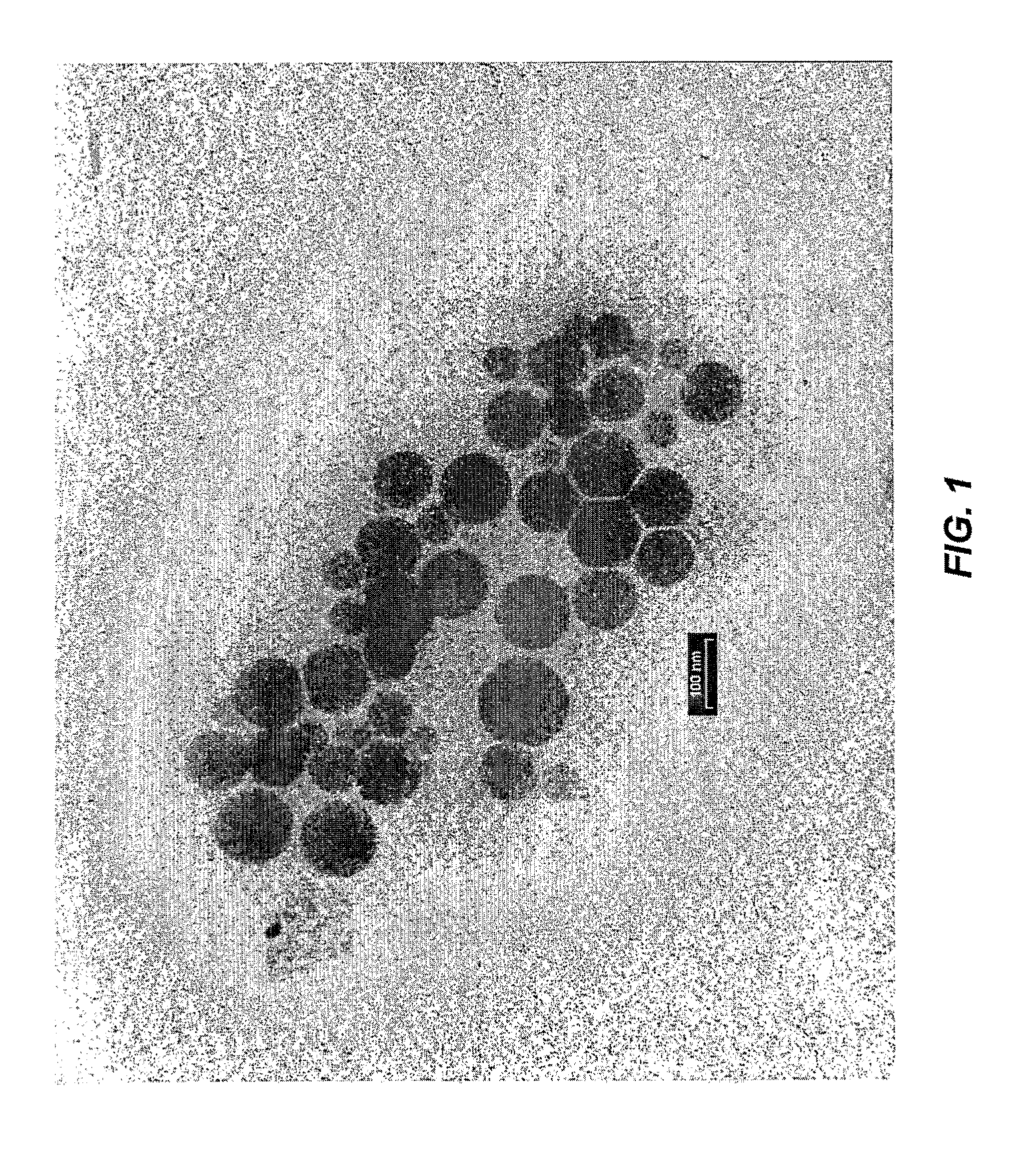
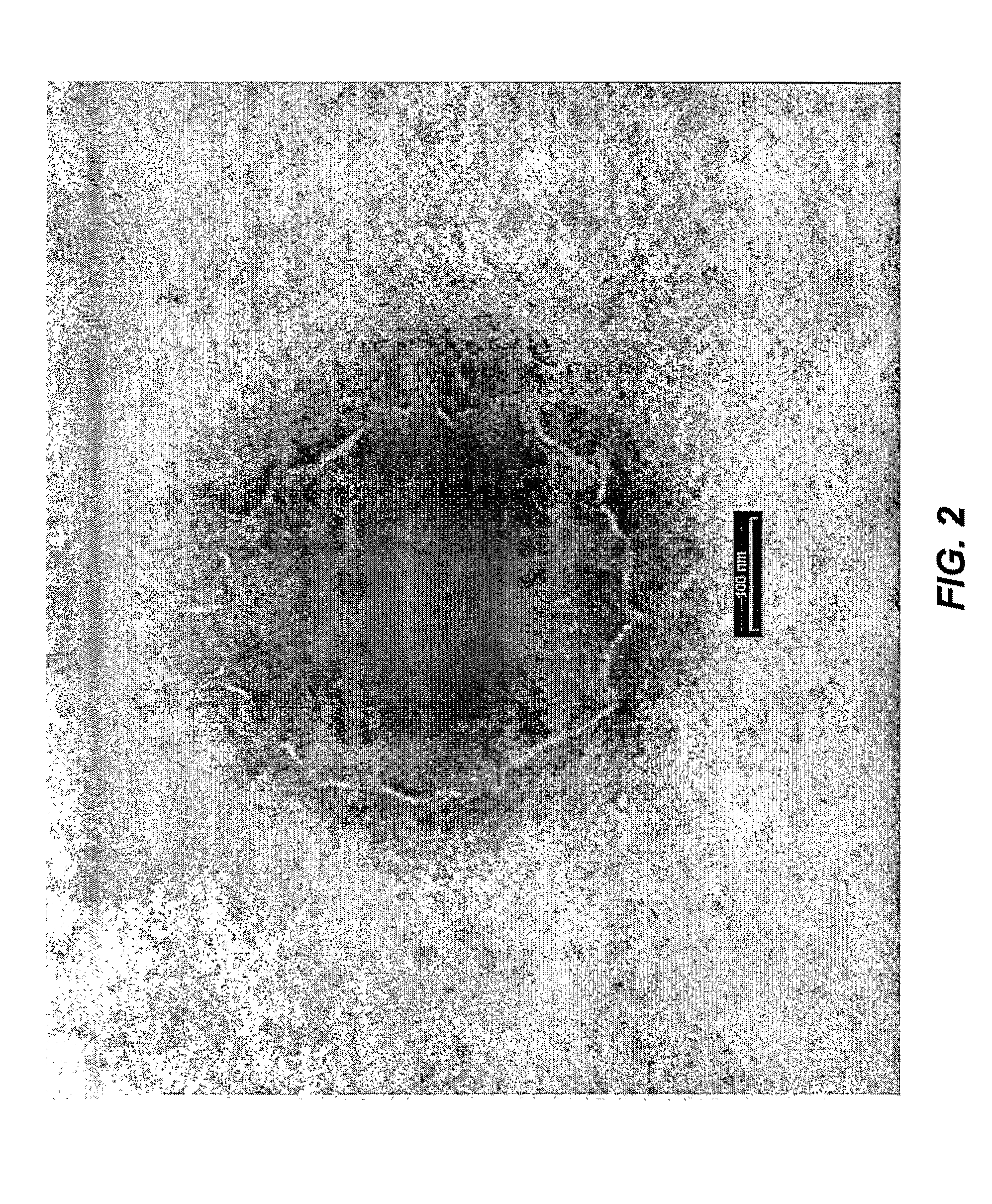
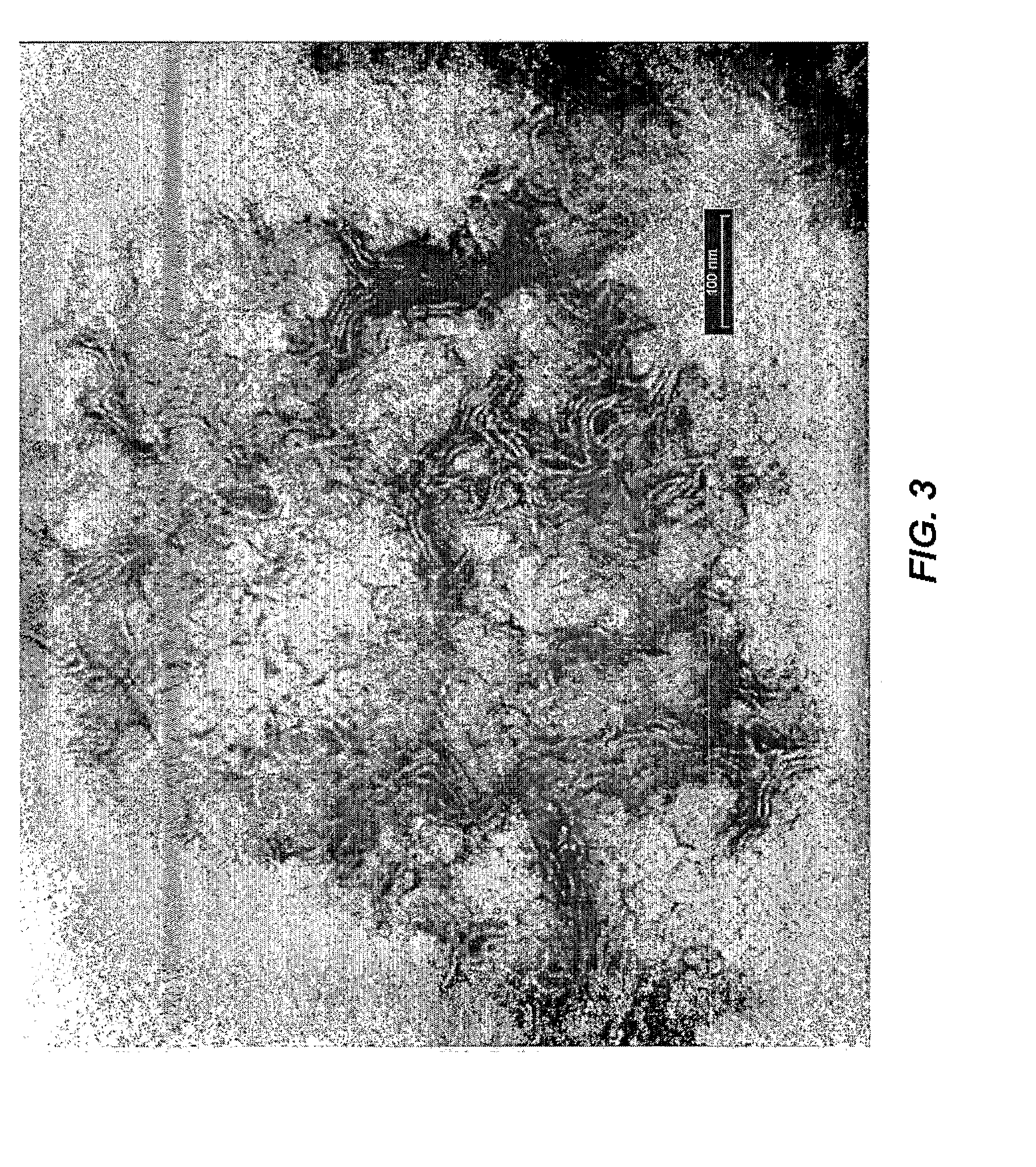
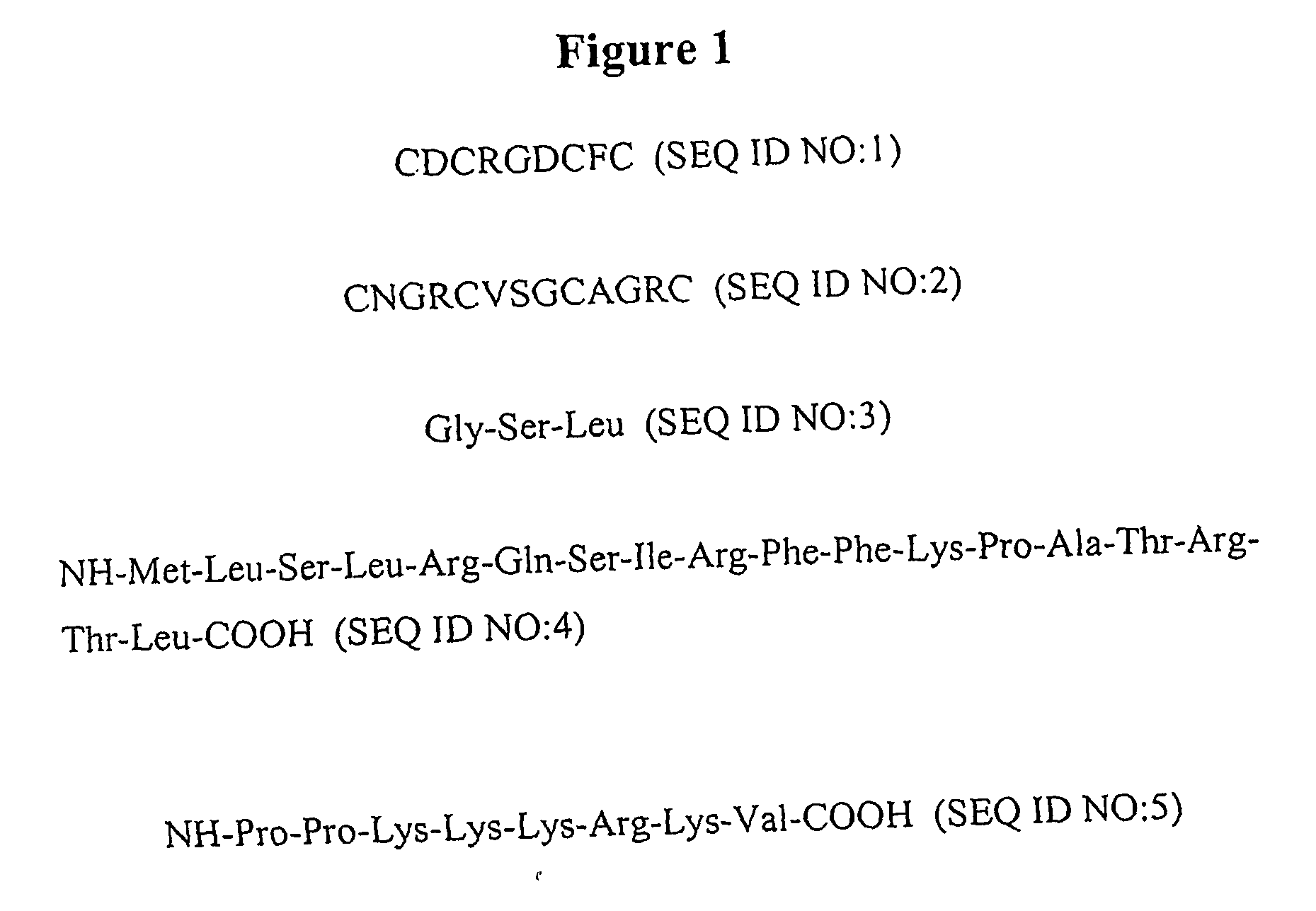
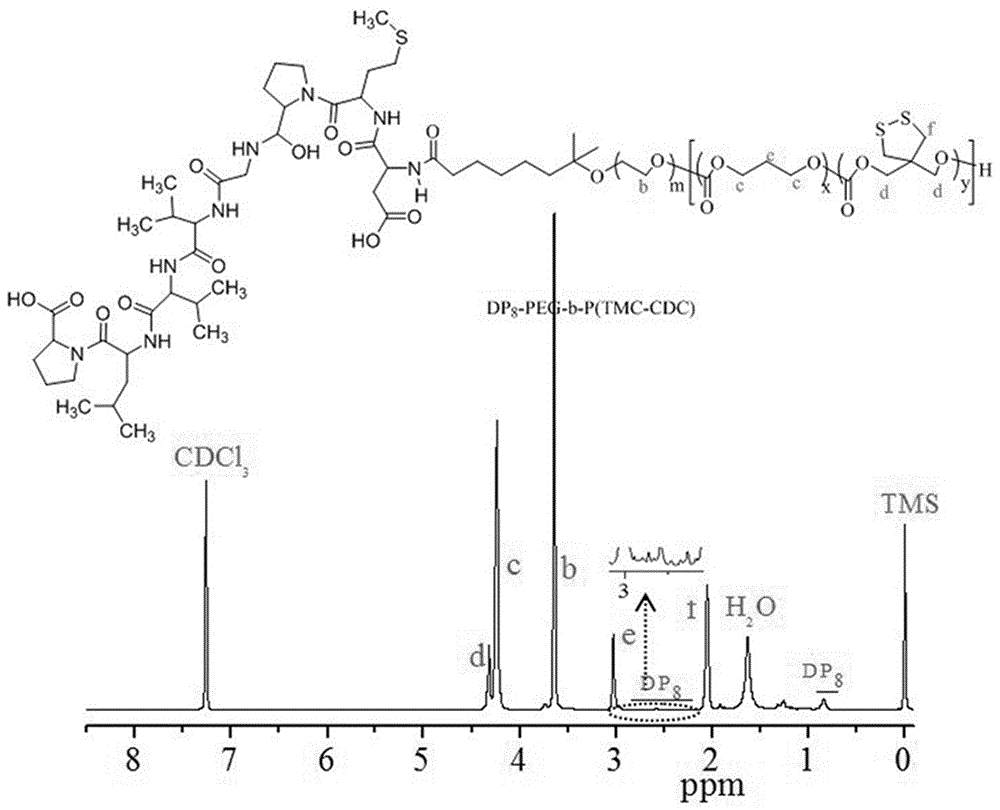
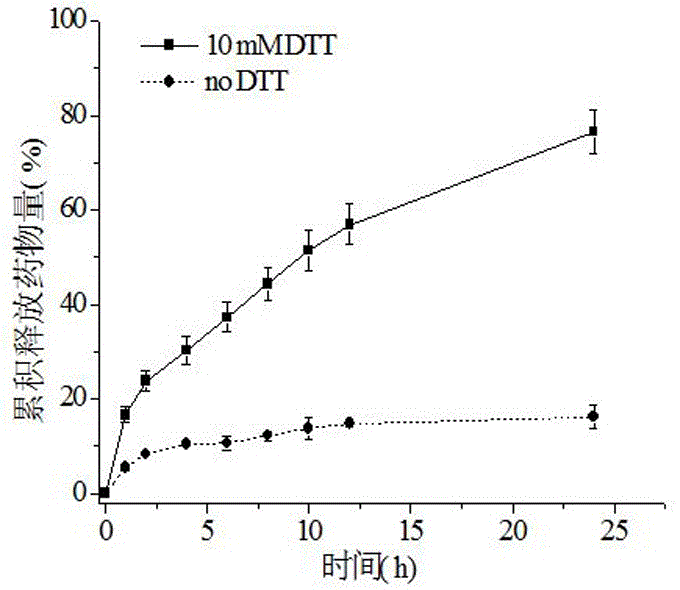
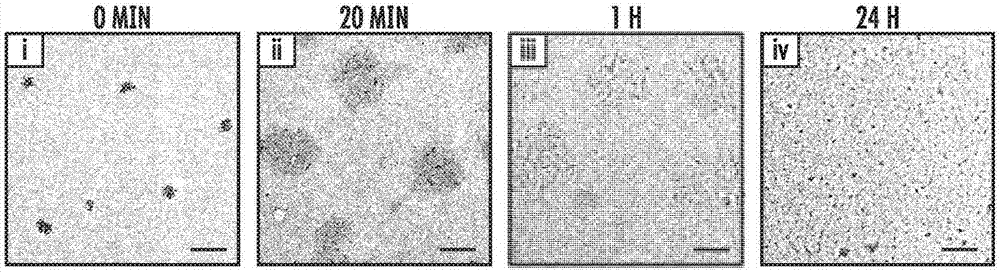
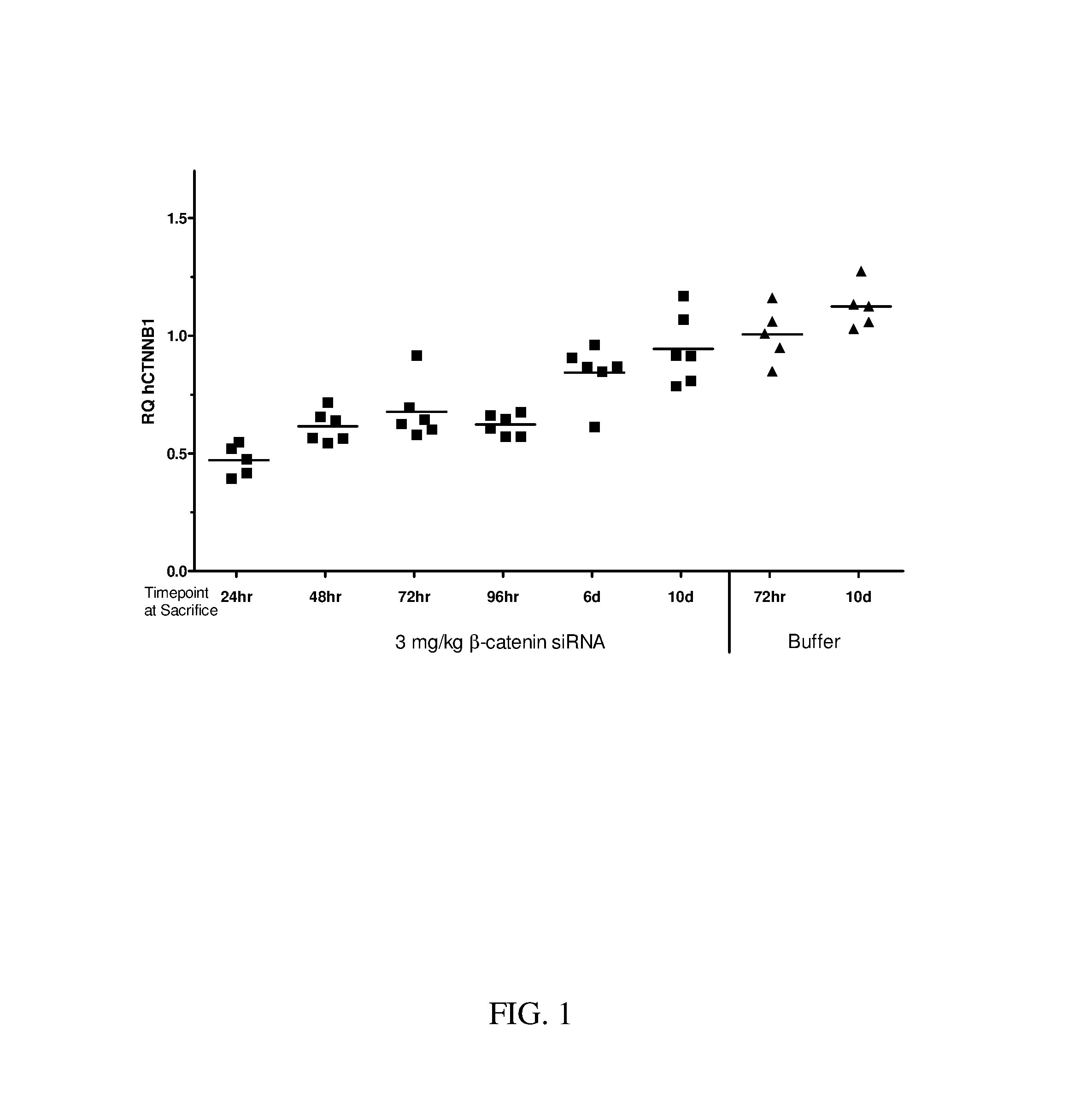
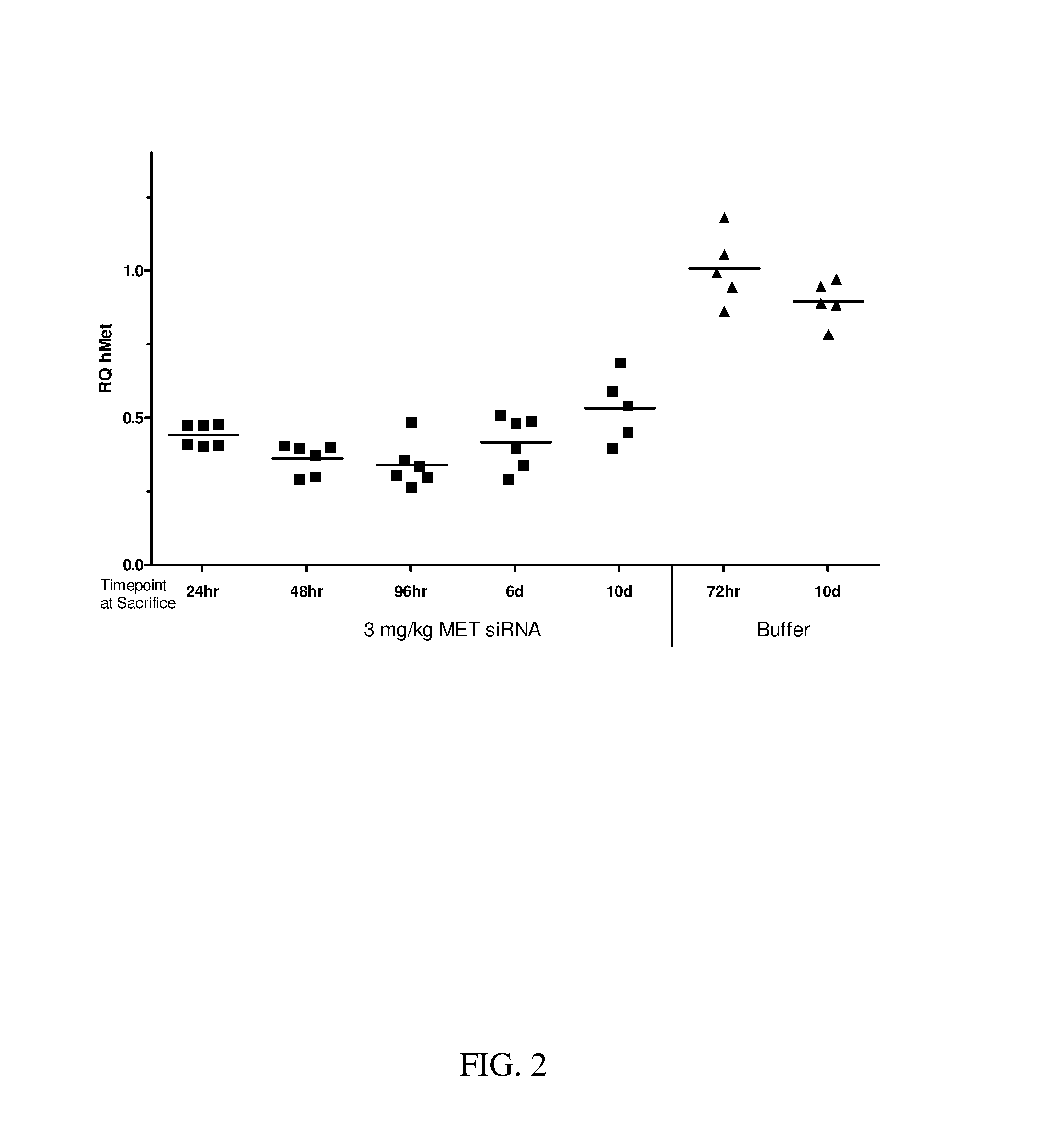
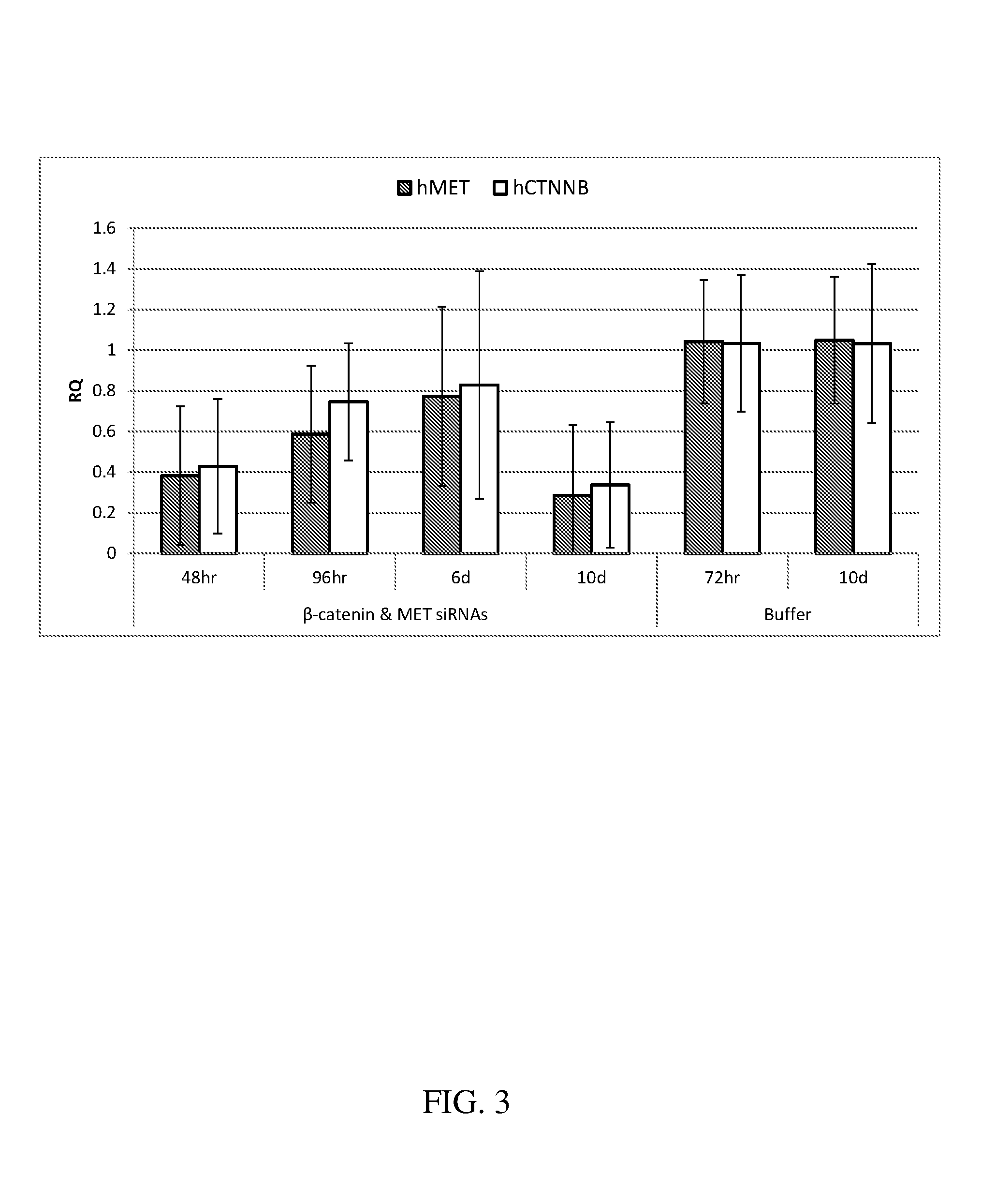
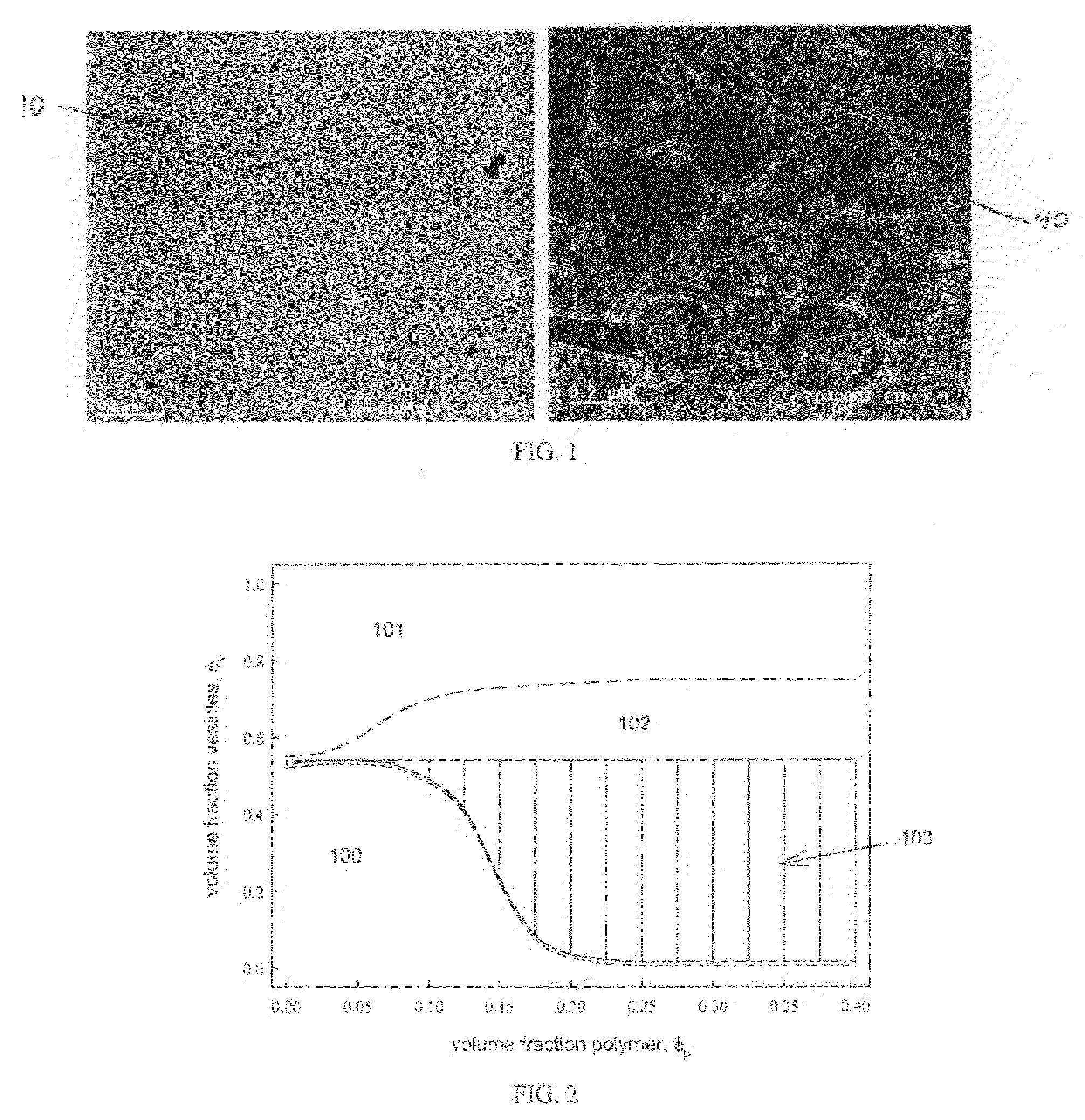
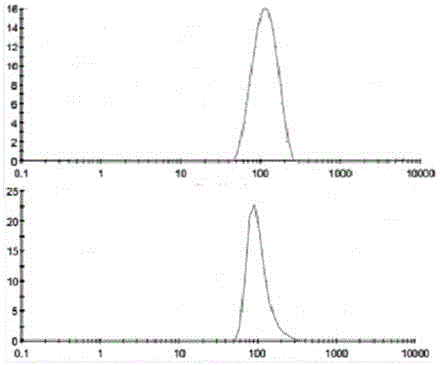
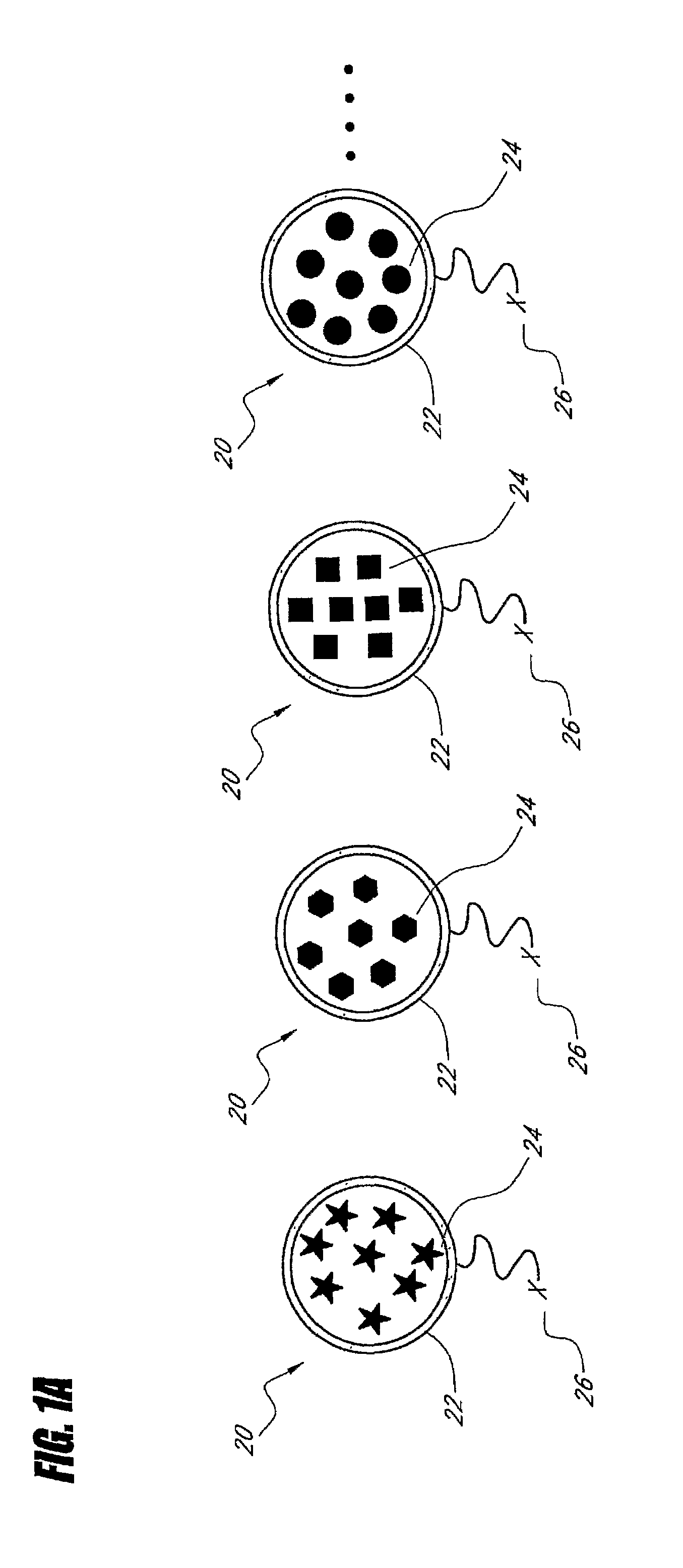
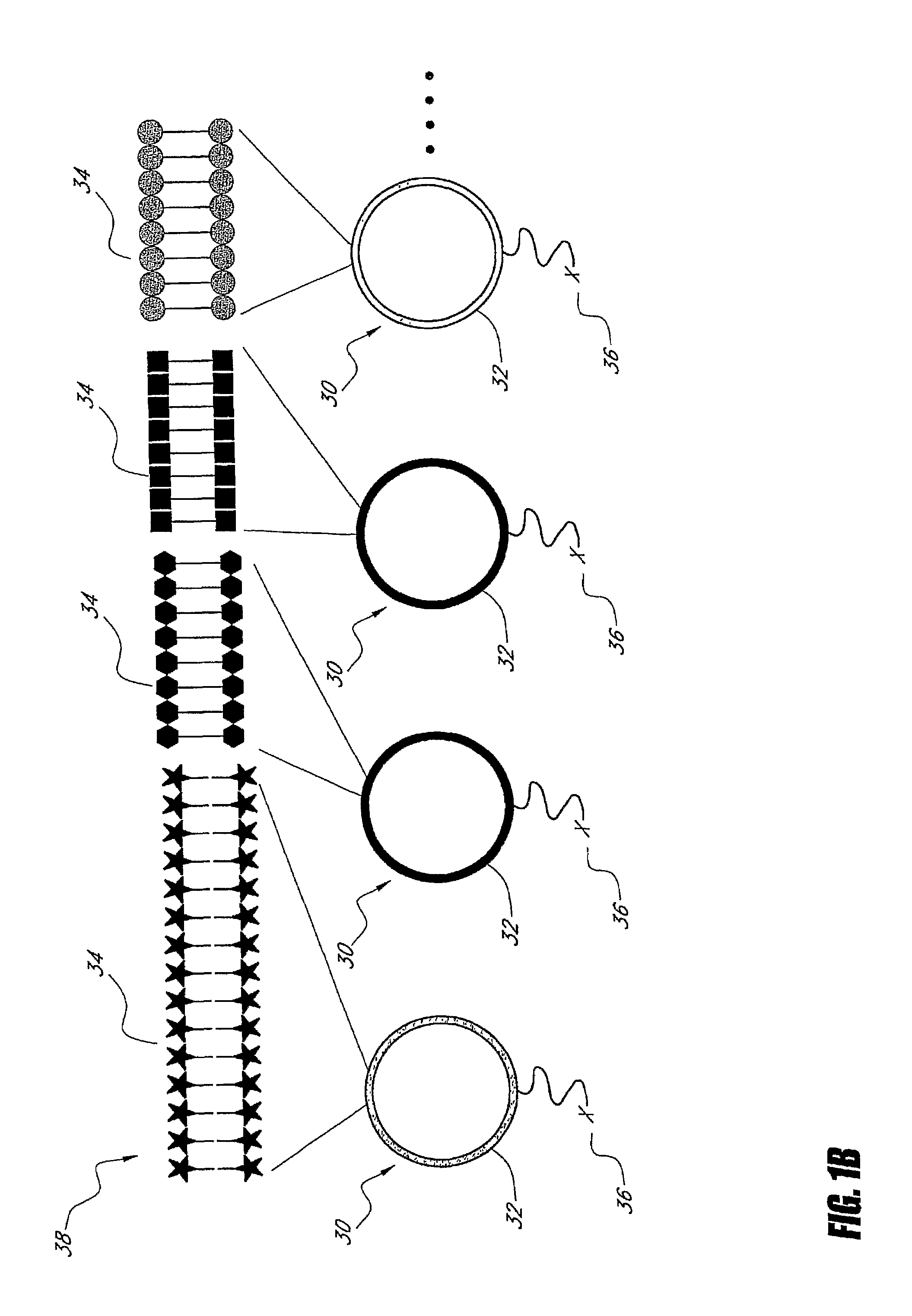
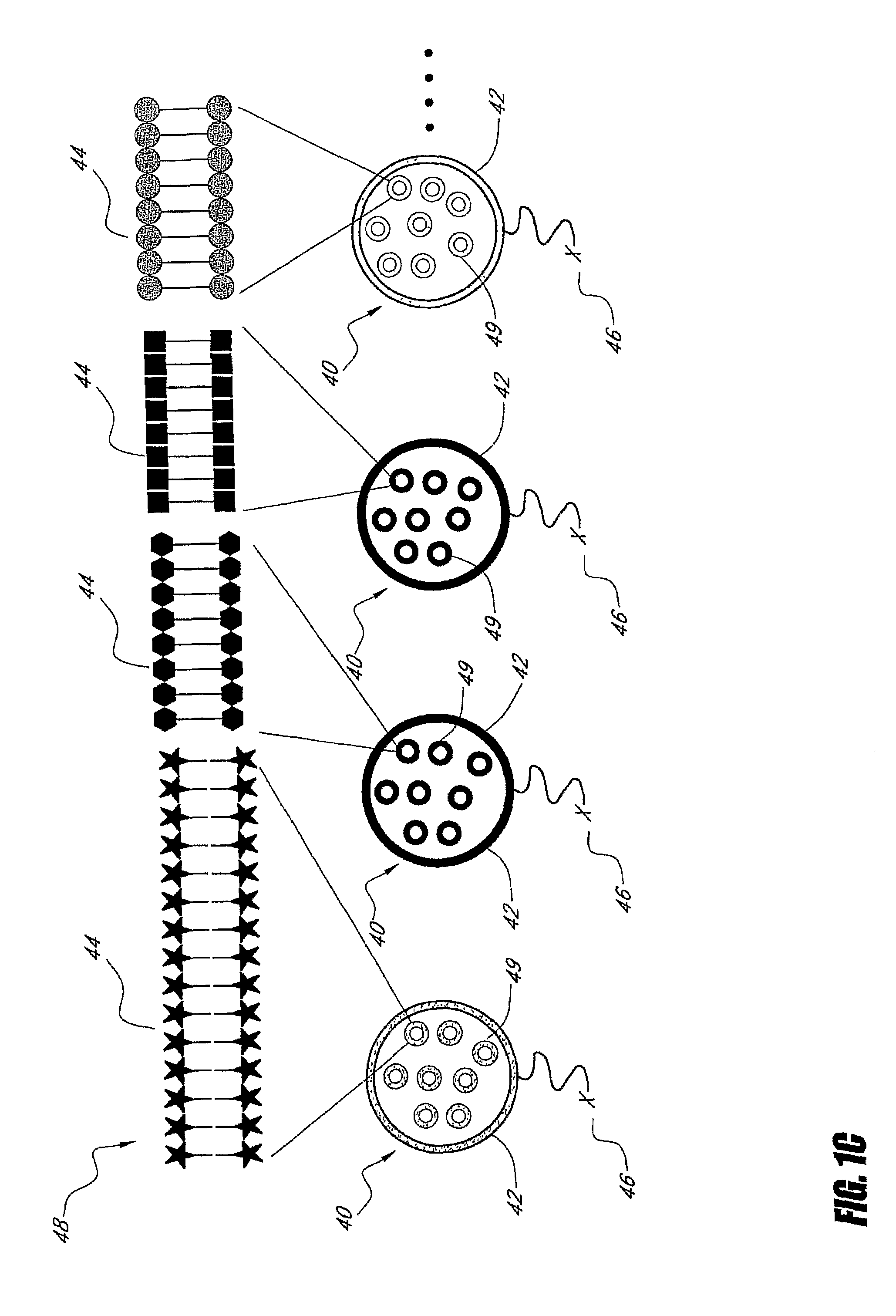
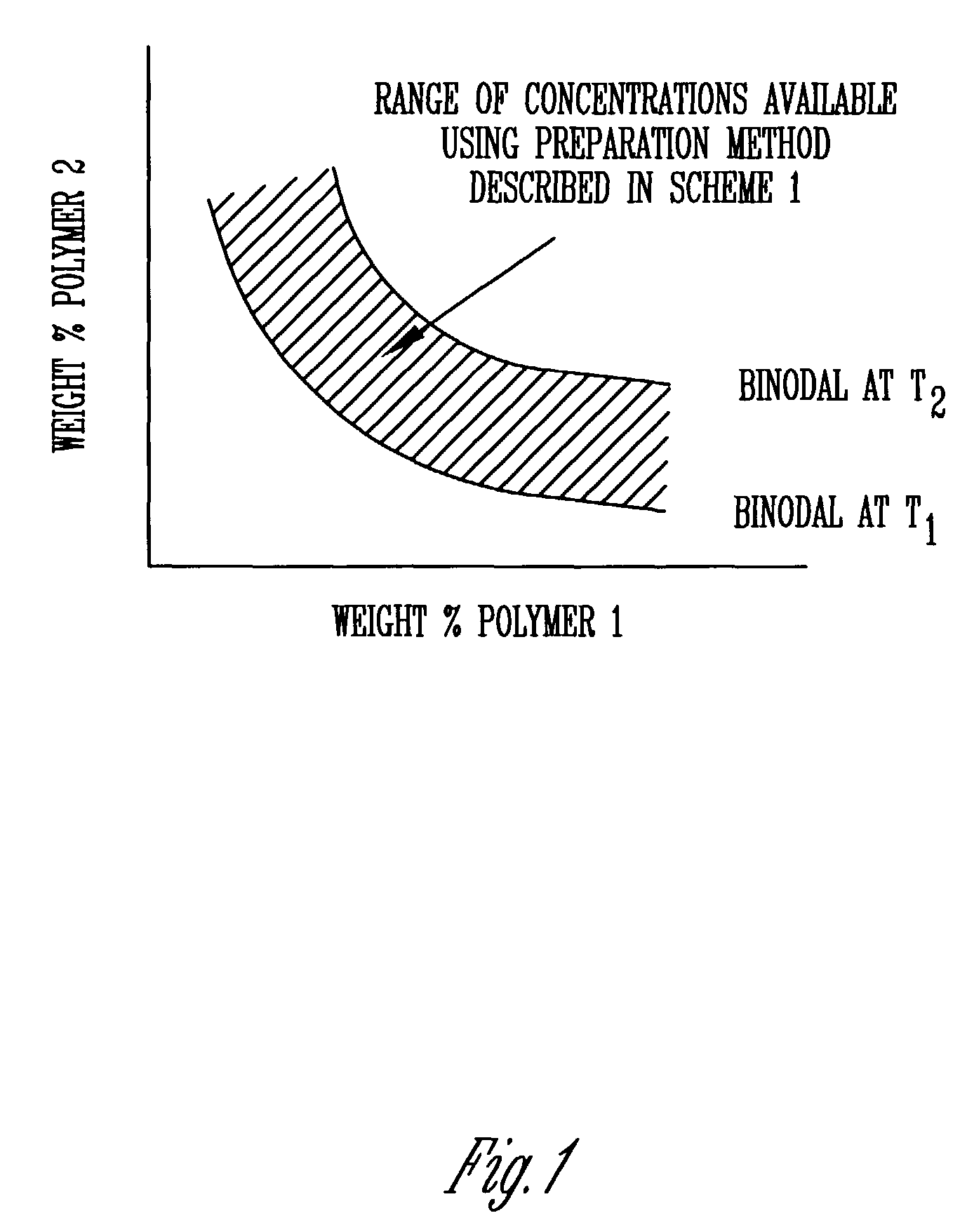
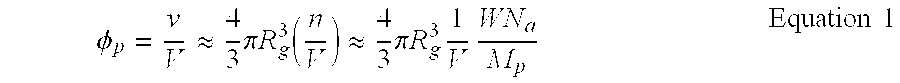Patents
Literature
604 results about "Vesicle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In cell biology, a vesicle is a structure within or outside a cell, consisting of liquid or cytoplasm enclosed by a lipid bilayer. Vesicles form naturally during the processes of secretion (exocytosis), uptake (endocytosis) and transport of materials within the plasma membrane. Alternatively, they may be prepared artificially, in which case they are called liposomes (not to be confused with lysosomes). If there is only one phospholipid bilayer, they are called unilamellar liposome vesicles; otherwise they are called multilamellar. The membrane enclosing the vesicle is also a lamellar phase, similar to that of the plasma membrane, and intracellular vesicles can fuse with the plasma membrane to release their contents outside the cell. Vesicles can also fuse with other organelles within the cell. A vesicle released from the cell is known as an extracellular vesicle.
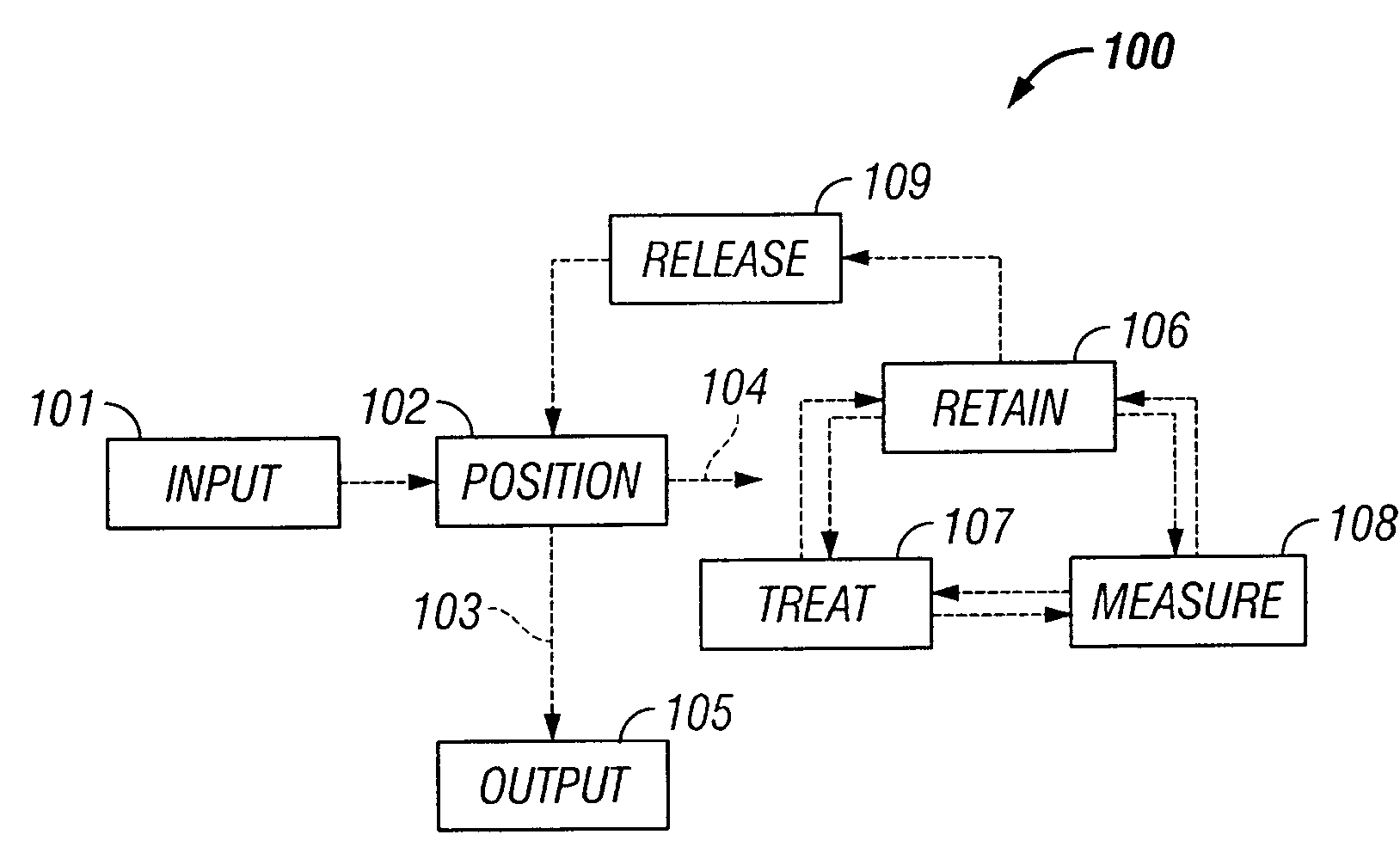
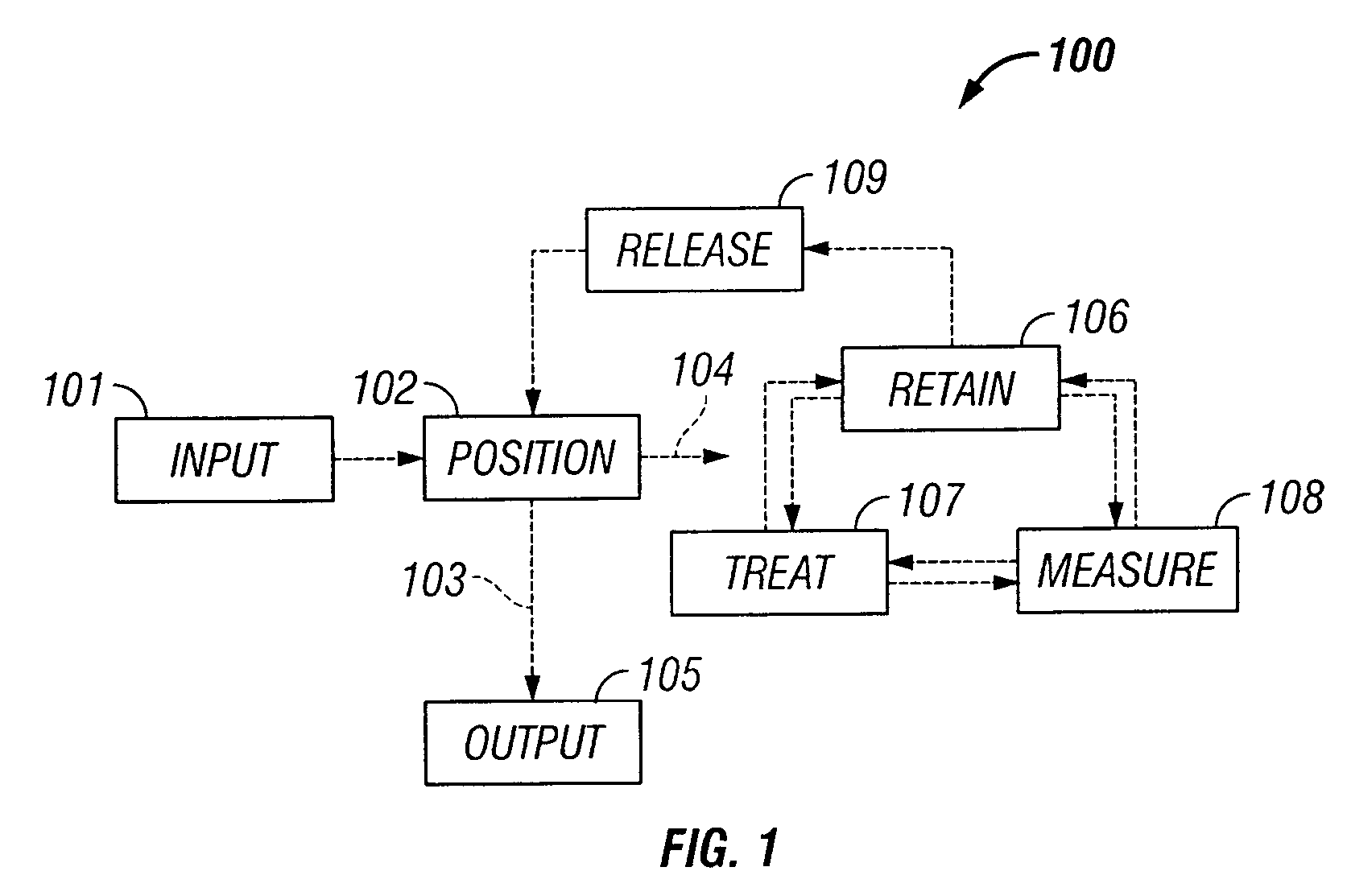
Microfluidic particle-analysis systems
ActiveUS7312085B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsReady to useMixed group
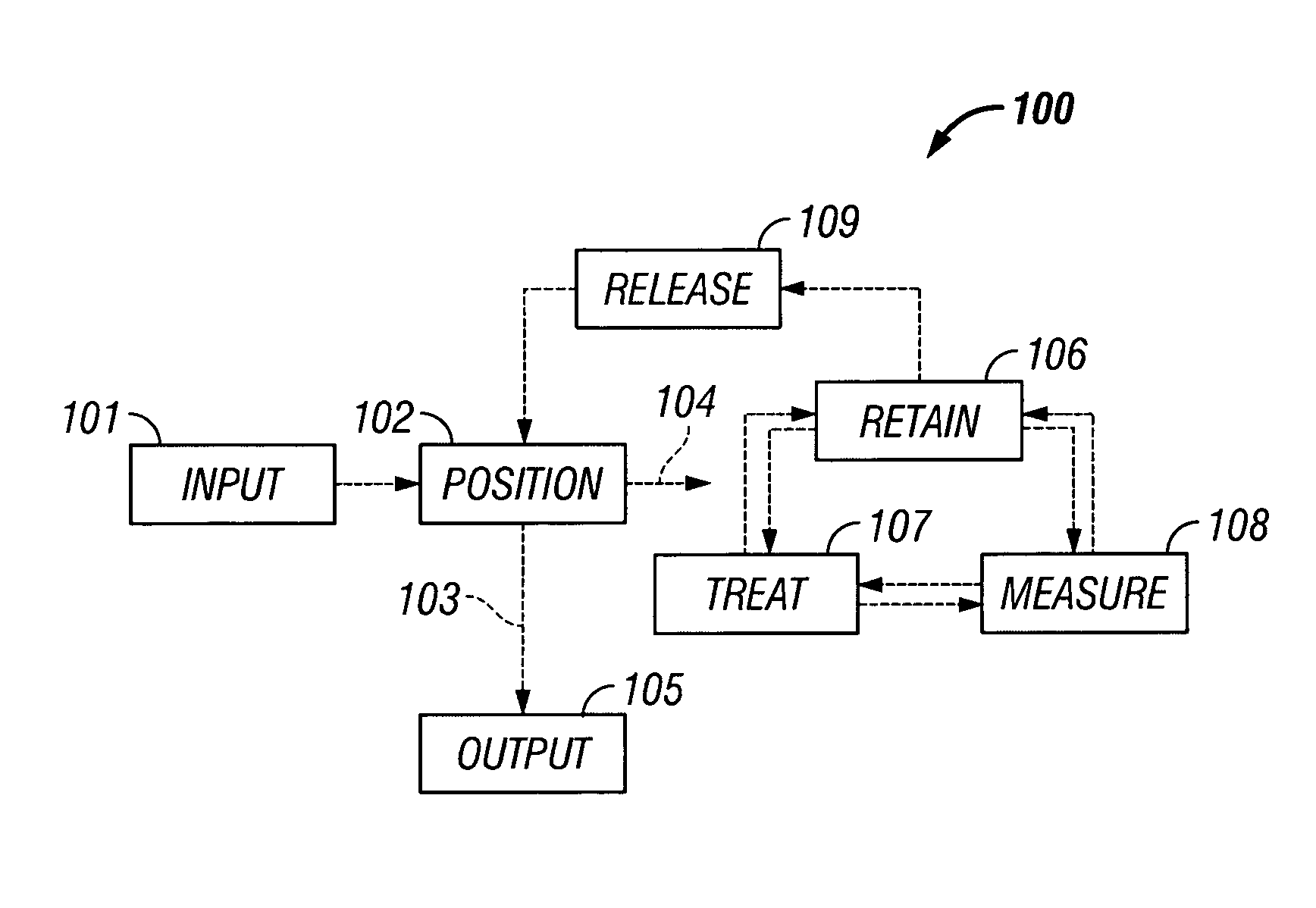
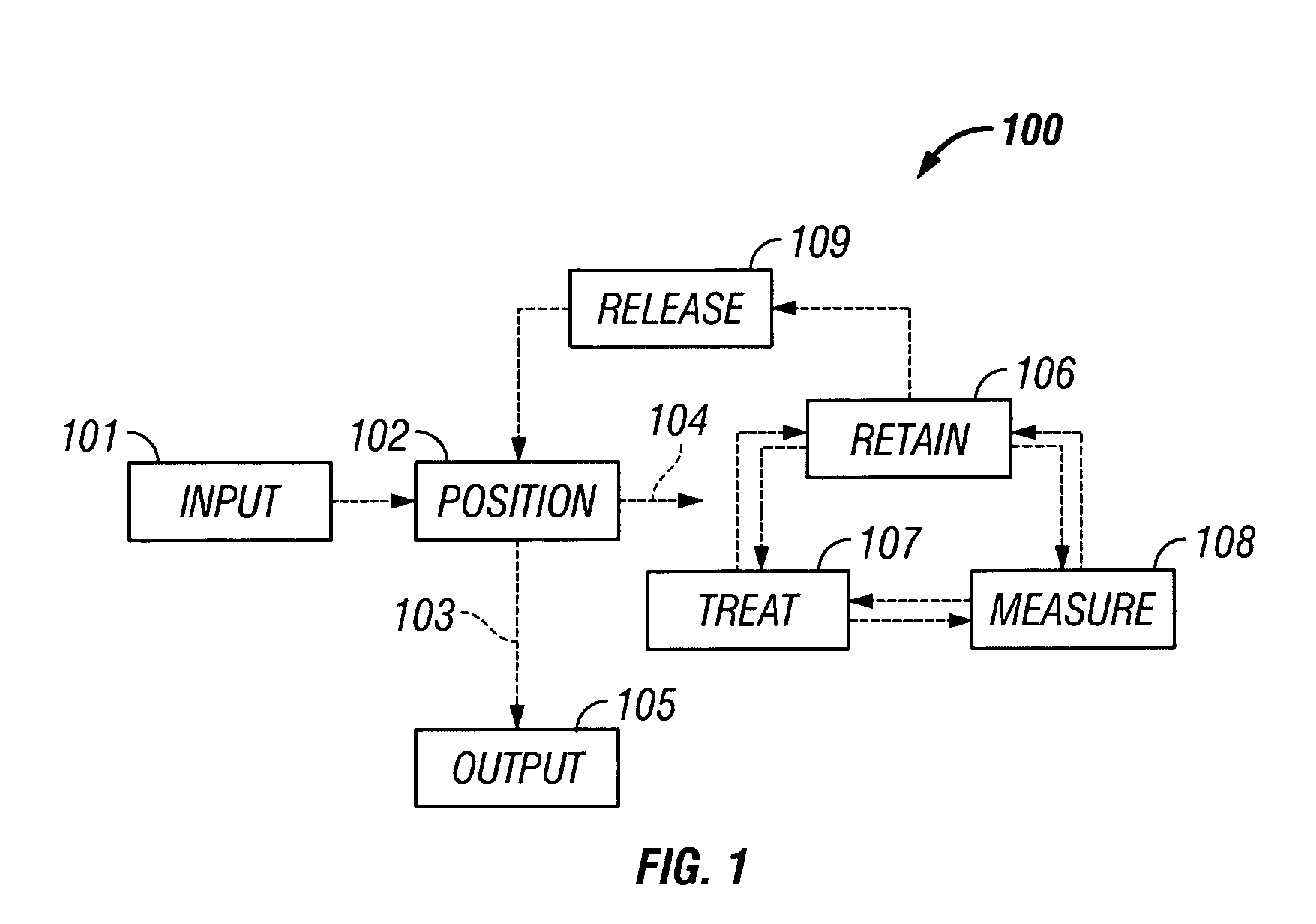
