Patents
Literature
266results about How to "Slide freely" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
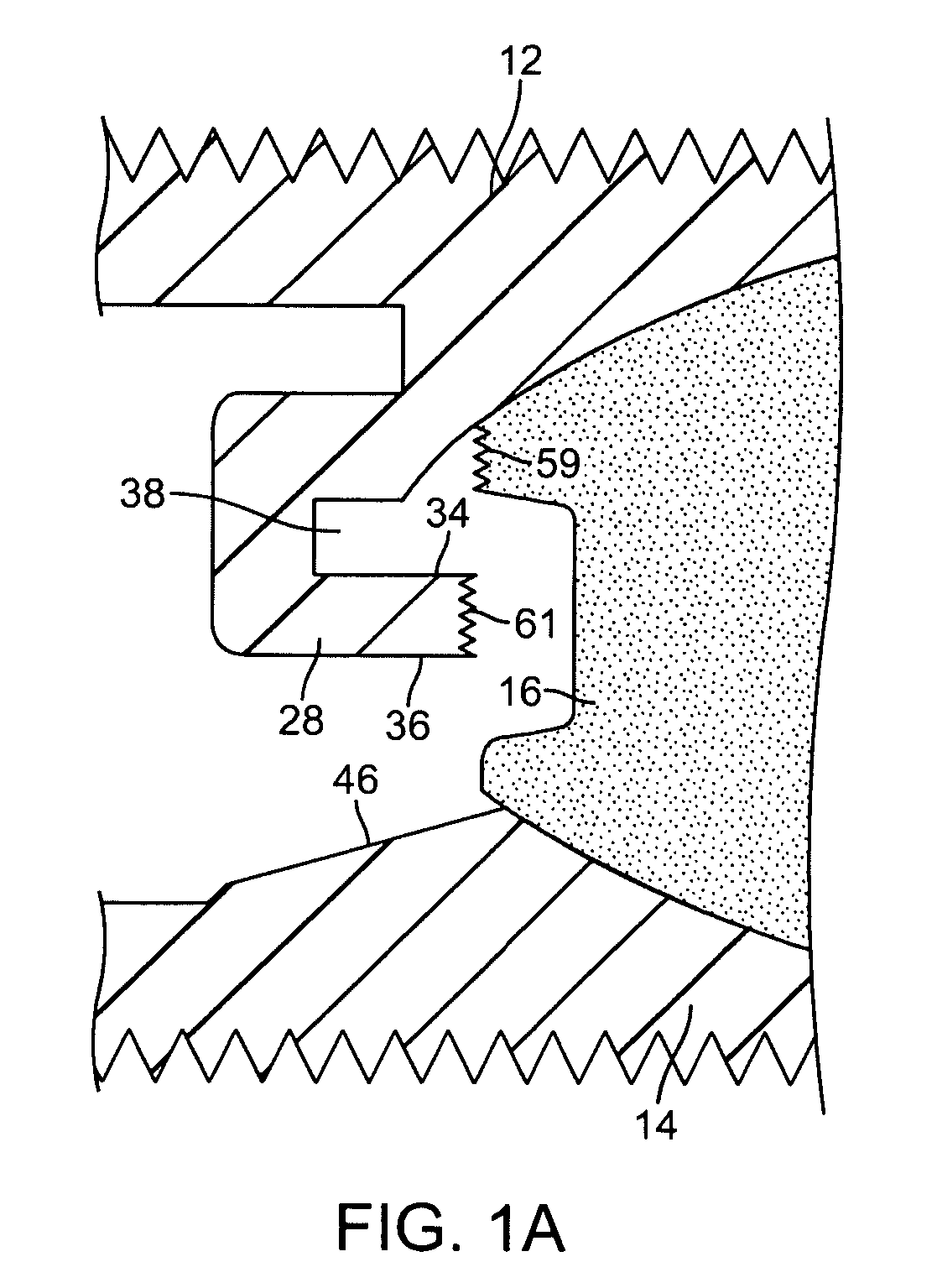
Methods and apparatus for mitral valve repair
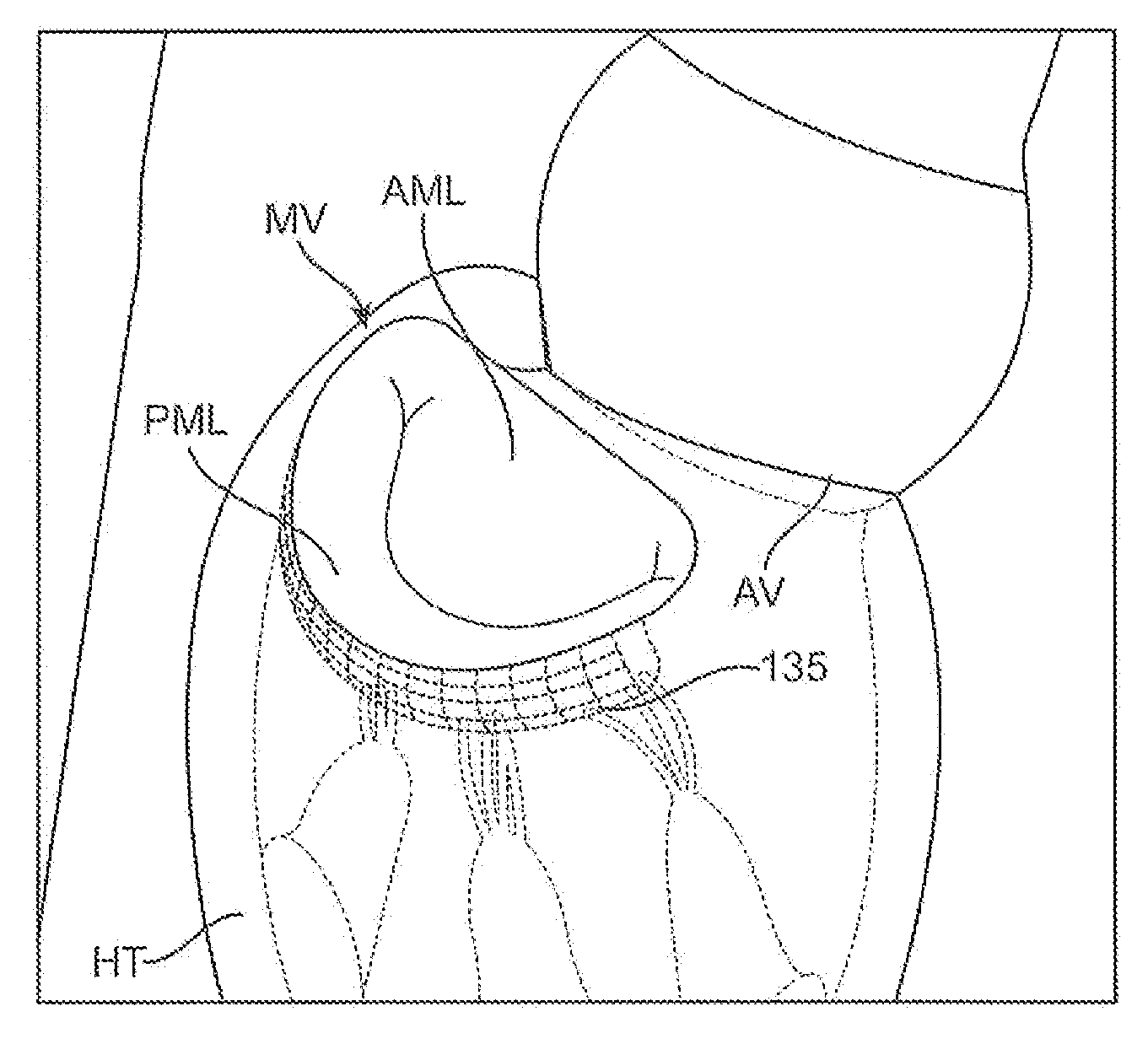
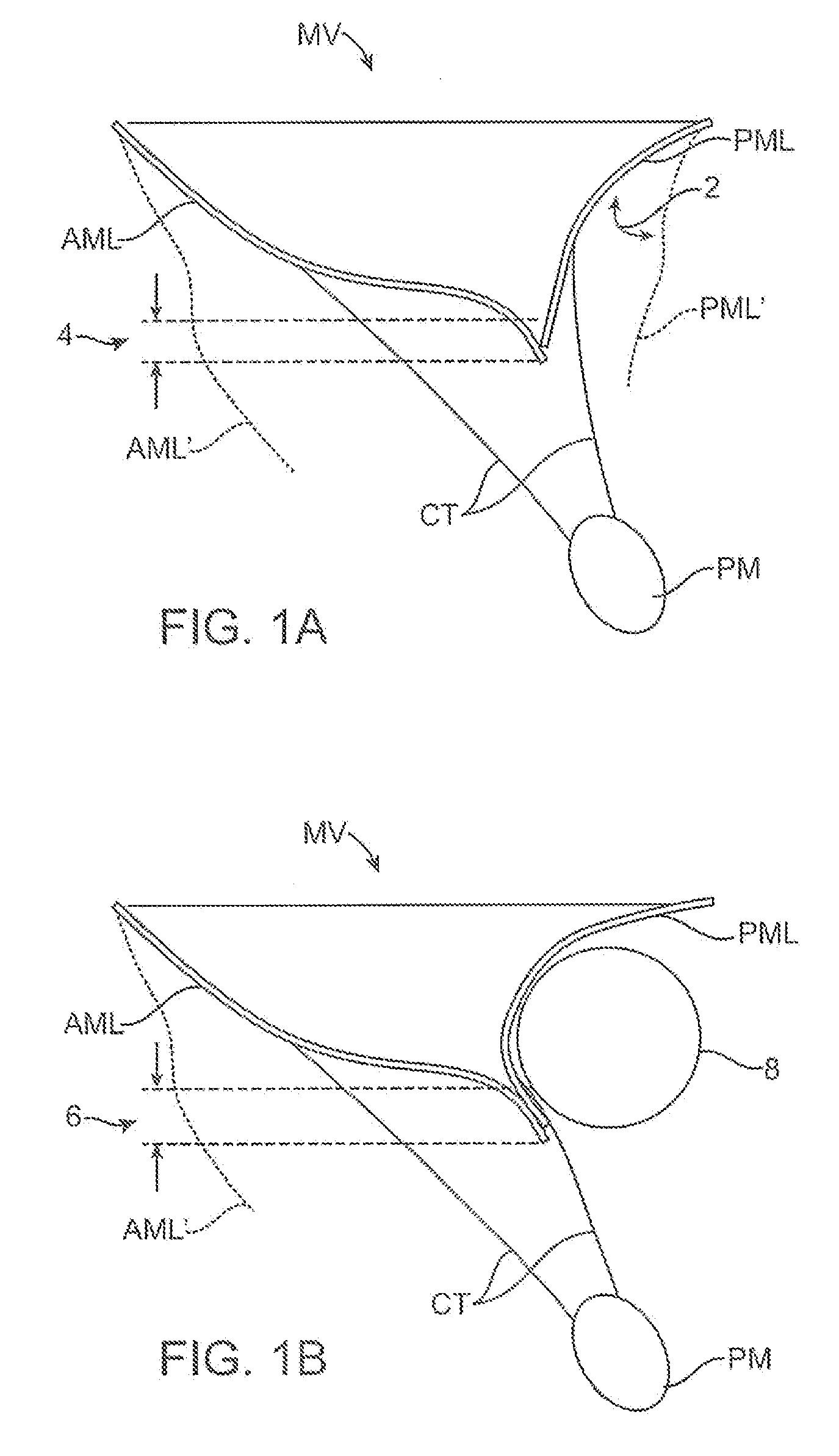
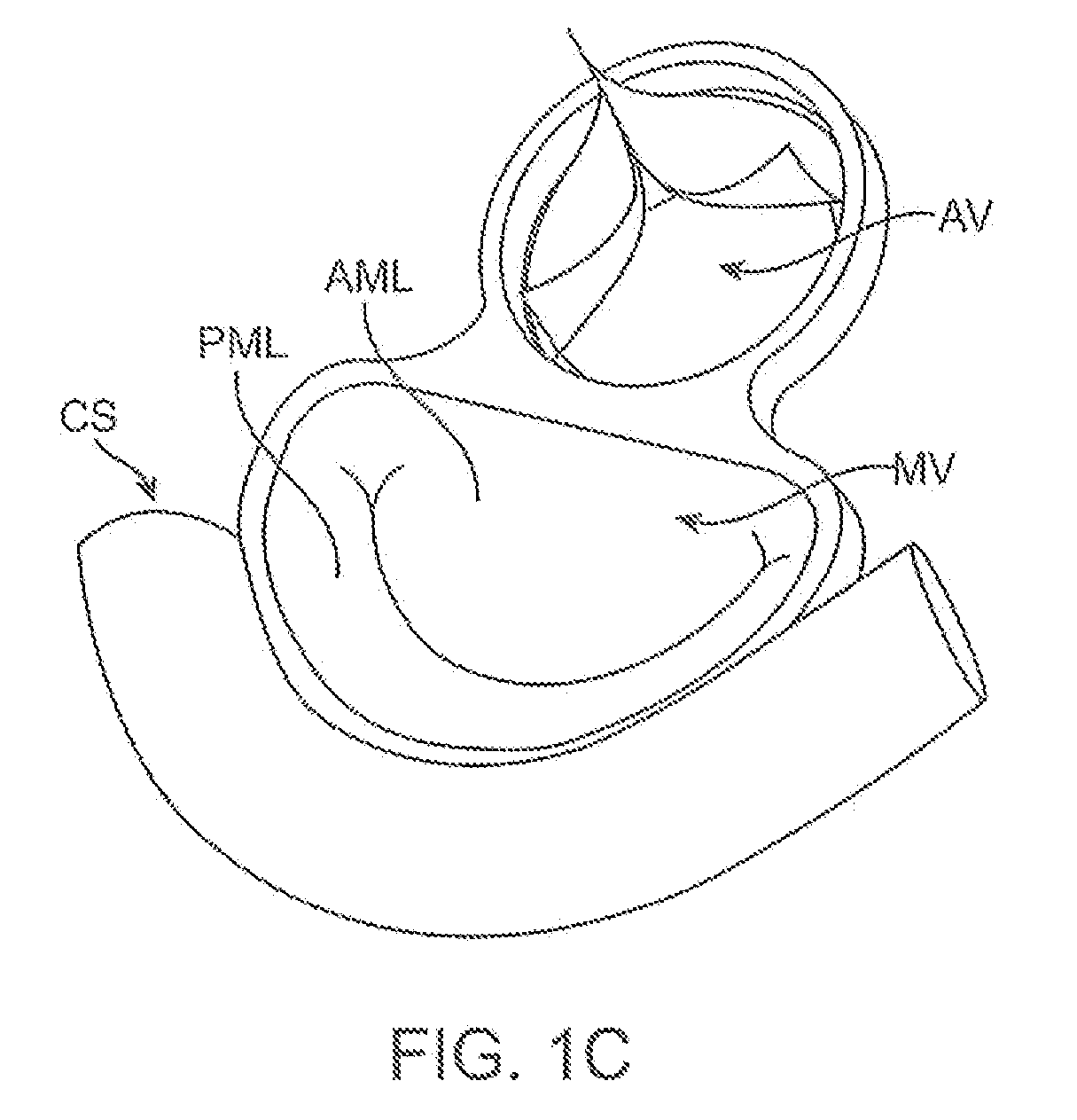
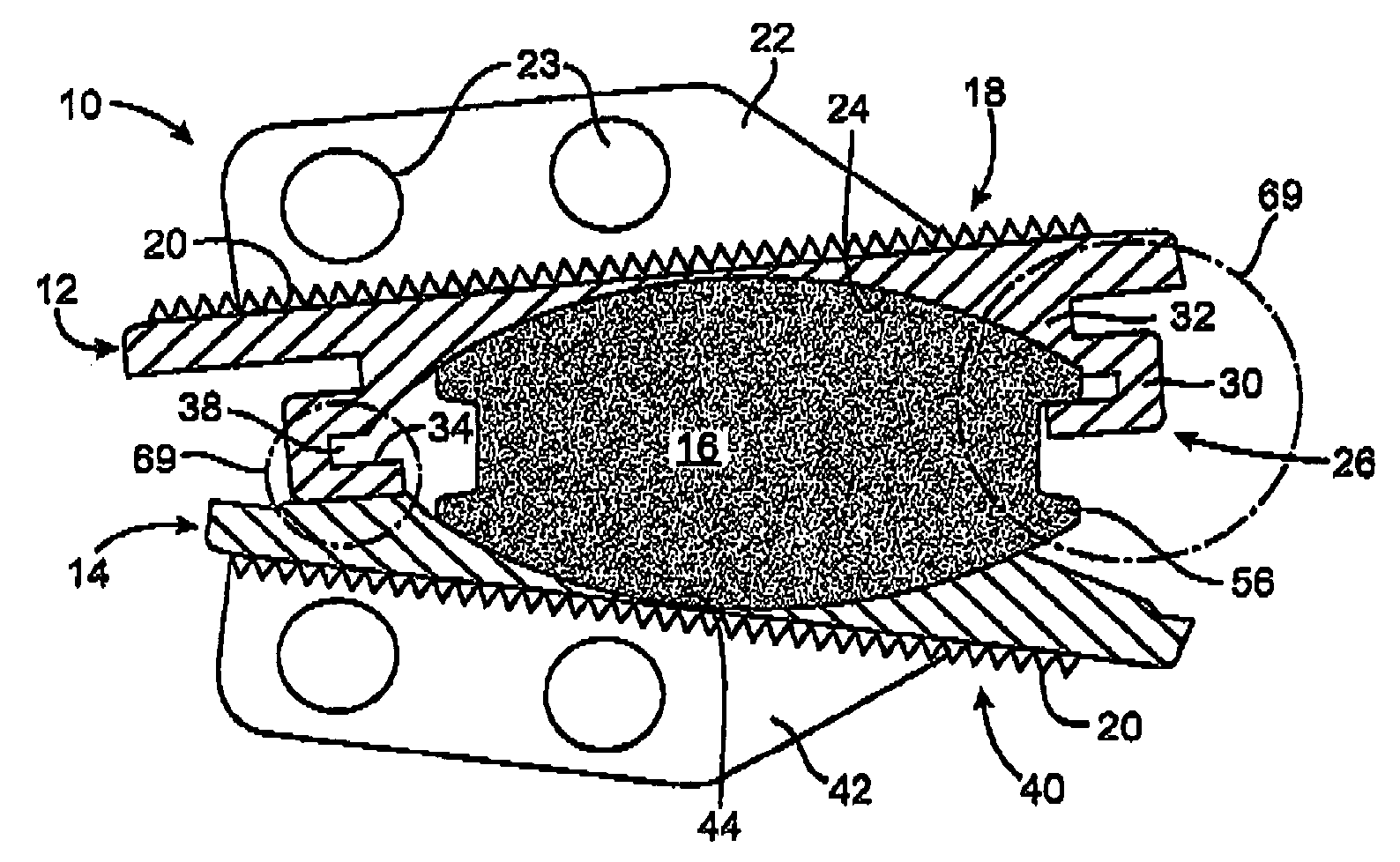
InactiveUS20080039935A1Inhibiting and preventing prolapseSlide freelyAnnuloplasty ringsPosterior leafletSystole
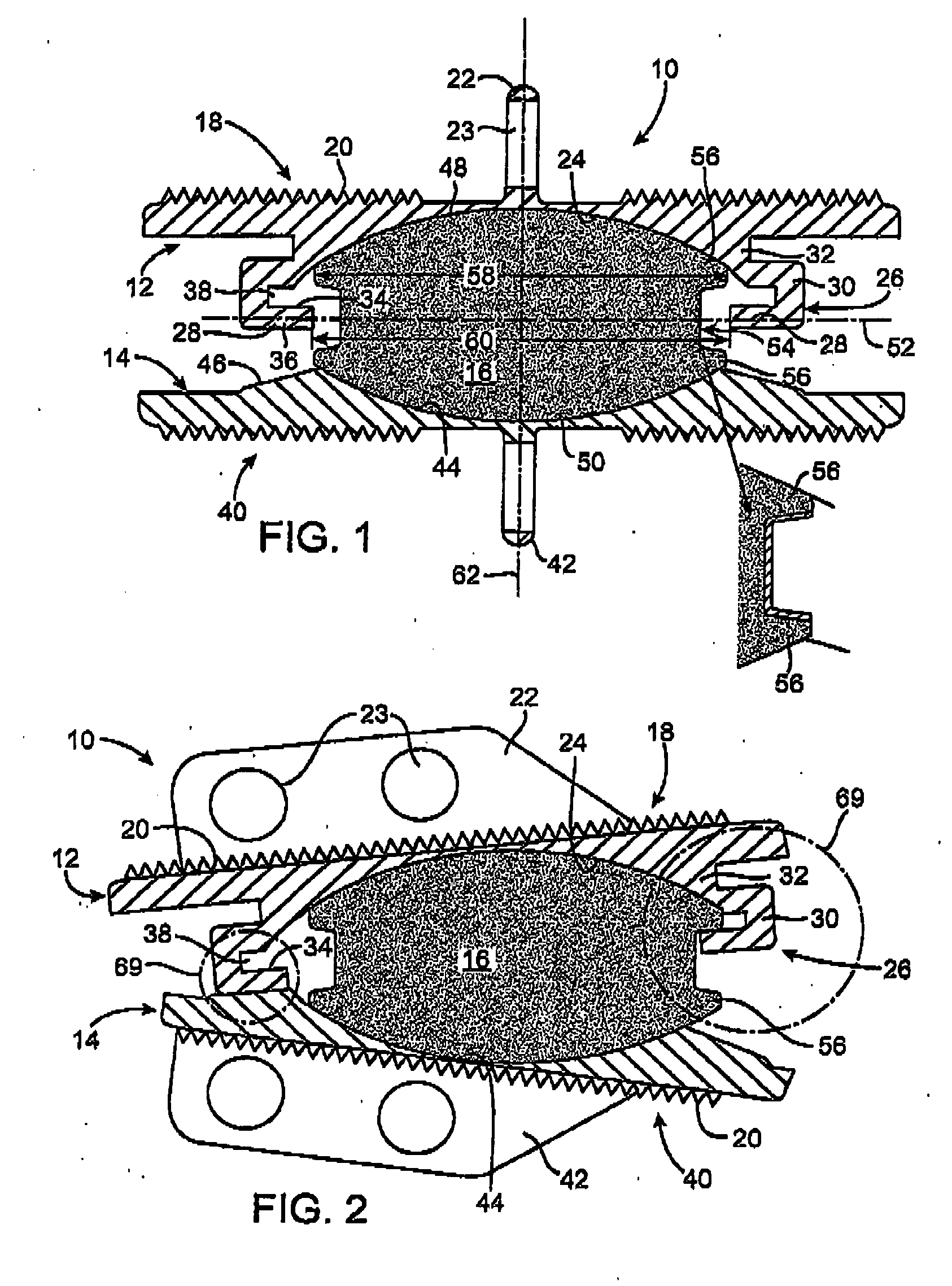
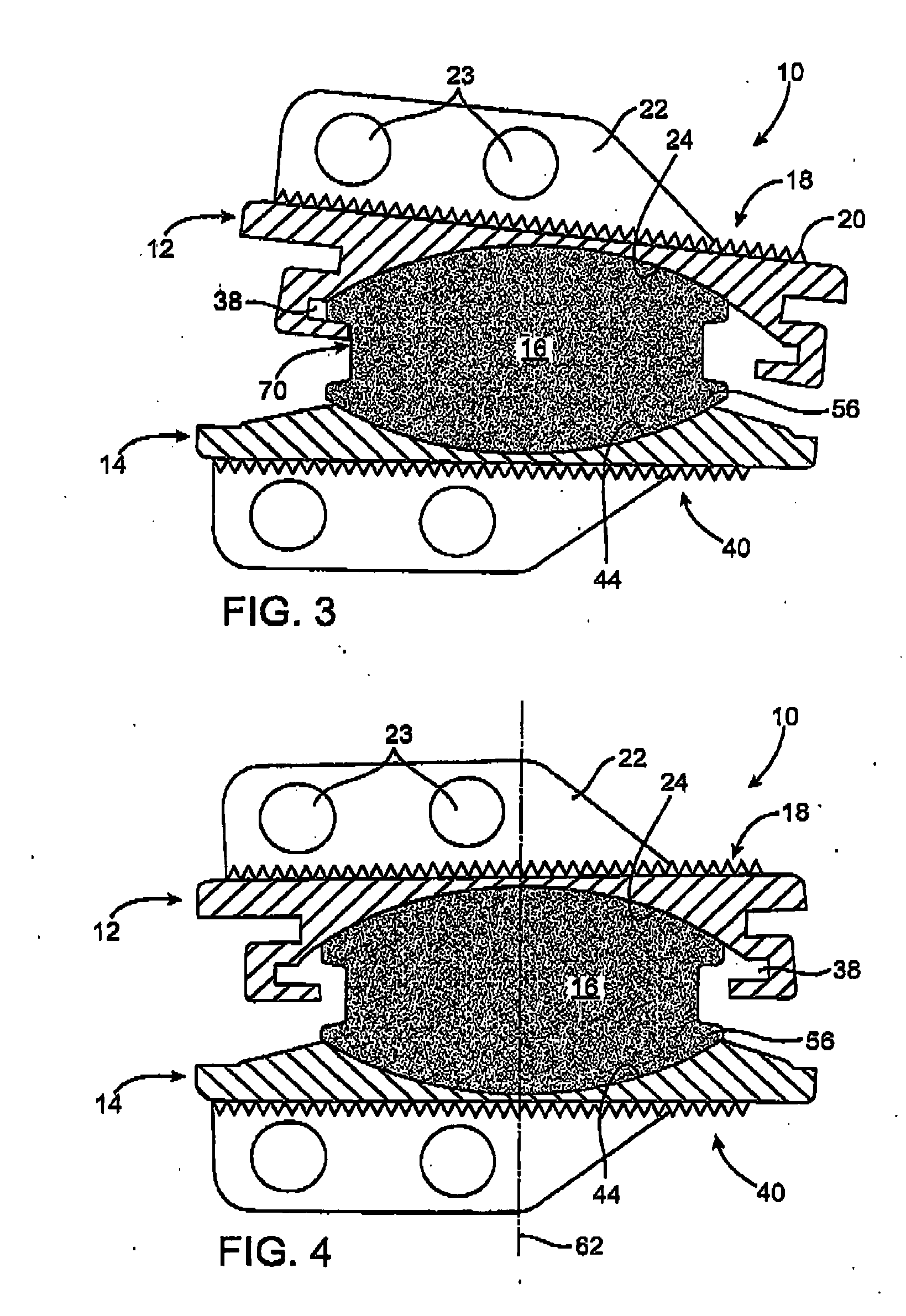
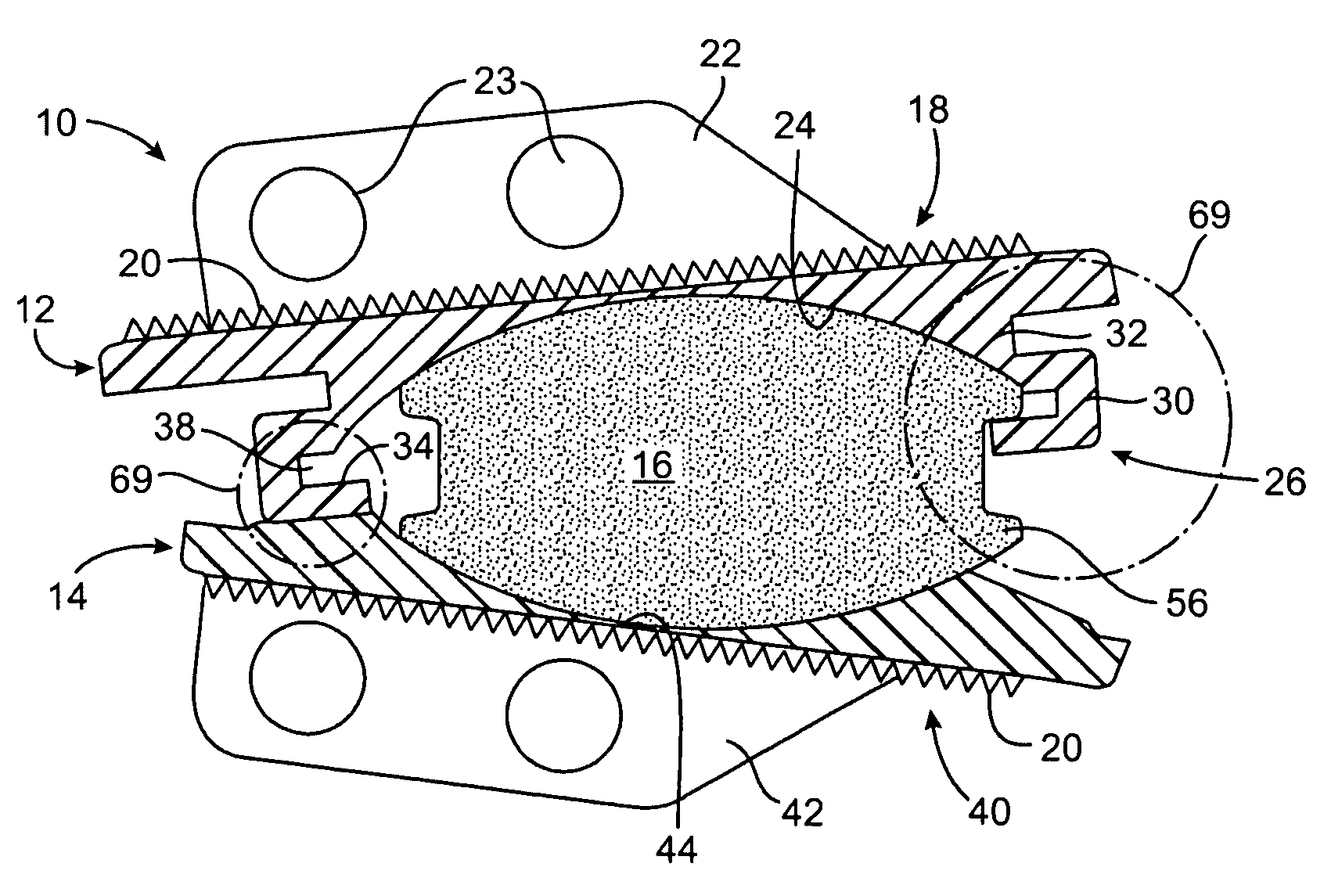
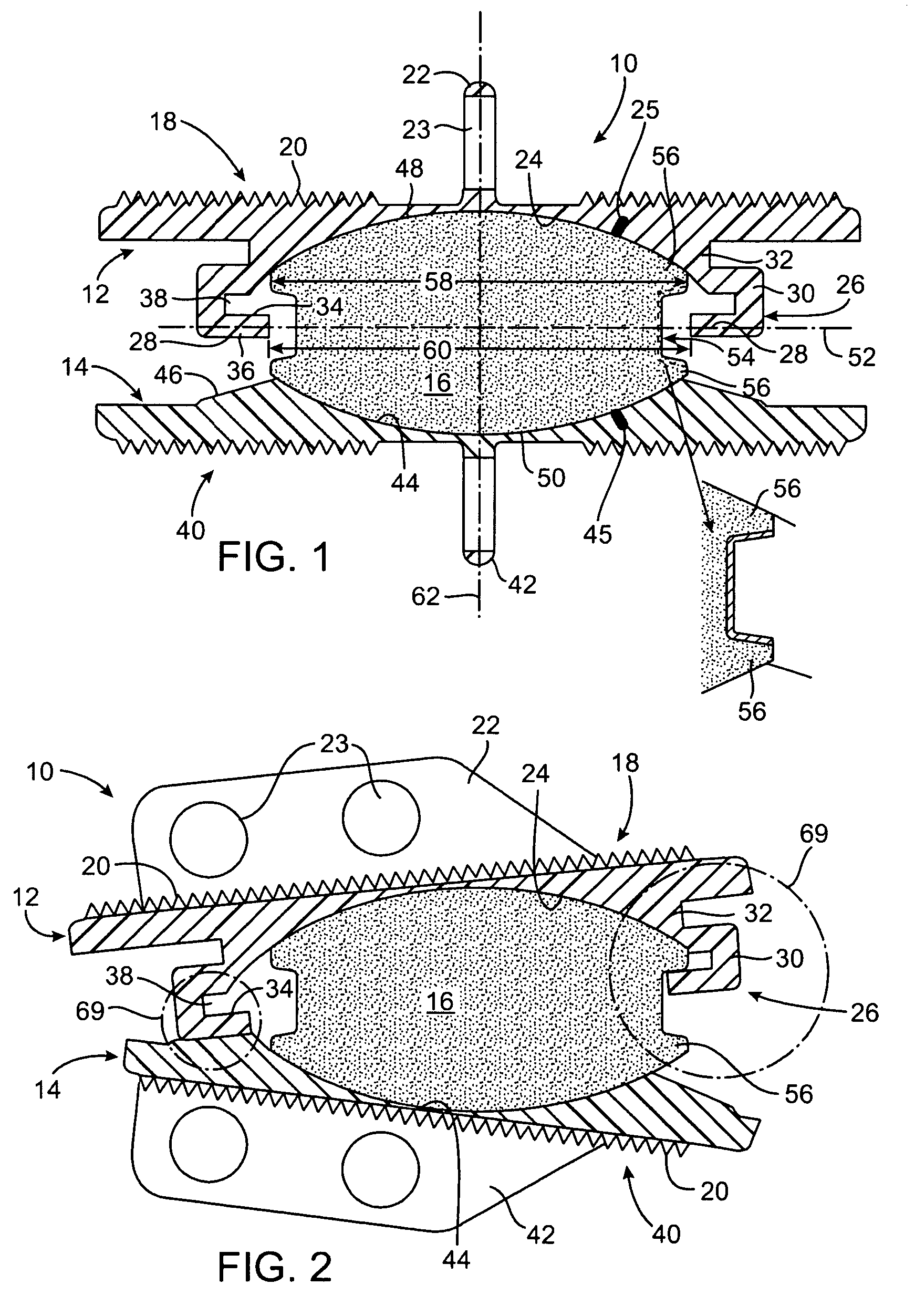
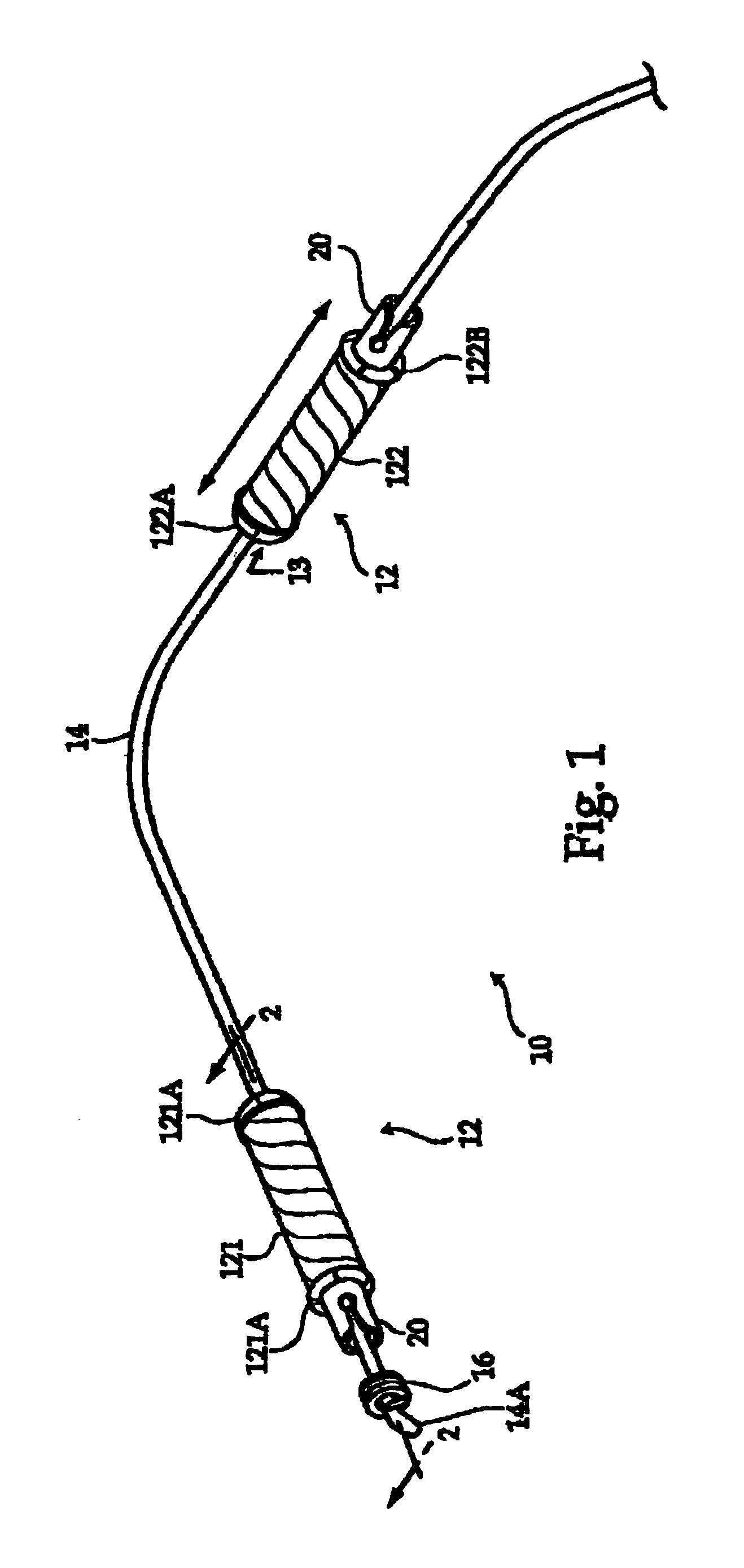
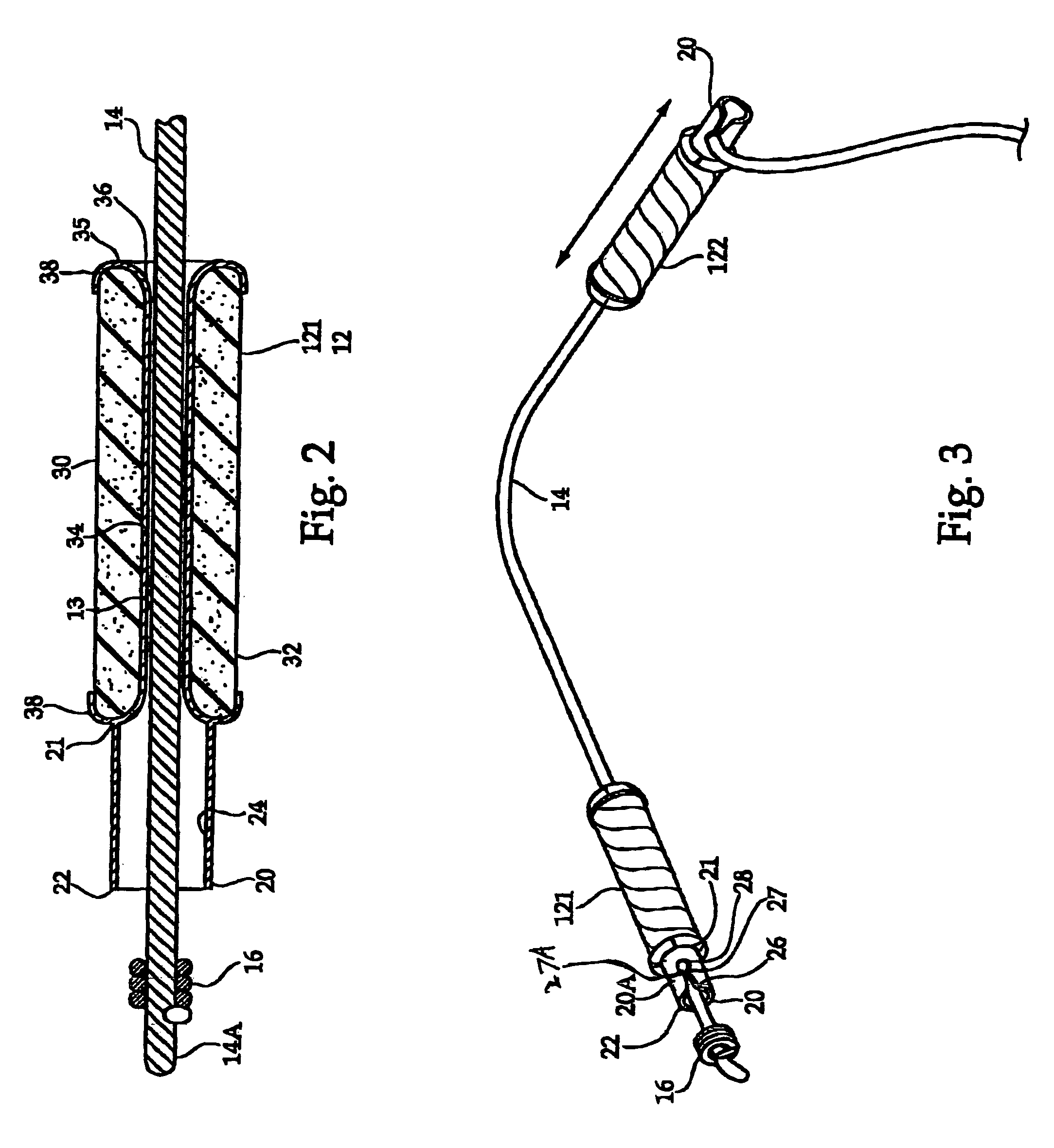
Methods and apparatus for mitral valve repair are disclosed herein where the posterior mitral leaflet is supported or buttressed in a frozen or immobile position to facilitate the proper coaptation of the leaflets. An implantable apparatus may be advanced and positioned intravascularly beneath the posterior leaflet of the mitral valve. The apparatus may include one or more individual balloon members, each of which may be optionally configured with supporting integrated structures. A magnet chain catheter may be positioned within the coronary sinus and adjacent to the mitral valve to magnetically secure the apparatus in position beneath the posterior mitral leaflet. Alternatively, a split-ring device may be placed about the chordae tendineae supporting the mitral valve such that the ring slides along the chordae tendineae alternately against the mitral leaflet and towards the papillary muscles during systole and diastole.
Owner:BUCH WALLY +1
Intervertebral prosthetic disc with metallic core
ActiveUS20060025862A1Inhibit wearAvoid tearingSpinal implantsCoatingsIntervertebral discCentre of rotation
