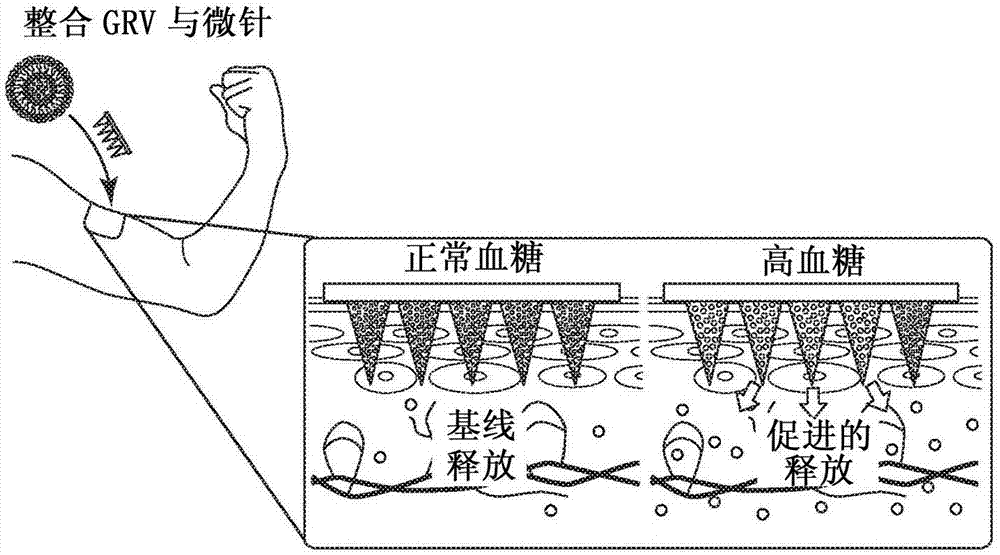
Glucose-responsive insulin delivery system using hyoxia-sensitive nanocomposites
A technology of sensitivity and insulin, applied in the direction of enzyme, drug combination, capsule delivery, etc., can solve the problem of glucose control accompanied by pain
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
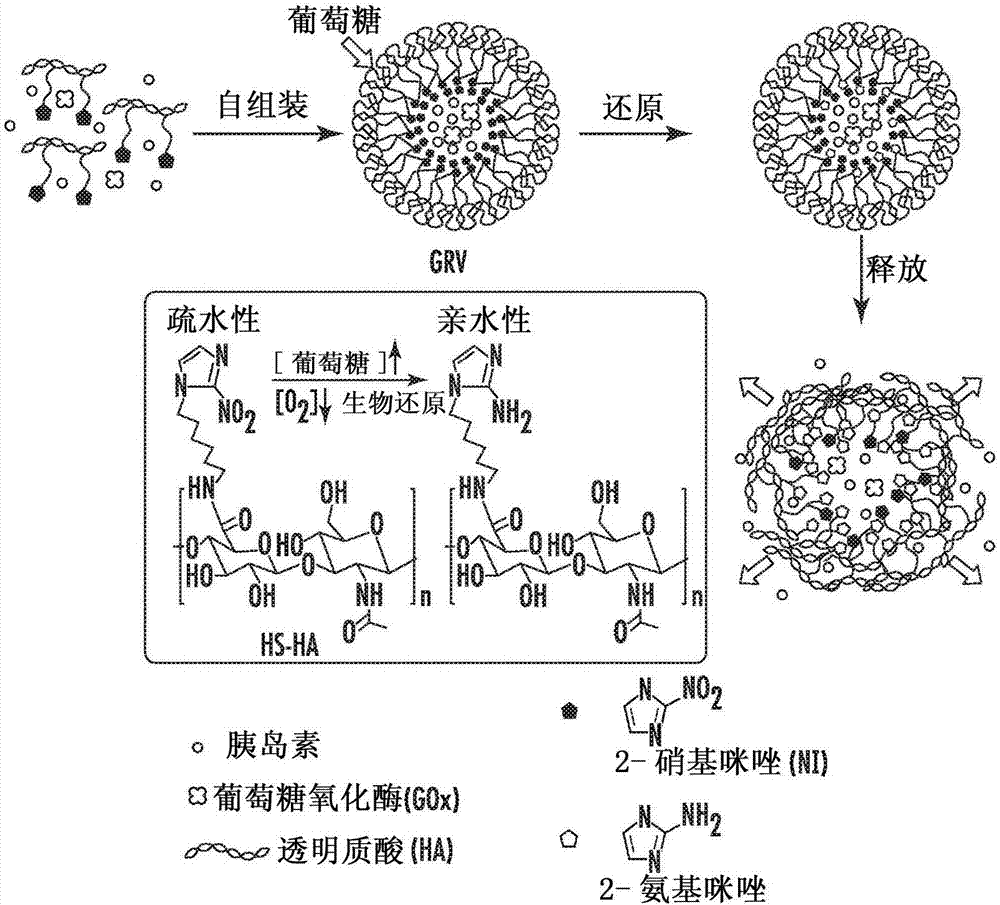
[0223] Representative synthesis of hypoxia-sensitive hyaluronic acid
[0224] Hypoxia-sensitive hyaluronic acid (HS-HA) was synthesized by chemically conjugating HA to 6-(2-nitroimidazole)hexylamine via amide formation. All chemicals were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA) and were used as received unless otherwise stated. Sodium hyaluronate (molecular weight 300 kilodaltons (kDa)) was purchased from Freda Biochem Co., Ltd. (Shandong China).
[0225] First, 6-(2-nitroimidazolium)hexylamine was synthesized for reaction with carboxylic acid of HA. Briefly, nitroimidazole (NI, 0.15 g, 1.3 mmol) was dissolved in DMF, to which was added K 2 CO 3 (0.28 g, 2.0 mmol). Then, 6-(tert-butoxycarbonylamino)hexyl bromide (ie, 6-(BOC-amino)hexyl bromide, 0.39 g, 1.4 mmol) was added dropwise to the solution and stirred at 80°0 for 4 hours. Solid impurities were removed from the reaction mixture by filtration and washed with methanol. The residual solvent was then evaporate...
Embodiment 2
[0229] Synthesis and Characterization of Glucose Responsive Vesicles (GRV)
[0230] GRVs were prepared by self-assembly in aqueous solution. Briefly, 20 mg of amphiphilic HS-HA was dissolved in water / methanol (2 / 1, v / v), followed by the addition of 10 mg of human insulin and 1.0 mg of GOx. Human recombinant insulin (zinc (Zn) salt, 