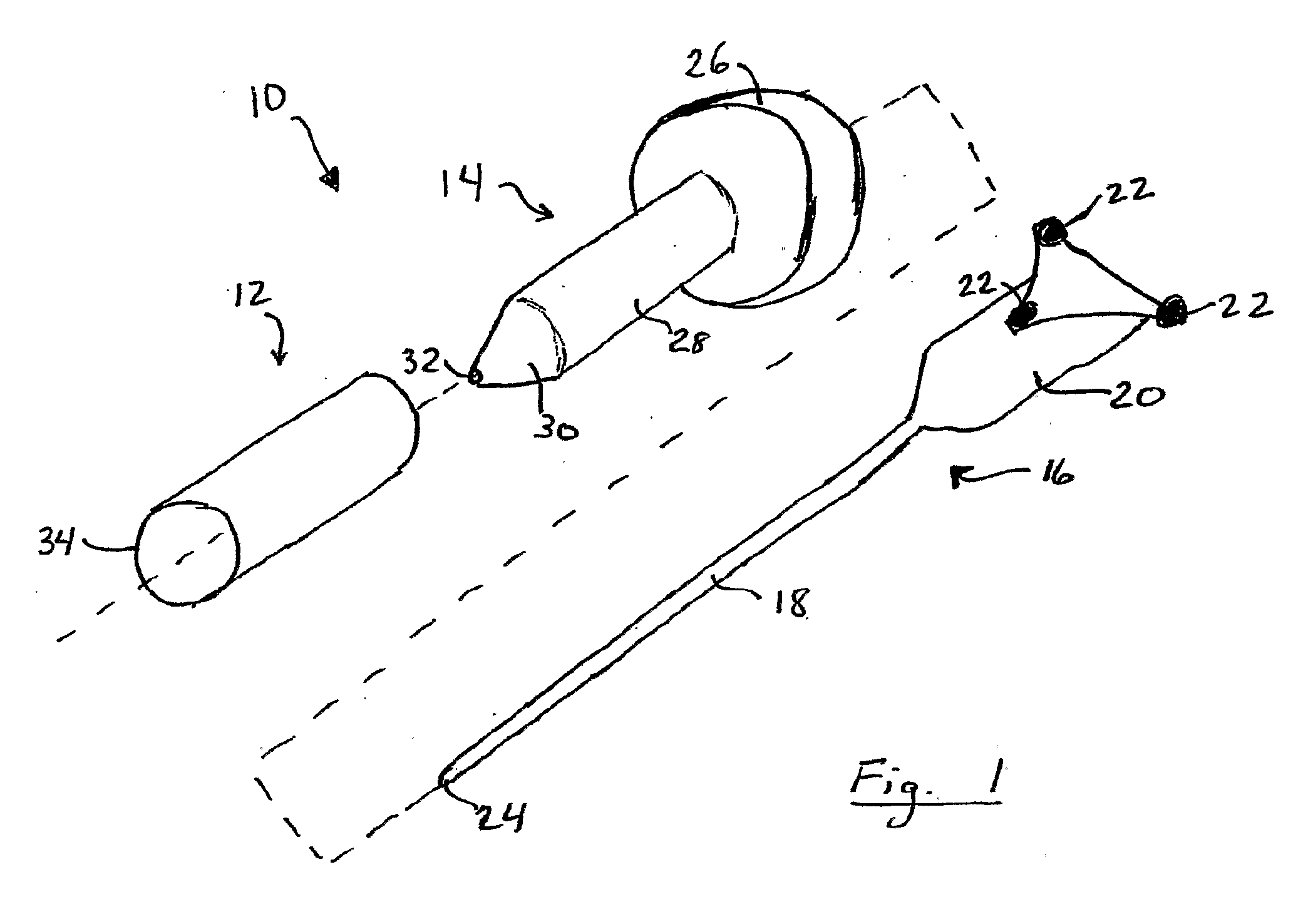
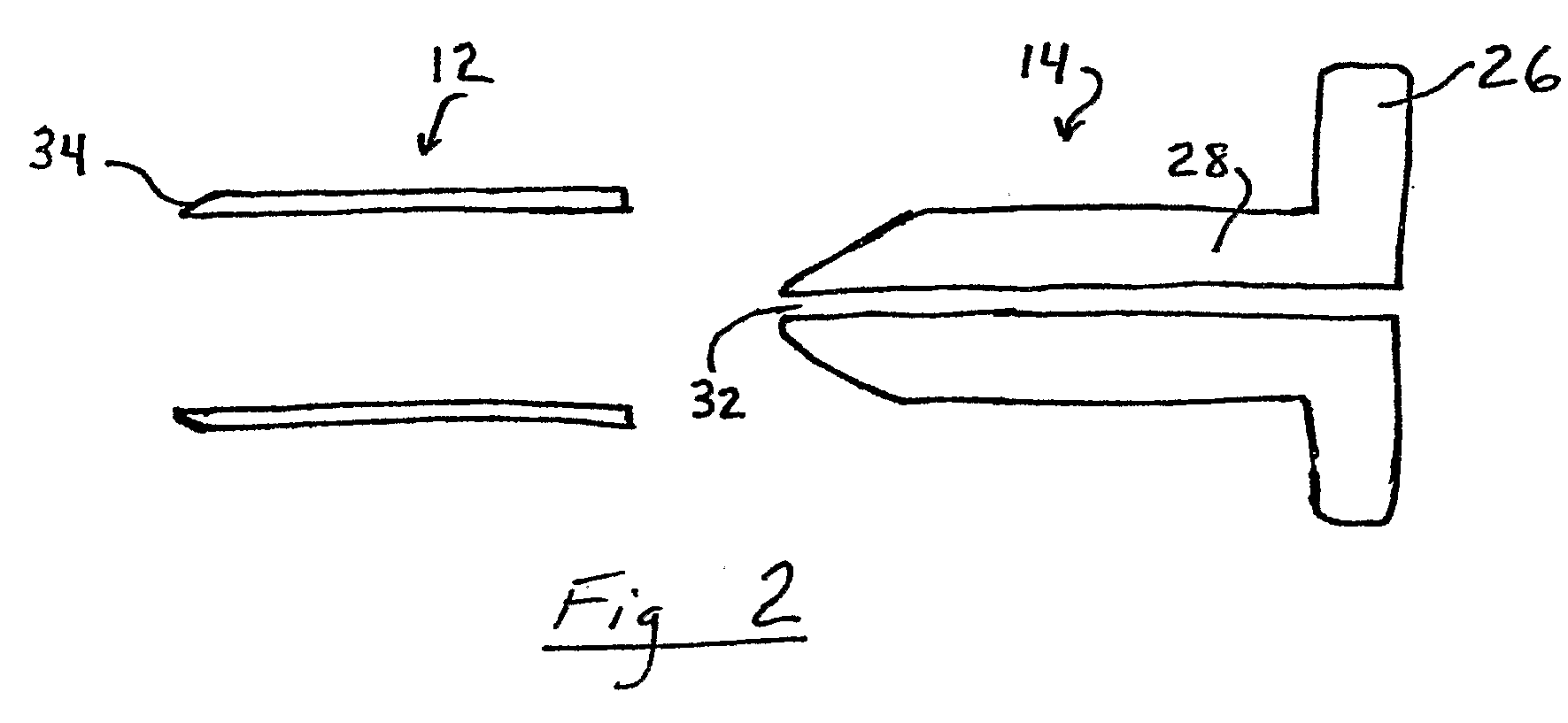
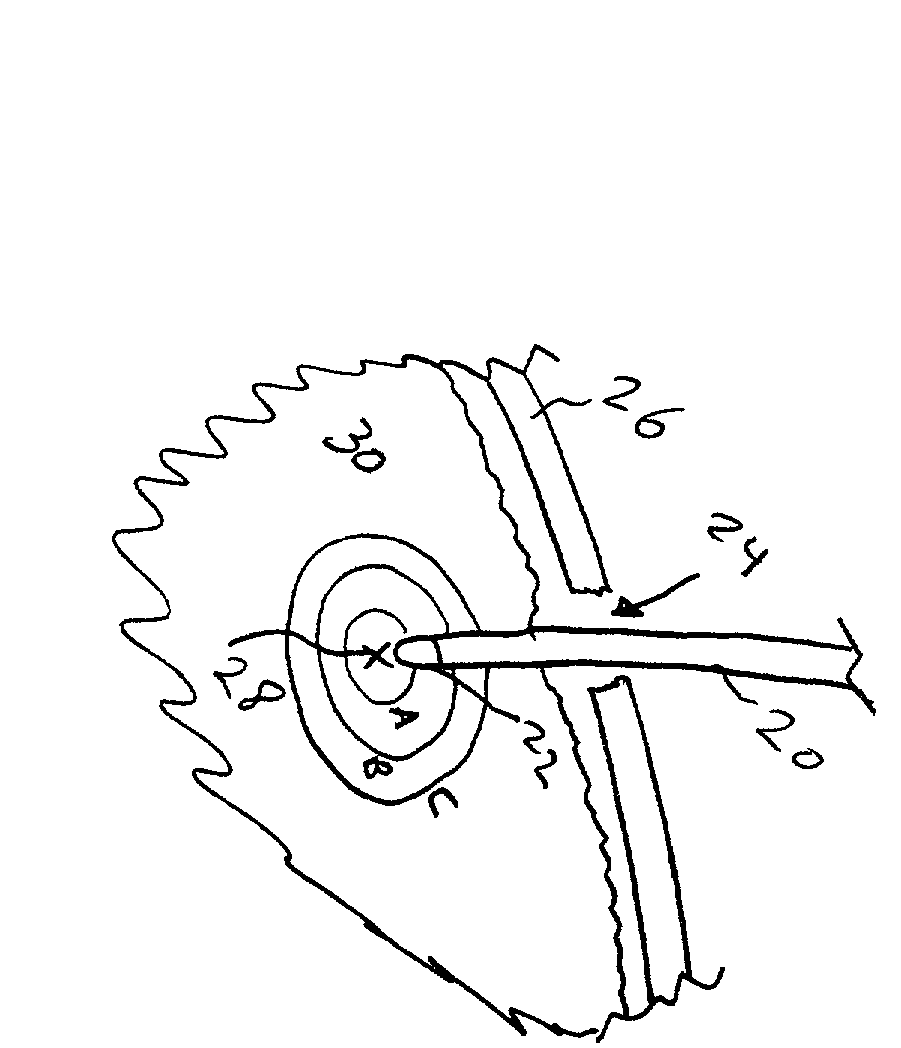
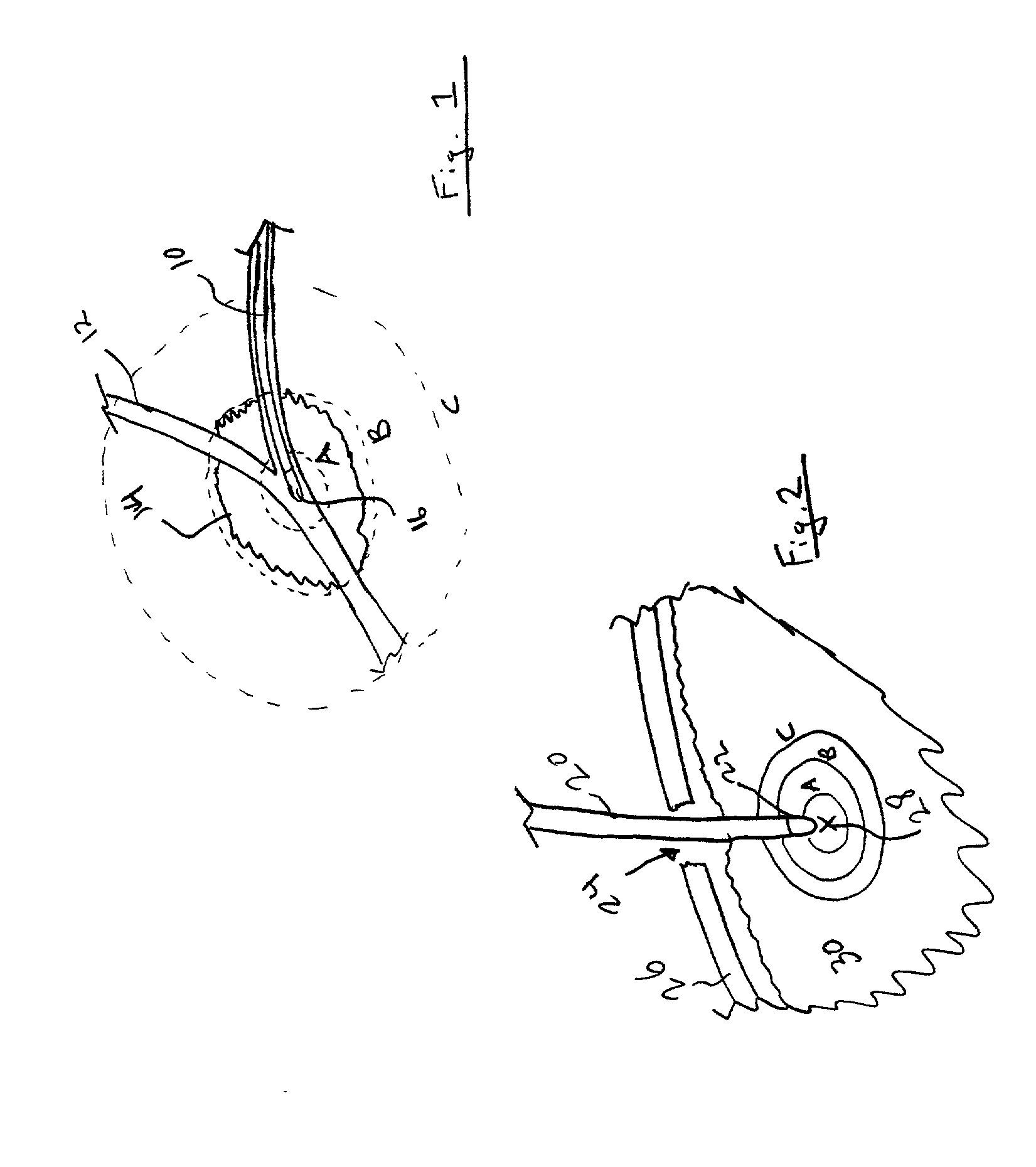
Patents
Literature
1297 results about "Brain tissue" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
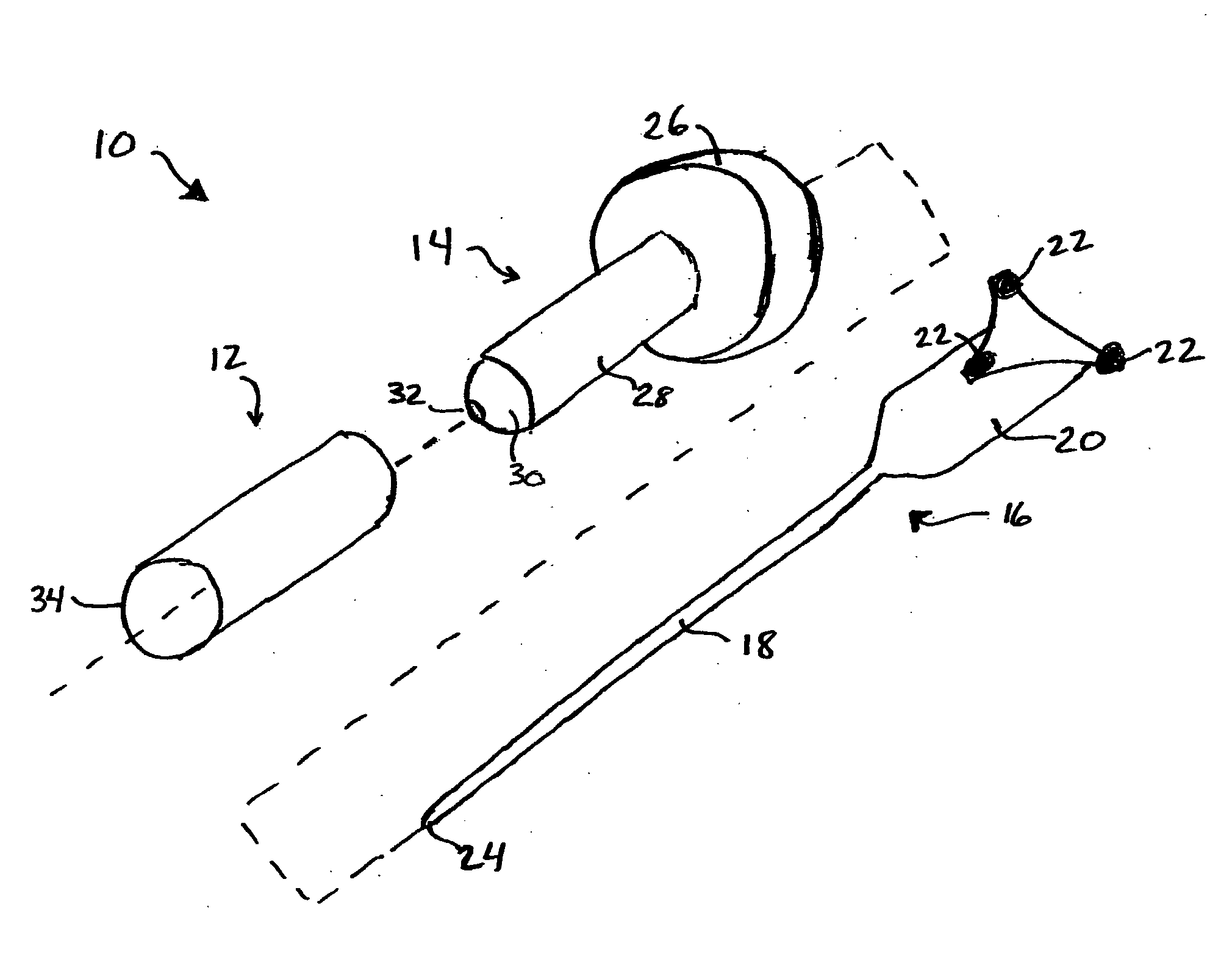
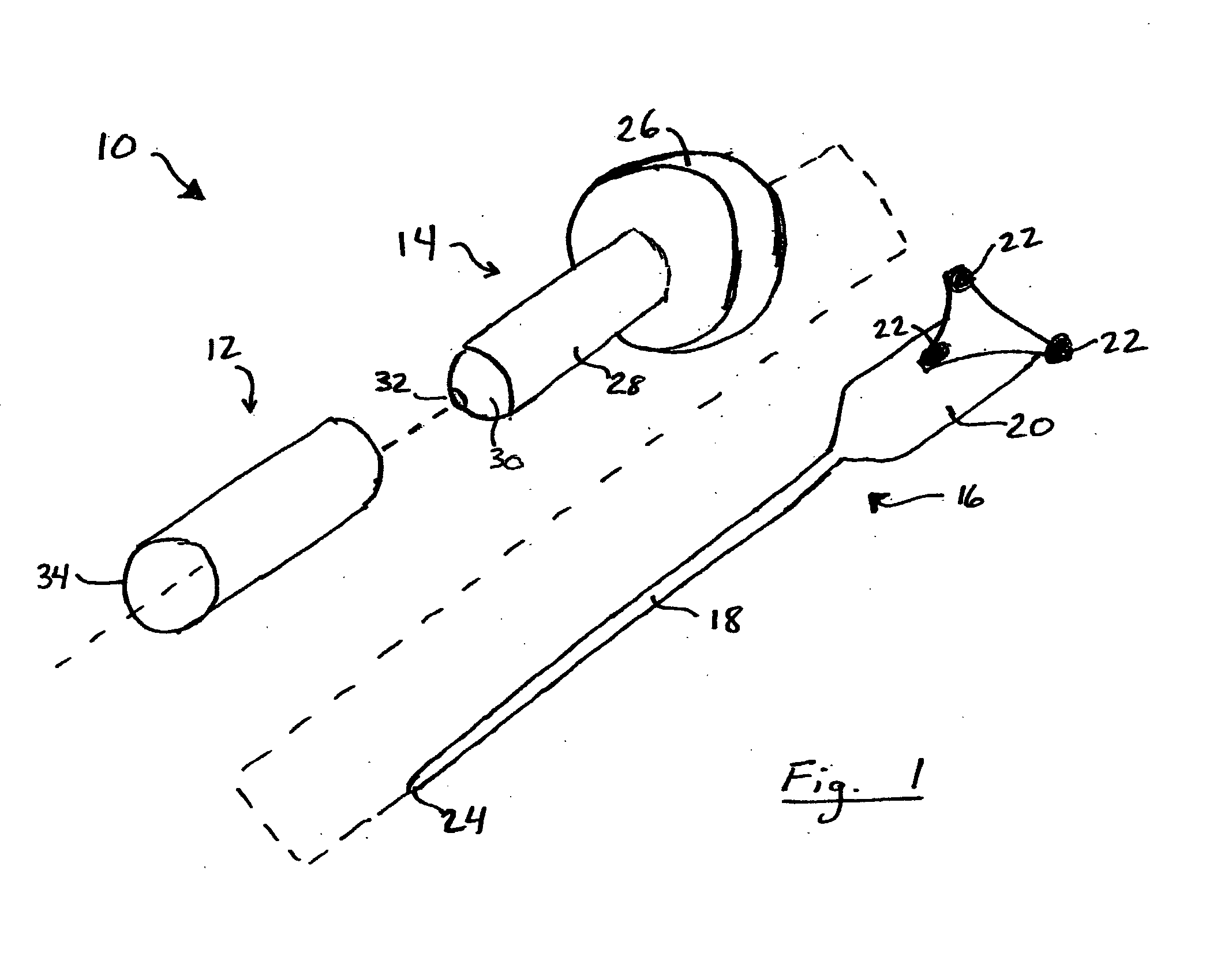
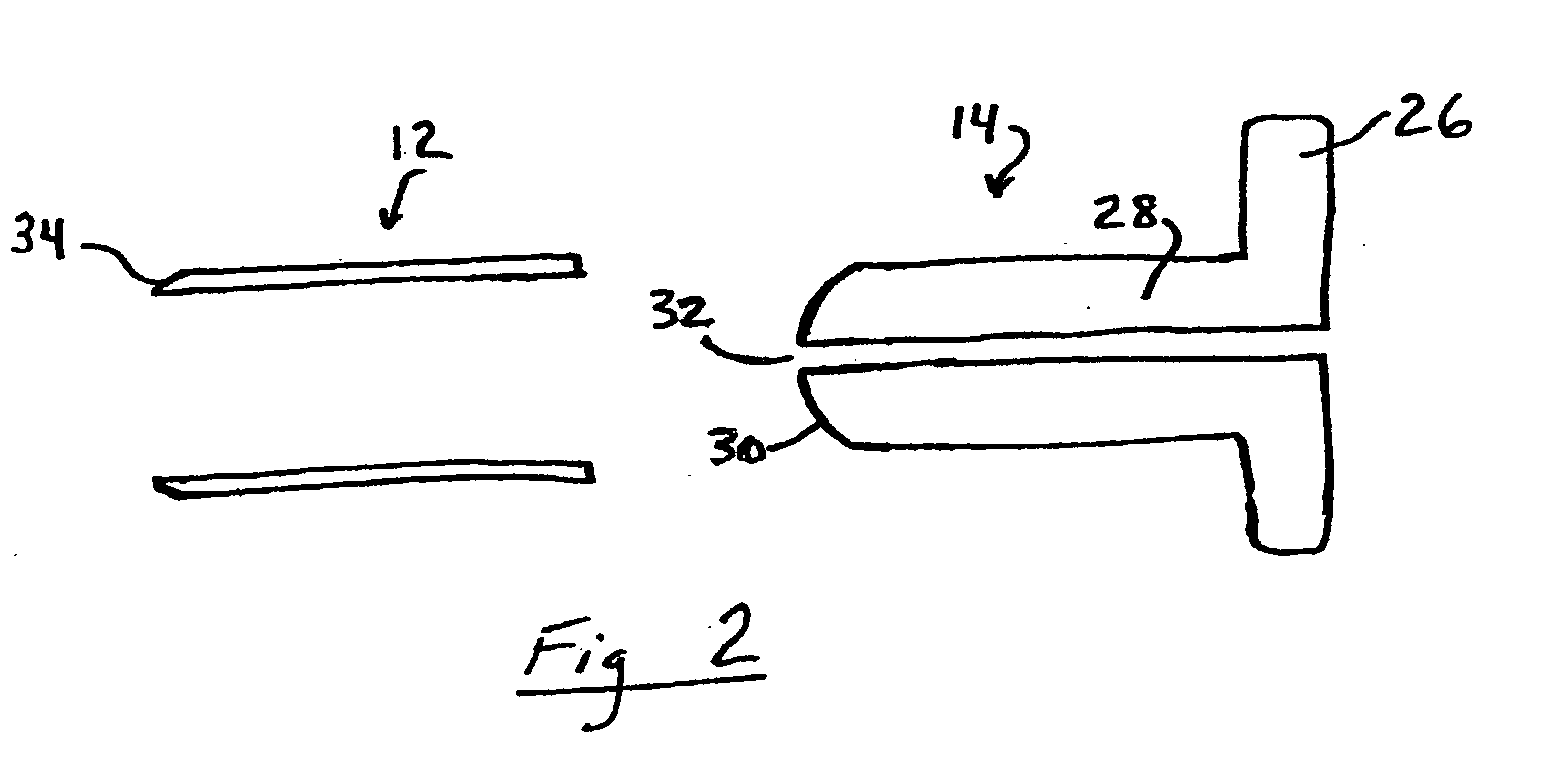
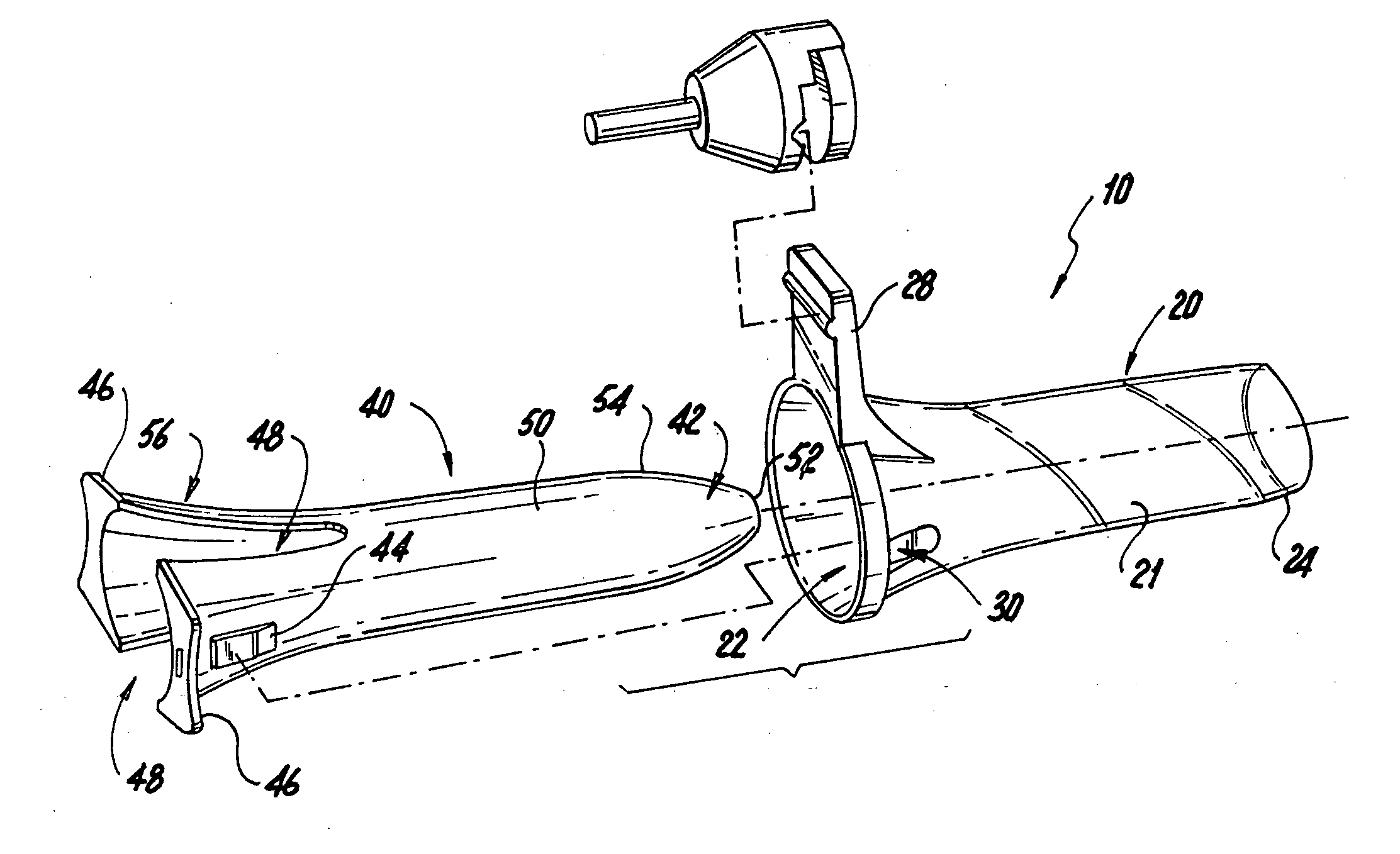
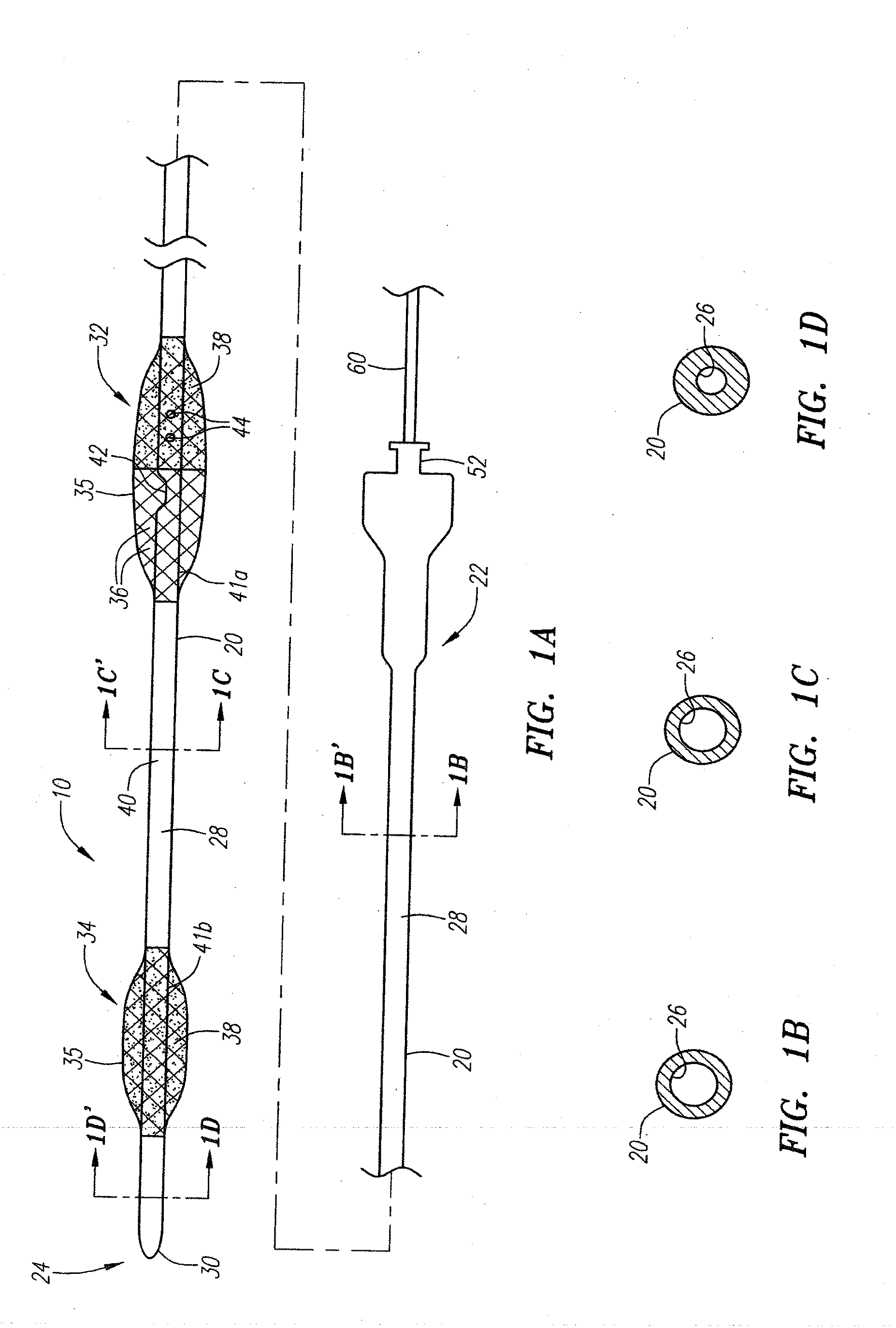
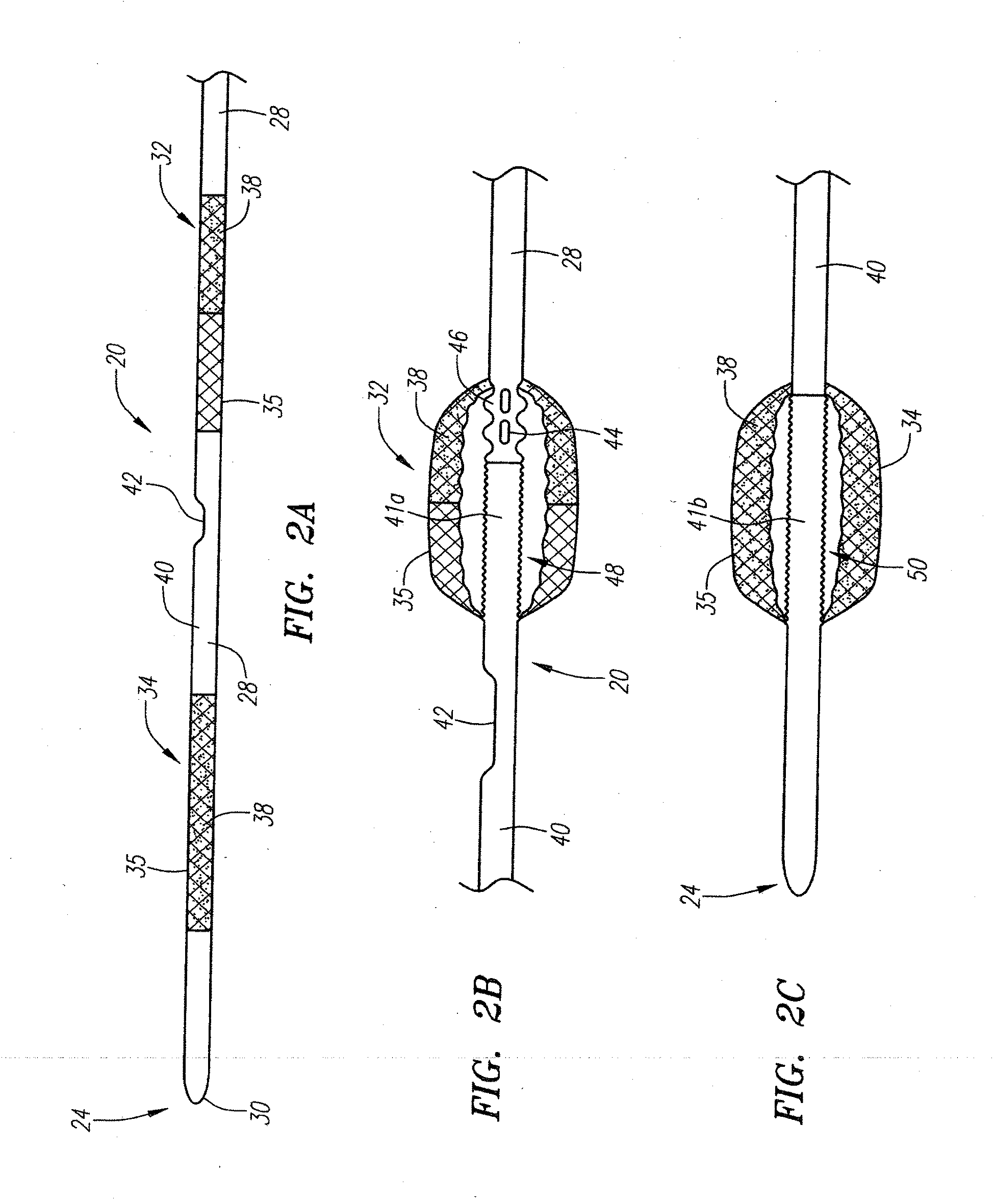
Potassium channel mediated delivery of agents through the blood-brain barrier
This invention includes pharmaceutical compositions, methods and kits for the treatment or diagnosis of a malignant tumors, including brain tumors, and diseases or disorders characterized by abnormal brain tissue.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
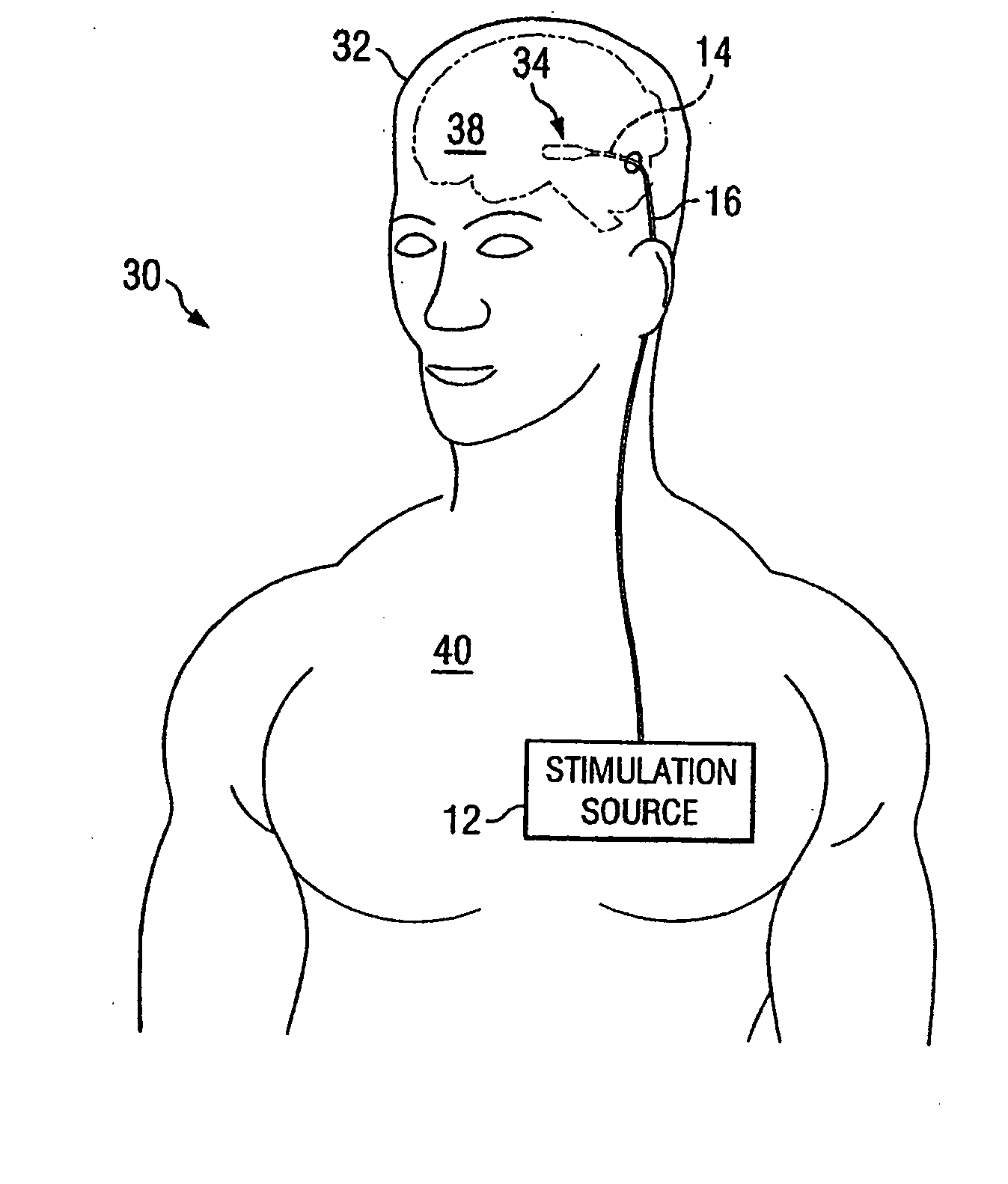
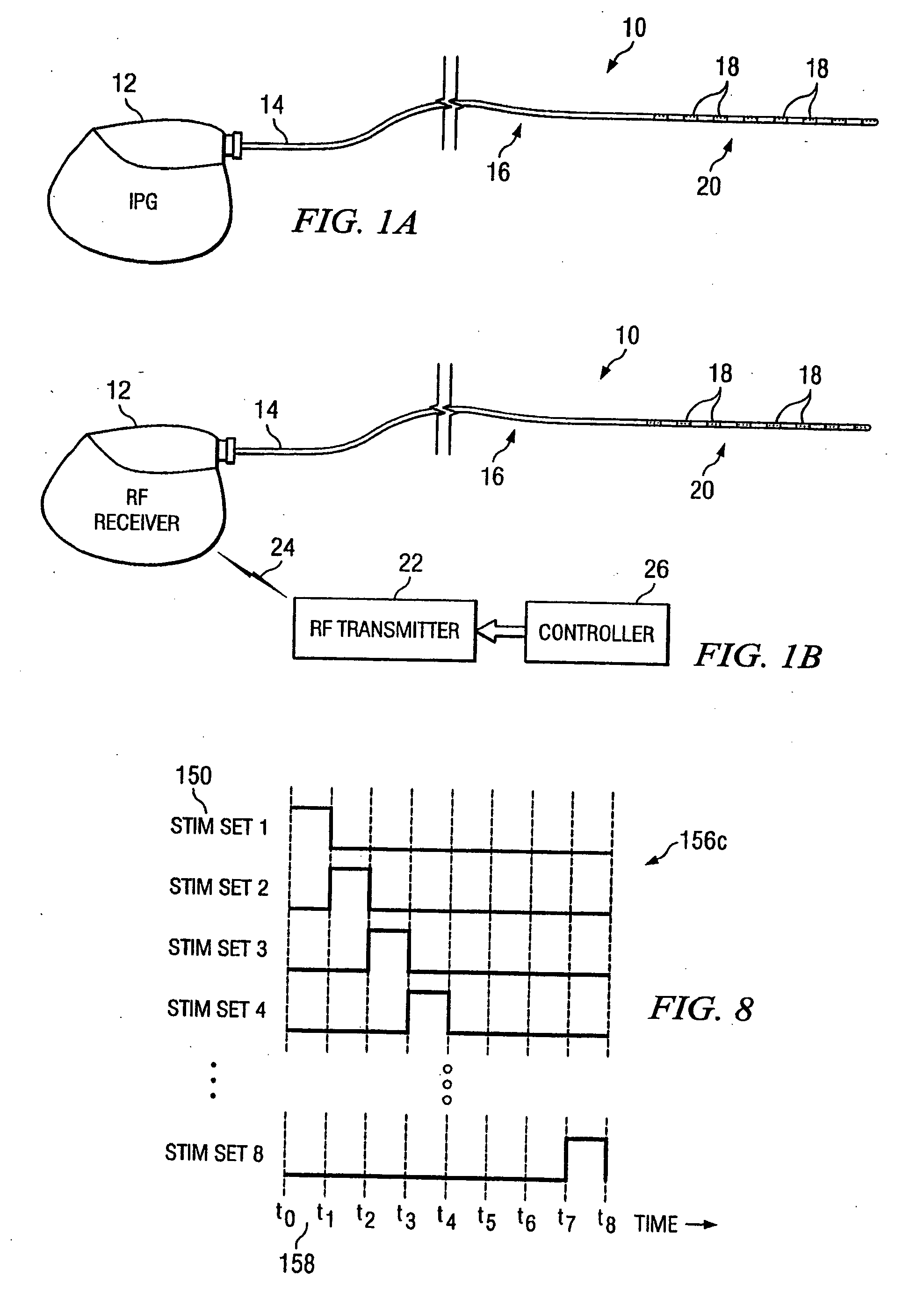
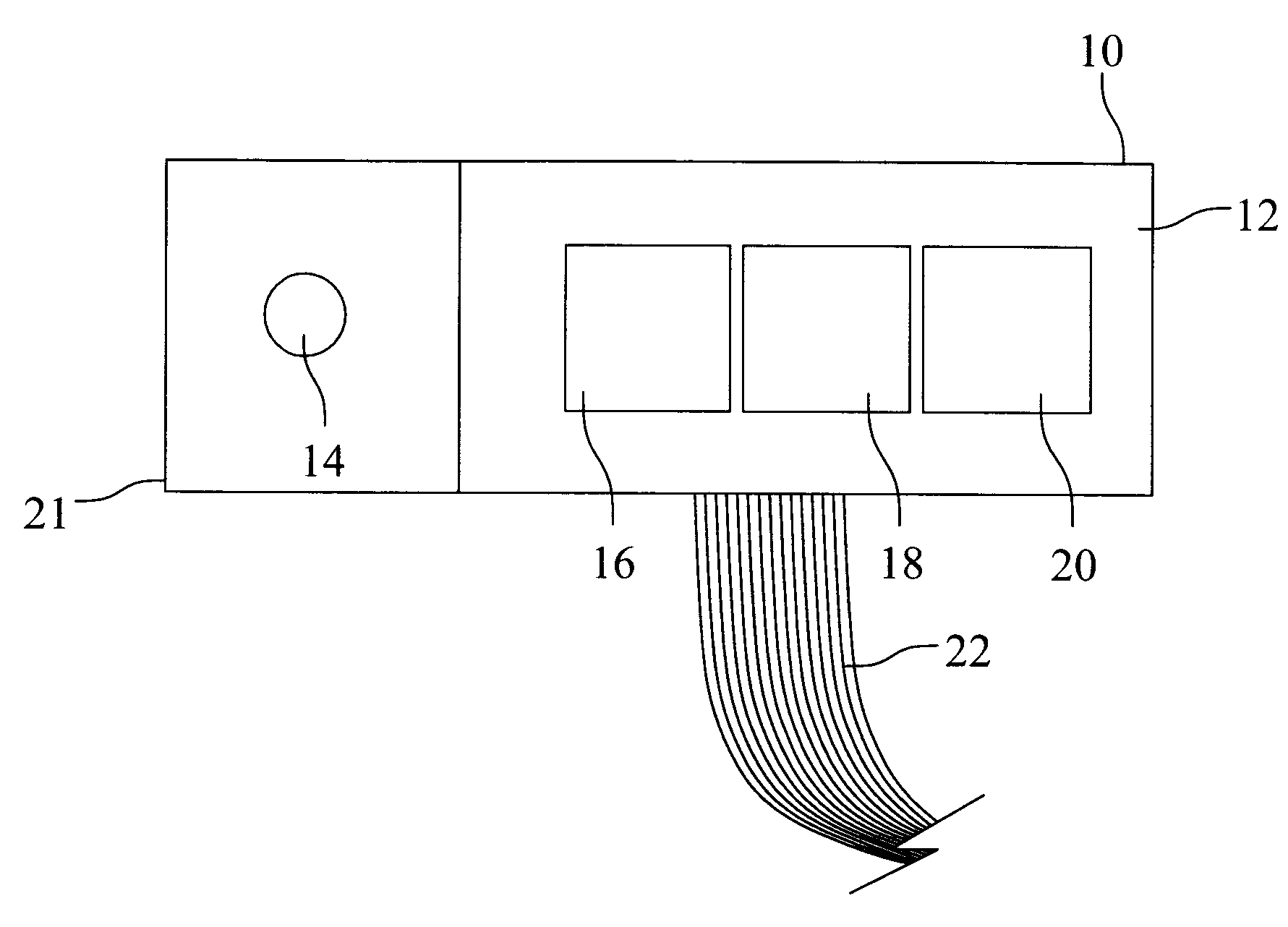
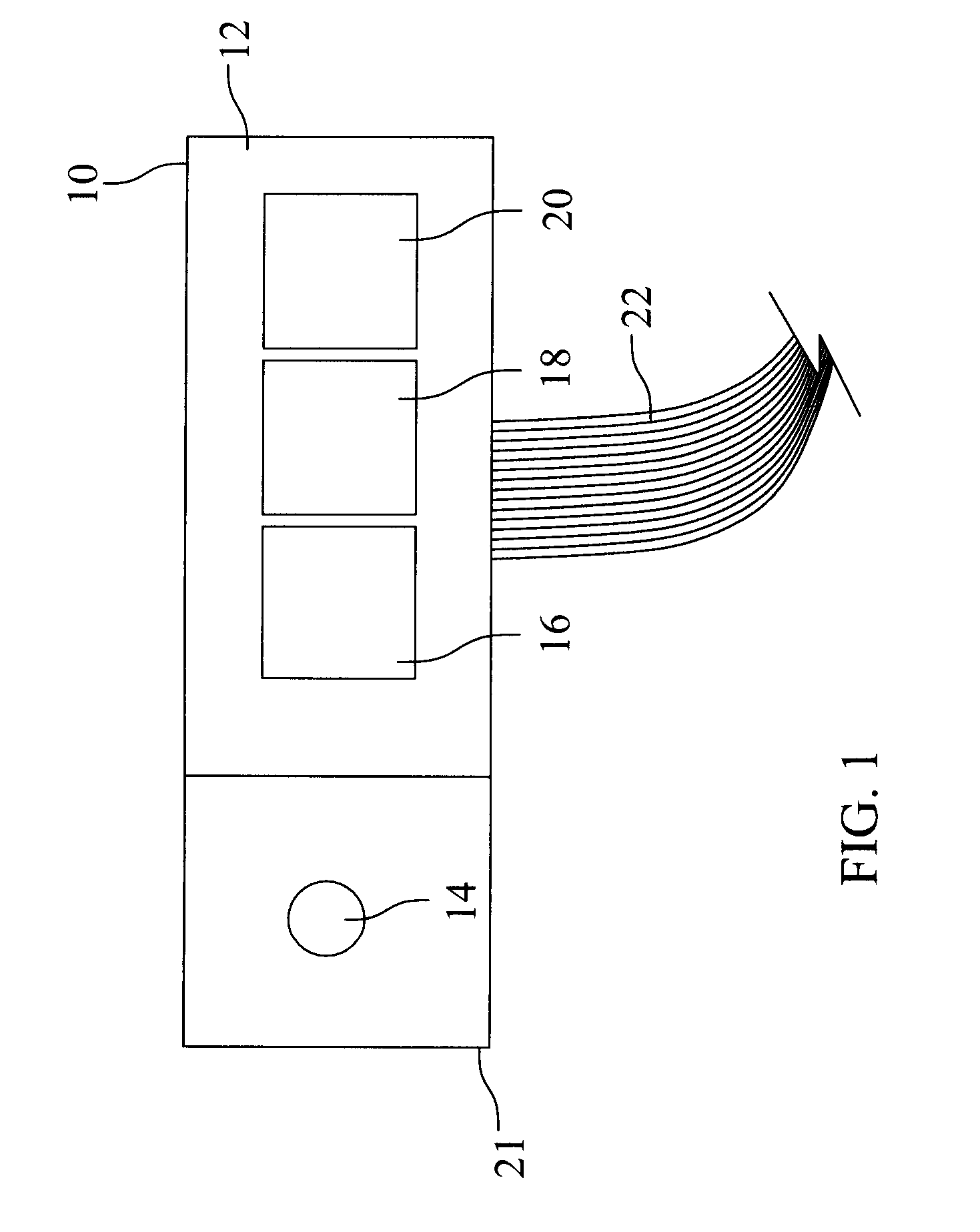
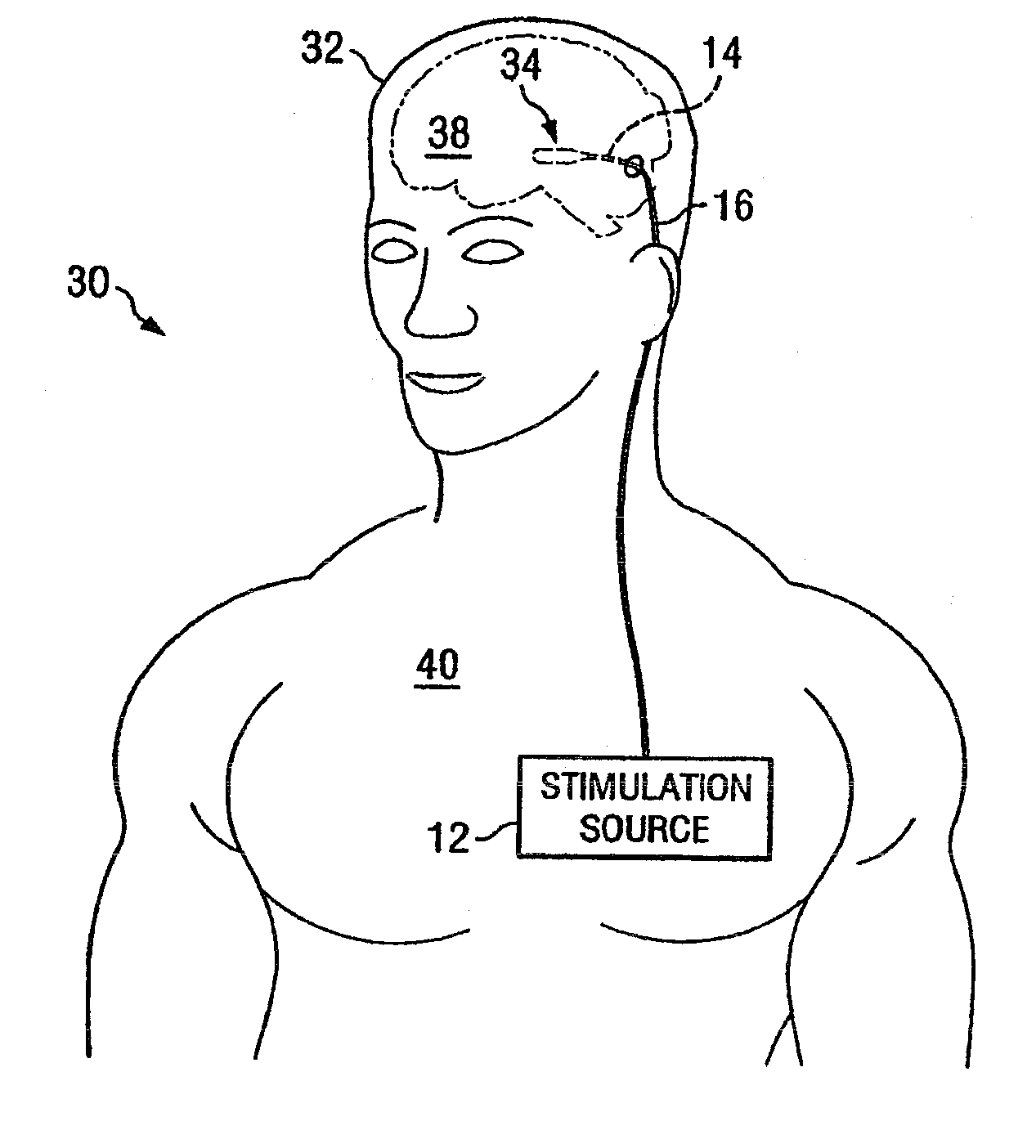
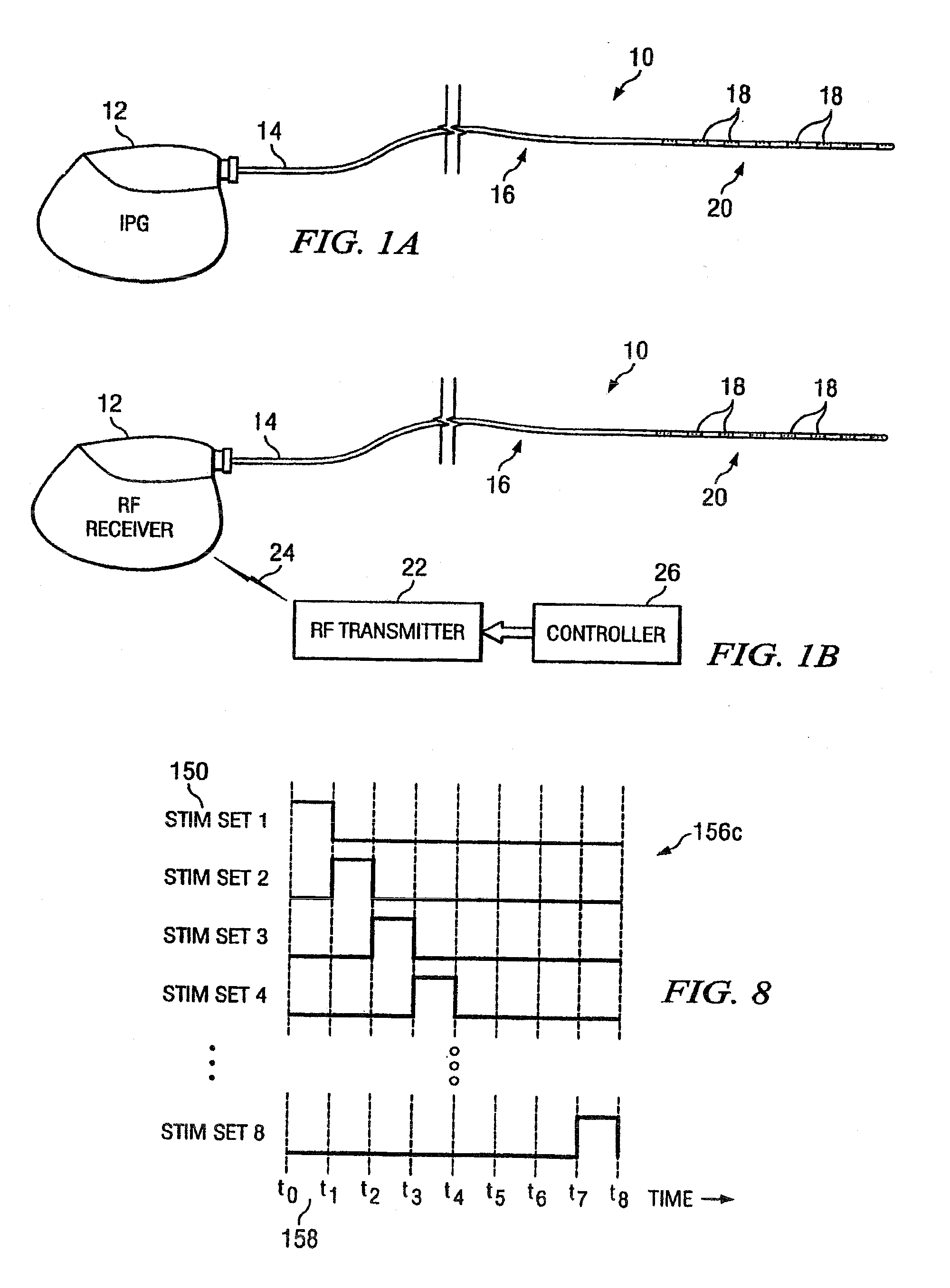
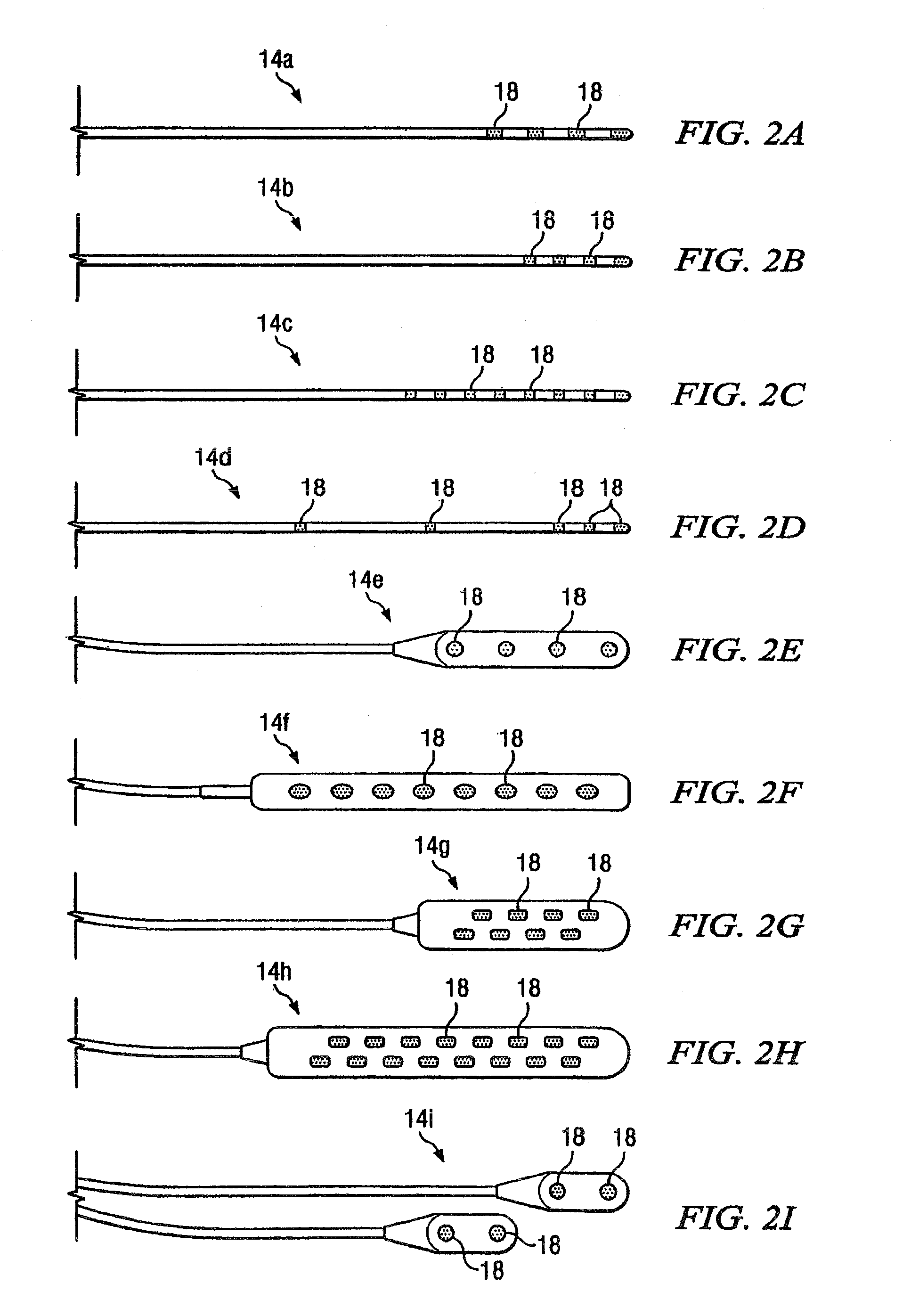
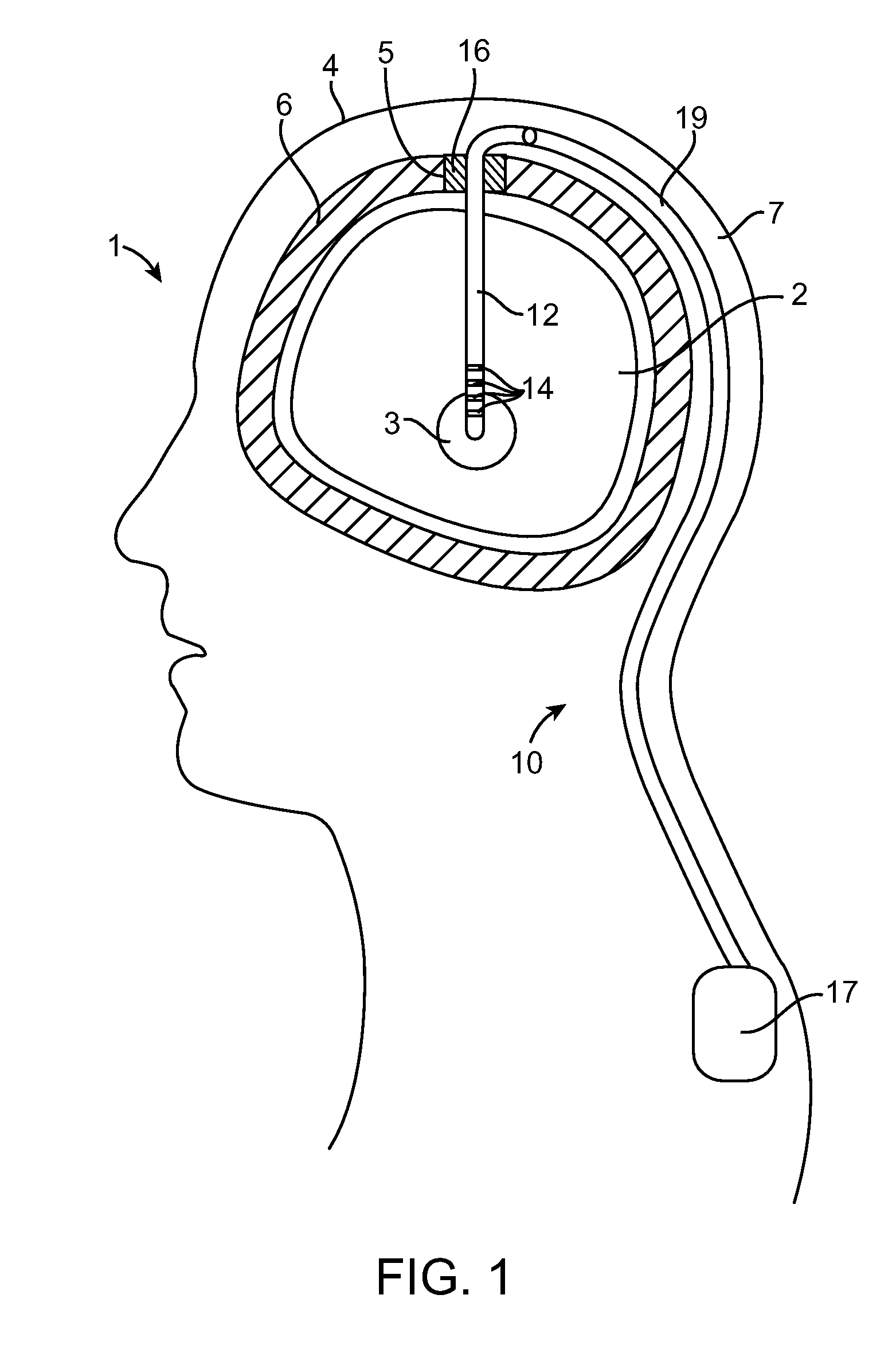
