Patents
Literature
51 results about "Costal cartilage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
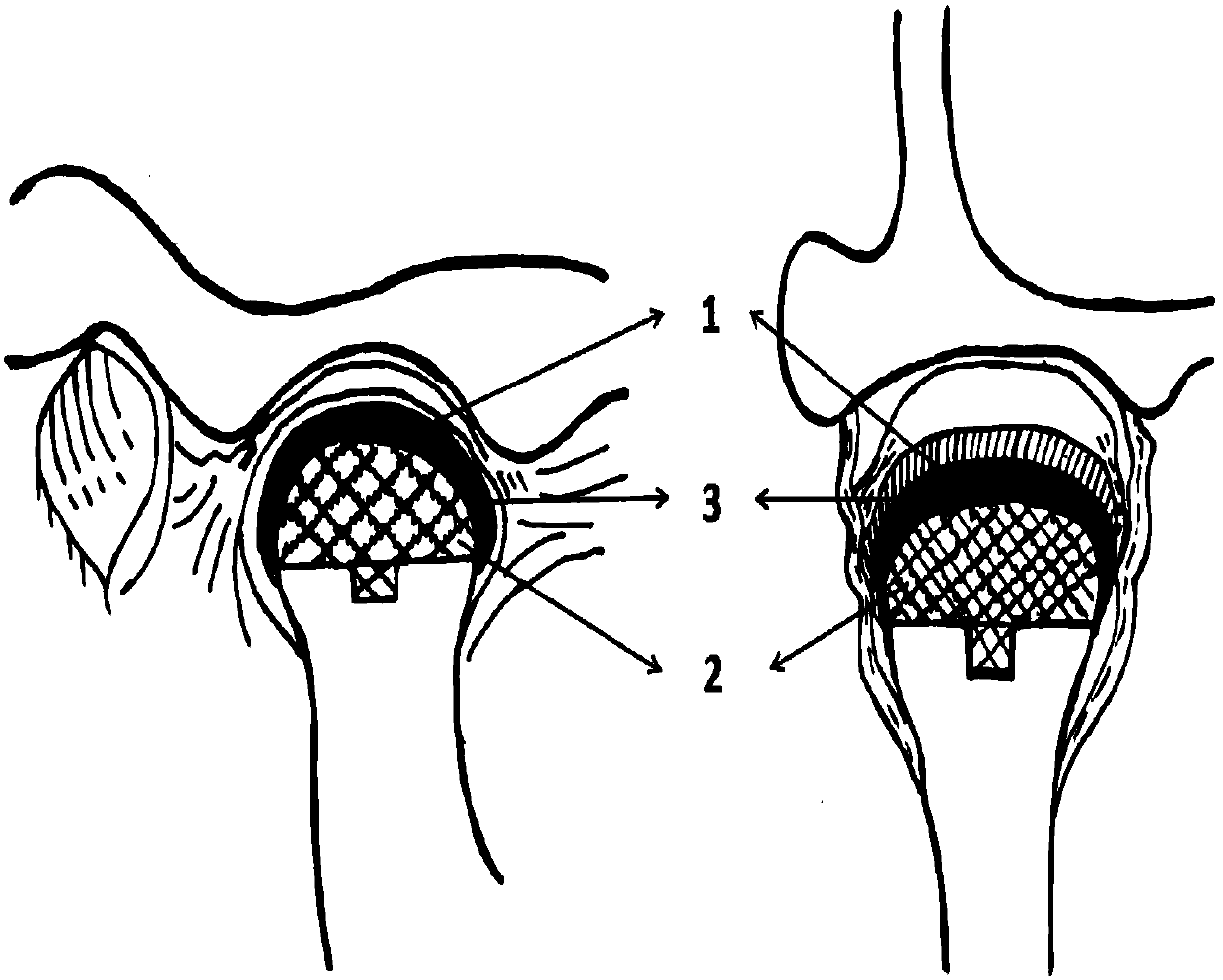
The costal cartilages are bars of hyaline cartilage that serve to prolong the ribs forward and contribute to the elasticity of the walls of the thorax. Costal cartilage is only found at the anterior ends of the ribs, providing medial extension.
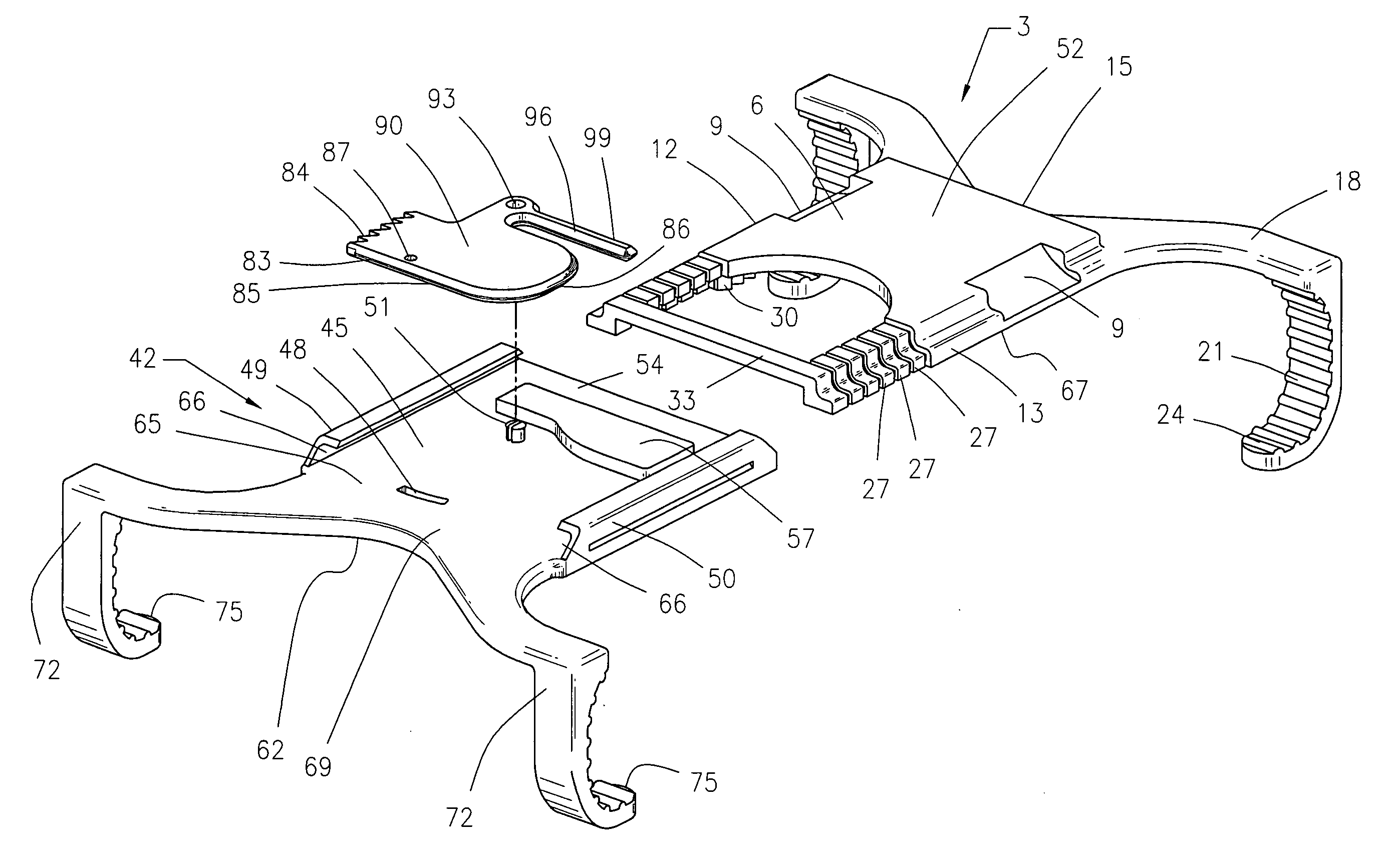
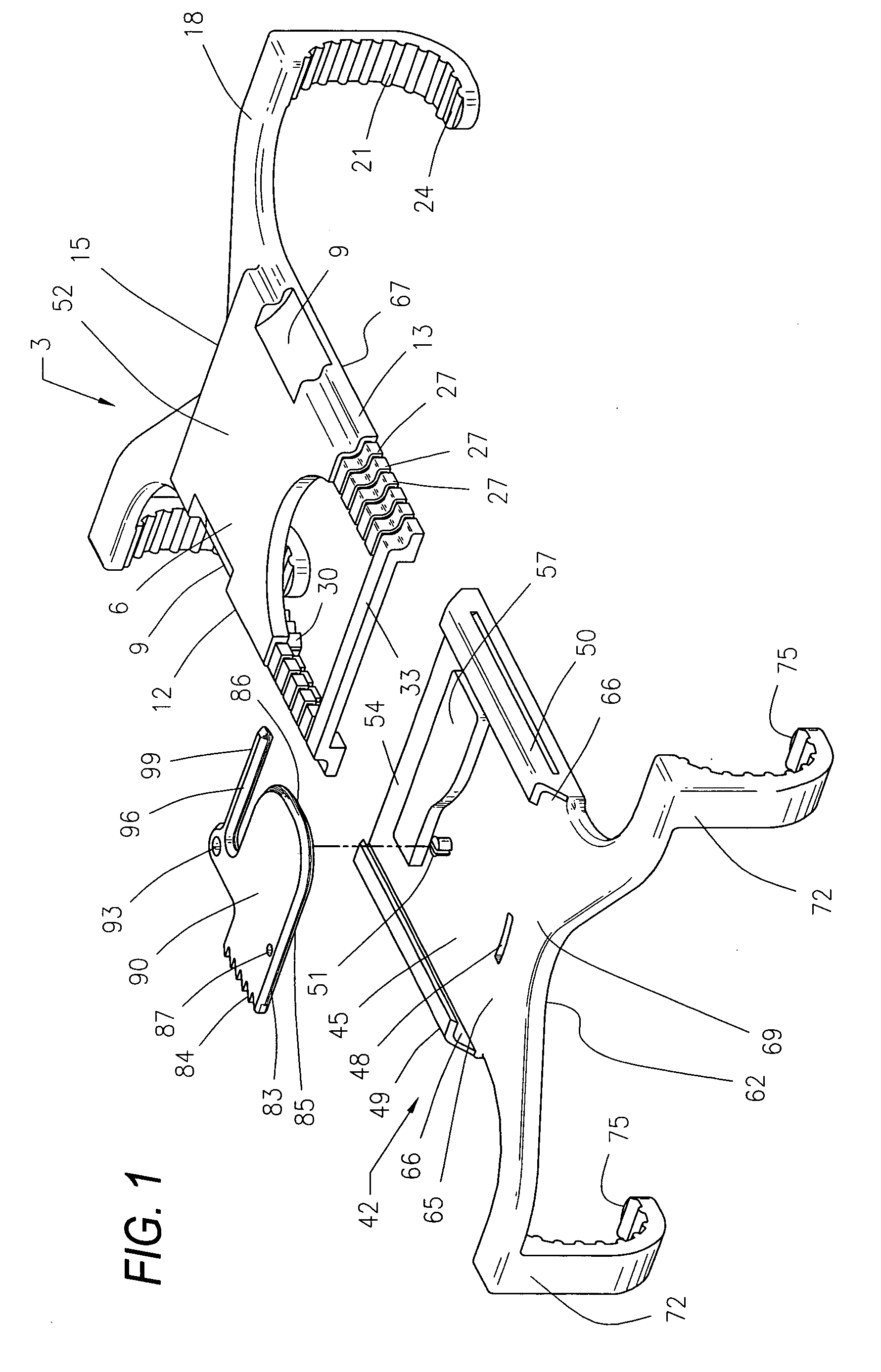
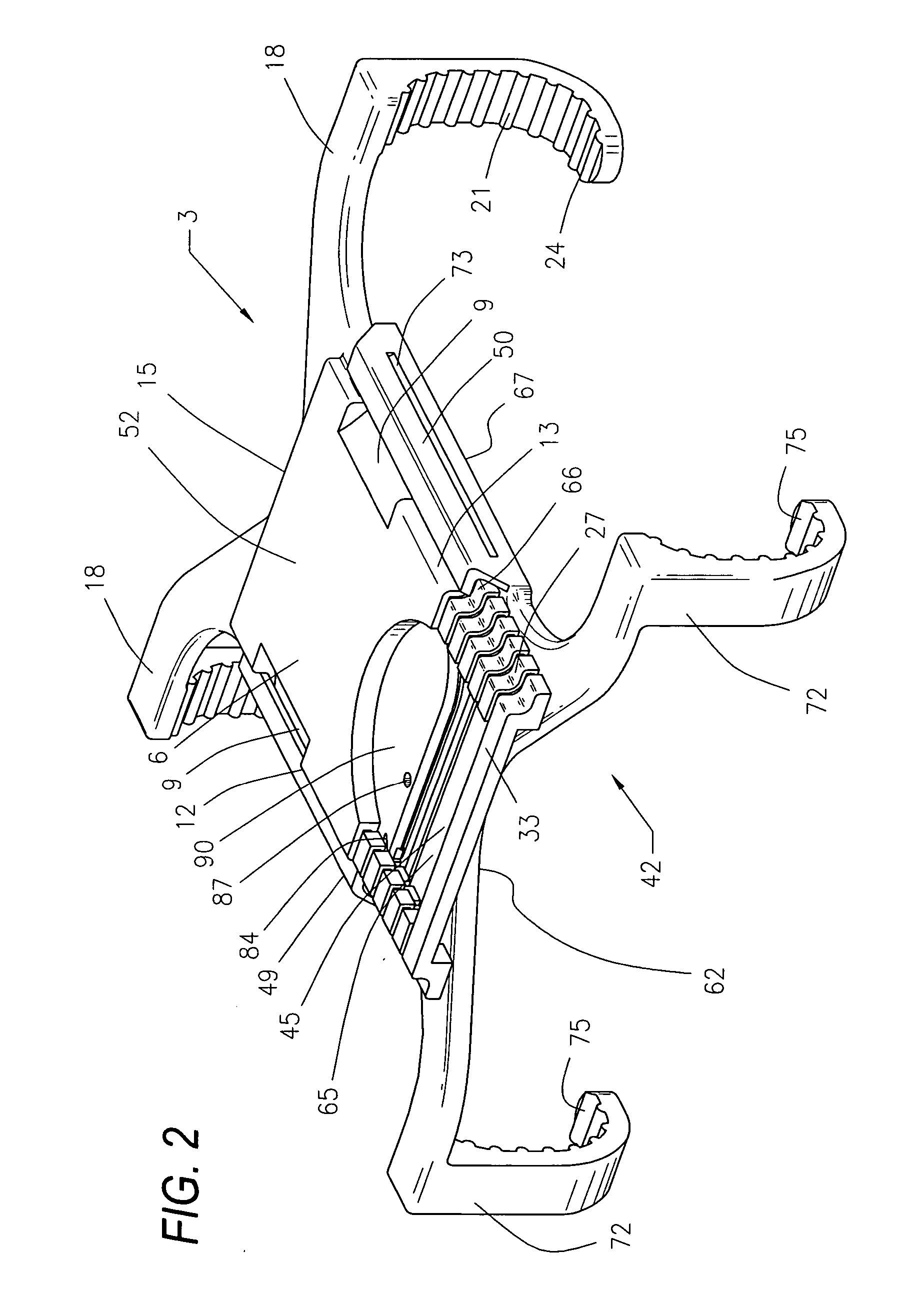
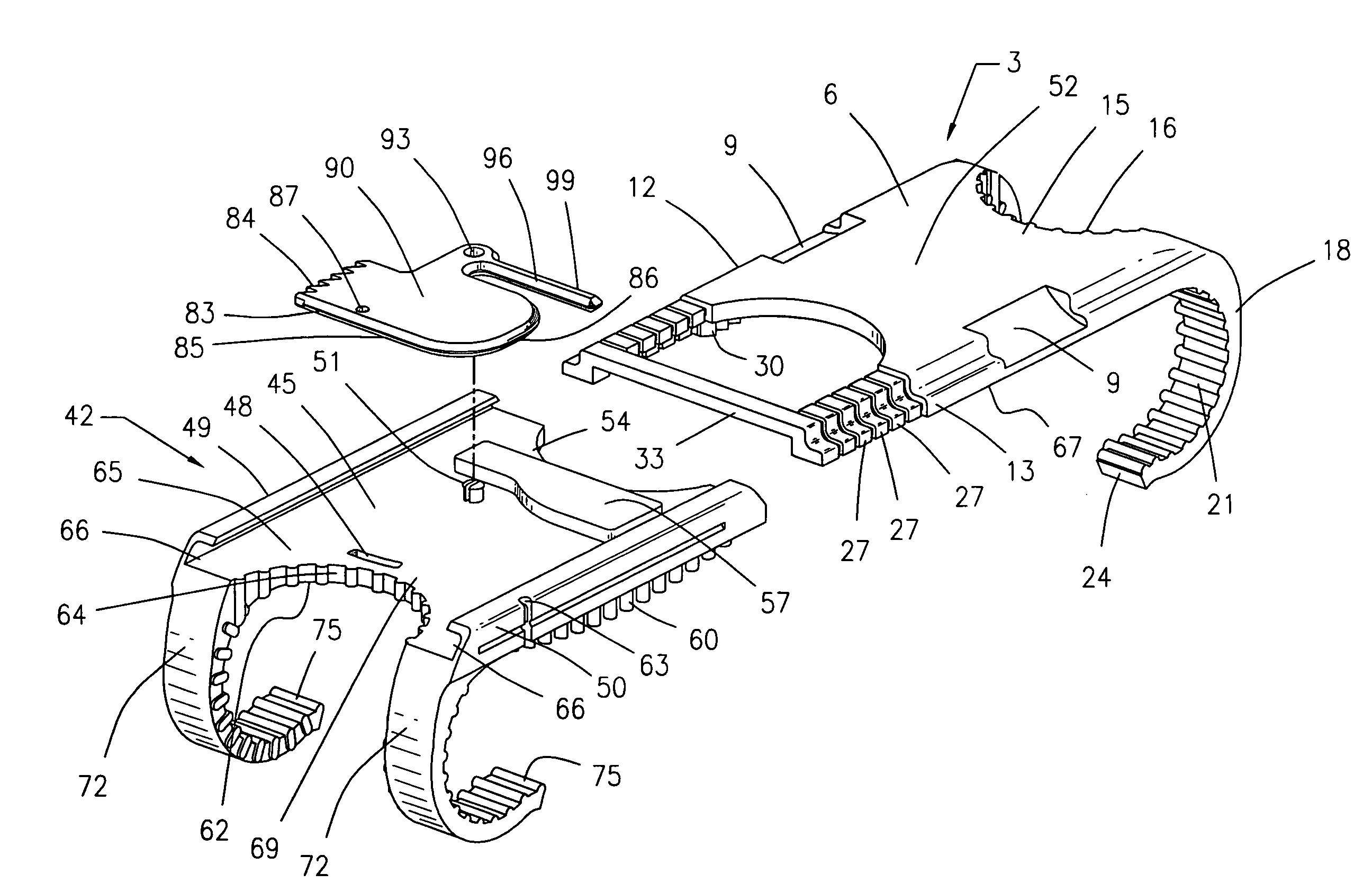
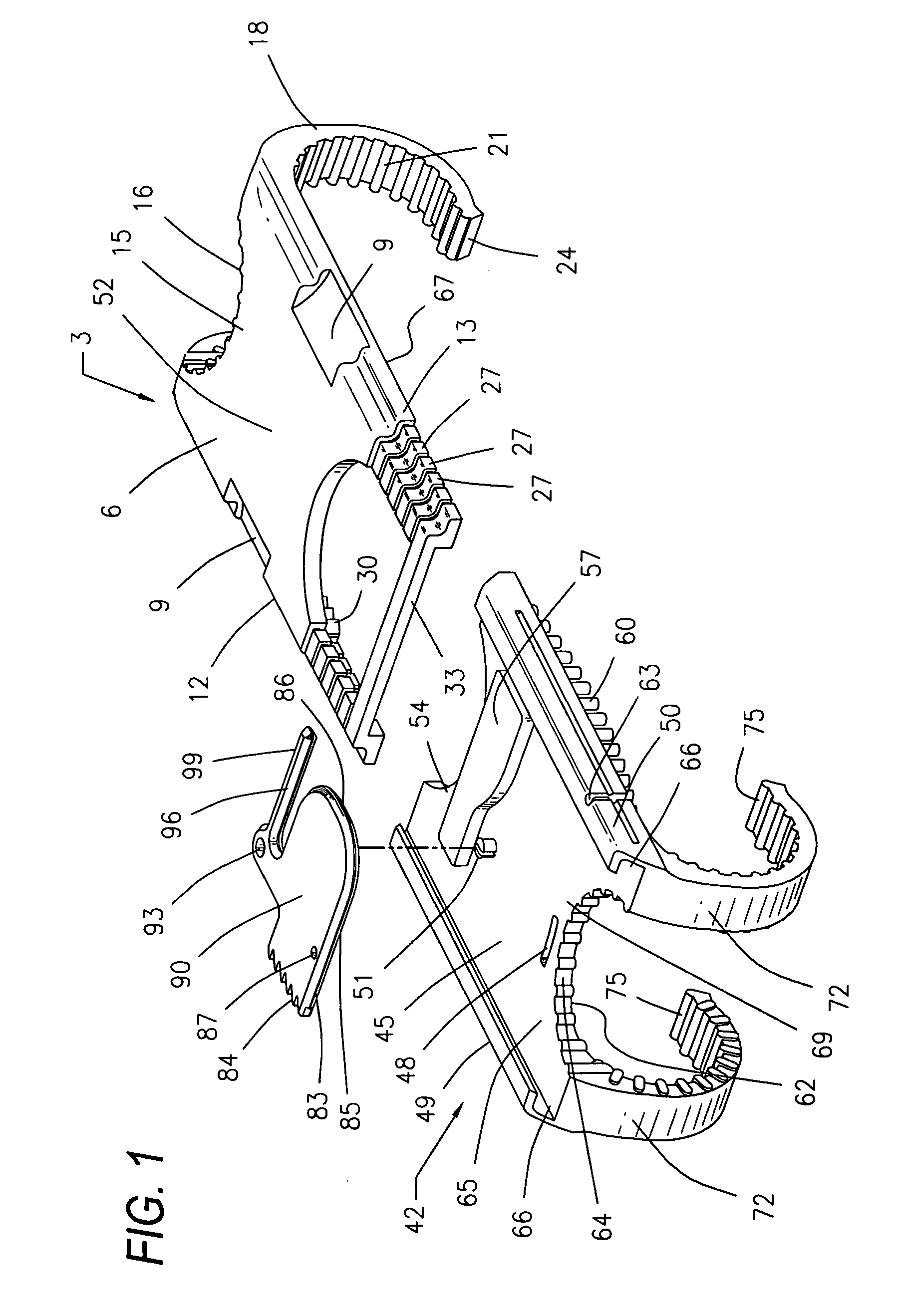
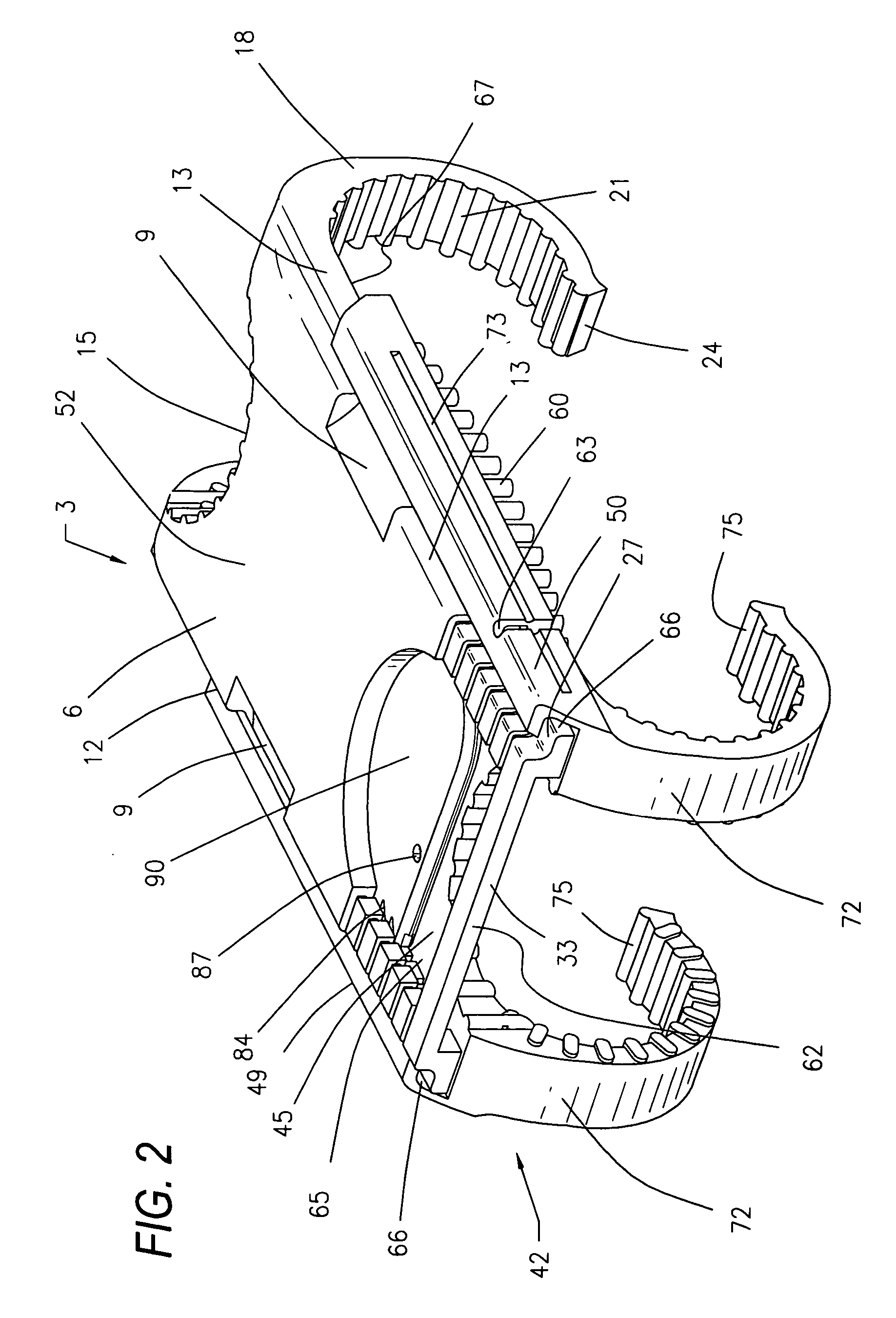
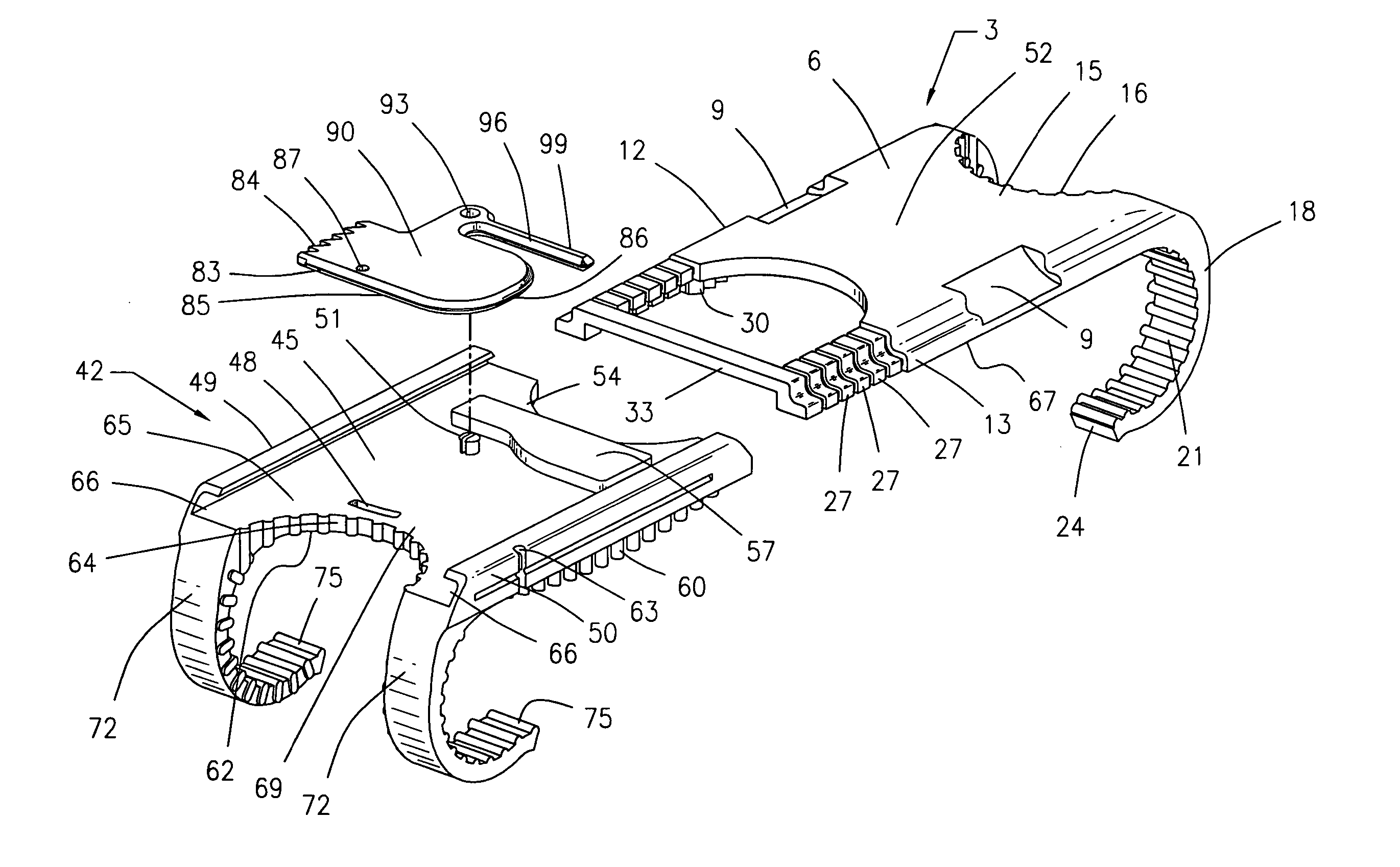
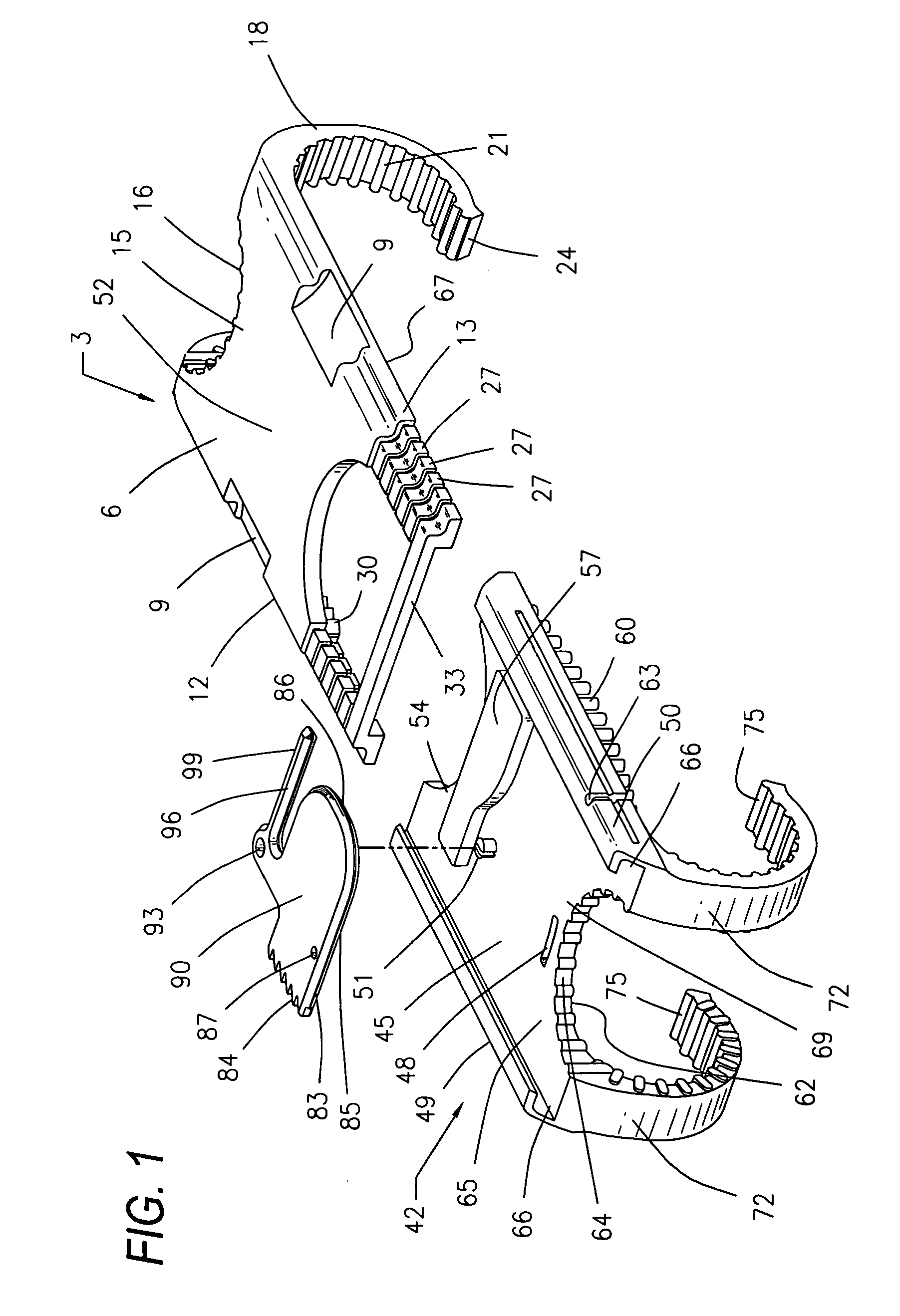
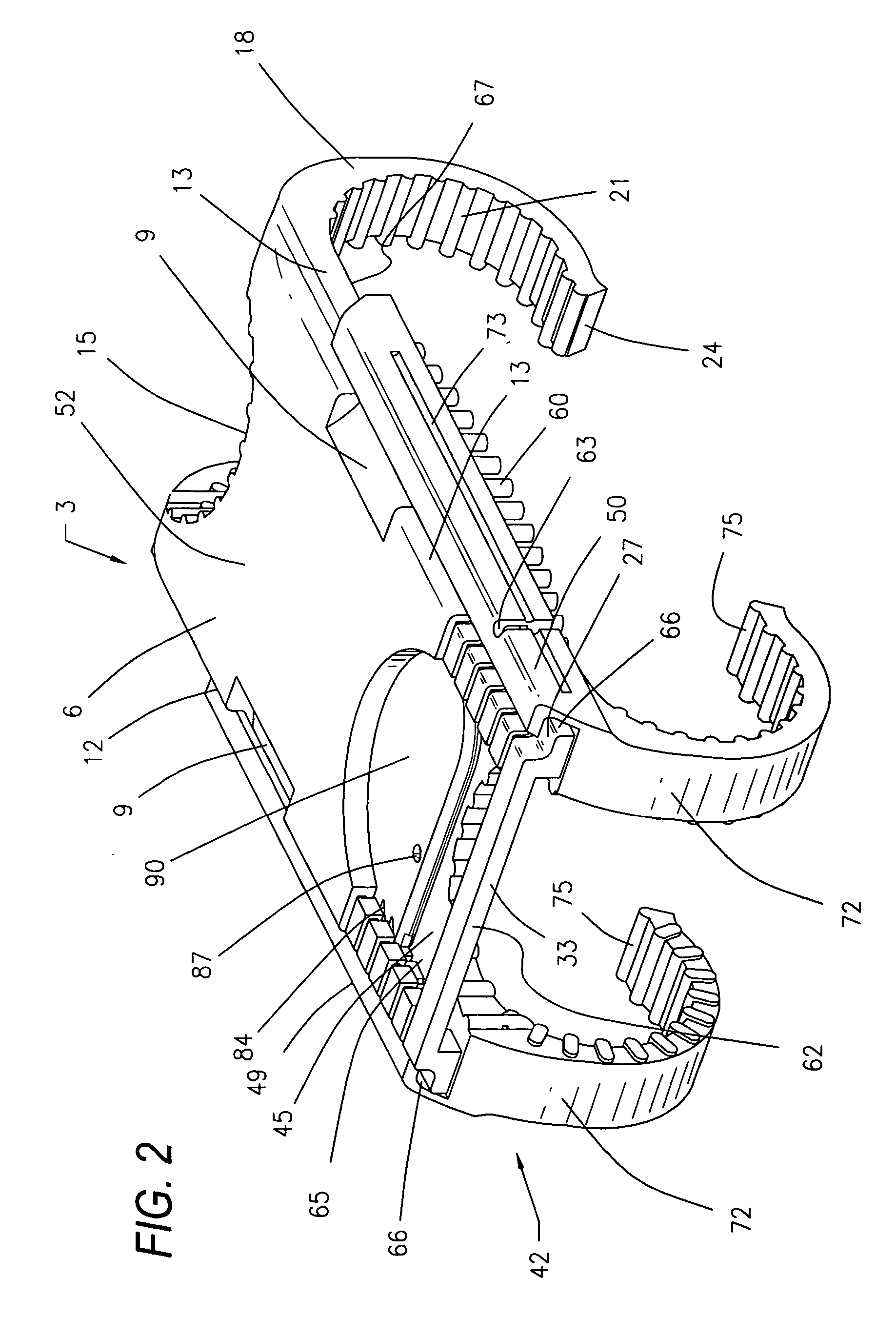
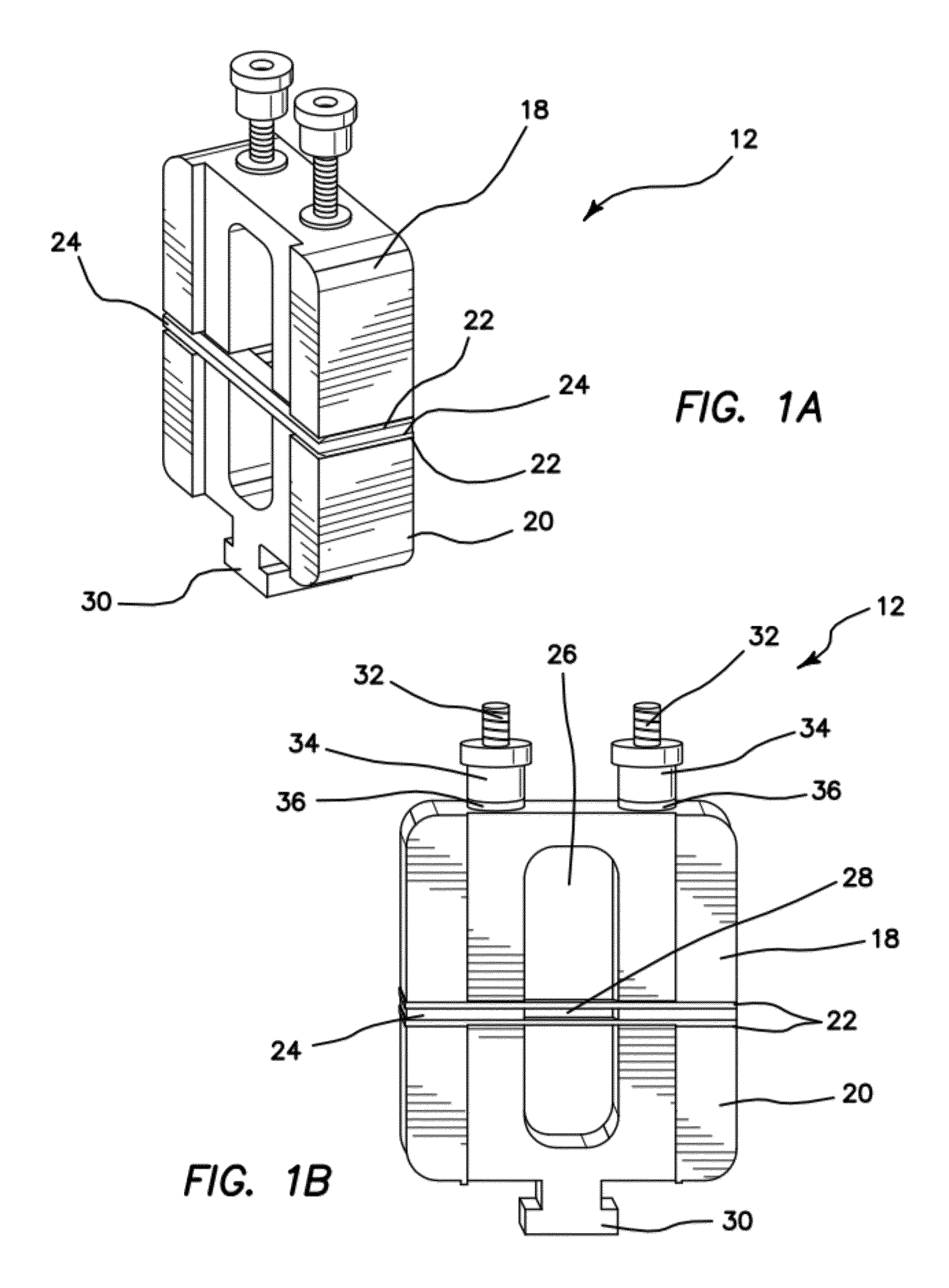
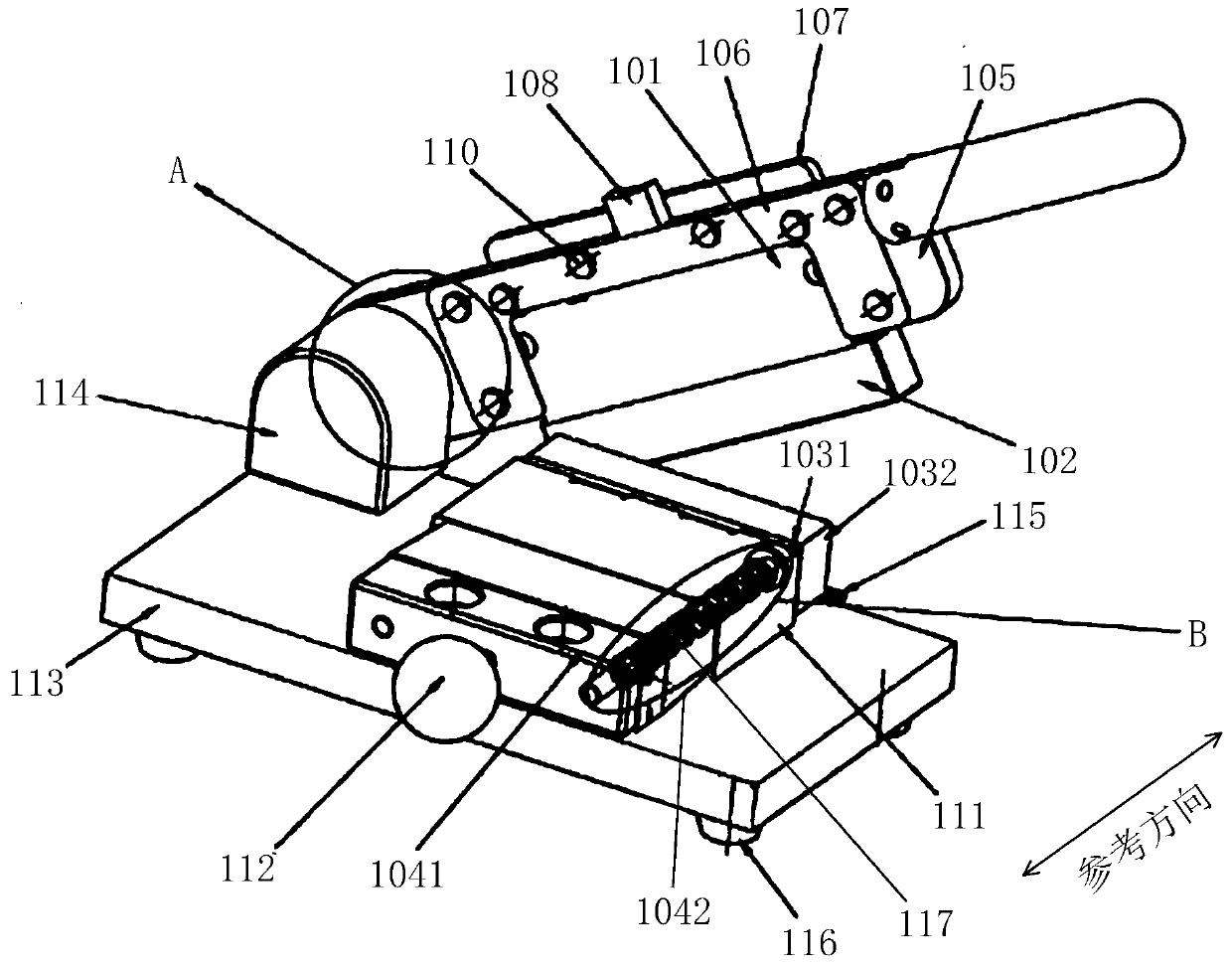
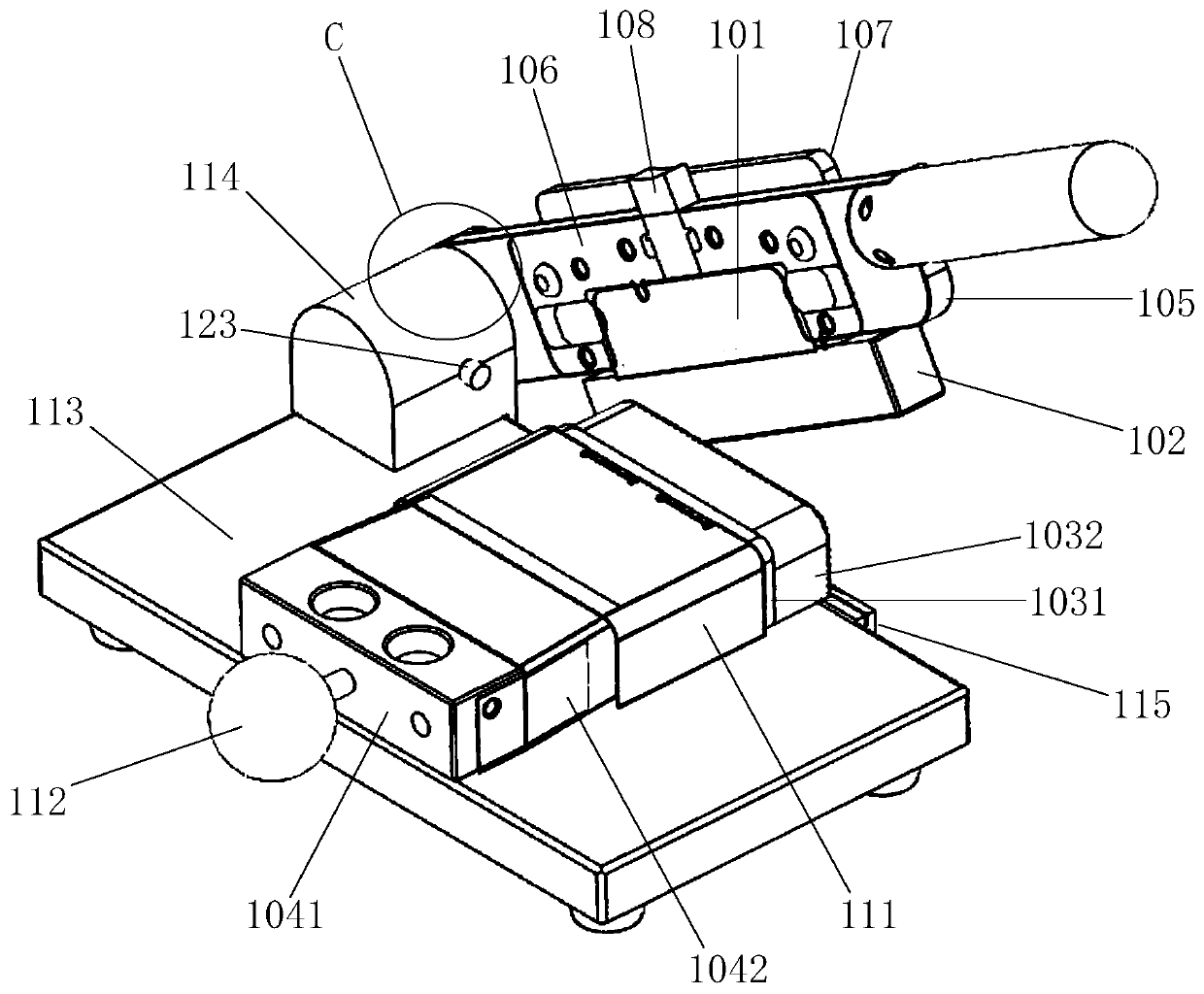
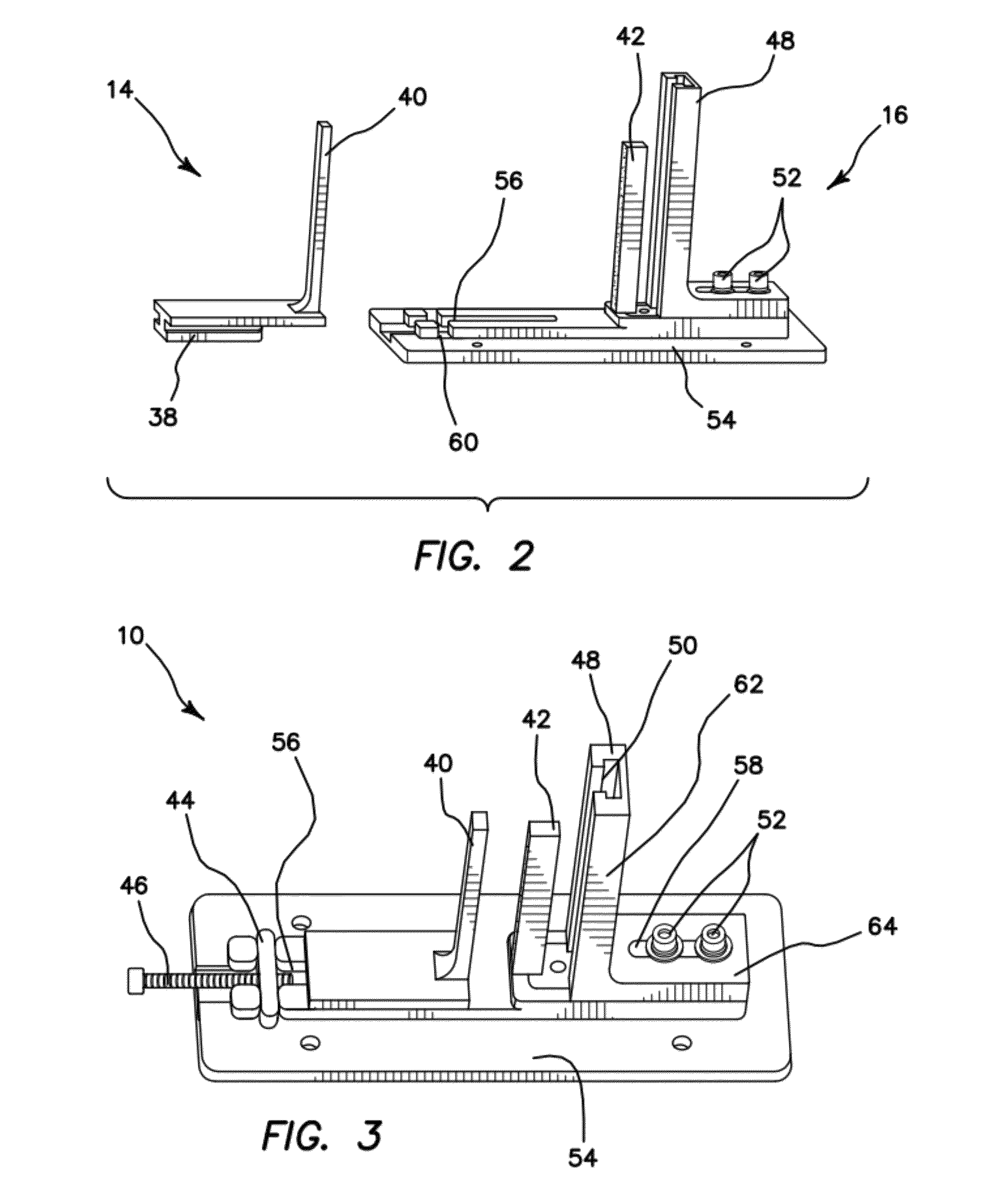
Surgical device for capturing, positioning and aligning portions of a horizontally severed human sternum
A surgical device for capturing, positioning and aligning portions of a horizontally severed human sternum via positioning around each of a paired set of ribs located on opposite sides of the severed sternum while simultaneously contacting and substantially surrounding the anterior and posterior portions of the sternum comprising impermanently joined insertion and insertion guide attachment members, each of the members having first and second end portions, first and second side portions, a body portion, anterior and posterior surfaces, two crescent formed leg portions with angularly displaced foot portions, a plurality of sternum, rib and costal cartilage engagement surfaces and, a rotary lock member pivotally attached to the insertion guide member, and further comprising a capturing mechanism having angularly displaced teeth-like structures on a first side cooperating with reciprocating teeth like structures integrated on a first side of the insertion member to position, secure in place and operatively combine the insertion member, rotary lock and insertion guide members.
Owner:MAVREX MEDICAL LLC
Surgical device for capturing, positioning and aligning portions of a severed human sternum
A surgical device for capturing, positioning and aligning portions of a severed human sternum via positioning around the costal cartilage portion of each of a paired set of ribs located on opposite sides of the severed sternum while simultaneously contacting and substantially surrounding the anterior and posterior portions of the sternum comprising impermanently joined insertion and insertion guide attachment members, each of the members having first and second end portions, first and second side portions, a body portion, anterior and posterior surfaces, two crescent formed leg portions with angularly displaced foot portions, a plurality of sternum, rib and costal cartilage engagement surfaces and, a rotary lock member pivotally attached to the insertion guide member, and further comprising a capturing mechanism having angularly displaced teeth-like structures on a first side cooperating with reciprocating teeth like structures integrated on a first side of the insertion member to position, secure in place and operatively combine the insertion member, rotary lock and insertion guide members.
