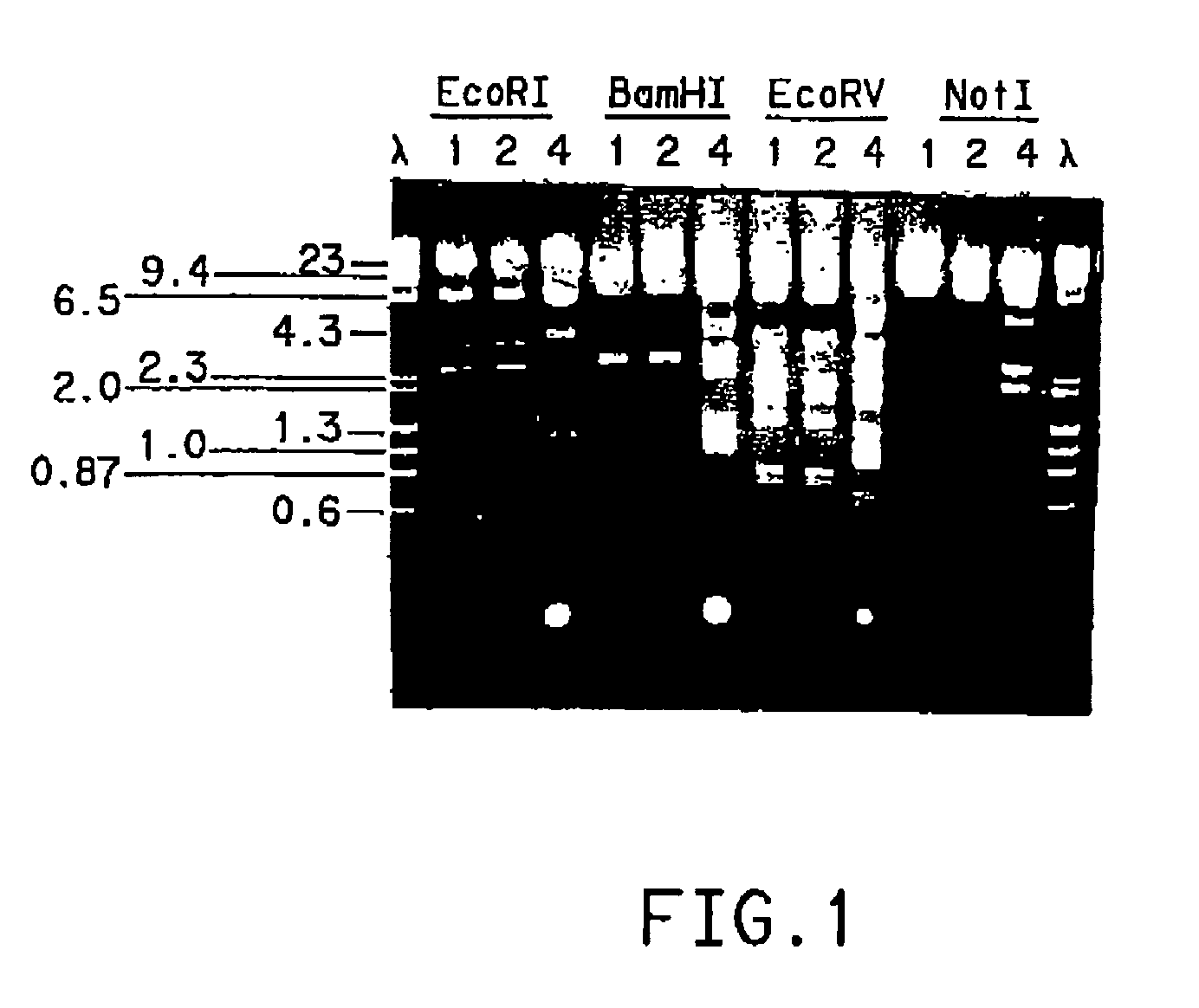
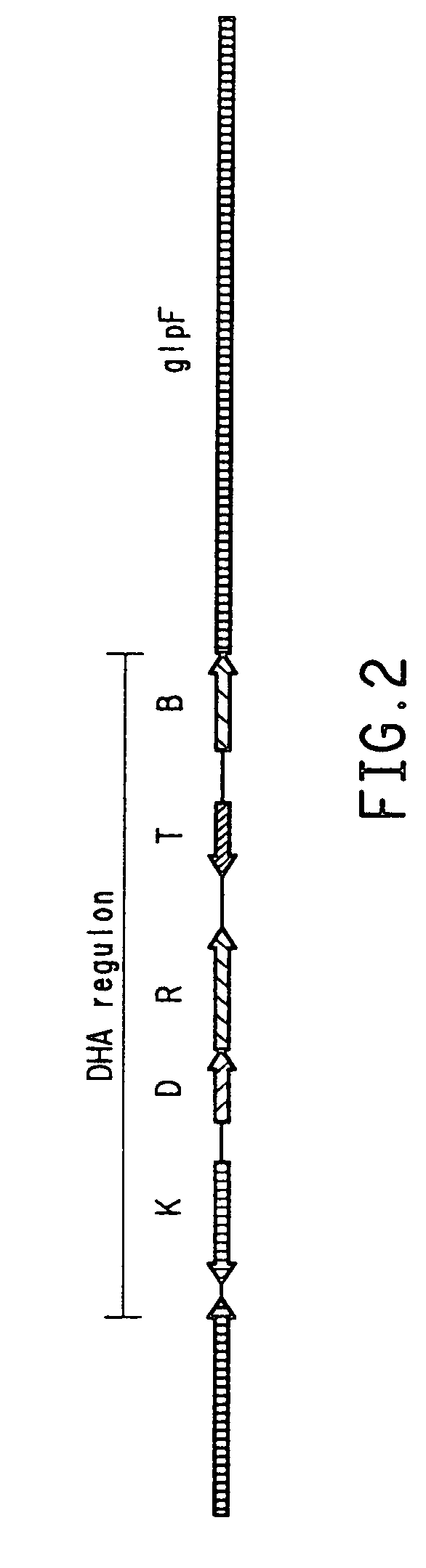
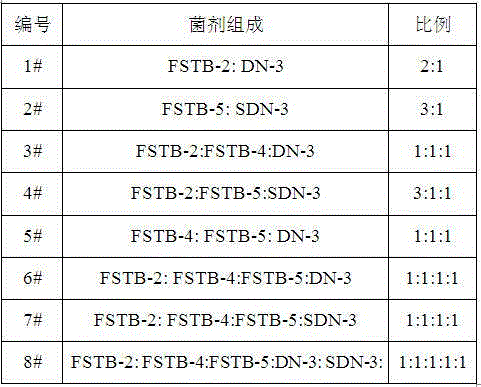
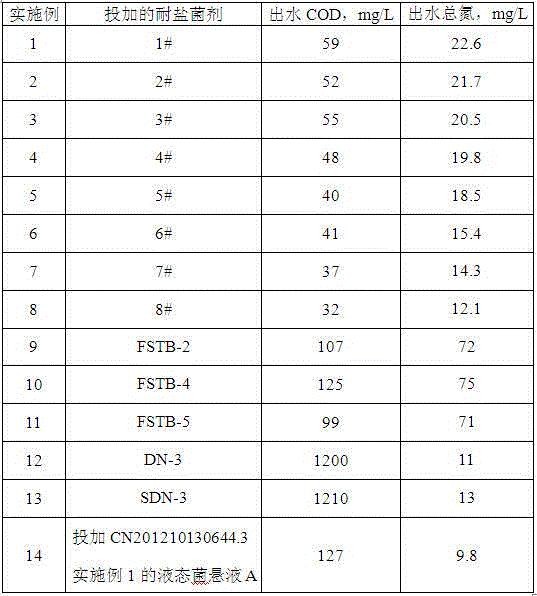
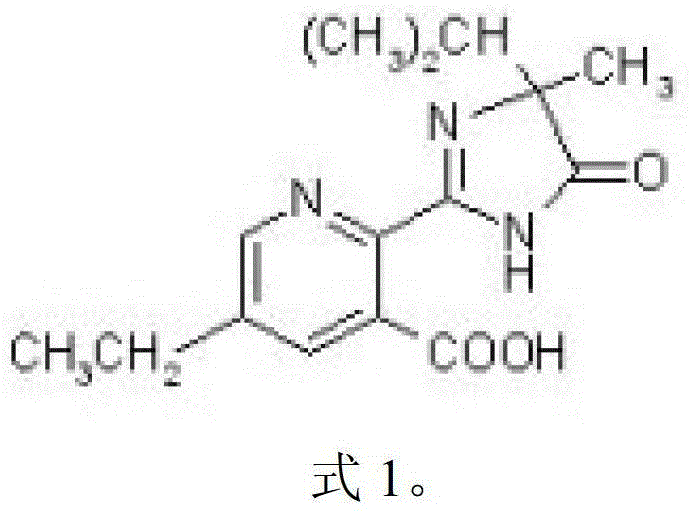
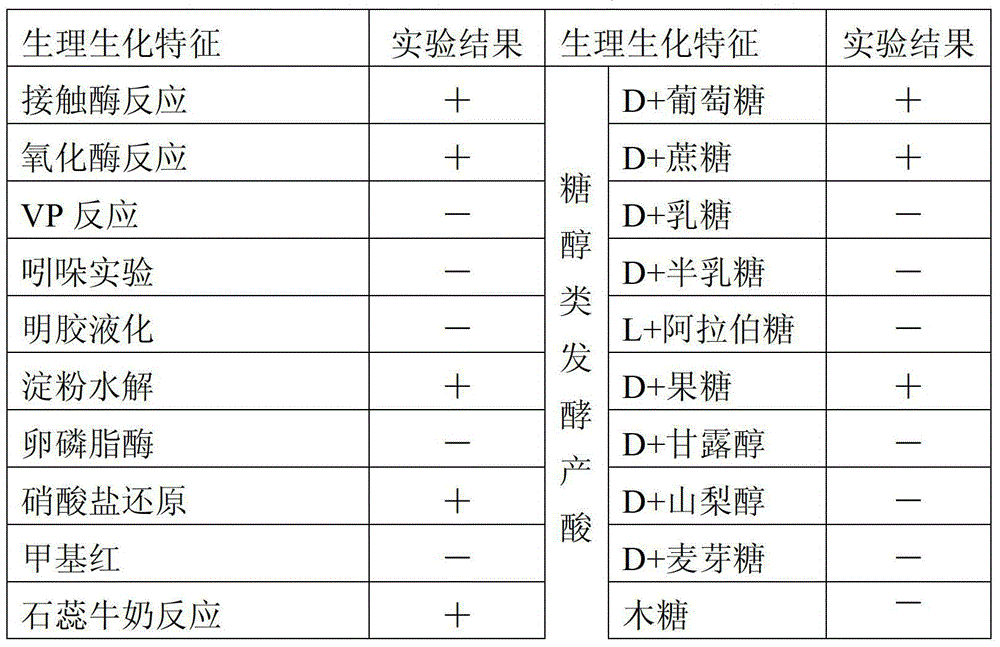
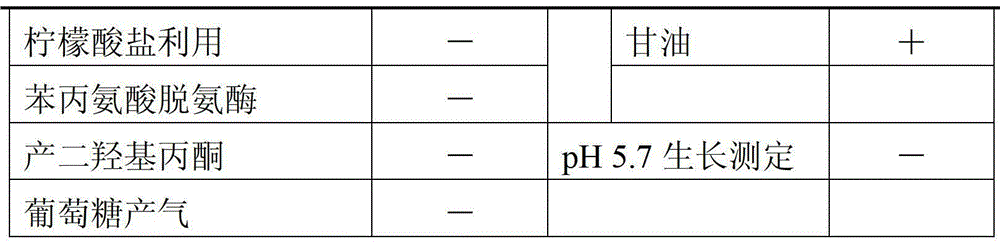
Patents
Literature
51 results about "Methylobacterium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The Methylobacteria are a genus of Rhizobiales. As well as its normal habitats in soil and water, Methylobacterium has also been identified as a contaminant of DNA extraction kit reagents, which may lead to its erroneous appearance in microbiota or metagenomic datasets.
