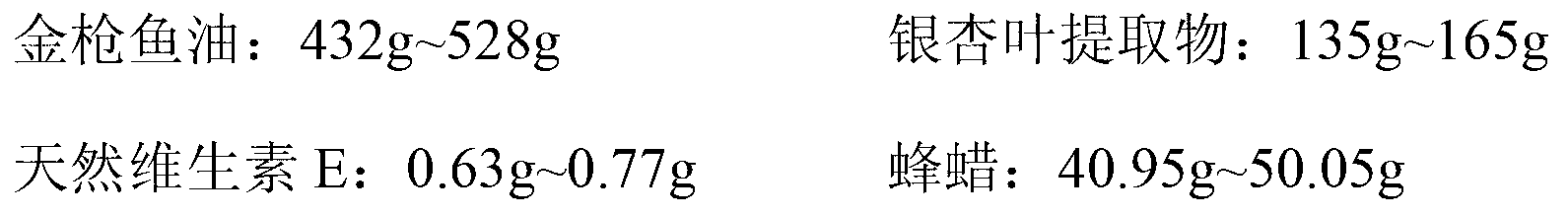Patents
Literature
272 results about "Tuna" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A tuna (also called tunny) is a saltwater fish that belongs to the tribe Thunnini, a subgrouping of the Scombridae (mackerel) family. The Thunnini comprise 15 species across five genera, the sizes of which vary greatly, ranging from the bullet tuna (max. length: 50 cm (1.6 ft), weight: 1.8 kg (4 lb)) up to the Atlantic bluefin tuna (max. length: 4.6 m (15 ft), weight: 684 kg (1,508 lb)). The bluefin averages 2 m (6.6 ft), and is believed to live up to 50 years.
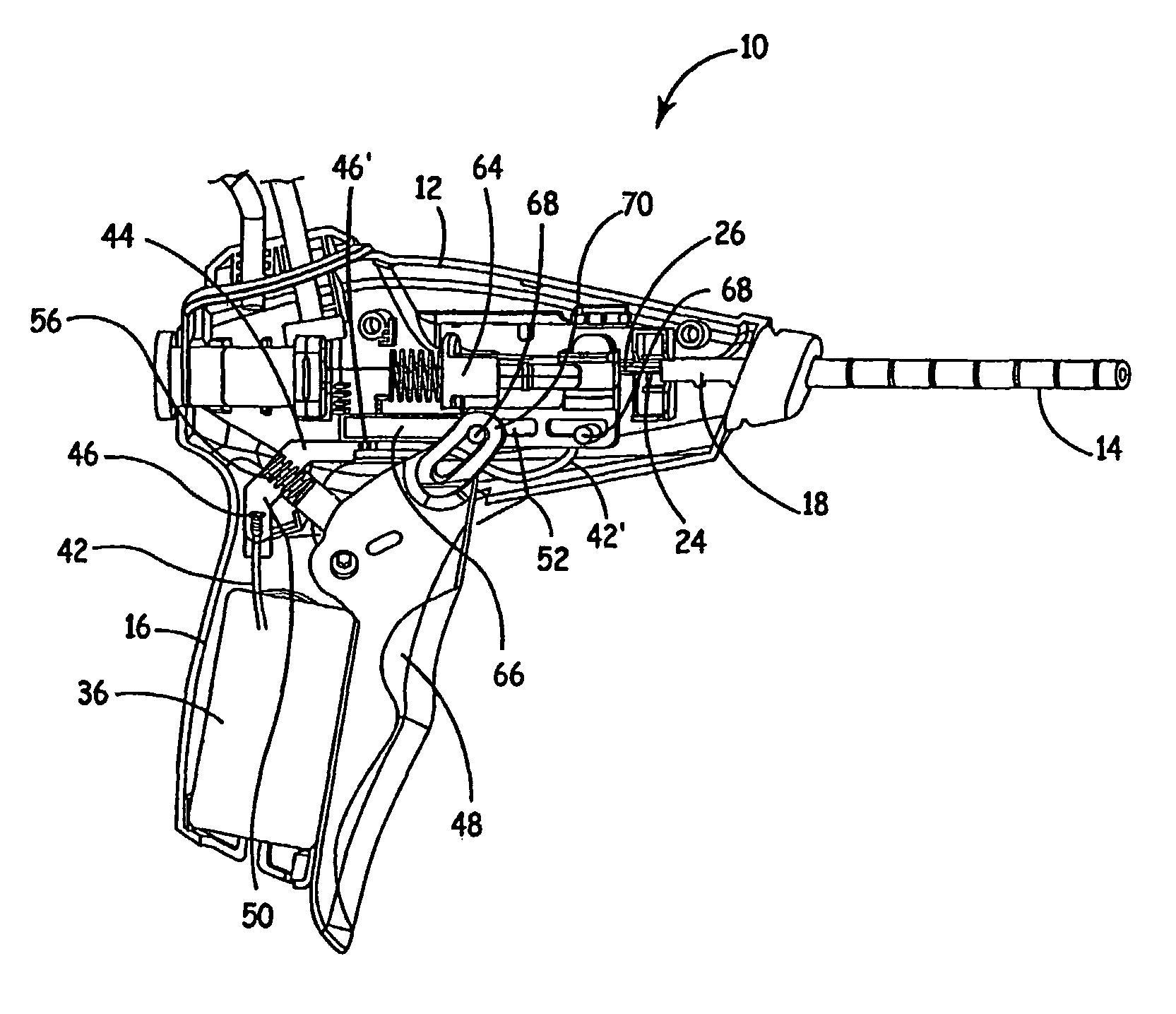
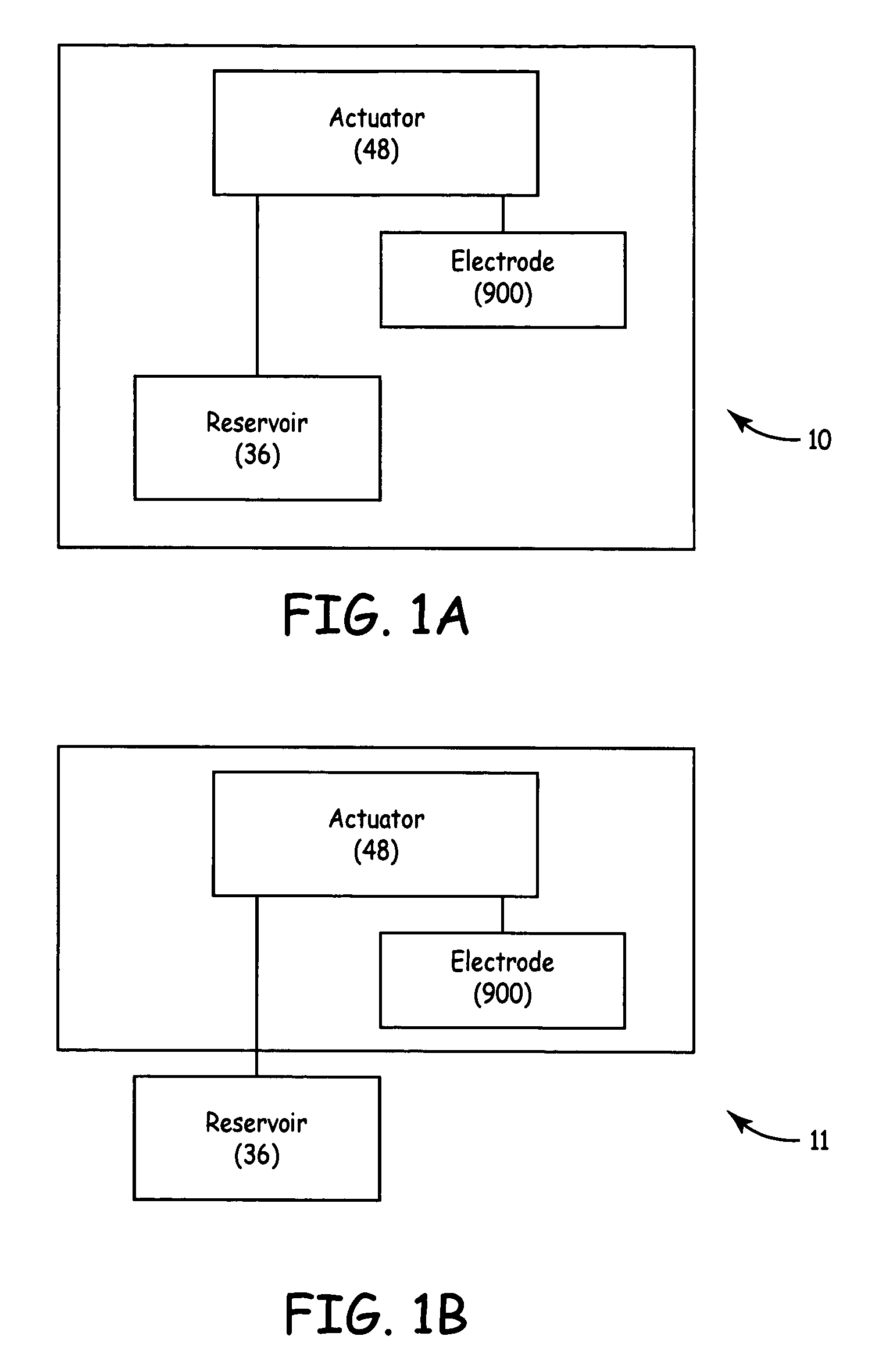
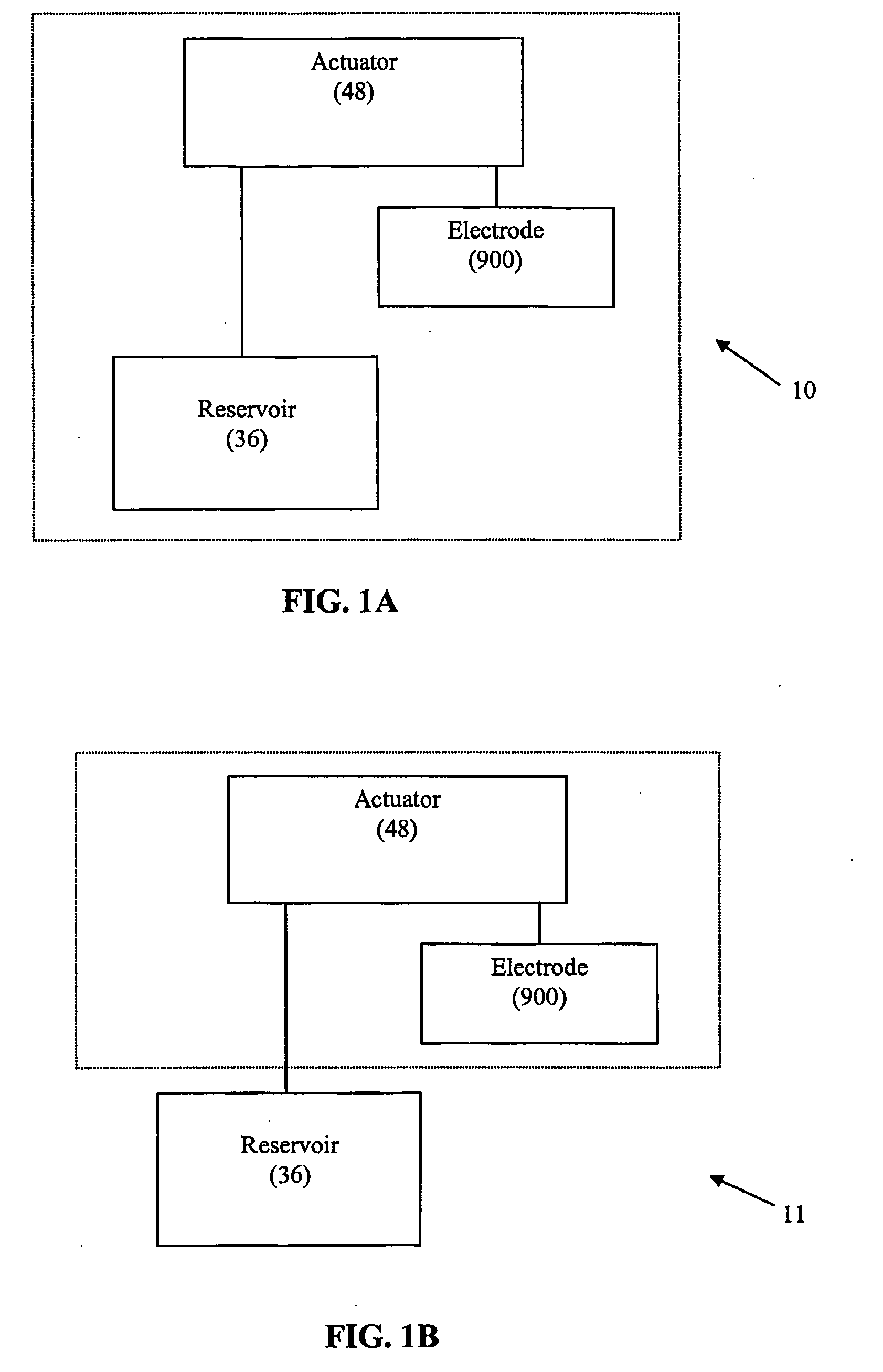
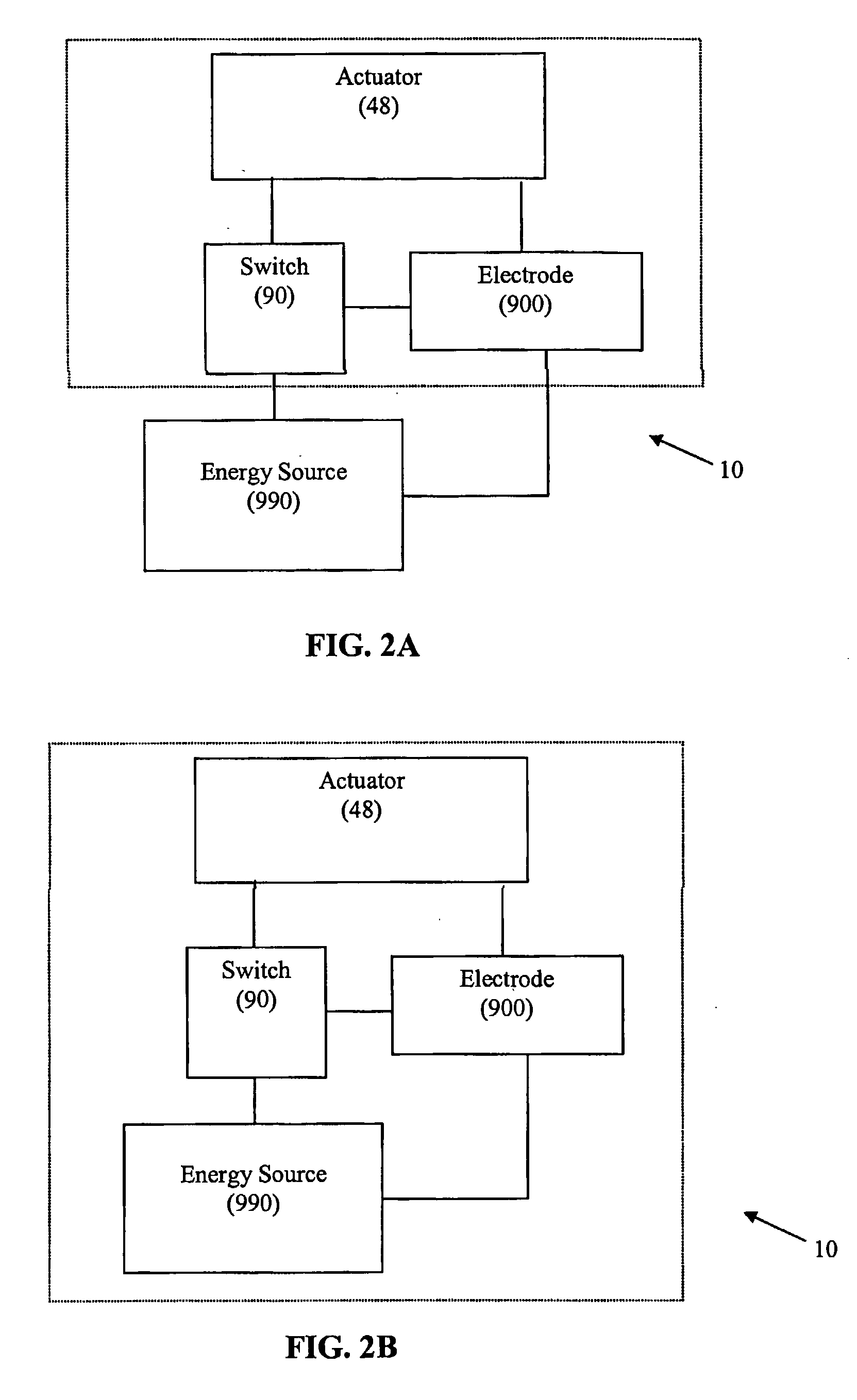
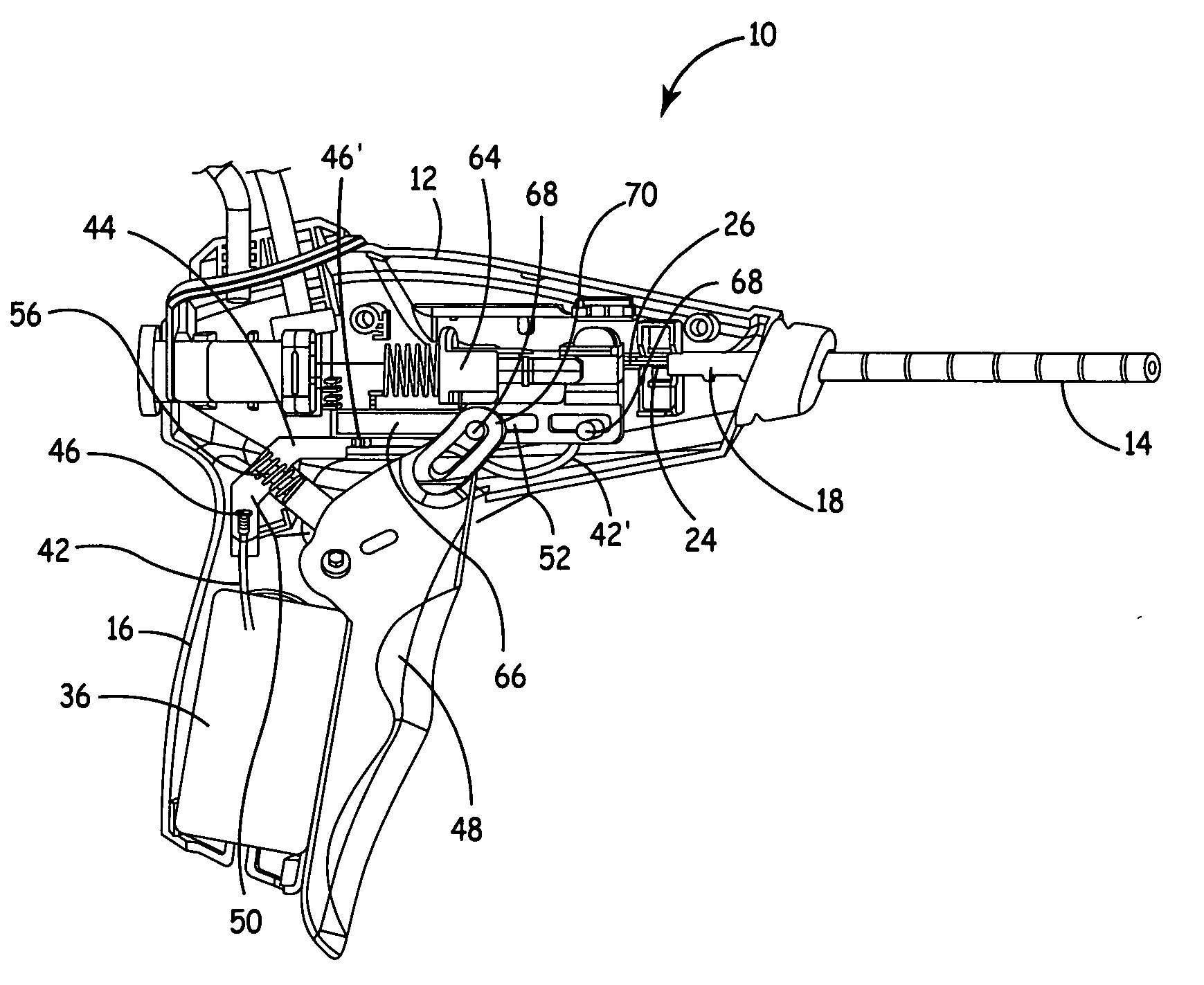
Tuna device with integrated saline reservoir
InactiveUS8911438B2Simplify wet electrode tissue ablation proceduresSimplify dry electrode techniquesSurgical needlesSurgical instruments for heatingActuatorTissue ablation
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
TUNA device with integrated saline reservoir
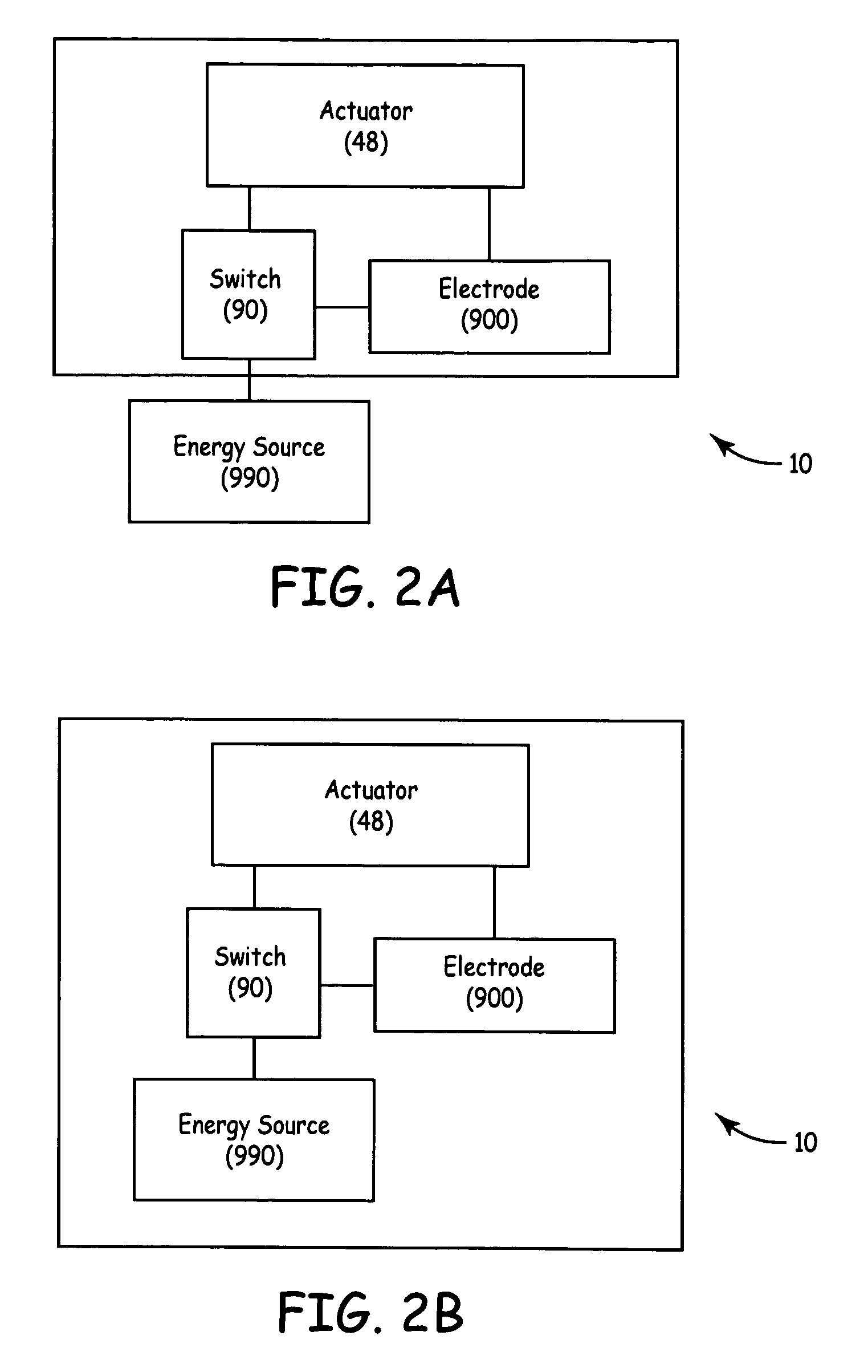
ActiveUS7322974B2Simplify wet electrode tissue ablation proceduresSimplify dry electrode techniquesSurgical needlesSurgical instrument detailsSaline waterActuator
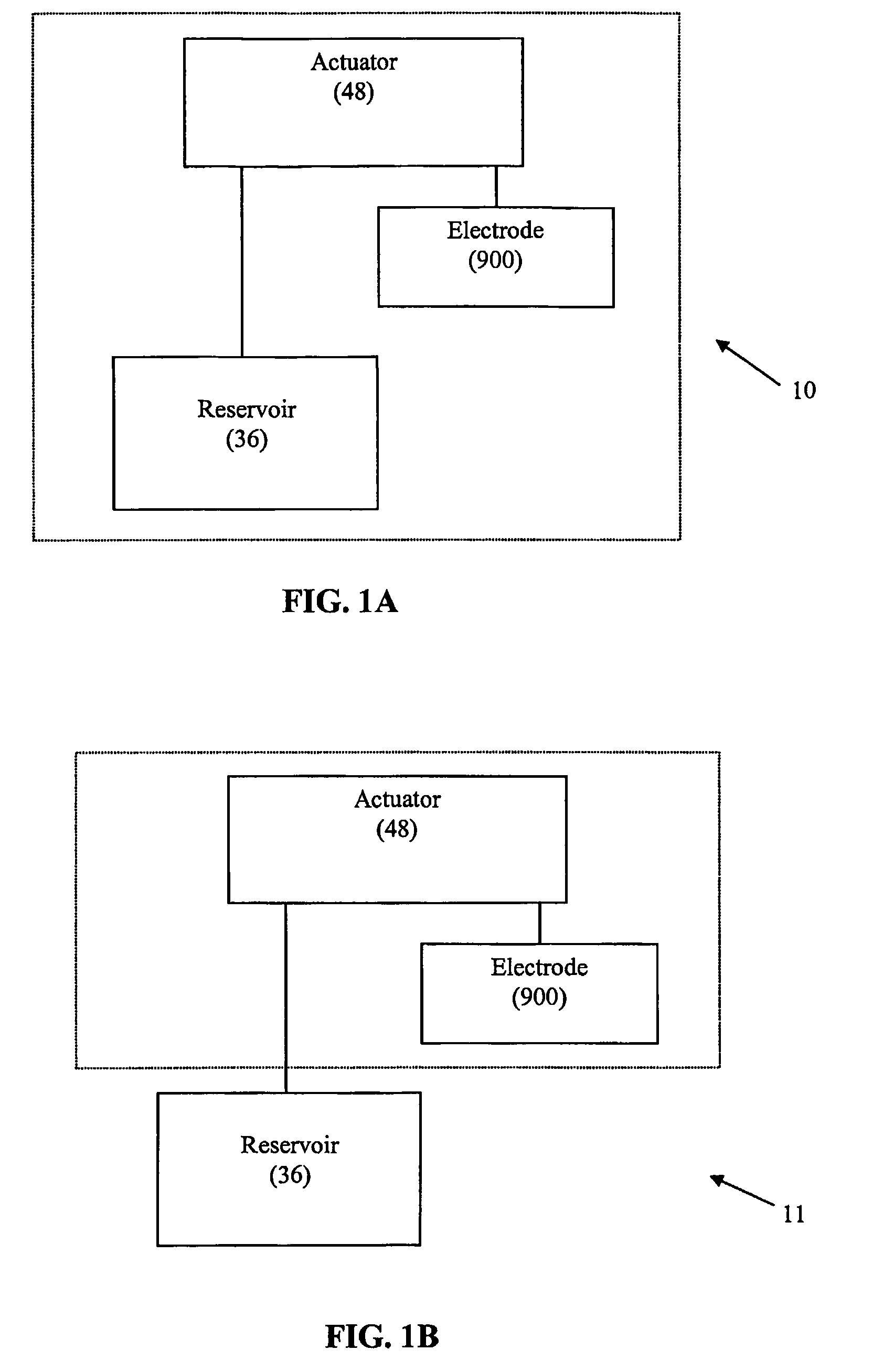
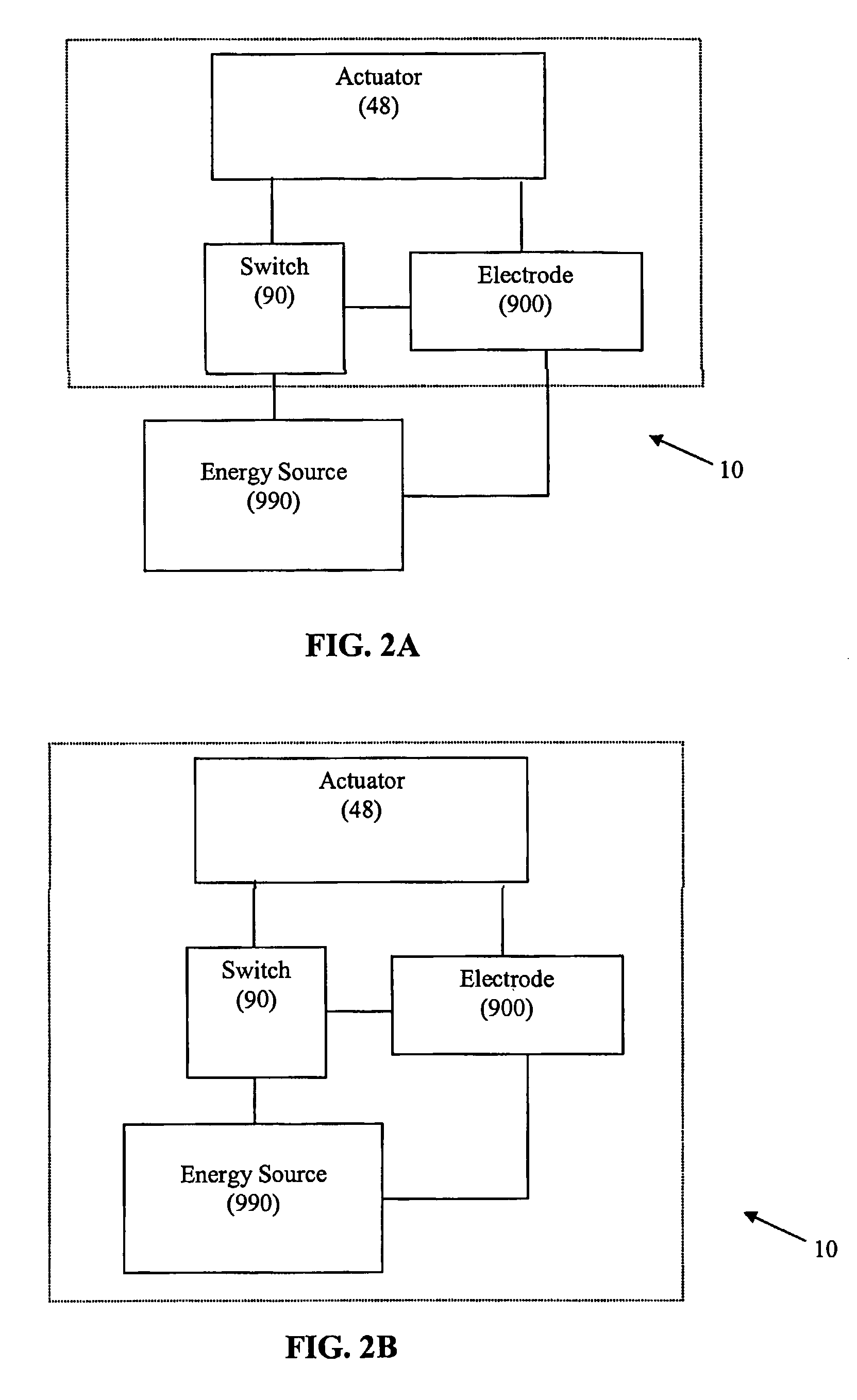
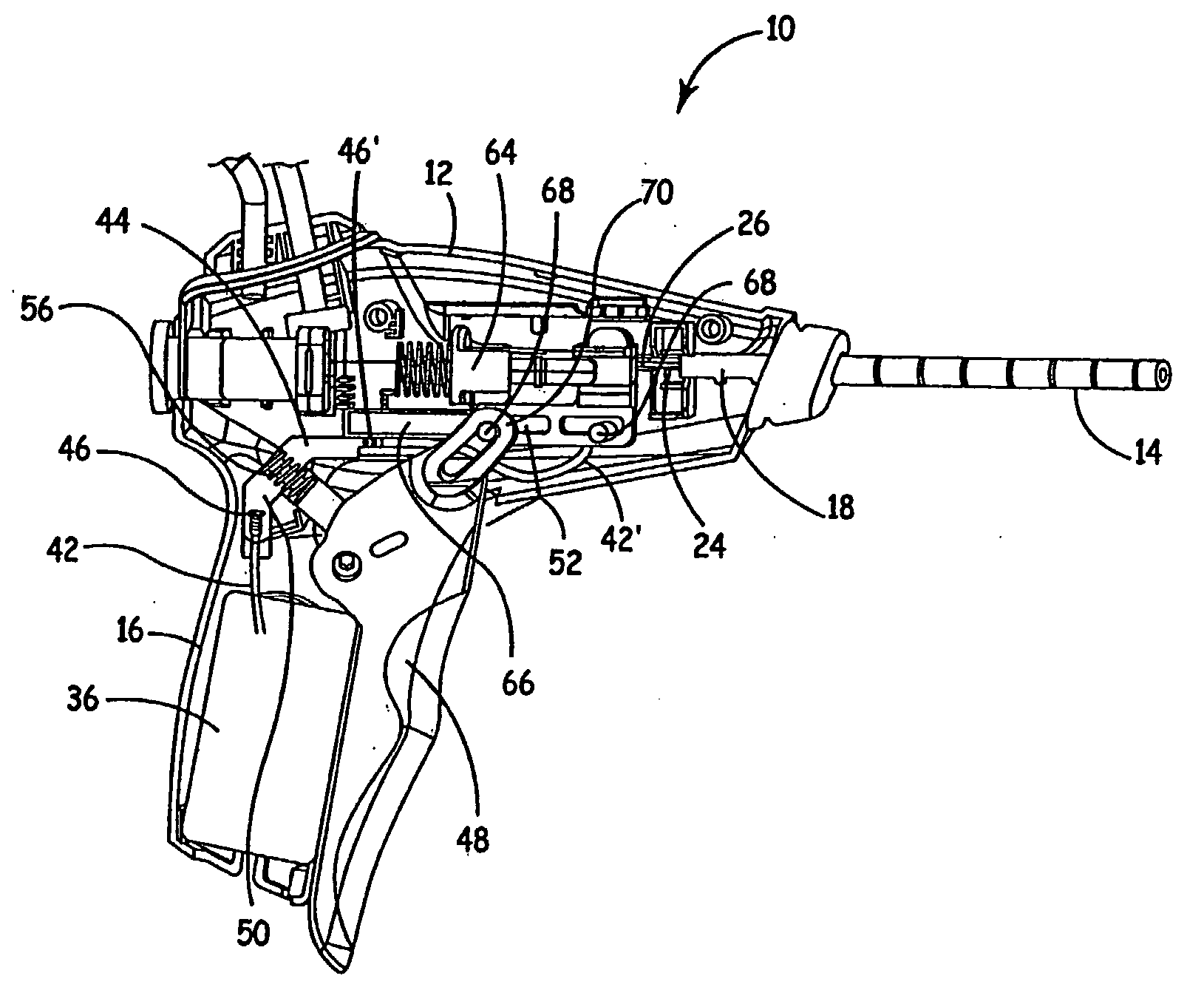
Methods and apparatus for ablating a target tissue are discussed. Such methods and apparatus include those that simplify tissue ablation. For example, a tissue ablation device having an actuator, such as a trigger mechanism, coupled to a power source and an electrode is discussed. A single step of engaging the actuator causes the electrode to be introduced into the target tissue and causes energy to be delivered from the power supply to the tissue via the electrode. By way of additional example, a tissue ablation device having an actuator coupled to a fluid source and an electrode is discussed. A single step of engaging the actuator causes conductive fluid to flow from the fluid source to the target tissue location and causes the electrode to be introduced to the target tissue location. The fluid source may be a conductive fluid, such as saline, which may increase the efficiency of ablation. Various other configurations and methods that simplify tissue ablation are also discussed.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Tuna Device with Integrated Saline Reservoir
InactiveUS20080262491A1Simplify wet electrode tissue ablation proceduresSimplify dry electrode techniquesSurgical needlesSurgical instruments for heatingActuatorTissue ablation
