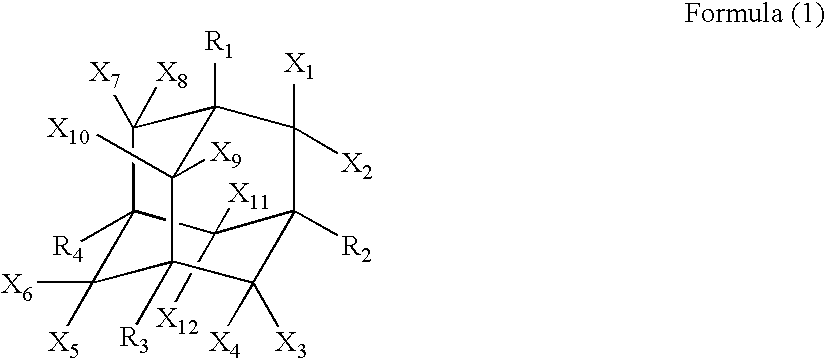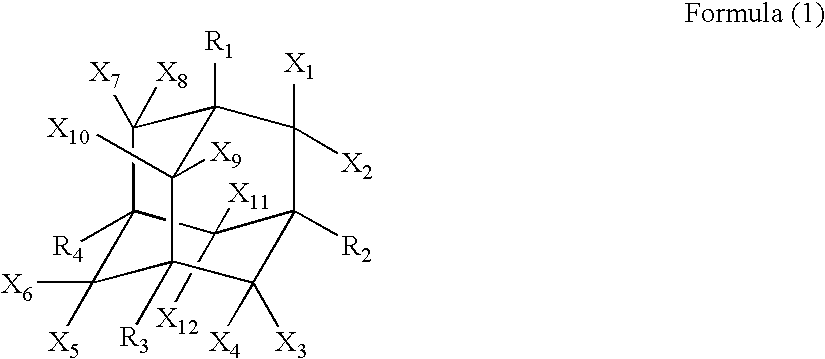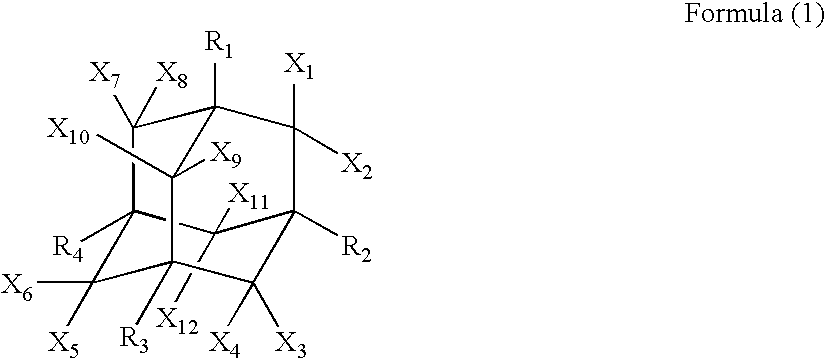Patents
Literature
53results about How to "Improve driving durability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
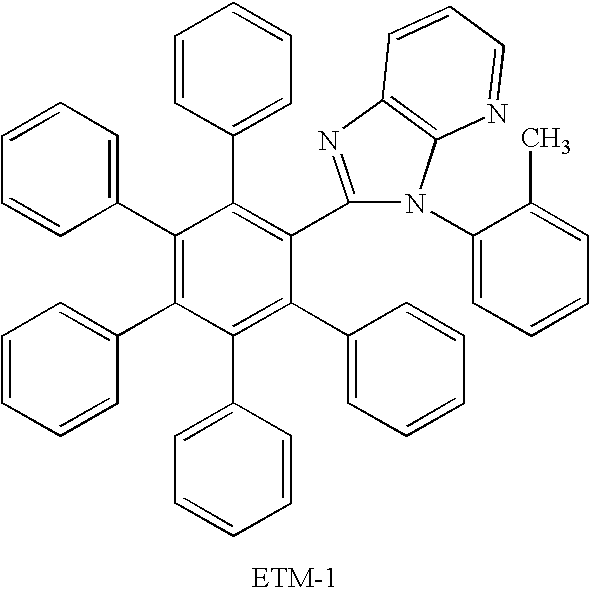
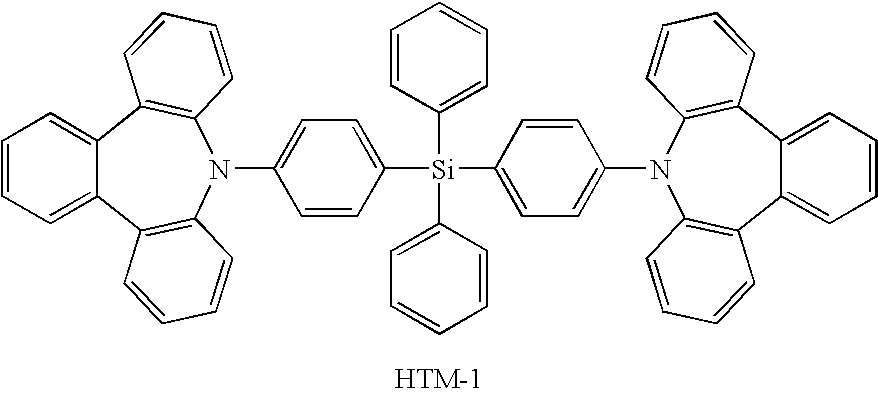
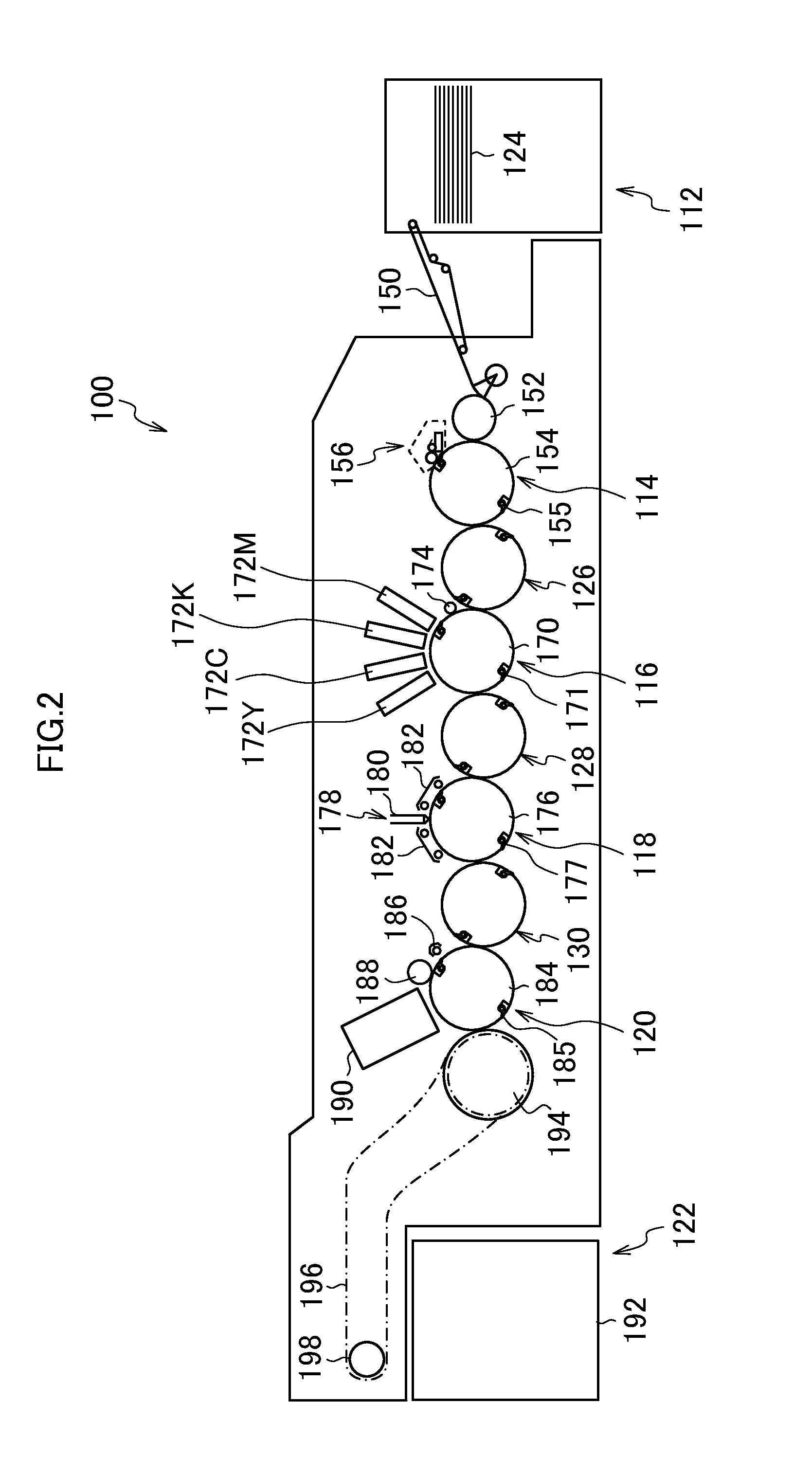
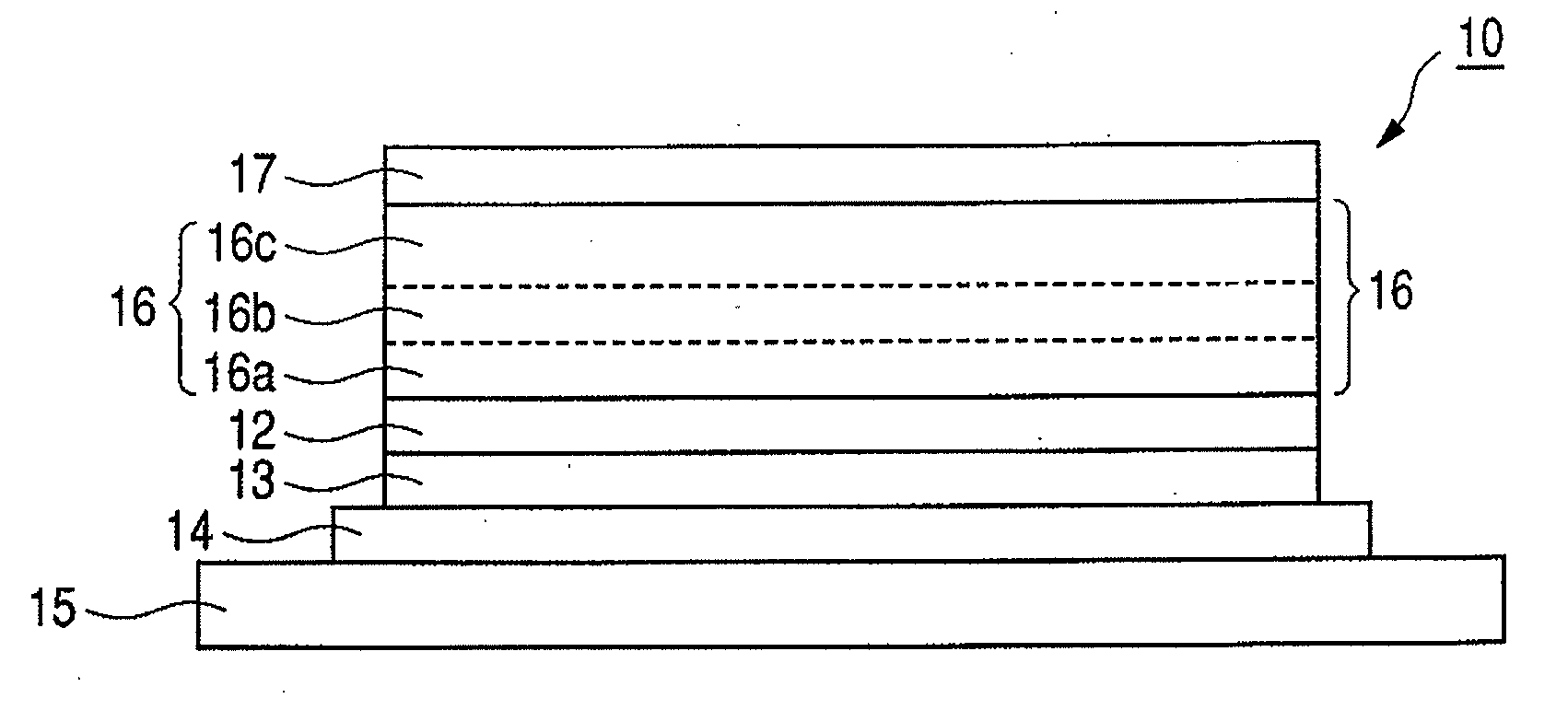
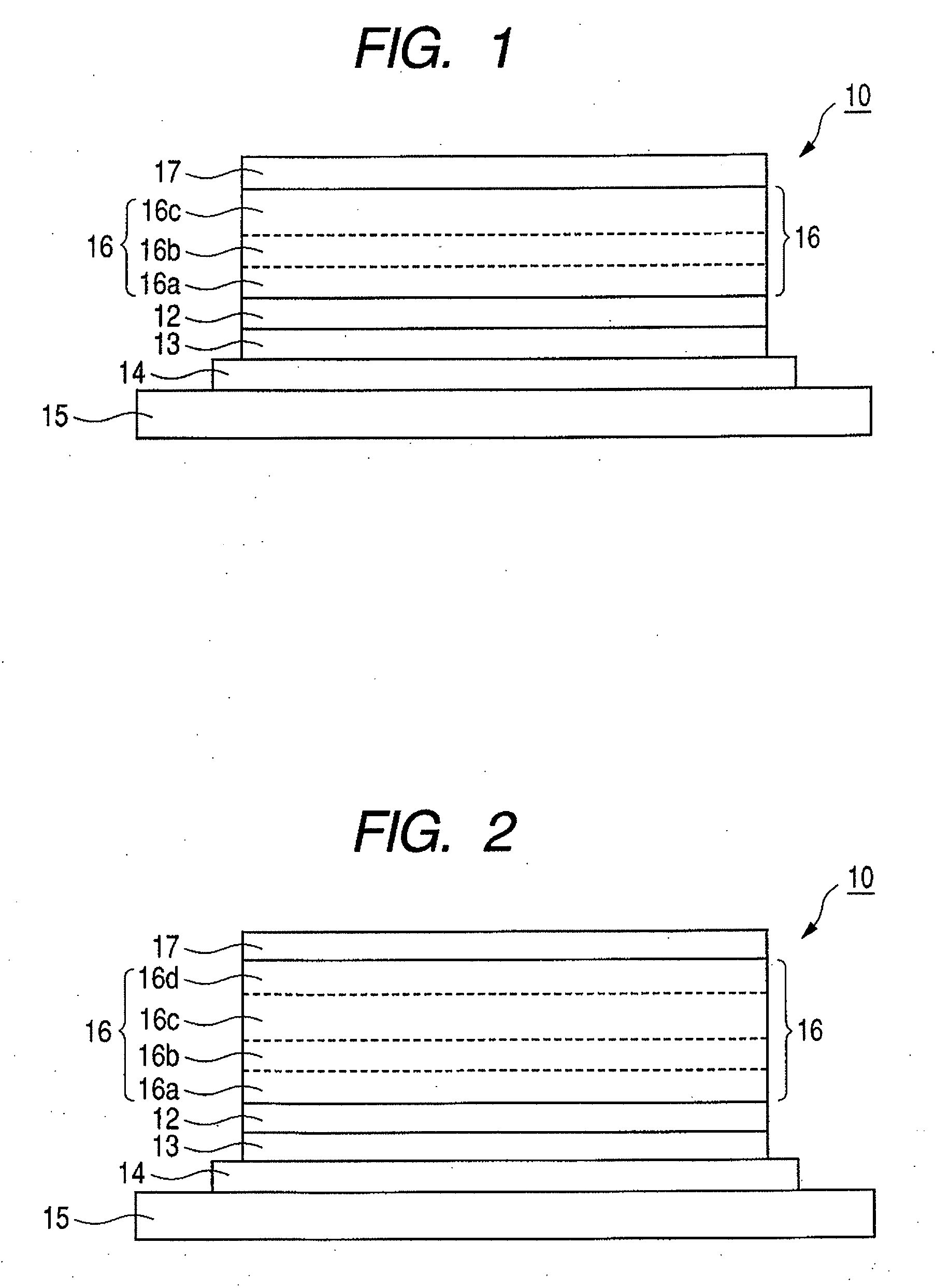
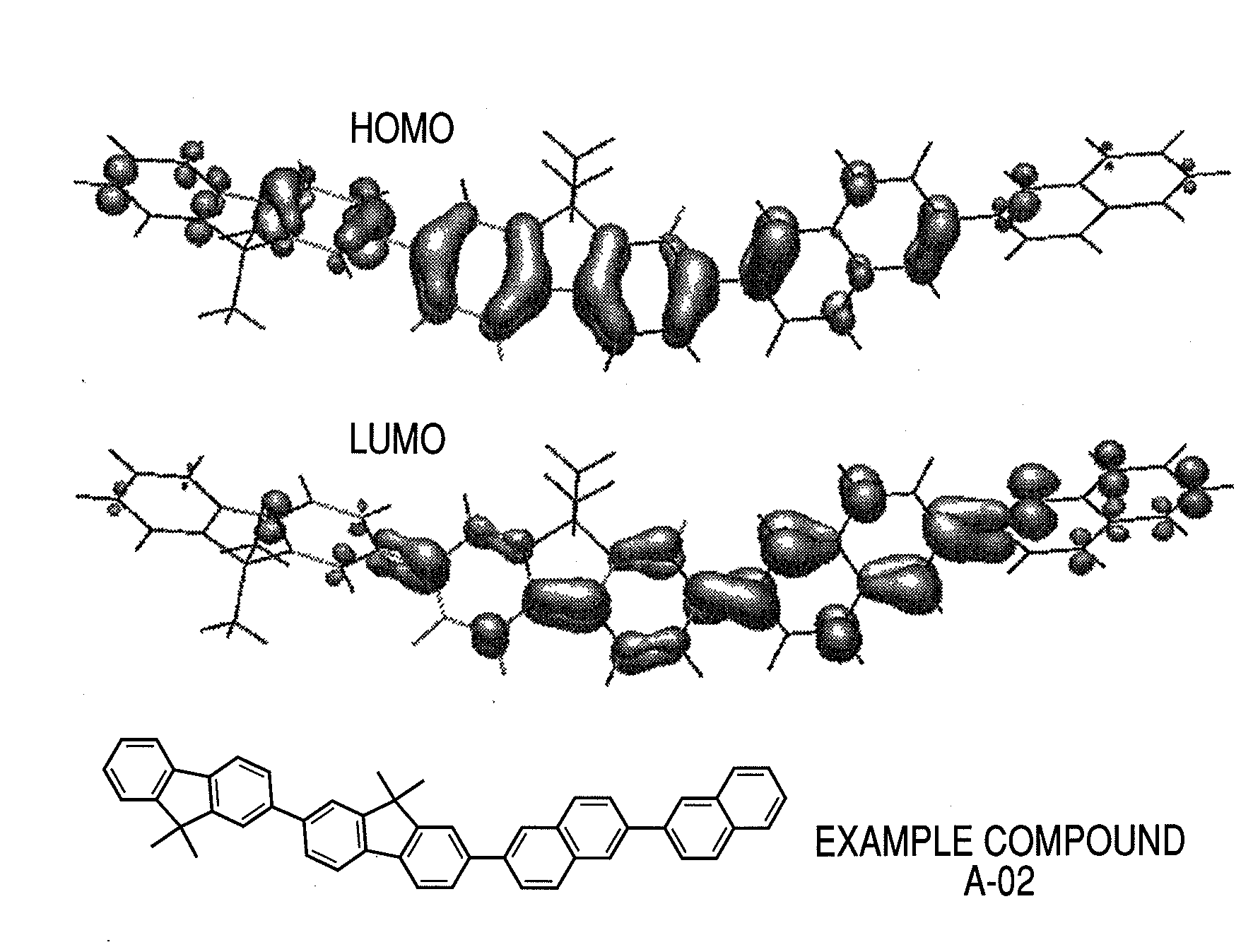
Organic electroluminescent device
InactiveUS20060105202A1Improve driving durabilityLow-voltage drivingDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesSimple Organic CompoundsHost material
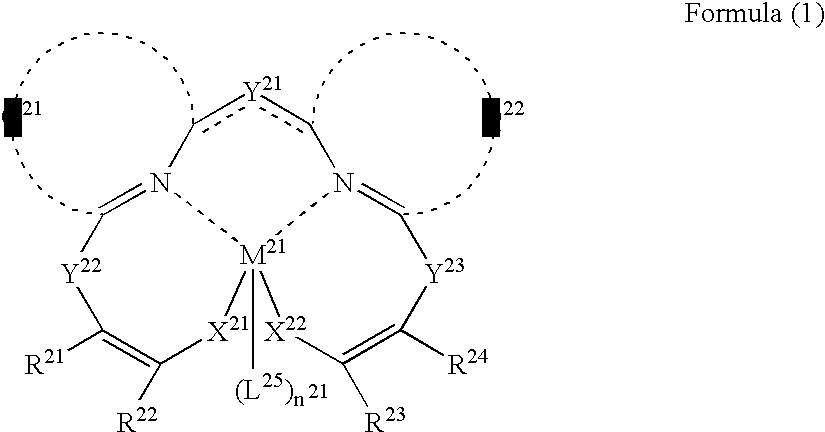
A first aspect of the invention is an organic electroluminescent device that includes a plurality of organic compound layers between a pair of electrodes. The plurality of organic compound layers include a luminescent layer and two or more hole-transporting