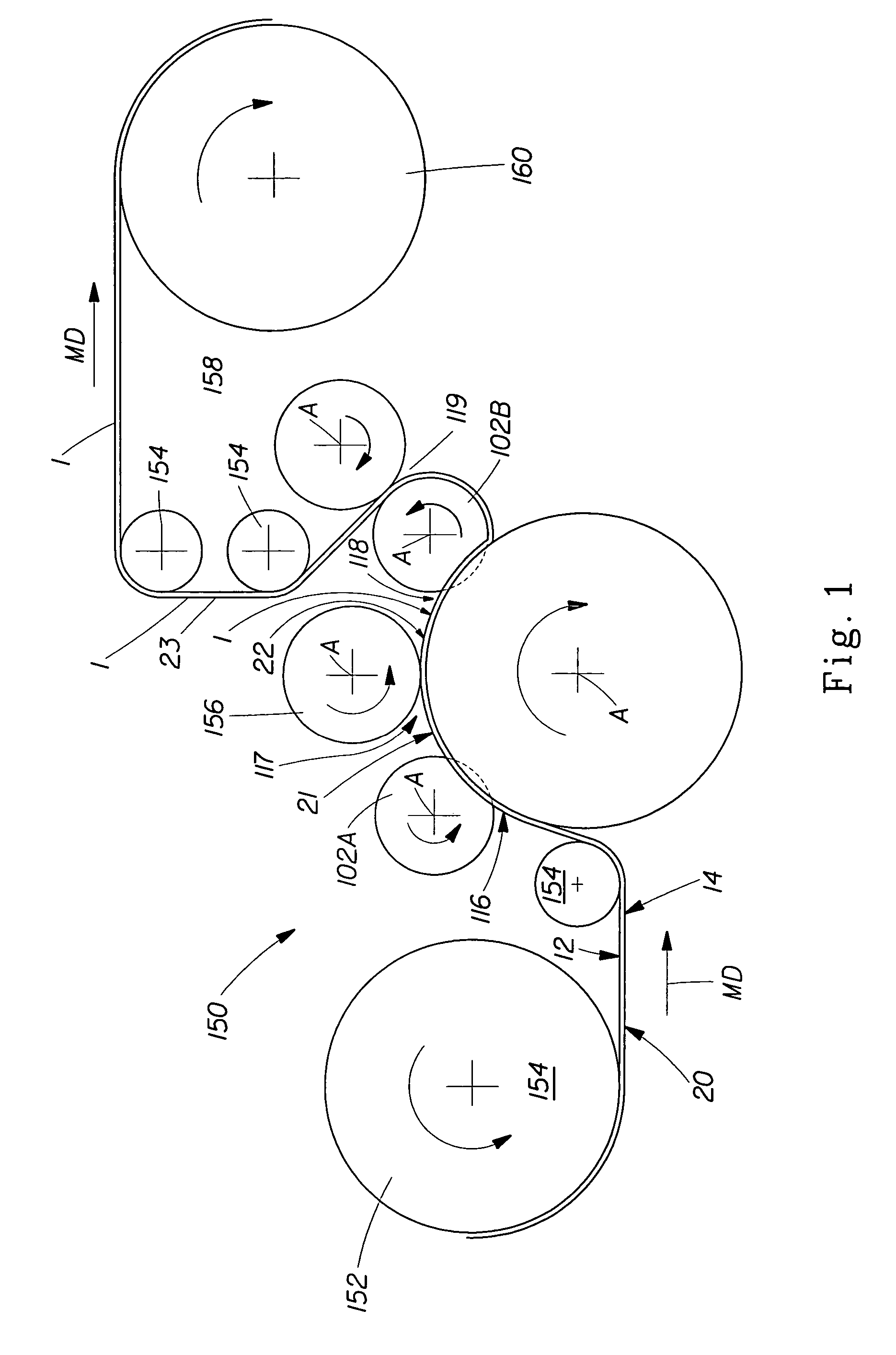
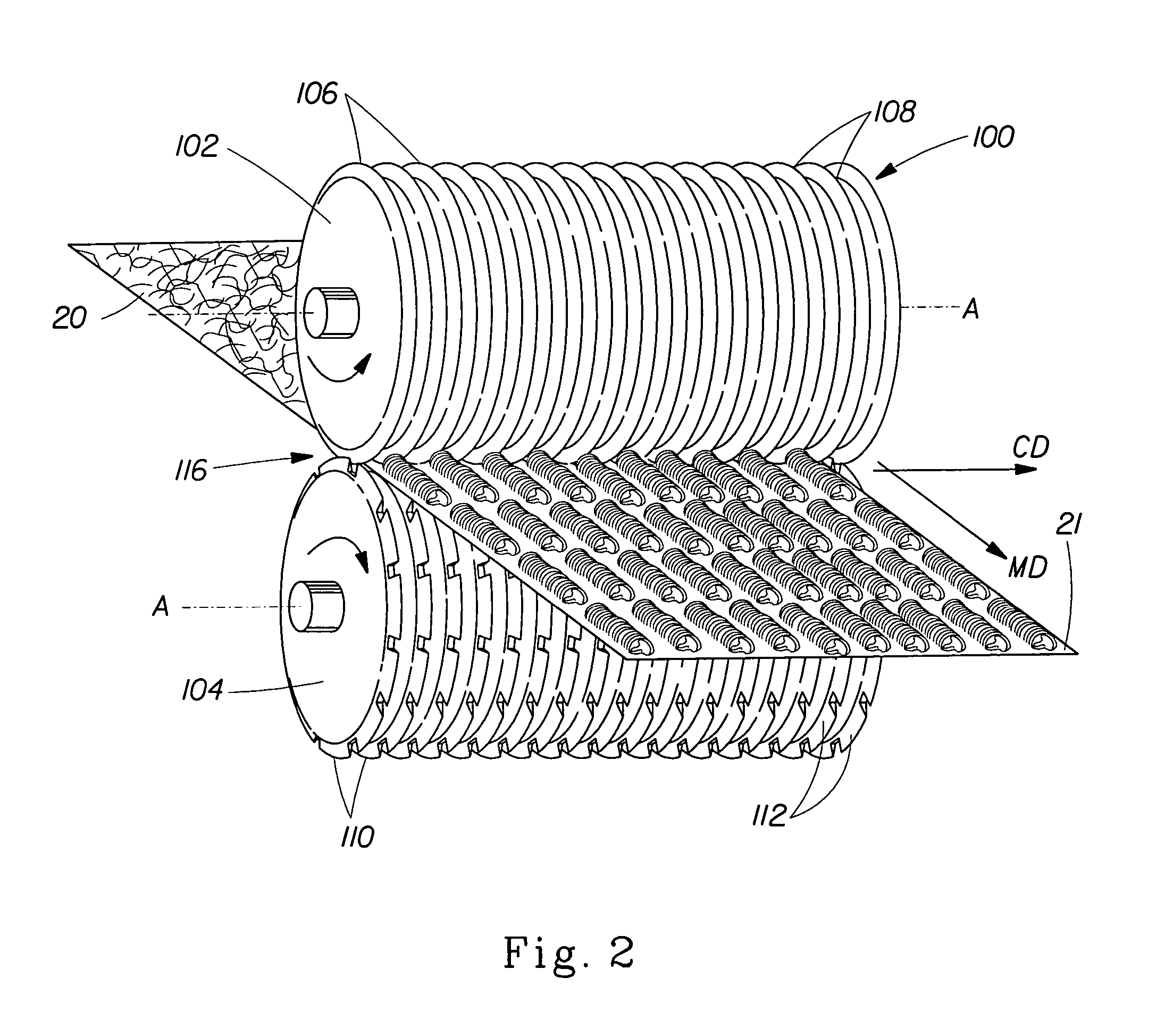
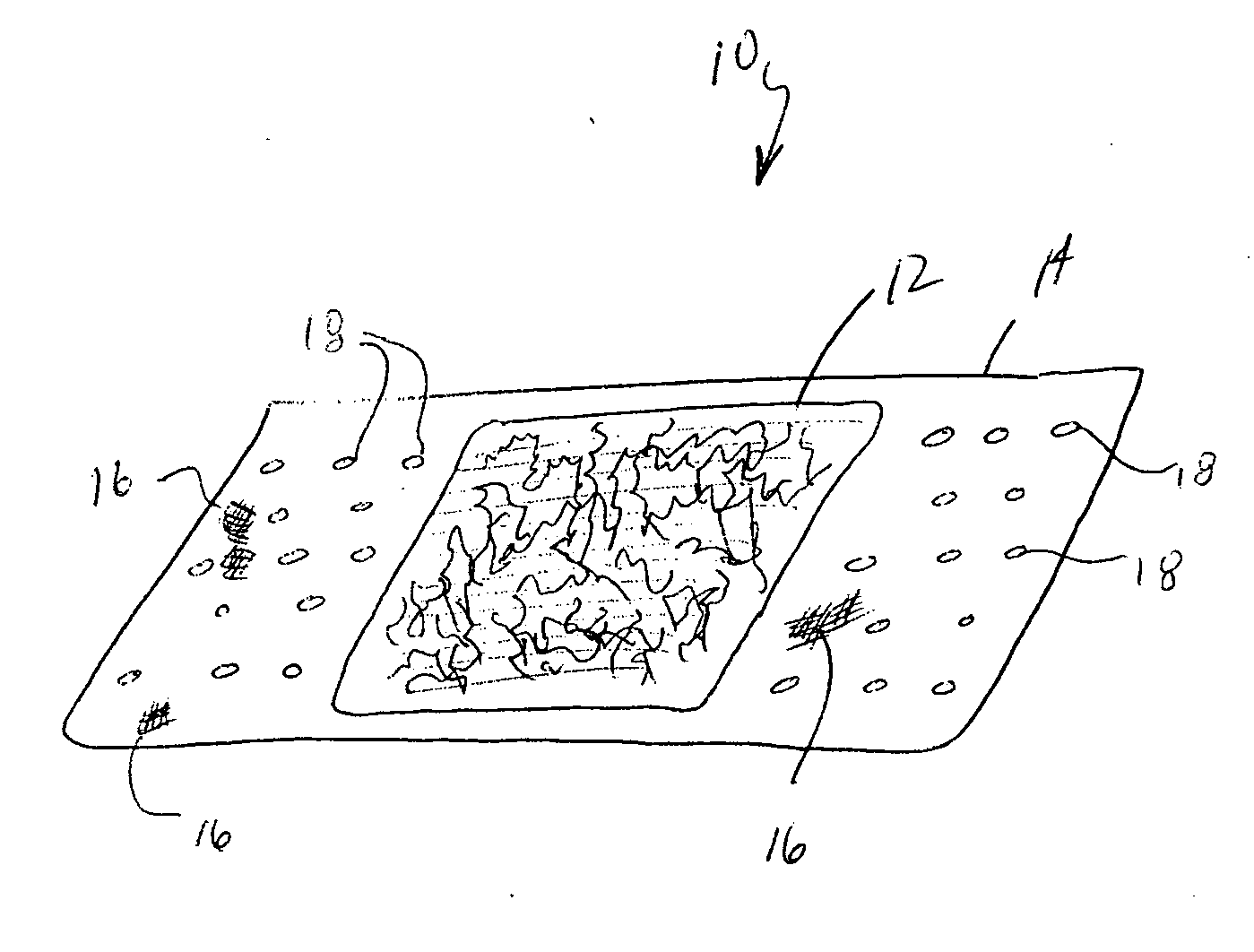
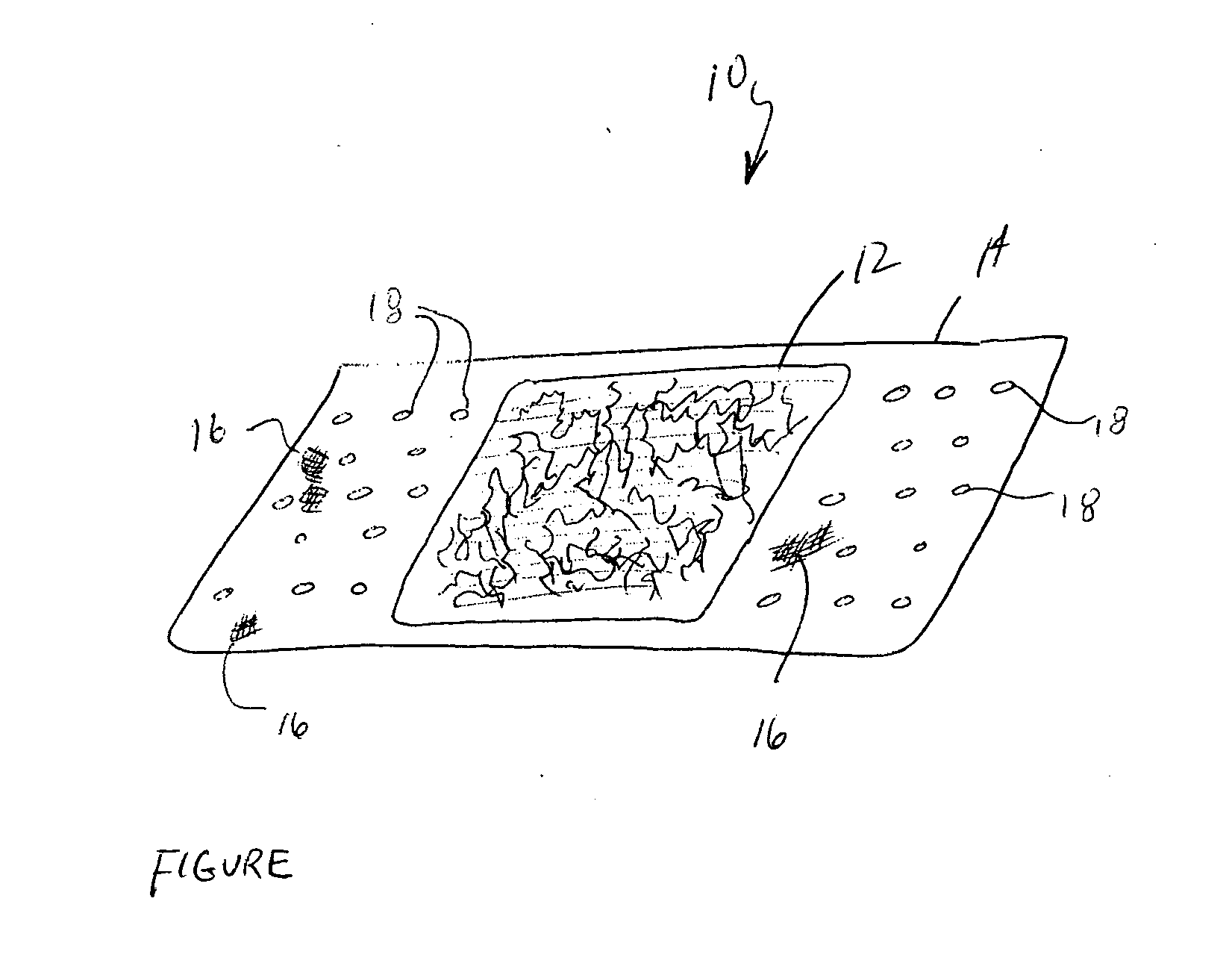
Patents
Literature
33795results about "Bandages" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
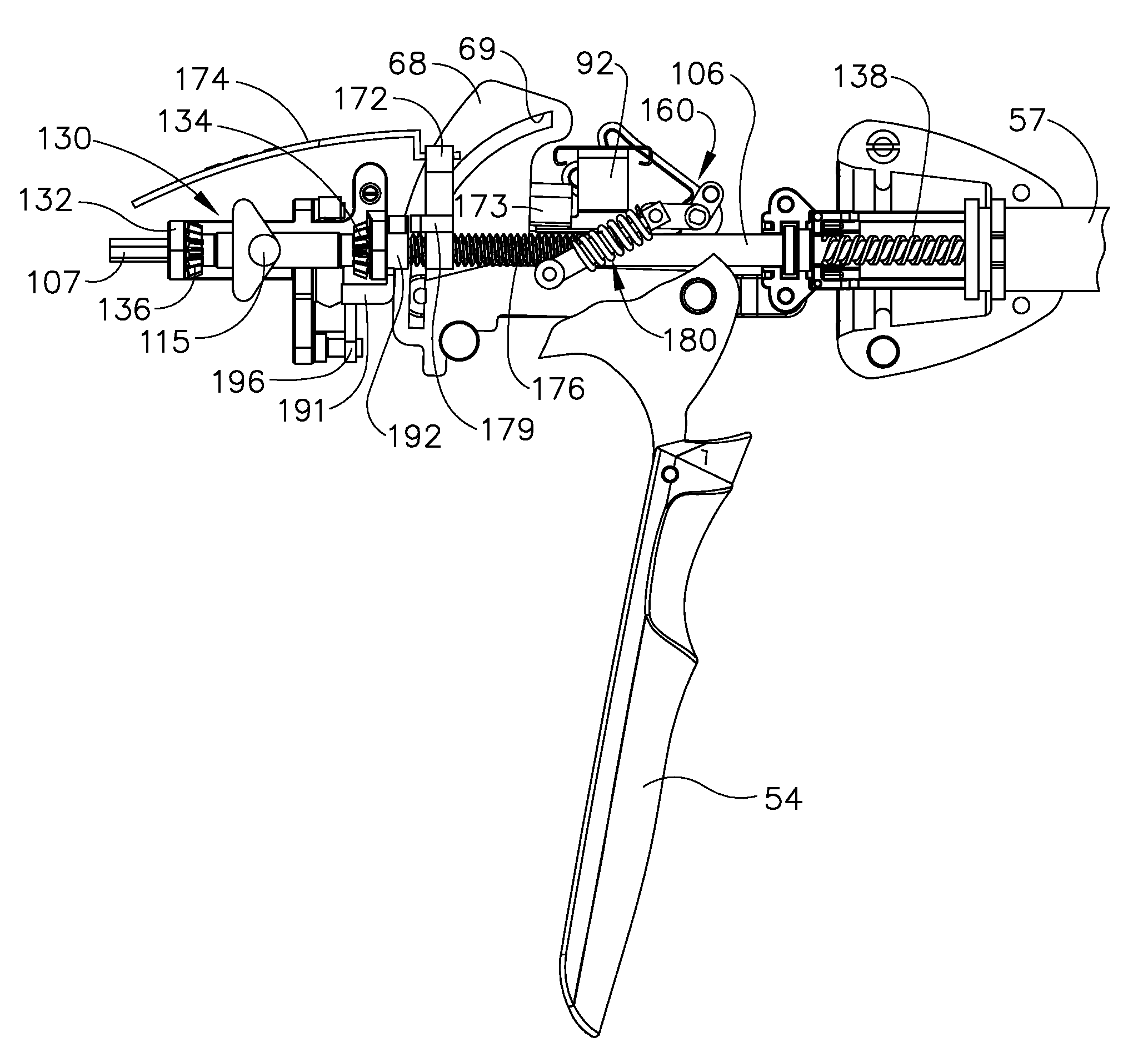
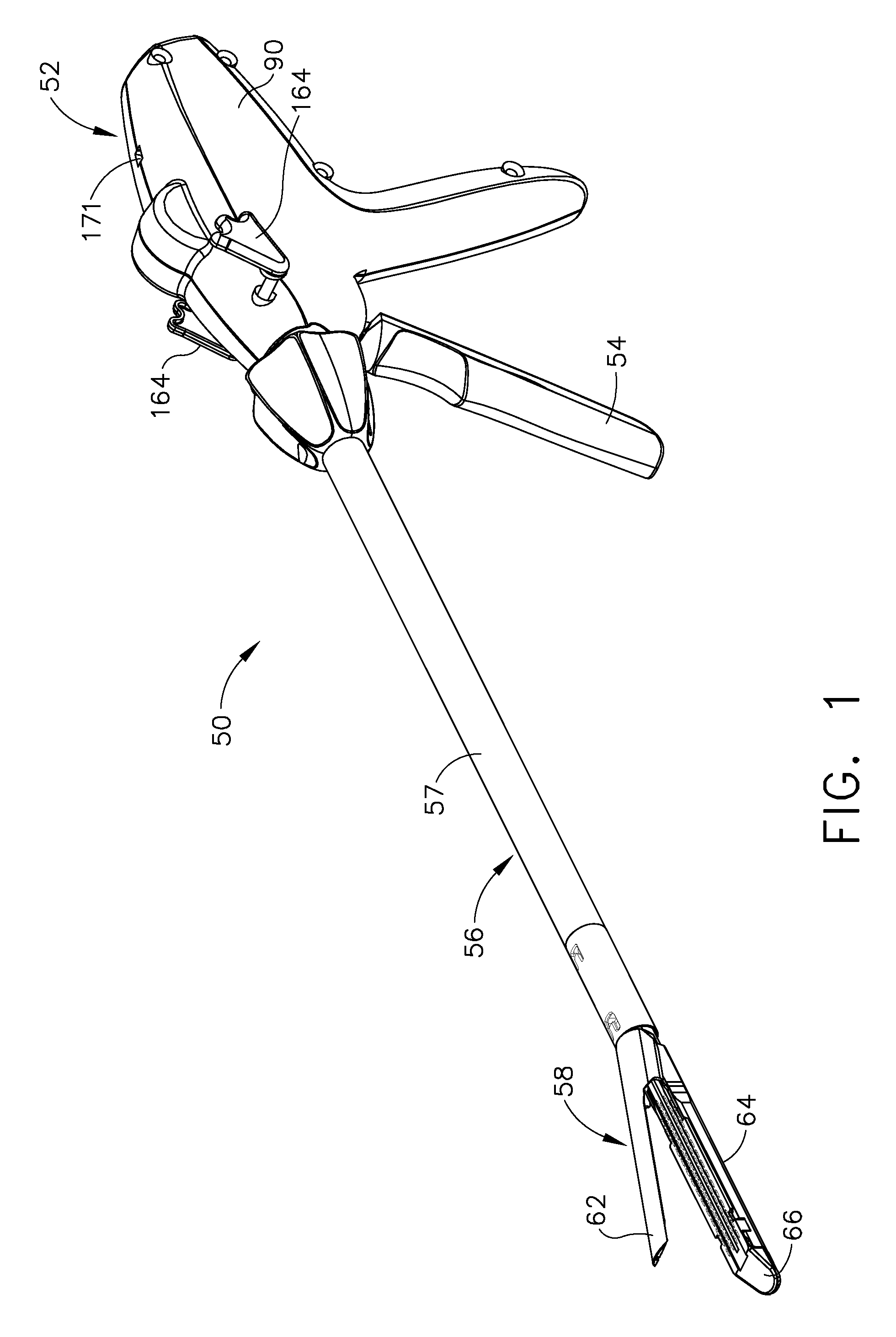
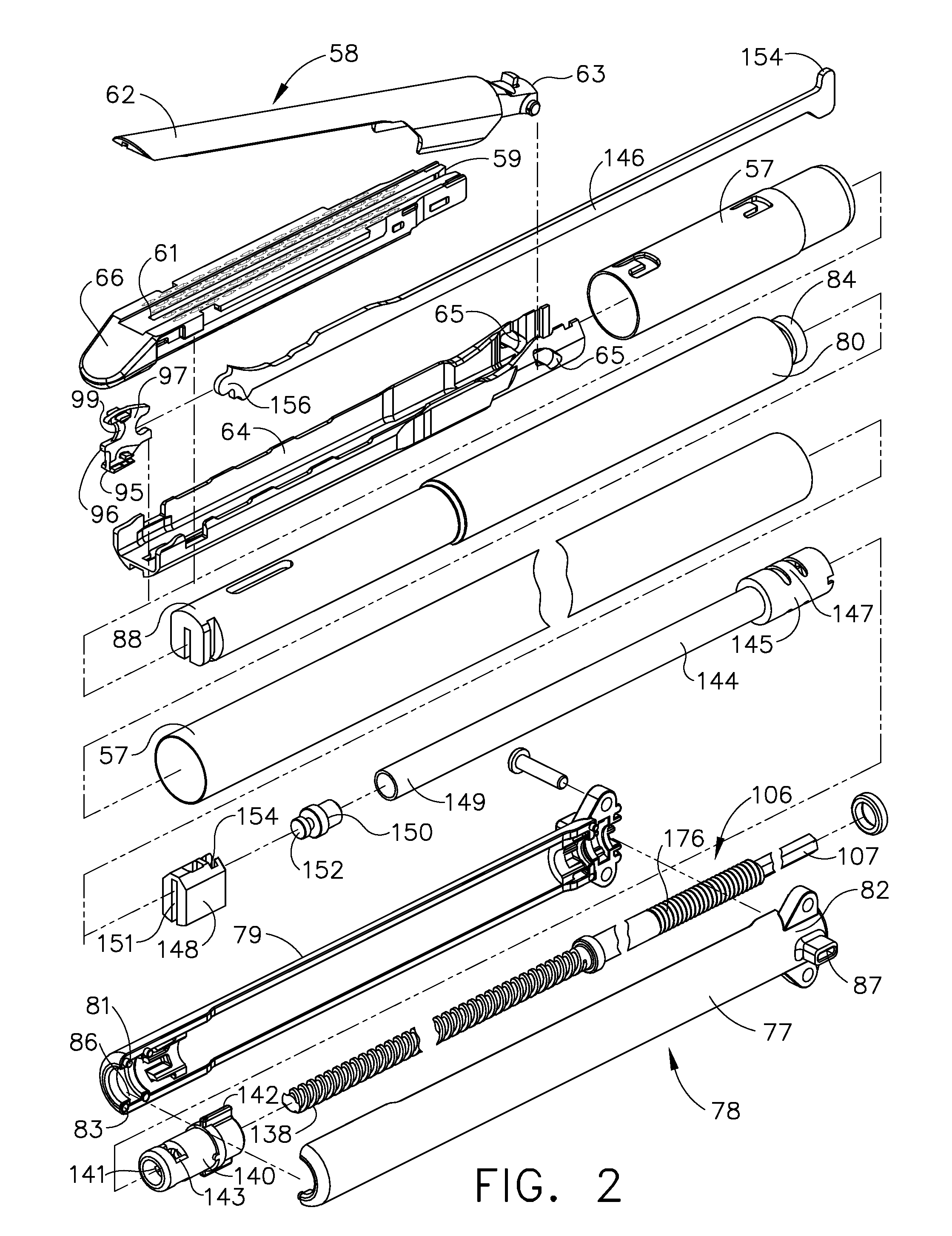
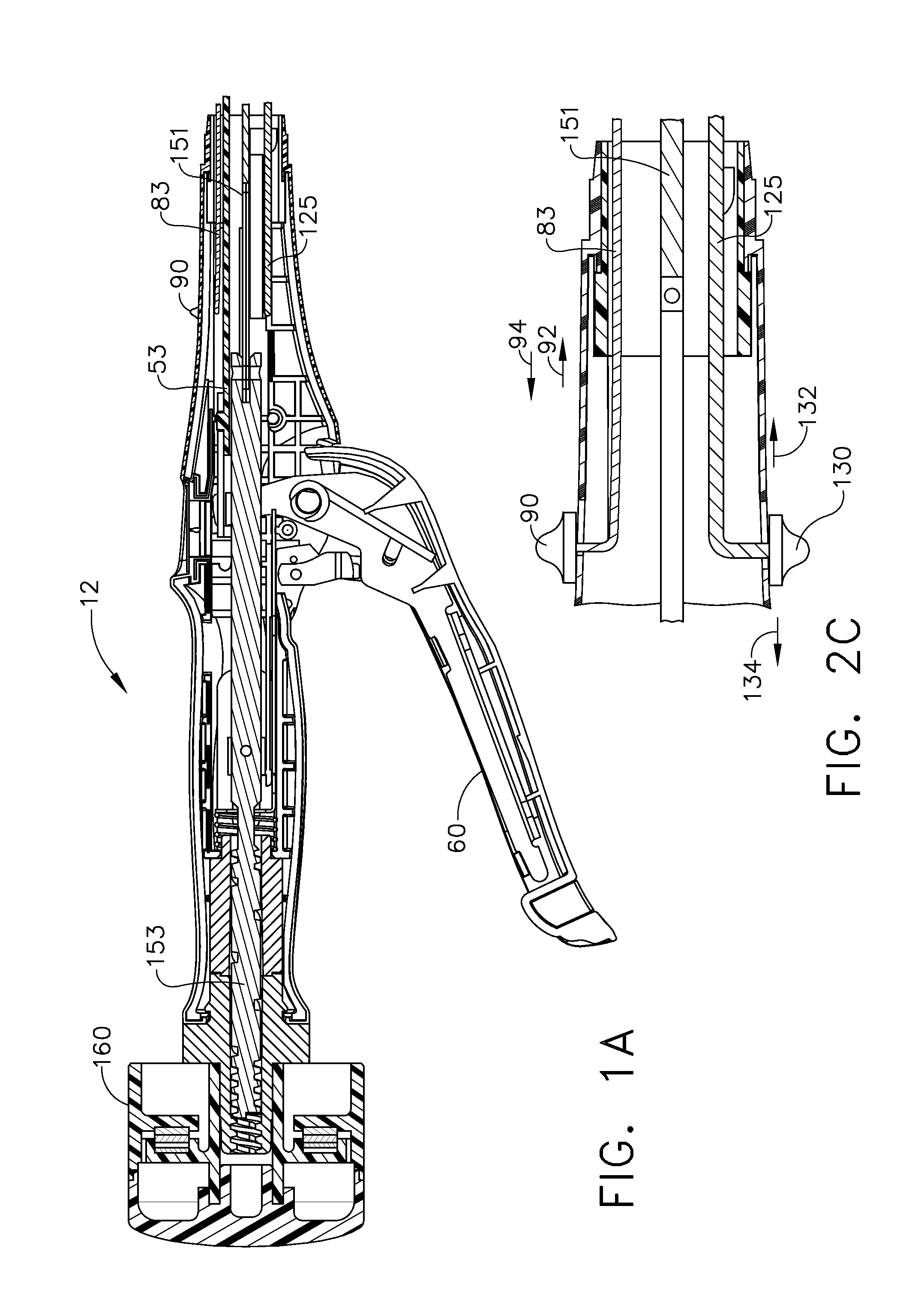
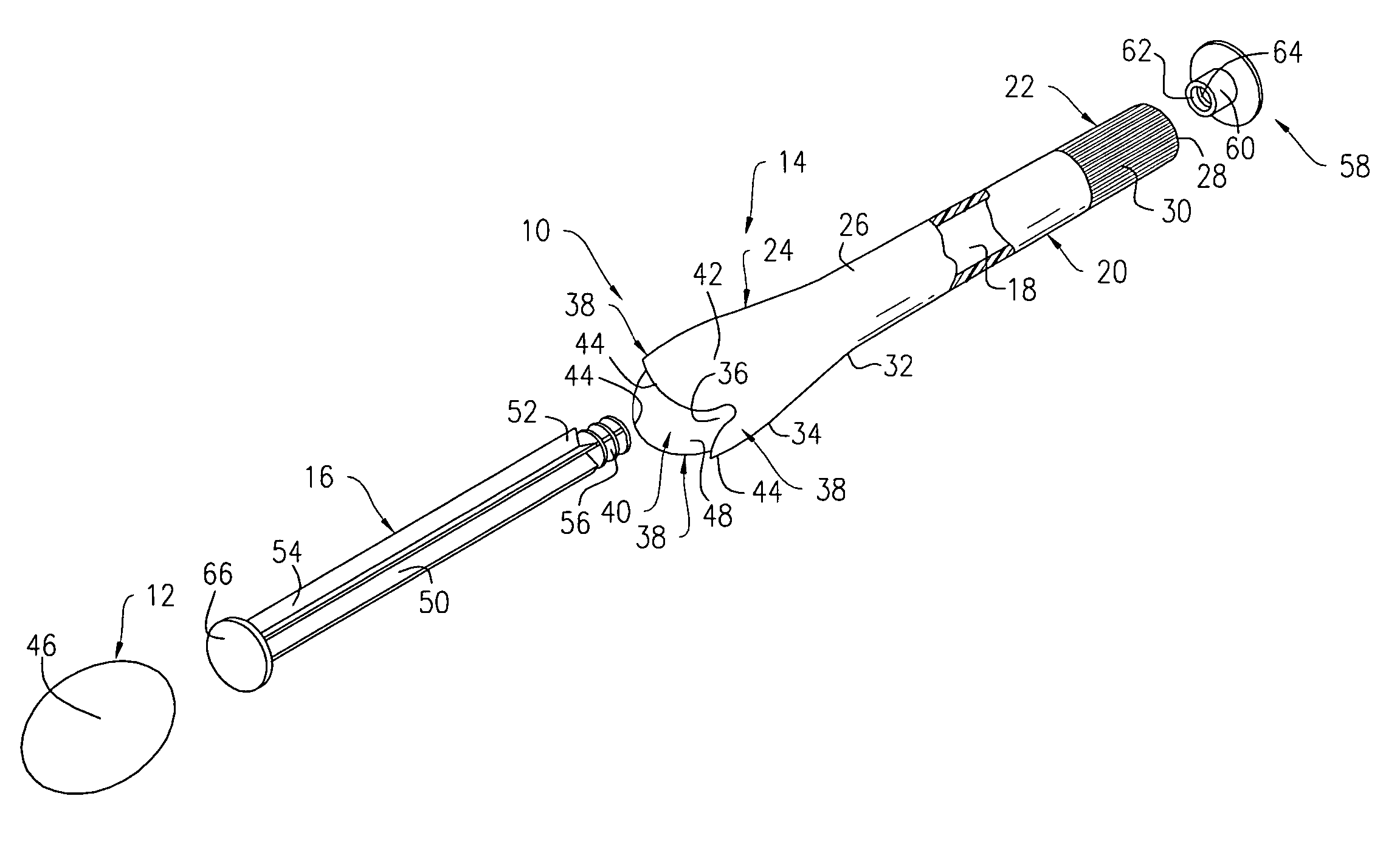
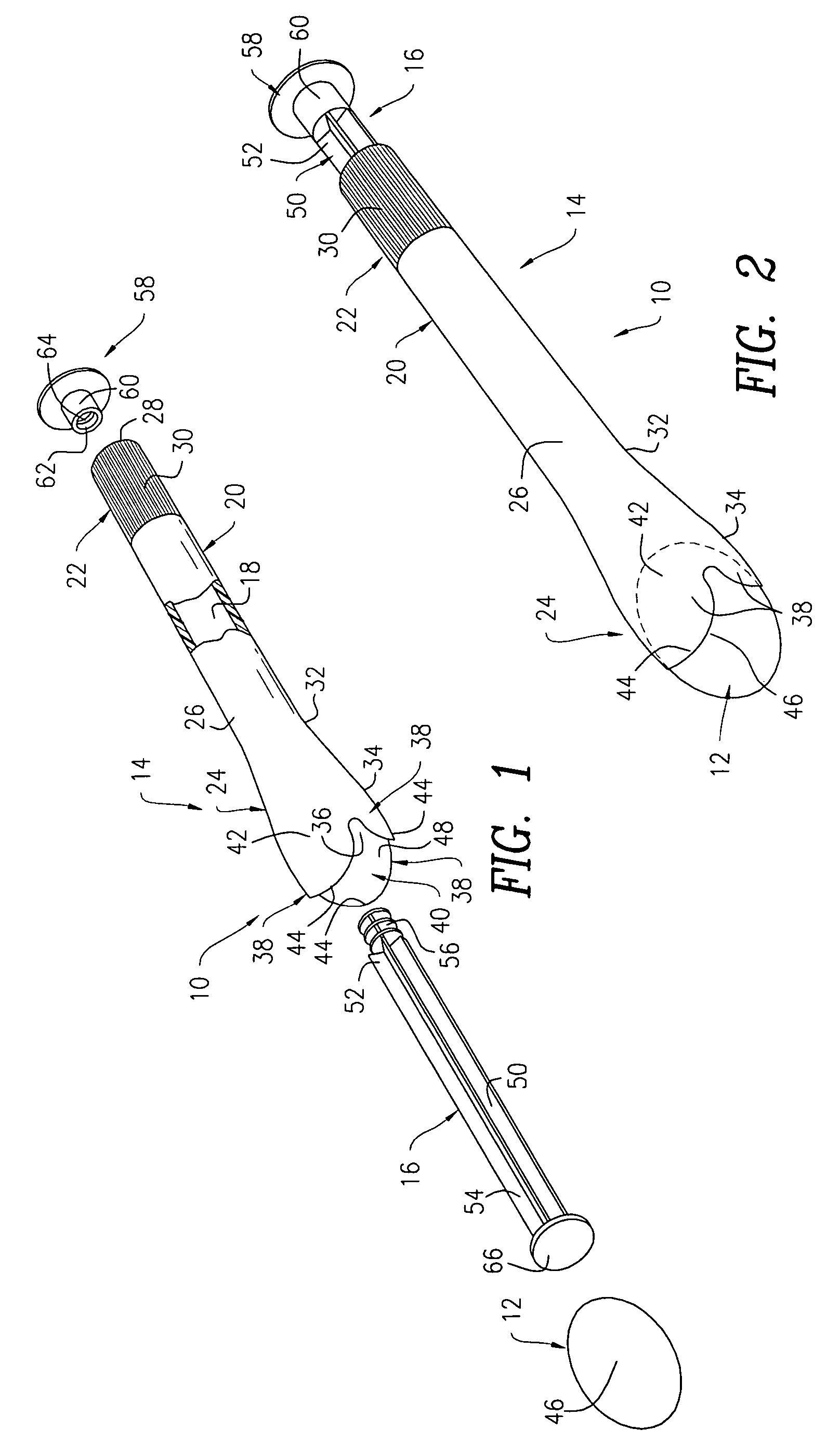
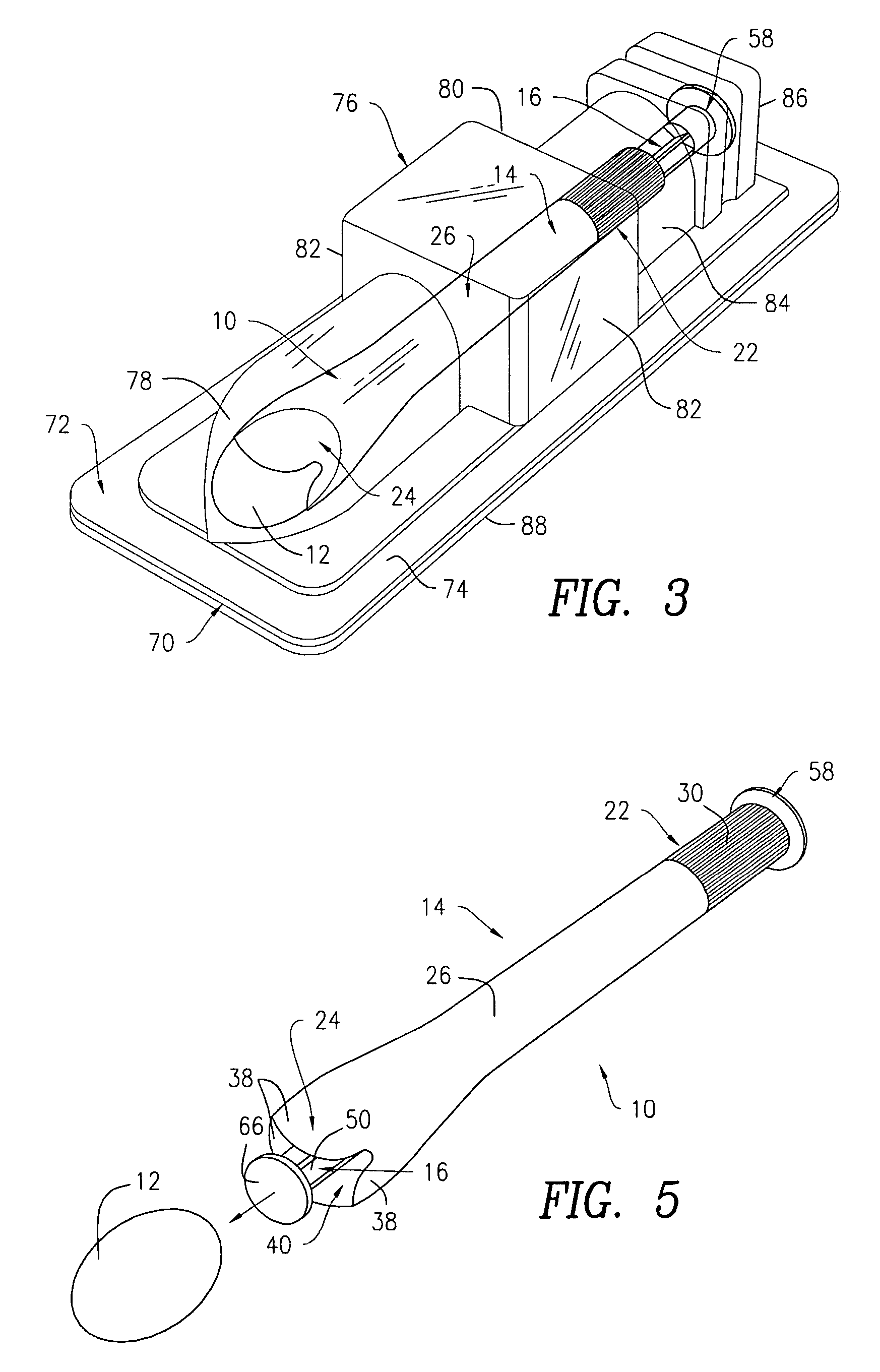
Surgical instrument having a common trigger for actuating an end effector closing system and a staple firing system
ActiveUS7819299B2Quickly and conveniently selectSuture equipmentsStapling toolsSurgical operationSurgical site
A surgical instrument including a trigger which can be configured to close a jaw member upon a first actuation of the trigger and advance a staple driver and / or cutting member upon a subsequent, or second, actuation of the trigger. Such a surgical instrument can allow a surgeon to position the surgical instrument in a surgical site and close