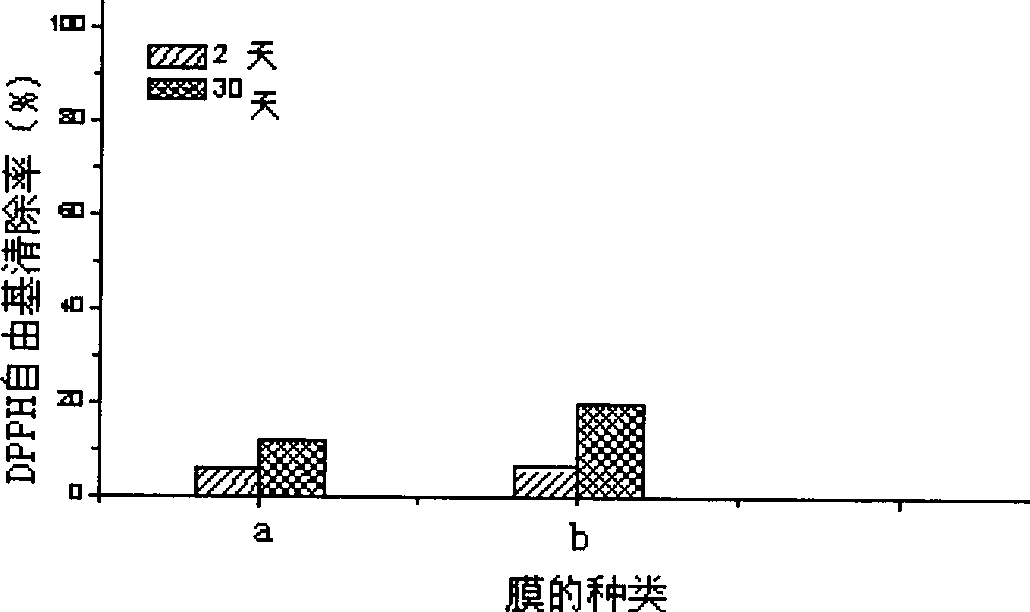
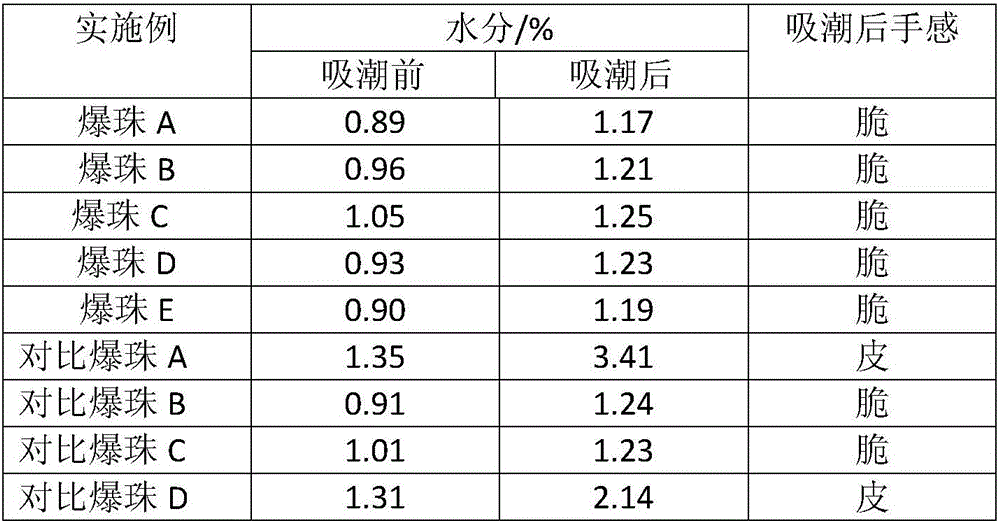
Patents
Literature
112 results about "Gelatin film" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Medical film
InactiveUS7718556B2Good biocompatibilityHigh strengthSuture equipmentsBiocideGelatin filmThin membrane
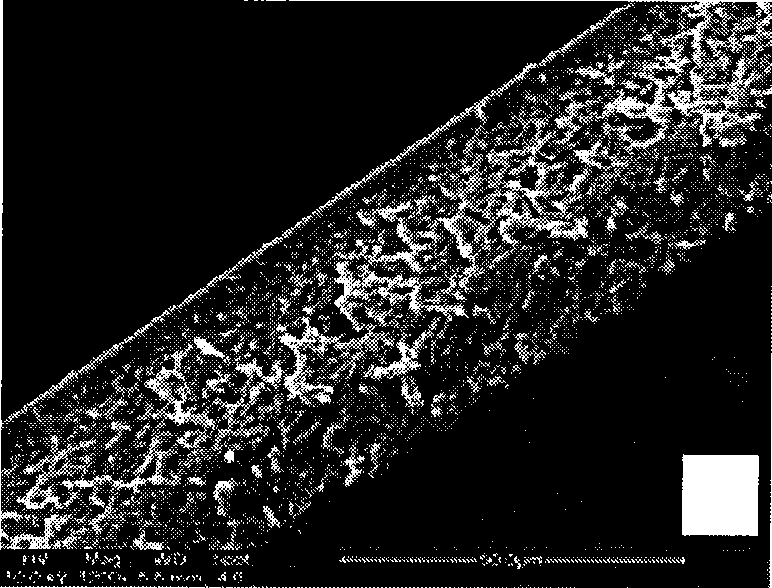
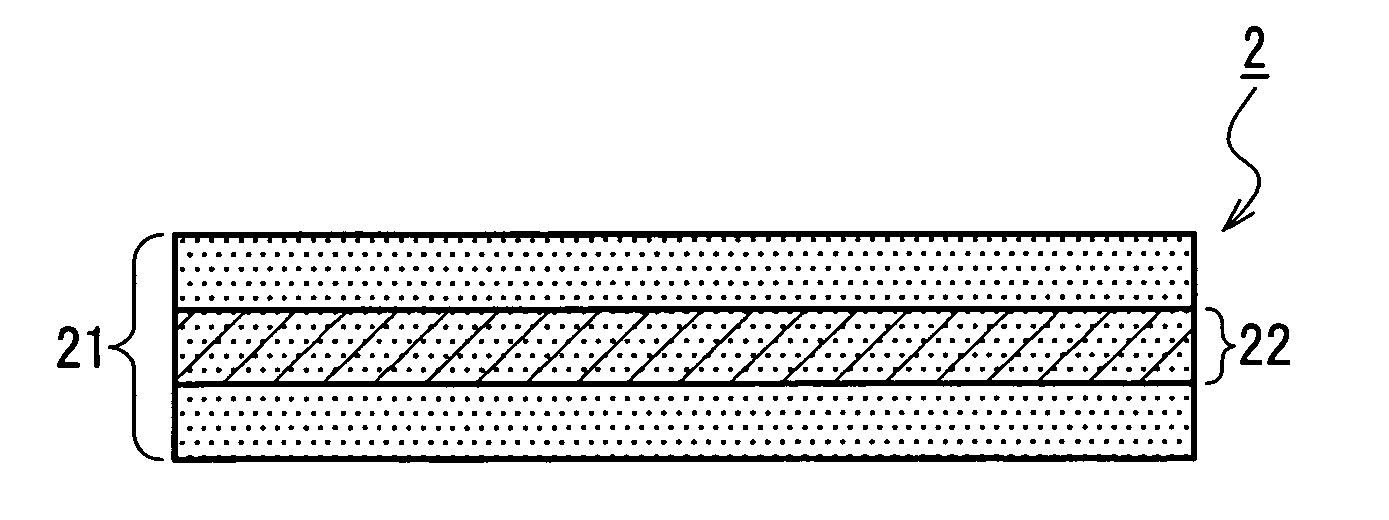
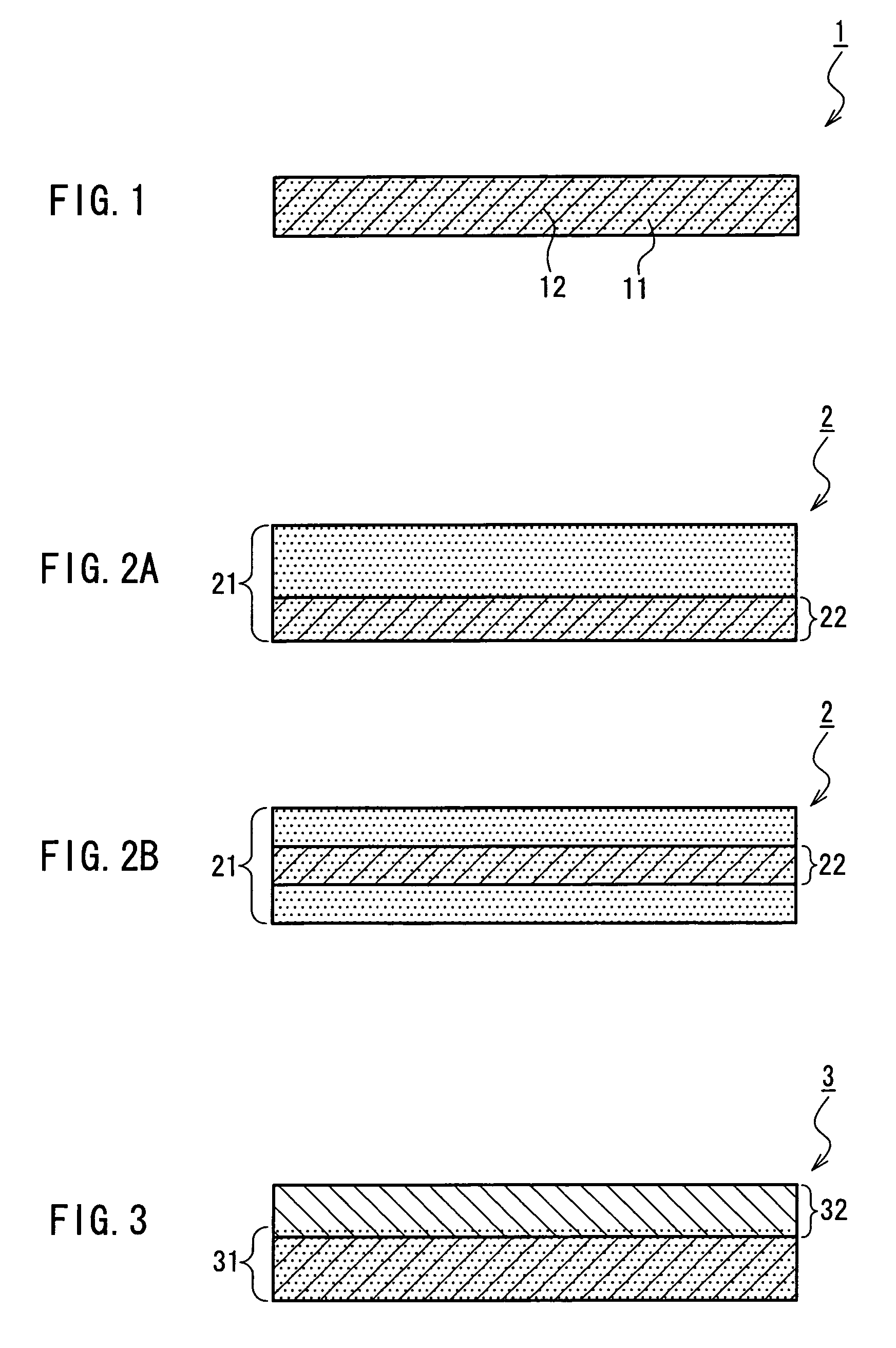
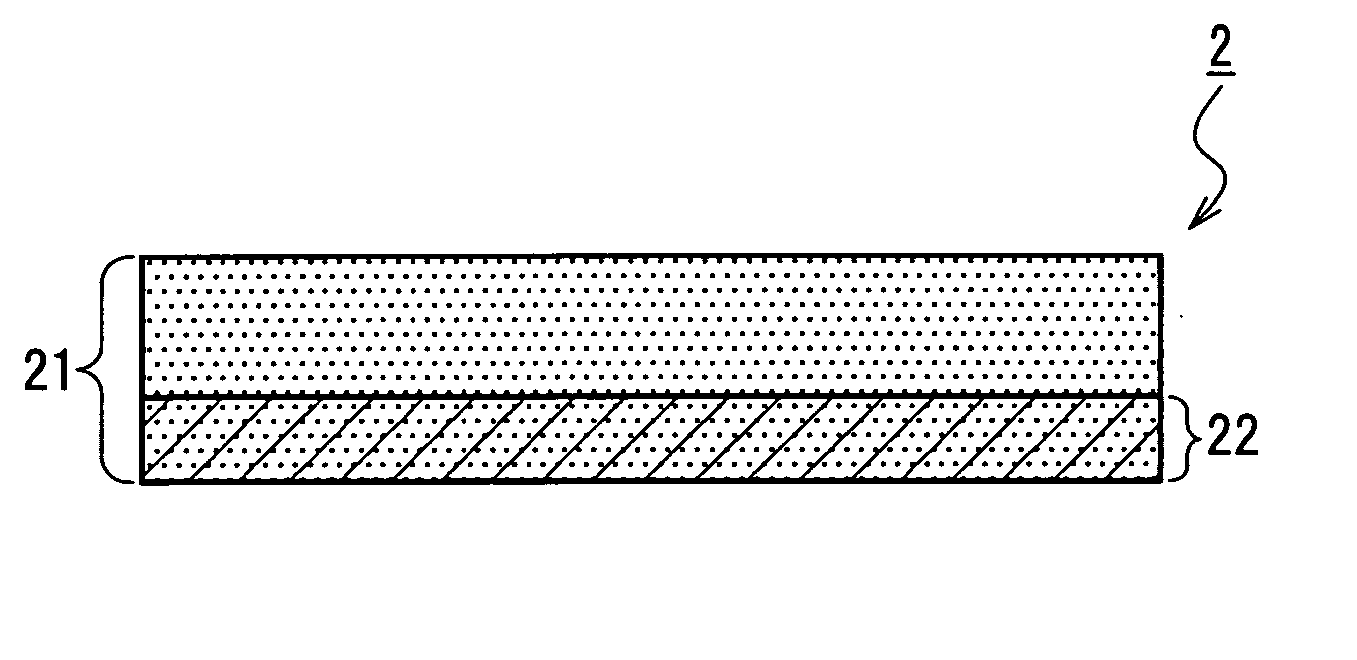
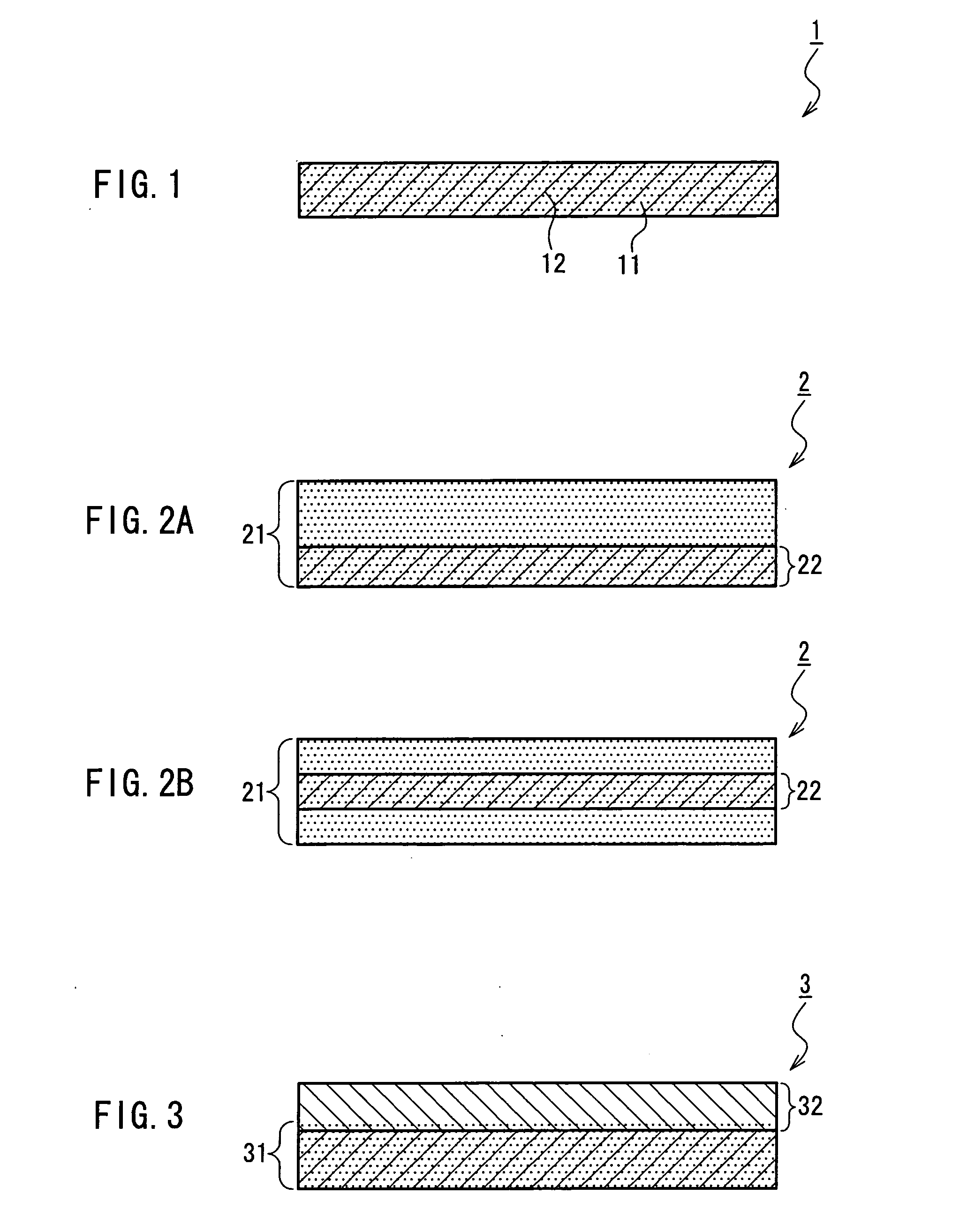
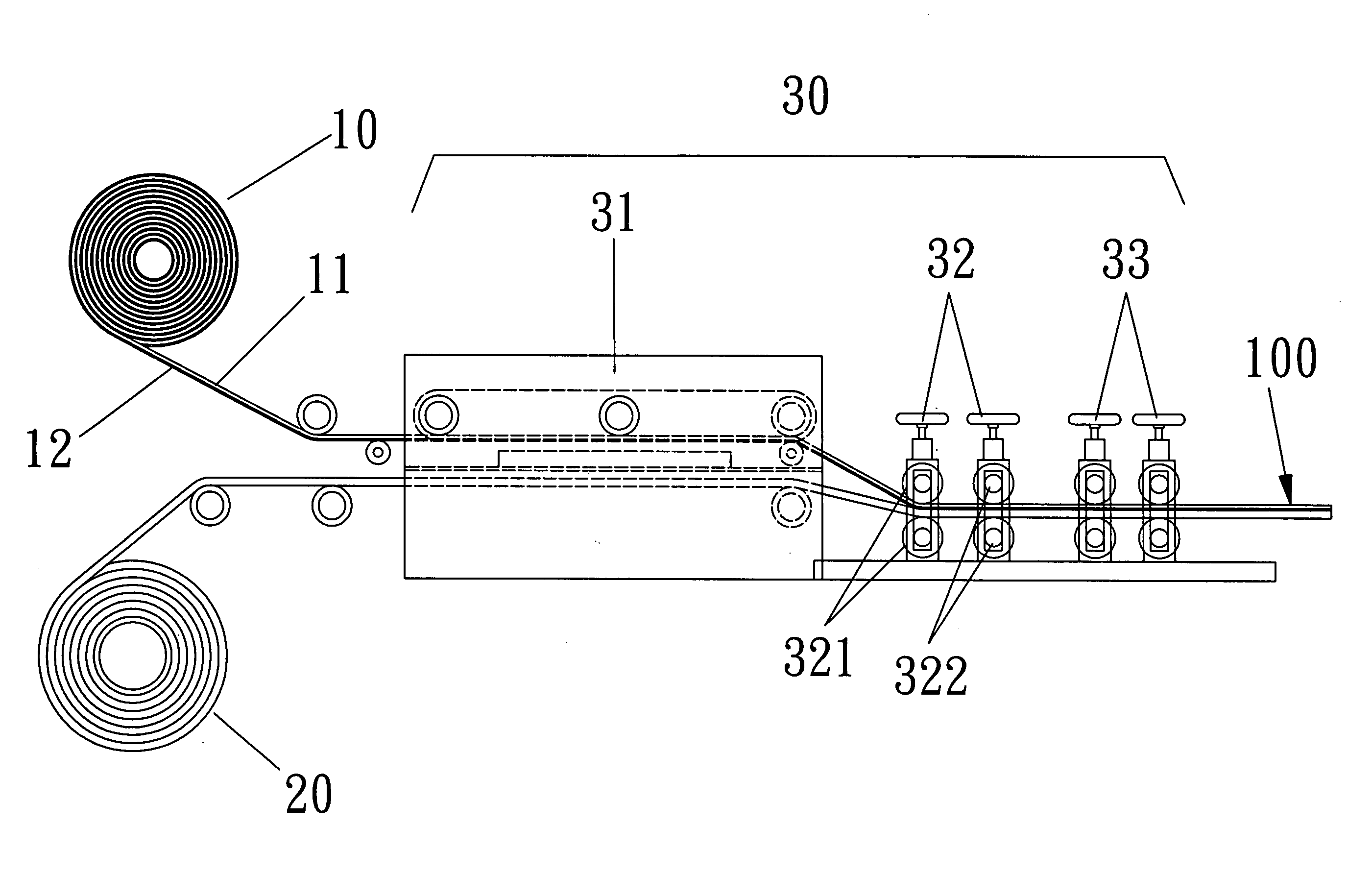
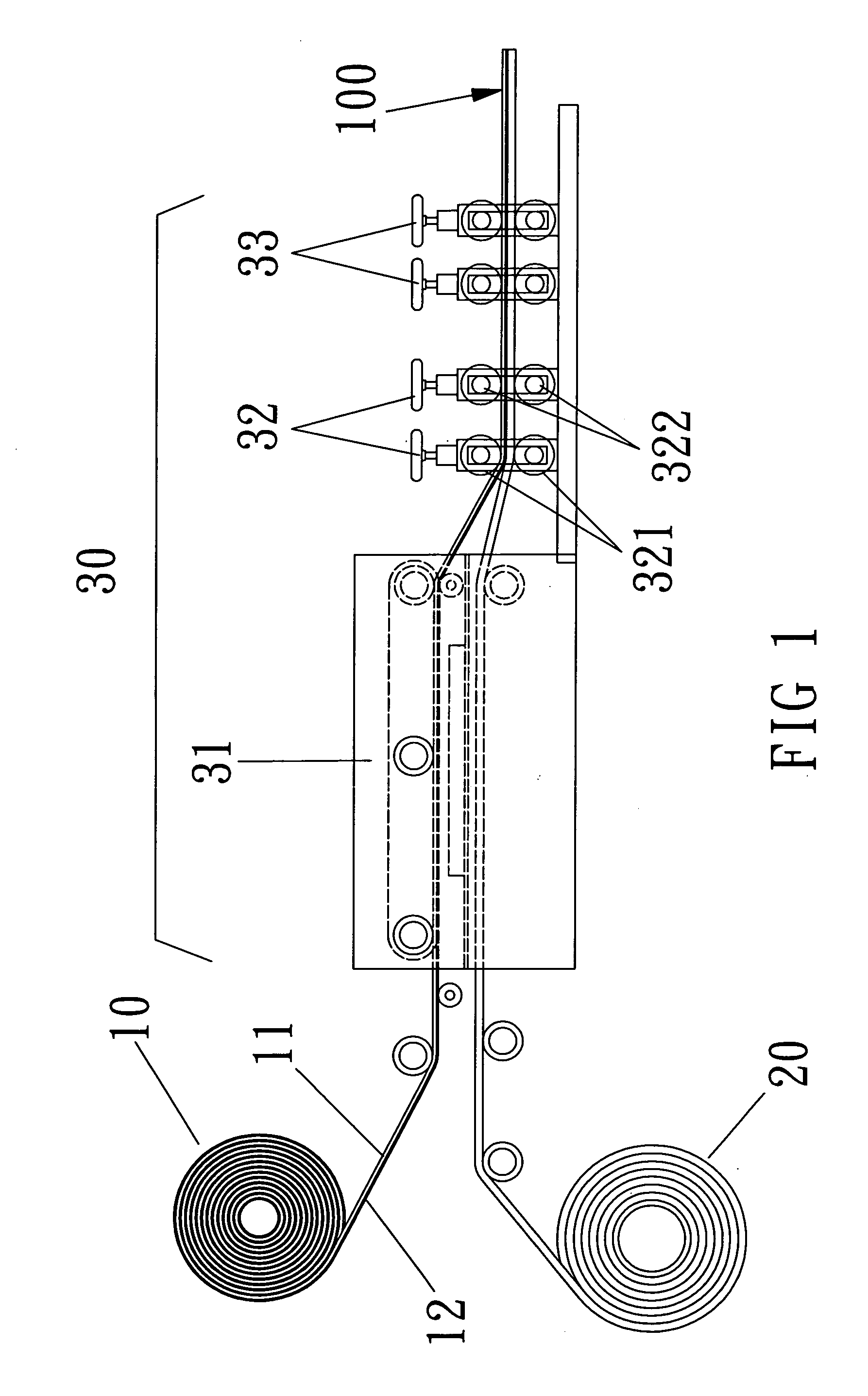
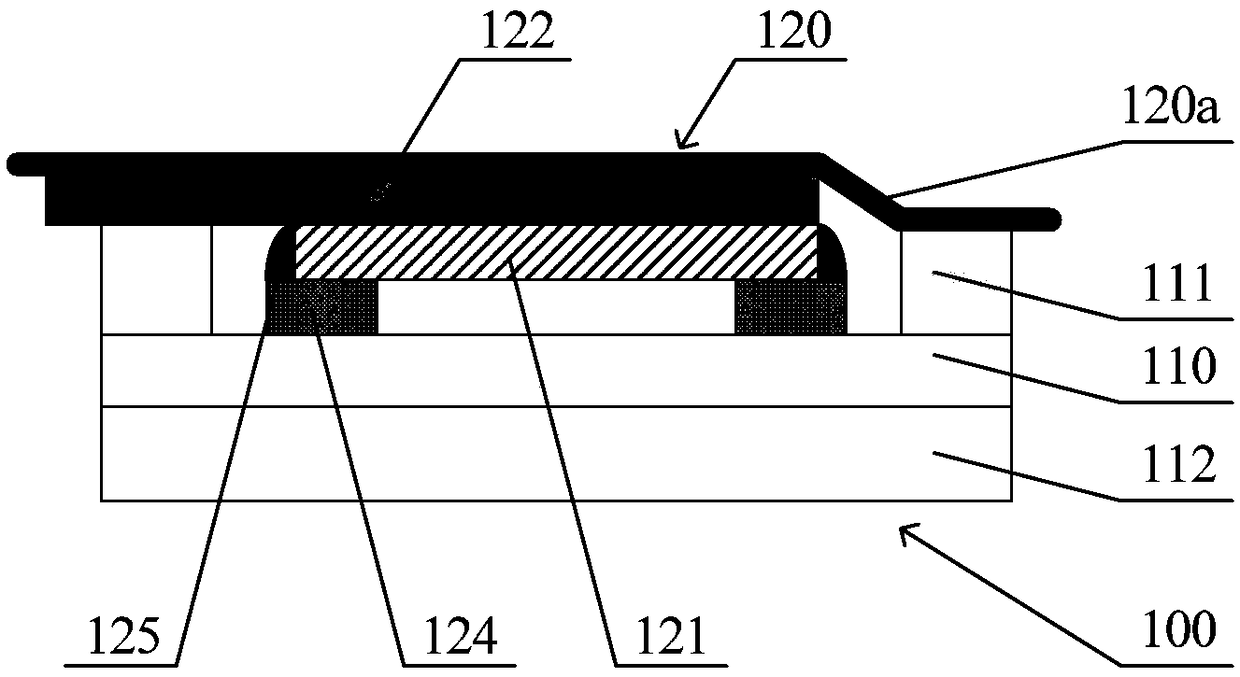
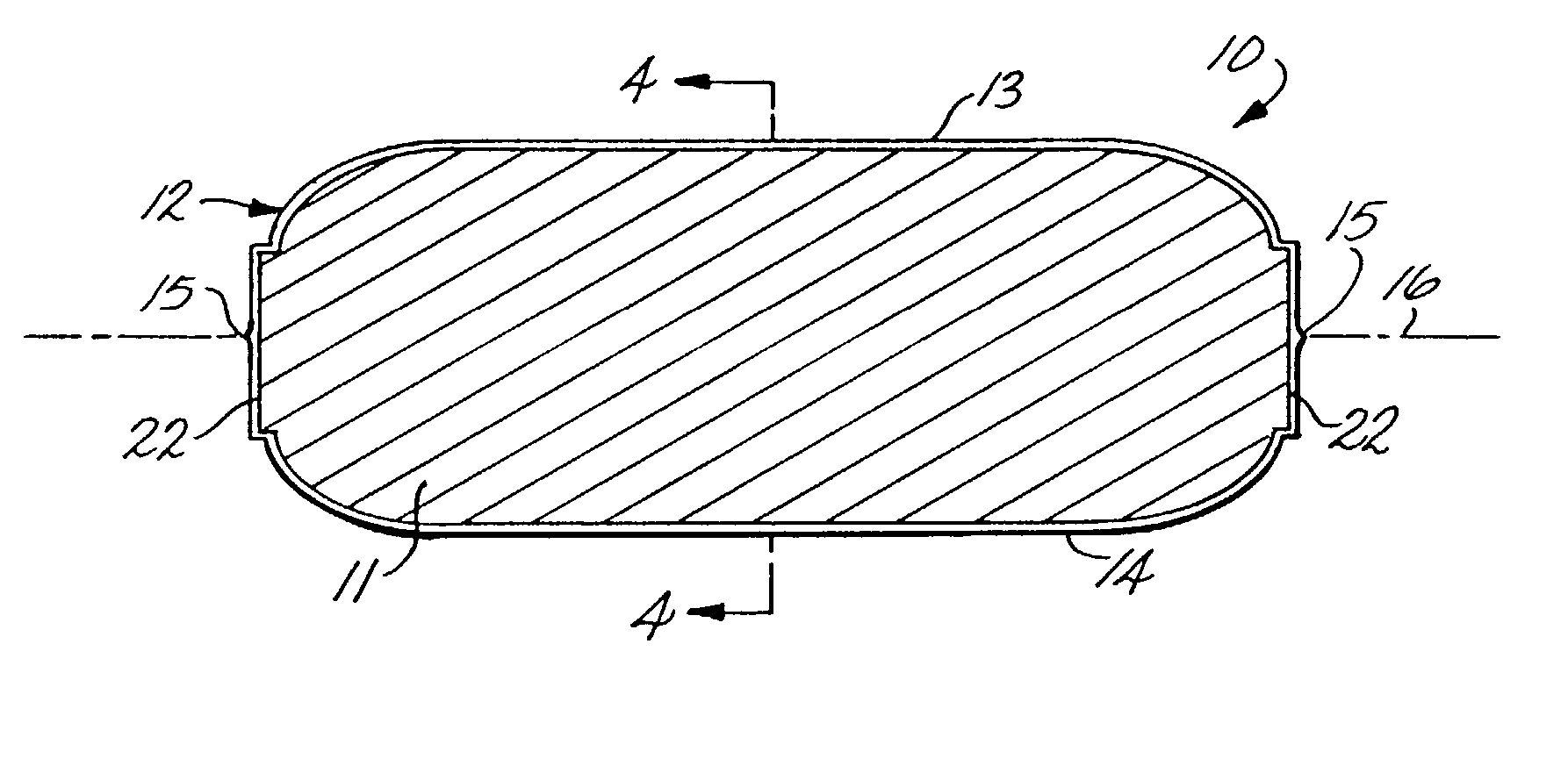
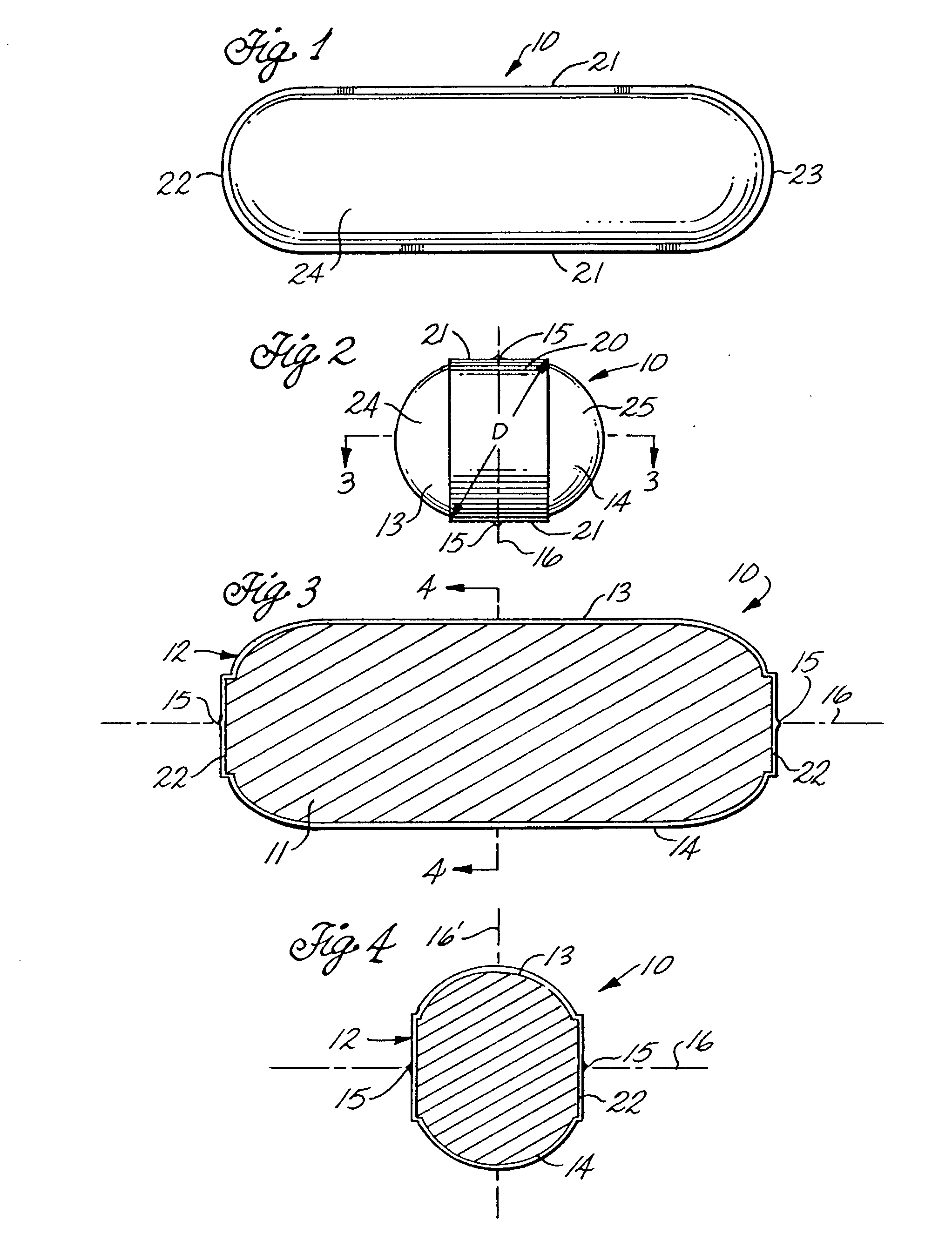
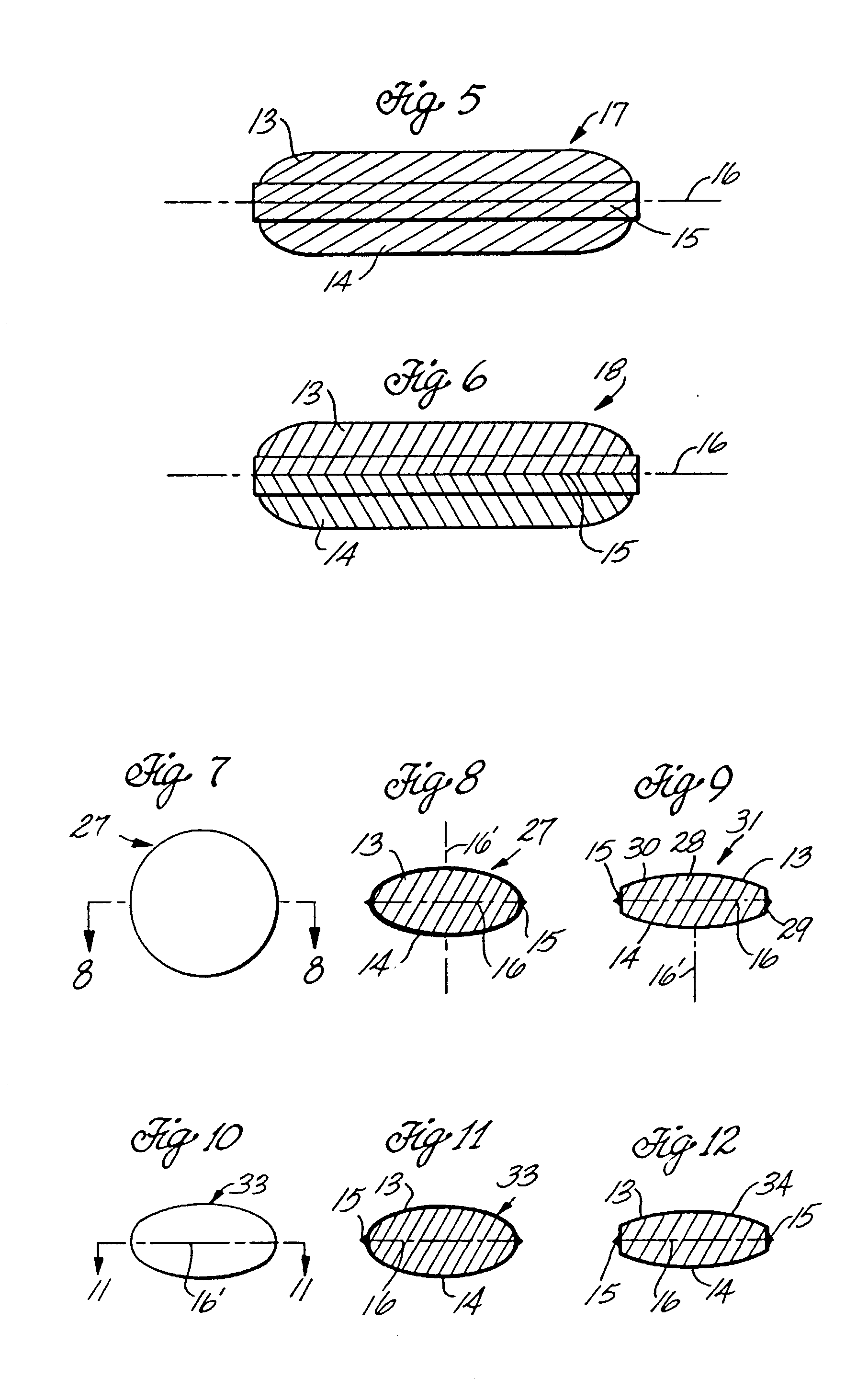
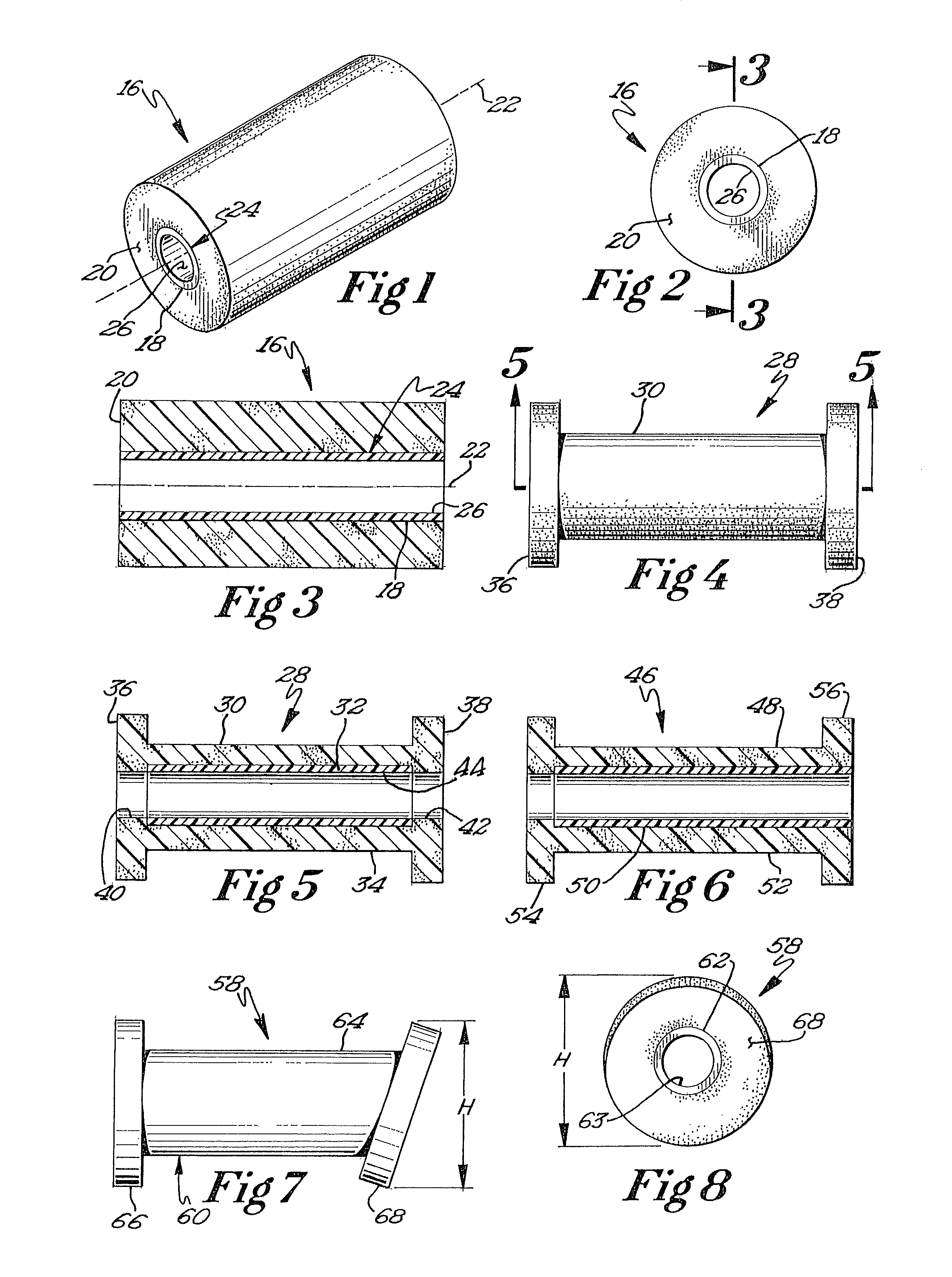
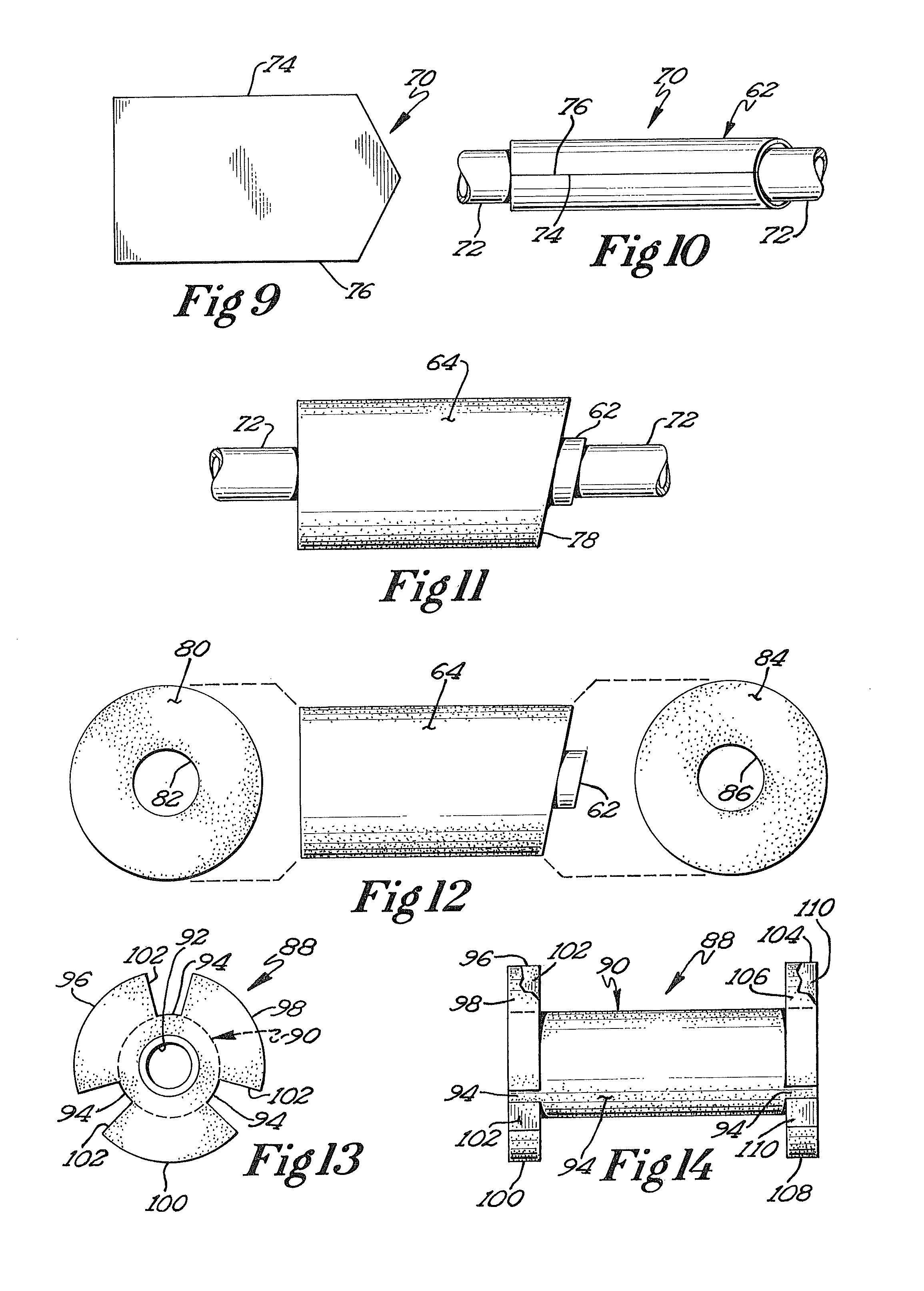
A medical film that is excellent in biocompatibility and bioabsorbability and has an excellent strength in suturing and bonding is provided. A reinforcing material 12 made of a biodegradable polymer is placed in a gelatin solution so as to allow the solution to infiltrate in the reinforcing material 12 and then the gelatin is dried. This allows the gelatin that has infiltrated entirely in an internal part of the reinforcing material 12 to gel, thereby forming a gelatin film 11. Thus, a medical film 1 in which the reinforcing material 12 and the gelatin film 11 are integrated is obtained. The gelatin film 11 preferably is a cross-linked gelatin film.