Methods and apparatus for ablating a target tissue are discussed. Such methods and apparatus include those that simplify tissue ablation. For example, a tissue ablation device having an actuator, such as a trigger mechanism, coupled to a power source and an electrode is discussed. A single step of engaging the actuator causes the electrode to be introduced into the target tissue and causes energy to be delivered from the power supply to the tissue via the electrode. Devices that include an electrode actuator for causing the electrode to be introduced into the target tissue and a fluid actuator for causing the fluid to flow to the target tissue are also discussed. Methods of causing the electrode to be introduced into the target tissue and fluid to flow to the target tissue with a single step and more than one step are also discussed.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Palatability enhancing compositions and foods for pets, and methods regarding the same
InactiveUS20080299286A1Simple compositionCost-effectiveAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsAnimal sciencePhosphate
Palatability enhancing compositions for pet foods, and pet foods with increased palatability, are provided. In some embodiments, the compositions and pet foods contain tea, such as green tea. In some embodiments, the compositions and pet foods contain brewer's yeast, liver hydrolysate, phosphate, and green tea. Shrimp meal and Tuna meal can also be utilized in these embodiments. In some embodiments, the compositions and pet foods comprise an ingredient having at least one of theanine; glutamine; tea; 1,5 octadien-3 one; 1,5-octadien-3-ol; and Camellia sinensis plant. In one example, green tea is used in a pet food palatability enhancing system at 0.1-25%, 1-15%, or 2-9% by weight of the system, and at 0.025-0.5% or 0.01 to 1.0% by weight of the pet food.
Owner:MANE SA
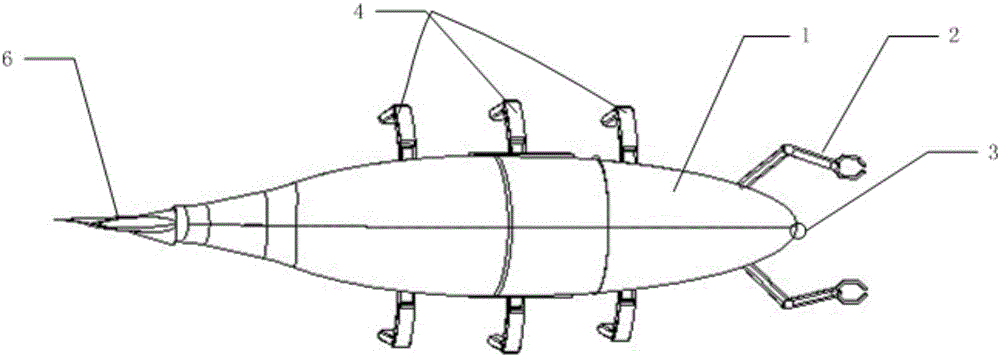
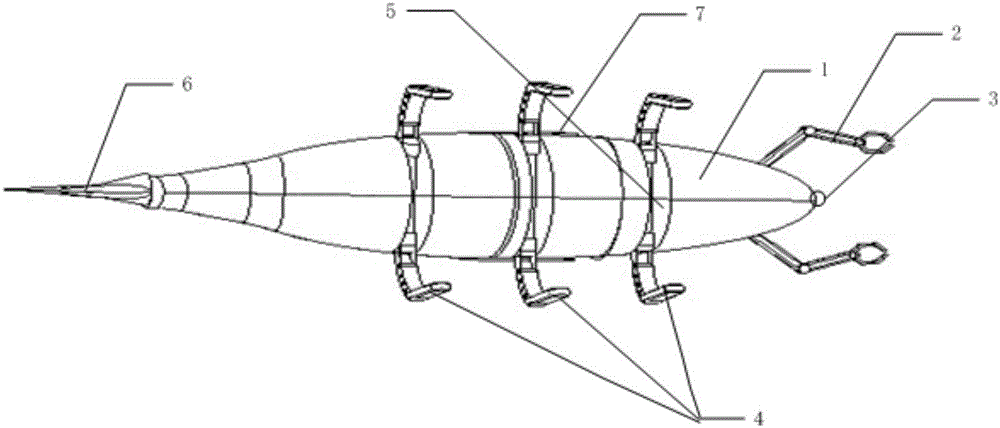
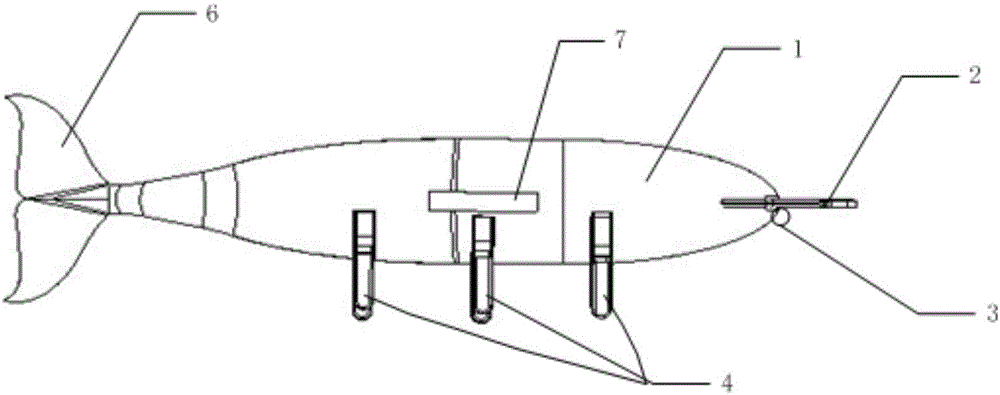
Bionic multi-navigation-state deep unmanned submersible
ActiveCN106628072ARealize the subsea walking functionFunction increaseUnderwater vesselsUnderwater equipmentManipulatorMarine navigation
The invention provides a bionic multi-navigation-state deep unmanned submersible. An underwater camera is arranged in the center of the bow of a deep unmanned submersible body, and telescopic mechanical arms are arranged on the two sides of the bow of the deep unmanned submersible body correspondingly. The two sides of the middle of the deep unmanned submersible body are each provided with side-scan sonar. A tuna bionic tail fin is arranged at the tail of the deep unmanned submersible body. Three sets of grooves are formed in the lower portion of the deep unmanned submersible body. A set of walking legs is arranged in each groove and includes two walking legs. Each walking leg comprises a first motor installed in the deep unmanned submersible body, a first arm hinged to an output shaft of the first motor, a second arm hinged to the end of the first arm, and a third arm hinged to the end of the second arm, wherein a second motor is arranged at the hinge position of the first arm and the second arm, a third motor is arranged at the hinge position of the second arm and the third arm, and the second arm is a bent arm. The bionic multi-navigation-state deep unmanned submersible can travel at the seabed and sample targets at the seabed.