the jaw member with an initial actuation of the trigger without deploying any staples into, or incising, the tissue. As a result, the surgeon can manipulate the position of the surgical instrument and then actuate the trigger a second time to deploy staples into, and / or incise, the tissue. In at least one such embodiment, the first actuation of the trigger which closes the jaw member can also unlock a firing drive configured to advance the staple driver and cutting member during the second actuation of the trigger.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
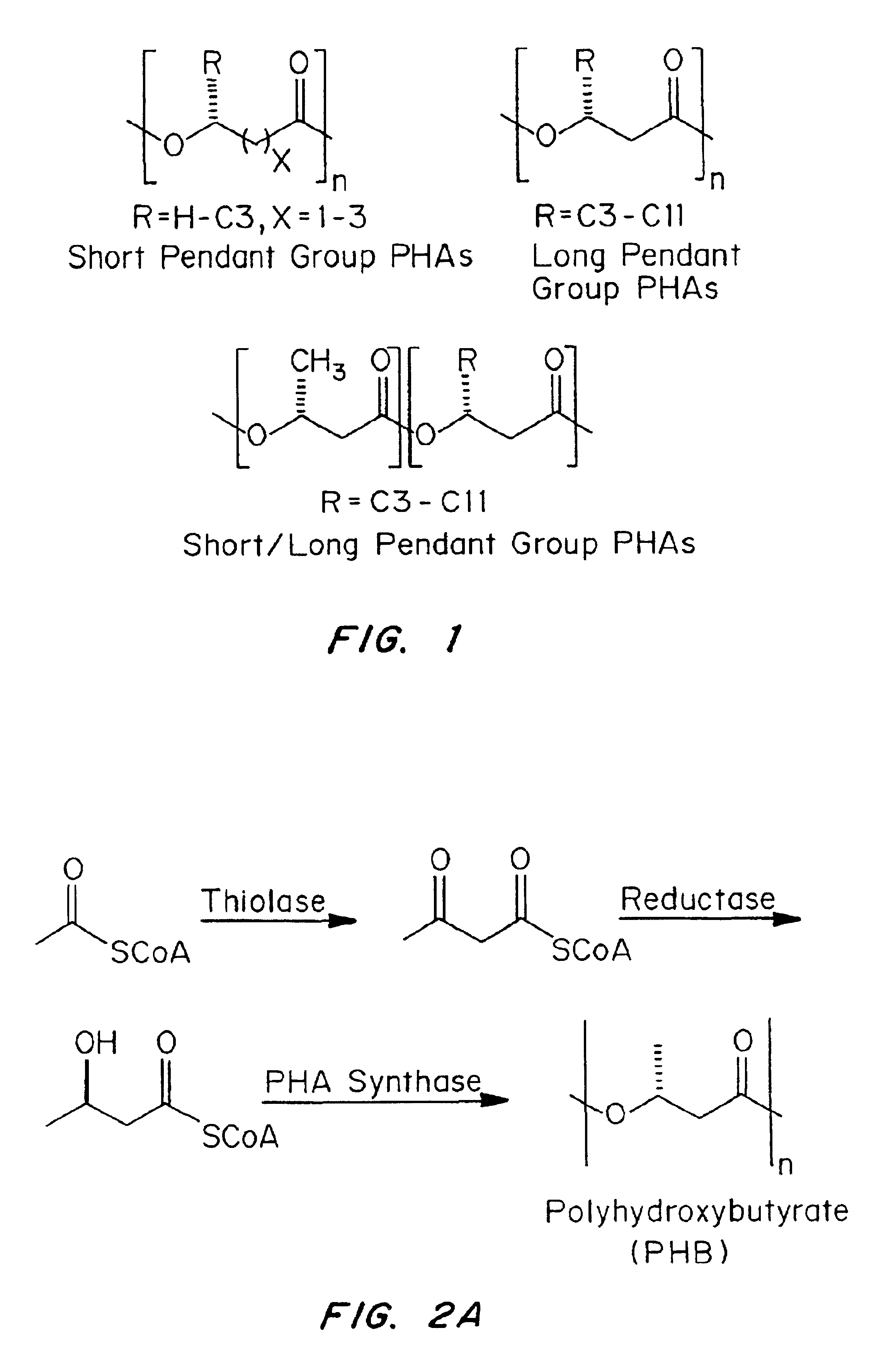
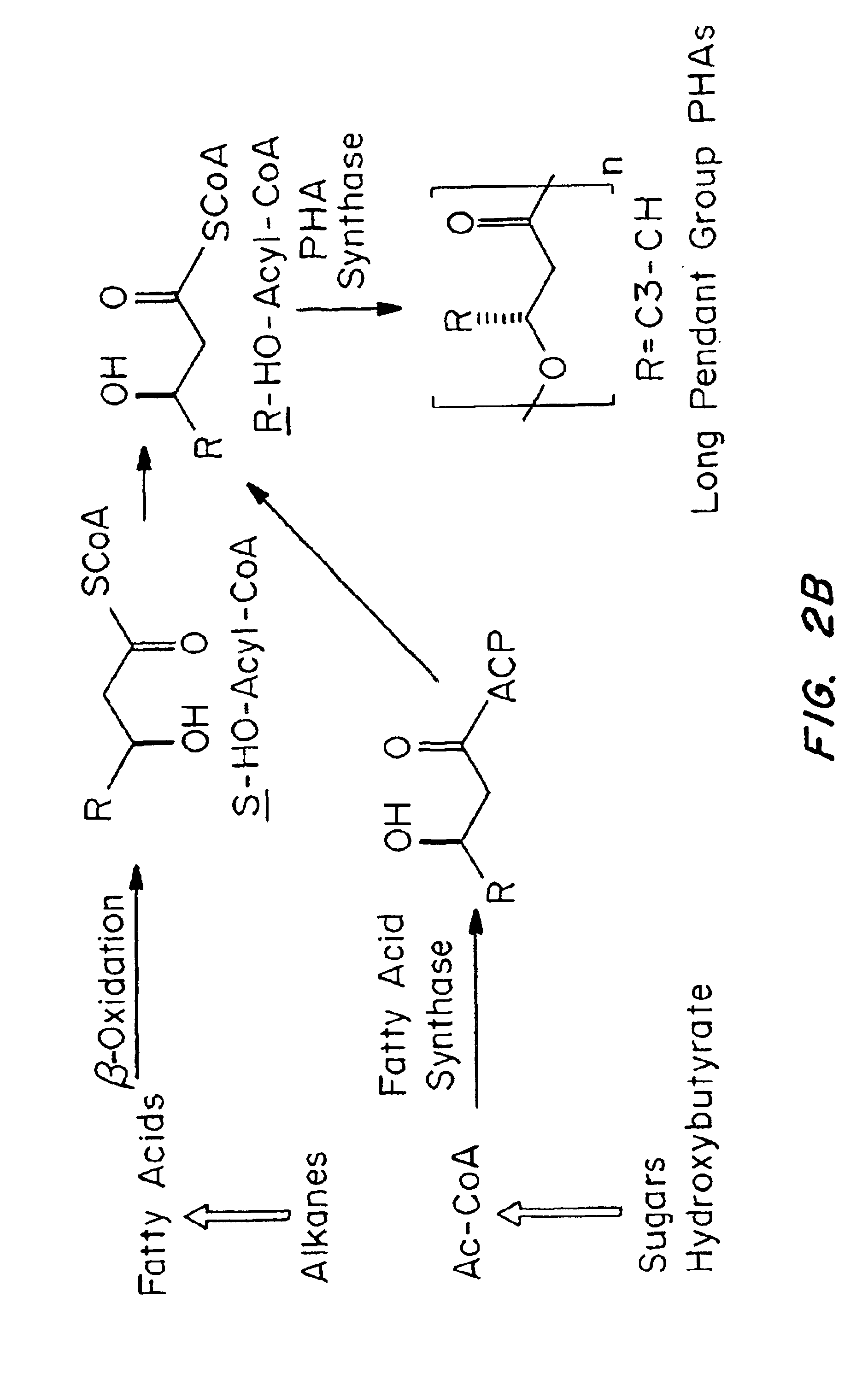
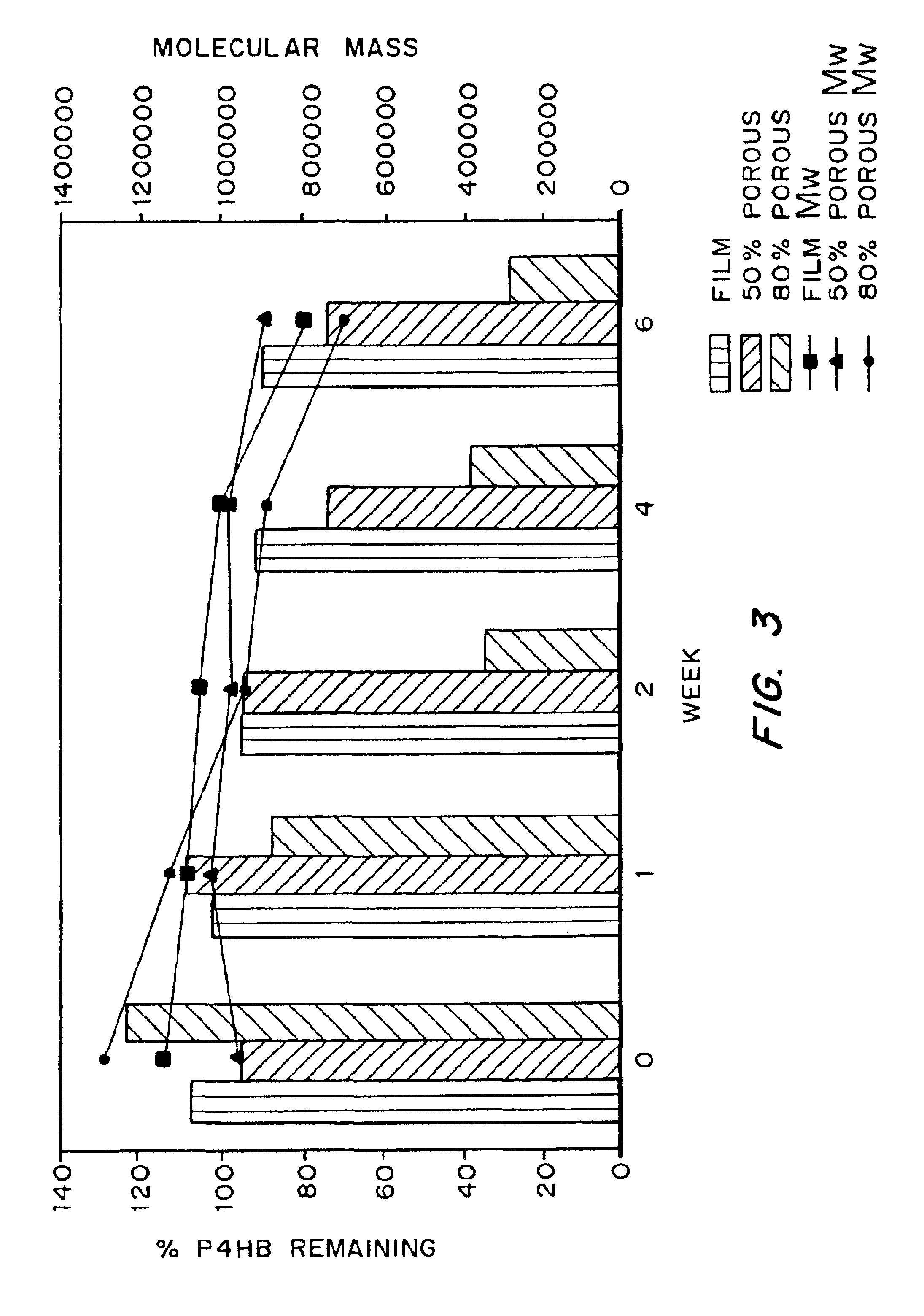
Medical devices and applications of polyhydroxyalkanoate polymers
InactiveUS6838493B2High porosityReduce probabilitySuture equipmentsOrganic active ingredientsTissue repairBiocompatibility Testing
Devices formed of or including biocompatible polyhydroxyalkanoates are provided with controlled degradation rates, preferably less than one year under physiological conditions. Preferred devices include sutures, suture fasteners, meniscus repair devices, rivets, tacks, staples, screws (including interference screws), bone plates and bone plating systems, surgical mesh, repair patches, slings, cardiovascular patches, orthopedic pins (including bone filling augmentation material), adhesion barriers, stents, guided tissue repair / regeneration devices, articular cartilage repair devices, nerve guides, tendon repair devices, atrial septal defect repair devices, pericardial patches, bulking and filling agents, vein valves, bone marrow scaffolds, meniscus regeneration devices, ligament and tendon grafts, ocular cell implants, spinal fusion cages, skin substitutes, dural substitutes, bone graft substitutes, bone dowels, wound dressings, and hemostats. The polyhydroxyalkanoates can contain additives, be formed of mixtures of monomers or include pendant groups or modifications in their backbones, or can be chemically modified, all to alter the degradation rates. The polyhydroxyalkanoate compositions also provide favorable mechanical properties, biocompatibility, and degradation times within desirable time frames under physiological conditions.
