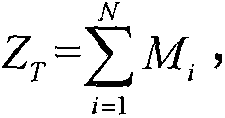Patents
Literature
278 results about "Belt speed" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
To figure the speed the belt is moving you need to know the diameter of the contact wheel, multiply that times 3.141592 (pi) to get the circumference of the wheel. Then multiply that times the rpm of the motor. That will give you inches per minute. To figure feet per minute just divide by 12.
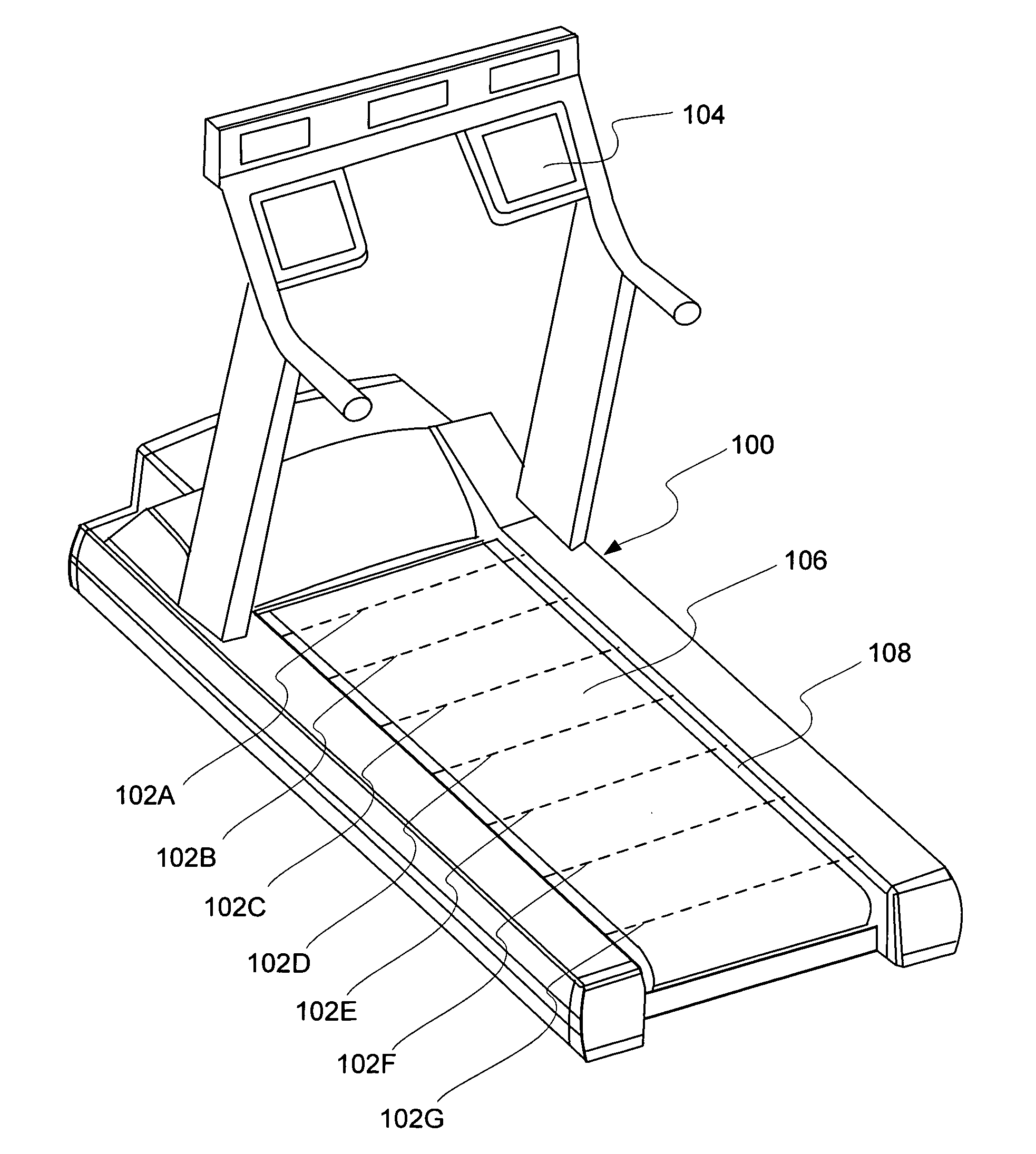
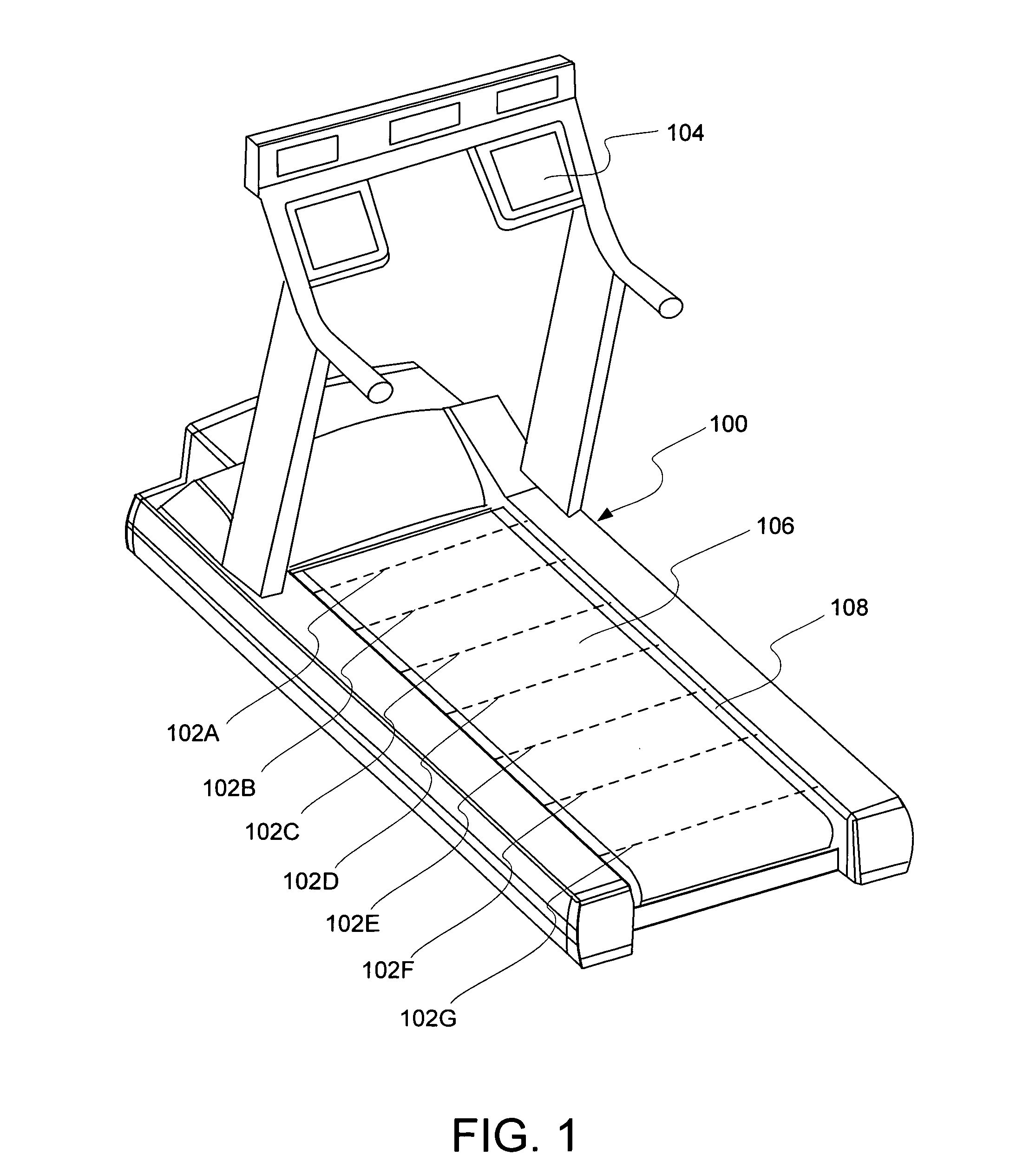
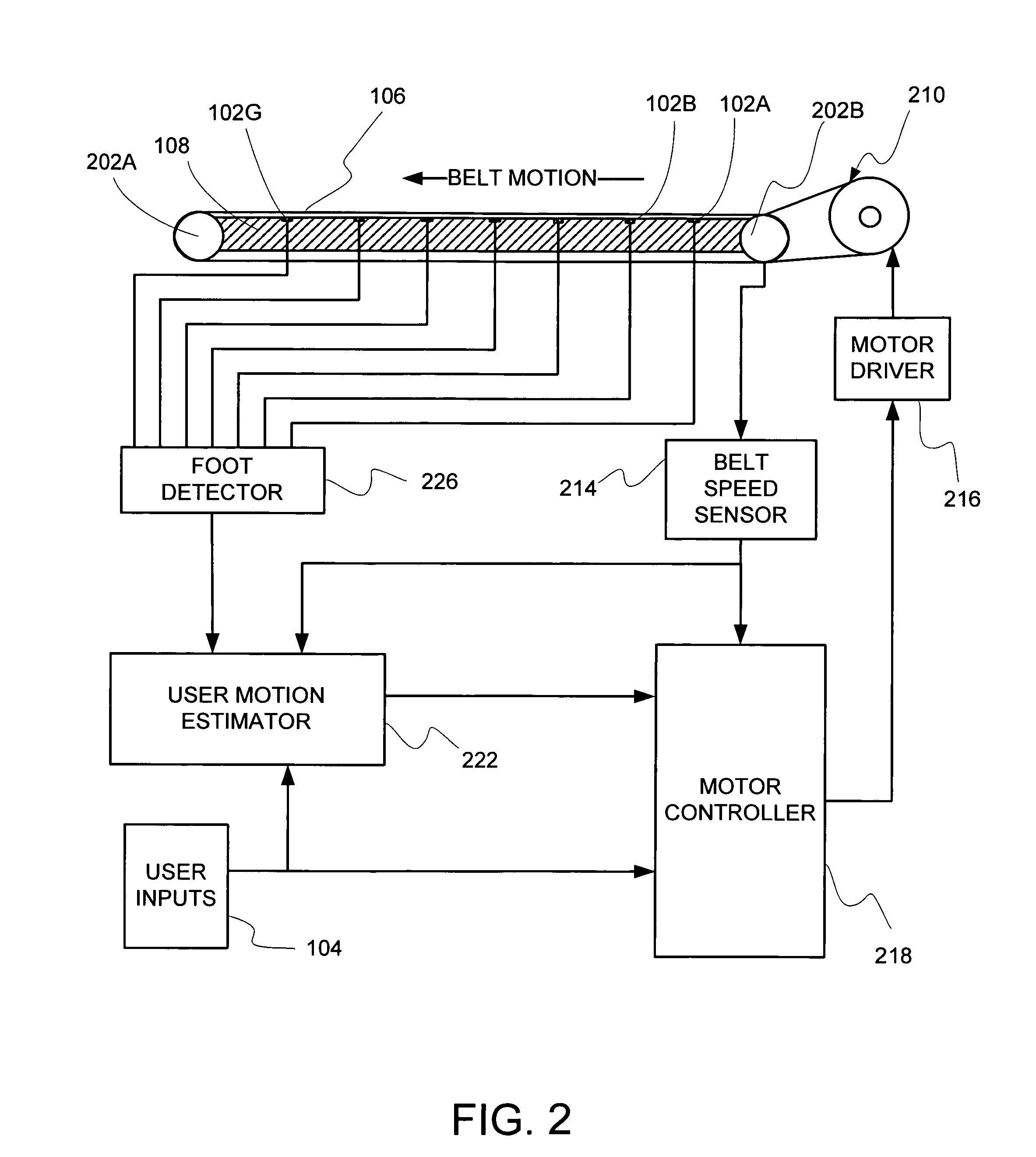
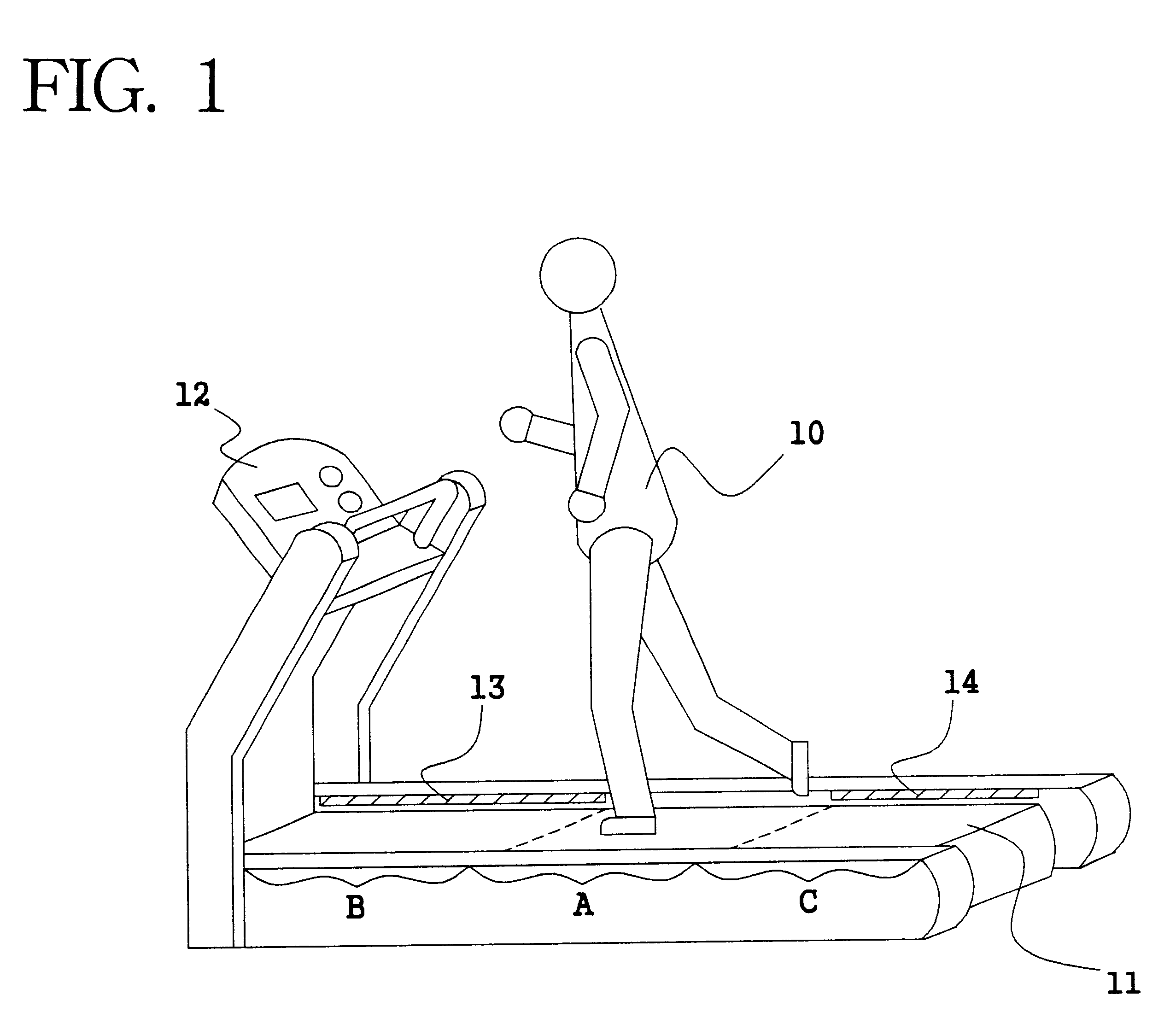
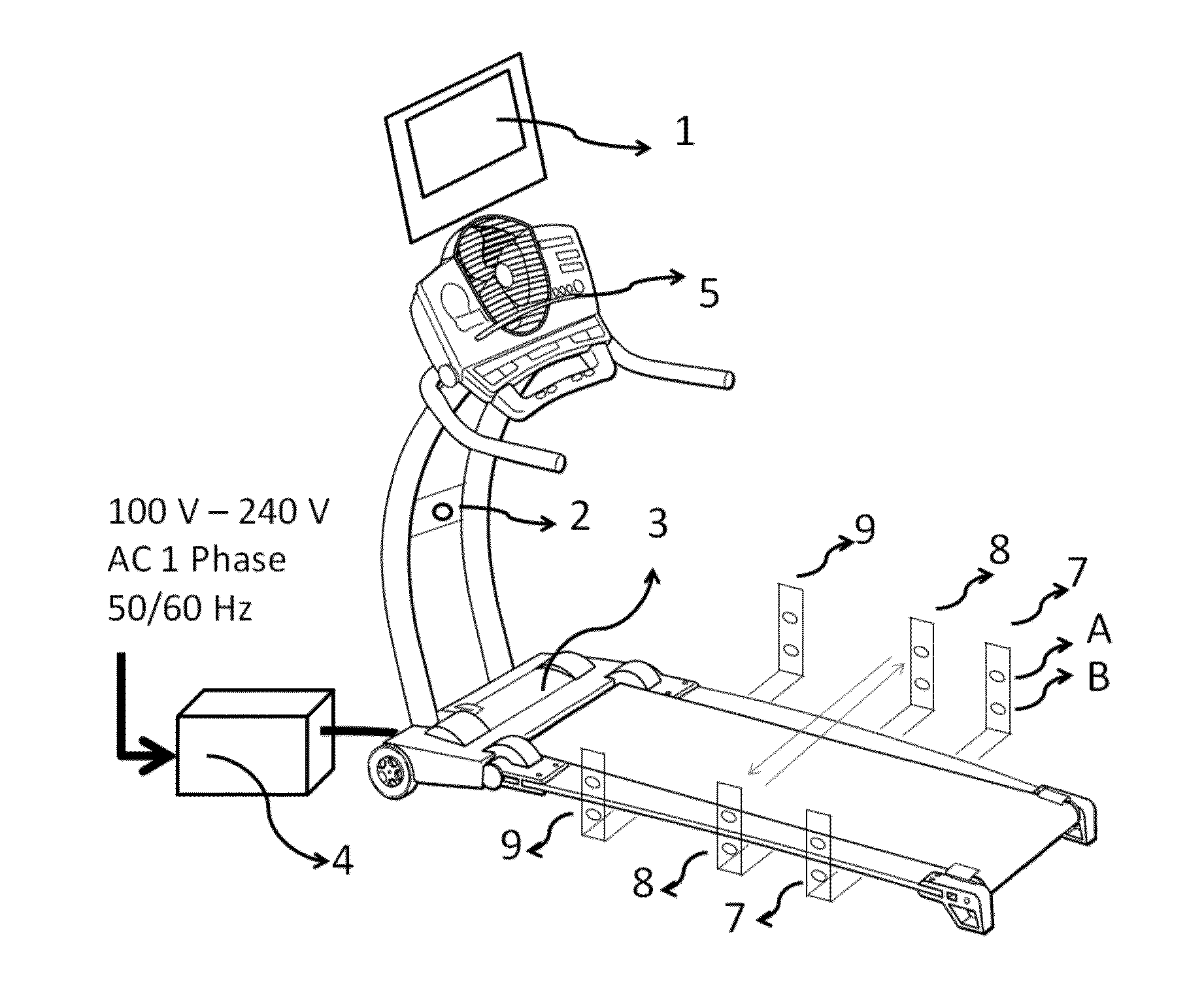
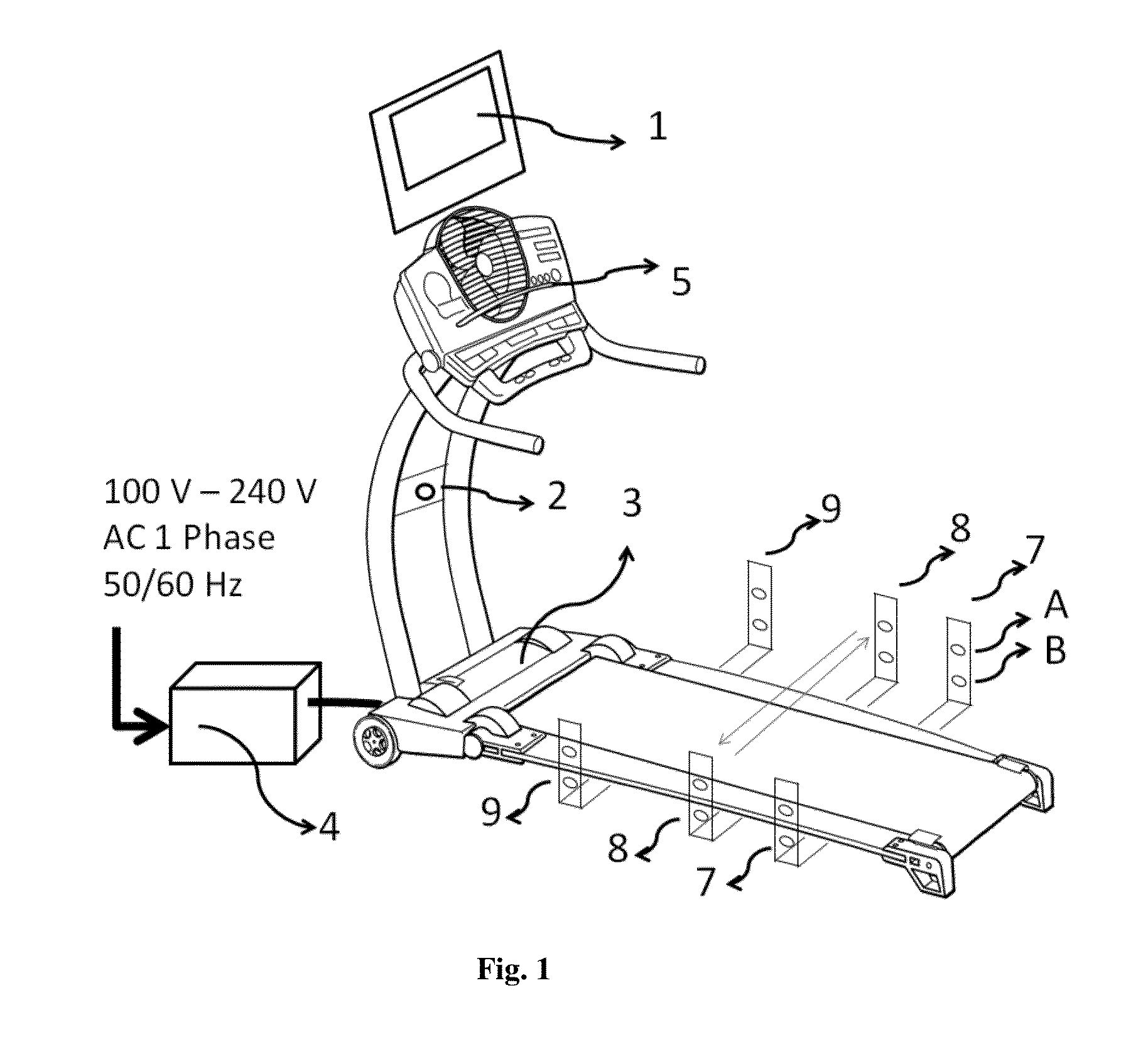
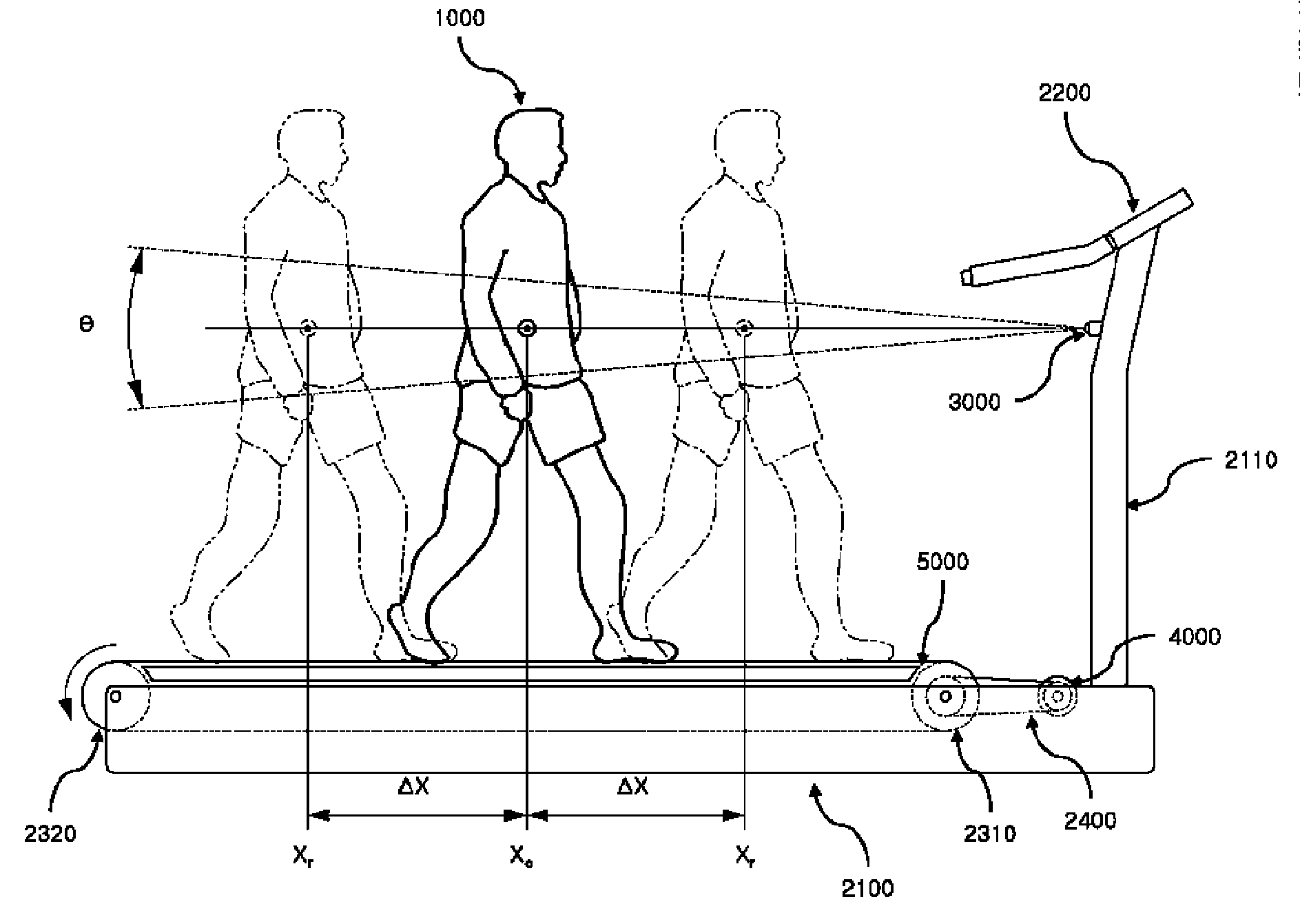
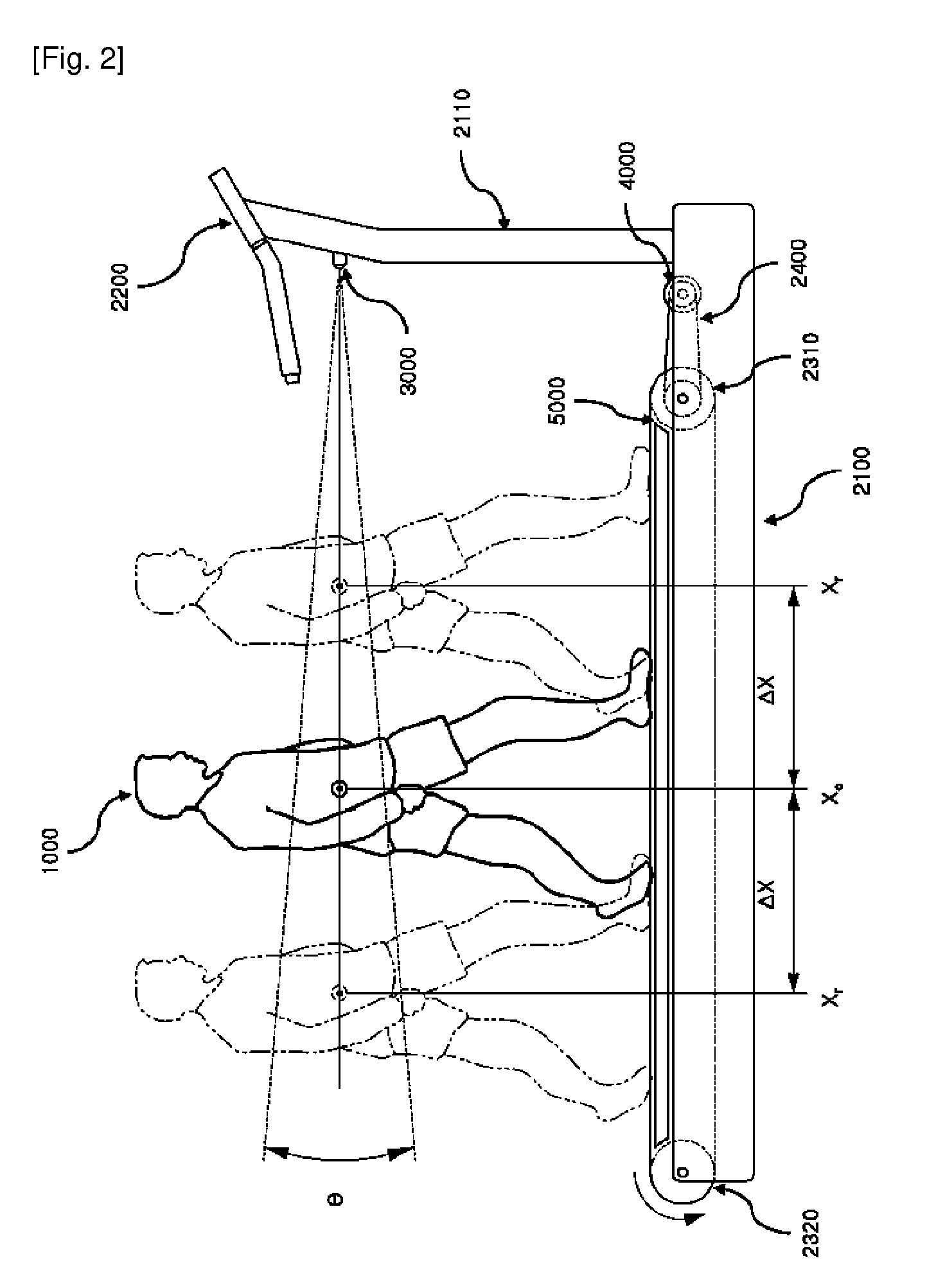
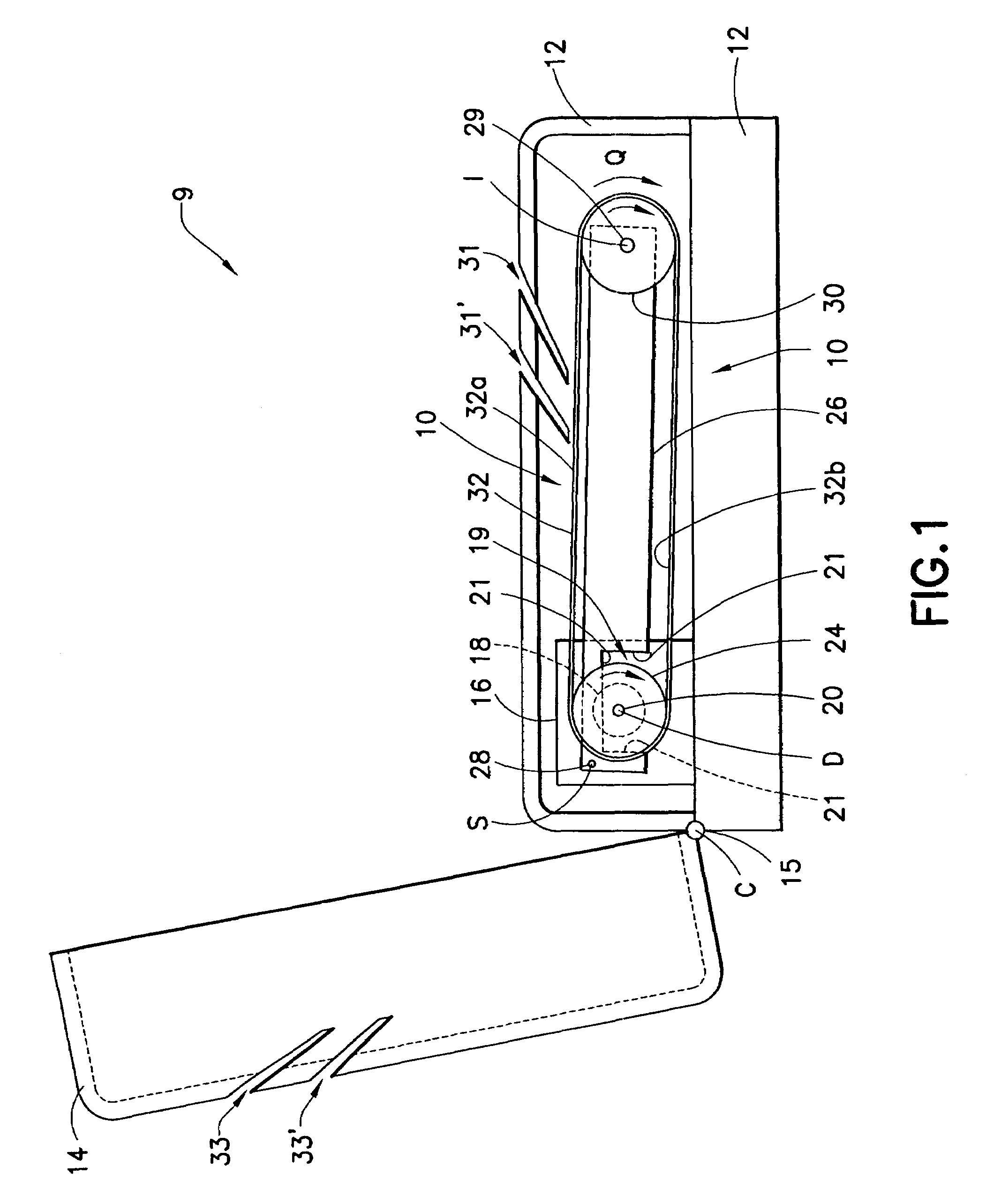
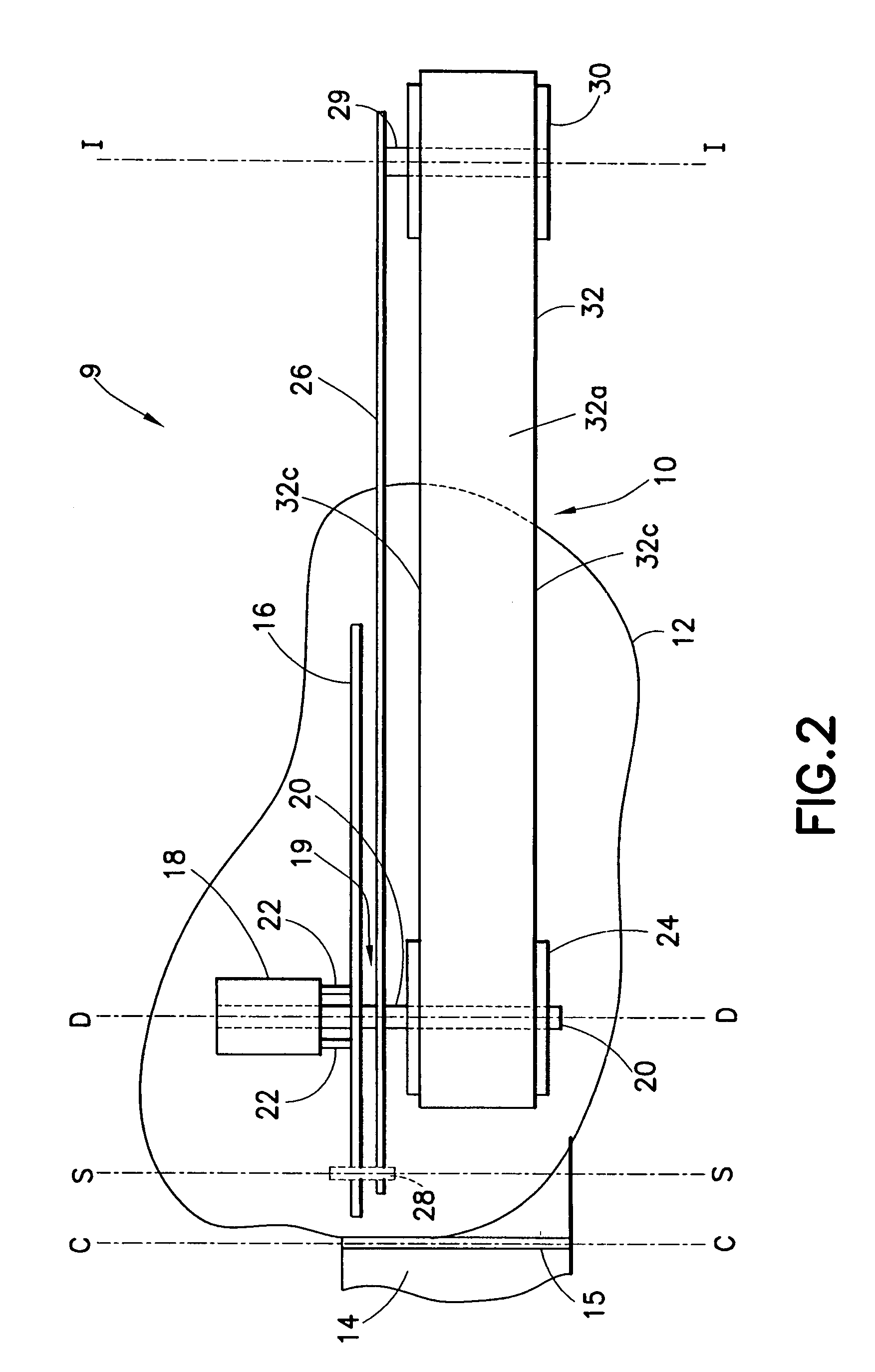
User footfall sensing control system for treadmill exercise machines
InactiveUS8480541B1The relative position is appropriateWiden meansClubsMovement coordination devicesProximity sensorTreadmill exercise
An improved treadmill control system which adjusts the speed of a moving tread belt to follow user motions. Equipment includes a tread base supporting a moving tread belt upon which a user can run or walk, a motor assembly and motor driver to move the tread belt, a plurality of foot sensors, a tread belt motion sensor, a measurement system to estimate user motion based on foot and tread belt sensor signals, and a motor controller to adjust motor assembly speed based on estimates of user motion. The system is capable of making improved user motion estimates and of using them to provide improved belt speed control. In one embodiment, user position, speed, and acceleration are estimated at each user footfall while estimates are continually revised between footfalls. In one embodiment, foot sensors are capacitive proximity sensors which are effective, fully concealable, and economical.
