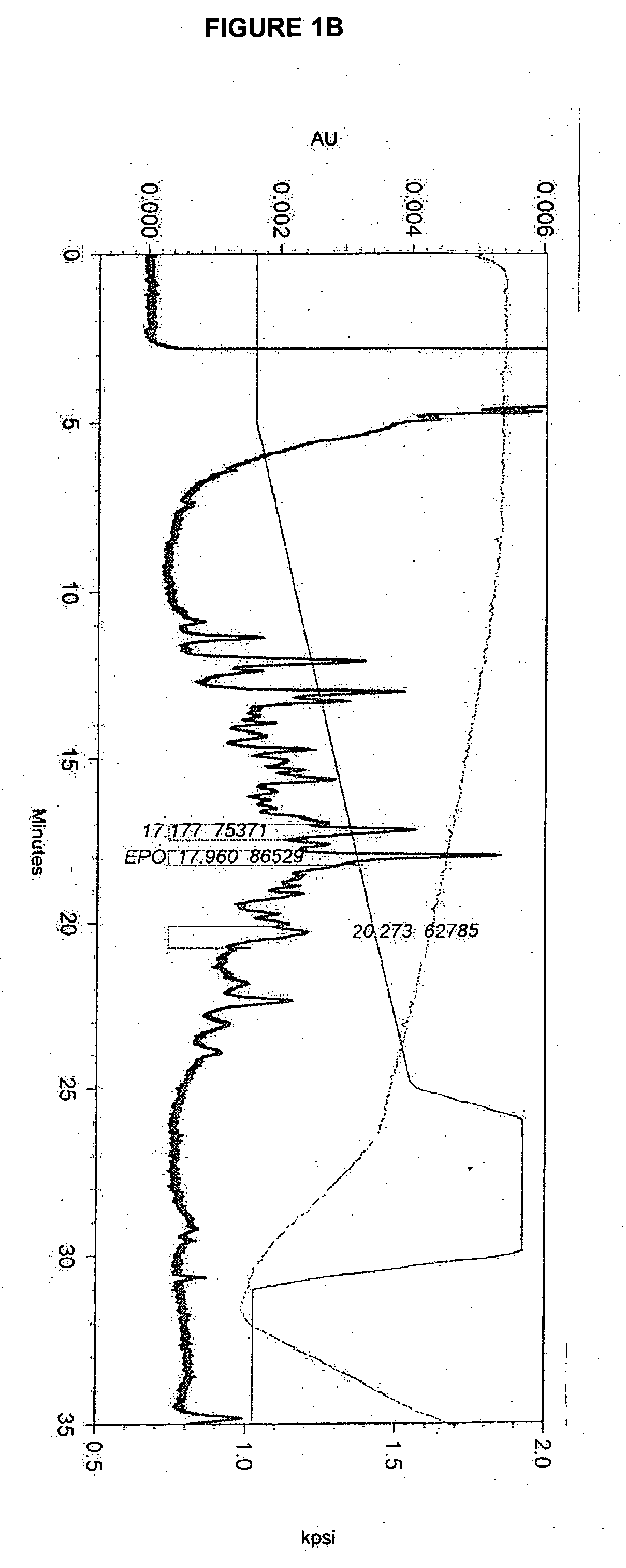
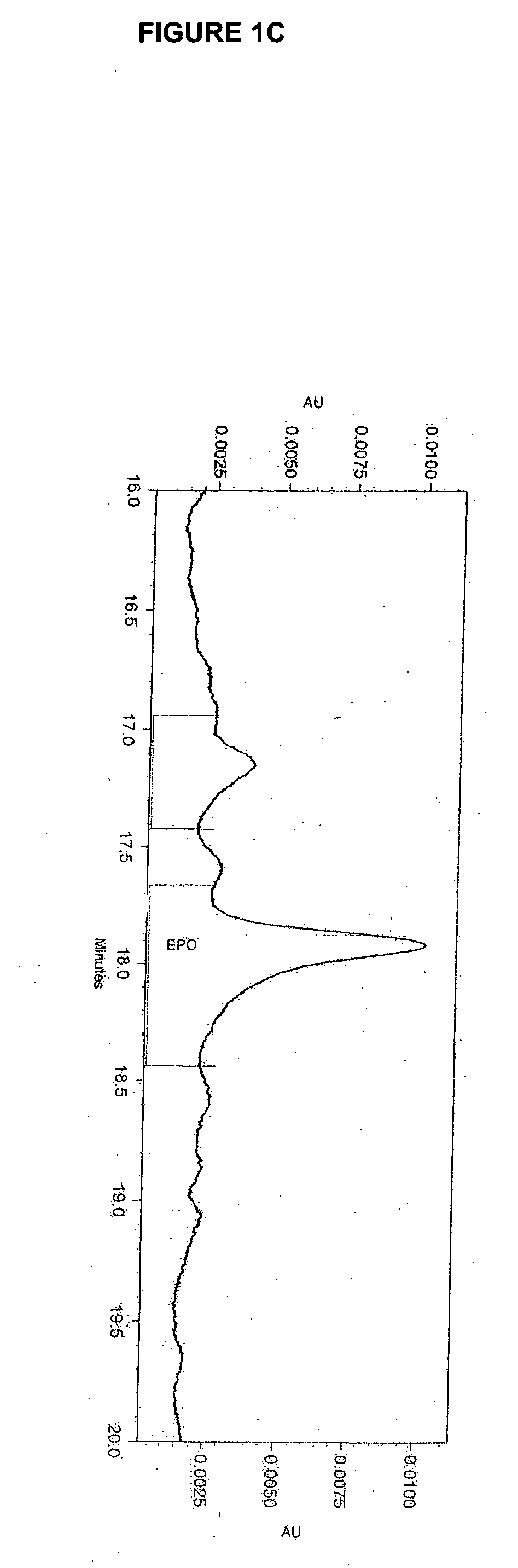
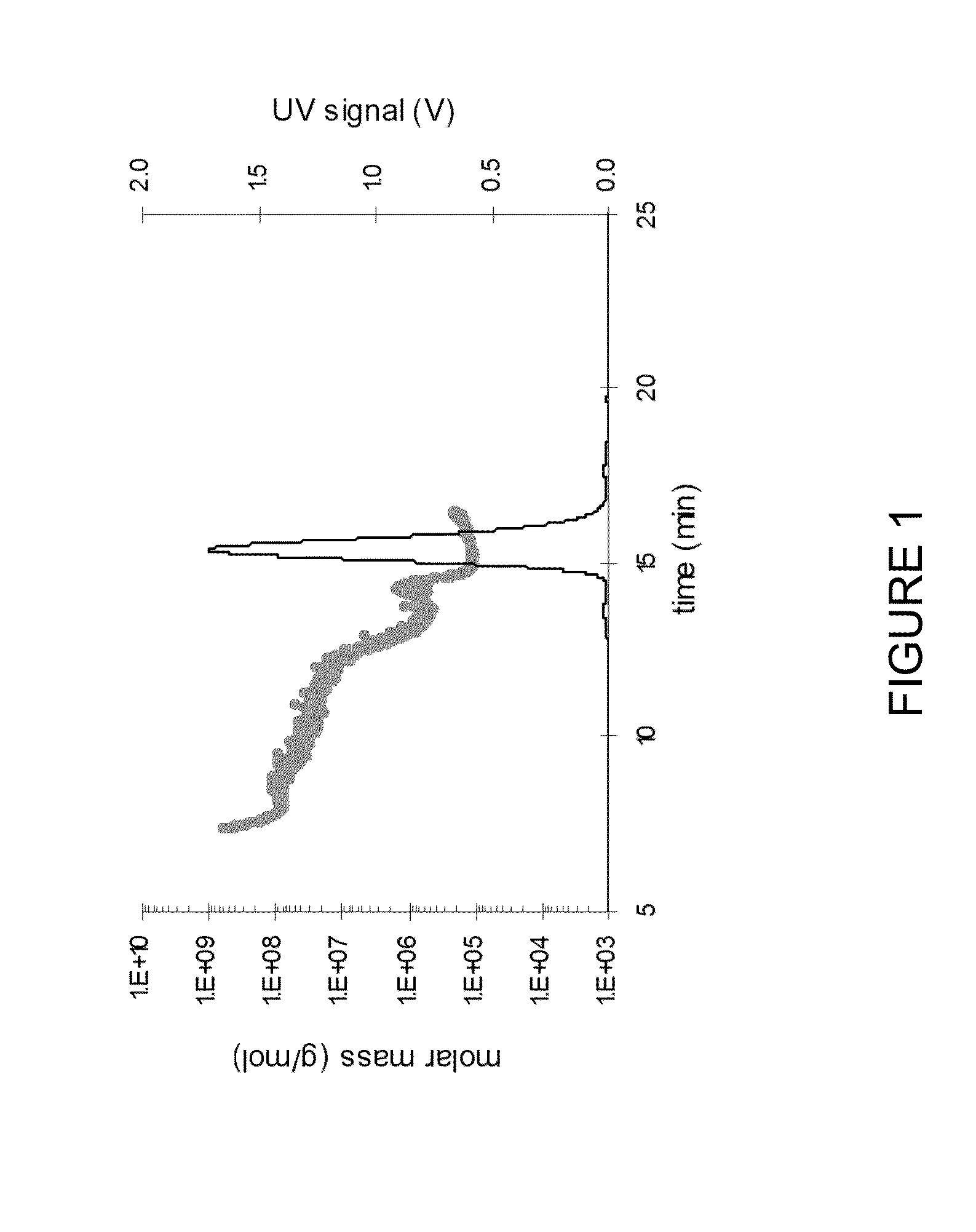
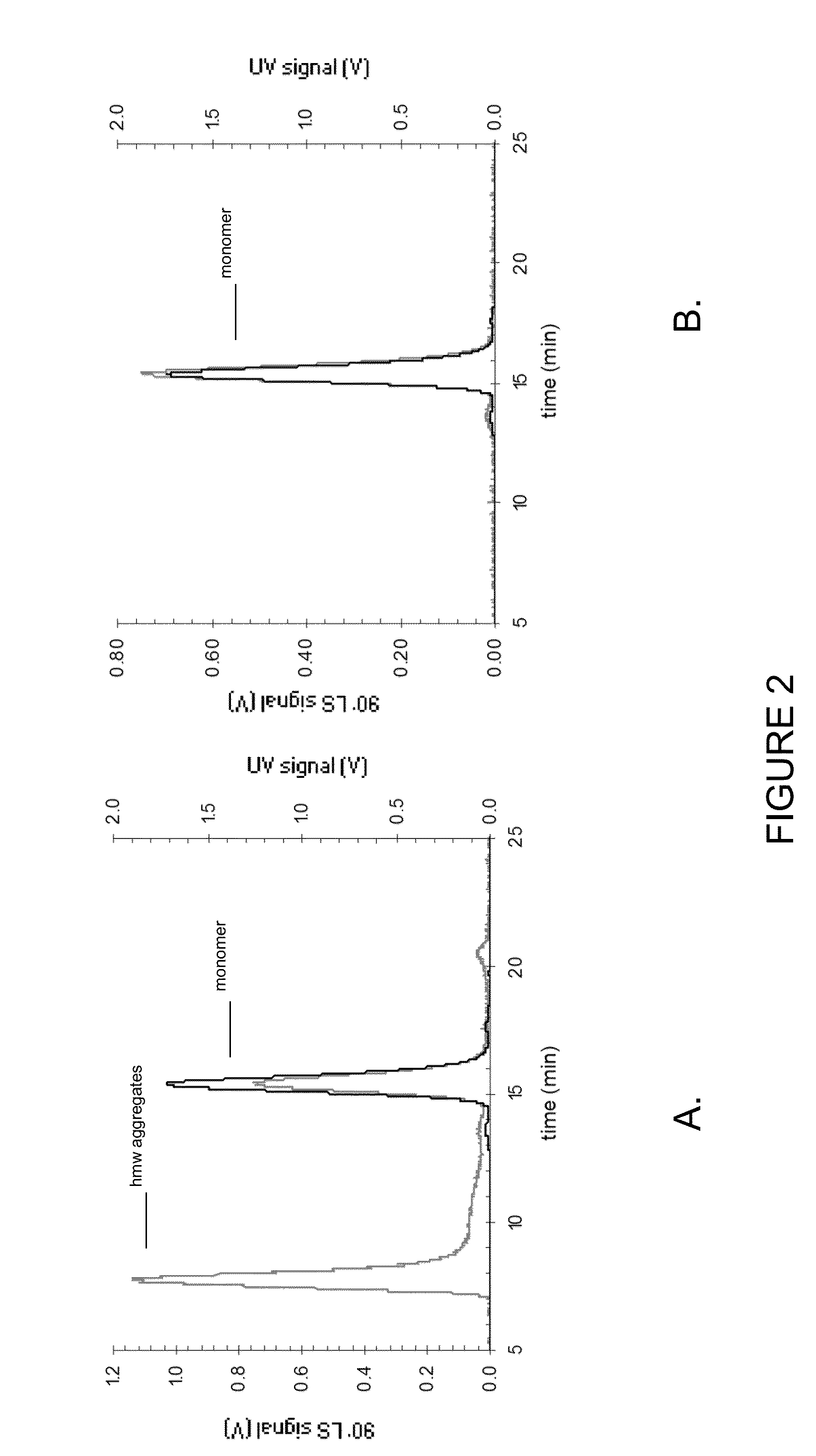
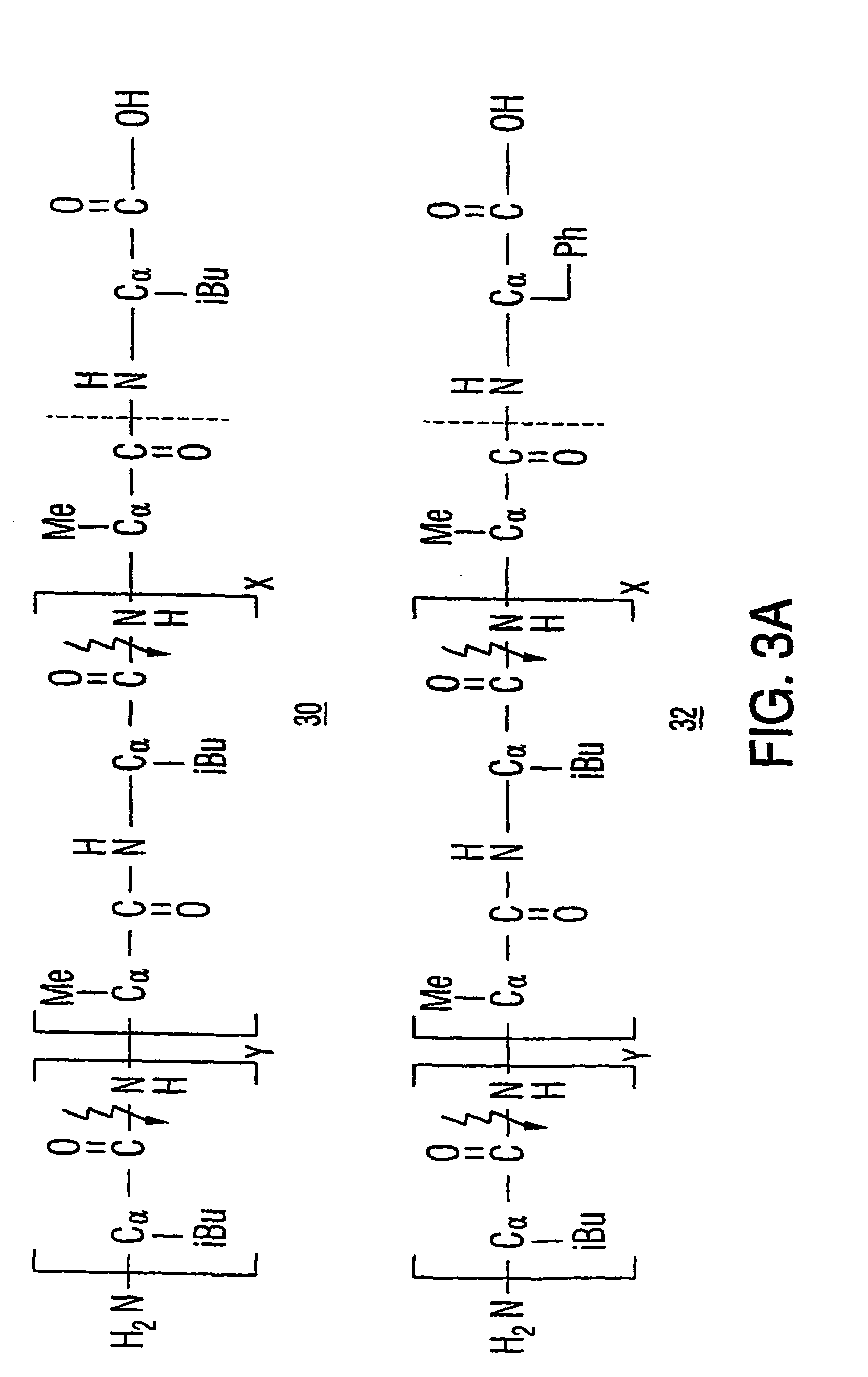Patents
Literature
911results about How to "High concentration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
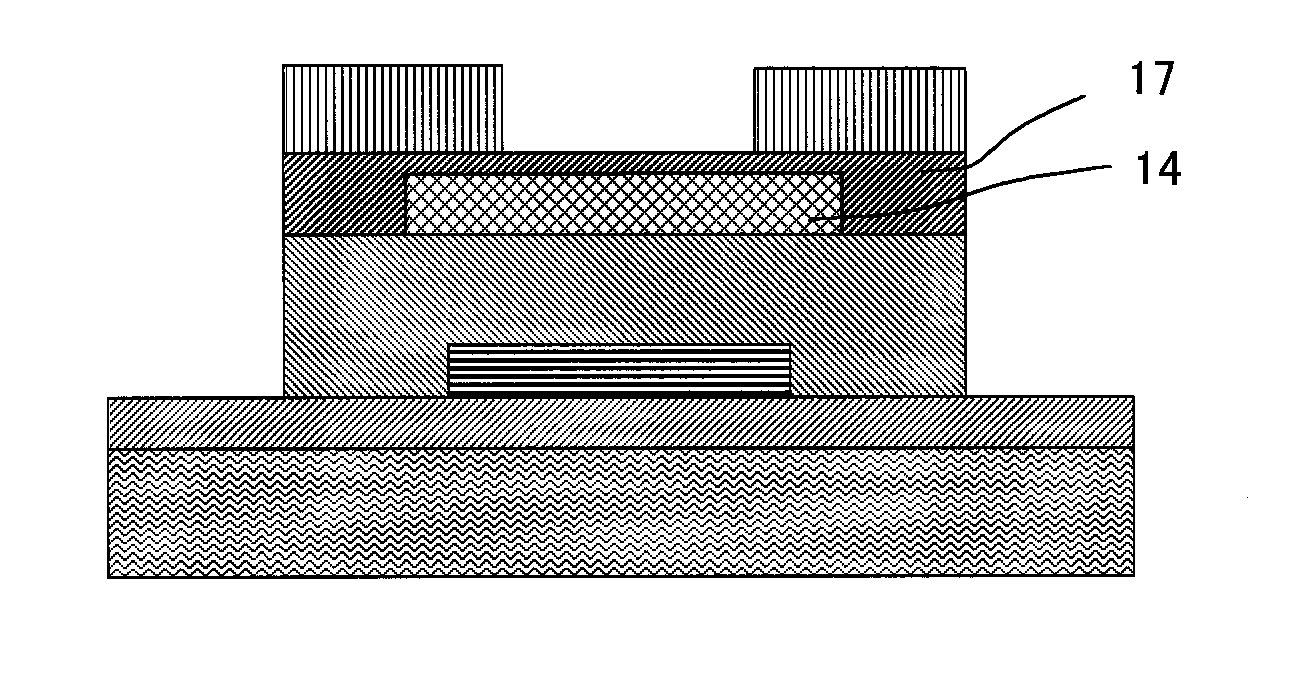
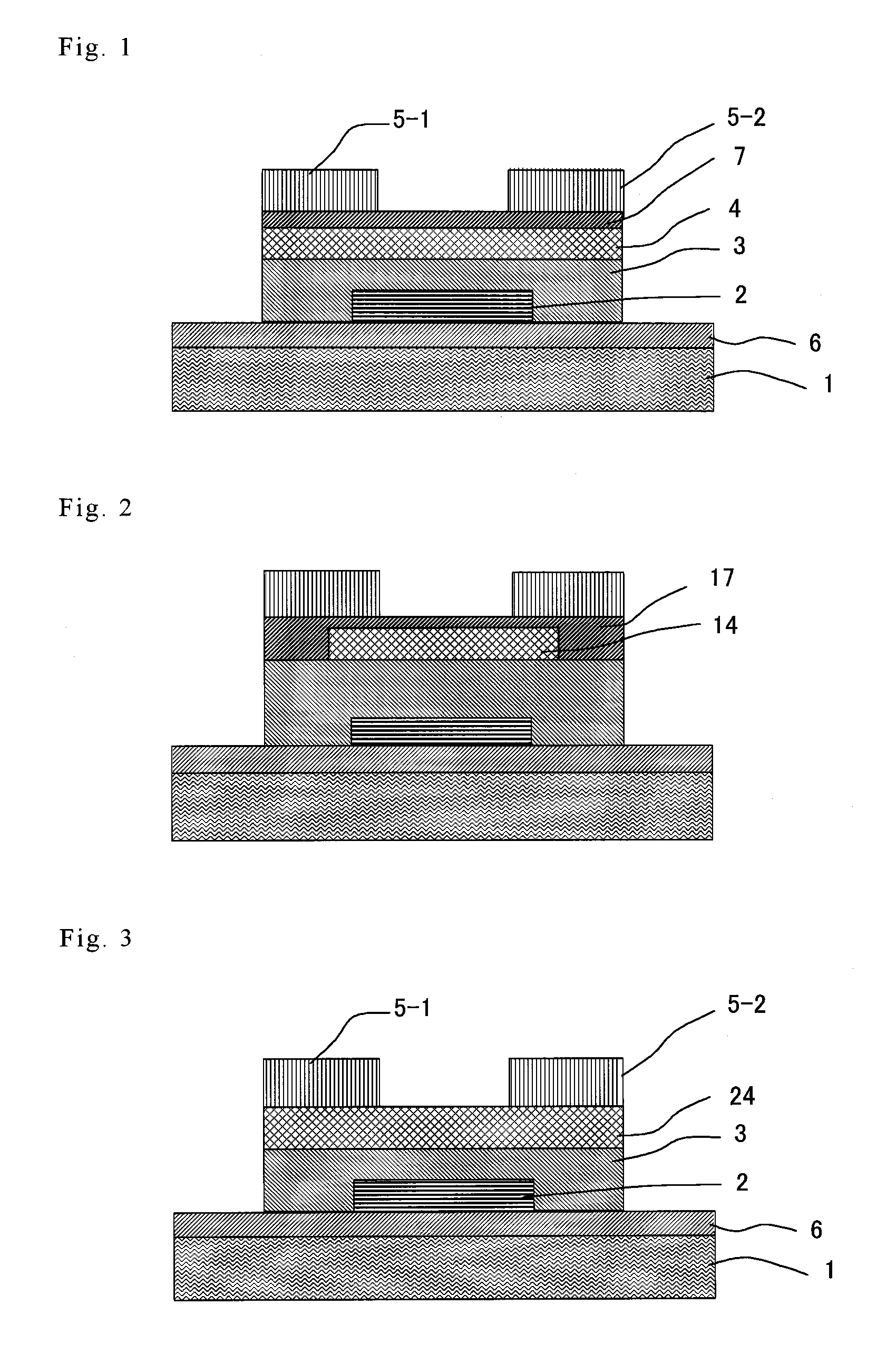
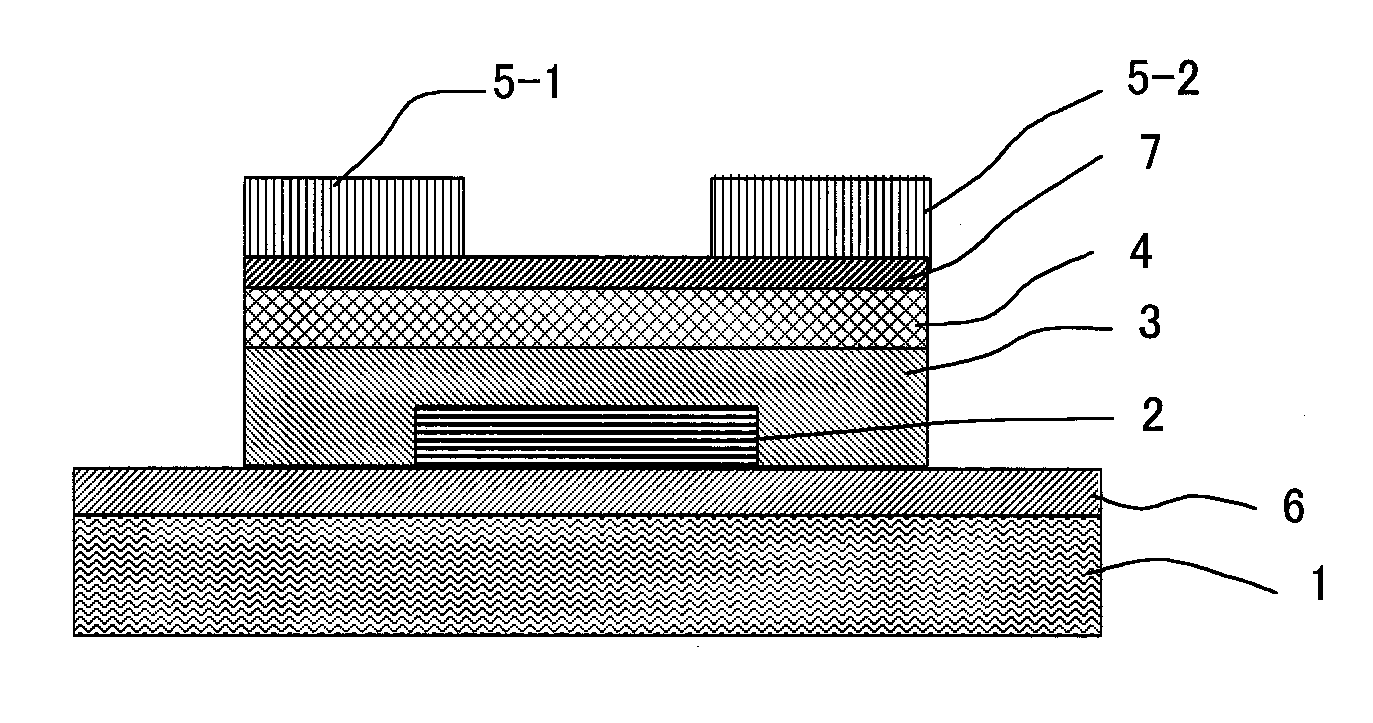
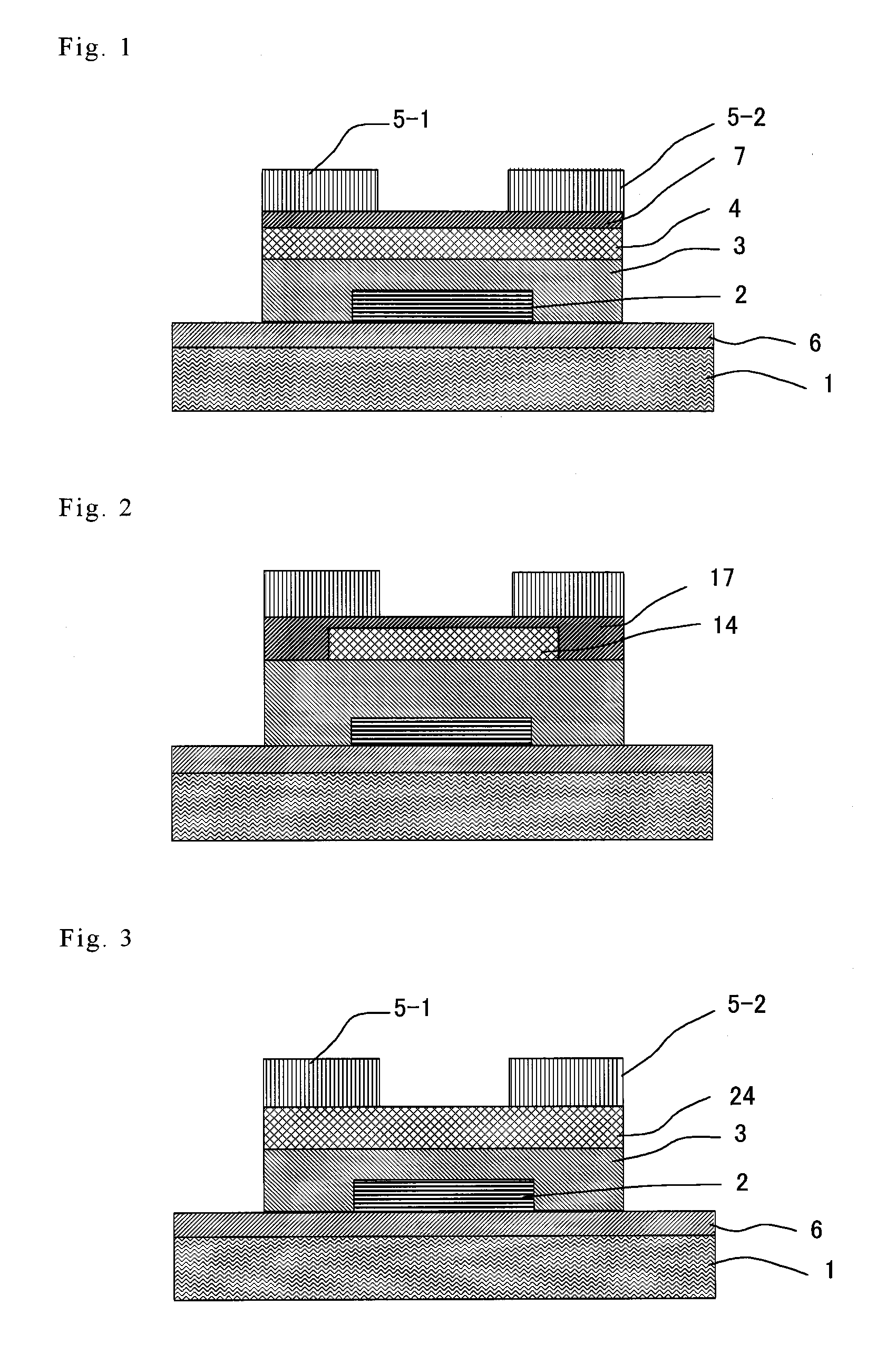
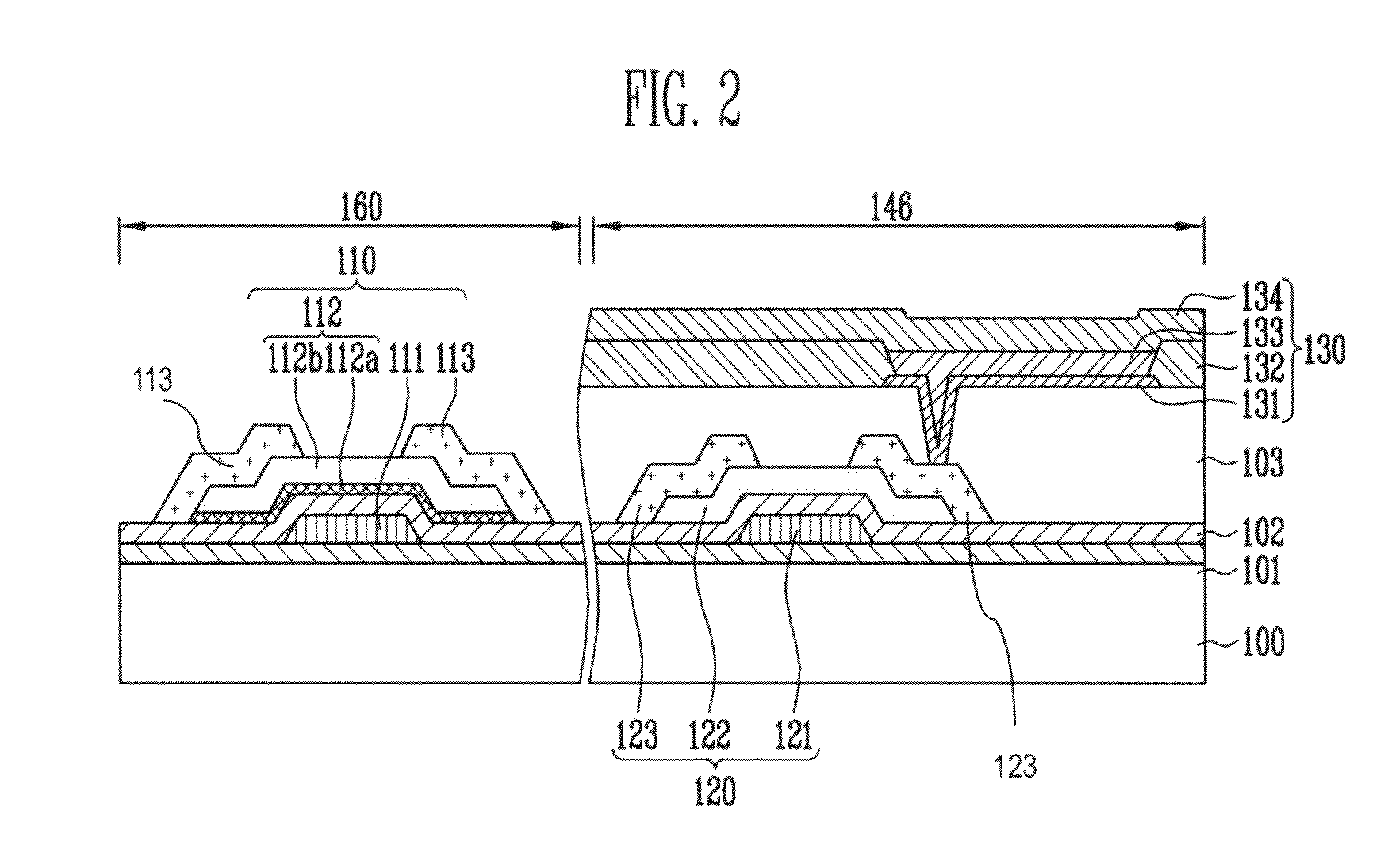
Thin film field effect transistor and display
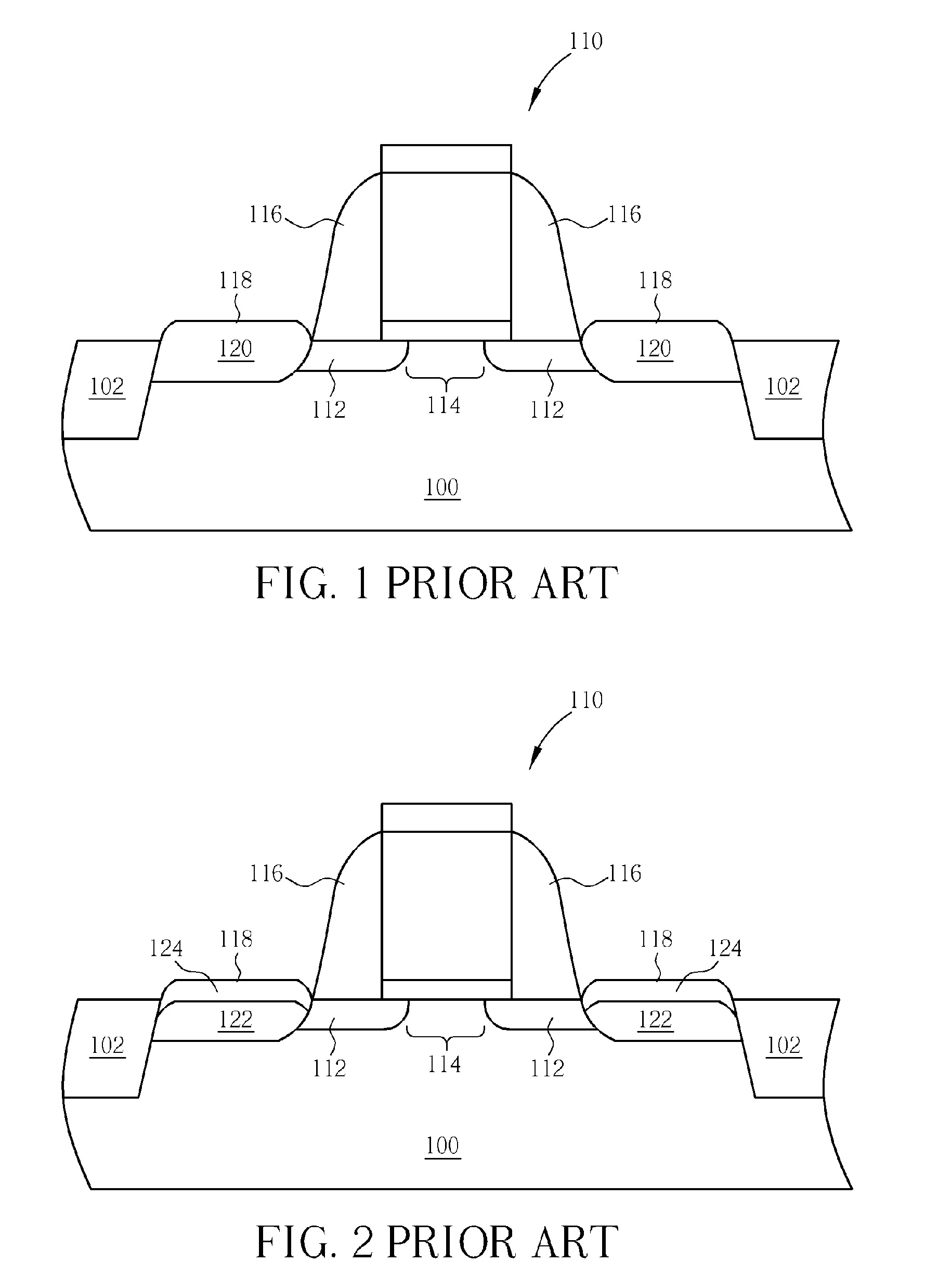
ActiveUS8188480B2High concentrationElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceField-effect transistor
A TFT is provided which includes, on a substrate, at least a gate electrode, a gate insulating layer, an active layer containing an amorphous oxide semiconductor, a source electrode and a drain electrode, wherein a resistance layer containing an amorphous oxide and having a thickness of more than 3 nm is disposed between the active layer and at least one of the source electrode or the drain electrode, and a band gap of the active layer is smaller than a band gap of the resistance layer. Also, a display using the TFT is provided.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
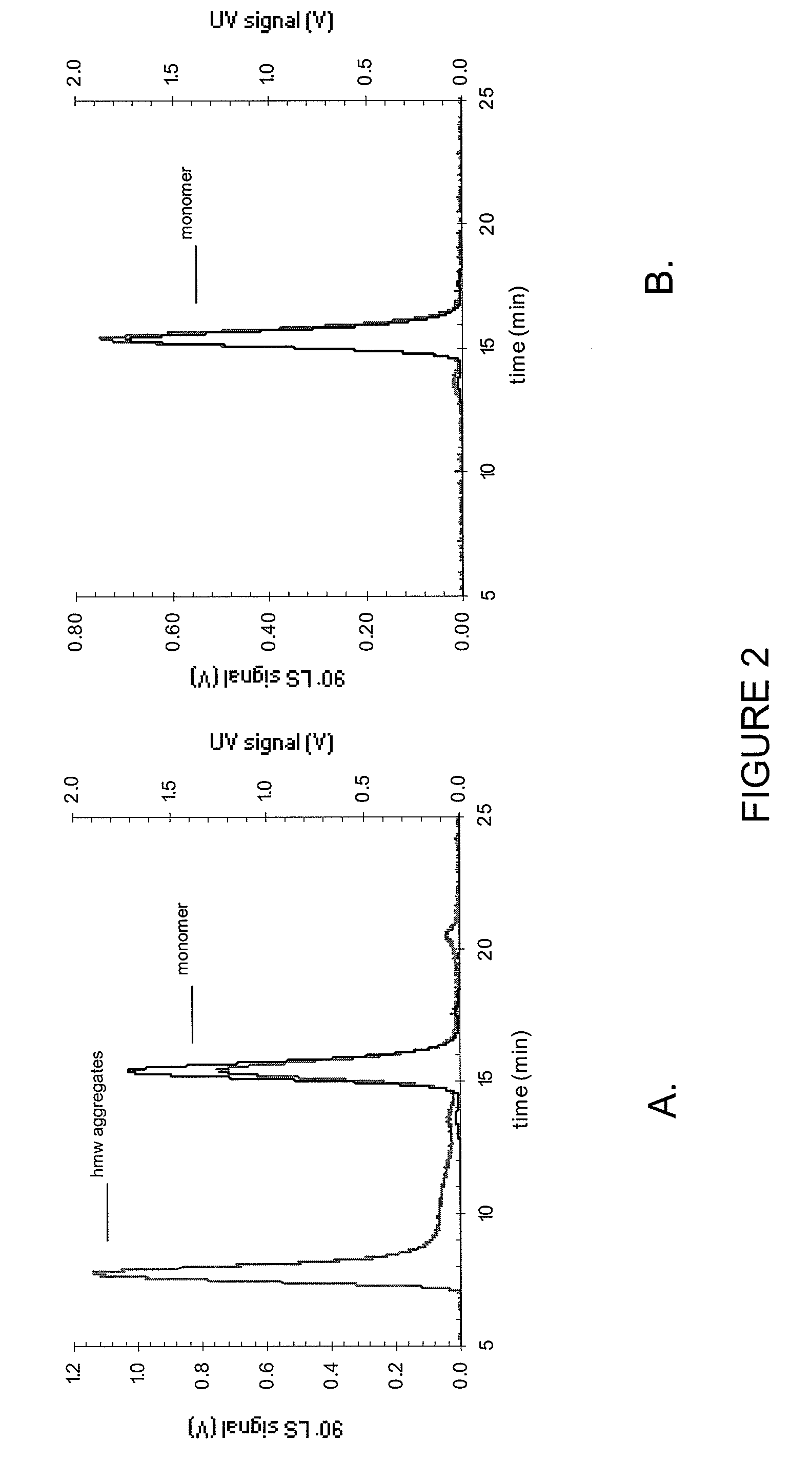
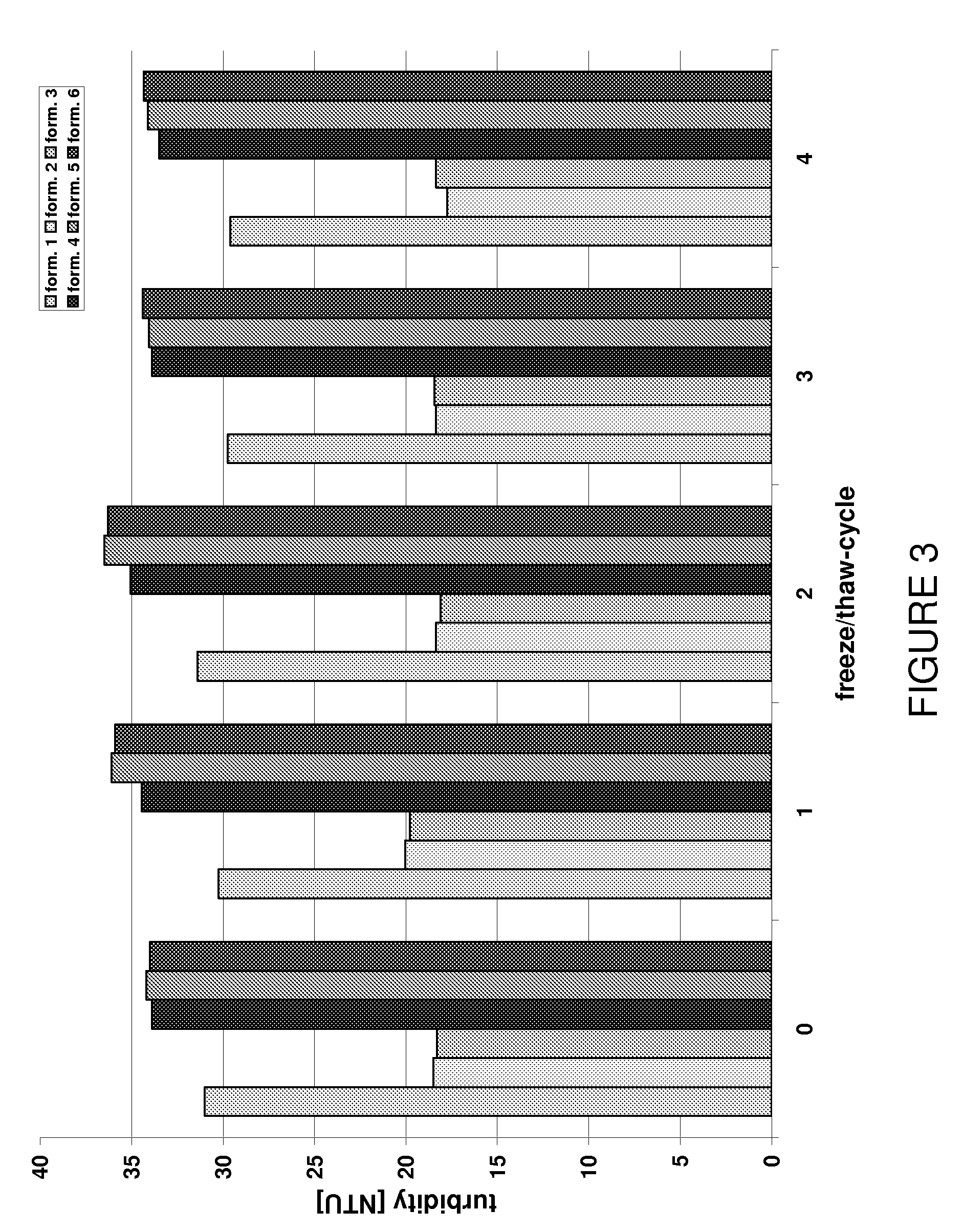
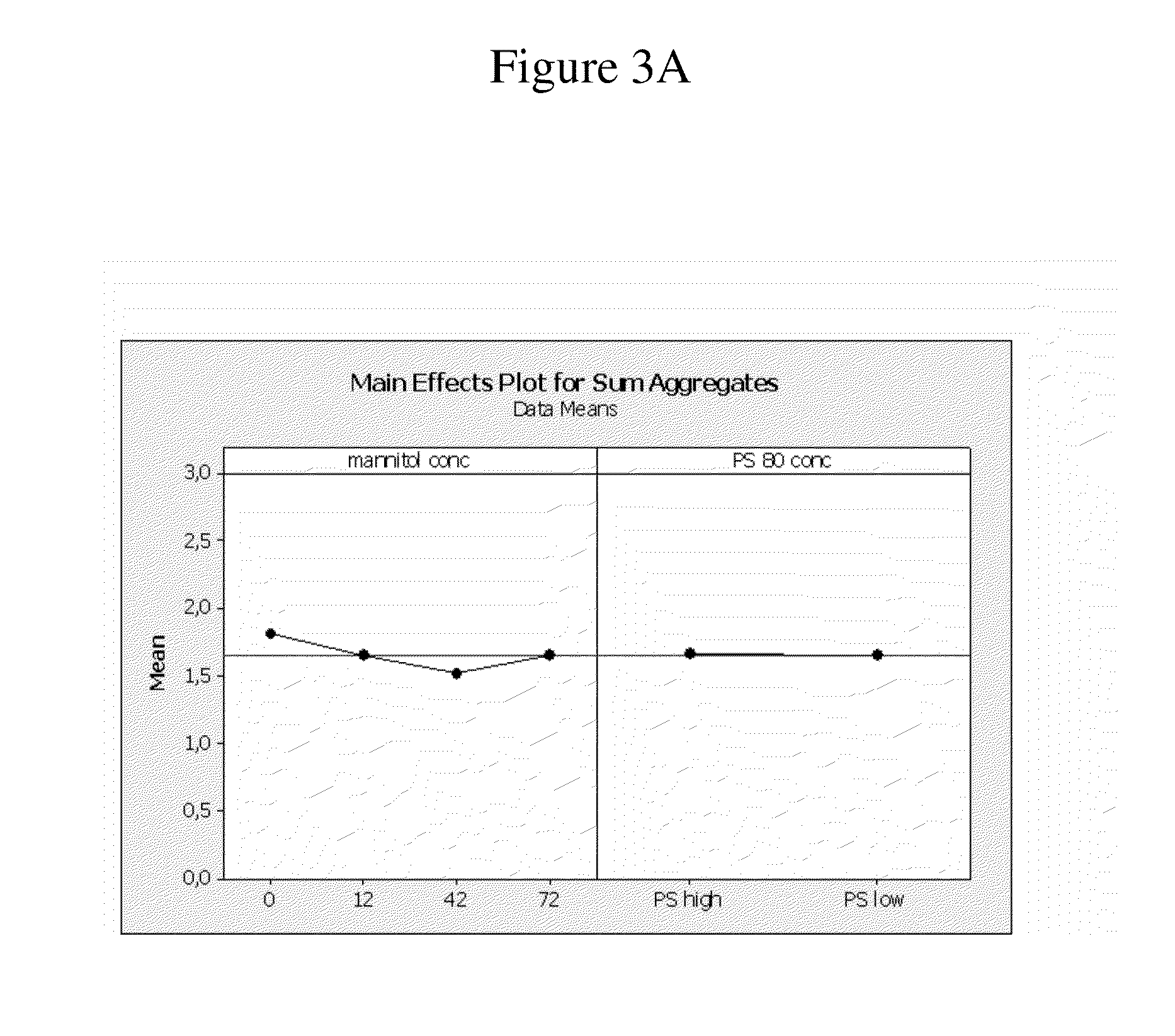
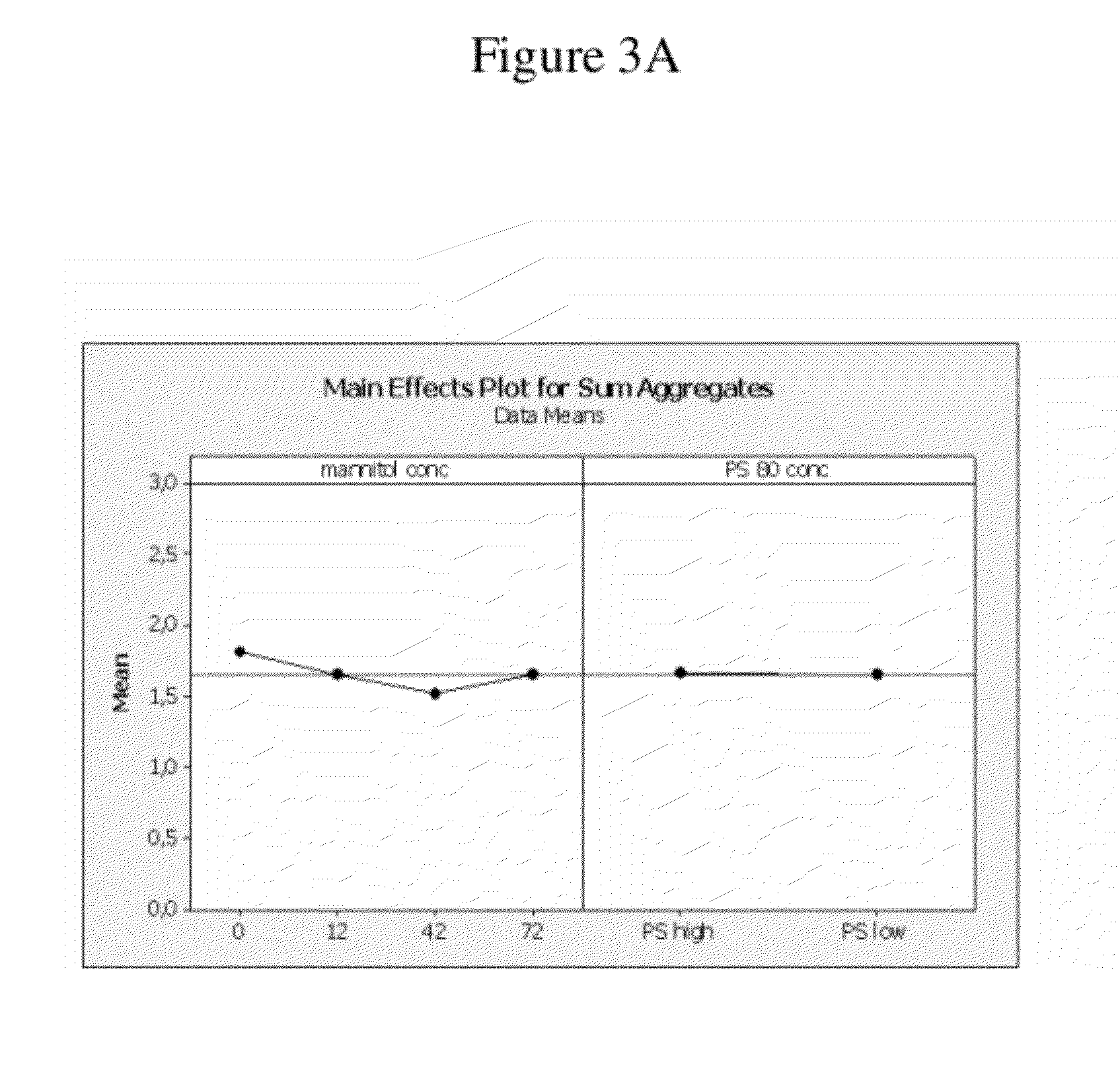
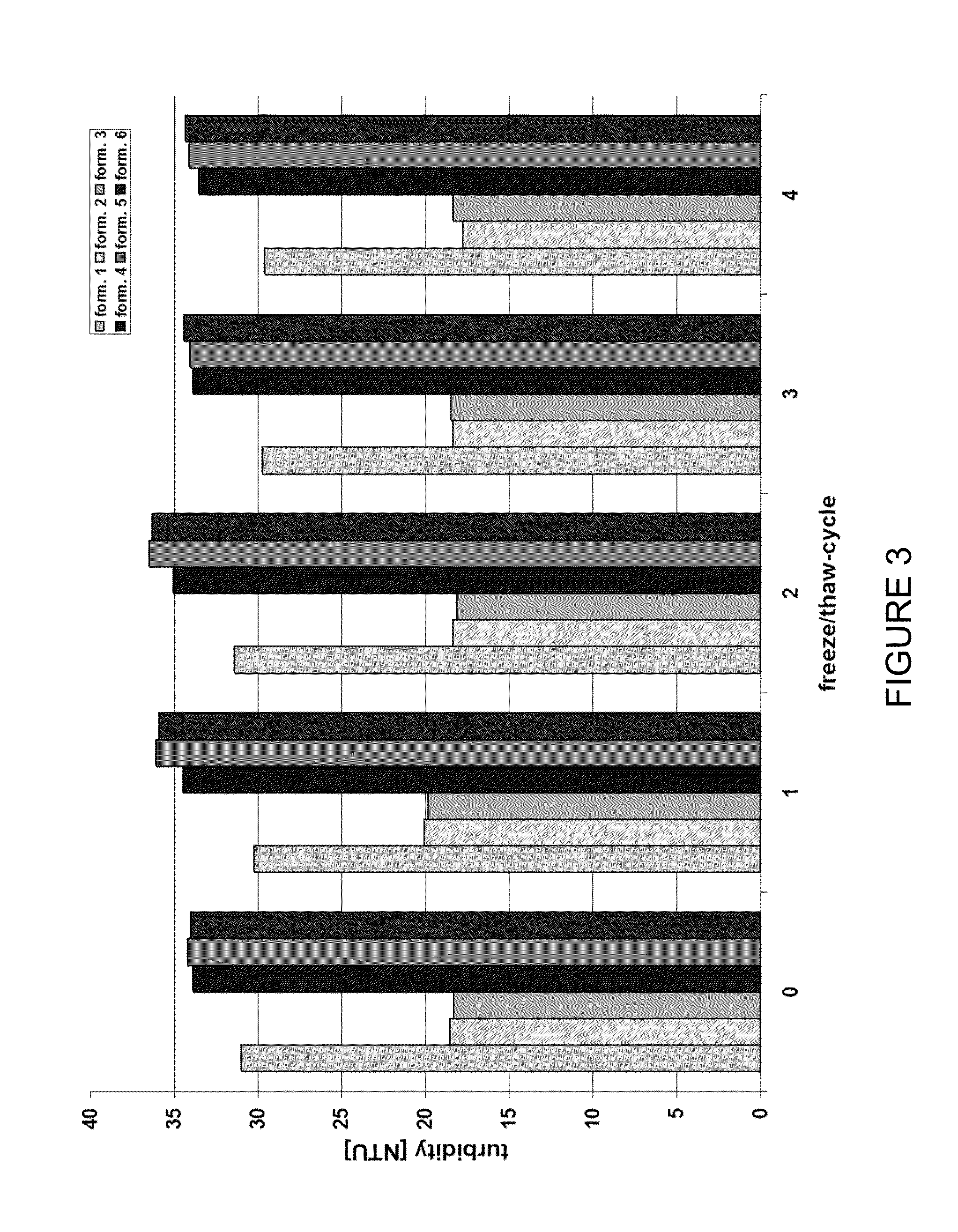
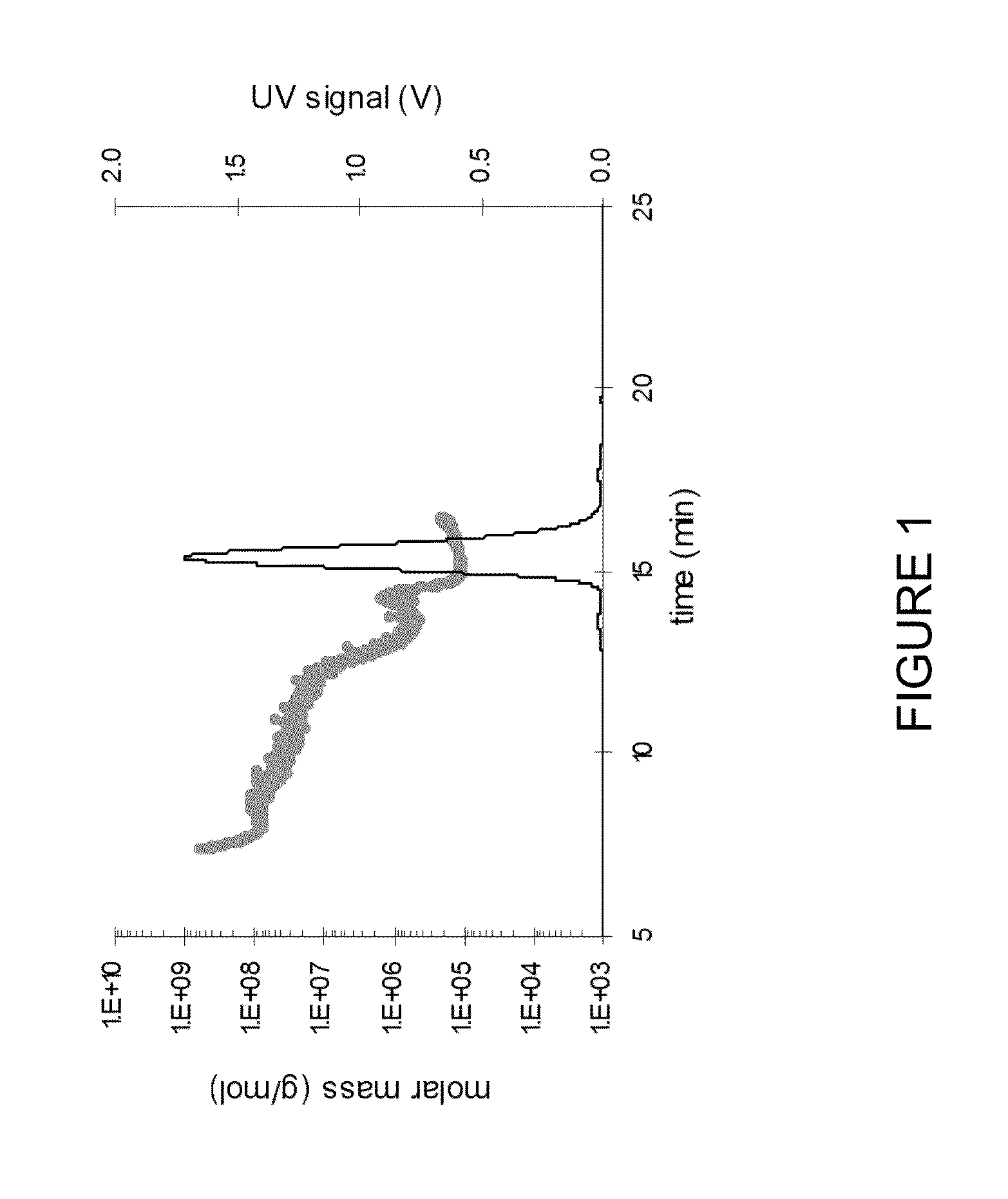
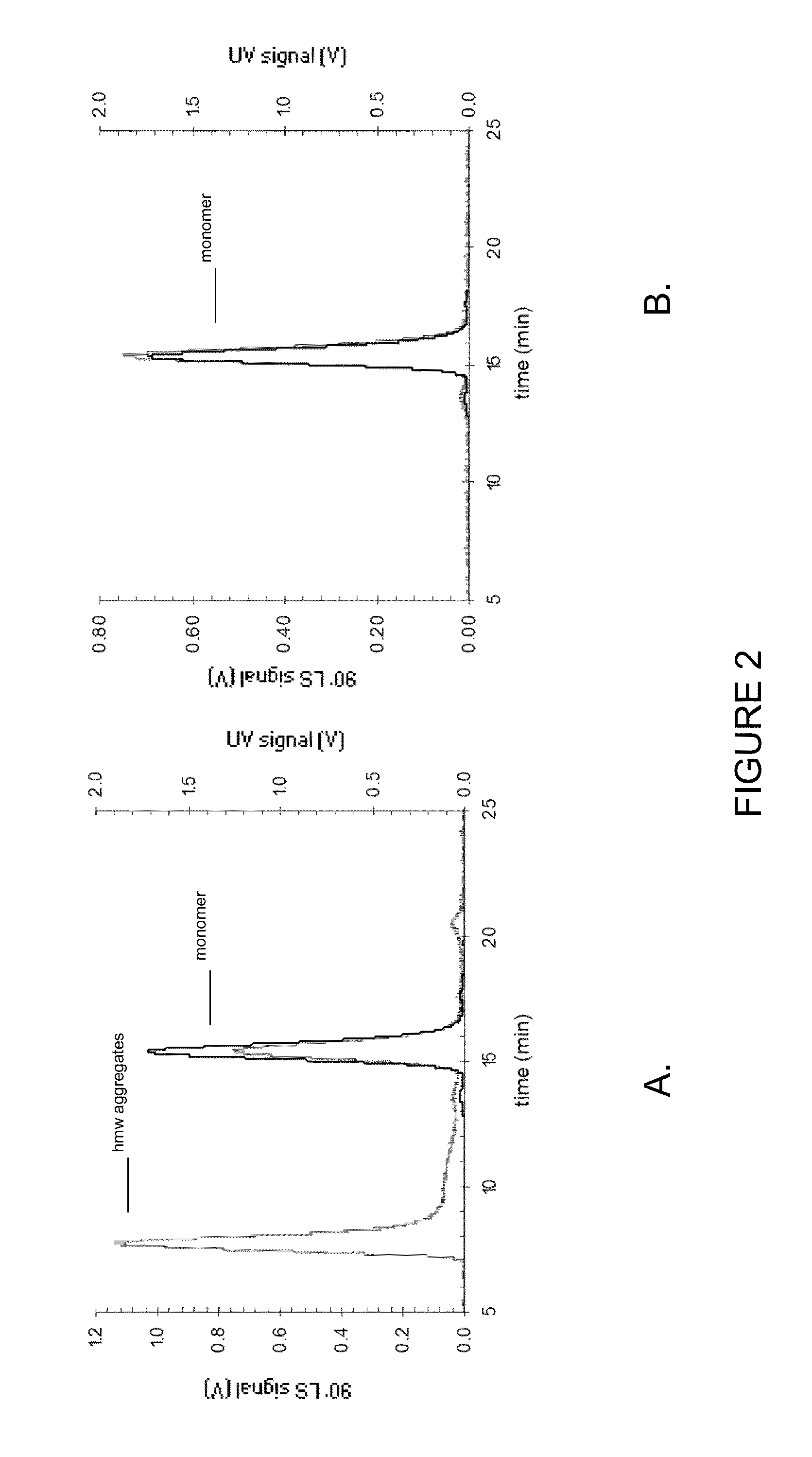
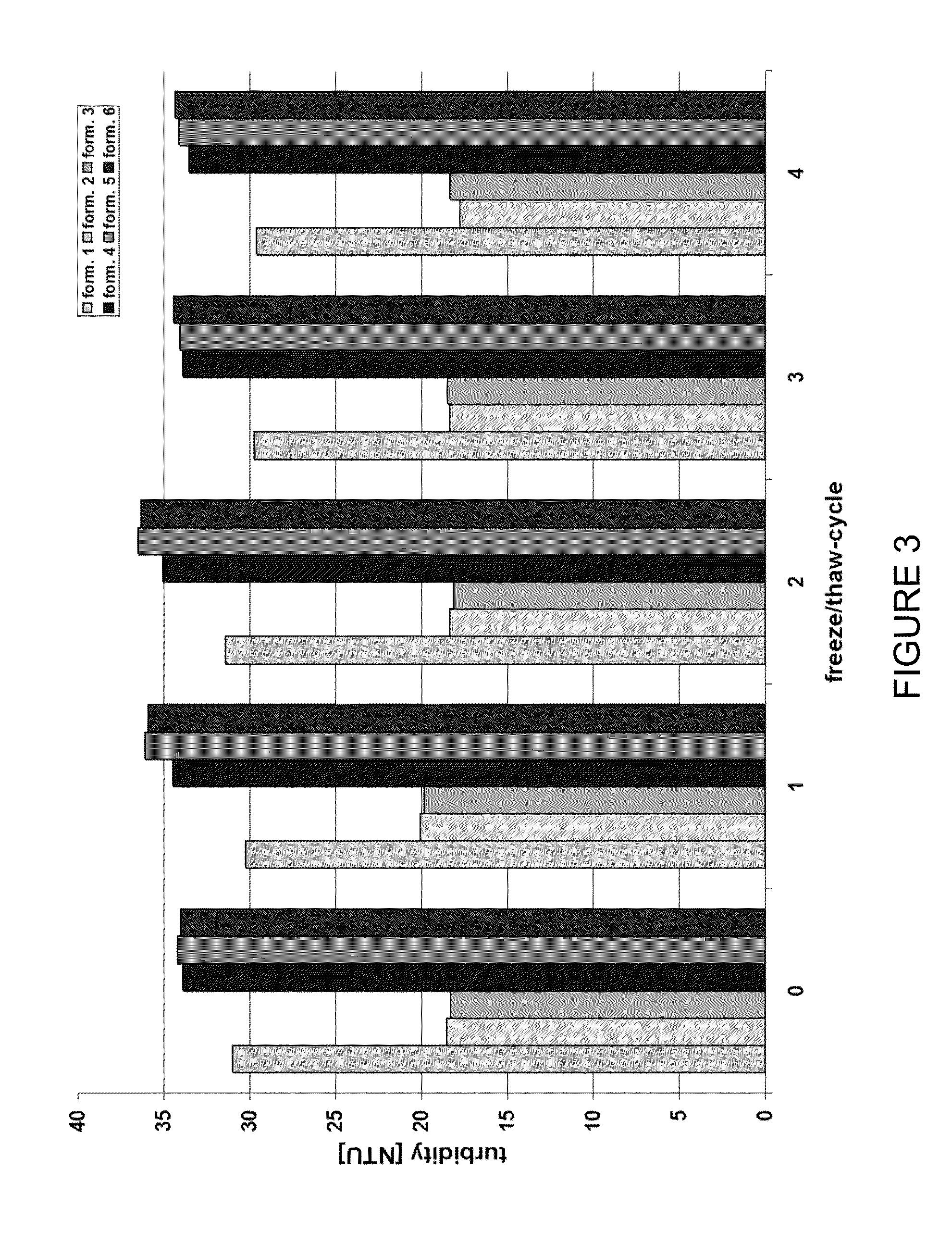
Stable high protein concentration formulations of human Anti-tnf-alpha-antibodies
InactiveUS20100278822A1Suitable viscosityIncrease concentrationAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderHigh concentrationPolyol
The invention provides a liquid pharmaceutical formulation which does not include NaCl and comprises more than 20 mg of a polyol and at least about 100 mg / mL of a human anti-TNF-alpha antibody, or antigen-binding portion thereof. The invention provides a high concentration antibody formulation having long-term stability and advantageous characteristics for subcutaneous administration.