Owner:TEPHA INC
Apparatus and methods for protecting adjacent structures during the insertion of a surgical instrument into a tubular organ
A device for protecting tissues and structures adjacent to a tubular organ during performance of a surgical procedure on a portion of the tubular organ. Various embodiments may comprise a member that may be deployed through a surgical instrument in a first configuration and expanded to a second configuration such that when in the second configuration, the protective member may extend substantially around an outer circumference of the portion of the tubular organ.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Dissolvable medical sealing device
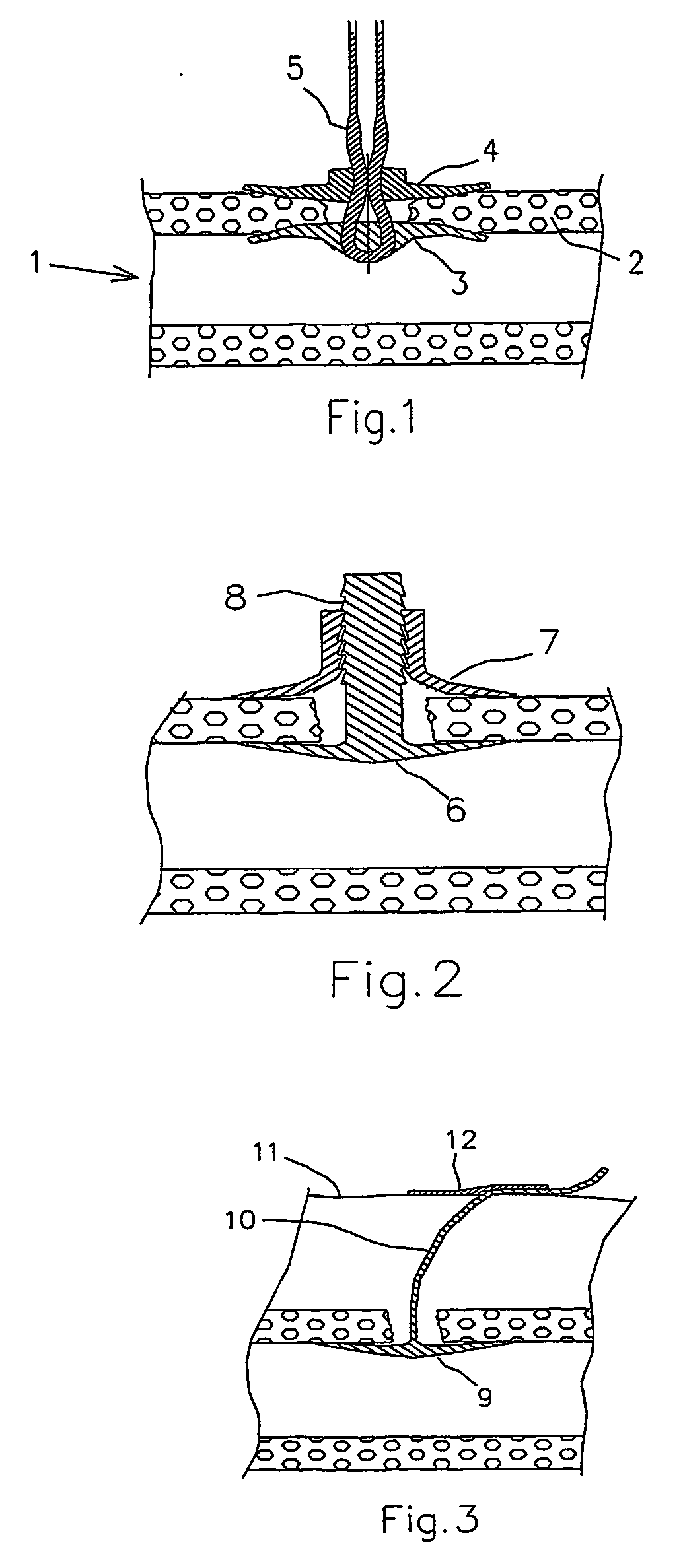
ActiveUS20050169974A1Shorten the timeSuture equipmentsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismOrganismal ProcessPolyvinyl alcohol
The present invention provides a dissolvable medical sealing device (3, 4; 6, 7; 9) for closing a wound in vessel. A sealing device (3, 4, 6, 7, 9) according to the invention is made of a material that dissolves by means of physical processes, rather than by means of chemical or biological processes. Such a sealing device (3, 4; 6, 7; 9) can be made of polyethylene glycol, polypropylene glycol, copolymers containing ethylene glycol and propylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol or polyvinyl pyrolidone, or any combinations thereof.
Owner:TERUMO MEDICAL CORP
Method for preparing two-layer bicomposite collagen material for preventing post-operative adhesions
InactiveUS6596304B1Improve propertiesAvoid stickingPeptide/protein ingredientsSurgerySurgical operationPost operative
A bicomposite material based on collagen is prepared which has two closely bound layers and is biocompatible, non-toxic, hemostatic and biodegradable in less than a month, and can be used in surgery to achieve hemostasis and prevent post-surgical adhesion. To prepare the material, a solution of collagen or gelatin, which may contain glycerine and a hydrophilic additive such as polyethylene glycol or a polysaccharide, is poured onto an inert support to form a layer 30 .mu.m to less than 100 .mu.m thick. Then a polymeric porous fibrous layer is applied during gelling of the collagen or gelatin, and the resultant material is dried. The polymeric porous fibrous layer may be made of collagen or a polysaccharide, and have a density of not more than 75 mg / cm.sup.2, a pore size from 30 .mu.m to 300 .mu.m and a thickness of 0.2 cm to 1.5 cm.
Owner:IMEDEX BIOMATERIAUX CHAPONOST
Absorbent material incorporating synthetic fibers and process for making the material
InactiveUS20030084983A1Reduce leakageWidespread acceptanceLayered productsBaby linensPolymer scienceHigh density
A process is provided for making a soft, high density, absorbent material with improved characteristics. A web is formed from material that includes a mixture of cellulosic fibers and synthetic polymer fibers. Then, the web is preferably compacted and embossed at an elevated temperature to further increase the web density and preferably to also create liquid-stable bonds between the synthetic polymer fibers and the cellulosic fibers in spaced-apart regions of the web.
Owner:EAM
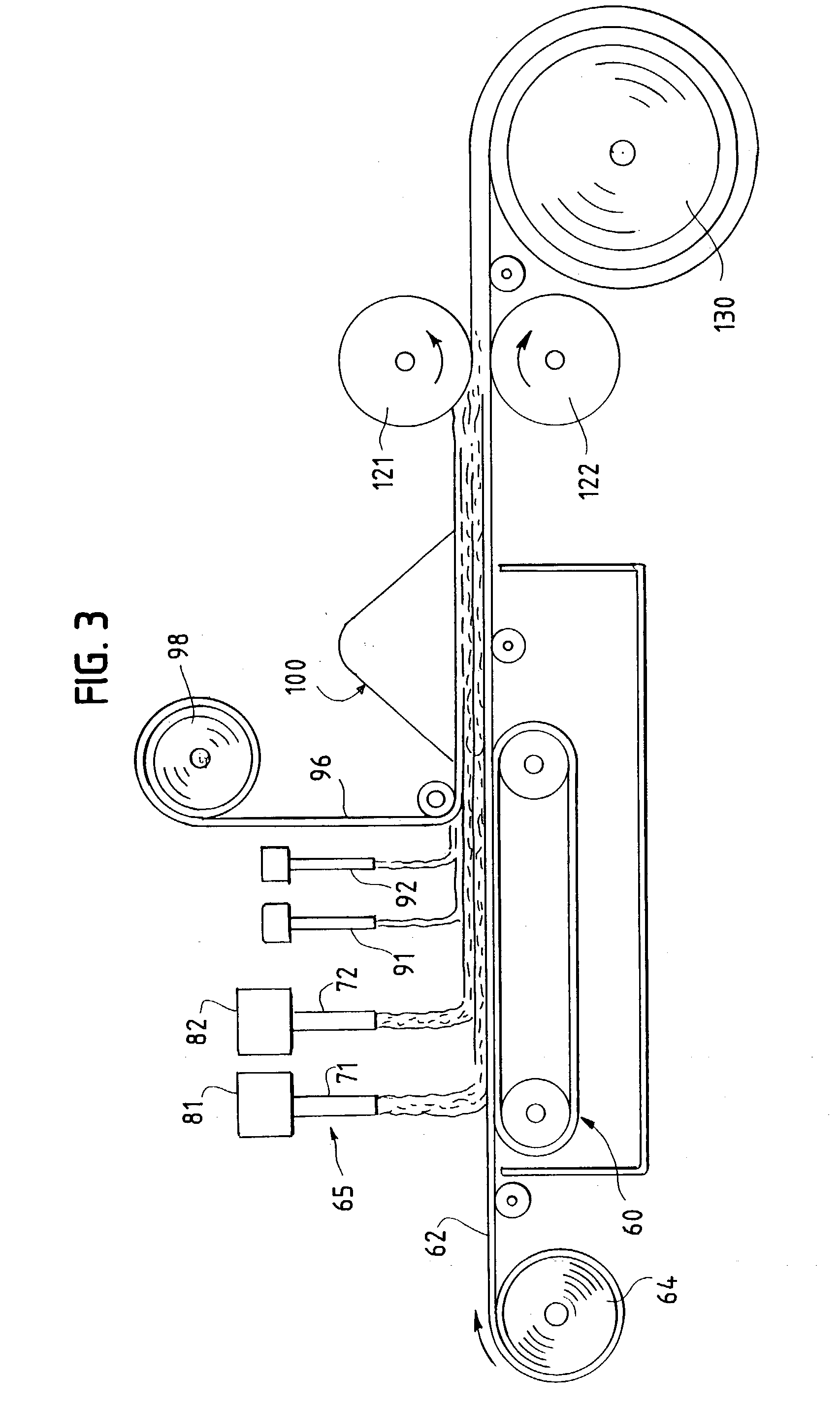
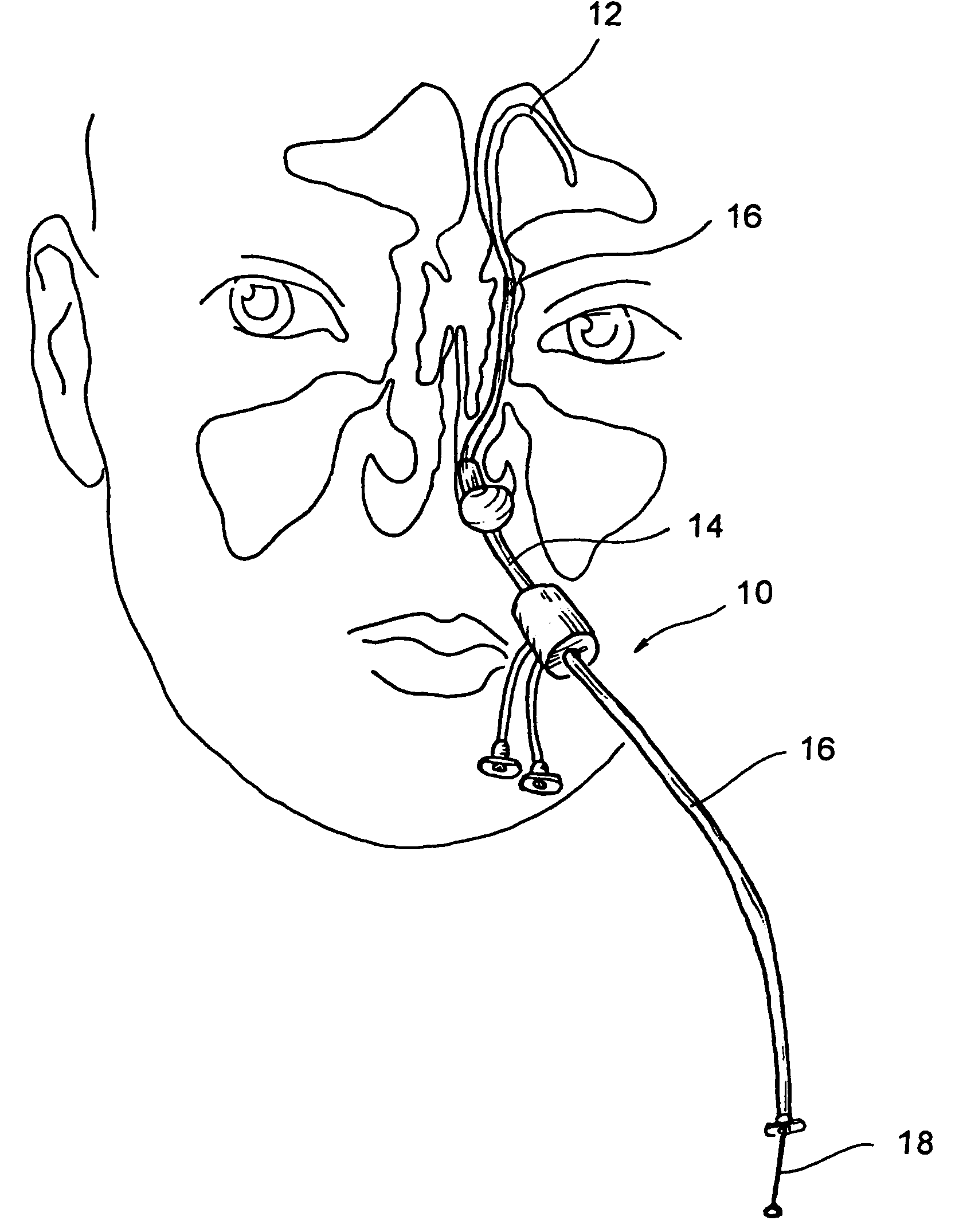
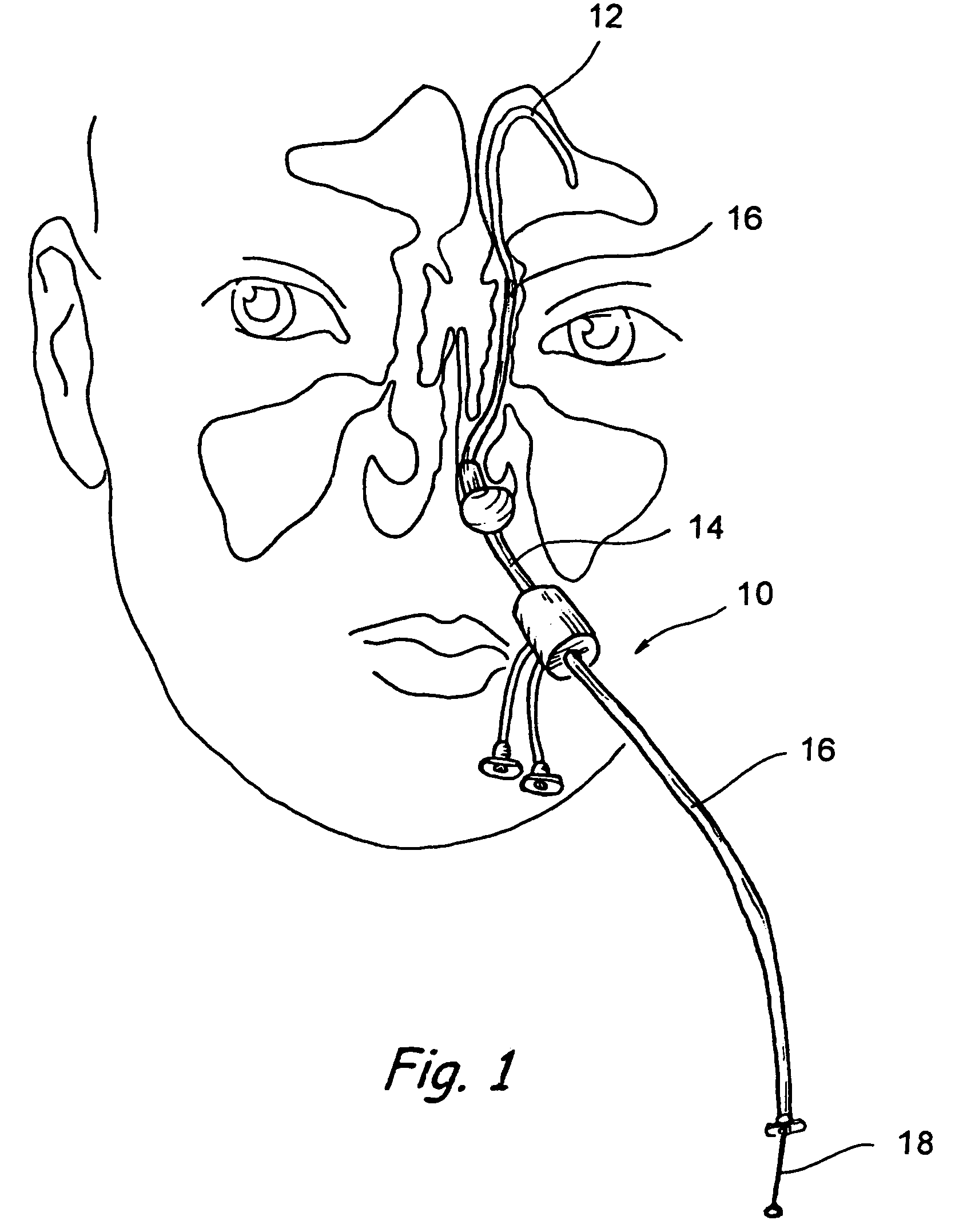
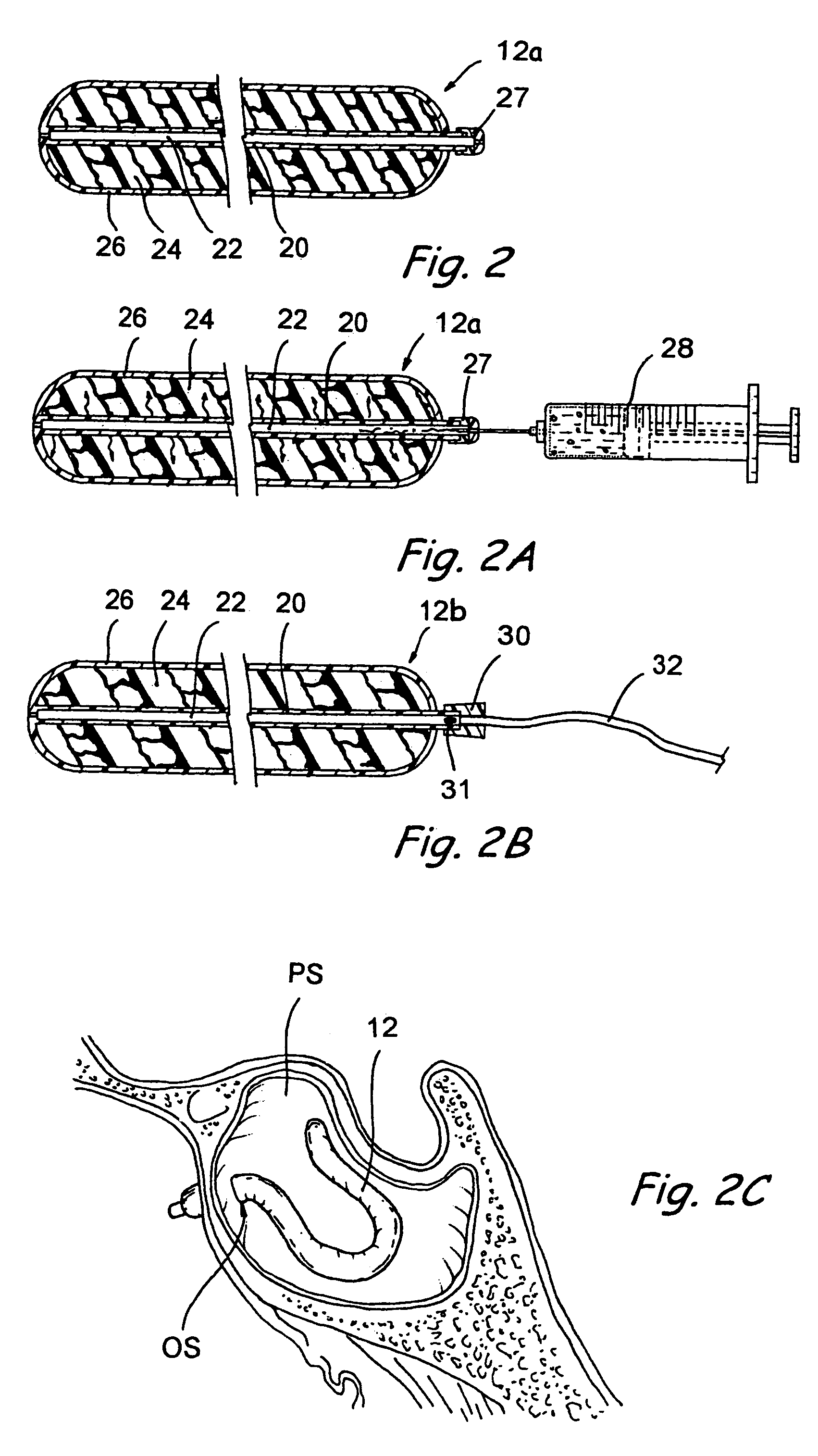
Implantable device and methods for delivering drugs and other substances to treat sinusitis and other disorders
Implantable devices and methods for delivering drugs and other substances to locations within the body of a human or animal subject to treat or diagnose sinusitis and a variety of other disorders. The invention includes implantable substance delivery devices that comprise reservoirs and barriers that control the rate at which substances pass out of the reservoirs. The delivery devices may be advanced into the body using guidewires, catheters, ports, introducers and other access apparatus. In some embodiments the delivery devices may be loaded with one or more desired substance before their introduction into the body. In other embodiments the delivery devices are loaded and / or reloaded with a desired substance after the delivery device has been introduced into the body.
