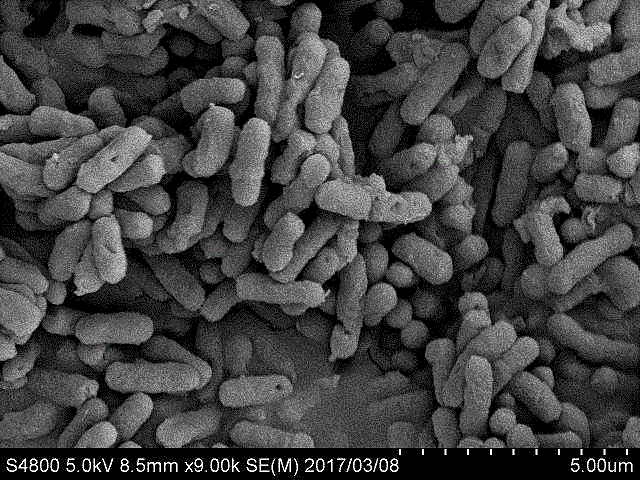
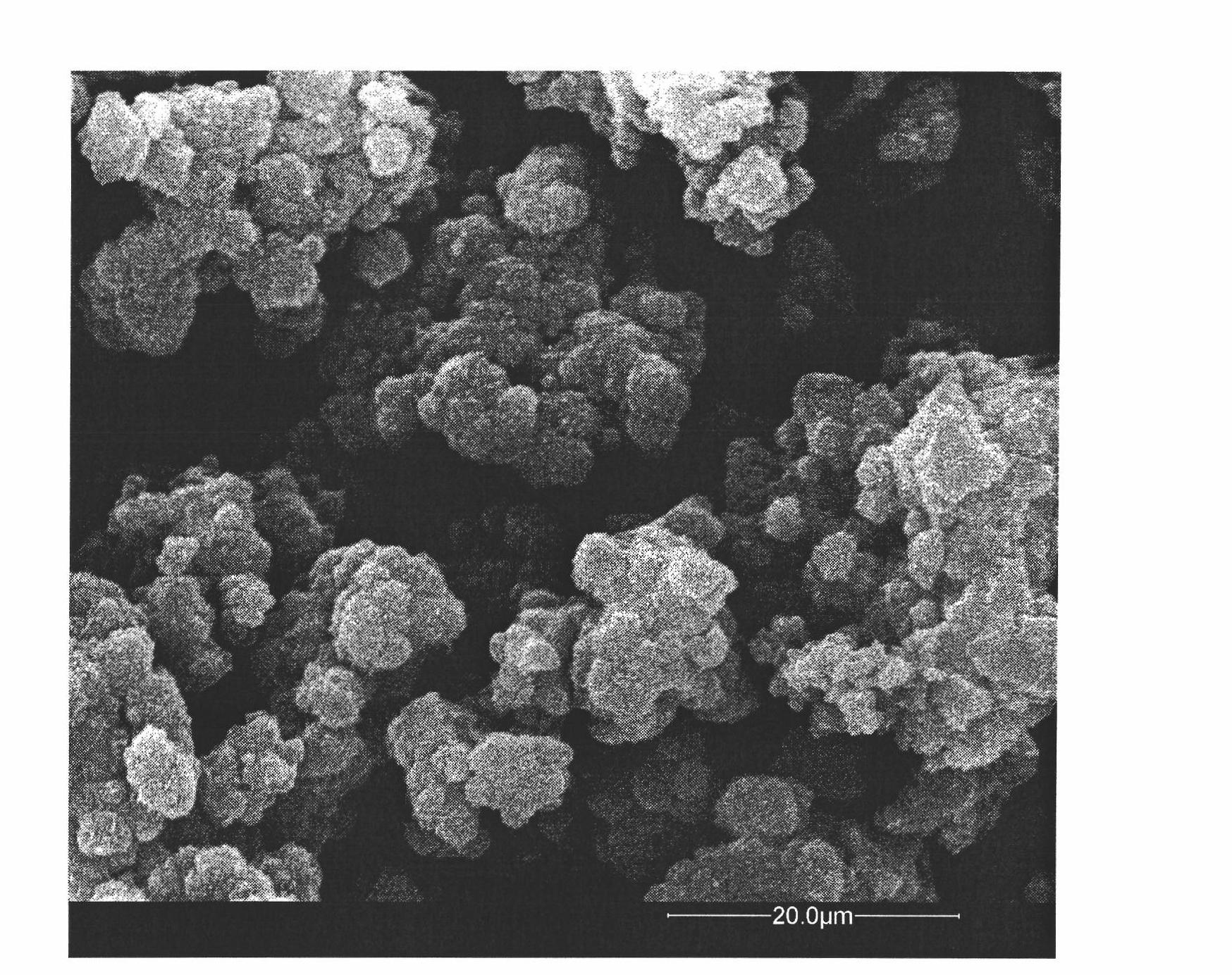
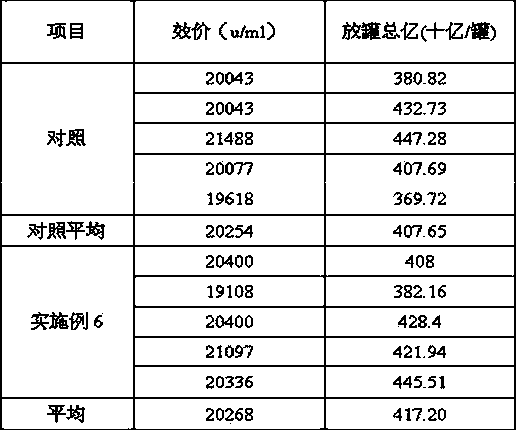
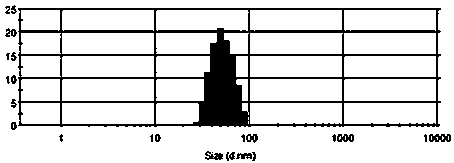
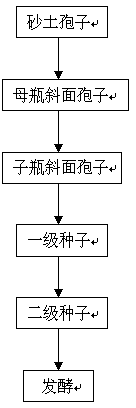
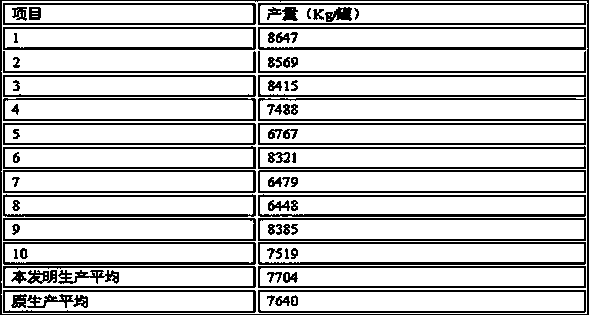
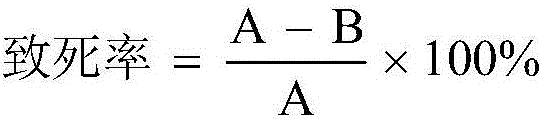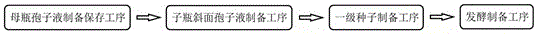Patents
Literature
85 results about "Chlortetracycline" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
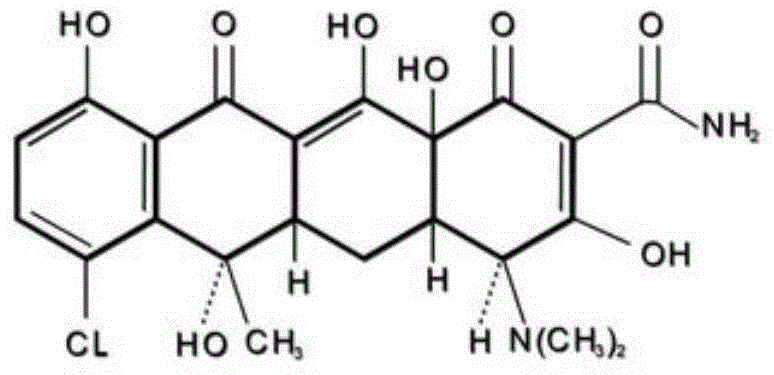
Chlortetracycline (trade name Aureomycin, Lederle Laboratories) is a tetracycline antibiotic, the first tetracycline to be identified. It was discovered in 1945 at Lederle Laboratories under the supervision of scientist Yellapragada Subbarow and his junior Benjamin Minge Duggar. Duggar identified the antibiotic as the product of an actinomycete he cultured from a soil sample collected from Sanborn Field at the University of Missouri. The organism was named Streptomyces aureofaciens and the isolated drug, Aureomycin, because of their golden color.
Degrading bacterium for TC (tetracycline) antibiotics and application of degrading bacterium
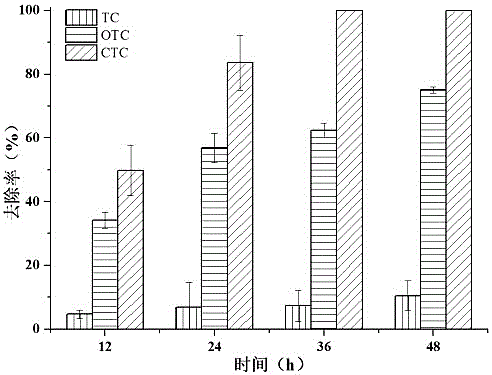
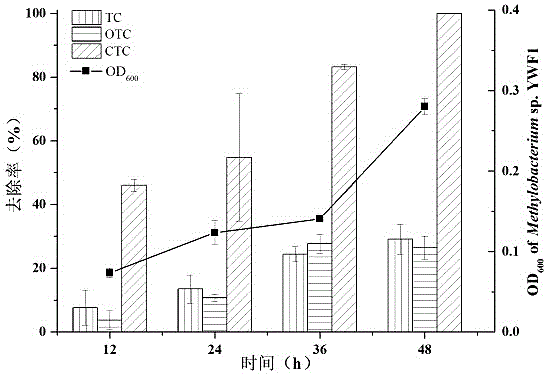
The invention relates to a degrading bacterium Methylobacterium sp. YWF1 capable of degrading three TC (tetracycline) antibiotics, namely, TC, OTC (oxytetracycline) and CTC (Chlorotetracycline) simultaneously. The degrading bacterium YWF1 is identified as Methylobacterium and was preserved in CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) on April 17, 2017 with preservation number being CGMCCNo. 14040. Methylobacterium sp. YWF1 can simultaneously degrade the three TC antibiotics, namely, TC, OTC and CTC, a microbial agent suspension can be prepared from the bacterium to be applied to degrading removal of TC antibiotic pollutants in different environment media such as livestock wastewater, TC pharmaceutical enterprise wastewater, medical wastewater or soil, and has good industrial application prospect and environmental benefits.
