Patents
Literature
737 results about "Thoracic structure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
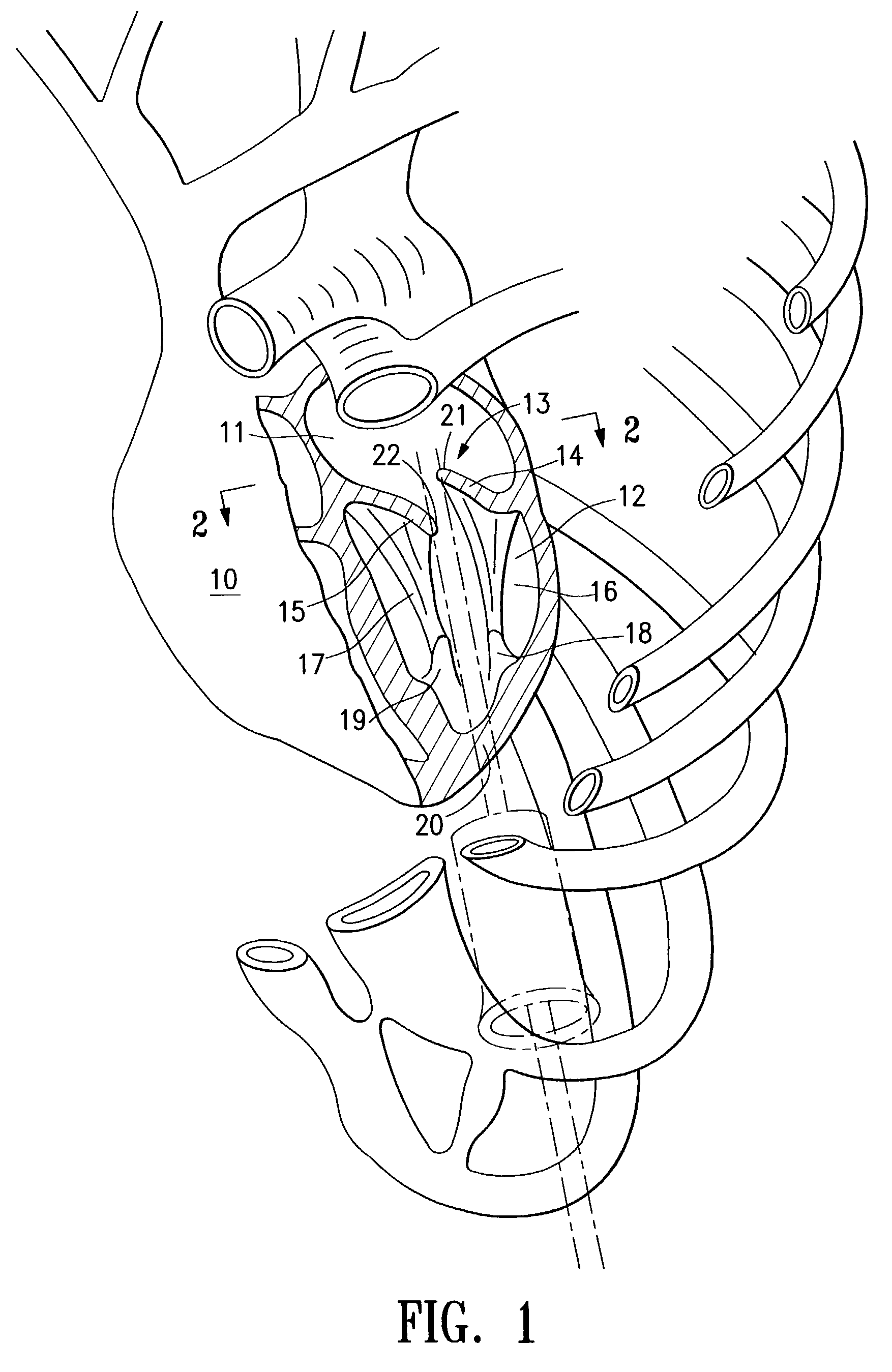
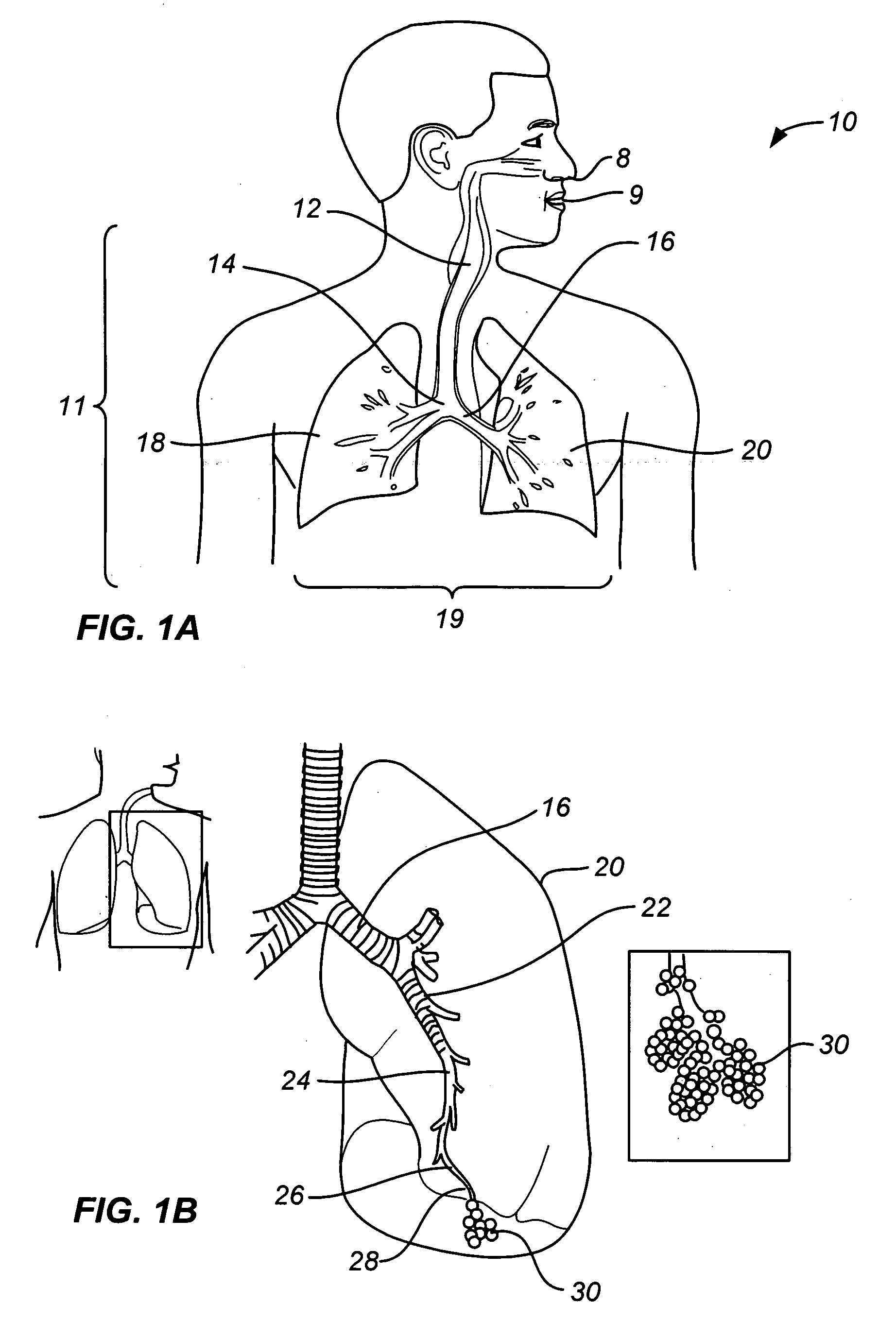
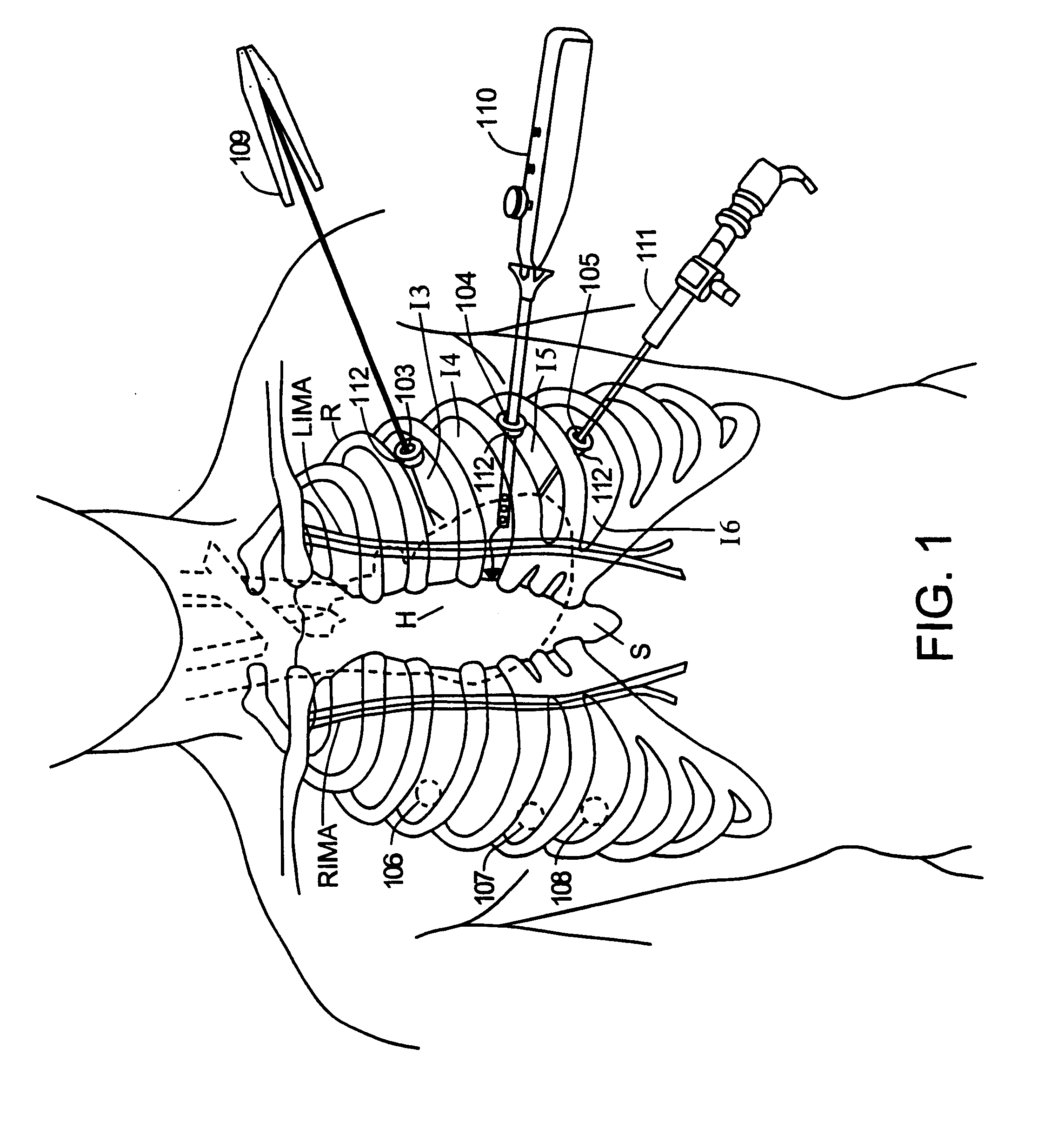
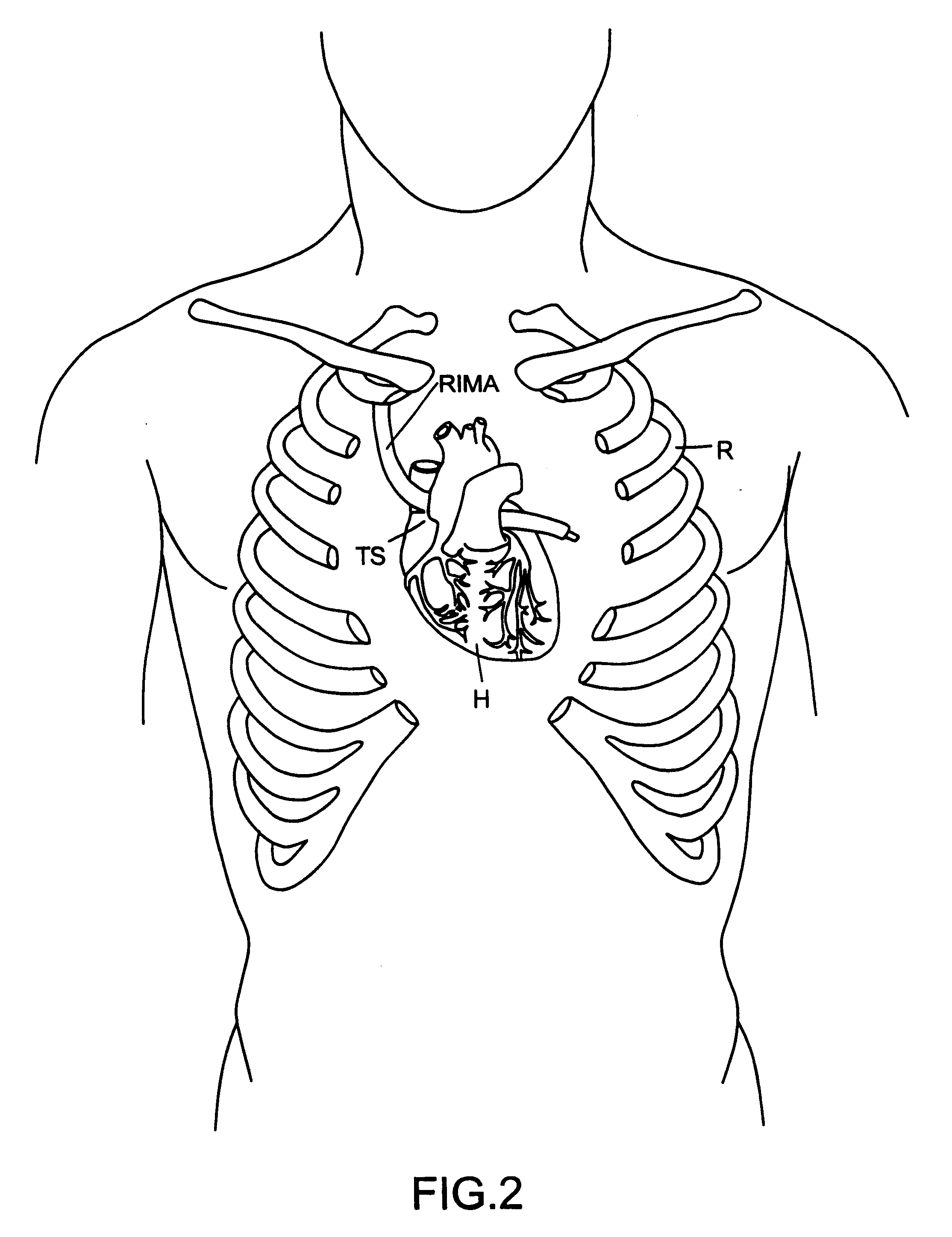
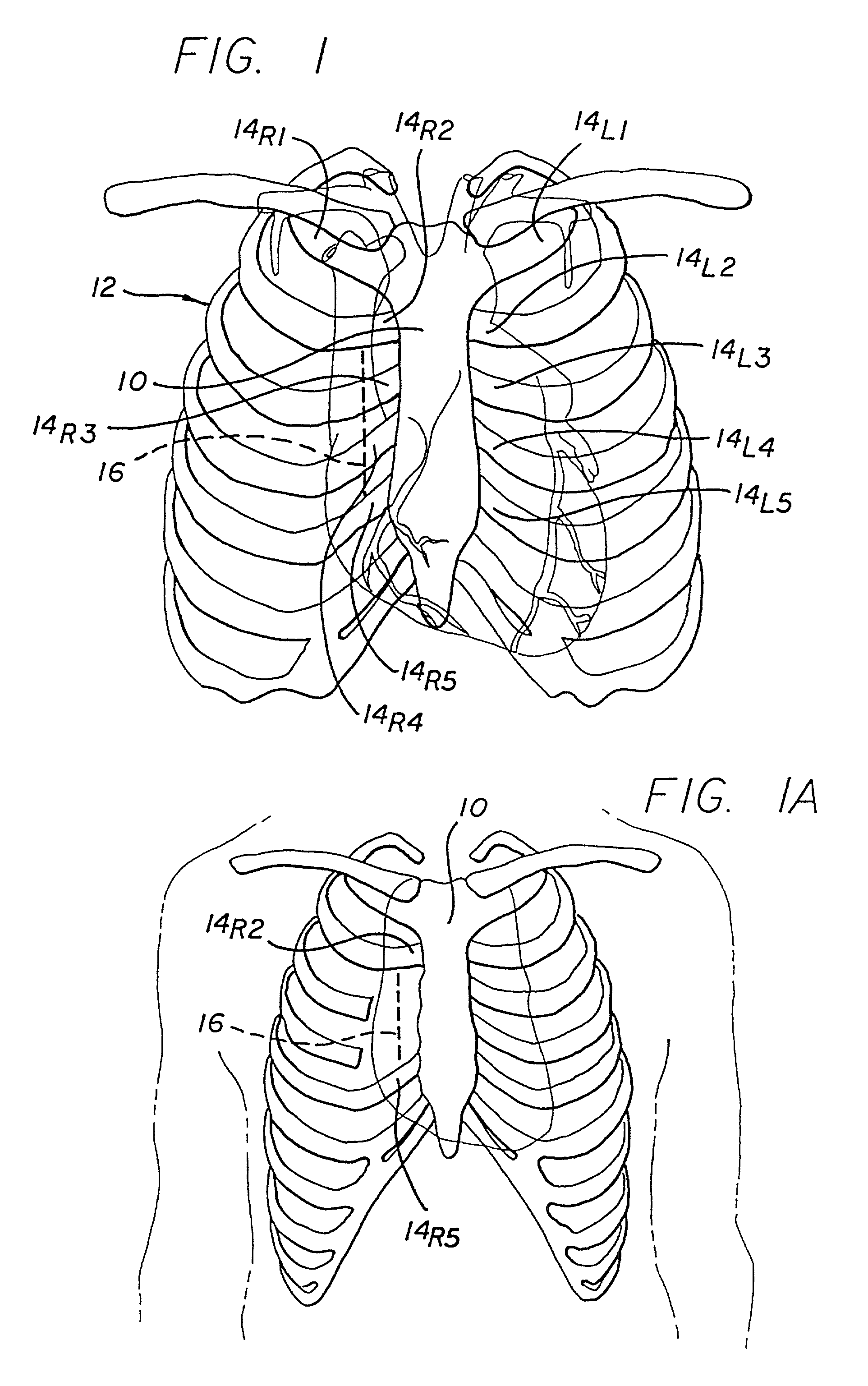
Structures within the thoracic cavity include: structures of the cardiovascular system, including the heart and great vessels, which include the thoracic aorta, the pulmonary artery and all its branches, the superior and inferior vena cava, the pulmonary veins, and the azygos vein
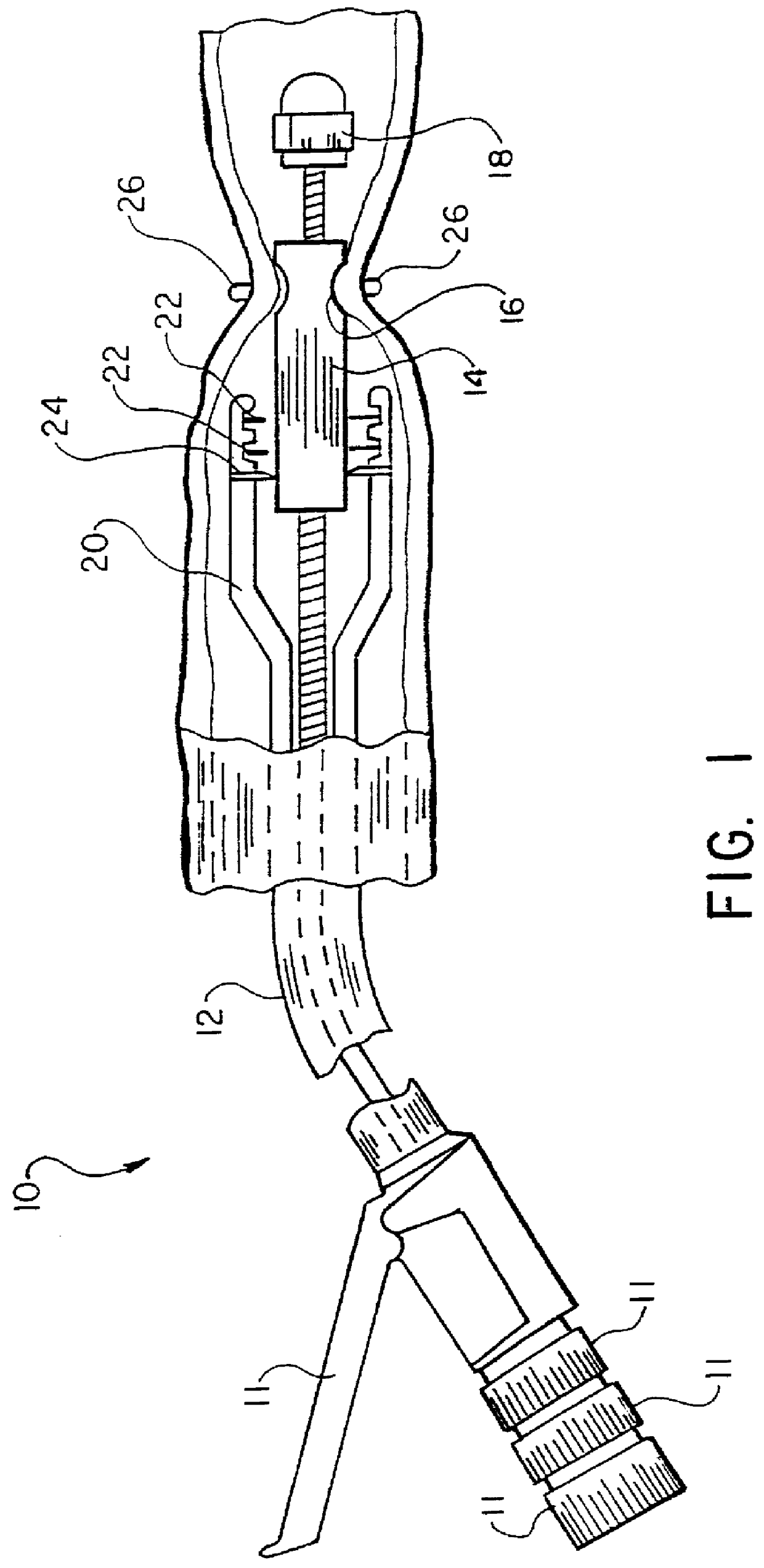
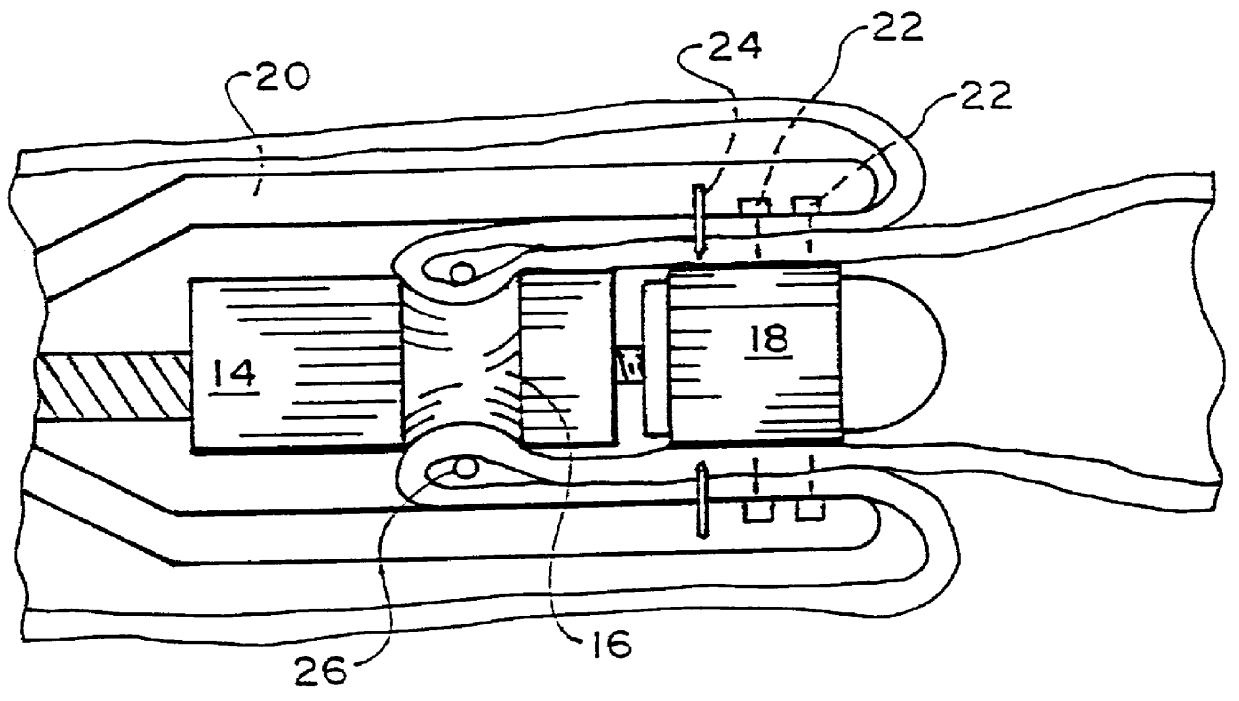
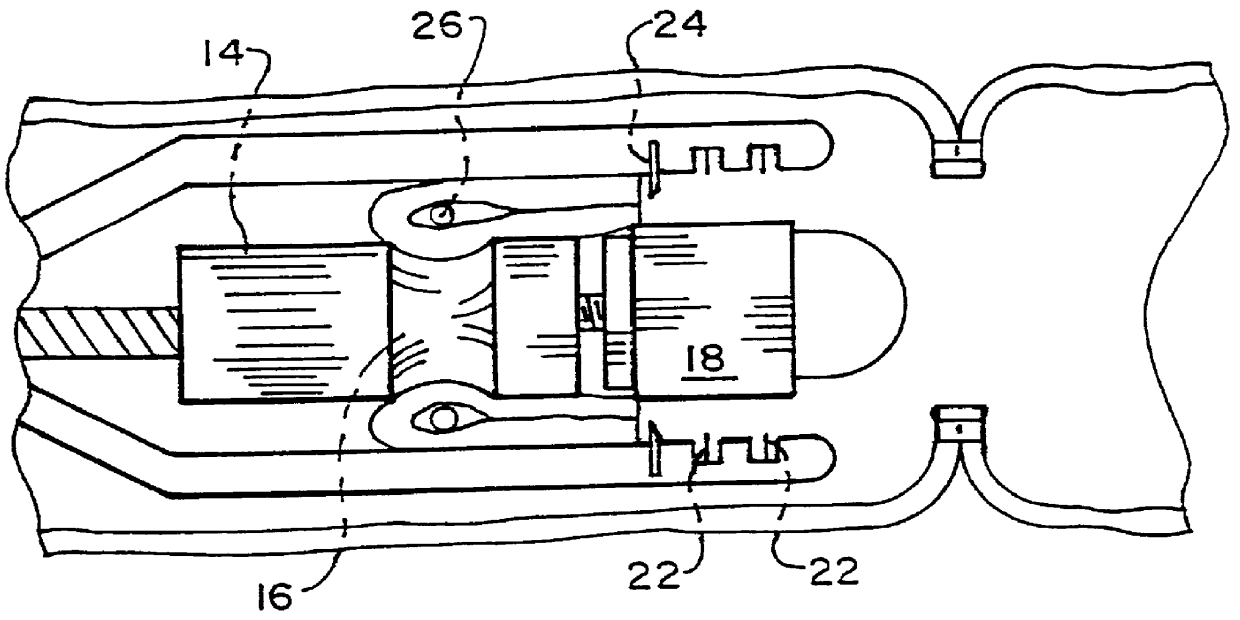
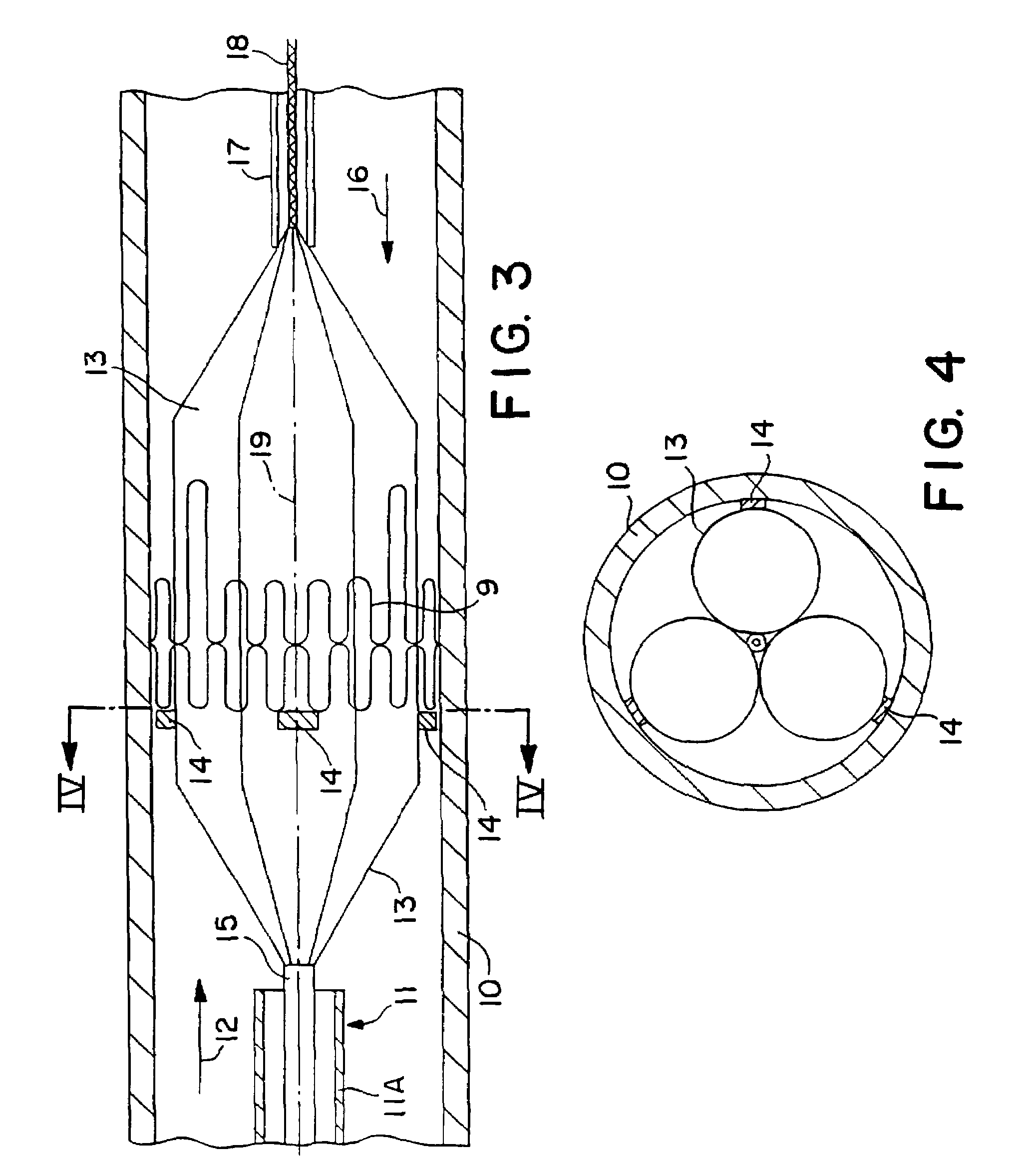
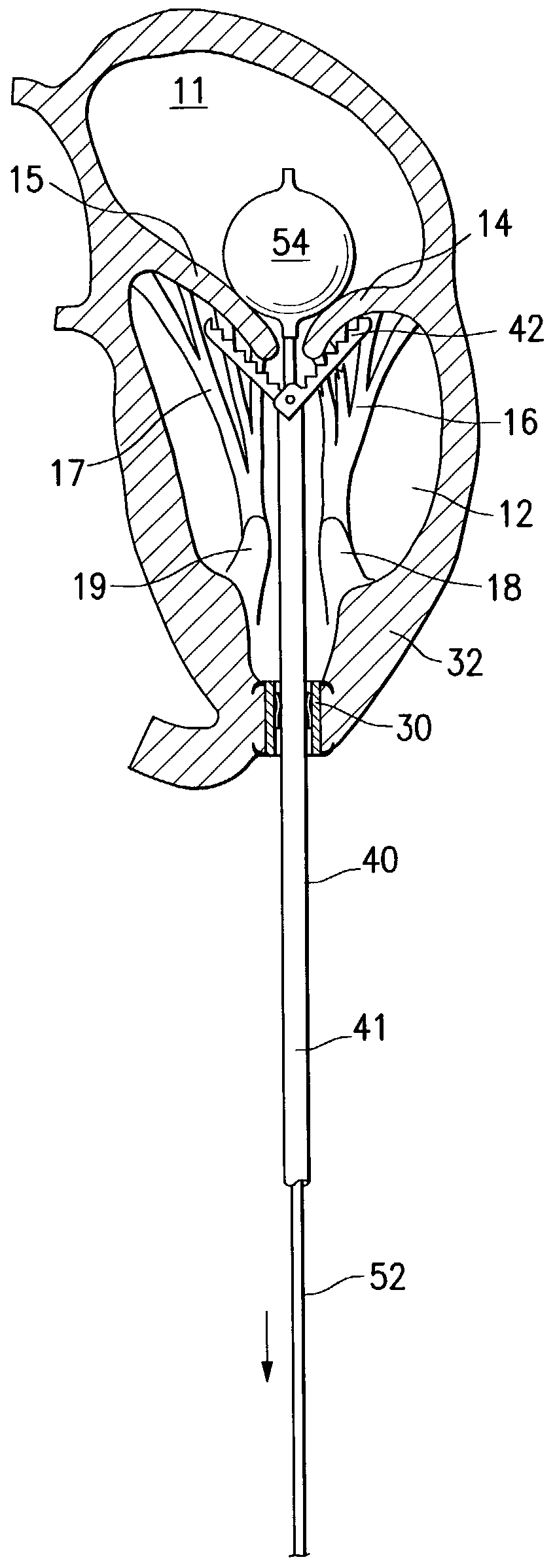
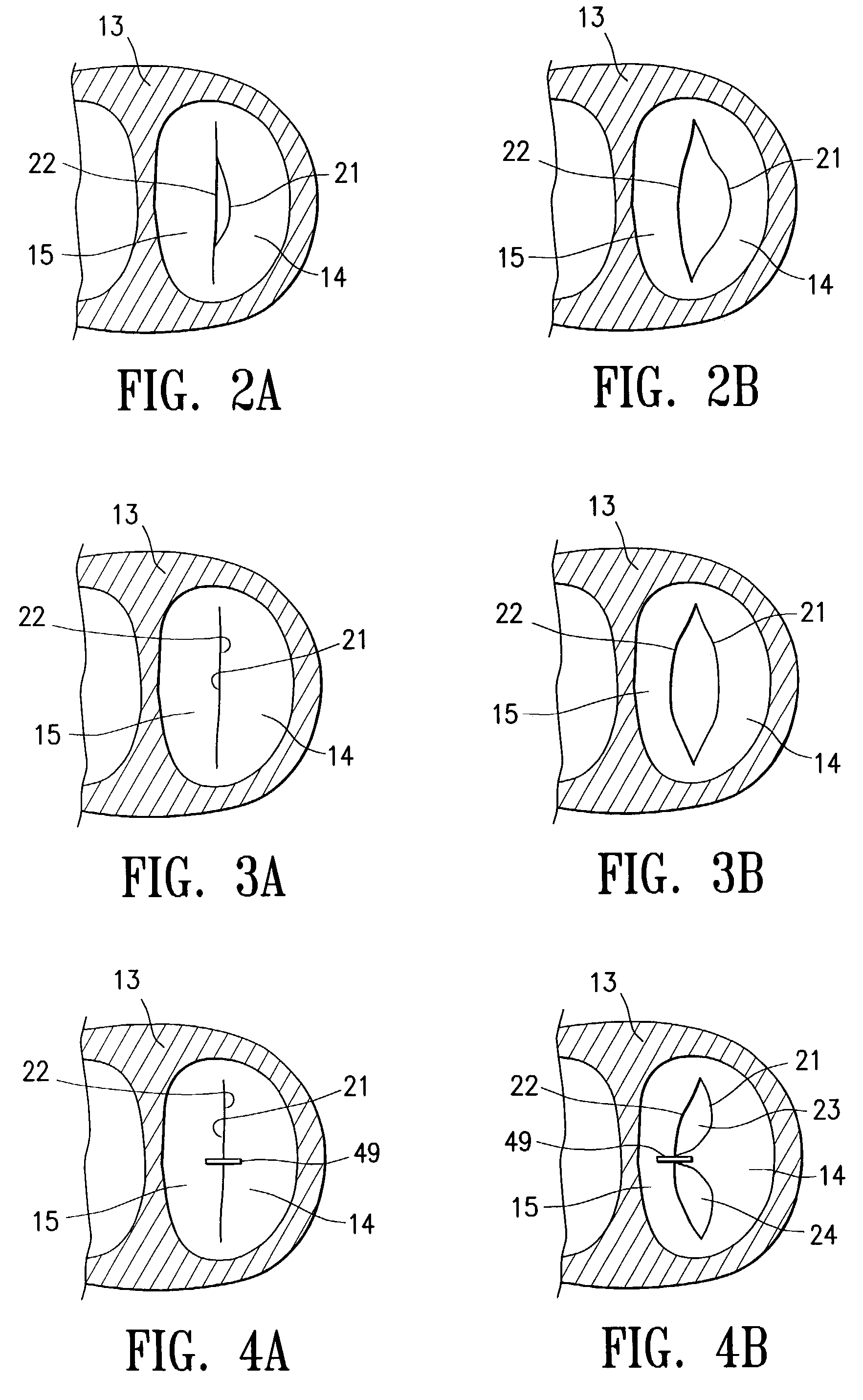
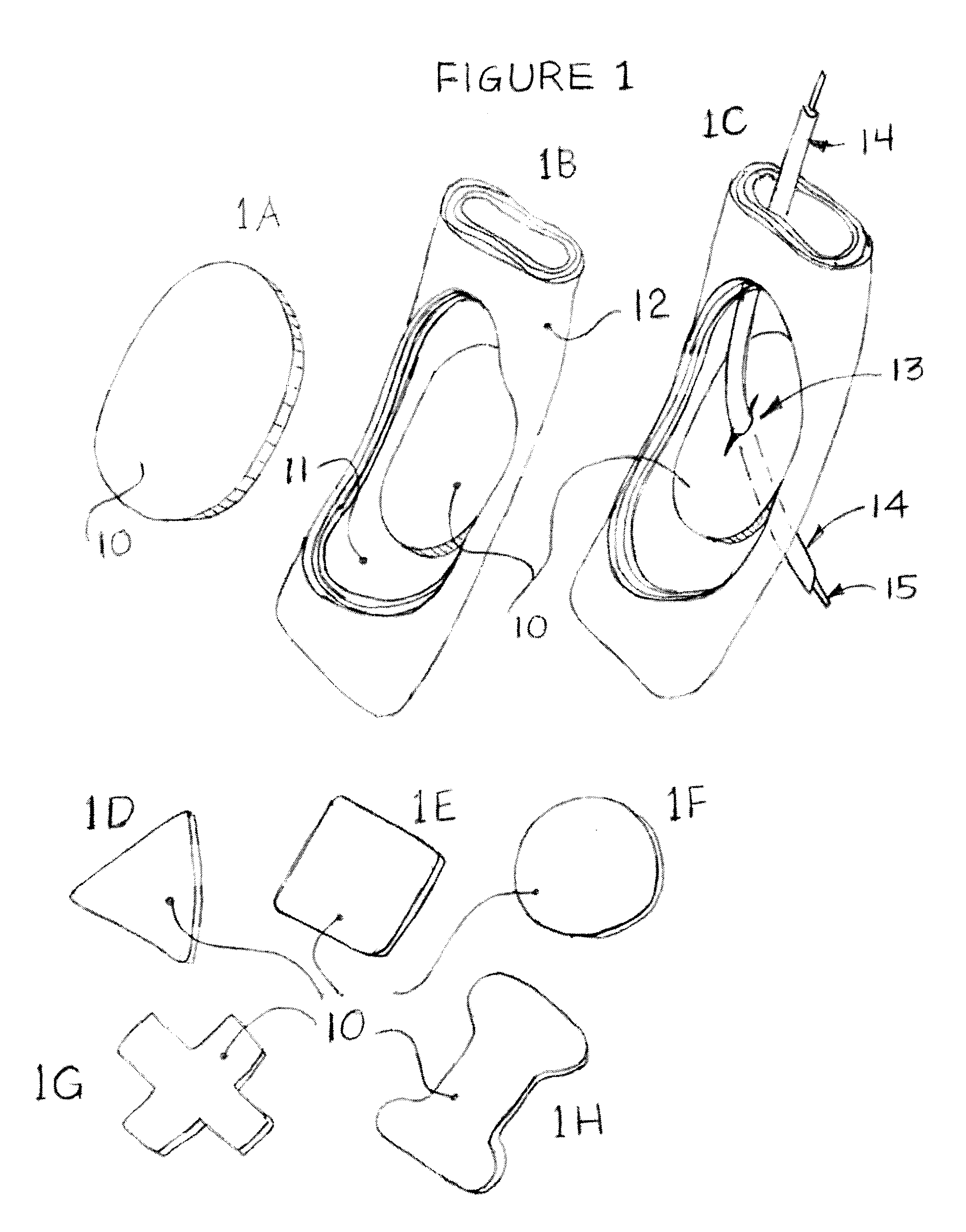
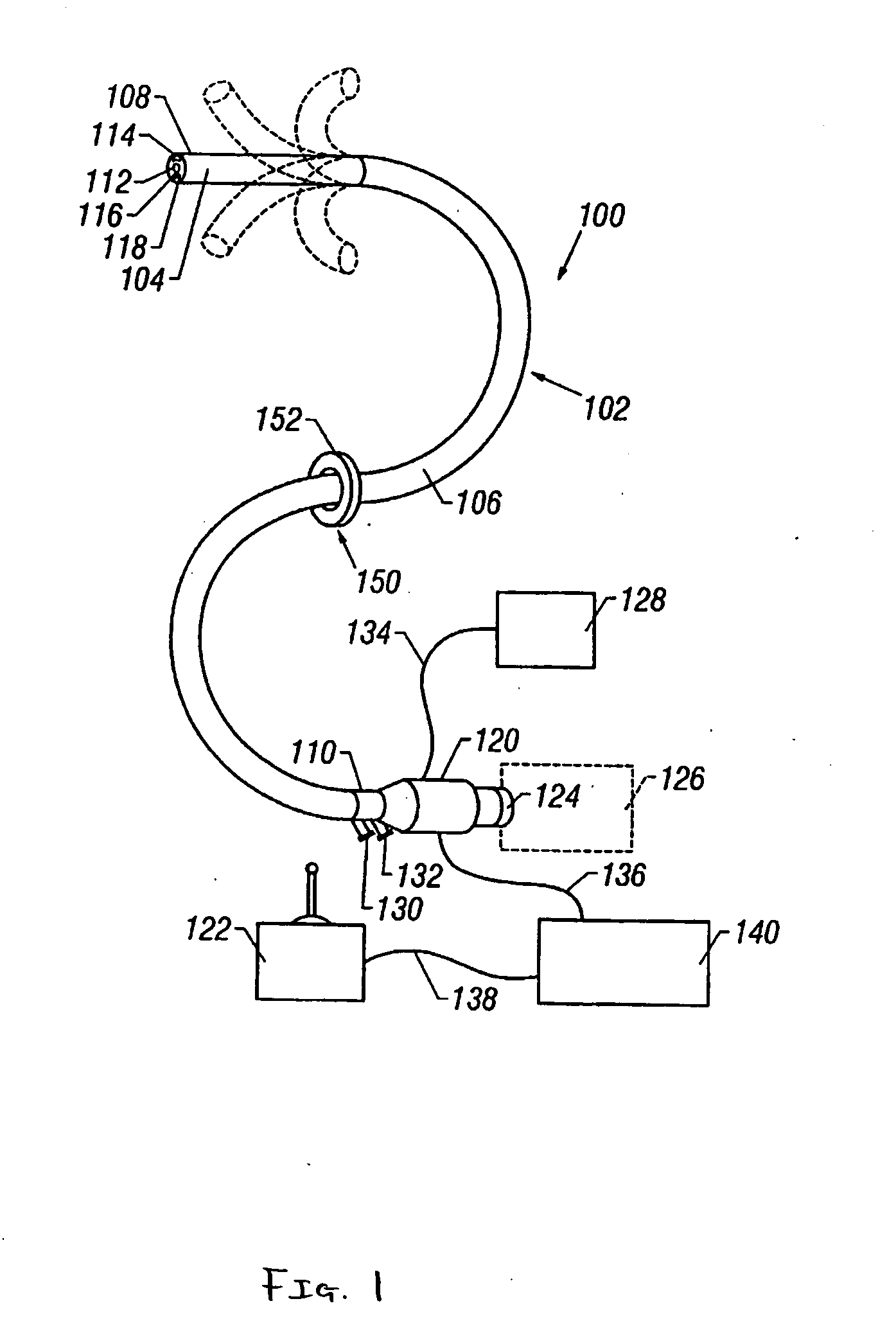
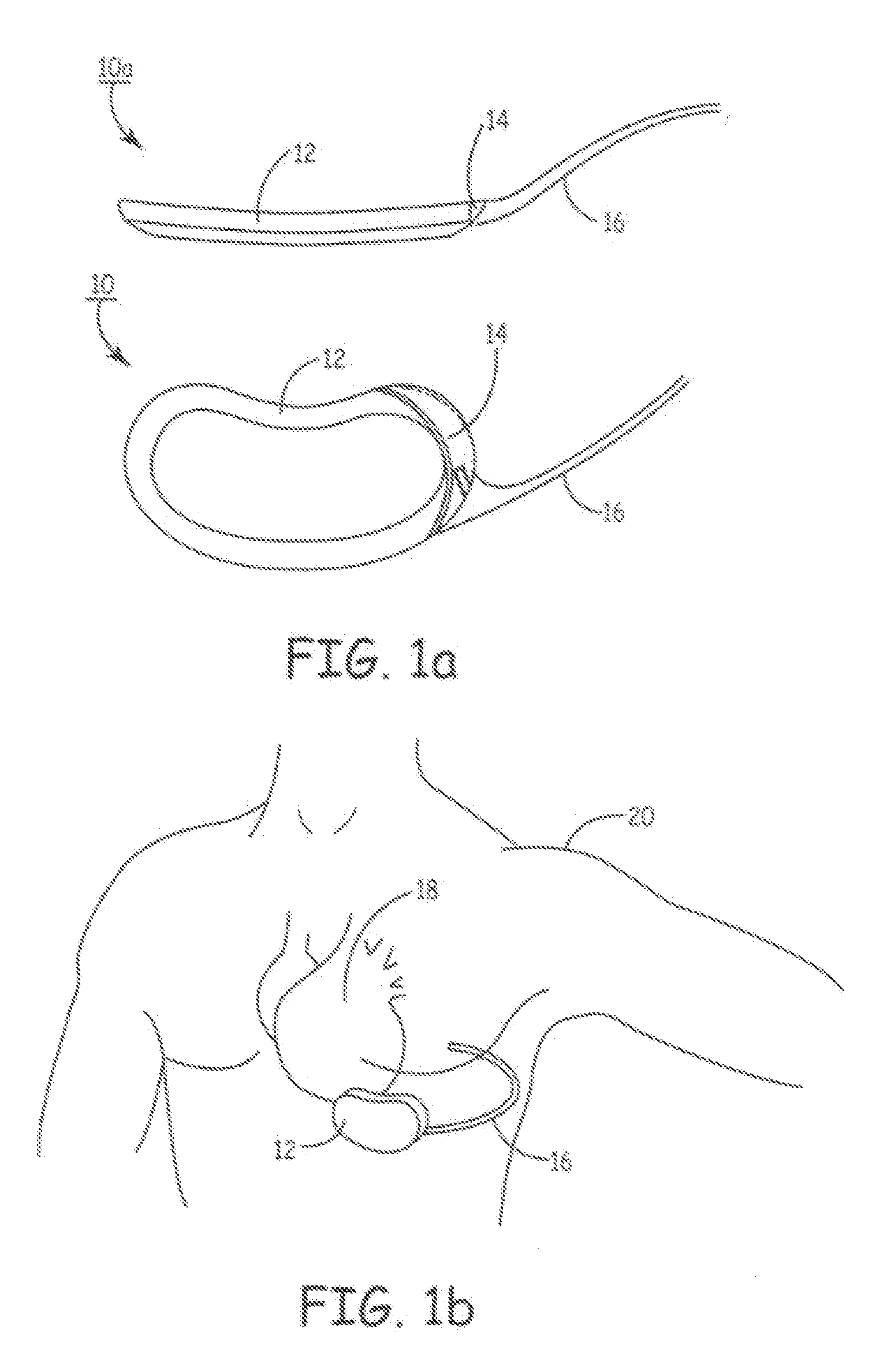
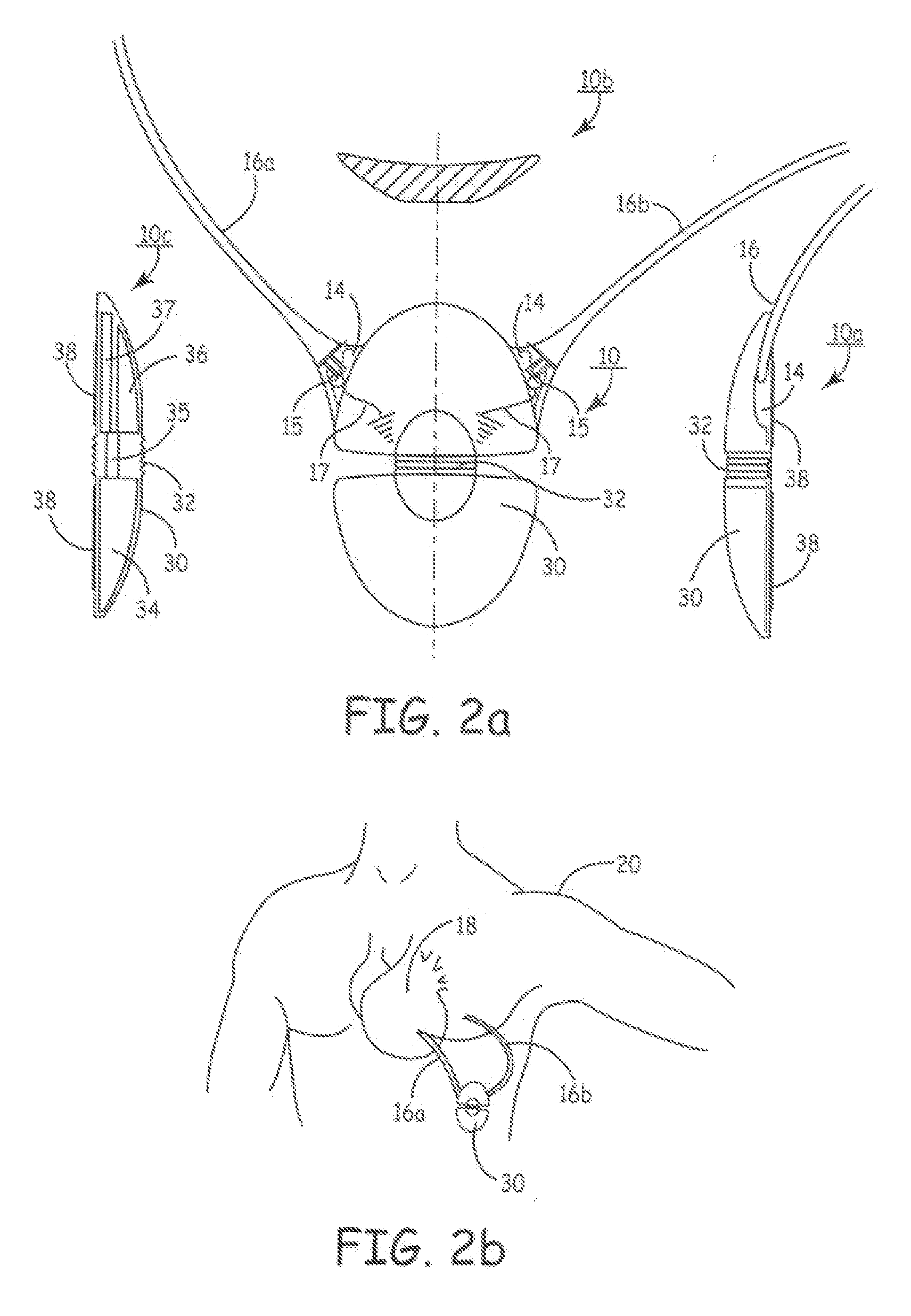
