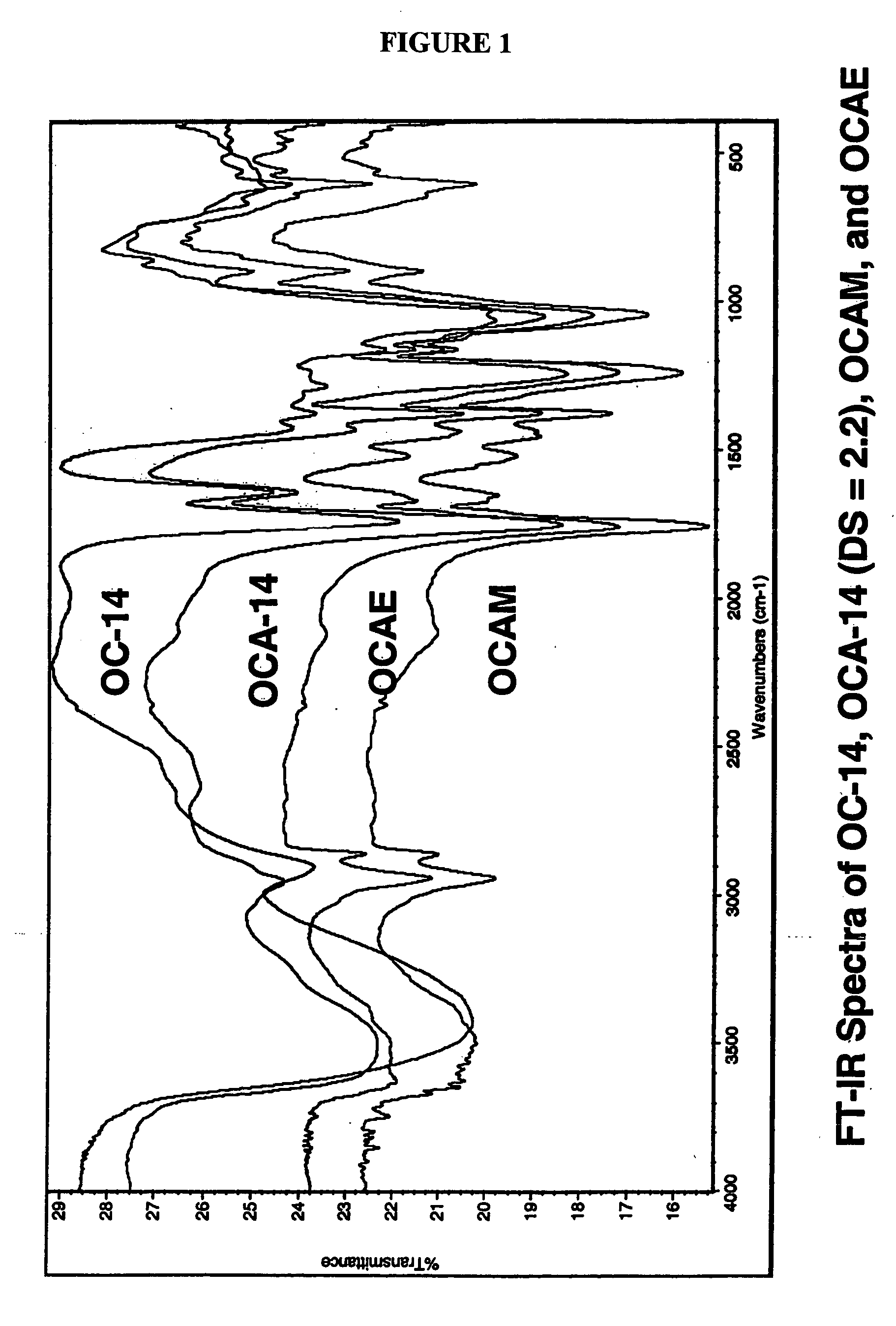
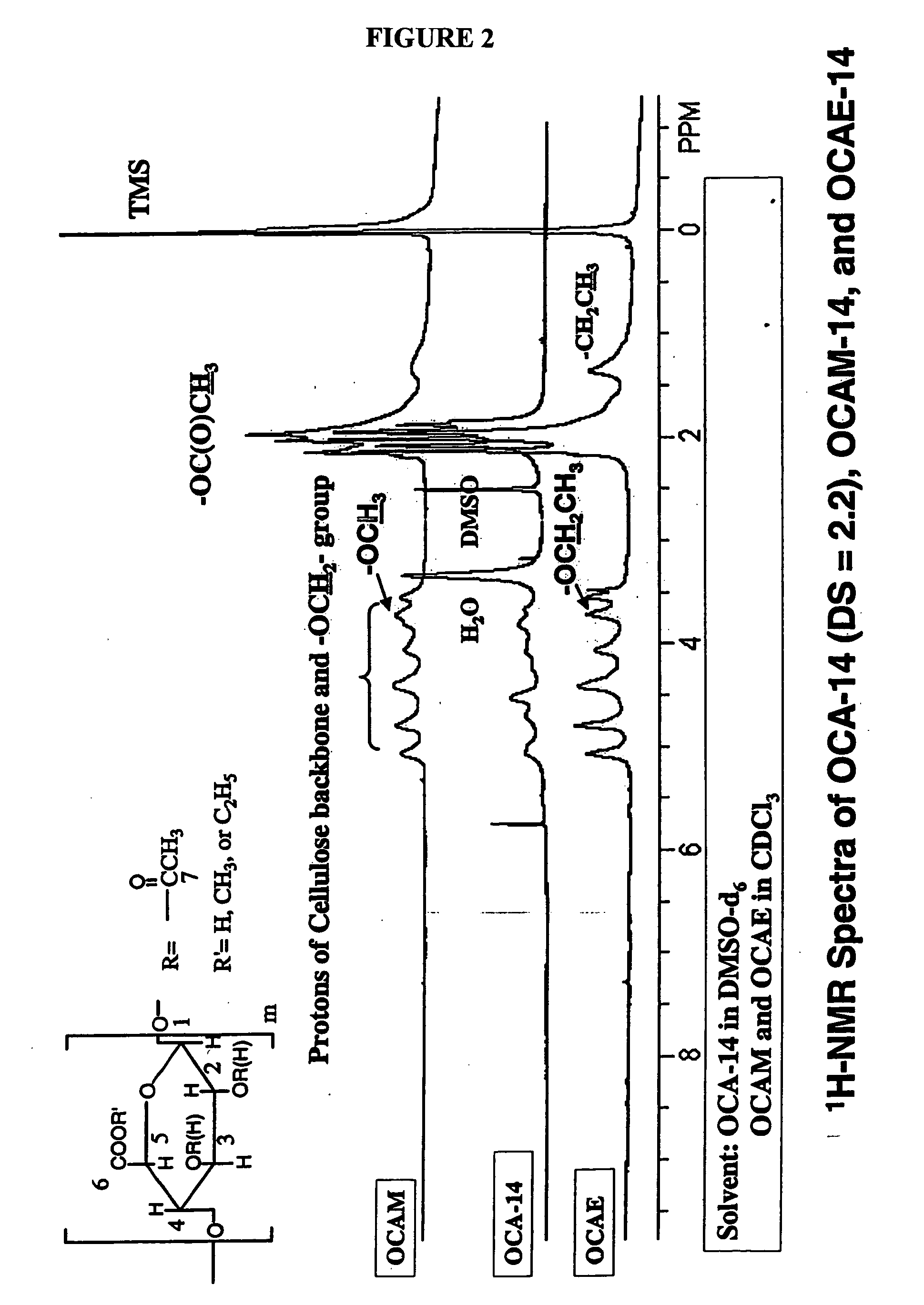
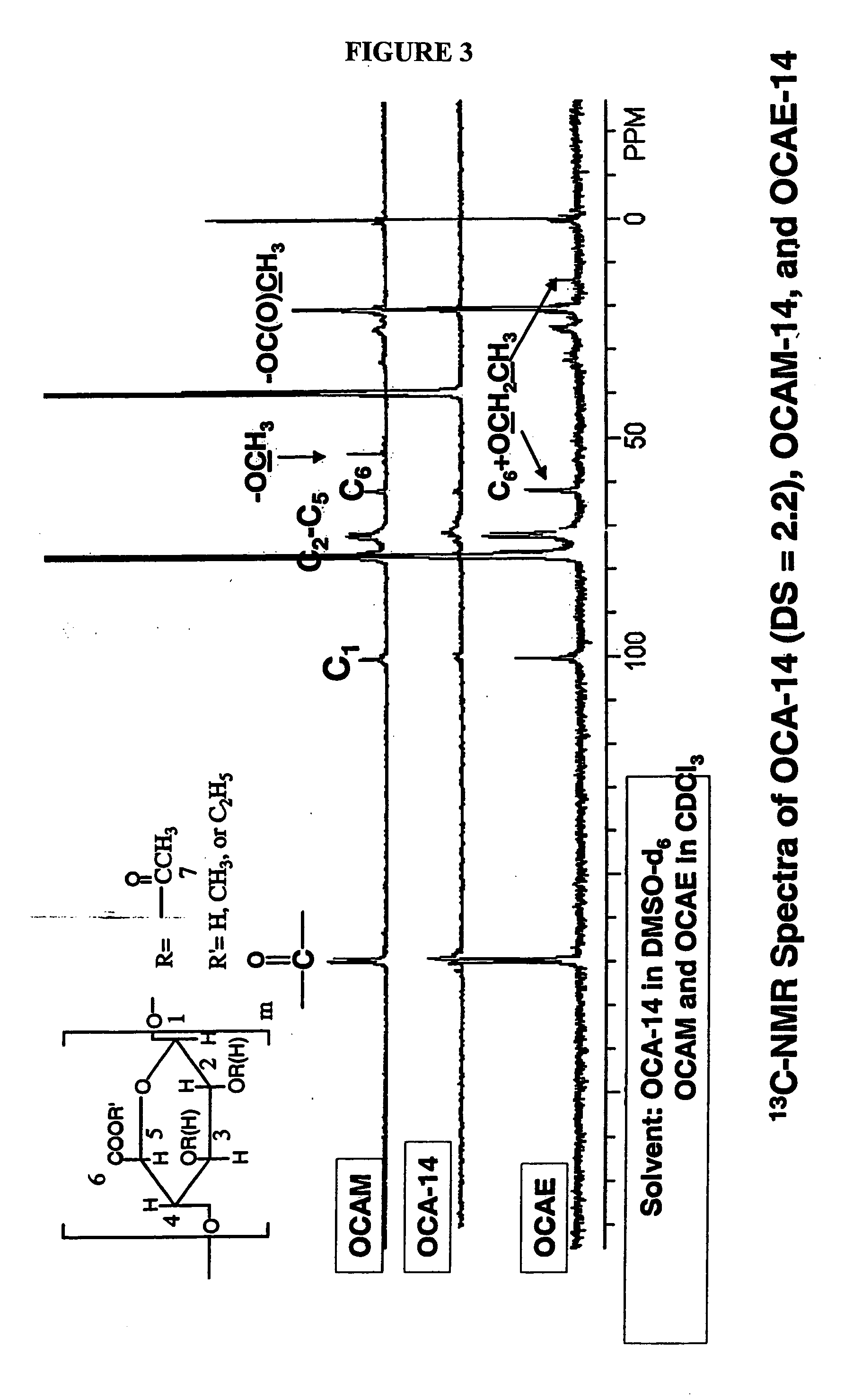
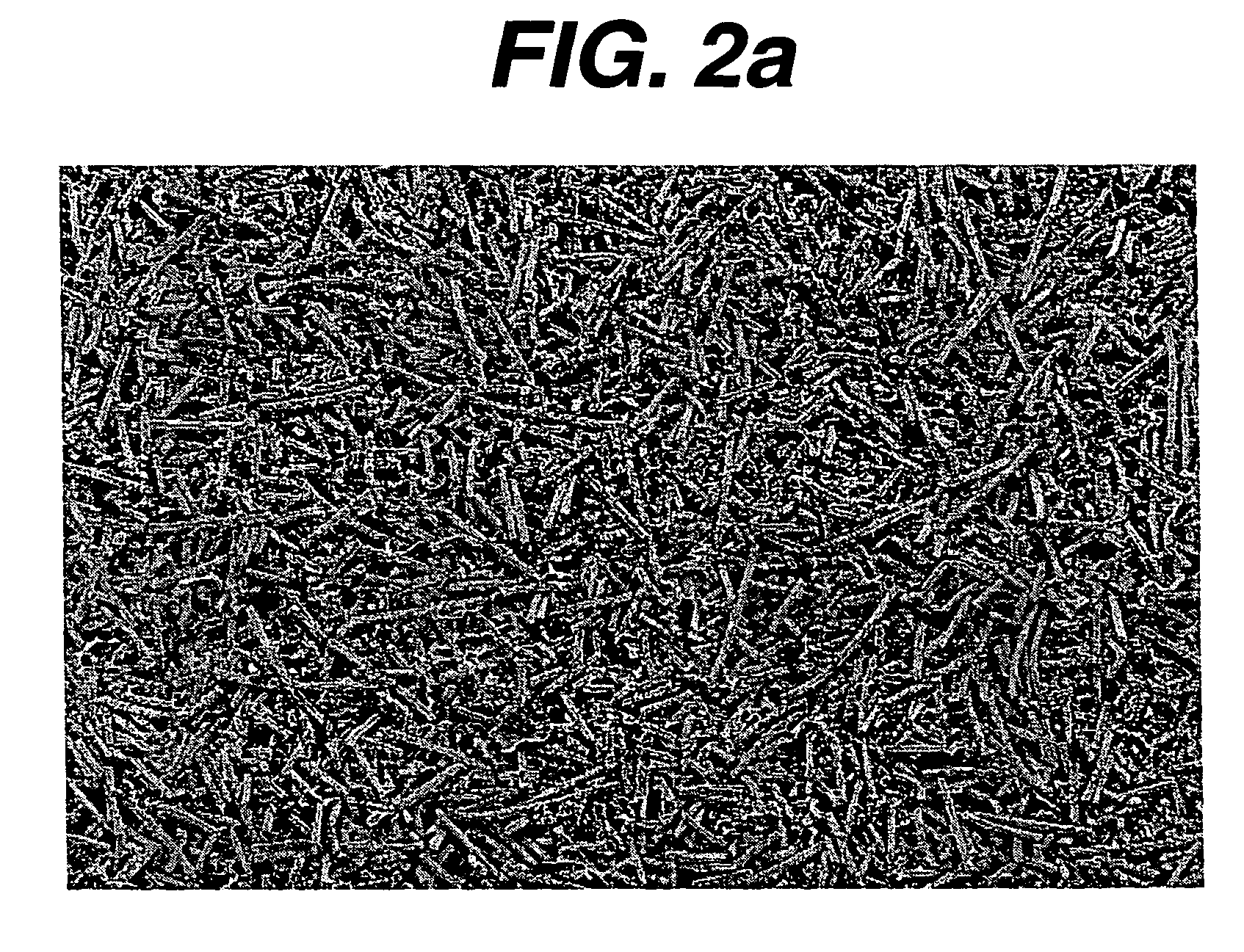
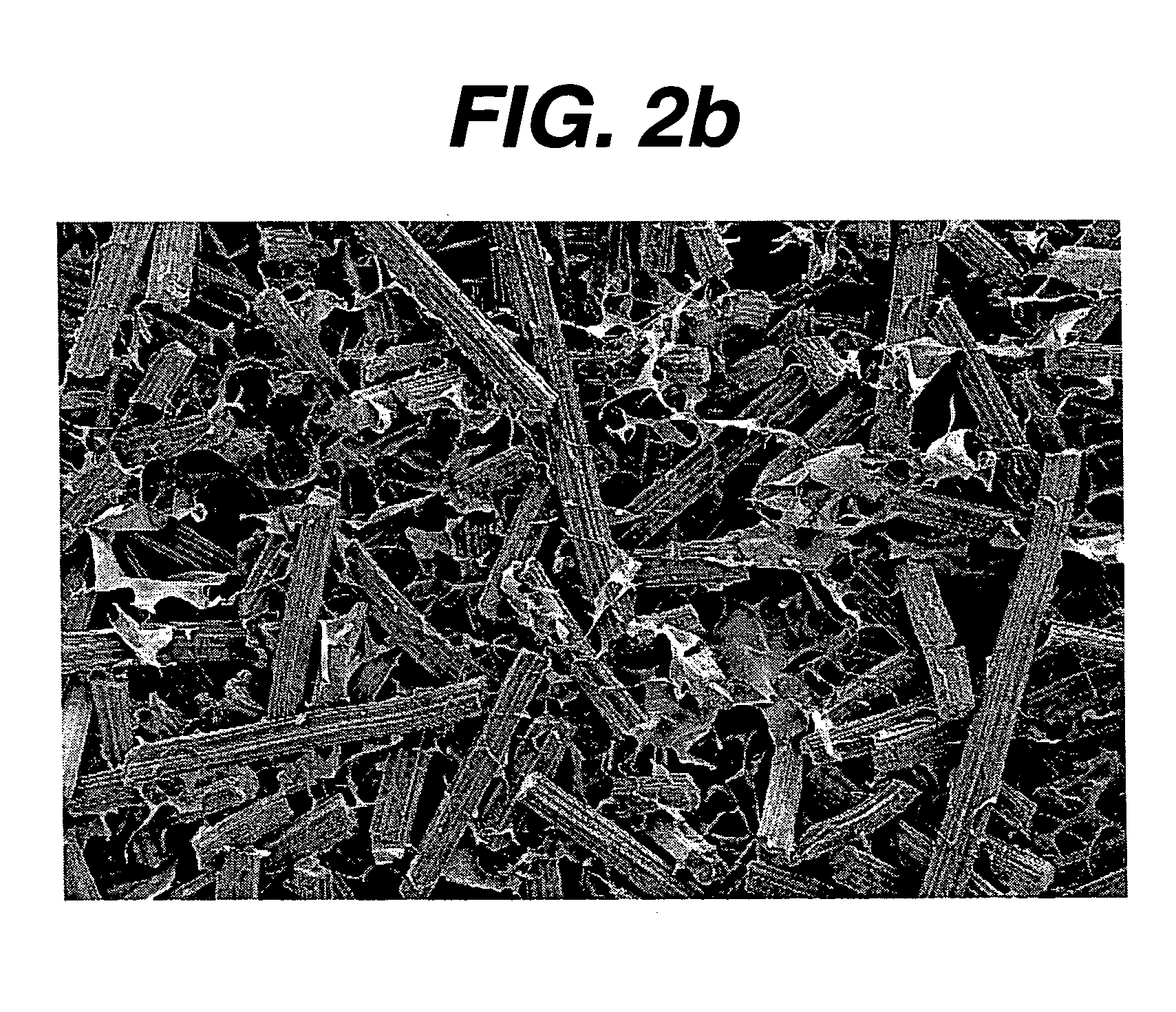
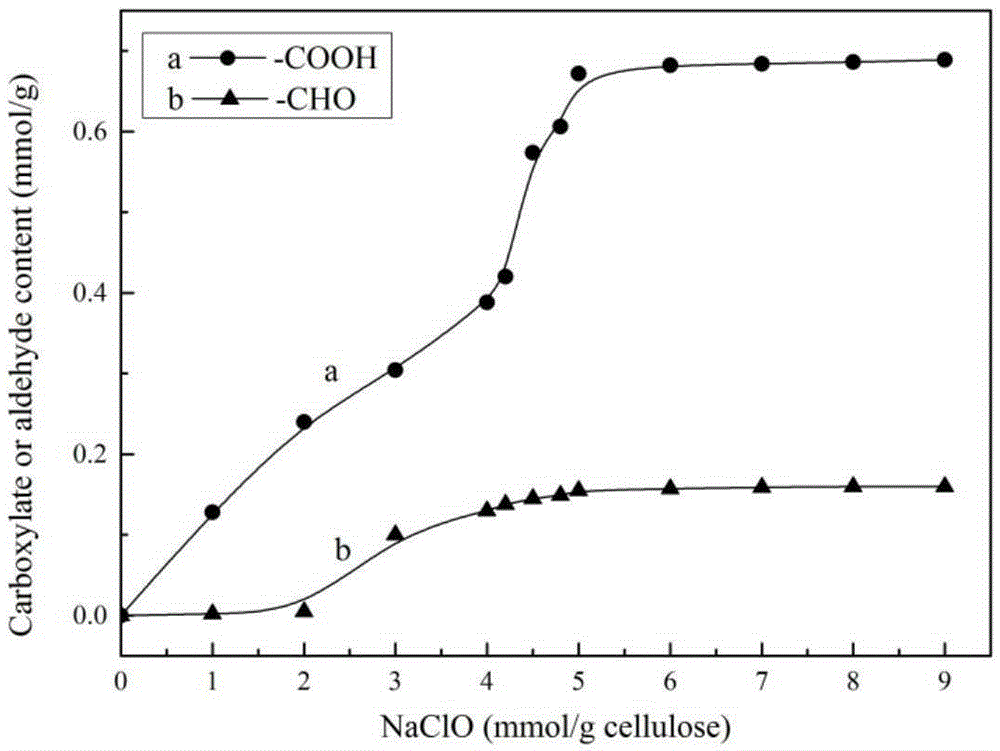
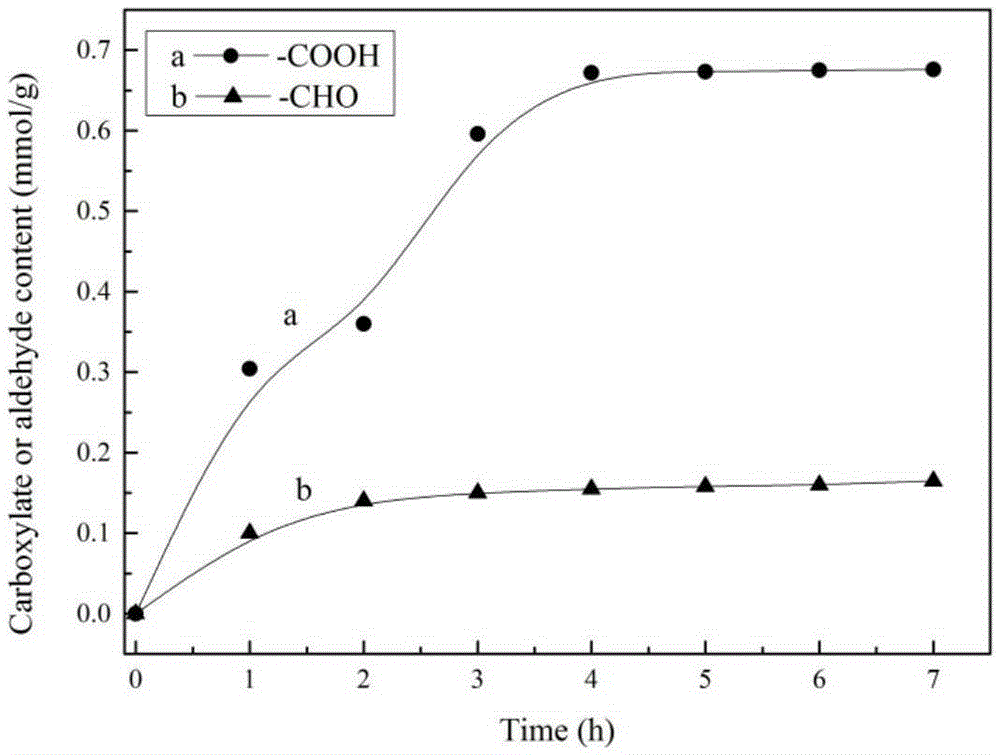
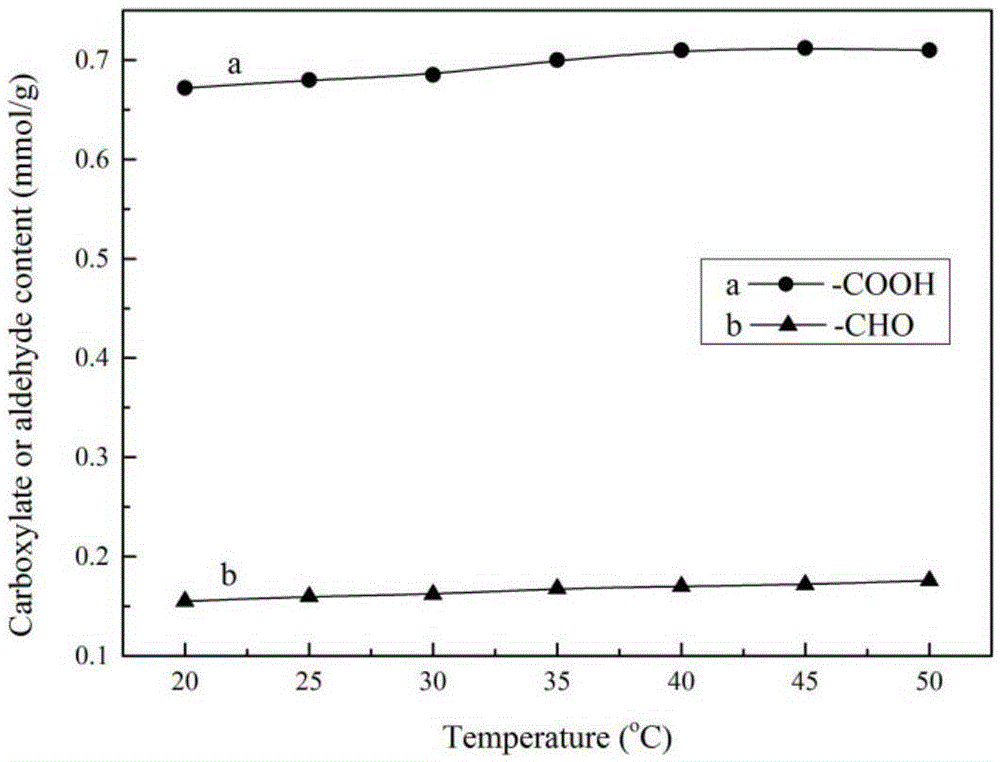
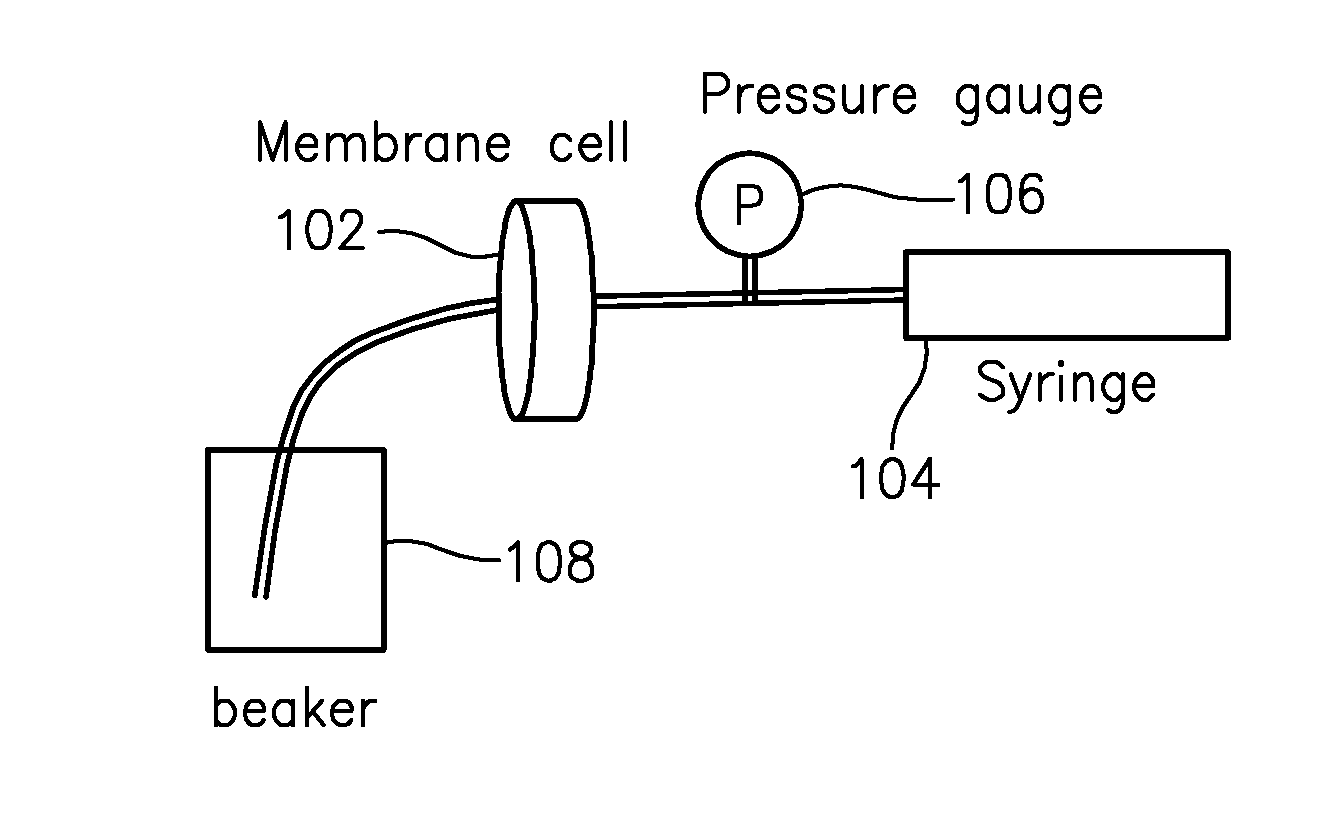
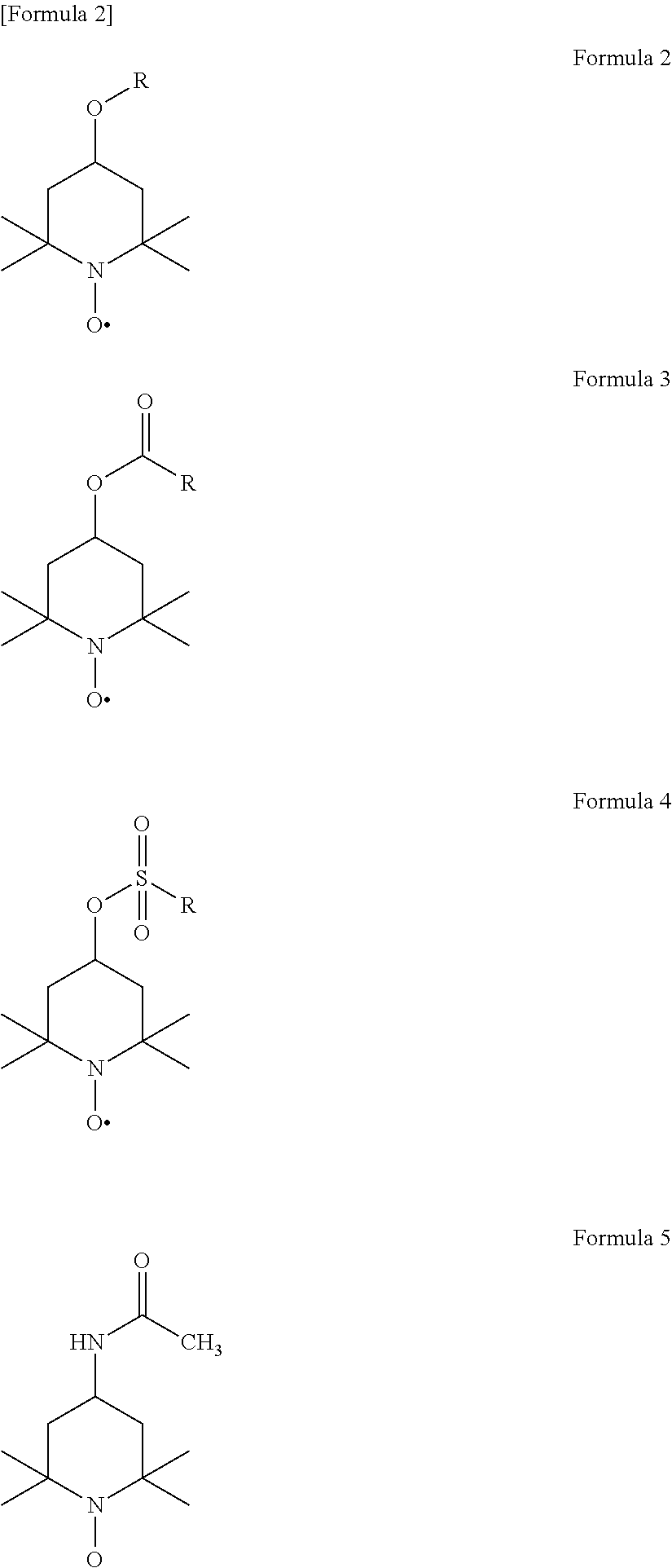
