Patents
Literature
37 results about "Ventricular cavity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
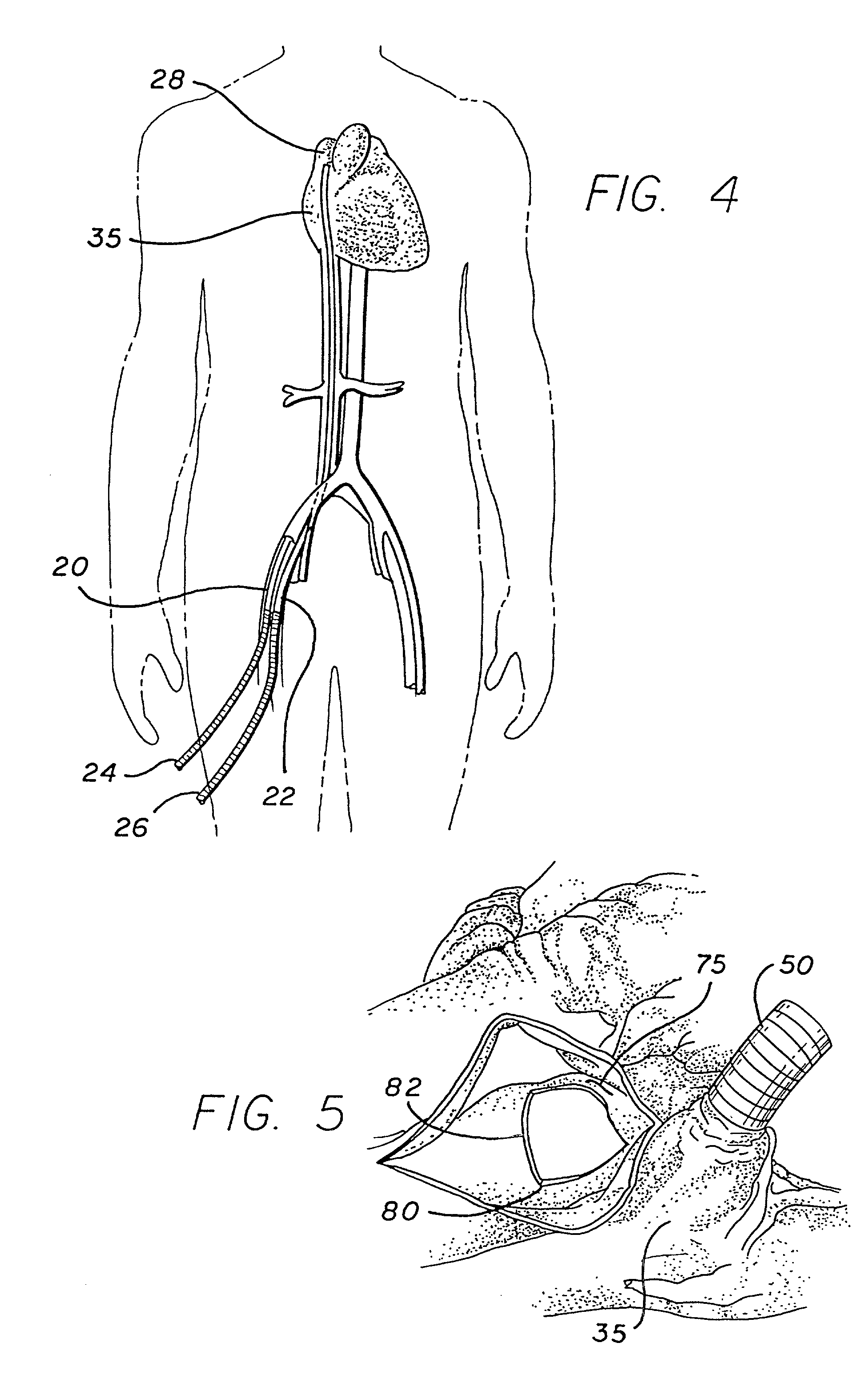
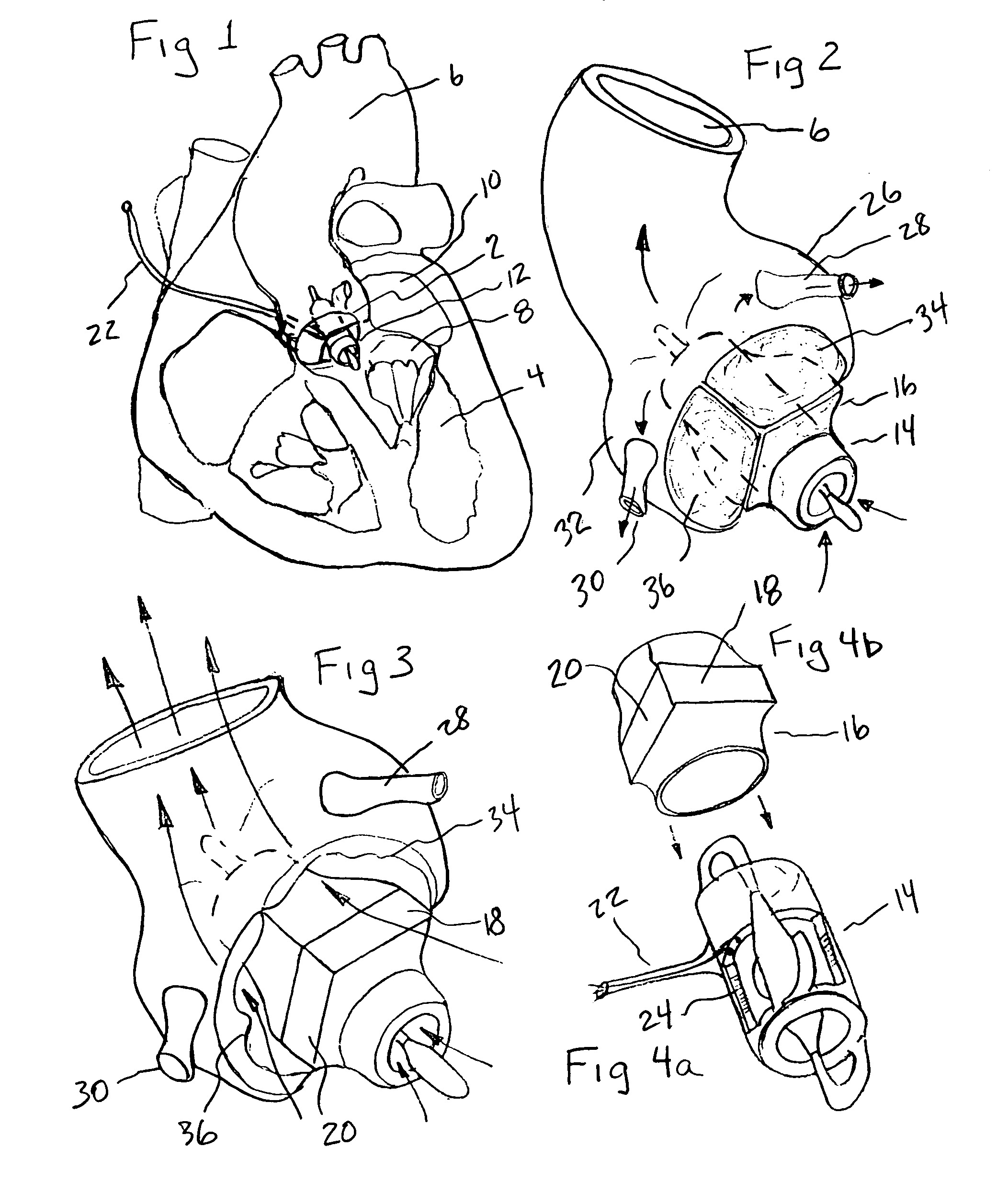
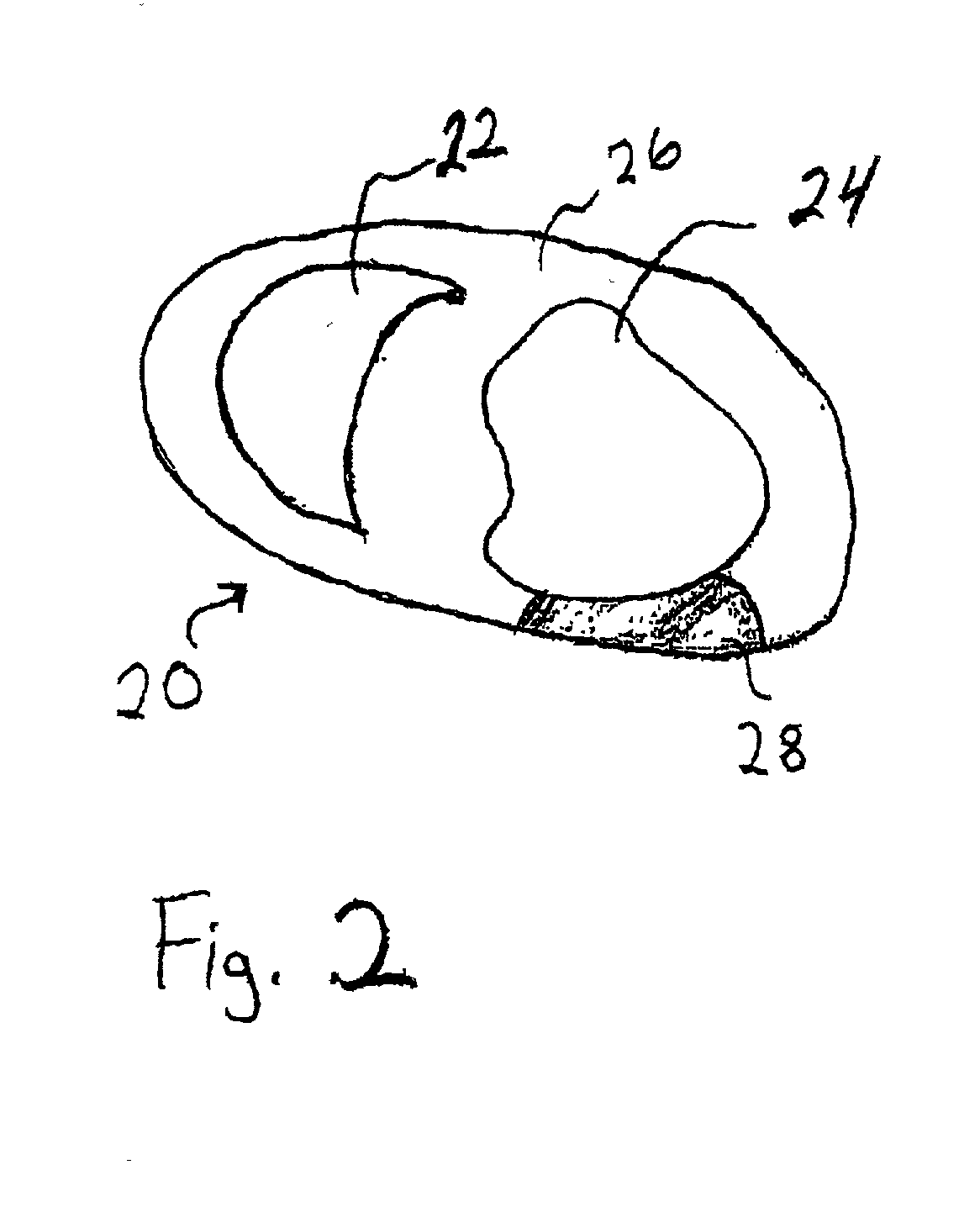
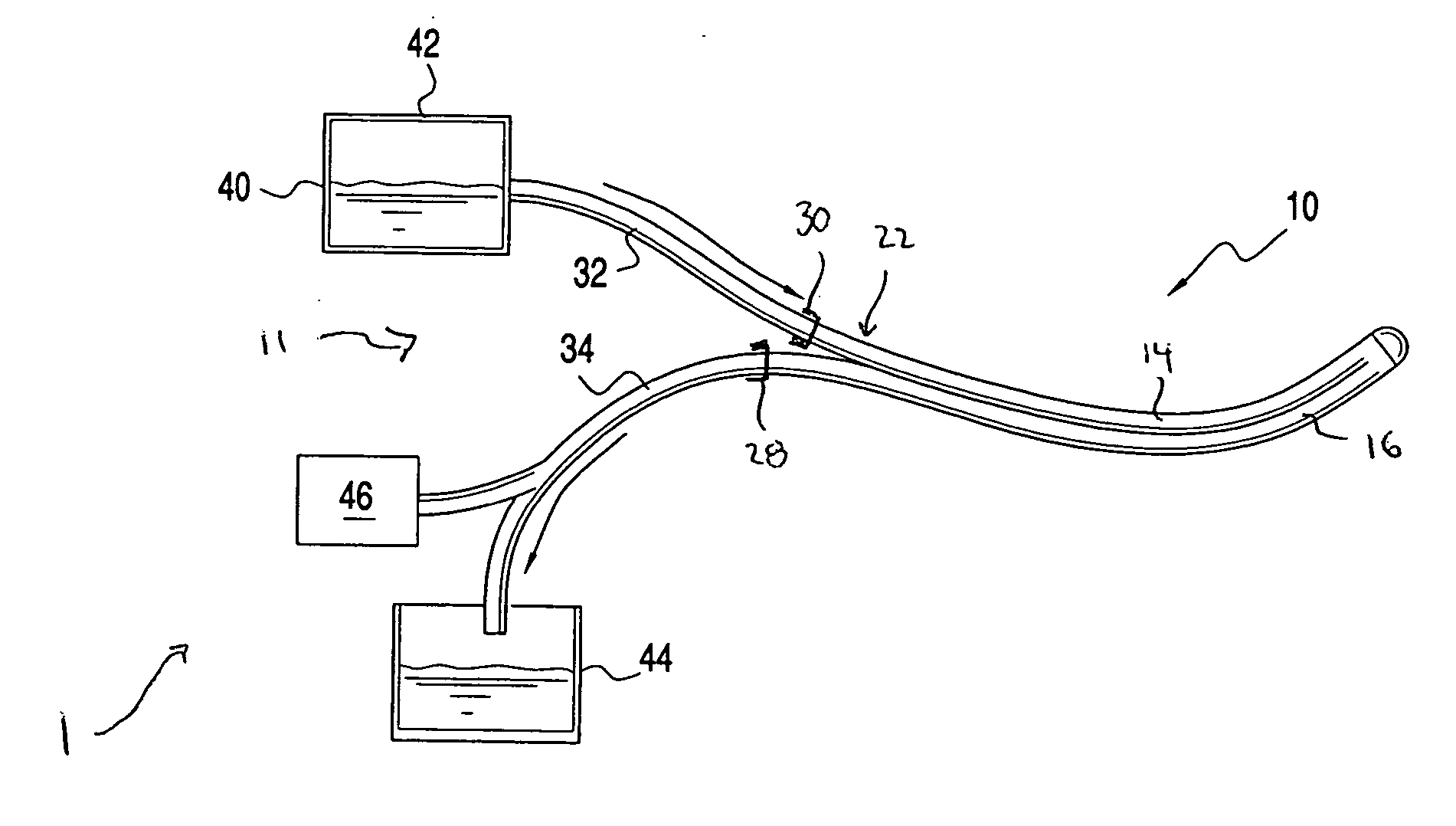
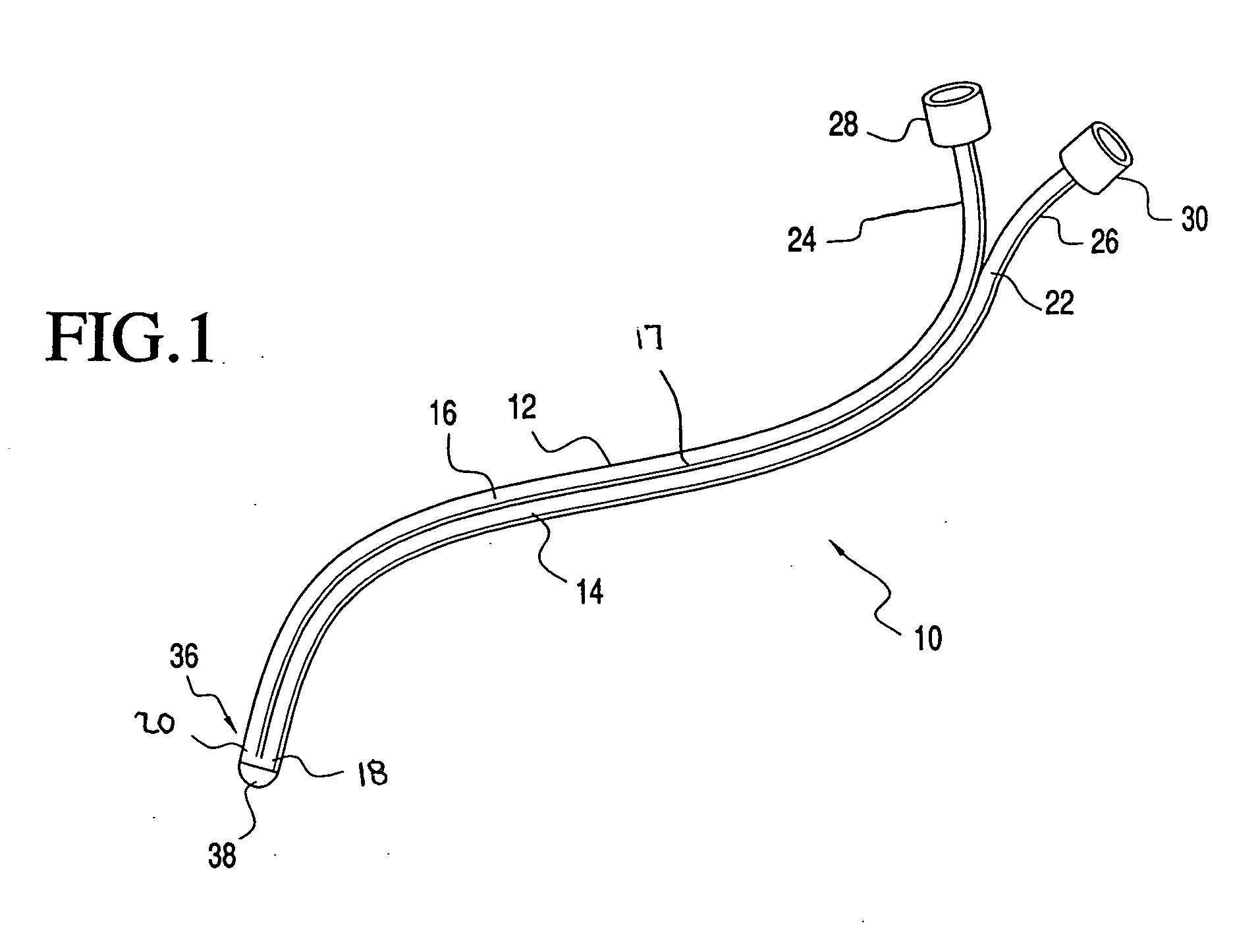
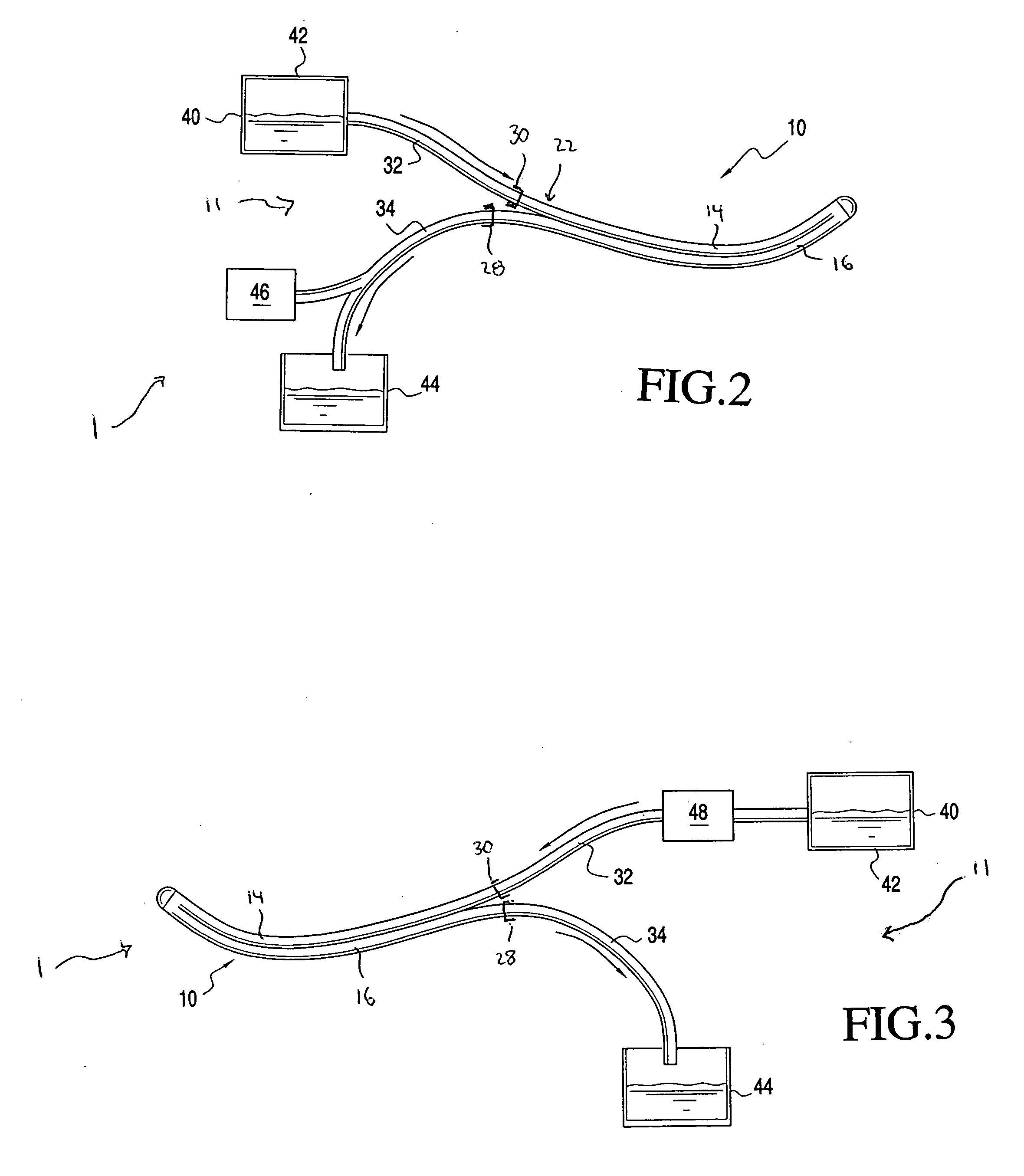
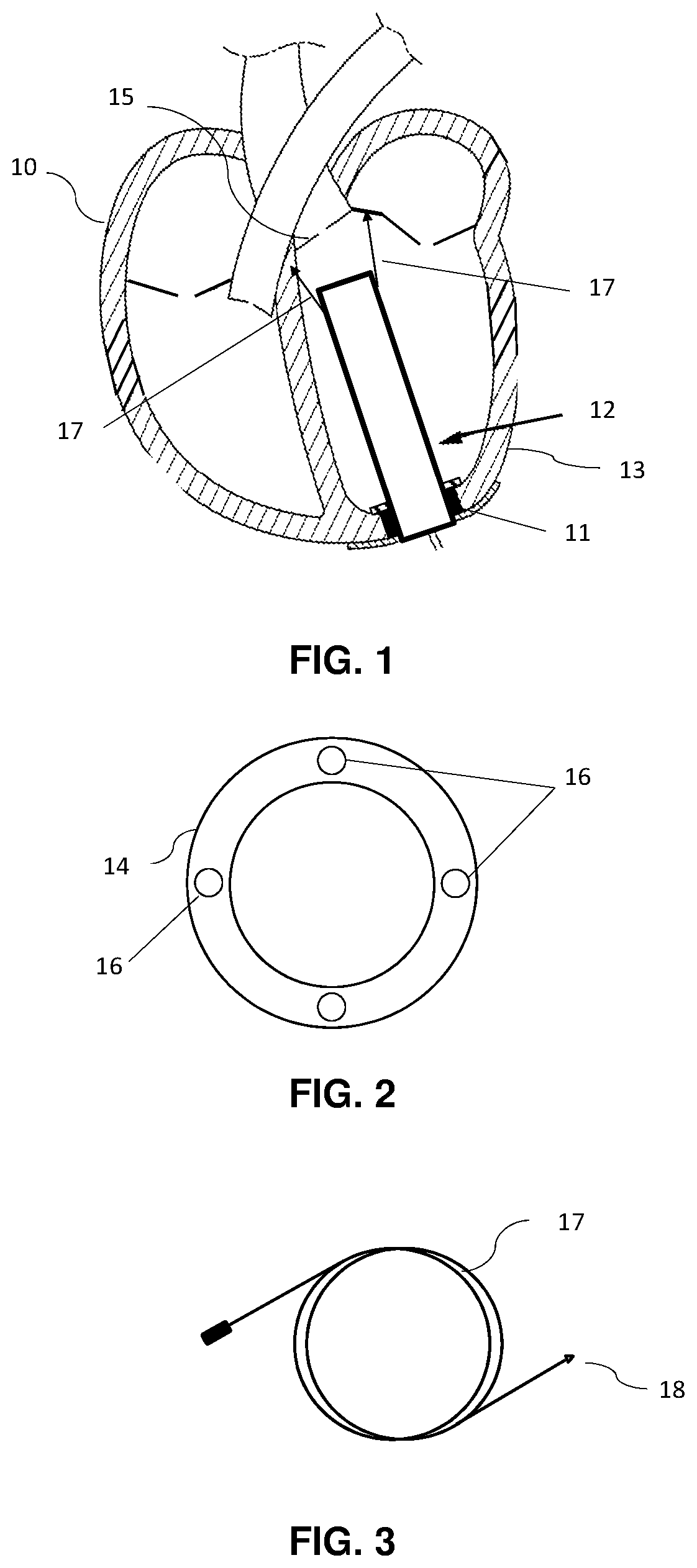
Minimally invasive transvalvular ventricular assist device
ActiveUS20060195004A1Highly effectiveHighly miniaturizedAdditive manufacturing apparatusBlood pumpsThree dimensional ctVentricular cavity
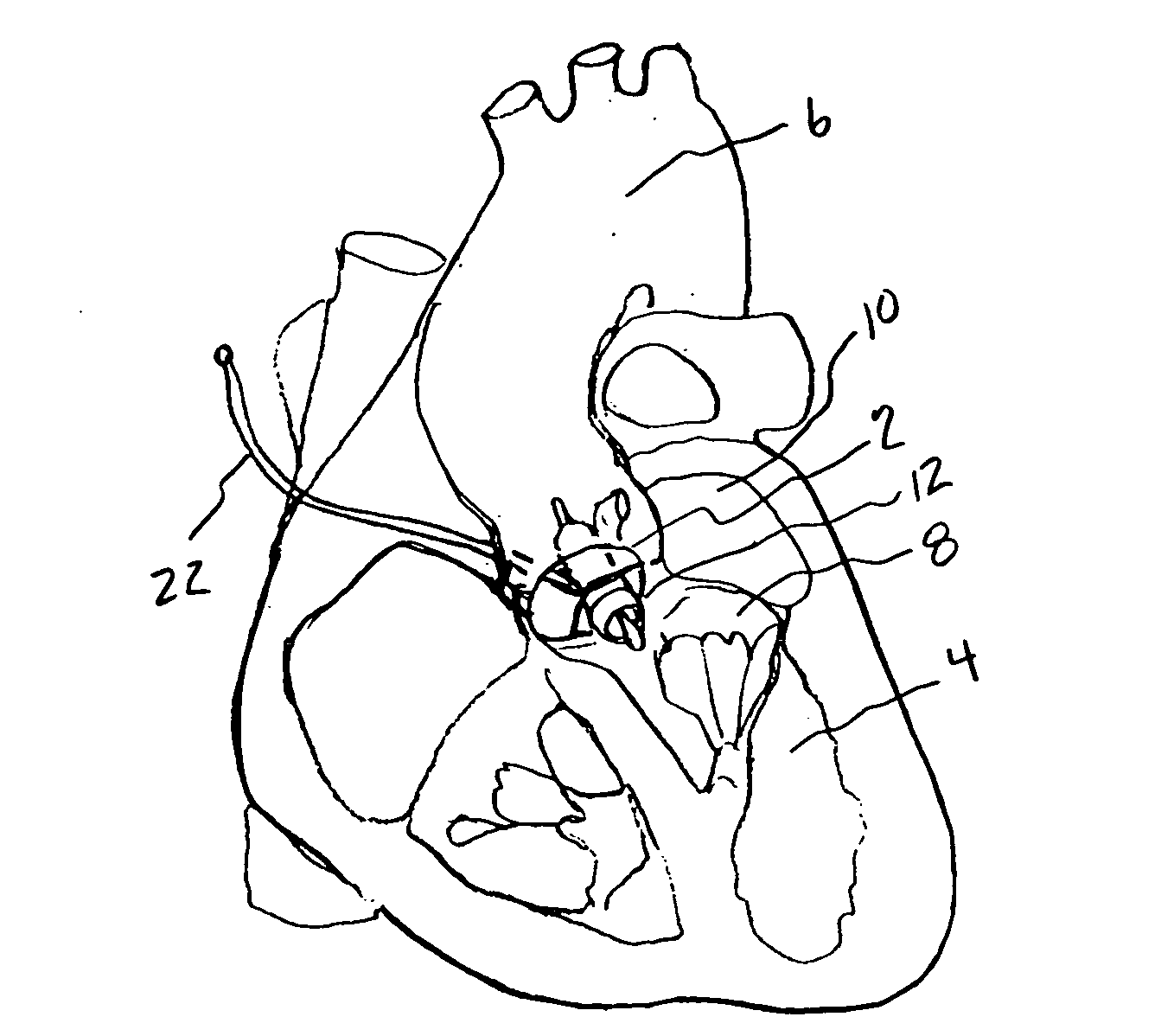
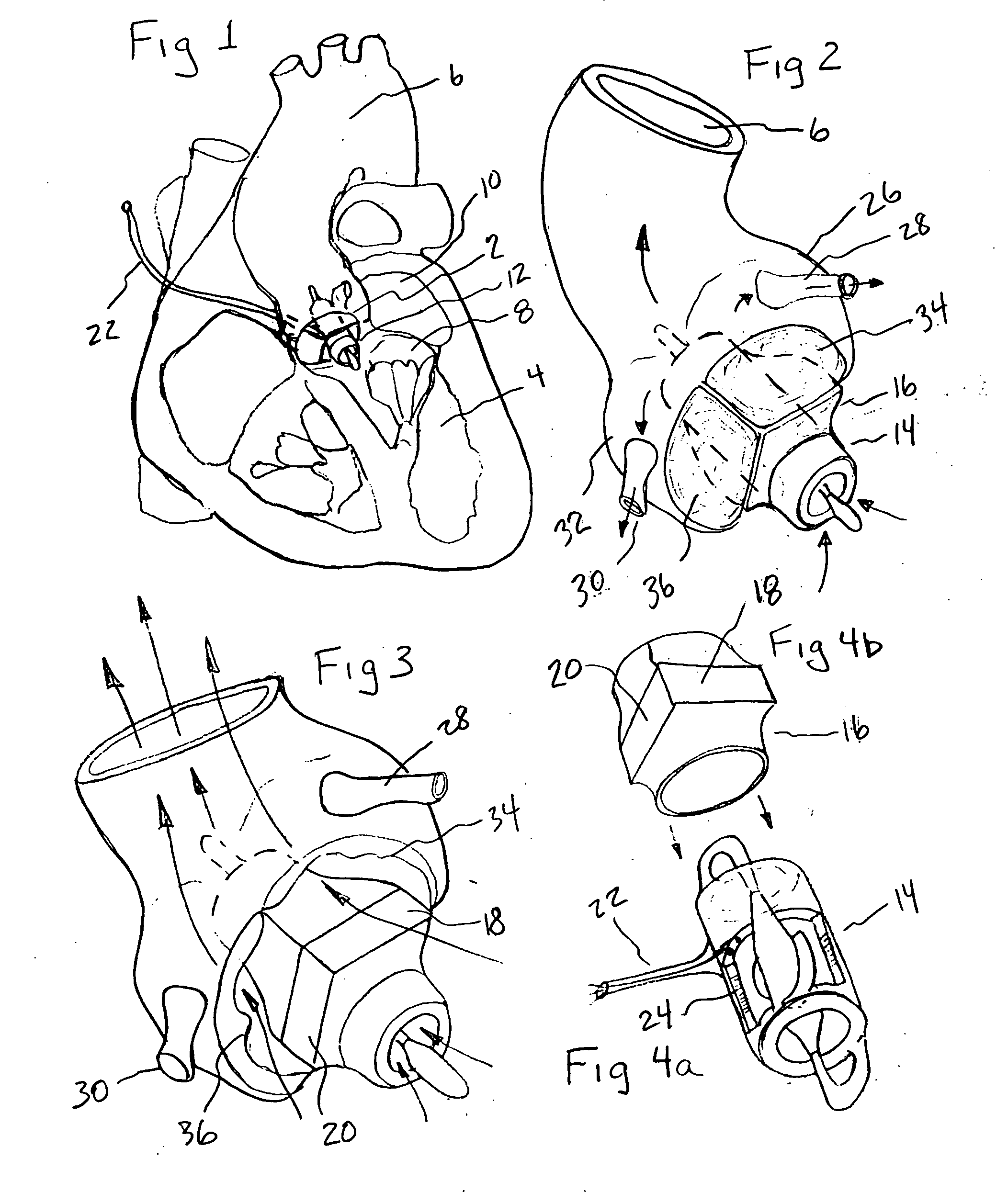
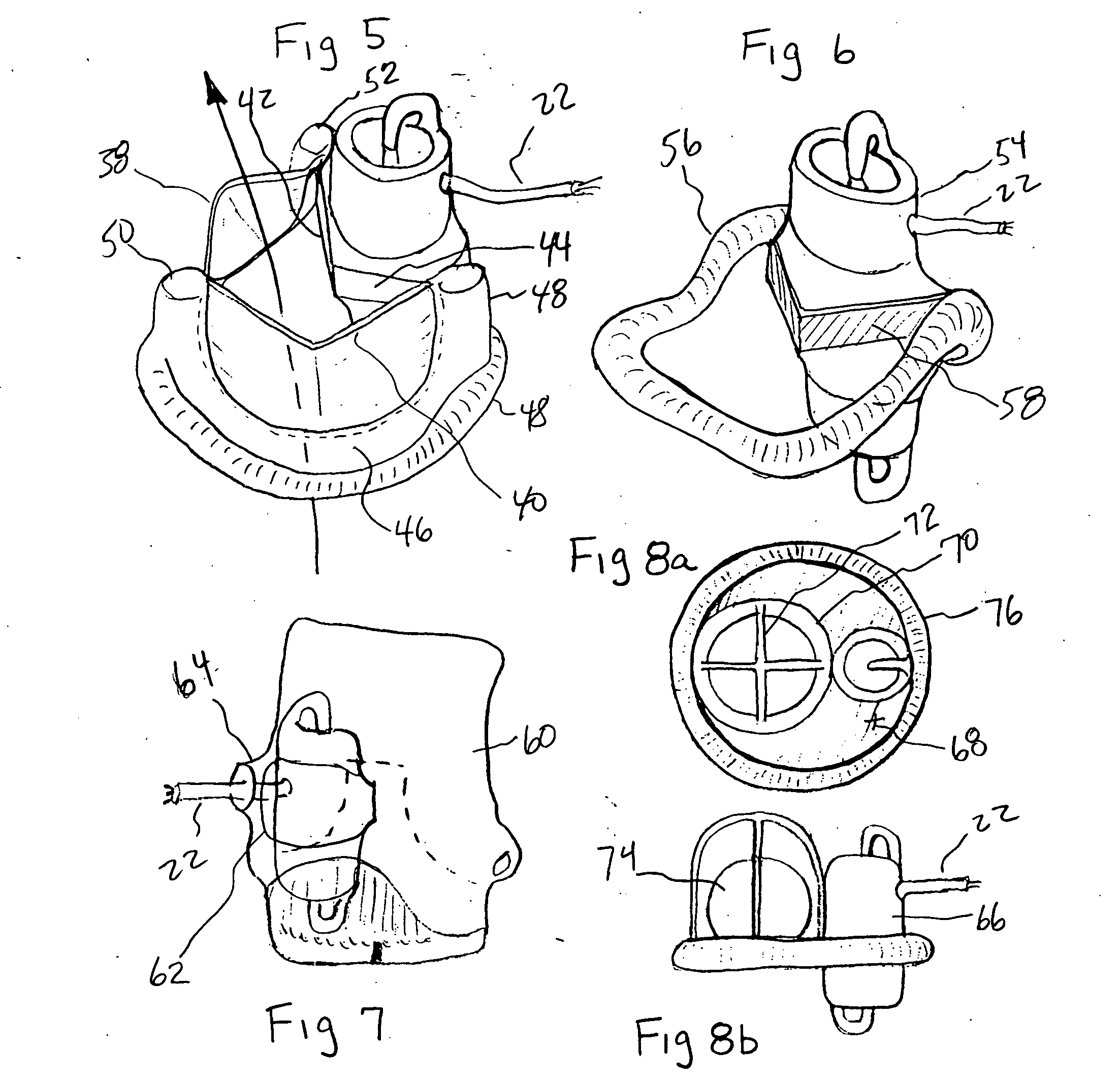
A tiny electrically powered hydrodynamic blood pump is disclosed which occupies one third of the aortic or pulmonary valve position, and pumps directly from the left ventricle to the aorta or from the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery. The device is configured to exactly match or approximate the space of one leaflet and sinus of valsalva, with part of the device supported in the outflow tract of the ventricular cavity adjacent to the valve. In the configuration used, two leaflets of the natural tri-leaflet valve remain functional and the pump resides where the third leaflet had been. When implanted, the outer surface of the device includes two faces against which the two valve leaflets seal when closed. To obtain the best valve function, the shape of these faces may be custom fabricated to match the individual patient's valve geometry based on high resolution three dimensional CT or MRI images. Another embodiment of the invention discloses a combined two leaflet tissue valve with the miniature blood pump supported in the position usually occupied by the third leaflet. Either stented or un-stented tissue valves may be used. This structure preserves two thirds of the valve annulus area for ejection of blood by the natural ventricle, with excellent washing of the aortic root and interface of the blood pump to the heart. In the aortic position, the blood pump is positioned in the non-coronary cusp. A major advantage of the transvalvular VAD is the elimination of both the inflow and outflow cannulae usually required with heart assist devices.
Owner:JARVIK ROBERT
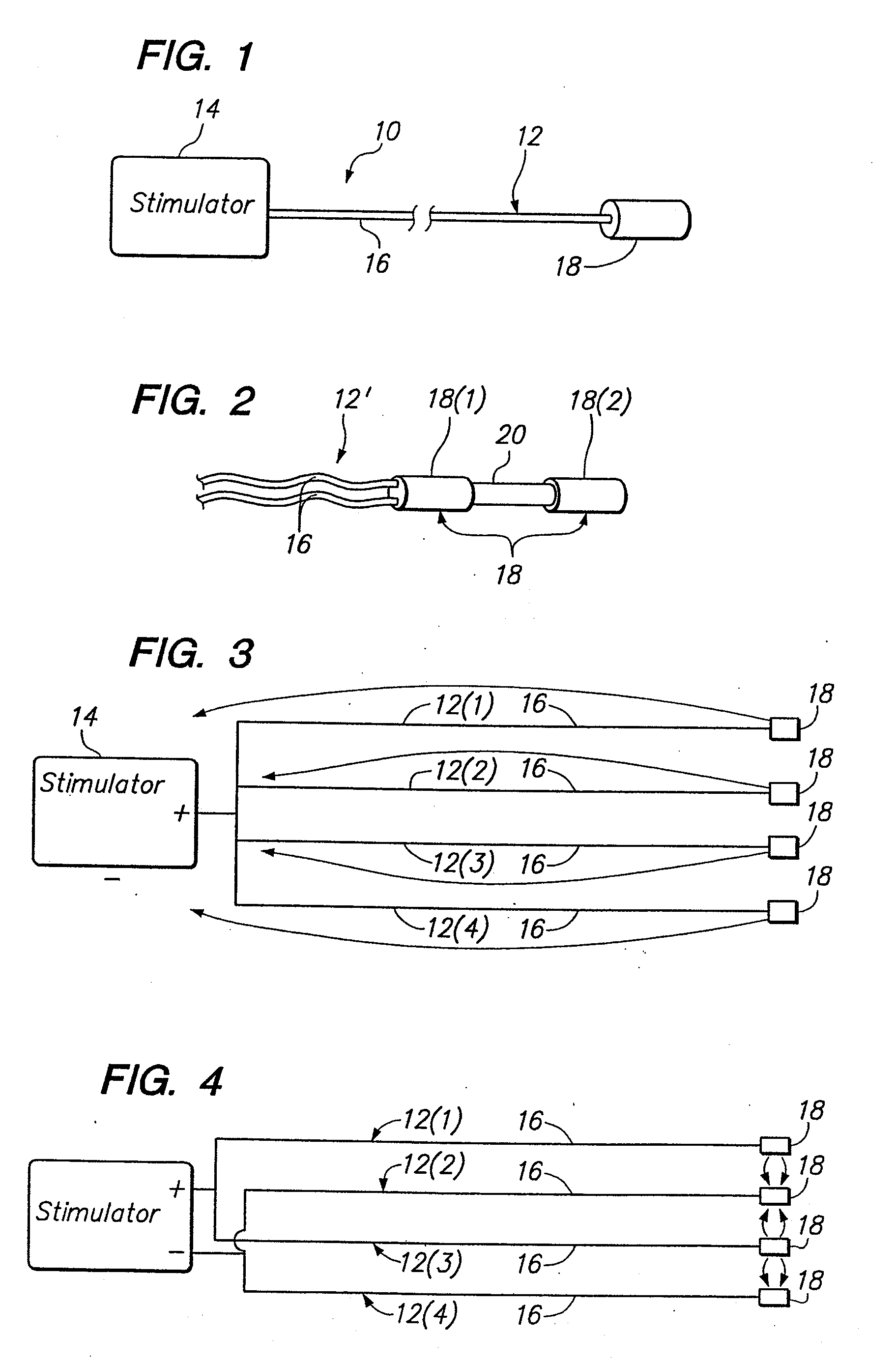
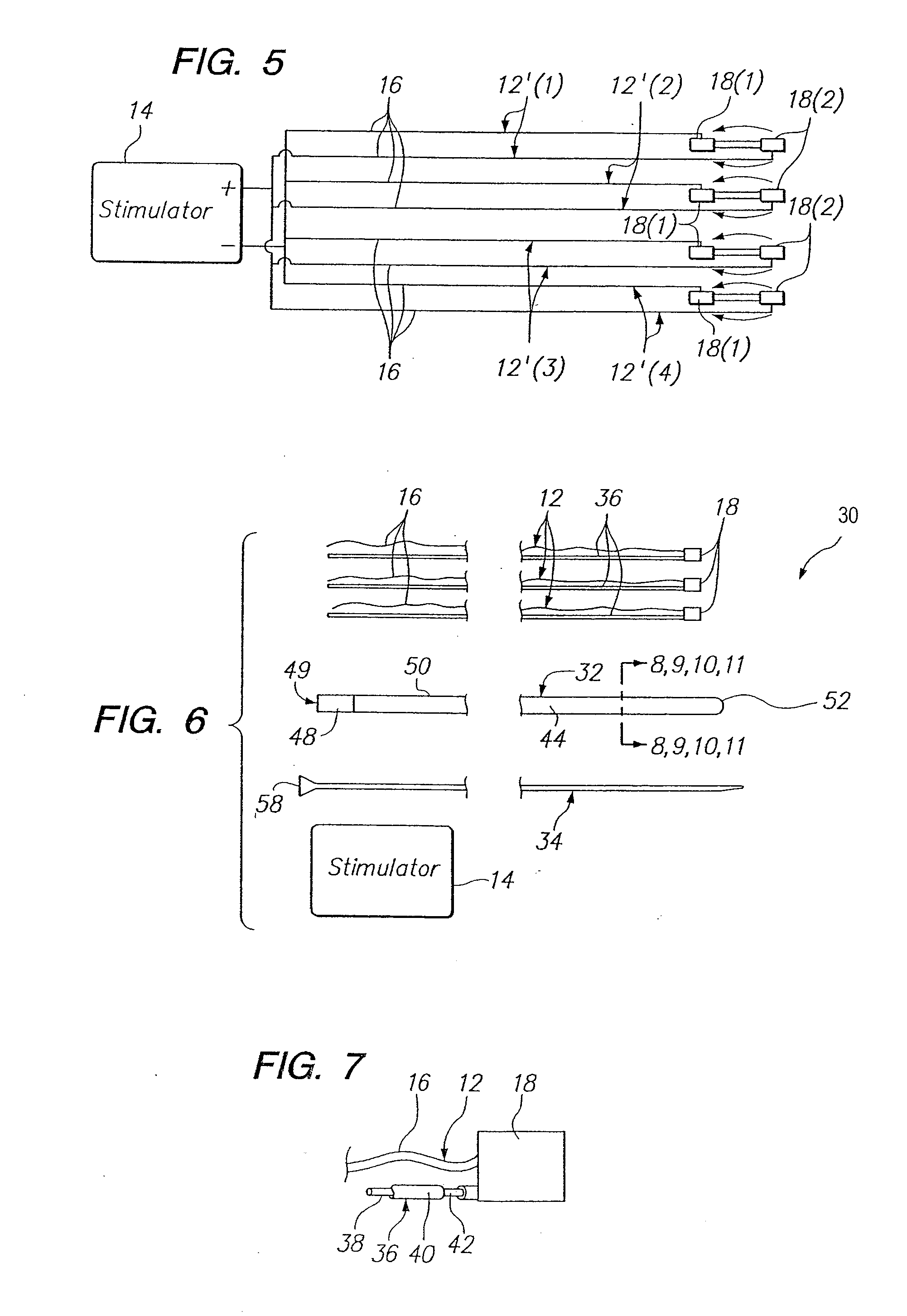
Method of intravascularly delivering stimulation leads into brain
A method of treating a neurological disorder in a patient is provided. The method comprises intravascularly delivering a stimulation lead within the head of the patient, and placing the stimulation lead adjacent brain tissue (e.g., cortical brain tissue or deep brain tissue), the stimulation of which will treat the neurological disorder. The stimulation lead can be placed into indirect contact with the brain tissue (e.g., through a blood vessel) or indirect contact with the brain tissue (e.g., when placed within the ventricular cavity or by being introduced through an exit point within a vessel wall). Optionally, the method comprises implanting a source of stimulation within the patient's body, and then electrically coupling the proximal end of the stimulation lead, which conveniently extends from the access point within the circulatory system, to the implanted stimulation source. Using the stimulation lead, the brain tissue can then be stimulated in order to treat the neurological disorder.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Minimally invasive cardiac surgery procedure
A minimally invasive approach for surgery on portions of the heart and great vessels. A parasternal incision is made extending across a predetermined number of costal cartilages, e.g., a right parasternal incision extending from the lower edge of the second costal cartilage to the superior edge of the fifth costal cartilage. One or more costal cartilages, e.g., the third and fourth, are then excised to provide access to the portion of the heart or great vessels of interest, for example between a point approximately three centimeters above supra annular ridge and the mid ventricular cavity, and a desired procedure completed. A minimally invasive procedure for repair or replacement of the aortic valve is disclosed that includes making a transverse incision of about 10 cm in length over the second or third intercostal space in the thorax of the patient, dividing the sternum transversely following the incision, retracting the transversely divided sternum, exposing the ascending aorta, and incising the ascending aorta to provide access to an area adjacent the aortic valve.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND +1