layers. The hole-transporting layers include a layer adjacent to the luminescent layer. The luminescent layer contains a host material and a luminescent material. The luminescent material is a metal complex containing a tri- or higher-dentate ligand. When the ionization potential of the luminescent layer is designated as Ip0, the ionization potential of the hole-transporting layer adjacent to the luminescent layer among the hole-transporting layers is designated as Ip1, and the ionization potential of the n-th hole-transporting layer from the luminescent layer among the hole-transporting layers is designated as IPn, these values satisfy the relationship represented by the following formula (1). In formula (1) n is an integer of 2 or more. Ip0>Ip1>Ip2> . . . >Ipn-1>Ipn formula (1)
Owner:UDC IRELAND
Organic electroluminescent device and method for producing the same
ActiveUS7745017B2Increase brightnessHigh luminous efficiencyGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsSolid-state devicesArylHydrogen atom
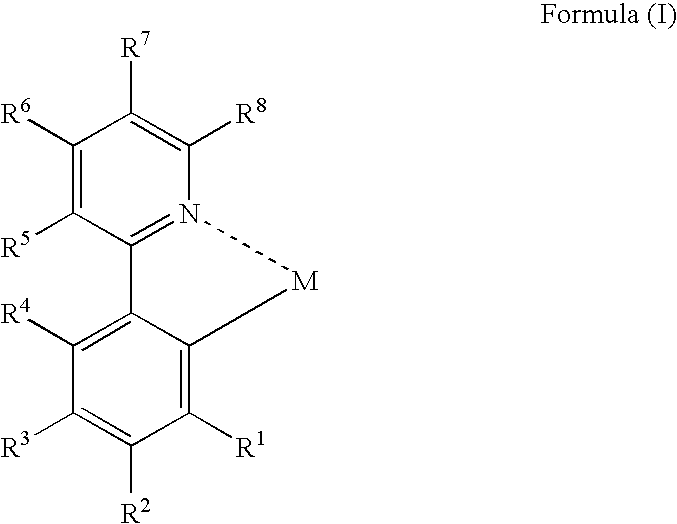
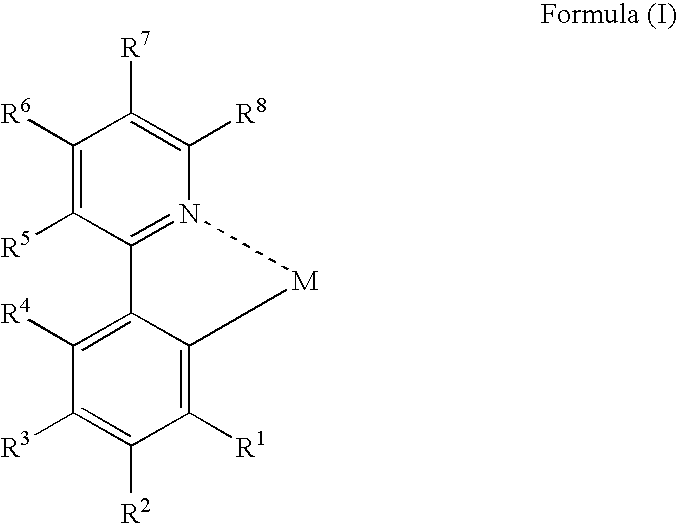
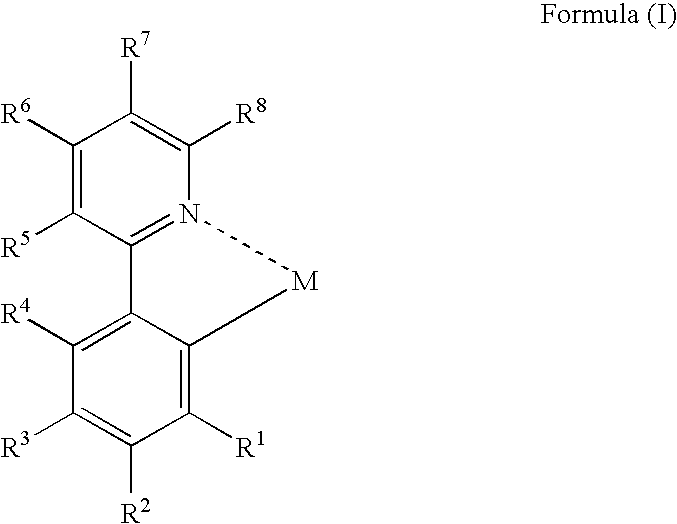
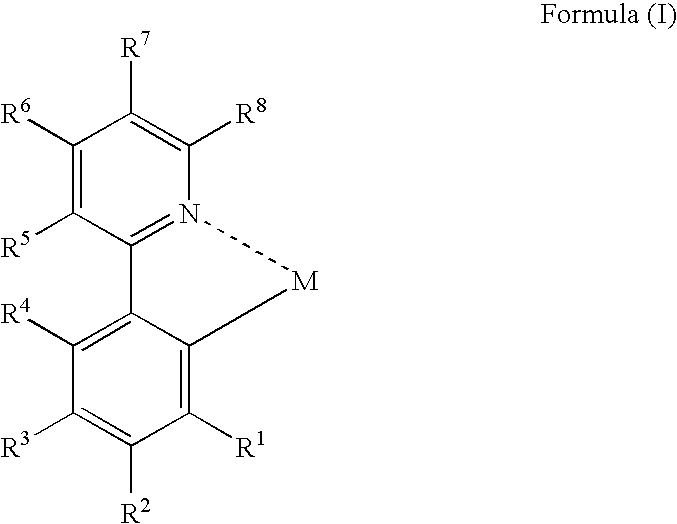
An organic electroluminescent device and a method for producing the same, the organic electroluminescent device including a luminescent layer produced by a vapor-deposition method disposed between a pair of electrodes, the luminescent layer containing at least one host material and at least one metal complex including a partial structure represented by formula (I):wherein M represents a metal atom, R1, R2 and R4 to R8 each independently represent a hydrogen atom or a substituent, and R3 represents a group represented by formula (II), an alkoxy group or an aryloxy group:wherein R11 to R13 each independently represent a hydrogen atom or a substituent, provided that at least two of them each independently represent an alkyl group or an aryl group.
