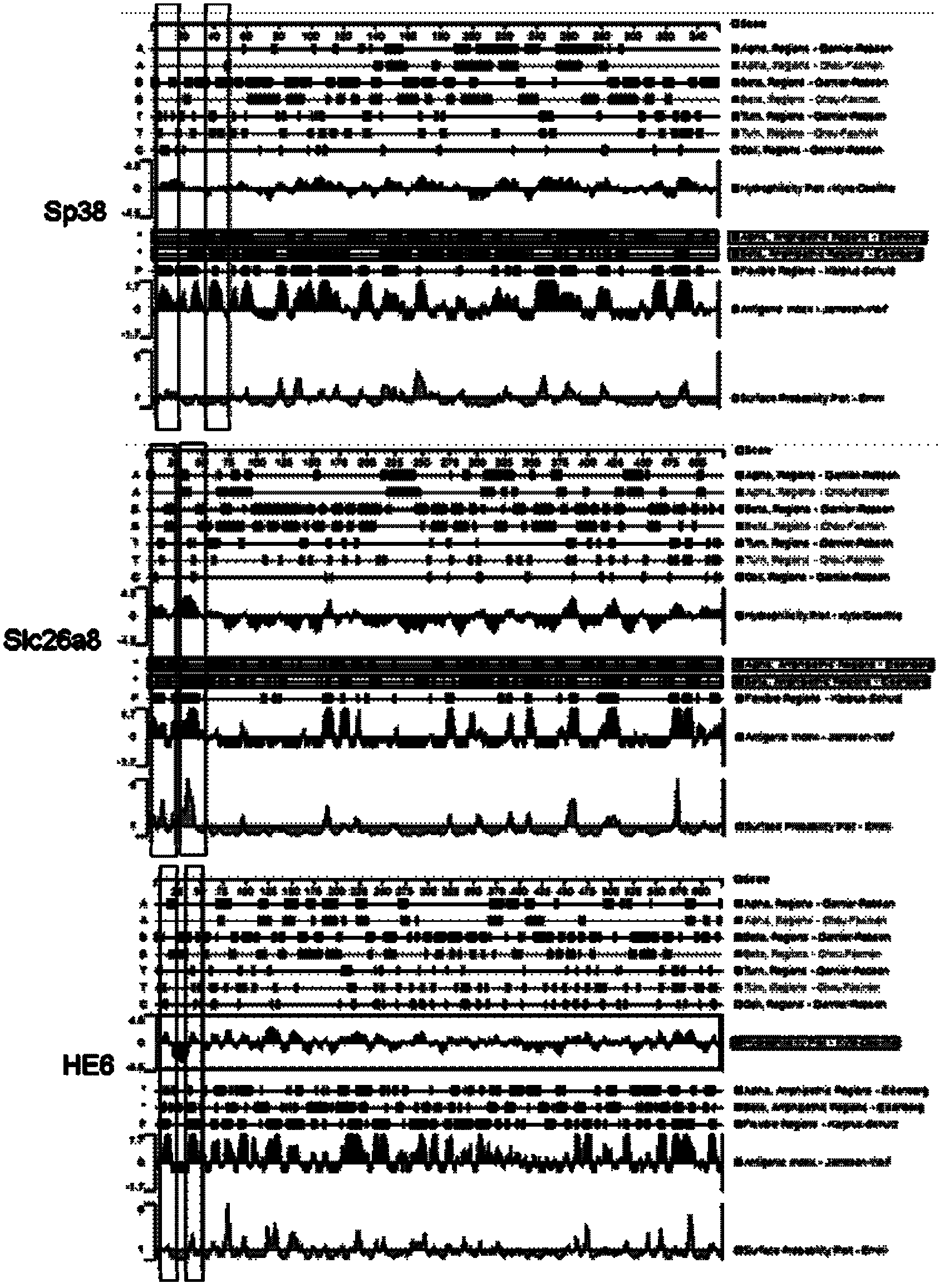
Patents
Literature
44 results about "Mixed group" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Mixed Group. Jump to navigation Jump to search. Mixed Group (Italian: Gruppo Misto, GM) is a parliamentary group active in both houses of the Italian Parliament, the Chamber of Deputies and the Senate. The groups comprise all the deputies and the senators, respectively, who are not members of any other parliamentary group.
Microfluidic particle-analysis systems
ActiveUS7312085B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsReady to useMixed group
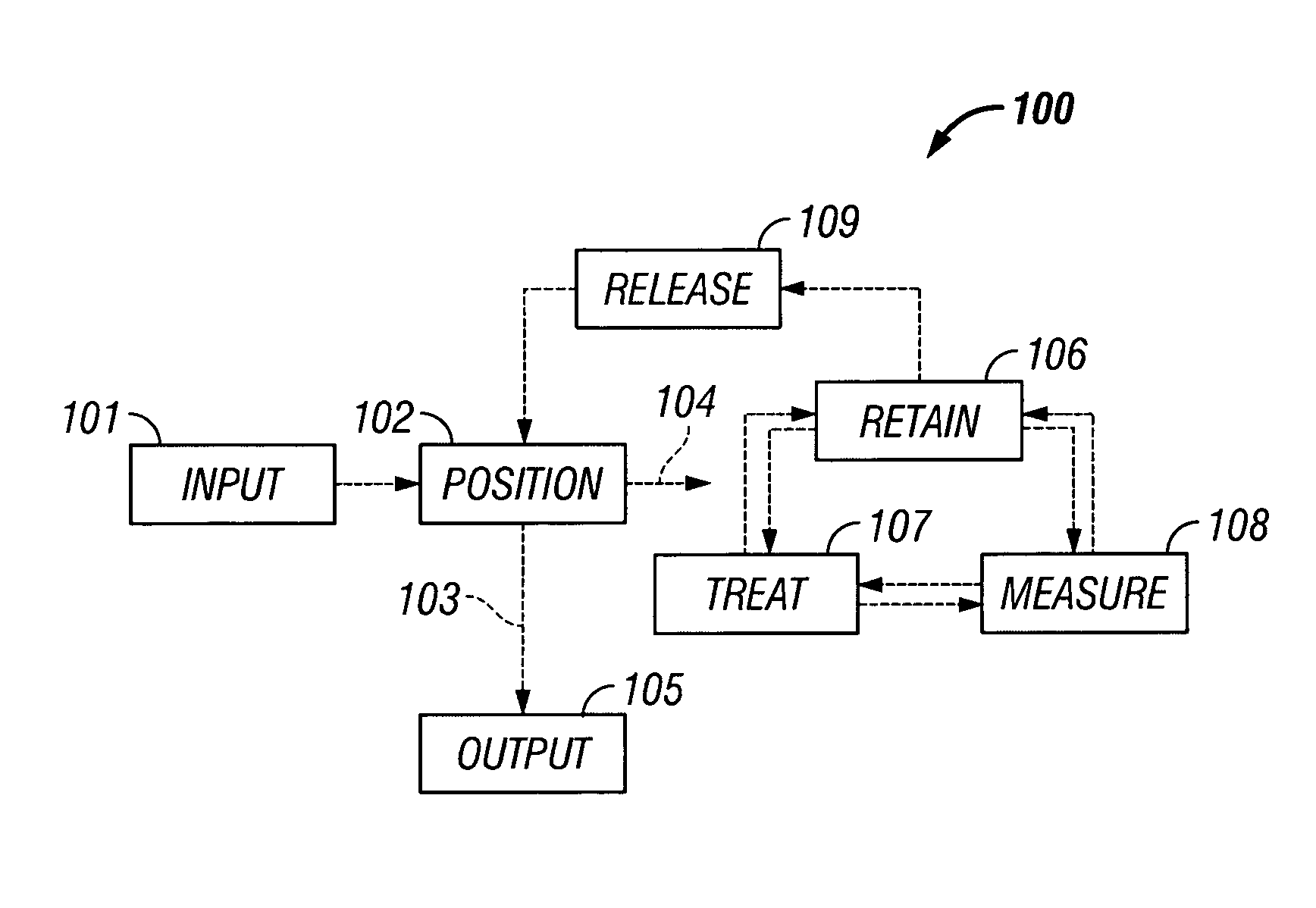
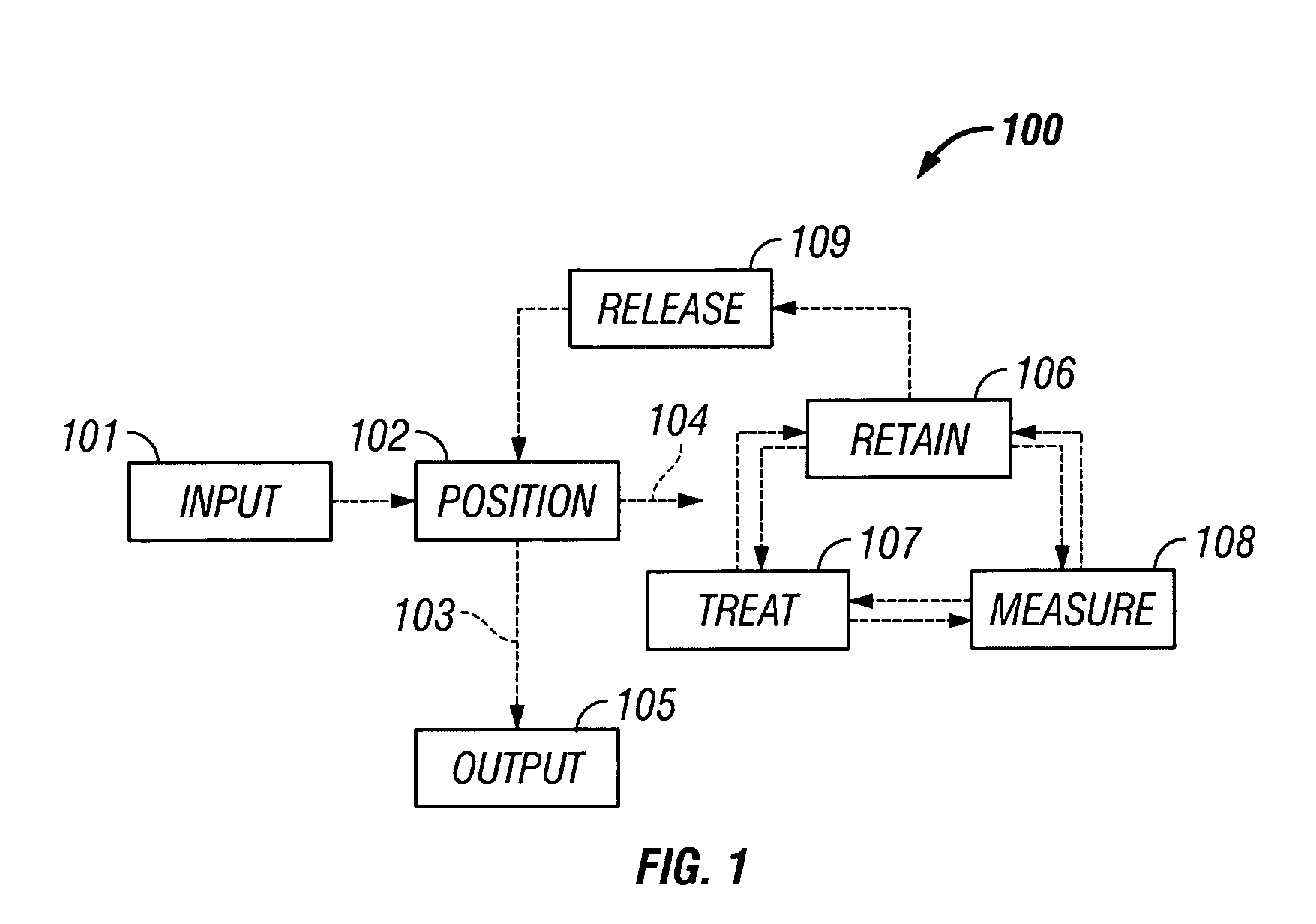
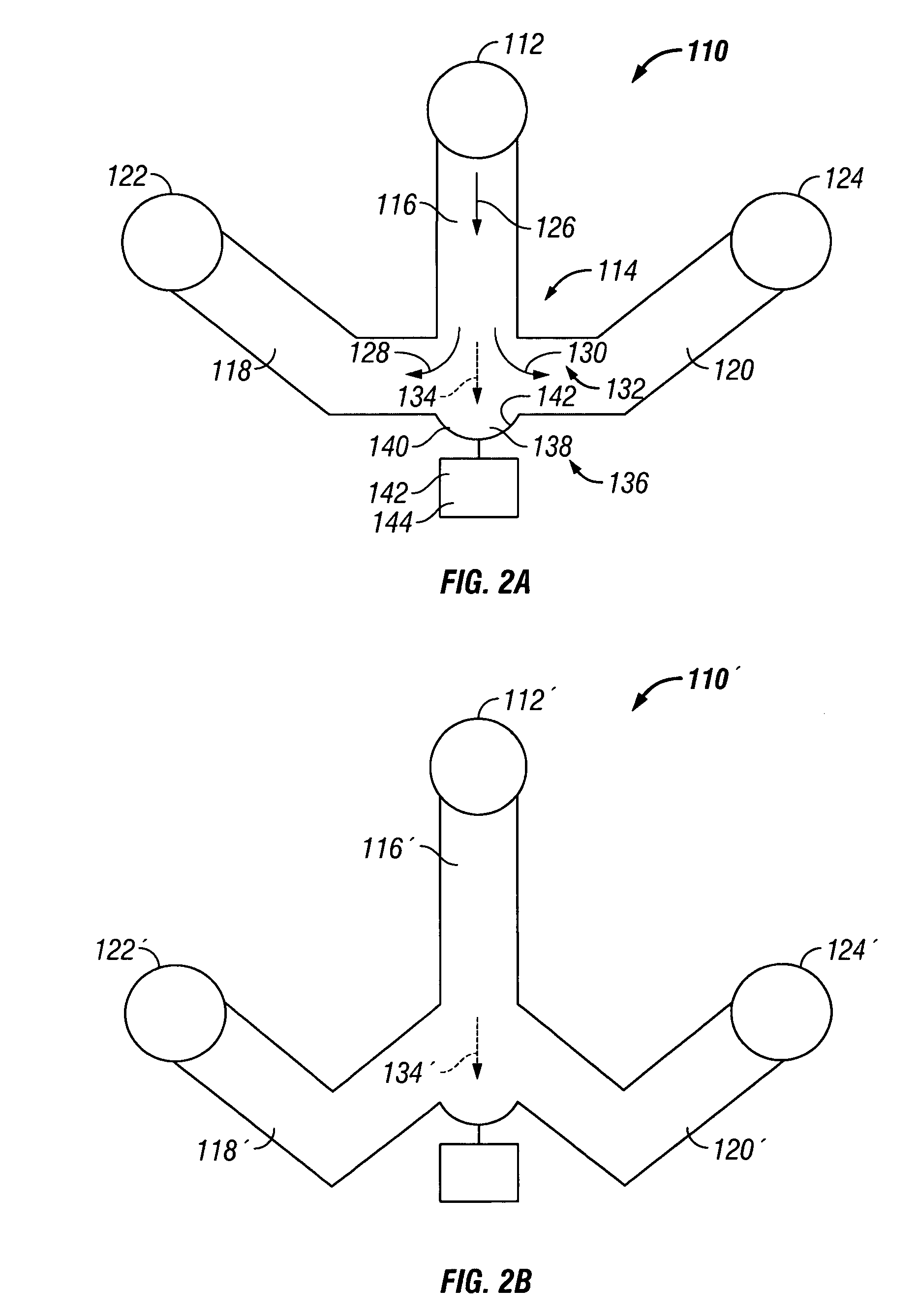
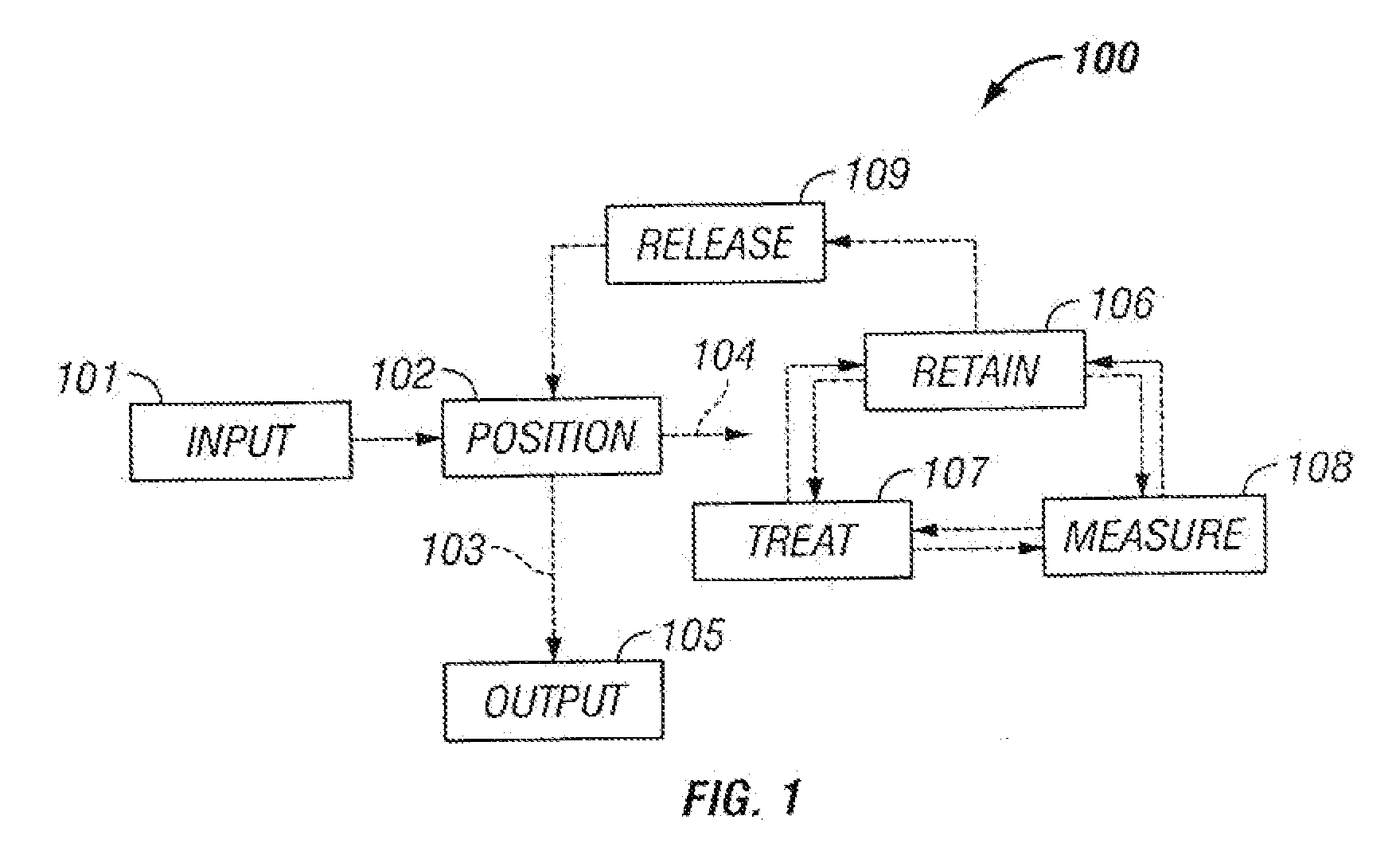
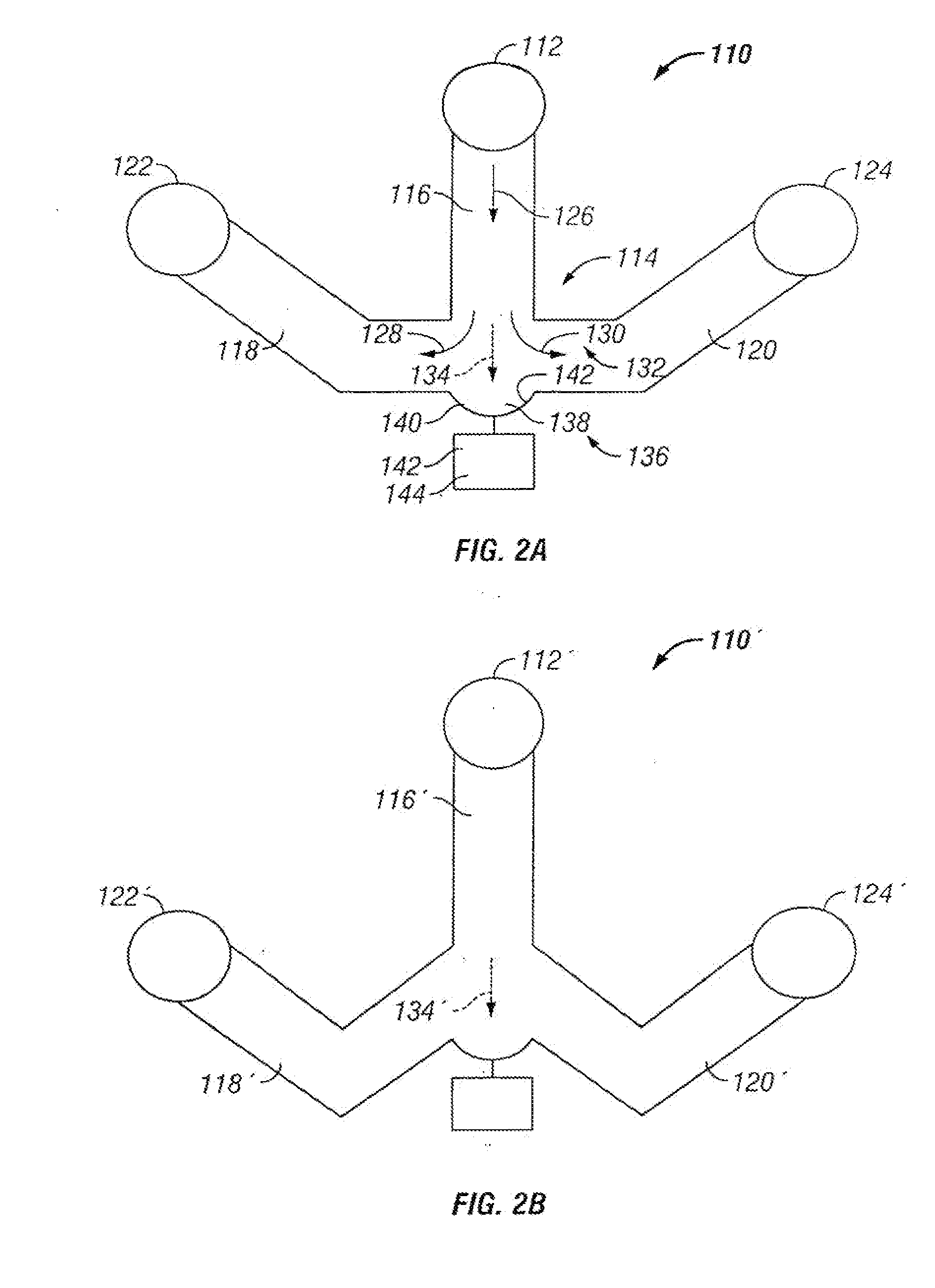
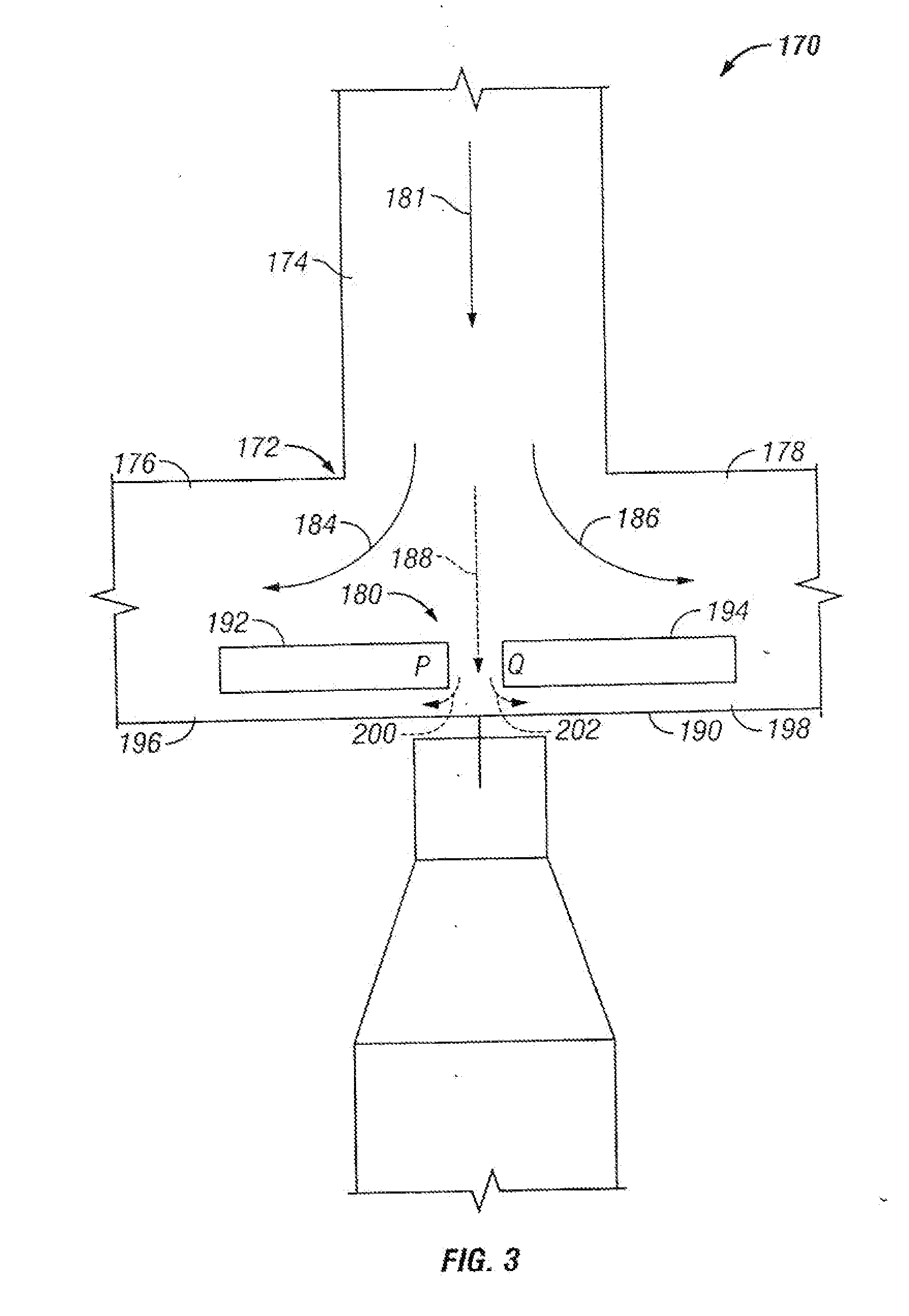
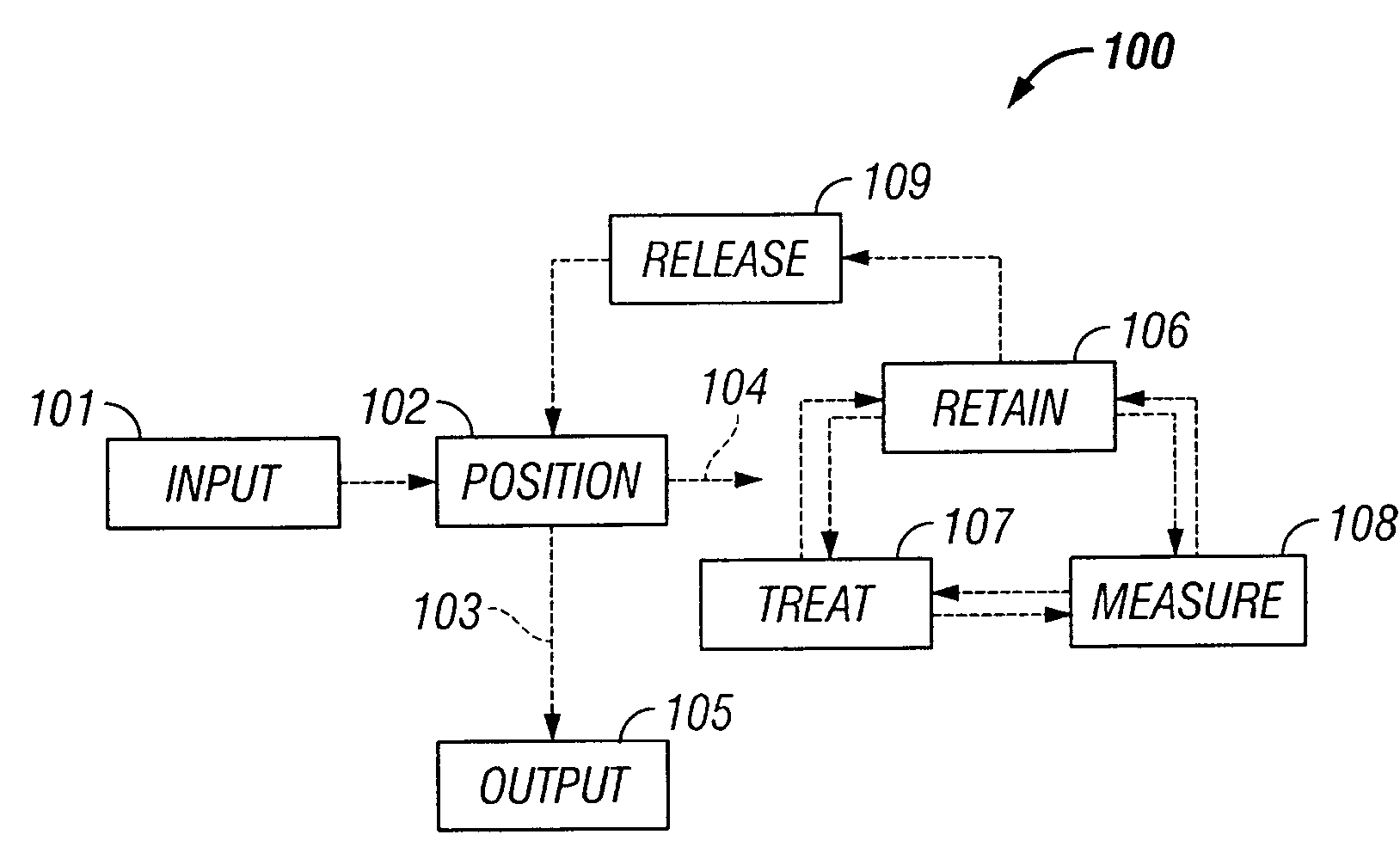
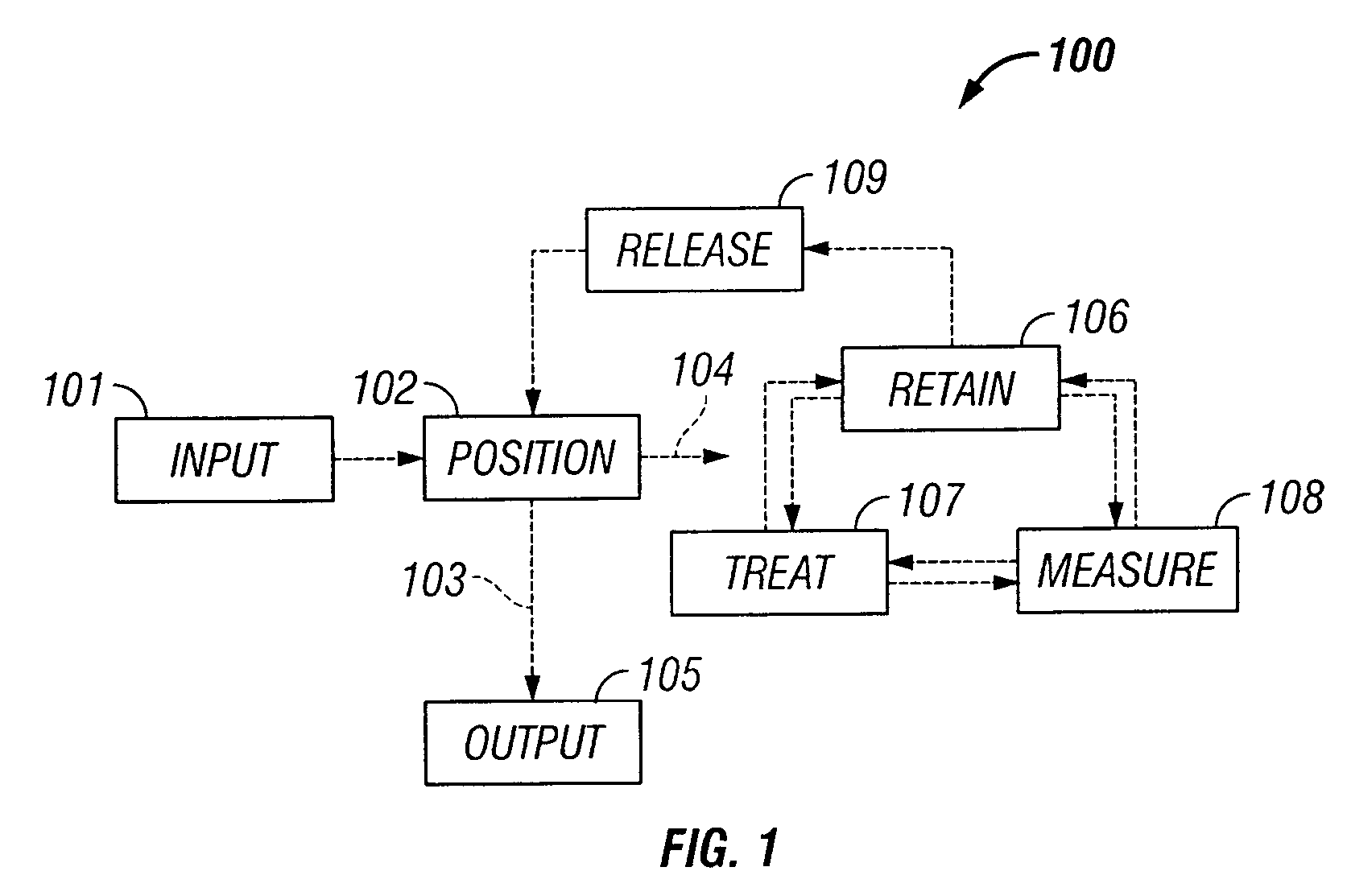
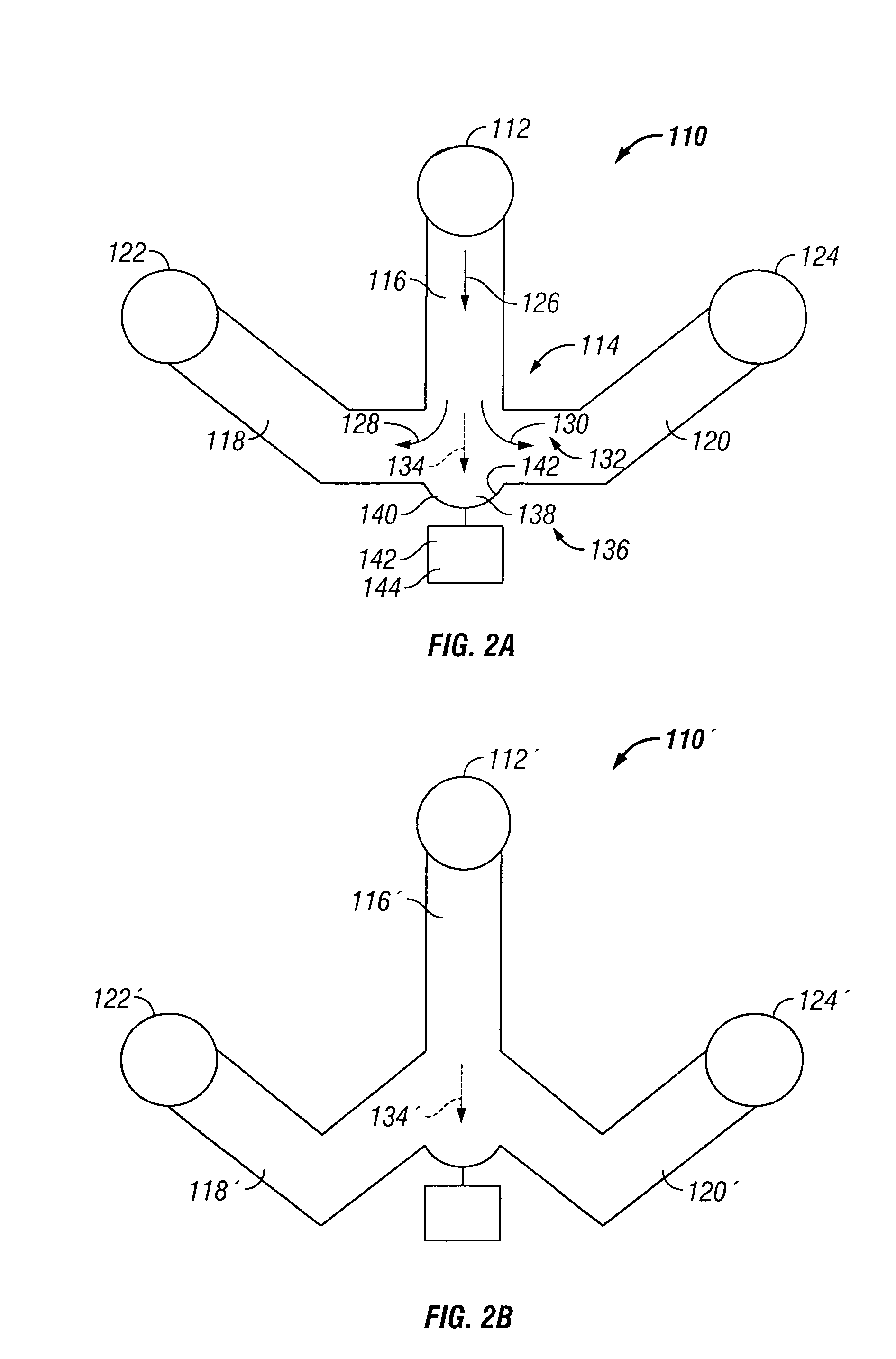
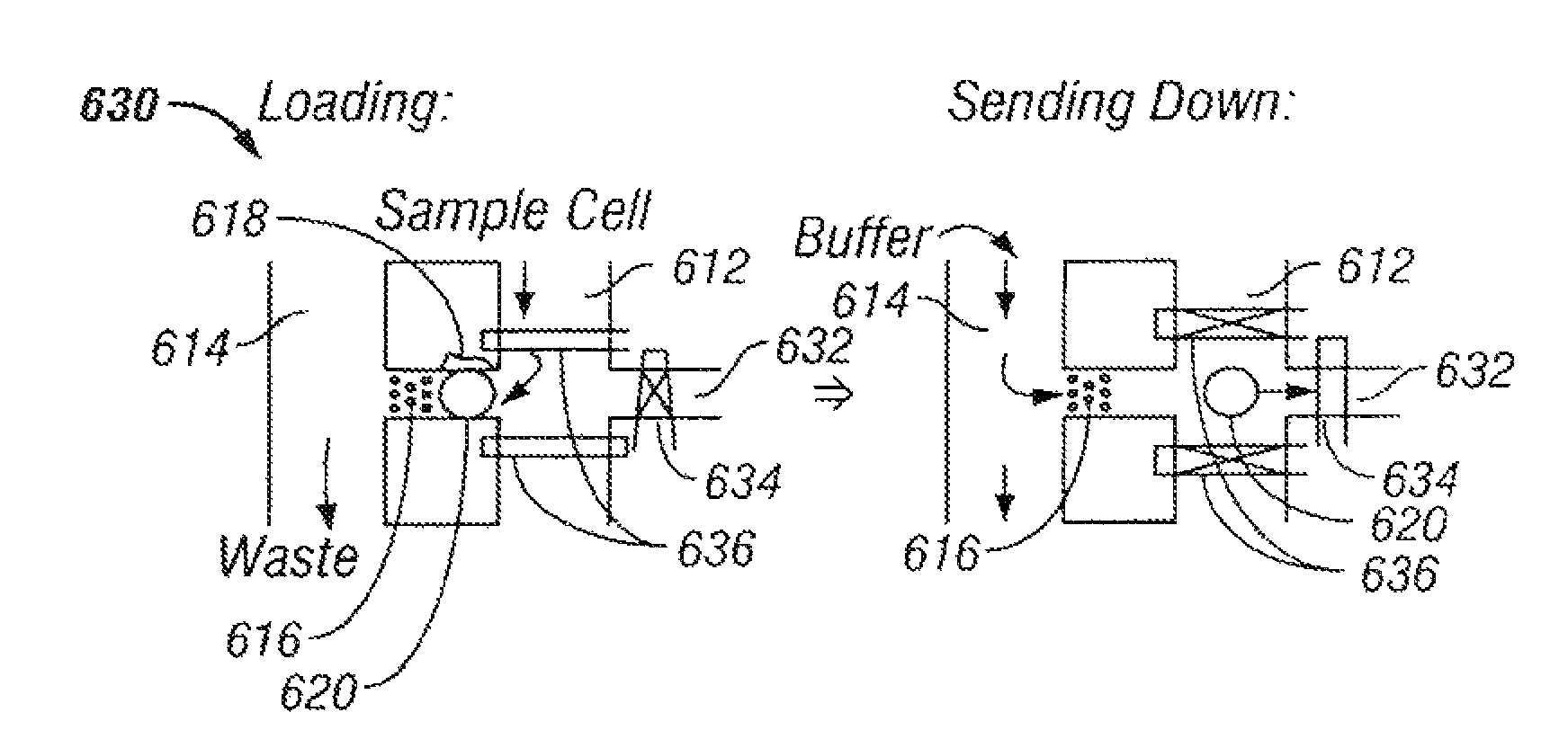
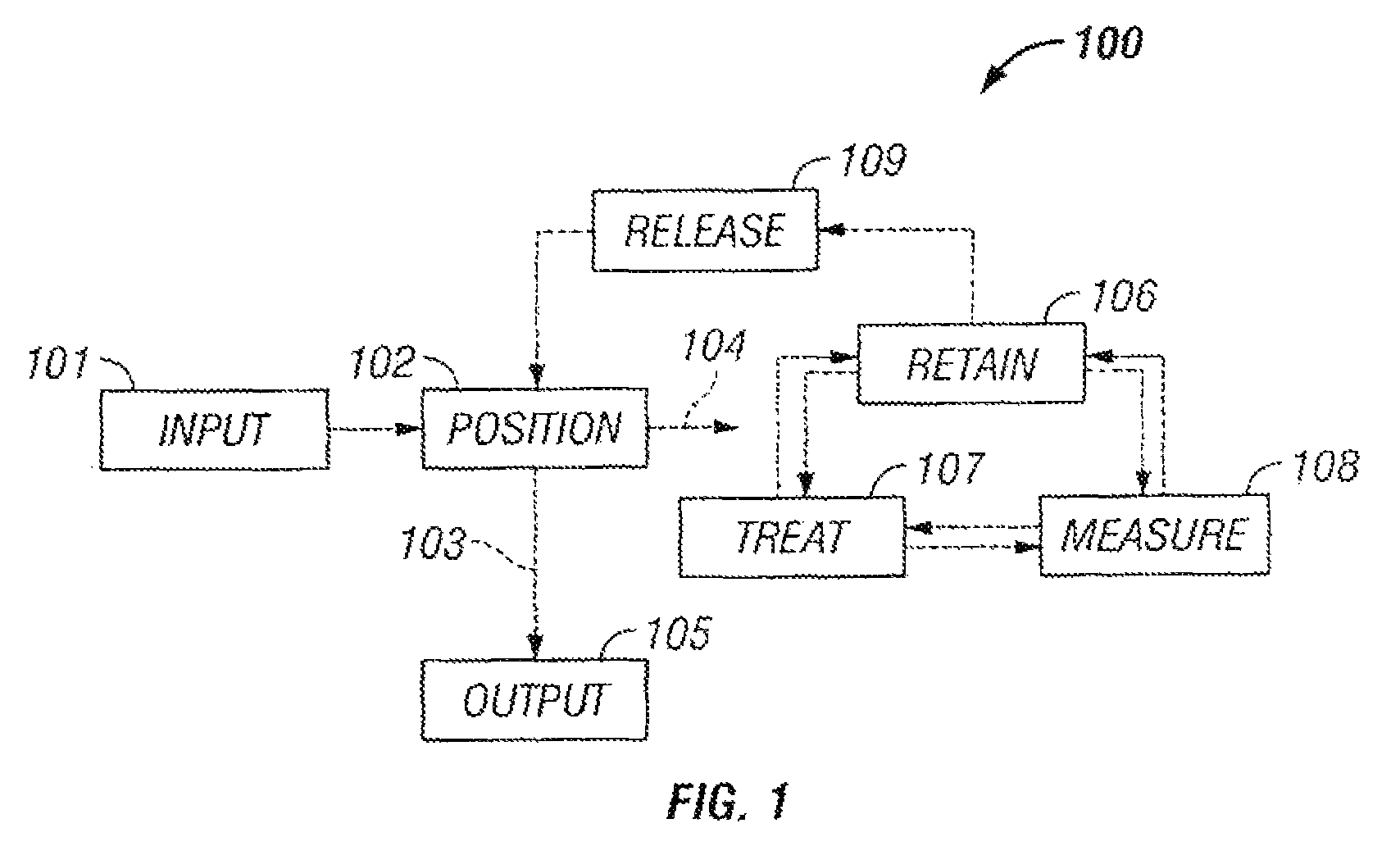
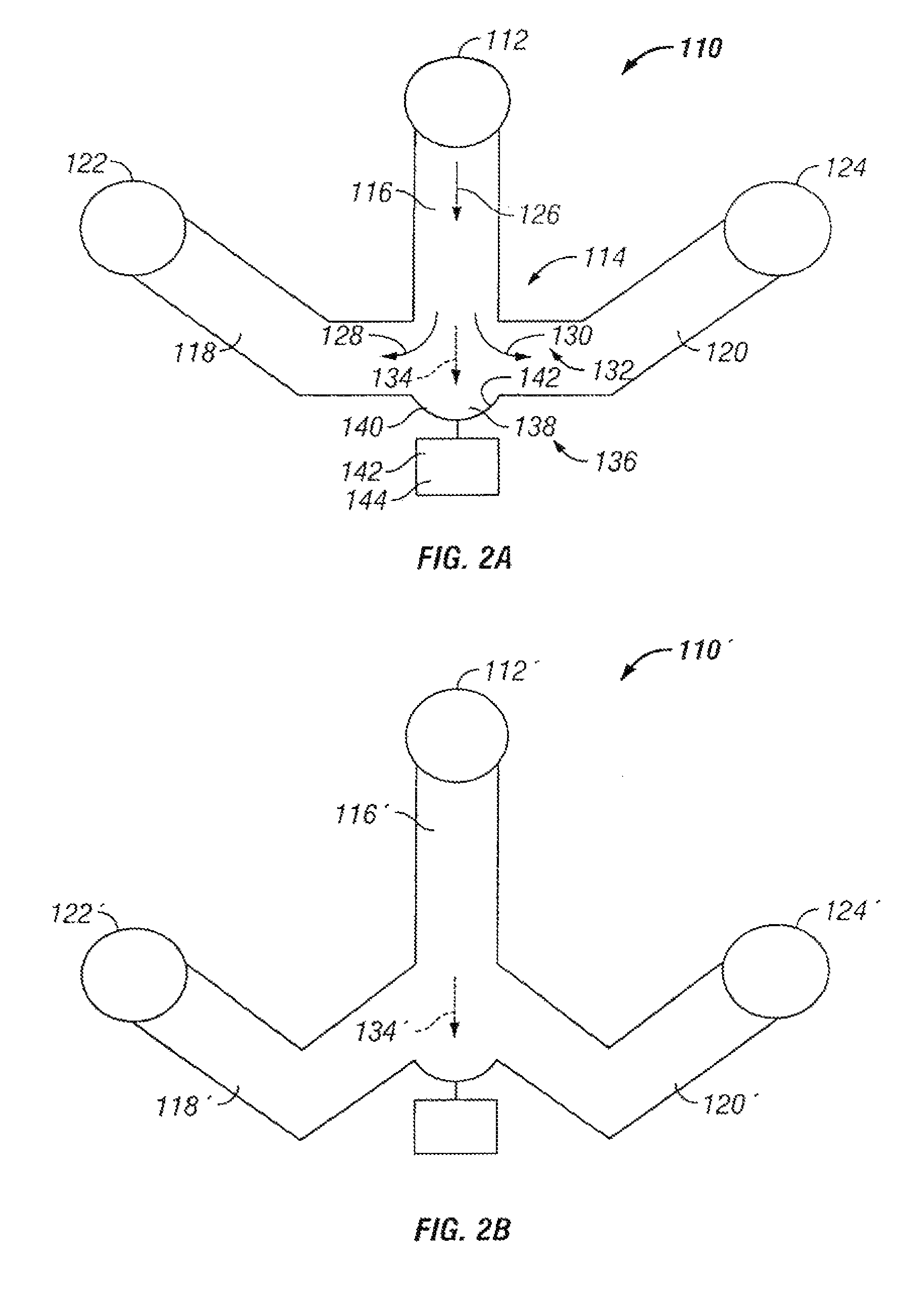
The invention provides systems, including apparatus, methods, and kits, for the microfluidic manipulation and / or detection of particles, such as cells and / or beads. The invention provides systems, including apparatus, methods, and kits, for the microfluidic manipulation and / or analysis of particles, such as cells, viruses, organelles, beads, and / or vesicles. The invention also provides microfluidic mechanisms for carrying out these manipulations and analyses. These mechanisms may enable controlled input, movement / positioning, retention / localization, treatment, measurement, release, and / or output of particles. Furthermore, these mechanisms may be combined in any suitable order and / or employed for any suitable number of times within a system. Accordingly, these combinations may allow particles to be sorted, cultured, mixed, treated, and / or assayed, among others, as single particles, mixed groups of particles, arrays of particles, heterogeneous particle sets, and / or homogeneous particle sets, among others, in series and / or in parallel. In addition, these combinations may enable microfluidic systems to be reused. Furthermore, these combinations may allow the response of particles to treatment to be measured on a shorter time scale than was previously possible. Therefore, systems of the invention may allow a broad range of cell and particle assays, such as drug screens, cell characterizations, research studies, and / or clinical analyses, among others, to be scaled down to microfluidic size. Such scaled-down assays may use less sample and reagent, may be less labor intensive, and / or may be more informative than comparable macrofluidic assays.
Owner:STANDARD BIOTOOLS INC
Microfluidic particle-analysis systems
InactiveUS20100120077A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAssayMixed group