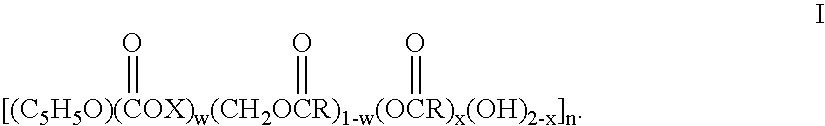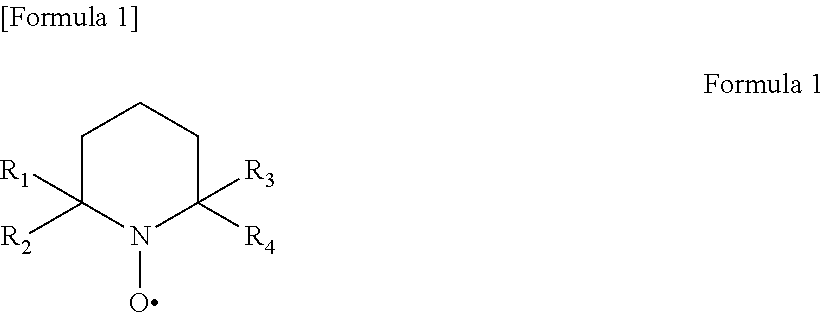Patents
Literature
92 results about "Oxidized cellulose" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
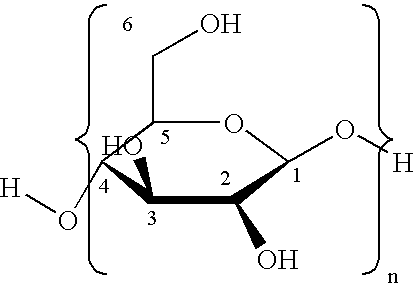
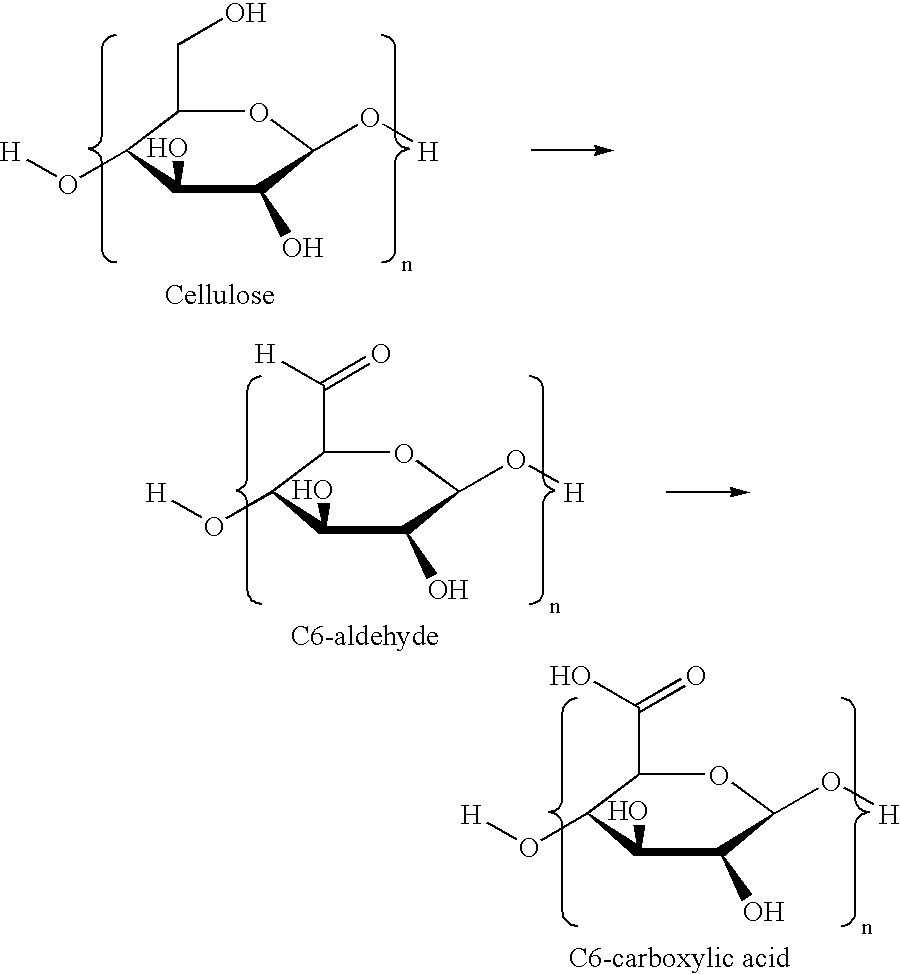
Oxidized cellulose is a water-insoluble derivative of cellulose. It can be produced from cellulose by the action of an oxidizing agent, such as chlorine, hydrogen peroxide, peracetic acid, chlorine dioxide, nitrogen dioxide, persulfates, permanganate, dichromate-sulfuric acid, hypochlorous acid, hypohalites or periodates and a variety of metal catalysts. Oxidized cellulose may contain carboxylic acid, aldehyde, and/or ketone groups, in addition to the original hydroxyl groups of the starting material, cellulose, depending on the nature of the oxidant and reaction conditions. It is an antihemorrhagic.