System and method for intraventricular treatment
Various methods and devices are provided for remodeling a heart's ventricular walls and improving of the function of the atrioventricular valves from within the ventricle or atrium through the use of tensioning structures. In one embodiment, a device for stabilizing a ventricle is provided and can include a superior tension member having a substantially arcuate shape that is sized and configured to improve a functioning of atrioventricular valve leaflets. The device can also include a descending tension member extending inferiorly from at least a portion of the superior tension member that is shaped to correspond to a wall of a ventricular cavity. The device can further include a plurality of anchors provided at least on the descending tension member that have attachment features for holding a wall of a ventricular cavity to the descending tension member.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Device and method to control volume of a ventricle
ActiveUS7530998B1Small sizePrevent further enlargement of a diseased heartHeart valvesHeart stimulatorsCardiac cycleReverse remodeling
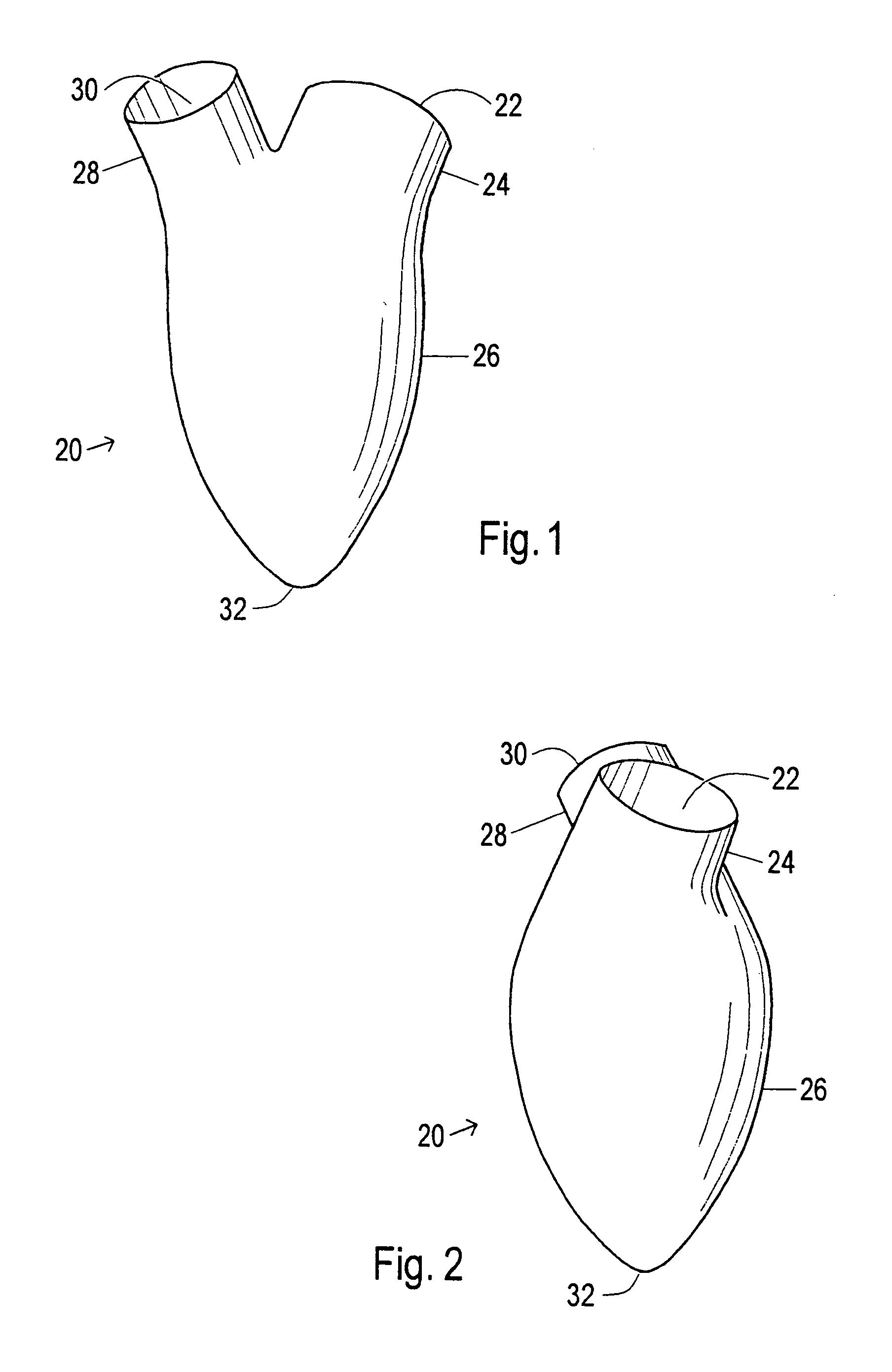
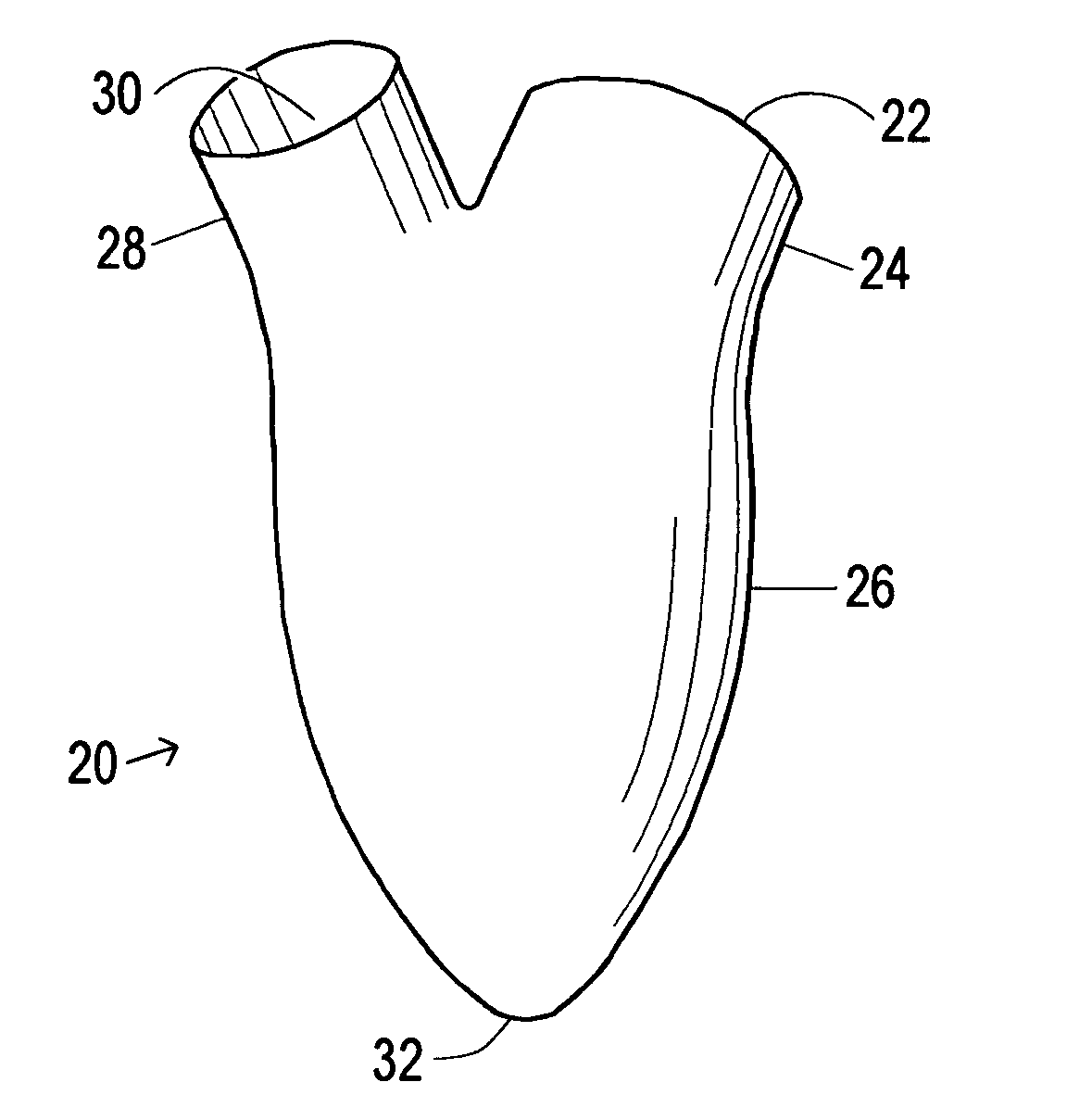
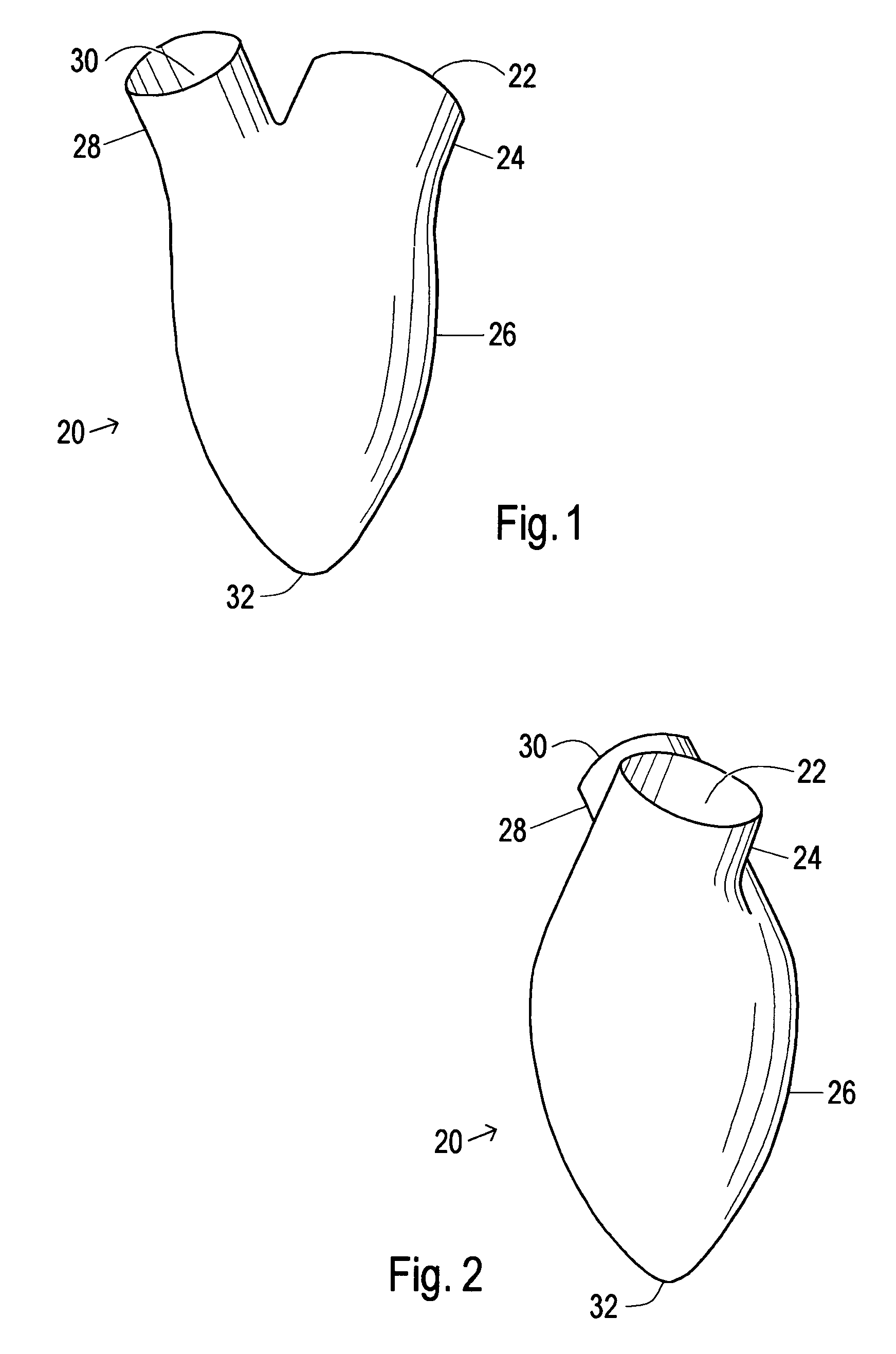
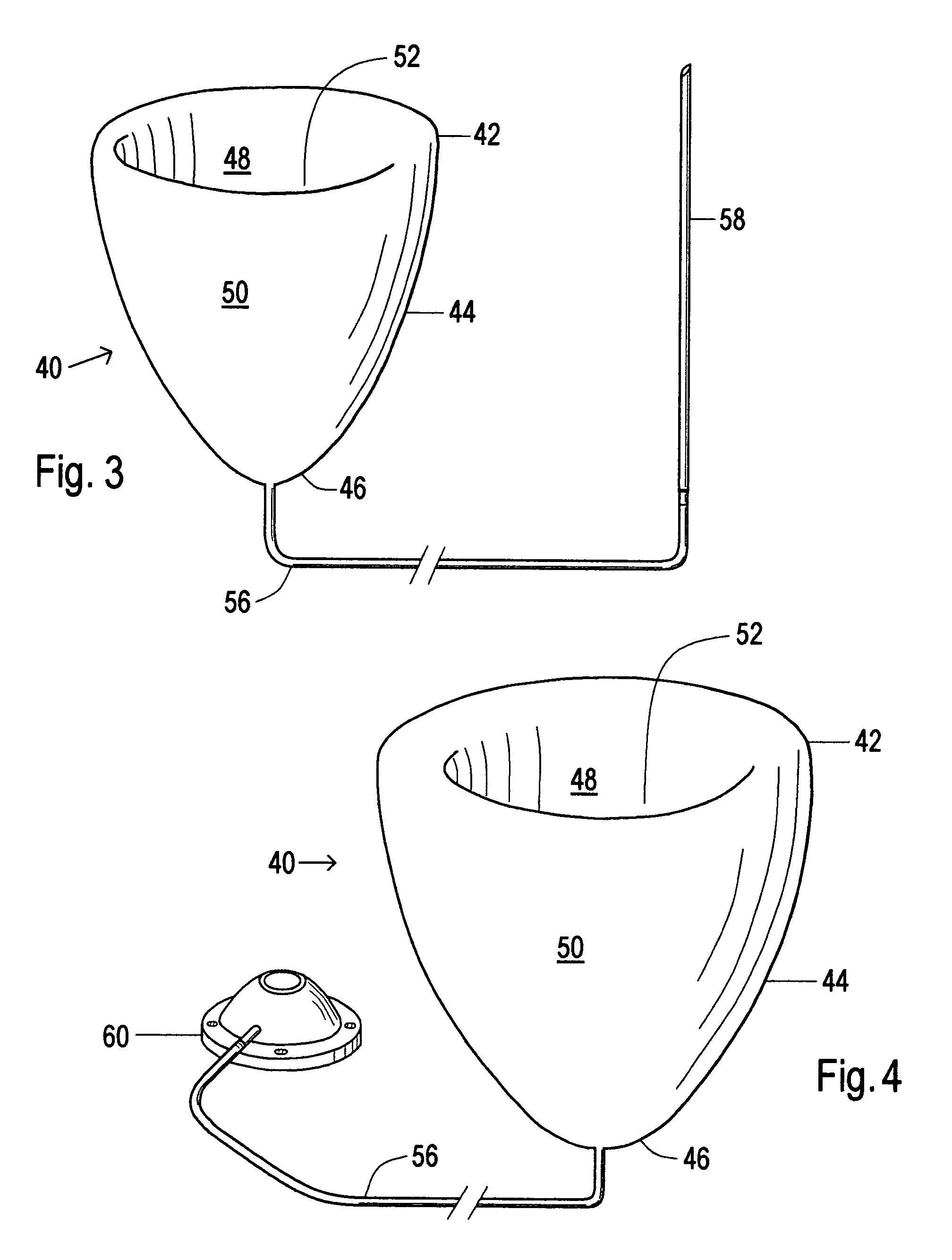
A device used to treat heart disease by decreasing the size of a diseased heart, or to prevent further enlargement of a diseased heart. The device works by limiting the volume of blood entering the heart during each cardiac cycle. The device partitions blood within the heart, and protects the heart from excessive volume and pressure of blood. The device is placed within the interior of the heart, particularly within a ventricular cavity. The device is a hollow sac, with two openings, which simulates the shape and size of the interior lining of a ventricle of a normal heart. It allows the ventricle to fill through one opening juxtaposed to the annulus of the inflow valve to a predetermined, normal volume, and limits filling of the heart beyond that volume. It then allows blood to be easily ejected through the second opening through the outflow valve. By limiting the amount of blood entering the ventricle, the ventricle is not subjected to the harmful effect of excessive volume and pressure of blood during diastole, the period of the cardiac cycle when the heart is at rest. This allows the heart to decrease in size, or to reverse remodel, and to recover lost function. In some applications, a second device may be simultaneously placed inside the heart to take up excessive space between the heart and the primary device.
Owner:STARKEY THOMAS DAVID
Device and method to limit filling of the heart
ActiveUS7341584B1Small sizeLimiting volume of bloodHeart valvesSurgical instrument detailsCardiac cycleReverse remodeling
A device used to treat heart disease by decreasing the size of a diseased heart, or to prevent further enlargement of a diseased heart. The device works by limiting the volume of blood entering the heart during each cardiac cycle. The device partitions blood within the heart, and protects the heart from excessive volume and pressure of blood. The device is placed within the interior of the heart, particularly within a ventricular cavity. The device is a hollow sac, with two openings, which simulates the shape and size of the interior lining of a ventricle of a normal heart. It allows the ventricle to fill through one opening juxtaposed to the annulus of the inflow valve to a predetermined, normal volume, and limits filling of the heart beyond that volume. It then allows blood to be easily ejected through the second opening through the outflow valve. By limiting the amount of blood entering the ventricle, the ventricle is not subjected to the harmful effect of excessive volume and pressure of blood during diastole, the period of the cardiac cycle when the heart is at rest. This allows the heart to decrease in size, or to reverse remodel, and to recover lost function. In some applications, a second device may be simultaneously placed inside the heart to take up excessive space between the heart and the primary device.
Owner:STARKEY THOMAS DAVID
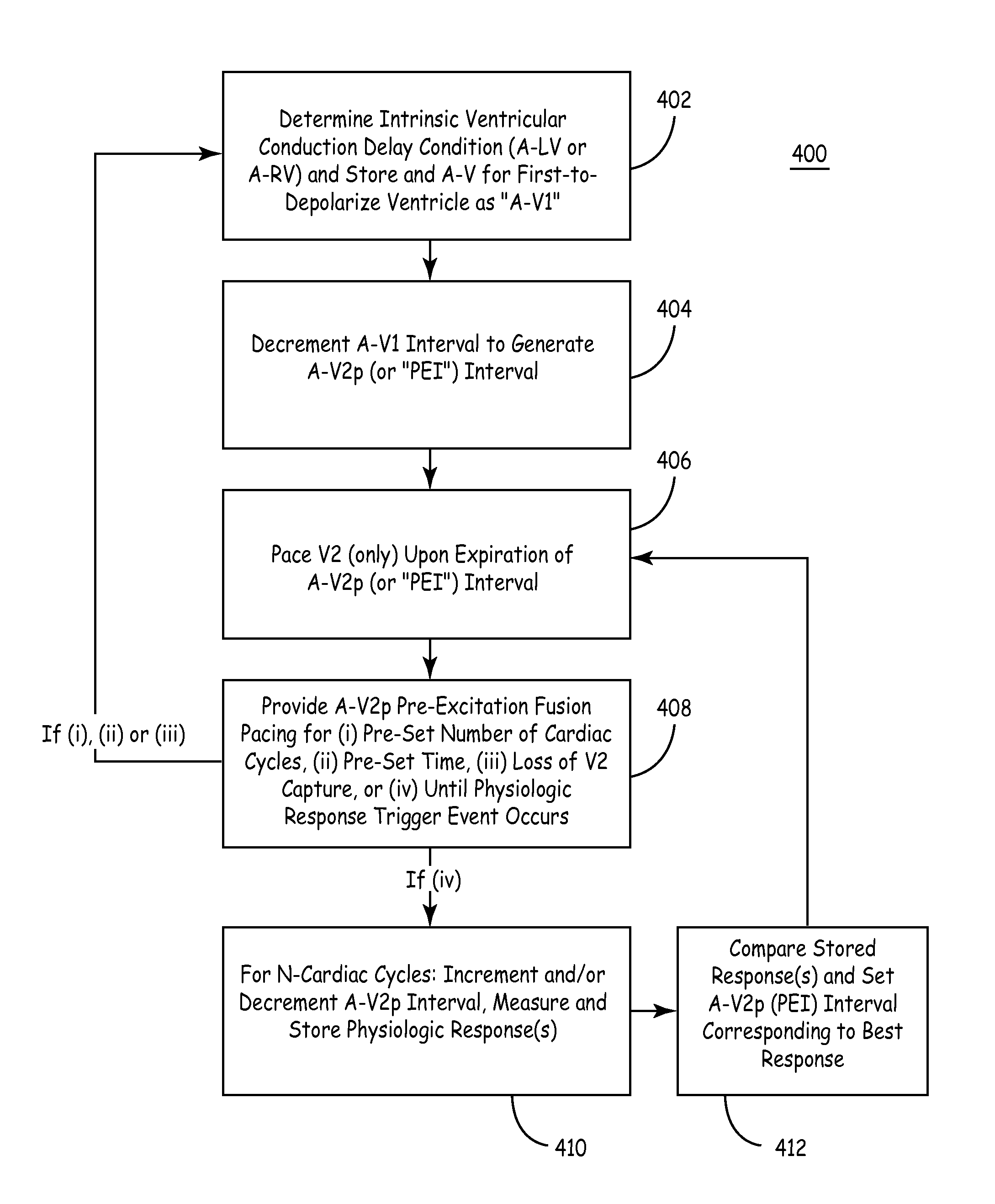
Fusion Pacing Enhancements
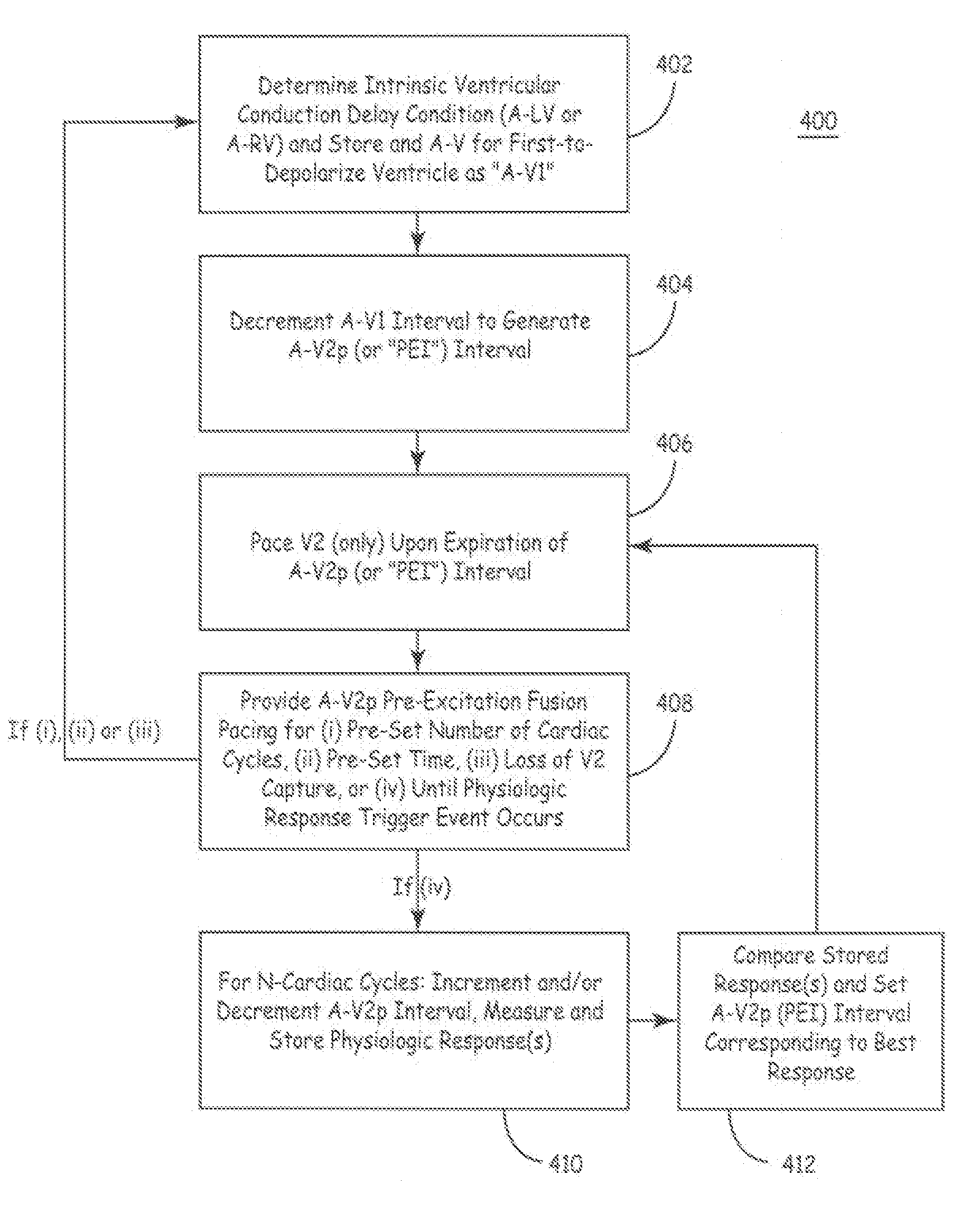
