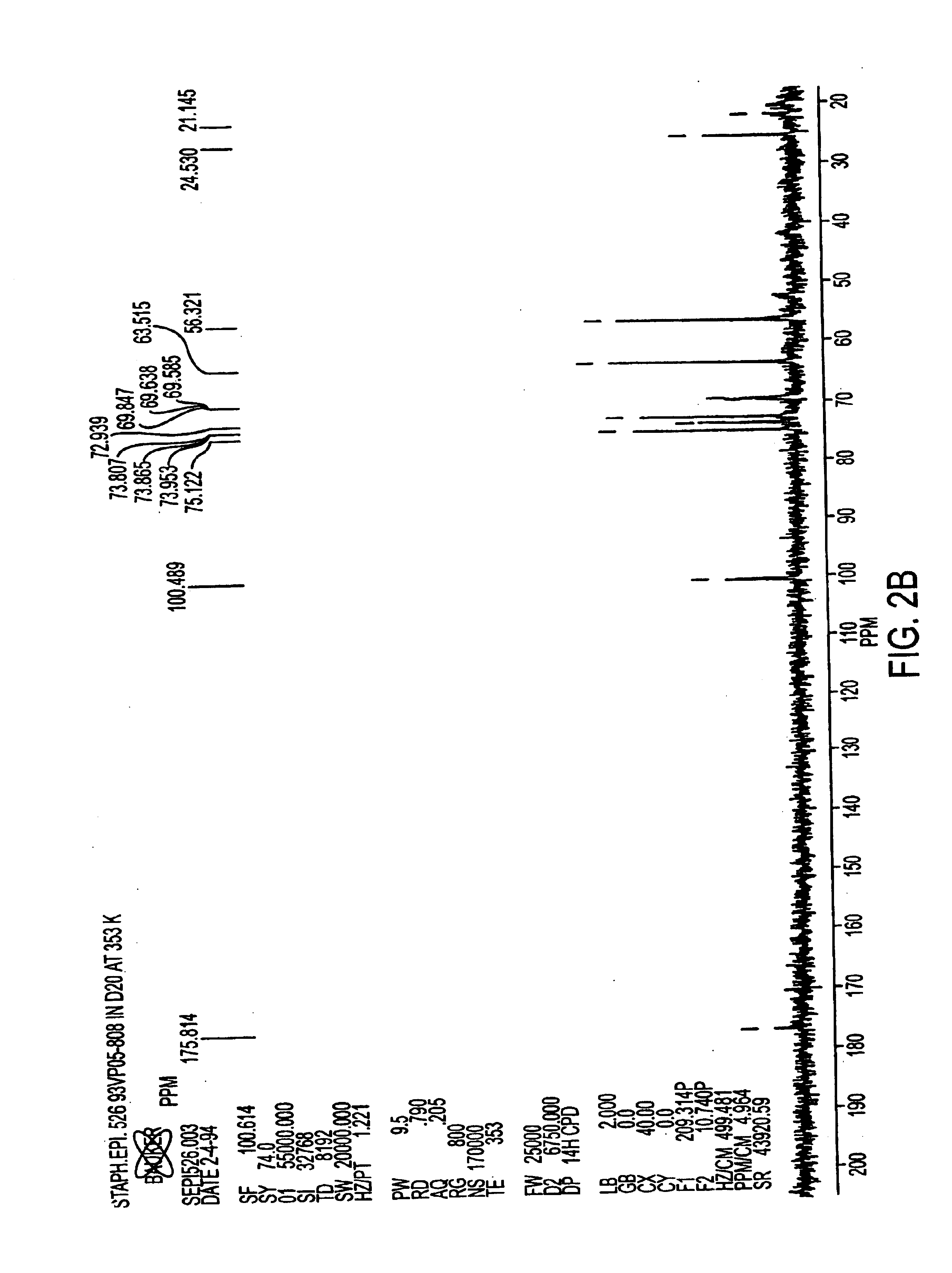
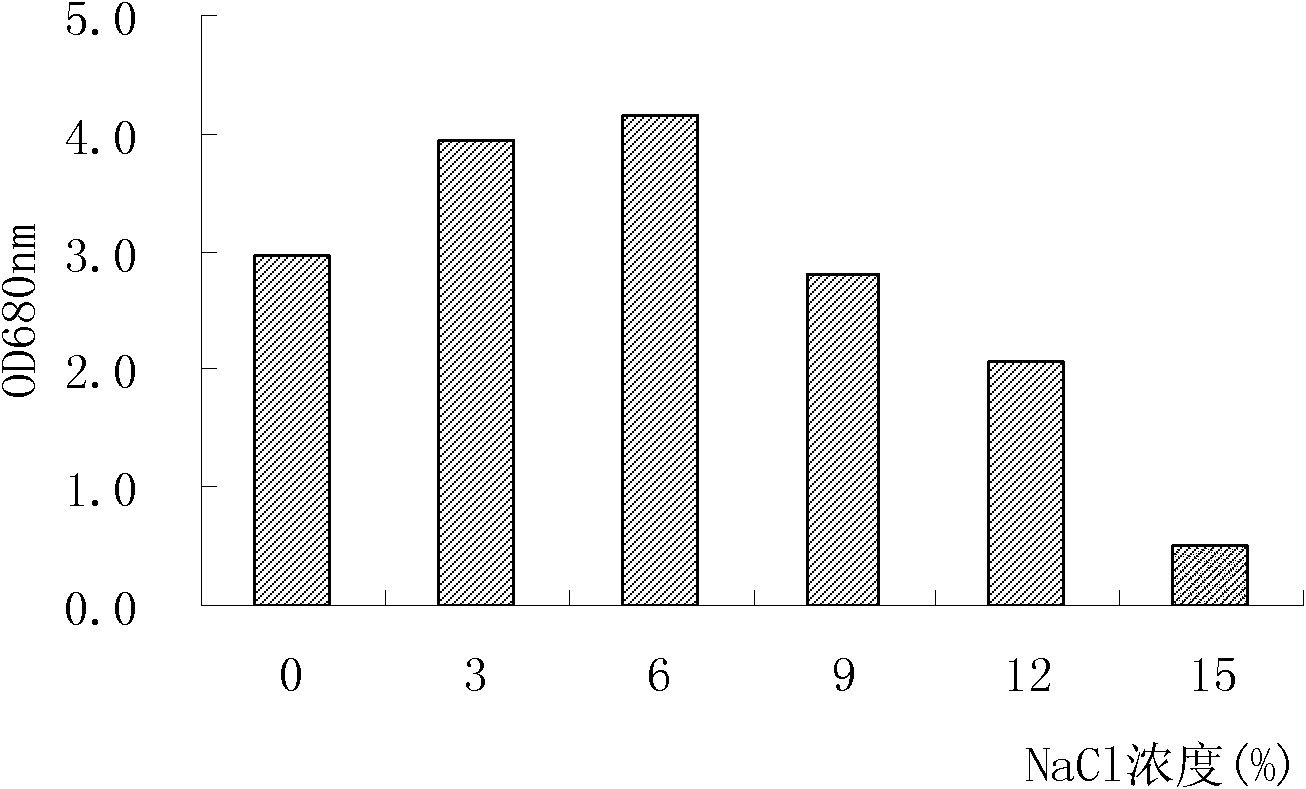
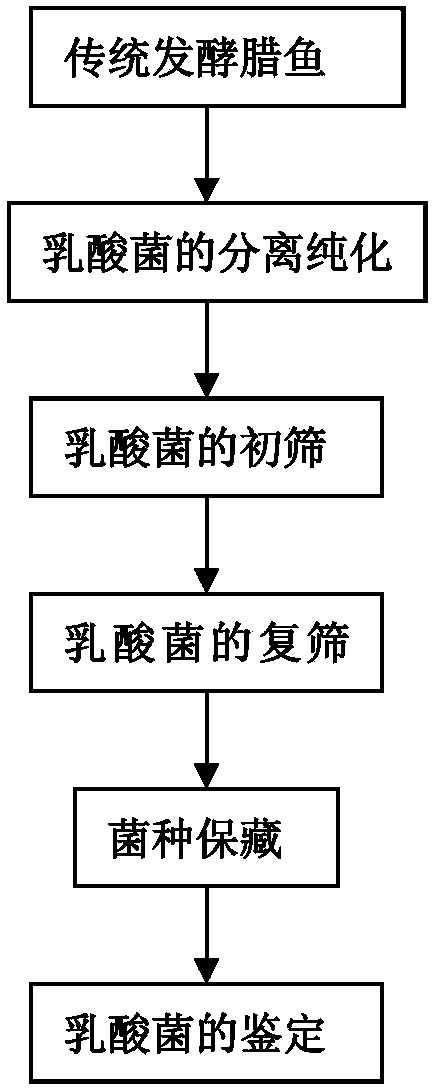
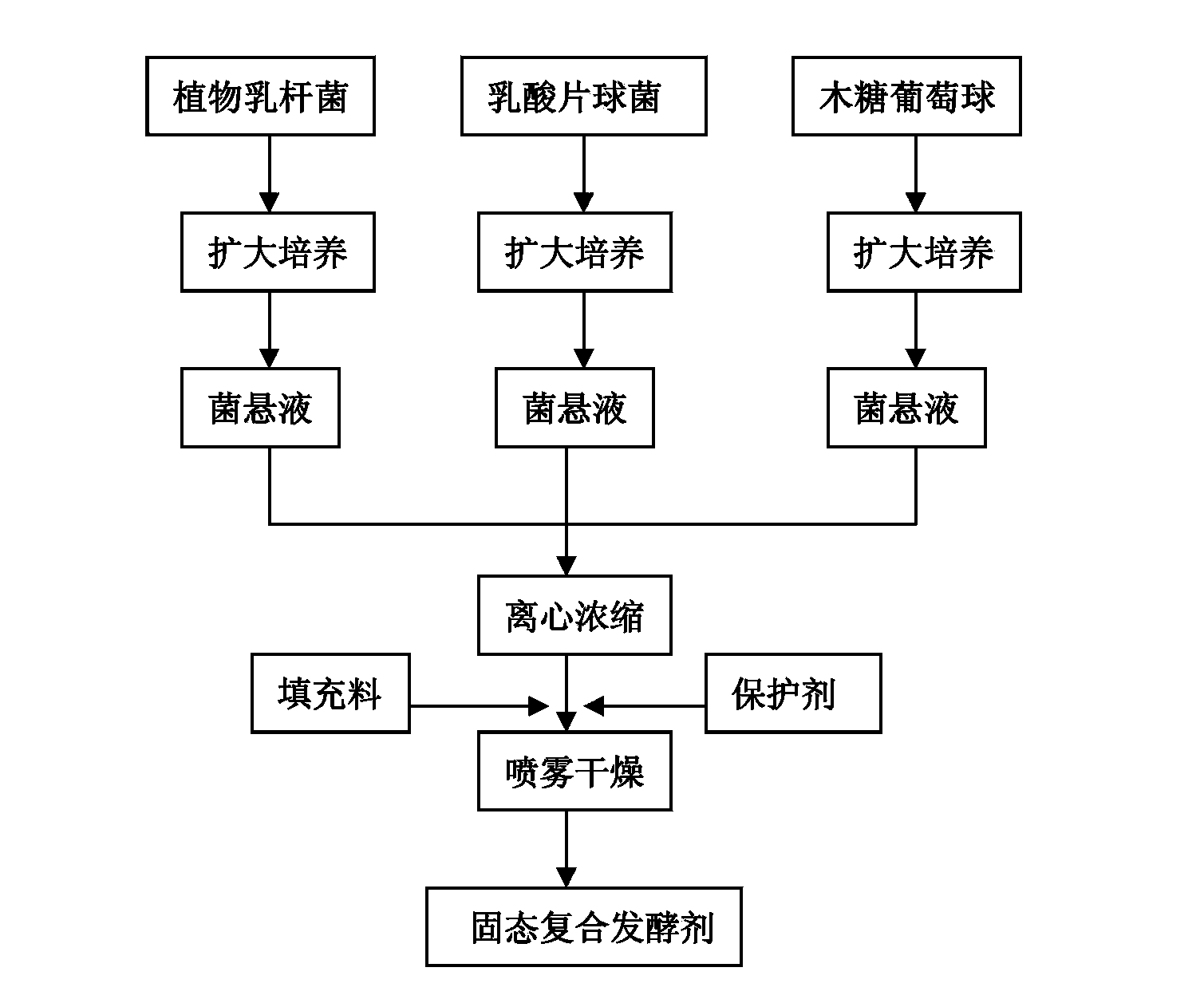
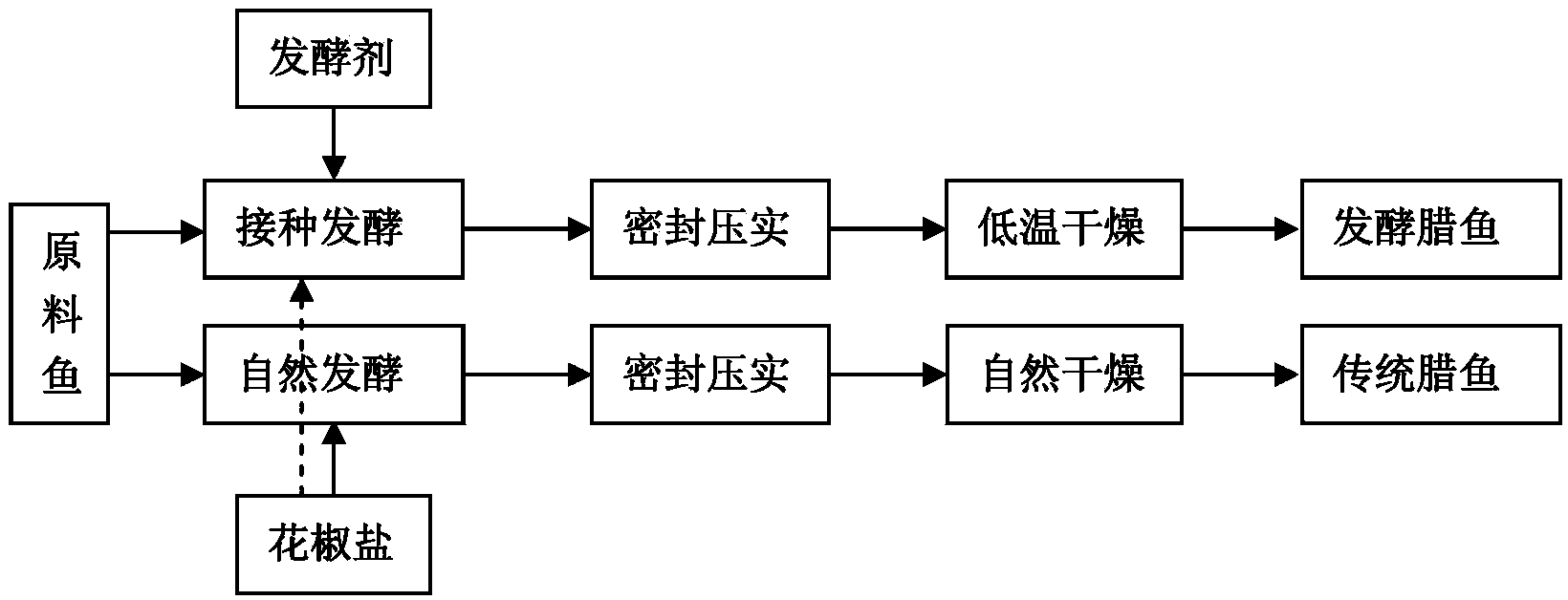
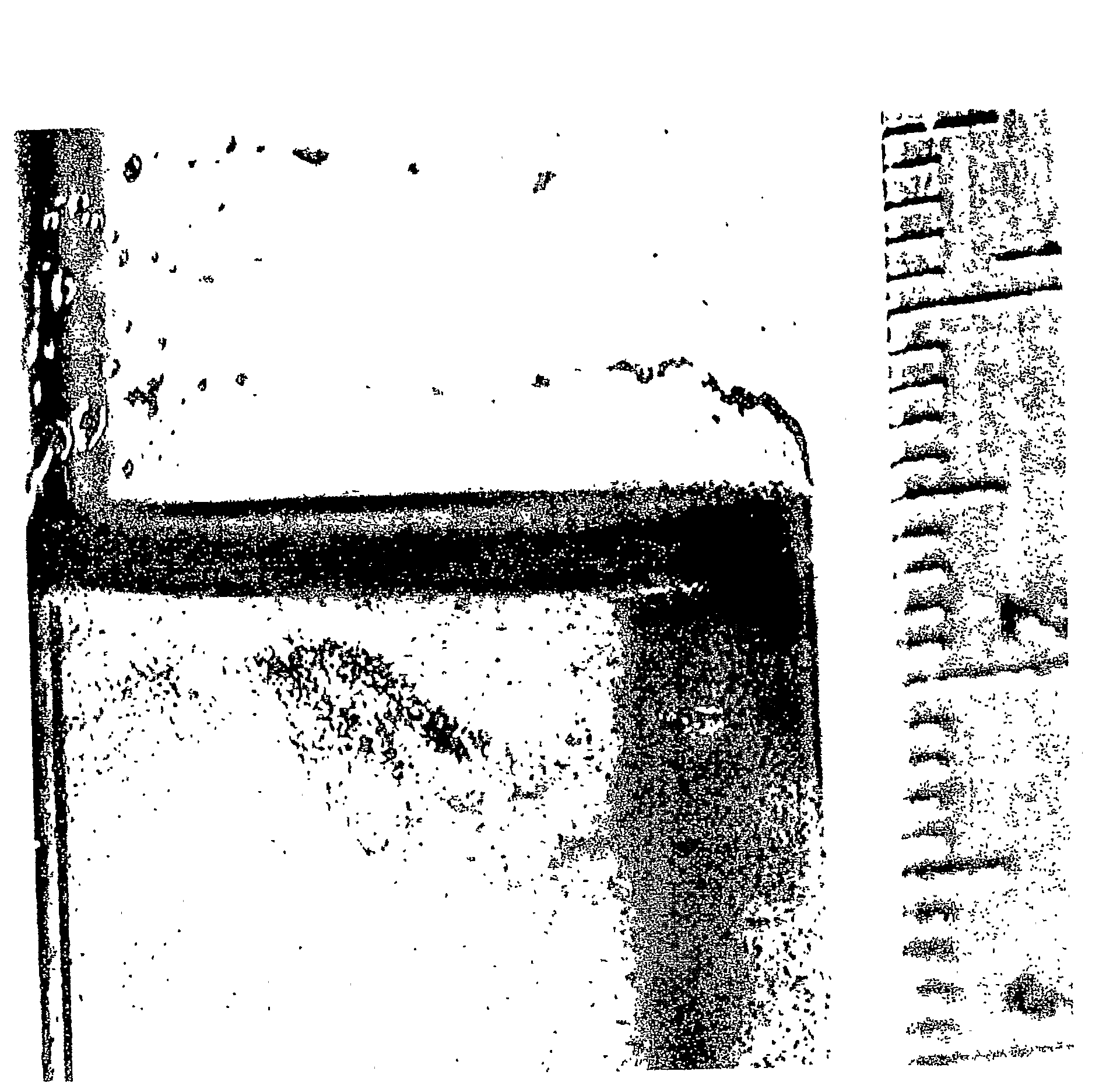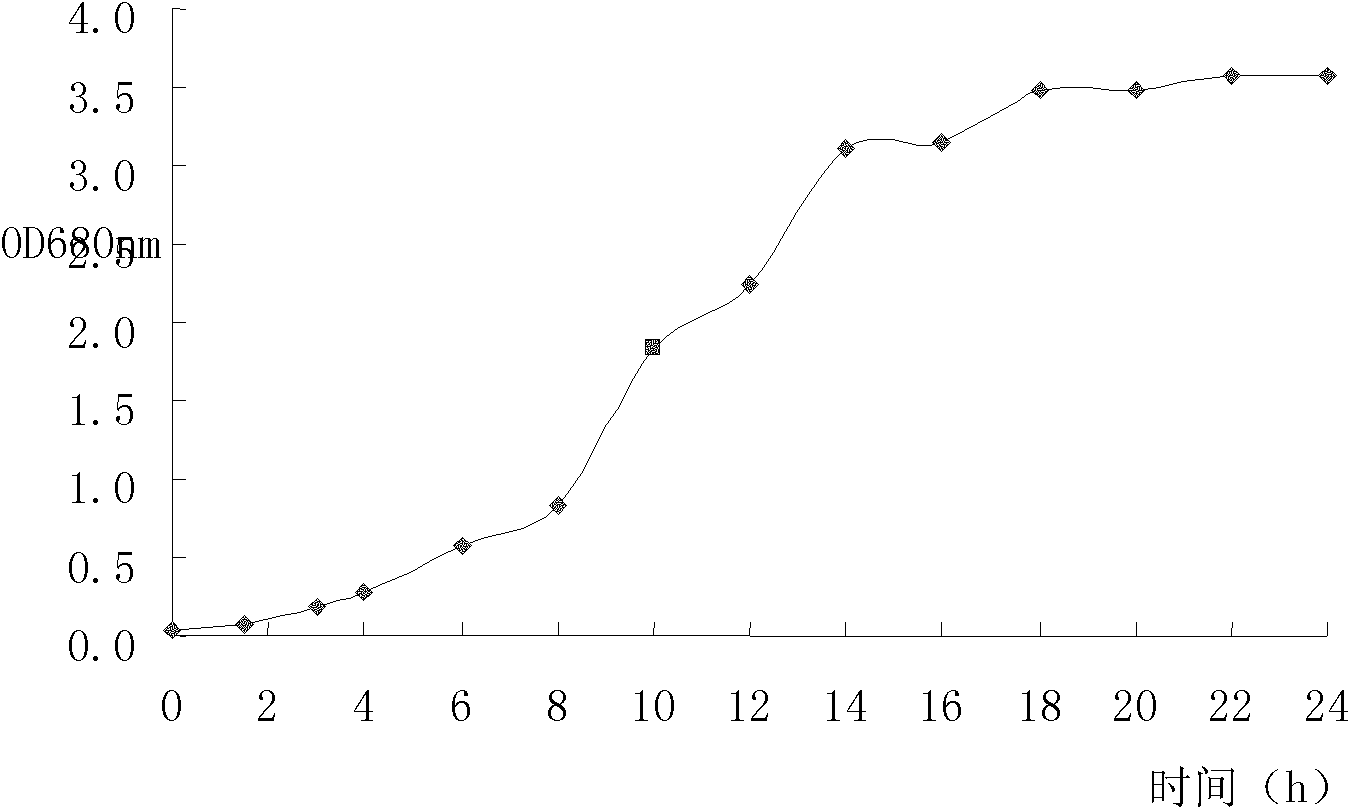Patents
Literature
330 results about "Staphylococcus xylosus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Staphylococcus xylosus is a species of bacteria belonging to the genus Staphylococcus. It is a Gram-positive bacterium that forms clusters of cells. Like most staphylococcal species, it is coagulase-negative and exists as a commensal on the skin of humans and animals and in the environment.
Nanosilver-containing antibacterial and antifungal granules and methods for preparing and using the same
InactiveUS6379712B1Improve solubilityPreventing mold build-upPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsEscherichia coliDisease
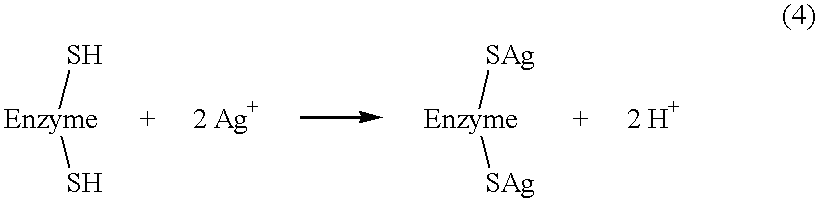
The present invention relates to nanosilver-containing antibacterial and antifungal granules ("NAGs"). The NAGs have longlasting inhibitory effect on a broad-spectrum of bacteria and fungi, which include, but are not limited to, Escherichia coli, Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Chlamydia trachomatis, Providencia stuartii, Vibrio vulnificus, Pneumobacillus, Nitrate-negative bacillus, Staphylococcus aureus, Candida albicans, Bacillus cloacae, Bacillus allantoides, Morgan's bacillus (Salmonella morgani), Pseudomonas maltophila, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus foecalis alkaligenes, Streptococcus hemolyticus B, Citrobacter, and Salmonella paratyphi C. The NAGs contain ground stalk marrow of the plant Juncus effusus L. which has been dispersed with nanosilver particles. The nanosilver particles are about 1-100 nm in diameter. Each of the nanosilver particles contain a metallic silver core which is surrounded by silver oxide. The present invention also provides a process for making the NAGs. The NAGs can be used in a variety of healthcare and industrial products. Examples of the healthcare products include, but are not limited to, ointments or lotions to treat skin trauma, soaking solutions or cleansing solutions for dental or women hygiene, medications for treating gastrointestinal bacteria infections, sexual related diseases, and eye diseases. Examples of industrial products include, but are not limited to, food preservatives, water disinfectants, paper disinfectants, construction filling materials (to prevent mold formation).