Owner:MAVREX MEDICAL LLC
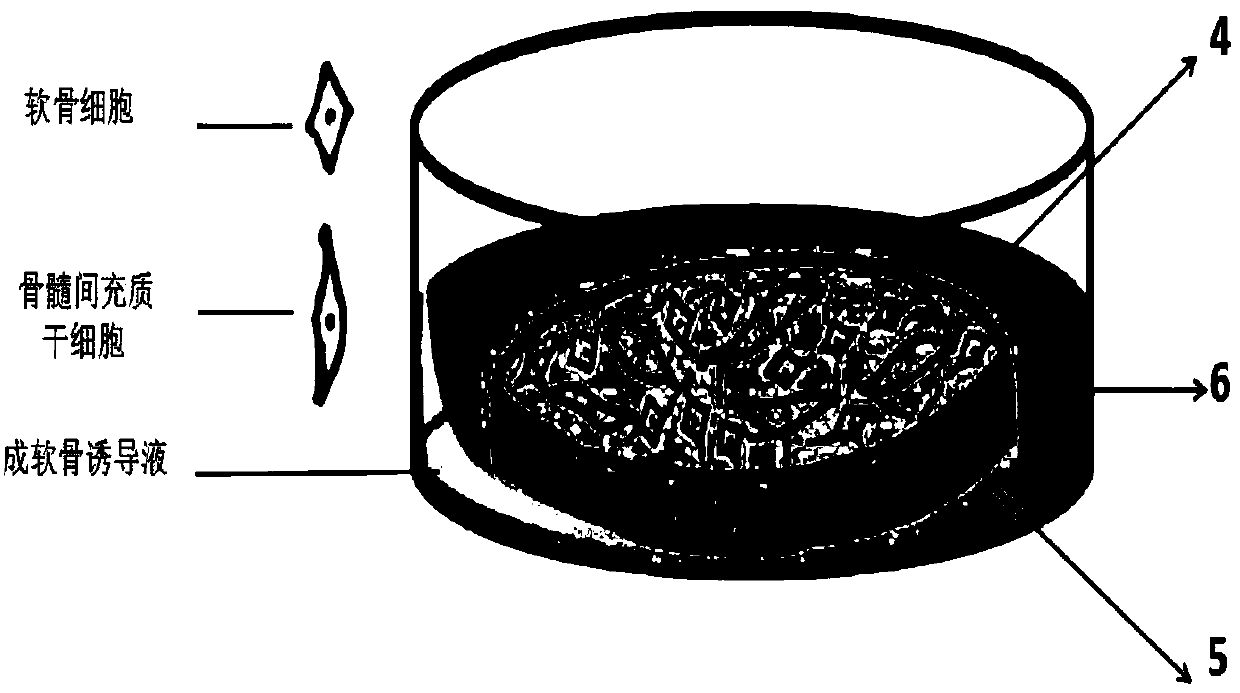
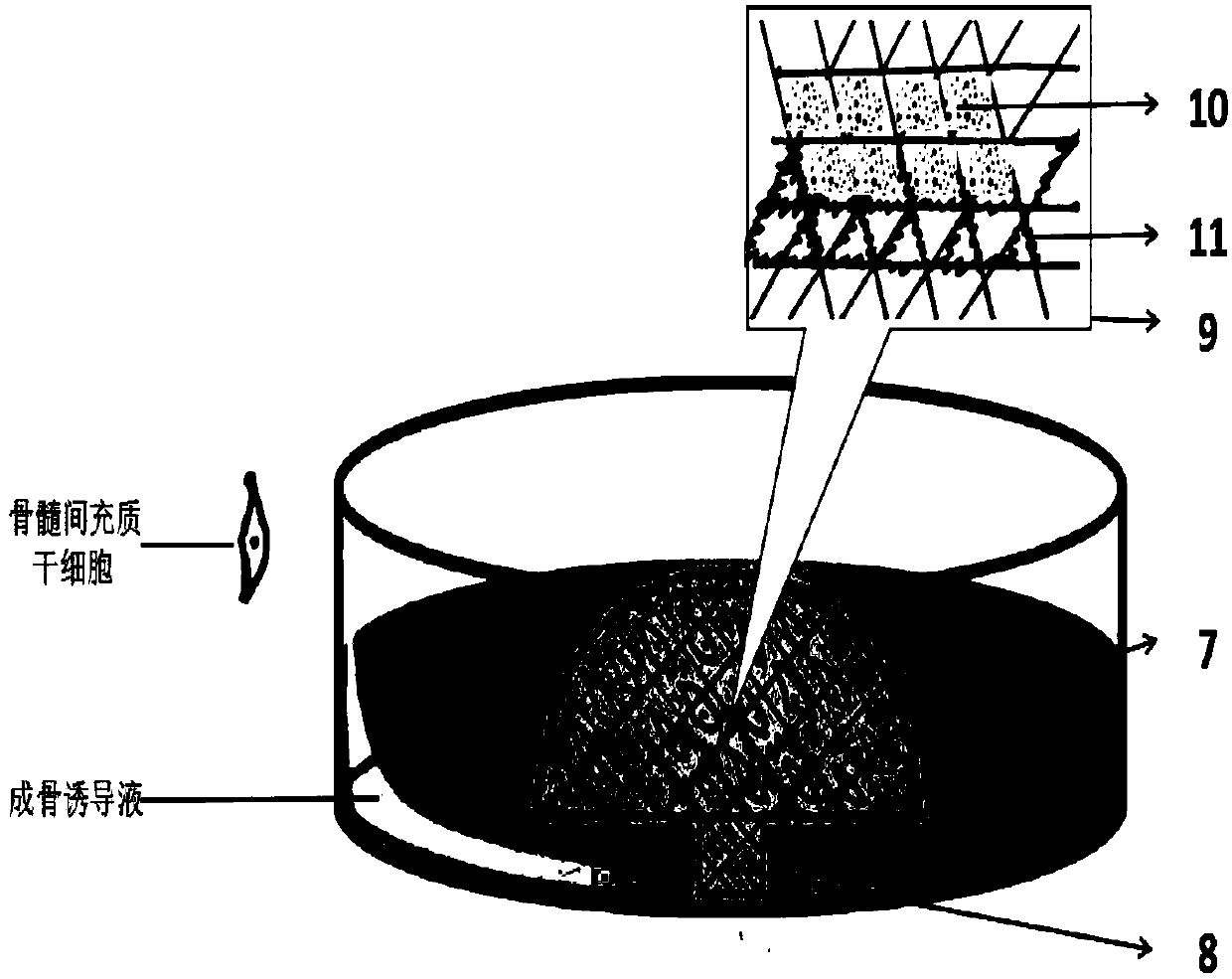
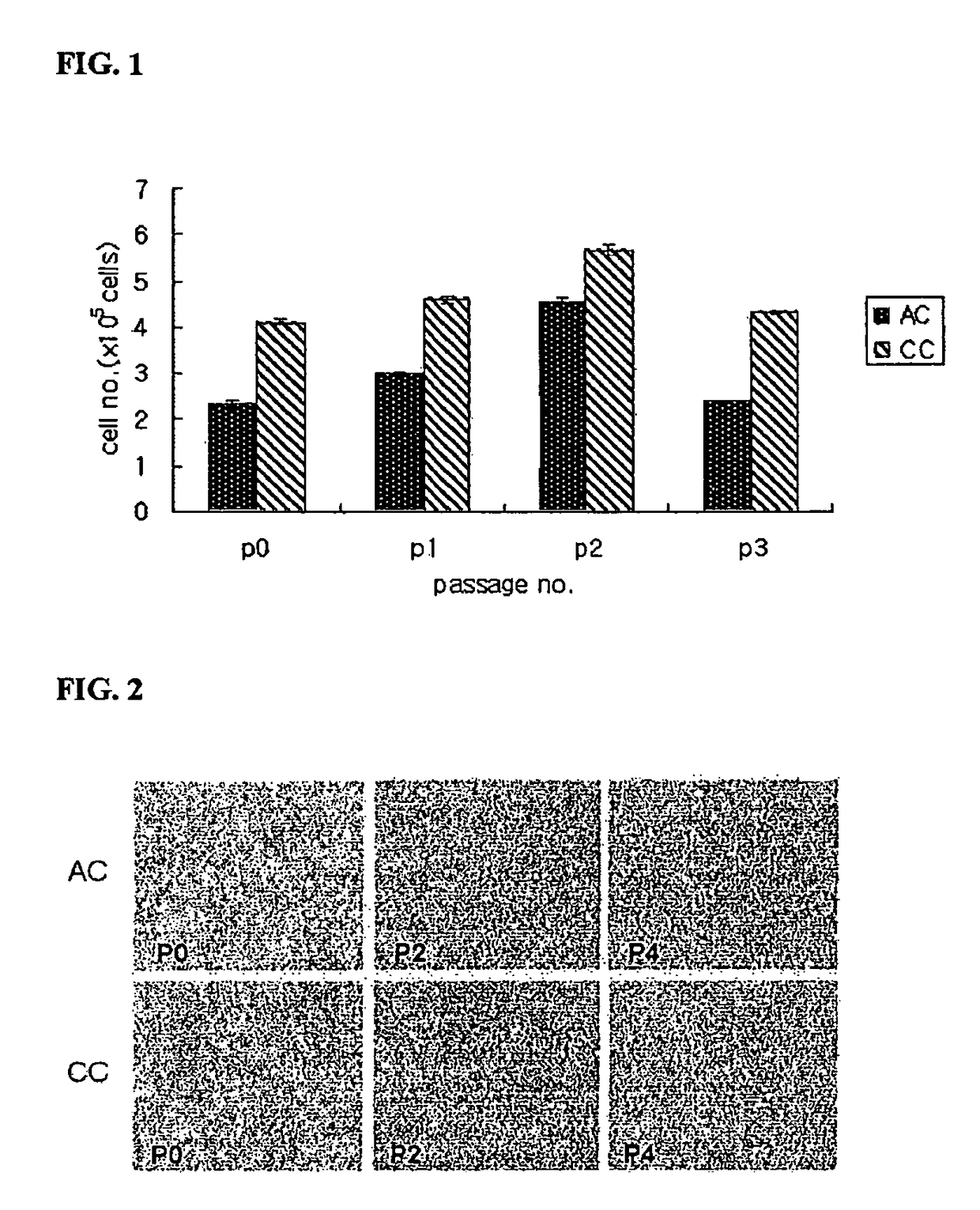
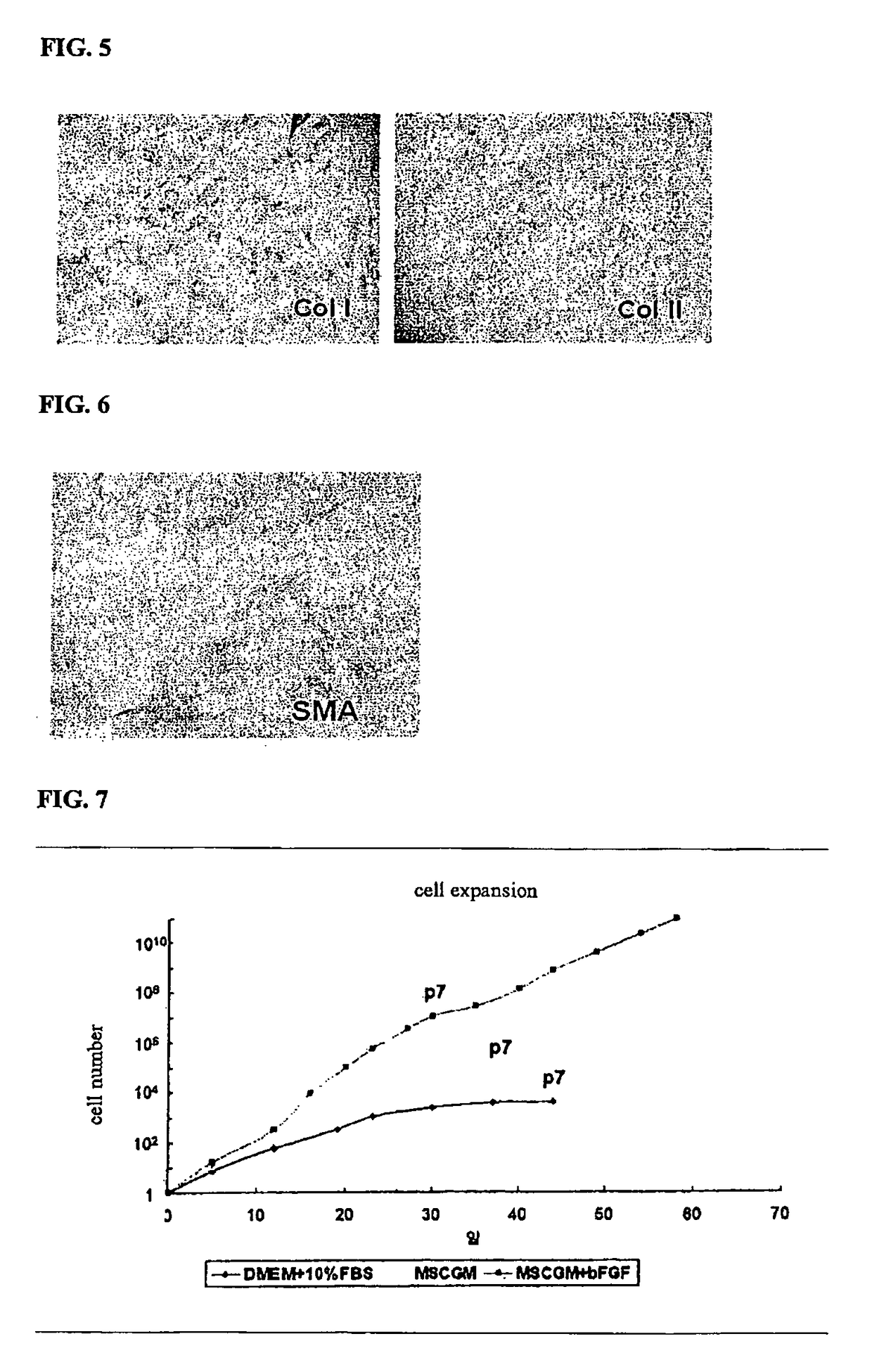
Artificial cartilage containing chondrocytes obtained from costal cartilage and preparation process thereof
ActiveUS20090228105A1Ability to useEfficient regenerationBone implantMammal material medical ingredientsMesenchymal stem cellCostal cartilage
The present invention relates to an artificial cartilage containing mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)-like dedifferentiated cells obtained by passage culturing costal chondrocytes, and a preparation process thereof.
Owner:BIO SOLUTION CO LTD +2
Surgical device for capturing, positioning and aligning portions of a severed human sternum
ActiveUS20050267475A1Prevent travelPrevent movementSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisBreast boneSurgical device
A surgical device for capturing, positioning and aligning portions of a severed human sternum via positioning around the costal cartilage portion of each of a paired set of ribs located on opposite sides of the severed sternum while simultaneously contacting and substantially surrounding the anterior and posterior portions of the sternum comprising impermanently joined insertion and insertion guide attachment members, each of the members having first and second end portions, first and second side portions, a body portion, anterior and posterior surfaces, two crescent formed leg portions with angularly displaced foot portions, a plurality of sternum, rib and costal cartilage engagement surfaces and, a rotary lock member pivotally attached to the insertion guide member, and further comprising a capturing mechanism having angularly displaced teeth-like structures on a first side cooperating with reciprocating teeth like structures integrated on a first side of the insertion member to position, secure in place and operatively combine the insertion member, rotary lock and insertion guide members.
Owner:MAVREX MEDICAL LLC
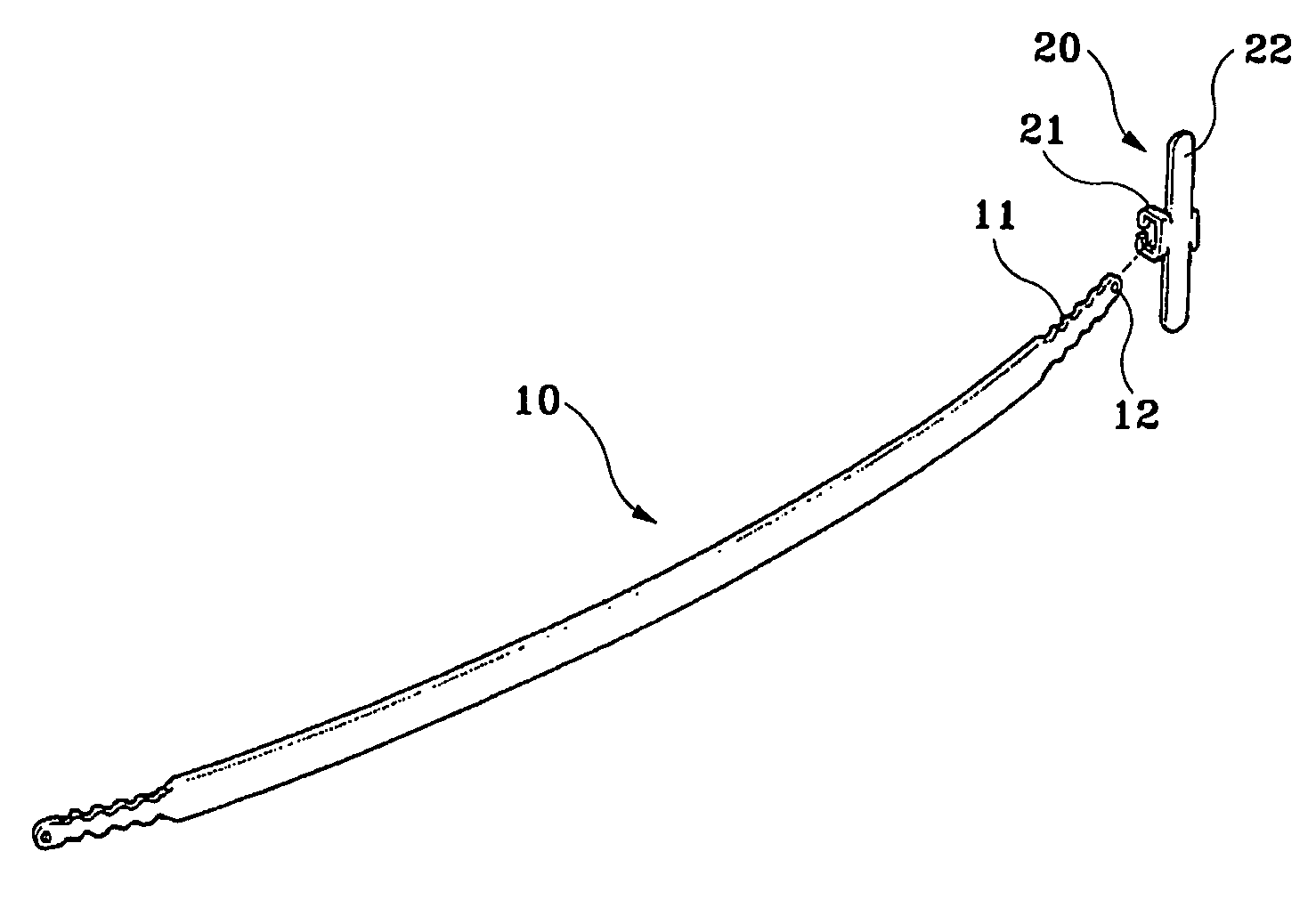
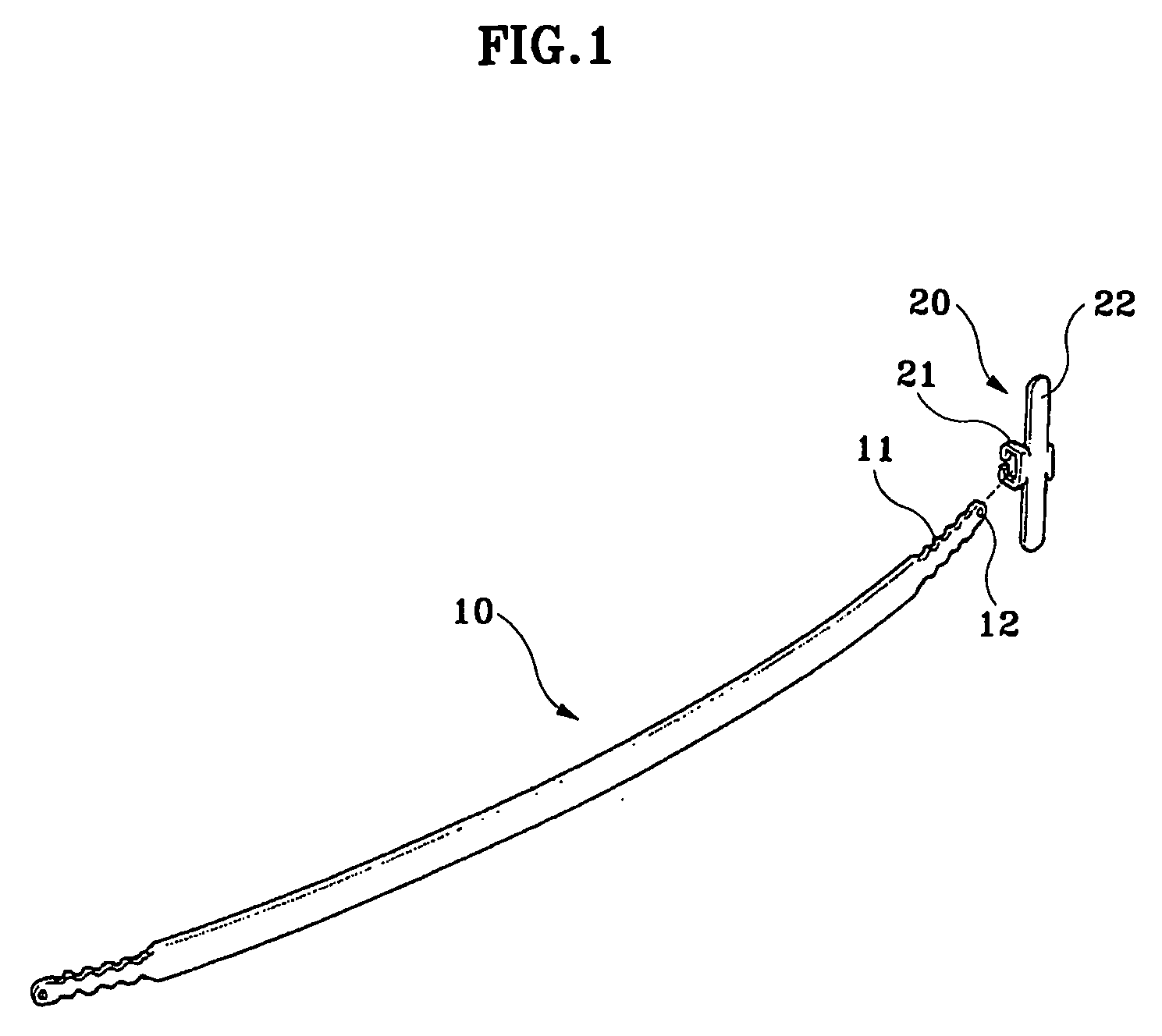
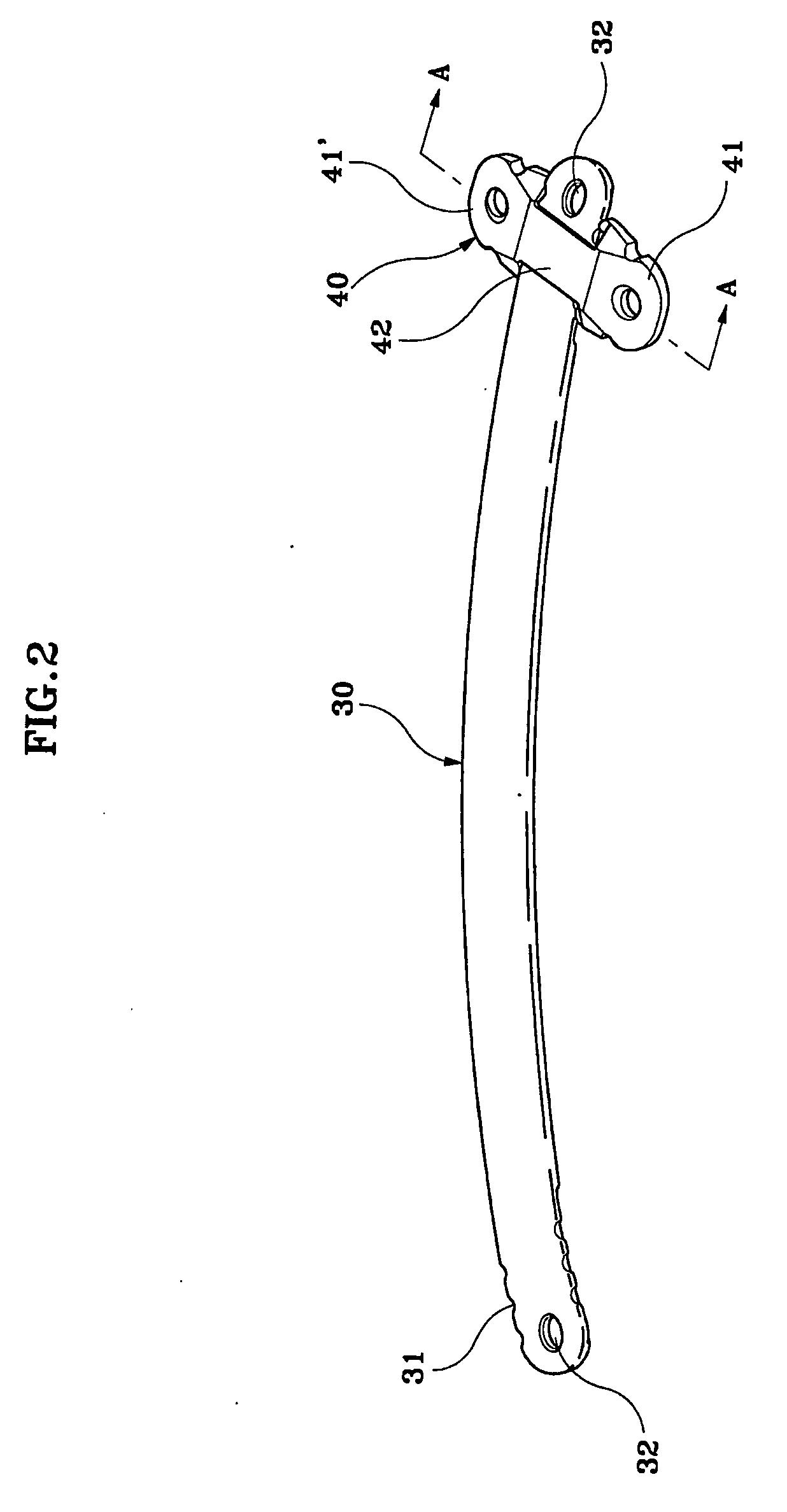
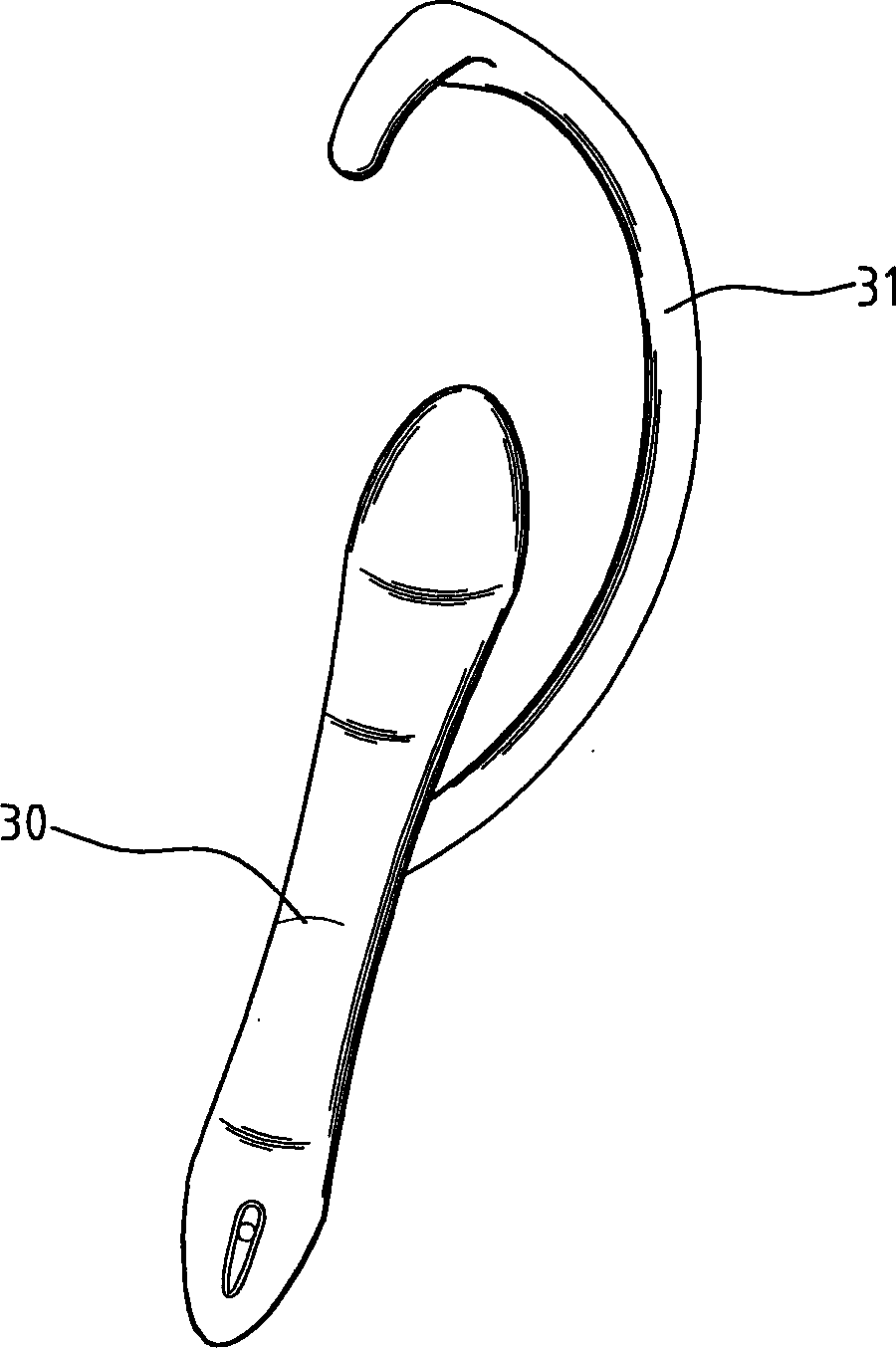
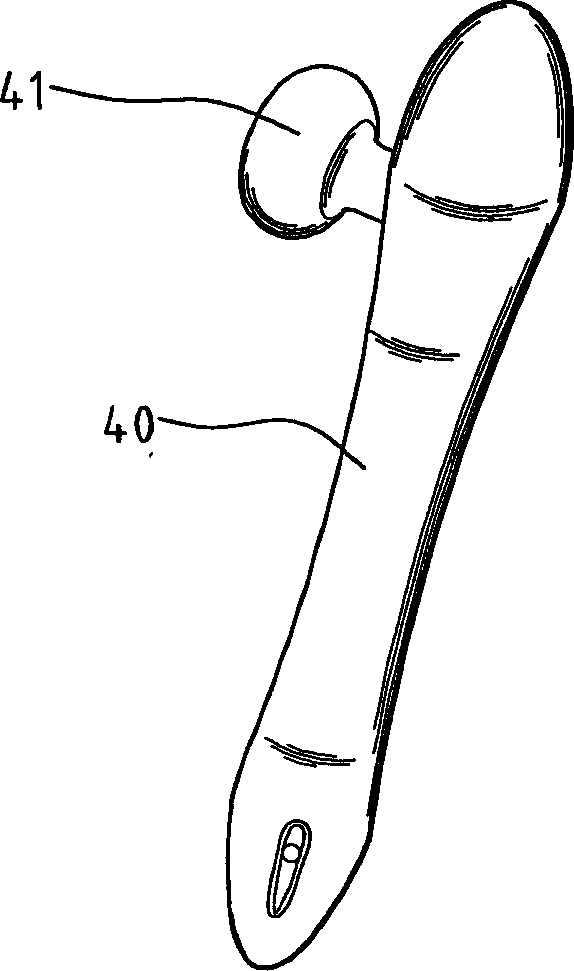
Implant for correction of pectus excavatum
InactiveUS20060058786A1Avoid infectionAvoid painJoint implantsBone platesBreast bonePectus excavatum
An implant for correcting pectus excavatum is disclosed, which comprises a chest correction bar (30) inserted into a body for lifting a depressed sternum and costal cartilages, and a stabilizer (40) for being inserted into a distal end of the chest correction bar (30) to prevent the chest correction bar from being rotated inside the body, wherein the chest correction bar (30) is formed at both jagged distal ends thereof with recesses (33) each of a predetermined length along the lengthwise direction of the chest correction bar (30), and wherein the stabilizer (40) comprises: two fixing plates (41, 41′) for being fixed to the body of a patient; a bridge (42) connecting the two fixing plates (41, 41′); two protruders (43, 43′) each generally opposed from the fixing plates (41, 41′) so as to be hitched by the recesses (33) at the distal ends of the chest correction bar (30) inserted from under the bridge (42), where there are formed two spaces (C) each of a predetermined size between the two protuders (43, 43′) and two lateral lengthwise surfaces of the bridge (42) so that the distal ends of the chest correction bar (30) can be inserted thereinto, thereby allowing the stabilizer (40) to be easily inserted into the chest correction bar (30), and once the insertion is made, pain and infection caused by stimulation on incised portions of a patient can be prevented.