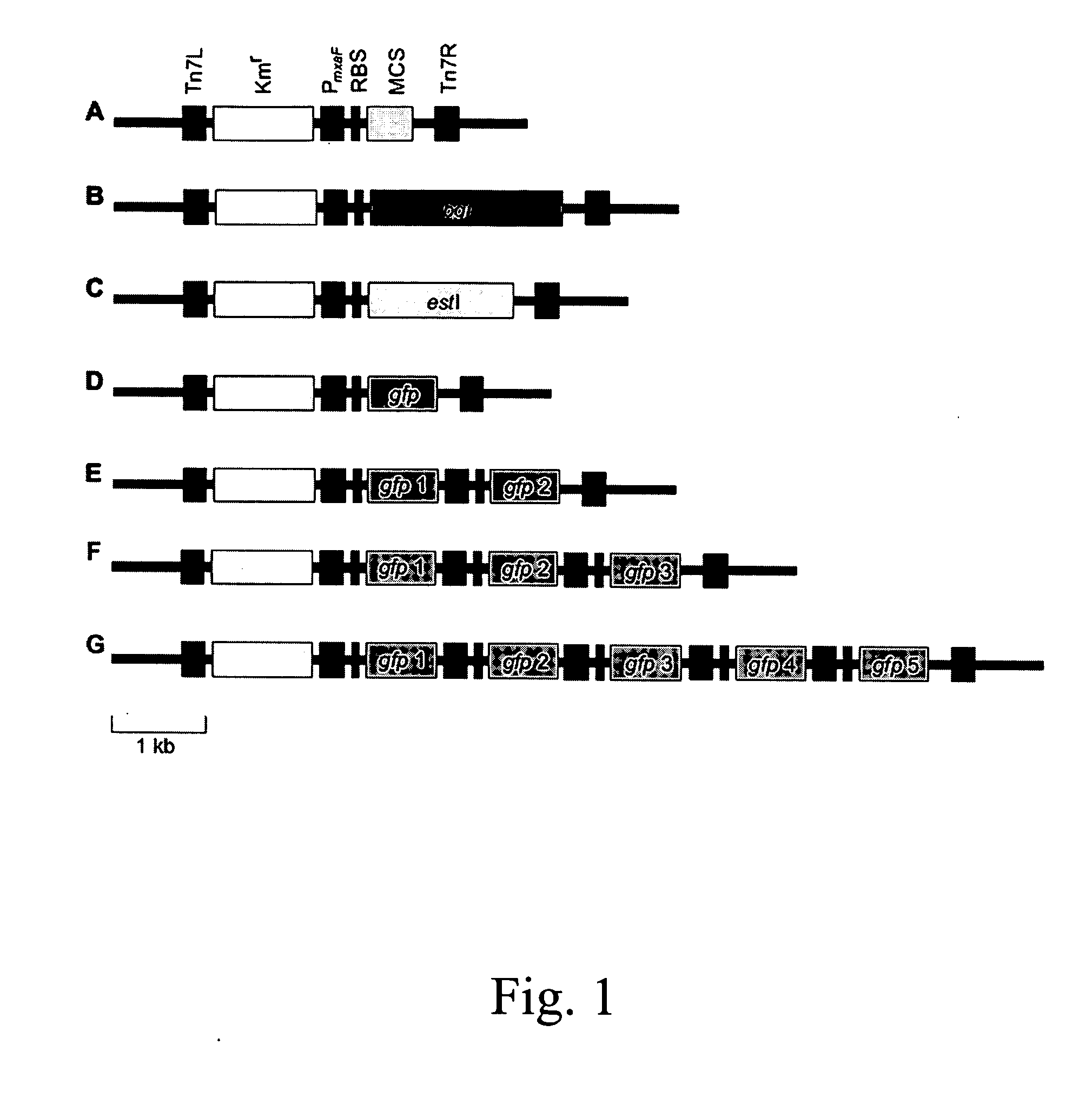
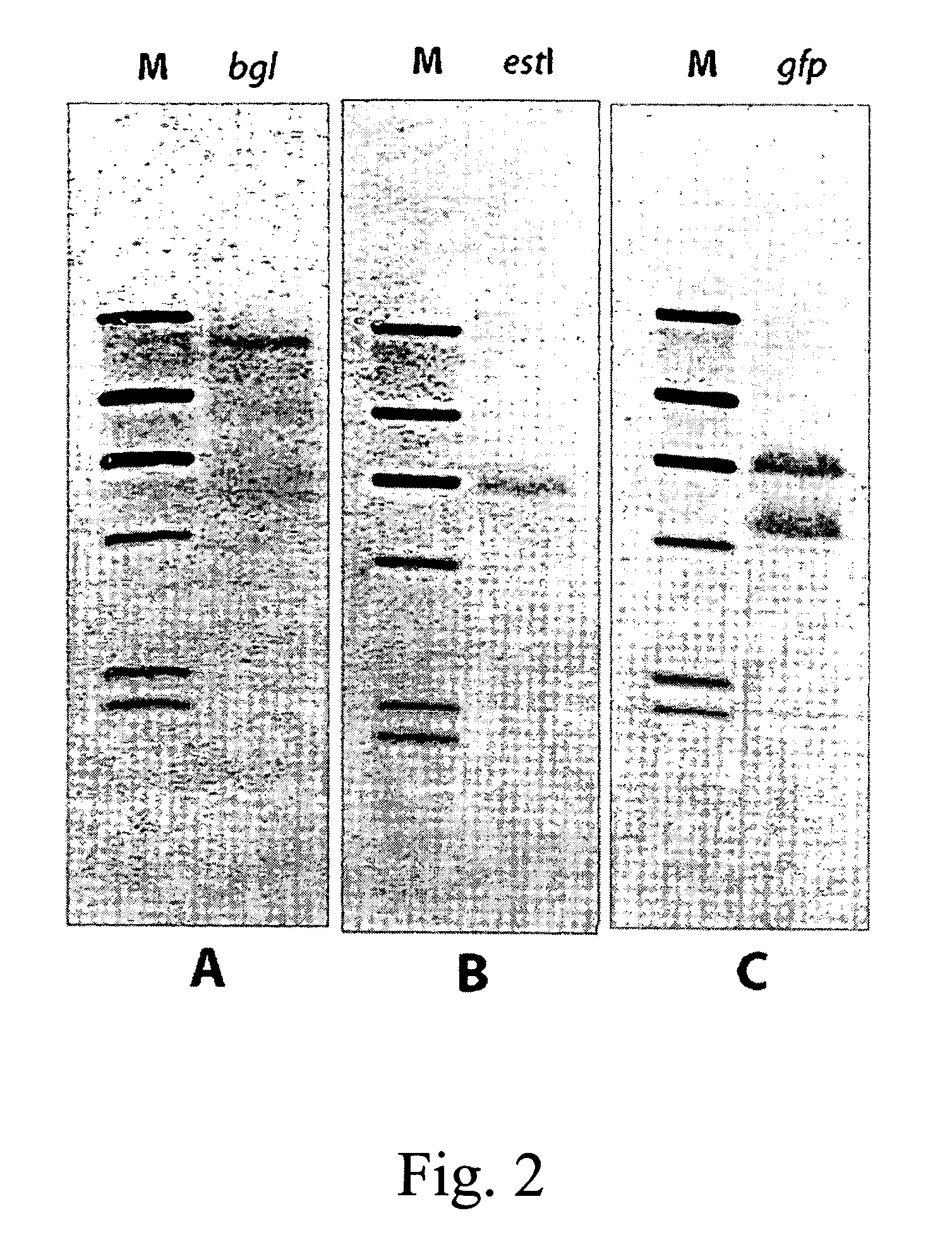
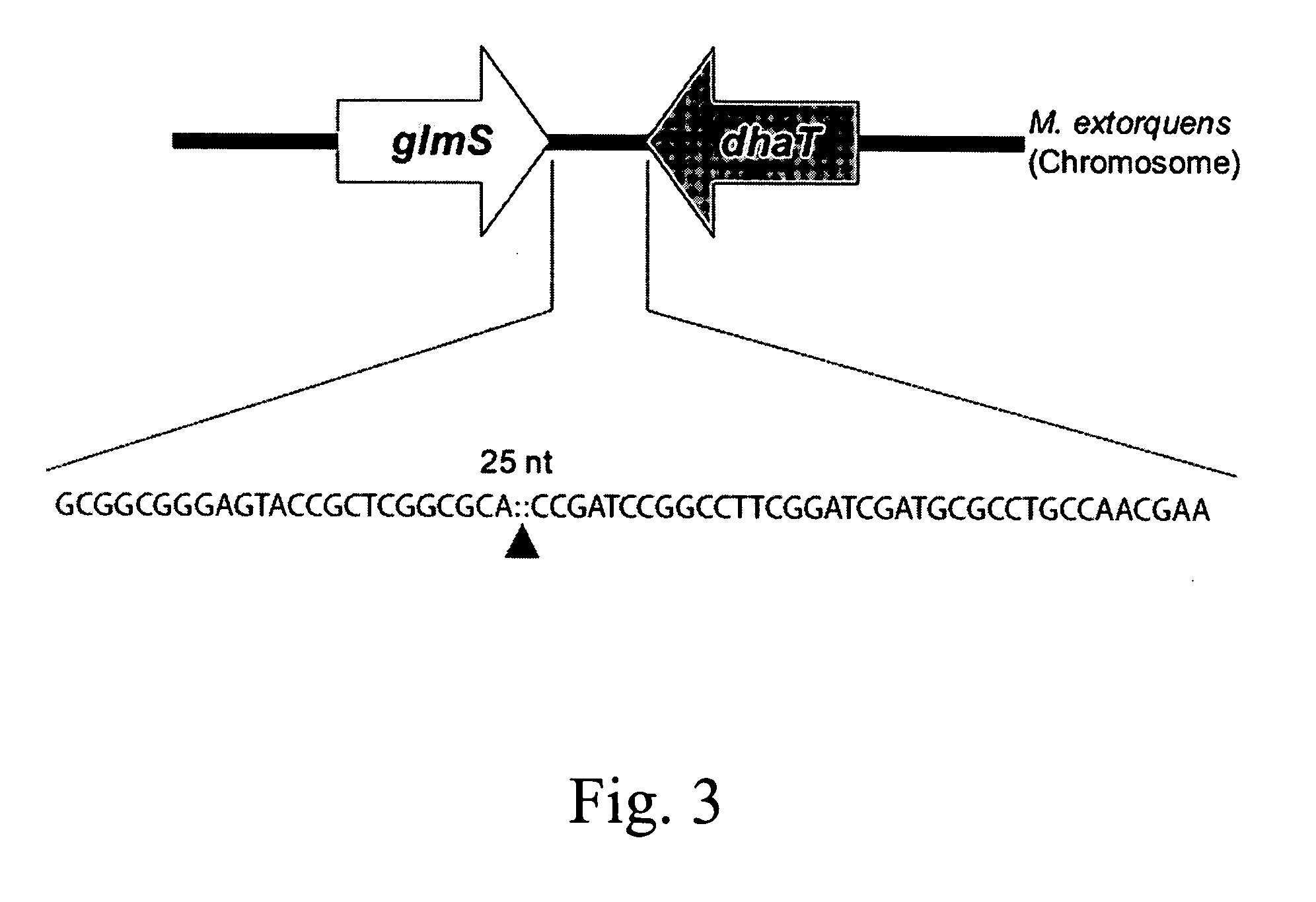
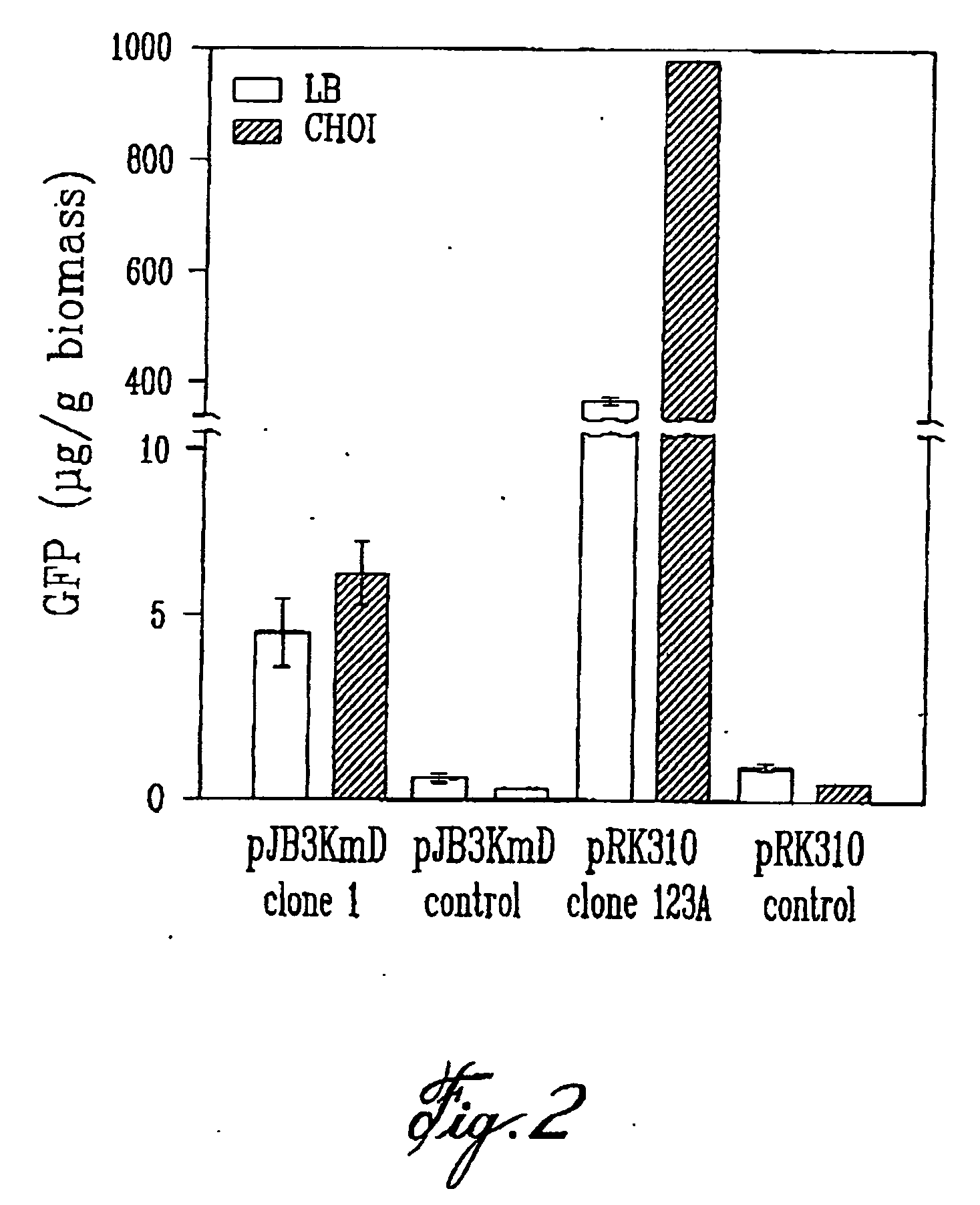
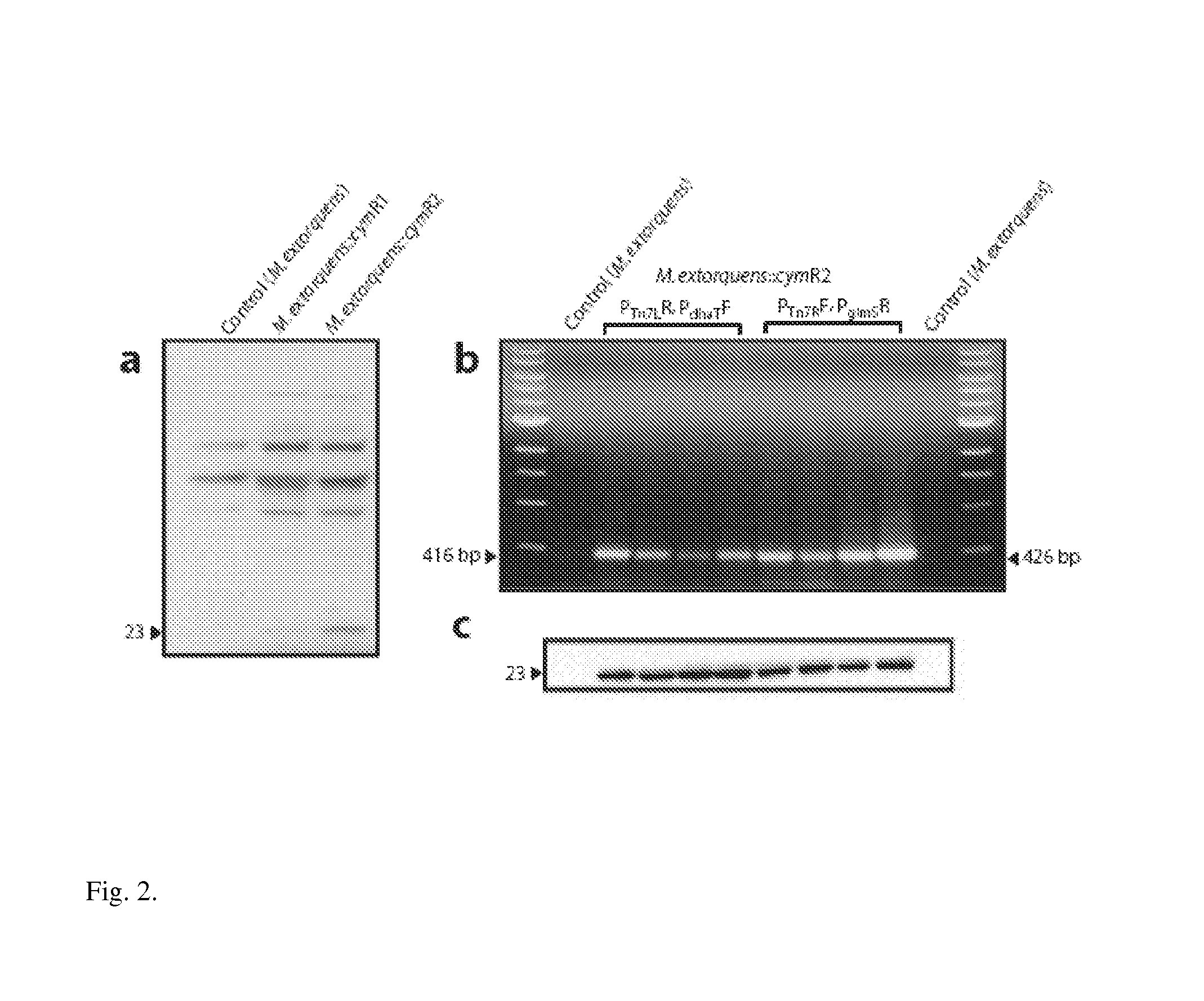
Multicopy-integration of heterologous genes and expression in methylobacterium
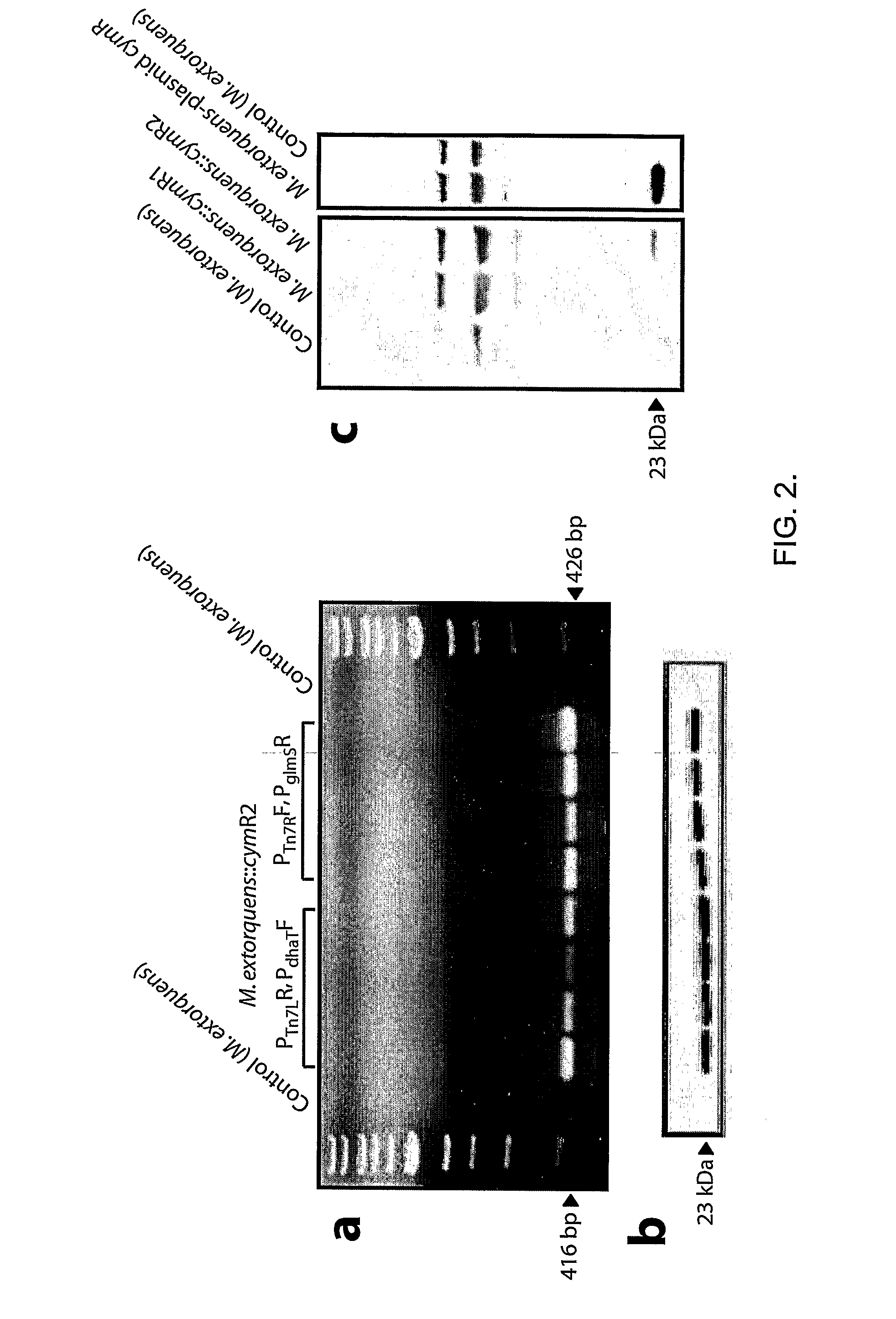
The integration of genes into methylobacterium, such as M. extorquens ATCC 55366 is disclosed, using a transposon system, preferably the mini-Tn7 transposon system, and under the control of a promoter, such as the strong methanol dehydrogenase promoter (PmxaF). Multicopy integration of genes of interest is also disclosed. The unique and specific attachment site for the Tn7 attachment (attTn7) is identified for M. extorquens.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
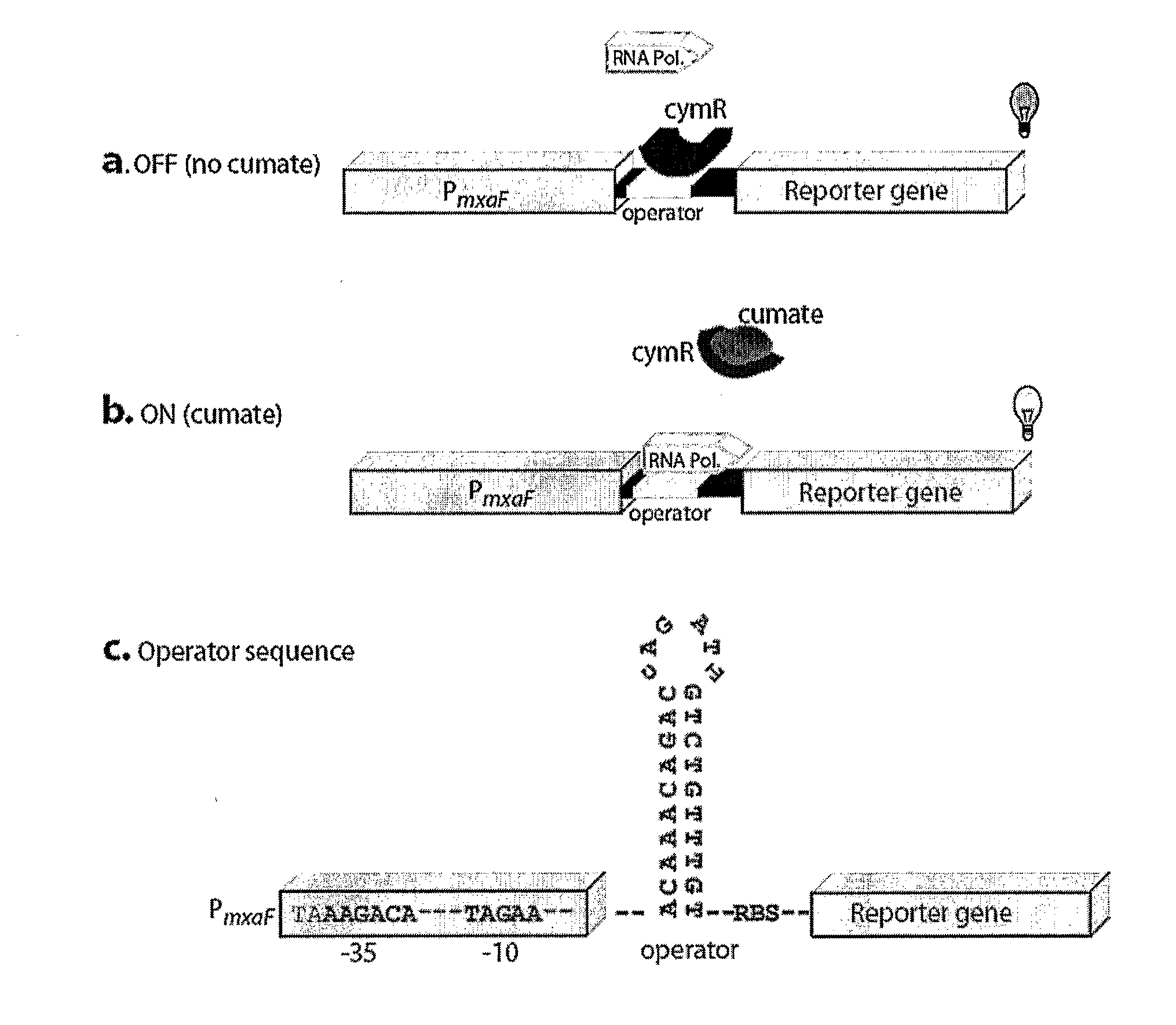
Regulation of heterologous recombinant protein expression in methylotrophic and methanotrophic bacteria
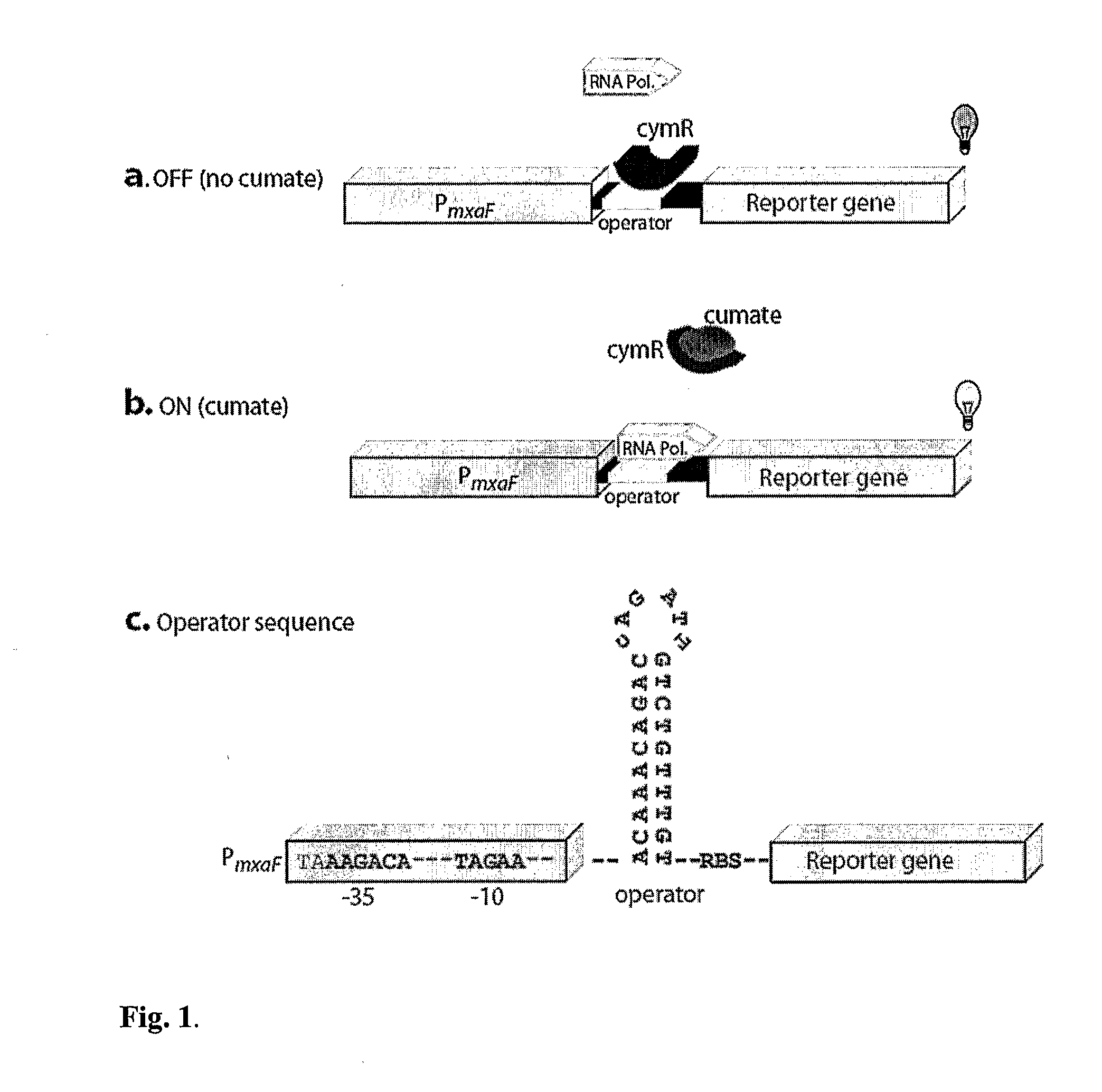
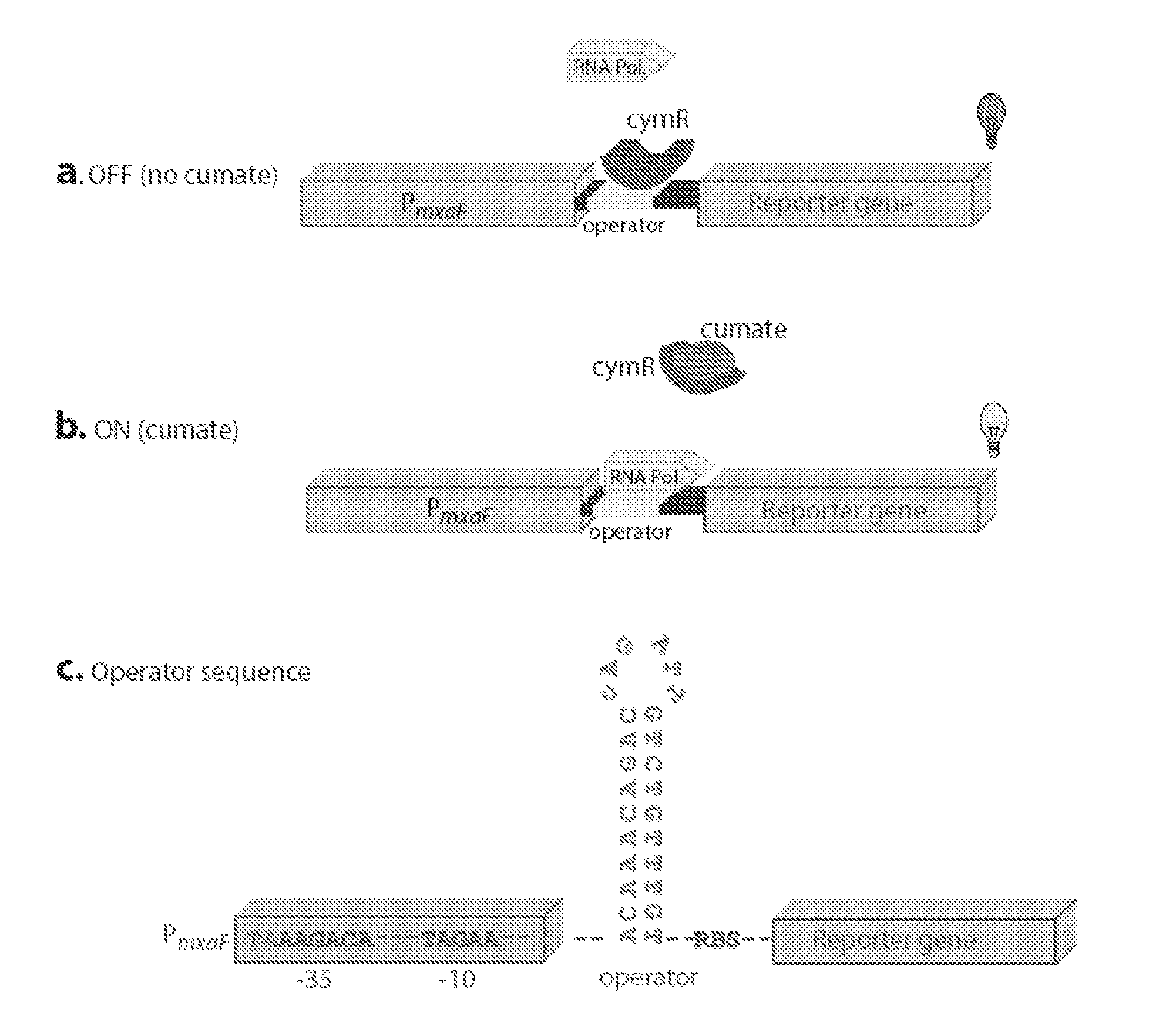
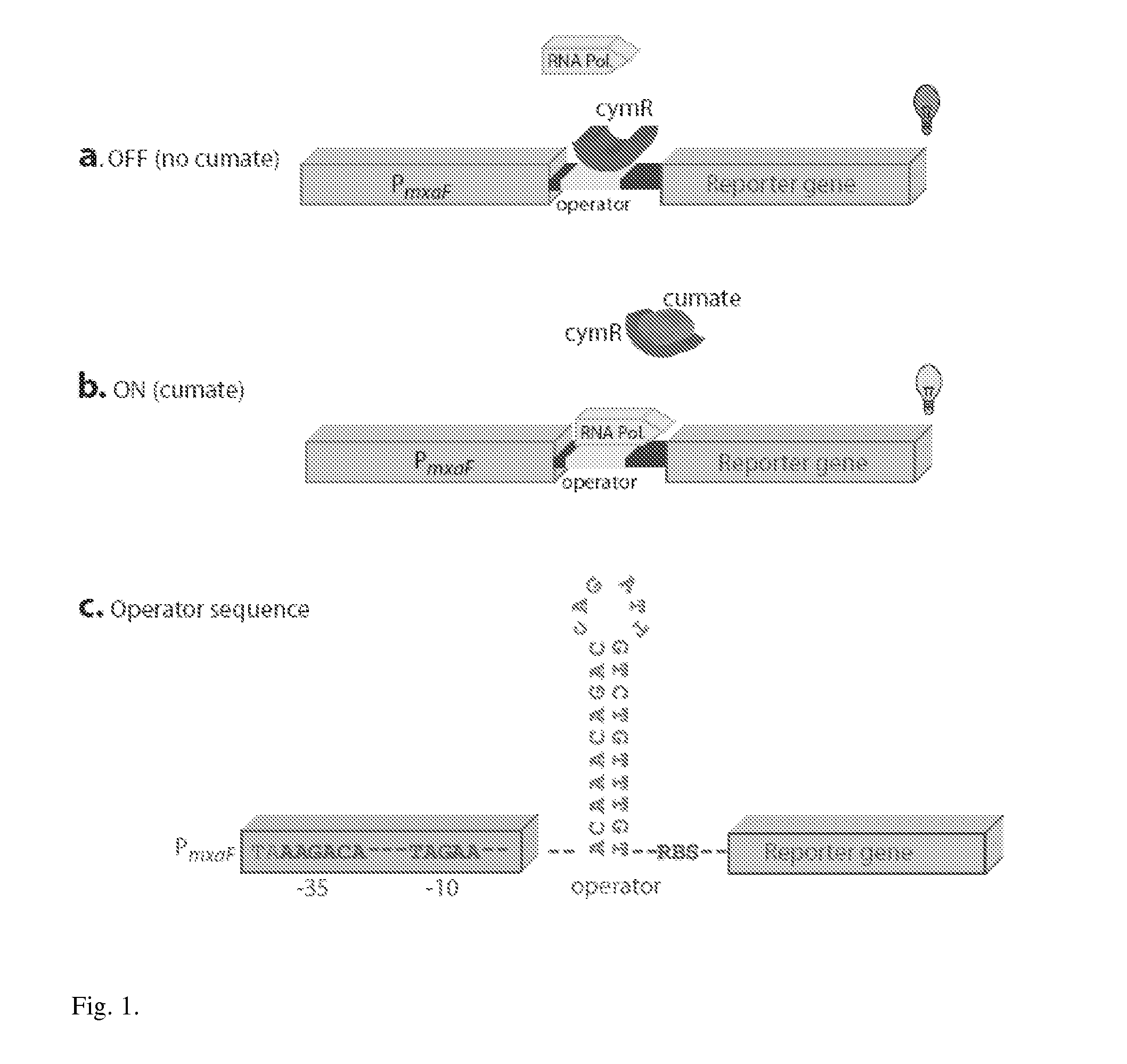
Methylotrophic or methanotrophic bacteria such as Methylobacterium are transformed with a gene of interest, and expression of the gene is regulated by means of a cumate repressor protein and an operator sequence which is operatively linked to the gene of interest, and the addition of an external agent. Specifically, the cymR repressor and cmt operator from Pseudomonas putida may serve to regulate gene expression in methylotrophic or methanotrophic bacteria with the addition of cumate.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
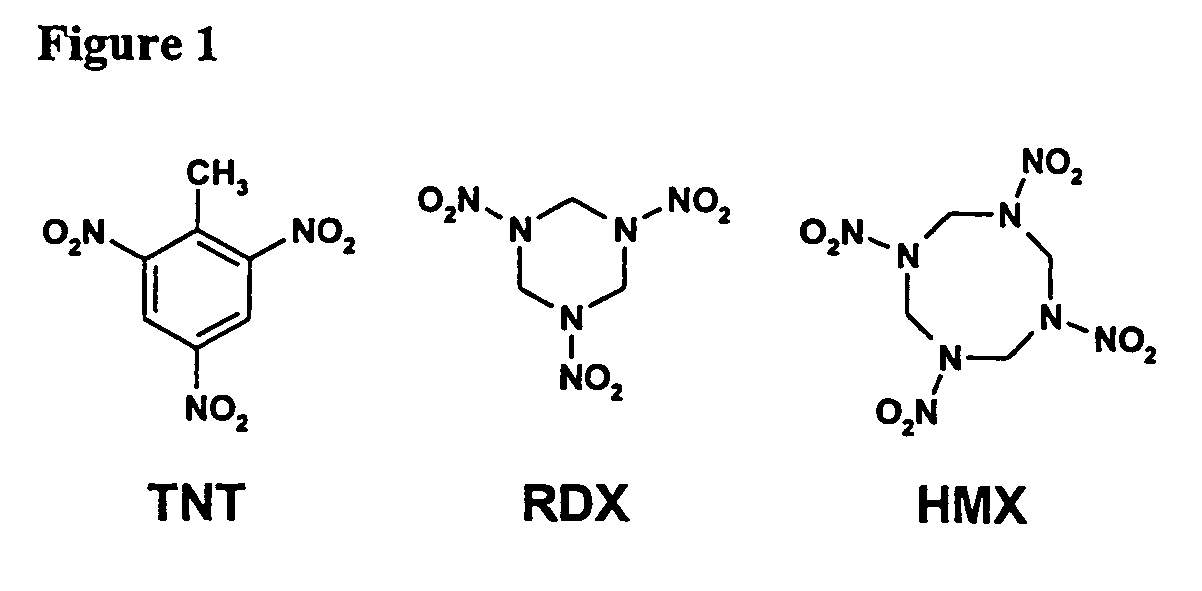
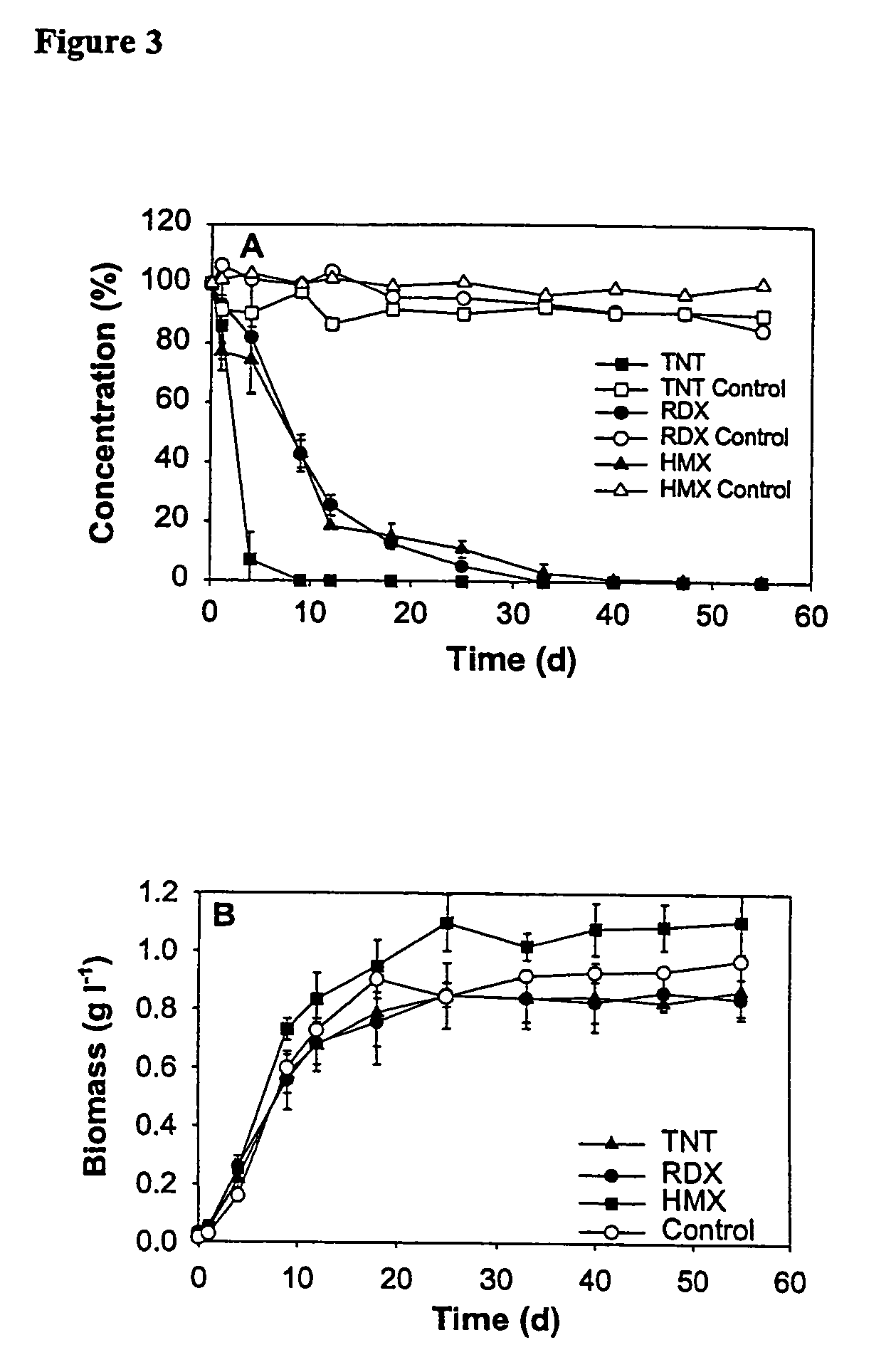
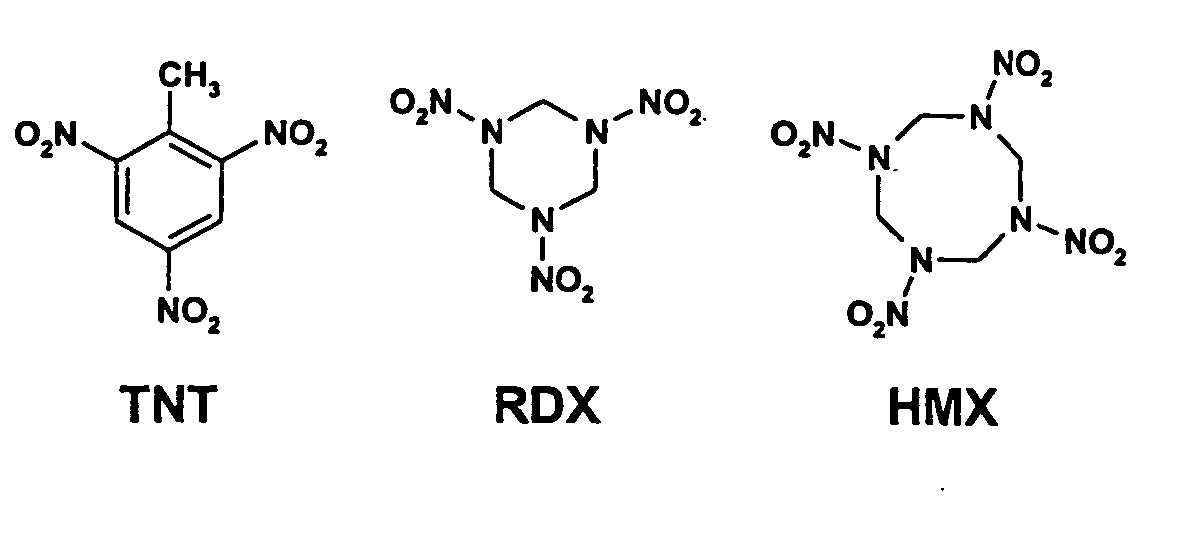
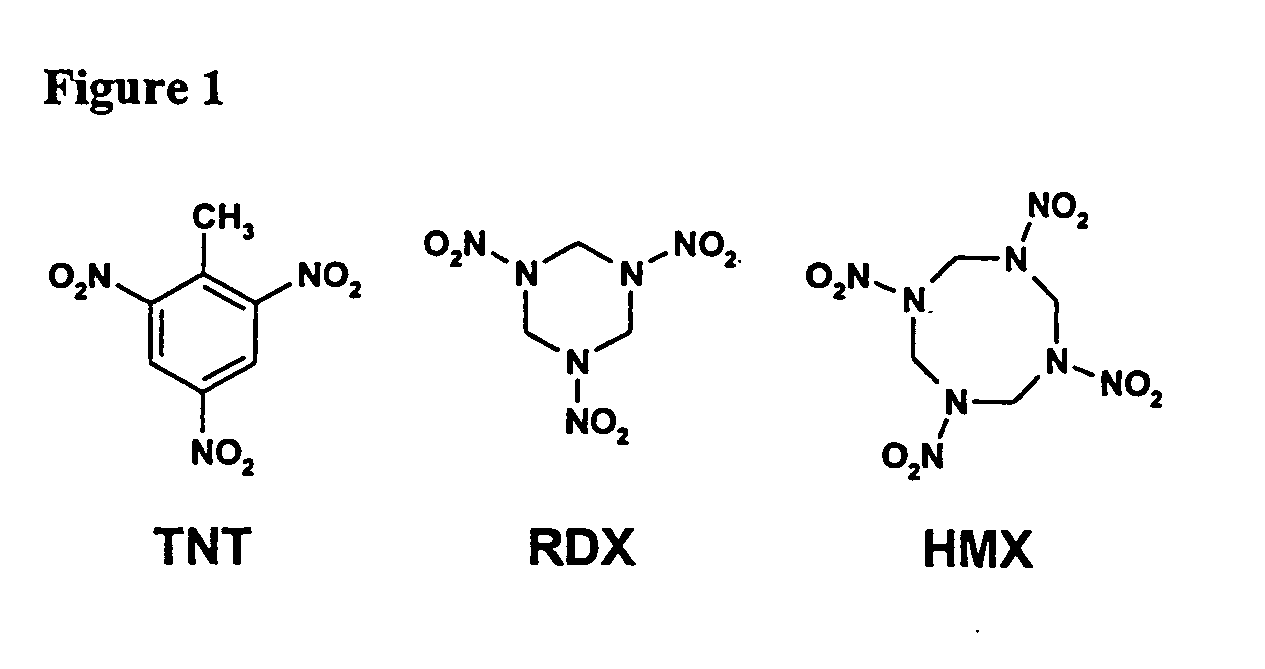
Methods and compositions for degradation of nitroaromatic and nitramine pollutants
InactiveUS7214509B2Low toxicityImprove abilitiesBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementNitroamineBioremediation
The invention relates to novel Methylobacterium species that are capable of degrading nitroaromatic and nitramine compounds. Compositions, kits and methods of using the Methylobacterium species for the degradation of nitroaromatic and nitramine pollutants are provided. More specifically, compositions and methods for the degradation or bioremediation of nitroaromatic and nitramine explosives and explosive residues are provided.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
Kitchen garbage degrading composite microbial inoculum and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106591178AEfficient degradationFast degradation rateBacteriaSolid waste disposalStaphylococcus cohniiStaphylococcus xylosus
The invention relates to a kitchen garbage degrading composite microbial inoculum and a preparation method and application thereof. The kitchen garbage degrading composite microbial inoculum is prepared by mixing a mixed inoculum of bacillus amyloliquefaciens, radiation-resistant methylobacterium, dispersed pantoea, pseudomonas oryzihabitans, citrobacter freundii and staphylococcus cohnii and a carrier, wherein the mass of the mixed inoculum accounts for 15-25% of the total mass of the kitchen garbage-degrading composite microbial inoculum; the mass ratio of the bacillus amyloliquefaciens, the radiation-resistant methylobacterium, the dispersed pantoea, the pseudomonas oryzihabitans, the citrobacter freundii and the staphylococcus cohnii is (1.5-3):(1-1.5):(1-1.5): (1-1.5):(1-1.5):(1-1.5); the kitchen garbage-degrading composite microbial inoculum is used for degrading kitchen garbage. Compared with the prior art, the kitchen garbage degrading composite microbial inoculum has the advantages as follows: the kitchen garbage degrading composite microbial inoculum can effectively degrade common vegetables, grains, fish, poultry meat and other kitchen garbage, has the degradation rate being above 80%, is high in degradation speed rate and small in odor, does not produce pollutants or poisonous substances, and is low in cost and stable in performance.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