The invention provides systems, including apparatus, methods, and kits, for the microfluidic manipulation and / or detection of particles, such as cells and / or beads. The invention provides systems, including apparatus, methods, and kits, for the microfluidic manipulation and / or analysis of particles, such as cells, viruses, organelles, beads, and / or vesicles. The invention also provides microfluidic mechanisms for carrying out these manipulations and analyses. These mechanisms may enable controlled input, movement / positioning, retention / localization, treatment, measurement, release, and / or output of particles. Furthermore, these mechanisms may be combined in any suitable order and / or employed for any suitable number of times within a system. Accordingly, these combinations may allow particles to be sorted, cultured, mixed, treated, and / or assayed, among others, as single particles, mixed groups of particles, arrays of particles, heterogeneous particle sets, and / or homogeneous particle sets, among others, in series and / or in parallel. In addition, these combinations may enable microfluidic systems to be reused. Furthermore, these combinations may allow the response of particles to treatment to be measured on a shorter time scale than was previously possible. Therefore, systems of the invention may allow a broad range of cell and particle assays, such as drug screens, cell characterizations, research studies, and / or clinical analyses, among others, to be scaled down to microfluidic size. Such scaled-down assays may use less sample and reagent, may be less labor intensive, and / or may be more informative than comparable macrofluidic assays.
Owner:STANDARD BIOTOOLS INC
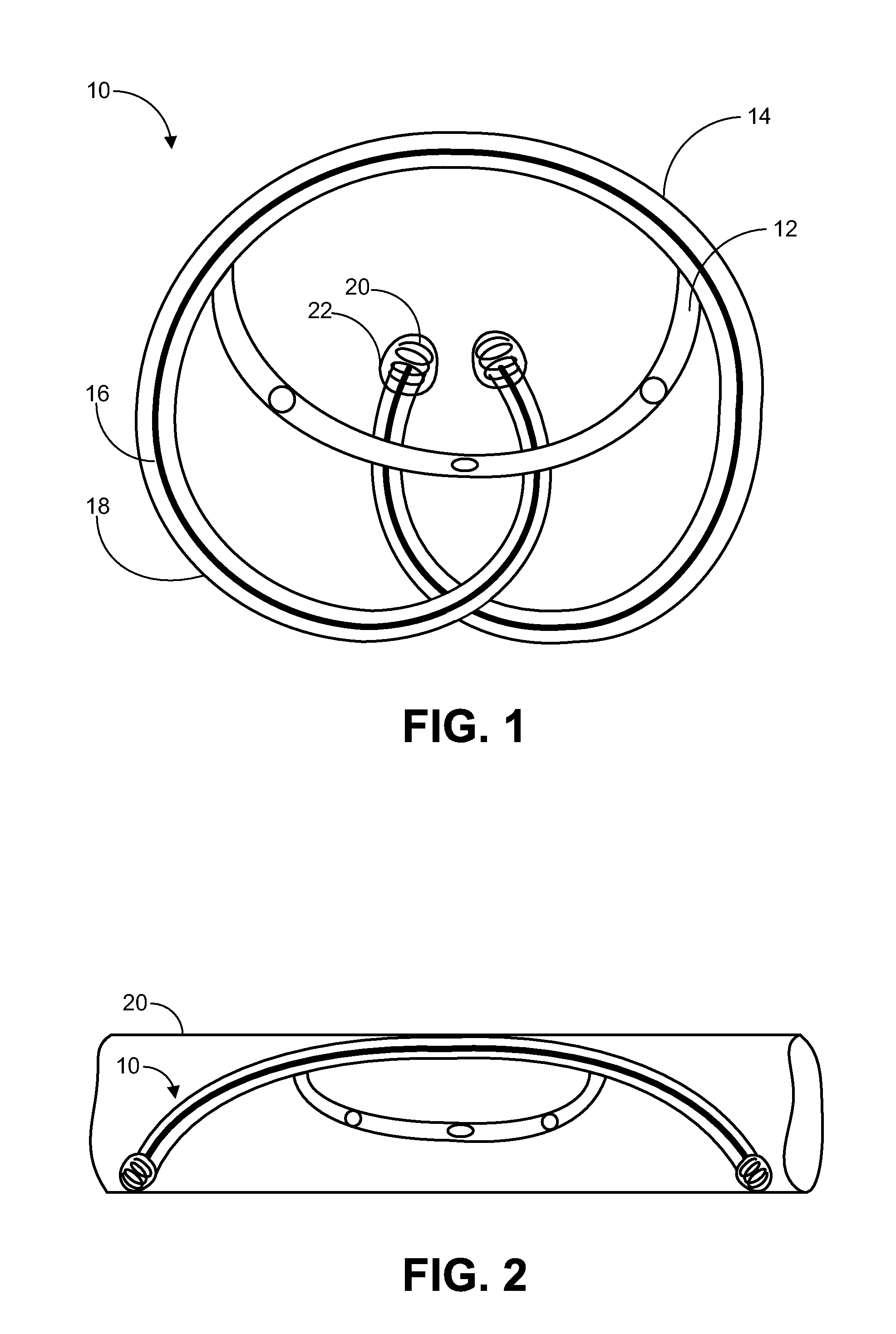
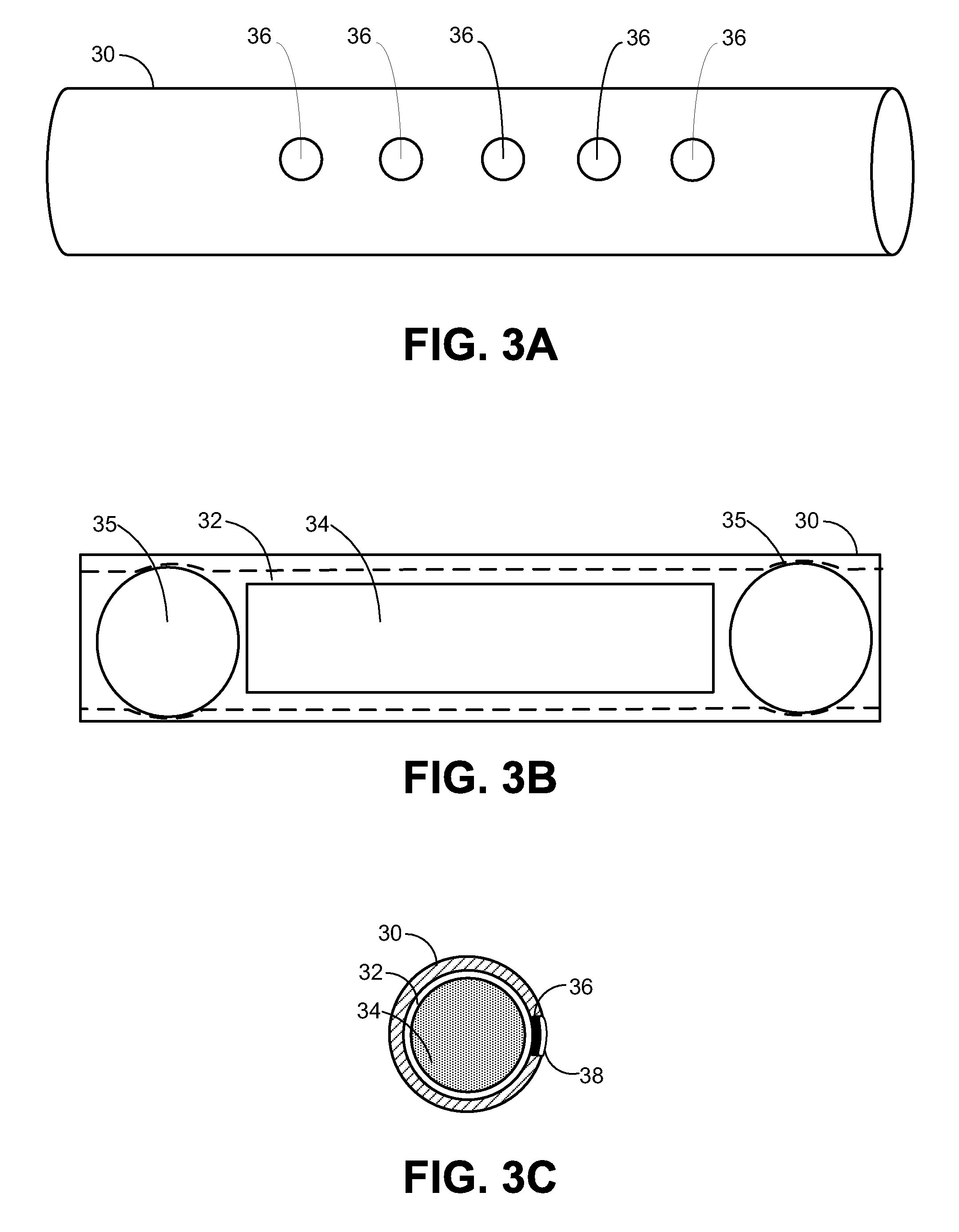
Implantable Drug Delivery Device and Methods for Treatment of the Bladder and Other Body Vesicles or Lumens
ActiveUS20090149833A1High plasma concentrationMinimize irritationBiocideMedical devicesDrug reservoirControlled drugs