Owner:LEGEND WIN FINANCE
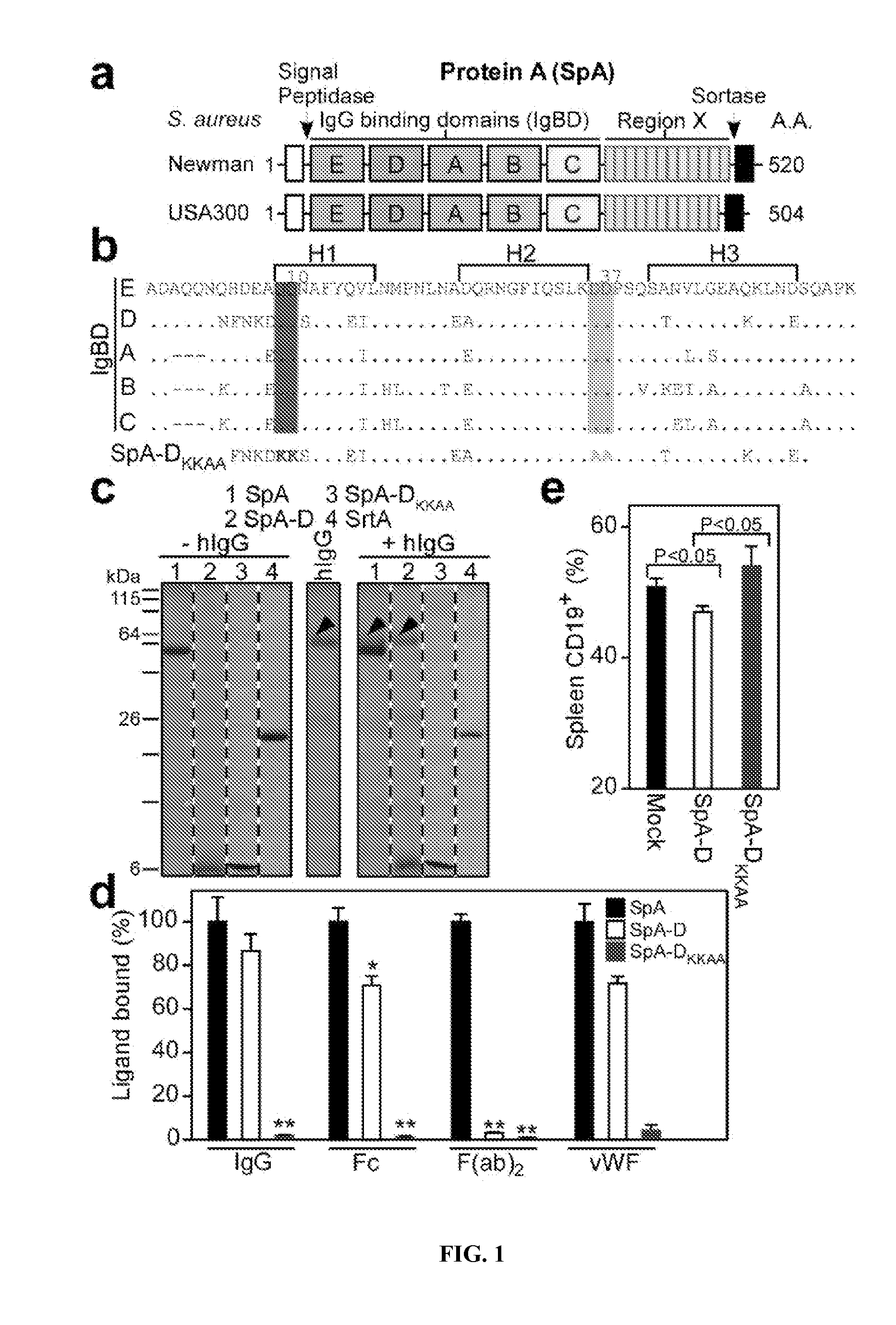
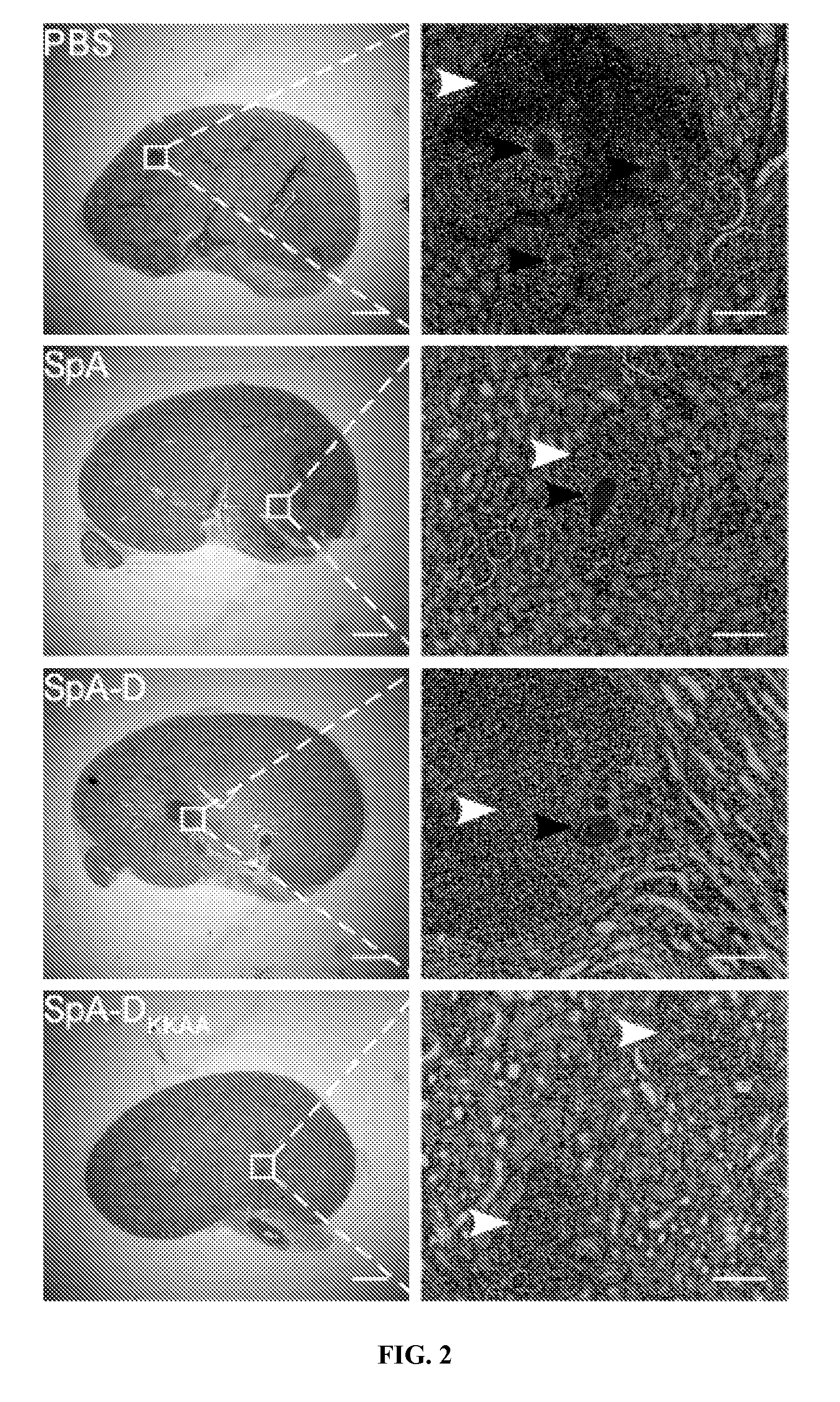
Compositions and methods related to protein a (SPA) variants
ActiveUS20120114686A1Reduced activityPrevents alleviates ameliorates symptomAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsStaphylococcus xylosusProtein A
Disclosed are methods and compositions for treating or preventing a Staphylococcus bacterial infection using a non-toxigenic Protein A (SpA) variant.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Staphylococcus antigen and vaccine
A negatively-charged Staphylococcus antigen contains amino acids and a N-acetylated hexosamine as a major carbohydrate component. The antigen is common to many coagulase-negative strains of Staphylococcus, including S. epidermidis, S. haemolyticus, and S. hominis. Staphylococcus strains that carry the antigen include many clinically significant strains of Staphylococcus. The antigen and antibodies to the antigen are useful in kits and assays for diagnosing Staphylococcus infection. Vaccines of the antigen and of whole cells that carry the antigen also are disclosed.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Composition to Treat Herpes, Pseudomonas, Staph, Hepatitis and Other Infectious Diseases
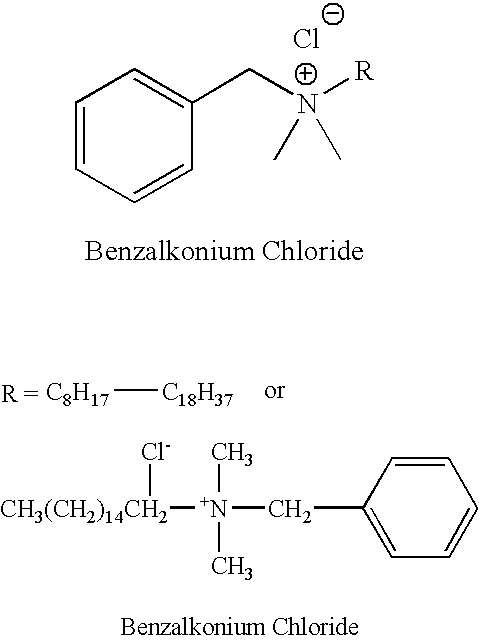
InactiveUS20090191288A1Safe and economical and effectiveGood and consistent resultOrganic active ingredientsBiocideBENZYL ALCOHOL/WATERInfectious illness
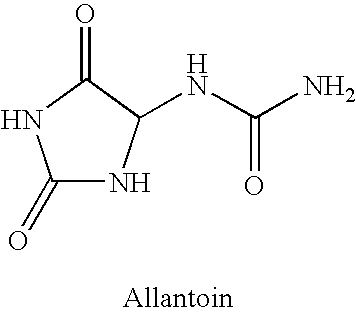
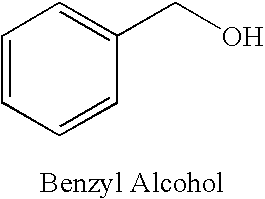
An improved method (process) and medicinal composition is provided to treat herpes, pseudomonas, hepatitis, staph (staphylococci) and other infectious diseases The inexpensive medicinal composition can be self-administered and maintained for a prescribed time. The attractive medicinal composition can comprise a quaternary ammonium salt surfactant, a skin protectant and an alcohol. The quaternary ammonium salt surfactant can comprise benzalkonium halide, preferably benzalkonium chloride. The skin protectant can comprise Allantoin. The alcohol can serve as a pain reliever and can comprise benzyl alcohol. The medicinal composition can also include other compounds, additives, herbal extracts and / or carriers.