The disclosure provides methods and apparatus of left ventricular pacing including automated adjustment of a atrio-ventricular (AV) pacing delay interval and intrinsic AV nodal conduction testing. It includes—upon expiration or reset of a programmable AV Evaluation Interval (AVEI)—performing the following: temporarily increasing a paced AV interval and a sensed AV interval and testing for adequate AV conduction and measuring an intrinsic atrio-ventricular (PR) interval for a right ventricular (RV) chamber. Thus, in the event that the AV conduction test reveals a physiologically acceptable intrinsic PR interval then storing the physiologically acceptable PR interval in a memory structure (e.g., a median P-R from one or more cardiac cycles). In the event that the AV conduction test reveals an AV conduction block condition or if unacceptably long PR intervals are revealed then a pacing mode-switch to a bi-ventricular (Bi-V) pacing mode occurs and the magnitude of the AVEI is increased.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Minimally invasive transvalvular ventricular assist device
ActiveUS7479102B2Highly effectiveHighly miniaturizedAdditive manufacturing apparatusBlood pumpsThree dimensional ctVentricular cavity
Owner:JARVIK ROBERT
Method of intravascularly delivering stimulation leads into brain to stimulate the spg
A method of treating a neurological disorder in a patient is provided. The method comprises intravascularly delivering a stimulation lead within the head of the patient, and placing the stimulation lead adjacent brain tissue (e.g., cortical brain tissue or deep brain tissue), the stimulation of which will treat the neurological disorder. The stimulation lead can be placed into indirect contact with the brain tissue (e.g., through a blood vessel) or indirect contact with the brain tissue (e.g., when placed within the ventricular cavity or by being introduced through an exit point within a vessel wall). Optionally, the method comprises implanting a source of stimulation within the patient's body, and then electrically coupling the proximal end of the stimulation lead, which conveniently extends from the access point within the circulatory system, to the implanted stimulation source. Using the stimulation lead, the brain tissue can then be stimulated in order to treat the neurological disorder.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
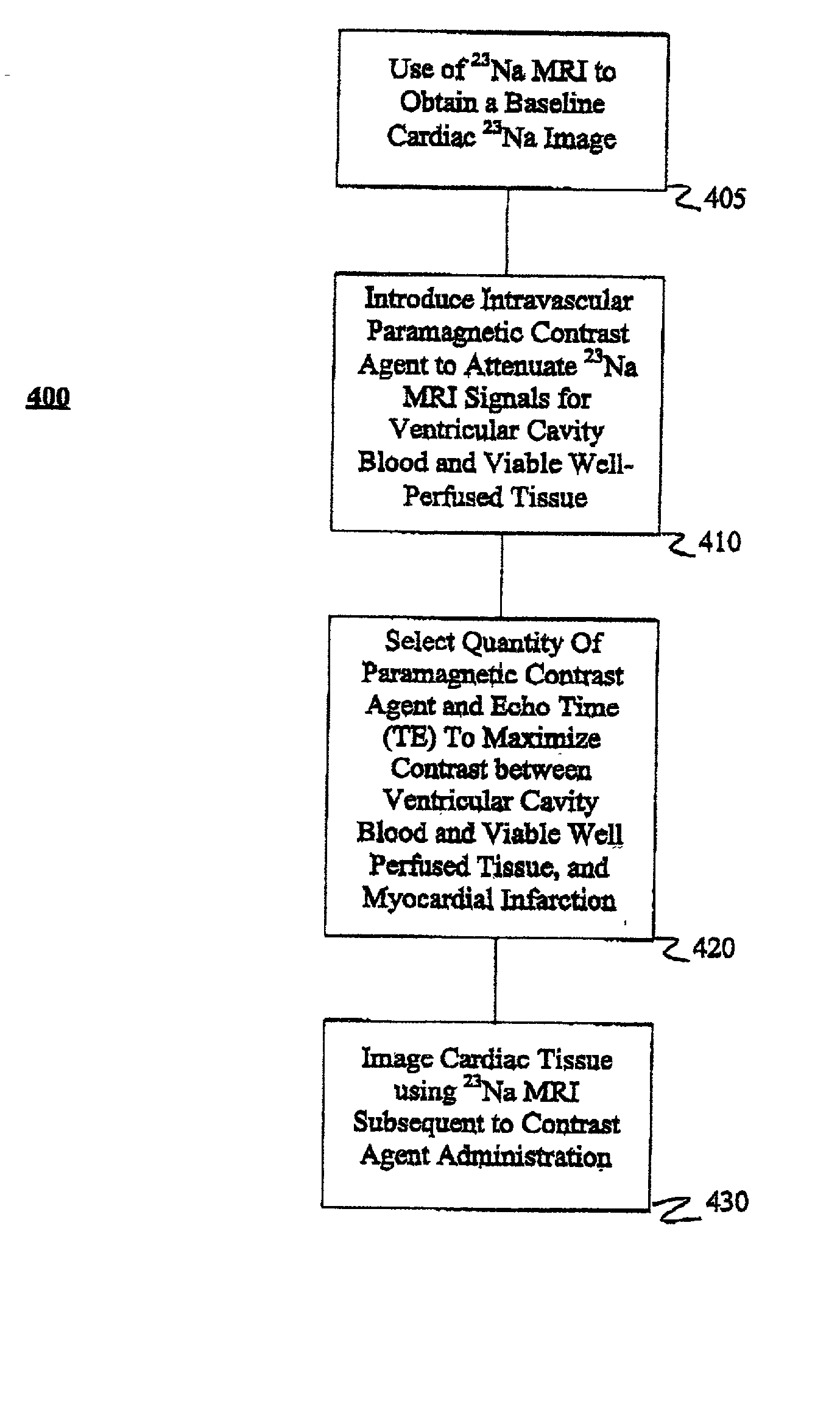
Magnetic resonance imaging methods and compositions
InactiveUS20030120151A1Minimize the differenceMaximize intensity differenceNanomedicineDiagnostic recording/measuringVentricular cavityBlood vessel
Methods and compositions are provided for magnetic resonance imaging of biological tissue, particularly methods and compositions for 23Na and 39K magnetic resonance imaging of cardiac tissue. In particular, methods of 23Na magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) cardiac imaging is presented for attenuating 23Na signals corresponding to ventricular cavity blood and viable well-perfused tissue and for visualizing myocardial infarction. Cardiac tissue is imaged using 23Na MRI after the introduction of an intravascular paramagnetic contrast agent. Optimally, the intravascular paramagnetic contrast agent is MION-46. The MION-46 suppresses the blood signal intensity in sodium images of ventricular cavities and signal for viable cardiac tissue. The quantity of MION-46 and the echo time (TE) for 23Na MRI of cardiac tissue may be selected to minimize signal intensity differences between ventricular cavity blood and well-perfused viable myocardium; maximize signal intensity differences between non-viable myocardium and ventricular cavity blood in myocardial infarction; and maximize signal intensity differences between non-viable myocardium and well-perfused viable myocardium in myocardial infarction.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Intra-thecal catheter and method for cooling the spinal cord and brain
A method for cooling of the brain includes the steps of positioning a cooling catheter within a ventricular cavity of the brain, the catheter including an inlet channel and outlet channel providing for the closed flow of cooling fluid into and out of the catheter, and cooling the catheter and ventricular cavity through the closed flow of cooling fluid through the catheter. An alternate method for cooling of the brain including the steps of positioning a cooling catheter within a spinal canal, the catheter including an inlet channel and outlet channel providing for the closed flow of cooling fluid into and out of the catheter, and cooling the catheter and brain through the closed flow of cooling fluid through the catheter.
