Patents
Literature
36 results about "Longissimus Thoracis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
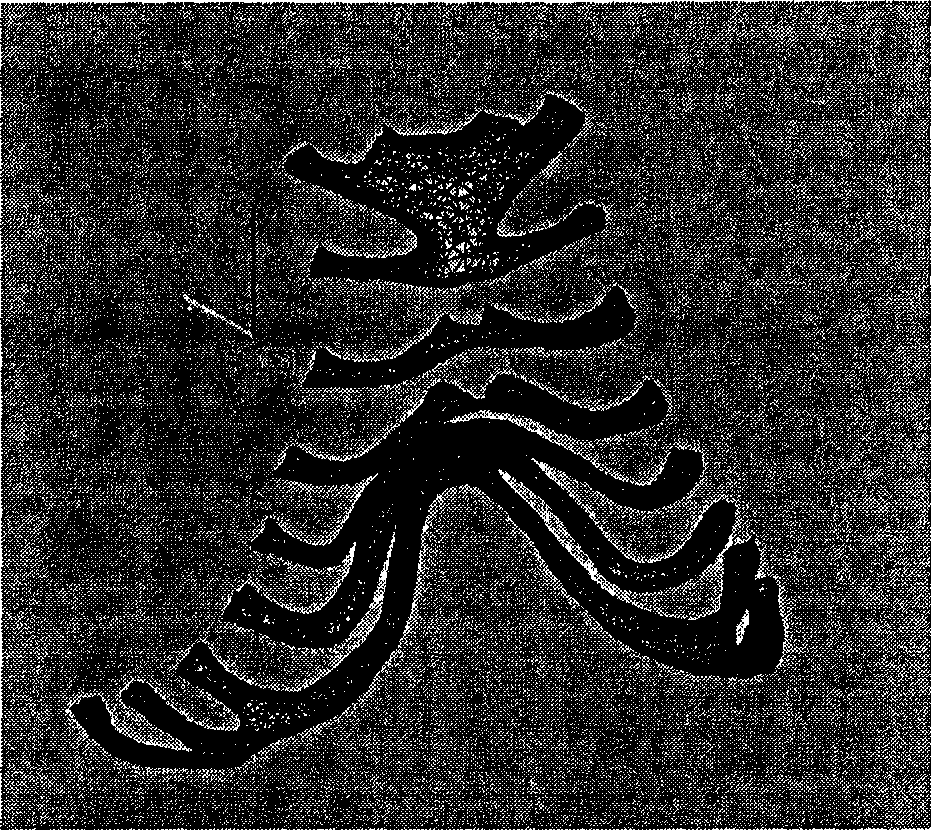
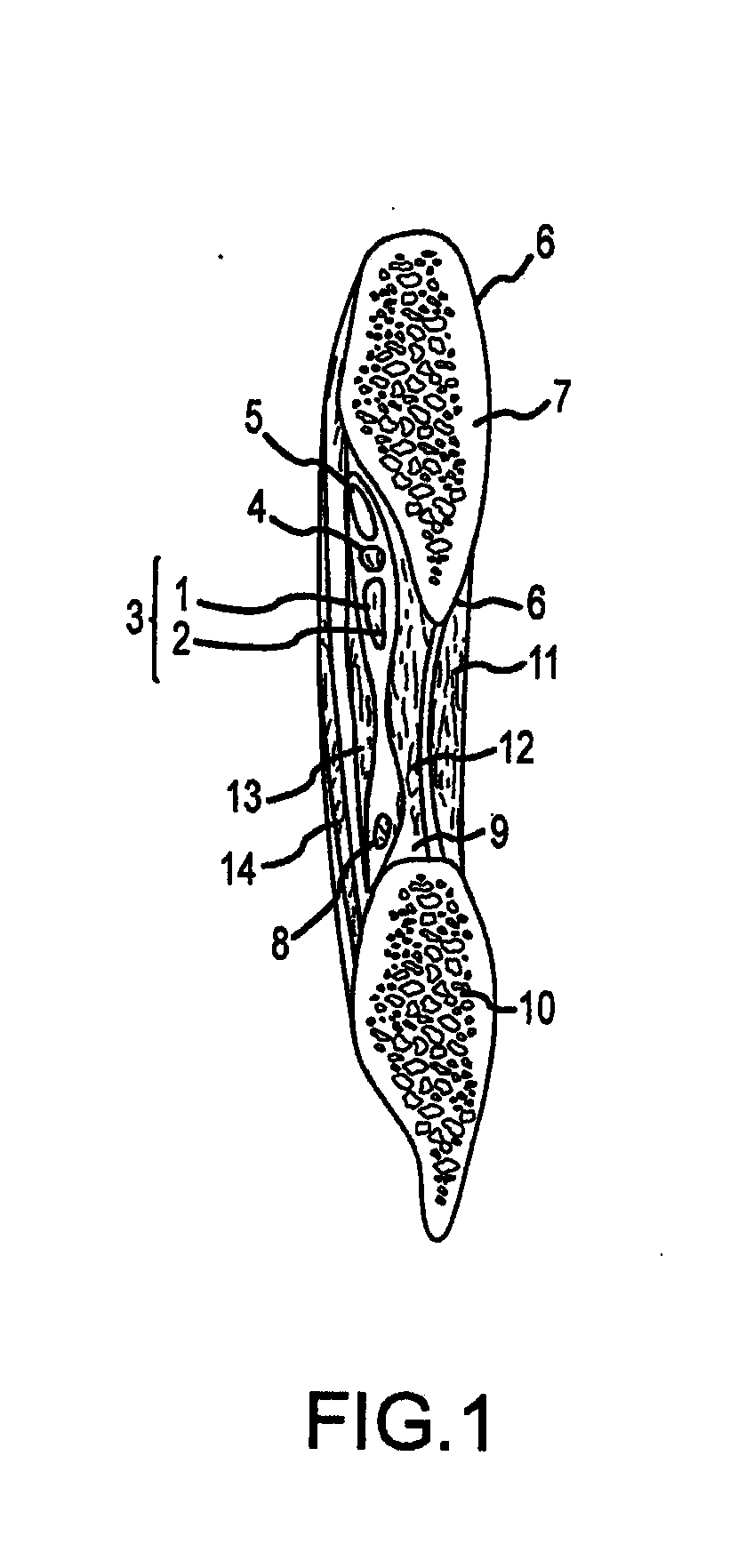
A muscle originating from the transverse processes of the lower thoracic vertebrae which inserts into the ribs between the angles and tubercles as well as the transverse and accessory processes of the upper lumbar vertebrae acting to extend the spine.
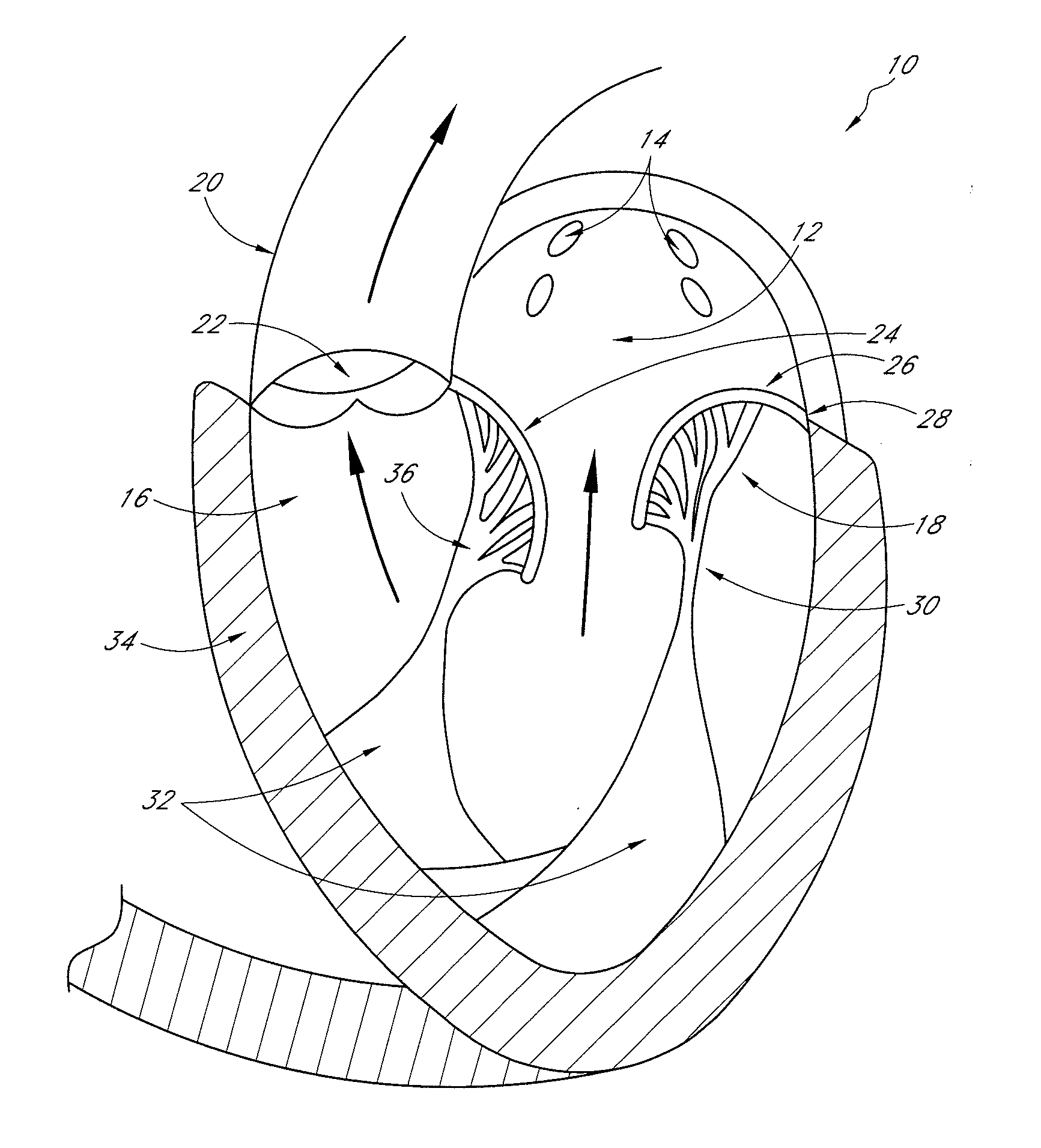
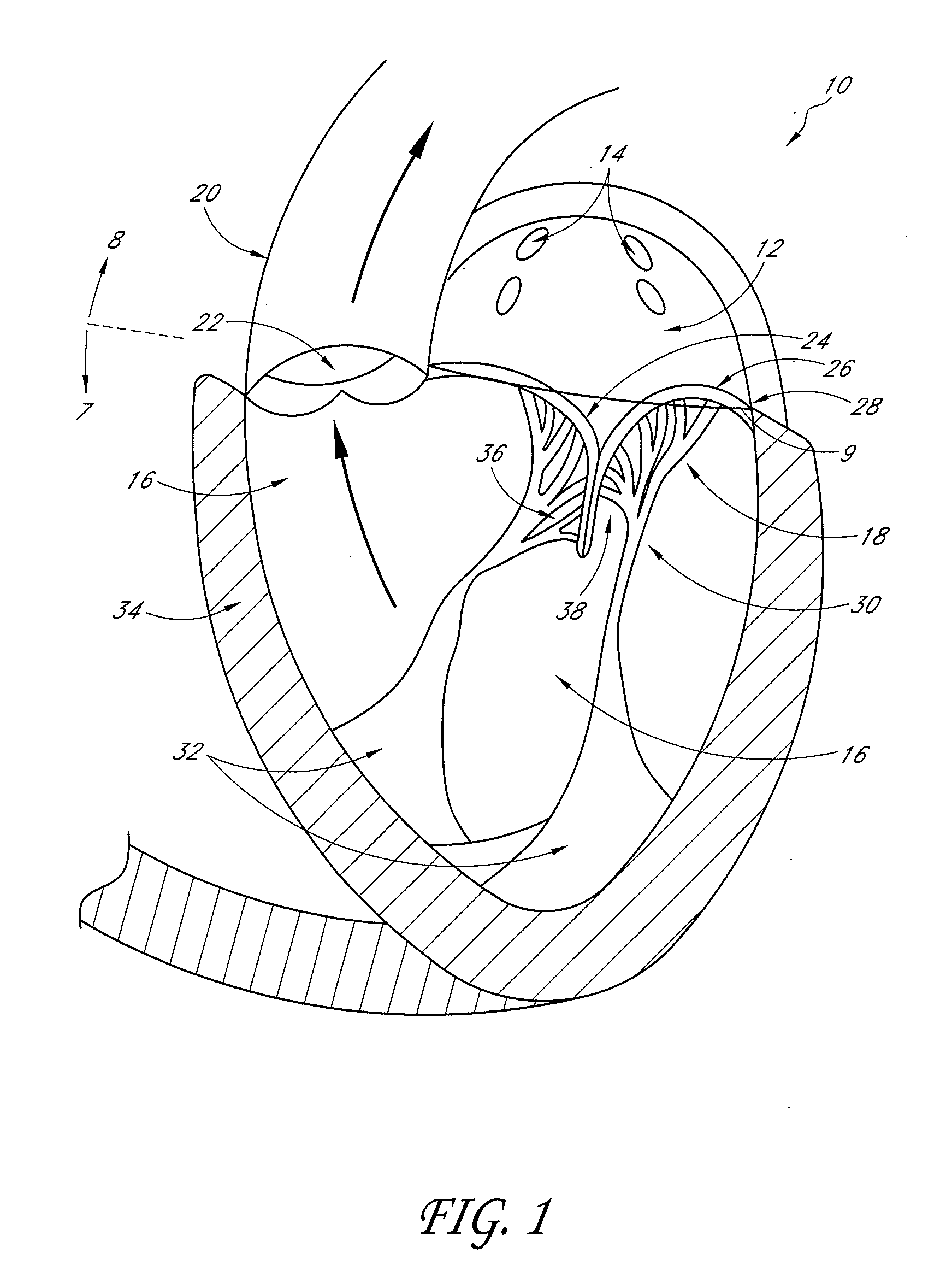
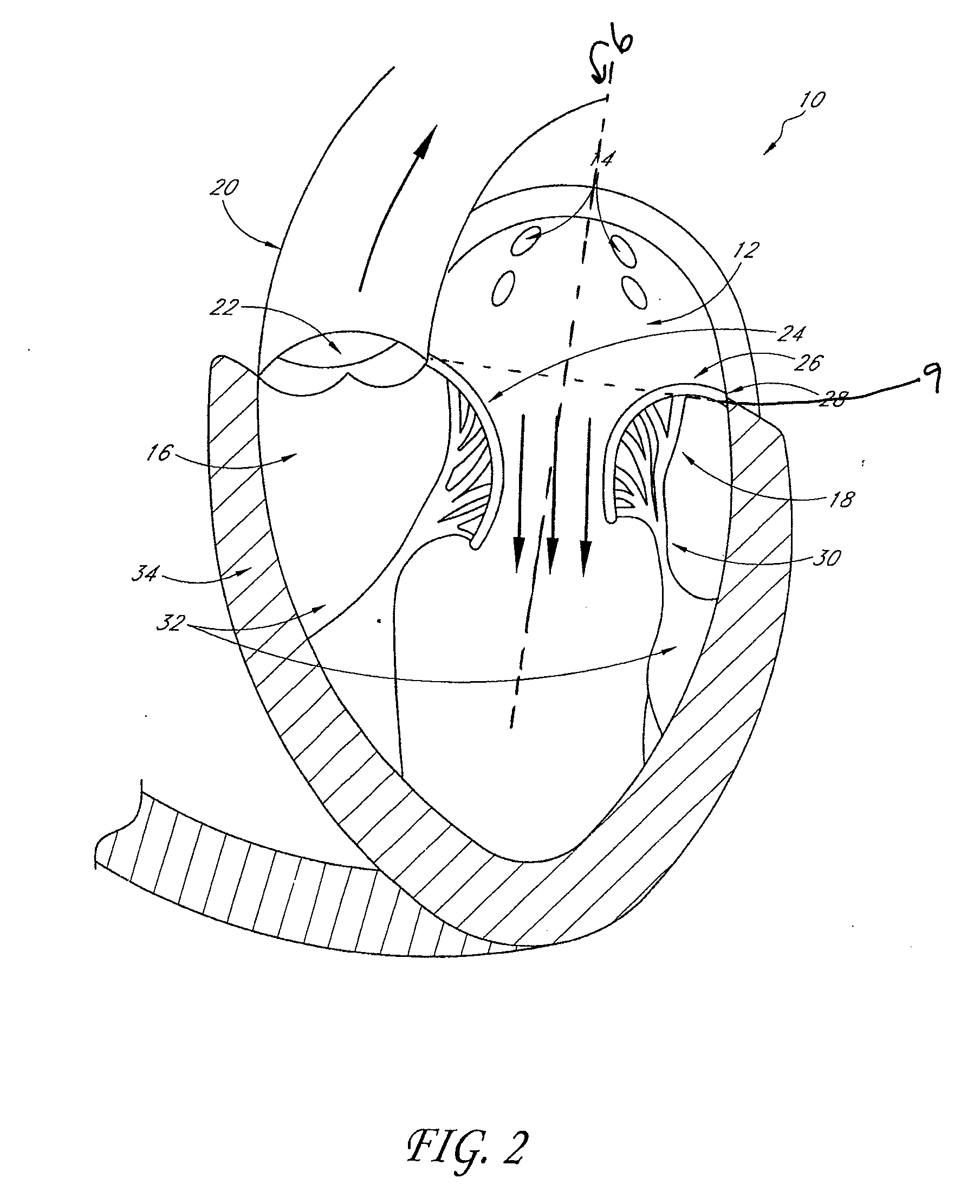