Owner:SQUIRES MERYL J
Novel antibiotic and nucleotide sequence, preparation method and application thereof
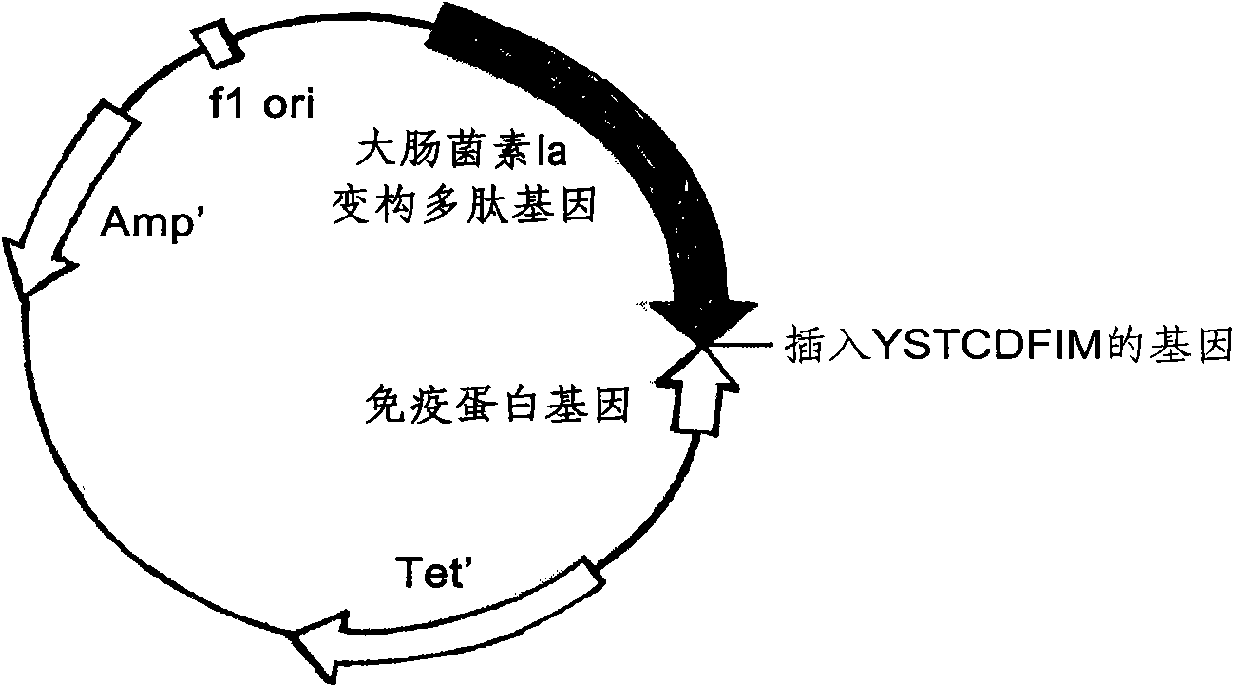
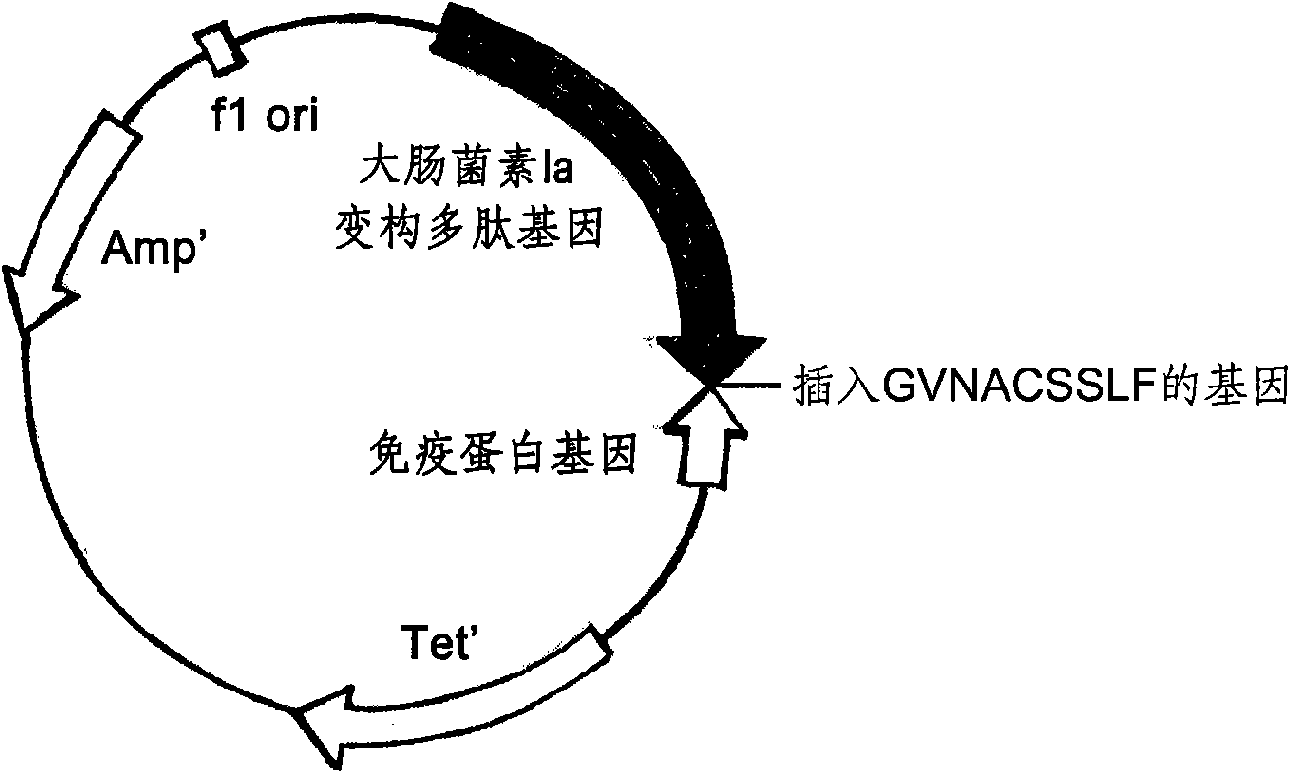
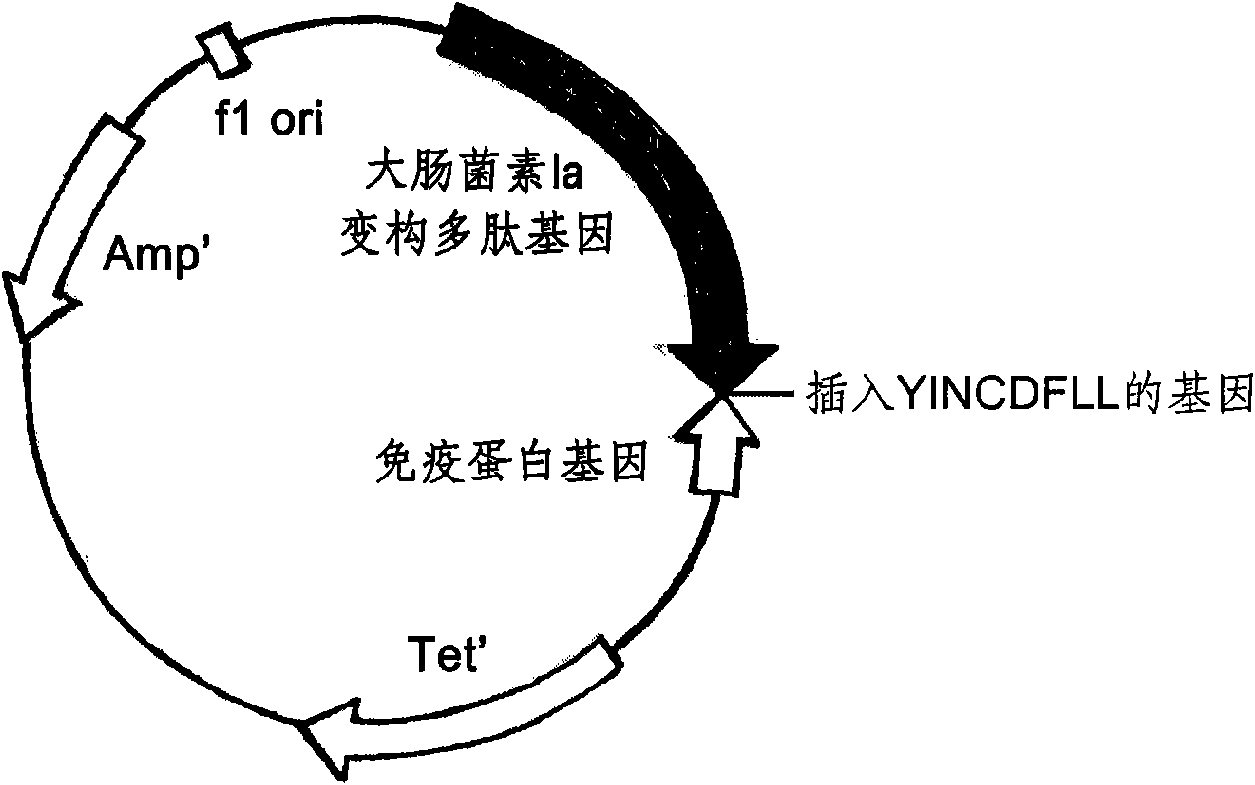
ActiveCN101643501AImprove the bactericidal effectOvercoming the disadvantages of hypersensitivityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsAeromonas veroniiStaphylococcus xylosus
The invention relates to a novel antibiotic and a nucleotide sequence, a preparation method and an application thereof, belonging to the biopharmaceutical field. The novel antibiotic comprises colicinallosteric polypeptide and staphylococcus pheromone peptide chain which are capable of specifically killing pathogenic bacteria combined by the specificity of the antibiotic without damaging the normal cells of human body and are linearly linked with each other to generate novel antibiotics resisting staphylococcus aureus, staphylococcus epidermidis and pseudomonas aeruginosa, has the antisepticeffect as thousand times as the conventional antibiotics, difficult generation of drug resistance, and safer use through overcoming the shortcoming of causing the hypersensitivity of human body of wild colicin.
Owner:美国信息菌素生物科技公司
Method for making fermented minced or cubed meat by utilizing fermenting agent
InactiveCN103704765AGood colorAdd flavorMeat/fish preservation using chemicalsFood ingredient for microbe protectionBiotechnologyFlavor
The invention provides a method for making fermented minced or cubed meat by utilizing a fermenting agent. The method comprises the steps of minced or cubed meat raw material pretreatment, preserving, fermenting, storing and the like, the above raw material selects cold meat or fresh meat, and a strain comprises one or more of lactic acid bacteria, Debaryomyces hansenii, Micrococcus Kristinae, Micrococcus varians and Staphylococcus xylosus. A fermented product obtained in the invention has the characteristics of fine texture, elasticity, rich and pure fragrance, possessing of the sour fragrance specially possessed by fermented meat products, good mouthfeel and unique flavor, and also has the advantages of high nutrition value, high safety, eating convenience, easy preservation, probiotic effect and the like.
Owner:胡永金
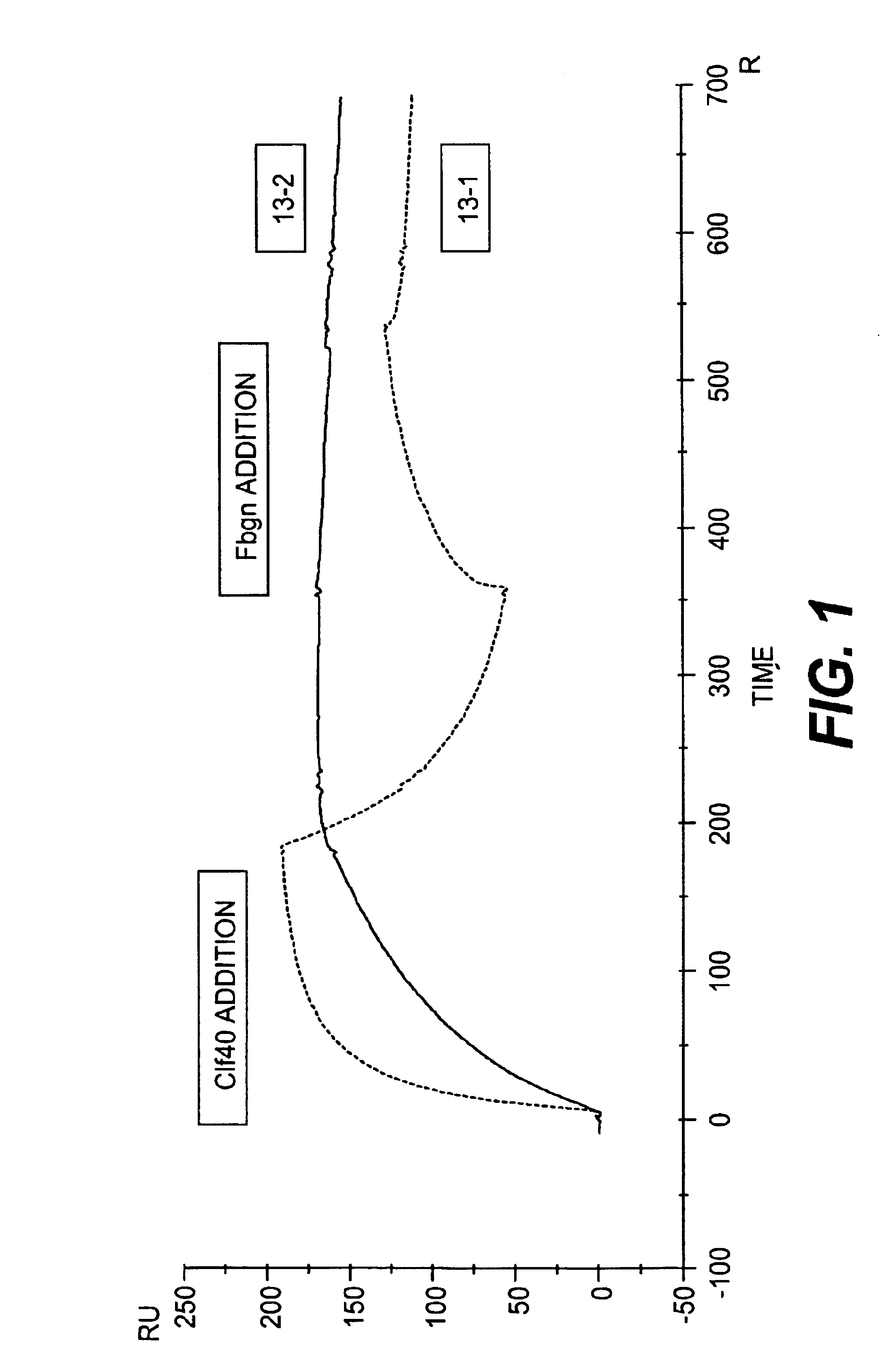
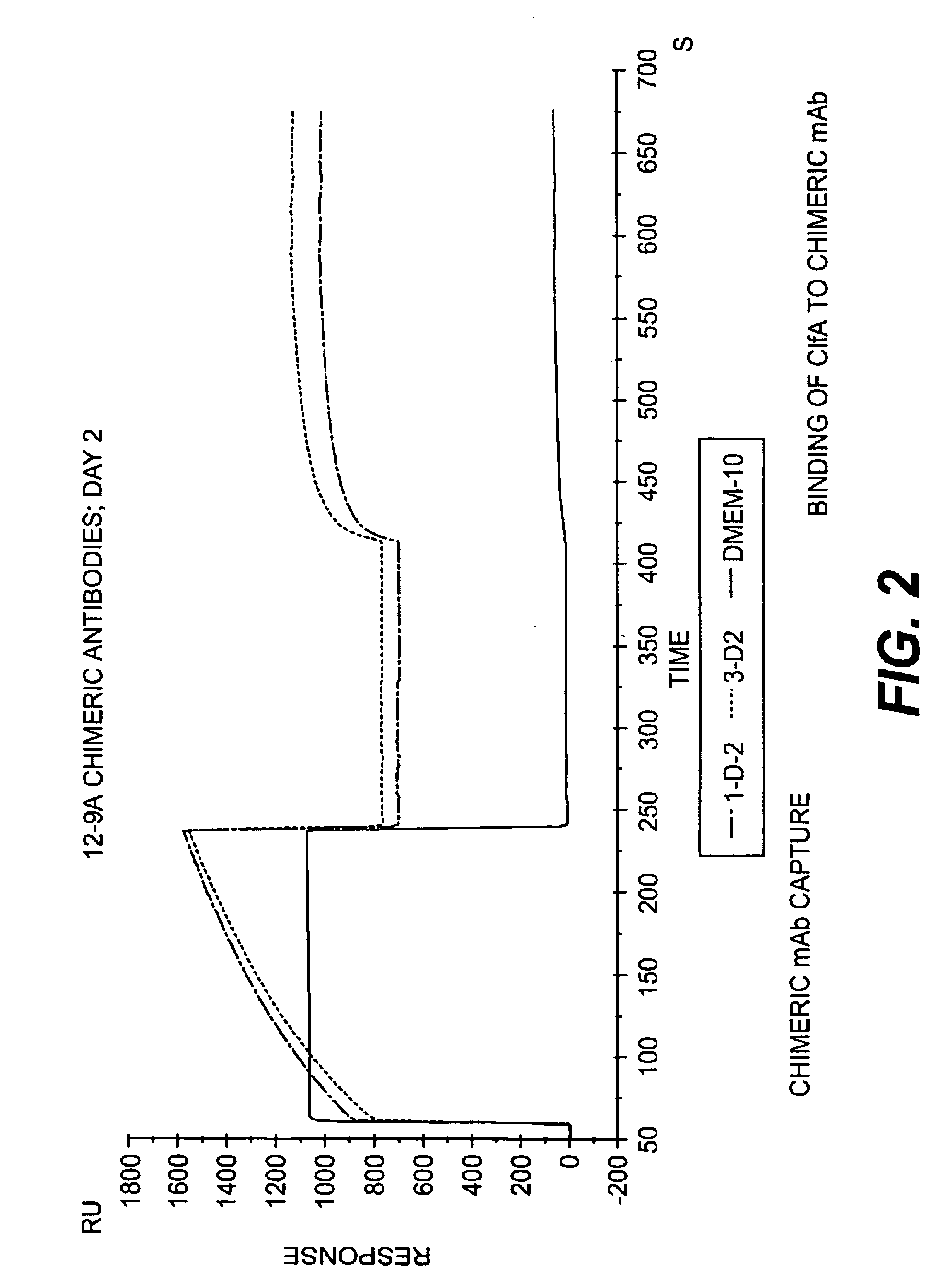
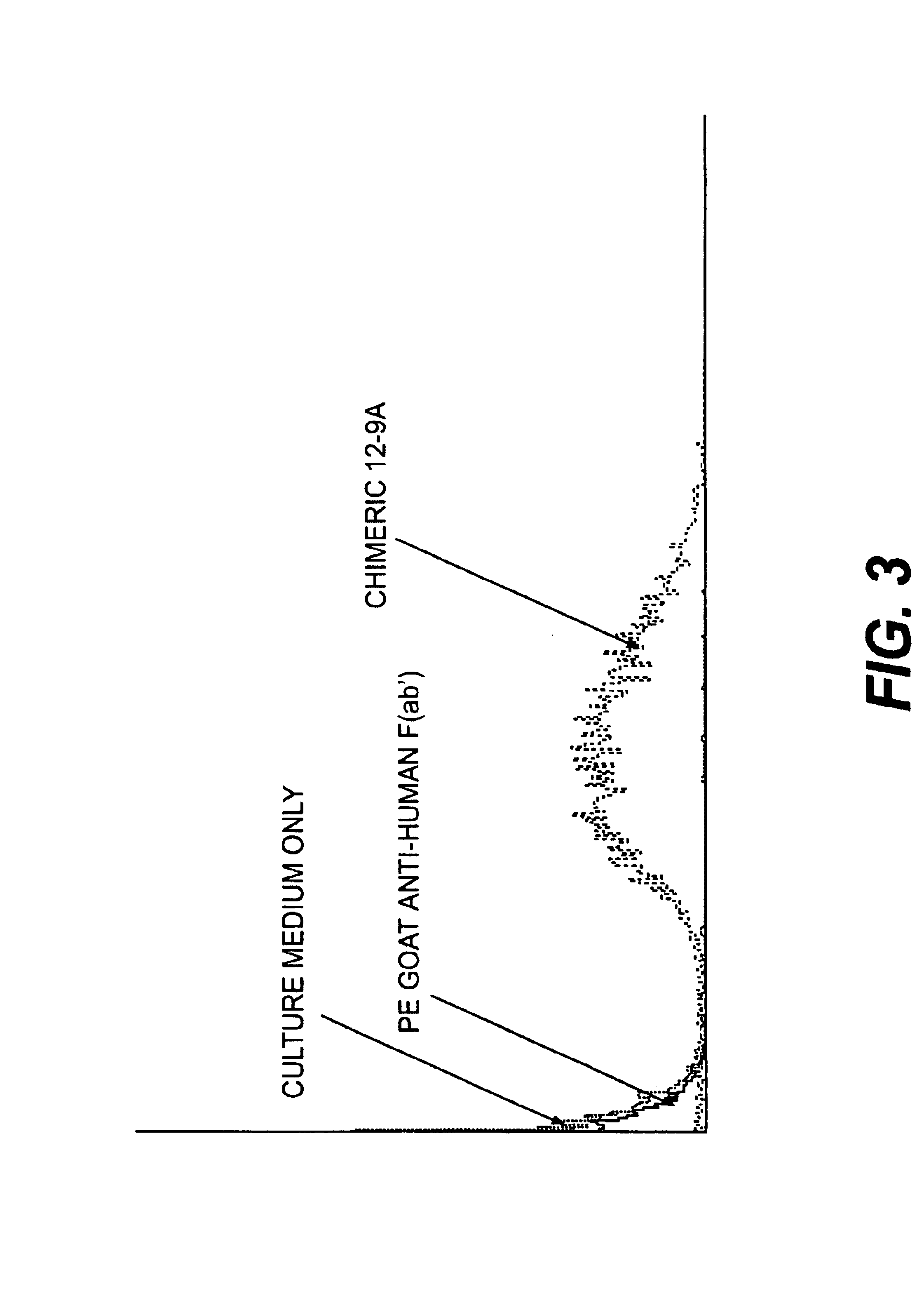
Monoclonal antibodies to the ClfA protein and method of use in treating or preventing infections
InactiveUS6979446B2Avoid stickingInhibiting or impairing the binding of the ClfA proteinAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteroidesStaphylococcus cohnii
Monoclonal antibodies which can bind to the ClfA protein and which are generated from binding subdomains or active fragments of the ClfA protein from Staphylococcus aureus, including the active fragments proteins from its fibrinogen binding domain such as Clf40 protein, the Clf33 protein, or ClfA N3, are provided which can be useful in the treatment and protection against infection from staphylococcal bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus. In addition, medical instruments can be treated using the monoclonal antibodies of the invention in order to reduce or eliminate the possibility of their becoming infected or further spreading the infection. In particular, the antibodies of the present invention are advantageous because they can prevent adherence of the bacteria to host cells by impairing or inhibiting the ability of S. aureus ClfA to bind to fibrinogen or fibrin, and thus can be utilized in methods or treating or preventing staphylococcal inventions.