Owner:GUNZE LTD
Multifunctional liquid rubber spray-coating material, preparation method, using method and special-purpose device
InactiveCN101235252AGood extensibilityImprove performanceSpraying apparatusConjugated diene hydrocarbon coatingsPolymer scienceSpray coating
Multifunctional liquid rubber spray coating comprises components of A, B, wherein A component comprises liquid rubber asphalt emulsion whose solid content is 50-75%, wherein 2-65% rubber elusion content, 30-97% asphalt elusion content, 0.0-5.0% carbon black, 0.0-6.0% ultra-fine powder, 0.025-2.50% anion dispersing agent and 0.025-3.00% anion surface activator, which is waterborne spray coating, and B component is water solution which comprises 3.0-18.0% concentration calcii chloridum (89.0-99.2%), sodium chloride (0.50-4.0%) and composite aluminum iron polymer (0.3-7.0%). The two components are sprayed on the same basal plane through adopting a double-component airless spraying device to form a gelatin film with 0.5-4mm after 3-5 seconds solidification, which has the characteristics of strong bonding, temperature resistance, weather resistance, and excellent chemical stability, heat insulation and puncture resistance. The A component can be individually sprayed, or can be combined with the double components.
Owner:大连美宸特环保节能产品有限公司
Medical film
InactiveUS20060094318A1Good biocompatibilityHigh strengthSuture equipmentsBiocideGelatin filmThin membrane
A medical film that is excellent in biocompatibility and bioabsorbability and has an excellent strength in suturing and bonding is provided. A reinforcing material 12 made of a biodegradable polymer is placed in a gelatin solution so as to allow the solution to infiltrate in the reinforcing material 12 and then the gelatin is dried. This allows the gelatin that has infiltrated entirely in an internal part of the reinforcing material 12 to gel, thereby forming a gelatin film 11. Thus, a medical film 1 in which the reinforcing material 12 and the gelatin film 11 are integrated is obtained. The gelatin film 11 preferably is a cross-linked gelatin film.
Owner:GUNZE LTD
Novel soft-gelatin capsule comprising S-adenosylmethionine and a method for producing the same
InactiveUS20020164369A1Easy to handleReadily availableBiocideSugar derivativesS-Adenosyl methionineGelatin film
The invention provides a novel soft gelatin capsule comprising a fill material consisting essentially of S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe) salt disposed within an enteric coated soft gelatin film.
Owner:ORCHID CHEM & PHARM LTD