Owner:ABBVIE BIOTECHNOLOGY LTD
Use of NSAIDs for prevention and treatment of cellular abnormalities of the lung or bronchial pathway
InactiveUS20030004142A1High concentrationMinimal exposureBiocideSalicyclic acid active ingredientsSurgeryNon steroidal anti inflammatory
Owner:PRIOR CHRISTOPHER P +2
Implantable Drug Delivery Device and Methods for Treatment of the Bladder and Other Body Vesicles or Lumens
ActiveUS20090149833A1High plasma concentrationMinimize irritationBiocideMedical devicesDrug reservoirControlled drugs
An implantable medical device is provided for controlled drug delivery within the bladder, or other body vesicle. The device may include at least one drug reservoir component comprising a drug; and a vesicle retention frame which comprises an elastic wire having a first end, an opposing second end, and an intermediate region therebetween, wherein the drug reservoir component is attached to the intermediate region of the vesicle retention frame. The retention frame prevents accidental voiding of the device from the bladder, and it preferably has a spring constant selected for the device to effectively stay in the bladder during urination while minimizing the irritation of the bladder.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Morphine controlled release system
InactiveUS20070003617A1Low administration frequencyAffecting extent of drug bioavailabilityBiocideNervous disorderMorphineDissolution
A composition for controlled release of an opioid from a pharmaceutical composition, the method comprises controlling the release of at least one opioid into an aqueous medium by erosion of at least one surface of a pharmaceutical composition comprising I) a matrix composition comprising a) polymer or a mixture of polymers, b) an opioid and, optionally, c) one or more pharmaceutically acceptable excipients, and (i) a coating. The matrix composition has a conus-like shape so the surface area exposed to the aqueous medium increases at least during initial erosion of the matrix composition, and the dissolution of the opioid-when tested in a Dissolution Test as described herein with or without application of sinkers-results in a zero order release of at least 80% of