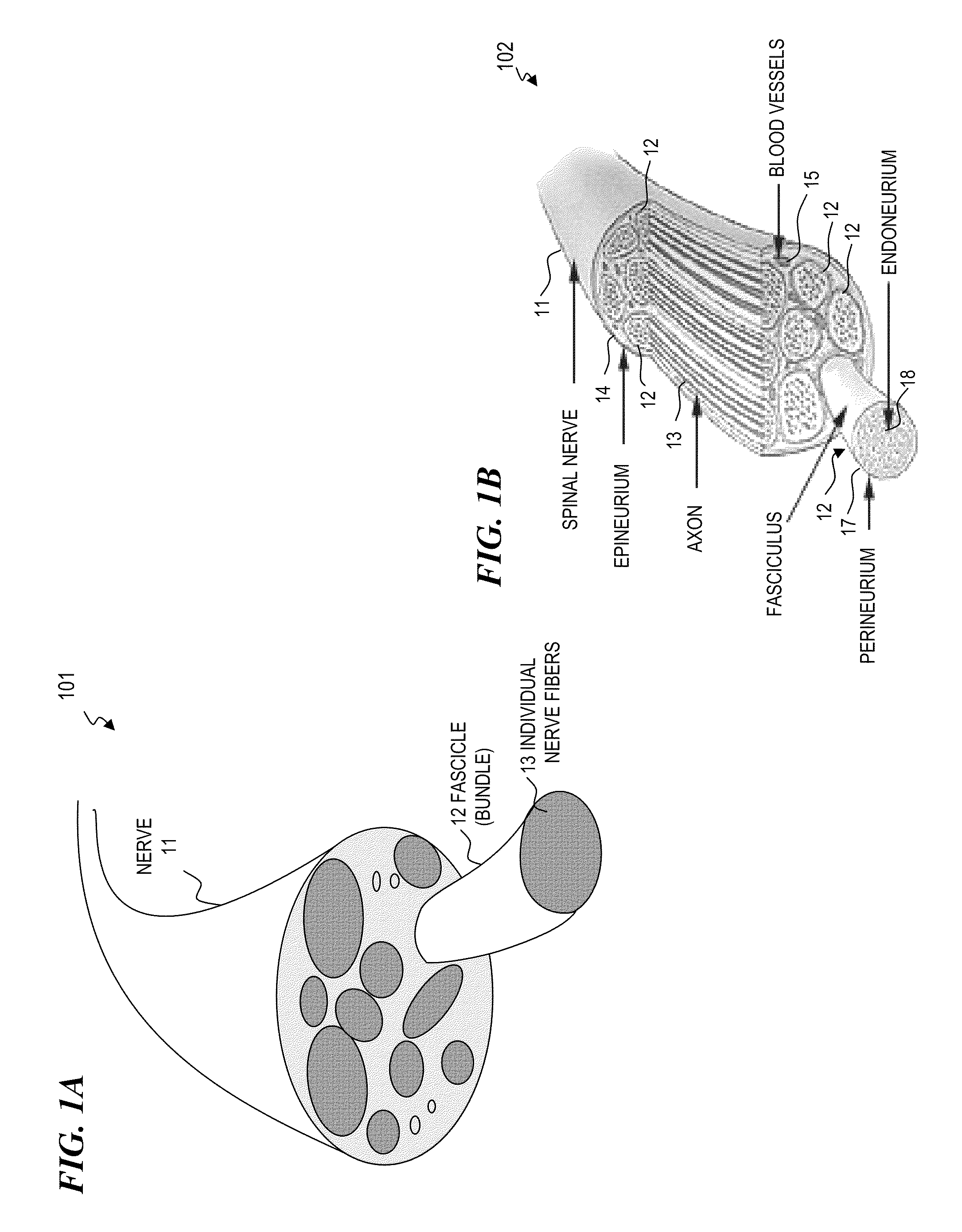
Electrical stimulation system and method for stimulating tissue in the brain to treat a neurological condition
InactiveUS20060004422A1Reduce and eliminate certain problem and disadvantageRemissionSpinal electrodesHead electrodesElectricityMedicine
According to one aspect, a stimulation system is provided for electrically stimulating a predetermined site to treat a neurological condition. The system includes an electrical stimulation lead adapted for implantation in communication with a predetermined site, wherein the site is brain tissue site. The stimulation lead includes one or more stimulation electrodes adapted to be positioned in the predetermined site. The system also includes a stimulation source that generates the stimulation pulses for transmission to the one or more stimulation electrodes of the stimulation lead to deliver the stimulation pulses to the predetermined site to treat a neurological disorder or condition.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
Near infrared spectroscopy device with reusable portion
InactiveUS7706853B2Small sizeFirmly attachedMaterial analysis by optical meansDiagnostic recording/measuringSurgical operationHigh energy
A NIRS sensor device for brain monitoring is small in size, provides reliable attachment to a patient, blocks ambient light, is easy to use, is hygienic, and supports data integration with surgical and monitoring systems. The sensor device is coupled to a remote near infrared light source via a hybrid cable. Since the light source is remotely located, a source adapted for providing high energy, short pulses can easily be used so that there is less chance of interference by superficial non-brain tissues and less interference from ambient light. In addition, the remote location avoids changes in output of local light sources experienced in the prior art during hypothermia procedures (e.g., bandwidth shifts in LEDs as a result of lowered temperature). The higher energy may be achieved by the use of laser diodes as opposed to locally-mounted LEDs typically used in the prior art. The sensor device is a two-piece design comprising a reusable portion containing the photodetector(s) and a disposable portion that receives the light from the reusable portion and bends it to direct the light into the brain.