The invention provides systems, including apparatus, methods, and kits, for the microfluidic manipulation and / or detection of particles, such as cells and / or beads. The invention provides systems, including apparatus, methods, and kits, for the microfluidic manipulation and / or analysis of particles, such as cells, viruses, organelles, beads, and / or vesicles. The invention also provides microfluidic mechanisms for carrying out these manipulations and analyses. These mechanisms may enable controlled input, movement / positioning, retention / localization, treatment, measurement, release, and / or output of particles. Furthermore, these mechanisms may be combined in any suitable order and / or employed for any suitable number of times within a system. Accordingly, these combinations may allow particles to be sorted, cultured, mixed, treated, and / or assayed, among others, as single particles, mixed groups of particles, arrays of particles, heterogeneous particle sets, and / or homogeneous particle sets, among others, in series and / or in parallel. In addition, these combinations may enable microfluidic systems to be reused. Furthermore, these combinations may allow the response of particles to treatment to be measured on a shorter time scale than was previously possible. Therefore, systems of the invention may allow a broad range of cell and particle assays, such as drug screens, cell characterizations, research studies, and / or clinical analyses, among others, to be scaled down to microfluidic size. Such scaled-down assays may use less sample and reagent, may be less labor intensive, and / or may be more informative than comparable macrofluidic assays.
Owner:STANDARD BIOTOOLS INC
Microfluidic particle-analysis systems
InactiveUS7452726B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMixed groupScale down
The invention provides systems, including apparatus, methods, and kits, for the microfluidic manipulation and / or detection of particles, such as cells and / or beads. The invention provides systems, including apparatus, methods, and kits, for the microfluidic manipulation and / or analysis of particles, such as cells, viruses, organelles, beads, and / or vesicles. The invention also provides microfluidic mechanisms for carrying out these manipulations and analyses. These mechanisms may enable controlled input, movement / positioning, retention / localization, treatment, measurement, release, and / or output of particles. Furthermore, these mechanisms may be combined in any suitable order and / or employed for any suitable number of times within a system. Accordingly, these combinations may allow particles to be sorted, cultured, mixed, treated, and / or assayed, among others, as single particles, mixed groups of particles, arrays of particles, heterogeneous particle sets, and / or homogeneous particle sets, among others, in series and / or in parallel. In addition, these combinations may enable microfluidic systems to be reused. Furthermore, these combinations may allow the response of particles to treatment to be measured on a shorter time scale than was previously possible. Therefore, systems of the invention may allow a broad range of cell and particle assays, such as drug screens, cell characterizations, research studies, and / or clinical analyses, among others, to be scaled down to microfluidic size. Such scaled-down assays may use less sample and reagent, may be less labor intensive, and / or may be more informative than comparable macrofluidic assays.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