Owner:ELEFTERIADES JOHN
Fusion pacing enhancements
The disclosure provides methods and apparatus of left ventricular pacing including automated adjustment of a atrio-ventricular (AV) pacing delay interval and intrinsic AV nodal conduction testing. It includes—upon expiration or reset of a programmable AV Evaluation Interval (AVEI)—performing the following: temporarily increasing a paced AV interval and a sensed AV interval and testing for adequate AV conduction and measuring an intrinsic atrio-ventricular (PR) interval for a right ventricular (RV) chamber. Thus, in the event that the AV conduction test reveals a physiologically acceptable intrinsic PR interval then storing the physiologically acceptable PR interval in a memory structure (e.g., a median P-R from one or more cardiac cycles). In the event that the AV conduction test reveals an AV conduction block condition or if unacceptably long PR intervals are revealed then a pacing mode-switch to a bi-ventricular (Bi-V) pacing mode occurs and the magnitude of the AVEI is increased.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
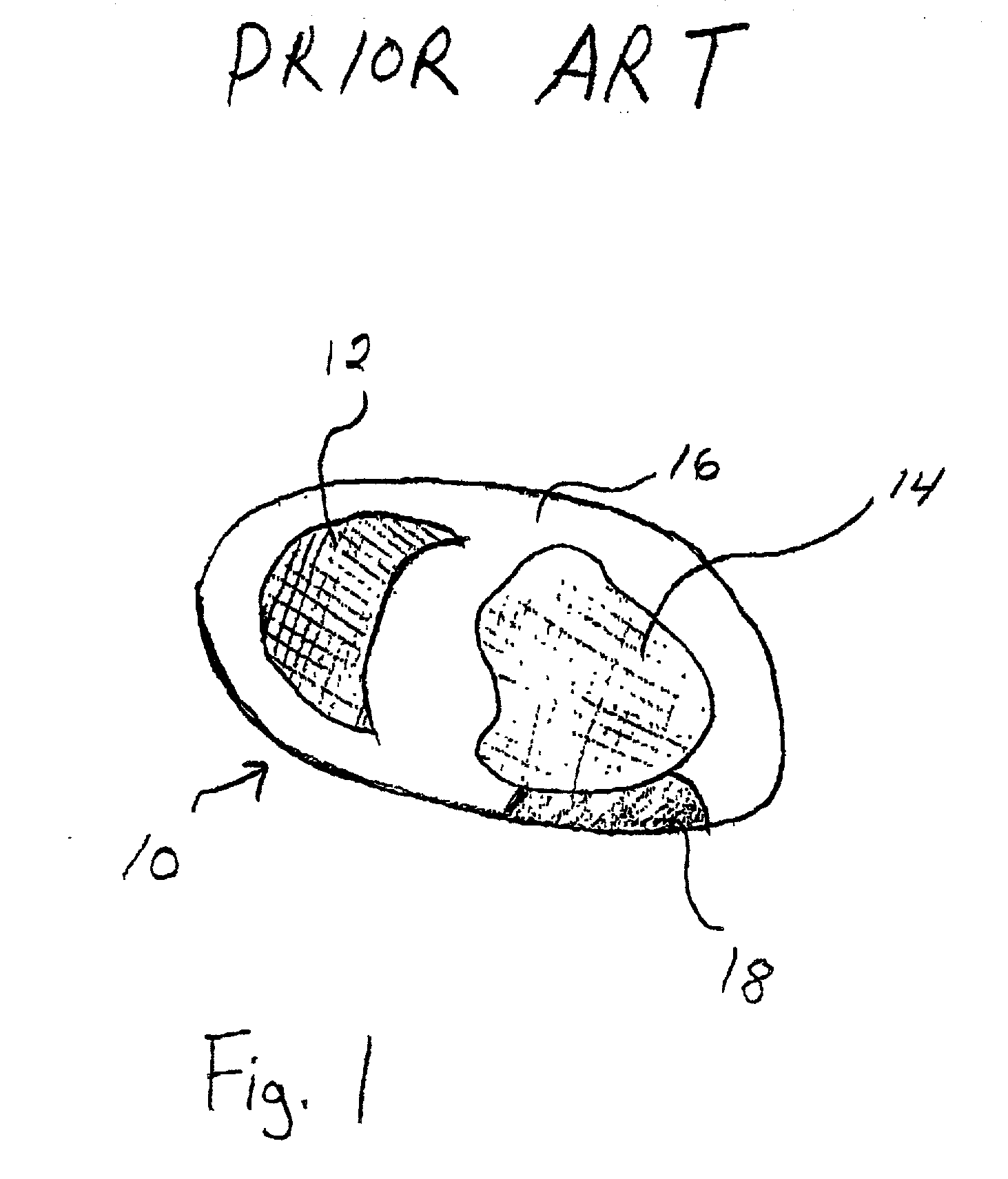
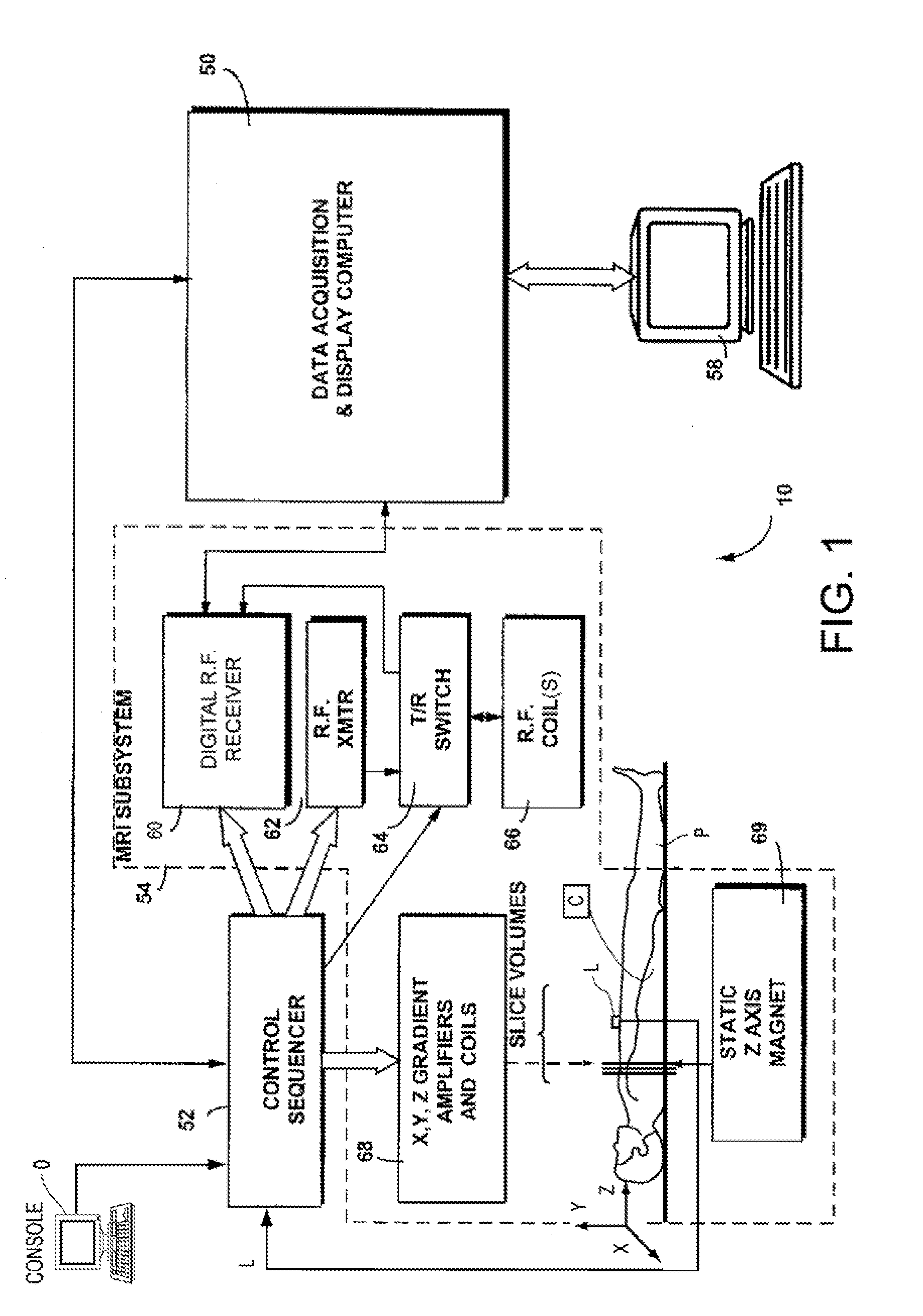
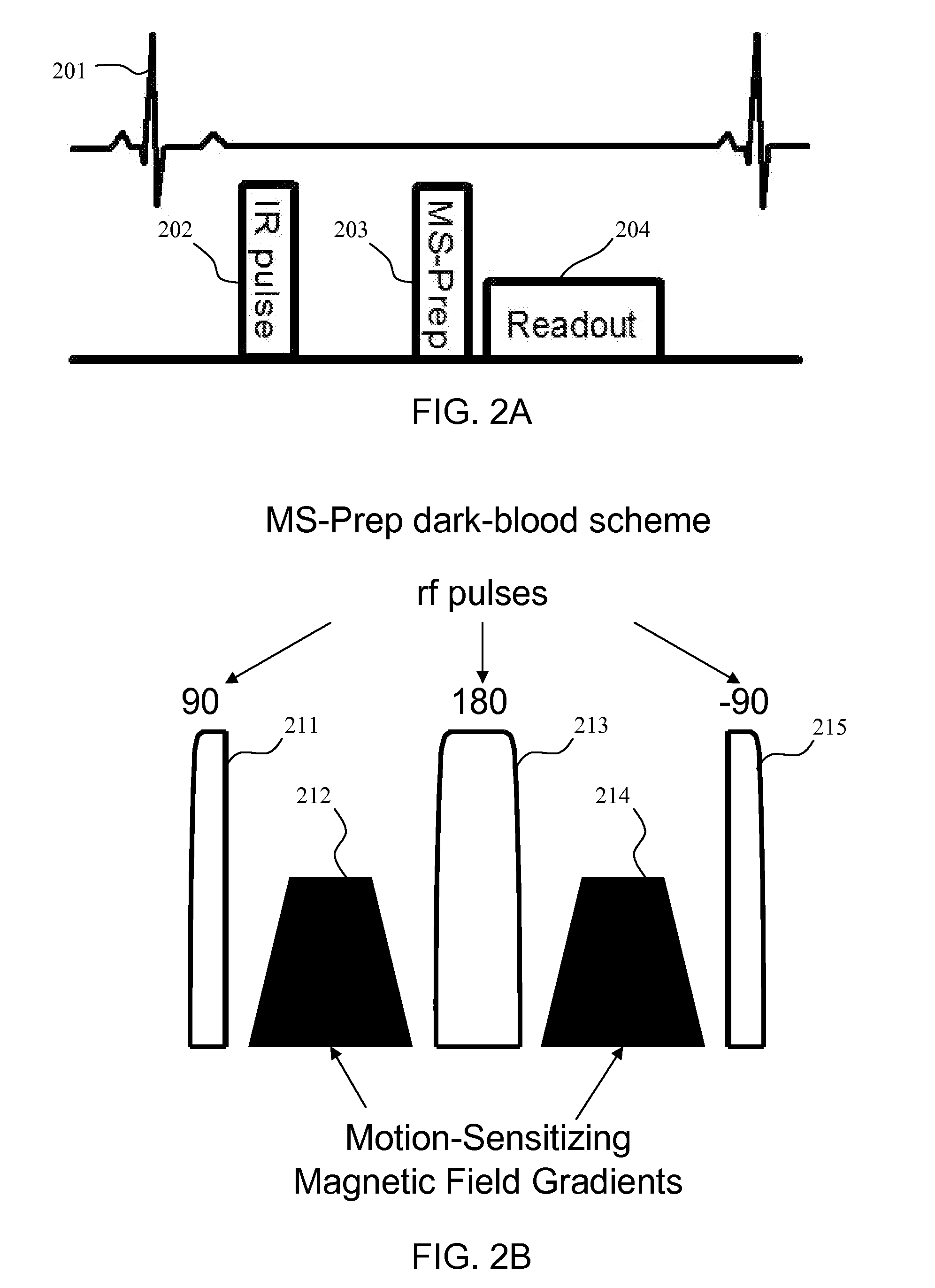
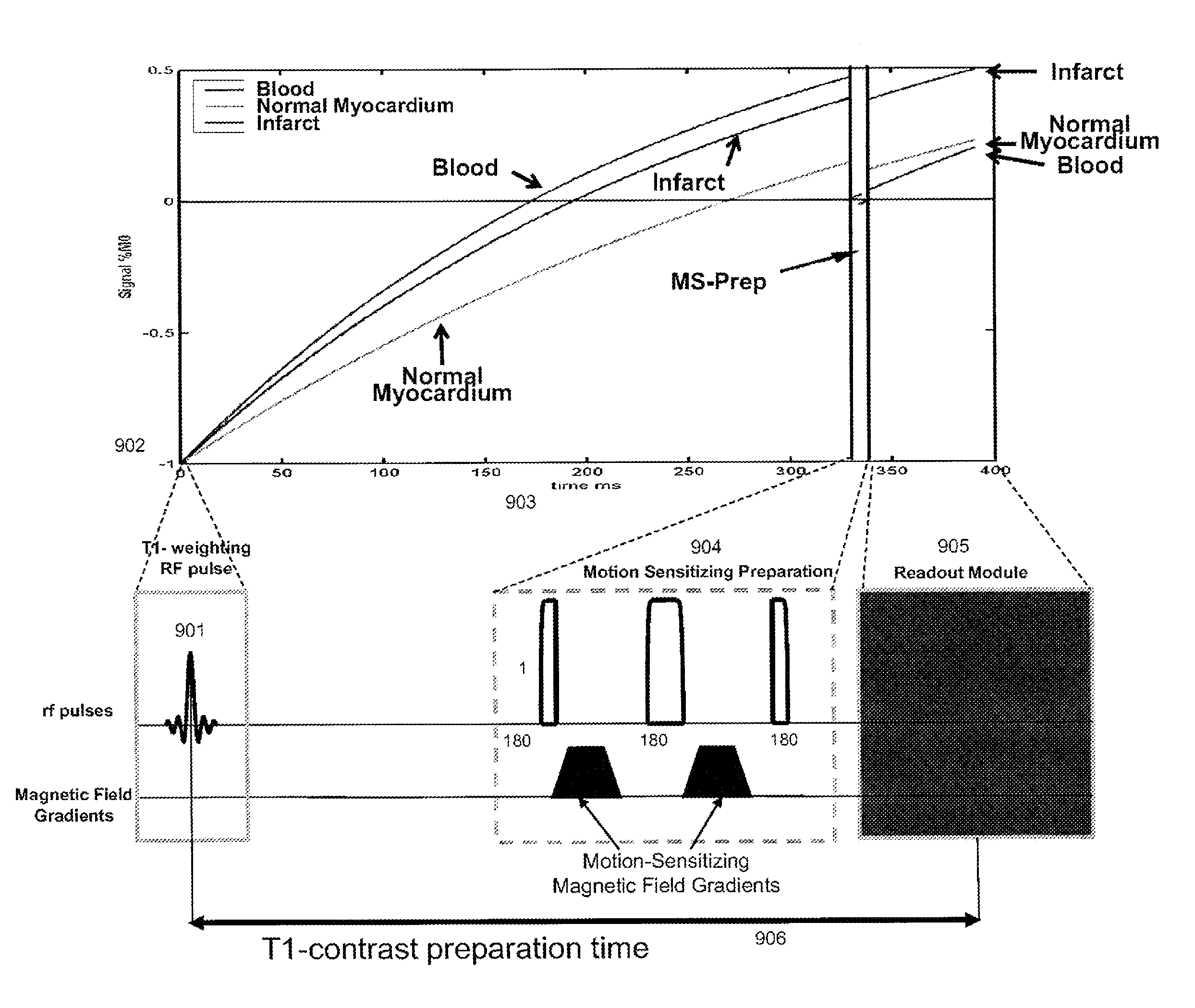
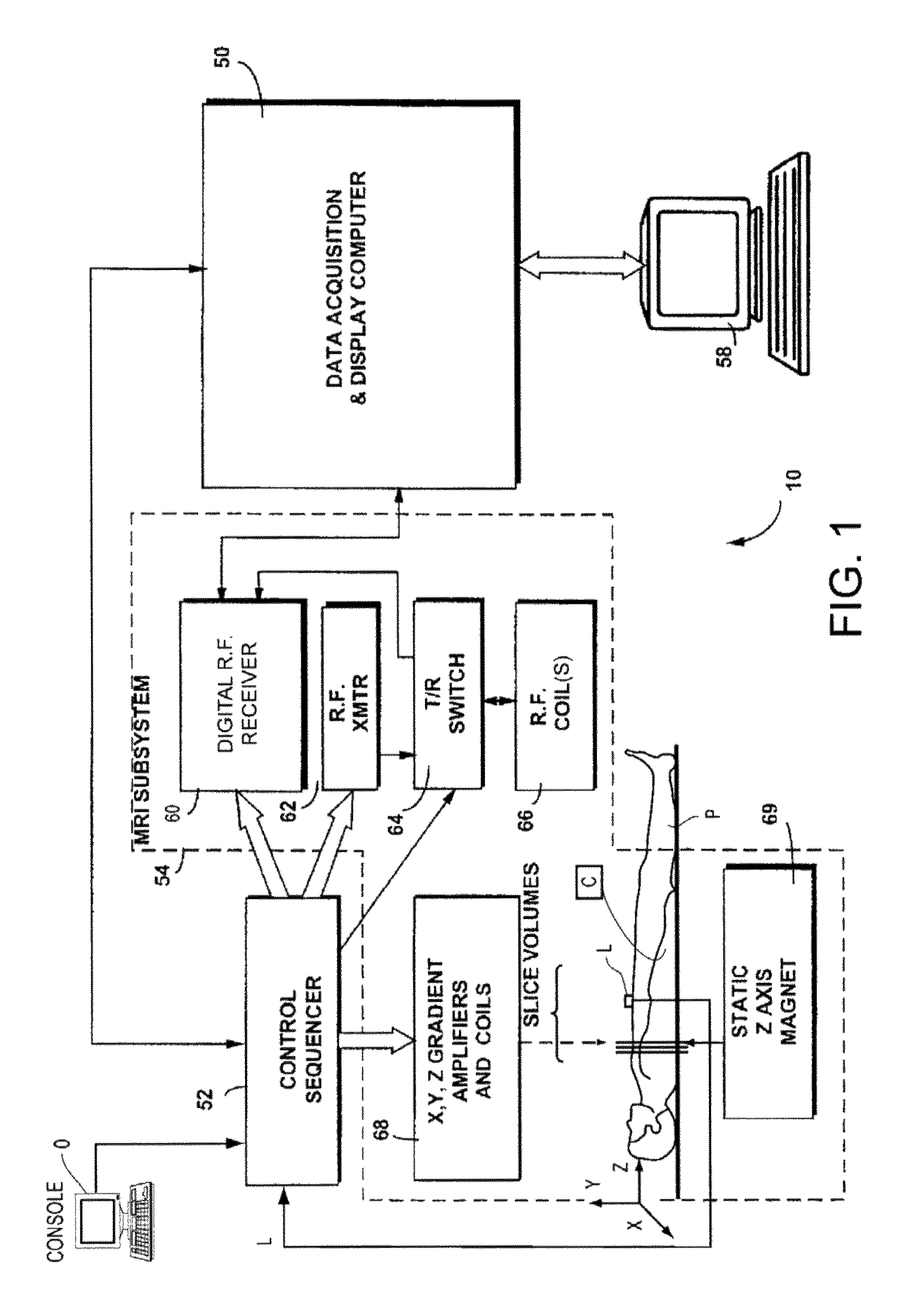
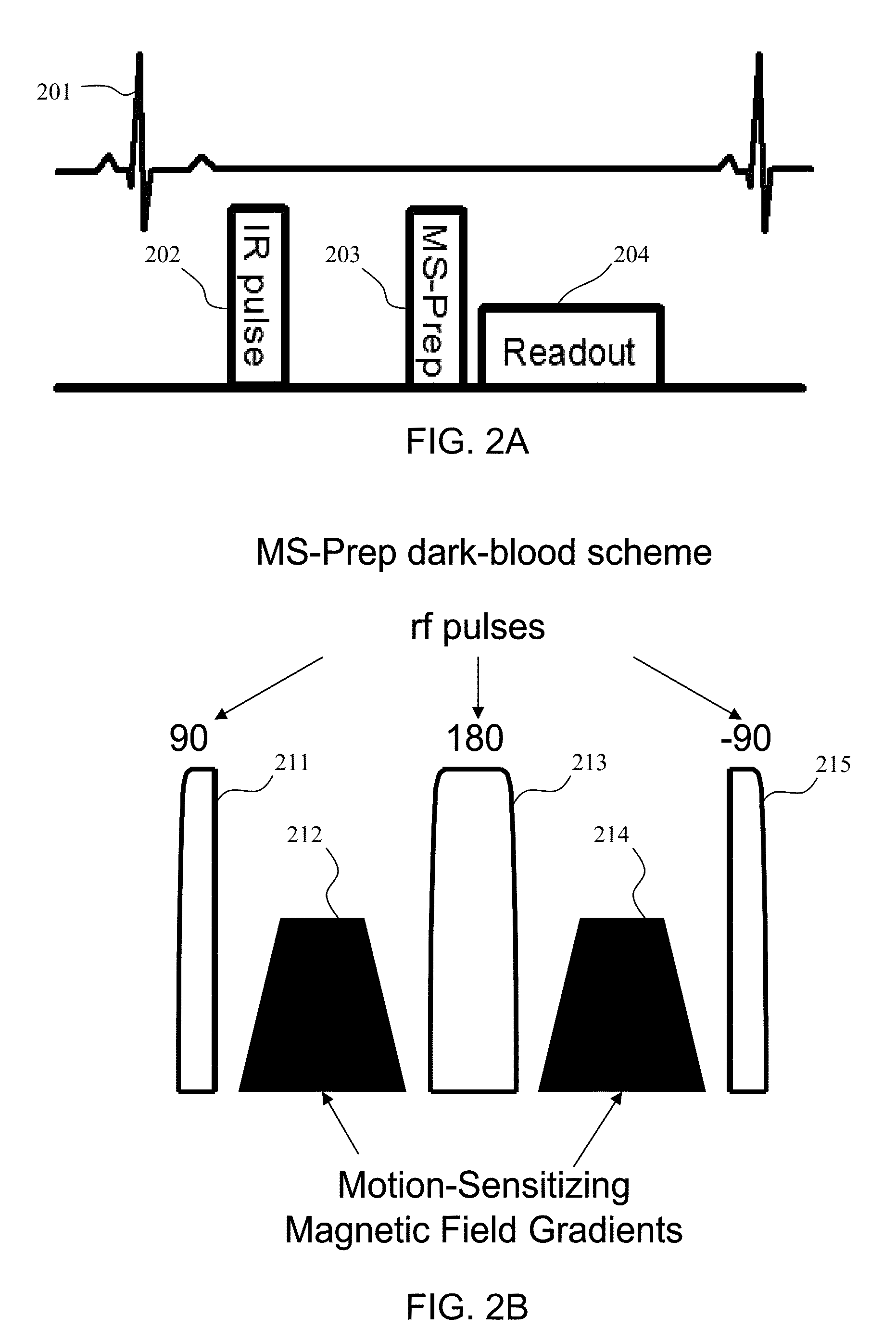
Motion-attenuated contrast-enhanced cardiac magnetic resonance imaging and related method thereof
ActiveUS20100191099A1Improve visualizationReduce signalingElectrocardiographyMagnetic measurementsContrast levelVentricular cavity
A system and method for providing a dark-blood technique for contrast-enhanced cardiac magnetic resonance, improving visualization of subendocardial infarcts or perfusion abnormalities that may otherwise be difficult to distinguish from the bright blood pool. In one technique the dark-blood preparation is performed using a driven-equilibrium fourier transform (DEFT) preparation with motion sensitizing gradients which attenuate the signal in the ventricular cavities related to incoherent phase losses resulting from non-steady flow within the heart. This dark-blood preparation preserves the underlying contrast characteristics of the pulse sequence causing a myocardial infarction to be bright while rendering the blood pool dark. When applied to perfusion imaging, this dark-blood preparation will help eliminate artifacts resulting from the juxtaposition of a bright ventricular cavity and relatively dark myocardium.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Motion-attenuated contrast-enhanced cardiac magnetic resonance imaging system and method
ActiveUS8700127B2Contrast-enhanced cardiac magnetic resonanceImprove visualizationElectrocardiographyMagnetic measurementsVentricular cavityPulse sequence