Owner:众心通慧(厦门)生态环保科技有限公司
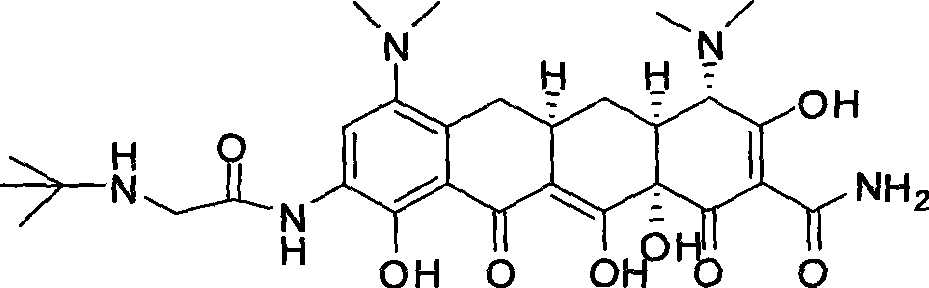
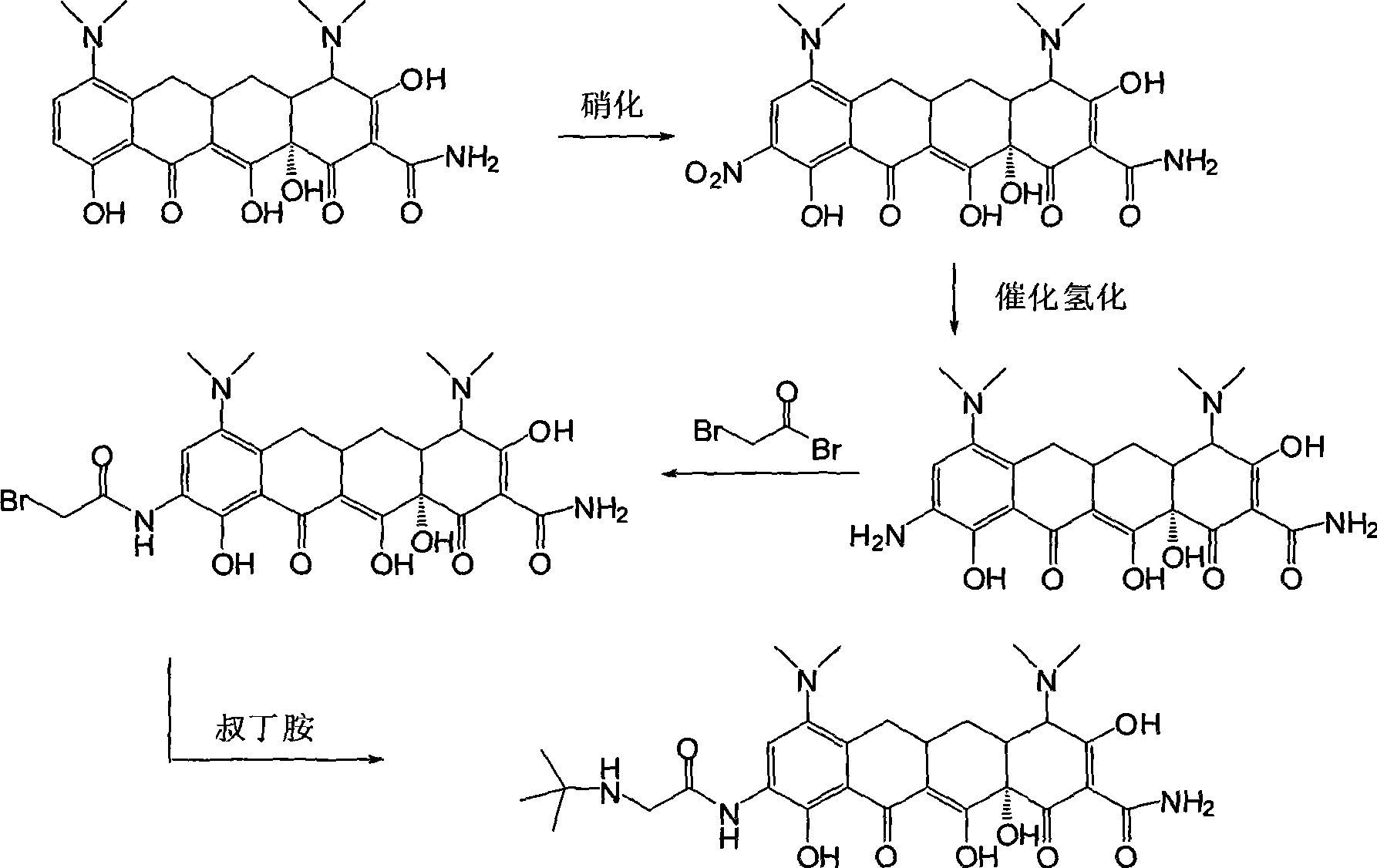
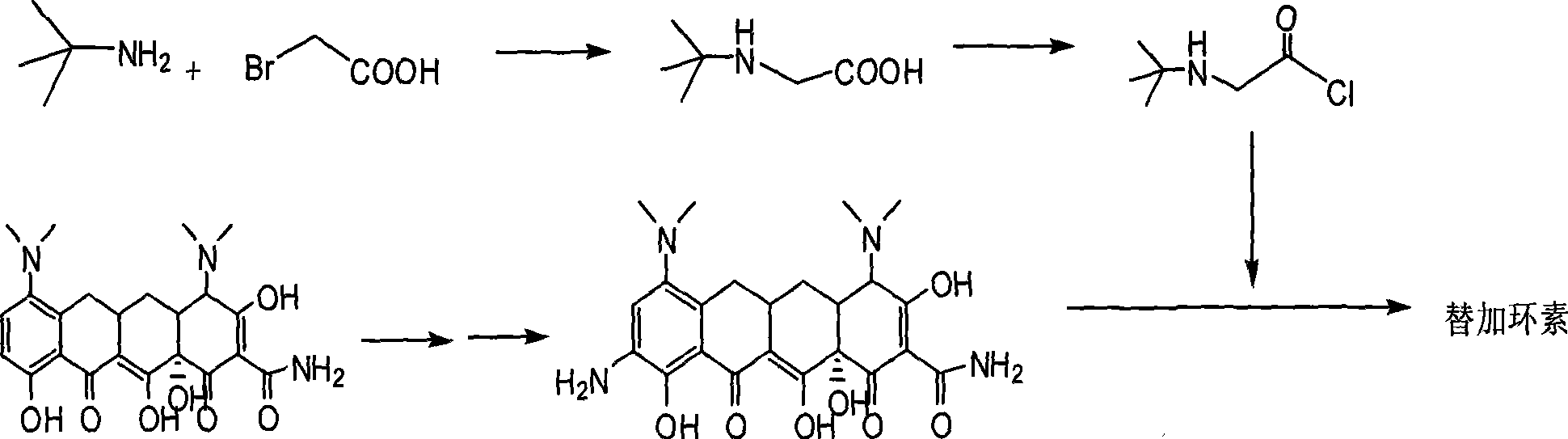
Synthetic method of tigecycline
ActiveCN101450916AEasy to operateProcess conditions are easy to controlOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid amides preparationDeoxidizationChlortetracycline
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing tigecycline. The method comprises: 6-demeclocycline is subjected to catalytic hydrogenation, nitration, selective deoxidization, amino prevention reaction, catalytic deoxidization, and a deprotection to form 9-amino minocycline hydrochloride; the 9-amino minocycline hydrochloride reacts with tert-butylamine acetyl chloride hydrochloride to form tigecycline. The invention uses 6-demeclocycline as a starting material, without synthesizing minocycline as the intermediate. The novel method has simple operation, easily controllable conditions, low requirements on equipment, low pollution, and great application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI LAIYI BIOMEDICAL RES & DEV CENT +1
Preparation method of molecular imprinting polymer with specific recognition capability to tetracycline family
InactiveCN101857664ARapid enrichment and purificationAccurate enrichment and purificationOther chemical processesCross-linkAcetic acid
The invention discloses a preparation method of a molecular imprinting polymer with specific recognition capability to a tetracycline family. The method comprises the following steps of: dissolving chlortetracycline, oxytetracycline chlortetracycline, functional monomers, a cross-linking agent and an initiating agent in acetonitrile by a certain proportions, mixing, then sealing and carrying out polymerization; carrying out extraction on generated polymer by firstly using a mixture solution of methanol and acetic acid to remove template molecules and then using methanol to extract and remove the acetic acid, and finally carrying out vacuum drying. The method is simple in operation; and the prepared molecular imprinting polymer has specific recognition capability to the tetracycline family, can carry out enriched purification on tetracycline antibiotic residues in a sample with speediness, sensitivity, accuracy and high efficiency and has the advantages of high recovery ratio, good reproducibility and high sensitivity.
Owner:HUBEI INSPECTION & QUARANTINE TECH CENT
Trichoderma LJ245 capable of degrading aureomycin
InactiveCN102604841AGrow fastImprove acid resistanceFungiWater contaminantsMicroscopic observationBioremediation
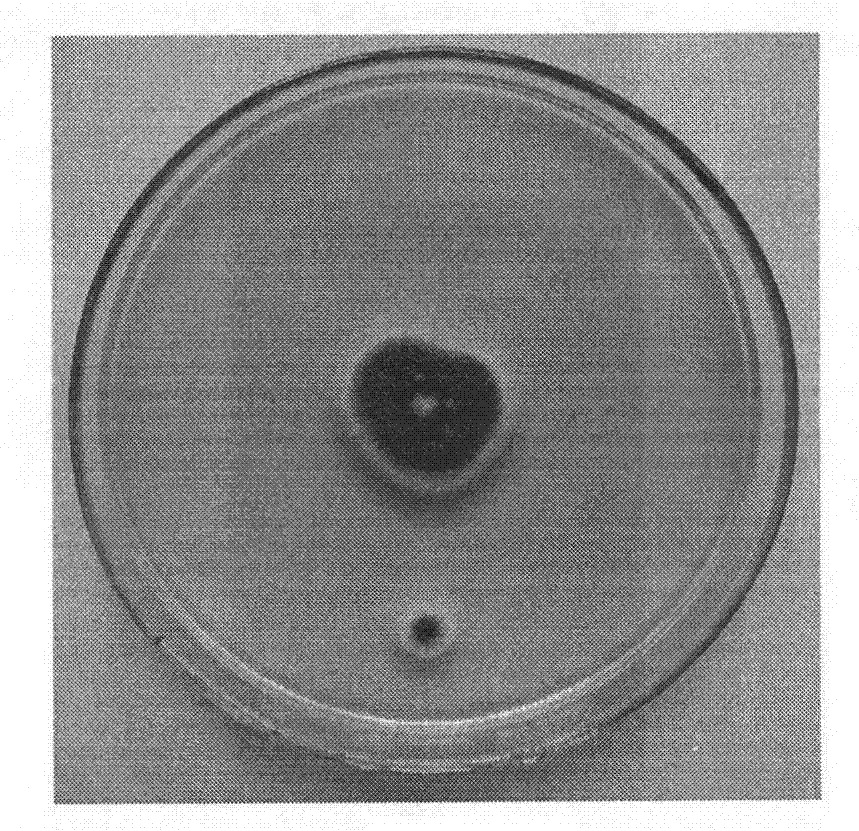
The invention relates to Trichoderma LJ245 capable of degrading aureomycin, belonging to the technical field of the microorganism. The 16S rDNA full sequence determination shows that: the strain LJ245 is Hypocrea lixii with the preservation number CGMCC No.5753. The strain LJ245 grows fast; mycelium is in the white flocculence and at the late growth stage, the mycelium is green yellow due to generation of conidium. The microscopic observation shows that: the mycelium is septate, colorless conidiophore vertically grows out and the conidium is spherical. The strain LJ245 has the function of degrading the aureomycin remained in the strain dregs and waste water, is also applied in treating the wastes from the aureomycin production enterprise, is also expected to be applied on the biological repair of the aureomycin polluted environment, especially is used as a sole carbon source, moreover the strain still grows well when the concentration of the aureomycin is low to 0.01g / L, thus the residual aureomycin is reduced to the hilt. Simultaneously, the strain is conveniently used and also used as the preparation raw material of an aureomycin degradation strain agent.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY +1
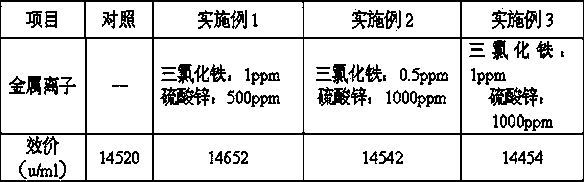
Fermentation technology for increasing the aureomycin yield by adding metal ions
InactiveCN103614446ARaise the level of fermentationIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationSulfateZinc
The invention provides a fermentation technology for increasing the aureomycin yield by adding metal ions. Certain amounts of zinc sulfate and ferric trichloride are added into a fermentation culture medium of aureomycin, thus achieving an objective of increasing the aureomycin yield. According to the technology, 500 ppm of the zinc sulfate and 1 ppm of the ferric trichloride are added into the conventional fermentation culture medium. The fermentation level by the fermentation technology provided by the invention is higher than the original fermentation level. The pilot potency and the yield are both increased, thus laying good foundations for industrial scale-up and application in the next stage.