Microfluidic particle-analysis systems
InactiveUS8658418B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAssayMixed group
The invention provides systems, including apparatus, methods, and kits, for the microfluidic manipulation and / or detection of particles, such as cells and / or beads. The invention provides systems, including apparatus, methods, and kits, for the microfluidic manipulation and / or analysis of particles, such as cells, viruses, organelles, beads, and / or vesicles. The invention also provides microfluidic mechanisms for carrying out these manipulations and analysis. These mechanisms may enable controlled input, movement / positioning, retention / localization, treatment, measurement, release, and / or output of particles. Furthermore, these mechanisms may be combined in any suitable order and / or employed for any suitable number of times within a system. Accordingly, these combinations may allow particles to be sorted, cultured, mixed, treated, and / or assayed, among others, as single particles, mixed groups of particles, arrays of particles, heterogeneous particle sets, and / or homogeneous particle sets, among others, in series and / or in parallel. In addition, these combinations may enable microfluidic systems to be reused. Furthermore, these combinations may allow the response of particles to treatment to be measured on a shorter time scale than was previously possible. Therefore, systems of the invention may allow a broad range of cell and particle assays, such as drug screens, cell characterizations, research studies, and / or clinical analysis, among others, to be scaled down to microfluidic size. Such scaled-down assays may use less sample and reagent, may be less labor intensive, and / or may be more informative than comparable macrofluidic assays.
Owner:STANDARD BIOTOOLS INC
Heavy-metal-polluted acidic soil repairing material as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102329620ARaise the pHReduced bioavailabilityAgriculture tools and machinesOther chemical processesSodium BentoniteSlag
The invention discloses a heavy-metal-polluted acidic soil repairing material as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The repairing material is prepared from the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 10-20% of biomass electric power plant ash, 10-20% of slag powder, 10-30% of steel slag powder, 5-10% of fly ash and 25-50% of bentonite by uniformly mixing in a dry powder state. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: firstly, drying the raw materials until the water content is smaller than or equal to 1%; then, respectively weighing the raw materials according to the percentage by weight; and finally, uniformly stirring. The in-situ repairing of heavy-metal-polluted acidic soil is achieved by covering a layer of repairing material on the soil surface, uniformly mixing the soil surface layer with the repairing material in plowing and stirring modes, and detecting the contents of Cd, Pb, Cr, Cu, Zn, Mn, Hg, As and Ni in the repaired soil and the soil pH value after 3-6 months until meeting the requirements of the second-level soil environment quality standard in GB15618-1995.