Methods and compositions for degradation of nitroaromatic and nitramine pollutants
InactiveUS20050054030A1Improve abilitiesReduced activityBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBioremediationMethylobacterium
The invention relates to novel Methylobacterium species that are capable of degrading nitroaromatic and nitramine compounds. Compositions, kits and methods of using the Methylobacterium species for the degradation of nitroaromatic and nitramine pollutants are provided. More specifically, compositions and methods for the degradation or bioremediation of nitroaromatic and nitramine explosives and explosive residues are provided.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
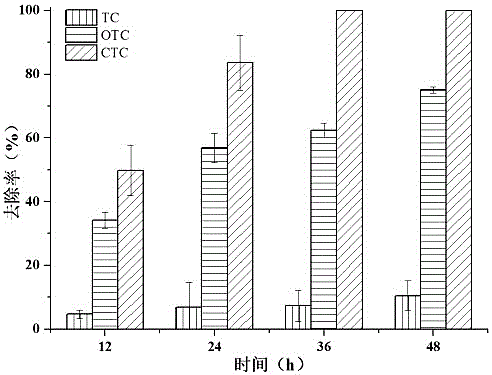
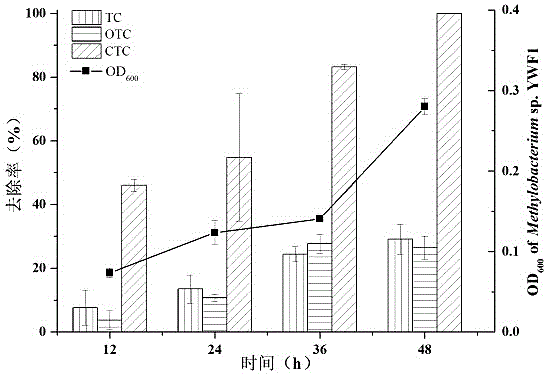
Degrading bacterium for TC (tetracycline) antibiotics and application of degrading bacterium
The invention relates to a degrading bacterium Methylobacterium sp. YWF1 capable of degrading three TC (tetracycline) antibiotics, namely, TC, OTC (oxytetracycline) and CTC (Chlorotetracycline) simultaneously. The degrading bacterium YWF1 is identified as Methylobacterium and was preserved in CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) on April 17, 2017 with preservation number being CGMCCNo. 14040. Methylobacterium sp. YWF1 can simultaneously degrade the three TC antibiotics, namely, TC, OTC and CTC, a microbial agent suspension can be prepared from the bacterium to be applied to degrading removal of TC antibiotic pollutants in different environment media such as livestock wastewater, TC pharmaceutical enterprise wastewater, medical wastewater or soil, and has good industrial application prospect and environmental benefits.