Owner:ZHUMADIAN HUAZHONG CHIA TAI
Preparation and application of nano silica-based doxycycline molecularly imprinted polymer
ActiveCN103554363ARecognizableOther chemical processesPreparing sample for investigationCross-linkN dimethylformamide
The invention relates to a preparation method for a nano SiO2-based doxycycline molecularly imprinted polymer. A doxycycline (DOC) molecularly imprinted polymer with nano silica (nano-SiO2) removed is obtained by using nano-SiO2 as a carrier and DOC as a template molecule, alpha-methylacrylic acid (MAA), ethylene glycol dimethacrylate (EDMA) and 2,2'-azodiisobutyronitrile (AIBN) as functional monomers, a cross-linking agent and an initiator respectively; N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) as a solvent and through the steps of dissolution, polymerization, SiO2 removal with hydrofluoric acid (HF) and elution. The imprinted polymer is used as a filler for a solid phase extraction column; the obtained solid phase extraction column has good recognizability for the template molecule (DOC) and three template molecule analogues such as tetracycline (TC), oxytetracycline (OTC) and chlortetracycline (CTC); an adsorption rate for DOC can reach 90.2%; an adsorption rate for TC can reach 85.4%; an adsorption rate for OTC can reach 83.7% and an adsorption rate for CTC can reach 86.1%. Therefore, the imprinted polymer can be used for sample pretreatment for residue detections of tetracycline antibiotics in animal derived foods.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
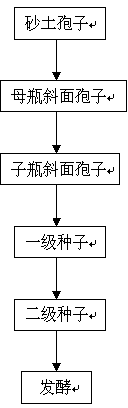
Method for high throughput screening of chlortetracycline high-yield strains
InactiveCN106191030AFast growthGood for plate cultureMutant preparationMicroorganism based processesHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsColor reaction
The invention discloses a method for high throughput screening of chlortetracycline high-yield strains and belongs to the technical field of metabolic engineering. Through a comparison of growth and yield of streptomyces aureofaciens on five flat plate culture mediums, an optimal culture medium is selected, and guarantee is provided for starting strains. Through a comparison of two primary screening methods which are color reaction between chlortetracycline and Sm3+ and a colorimetric method of co-heat of chlortetracycline and hydrochloric acid, the simple and accurate color reaction is selected as the primary screening method. Repeatability and accuracy of nitric acid color reaction serving as a primary screening means are verified.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for detecting chlortetracycline by fluorescent carbon dots prepared by using p-phenylenediamine and acetic acid as carbon source
ActiveCN109324027AImprove uniformityEasy to operateFluorescence/phosphorescenceAcetic acidLinear relationship
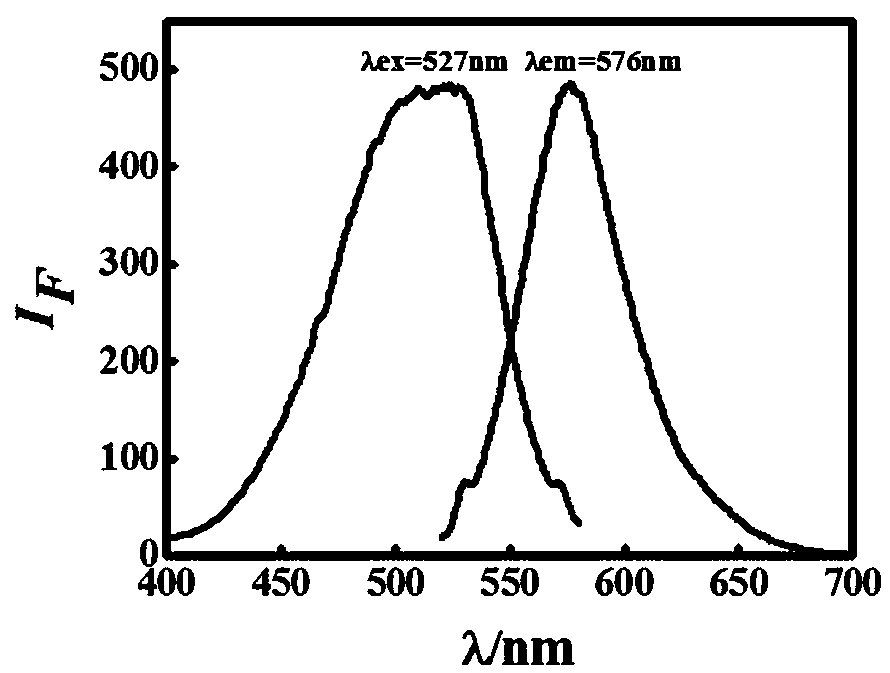
The invention discloses a method for detecting chlortetracycline by fluorescent carbon dots prepared by using p-phenylenediamine and acetic acid as carbon sources. An orange-red fluorescent carbon dotsolution is synthesized under the heating condition of a solvothermal reaction kettle by using p-phenylenediamine and acetic acid as carbon sources and ethanol as a dispersion system. The synthesizedcarbon dots have fluorescence characteristics with a maximum excitation wavelength of 527 nm and a maximum emission wavelength of 576 nm. After the reaction of the carbon dot solution with differentconcentrations of chlortetracycline solution, the fluorescence intensity value of the fluorescent carbon dot solution and the chlortetracycline concentration shows a good linear relationship (I<F> -I<F0>) / I<F0>=2.9257x10<6> c+0.3473, wherein I<F> is the fluorescence intensity value, c is the chlortetracycline concentration. The range of chlortetracycline concentration of detectable solutions is 1.0x10<-8>-1.0x10<-5>mol L<-1>, and the detection limit is: 1.5x10<-9>mol L<-1>. The method for detecting chlortetracycline by fluorescent carbon dots prepared by using p-phenylenediamine and acetic acid as carbon sources of the invention has simple process, can rapidly prepare fluorescent carbon dots, and can accurately measure the chlortetracycline concentration of the solution. According to the linear relationship, three synthetic samples are measured, and the measured recovery rate is 97.10%-99.20%, indicating that the method has good practical application value.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Chlortetracycline fermentation production method using refined protein powder
InactiveCN106047977AEfficient productionLow input costMicroorganism based processesFermentationStreptomyces auratusAntibiotic Y
The invention relates to the field of fermentation production processes, and discloses a chlortetracycline fermentation production method using refined protein powder. According to the present invention, Streptomyces aureus is adopted as a starting strain, and pure culture and two-stage fermentation are performed to produce chlortetracycline; with the application of the 100% refined protein powder to replace the soybean cake powder, the chemical titer is increased by 2.3% compared to the application of the soybean cake powder, and the yield is increased by 1.8% compared to the unimproved method, such that the yield is effectively increased; and the raw material cost input per tank can be reduced by about 540 yuan after the cost accounting, the effect is good, the fermentation production level is stably increased, and the theoretical and applied basis is provided for the industrial production of the antibiotics and the scientific research.
Owner:PUCHENG CHIA TAI BIOCHEM
Oil-in-water compound chlortetracycline nanoemulsion
InactiveCN104352566AImprove bioavailabilityPromote and enhance antibacterial abilityAntibacterial agentsTetracycline active ingredientsSurface-active agentsBioavailability
The invention discloses oil-in-water compound chlortetracycline nanoemulsion, and belongs to the technical field of medicines. The oil-in-water compound chlortetracycline nanoemulsion comprises the following components in parts by weight: 1-18 parts of aqueous magnolia officinalis extract, 25-45 parts of a surfactant, 0-20 parts of a co-surfactant, 1-20 parts of chlortetracycline, 1-20 parts of oil and 20-70 parts of water. The oil-in-water compound chlortetracycline nanoemulsion has relatively narrow emulsion particle size distribution, is transparent, has high stability, relatively low surface tension and good mobility, and is convenient to take; a nanoemulsion preparation improves solubility and permeability of the chlortetracycline, so that the bioavailability of a medicine is improved; after the aqueous magnolia officinalis extract and the chlortetracycline are compounded, antibacterial abilities of the aqueous magnolia officinalis extract and the chlortetracycline are mutually promoted and enhanced, so that the antibacterial effect of the oil-in-water compound chlortetracycline nanoemulsion is more stable.
Owner:HENAN SOAR VETERINARY PHARMA
Aureomycin strain breeding culture medium and strain breeding method
InactiveCN104988103AShorten breeding timeImprove breeding efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesYeastMonopotassium phosphate
The invention discloses an aureomycin strain breeding culture medium and a strain breeding method. The culture medium comprises, by weight, 6.0%-7.5% of corn starch, 3.5%-4.5% of soybean cake powder, 0.15%-0.25% of yeast powder, 0.55%-0.65% of calcium carbonate, 0.3%-0.4% of ammonium sulfate, 0.2%-0.3% of sodium chloride, 0.02%-0.03% of magnesium sulfate, 0.02%-0.03% of monopotassium phosphate, 2.86%-4.28% of soya-bean oil and the balance water. An aureomycin strain breeding culture medium formula is improved, a strain culturing and strain fermentation cultivation second-level fermentation mode is changed into a primary fermentation mode, strain breeding time is greatly shortened, strain breeding efficiency is improved, the using quantity of shaking flasks and shaking tables is reduced, cost is lowered, the probability of strain pollution is lowered, and accordingly the culture medium and the method are suitable for large-scale strain screening.
Owner:金河生物科技股份有限公司
A fermentation production method for aureomycin by utilizing mycoprotein in place of a portion of yeast powder
InactiveCN103614445ALow input costLow costMicroorganism based processesFermentationAmylaseMycoprotein
The invention provides a technology method used in an aureomycin fermentation production process by utilizing mycoprotein in place of a portion of yeast powder. The mycoprotein is added into an aureomycin basal culture medium according to a certain ratio to replace the portion of the yeast powder, thus achieving an objective of reducing the production cost of aureomycin. The method is characterized in that culture medium aqueous solution per liter in a fermentation tank in a fermentation preparation process comprises following components: 20 g of groundnut meal, 10 g of soybean cake powder, 60 g of the corn starch, 0.1 g of amylase, 2 g of sodium chloride, 7.3 g of ammonium sulfate, 5.7 g of calcium carbonate, 4.35 g of the yeast powder, 4.35 g of the mycoprotein, 13.3 g of corn steep liquor, 0.22 g of magnesium sulfate, 0.1 g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate and 0.17 g of soybean oil. When the basal culture medium sterilization is completed and the temperature is decreased to 30-35 DEG C, a second-stage seed is transferred into the fermentation tank. After seed transference, fermentation production is controlled by changing temperature. The culture pressure is controlled at 0.01-0.04 MPa. The fermentation culture viscosity is controlled at 1-35 s. The fermentation period is 90-124 h. According to the method, the mycoprotein is adopted in the fermentation process to replace 50% of the yeast powder, the production is almost the same as that of common fermentation, products are qualified and the cost of raw materials for one tank is reduced by 1040 Yuan, and therefore the cost of the raw materials is reduced in the case of guaranteeing production stability.
Owner:ZHUMADIAN HUAZHONG CHIA TAI
Aspergillus oryzae LJ366 strain used for degrading aureomycin
InactiveCN103421697AEasy to usePromote degradationFungiMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismAspergillus oryzae
The invention relates to an Aspergillus oryzae LJ366 strain used for degrading aureomycin and belongs to the microbial technical field. The bacterial strain has already been preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on Aug 27, 2013 and the preservation number is CGMCC No.8078. The ITS gene sequence of the Aspergillus oryzae LJ366 strain used for degrading the aureomycin is composed of 593 bases. The bacterial strain can degrade the aureomycin and can be used for processing residual aureomycin in solid waste and liquid.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY +1
Rumen bypass chlortetracycline micro-pills and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105997939ADoes not affect sexual functionDoes not affect digestionAntibacterial agentsTetracycline active ingredientsAdhesiveGrowth promoting
The invention aims at providing rumen bypass chlortetracycline micro-pills and a preparation method thereof. The rumen bypass chlortetracycline micro-pills sequentially comprise drug-containing pill cores and coating layers from inside to outside, wherein the drug-containing pill cores are prepared from, by weight, 10-25 parts of chlortetracycline, 10-30 parts of corn starch, 30-40 parts of calcium carbonate, 0.8-3.2 parts of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, 5-10 parts of adhesive and 7-25 parts of coating layer. The coating layers of the rumen bypass chlortetracycline micro-pills prepared by means of the preparation method are complete in rumen, and no chlortetracycline is released; then the micro-pills reach the stomach, the coating layers are damaged in a gastric acid environment, the chlortetracycline is released, and accordingly antibacterial and growth-promoting effects are achieved; meanwhile, the physiological habits of ruminants are not affected, and the micro-pills are convenient to use.