Owner:WUHAN KAIDI ENG TECH RES INST CO LTD
Resin plastic wood and its manufacturing method
InactiveCN102286193AStable structureLow costPolyethylene terephthalate glycolPolyethylene terephthalate
The present invention relates to a resin plastic wood and its manufacturing method. The resin plastic wood is made by extrusion molding and injection molding of a mixture, and the mixture contains a wood powder mixed in a predetermined ratio. Components, a plastic component, a compatibilizer component and a modifier component, the plastic component includes a first plastic and a second plastic mixed in a predetermined ratio, the first plastic is poly Ethylene phthalate (PET). By mixing PET and wood powder components, a relatively small amount of wood powder components can be combined with plastic components, and combined with the characteristics of PET's easy processing and molding, plastic wood with a predetermined shape can be smoothly produced, and better The wood-like texture, plus the easy recycling of PET plastics, makes the resin-plastic wood of the present invention also have the characteristics of low cost and environmental protection.
Owner:PLASTICS INDUSTRY DEVELOPMENT CENTER
Hybrid power supply and technology of electric motorcar
InactiveCN102347631AReduce the number of configurationsAvoid impact damageElectrical storage systemBatteries circuit arrangementsElectrical batteryElectric cars
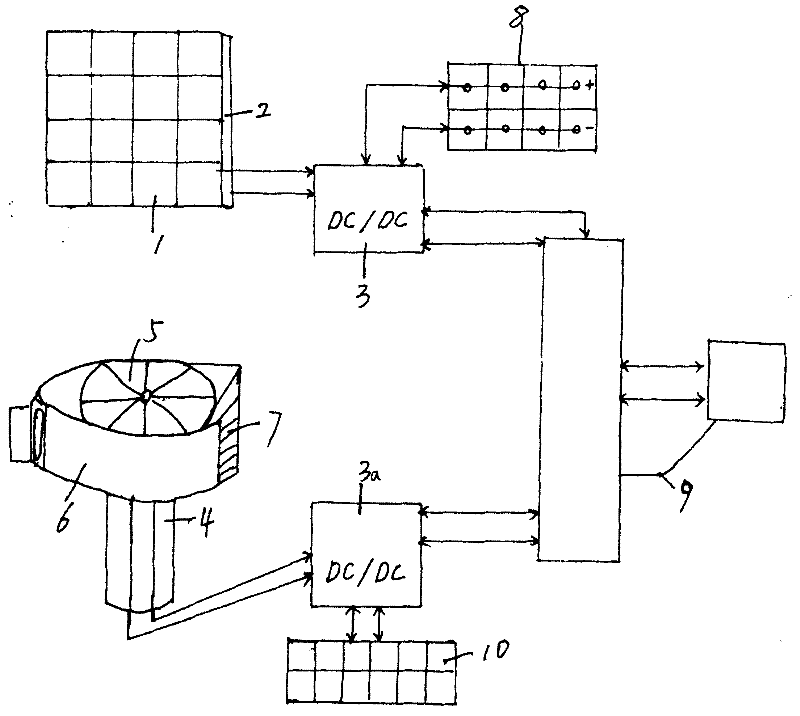
The invention provides a hybrid power supply and a technology of an electric motorcar. The hybrid power supply consists of four parts, i.e. a solar battery, a wind turbine, a super charging capacitor and a storage battery which are grouped in a mixing way. The solar battery and the wind turbine are a power generation power supply unit; and the super charging capacitor and the storage battery are a power storage power supply unit; with the adoption of the combination, the power supply system overcomes the disadvantages that the power storage function of various electric motorcars is single, the storage capacity is small, dynamic charging cannot be performed, the driving range is short and the electric motorcar is charged frequently. With the adoption of the mixed grouping design of reproducible energy dynamic power supply and stored static power supply, the configuration quantity of the storage battery of the electric motorcar can be reduced, the overall weight and space in the car can be reduced, the complementing time of traditional electrical energy can be reduced, and the traveling power and speed of a vehicle can be increased.
Owner:大庆市海丰能源技术研究有限公司
Triarylsulfonium salt as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103274978AHigh reactivityExcellent surface curingOrganic chemistryEpoxy resin coatingsSolubilityUltraviolet absorption
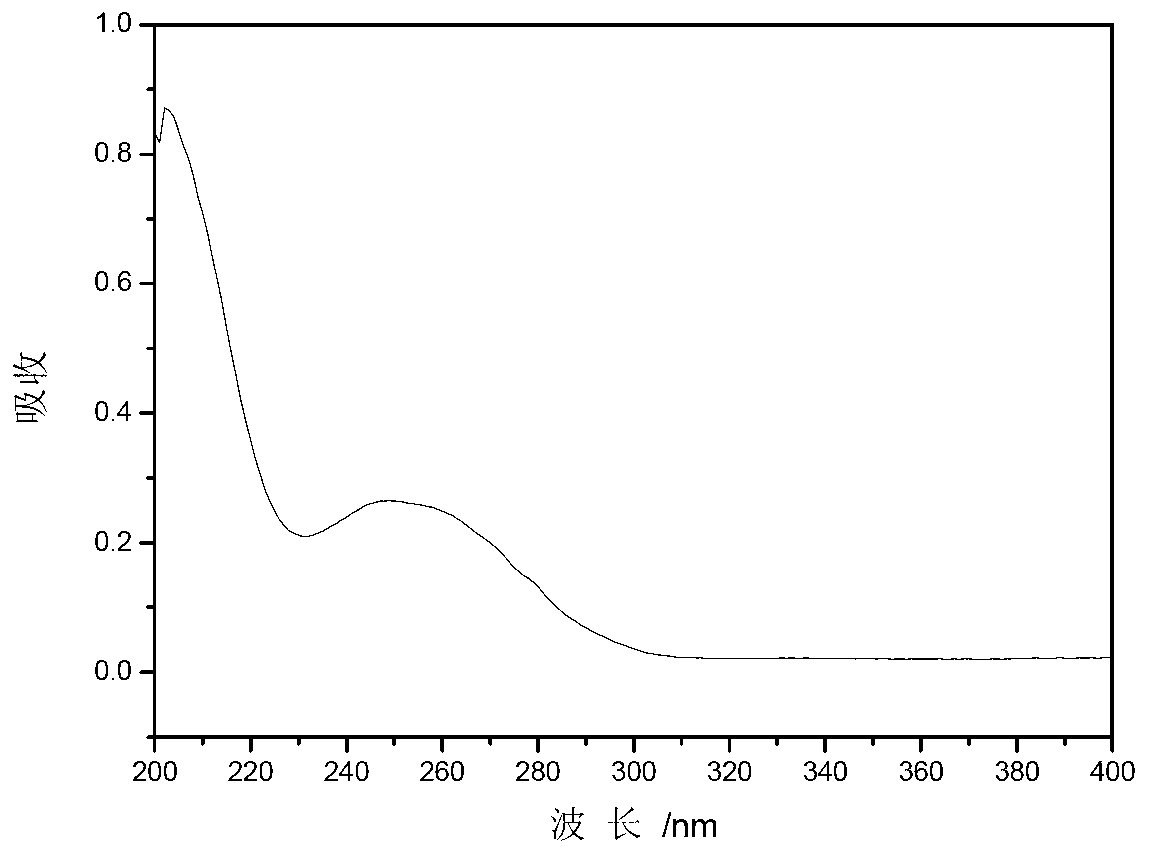
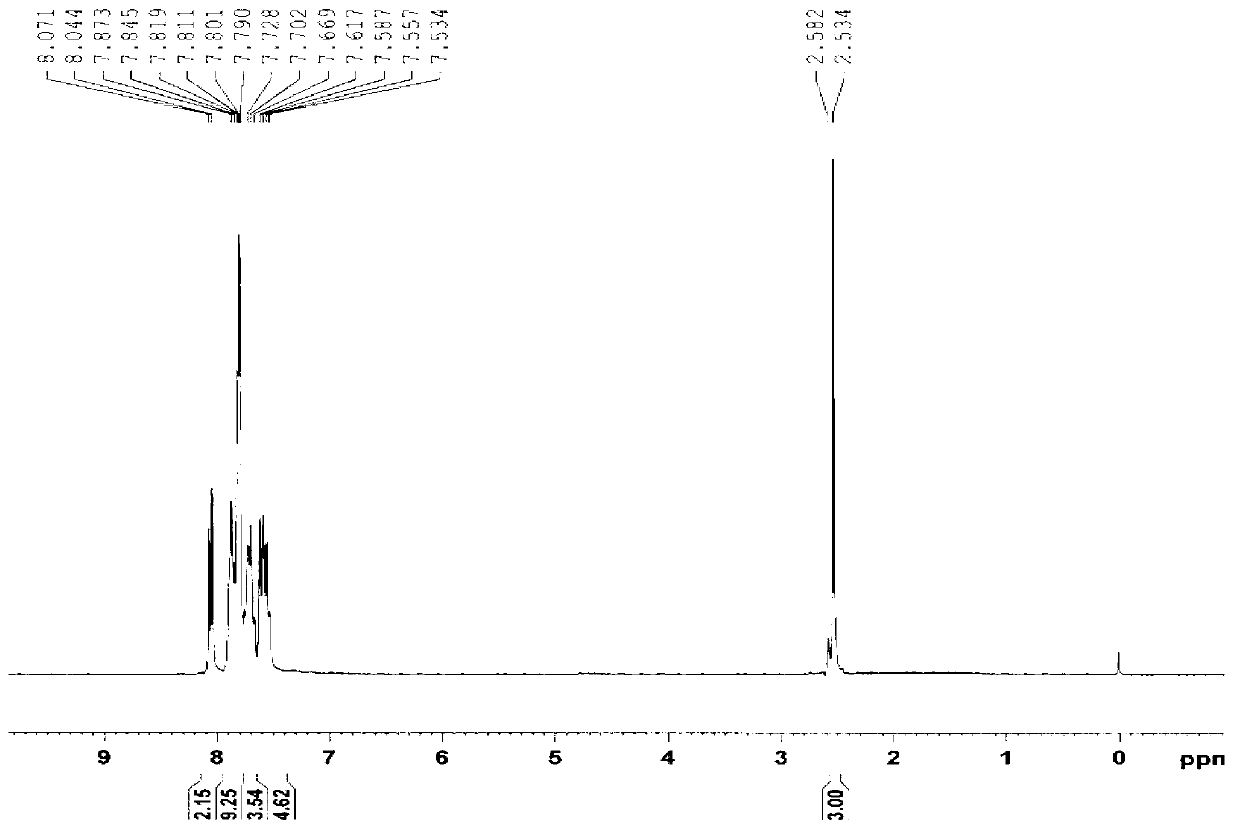
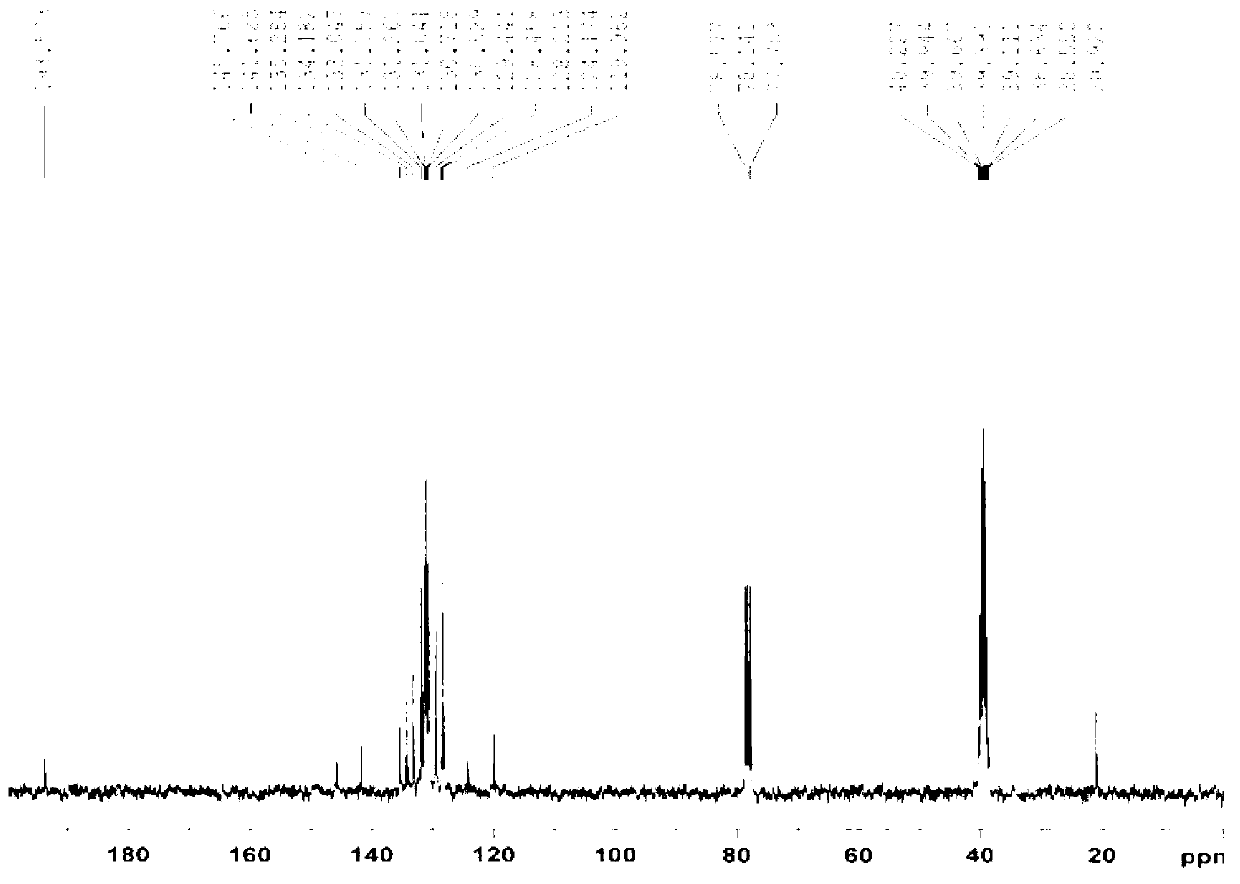
The invention discloses a triarylsulfonium salt with a benzophenone framework as well as a preparation method and application of the triarylsulfonium salt. According to the method, 4-benzoyl-4'-methyl-diphenyl sulfide (BMS) is used as a raw material to react with a diaryliodonium salt under the copper-catalyzed condition to prepare the triarylsulfonium salt; and the maximum ultraviolet absorption wavelength range of the compound can be shifted to 250nm, and meanwhile, the ultraviolet absorption wavelength range is widened due to the existence of free radicals and cation ion initiating groups. The prepared triarylsulfonium salt can be used as a photoinitiator for an ultraviolet photo-cured compound and particularly for an ultraviolet photo-cured coating, and has favorable reaction activity, surface curing capability and solubility; and the mixed groups exist in a molecule to ensure that the molecule is relatively stable, so that the light inhibiting performance is effectively improved.
Owner:山西亮龙涂料有限公司
Molecular marking method for distinguishing Jian carps
InactiveCN101974649AAvoid Germplasm MixingMicrobiological testing/measurementResearch ObjectWild type
The invention relates to a molecular marking method for distinguishing Jian carps, which comprises the following steps of: selecting a mixed group of the selfing F1 generation of Jian carps and the hybridization F1 generation of Yellow river carp male parent and Jian carp female parent as a research object, randomly selecting 48 carps, respectively sampling blood, and respectively extracting a DNA sample by using a DNA extraction method; carrying out PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification by using IGF2a gene intron 2, and taking the extracted DNA sample of the mixed group as a template; detecting the amplified PCR product as 693bp through electrophoresis, and sequencing to obtain the amplified nucleotide sequence; and comparing the sequences according to the result of given wile type basic group C and mutant type basic group CA for contrast after the nucleotide sequence is obtained, and judging the comparison result. The invention has the advantages of separating germ plasm from Jian carps, Yellow river carps and the forward hybridization F1 generation of Jian carps, providing a reference path for treating river germ plasm mixed hybridization and providing a method for breeding improvement to avoid germ plasm mixed hybridization.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Impermeable material based on flue gas desulfurization byproduct and usage in garbage landfill thereof
InactiveCN101157528AOvercoming the problem of stacking land occupationEnhanced advantageSolid waste managementSodium BentoniteMetallurgy
The invention discloses an impermeable material based on flue gas desulphurization by-product and the usage in trash burying. The impermeable material is compounded evenly according the weight by 60-90 percent of circulating fluidized bed flue gas desulphurization dreg and 10-40 percent of chemical additive under the dried powder ugh condition. The chemical additive is the one kind or two kinds of combination of bentonite and kleit at random proportion, and the impermeable material can be applied to be used as an anti-seepage layer in trash burying, wherein, the anti-seepage layer used as the underlay of the trash burying field has a thickness of 80cm to 120cm; the anti-seepage layer used as the intermediate coating has a thickness of 15cm to 30cm; and the anti-seepage layer used as the full closure field has a thickness of 60cm to 100cm. The impermeable material can not only prevent from polluting the underground water of the trash burying field, reduce the treatment of trash infiltrated liquid and ensure that the trash buried gases are collected orderly, but also make full use of the huge desulphurization dreg and change waste into resources, thereby realizing the win-win benefit.