A system and method for providing a dark-blood technique for contrast-enhanced cardiac magnetic resonance, improving visualization of subendocardial infarcts or perfusion abnormalities that may otherwise be difficult to distinguish from the bright blood pool. In one technique the dark-blood preparation is performed using a driven-equilibrium fourier transform (DEFT) preparation with motion sensitizing gradients which attenuate the signal in the ventricular cavities related to incoherent phase losses resulting from non-steady flow within the heart. This dark-blood preparation preserves the underlying contrast characteristics of the pulse sequence causing a myocardial infarction to be bright while rendering the blood pool dark. When applied to perfusion imaging, this dark-blood preparation will help eliminate artifacts resulting from the juxtaposition of a bright ventricular cavity and relatively dark myocardium.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
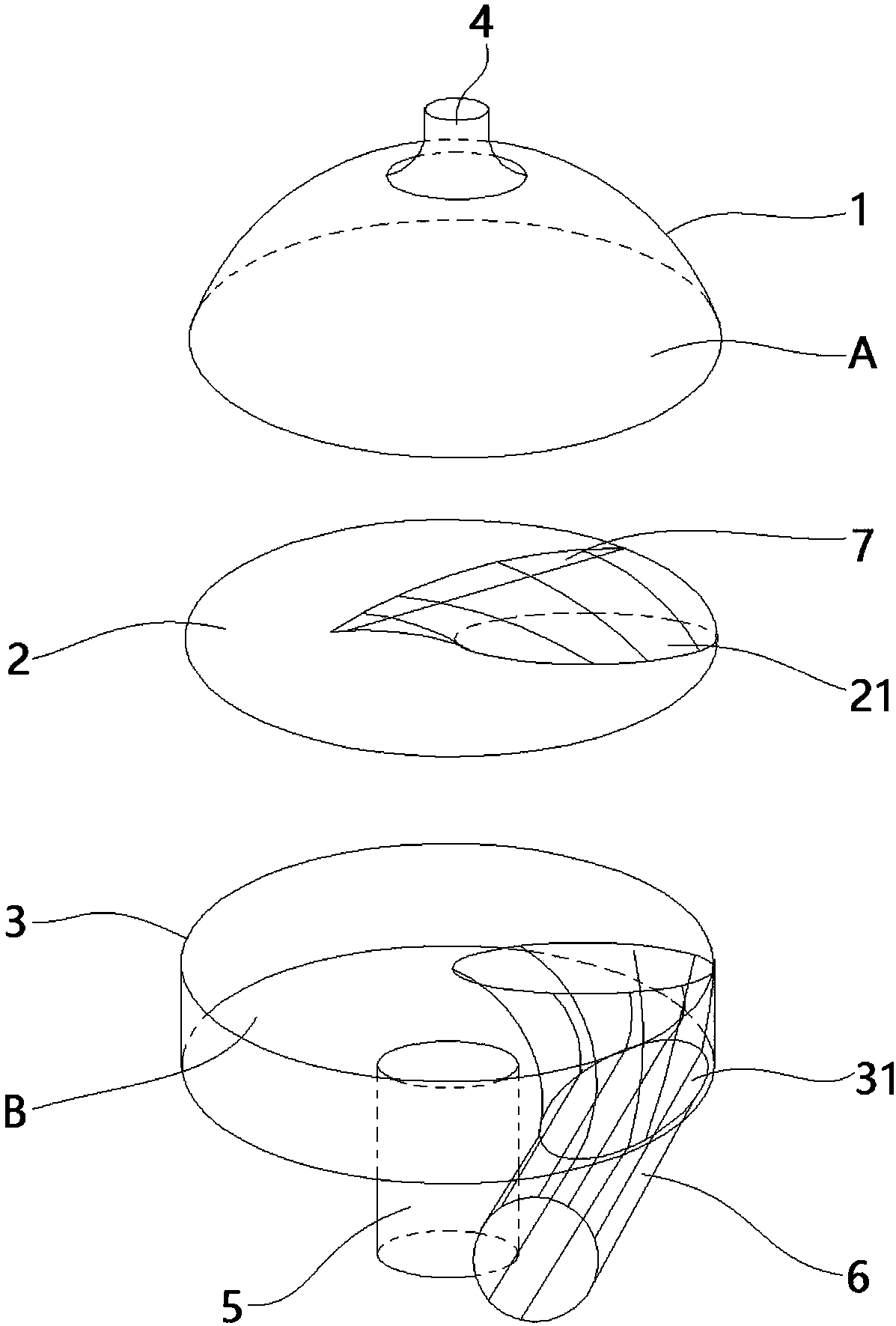
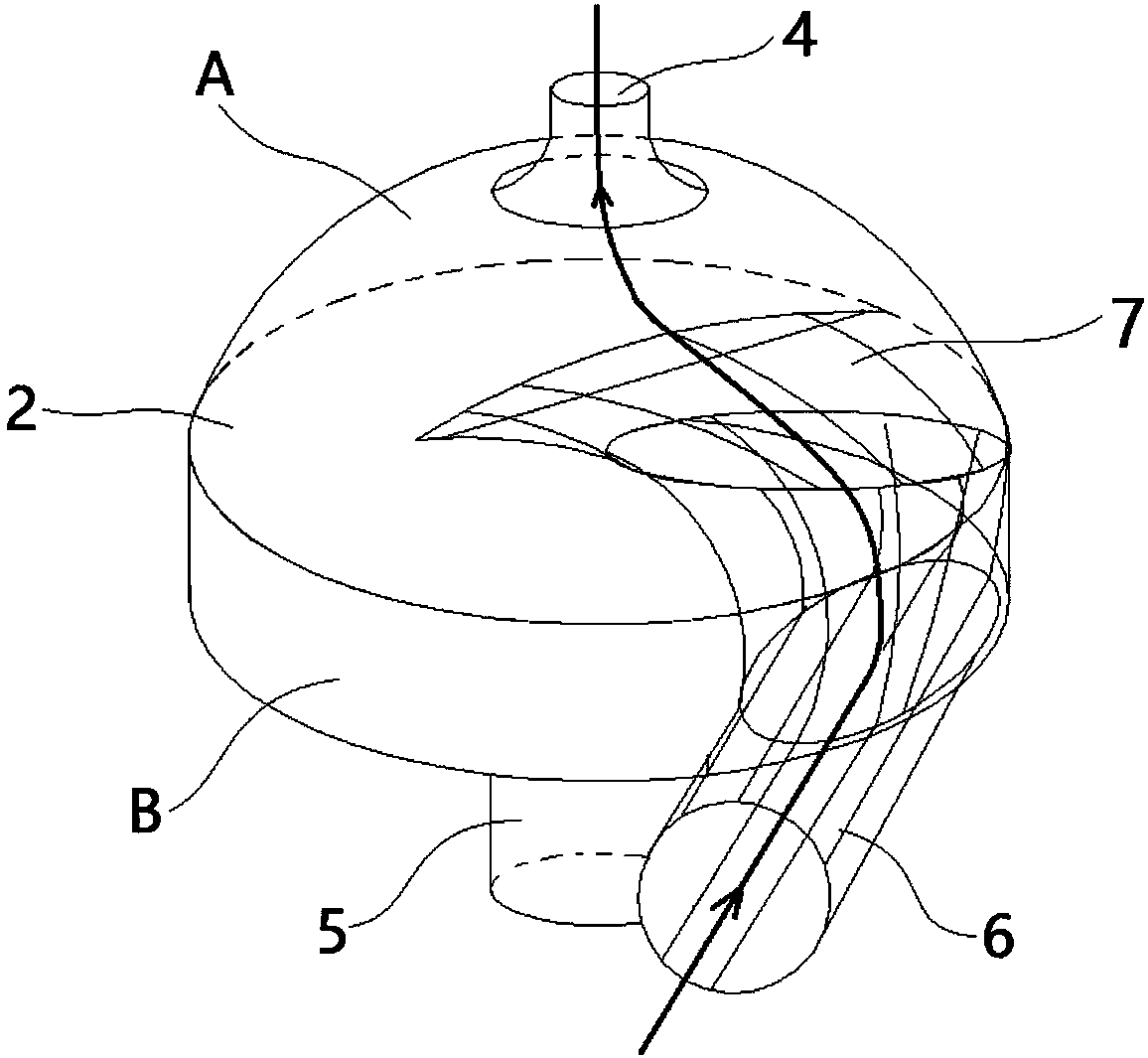
Cystic cavity pulmonary circulation assisting device
ActiveCN108653840ACompact internal structureReduce volumeMedical devicesIntravenous devicesVeinPulmonary vasculature
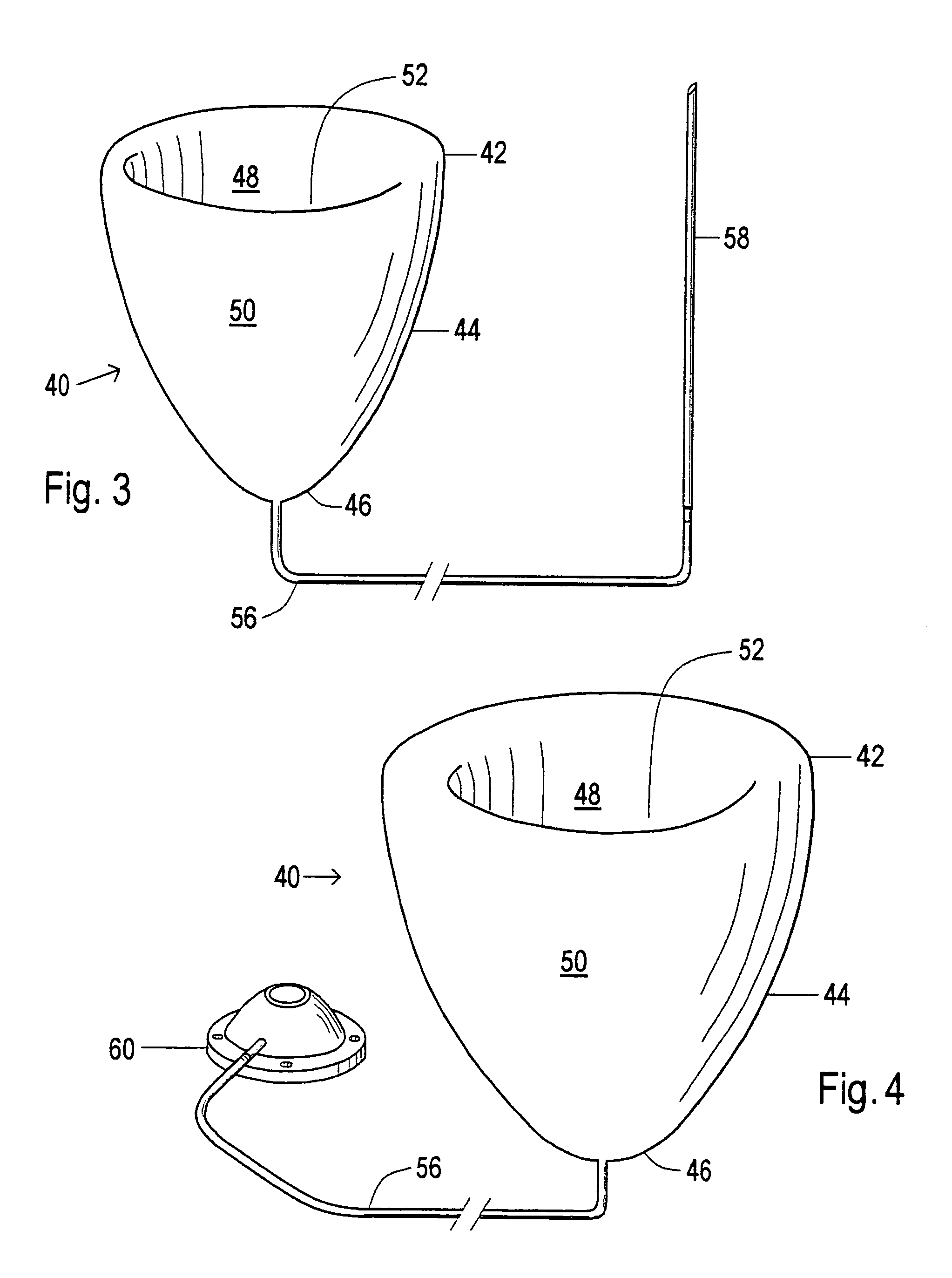
The invention relates to a cystic cavity pulmonary circulation assisting device, which comprises a shell, a flow-in tube (6) and a flow-out tube (4), wherein a blood storage cavity (A) and a power cavity (B) are arranged in the shell; the power cavity (B) is used for offering systolic and diastolic power to the blood storage cavity (A); the flow-in tube (6) is arranged on the part, which corresponding to the power cavity (B), of the shell, and the outer end communicates with vana cava while the inner end runs through the power cavity (B) and communicates with the blood storage cavity (A); theflow-out tube (4) is arranged on the part, corresponding to the blood storage cavity (A), of the shell, and the outer end communicates with pulmonary artery while the inner end communicates with the blood storage cavity (A). With the application of the assisting device, a single ventricular cavity can be assisted in pulmonary circulation, and repeated blood extracting and blood pumping actions canbe achieved, so that power required by pulmonary circulation can be offered and blood flow in the human body is close to be normal; and the circulating device is more compact in inner structure and is relatively small in overall volume since the arrangement of the flow-in tube occupies a space in the power cavity; and moreover, the full use of the power of the power cavity can be achieved.