Polyvinyl butyral transparent film and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102863917ANon-macromolecular adhesive additivesFilm/foil adhesivesPolymer scienceComposite film
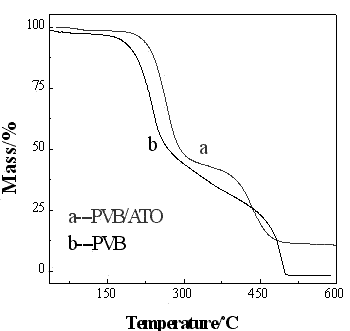
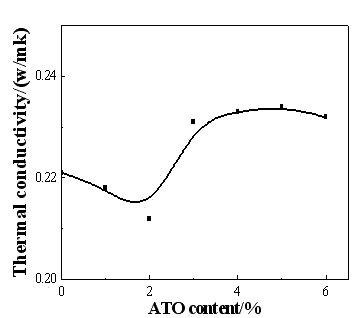
The invention belongs to the field of polymer / nanoparticle composite materials, and relates to an infrared thermal reflection and anti-ultraviolet polyvinyl butyral (PVB) transparent film for laminated safety glass and a preparation method thereof. According to the method, nano-indium stannum oxide (ATO) is selected as functional particles, is subjected to double processing through a coupling agent and a dispersing agent and is poured into a mold to be formed and compounded after being directly and uniformly mixed with purchased or self-made polyvinyl butyral, plasticizer, antioxidant and filming agent by means of ultrasonic wave to prepare a heat-insulating PVB nano composite film. The nano-ATO particles are subjected to the double processing and the special ultrasonic dispersion process, so that the problem of agglomeration of the ATO is effectively improved; and the prepared PVB nano composite film has superior mechanical property and higher infrared reflectivity and visible light transmittance, and can be directly used for processing and producing heat-insulating, sound-insulating, anti-ultraviolet, transparent and impact-resistant multi-functional safety glass.