the opioid contained in the composition. Such compositions are especially suitable for controlled release of an opioid to obtain a delayed pead concentration and a prolonged therapeutically effective plasma concentration upon oral administration. Once or twice daily administration is possible. The matrix typically comprises PEO and the active substance is typically an opioid such as morphine or a glucuronide thereof.
Owner:EGALET LTD
Field effect transistor and manufacturing method thereof
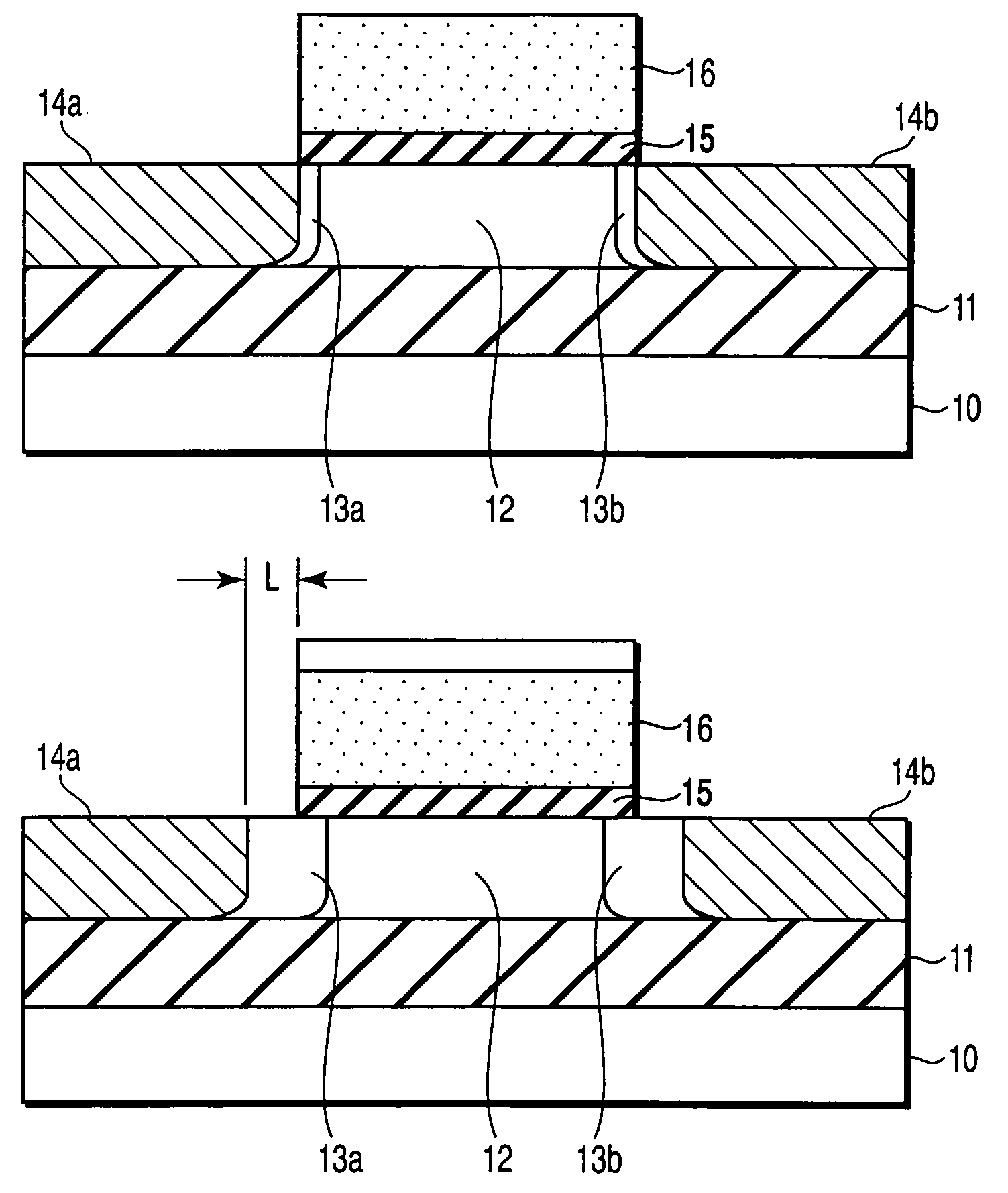
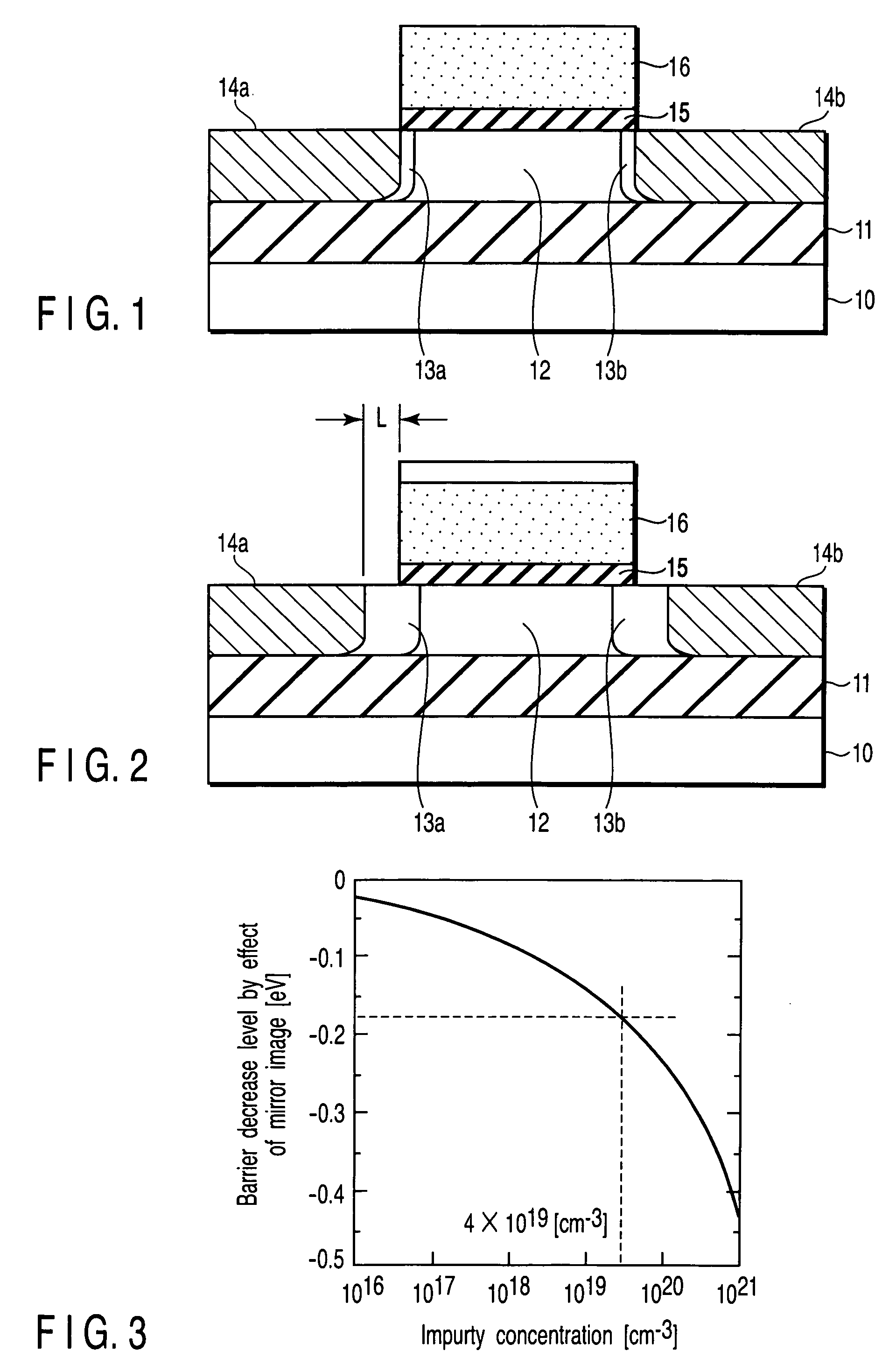
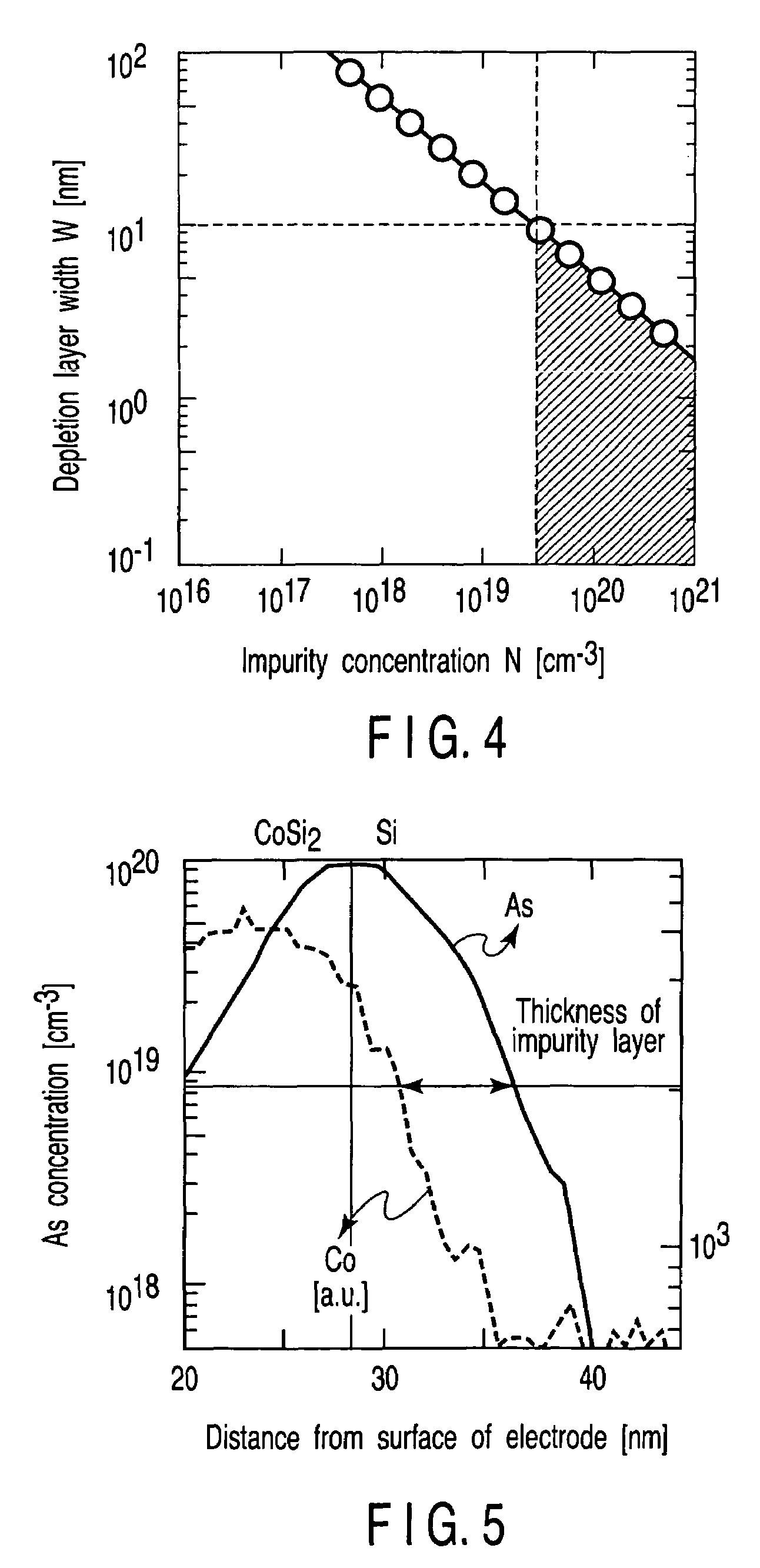
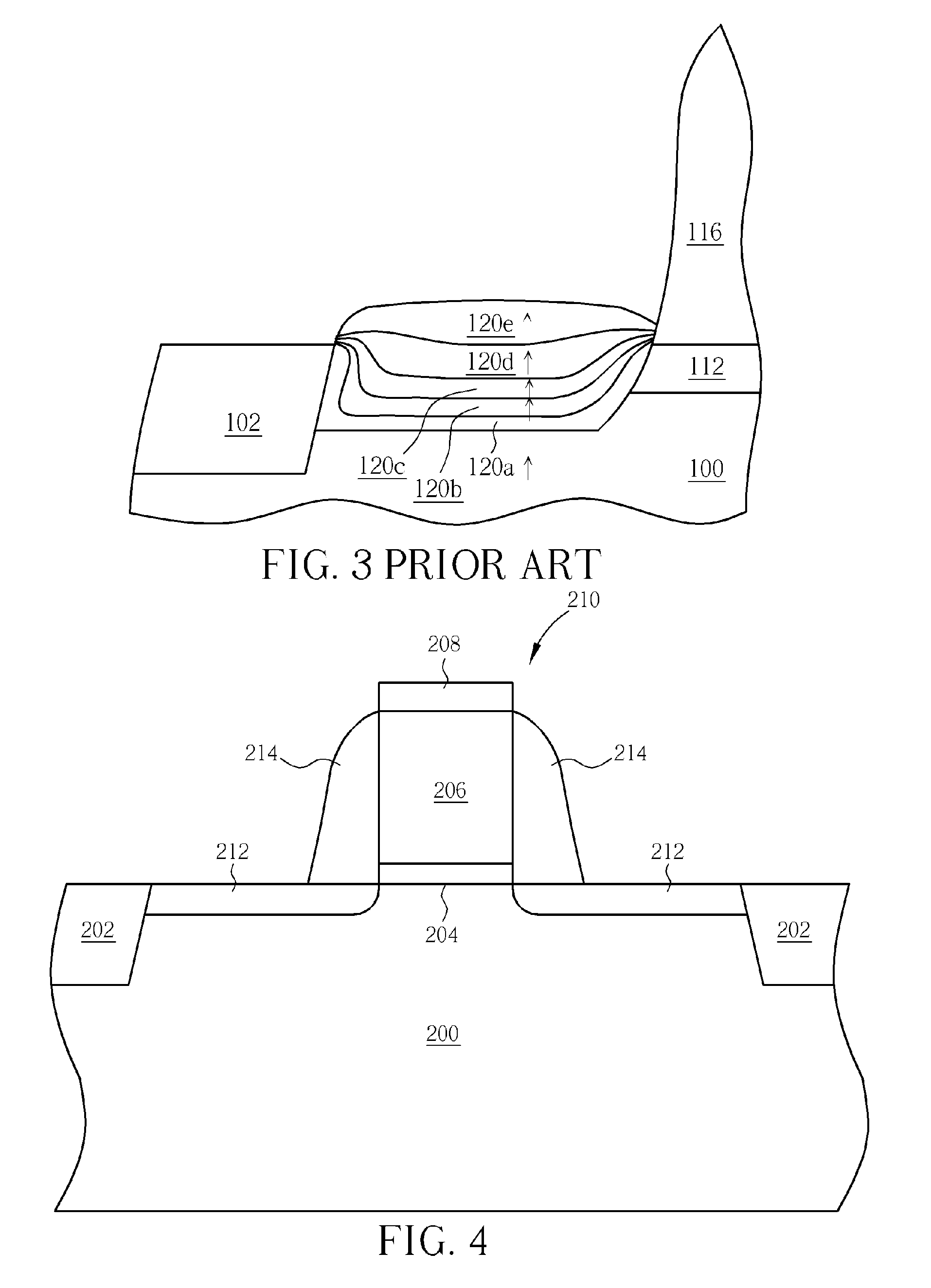
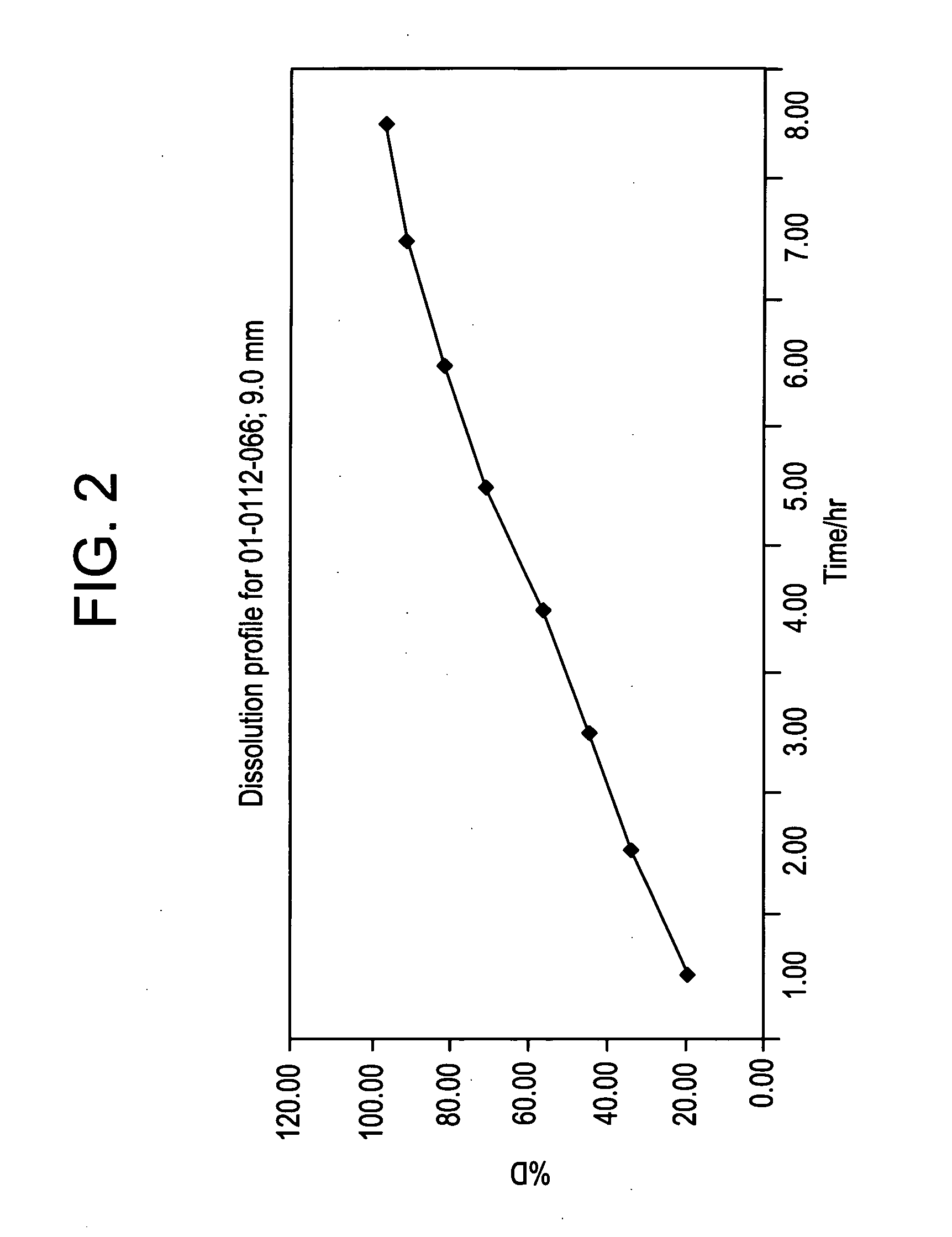
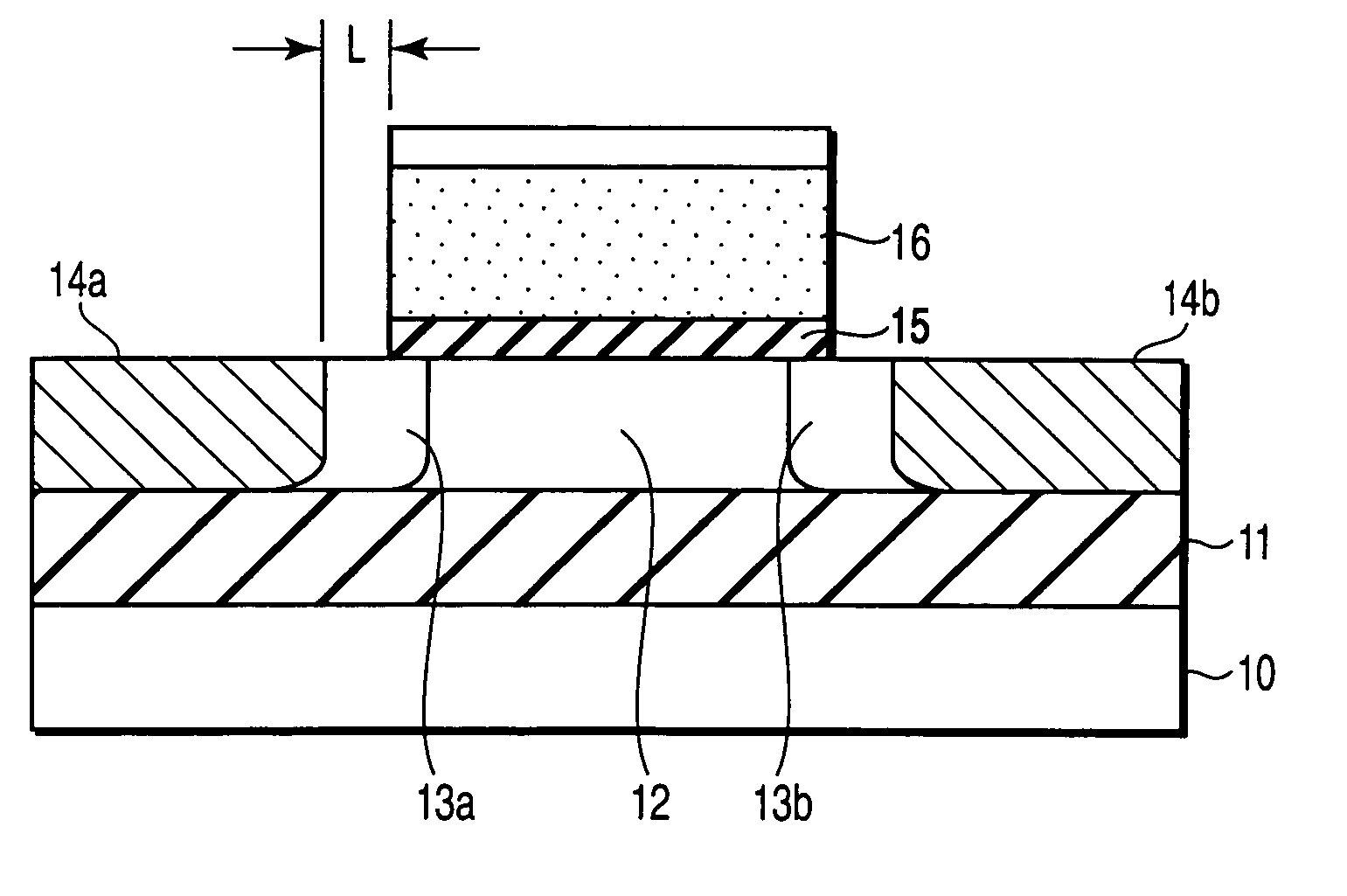
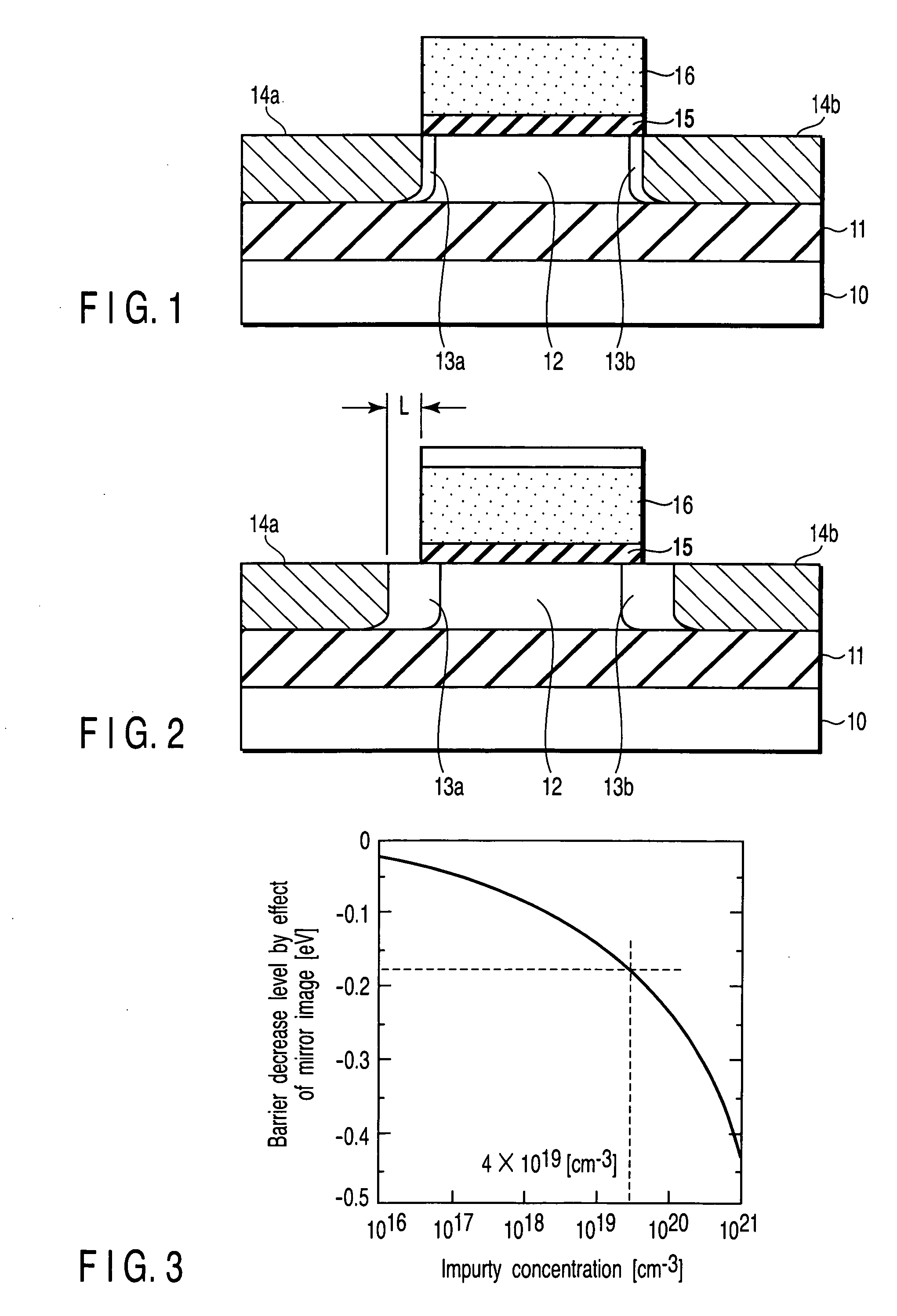
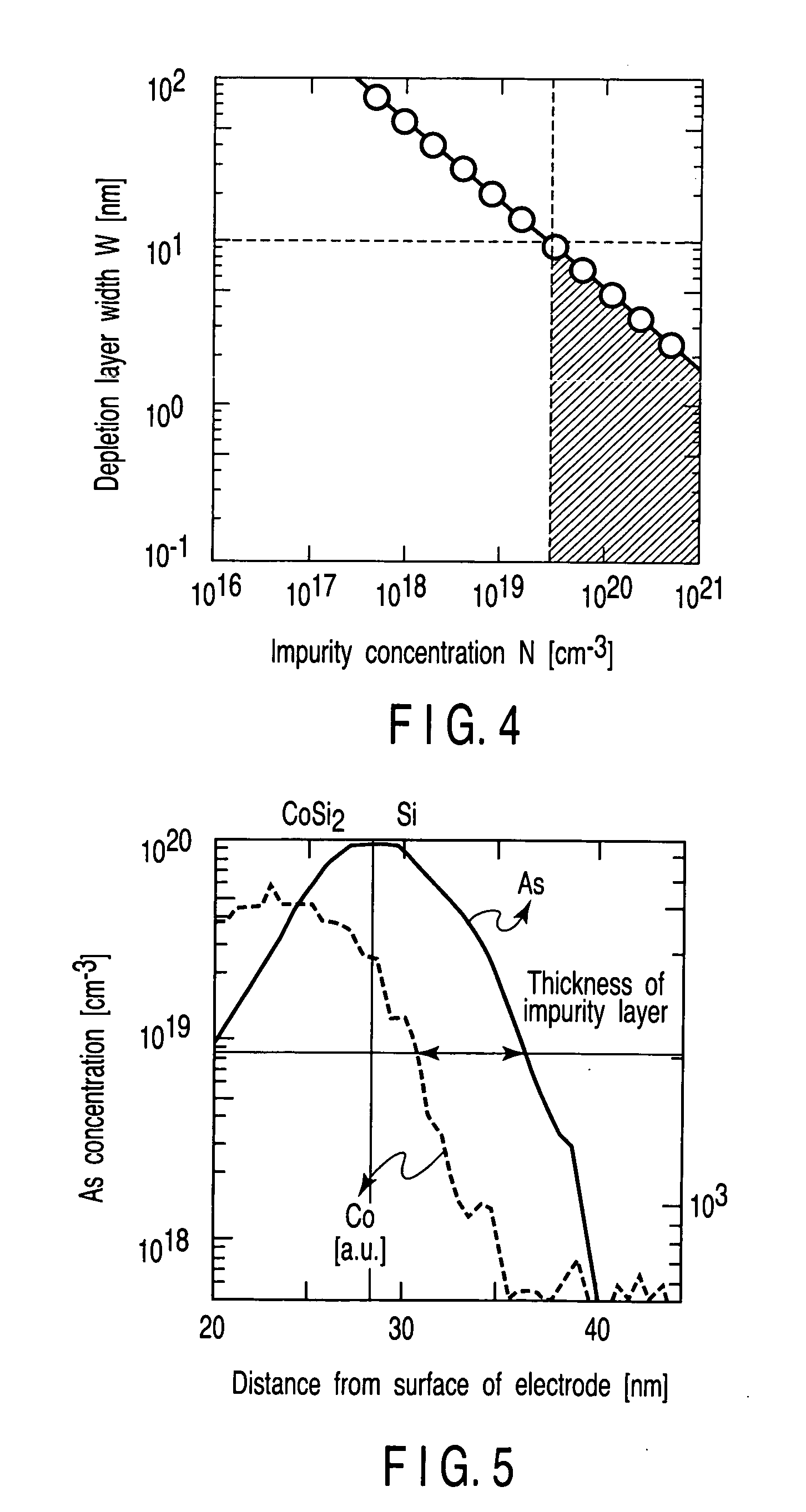
InactiveUS7119402B2High concentrationReduce parasitic resistanceTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringField-effect transistor
A field effect transistor includes a first semiconductor region forming a channel region, a gate electrode insulatively disposed above the first semiconductor region, source and drain electrodes formed to sandwich the first semiconductor region in a channel lengthwise direction, and second semiconductor regions formed between the first semiconductor region and the source and drain electrodes and having impurity concentration higher than the first semiconductor region. The thickness of the second semiconductor region in the channel lengthwise direction is set to a value equal to or less than depletion layer width determined by the impurity concentration so that the second semiconductor region is depleted in a no-voltage application state.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
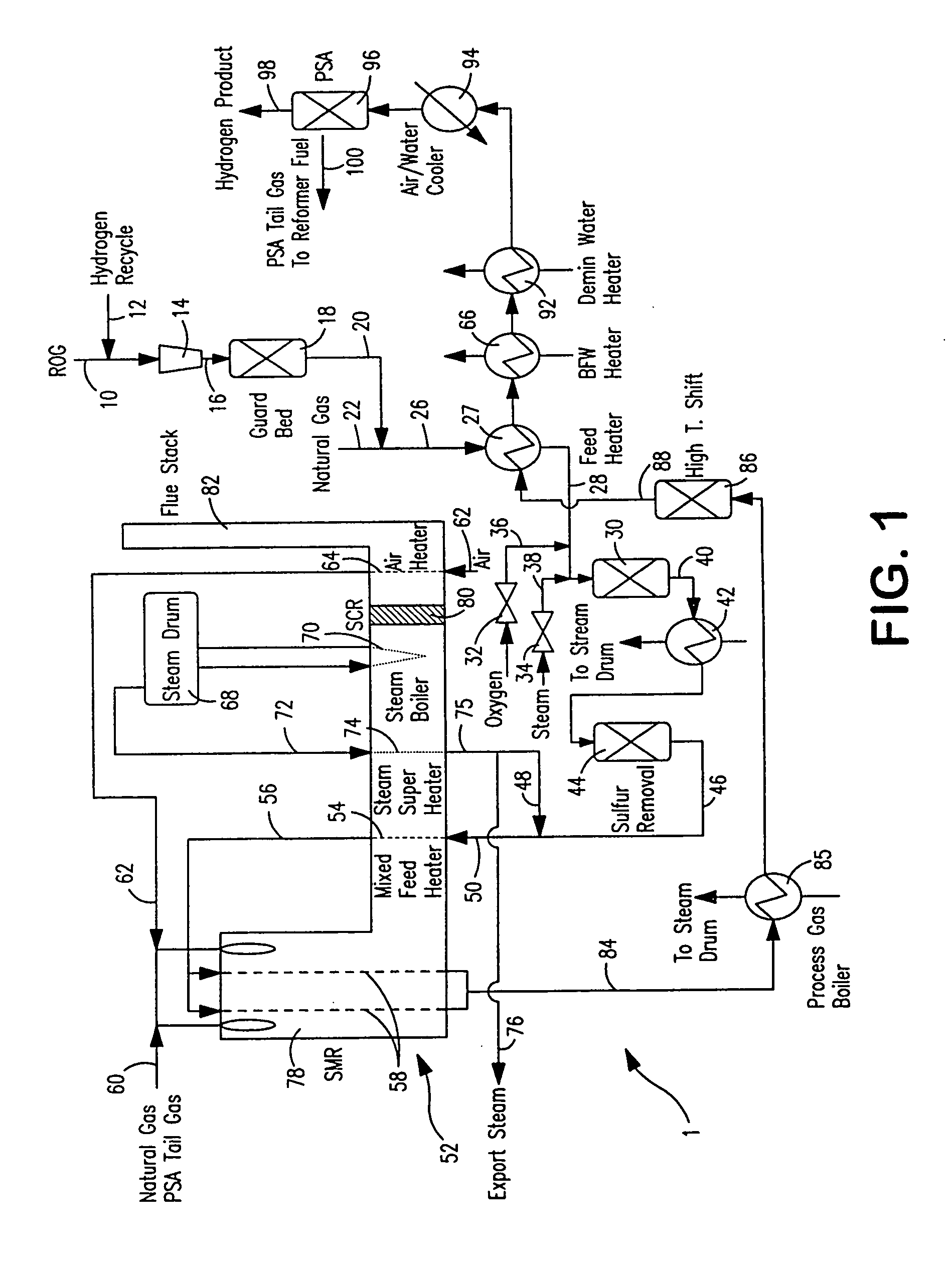
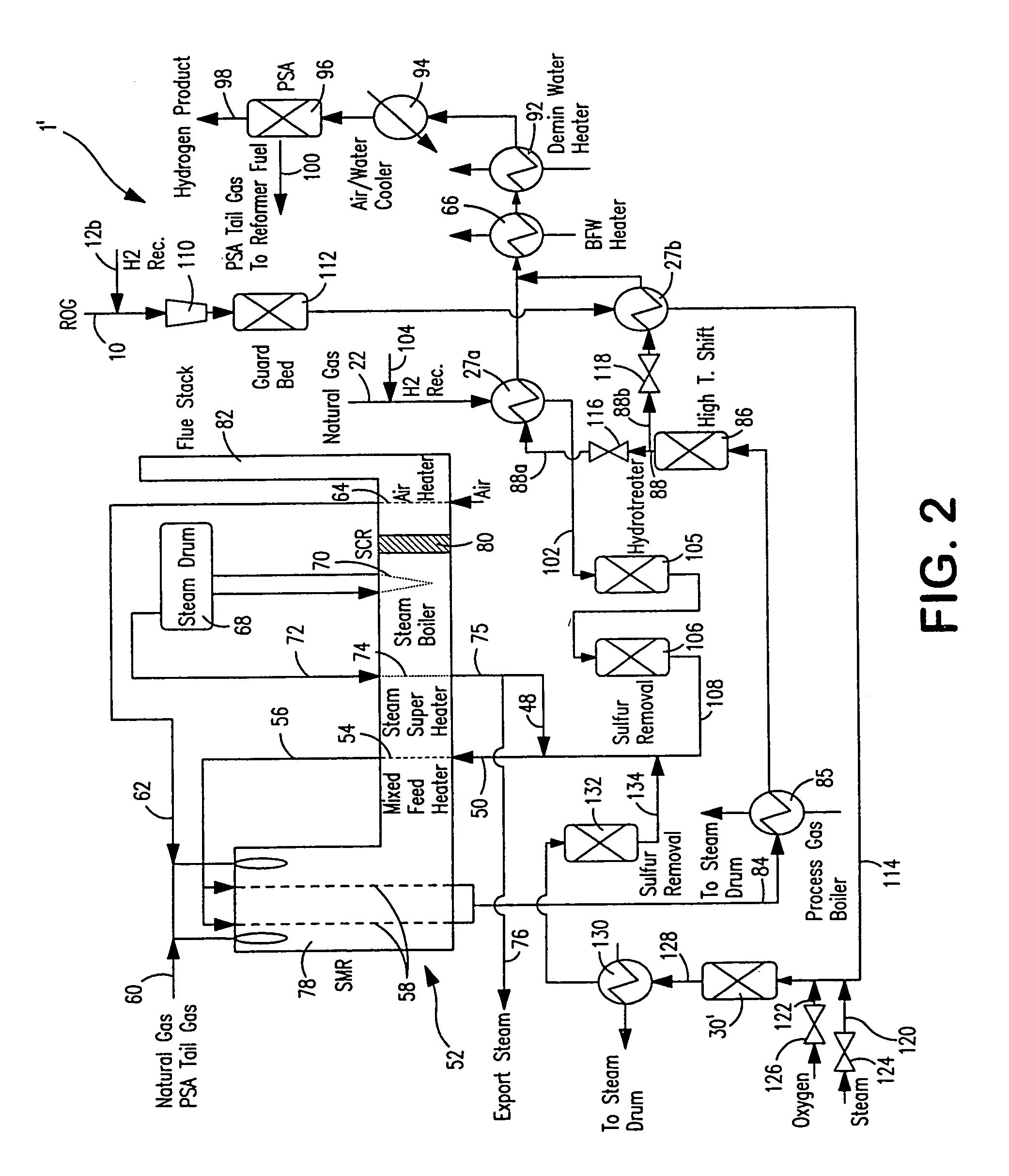
Steam methane reforming method
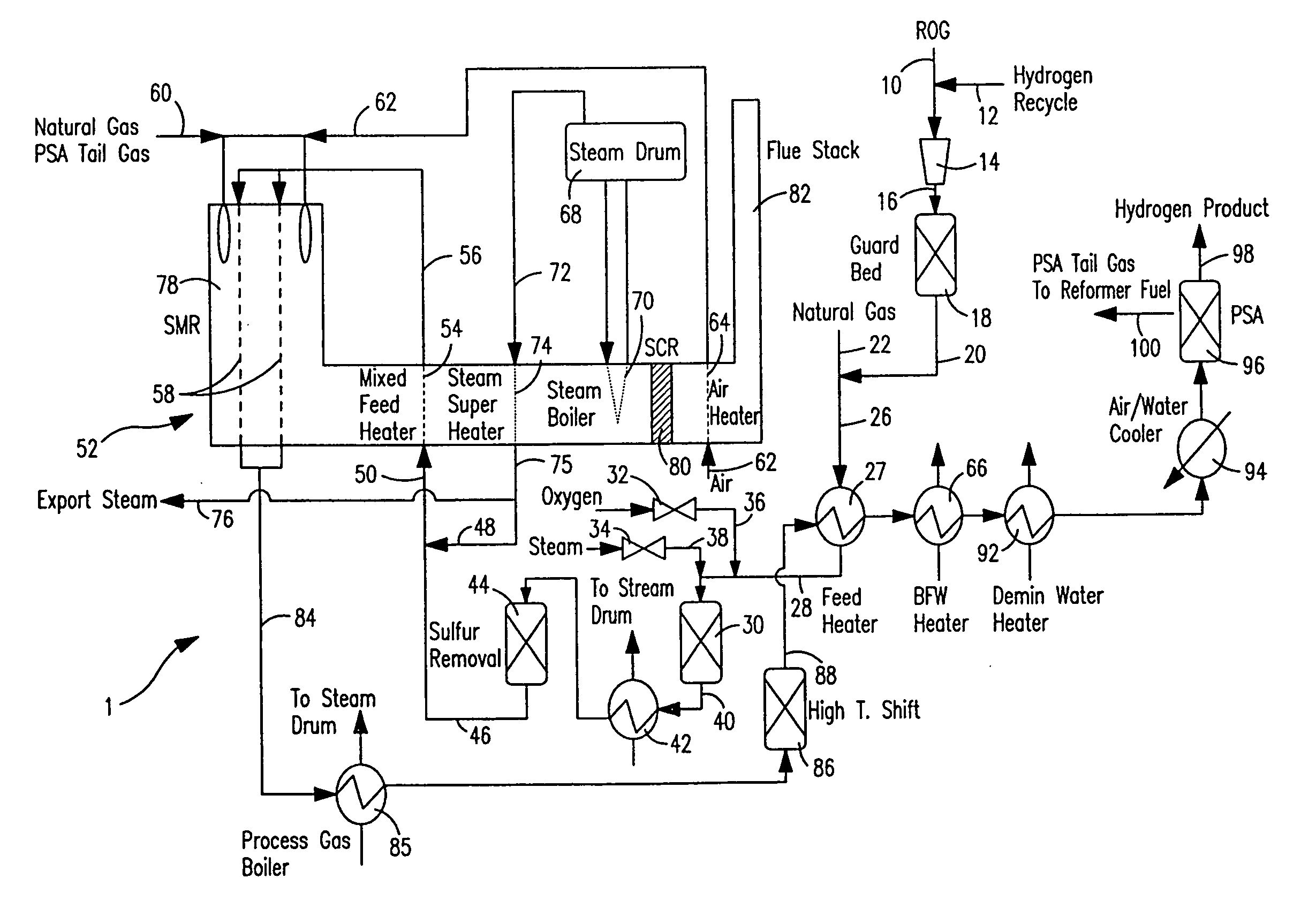
ActiveUS7037485B1Reduce fuel usageReduce firing rateHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesHydrogen separation using solid contactMethane reformerAlkane