Owner:WUHAN KAIDI ELECTRIC POWER ENVIRONMENTAL
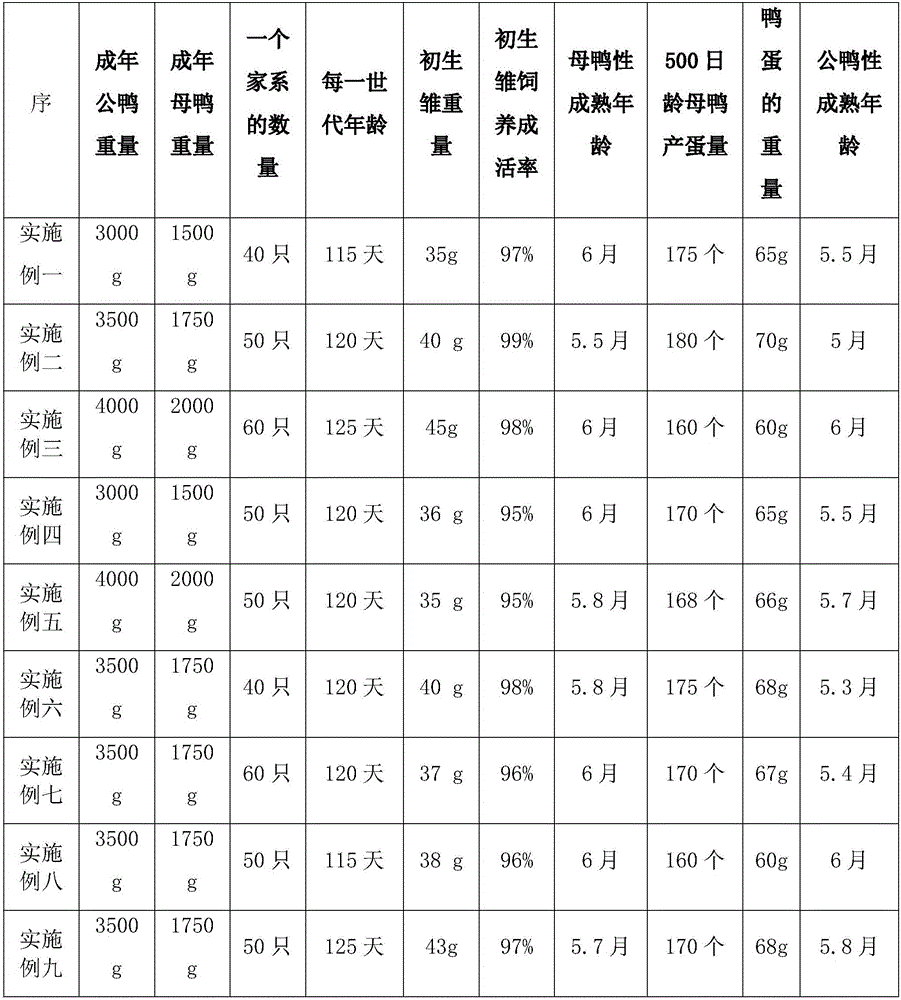
Breed protection and selection method of Muscovy ducks
InactiveCN105766799AEarly sexual maturityConsiderable egg productionAnimal husbandryAdult femaleMixed group
The invention belongs to the technical field of livestock and poultry breeding and particularly relates to a breed protection and selection method of Muscovy ducks. The method includes the steps of firstly, selecting the Muscovy ducks conforming to the variety features of Yongchun Muscovy ducks for cultivation so as to obtain adult male ducks and adult female ducks, selecting and eliminating the Muscovy ducks which do not conform to the variety features of the Yongchun Muscovy ducks from the adult male ducks and the adult female ducks and selecting the population conforming to the variety features of the Yongchun Muscovy ducks through a series of cultivation, selection, eliminating and cultivation; secondly, selecting the adult male ducks and the adult female ducks to build an underlying group; thirdly, building generation zero, to be more specific, in the underlying group, randomly selecting dozens of the adult male ducks and the adult female ducks to form a family, and performing breeding of several families; fourthly, performing subculture breeding, to be more specific, giving wing tags to the newborn ducks in the third step, making pedigree records, and performing mixed-group feeding. By the breed protection and selection method, the problem that the preservation of the Yongchun Muscovy ducks is severely affected due to the fact that existing Yongchun Muscovy ducks raisers blindly import hybridization and improvement is solved.
Owner:YONGCHUN YUNHE WHITE MUSCOVY DUCK CONSERVATION BREEDING CO LTD
Method for setting parallel incomplete disassembly line for disassembling waste products
ActiveCN110580547AImprove global search performanceEasy to implementForecastingManufacturing computing systemsWaste productMixed group
The invention discloses a method for setting a parallel incomplete disassembly line for disassembling waste products. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) constructing a mathematical modelaiming at minimizing the disassembly depth, the number of workstations, the idle time balance index of the workstations and the number of disassembly resources; (2) generating an initial population;(3) obtaining neighborhood individuals of the initial population; (4) comparing the target function value of a mixed group composed of the neighborhood individuals and the population individuals through Pareto, updating the population, and outputting a Pareto optimal solution to an external file; (5) performing simulated annealing operation on the population updated in the step (4) to obtain a newpopulation; (6) comparing a target function value of a mixed group consisting of the group subjected to simulated annealing operation and an external file by adopting Pareto, and outputting a Paretooptimal solution to the external file; (7) repeating the steps (3)-(6) according to the set number of times; and (8) outputting a Pareto optimal solution in the external file as a disassembly task allocation scheme. The method is easy to implement and high in search capacity.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
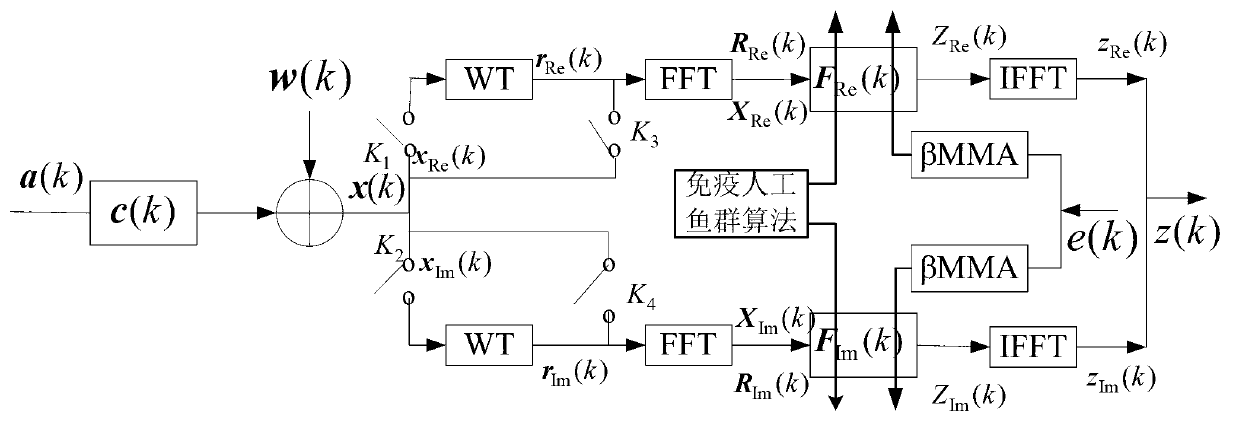
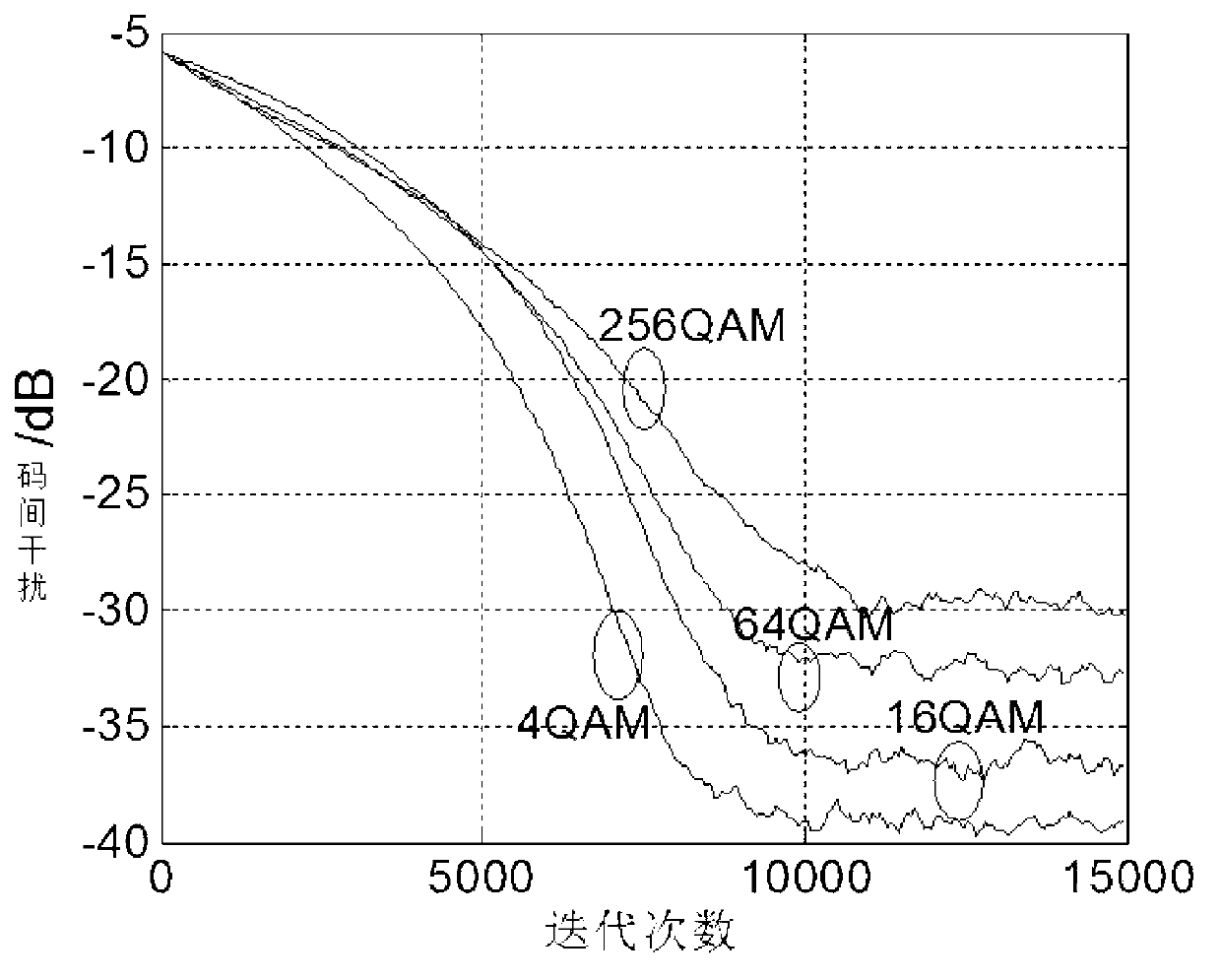
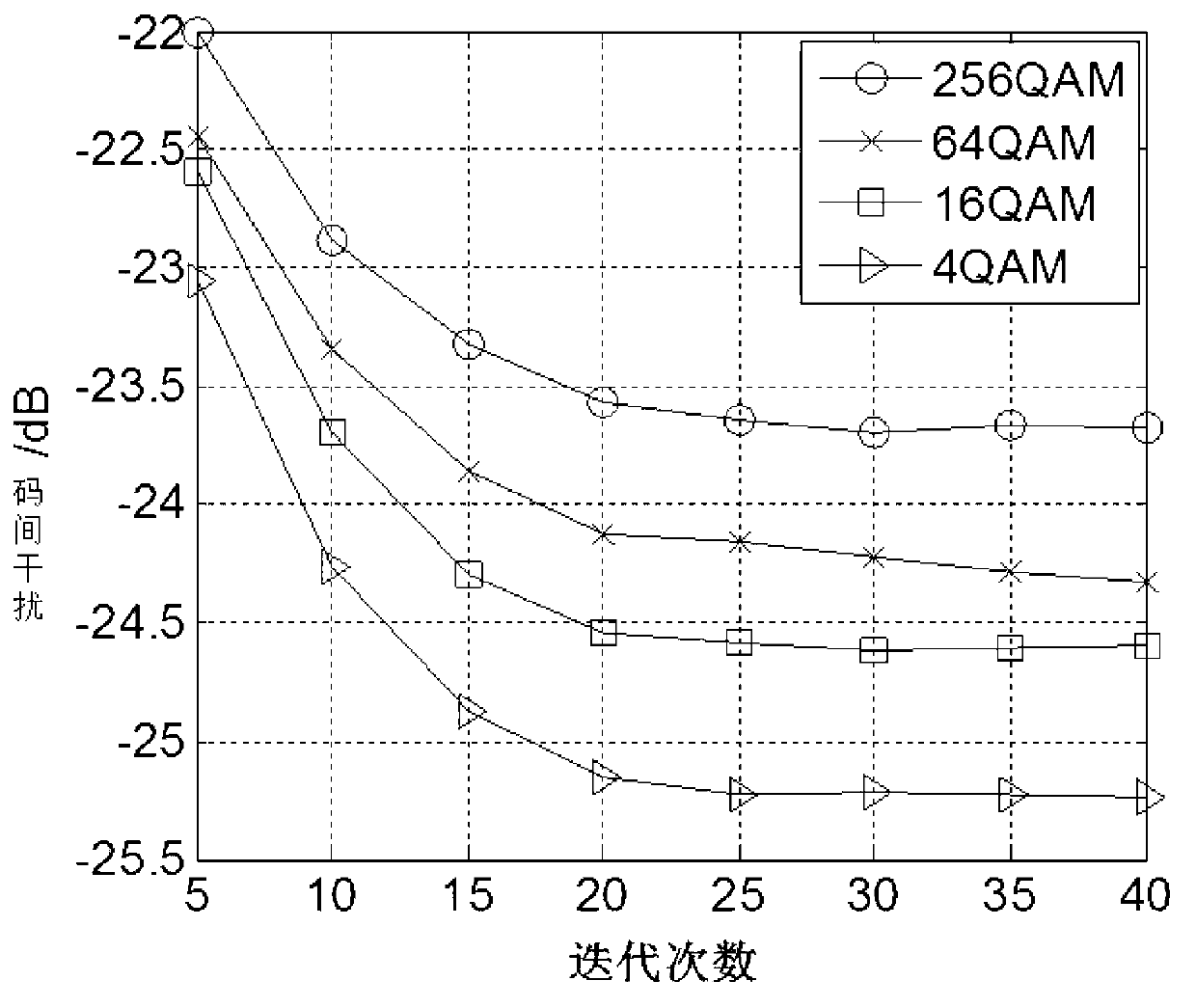
Frequency-domain self-adaptation wavelet multi-mode blind equalization method for immune artificial shoal optimization
InactiveCN103346987AStrong global search capabilityFast convergenceTransmitter/receiver shaping networksMultiple carrier systemsBlind equalizationMixed group
The invention discloses a frequency-domain self-adaptation wavelet multi-mode blind equalization method for immune artificial shoal optimization. The frequency-domain self-adaptation wavelet multi-mode blind equalization method for the immune artificial shoal optimization comprises the following steps that an immune artificial shoal is a mixed group of an artificial shoal and an immune system antibody shoal, position vectors of the artificial shoal and antibody vectors of an immune system of a set of immune artificial shoal are initialized in a random mode, the position vectors and the antibody vectors serve as decision variables of an immune artificial shoal method, input signals of an orthogonal wavelet converter serve as input signals of the immune artificial shoal method, a fitness function of the immune artificial shoal is determined by a cost function of the frequency-domain self-adaptation wavelet multi-mode blind equalization method, and initialization weight vectors of the frequency-domain self-adaptation wavelet multi-mode blind equalization method are determined by an immune artificial shoal optimization method. The frequency-domain self-adaptation wavelet multi-mode blind equalization method for the immune artificial shoal optimization is high in rate of convergence, low in steady-state error, low in complexity and good in practicability when the frequency-domain self-adaptation wavelet multi-mode blind equalization method for the immune artificial shoal optimization is used for processing high-order QAM signals.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Heavy-metal-polluted acidic soil repairing material as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102329620BRaise the pHReduced bioavailabilityAgriculture tools and machinesOther chemical processesSodium BentoniteSlag
The invention discloses a heavy-metal-polluted acidic soil repairing material as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The repairing material is prepared from the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 10-20% of biomass electric power plant ash, 10-20% of slag powder, 10-30% of steel slag powder, 5-10% of fly ash and 25-50% of bentonite by uniformly mixing in a dry powder state. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: firstly, drying the raw materials until the water content is smaller than or equal to 1%; then, respectively weighing the raw materials according to the percentage by weight; and finally, uniformly stirring. The in-situ repairing of heavy-metal-polluted acidic soil is achieved by covering a layer of repairing material on the soil surface, uniformly mixing the soil surface layer with the repairing material in plowing and stirring modes, and detecting the contents of Cd, Pb, Cr, Cu, Zn, Mn, Hg, As and Ni in the repaired soil and the soil pH value after 3-6 months until meeting the requirements of the second-level soil environment quality standard in GB15618-1995.
Owner:WUHAN KAIDI ENG TECH RES INST CO LTD
Universal infusion head with automatic infusion continuing function
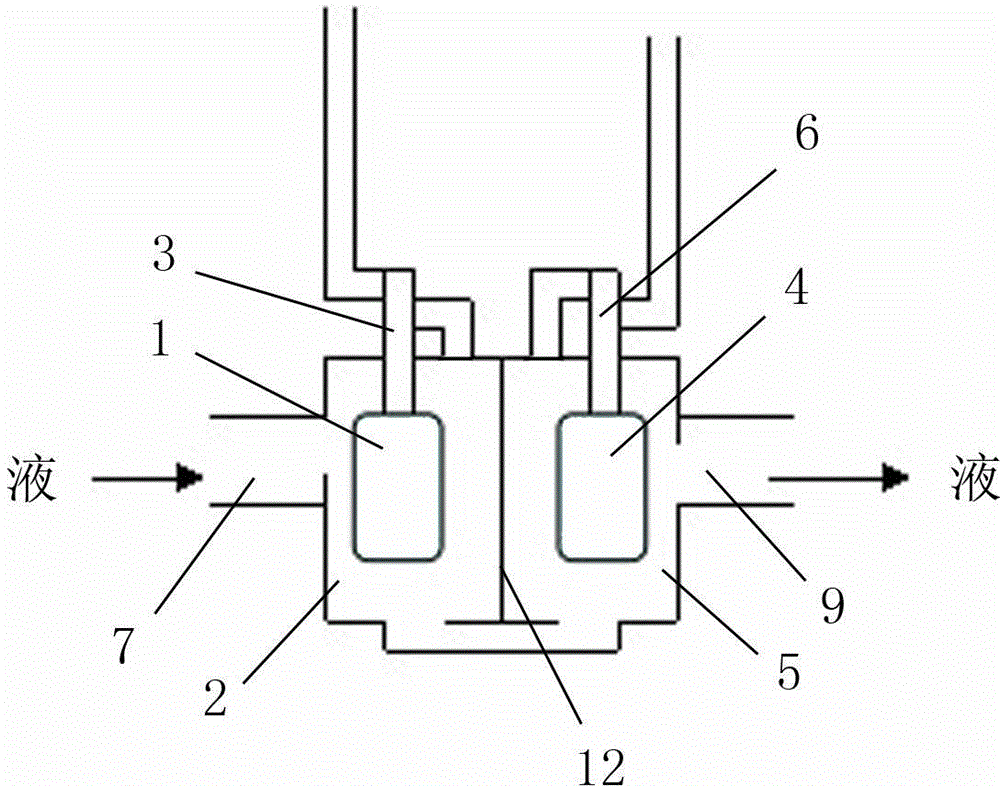
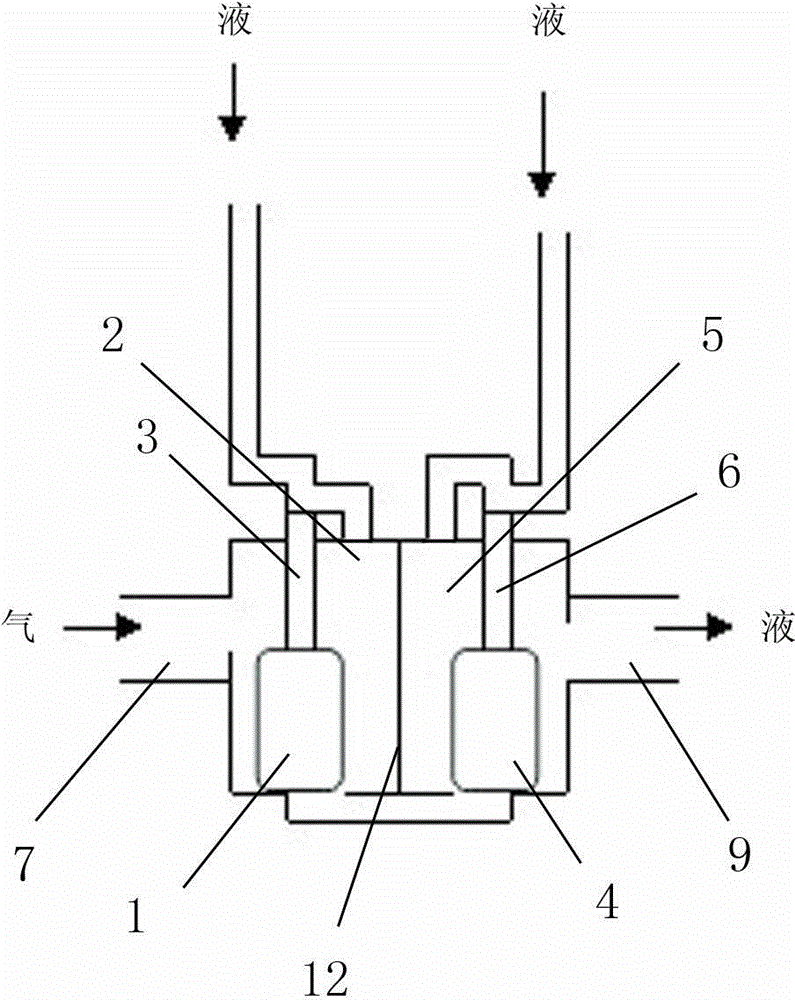
The invention relates to a universal infusion head with an automatic infusion continuing function. The infusion head comprises an infusion head body, two infusion passages and an automatic infusion continuing control chamber. A partition is disposed in the middle of the automatic infusion continuing control chamber to separate the automatic infusion continuing control chamber into a first floating valve chamber and a second floating valve chamber. The bottoms of the first floating valve chamber and the second floating valve chamber are communicated. The first floating valve chamber and the second floating valve chamber respectively correspond to the two infusion passages. A floater valve switch is disposed in each of the first floating valve chamber and the second floating valve chamber. The first floating valve chamber is connected with a liquid inlet tube, and the second floating valve chamber is connected with a liquid outlet tube. The floater valve switch in the two floating valve chambers moves upwards to block the infusion passage of a current bottle or bag by the buoyancy of liquid medicine entering through the liquid inlet tube, and the infusion passage of the current bottle or bag is smooth when the no liquid medicine enters from the liquid inlet tube, air enters the liquid inlet tube, and the floater valve switches naturally fall. The universal infusion head has the advantages that the physical principles of liquid, gas and the floater switches are utilized to achieve automatic infusion continuing of multi-form infusion groups including an infusion bag group, an infusion bottle group or an infusion bottle-bag mixed group, and the application range of continuous infusion devices is widened.