Owner:TERUMO CARDIOVASCULAR SYST CORP
Technique for using heat flow management to treat brain disorders
InactiveUS6248126B1Prevent and reduce occurrenceModulates seizureImplantable neurostimulatorsSurgical instruments for heatingDiseaseBrain section
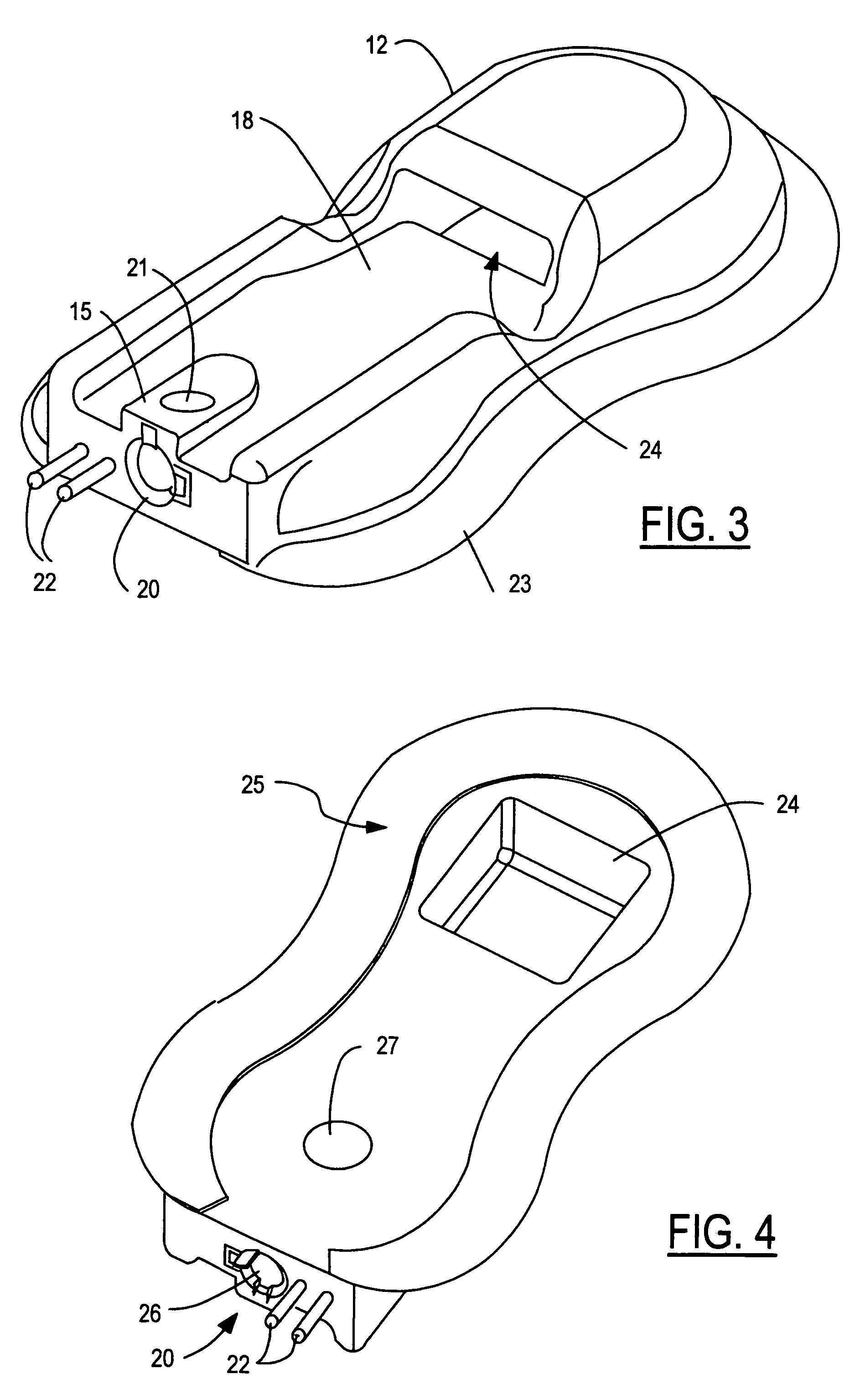
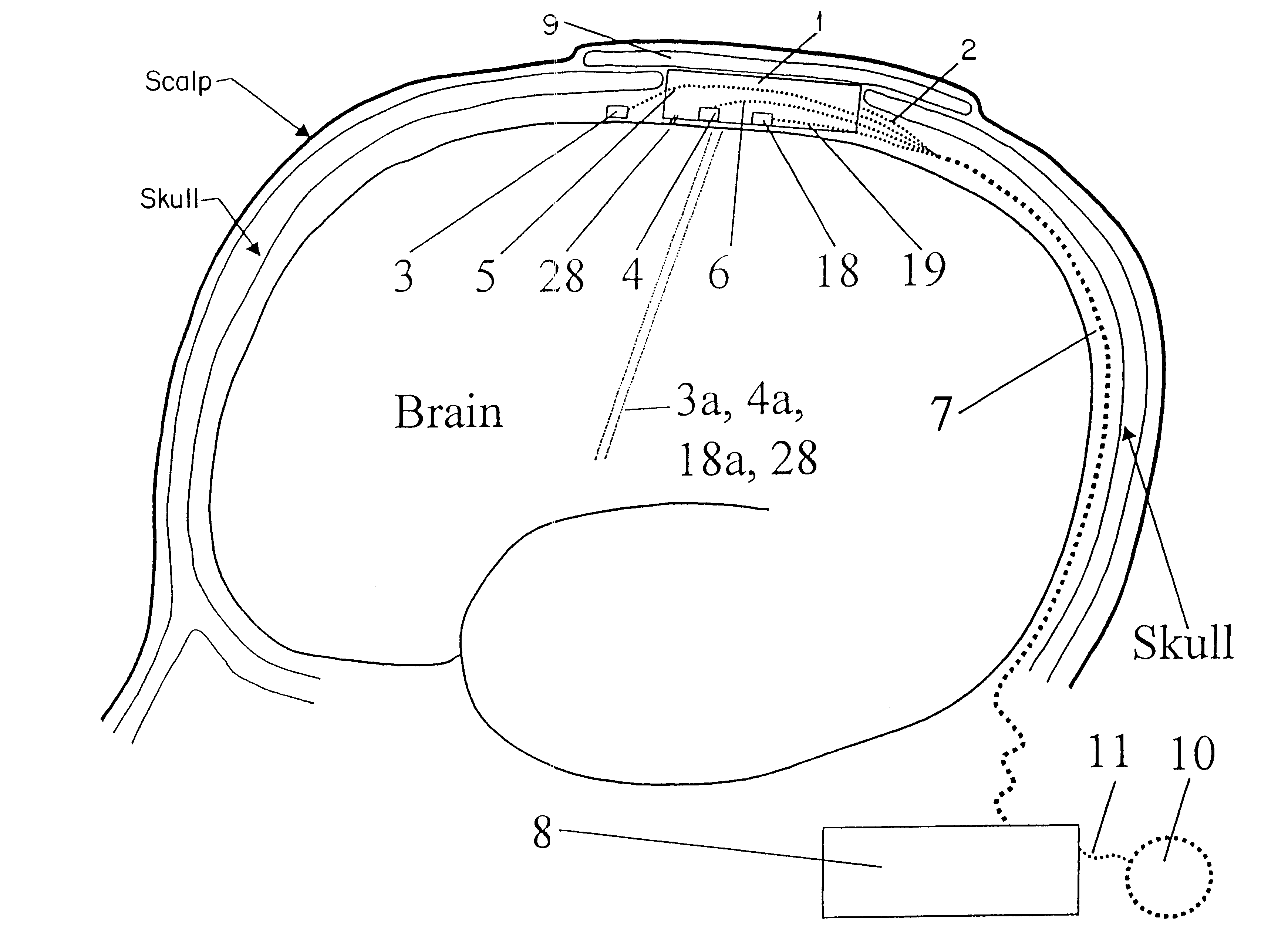
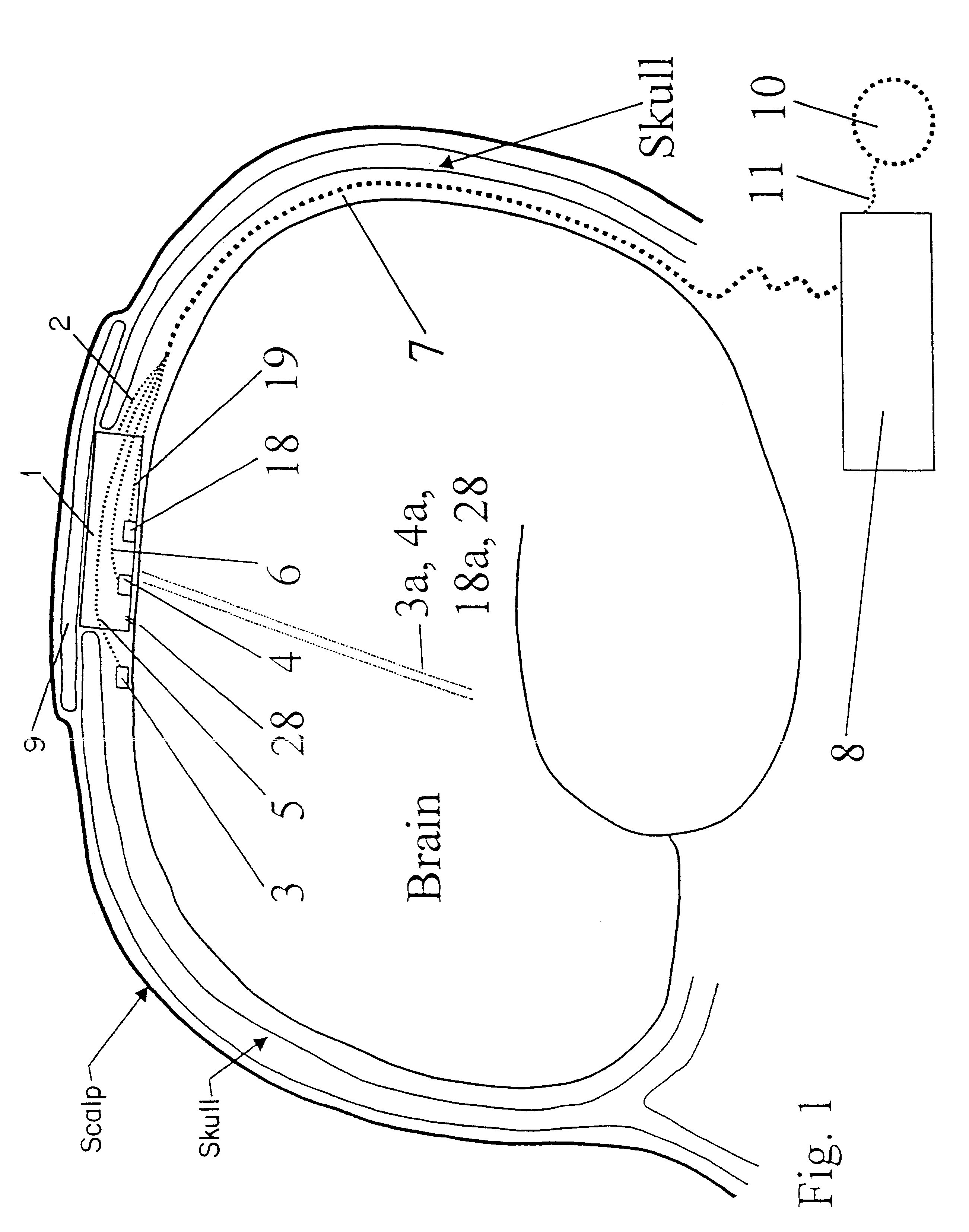
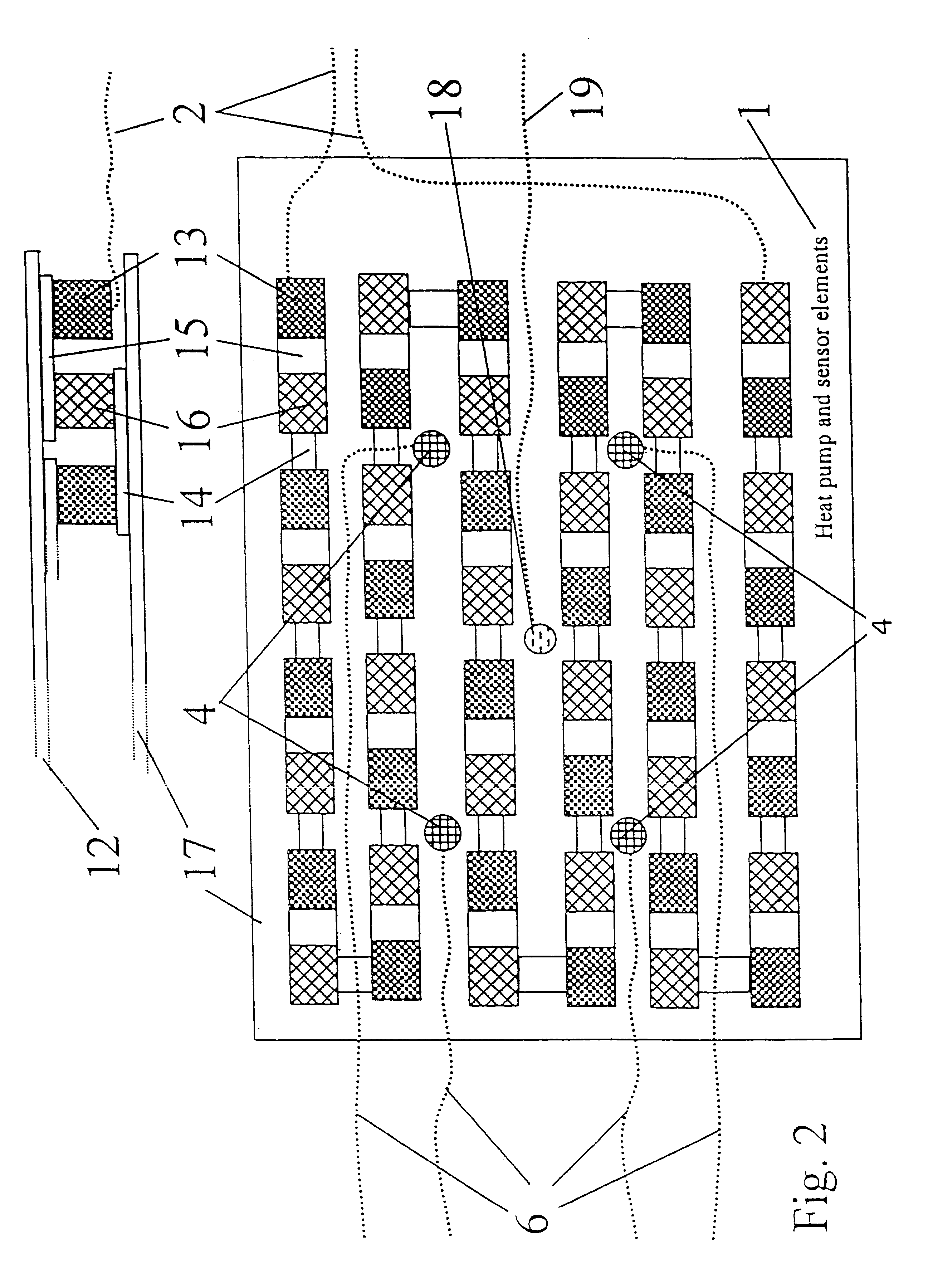
A method of treating a brain disorder by heat transfer from brain tissue comprising the steps of surgically cutting a heat transfer aperture into a patient's skull, thereby exposing a predetermined portion of patient's brain; surgically implanting into said heat transfer aperture a heat pump having one or more electrical sensor elements and one or more temperature sensor elements; surgically implanting a heat transfer management unit in a body cavity of said patient such that a micro controller of the heat transfer management unit is connected to one or more activity sensor elements and one or more temperature sensor elements contacting brain tissue and connecting the heat transfer management unit to said heat pump via a lead bundle. Optionally, the heat transfer unit may be located external to the patient's body. Responsive to signals from one or more activity or temperature sensor elements, mathematical algorithms of the heat transfer management unit determine abnormal brain activity, causing the heat pump to remove heat from the brain tissue into a heat sink, thereby cooling the predetermined portion of the patient's brain. This technique utilizes acute hypothermia by means of a Peltier cooler or similar device to cool the brain temperature to reduce or prevent seizure initiation and / or propagation. The method may be used in association with brain stimulation and / or drug application to acutely avoid the occurrence of a seizure episode.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Stimulation for treating and diagnosing conditions
InactiveUS20050159790A1Increasing and reducing cortical blood flowMinimize damageHead electrodesMedical devicesPower flowWhole body
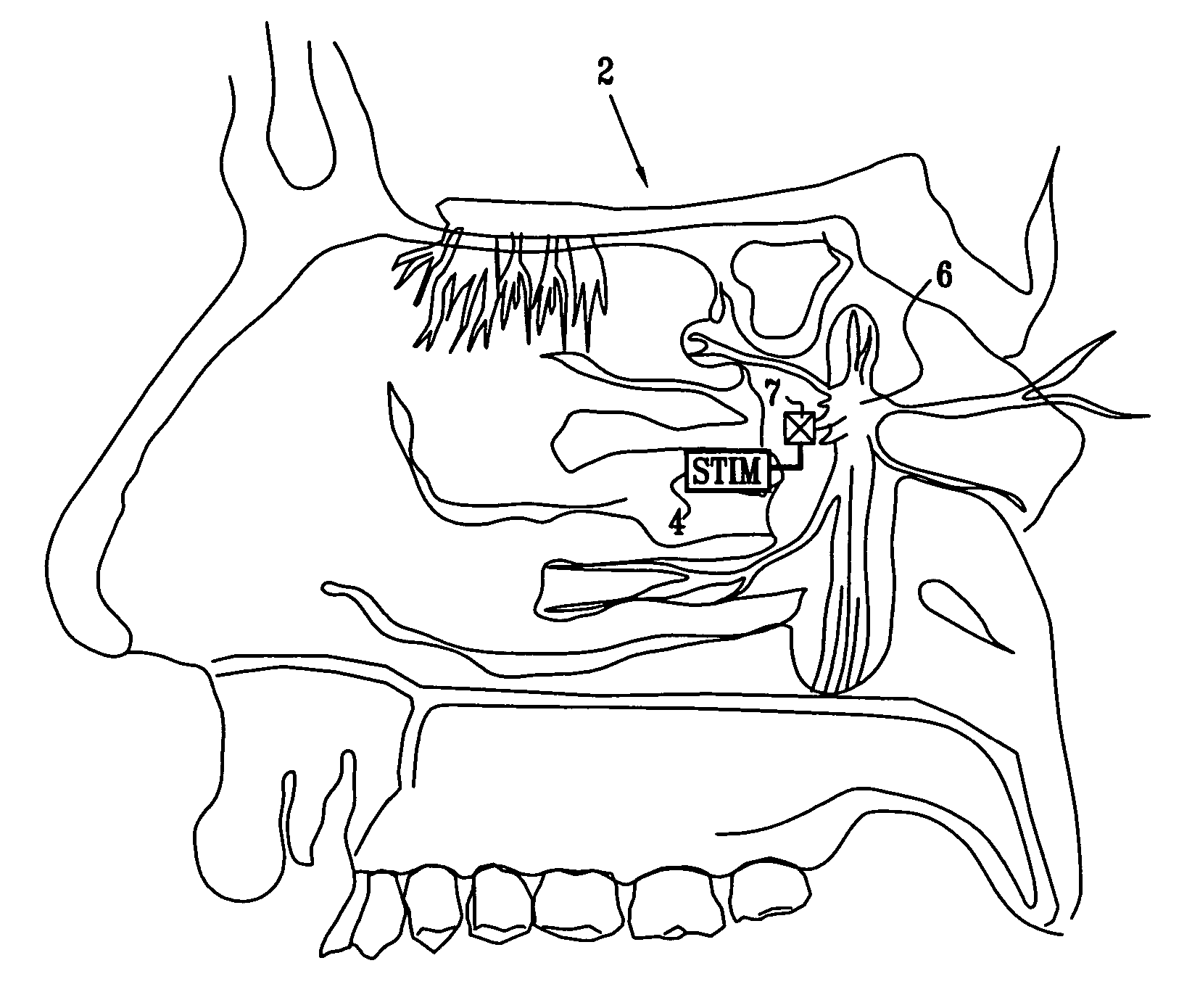
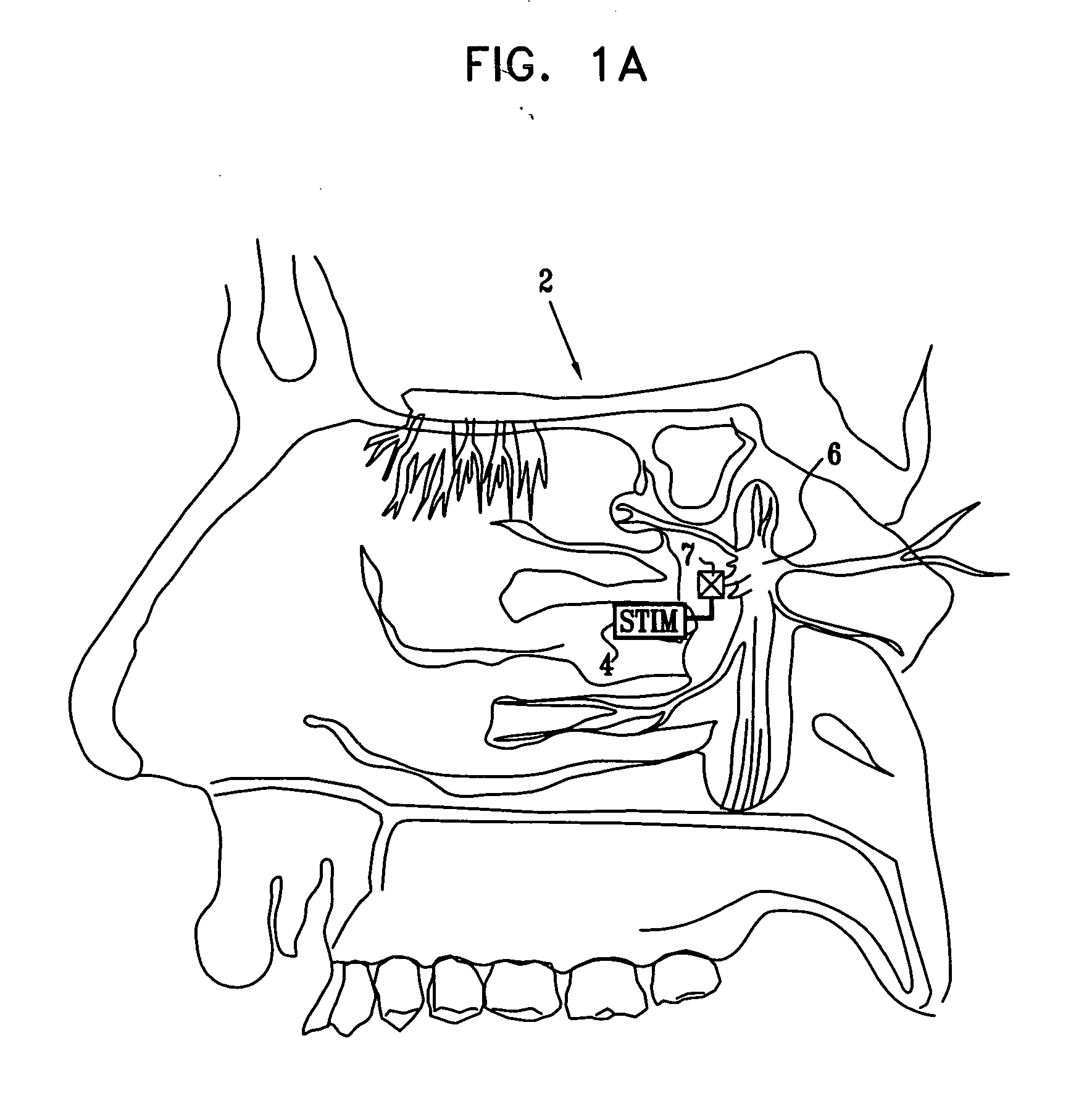
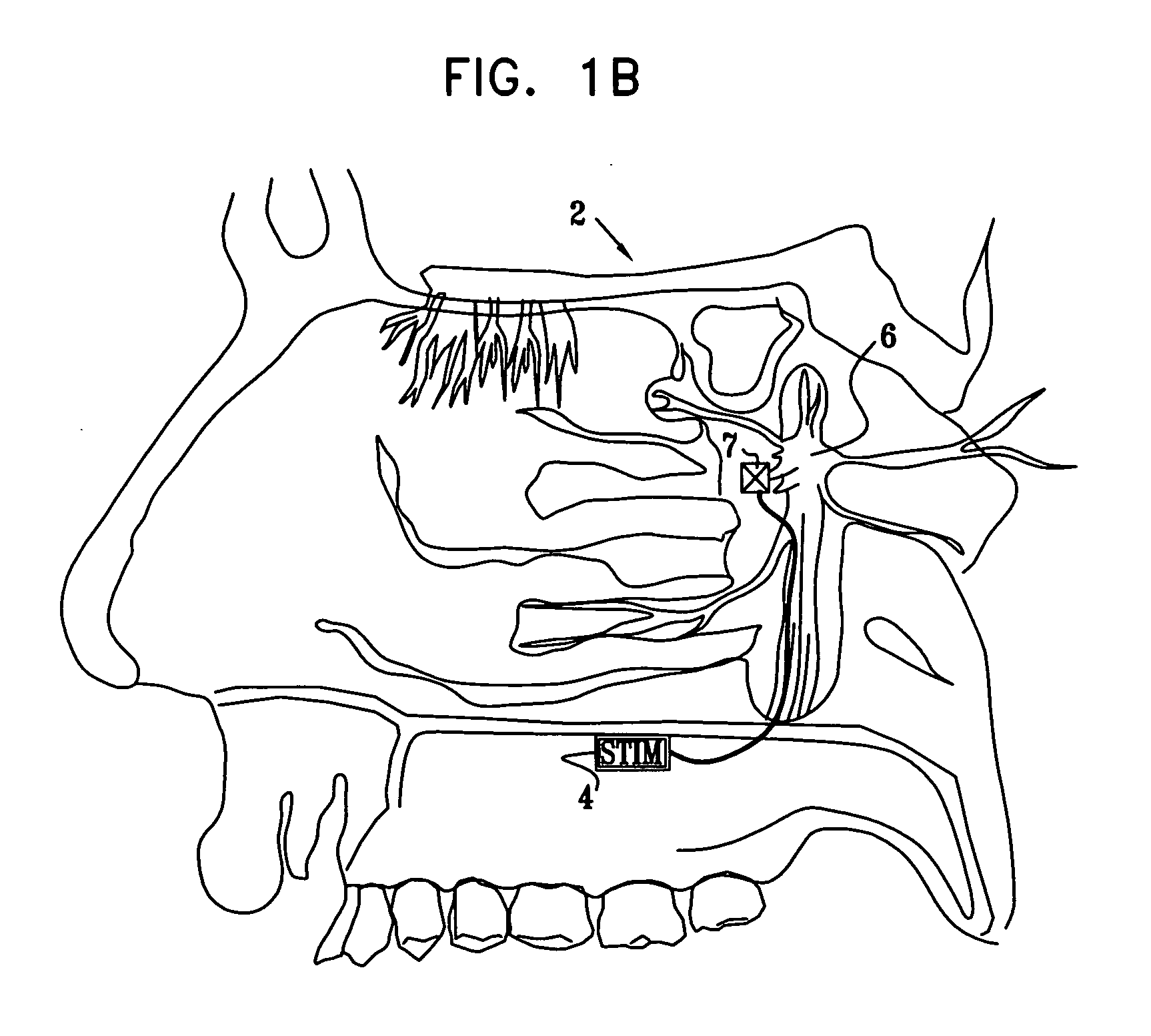
A method is provided for facilitating a diagnosis of a condition of a subject, including applying a current to a site of the subject selected from the list consisting of: a sphenopalatine ganglion (SPG) of the subject, and a neural tract originating in or leading to the SPG, and configuring the current to increase conductance of molecules from brain tissue of the subject through a blood brain barrier (BBB) of the subject into a systemic blood circulation of the subject. The method also includes sensing a quantity of the molecules from a site outside of the brain of the subject, following initiation of application of the current.