Owner:BRUNTS RANDALL THOMAS
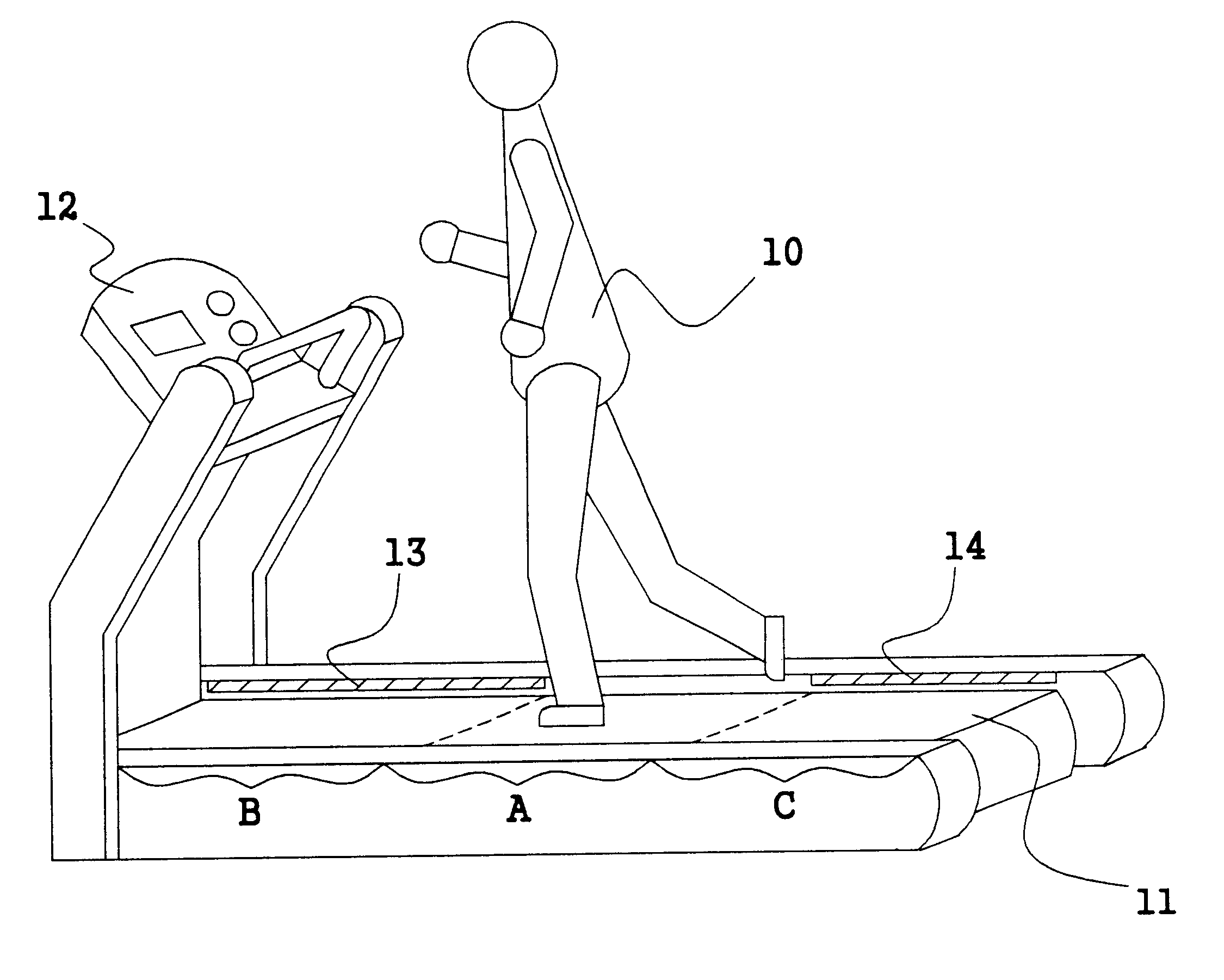
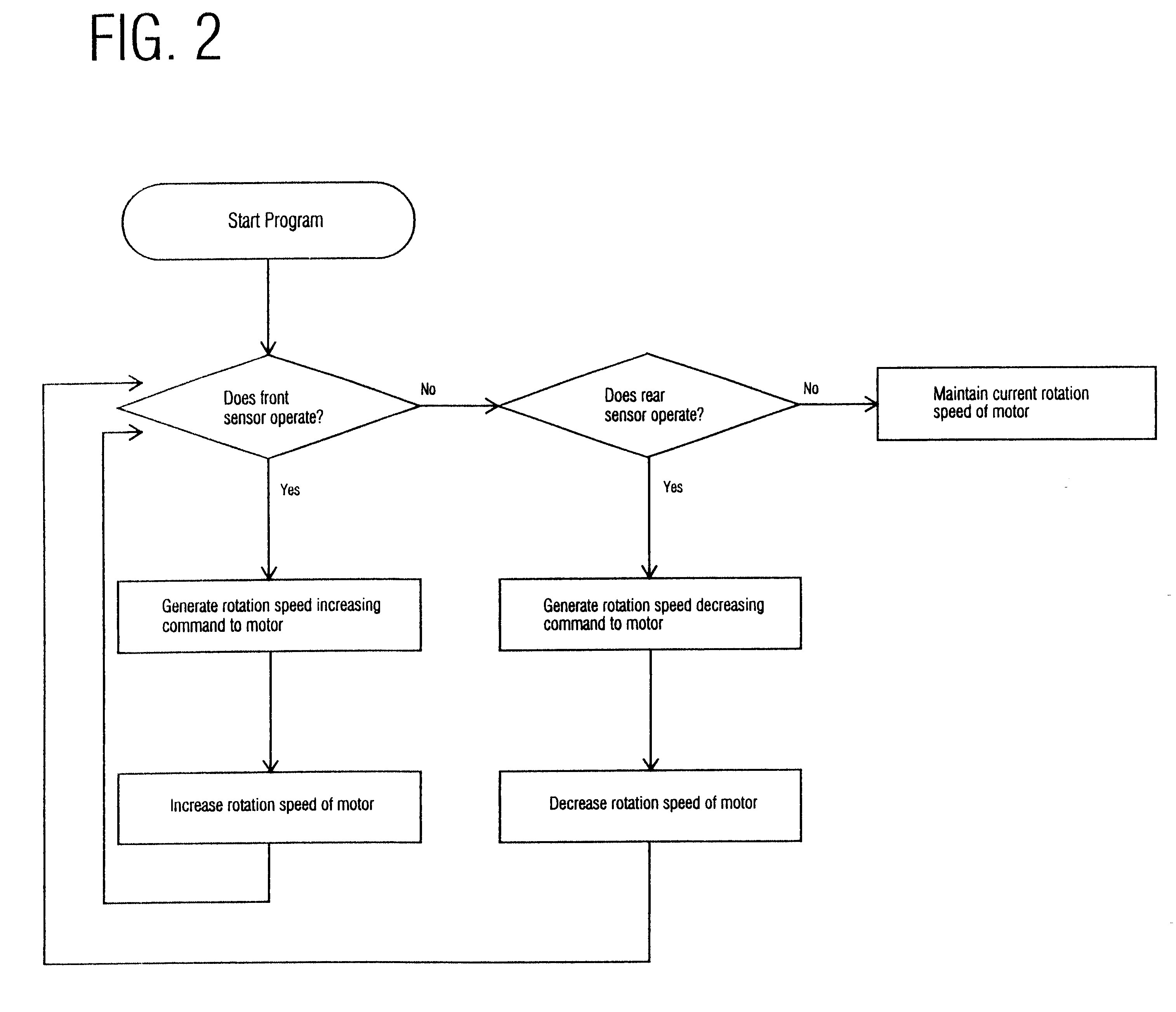
Treadmill having a walking belt whose running speed is automatically adjusted
InactiveUS6416444B1Increase and decrease rotation speedShort timeMovement coordination devicesCardiovascular exercising devicesBelt speedEngineering
A treadmill having a walking belt whose running speed is automatically adjusted in conformity with the walking or running speed of a user, without any manipulation of a walking belt speed control button, and a method for automatically adjusting the running speed of a walking belt in a treadmill. The treadmill of the present invention first checks and determines whether the rotation speed of the motor is deviated from an initial set range or the user is deviated from his original position and then if any one of the two deviations is checked, automatically increase or decrease the rotation speed of the motor.
Owner:SNS CARE
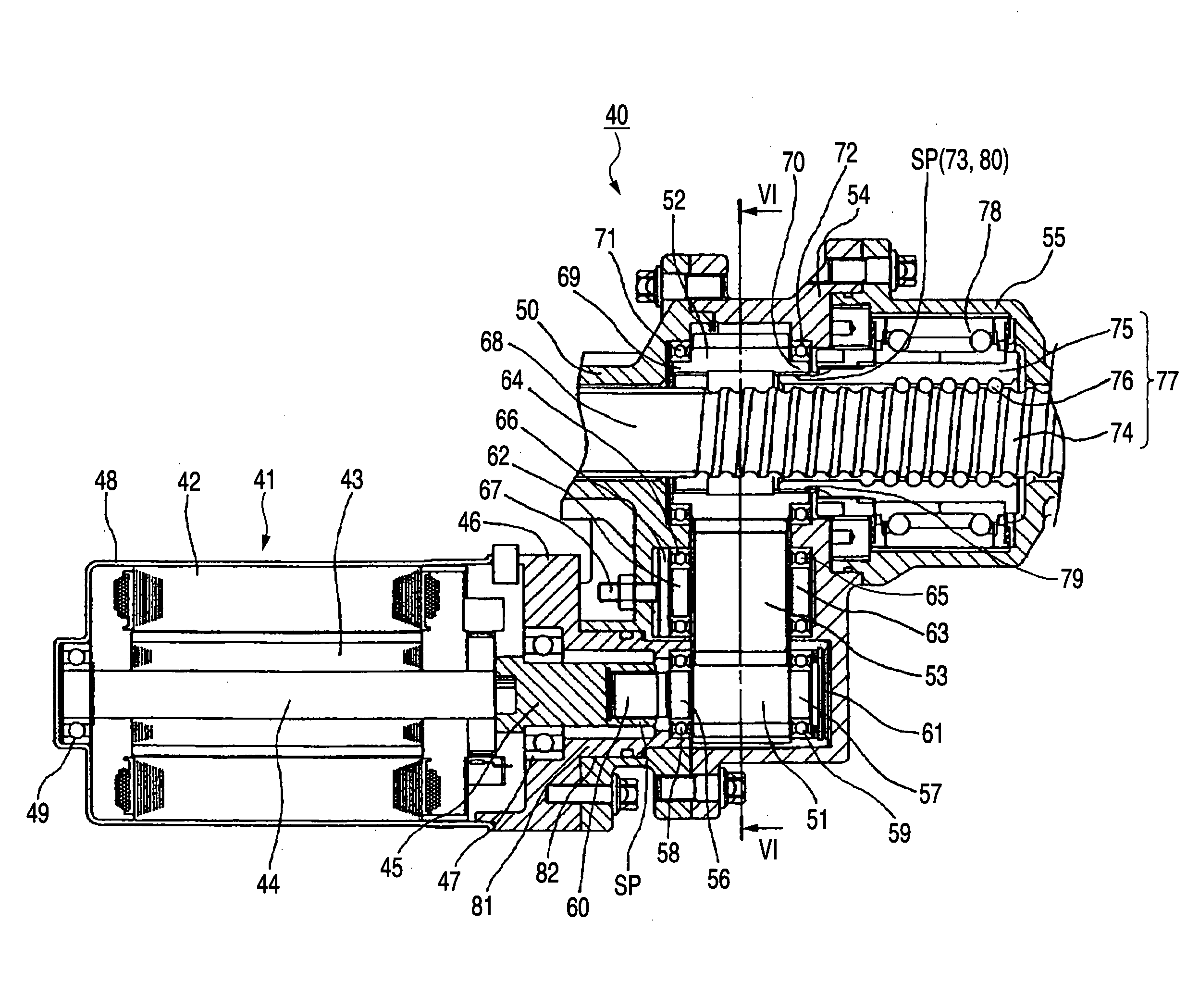
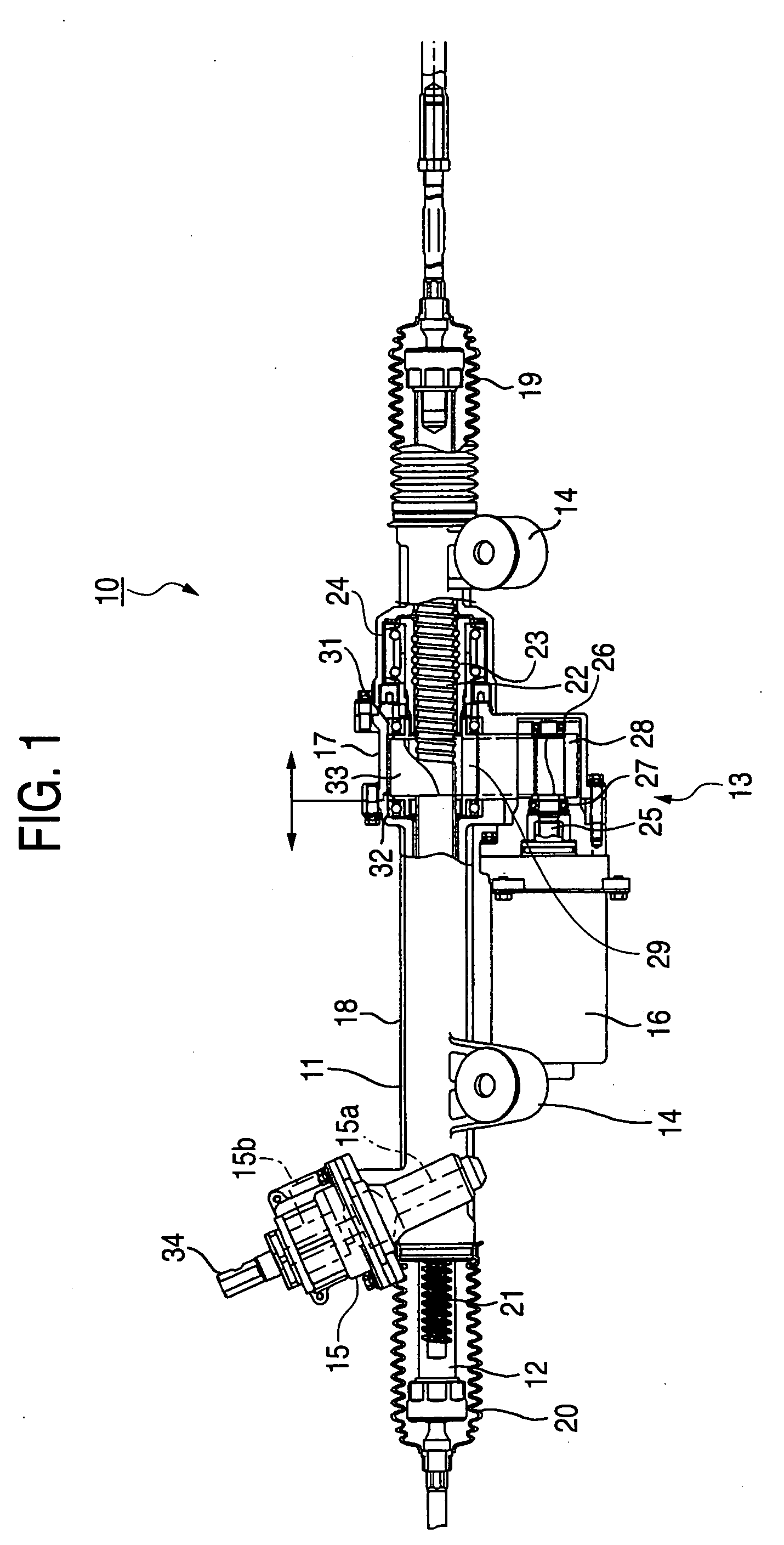
Belt speed reducing apparatus for electric power steering apparatus and electric power steering apparatus
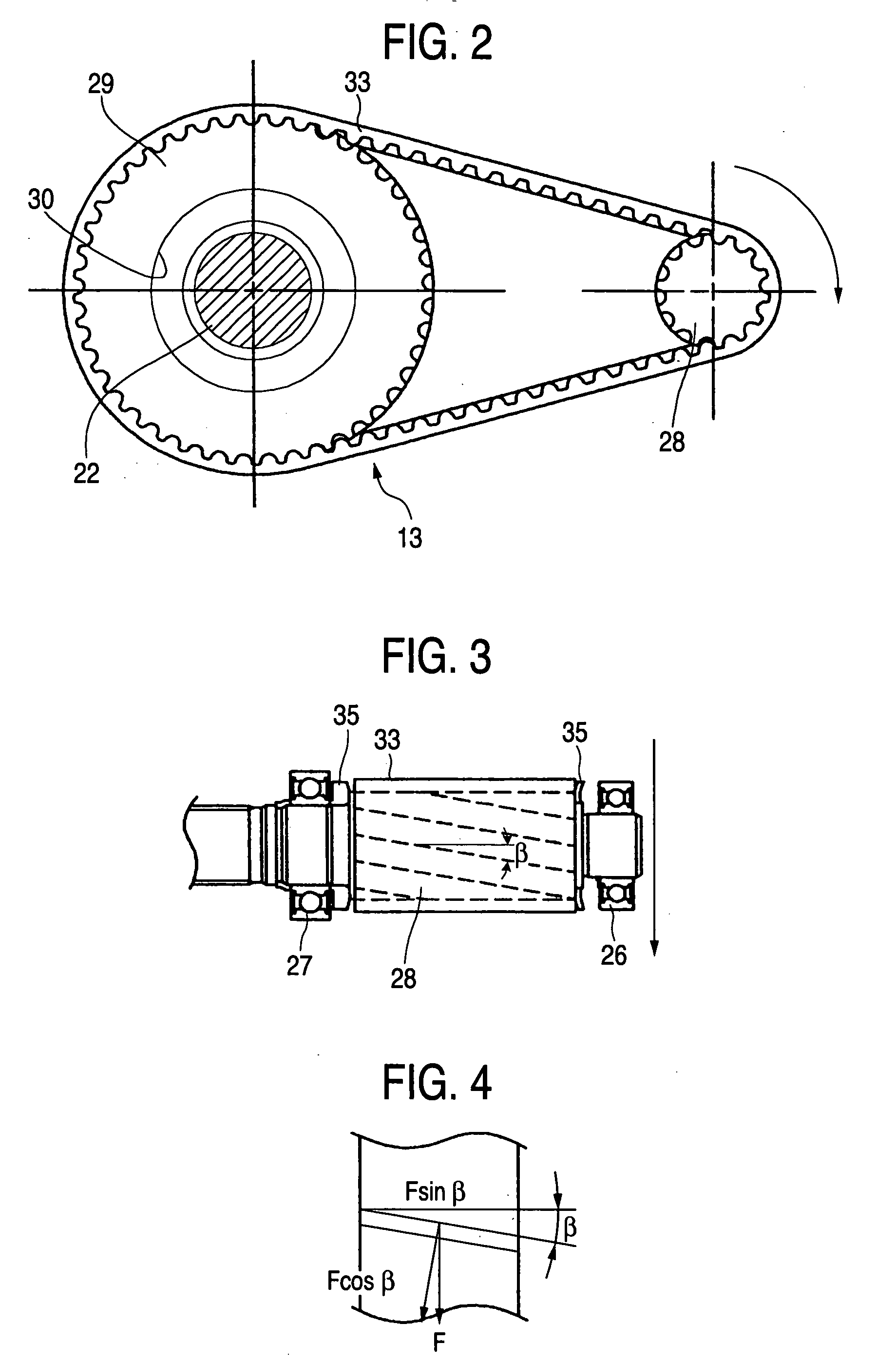
ActiveUS20050121251A1Improve driving durabilityIncrease the angleToothed gearingsElectrical steeringElectric power steeringBelt speed
A belt speed reducing apparatus for an electric power steering apparatus includes a drive pulley having a first helical gear, a driven pulley having a second helical gear and a drive belt having a third helical gear in which a relationship of tan β<μ is established between a twist angle β of the respective helical gears and a friction coefficient μ between the first or the second helical gear and the third helical gear. Further, an electric power steering apparatus for adjusting a backlash between gears of a speed reducing apparatus brought in mesh with each other or adjusting a tension of a belt of a speed reducing apparatus.