Owner:UDC IRELAND
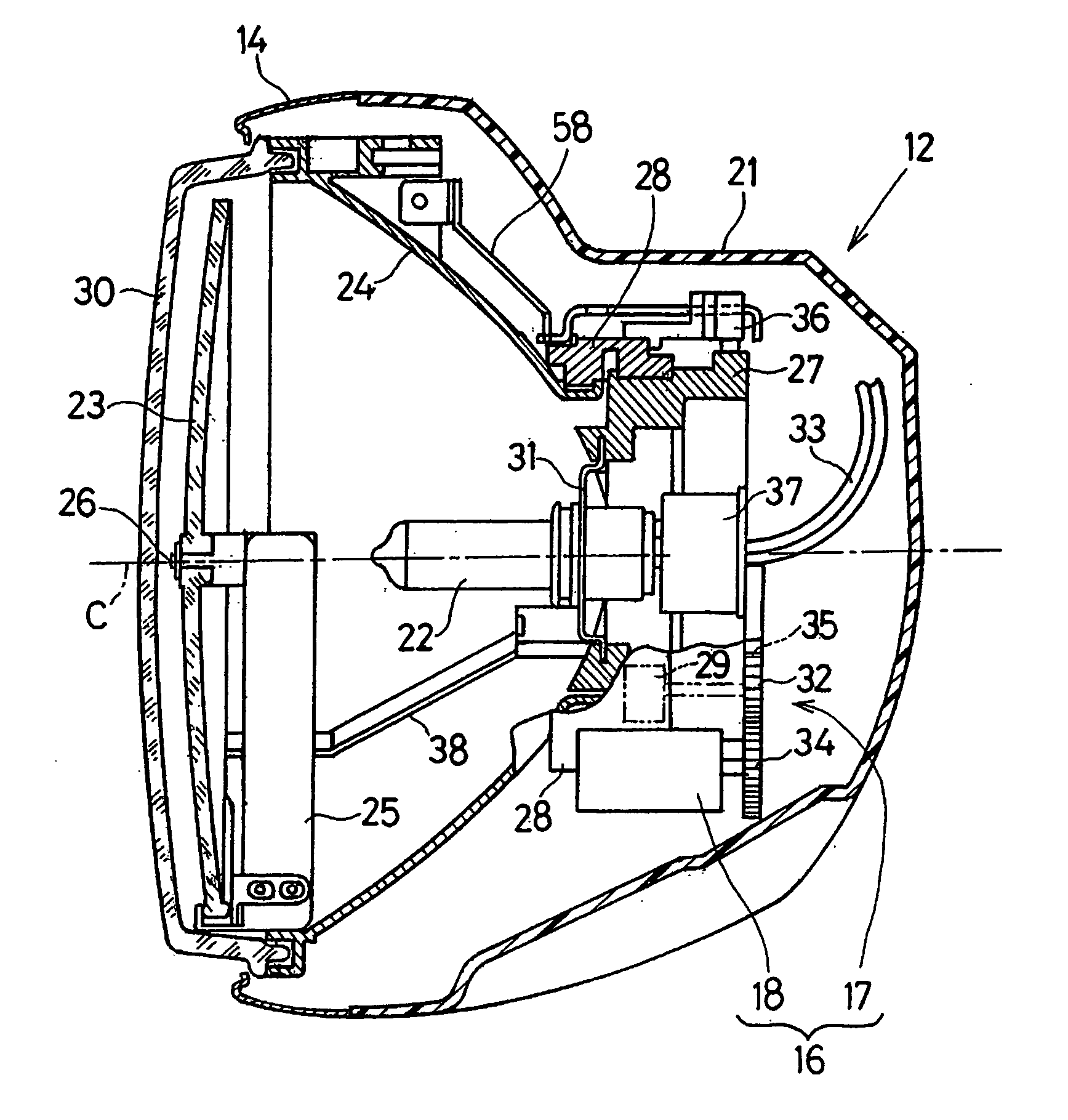
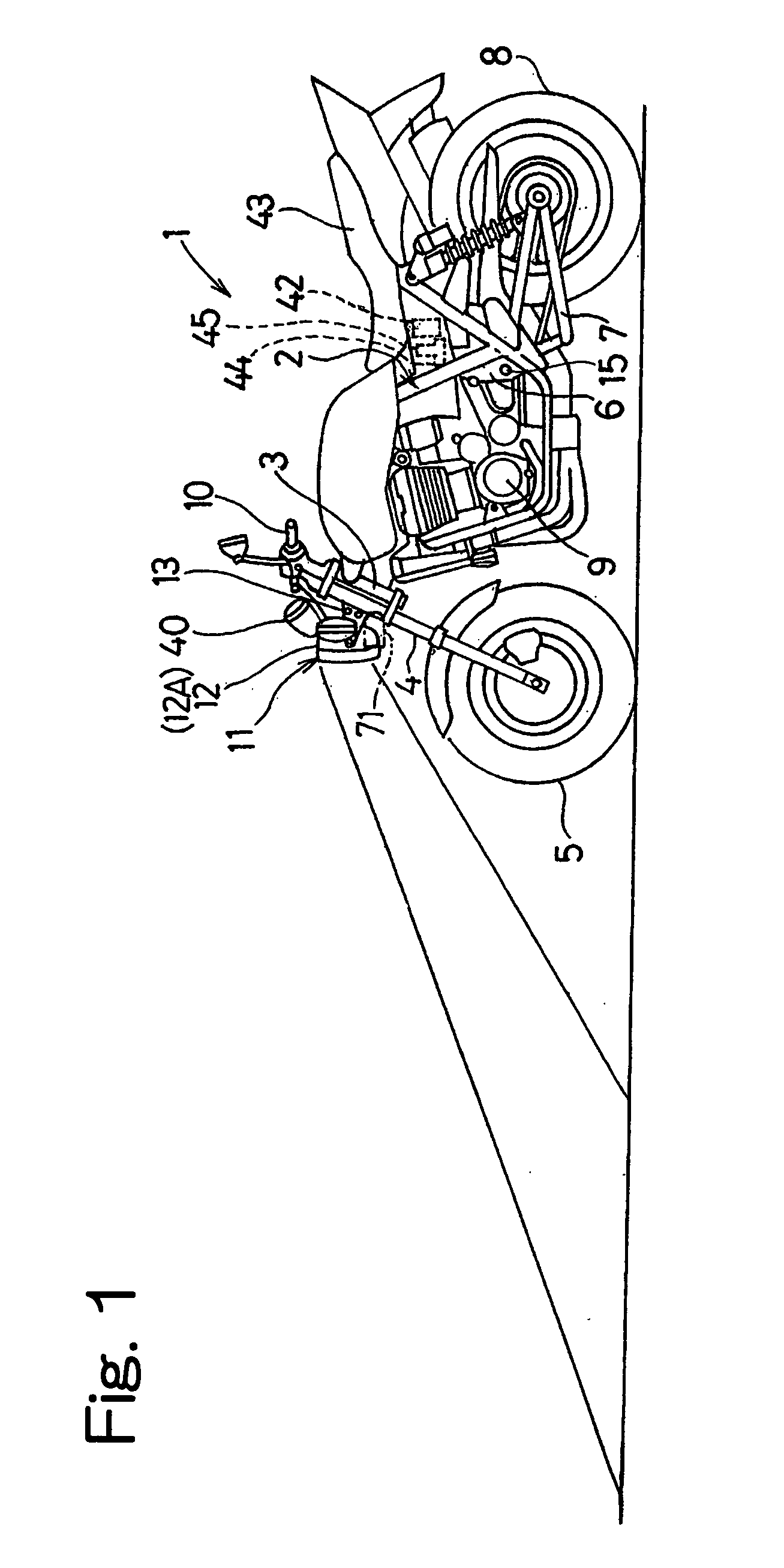
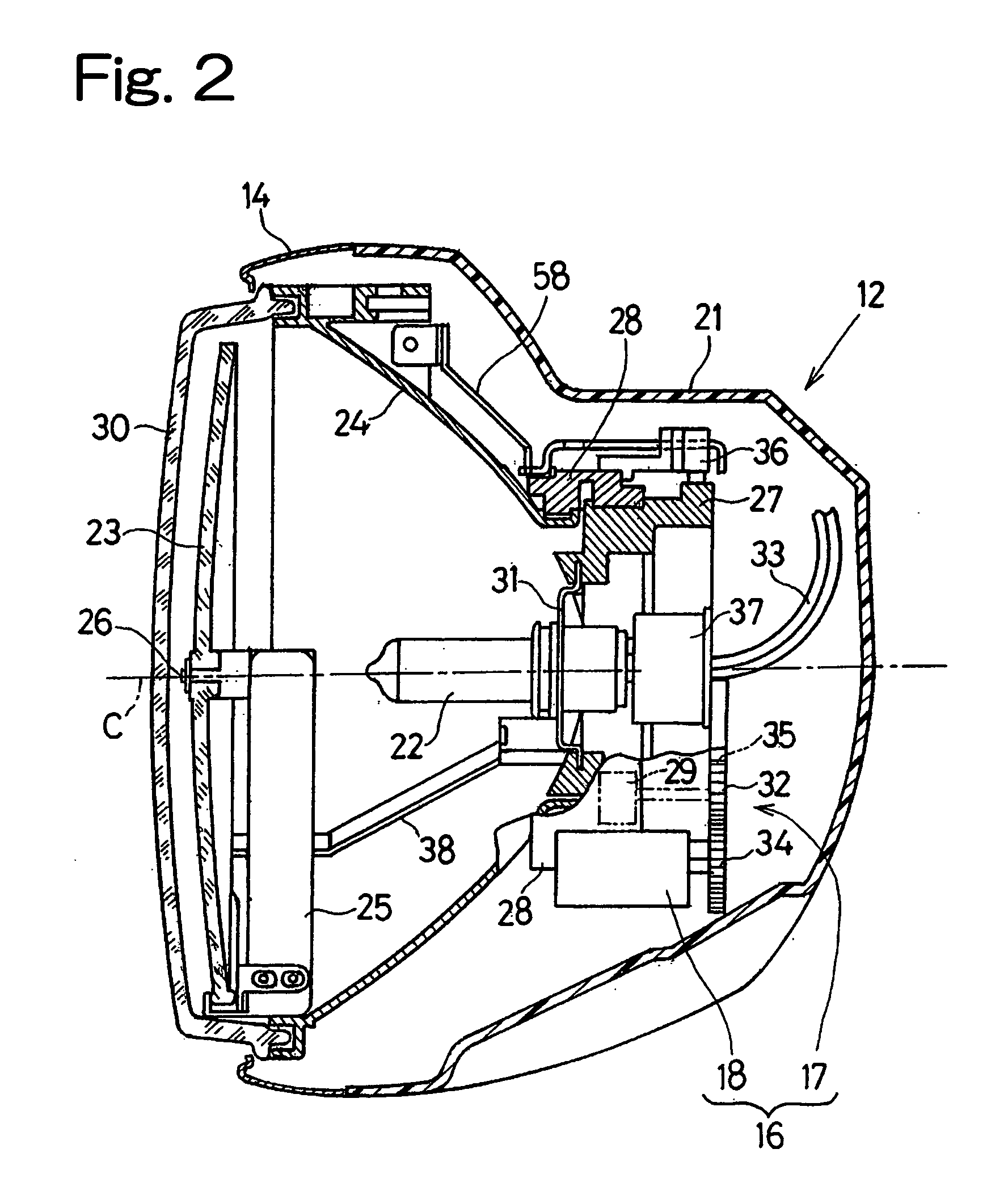
Motorcycle headlight device
ActiveUS20080112174A1Avoid possibilityDrive stabilityNon-electric lightingVehicle headlampsAngular velocityEngineering
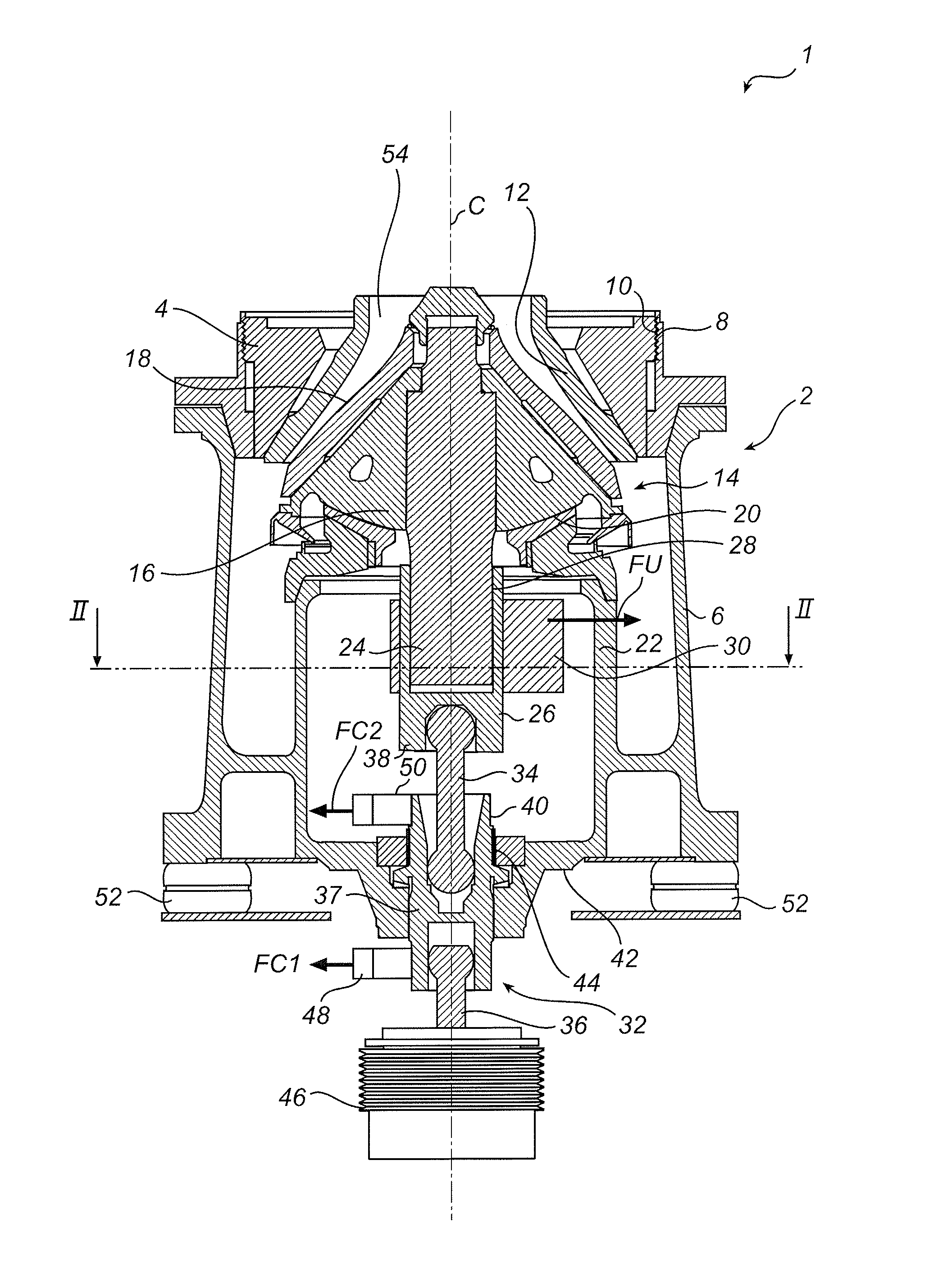
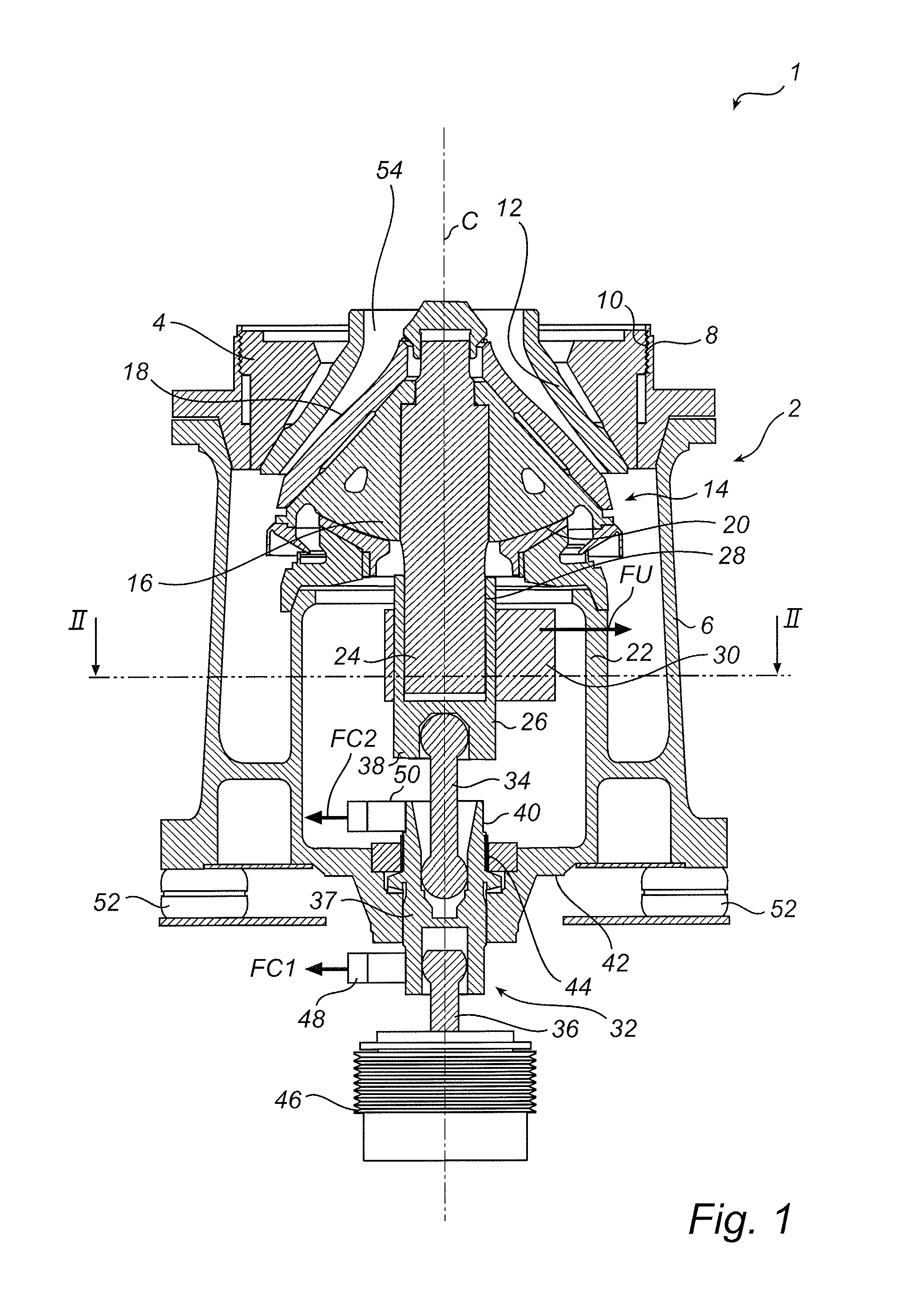
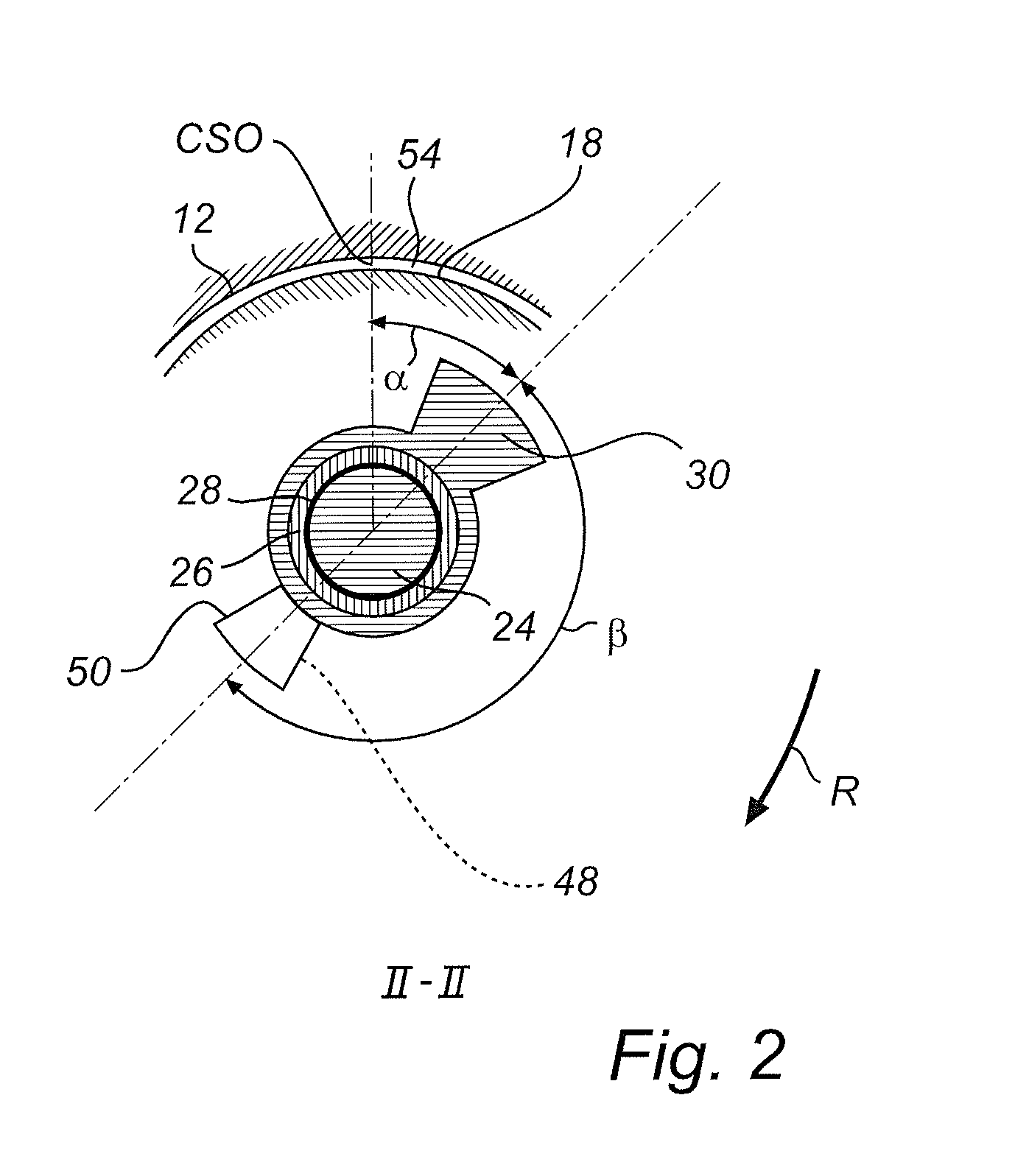
To provide a headlight device, in which a change of the region of illumination afforded by the headlamp can be initiated substantially punctual to the start of cornering of the motorcycle, the headlight device includes a headlamp for illuminating forwardly of the motorcycle, a light-distribution adjusting mechanism for changing a region of illumination, a bank angle detecting unit for detecting a bank angle δ of the motorcycle in reference to an angular velocity ωy about a vertical axis of the motorcycle, an angular velocity ωr about a longitudinal axis of the motorcycle and a motorcycle velocity v, and a light-distribution controller for controlling the light-distribution adjusting mechanism based on the detected bank angle δ to change the region of illumination into an area further away from and at least inwardly of a direction of turn of the motorcycle during a cornering.