A prosthetic disc for insertion between adjacent vertebrae includes a core having upper and lower curved surfaces and upper and lower plates. At least one of the curved surfaces of the core is metallic, and in some embodiments the entire core is metallic. Each plate has an outer surface which engages a vertebra and a metallic inner curved surface which is shaped to slide over one of the curved surfaces of the core. In some embodiments, the center of rotation of the core is free to move relative to the upper and lower metallic plates. In some embodiments, one or more channels extend across one or both of the curved surfaces of the core for allowing passage of bodily fluid to promote lubrication between the core and at least one of the plates.
Owner:SIMPLIFY MEDICAL PTY LTD
Intervertebral prosthetic disc with metallic core
Owner:SIMPLIFY MEDICAL PTY LTD
Endoscopic System and Method for Therapeutic Applications and Obtaining 3-Dimensional Human Vision Simulated Imaging With Real Dynamic Convergence
An endoscopic system and method that is adaptable for therapeutic applications as well as sensor operation and is capable of producing 3-dimensional human vision simulated imaging with real dynamic convergence, not virtual convergence. Applications may include use in any space, including but not limited to, intra-abdominal cavities, intra-thoracic cavities, and intra-cranial cavities. Further, two or more diagnostic / sensor probes may be used, with at least two being the same kind to create the 3-dimensional effect, such as but not limited to, camera, ultrasound, and magnetic-resonance imaging. Diagnostic / sensor probes are each mounted to the end of a different arm, with the other ends of the two arms both being attached to the same hinge that allows them to turn freely on the same axis from side-to-side within a 180 degree angle range of movement on the distal end of a main tubular shaft system. Medical, as well as other applications, are contemplated.
Owner:ABOU EL KHEIR TAREK AHMED NABIL
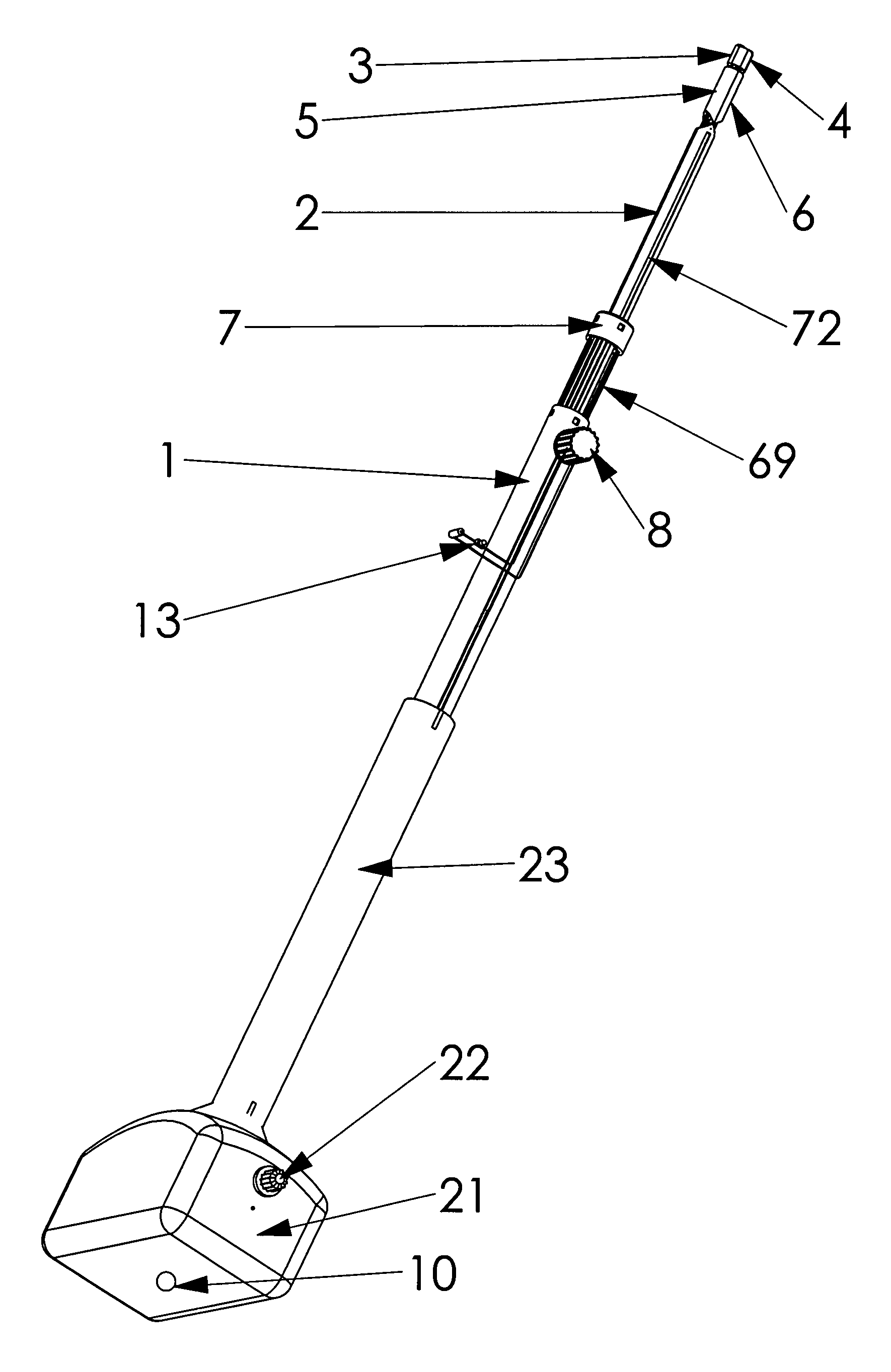
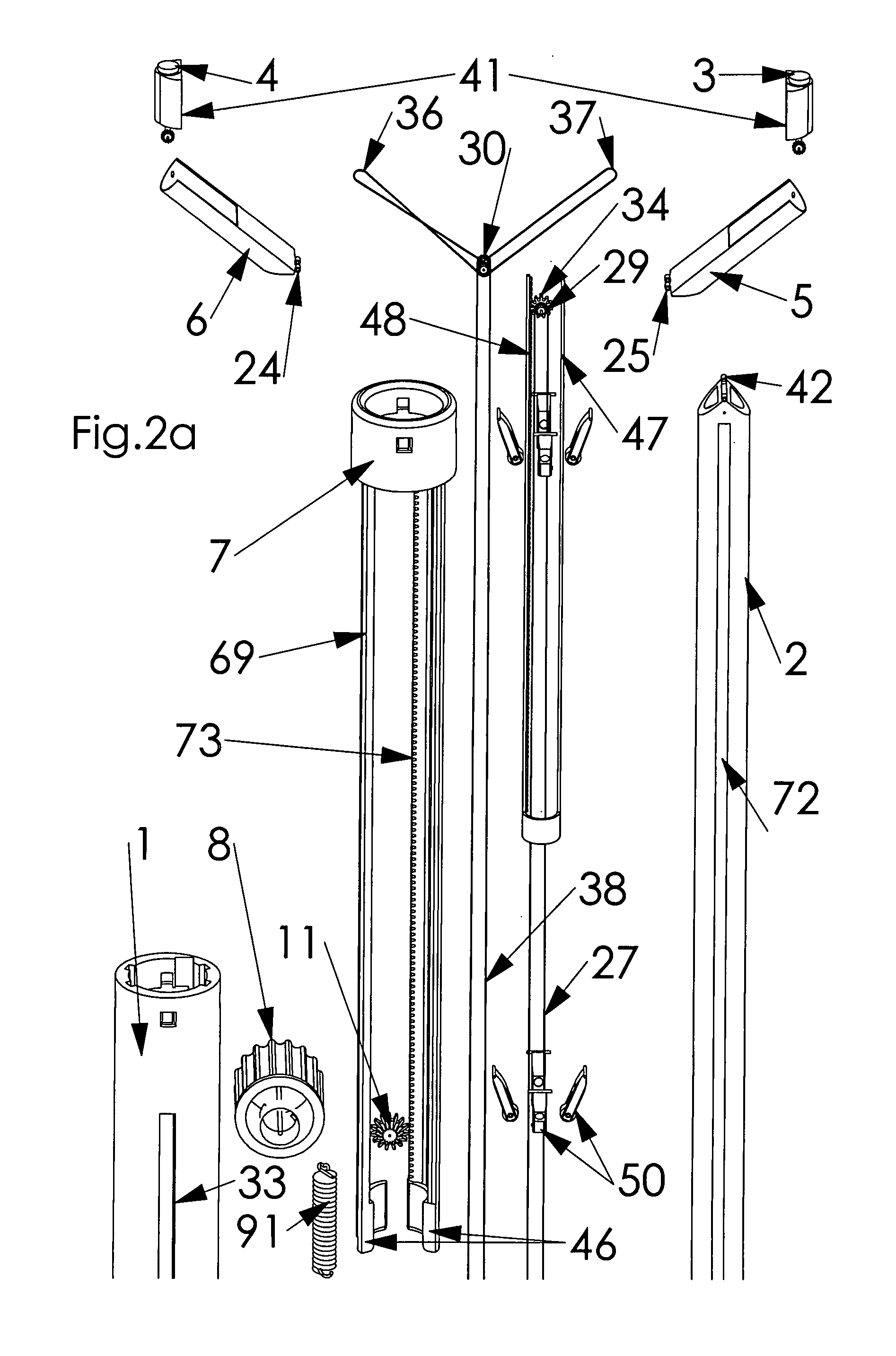
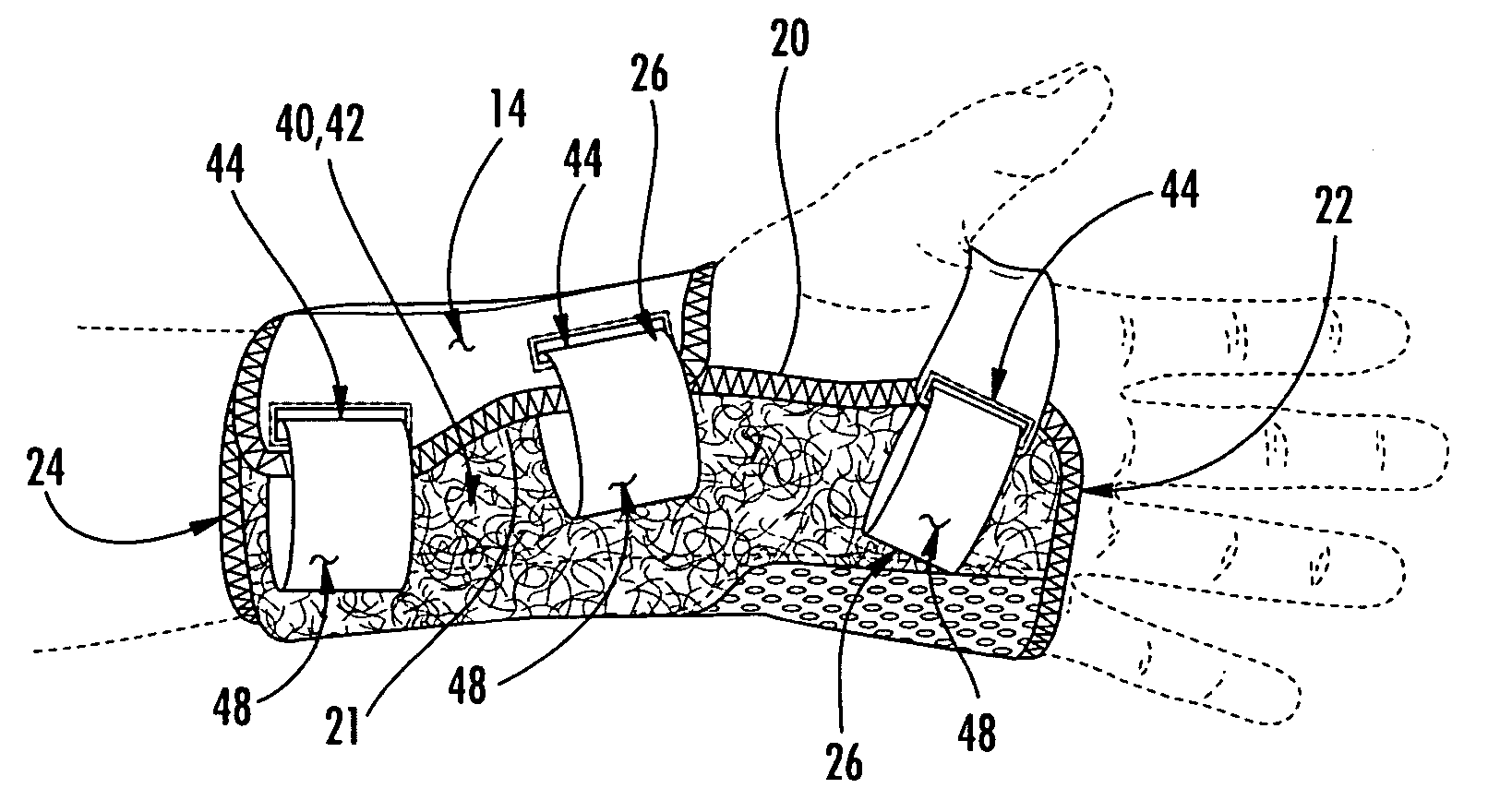