Owner:ZHUMADIAN HUAZHONG CHIA TAI
Penicillium spinulosum LJ220 strain for degrading aureomycin
InactiveCN102732431AImprove adaptabilityGrow fastFungiMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismPenicillium spinulosum
The invention relates to a Penicillium spinulosum LJ220 strain for degrading aureomycin, belonging to the technical field of microorganism. The Penicillium spinulosum LJ220 strain disclosed herein is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) with the preservation number of CGMCC No.5754 on 14 Feb, 2012. The gene sequence of the strain is obtained by genome DNA extraction, rDNA-ITS sequence-based amplification and complete sequence determination and analysis. The LJ220 strain can grow in a medium with aureomycin as the sole carbon source. The strain is convenient for usage, and has efficient degradation on residual aureomycin in bacteria residues.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY +1
OAP-MIP multiple binding site affinity membrane chlortetracycline (CTC) sensor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105092671AMeet the requirements of trace analysisQuick responseMaterial electrochemical variablesFunctional monomerBinding site
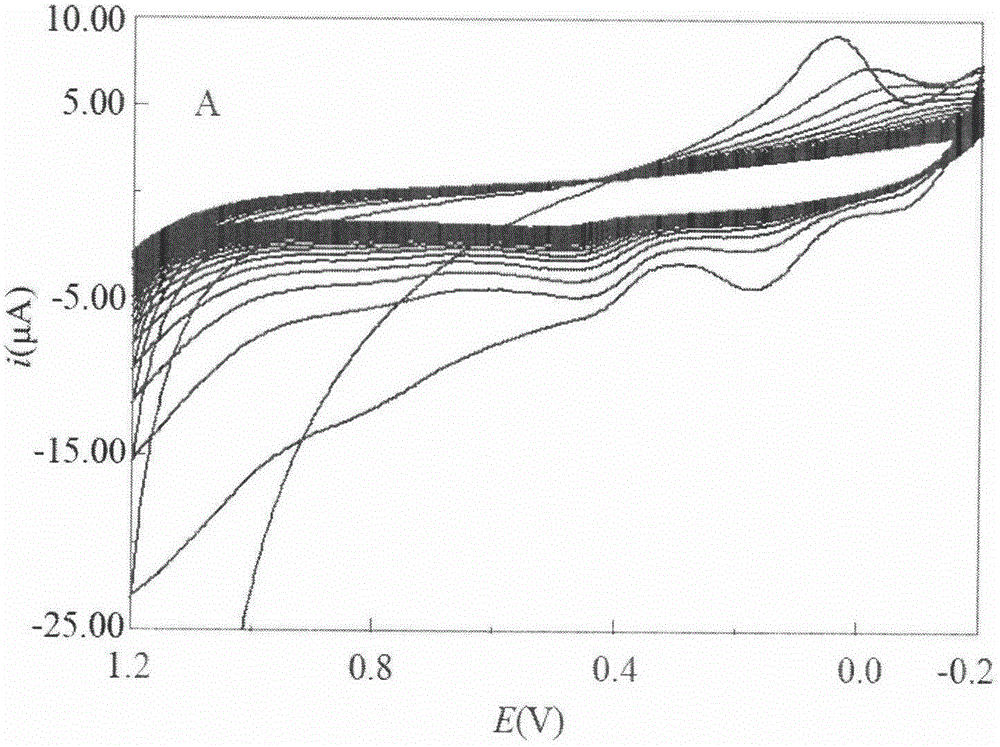
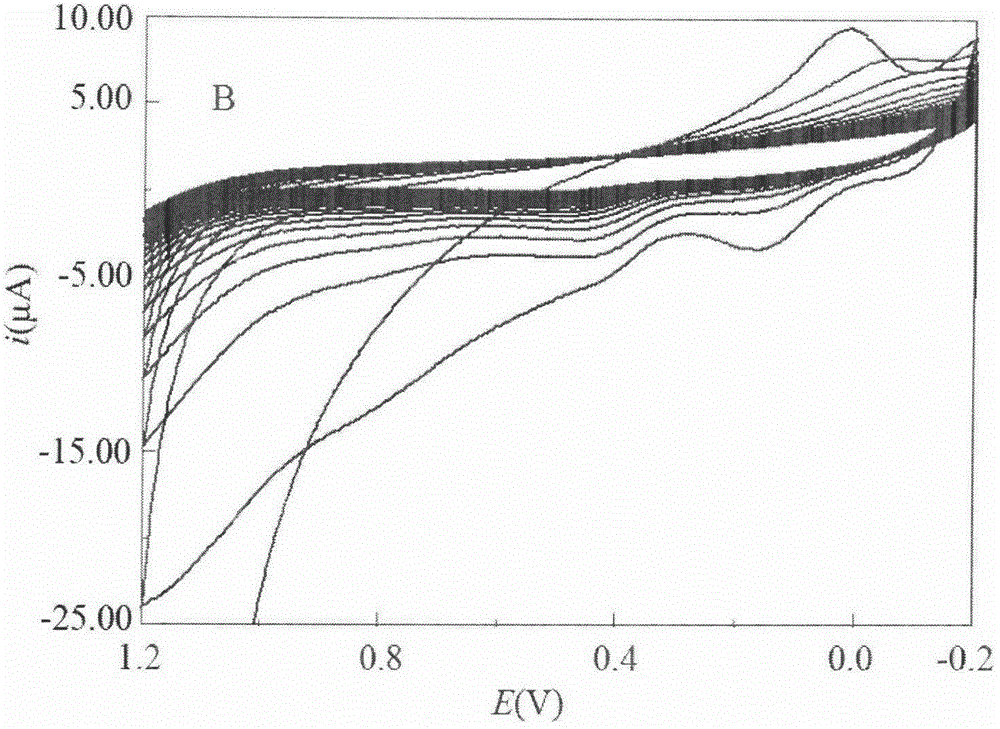
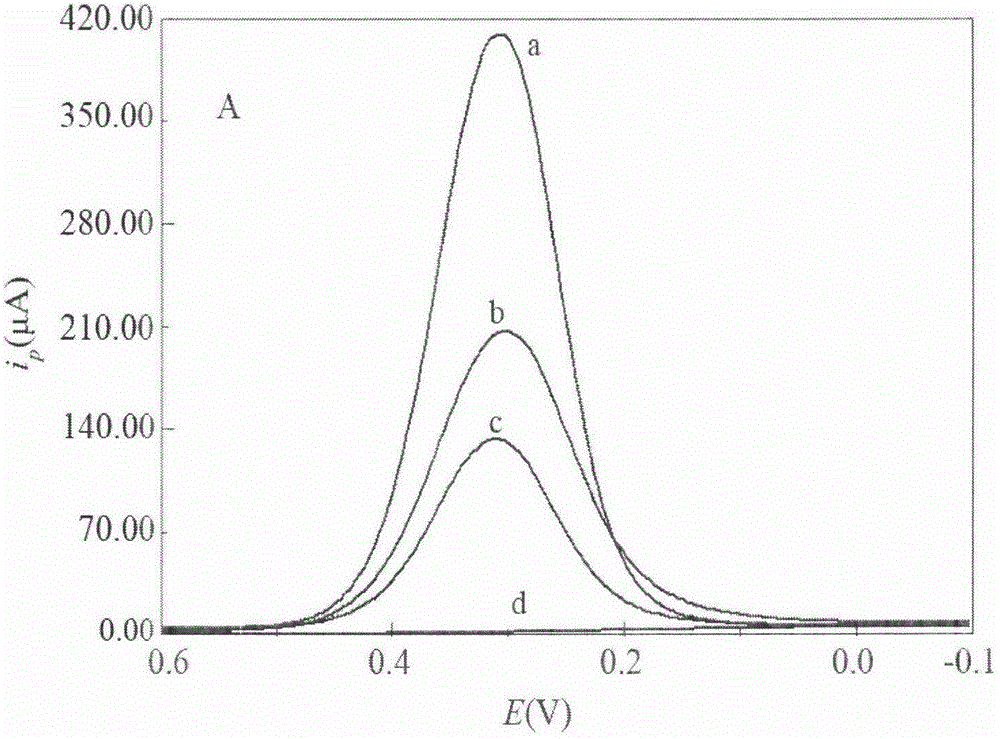
The invention relates to a chlortetracycline (CTC) molecularly imprinted (MIP) affinity membrane sensor and a preparation method thereof. The specific affinity membrane is formed based on an electropolymerization method, and CTC as a template molecule and o-aminophenol (OAP) as a functional monomer form a molecularly imprinted polymer membrane on the surface of a glassy carbon electrode by an electrochemistry method. CTC contains a phenolic hydroxyl group, an enol group and a dimethylamino group and the hydroxyl group in the OAP structure can be used as a latent coordination site so that OAP amino group, and phenolic hydroxyl group and enol group of CTC undergo intermolecular hydrogen bond interaction. OAP hydroxyl group and CTC dimethylamino group undergo a reaction so that multiple binding sites between OAP and CTC exist and the prepared molecularly imprinted polymer has very high CTC selectivity and bonding capability. The sensor can be used for on-site fast detection, does not need specimen pre-treatment, and has a low cost, simple processes and high sensitivity. The sensor has a detection linear range of 20-610nM and sensitivity of 15nM.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Fattening swine feed
InactiveCN104413274AIncrease spawn rateImprove qualityAnimal feeding stuffAnimal scienceChlortetracycline
The invention relates to a swine feed and specifically relates to a fattening swine feed. The swine feed comprises the raw materials in parts by weight: corn 650-700, soybean meal 50-60, stone powder 10-13, cottonseed meal 40-50, fish meal 1-5, chlortetracycline 0.3-0.6, betaine 0.7-0.9, choline 0.8-1.2, compound enzyme 0.8-1.2, salt 1-1.5, vitamin C 0.01-0.04, vitamin D 0.5-0.8, vitamin B6 0.5-0.8, vitamin B12 0.4-0.6, vitamin E 0.7-0.9, Radix Astragali 10-15, Argy Wormwood leaf 10-15, Chinese Arborvitae 7-10 and pine needle powder 4-7.
Owner:赵贵喜
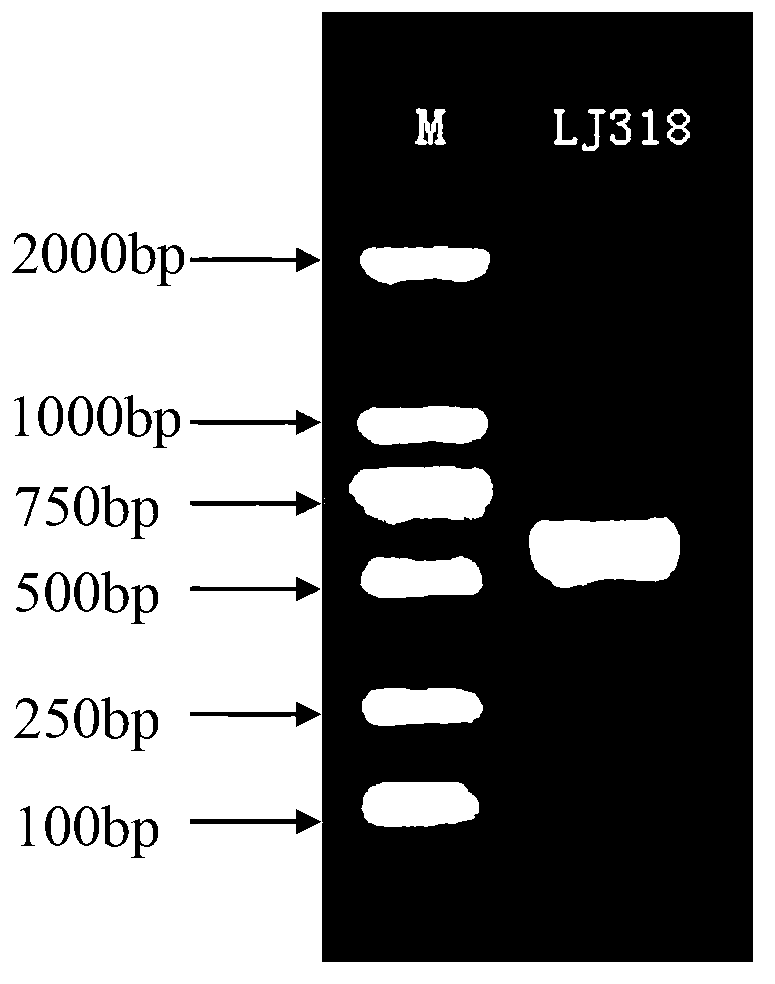
Penicillium citrinum LJ318 for degrading chlortetracycline
InactiveCN103289904APromote degradationGrow fastFungiMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismRibosomal DNA
The invention relates to a strain of Penicillium citrinum LJ318 capable of degrading chlortetracycline and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. The strain is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) in March 3rd, 2012, and the preservation number of the strain is CGMCC No.5850. An rDNA-ITS (Ribosomal DNA internal transcribed spacer) gene sequence of the chlortetracycline degrading strain LJ318 consists of 544 basic groups. The strain is wide in chlortetracycline-tolerating range and has relatively good degradation effects on the residual chlortetracycline in both liquid and solid wastes.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY +1