Owner:刘玮
Two-bee-specie dual queen mixed group construction, mixed royal jelly and production method thereof
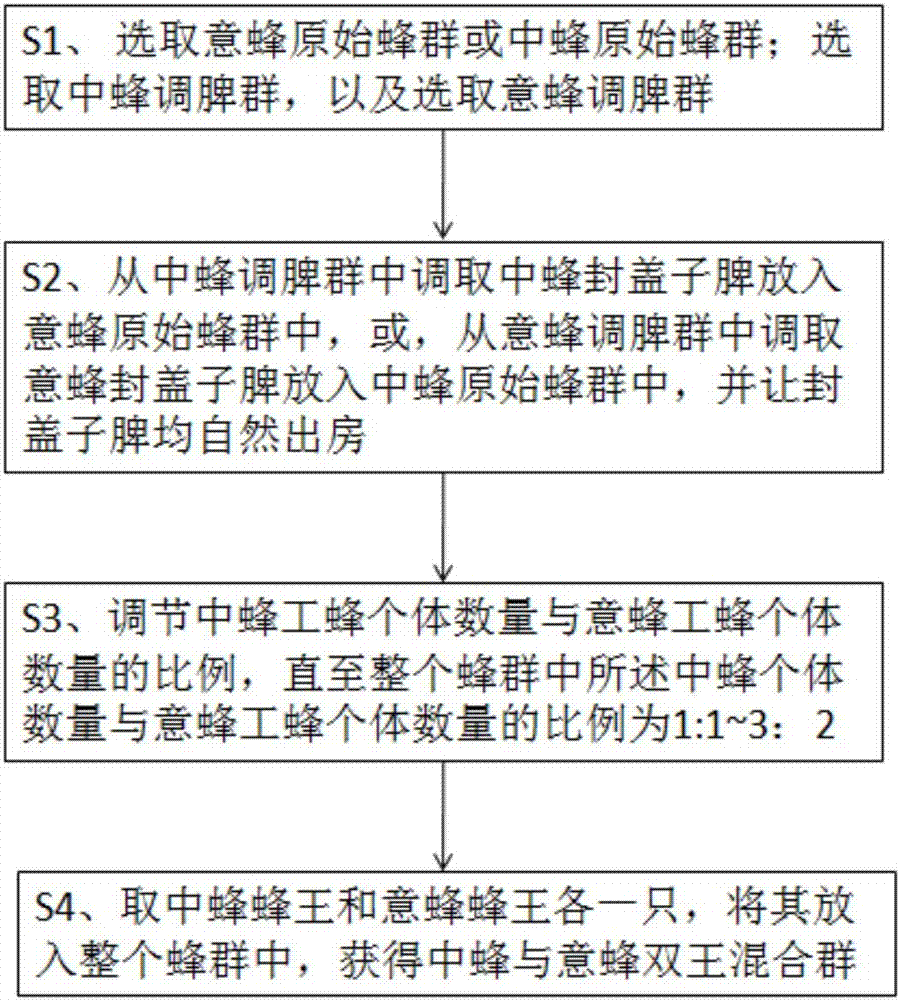
ActiveCN107047486AEffective establishmentIncrease productivityAnimal husbandryFood scienceApis ceranaMixed group
The invention discloses a two-bee-specie dual queen mixed group construction, and mixed royal jelly and a production method thereof. The two-bee-specie dual queen mixed group construction method includes: S1, selecting an Apis mellifera group or an Apis cerana group as an original bee group; and selecting an Apis cerana comb adjustment group and an Apis mellifera comb adjustment group; S2, putting a sealed sub comb to the original bee group, and allowing bees in the selected sealed sub comb and a sealed sub comb of the original bee group to naturally fly out of the combs; S3, adjusting the proportion of the number of Apis cerana worker bee individuals and the number of Apis mellifera worker bee individuals; and S4, putting an Apis cerana queen and an Apis mellifera queen to the whole bee group, and acquiring an Apis cerana and Apis mellifera mixed group. The Apis cerana and Apis mellifera mixed group can be effectively established, and has two queens of the two bee species; a strong group can be maintained for long time, and respective advantage roles of the Apis cerana and the Apis mellifera can be fully played; various kinds of mixed royal jelly can be produced, the production efficiency of the mixed royal jelly can be improved, and the quality of the mixed royal jelly is ensured.
Owner:JIANGXI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
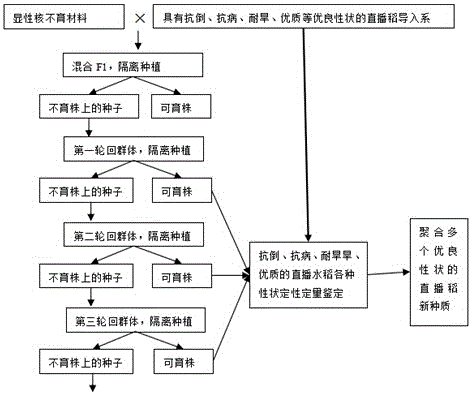
Method for quickly breeding directly seeded rice varieties suitable for wheat stubble along Huaihe region
InactiveCN106305410AQuick eliminationReduce workloadPlant genotype modificationFiltrationMultiple traits
The invention discloses a method for quickly breeding directly seeded rice varieties suitable for wheat stubble along the Huaihe region. The quick breeding method comprises the following specific steps of: S1, testing in a seeding date and observing adaptability; S2, taking a dominant sterile material as a female parent and respectively hybridizing with rice varieties to gain F1; S3, implementing mixed planting of the F1 and isolating with surrounding rice, implementing mixed pressing and pollination of pollen in a full-blossom period; S4, implementing mixed harvesting of sterile plants in the mixed group; S5, isolating and planting a first cycle of groups; S6, isolating and planting a second cycle of groups; S7, screening out new directly seeded rice varieties aggregated with multiple traits; S8, finally selecting new target strains. In the quick breeding method, the dominant sterile material is used as a hybrid medium to quickly aggregate good genes, meanwhile a molecular marker-assisted breeding technique is applied to indoor filtration so that a non-target material can be quickly obsoleted, farm workload is greatly reduced and breeding efficiency is effectively increased.
Owner:安徽省东昌农业科技有限公司
Device capable of preventing pigs from fighting
ActiveCN106386556AStop fightingAvoid fightingAnimal housingTaming and training devicesFree rangeEngineering
The device provides a device capable of preventing pigs from fighting and aims to provides the welfare device capable of preventing the pig from fighting .The device reduces or avoids harm to pigs due to fighting behaviors caused by mixed groups in a free-ranging large hoggery, enhances a welfare grade of pig breed, improves free-ranging technology of a large free-ranging pig hoggery, and is beneficial to application and popularization of the device. The device capable of preventing the pigs from fighting comprises a aisle support (2), a side plate (3), a rotary plate (1), a first toy device (5), a second toy device (6) and a third toy device (7).
Owner:CHONGQING ACAD OF ANIMAL SCI
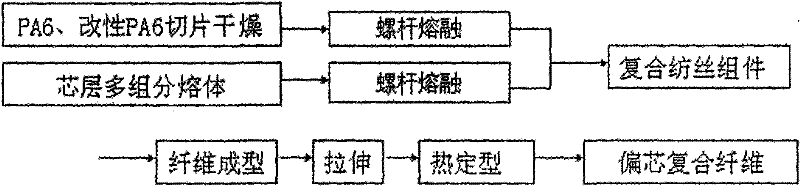
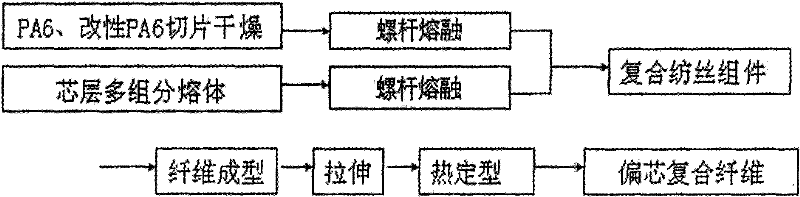
A kind of multi-component composite eccentric fiber and its preparation method
InactiveCN101798713BPermanent curl elasticGood miscibilityFilament/thread formingConjugated synthetic polymer artificial filamentsFiberChemical composition
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV +1
Double-dominant marker for accurately authenticating S/N cytoplasm genotype of onions and application of double dominant marker
ActiveCN107881255AAvoid misclassificationGuaranteed accuracy and reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenotypeMixed group
The invention discloses a double-dominant marker for accurately authenticating an S / N cytoplasm genotype of onions and application of the double-dominant marker. The length of a specific fragment of an S-form cytoplasm in the double-dominant marker is 232bp, and the length of a specific fragment of an N-form cytoplasm is 196bp. The invention further discloses SCAR marking primers SEQ ID NO.5 and SEQ ID NO.6. A prepared SCAR molecular marker is utilized for rapidly and accurately judging cytoplasm types of onion materials, so that the misclassification of cytoplasm genotypes caused due to experimental operate miss and invalid PCR amplification can be avoided; and furthermore, DNA can be extracted from mixed group samples when a maintainer line is selected in a large group and can be used for primarily screening whether a maintainer line single plant exists, so that the selection efficiency is greatly improved, the time and the cost are saved, and the double-dominant marker has importantsignificances to the matching of a breeding sterile line and a maintainer line of the onions and the breeding of hybrid varieties of the onions.
Owner:VEGETABLE RES INST OF SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Method for preparing pannage with blackberry pomace
InactiveCN101715887ANutritional balanceImprove palatabilityFood processingAnimal feeding stuffManufacturing technologyVegetable oil
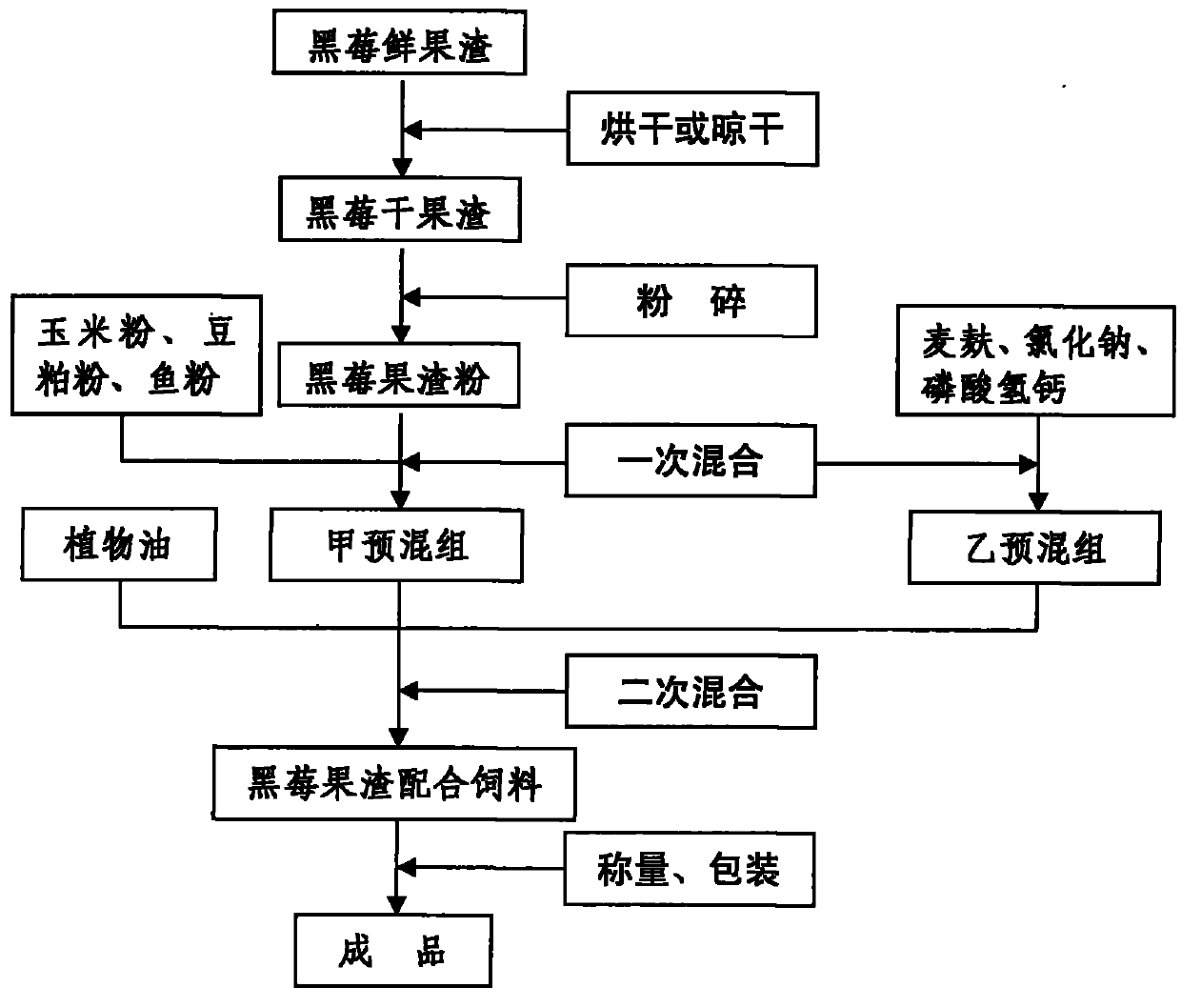
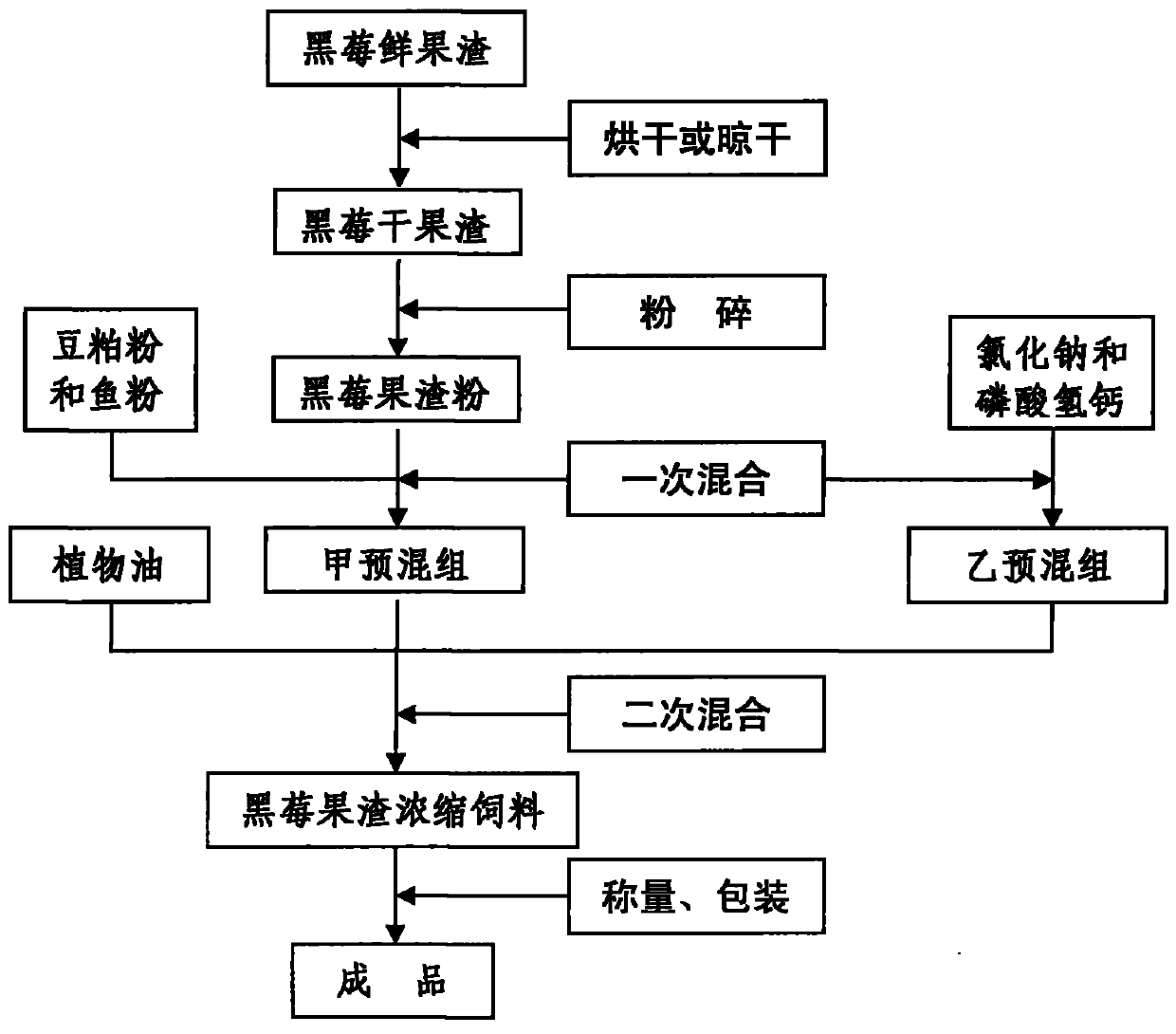
The invention provides a method for preparing pannage with blackberry pomace, relating to the technical field of preparing feedstuff. The method takes pomace which is produced by juicing fresh blackberry as raw materials, and adopts a second mixing technology to prepare the pannage. The method specifically comprises the following steps: mixing blackberry pomace powder, corn powder, soybean meal powder or fish powder according to a certain proportion to obtain a previously-mixed group A; mixing wheat bran, sodium chloride or calcium hydrophosphate according to a certain proportion to obtain a previously-mixed group B; mixing the previously-mixed group A, the previously-mixed group B and plant oil with a certain proportion; and packing to prepare blackberry pomace compound feedstuff or concentrated feedstuff. The method has the following characteristics: the blackberry pomace feedstuff has low cost, simple manufacture technology, universal equipment, less investment, easy operation and control, abundant nutrition, stable quality and easy digestion, and is easy in large-scale industrial production. The perpetration of the blackberry pomace feedstuff not only can recycle waste, but also can remove environment pollution during processing the blackberry.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY JIANGSU PROVINCE & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for identifying silkworm silk color in larval stage
InactiveCN102808033AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationComplementary deoxyribonucleic acidGenetic engineering
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and discloses a method for identifying a silkworm silk color in a larval stage. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: extracting the ribonucleic acid (RNA) of a silkworm silk gland of a 5th instar stage to be detected by utilizing a genetic engineering technology; performing reverse transcription to synthesize complementary deoxyribonucleic acid (cDNA); taking the obtained cDNA as a template, performing reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) amplification reaction by using a specific primer; judging whether a silkworm spins yellow silk or green silk or white silk by detecting the type and the length of a PCR amplification product by agarose electrophoresis; and further judging whether the silkworm which spins the yellow silk is a homozygous yellow silk spinning silkworm or a heterozygous yellow silk spinning silkworm, and other silkworms spin green silk or white silk by analyzing the content of the RT-PCR amplification product relative to an electrophoresis gel product. By the method provided by the invention, the pedigree with consistent internal cocoon color and external cocoon color and high color fastness also can be identified and separated from a mixed group with different cocoon layer colors and chromaticities. The identification method provided by the invention is simple, convenient and rapid to operate; and the accuracy for identifying the color of the silkworms is high.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Method for artificially cultivating soft-shell blue crabs