Biodegradable oxidized cellulose esters and their uses as microspheres
A new cellulose excipient, OCCAE, suitable for use as a binder, filler, and / or disintegrant in the development of solid dosage forms and as a bodying agent or a drug carrier in the preparation of topical formulations is described. The cellulose excipient is formed by reacting an oxidized cellulose ester with an alcohol in the presence of a catalyst. The invention also describes the formation of controlled release microspheres using OCCAE and / or oxidized cellulose esters that may be used to control the release of drug in a patient over a time period of several hours to several days.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
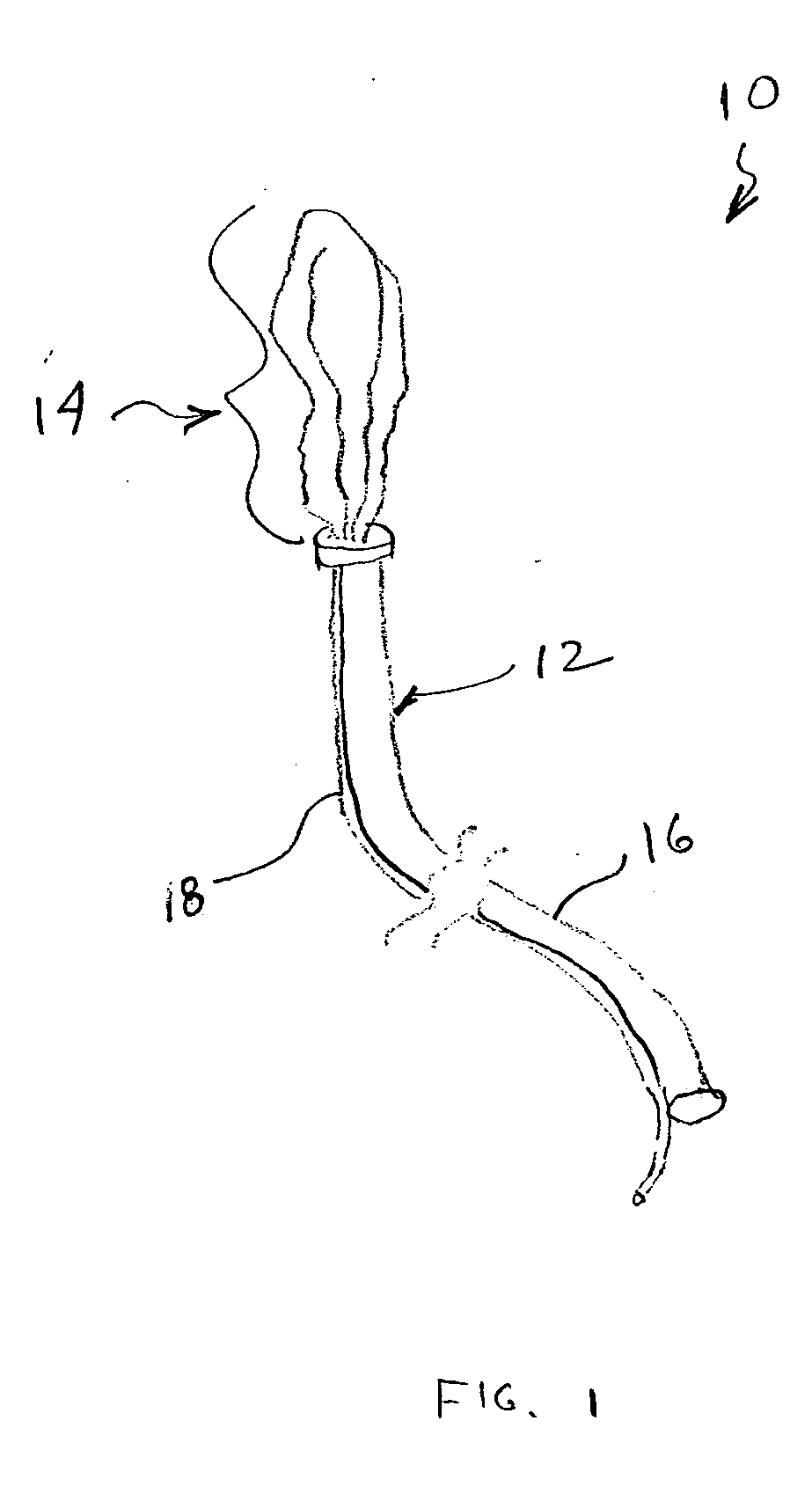
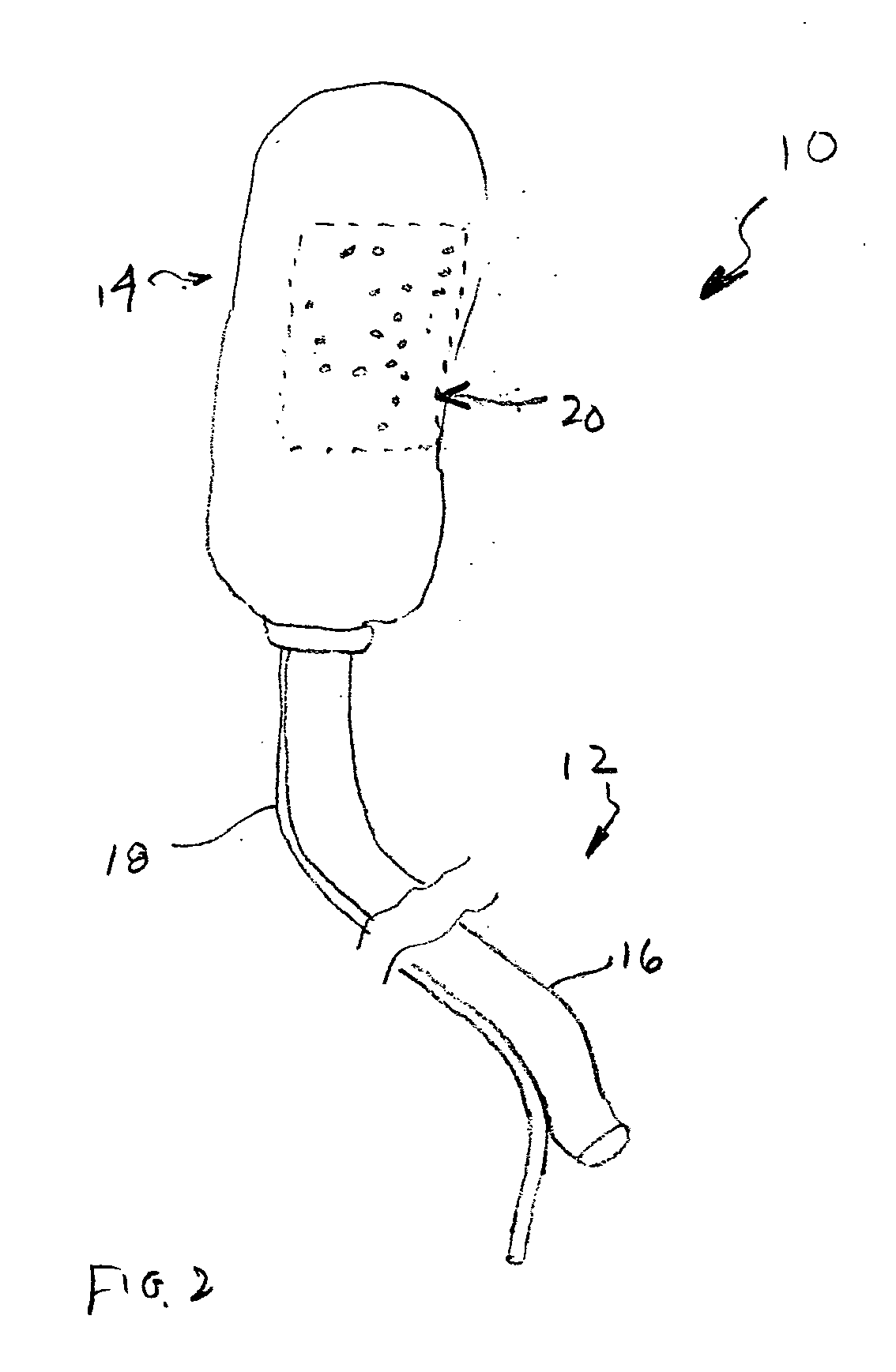
Devices and methods for promoting the formation of blood clots in esophageal varices
InactiveUS20070167971A1Inhibit injectionPromote formationBalloon catheterSurgeryThrombusSilicon dioxide
A device for promoting the clotting of blood in body cavities includes a flexible body portion; an expandable member located on the flexible body portion; and a blood clotting material attached to the expandable member. When used, insertion of at least a portion of the blood clotting material into the body cavity causes at least a portion of the blood clotting material to contact blood emanating from a bleed site. Methods of providing therapies to tube-shaped organs include the steps of providing suitable devices having expansion capabilities, positioning the devices at the appropriate bleed sites, and expanding the devices to cause blood clotting materials to contact the bleed sites. Materials that may be used as the blood clotting material include zeolites, molecular sieve materials, diatomaceous earth, clay, silica-based materials, oxidized cellulose, carboxymethyl cellulose, bioactive glass, biological hemostats, chitosan, and combinations of the foregoing.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
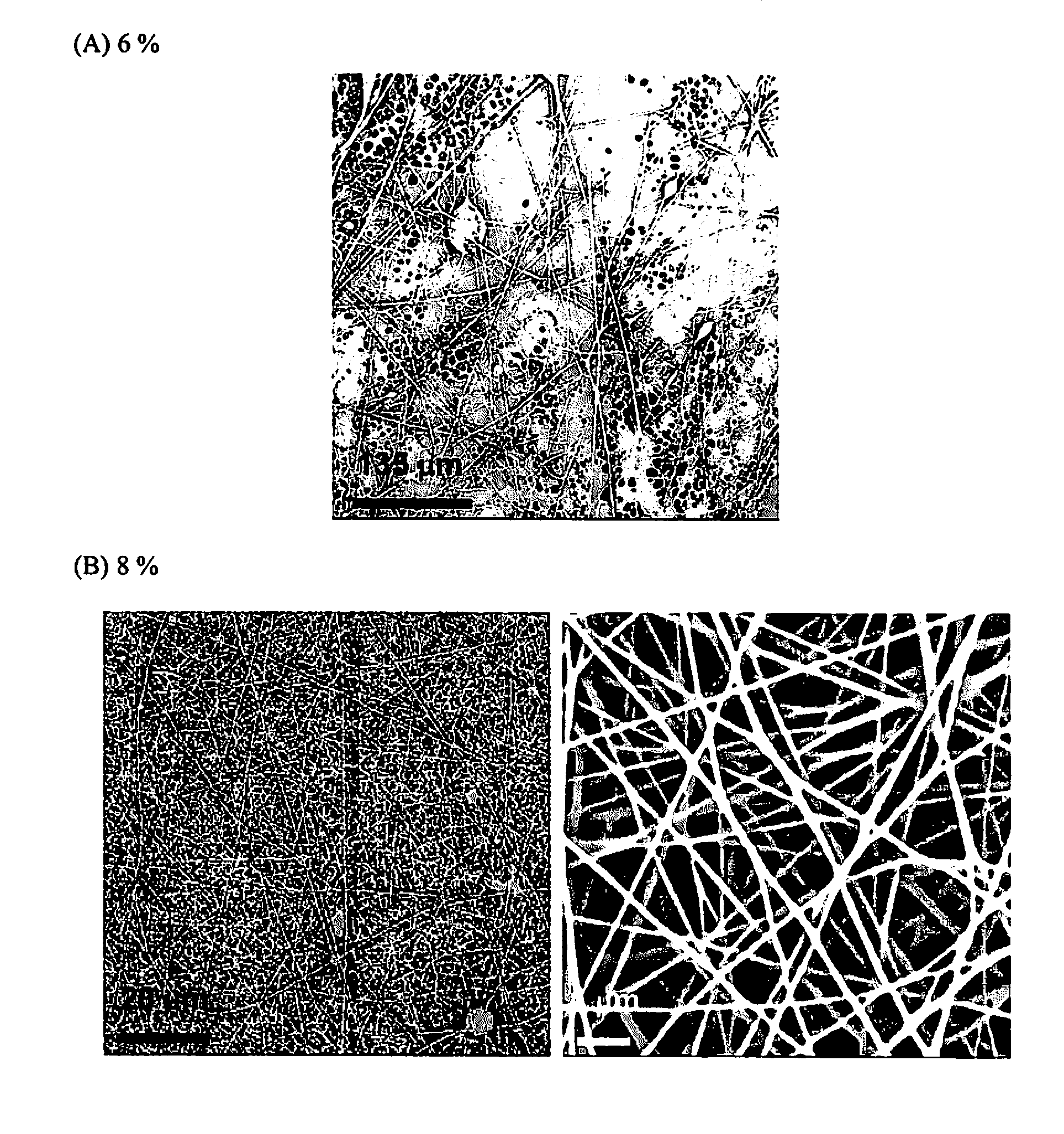
High flux high efficiency nanofiber membranes and methods of production thereof
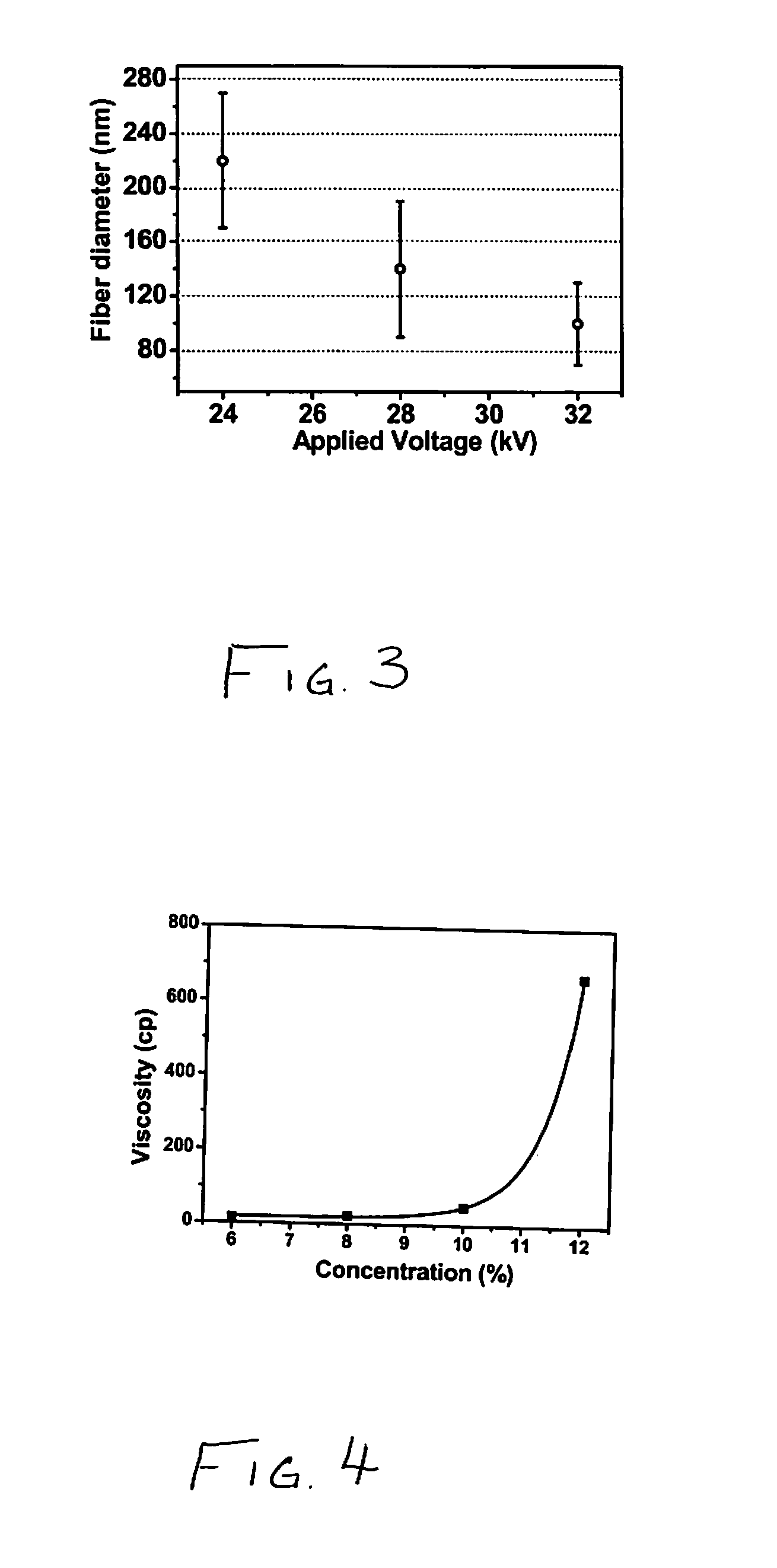
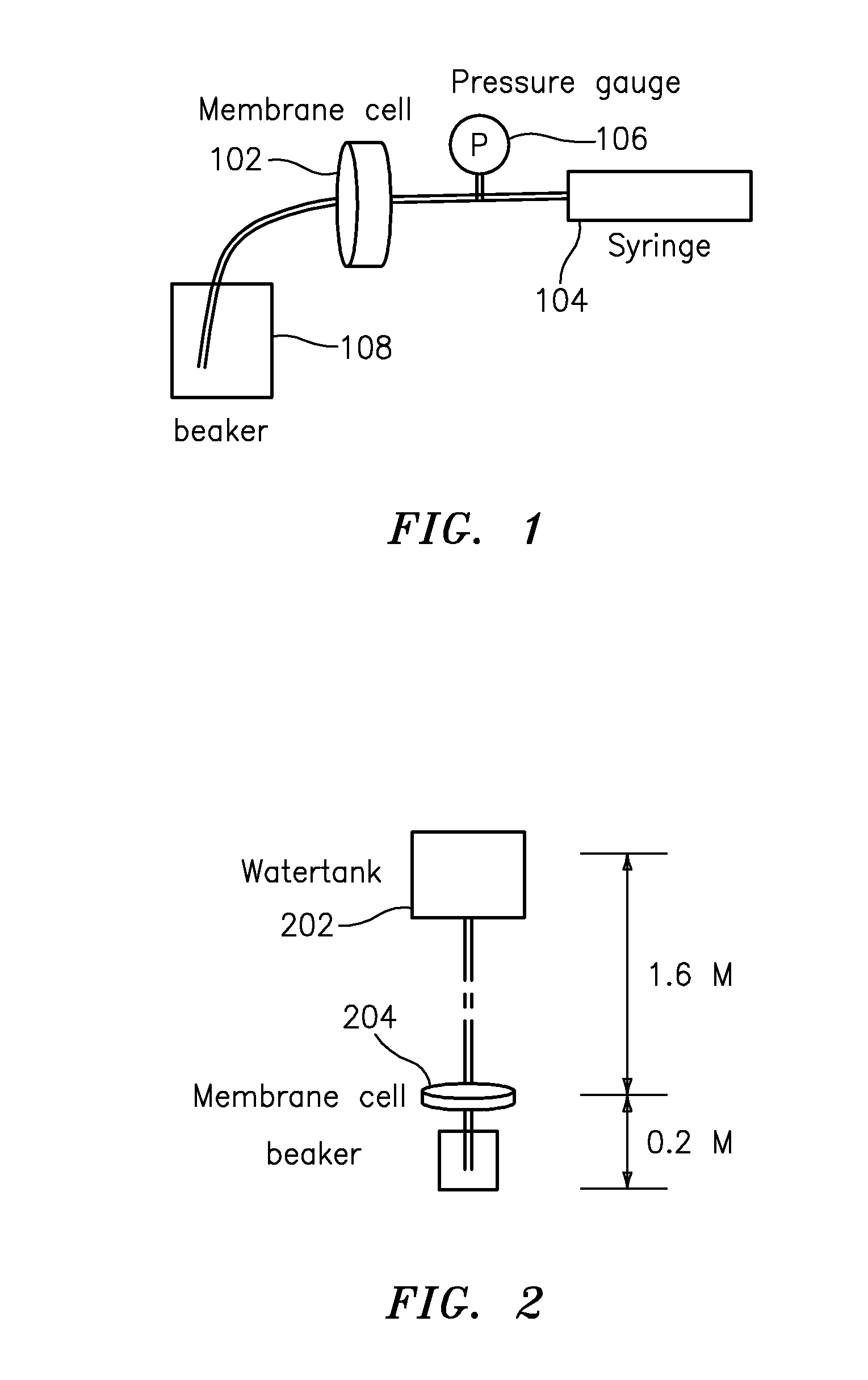
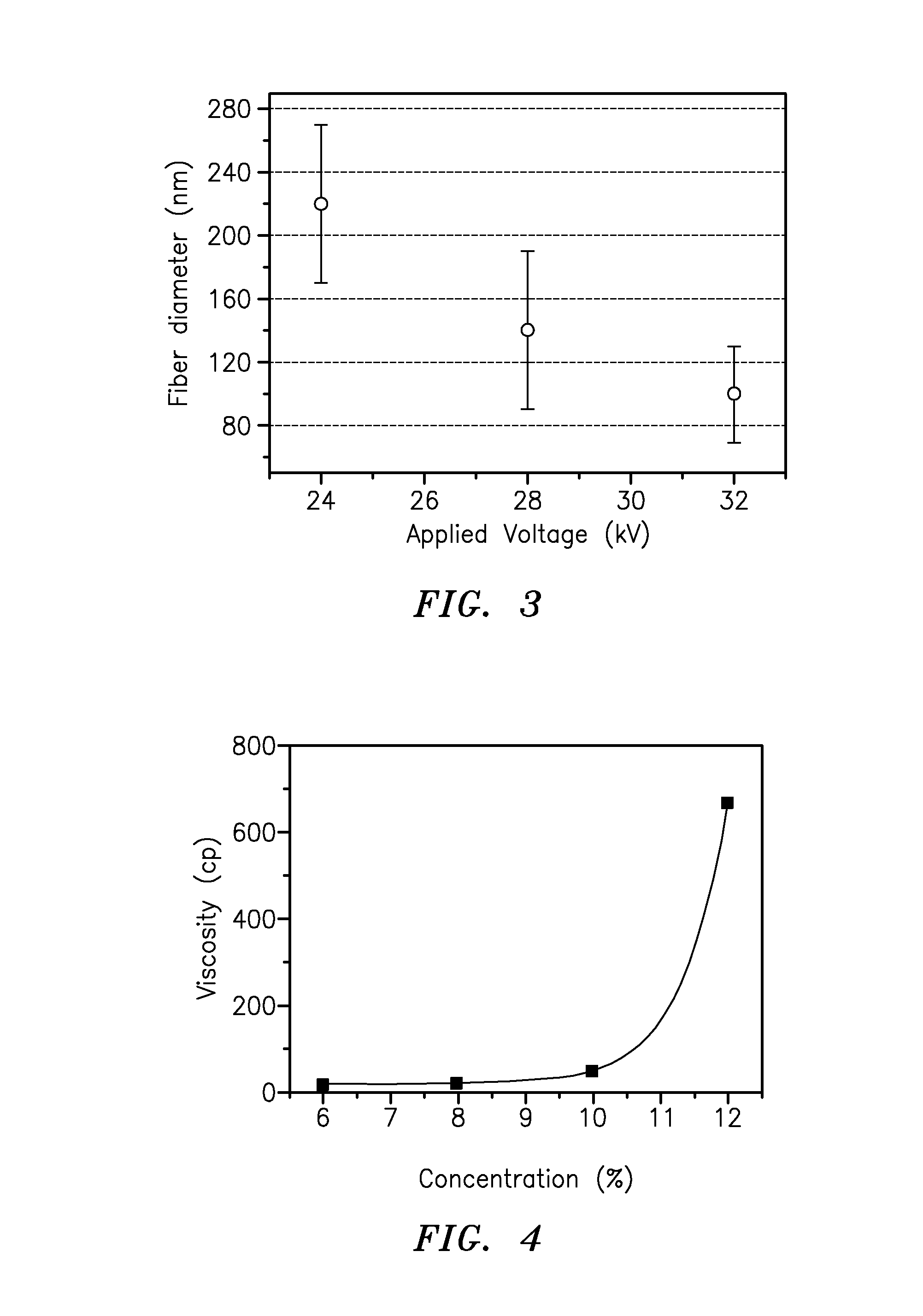
A membrane is provided including a coating layer having cellulose nanofibers produced from oxidized cellulose microfibers and an electrospun substrate upon which the coating layer is applied. The nanofibers of the electrospun substrate have a diameter greater than that of the cellulose nanofibers. The membrane also has non-woven support upon which the electrospun substrate is disposed. Microfibers of the non-woven support have a diameter greater than that of the nanofibers of the electrospun substrate. Application of electrospun membrane is in microfiltration area, while the cellulose nanofiber membrane serves in ultra-filtration, nanofiltration, and reverse osmosis after chemical modification.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Cellulose oxidation by nitrogen dioxide in a perfluorinated tertiary amine solvent
ActiveUS20070054880A1Efficiently oxidizedReduce usageBiocideOrganic active ingredientsNitrogen dioxideAqueous alcohol
This invention relates to a process for preparing bioabsorbable oxidized cellulose comprising combining cellulose material, with nitrogen dioxide and a nonaqueous solvent chosen from the class of perfluorinated tertiary amines. This invention also relates to a method of oxidizing cellulose material comprising introducing a solvent into the vessel, circulating the solvent through the cellulose material, adding nitrogen dioxide to said vessel containing the solvent and cellulose in the required amounts, circulating the solution for 7 to 24 hours while controlling the reaction temperature, and isolating the oxidized material. Preferably, isolation of the oxidized product is followed by first washing the oxidized cellulose material with cold water, then washing the oxidized cellulose material with an aqueous alcohol solution several times, then washing the material with 100% alcohol several times, and finally drying the oxidized material.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Biodegradable oxidized cellulose esters
InactiveUS20060093672A1Less-expensive to produceOrganic active ingredientsBiocideOrganic solventMicrosphere
The present invention relates to the preparation of a series of oxidized cellulose esters suitable for use as a drug carrier in the development of biodegradable controlled and / or sustained release pharmaceutical, agricultural, and veterinary compositions, such as films, compacts, microspheres, and pellets. The esters are prepared by acylation of oxidized cellulose having at least 3% carboxyl groups. The resulting oxidized cellulose esters are soluble in aqueous alkaline solutions, water, and a variety of organic solvents.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
Resorbable Oxidized Cellulose Embolization Microspheres
A method for forming an embolism within a blood vessel is disclosed. The method includes including: implanting a plurality of oxidized cellulose microspheres into a lumen of a blood vessel to at least partially block the lumen.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Hemostatic devices and methods of making same
The present invention includes compositions suitable for use in a hemostatic device and hemostatic devices utilizing such compositions, as well as methods of making the compositions and the medical devices utilizing such compositions where the compositions contain biocompatible, oxidized cellulose particles having an average designated nominal particle size of about 0.035-4.35 mm and a biocompatible, water-soluble or water-swellable polysaccharide porous binder component.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Hypochlorite free method for preparation of stable carboxylated carbohydrate products
InactiveUS6919447B2Low costEnvironmental lossPulp properties modificationSugar derivativesHydroxylamineHypochlorite
Owner:INT PAPER CANADA PULP HLDG ULC
Composition for film formation, laminate, film, sheet base material, method for producing composition for film formation, and method for preparing a cellulose dispersion