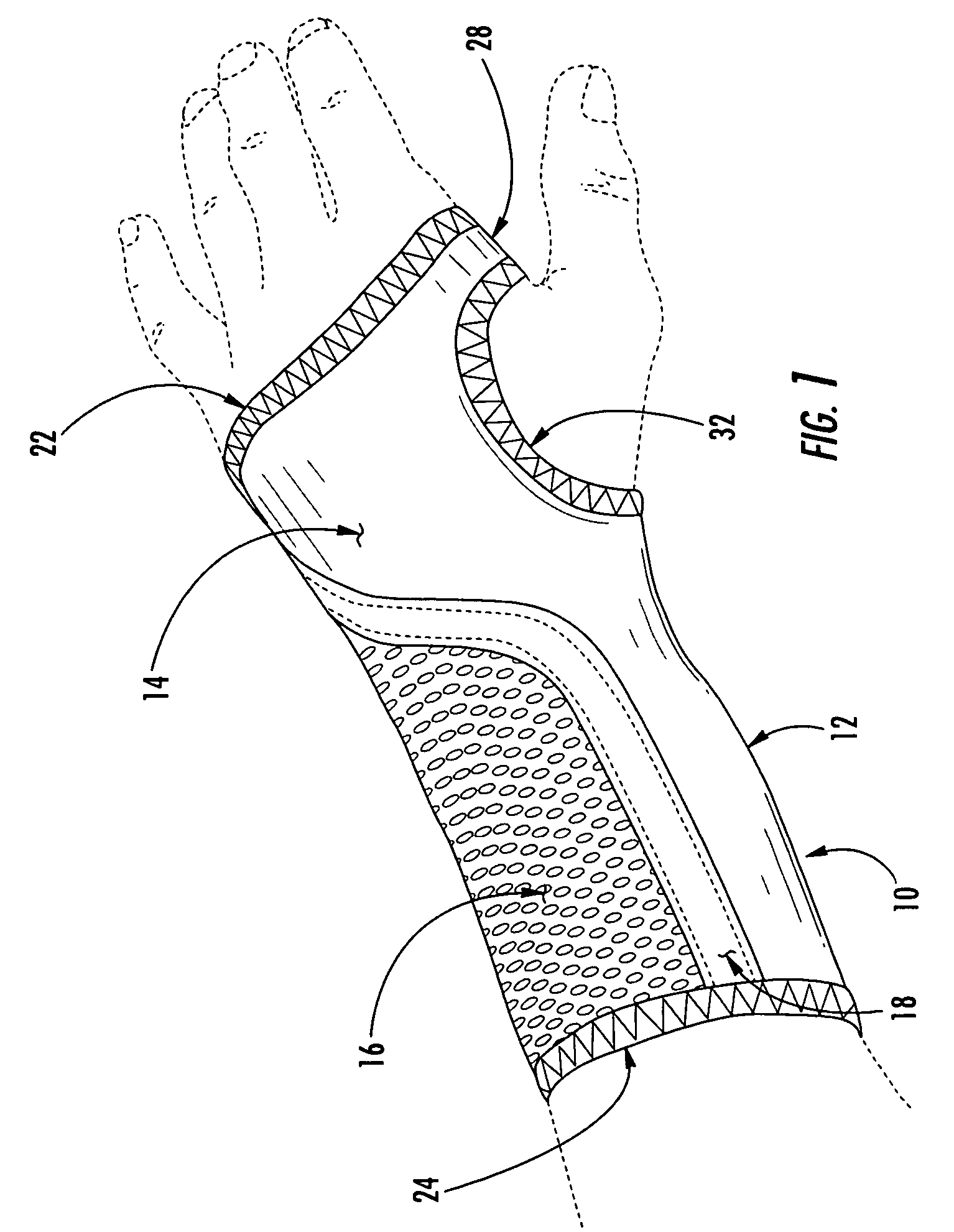
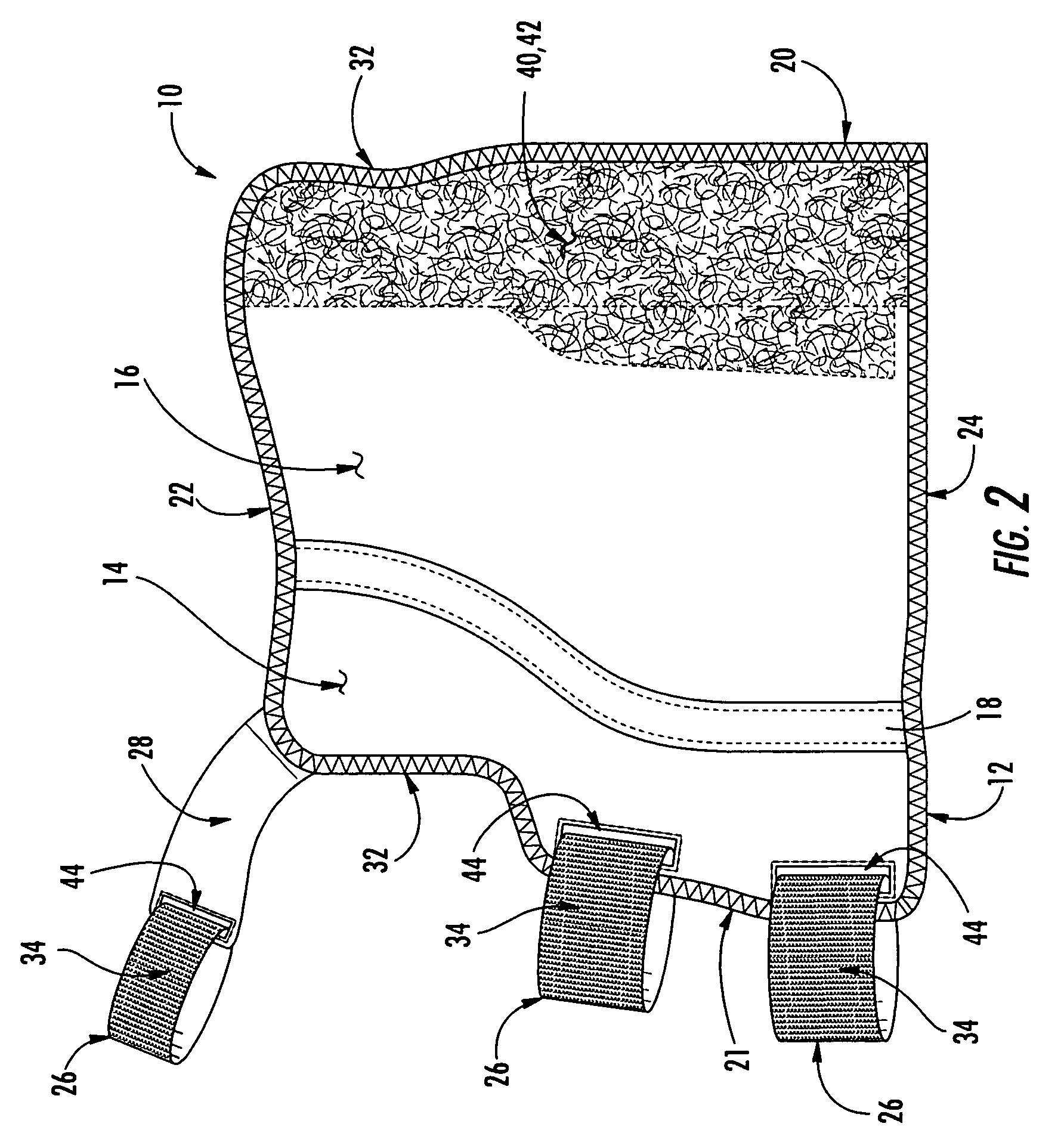
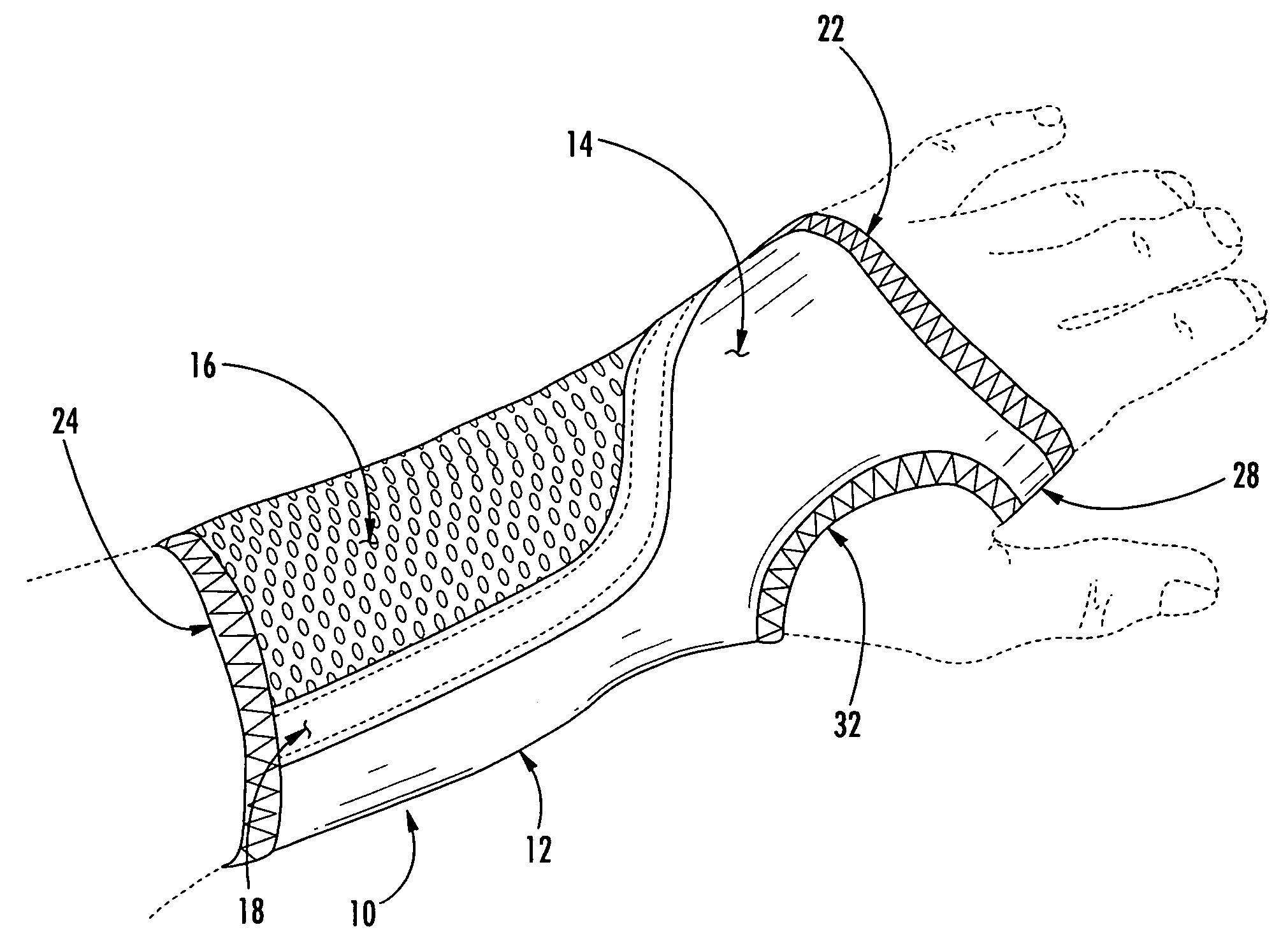
Wrist brace having continuous loop straps and method of using the same
InactiveUS7318812B2Slide freelyThe process is convenient and fastFinger bandagesFeet bandagesEngineeringWrist brace
A reversible wrist brace includes a sheet of flexible material that overlies and supports a wearer's wrist, wherein the sheet of material includes opposing surfaces each having one or more portions of loop material. The flexible sheet has at least one opening in the vicinity of a lateral edge to accommodate at least one fastening strap, such that the strap may slide within the opening. The fastening strap is a continuous loop of sheet material having an outer surface with a hook-bearing portion. The fastener is designed so as to enable a wearer to switch the wrist brace between right and left hands by orienting the hook-bearing portion so that it is coincident with the loop-bearing portion when the wrist brace is worn on either hand. The wrist brace may include a splint that may be inserted within a pocket located on the flexible material to further immobilize the wrist.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
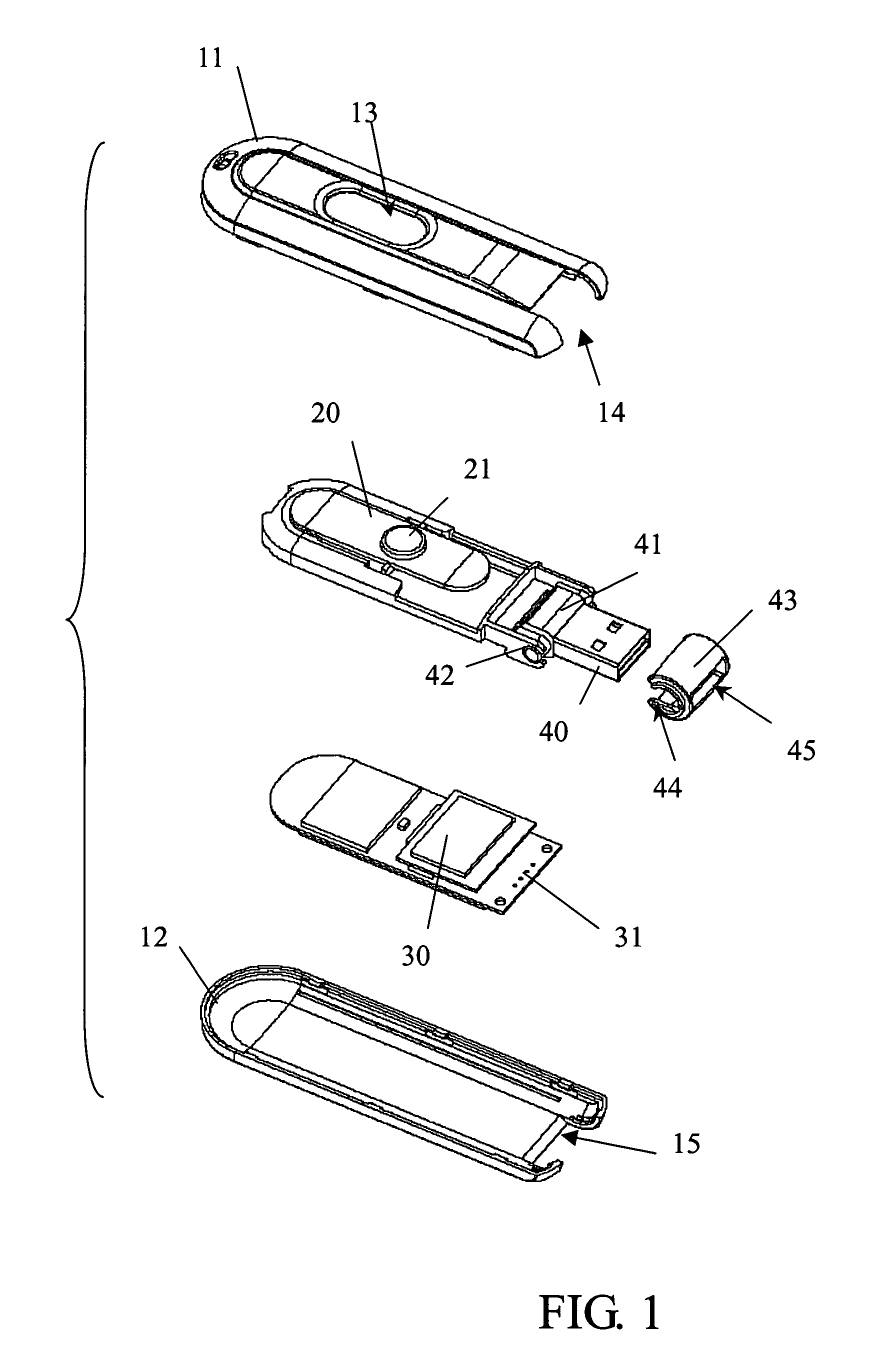
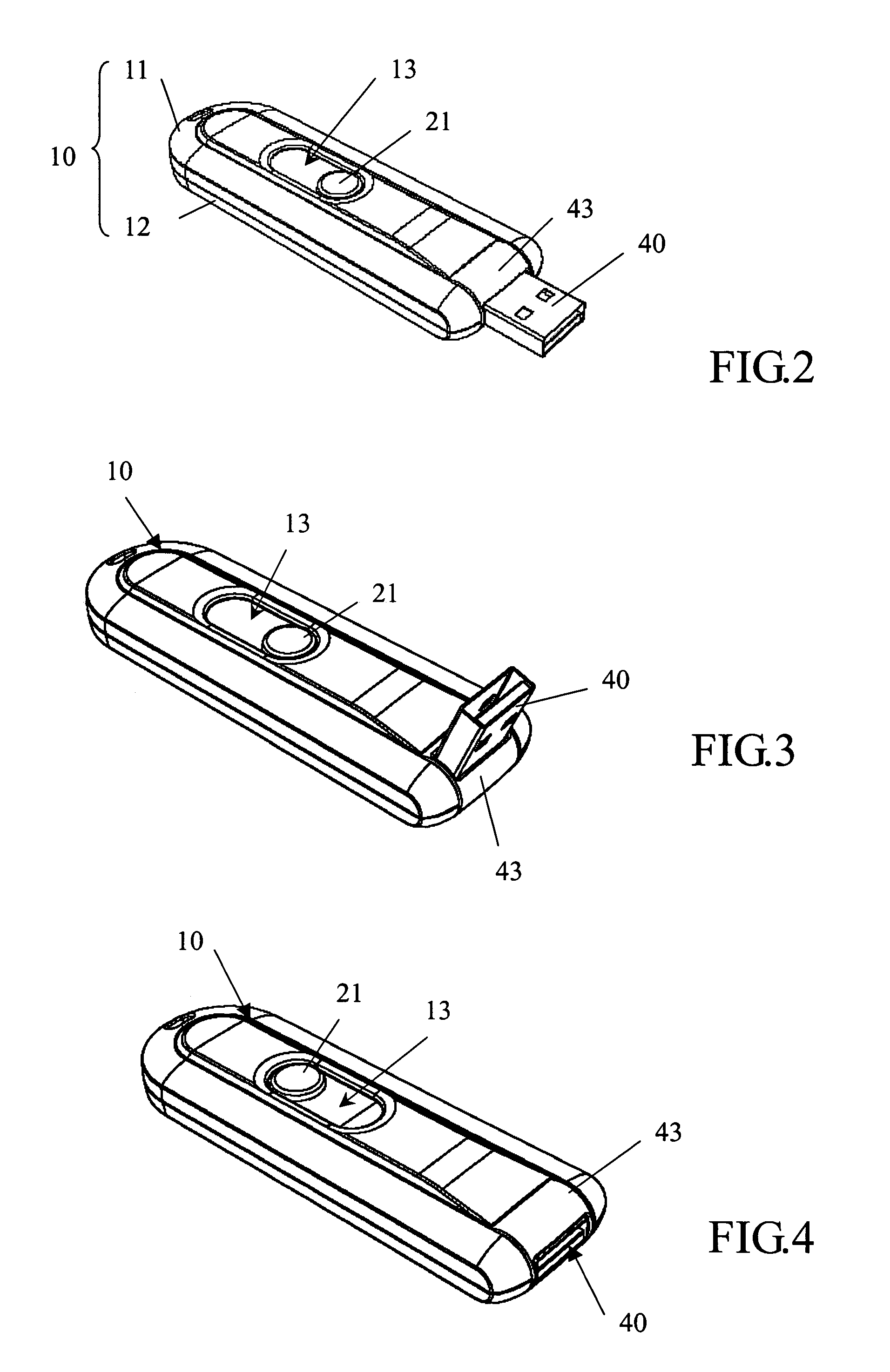
Memory device having a hiding and swing plug and method for hiding and swing a plug thereof
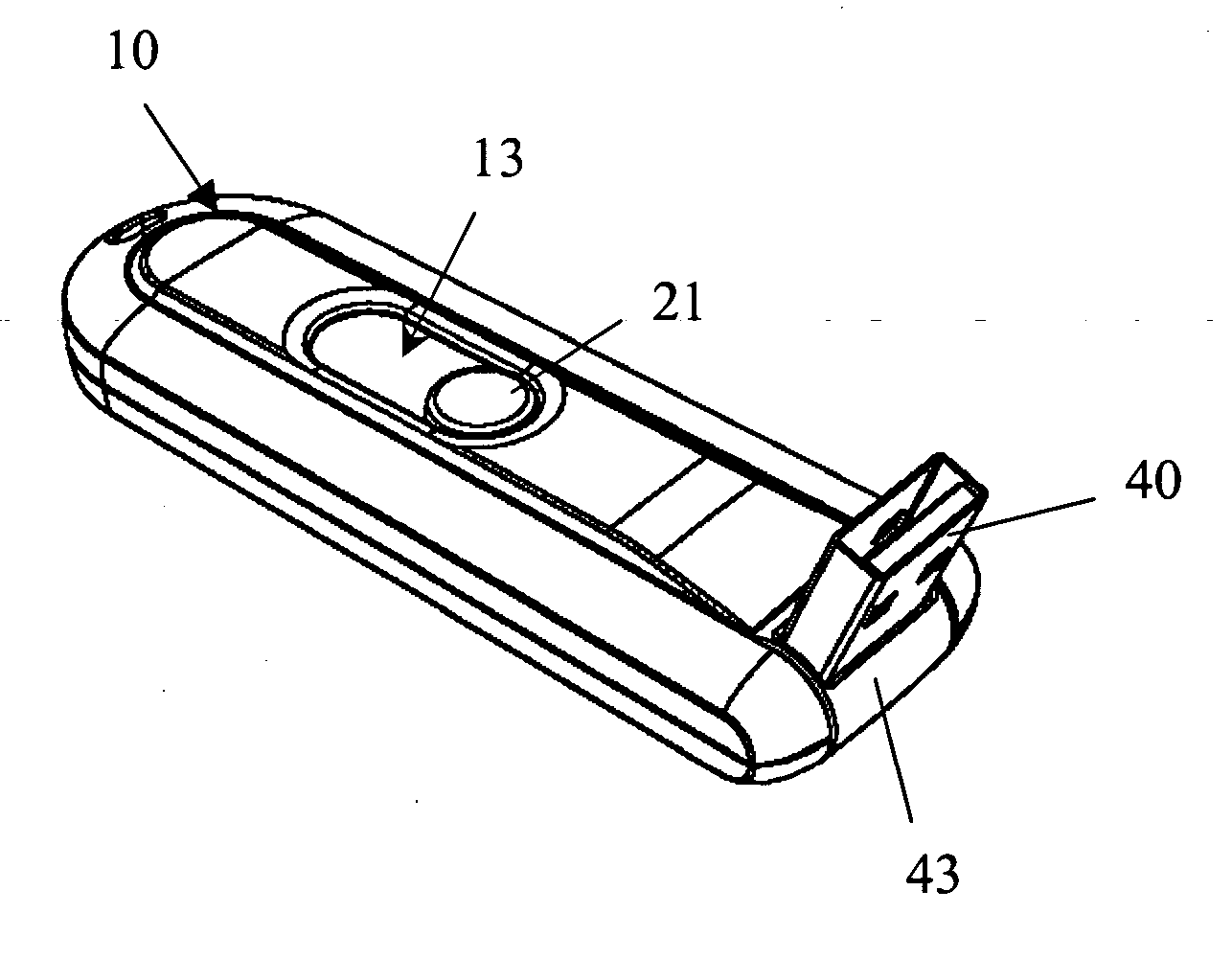
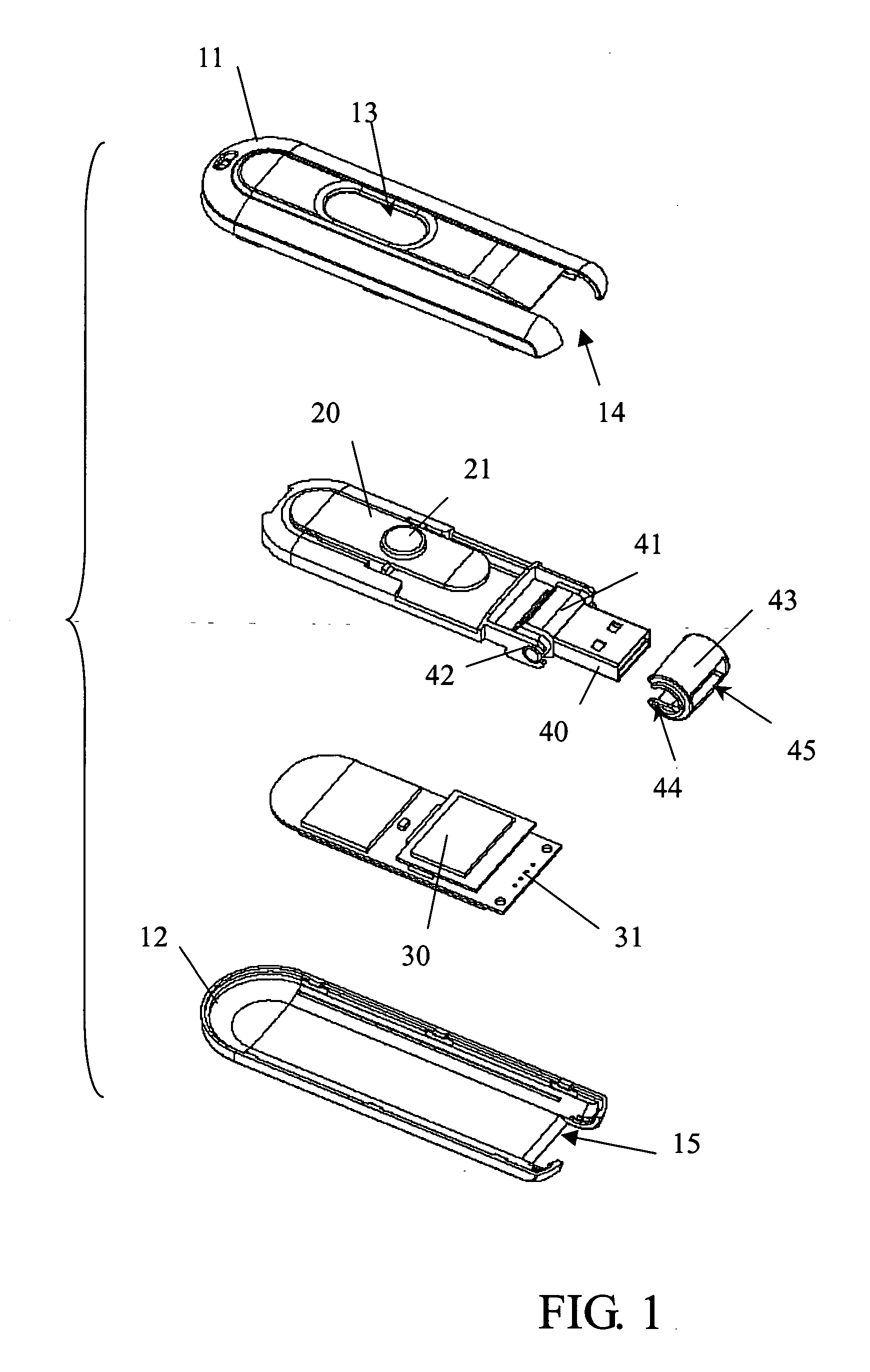
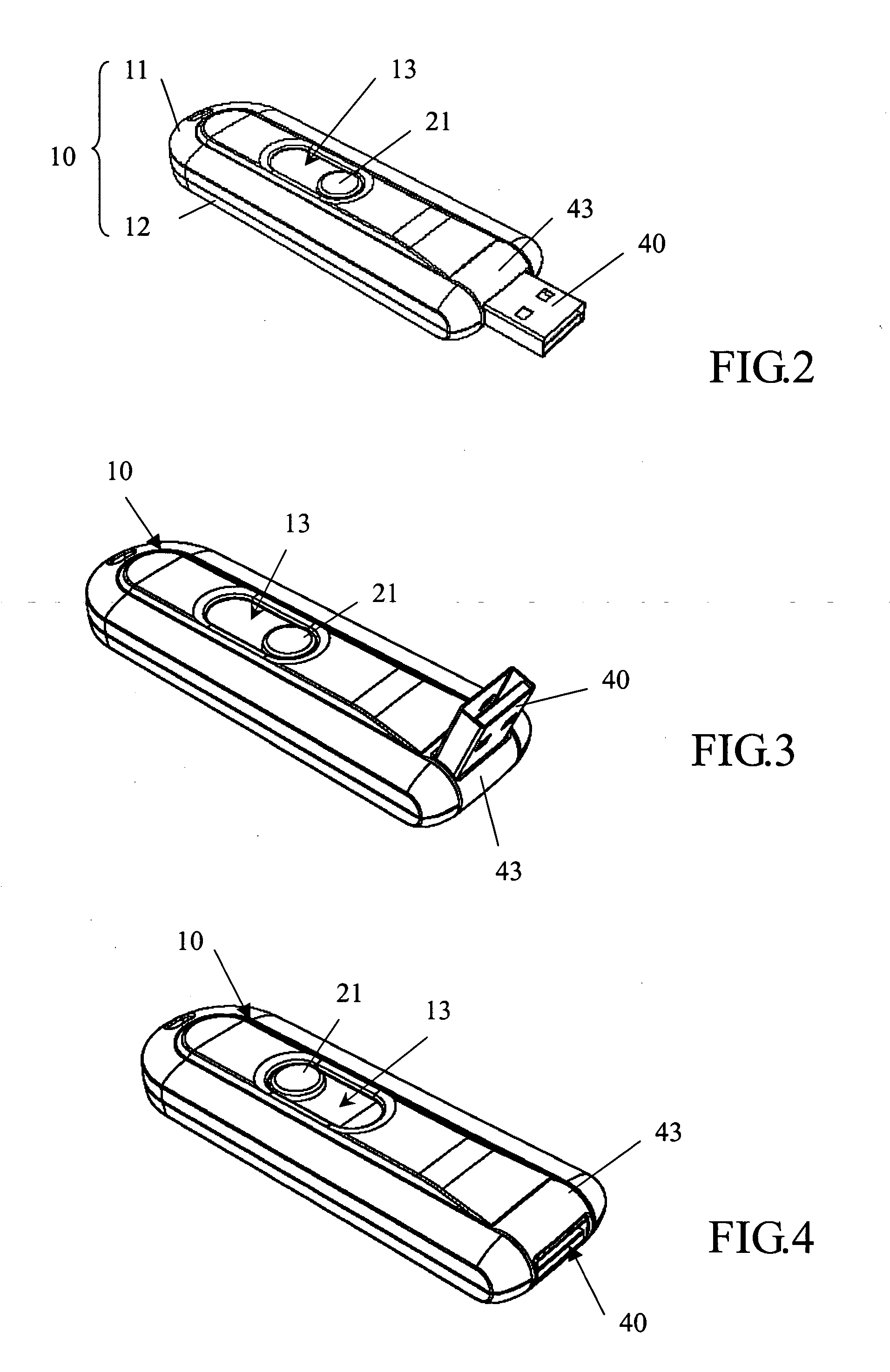
InactiveUS7179099B2Improve compatibilitySlide freelyRotary current collectorTwo-part coupling devicesElectricityEngineering
The mean for the universal serial bus hide and swing, its body inside have a sliding unit its head pivot to establish on can swing from as of deal with USB, and a memory to equip the electricity conjunction in deal with USB. The USB can conceal in the body, or along with the sliding unit to swing after being moved the indentation of the body.