Owner:INHIBITEX INC
Species-specific, genus-specific and universal DNA probes and amplification primers to rapidly detect and identify common bacterial and fungal pathogens and associated antibiotic resistance genes from clinical specimens for diagnosis in microbiology laboratories
InactiveUS20040185478A1Reduce usageDetermine rapidly the bacterial resistance to antibioticsMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationBacteroidesNeisseria meningitidis
DNA-based methods employing amplification primers or probes for detecting, identifying, and quantifying in a test sample DNA from (i) any bacterium, (ii) the species Streptococcus agalactiae, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Enterococcus faecium, Neisseria meningitidis, Listeria monocytogenes and Candida albicans, and (iii) any species of the genera Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, Enterococcus, Neisseria and Candida are disclosed. DNA-based methods employing amplification primers or probes for detecting, identifying, and quantifying in a test sample antibiotic resistance genes selected from the group consisting of blatem, blarob, blashv, blaoxa, blaZ, aadB, aacC1, aacC2, aacC3, aacA4, aac6'-lla, ermA, ermB, ermC, mecA, vanA, vanB, vanC, satA, aac(6')-aph(2''), aad(6'), vat, vga, msrA, sul and int are also disclosed. The above microbial species, genera and resistance genes are all clinically relevant and commonly encountered in a variety of clinical specimens. These DNA-based assays are rapid, accurate and can be used in clinical microbiology laboratories for routine diagnosis. These novel diagnostic tools should be useful to improve the speed and accuracy of diagnosis of microbial infections, thereby allowing more effective treatments. Diagnostic kits for (i) the universal detection and quantification of bacteria, and / or (ii) the detection, identification and quantification of the above-mentioned bacterial and fungal species and / or genera, and / or (iii) the detection, identification and quantification of the above-mentioned antibiotic resistance genes are also claimed.
Owner:GENEOHM SCI CANADA
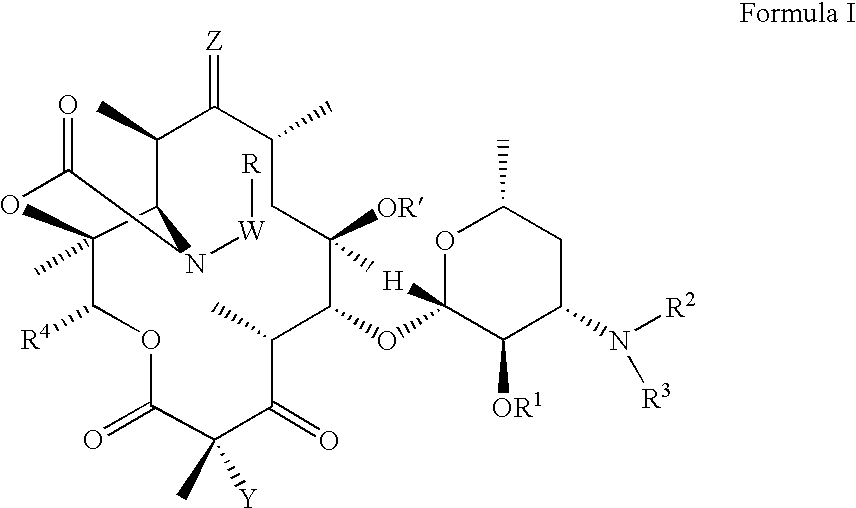
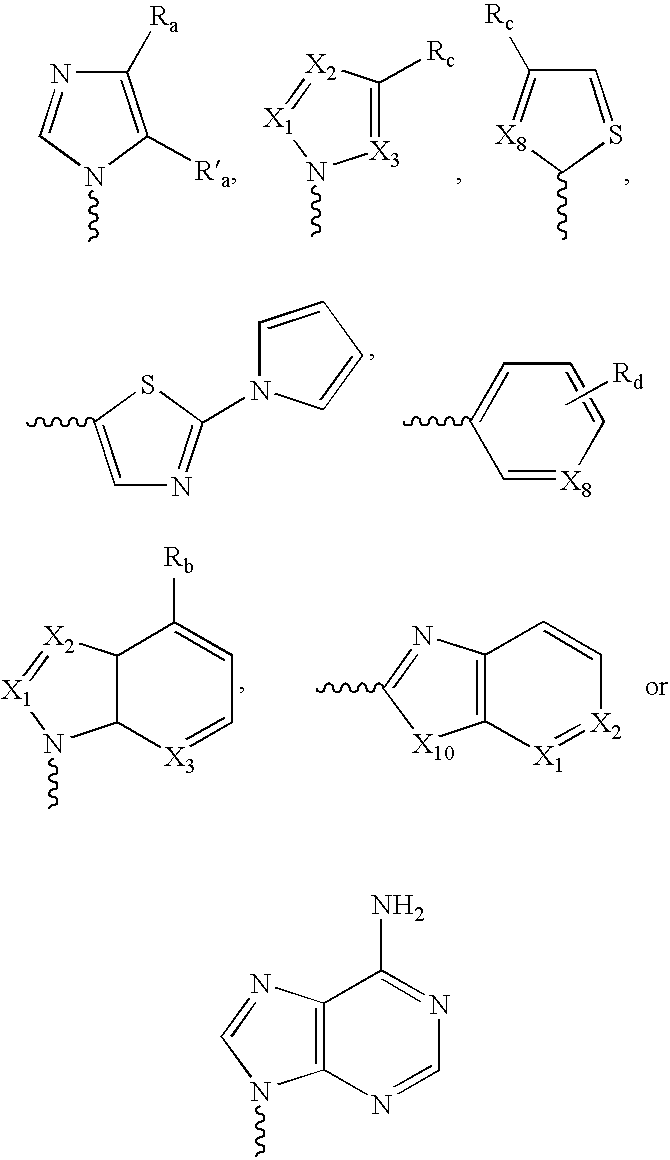
Ketolide Derivatives as Antibacterial Agents
The present invention provides ketolide derivatives, which can be used as antibacterial agents. In particular, compounds described herein can be used for treating or preventing conditions caused by or contributed to by Gram-positive, Gram-negative or anaerobic bacteria, more particularly against, for example, Staphylococci, Streptococci, Enterococci, Haemophilus, Moraxalla spp. Chlamydia spp., Mycoplasm, Legionella spp., Mycobacterium, Helicobacter, Clostridium, Bacteroides, Corynebaclerium, Bacillus or Enterobactericeae. Also provided are processes for preparing such ketolide derivatives, pharmaceutical compositions thereof, and methods of treating bacterial infections.