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
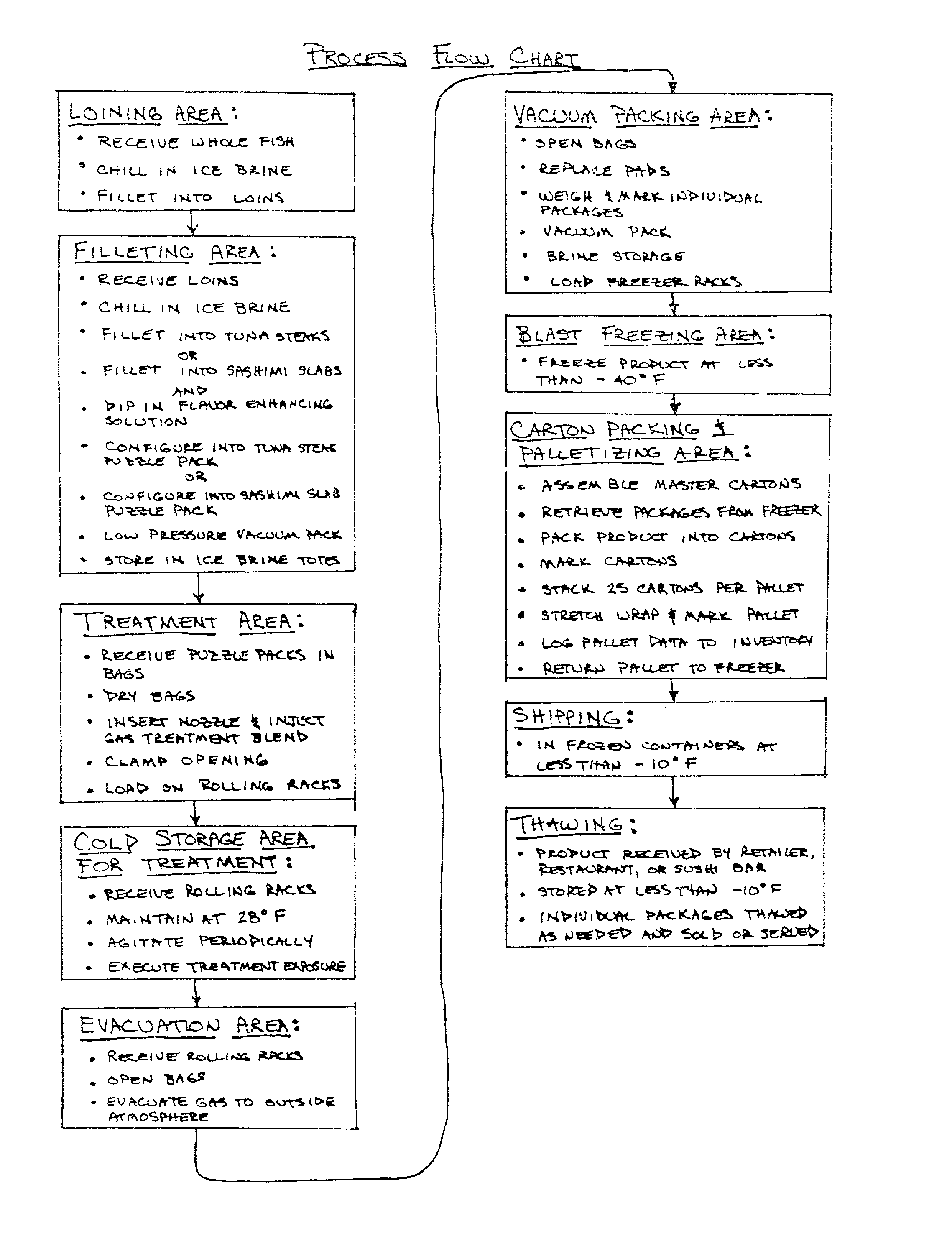
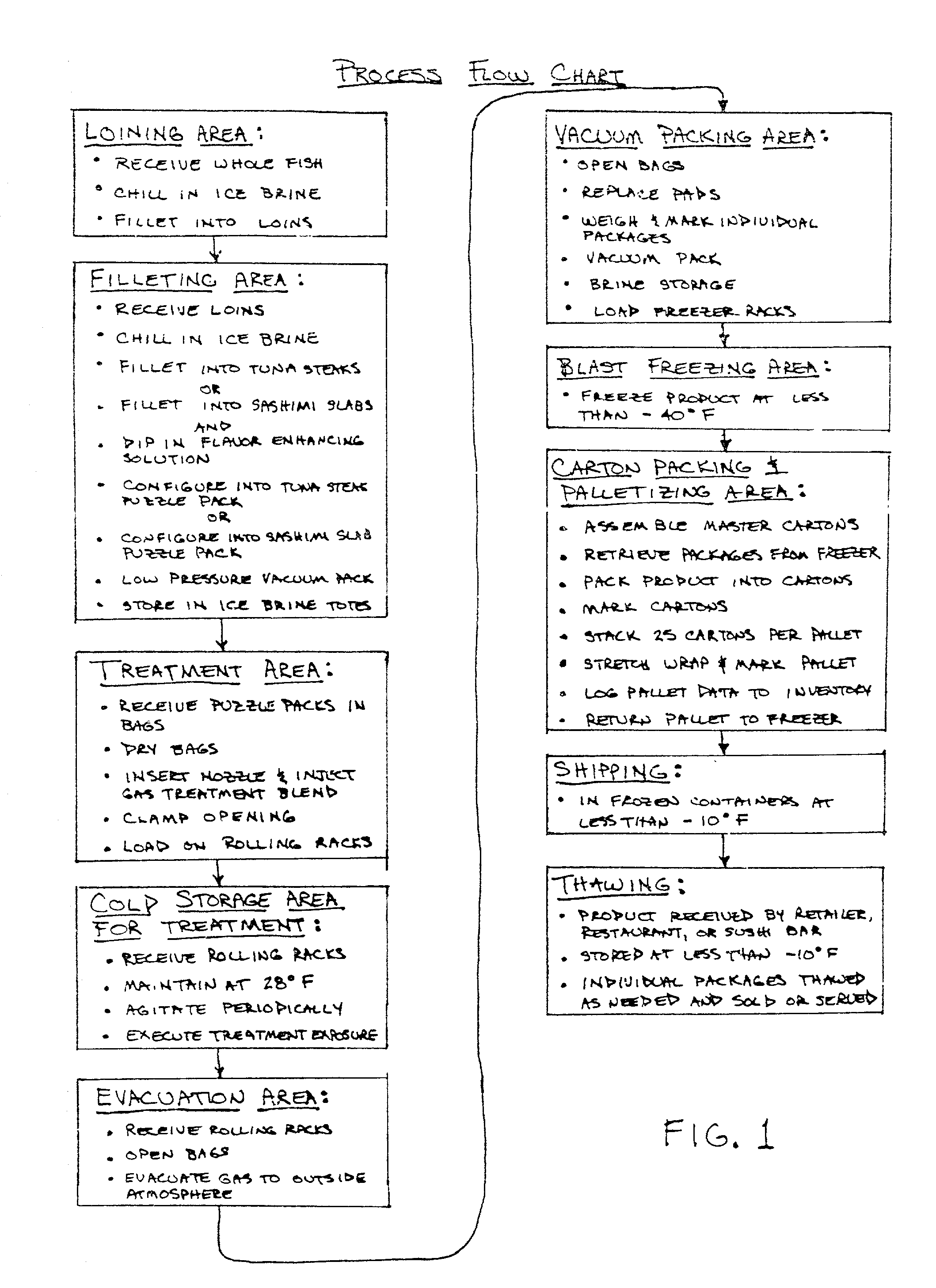
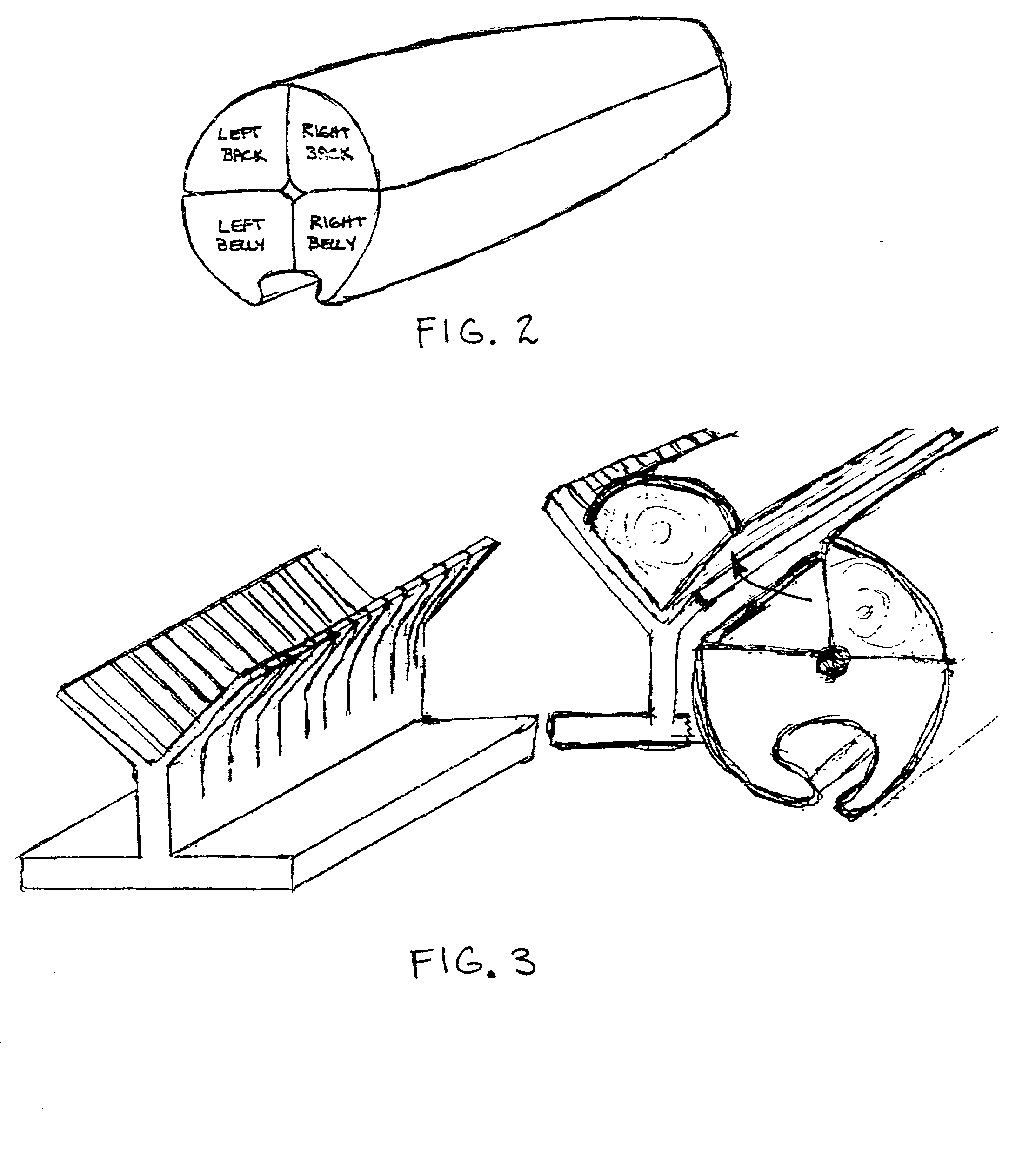
Process for the filleting, treating, packaging, freezing, and thawing of varying types of tuna and other pelagic species
InactiveUS20020012724A1Efficiently filletEffective treatmentReady-for-oven doughsMilk preservationSaline waterVacuum pack
A method of treating fish to maintain freshness after freezing and thawing. A whole fish is chilled and cut into four loins, each with two flat sides forming a corner. The loins are chilled and either sliced cross sectionally to form steaks or sliced parallel to one of the flat sides to form sashimi slabs. If sashimi slabs are formed, the slabs are then preferably dipped in a warm flavor enhancing solution. The steaks or slabs are then sealed in non-permeable bags, preferably in a "puzzle pack" configuration that maximizes density and minimizes interstices. The bag with the steaks or sashimi slabs is then submerged in a brine solution. A treatment gas is then injected into the bag. After a treatment time, the gas is removed and the bag is vacuum packed. The bags are then frozen for shipping and storage. When needed, the bags can be thawed in a brine solution.
Owner:KOWALSKI WILLIAM R
Method for preparing antihypertensive peptides through enzymolysis of ground meat proteins of tuna
InactiveCN102808010AIncrease added valueRich sourcesPeptide preparation methodsFermentationChemical synthesisAlkaline protease
The invention discloses a method for preparing antihypertensive peptides through enzymolysis of ground meat proteins of a tuna. The method comprises the steps of: (1) regarding the ground meat of the tuna as the raw material, mixing and homogenizing the raw material and a buffer solution according to a weight / volume ratio of 1 g: 3-5 ml, and then adjusting the pH value to 9.5-10 to obtain a mixed solution; (2) heating the mixed solution to 55-60 DEG C for pre-heating, and adding alcalase according to 1.0%-1.5% of the raw material for enzymolysis at an enzymolysis temperature of 55-60 DEG C for 4-6 h; and (3) performing enzyme deactivation on the obtained enzymolysis product to obtain an enzymolysis solution and then enabling the enzymolysis solution to sequentially suffer from ultrafiltration, desalination, freeze drying and chromatography to obtain the antihypertensive peptides. The method for preparing the antihypertensive peptides through the enzymolysis of