Owner:TUL CORP
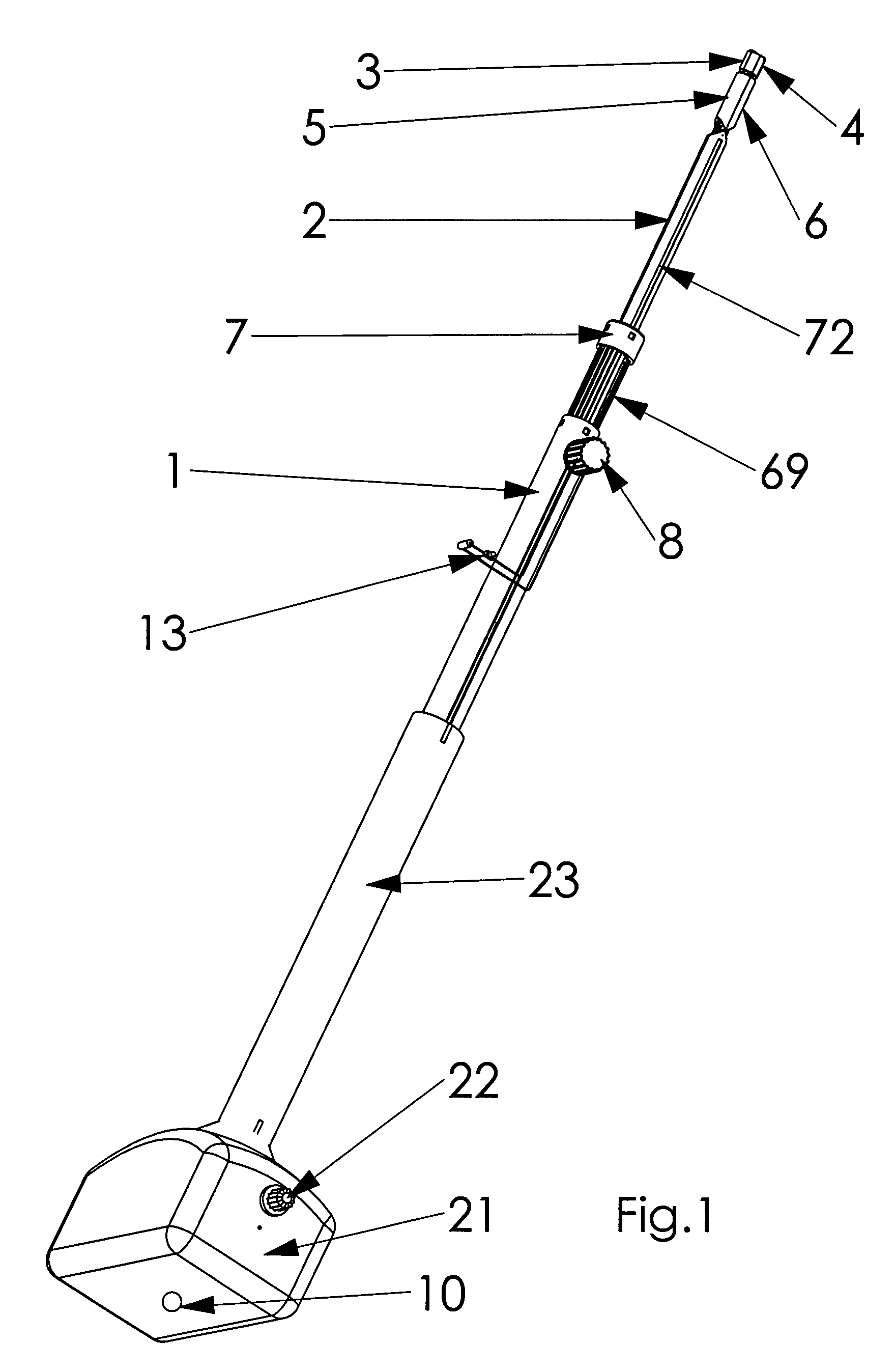
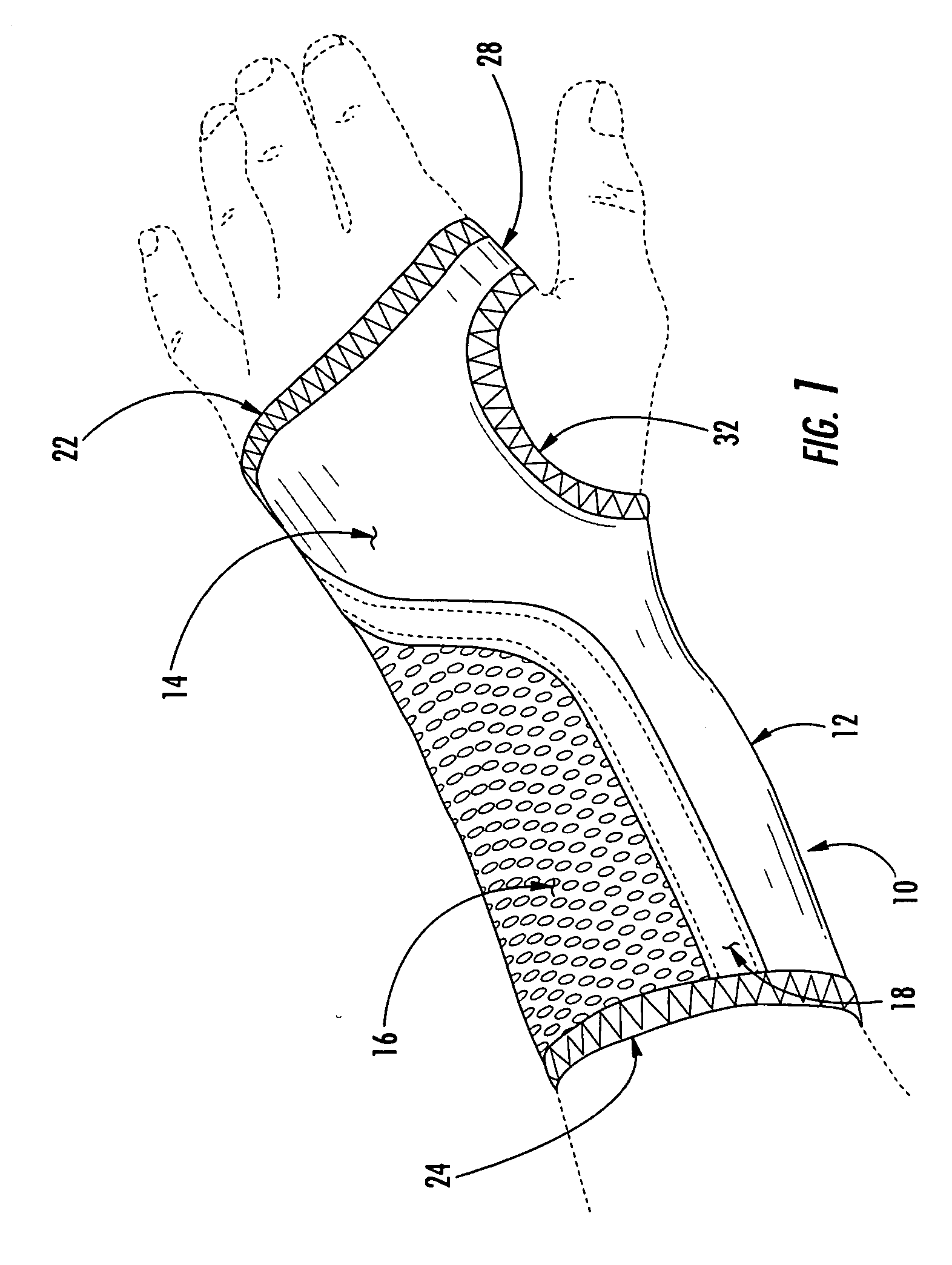
Wrist brace having continuous loop straps and method of using the same
InactiveUS20050197608A1Quickly and easily slideAvoid scratchesFinger bandagesFeet bandagesWrist supportEngineering
A reversible wrist brace includes a sheet of flexible material that overlies and supports a wearer's wrist, wherein the sheet of material includes opposing surfaces each having one or more portions of loop material. The flexible sheet has at least one opening in the vicinity of a lateral edge to accommodate at least one fastening strap, such that the strap may slide within the opening. The fastening strap is a continuous loop of sheet material having an outer surface with a hook-bearing portion. The fastener is designed so as to enable a wearer to switch the wrist brace between right and left hands by orienting the hook-bearing portion so that it is coincident with the loop-bearing portion when the wrist brace is worn on either hand. The wrist brace may include a splint that may be inserted within a pocket located on the flexible material to further immobilize the wrist.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Intervertebral Prosthetic Disc With Metallic Core
InactiveUS20090210060A1Inhibit wearAvoid tearingSpinal implantsCoatingsBody fluidIntervertebral disk
A prosthetic disc for insertion between adjacent vertebrae includes a core having upper and lower curved surfaces and upper and lower plates. At least one of the curved surfaces of the core is metallic, and in some embodiments the entire core is metallic. Each plate has an outer surface which engages a vertebra and a metallic inner curved surface which is shaped to slide over one of the curved surfaces of the core. In some embodiments, the center of rotation of the core is free to move relative to the upper and lower metallic plates. In some embodiments, one or more channels extend across one or both of the curved surfaces of the core for allowing passage of bodily fluid to promote lubrication between the core and at least one of the plates.
Owner:SIMPLIFY MEDICAL PTY LTD
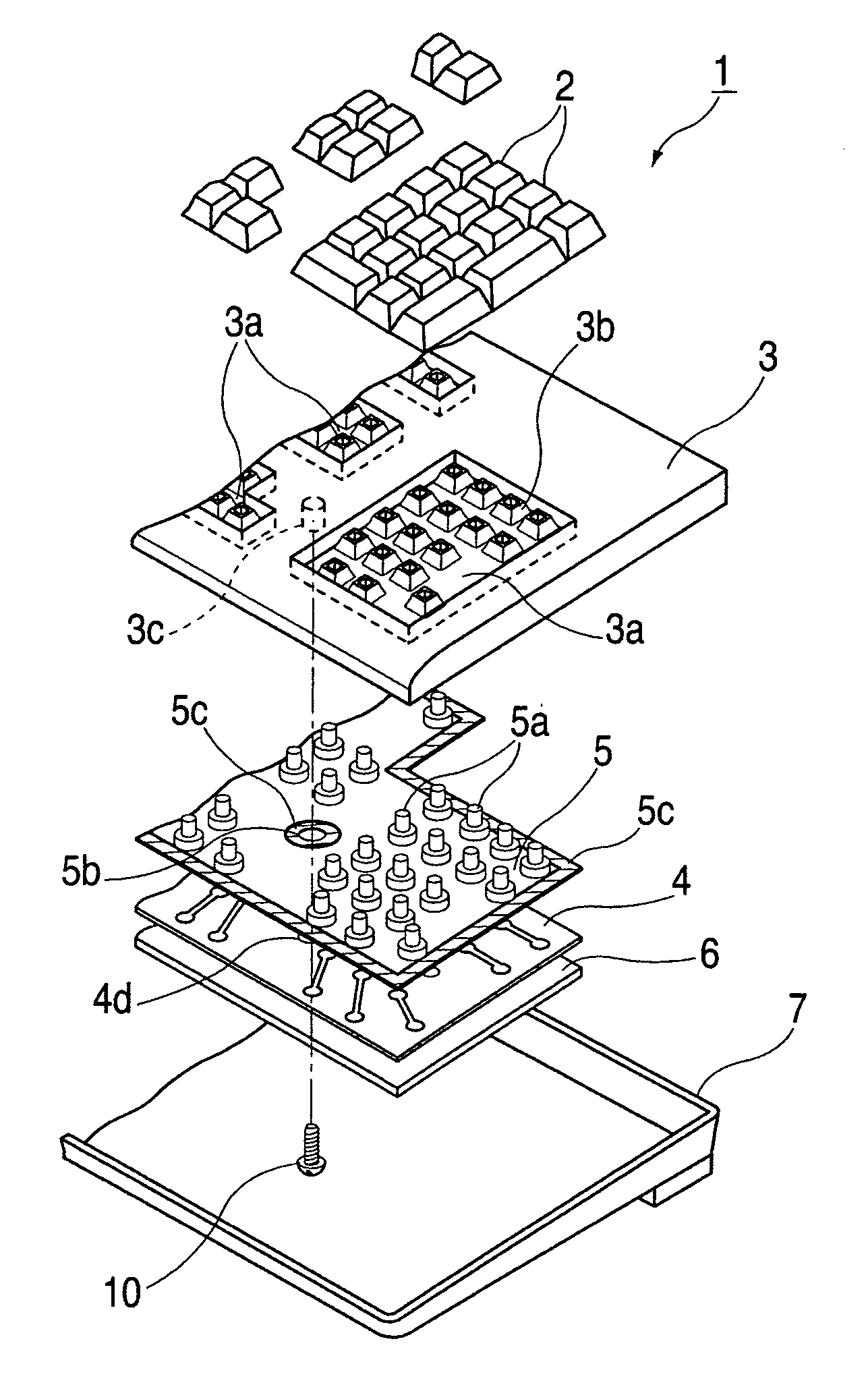
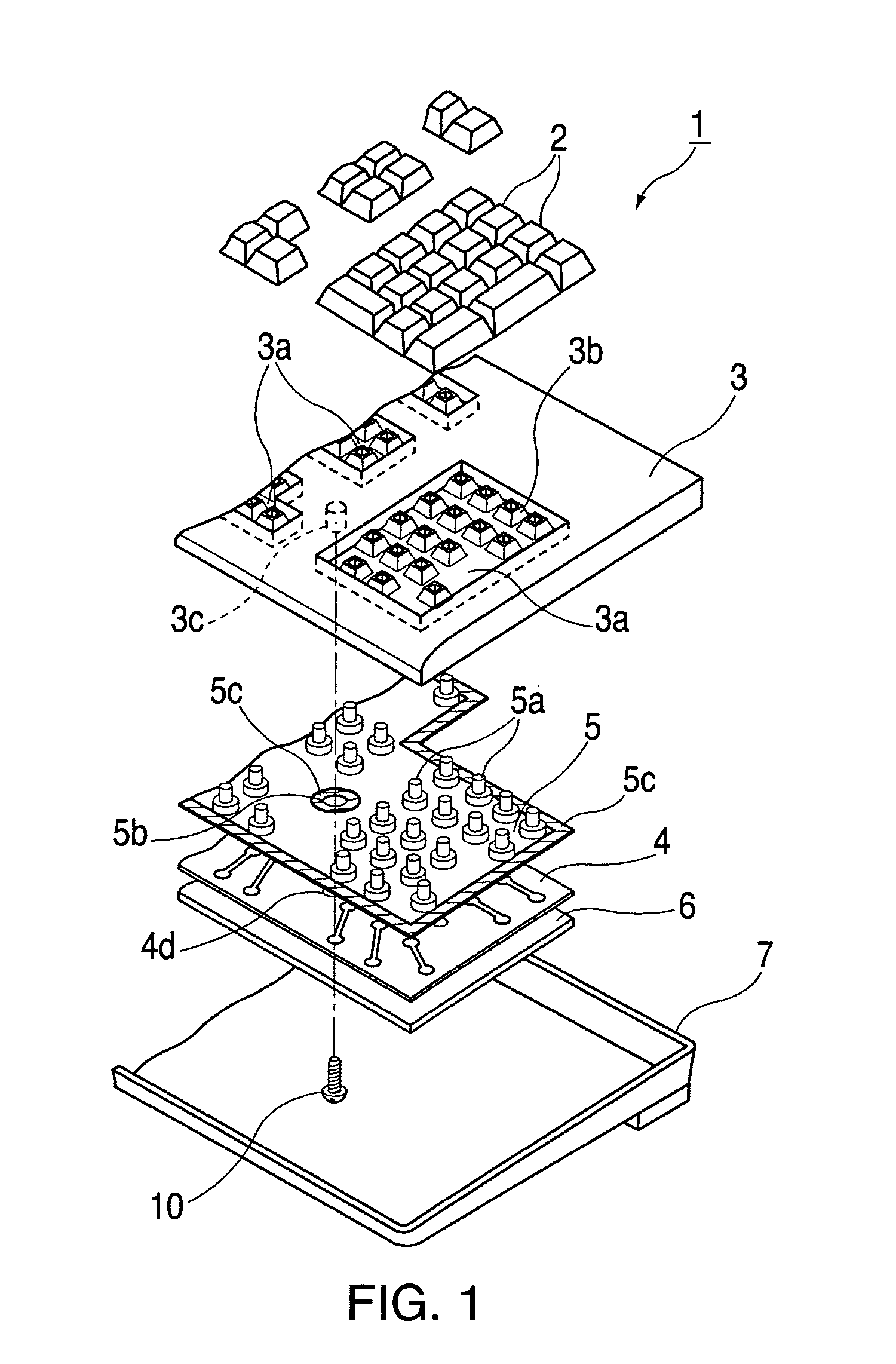
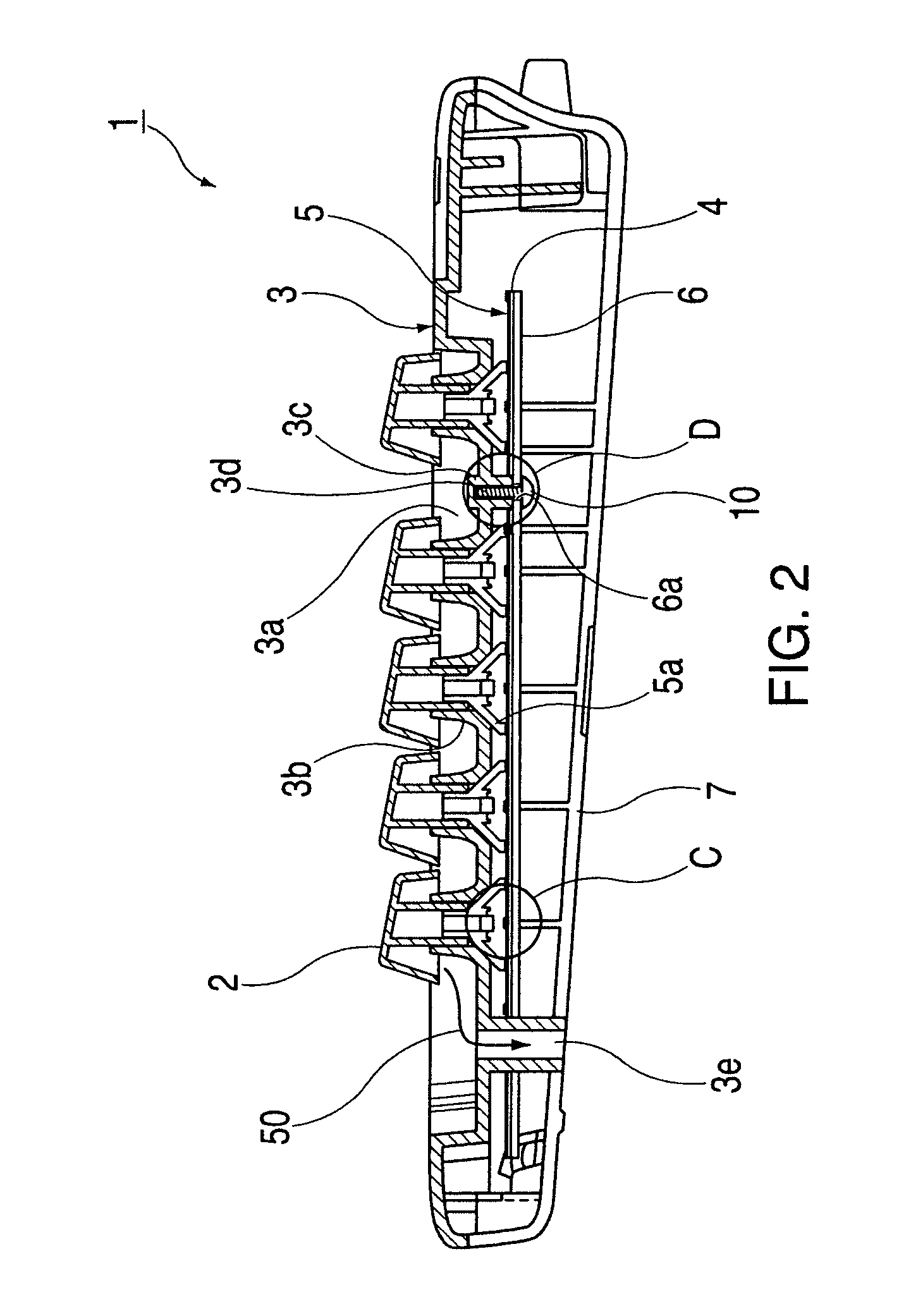
Keyboard spill-proofing mechanism
ActiveUS7030330B2Minimize manufacturing costImprove work efficiencyInput/output for user-computer interactionEmergency casingsElectronic circuitEngineering
This keyboard spill-proofing mechanism reduces and prevents damage to the electronic circuitry in keyboard that would normally occur due to inadvertent spillages of liquids, such as water, coffee or soda, onto the keyboard. This keyboard spill-proofing mechanism features a membrane sheet positioned below the top case. The membrane sheet includes multiple layers that have electrical circuits. The electrical circuits detect the off / on state of the key caps when they are pressed. The keyboard design features a waterproof base sheet made of an adhesive material that is positioned between the top case and the membrane sheet. The waterproof base sheet is designed such that a plurality of rubber springs connected thereon transmit the off / on state of the key caps to the electrical circuits in the membrane sheet. The waterproof base sheet is also designed so that it has multiple blocking portions which project upward from the waterproof base sheet so as to prevent spilled liquid from flowing downward onto the membrane sheet thereby preventing or reducing possible damage to the electrical circuits in the membrane sheet of the keyboard.
Owner:LITE ON SINGAPORE PTE LTD
Thermal-mechanical positioning for radiation tracking
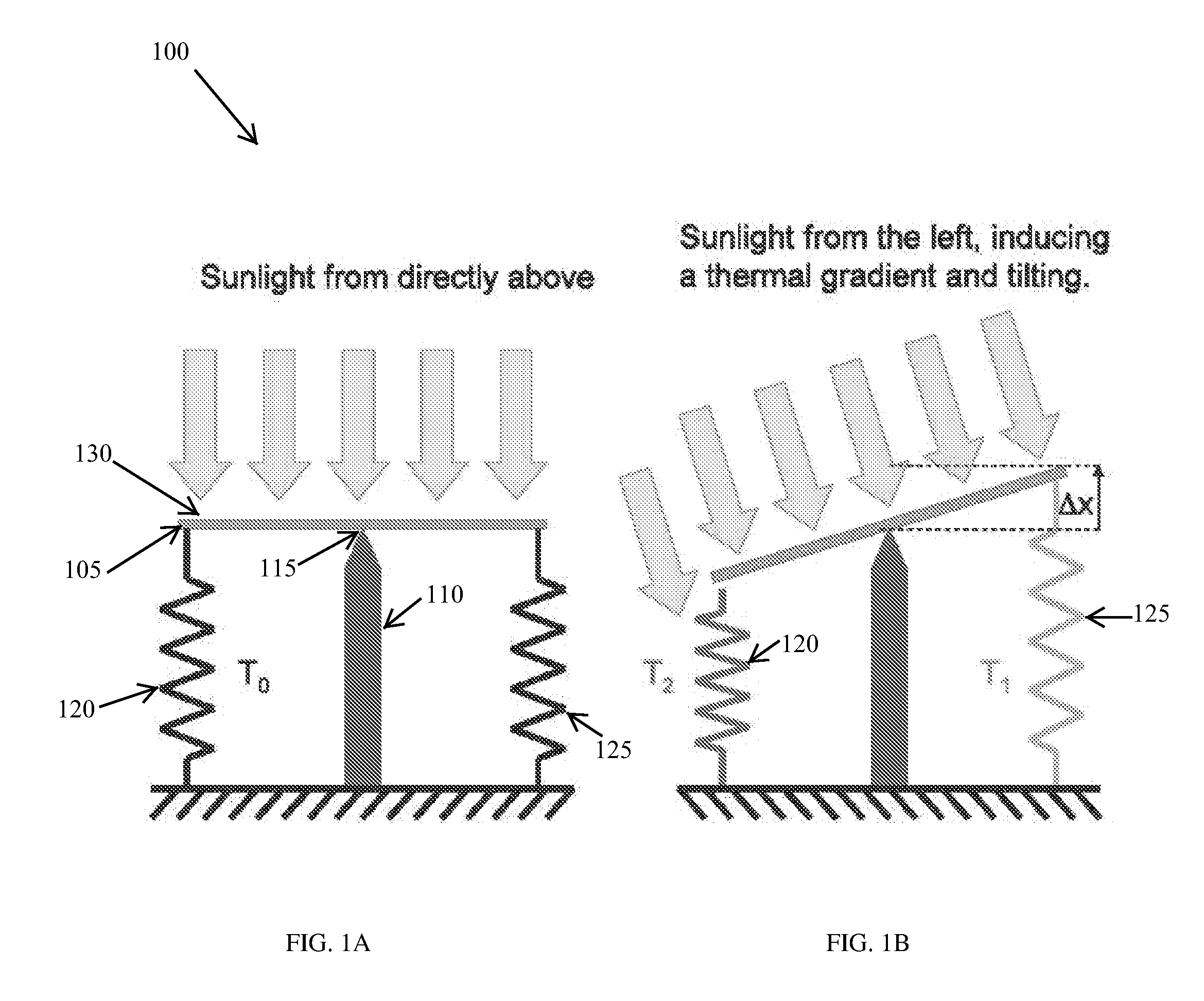
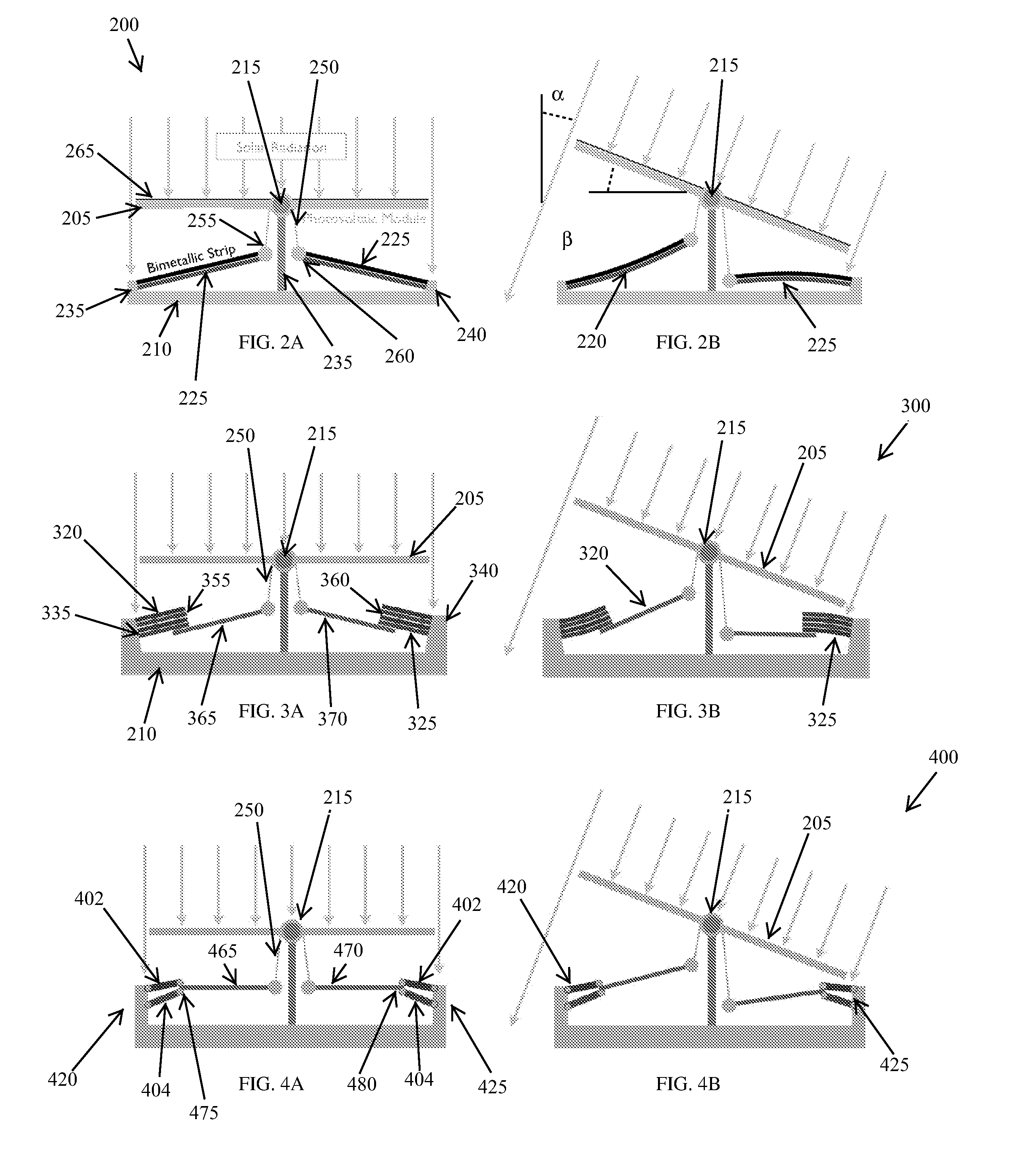
InactiveUS20100275904A1Low costHigh efficiencyPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyRadiationThermodynamics
The invention relates to systems and methods for controlling angular position of a pivotable platform relative to a radiation source. In one embodiment, an apparatus for controlling angular position of a pivotable platform relative to a radiation source includes a frame, a thermal actuation element coupled to the frame, a pivotable platform positioned between the radiation source and the thermal actuation element so as to at least partially block energy from the radiation source from impinging on the thermal actuation element, and apparatus for pivoting the pivotable platform in response to a thermally controlled deformation of the thermal actuation element.