An implantable medical device is provided for controlled drug delivery within the bladder, or other body vesicle. The device may include at least one drug reservoir component comprising a drug; and a vesicle retention frame which comprises an elastic wire having a first end, an opposing second end, and an intermediate region therebetween, wherein the drug reservoir component is attached to the intermediate region of the vesicle retention frame. The retention frame prevents accidental voiding of the device from the bladder, and it preferably has a spring constant selected for the device to effectively stay in the bladder during urination while minimizing the irritation of the bladder.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Microfluidic particle-analysis systems
InactiveUS7452726B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMixed groupScale down
The invention provides systems, including apparatus, methods, and kits, for the microfluidic manipulation and / or detection of particles, such as cells and / or beads. The invention provides systems, including apparatus, methods, and kits, for the microfluidic manipulation and / or analysis of particles, such as cells, viruses, organelles, beads, and / or vesicles. The invention also provides microfluidic mechanisms for carrying out these manipulations and analyses. These mechanisms may enable controlled input, movement / positioning, retention / localization, treatment, measurement, release, and / or output of particles. Furthermore, these mechanisms may be combined in any suitable order and / or employed for any suitable number of times within a system. Accordingly, these combinations may allow particles to be sorted, cultured, mixed, treated, and / or assayed, among others, as single particles, mixed groups of particles, arrays of particles, heterogeneous particle sets, and / or homogeneous particle sets, among others, in series and / or in parallel. In addition, these combinations may enable microfluidic systems to be reused. Furthermore, these combinations may allow the response of particles to treatment to be measured on a shorter time scale than was previously possible. Therefore, systems