Owner:KAWASAKI MOTORS LTD
Organic electroluminescent element
ActiveUS20060057427A1Solve low luminous efficiencyImprove driving durabilityDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesOrganic electroluminescenceIonization
The present invention provides an organic electroluminescent element that includes a pair of electrodes and a plurality of organic compound layers being disposed between the pair of electrodes. The organic compound layers include a luminescent layer containing a blue phosphorescent luminescent material and a host material having the lowest excited triplet energy (T1) of 272 kJ / mol (65 kcal / mol) or more, and hole transport layers. One of the hole transport layers is a layer adjacent to the luminescent layer, and when the ionization potentials of the luminescent layer, the hole transport layer adjacent to the luminescent layer, and another of the hole transport layers, respectively, designated to Ip1, Ip2 and Ip3, the relationship Ip1>Ip2>Ip3 is satisfied.
Owner:UDC IRELAND
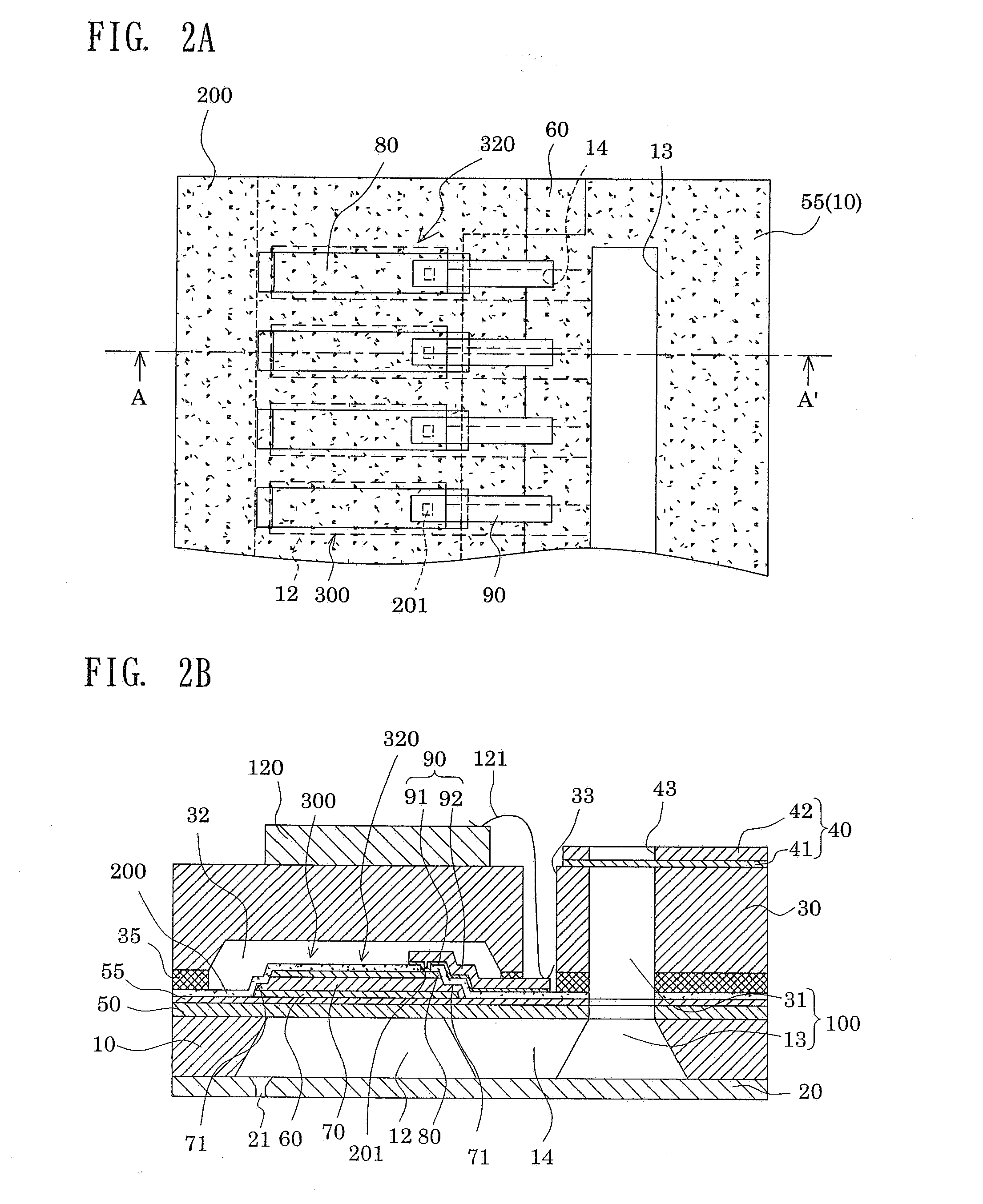
Actuator device, liquid-jet head and liquid-jet apparatus
ActiveUS20080012907A1High crystallinityImprove driving durabilityPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyInking apparatusLiquid jetActuator
Provided is an actuator device including piezoelectric elements which are displaceably provided on a substrate. Each piezoelectric element is formed of a lower electrode, a piezoelectric layer and an upper electrode. In the actuator device, longitudinal end portions of the upper electrode define longitudinal end portions of a piezoelectric active portion to be a substantial driver of the piezoelectric element. The