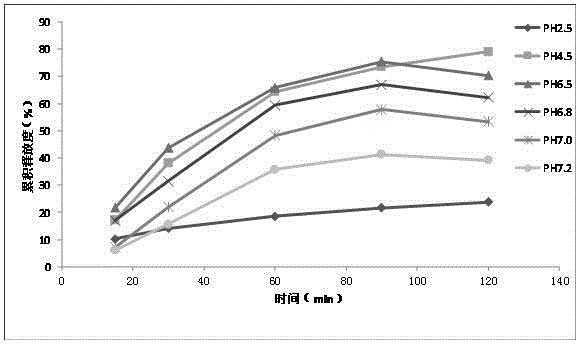
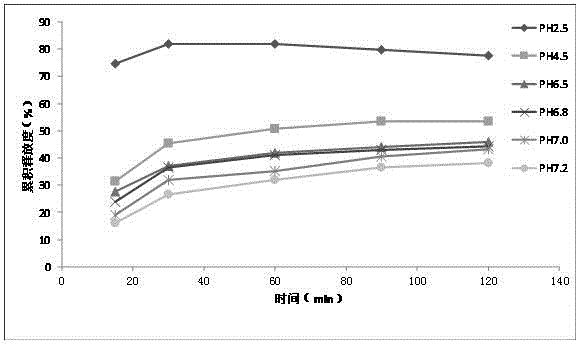
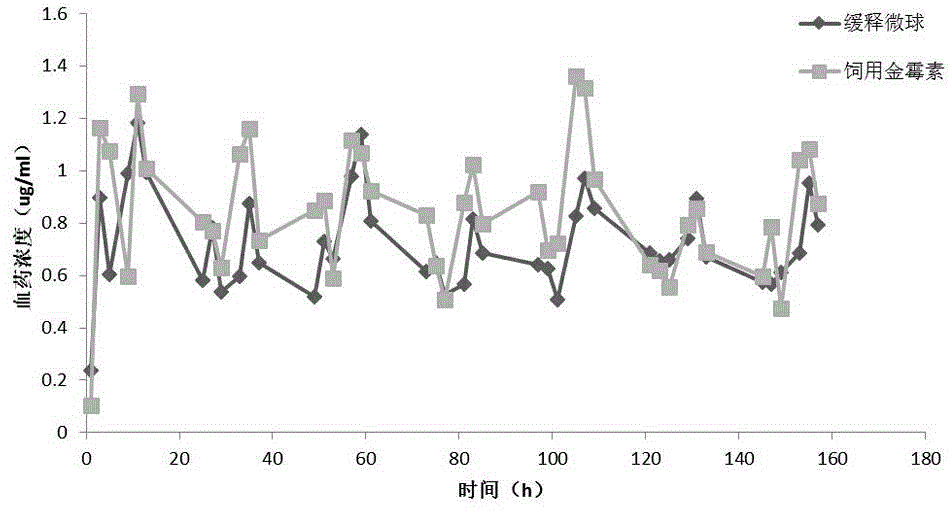
Preparation method of chlortetracycline sustained-release microspheres
ActiveCN104666250AIncrease profitSpherical RegularityAntibacterial agentsTetracycline active ingredientsMicrosphereMontmorillonite
The invention discloses a preparation method of chlortetracycline sustained-release microspheres. The method comprises steps as follows: mixing chlortetracycline with montmorillonite, adding the mixture to water to prepare a suspension, adding the suspension to a sodium alginate solution, evenly mixing the mixture, dropping the mixture into a calcium chloride solution for crosslinking, and collecting and air-drying gel spheres to obtain the chlortetracycline sustained-release microspheres. The condition of mixing of the chlortetracycline-montmorillonite suspension with the sodium alginate solution is optimized, the problems that mixtures are higher in viscosity and difficult to stir are well solved by the aid of high-speed magnetic stirring and even mixing, the mixture is evenly dispersed through full stirring, and stabilization of the chlortetracycline and formation of the sustained-release microspheres are facilitated. Besides, the drying method is also optimized, defects of other drying methods are overcome due to adoption of an ethanol soaking and air-drying method, the dried microspheres are regular in form, the drying time is shorter, and soaking of the microspheres with ethanol and the room temperature environment are beneficial to stabilization of properties of the chlortetracycline.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
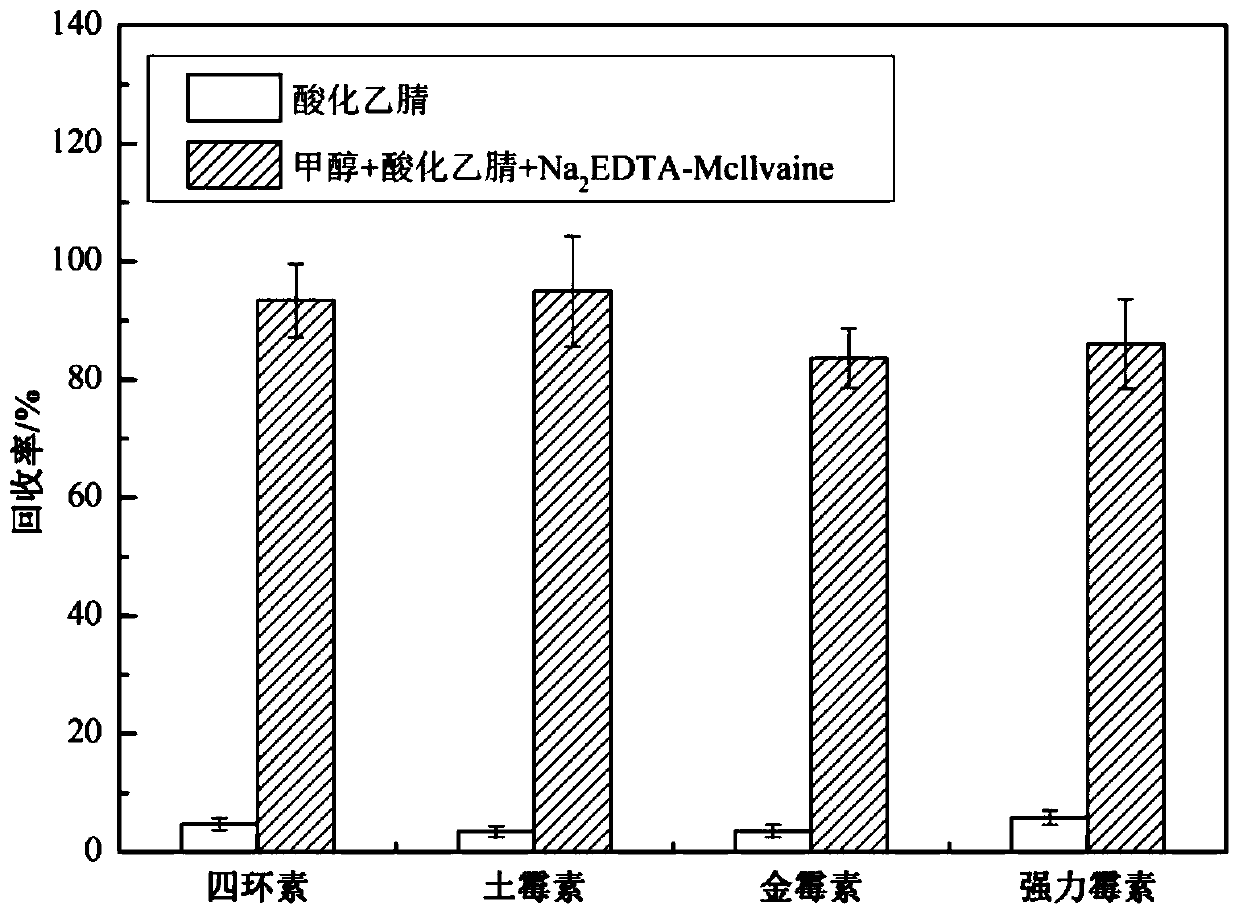
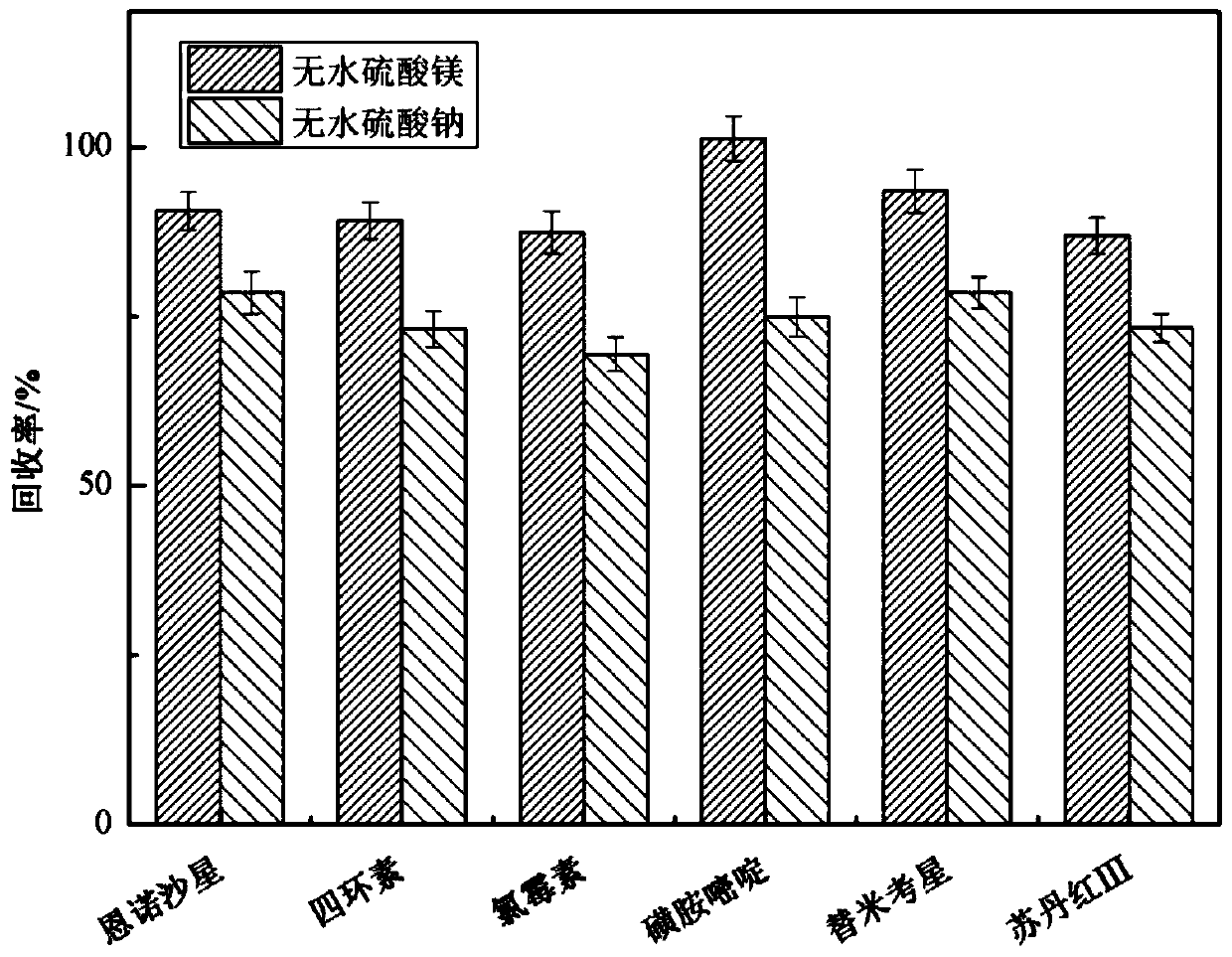
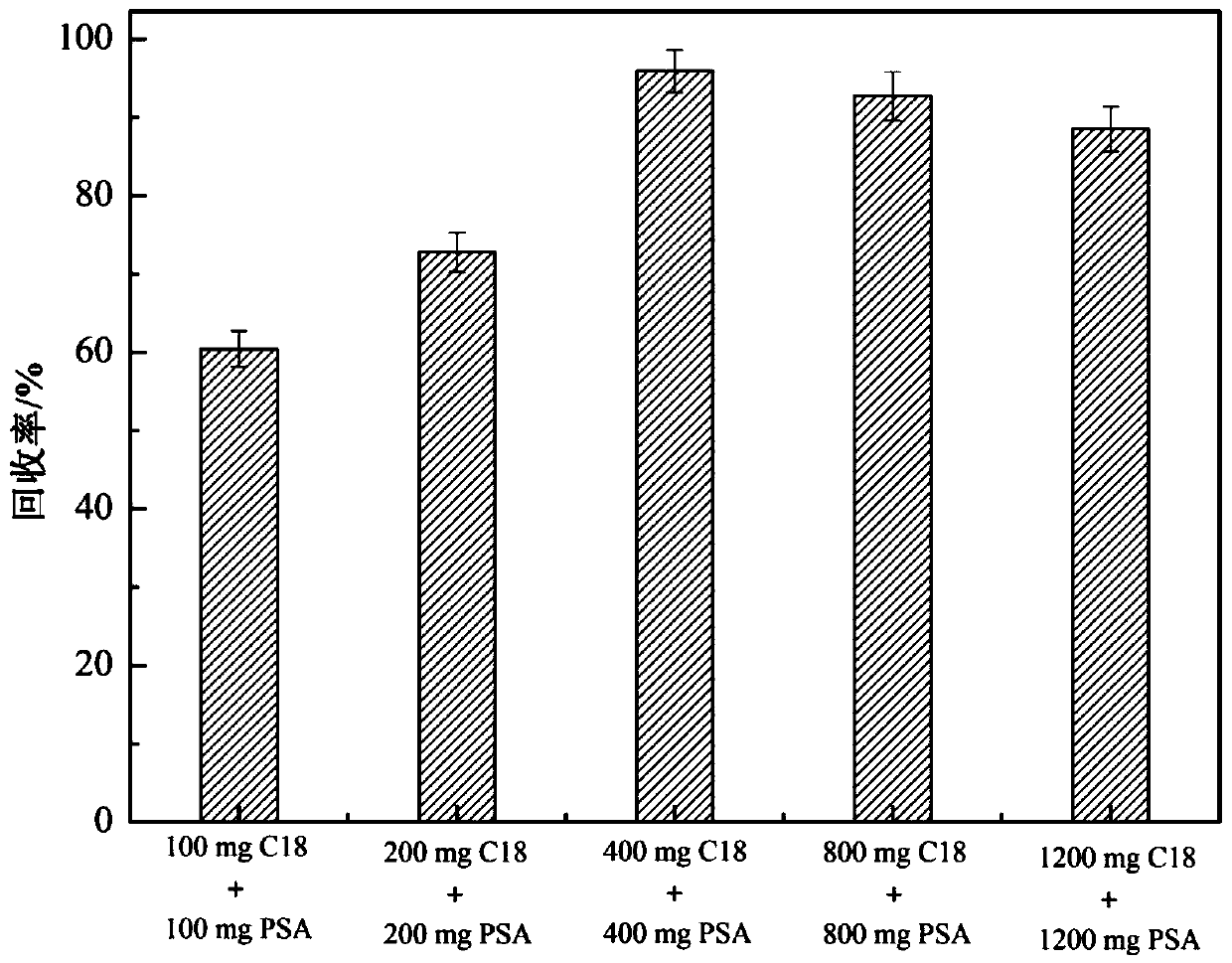
Method for simultaneously screening multiples categories of drug residues in fish by using ultra performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole rod time-of-flight mass spectrometry
InactiveCN109917047AHigh recovery rateImprove solubilityComponent separationPretreatment methodSudan III
The invention relates to a method for simultaneously screening multiples categories of drug residues in fish by using ultra performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole rod time-of-flight mass spectrometry. The multiples categories of drugs screened simultaneously comprise enrofloxacin, danofloxacin, tetracycline, oxytetracycline , chlortetracycline, doxycycline, chloramphenicol, thiamphenicol, florfenicol, sulfamethoxazole, sulfamethoxazole, sulfathiazole, sulfadiazine, sulfadoxine, sulfisoxazole, sulfaphenirazole, sulfacetamide, sulfamethazine, azithromycin, tilmicosin, medimycin, roxithromycin, acetylspiramycin, doramectin, sudan I, sudan II, sudan III, sudan IV and rhodamine B. By optimizing the parameters of a d-SPE pretreatment method, all target drugs can obtain good recovery rates.29 kinds of target drugs are simultaneously screened by an optimized chromatographic mass spectrometry condition, thereby achieving simultaneous screening of common multiples categories of drug residues in fish. The method has a good application prospect in the field of fish food.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
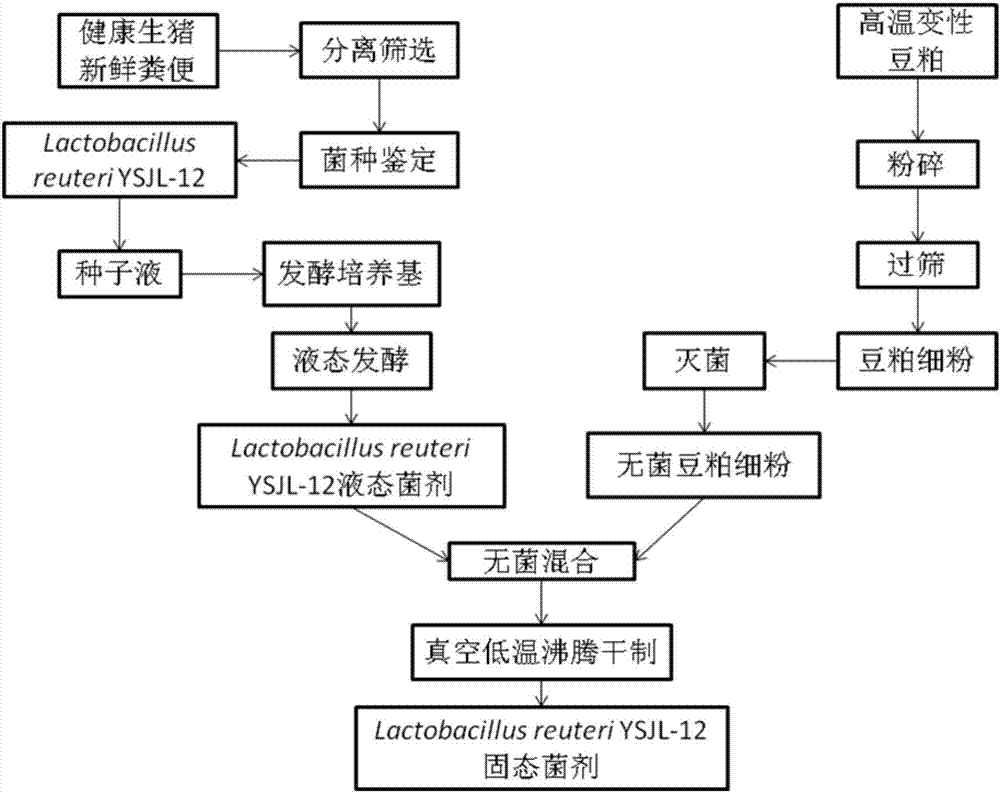
Swine-origin lactobacillus reuteri and prepared solid probiotics
The invention relates to swine-origin lactobacillus reuteri and prepared solid probiotics. The bacterial strain is separated from fresh night soil of healthy live pig, and is indentified as Lactobacillus reuteri YSJL-12 through a morphological biochemistry and molecular biology method, and a preservation number is CGMCC No. 9062. The bacterial strain inhibits Listeria monocytogenes CICC21633 to positive. The prepared solid probiotics contain soybean meal and active Lactobacillus reuteri YSJL-12, can substitute aureomycin for preventing and treating diarrhoea while added in a live pig basic feed, and the feed-gain ratio of the breeding pork pig at age in days of 28-168 is 2.61. The bacterial strain has the characteristics of strong host specificity, large live bacteria quantity, low cost and high cost performance, added value of high temperature soybean meal is increased, and the green live pig culture cost is reduced.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Penicillium oxalicum LJ302 capable of degrading chlortetracycline