ActiveUS20140206798A1Improve barrier propertiesSuppress infiltrationPolyureas/polyurethane adhesivesCellulose coatingsPolymer scienceInorganic compound
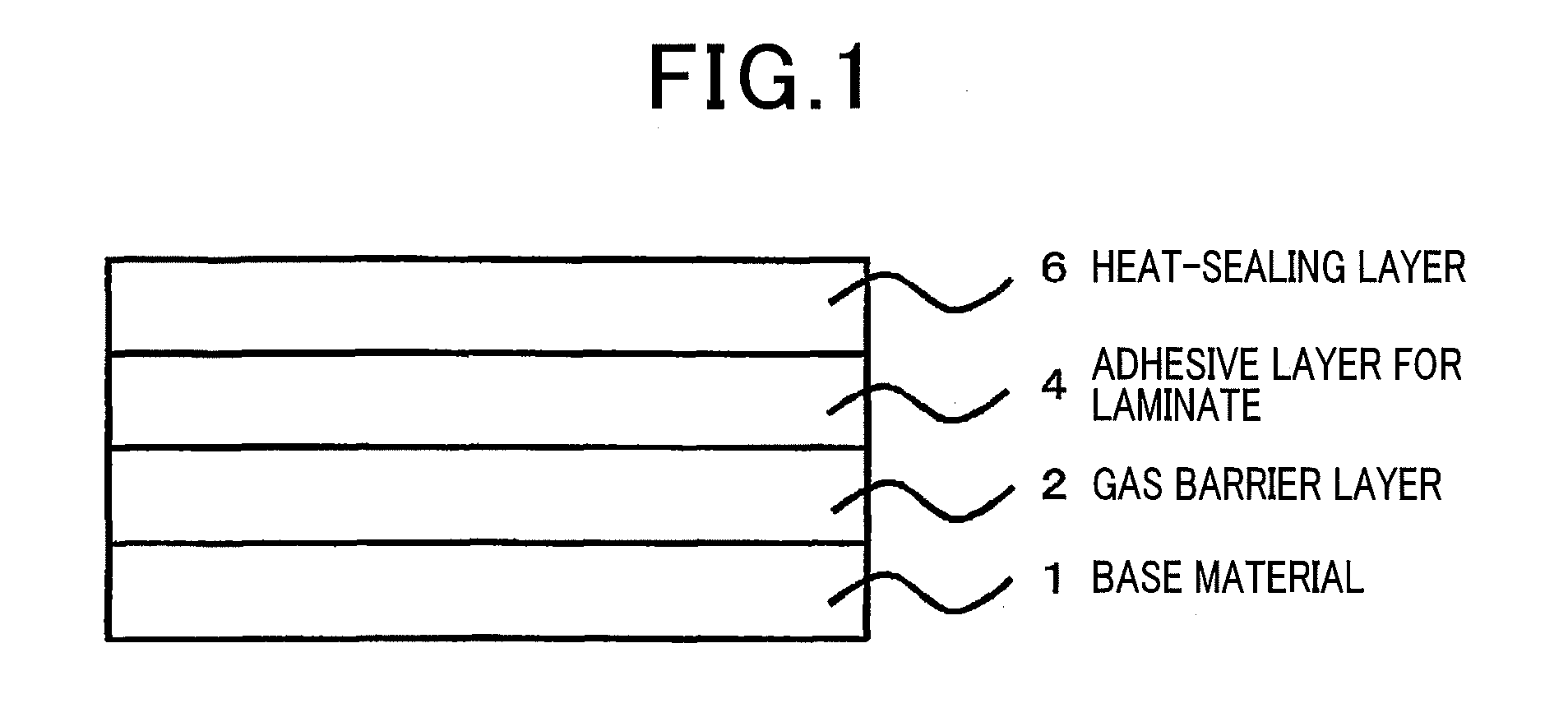
[Problem] To provide a composition for film formation comprising cellulose fibers, a layered inorganic compound, and a water-soluble polymer, which are each dispersed on nano level, a method for preparing a cellulose dispersion capable of forming a moisture-resistant film containing cellulose nanofibers, a gas-barrier laminate obtained by use of the dispersion, and a packaging material using the laminate. [Solution] A film-forming composition comprising at least cellulose fibers and a swollen inorganic compound is prepared. The method of preparing a cellulose dispersion comprises the steps of oxidizing cellulose, fibrillating the thus oxidized cellulose to prepare cellulose nanofibers, and adding a water-soluble polymer and inorganic particles to the dispersion containing the cellulose nanofibers.
Owner:TOPPAN PRINTING CO LTD
Method for preparing adsorbable oxycellulose through ramie oxidation degumming process
InactiveCN105061606AAdsorptiveImprove adsorption capacityOther chemical processesPaper material treatmentOxidized cellulosePeroxide
The invention provides a method for preparing adsorbable oxycellulose through a ramie oxidation degumming process. The method includes the steps that ramie original hemp serves as a raw material, the original hemp is smashed into short fibers through a smashing machine, and the short fibers are added with deionized water and soaked for pretreatment; a degumming solution is prepared from an oxidizing agent, a stabilizing agent, a fiber expanding agent, a penetrating agent, a chelating agent and water, the ramie original hemp and the degumming solution are mixed, gum in the ramie original hemp is fully removed by means of oxidizability of hyperoxide, and cellulose with active hydroxyl groups is oxidized into oxycellulose containing a great number of formyl groups; the oxycellulose is separated from water and dried to obtain the oxycellulose in the powder state. The method is simple in flow path, environmentally friendly, low in requirement for equipment and beneficial for large-scale production and has good economic and social benefits, the total reaction time is shortened, chemicals and cost are saved, efficiency is greatly improved, reaction conditions are moderate, and additional value of the cellulose is substantially increased.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Method for preparing cellulose nanofibers
The invention discloses a method for preparing cellulose nanofiber dispersion liquid, which comprises the following steps: dispersing a cellulose raw material in a drainage buffer solution system with a pH value of 4-5, and adding laccase and TEMPO so as to prepare a laccase-TEMPO oxidation system; continuously pumping oxygen into a reaction system so as to carry out oxidation reaction for 24-130 hours; after the reaction is completed, carrying out centrifugal filtration on the obtained object so as to obtain supernatant for repeated use; cleaning an obtained precipitate (i.e. water-insoluble oxidized cellulose) to be neutral by using deionized water; and adding deionized water, stirring the obtained mixture so as to obtain an oxidized cellulose water suspension, carrying out homogenation and ultrasonic treatment, and centrifugalizing the obtained object so as to obtain supernatant, i.e. oxidized cellulose nanofiber dispersion liquid. According to the invention, the oxidation efficiency is guaranteed, and the pollution caused by halogen elements to the environment is avoided; and the reaction system can be repeatedly used, so that the utilization rate of the oxidation system is improved, the oxidation effect is uniform, the yield of cellulose nanofibers is increased, and high-length-to-diameter-ratio nanofibers can be obtained.
Owner:贝尔纳丝新材料(江苏)有限公司
Processes for producing cellulose nanofibers
InactiveUS8287692B2Fast preparationCellulosic pulp after-treatmentNanostructure manufactureFiberNanofiber
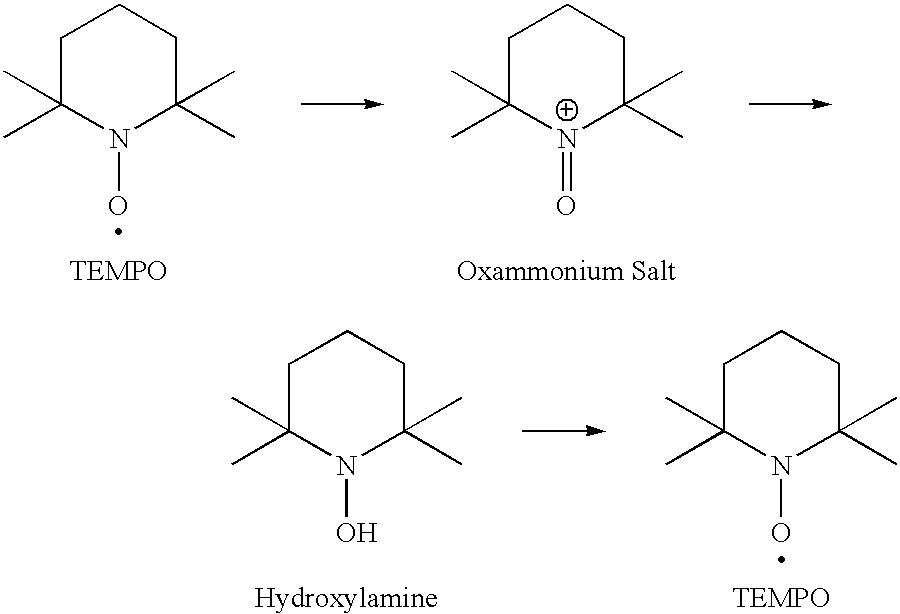
Cellulose nanofibers are produced using a 4-hydroxy TEMPO derivative by treating a cellulosic material with an oxidizing agent in water in the presence of a cellulose oxidation catalyst containing an N-oxyl compound to prepare oxidized cellulos, and microfibrillating the oxidized cellulose.
Owner:NIPPON PAPER IND CO LTD
Preparation method of corn stalk modified cellulose gel
InactiveCN104387617ALow toxicityImprove adsorption capacityOther chemical processesPaper material treatmentCobalt acetateThiourea
The invention discloses a preparation method of corn stalk modified cellulose gel capable of adsorbing heavy metal ions. The preparation method comprises the steps of stripping and shearing air-dried corn stalks to obtain two raw materials including basts and piths, respectively carrying out glacial acetic acid / hydrogen peroxide / cobalt acetate treatment, and then, further reacting after dropwise adding a potassium hydroxide solution to obtain two parts of cellulose; dissolving bastuse by using a low-temperature lithium hydroxide / thiourea method; oxidizing pith cellulose by using a piperidine-N-oxide radical / cooxidation system method to obtain a product, carrying out solid-liquid separation on the product, carrying out alcohol precipitation and freeze drying on filtrate to obtain pith oxidized cellulose, dispersing the product into a chitosan / acetic acid solution, and heating to obtain an oxidized cellulose / chitosan cross-linked product; and mixing the cross-linked product and a bastuse solution, molding by using a mold, carrying out alcohol bath dehydration, washing and drying to obtain the corn stalk modified cellulose gel. The gel prepared by using the method is microporous and flaky and has relatively high adsorption capacity for heavy metal ions such as Zn<2+>, Fe<3+>, Cd<3+> and Cu<2+>.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Macromolecule cross-linking agent based on oxidized cellulose, gelatin film thereof and preparation method
InactiveCN105237645ADirect connectionImprove light blocking performanceFlexible coversWrappersCross-linkPhosphate
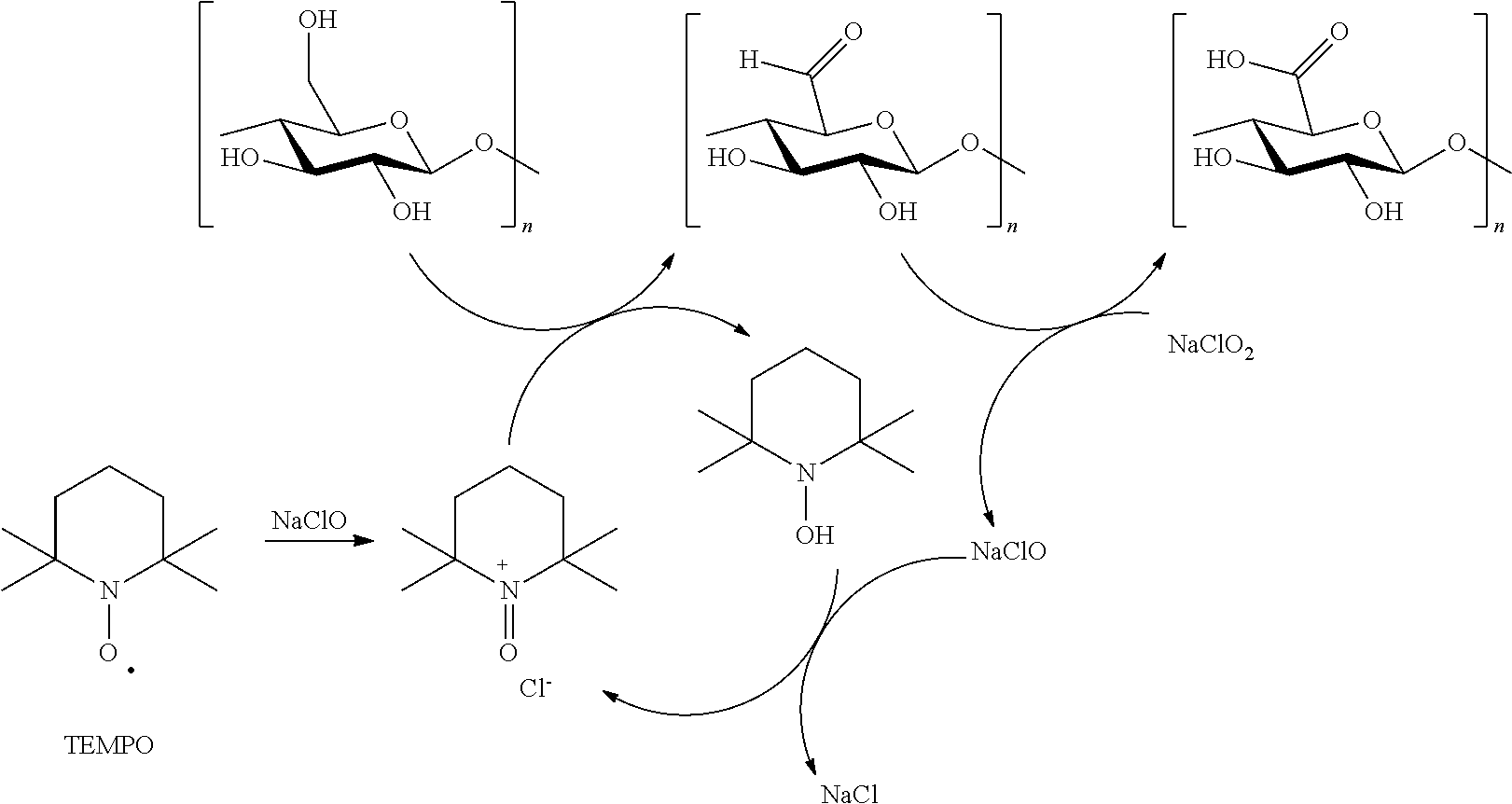