A steam methane reforming method in which a feed stream is treated in a reactor containing a catalyst that is capable of promoting both hydrogenation and partial oxidation reactions. The reactor is either operated in a catalytic hydrogenation mode to convert olefins into saturated hydrocarbons and / or to chemically reduce sulfur species to hydrogen sulfide or a catalytic oxidative mode utilizing oxygen and steam to prereform the feed and thus, increase the hydrogen content of a synthesis gas produced by a steam methane reformer. The method is applicable to the treatment of feed streams containing at least 15% by volume of hydrocarbons with two or more carbon atoms and / or 3% by volume of olefins, such as a refinery off-gas. In such case, the catalytic oxidative mode is conducted with a steam to carbon ratio of less than 0.5, an oxygen to carbon ratio of less than 0.25 and a reaction temperature of between about 500° C. and about 860° C. to limit the feed to the steam methane reformer to volumetric dry concentrations of less than about 0.5% for the olefins and less than about 10% for alkanes with two or more carbon atoms.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
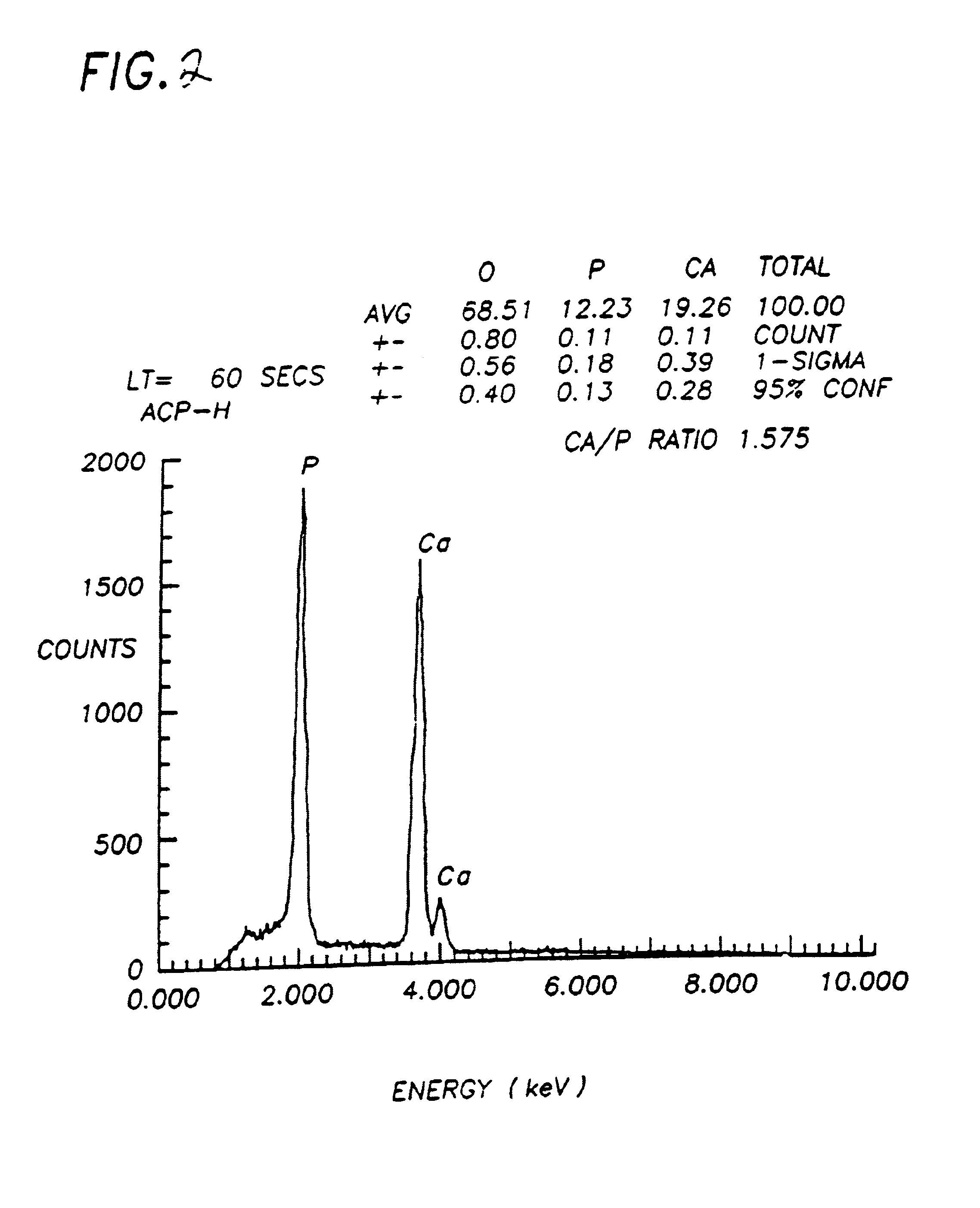
Bioceramic compositions
InactiveUS6972130B1Good biocompatibilityEasy to processBiocideInorganic phosphorous active ingredientsDiseaseDelivery vehicle
The present invention provides a synthetic, poorly crystalline apatite (PCA) calcium phosphate containing a biologically active agent and / or cells (preferably tissue-forming or tissue-degrading cells). The compositions provided by the present invention are useful for a variety of in vivo and in vitro applications, including drug delivery (for example, to bony sites, the central nervous system, intramuscular sites, subcutaneous sites, interperitoneal sites, and occular sites) tissue growth (preferably bone or cartilage) osseous augmentation, and methods of diagnosing disease states by assaying tissue forming potential of cells isolated from a host. The invention also provides methods of preparing delivery vehicles, of altering delivery vehicle characteristics, and of delivering biologically active agents to a site. The invention further provides in vitro cell culture systems and cell encapsulation materials. The invention is useful for both medical and veterinary applications.