the ground meat proteins of the tuna, disclosed by the invention, has the advantages of abundant source of the raw material, low price, simple preparation process, relatively strong activity of the prepared antihypertensive peptides; compared with a chemosynthetic ACE (Angiotensin Converting Enzyme) inhibitor, the ACEP (ACE Inhibitive Bioactive Peptide) prepared through enzymolysis of the ground meat of the tuna has the advantages of being safe and nontoxic, specific in antihypertensive efficacy, easy to digest and absorb and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Method for preparing tuna food
The invention relates to a method for preparing tuna food, which comprises technical processes of carrying out a heat cutting and numbles removing to the tuna, washing with clean water and canning of products. In order to keep the color of the tuna, the mixing water solution containing 2-15 percent of salt and 0.1-1.0 percent of sodium isoascorbate is used for soaking and treating the tuna for 20min-180min and then the tuna is washed with the clean water. The weight proportion between the tuna and the mixing water solution is 1 : 0.8-2.0. Or when the products are canned, 0.1-0.5 percent of the sodium isoascorbate is added according to the weight of herb broth so that the weight proportion between the canning tuna and the herb broth is 5.0-2.0 : 1. Or the two proposals are used at the same time. Certain quantitative of the sodium isoascorbate is used for keeping the color of the tuna in the processing, therefore, the products has improved color and the flesh-color is fresh and stable.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GONGSHANG UNIVERSITY
Tuna fresh keeping method
ActiveCN105076349AGuaranteed food qualityExtend freshnessMeat/fish preservation using chemicalsMeat/fish preservation by dryingPropolisSodium erythorbate
The invention discloses a tuna fresh keeping method to solve a problem that present tuna fresh keeping methods reduce the quality of tuna. The method mainly comprises the following steps: 1, preprocessing tuna bodies; 2, immersing tuna in a composite fresh keeping agent; 3, carrying out surface air drying; and 4, packaging, and refrigerating. The composite fresh keeping agent comprises, by mass, 5-10% of mycose, 0.03-0.05% of nisin, 0.05-0.1% of konjak mannan, 0.1-0.3% of sodium phytate, 2-3% of calcium chloride, 0.2-0.5% of chitosan, 3-5% of disodium EDTA, 0.3-0.5% of sodium erythorbate, 0.3-0.5% of sodium citrate, and the balance of a propolis water extraction liquid. The fresh keeping method has the advantages of easy implementation, high efficiency, low cost, good fresh keeping effect, great prolongation of the fresh keeping time of tuna, maintenance of the original eating quality of tuna, good safety, facilitation of improvement of the economic benefit of ships, and suitableness for being popularized and applied.