The invention discloses a macromolecule cross-linking agent based on oxidized cellulose, a gelatin film thereof and a preparation method. The preparation method of the gelatin film comprises the following steps: 1, oxidizing a primary amino group on the C6 position of cellulose into carboxyl through a TEMPO / NaBr / NaClO system, and obtaining oxidized cellulose TOMCC; 2, treating N-hydroxy succinimide and TOMCC obtained in step 1 as raw materials, and manufacturing a macromolecule cross-linking agent TMN; 3, making the macromolecule cross-linking agent TMN be subjected to chemical cross-linking with a gelatin film, and obtaining the food package gelatin film based on oxidized cellulose chemical cross-linking. Light-blocking performance, thermal stability, anti-biodegradation capability, the mechanical property (elasticity) and hydrophobicity of the gelatin film are all improved to a large extent, and a favorable condition is provided for application of the gelatin film to the food package field. In addition, biodegradation mechanisms of a modified gelatin film and a pure gelatin film in a phosphate buffered solution (PBS) and lysozyme are explored and analyzed as well.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing bleeding stopping oxidized celluloses in ramie oxidation degumming procedures
ActiveCN106478825AChange structureWith hemostatic functionSurgical adhesivesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismOrganic solventColloid
The invention provides a method for preparing bleeding stopping oxidized celluloses in ramie oxidation degumming procedures. The method includes smashing raw ramie to obtain short fibers and soaking the short fibers to sufficiently moisten the short fibers and allow the short fibers to sufficiently swell; mixing the pretreated raw ramie short fibers and degumming solution with one another to obtain mixtures, heating the mixtures, then preserving heat, sufficiently removing colloid in the raw ramie by the aid of oxidability of specific oxidizing agents and simultaneously oxidizing celluloses with active hydroxyl to obtain oxidized celluloses with a large quantity of carboxyl; soaking oxidized and treated fibers by the aid of organic solvent aqueous solution and removing the unreacted oxidizing agents; separating the oxidized celluloses from water and carrying out drying treatment on the oxidized celluloses to ultimately obtain the powdery bleeding stopping oxidized celluloses. The method has the advantages that processes are simple, the original two working procedures are combined into a single working procedure, accordingly, the total reaction time can be shortened, medicines and the cost can be saved, and the efficiency can be greatly improved; the bleeding stopping oxidized celluloses which are products prepared by the aid of the method are high in bleeding stopping speed and bleeding stopping efficiency and can be widely applied to quickly stopping bleeding under conditions of war wound, trauma and the like, and stable effects can be realized.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Method for preparing heavy metal ion adsorbents in ramie oxidization degumming procedures
InactiveCN106475065APromote regenerationIncrease added valueOther chemical processesWater contaminantsAbsorption capacitySorbent
The invention provides a method for preparing heavy metal ion adsorbents in ramie oxidization degumming procedures. The method includes smashing raw ramie to obtain short fibers, adding the short fibers into deionized water and soaking the short fibers; mixing the raw ramie and degumming solution with each other to obtain mixtures, heating the mixtures, sufficiently removing colloid in the raw ramie by the aid of oxidizing agents, and simultaneously oxidizing celluloses with active hydroxyl into oxidized celluloses with aldehyde; soaking reacted fibers in organic solvent aqueous solution and removing the unreacted oxidizing agents; separating the oxidized celluloses from water and drying the oxidized celluloses to obtain powdery oxidized cellulose adsorbents; preparing heavy metal solution, adding the oxidized cellulose absorbents into the heavy metal solution, carrying out vibration adsorption at the room temperature and measuring heavy metal ion absorption capacity numerical values. The method has the advantages that the adsorbents prepared by the aid of the method are low in residual gum content, moderate in crystallinity degree and polymerization degree and high in aldehyde content, and excellent heavy metal ion adsorption effects can be realized; working procedures are simplified, the total reaction time can be shortened, medicines and the cost can be saved, and the efficiency can be greatly improved.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
High flux high efficiency nanofiber membranes and methods of production thereof
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Hemostatic wound dressing and its producing method
The present invention is directed to a hemostatic wound dressing that utilizes a fibrous, fabric substrate made from carboxylic-oxidized cellulose and containing a first surface and a second surface opposing the first surface, the fabric having flexibility, strength and porosity effective for use as a hemostat; and further having a porous, polymeric matrix substantially homogeneously distributed on the first and second surfaces and through the fabric, the porous, polymeric matrix being made of a biocompatible, water-soluble or water-swellable cellulose polymer, wherein prior to distribution of the polymeric matrix on and through the fabric, the fabric contains about 3 percent by weight or more of water-soluble oligosaccharides.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Functional nano-crystalline cellulose hydrogel and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109180988AConducive to growth and migrationIncrease moisture contentProsthesisBiocompatibility TestingMechanical property