Owner:LIFE SCI ENTERPRISES
Non-flammable quasi-solid electrolyte and non-lithium alkali metal or alkali-ion secondary batteries containing same
ActiveUS20150064574A1High concentrationImprove solubilityNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsCell electrodesSolventVapor pressure
A non-flammable quasi-solid electrolyte and a rechargeable non-lithium alkali metal cell containing this electrolyte. The electrolyte comprises an alkali metal salt dissolved in an organic liquid solvent with a concentration higher than 2.5 M (preferably >3.5 M) or a molecular ratio greater than 0.2 (preferably >0.3), wherein the alkali metal is selected from Na, K, a combination of Na and K, or a combination of Na and / or K with Li. The alkali metal salt concentration is sufficiently high so that the electrolyte exhibits a vapor pressure <0.01 kPa when measured at 20° C., a vapor pressure <60% of the vapor pressure of thet organic solvent when measured alone, a flash point at least 20 degrees Celsius higher than a flash point of the organic liquid solvent when measured alone, a flash point higher than 150° C., or no detectable flash point.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
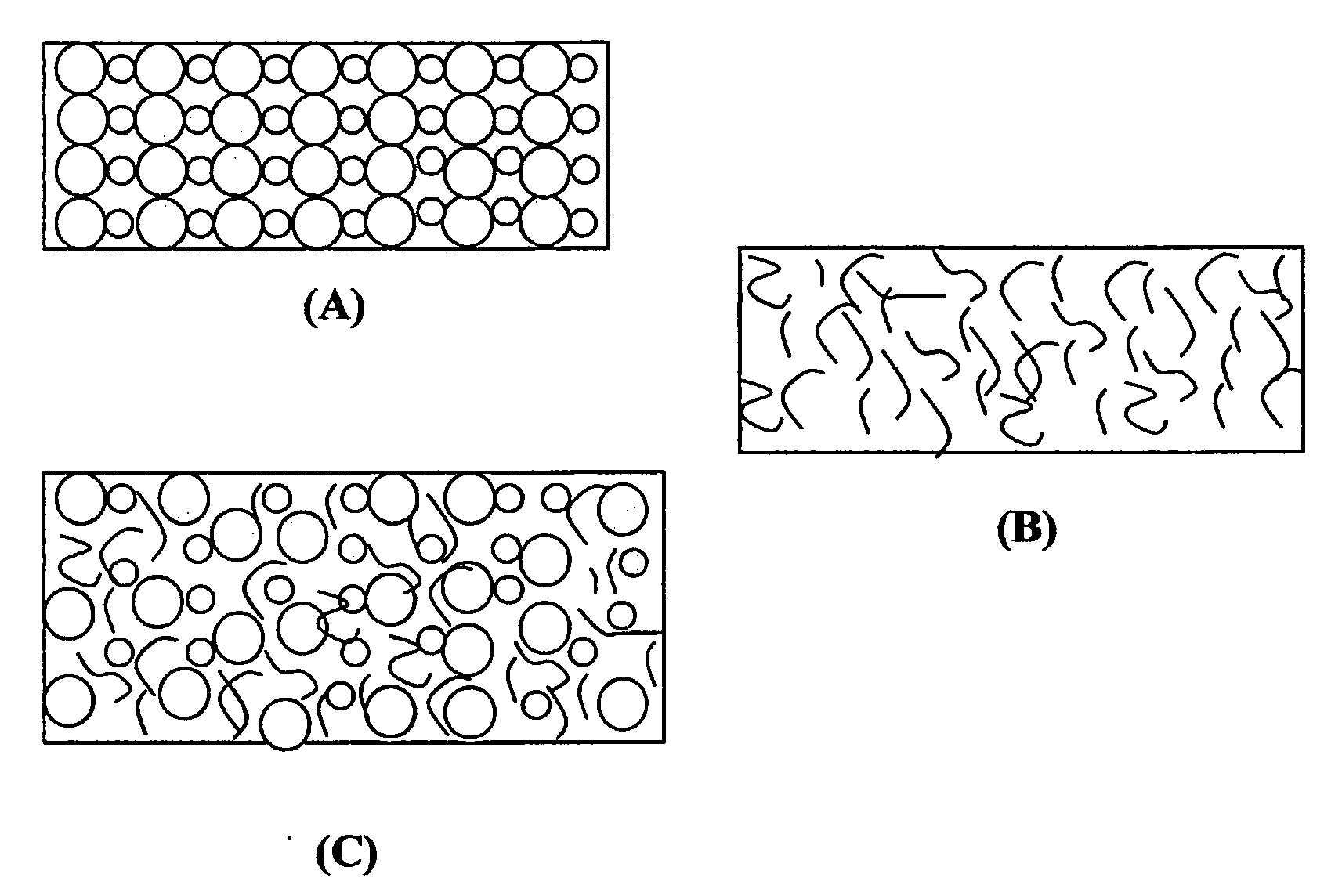
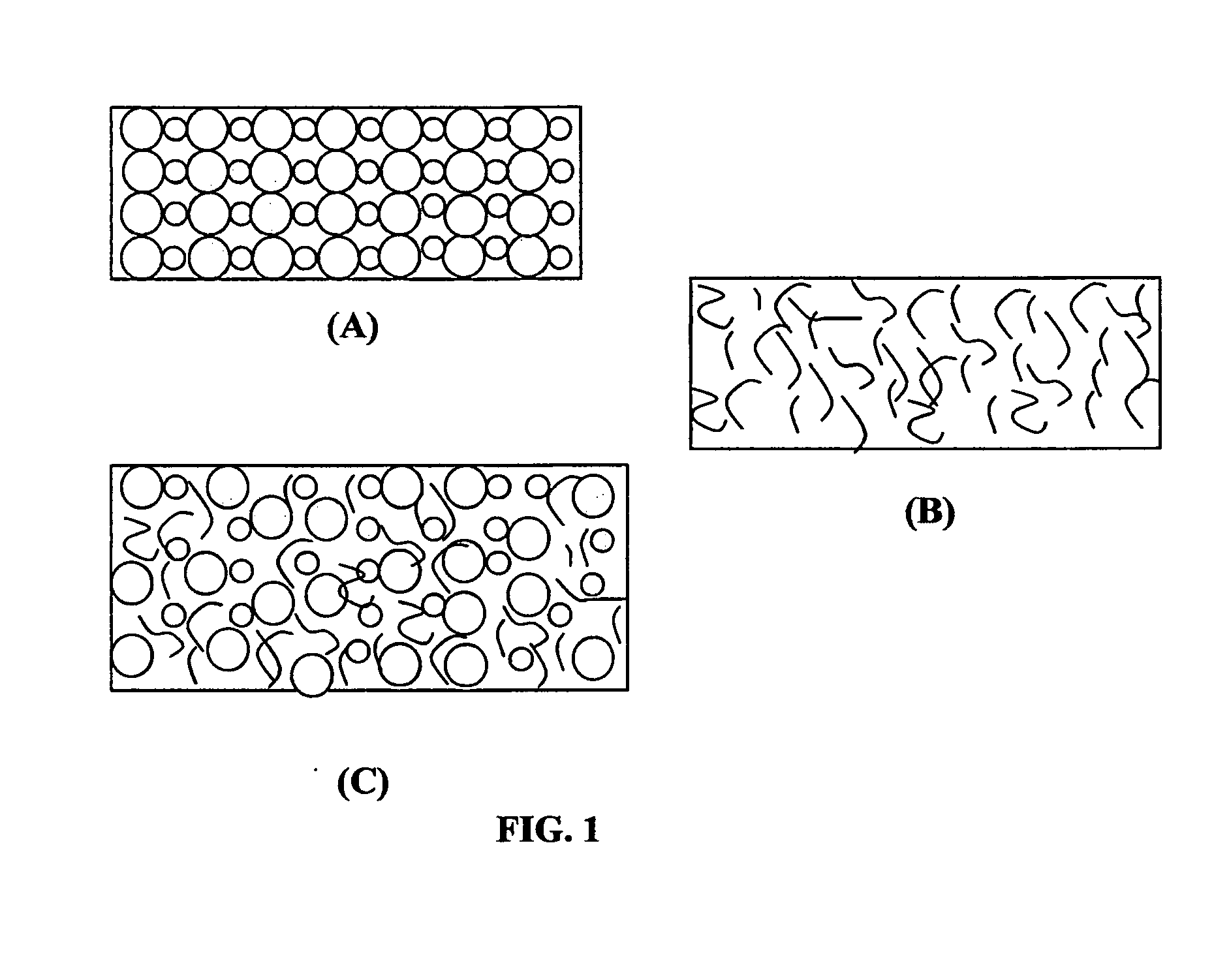
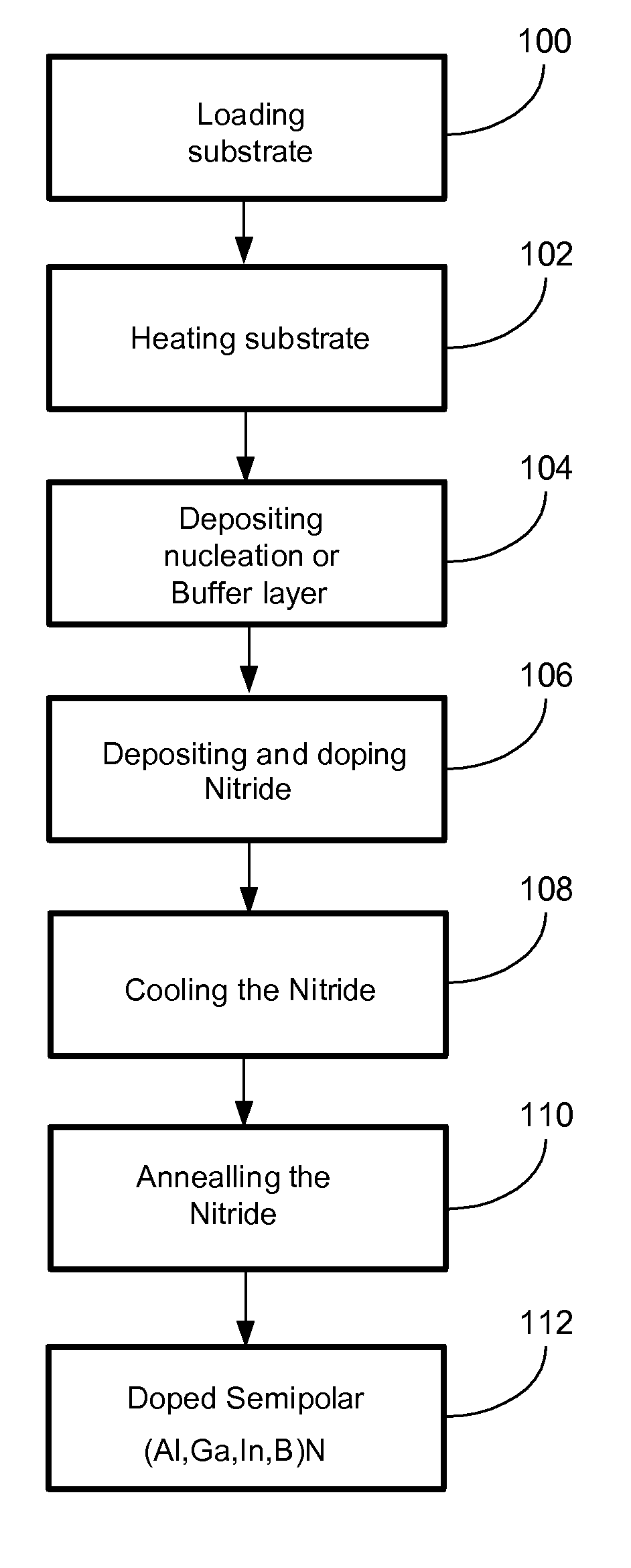
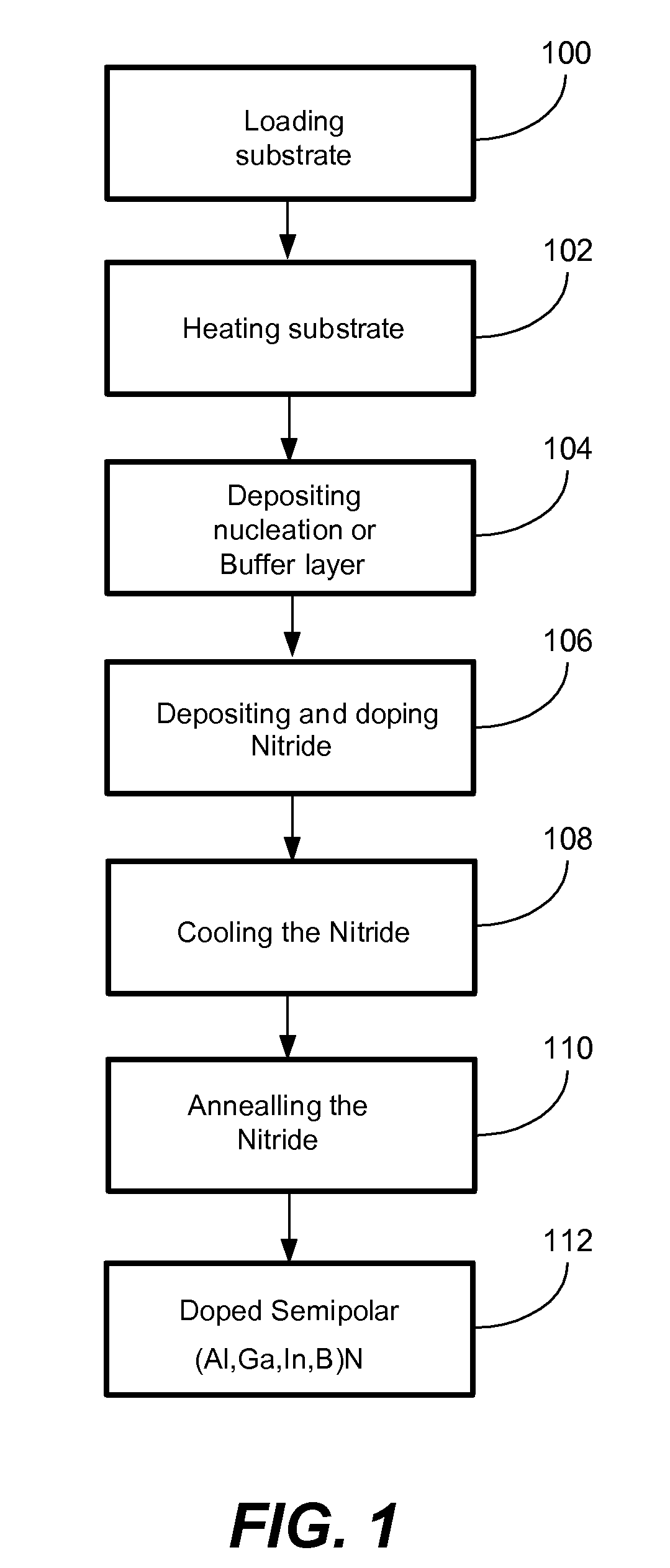
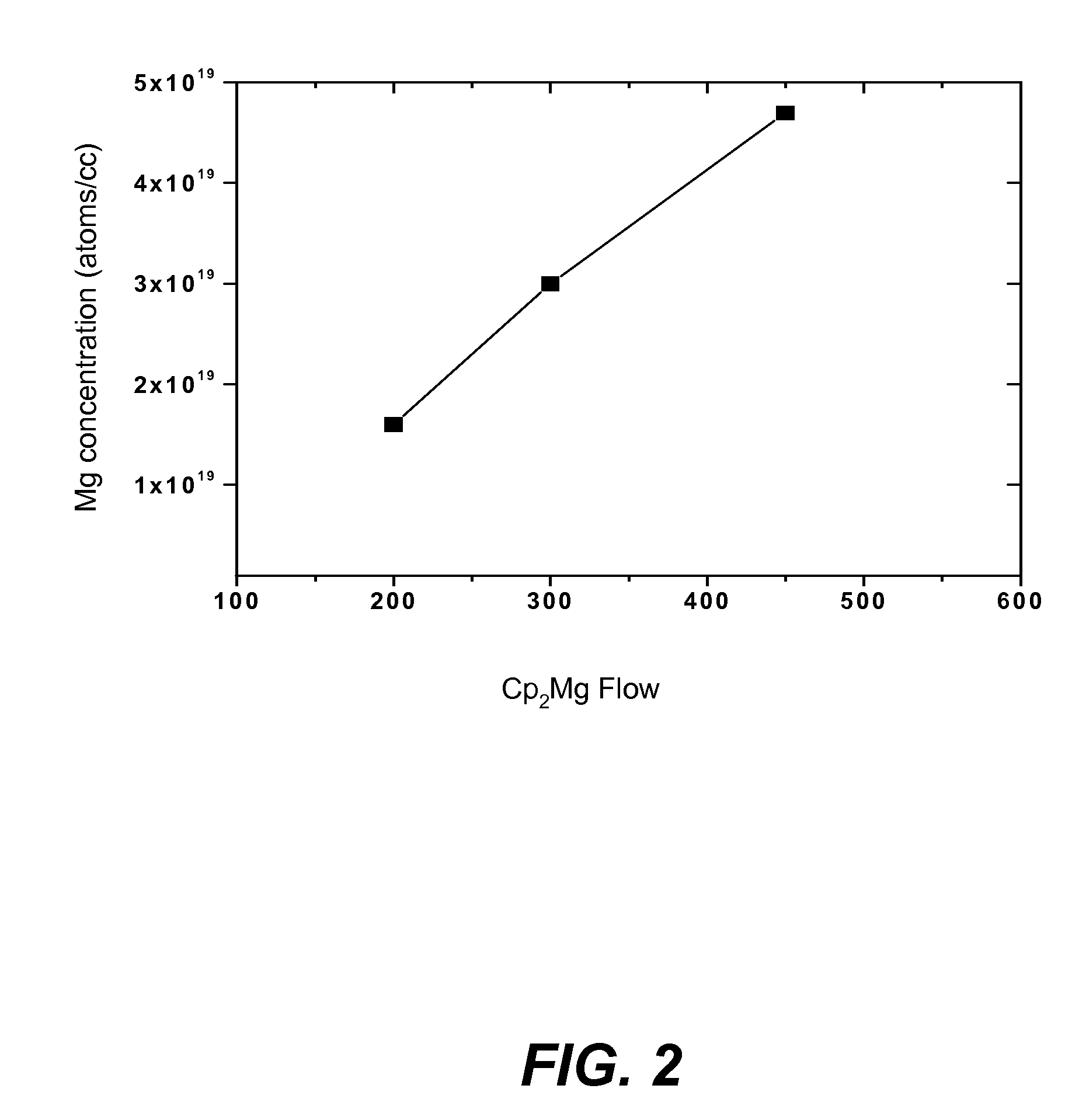
METHOD FOR CONDUCTIVITY CONTROL OF (Al,In,Ga,B)N
ActiveUS20070190758A1Improve conductivityEnhancing or tailoring conductivity propertiesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesElectronic statesSpinel
A method of controlled p-type conductivity in (Al,In,Ga,B)N semiconductor crystals. Examples include {10 11} GaN films deposited on {100} MgAl2O4 spinel substrate miscut in the <011> direction. Mg atoms may be intentionally incorporated in the growing semipolar nitride thin film to introduce available electronic states in the band structure of the semiconductor crystal, resulting in p-type conductivity. Other impurity atoms, such as Zn or C, which result in a similar introduction of suitable electronic states, may also be used.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
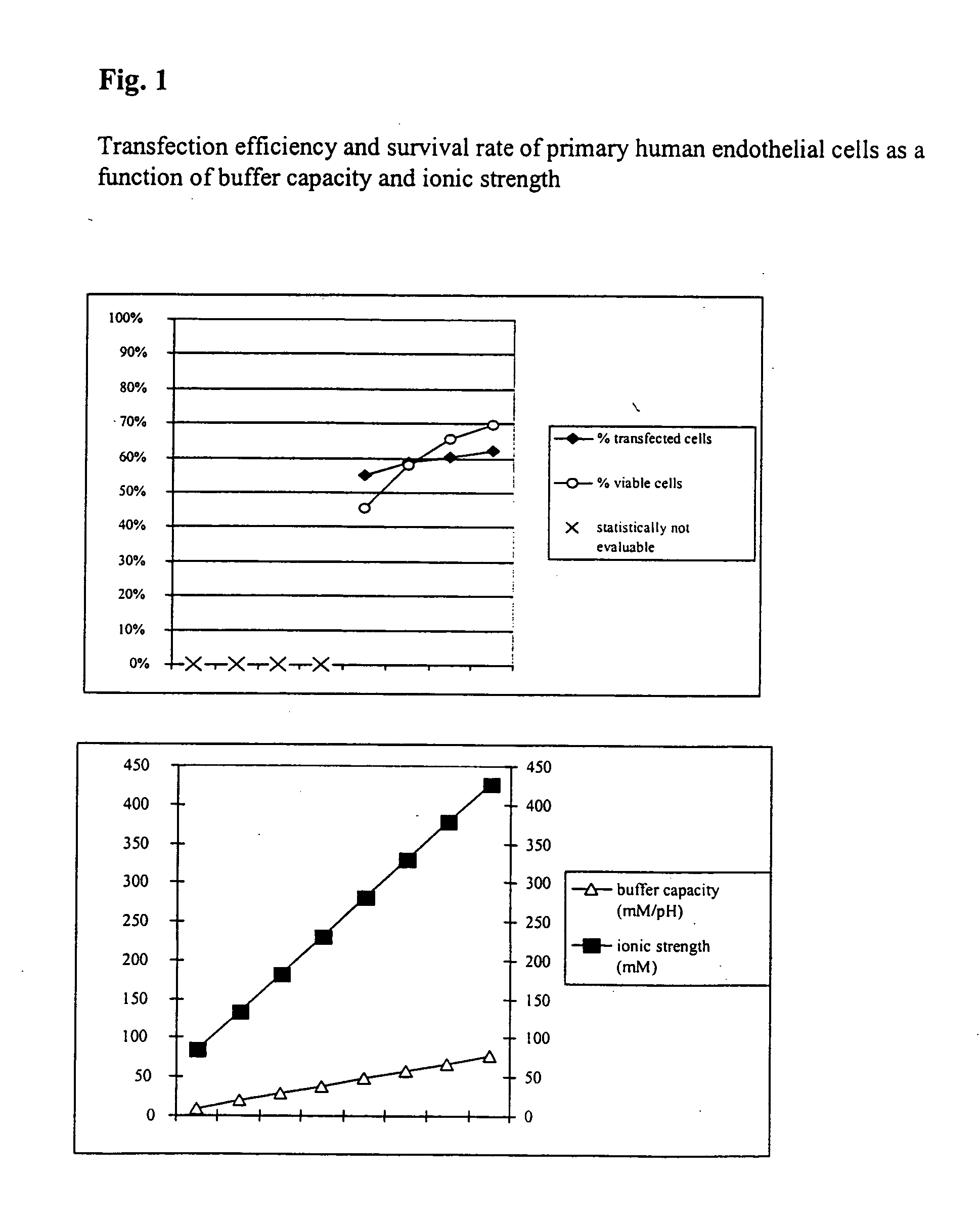
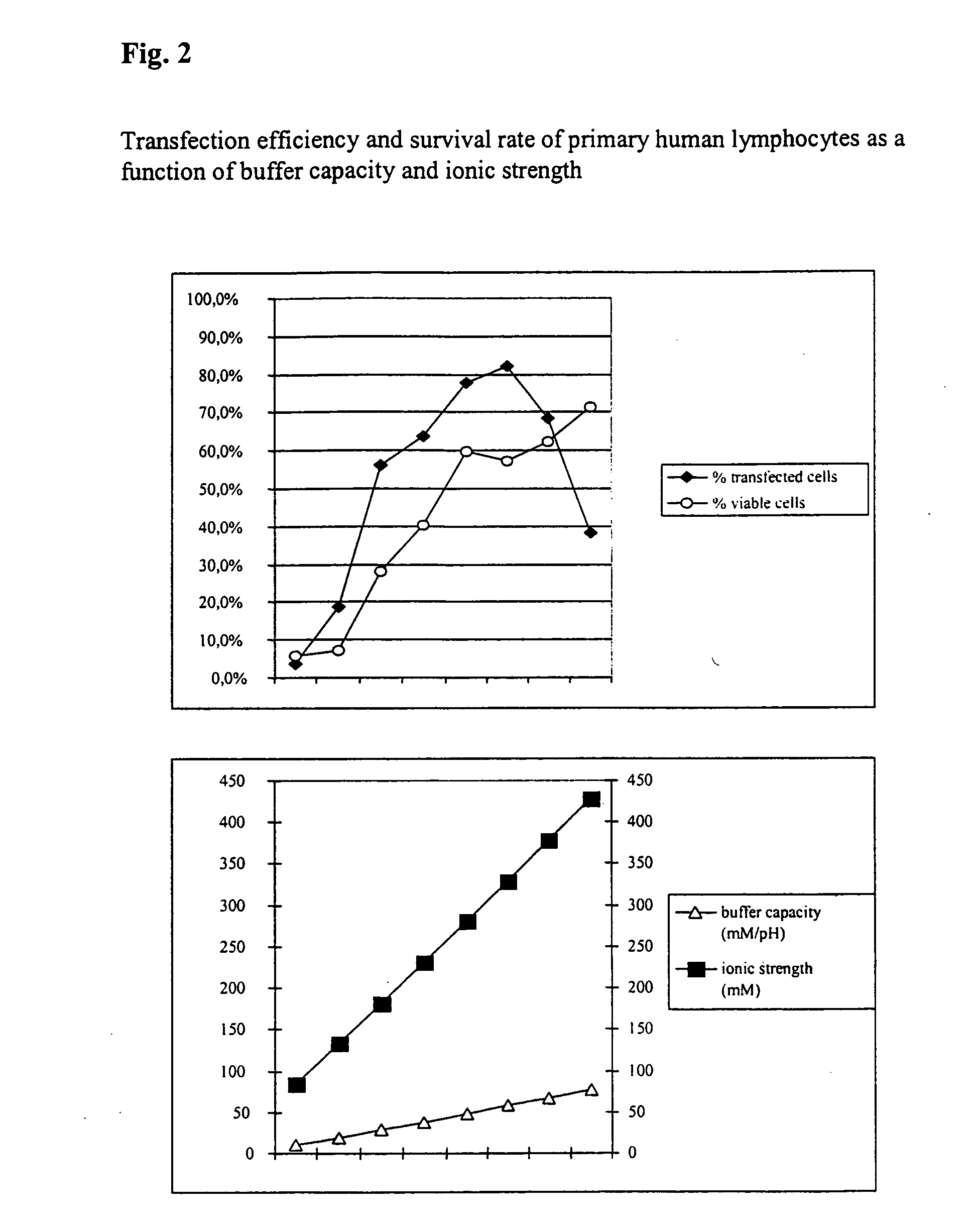
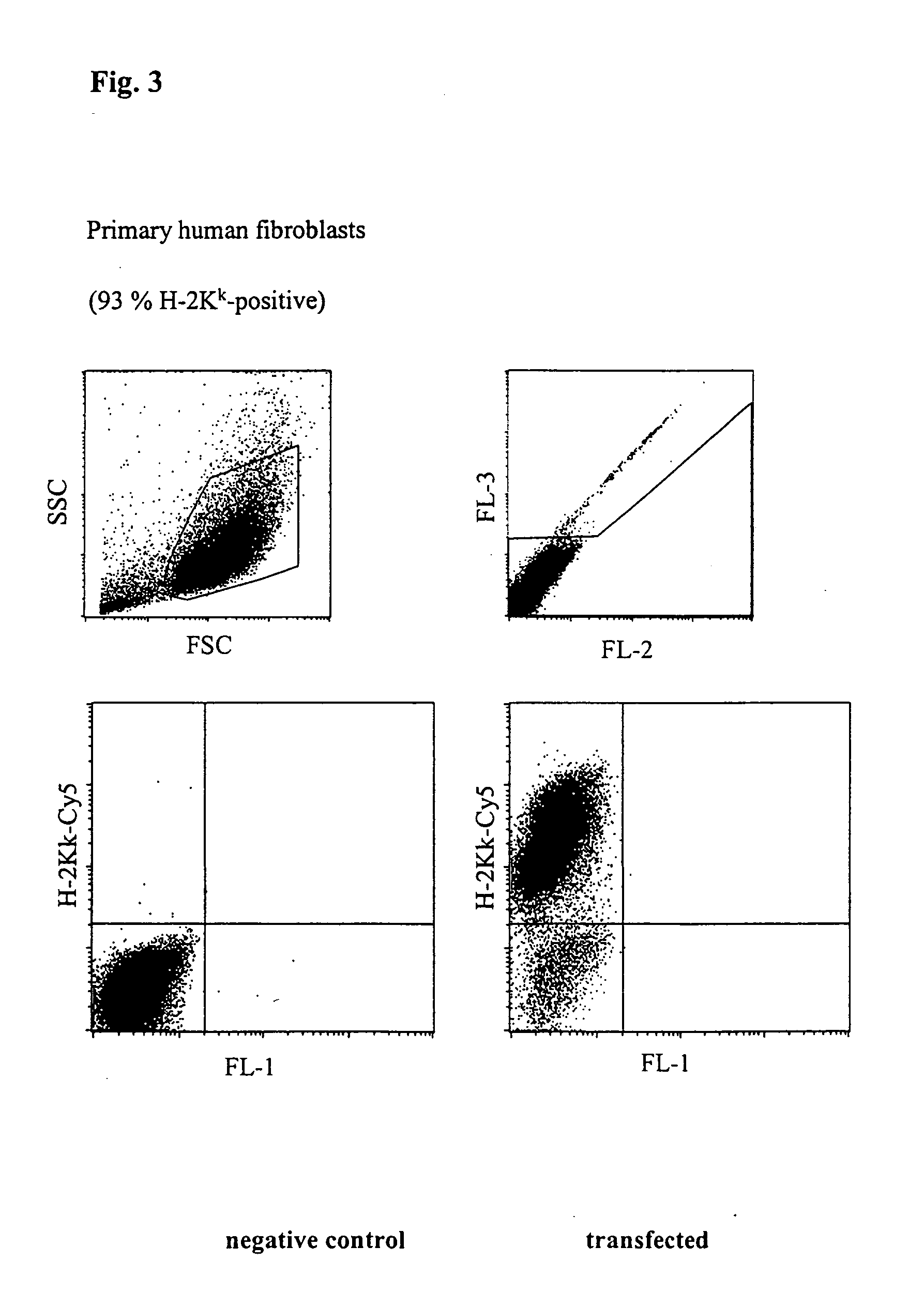
Buffer solution for electroporation and a method comprising the use of the same
InactiveUS20050064596A1High transfection efficiencyReduce cell deathPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsElectroporationIon
The invention relates to a buffer solution for suspending animal or human cells and for dissolving biologically active molecules in order to introduce said biologically active molecules into the cells using an electric current and to a method for introducing biologically active molecules into animal or human cells using an electric current and a buffer solution. The inventive buffer solution has a buffering capacity of at least 20 mmol*I−1*pH−1 and an ionic strength of at least 200 mmol*I−1 during a change to the pH value from pH 7 to pH 8 and at a temperature of 25° C. The use of a buffer solution of this type in the corresponding method allows biologically active molecules to be introduced into animal and human cells with a high degree of transfection efficiency and at the same time a low cell mortality. Different cell types, in particular dormant and actively dividing cells of low activity, can be successfully transfected in said buffer solution.