Owner:GUANGDONG CARDIOVASCULAR INSITITUTE
Test bench assembly for the simulation of cardiac surgery and/or interventional cardiology operations and/or procedures
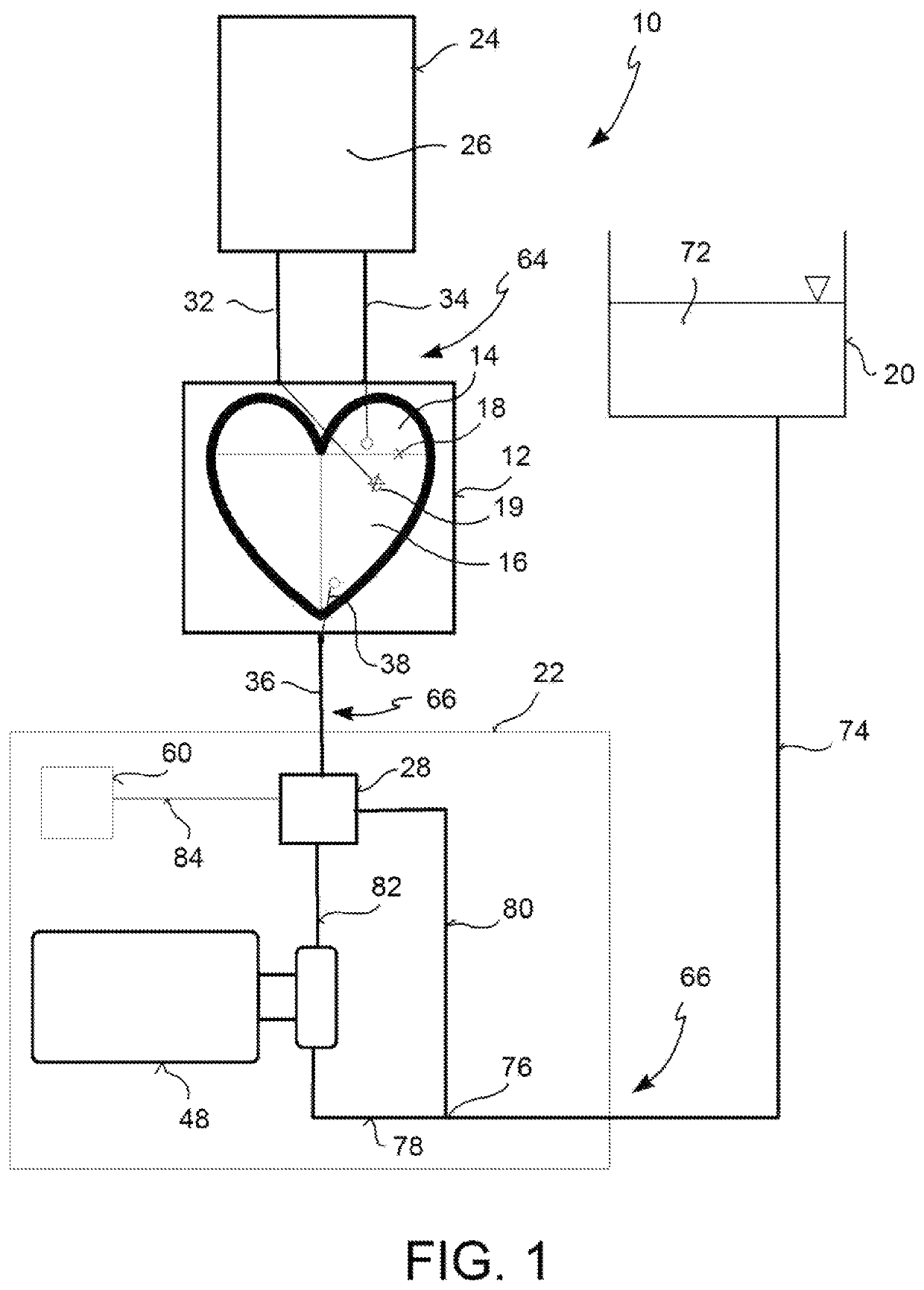
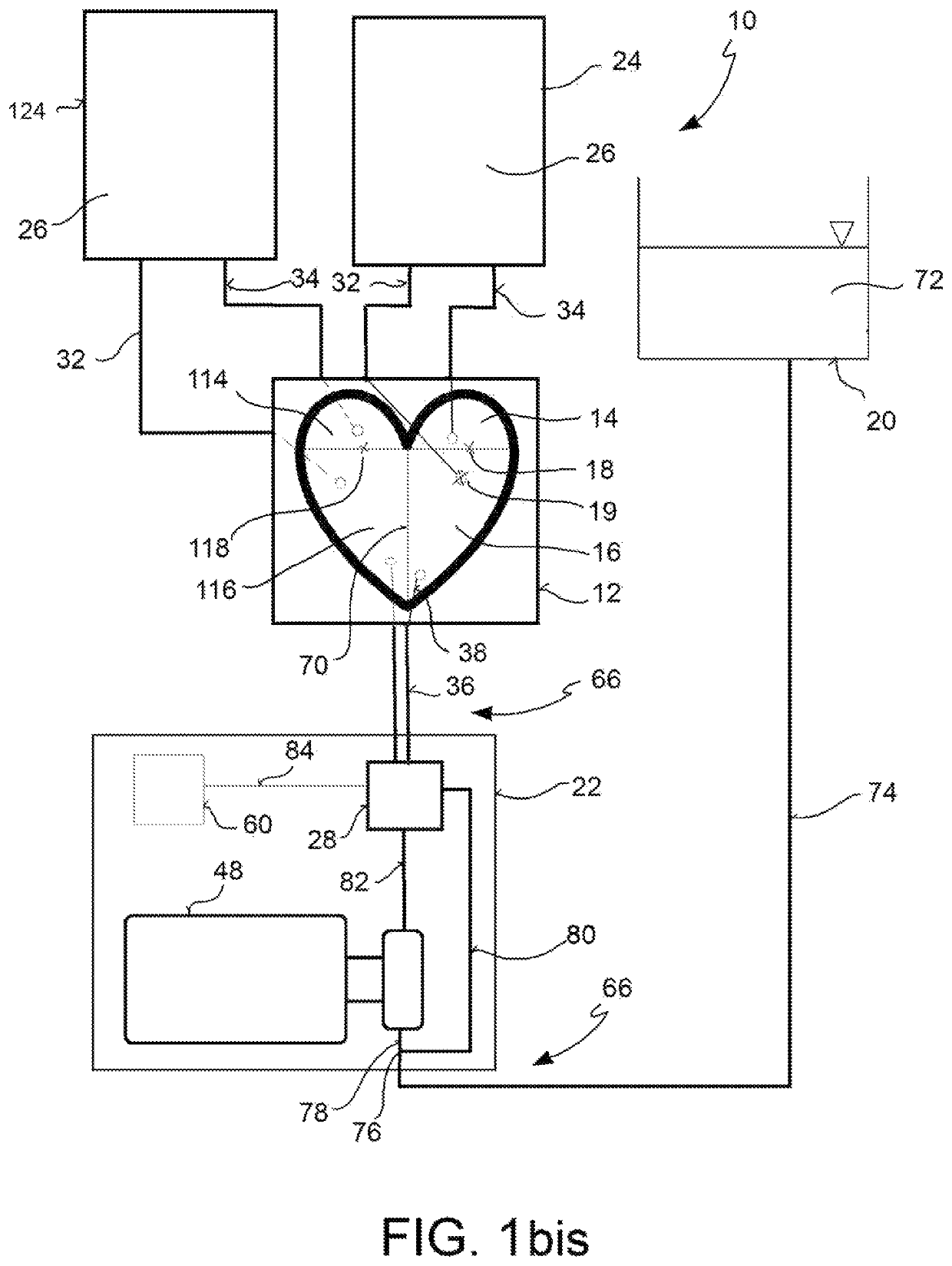
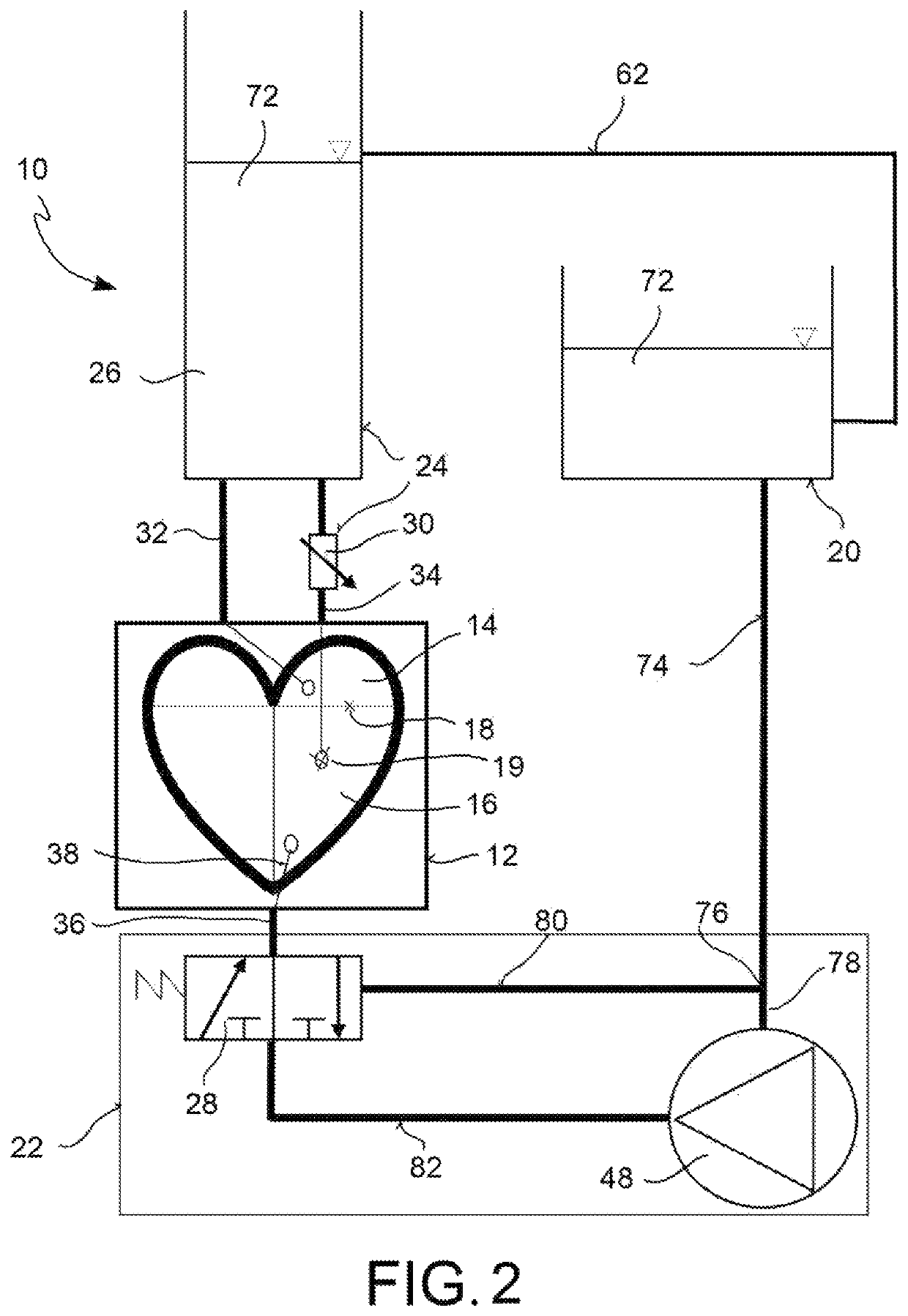
A test bench assembly for simulating cardiac surgery includes a passive heart having at least one pair of cardiac chambers with an atrial chamber and a ventricular chamber. A reservoir is adapted to house working fluid. A pressure generator fluidically connects both to the ventricular chamber of the passive heart and to the reservoir. A pressure regulation device provides working fluid in input to the atrial chamber with preload pressure, and working fluid in output from the ventricular chamber with afterload pressure. The pressure regulation device fluidically connects both to the atrial chamber of the passive heart and to the ventricular chamber of the passive heart. The pressure regulation device has a single compliant element for each pair of cardiac chambers, which provides working fluid with both preload, and afterload pressures.
Owner:POLITECNICO DI MILANO +1
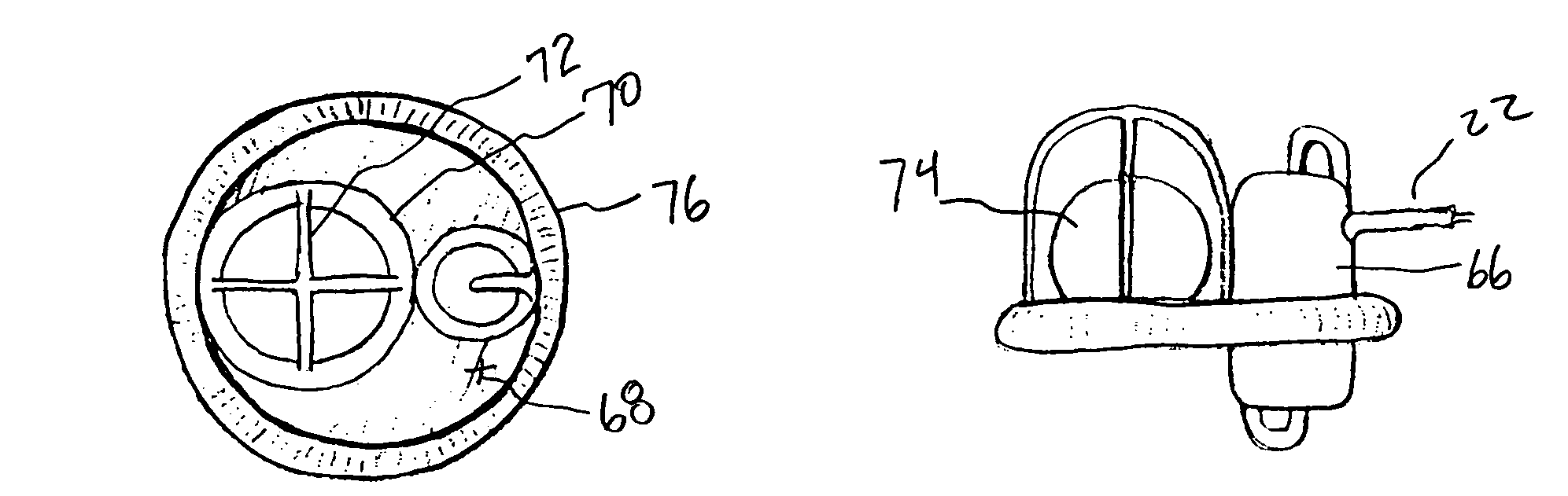
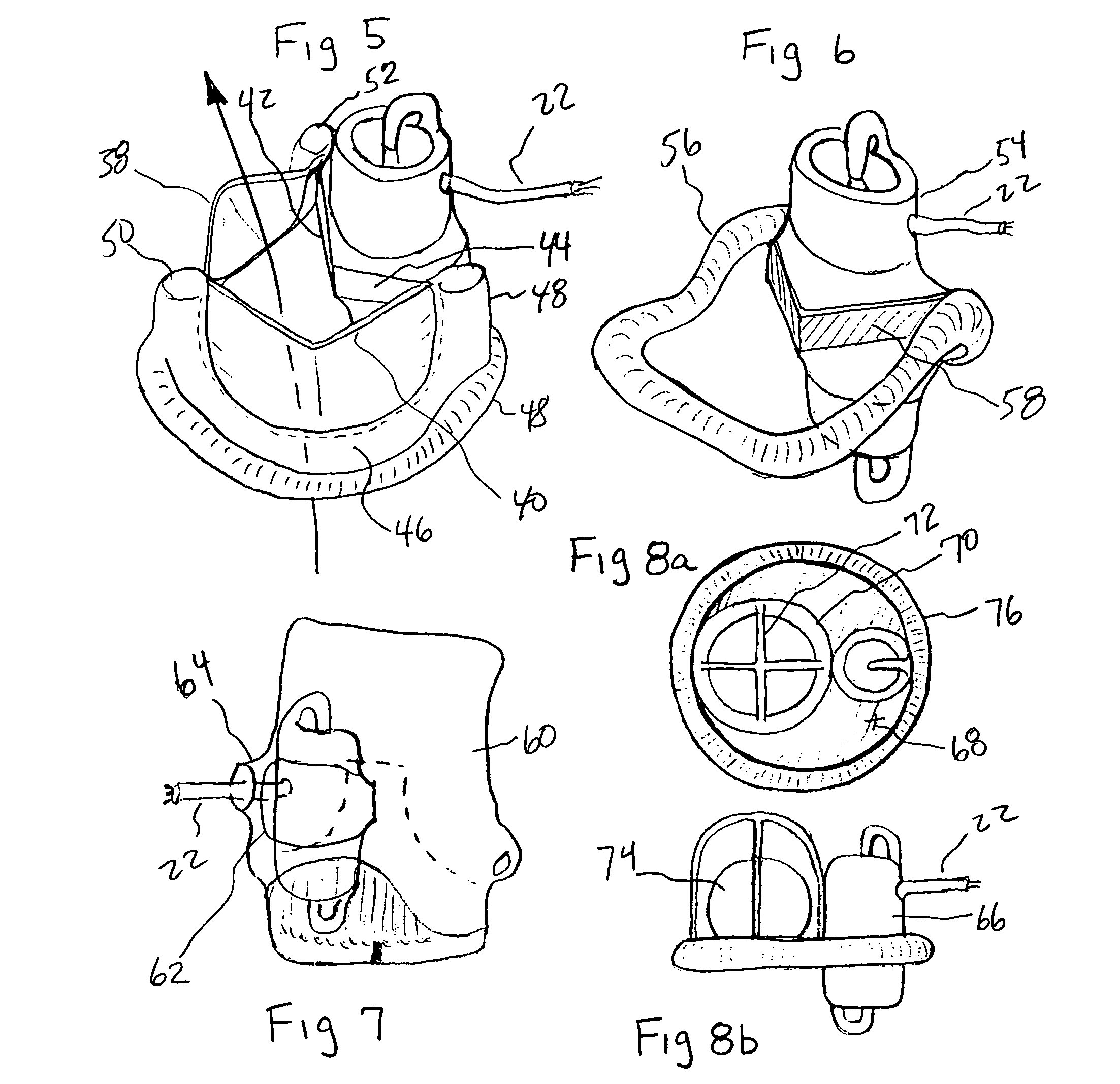
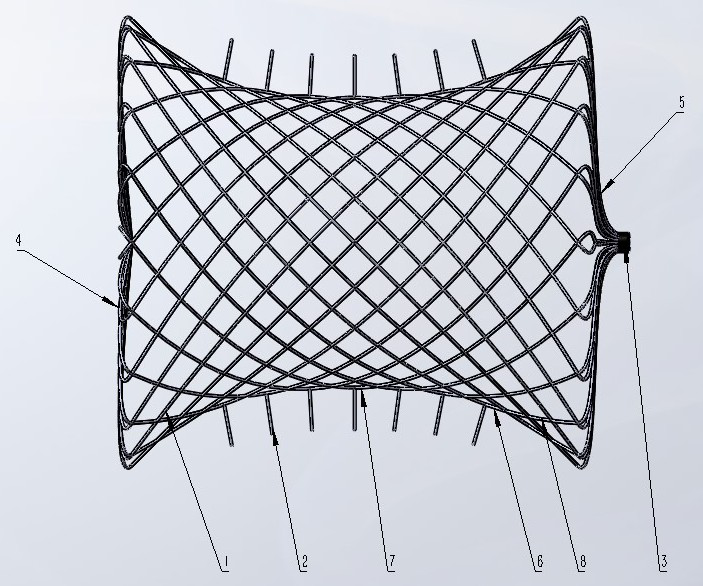
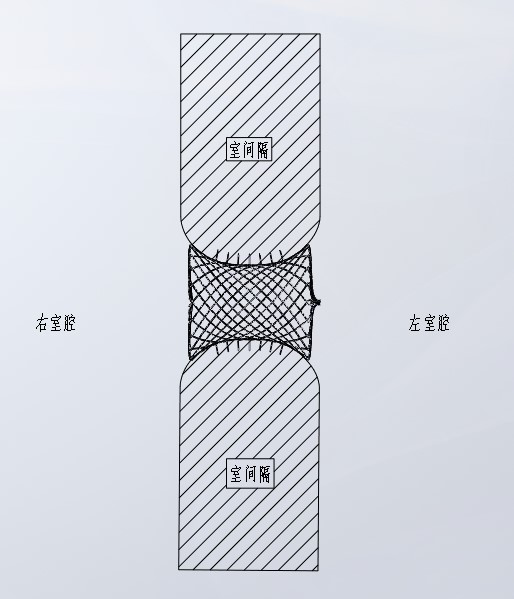
Bioactive implant for myocardial regeneration and ventricular chamber restoration
InactiveUS8968417B2Limit chronic dilationRestore native elliptical shapeHeart valvesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismSystolic functionCaprolactone
Bioactive implant for myocardial regeneration and ventricular chamber support including an elastomeric microporous membrane. The elastomeric microporous membrane being at least one non-degradable polymer and at least one partially degradable polymer. The non-degradable polymer is selected from polyethylacrylate and polyethylacrylate copolymerized with a hydroxyethylacrylate comonomer. The partially degradable polymer is selected from caprolactone 2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyl ester and caprolactone 2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyl ester copolymerized with ethylacrylate. The elastomeric microporous membrane further includes a nanofiber hydrogel, and cells. The bioactive implant, having one or two helical loops, contributes to the restauration of the heart conical shape. Cardiac wrapping by ventricular support bioprostheses of the present invention, having reinforcement bands spatially distributed as helicoids, recovers the sequential contraction of the myocardium resulting in the successive shortening and lengthening of the ventricles, therefore improving the ejection (systolic function) and suction of blood (diastolic function).
Owner:INSTITUT QUIMIC DE SARRIA +3
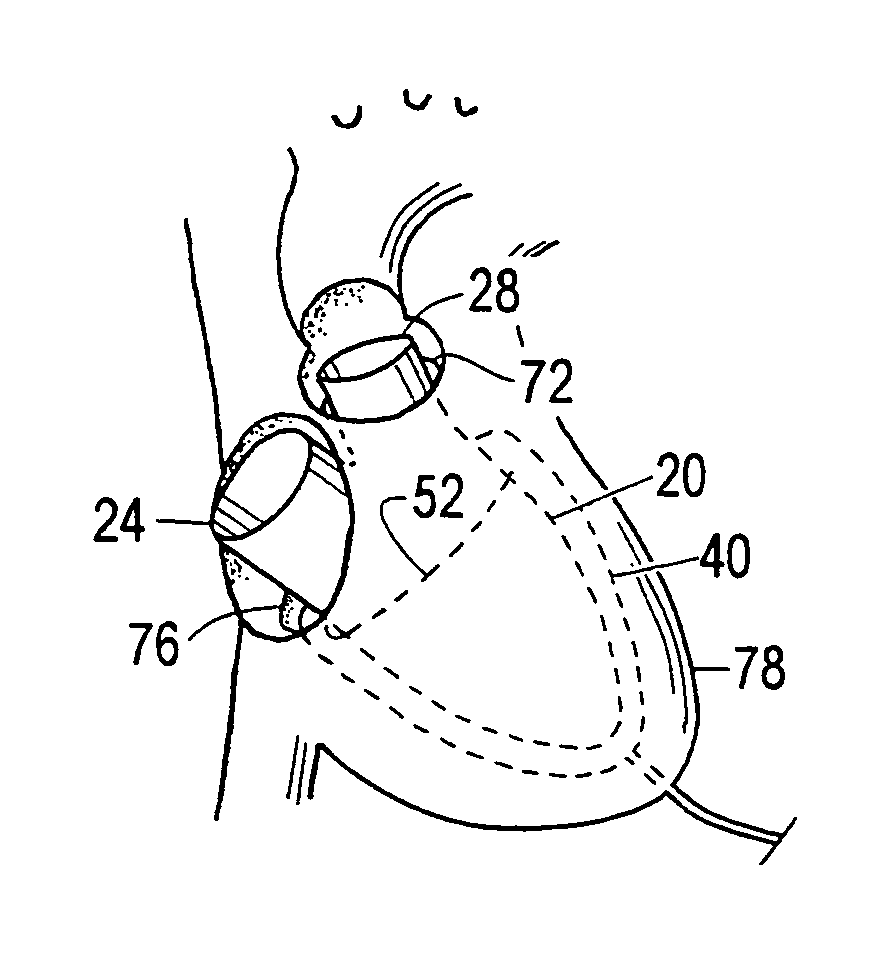
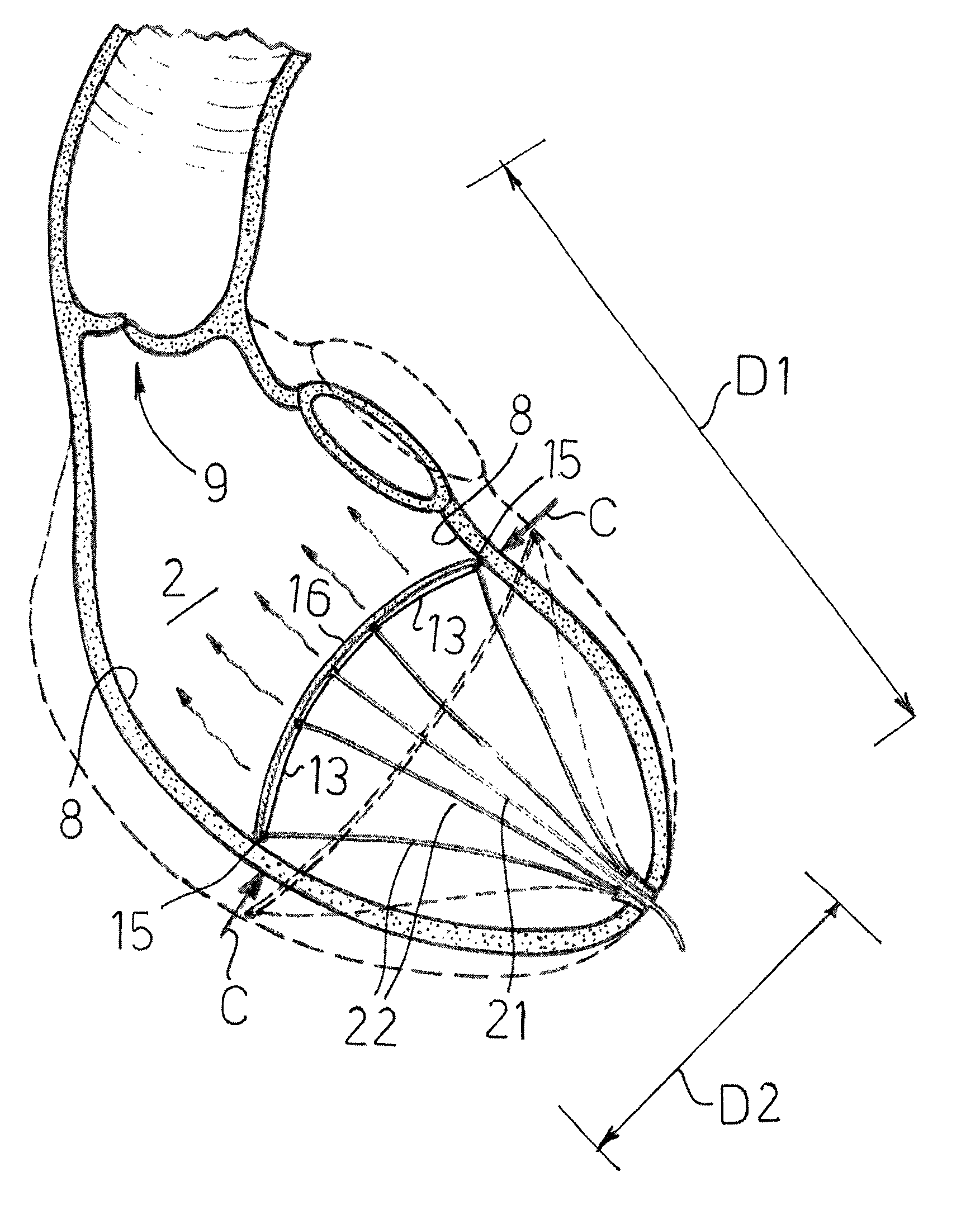
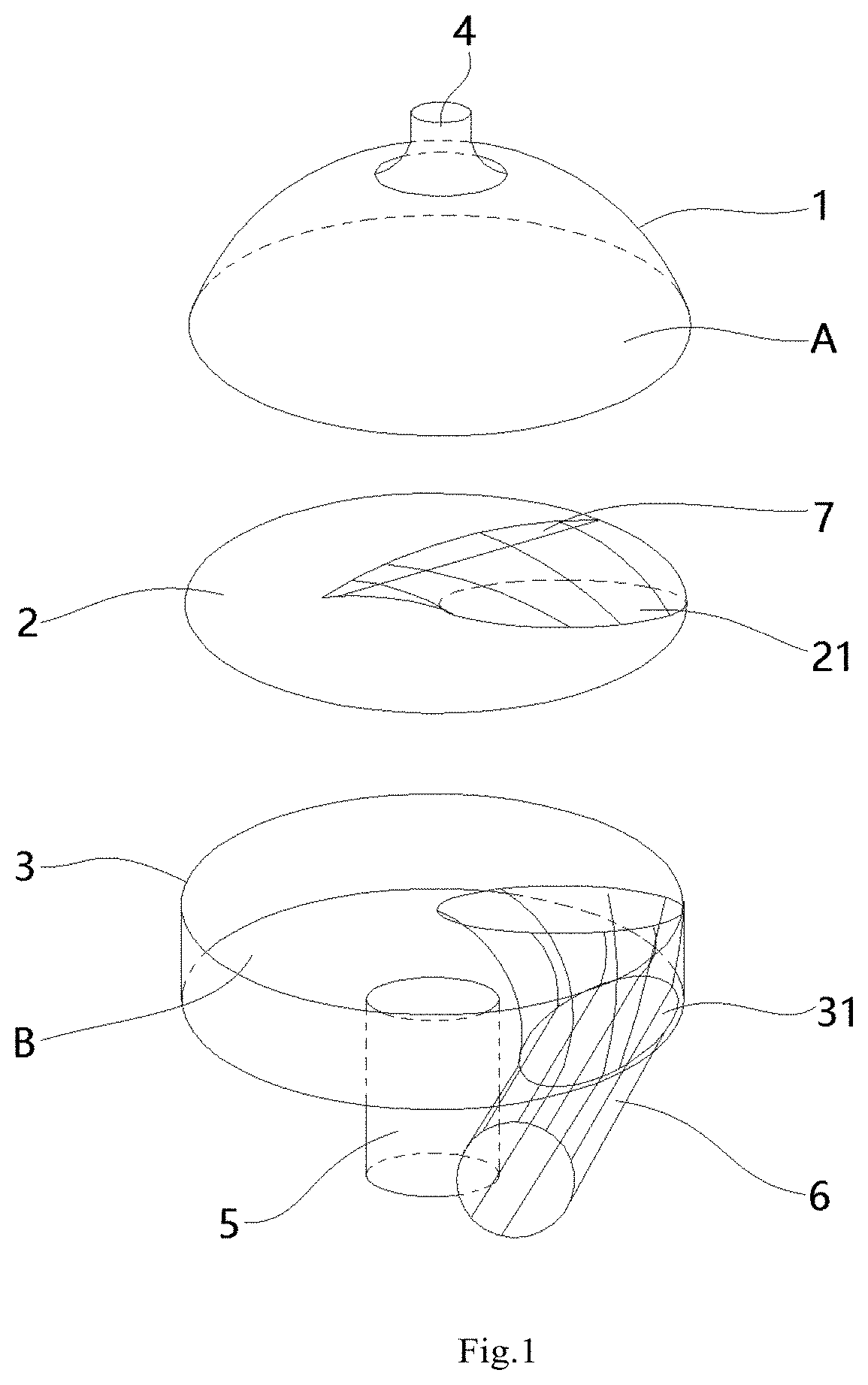
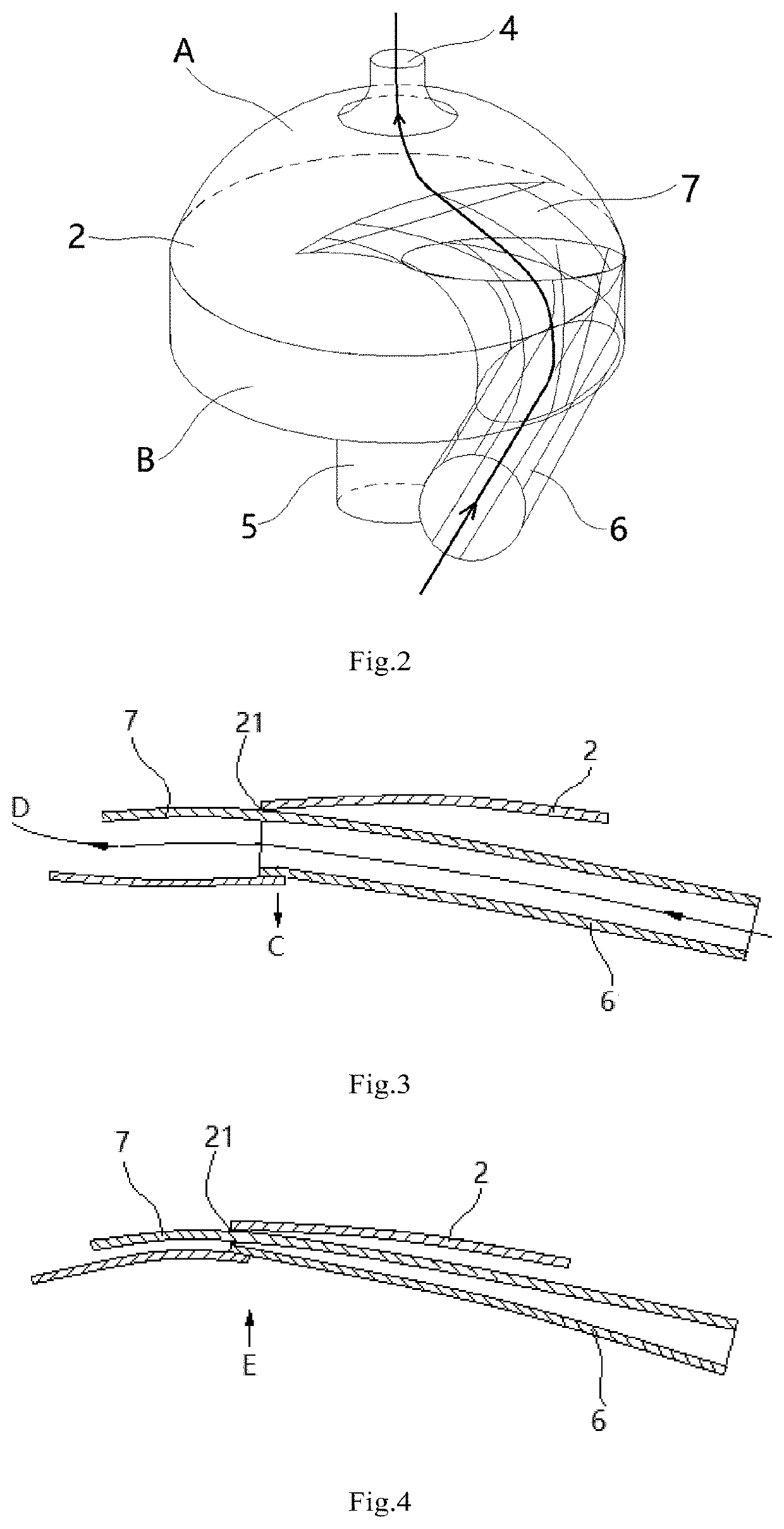
Cardiovascular device
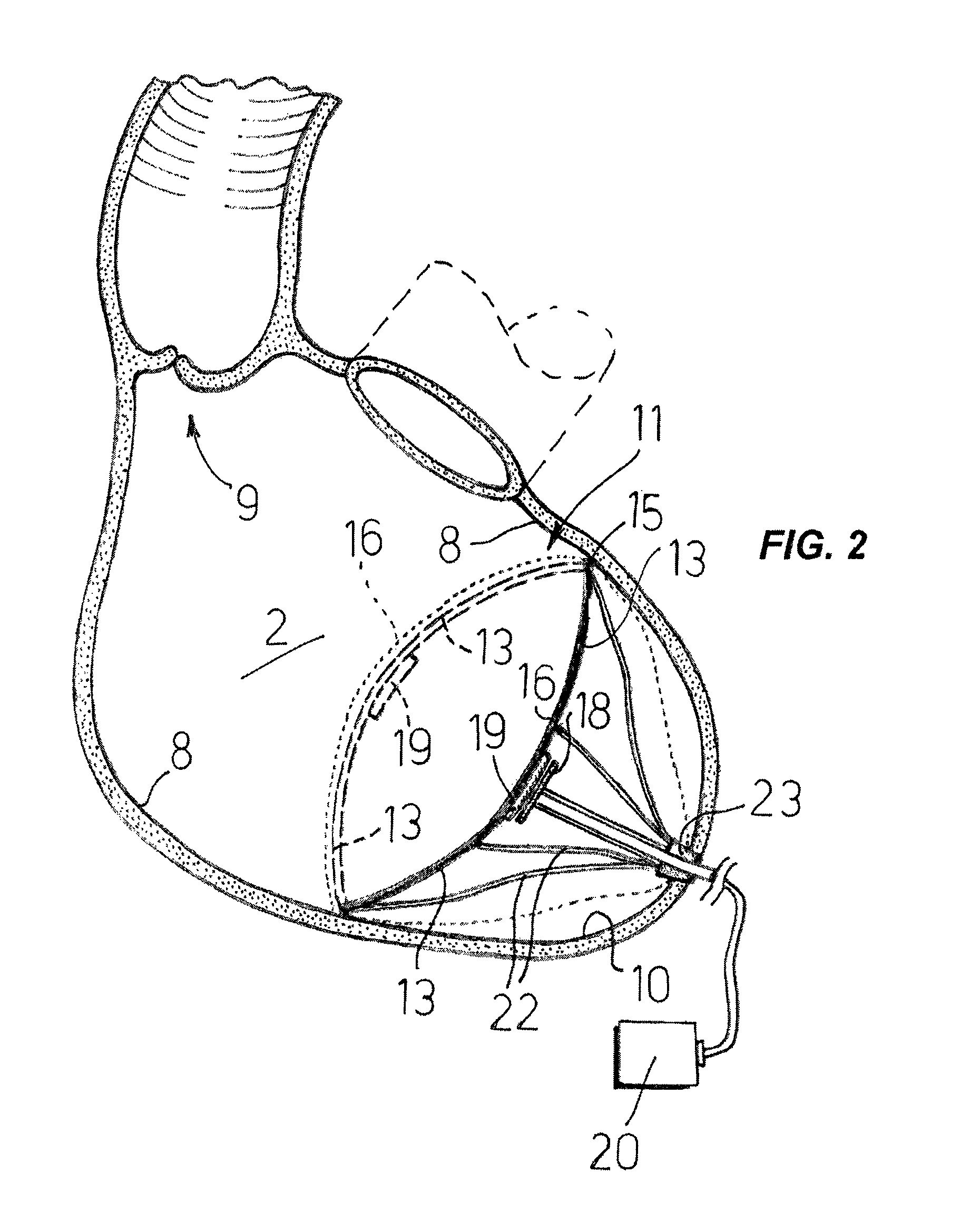
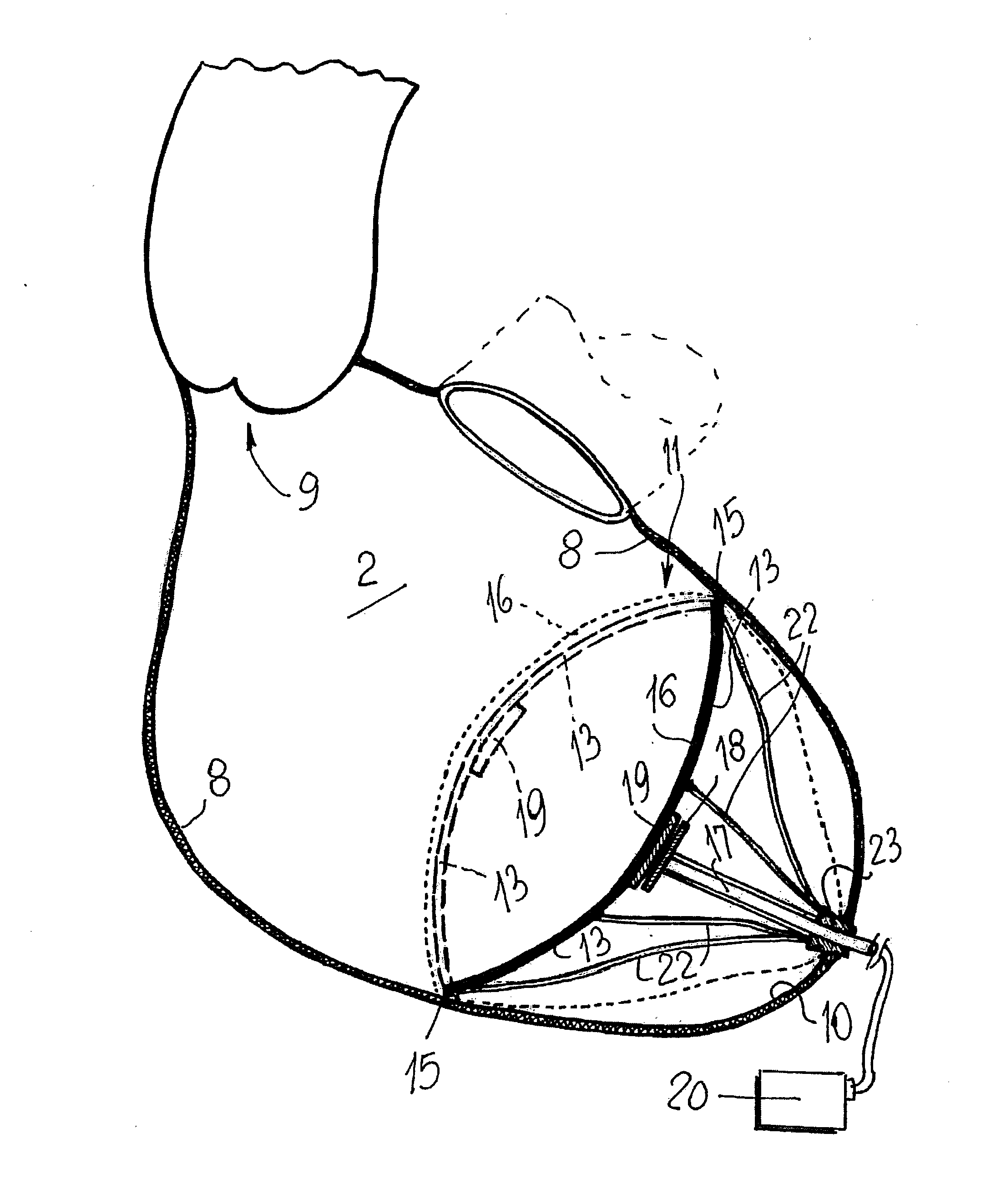
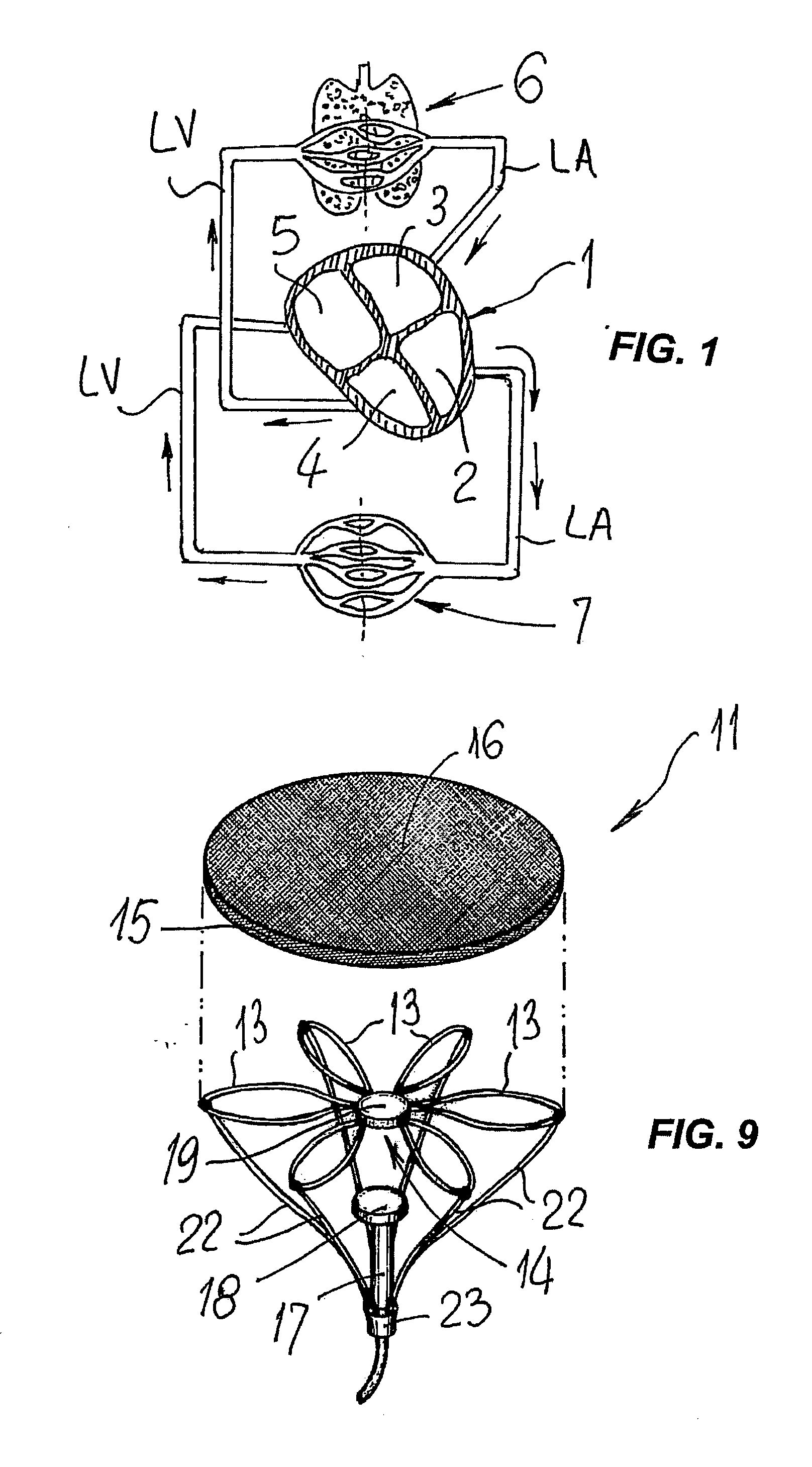
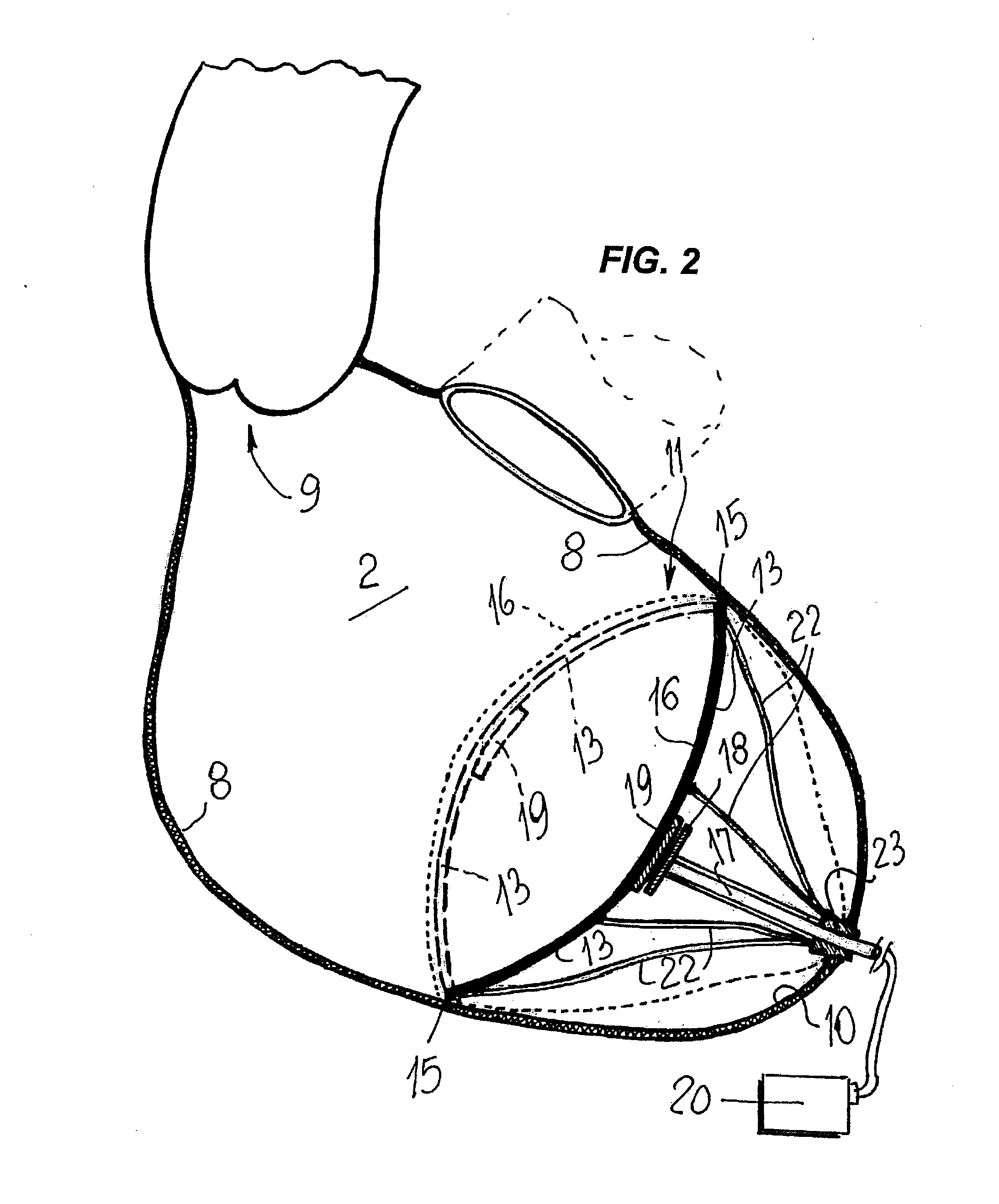
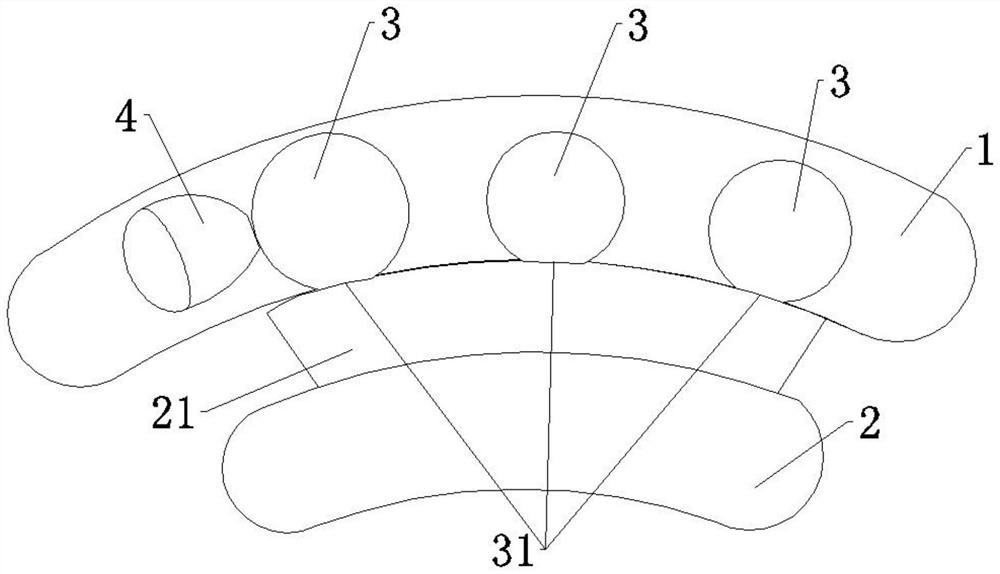
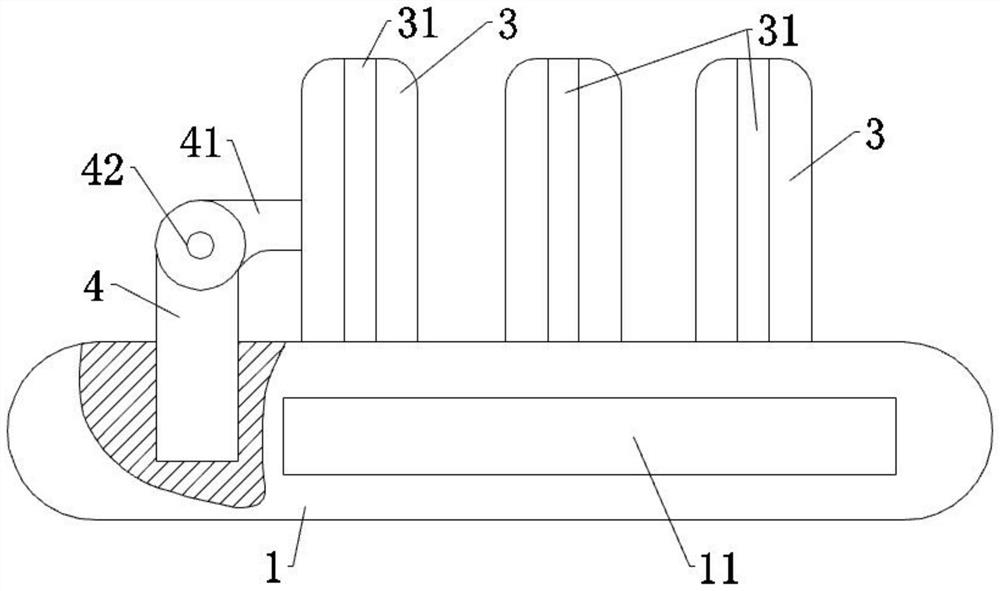
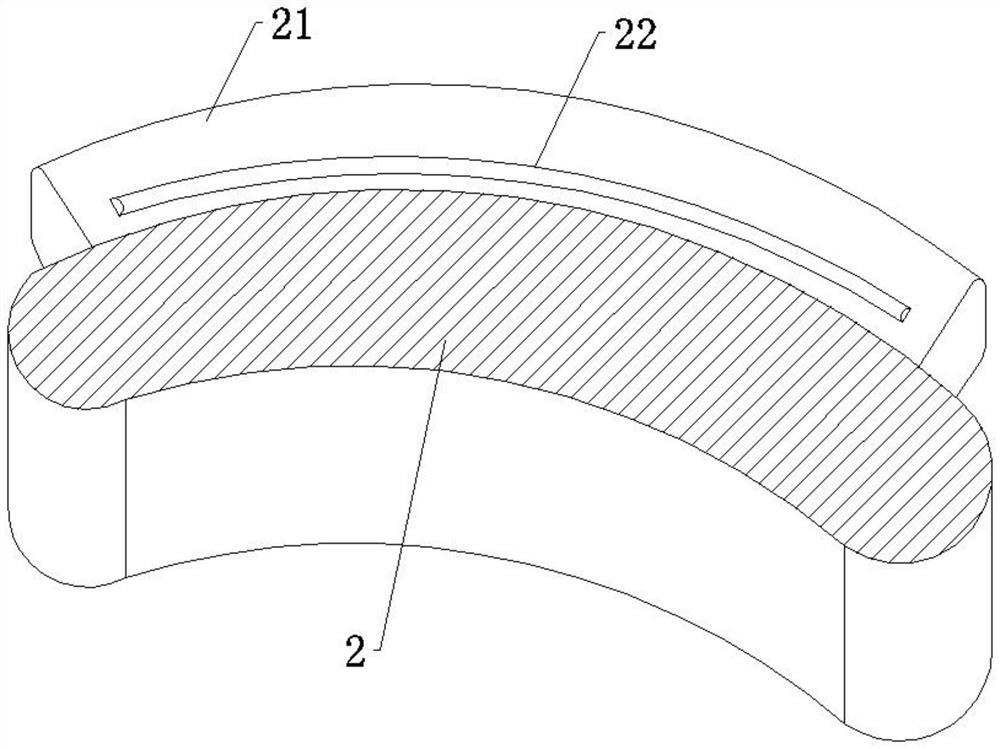
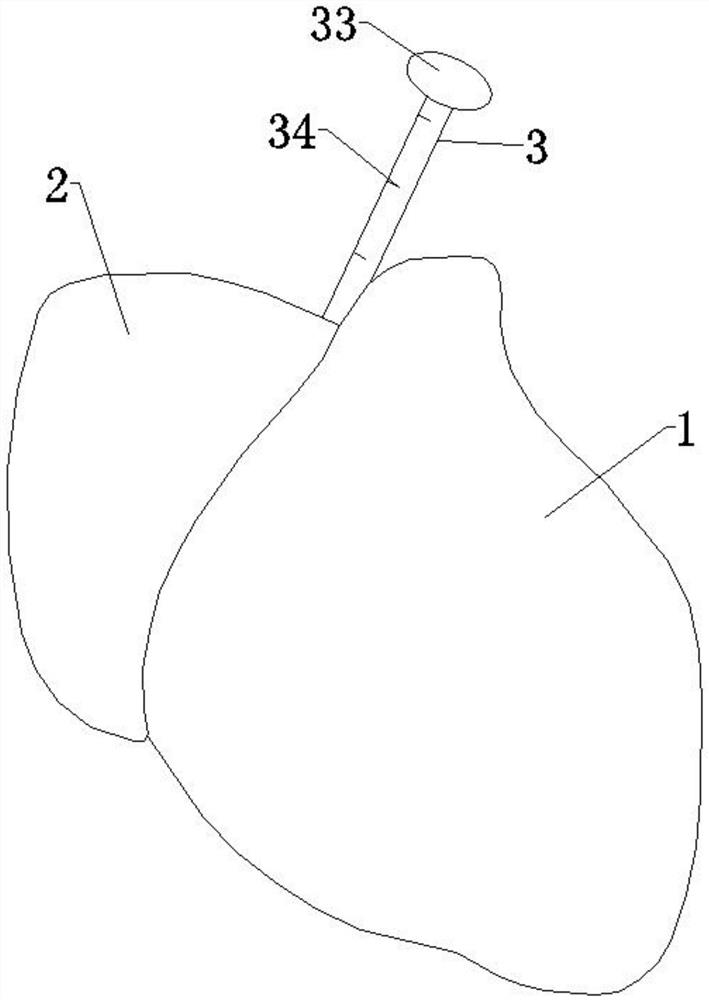
ActiveUS8684906B2Quickly remedy heart failureEasy to installControl devicesIntravenous devicesVentricular volumeVentricular cavity
A cardiovascular device (11), adapted to be fitted into a cardiac ventricular cavity (2) having a volume with blood flowing therethrough, which is bounded by walls (8) and has a larger longitudinal dimension (D1) and a smaller transverse dimension (D2). The device includes a diaphragm (16) that can be disposed in the ventricular cavity (2) substantially transverse to the larger longitudinal dimension (D1), in such an arrangement as to reduce ventricular volume, the diaphragm (16) having a peripheral edge (15) which can be sealingly engaged with the ventricle walls (8) and being adapted to be alternately driven between an active blood pushing displacement and an inactive return displacement.