of the invention may allow a broad range of cell and particle assays, such as drug screens, cell characterizations, research studies, and / or clinical analyses, among others, to be scaled down to microfluidic size. Such scaled-down assays may use less sample and reagent, may be less labor intensive, and / or may be more informative than comparable macrofluidic assays.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
Biomimetic membranes and uses thereof
InactiveUS20120080377A1General water supply conservationSeawater treatmentEmulsion liquid membraneDesalination
A liquid membrane system is disclosed in the form of a biochannel containing bulk liquid membrane (BLM), biochannel containing emulsion liquid membrane (ELM), and biochannel containing supported (immobilised) liquid membrane (SLM), or a combination thereof, wherein said liquid membrane system is based on vesicles formed from amphiphilic compounds such as lipids forming a bilayer wherein biochannels have been incorporated and wherein said vesicles further contain a stabilising oil phase. The uses of the membrane system include water extraction from liquid aqueous media by forward osmosis, e.g. for desalination of salt water.
Owner:AQUAPORIN AS
Delivery System for Topically Applied Compounds
A delivery system for topically applied compounds is disclosed. The delivery system contains a fatty acid, a phospholipid, and an oil, and is activated by the addition of water. The delivery system is admixed with a topically applied compound and water to provide a composition suitable for application to the skin or hair. The relative amounts of delivery system ingredients provide round, flexible vesicles that allow penetration of the topically applied compound to the epidermis and dermis, vesicles having a partially ruptured membrane for a controlled delivery of the topically applied drug to the epidermis and dermis, completely ruptured vesicles in the form of lamellar sheets that allow the topically applied compound to be retained in the stratum corneum, and mixtures thereof.