Owner:LONZA COLOGNE
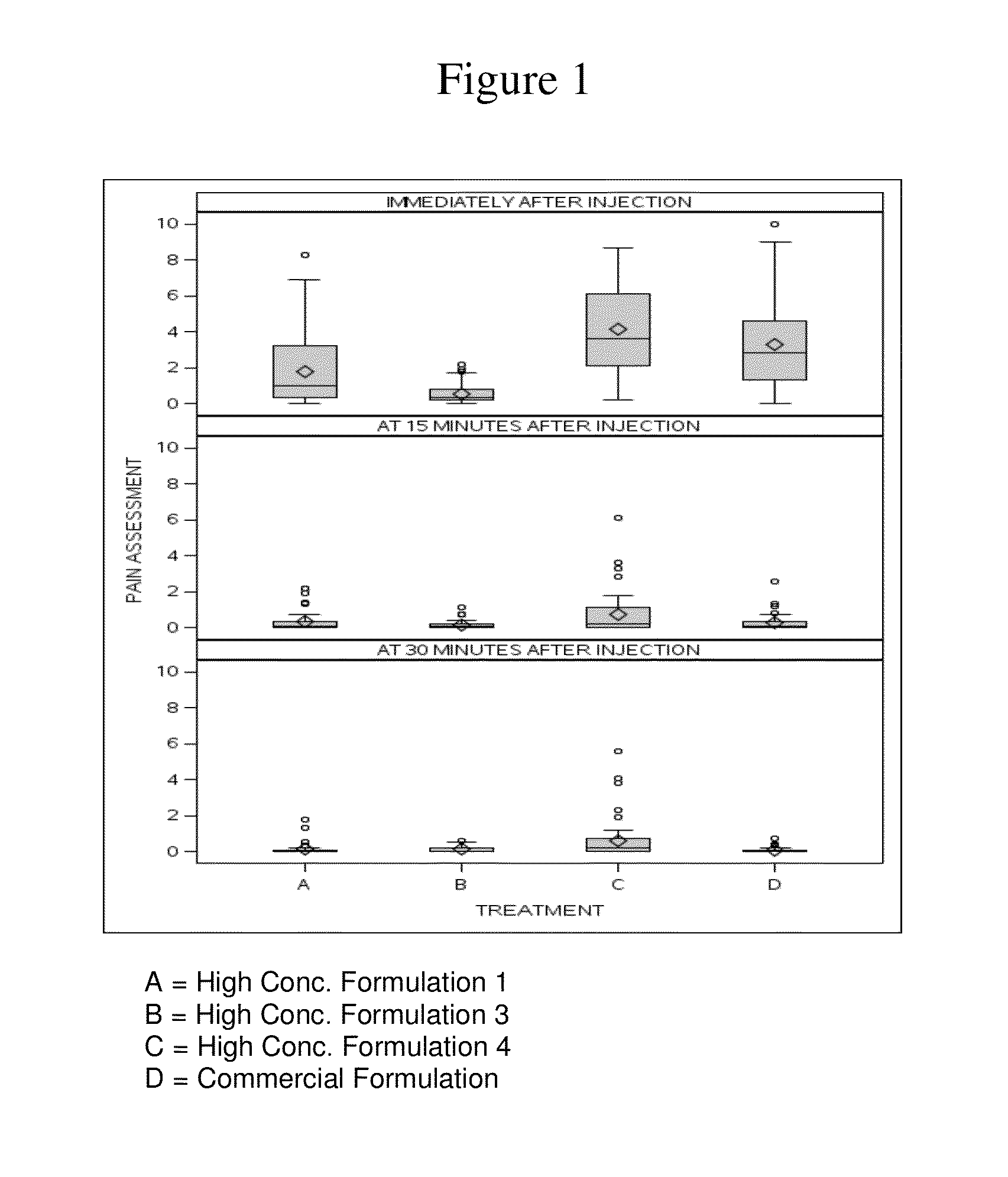
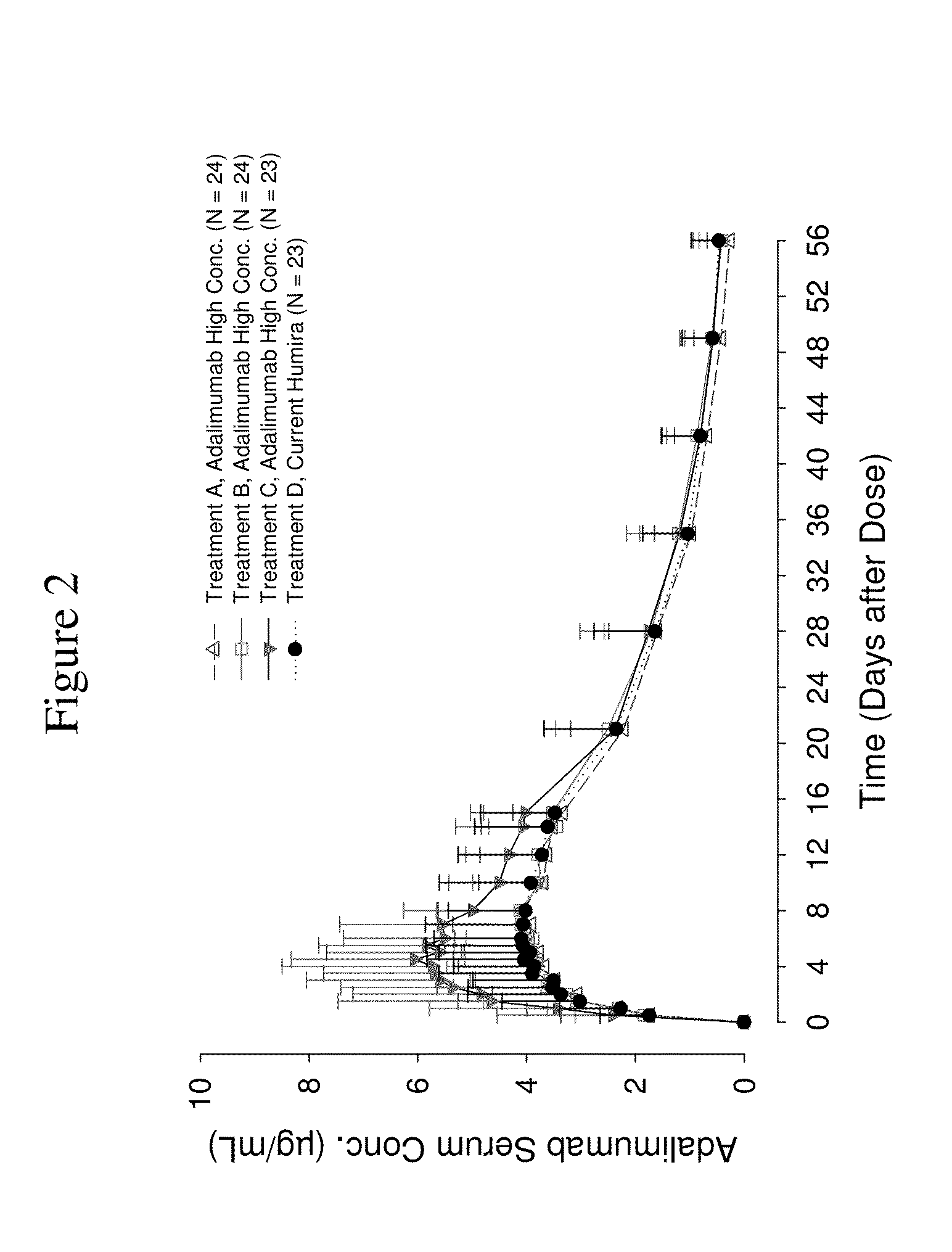
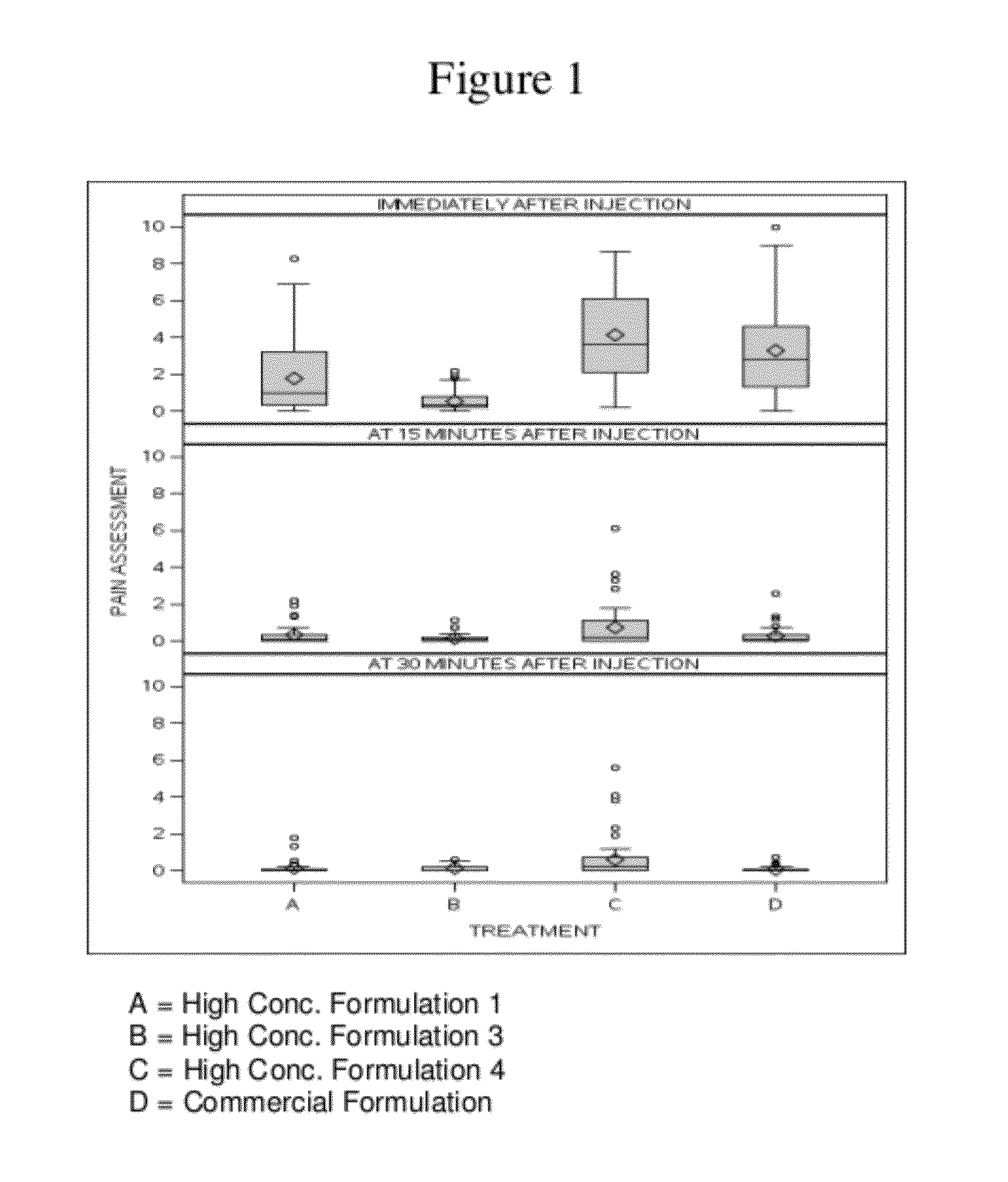
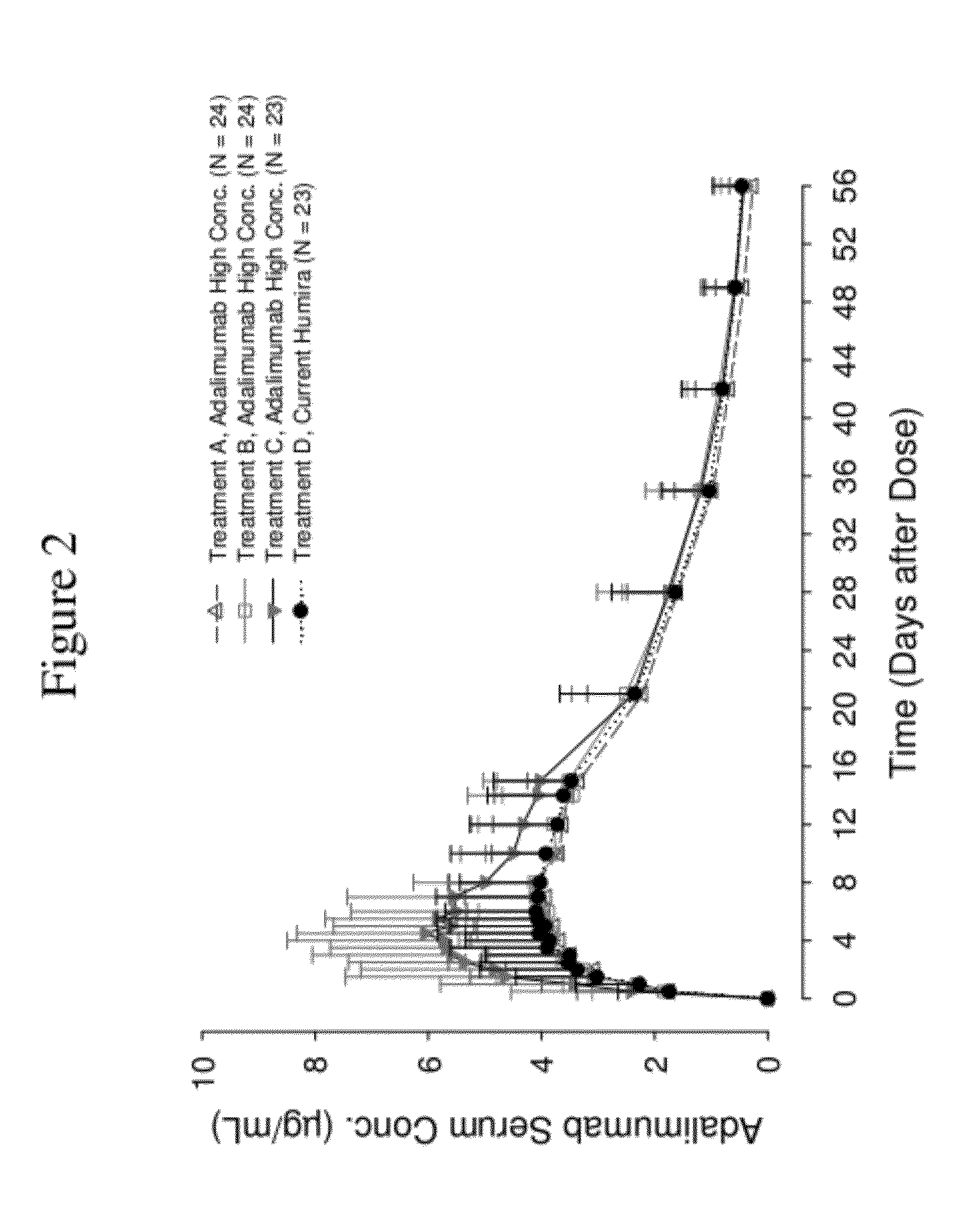
High concentration anti-TNFα antibody liquid formulations
ActiveUS8821865B2Improve bioavailabilityRelieve painSenses disorderNervous disorderAntiendomysial antibodiesTherapeutic protein
The invention provides a liquid aqueous pharmaceutical formulation comprising a human anti-TNFa antibody, or antigen-binding portion thereof, which reduces pain associated with injection in a subject by at least about 50% when compared to injecting an otherwise identical formulation comprising at least one salt and / or at least one buffer. The invention also provides a liquid aqueous pharmaceutical formulation comprising a human anti-TNFa antibody, or antigen-binding portion thereof, having increased bioavailability upon subcutaneous administration into a subject. The formulation may comprise a therapeutic protein, such as a human anti-TNF-alpha antibody, or an antigen-binding portion thereof, or a biosimilar thereof.
Owner:ABBVIE BIOTECHNOLOGY LTD
Thin film field effect transistor and display
ActiveUS20090236596A1Small band gapHigh concentrationTransistorElectroluminescent light sourcesDisplay deviceField-effect transistor
A TFT is provided which includes, on a substrate, at least a gate electrode, a gate insulating layer, an active layer containing an amorphous oxide semiconductor, a source electrode and a drain electrode, wherein a resistance layer containing an amorphous oxide and having a thickness of more than 3 nm is disposed between the active layer and at least one of the source electrode or the drain electrode, and a band gap of the active layer is smaller than a band gap of the resistance layer. Also, a display using the TFT is provided.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
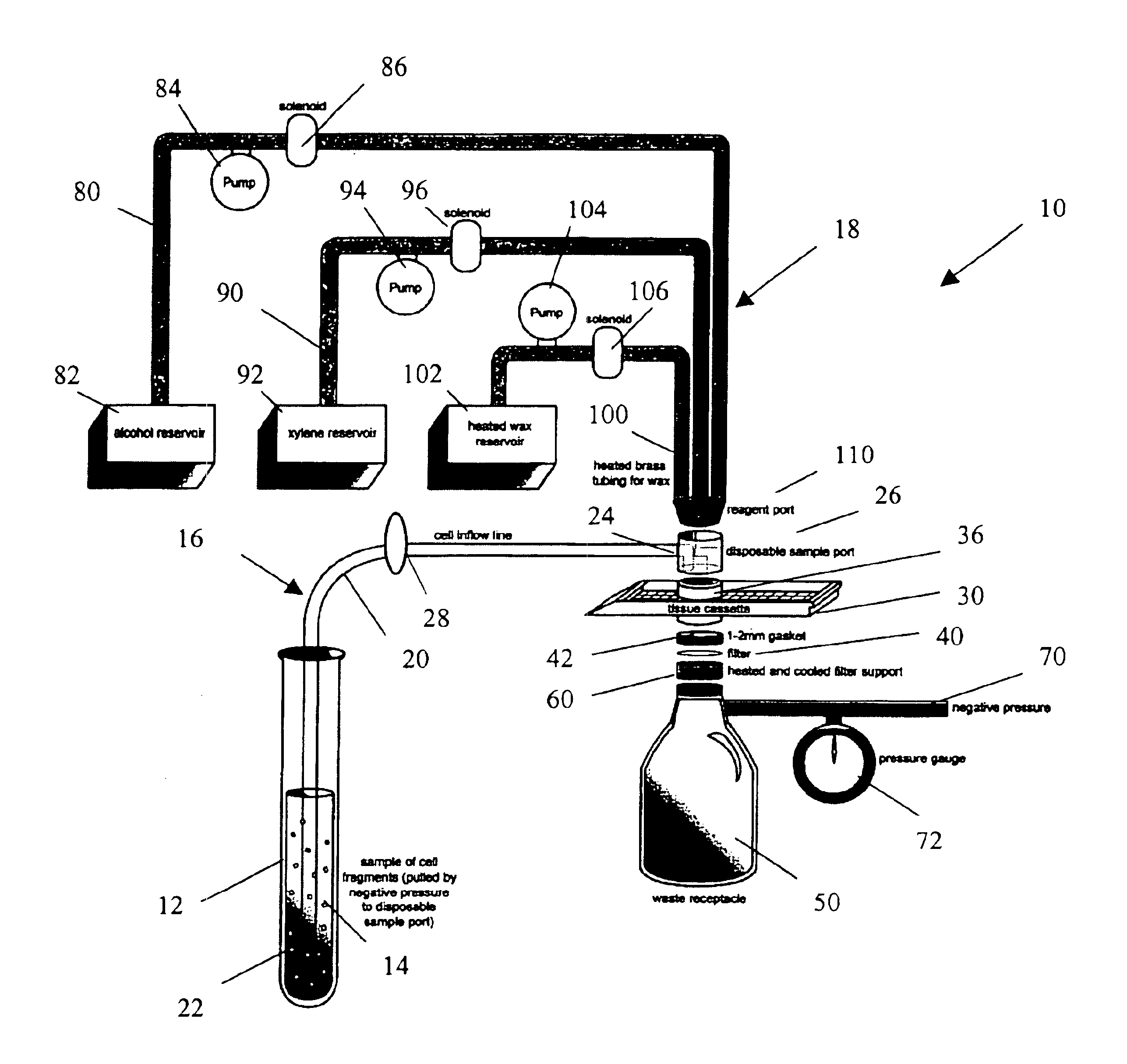
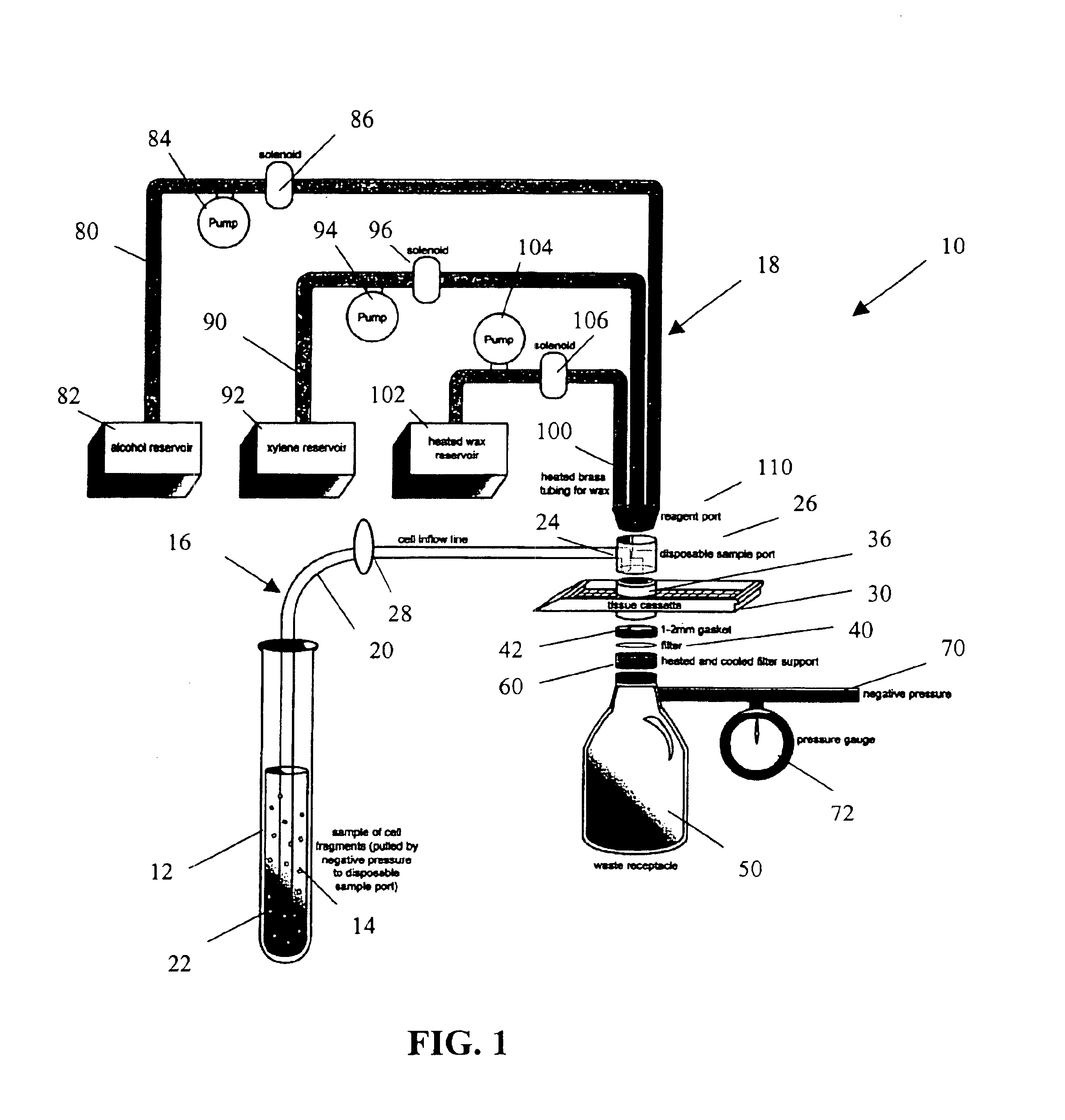
Rapid cell block embedding method and apparatus
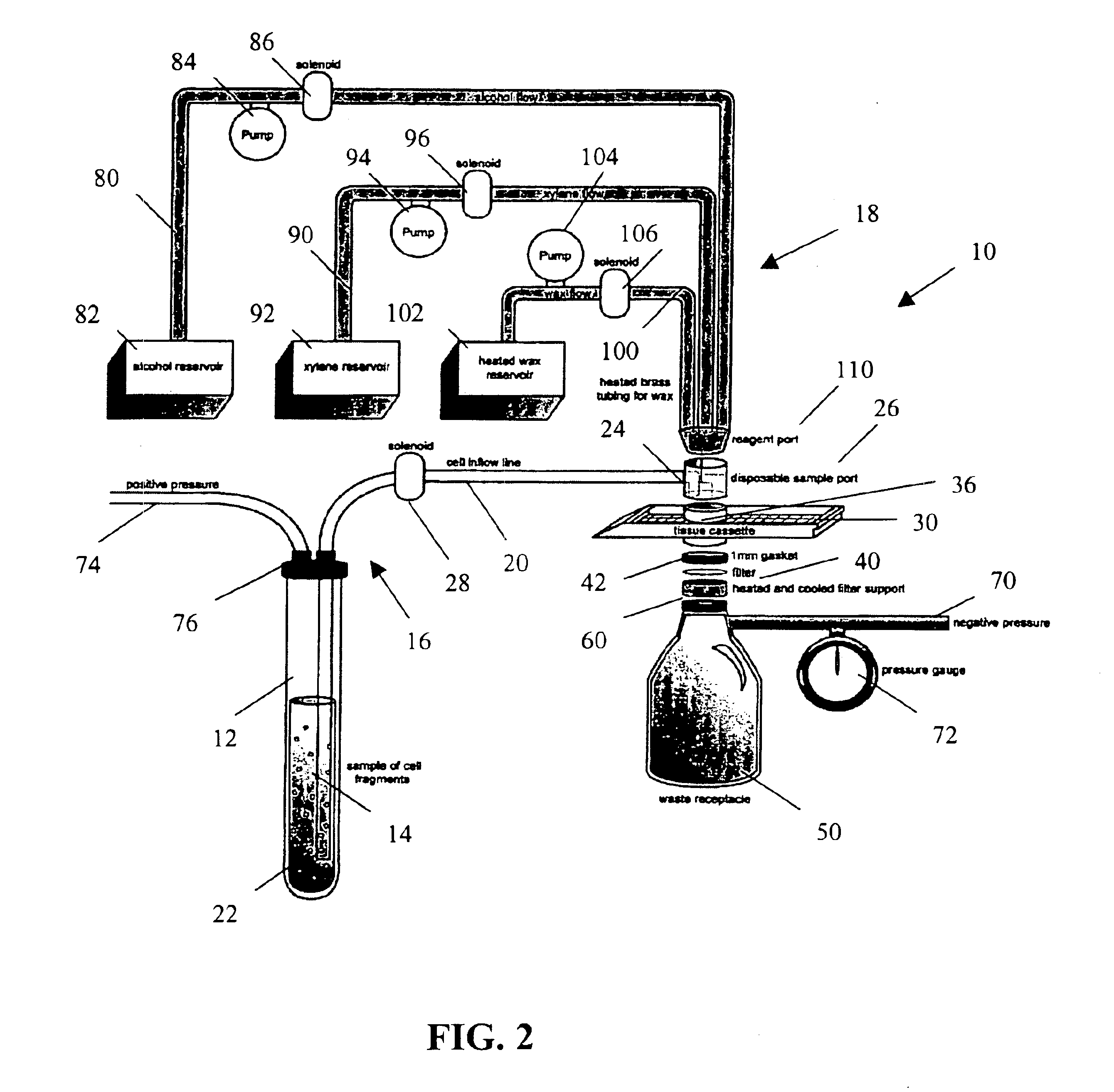
ActiveUS6913921B2Maximize efficiencyReduce amountBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringReagent
A method and apparatus for embedding cells that utilizes a flow-through embedding technique maximizes the efficiency of extractions and decreases time for embedding the cell fragments, minimizes cell loss, and automatically positions cell samples at the position in which a microtome blade will section them. The apparatus includes a cell flow pathway defined by an inflow tube for delivering cell fragments from a cell sample to a sample port. The sample port is in fluid communication with a tissue cassette having attached thereto a filter. The cell flow pathway is in communication with a reagent flow pathway for delivering the reagents through the sample port to the cassette. The apparatus is configured such that the application of pressure directs the cell fragments from the cell sample through the cell flow pathway, and effects delivery of the reagents through the reagent flow pathway. The apparatus produces an embedded cell block having concentrated cells near the plane of the block to be sectioned in a quick and efficient manner.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS UNIV OF
Process for the recovery of value metals from base metal sulfide ores
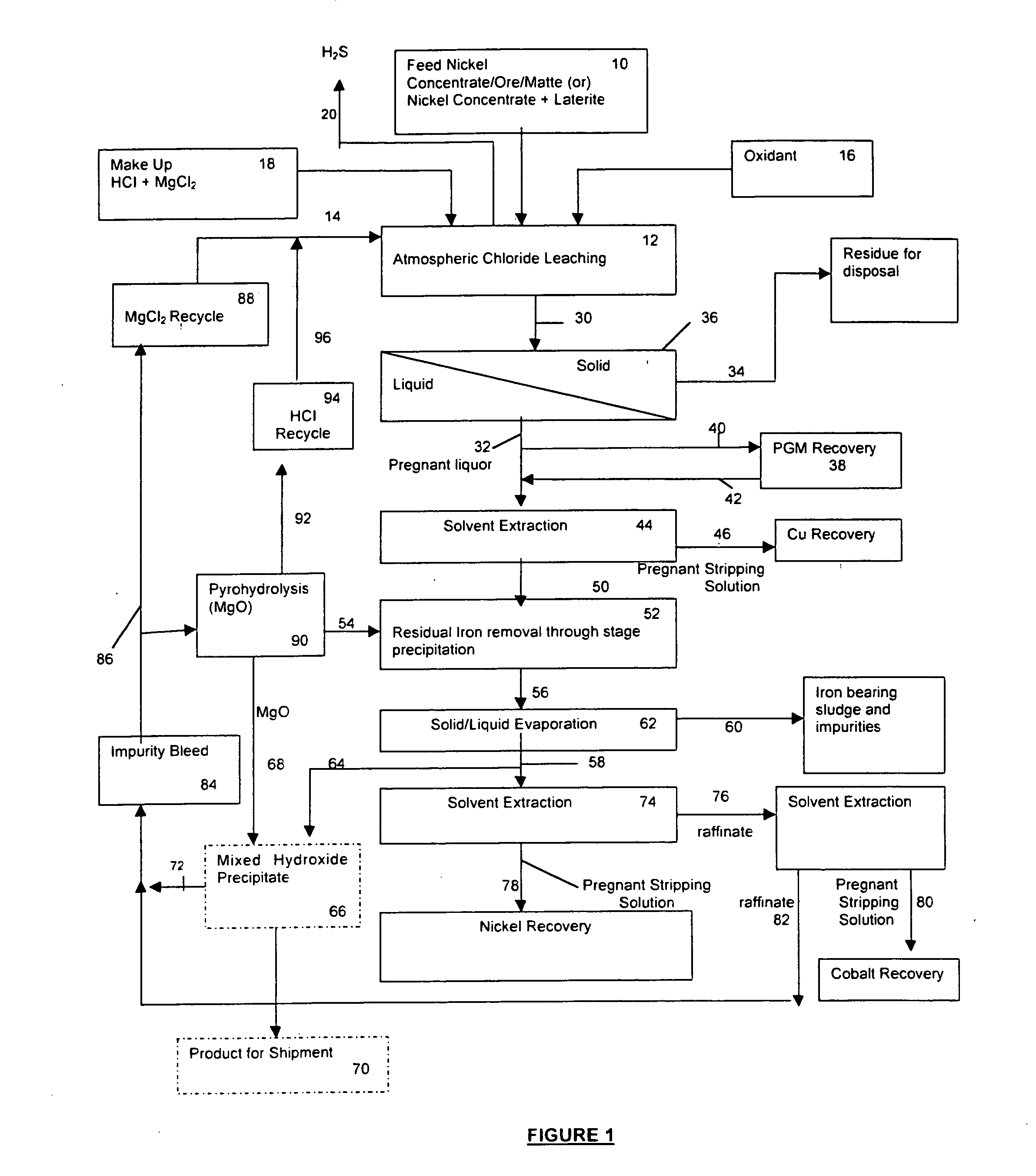
InactiveUS20050118081A1Simple gas/liquidReduce the amount requiredSulfur compoundsSolid sorbent liquid separationSulfideDissolution
A process for leaching a value metal from a base metal sulfide ore, comprising the step of leaching the ore with a lixiviant comprising a chloride, an oxidant and hydrochloric acid is disclosed. The leaching is controlled, by use of low concentrations of hydrochloric acid and a redox potential, to effect formation of hydrogen sulfide from the base metal sulfide ore. The hydrogen sulfide is stripped from the leach solution, thereby reducing the amount of sulfate generated in the leach to very low levels. The leaching may also be conducted to limit the co-dissolution of platinum group metals and gold with the base value metals. The leach forms a value metal-rich leachate and a solids residue. The solids residue may be subsequently leached to recover the platinum group metals and gold. The value metal-rich leachate can be is oxidized and neutralized to recover the value base metals. In an embodiment, the chloride is magnesium chloride and lixiviant solution is regenerated.