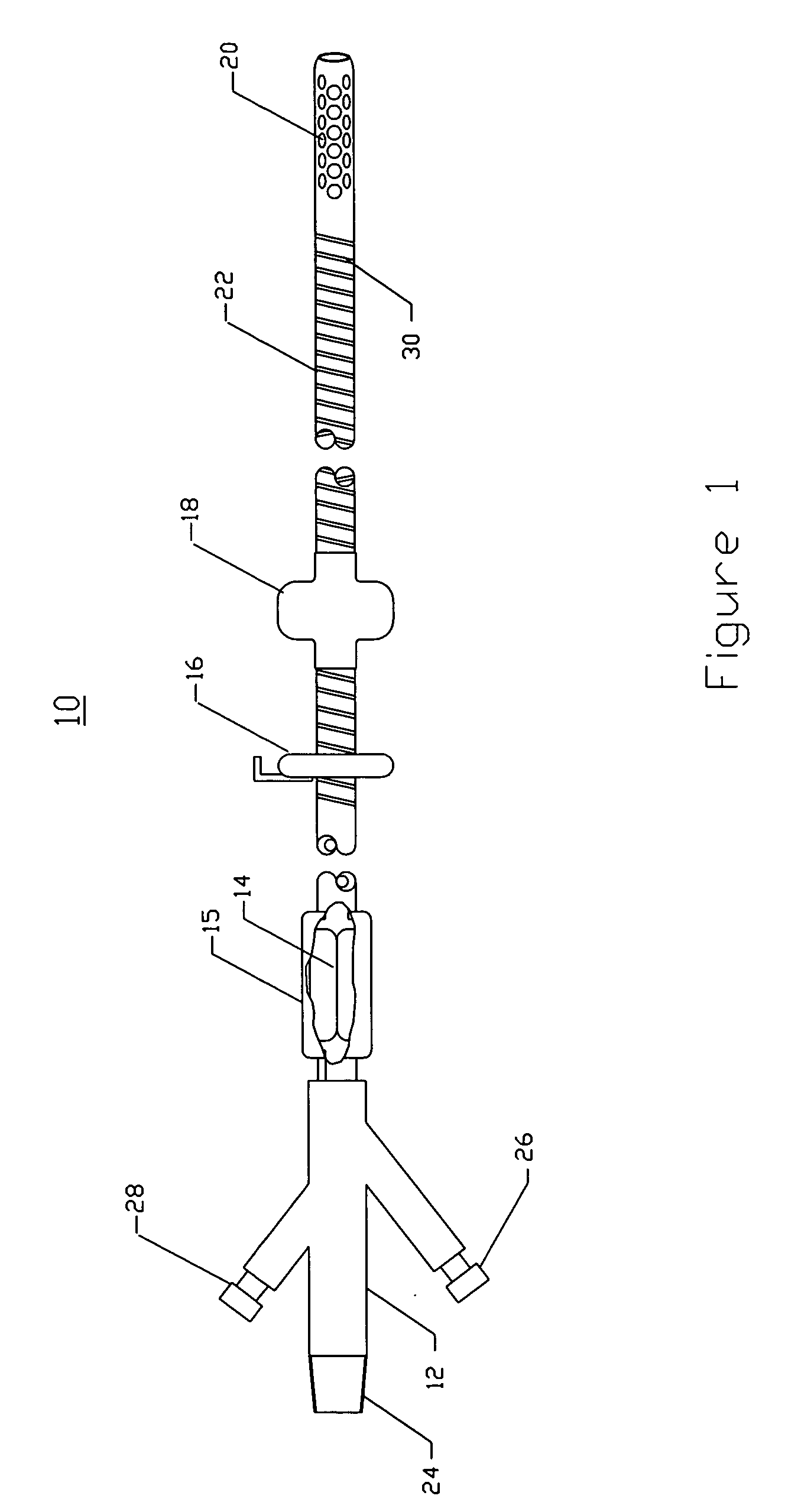
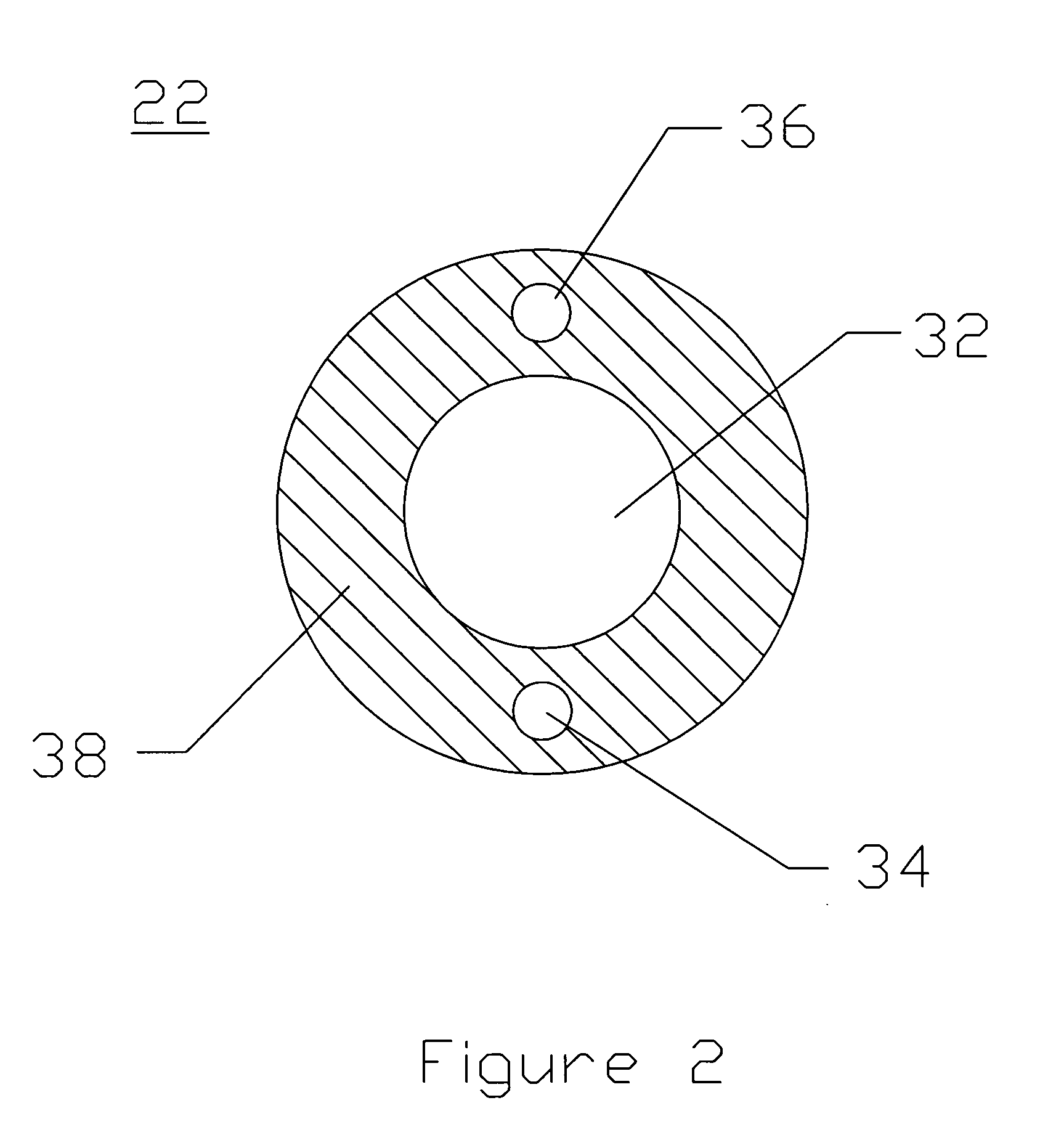
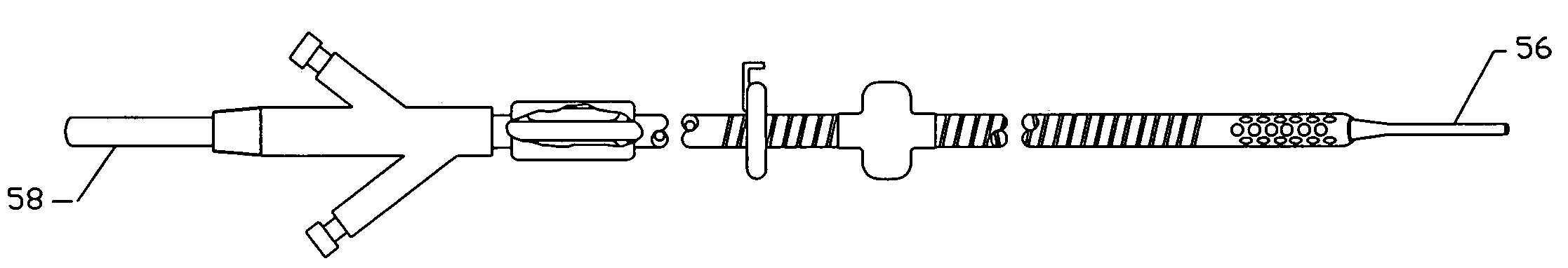
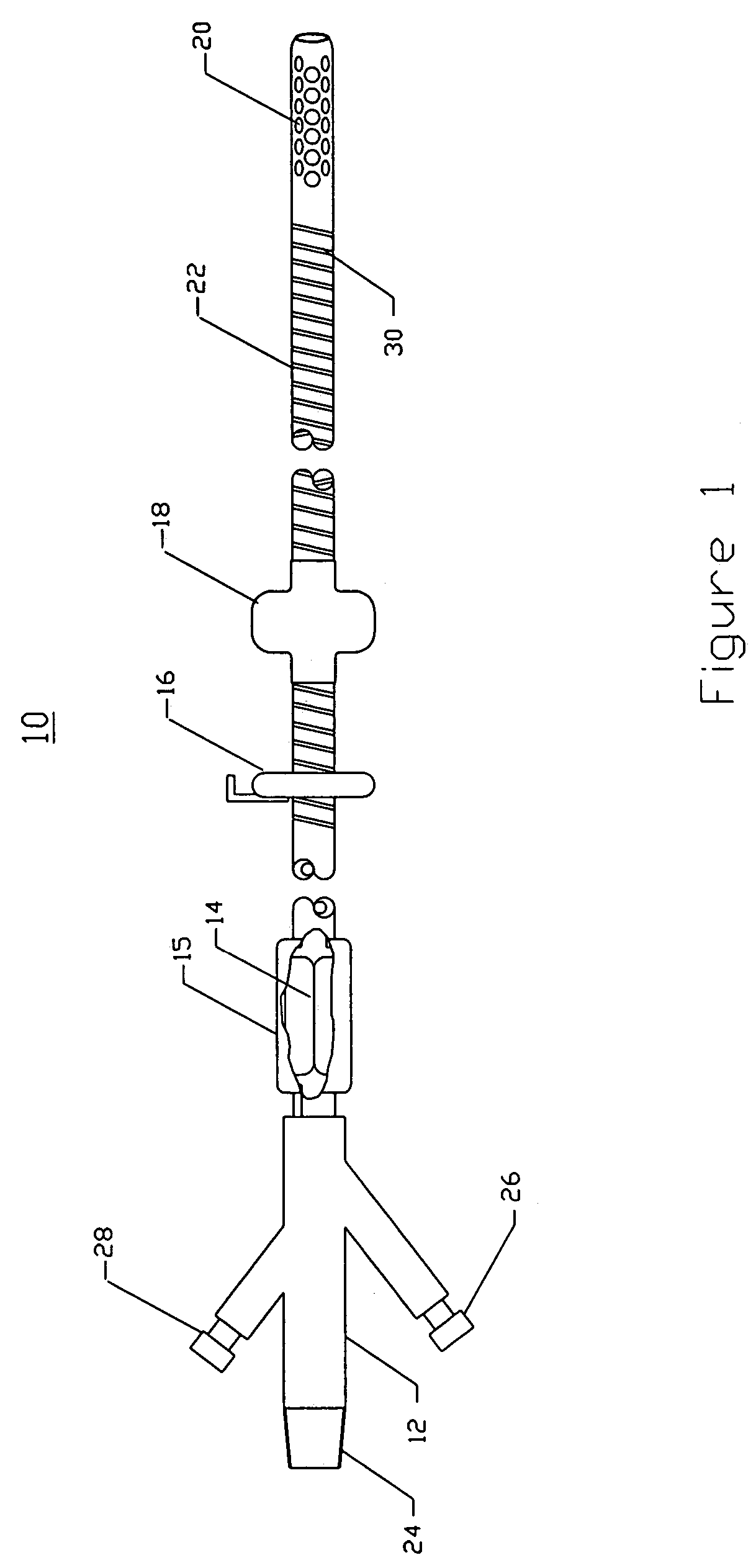
Intraluminal anastomotic device
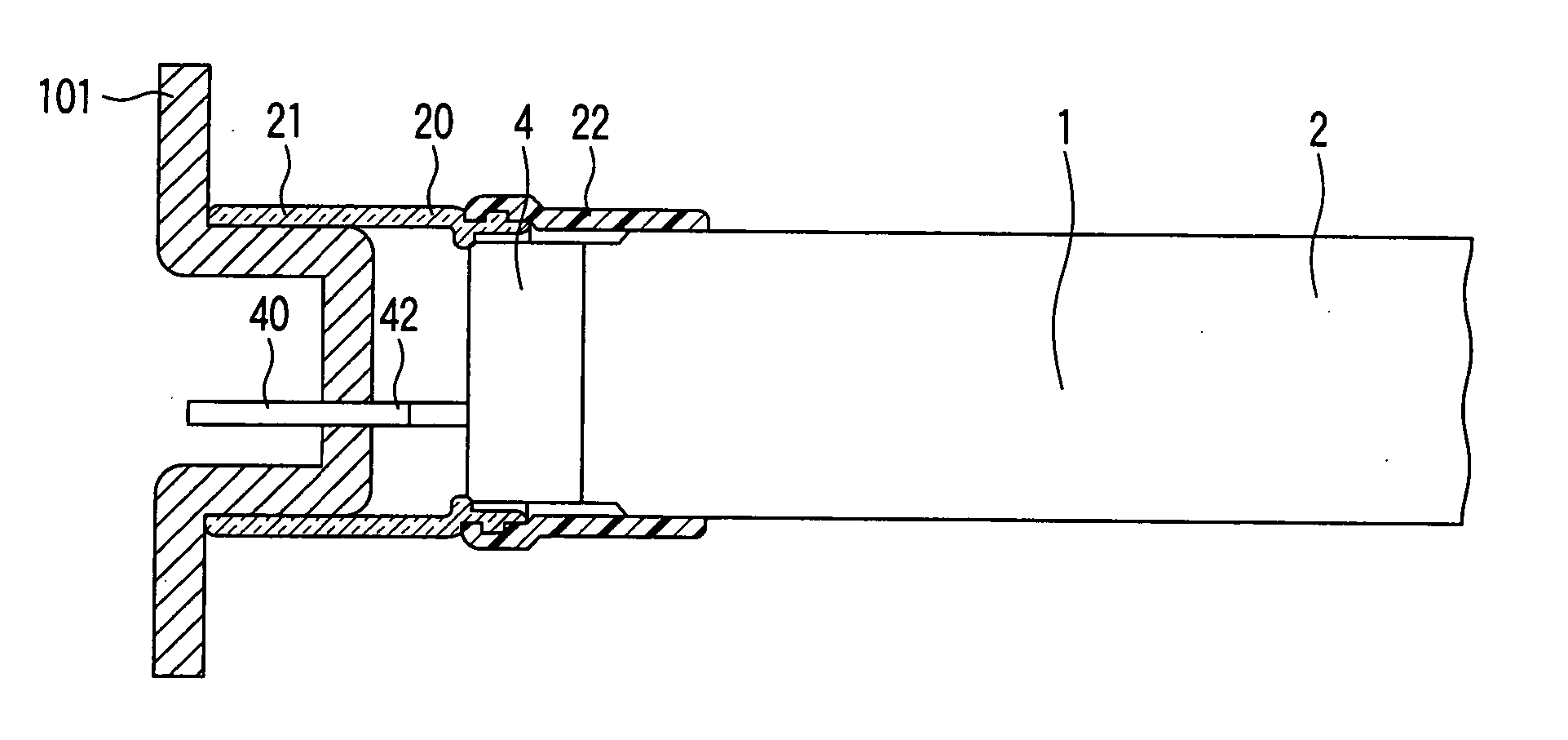
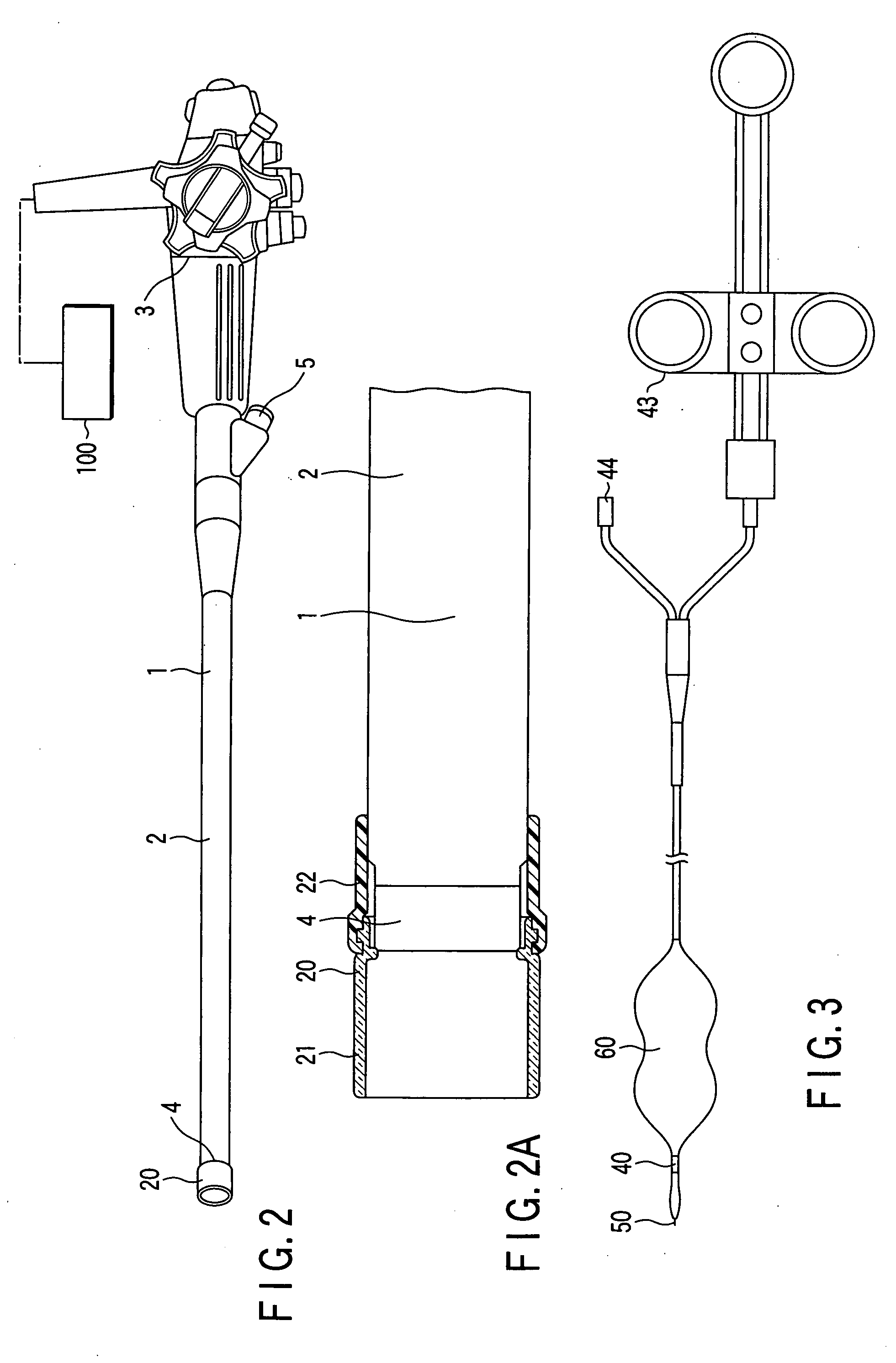
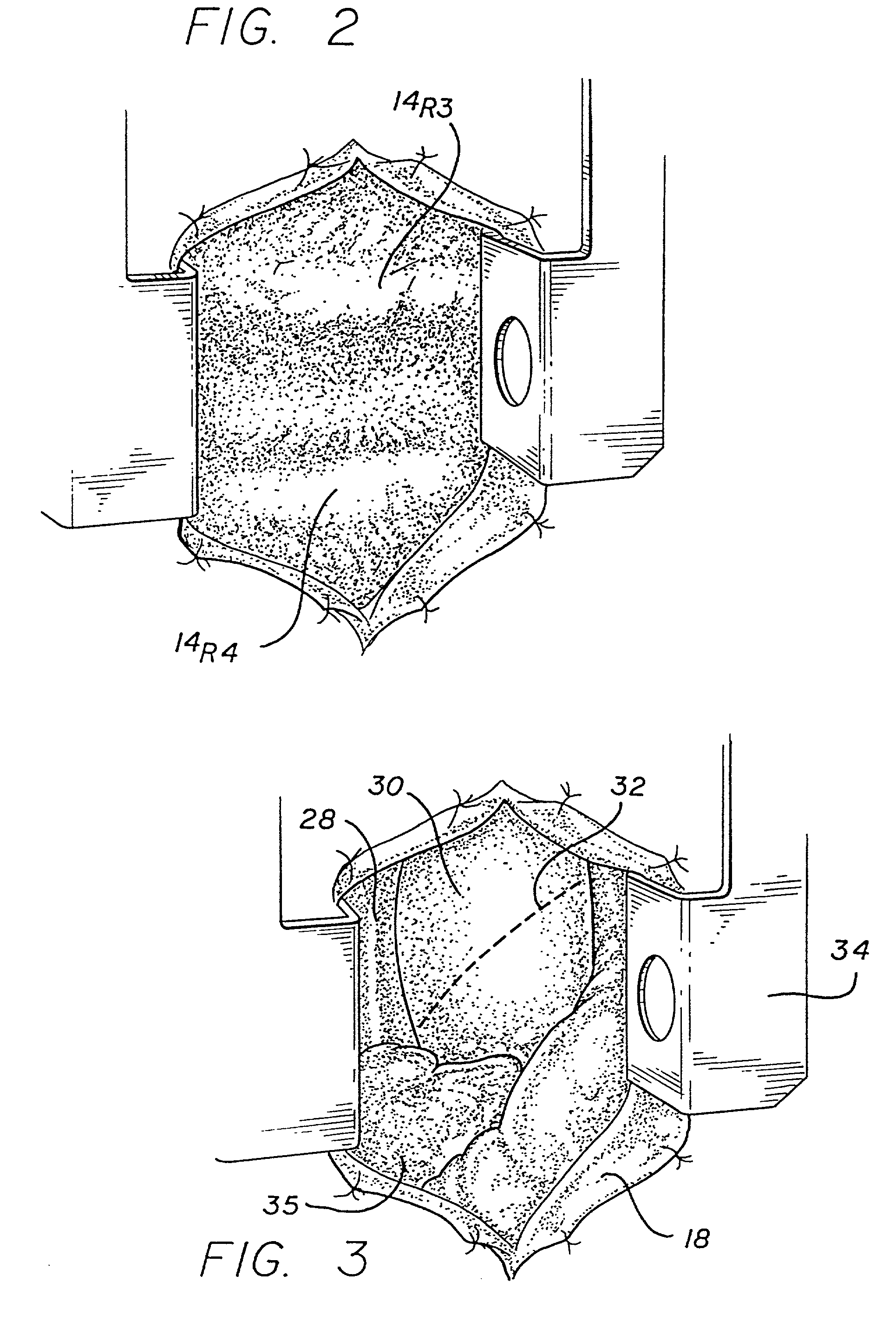
InactiveUS6117148AEasy to disassembleSuture equipmentsStapling toolsThoracic structureAbdominal cavity
An intestinal intraluminal reconstruction and resection device includes a mechanism for intussusception of the bowel, a bowel anastomosis mechanism and a mechanism for severing the resected bowel. The surgical device allows the user to carry out intraluminally an anastomosis first, prior to resection of the intestine or any hollow viscus, therefore not exposing the dirty intraluminal content to the clean abdominal or thoracic cavities. The above is achieved by first intussuscepting the hollow viscus, then anastomosis and finally intraluminal resection.
Owner:RAVO BIAGIO +1