Owner:LIPO CHEM
Chemical address tags
The present invention provides methods and compositions related to the fields of chemoinformatics, chemogenomics, drug discovery and development, and drug targeting. In particular, the present invention provides subcellular localization signals (e.g., chemical address tags) that influence (e.g., direct) subcellular and organelle level localization of associated compounds (e.g., drugs and small molecule therapeutics, radioactive species, dyes and imagining agents, proapoptotic agents, antibiotics, etc) in target cells and tissues. The compositions of the present invention modulate the pharmacological profiles of associated compounds by influencing the compound's accumulation, or exclusion, from subcellular loci such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, cytoplasm, vesicles, granules, nuclei and nucleoli and other subcellular organelles and compartments. The present invention also provides methods for identifying chemical address tags, predicting their targeting characteristics, and for rational designing chemical libraries comprising chemical address tags.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Polymersomes and related encapsulating membranes
InactiveUS7217427B2Easy to measureMaintaining semi-permeabilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBiocideAqueous solutionMembrane configuration
The present invention provides biocompatible vesicles comprising semi-permeable, thin-walled encapsulating membranes which are formed in an aqueous solution, and which comprise one or more synthetic super-amphiphilic molecules. When at least one super-amphiphile molecule is a block copolymer, the resulting synthetic vesicle is termed a “polymersome.” The synthetic, reactive nature of the amphiphilic composition enables extensive, covalent cross-linking of the membrane, while maintaining semi-permeability. Cross-linking of the polymer building-block components provides mechanical control and long-term stability to the vesicle, thereby also providing a means of controlling the encapsulation or release of materials from the vesicle by modifying the composition of the membrane. Thus, the encapsulating membranes of the present invention are particularly suited for the reliable, durable and controlled transport, delivery and storage of materials.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
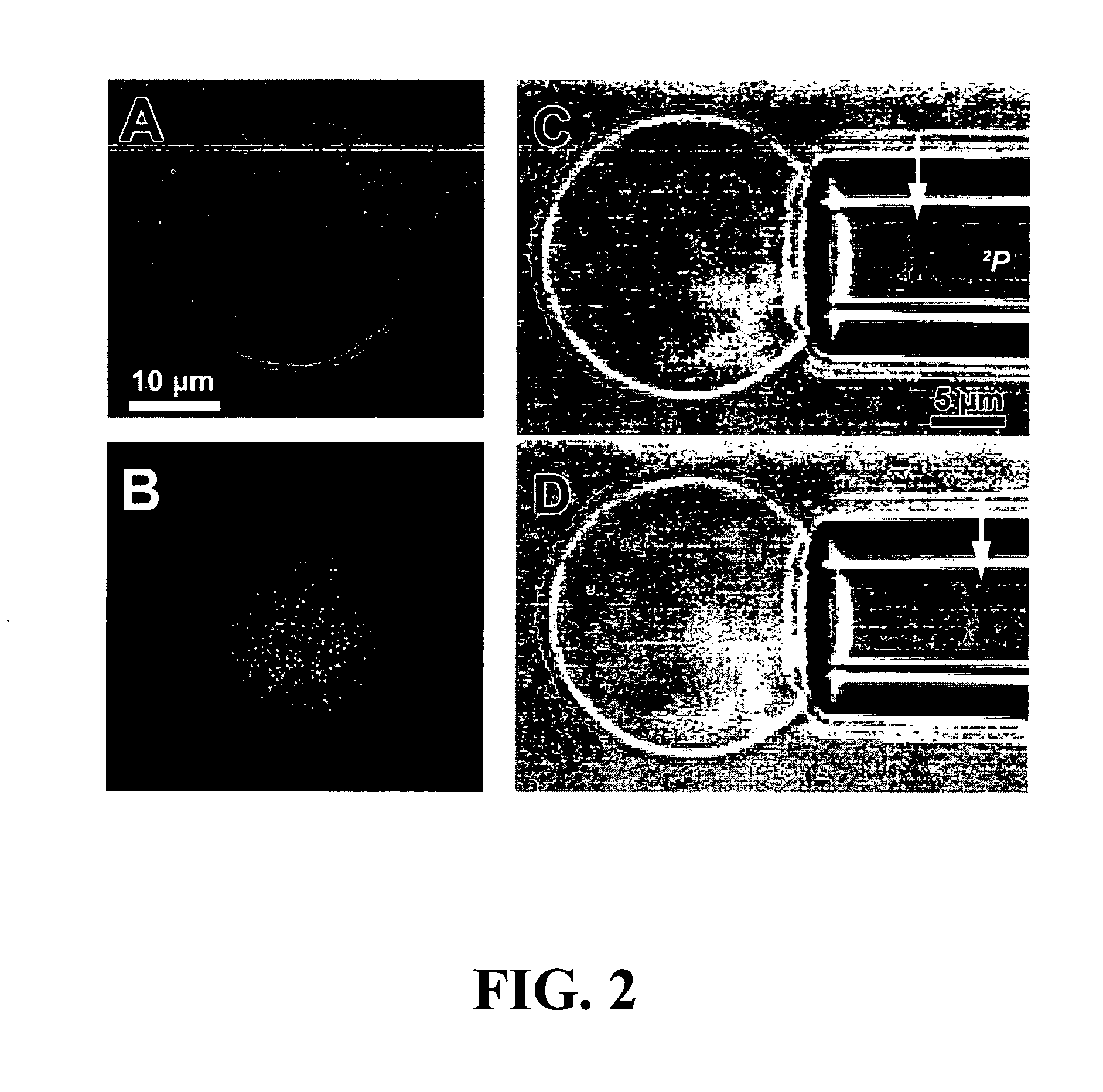
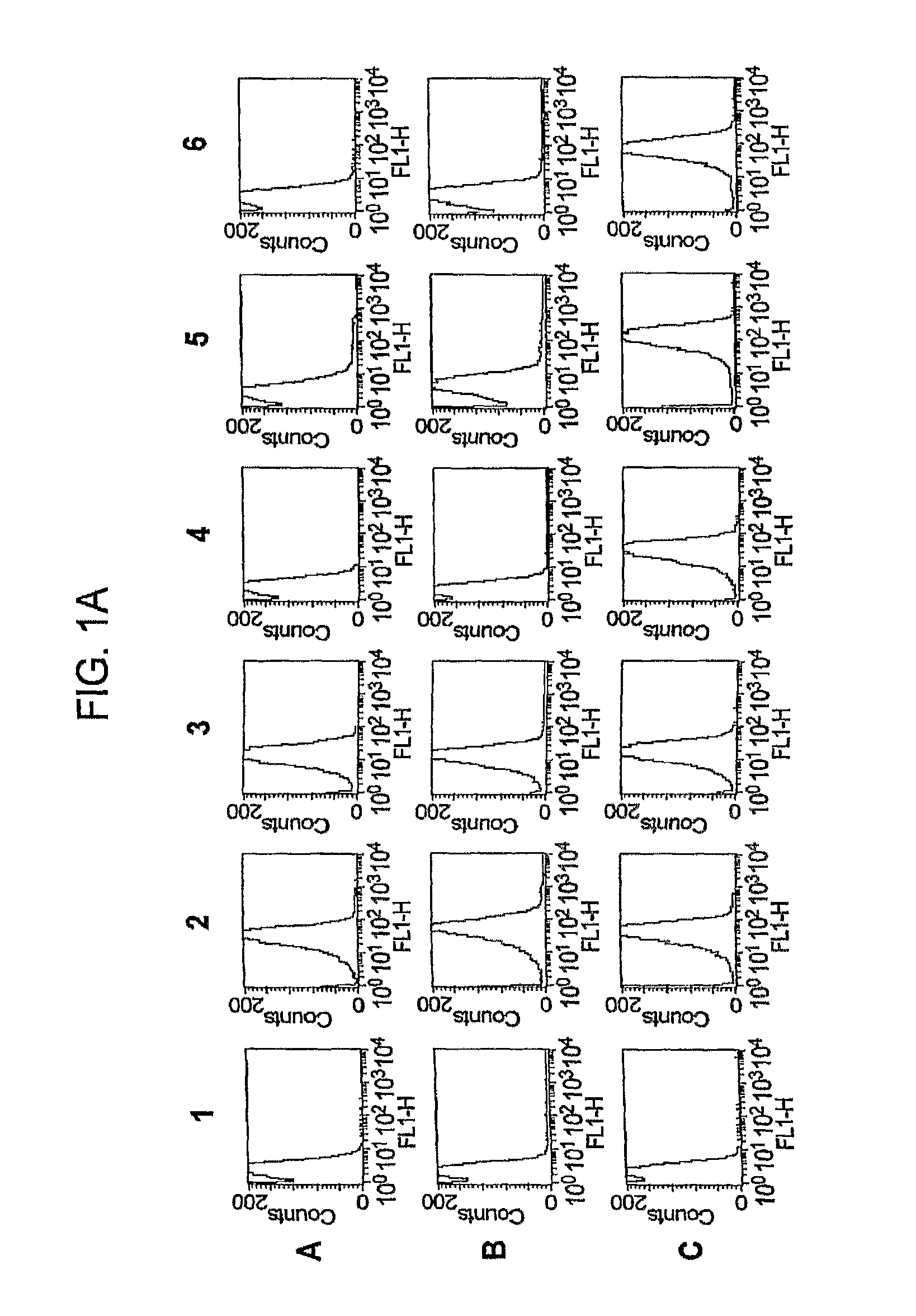
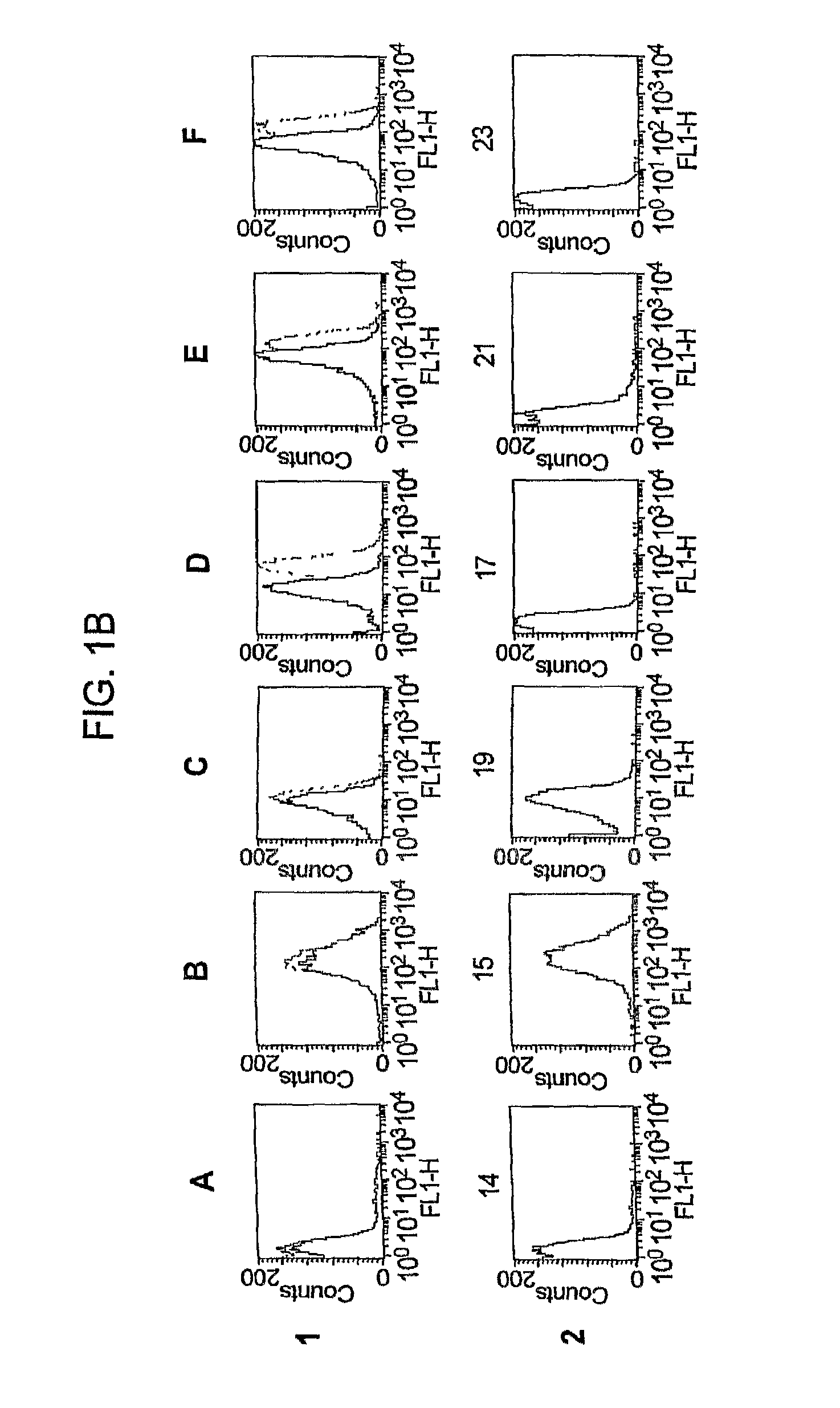
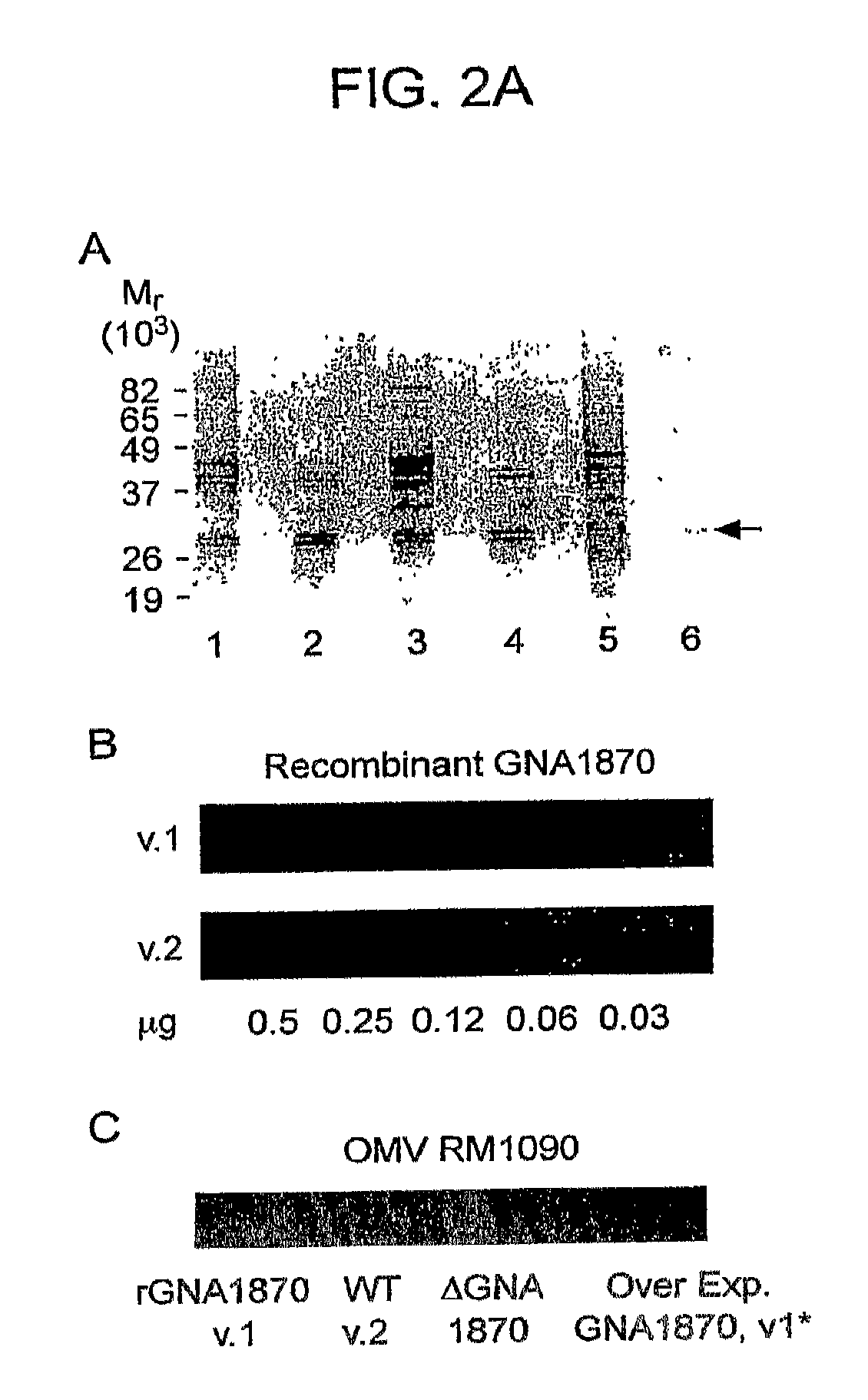
GNA1870-based vesicle vaccines for broad spectrum protection against diseases caused by Neisseria meningitidis
ActiveUS8968748B2Broad protectionReduce expressionAntibacterial agentsBiocideTGE VACCINENeisseria meningitidis
Owner:CHILDREN S HOSPITAL &RES CENT AT OAKLAN
Device for the production of capillary jets and micro-and nanometric particles
InactiveUS20050116070A1Eliminate the effects ofIncreasing drag effectFuel injection apparatusMachines/enginesNanoparticleMicrometer
The invention relates to a method and devices for the production of capillary microjets and microparticles that can have a size of between hundreds of micrometers and several nanometers. The inventive method makes use of the combined effects of electrohydrodynamic forces, fluid-dynamic forces and a specific geometry in order to produce micro- and nano-capsules or fluid jets, single- or multi-component, which, upon disintegrating or splitting, form a significantly monodispersed spray of drops which have a controlled micro- or nanometric size and which can also comprise a specific internal structure, such as, for example, a nucleus which is surrounded by a cortex of a different substance or several concentric or non-concentric nuclei or vesicles which are surrounded by a cortex.
Owner:UNIV DE SEVILLA
Red blood cell-derived vesicles as a nanoparticle drug delivery system
Red blood cell-derived vesicles (RDV) as a nanoparticle drug delivery system. The RDV are smaller than one micrometer, capable of encapsulating and delivering an exogenous substance into cells. The substance may be at least one selected from the group consisting of fluorophores, nucleic acids, superparamagnetic compounds and therapeutic agents. The RDV are capable of delivering encapsulated substances into cells including stem cells. The delivered substance within the cell or stem cell may be traced or tracked using a suitable device either in vitro or in vivo.