Owner:众心通慧(厦门)生态环保科技有限公司
Processes for the bioconversion of a fermentable carbon source to 1,3-propanediol by a single microorganism
A process is provided for the bioconversion of a carbon substrate to 1,3-propanediol by a single organism utilizing microorganisms, such as, Citrobacter, Enterobacter, Clostridium, Klebsiella, Aerobacter, Lactobacillus, Aspergillus, Saccharomyces, Zygosaccharomyces, Pichia, Kluyveromyces, Candida, Hansenula, Debaryomyces, Mucor, Torulopsis, Methylobacter, Escherichia, Salmonella, Bacillus, Streptomyces and Pseudomonas, containing the genes encoding for an active glycerol or diol dehydratase enzyme by contacting these organisms with a carbon substrate under the appropriate fermentation conditions. Specifically, Citrobacter and, Klebsiella provide the source of exogenous genes for such active dehydratase enzyme.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO +1
Salt-tolerant COD removal denitrifying microbial agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106635861ASimple compositionRapid cultivationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSynechococcusMicrobial agent
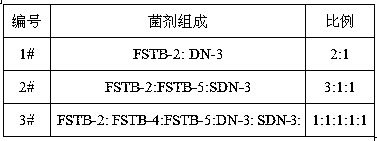
The invention relates to a salt-tolerant COD removal denitrifying microbial agent. The microbial agent consists of at least one of paracoccus sp FSTB-2, microbacterium kitamiense FSTB-4 and pseudomonas stutzeri FSTB-5, and further consists of at least one of paracoccus denitrificans DN-3 and methylobacterium phyllosphaerae SDN-3, wherein the paracoccus sp FSTB-2, the microbacterium kitamiense FSTB-4 and the pseudomonas stutzeri FSTB-5 are preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on June 1, 2015, with preservation numbers of CGMCC No.10938, CGMCC No.10939 and CGMCC No.10940; and the paracoccus denitrificans DN-3 and the methylobacterium phyllosphaerae SDN-3 are disclosed in CN102465104A and CN102465103, and the preservation numbers of the paracoccus denitrificans DN-3 and the methylobacterium phyllosphaerae SDN-3 are CGMCC No.3658 and CGMCC No.3660. The microbial agent can be used for directly processing total nitrogen and COD in high-salinity wastewater, and the microbial agent can be also added to various biochemical reaction constructions so as to improve microbiological composition, optimize the salt tolerance of a microbial system in wastewater treatment and improve total nitrogen and COD removal rate of the entire process.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Methylotrophs for aquaculture and animal feed
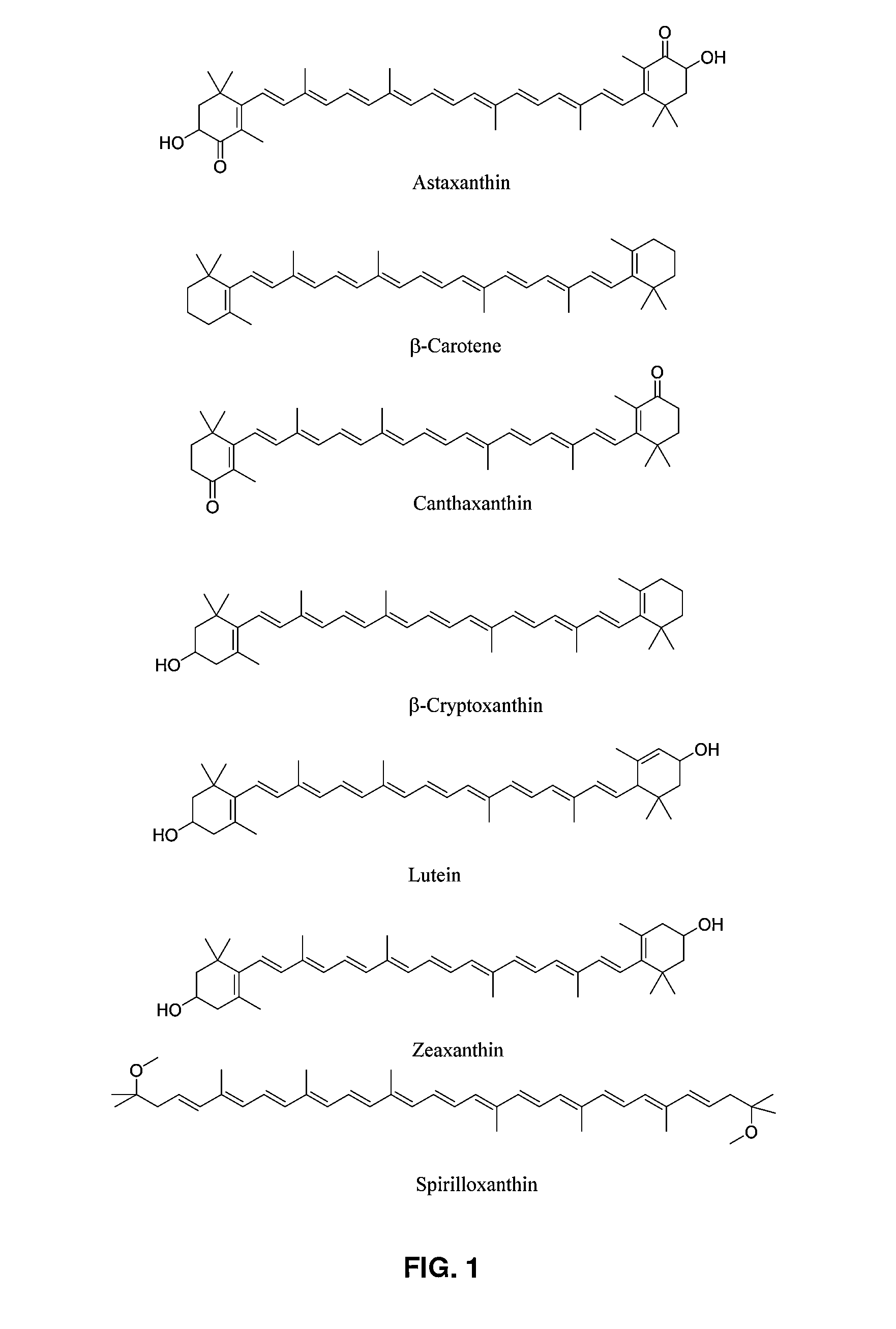
Disclosed are methods of producing carotenoid compounds in a methylotrophic bacterial host cell. Such a host cell may be an unmodified Methylobacterium, spontaneous mutant, or transformed cell, any of which exhibit favorable properties, such as overproduction of carotenoid compounds, increased carbon flux, improved growth, or the production of additional nutrients, such as protein, vitamins, antioxidants, or fatty acids. Also disclosed are feed compositions for use in aquaculture, or as animal feed, or as human nutritional supplements containing processed or unprocessed biomass from such cells, as are methods of preparation of the feed compositions.
Owner:KNIPBIO INC
Methylotrophic bacterium for the production of recombinant proteins and other products
InactiveUS20060234336A1Overcome problemsLow costSugar derivativesBacteriaMethylobacterium extorquensRecombinant peptide
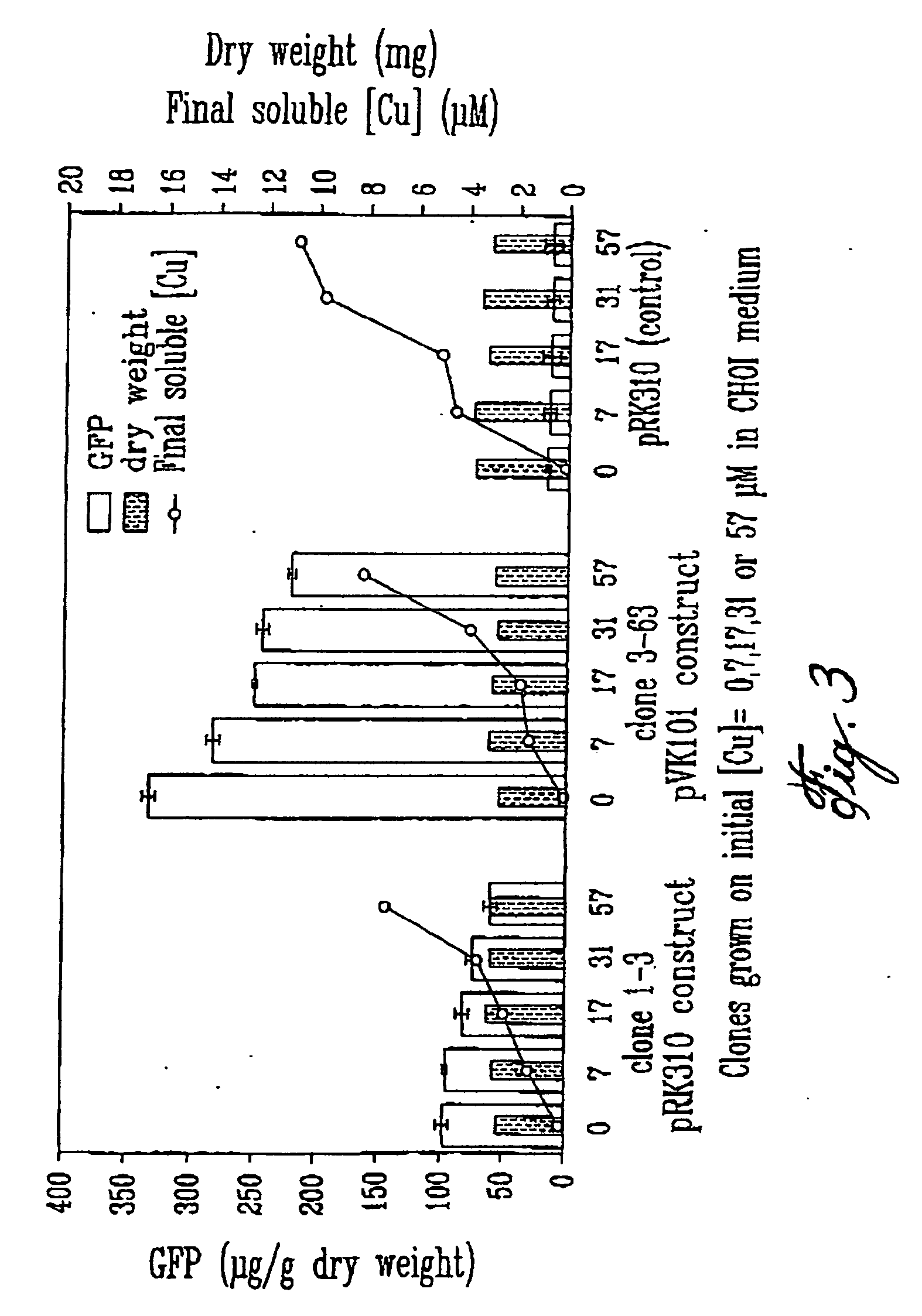
The present invention relates to a method of producing a recombinant peptide, a recombinant protein, or a product from metabolic engineering using a genetically modified methylotrophic bacterium, and more particularly to Methylobacterium extorquens ATCC 55366. The method comprises introducing am expression vector into the methylotrophic bacterium, the expression vector comprising a polynucleotide sequence, coding for a peptide or protein, or allowing for production of a product from metabolic engineering under the control of a regulated promoter. the method also comprises growing the genectically modified methylotrophic bacterium in a minimal salts medium lacking organic sugars and containing methanol. A metal ion may be used for regulating the expression of the polynucleotide sequence by the promoter.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WARWICK +1
Kitchen waste composite microbial degradation agent as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN111961606AEfficient degradationImprove microbial activityFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyAmylase
The invention discloses a kitchen waste composite microbial degradation agent as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The degradation agent is prepared from Bacillus subtilis, Streptomyces thermodiastaticus, Bacillus stearothermophilus, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Enteromorpha protease, Methylobacterium radiora, Pantoea dispersa, Pseudomonas oryzihabitans,Citrobacter freundii and Staphylococcus cohnii. The mixed strain accounts for 15-25% of the total mass of the degradation agent, the mass percentage of water in the degradation agent is 10-20%, the pH value of the degradation agent is 5.5-8.5, and each gram of the degradation agent contains 106-109 viable bacteria. The degradation agent has the beneficial effects that: kitchen waste containing various substances such as vegetables, grains and meat can be effectively degraded, the activity of microorganisms in the degrading agent is high, the degrading rate reaches 80% or above, the degradingrate is high, the use amount is small when the kitchen waste is treated, generated peculiar smells are small, the cost is low, use is convenient, toxic and harmful substances are not generated, and safety, reliability and environment friendliness are achieved.