Owner:NSK LTD +1
Intelligent Treadmill and Enhancements to Standard Treadmills
InactiveUS20160213976A1Improve transient responseImprove energy efficiencyMovement coordination devicesCardiovascular exercising devicesInduction motorBelt speed
An intelligent treadmill is described with modifications to existing treadmills, and associated methodology. The invention allows the conveyor belt automatically keeps track of and fixes the user's position dynamically with respect to a stationery reference point of the treadmill by adjusting its own speed free hands. Two position measurement techniques and their corresponding belt speed control algorithms are described. Other features of the invention allow users to perceive in real time how their surroundings would be changing by means of video, incline of platform, fan speed, sound and illumination as if they were in fact running in the natural environment. Real time positions of the runner and his partners on other treadmills with respect to a chosen track are displayed. The invention also utilizes a vectored controlled 2 / 3-phase AC induction motor or a BLDC motor to drive the conveyor belt for energy efficiency and fast response.
Owner:SO ALBERT TING PAT +2
Belt conveyor control system and method capable of adjusting belt speeds automatically according to material flows or material levels
ActiveCN102942039AExtend your lifeReduce usage costsControl devices for conveyorsFrequency changerProgrammable logic controller
The invention provides a belt conveyor control system capable of adjusting belt speeds automatically according to material flows or material levels, and belongs to the belt conveyor control technology. The control system comprises a frequency conversion system, a programmable logic controller (PLC) system, a monitoring system and a detection system. The frequency conversion system comprises a power wire inlet device, a power feed device and a frequency converter. The PLC system comprises a power wire inlet control device, a power feed control device and a PLC device. The monitoring system comprises an operation platform and a display screen. The detection system comprises a material sensor which can use a contactless sensor. The control system sets the operation speed of a belt conveyor reasonably according to material flows or material levels and the operation state of a front conveyor and in additional conditions of time and motor currents, and the belt speed is adjusted by the controlling of the output frequency of the frequency converter.
Owner:SHANXI SANYUAN COAL IND +1
Method and apparatus for monitoring and controlling conveyor position
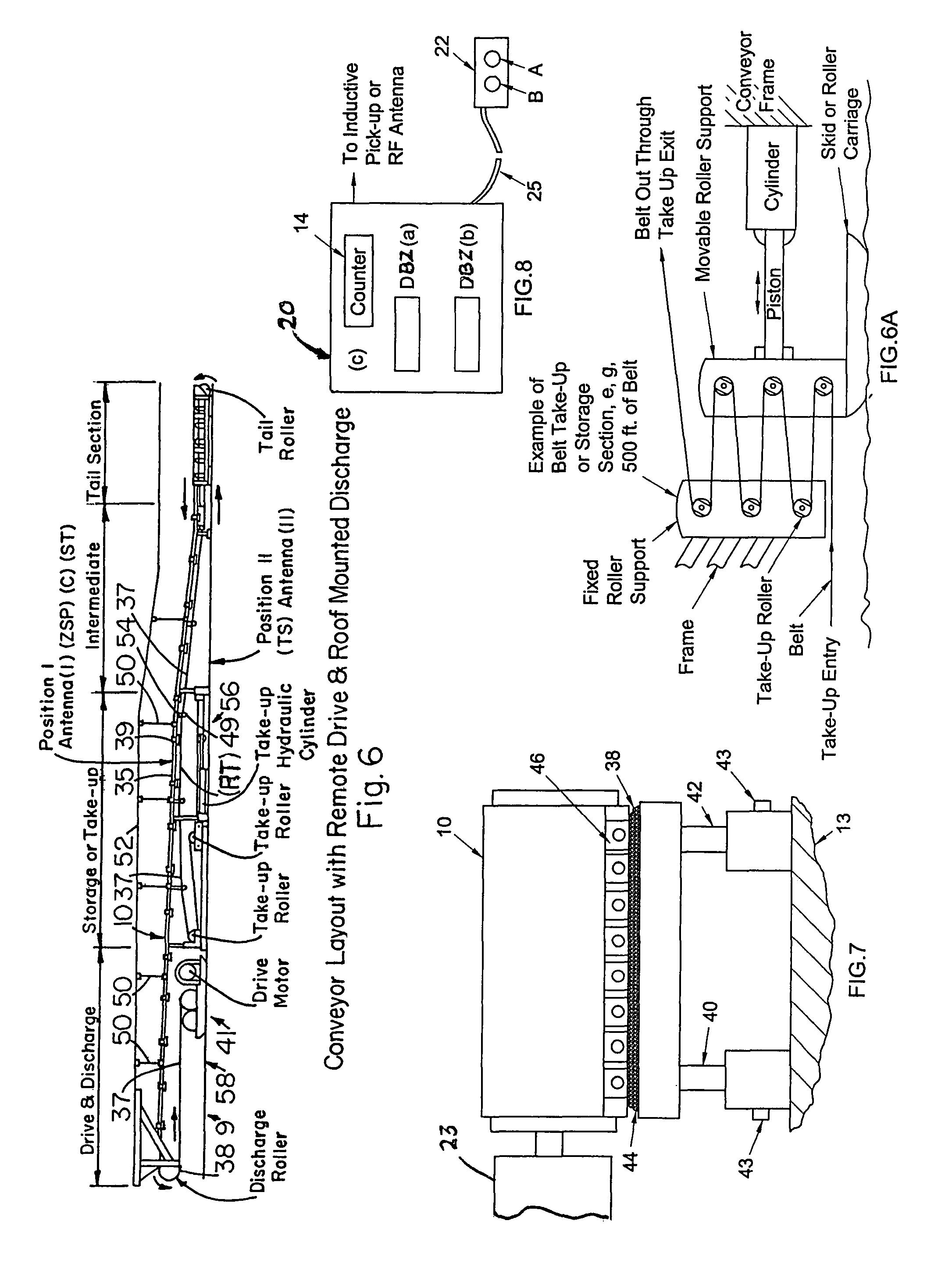
A Belt Positioning Unit “BPU” operation which in use for facilitating the maintenance of long, heavy conveyor belts of conveyor systems comprises the steps of (a) monitoring a conveyor belt for event sites, (b) spotting an event site and logging into a computer (1), sufficient data from which the computer determines and records the footage location of the event site on the belt, (2) belt drift footage data, and (3) take up belt footage data, and (c) using said data to control operational aspects of the conveyor system components, e.g., belt speed, drive motor power-off point (POP), or belt scraper pressure which affect the maintenance or condition of said event site.
Owner:BAKER CAPITAL LIMITED A PENNSYLVANIA
Continuously variable belt drive system
InactiveUS20060019781A1Slide freelyIncrease axial forceGearingPortable liftingAxial pressureTransfer system
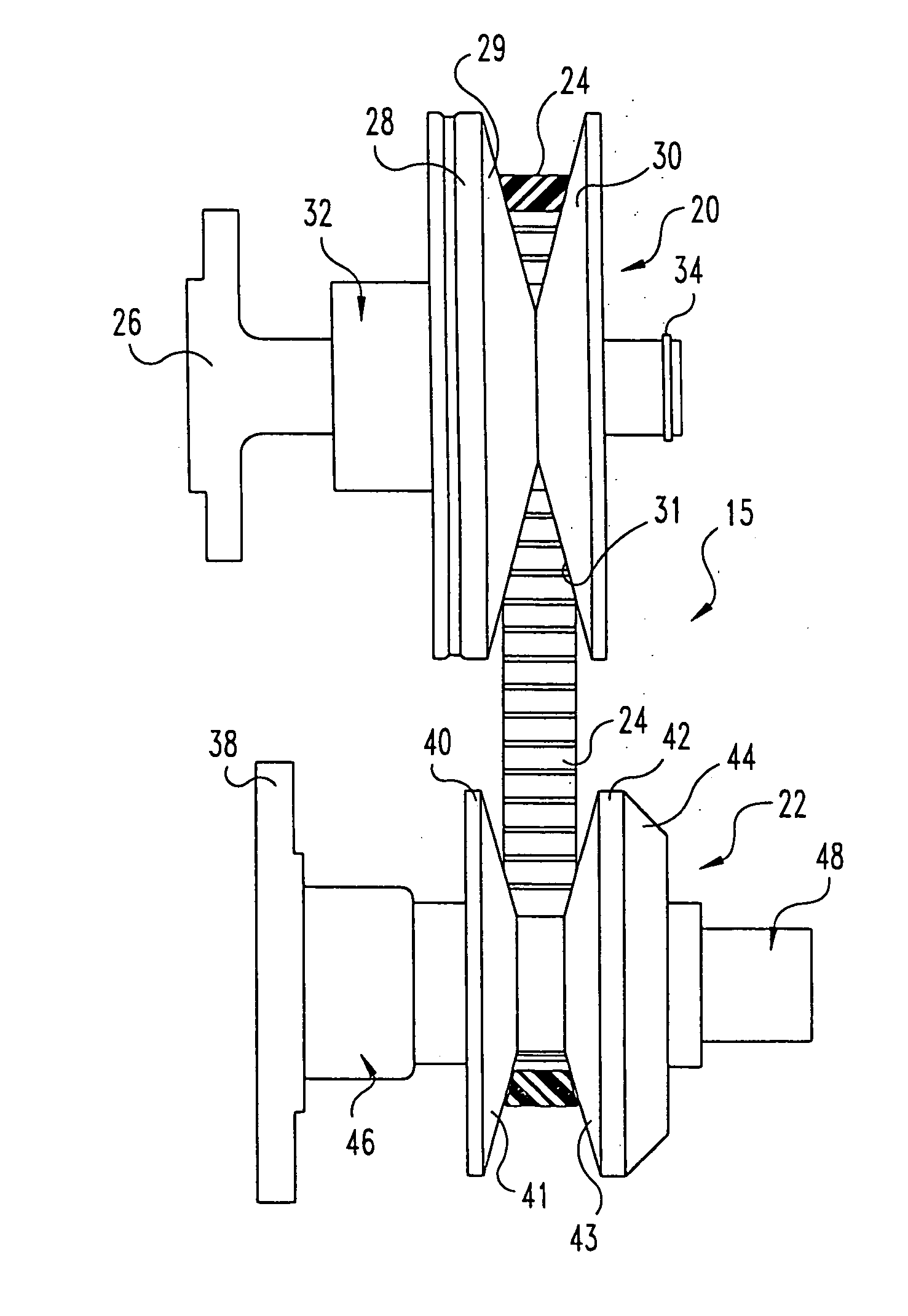
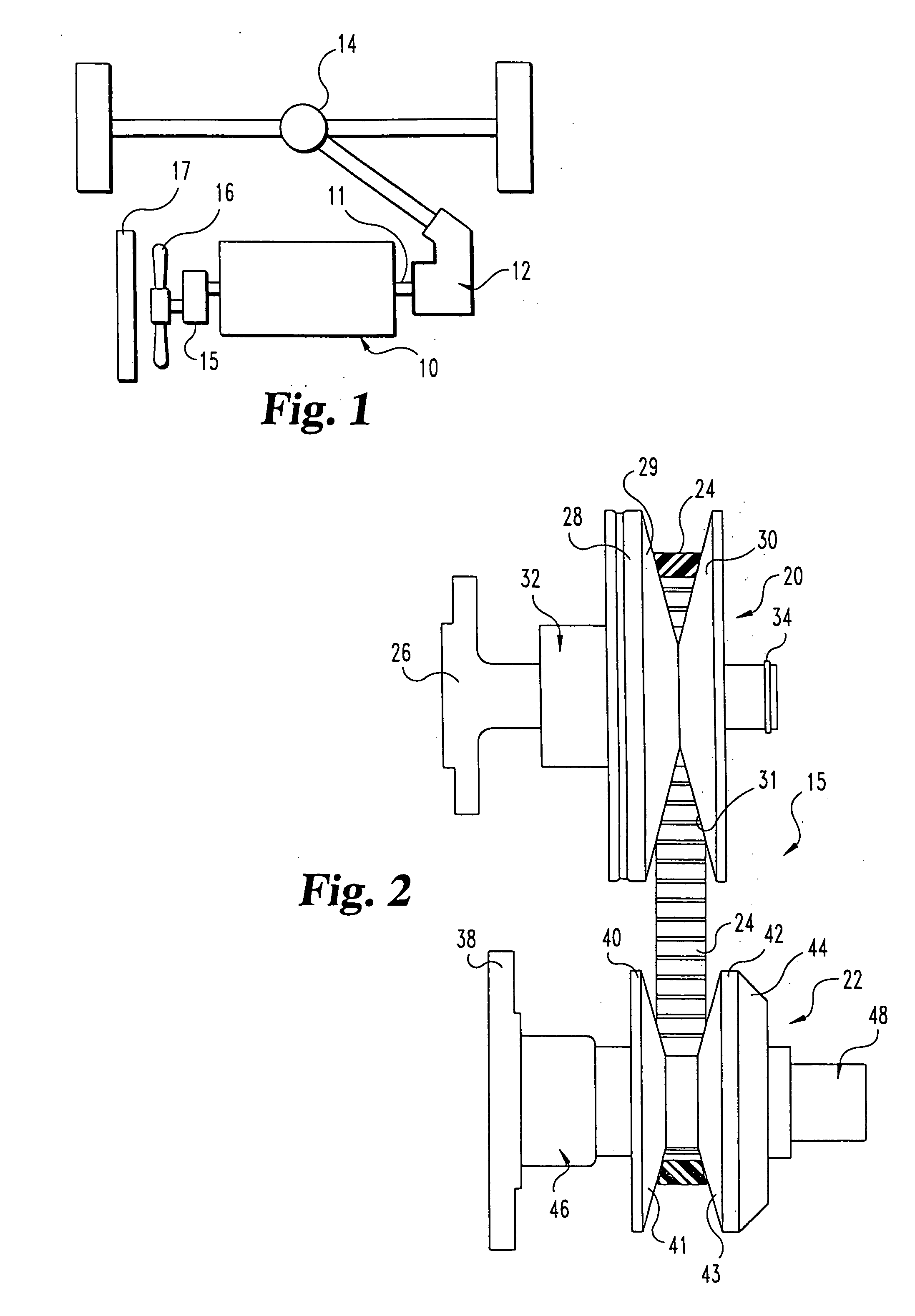
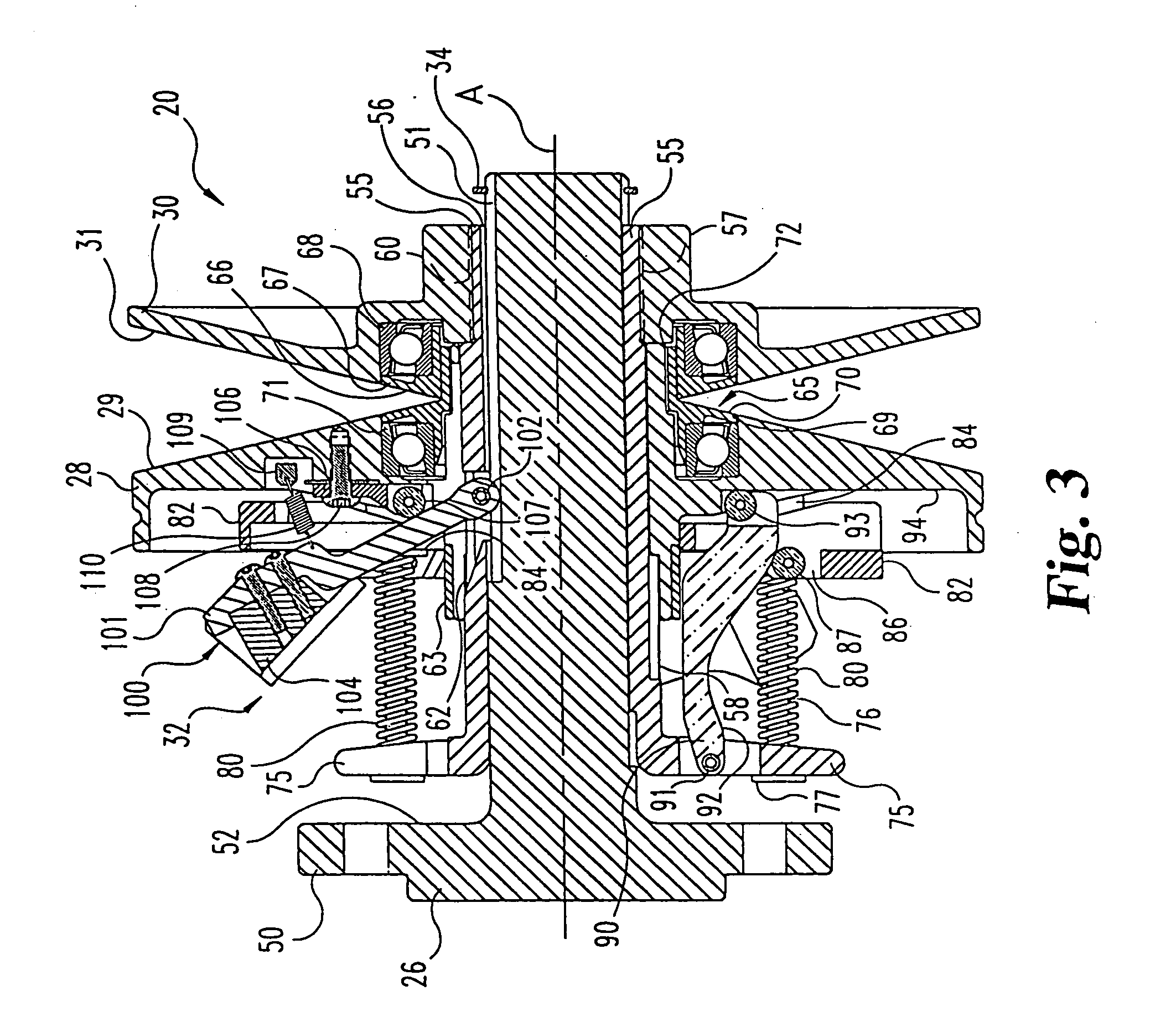
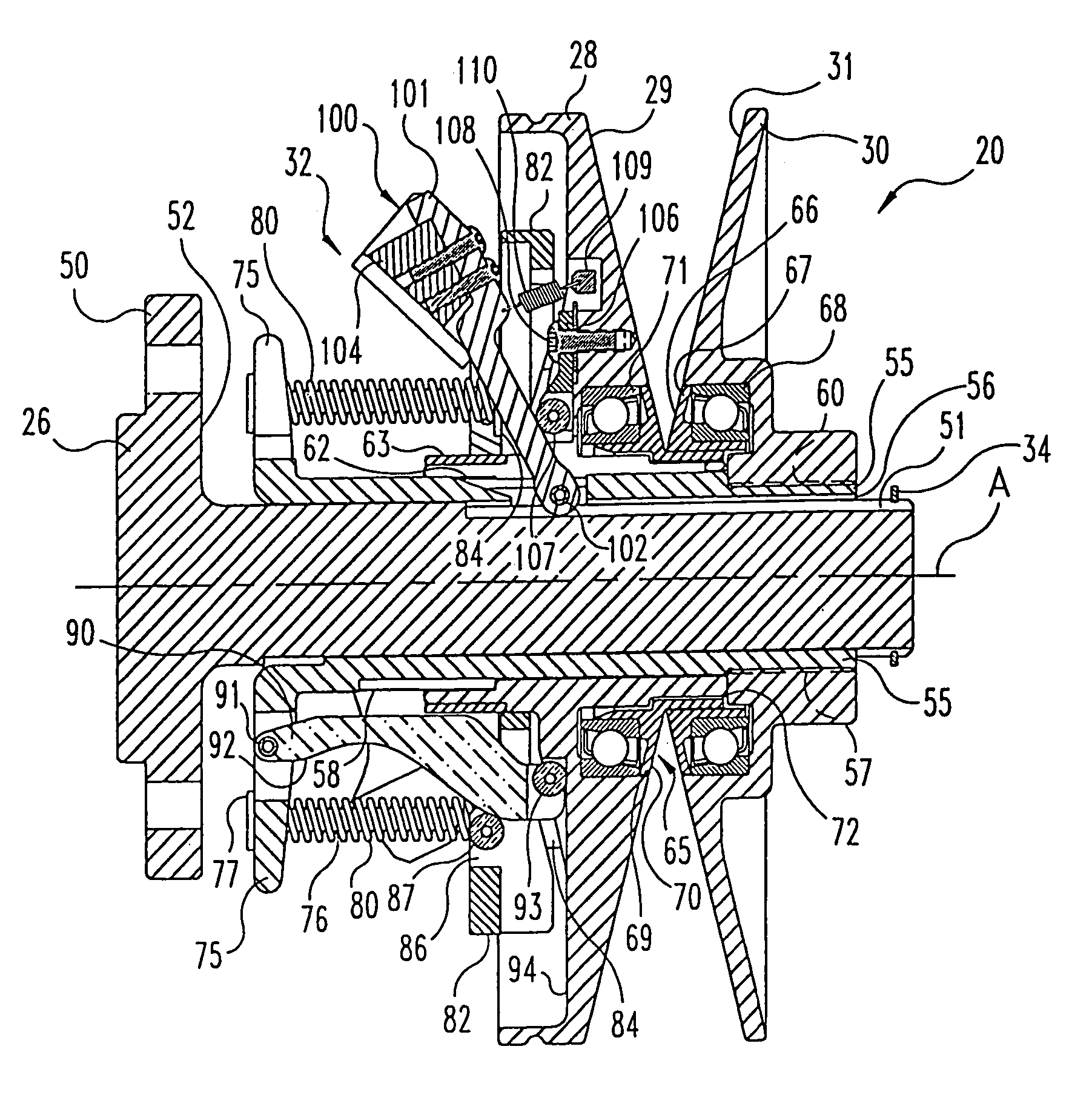
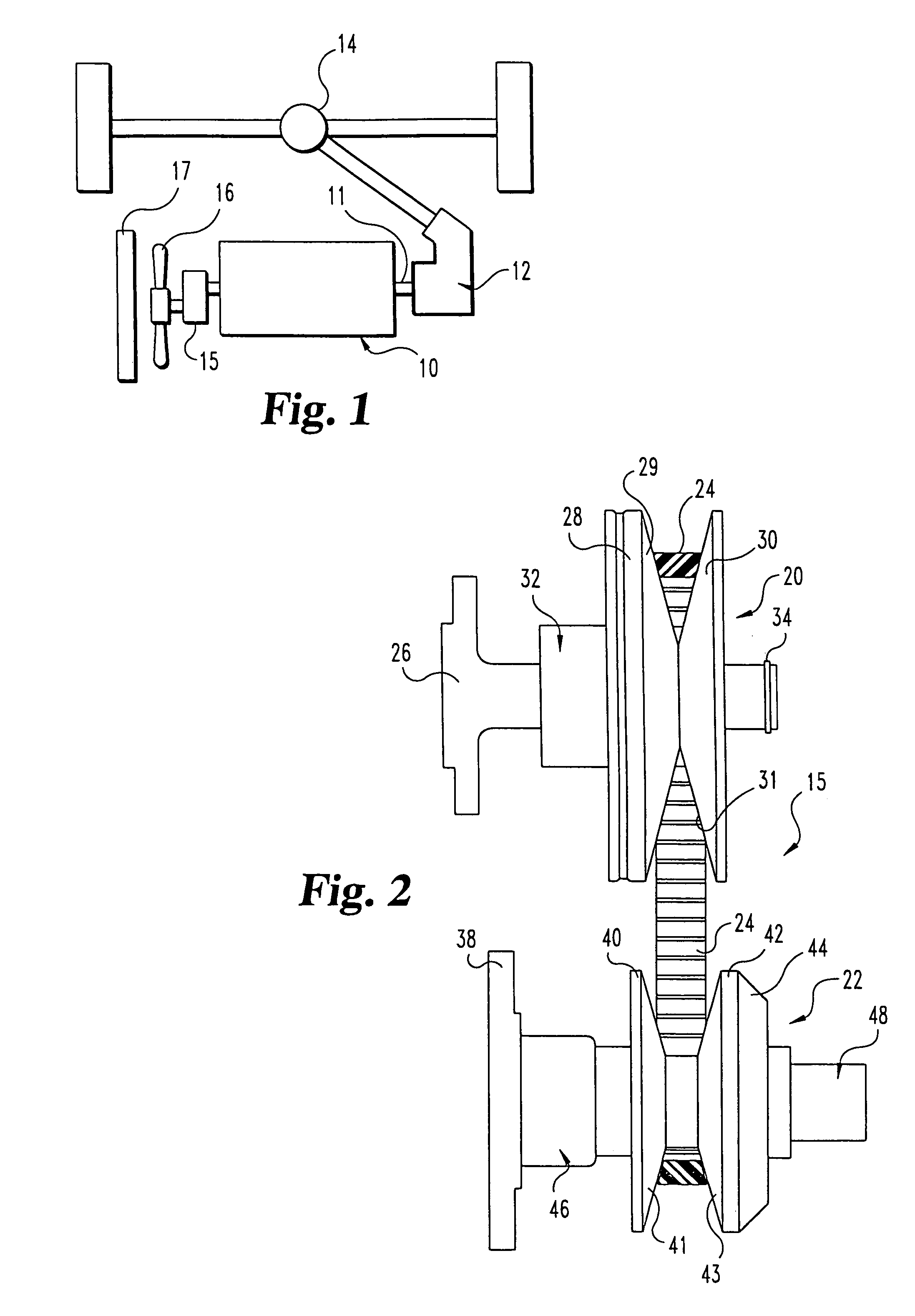
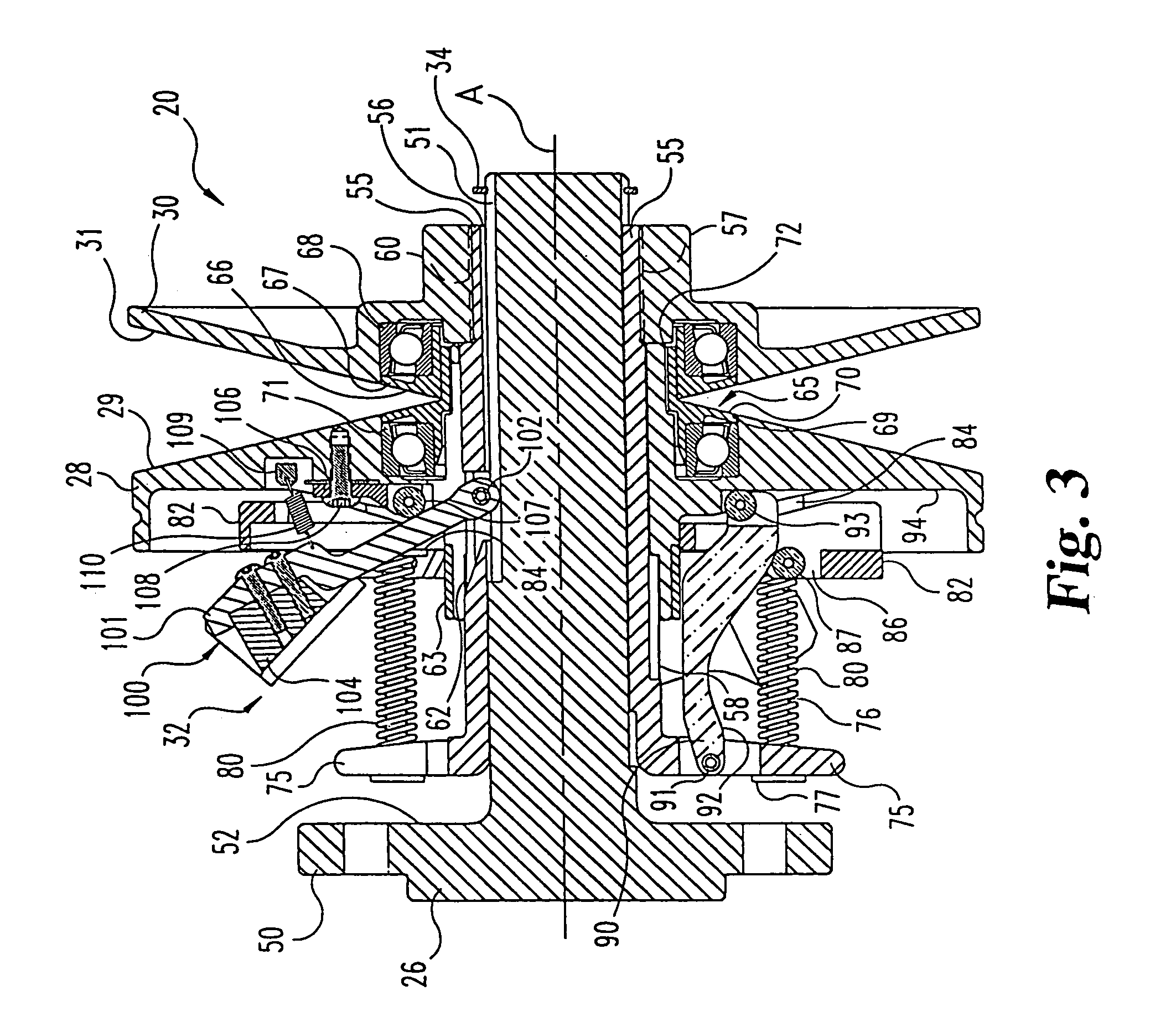