InactiveCN103266064APromote growthPromote degradationFungiWater contaminantsMicroorganismBiotechnology
The invention relates to penicillium oxalicum LJ302 capable of degrading chlortetracycline, and belongs to the technical field of microbes. The penicillium oxalicum LJ302 is named, and is preserved in General Microorganism Centre of China Microbiological Preservation and Management Committee in Dec 19, 2012 with an accession number of CGMCC No. 7019. The rDNA-ITS sequence of the LJ302 bacterial strain is composed of 572 bases. The LJ302 bacterial strain can grow in a medium with chlortetracycline as a sole carbon source, and has a good degradation effect on chlortetracycline remained in wastes.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY +1
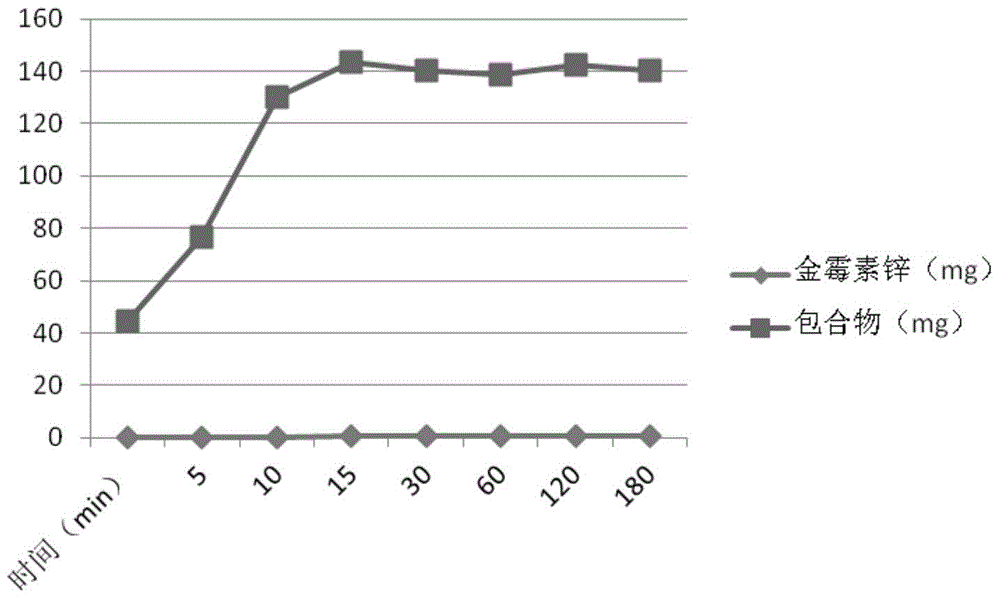
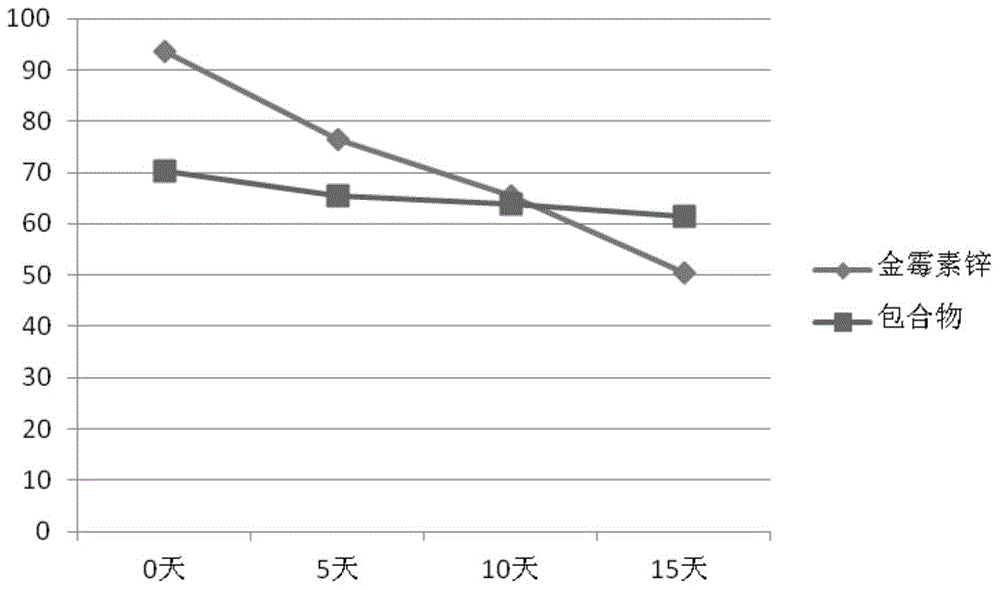
Clathrate compound of aureomycin zinc complex, and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104399086AOvercome the main disadvantage of poor water solubilityImprove stabilityAntibacterial agentsTetracycline active ingredientsSolubilitySide effect
The invention belongs to the technical field of drug preparation, particularly relates to a clathrate compound of an aureomycin zinc complex, and a preparation method thereof, and aims to solve the technical problem that the aureomycin zinc complex is poor in solubility and small in dissolution rate. Through the technical scheme, the clathrate compound of the aureomycin zinc complex comprises a clathrate material and the aureomycin zinc complex according to a weight ratio of (1-3): 1, and the clathrate material is cyclodextrin or a cyclodextrin derivative. The invention further provides an oral preparation prepared from the clathrate compound. The invention further provides a preparation method for the clathrate compound of the aureomycin zinc complex. The aureomycin zinc complex in the clathrate compound is good in solubility in water and high in dissolution rate, and has the advantages of good water solubility, high stability, good curative effect, little side effect and the like.
Owner:CHONGQING ACAD OF ANIMAL SCI +2
Semi-artificial feedstuff for sesamie inferens and preparation method of feedstuff
InactiveCN103110009ARealize long-term feedingImprove survival rateAnimal feeding stuffSucroseVitamin C
The invention relates to semi-artificial feedstuff for sesamie inferens and a preparation method of the feedstuff, belonging to artificial feedstuff for insects and feedstuff preparation technologies. The semi-artificial feedstuff is characterized in that each kilogram of feedstuff contains 21-27 grams of soybean flour, 25-60 grams of water bamboo flour, 18-36 grams of rice stem powder, 22-30 grams of corn flour, 16-22 grams of malt flour, 10-20 grams of rice sprout powder, 35-70 grams of yeast, 10-14 grams of cane sugar, 20-30 grams of casein, 1.5-2.8 grams of vitamin C, 0.05-0.15 gram of cholesterol, 5-8 grams of Wesson salt mixture, 2-4 grams of sorbic acid, 1.5-3.0 grams of chlortetracycline, 12-13 grams of agar, and the balance of distilled water. When the semi-artificial feedstuff is used to breed newly hatched larvae of sesamie inferens, the survival rate of the larvae of 12 days is more than 92%, the proportion of the larvae growing to pupas is more than 85%, and 10 generations of larvae can be continuously raised; during the breeding of each generation of larvae, the feedstuff only needs to be replaced once, thus simplifying the operation; and the raw materials are readily available and low in cost.