Owner:人与自然环保生物科技(南京)有限公司
Methylobacterium strain and application thereof
InactiveCN108753660AReduce usageImprove protectionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMethylobacterium extorquensMicroorganism
The invention belongs to the technical field of microorganisms and particularly relates to a Methylobacterium strain and application thereof. The Methylobacterium strain has taxonomic name, Methylobacterium extorquens, collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on May, 21, 2018 under CGMCC No. 15777. Application of the Methylobacterium strain in the preparation of microbial fertilizers is also provided. Further, a microbial seed coating agent made with the Methylobacterium strain is provided. The Methylobacterium strain and application thereof have the advantages thatthe consumption of chemical fertilizers and pesticides in corn planting is decreased so that high yield is achieved; the Methylobacterium strain is more important to seeds that are inactivated easily.
Owner:MOON (GUANGZHOU) BIOTECH CO LTD
Vancomycin production wastewater treatment method
ActiveCN106746160AEfficient removalImprove processing efficiencyMultistage water/sewage treatmentStaphylococcus cohniiTotal nitrogen
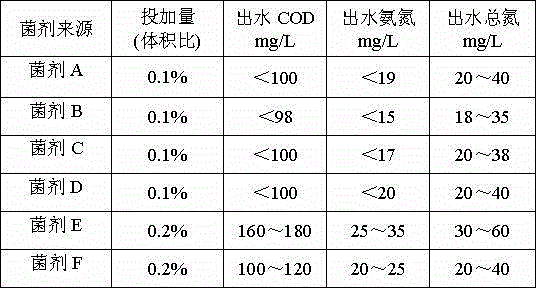
The present invention relates to a vancomycin production wastewater treatment method, which comprises: (1) carrying out coagulation precipitation treatment on vancomycin production wastewater, and filtering to remove precipitate; (2) carrying out anaerobic biochemical treatment on the effluent obtained in the step (1), and pouring Pseudomonas stutzeri FSTB-5; and (3) carrying out aerobic biochemical treatment on the effluent obtained in the step (2), and pouring a COD removing denitrogenation bacterial agent, wherein the COD removing denitrogenation bacterial agent comprises at least one selected from Pseudomonas stutzeri FSTB-5, Paracoccus denitrificans DN-3 and Methylobacterium SDN-3, at least one selected from Arthrobacter FDN-1 and Flavobacterium aquatile FDN-2, and at least one selected from Kocuria palustris FSDN-A and Staphylococcus cohnii FSDN-C. According to the present invention, the coagulation precipitation-anaerobic biochemical treatment-aerobic biochemical treatment combination treatment process is used, the specific COD removing bacterial agent is poured into the anaerobic unit, and the specific COD removing denitrogenation bacterial agent is poured into the aerobic unit, such that the efficient removal of the COD and the total nitrogen from wastewater is achieved, and the treatment method has characteristics of simple process, high treatment efficiency, low treatment cost, and the like.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method and bacterium for promoting the growth of racomitrium canescens and seed plants
InactiveUS20110028321A1Promote growthShorten the time periodPlant growth regulatorsBiocideProtozoaNicotiana tabacum
Disclosed are bacteria and methods for promoting growth of Racomitrium canescens, tobacco, barley and soybean. The bacteria are selected from the methanol-utilizing bacteria deposited under Accession numbers FERM BP-11078, FERM BP-11079, FERM BP-11080 and FERM BP-11071, respectively which bacteria belong to the genus Methylobacterium. The methods are a method for promoting growth of protonemata of Racomitrium canescens which method is characterized by culturing the protonemata in the presence of the bacteria and a method for promoting growth of a seed plant selected from the group consisting of tobacco, barley and soybean which method is characterized by culturing seeds of the seed plant while contacting the seeds with the bacterium deposited under Accession number FERM BP-11078 which is one of the above-mentioned bacteria.
Owner:UNIV OKAYAMA +1
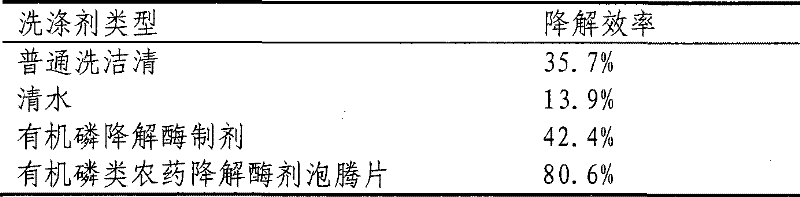
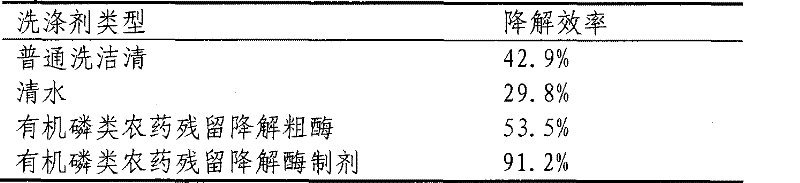
Organic phosphorus degrading enzyme preparation and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to microbe technology, in particular to a degrading enzyme preparation for degrading residual organic phosphorus on vegetables and fruits and a preparation method thereof. The invention particularly relates to organic phosphorus degrading enzyme preparation obtained by fermenting Methylobacterium. The preparation process comprises the following steps: after fermenting the inoculated strain, centrifugally collecting thalli, and breaking thalli to obtain the organic phosphorus degrading enzyme preparation. The organic phosphorus pesticide degrading enzyme preparation can degrade residual organic phosphorus pesticides on vegetables and fruits.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Treating method for reverse osmosis (RO) concentrated water
ActiveCN108117221ASolve removal puzzlesReduce concentrationMultistage water/sewage treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentMicrobial agentReverse osmosis
The invention relates to a treating method for RO concentrated water. The treating method mainly comprises the following steps: (1) treatment with an advanced oxidation unit: subjecting RO concentrated water to advanced oxidation to improve the biodegradability of the RO concentrated water; and (2) biologically strengthened treatment: allowing the RO concentrated water having undergone advanced oxidation to enter a biologically strengthened treatment unit, and adding a salt-tolerant COD-removing denitrifying microbial agent into a treatment system, wherein the microbial agent comprises at least one selected from a group consisting of Paracoccus sp. FSTB-2, Microbacterium kitamiense FSTB-4 and Pseudomonas stutzeri FSTB-5, and further comprises at least one selected from a group consisting of Paracoccus denitrificans DN-3 and Methylobacterium phyllosphaerae SDN-3. The treating method of the invention adopts a combination of an advanced oxidation treatment process and a biologically strengthened treatment process, and the salt-tolerant microbial agent is added into the biologically strengthened treatment unit, so COD and total nitrogen in the RO concentrated water are both removed efficiently, and effluent meets emission requirements.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Biological processing method of ammonia-containing wastewater
ActiveCN105712487AImprove impact performanceEasy to handleWater contaminantsBiological water/sewage treatmentStaphylococcus cohniiMicrobial agent
The invention discloses a biological processing method of ammonia-containing wastewater. According to the method, sludge in sewage disposal plants is taken as the microbial carrier, a denitrification microbial agent is added under MLSS of 2000 to 3000 g / L; when the removal rate of ammonia nitrogen reaches 50 to 70%, the DO is reduced to 1.0 to 2.0 mg / L, and when the removal rate of ammonia nitrogen reach more than 80%, the DO is reduced to 0.1 to 1.0 mg / L. The microbial agent comprises Arthrobacter creatinolyticus FDN-1, Flavobacterium mizutaii FDN-2, Paracoccus denitrificans DN-3, Methylobacterium phyllosphaerae SDN-3, Kocuria palustris FSDN-A, and Staphylococcus cohnii FSDN-C. According to denitrification characteristics of added microbial agent, the concentration of dissolved oxygen (DO) is controlled so as to efficiently remove ammonia nitrogen and total nitrogen in a reactor; moreover, degradation-resistant organic pollutants in wastewater can be removed efficiently, and the effluent quality is improved.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Biological air purifier
PendingCN108131736AImprove economyEnvironmentally friendlyMechanical apparatusLighting and heating apparatusOrganic compoundPhotosynthetic bacteria
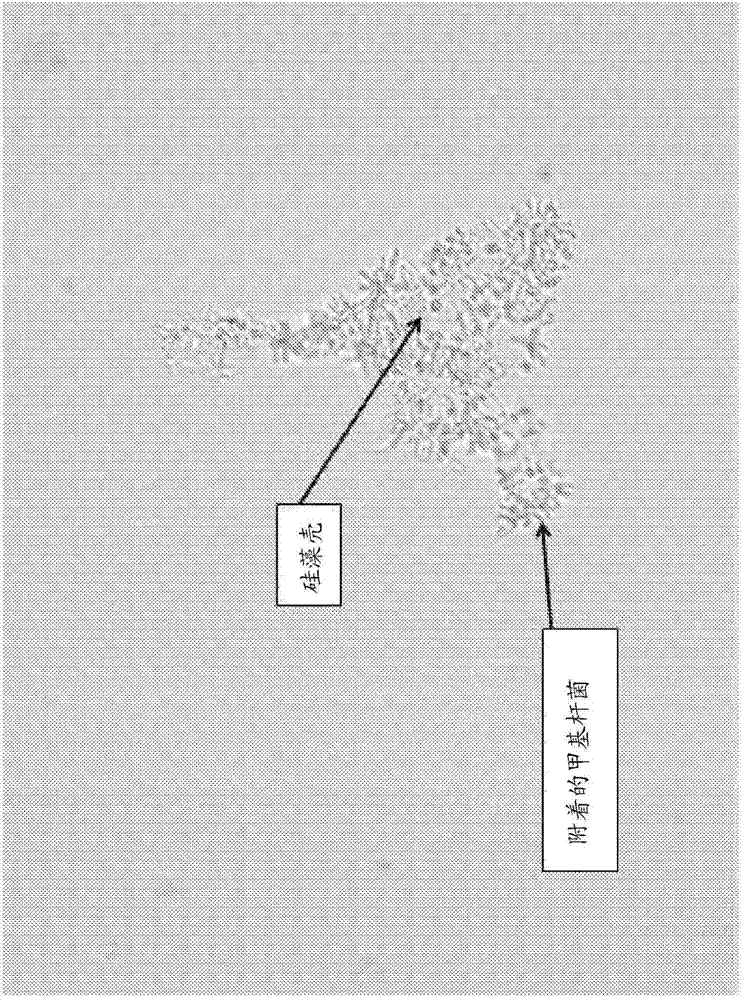
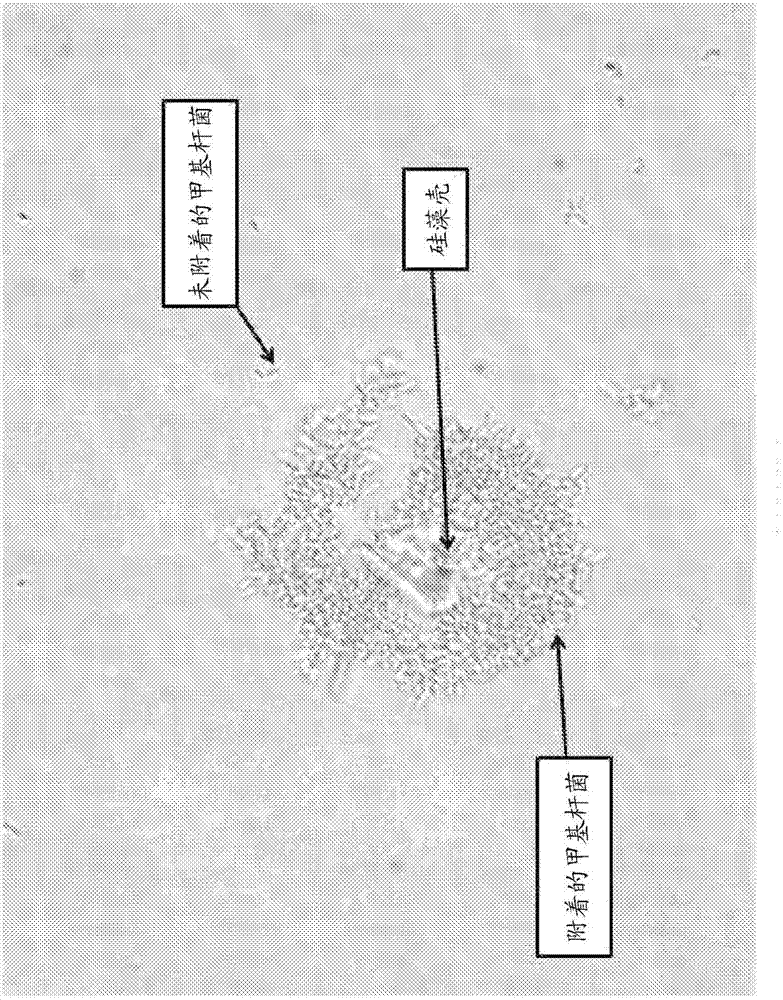
The invention relates to a biological air purifier, and belongs to the technical field of air purification. Methylobacterium sponge balls are obtained in the mode that methylobacterium having specificformaldehyde metabolic pathways and capable of removing pollution benzene series and improved photosynthetic-bacterium inorganic salt culture media are embedded and fixed with sodium alginate and carboxymethyl cellulose, photosynthetic-bacterium sponge columns are obtained in the mode that photosynthetic bacteria having formaldehyde photosynthetic assimilation pathways and inorganic salt culturemedia are embedded and fixed with sodium alginate and carboxymethyl cellulose, and the methylobacterium sponge balls and the methylobacterium sponge columns serve as air purification materials. The sponge balls embedded with the methylobacterium are arranged in a gas purification area, photosynthetic-bacterium sponge strips are soaked in water of a water tank, the photosynthetic-bacterium sponge columns in the water tank can also be replaced with hydroponic plants, the air purifier based on the bioreactor principle is established, polluting formaldehyde and other toxic organic compounds in airare purified, and the aim of purifying indoor air is achieved. The biological air purifier has the advantages of being economical, practical and environmentally friendly, and meets the green and environment-friendly theory requirements in living facilities of modern people.
Owner:YUNNAN WAN KUI BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH CO LTD
Microbial fermentation methods and compositions
The present invention provides methods for the cultivation of the Methylobacterium genus of bacteria. In particular the method provides methods for the efficient and inexpensive cultivation of these bacteria. Additionally, the invention provides methods for the utilization of these bacterial cultures to improve plant agriculture.