Owner:NAT INST OF HEALTH REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES NAT INST OF HEALTH
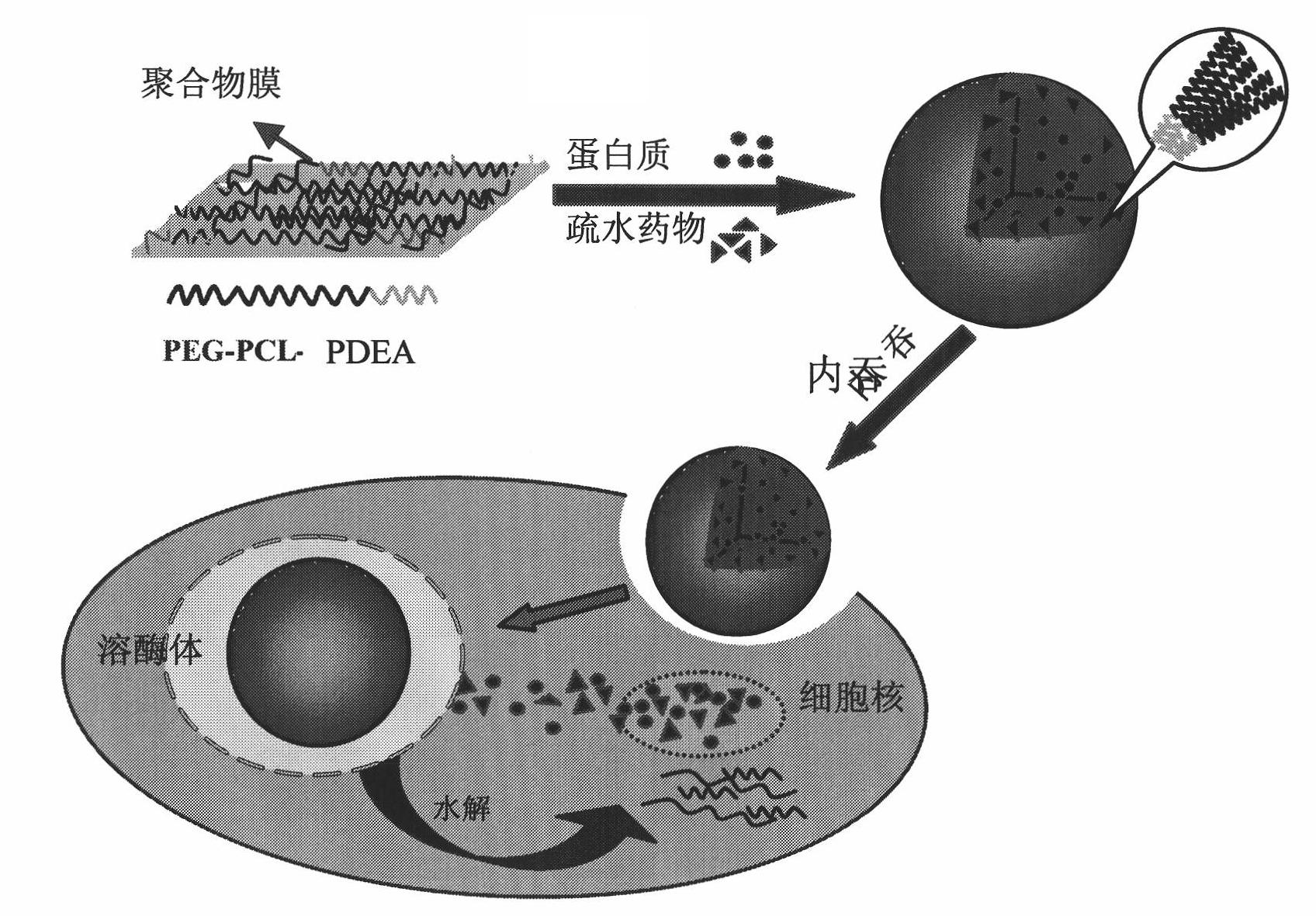
Biodegradable polymer vesicles and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN101792516AEfficient packagingEliminate drug resistancePharmaceutical non-active ingredientsPolymer sciencePolyethylene glycol
The invention relates to a medicament carrier and a preparation method thereof, in particular to a medicament delivery system comprising biodegradable polymer vesicles with asymmetric membranes. The invention discloses the biodegradable polymer vesicles and preparation and application thereof. The biodegradable polymer vesicles are prepared from A-B-C type block polymer, wherein a block A is polyethylene glycol (PEG) distributed on outer surfaces of the vesicles; a block B is hydrophobic biodegradable polymer to form the nucleuses of the vesicles; and a block C is polyelectrolyte distributed on inner walls of the vesicular membranes and used for efficiently loading medicaments with opposite electric charge. The biodegradable polymer vesicles are formed in aqueous solution directly, can efficiently load protein and polypeptide medicaments, nucleic acid medicaments and micro-molecular medicaments, and are expected to be applied to the protein therapy and the combination therapy of cancers.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Novel strategies for protein vaccines
InactiveUS20060275777A1Microbiological testing/measurementCancer antigen ingredientsTarget antigenPathogen
A prerequisite for clinical vaccines is the construction of safe and highly immunogenic reagents able to generate efficient immune responses against target antigens. Lipid based delivery vesicles, including virosomes, as clinically approved safe vaccines, can be used to elicit both humoral and cell-mediated responses against protein antigens and mediate effective immune responses against the target pathogen and / or induce tumor rejection. Thus the compositions of the present invention are useful either as a primary vaccination or as a boost in combination with other vaccines in a context of an adjuvant treatment plan.
Owner:PEVION BIOTECH
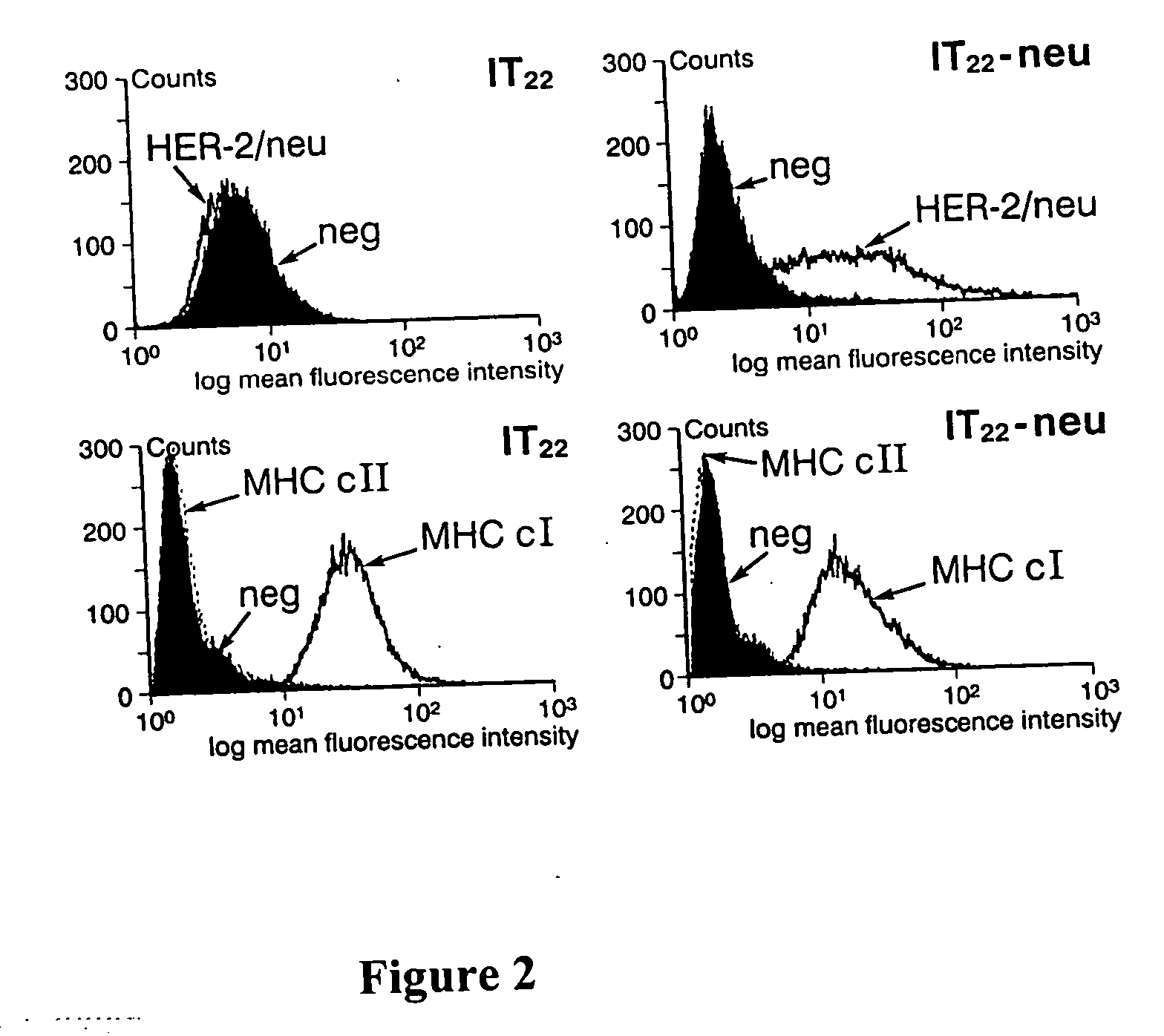
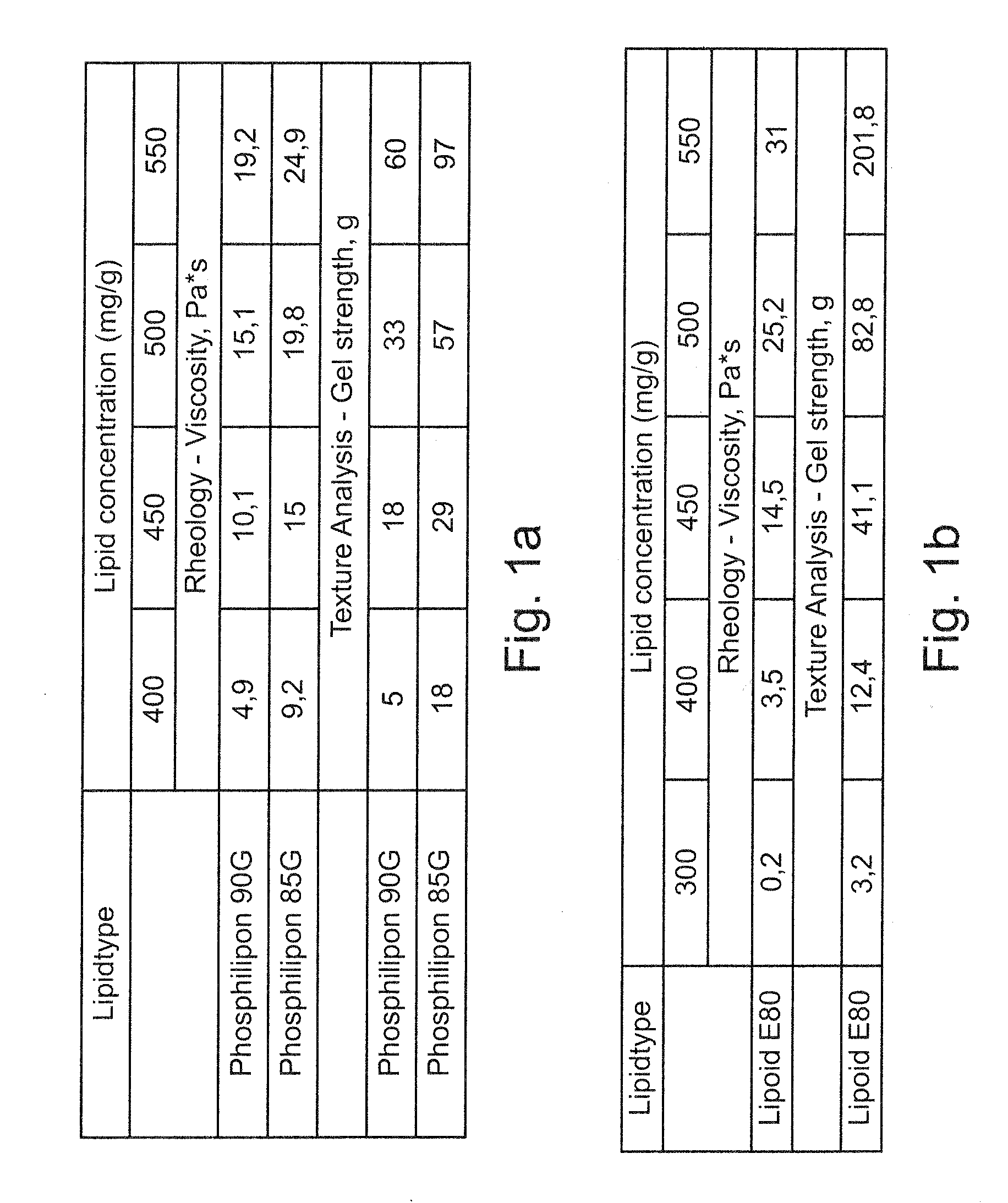
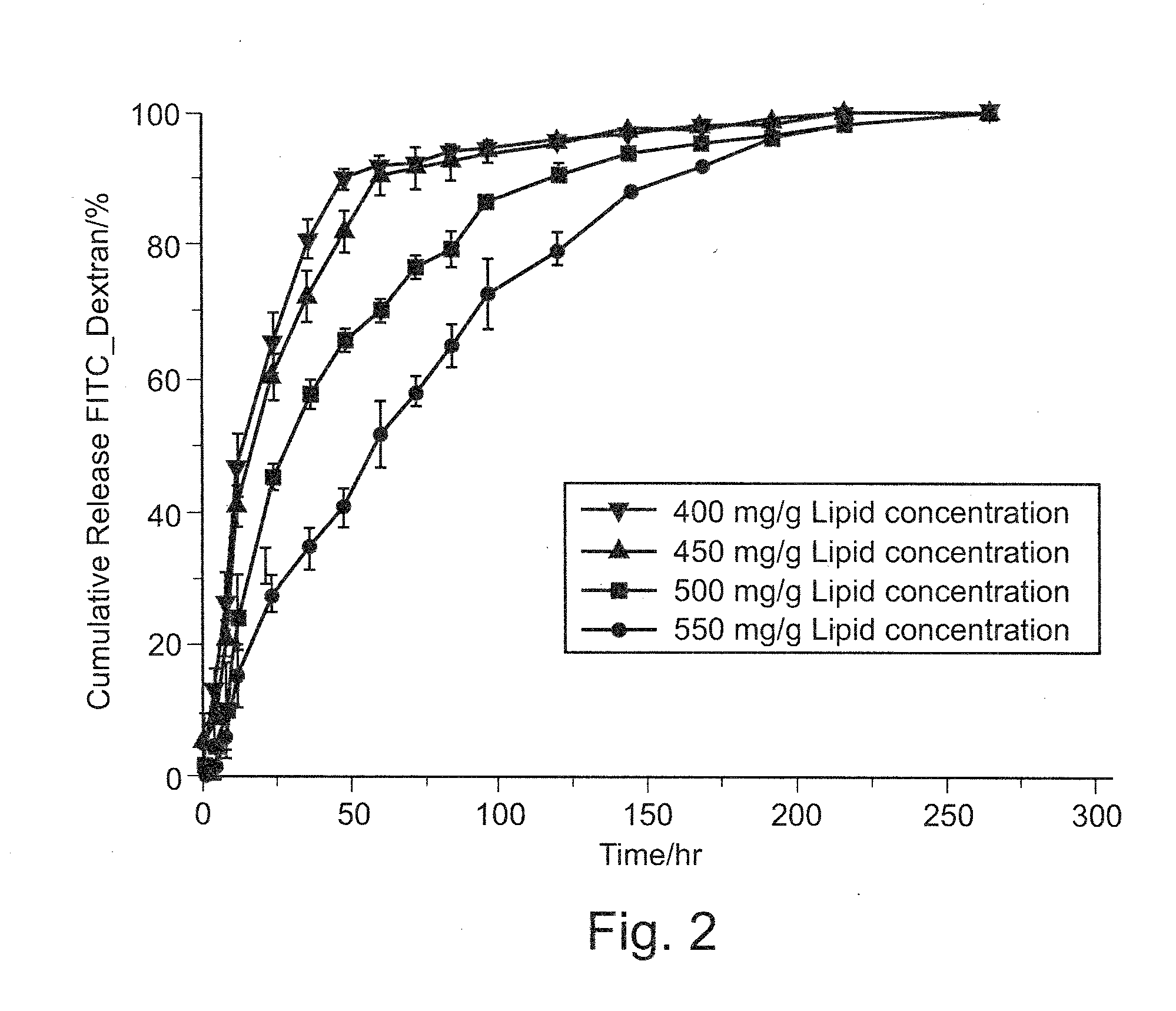
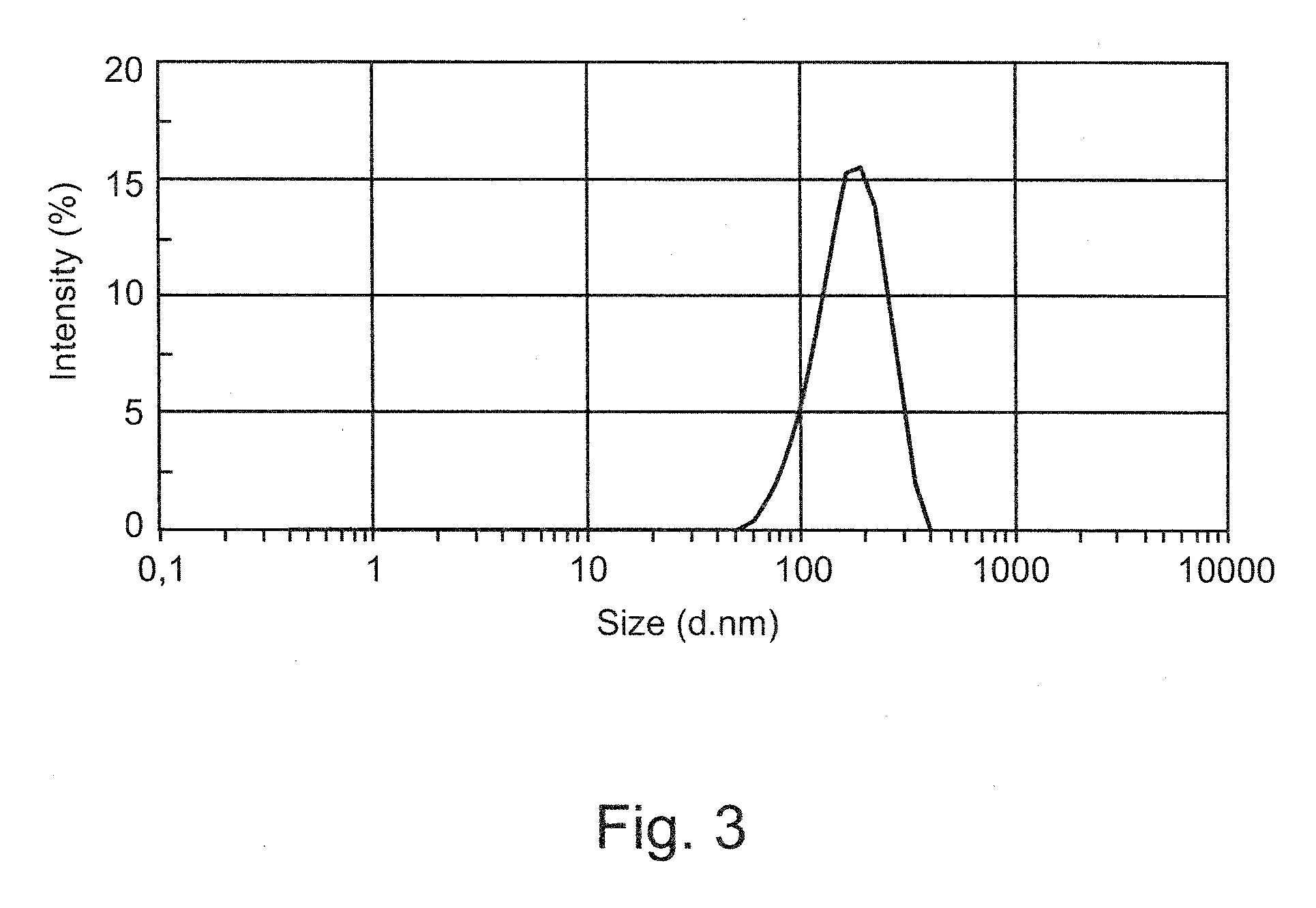
Vesicular phospholipid gels comprising proteinaceous substances
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition for sustained release of a pharmaceutically active compound, the composition comprising a vesicular phospholipid gel. More particularly, the invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising at least one proteinaceous substance as the pharmaceutically active compound in encapsulated form, the at least one proteinaceous substance being a biologically active protein, peptide or polypeptide. Furthermore, the present invention relates to a method for the production of said pharmaceutical composition comprising dual asymmetric centrifugation and to the use of said pharmaceutical composition for immunotherapy and / or for stimulating selective tissue regeneration in the treatment of surgical defects in the course of surgical interventions.
Owner:WINTER GERHARD DR
Vesicle dispersion and cosmetic containing the same
A vesicle dispersion comprising (A) sucrose fatty acid ester, (B) a sphingosine and / or its derivative, and (C) an aqueous component and a cosmetic composition comprising the vesicle dispersion are disclosed. The vesicle dispersion can stably contain sphingosines such as a ceramide, excelling in a moisturizing effect of the skin, and the cosmetic composition comprising the vesicle dispersion exhibits an excellent moisturizing effect, storage stability, and the like.
Owner:KOBAYASHI KOSE CO LTD
Preparation method of metal polyphenol vesicle material with micrometer/nanometer multilayer composite structure
InactiveCN106565964ARich functionalityOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsMicrometerSurface roughness
The invention discloses a preparation method of a metal polyphenol vesicle material with a micrometer / nanometer multilayer composite structure. The metal polyphenol vesicle material with the multilayer composite structure is obtained by etching polyphenol by taking a metal organic framework compound serving as a template. The precise control on an internal structure of a vesicle and the surface roughness of the vesicle is realized through controlling experiment parameters such as etching time and a pH value. The functionality of the obtained vesicle material is also greatly enriched by introducing a polyphenol structural unit to an assembly system, and the preparation method is favorably applied to aspects such as catalytic reaction and drug delivery.