Owner:MARINE FISHERIES RES INST OF ZHEJIANG
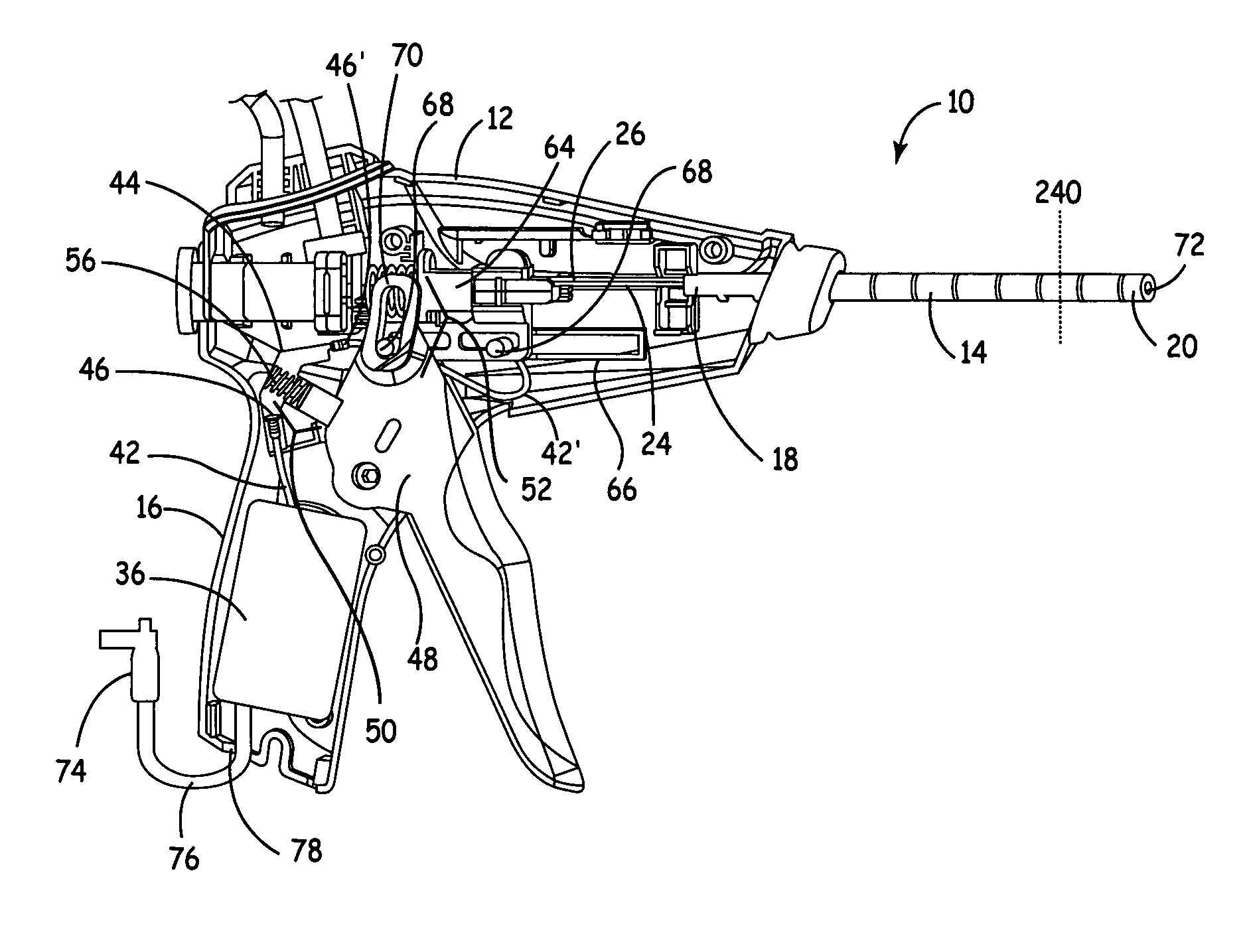
TUNA device with integrated saline resevoir
ActiveUS20060036235A1Simplify wet electrode tissue ablation procedureSimplify wet electrode tissue ablation proceduresSurgical needlesSurgical instruments for heatingSaline waterActuator
Methods and apparatus for ablating a target tissue are discussed. Such methods and apparatus include those that simplify tissue ablation. For example, a tissue ablation device having an actuator, such as a trigger mechanism, coupled to a power source and an electrode is discussed. A single step of engaging the actuator causes the electrode to be introduced into the target tissue and causes energy to be delivered from the power supply to the tissue via the electrode. By way of additional example, a tissue ablation device having an actuator coupled to a fluid source and an electrode is discussed. A single step of engaging the actuator causes conductive fluid to flow from the fluid source to the target tissue location and causes the electrode to be introduced to the target tissue location. The fluid source may be a conductive fluid, such as saline, which may increase the efficiency of ablation. Various other configurations and methods that simplify tissue ablation are also discussed.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Marine folding tower
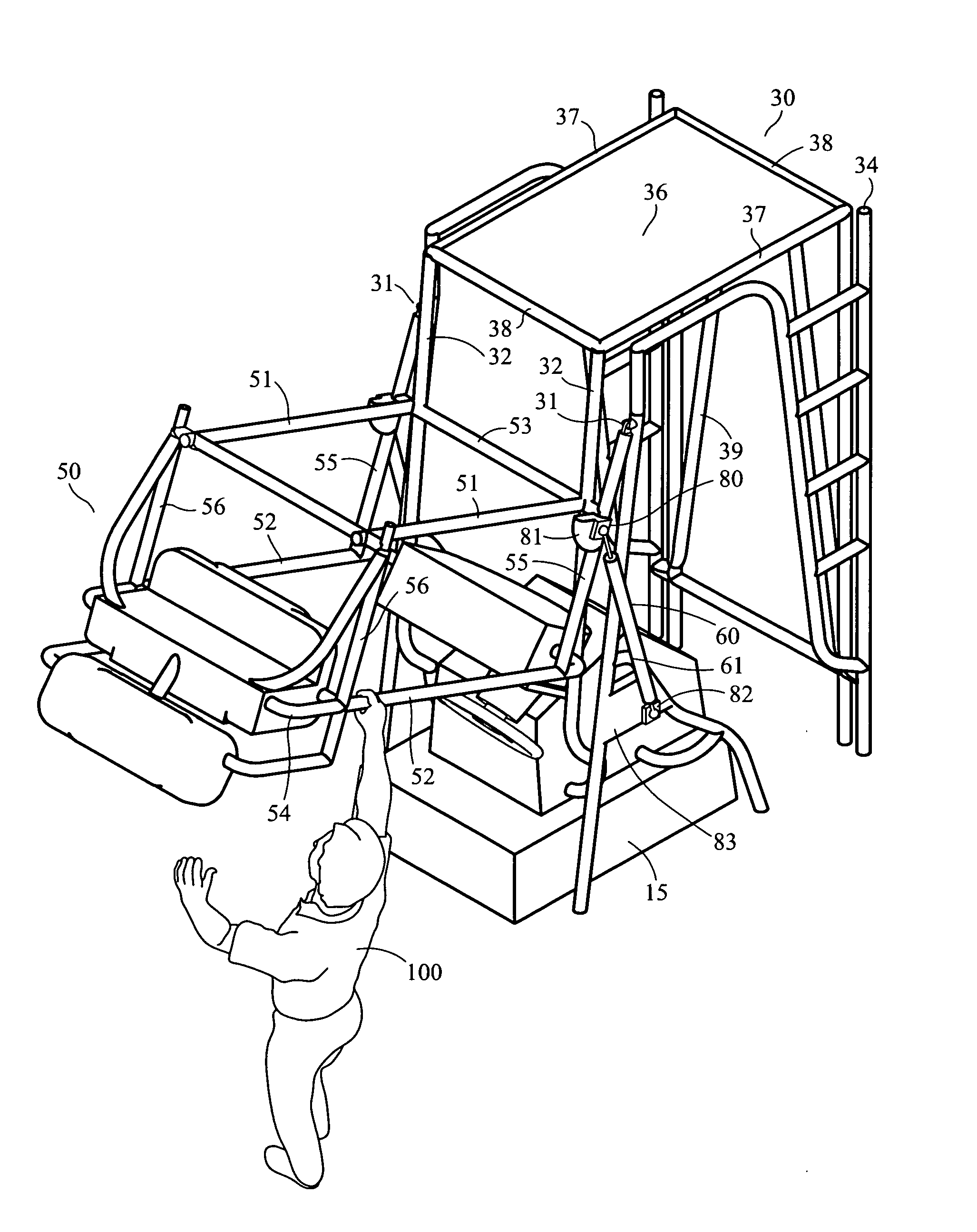
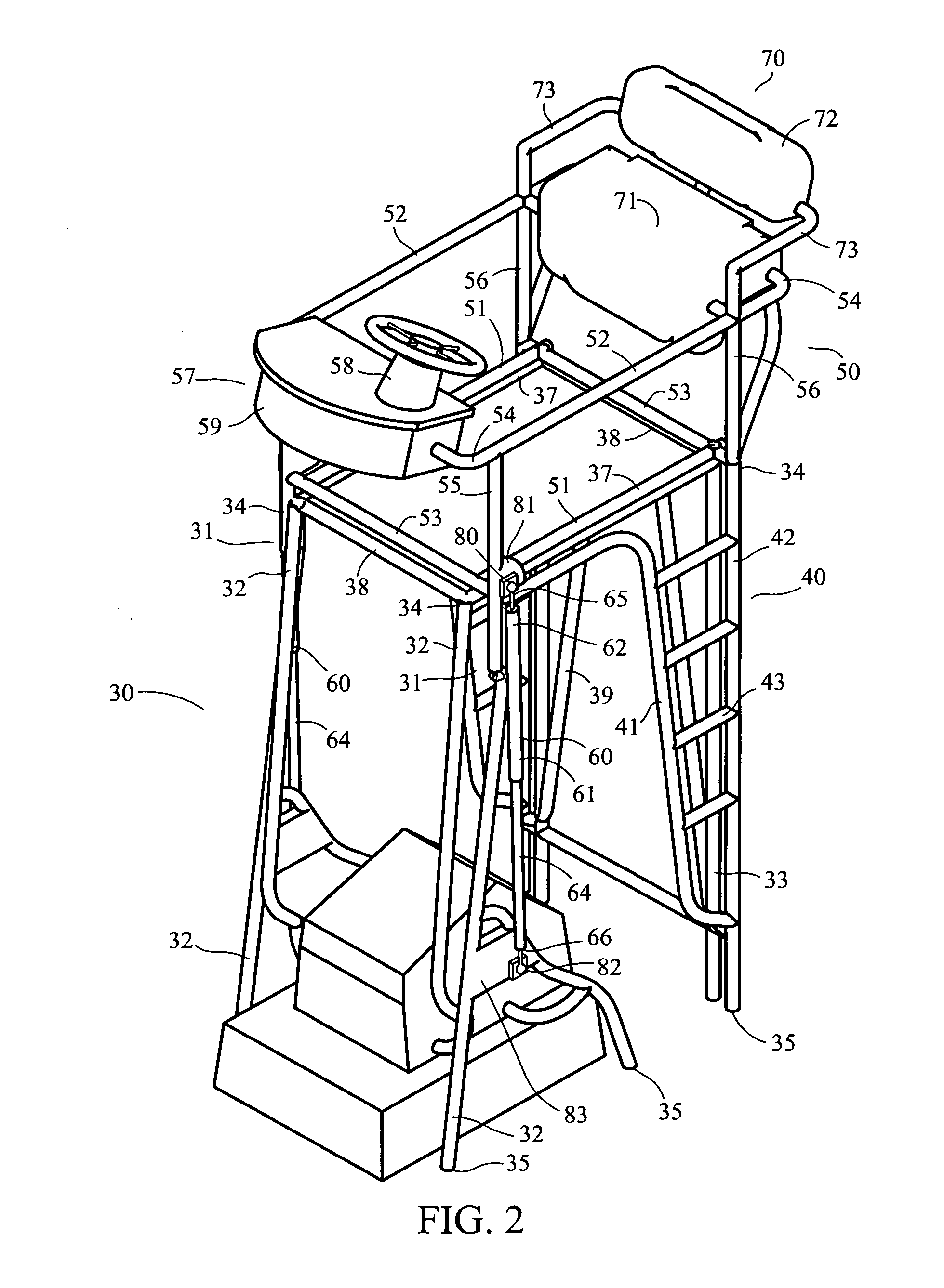
InactiveUS20090320738A1Less manual effortPromotes downward movementVessel partsFloating buildingsGas springEngineering
A system that will result in less physical effort in the lowering or raising of a marine folding tower, spotting station, driving station, fishing tower, or tuna tower. The system will be installed on a fishing boat, pleasure boat, or other marine vessel. The system comprises at least one gas spring, or hydraulic or electric ram or shock absorber of any size or style that attaches to both the upper frame assembly and lower frame assembly of the tower or other station.
Owner:BLUMBERG RYAN
A method for preparing tuna skin gelatin
InactiveCN103289576AImprove qualityScientific and reasonable processGlue/gelatin preparationActivated carbon filtrationIon exchange
The present invention discloses a method for preparing tuna skin gelatin, belonging to the technical field of fish resources utilization. According to the invention, skin tuna skin is subjected to pretreatment, degreasing, acid and alkali treatment, and then is subjected to gelatin extraction, and deodorization by filtering through activated carbon, and ion-exchange purification to remove heavy metal ions, and then concentration under vacuum and spray-drying to obtain finished products of tuna skin gelatin with quality meeting the edible gelatin standards specified in national standards. The tuna skin gelatin of the invention can be further processed for use and can be used in medicine, food and cosmetic industries, achieving the purposes of turning waste into treasure, and comprehensively and efficiently developing high value-added tuna by-products. The method of the invention has advantages of: 1, a scientific and reasonable process is adopted, the temperature in the reaction process is low and easy to control, which saves energy and controls the molecular weight of the skin gelatin in a relatively narrow range, and the quality of obtained gelatin is high; and 2, activated carbon is used for filtering for deodorization, improving the taste of the product.