Owner:BRAINSGATE LTD
Shape-memory polymer coated electrodes
There is provided a slowly implantable electrode. A coating for an electrode, the coating includes a shape-memory polymer. A method for inserting an electrode into brain tissue by inserting an implantable electrode having a shape-memory polymer coated electrode into brain tissue.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Directional brain stimulation and recording leads
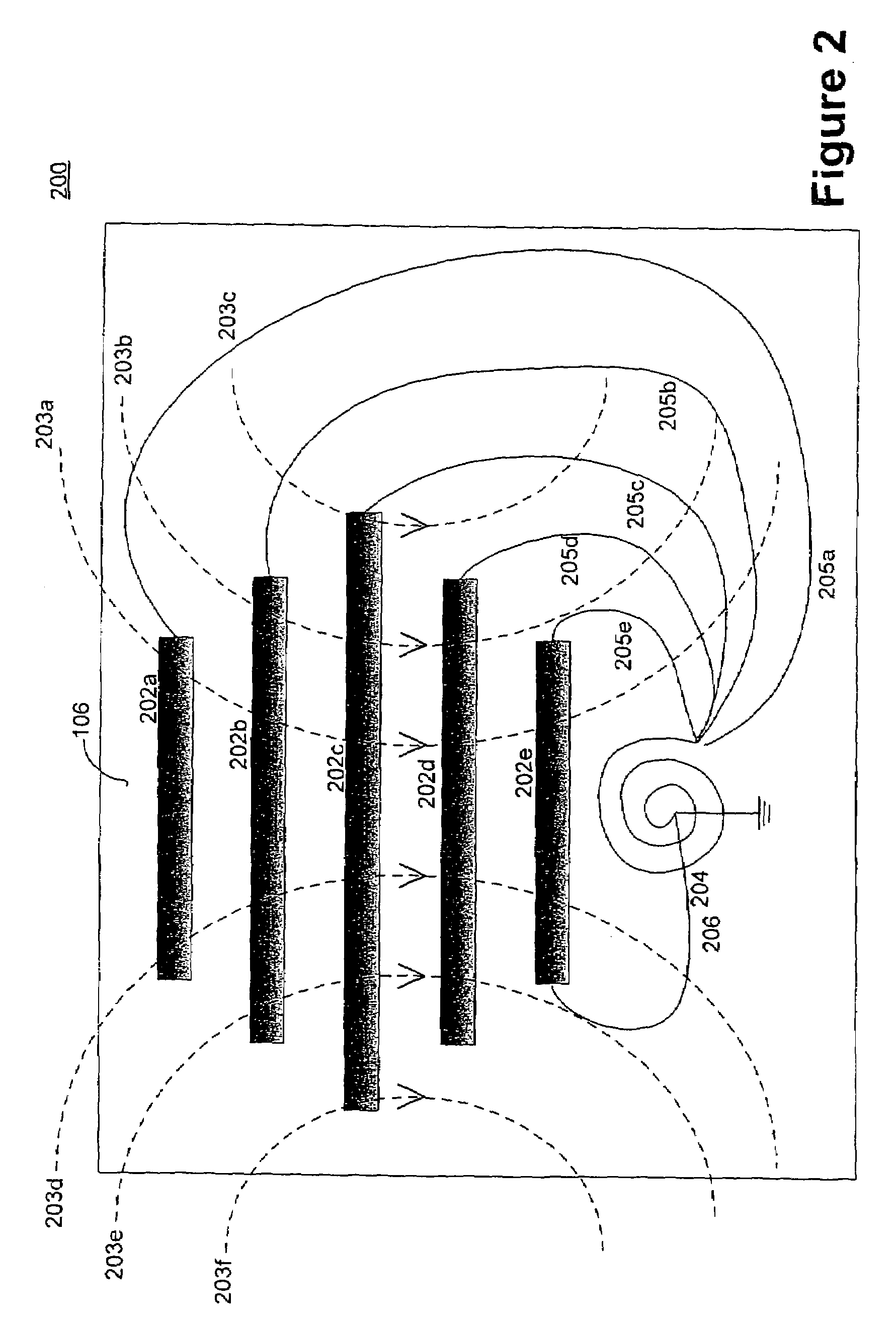
InactiveUS7212867B2Improve abilitiesLess interferenceHead electrodesExternal electrodesElectricitySide effect
A directional brain stimulation lead assembly provides a lead body and an insulating member defining one or more windows that selectively expose portions of electrodes carried by the lead body to produce a directional stimulation current field. The lead assembly can achieve more effective localization of electrical stimulation to very small brain targets, and thereby reduce the incidence of material side effects caused by collateral stimulation of brain tissue adjoining a desired brain target. In addition, the directional lead can sense brain activity on a more localized basis.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Multi-modal system for detection and control of changes in brain state
ActiveUS7204833B1Increase temporo-spatial resolutionWithout of complications and without in performanceElectroencephalographyInternal electrodesBrain stateElectrical stimulations
A multi-purpose device mechanism for sensing and control of changes in brain state includes a shaft portion and extendible elements structured for insertion into target tissue of the brain of a subject patient, cooling means configured to operatively apply cooling therapy to the target tissue, stimulation means having at least one electrical contact structured to operatively apply electrical stimulation therapy to the target tissue, sensing means including at least one sensor monitoring a biological signal of the subject patient, control means responsive to the sensing means wherein the control means is structured to, in response to signals from the sensing means that indicate the presence of a pre-determined physiological condition or occurrence of an undesirable state change, automatically cause the cooling means and / or the stimulation means to initiate or terminate the cooling therapy and / or the electrical stimulation therapy respectively and an energy source for powering the various components of the multi-purpose device mechanism. A modified embodiment includes a least one spiral conduit and at least one return conduit for cycling coolant or refrigerant to and from the shaft portion and an external reservoir. Another modified embodiment includes pressurizing means for extending at least one extendable tube into brain tissue surrounding the shaft portion.
Owner:FLINT HILLS SCI L L C
Pulsewidth electrical stimulation
A process for stimulating tissue such as cardiac tissue, nerve tissue, and brain tissue. In one step of the process, there is delivered an electrical stimulating signal to the tissue that contains from about 10 to about 1,000 individual pulses. Each individual pulse has a duration of from about one microsecond to about 100 microseconds and is discontinuous, with a spacing between adjacent pulses of at least from about 1 microsecond to about 100 microseconds. The individual pulses have a voltage of from about 10 millivolts to about 100 volts.
Owner:BIOPHAN TECH
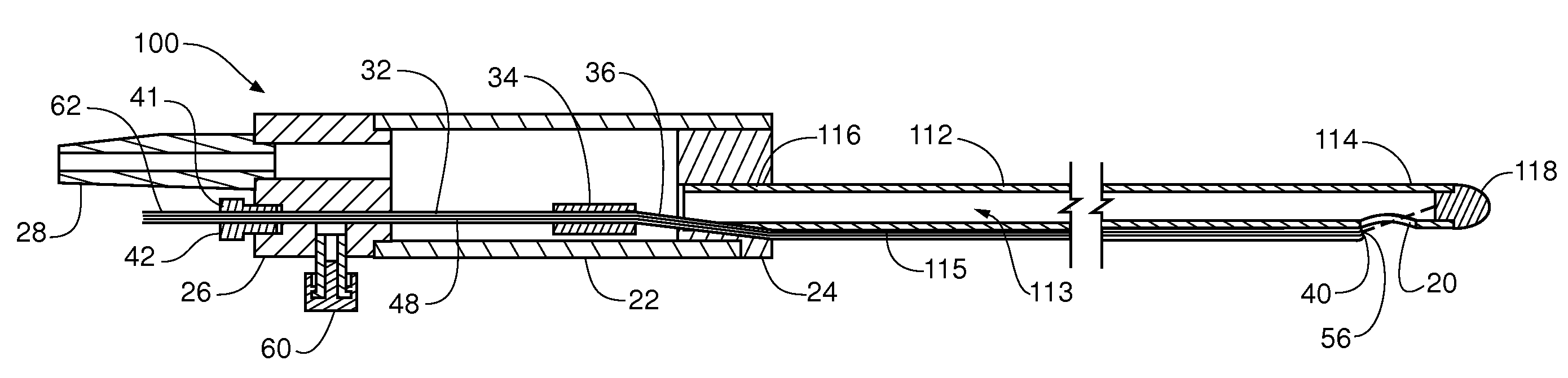
Occlusion device and method of use
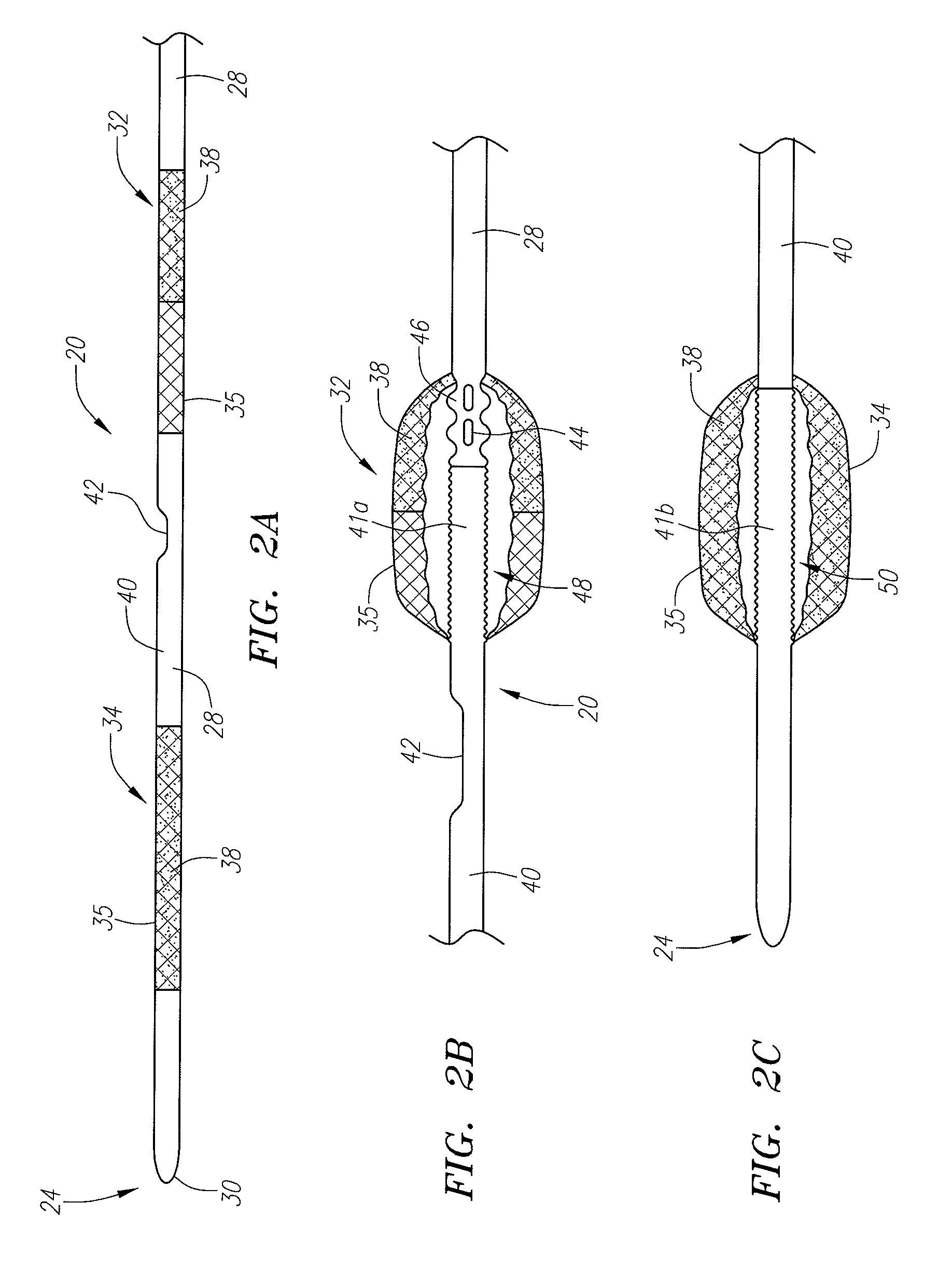
ActiveUS20080200946A1Small outer diameterReduce intervention timeStentsSurgeryDistal portionBlood vessel
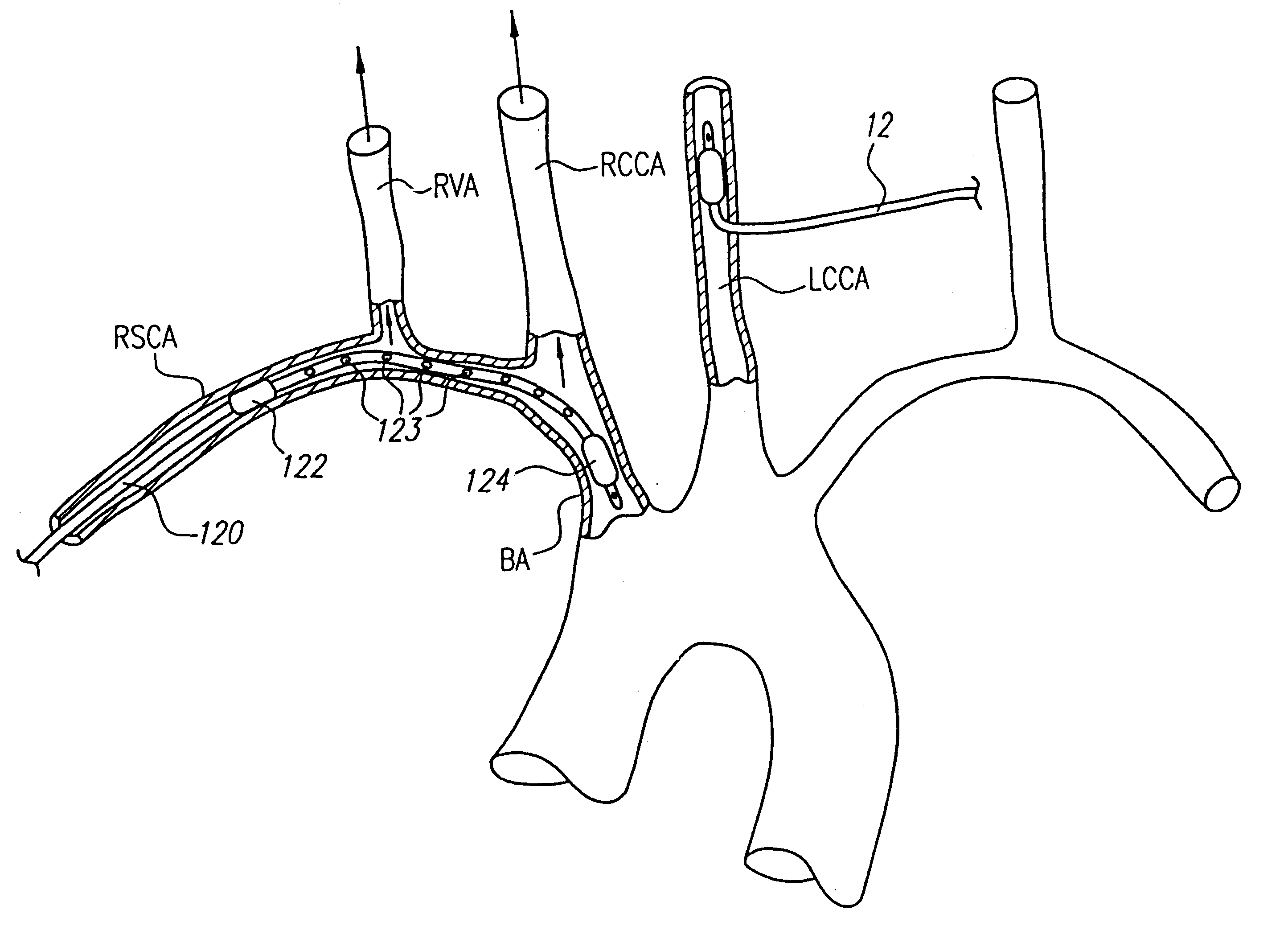
A device for protecting cerebral vessels or brain tissue during treatment of a carotid vessel includes a catheter having a distal portion, a proximal portion and a lumen extending therebetween, the catheter including first and second expandable areas for vessel occlusion provided over the length of the catheter. The device further includes an elongate stretching member insertable longitudinally through the lumen of the catheter, the elongate stretching member being configured for stretching at least a portion of the catheter and causing the first and second expandable areas to transition from an expanded state to a collapsed state, and wherein the elongate stretching member is retracted proximally relative to the catheter causes the first and second expandable areas to transition from the collapsed state to a radially, or laterally expanded state.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
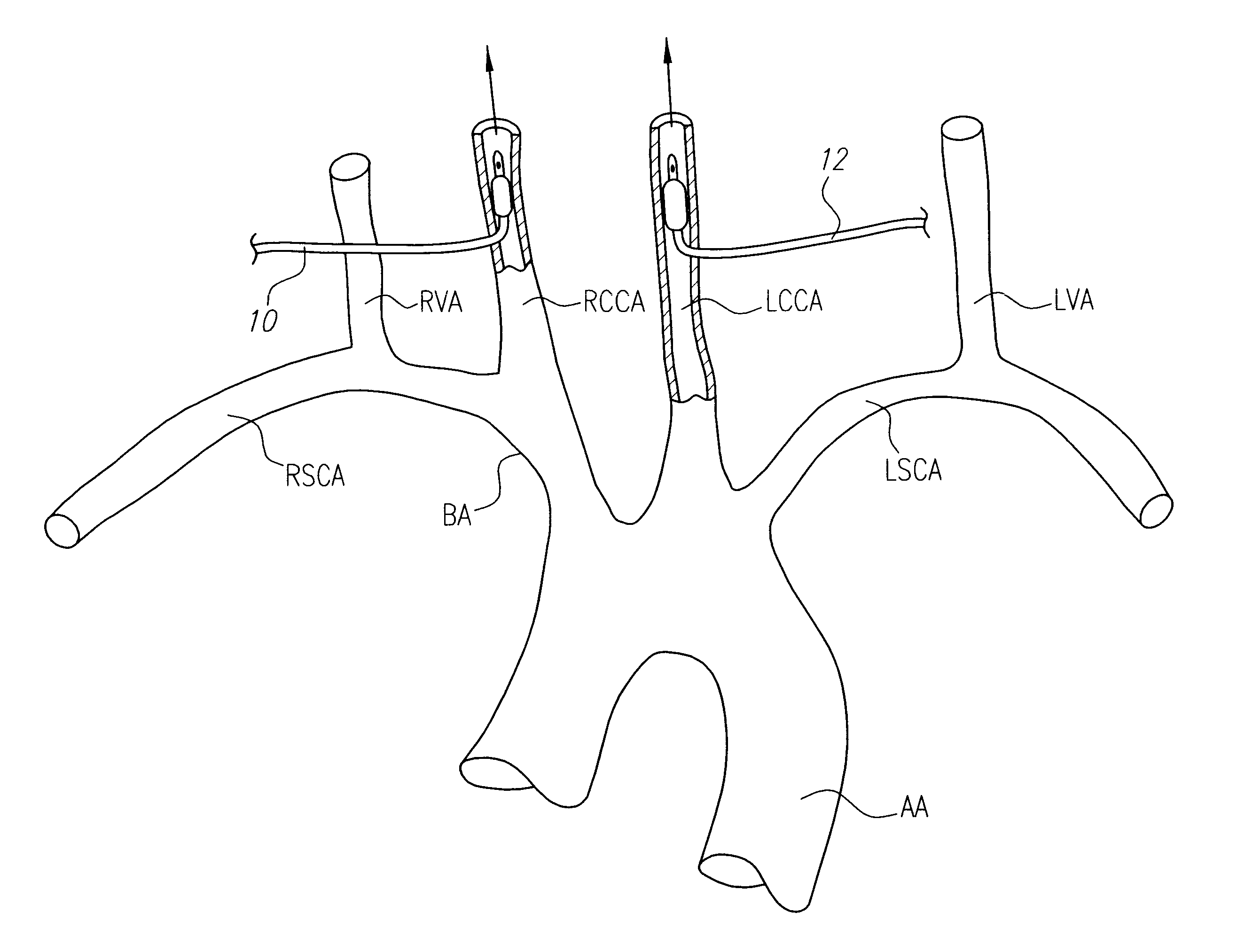
Intravascular methods and apparatus for isolation and selective cooling of the cerebral vasculature during surgical procedures
InactiveUS6555057B1Reduce riskIncrease perfusionOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesRisk strokeSurgical department
Patients having diminished circulation in the cerebral vasculature as a result of stroke or from other causes such as cardiac arrest, shock or head trauma, or aneurysm surgery or aortic surgery, are treated by flowing an oxygenated medium through an arterial access site into the cerebral vasculature and collecting the medium through an access site in the venous site of the cerebral vasculature. Usually, the cold oxygenated medium will comprise autologous blood, and the blood will be recirculated for a time sufficient to permit treatment of the underlying cause of diminished circulation. In addition to oxygenation, the recirculating blood will also be cooled to hypothermically treat and preserve brain tissue. Isolation and cooling of cerebral vasculature in patients undergoing aortic and other procedures is achieved by internally occluding at least the right common carotid artery above the aortic arch. Blood or other oxygenated medium is perfused through the occluded common carotid artery(ies) and into the arterial cerebral vasculature. Usually, oxygen depleted blood or other medium leaving the cerebral vasculature is collected, oxygenated, and cooled in an extracorporeal circuit so that it may be returned to the patient. Occlusion of the carotid artery(ies) is preferably accomplished using expansible occluders, such as balloon-tipped cannula, catheters, or similar access devices. Access to the occlusion site(s) may be open surgical, percutaneous, or intravascular.