Owner:JAGUAR NICKEL INC
Method for forming a semiconductor device
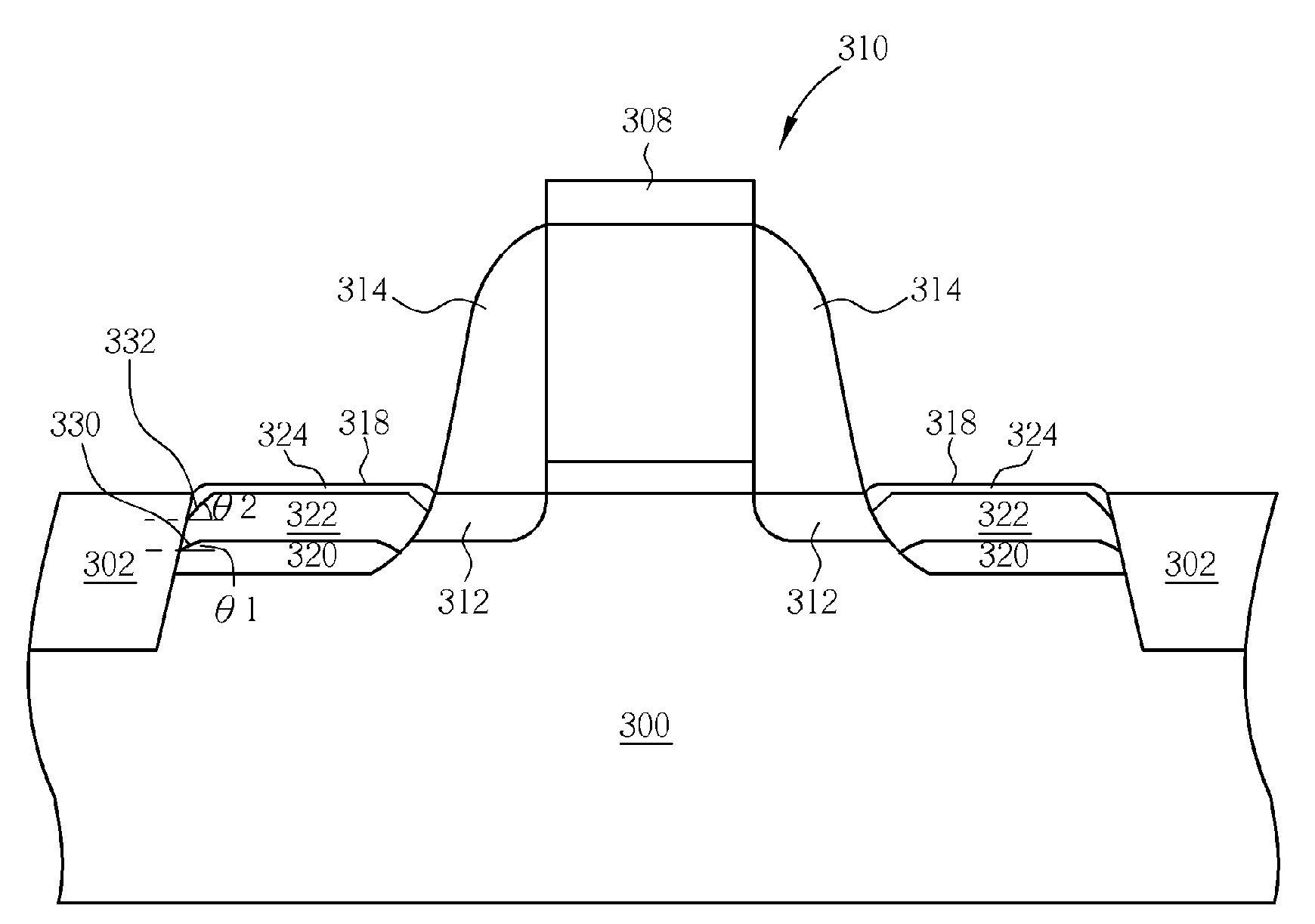
ActiveUS20100093147A1High Ge concentrationReduce difficultySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingEngineeringSemiconductor
A method for forming a semiconductor device includes providing a substrate having at least a gate positioned thereon, forming at least a recess in the substrate adjacent to the gate, performing a first selective epitaxial growth (SEG) process to form a first epitaxial layer in the recess, performing an etching process to remove a portion of the first epitaxial layer to expose the substrate, and performing a second SEG process to form a second epitaxial layer on the first epitaxial layer.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Organic light emitting display device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20100176383A1High carrier concentrationStable and uniform functional propertyElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceLight-emitting diode
Disclosed is an organic light emitting display device and a method of manufacturing the same. The organic light emitting display device includes the thin film transistor of the drive unit that has the activation layer formed in a structure where the first oxide semiconductor layer and the second oxide semiconductor layer are stacked, the thin film transistor of the pixel unit that has the activation layer formed of the second oxide semiconductor layer, and the organic light emitting diode coupled to the thin film transistor of the pixel unit. The thin film transistor of the drive unit has channel formed on the first oxide semiconductor layer having a higher carrier concentration than the second oxide semiconductor layer, having a high charge mobility, and the thin film transistor of the pixel unit has a channel formed on the second oxide semiconductor layer, having a stable and uniform functional property.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
HIGH CONCENTRATION ANTI-TNFalpha ANTIBODY LIQUID FORMULATIONS
ActiveUS20120263731A1Improve bioavailabilityRelieve painSenses disorderNervous disorderHigh concentrationBiosimilar Pharmaceuticals
The invention provides a liquid aqueous pharmaceutical formulation comprising a human anti-TNFa antibody, or antigen-binding portion thereof, which reduces pain associated with injection in a subject by at least about 50% when compared to injecting an otherwise identical formulation comprising at least one salt and / or at least one buffer. The invention also provides a liquid aqueous pharmaceutical formulation comprising a human anti-TNFa antibody, or antigen-binding portion thereof, having increased bioavailability upon subcutaneous administration into a subject. The formulation may comprise a therapeutic protein, such as a human anti-TNF-alpha antibody, or an antigen-binding portion thereof, or a biosimilar thereof.
Owner:ABBVIE BIOTECHNOLOGY LTD
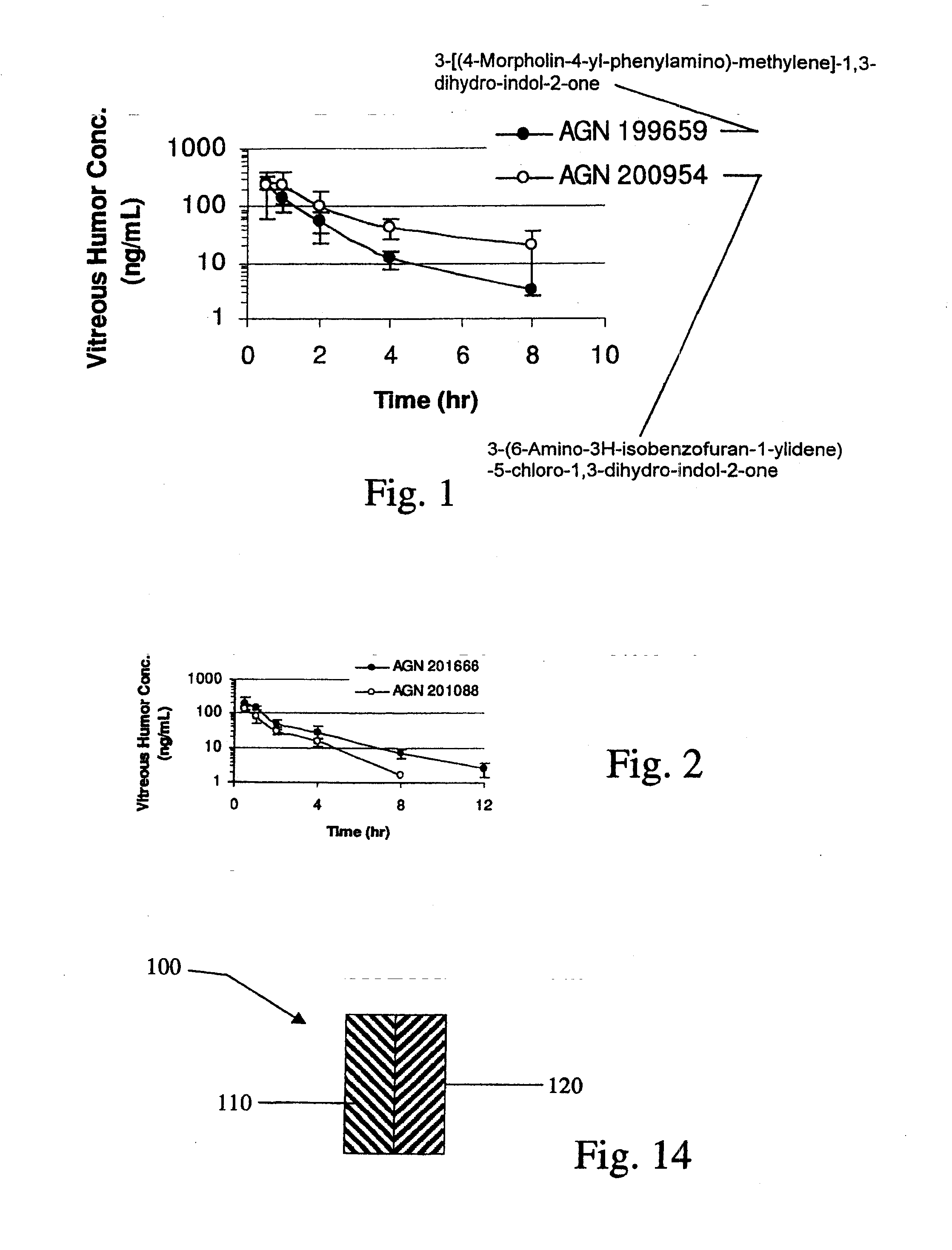
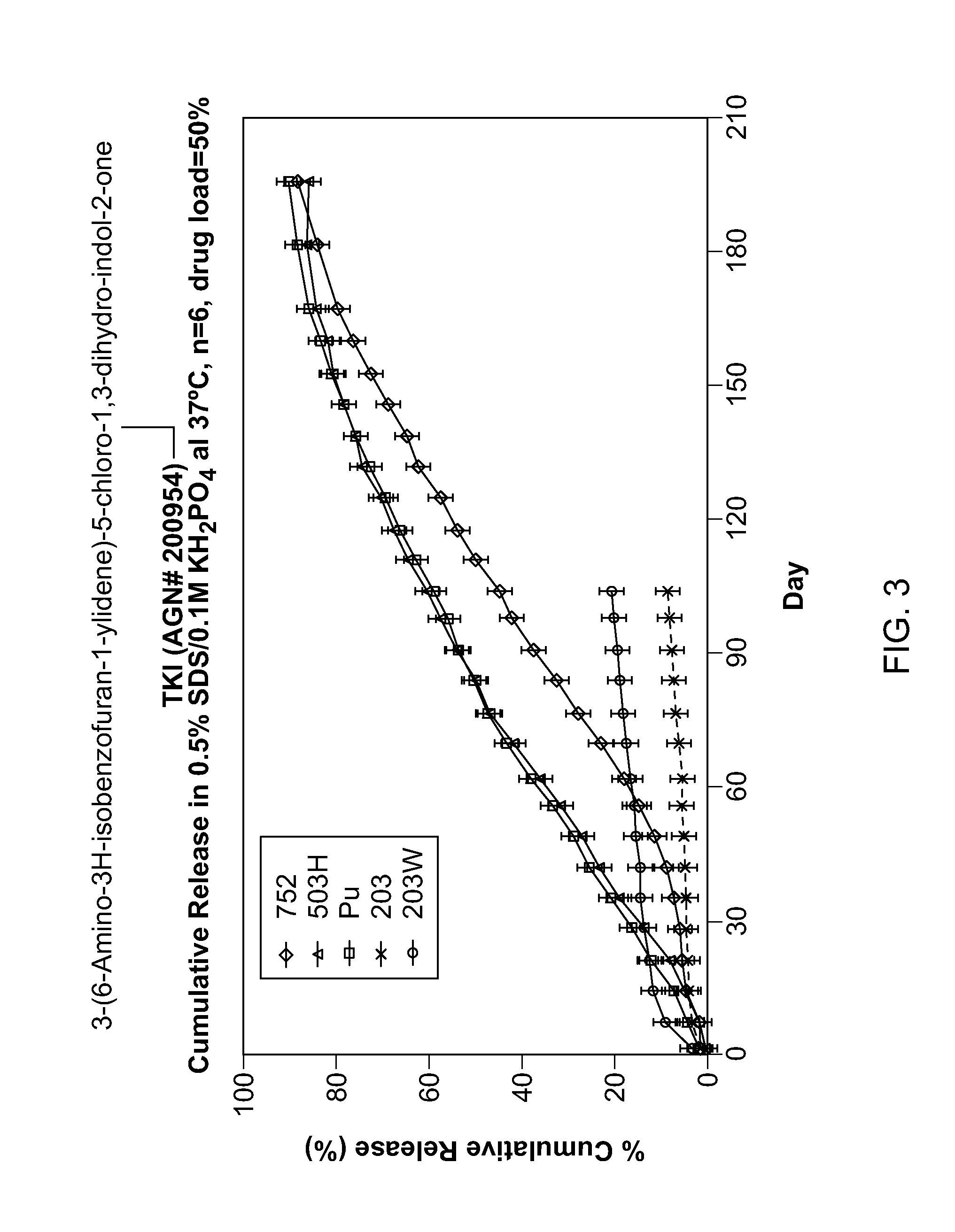
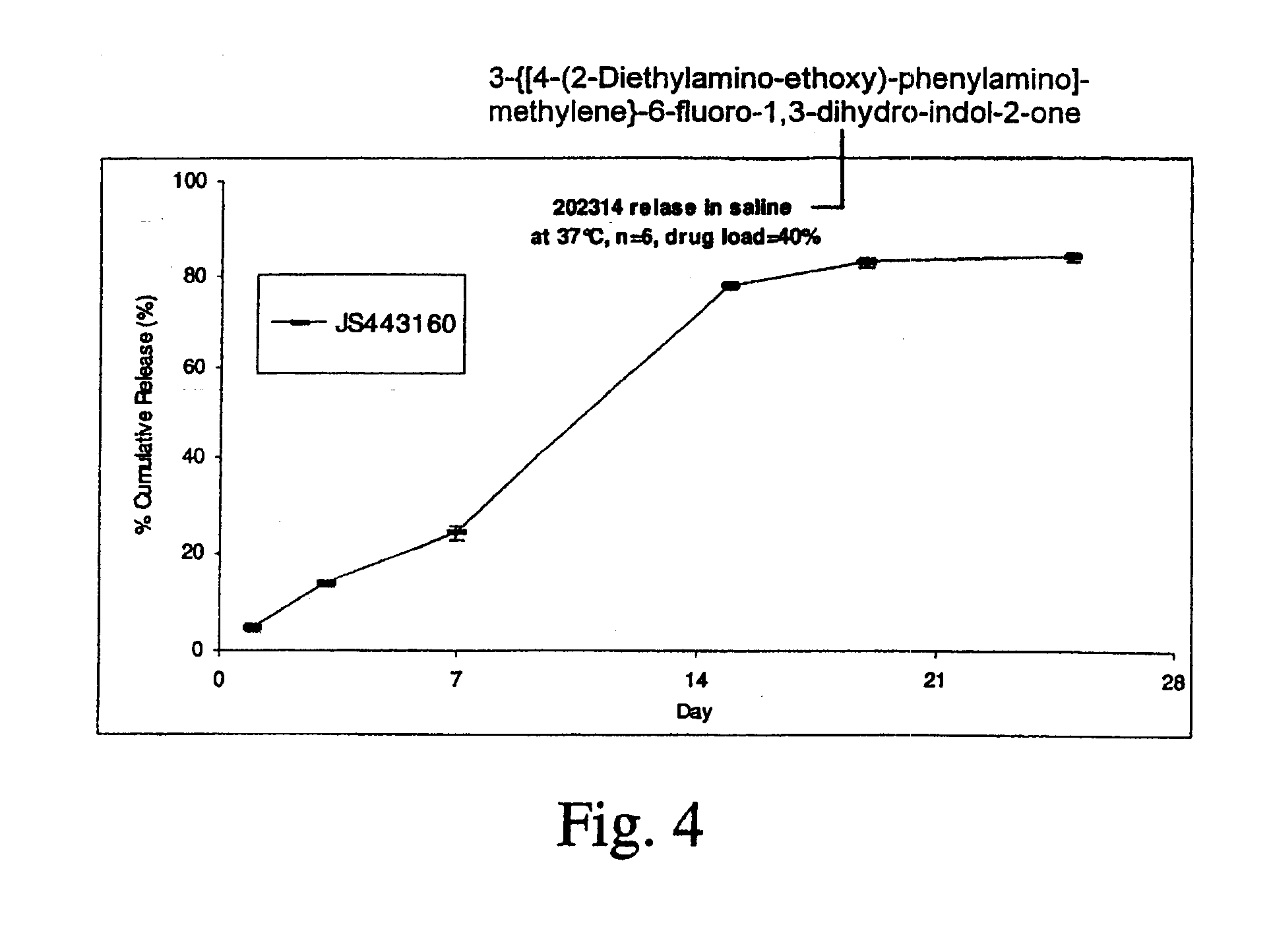
Biodegradable Intravitreal Tyrosine Kinase Implants
ActiveUS20140031408A1Reduce deliveryFacilitate obtaining successful treatment resultsBiocideSenses disorderOphthalmologyPolyvinyl alcohol
Biocompatible intraocular implants include a tyrosine kinase inhibitor and a biodegradable polymer that is effective to facilitate release of the tyrosine kinase inhibitor into the vitreous of an eye for an extended period of time. The therapeutic agents of the implants may be associated with a biodegradable polymer matrix, such as a matrix that is substantially free of a polyvinyl alcohol. The implants can be placed in an eye to treat or reduce the occurrence of one or more ocular conditions.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
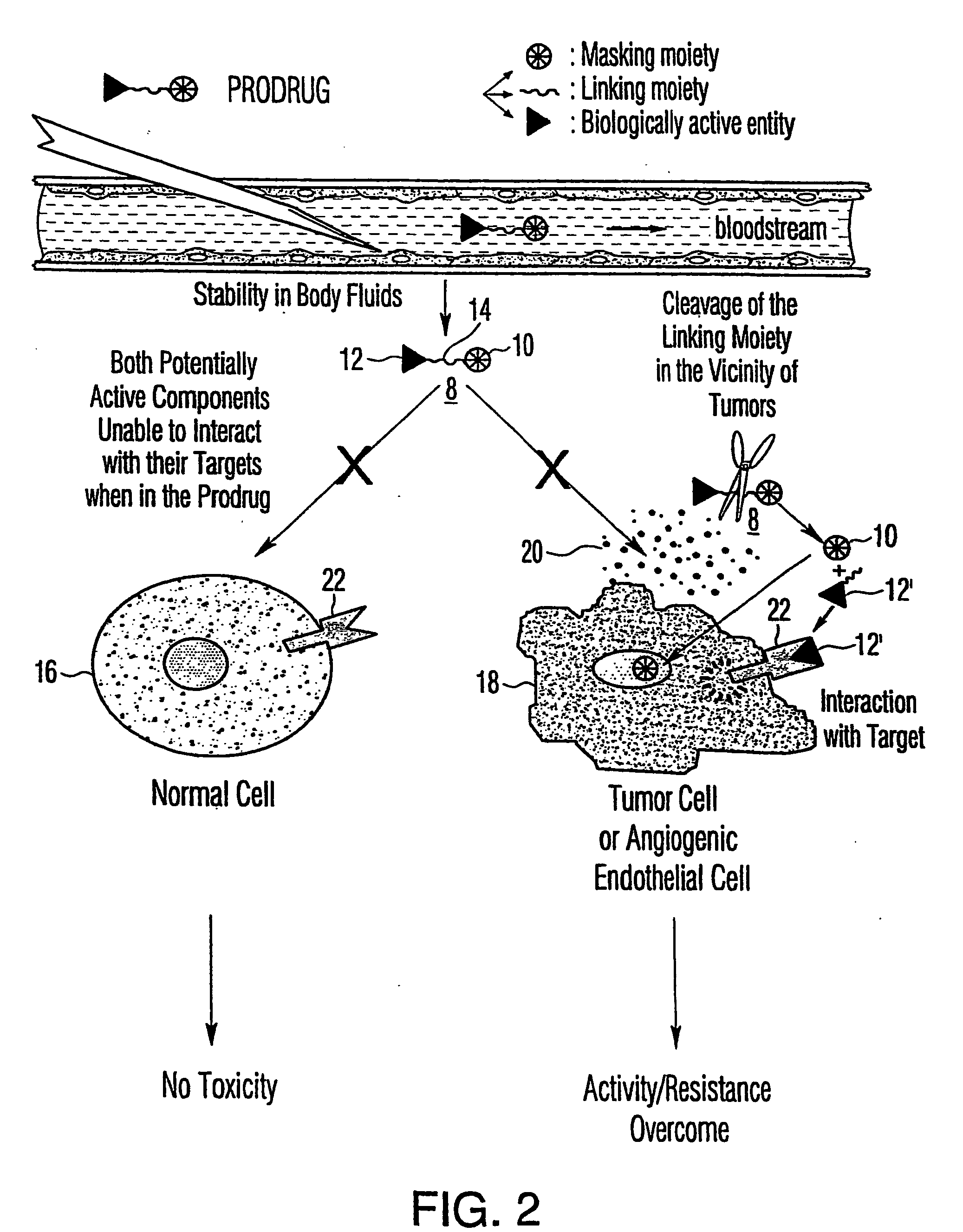
Tumor activated prodrug compounds and methods of making and using the same
InactiveUS20040014652A1Improved therapeutic propertyLow toxicityIn-vivo radioactive preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsHalf-lifeIn vivo
The invention is directed to novel prodrug compounds, compositions comprising the prodrug compounds, methods of making the prodrug compounds and methods of using the prodrug compounds. The prodrug compounds comprise a biologically active entity linked to a masking moiety via a linking moiety. The prodrug compounds are selectively activated at or near target cells and display lower toxicity and possibly a longer in vivo or serum half-life than the corresponding naked biologically active entity.
Owner:UNIVERSITE CATHOLIQUE DE LOUVAIN
Morphine polymer release system
InactiveUS20080254123A1Affecting extent of drug bioavailabilityReduce frequencyBiocidePowder deliveryControlled releaseMedicine
A pharmaceutical composition for controlled release of an active substance is provided. The active substance is released into an aqueous medium by erosion of at least one surface of the composition. The composition comprises i) a matrix comprising a) polymer or a mixture of polymers, b) an active substance and, optionally, c) one or more pharmaceutically acceptable excipients, and ii) a coating.
Owner:EGALET LTD
Field effect transistor and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20050093033A1High impurity concentrationHigh concentrationTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringField-effect transistor
A field effect transistor includes a first semiconductor region forming a channel region, a gate electrode insulatively disposed above the first semiconductor region, source and drain electrodes formed to sandwich the first semiconductor region in a channel lengthwise direction, and second semiconductor regions formed between the first semiconductor region and the source and drain electrodes and having impurity concentration higher than the first semiconductor region. The thickness of the second semiconductor region in the channel lengthwise direction is set to a value equal to or less than depletion layer width determined by the impurity concentration so that the second semiconductor region is depleted in a no-voltage application state.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Betaine with Calcium and/or Strontium Antiperspirants
InactiveUS20070020211A1Good curative effectImprove skinCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsAntiperspirantsBetaine
Aluminum and aluminum-zirconium antiperspirant compositions comprising basic aluminum chlorides that have a particular molecular size distribution defined by having an SEC-HPLC Band III / II ratio of at least 0.5, having SEC-HPLC Band III plus Band II area of at least 70% of the total area and having SEC-HPLC Band I content no more than 5% and containing betaine (trimethylglycine), calcium and / or strontium are disclosed. Also disclosed are the methods of making these compositions and the use thereof in consumer acceptable antiperspirant vehicles such as aerosols, gels, roll-on, sticks and soft solids.