Owner:BEIHAI GOFAR MARINE BIOLOGICAL IND CO LTD
Liver injury and repair type active peptide prepared from tuna offal
ActiveCN106632605AIncrease valueReduce manufacturing costPeptide preparation methodsFermentationMedicineAquatic product
The invention discloses a liver injury and repair type active peptide prepared from tuna offal. The active peptide is shown as an amino acid sequence of Met-Thr-His-Asp-Asp-Val-Asp-Glu. The active peptide has the advantages that the collagen peptide with the liver injury and repair functions is extracted from an aquatic product processing byproduct, namely tuna offal simply and easily at a low production cost, so that the aquatic product processing byproduct value can be increased remarkably, waste is avoided and environment protection is achieved, and preliminary basis can be provided for related functional food.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Real-time fish stock monitoring and fish amount estimating system based on wireless communication network
InactiveCN105116414AAchievement distanceRealize the display effectAcoustic wave reradiationFish stockingReflection mapping
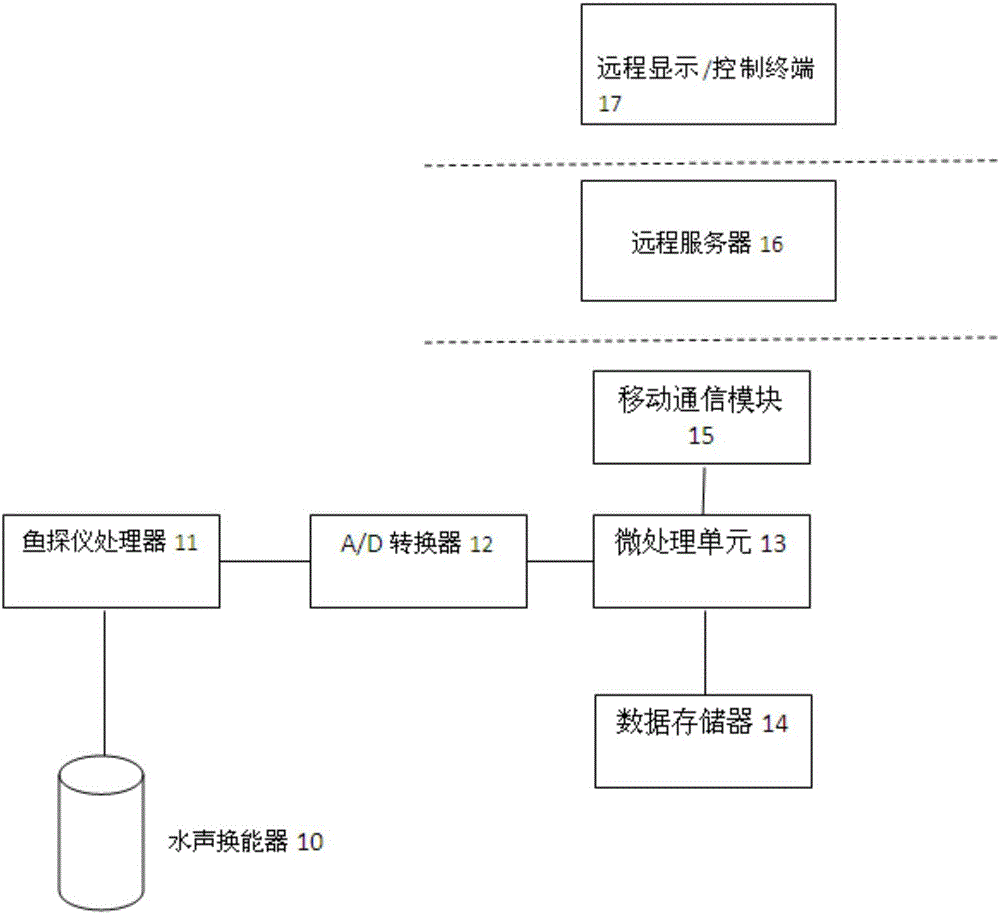
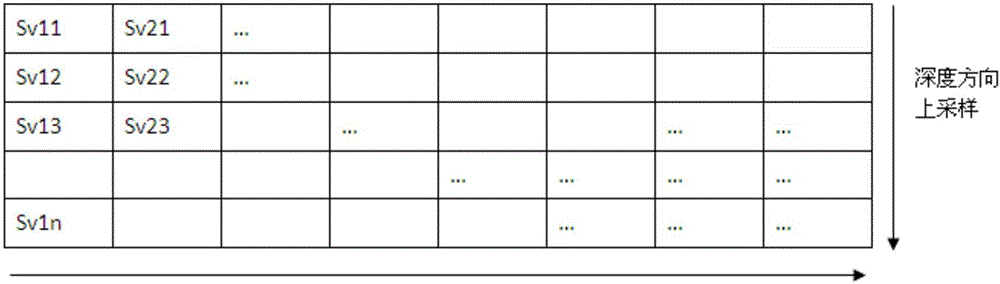
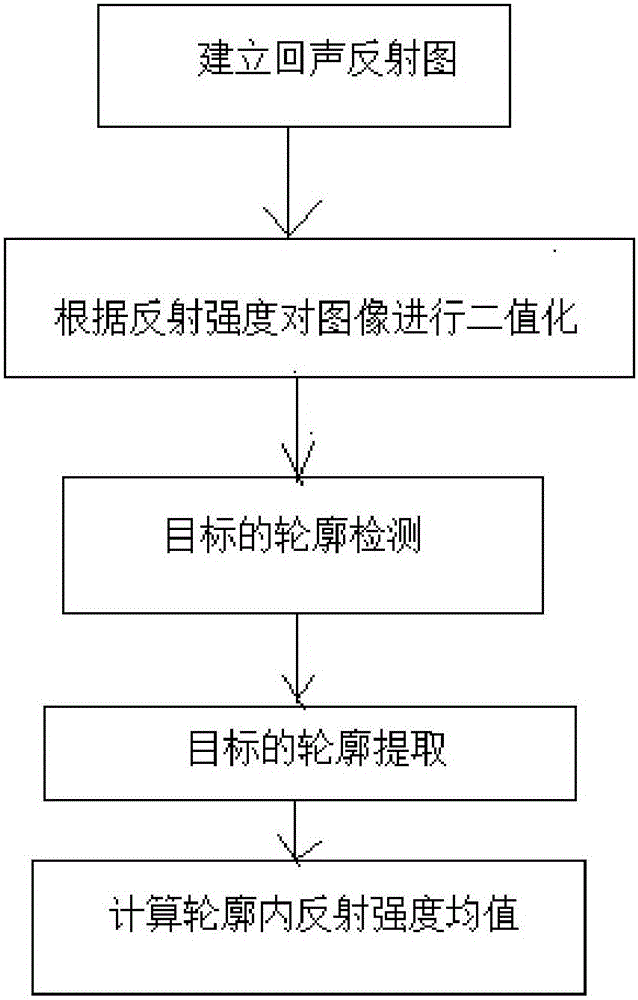
The invention provides a real-time fish stock monitoring and fish amount estimating system based on a wireless communication network, which mainly comprises an underwater acoustic transducer, a fish finder processor and a micro-processing unit, wherein the micro-processing unit detects echo reflection signals of a fish stock and extracts an average value of the rear echo reflection strength within a period of time in a specific water depth range; and fish stock mapping information in an echo reflection mapping graph formed by echo signals is extracted, and remote transmission and display of fish stock information are realized. The system can also be used for predicating the fishing yield besides displaying fish finder images in real time. The system provided by the invention can be applied to a plurality of fields such as real-time monitoring for fixed net fishery and the sea net cage breeding industry, observation of artificial reef fish-gathering effects, fish stock detection under an artificial fish-gathering device in tuna seine purse fishery and the like, and has very important significance for improving the production efficiency of marine fishery.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV +1
Tuna preservation method
ActiveCN103053672AEnvironmental protection and effective long-term freshness preservationSmall meatMeat/fish preservation using chemicalsFish processingSurface-active agentsProduct processing
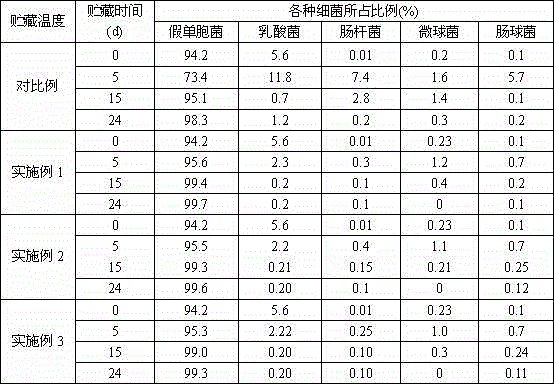
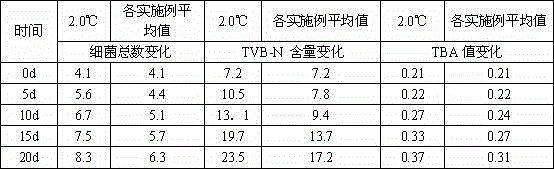
The invention relates to the technical field of aquatic product processing, and specifically relates to a tuna preservation method. The method specifically comprises the following steps of: firstly, removing internal organs and gills of the catched fresh tuna, and washing the surface and the inside of the tuna with cleaning fluid; then, soaking the tuna in a lysozyme-containing soak solution, of which pH is 5.5-6.5, for 20-30min; and finally, storing the soaked tuna in binary ice, wherein the binary ice is prepared by dissolving the following constituents by weight percent in water: 0.5-2% of foaming agent, 0.5-3% of organic acid, 6-15% of sodium chloride, 0.1-0.3% of surface active agent and 1-3% of vitamin E1. The method provided by the invention can effectively inhibit the reproduction of various bacteria in flesh of fish for long time, the flesh quality and the appearance of the preserved tuna change less, the residual quantity of harmful chemical substances is low, thus, the method can preserve the tuna for long time on the basis of guaranteeing the flesh quality of the tuna.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MARINE DEV RES INST
Ginkgo biloba extract and fish oil soft capsule and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103238840AHigh in DHAIncrease blood oxygen levelsFood preparationAdditive ingredientFish oil
The invention relates to a ginkgo biloba extract and fish oil soft capsule. Memory deterioration is one of body function debilitating symptoms of elders, the memory deterioration commonly occurs in youngsters and adults with the increasingly fierce social competition, and chemotherapy has a by-effect. The ginkgo biloba extract and fish oil soft capsule content is prepared by tuna oil, ginkgo biloba extract, natural vitamin E, beewax and soybean oil according to a proportion of parts by weight of (432-528):(135-165):(0.63-0.77):(40.95-50.05):(21.42-26.18). The invention further relates to a preparation of ginkgo biloba extract and fish oil soft capsule. The ginkgo biloba extract and fish oil soft capsule provided by the invention can be used for effectively improving the intracerebral DHA content, optimizing the brain tissue ingredients, improving the brain blood oxygen content and perfecting the memory, thereby being suitable for people of all agents and particularly suitable for elders with memory deterioration and brain function decline.
Owner:BY HEALTH CO LTD
Method for extracting blood pressure lowering peptide from tuna
InactiveCN102051399ACheap and easy to getThe preparation method is scientific and reasonablePeptide preparation methodsFermentationWater bathsHydrolysate
The invention relates to a preparation method of a tuna blood pressure lowering peptide. The preparation method comprises steps of homogenizing tuna tissue, adding pepsin or papain of 1,000-13,000 U / g fish pulp at the pH value of 2-5, heating to 35-50 DEG C, performing enzymolysis in a water bath for 1-4 hr, heating hydrolysate with boiled water for 5-15 min for deactivating enzyme, cooling, centrifuging, and purifying with macroporous resin or dextrane gel resin. The preparation method is scientific and reasonable, and extracts blood pressure lowering peptide with the leftovers of natural tuna as raw material. The blood pressure lowering peptide prepared by hydrolysis has good effect, easily-accessible raw material and low cost, and can be used for developing health products or medical preparations. The extraction method is simple, economic and easy for operation, and can be carried out in a common biochemical laboratory.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MARINE DEV RES INST +2
Tuna bone collagen peptide preparation method
ActiveCN105087729APromote absorptionShorten the production cyclePeptide preparation methodsFermentationHuman bodyDrug development