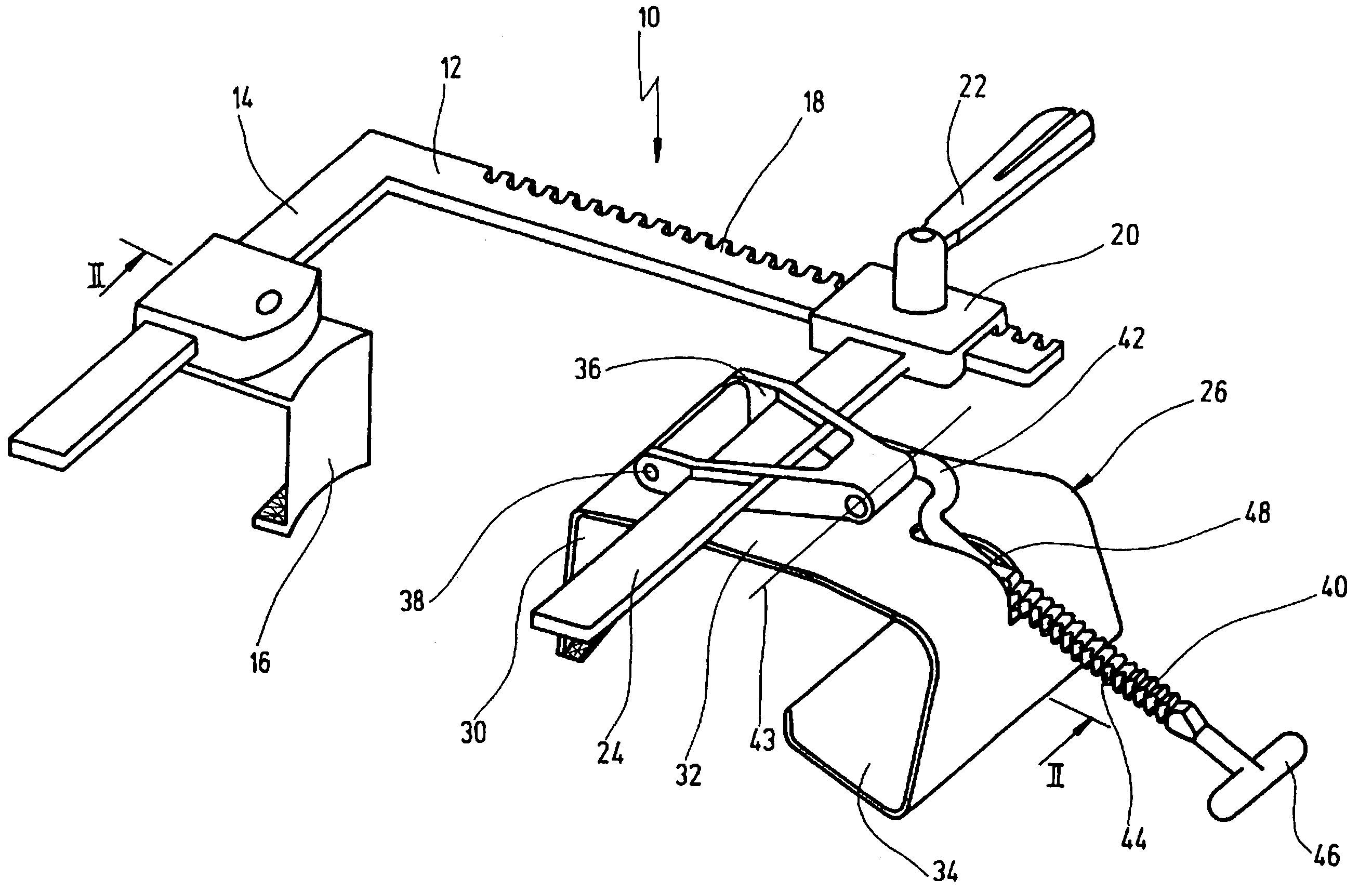
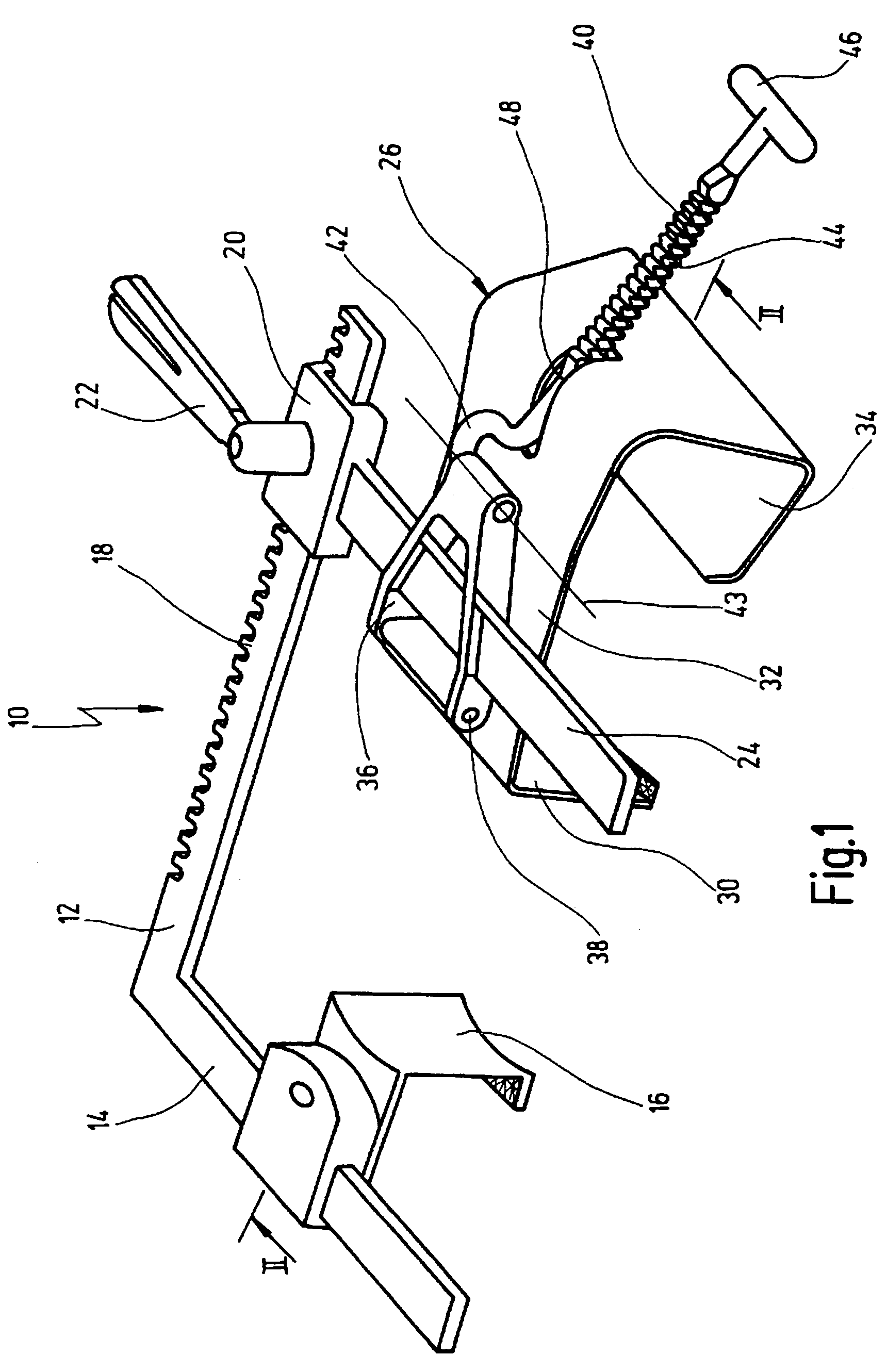
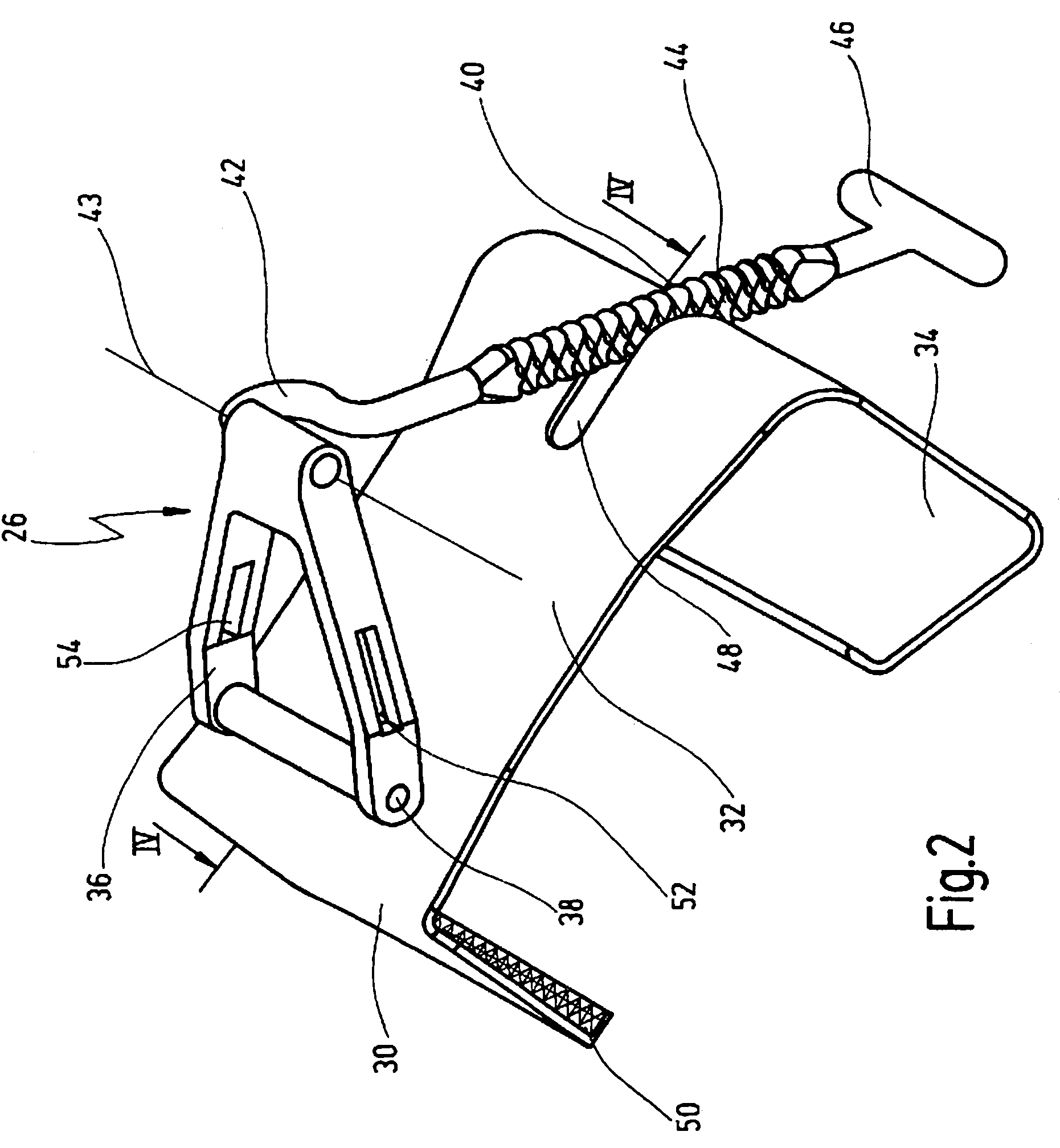
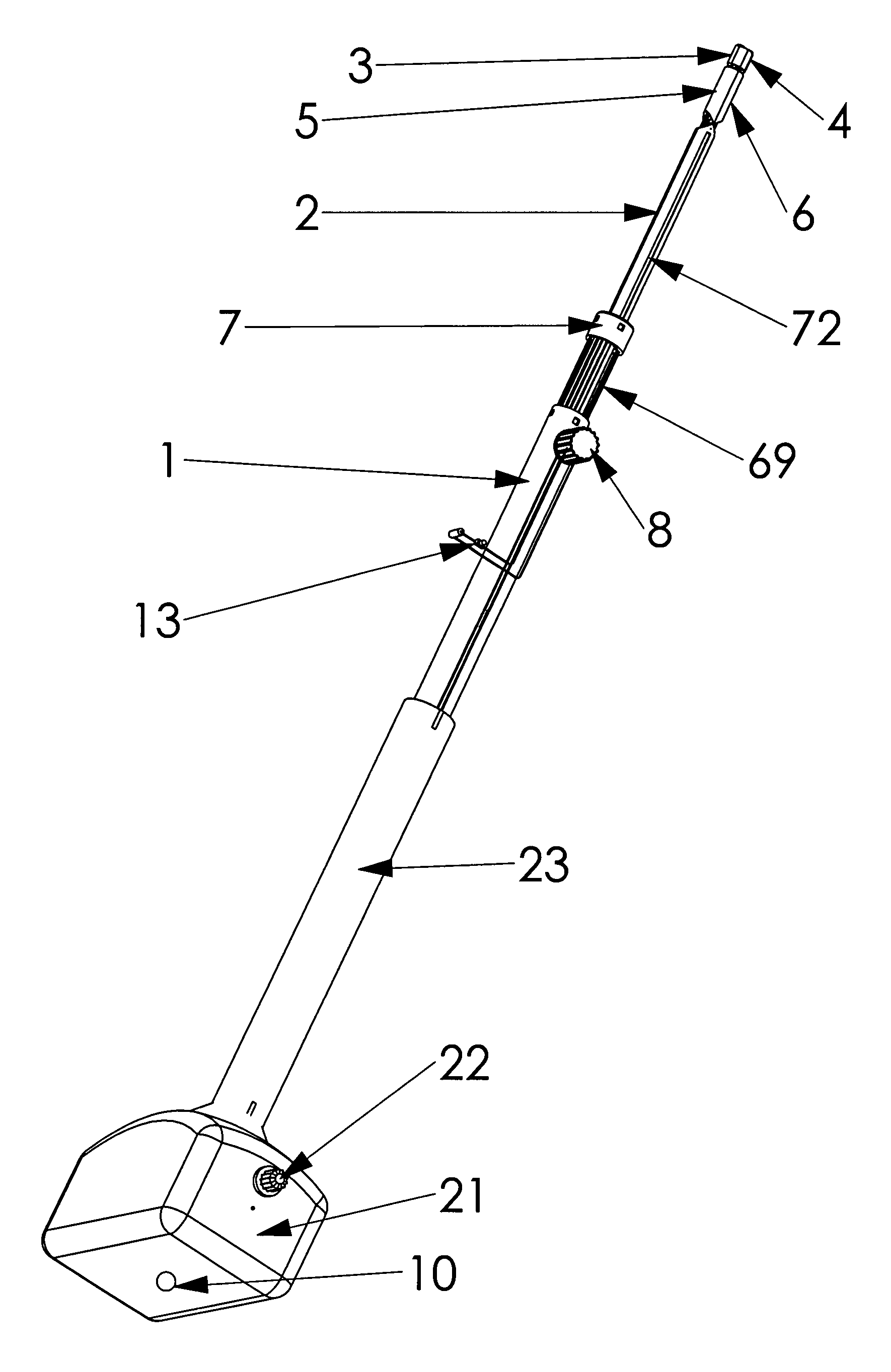
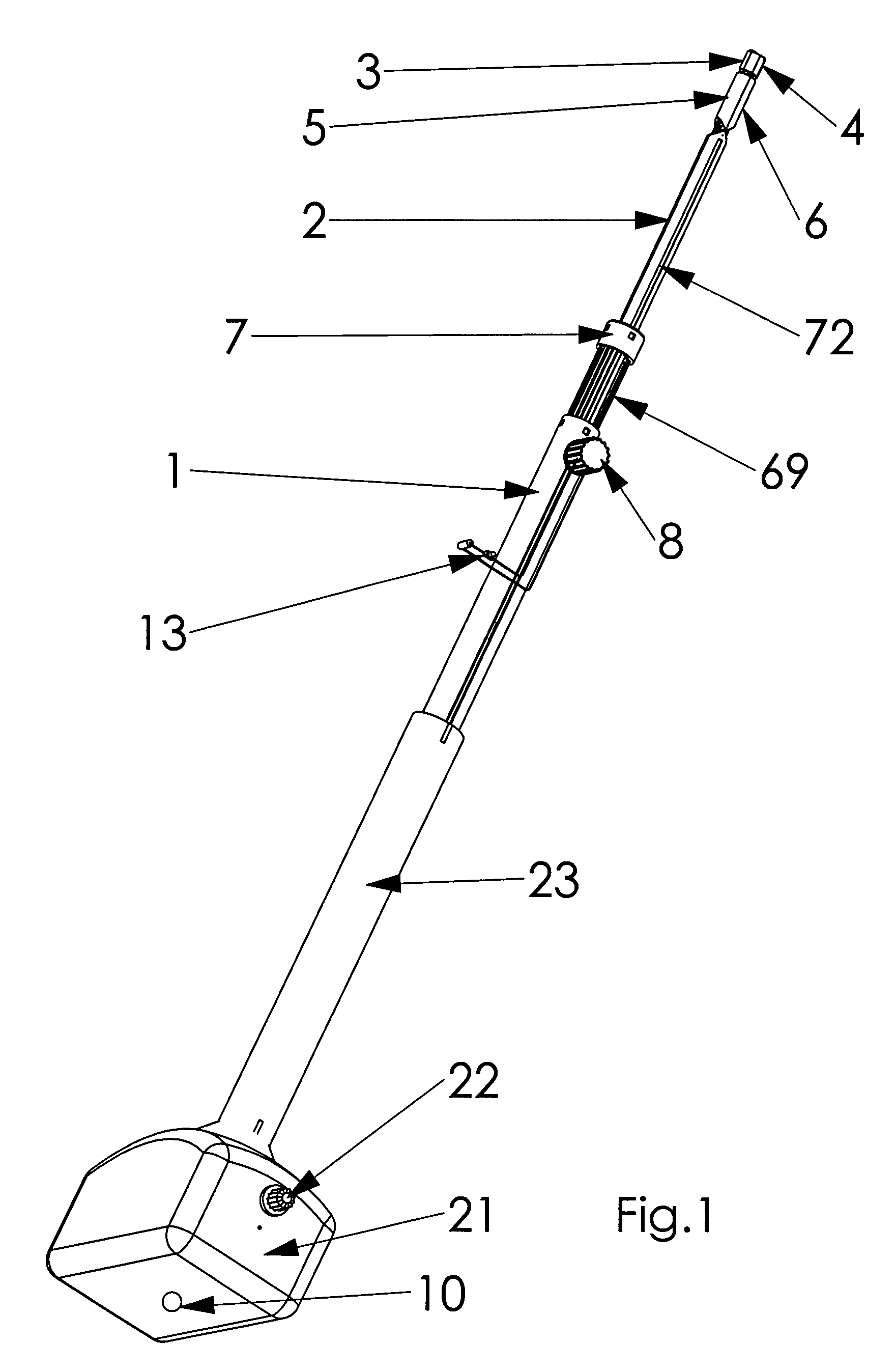
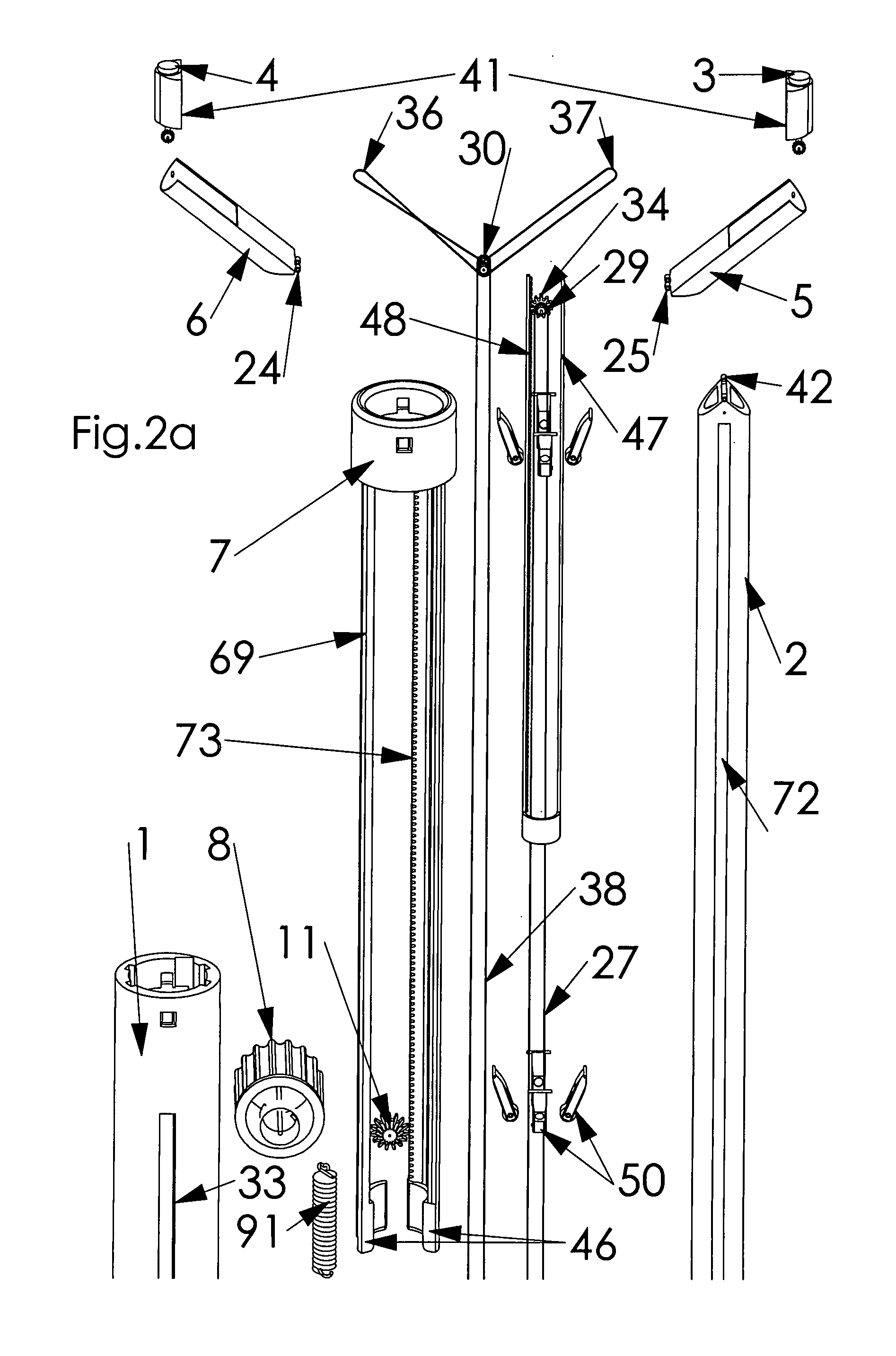
Retractor for performing heart and thorax surgeries
A retractor has a rail, a first holding arm protruding from this rail at an angle at a second holding arm extending approximately parallel to the first holding arm. A distance between the two arms being modifiable. At least one functional element is mounted on one of these holding arms, which functional element has a section extending transversely to the holding arms and a swivel bracket protruding from this transverse section. The functional element being pivotable about a pin extending roughly parallel to the arms via the swivel bracket, a swiveled position can be set by grasping the function element with a hand. A locking mechanism serves for locking the functional element in a swiveled position.