Owner:ACCLARENT INC
Drug depot implant designs
ActiveUS7727954B2Uniform drug distributionMinimal disruptionPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsSkeletal injuryChronic pain
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
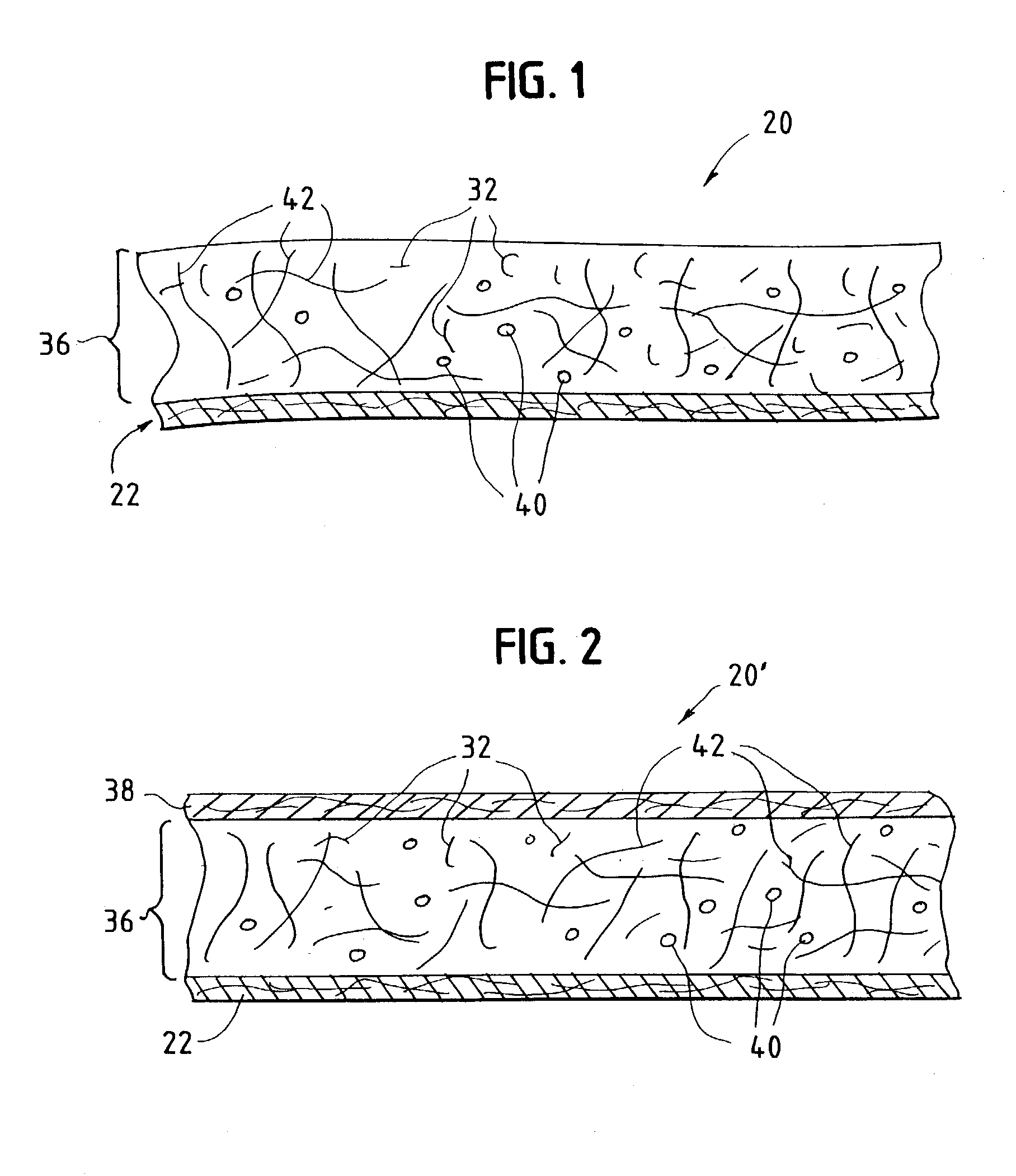
Tufted fibrous web
A fibrous web having a first surface and a second surface. The fibrous web has a first region and at least one discrete second region, the second region being a discontinuity on the second surface and being a tuft comprising a plurality of tufted fibers extending from the first surface. The tufted fibers define a distal portion, the distal portion comprising portions of the tufted fibers being bonded together. Bonding can be thermal melt-bonding. In another embodiment the second surface of the web can have non-intersecting or substantially continuous bonded regions, which also can be thermal melt-bonding.
Owner:PROCTER & GAMBLE CO
Agents and devices for providing blood clotting functions to wounds
InactiveUS20070190110A1Promote healingShorten the timePhysical treatmentAntithrombogenic treatmentNitrogen dioxideMedicine
Hemostatic agents and devices are made from oxidized cellulose fiber, the oxidized cellulose having a carboxylation content increased by the action of nitrogen dioxide on virgin cellulose fiber. A composition may be incorporated into the oxidized cellulose fiber to cause a pharmacological effect on a wound to which the hemostatic agents and devices are applied. When applied, the oxidized cellulose fiber causes blood emanating from the wound to clot. The oxidized cellulose fiber can either be resorbed into the wound or removed from the wound after healing. A hemostatic bandage includes a pad of unwoven oxidized cellulose fibers mounted on a substrate. Methods of arresting a flow of blood emanating from a wound using such devices are also disclosed. Methods of fabricating oxidized cellulose are also disclosed.
Owner:PAMEIJER CORNELIS H +1
Hemostatic compositions for arresting blood flow from an open wound or surgical site
A hemostatic composition for stopping or decreasing blood flow from an open wound or medical or surgical procedure. Compositions of the invention comprise a mixture of a cationic polymer and a cation exchange material. In one embodiment, the composition comprises a mixture: (1) a high molecular weight copolymer of diallyl dimethyl ammonium chloride (DADMAC) and acrylamide [DADMAC copolymer], and (2) the hydrogen form of a crosslinked, sulfonated polystyrene (hydrogen resin). In an exemplified embodiment, a composition of the invention comprises the mixture of DADMAC copolymer and hydrogen resin provided in a dry powdered form. The compositions of the invention may be applied directly to a wound or treatment site, or they may be incorporated into a wound dressing, such as a bandage. The seal formed at a wound or treatment site treated with the present invention is adhesive and exhibits considerable toughness.
Owner:BIOLIFE
Plasma protein matrices and methods for their preparation
InactiveUS7009039B2Rapid cell growthRapid vascularizationBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsBiological propertyFreeze-drying
A freeze dried biocompatible matrix comprising plasma proteins, useful as implants for tissue engineering as well as in biotechnology, and methods of producing the matrix are provided. Mechanical and physical parameters can be controlled by use of auxiliary components or additives which may be removed after the matrix is formed in order to improve the biological properties of the matrix. The matrices according to the present invention may be used clinically per se, or as a cell-bearing implant.
Owner:PROCHON BIOTECH
Disposable Absorbent Article With Improved Acquisition System
A disposable absorbent article comprising a chassis including a topsheet and a backsheet, a substantially cellulose free absorbent core located between the topsheet and the backsheet and having a wearer facing side oriented toward a wearer when the article is being worn and an opposed garment facing side, and a liquid acquisition system disposed between the liquid permeable topsheet and the wearer facing side of the absorbent core comprising chemically cross-linked cellulosic fibers.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Absorbent articles comprising nanoparticles
Owner:NANO MET ZERO
Medical system and method for remodeling an extravascular tissue structure
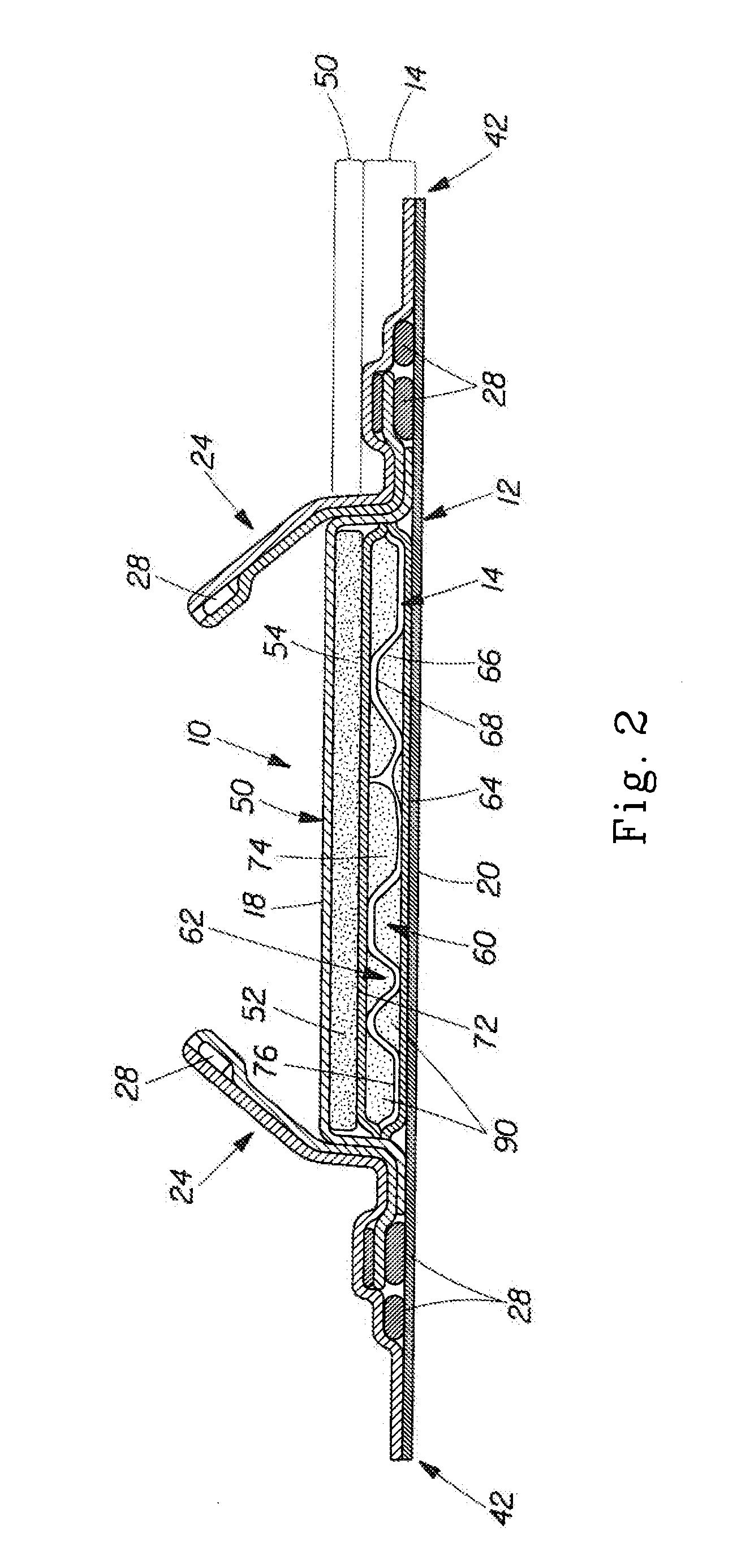
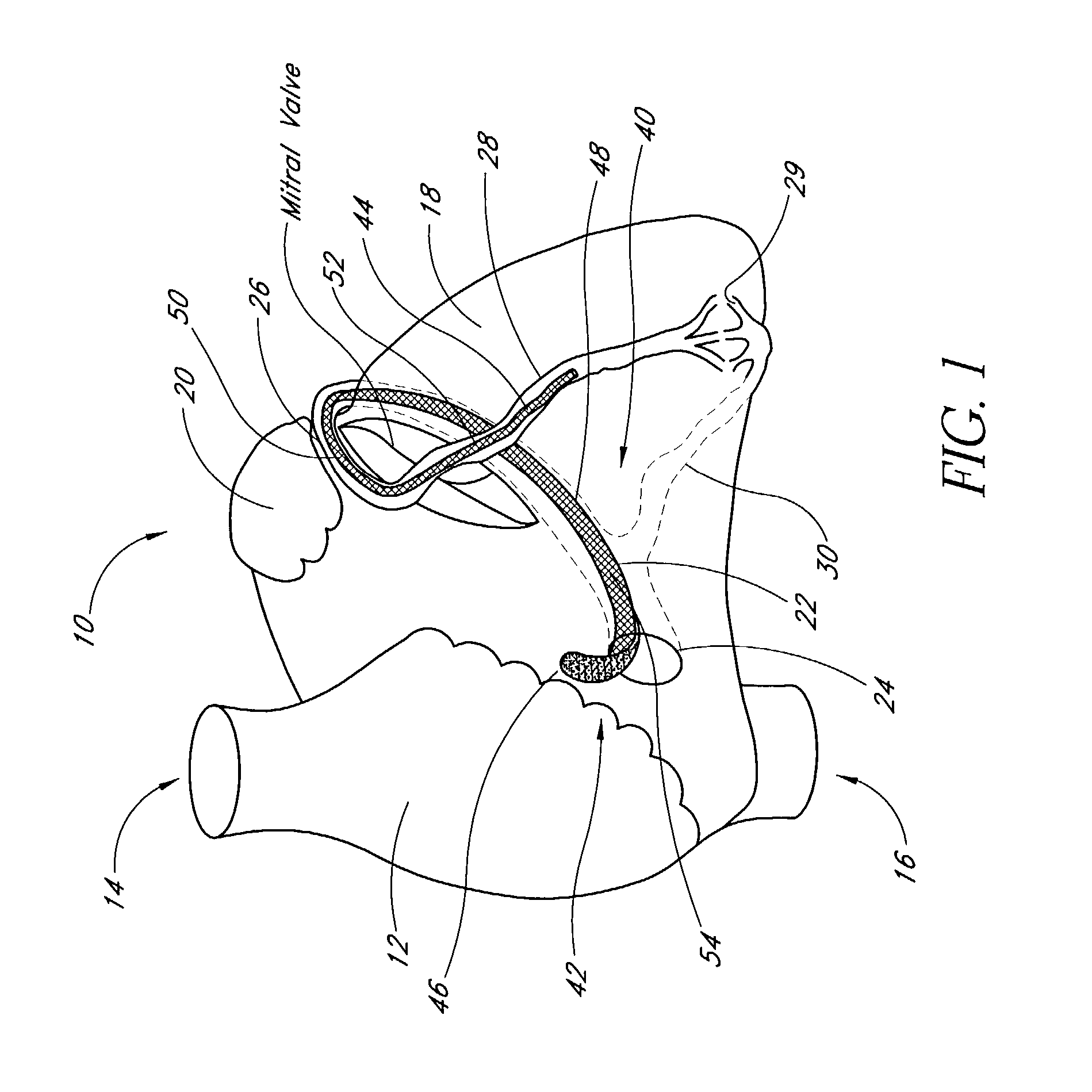
A medical apparatus and method suitable for remodeling a mitral valve annulus adjacent to the coronary sinus. The apparatus comprises an elongate body having a proximal region and a distal region. Each of the proximal and distal regions is dimensioned to reside completely within the vascular system. The elongate body may be moved from a first configuration for transluminal delivery to at least a portion of the coronary sinus to a second configuration for remodeling the mitral valve annulus proximate the coronary sinus. A forming element may be attached to the elongate body for manipulating the elongate body from the first transluminal configuration to the second remodeling configuration. Further, the elongate body may comprise a tube having a plurality of transverse slots therein.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES AG
Method of preparation of bioabsorbable porous reinforced tissue implants and implants thereof
A biocompatible tissue implant. The tissue implant may be bioabsorbable, consists of a biocompatible polymeric foam. The tissue implant also includes a biocompatible reinforcement member. The polymeric foam and the reinforcement member are soluble in a lyophilizing solvent. The reinforcement may be annealed and / or coated.