The invention relates to a tuna bone collagen peptide preparation method. The tuna bone collagen peptide preparation method includes: crushing tuna bones, subjecting the crushed tuna bones to pretreatment, adding additives to prepare collagen and performing enzymolysis to obtain a tuna bone collagen peptide. The preparation method is short in preparation cycle, high in yield and product purity and capable of removing bitter fishy smell, provides technical assistance for development of selenium-supplementing health food and drugs and also provides a new thought for high-value application of the tuna bones, and the tuna bone collagen peptide is good in taste and beneficial to absorption of human bodies.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MARINE DEV RES INST
Preparation method of selenium-chelated collagen peptide with tuna bone collagen serving as source
ActiveCN105087728APromote absorptionWide variety of sourcesPeptide preparation methodsFermentationPeptideTuna
The invention relates to a preparation method of a selenium-chelated collagen peptide with tuna bone collagen serving as a source. The preparation method includes: crushing tuna bones, subjecting the crushed tuna bones to pretreatment prior to enzymolysis and adding selenium-enriched yeast so as to obtain the selenium-chelated collagen peptide. The preparation method is short in preparation cycle, high in yield and product purity and capable of removing bitter fishy smell, provides technical assistance for development of selenium-supplementing health food and drugs and also provides a new thought for high-value application of the tuna bones, and the selenium-chelated collagen peptide is good in taste and beneficial to absorption of human bodies.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MARINE DEV RES INST
Method for preparing fish oil by virtue of leftovers of tuna
ActiveCN103060076ARapid responseShort growth arrest timeFatty-oils/fats productionEmulsionAquatic product
The invention relates to the technical field of aquatic product processing, and particularly relates to a method for preparing fish oil by virtue of the leftovers of tuna. The specific scheme disclosed by the invention is as follows: the method comprises the following steps of: removing impurities from the leftovers of tuna and cleaning, and then crushing to obtain a feedstock; then performing primary enzymolysis on the feedstock by virtue of immobilized lipase, then performing secondary enzymolysis, filtering the obtained secondary enzymolysis solution to remove residue, performing centrifugal treatment, and separating to obtain lower-layer emulsion and upper-layer crude fish oil; and demulsifying the lower-layer emulsion, and forming the tuna fish oil with the upper-layer crude fish oil. According to the technical scheme disclosed by the invention, the fish oil is prepared by virtue of the leftovers of tuna; and the fish oil is high in extraction rate, complete in active ingredients and high in content, and the method is low in energy consumption and environment-friendly.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MARINE DEV RES INST
Tuna ground meat polypeptide angiogenesis inhibiting factor as well as preparation method and application thereof
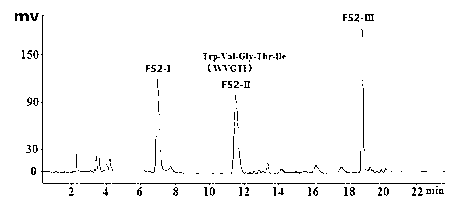
InactiveCN103275181AHigh activityScientific and reasonable processPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsProstate cancer cellESI mass spectrometry
The invention discloses a tuna ground meat polypeptide angiogenesis inhibiting factor as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the polypeptide angiogenesis inhibiting factor is Trp-Val-Thr-Gly-Ile (WVTGI), and ESI / MS (electrospray ionization / mass spectrometry) detection shows that a molecular ion peak (m / z) is 575.42Da ([M+H]+). The tuna ground meat polypeptide angiogenesis inhibiting factor Trp-Val-Thr-Gly-Ile (WVTGI) can be used for effectively inhibiting angiogenesis of chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) of chicken embryo and multiplication of prostate cancer cell DU-145. The tuna ground meat polypeptide angiogenesis inhibiting factor Trp-Val-Thr-Gly-Ile (WVTGI) can be used for preparing a medicine used for inhibiting angiogenesis and preventing and treating prostate cancer.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
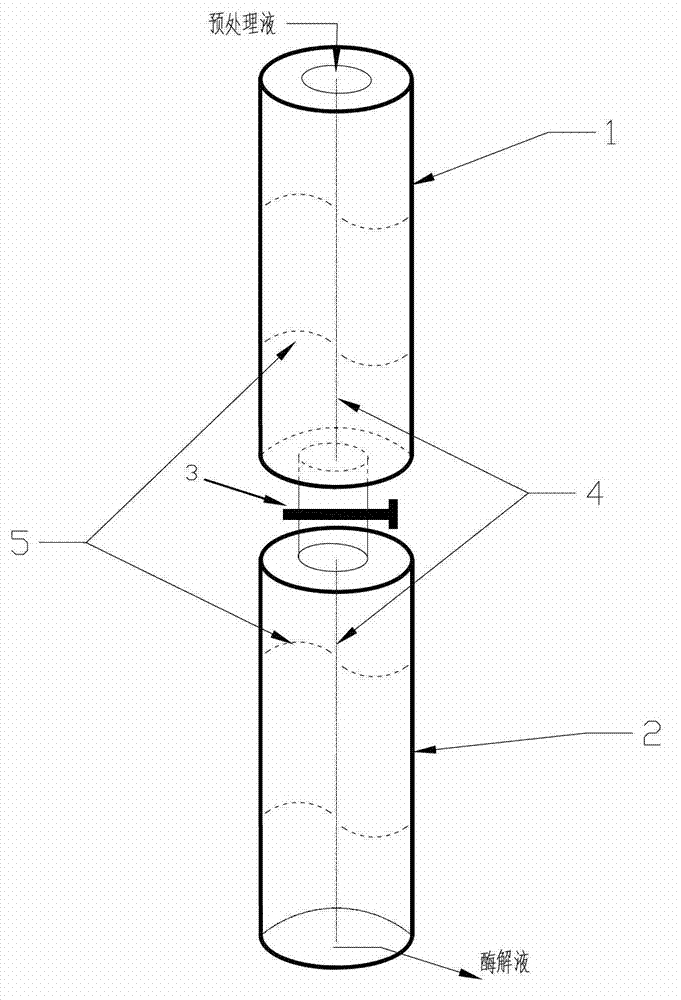
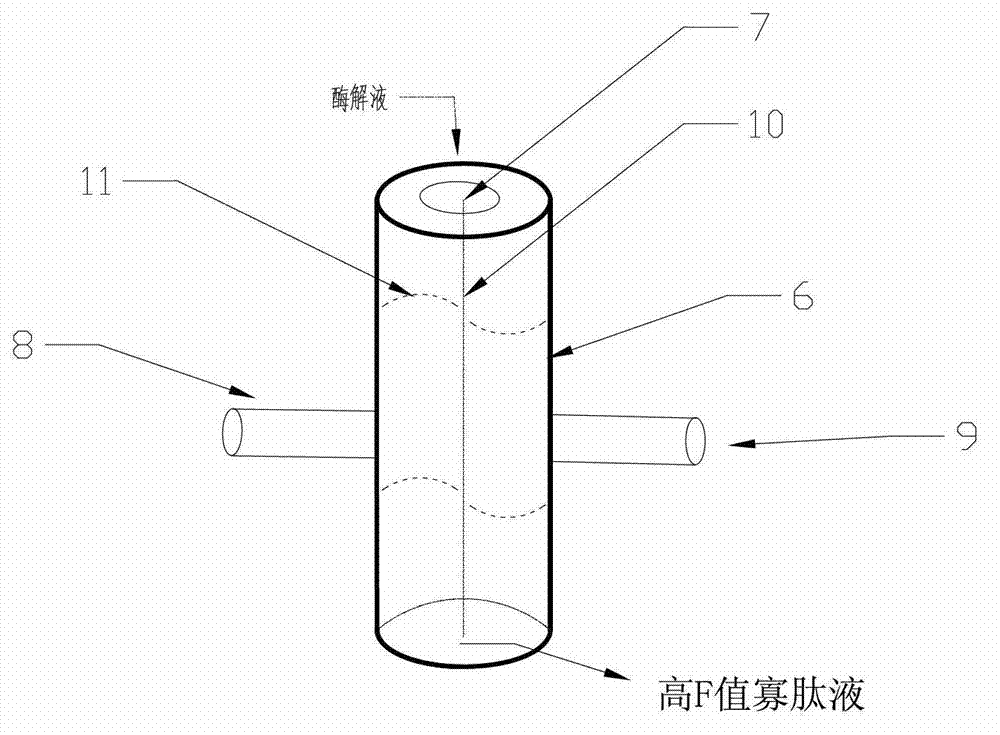
Preparation method of high-F-value tuna oligopeptide
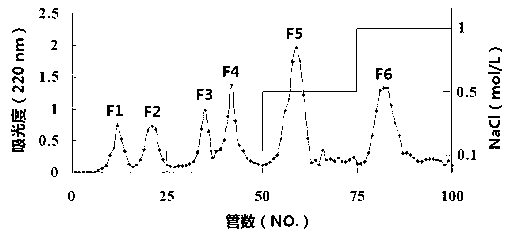
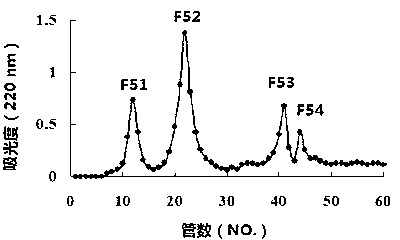
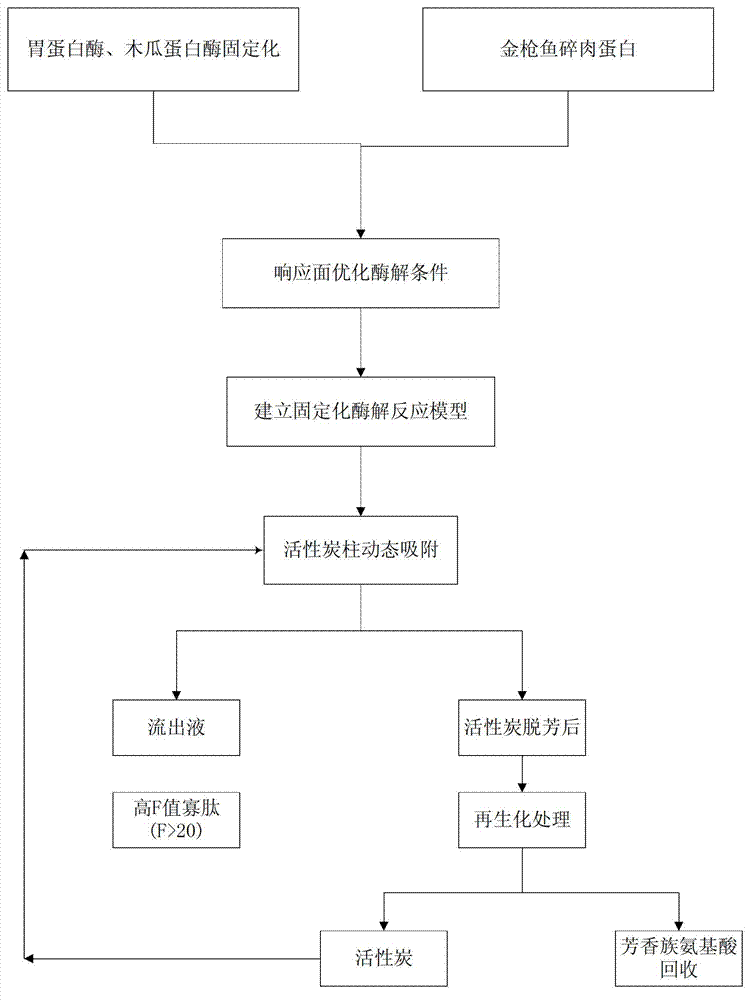
InactiveCN102776262AEnzyme hydrolysis efficiency decreasedImprove enzymatic hydrolysis efficiencyPeptide preparation methodsOn/in organic carrierStereochemistryTuna
The invention belongs to the technical field of oligopeptide preparation, and in particular relates to a preparation method of high-F-value tuna oligopeptide. According to the invention, an immobilized enzymolysis method and an active carbon dynamic absorption method are adopted, and the preparation method has favorable enzymolysis efficiency, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
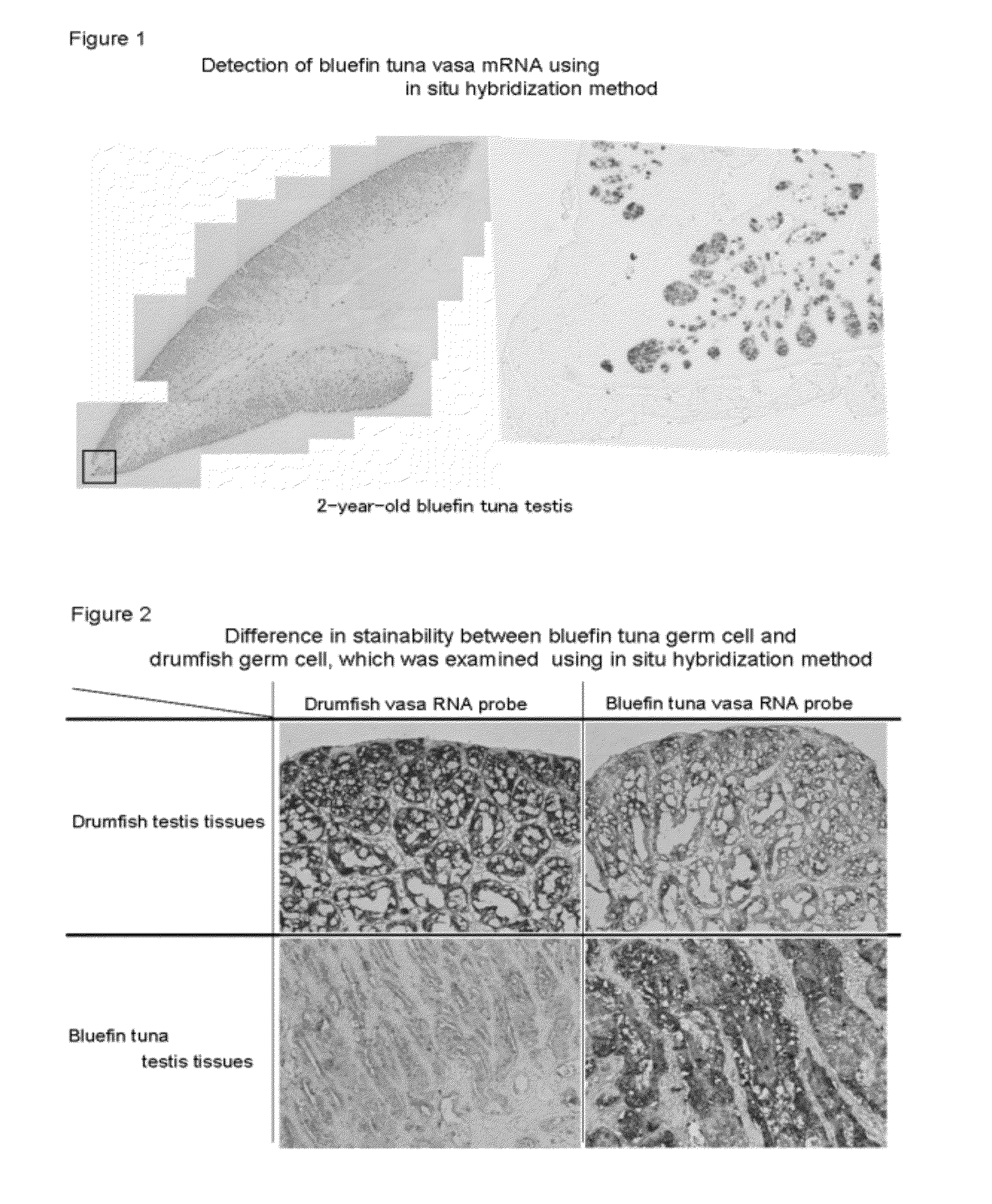
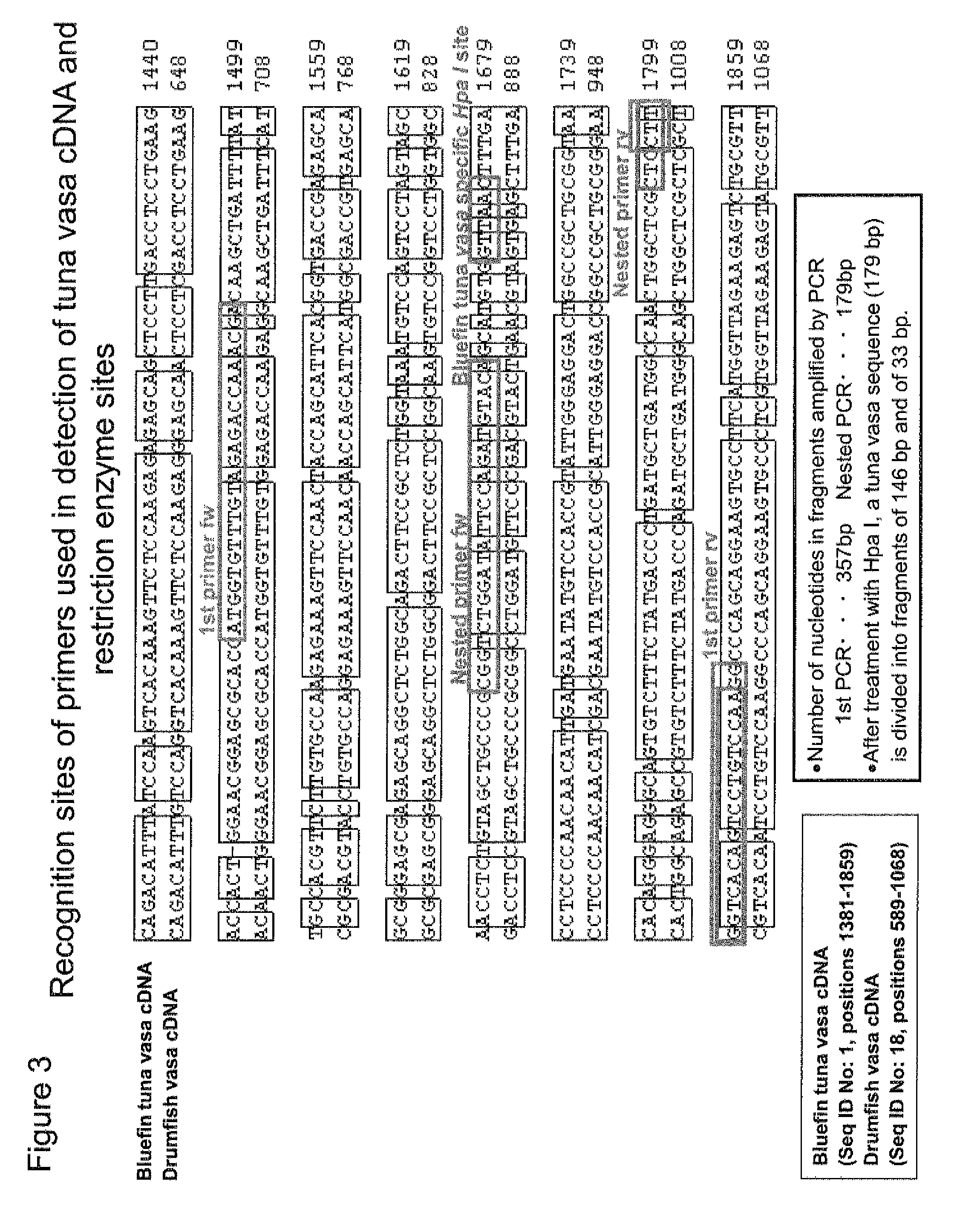
Germ cell marker using fish vasa gene
Owner:NIPPON SUISAN KAISHA LTD
Electric-nose-analysis-based determination method of tuna oil corruption degree in storage process
InactiveCN105527391AEfficient determinationEasy to operateTesting foodNosePrincipal component analysis
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Flavored morchella raw fish and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a flavored morchella raw fish which is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 90-110 parts of frozen tuna, 15-16 parts of lyophilized royal jelly powder, 22-24 parts of grape pulp, 8-9 parts of morchella, 5-7 parts of steamed bun, 9-11 parts of mango juice, 17-18 parts of walnut kernel, 7-8 parts of honey, 0.5-1 part of a mulberry root, 0.4-1 part of penthorum Chinese pursh, 1.8-2 parts of wax gourd seeds, 0.2-0.3 part of sodium glutamate, 0.1-0.3 part of ethyl maltol, 0.1-0.2 part of phosphate, 1-2 parts of lactic acid bacteria, 300mmol / L of CaCl2 solution, refined salt and a proper amount of sugar. The flavored morchella raw fish has the advantages of unique taste, long shelf life and good health effect; the flavored morchella raw fish is unfrozen by a pickling method and is pickled by an injection method; the technology is unique and novel; the value-added space and the extension benefits of the raw fish product are increased; and due to the addition of traditional Chinese medicine components such as mulberry root and penthorum Chinese pursh, walnut kernel is endowed with the health effects of moistening the lung for removing phlegm and clearing away heat and toxic materials.