Owner:KARL STORZ GMBH & CO KG
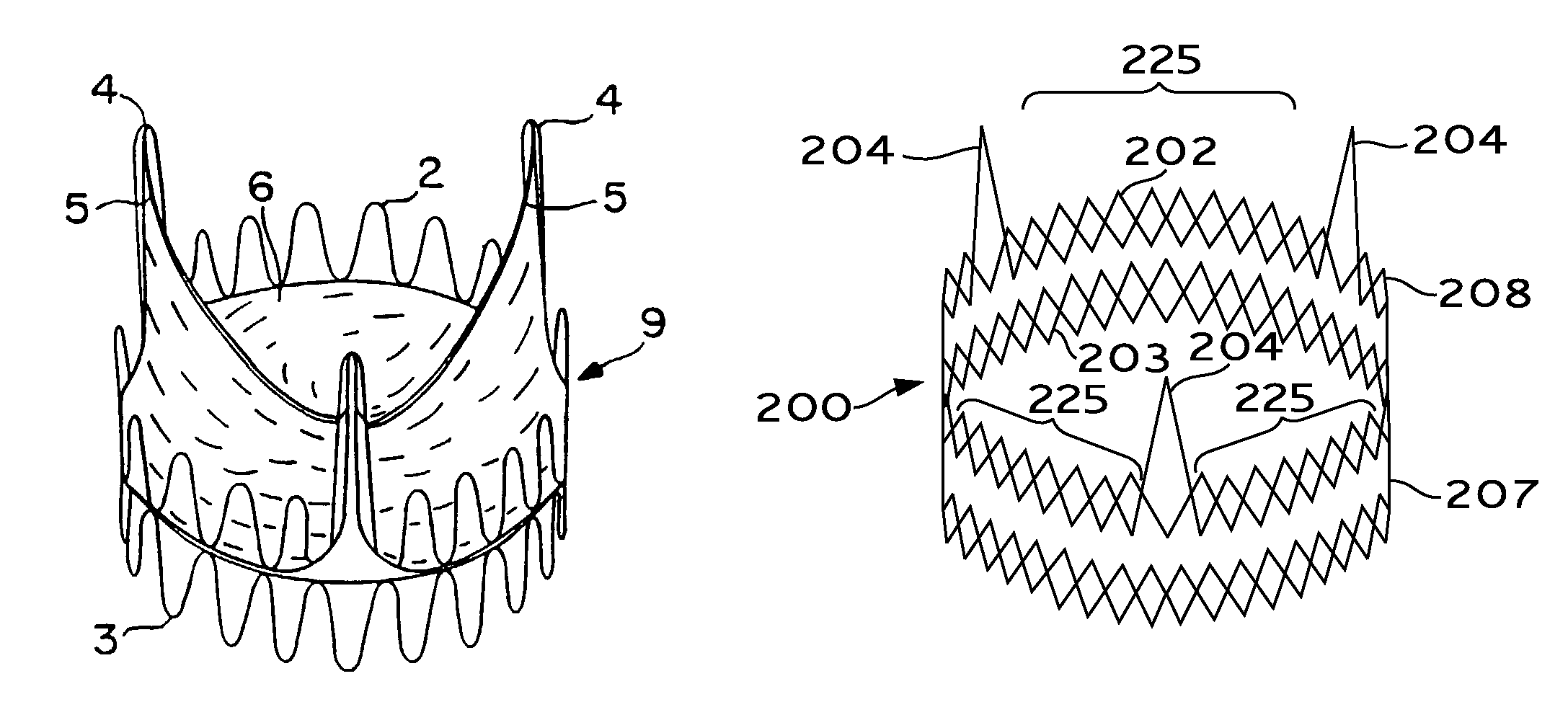
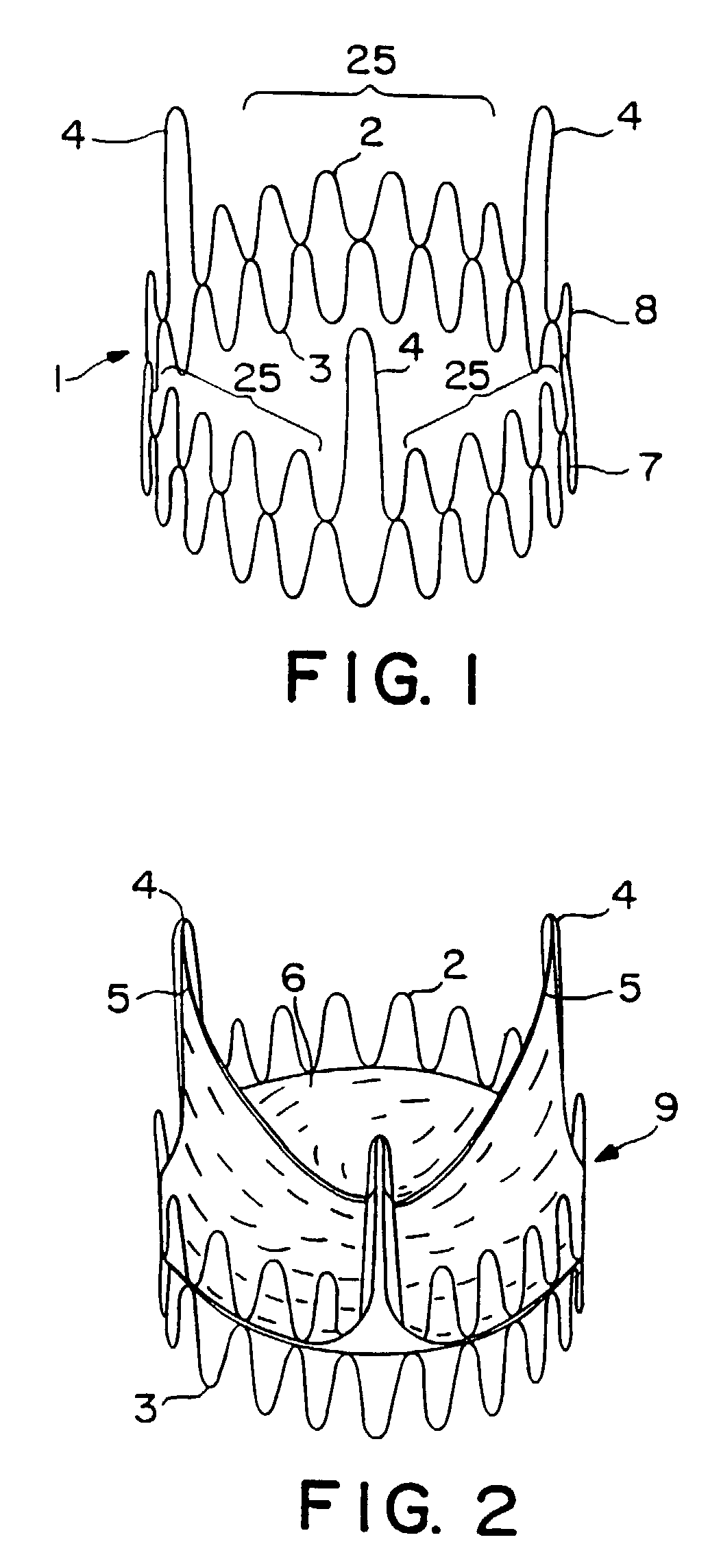
Valve prosthesis for implantation in the body and a catheter for implanting such valve prosthesis
InactiveUS7618446B2Inhibition of contractionEasy to shapeStentsBalloon catheterSurgical operationThoracic structure
A valve prosthesis for implantation in the body by use of a catheter includes a stent made from an expandable cylinder-shaped thread structure including several spaced apices. The elastically collapsible valve is mounted on the stent as the commissural points of the valve are secured to the projecting apices. The valve prosthesis can be compressed around balloons of the balloon catheter and inserted in a channel, for instance, in the aorta. When the valve prosthesis is placed correctly, the balloons are inflated to expand the stent and wedge it against the wall of the aorta. The balloons are provided with beads to ensure a steady fastening of the valve prosthesis on the balloons during insertion and expansion. The valve prosthesis and the balloon catheter make it possible to insert a cardiac valve prosthesis without a surgical operation involving opening the thoracic cavity.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES AG
Treatment for patient with congestive heart failure
Owner:TRANSCARDIAC THERAPEUTICS
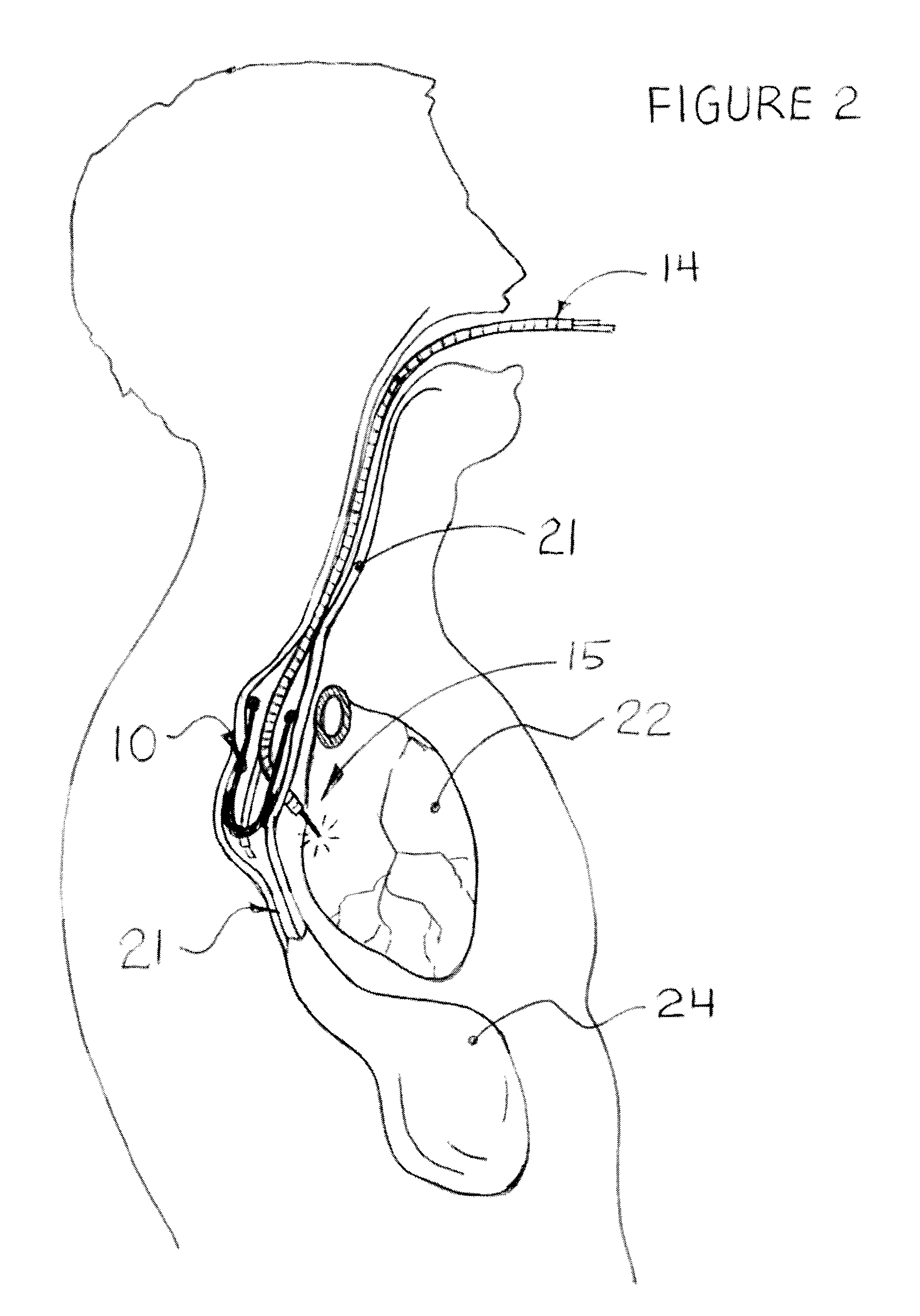
Methods and systems for ultrasound imaging of the heart from the pericardium
InactiveUS20050203410A1Low costOptimize locationSurgeryHeart/pulse rate measurement devicesUltrasound imagingThoracic structure
A peritoneal ultrasound imager includes an elongated body less than about 20 inches in length that is adapted to be inserted through a cannula into or near the pericardium space, and an ultrasound transducer array at one end of the body that is suitable for ultrasound echocardiography. The cannula and ultrasound imager may be of a single piece construction. A method for imaging the heart includes introducing a cannula into the wall of a patient's chest, inserting the elongated body into the cannula, moving the inserted elongated body to a position near the heart, and imaging the heart with ultrasound echo.
Owner:EP MEDSYST
Apparatus and methods for facilitating treatment of tissue via improved delivery of energy based and non-energy based modalities
InactiveUS20050020901A1Avoid excessive forceAccurately advancedEndoscopesCatheterThoracic structureAutomatic control
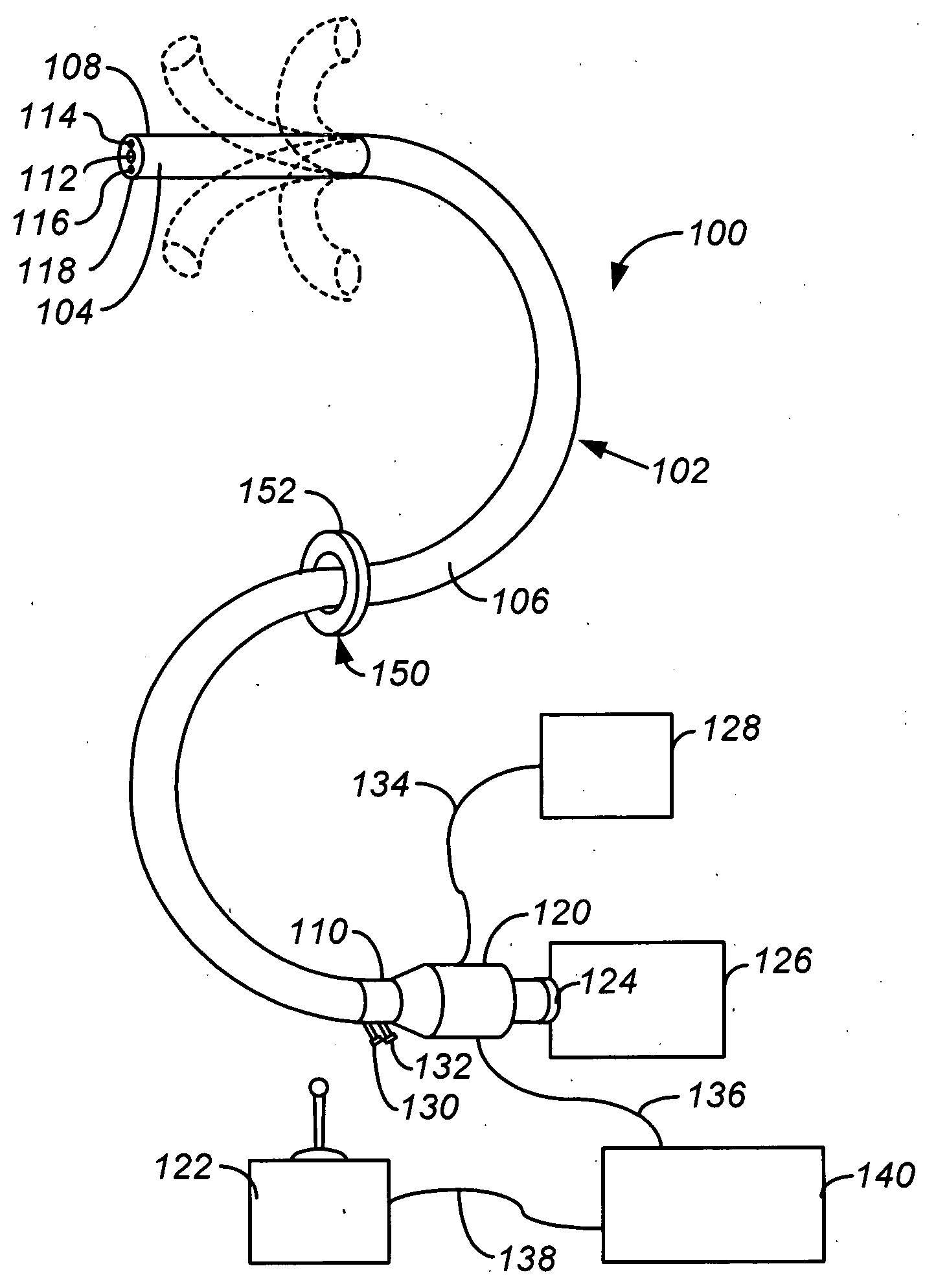
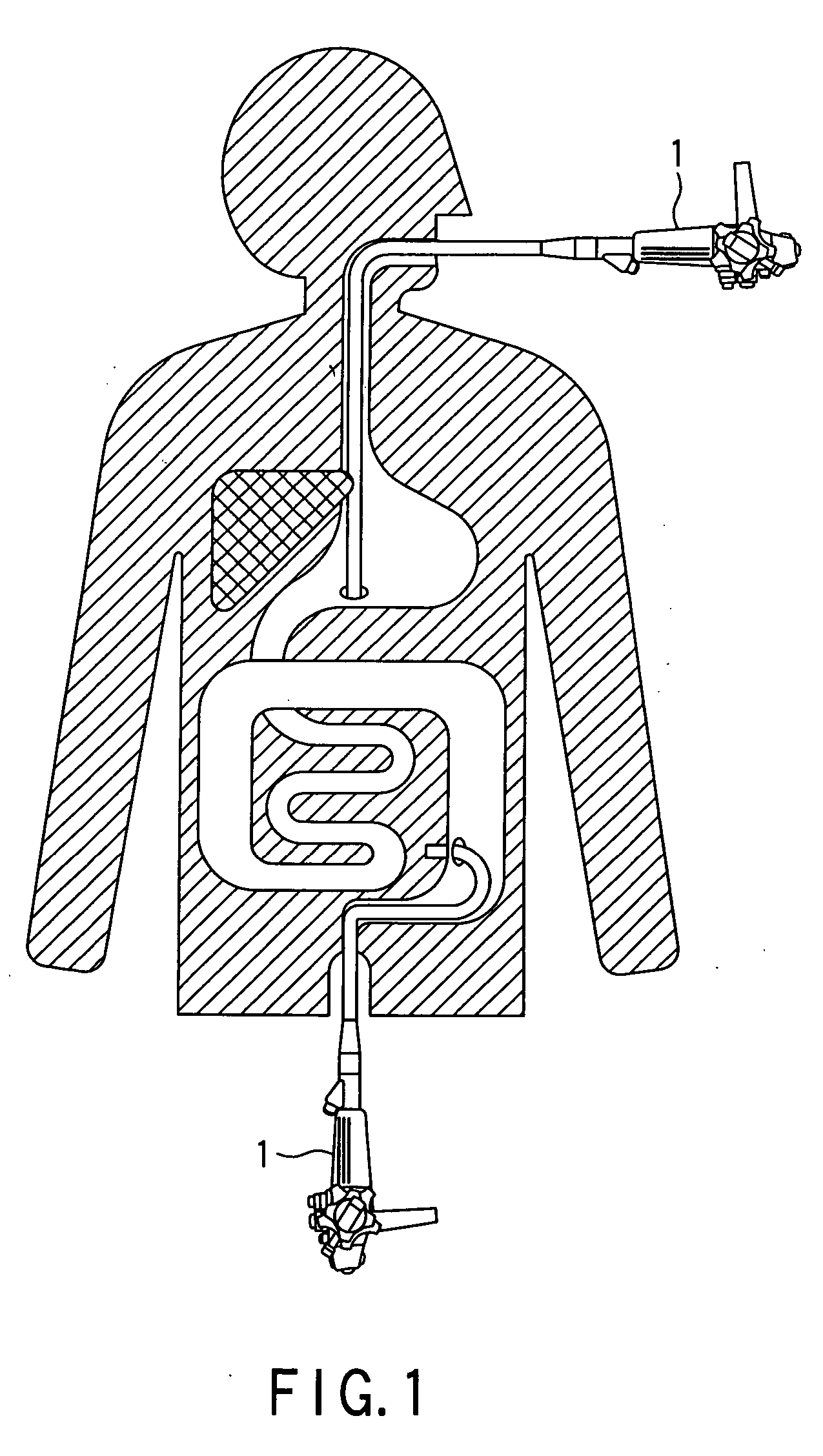
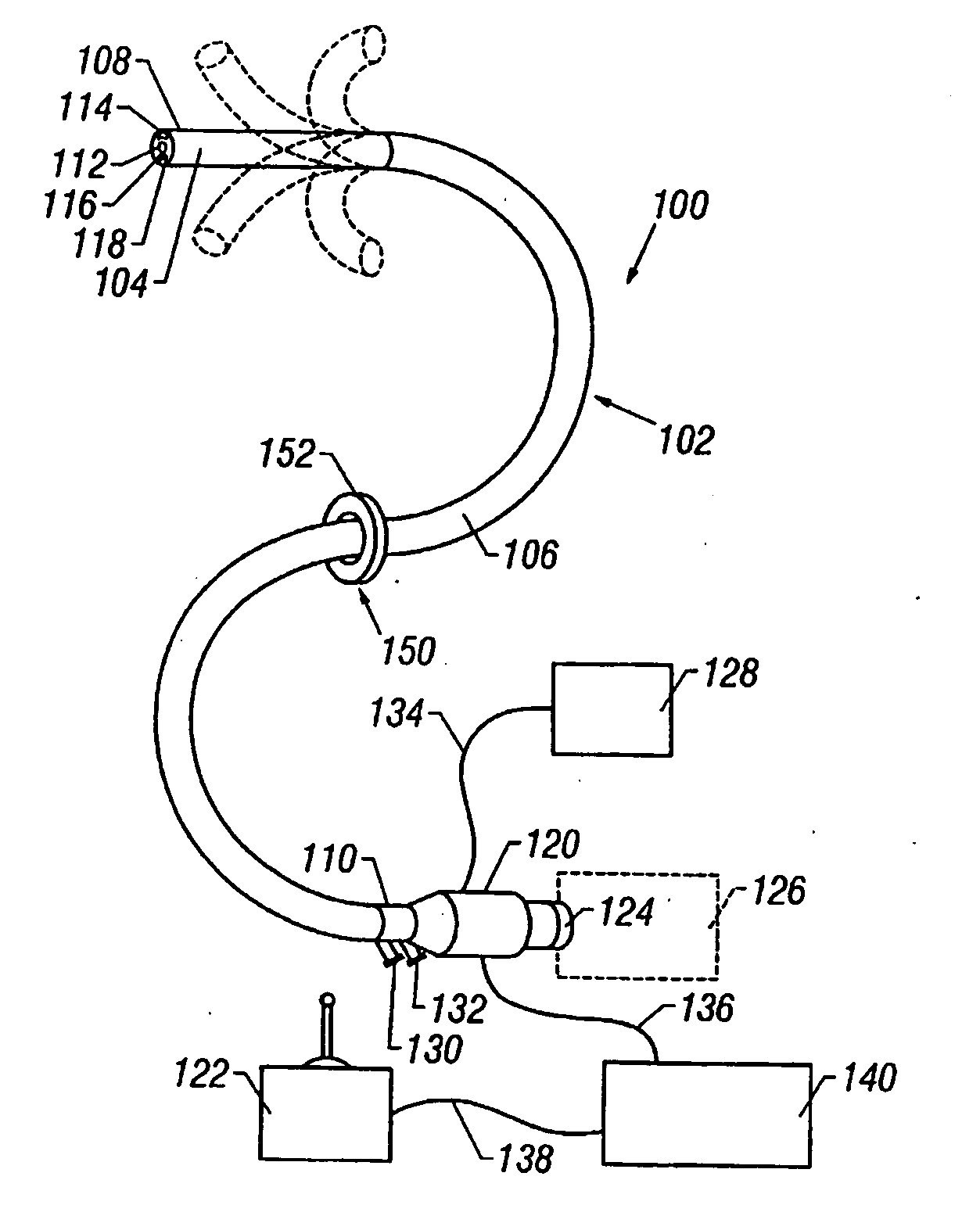
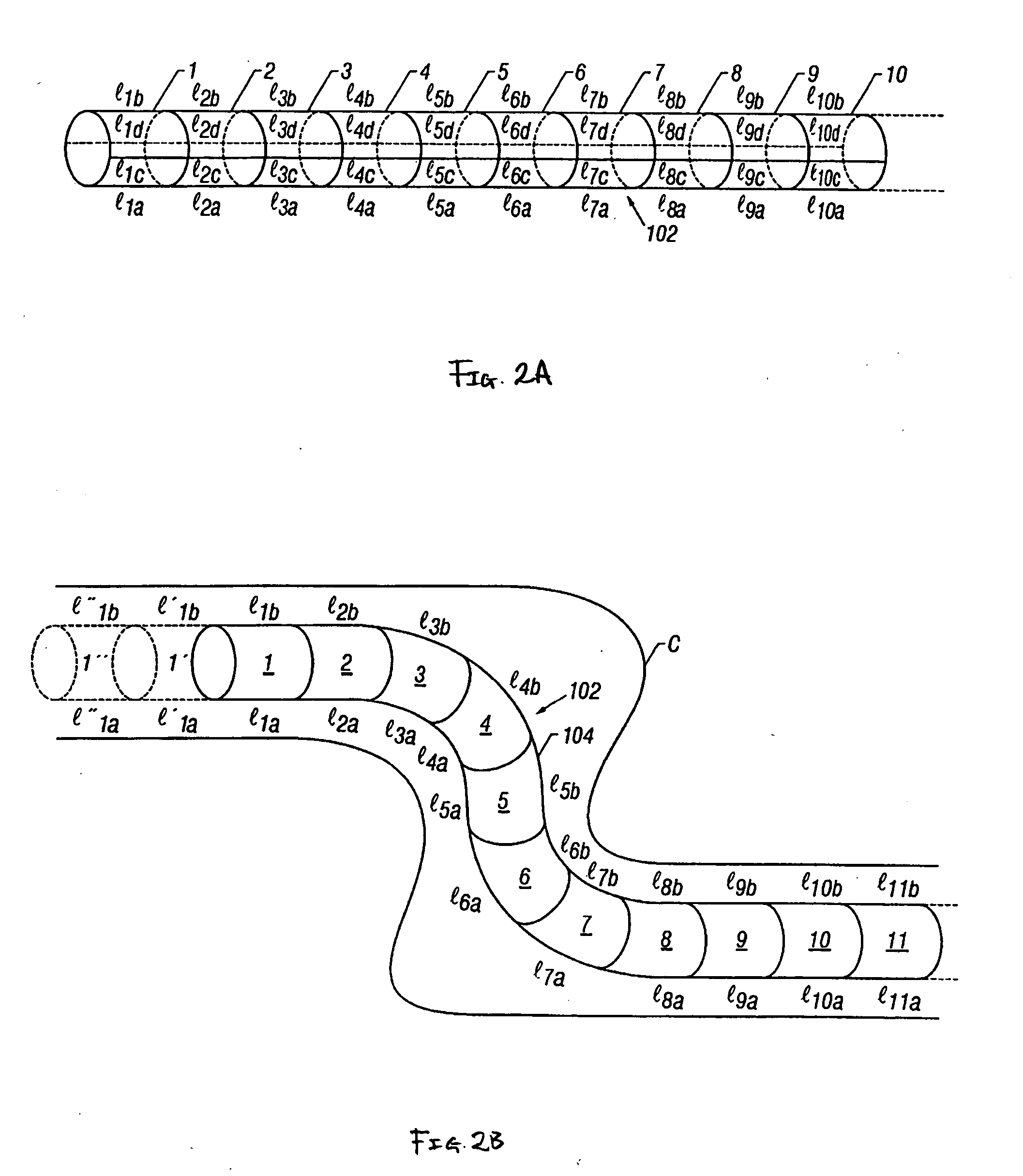
Methods and apparatus for accessing and treating regions of the body are disclosed herein. Using an endoscopic device having an automatically controllable proximal portion and a selectively steerable distal portion, the device generally may be advanced into the body through an opening. The distal portion is selectively steered to assume a selected curve along a desired path within the body which avoids contact with tissue while the proximal portion is automatically controlled to assume the selected curve of the distal portion. The endoscopic device can then be used for accessing various regions of the body which are typically difficult to access and treat through conventional surgical techniques because the device is unconstrained by “straight-line” requirements. Various applications can include accessing regions of the brain, thoracic cavity, including regions within the heart, peritoneal cavity, etc., which are difficult to reach using conventional surgical procedures.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Lung device with sealing features
InactiveUS20060025815A1Reduce air leakageMitigates pneumothorax and hemothoraxSurgical needlesMedical devicesThoracic structureThoracic cavity
This invention relates generally to a design of lung devices for safely performing a transthoracic procedure. In particular, the invention provides devices and methods of using these devices to access the thoracic cavity with minimal risk of causing pneumothorax or hemothorax. More specifically, the invention enables diagnostic and therapeutic access to a thoracic cavity using large bore instruments. This invention also provides a method for diagnostic and therapeutic procedures using a device capable of sealing the wound upon withdrawal of the device. The invention includes a device comprising an elongated body adapted to make contact with a tissue of a subject through an access hole, and a sealant delivery element. The invention also includes a method of performing tissue treatment or diagnosis in a subject.