Owner:MEDIXALIGN
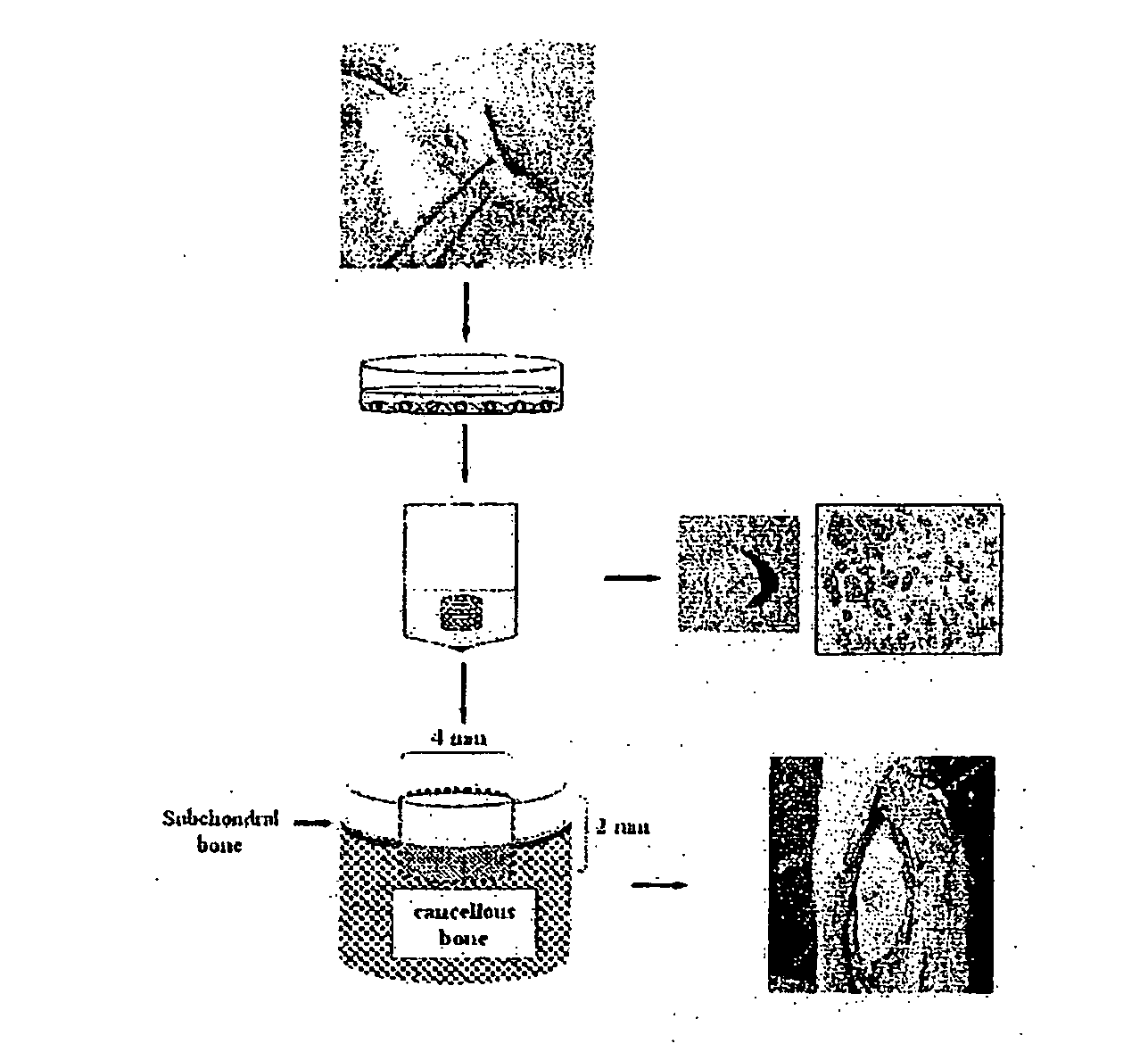
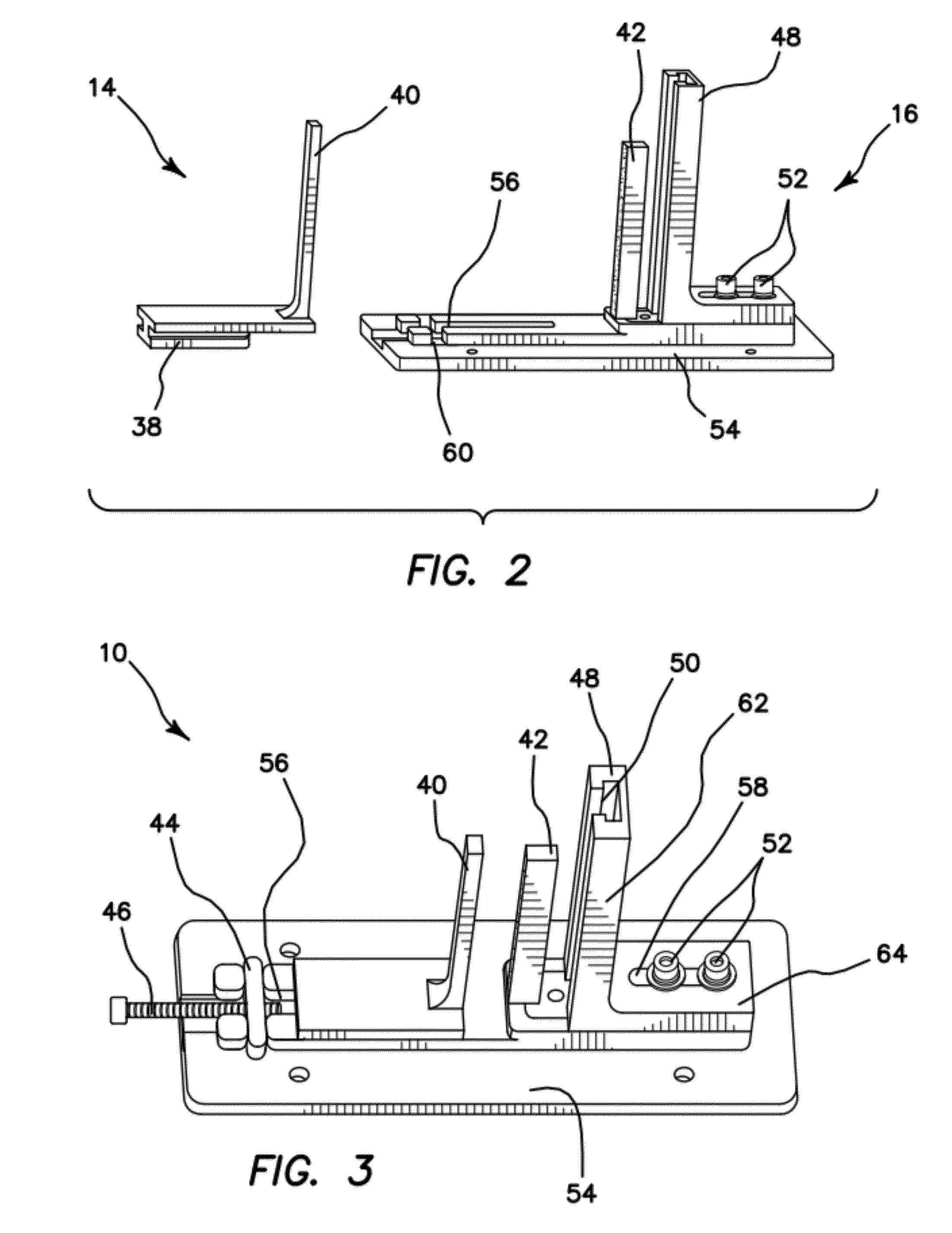
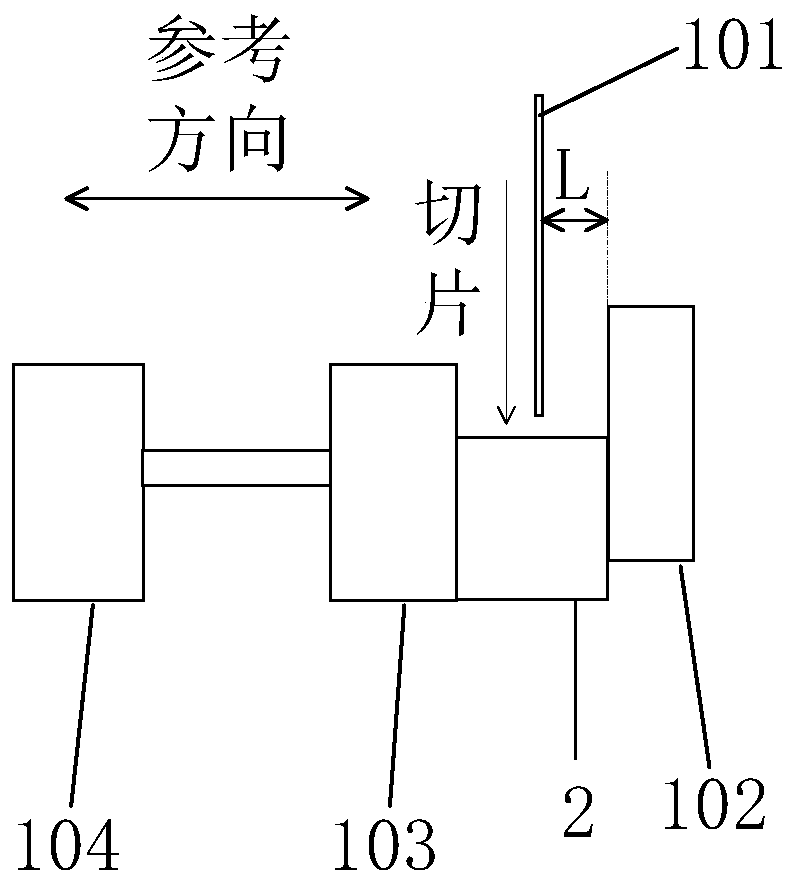
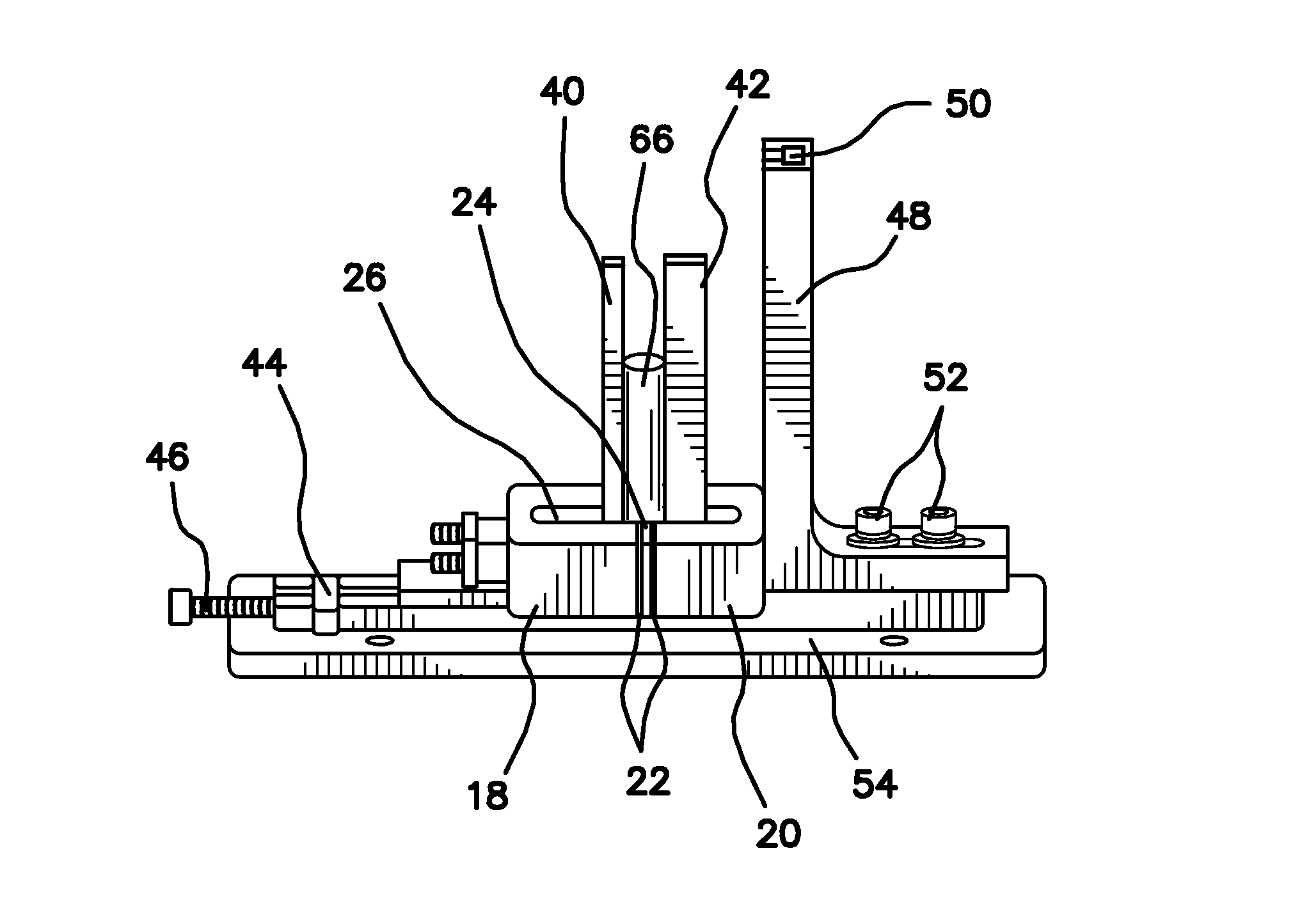
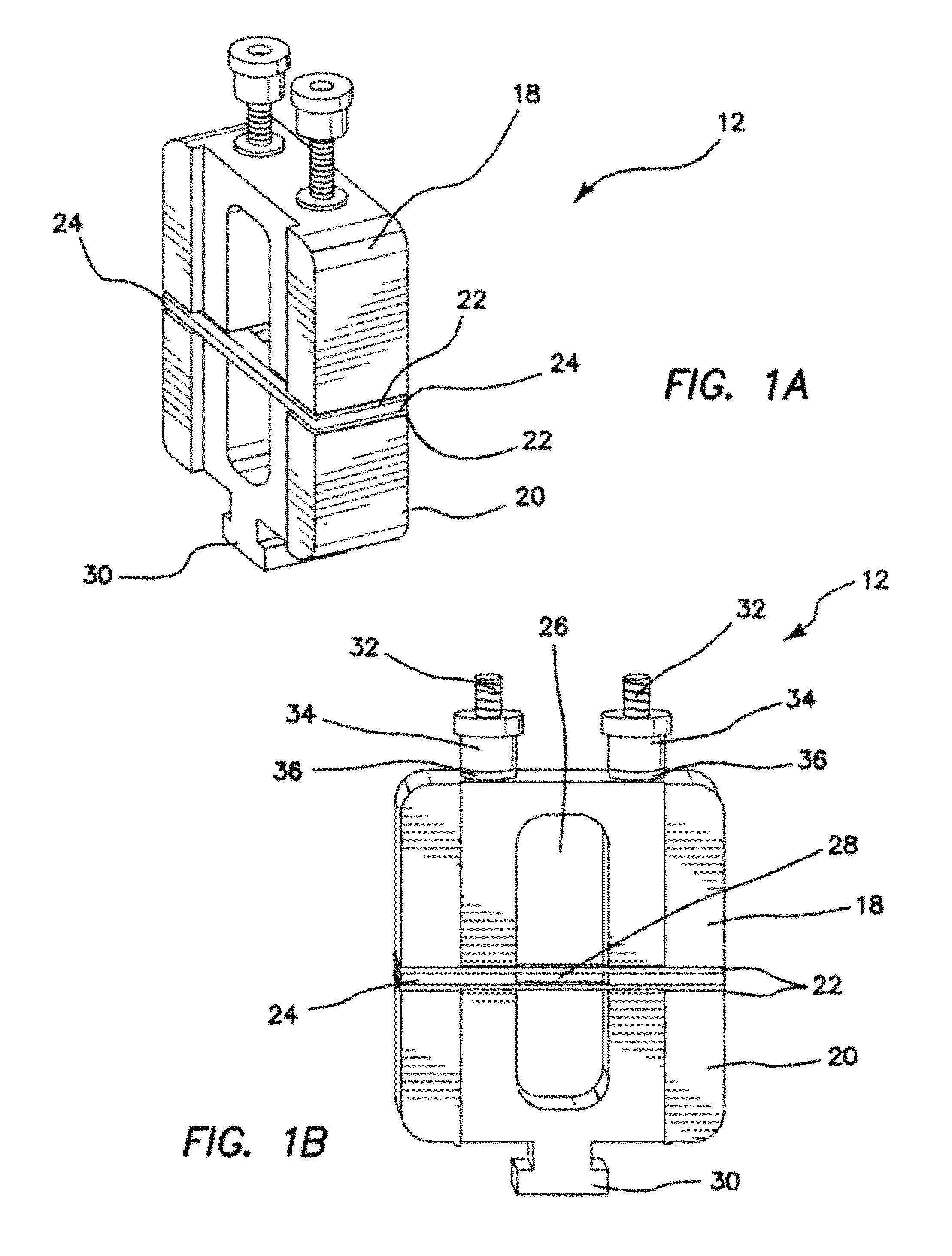
Apparatus and Method for Cutting Costal Cartilage
A double-bladed cutting device providing a practical method for obtaining costal cartilage specimens in both an operating room and research setting. The device reduces the skill and time required to fashion cartilage slices, while increasing the uniformity of the cut specimens. Furthermore, via an adjustable guide, slices can be obtained precisely from the central core of the rib. Although specimen lengths up to 4 cm are preferred, longer lengths can be attained without modification of the device. The cartilage specimen may be held in place within the device via means of compression or tension.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Simulation method for funnel breast orthopaedic surgery
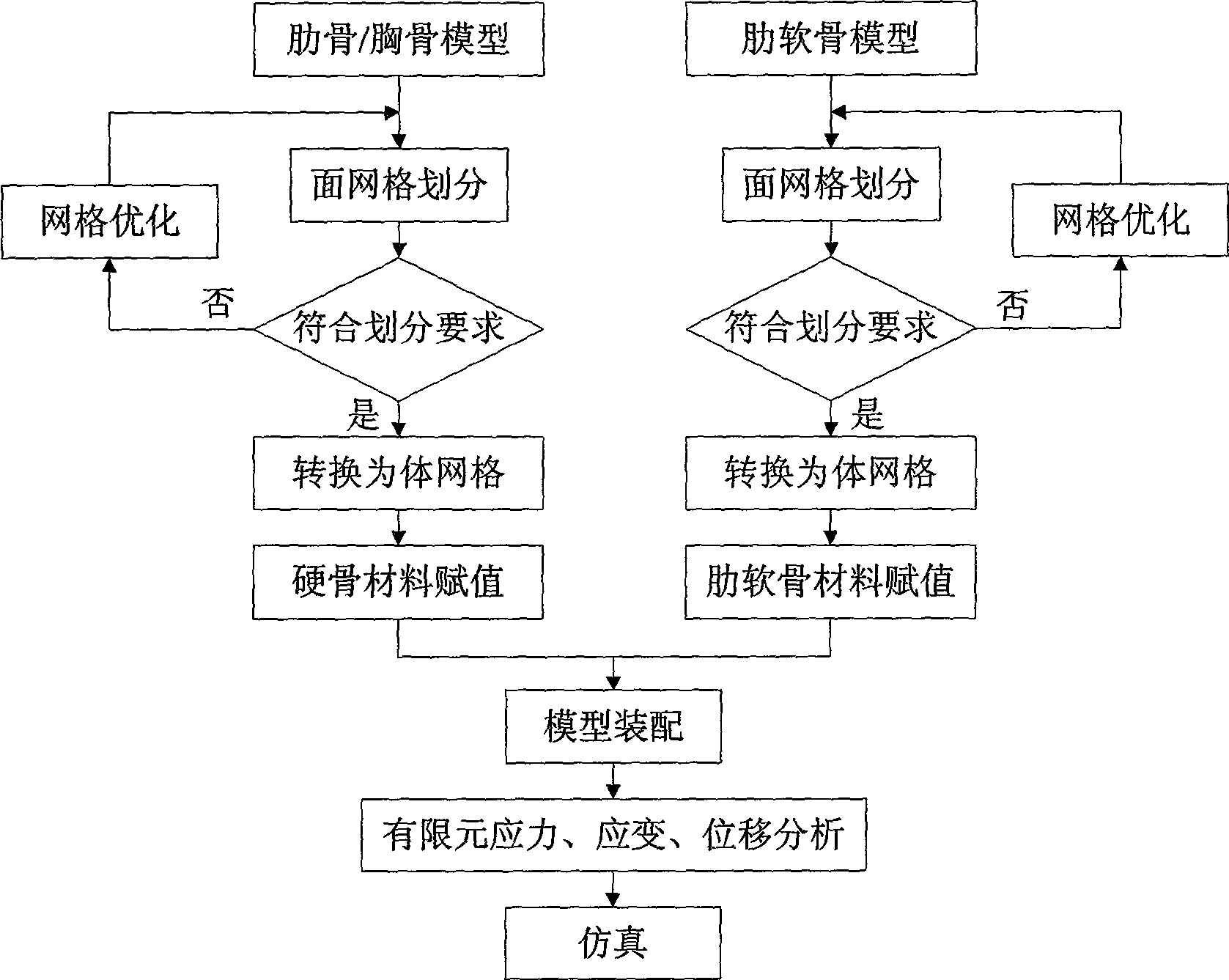
InactiveCN101488236AIncrease success rateInternal osteosythesisDiagnostic recording/measuringMechanical modelsElement analysis
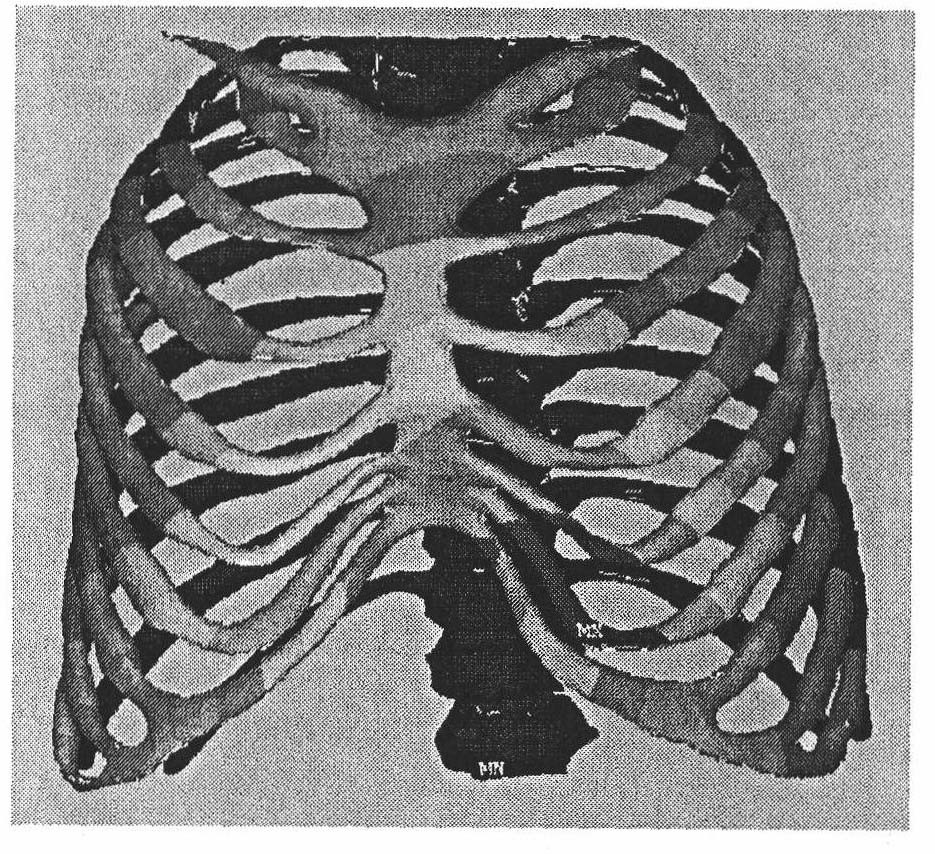
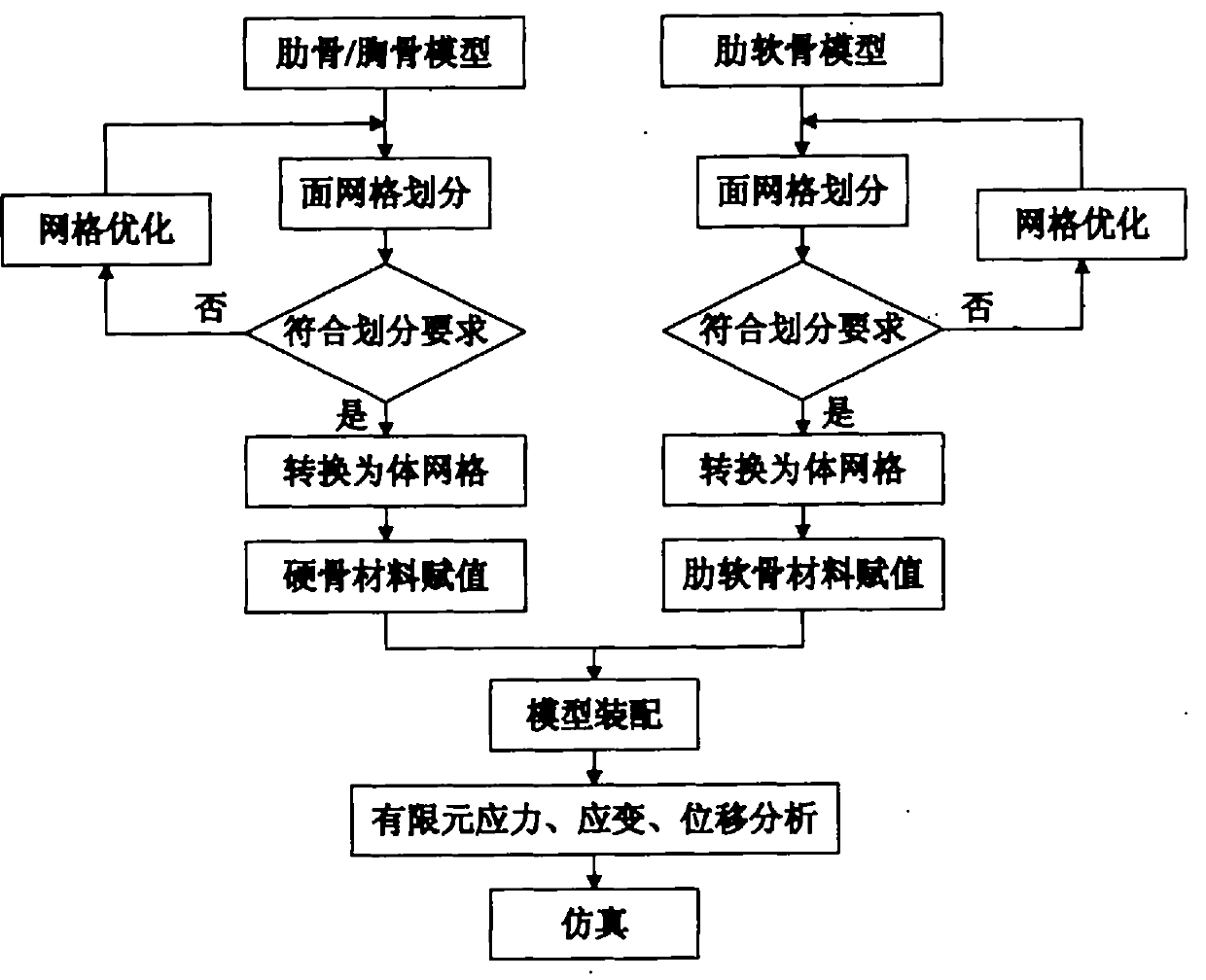
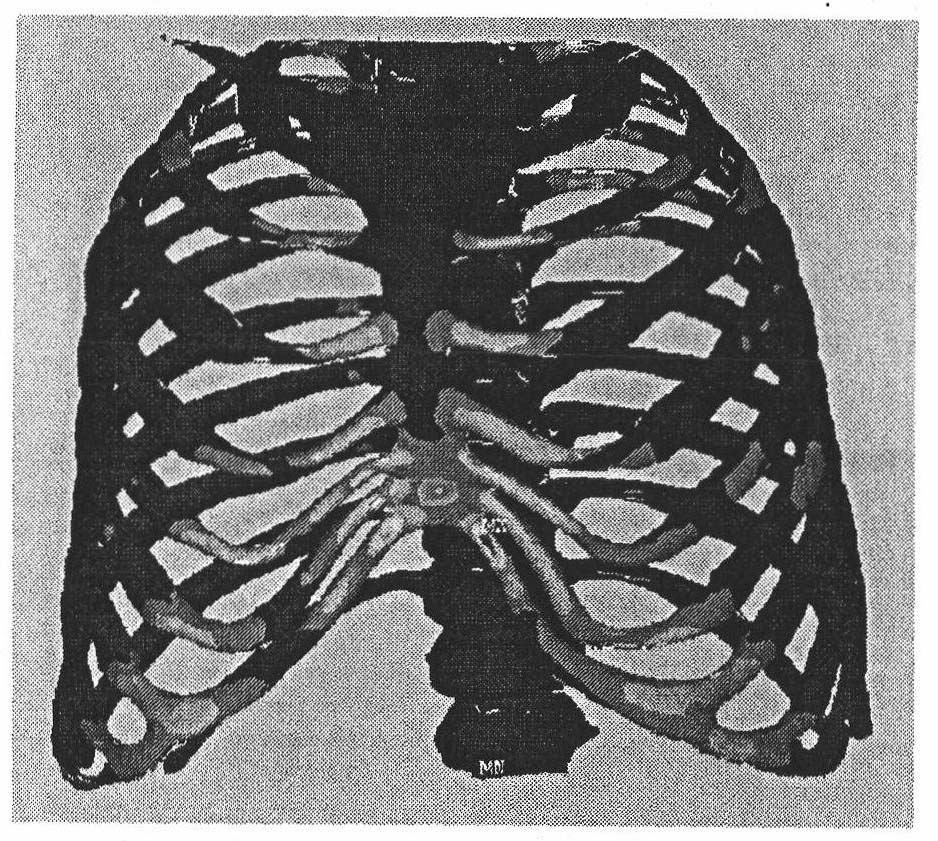
The invention discloses a funnel chest orthopaedic surgery simulation method; chest three-dimension visualization bone models and costal cartilage models are respectively processed by face mesh division, and the mesh is optimized; a mesh conversion is used on the basis of mesh optimization, and a chest model is converted into a body mesh from a face mesh; rib, costal cartilage and breast bone are respectively material-evaluated, and skeleton body mesh model of each part is assembled so as to obtain a complete chest three-dimensional mechanical model; boundary conditions and loading force moment are determined, and the chest model is processed by finite element analysis so as to obtain the stress, strain and displacement conditions of each skeleton part under the action of different external forces; the incision position, support plate material, fixing method and supporting force moment of funnel chest surgery are simulated so that the success ratio of funnel chest surgery is increased to over 98% from 70-90% of the prior art.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
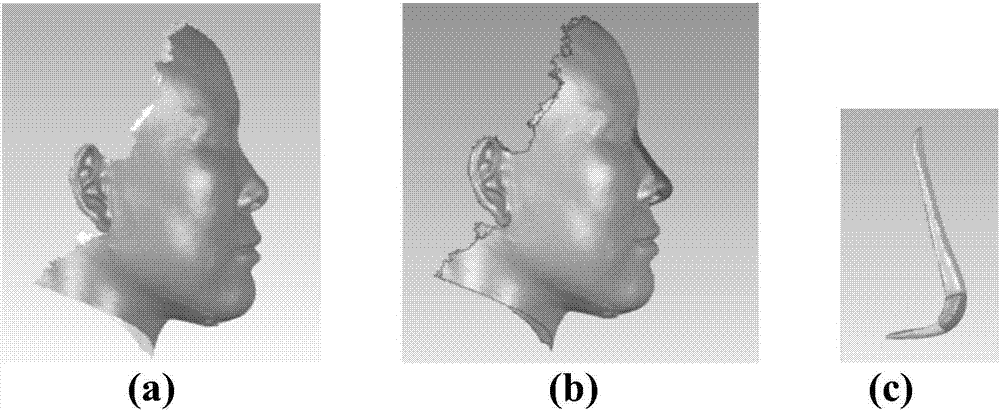
Three-dimensional modelling approach for children's funnel chest
InactiveCN101366639ASolve invisibleImplement cartilage modelingImage analysisComputerised tomographsLongissimus ThoracisFunnel Chest
The invention discloses a three-dimensional modeling method for the funnel chest of a child. Firstly, aiming at an original spiral CT picture of the funnel chest of the child, a region search method is adopted to model a thoracic hard bone part; a gray value of a cartilage region of a thoracic three-dimensional model is measured, and masking separation costal cartilage image data are created after the modification; a region growing method is adopted to apply region growing separation costal cartilage image data to a combining end of a hard bone and a cartilage of each rib; the costal cartilage data which is subjected to secondary data separation is three-dimensionally drafted to generate a three-dimensional funnel costal cartilage model; the three-dimensional funnel costal cartilage model is subjected to Gaussian smooth processing, and the model of the thoracic hard bone part of the funnel chest of the child and the three-dimensional costal cartilage model are overlapped to obtain an integral three-dimensional model of the funnel chest of the child. The region search method is adopted to process cartilages at the positions where with hard bones are combined, and the region growing method is adopted to solve the problem that a CT image of the cartilages is invisible, so the created three-dimensional model ensures that costal cartilages are not adhered to each other and each costal cartilage is round and smooth, and has high simulation degree.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Temporo-mandibular joint biological condyle constructed based on tissue engineering related technology
ActiveCN107899087ASolve the biggest bottleneck that cannot achieve joint function reconstructionImprove joint symptomsTissue regenerationCoatingsUpper floorCostal cartilage