Owner:CHINA NAT RICE RES INST +1
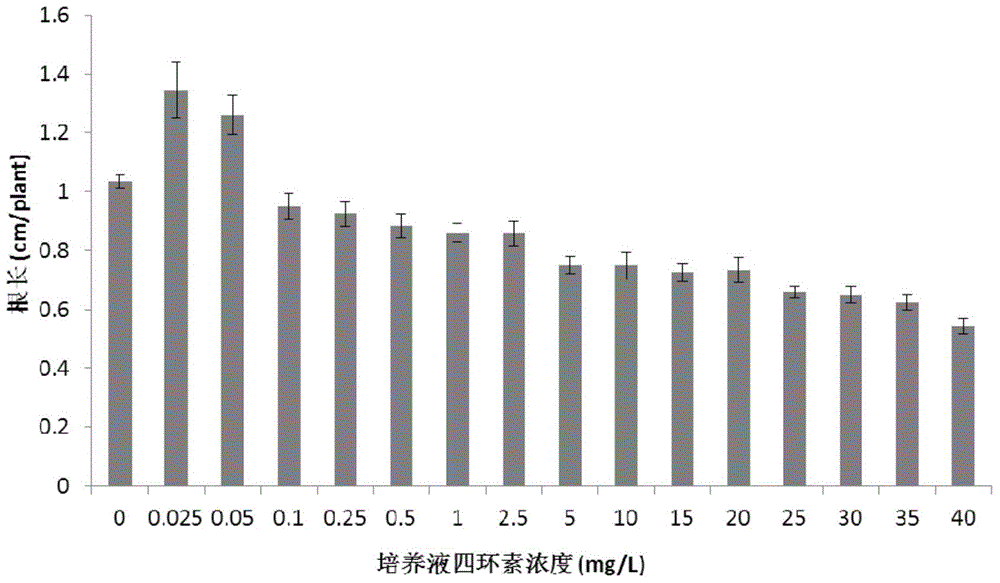
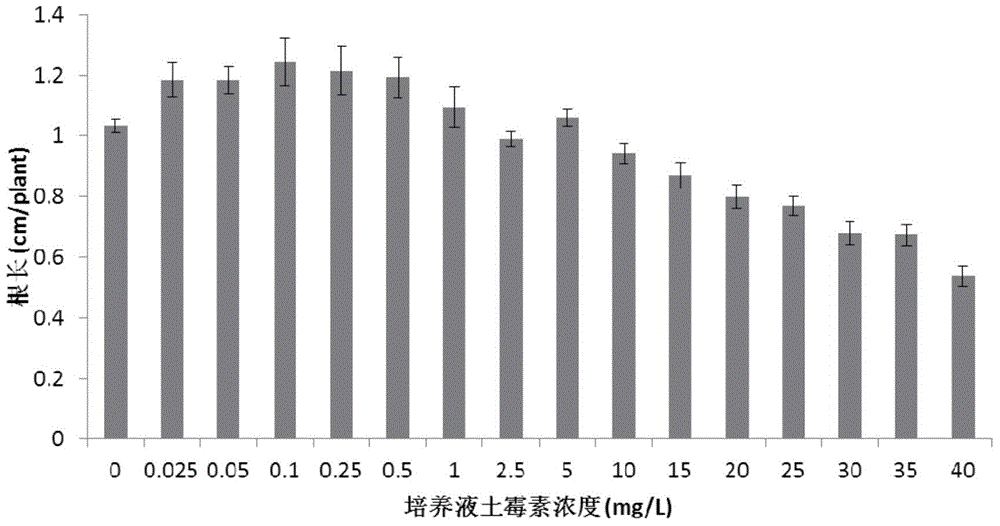
Method for diagnosing soil contamination by tetracycline antibiotics
InactiveCN104950094ASimple methodMethod is fast and cheapEarth material testingSoil contaminationPlanting seed
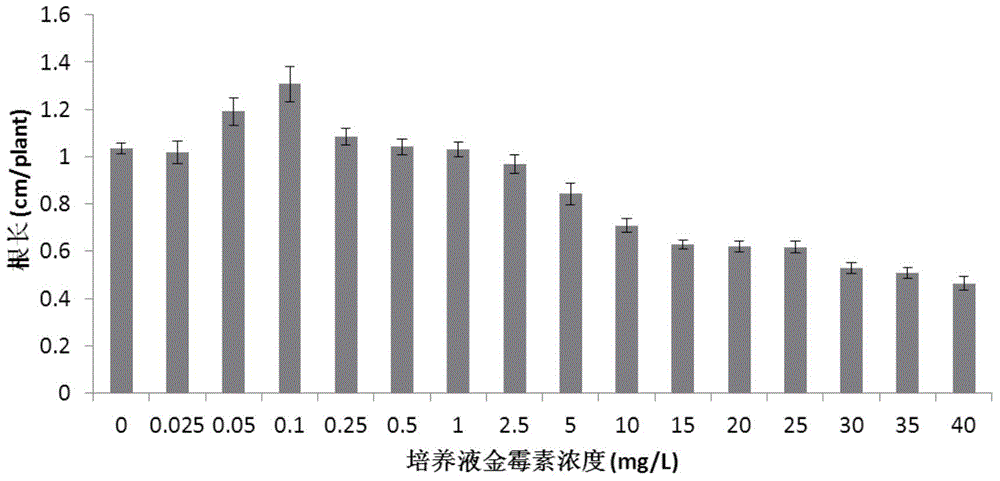
The invention discloses a method for diagnosing soil contamination by tetracycline antibiotics. The method includes the following steps: placing plant seeds in a group of soil with the antibiotic concentration being in gradient distribution for cultivation, after three days of cultivation, detecting the length of the root systems of the plant seeds and calculating the average value of the root length; establishing a relation curve between the antibiotics concentration in the soil and the average value of the root length; performing pretreatment on the to-be-detected soil containing antibiotics, placing plant seeds in the to-be-detected soil for cultivation, after three days of cultivation, detecting the length of the root systems of the plant seeds, and calculating the concentration of antibiotics in the to-be-detected soil according to the relation curve, wherein the plant seeds are Zaoshu No.8, the soil is blue purple clay soil, antibiotics are oxytetracycline and chlortetracycline, and the gradient range of antibiotic concentration in the soil is 0-5 mg.kg<-1>. The method provided by the invention can reflect the concentration of antibiotics in the to-be-detected sample, and has the characteristics of being simple, fast and low in cost, and the limitations of the traditional antibiotics detection method are overcome.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Organic fertilizer prepared from chlortetracycline residues and preparation method of organic fertilizer
InactiveCN109053238AEfficient use ofBio-organic fraction processingBioloigcal waste fertilisersOrganic contentOrganic fertilizer
The invention relates to a method for preparing an organic fertilizer from chlortetracycline residues. The method comprises the following steps: enzymolysis separation: adding a reaction enzyme into chlortetracycline residue paste, adjusting a pH value to 4-7 with an inorganic base solution after uniform mixing, and carrying out solid-liquid separation after the mixture is kept in a static state for 1-2 hours at a temperature of 20-30 DEG C to obtain chlortetracycline residues subjected to enzymolysis; fermentation: adding rice bran into the chlortetracycline residues subjected to enzymolysis,mixing uniformly, adding fermented compound bacteria, carrying out fermentation at a temperature of 20-70 DEG C, turning over the mixture every 2-4 days during the fermentation, and carrying out drying, sieving and granulation after the fermentation continues for 10-30 days to obtain the organic fertilizer. According to the organic fertilizer prepared with the technique, the organic content (on adry basis) is equal to or larger than 70.0%, the total nutrient content (N+P2O5+K2O, on a dry basis) is equal to or larger than 7.0%, and no chlortetracycline is detected.
Owner:FUJIAN FUKANG PHARMA
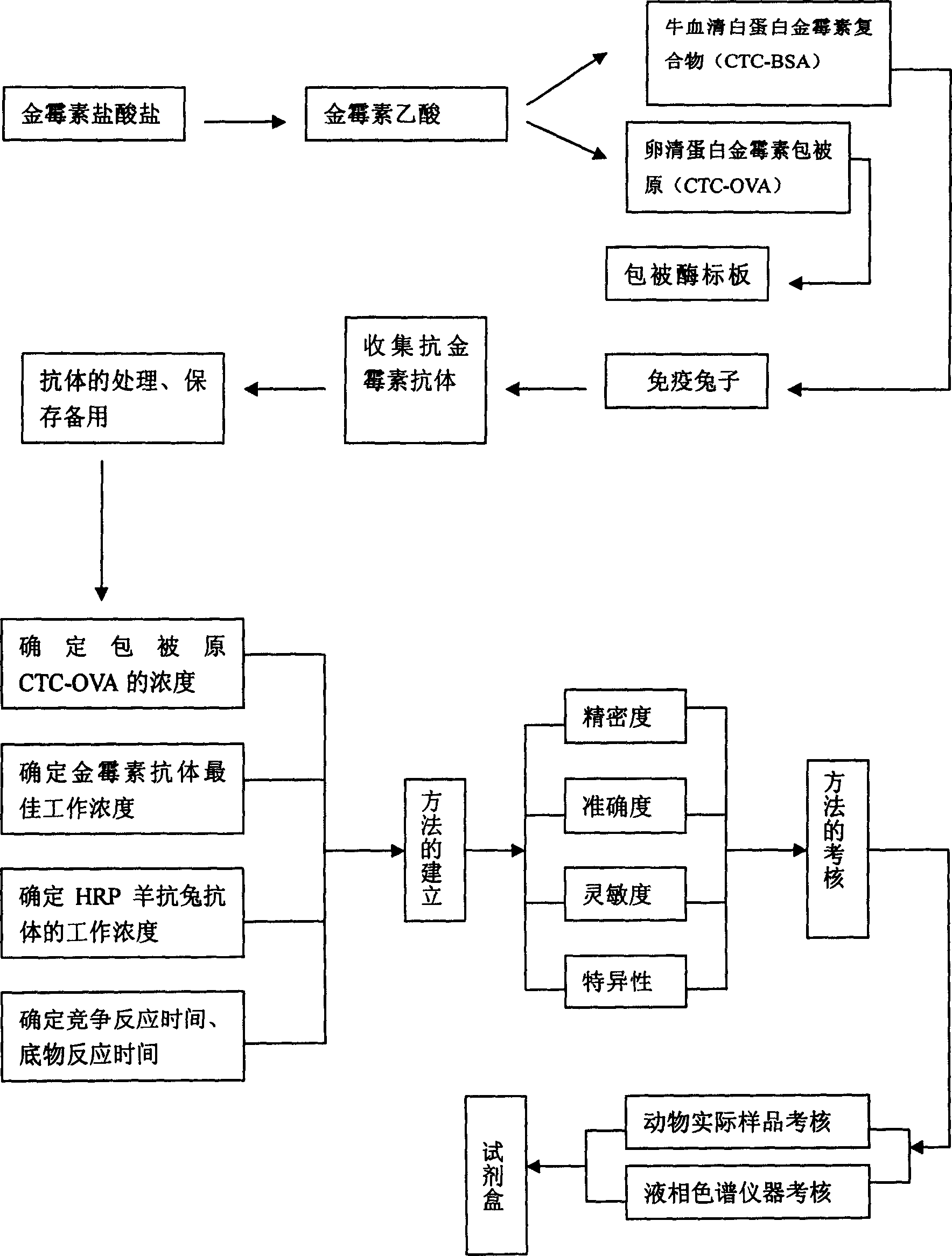
Enzyme-linked immune assay kit adapted to biomycin residue analysis and application
InactiveCN1811435AStrong specificityEffectively eliminate interferenceMaterial analysisAntigenBovine serum albumin
The present invention discloses an ELIA kit applicable to aureomycin recidue analysis and its application. Said kit includes kit body, enzyme-labelled plate and reagent, in which said reagent includes washing solution, sample diluent, horseradish peroxidase labeled antibody, substrate solution, color developing solution and stop buffer. The invented kernel lies in that it has the coated antigen, which is coated by coating solution and can be specifically reacted with aureomycin antibody, aureomycin standard solution and aureomycin antibody. Said antibody is the blood serum that is obtained by immunizing rabbit by utilizing artificial immune source, the coated antigen is the compound formed from aureomycin acetic acid and egg-white albumin, and the artificial immune source is the compound composed of aureomycin acetic acid and bovine serum albumin.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Chemiluminescence detection kit of aureomycin and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107543928AHigh sensitivityImprove featuresChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceBiological testingAntigenMicroparticle
The invention discloses a chemiluminescence detection kit of aureomycin and a preparation method thereof. The kit comprises the following components: an acridinium ester labelled aureomycin antigen orantibody, a magnetic particle coupled antibody or antigen, an aureomycin series standard substance solution, chemiluminescence preexcitation liquid A, chemiluminescence preexcitation liquid B, and cleaning fluid. The kit combines chemiluminescence technology and immunomagnetic particles, and provides a reaction system approaching to a homogeneous phase. Compared with the prior art, the kit has the advantages of high sensitivity, good specificity, short reaction time, and the like.
Owner:太原瑞盛生物科技有限公司
Detection method for antibiotic residual in livestock meat
InactiveCN107179357ASimplified processing stepsReduce processing costsComponent separationMuscle tissueCombined method
The invention discloses a detection method for antibiotic residual in livestock meat. The detection method comprises the following steps: cleaning the livestock meat, blowing moisture on a surface to be dry, and then, cutting the livestock meat into slices of which the thickness is about 0.1-1.0cm for standby; spraying solid weak base on the slices or spraying weak base aqueous solution on the slices; putting the slices in a drying oven to be dried at the temperature of 30-60 DEG C, taking out the slices when the moisture content is 30-50%, washing in distilled water for 1-3 times, and then, continuously drying until the moisture content of the slices is not higher than 10%; grinding the slices, adding extractant for extraction, carrying out centrifugation, and taking supernate; after the supernate passes through a microfiltration membrane, adopting a ultra-high performance liquid chromatography and mass spectrum combined method to measure the antibiotic residual, wherein the antibiotics can be oxytetracycline, tetracycline, doxycycline and aureomycin. The detection method is characterized in that the influence of high protein muscle tissues on an antibiotic recovery rate can be avoided especially in the early-stage treatment of a sample, and detection accuracy is high.