InactiveCN101946739BShorten the cultivation cycleIncrease profitClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaCalcium in biologyCALCIUM HYDROXIDE SOLUTION
The invention provides a method for artificially cultivating soft-shell blue crabs, which relates to a method of breeding blue crabs. By using the method, the soft-shell crabs can be obtained quickly and the survival rate of the soft-shell crab can be improved. The method comprises the following steps: dividing the blue crabs into three classes, and choosing the blue crabs in the first and second classes as the cultivated objects of the soft-shell crabs; putting a single blue crab in the first class in a crab pot, stacking and binding 3 to 5 crab pots together to be a group of crab pots, and then putting the groups of crab pots into a cultivating pool for intensive cultivation; during the cultivation period, transferring the whole group of crab pots to a black barrel or a small pond in which a natural shell-removing agent is added to soak every day; putting the crab pots into calcium hydroxide solution to soak and disinfect and promote calcium absorption and shell removal, and then putting the blue crabs subjected to socking into the original cultivating pool again; timely selecting out the blue crabs which just remove shells and transferring, then carrying out low-temperature paralysis fresh preservation or cryopreservation on the selected blue crabs; carrying out mixed group cultivation on the blue crabs in the second class in a cultivating pool, after the state of the blue crab in the second class in the shell removing cycle enters the state of the blue crab in the first class, selecting out and transferring the blue crabs to the crab pots, then cultivating the blue crabs to be the soft-shell crabs.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Preparation method of amphoteric surfactant containing plurality of polar heads
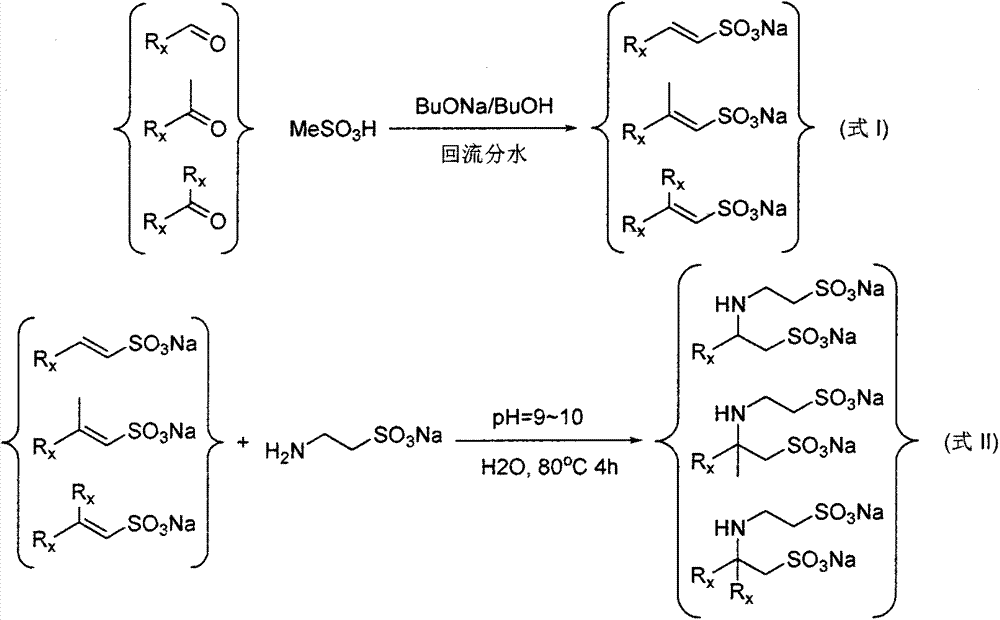
InactiveCN107325026AReduce utilizationEasy to separate and purifySulfonic acids salts preparationHigh sodiumSulfonate
This invention discloses a synthetic method of an amphoteric surfactant 1-(substituent)-amine diethanesulfonate (hereinafter the same) containing multiple polar heads. This invention comprises the following steps: the first step, using n-butanol as solvent and water-carrying agent, sodium n-butoxide as reaction reagent, mixing aldehydes, ketones and methanesulfonic acid with Rx group to prepare β- Sodium Rx ethylene sulfonate; the second step, water is used as a solvent, and sodium hydroxide is used as a reagent to mix β-Rx sodium ethylene sulfonate and aminoethanesulfonic acid to prepare 1-(substituent) of the formula II structure ‑Amine diethylsulfonate sodium. This invention realizes high utilization and low-cost preparation of 1-(substituent)-amine diethanesulfonate by improving conditions such as solvent, temperature, and pH.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Method of artificial breeding Pianniu
The invention provides a method of artificial breeding Pianniu, which comprises the following steps: breed two-way cross bulls and select a breeding cattle from the two-way cross bulls; introduce the bull and add electrolytic multivitamins in the drinking-water of the bull 3-5 days before the introduction; breed the bull in a mode combining warm house+ supplementary feeding 15 days before the introduction; train the bull for eating 5 days after the introduction; breed the bull in a mode combining grazing+ supplementary feeding 15 days after the introduction; put the bull together with female yaks for production from the second month of the introduction, and breed the female yaks in the mixed group in a mode combining grazing+ supplementary feeding, and breed the bull in the mixed group in a mode combining grazing+ supplementary feeding+ warm house; when he female yaks are oestrus, carry out artificial breeding. The artificial breeding Pianniu method provided by the invention has the advantages of simple and easy operation.
Owner:SICHUAN ACAD OF GRASSLAND SCI
Method for artificially cultivating soft-shell blue crabs
InactiveCN101946739AIncrease profitImprove survival rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaCalcium in biologyCALCIUM HYDROXIDE SOLUTION
The invention provides a method for artificially cultivating soft-shell blue crabs, which relates to a method of breeding blue crabs. By using the method, the soft-shell crabs can be obtained quickly and the survival rate of the soft-shell crab can be improved. The method comprises the following steps: dividing the blue crabs into three classes, and choosing the blue crabs in the first and secondclasses as the cultivated objects of the soft-shell crabs; putting a single blue crab in the first class in a crab pot, stacking and binding 3 to 5 crab pots together to be a group of crab pots, and then putting the groups of crab pots into a cultivating pool for intensive cultivation; during the cultivation period, transferring the whole group of crab pots to a black barrel or a small pond in which a natural shell-removing agent is added to soak every day; putting the crab pots into calcium hydroxide solution to soak and disinfect and promote calcium absorption and shell removal, and then putting the blue crabs subjected to socking into the original cultivating pool again; timely selecting out the blue crabs which just remove shells and transferring, then carrying out low-temperature paralysis fresh preservation or cryopreservation on the selected blue crabs; carrying out mixed group cultivation on the blue crabs in the second class in a cultivating pool, after the state of the blue crab in the second class in the shell removing cycle enters the state of the blue crab in the first class, selecting out and transferring the blue crabs to the crab pots, then cultivating the blue crabs to be the soft-shell crabs.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Cluster setting rate improving method by mixed cropping of different corn varieties
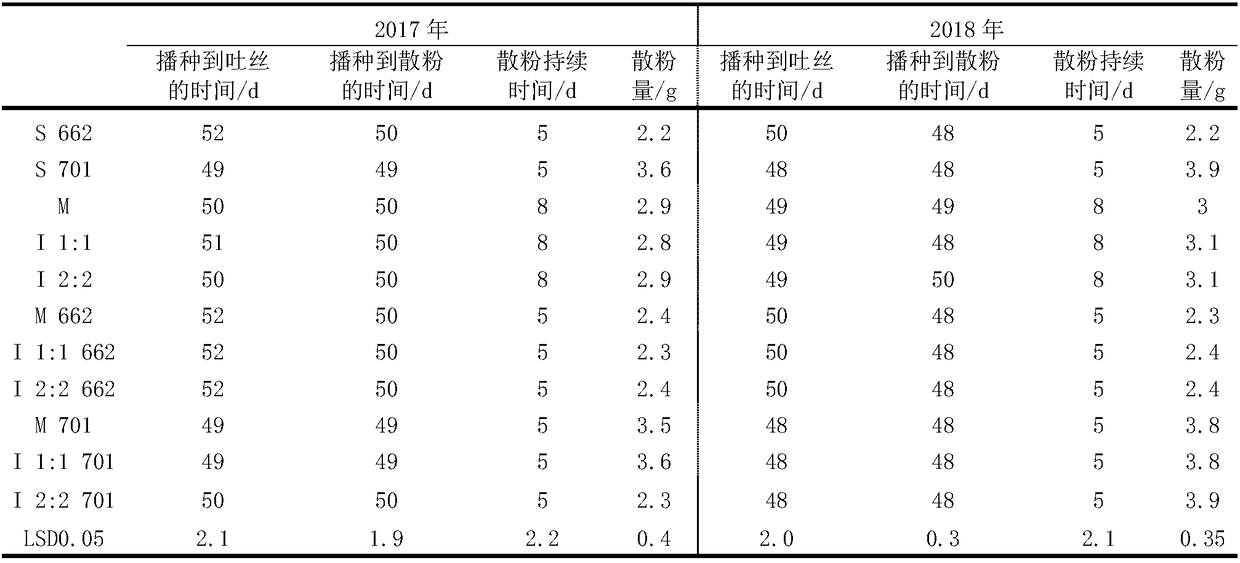
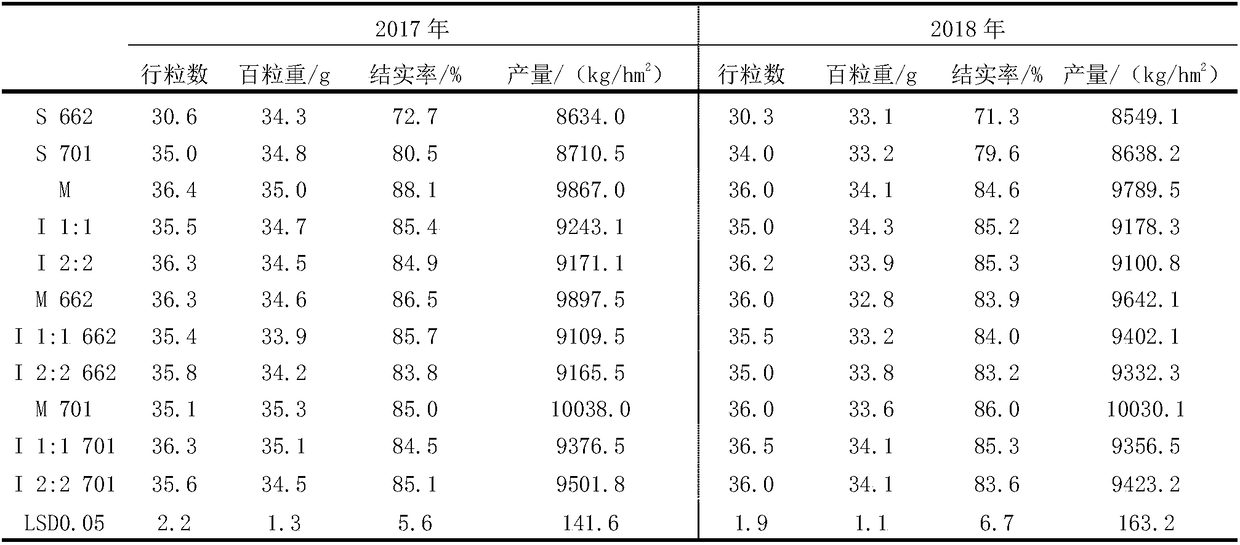
ActiveCN109197435AIncrease the amount of effective pollenExtend the duration of loose powderCereal cultivationHigh resistancePollen
The invention discloses a cluster setting rate improving method by mixed cropping of different corn varieties. Varieties with high resistance in the adverse condition are mixed cropped reasonably to prolong pollen dispersal duration of a mixed cropped group, provide sufficient high-quality pollen for insemination and setting of gynoecium, improve the group setting rate, and solve the problems thatadverse growth of male and female ears in the adverse condition causes unsatisfied encountering state of florescence, relatively low pollen quality and less pollen. Fertility and habit change of thevarieties in meteorological disasters are used ingeniously to match and combine the variables properly, a reasonable mixed cropping plantation belt is formed, the cluster setting rate of the mixed group is improved, and the group output is improved. The pollen complementary effect can be used to overcome the problem that gynoecium in the variety with early fusule but late pollen dispersal in the adverse condition needs to wait for pollen, there is pollen when filaments are provided to realize insemination, and insemination is completed when the filaments are most vital.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Mouse-specific anti-fertility polypeptide
InactiveCN102827285APeptide/protein ingredientsMacromolecular non-active ingredientsMixed groupFertility
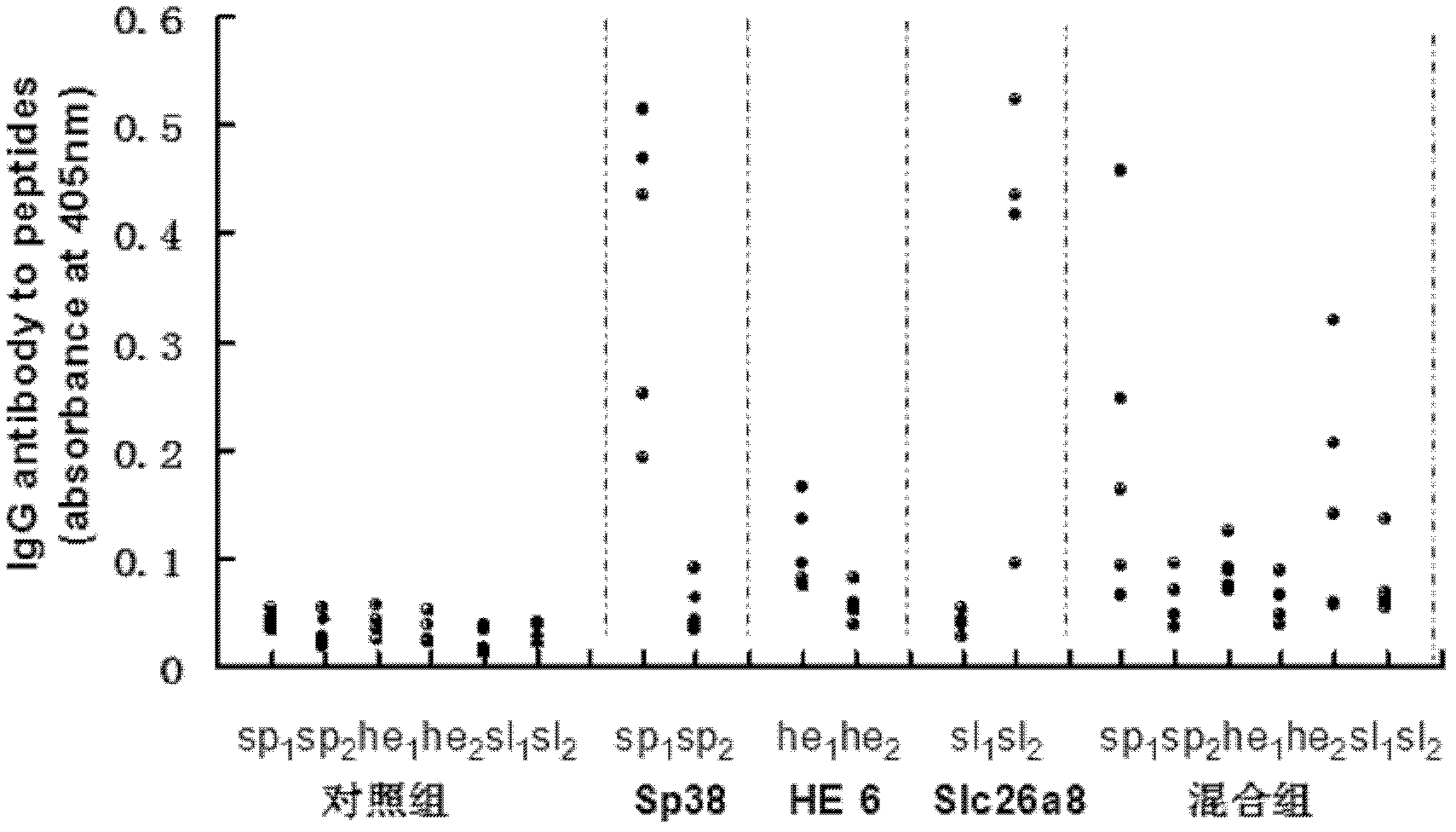
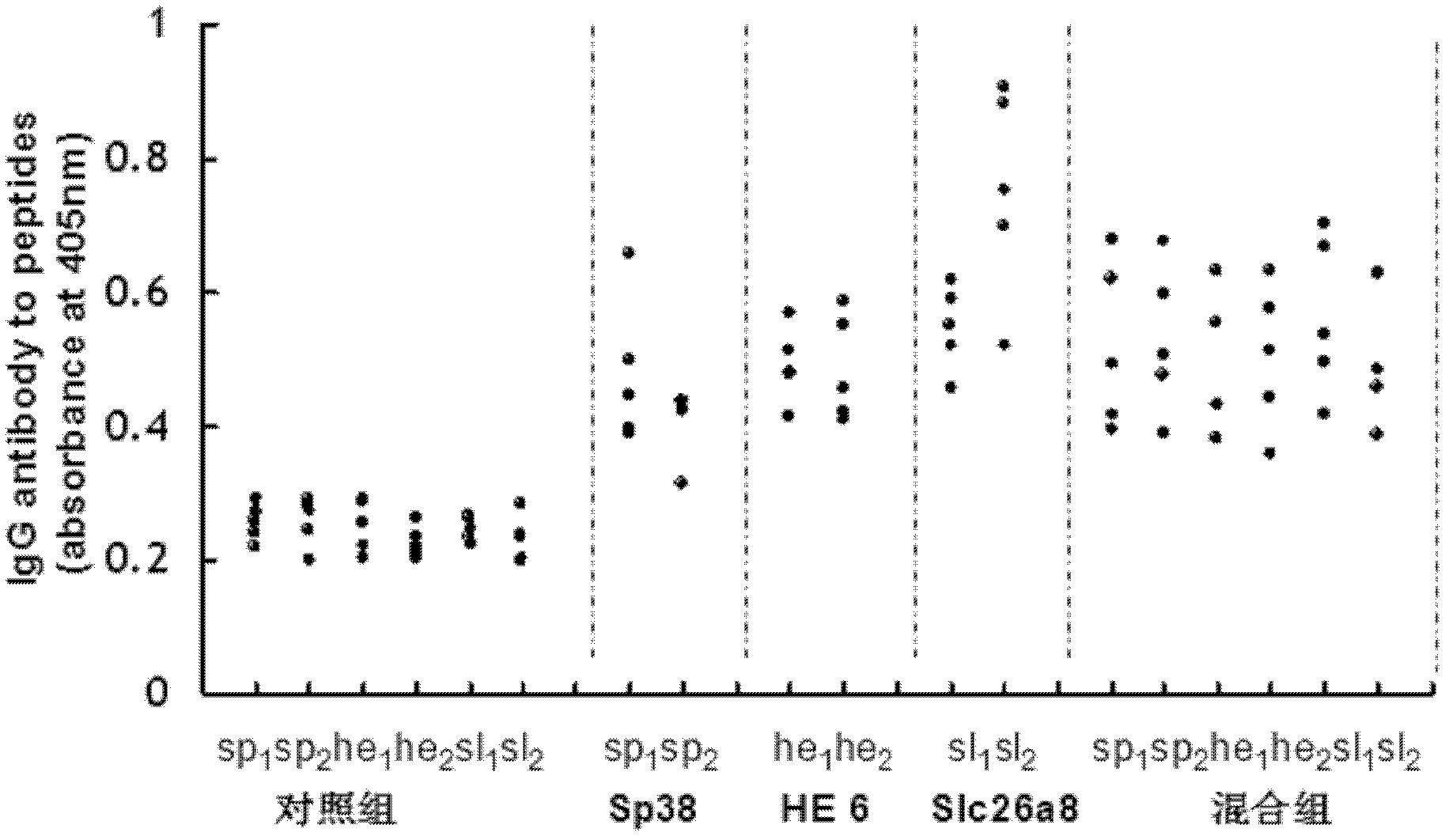
The invention discloses six immune anti-fertility polypeptide segments, all of which have excellent immunogenicity. The six immune anti-fertility polypeptide segments can stimulate the organisms to generate specific antibodies and induce the anti-fertility function. According to the fertility comparison of antigen polypeptide immunized mice and the immunized mice in a control group (KLH (keyhole limpet homocyanin) control group), immunization by the six polypeptide antigens mixed group can significantly reduce the farrowing rate of the male and the female mice, wherein litter sizes in the male and the female mice is respectively reduced by 62.8% and 50%. The athletic ability and activity of sperms are significantly reduced in the HE6 polypeptide group or the mixed group immunized male mice. The polypeptide with high-efficiency anti-fertility effect establishes the foundation for research of the mouse-specific immune anti-fertility vaccines, and can be used for application of various anti-fertility preparations.