Owner:CHANGZHOU XIAOGUO INFORMATION SERVICES
Method for preparing antioxidation gelatine membrane containing tea polyphenol-chitosan nano grain
InactiveCN101461535AControlled releaseImprove antioxidant capacityFood shapingFood preparationFlavorControlled release
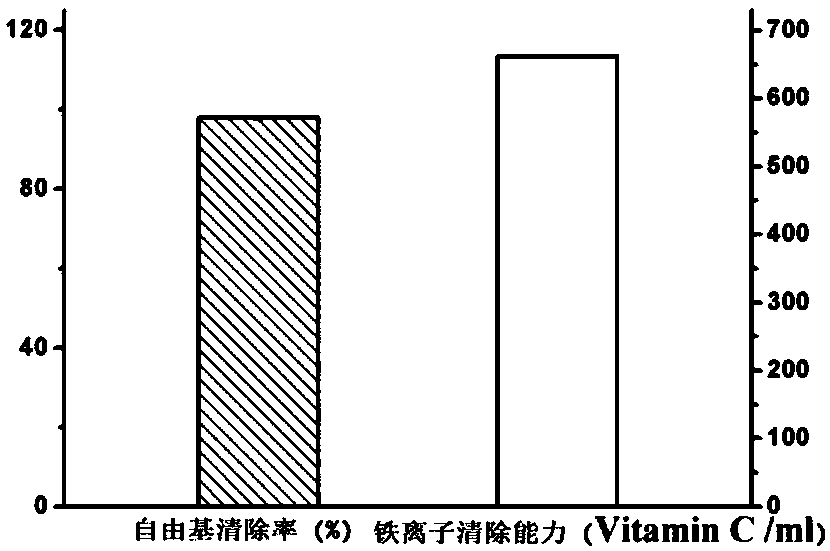
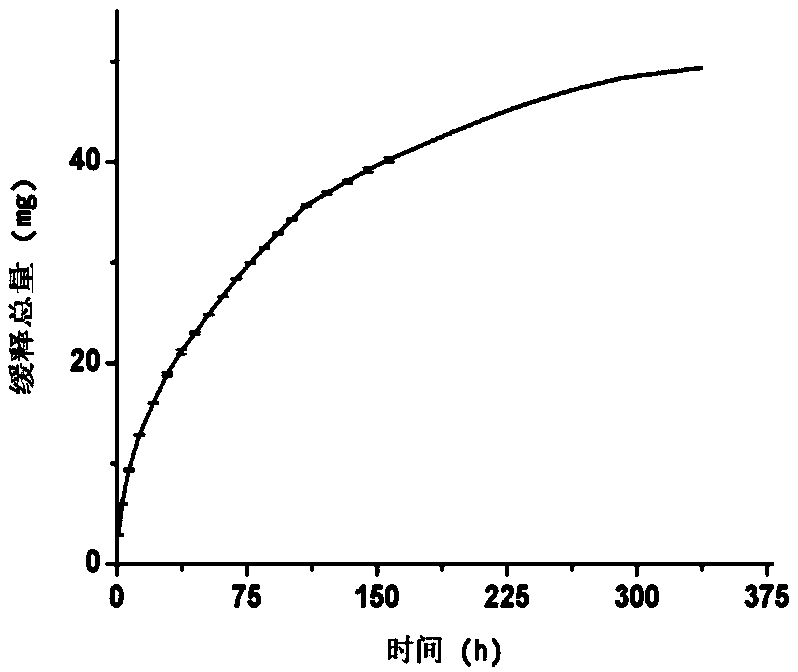
The invention relates to a preparation of oxidation resistant gelatin film containing tea polyphenol-chitosan nano granule, pertains to the field of applying chitosan controlled release and oxidation resistance in the gelatin film. The oxidation resistant gelatin film component comprises tea polyphenol-chitosan nano granules, gelatin and glycerin. The preparation includes dissolving gelatin and glycerin into deionized water in proportion to produce a gelatin solution, charging a predetermined amount of tea polyphenol-chitosan nano granule suspension, mixing uniformly, hypersonic de-gassing, removing dried film spreading on the organic glass board. The prepared nano tea polyphenol-chitosan gelatin film has oxidation resistance greatly improved comparing with the simple gelatin film phase, and oxidation resistance of the gelatin film is capable of lasting for longer time due to protection function of the chitosan to the tea polyphenol and slowly-releasing of the tea polyphenol. The oxidation resistant gelatin film can be biologically degraded, without environment pollution during application process; is capable of having functions of preventing loss of flavor substance in the food, preventing food oxidation, so as to reach the effect of anti-staling and prolonging storage period.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for preparing antioxidation gelatine membrane containing tea polyphenol nano lipidosome
InactiveCN101461534AControl releaseImprove antioxidant capacityFood shapingFood preparationPhenolic content in teaGlycerol
The invention relates to preparation of an oxidation resistant gelatin film containing a tea polyphenol nano-liposome, pertains to the application technology field of nano-liposome controlled release and oxidation resistance. The oxidation resistant gelatin film component comprises tea polyphenol nano-liposome, gelatin and glycerin. The preparation includes dissolving gelatin and glycerin into deionized water in proportion to produce a gelatin solution, charging a predetermined amount of tea polyphenol nano-liposome suspension, mixing uniformly, hypersonic de-gassing, and removing dried film spreading on the organic glass board. The prepared oxidation resistant gelatin film has oxidation resistance greatly improved comparing with the simple gelatin film phase, and oxidation resistance of the gelatin film is capable of lasting for longer time due to protection function of the liposome to the tea polyphenol and slowly-releasing of the tea polyphenol. The gelatin film can be biologically degraded, without environment pollution during application process; has functions of preventing loss of flavor substance in the food, preventing food oxidation, so as to reach the effect of anti-staling and prolonging storage period.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Soft-gelatin capsule comprising S-adenosylmethionine and a method for producing the same
InactiveUS6759395B2Easy to swallowGood optionBiocideSugar derivativesS-Adenosyl methionineGelatin film
The invention provides a novel soft gelatin capsule comprising a fill material consisting essentially of S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe) salt disposed within an enteric coated soft gelatin film.
Owner:ORCHID CHEM & PHARM LTD
Gelatin capsules
InactiveUS20050058703A1Connective tissue peptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsGelatin filmGelatin capsule
The invention relates to recombinant gelatins, and to recombinant gelatins useful in gelatin capsule manufacture, and to compositions, gelatin capsules, and gelatin films comprising these, as well as methods of production.
Owner:FIBROGEN INC
High-weatherability cigarette blasting bead rubber material and preparation method thereof
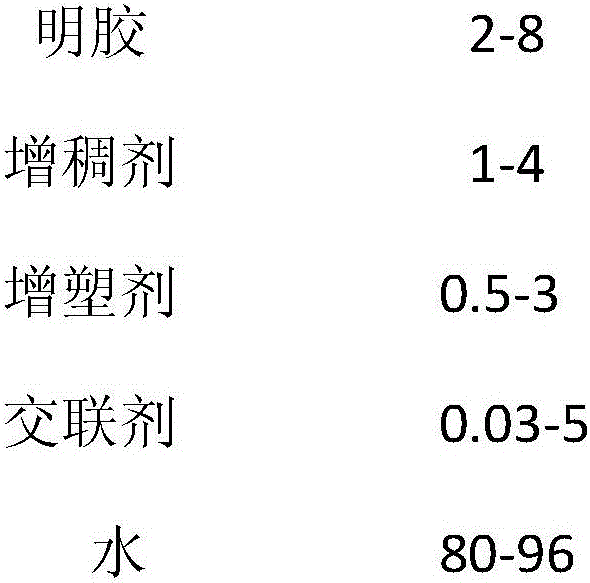
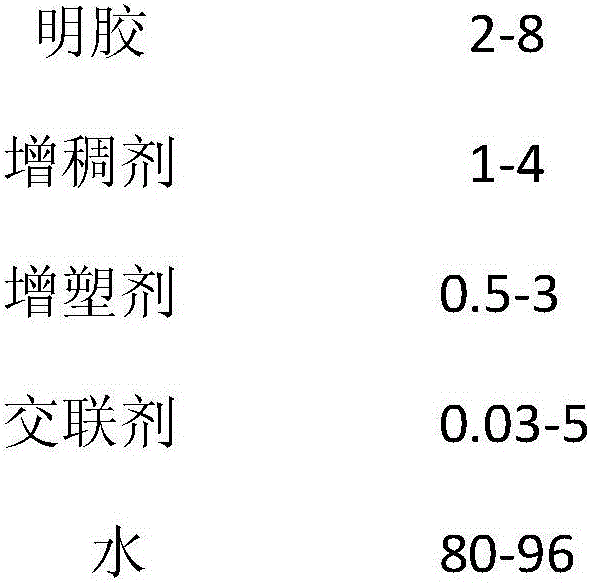
ActiveCN106497088AImprove performanceEquilibrium moisture content decreasedTobacco smoke filtersRubber materialWater baths
The invention provides a high-weatherability cigarette blasting bead rubber material and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the blasting bead rubber material includes the steps: mixing 1-4 parts of thickening agents and 80-96 parts of water by weight; heating mixture in a water bath to reach the temperature of 50-90 DEG C; stirring and dissolving the mixture into uniform solution and then adding 2-8 parts of gelatin and 0.5-3 parts of plasticizers; continuing heating and dissolving for 1-2 hours at the temperature of 50-70 DEG C; uniformly mixing the mixture and adding 0.03-5 parts of cross-linking agents; performing stirring reaction for 15 minutes to 1 hour; standing; filtering the mixture in a heat insulation state after foam floats and the filtrate is filtered to obtain the cigarette blasting bead rubber material. The cross-linking agents are added into a gelatin system, the performance of a gelatin film is improved by the cross-linking function of aldehydes for the gelatin, so that the equilibrium moisture content of blasting bead rubber is reduced, a blasting bead prepared from the rubber material is good in weatherability, and adaptability of the blasting bead to environmental temperature-humidity change in a high-humidity environment is improved.
Owner:HUBEI CHINA TOBACCO IND
Preparation method of fish scale gelatin starch antioxidant edible composite film
The invention relates to a preparation method of a fish scale gelatin starch antioxidant edible composite film. The preparation method comprises the following steps of extracting tea polyphenol from tea leaves, and preparing a tea polyphenol solution for preparation of the film; respectively dissolving the gelatin and starch in the tea polyphenol to prepare gelatin tea polyphenol solution and starch tea polyphenol solution with different mass fractions, mixing according to a volume ratio of 1 to 1, adding glycerol and preparing the composite film solution. The edible composite film prepared by the preparation method disclosed by the invention is degradable, and the preparation method is simple and free of environmental pollution; compared with the pure gelatin film and starch film, the edible composite film has the advantages of strong oxidation resistance, high tensile strength and low solubility and can be applied in food packaging; the migration and diffusion of water, oil and other ingredients in food are delayed, the oxidization of the food is decreased, the shelf life of the food is prolonged, the food is ensured to be nutritional and safe and the nutrition of the food is increased. The preparation method provides a novel method for the preparation of the antioxidant edible composite film, especially the manufacturing of the composite film having the advantages of high oxidation resistance, high tensile strength and low solubility.
Owner:JIANGXI NORMAL UNIV
Method of fabricating substrate of paper-made food container
InactiveUS20090277567A1Simple processReduce manufacturing costSynthetic resin layered productsLaminationCross-linkGelatin film
A method of fabricating a substrate of a paper-made food container includes: (1) a paper layer of an original paper roll is processed with preheating and electrostatic process in advance, and a gelatin film then is coated on a single face lamination or double face lamination of the paper layer to form a complex layer. Alternatively, the double face lamination does not to be coated. The gelatin film is biodegradable material or non-biodegradable material. (2) Biodegradable material or non-biodegradable material is utilized to prepare an electronic cross-linked foam layer as a roll. (3) The complex layer is conveyed to the continuous thermal laminator. The thermal processing device of the continuous thermal laminator then is utilized to perform melting point heating for one face lamination or double face laminations of surfaces between the complex layer and the electronic cross-linked foam layer. Two rollers of the rolling (laminating) device then roll the complex layer and the electronic cross-linked foam layer to form the substrate that can be subsequently cut to make various food containers having heat insulation, warm-keeping and cold insulation functions.