A belt-type continuously variable transfer system (15) includes a driving pulley assembly (20), a driven pulley assembly (22) and a V-shaped belt (24) engaged to transfer rotary power therebetween. The driven pulley assembly (22) can include a ratio adjustment mechanism (46) that adjusts the position of a rear sheave (40) relative to a forward sheave (42). The adjustment mechanism (46) includes a motor (170) and a worm gear mechanism (171, 172) that rotates an actuation screw (154). Rotation of the actuation screw (154) is reacted by a split nut (158) so that as the screw (154) rotates is translated along the axis (B) of the driven pulley assembly (22). Translation of the actuation screw (154) exerts pressure against the rear sheave (40) to push it toward the forward sheave (42), thereby altering the drive ratio of the pulley assembly. In one feature, the driven pulley assembly (22) includes a fail-safe mechanism (48) that operates when power is supplied to the motor (170) to hold the split nut (158) together. Once power is disrupted, the fail-safe mechanism (48) allows the components (1 58a-c) of the split nut (158) to be separated, disrupting the threaded engagement with the actuation screw (154). At this point, the actuation screw (154) is driven forward by a compression spring (190), thereby driving the rear sheave (40) forward to a predetermined drive ratio position. In another aspect of the invention, the driving pulley assembly (20) includes an idler pulley portion (65) radially inboard from the normal driving sheave surface (29, 31). As the belt speed decreases, the belt (24) migrates downward within the driving pulley assembly (20) until it falls within the idler pulley portion (65). At this point, the belt (24) is isolated from the rotation of the driving pulley assembly (20). The driving pulley assembly (20) also includes a belt tensioning mechanism (32) that maintains proper belt tension at all speeds and drive ratios. The tensioning mechanism (32) relies upon a pivotably mounted centrifugal weight arm (101) to provide tensioning as a function of speed. A compression spring (80) provides axial pressure to maintain belt tension over all drive ratios. The spring (80) acts against a specially curved cam edge (92) on a pivoting lever arm (90), which arm (90) transfers an axial force to the rear sheave (28) of the driven pulley assembly (20).
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
Treadmill with automatic speed control, control module of the same and control method of the same
ActiveUS20100210419A1Feel goodIncrease decelerationMotor/generator/converter stoppersDynamo-electric converter controlObservational errorAutomatic control
The present invention provides a treadmill with an automatic speed control function, including: a body having a belt for supporting an exerciser; an exerciser detecting portion installed in a predetermined area of the body to detect movement of the exerciser; a driving motor coupled to the body to drive the belt; a control portion for generating a control signal for adjusting a rotation speed of the driving motor based on a signal received from the exerciser detecting portion; and a motor driving portion for adjusting the rotation speed of the driving motor according to the control signal received from the control portion, wherein a provision braking torque provided corresponding to the control signal is varied as the rotation speed of the driving motor is reduced. The treadmill quickly follows acceleration or deceleration of an exerciser, realizes a feeling like what an exerciser has while exercising on the ground to thereby improve an exerciser's exercising feeling, accepts various exercising patterns of an exerciser, resolves a problem in that a motor driving portion is tripped due to a load caused by quick deceleration, and pre-processes measured values of an exerciser's position to resolve a problem in that a speed of a belt can not be controlled due to measurement errors contained in measured values.
Owner:KAESUN SPORTS
Control method for reflux welding curve on surface sticking process rpoduction line
InactiveCN101052293AImprove reliabilityPrinted circuit assemblingElectrical componentsHeating timeTime segment