Owner:SUNPOINT TECH
Exercise device with integrated handle and stopping device
InactiveUS6860841B1Quickly “ pumping up ”Toning individual muscle groups of a userResilient force resistorsTherapy exerciseEngineeringStops device
An exercise device, having a pair of handles—namely a first handle and second handle, and an elastic cord extending through the handles. The elastic cord has a fixed end, the first handle located adjacent to the fixed end. The second handle located along the elastic cord further away from the fixed end than the first handle. The second handle can selectively slide freely along the elastic cord toward and away from the first handle. A stopping device is attached to at least one of the first handle and second handle. The stopping device is capable of fixing the position of its associated handle along the elastic cord so that the elastic cord may then be tensioned to allow exercises to be performed.
Owner:MORTORANO MICHAEL PETER
Device and method for transferring force to a targeted objected
InactiveUS7191685B2Increase or decreaseReduce shockConstructionsReciprocating drilling machinesHead movementsMechanical engineering
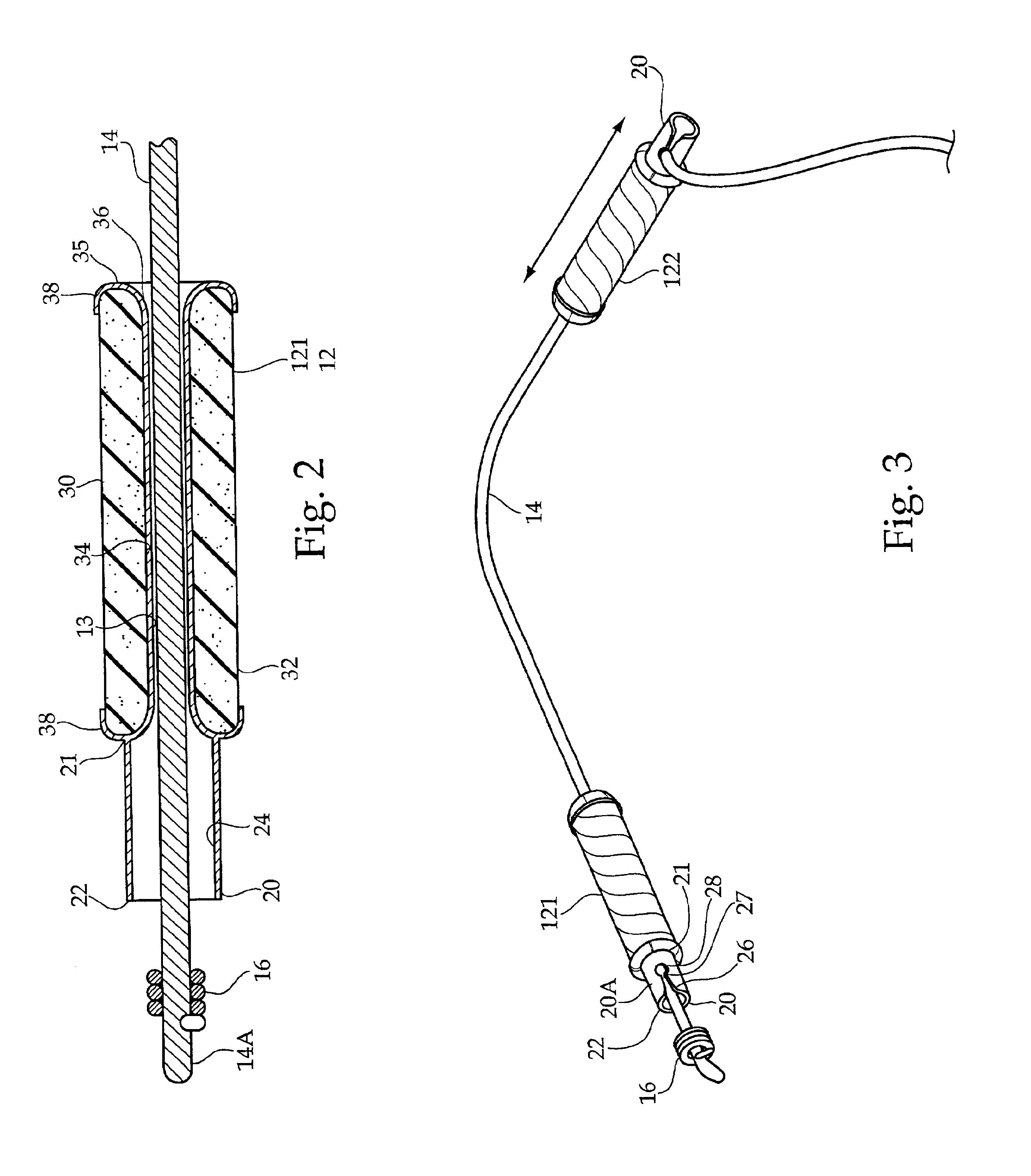
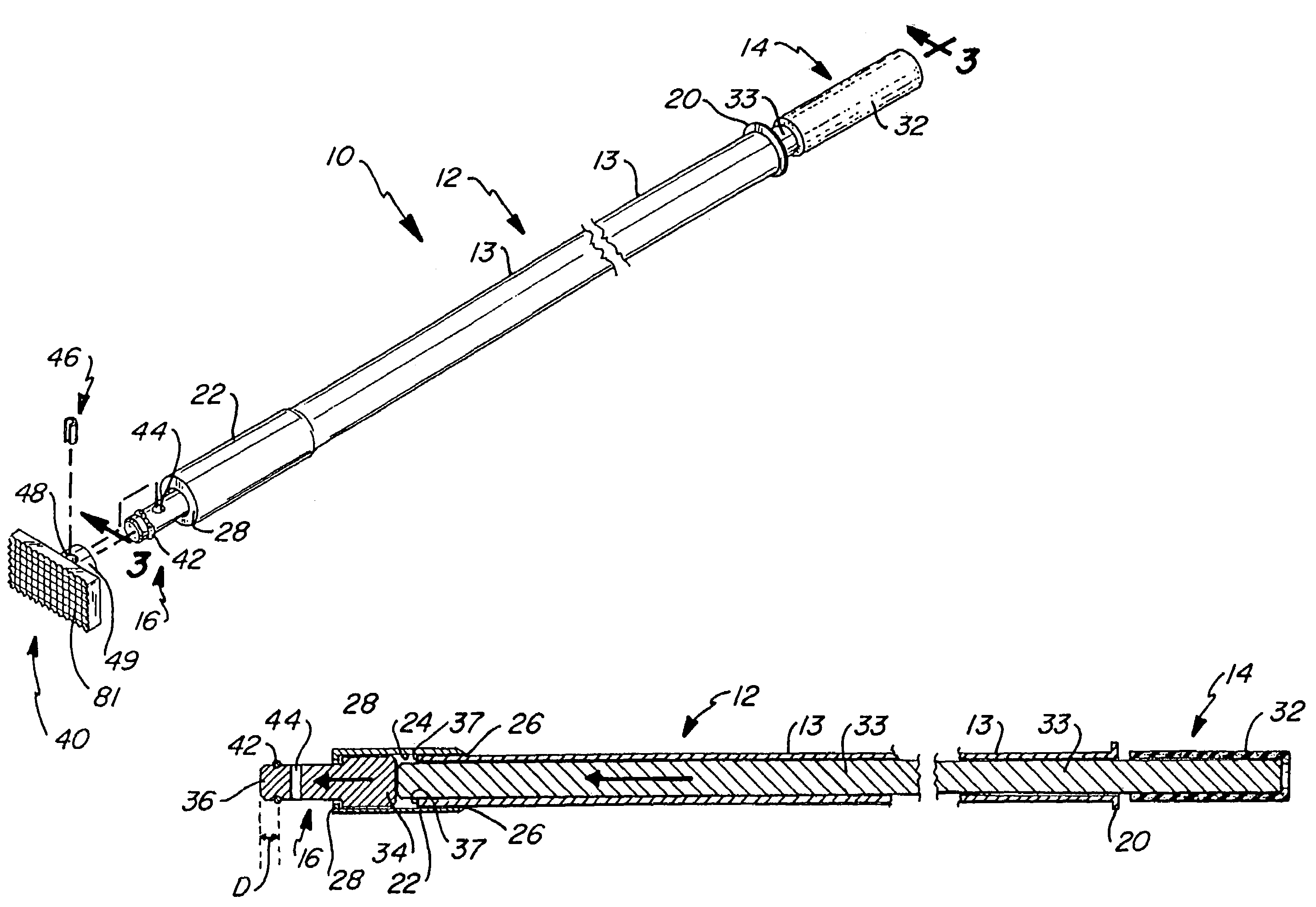
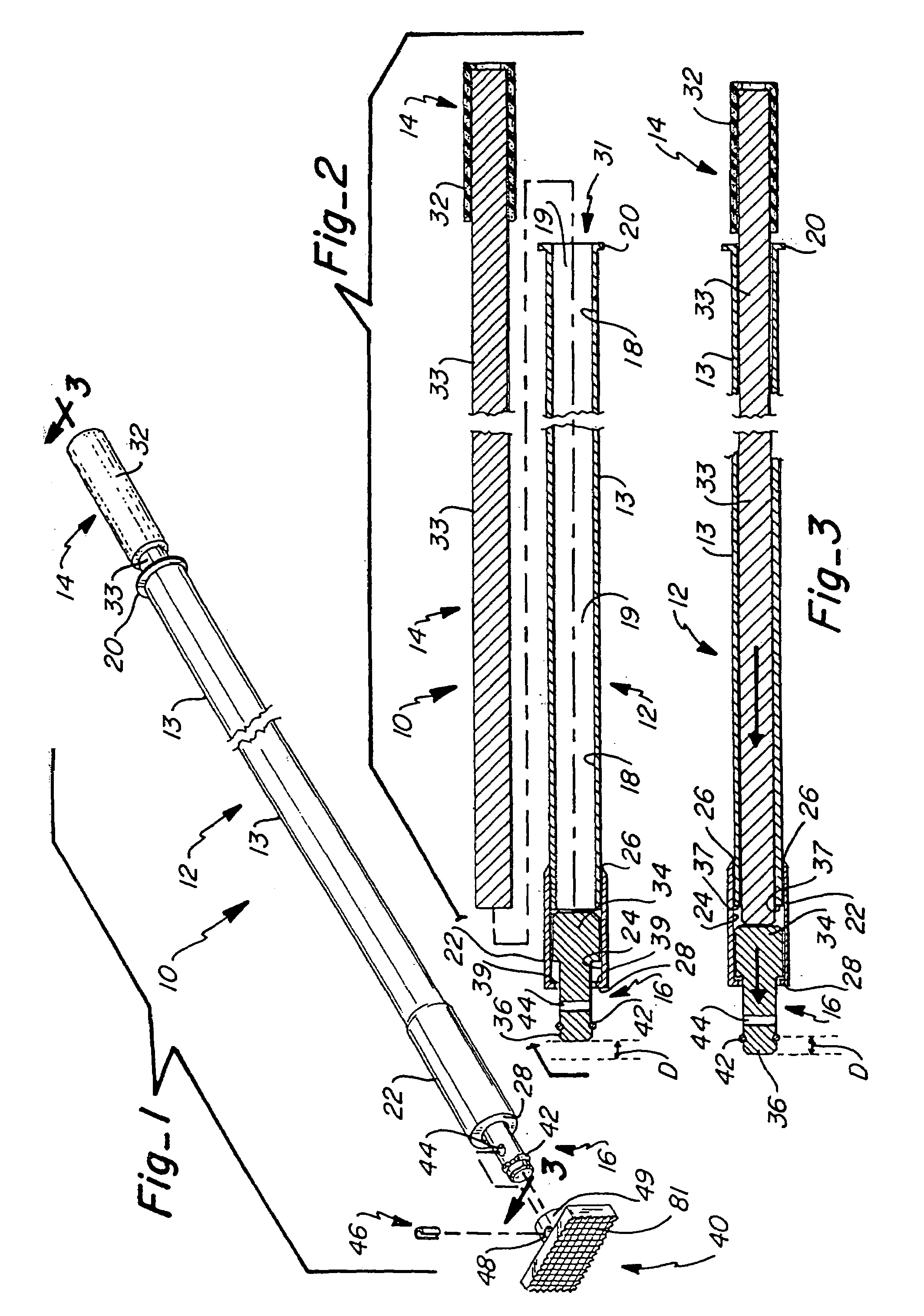
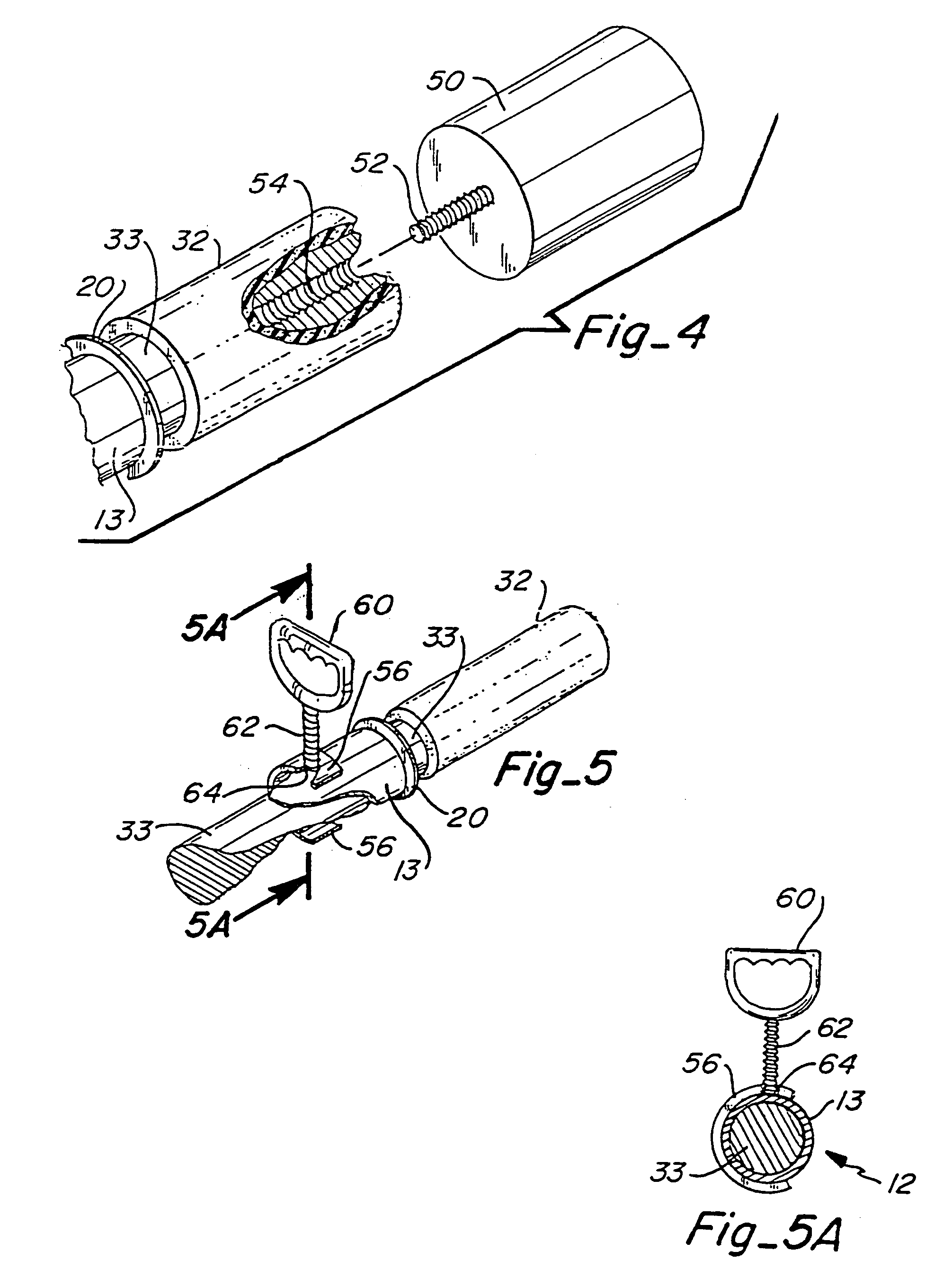
A slide hammer includes three major components, namely, a guide sleeve, a plunger and an impact head. The plunger is inserted within the guide sleeve. The impact head is secured within the distal end of the guide sleeve, and has a portion which protrudes from the guide sleeve distal end. The impact head is able to freely slide within a segmented portion of the guide sleeve distal end, or the impact head movement may be controlled by a spring. The plunger is slid within the guide sleeve at a selected velocity in order to contact the portion of the impact head slidably secured within the guide sleeve. The force of the plunger striking the impact head is transmitted through the impact head to a targeted object in contact with the protruding portion of the impact head. The impact head may be fitted with various types of tips. Each of the tips has particular advantages in applying force to a targeted object.