Owner:CHANG HSI CHING
Macromolecule cross-linking agent based on oxidized cellulose, gelatin film thereof and preparation method
InactiveCN105237645ADirect connectionImprove light blocking performanceFlexible coversWrappersCross-linkPhosphate
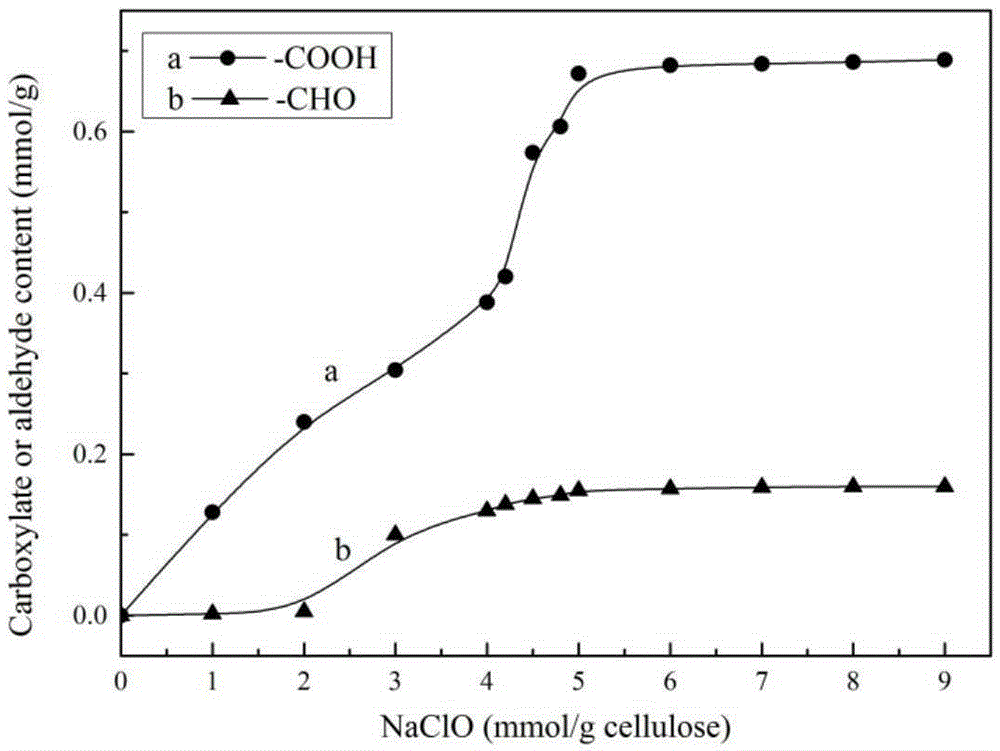
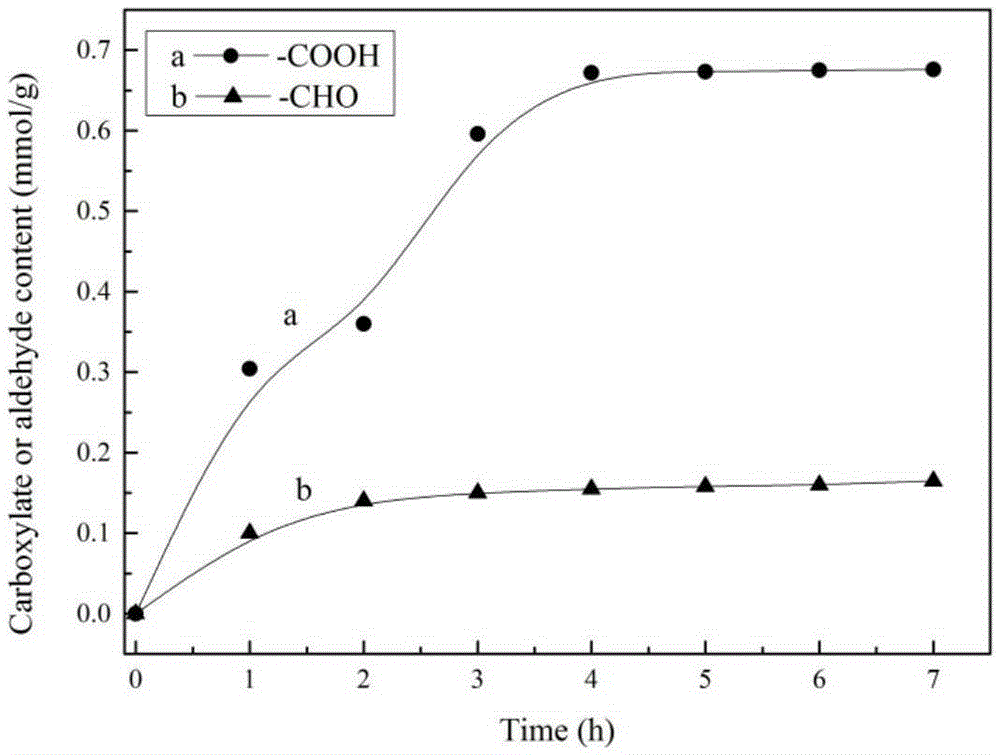
The invention discloses a macromolecule cross-linking agent based on oxidized cellulose, a gelatin film thereof and a preparation method. The preparation method of the gelatin film comprises the following steps: 1, oxidizing a primary amino group on the C6 position of cellulose into carboxyl through a TEMPO / NaBr / NaClO system, and obtaining oxidized cellulose TOMCC; 2, treating N-hydroxy succinimide and TOMCC obtained in step 1 as raw materials, and manufacturing a macromolecule cross-linking agent TMN; 3, making the macromolecule cross-linking agent TMN be subjected to chemical cross-linking with a gelatin film, and obtaining the food package gelatin film based on oxidized cellulose chemical cross-linking. Light-blocking performance, thermal stability, anti-biodegradation capability, the mechanical property (elasticity) and hydrophobicity of the gelatin film are all improved to a large extent, and a favorable condition is provided for application of the gelatin film to the food package field. In addition, biodegradation mechanisms of a modified gelatin film and a pure gelatin film in a phosphate buffered solution (PBS) and lysozyme are explored and analyzed as well.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
Multilayer composite film dressing and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105497969AImprove breathabilityGood cell compatibilityAbsorbent padsBandagesFiberComposite film
The invention discloses a multilayer composite film dressing, which comprises a gelatin layer and a polyurethane layer. The gelatin film layer and / or the polyurethane film layer are / is a nano-fiber material. The polyurethane film layer includes an antibacterial component. The preparation method of the multilayer composite film dressing consists of the step of continuous preparation of the polyurethane film layer or gelatin film layer with a well prepared gelatin film layer or polyurethane film layer as the substrate, or includes the step of hot-pressing of the gelatin film layer and the polyurethane film layer respectively. The multilayer composite film dressing provided by the invention has a multilayer structure, different layers have no interference to each other and can cooperate with each other to complete a variety of functions, so that the multilayer composite film dressing has good broad-spectrum antibacterial activity, hemostatic properties, air permeability, cell compatibility, liquid absorption rate, surface waterproof performance, water vapor permeability and other performance. The preparation method of the multilayer composite film dressing has very simple operation steps, and at the same time the operation process is very easy to grasp.
Owner:POLYU RES BASE SHENZHEN
A bonding method of a display device and a fingerprint module
ActiveCN109460731AReduce manufacturing costAchieve integrationStatic indicating devicesDigital data processing detailsGelatin filmFlexible circuits
The embodiment of the invention discloses a bonding method of a display device and a fingerprint module. The display device comprises a display panel, a fingerprint module and a functional flexible circuit board FPC. A colloidal film is attached to the side of the display panel away from the light emitting surface, and an opening area is arranged in the colloidal film. A functional FPC is attachedto the side of the display panel away from the light emitting surface through a scattering film. The fingerprint module is arranged on the side of the functional FPC close to the display panel, and the fingerprint module is embedded in the opening area of the gelatin film through the functional FPC. The embodiment of the invention solves the problem of high cost of the display device due to the need of additional special FPC carrier and the need of using a special machine to execute additional device mounting process in the integration and bonding mode of the fingerprint module in the prior display device.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Method for improving thermal stability of fish skin gelatin film
InactiveCN105602261AImprove thermal stabilitySimple UV irradiation techniqueFlexible coversFruit and vegetables preservationGlycerolPollution
The invention relates to a method for improving thermal stability of a fish skin gelatin film. The method includes the following steps that firstly, a cold fish skin gelatin solution, nano microcrystalline cellulose and glycerol are mixed to be prepared into a mixed solution; secondly, riboflavin is added in the mixed solution obtained in the first step; thirdly, the solution obtained in the second step is poured into an ultrasonic smasher to be subjected to ultrasonic smashing; fourthly, the solution obtained in the third step is poured on an acrylic flat plate and irradiated with an ultraviolet lamp; fifthly, the irradiated solution is dried and preserved at room temperature. The riboflavin is added, the thermal stability of the film is improved through an ultraviolet irradiation method, the method is easy and convenient and facilitates operation, the raw materials are non-toxic and free of pollution, and the thermal stability of the film can be well improved. The method is widely applied to the fields of food packaging and freshness retaining of casing for sausages and vegetables.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Seaweed flavoured tuna bone gelatine edible film and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104558648AIncrease added valueReduce pollutionProtein composition from fishFlexible coversBiotechnologyGelatin film
The invention discloses a preparation method of a seaweed flavoured tuna bone gelatine edible film. The preparation method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: preparing tuna bone gelatine, extracting active and flavour components of seaweeds, preparing seaweed flavoured tuna bone gelatine film-forming solution, stirring, defoaming and the like, and finally, pouring the successfully prepared film solution on a polyvinyl chloride crystal plate to scrape, dry and uncover a film so as to obtain the seaweed flavoured tuna bone gelatine edible film. According to the invention, tuna processing leftovers, namely bones, are used as the main raw materials; a new way is opened for recycling and high value of bones; the prepared gelatine film has the properties of the common edible film and also has the obvious characteristics of being oxidation-resistant, unique in flavour and the like; and thus, the preparation method disclosed by the invention has good market application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Enrobed core medicament
InactiveUS20030059614A1More resistance to breakageMore strengthGlass/slag layered productsWood layered productsGelatin filmPlasticizer
A medicine tablet is described as a new article of manufacture. The tablet is enrobed in a gelatin coating formed by application of respective layers of elastic gelatin film to opposite sides of the tablet. The applied gelatin layers conform tightly to the tablet surface, bond securely to the tablet, and are sealed together in essentially edge-to-edge manner at a seal line which extends around the tablet at a desired place on the tablet. The gelatin layers can be colored differently from the tablet and differently from each other. A range of formulations are described for film which can be peelable from a tablet or other product core, and for films which bond to the core. A presently preferred formulation for producing tablets having a bonded tamper-evident coating comprises a water-based gelatin preparation having about 45% gelatin and about 9% plasticizer (glycerin and / or sorbitol) by weight Method and apparatus for producing such new products are also described. Product cores can be dispensed on a self-timed basis into essentially simultaneous contact with two enrobing films which are supported on locally recessed coacting rotary dies. The cores contact the films adjacent a nip between the dies at places on the films which overlie die recesses which are oversize relative to the cores.. The films deform around each core and are sealed by the dies to each other before the dies coact to cut the enrobed cores from the films. A core feeding mechanism can include an alignment device which causes the cores to have a desired orientation as they are handled by the dies.
Owner:SADEK HANI +1
Films for use as dosage forms
InactiveUS20120100278A1Easy to transportPretreated surfacesSpecial surfacesPolymer scienceGelatin film
Non-gelatin film materials, e.g. films of modified cellulose materials find use as dosage forms. Substances are incorporated into the film matrix and films thus prepared may be administered orally, or otherwise internally, or epidermally. The administable form may comprise a matrix which contains at least one water soluble polymer in the form of a film, in addition to at least one active ingredient, to produce a therapeutic, organoleptic or cosmetic effect.