The method comprises: the total temperature rise length of the target backflow curve is divided by the backflow oven heating length to get the belt speed of the oven; using each heating area length of the oven to divide the belt speed to get the stay time of the assembled electronic product in each heat area; according to the trace of the backflow curve, determining the temperature rise in the stay time of each heating area; using the temperature rise of the target backflow curve in each heating time interval as the difference value of each heating area temperature in backflow oven in order to set the heat source temperature parameters of each heat interval into a combined parameter; the combined parameters is represented by the temperature of the last heat area in adjacent cooling area, and is set at a temperature being 5-25deg.c higher than the peak temperature of the target backflow curve; the risen temperature value is adjusted based on the bounding point character; the temperature at cooling area can be set as 100-120deg.c lower than the fusion point of soldering past so as to get a complete control parameter setting of the backflow oven.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
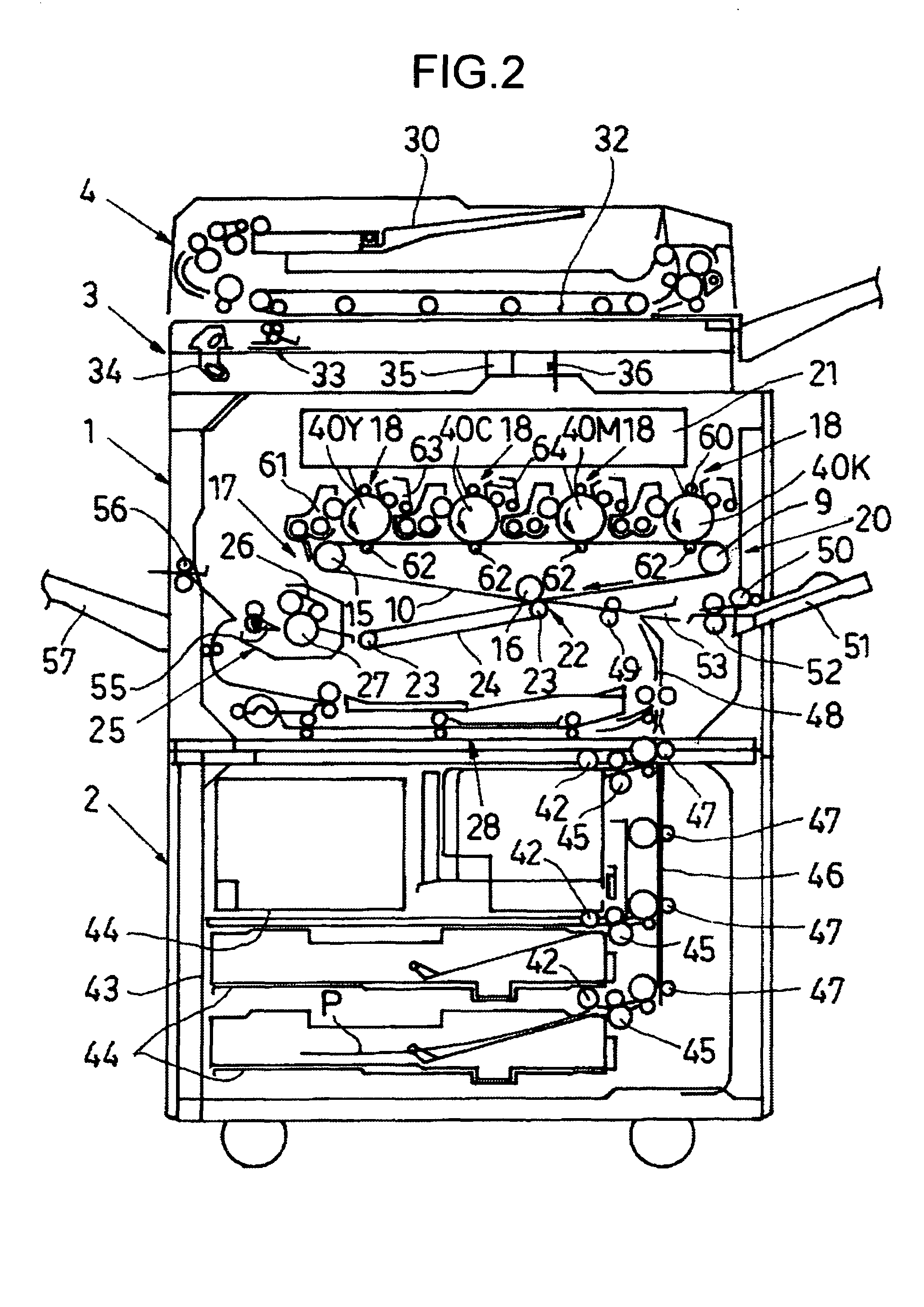
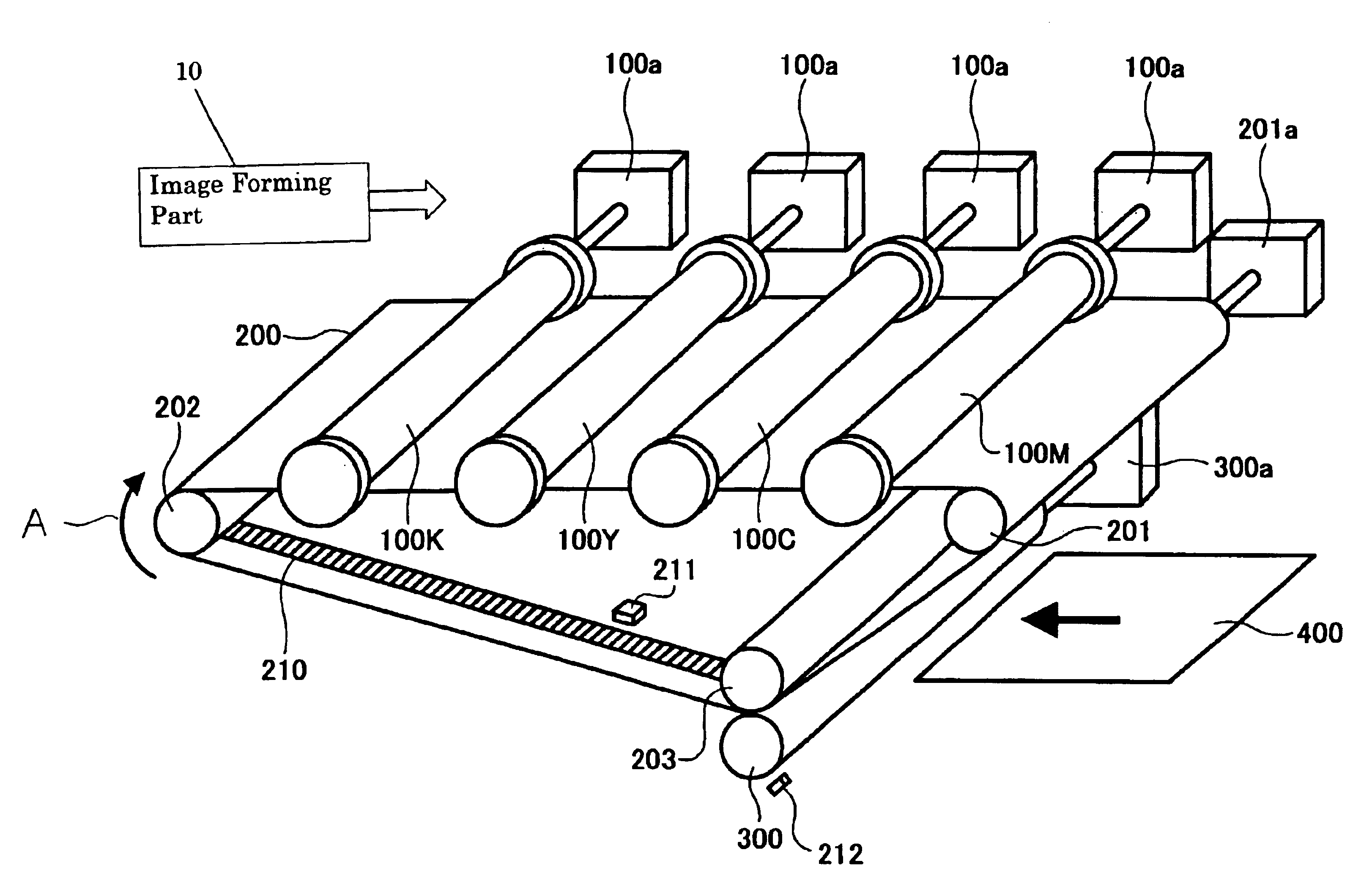
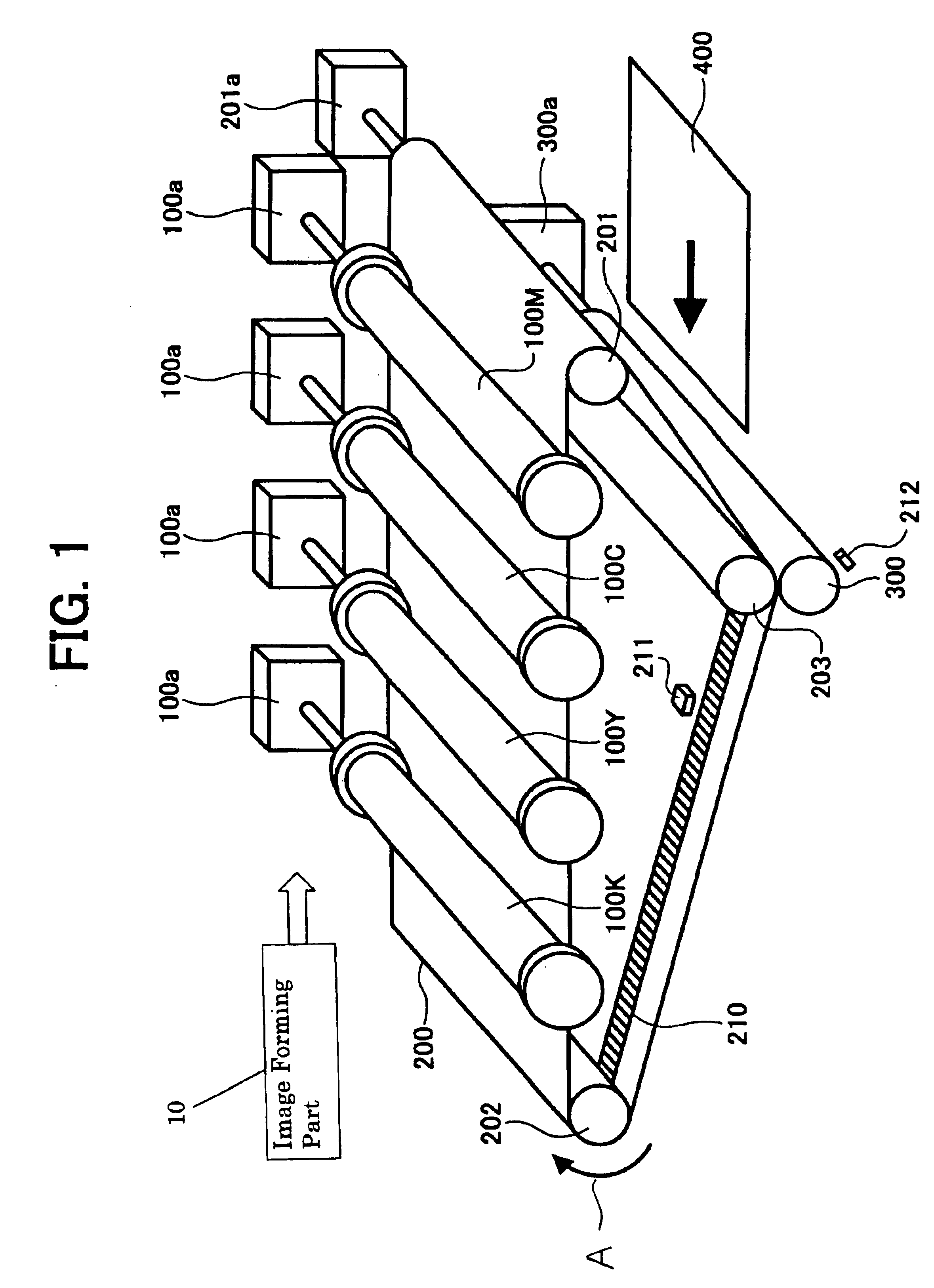
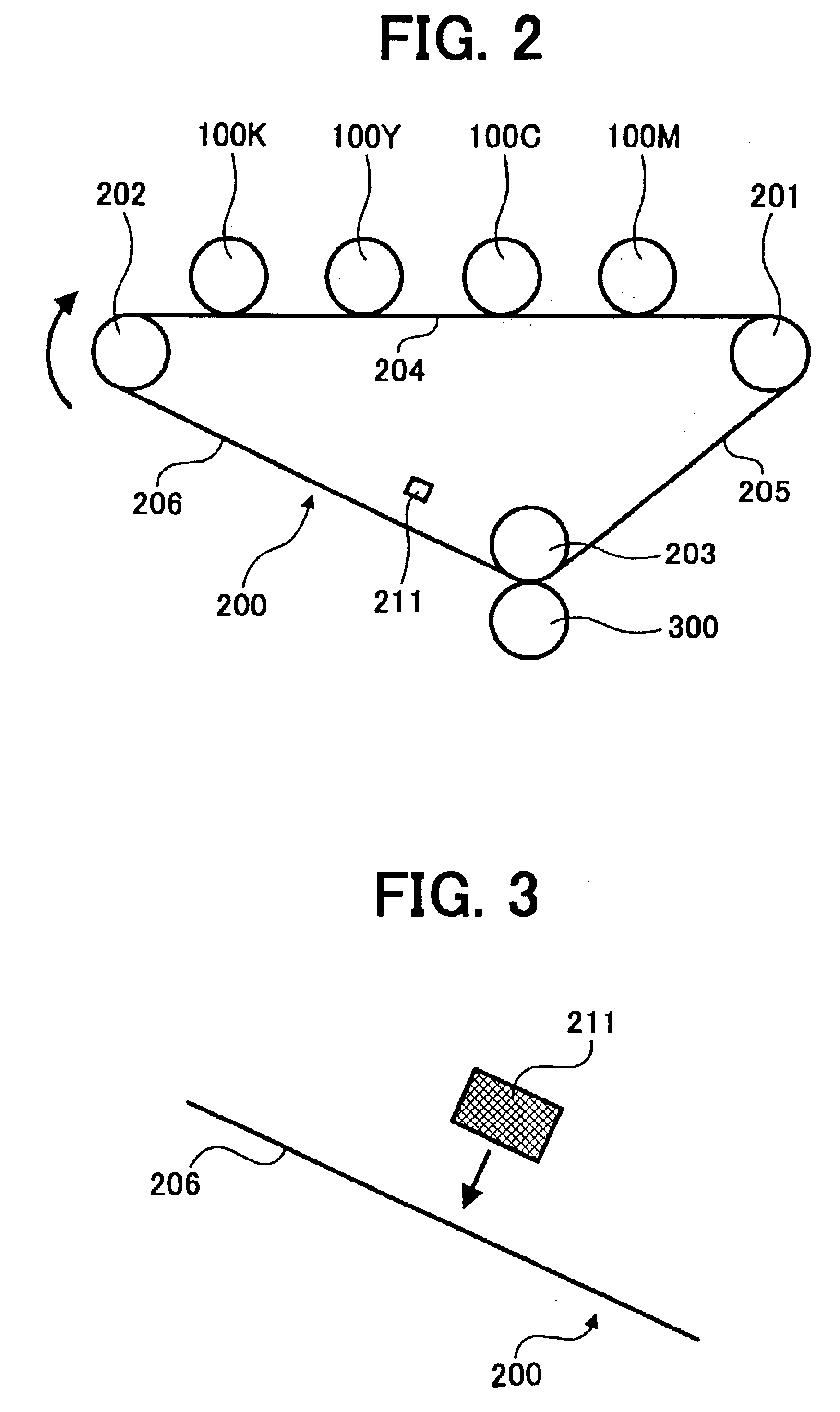
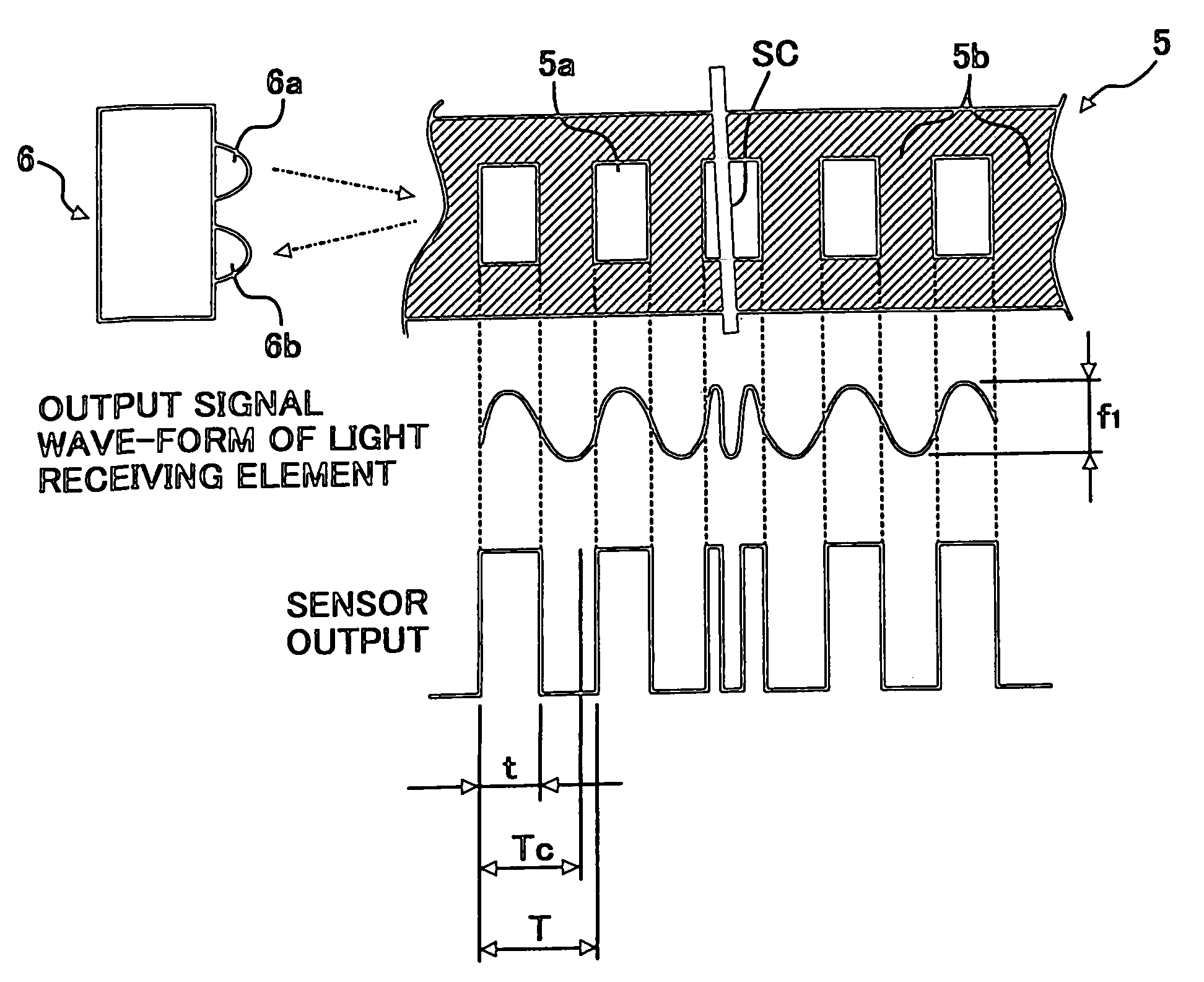
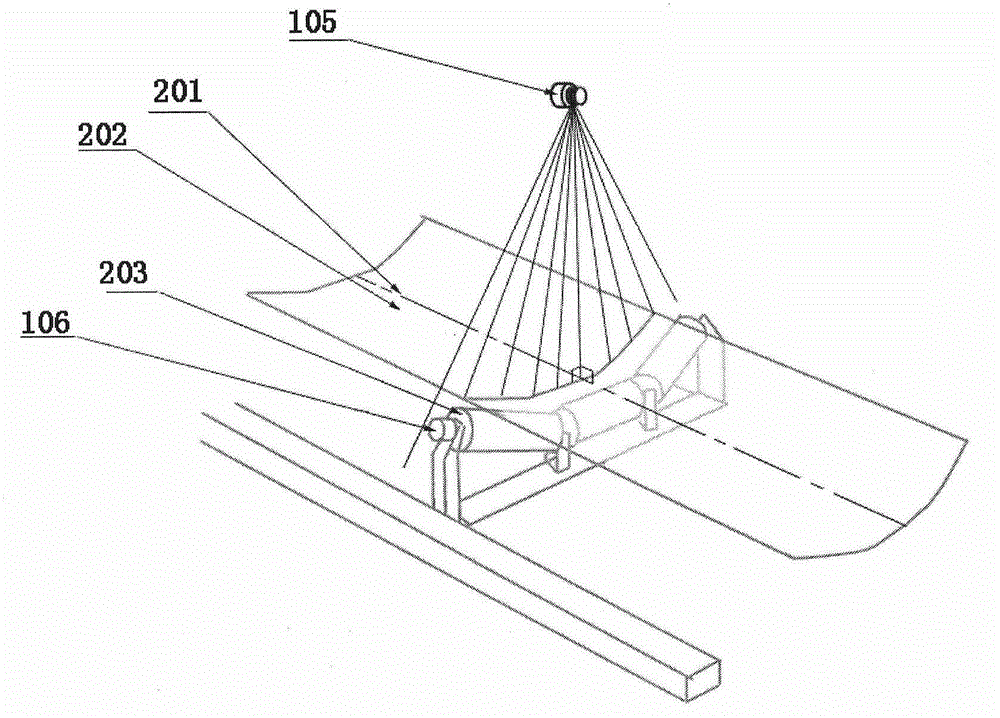
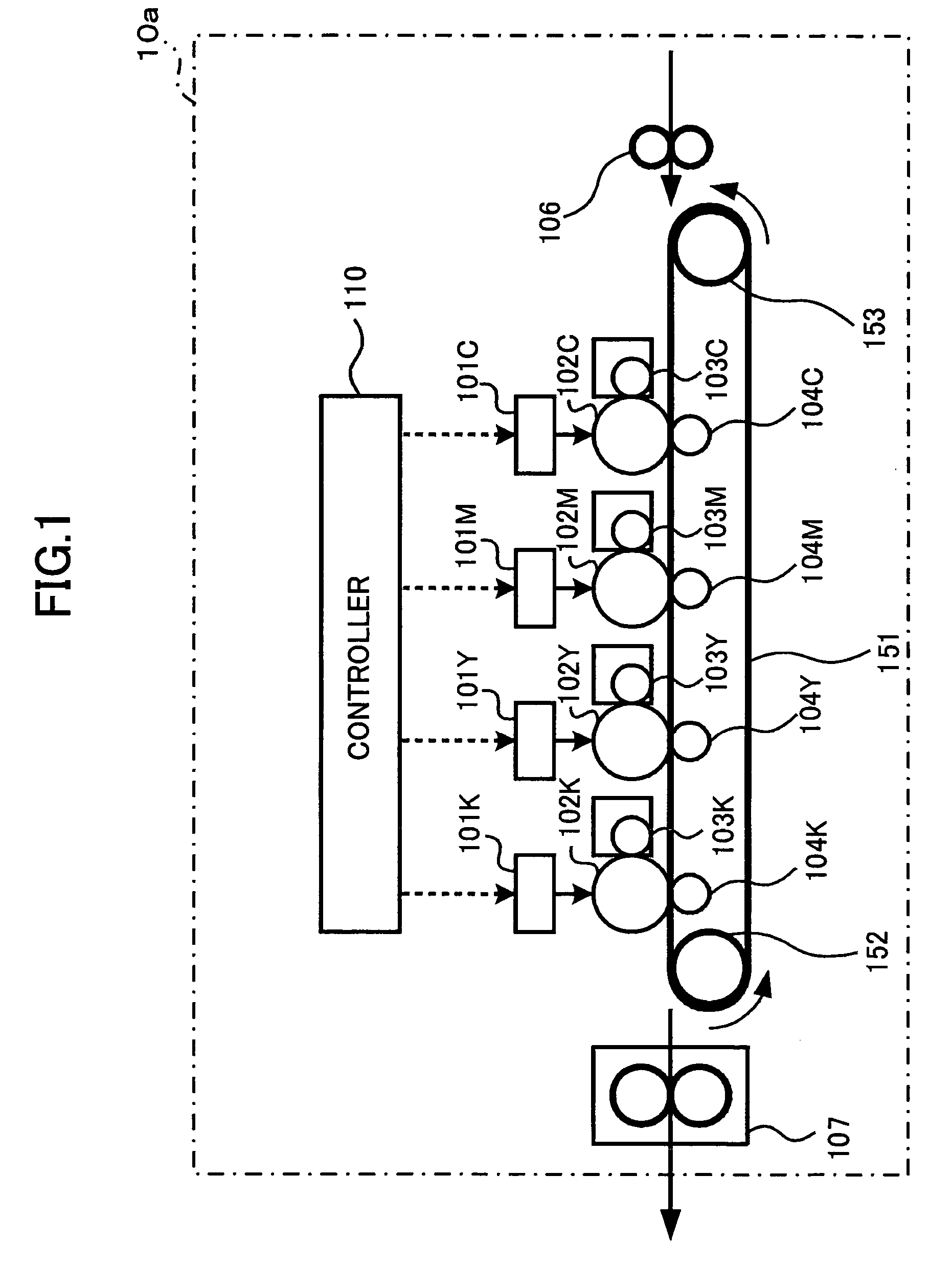
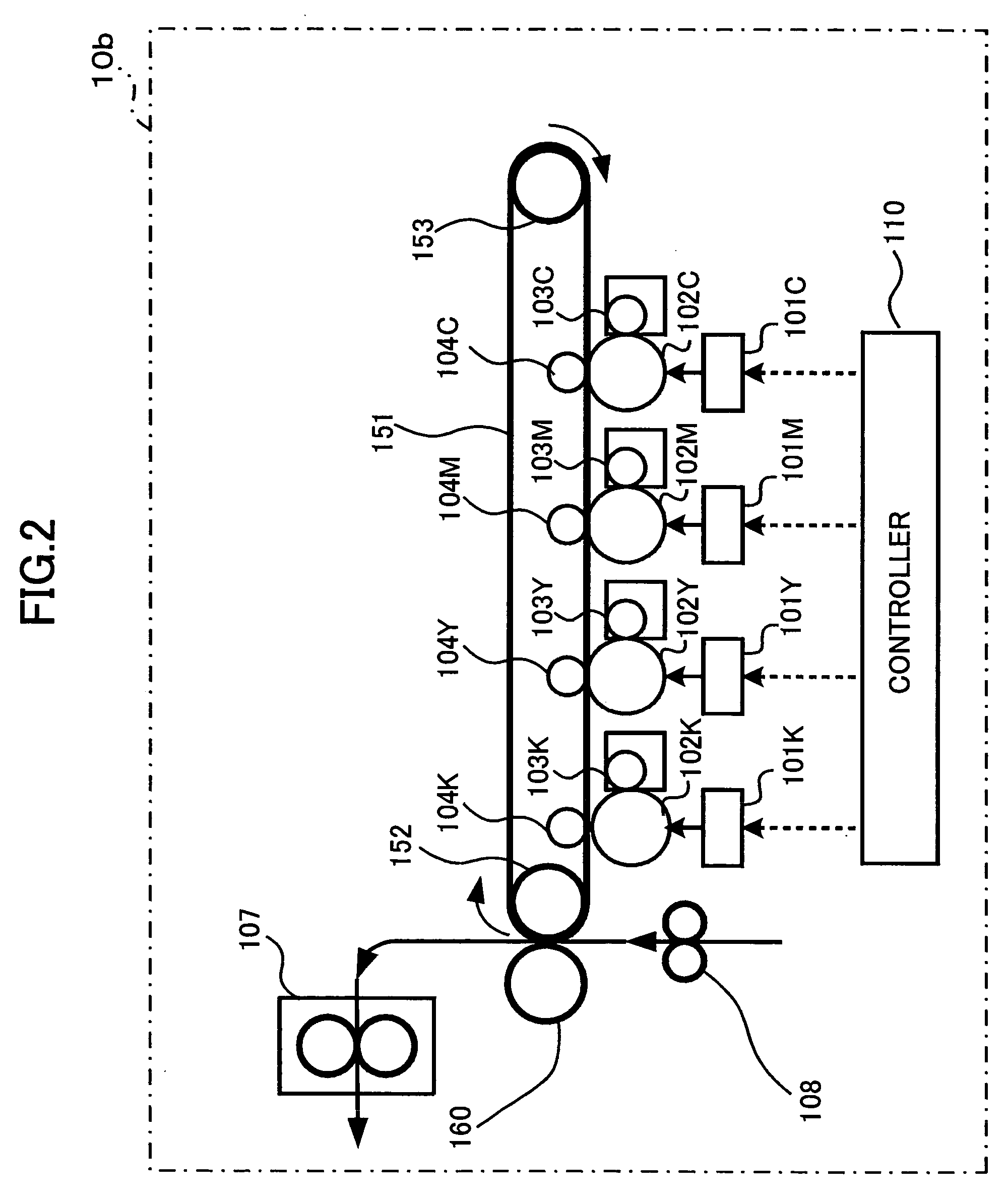
Transfer apparatus, image forming apparatus, and method of correcting moving speed of belt
A scale is provided along at least one side of a portion of a belt. A sensor reads the scale on the belt to obtain scale information. An actual speed calculating unit calculates a speed of the belt from the scale information. A speed calculating unit calculates a speed of the belt from information other than the scale information. A control unit that provides a control to correct speed of the belt according to the speed calculated by the actual speed calculating unit when the speed calculated by the actual speed calculating unit is normal, and provides a control to correct speed of the belt according to the speed calculated by the speed calculating unit when the speed calculated by the actual speed calculating unit is abnormal.
Owner:RICOH KK
Electric booster brake device for vehicle
InactiveCN102205838AWith intelligent automatic braking modeAvoid empty tripsBraking action transmissionFoot actuated initiationsDrive shaftReduction drive
The invention relates to a brake device for a vehicle, in particular to an electric booster brake device. The electric booster brake device for the vehicle comprises a pedal, an input force push rod connected with the pedal, a booster connected with the input force push rod, an output force push rod connected with the booster and a master cylinder connected with the output force push rod. The booster comprises racks connected between the input force push rod and the output force push rod, a gear engaged with the racks, a direct-current motor belt speed reducer assembly connected with the gear via a transmission shaft, an electronic control unit (ECU) and a speed sensor connected to the input force push rod; and the speed sensor is connected with the ECU which is connected with the direct-current motor belt speed reducer assembly. The electric booster brake device for the vehicle has the characteristics that the brake boost can be automatically adjusted according to requirements and has an intelligent automatic brake mode, idle stroke and poor rigidity are effectively avoided, and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAPU AUTOMOBILE CO LTD +1
Sorting method of low grade vanadium titano-magnetite
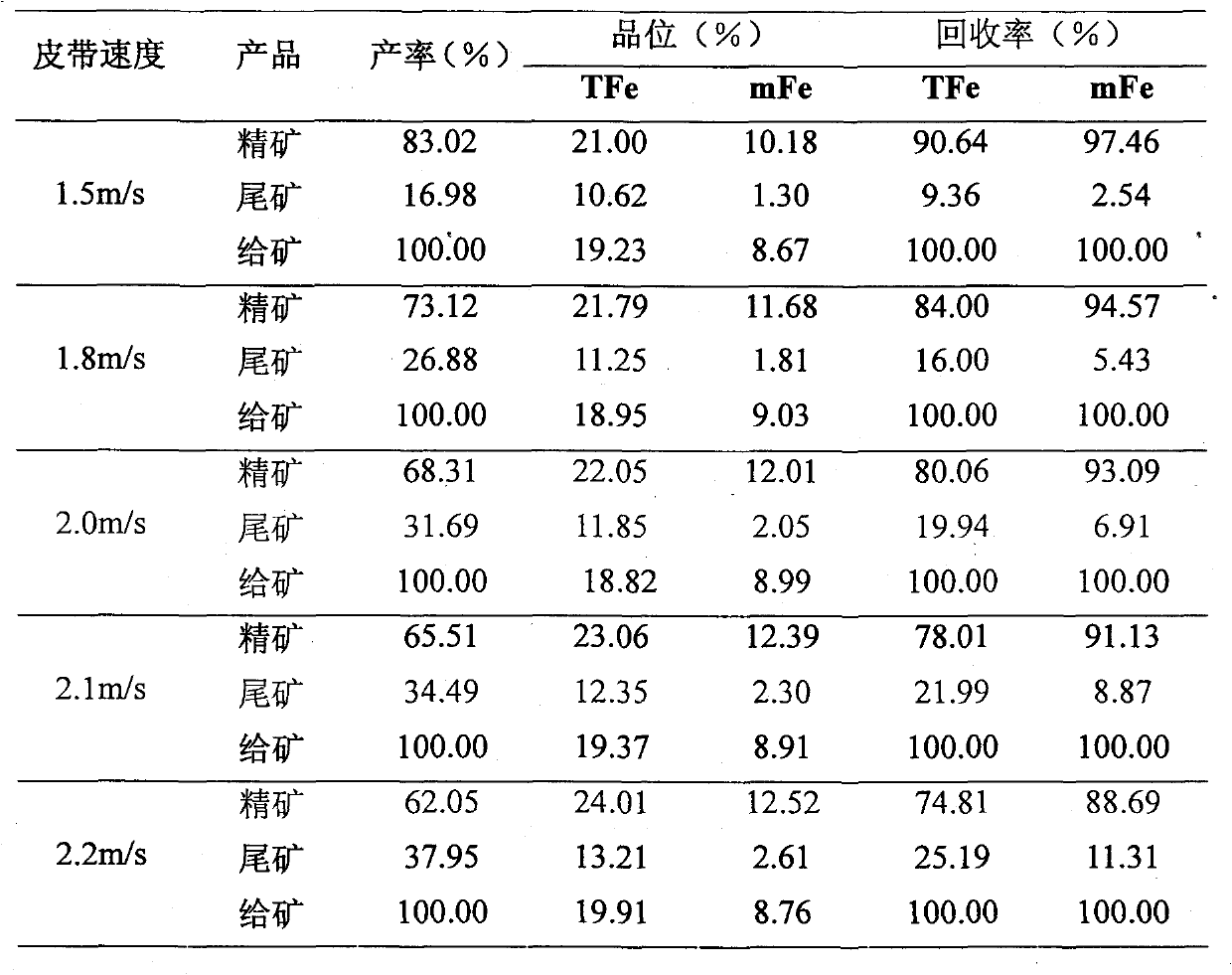
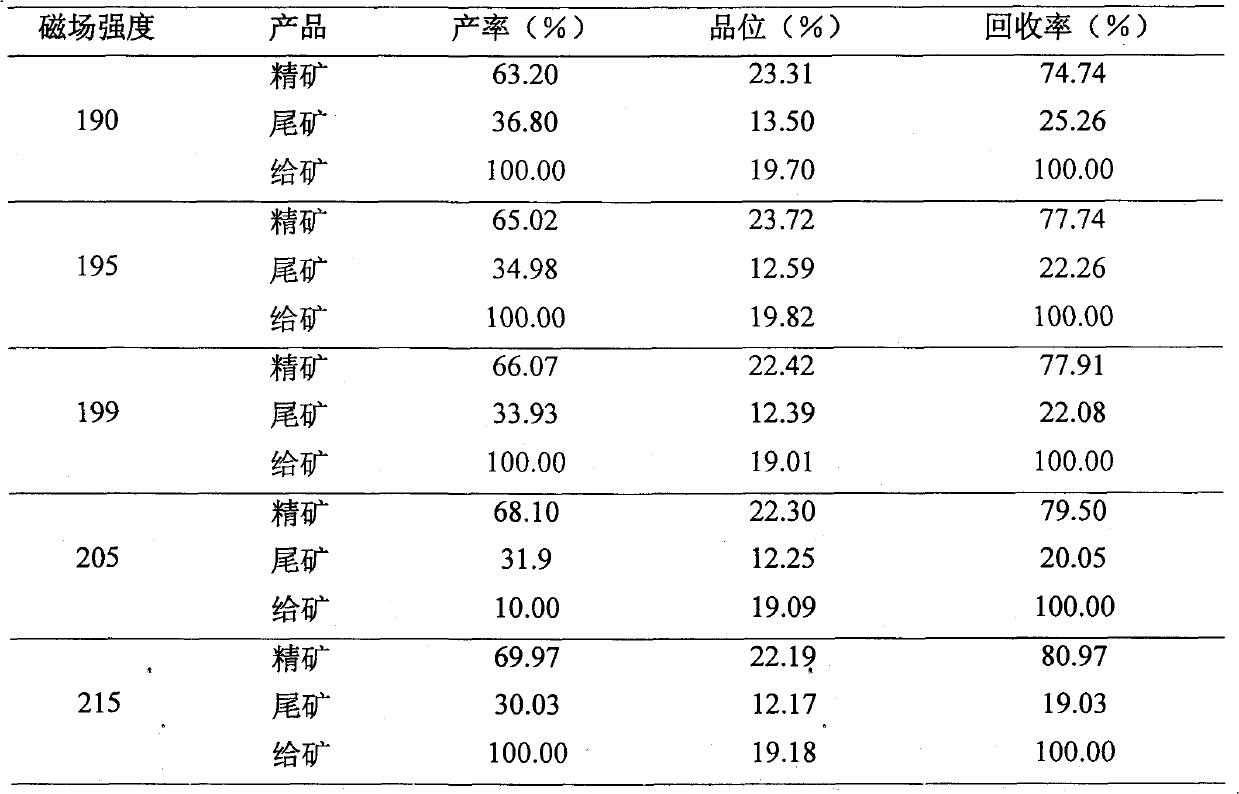
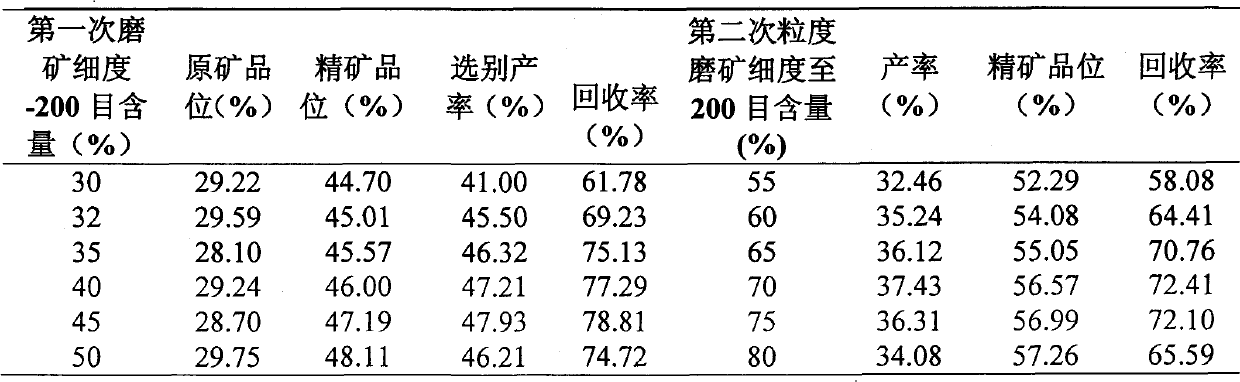
The invention provides a sorting method of low grade vanadium titano-magnetite. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, crushing raw ore, screening, performing magnetic separation while controlling the magnetic-field intensity and belt speed, discarding tailings, and performing twice grinding-magnetic separation to obtain high grade vanadium titano-magnetite concentrate, wherein the magnetic-field intensity is 195-205KA / m and the belt speed is 2.0-2.2 m / s during magnetic separation. The sorting method fully utilizes low grade vanadium titano-magnetite and completely realizes the comprehensive recovery and utilization of resources.