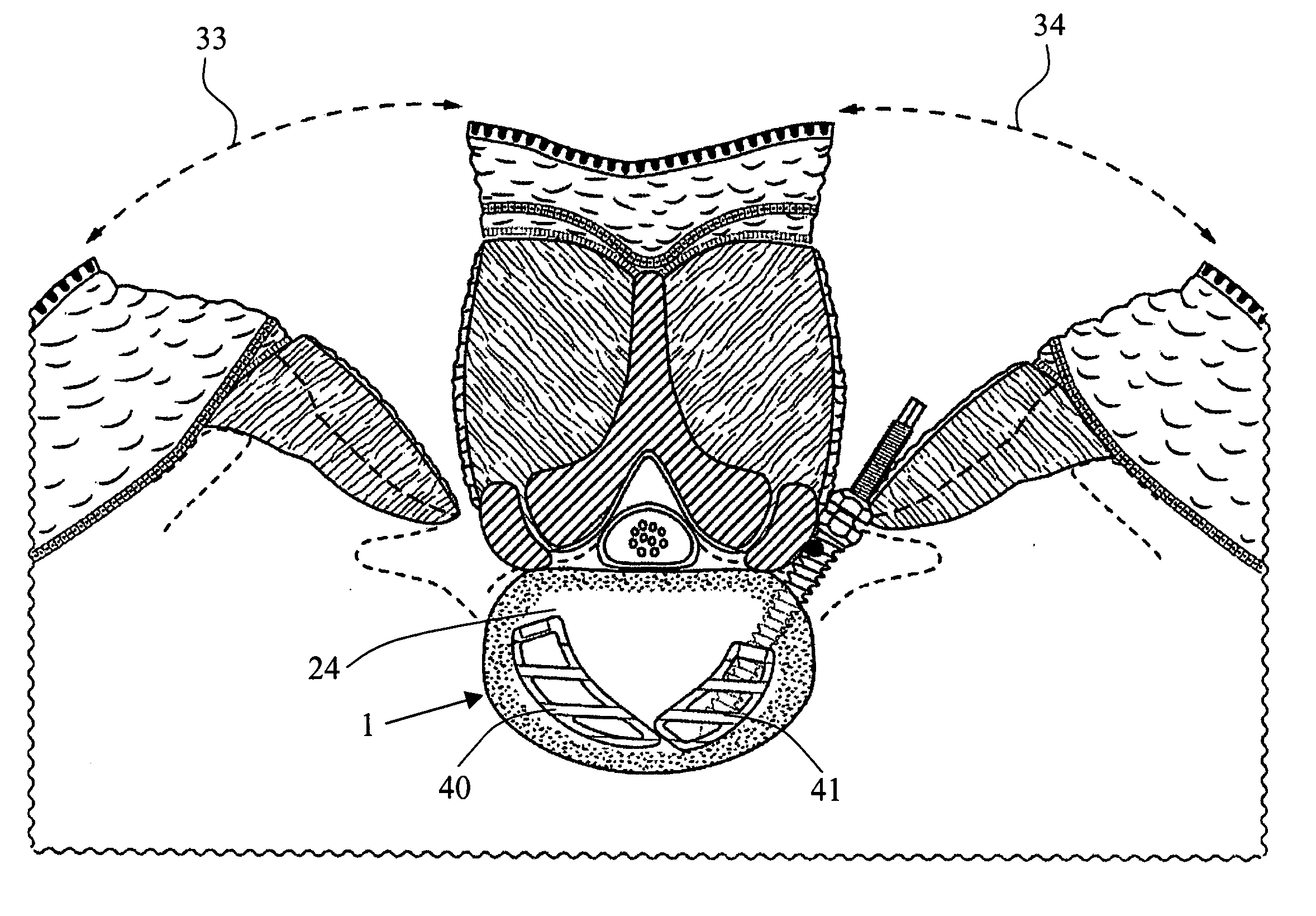
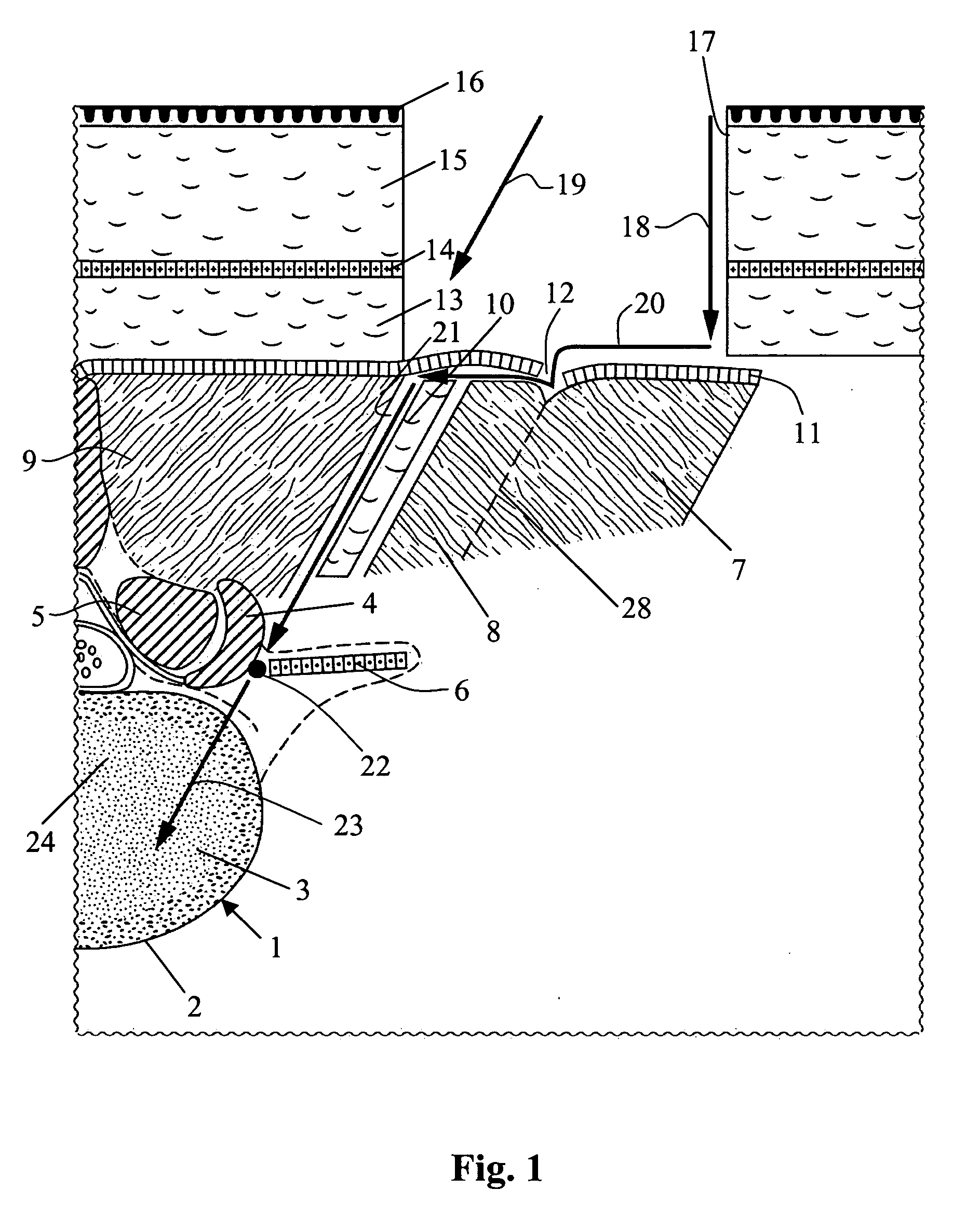
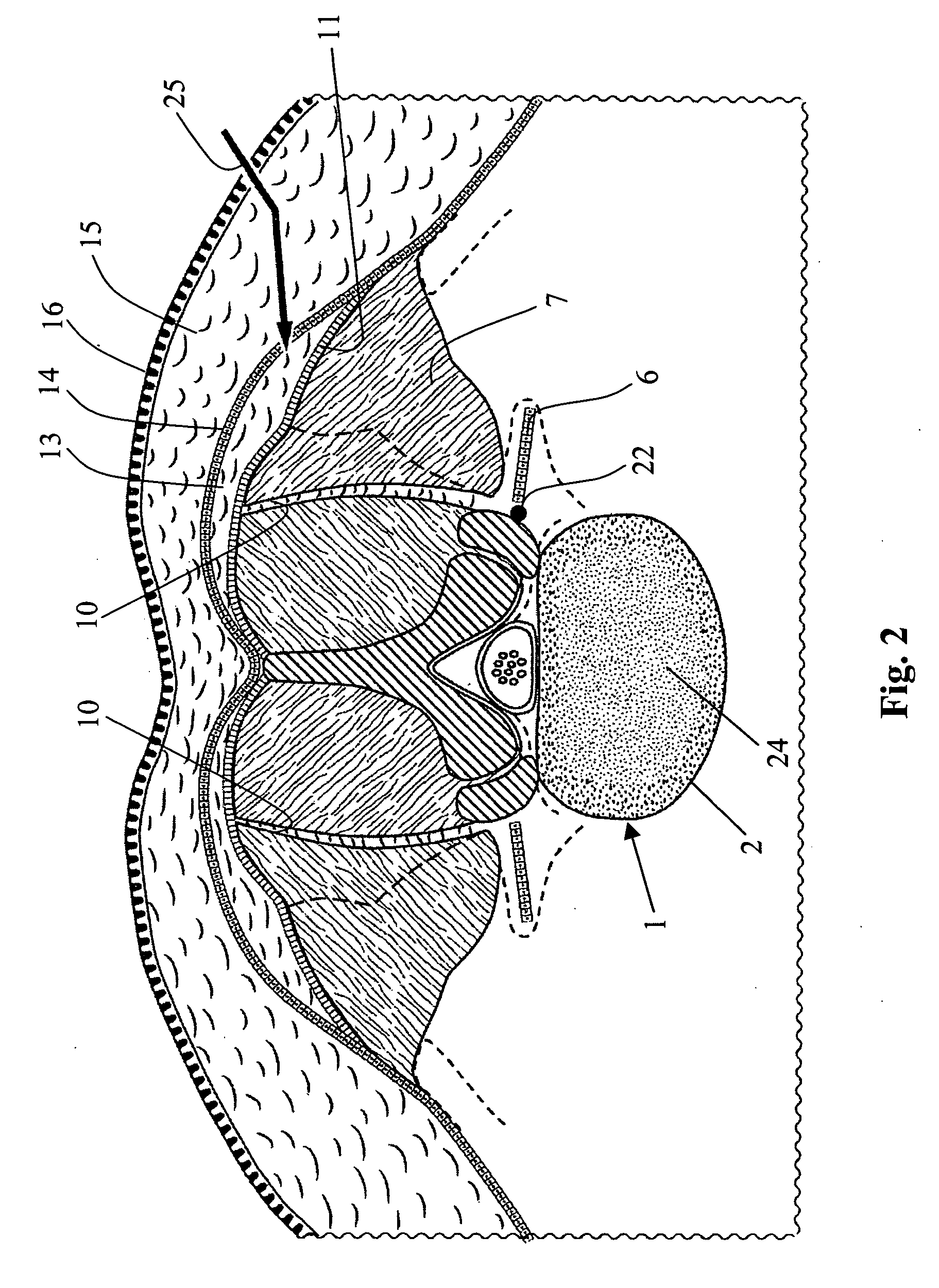
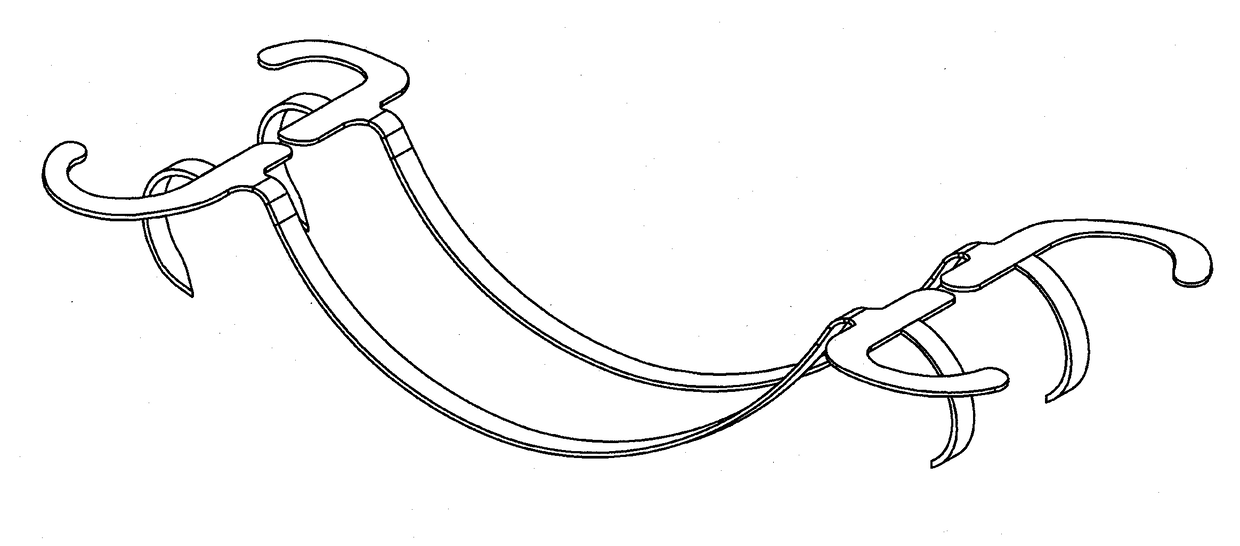
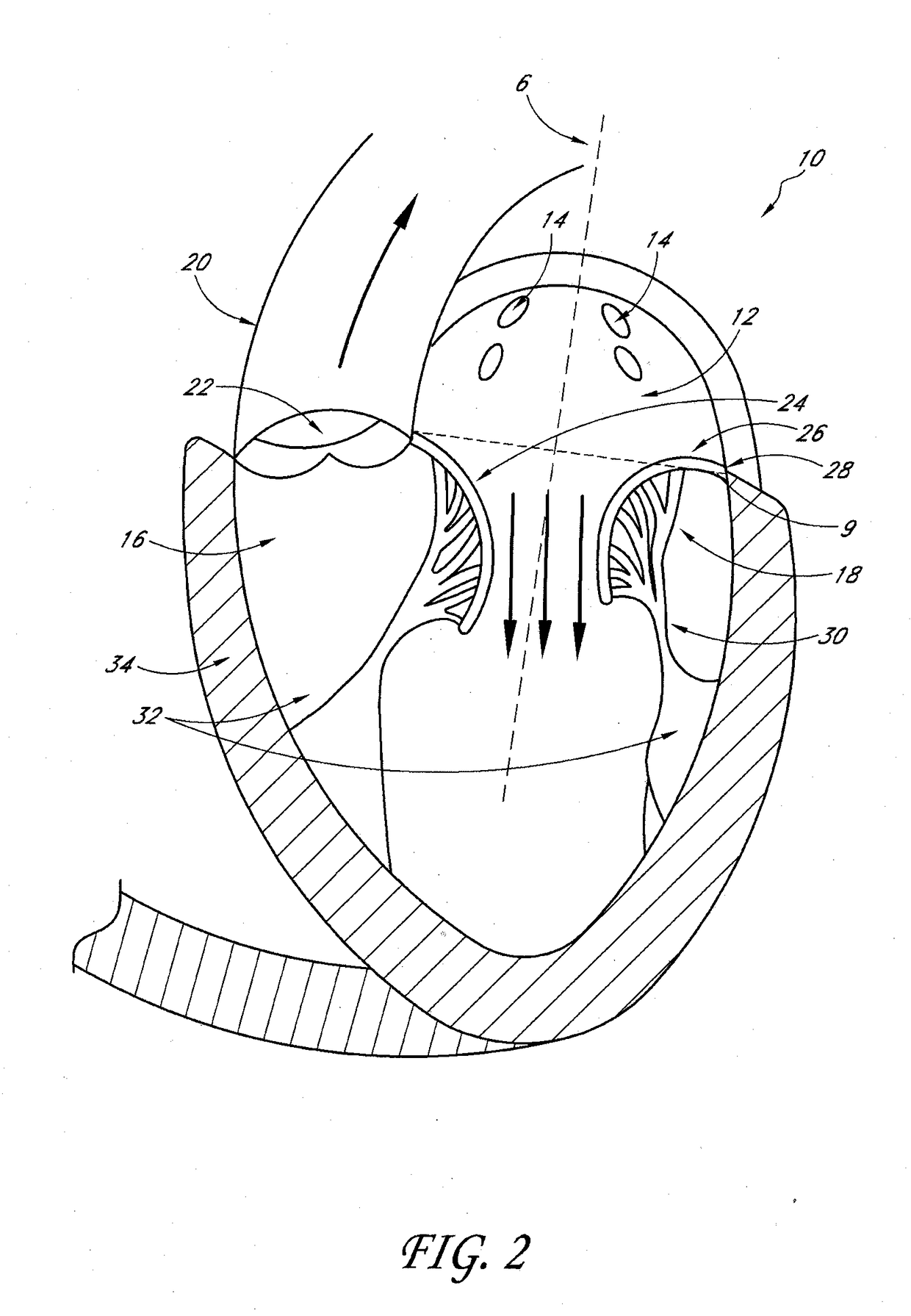
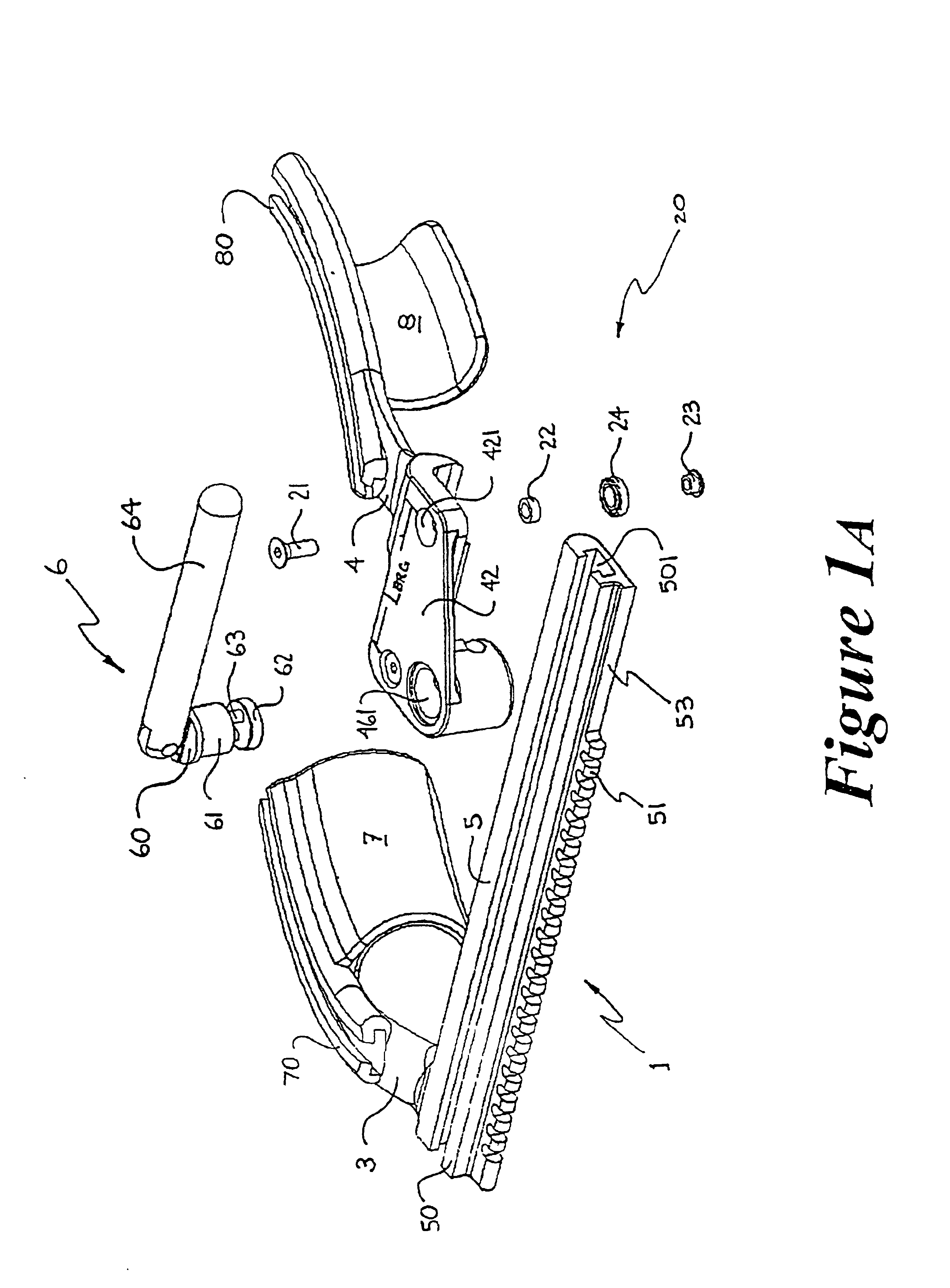
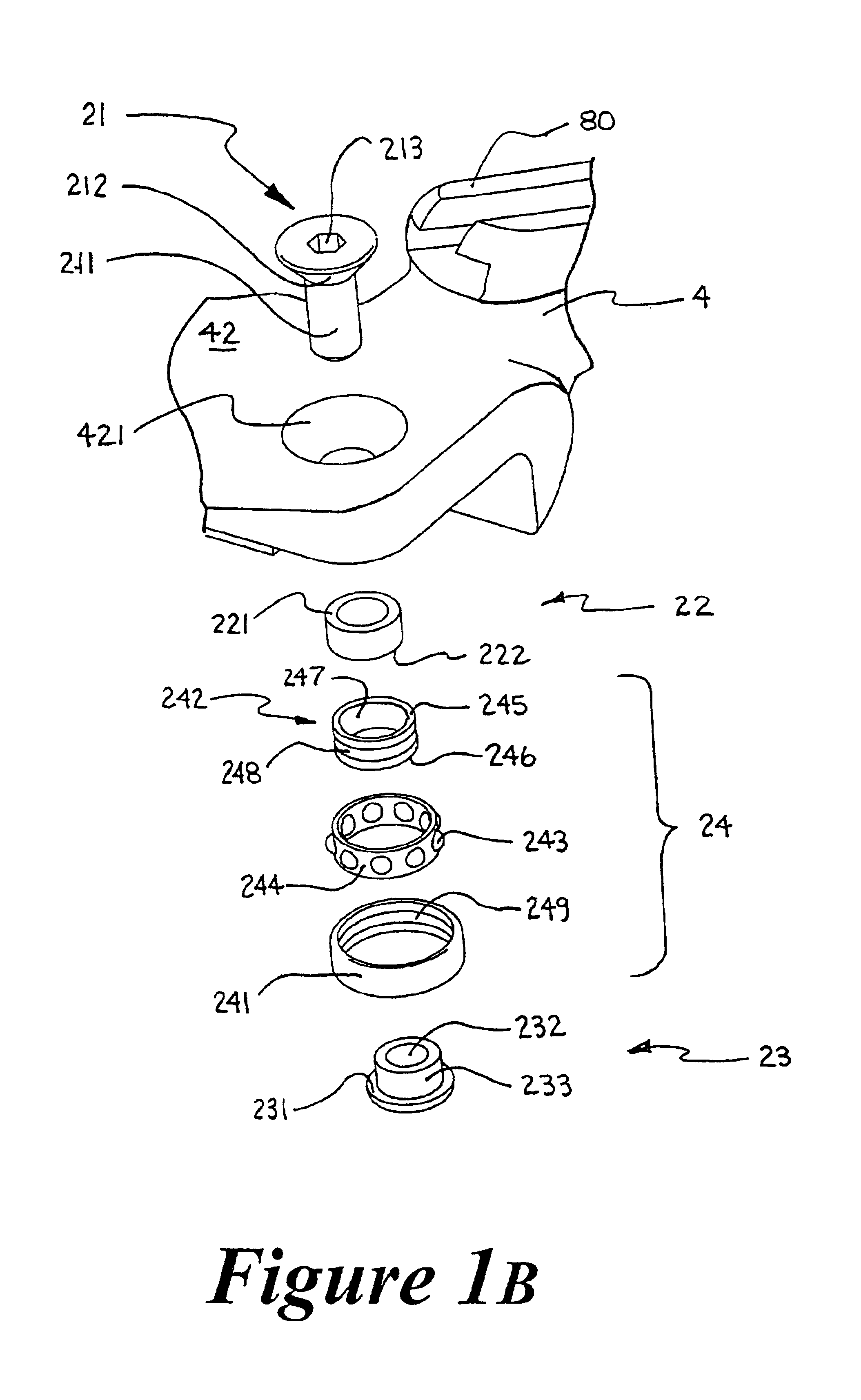
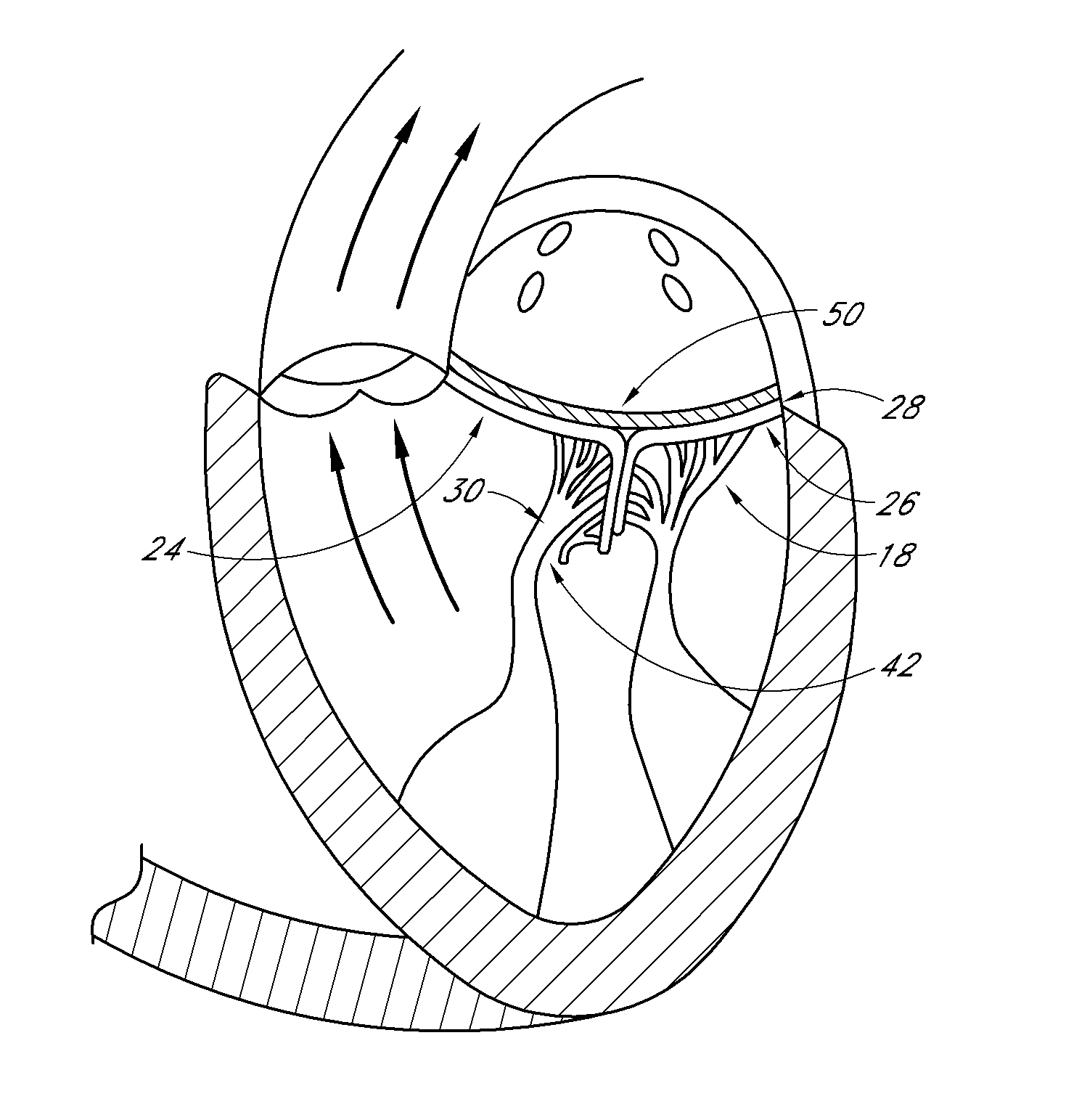
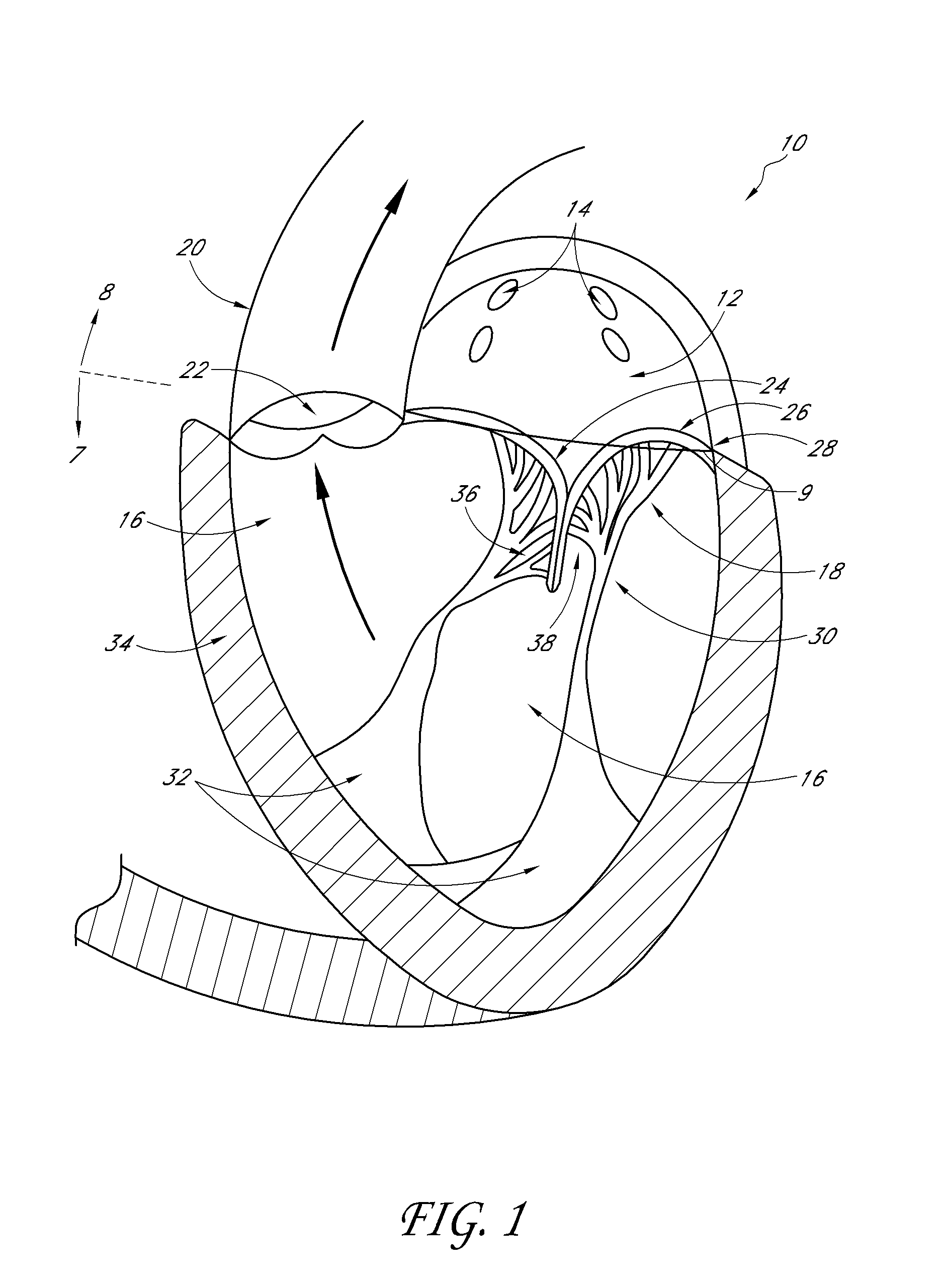
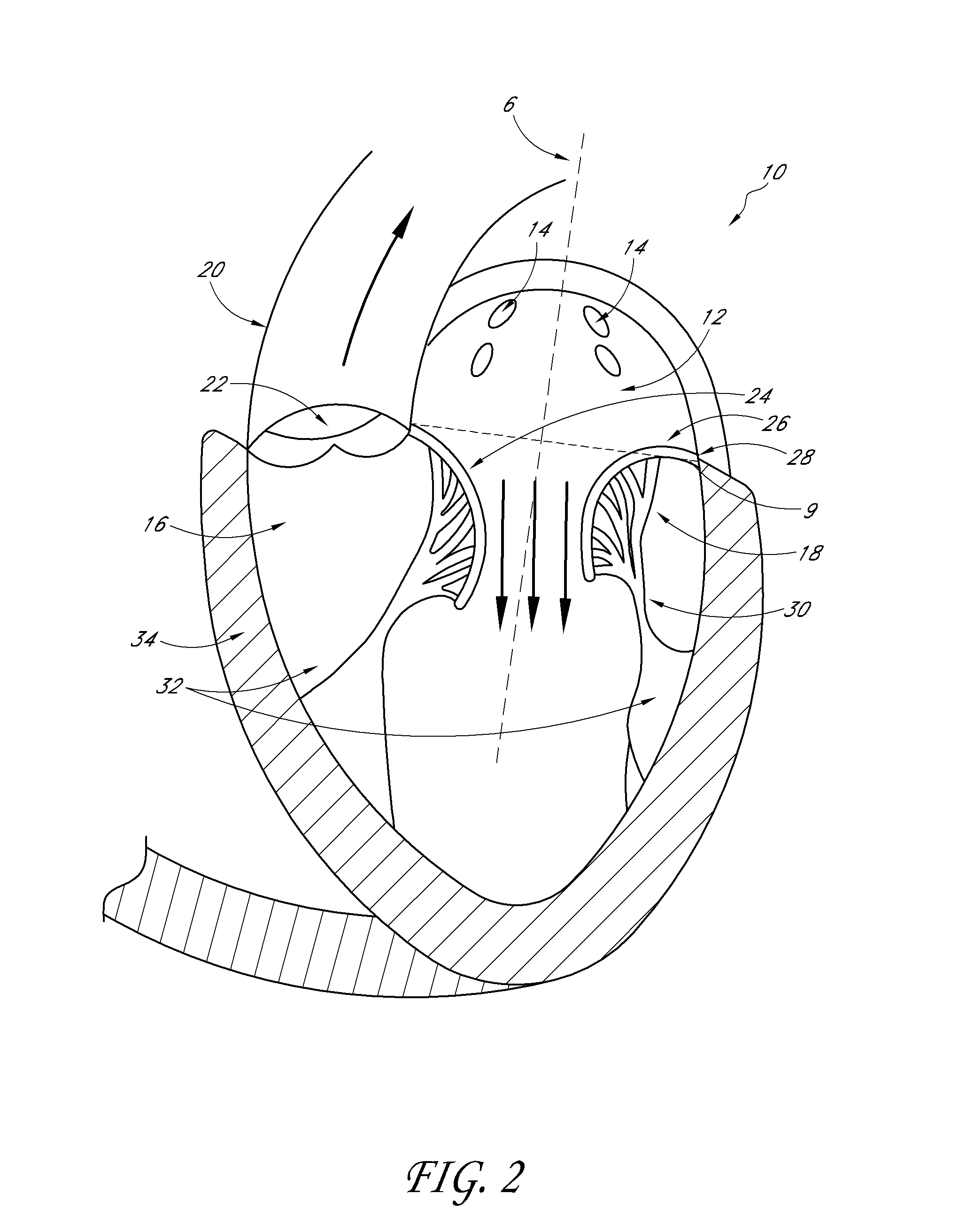
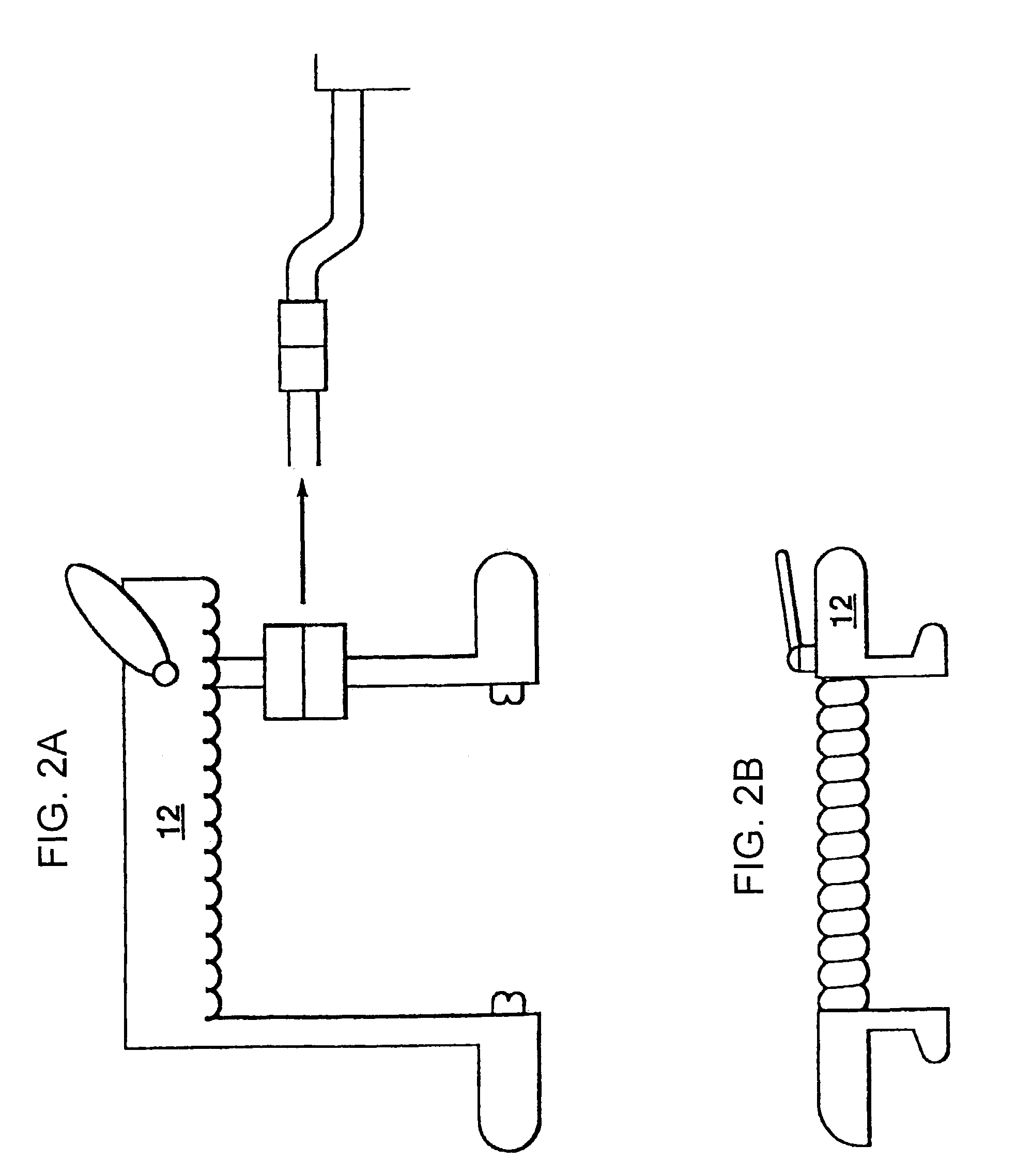
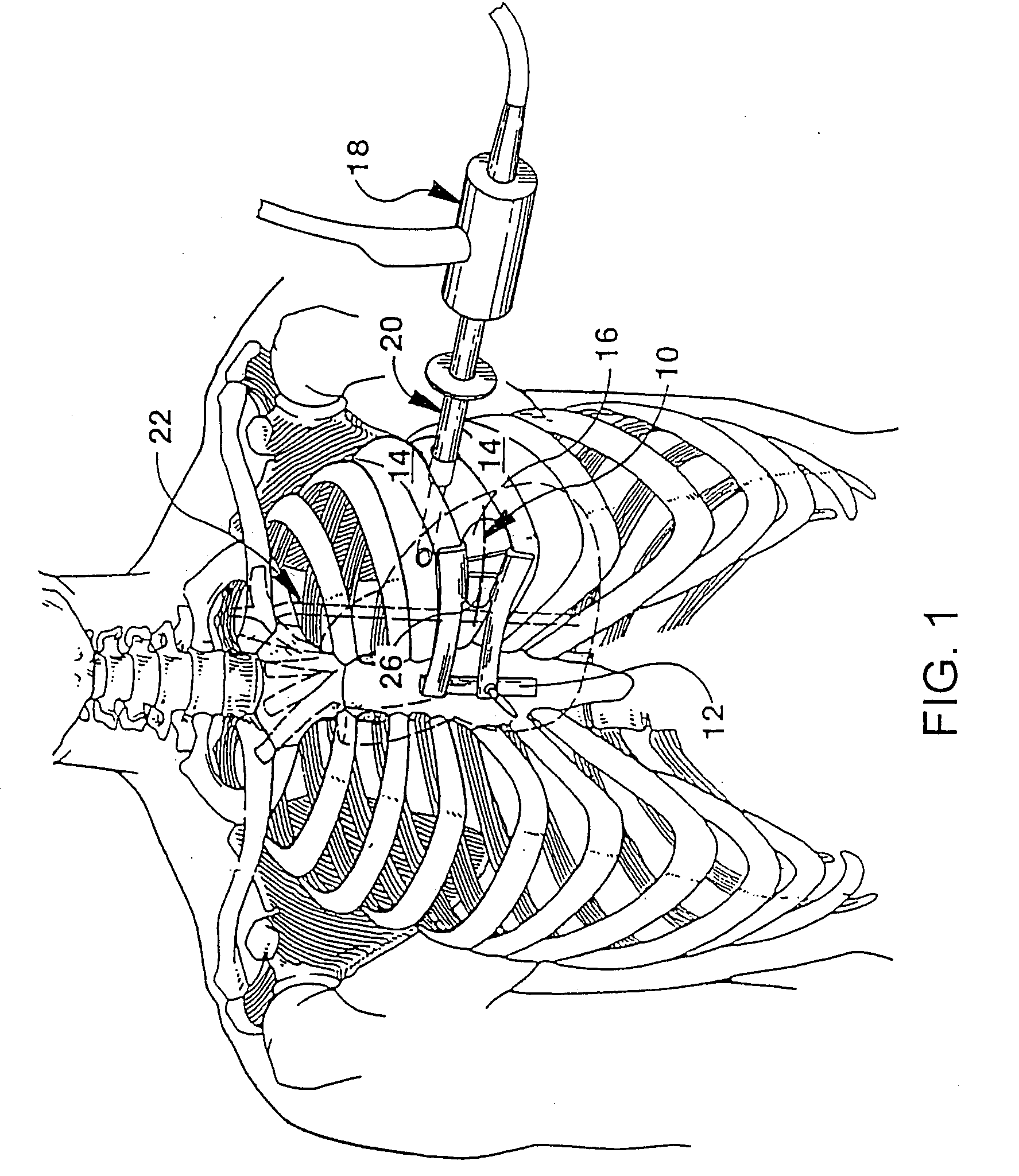
Percutaneous transvalvular intrannular band for mitral valve repair
Mitral valve prolapse and mitral regurgitation can be treating by implanting in the mitral annulus a transvalvular intraannular band. The band has a first end, a first anchoring portion located proximate the first end, a second end, a second anchoring portion located proximate the second end, and a central portion. The central portion is positioned so that it extends transversely across a coaptive edge formed by the closure of the mitral valve leaflets. The band may be implanted via translumenal access or via thoracotomy.