27.5 international units per milligram (IU / mg)) was purchased from Life Technology (Carlsbad, California, United States of America). Place the emulsion at 4°. Stir for 2 hours. Methanol was then removed by dialysis against deionized water for 1 day. The pH of the resulting GRV solution was adjusted to 5.3 (the isoelectric point (pI) of insulin) to remove unloaded insulin by centrifugation at 8,000 rpm for 10 minutes and passed through a centrifugal filter (100,000 Da molecular weight cutoff, Millipore, Billerica, Massachusetts, United States of America) was further filtered at pH 7.4. The final GRV solution was stored at 4°C for subsequent stud...
Embodiment 3
[0234] In vitro glucose-responsive insulin release from GRV
[0235] To assess the glucose responsiveness of GRV, GRV was incubated with 100 μM NADPH and 5 μg / mL cytochrome c reductase in 600 μL PBS buffer (NaCl, 137 mM; KCl, 2.7 mM; NaCl, 2.7 mM; 2 HPO 4 , 10mM; KH 2 PO 4 , 2mM; pH 7.4). Different amounts of glucose were added to provide solutions with a final glucose concentration of 0 mg / dL, 100 mg / dL or 400 mg / dL. The 400 mg / dL glucose concentration solution represents a typical hyperglycemic glucose level, the 100 mg / dL glucose concentration solution represents a normoglycemic glucose level, and the 0 mg / dL glucose concentration solution is used as a control. The mixture was incubated at 37°7 in a vessel with an oxygen concentration of 21% by adjusting with a mass flow meter. At predetermined times, the pH of each mixture was recorded using a pH meter (AB15, Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, Massachusetts, United States of America), and then adjusted to the pI ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com