Owner:EKOS CORP
Method for cryospray ablation
InactiveUS20090192505A1Increase load capacityAdequate doseUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsEchographic/ultrasound-imaging preparationsThoracic structureDisease
The present invention relates to methods for treating tissue in the thoracic cavity of a subject by the application of a cryogen, or using the cryogen to create an isotherm in proximity to the tissue to be treated. A wide variety of conditions may be treated using the methods of the invention including asthma, neoplastic disease and a variety of conditions characterized by inflammation in lung and chest tissue.
Owner:RESET MEDICAL
Endoscopic system for treating inside of body cavity
InactiveUS20060025654A1Safe and reliableHelp positioningCannulasSurgical needlesThoracic structureHuman body
There is provided an endoscopic inserting system. The system includes an endoscope which is inserted into a lumen inside a body through a natural opening of a human body, an opening member which forms an opening for inserting the endoscope into a thoracic cavity or an abdominal cavity from the lumen inside the body at a wall portion of the lumen, and a retracting member which, when forming the opening, retracts the wall portion of the lumen.
Owner:APOLLO ENDOSURGERY INC
Devices and methods for port-access multivessel coronary artery bypass surgery
InactiveUS6478029B1Reduce oxygen demandReduce the temperatureSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsDiseaseSurgical approach
Surgical methods and instruments are disclosed for performing port-access or closed-chest coronary artery bypass (CABG) surgery in multivessel coronary artery disease. In contrast to standard open-chest CABG surgery, which requires a median sternotomy or other gross thoracotomy to expose the patient's heart, post-access CABG surgery is performed through small incisions or access ports made through the intercostal spaces between the patient's ribs, resulting in greatly reduced pain and morbidity to the patient. In situ arterial bypass grafts, such as the internal mammary arteries and / or the right gastroepiploic artery, are prepared for grafting by thoracoscopic or laparoscopic takedown techniques. Free grafts, such as a saphenous vein graft or a free arterial graft, can be used to augment the in situ arterial grafts. The graft vessels are anastomosed to the coronary arteries under direct visualization through a cardioscopic microscope inserted through an intercostal access port. Retraction instruments are provided to manipulate the heart within the closed chest of the patient to expose each of the coronary arteries for visualization and anastomosis. Disclosed are a tunneler and an articulated tunneling grasper for rerouting the graft vessels, and a finger-like retractor, a suction cup retractor, a snare retractor and a loop retractor for manipulating the heart. Also disclosed is a port-access topical cooling device for improving myocardial protection during the port-access CABG procedure. An alternate surgical approach using an anterior mediastinotomy is also described.
Owner:HEARTPORT
Methods and apparatus for transesophageal microaccess surgery
The current invention describes methods of transesophageal access to the neck and thorax to perform surgical interventions on structures outside the esophagus in both the cervical and the thoracic cavity. It describes a liner device made of a complete or partial tubular structure, or a flat plate, the liner having means to facilitate creation of a side opening, which may include a valve. The liner with its side opening form a port structure inside the esophageal lumen. The port structure allows elongated surgical devices to pass through a perforation across the full thickness of the esophageal wall to outside location, in a controlled way. The elongated surgical devices can be diagnostic scopes, therapeutic scopes, manual elongated surgical devices, robotic arms or the like. After being deployed outside the esophagus, the surgical devices can access structures outside the esophagus, in the neck and thorax in 360 degrees of freedom around the esophageal circumference. These structures can be bony, cartilaginous, spinal, vascular, soft tissue, deep tissues, lymph nodal, cardiac, pulmonary, tracheal, nervous, muscular or diaphragmatic, skin and subcutaneous tissues of the neck, skin and subcutaneous tissues of the anterior chest wall, skin and subcutaneous tissues of the skin of the back, and skin and layers of the breast.
Owner:MICROACCESS
Endoscopic System and Method for Therapeutic Applications and Obtaining 3-Dimensional Human Vision Simulated Imaging With Real Dynamic Convergence