Owner:TAIHE IRON MINE CHONGQING IRON & STEEL GROUP MINING
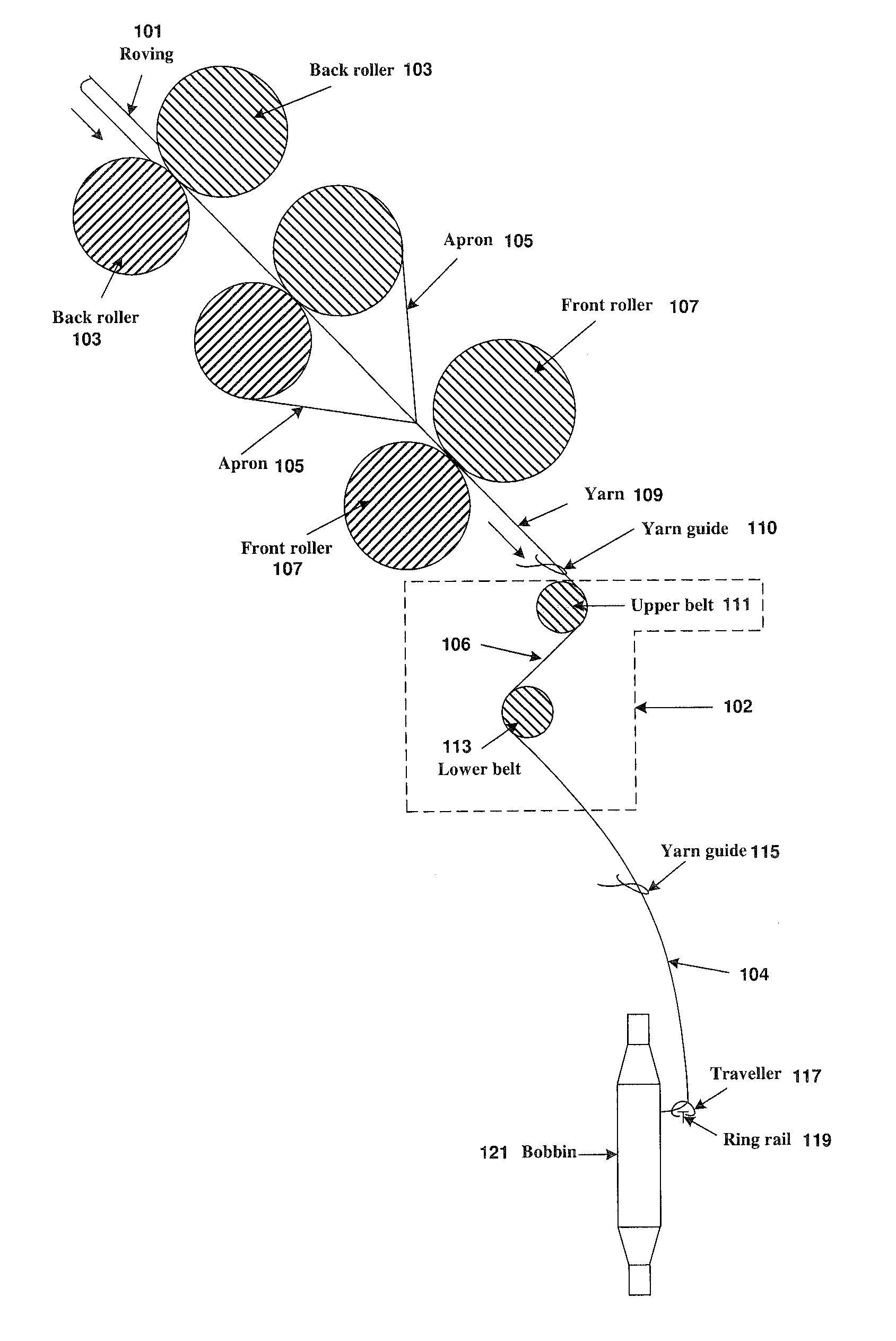
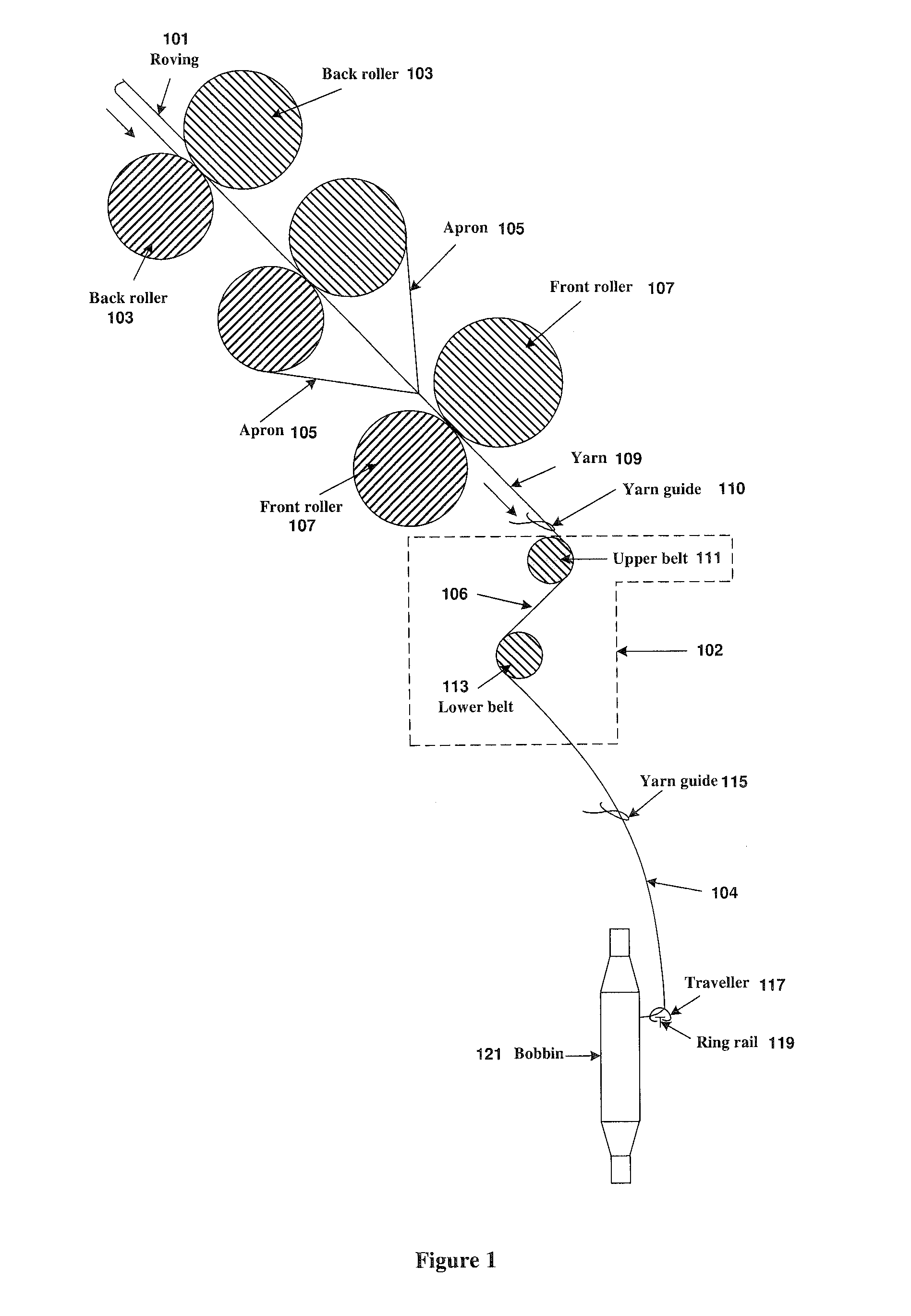
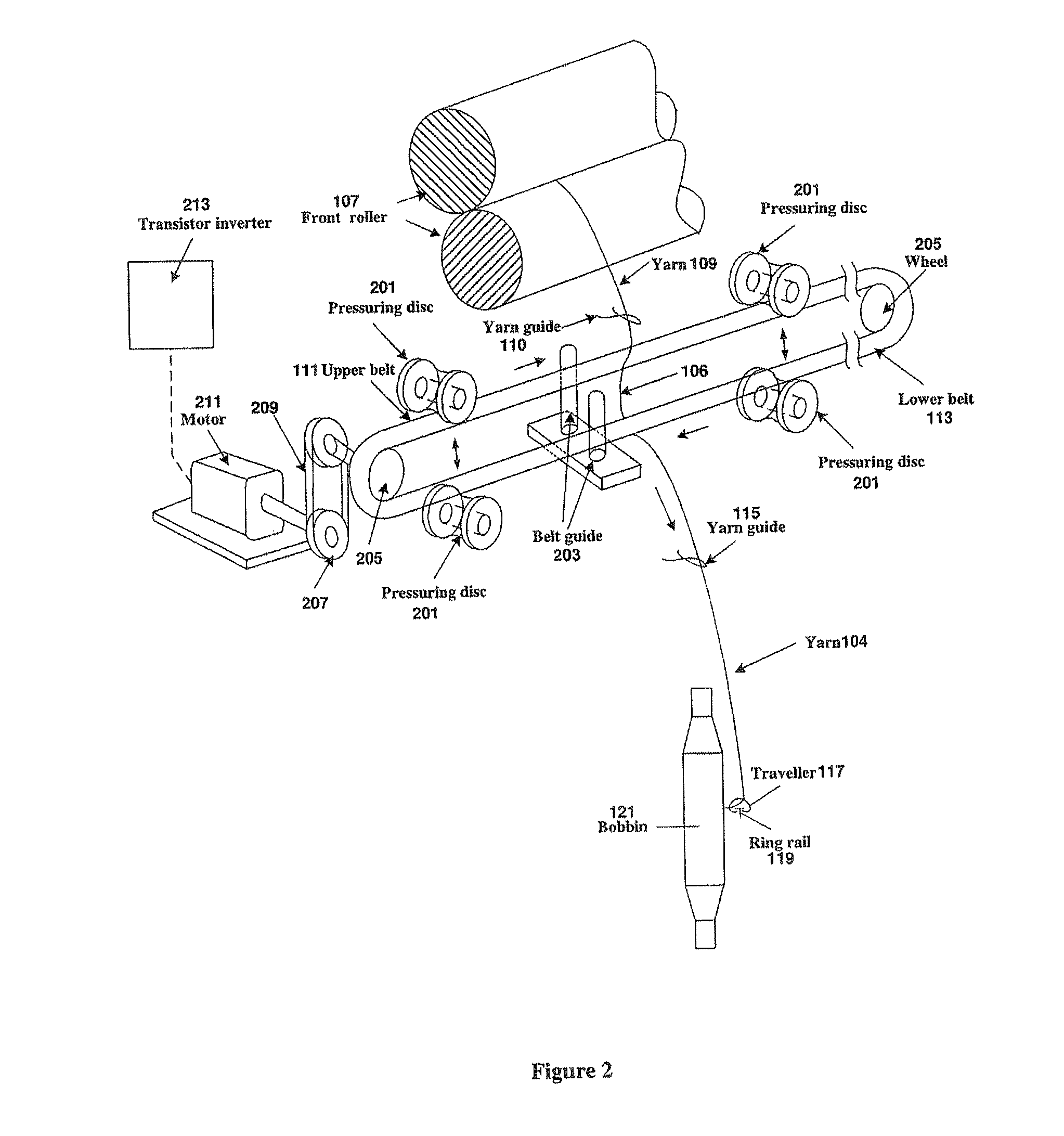
Method And Apparatus For Reducing Residual Torque And Neps In Singles Ring Yarns
ActiveUS20120151894A1High false twist efficiencyLow investment costDrafting machinesContinuous wound-up machinesFiberYarn
Method and apparatus for reducing residual torque in singles ring yarns, achieved by imparting two separate false twisting points on the traveling strand of fibers (or yarn) after the strand exits from the spinning triangle with a proper ratio between the belt speed and the strand feeding speed. In addition to reducing the residual torque, this double false twist technique also reduces yarn hairiness to the same level as achieved by more expensive compact spinning devices, reduces yarn twist by more than 20% and significantly enhances yarn and fabric softness. Furthermore, by combining the double false twist technique with a compact spinning device, the numbers of neps, thick and thin places are significantly reduced to produce high-quality yarns and fine-count yarns.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Continuously variable belt drive system
A continuously variable belt drive system including a driving pulley assembly, a driven pulley assembly, and a V-shaped belt engaged to transfer rotary power therebetween is disclosed herein. The driving pulley assembly includes an idler pulley portion. As the belt speed decreases, the belt migrates downward within the driving pulley assembly until it falls within the idler pulley portions, thereby isolating the belt from the rotation of the driving pulley assembly. The driving pulley assembly also includes a belt tensioning mechanism that maintains proper belt tension at all speeds and drive ratios. The tensioning mechanism relies upon a pivotably mounted centrifugal weight arm to provide tensioning as a function of speed. A compression spring provides axial pressure to maintain belt tension over all drive ratios. The spring, acts against a curved cam edge on a pivoting lever arm, which arm transfers an axial force to the rear sheave of the driven pulley assembly.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
Friction transmission belt
ActiveUS20070082777A1Increased durabilityExcellent in power transmission propertyV-beltsRopes and cables for vehicles/pulleyPlasticizerTransmission belt
Owner:MITSUBOSHI BELTING LTD
Belt moving device and image forming apparatus using same
InactiveUS20080213009A1Prevent color shiftHigh quality imagingElectrographic process apparatusColor shiftBelt speed
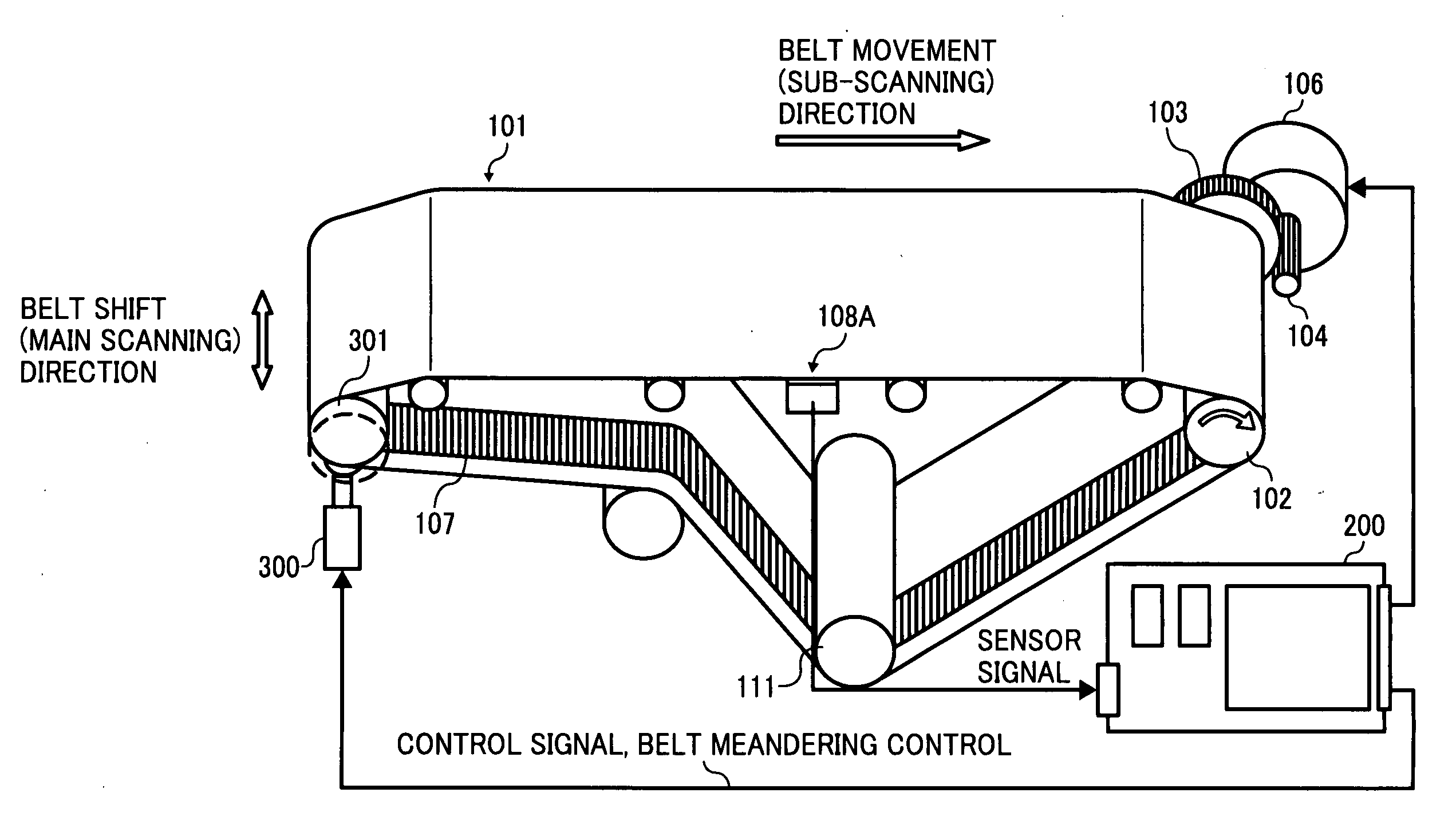
In a belt moving device that is capable of reducing belt speed fluctuation and positional deviation from a target belt position in a sub-scanning direction and performing highly precise position control in a main scanning direction, and an image forming apparatus that uses this belt moving device to prevent color shift in both the main scanning direction and sub-scanning direction of a formed image such that a high-quality image can be formed, belt shift control means reduce shift position variation within a single round trip of an endless belt by feeding back a target value for canceling out the shift position variation within a single round trip of the endless belt and feeding forward a value obtained by multiplying an inverse transfer characteristic of moving means by a transfer characteristic of a target value of the moving means in relation to the control content of the moving means.
Owner:RICOH KK
Knife sharpening apparatus
Owner:FUCHS RICHARD W
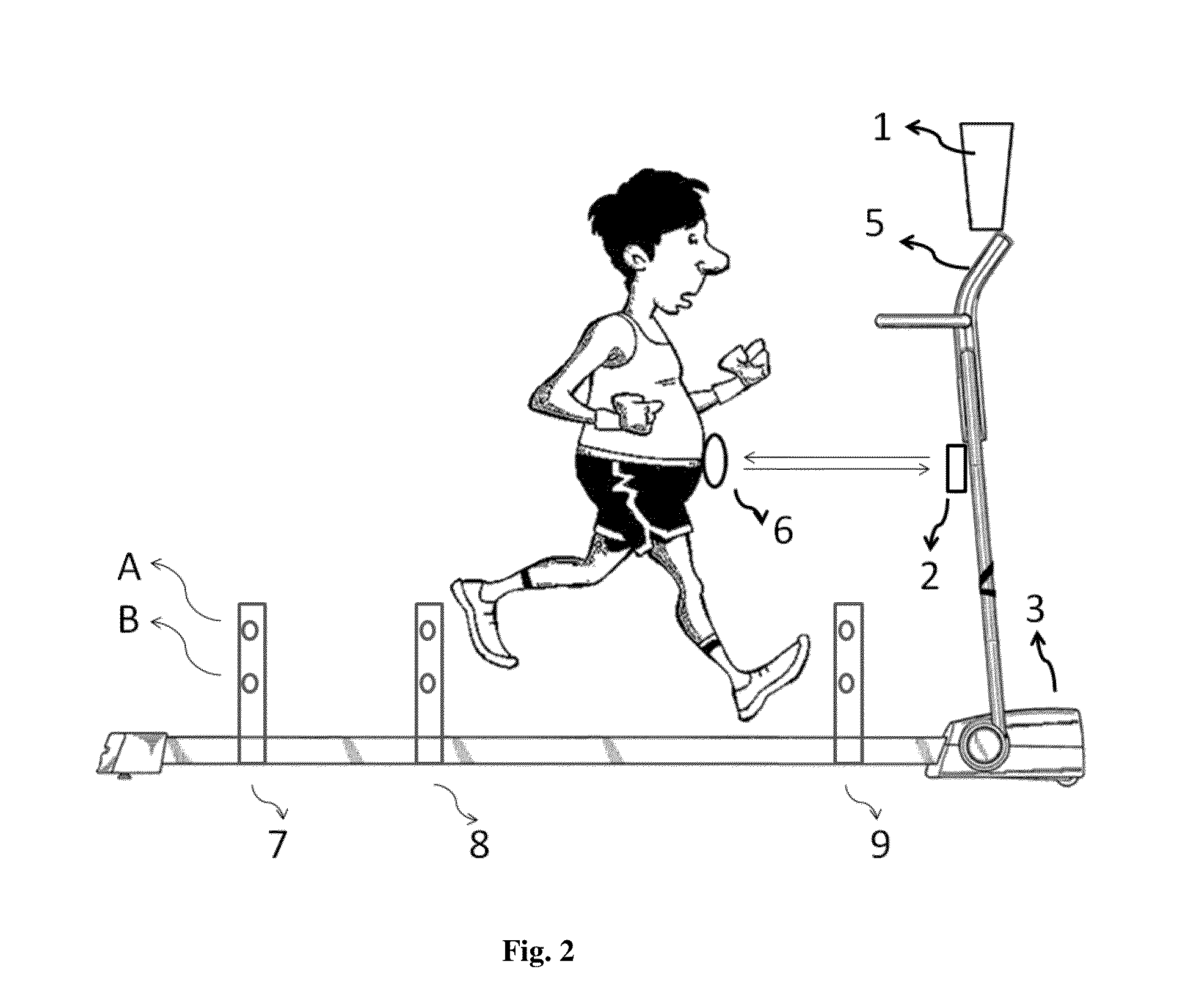
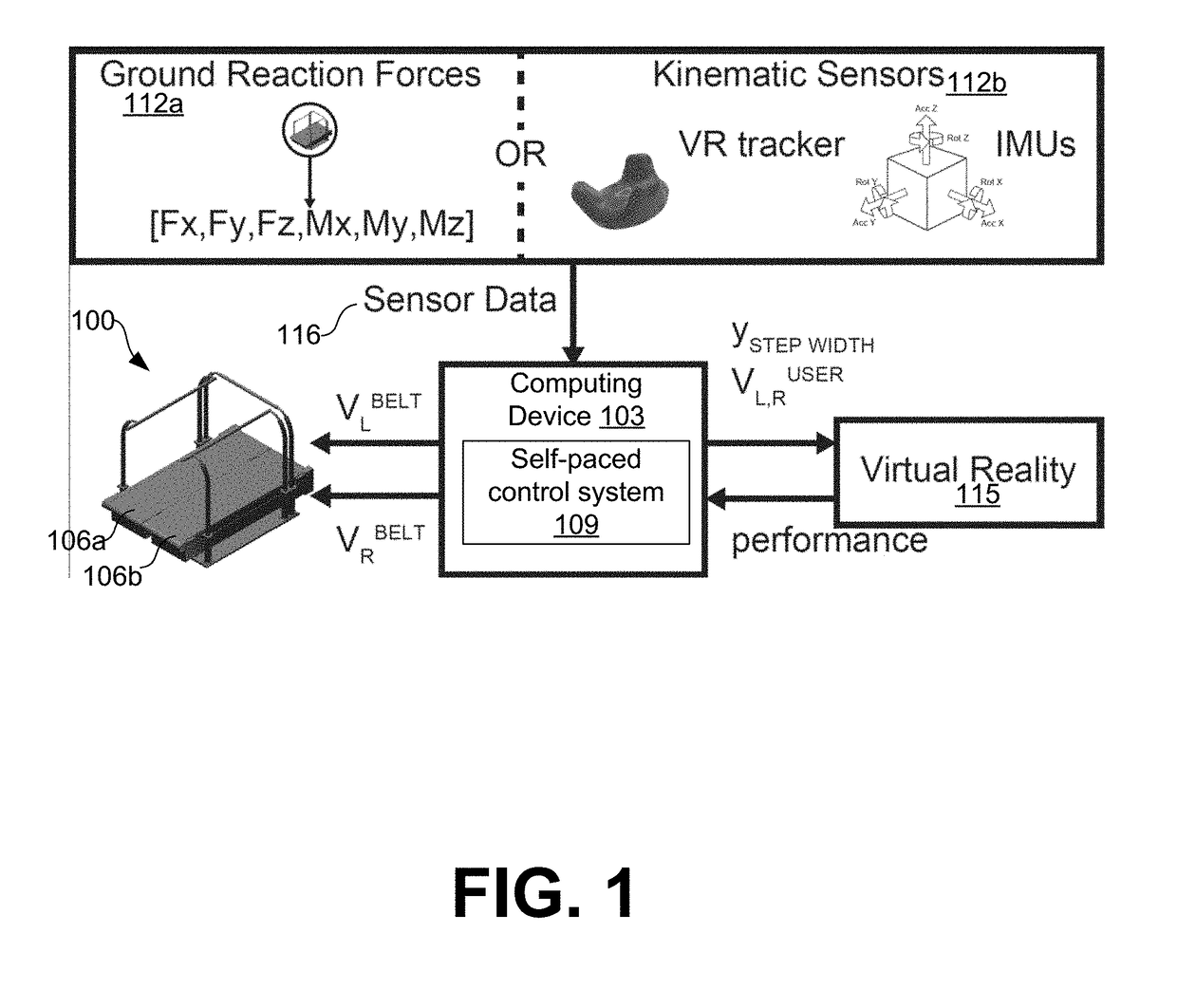
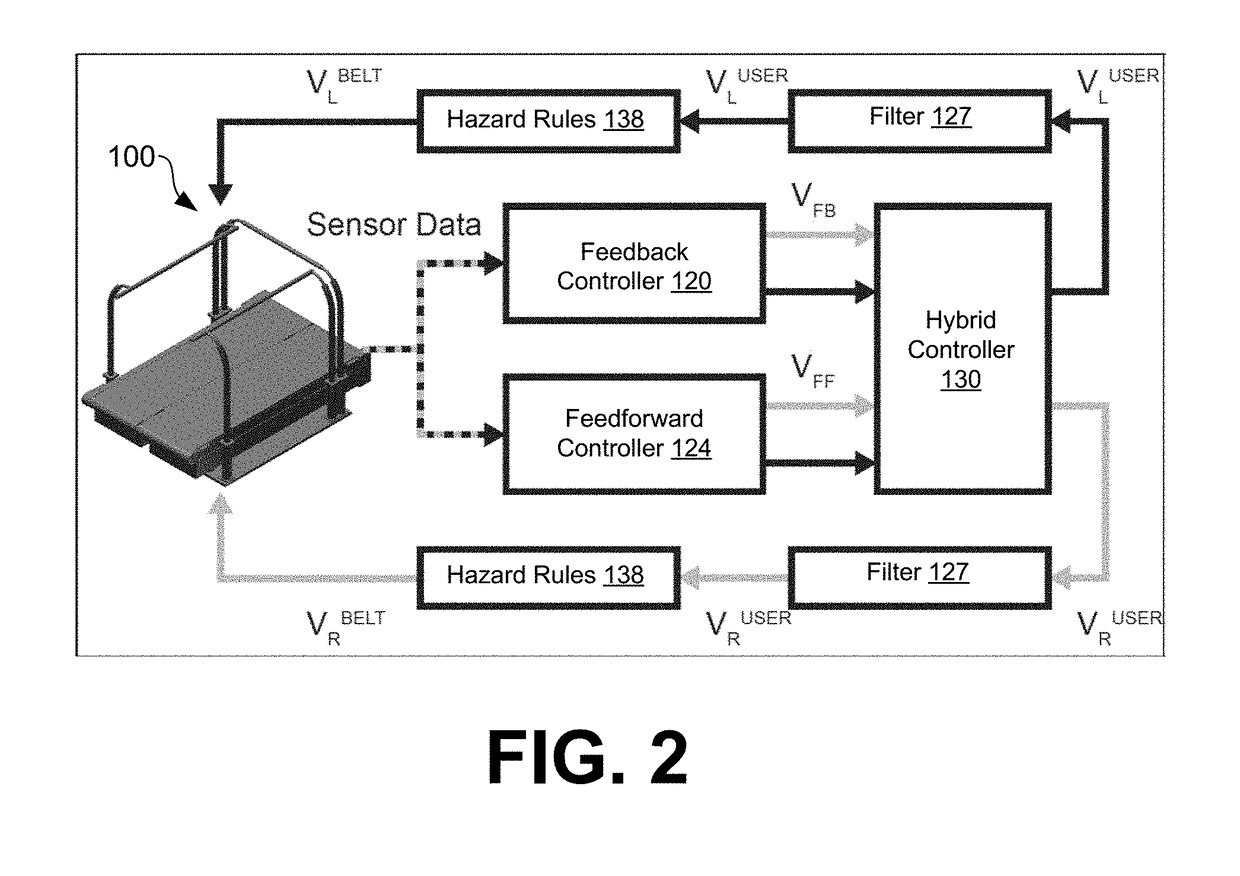
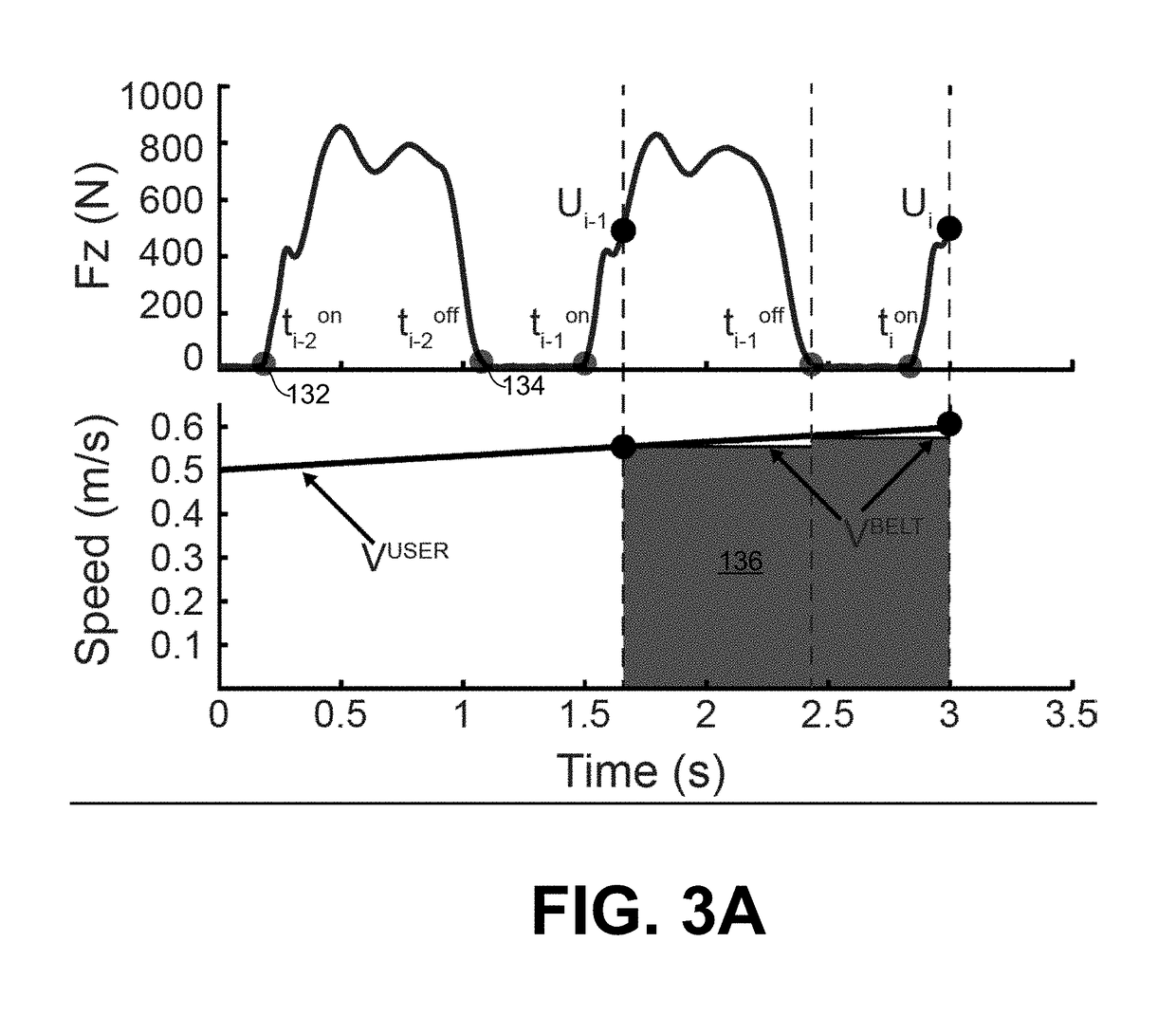
Systems and methods for controlling a self-paced treadmill using predicted subject velocity
ActiveUS20180345070A1Movement coordination devicesCardiovascular exercising devicesKaiman filterStride length
Systems and methods are provided for enabling a split belt treadmill having two belts to self-pace. A feedback process estimates a first current step speed for a user on each belt by measuring stride length and step duration. A feed-forward process estimates a second current step speed for the user on each belt by measuring three forces and three moment components associated with foot contact with the belt. A command speed for each belt is produced by combining the first and second current step speeds with a Kalman filter. A belt speed associated with each belt is adjusted based upon the command speed.