Owner:NEWLEAF SYMBIOTICS INC
Bacterium for degrading herbicide imazethapyr and application of bacterium
The invention discloses a bacterium for degrading a herbicide imazethapyr and application of the bacterium. The bacterium for degrading imazethapyr is methylobacterium sp. PST1991, which is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center by a preservation number of CGMCC No.7773. The methylobacterium sp. PST1991 CGMCC No.7773 reaches a degrading rate of 71.06% on 8mg / L of imazethapyr in an organic salt culture medium within 7d, showing that the strain can effectively degrade the imazethapyr; the bacterium has a wide application prospect in an aspect of repairing imazethapyr pollution of soil.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
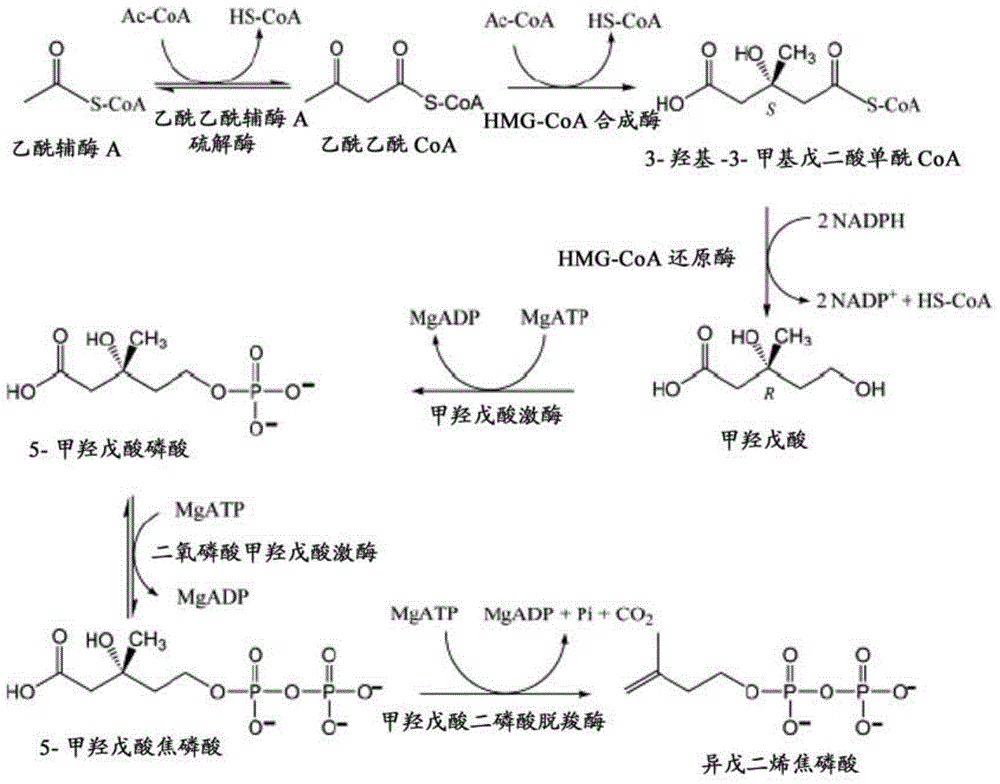
Isoprene producing bacterial and isoprene producing method
The invention relates to isoprene producing bacterial and an isoprene producing method, specifically to bacterial for producing isoprene by adopting methanol as a raw material and belonging to Methylobacterium, wherein the bacterial is modified so as to express isoprene synthetase (IspS).
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
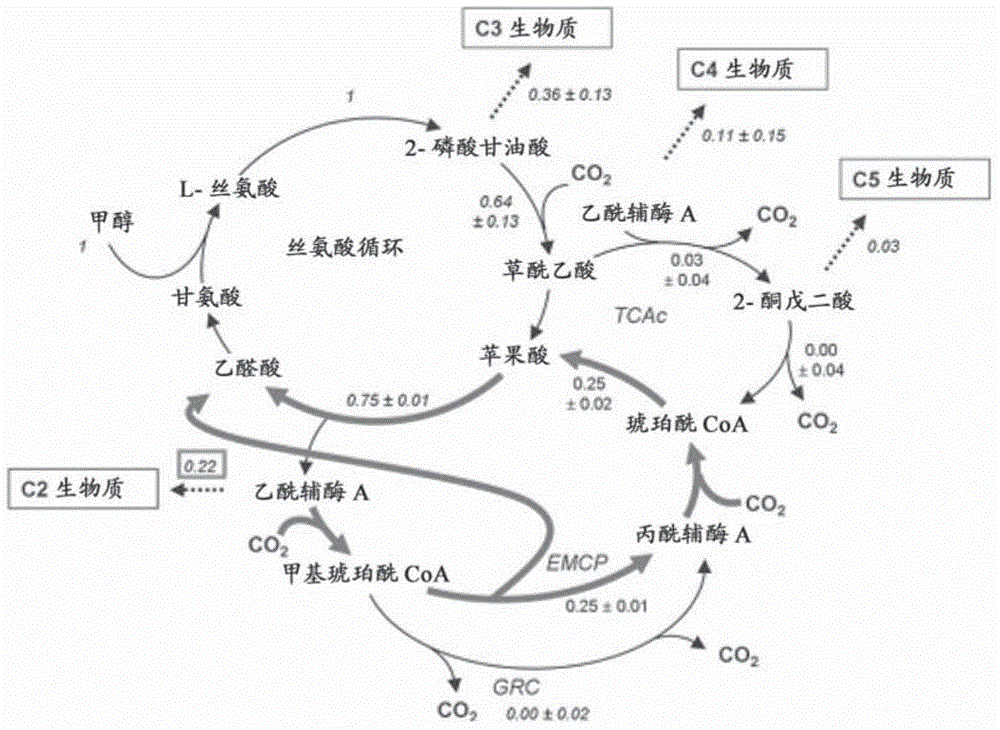
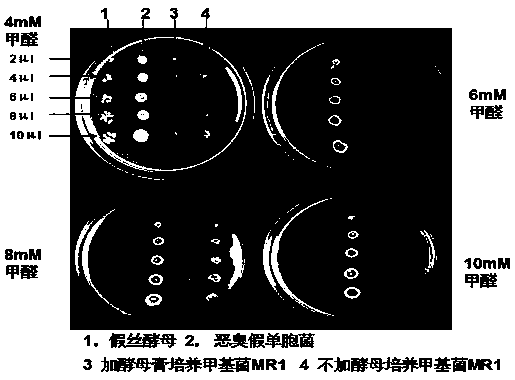
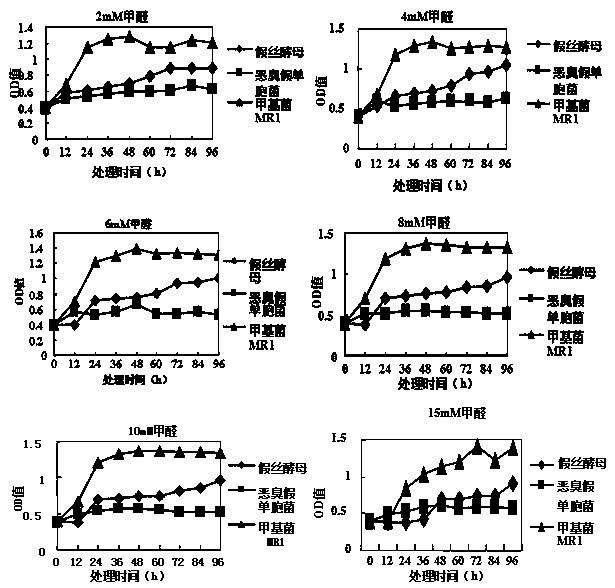
Novel methylobacterium MR1 and applications thereof
ActiveCN107674844AStrong resistancePromote growthGas treatmentBacteriaActivated sludgeHigh concentration
The invention relates to a methylobacterium zatmanni strain MR1. The methylobacterium zatmanni strain MR1 is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection, and is assigned with the accession number of CCTCC M 2017322. The methylobacterium is methylotrophic bacterium obtained by adopting activated sludge embedded by sodium alga acid domesticated by formaldehyde as the material and through separation of an inorganic salt culture medium of the methylobacterium, the methylobacterium can grow in the culture medium taking formaldehyde as the unique carbon source, has the resistance achieving 30mM for formaldehyde on a solid culture medium, grows normally in a liquid culture medium in which 5mM methanol and 2-15 mM formaldehyde are added, and has relatively high removal rate for formaldehyde with high concentration in the culture medium. MR1 also can grow in the inorganic salt culture medium adopting sodium acetate, sodium malate or sodium citrate as the unique carbon source, andthe growth is the best when sodium malate is adopted as the carbon source. When MR1 grows in the culture medium containing sodium acetate, sodium malate or sodium citrate, the added benzene series compounds can be removed, and the removal rate achieves 100%.
Owner:YUNNAN WAN KUI BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH CO LTD
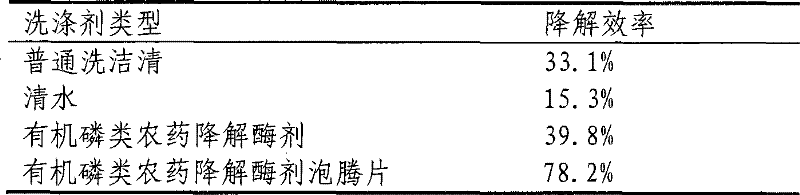
Organic phosphorus degrading enzyme preparation and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to microbe technology, in particular to a degrading enzyme preparation for degrading residual organic phosphorus on vegetables and fruits and a preparation method thereof. The invention particularly relates to organic phosphorus degrading enzyme preparation obtained by fermenting Methylobacterium. The preparation process comprises the following steps: after fermenting the inoculated strain, centrifugally collecting thalli, and breaking thalli to obtain the organic phosphorus degrading enzyme preparation. The organic phosphorus pesticide degrading enzyme preparation can degrade residual organic phosphorus pesticides on vegetables and fruits.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPLIED ECOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Quick starting method of waste water treatment system short-cut nitrification denitrification
ActiveCN105645582AImprove processing efficiencyReduce the difficulty of startingTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesActivated sludgeStart time
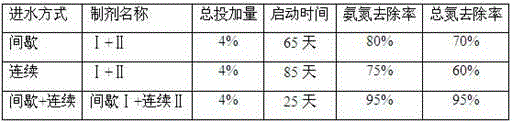
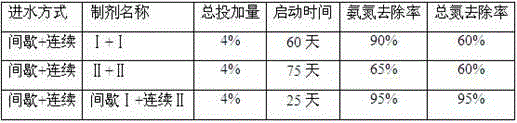
The invention discloses a quick starting method of waste water treatment system short-cut nitrification denitrification. The quick starting method comprises following steps: (1) firstly, a bioreactor is inoculated with aerobic activated sludge from wastewater treatment plants; (2) batch water injection is adopted, and then continuous water injection is adopted for system starting; and (3) denitriding microbial preparations are added at different ratio for different water injection modes, wherein the denitriding microbial preparations are mainly composed of Arthrobacter creatinolyticus FDN-1, Flavobacterium mizutaii FDN-2, Paracoccus denitrificans DN-3, and Methylobacterium phyllosphaerae SDN-3, volume ratio of the microbial preparations added in batch water injection is 1:2:(8-15):(8-15), and volume ratio of the microbial preparations added in continuous water injection is (8-15):(8-15):2:1. The quick starting method is capable of reducing starting difficulty of short-cut nitrification greatly and shortening start time obviously, ensuring long-term stable operation of reactors, achieving high waste water treatment efficiency, and realizing simultaneous removing of ammonia nitrogen, total nitrogen, and COD.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Regulation of heterologous recombinant protein expression in methylotrophic and methanotrophic bacteria
Methylotrophic or methanotrophic bacteria such as Methylobacterium are transformed with a gene of interest, and expression of the gene is regulated by means of a cumate repressor protein and an operator sequence which is operatively linked to the gene of interest, and the addition of an external agent. Specifically, the cymR repressor and cmt operator from Pseudomonas putida may serve to regulate gene expression in methylotrophic or methanotrophic bacteria with the addition of cumate.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Sporidiobolus pararoseus strain and application thereof
ActiveCN109868228AGood effectEasy to prepareBiocidePlant growth regulatorsMicroorganismSporidiobolus pararoseus
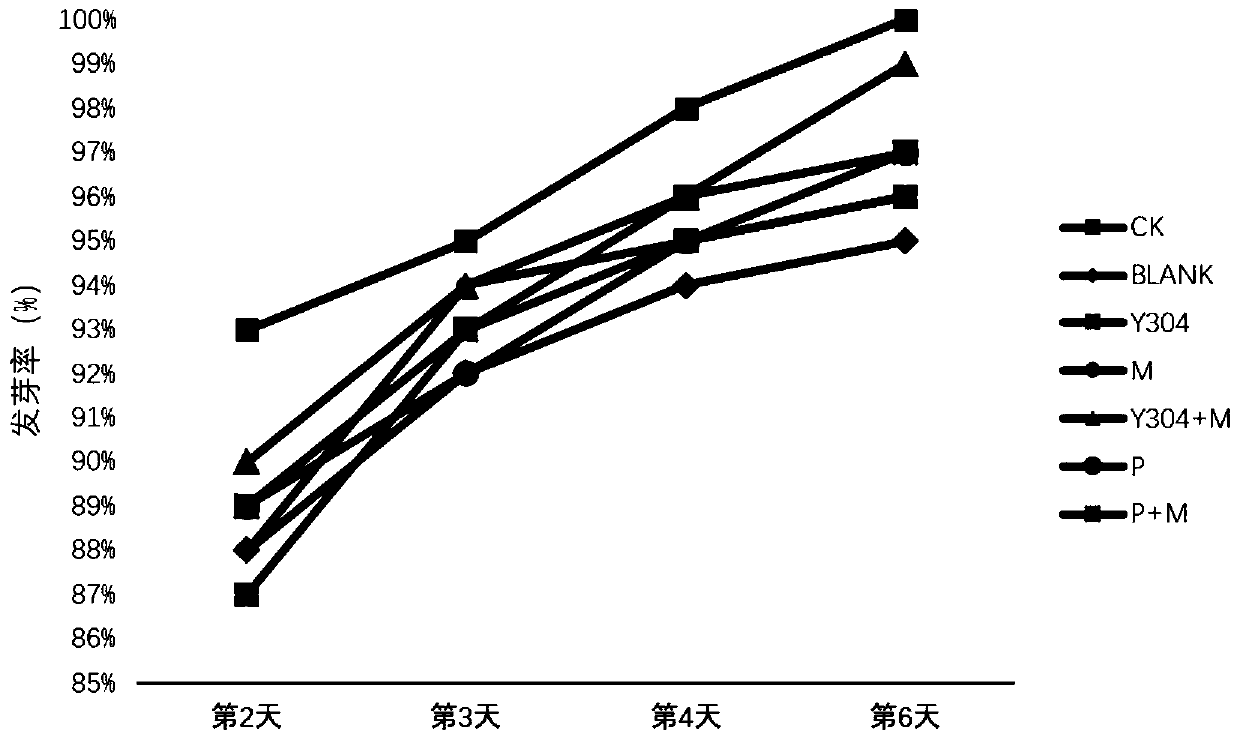
A method carries out isolated culture and identification to obtain a Sporidiobolus pararoseus strain, which is preserved in Guangdong Microbial Culture Collection Center with a preservation number ofGDMCC NO:60486. According to the embodiment of the invention, the Sporidiobolus pararoseus strain and Methylotrophic bacteria are used together to prepare a microbial seed coating agent; a contrast test is set to observe the influence of the microbial seed coating agent on the germination rate of wheat seeds and the growth condition of wheat seedling plants compared with other microbial seed coating agents; results show that the microbial seed coating agent prepared from the Sporidiobolus pararoseus strain and the Methylotrophic bacteria improves the germination rate of wheat seeds and improves the physiological status indexes of wheat seedling plants.