Owner:BARBUT DENISE +3
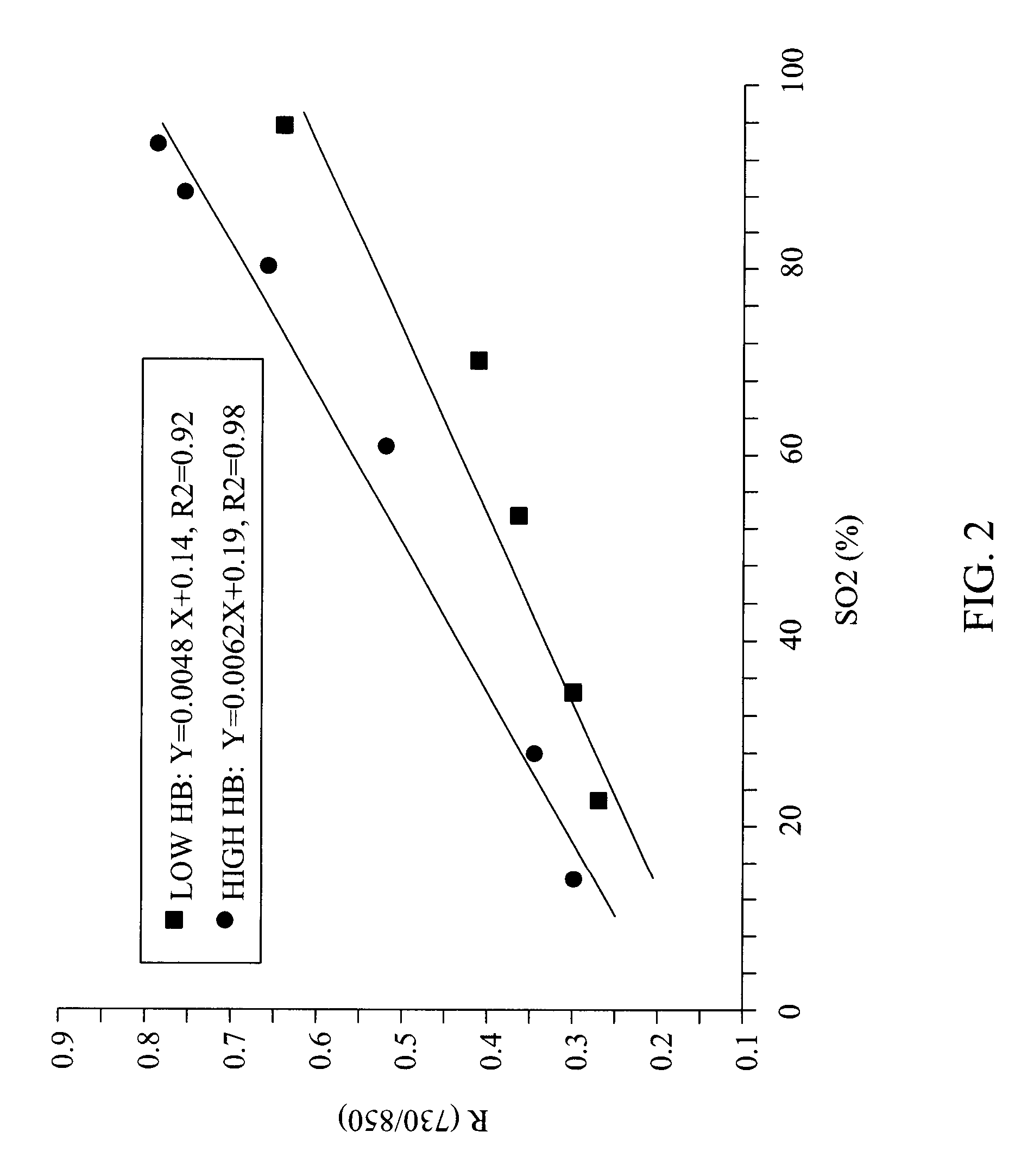
Multi-Wavelength Spatial Domain Near Infrared Oximeter to Detect Cerebral Hypoxia-Ischemia
InactiveUS20080139908A1Material analysis by optical meansDiagnostic recording/measuringTissue oxygenationMulti wavelength
Methods and apparatus for measuring cerebral O2 saturation and detecting cerebral hypoxia-ischemia using multi-wavelength near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS). Near-infrared light produced by an emitter is directed through brain tissue. The intensity of the light that passes through the brain tissue is measured using photodiode detectors positioned at distinct distances from the emitter. This process is conducted for at least three wavelengths of near-infrared light. One of the wavelengths used is substantially at an isobestic point for oxy-hemoglobin and deoxy-hemoglobin, but the other two may be any wavelengths within the near-infrared spectrum (700 nm to 900 nm), so long as one of the additional wavelengths is greater than the isobestic point and the other is less than the isobestic point. Tissue oxygenation is calculated using an algorithm derived from the Beer-Lambert law. Cerebral hypoxia-ischemia may be diagnosed using the calculated tissue oxygenation value.
Owner:KURTH CHARLES DEAN
Electrical stimulation system and method for stimulating tissue in the brain to treat a neurological condition
ActiveUS20090287274A1Reduce and eliminate certain problem and disadvantageRemissionSpinal electrodesHead electrodesElectricityMedicine
According to one aspect, a stimulation system is provided for electrically stimulating a predetermined site to treat a neurological condition. The system includes an electrical stimulation lead adapted for implantation in communication with a predetermined site, wherein the site is brain tissue site. The stimulation lead includes one or more stimulation electrodes adapted to be positioned in the predetermined site. The system also includes a stimulation source that generates the stimulation pulses for transmission to the one or more stimulation electrodes of the stimulation lead to deliver the stimulation pulses to the predetermined site to treat a neurological disorder or condition.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
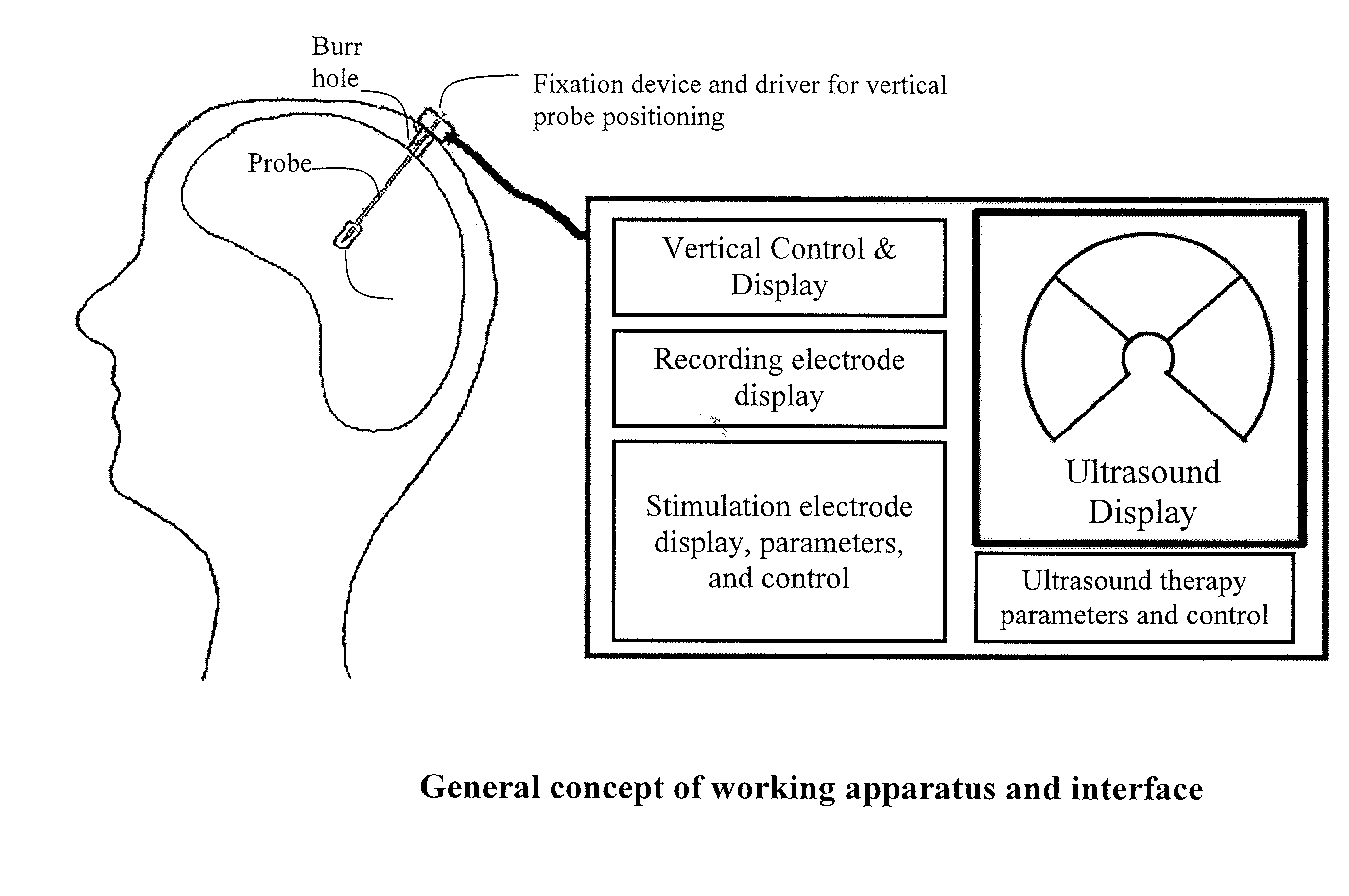
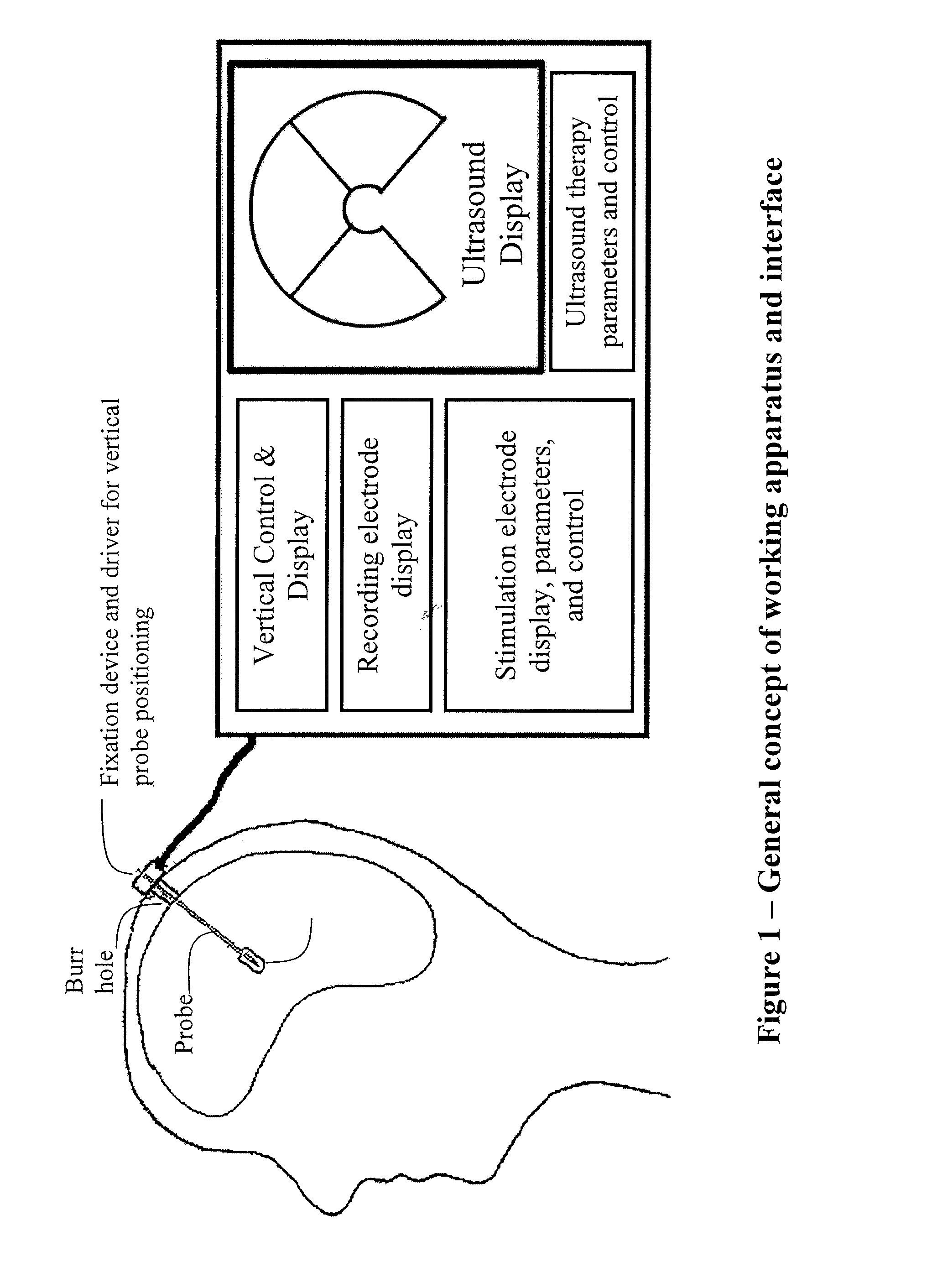
Hybrid ultrasound/electrode device for neural stimulation and recording
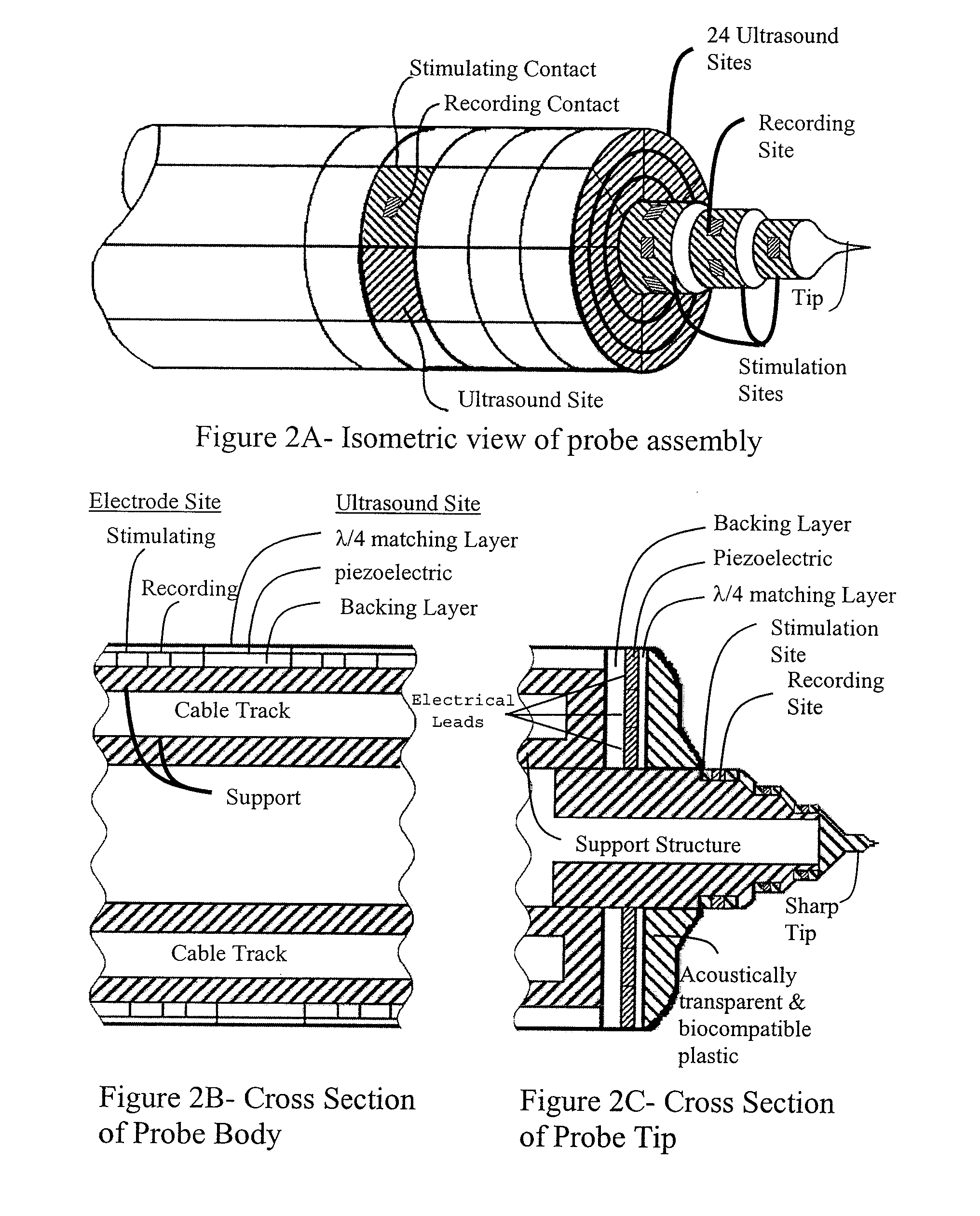
InactiveUS20090254134A1ElectroencephalographyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBrain tissueElectricity
An invasive device that uses electrodes in conjunction with ultrasound is used to enhance and localize electrical recordings and stimulation of neurons. The current design is confined to operate within an elongated geometry for ease of insertion and minimal disruption to brain tissue.
Owner:MEDTRODE
Method of intravascularly delivering stimulation leads into brain
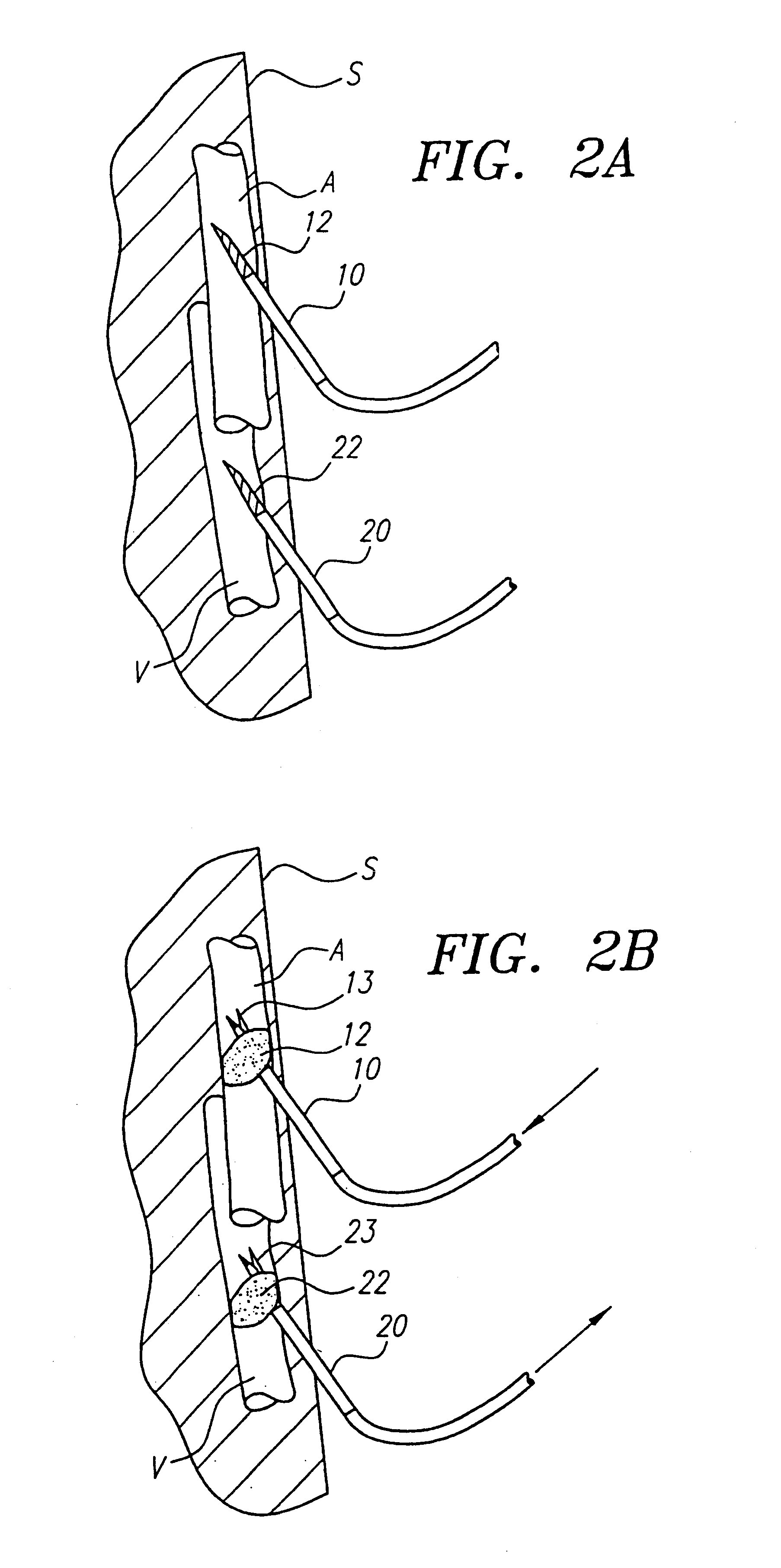
A method of treating a neurological disorder in a patient is provided. The method comprises intravascularly delivering a stimulation lead within the head of the patient, and placing the stimulation lead adjacent brain tissue (e.g., cortical brain tissue or deep brain tissue), the stimulation of which will treat the neurological disorder. The stimulation lead can be placed into indirect contact with the brain tissue (e.g., through a blood vessel) or indirect contact with the brain tissue (e.g., when placed within the ventricular cavity or by being introduced through an exit point within a vessel wall). Optionally, the method comprises implanting a source of stimulation within the patient's body, and then electrically coupling the proximal end of the stimulation lead, which conveniently extends from the access point within the circulatory system, to the implanted stimulation source. Using the stimulation lead, the brain tissue can then be stimulated in order to treat the neurological disorder.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Laser energy device for soft tissue removal
InactiveUS20080208105A1Reduce the cross-sectional areaHigh potential for occlusionElectrotherapyDiagnosticsLiposuctionIn vivo
This invention relates to a device and method for improving the surgical procedure of soft tissue removal by aspiration and more particularly to a device and method utilizing laser energy directed substantially across the inlet port to more readily and safely facilitate the separating of soft tissue from a patient in vivo. This invention has immediate and direct application to the surgical procedure of liposuction or body contouring as well as application in the surgical procedures of other soft tissue removal such as brain tissue, eye tissue, and other soft tissue inaccessible to other soft tissue aspiration techniques.
Owner:CURVE MEDICAL LLC
Apparatus and Methods for Performing Brain Surgery
InactiveUS20080109026A1Easy to installAssisting understandingCannulasInfusion syringesLess invasive surgeryMedicine
Less invasive surgical techniques for performing brain surgery are disclosed in which a dilating obturator and cannula assembly is inserted into brain tissue until the obturator tip and cannula are adjacent the target tissue. The obturator is removed and surgery is performed through the cannula. In preferred embodiments the obturator and cannula are placed using image guidance techniques and systems to coordinate placement with pre-operative surgical planning. A stylet with associated image guidance may he inserted prior to insertion of the obturator and cannula assembly to guide insertion of the obturator and cannula assembly. Surgery preferable is performed using an endoscope partially inserted into the cannula with an image of the target tissue projected onto a monitor.
Owner:NICO CORP
Method of using cryotreatment to treat brain tissue
A method is disclosed for treating brain tissue with cryotreatment. A surgical tool, such as a catheter is disposed proximate to a target region of brain tissue. The tool or catheter provided includes a cryotreatment element. The cryotreatment element may be a cryochamber for enclosing the flow of a fluid refrigerant therein. The cryotreatment element is disposed at the situs of brain tissue to be treated, either through endovascular insertion, or via an opening in the cranium. A refrigerant flow within the cryochamber creates endothermic cooling with respect to the surrounding brain tissue, inducing hypothermia and forming iceballs proximate said tissue. The cooling may be reversible and non-permanent, or may be permanent leading to cell death, necrosis, apoptosis and / or surgical excision or ablation of tissue. Mapping using conventional techniques may be used to measure and assess brain function before and after cryotreatment, and cryotreatment itself may be integrally and progressively used to map brain function and treat tissue.
Owner:MEDTRONIC CRYOCATH LP
Apparatus and methods for performing brain surgery
ActiveUS20090048622A1Many of techniqueEasy to installCannulasSurgical needlesLess invasive surgeryLess invasive
Less invasive surgical techniques for performing brain surgery are disclosed in which a dilating obturator and cannula assembly is inserted into brain tissue until the obturator tip and cannula are adjacent to the target tissue. The obturator is removed and surgery is performed through the cannula. In preferred embodiments the obturator and cannula are placed using image guidance techniques and systems to coordinate placement with pre-operative surgical planning. A stylet with associated image guidance may be inserted prior to insertion of the obturator and cannula assembly to guide insertion of the obturator and cannula assembly. Surgery preferably is performed using an endoscope partially inserted into the cannula with an image of the target tissue projected onto a monitor. Dilating obturator structures having a rounded or semi-spherical tip and / or an optical window for visualizing brain tissue during expansion are contemplated.
Owner:VYCOR MEDICAL INC
Surgical access instruments for use with delicate tissues
InactiveUS20060287583A1Lightweight materialEasy to operateCannulasSurgical needlesButtressSurgical site
One or more surgical instruments provide access to delicate tissue, such as brain tissue or breast tissue, through a transcutaneous incision, for a variety of reasons, such as to access a surgical site for providing a working channel for accessing delicate tissue by surgical instruments, to provide access to insert an inflatable prosthesis, or for providing an external buttress channel for supporting tissue thereon. The surgical instrument assembly includes an interleaved combination of an open sleeve hollow retractor and a tapered tipped wedge introducer. The wedge introducer is introduced into an area adjacent to the hollow sleeve. The distal tip of the wedge introducer extends beyond a distal end of the hollow retractor, forward of a distal end of the hollow retractor, so that the wedge introducer traverses delicate tissue ahead of the distal end of the hollow retractor, guiding the hollow retractor into place to the delicate tissue.