Owner:BIOENG RES INST OF THE ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI
Fractional slot winding configuration for electric motor
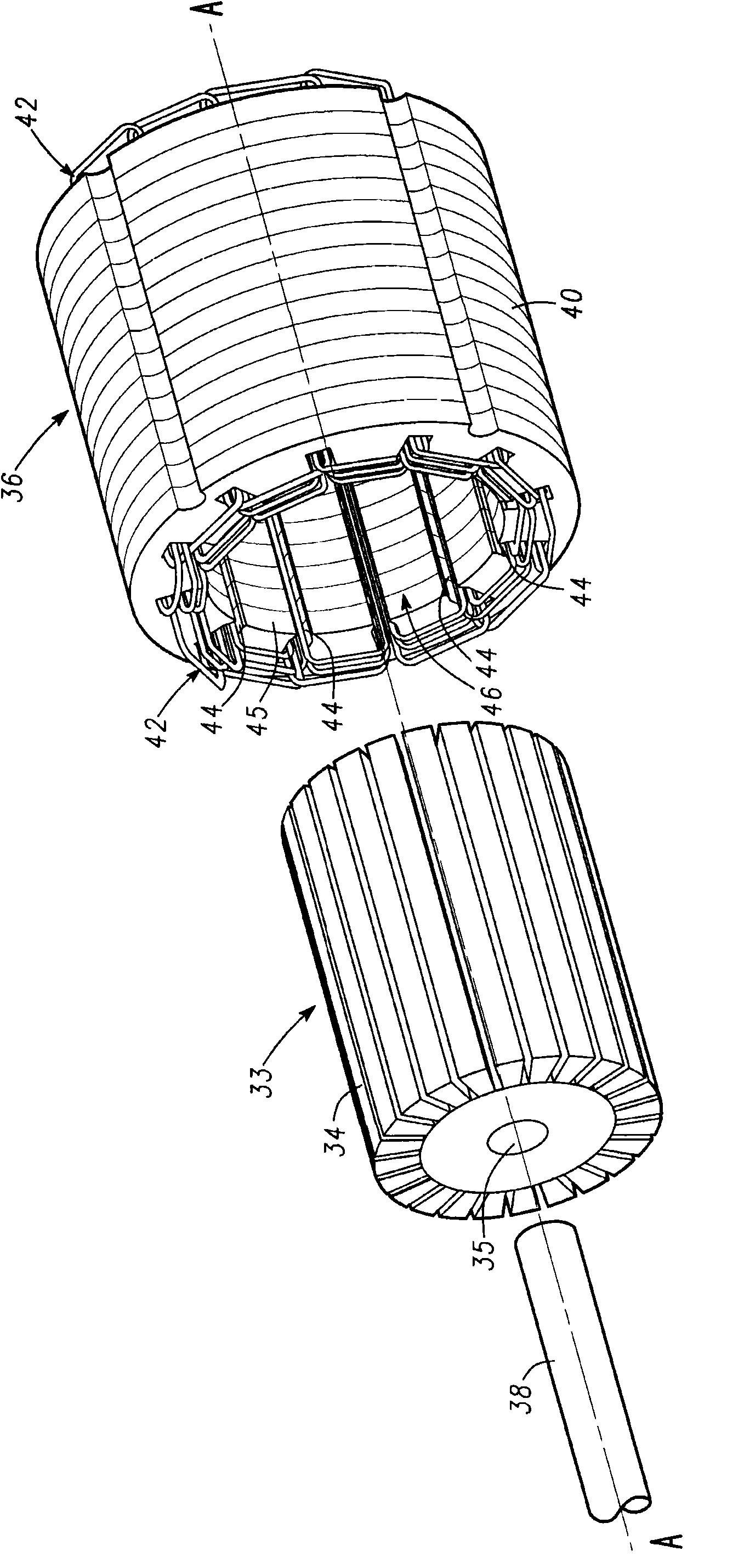
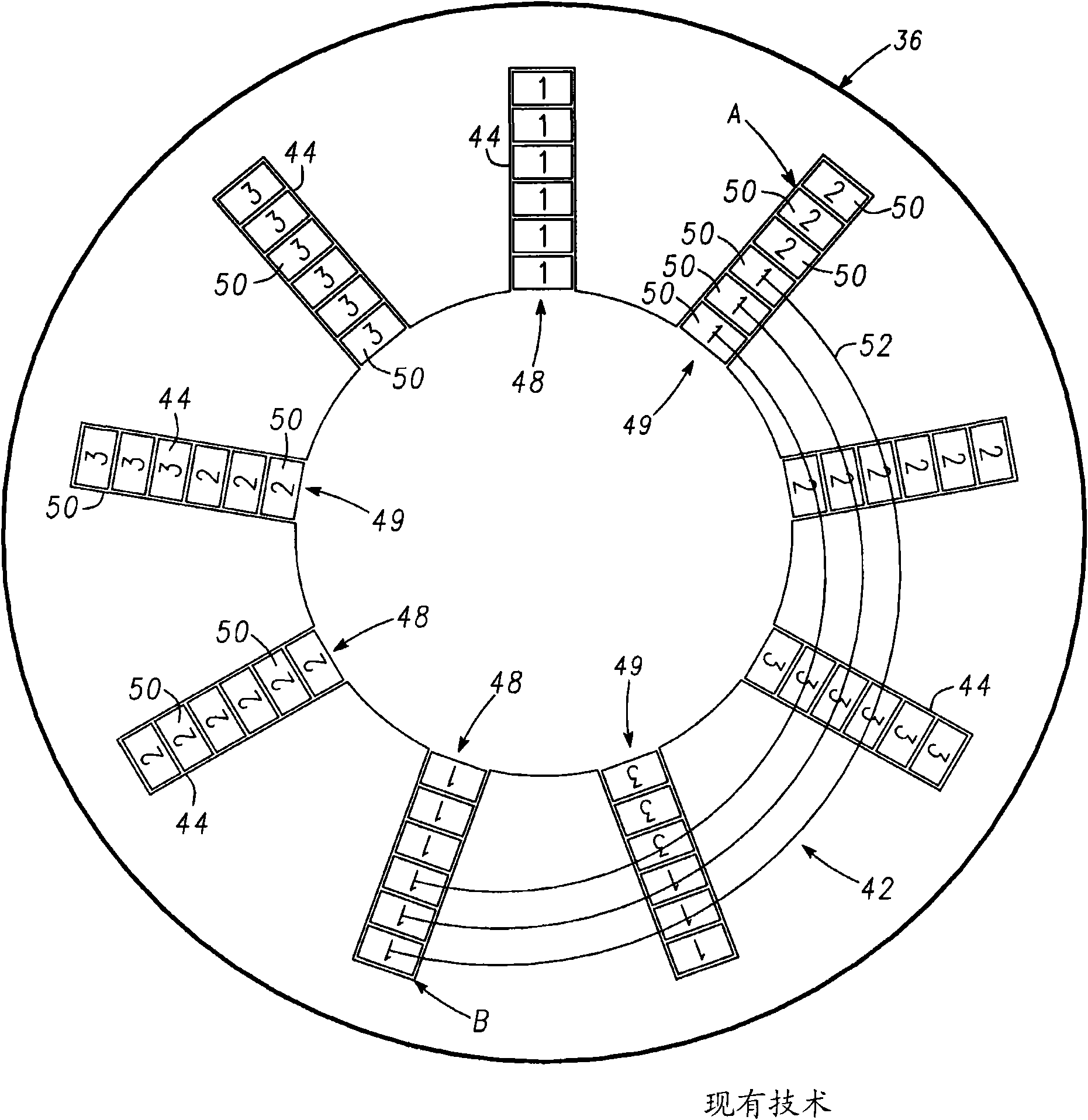
InactiveCN101958586AMagnetic circuit stationary partsManufacturing dynamo-electric machinesElectrical conductorMixed group
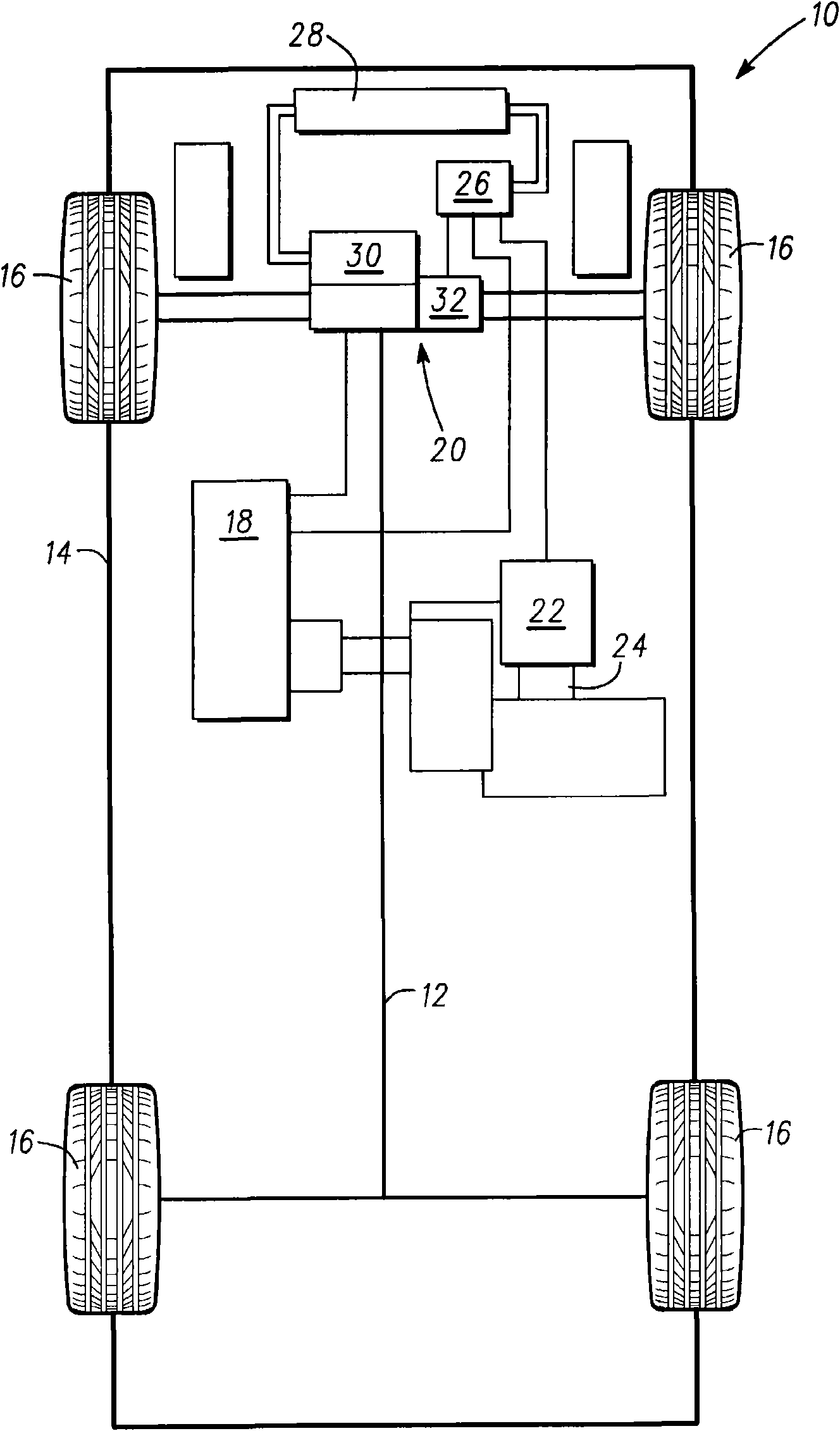
The invention relates to fractional slot winding configuration for electric motors. Methods and apparatus are provided for stator assembly for use with an electric motor assembly. The stator assembly includes, but is not limited to a stator core that has an inner surface and a plurality of stator slots defined in the inner surface. A fractional slot winding having a plurality of conductors is coupled to the stator core. Each stator slot contains a group of the conductors arranged in a radially adjacent configuration. The groups of conductors in each of the stator slots together form a plurality of concentric rings of conductors. The conductors in each mixed group are arranged such that conductors carrying differing phases of electric current are arranged in a radially alternating configuration.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method for preparing medical dressing
The invention discloses a preparation method of a medical dressing used for treating burns and scalds after operation. Combining 60-70% (w / w) of carboxyvinyl polymer and 40%-30% (w / w) of lauryl polyoxyethylene ether into a polymer compound is group A, and take 40-50ml of propylene glycol and 40-50g of glycerin , 60-70g of liquid paraffin and 1000ml of purified water are mixed under high-shear stirring to make a mixed liquid group B, take 20-30g of emulsified silicone oil and 10-20g of water-soluble laurozone to make a mixed group C, take 20-30g of tea tree oil and water-soluble tea tree dew 300-500g to make solution group D after stirring and strengthening, then place group A in a slow-stirring reaction kettle and add group B, group C and group D respectively to form a gel-like sol. Soak the sol into medium-density polyurethane sponge or degreasing gauze, wool felt, various medical non-woven fabrics and seal the package. It can promote skin metabolism, antibacterial, sterilizing, moisten the wound, relieve pain, no sticky feeling, accelerate wound healing, and minimize external skin damage.
Owner:ROOSIN MEDICAL CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com