The invention discloses a temporo-mandibular joint biological condyle constructed based on a tissue engineering related technology. The temporo-mandibular joint biological condyle is characterized bycomprising an upper cartilage layer, a middle cellular hydrogel layer and a lower phrenological compound layer which are mutually laminated, wherein the upper cartilage layer comprises a tissue surface making contact with an upper articular disc, a connecting surface making contact with the middle cellular hydrogel layer and a dense tissue layer positioned between the tissue surface and the connecting surface. According to the temporo-mandibular joint biological condyle disclosed by the invention, on the basis of ensuring accurate control over a three-dimensional morphological structure, functional reconstruction of a temporo-mandibular joint is realized; besides, the temporo-mandibular joint biological condyle has the advantages of reducing operative wound, facilitating the use in the operation, reducing osteotomy and bone grinding change, avoiding skull base damage and massive hemorrhage risk and the like so as to overcome the defects of current artificial joint replacement and costal cartilage grafting; transformation from joint reconstruction and replacement to joint reconstruction and regeneration is realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Adjustable costal cartilage cutter and ear and nose surgical instrument
Owner:DALIAN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
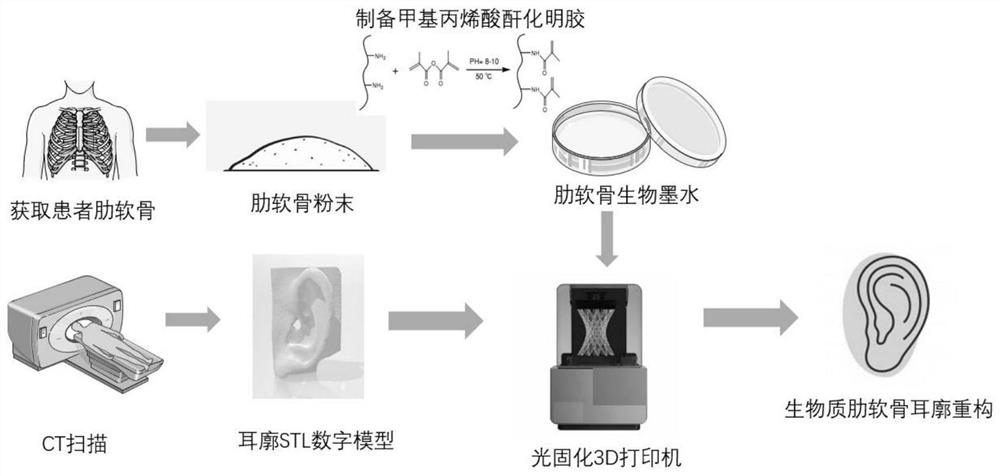
3D printed bio-ink based on costal cartilage as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111671978AEnable accurate modelingAccurate modelingAdditive manufacturing apparatusTissue regeneration3d printTissue reconstruction
The invention discloses 3D printed bio-ink based on costal cartilage as well as a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biomedical materials. The 3D printedbio-ink comprises costal cartilage powder, photocurable hydrogel and phenyl-2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyl lithium phosphonate, and an artificial auricle can be successfully prepared by adopting the 3D printed bio-ink through a reverse engineering system and a photocurable 3D printing technology. The 3D printed autologous costal cartilage auricle prepared by the 3D printed bio-ink has the advantages of high adaptive individuation, simple and fast preparation process, high appearance precision, full utilization of donor autologous materials, great reduction of costal cartilage taking amount and good biocompatibility and tissue reconstruction capability, and has great clinical application value in a microtia reconstruction operation.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
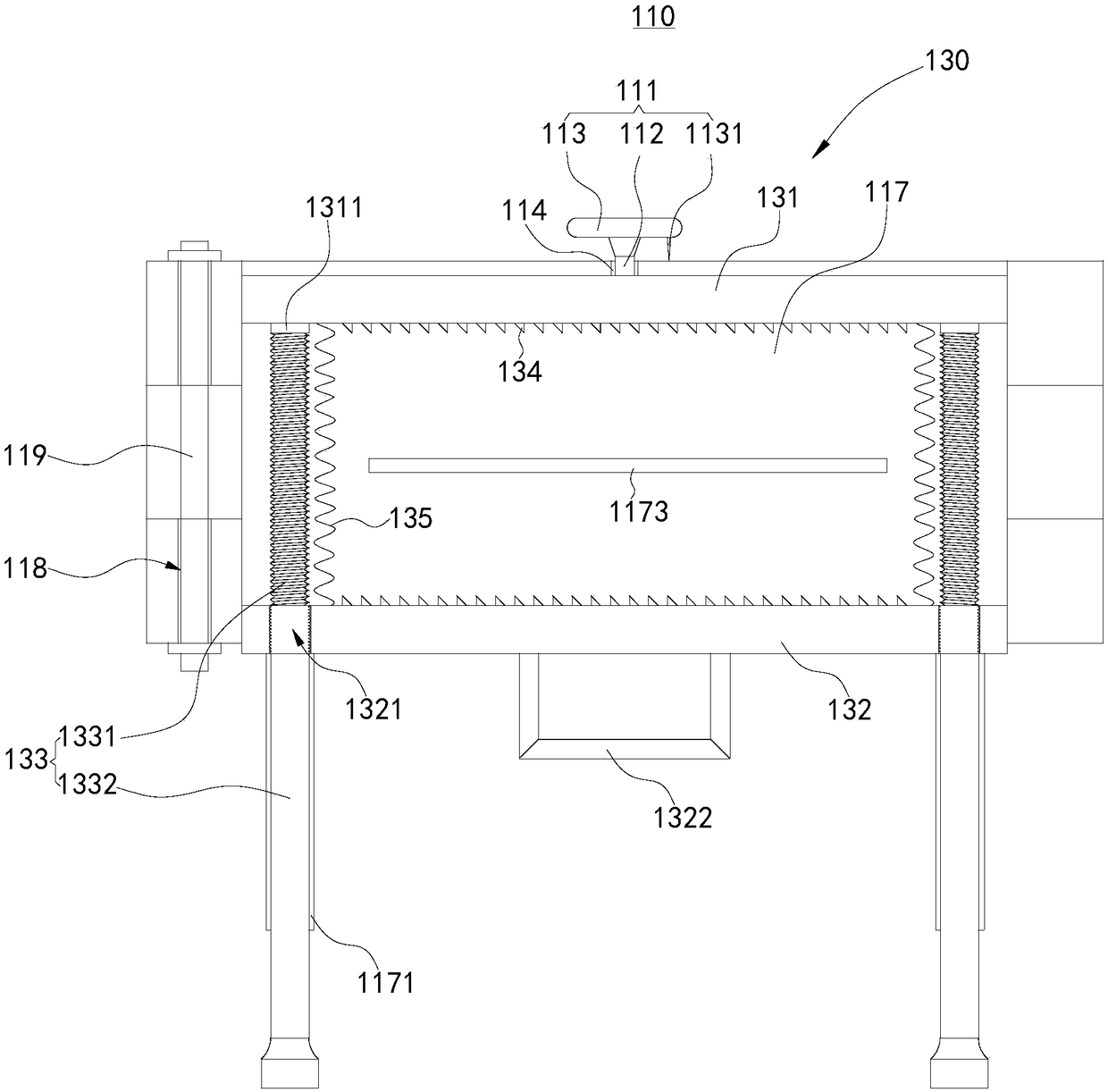
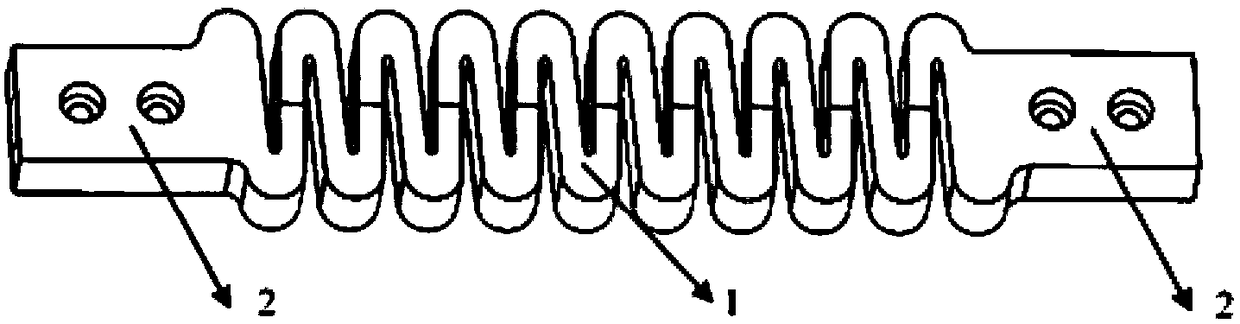
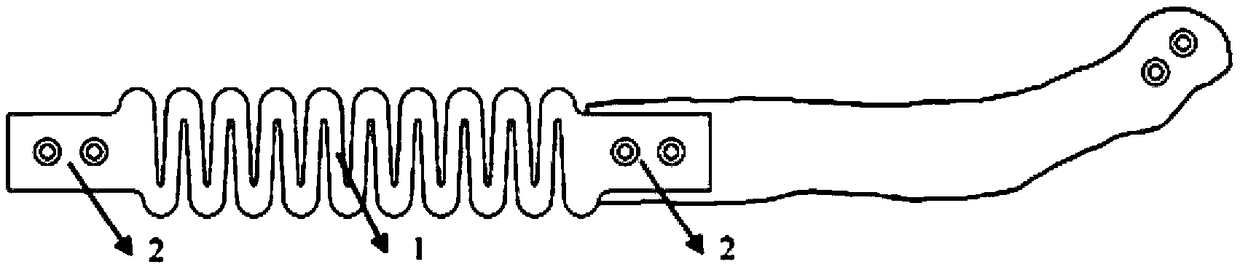
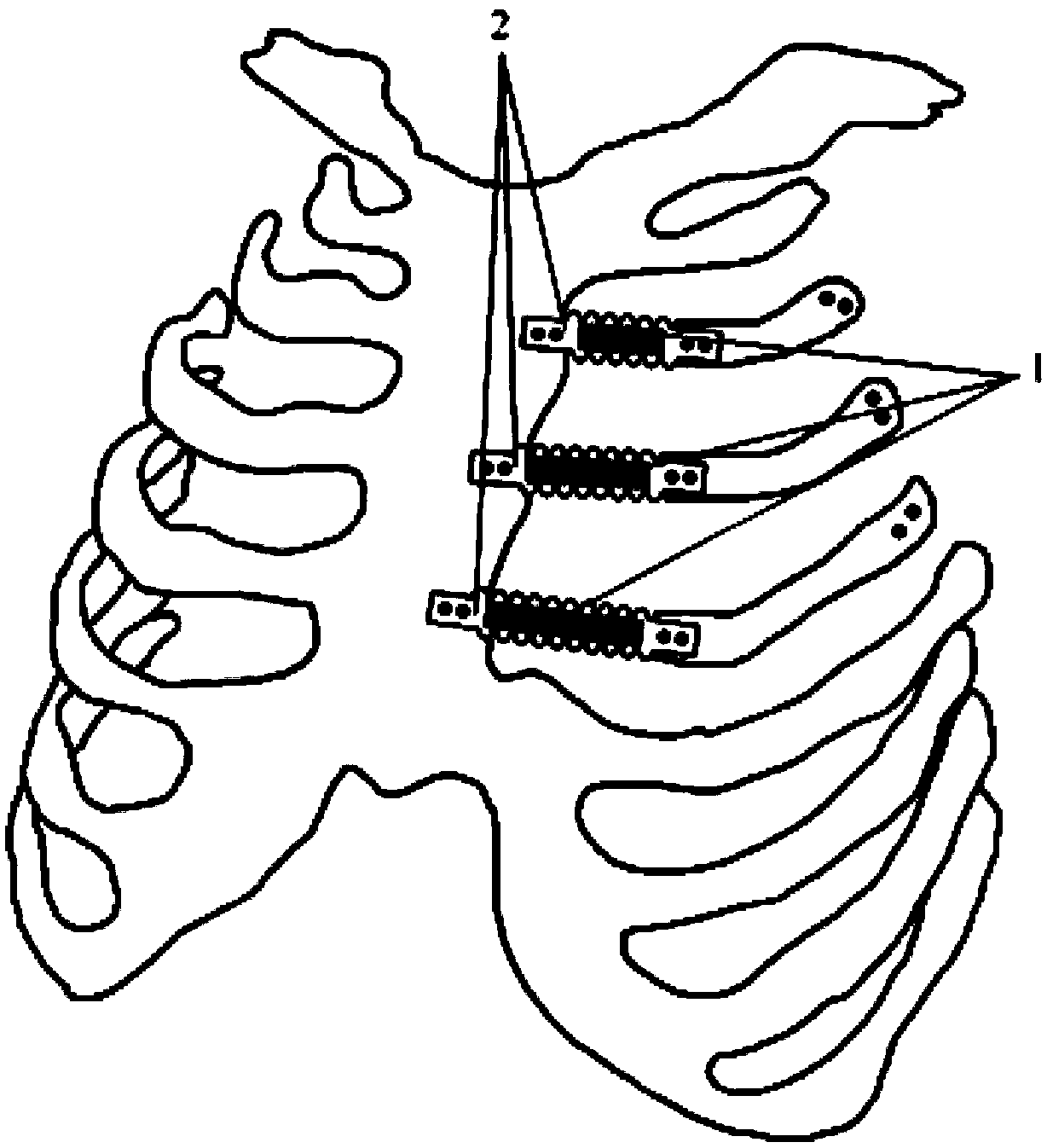
A biomimetic designed costal cartilage prosthesis implant and a preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109199644AMeet strength requirementsImprove toughnessJoint implantsReticular formationMechanical property
The invention discloses a biomimetic costal cartilage prosthesis implant and a preparation method thereof, as that costal cartilage prosthesis implant is integrally in the shape of a strip, comprisesan intermediate elastic structure and a two-end fixing structure, wherein the elastic structure in the middle of the costal cartilage prosthesis is a mechanical wave structure, a reticular structure or a spiral structure, and the elastic coefficient of the costal cartilage prosthesis can be changed according to different implant positions by changing parameters of the intermediate elastic structure. The costal cartilage prosthesis implant has two end fixing structures, corresponding ribs and sternum, and has a structure for mounting fixing substitutes. The costal cartilage prosthesis implant has two end fixing structures. The costal cartilage prosthesis implant provided by the invention has mechanical properties close to the real costal cartilage, It can be used in combination with sternalrib prosthesis to improve the physiological function of sternal rib prosthesis after replacement in personalized chest wall bone reconstruction surgery, effectively reduce the postoperative respiratory function inhibition of clinical problems, and has a positive effect on postoperative recovery of patients.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
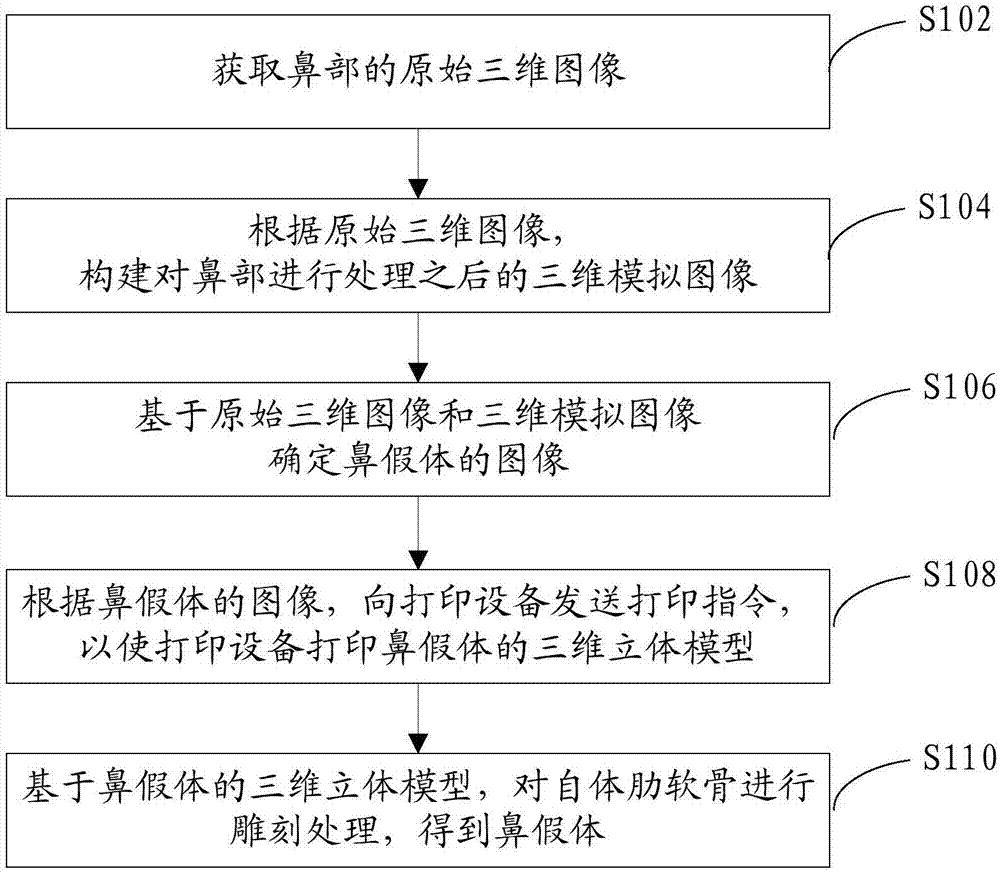
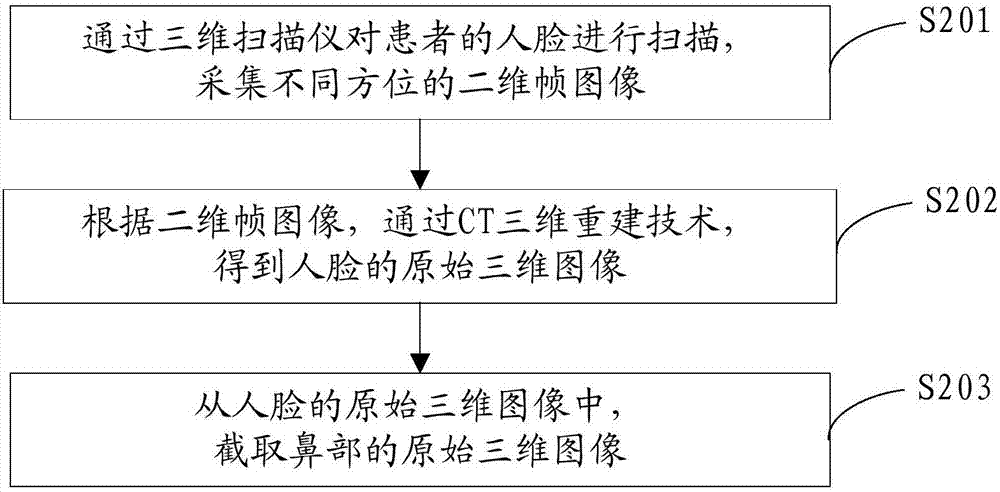
Method and device for preparing nasal prosthesis
InactiveCN106974744AReduce variance in actual requirementsReduce human errorNose implantsThree dimensional simulationNasal prosthesis
The invention provides a method and device for preparing a nasal prosthesis, and relates to the field of nasal prosthesis preparing. The method comprises the following steps that an original three-dimensional image of a nose is obtained; according to the original three-dimensional image, the three-dimensional simulation image after processing the nose is constructed; the nasal prosthesis is determined based on the original three-dimensional image and the three-dimensional simulation image; according to the image of the nasal prosthesis, a printing command is sent to a printing device so that the three-dimensional model of the nose prosthesis is printed by the printing device; the nasal prosthesis is obtained by processing the autogenous costal cartilage in a carving mode based on the three-dimensional model of nasal prosthesis. According to the method and device for preparing the nasal prosthesis, the technical problem that the rhinoplasty effect is not ideal in the prior art is solved.