An endoscopic system and method that is adaptable for therapeutic applications as well as sensor operation and is capable of producing 3-dimensional human vision simulated imaging with real dynamic convergence, not virtual convergence. Applications may include use in any space, including but not limited to, intra-abdominal cavities, intra-thoracic cavities, and intra-cranial cavities. Further, two or more diagnostic / sensor probes may be used, with at least two being the same kind to create the 3-dimensional effect, such as but not limited to, camera, ultrasound, and magnetic-resonance imaging. Diagnostic / sensor probes are each mounted to the end of a different arm, with the other ends of the two arms both being attached to the same hinge that allows them to turn freely on the same axis from side-to-side within a 180 degree angle range of movement on the distal end of a main tubular shaft system. Medical, as well as other applications, are contemplated.
Owner:ABOU EL KHEIR TAREK AHMED NABIL
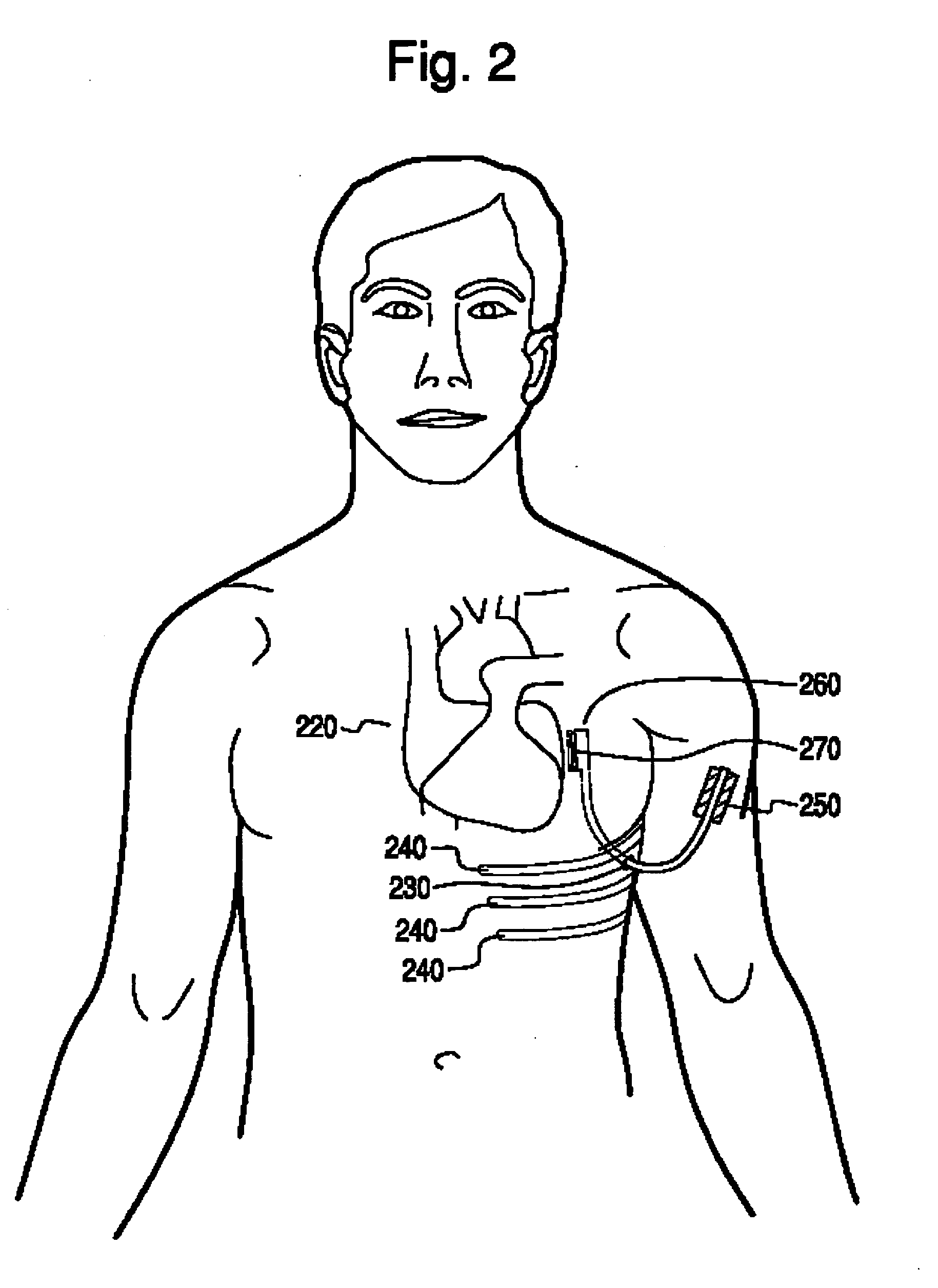
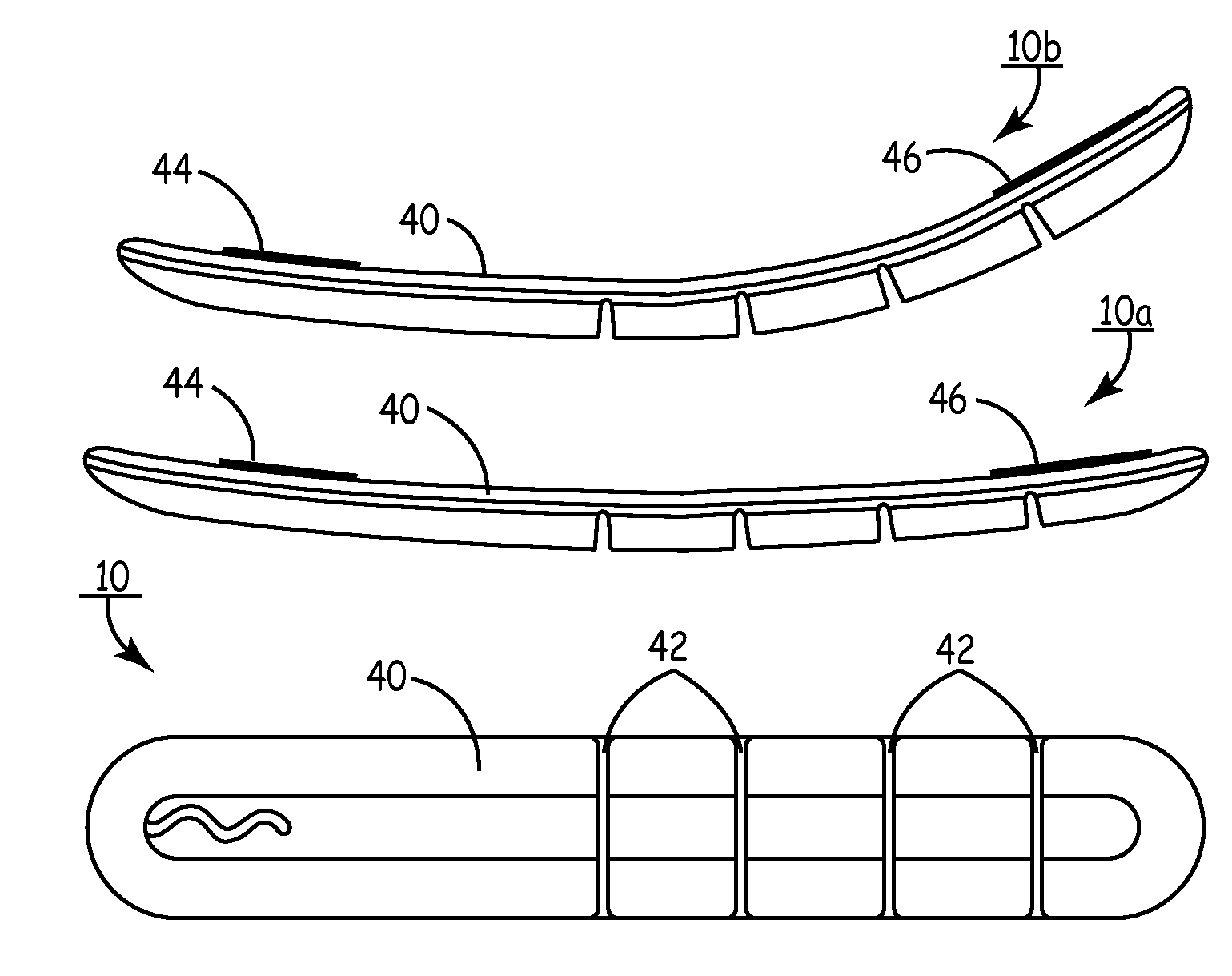
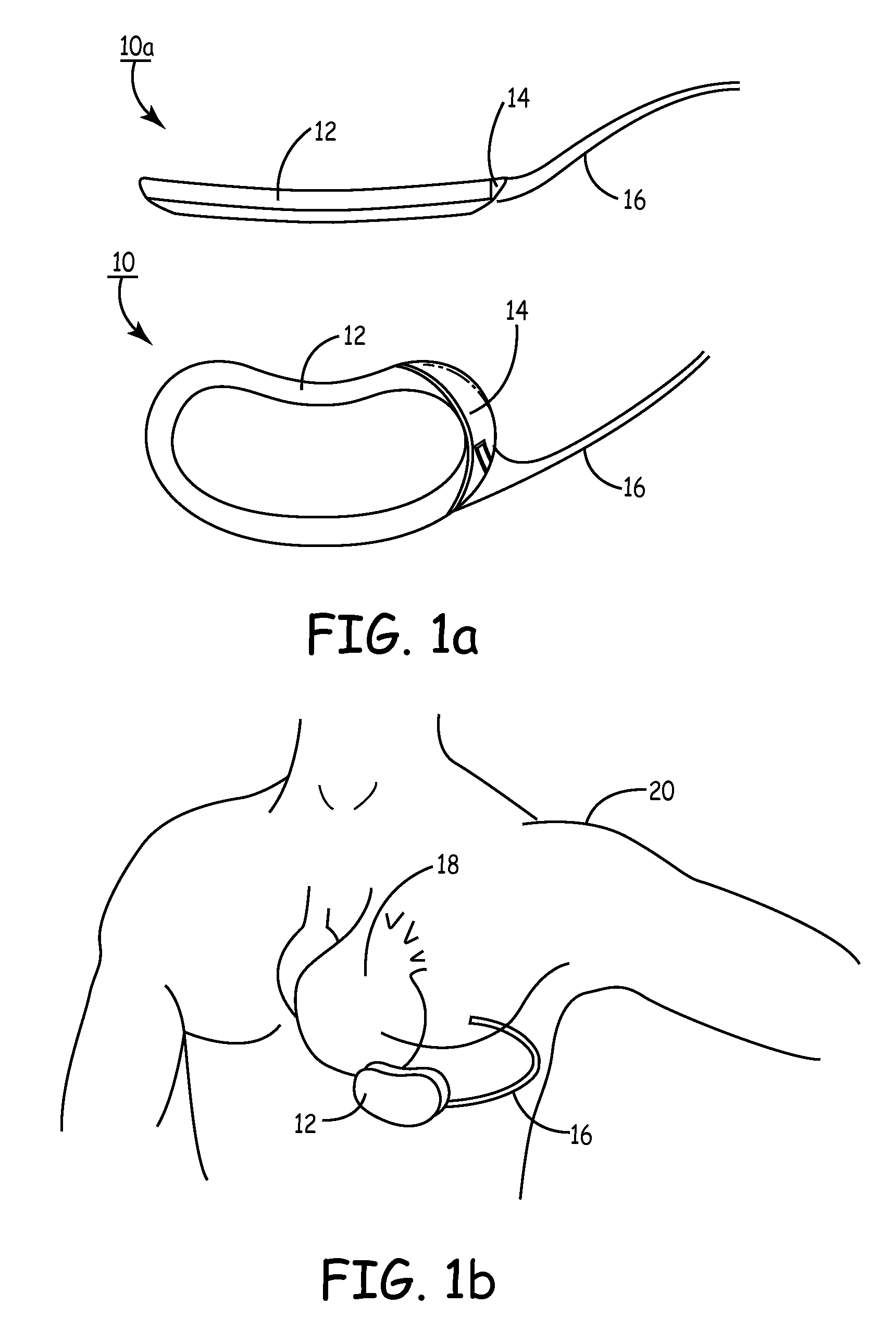
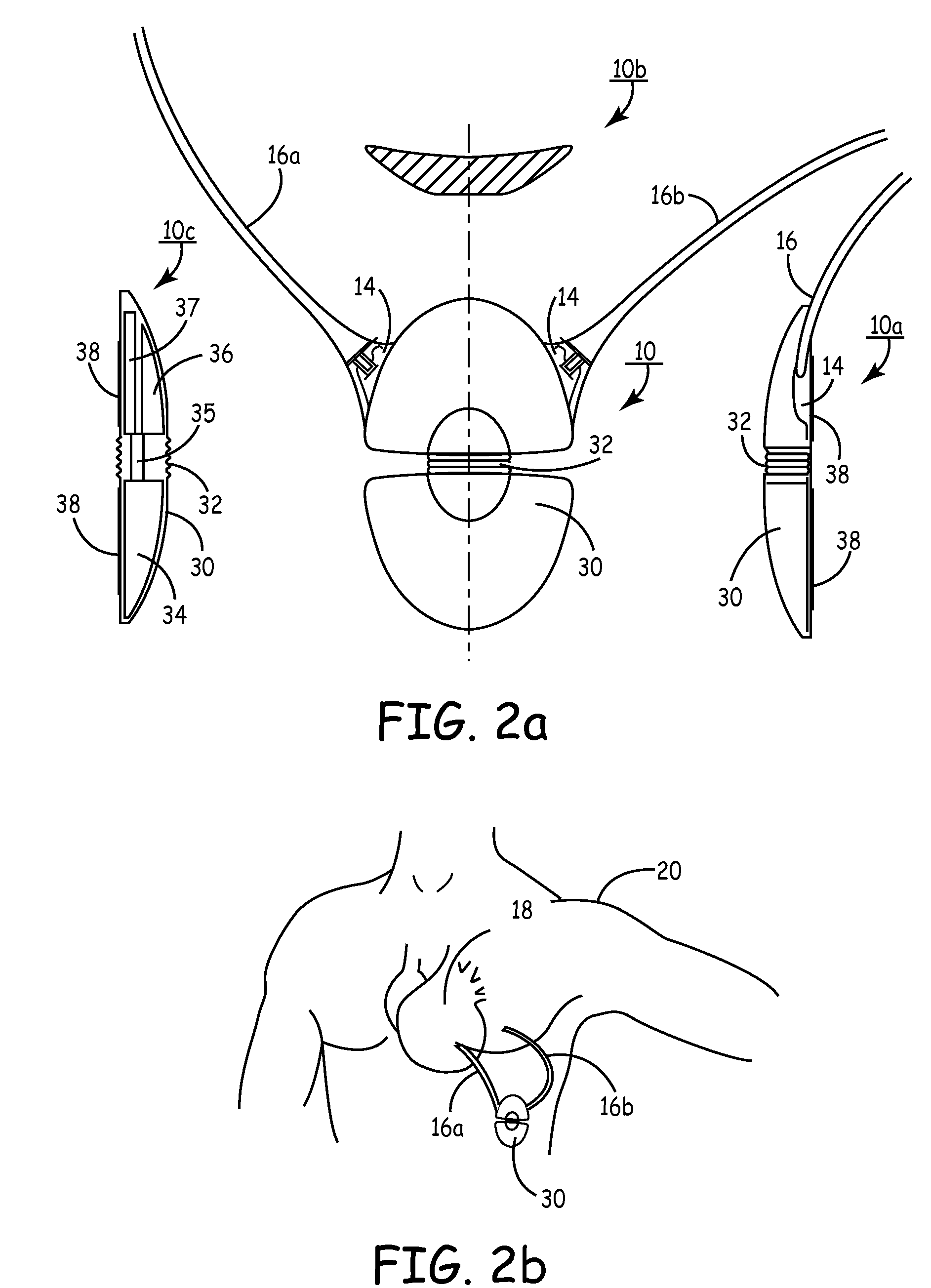
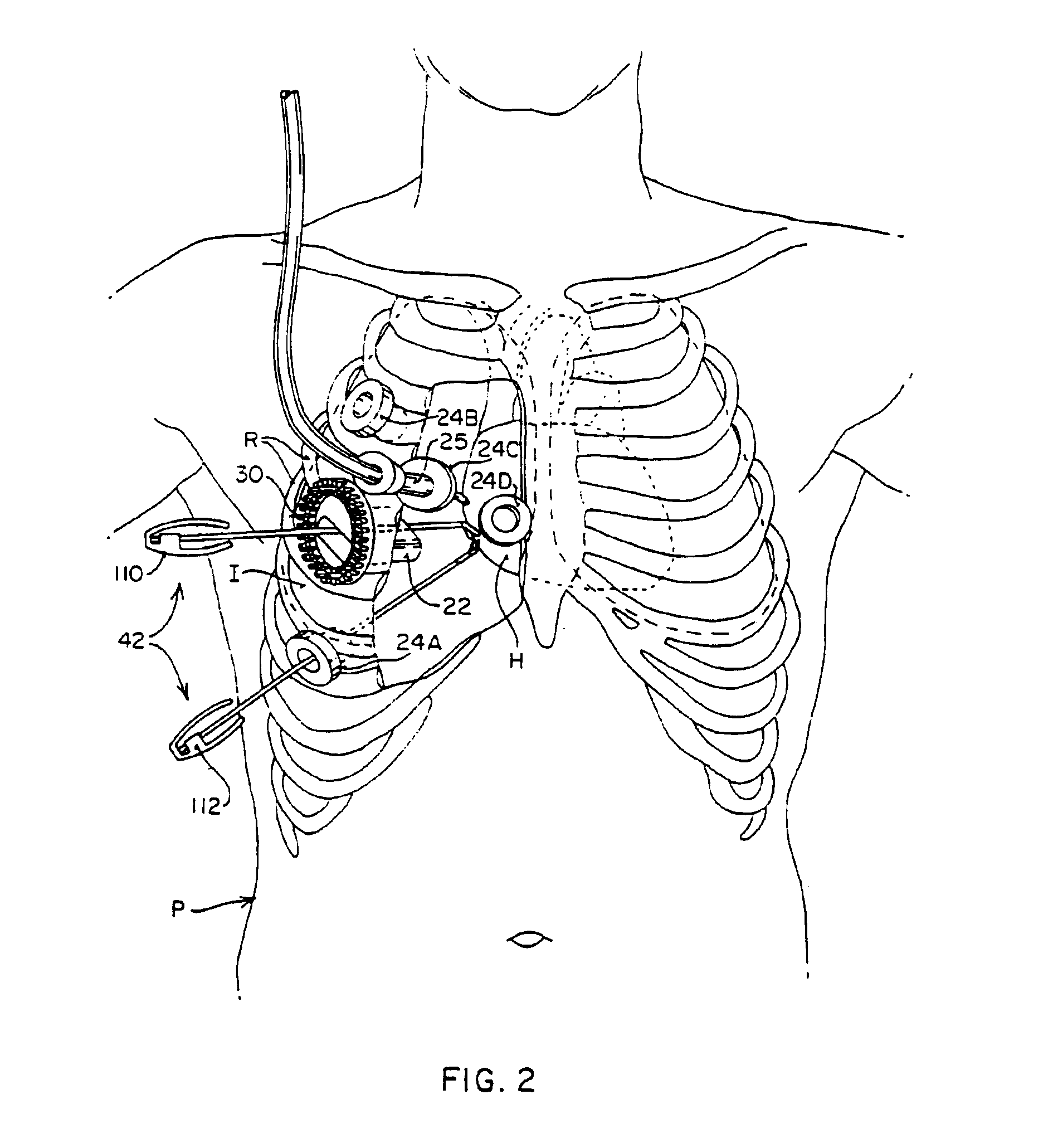
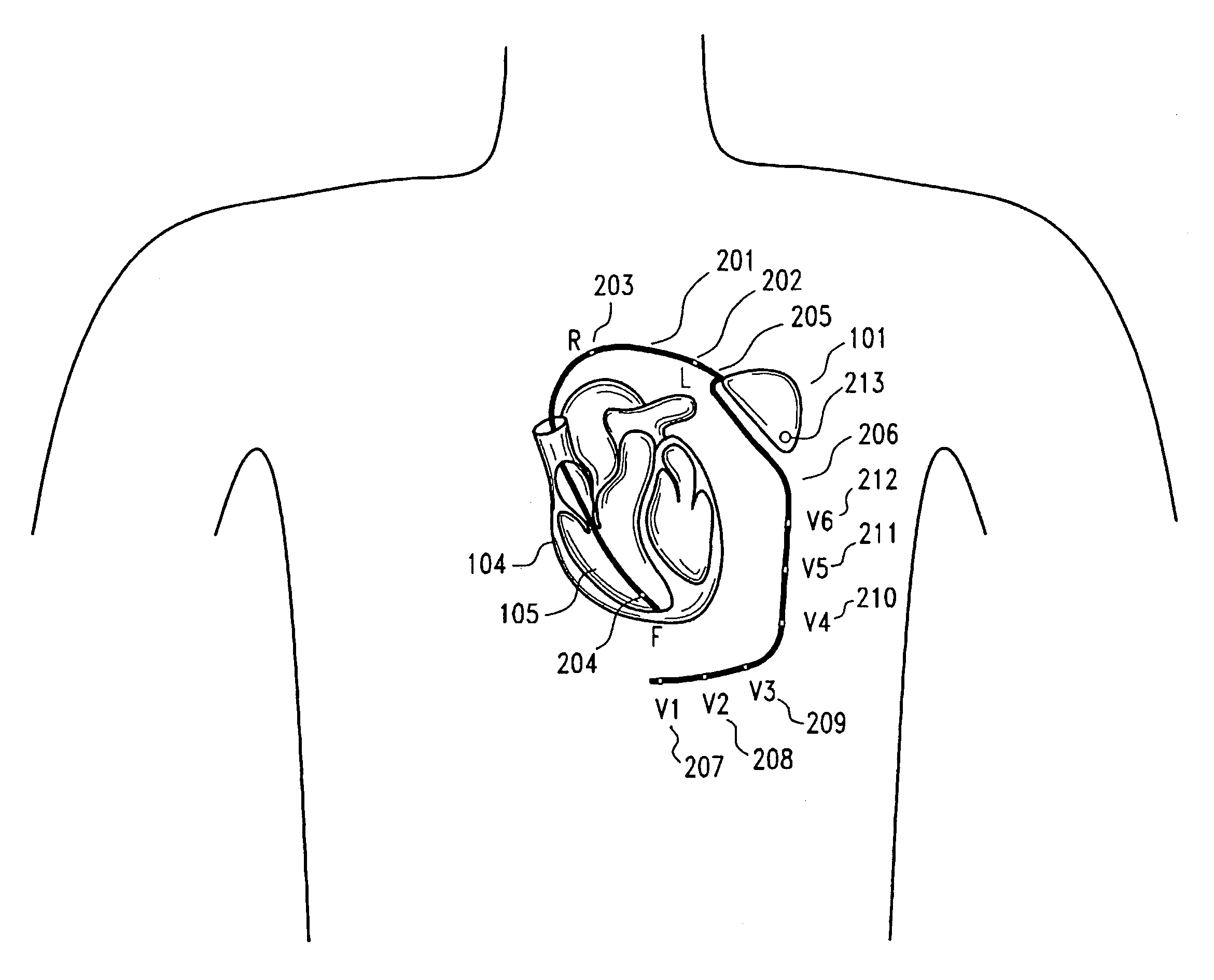
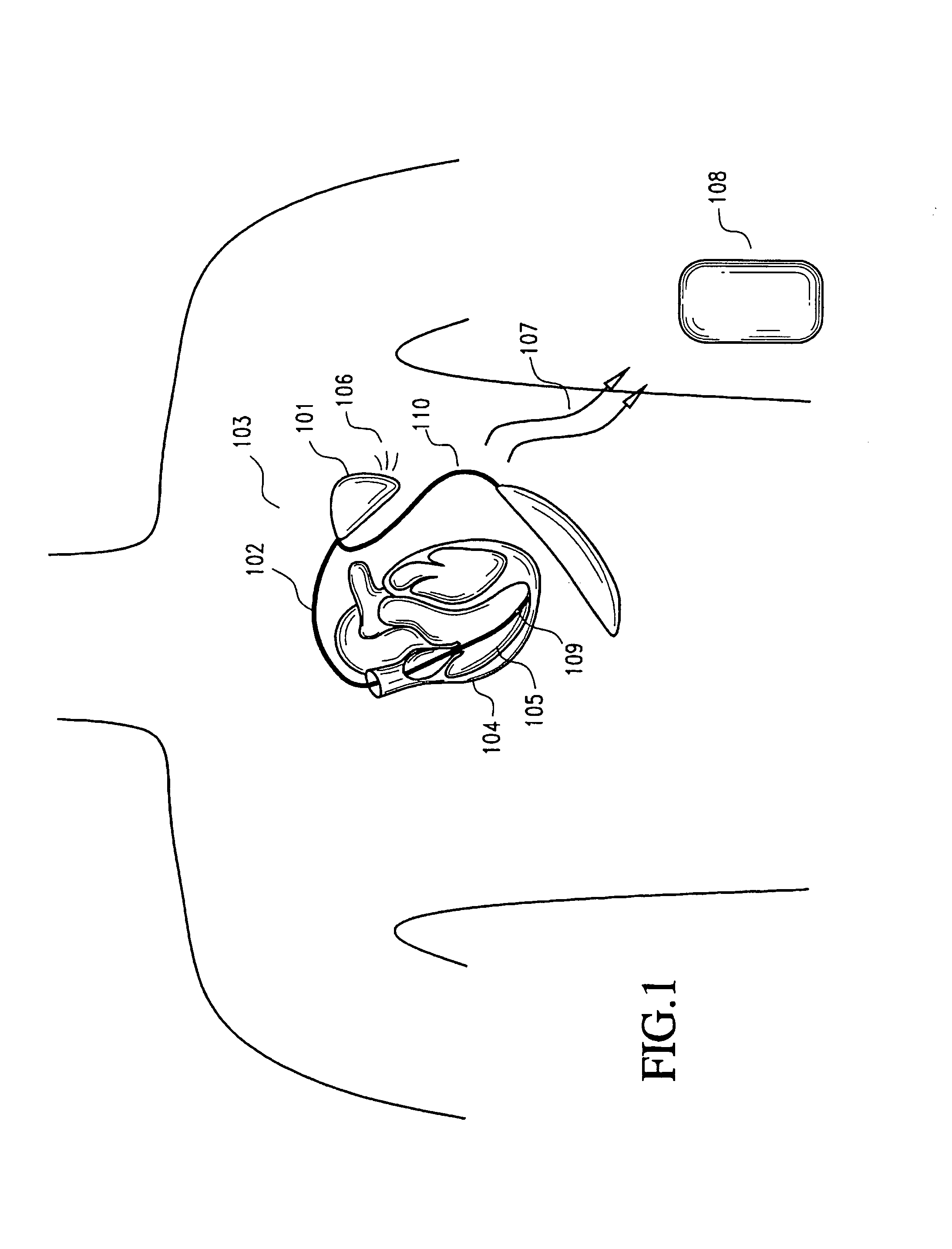
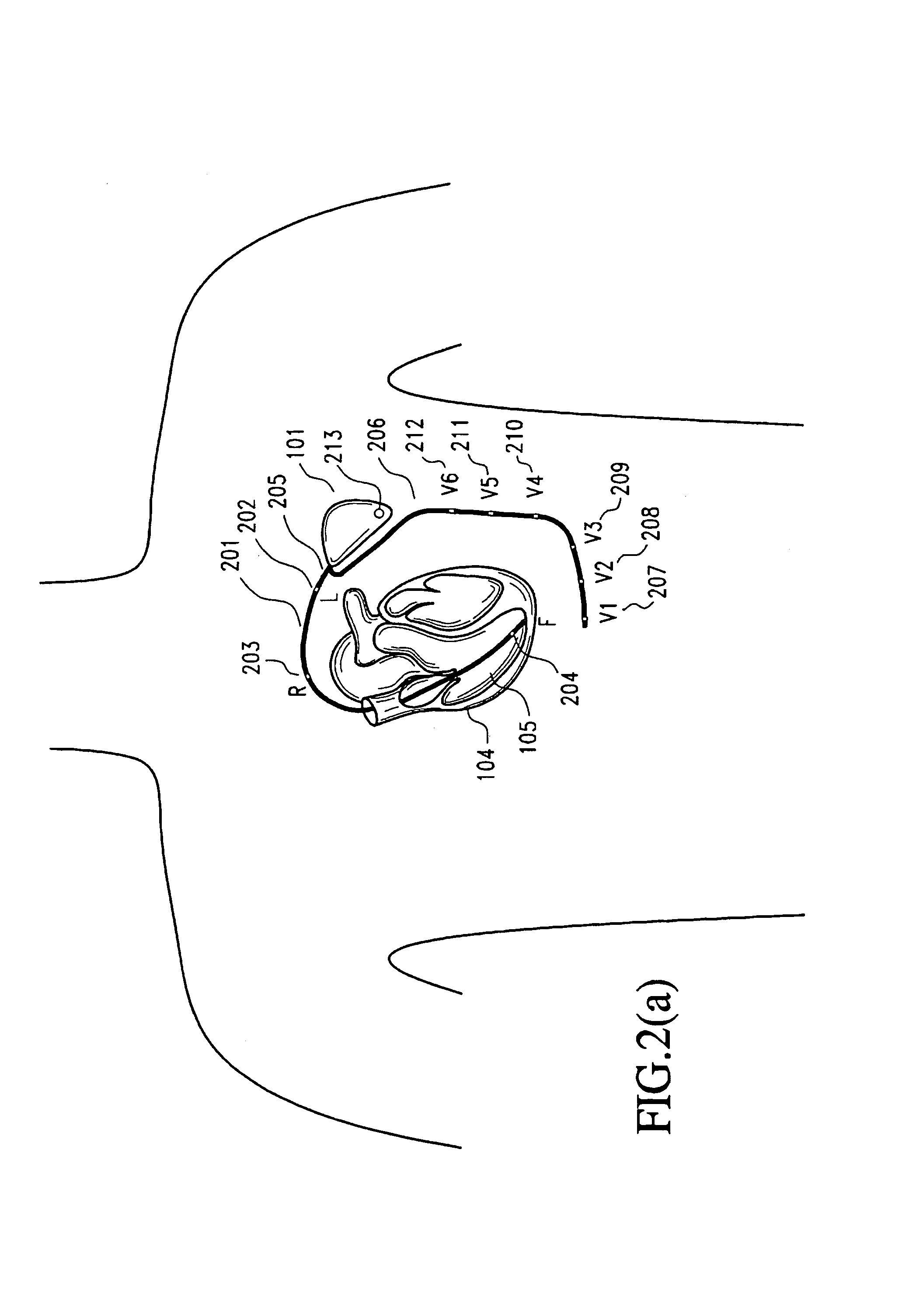
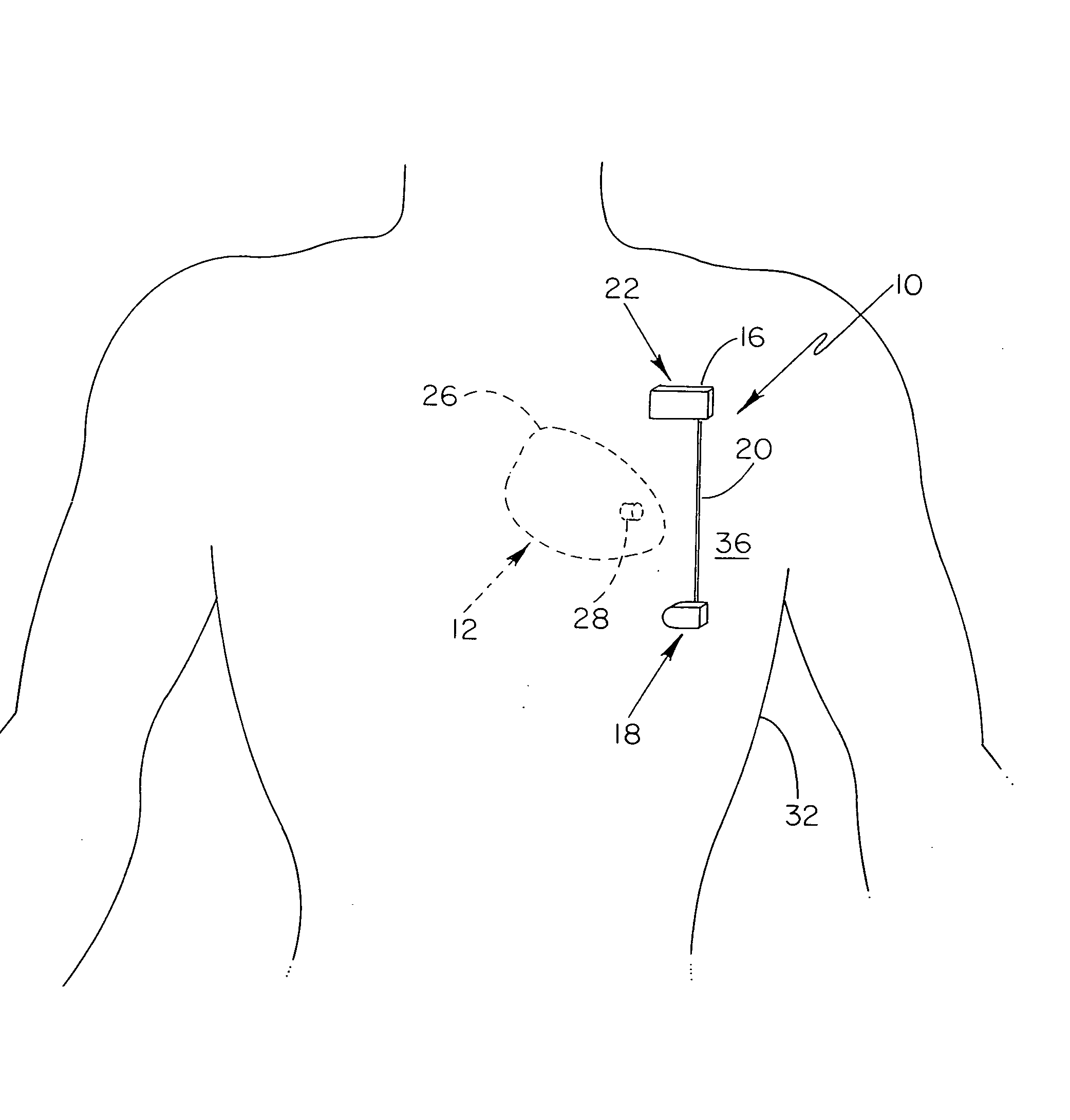
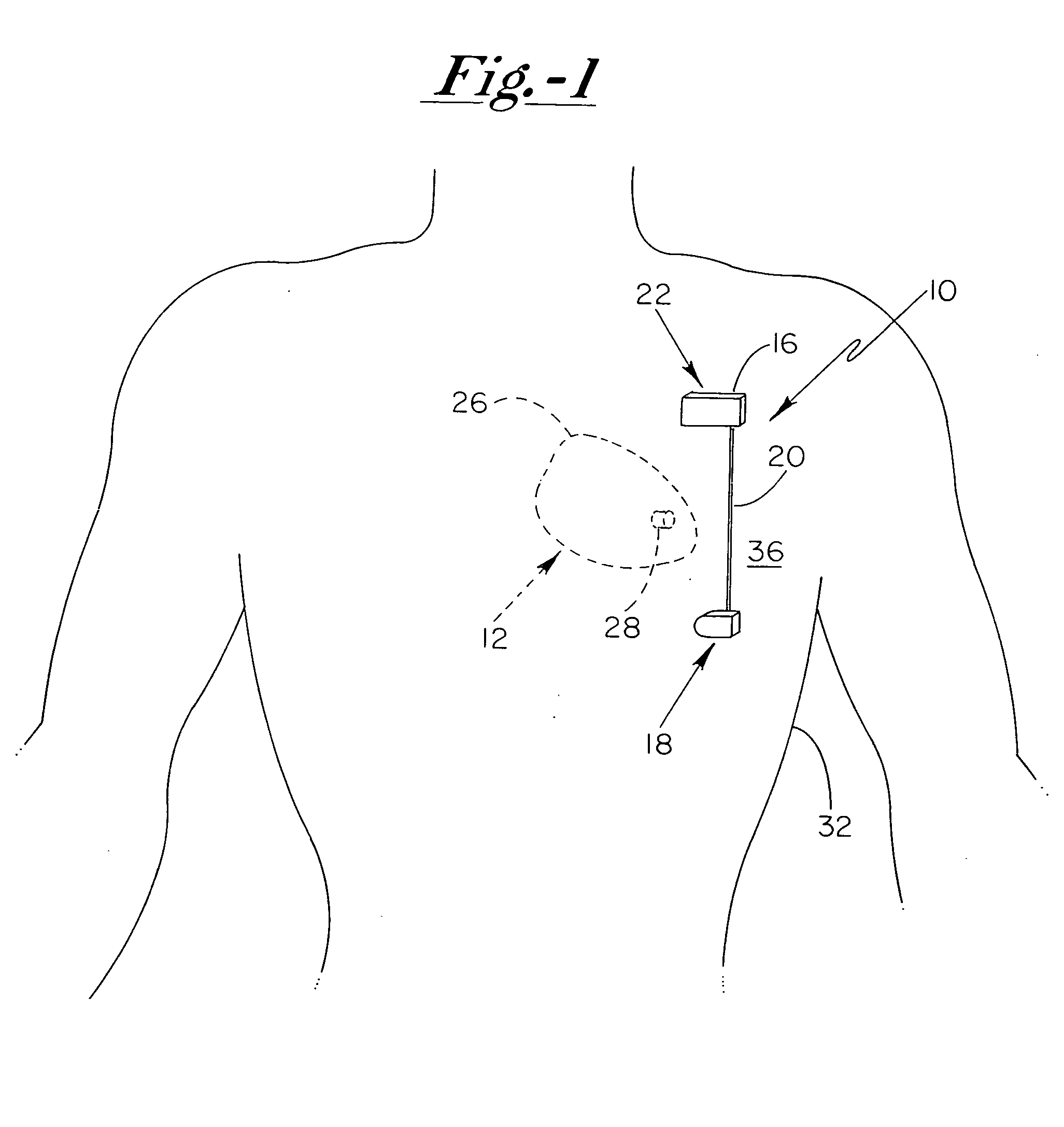
Subcutaneous cardioverter-defibrillator
SubQ ICDs are disclosed that are entirely implantable subcutaneously with minimal surgical intrusion into the body of the patient and provide distributed cardioversion-defibrillation sense and stimulation electrodes for delivery of cardioversion-defibrillation shock and pacing therapies across the heart when necessary. Configurations include one hermetically sealed housing with 1 or, optionally, 2 subcutaneous sensing and cardioversion-defibrillation therapy delivery leads or alternatively, 2 hermetically sealed housings interconnected by a power / signal cable. The housings are generally dynamically configurable to adjust to varying rib structure and associated articulation of the thoracic cavity and muscles. Further the housings may optionally be flexibly adjusted for ease of implant and patient comfort.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Methods and apparatus for accessing and treating regions of the body
InactiveUS20050165276A1Avoid excessive forceAccurately advancedEndoscopesLaproscopesThoracic structureAutomatic control
Methods and apparatus for accessing and treating regions of the body are disclosed herein. Using an endoscopic device having an automatically controllable proximal portion and a selectively steerable distal portion, the device generally may be advanced into the body through an opening. The distal portion is selectively steered to assume a selected curve along a desired path within the body which avoids contact with tissue while the proximal portion is automatically controlled to assume the selected curve of the distal portion. The endoscopic device can then be used for accessing various regions of the body which are typically difficult to access and treat through conventional surgical techniques because the device is unconstrained by “straight-line” requirements. Various applications can include accessing regions of the brain, thoracic cavity, including regions within the heart, peritoneal cavity, etc., which are difficult to reach using conventional surgical procedures.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL
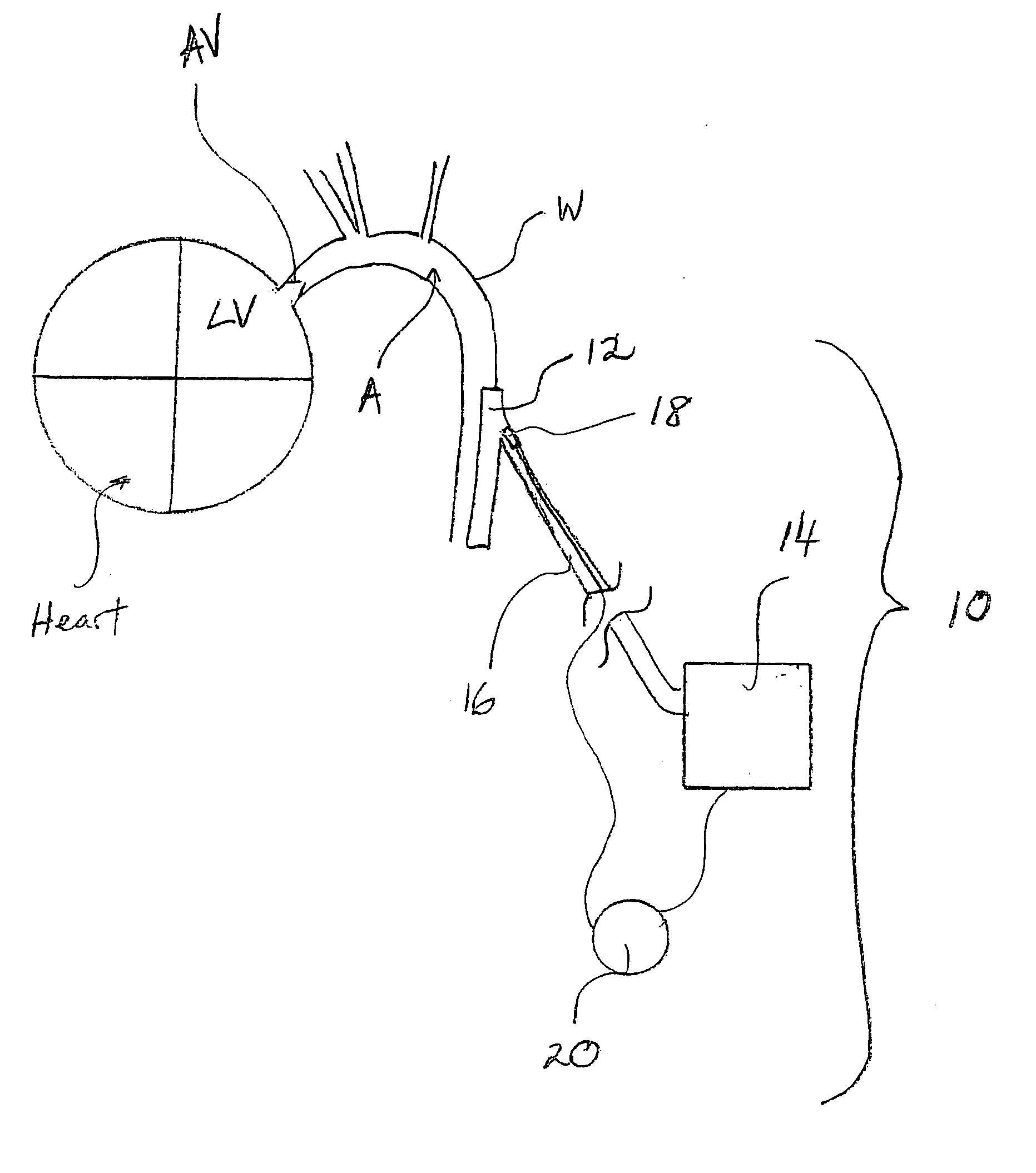
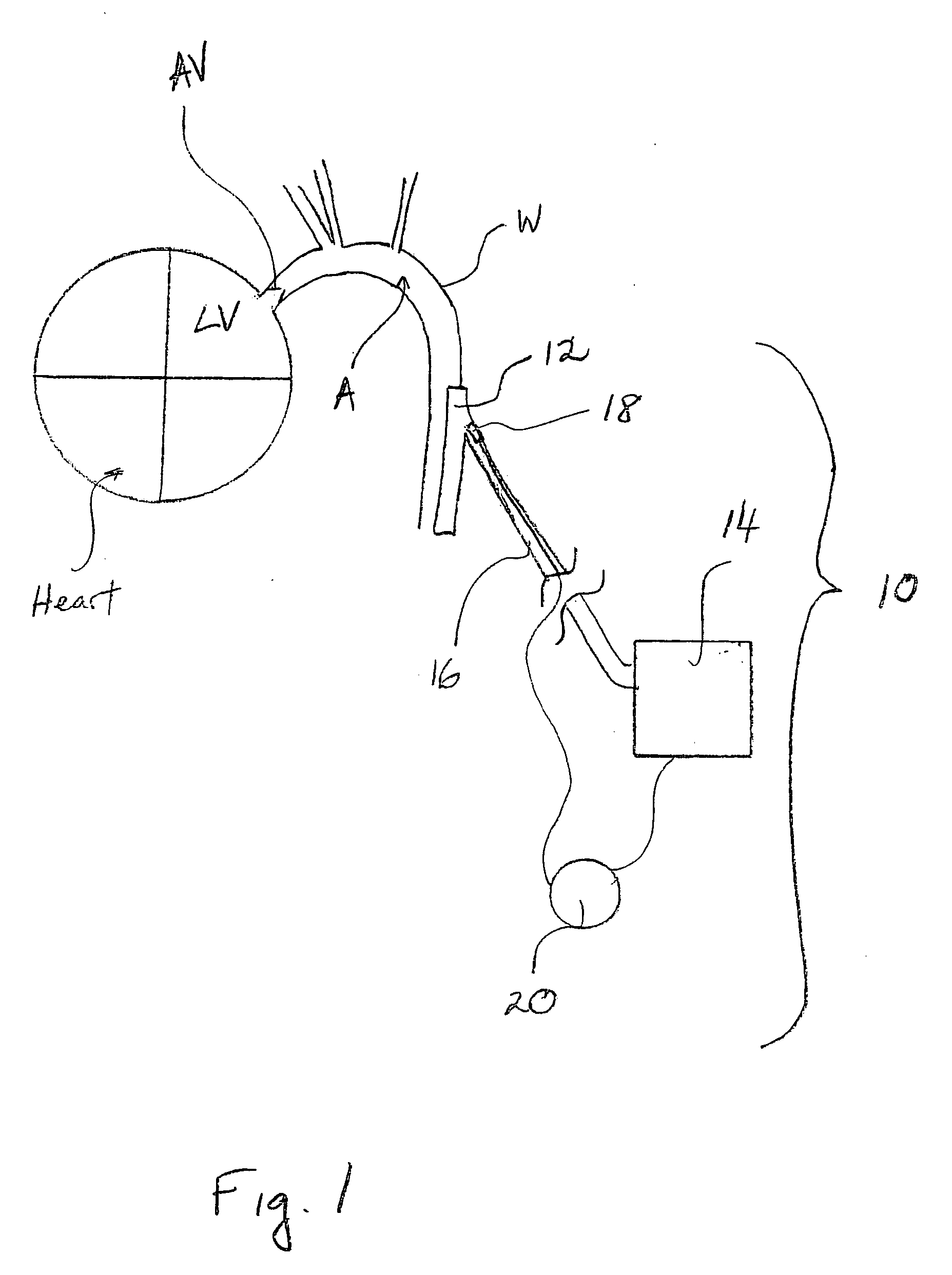
Synchronization system between aortic valve and cardiac assist device
ActiveUS20060030747A1Achieve synchronizationControl devicesMedical devicesAccelerometerThoracic cavity
A cardiac assist device synchronization system includes a cardiac assist device and an acoustic or accelerometer sensor that provides a signal input to the cardiac assist device indicative of aortic valve closure. The cardiac assist device is coupled to a mammalian aorta and includes an inflatable chamber and a fluid pump. A fluid conduit is in communication between the chamber and the pump to provide for selective inflation of the chamber. A pump controller triggers the pump in counter-pulsation to a mammalian heart upstream from the aorta. A process for synchronizing a cardiac assist device in counter-pulsation with a left ventricle includes locating an acoustic or accelerometer sensor within a thoracic cavity of a mammal having the assist device coupled to the aorta of the mammal. Through the measurement of an acoustic or acceleration property of an aortic valve of the mammal, and the transmission of aortic valve closure measurement through a controller for the cardiac assist device, counter-pulsatile synchronization for the cardiac assist device is achieved.