Owner:RANBAXY LAB LTD
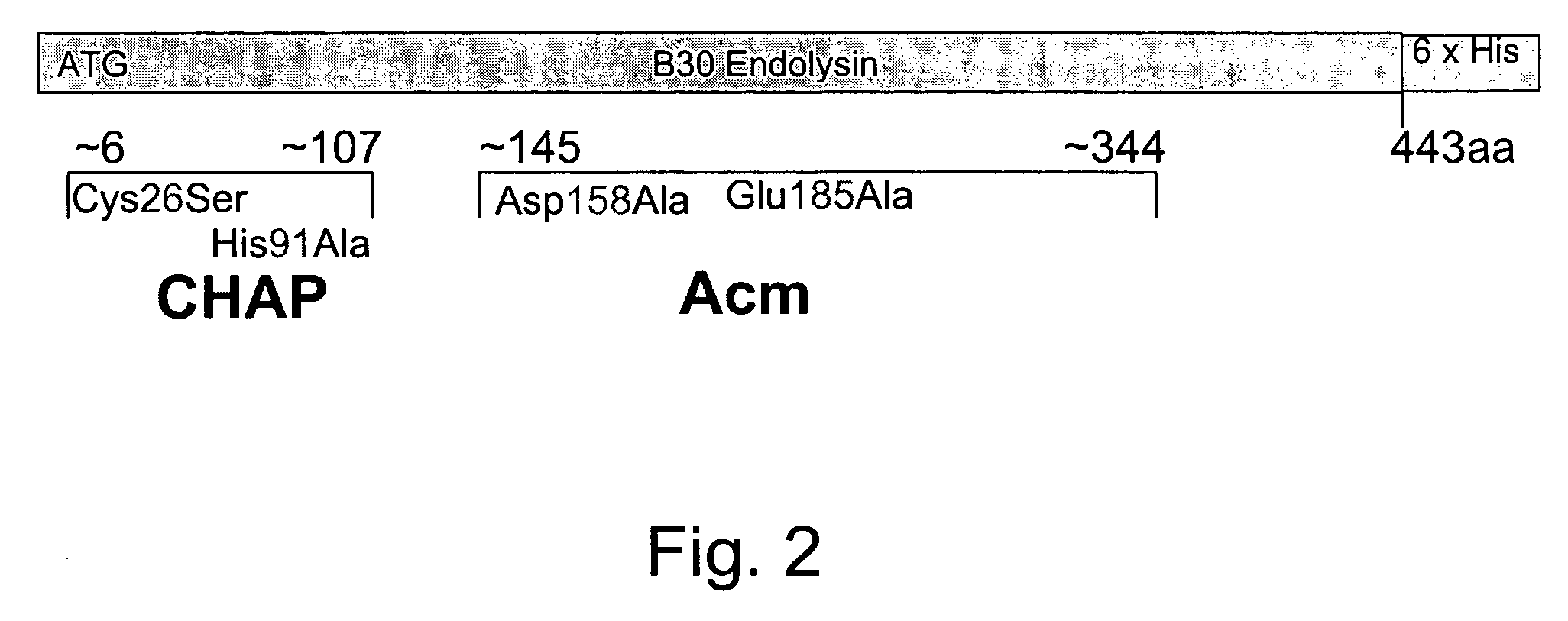
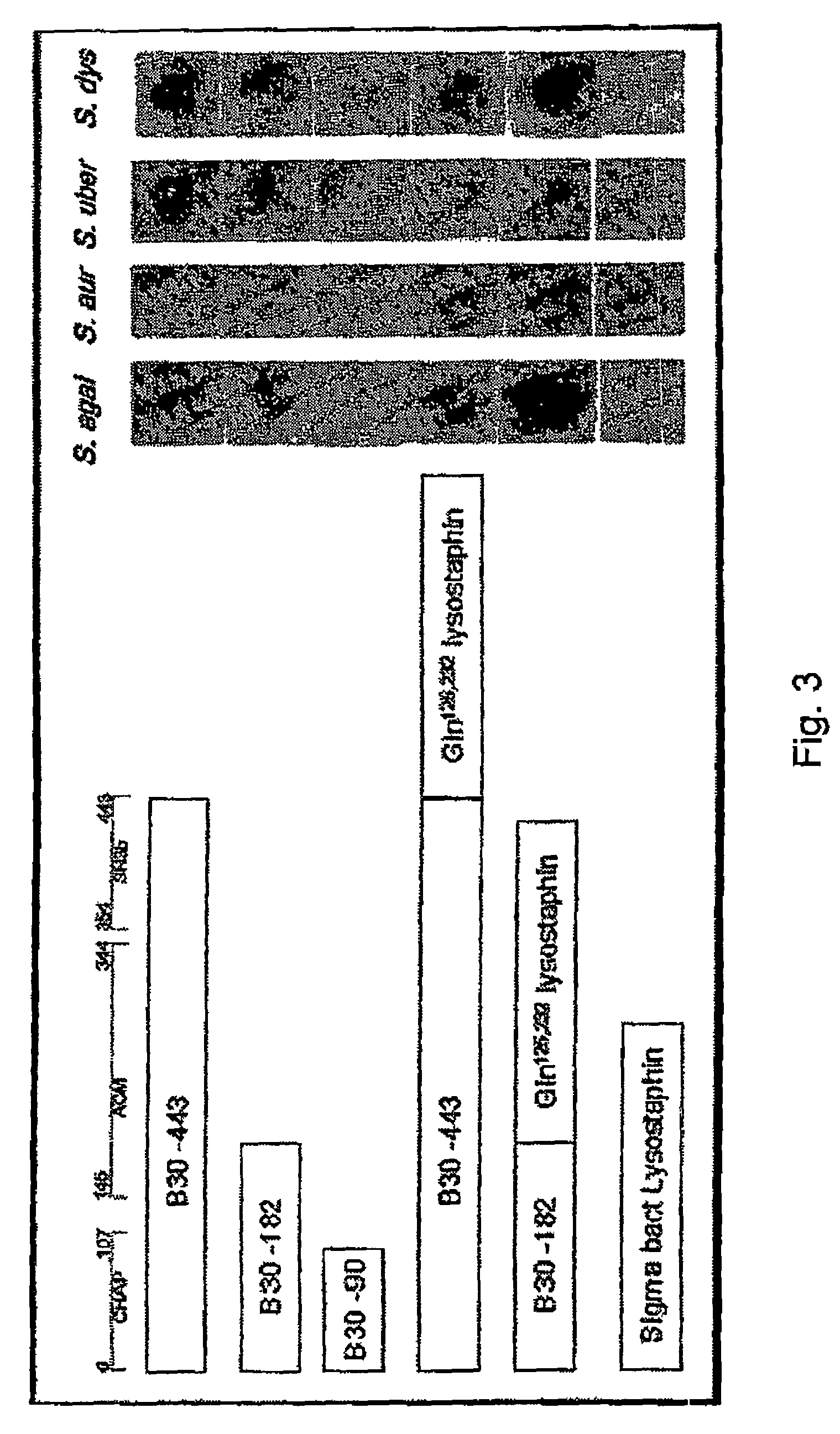
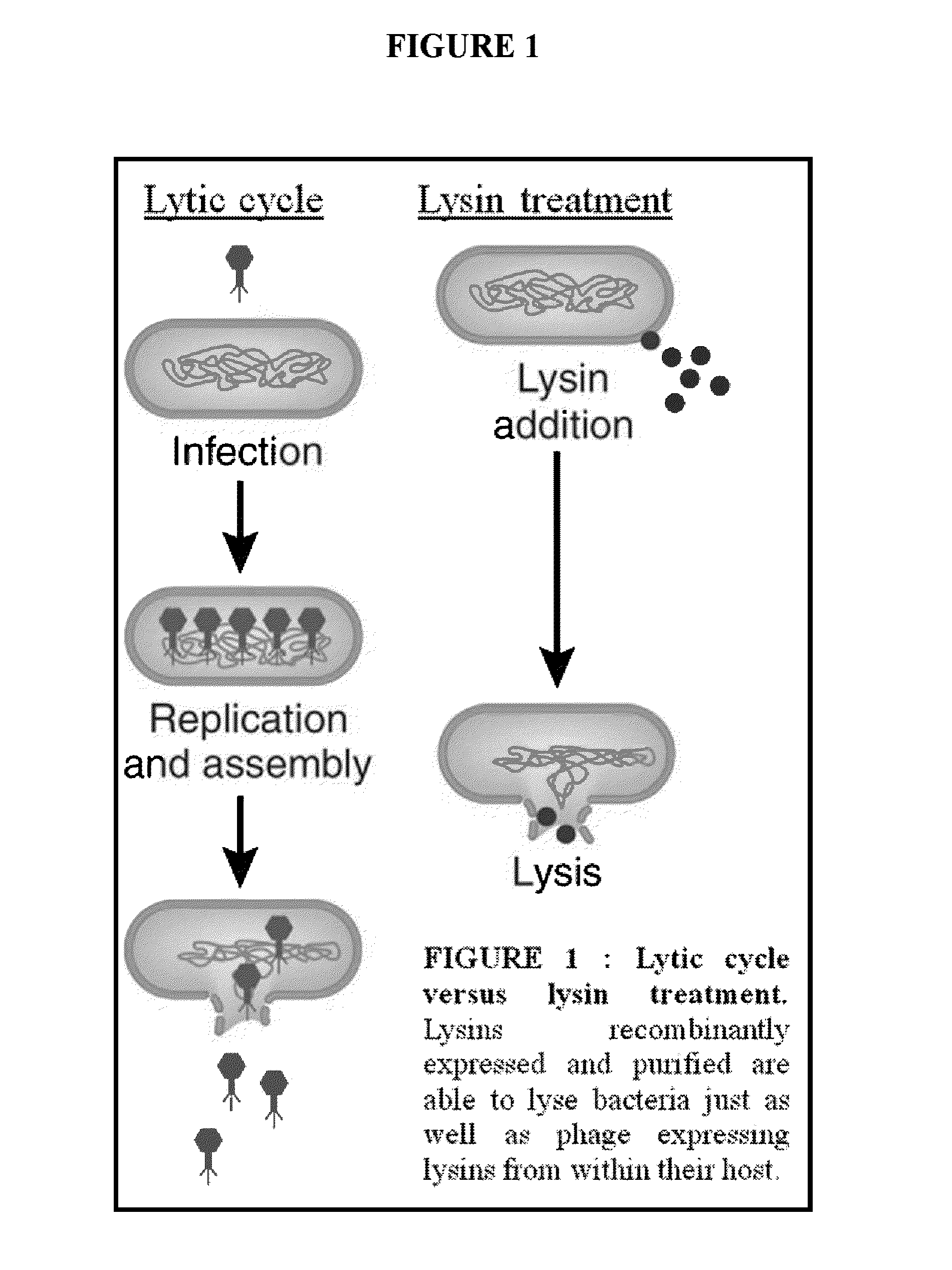
Nucleic acid encoding endolysin fusion protein
The invention concerns a recombinant nucleic acid molecule encoding an antimicrobial fusion peptidoglycan endopeptidase. The recombinant nucleic acid molecule according to the invention is formed from a nucleic acid encoding a bacterial endopeptidase (lysostaphin) from Staphylococcus simulans and a nucleic acid encoding a second endopeptidase (endolysin) module from Group B streptococcal bacteriophage B30. The encoded fusion endopeptidase has antimicrobial activity and kills both Staphylococcus bacteria and Streptococcus bacteria.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Species-specific, genus-specific and universal DNA probes and amplification primers to rapidly detect and identify common bacterial and fungal pathogens and associated antibiotic resistance genes from clinical specimens for diagnosis in microbiology laboratories
InactiveUS20030049636A1Low costRapid positioningMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationBacteroidesNeisseria meningitidis
DNA-based methods employing amplification primers or probes for detecting, identifying, and quantifying in a test sample DNA from (i) any bacterium, (ii) the species Streptococcus agalactiae, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Enterococcus faecium, Neisseria meningitidis, Listeria monocytogenes and Candida albicans, and (iii) any species of the genera Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, Enterococcus, Neisseria and Candida are disclosed. DNA-based methods employing amplification primers or probes for detecting, identifying, and quantifying in a test sample antibiotic resistance genes selected from the group consisting of blatem, blarob, blashv, blaoxa, blaZ, aadB, aacC1, aacC2, aacC3, aacA4, aac6'-lla, ermA, ermB, ermC, mecA, vanA, vanB, vanC, satA, aac(6')-aph(2''), aad(6'), vat, vga, msrA, sul and int are also disclosed. The above microbial species, genera and resistance genes are all clinically relevant and commonly encountered in a variety of clinical specimens. These DNA-based assays are rapid, accurate and can be used in clinical microbiology laboratories for routine diagnosis. These novel diagnostic tools should be useful to improve the speed and accuracy of diagnosis of microbial infections, thereby allowing more effective treatments. Diagnostic kits for (i) the universal detection and quantification of bacteria, and / or (ii) the detection, identification and quantification of the above-mentioned bacterial and fungal species and / or genera, and / or (iii) the detection, identification and quantification of the above-mentioned antibiotic resistance genes are also claimed.
Owner:BERGERON MICHEL G +3
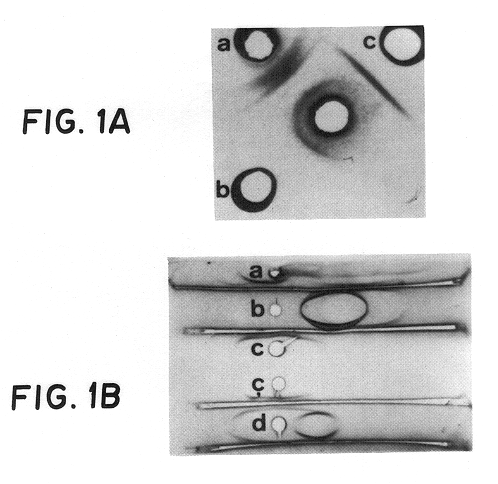
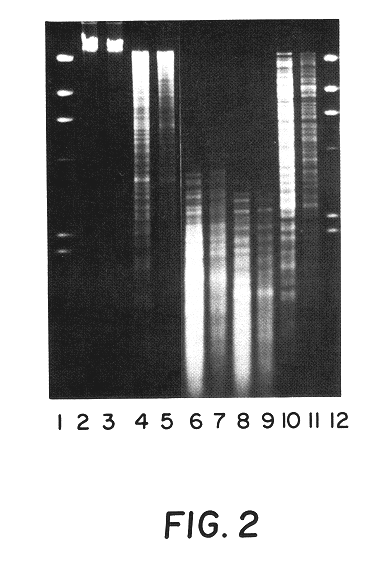
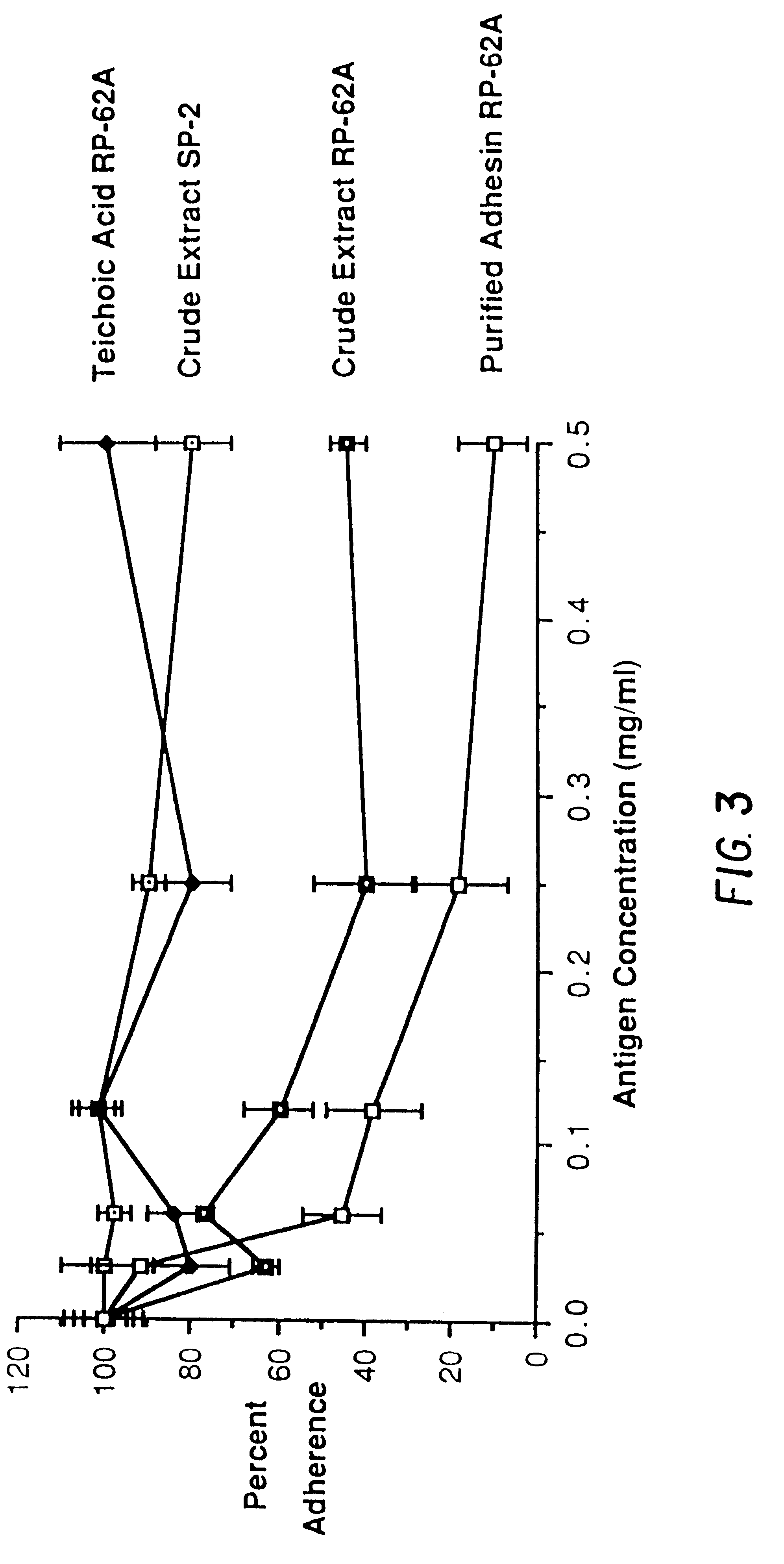
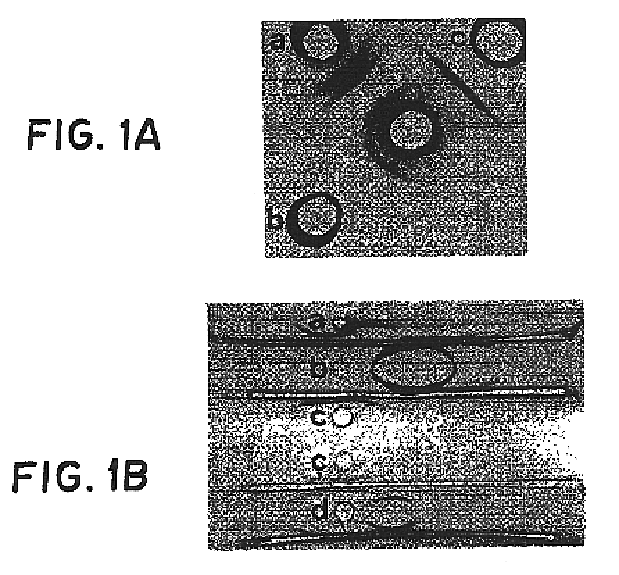
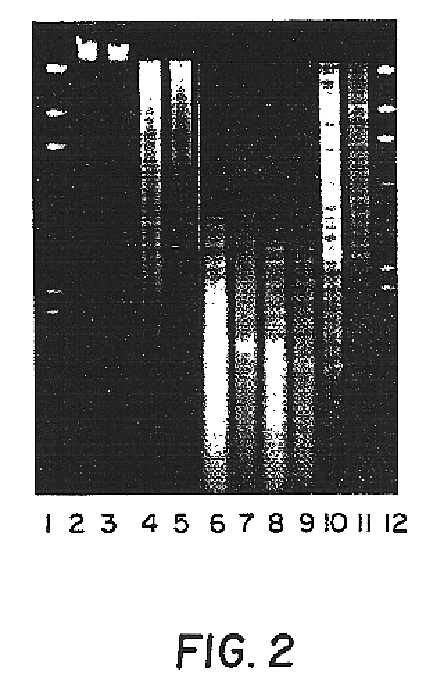
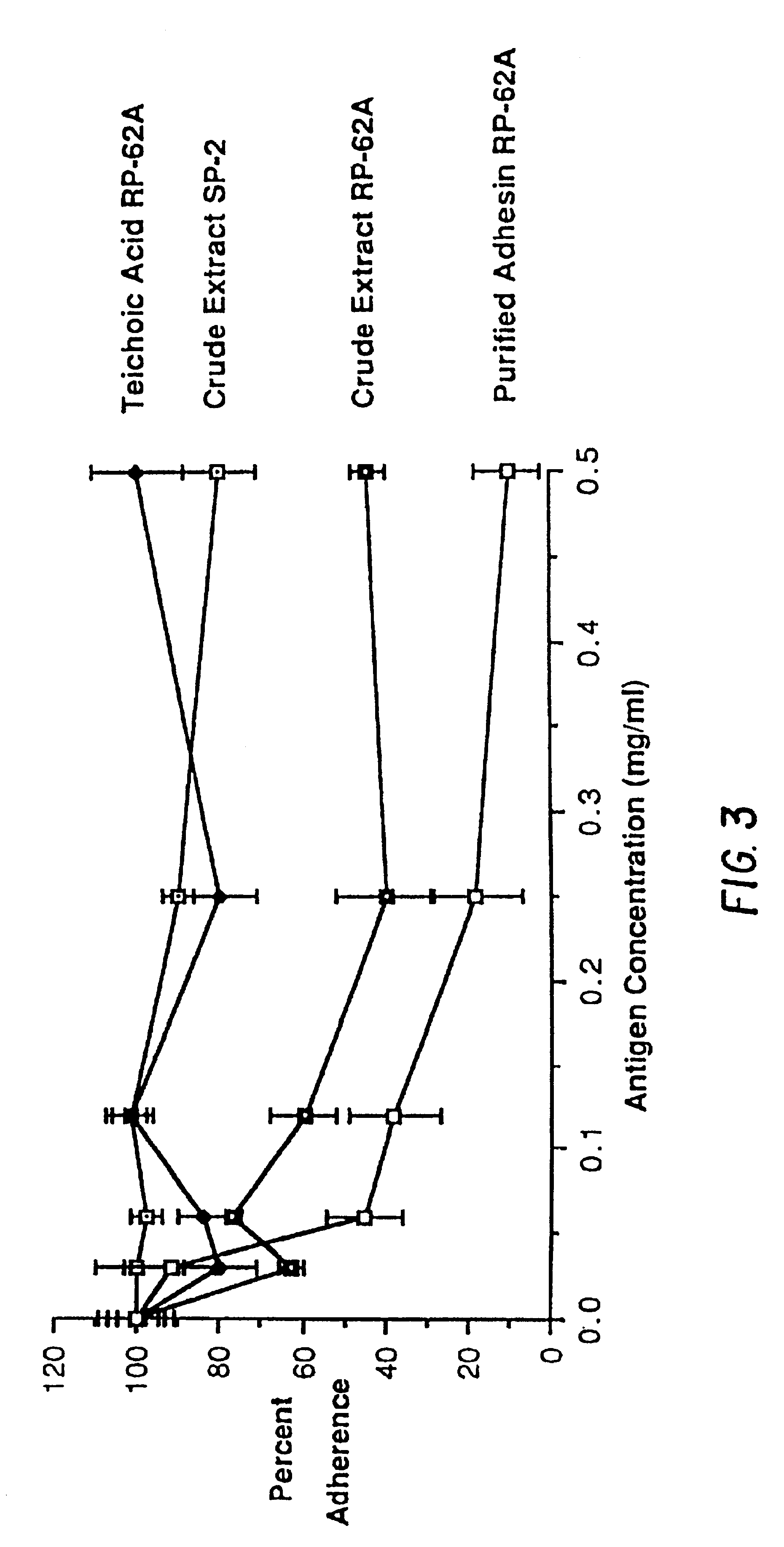
Capsular polysaccharide adhesin antigen, preparation, purification and use