Owner:PLASTIC SURGERY HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Cartilage slicing knife
PendingCN111166531AGuaranteed stabilityAvoid deformationNose implantsBone implantSurgeryKnife blades
The invention relates to a cartilage slicing knife. The cartilage slicing knife is used for cutting cartilage pieces from a costal cartilage, and comprises a cutting knife and a base, wherein the cutting knife is a dual-edge cutting knife with two knife blades; a gap of which the width corresponds to the thickness of each cartilage piece is formed between the two knife blades; a material placing groove allowing the costal cartilage to be placed is formed in the base; and a cutting empty groove of which the width corresponds to that of the cutting knife is formed in the bottom of the material placing groove. The cartilage slicing knife disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that the dual-edge cutting knife is adopted, so that cutting and shaping can be performed in one time,and the operation is convenient and high in efficiency; the material placing groove is in sliding cooperation with a knife bar, so that the stability of the moving of the cutting knife in the horizontal direction is guaranteed; a cutting knife guide block for elastically compacting the costal cartilage from the front end is arranged, so that the costal cartilage can be stably positioned and fixed;and a knife blade guide groove which is in sliding cooperation with the knife blade is formed in the cutting knife guide block, and can be used for supporting and positioning the knife blade in the cutting process, so that the situation that in the cutting process, the knife blade is deformed is avoided, the cutting effect and the cutting precision are guaranteed.
Owner:FIRST HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
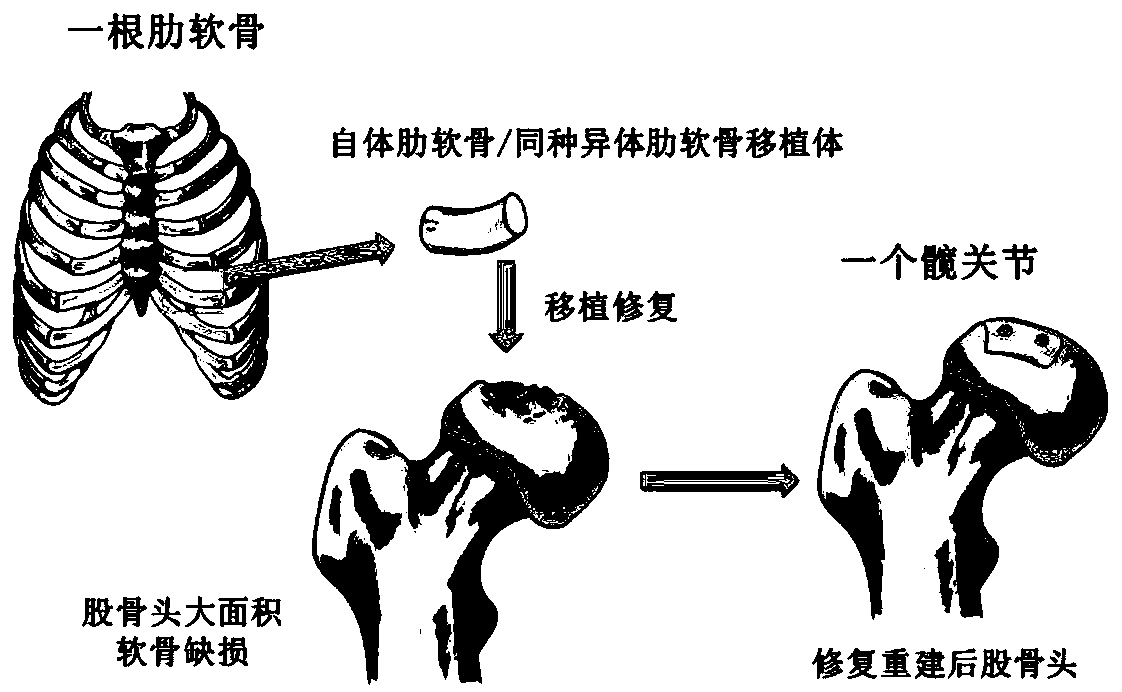
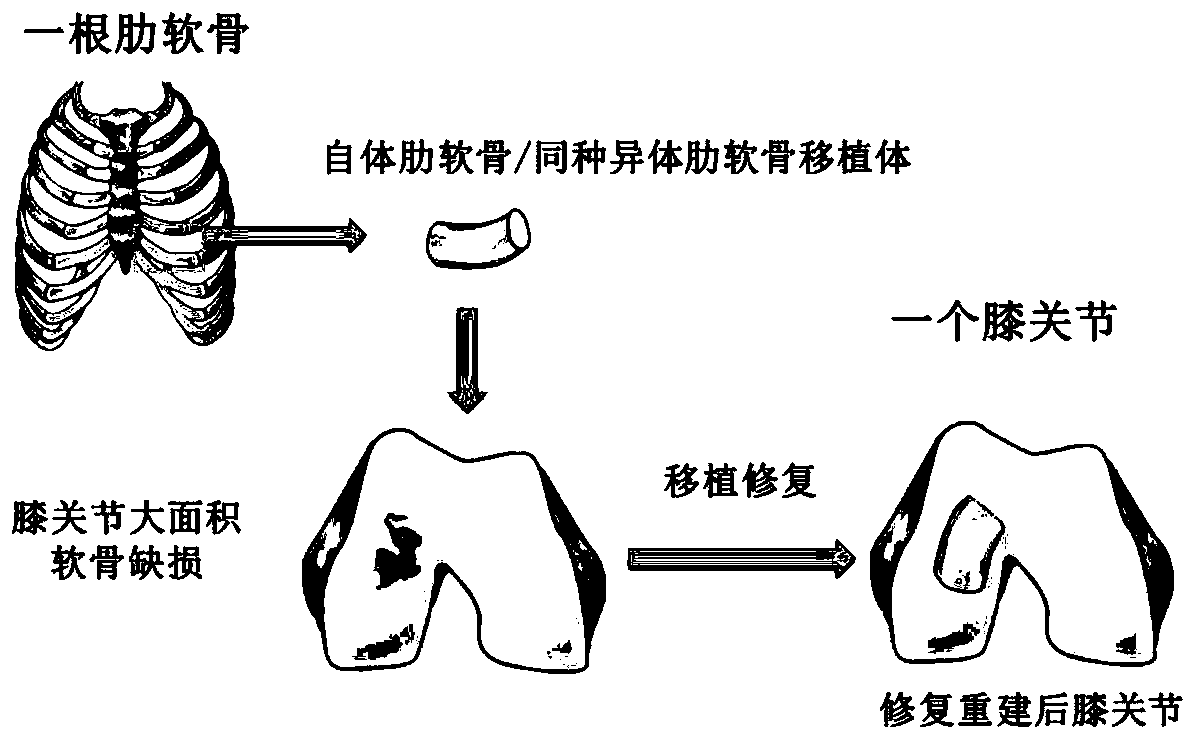
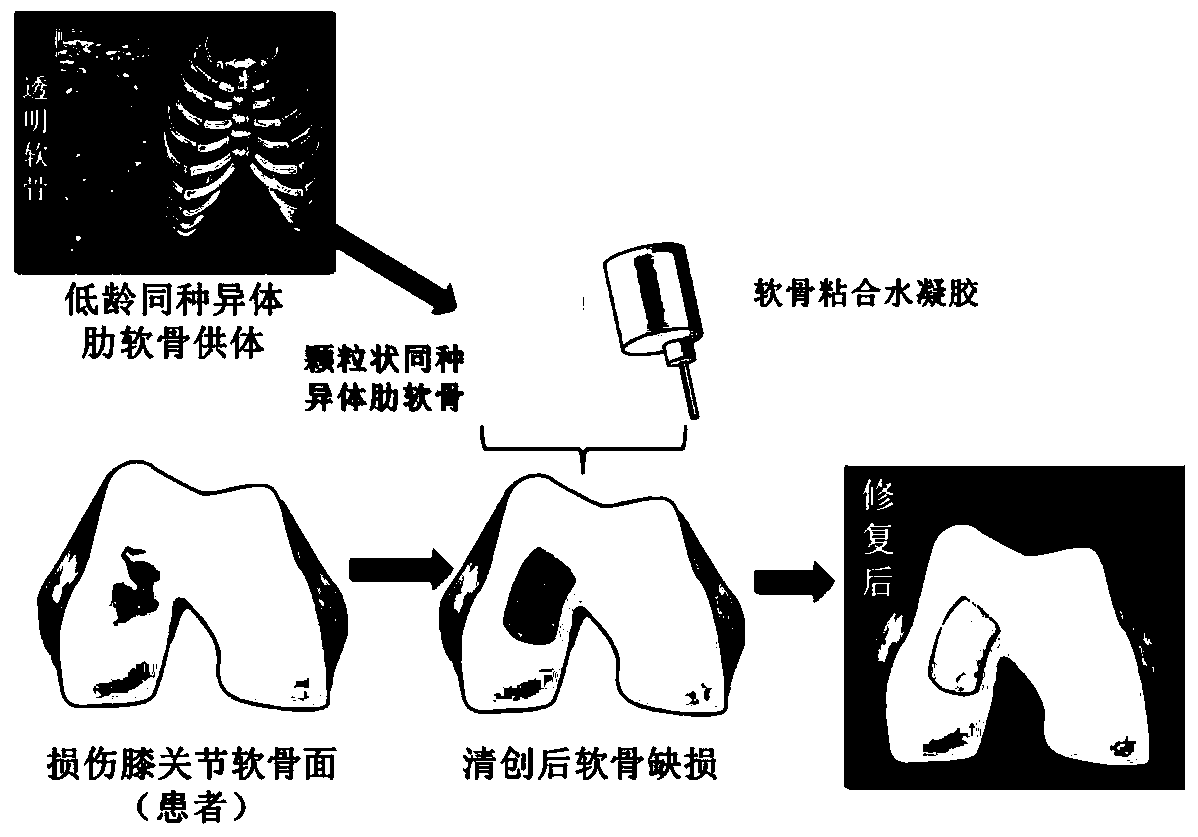
Transplant and method for repairing articular cartilage defects
InactiveCN109893301AAvoid painReduce riskBone implantJoint implantsArtificial jointsSacroiliac joint
The invention provides a transplant for repairing articular cartilage defects. The transplant comprises at least one of autologous costicartilage and allogeneic costicartilage; the transplant can be specially a whole-section costicartilage or cartilage particle combined hydrogel transplant. The invention further relates to application of the transplant and a method for repairing the articular cartilage defects. The transplant and method for repairing the articular cartilage defects and the application of the transplant have the advantages that by adopting costal cartilage grafting, vice-damageis small, and minimally invasive operation can be carried out to avoid the risk of prosthesis loosening, infection and other complications which are caused by artificial joint replacement; the amountof the costicartilage is sufficient, and the needs of multiple times of cartilage reconstruction and revision surgeries can be met; it can be achieved that the reconstruction of the damaged articularcartilage surface is personalized, and the repairing method with higher safety and stronger operability is provided for patients with the articular cartilage defects.
Owner:SHANGHAI SIXTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL
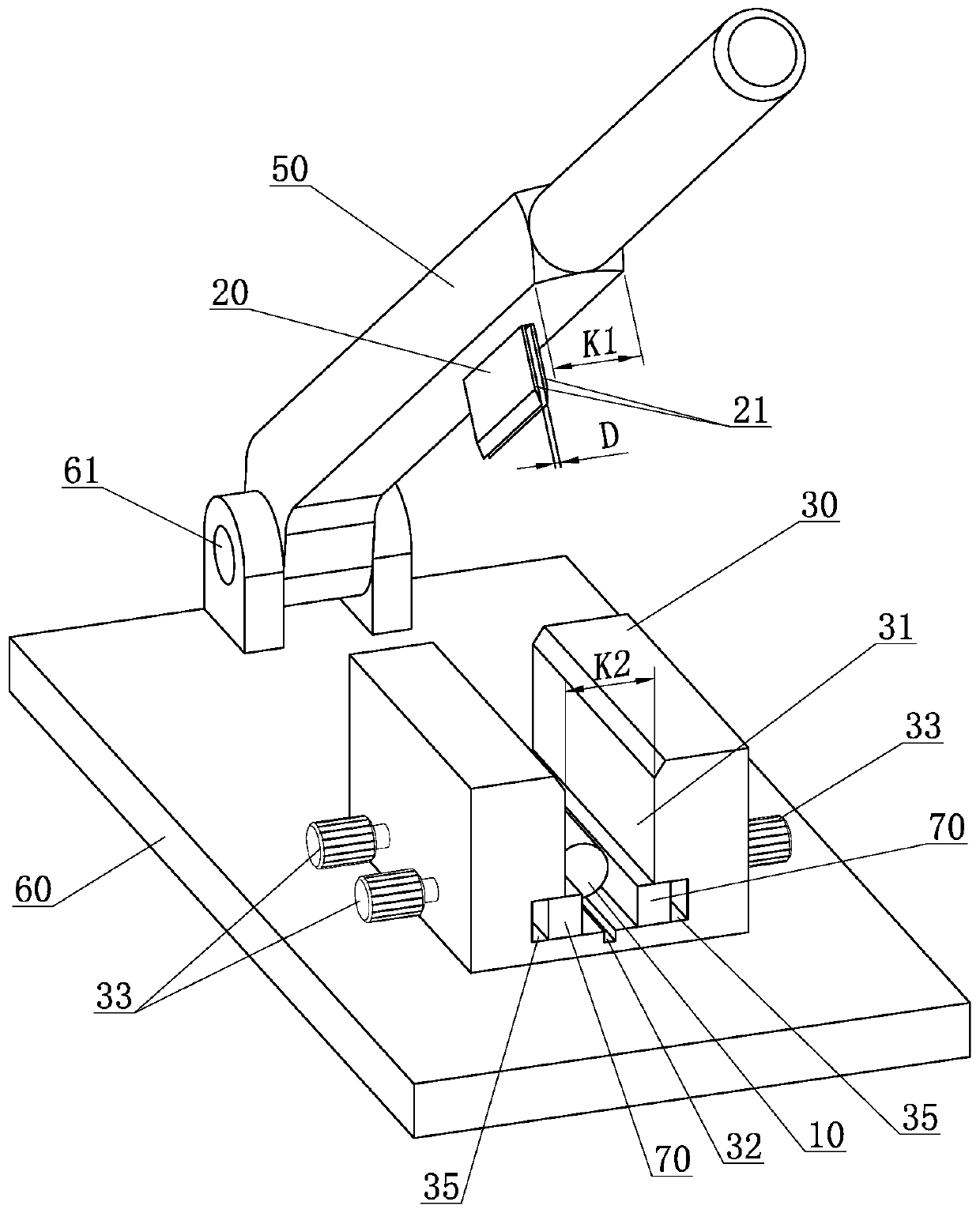
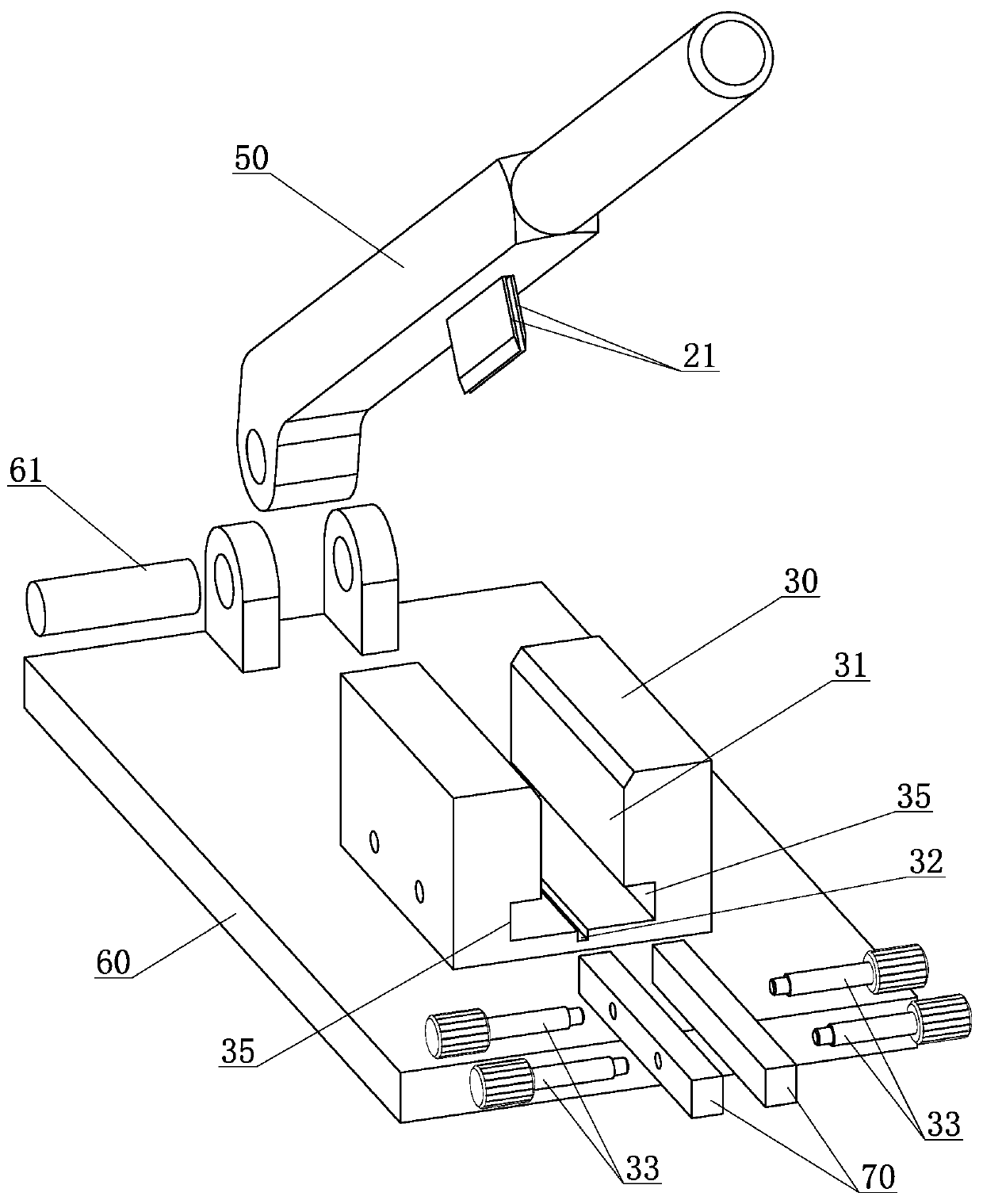
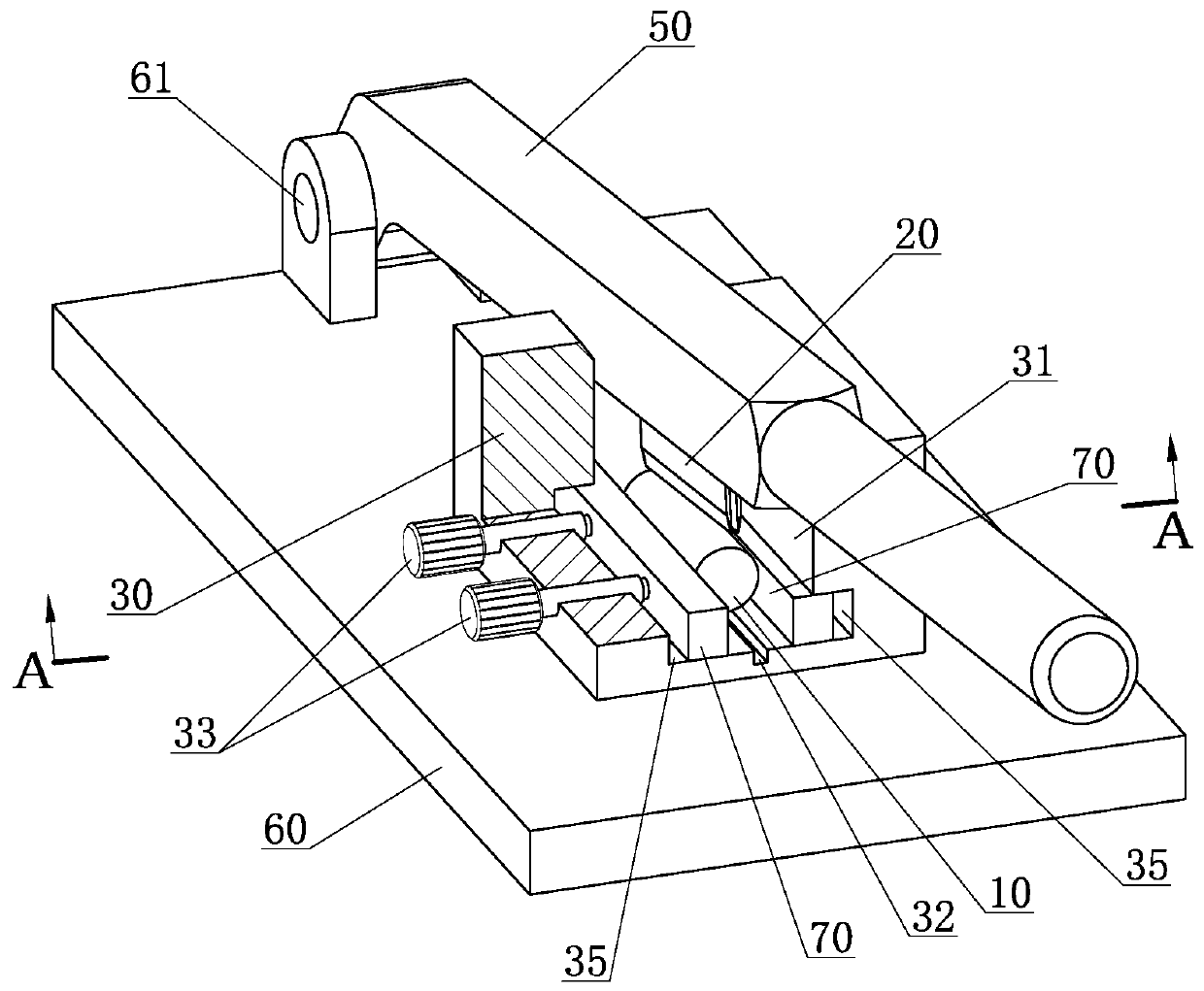
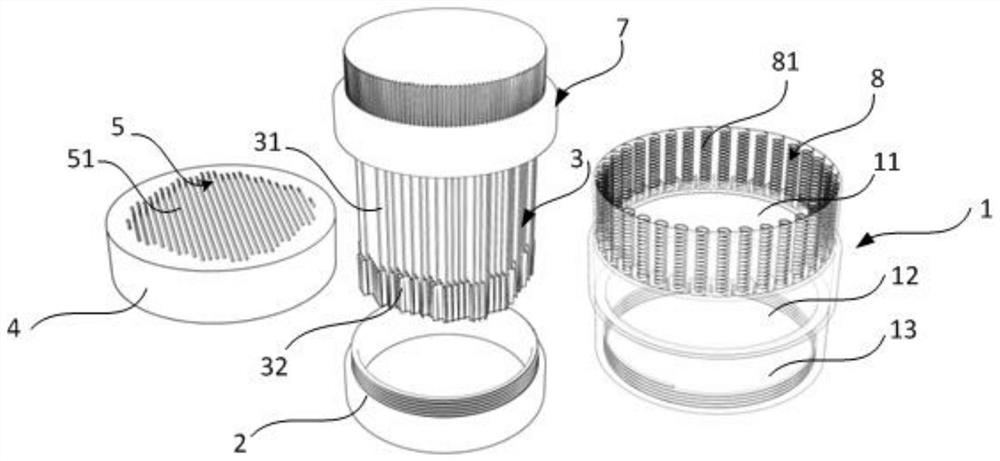
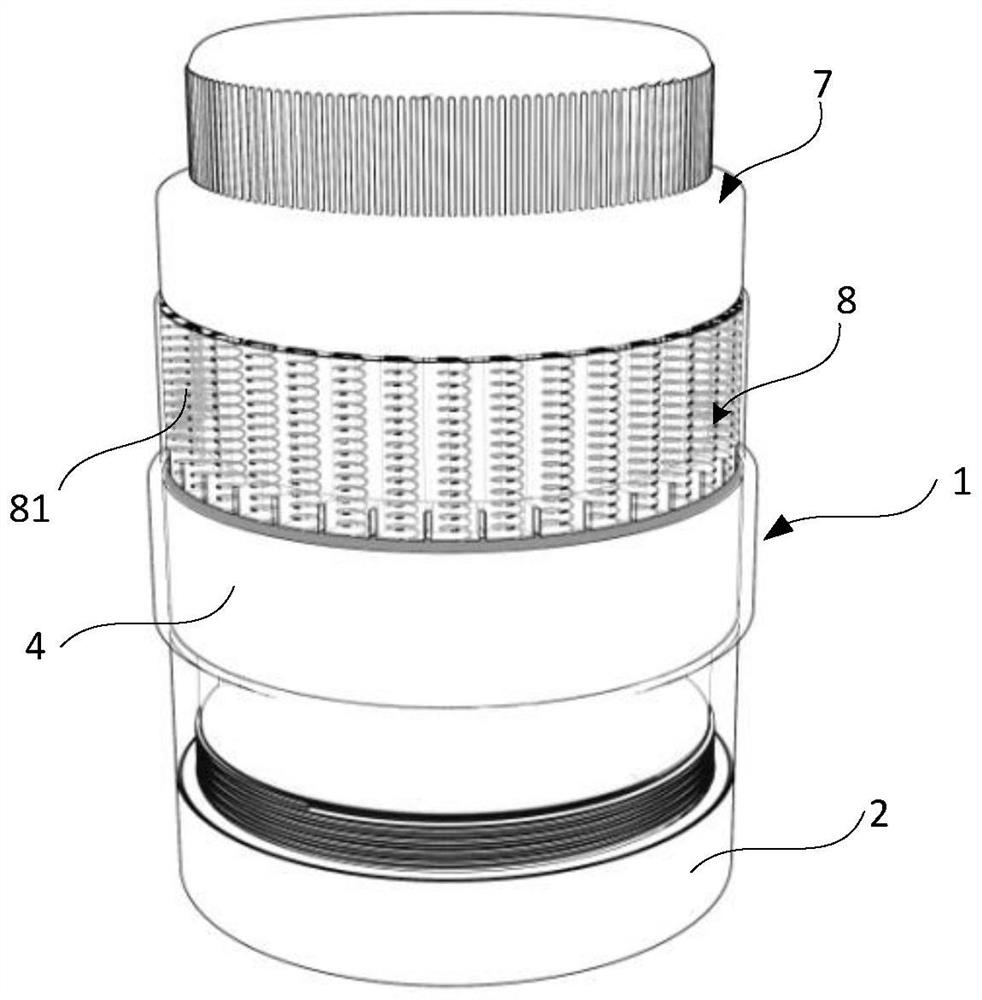
Costal cartilage slicer
The invention provides a costal cartilage slicer. The costal cartilage slicer comprises a base, a knife holder, a fixing structure, a chuck structure, a knife rest and a stop block, wherein the kniferest is used for detachably mounting a blade; the knife holder is arranged on the base; one end of the knife rest is rotationally connected to the knife holder, so that the blade is driven to cut a costal cartilage block through rotation of the knife rest; the stop block is arranged on the lower side of the knife rest; the chuck structure can move in a reference direction relative to the fixing structure; the fixing structure is arranged on a first side of the chuck structure in the reference direction; the stop block is located on a second side of the chuck structure in the reference direction; and the costal cartilage block to be sliced can be tightly clamped between the stop block and the chuck structure. The thickness of a costal cartilage slice sliced by the costal cartilage slicer can be uniform and consistent.