Owner:HEART REPAIR TECH INC
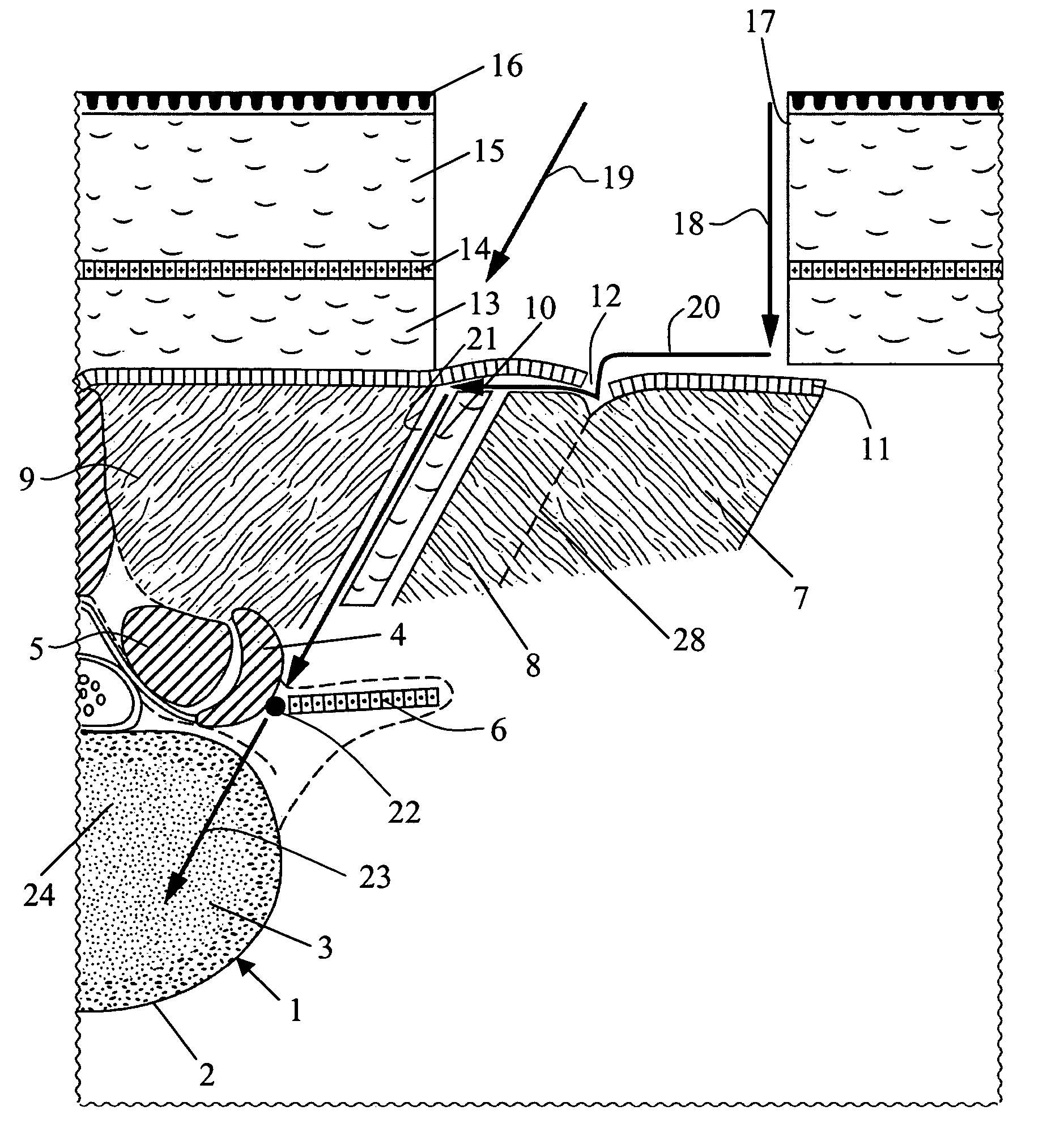
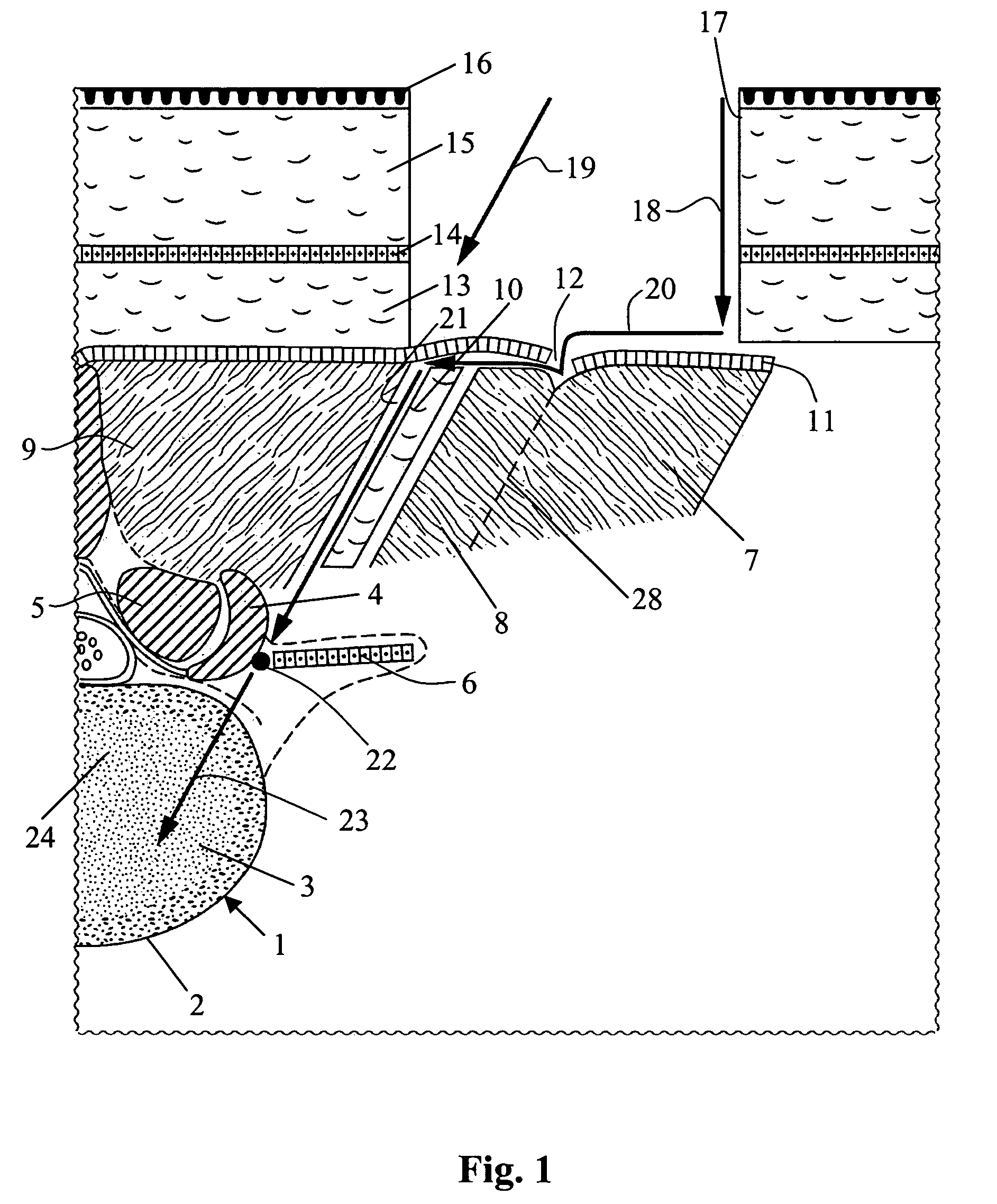
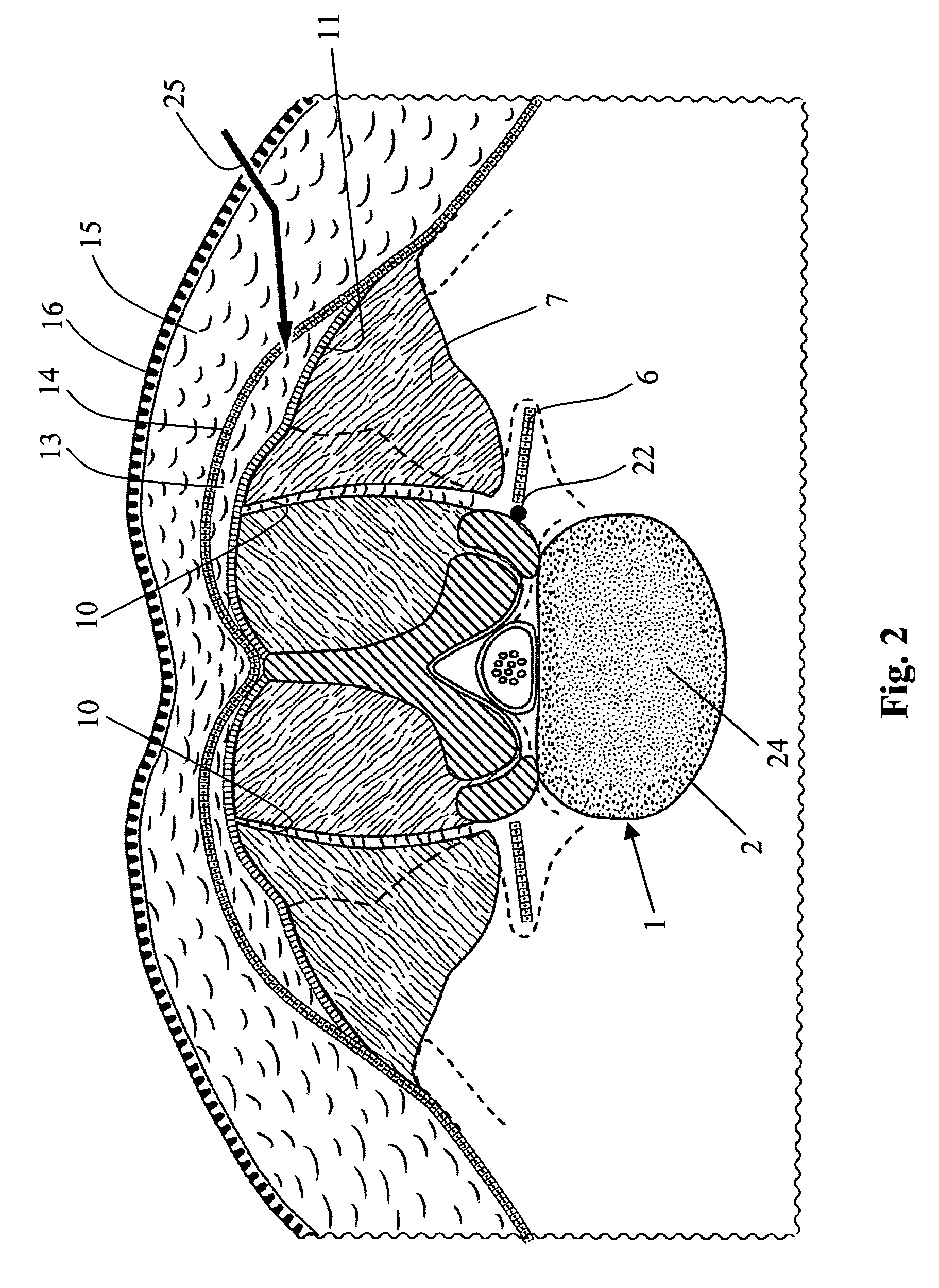
Method for repair of a spine and intervertebral implant
Repair of a spine from a posterior approach especially for locating an implant between a lower and upper human vertebra includes making an incision in the skin lateral to the midline, making an incision through the Erector Spinae Aponeurosis (ESA) following the ELIF groove, separating the ESA from the Longissimus Thoracis Pars Lumborum (LTPL), atraumatic separating the Multifidus from the LTPL using the interfascial boundary between the Multifidus and the LTPL, and creating a surgical plane having an angle of 20°-60°.
Owner:LIGNE
Transvalvular intraannular band for mitral valve repair
Mitral valve prolapse and mitral regurgitation can be treating by implanting in the mitral annulus a transvalvular intraannular band. The band has a first end, a first anchoring portion located proximate the first end, a second end, a second anchoring portion located proximate the second end, and a central portion. The central portion is positioned so that it extends transversely across a coaptive edge formed by the closure of the mitral valve leaflets. The band may be implanted via translumenal access or via thoracotomy.
Owner:HEART REPAIR TECH INC
Method for repair of a spine and intervertebral implant
Repair of a spine from a posterior approach especially for locating an implant between a lower and upper human vertebra includes making an incision in the skin lateral to the midline, making an incision through the Erector Spinae Aponeurosis (ESA) following the ELIF groove, separating the ESA from the Longissimus Thoracis Pars Lumborum (LTPL), atraumatic separating the Multifidus from the LTPL using the interfascial boundary between the Multifidus and the LTPL, and creating a surgical plane having an angle of 20°-60°.
Owner:LIGNE
Thoracic retractors and methods
InactiveUS20120330106A1Pain minimizationAvoid contactSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesIntercostal nervesLongissimus Thoracis
A surgical thoracic retractor has retraction members that grip the anterior and posterior surfaces of the ribs between vice-like jaws to prevent a crushing or other force being applied to the intercostal nerves, thus minimizing the patient's post-operative pain.
Owner:GENESEE BIOMEDICAL
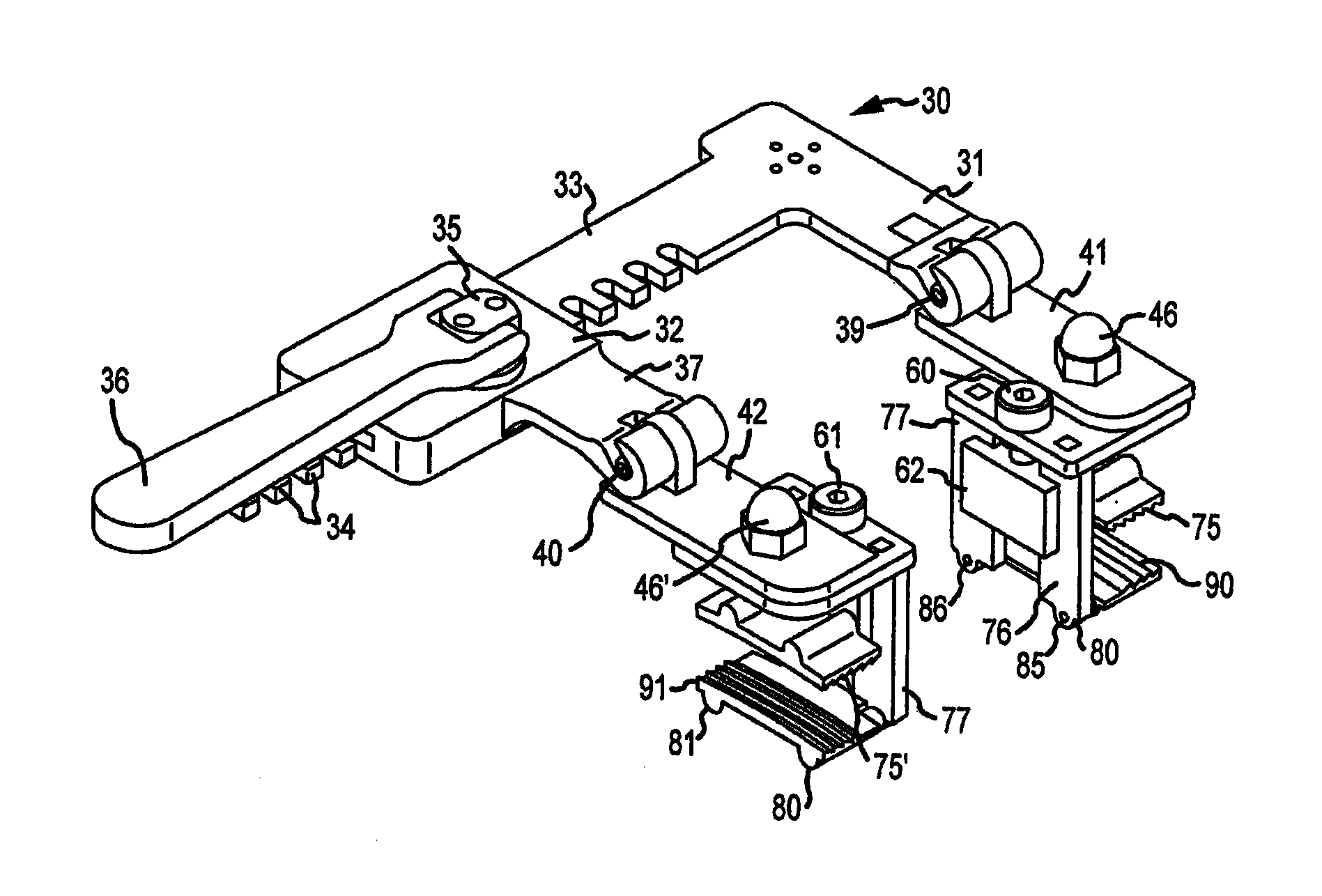
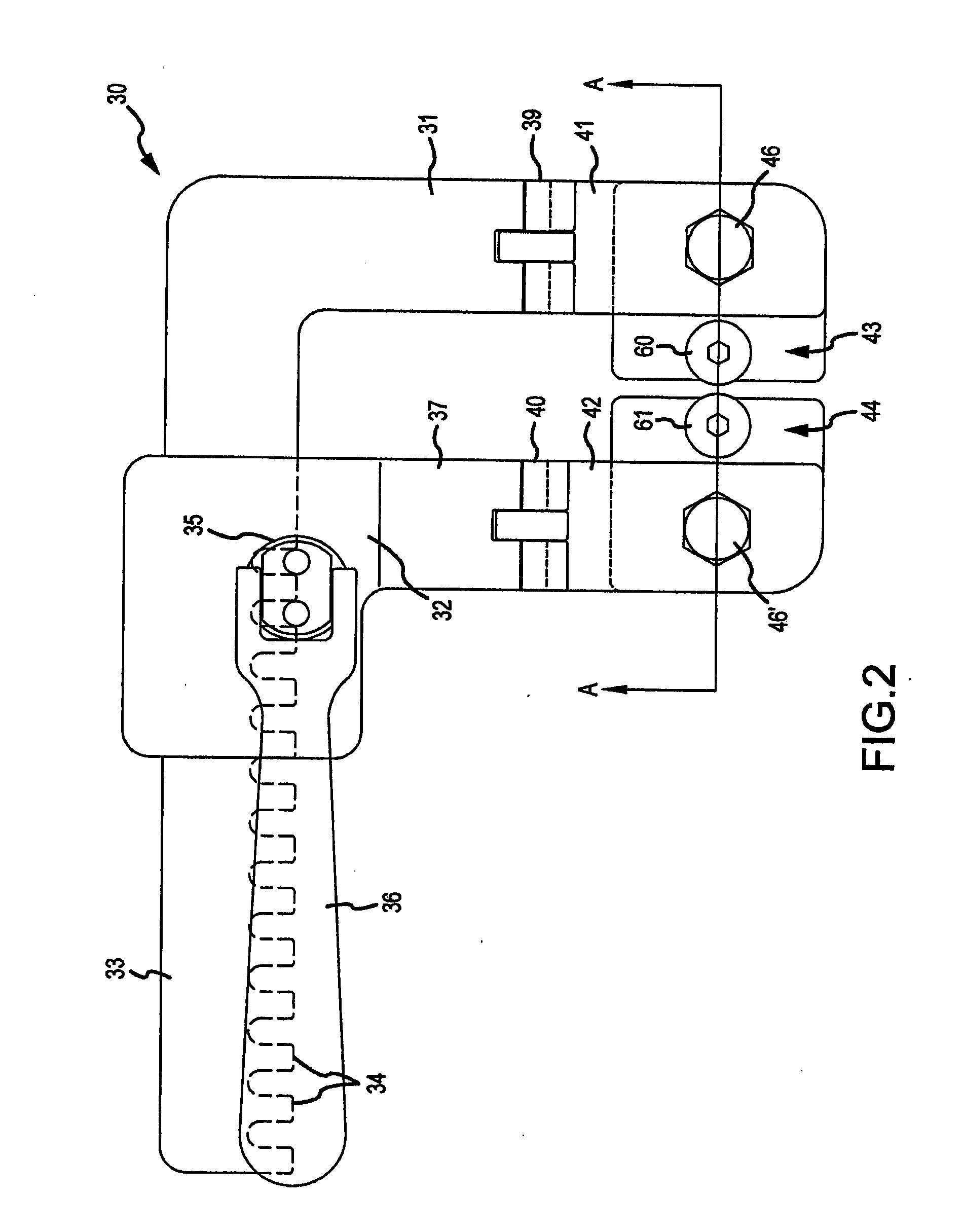
Surgical retractor having low-friction actuating means and contoured blade arms
A retractor for performing surgery, for instance cardiac surgery on the coronary organs of a patient, which has a driving member to which the surgeon input is applied in the form of a mechanical force or torque, a thoracic structure engaging member which interfaces and retracts the patient's thoracic structure when surgeon input is applied to the movable driving member, and a surgeon input load-reducing and load-normalizing mechanism provided in at least one mechanical interface between retractor components where relative motion therebetween occurs. The load-reducing and load-normalizing mechanisms are preferably non-lubricated, thereby tending to ensure an inert and sterile environment during surgery. The retractor is comprised of a locking arrangement allowing a retractor spreader arm to be secured at any longitudinal position along the rack bar, independently of the pinion's position. The thoracic retractor according to this invention tends to improve the efficiency and safety of surgery by reducing the surgeon input required to achieve retraction, and by allowing said input to be applied more uniformly and in a controlled manner free from sudden movements through the normalization of retractor variables.
Owner:CORONEO
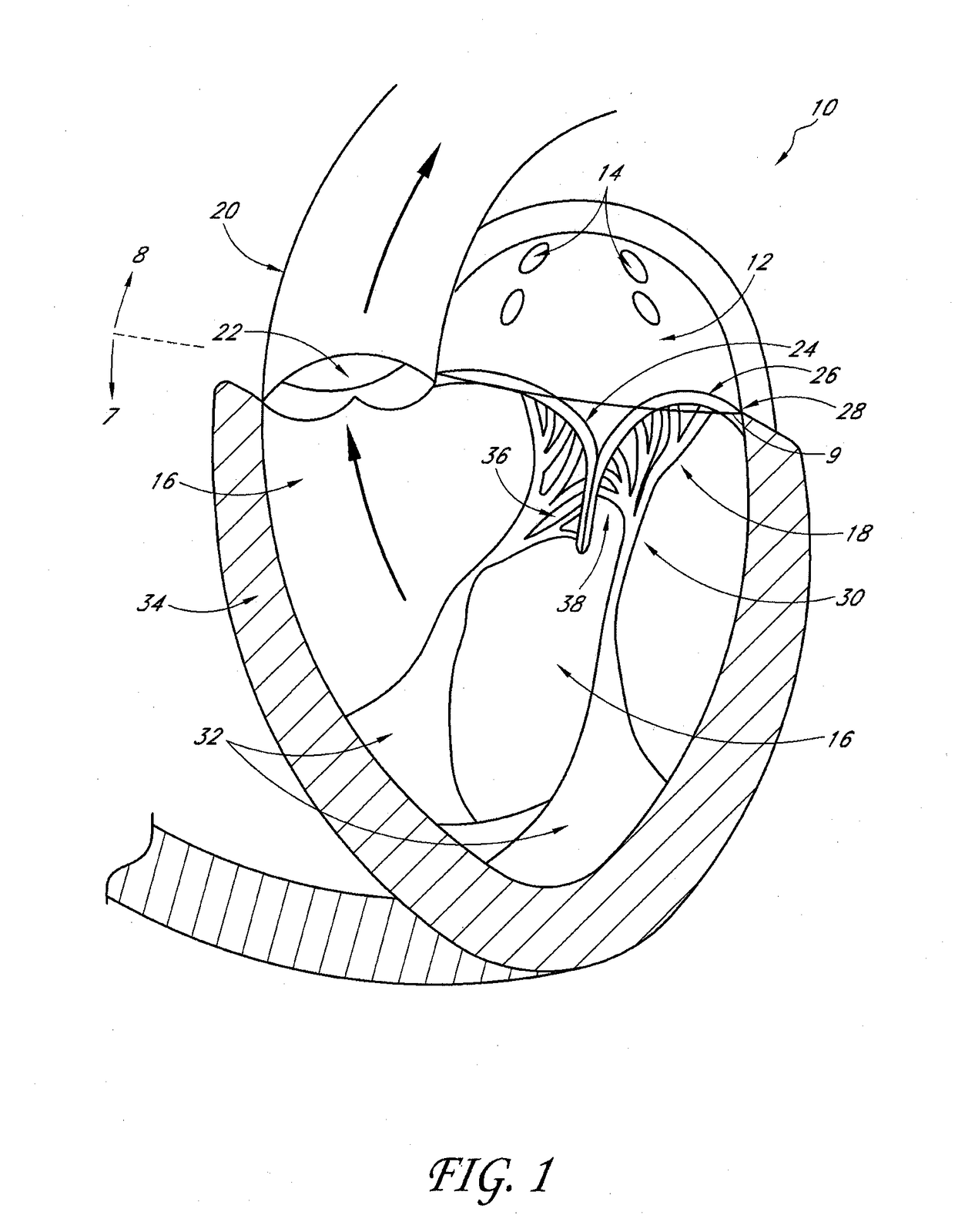
Transvalvular intraannular band for aortic valve repair
ActiveUS20130103142A1Reduce distanceImprove aortic leaflet coaptivityBone implantAnnuloplasty ringsAortic valve repairLongissimus Thoracis
Aortic regurgitation can be treating by implanting in the aortic annulus a transvalvular intraannular band. The band has a first end, a first anchoring portion located proximate the first end, a second end, a second anchoring portion located proximate the second end, and a central portion. The central portion is positioned so that it extends transversely across a coaptive edge formed by the closure of the aortic valve leaflets. The band may be implanted via translumenal access or via thoracotomy.