A substantially pure capsular exopolysaccharide adhesin of coagulase-negative staphylococcal strains, and a general method to prepare such adhesins, are described. Vaccines composed of such adhesins, and uses of such adhesins to produce polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies against such adhesins, are also disclosed. The adhesins are useful in coating polymeric medical materials to prevent colonization by coagulase-negative staphylococcal strains, and as a probe in selecting desirable polymeric medical materials. Such adhesin antibodies are useful in vivo to prevent infection by nosocomial coagulase-negative staphylococcal strains, in assays for the detection of such bacteria, in assays for the estimation of such adhesins in complex mixtures, and as an affinity chromatography matrix.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMENS HOSPITAL INC
Streptococcus bacteriophage lysins for detection and treatment of gram positive bacteria
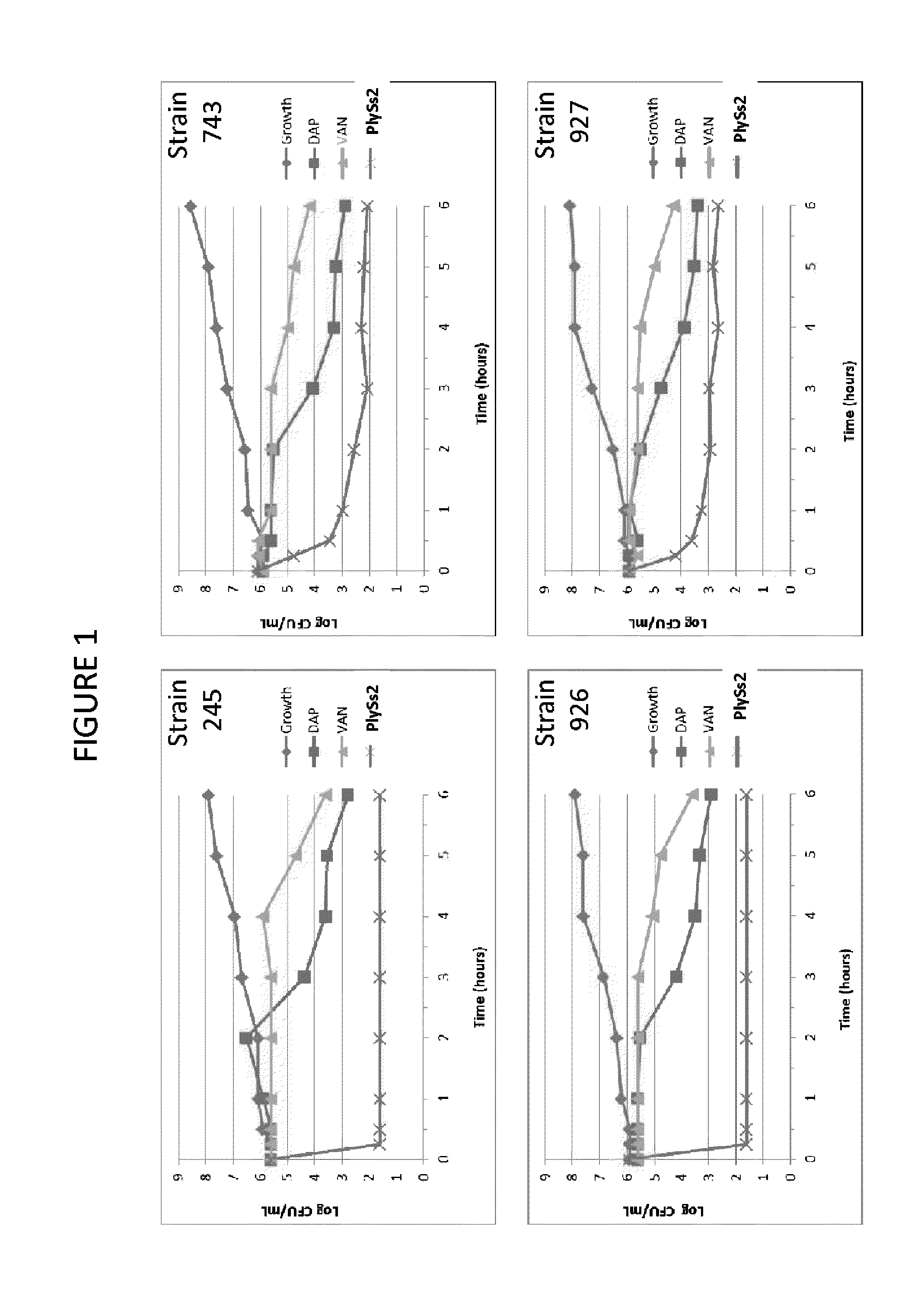
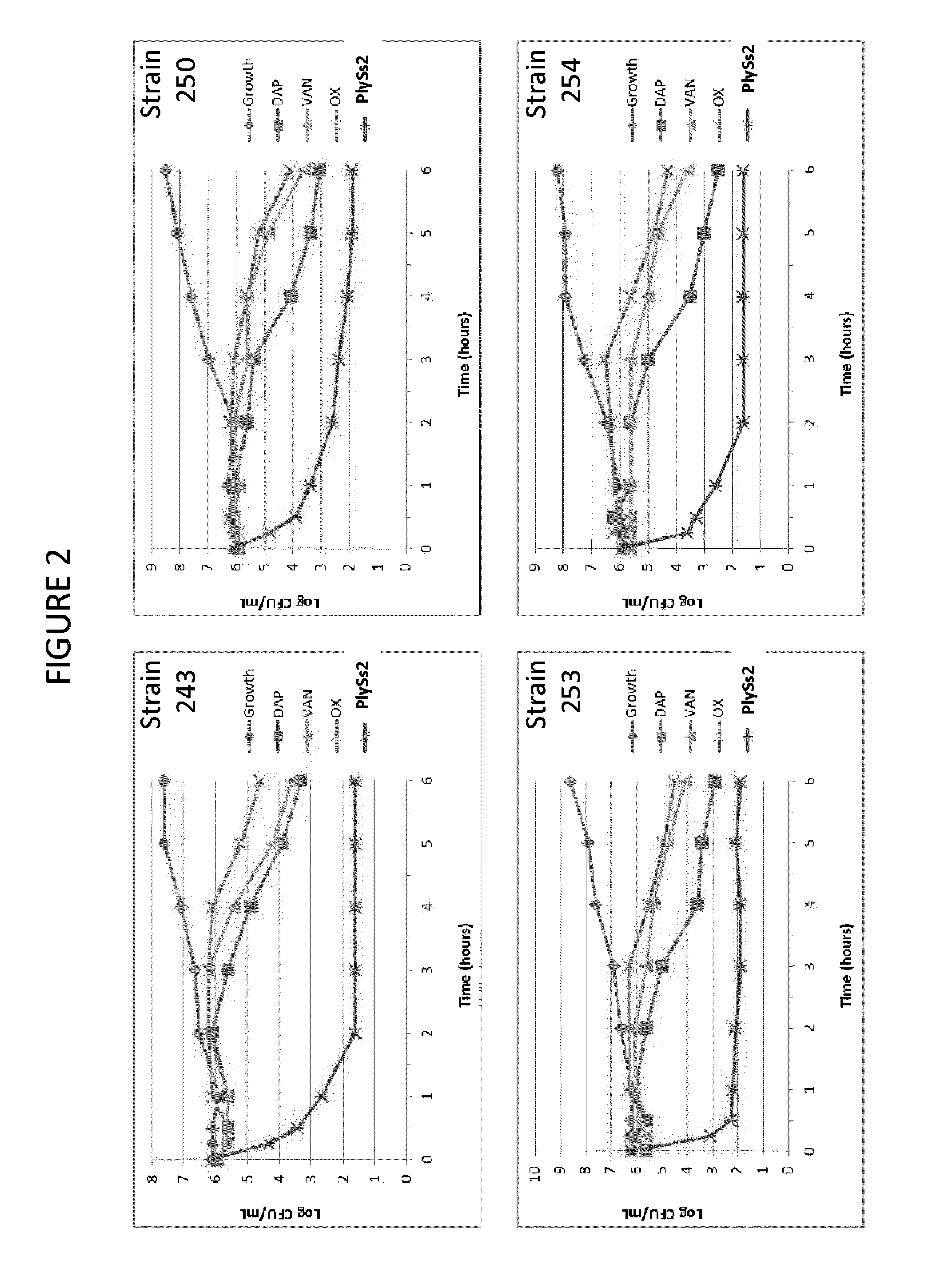
ActiveUS9034322B2Efficient killingReduce in quantityAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryStreptococcus constellatusStaphylococcus xylosus
The present invention provides methods, compositions and articles of manufacture useful for the prophylactic and therapeutic amelioration and treatment of gram-positive bacteria, including Streptococcus and Staphylococcus, and related conditions. The invention provides compositions and methods incorporating and utilizing Streptococcus suis derived bacteriophage lysins, particularly PlySs2 and / or PlySs1 lytic enzymes and variants thereof, including truncations thereof. Methods for treatment of humans are provided.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
Technological process for preparing fermentation dehydrated beef using composite leaven
InactiveCN101248884AImprove organizational structureEnhance sensory effectFood preparationLactobacillusOrganoleptic
The invention provides a method for producing fermented beef jerky with compound leaven. The bacteria strain used in fermentation is lactobacillus casei and staphylococcus xylosus with volume ratio of 1:3 and volume of addition of 1-1.5%, the fermentation temperature is 20 DEG C, and the fermentation time is 5 days. The addition of lactobacillus casei reduces pH value of the product, improves safety, improves the texture of the product, and shortens fermentation period. At the same time, the addition of staphylococcus xylosus generates a large amount of flavoring substances during fermentation process, improves sensing effect of the product, and the final product has thick fragrance, good taste, and infinitive aftertaste. The inventive method is especially suitable for producing fermented beef jerky, as well as air dried sausage and sausage.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Capsular polysaccharide adhesin antigen, preparation, purification and use
A substantially pure capsular exopolysaccharide adhesin of coagulaso-negative staphylococcal strains, and a general method to prepare such adhesins, are described. Vaccines composed of such adhesins, and uses of such adhesins to produce polyclonal and mono-clonal antibodies against such adhesins, are also disclosed. The adhesins are useful in coating polymeric medical materials to prevent colonization by coagulase-negative staphylococcal strains, and as a probe in selecting desirable polymeric medical materials. Such adhesin antibodies are useful in vivo to prevent infection by noso-comial coagulase-negative staphylococcal strains, in assays for the detection of such bacteria, in assays for the estimation of such adhesins in complex mixtures, and as an affinity chromatography matrix.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
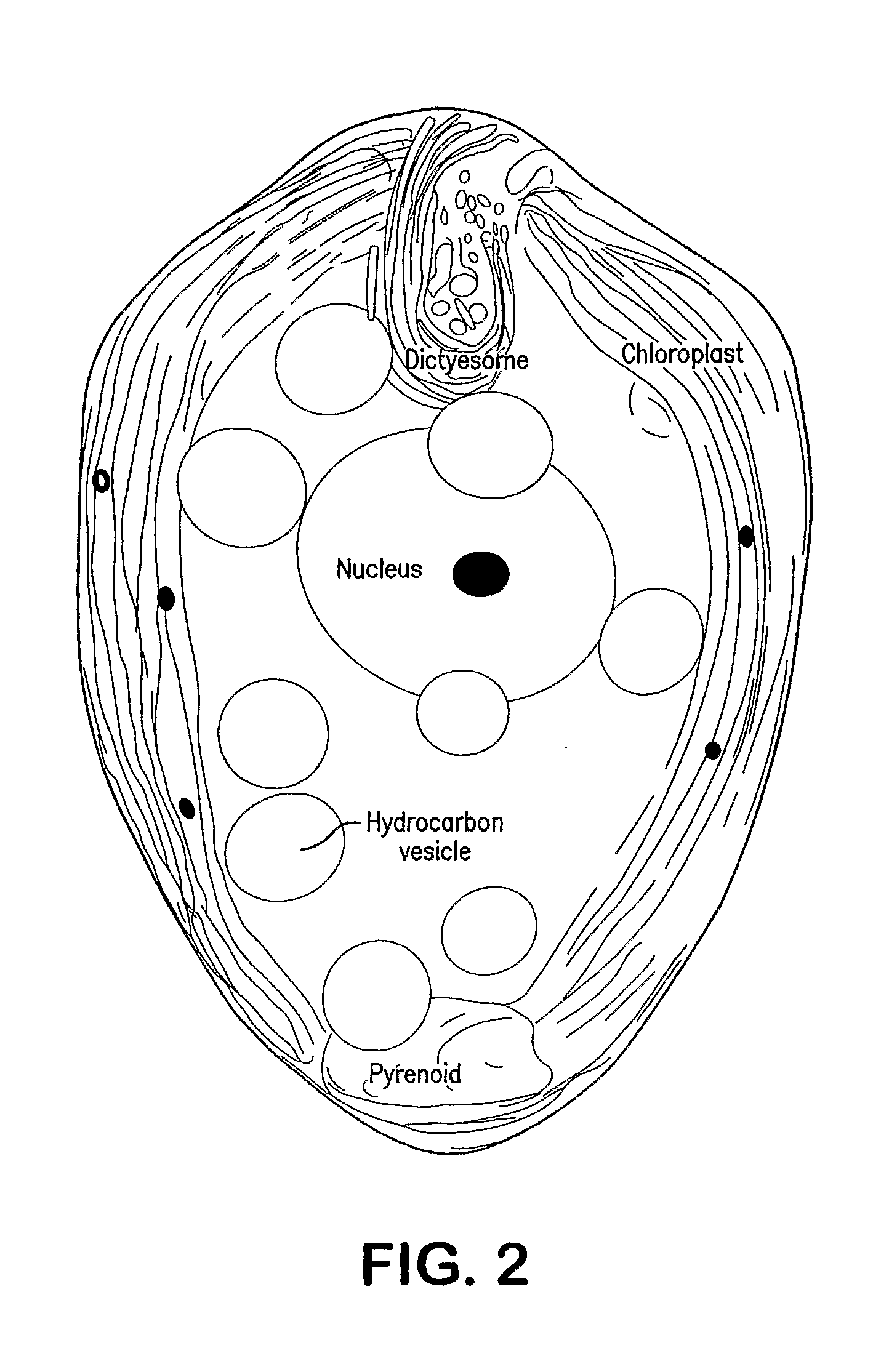
Methods and compositions for growth hydrocarbons in botryococcus sp.