Owner:BIOPROGRESS TECH
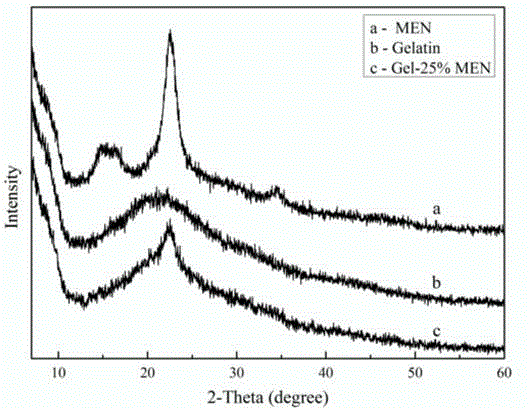
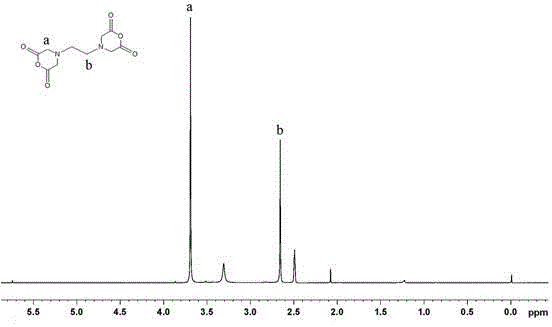
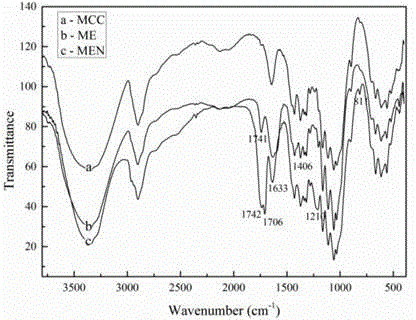
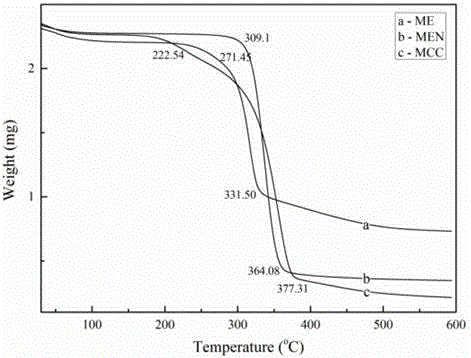
Cellulose chemical crosslinking based gelatin film and preparation method thereof
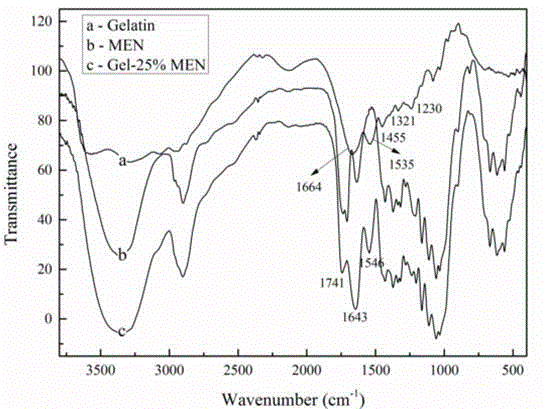
InactiveCN104861182AImprove thermal stabilityImprove resistance to degradationCross-linkEthylene diamine
The invention discloses a cellulose chemical crosslinking based gelatin film and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of modified gelatin. The preparation method of the cellulose chemical crosslinking based gelatin film comprises steps as follows: 1), EDTA (ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid) dianhydride and microcrystalline cellulose are taken as raw materials to prepare EDTA dianhydride functionalized microcrystalline cellulose ME; 2), N- hydroxysuccinimide and ME obtained in the step 1) are taken as raw materials to prepare the macromolecular cross-linking agent MEN; 3), the macromolecular cross-linking agent MEN and the gelatin film are subjected to chemical crosslinking to prepare the cellulose chemical crosslinking based gelatin film. The ester group in the cross-linking agent MEN can have a crosslinking reaction with primary amino in gelatin, the gelatin film is modified in a chemical reaction manner, and the limitation of gelatin modification through cellulose macromolecule blending in the prior art is broken. The heat stability, the degradation resistance, the mechanical property (elasticity), the light blocking performance and the hydrophobicity of the gelatin film are improved to a greater degree.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
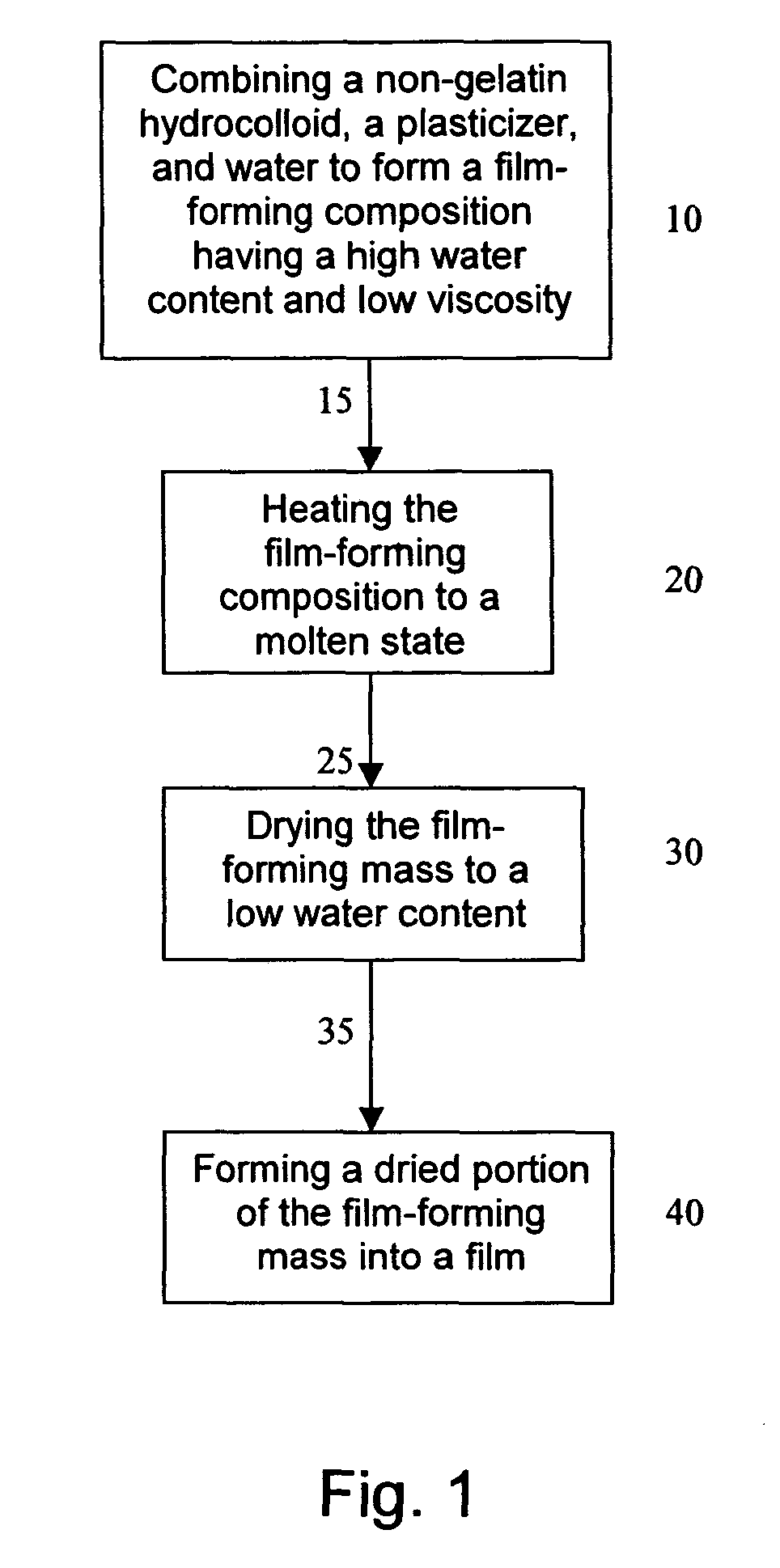
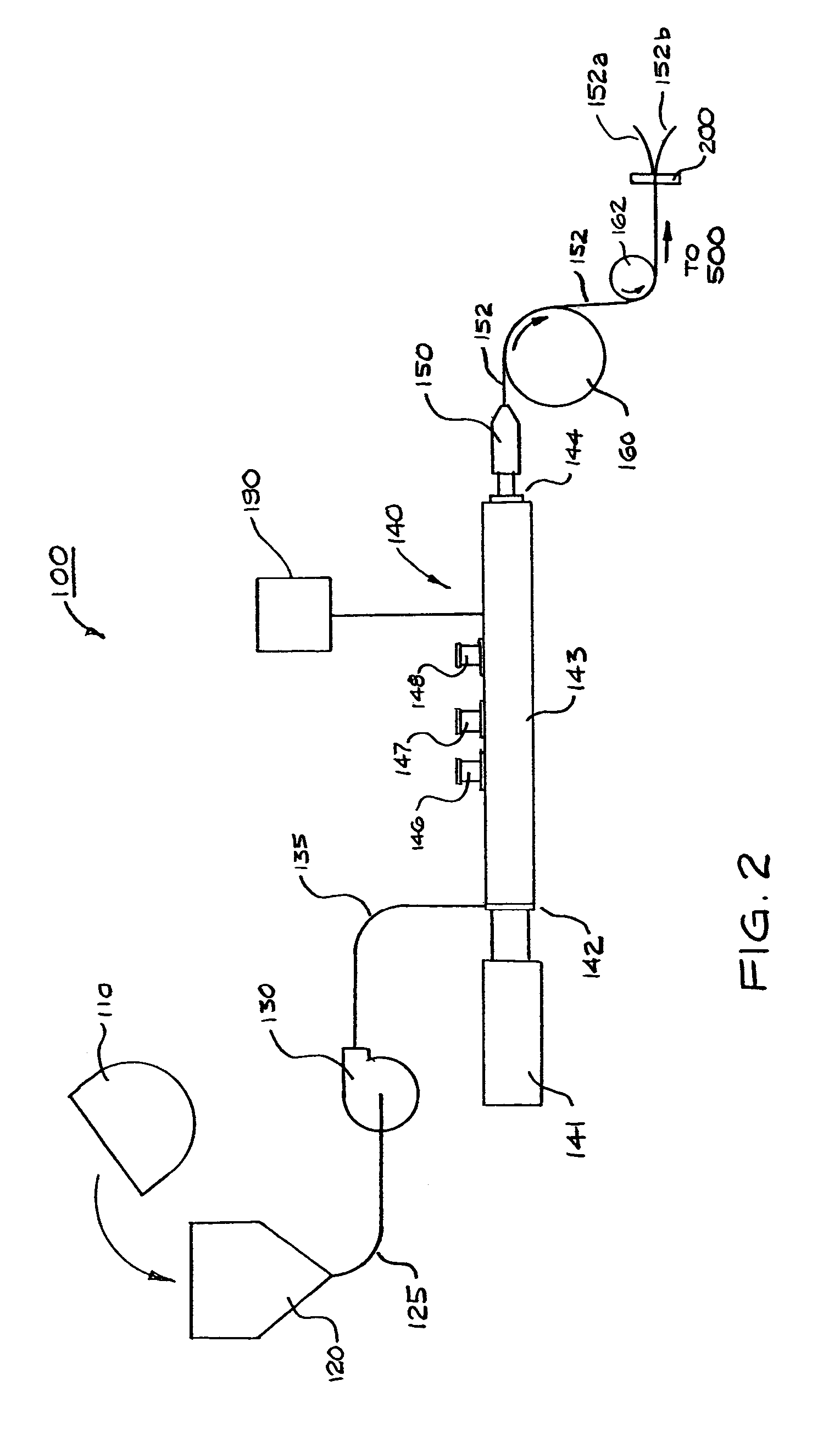
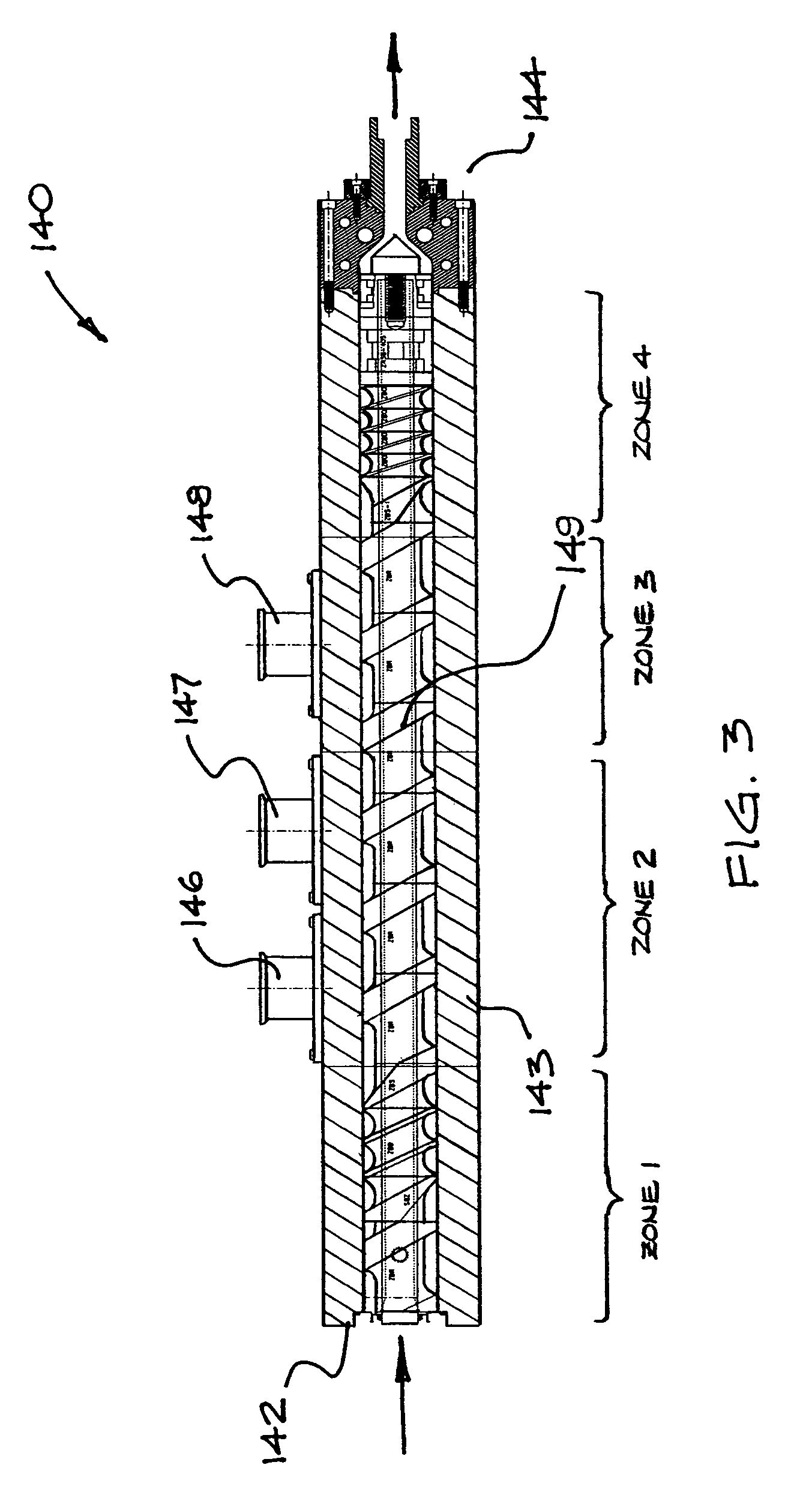
Non-gelatin film and method and apparatus for producing same
A film-forming composition comprising a hydrocolloid, a plasticizer, and water is described. A process and apparatus for producing a non-gelatin film comprising a hydrocolloid, a plasticizer, and water is also disclosed. The process includes combining at least one non-gelatin hydrocolloid, water, and at least one plasticizer into a substantially homogeneous film-forming composition comprising at least about 40 percent water by weight. A substantial portion of the water is then extracted from the film-forming composition to form a dried portion having a water content of less than or equal to about 25 percent by weight. The dried portion of the film-forming composition is formed into a film. A film produced according to the process preferably has a tensile strength at rupture of at least about 0.4 N / mn2, and a percent elongation of at least about 50 percent at rupture at room temperature. An apparatus for performing the process is also described, as well oral dosage forms encapsulated or enrobed in the produced film.