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG UNIVERSITY
Reversible crosslinked biodegradable polymer vesicle having positive charges on inner membrane, preparation method thereof and application in preparation of antineoplastic drugs
ActiveCN106137968AEfficient specific bindingEfficient combinationPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsTumor targetingApoptosis
The invention discloses a reversible crosslinked biodegradable polymer vesicle having positive charges on an inner membrane, a preparation method thereof and application in preparation of antineoplastic drugs. The biodegradable polymer vesicle based on tumor targeting of a block polymer PEG-P (TMC-DTC)-SP or PEG-P (LA-DTC)-SP, having the positively charged membrane, reversibly crosslinked in reduction sensitivity and intracellularly solvable and crosslinked can effectively support and protect biological macromolecules such as proteins, DNA and siRNA and micromolecular drugs with negative charges in a physical environment and can be delivered to intravital tumor cells to induce apoptosis. The system has lots of unique advantages including simple and easy controllability of preparation, excellent biocompatibility, excellent controlled drug release property, super-strong in-vivo circulation stability, superior cancerous cell targeting and remarkable cancer cell apoptosis capability and the like. Therefore, the reversible crosslinked biodegradable polymer vesicle is expected to become a simple, stable, multifunctional nano system platform integrating multiple advantages and is used for efficient, active and targeted delivery from nucleic acids to in-situ tumors.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
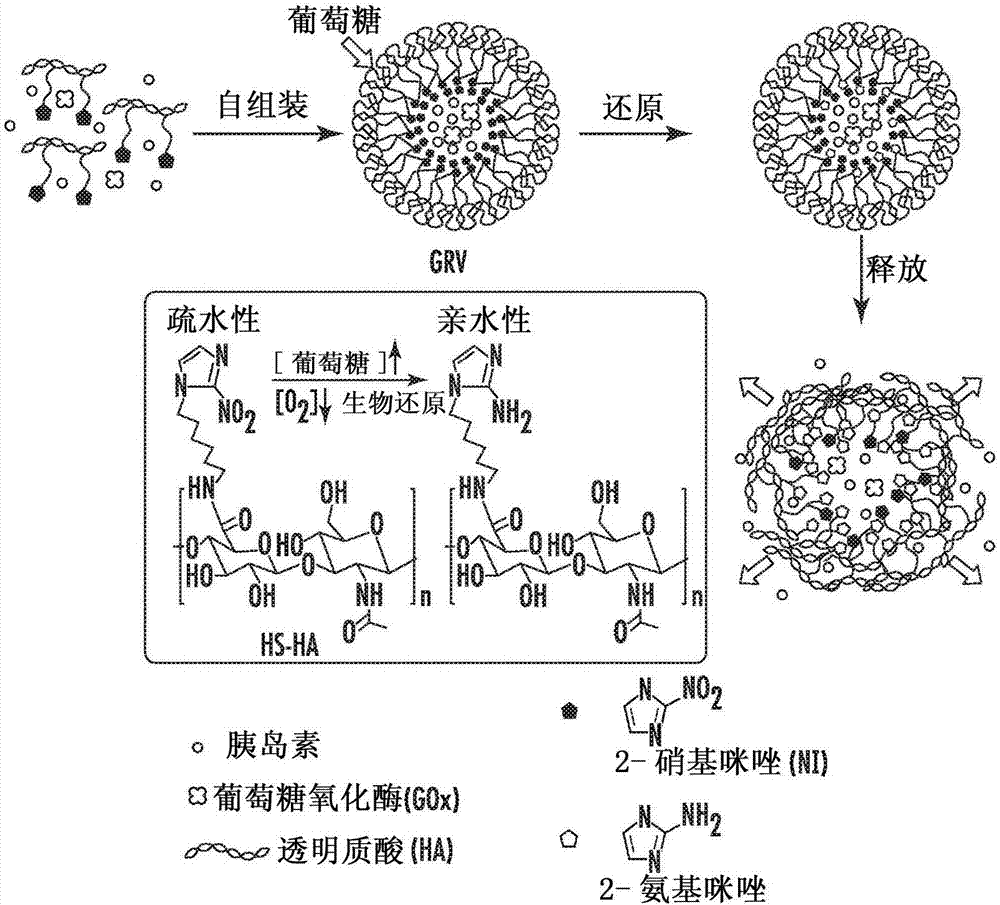
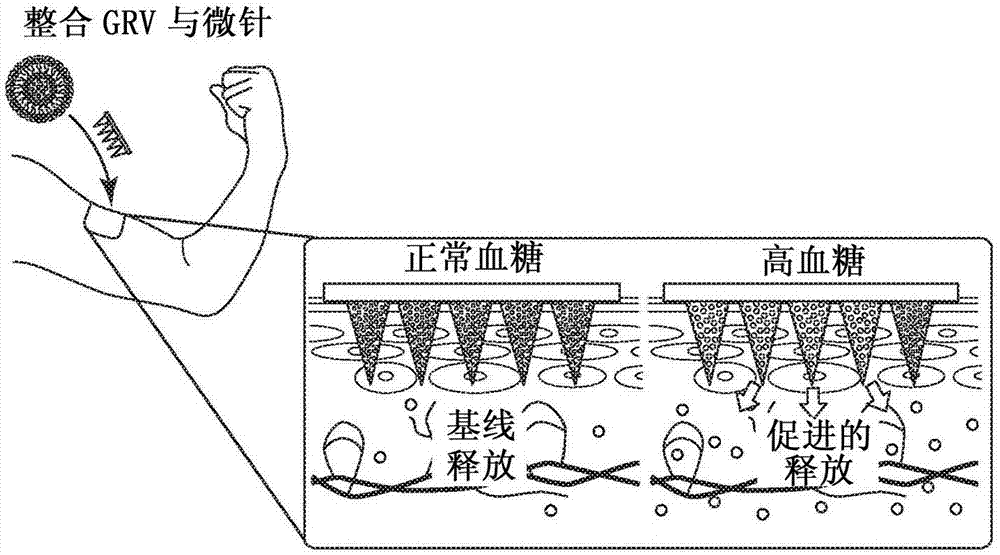
Glucose-responsive insulin delivery system using hyoxia-sensitive nanocomposites
A closed-loop insulin delivery system is described. More particularly, the presently disclosed insulin delivery system can comprise glucose-responsive vesicles that release insulin in response to hypoxia triggered by enzymatic reduction of glucose. In addition or as an alternative to insulin, the delivery system can release other diabetes treatment agents, such as non-insulin-based diabetes treatment agents. The vesicles can be prepared from a hypoxia sensitive polymer, such as a hypoxia-sensitive hyaluronic acid (HS-HA). The HS-HA can comprise hydrophobic groups that can be reduced in hypoxicenvironments to form hydrophilic groups. The vesicles can be loaded into microneedles and microneedle array patches for use in the treatment of diabetes or to otherwise regulate blood glucose levelsin subjects in need of such treatment.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Block copolymers
ActiveUS20160206750A1Efficient deliverySpecial deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsLipofectamineCell membrane
Described herein are block copolymers, and methods of making and utilizing such copolymers. The described block copolymers are disruptive of a cellular membrane, including an extracellular membrane, an intracellular membrane, a vesicle, an organelle, an endosome, a liposome, or a red blood cell. Preferably, in certain instances, the block copolymer disrupts the membrane and enters the intracellular environment. In specific examples, the block copolymer is endosomolytic and capable of delivering an oligonucleotide (e.g., an mRNA) to a cell. Compositions comprising a block copolymer and an oligonucleotide (e.g., an mRNA) are also disclosed.
Owner:GENEVANT SCI GMBH
Fabric enhancers comprising nano-sized lamellar vesicle
InactiveUS20090042765A1Enough disruptionCationic surface-active compoundsFibre treatmentNanometrePolymer chemistry
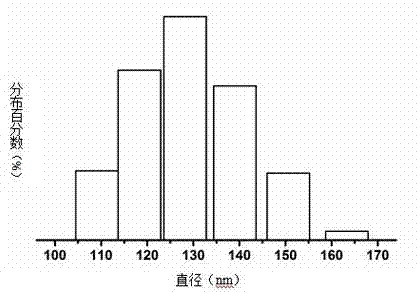
A fabric enhancer comprising: at least one cationic softening compound, wherein said cationic softening compound comprises a plurality of lamellar vesicles, said lamellar vesicles having an average diameter from about 10 nm to about 170 nm, wherein said fabric enhancer is capable of forming phase stable mixtures with enhanced stability in the presence of at least one cationic polymer and processes for making the same.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Small interfering ribonucleic acid (siRNA) lipid nanometer vesicles with targeted hepatic stellate cells, and application of siRNA lipid nanometer vesicles
InactiveCN105688229AAchieve targetedAchieve deliveryOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsGene deliveryPharmaceutical drug
The invention relates to the technical field of gene therapy drugs, and in particular discloses small interfering ribonucleic acid (siRNA) lipid nanometer vesicles with targeted hepatic stellate cells, and the application of the siRNA lipid nanometer vesicles. The nanometer vesicles respectively comprise a treatment component and a delivery component, wherein the treatment component is siRNA having a targeted gene inhibition effect, and the delivery component is a lipid carrier. The nanometer vesicles formed by encapsulating the treatment component by the delivery component are prepared by an ethanol dilution method; a gene delivery system existing in a form of nanometer vesicles is capable of effectively overcoming the obstacles preventing the delivery of the gene therapy drugs in the body.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Polymer nano-vesicle for co-delivering drug and perfluorooctylbromide, as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104725645AAvoid premature releaseImproved particle size is largerEchographic/ultrasound-imaging preparationsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsPhenylboronic acidPolyethylene glycol
The invention relates to an acid-sensitive amphipathic tri-block polymer. The polymer is composed of a polyethylene glycol-acid sensitive segment 1-acid sensitive segment 2 tri-block copolymer, wherein the acid sensitive segment 1 is poly(acrylamidophenylboronic acid); the acid sensitive segment 2 is poly(aminoacyl dimethyl-ethylenediamine); the molecular weight of the polyethylene glycol is 2000-5000, the molecular weight of the acid sensitive segment is 2000-6000, and the molecular weight of the acid sensitive segment is 1000-2000. The invention further relates to application of the acid sensitive amphipathic tri-block polymer in preparation of polymer nano-vesicle for co-delivering drug and perfluorooctylbromide. The nano-vesicle has a uniform nano-diameter, can stably circulate in a body and can be enriched in a tumor position, has excellent capability of reinforcing ultrasonic development to realize application of ultrasonic development under diagnostic ultrasound, and has ultrasonic sensitivity to stimulate the cavitation effect under a condition of low-frequency high-energy ultrasonic-radiation so as to realize controllable release of drugs.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
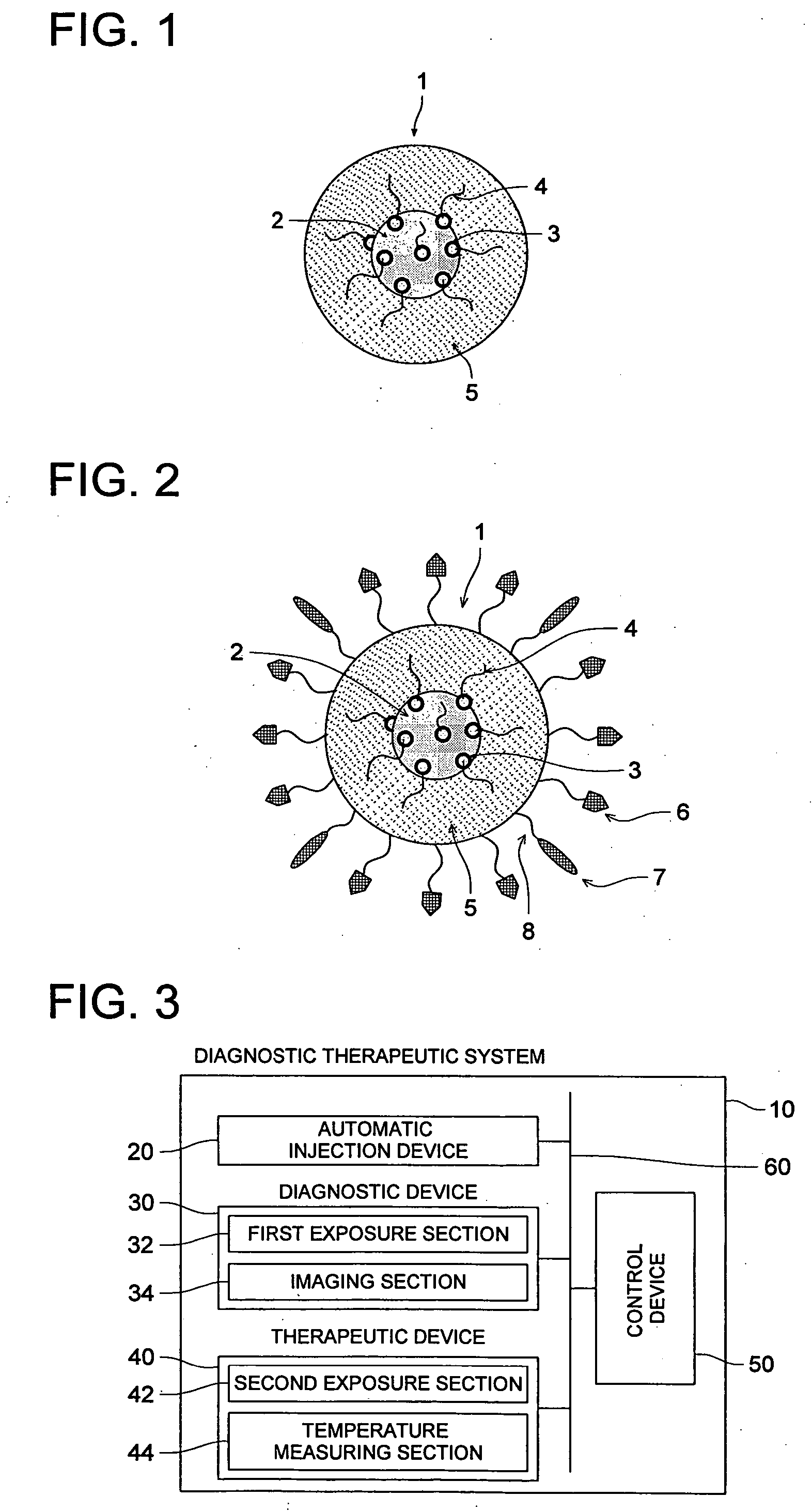
Pharmaceutical preparation containing magnetic vesicular particles, manufacturing method thereof and diagnostic therapeutic system
InactiveUS20060171894A1Improve abilitiesIncrease temperatureUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringLipid formationParticulates
A pharmaceutical preparation comprising magnetic vesicular particles, wherein the magnetic vesicular particles each include one or more magnetic microparticles within a lipid membrane, the magnetic microparticle having particulate gold attached to the surface of the magnetic microparticles and further having an organic compound bound to the particulate gold; and the vesicular particles meet the following requirement: 0.02≦R / (r×100)≦0.03 wherein R is an average particle size of the magnetic vesicular particles and r is an average particle size of the magnetic microparticles included in the magnetic vesicular particles.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA MEDICAL & GRAPHICS INC
Multiplex detection probes
InactiveUS7595155B2Increase intensityHighly sensitive multiplex analysisTime-of-flight spectrometersSugar derivativesAnalyteBiology
The present invention comprises detection probes utilizing vesicles or soluble bodies to retain multiple mass tag molecules. The detection probes may be used to simultaneously assay a plurality of different biological samples, each comprising a plurality of analytes, by immobilizing the analytes from each of the samples on a surface incubating the surface with a set of the detection probes, each having mass tag molecules with different masses, removing the unbound detection probe, collecting the first and second mass tag molecules from the bound detection probe, and quantifying the first and second mass tag molecules collected.