Owner:DEPUY MITEK INC
Bi-phasic compressed porous reinforcement materials suitable for implant
ActiveUS8389588B2Efficient use ofHigh and low porosity zoneBone implantSkeletal disorderFluid migrationUltimate tensile strength
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Porous medical device and method for its manufacture
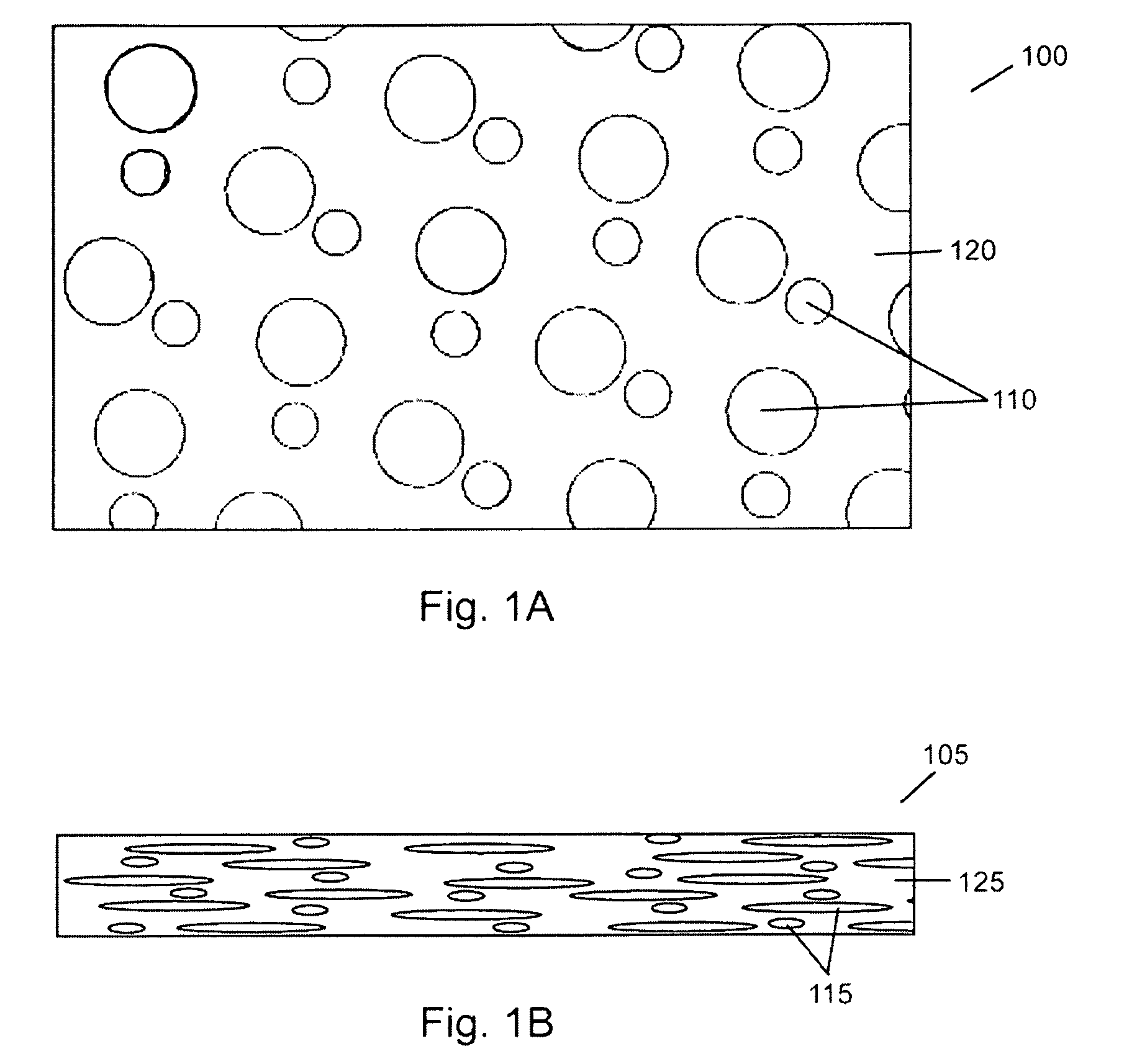
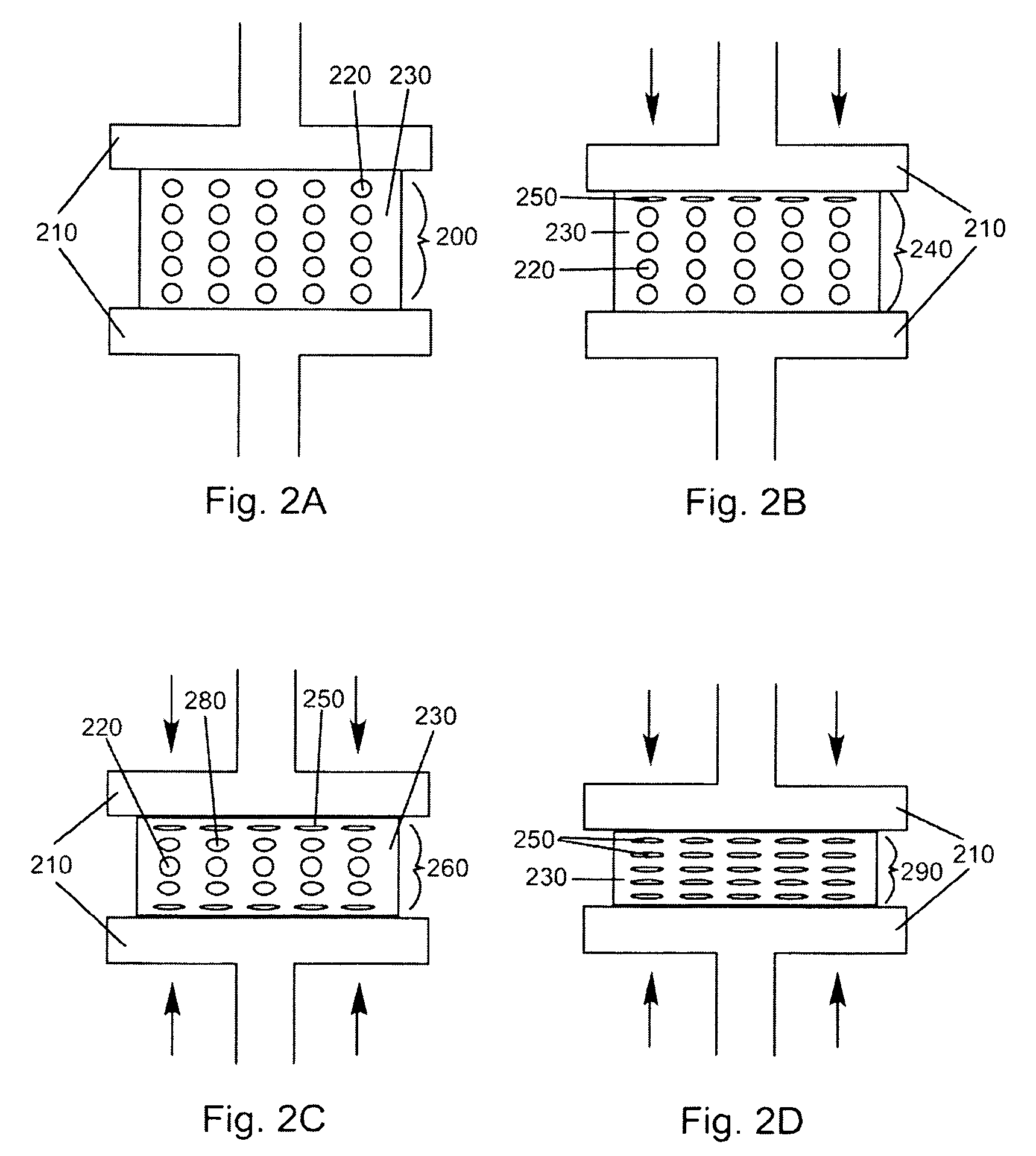
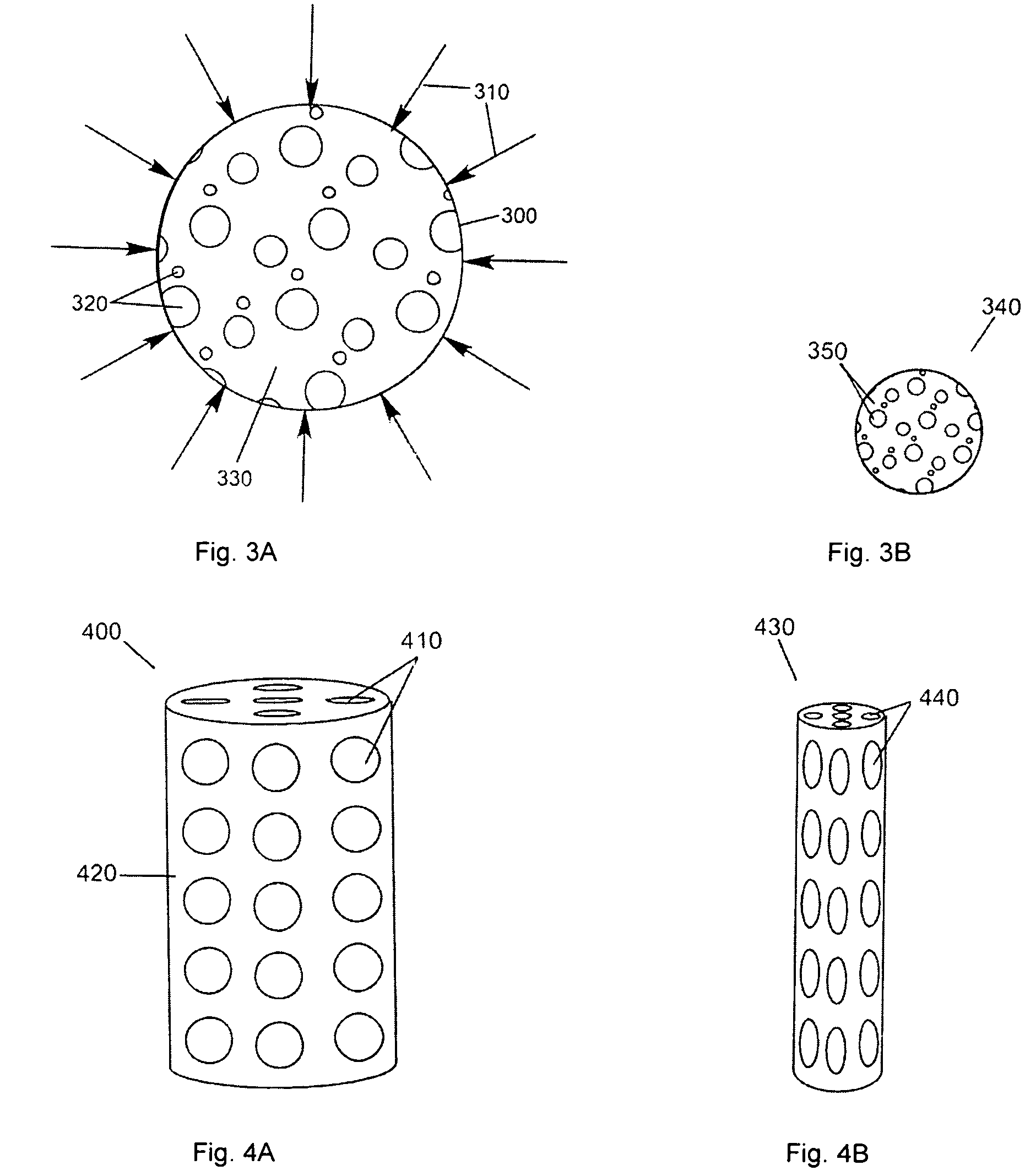
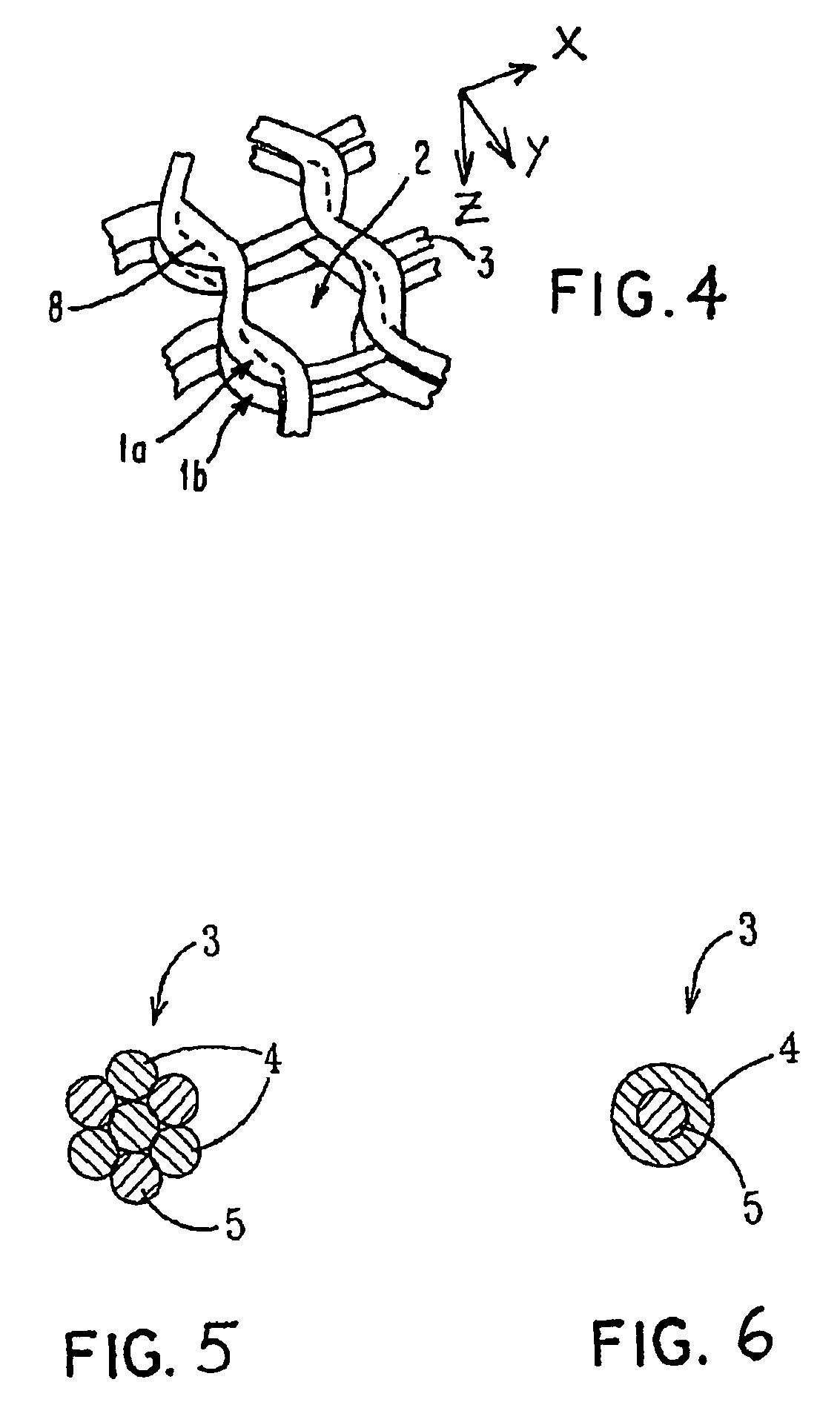
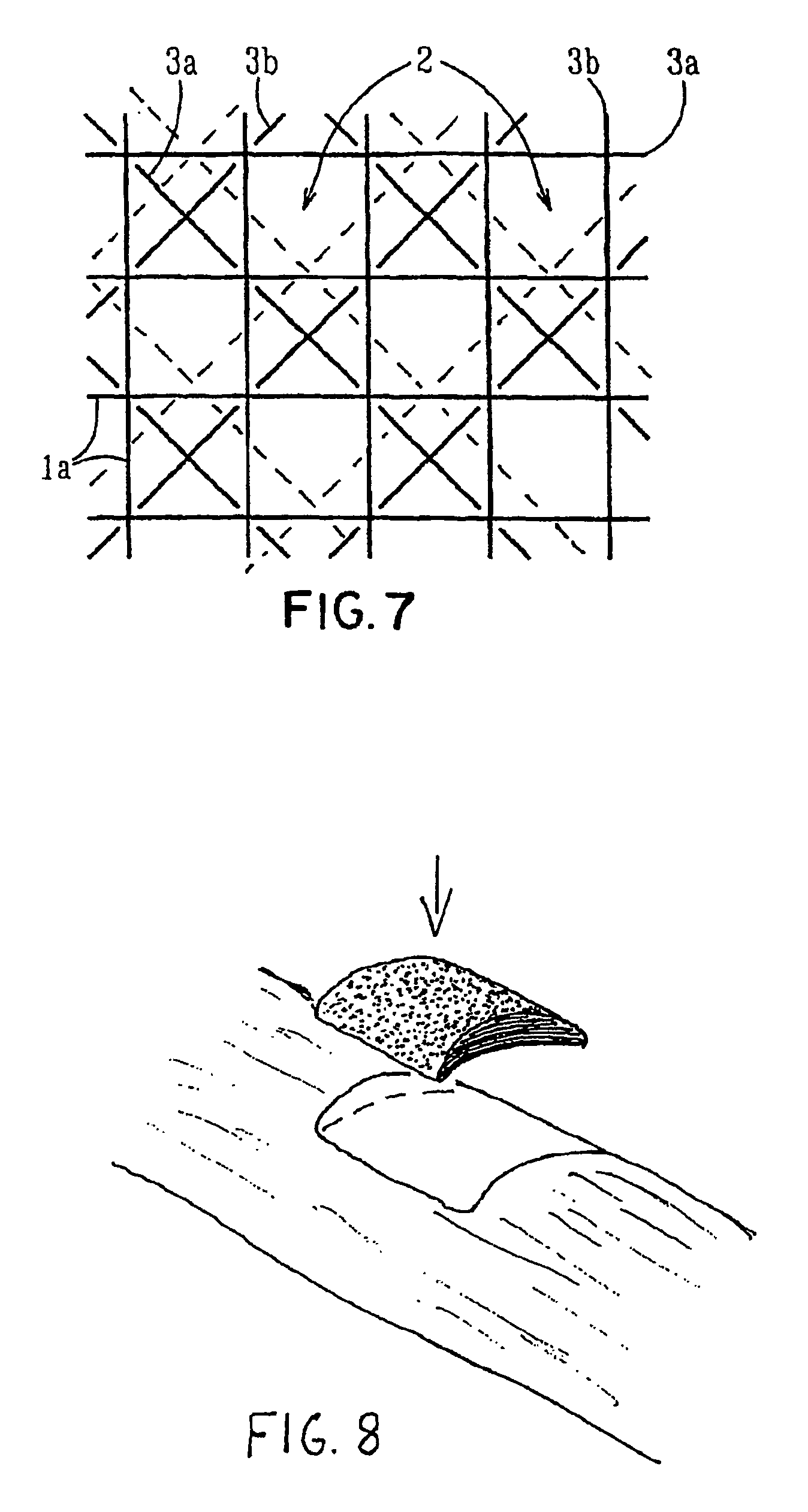
ActiveUS7964206B2Thickness of device can be variedControllable porosityBiocideGenetic material ingredientsFiberBioceramic
Porous bioabsorbable, bioactive and load-bearing composite medical device structure includes a plurality of regular textile planar layers (1a, 1b . . . ) formed of continuous bioabsorbable polymer matrix and bioceramic fibers acting as reinforcements, both included in continuous fibrous elements (3) forming the textile layers. The layers are placed on top of each other to form a structure having two dimensions (x, y) at right angles to each other according to the two dimensions of the textile layer and a third dimension (z) perpendicular to them and resulting from the piling of the layers. A plurality of passages extend through the layers as a result of the openings (2) defined by portions of the continuous fibrous elements (3) extending substantially in the direction of the plane. The continuous fibrous elements (3) comprise both bioactive ceramic reinforcing fibers which form a reinforcing structure and a bioabsorbable polymer matrix material which forms a matrix which binds the layers together and also binds the portions of continuous fibers defining the openings together, thereby forming the passages and stiffening the structure. This bioactive and bioabsorbable composite structure is suitable to be used as a basic structure in medical devices, especially in osteochondral applications where the load-bearing properties of implant are required.