Owner:VYCOR MEDICAL LLC
Reducing discomfort caused by electrical stimulation
The invention is directed to a novel method for reducing discomfort caused by transcutaneous stimulation. The novel method includes providing transcutaneous stimulation, reducing the transcutaneous stimulation at a first location, and substantially maintaining the transcutaneous stimulation at a second location. The transcutaneous stimulation may be created by electric and / or magnetic fields. The first location may be relatively proximate to the cutaneous surface and may comprise tissue, nerves and muscle. Also, the second location may be relatively deeper than the first location and include, for example, brain tissue that requires the transcutaneous stimulation for treatment purposes. The invention further may include locating a conductor on a treatment area and / or a transcutaneous stimulation device relative to the first location. In addition, the method may further include adjusting how much the transcutaneous stimulation is reduced at the first location.
Owner:NEURONETICS
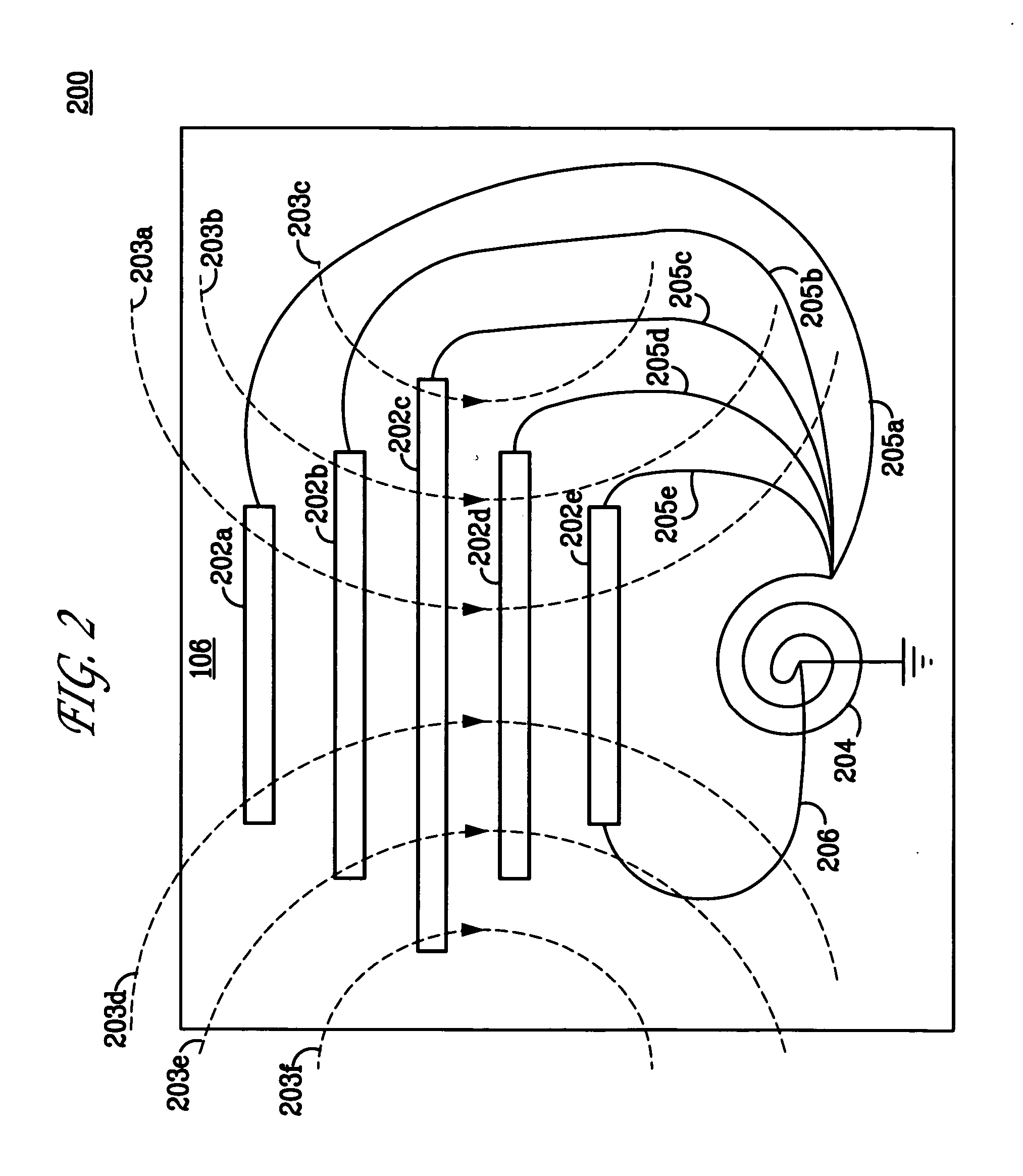
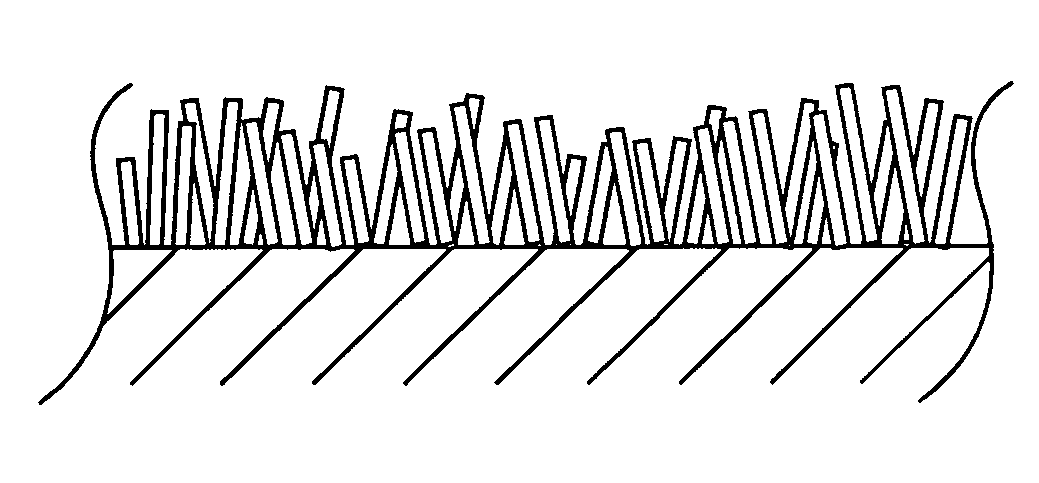
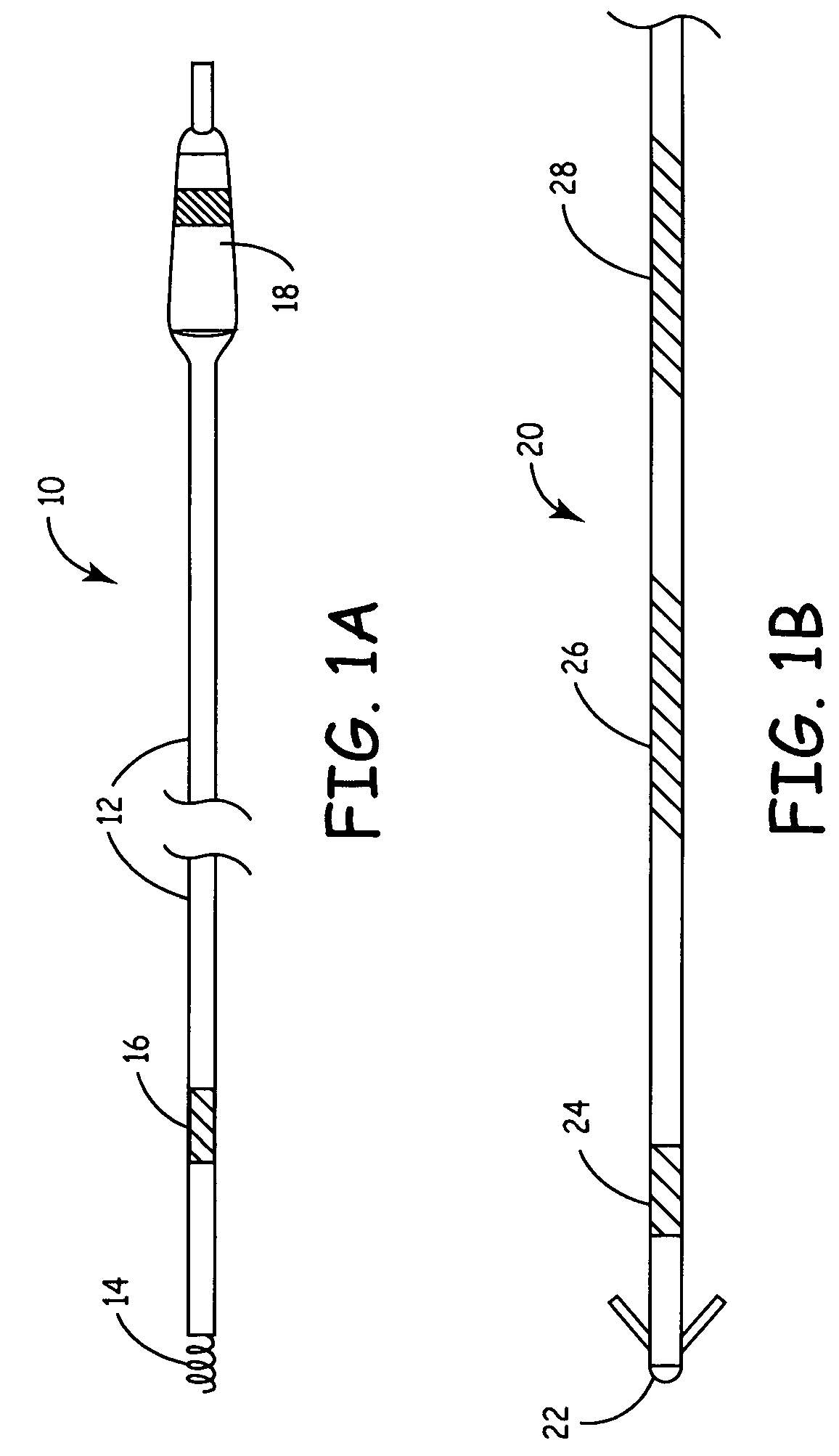
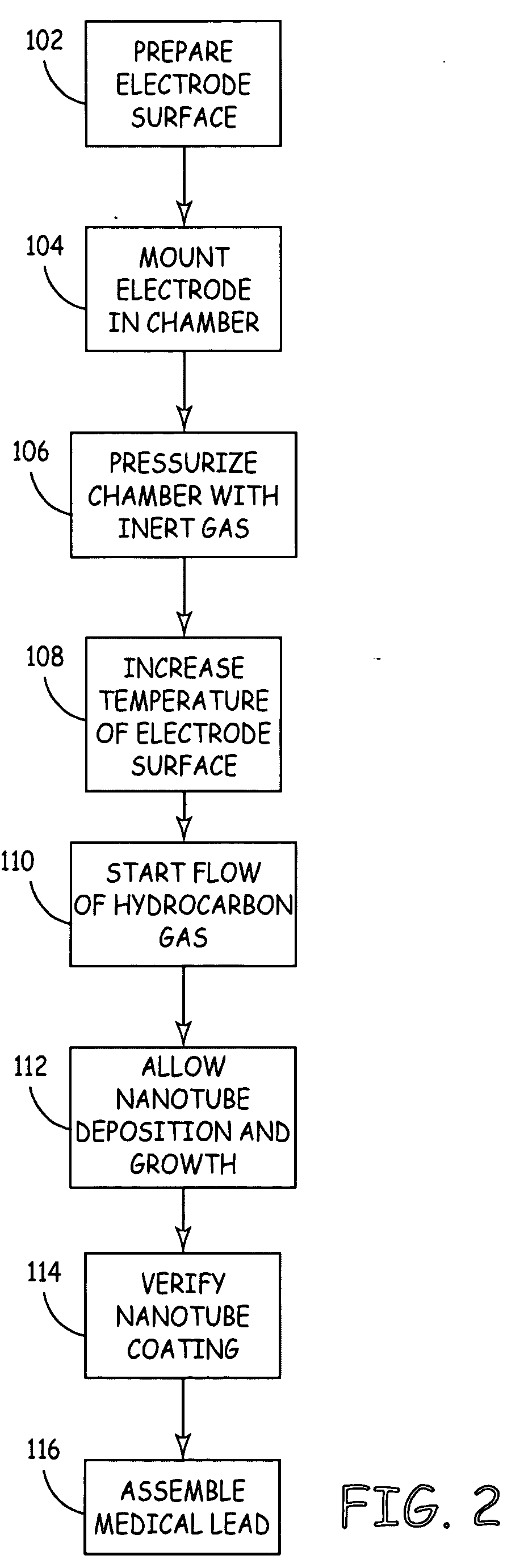
Medical devices incorporating carbon nanotube material and methods of fabricating same
InactiveUS7596415B2High strengthStable stateNanotechTransvascular endocardial electrodesMuscle tissueCarbon nanotube
The present invention relates generally to medical devices; in particular and without limitation, to unique electrodes and / or electrical lead assemblies for stimulating cardiac tissue, muscle tissue, neurological tissue, brain tissue and / or organ tissue; to electrophysiology mapping and ablation catheters for monitoring and selectively altering physiologic conduction pathways; and, wherein said electrodes, lead assemblies and catheters optionally include fluid irrigation conduit(s) for providing therapeutic and / or performance enhancing materials to adjacent biological tissue, and wherein each said device is coupled to or incorporates nanostructure or materials therein. The present invention also provides methods for fabricating, deploying, and operating such medical devices.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method and system for selective or isolated integrate cerebral perfusion and cooling
InactiveUS6736790B2Reduce riskImproving cerebral perfuisionBronchoscopesLaryngoscopesOxygenPerfusion
Patients having diminished circulation in the cerebral vasculature as a result of cardiac arrest or from other causes are treated by flowing an oxygenated medium through an arterial access site into the cerebral vasculature and collecting the medium through an access site in the venous site of the cerebral vasculature. In addition to oxygenation, the recirculating blood may also be cooled to hypothermically treat and preserve brain tissue. Isolation and cooling of cerebral vasculature in patients undergoing aortic and other procedures is achieved by internally occluding at least the right common carotid artery above the aortic arch. Blood or other oxygenated medium is perfused through the occluded common carotid artery(ies) and into the arterial cerebral vasculature. Usually, oxygen depleted blood or other medium leaving the cerebral vasculature is collected, oxygenated, and cooled in an extracorporeal circuit so that it may be returned to the patient.
Owner:BARBUT DENISE & PATTERSON RUSSEL +1
Burr hole plug designs
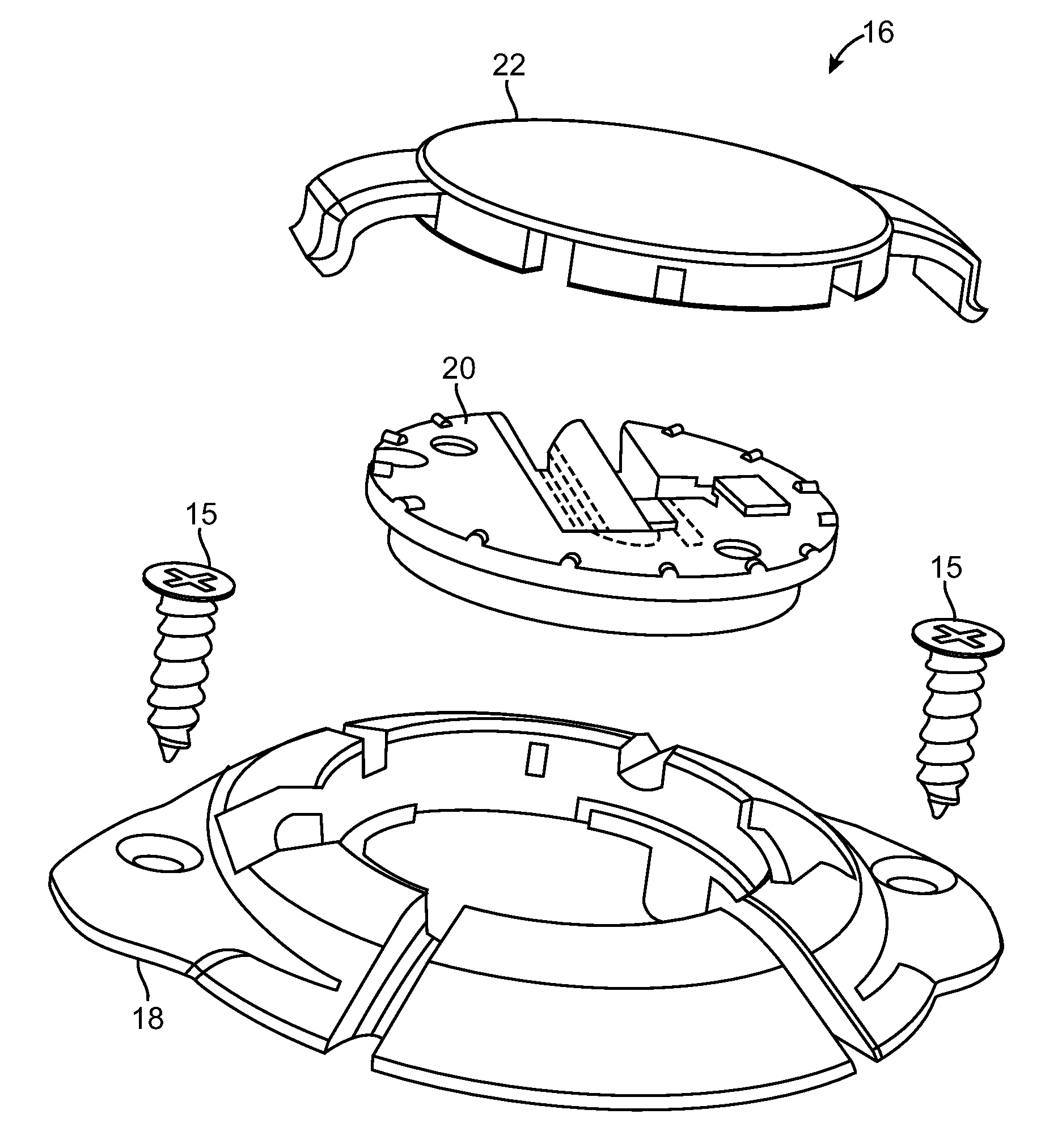
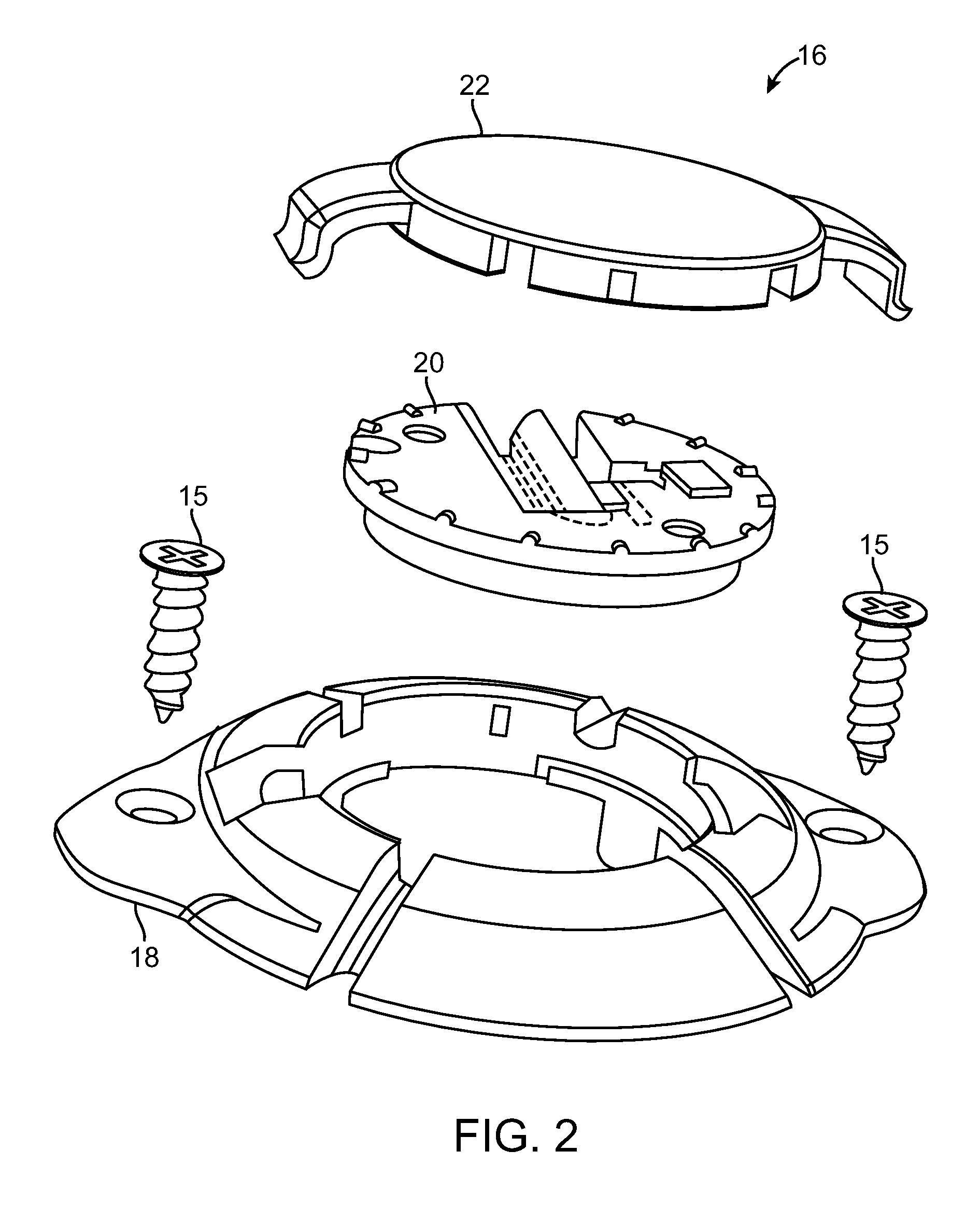
InactiveUS20090112327A1Facilitates the securing of moreImprove securityHead electrodesBone implantBurr holesEngineering
A burr hole plug comprises a plug base including a flange configured for being mounted around a burr hole, an aperture through which an elongated medical device may pass, and tabs configured for extending within the cranial burr hole to center the plug base relative to the cranial burr hole. The burr hole plug further comprises a retainer configured for being mounted within the aperture of the plug base to secure the medical device. A method may comprise locating the plug base within a burr hole, such that the tabs are disposed within the burr hole to center the plug base relative to the cranial burr hole, introducing the elongated medical device through the cranial burr hole and into the brain tissue of the patient, mounting the retainer within the aperture of the plug base, and actuating the retainer to secure the medical device.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Reducing discomfort caused by electrical stimulation
The invention is directed to a novel method for reducing discomfort caused by transcutaneous stimulation. The novel method includes providing transcutaneous stimulation, reducing the transcutaneous stimulation at a first location, and substantially maintaining the transcutaneous stimulation at a second location. The transcutaneous stimulation may be created by electric and / or magnetic fields. The first location may be relatively proximate to the cutaneous surface and may comprise tissue, nerves and muscle. Also, the second location may be relatively deeper than the first location and include, for example, brain tissue that requires the transcutaneous stimulation for treatment purposes. The invention further may include locating a conductor on a treatment area and / or a transcutaneous stimulation device relative to the first location. In addition, the method may further include adjusting how much the transcutaneous stimulation is reduced at the first location.