Owner:SHANGHAI YUNXI MEDICAL CO LTD
Apparatus and method for cutting costal cartilage
ActiveUS8535315B2Reduces skill and timeImprove uniformitySurgeryProsthesisResearch settingBiomedical engineering
A double-bladed cutting device providing a practical method for obtaining costal cartilage specimens in both an operating room and research setting. The device reduces the skill and time required to fashion cartilage slices, while increasing the uniformity of the cut specimens. Furthermore, via an adjustable guide, slices can be obtained precisely from the central core of the rib. Although specimen lengths up to 4 cm are preferred, longer lengths can be attained without modification of the device. The cartilage specimen may be held in place within the device via means of compression or tension.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
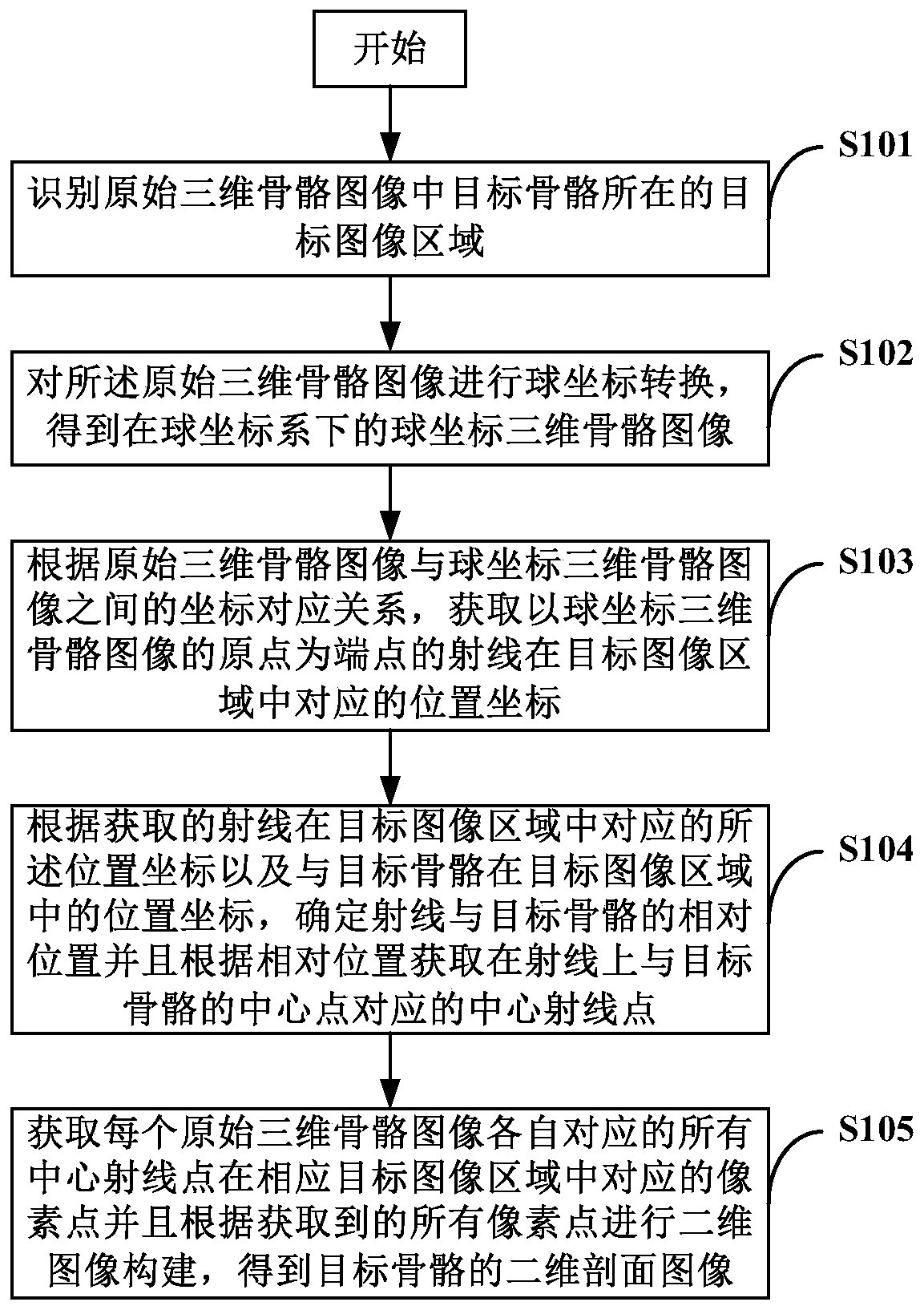
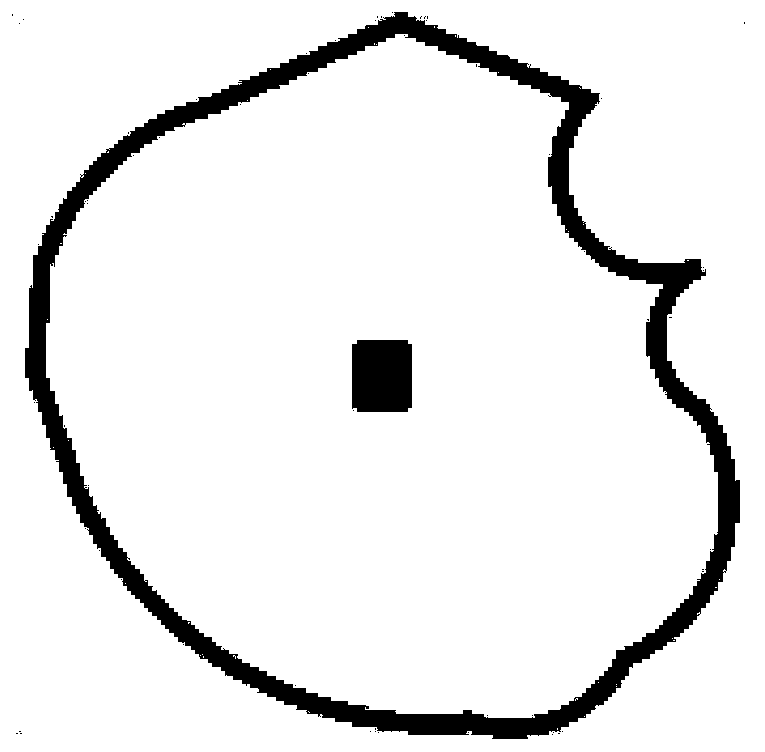
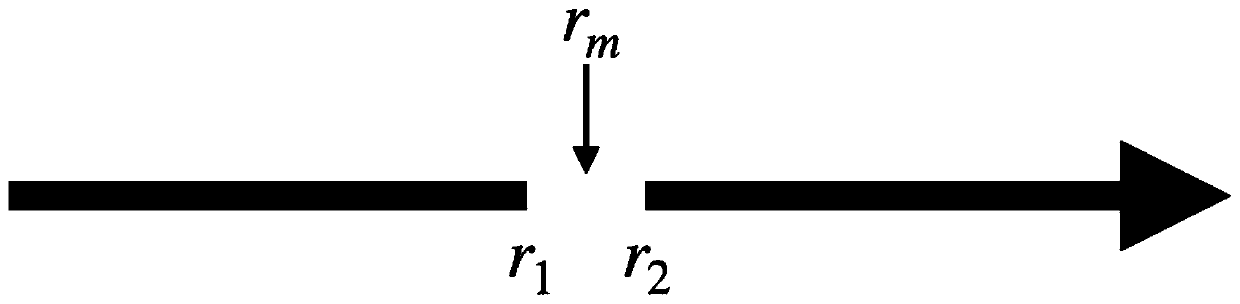
Two-dimensional bone image acquisition method, system and device
ActiveCN110916707AEasy to operateDoes not involve operation contentGeometric image transformationComputerised tomographsShoulder bonesImaging processing
The invention relates to the technical field of image processing, particularly provides a two-dimensional bone image acquisition method, system and device, and aims to solve the problem of how to conveniently and reliably convert a three-dimensional skeleton image of any skeleton type (such as ribs, sternum, costal cartilage and shoulder blades) into a clear two-dimensional skeleton image. According to the embodiment of the invention, the method comprises the steps: carrying out the image coordinate conversion of a three-dimensional image in a three-dimensional space, determining the central points of bones in the image according to the coordinate corresponding relation between the images before and after conversion, and extracting the corresponding pixel points of all central points in anoriginal three-dimensional bone image; a skeleton two-dimensional profile image of any skeleton type is obtained by using the pixel points, the operation is simple, complex operation contents are notinvolved, and meanwhile, random errors are not introduced in the steps of coordinate conversion, center point determination, pixel point extraction and the like, so that a two-dimensional image witha clear imaging effect can be obtained.
Owner:上海皓桦科技股份有限公司
Decellularized cartilage material from pig costal cartilage as well as preparation method and application of decellularized cartilage material
InactiveCN113599577AEfficient removalLow residual DNA contentTissue regenerationProsthesisCell-Extracellular MatrixECM Protein
The invention relates to a decellularized cartilage material from pig costal cartilage and a preparation method and application of the decellularized cartilage material. The preparation method comprises a decellularization step: specifically, a phosphate buffer solution containing trypsin and disodium ethylene diamine tetraacetate is adopted as a decellularized solution, a costal cartilage material is added into the decellularized solution and put into a shaking table, the volume ratio of the decellularized solution to the costal cartilage material is 20: 1, the rotating speed of the shaking table is set to be 150r / min, the action lasts for 72 hours, the temperature is 37 DEG C, and the decellularized solution is replaced every 24 hours. The prepared decellularized cartilage material basically retains the structure and function of an extracellular matrix, a stable environment is provided for cell proliferation and tissue regeneration, most collagenous fiber components in the extracellular matrix are retained, in the costal cartilage defect repairing process, cell migration differentiation and tissue regeneration can be induced, and mechanical support is provided, so that the effect of improving local thoracic depression and deformity is achieved.
Owner:PLASTIC SURGERY HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Cartilage morcellator
PendingUS20210236302A1Efficient crushingEnhanced couplingSurgeryJoint implantsPlastic surgeryKnife blades
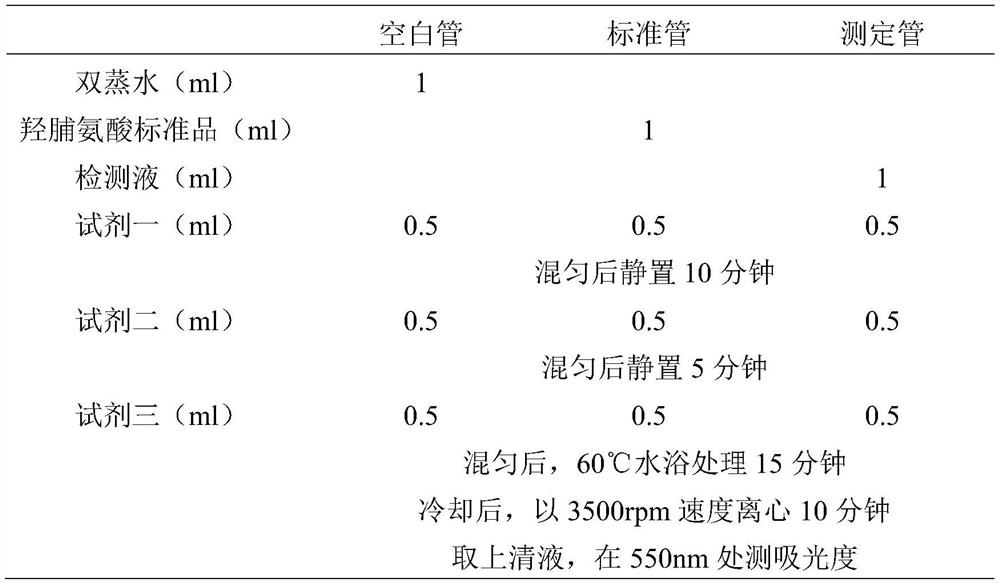
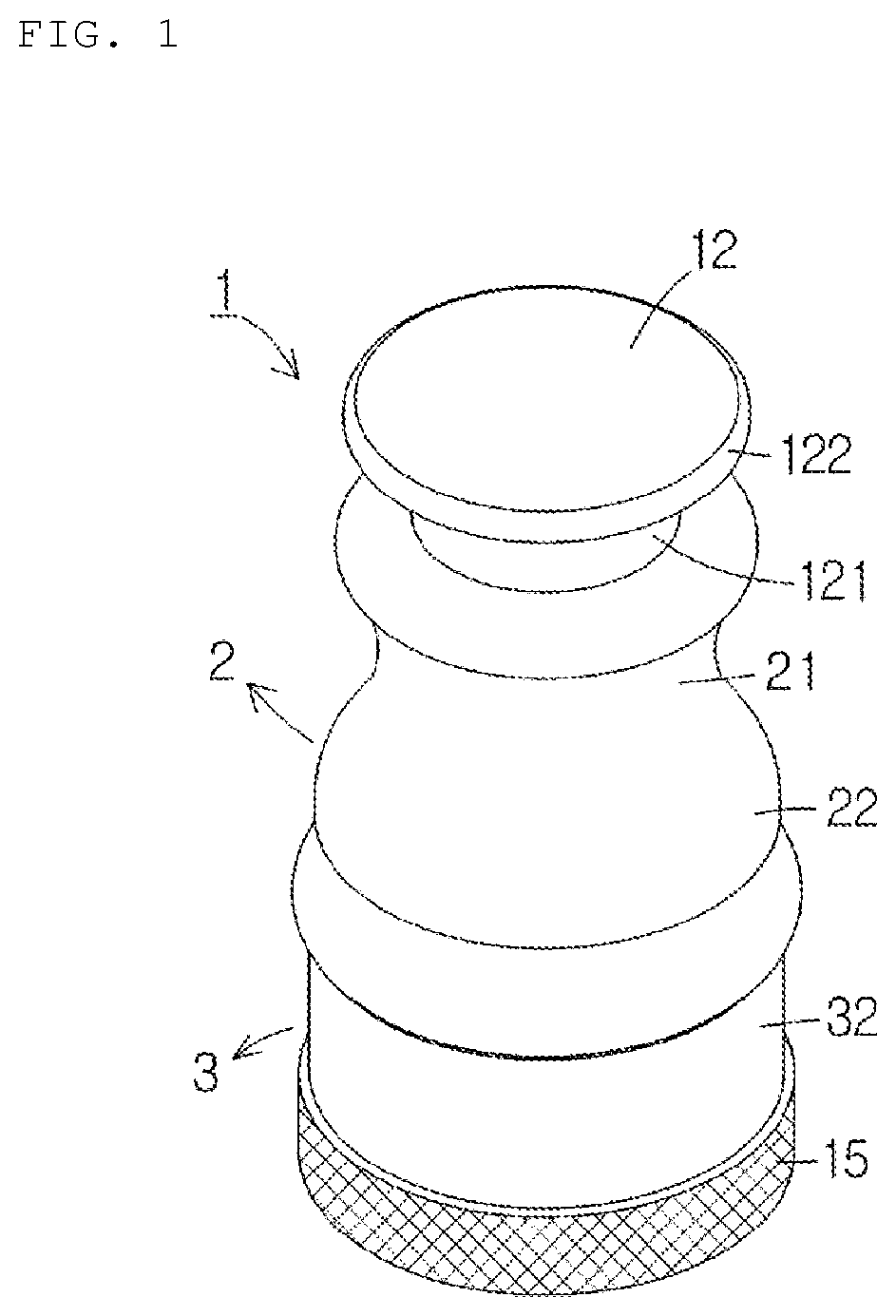
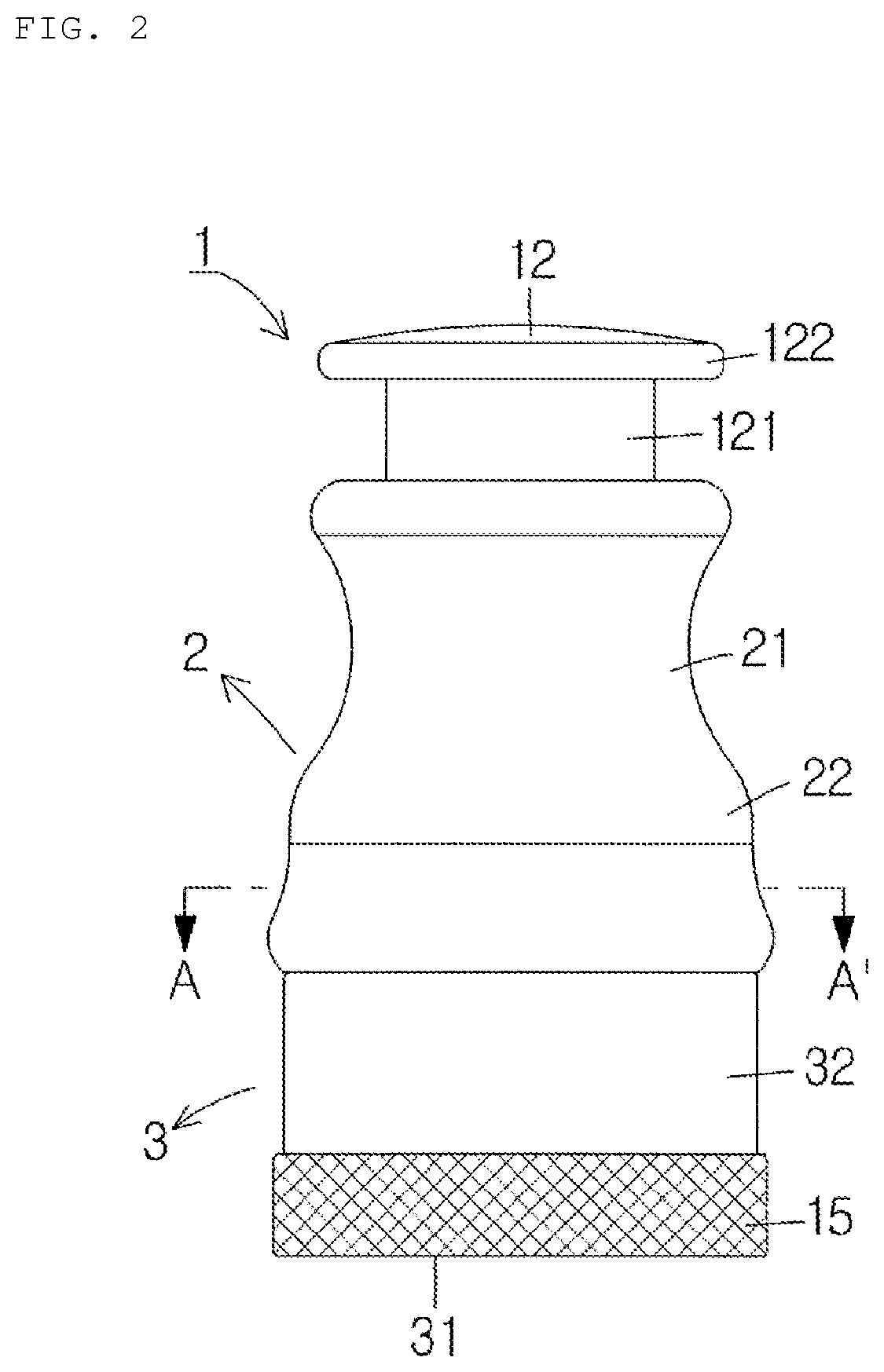
The present invention relates to cartilage morcellator for cutting various kinds of cartilage (including costal cartilage and the like) into small pieces by using an elevating-type cutting knife having a simple configuration such that same can be supplied to a plastic surgery part. The cartilage morcellator comprises: an upper body (2) and a lower body (3), which are separated from / coupled to each other; an upper groove (4) and a lower groove (5) formed on the upper and lower portions of the upper body (2), respectively; an isolation portion (6) formed between the upper groove (4) and the lower groove (5); a through-hole (7) formed perpendicularly at the center of the isolation portion (6); an elevating rod (8) fitted to the through-hole (7); a morcellating knife (10) fixed to the bottom surface of the elevating rod (8), the morcellating knife (10) having a zigzag-shaped knife portion (102) and a blade portion (103) formed thereon; a spring (11) fitted to the outer periphery of the elevating rod (8); and a striking portion (12) fastened to the upper portion of the elevating rod (8) and elastically supported by a spring (11). The cartilage morcellator further comprises: a morcellation chamber (13) formed in the lower body (3) and provided with a bottom; a prop plate (14) formed on the bottom of the morcellation chamber (13); a first gripping portion (21) formed on the outer periphery of the upper body (2) so as to have an outer diameter smaller than the outer diameter of the upper end of the upper body (2); a second gripping portion (22) formed to have an outer diameter larger than the outer diameter of the first gripping portion (21); and a plate body (101) having a predetermined thickness, which is fixed to the upper portion of the knife portion (102).