Owner:KANTROWITZ ALLEN B +1
Method and system for performing closed-chest bypass
InactiveUS6869437B1Addressing slow performancePromote recoverySurgical staplesWound clampsMeasurement deviceThoracic cavity
A coronary artery bypass graft procedure is performed through one or more openings made in the patient to create a point of entry to the thoracic cavity. A vein measurement device measures the distance between the proximal and distal anastomotic sites for each graft. A proximal anastomosis tool splits to release a graft vessel after deploying an anastomosis device at the proximal anastomosis site. The tool may be articulated. An integrated stabilizer stabilizes one or more tools relative to the surface of the beating heart at a distal anastomotic site. A distal anastomotic tool may be provided as part of the integrated stabilizer, and connects one end of the graft vessel to a target vessel. An epicardial dissector may be provided as part of the integrated stabilizer, and dissects the epicardium from the target vessel at a distal anastomotic site, as needed.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
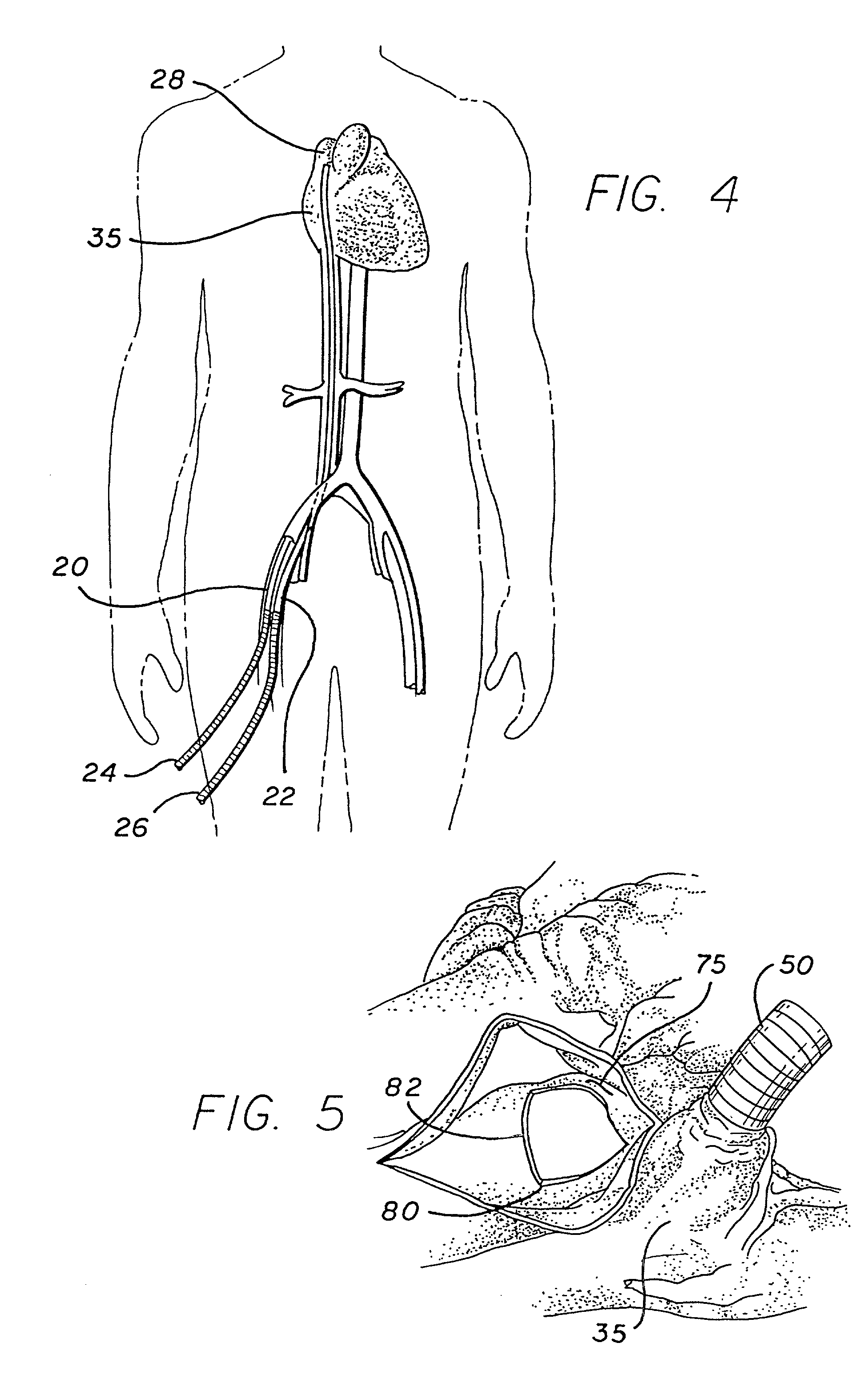
Minimally invasive cardiac surgery procedure
A minimally invasive approach for surgery on portions of the heart and great vessels. A parasternal incision is made extending across a predetermined number of costal cartilages, e.g., a right parasternal incision extending from the lower edge of the second costal cartilage to the superior edge of the fifth costal cartilage. One or more costal cartilages, e.g., the third and fourth, are then excised to provide access to the portion of the heart or great vessels of interest, for example between a point approximately three centimeters above supra annular ridge and the mid ventricular cavity, and a desired procedure completed. A minimally invasive procedure for repair or replacement of the aortic valve is disclosed that includes making a transverse incision of about 10 cm in length over the second or third intercostal space in the thorax of the patient, dividing the sternum transversely following the incision, retracting the transversely divided sternum, exposing the ascending aorta, and incising the ascending aorta to provide access to an area adjacent the aortic valve.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND +1
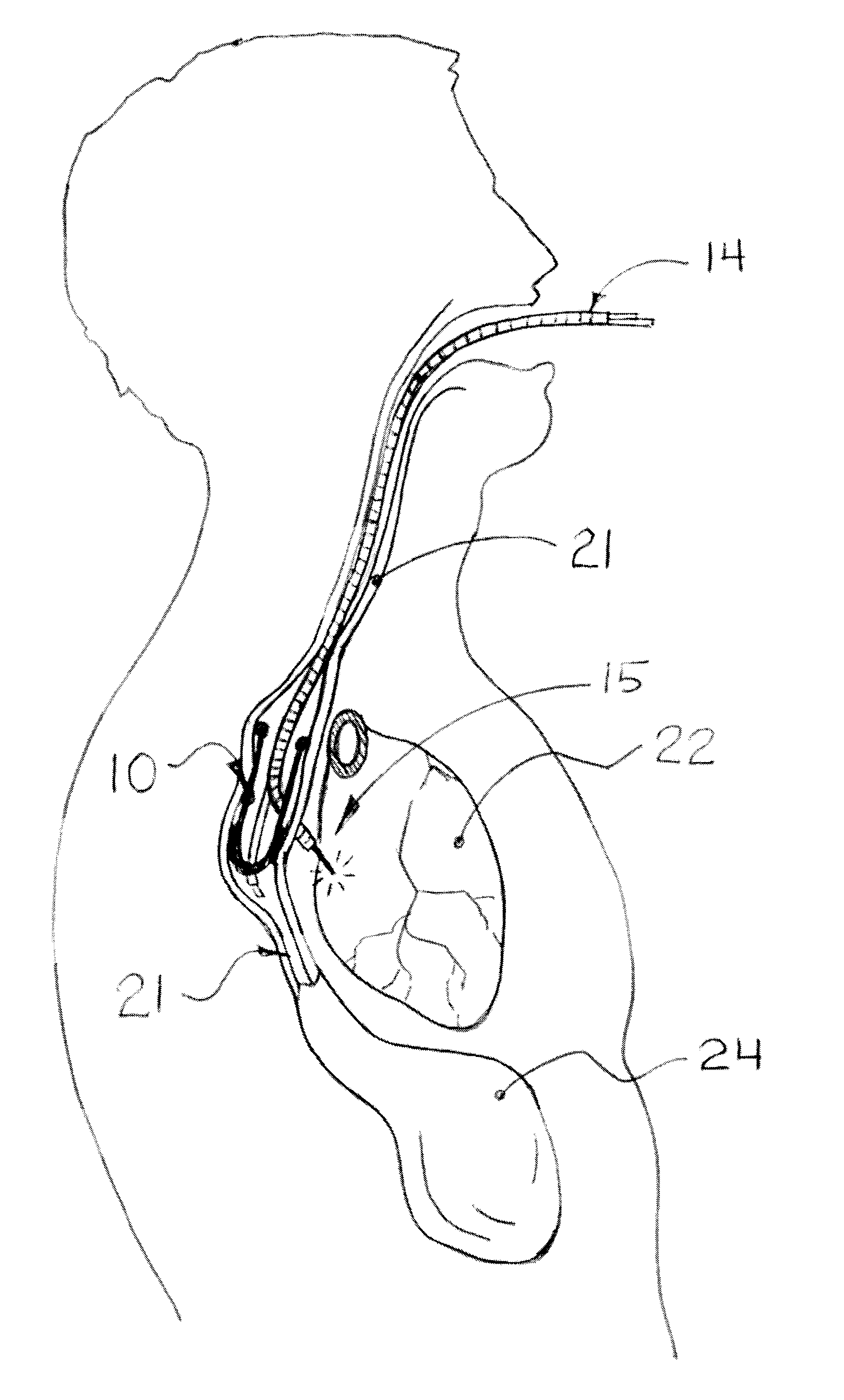
Devices and methods for intracardiac procedures
InactiveUS6899704B2Easy to replaceEasy to interveneSuture equipmentsCannulasAtrial cavityThoracic cavity
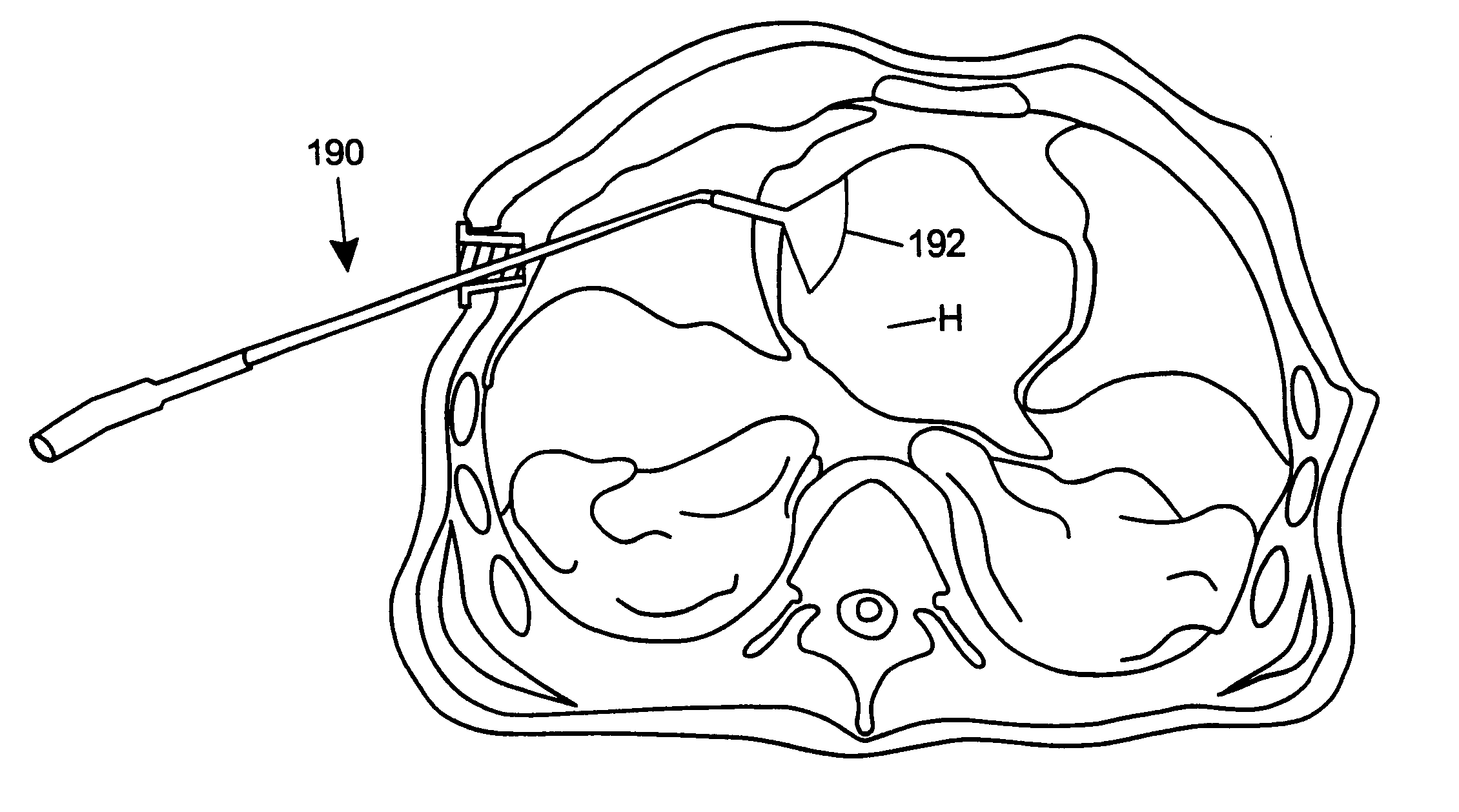
The invention provides devices and methods for performing less-invasive surgical procedures within an organ or vessel. In an exemplary embodiment, the invention provides a method of closed-chest surgical intervention within an internal cavity of a patient's heart or great vessel. According to the method, the patient's heart is arrested and cardiopulmonary bypass is established. A scope extending through a percutaneous intercostal penetration in the patient's chest is used to view an internal portion of the patient's chest. An internal penetration is formed in a wall of the heart or great vessel using cutting means introduced through a percutaneous penetration in an intercostal space in the patient's chest. An interventional tool is then introduced, usually through a cannula positioned in a percutaneous intercostal penetration. The interventional tool is inserted through the internal penetration in the heart or great vessel to perform a surgical procedure within the internal cavity under visualization by means of the scope. In a preferred embodiment, a cutting tool is introduced into the patient's left atrium from a right portion of the patient's chest to remove the patient's mitral valve. A replacement valve is then introduced through an intercostal space in the right portion of the chest and through the internal penetration in the heart, and the replacement valve is attached in the mitral valve position.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
Implantable myocardial ischemia detection, indication and action technology
InactiveUS7277745B2Reduce capacityReduce mechanical performance requirementsElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsThoracic structureCardiac muscle
One embodiment enables detection of MI / I and emerging infarction in an implantable system. A plurality of devices may be used to gather and interpret data from within the heart, from the heart surface, and / or from the thoracic cavity. The apparatus may further alert the patient and / or communicate the condition to an external device or medical caregiver. Additionally, the implanted apparatus may initiate therapy of MI / I and emerging infarction.
Owner:INFINITE BIOMEDICAL TECH
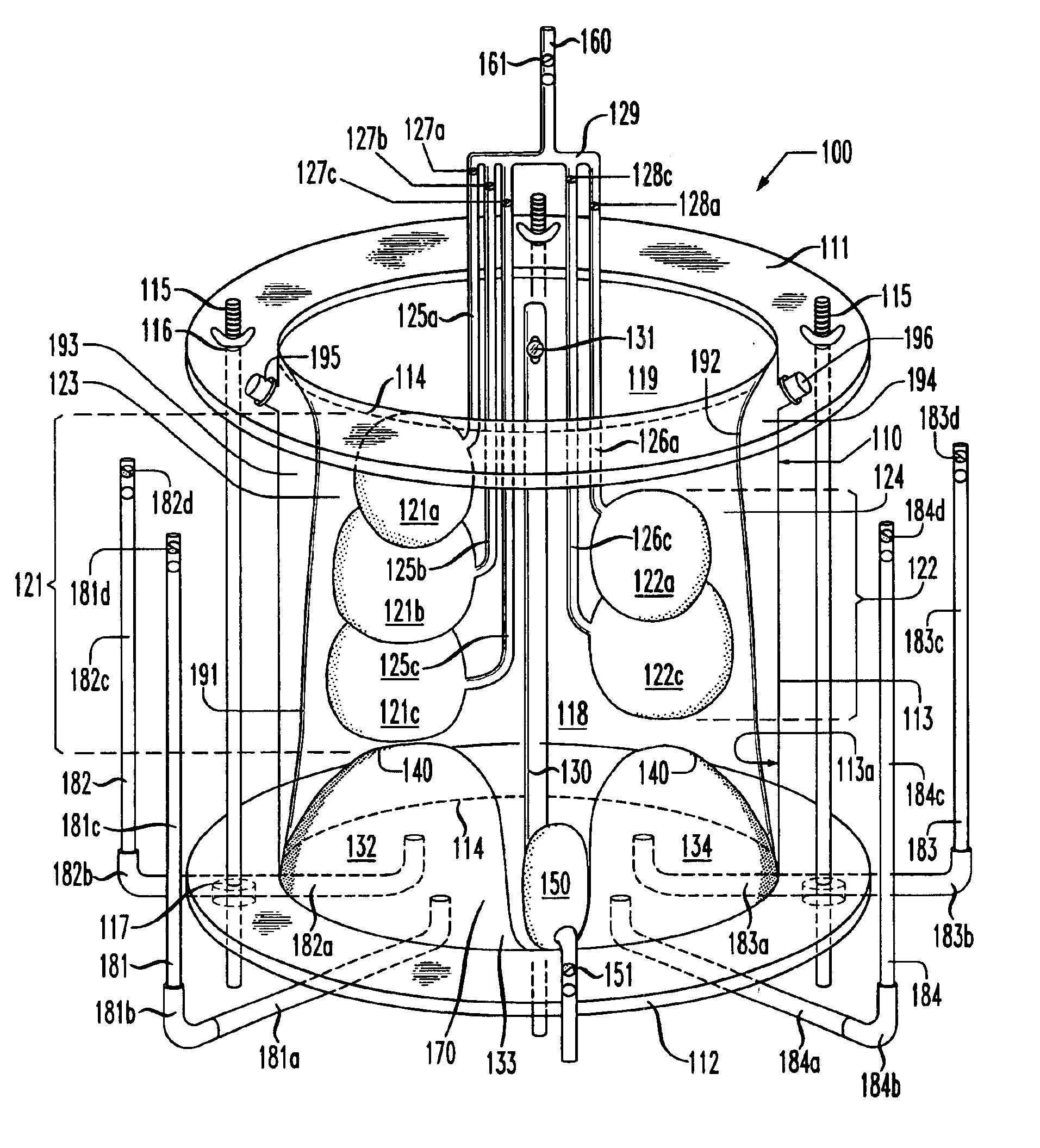
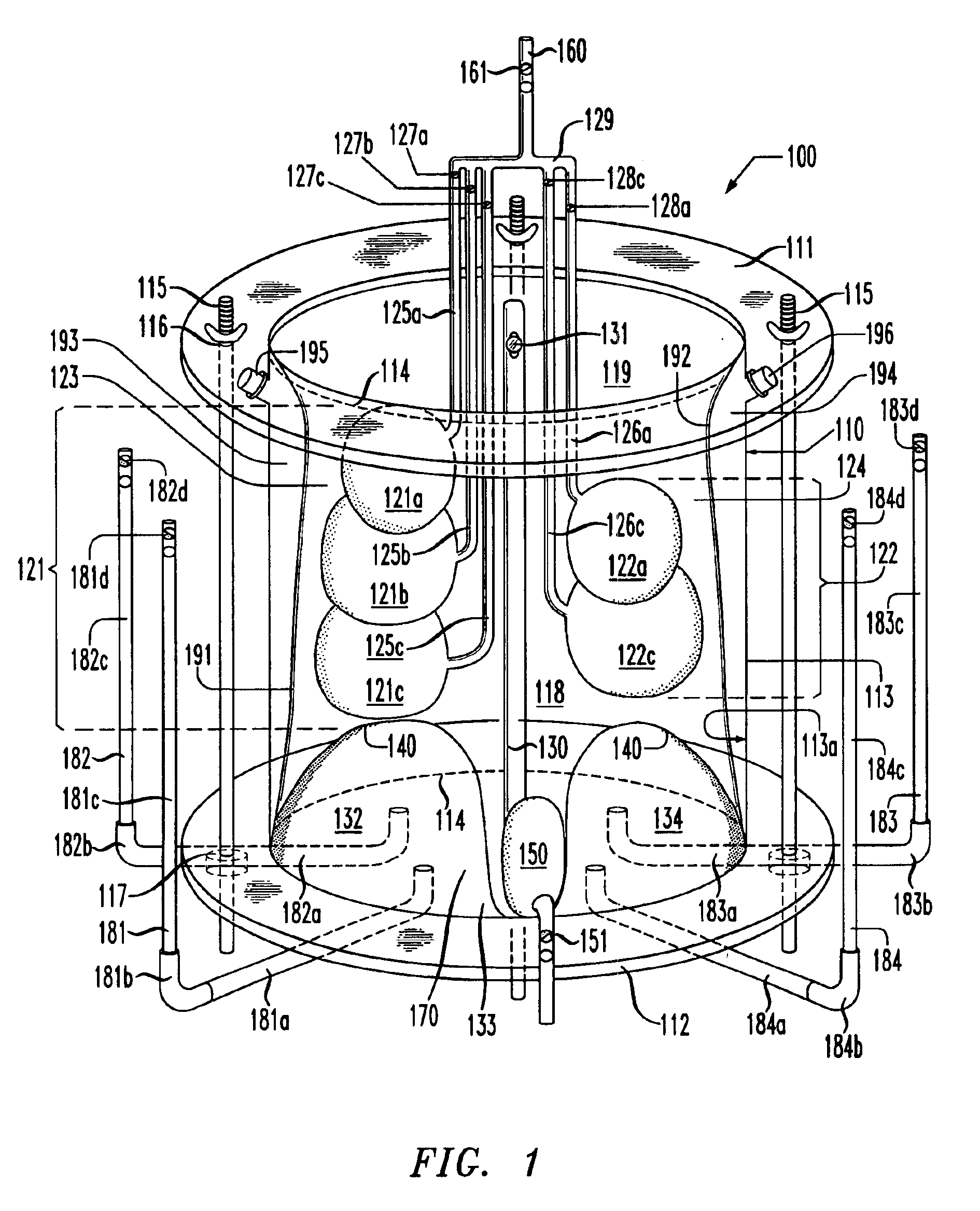
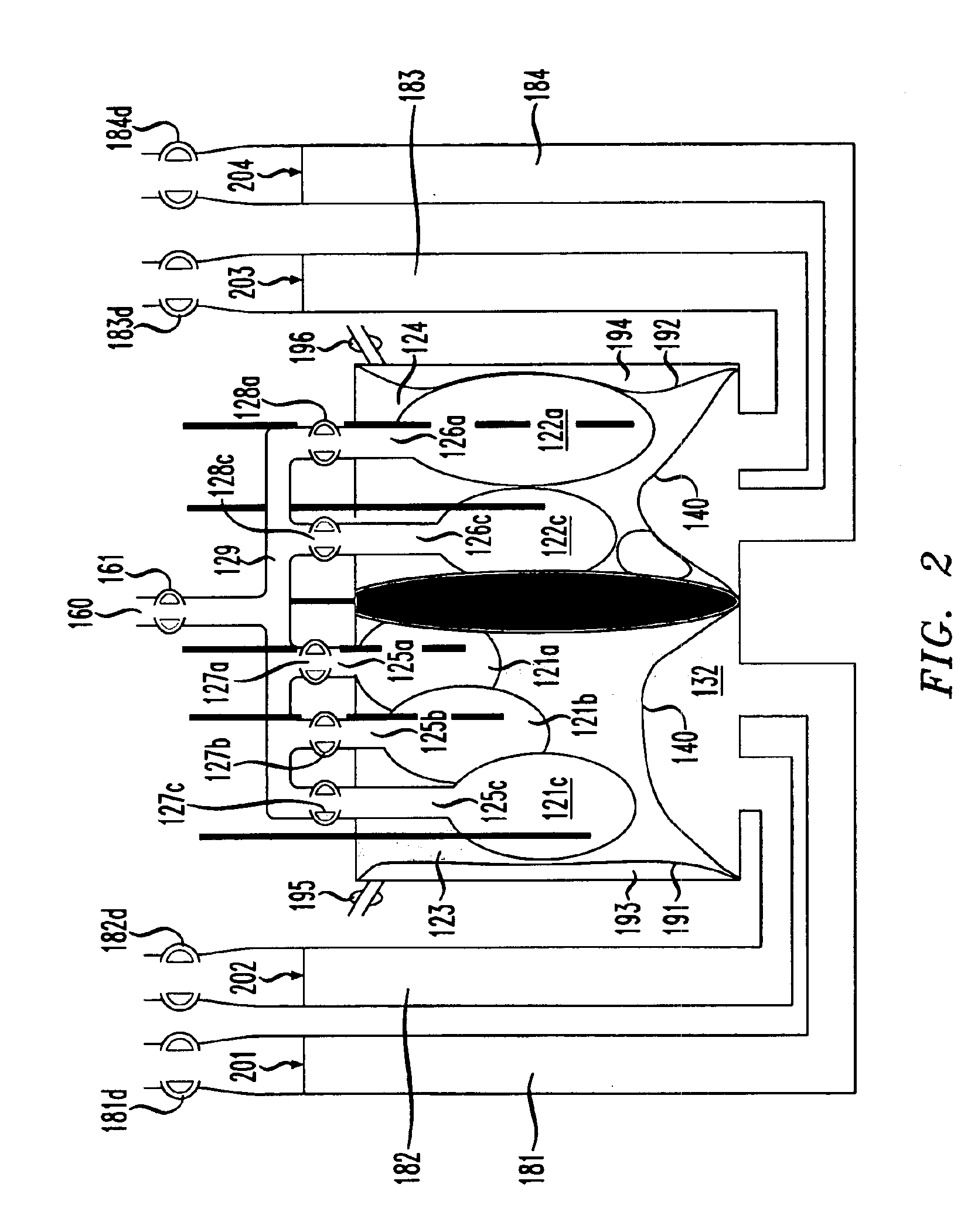
Lung simulator
The present invention provides a lung simulator comprising a substantially-rigid, fluid-tight, translucent housing simulating a human thoracic cavity and at least one flexible air-tight bag simulating a lung having a plurality of simulated lung lobes, and a corresponding plurality of valves, each of the plurality of valves coupled to a one of the plurality of simulated lung lobes and configured to simulate varying degrees of fluid flow resistance. In a preferred embodiment, the substantially-rigid, fluid-tight, transparent housing has isolated simulated left and right thoracic cavities therein and the at least one flexible air-tight bag is located within one of the simulated thoracic cavities. The present invention further provides a method of manufacturing a lung simulator.
Owner:ESTETTER ROBERT H +2
Methods and Apparatus for Selectively Shunting Energy in an Implantable Extra-Cardiac Defibrillation Device
InactiveUS20080183230A1Sufficient massEasy to implantSubcutaneous electrodesExternal electrodesPatient comfortThoracic cavity
The disclosure provides methods and apparatus for simultaneously providing protection to an implantable medical device, such as an extra-cardiac implantable defibrillator (EID), while allowing efficacious therapy delivery via an external defibrillator (e.g., an automated external defibrillator, or AED). Due to the orientation of the electrodes upon application of therapy via, for example, via an AED the structure of the EID essentially blocks therapy delivery. In addition, but for the teaching of this disclosure sensitive circuitry of an EID can be damaged during application of external high voltage therapy thus rendering the EID inoperable. EIDs are disclosed that are entirely implantable subcutaneously with minimal surgical intrusion into the body of the patient and provide distributed cardioversion-defibrillation sense and stimulation electrodes for delivery of cardioversion-defibrillation shock and pacing therapies across the heart when necessary. Configurations include one hermetically sealed housing with one or, optionally, two subcutaneous sensing and cardioversion-defibrillation therapy delivery leads or alternatively, two hermetically sealed housings interconnected by a power / signal cable. The housings are generally dynamically configurable to adjust to varying rib structure and associated articulation of the thoracic cavity and muscles. Further the housings may optionally be flexibly adjusted for ease of implant and patient comfort. One aspect includes partially insulating a surface of an EID that faces away from a heart while maintaining a major conductive surface facing the heart.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Anti-coagulation and demineralization system for conductive medical devices
ActiveUS20060009804A1Prevention and elimination of blood component depositElectrotherapyArtificial respirationThoracic structureElectricity
A system for minimizing and / or eliminating coagulative or mineral deposits on respective blood-contacting surfaces of implanted medical devices includes an implantable system having a current generating device that is electrically coupled to at least first and second electrodes for developing a current therebetween. The at least first and second electrodes are disposed across a patient's thoracic cavity in a manner so that a particular implanted medical device having at least a portion thereof that is fabricated from an electrically conductive material is disposed in a path substantially between such electrodes, thereby focusing the generated electrical current at the electrically conductive portion of the implanted medical device for therapeutic treatment thereat.
Owner:MEDTRONIC PS MEDICAL
Lung device with sealing features
InactiveUS7766891B2Reduce air leakageMitigates pneumothorax and hemothoraxSurgical needlesMedical devicesThoracic structureThoracic cavity
This invention relates generally to a design of lung devices for safely performing a transthoracic procedure. In particular, the invention provides devices and methods of using these devices to access the thoracic cavity with minimal risk of causing pneumothorax or hemothorax. More specifically, the invention enables diagnostic and therapeutic access to a thoracic cavity using large bore instruments. This invention also provides a method for diagnostic and therapeutic procedures using a device capable of sealing the wound upon withdrawal of the device. The invention includes a device comprising an elongated body adapted to make contact with a tissue of a subject through an access hole, and a sealant delivery element. The invention also includes a method of performing tissue treatment or diagnosis in a subject.