Owner:NONOMURA ARTHUR M
Staphylococcus aureus polynucleotides and polypeptides
The present invention relates to novel genes from S. aureus and the polypeptides they encode. Also provided are vectors, host cells, antibodies and recombinant methods for producing the same. The invention further relates to screening methods for identifying agonists and antagonists of S. aureus polypeptide activity. The invention additionally relates to diagnostic methods for detecting Staphylococcus nucleic acids, polypeptides and antibodies in a biological sample. The present invention further relates to novel vaccines for the prevention or attenuation of infection by Staphylococcus.
Owner:HUMAN GENOME SCI INC
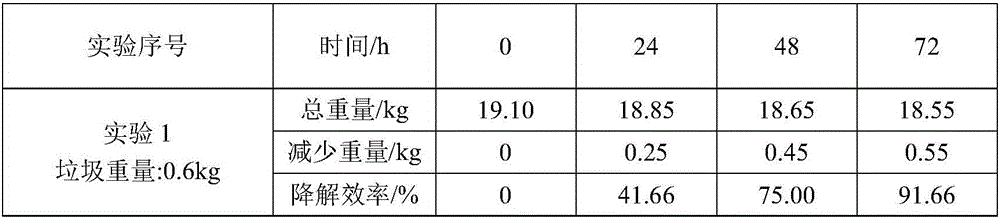
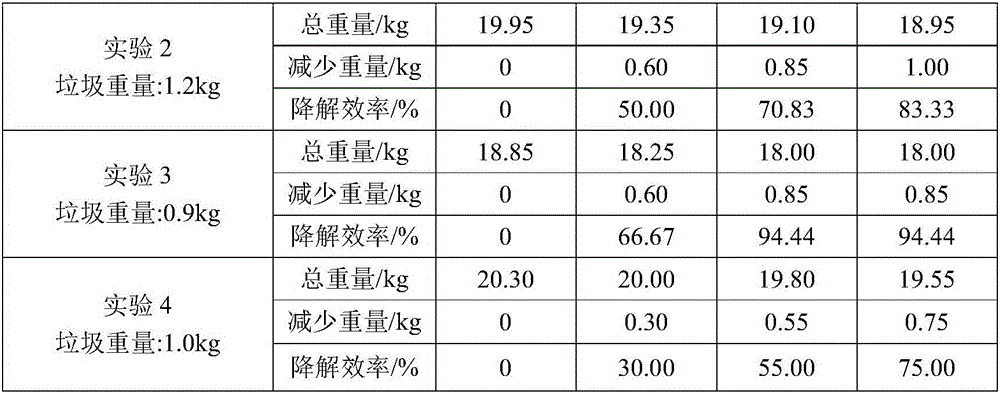
Kitchen garbage degrading composite microbial inoculum and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106591178AEfficient degradationFast degradation rateBacteriaSolid waste disposalStaphylococcus cohniiStaphylococcus xylosus
The invention relates to a kitchen garbage degrading composite microbial inoculum and a preparation method and application thereof. The kitchen garbage degrading composite microbial inoculum is prepared by mixing a mixed inoculum of bacillus amyloliquefaciens, radiation-resistant methylobacterium, dispersed pantoea, pseudomonas oryzihabitans, citrobacter freundii and staphylococcus cohnii and a carrier, wherein the mass of the mixed inoculum accounts for 15-25% of the total mass of the kitchen garbage-degrading composite microbial inoculum; the mass ratio of the bacillus amyloliquefaciens, the radiation-resistant methylobacterium, the dispersed pantoea, the pseudomonas oryzihabitans, the citrobacter freundii and the staphylococcus cohnii is (1.5-3):(1-1.5):(1-1.5): (1-1.5):(1-1.5):(1-1.5); the kitchen garbage-degrading composite microbial inoculum is used for degrading kitchen garbage. Compared with the prior art, the kitchen garbage degrading composite microbial inoculum has the advantages as follows: the kitchen garbage degrading composite microbial inoculum can effectively degrade common vegetables, grains, fish, poultry meat and other kitchen garbage, has the degradation rate being above 80%, is high in degradation speed rate and small in odor, does not produce pollutants or poisonous substances, and is low in cost and stable in performance.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
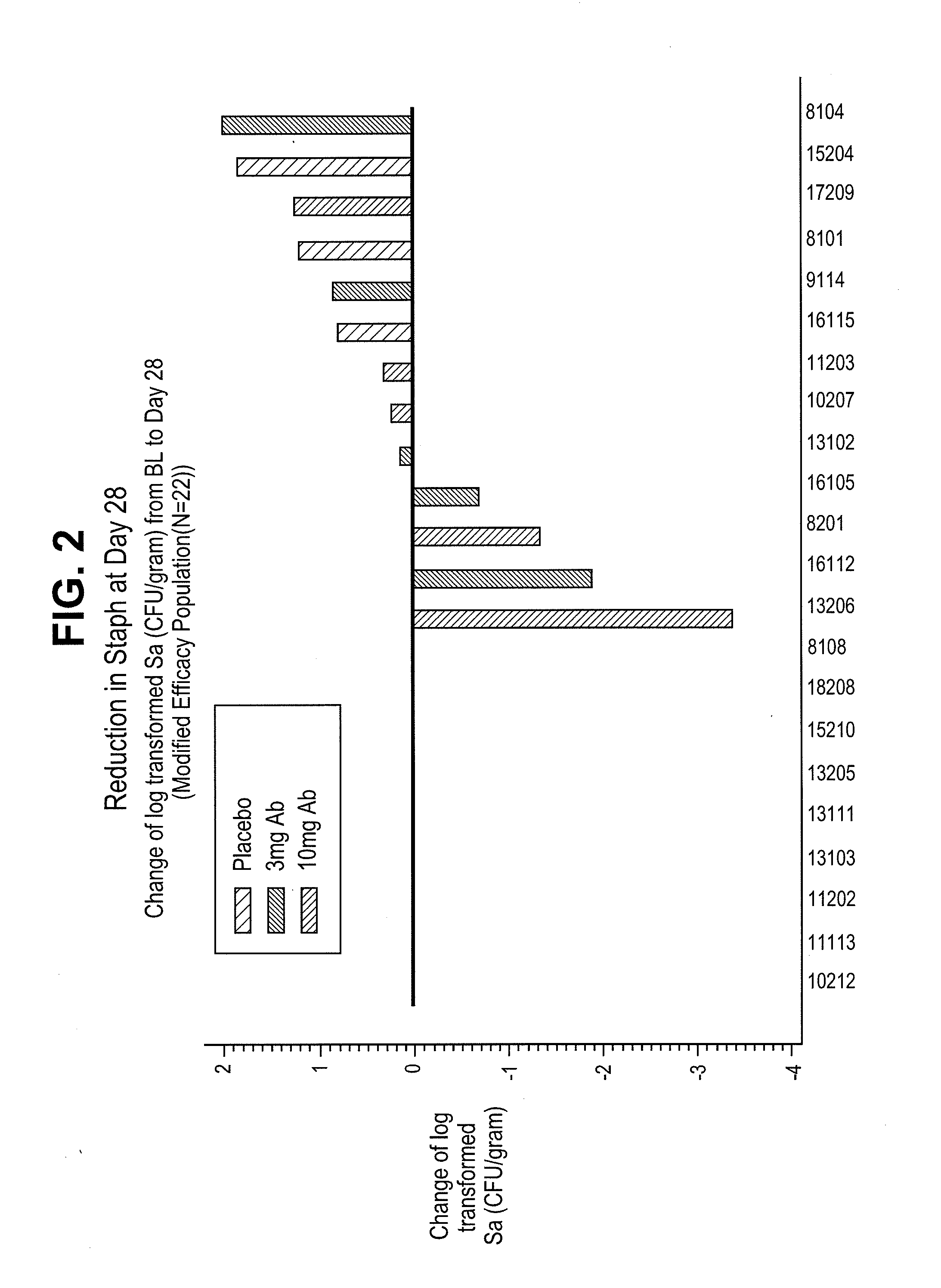
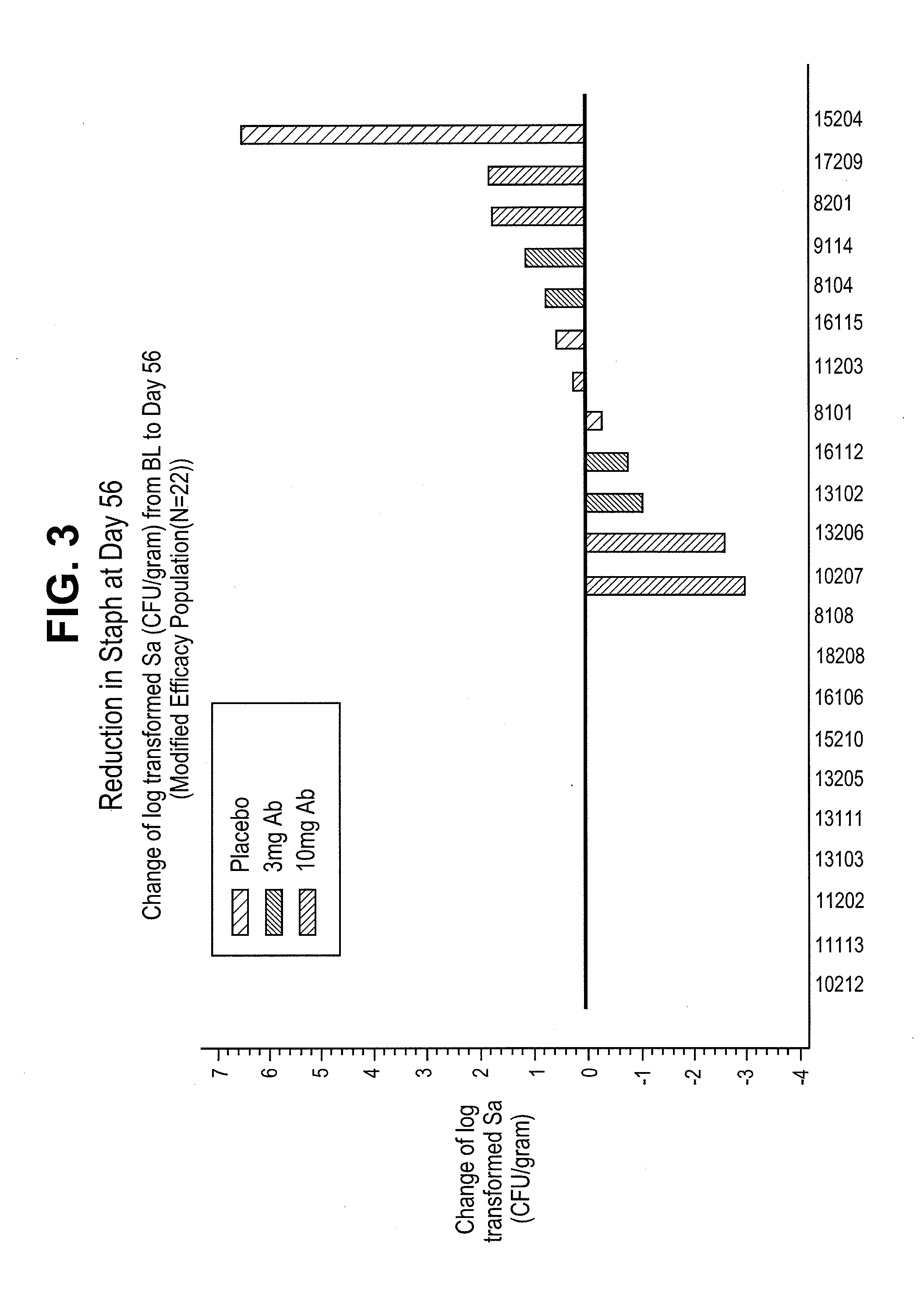
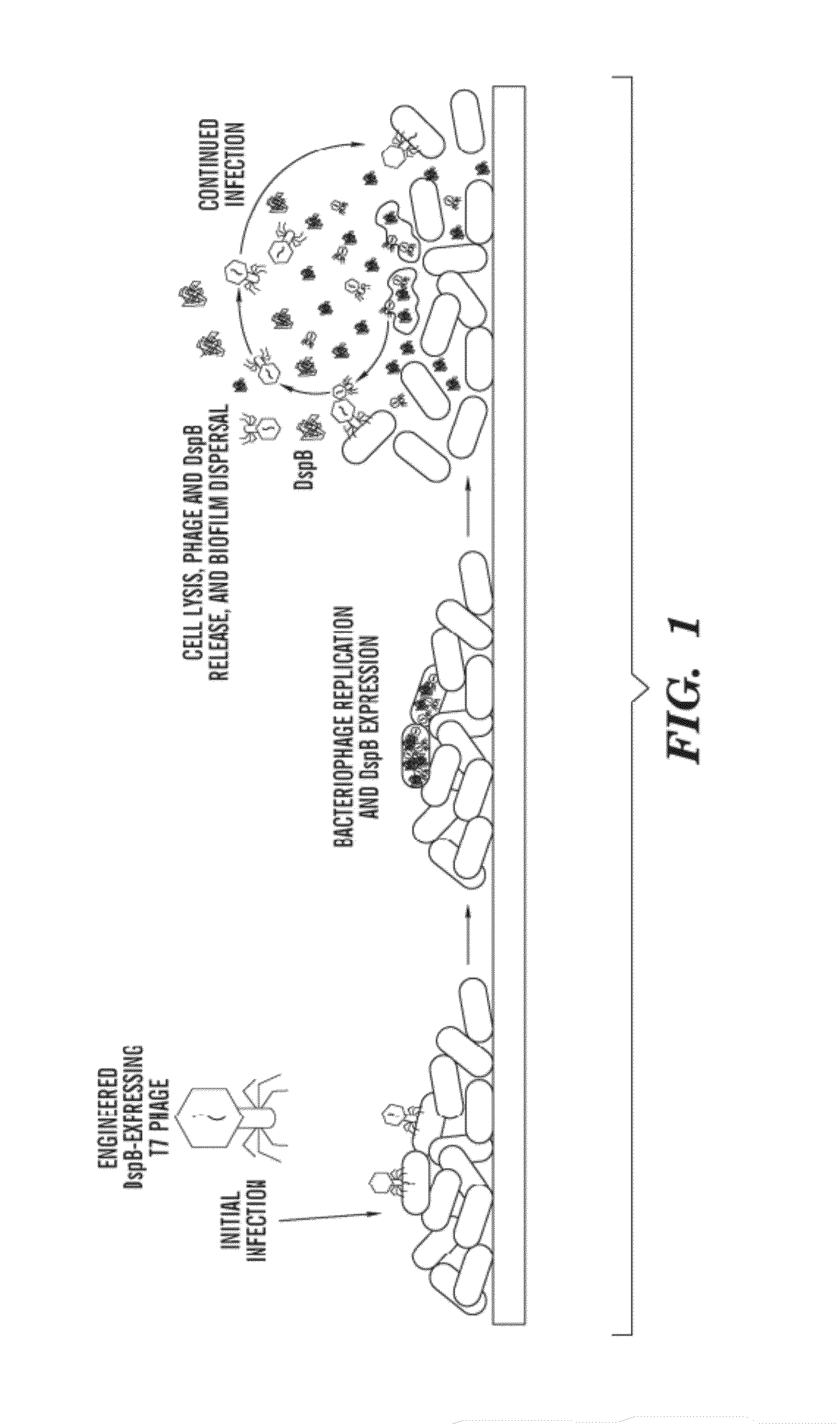
Engineered enzymatically active bacteriophage and methods for dispersing biofilms
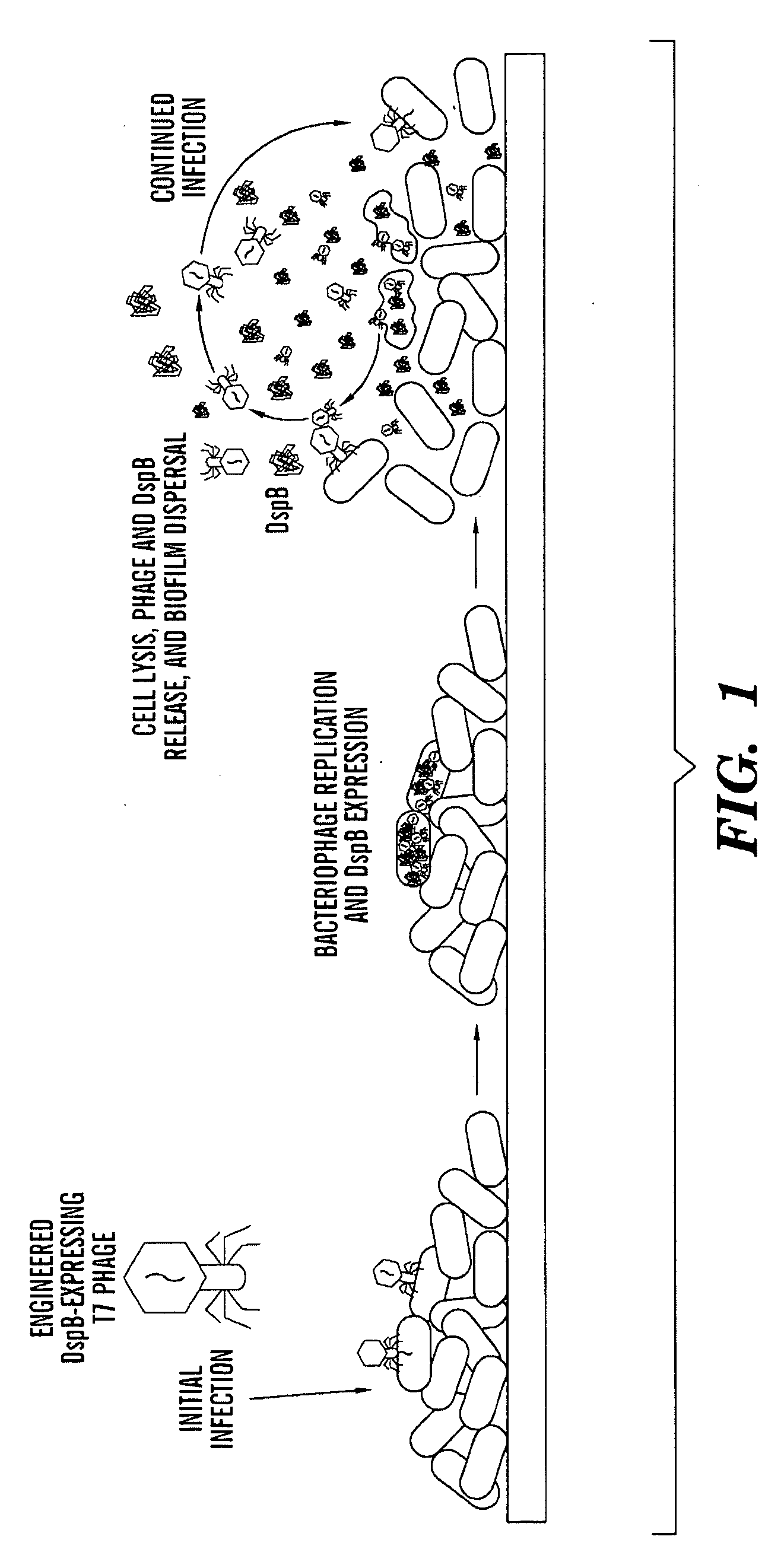
ActiveUS20090155215A1High concentrationReduce and eliminate multiple applicationBiocideGenetic material ingredientsEscherichia coliBiofilm
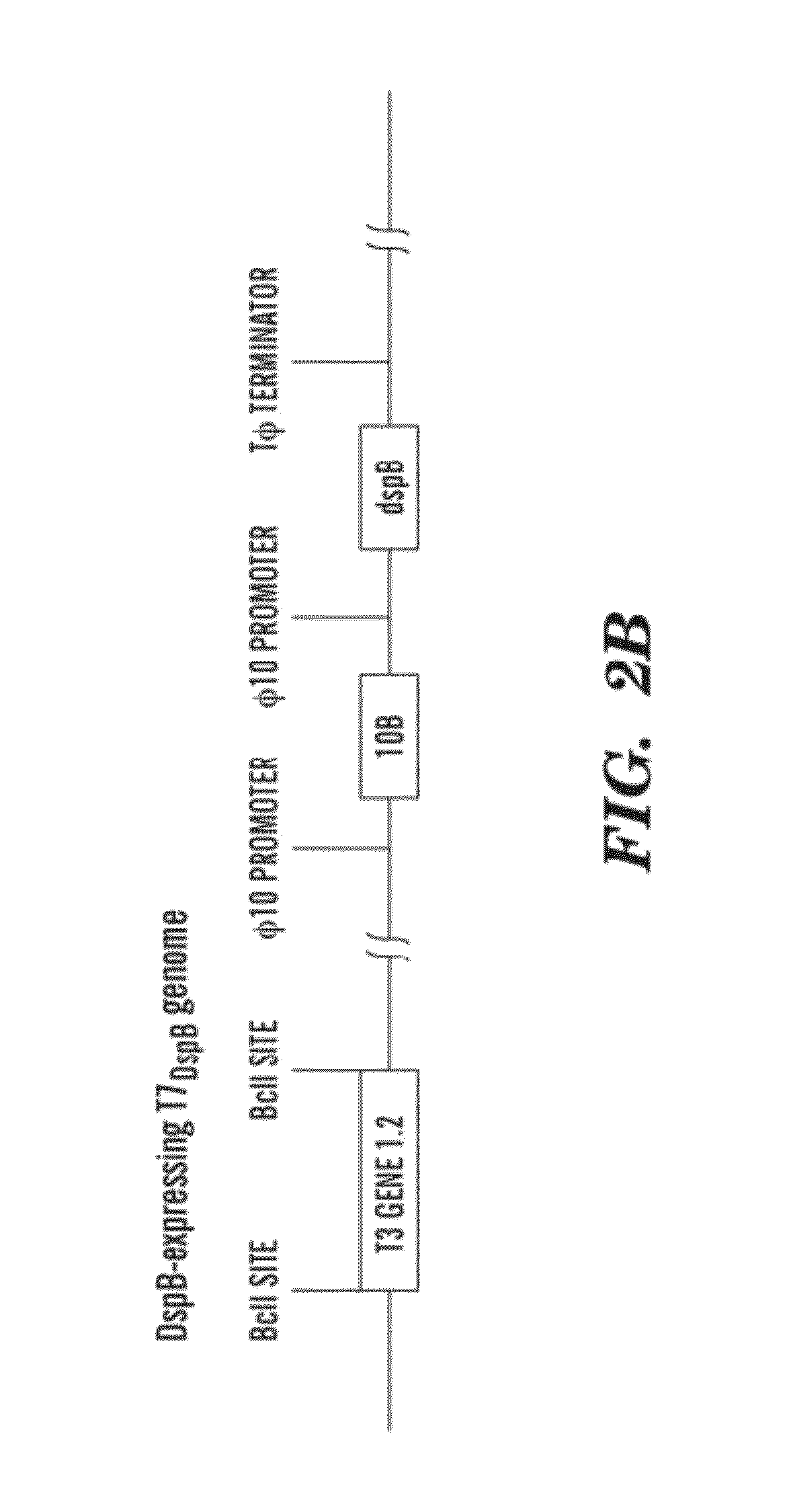
The present invention is directed to engineered enzymatically active bacteriophages that are both capable of killing the bacteria by lysis and dispersing the bacterial biofilm because they have been also engineered to express biofilm-degrading enzymes, particularly dispersin B (DspB), an enzyme that hydrolyzes β-1,6-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine, a crucial adhesion molecule needed for biofilm formation and integrity in Staphylococcus and E. coli, including E. coli K-12, as well as clinical isolates.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
Method of treating a staphylococcus infection in a patient having a low-level pathogenic pseudomonas aeruginosa infection
InactiveUS20110165172A1Lower Level RequirementsLow levelAntibacterial agentsAntibody ingredientsStaphylococcal infectionsPseudomonas
This invention provides methods of treating patients having a Staphylococcus infection where the patient also has a low level of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The methods comprise administering an antagonist of the Pseudomonas Type III Secretion System, e.g., an anti-PcrV antibody antagonist.
Owner:KALOBIOS PHARMA
Compositions and methods for treatment of staphylococcal infection while suppressing formation of antibiotic-resistant strains
Co-administration of a lysostaphin or other anti-staphylococcal agent which cleaves cross-links of peptidoglycans of staphylococci cell walls such as lysostaphin and an antibiotic effective against staphylococci due to antibiotic activity mediated by cell-wall activity is effective against staphylococcal infection, even staphylococci that may be resistant to one or other of lysostaphin or the cell-wall active antibiotic. Co-administration simultaneously suppresses the generation of antibiotic-resistant mutant strains. Effective cell-wall active antibiotics include β-lactams and glycopeptides.
Owner:NUTRITION 21 INC
Fermentation agent for low ergamine salami sausage and method of use thereof
InactiveCN101176559ALowers histamine levelsExcellent flavorMeat/fish preservation using acidsFood preparationFlavorDecarboxylase activity
The invention discloses a fermentation agent and the application method for processing low histamine salami sausage, comprising the followings: 1. The selected strains of fermentation agent are CGMCCNo.1923-pediococcus pentosaceus and CGMCCNo.1572-staphylococcus xylosus both without decarboxylase activity; 2. The matching proportion between the CGMCCNo.1923-pediococcus pentosaceus and the CGMCCNo.1572-staphylococcus xylosus is 1:1; 3. The fermentation agent dosage of the pediococcus pentosaceus and the staphylococcus xylosus are 100kg respectively every 100g of mince when processing, the inoculated-pathogen quantity can be up to 1 x 10<7>cfu / g. The adding method is as follow: to make fermentation liquid by mixing the pediococcus pentosaceus fermentation agent and the staphylococcus xylosus fermentation agent with equal ratio and being dissolved in 500g water, spread the fermentation liquid uniformly on the mix mince surface, and mix the mince and the fermentation liquid thoroughly; 4. The preserved preparation used is as follow: the mass ratio to the material mince is salt 3.0%, glucose 1.5%, sodium nitrite 0.015%, and ascorbic acid 0.08%; 5. Using the fermentation agent, preserved preparation and processing technology, the histamine content of salami product is reduced by more than 40% and meets with the food histamine content limitation requirement of the European Union. The invention is tested according to the regulated hygienic standards of cured meat products in the GB2730-2005 hygienic standard for cured meat products, the hygienic state of products meets with the standard, the product flavor and the hygienic safety are better than the traditional technologic product evidently. The invention has the advantages of good application prospect in the aspects of quality improvement and new product development of salami products.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Engineered enzymatically active bacteriophage and methods for dispersing biofilms
ActiveUS8153119B2High concentrationReduce and eliminate multiple applicationBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsEscherichia coliBiofilm
The present invention is directed to engineered enzymatically active bacteriophages that are both capable of killing the bacteria by lysis and dispersing the bacterial biofilm because they have been also engineered to express biofilm-degrading enzymes, particularly dispersin B (DspB), an enzyme that hydrolyzes β-1,6-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine, a crucial adhesion molecule needed for biofilm formation and integrity in Staphylococcus and E. coli, including E. coli K-12, as well as clinical isolates.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