Owner:PATHEON SOFTGELS INC
Cellulose based macromolecular cross-linking agent, preparation method thereof and application of cellulose based macromolecular cross-linking agent in preparation of modified gelatin
InactiveCN104861078AImprove thermal stabilityImprove resistance to degradationCross-linkEthylene diamine
The invention discloses a cellulose based macromolecular cross-linking agent, a preparation method thereof and an application of the cellulose based macromolecular cross-linking agent in preparation of modified gelatin, and belongs to the field of gelatin cross-linking agents. The preparation method of the cross-linking agent comprises steps as follows: 1), EDTA (ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid) dianhydride and microcrystalline cellulose are taken as raw materials to prepare EDTA dianhydride functionalized microcrystalline cellulose ME; 2), N- hydroxysuccinimide and ME obtained in the step 1) are taken as raw materials to prepare the macromolecular cross-linking agent. The ester group in the cross-linking agent can have a cross-linking reaction with primary amino in gelatin, a gelatin film is modified in a chemical reaction manner, and the limitation of gelatin modification through cellulose macromolecule blending in the prior art is broken. The heat stability, the degradation resistance, the mechanical property (elasticity), the light blocking performance and the hydrophobicity of the gelatin film are improved to a greater degree.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing edible biological gelatin film with EGCG (epigallocatechin gallate) controlled-release performance
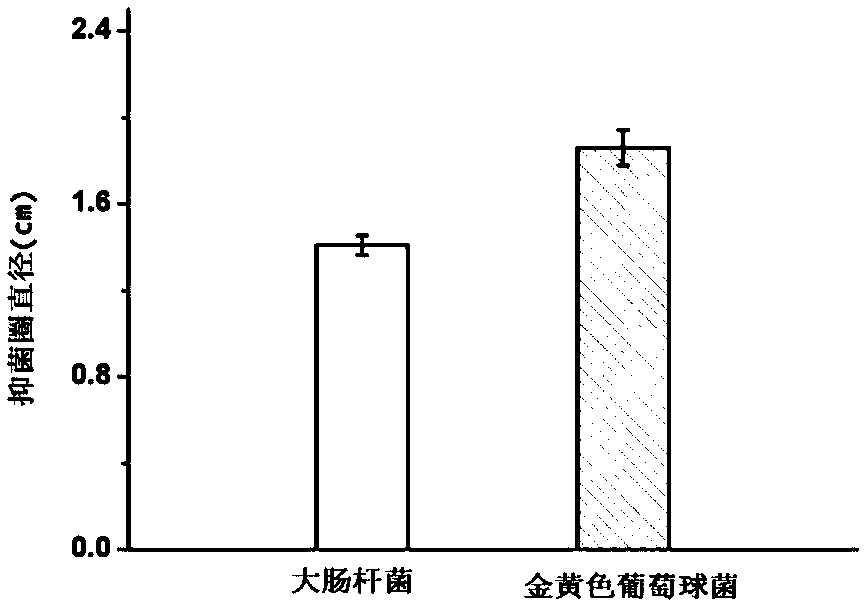
The invention discloses a method for preparing an edible biological gelatin film with an EGCG (epigallocatechin gallate) controlled-release performance. The method includes: step 1, preparing gelatinsolution; step 2, cooling gelatin solution prepared in the step 1 to the room temperature, adding EGCG, stirring to dissolve, and standing for cross linking at 2-8 DEG C for 10-14h to obtain film forming liquid; step 3, dissolving the film forming liquid obtained in the step 2 by water-bath heating, transferring into a mould, and drying in a constant-temperature air dry oven to form the film. By adding of EGCG, antibacterial and antioxidant performances of the gelatin film are improved.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY
Biodegradable prosthesis
A body compatible and resorbable prosthesis has a tubular body incorporating denatured gelatin sponge material, either as a unitary gelatin sponge or as fragmented or powdered sponge material dispersed throughout a structurally self supporting medium. One version of the prosthesis uses the fragmented or powdered form of the gelatin sponge and is substantially homogeneous. An alternative prosthesis employs an inner tubular layer of gelatin film. The gelatin film layer is surrounded by an outer tubular layer, formed either of the gelatin sponge or the fragmented medium incorporating the gelatin sponge dispersion.
Owner:SKOVLUND MEDICAL PROD
Medical film
InactiveCN1726056AEasy to fixAvoid reactionSynthetic resin layered productsSurgeryBiological bodyGelatin film
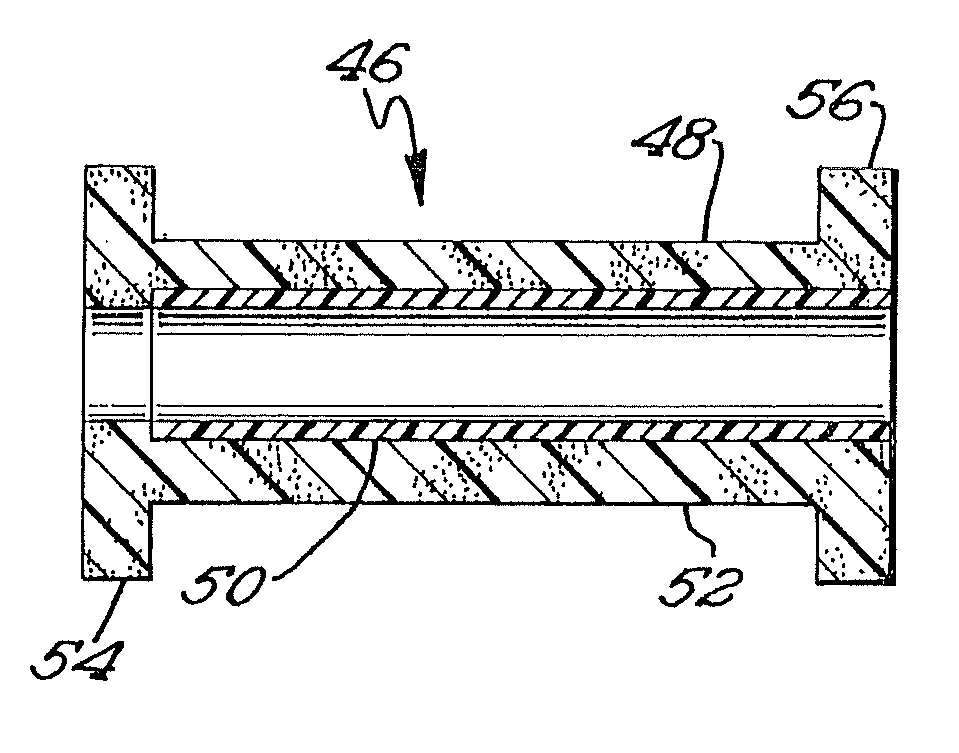
It is intended to provide a medical film which is excellent in biocompatibility and bioabsorbability and has a high strength in suturing and bonding. A reinforcing material (12) made of a biodegradable and bioabsorbable polymer is located in a gelatin solution. After allowing the solution to penetrate into the reinforcing material (12), the gelatin is dried. Thus, the gelatin having penetrated into the reinforcing material (12) sets to gel to thereby form a gelatin film (11) so that a medical film (1 )composed of the reinforcing material (12) and the gelatin film (11) integrated together can be obtained. It is preferable that the above-described gelatin film (11) is a crosslinked gelatin film.
Owner:GUNZE LTD +1
Responsive slow-release active packaging film as well as preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN111995785ASolve the incentive mechanismGuaranteed active efficacyFlexible coversWrappersPolymer scienceMagnetite Nanoparticles
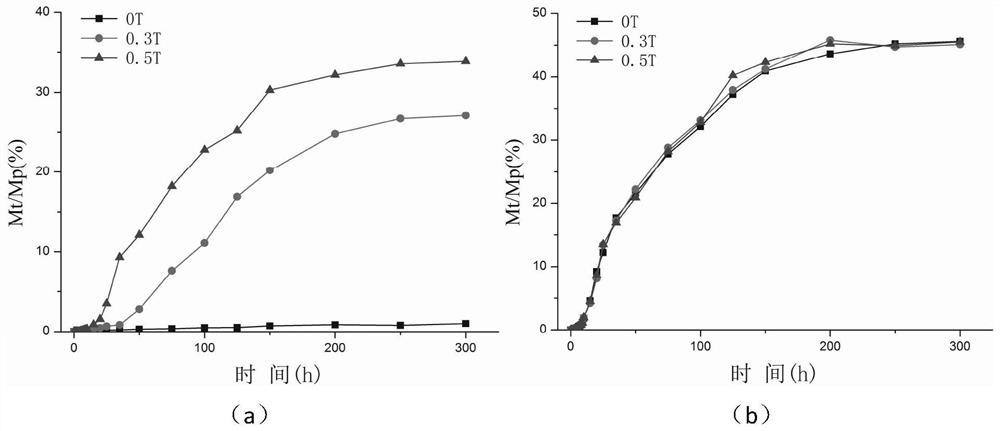
The invention provides a responsive slow-release active packaging film as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The active packaging film is of a multi-layer structure formed by compounding an inner layer, a middle layer and an outer layer, the inner layer is a gelatin film containing magnetite nanoparticles and has a magnetic field response function, the middle layer is a gelatin film containing a water-soluble antibacterial agent or a water-soluble antioxidant, and the outer layer is a common polymer film. The invention discloses a packaging film. Under the action of an external magnetic field, the permeability of the inner layer of the film can be changed, release of active substances of the middle layer is stimulated, the active film is in a releasable state only after being packaged and used, the active effect of the prepared film is effectively guaranteed, and the film is applied to food packaging and more beneficial to food protection and food shelf life prolonging. Therefore, the packaging film solves the problem of an excitation mechanism of an active film, so that the packaging film is in a controllable state in the whole circulation use process.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Aesculin sturgeon skin gelatin film with antioxidant activity and enterococcus faecalis detection ability and a method of preparing the same
ActiveUS20190031840A1Special physicochemical propertyGood film formingFlexible coversWrappersGelatin filmDistilled water
A method of preparing an aesculin sturgeon skin gelatin with antioxidant activity and Enterococcus faecalis detection ability includes: 1) mixing a sturgeon skin gelatin and distilled water in a ratio of 1:15-1:25 (w / v) at 50-70° C. and filtering to obtain a sturgeon skin gelatin solution; 2) adding aesculin and a glycerin solution to the sturgeon skin gelatin solution, stirring the resulted sturgeon skin gelatin solution at 30-50° C. for 30 minutes, and filtering; and 3) removing air bubbles from the sturgeon skin gelatin solution of step 2) under reduced pressure, placing the sturgeon skin gelatin solution on an acrylic glass, and drying the sturgeon skin gelatin solution at in a vented oven 25° C. and 45-55% relative humidity for 24 hours to obtain the aesculin sturgeon skin gelatin film.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method for preparing porous gelatin film from GO (graphene oxide) stabilized Pickering emulsion
The invention discloses a preparation method for preparing a porous gelatin film from a GO (graphene oxide) stabilized Pickering emulsion. The method comprises the steps as follows: a proper amount ofGO is added to deionized water, a GO suspended dispersion liquid is prepared, and ultrasonic treatment is performed; a gelatin solution is dissolved in the GO suspension, benzoate is added to serve as an oil phase, and ultrasonic treatment is performed; a sample in placed in a water bath, then casting is performed, and a non-crosslinked film is obtained; the non-crosslinked film is impregnated ina solution containing a crosslinking agent for a period to be crosslinked, then, the film is washed with ethanol and deionized water, finally, the film is dried, and the gelatin film adopting a porous structure is obtained. The preparation process for preparing the porous gelatin film from the Pickering emulsion is simple, green, environmentally friendly, has low equipment requirement, high aqueous solution stability and uniform porous structure, is prone to large-scale production and has wide application prospects in wastewater separation, gas separation, food emulsification, catalysis, heavy metal ion detection and other fields.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Poly(L-lactide-co-epsilon-caprolactone)nano-fiber nerve conduit and preparation method thereof
The present invention discloses a poly(L-lactide-co-epsilon-caprolactone)nano-fiber nerve conduit and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises: (1) dissolving poly(L-lactide-co-epsilon-caprolactone) in a mixed solvent of tetrahydrofuran and N,N-dimethyl formamide; (2) immersing a nano-fiber acceptable metal rod in a gelatin solution, taking out, and carrying out air-drying so as to form a gelatin film layer on the outer layer of the metal rod; (3) carrying out electrostatic spinning of the poly(L-lactide-co-epsilon-caprolactone) / tetrahydrofuran / N,N-dimethyl formamide solution so as to make the metal rod coated with the gelatin film accept the nano-fibers; and (4) after completing the electrostatic spinning, and immersing the metal rod into warm water to dissolve the gelatin so as to take out the nerve conduit. According to the present invention, the nerve conduit has characteristics of good biocompatibility and good mechanical strength, the conduit wall has rich micropores so as to easily perform nutrient exchange, and the nerve conduit degradation time and the autologous nerve regeneration time are matched; and the preparation method has characteristics of simpleness, no environment pollution, and high economic benefit.
Owner:山东隽秀生物科技股份有限公司
Epiderm substitute for tissue engineering and its prepn process
InactiveCN1739813AIncrease clinical restoration effectEasy access to technologyProsthesisGelatin filmCuticle
The present invention relates to biological material and tissue engineering technology, and is especially one kind of tissue engineering epiderm substituent and its preparation process. The tissue engineering epiderm substitute features that the chitosan-gelatin film or rack possesses pores of 20-50 micron size. Compared with available technology, the present invention adopts chitosan and gelatin as the material for the cell carrying system as the cell substituent, and has the features of easy-to-obtain material, simple technological process, high ventilation and raised clinical repair effect.
Owner:上海蓝融股权投资基金管理有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com