Owner:WEST VIRGINIA UNIVERSITY
Belt apparatus and image forming apparatus
A belt apparatus including a belt configured to rotate around a plurality of belt rollers, a belt speed detection system configured to detect a speed of the belt, and a contact roller configured to contact the belt. A control device is configured to control the contact roller based on a detected speed of the belt. An image forming apparatus includes an image forming part configured to form an image, a first image transfer device, a transfer belt configured to rotate around a plurality of belt rollers and to hold the image transferred by the first image transfer device, a transfer belt speed detection system configured to detect a speed of the transfer belt, and a second transfer roller configured to transfer the image held on the transfer belt to a paper. A control device configured to control the second transfer roller based on a detected speed of the transfer belt.
Owner:RICOH KK
Energy-saving control device for belt conveyor units
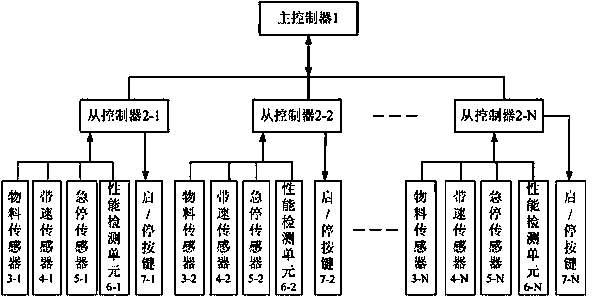
InactiveCN103818704AAccurate account openingExact stop timeControl devices for conveyorsStart timeStop time
The invention provides an energy-saving control device for belt conveyor units. The energy-saving control device comprises a belt conveyor unit composed of a plurality of belt conveyors. Each belt conveyor is provided with a slave controller. The slave controllers are all interactively connected with a master controller. The input end of the slave controller is connected with the output end of each of a material sensor, a belt speed sensor, an emergency stop sensor and a performance detection unit disposed on the corresponding belt conveyor. The output end of each slave controller is connected with a start / stop button of the corresponding belt conveyor. The slave controllers on the belt conveyors are all interactively connected with the master controller, actual time of the former belt conveyor serves as delayed start time of the second belt conveyor, and accordingly start or stop time of each belt conveyor is more accurate; chances of the belt conveyors being idle are avoided, transporting efficiency is improved, normal effective transport modes are ensured, energy resources are saved, and the service lives of the belt conveyors are prolonged.
Owner:SUZHOU ZHONGKUANG SANJIE TECH
Multistage belt conveyer coordination control system based on internet of things and method
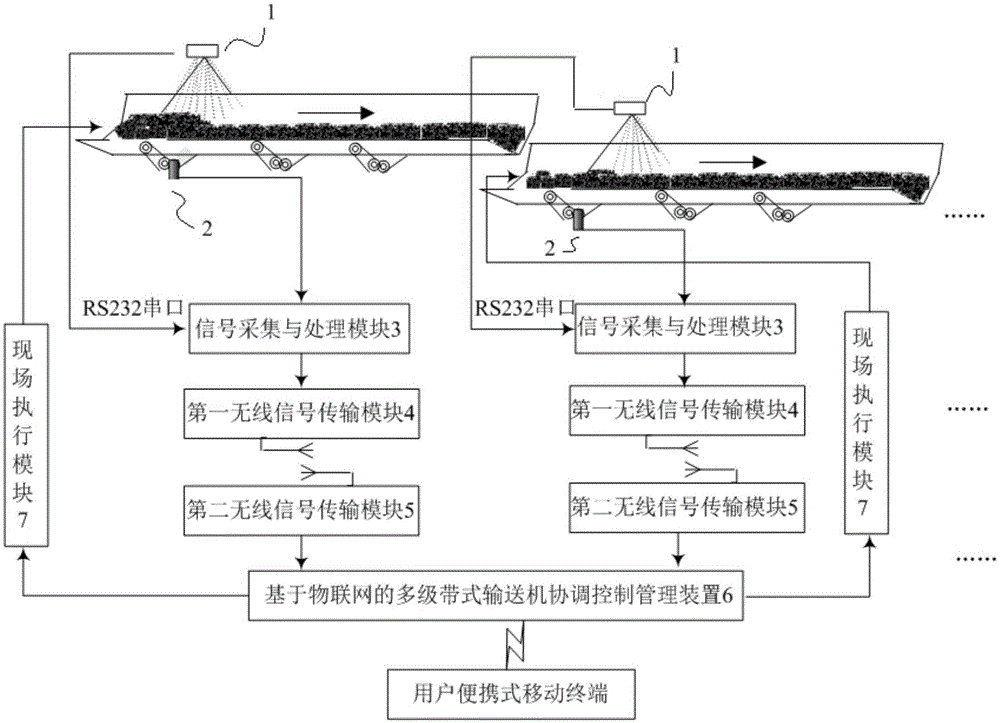
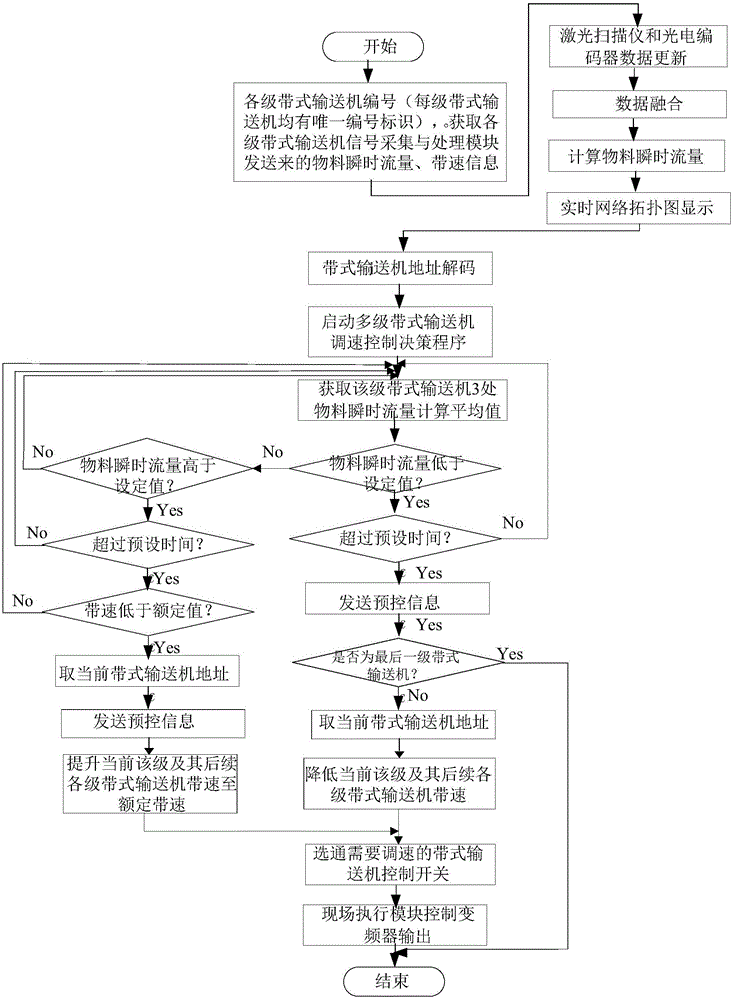
InactiveCN105022273AOptimizing the operation process of speed regulation and energy saving controlImprove the intelligent level of speed controlAdaptive controlThe InternetBelt speed
The invention discloses a multistage belt conveyer coordination control system based on internet of things, which comprises a material flow status laser acquisition apparatus, a photoelectric encoder, a signal acquisition and processing module, a first wireless signal transmission module, a second wireless signal transmission module, a multistage belt conveyer coordination control management apparatus based on internet of things, and an on-site execution module. The invention also discloses a multistage belt conveyer coordination control method based on the internet of things, which comprises the steps of collecting a material instantaneous flow signal and a belt speed signal; calculating the belt speed variance of the multistage belt conveyer according to the instantaneous flow signal and the belt speed signal; and controlling the belt conveyer in each stage through the on-site execution module. The invention has the advantages of simple structure, convenient installation and usage, strong application way, high automation degree, and high safety and reliability, and the belt speed coordination control of a harbor large-scale multistage belt conveyer system can be realized.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
Knife sharpening apparatus
InactiveUS20070243799A1Reduce tensionLittle strengthBelt grinding machinesGrinding feed controlBelt speedPulley
A sharpening apparatus having at least one guide slot, a drive pulley drivingly coupled to a frame and at least one idler pulley rotatably coupled to a support member. The support member is pivotably coupled to the frame. The apparatus includes an endless abrading belt rotatable in a path over the drive pulley and the at least one idler pulley and a biasing member coupled to the frame for biasing the support member toward an engaged position. Pivotal movement of the support member adjusts tension in the belt. A tool is traversed into the guide slot for sharpening a cutting edge thereof. The belt and support member respond to application and release of a force applied to the belt by the cutting edge to decrease and increase, respectively, belt speed to preclude overheating of the cutting edge and damage to the belt and cutting edge.
Owner:FUCHS RICHARD W
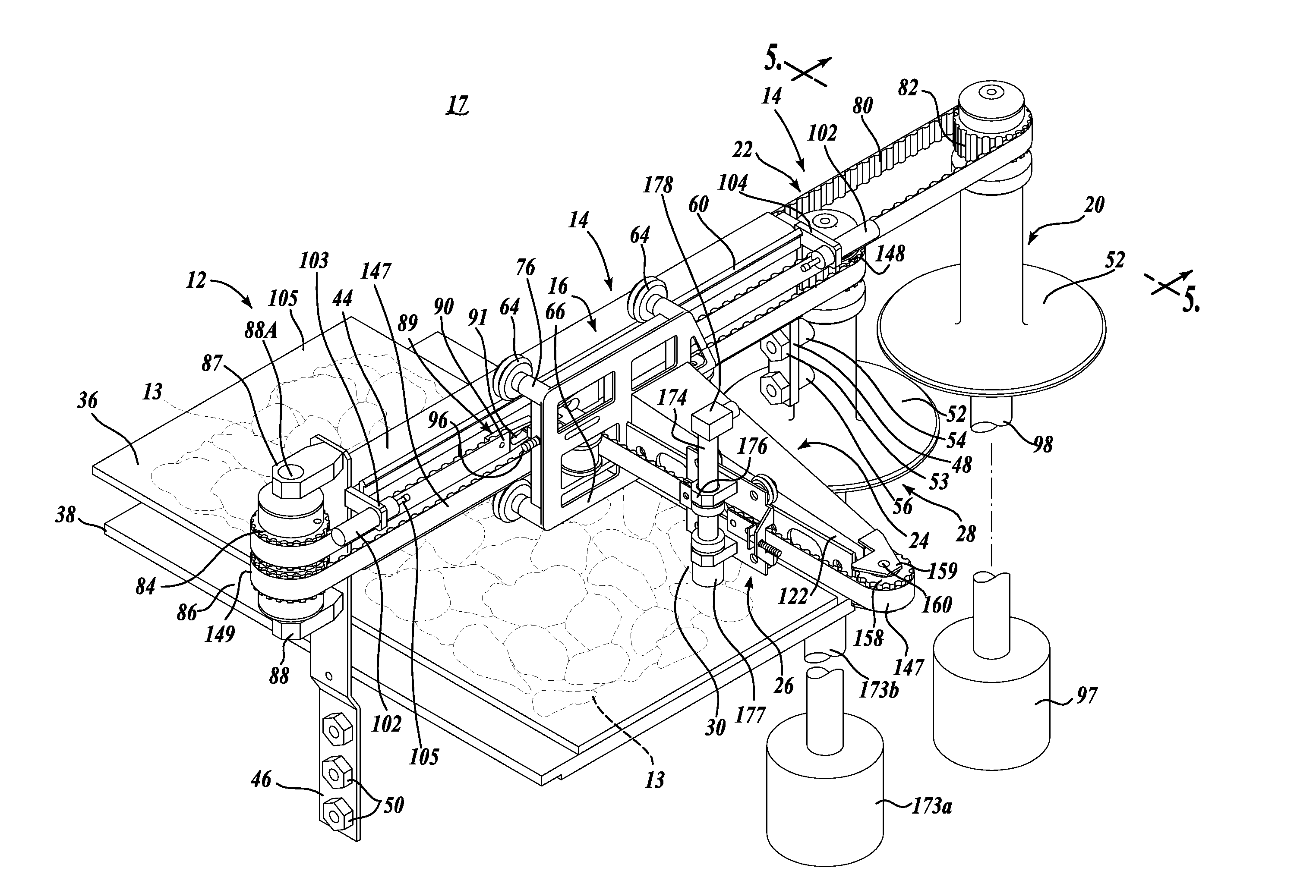
Two-axis dicing of a work product with a fluid jet portioner
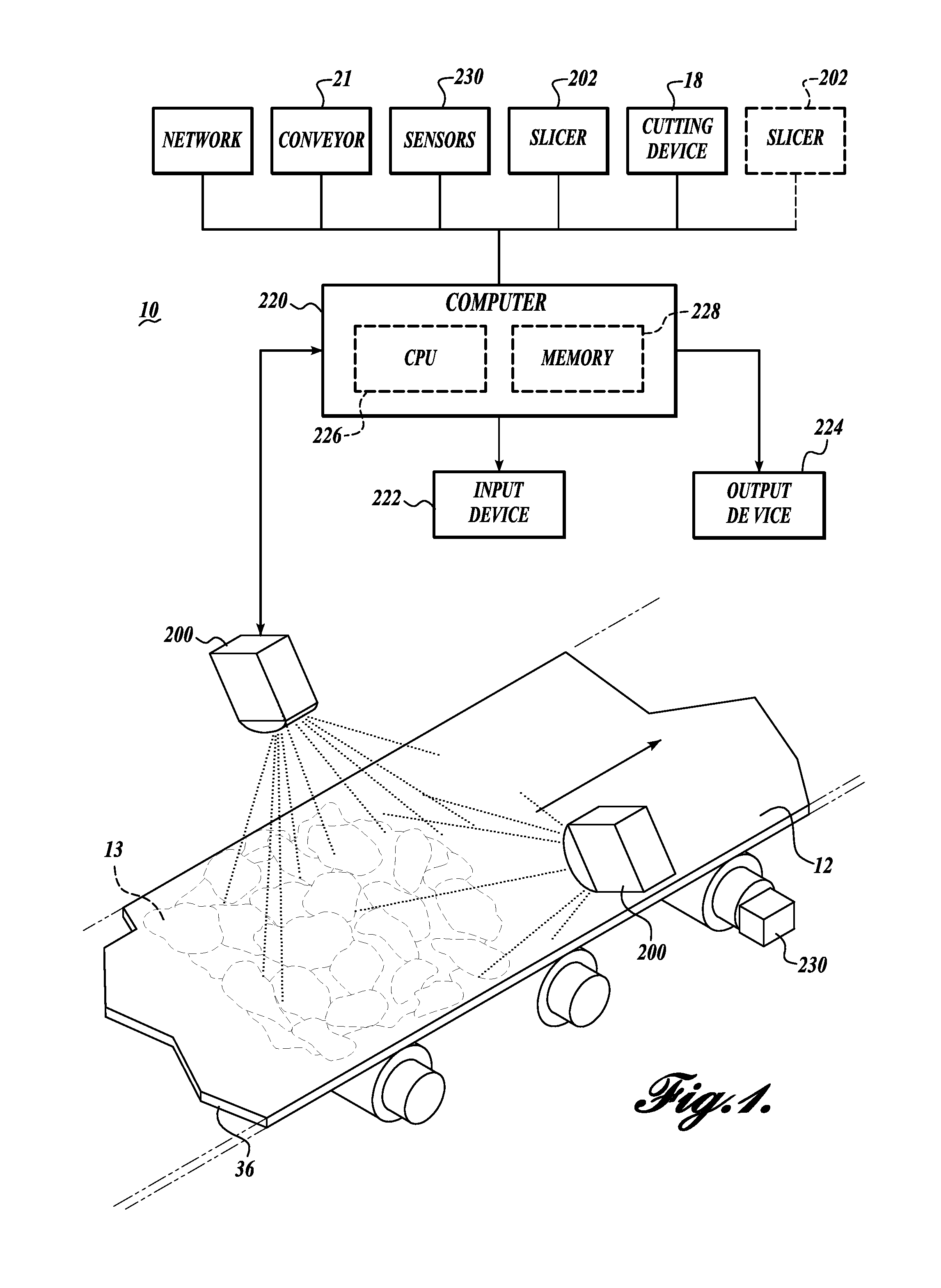
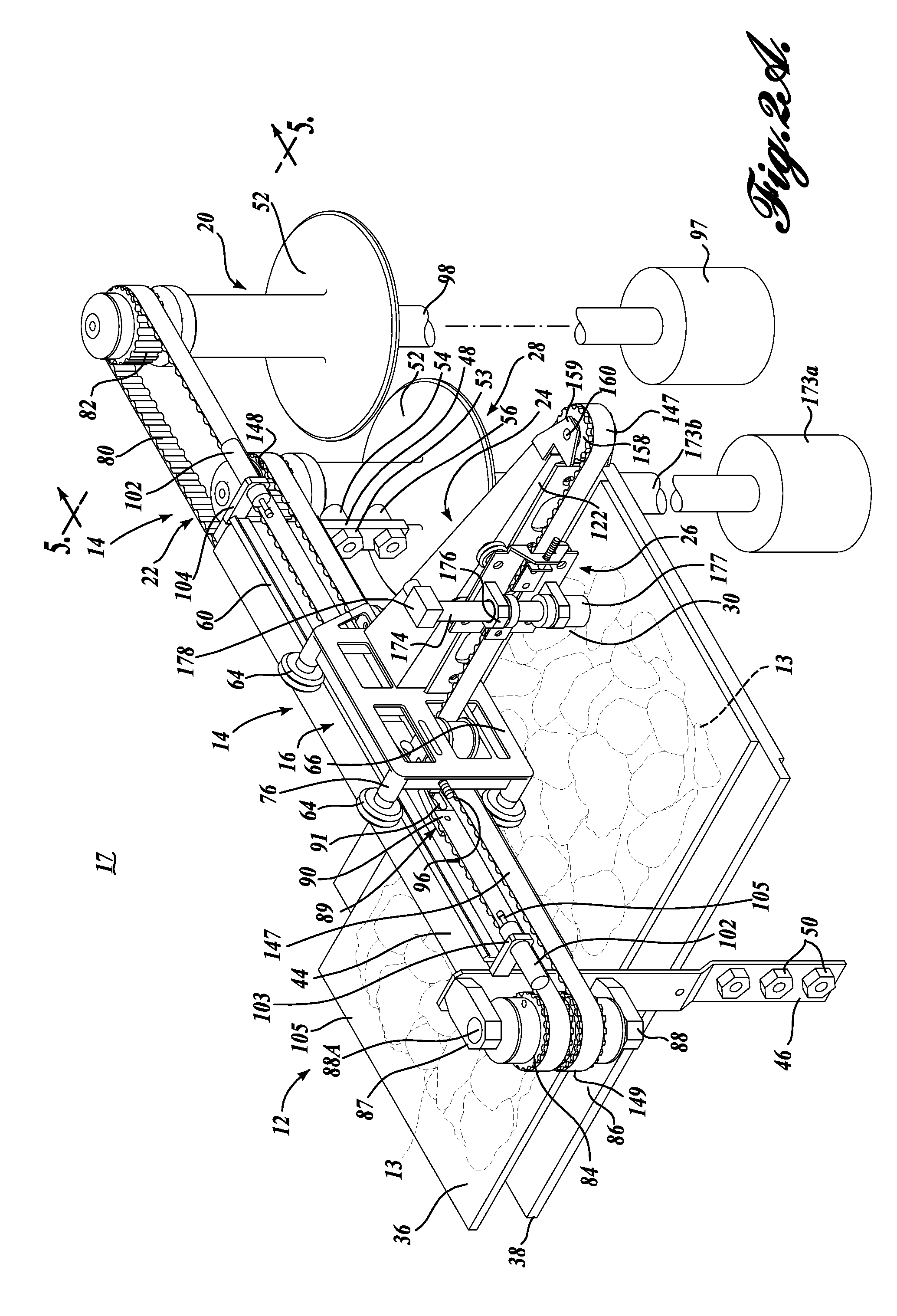
A portioning system (10) for cutting a work product (13) into a diced pattern as the work product is being carried by a conveyor (12). A cutter actuator (17) moves at least one cutter (18) parallel and transverse to the conveyor (12) either singularly or simultaneously at a speed significantly faster than the travel speed of the conveyor. A control system (220) is capable of controlling the direction and speed of movement of the cutter (18) and the conveyor (12) according to one or more directly controlled parameters including cutter pattern width, belt speed, cutter movement speed, cutter direction of movement, shape of desired end product(s), weight of desired end product(s), size of desired end product(s).
Owner:JOHN BEAN TECH CORP
Dual-belt type microwave quick sterilizing device
PendingCN107535796AReduce in quantityImprove securityFood processingFood preservationResonant cavityBelt speed
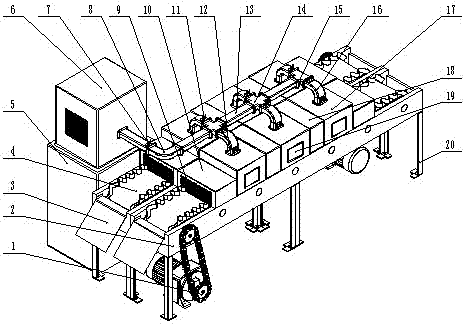
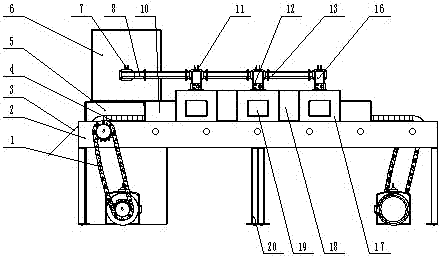
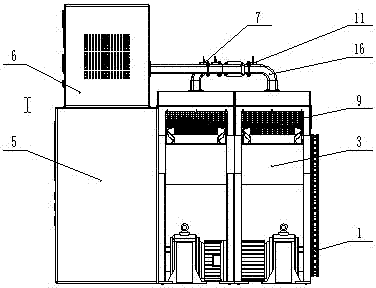
The invention belongs to the technical field of food processing, and relates to a dual-belt type microwave quick sterilizing device. The dual-belt type microwave quick sterilizing device comprises a dual-conveyer-belt transporting device (4). The dual-belt type microwave quick sterilizing device is characterized in that the belt speed of the dual-conveyer-belt transporting device (4) can be adjusted according to different materials; sterilizing resonance cavities (17) are arranged on a single conveyer belt, and are mutually independent; a vertical wave guide pipe (16) communicates with the corresponding sterilizing resonance cavity (17); an independent microwave adjusting switch (12) and a microwave detecting device (11) are arranged on the vertical wave guide pipe (16), and the sterilizing process of each sterilizing resonance cavity can be controlled through a microwave master console (5), and the number of the microwave resonance cavities (17) can be increased and reduced to changethe microwave sterilization efficiency. The dual-belt type microwave quick sterilizing device disclosed by the invention is reasonable in structure, energy-saving, low in consumption, is suitable forfoods of different sizes and kinds, economical and practical, safe and environmental-friendly.
Owner:SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Belt material measuring system based on laser ranging
The invention discloses a belt material measuring system based on laser ranging, and belongs to a non-contact belt scale system. The system scans the surface of material through laser scanning ranging equipment and obtains the distance value between a laser head and the surface of the material, cross-section shape and area of the material are obtained through the distance value, and combining real-time running speed of a belt obtained by belt speed measurement equipment, instant volume and weight of the material transported on the belt are obtained. The adoption of centralized type data processing method, accurate measurement and monitoring for multiple belts can be achieved at the same time. Equipment and original parts of the system are much less. The belt material measuring system based on laser ranging has the advantages of simple structure, high measurement accuracy, safe and reliable operation, low implementation cost and convenient application and popularization in various industries with the application of travelling belts.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING)
Image forming apparatus with transfer belt speed control
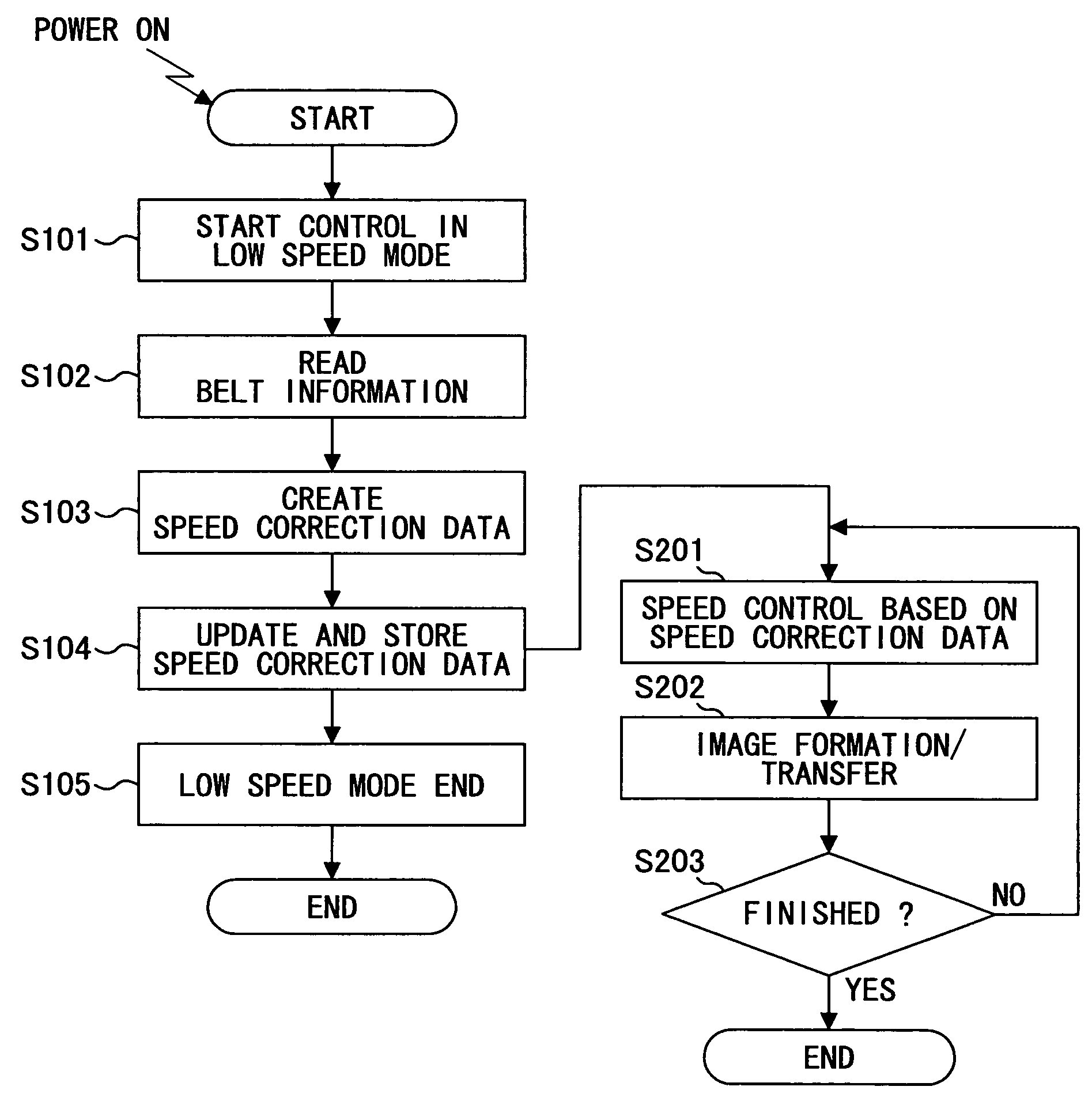
An image forming apparatus is disclosed that is capable of automatically acquiring thickness variation data of a transfer belt newly installed in the image forming apparatus without manual operation of setting the thickness variation data, and capable of controlling the moving speed of the newly installed transfer belt to be constant based on the acquired data so as to output images of high quality constantly. The transfer belt includes a belt information mark recorded with information used for creating rotational speed correction data, and the rotational speed control unit includes a storage unit configured to store the rotational speed correction data. A rotational speed control unit is provided that includes a belt information reading unit for reading the belt information mark to obtain the belt information, and a correction data updating unit for updating and storing the rotational speed correction data based on the obtained belt information.