Owner:HEART REPAIR TECH INC
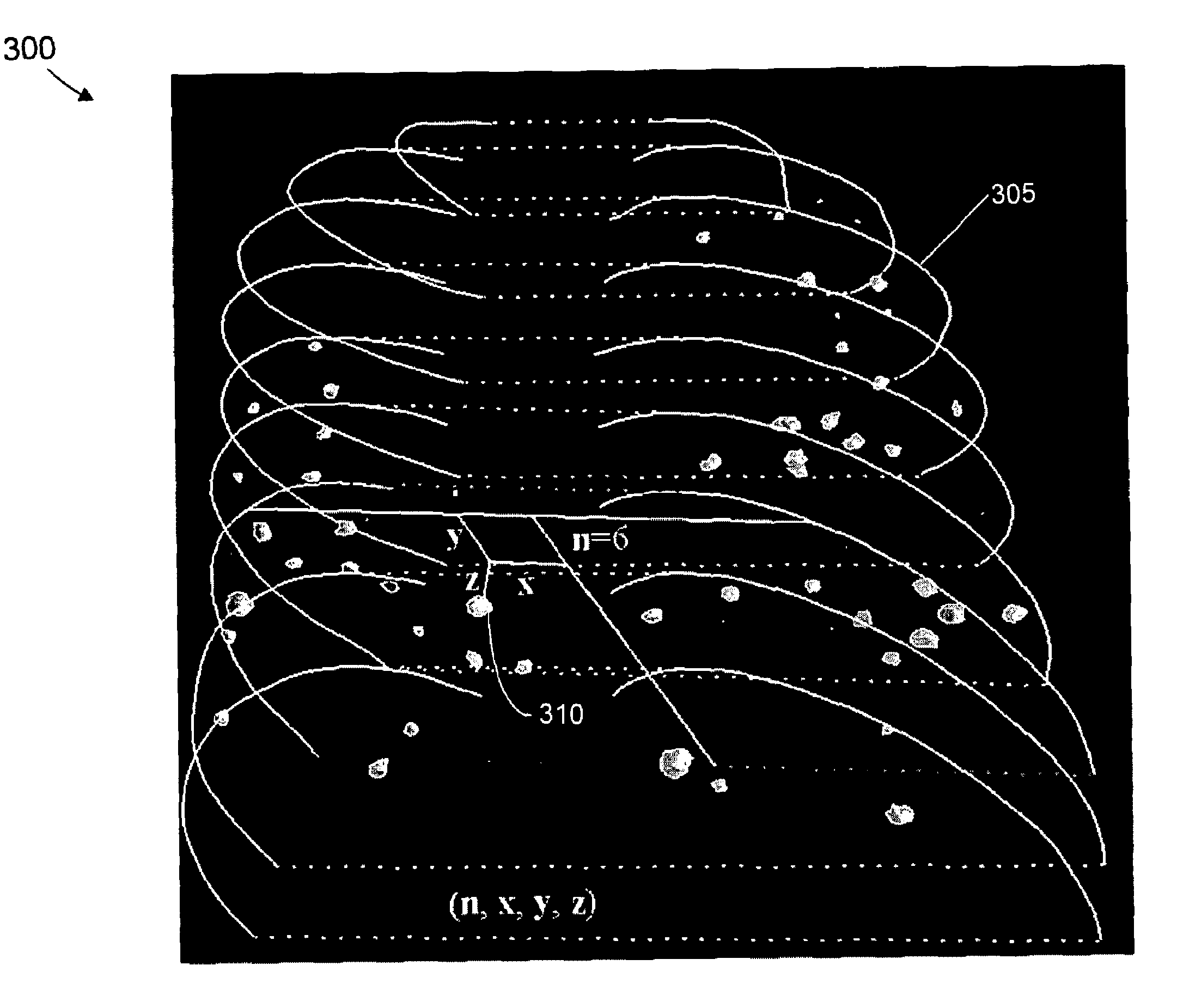
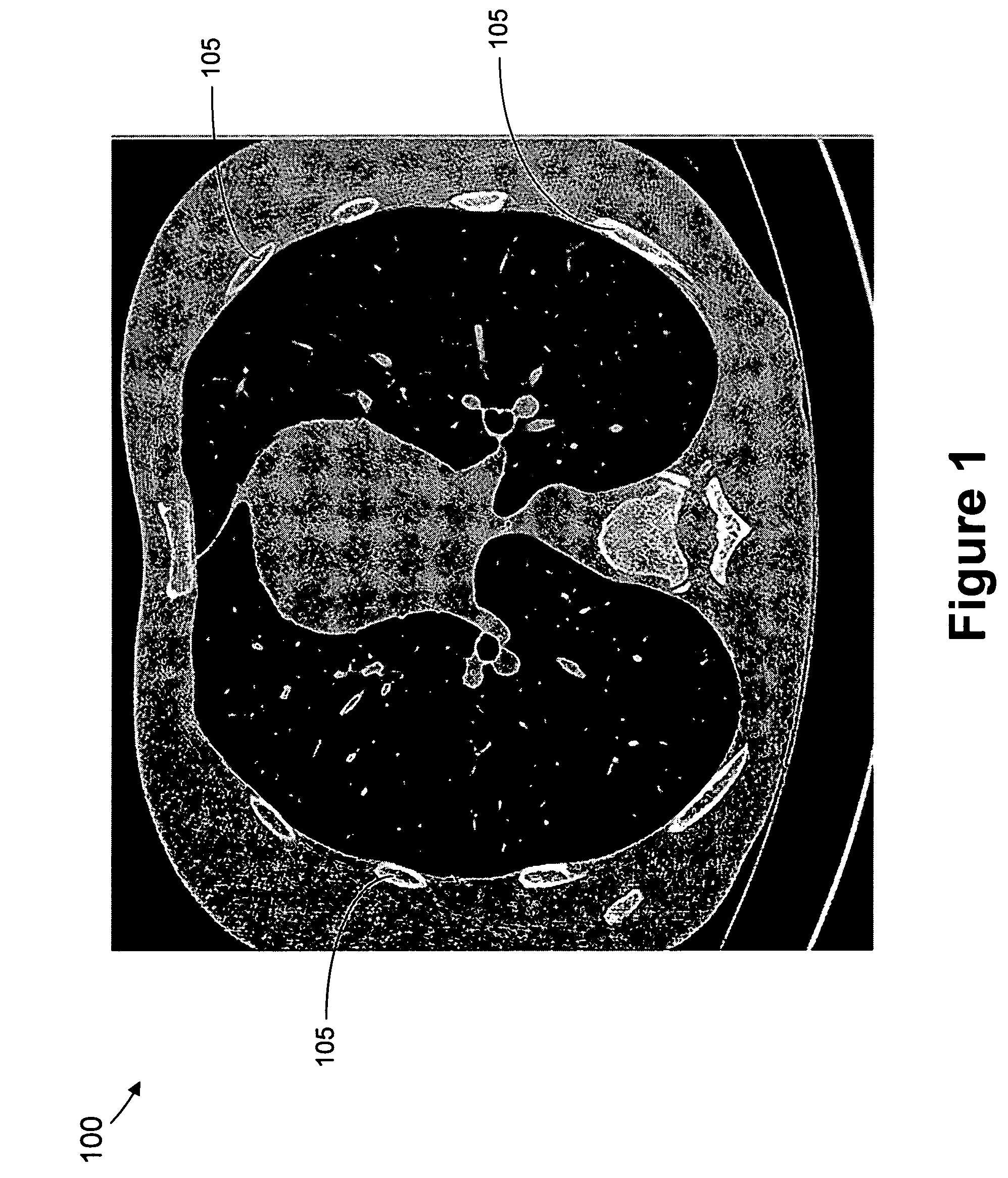
Thoracic cage coordinate system for recording pathologies in lung CT volume data
We introduce a thoracic cage coordinate system for recording pathology locations in lung CT volume data. The centerlines of each individual rib are extracted and labeled from top to bottom. For each pair of ribs, a three-dimensional (“3D”) orthogonal basis is computed by eigen-analysis of the rib centerline points, which are taken as the x, y, and z axes. The rib pairs form a set of reference planes. Therefore, there are a set of coordinate systems (x, y, z), each of which is locally valid between two adjacent planes. To define a location globally, a fourth parameter, n, is added to identify the serial number of the reference plane. The complete coordinate is recorded as (n, x, y, z). This system is robust against deformations due to bending and twisting, and is relatively stable over inhalation. Further, this system may be readily adapted in other 3D modalities, such as MRI volume data.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
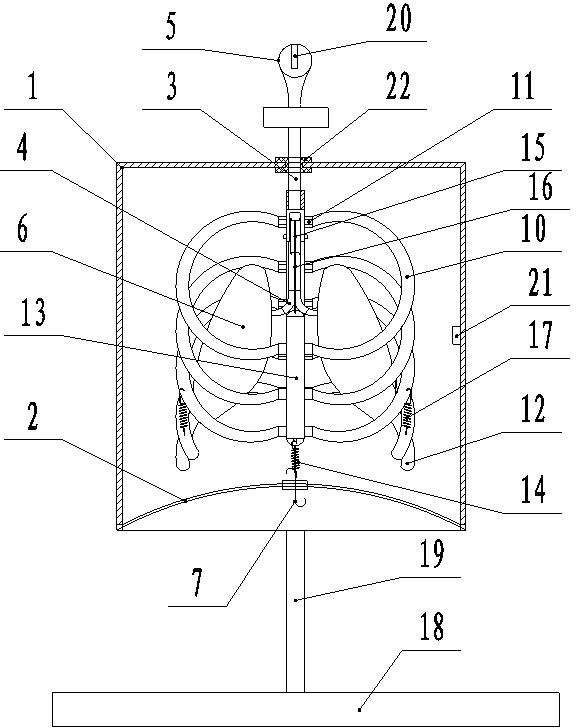
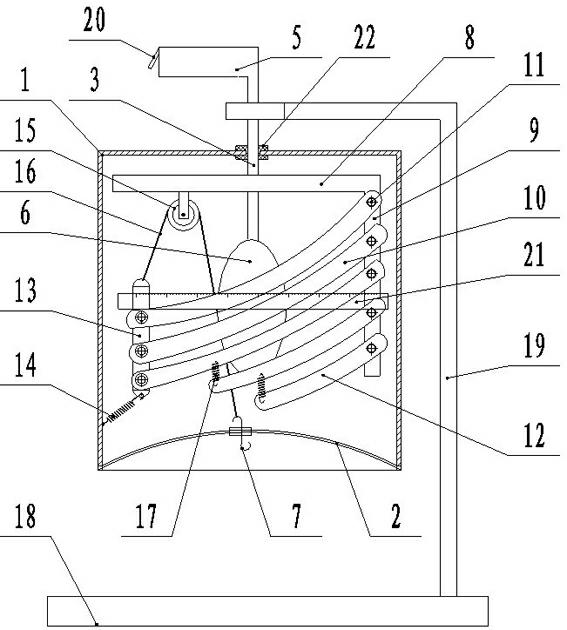
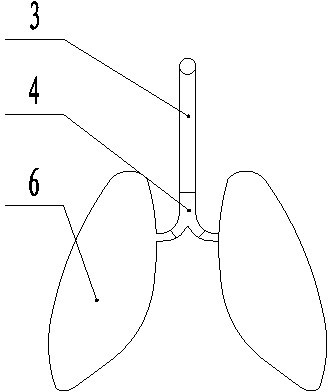
Human breathing demonstration instrument
The invention provides a human breathing demonstration instrument, which comprises a simulative thorax, simulative lungs and a simulative skeleton; the simulative skeleton is arranged in the simulative thorax, and comprises a vertical rod as the spinal column and curved rods as the ribs, the curved rods are curved, one end of each of each pair of curved rods is articulated with the vertical rod through a bolt, and the other ends of each pair of curved rods are articulated with a connecting rod as the sternum through bolts; the connecting rod is vertically arranged, the lower end of the connecting rod is connected with a restoring spring, the other end of the restoring spring is connected with a housing, and the restoring spring can downwardly pull the connecting rod; the upper end of the connecting rod is connected with a string, and the string passes through a pulley arranged on a cross rod, and is connected with a hook. The human breathing demonstration instrument not only can demonstrate the entry of the air into the lungs, the expansion and contraction of the lungs, the motion of the diaphragms and the expansion and contraction of the thorax when the human body breathes, but also can demonstrate the motion of the ribs, the sternum and other thoracic bones.
Owner:赵泽洪
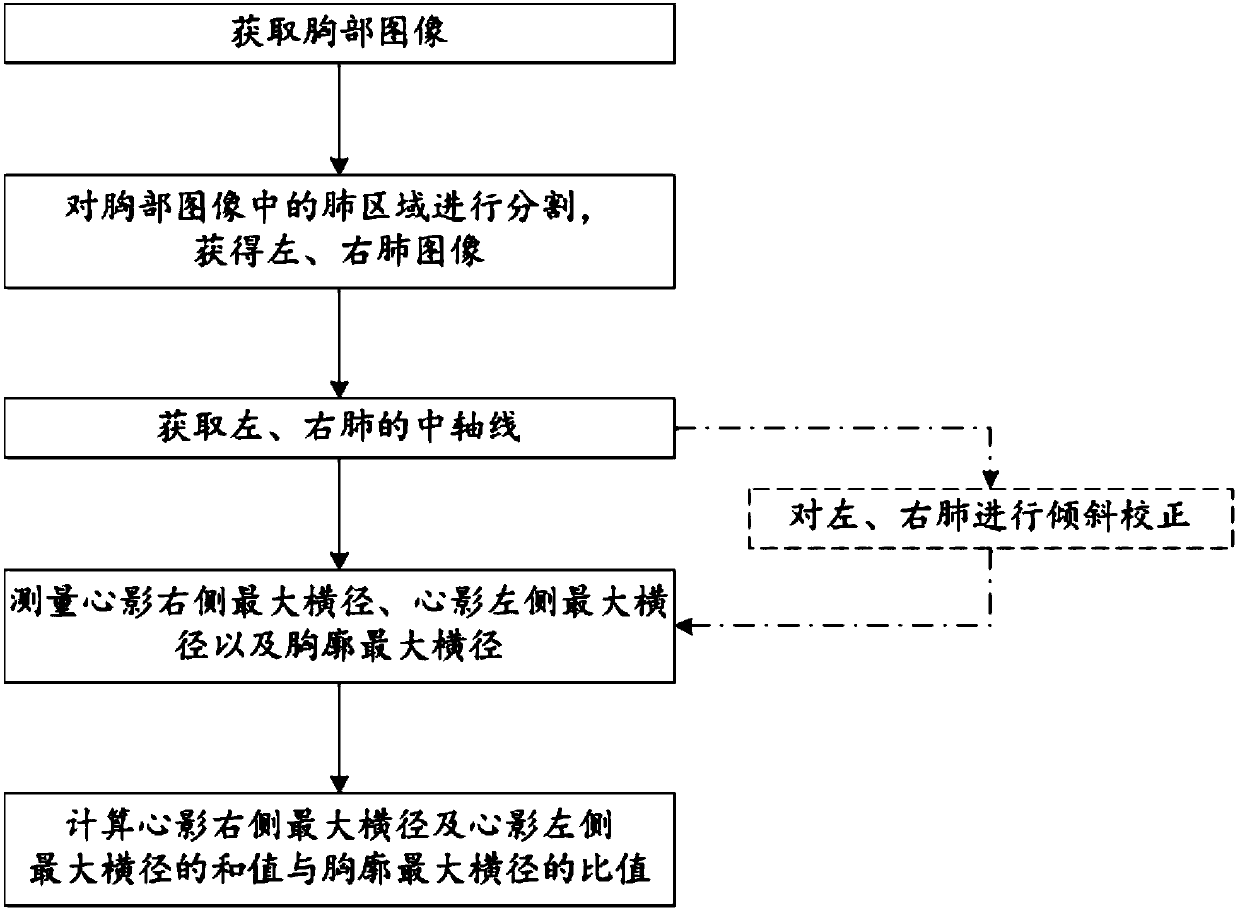
Method for cardio-thoracic proportion calculation of medical image
ActiveCN107665497AConvenient automatic measurementImage enhancementImage analysisLeft lungChest region
The invention discloses a method for cardio-thoracic proportion calculation of a medical image. The method includes steps of acquiring a thorax image; performing segmentation on a lung area in the thorax image and acquiring a left lung image and a right lung image; acquiring the central axis of the left lung and the right lung; measuring a podoid right side maximal cross diameter, a podoid left side maximal cross diameter and a thorax maximal cross diameter; calculating the proportion between the sum of the podoid right side maximal cross diameter and the podoid left side maximal cross diameter and the thorax maximal cross diameter. According to the invention, on the basis of lung segmentation, the podoid maximal cross diameter and the thorax maximal cross diameter are measured automatically and the cardio-thoracic proportion is calculated.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
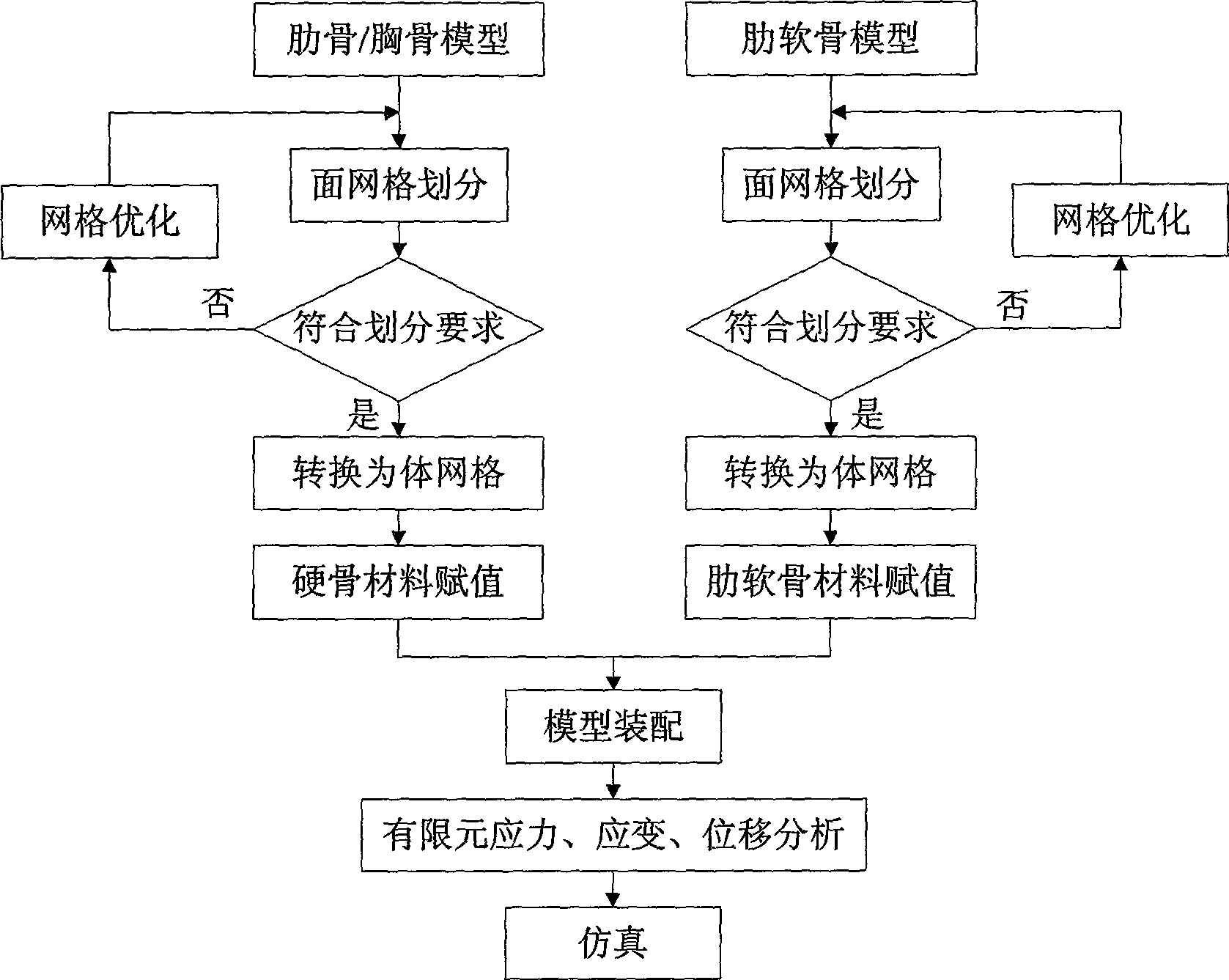
Simulation method for funnel breast orthopaedic surgery
InactiveCN101488236AIncrease success rateInternal osteosythesisDiagnostic recording/measuringMechanical modelsElement analysis
The invention discloses a funnel chest orthopaedic surgery simulation method; chest three-dimension visualization bone models and costal cartilage models are respectively processed by face mesh division, and the mesh is optimized; a mesh conversion is used on the basis of mesh optimization, and a chest model is converted into a body mesh from a face mesh; rib, costal cartilage and breast bone are respectively material-evaluated, and skeleton body mesh model of each part is assembled so as to obtain a complete chest three-dimensional mechanical model; boundary conditions and loading force moment are determined, and the chest model is processed by finite element analysis so as to obtain the stress, strain and displacement conditions of each skeleton part under the action of different external forces; the incision position, support plate material, fixing method and supporting force moment of funnel chest surgery are simulated so that the success ratio of funnel chest surgery is increased to over 98% from 70-90% of the prior art.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
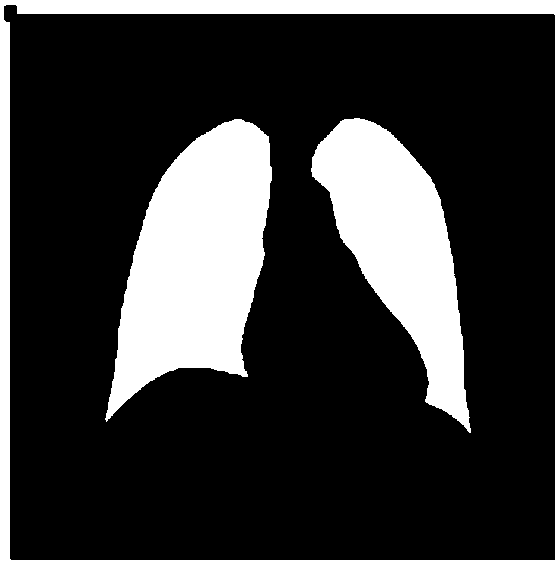
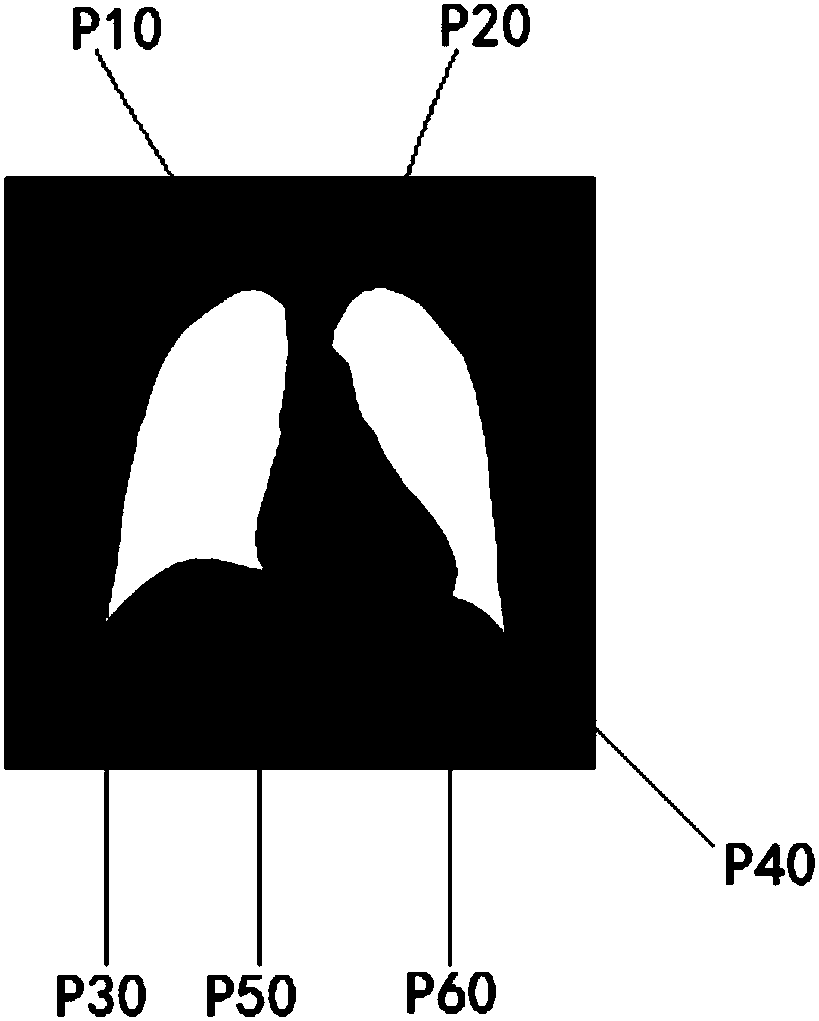
Three-dimensional modelling approach for children's funnel chest
InactiveCN101366639ASolve invisibleImplement cartilage modelingImage analysisComputerised tomographsLongissimus ThoracisFunnel Chest
The invention discloses a three-dimensional modeling method for the funnel chest of a child. Firstly, aiming at an original spiral CT picture of the funnel chest of the child, a region search method is adopted to model a thoracic hard bone part; a gray value of a cartilage region of a thoracic three-dimensional model is measured, and masking separation costal cartilage image data are created after the modification; a region growing method is adopted to apply region growing separation costal cartilage image data to a combining end of a hard bone and a cartilage of each rib; the costal cartilage data which is subjected to secondary data separation is three-dimensionally drafted to generate a three-dimensional funnel costal cartilage model; the three-dimensional funnel costal cartilage model is subjected to Gaussian smooth processing, and the model of the thoracic hard bone part of the funnel chest of the child and the three-dimensional costal cartilage model are overlapped to obtain an integral three-dimensional model of the funnel chest of the child. The region search method is adopted to process cartilages at the positions where with hard bones are combined, and the region growing method is adopted to solve the problem that a CT image of the cartilages is invisible, so the created three-dimensional model ensures that costal cartilages are not adhered to each other and each costal cartilage is round and smooth, and has high simulation degree.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Adult simulation thorax structure
The invention discloses an adult simulation thorax structure. The adult simulation thorax structure is characterized in that the shape of a thorax and the size of each internal part refer to 50-percentile shape parameters of a Chinese adult body; the thorax is provided with a rigid manubrium, flexible rib cartilages, resilient ribs, a rigid xiphoid process structure and a spine; the thorax adopts an integral suspended structure and is completely made based on thorax dissection data of a real human body, characteristics of structural bionics and mechanic equivalent are realized through combination of different materials, and a support can be provided for a simulation research on the real human body in various experiments and teaching in need of testing human body stress.