Owner:SUMMIT RES LAB
Manufacturing process for the production of peptides grown in insect cell lines
InactiveUS20060246544A1Improve purityHigh concentrationHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptideGlycosyltransferase
The present invention provides a manufacturing method for the production of peptides that are grown in insect cell lines. The peptides are grown in insect cell cultures that are infected with baculovirus particles in a culture supplemented with a lipid mixture. The peptides are then isolated from the insect cell culture using a method that employs a tangential flow filtration cascade. The isolated peptides are glycopeptides having an insect specific glycosylation pattern. The glycopeptides may then be conjugated to a modifying group via linkage through a glycosyl linking group interposed between and covalently attached to the peptide and the modifying group. The conjugates are formed from glycosylated peptides by the action of a glycosyltransferase.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Stable high protein concentration formulations of human Anti-tnf-alpha-antibodies
InactiveUS20140141007A1High concentrationIncrease concentrationAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderHigh concentrationPolyol
The invention provides a liquid pharmaceutical formulation which does not include NaCl and comprises more than 20 mg of a polyol and at least about 100 mg / mL of a human anti-TNF-alpha antibody, or antigen-binding portion thereof. The invention provides a high concentration antibody formulation having long-term stability and advantageous characteristics for subcutaneous administration.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC +1
Stable high protein concentration formulations of human Anti-tnf-alpha-antibodies
InactiveUS20140141008A1High concentrationIncrease concentrationAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderHigh concentrationPolyol
The invention provides a liquid pharmaceutical formulation which does not include NaCl and comprises more than 20 mg of a polyol and at least about 100 mg / mL of a human anti-TNF-alpha antibody, or antigen-binding portion thereof. The invention provides a high concentration antibody formulation having long-term stability and advantageous characteristics for subcutaneous administration.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC +1
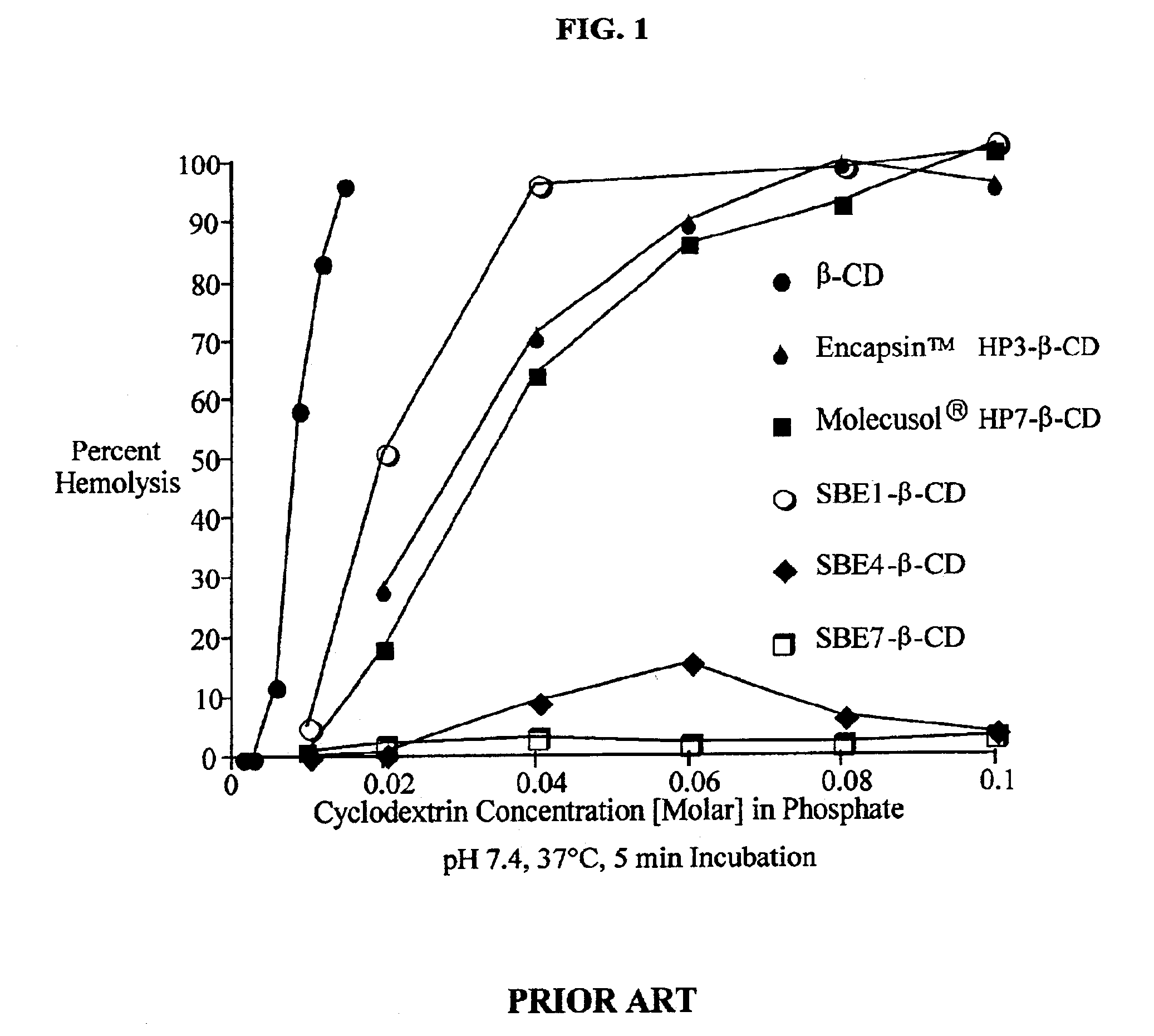
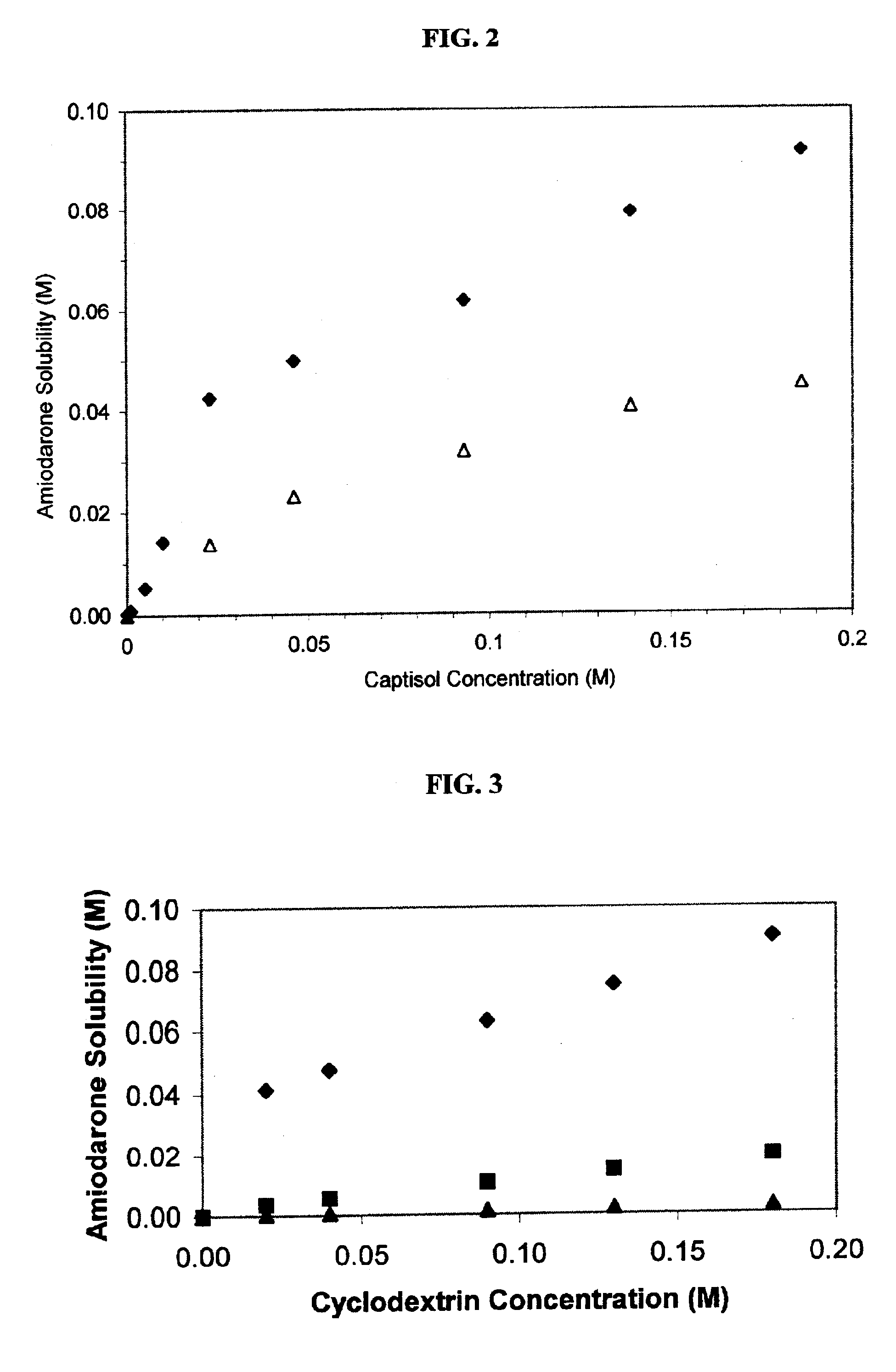
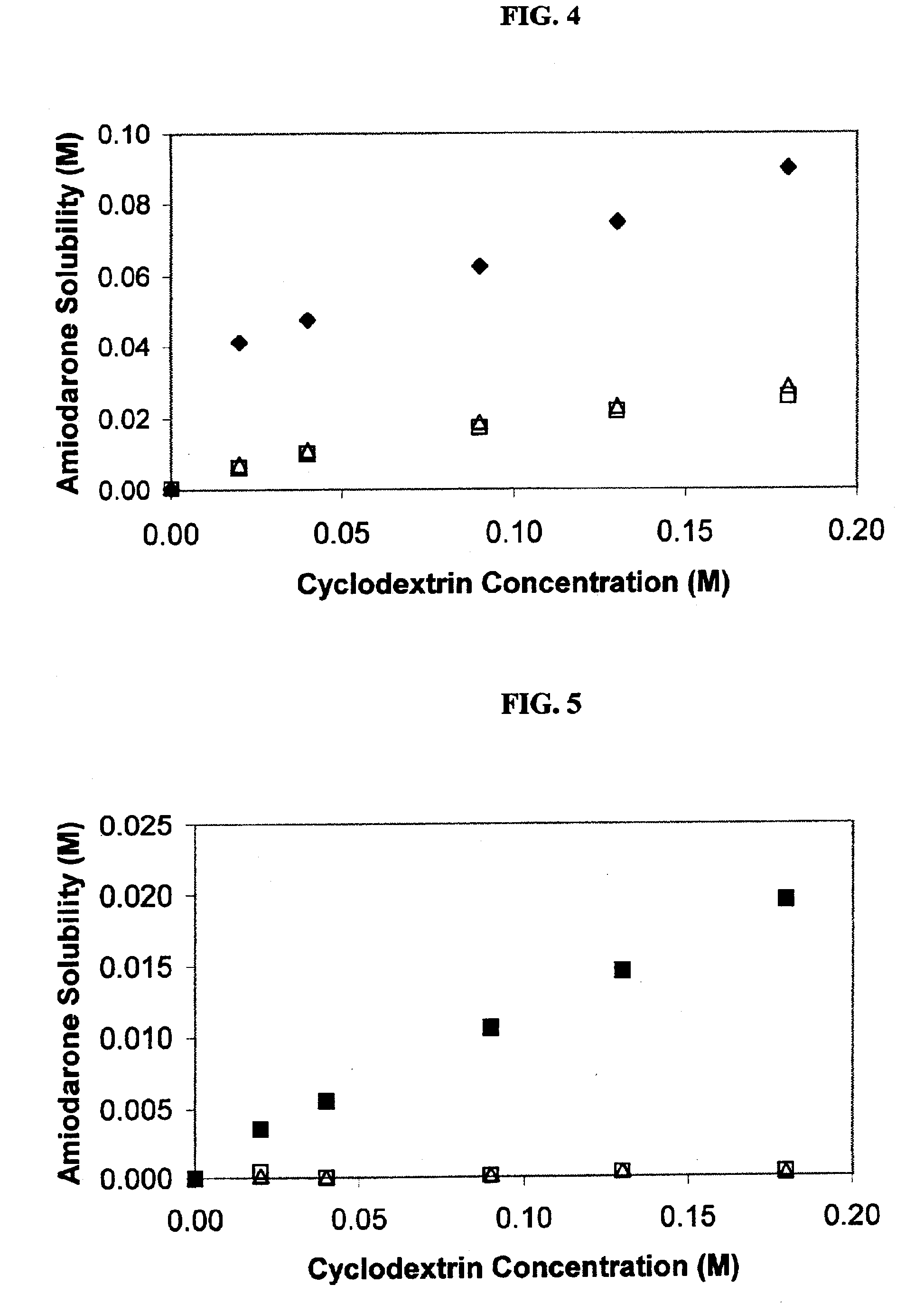
Formulations containing amiodarone and sulfoalkyl ether cyclodextrin
InactiveUS6869939B2Increase surface tensionAccurate doseCompounds screening/testingPowder deliveryCyclodextrinRoom temperature
The present invention provides aqueous parenteral formulations containing an antiarrhythmic agent, such as amiodarone, and a sulfoalkyl ether cyclodextrin. The liquid formulations are clear, sterilizable, and chemically and physically stable. The liquid formulations do not require a surfactant and do not precipitate upon dilution with distilled water or other pharmaceutically acceptable liquid carrier. The sulfoalkyl ether cyclodextrin-containing formulation provides significant advantages over other cyclodextrin-containing formulations of amiodarone. The formulation can be prepared in acidic, neutral and slightly basic medium while providing acceptable concentrations of amiodarone suitable for parenteral administration. An SAE-CD-containing formulation of amiodarone can be provided in liquid form or as a reconstitutable powder. Moreover, highly concentrated solutions exceeding 200 mg of amiodarone per mL can be prepared. Solutions can be made either dilutable or non-dilutable with water at room temperature or under conditions typically encountered in the clinic.
Owner:CYDEX PHARMACEUTICALS INC
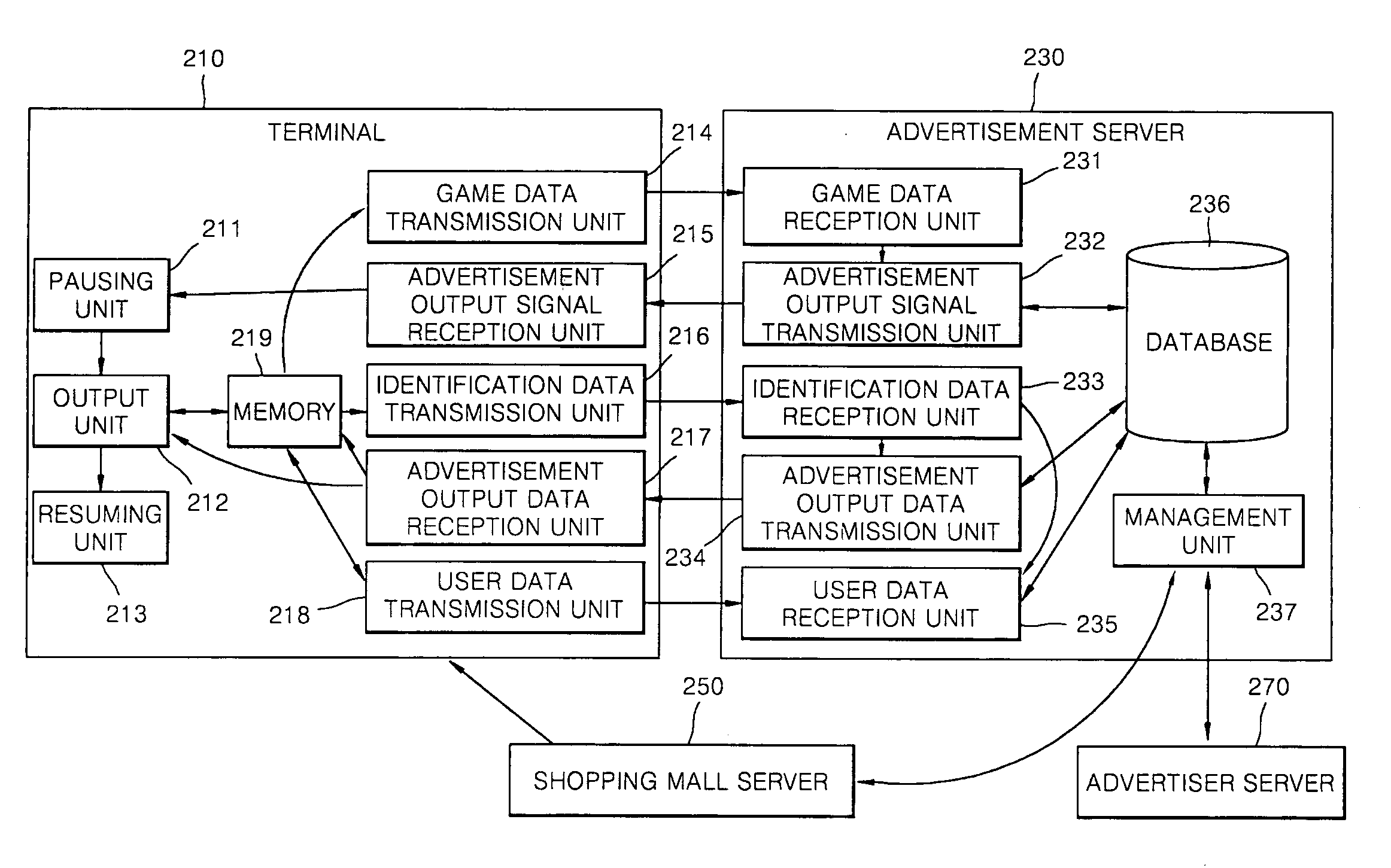
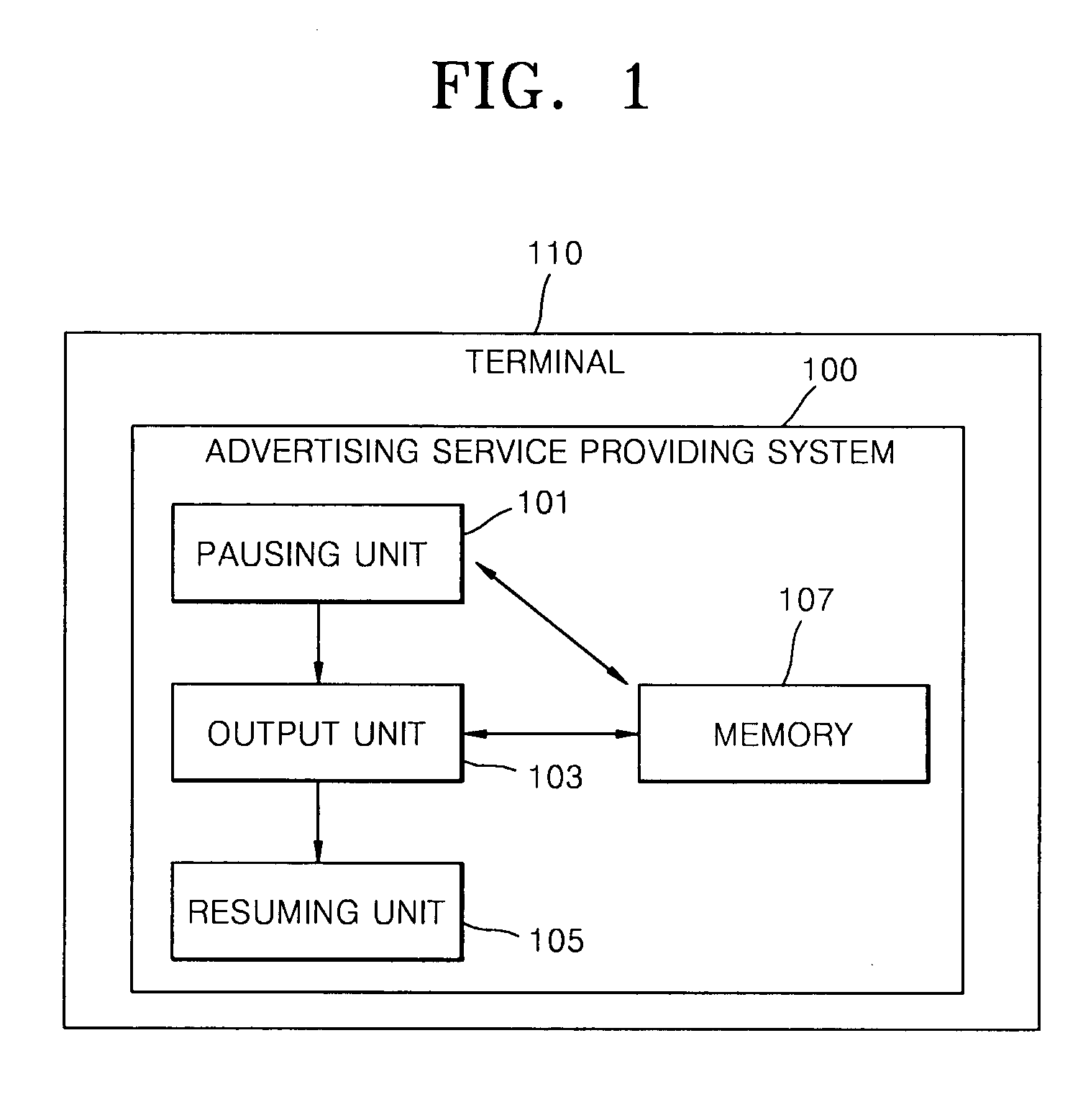
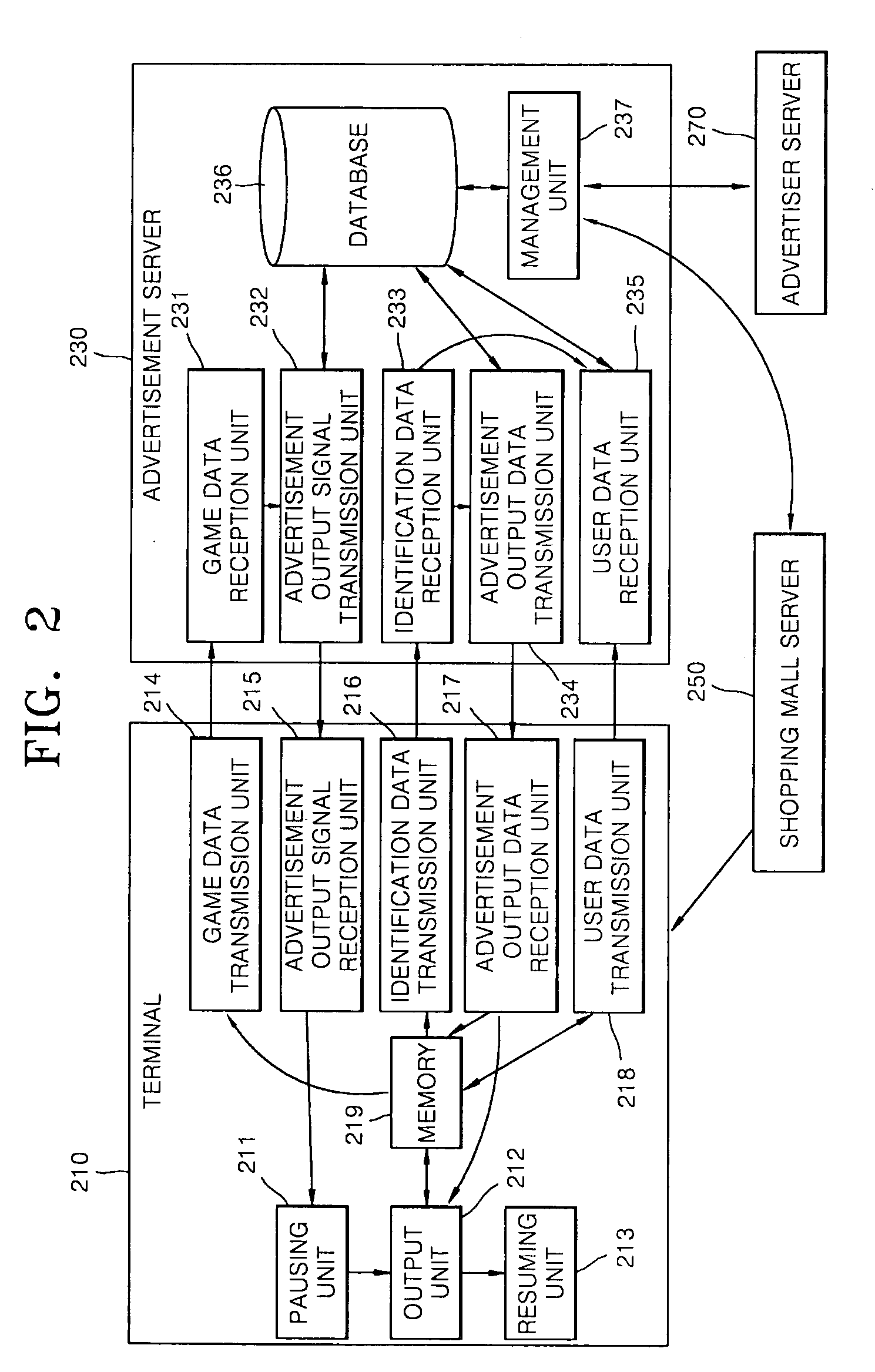
Advertising service method providing separate advertisement of moving picture during the game play and system thereof
InactiveUS20090327077A1Good effectImprove visibilityMultiple digital computer combinationsApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingService provisionGame play
Provided are an advertising service providing method and advertising service providing system for providing a separate video advertisement once a video game is paused. The advertising service providing method includes pausing a game in a terminal if a predetermined first condition is satisfied while the video game is being played in the terminal; outputting an advertisement including video data once the video game is paused; and resuming the video game once the advertisement is completely output. According to the present invention, by pausing a game when the concentration of users is high and primarily outputting an advertisement that is separate from the game, the advertisement may be noticed and effectively advertised, and users may use the video game for free or at an inexpensive price as a result of employing this effective form of advertising since a game provider may a stably profit from advertisement fees paid by an advertiser.
Owner:ARUON GAMES
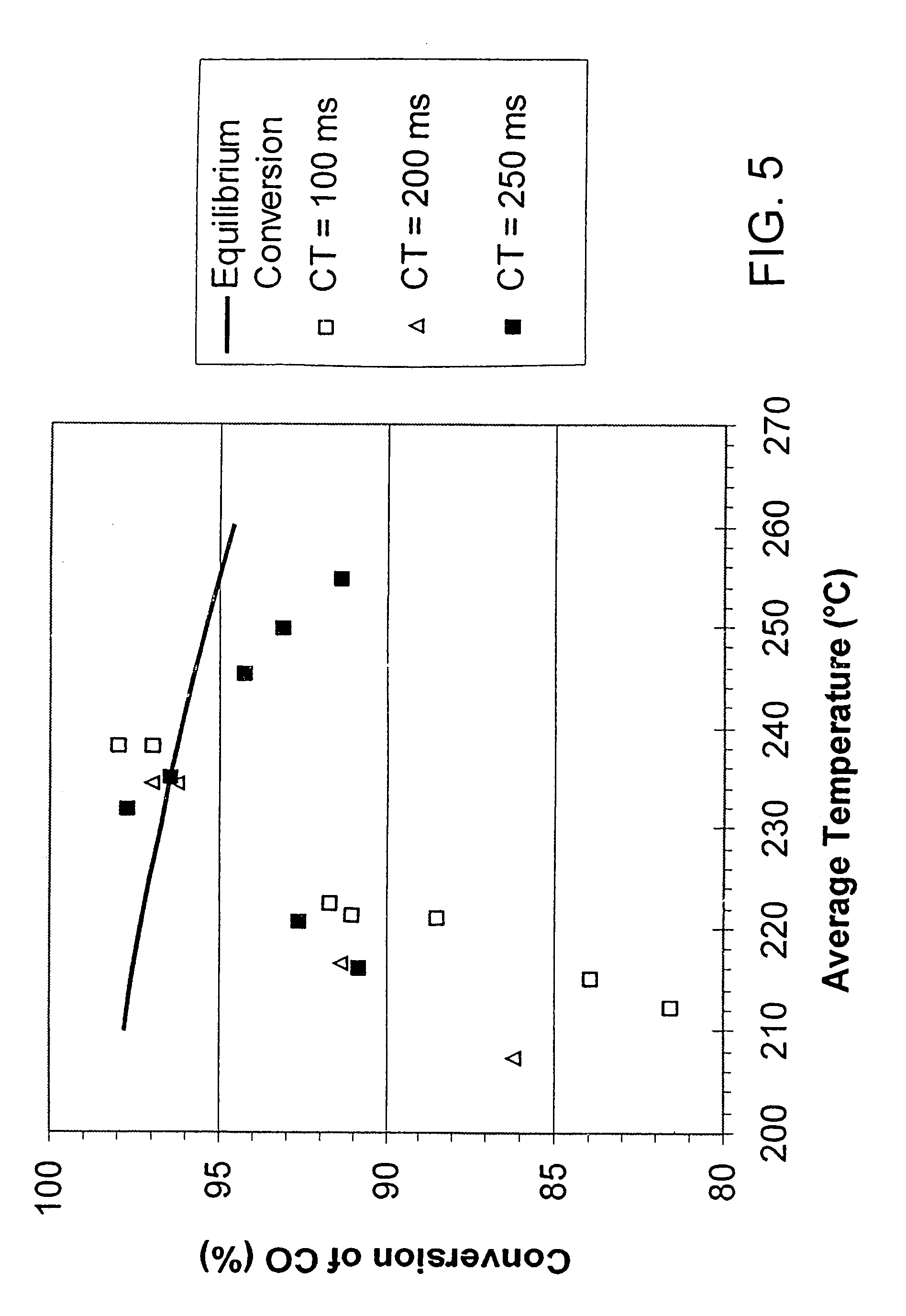
Process for conducting an equilibrium limited chemical reaction in a single stage process channel
ActiveUS6969505B2High concentrationOrganic compounds purification/separation/stabilisationOrganic compound preparationChemical reactionSingle stage
This invention relates to a process for conducting an equilibrium limited chemical reaction in a single stage process channel. A process for conducting a water shift reaction is disclosed. A multichannel reactor with cross flow heat exchange is disclosed.
Owner:VELOCYS CORPORATION
Two-part dental bleaching systems having improved gel stability and methods for bleaching teeth using such systems
InactiveUS6503485B1Maintain bleaching potencyHigh concentrationCosmetic preparationsGum massageParticulatesAlkaline earth metal
Dental bleaching systems that include a bleaching component and a neutralizing component which, when mixed together, yield a mixed composition having a desired bleaching activity and viscosity. The bleaching composition includes a suitable bleaching agent, such as aqueous hydrogen peroxide, in a concentration of about 3% to about 95% by weight of the bleaching composition component. The neutralizing component includes a particulate base dispersed within a stable gel that includes at least one polymeric thickening agent. The neutralizing component is substantially water-free to prevent destruction of the gelling capability of the thickening agent by the base. The particulate base may include oxides, hydroxides or carbonates of alkali metals or alkaline earth metals. Maintaining the bleaching agent and neutralizing agent in separate components provides increased stability during storage and transport.
Owner:ULTRADENT PROD INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com