Owner:NEURONETICS
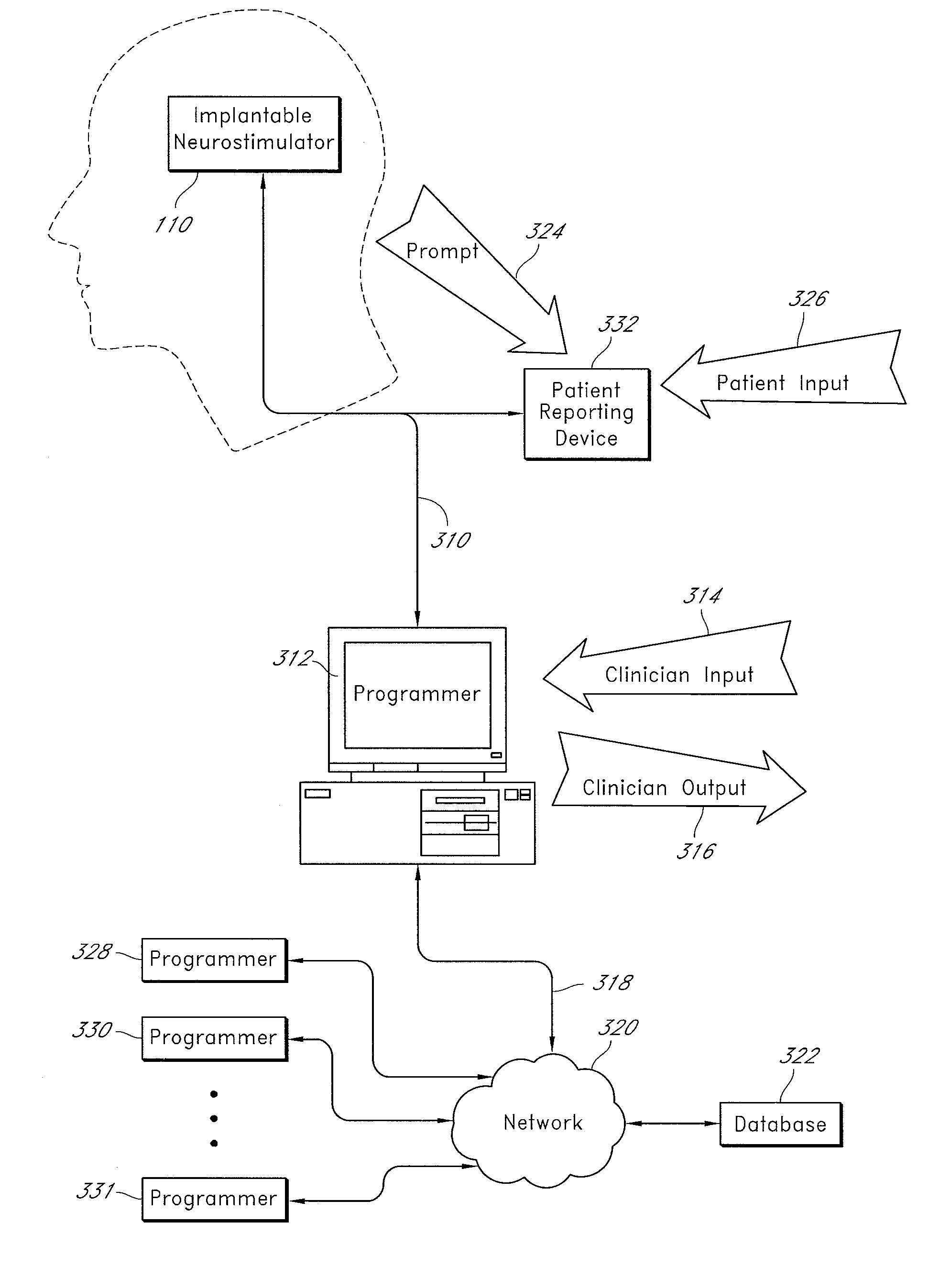
Auto adjusting system for brain tissue stimulator
An implantable neurostimulator for treating disorders such as epilepsy, pain, movement disorders and depression includes a detection subsystem capable of detecting a physiological condition and a therapy subsystem capable of providing a course of therapy in response to the condition. The therapy subsystem includes an auto-adjust module for automatically adjusting one or more parameters of the therapy so that the therapy subsystem can provide an adjusted parameter to the patient and solicit the patient's feedback concerning the adjustment without requiring the presence of, or immediate involvement with, a clinician or physician. The patient feedback can be analyzed by computer, clinician or a combination of both to determine an optimal range of parameters for subsequent courses of therapy. In this manner, information useful in tuning the neurostimulator therapy parameters to optimize them for individual patient can be acquired automatically outside of the traditional clinical setting, saving time and minimizing patient fatigue that otherwise would be experience in marathon, in-clinic tuning sessions. The auto-adjust module also can be configured to prompt the patient to provide feedback even when parameters are not being adjusted, so as to acquire information for a baseline or about any placebo effect when the patient is otherwise expecting changes to the therapy to be made.
Owner:NEUROPACE
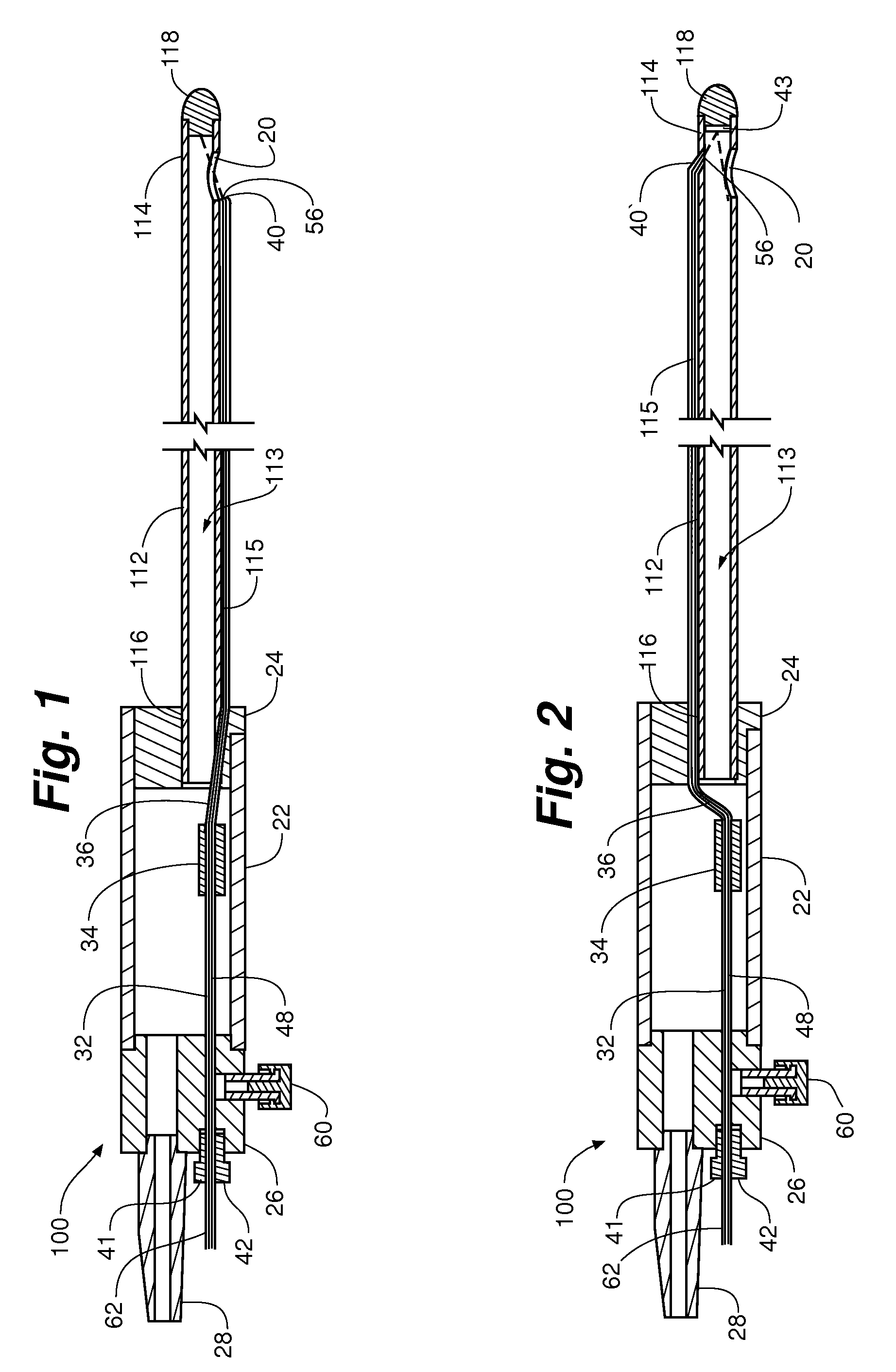
Occlusion device and method of use
InactiveUS20120022572A1Small outer diameterIncrease flexibilityDilatorsOcculdersDistal portionBlood vessel
A device for protecting cerebral vessels or brain tissue during treatment of a carotid vessel includes a catheter having a distal portion, a proximal portion and a lumen extending therebetween, the catheter including first and second expandable areas provided over the length of the catheter. The device includes a first elongate member insertable longitudinally through the lumen of the catheter, the first elongate member being configured for stretching at least a portion of the catheter and causing one of the first and second expandable areas to transition from an expanded state to a collapsed state. The device further includes a second elongate member insertable longitudinally through the lumen of the catheter, the second elongate member being configured for stretching at least a portion of the catheter and causing the other of the first and second expandable areas to transition from an expanded state to a collapsed state.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
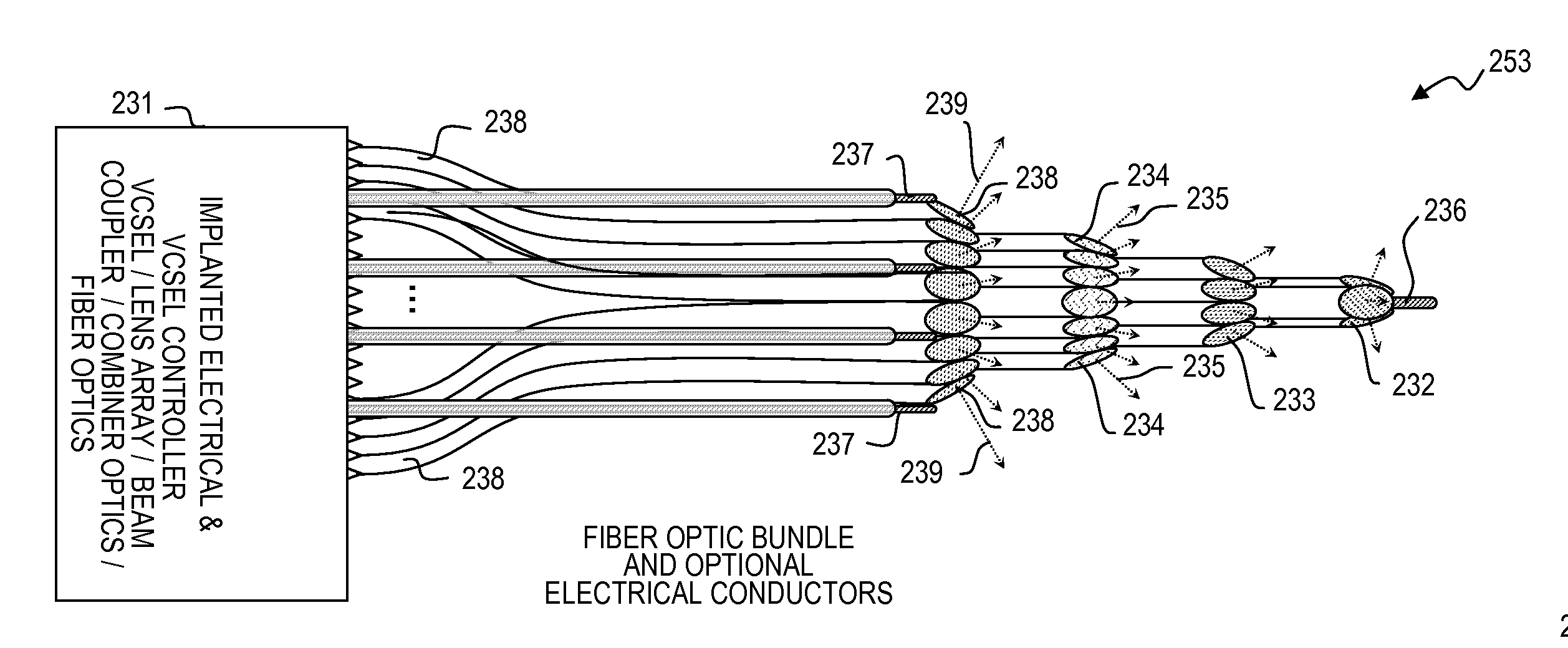
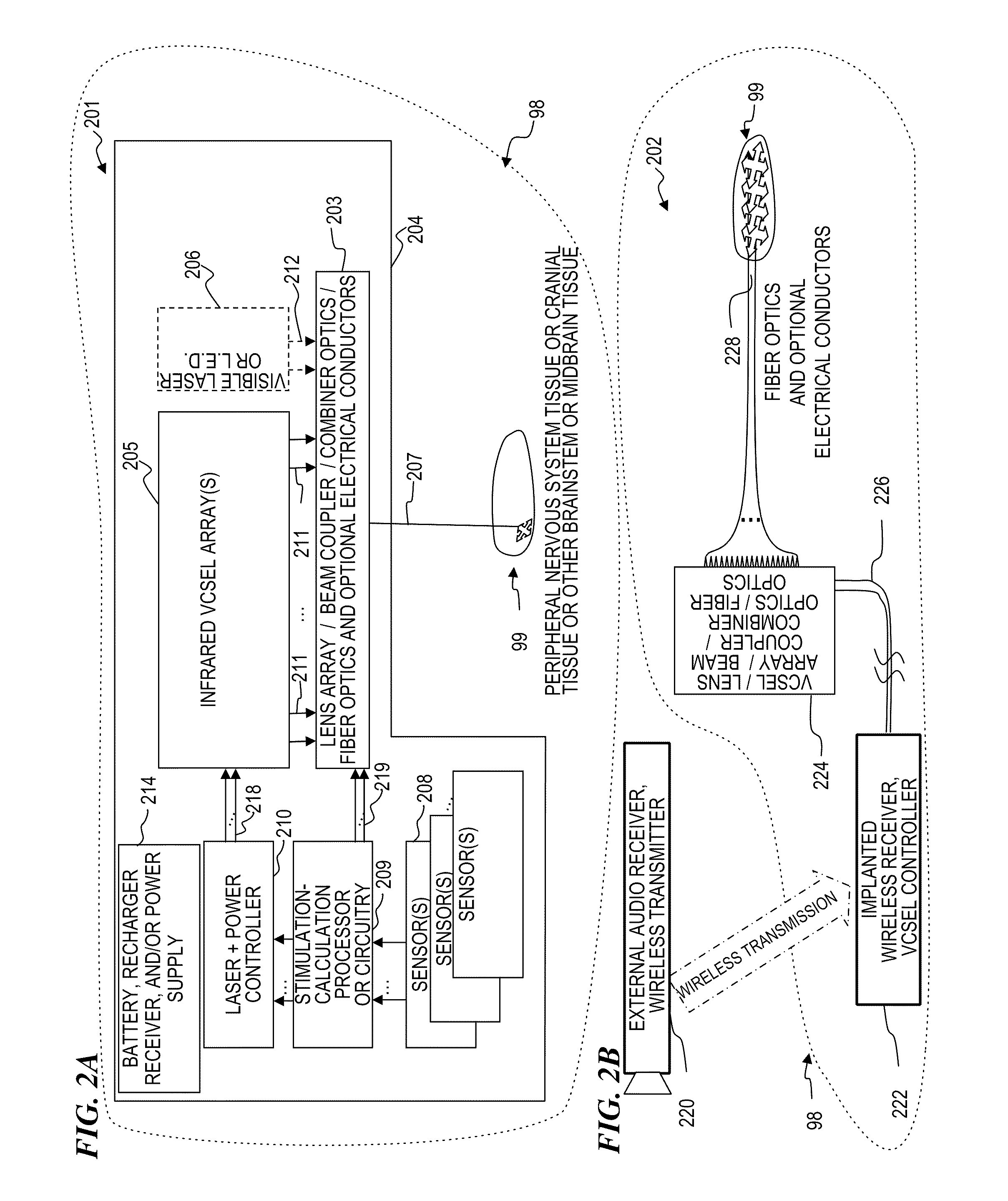
Implantable infrared nerve stimulation devices for peripheral and cranial nerve interfaces
InactiveUS20110295345A1Efficacious generationImprove accuracyHead electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsNervous systemCranial nerves
Apparatus and method for making and using devices that generate optical signals, and optionally also electrical signals in combination with one or more such optical signals, to stimulate (i.e., trigger) and / or simulate a sensory-nerve signal in nerve and / or brain tissue of a living animal (e.g., a human), for example to treat nerve damage in the peripheral nervous system (PNS) or the central nervous system (CNS) and provide sensations to stimulate and / or simulate “sensory” signals in nerves and / or brain tissue of a living animal (e.g., a human) to treat other sensory deficiencies (e.g., touch, feel, balance, visual, taste, or olfactory) and provide sensations related to those sensory deficiencies, and / or to stimulate (i.e., trigger) and / or simulate a motor-nerve signal in nerve and / or brain tissue of a living animal (e.g., a human), for example to control a muscle or a robotic prosthesis.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Medical devices incorporating carbon nanotube material and methods of fabricating same
InactiveUS20050203604A1High strengthStable stateNanotechTransvascular endocardial electrodesMuscle tissueCarbon nanotube
The present invention relates generally to medical devices; in particular and without limitation, to unique electrodes and / or electrical lead assemblies for stimulating cardiac tissue, muscle tissue, neurological tissue, brain tissue and / or organ tissue; to electrophysiology mapping and ablation catheters for monitoring and selectively altering physiologic conduction pathways; and, wherein said electrodes, lead assemblies and catheters optionally include fluid irrigation conduit(s) for providing therapeutic and / or performance enhancing materials to adjacent biological tissue, and wherein each said device is coupled to or incorporates nanostructure or materials therein. The present invention also provides methods for fabricating, deploying, and operating such medical devices.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
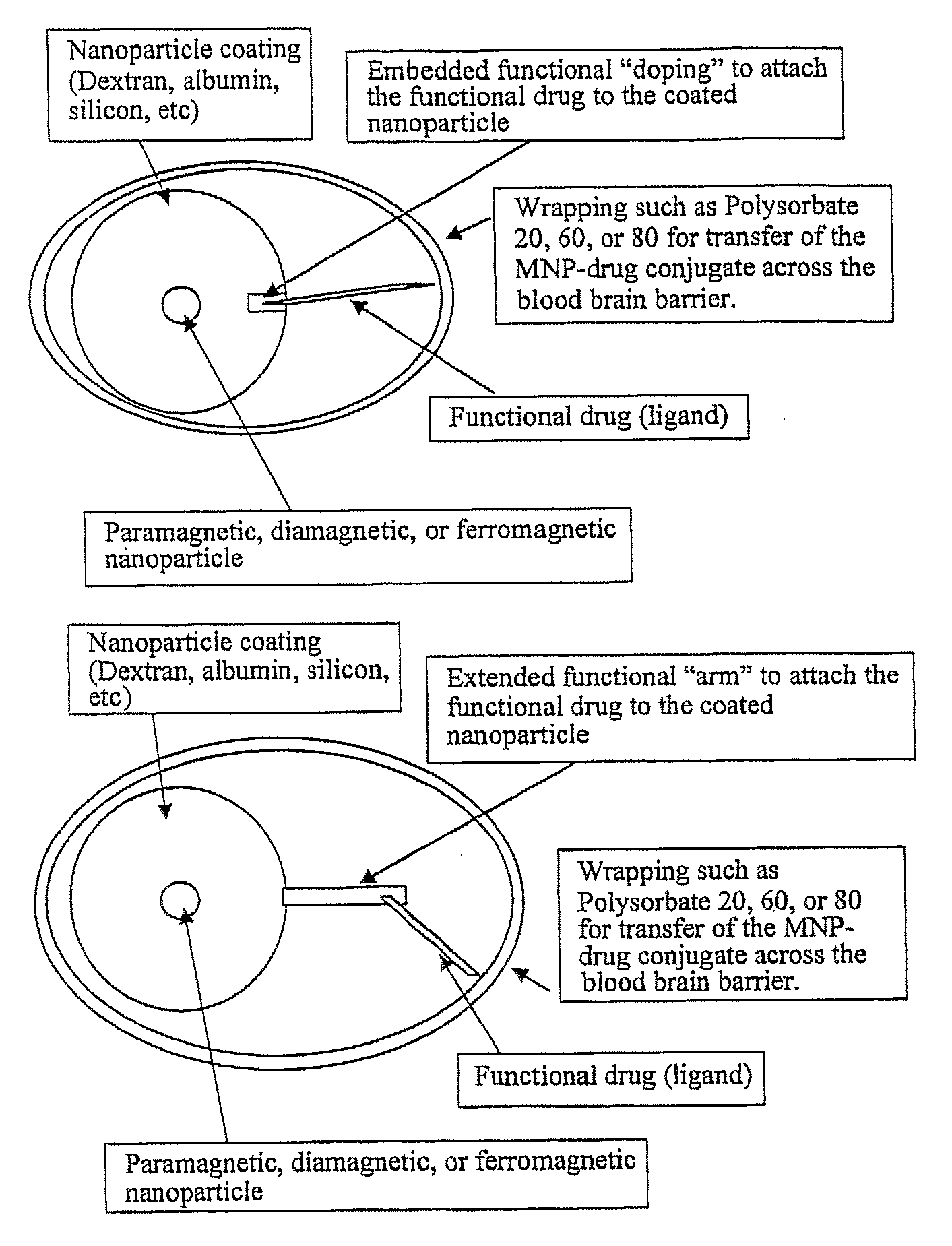
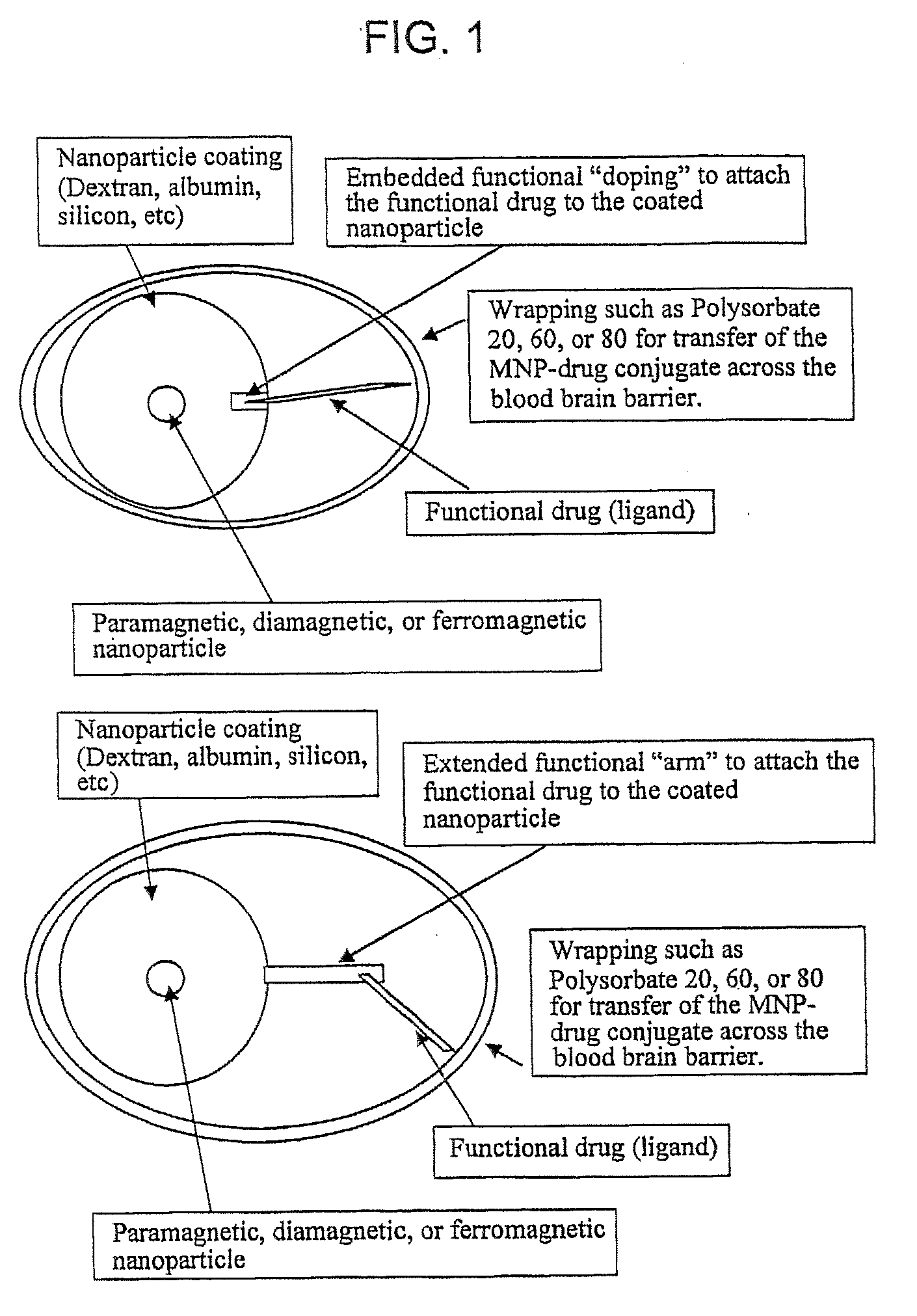
Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles and Methods of Use Thereof
The present invention provides functionalized magnetic nanoparticles comprising a functional group, which functionalized magnetic nanoparticles exhibit differential binding to a tissue, indulging brain tissue, bone, and vascular tissues. The present invention further provides compositions, including pharmaceutical compostions, comprising a subject functionalized magnetic nanoparticle. The present invention further provides diagnostic and research methods including use of subject functionized magnetic nanoparticles. The present invention further provides a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-visible drug delivery system; drugs using MRI, as well as tissue-specific drug delivery.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com