Owner:BIORETEC
Mesh implant
The present disclosure relates to implants including a porous substrate, a first hydrogel precursor, a second hydrogel precursor and a mesh. The first and second hydrogel precursors are applied to the porous substrate. The mesh has a first portion in contact with the porous substrate and a second portion exposed for tissue contact.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Method of producing sustained-release preparation
InactiveUS6267981B1Maintain good propertiesEnhancement of entrapmentPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsEntrapmentBiodegradable polymer
This invention provides a sustained-release preparation comprising a biodegradable polymer metal salt and broactive polypeptide, with enhanced entrapment of the bioactive polypeptides, a suppression of initial burst, and a constant long-term release of the bioactive polypeptides.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Method of preparation of bioabsorbable porous reinforced tissue implants and implants thereof
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Applicator device for suppositories and the like
An applicator for delivering pharmaceutical products or the like to a bodily cavity includes a barrel member having a distal end which is equipped with an opening. The applicator also includes a plurality of petals extending outwardly from the distal end in a generally axial direction. The petals cooperate with the opening so as to form a receptacle for releasably receiving a pharmaceutical product in the distal end of the barrel member. Each of the petals has a truncated flexible tip sized and shaped so as to engage a substantially central portion of the pharmaceutical product such that a large section of the pharmaceutical product extends outwardly beyond the petals so as to facilitate the release of the pharmaceutical product from the receptacle. The device also includes a plunger member for releasing the pharmaceutical product from the receptacle. In accordance with the present invention, the device can be packaged in a package together with the pharmaceutical product received in the receptacle.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON CONSUMER COPANIES
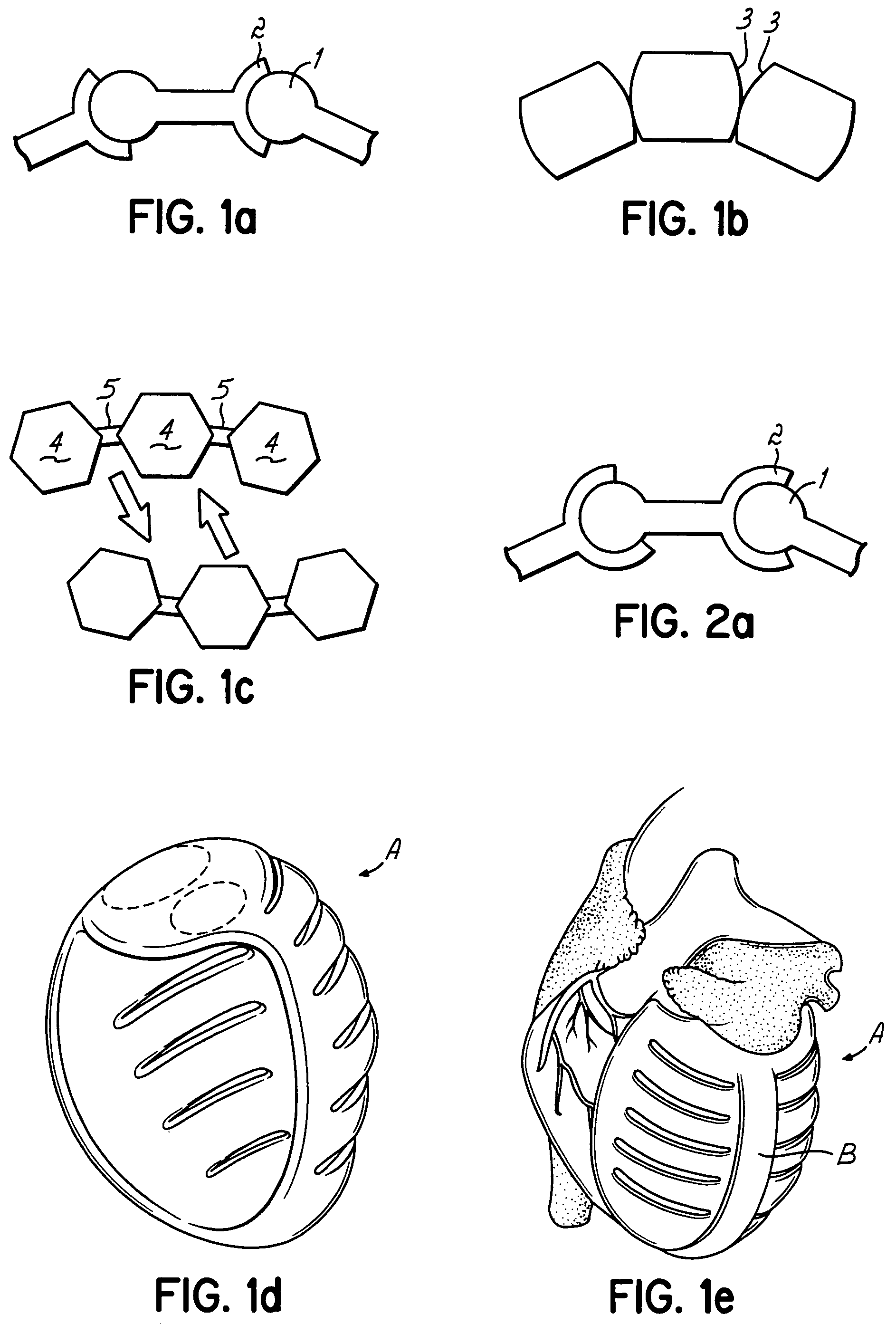
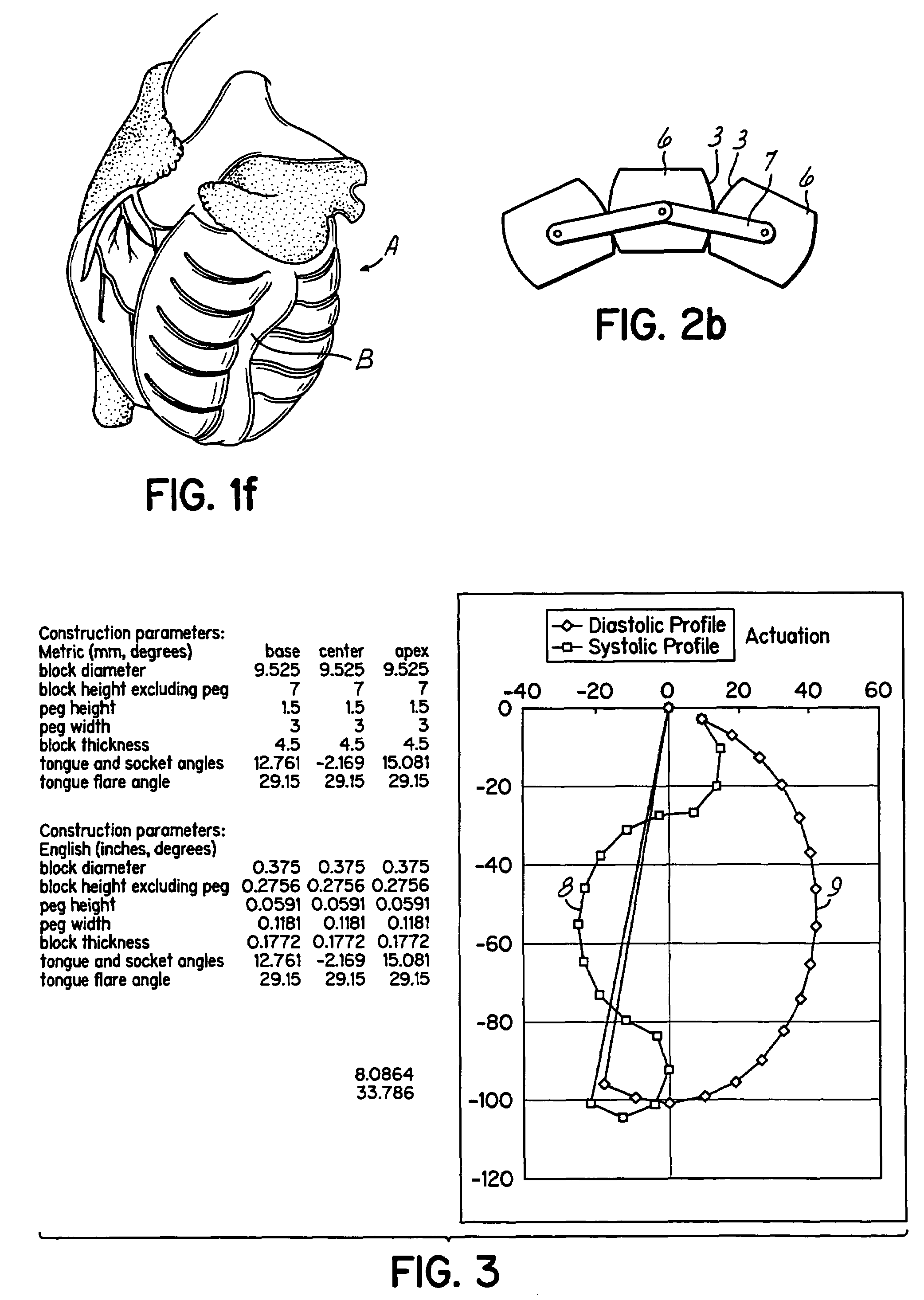
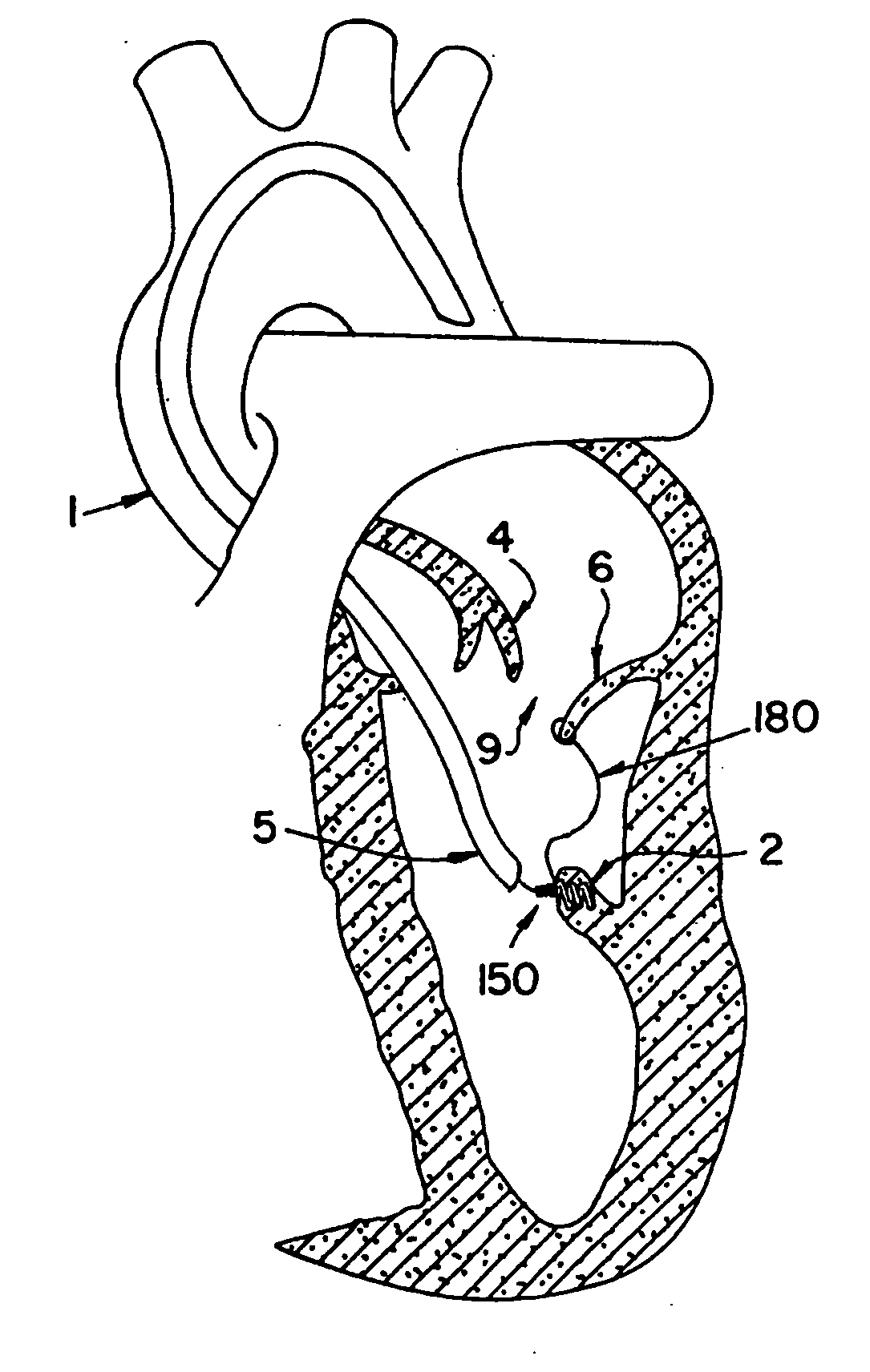
Actuation mechanisms for a heart actuation device
An actuation mechanism for assisting the operation of the natural heart has a varying shape for deforming the heart. In one embodiment, a plurality of links articulates with respect to each other for varying the shape of the actuation mechanism. The plurality of links is configured for being positioned proximate to an outer surface of the heart for deforming the heart by varying the shape of the actuation mechanism. In another embodiment, a jacket for coupling with an outer surface of the heart has a tether coupled to successive sections of the jacket. The tether is operable to be translated with respect to the jacket sections to vary the shape of the jacket for deforming the heart. In another embodiment, a plurality of concentric ring structures are coupled together to move with respect to each other in a concentric fashion. A movement mechanism coupled to the rings is operable to vary their positions with respect to each other to vary the overall shape for deforming the heart.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI +1
Cartridge shipping aid
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Biointerface membrane with macro-and micro-architecture
Disclosed herein are biointerface membranes including a macro-architecture and a micro-architecture co-continuous with and bonded to and / or located within at least a portion of the macro-architecture. The macro- and micro-architectures work together to manage and manipulate the high-level tissue organization and the low-level cellular organization of the foreign body response in vivo, thereby increasing neovascularization close to a device-tissue interface, interfering with barrier cell layer formation, and providing good tissue anchoring, while reducing the effects of motion artifact, and disrupting the organization and / or contracture of the FBC. The biointerface membranes of the preferred embodiments can be utilized with implantable devices such as devices for the detection of analyte concentrations in a biological sample (for example, from a body), cell transplantation devices, drug delivery devices, electrical signal delivering or measuring devices, and / or combinations thereof.
Owner:DEXCOM
Drug-eluting medical devices
Owner:ZILBERMAN MEITAL
Apparatus and method for steam reprocessing flexible endoscopes
A system for reprocessing flexible endoscopes having lumen therein. The reprocessing system deploys steam to disinfect and / or sterilize the endoscopes, and designs, components, and methods for reducing or balancing the reprocessing cycle time and the effects of thermal expansion and contraction on the endoscopes.