Owner:RICOH KK
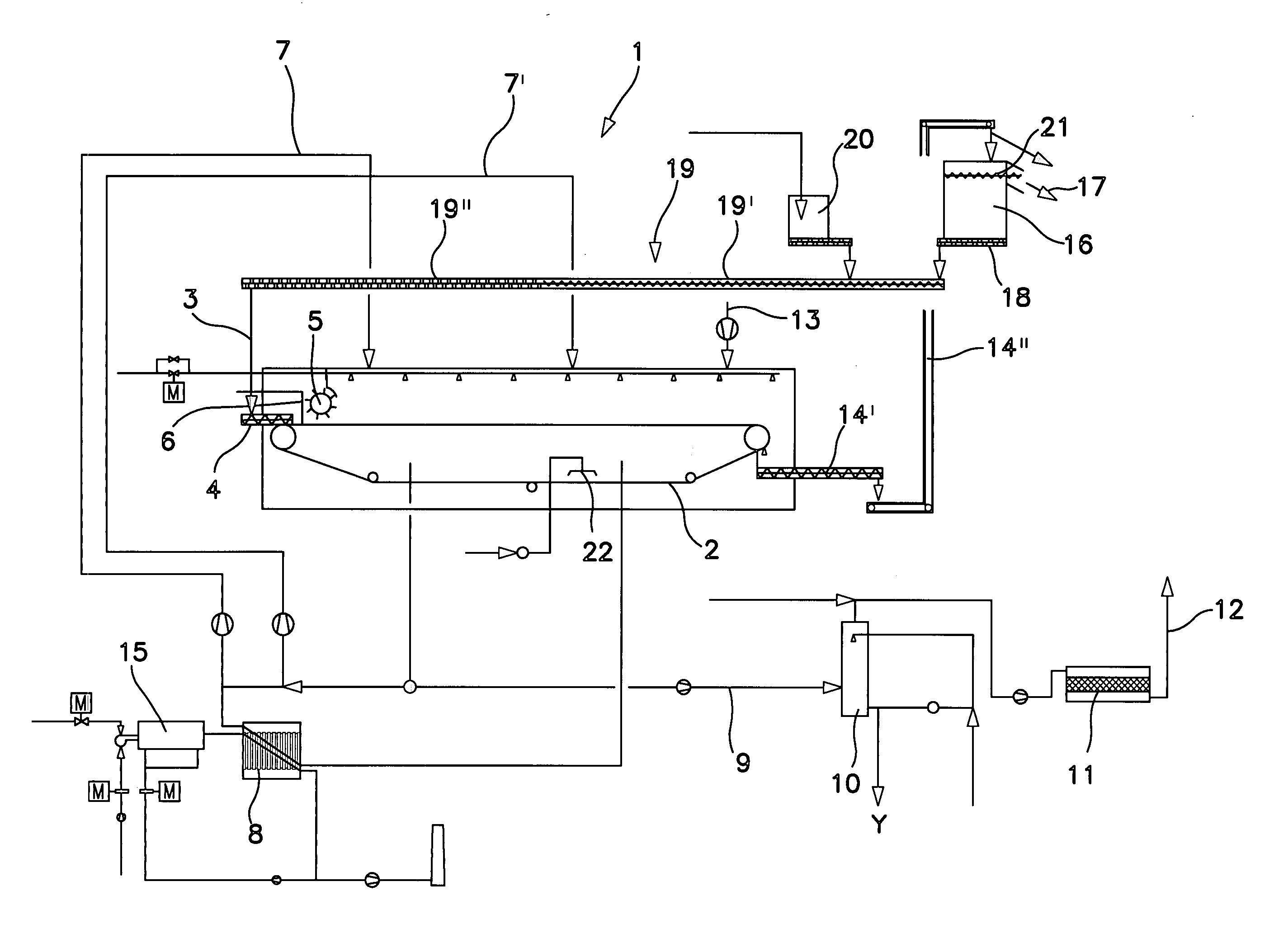
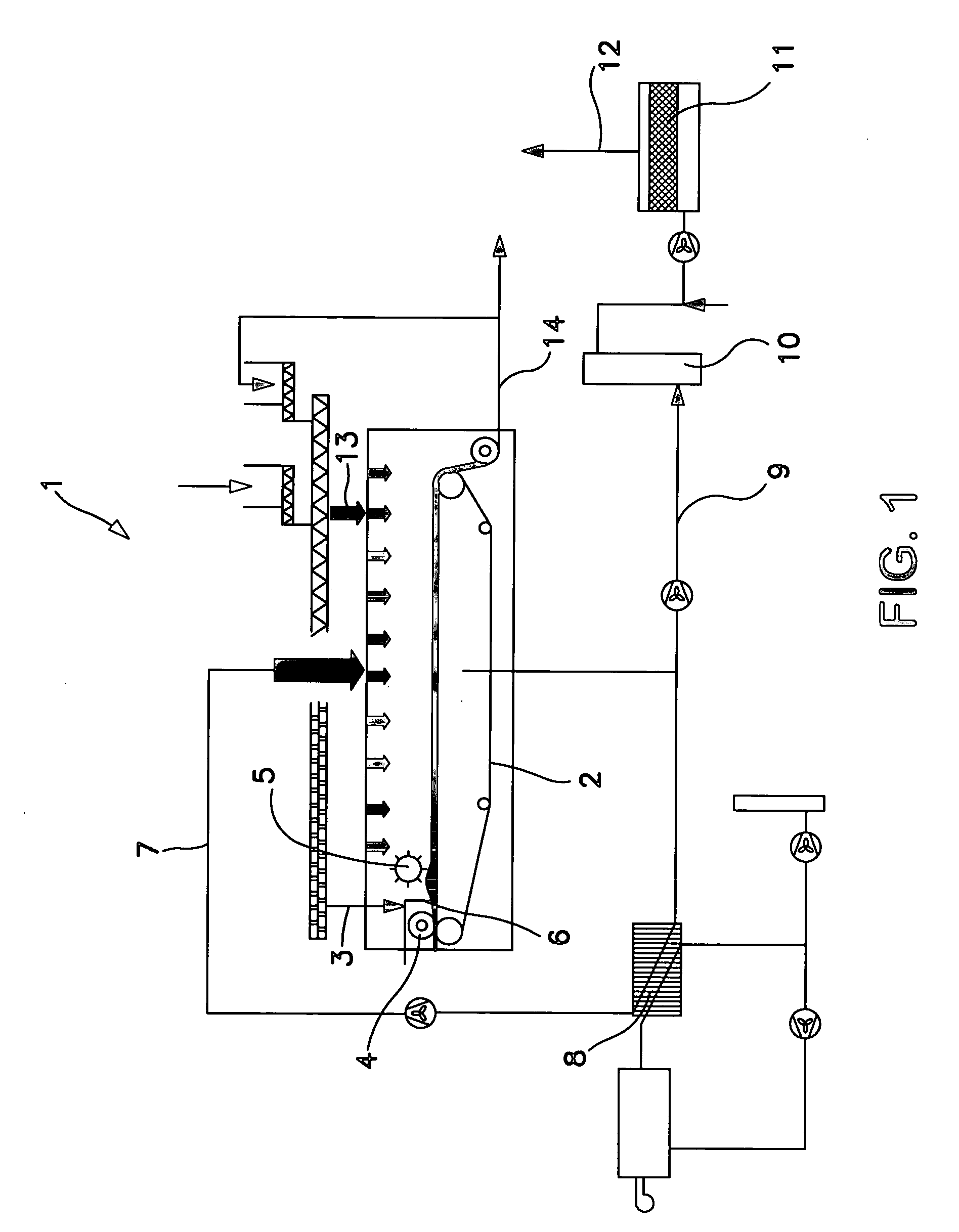
Device for continuous drying of material
ActiveUS20050241173A1Reduce environmental pollutionGuaranteed allocationDrying using combination processesDrying solid materials with heatSludgeBelt speed
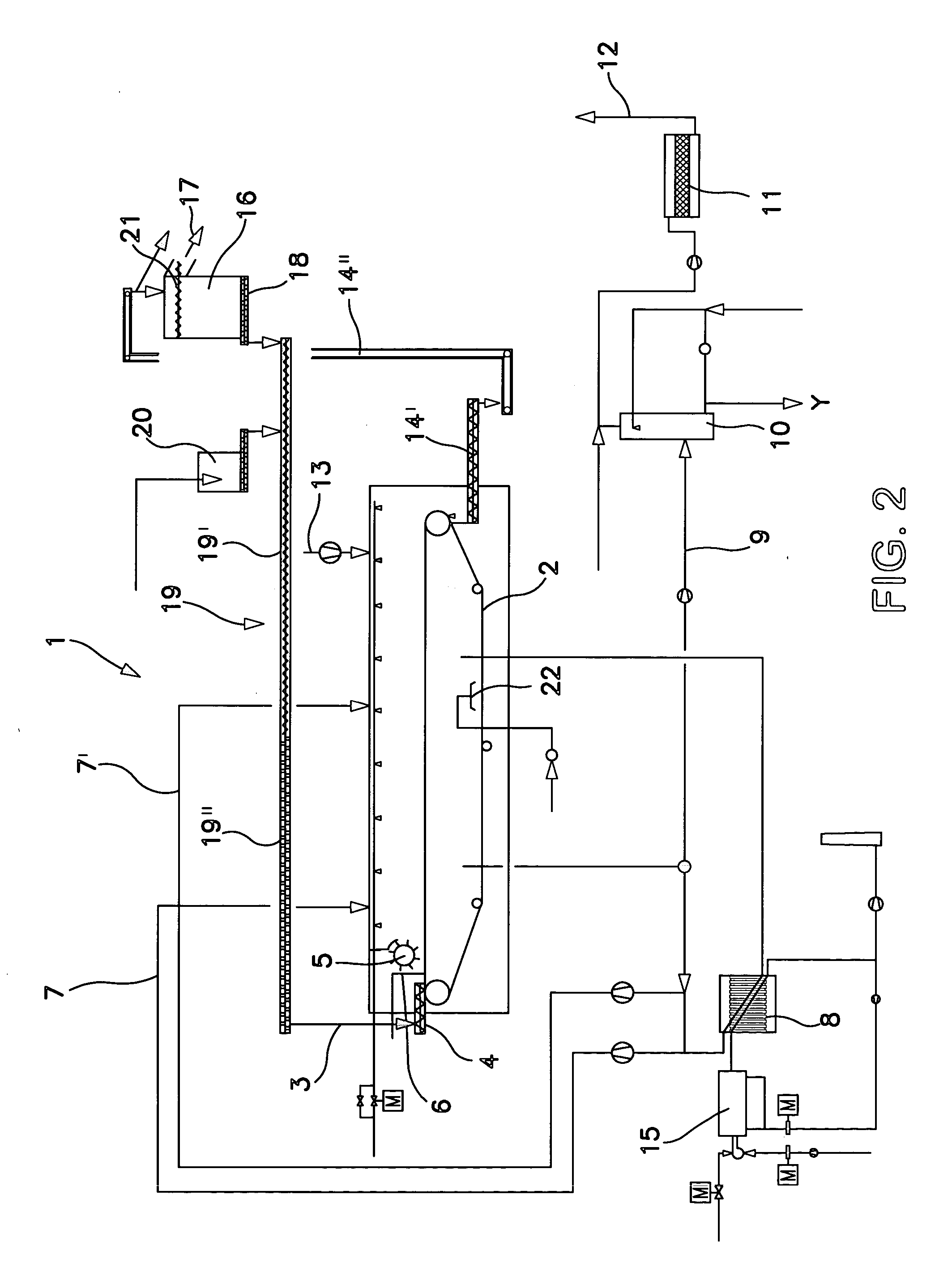
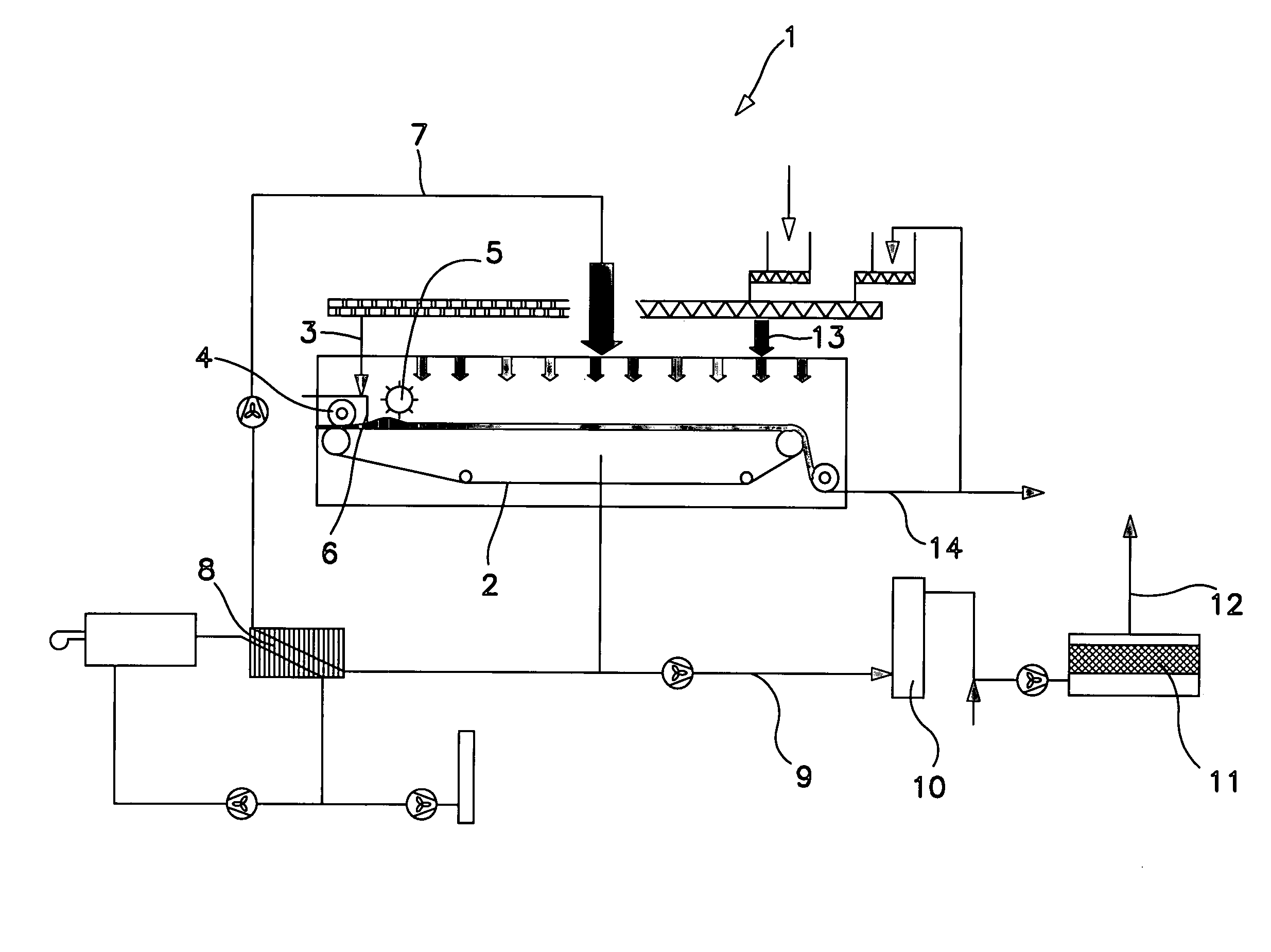
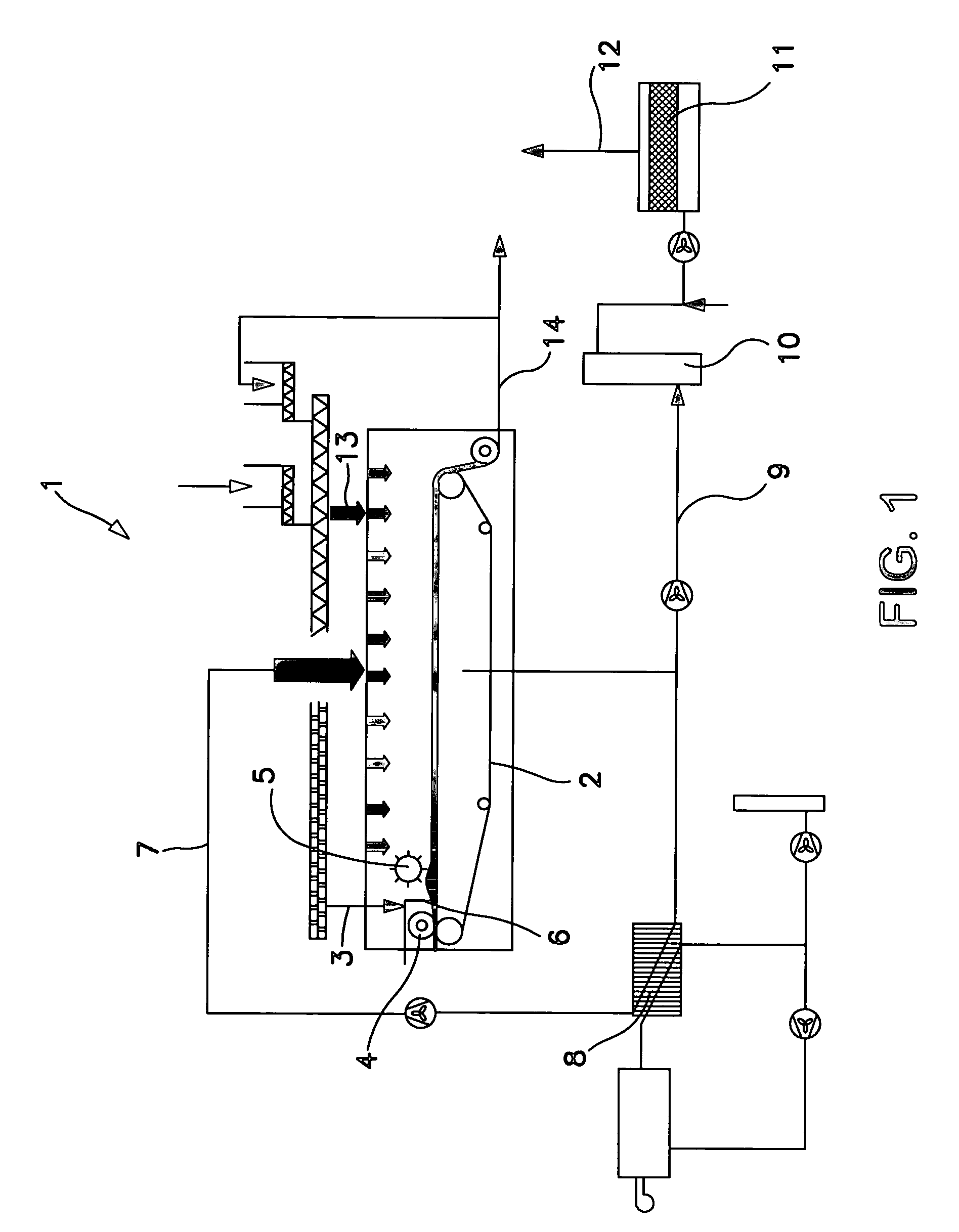
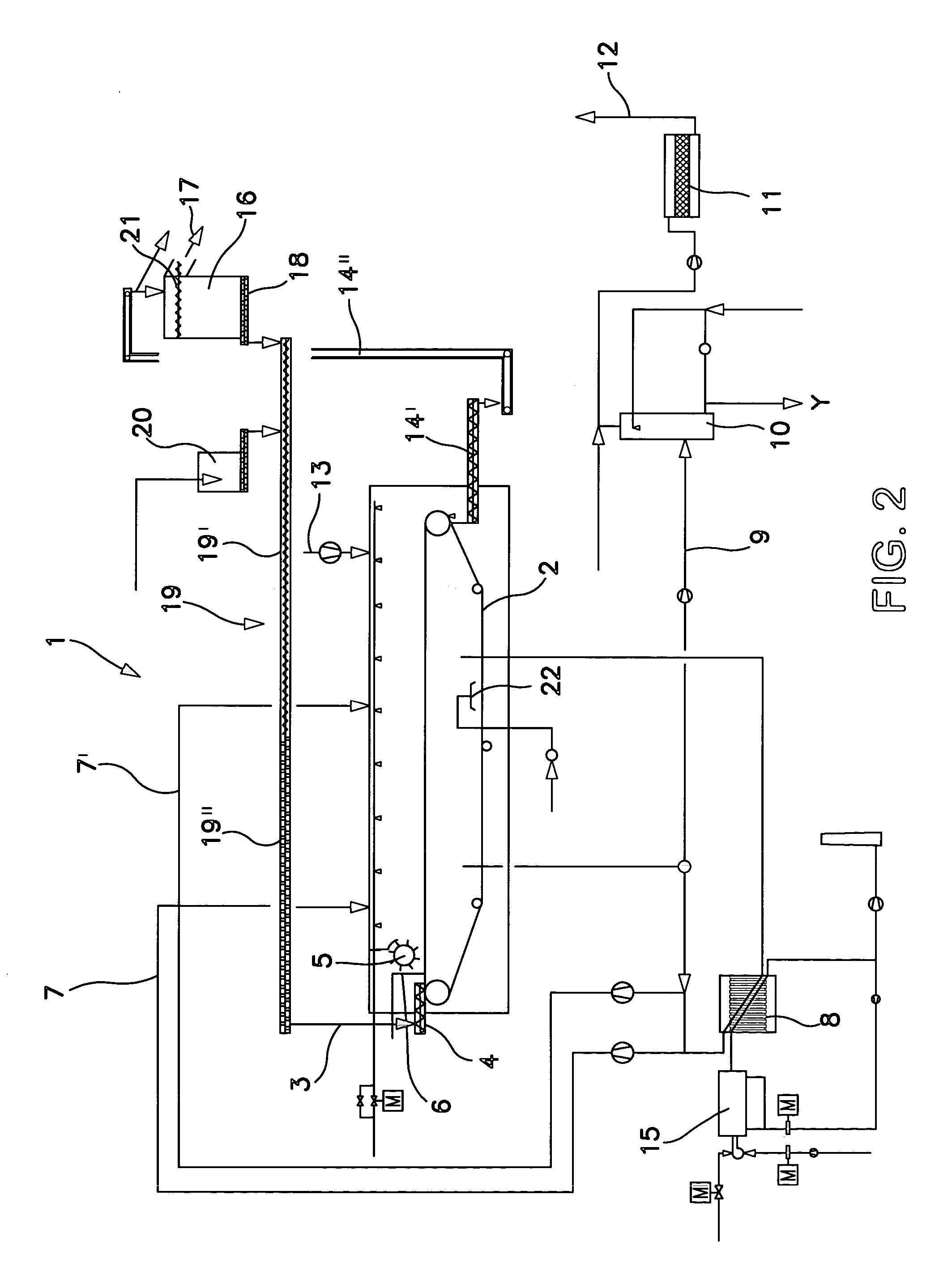
The invention relates to a device for device for continuous drying of material, particularly sewage sludge, which has a belt 2, particularly a filter belt, on which the material is conveyed. It is characterised by a distribution screw 4 being mounted above the belt 2, particularly filter belt, at the inlet in order to feed the material onto the belt 2, particularly filter belt. In addition, the invention relates to a process for drying material, particularly sewage sludge, where the material is conveyed on a belt 2, particularly a filter belt, through a dryer 1, which process is characterised by the material being fed in through a distribution screw 4, where the level can be changed by altering the belt speed.
Owner:ANDRITZ INC
Device for continuous drying of material
ActiveUS7028414B2Guaranteed allocationDrying using combination processesDrying solid materials with heatSludgeBelt speed
The invention relates to a device for device for continuous drying of material, particularly sewage sludge, which has a belt 2, particularly a filter belt, on which the material is conveyed. It is characterised by a distribution screw 4 being mounted above the belt 2, particularly filter belt, at the inlet in order to feed the material onto the belt 2, particularly filter belt. In addition, the invention relates to a process for drying material, particularly sewage sludge, where the material is conveyed on a belt 2, particularly a filter belt, through a dryer 1, which process is characterised by the material being fed in through a distribution screw 4, where the level can be changed by altering the belt speed.
Owner:ANDRITZ INC
Suspension-type electronic belt scale capable of detecting tare weight in real time
InactiveCN101561311AImprove stabilityGuaranteed accuracyWeighing apparatus for continuous material flowWeighing auxillary devicesSingle supportBelt speed
The invention relates to a suspension-type electronic belt scale capable of detecting the tare weight in real time, which is characterized by mainly comprising a belt conveyor, suspension-type single-support roller weighing supports, an online real-time tare weight detector, a plurality of weighing sensors, a belt speed detector, a signal transmitter and a signal processor, wherein the single-support roller weighing supports are suspended by being directly supported by the weighing sensors; two or more than two suspension-type single-support roller weighing supports form a suspension-type weighing platform which is placed inside the belt conveyor; the online real-time tare weight detector is connected with the weighing sensors which are connected with the signal transmitter; the signal transmitter is connected with the signal processor; and the belt speed detector contacts a belt of the belt conveyor and is connected with the signal processor. The suspension-type electronic belt scale eliminates the speed detection deviation caused by various intermediate conversion links, can precisely detect the tare weight in real time at any moment, has a simple, concise and compact structure and high measuring accuracy, and is convenient to assemble and maintain.
Owner:玉溪市浩森工贸有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com