Owner:HITACHI CHEM RES CENT +1
Encapsulation of aqueous phase systems within microscopic volumes
InactiveUS7803405B2Increase ionic strengthReduce interfacial tensionIn-vivo radioactive preparationsMicroencapsulation basedLipid filmChemical compound
A means and method for preparing vesicles and freestanding two-dimensional assemblies using aqueous two-phase systems (ATPS) is described. The surface tension of the ATPS is sufficient to support the assembly of various types of particles, and provide the advantage of being biocompatible with DNA and other types of biological molecules that may be used in the assembly. Vesicles are formed by mixing chemically dissimilar compounds in appropriate concentrations and at a temperature sufficient to form a monophasic mixture. This mixture is then heated above the temperature at which the polymer mixture is monophasic, added to a lipid film, and allowed to hydrate at this elevated temperature.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Method for loading lipid like vesicles with drugs or other chemicals
InactiveUS20040208922A1Reduce toxic effectsImprove stabilityLiposomal deliveryPh gradientAmount of substance
A method for accumulating drugs or other chemicals within synthetic, lipid-like vesicles by means of a pH gradient imposed on the vesicles just prior to use is described. The method is suited for accumulating molecules with basic or acid moieties which are permeable to the vessels membranes in their uncharged form and for molecules that contain charge moieties that are hydrophobic ions and can therefore cross the vesicle membranes in their charged form. The method is advantageous over prior art methods for encapsulating biologically active materials within vesicles in that it achieves very high degrees of loading with simple procedures that are economical and require little technical expertise, furthermore kits which can be stored for prolonged periods prior to use without impairment of the capacity to achieve drug accumulation are described. A related application of the method consists of using this technology to detoxify animals that have been exposed to poisons with basic, weak acid or hydrophobic charge groups within their molecular structures.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Polylactic acid stereo complex magnetic nanometer vesicle preparation method
The present invention belongs to the field of polymer materials and biomedical engineering, and particularly relates to a polylactic acid stereo complex magnetic nanometer vesicle preparation method, which specifically comprises that: L-polylactic acid and D-polylactic acid respectively react with polyethylene glycol to synthesize two different block copolymers, then stereo compounding is performed, and nanometer magnetic particles are entrapped so as to form the polylactic acid stereo complex magnetic nanometer vesicle adopting the hydrophobic stereo composite polylactic acid as the film and having the inner layer and the outer layer being the hydrophilic polyethylene glycol chains, wherein the obtained nanometer vesicle has excellent stability due to the strong intermolecular interaction of the stereo complex, and the magnetic particles are wrapped in the compact polylactic acid film structure so as not to be easily leaked. According to the present invention, the magnetic nanometer vesicles can be used as the enhancement contrast agent in the clinical magnetic resonance imaging, and can further load drugs or biological macromolecules so as to be used as the release controlling nanometer carrier of drug or gene therapy.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
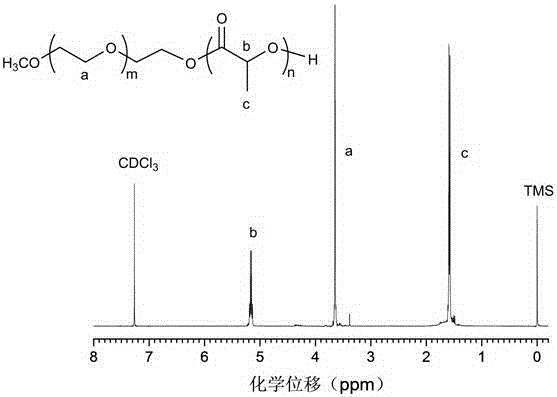
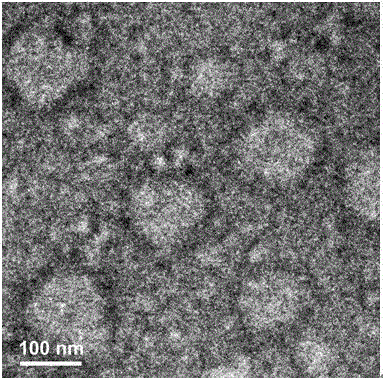
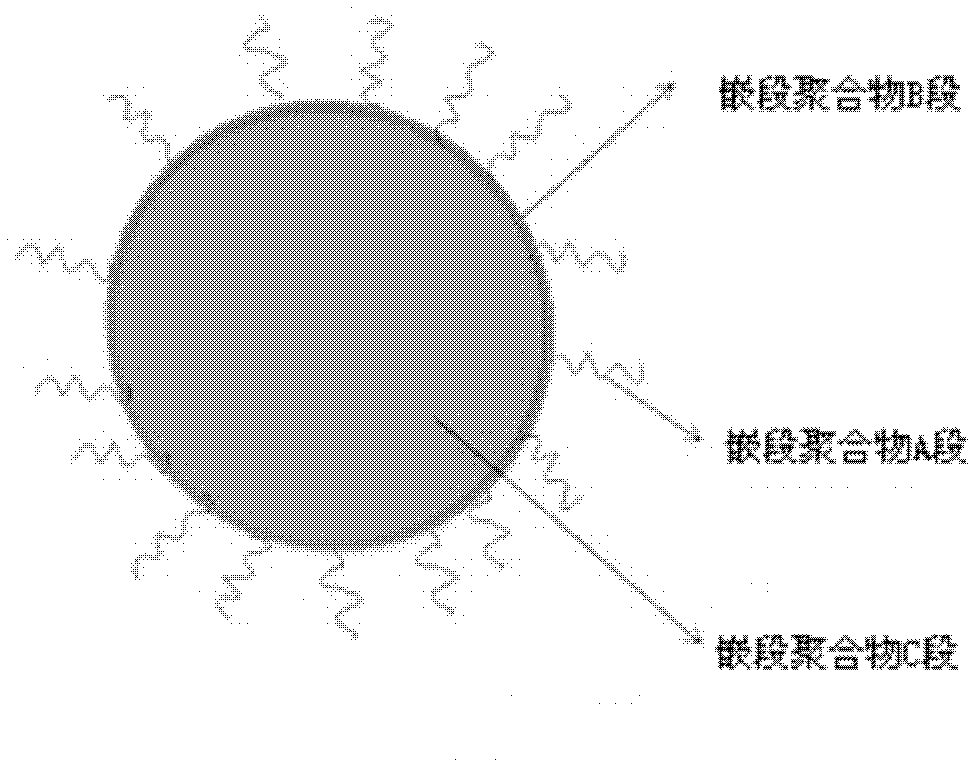
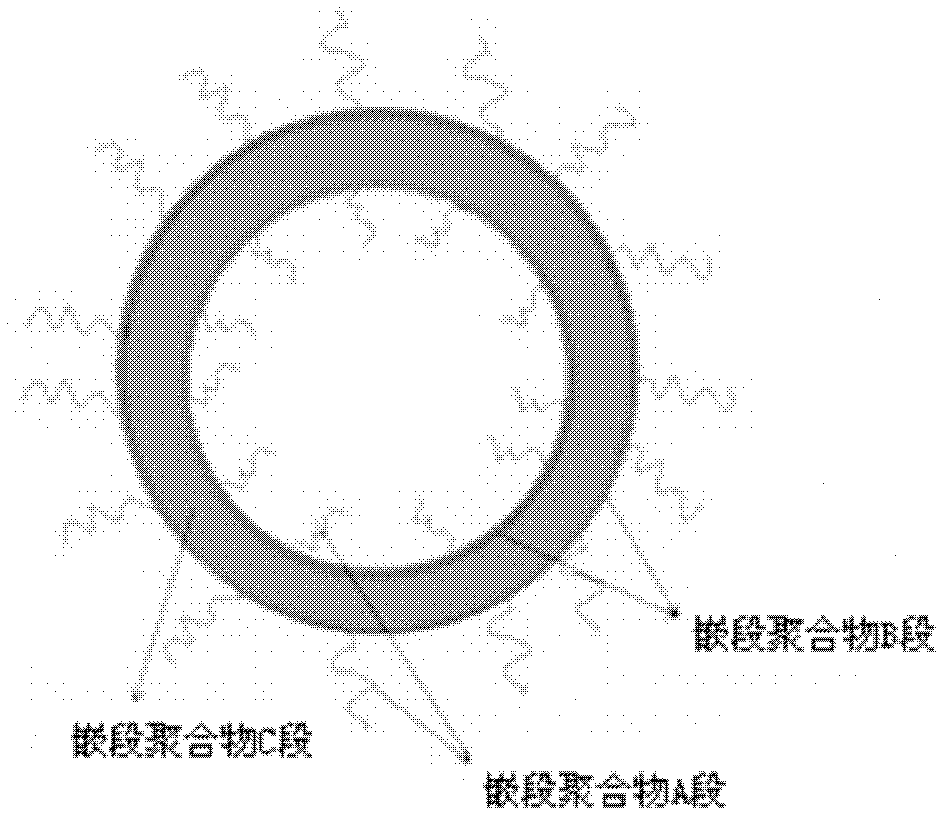
Cross-linked biologically degradable carrier polymer, micelle and vesicle, and preparation method and application of the cross-linked biologically degradable carrier polymer, micelle and vesicle
ActiveCN102604065ALoad implementationOxygen-carrying functionPowder deliveryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCross-linkPolyester
The invention provides a cross-linked biologically degradable carrier polymer, a micelle and a vesicle, and a preparation method and an application of the cross-linked biologically degradable carrier polymer, micelle and vesicle, belonging to the field of biological medical material and solving a poor stability problem of the existing polymer micelle and vesicle. The carrier polymer is an A-B-C tri-block polymer, wherein the block A is polyethylene glycol, the block B is the polyethylene glycol containing functional groups in a lateral chain, and the block C is biologically degradable polyester. The invention also provides the polymer micelle and vesicle, which is formed by self assembly of the carrier polymer, wherein the size of the polymer micelle is 20-1000nm, and the size distribution is 0.01-0.50; the size of the vesicle is 20-1000nm, and the size distribution is 0.01-0.50. The polymer micelle provided by the invention can package fat-soluble matters; and the polymer vesicle canpackage water-soluble matters and the fat-soluble matters at the same time; and the polymer micelle or the vesicle has better mechanical strength and stability because the polymer micelle or the vesicle contains a transitional layer formed by the cross-linked block B.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY STORAGE MATERIALS &DEVICES
Active detection method for concealed spore egg vesicle and Giardia sporocyst in drinking water
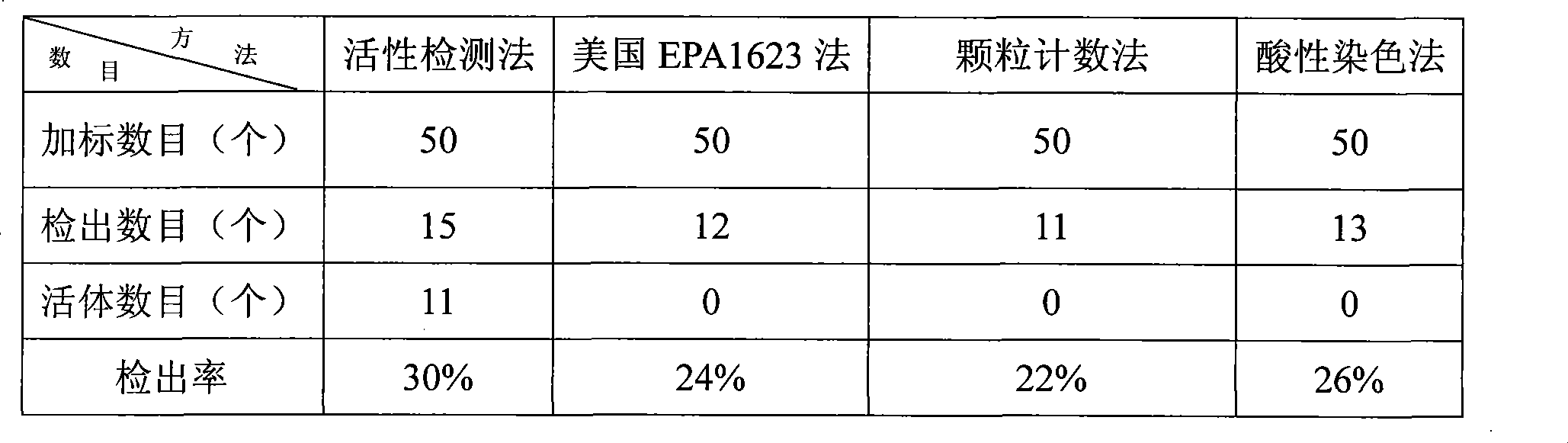
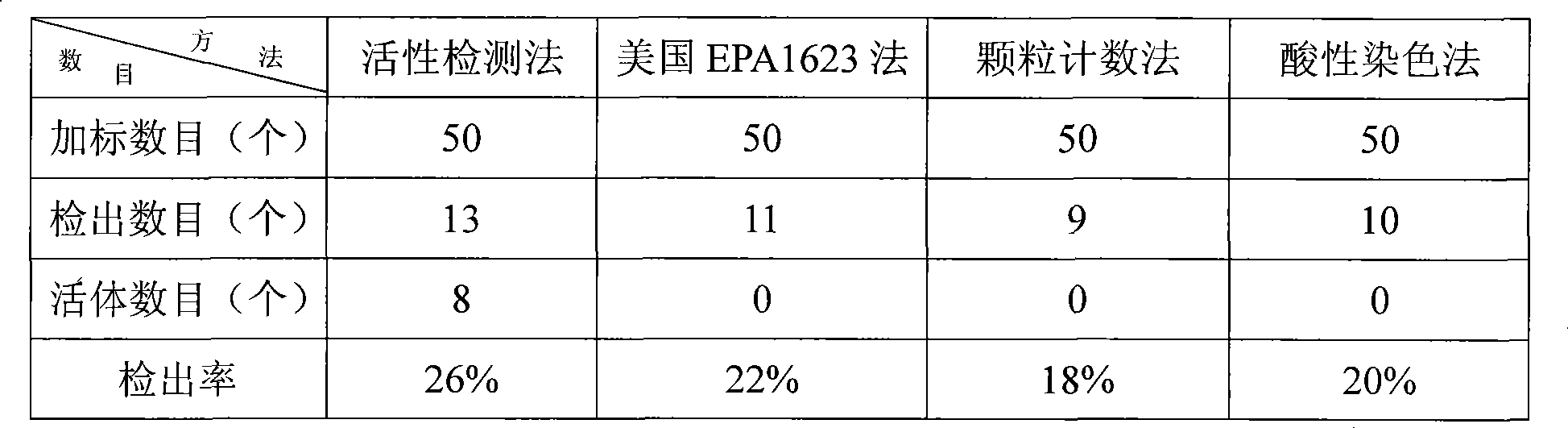
InactiveCN101430281AReduce probabilityHigh precisionMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceSporelingStaining
The invention relates to a method for detecting the activity of cryptosporidium cyst and giardia lamblia sporocyst in drinking water. The method solves the problem that the existing method for detecting the cryptosporidium cyst and the giardia lamblia sporocyst in the drinking water has high cost and low precision and can not confirm the activity of the cryptosporidium cyst and the giardia lamblia sporocyst. The method comprises the steps as follows: 1, water sample pretreatment; 2, elution; 3, condensation; 4 the purification of the cryptosporidium cyst and the giardia lamblia sporocyst; 5, dying; 6, microscopical examination for observing the cryptosporidium cyst and the giardia lamblia sporocyst; and the detection of the cryptosporidium cyst and the giardia lamblia sporocyst in the drinking water is realized. The method does not require complex instrument and equipment; the method is simple and easy for grasping, thereby reducing the investment on the equipment greatly and reducing the detection cost; and the method can detect whether the cryptosporidium cyst and the giardia lamblia sporocyst have the activity or not and has the high precision of detection result.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
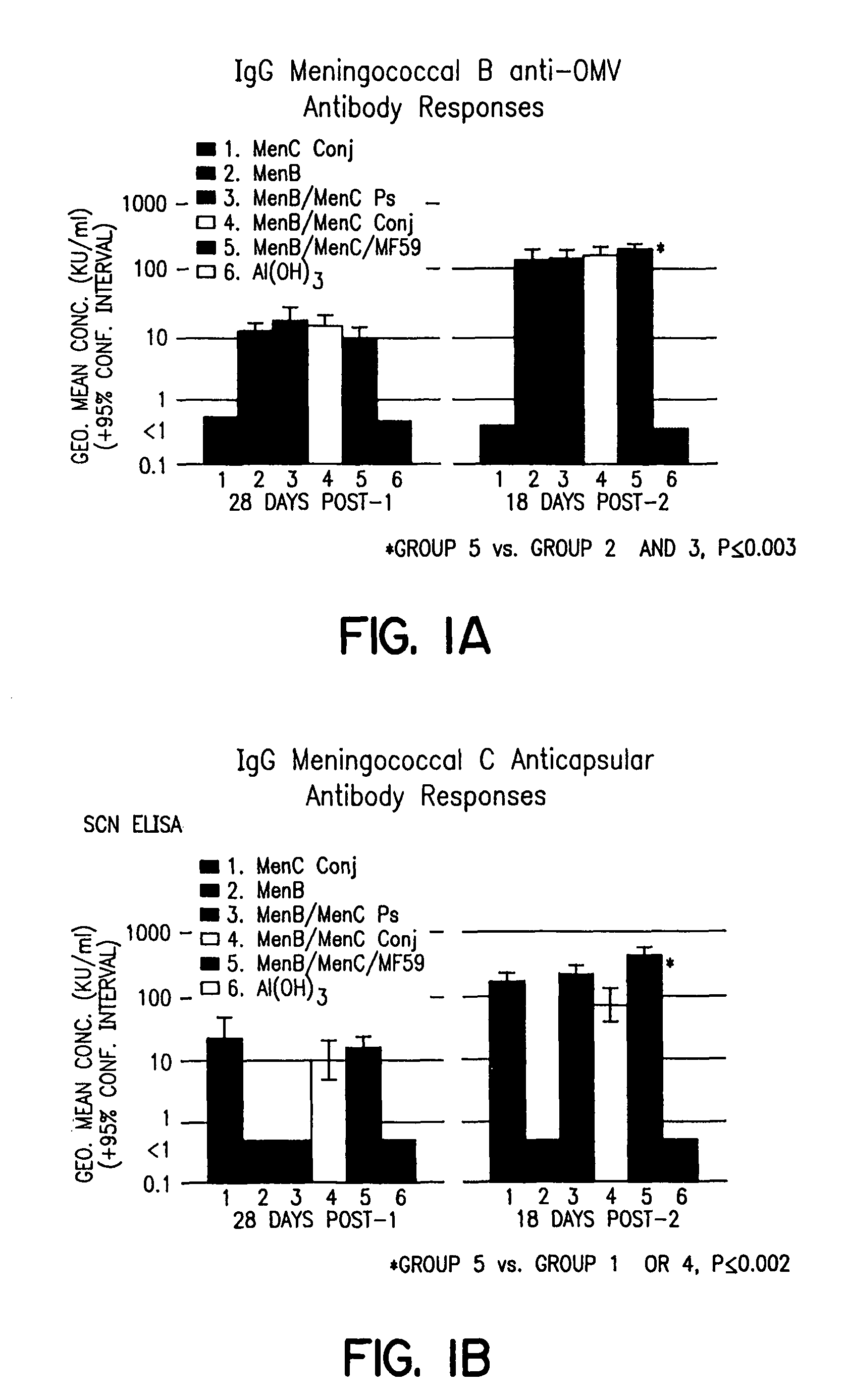
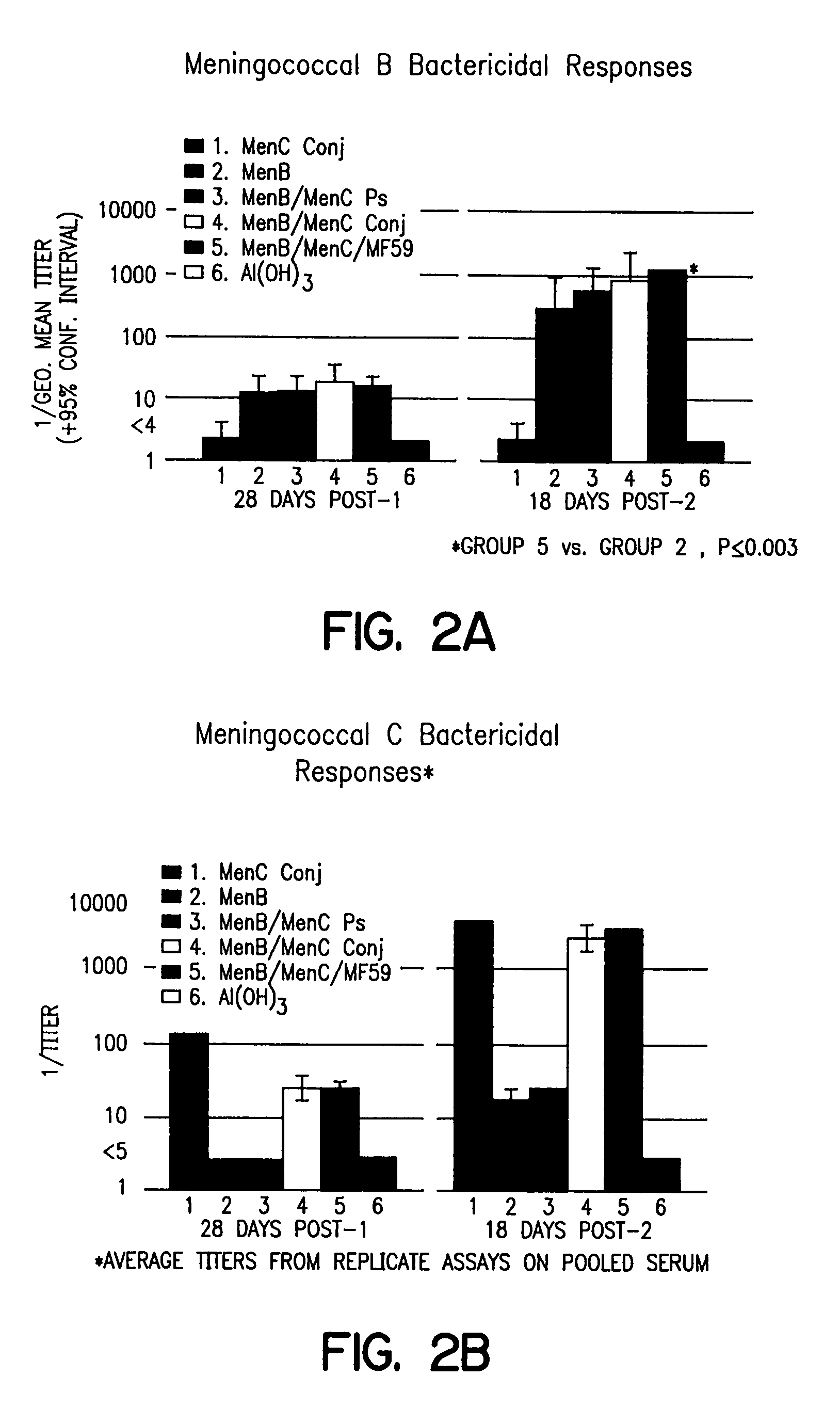
Combination meningitidis B/C vaccines
InactiveUS8007815B1Antibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsLiposome VesicleNeisseria meningitidis
Combination vaccines for treating or preventing Neisseria meningitidis infection are described. The vaccines include Neisseria meningitidis serogroup B proteoliposomic vesicles and Neissera meningitidis serogroup C conjugated oligosaccharides.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG +2
Vesicle guiding immunocyte and application of the same in preparing antineoplastic medicine
The invention provides an immunological active Chinese medicinal composition which comprises effective dose of vesicle oriented immunological cell and medicinal carrier material. The invention also provides a method for preparing the immunological active Chinese medicinal composition, and provides preparation method of vesicle oriented immunological cell. The invention also provides an application of the immunological active Chinese medicinal composition in preparing medicament for resisting tumor, and inhibiting autoimmune disease and / or inhibiting rejection reaction.
Owner:项雯华 +1
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com