Owner:PARRAVICINI ROBERTO
Temporary pacing lead
ActiveUS10773076B2Easy to placeMaximize good positionTransvascular endocardial electrodesExternal electrodesHeart chamberVentricular cavity
A temporary pacing lead has an atraumatic curled distal region with multiple cathodes and distal pressure measurement to allow positioning and repositioning within the heart chamber without fluoroscopic or echo guidance. The curled distal region provides definite contact with two opposing walls of the ventricular chamber to ensure electrical signal capture without trauma to the endocardial surface. A stylet located in the pacing lead lumen assists in introducing, placing, and removing the pacing lead from the heart. The flexible distal region provides safe removal of the temporary lead following completion of use.
Owner:NEXTERN INNOVATION LLC
Cardiovascular device
ActiveUS20130079583A1Quickly remedy heart failureEasy to installControl devicesBlood pumpsVentricular cavityBiomedical engineering
A cardiovascular device (11), adapted to be fitted into a cardiac ventricular cavity (2) having a volume with blood flowing therethrough, which is bounded by walls (8) and has a larger longitudinal dimension (D1) and a smaller transverse dimension (D2), characterized in that it comprises diaphragm means (16) that can be disposed in said ventricular cavity (2) substantially transverse to said larger longitudinal dimension (D1), in such an arrangement as to reduce said volume, said diaphragm means (16) having a peripheral edge (15) which can be sealingly engaged with said walls (8) and being adapted to be alternately driven between an active blood pushing displacement and an inactive return displacement.
Owner:PARRAVICINI ROBERTO
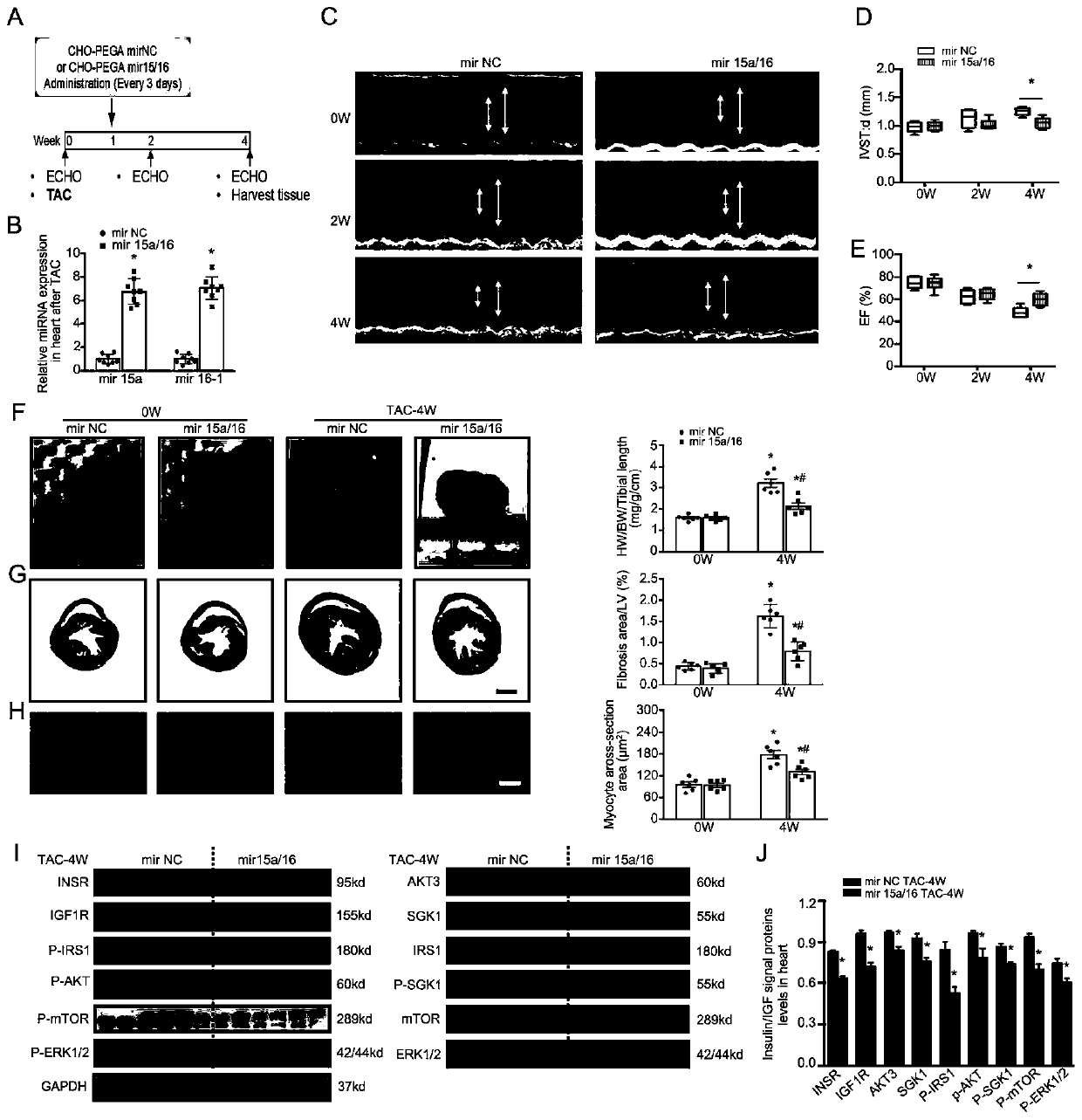
Application of miRNA in treating cardiac hypertrophy
ActiveCN111184734APrevent hypertrophyPrevent heart failureOrganic active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderNucleotideVentricular cavity
The invention relates to an application of miRNA in treating cardiac hypertrophy. Particularly, the miRNA is hsa-miR-15a-5p / hsa-miR-16-5p, and the nucleotide sequences of the miRNA are shown as SEQ IDNO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2. The cardiac hypertrophy refers to a pathophysiological process which is caused by overloading of a heart due to genetic factors, hypertension, myocardial infarction, valve diseases and the like and mainly takes thickening of ventricular muscles and narrowing of ventricular cavities as main characteristics. The invention also relates to an application of a complex loaded withthe hsa-miR-15a-5p / hsa-miR-16-5p in preparing a medicament for treating cardiac hypertrophy, wherein the complex is a CHO-PGEA-nucleic acid complex.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF HEART LUNG & BLOOD VESSEL DISEASES
Saccular Cavopulmonary Assist Device
ActiveUS20200009305A1Restore biventricular blood flowSmall volumeControl devicesMedical devicesPulmonary vasculatureVein
The present disclosure relates to a saccular cavopulmonary assist device, including a shell, an inflow tube (6) and an outflow tube (4), wherein a blood storage cavity (A) and a power cavity (B) are arranged in the shell, and the power cavity (B) is used for providing contraction and relaxation power for the blood storage cavity (A); the inflow tube (6) is arranged at a position corresponding to the power cavity (B) on the shell, an outer end is used for communicating with the vena cava, and an inner end communicates with the blood storage cavity (A) after passing through the power cavity (B); the outflow tube (4) is arranged at a position corresponding to the blood storage cavity (A) on the shell, an outer end is used for communicating with the pulmonary artery, and an inner end communicates with the blood storage cavity (A). This device can assist the cavopulmonary circulation of the single ventricle, realize repeated blood drawing and pumping actions, provide the required power for the pulmonary circulation of the patient, and restore the biventricular blood flow in the human body; and because the arrangement of the inflow tube in the power cavity, the internal structure of this device is more compact, the overall shape is smaller, and the energy of the power cavity can be fully utilized.
Owner:GUANGDONG CARDIOVASCULAR INSITITUTE
Multi-mode atrial fibrillation demonstration model
The invention discloses a multi-mode atrial fibrillation demonstration model. The model comprises a model base; the side connecting column is vertically fixed on one side of the upper end surface of the model base; the atrium model is obliquely erected on the model base through the side linkage columns; the first expansion and shrinkage assembly is correspondingly arranged in the atrium cavity of the atrium model; the first expansion and contraction assembly is correspondingly arranged in a ventricular cavity of the atrium model, the second expansion and contraction assembly is correspondingly arranged in the ventricular cavity of the atrium model, the composition structure of the first expansion and contraction assembly is similar to that of the second expansion and contraction assembly, and the first expansion and contraction assembly and the second expansion and contraction assembly synchronously move for expansion and contraction and are in opposite movement mode states; and the micro-wall expansion and contraction assembly is arranged in the atrial cavity and the ventricular cavity of the atrial model.
Owner:李永前
Atrial fibrillation demonstration model
PendingCN112837592AImprove reliabilityEasy to useEducational modelsIrregular heart rhythmHEART THROBBING
The invention discloses an atrial fibrillation demonstration model in the technical field of heartbeat models, which comprises a ventricular cavity cover, a closed cavity with a ventricular shape outside, a plurality of ventricular elastic strips uniformly and fixedly connected to the inner wall, a ventricular limiting shaft fixed inside, a ventricular contraction and expansion wheel rotatably mounted on the ventricular limiting shaft, and a ventricular contraction and expansion wheel rotatably mounted on the ventricular contraction and expansion wheel. The other ends of the ventricular elastic strips are fixedly connected with the ventricular contraction and expansion wheel, the rhythm of the heartbeat can be simulated, contraction and expansion of the ventricle and the atrium of the heartbeat can be displayed, and the device is specially used for displaying the rhythm of the atrial fibrillation, is used for simulating the heartbeat of different rhythms, and can perform visual simulation display on the atrial fibrillation. The heartbeat rhythm during arrhythmia can be displayed through various different atrial and ventricular beating rhythms, meanwhile, beating simulation can be conducted according to different atrial and ventricular proportions, manufacturing is easier, displaying is more visual, and carrying is more convenient.
Owner:中国人民解放军联勤保障部队第九〇〇医院
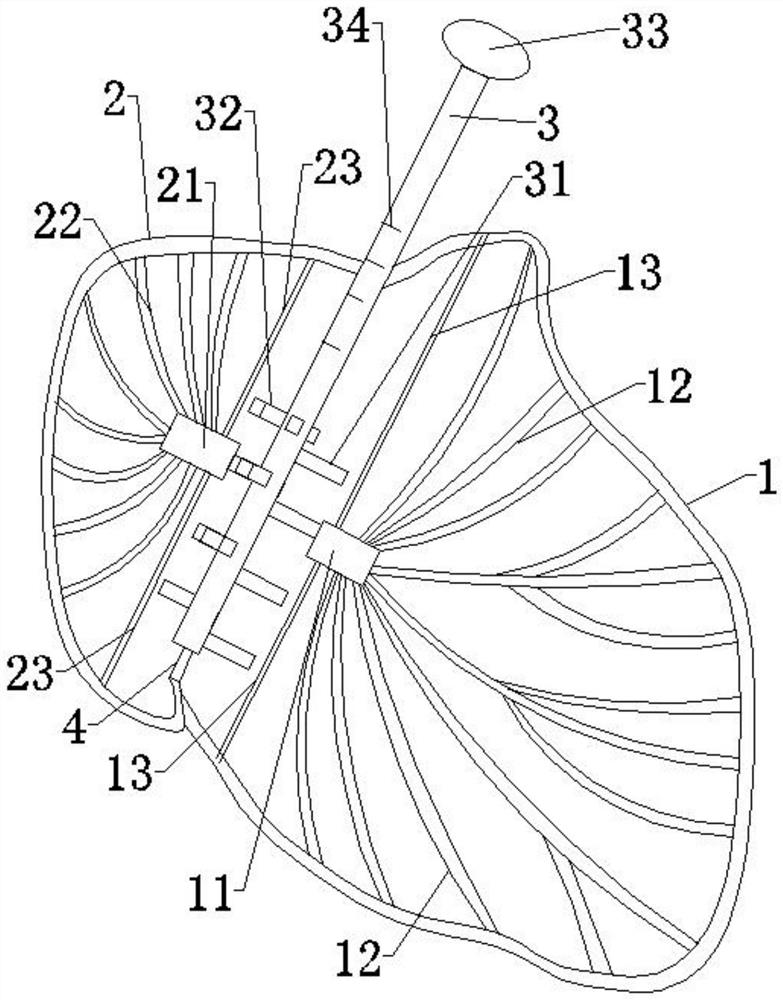
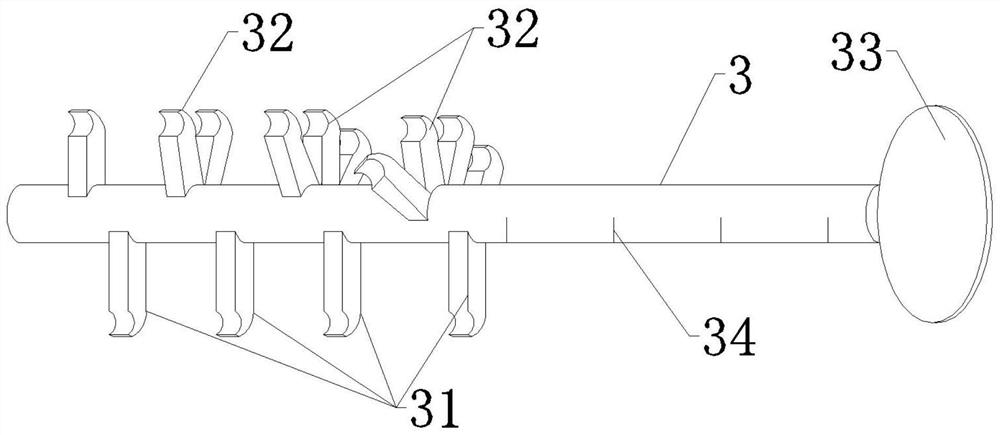
Ventricular assistance assembly with stabilized cardiac pump
ActiveUS20210052792A1Simple designEasy to operateBlood pumpsIntravenous devicesDevice implantVentricular assistance
A ventricular assist assembly, for assisting a heart,includes an anchoring device, a cardiac pump and a stabilizing device. The anchoring device anchors a cardiac pump, is intended to be assembled with an opening in a ventricular wall of the heart, and delimits an internal passage.The cardiac pump is intended to be attached to the anchoring device, is configured for intra-ventricular insertion into the heart, and has a distal end.The cardiac pump extends through the internal passage into the heart when attached to the anchoring device implanted in the opening so that its distal end is placed in a ventricular chamber.The stabilizing device stabilizes the cardiac and includes at least two elongate, biocompatible and flexible connecting members, each elongate connecting member being intended to connect a part of the cardiac pump that is positioned in the ventricular chamber to an internal wall of the ventricular chamber.
Owner:FINEHART
Guide steel wire for hybrid therapy of muscular ventricular septal defect and positioning and conveying device of guide steel wire
The invention relates to a guide steel wire for the hybrid therapy of a muscular ventricular septal defect and a positioning and conveying device of the guide steel wire. The positioning and conveyingdevice comprises a detecting sheathing canal, the guide steel wire and a steel wire ring part catcher. The detecting sheathing canal is hollow and has an obtuse head part. The head end of the guide steel wire is bent into a water-drop-shaped ring part. The steel wire ring part catcher is composed of a handle and a ring hook. The ring hook is located at the position, close to the top end, in the handle. The positioning and conveying device has the advantages that the L-shaped detecting sheathing canal with the obtuse head part conveniently conducts detection on the muscular ventricular septaldefect at the deep part of a ventricular cavity from a ventriculus dexter; the guide steel wire can directly arrive at and penetrate through the muscular ventricular septal defect along a canal cavityof the detecting sheathing canal, and through the design of the water-drop-shaped ring of the head part, it is avoided that the head end of the guide steel wire enters a ventriculus sinister and accidentally injures a ventricular wall or valve tissue; the top end of the steel wire ring part catcher is obtuse, and the accidental injuries caused to valves, chordae tendineae, musculi papillares andventricular walls when the guide steel wire goes deep into the ventriculus sinister are reduced; the ring part of the guide steel wire can be conveniently caught by the ring hook, the guide steel wireis pulled out of a heart to be fixed, and a stable steel wire guide route is established.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Ventricular assistance assembly with stabilized cardiac pump
ActiveUS11458296B2Simple designEasy to operateBlood pumpsIntravenous devicesDevice implantVentricular assistance
A ventricular assist assembly, for assisting a heart,includes an anchoring device, a cardiac pump and a stabilizing device. The anchoring device anchors a cardiac pump, is intended to be assembled with an opening in a ventricular wall of the heart, and delimits an internal passage.The cardiac pump is intended to be attached to the anchoring device, is configured for intra-ventricular insertion into the heart, and has a distal end.The cardiac pump extends through the internal passage into the heart when attached to the anchoring device implanted in the opening so that its distal end is placed in a ventricular chamber.The stabilizing device stabilizes the cardiac and includes at least two elongate, biocompatible and flexible connecting members, each elongate connecting member being intended to connect a part of the cardiac pump that is positioned in the ventricular chamber to an internal wall of the ventricular chamber.
Owner:FINEHART
EY ventricular septal defect plugging device
The invention relates to an EY ventricular septal defect plugging device. A rivet structure is used for penetrating into cardiac muscle to anchor the device; as a disc-shaped structure is not contained, the implant does not protrude into a ventricular cavity at all after being implanted, and the influence on the heart structure function can be reduced; the shape of the plugging device is specially designed for non-membrane ventricular septal defect plugging treatment, and equipment guarantee is provided for interventional treatment of the type of ventricular septal defect.
Owner:梁怀民
Electrode guide wire shaping device of cardiac pacemaker
PendingCN114768097AReduce uncertaintyImprove stabilityElectrotherapyCardiac pacemakerVentricular cavity
The invention discloses an electrode guide wire shaping device of a cardiac pacemaker in the technical field of cardiac pacemaker implantation, and the electrode guide wire shaping device comprises a guide clamping seat, clamping columns, a clamping block and a lifting column, the vertical side wall is a cambered surface, and the multiple clamping columns are sequentially and uniformly arranged at the top of the guide clamping seat in an arc shape; the vertical side wall of one side of each clamping column protrudes out of the inner arc surface of the guide clamping seat, the electrode guide wire can be clamped at a specific angle through a specific shape, the electrode guide wire is drawn and shaped under the clamping of the specific radian, stable deformation at a set angle is formed, the radian of the guide clamping seat can be changed, and the clamping effect is good. Adjustment is carried out according to the size and the shape of a ventricular cavity of a patient, so that the shaping radian of the guide wire is changed, the deformation and the angle of the electrode guide wire are more suitable for the size, the angle and the like of the ventricular cavity of the corresponding patient, meanwhile, shaping of the electrode guide wire is more convenient, the shaping angle is more stable, and the success rate is higher.
Owner:中国人民解放军联勤保障部队第九〇〇医院
Heart rhythm demonstration model capable of adjusting beating rhythm
PendingCN112837594AImprove reliabilityEasy to useEducational modelsVentricular contractionVentricular cavity
The invention discloses a heart rhythm demonstration model capable of adjusting beating rhythm in the technical field of heart beating models, which comprises a ventricular cavity cover, a closed cavity with a ventricular shape outside, a plurality of ventricular elastic strips uniformly and fixedly connected to the inner wall, and a ventricular limiting shaft fixed inside, one end of each ventricular elastic strip is fixedly connected with the ventricular limiting shaft, a ventricular contraction and expansion wheel is rotatably mounted on the ventricular limiting shaft, the other ends of the ventricular elastic strips are fixedly connected with the ventricular contraction and expansion wheel, the rhythm of heartbeat can be simulated, and contraction and expansion of ventricles and atriums of the heartbeat can be displayed, meanwhile, the atrial and ventricular beating at different frequencies can be displayed, the heartbeat of different arrhythmias can be simulated, the arrhythmias can be visually simulated and displayed, the heartbeat rhythm of the arrhythmias can be displayed at different atrial and ventricular beating frequencies, the manufacturing is simpler, the display is more visual, and the carrying is more convenient.
Owner:中国人民解放军联勤保障部队第九〇〇医院
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com