Owner:SICHUAN LINSHENG HIGH TECH CO LTD
Individualized sternum prosthesis with computer-aided design and manufacturing method
PendingCN107307925AThe postoperative range of motion of the upper limbs was preserved due to the design of micro-movement factorsThe problem of limited range of motion of the upper limbs after surgery caused by the design of fretting factors is retainedBone implantJoint implantsPatient needAnatomical structures
The invention relates to an individualized sternum prosthesis with computer-aided design and a manufacturing method. The method comprises the steps of collecting CT data of the chest of a patient, and establishing a three-dimensional chest model; measuring parameters of the sternum of the patient; utilizing modeling software to design the shape of manubrium of the prosthesis with the shape of biological manubrium as a reference; designing a plurality of hole channels at the connection edges of the clavicles and the ribs on the manubrium of the prosthesis; designing the size of the part, inserted in the cavity of the sternum, of the sternum prosthesis according to the size of the inner cavity of the sternum of the patient, wherein the sternum part of the prosthesis is vertically provided with hole channels, the diameter of the hole channels is 5-6 mm, the top end of the sternum of the patient needs to be excised 10-12 mm before the sternum prosthesis is placed into the cavity of the sternum, the placement position of the sternum prosthesis is completely identical to the position of the computer-aided design, and the upper end of the sternum of the prosthesis and the connection portions of the manubrium are additionally provided with ladder-like bulges. Through the adoption of the individualized sternum prosthesis with the computer-aided design, regarding the characteristics of an anatomical structure of the chest of an individual, the accurate data measurement of the sternum of the patient are achieved, the thoracic structure of the patient is perfectly matched, and the problem that the movement range of the upper limbs of the patient is limited is solved through ligament connection.
Owner:TIANJIN HOSPITAL
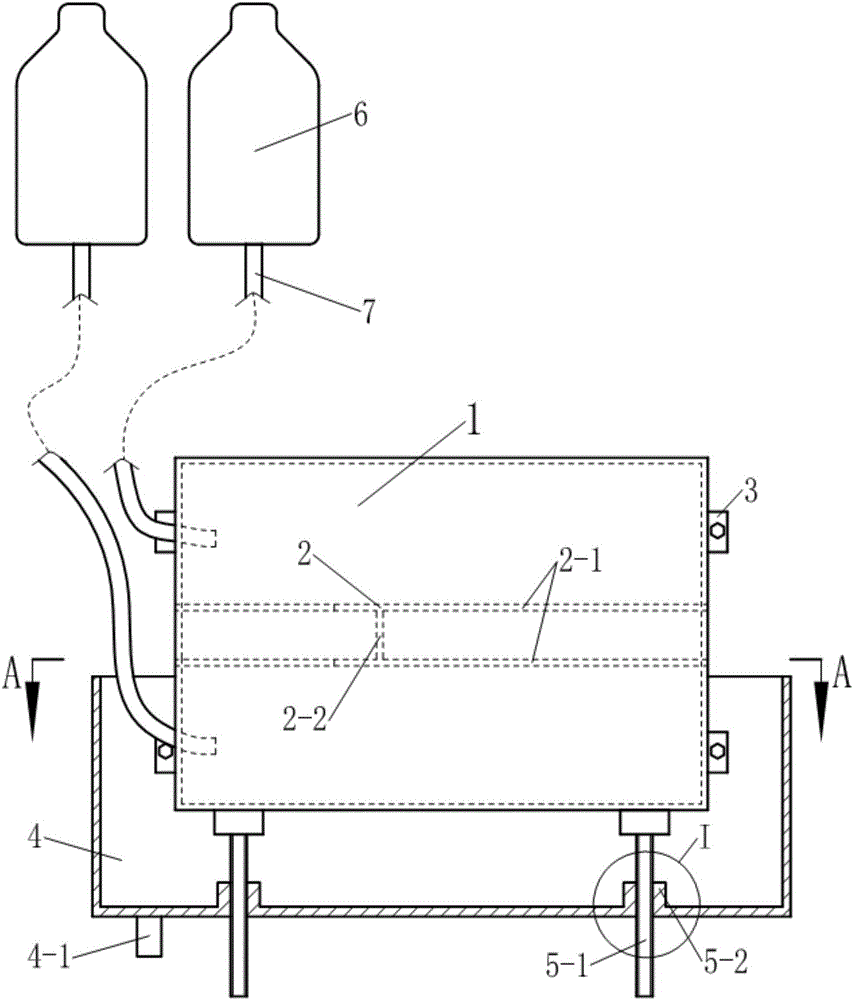
Thoracoscopic surgery simulation training box
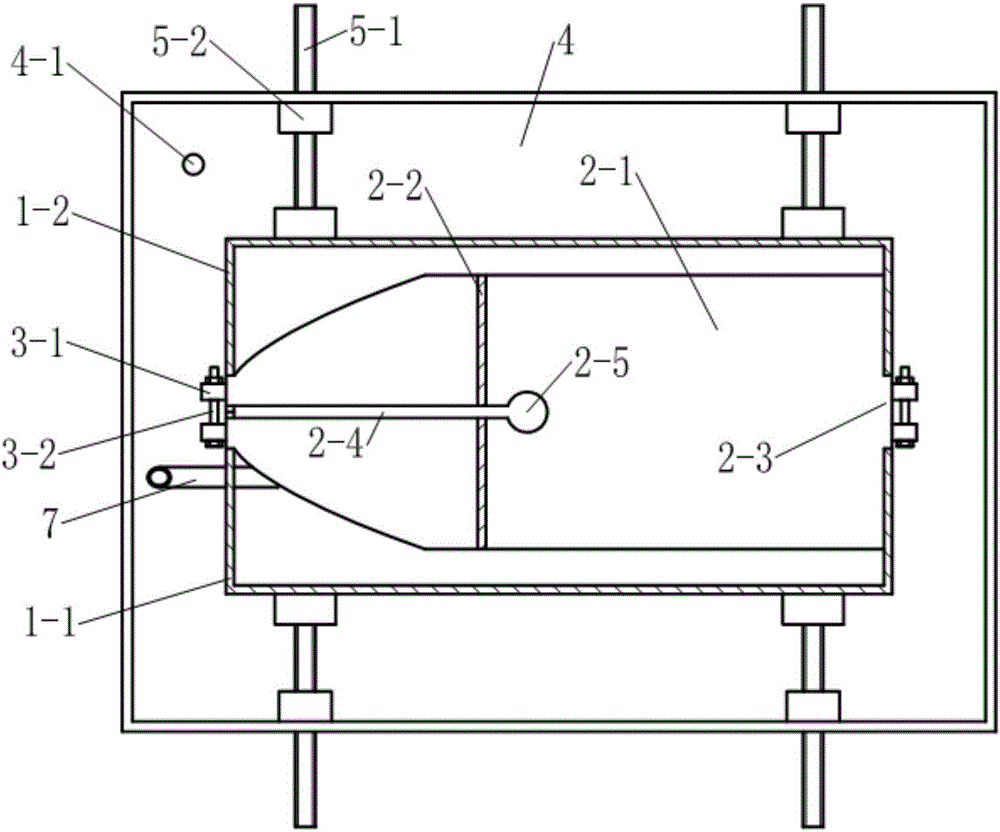
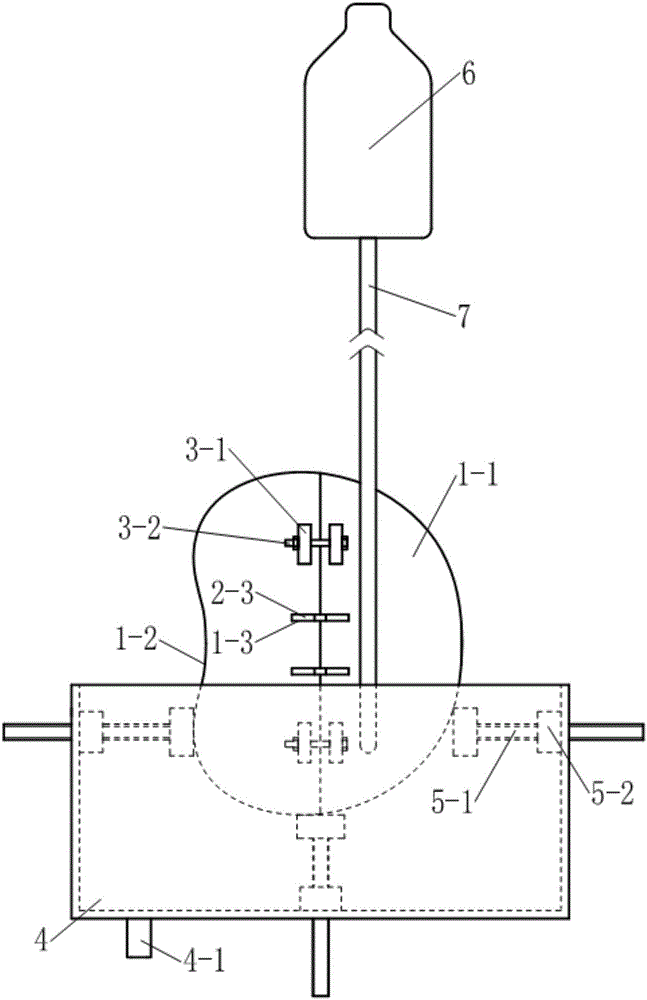
The invention discloses a medical model, in particular, a thoracoscopic surgery simulation training box. The training box comprises a thoracic cavity prosthesis. The thoracoscopic surgery simulation training box is characterized in that the thoracoscopic surgery simulation training box further comprises a blood flow simulation device and a supporting device; the cross section of the thoracic cavity prosthesis is similar to the cross section of the thorax of a human body; the thoracic cavity prosthesis is divided into a front thoracic cavity prosthesis and a rear thoracic cavity prosthesis through a plane where midaxillary lines at two sides of the thoracic cavity prosthesis are located; a mediastinum prosthesis is arranged in the thoracic cavity prosthesis; the mediastinum prosthesis is composed of mediastinum plates located at two sides of the median sagittal plane of the thoracic cavity prosthesis and a connecting plate connected with the two mediastinum plates; the blood flow simulation device is composed of two perfusion bottles and two perfusion catheters of the thoracic cavity prosthesis; the supporting device includes a cuboid supporting box of which the top is open and supporting push rods which are located at the two sides and bottom of the supporting box; and the bottom of the supporting box is provided with a perfusion liquid recovery opening; the supporting push rod is composed of a push rod seat fixed on the box body and a push rod which passes through the push rod seat and is supported on the thoracic cavity prosthesis, wherein the push rod is in threaded connection with the push rod seat.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Postoperative rehabilitation training device for patients in thoracic surgery department
The invention belongs to the technical field of a rehabilitation training device, in particular to a postoperative rehabilitation training device for patients in thoracic surgery department. The device comprises a bottom table and a side plate welded in a position of one side of the upper surface of the bottom table, wherein a position, near the side plate, of the upper surface of the bottom tableis fixedly connected with an air pump through a screw bolt; the output end of the air pump is connected with a seat table in a screwing way through screw threads. In the use process, the patient sitson the seat table and leans in the direction towards a first cotton back plate; in the process, the position of the back part of the thoracic cavity of the patient is in contact with the rotating plate at one end of the rotating plate; meanwhile, certain backward pressure is exerted onto the linkage plate; then, the two hands are put at the front lower sides of the thoracic; the air is deeply breathed in through the nose and is then slowly breathed out through the slightly opened mouth; during the deep breathing in each time, the thoracic is tried to be expanded as much as possible; certain thrust is provided for the thoracic cavity air lifting expansion process under the elasticity effect of the second spring between one side of the linkage plate and the slide block, so that the breathing training is efficiently performed.
Owner:HENAN CANCER HOSPITAL
Model for demonstrating pulmonary ventilation disfunction
InactiveCN102750859ASimple structureIntuitive imageEducational modelsLongissimus ThoracisThoracic cavity
The invention discloses a model for demonstrating pulmonary ventilation disfunction and relates to a pathophysiology training aid. The model for demonstrating pulmonary ventilation disfunction comprises a thorax model, a thoracic central airway model, an intrathoracic central airway model, a thoracic cavity model, a pulmonary alveoli model, a diaphragm muscle model, airway foreign body models, a pulmonary atelectasis model, a pleural effusion model, an aerothorax model and a diaphragm muscle model, wherein the thoracic central airway model is positioned outside the thorax model, the intrathoracic central airway model and the pulmonary alveoli model are positioned in the thorax model, the intrathoracic central airway model is downwards divided into a left bronchus and a right bronchus which are respectively communicated with the pulmonary alveoli model, the thoracic central airway model and the intrathoracic central airway model are provided with the airway foreign body models, and the pleural effusion model and the aerothorax model are arranged between the pulmonary atelectasis model and the thorax model. The diaphragm muscle model is an elastic film. The model disclosed by the invention can be used for visually and vividly demonstrating the influence of obstructive hypoventilation and restrictive hypoventilation on respiratory failure.