Owner:SUZHOU POLYTECHNIC INST OF AGRI
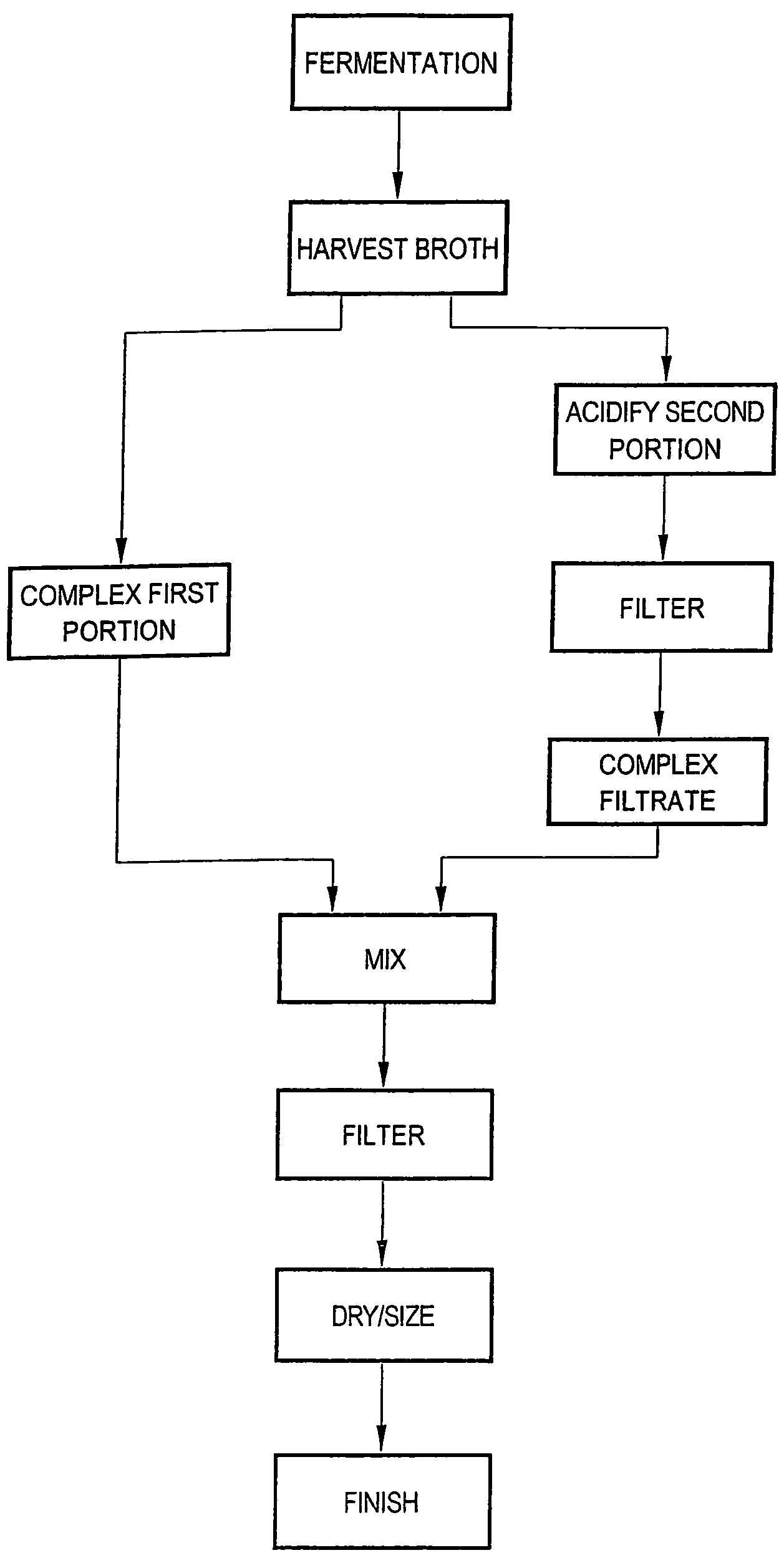
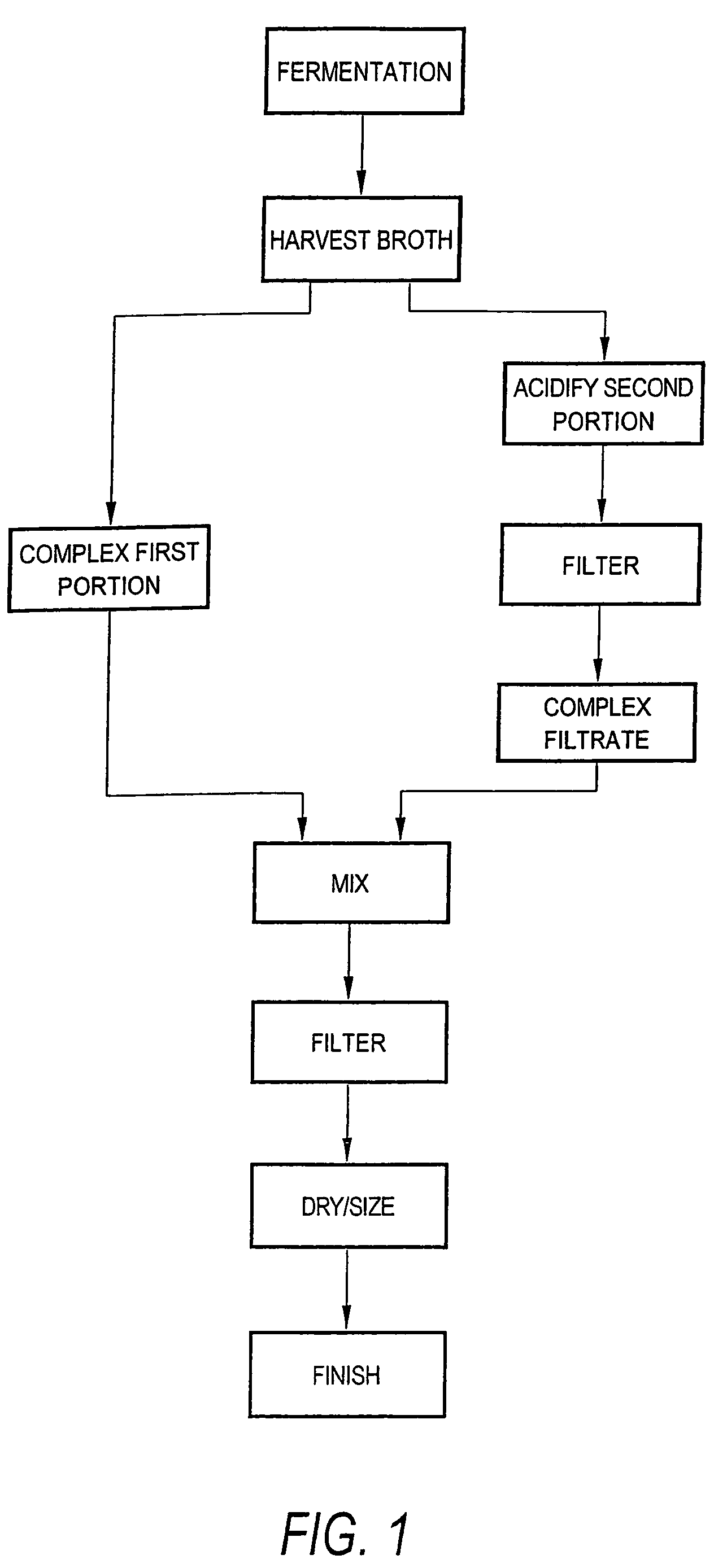
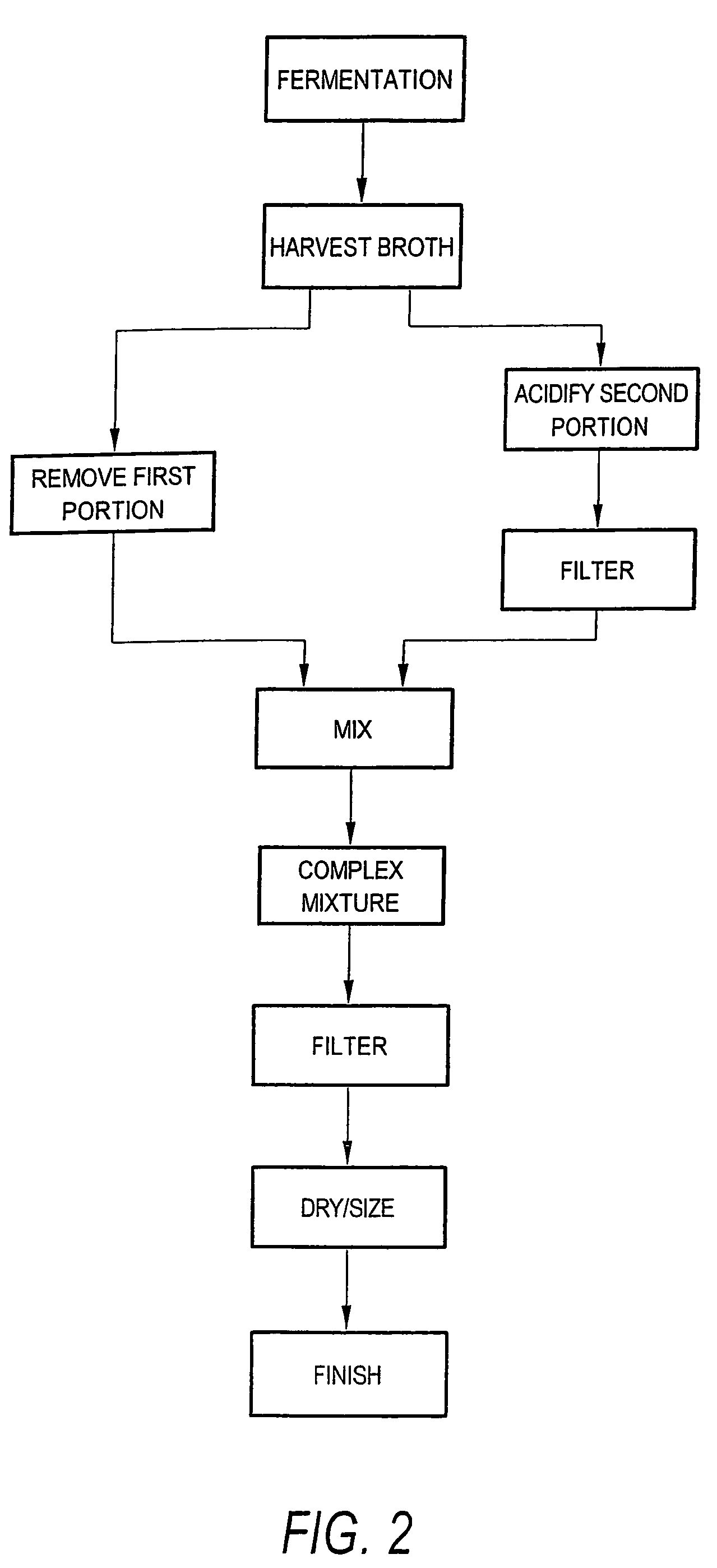
Process and apparatus for the preparation of chlortetracycline-containing animal feed compositions
InactiveUS7504112B1Less roomLess storage spaceBiocideAnimal feeding stuffChlortetracyclineIndividual animal
The present invention provides improved chlortetracycline-containing animal feed compositions and processes and apparatuses for their preparation. In certain embodiments, raw fermentation broth comprising chlortetracycline is divided into two portions. The first portion is mixed with a compound that complexes chlortetracycline. The second portion is acidified and the solids are removed. The acidified liquid is treated with a complexing agent to produced a chlortetracycline complex. The first and second portions thus treated are then mixed and the mixture is passed on to a filter press or other means for separation of the solids to produce a wet cake comprising complexed chlortetracycline. In alternative embodiments, the second portion may be acidified and filtered and admixed with the first portion prior to the complexing step. The resulting mixture is passed on to a filter press or other means for separation of the solids. In still further embodiments, the complexing steps are replaced with neutralizing or basification steps to yield the free base form of chlortetracycline. The wet filter cake comprising chlortetracycline and fermentation solids is dried and sized to produce a dried semi-finished product in the form of a powder, meal, granules, pellets, tablets, etc. The semi-finished product may be standardized to produce an animal feed supplement having a desired potency. In a further aspect, the present invention relates to a method of combating microbial infection and promoting growth in animals comprising orally administering to said animals an effective amount of an animal composition according to the present invention.
Owner:PENNFIELD OIL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com