Owner:KIM CHANWOO
Simulation method for funnel breast orthopaedic surgery
InactiveCN101488236BIncrease success rateInternal osteosythesisDiagnostic recording/measuringThoracic boneMechanical models
The invention discloses a funnel chest orthopaedic surgery simulation method; chest three-dimension visualization bone models and costal cartilage models are respectively processed by face mesh division, and the mesh is optimized; a mesh conversion is used on the basis of mesh optimization, and a chest model is converted into a body mesh from a face mesh; rib, costal cartilage and breast bone arerespectively material-evaluated, and skeleton body mesh model of each part is assembled so as to obtain a complete chest three-dimensional mechanical model; boundary conditions and loading force moment are determined, and the chest model is processed by finite element analysis so as to obtain the stress, strain and displacement conditions of each skeleton part under the action of different external forces; the incision position, support plate material, fixing method and supporting force moment of funnel chest surgery are simulated so that the success ratio of funnel chest surgery is increasedto over 98% from 70-90% of the prior art.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
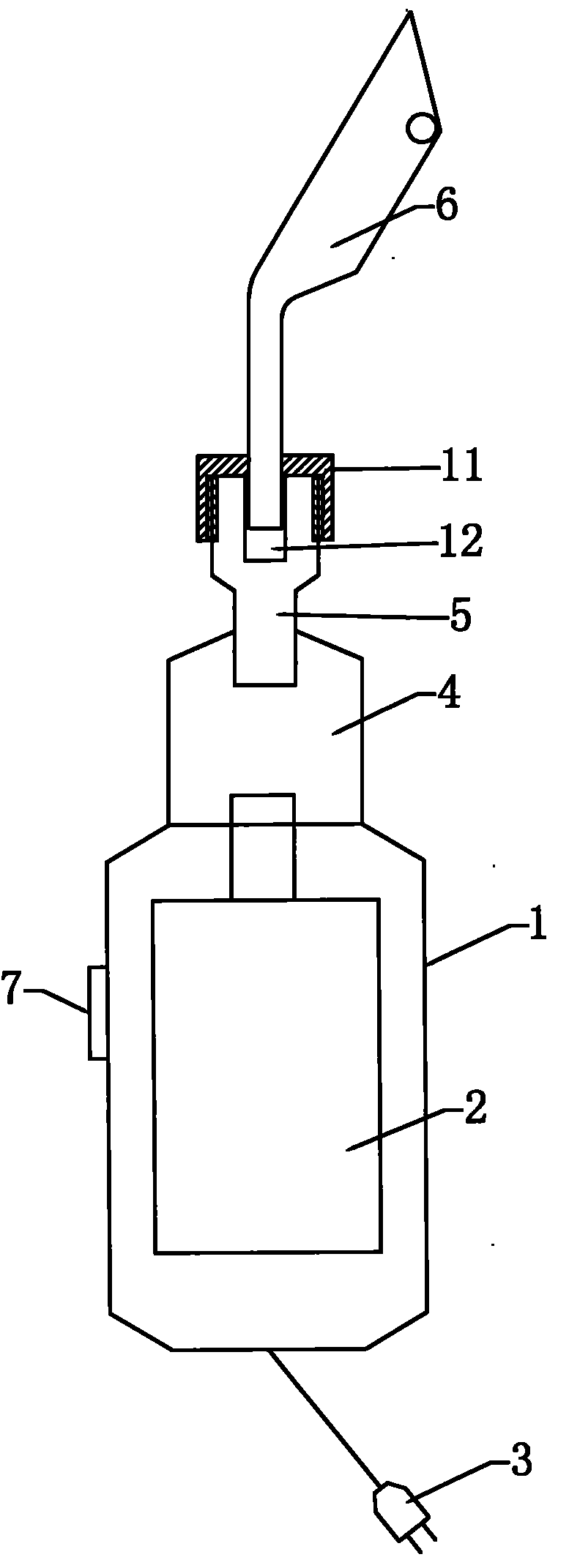
Electric costal cartilage cutter
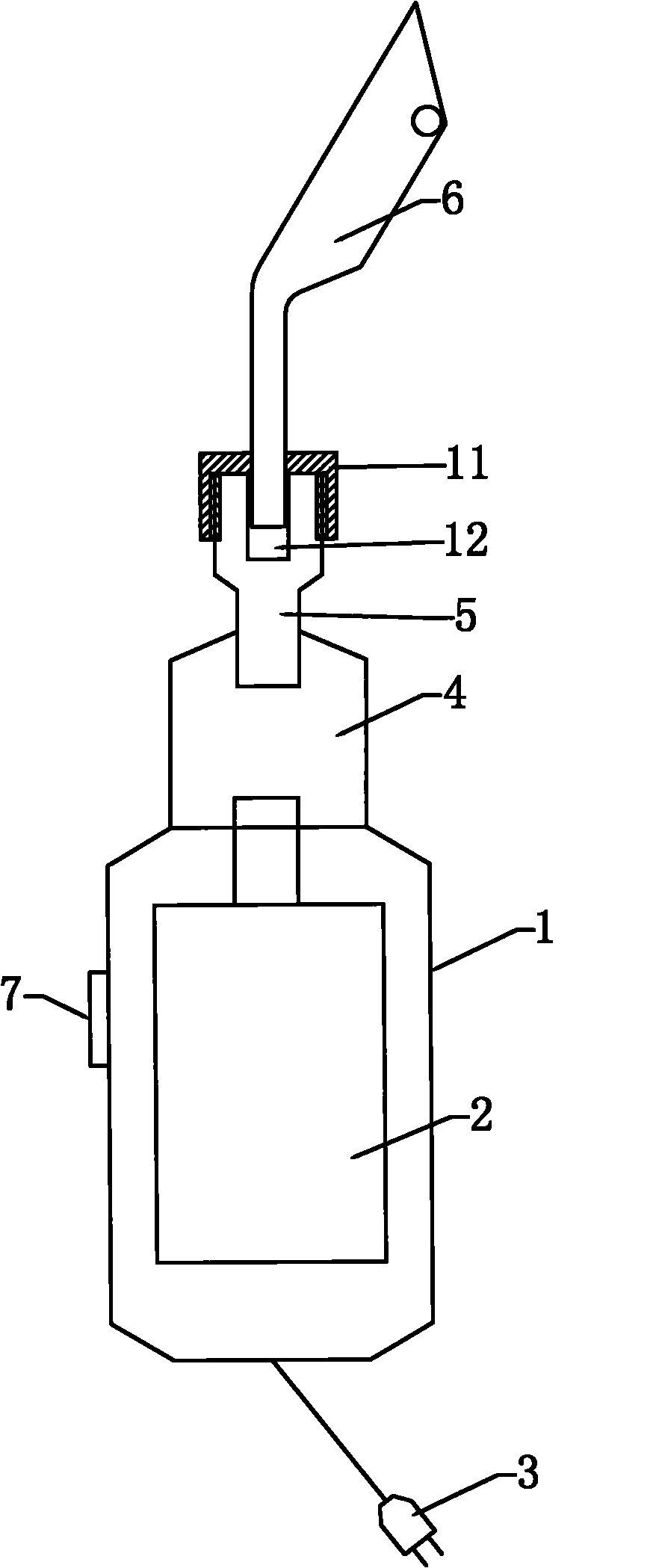
The invention discloses a medical instrument, and specifically discloses an electric costal cartilage cutter. The electric costal cartilage cutter is characterized by comprising a handle, wherein, the handle is internally equipped with a motor; the motor is connected with a power plug; a rotating shaft of the motor is connected with a direction converter; the front end of the direction converter is connected with a reciprocating center shaft; and the front end of the reciprocating center shaft is equipped with a cutter. In the invention, only an incision of 2-2.5cm is opened at the position of costal cartilage at the chest of a patient while cutting the costal cartilage, and then one or more than one of costal cartilage pieces can be easily removed; and the costal cartilage pieces or costal cartilage strips has regular shape and consistent thickness, thus being beneficial to engraving, causing little wound of the patient, achieving quick recovery, alleviating pain of the patient and obtaining obvious curative effects.
Owner:姜言舟
Cartilage extractor for plastic surgery
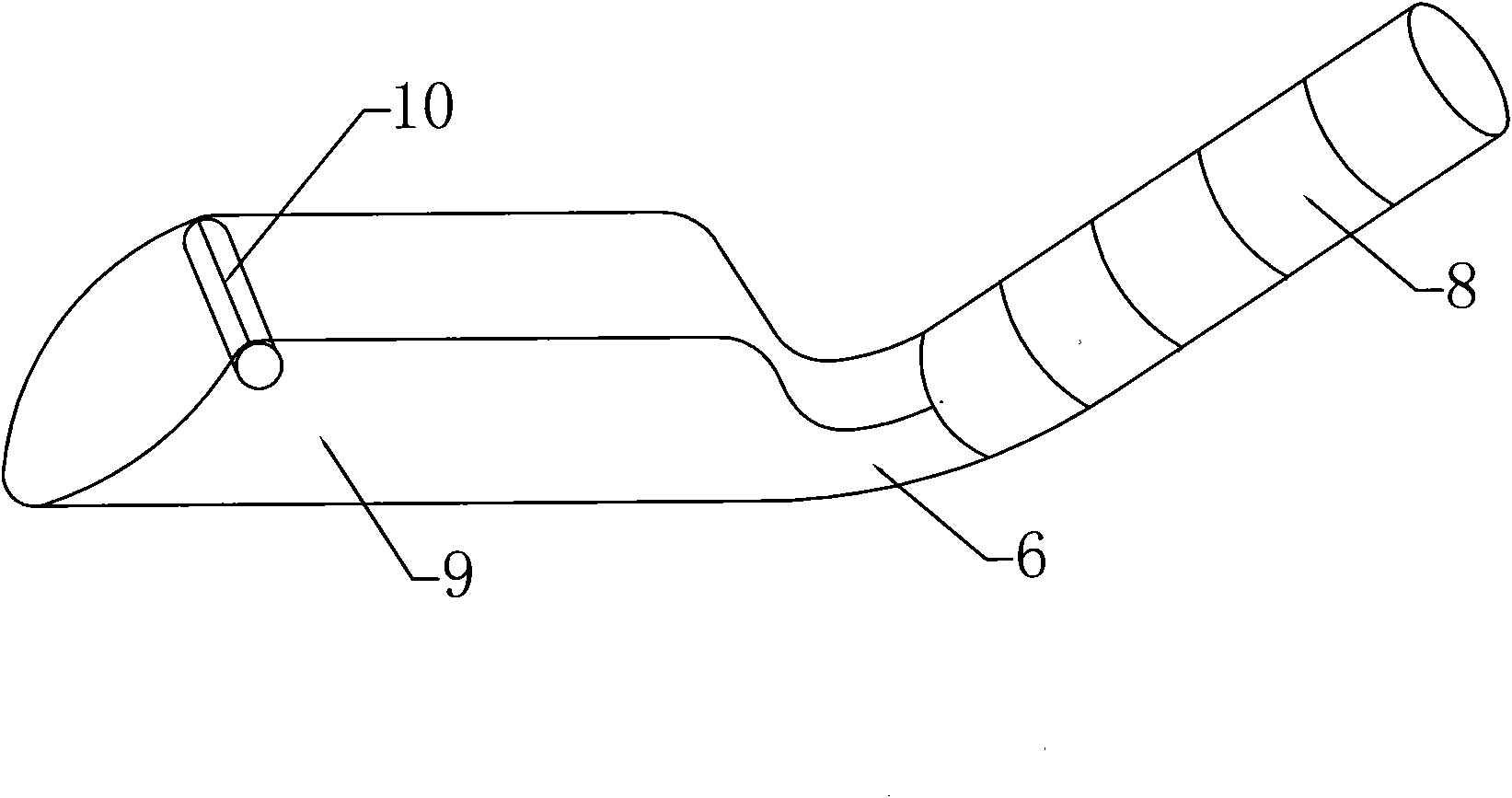
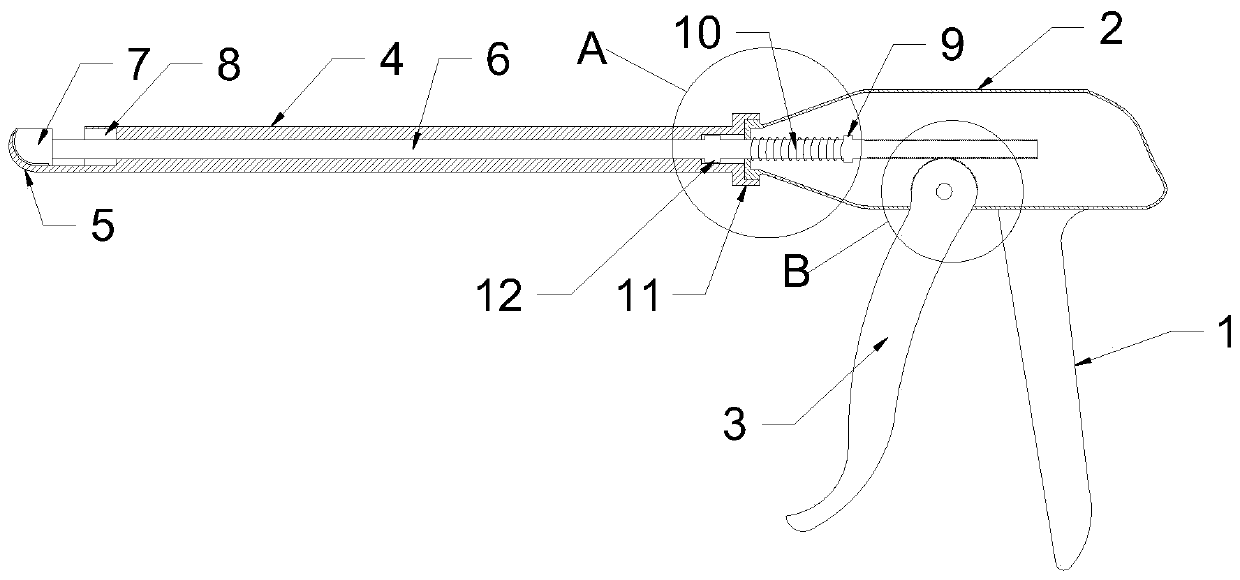
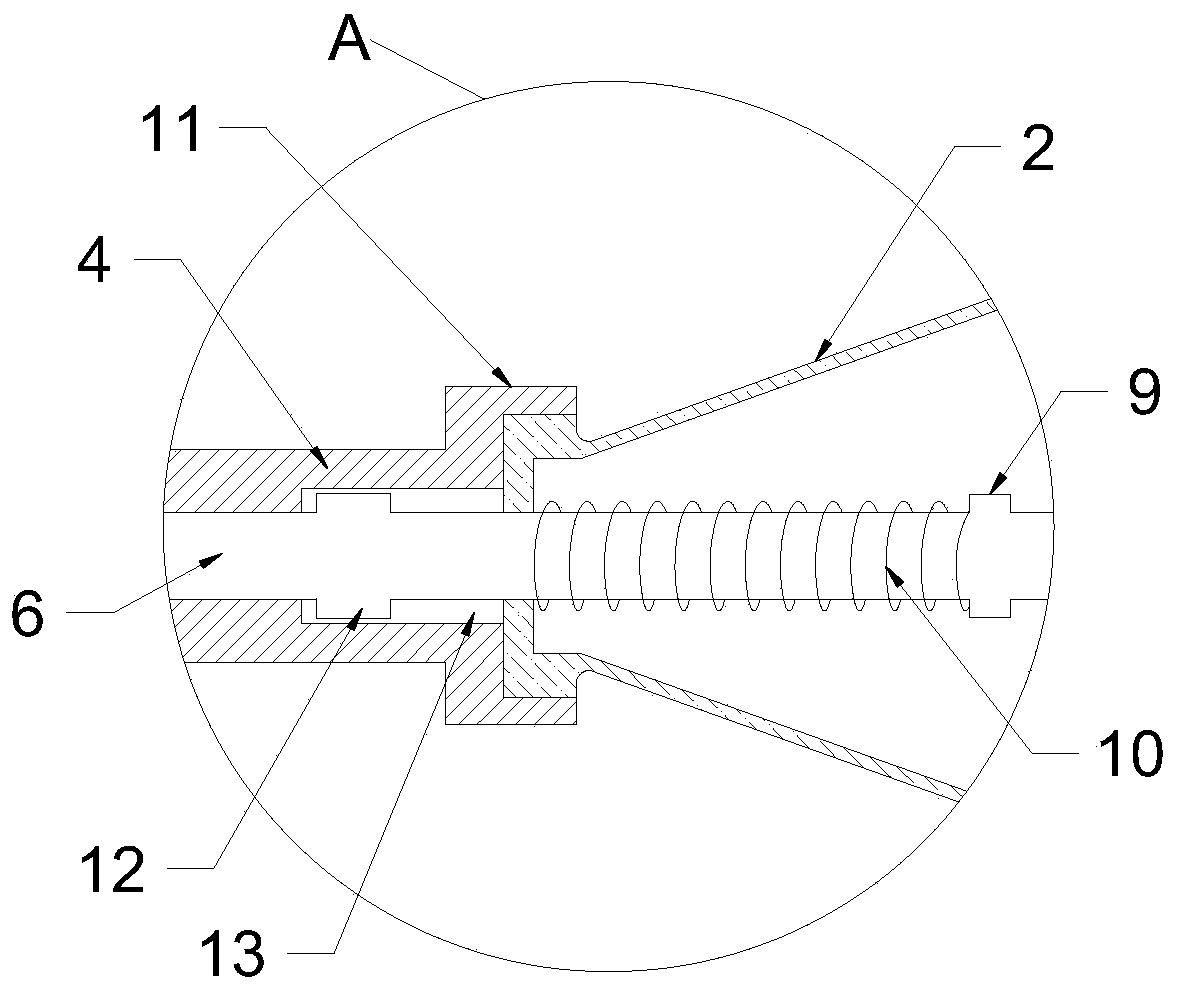
PendingCN110811759AGuaranteed complete cutting at one timeAvoid nerve damageSurgeryEngineeringApparatus instruments
The invention relates to the technical field of medical instruments, and discloses a cartilage extractor for plastic surgery. The cartilage extractor comprises a shell with a handle, wherein a triggerrod is hinged on the shell; an extension pipe is arranged at the front end of the shell, a hook is arranged at one end, far away from the shell, of the extension pipe, and the front end of the hook is a round blunt metal sheet; a force transmission rod is inserted into the extension pipe, one end of the force transmission rod extends into the shell, and a blade is arranged at the other end of theforce transmission rod; a plurality of tooth sockets are arranged at the end of the force transmission rod positioned in an inner cavity of the shell; and an edge of the hinge end of the trigger rodis provided with teeth which can be meshed with the tooth sockets. According to the invention, a costal cartilage is hooked by the hook, and then the trigger rod controls a blade to cut the costal cartilage, so that the stripped costal cartilage can be hooked and cut. The whole process can be operated by one person, operation is simple, and operation time is shortened. In addition, the blade partof the blade can be attached to the inner wall of the hook, so that the costal cartilage can be completely cut at one time, and safety of a cutting process and integrity of the broken end of the costal cartilage are improved.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
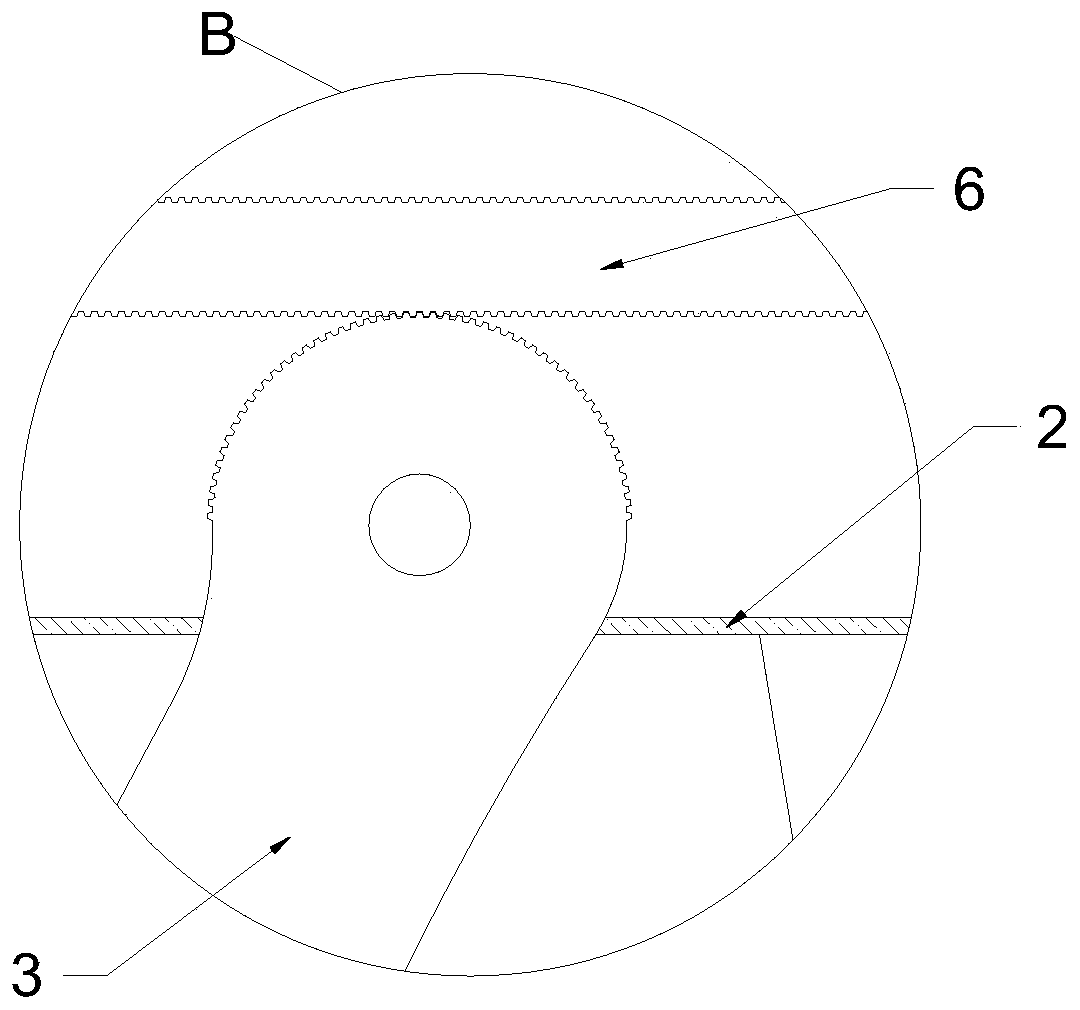
Telecommunication earphone structure
InactiveCN1780491AImprove shortcomingsEliminate discomfortEarpiece/earphone attachmentsTelephone set constructionsHeadphonesOuter ear
An ear canal type earphone is set at inner sidewall of the body, and a protruding block is set at upper end and inner side of body and near the ear canal type earphone. A hook part is set at the side of upper end of the body. The ear canal type earphone can be fixed in ear hole, and the protruding block is against the earlap to make the earphone steadily clipped on the first ear of user. When using second ear, the communication ear phone is rotated 180 degree to make the ear canal type earphone fixed in the second ear, and the hook part attach the inside of costal cartilage at top edge of external ear so that the communication earphone can be steadily clipped on the second ear of user.
Owner:久易科技股份有限公司 +1
Artificial cartilage containing chondrocytes obtained from costal cartilage and preparation process thereof
ActiveUS9694034B2Ability to useEfficient regenerationBone implantMammal material medical ingredientsMesenchymal stem cellCostal cartilage
The present invention relates to an artificial cartilage containing mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)-like dedifferentiated cells obtained by passage culturing costal chondrocytes, and a preparation process thereof.
Owner:BIO SOLUTION CO LTD +2
Nasal plastic stent
InactiveCN112043461ATroubleshoot bend characteristicsAvoid causing postoperative bending deformationNose implantsNasal bridgeNasal tip
The invention discloses a nasal plastic stent. The nasal plastic stent comprises a stent body; the stent body comprises a nose bridge, a nasal columella and a nasal tip cap; a left extension part anda right extension part are arranged on the two sides of the nose bridge respectively; the nasal tip cap is arranged at the front end of the nose bridge, and the nasal columella is arranged at the front end of the nose bridge and located at the lower end of the nasal tip cap; the left extension part and the right extension part are adjustably connected with the nose bridge respectively; the stent body comprises the nose bridge, the nasal columella and the nasal tip cap; the left extension part and the right extension part are adjustably connected with the nose bridge respectively and are arranged in the length direction of the nose bridge; compared with a thick and heavy costal cartilage stent, the nose bridge in the stent body can be light and thin; the left extension part and the right extension part can play a role in enhancing the stability in the length direction of the nose bridge, so that the problem of the bending characteristic of the costal cartilage is solved, the postoperative bending deformation of the costal cartilage nose bridge is avoided, and the phenomena that the postoperative nasal columella is too thick and too hard or moves backwards, the nasal tip is too hardand too top, and a stone-like nose is formed are avoided.
Owner:武汉华美整形外科医院有限公司
Composite artificial stent for total auricle reconstruction and preparation method of composite artificial stent
PendingCN113693781AAvoid discomfortStrong resilienceAdditive manufacturing apparatusEar implantsHuman bodyMetal strips
The invention discloses a composite artificial stent for all auricle reconstruction. The composite artificial stent comprises a stent and a silica gel body, the stent comprises an auricle bulge and a metal body, and the metal body is composed of a plurality of groups of metal strips in different directions. The composite artificial stent is made of the memory alloy, a layer of silica gel body is poured on the outer surface of the composite artificial stent, the elasticity of the composite artificial stent is improved, meanwhile, the compatibility of the composite artificial stent and the human body is better, and the composite artificial stent can be produced in batches. The composite artificial stent is provided with structures similar to auricle helixes, helix feet, antihelixes and the like. The shape and the size of the auricle stent are set according to the shape and the size of the normal adult auricle obtained through big data, the size layering code number is set, so that the artificial auricle stent is closer to the structure of a real auricle, the number can be directly selected for use, one-by-one customization by using a 3D technology according to the data of each patient is not needed, the costal cartilage does not need to be cut out through a thoracic operation, more convenience and rapidness are achieved, the operation and manufacturing time and the equipment cost are reduced, and meanwhile, the pain of the patient is relieved, and various costs are reduced.
Owner:雅安市人民医院
Costal cartilage cutting and crushing device
PendingCN113730050ASave operating timeReduce labor costsNose implantsJoint implantsApparatus instrumentsSurgery
The invention relates to the field of medical instruments, in particular to a costal cartilage cutting and crushing device. The device comprises a shell and a cartilage placement part which are detachably connected, and a cavity of the shell sequentially comprises a pressing cavity, a cleaning cavity and a transition cavity from the top to the bottom; a cutting assembly is arranged in the shell and comprises a gang tool body and a cutting part which are connected, the gang tool body extends into the cleaning cavity from the pressing cavity, the cutting part is arranged in the cleaning cavity, a cleaning part is arranged in the cleaning cavity, and the cleaning part sequentially comprises a gang tool body passing groove and a cutting part passing groove which are communicated from top to bottom; a rotary pressing part is arranged at the end, away from the cartilage placement part, of the cutting assembly, and an elastic piece matched with the rotary pressing part is arranged on the cavity wall of the pressing cavity. According to the device, the operation time of a doctor in an operation can be effectively shortened, the fatigue degree caused by repeated operation processes can be reduced, the labor cost can be greatly reduced, and the device has a good industrialization prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
costochondral junction incision stripper
The invention discloses a costal cartilage joint cutting peeler which comprises a knob and an adjusting mechanism. Part of the knob is exposed to an outer shell, the adjusting mechanism is positioned in the outer shell and comprises a first bevel gear connected with the knob, the first bevel gear is meshed with a second bevel gear and connected with a second conveying shaft, the second bevel gear is connected with a first conveying shaft, the other end of the first conveying shaft is connected with a third bevel gear, the third bevel gear is meshed with a fourth bevel gear, the fourth bevel gear is connected with a supporting column, the supporting column is connected with a bottom plate, and an inner shell can be far away from or close to a video playback device in a pushed manner. According to the costal cartilage joint cutting peeler, focal distance can be conveniently, effectively and stably adjusted.
Owner:刘波
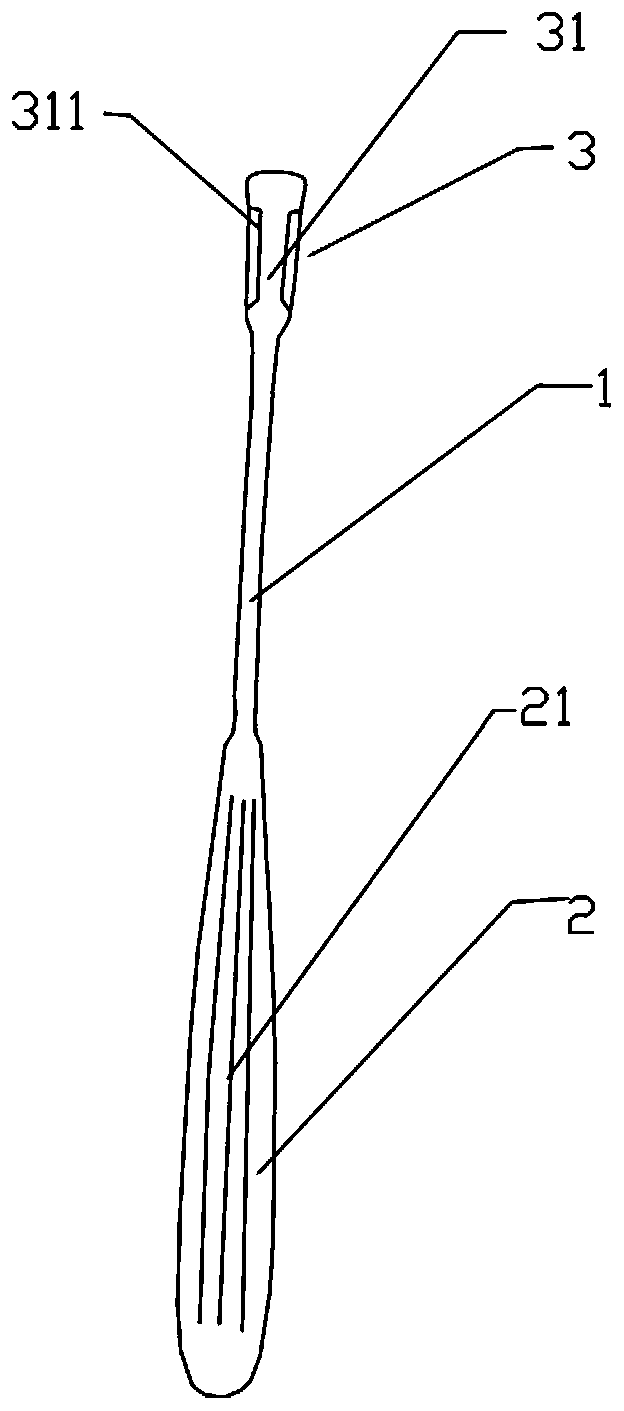
A costal cartilage slicer
Owner:上海迪派生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com