Owner:MOON (GUANGZHOU) BIOTECH CO LTD
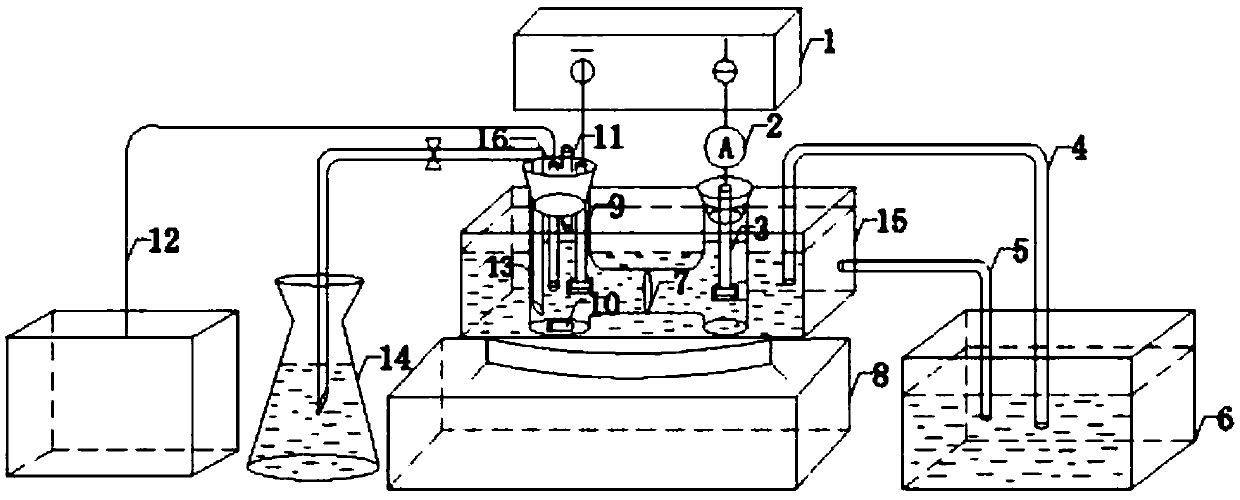
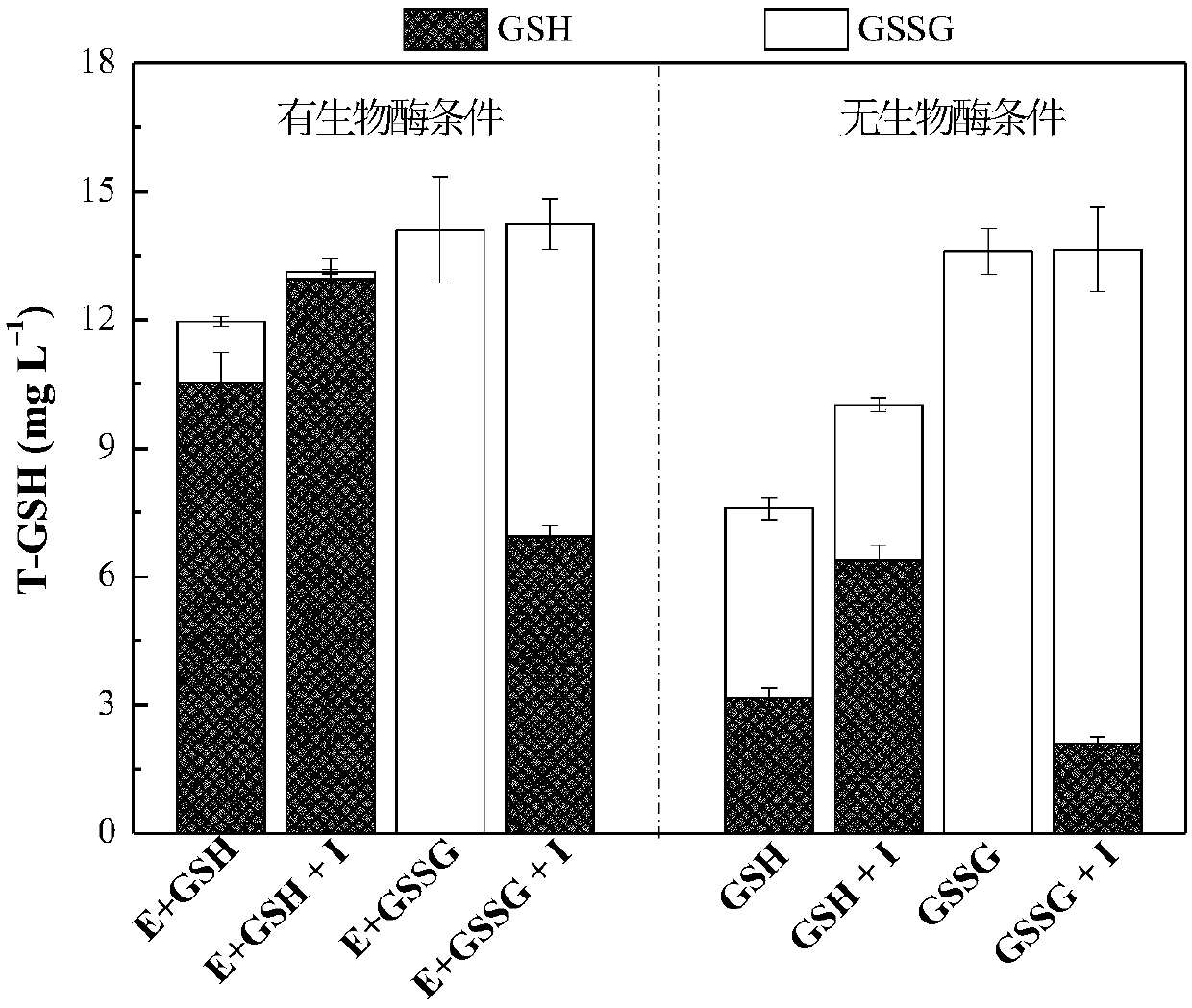
Method for regenerating coenzyme-reduced glutathione based on electrochemistry and enzyme electrode
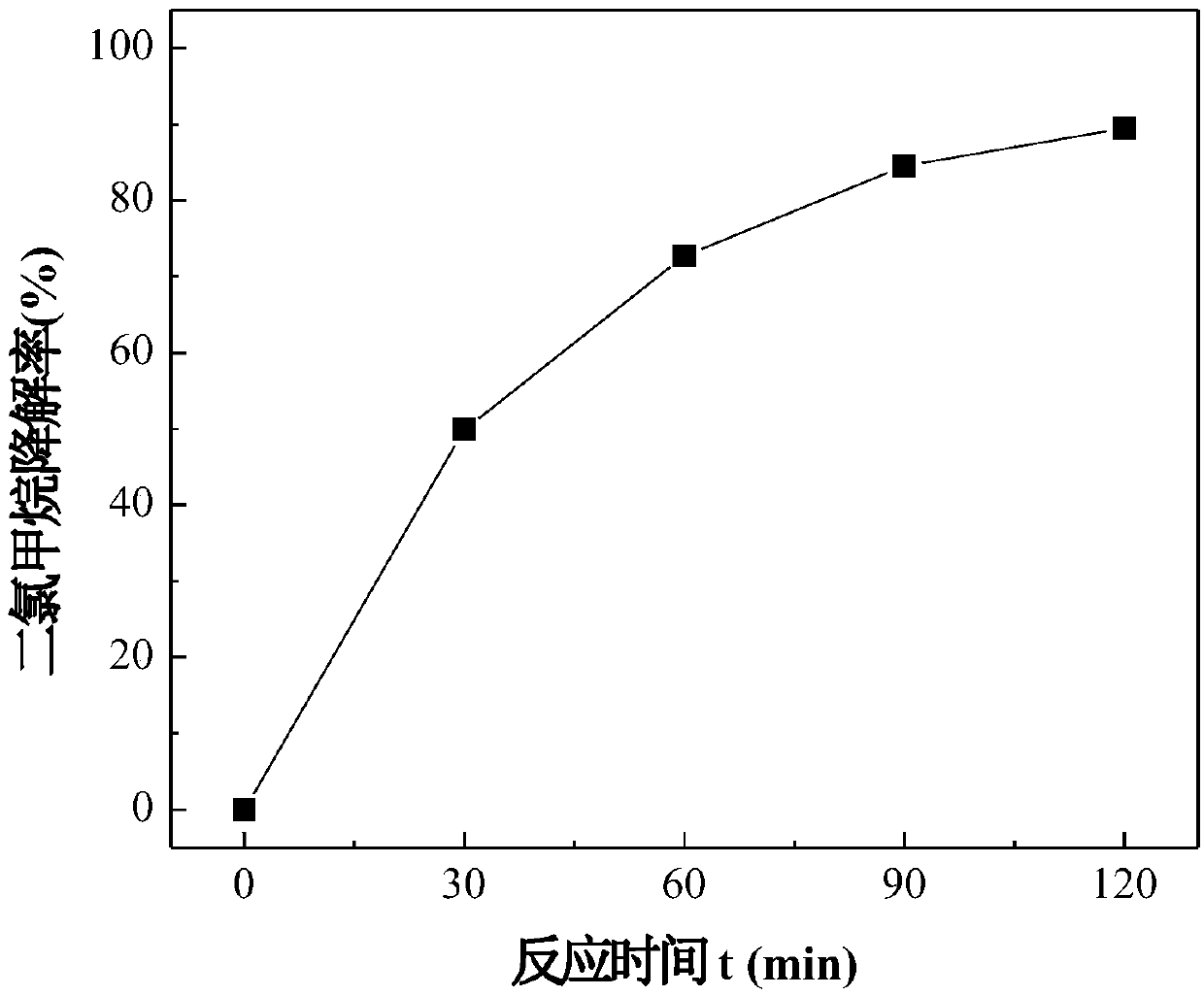
The invention discloses an enzyme electrode, which is prepared by the following steps of: preparing recombinant engineering bacteria by using a DCM degrading bacterium Methylobacterium H13, and obtaining DCM dehalogenase pure enzyme solution through induction culture expression and purification; mixing the DCM dehalogenase pure enzyme solution with sodium alginate to obtain an embedding material;spreading the embedding material on the surface of an electrode matrix, and fixing the embedding material by Ca (NO3)2 and the like to obtain the enzyme electrode. The invention also provides a methodfor regenerating coenzyme-reduced glutathione based on electrochemistry by using the enzyme electrode, which comprises the following steps of: injecting DCM-containing wastewater into a cathode electrolytic tank, and performing constant current electrolysis on the reduced glutathione GSH serving as coenzyme. The method utilizes electrochemical technology and a medium of the enzyme electrode to provide sufficient electrons for regenerating coenzyme GSH and promote GSSG to regenerate GSH.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
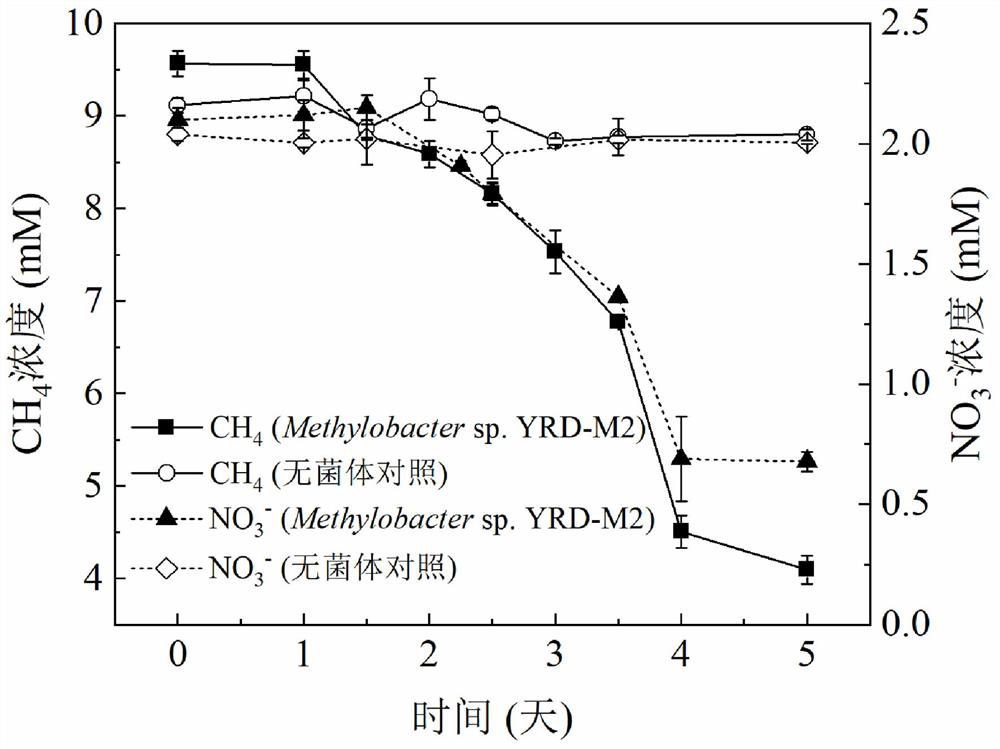
Methylobacterium with denitrification function and hypoxia stress resistance and application thereof
The invention provides a methylobacterium with a denitrification function and hypoxia stress resistance and application thereof. The methylobacterium can efficiently degrade nitrate under different environmental conditions and simultaneously perform a methane oxidation process, has stress resistance to an anoxic environment, is simple to culture, low in cost, strong in strain adaptability and good in stability, and has a wide application prospect in the field of sewage treatment. The strain utilizes methane and nitrate as a carbon source and a nitrogen source to form mycoprotein, can be used as feed and the like, realizes conversion of pollutants into products with higher additional values, and has advantage of comprehensive pollution treatment.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF ECO ENVIRONMENT & SOIL SCI
Bacteriophage for lysis of Methylobacterium and compositions and uses thereof
The invention relates to a novel bacteriophage which is lytic for species of the genus Methylobacterium, Human Blood Bacterium (HBB) or both, and derivatives, progeny and recombinant and mutated forms thereof. The invention further relates to compositions, methods and kits for using the bacteriophage of the invention in agricultural and therapeutic settings.
Owner:SALISBURY UNIVERSITY
In-situ repair agent for efficient degradation of tetracycline antibiotics in soil and preparation method of the in-situ repair agent
ActiveCN110303040ASimple methodEasy to operateBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationPhotocatalytic degradationBiology
The invention discloses an in-situ repair agent for efficient degradation of tetracycline antibiotics in soil and a preparation method of the in-situ repair agent. The in-situ repair agent is characterized in that the in-situ repair agent is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 30-40 parts of Pt / TiO2 modified porous silkworm excrement, 2-6 parts of graphene, 1-5 parts of cation exchange resin, 4-6 parts of methylobacterium and 4-6 parts of pseudomonas hibiscicola; the methylobacterium and the pseudomonas hibiscicola are obtained by an original strain in a basic solid medium containing tetracycline through continuous passage and domestication. The preparation process of the Pt / TiO2 modified porous silkworm excrement includes the steps that original silkworm excrement is swelled in 6-12% of a urea solution, dried, carbonized for 1-2 hours at 180-200 DEG C under the action of protective gas, quenched by being added with 0.1-1% of a bromoplatinic acid solution and tetrabutyl titanate diluents, then heated to 450-500 DEG C, and roasted for 3-5 hours. According to the in-situ repair agent for efficient degradation of the tetracycline antibiotics in the soil and thepreparation method of the in-situ repair agent, the soil polluted by the tetracycline antibiotics can be directly repaired in situ, the cycle is short, in-situ removal is carried out in combination with means of physical adsorption, photocatalytic degradation, biodegradation and the like, and the conversion rate is high.
Owner:四川好土优土农业开发有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com