Owner:关真民
Method for coronary artery bypass
InactiveUS7219671B2Easy to harvestBronchoscopesLaryngoscopesOff-pump coronary artery bypassArterial blood supply
The invention comprises a method for performing a coronary artery bypass graft on a beating heart under thoracoscopic visualization without opening the chest wall. At least one small opening is formed in the patient's chest, a target artery for an arterial blood supply is located, instruments are introduced through one or more small openings formed in the patient's chest to prepare the target artery for fluid connection to the coronary artery, and instruments are introduced through one or more small openings formed in the patient's chest to connect the target artery to the coronary artery distal from a stenosis. In a preferred embodiment, a minimal left anterior intercostal thoracotomy provides access to form an anastomosis between the left internal mammary artery (LIMA) and the left anterior descending artery (LAD) while thoracoscopic viewing facilitates harvesting the LIMA. In other embodiments, access to the patient's heart may be obtained through a trocar sheath or other means for providing percutaneous access to the patient's thoracic cavity without opening the chest wall. Thoracoscopic visualization, depending on the procedure, is used to locate the arterial blood supply, the location of the coronary artery to be bypassed and the location of the occlusion in the artery. In other embodiments, the diagonal (Dx) or circumflex (Cx) arteries may be bypassed.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
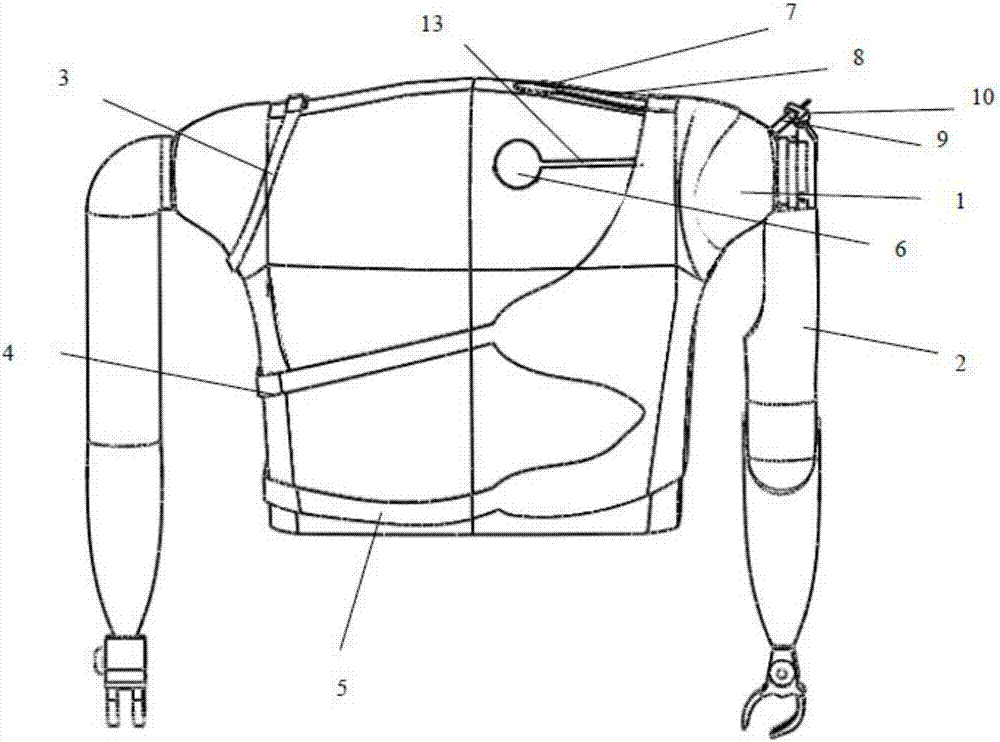
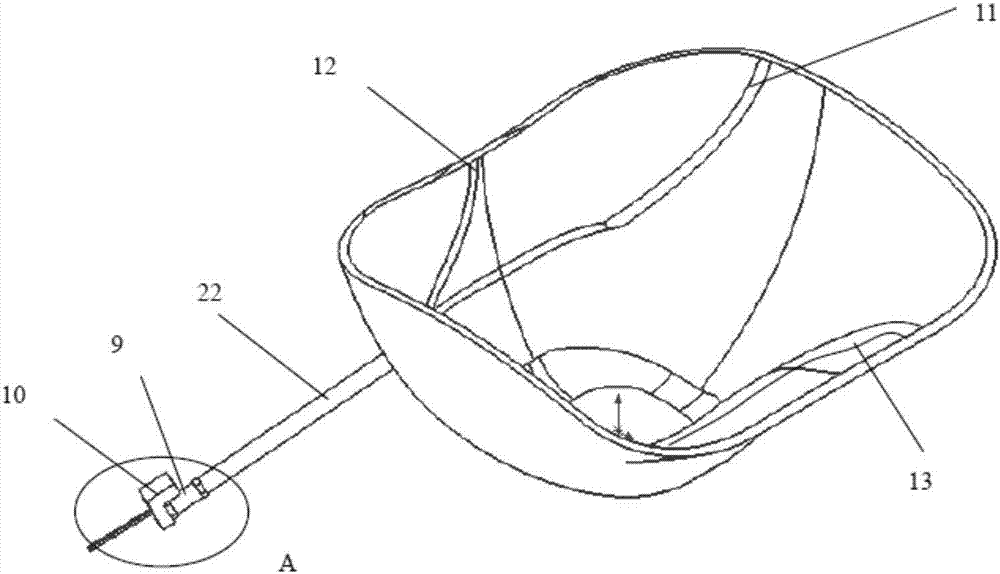
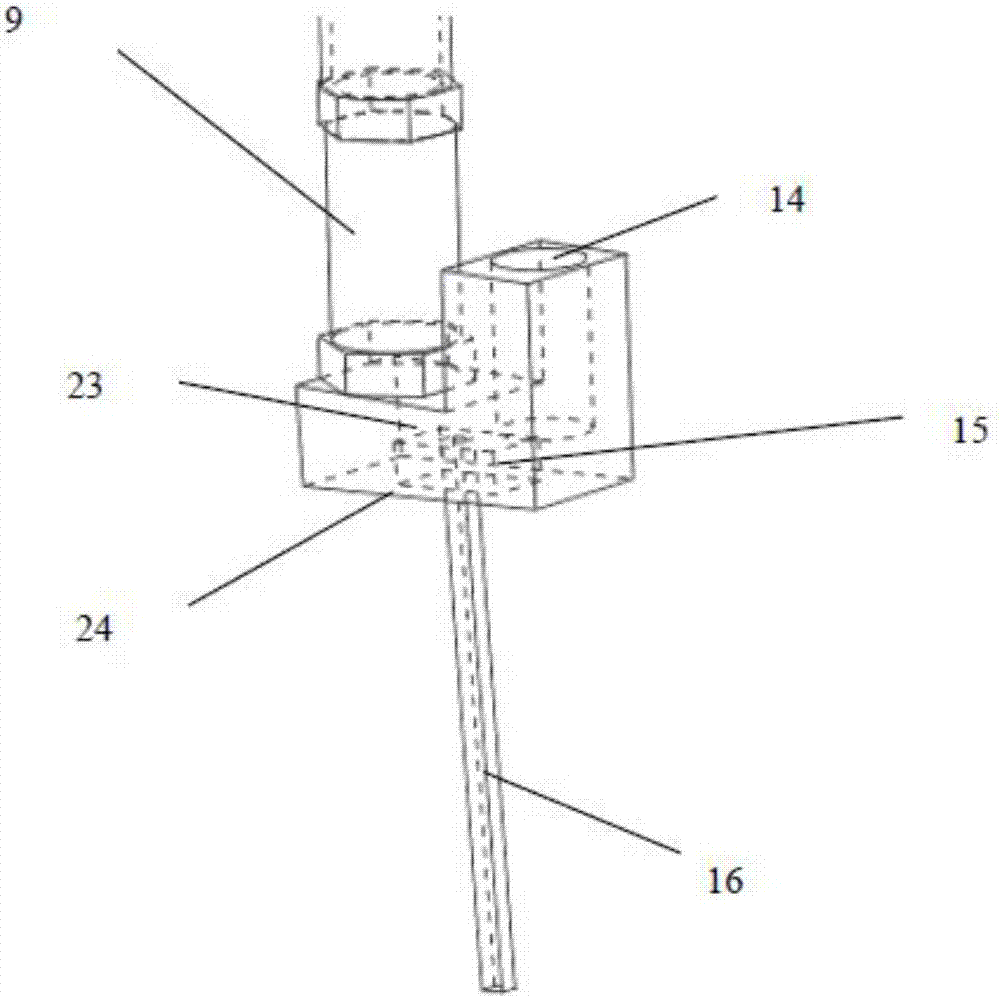
Fixing device for upper limb prosthesis
The invention relates to a fixing device for an upper limb prosthesis, used for fixing the upper limb prosthesis to a human body residual limb. The fixing device for the upper limb prosthesis comprises a prosthetic socket, a decompression pectoral girdle used for fixing the prosthetic socket and a socket fastener used for fastening the prosthetic socket on a human body, wherein the prosthetic socket is in a shape of rectangular cover body, can sleeve the human body residual limb and can be in tight contact to the human body residual limb; the decompression pectoral girdle is composed of an axilla decompression pectoral girdle, a thorax decompression pectoral girdle and a waist decompression pectoral girdle; the upper limb prosthesis can be detachably connected with the prosthetic socket; an opening end of the prosthetic socket is tightly connected with a human body residual limb end; and the axilla decompression pectoral girdle, the thorax decompression pectoral girdle and the waist decompression pectoral girdle are all connected with the prosthetic socket and can pass through an axilla, a thorax and a waist of the human body respectively to be connected with the front side and the back side of the prosthetic socket. According to the fixing device for the upper limb prosthesis, the prosthesis can be accurately fixed on the residual limb, so that the upper limb prosthesis is easily worn and taken off.
Owner:国家康复辅具研究中心
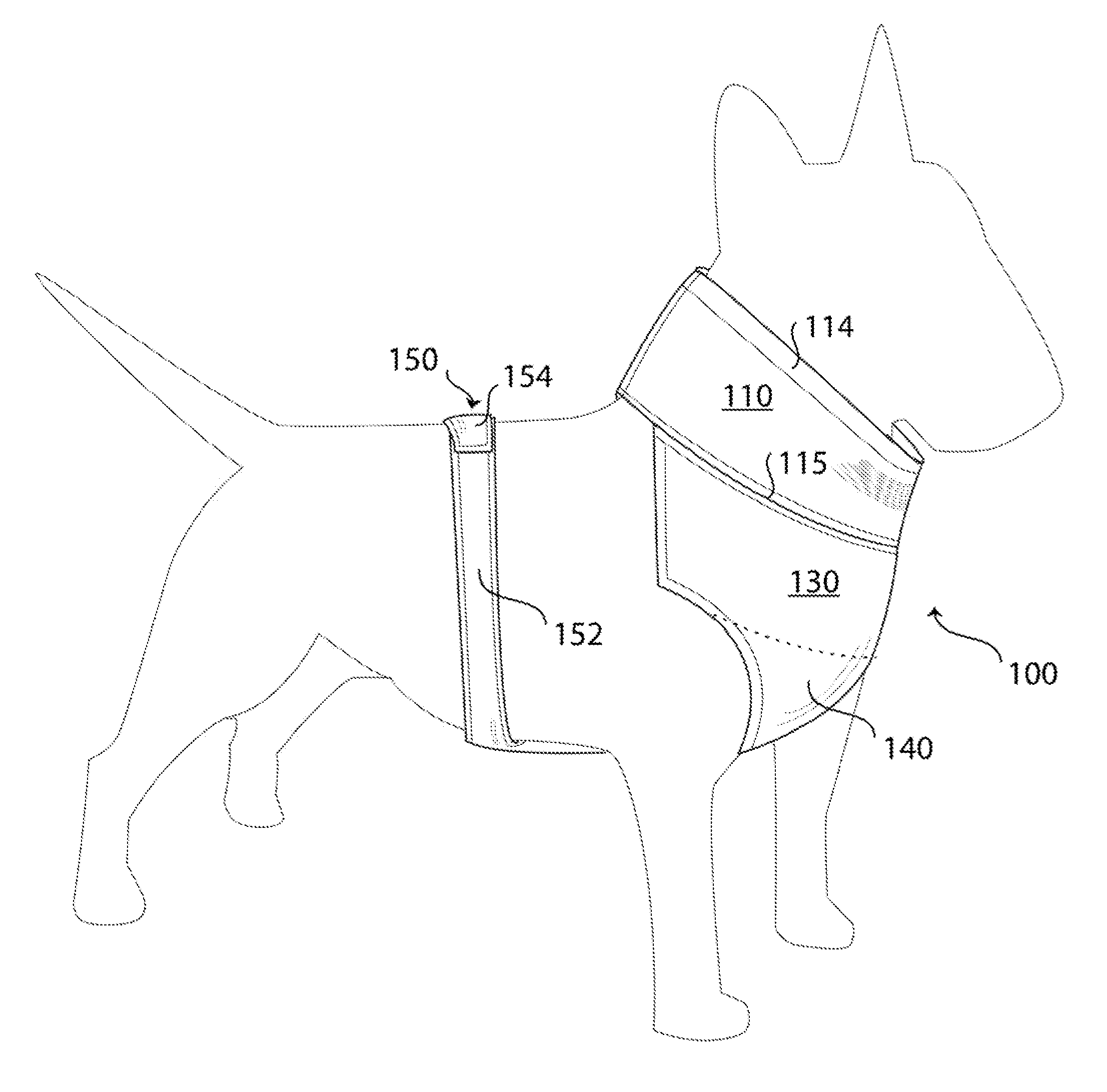
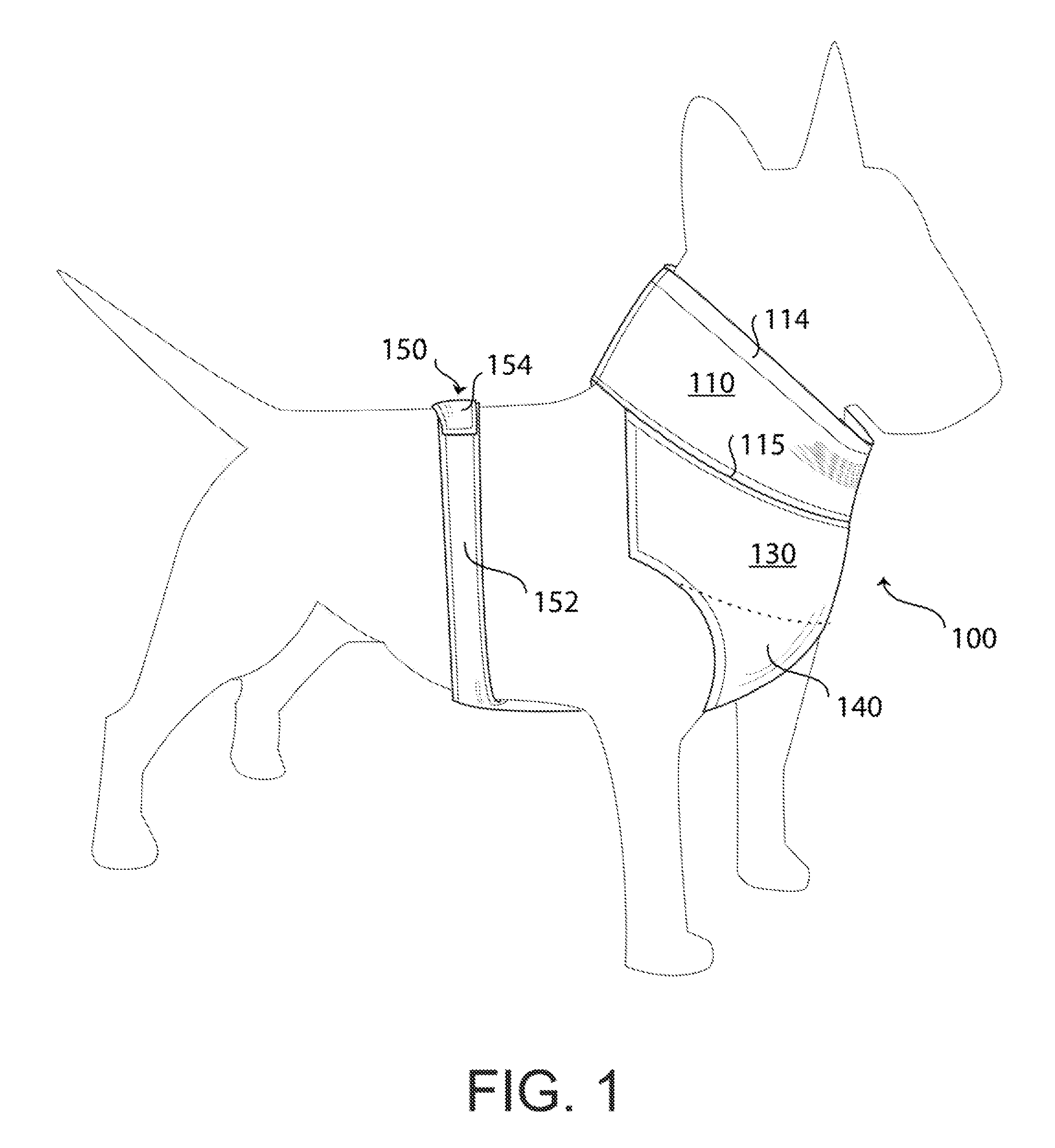
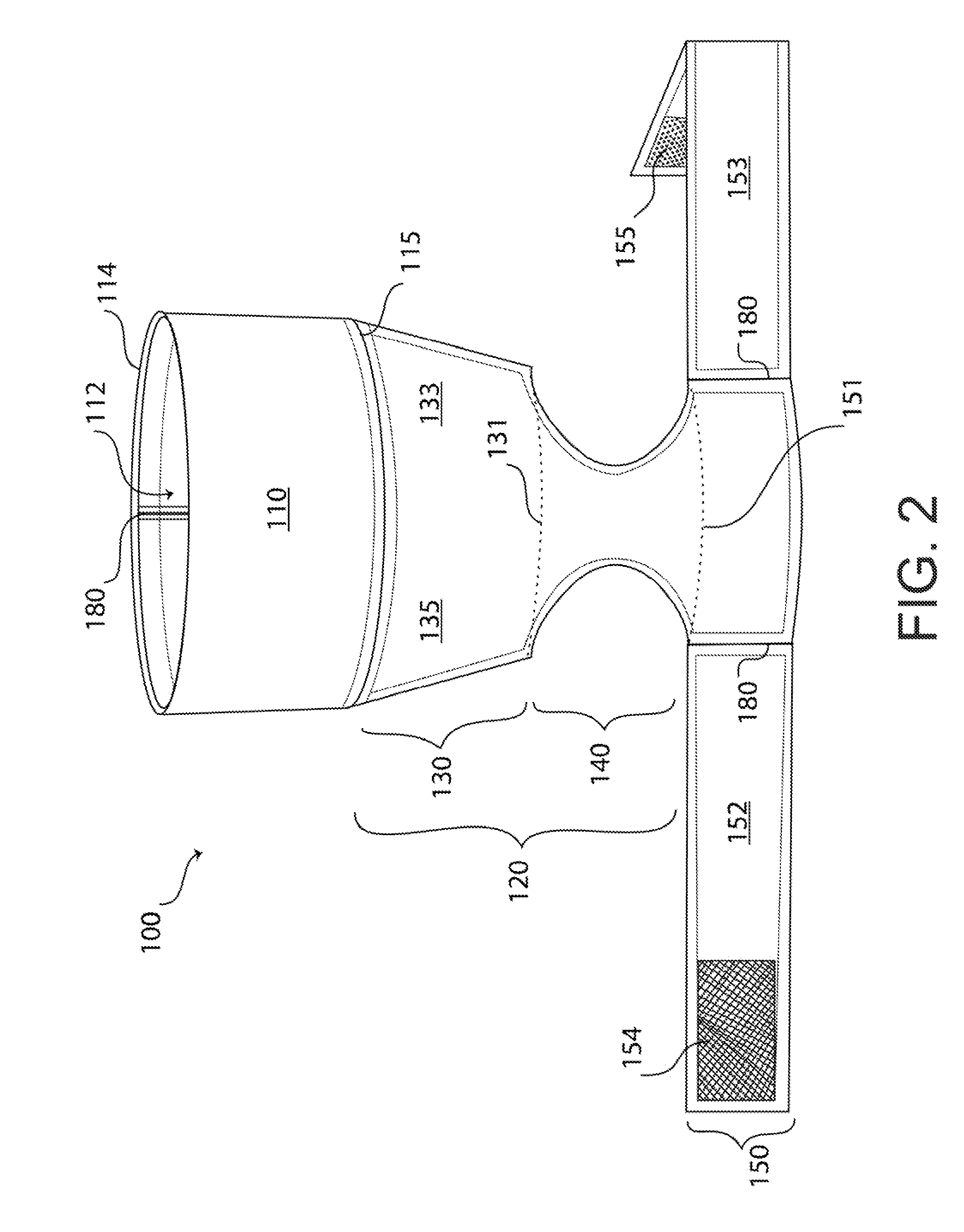
Dog Garment
InactiveUS20140230754A1Easy to fixEasy to disassembleGrooming devicesLongissimus ThoracisCanis lupus familiaris
A dog garment for retaining body heat comprises a tubular neck portion for slipping over a dog's head, a torso portion and an anchoring portion, each including heat-retentive material. The torso portion depends downwardly from the neck portion and extends posteriorly on the dog to an anchoring portion that surrounds the sides of a rib cage of the dog in the posterior section of the dog's rib cage. The torso portion has a chest covering and an intermediate portion situated between the chest covering and the anchoring portion. In the region on the back and sides of the dog, between the neck portion and the anchoring portion, the garment is sufficiently free of material so that the garment can be secured to the dog when the dog is wearing a typical harness without interfering with operation of the harness.