Owner:SLIDE SLEDGE
Parking caliper assembly
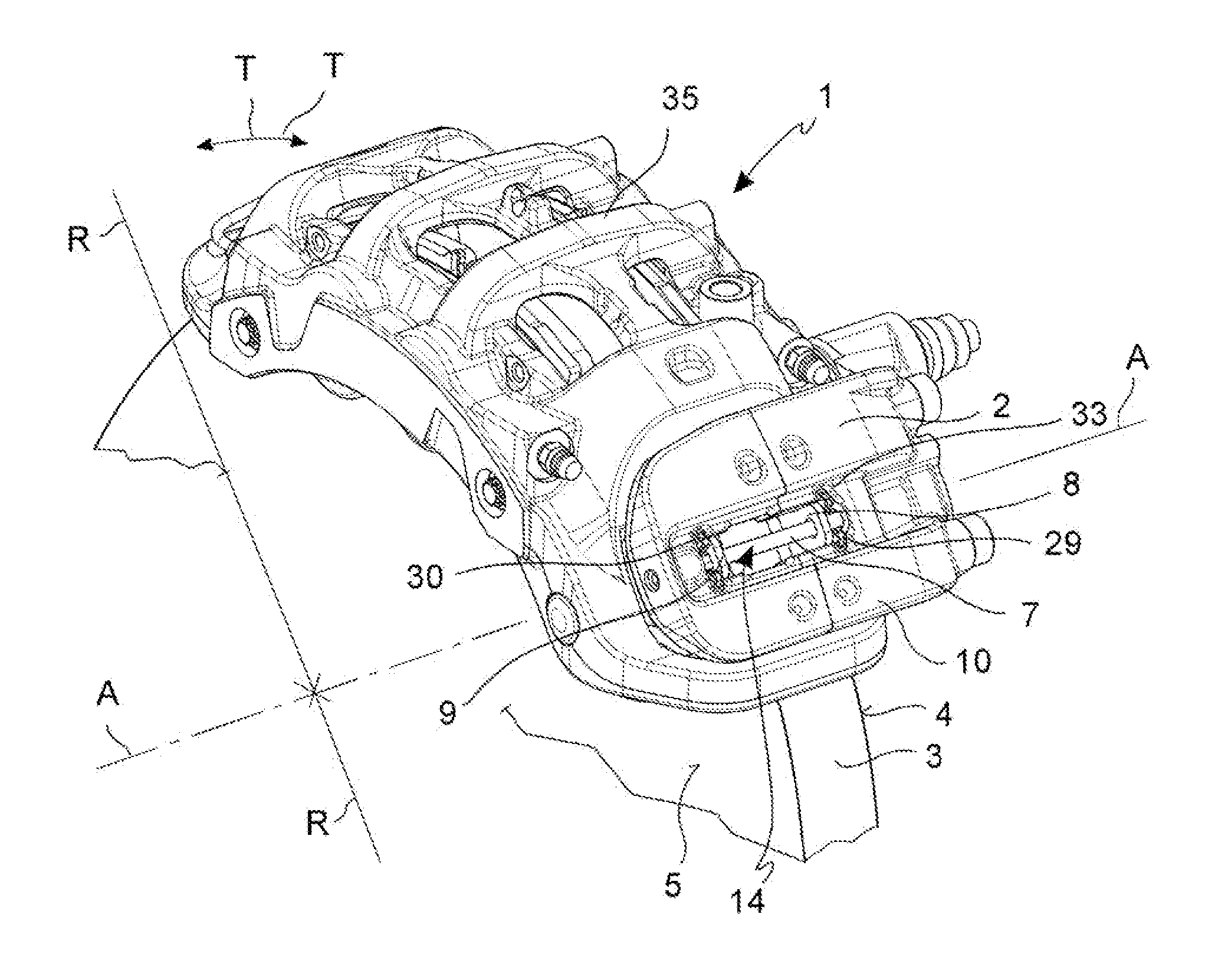
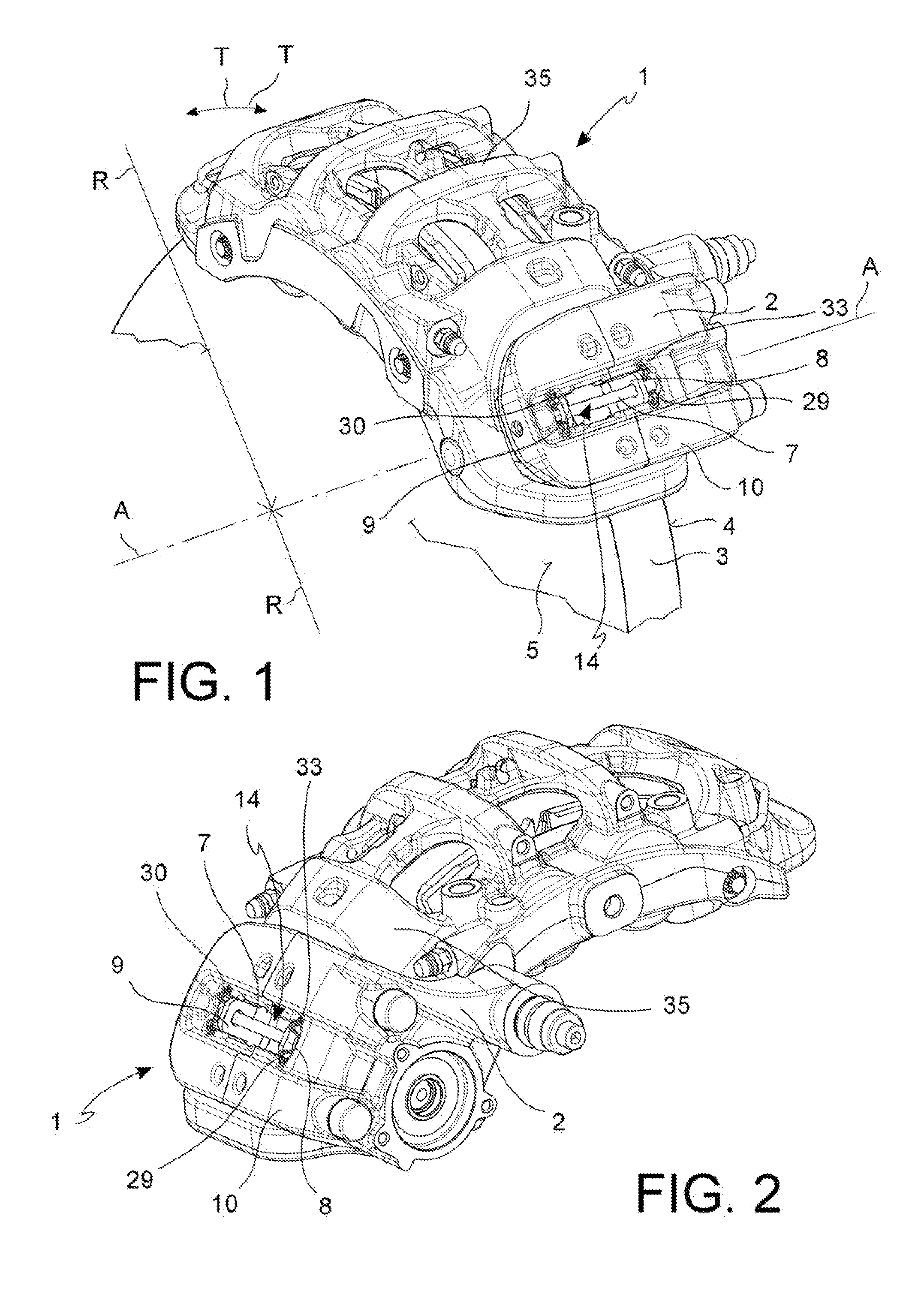
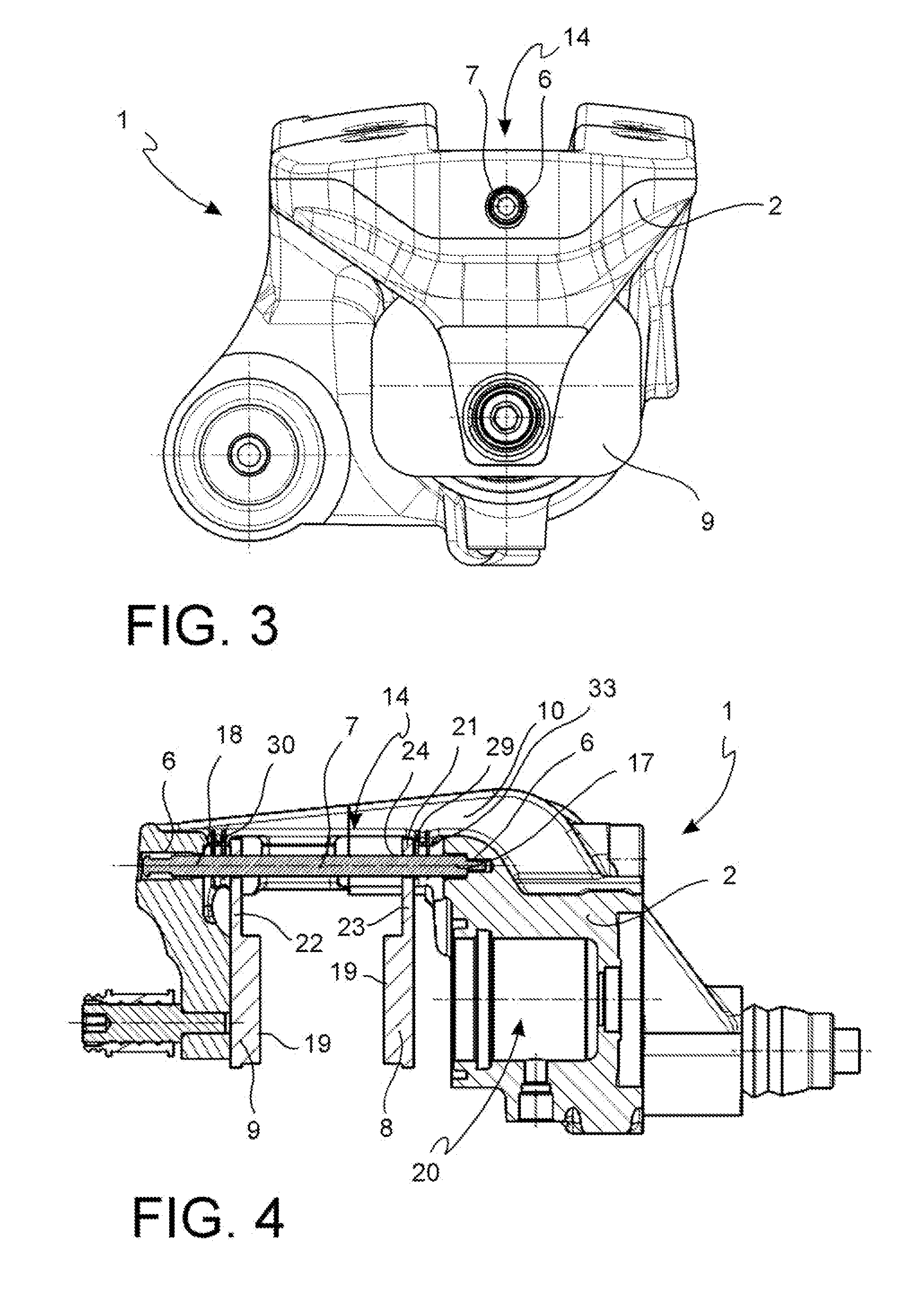
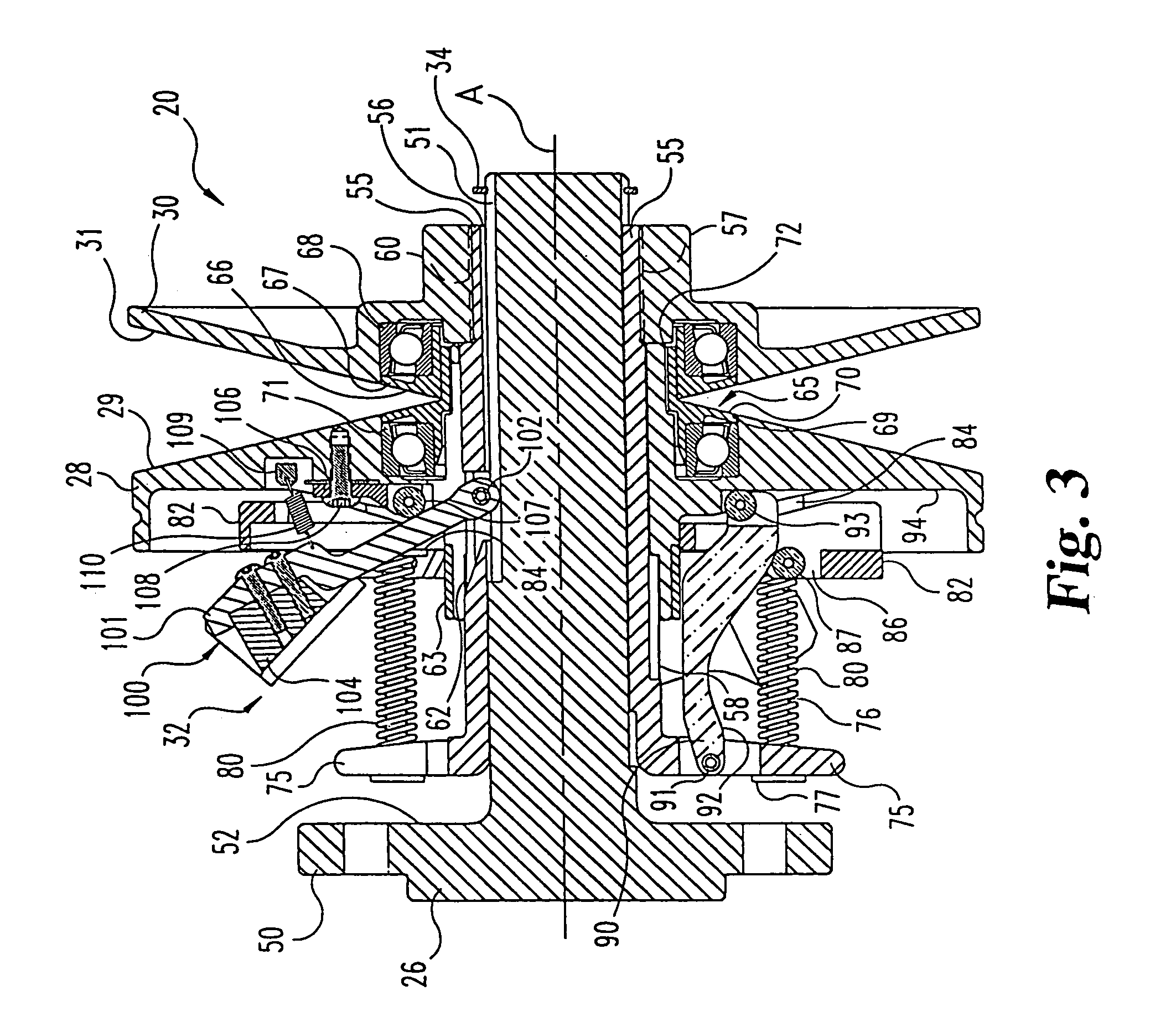
ActiveUS20150027821A1Slide freelyReduced dimensionBraking element arrangementsAxially engaging brakesAbutmentCalipers
An assembly comprising a caliper body (2) of a caliper assembly for parking disc brake, said caliper body (2) comprising a channel (14), said axial channel (14) being defined by at least one wall having at least one flattened length forming at least one guide surface (15; 16); at least one portion of caliper body (10) projecting towards the disc or above the disc (3), said portion of caliper body (10) comprising a surface facing the disc (11) or at least the friction material (12) of said pad (8), and wherein said surface facing the disc (11) has a flattened length forming at least one abutment surface (12; 13) and wherein said at least one guide surface (15; 16) is oriented differently with respect to said at least one abutment surface (12; 13) so as to avoid that they are mutually coplanar; said guide surface (15; 16) is suitable to face an opposite guide surface (25; 26) provided for on an associable supporting plate (21, 22) of an associable pad (8) in order to allow the positioning and sliding thereof against the caliper body (2) and wherein, in said abutment surface (12, 13), it is suitable to face an opposite abutment surface (27, 28) provided for on the supporting plate (21, 22) of at least one associable pad (8) so as to allow the pad to abut and slide against said abutment surface (12; 13).
Owner:FRENI BREMBO SPA
Resin matrix composite with super-hydrophobic bionic surface and preparation method of resin matrix composite
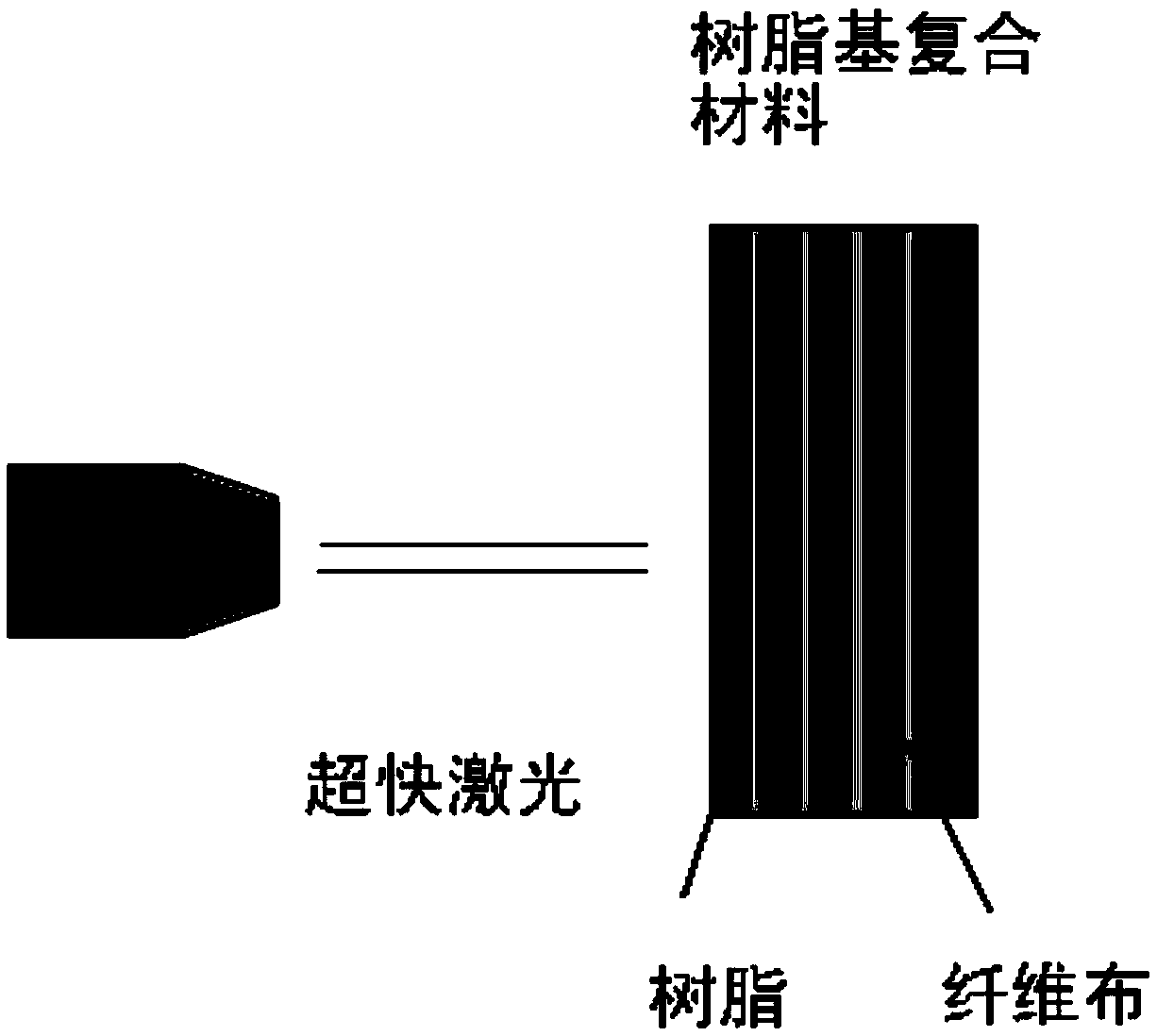
ActiveCN105504324AImprove environmental adaptabilityAvoid heat damageCoatingsMicrostructureResin matrix
The invention provides a resin matrix composite with a super-hydrophobic bionic surface and a preparation method of the resin matrix composite. The method comprises steps as follows: the surface of a matrix of the resin matrix composite is polished until the surface turns white; the matrix of the resin matrix composite is processed through ultrafast laser, and a microstructure is formed on the surface; a first coating is sprayed on the microstructure surface of the matrix of the resin matrix composite through a pneumatic type paint spray gun to form a bonding layer, a second coating containing nanosilicon dioxide particles is sprayed to form a surface hydrophobic function layer, and the resin matrix composite with the super-hydrophobic bionic surface is obtained. The preparation method is simple to operate and facilitates production, the prepared resin matrix composite with the super-hydrophobic bionic surface can allow water drops to freely slip off, and the real self-cleaning super-hydrophobic function is realized.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING AERONAUTICAL MFG TECH RES INST
Universal stand for vehicle engines and gearboxes
InactiveUS7237758B2Slide freelyEasy to processPortable framesStands/trestlesEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:NIKOLIC LJUBOMIR
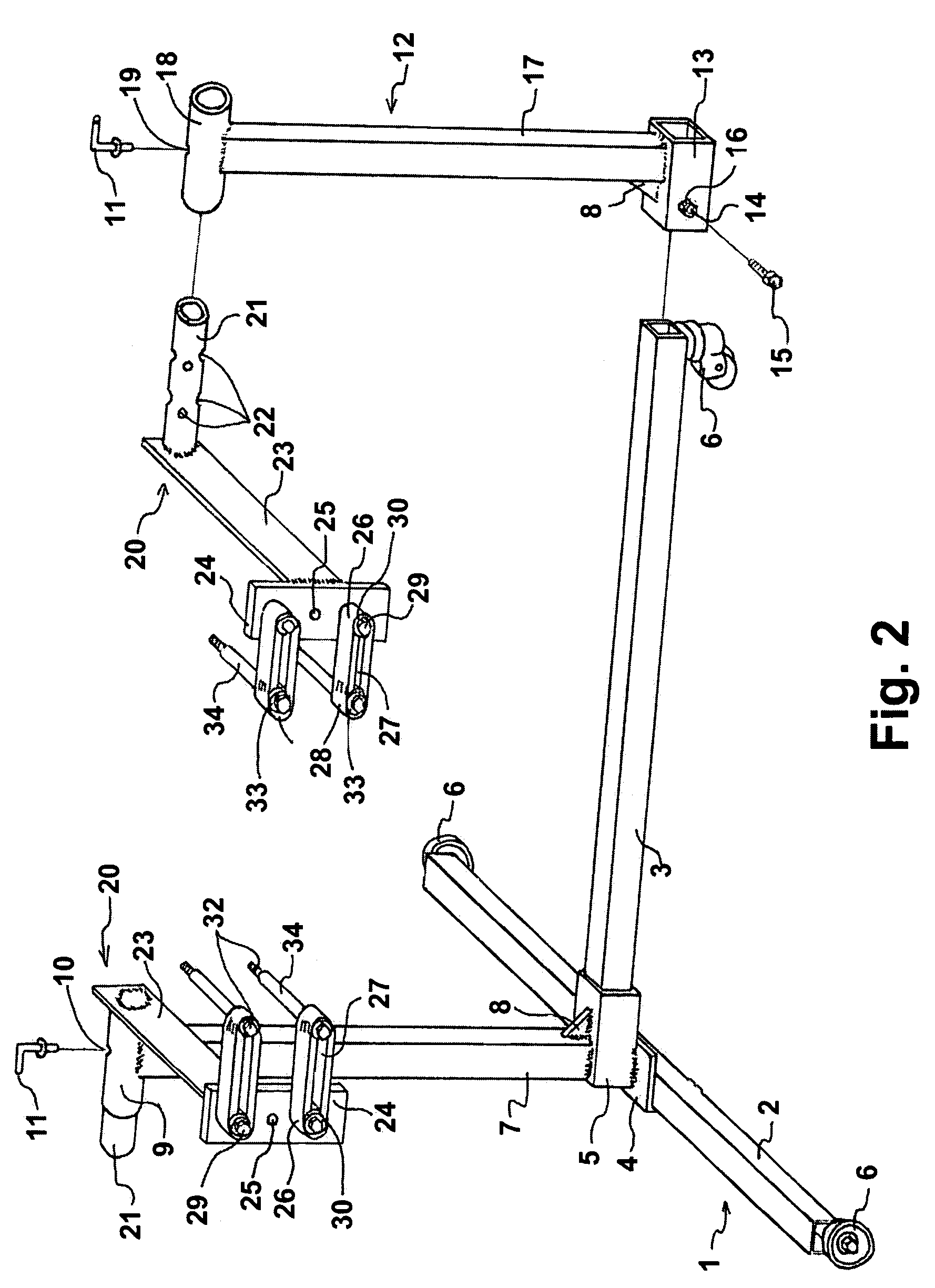
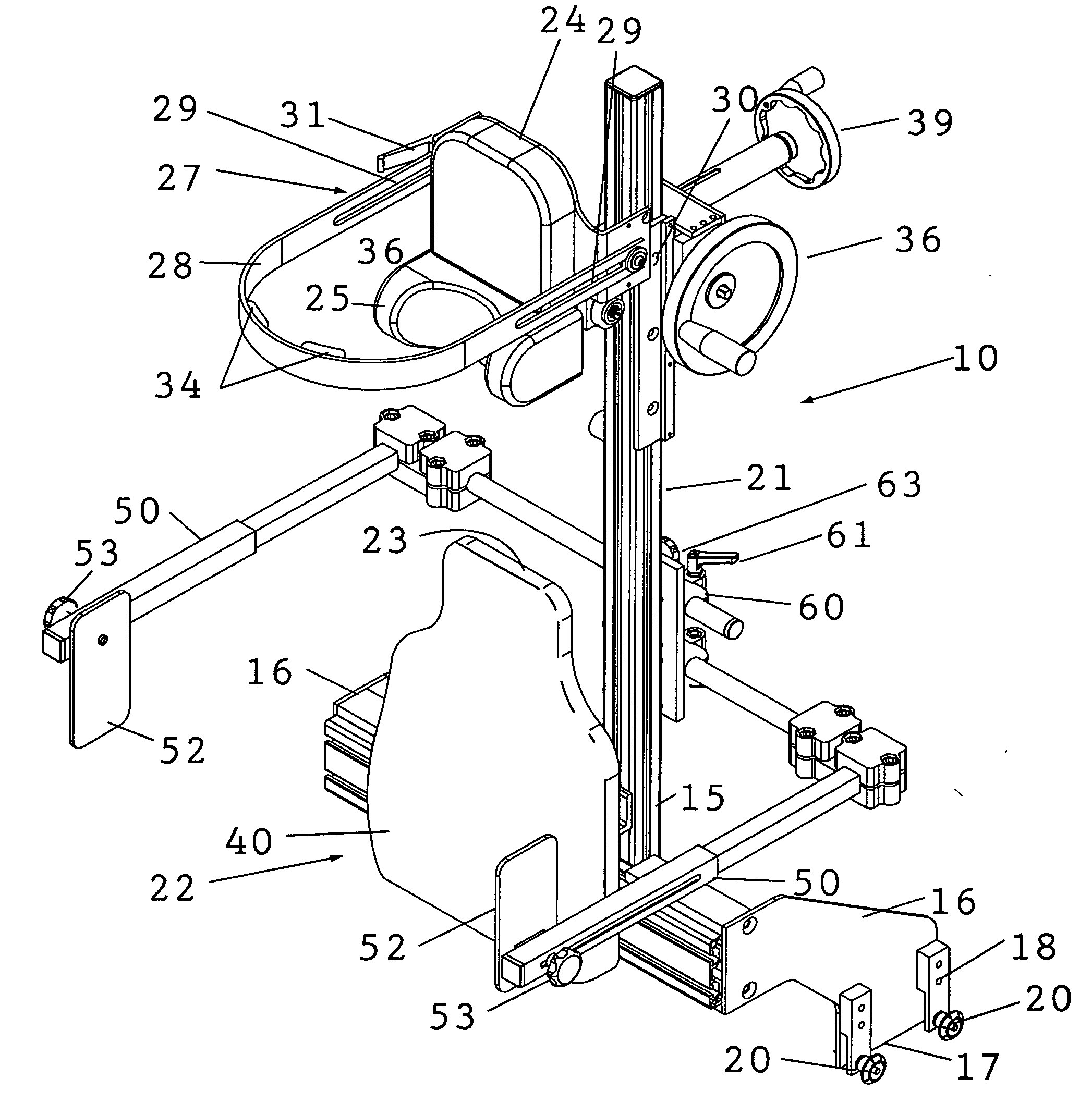
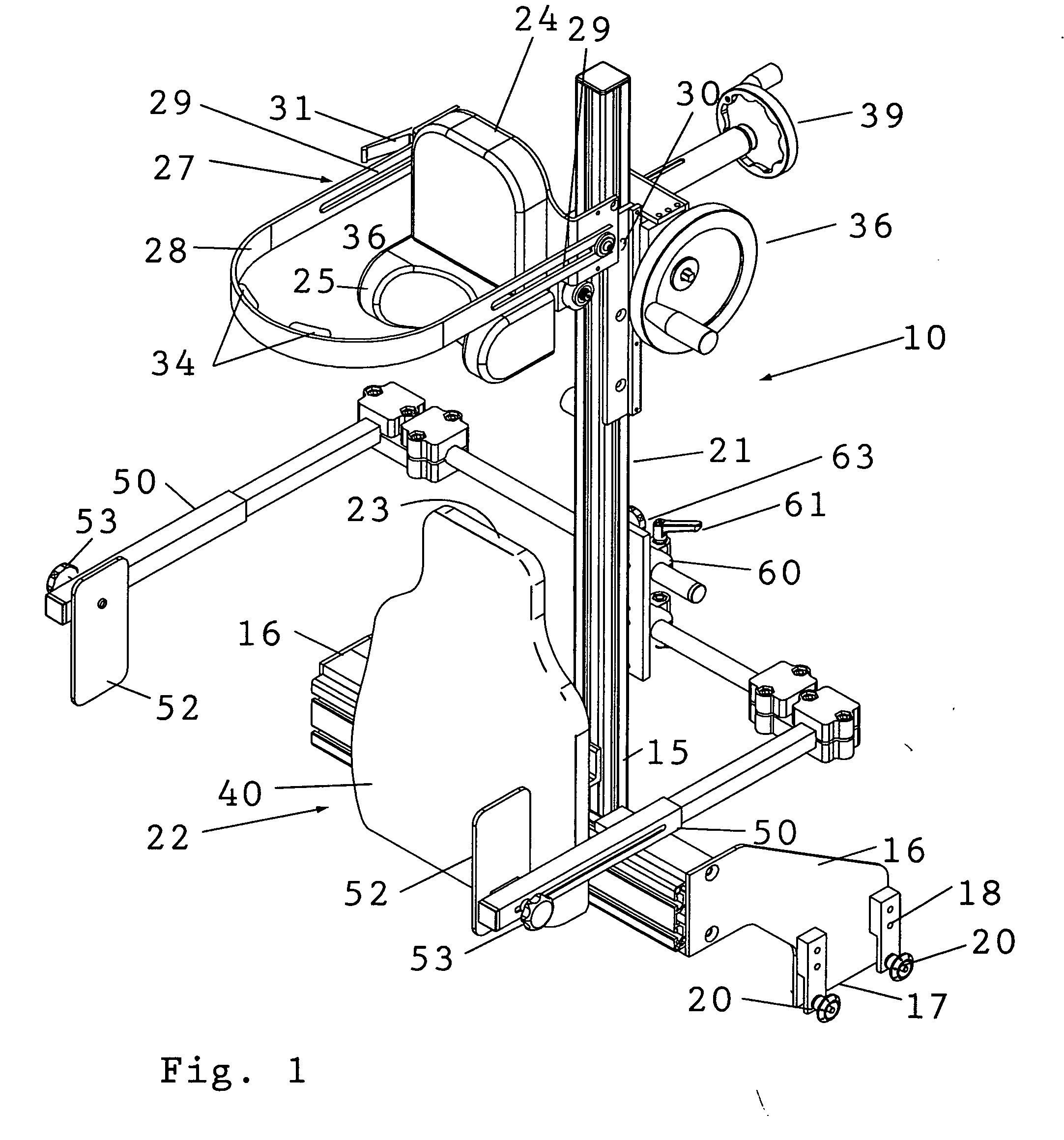
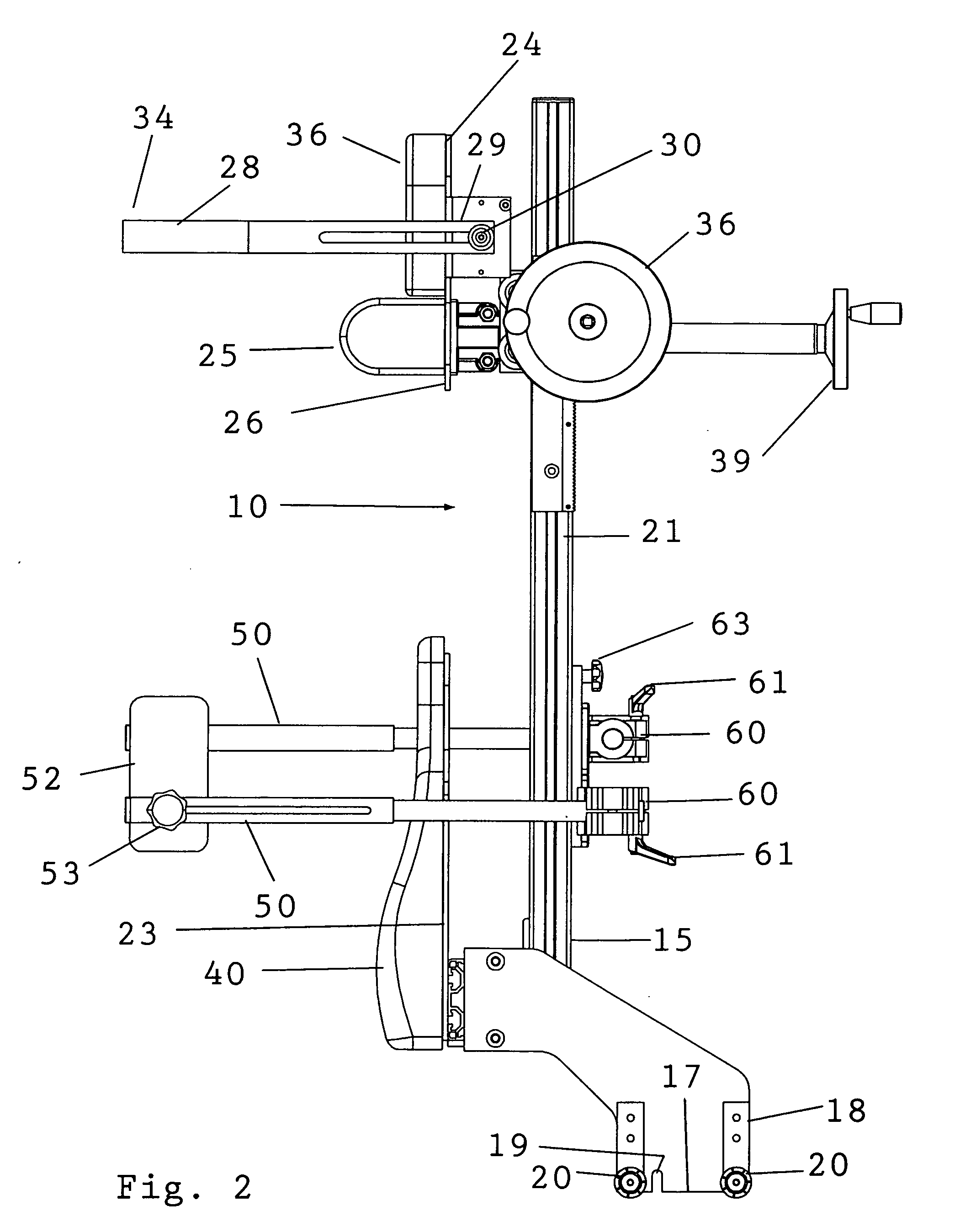
Shoulder surgery attachment for a surgical table
ActiveUS20090307845A1Guarantees proper engagementSlide freelyOperating tablesSofasEngineeringHead fixation
A shoulder surgery attachment for a surgical table having an articulated leg section with accessory attachment rails on opposite sides. An upright chair back assembly is supported at its base or bottom end thereof for attachment to the accessory attachment rails and the chair back assembly includes a headrest assembly positioned above a back support. The headrest assembly includes a removable neck support and a head fixation assembly. The headrest assembly is adjustably moveable up and down the chair back assembly. The neck support is positioned below the head fixation assembly and protrudes from the front of the headrest assembly for engagement with the back of the patient's neck. The head fixation assembly includes a forward protruding U-shaped forehead clamp having two distal rearwardly extending free ends that are adjustably secured to the headrest assembly whereby the head clamp may be adjusted for engaging the forehead of the patient to clamp the patient's head against the headrest assembly.