Owner:MEDIVATORS INC
Disposable Absorbent Article With Substantially Continuously Distributed Absorbent Particulate Polymer Material And Method
A disposable absorbent core comprises first and second absorbent layers each comprising an absorbent particulate polymer material such that the absorbent particulate polymer material is substantially continuously distributed across an absorbent particulate polymer material area. A disposable absorbent article and method for making the absorbent core are also disclosed.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
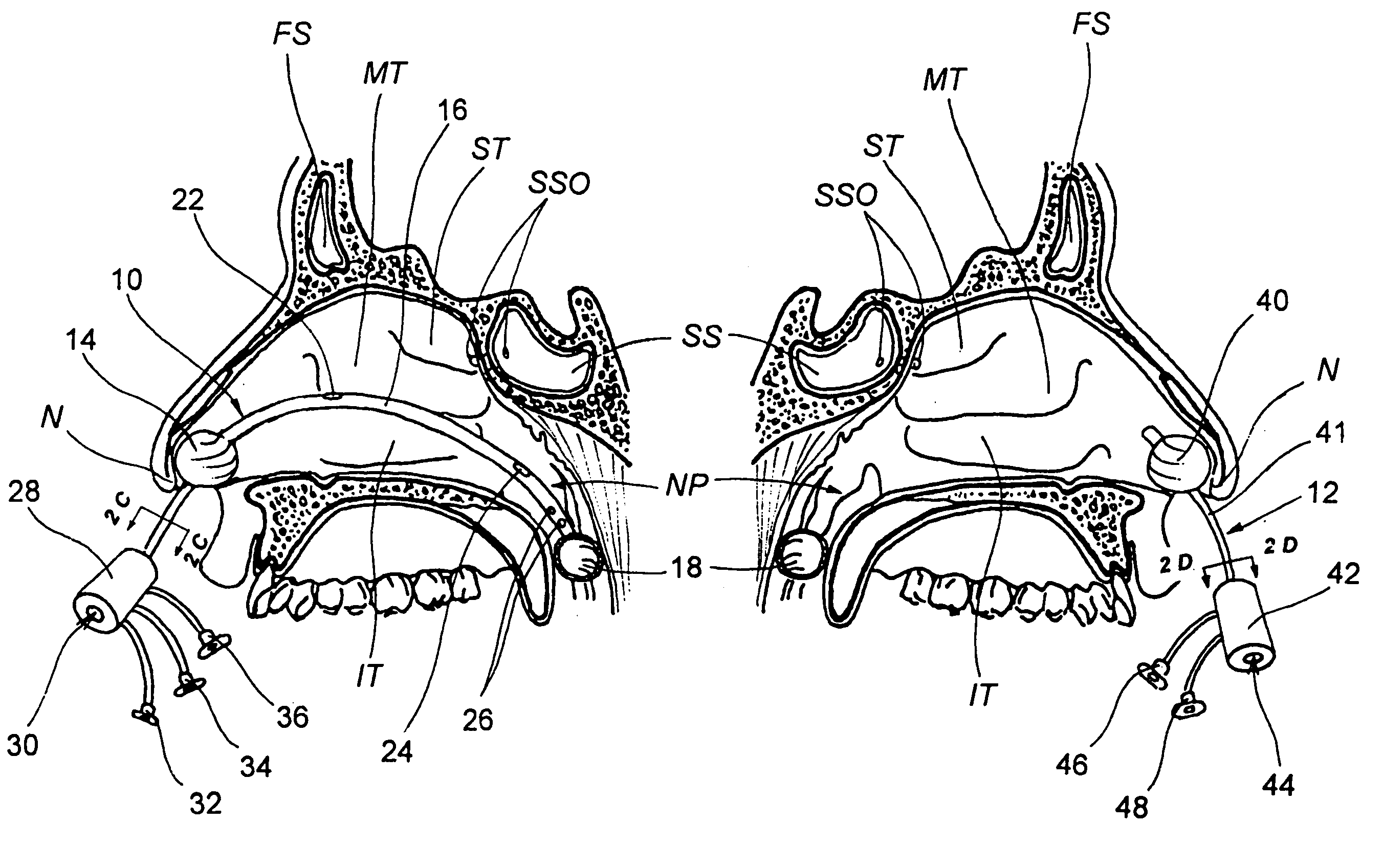
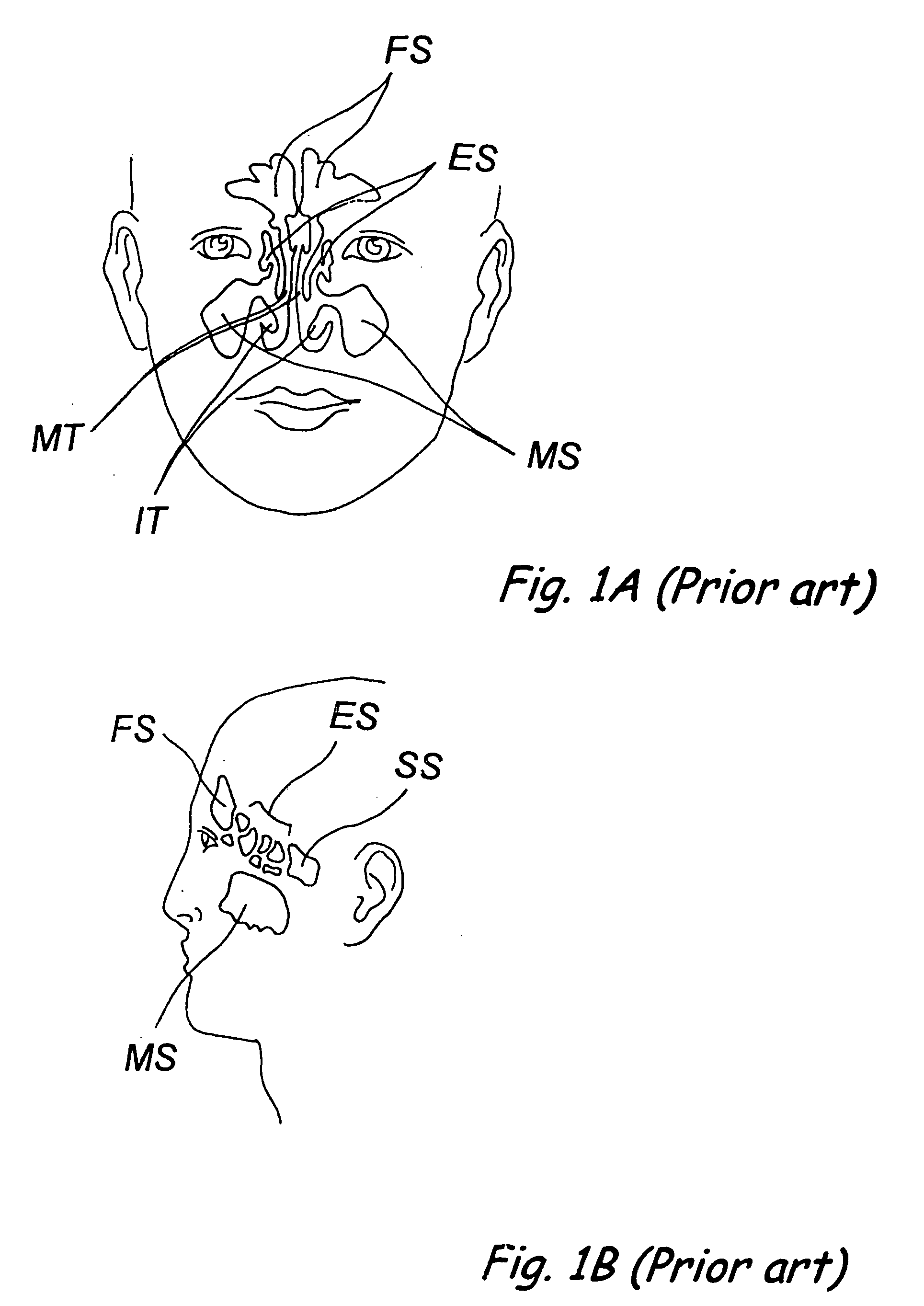
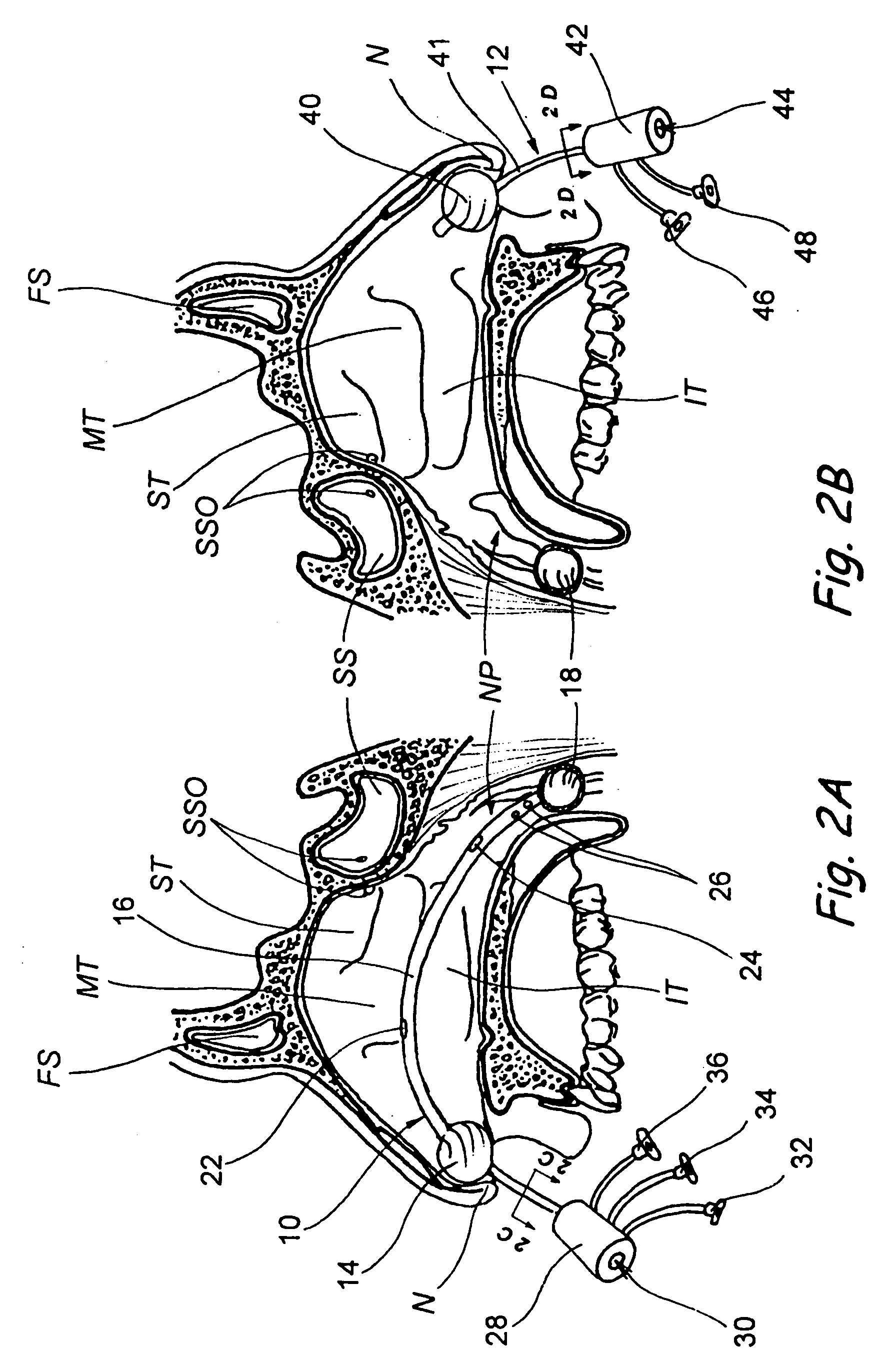
Devices, systems and methods for diagnosing and treating sinusitus and other disorders of the ears, nose and/or throat
Sinusitis, enlarged nasal turbinates, tumors, infections, hearing disorders, allergic conditions, facial fractures and other disorders of the ear, nose and throat are diagnosed and / or treated using minimally invasive approaches and, in many cases, flexible catheters as opposed to instruments having rigid shafts. Various diagnostic procedures and devices are used to perform imaging studies, mucus flow studies, air / gas flow studies, anatomic dimension studies, endoscopic studies and transillumination studies. Access and occluder devices may be used to establish fluid tight seals in the anterior or posterior nasal cavities / nasopharynx and to facilitate insertion of working devices (e.g., scopes, guidewires, catheters, tissue cutting or remodeling devices, electrosurgical devices, energy emitting devices, devices for injecting diagnostic or therapeutic agents, devices for implanting devices such as stents, substance eluting devices, substance delivery implants, etc.
Owner:ACCLARENT INC
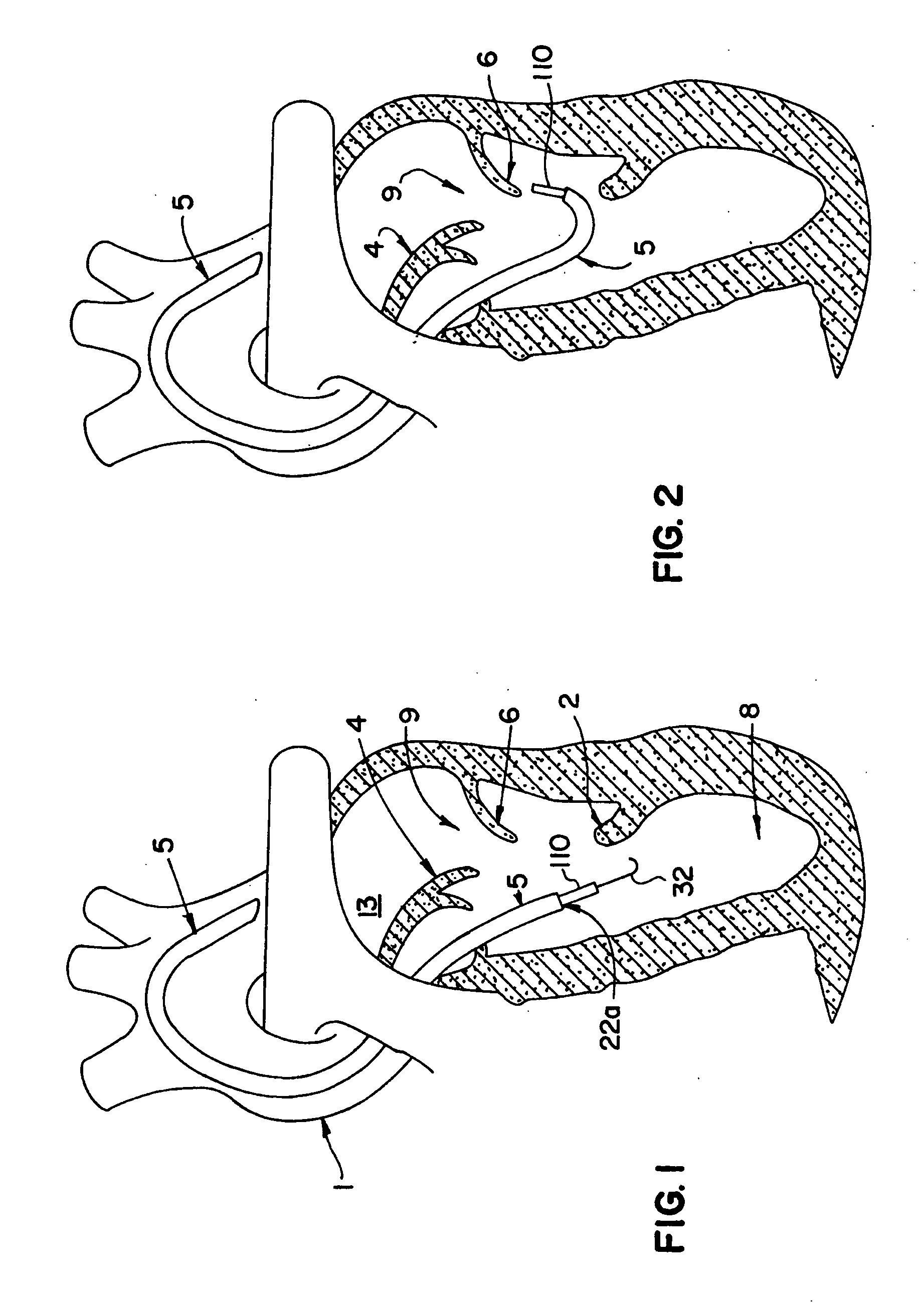
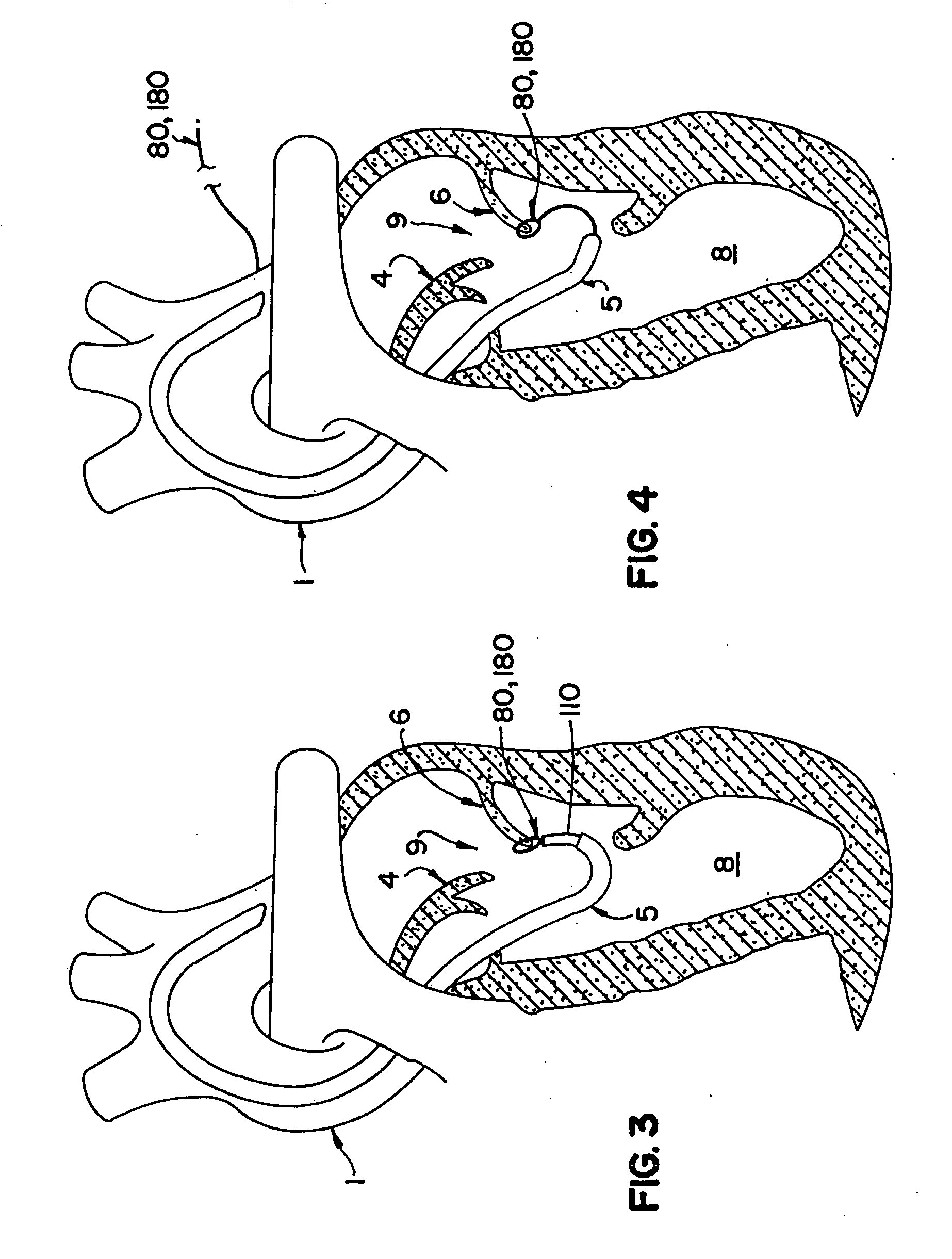
Percutaneous cardiac valve repair with adjustable artificial chordae
InactiveUS20070118151A1Reduction of mitral valve regurgitationEasy to operateSuture equipmentsHeart valvesExtracorporeal circulationCardiopulmonary bypass time
The invention includes a novel method and system to achieve leaflet coaptation in a cardiac valve percutaneously by creation of neochordae to prolapsing valve segments. This technique is especially useful in cases of ruptured chordae, but may be utilized in any segment of prolapsing leaflet. The technique described herein has the additional advantage of being adjustable in the beating heart. This allows tailoring of leaflet coaptation height under various loading conditions using image-guidance, such as echocardiography. This offers an additional distinct advantage over conventional open-surgery placement of artificial chordae. In traditional open surgical valve repair, chord length must be estimated in the arrested heart and may or may not be correct once the patient is weaned from cardiopulmonary bypass. The technique described below also allows for placement of multiple artificial chordae, as dictated by the patient's pathophysiology.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com