Owner:MCGRAW LINDSEY J
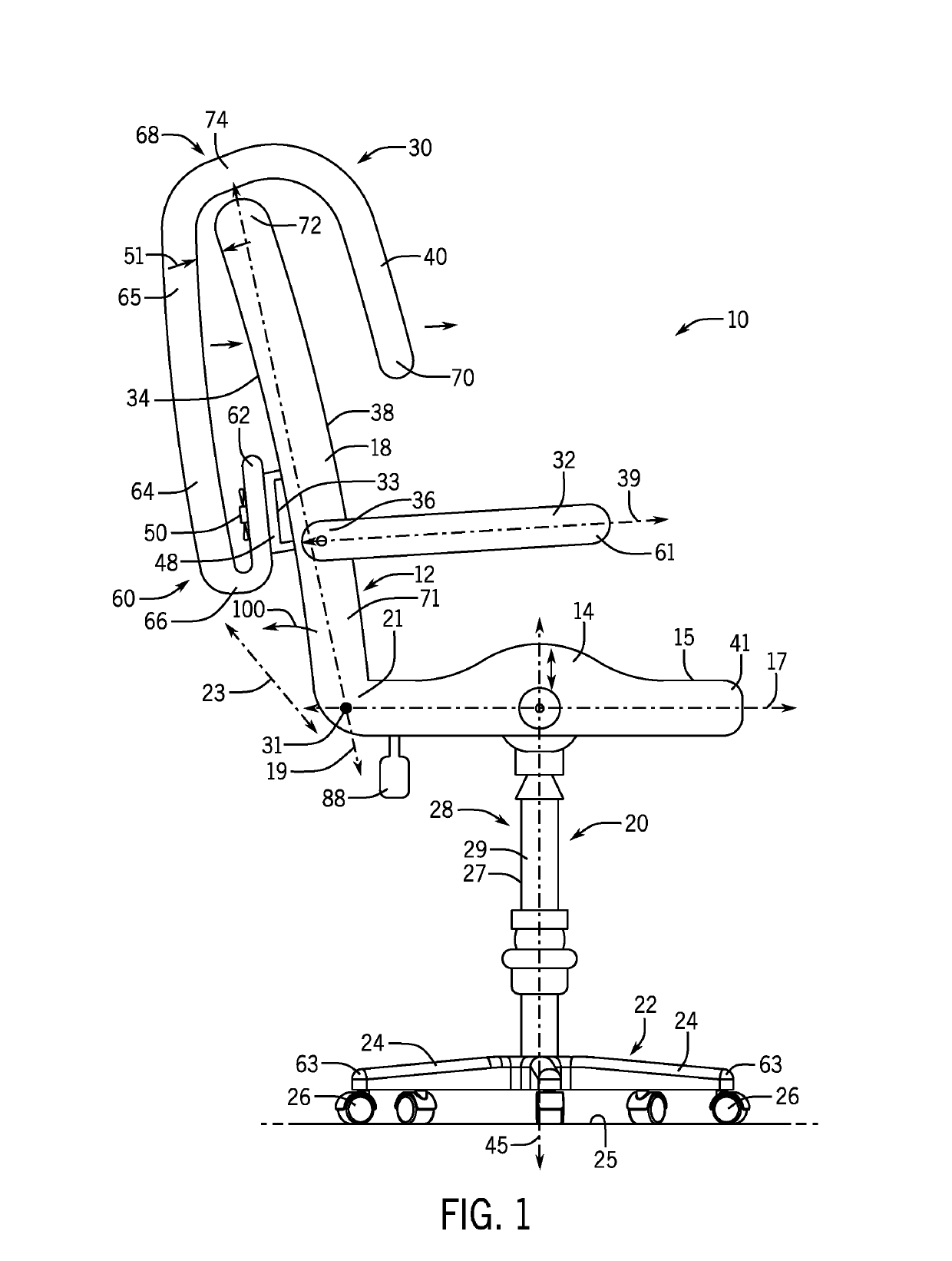
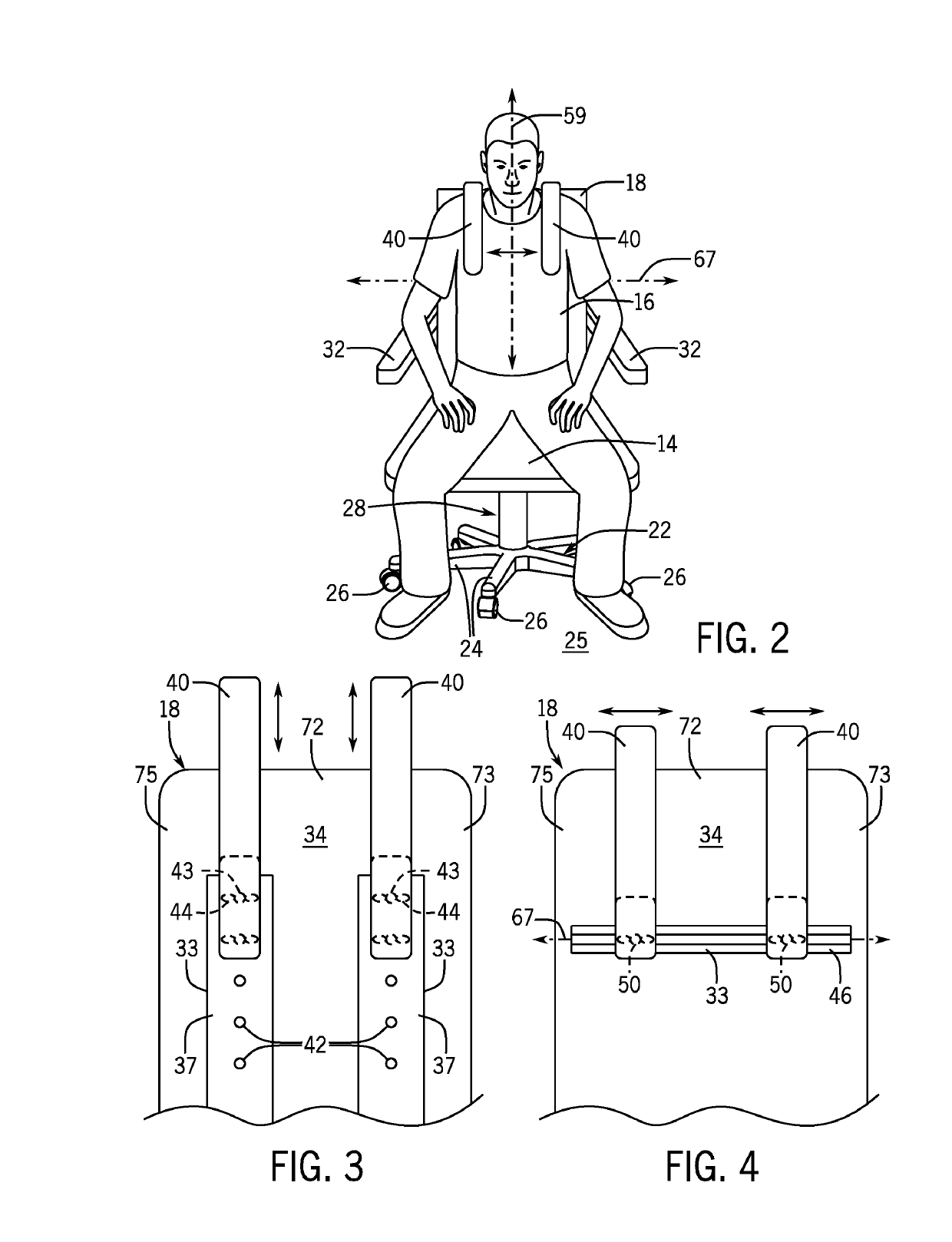
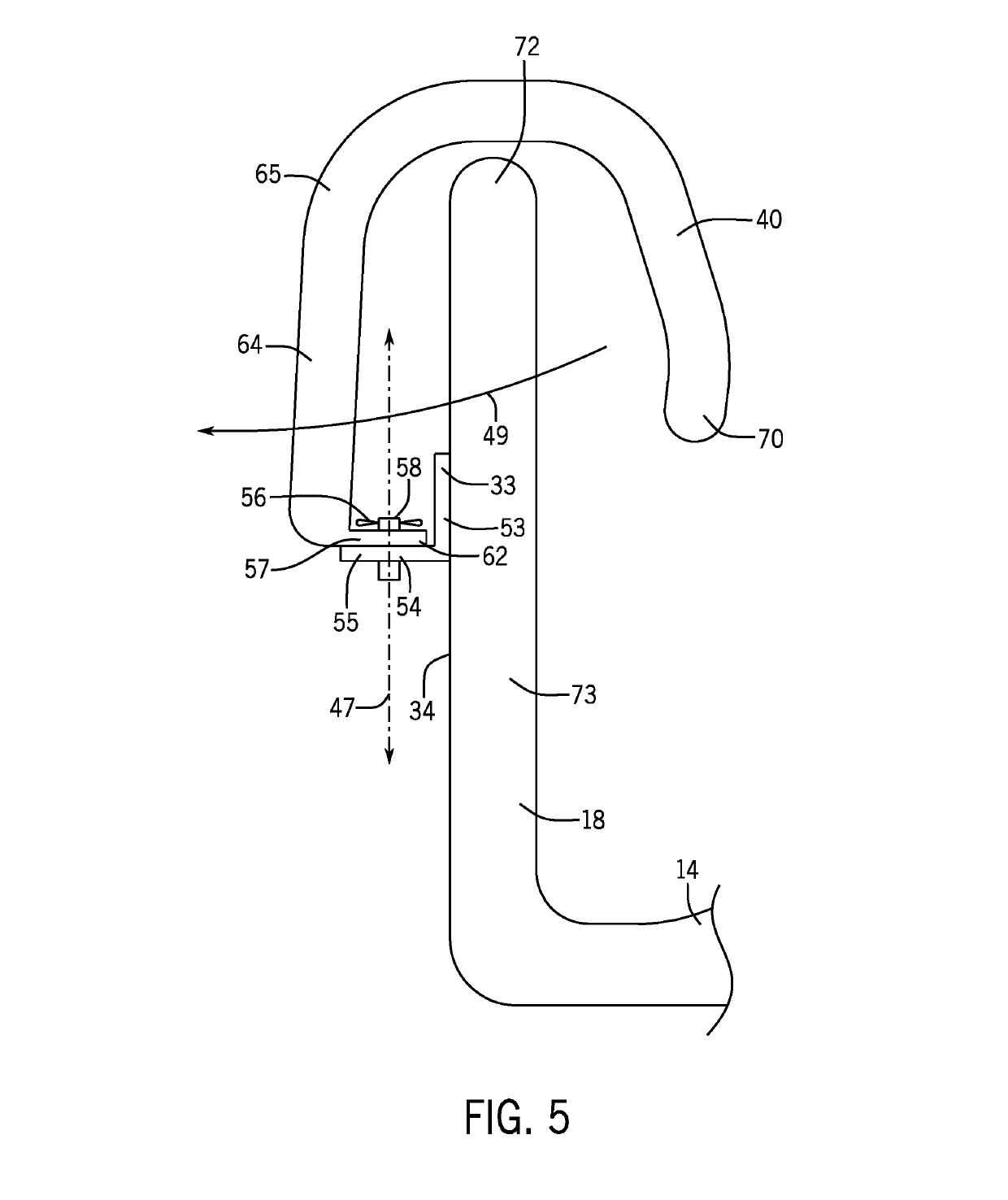
Ergonomically Configured Muscle Release Office Chair
ActiveUS20190159597A1Release muscle tensionRelease tensionStoolsMuscle exercising devicesPectoralis minor muscleScalene muscles
An office chair that is ergonomically configured to allow for the coordination of stretches to the pectoralis minor muscle, trapezius muscle, and scalene muscles to open up the thoracic outlet, release muscle tension, and reinforce proper structure is provided. The stretches may be performed by an average human user while sitting in the office chair throughout the workday. The ergonomically configured chair assembly may have a brace supported by the seatback and extending downwardly therefrom over a left and right shoulder of the seated average human in a cantilevered fashion and an arm restraining device positioned rearward with respect to the rear face of the upstanding seat back.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Method for coronary artery bypass
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
Stabilizing and Mobility-Enhancing Brace for the Shoulder Joint
A stabilizing and mobility-enhancing brace for the shoulder joint is a device for providing structural support to the user's shoulder joint while allowing a degree of mobility for the user's shoulder and the user's arm. The device includes a shoulder joint brace for providing stability to the shoulder as well as an elbow brace for providing stability to the arm. The elbow brace is connected to the shoulder joint brace through a mobility strap and a deltoid connector strap that enable movement of the user's arm. The mobility strap is engaged through a strap groove on the shoulder joint brace and is able to slide over a roller assembly within the strap groove. The shoulder joint brace is also secured to a lateral thoracic brace worn on the user's body via a torso strap assembly. The elbow brace is fastened in place via a plurality of elbow securing straps.
Owner:PAPPADY ROJAN JOHN
Method to evaluate patients for thoracic outlet syndrome
ActiveUS8965481B1Accurate assessmentMedical imagingDiagnostic recording/measuringLongissimus ThoracisMR - Magnetic resonance
Improvements in magnetic resonance imaging methods to obtain three-dimensional models and diagnoses of Thoracic Outlet Syndrome are described.
Owner:VANGUARD SPECIALTY IMAGING
Metal Sternal Frame Device
ActiveCN106109057BEffective protectionEase the pain of oppressionBone implantBreathing problemsThoracic structure
The invention discloses a metal breastbone skeleton device, and especially suits the chest wall defection and clavicle defection conditions caused by tumor operation; the metal breastbone skeleton device mainly comprises a metal breastbone skeleton; the metal breastbone skeleton comprises an artificial breastbone main part and a rib grasp part moulded in one piece; the artificial breastbone main part comprises an artificial breastbone handle and an artificial breastbone body; the rib grasp part and the artificial breastbone body are integrated; the metal breastbone skeleton device is characterized by also comprising clavicle connectors and movable connecting nails; in application, the bottom of the clavicle connector is movably connected with the artificial breastbone handle through the movable connecting nails; the top of the clavicle connector is provided with a connecting portion used for connecting with a clavicle nub end. The metal breastbone skeleton and the clavicle connectors are respectively made of pure titanium material; the artificial breastbone skeleton is simple in structure, can replace the original ribcage, can friendly coexist with internal residual breastbones, thus effectively protecting thoracic cavity internal organs, and solving patient hard breathing problems.
Owner:CHANGZHOU WASTON MEDICAL APPLIANCE CO LTD
Intrathoracic cardiac compression device
InactiveCN110025470AAvoid bleedingElectrotherapyHeart stimulationLeft ventricular surfaceLongissimus Thoracis
The invention discloses an intrathoracic cardiac compression device. The intrathoracic cardiac compression device comprises a positioning plate, an air sac and a gas transporting pipe, wherein a chestwall fixing part for positioning the positioning plate on the inner side of the left side chest wall of a human body is arranged on the positioning plate; the air sac is fixed on the inner side of the positioning plate and communicates with the gas transporting pipe; and the air sac is inflated through the gas transporting pipe to expand facing a left ventricle of the heart and gradually press the surface of the left ventricle. According to the intrathoracic cardiac compression device disclosed by the invention, avoiding influencing the development of normal functions of the heart is facilitated, and when the heart normally beats, the intrathoracic cardiac compression device cannot separate from the heart; when cardiac compression is needed, the air sac is inflated through the gas transporting pipe and gradually expands, in the expanding process, the air sac is gradually close to the left ventricle to form compression on the left ventricle, after compression achieves a certain degree,the air sac is deflated through the gas transporting pipe to be contracted, in the contracting process, the air sac gradually be away from the left ventricle, then the left ventricle returns, and thecirculation is performed, so that an intrathoracic cardiac compression measure in a certain frequency is formed.
Owner:FUWAI HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI & PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE
Cervical vertebra and lumbar vertebra traction bed and using method thereof
InactiveCN109938905AMeet the needs of usePrecisely adjust the rotation angleFractureLumbar vertebraeLongissimus Thoracis
The invention relates to a cervical vertebra and lumbar vertebra traction bed and a using method thereof. The traction bed comprises a bed body, a lumbar vertebra traction device, a thorax fixing device and a cervical vertebra traction device, wherein the lumbar vertebra traction device, the thorax fixing device and the cervical vertebra traction device are sequentially arranged on the bed body, the lumbar vertebra traction device and the thorax fixing device are fixedly installed on the bed body, the cervical vertebra traction device is rotatably connected with the bed body, and the rotatingangle is adjusted under driving of a power mechanism. The cervical vertebra and lumbar vertebra traction bed simultaneously has the two functions of lumbar vertebra traction and cervical vertebra traction, lumbar vertebra traction and cervical vertebra traction can be conducted separately and simultaneously, and the using requirements of different patients are met.
Owner:贺琨
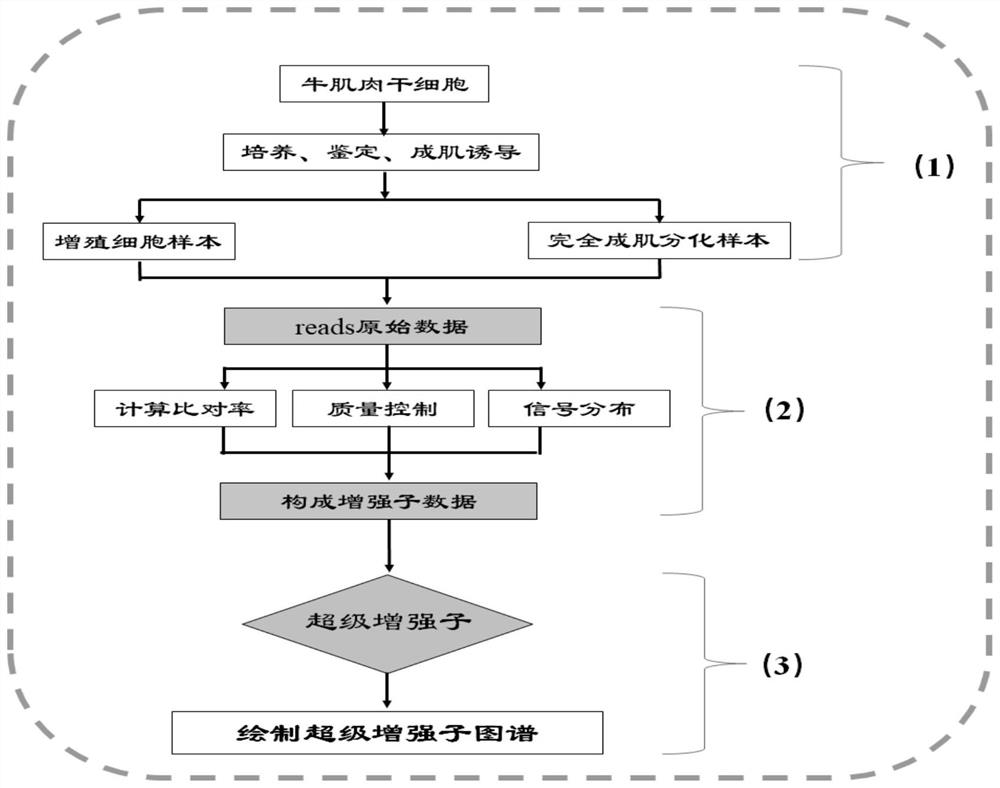
Muscle tissue extraction method for separating bovine muscle stem cells and application of muscle tissue extraction method
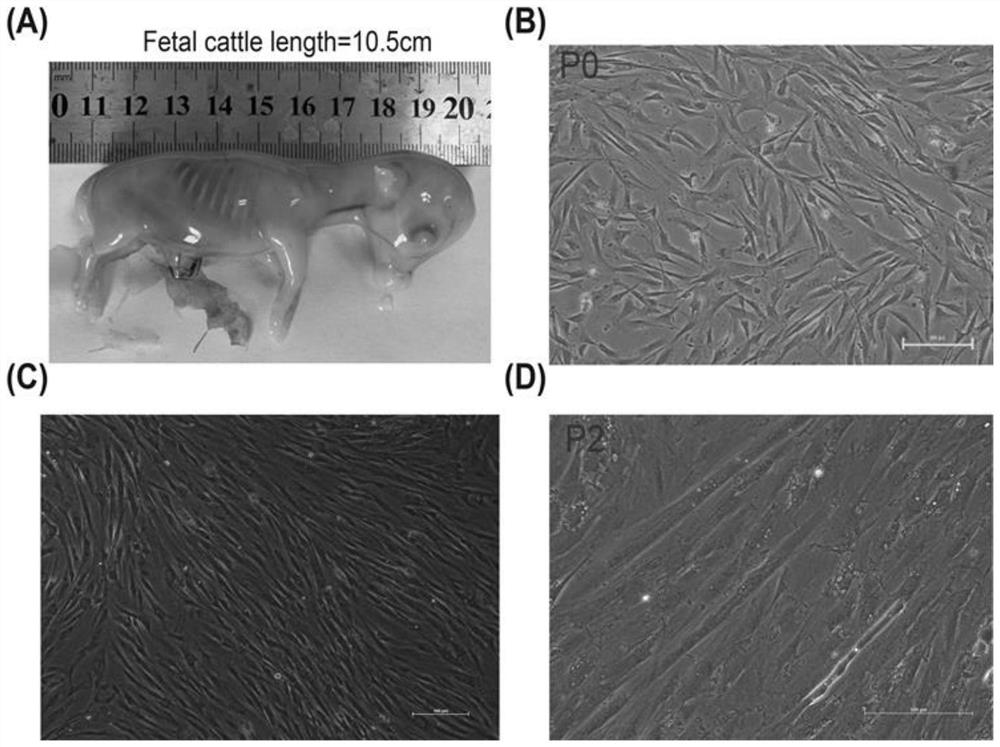
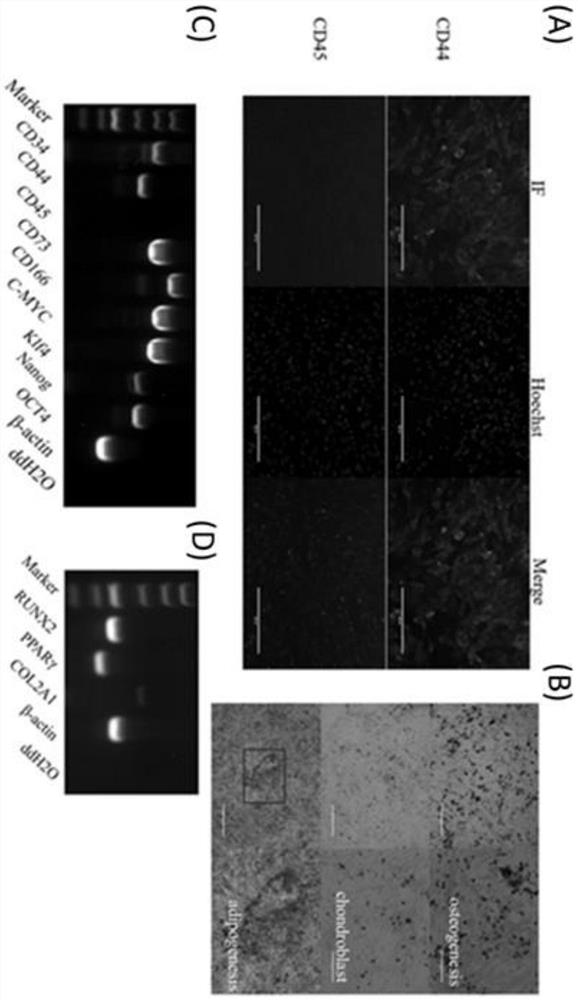
PendingCN114525249ALow costCell dissociation methodsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsMuscle tissueLongissimus
The invention belongs to the technical field of cell engineering, and particularly relates to an extraction method for separating muscle tissues of bovine muscle stem cells and application of the extraction method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) wiping the surface of cattle skin with alcohol, collecting muscular tissues of longissimus on the back of the cattle, and immediately rinsing with a phosphate buffer solution; (2) removing fascia and white film on the surface; and (3) rinsing with triple distilled water, and then rinsing with a phosphate buffer solution, alcohol and a phosphate buffer solution in sequence. The extraction method is different from the conventional method for treating by singly using a phosphate buffer solution, and the cost is reduced by combined treatment of three washing solutions. The method comprises the following steps: extracting muscle tissue, separating muscle stem cells from the extracted muscle tissue, using the muscle stem cells to construct a super enhancer, and optimizing and forming a method for analyzing the bovine muscle super enhancer by using an H3K4me1 and H3K27ac double-labeling method on the basis of chromosome co-immunoprecipitation high-throughput data basic analysis, which is different from a single labeling method in the prior art.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Three-dimensional modeling method for funnel chest of children
InactiveCN100588370CSolve invisibleImplement cartilage modelingImage analysisComputerised tomographsLongissimus ThoracisImaging data
The invention discloses a three-dimensional modeling method for the funnel chest of a child. Firstly, aiming at an original spiral CT picture of the funnel chest of the child, a region search method is adopted to model a thoracic hard bone part; a gray value of a cartilage region of a thoracic three-dimensional model is measured, and masking separation costal cartilage image data are created afterthe modification; a region growing method is adopted to apply region growing separation costal cartilage image data to a combining end of a hard bone and a cartilage of each rib; the costal cartilagedata which is subjected to secondary data separation is three-dimensionally drafted to generate a three-dimensional funnel costal cartilage model; the three-dimensional funnel costal cartilage modelis subjected to Gaussian smooth processing, and the model of the thoracic hard bone part of the funnel chest of the child and the three-dimensional costal cartilage model are overlapped to obtain an integral three-dimensional model of the funnel chest of the child. The region search method is adopted to process cartilages at the positions where with hard bones are combined, and the region growingmethod is adopted to solve the problem that a CT image of the cartilages is invisible, so the created three-dimensional model ensures that costal cartilages are not adhered to each other and each costal cartilage is round and smooth, and has high simulation degree.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Thoracic and abdominal postoperative expectoration-assisting device
ActiveCN109875738AEliminate psychological barriersRelieve painNon-surgical orthopedic devicesSuction-kneading massageLongissimus ThoracisThoracic cavity
The invention relates to a thoracic and abdominal postoperative expectoration-assisting device. The thoracic and abdominal postoperative expectoration-assisting device comprises a thoracic fixing device, an abdominal presser fixing device and a connecting bracket, the connecting bracket comprises a pair of longitudinal arms and a lateral arm, one ends of a pair of the longitudinal arms are respectively fixedly connected to two ends of the lateral arm, a middle portion of the lateral arm is fixedly connected with the abdominal presser fixing device, the abdominal presser fixing device is detachably and fixedly connected to the bottom end of an abdominal presser, the other end of the pair of the longitudinal arms is provided with fixing bolts, the thoracic fixing device is provided with a plurality of adjustment holes capable of adjusting a length, the fixing bolt passes through the adjustment hole, and a pair of the longitudinal arms are respectively fixedly connected with one of the thoracic fixing device. The expectoration-assisting device aims at the problem of expectoration difficulty in patients after thoracic and abdominal operation, and the device can fix the chest of the patient, prevents the injury of the incision and reduces the pain of the patient, effectively cleans sputum in the patient's airway, has safe and simple operation, and saves human resources.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com