Owner:ORTHOPEDIC POSITIONING SOLUTIONS LLC +1
Memory device having a hiding and swing plug and method for hiding and swing a plug thereof
InactiveUS20060084284A1Increase compatibilityImprove compatibilityRotary current collectorTwo-part coupling devicesElectricityHead parts
The mean for the universal serial bus hide and swing, its body inside have a sliding unit its head pivot to establish on can swing from as of deal with USB, and a memory to equip the electricity conjunction in deal with USB. The USB can conceal in the body, or along with the sliding unit to swing after being moved the indentation of the body.
Owner:TUL CORP
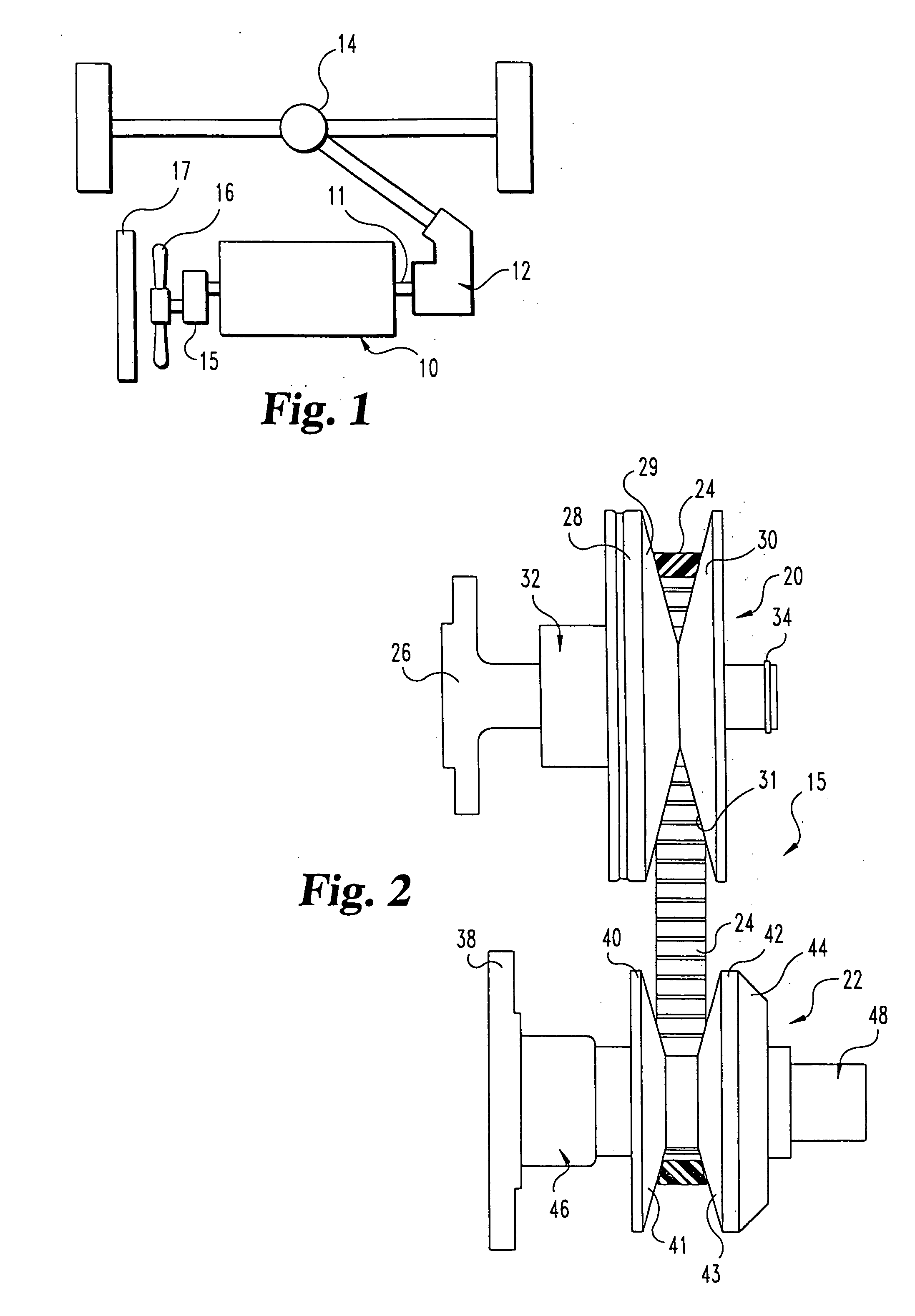
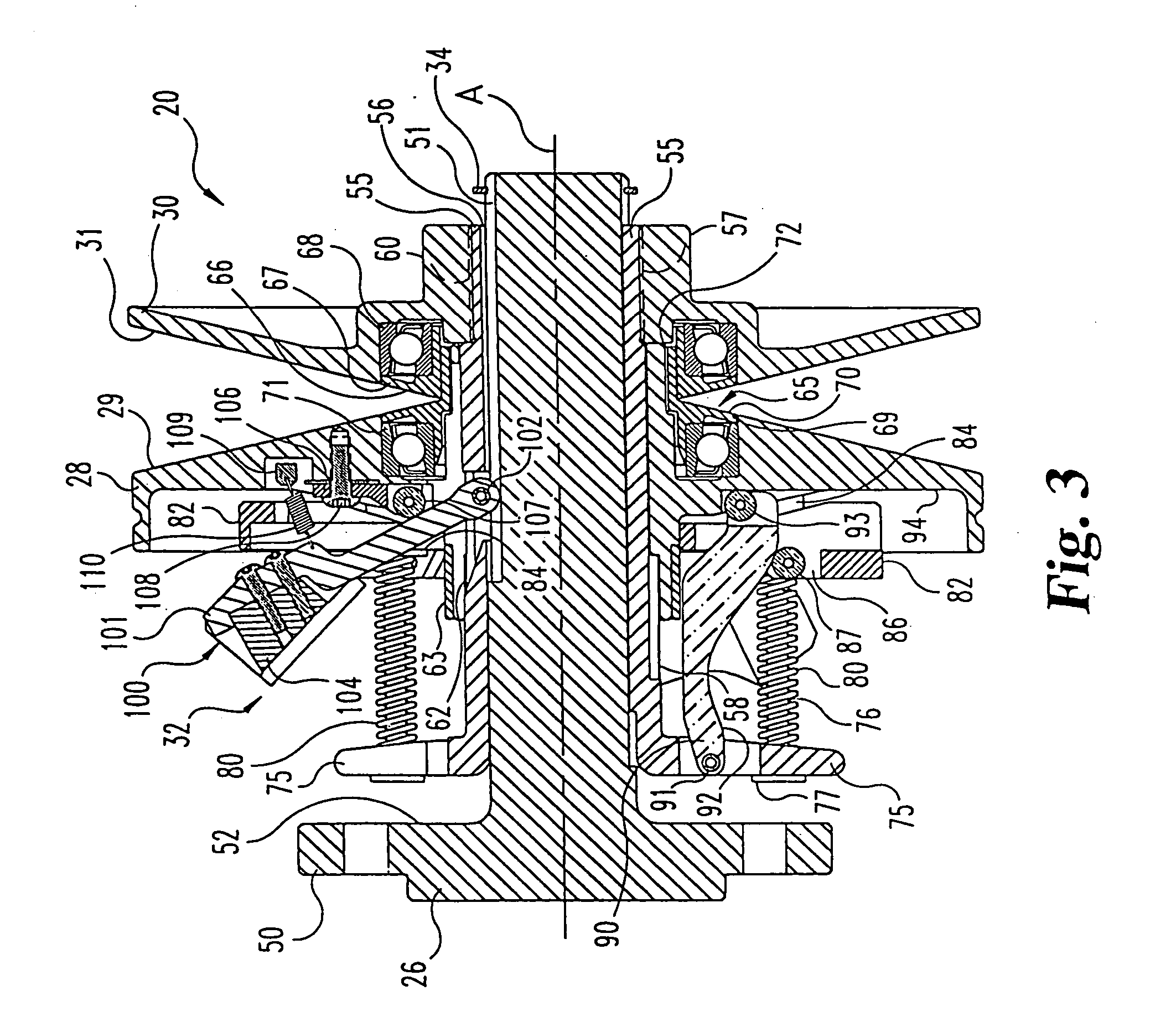
Continuously variable belt drive system
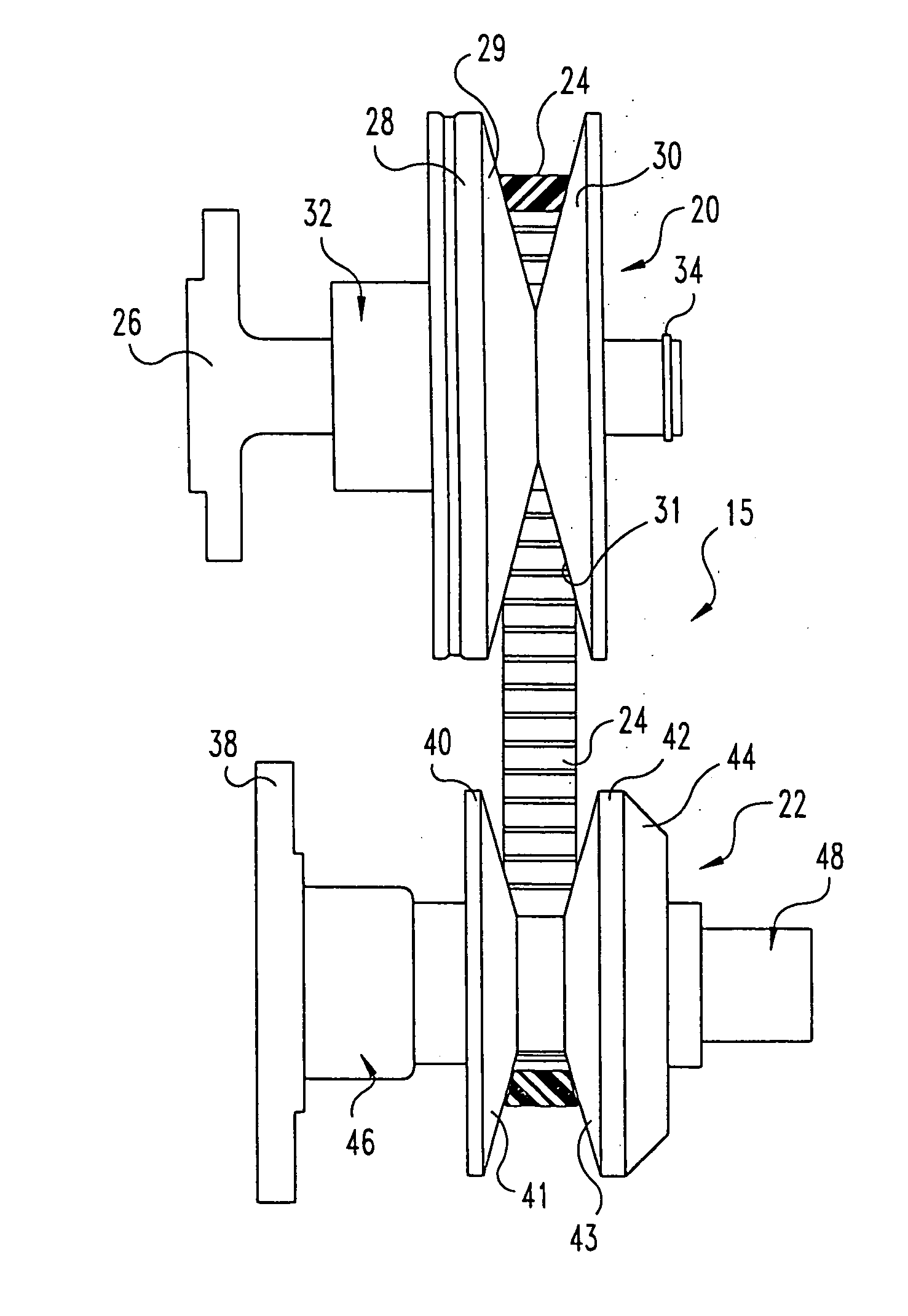
InactiveUS20060019781A1Slide freelyIncrease axial forceGearingPortable liftingAxial pressureTransfer system
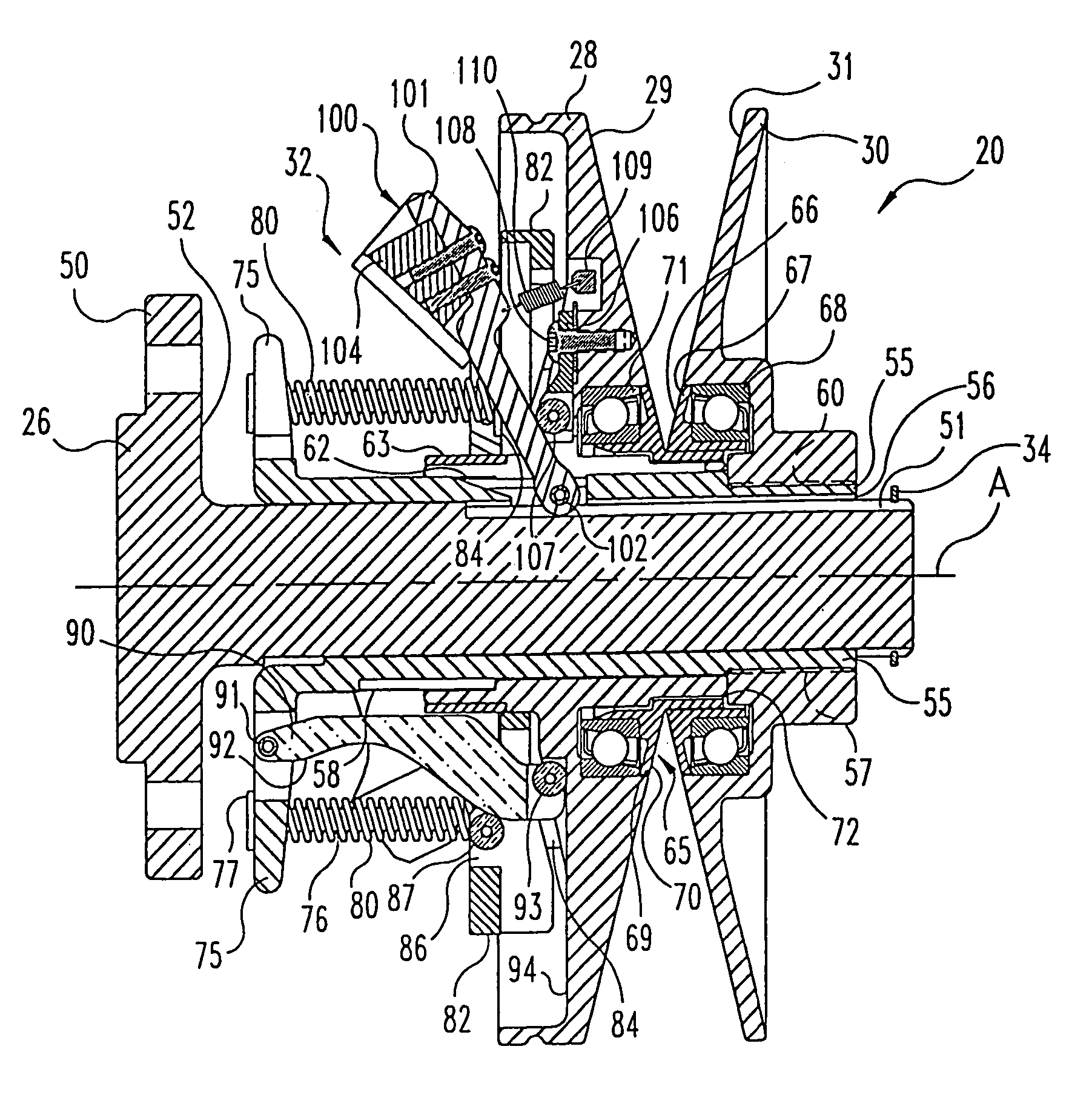
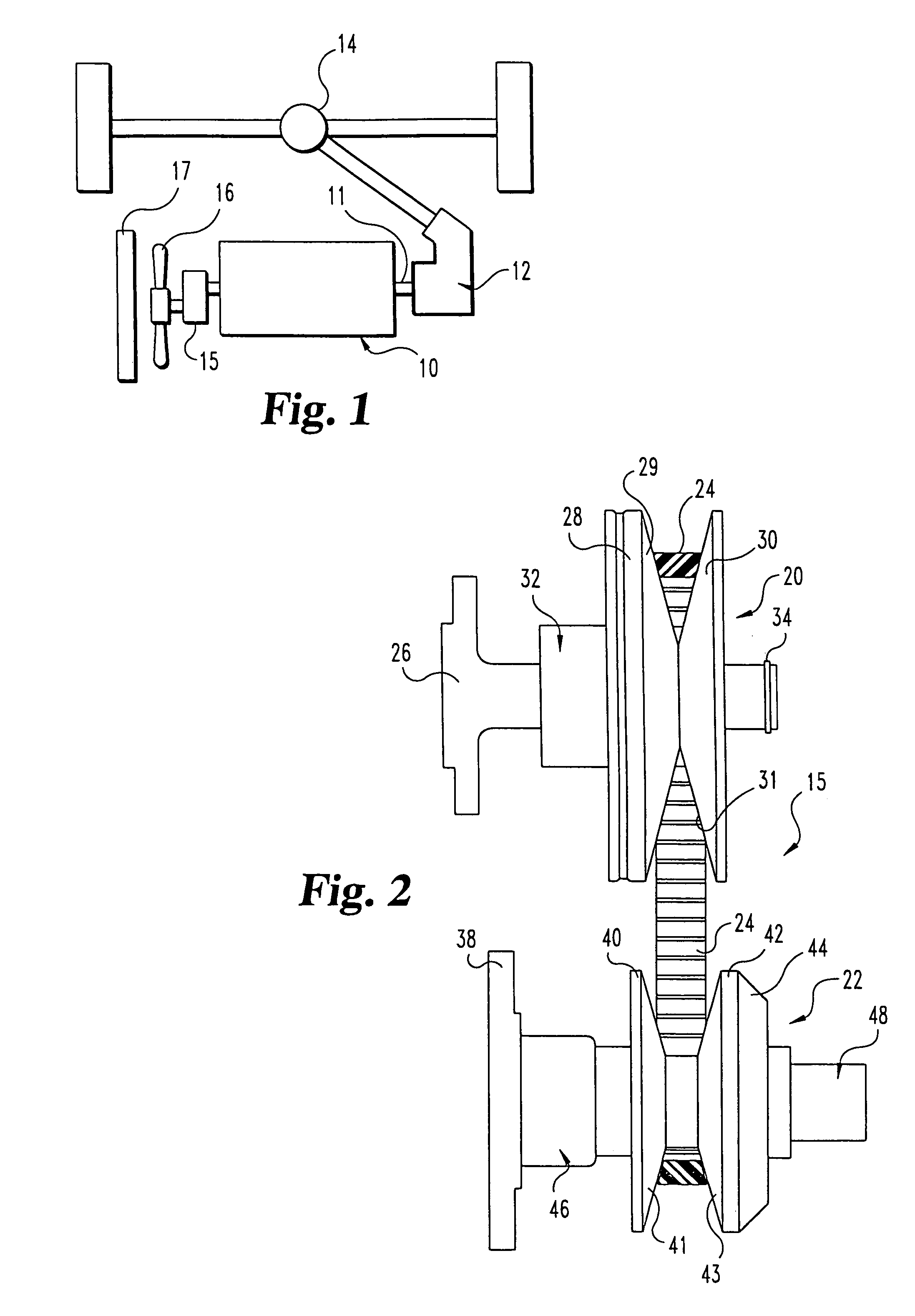
A belt-type continuously variable transfer system (15) includes a driving pulley assembly (20), a driven pulley assembly (22) and a V-shaped belt (24) engaged to transfer rotary power therebetween. The driven pulley assembly (22) can include a ratio adjustment mechanism (46) that adjusts the position of a rear sheave (40) relative to a forward sheave (42). The adjustment mechanism (46) includes a motor (170) and a worm gear mechanism (171, 172) that rotates an actuation screw (154). Rotation of the actuation screw (154) is reacted by a split nut (158) so that as the screw (154) rotates is translated along the axis (B) of the driven pulley assembly (22). Translation of the actuation screw (154) exerts pressure against the rear sheave (40) to push it toward the forward sheave (42), thereby altering the drive ratio of the pulley assembly. In one feature, the driven pulley assembly (22) includes a fail-safe mechanism (48) that operates when power is supplied to the motor (170) to hold the split nut (158) together. Once power is disrupted, the fail-safe mechanism (48) allows the components (1 58a-c) of the split nut (158) to be separated, disrupting the threaded engagement with the actuation screw (154). At this point, the actuation screw (154) is driven forward by a compression spring (190), thereby driving the rear sheave (40) forward to a predetermined drive ratio position. In another aspect of the invention, the driving pulley assembly (20) includes an idler pulley portion (65) radially inboard from the normal driving sheave surface (29, 31). As the belt speed decreases, the belt (24) migrates downward within the driving pulley assembly (20) until it falls within the idler pulley portion (65). At this point, the belt (24) is isolated from the rotation of the driving pulley assembly (20). The driving pulley assembly (20) also includes a belt tensioning mechanism (32) that maintains proper belt tension at all speeds and drive ratios. The tensioning mechanism (32) relies upon a pivotably mounted centrifugal weight arm (101) to provide tensioning as a function of speed. A compression spring (80) provides axial pressure to maintain belt tension over all drive ratios. The spring (80) acts against a specially curved cam edge (92) on a pivoting lever arm (90), which arm (90) transfers an axial force to the rear sheave (28) of the driven pulley assembly (20).
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
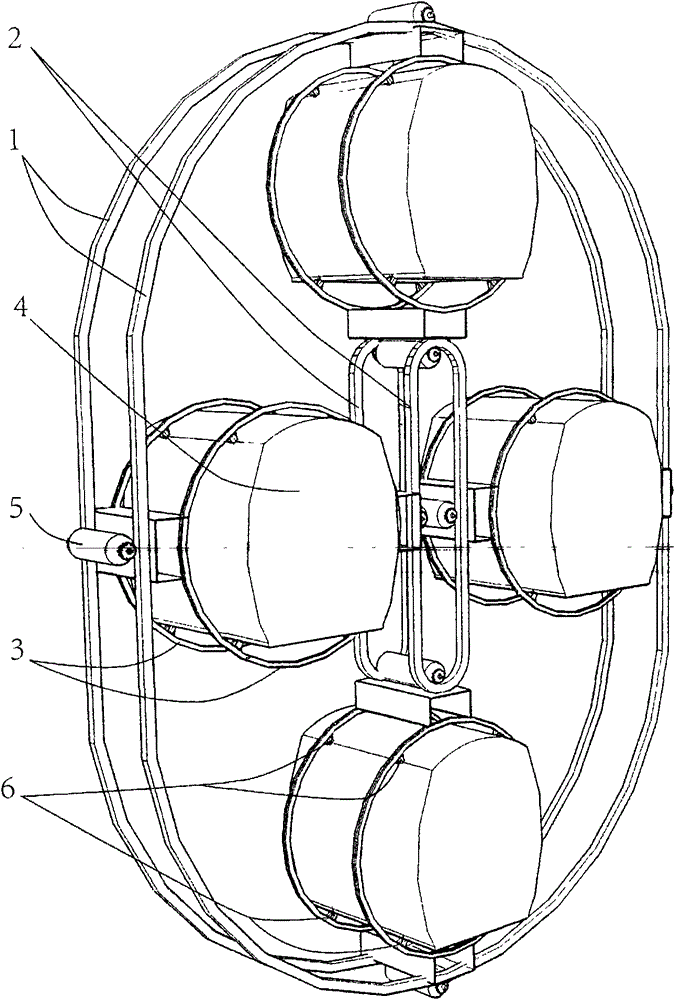
Multi-car individual drive 360-degree circular rail superhigh-rise elevator device
InactiveCN104787647AReduce noiseTimely response to call signalsElevatorsBuilding liftsAutomotive engineeringControl theory
The invention discloses a multi-car individual drive 360-degree circular rail superhigh-rise elevator device. The device consists of a rail, a car (4), a driving device (5), a braking device, a rail changing device, a balancing device and a control device, wherein the rail comprises a revolution rail and a rotation rail; the revolution rail comprises an inner rail (2) and an outer rail (1); the rotation rail (3) is clamped between the inner rail (2) and the outer rail (1) of the revolution rail, and is connected with the inner rail (2) and the outer rail (1) through the driving device (5) mounted on a frame of the rotation rail (3); a roller (6) on the wall of the car (4) is clamped in the rotation rail (3); the braking device is positioned on the frame of the rotation rail (3) and on the inner rail (2) and the outer rail (1); the balancing device is positioned at the bottom of the car (4); and the control device is connected with the driving device and the balancing device of each car through signal wires. The multi-car individual drive 360-degree circular rail superhigh-rise elevator device has the advantages of high transportation efficiency, safety, reliability and convenience for maintenance.
Owner:吴平安
Unison ring assembly for an axial compressor casing
InactiveUS8123472B2Minimal frictionSlide freelyWind motor controlPump componentsAxial compressorMechanical engineering
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Belt tracking regulator
InactiveUS7614493B2Prevent disengagementSlide freelyConveyorsControl devices for conveyorsAcute angleEngineering
A roller assembly for supporting a moving belt and including at least one roller mounted for rotation about a roller axis; and a support arrangement, the roller assembly being mounted on the support arrangement for pivotal displacement about a pivot point, characterized in that the belt tracking regulator includes guide means operable, in use, to constrain the pivotal displacement of the roller assembly to move in a plane containing the pivot and tilted at an acute angle with respect to a horizontal plane defined through the pivot point.