Owner:合肥市韩林家庭农场有限公司
Stewing process of tuna
ActiveCN103070421AGreat tastePromote absorptionFood preparationMonosodium glutamateSodium bicarbonate
The invention relates to the technical field of aquatic product processing, and in particular relates to a stewing process of tuna. The method comprises the specific steps of: first, cleaning the tuna with a cleaning fluid, rinsing the tuna with clean water and draining for standby; then subjecting the cleaned tuna to ultrasonic immersion treatment in a soaking liquid for 20-30 min, wherein the soaking liquid is an aqueous solution comprising the following components by weight: 5-12% of sodium chloride, 1-3% of sodium bicarbonate, 0.3-0.5% of sodium succinate, 0.6-1.3% of monosodium glutamate, 0.4-1% of beta-carotene and the balance of water; and finally stewing the soaked tuna in a stewing liquid for 8-15 min, and then steaming the tuna at 102-105 DEG C for 3-10min. Through the method provided by the invention, the tuna has few nutrient loss, gains good taste, and is easy to absorb and not easy to breed bacteria, so as to facilitate later preservation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MARINE DEV RES INST
Preparation method for dried tuna
ActiveCN105146591ADeliciousReduce nutrient lossFood ingredient as antioxidantLipidic food ingredientsDried fishAquatic product
The invention relates to the technical field of aquatic product processing, and discloses a preparation method for dried tuna, which includes: (1) thawing: tunas are taken out of a freezer and thawed; (2) washing and cutting: offal is removed from the tunas, and the fish bodies are then cut into pieces after being washed; (3) preprocessing of the fillets: the fillets are soaked in preprocessing liquid, and after soaking, the fillets are washed and pickled; (4) cooking: the fillets and auxiliary materials are added into water and cooked; (5) dehydration: after the water of the fillets is drained, the fillets are put into a vacuum drier and dehydrated; (6) roasting: sauce is applied on the surfaces of the fillets, tinfoils are then used for wrapping the fillets, and the fillets wrapped by the tinfoils are roasted; (7) rolling: the fillets are rolled; (8) packaging and sterilization: the dried tuna is packaged and sterilized. The taste of the dried tuna prepared by the preparation method is delicious, the loss of nutrients is little, and the shelf life is long.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MARINE DEV RES INST
Comprehensive utilization method of tuna leftovers
InactiveCN104342474AReduce manufacturing costIncrease productionFermentationWAS PROTEINAlkaline protease
The invention relates to a comprehensive utilization method of tuna leftovers to solve the problem that existing tuna leftovers cannot be comprehensively utilized. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out enzymolysis on tuna leftovers by virtue of alkaline protease until fish is separated from fine bones; separating out fish bones on the lower layer, wherein upper liquid is hydrolysate; separating out sediments and supernate after centrifuging the hydrolysate, wherein the sediments are protein and hydrolysate thereof; and separating an oil phase from a water phase in the supernate, wherein the oil phase mainly is a tuna fat substance; and the water phase mainly is protein hydrolysate. The separated fish bones, protein, and hydrolysate and fish oil thereof can be respectively applied to production and processing of collagen, gelatin, fish meal and the like, and the economic benefits of fish product processing enterprises are improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
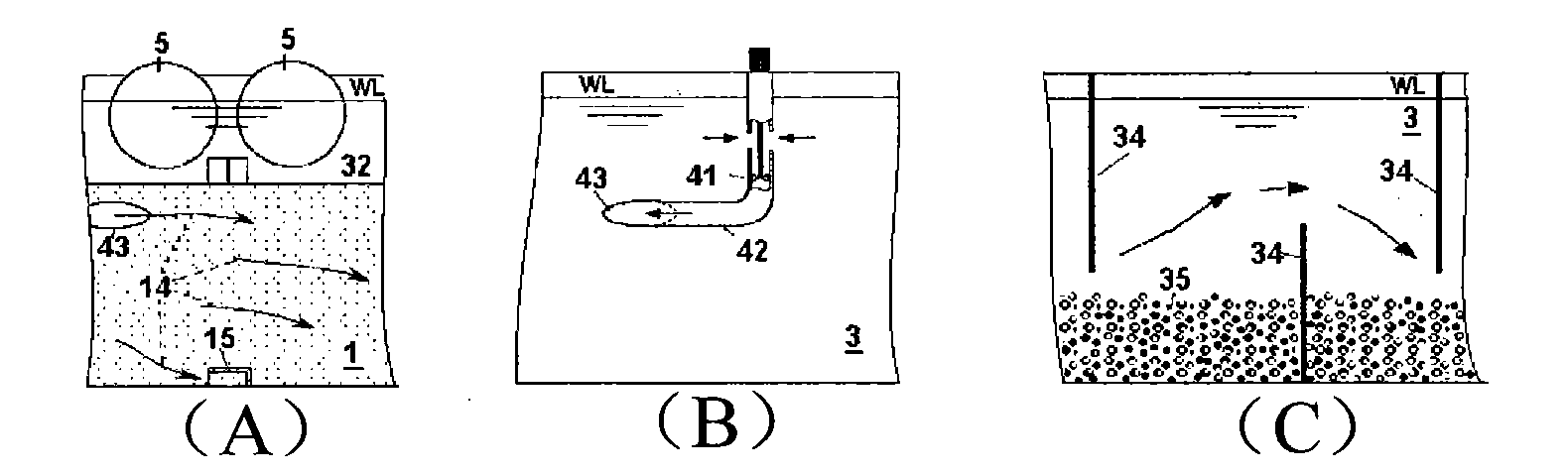
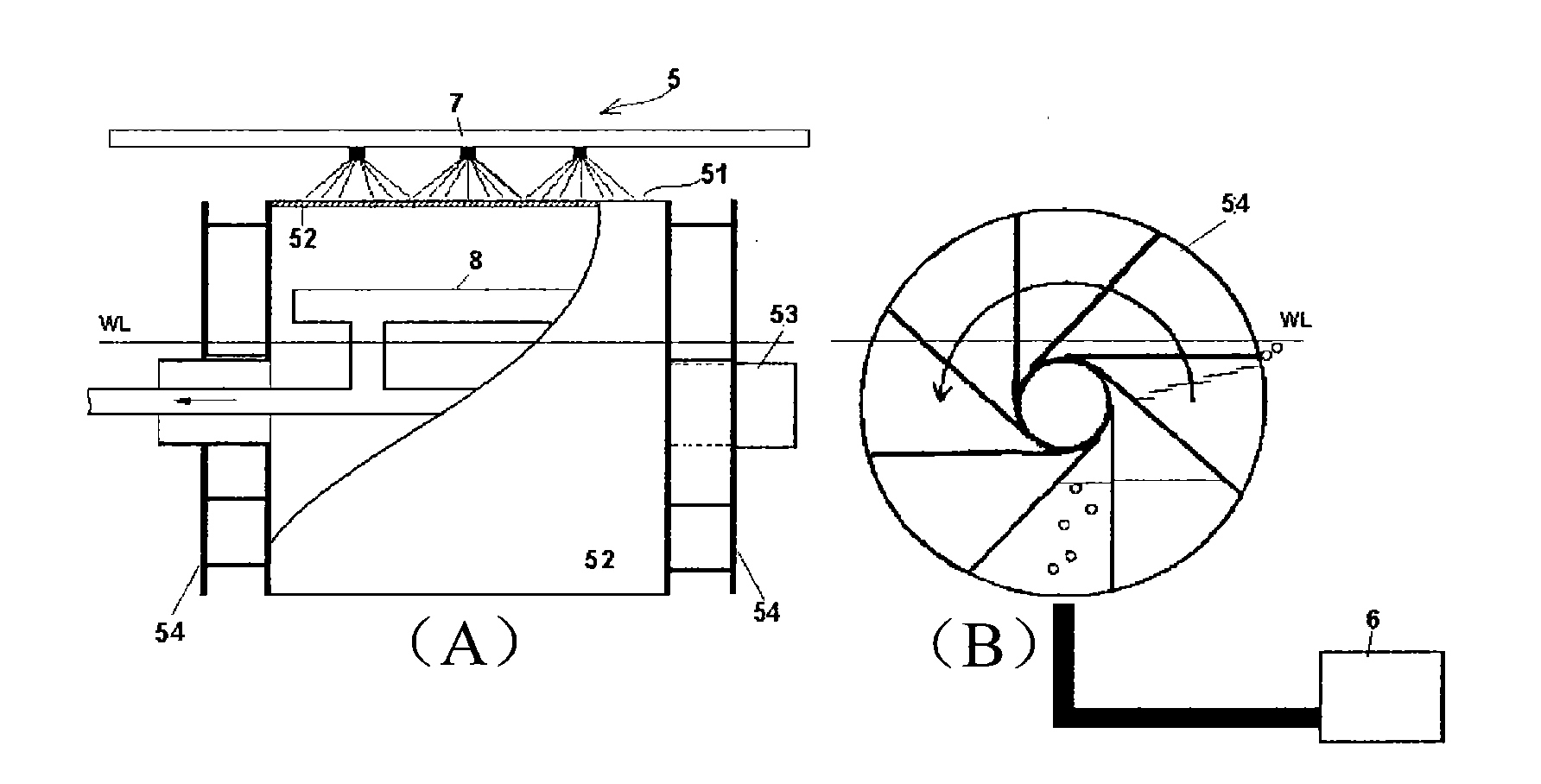
Equipment for migratory fish breeding
Owner:鹫山 一郎
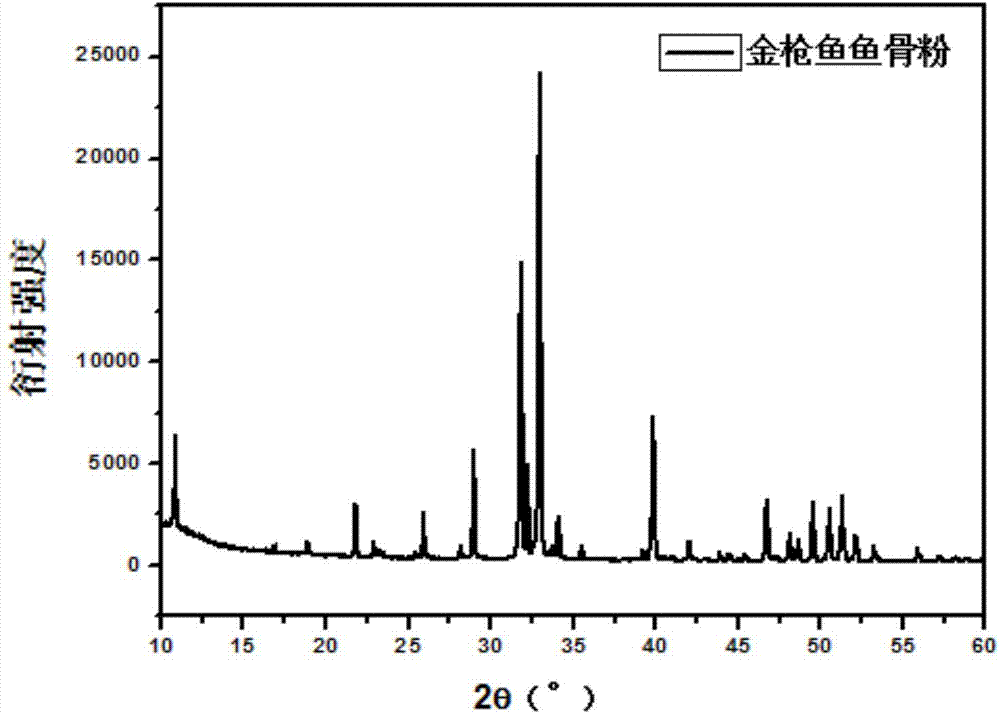
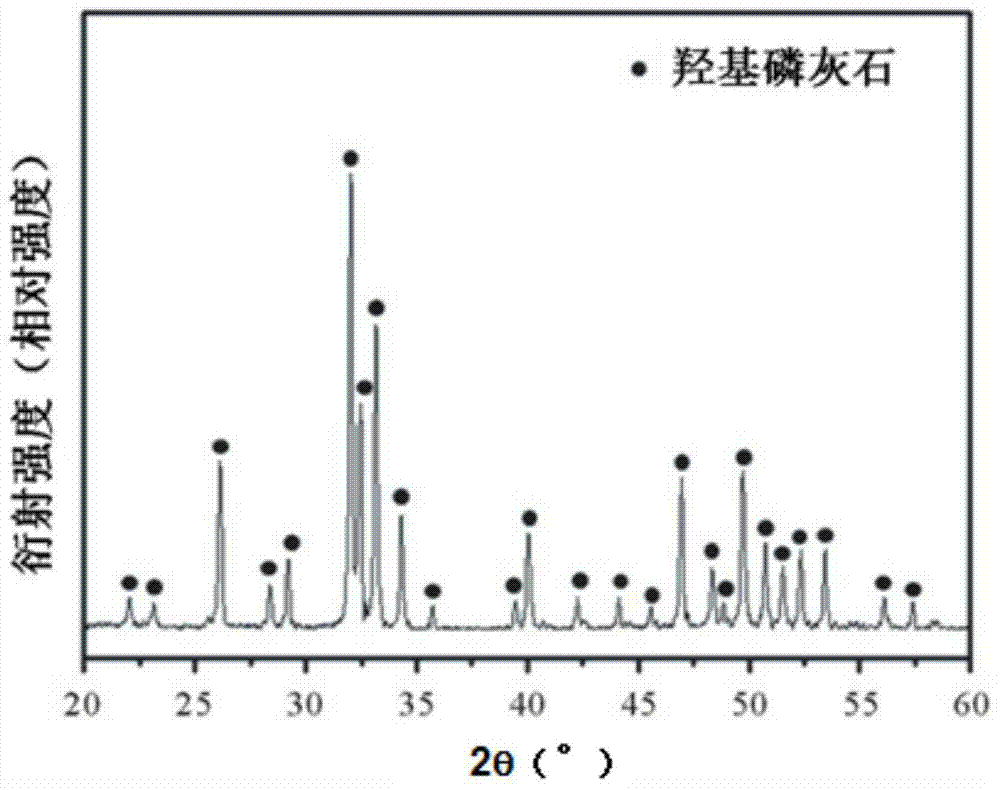
Tuna fishbone meal material, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104841016AQuality is easy to controlEasy to introduceProsthesisDental filling materialsHydrogen
The invention provides a tuna fishbone meal material, a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method of the tuna fishbone meal material provided by the invention includes: conducting preliminary crushing on tuna fishbone to obtain a fishbone preliminary material, cooking the fishbone preliminary material at 90-100DEG C and under 1.0-1.1bar for 1-4h to obtain a fishbone initial material; soaking the fishbone initial material in a sodium hydrogen sulfite buffer solution with a mole concentration of 4-7% for 2-4h, then conducting calcinations at 800-1000DEG C for 4-10h to obtain a fishbone material, and then carrying out crushing and sieving treatment to obtain fishbone meal material with different particle size ranges. The invention additionally provides the tuna fishbone meal material prepared by the method. The invention also provides application of the tuna fishbone material as a medical orthopaedic filling material. The tuna fishbone material can be used as an individual bone filling material and dental filling material, and also can be compounded with other materials into widely applied biomedical materials.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com