The invention relates to functional nano-crystalline cellulose hydrogel and a preparation method thereof. The interior of the hydrogel is of a uniform porous mesh structure, and the pore size of the hydrogel is 30-100 microns. The hydrogel is prepared by the following steps: dispersing TEMPO oxidized cellulose in water to prepare nano-cellulose dispersion, mixing with cells to prepare bio-ink, andprinting into an ionic crosslinking agent by utilizing a 3D bio-printing technology, thereby obtaining the product. The shape of the product can be designed according to needs. The renewable resourcecellulose serves as a raw material, and the functional nano-crystalline cellulose hydrogel with advantages of being excellent in mechanical property, excellent in biocompatibility and applicable to bio-printing is prepared. The prepared hydrogel serves as a nano-cellulose based tissue engineering material, is particularly one of tissues such as bones, cartilage, skin, blood vessels, liver, heartand the like, the application range of the cellulose is widened, and a novel pathway is provided for application research of the cellulose in the biomedical field.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Microspheres Including Oxidized Cellulose
A process for forming microspheres is disclosed. The process includes: forming a first plurality microspheres comprising at least one bioactive agent and modified cellulose; contacting the first plurality of microspheres with a solution of a biodegradable polymer to form a discontinuous phase liquid; contacting the discontinuous phase liquid with a continuous phase liquid to form an emulsion; and extracting a second plurality of microspheres from the emulsion, the second plurality of microspheres comprising the first plurality of microspheres.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Preparation method and application of cellulose-based nitrogen-doped fluorescent carbon quantum dots
InactiveCN108485660AExpensive to solveHigh fluorescence intensityMaterial nanotechnologyNanoopticsSolubilityEvaporation
The invention discloses a preparation method of cellulose-based nitrogen-doped fluorescent carbon quantum dots, and belongs to the field of fluorescent nano material science. The method comprises thefollowing steps of: (1) placing cellulose in a HNO3 / H3PO4 / NaNO2 oxidation system, performing selective oxidation on C-6 hydroxyl groups, adding ultrapure water, performing static settlement, performing centrifugation, washing, drying and ultrasonic treatment to obtain an aqueous solution of oxidized cellulose nanoparticles; and (2) mixing the aqueous solution of the oxidized cellulose nanoparticles with ammonia water, pouring the mixture into a reaction kettle, performing a hydrothermal reaction, cooling to room temperature, performing ultrasonication and centrifugation so as to remove insoluble precipitate thoroughly and obtain supernatant, and finally conducting rotary evaporation on the supernatant to obtain the cellulose-based nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots. The raw materials haverich sources and low price, and the preparation process is green and simple, and needs no expensive equipment; the prepared cellulose-based nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots have high fluorescence intensity, low toxicity and good water solubility, and can be applied to detection of Fe<3+>.
Owner:DALIAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing oxidized cellulose
The invention discloses a method for preparing oxidized cellulose. The preparation method comprises the following steps: a, putting an oxidized cellulose material into inert solution; b, adding an oxidant into the inert solution, sealing the solution, stirring the solution for 10 to 12 hours by using a magnetic stirrer at the temperature of between 20 and 60 DEG C; c, taking the oxidized cellulose material out, and washing the oxidized cellulose material with purified water; d, drying the oxidized cellulose material by using a centrifugal machine, and then washing the oxidized cellulose material by cleaning solution; and e, drying the oxidized cellulose material to obtain a finished product. Because the inert solution is used as a reaction solvent, the oxidization reaction can be performed under the controllable conditions, the reaction is even, and the manufactured oxidized cellulose and oxidized regenerated cellulose products are stable and easy to store; and the reaction solvent and the oxidant can be reclaimed for recycle, so the method is economic and environment-friendly, and the production cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:GUIZHOU JINJIU BIOTECH
Preparation method of oxidized cellulose nanofiber membrane sheet with fast bleeding stopping function
ActiveCN106120327APromote aggregationImprove solubilityPharmaceutical delivery mechanismFilament/thread formingCellulose acetateBiocompatibility Testing
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical materials, and particularly relates to a preparation method of an oxidized cellulose nanofiber membrane sheet with a fast bleeding stopping function. According to the method, cellulose derivatives such as cellulose acetate, cellulose acetate butyrate and ethyecellulose are used as raw materials; a nanofiber membrane of the cellulose derivatives is prepared through an electrostatic spinning process. Then, through processes of hydrolysis, oxidization and the like, the oxidized cellulose nanofiber membrane sheet is obtained. The method has the characteristics that the process is simple; the reaction is mild; safety and environment protection are realized. The oxidized cellulose nanofiber membrane sheet prepared by the method has good biocompatibility and biodegradability; the gathering of blood platelets in a wound can be effectively promoted; the fast bleeding stopping can be realized.
Owner:广州永翔科技发展有限公司
Synthetic method of oxidized cellulose
The invention discloses a synthetic method of oxidized cellulose. According to the method, firstly, cellulose materials are pretreated through an NaOH or LiOH solution by combining an ultrasonic technology; then, an NaClO4 and K2FeO4 oxidation system is used for further oxidizing the materials through regulating the pH values in the mixed material via NaAc; the oxidation temperature is 30 to 42 DEG C; the oxidization time is 1 to 3h; finally, an oxidized product is cleaned and dried. The method has the advantages that the cellulose oxidization time can be greatly shortened; in addition, the obtained oxidized cellulose has high-content carboxyl; the content of the carboxyl can reach 21.6 percent to 35.8 percent; the oxidized cellulose belongs to a medical material with better application prospects.