Method for pickling fresh water fish
InactiveCN101356981AIncreased concentration activates the enzymeSuppress generationMeat/fish preservation using acidsFood preparationPediococcus speciesBiological activation
The invention discloses a method for preserving fresh water fish. The method comprises the steps of killing, washing, preserving, drying and packing. The preserving steps comprise after being processed, round fish is placed in pickle at the temperature of 10-15 DEG C for 24-36 hours; wherein, the prepared pickle is of 4% salt solution containing 2%-3%(W / W) of glucose, 3 per thousand-4 per thousand (W / W) of zinc ion, 1%-2%(W / W) of a blended leaven; the blended leaven is selected from the mixture of two or more than two of Lactobacillus casei (L.casei), Lactobacillus plant arum (L.plantarum), Staphylococcus xylosus (S.xylosus) or Pediococcus pentosaceus (L.pentosaceus) with the same mass. In the method, the pickle with low baume degree is added with beneficial microbes and the zinc ion to increase substrate concentration activation enzyme, breed the beneficial microbes, and restrain the generation of molds. The preserved fish has low salt content and good flavor, and is easy to store.
Owner:KUSN ZHOUZHUANG LVERKANG FOOD
Monoclonal antibodies to the ClfA protein and method of use in treating or preventing infections
InactiveUS20050287164A1Avoid stickingInhibiting or impairing the binding of the ClfA proteinAntibacterial agentsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBacteroidesStaphylococcus cohnii
Monoclonal antibodies which can bind to the ClfA protein and which are generated from binding subdomains or active fragments of the ClfA protein from Staphylococcus aureus, including the active fragments proteins from its fibrinogen binding domain such as Clf40 protein, the Clf33 protein, or ClfA N3, are provided which can be useful in the treatment and protection against infection from staphylococcal bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus. In addition, medical instruments can be treated using the monoclonal antibodies of the invention in order to reduce or eliminate the possibility of their becoming infected or further spreading the infection. In particular, the antibodies of the present invention are advantageous because they can prevent adherence of the bacteria to host cells by impairing or inhibiting the ability of S. aureus ClfA to bind to fibrinogen or fibrin, and thus can be utilized in methods or treating or preventing staphylococcal inventions.
Owner:INHIBITEX INC
Bacteriophage lysin and antibiotic combinations against gram positive bacteria
ActiveUS20130302306A1Quick killBroad killing activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsLysinLinezolid
The present invention provides compositions and methods for prevention, amelioration and treatment of gram positive bacteria, particularly Staphylococcal bacteria, with combinations of lysin, particularly Streptococcal lysin, particularly the lysin PlySs2, and one or more antibiotic, including daptomycin, vancomycin, oxacillin, linezolid, or related antibiotic(s).
Owner:CONTRAFECT CORP
Compositions and methods for treatment of staphylococcal infection while suppressing formation of antibiotic-resistant strains
Co-administration of a lysostaphin or other anti-staphylococcal agent which cleaves cross-links of peptidoglycans of staphylococci cell walls such as lysostaphin and an antibiotic effective against staphylococci due to antibiotic activity mediated by cell-wall activity is effective against staphylococcal infection, even staphylococci that may be resistant to one or other of lysostaphin or the cell-wall active antibiotic. Co-administration simultaneously suppresses the generation of antibiotic-resistant mutant strains. Effective cell-wall active antibiotics include β-lactams and glycopeptides.
Owner:NUTRITION 21 INC
Staphylococcus xylosus YG-27 and application thereof to preparation of fish-fermented sausage
The invention provides a Staphylococcus xylosus YG-27 separated from salt fish and application thereof to preparation of a fish-fermented sausage. The stain is collected in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center with a collection number of CGMCCNo. XXXX in 2010. The invention has the advantages that: the Staphylococcus xylosus YG-27 separated from the salt fish and the application thereof to the preparation of the fish-fermented sausage are provided; and in the fish-fermented sausage produced by mixing the strain and lactic acid bacteria for fermentation, the flavor of the product is remarkably superior to that of a product which is synchronously produced and is only added with the lactic acid bacteria.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Lactobacillus plantarum for freshwater fish fermentation product and application thereof
InactiveCN103421704AAchieving enhanced fermentationShort fermentation timeBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismAquatic product
The invention belongs to the technical field of agricultural microorganisms and aquatic product processing, and particularly relates to a compound starter for lactobacillus plantarum and application thereof, wherein the compound starter is used as a microbial starter, is especially suitable for freshwater fish fermentation, and is composed of lactobacillus, pediococcus acidilactici and staphylococcus xylosus. A lactic acid bacterium, namely lactobacillus plantarum, suitable for freshwater fish fermentation is obtained through self separation and screening, and the preservation number in the China center for typical culture collection is CCTCC NO: M2012396. The compound microbial starter is prepared from lactobacillus plantarum, pediococcus acidilactici and staphylococcus xylosus, is suitable for fish product fermentation and particularly suitable for the application to preserved fish fermentation, has a sound fermenting property, has typical fermentation fragrance, and facilitates industrial production.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV +1
Novel staphylophage and composition, as well as preparation methods and application thereof
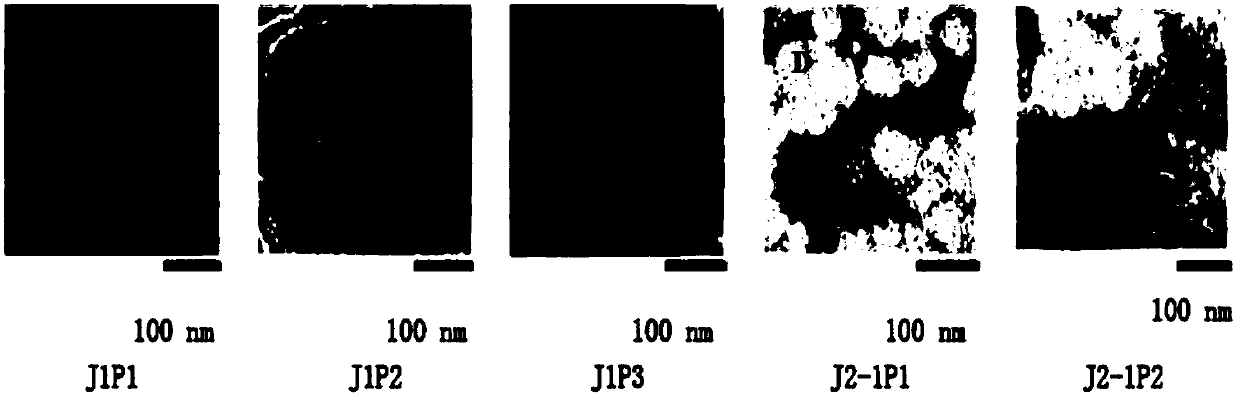
ActiveCN107779439AEfficient killingNon-toxicAntibacterial agentsViral/bacteriophage medical ingredientsMicroorganismStaphylococcal Phages
The invention relates to the field of microorganisms, and specifically provides a novel staphylophage and a composition, as well as preparation methods and application thereof. The phage is aureus staphylophage J1P1 with the storage number of CCTCC NO: M2016284, aureus staphylophage J1P2 with the storage of CCTCC NO: M2016285, aureus staphylophage J1P3 with the storage of CCTCC NO: M2016286, aureus staphylophage J2-1P1 with the storage of CCTCC NO: M2016287, or aureus staphylophage J2-1P2 with the storage of CCTCC NO: M2016288. The phage is capable of preventing and treating human or animal bacterial infectious diseases caused by various staphylococcocci, particularly by aureus staphylophage; a good phage resource is provided to develop novel antimicrobial preparations; the novel staphylophage has a good application and development prospect.
Owner:PHAGELUX (NANJING) BIO-TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com