Owner:DOWLING JOHN +1
Tissue morcellating device
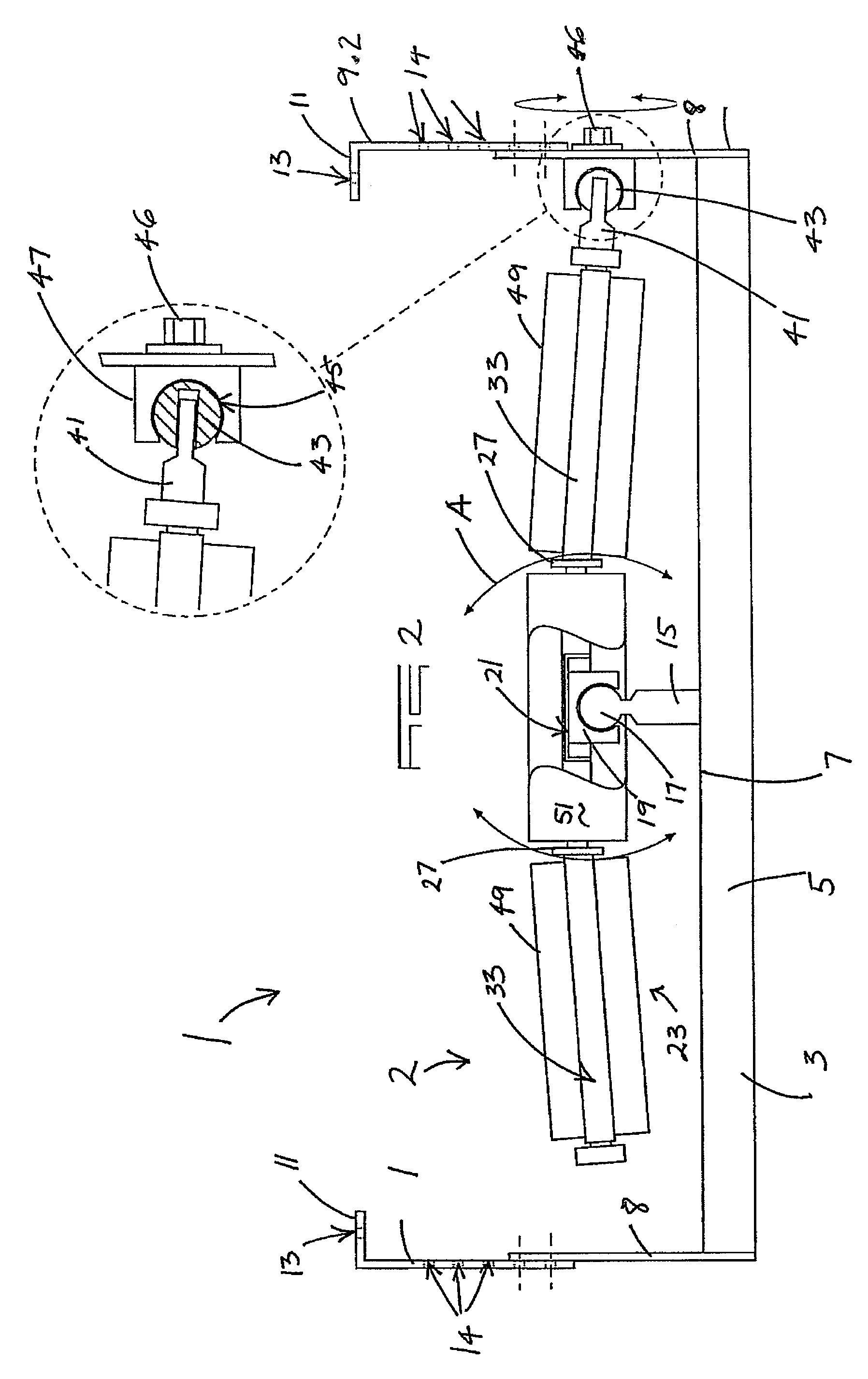
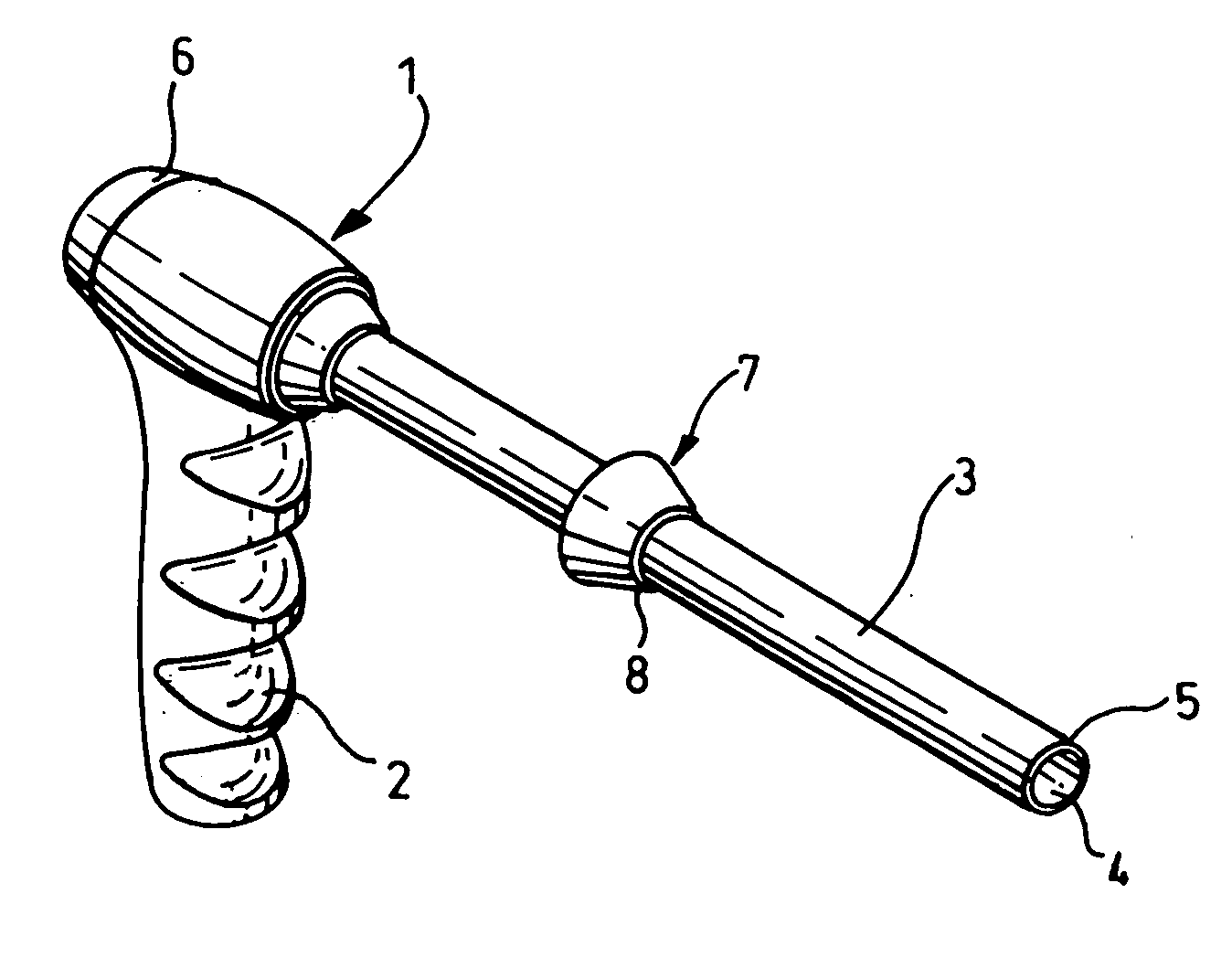
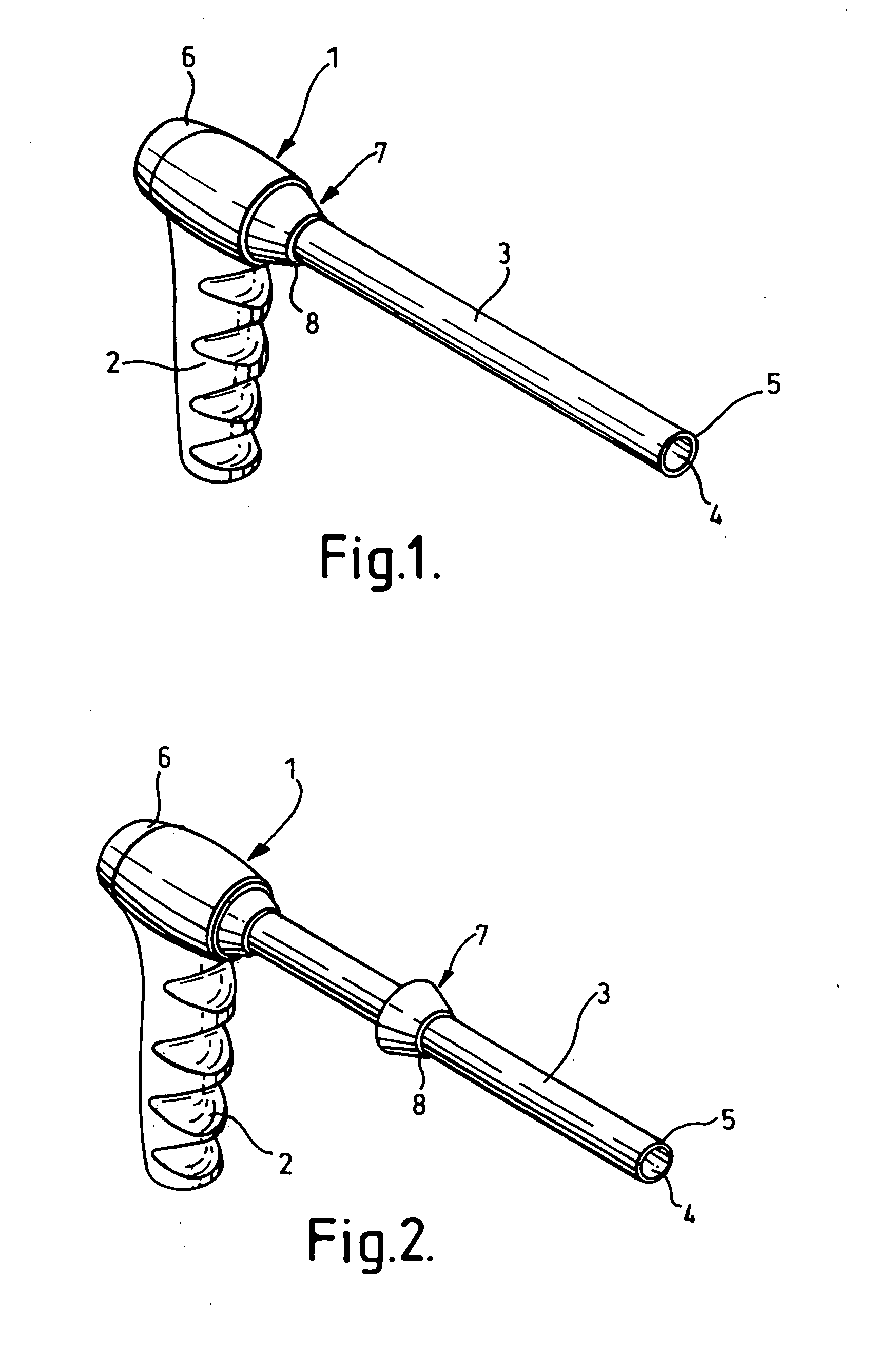
InactiveUS20080065129A1Increase in sizeSlide freelyDiagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsBiomedical engineeringBody cavity
A tissue morcellating device (1) is provided for morcellating tissue within a body cavity of a patient. The morcellating device (1) comprisies a hollow tube (3) having a distal end portion, and tissue cutting means (5) located at the distal end of the tube, such that, when relative movement is initiated between the tube and the tissue, a core of severed tissue is formed within the tube for removal from the body cavity of the patient through the hollow tube. The hollow tube (3) is provided with a stop mechanism (7) which is longitudinally adjustable with respect to the hollow tube (3), the stop mechanism being provided with a shoulder (8) for limiting the longitudinal insertion of the tube into the patient's body.
Owner:GYRUS MEDICAL LTD
Quick-change attachment configuration for a hole saw
ActiveUS9248513B2Reduce forceReduce construction difficultyTransportation and packagingChucksDrill bit shankHole saw
A quick-change attachment configuration is directed to a tool for use with a hole saw for boring holes on a wooden plank, particularly the quick-change attachment configuration is arranged for quickly replacing a longitudinal body, which is a drill bit shank having a driving end, a tool end, and a limiting portion. The configuration includes a quick-change attachment for assembling a longitudinal body and a hole saw which has an axial hole for allowing a longitudinal body to move on the quick-change attachment, and a locking component for locking and releasing the longitudinal body on and from the quick-change attachment. The locking component has a first component and a second component, which when used, the longitudinal body is easily moved slidably and locked so the shreddings emerging from the hole saw are cleaned.
Owner:ROTE MATE IND
Blood collection tube stocker and device for preparing blood collection tubes
InactiveCN102460179AReduce max widthMiniaturizationPharmaceutical product form changeBlood sampling devicesBlood Collection TubeComputer module
Provided is a blood collection tube preparing apparatus which is simple, downsized, portable, capable of being easily placed on a desk or the like, excellent in responding to an emergency such as a disaster, and capable of preparing various kinds of blood collection tubes depending on a blood collection instruction from a doctor. A blood collection tube holding member is arranged along one transferring belt and between a forward-side transferring belt and a backward-side transferring belt of the one transferring belt, and lower end surfaces of a cap of a blood collection tube is supported on upper end surfaces of the blood collection tube holding member and the forward-side transferring belt. The forward-side transferring belt applies a transferring force to the blood collection tube through the cap. Further, the members constituting a storage box are accommodated in one module, and the storage box is detachably mounted onto a mounting portion of an apparatus main body. Further, the storage box is in the form of module, and hence an operation in the case of failure or during maintenance is significantly facilitated.
Owner:AFC MINNESOTA
Continuously variable belt drive system
A continuously variable belt drive system including a driving pulley assembly, a driven pulley assembly, and a V-shaped belt engaged to transfer rotary power therebetween is disclosed herein. The driving pulley assembly includes an idler pulley portion. As the belt speed decreases, the belt migrates downward within the driving pulley assembly until it falls within the idler pulley portions, thereby isolating the belt from the rotation of the driving pulley assembly. The driving pulley assembly also includes a belt tensioning mechanism that maintains proper belt tension at all speeds and drive ratios. The tensioning mechanism relies upon a pivotably mounted centrifugal weight arm to provide tensioning as a function of speed. A compression spring provides axial pressure to maintain belt tension over all drive ratios. The spring, acts against a curved cam edge on a pivoting lever arm, which arm transfers an axial force to the rear sheave of the driven pulley assembly.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
Device for correcting scoliosis and controlling vertebral arthrodesis
InactiveUS20130338712A1Slide freelyPrevent vertebral arthrodesisInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsJoint arthrodesisEngineering
The present invention provides a scoliosis correction device comprising a pair of distraction rods (2, 3) and a member (4) for linking the distraction rods provided with means (8) for guiding each of the rods relative to each other inside said linking member. This device further comprises at least one member (6) for suspension of the distraction rods (2, 3) that can provide flexibility and exert a longitudinal pre-load on the rods in order to augment comfort and prevent vertebral arthrodesis of the spine of a patient instrumented with the correction device. Finally, it comprises a structure for cushioning and locking the distraction rods in translation in the linking member, said structure being active only when compressive forces are applied by the spine of a patient to the distraction rods (2, 3) so as to absorb and oppose said compressive forces and augment patient comfort, thereby preventing vertebral arthrodesis of the patient's spine.
Owner:UNIV CLAUDE BERNARD LYON 1 +1
Satellite navigation and inertial measurement combined orbit measuring system and method
ActiveCN103207403AEasy to analyzeSmooth slidingSatellite radio beaconingOriginal dataData acquisition
The invention discloses a satellite navigation and inertial measurement combined orbit measuring system and method. The satellite navigation and inertial measurement combined orbit measuring system comprises a measuring unit and a data post-processing unit. The measuring unit comprises two satellite navigation and inertial measurement combined orbit measuring devices which are placed on two monorails. A drawing device draws a satellite navigation and inertial measurement combined system to perform real-time online measurement, record original data of a dual-rail geometrical state and an equipment running state and perform offline processing through the data post-processing unit. The satellite navigation and inertial measurement combined orbit measuring method comprises performing preprocessing on original measurement data; establishing a directional mileage measurement curve and an ideal curve; calculating absolute and relative irregularity of a rail direction; establishing a slope angle mileage measurement curve and a slope angle ideal curve; and calculating absolute and relative irregularity of the height. According to online data collection, an offline data processing mode and a dual-rail parallel measuring mode, external geometrical information and internal geometrical irregularity of orbits are determined.
Owner:SAFEWAY XIAN NAVIGATION TECH
Exercise device and stopping device therefor
InactiveUS7465258B1Quickly “ pumping up ”Toning individual muscle groups of a userResilient force resistorsTherapy exerciseStops deviceEngineering
An exercise device, having a pair of handles—namely a first handle and second handle, and an elastic cord extending through the handles. The elastic cord has a fixed end, the first handle located adjacent to the fixed end. The second handle located along the elastic cord further away from the fixed end than the first handle. The second handle can selectively slide freely along the elastic cord toward and away from the first handle. A novel stopping device is attached to at least one of the first handle and second handle, which is capable of fixing the position of its associated handle along the elastic cord so that the elastic cord may then be tensioned to allow exercises to be performed. The novel stopping device includes a keyhole type slot for the cord terminating in a circular opening and forming a pair of pinch points with a tapering slot whereby the cord is securely held in the circular opening against slippage or accidental removal from the opening.
Owner:MORTORANO MICHAEL PETER
Instrument holder for surgical instrument
Owner:VIANT AS&O HLDG LLC
Vehicle wheel lathe fixture
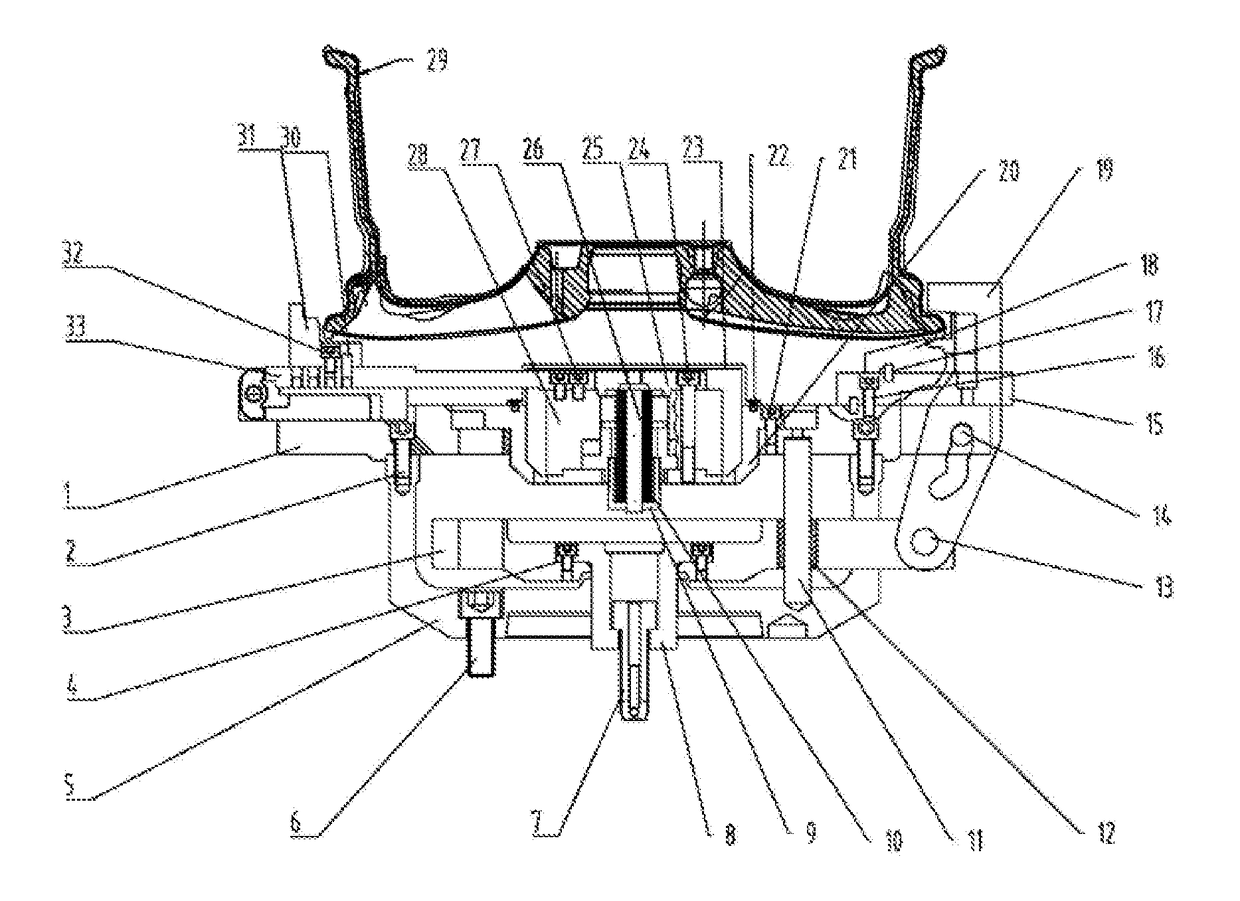
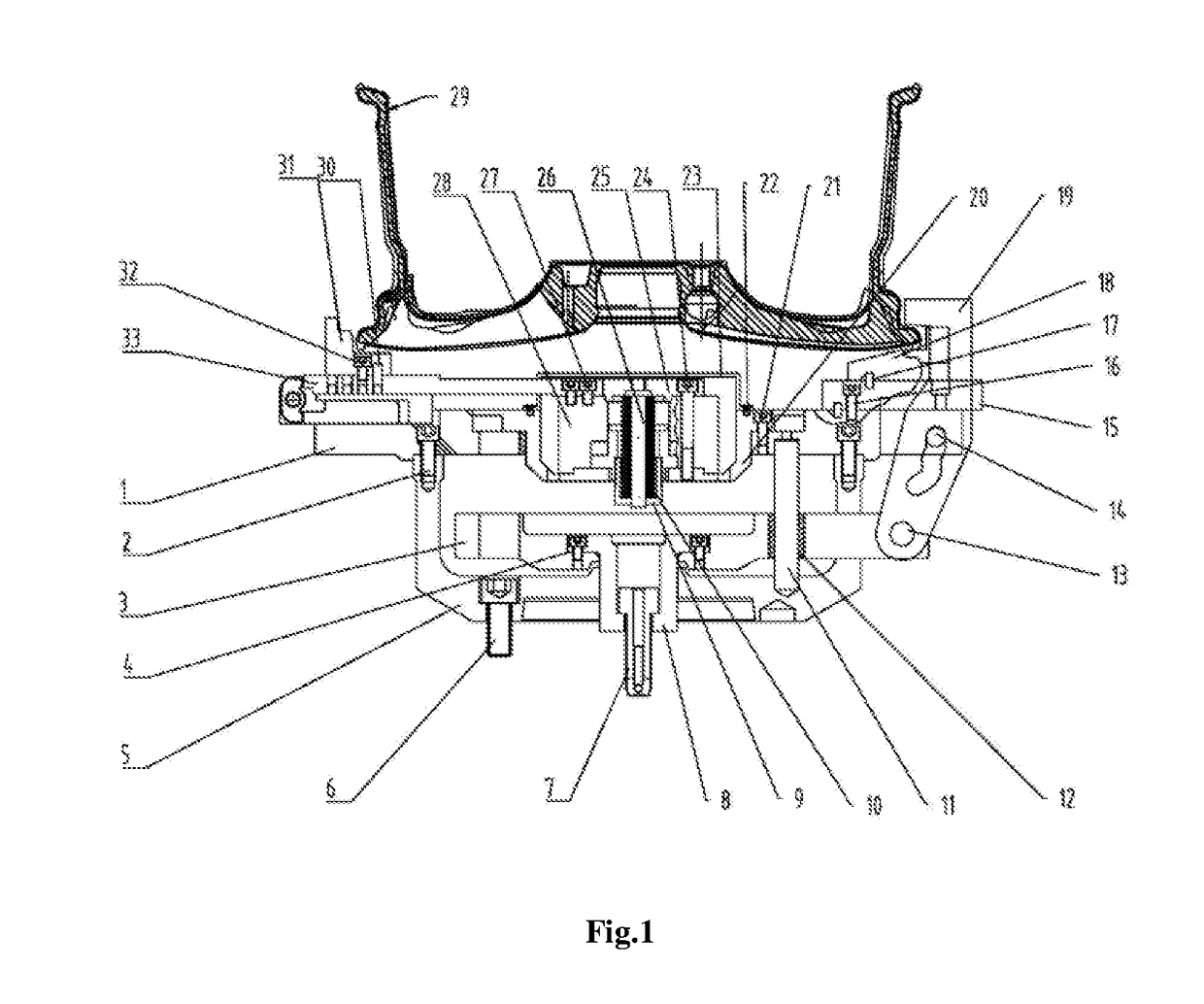
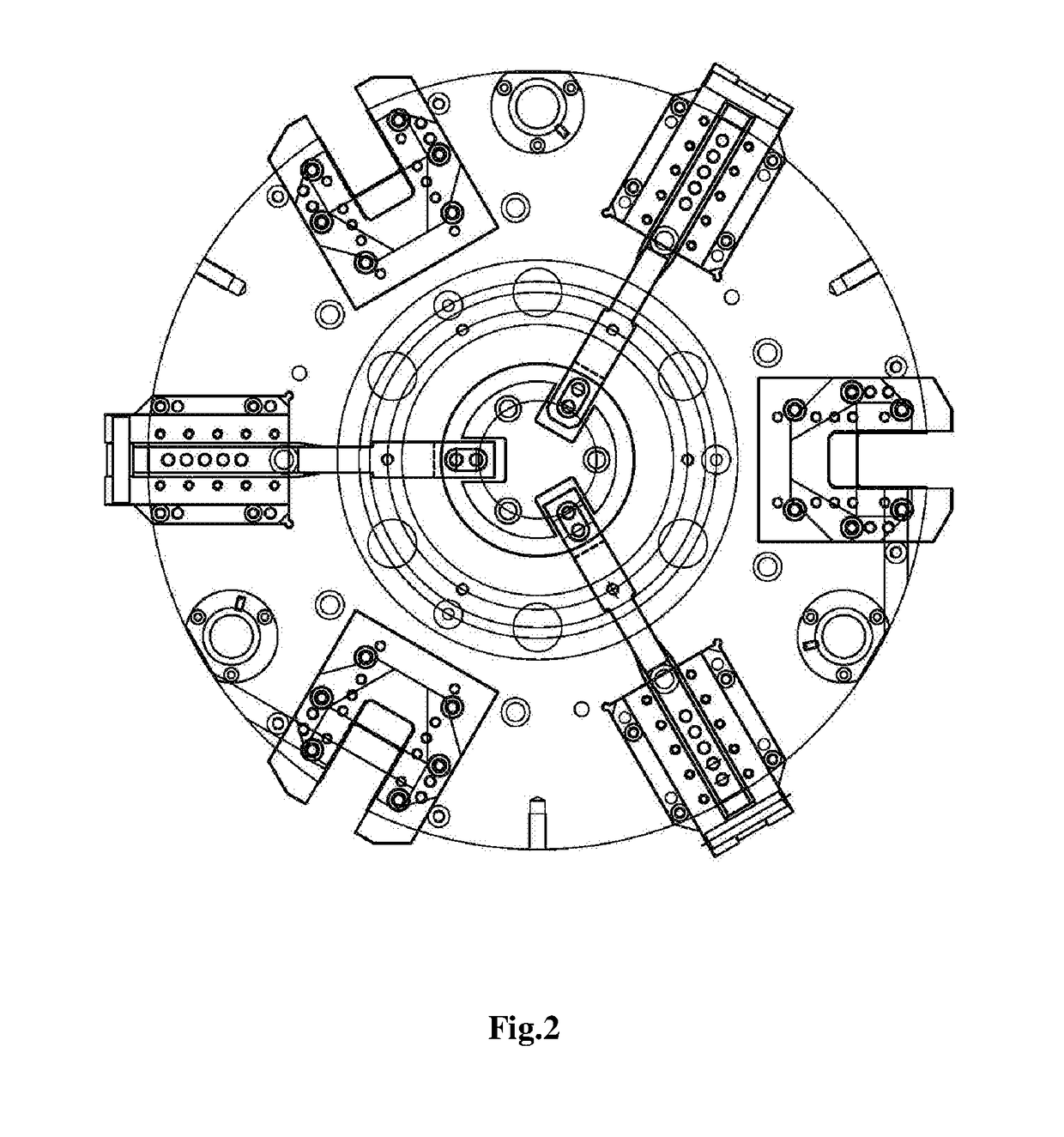
InactiveUS20170312834A1Work reliablyGuaranteed uptimeStatic/dynamic balance measurementTyresCouplingEngineering
A vehicle wheel lathe fixture, including an upper cover, a coupling base, a floating disc, a driving seat, a sliding sleeve, a finger-shaped press jaw, a rotating shaft, a sliding shaft, an end-face positioning block base, an end-face positioning block, a positioning pin, a radial positioning block, a radial pull rod, a hydraulic power chuck, a disc spring sleeve, a disc spring, a disc spring positioning column, a press cover, a hydraulic power chuck mounting base and a dust cover. Embodiments of the invention have the characteristics of reliable work, stable operation and wide compatibility range, and is applicable to vehicle wheel mechanical processing lathes.
Owner:CITIC DICASTAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com