Owner:JIANGSU LANWAN BIOTECH
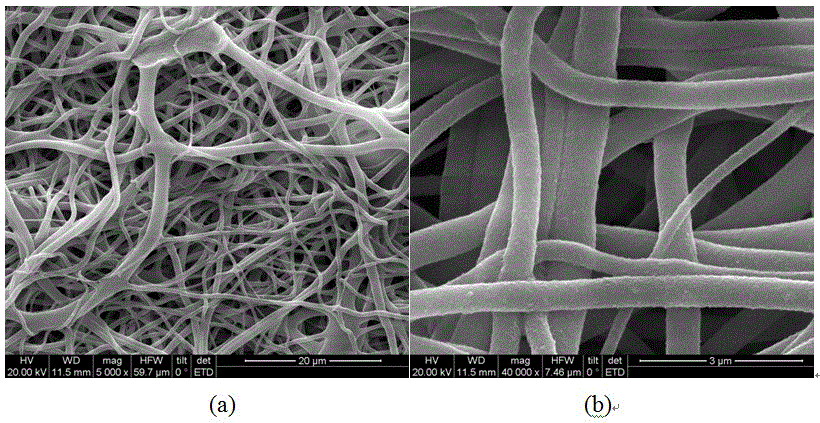
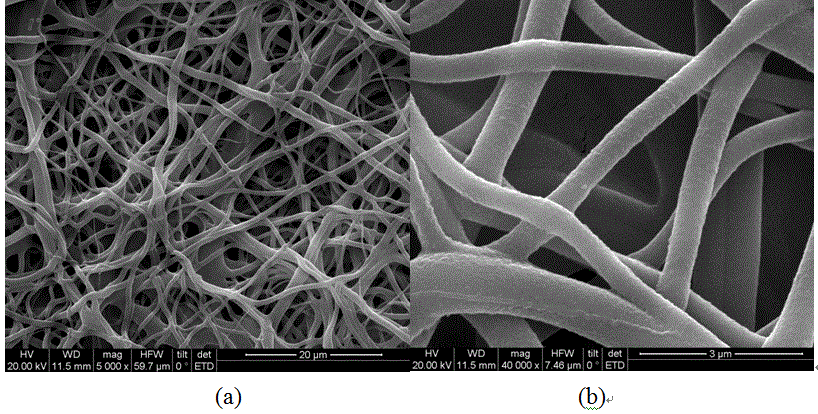
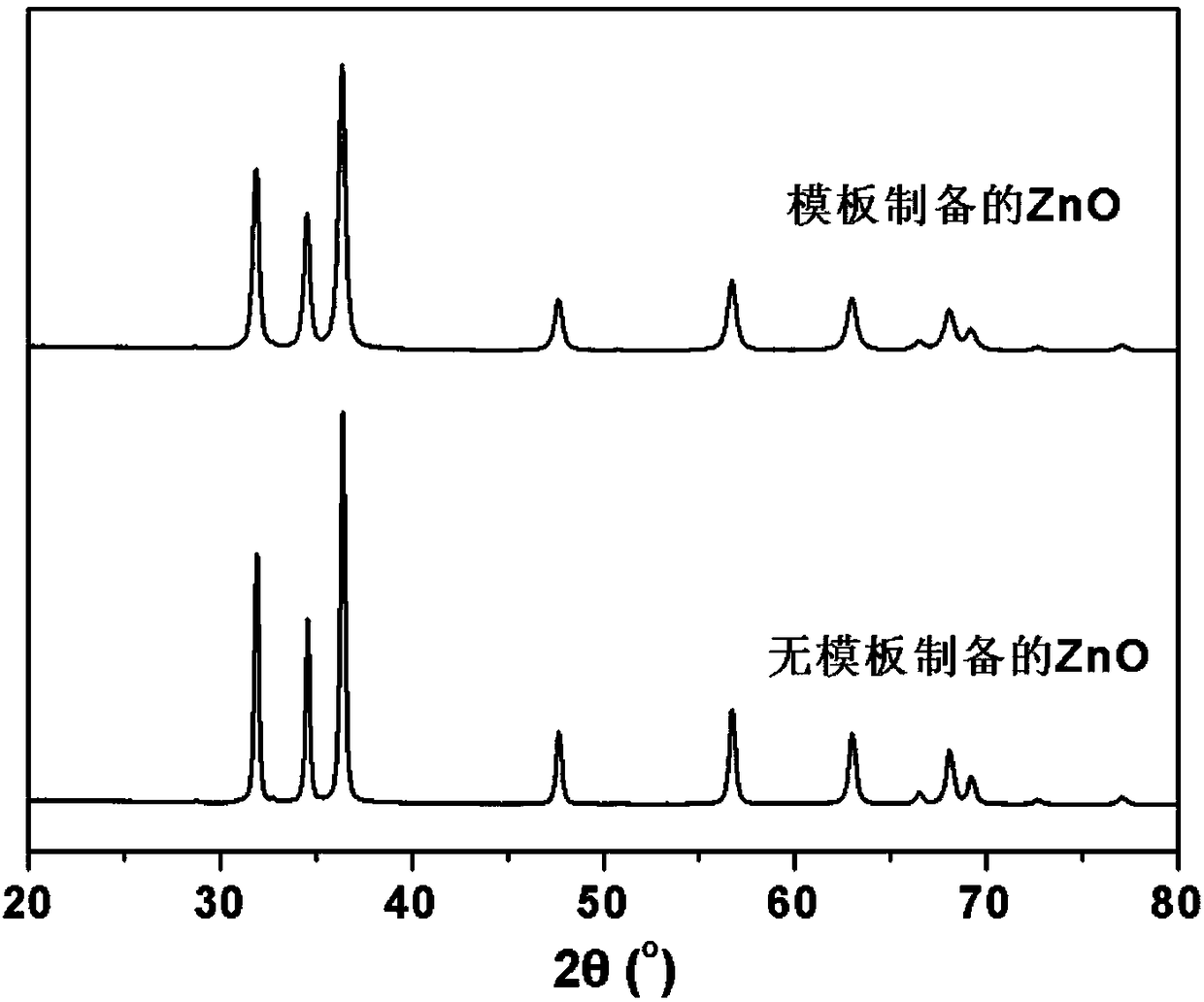
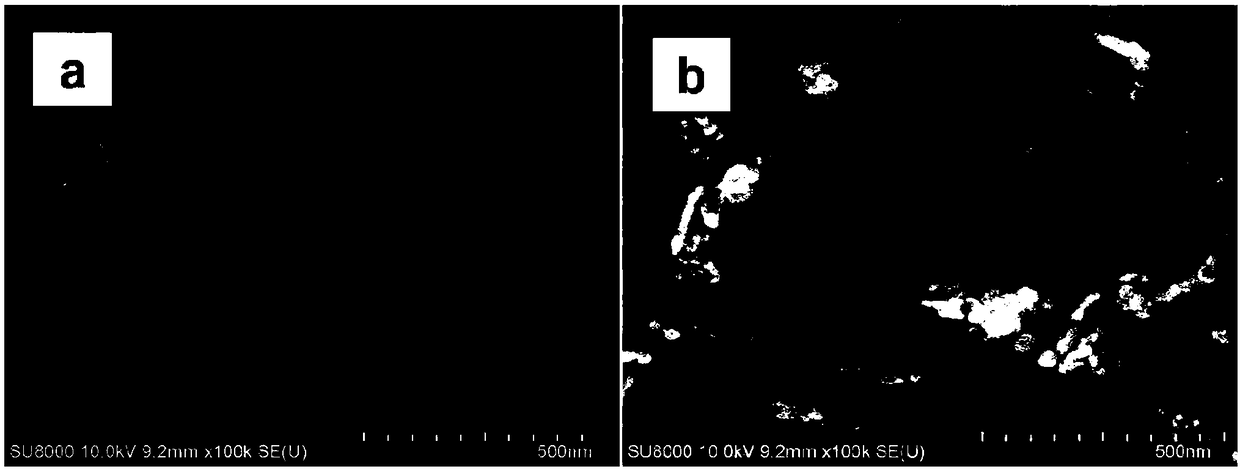
Preparation method of zinc oxide nanocrystal
ActiveCN108128800AHigh crystal contentIncrease the areaZinc oxides/hydroxidesChemical industryPolymer science
The invention belongs to the field of a chemical industry, and particularly relates to a preparation method of a zinc oxide nanocrystal, so that the photocatalytic activity of zinc oxide is improved.The method comprises the steps of firstly preparing TEMPO oxidized cellulose, then respectively grafting a polymer containing carboxyl, a polymer containing sulfonyl, or a polymer containing an epoxygroup through a heterogeneous free radical polymerization method, preparing to obtain modified TEMPO oxidized cellulose, then adopting the modified TEMPO oxidized cellulose as a template, adsorbing aprecursor zinc acetate of zinc oxide, obtaining cellulose / zinc oxide compound under hydrothermal reaction, calcining to remove the template, and finally obtaining the zinc oxide nanocrystal. The ZnOnanocrystal prepared through the method provided by the invention can replace an existing ZnO photocatalytic material, has the characteristics of high wurtzite crystal form content, large specific surface area and large pore volume, shows a better photocatalytic performance, is simple in preparation process, and belongs to an environment-friendly material.
Owner:SHANDONG HUATAI PAPER
Preparation method of nano cellulose/carbon nanotube flexible tactile sensor
ActiveCN110305345AStrong mechanical propertiesHigh sensitivityCatheterSensorsCarbon nanotubeTactile sensor
The invention discloses a preparation method of a nano cellulose / carbon nanotube flexible tactile sensor. The nano cellulose / carbon nanotube flexible tactile sensor is made by dispersing TEMPO oxidized cellulose in water to obtain a nano cellulose dispersion, mixing well the nano cellulose dispersion with carbon nanotubes, and carrying out ion crosslinking and silk copying. Cellulose as a crystal-structured polysaccharide is the richest natural polymer on earth, is regenerable, biologically degradable and well biocompatible, and has a wide range of origins. Electronic skin herein is made fromthe renewable resource cellulose and carbon nanotubes; the preparation technique is simple, time consumption is low, and the expenditure is low; the defects of high cost and complex time-consuming process due to the use of traditional photolithography, chemical corrosion and other traditional methods are avoided; the sensor of the invention has good sensing performance, the applicable range of cellulose is widened greatly, and a new approach is provided for the research on the application of cellulose in the sensing field.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Synthesis method of high-carboxylation-degree oxidized cellulose
The invention discloses a synthesis method of high-carboxylation-degree oxidized cellulose, comprising the steps of combining pre-treatment and multistep oxidization to fully oxidize a cellulosic material, namely, first sealing, mixing and ball-milling the cellulosic material and dry ice and exposing a sample to air to realize the pre-treatment process after finishing ball-milling, then adopting NaNO3 and H2SO4 for carrying out primary oxidization on the material, and carrying out secondary oxidization by adopting KCLO4 as an oxidizing agent, wherein a reaction is performed at the temperature of 30 to 40 DEG C and the reaction time is 30 to 60 min; finally, further oxidizing the material subjected to the secondary oxidization by adopting KCLO, wherein the oxidization temperature is 50 to 60 DEG C and the time is 50 to 65 min. An oxidized cellulose product obtained through the synthesis method is relatively high in content of carboxyl, the content of the carboxyl can reach up to 35.6 percent to 48.7 percent, and the product has good application prospect in the technical field of biological medicine materials.
Owner:JIANGSU LANWAN BIOTECH
Method for making and using a dye sorbent
A method for producing a modified sawdust sorbent. The method involves sulfonating sawdust with sulfuric acid and oxidizing the sulfonated sawdust with hydrogen peroxide. The method yields a modified sawdust sorbent containing sulfonated and oxidized cellulose. The modified sawdust sorbent has a higher surface area, higher organic dye adsorption capacity, and more rapid organic dye adsorption rate than unmodified sawdust. Also disclosed is a method of using the modified sawdust sorbent for organic dye removal from water.
Owner:PRINCE MOHAMMAD BIN FAHD UNIV
Oxidized cellulose-based material, method for obtaining same and use thereof as compress
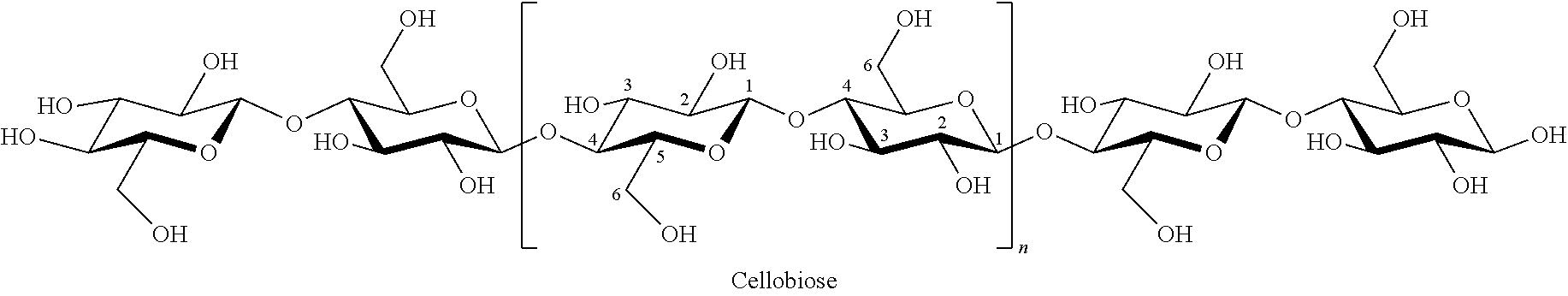
The present invention relates to a method of obtaining a solid material based on a polymer having its cellobiose units exhibiting the following characteristics:at least some of the cellobiose units have at least one carboxylic acid function attached to the C6 carbon, the other C6 carbons having a primary alcohol function attached thereto; andat least some of the cellobiose units have at least one of the two rings open between the C2 and C3 carbons, the other C2 and C3 carbons forming a ring and having an alcohol function attached thereto.Such a material, advantageously a textile, may be used as a compress.
Owner:SYMATESE
Method for producing cellulose nanofibers
ActiveUS20140053828A1Improve liquidityLow viscosityArtificial filaments from cellulose solutionsPulp properties modificationPolymer scienceNanofiber
Cellulose nanofibers are produced by means of a method comprising a step (A) of oxidizing a cellulosic starting material in the presence of an N-oxyl compound and a step (B) of forming the oxidized cellulosic starting material into nanofibers by defibrating the oxidized cellulosic starting material, and a step (C) of performing at least one selected from the following steps: a step (C-1) of treating the cellulosic starting material in water having a hydroxide ion concentration of 0.75 to 3.75 mol / L prior to performing the step (A); and a step (C-2) of subjecting the oxidized cellulosic starting material obtained from the step (A) to hydrolysis in an alkaline solution having a pH between 8 and 14 after performing the step (A) and prior to performing the step (B).
Owner:NIPPON PAPER IND CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com