Owner:EKOS CORP
Subcutaneous cardioverter-defibrillator
ActiveUS20060247688A1Convenient to implantHeart defibrillatorsSubcutaneous electrodesThoracic structureThoracic cavity
SubQ ICDs are disclosed that are entirely implantable subcutaneously with minimal surgical intrusion into the body of the patient and provide distributed cardioversion-defibrillation sense and stimulation electrodes for delivery of cardioversion-defibrillation shock and pacing therapies across the heart when necessary. Configurations include one hermetically sealed housing with 1 or, optionally, 2 subcutaneous sensing and cardioversion-defibrillation therapy delivery leads or alternatively, 2 hermetically sealed housings interconnected by a power / signal cable. The housings are generally dynamically configurable to adjust to varying rib structure and associated articulation of the thoracic cavity and muscles. Further the housings may optionally be flexibly adjusted for ease of implant and patient comfort.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Progressive biventricular diastolic support device
InactiveUS7468029B1Easy accessIncrease acceptanceHeart valvesIntravenous devicesAtrial cavityLeft anterior axillary line
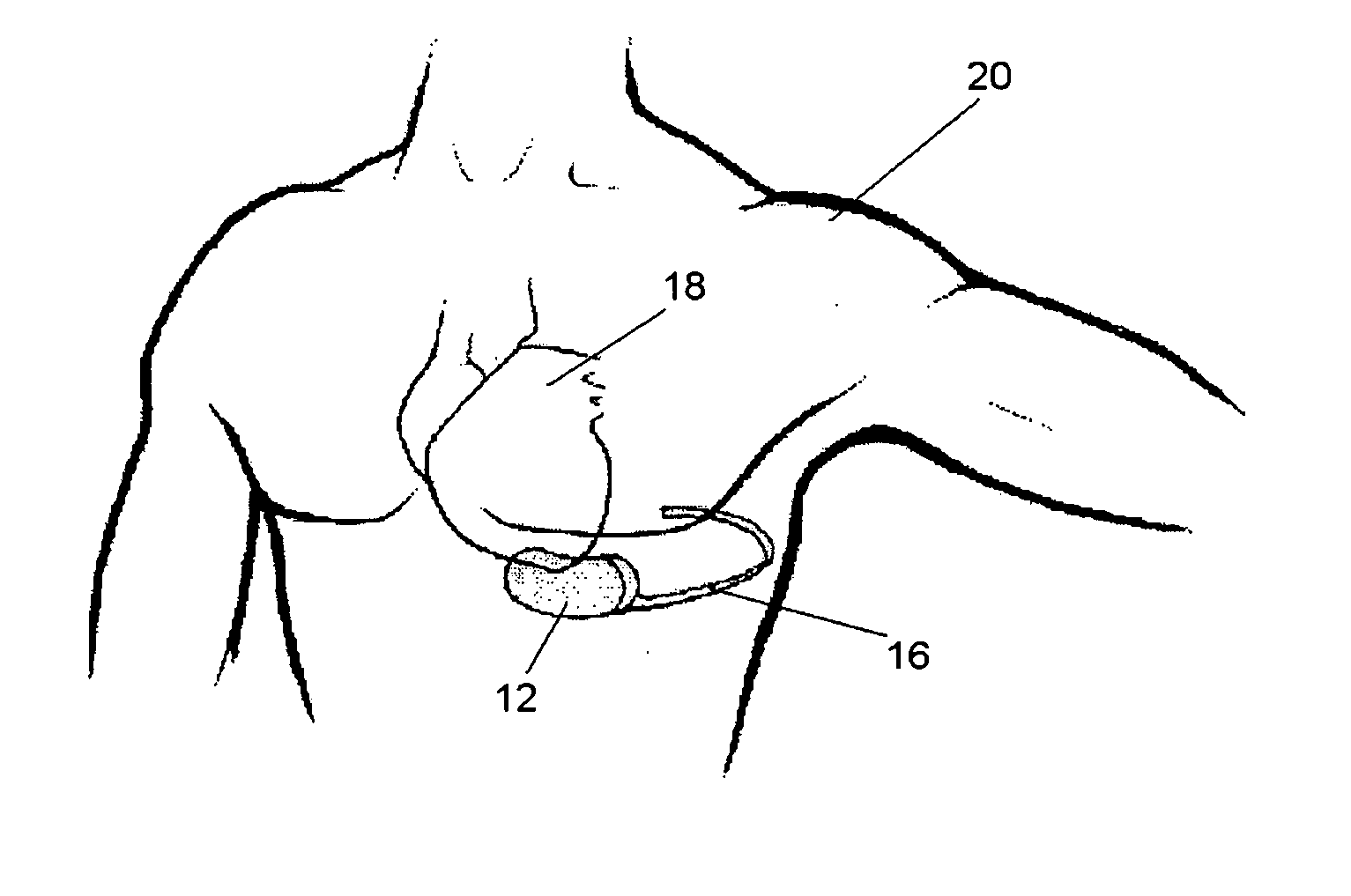
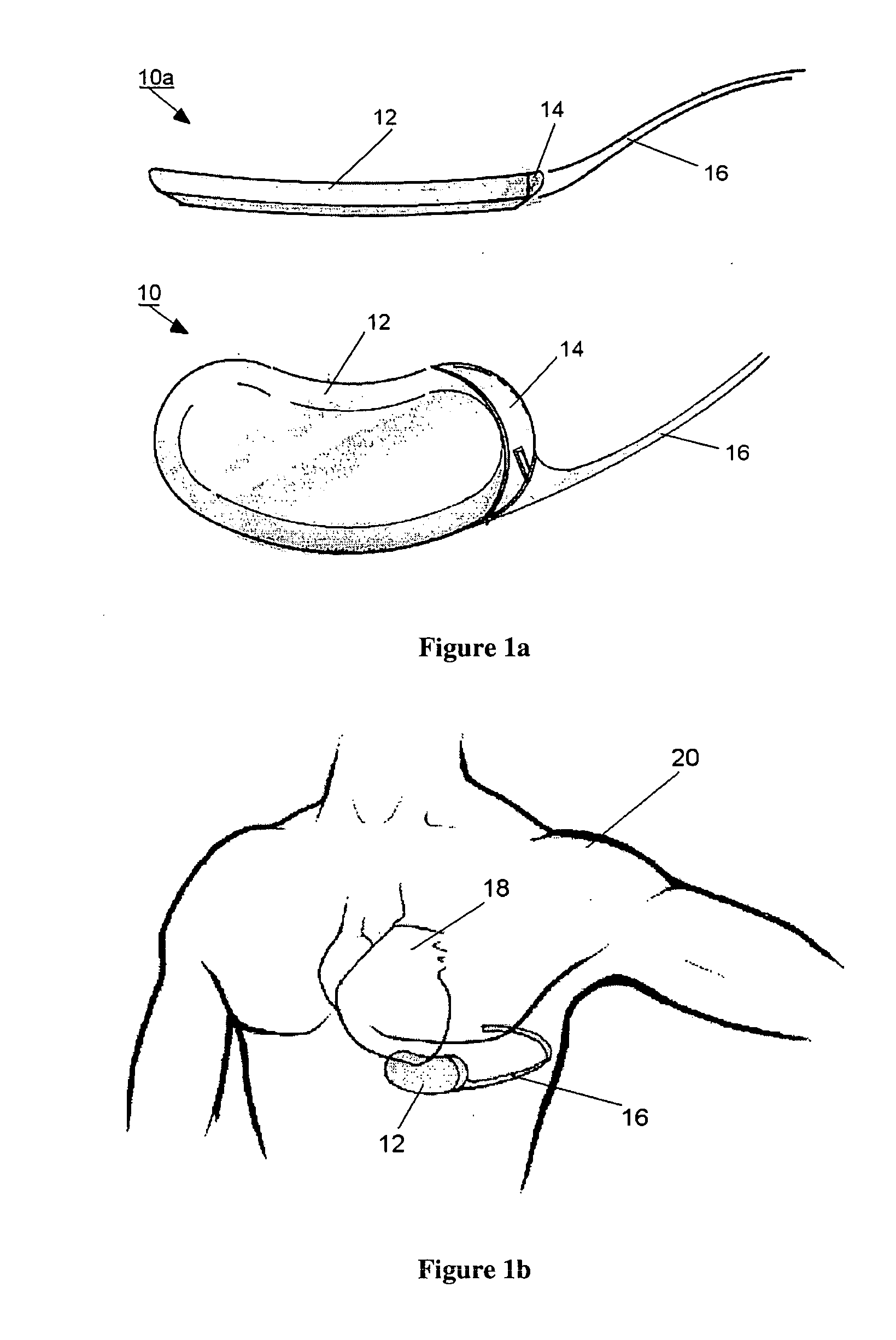
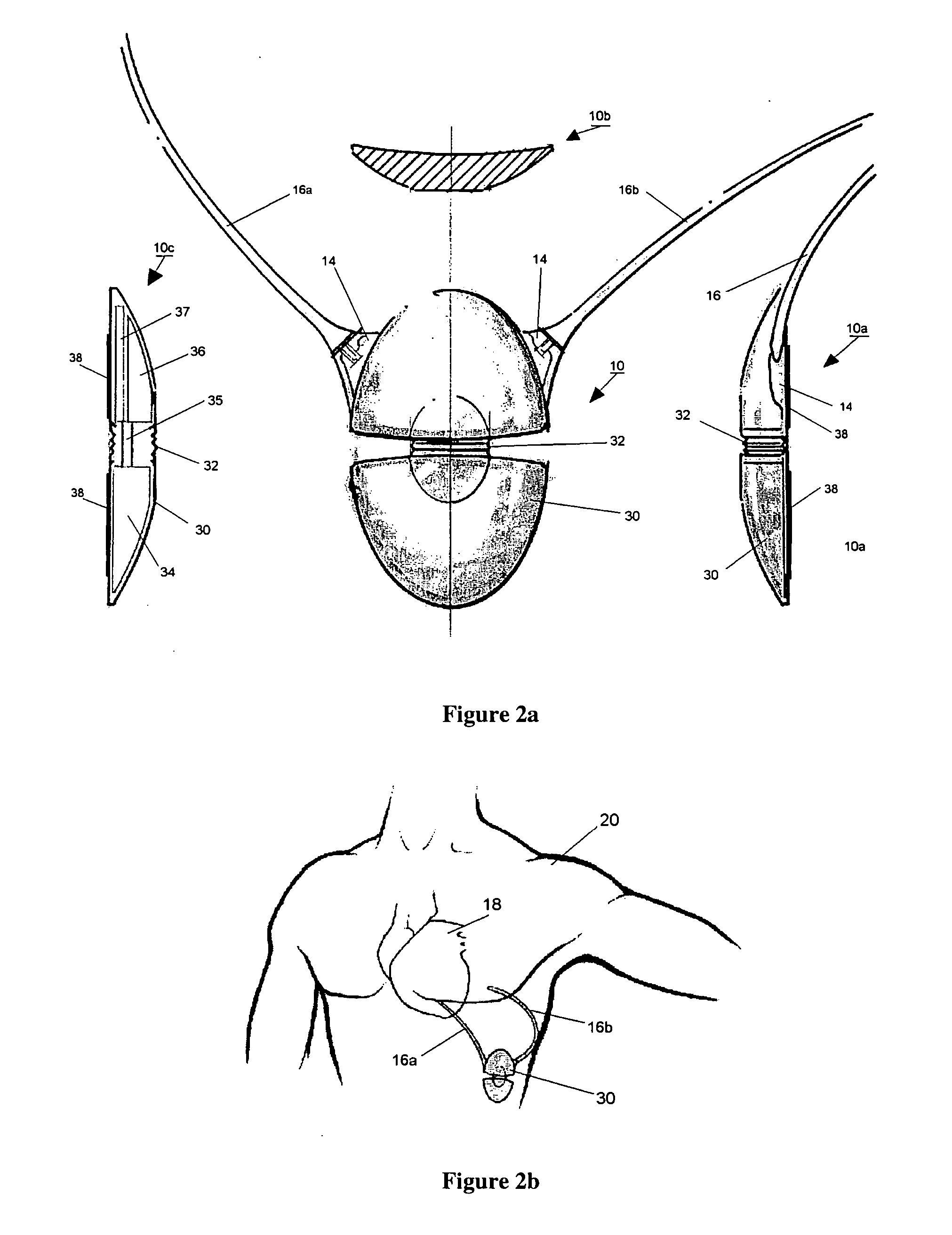
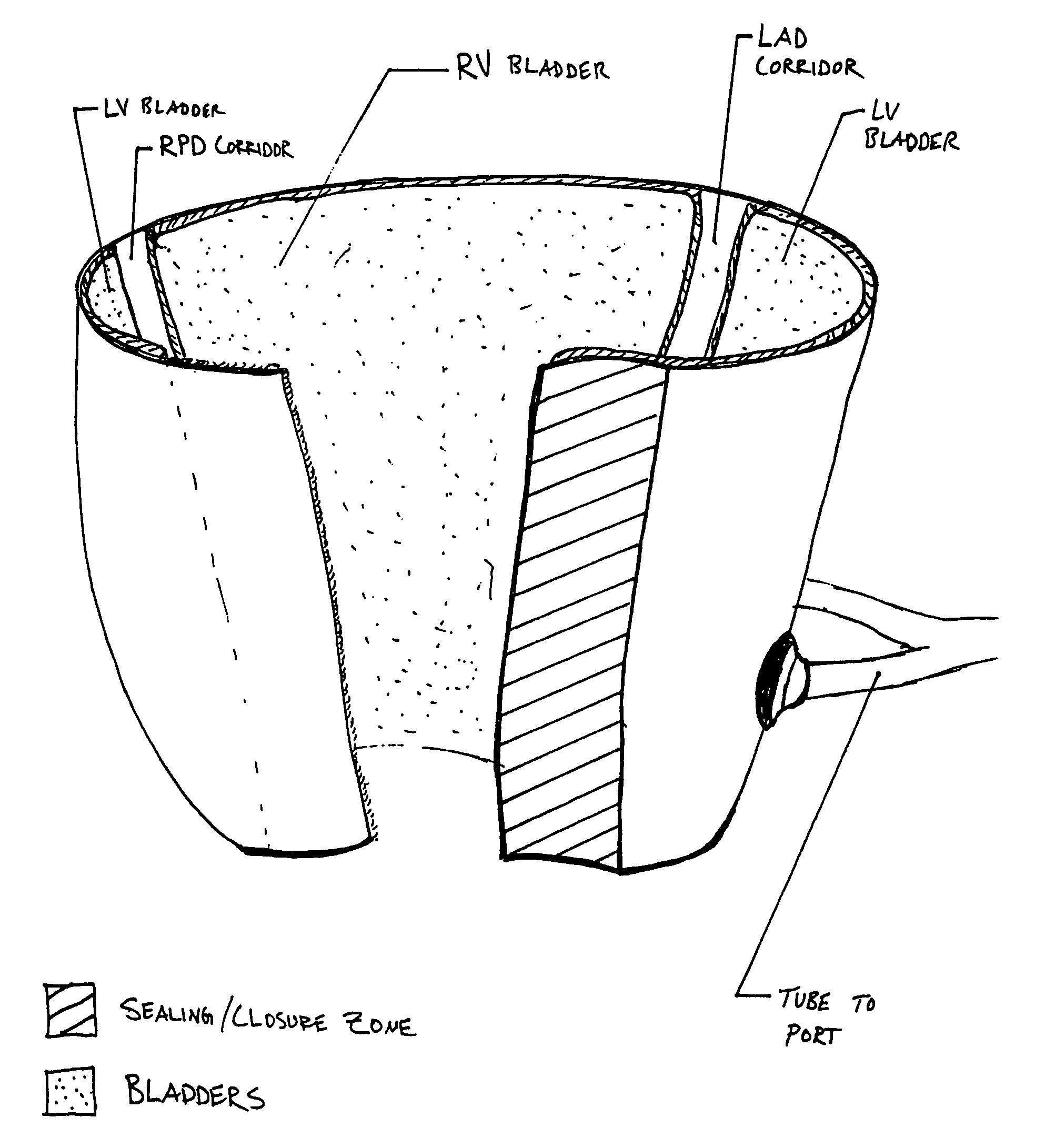
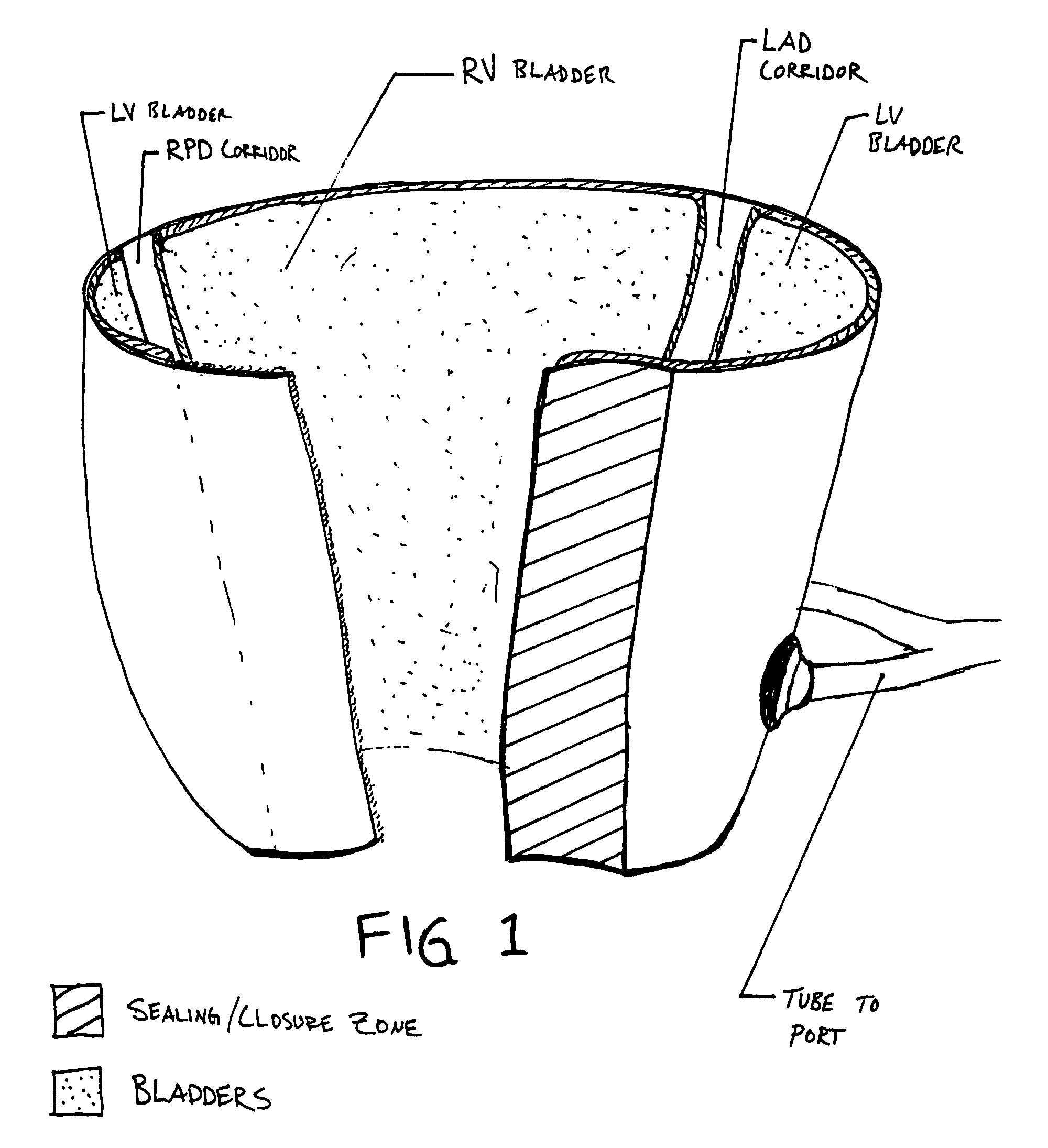
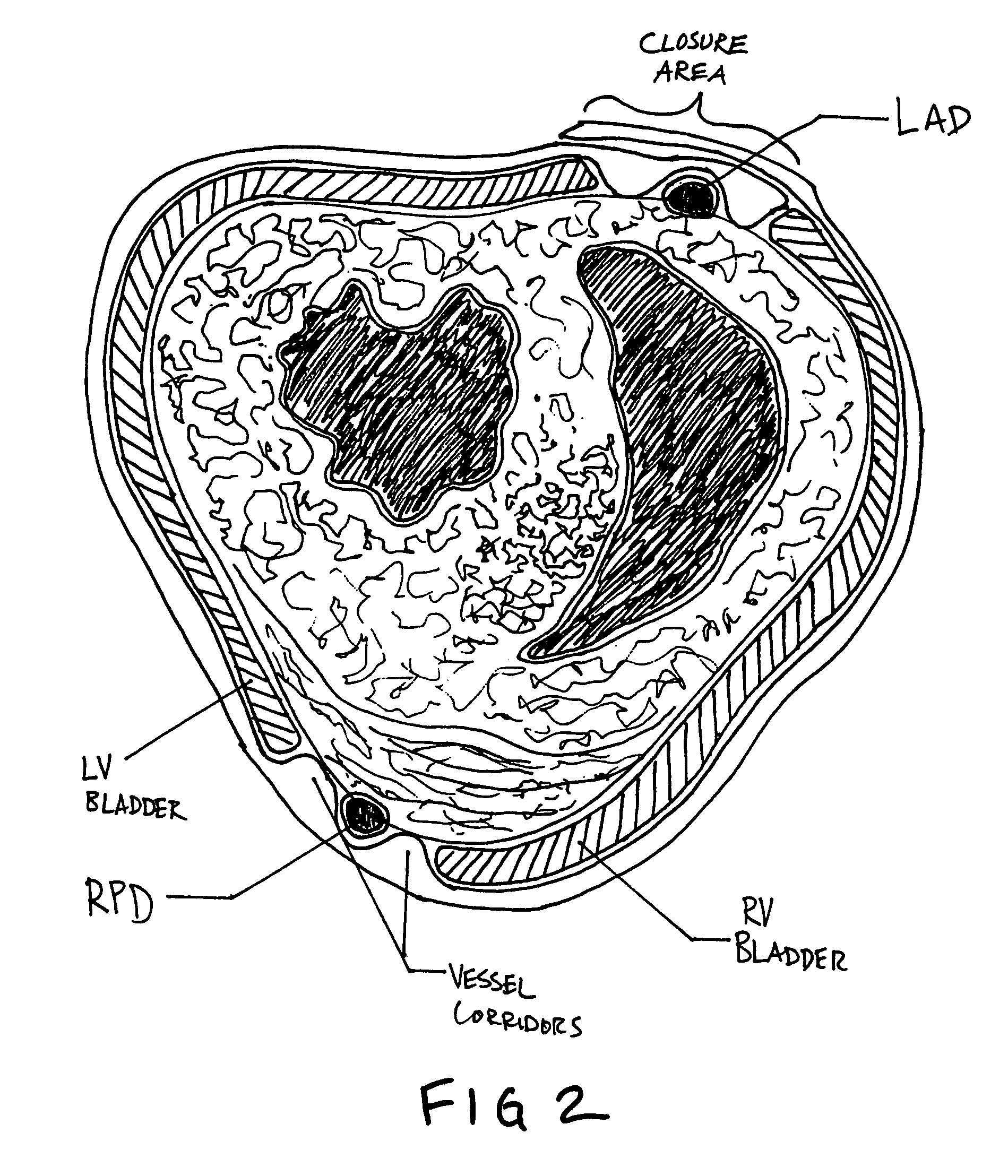
A device is proposed to progressively reduce the hemodynamic cardiac symptoms of congestive heart failure as well as those induced by dilated cardiomyopathies. This device affords progressive diastolic ventricular control by offering a method for percutaneous access and adjustments of its gas filled bladders surrounding the heart. After opening the pericardium, the device is not attached to the heart muscle but may be anchored to the pericardial sac. The device actually extends primarily around the heart from below the atrio-ventricular canal to the cardiac apex. Between the device exterior, made of non-elastic material and the epicardium, two independent elastic bladders or chambers provide variable compressive diastolic support to the right and left ventricles, while allowing adequate blood flow to the anterior and posterior descending epicardial branches of the coronary arteries and veins. Progressive hemodynamic increases in diastolic pressures for the right and left ventricles can be individually and repeatedly monitored by pressure gauges and an inert gas separately injected or removed in the enclosed chest through self-sealing access ports. These ports are subcutaneously implanted in the left anterior axillary line and connected by thin tubes across the 4th or 5th intercostal spaces to the pericardial bladders or chambers described above.
Owner:ROBERTSON JR ABEL L
Pulmonary Monitoring System
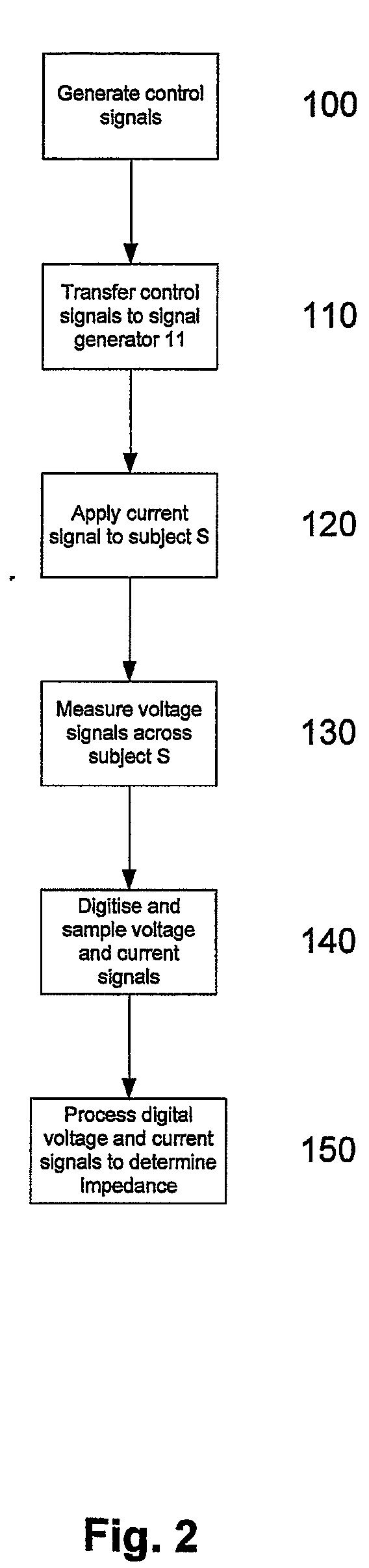
InactiveUS20090143663A1Noise signalUser identity/authority verificationDiagnostic recording/measuringThoracic structureMonitoring system
A method of monitoring pulmonary oedema in a subject using a processing system. The method includes, determining a measured impedance value for at least two body segments, at least one of the body segments being a thoracic cavity segment. For each body segment, the measured impedance values are used to determine an index, which is in turn used to determine the presence, absence or degree of pulmonary oedema using the determined indices.
Owner:IMPEDANCE CARDIOLOGY SYST +1
Apparatus and methods for facilitating treatment of tissue via improved delivery of energy based and non-energy based modalities
InactiveUS8517923B2Accurately advancedMinimize damageEndoscopesCatheterThoracic structureAutomatic control
Methods and apparatus for accessing and treating regions of the body are disclosed herein. Using an endoscopic device having an automatically controllable proximal portion and a selectively steerable distal portion, the device generally may be advanced into the body through an opening. The distal portion is selectively steered to assume a selected curve along a desired path within the body which avoids contact with tissue while the proximal portion is automatically controlled to assume the selected curve of the distal portion. The endoscopic device can then be used for accessing various regions of the body which are typically difficult to access and treat through conventional surgical techniques because the device is unconstrained by “straight-line” requirements. Various applications can include accessing regions of the brain, thoracic cavity, including regions within the heart, peritoneal cavity, etc., which are difficult to reach using conventional surgical procedures.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Single-phase surgical procedure for creating a pneumostoma to treat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
InactiveUS20090209970A1Stable artificial apertureAvoid cavitiesEar treatmentBreathing masksObstructive Pulmonary DiseasesThoracic cavity
A single-phase surgical procedure is disclosed for creating a pneumostoma to treat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. In a single-phase technique the pleurodesis is formed at the same time as the pneumostoma and does not require a separate step. The thoracic cavity is accessed to visualize the lung, the pneumostomy catheter is inserted into the lung and then the lung is secured to the channel through the chest wall creating a sealed anastomosis which matures into a pleurodesis after the procedure.
Owner:PORTAERO
Method and apparatus for chest drainage
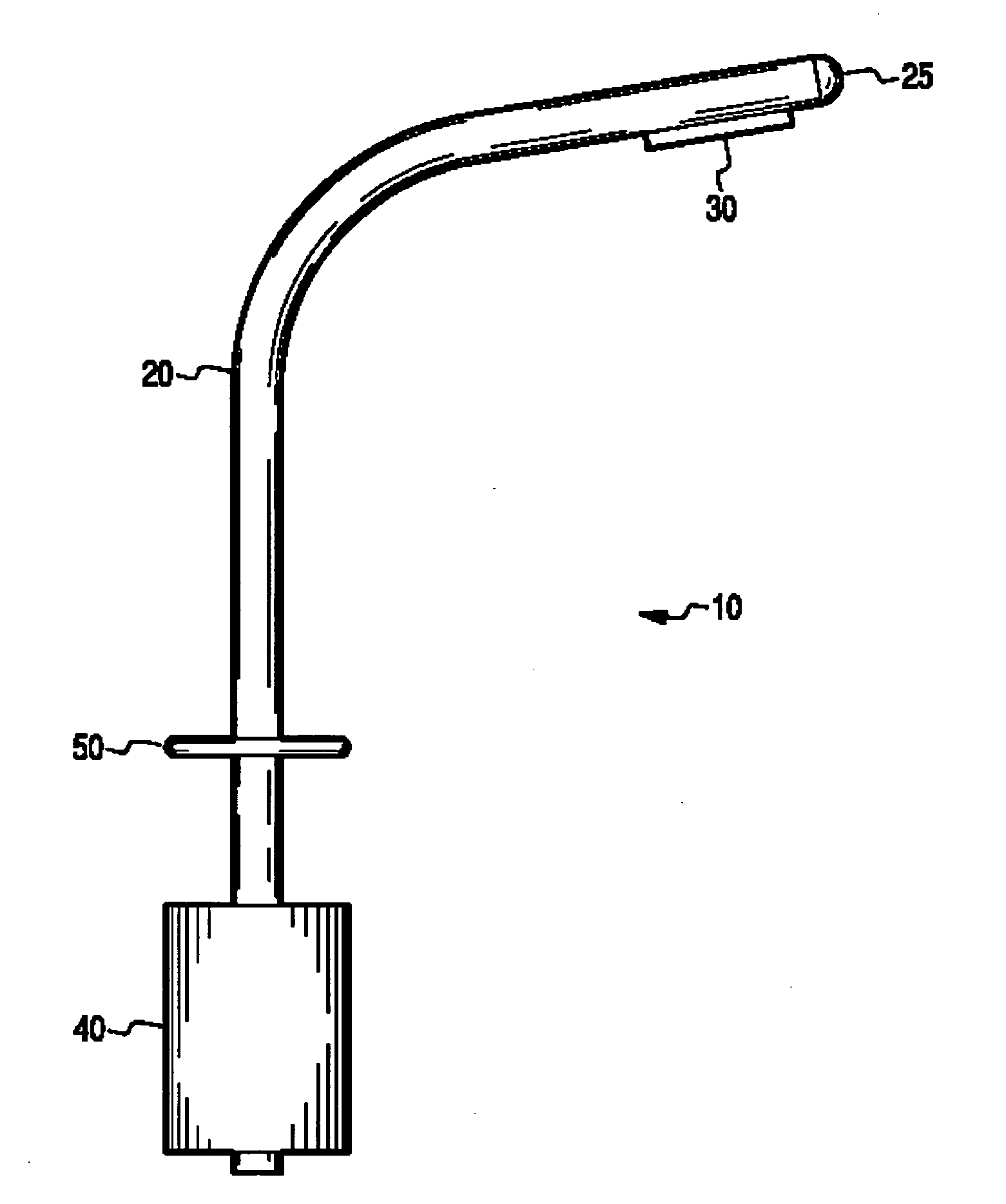
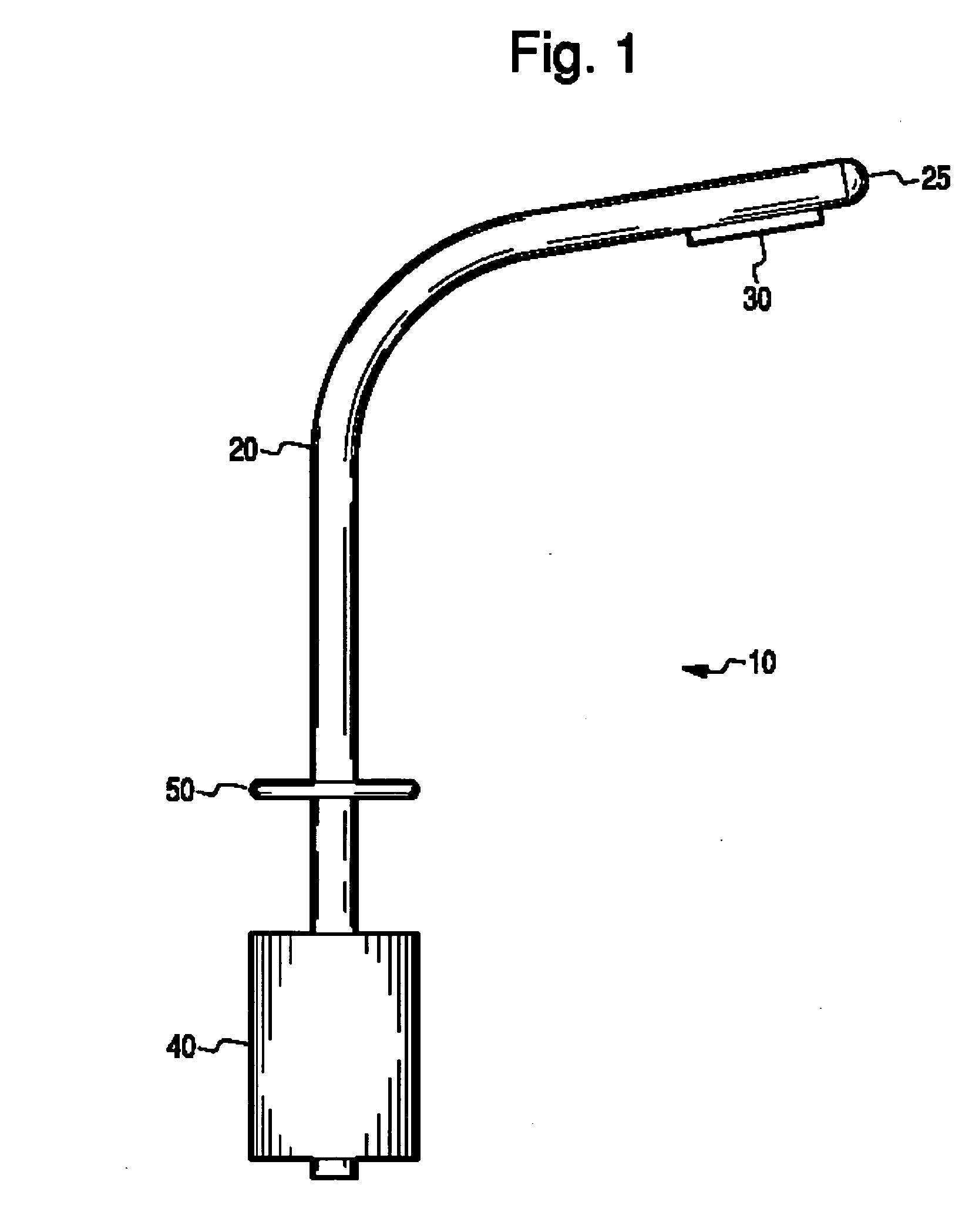
InactiveUS20060206097A1Reduce stepsReduce errorsWound drainsMedical devicesThoracic structurePneumothorax
The present invention describes a device for placement in the thoracic cavity of a patient. The device is a cannula, tube or catheter for chest drainage. The device serves as a conduit for drainage of excessive fluid or air buildup in the chest to a receptacle outside the body. The device also serves to prevent influx of fluid or air into the chest cavity, thus preventing pneumothorax or infection. The device incorporates systems for anchoring the chest drainage cannula to the chest and for steering the chest drainage cannula into the thoracic cavity.
Owner:BREZNOCK EUGENE M +1
Method and apparatus for chest drainage
InactiveUS7326197B2Minimizing chanceReducing chance of iatrogenic injuryInfusion syringesWound drainsThoracic structurePneumothorax
The present invention describes a device for placement in the thoracic cavity of a patient. The device is a cannula, tube or catheter for chest drainage. The device serves as a conduit for drainage of excessive fluid or air buildup in the chest to a receptacle outside the body. The device also serves to prevent influx of fluid or air into the chest cavity, thus preventing pneumothorax or infection. The device incorporates systems for anchoring the chest drainage cannula to the chest and for steering the chest drainage cannula into the thoracic cavity.
Owner:BREZNOCK EUGENE M +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com