lower electrode and the piezoelectric layer are provided continuously to the longitudinal outside of the piezoelectric active portion. Regions of the piezoelectric layer outside of the piezoelectric active portion are formed so that thin film portions may have a thin thickness.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Piezoelectric element, ink jet head, and ink jet recording device
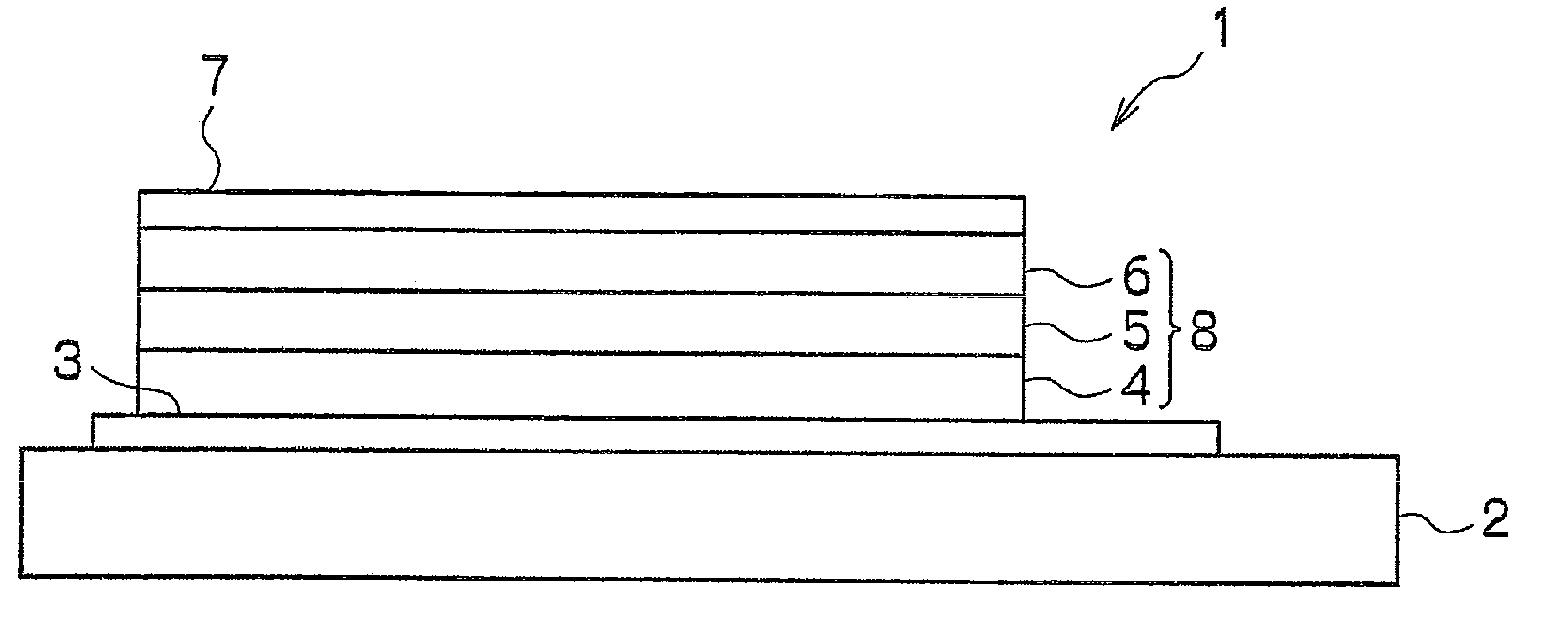
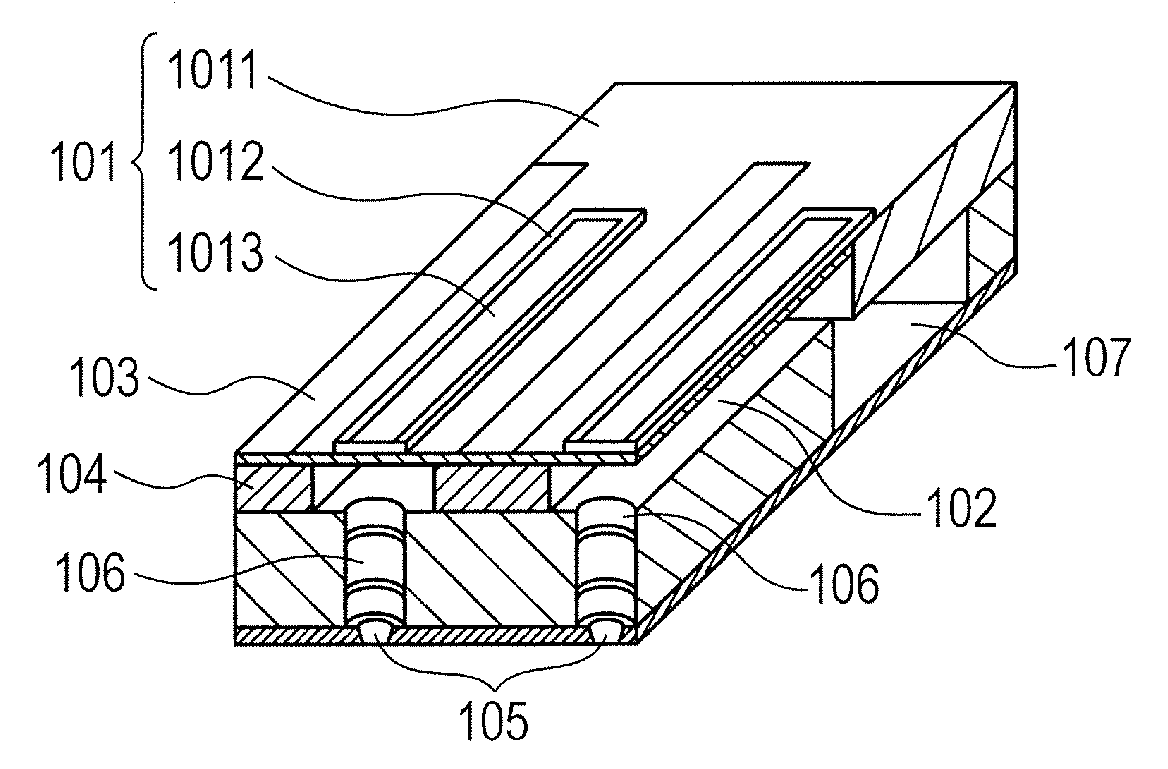
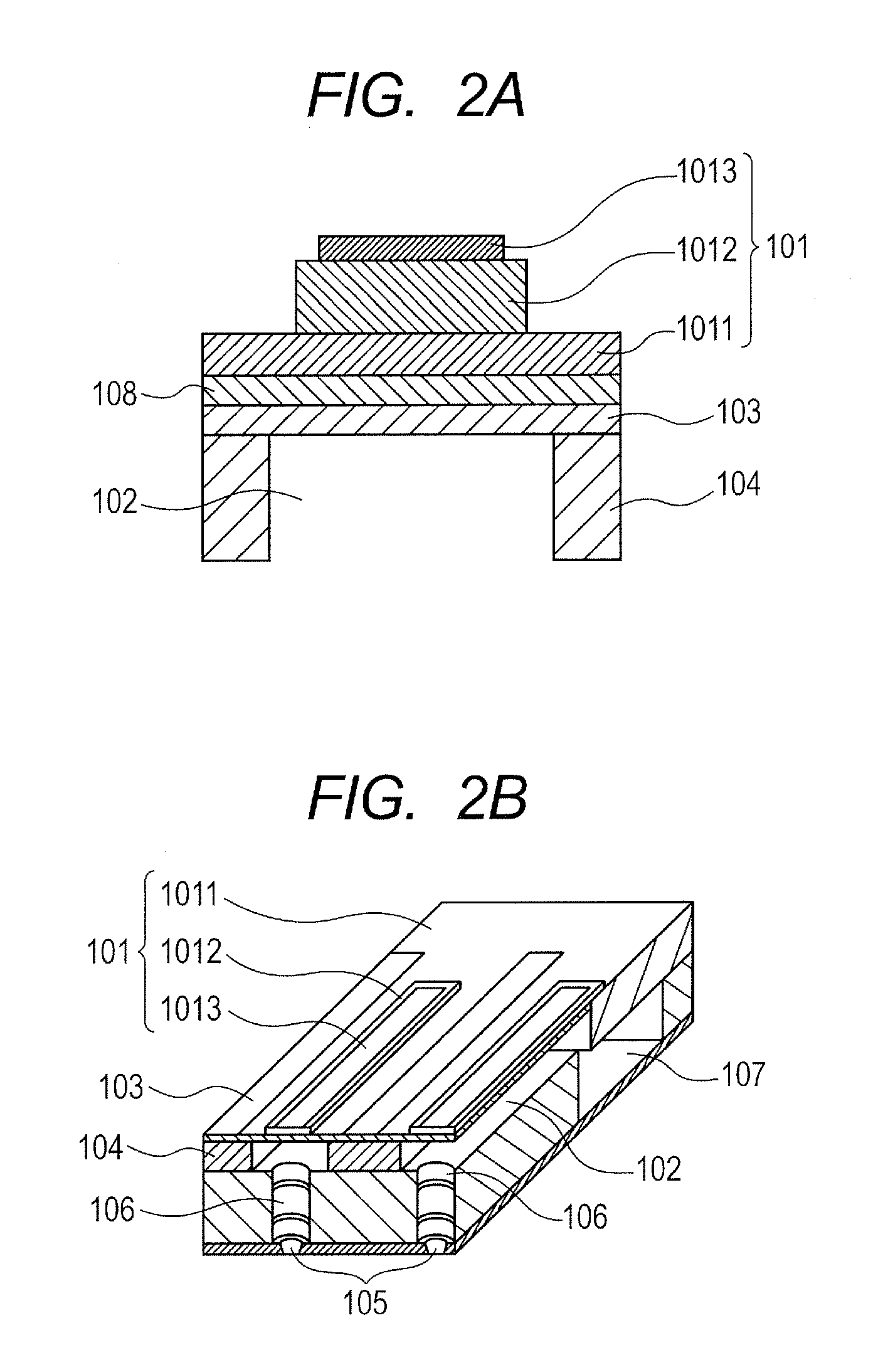
ActiveUS20080259133A1Improve efficiencyImprove driving durabilityInking apparatusPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesEngineeringLead electrode
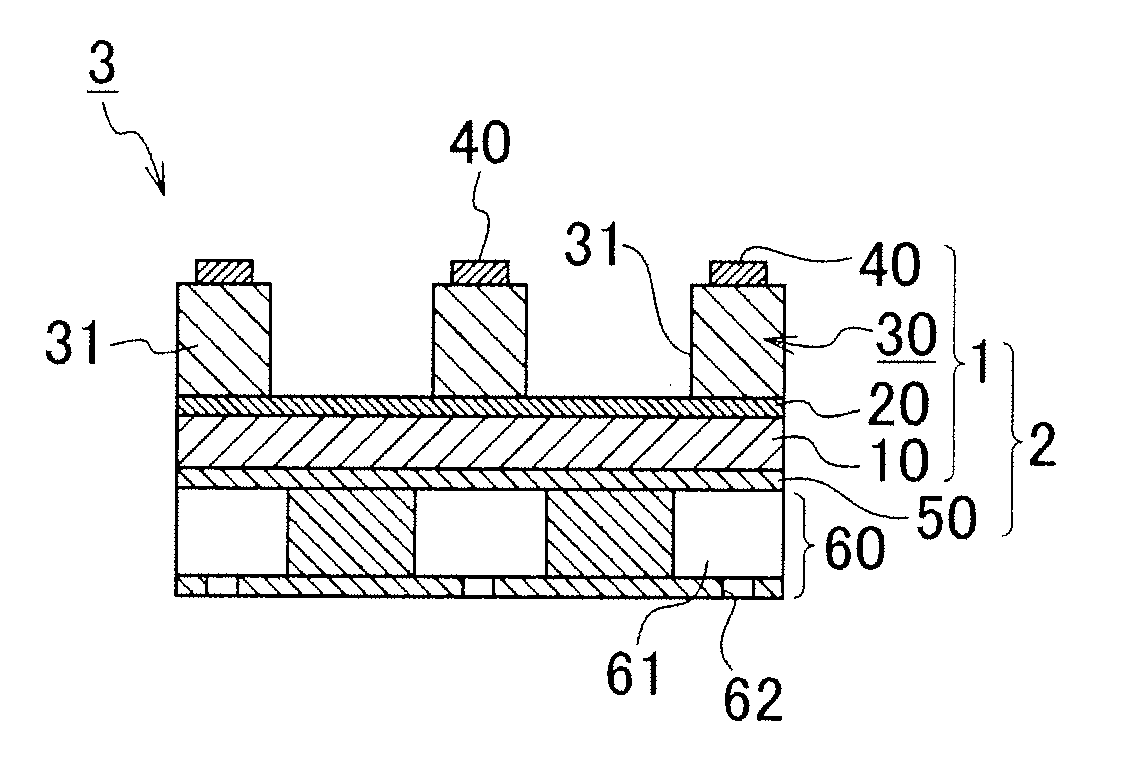
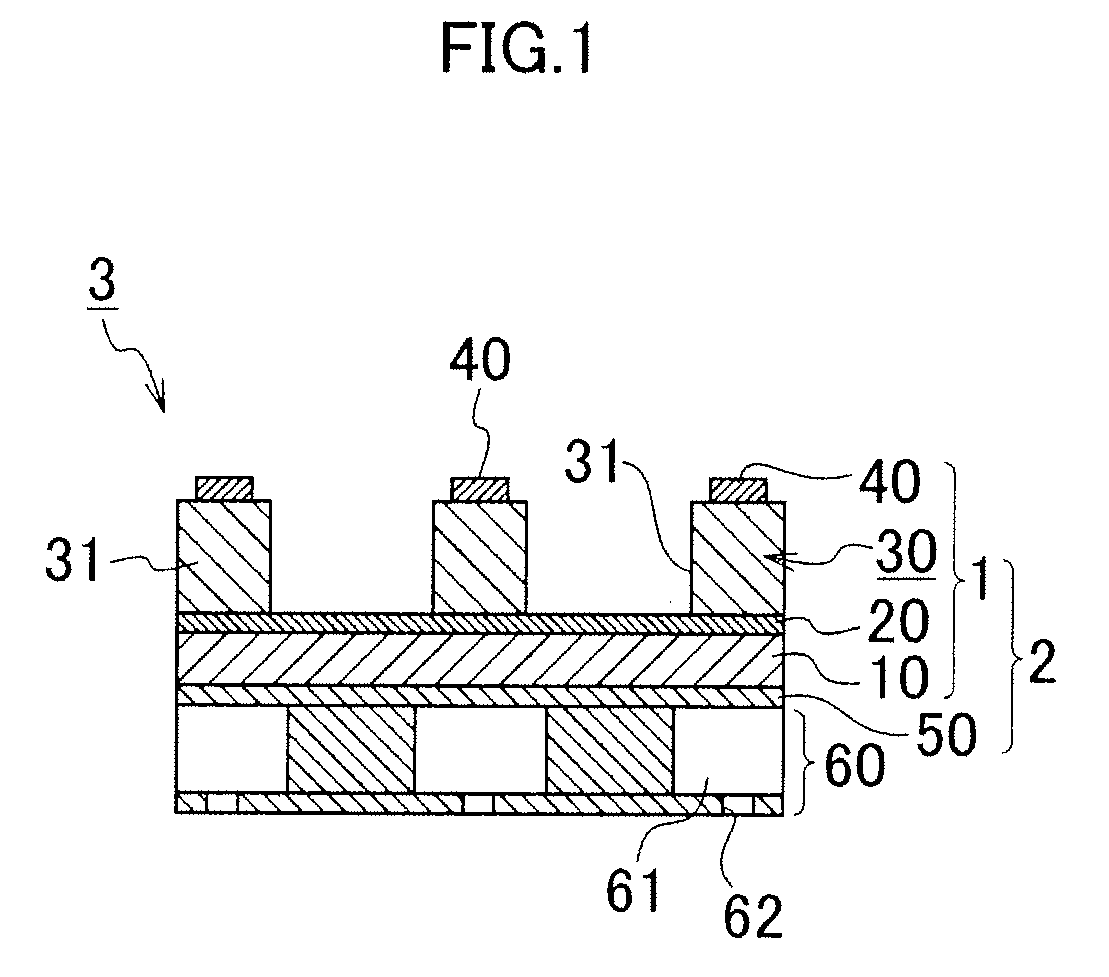
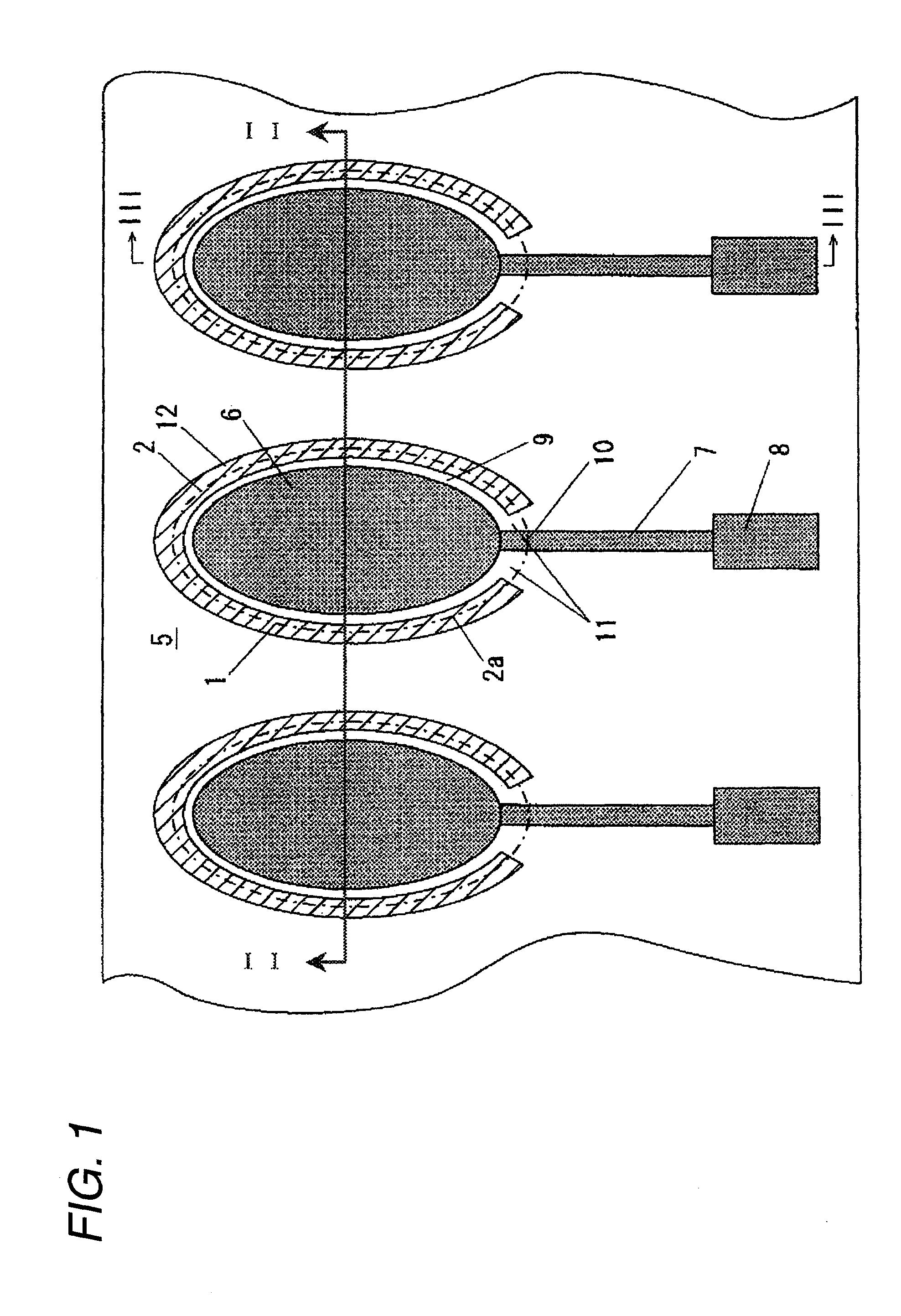
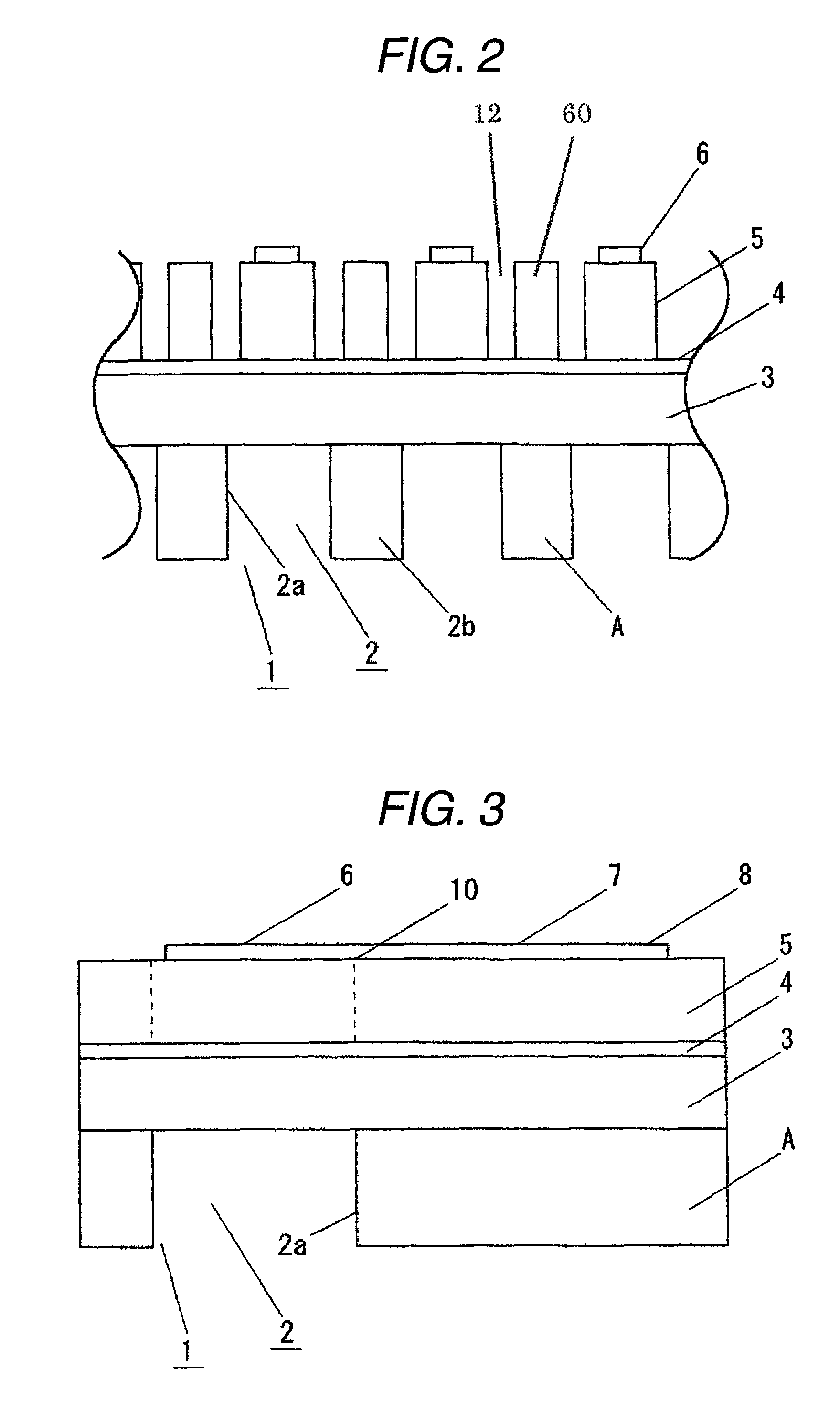
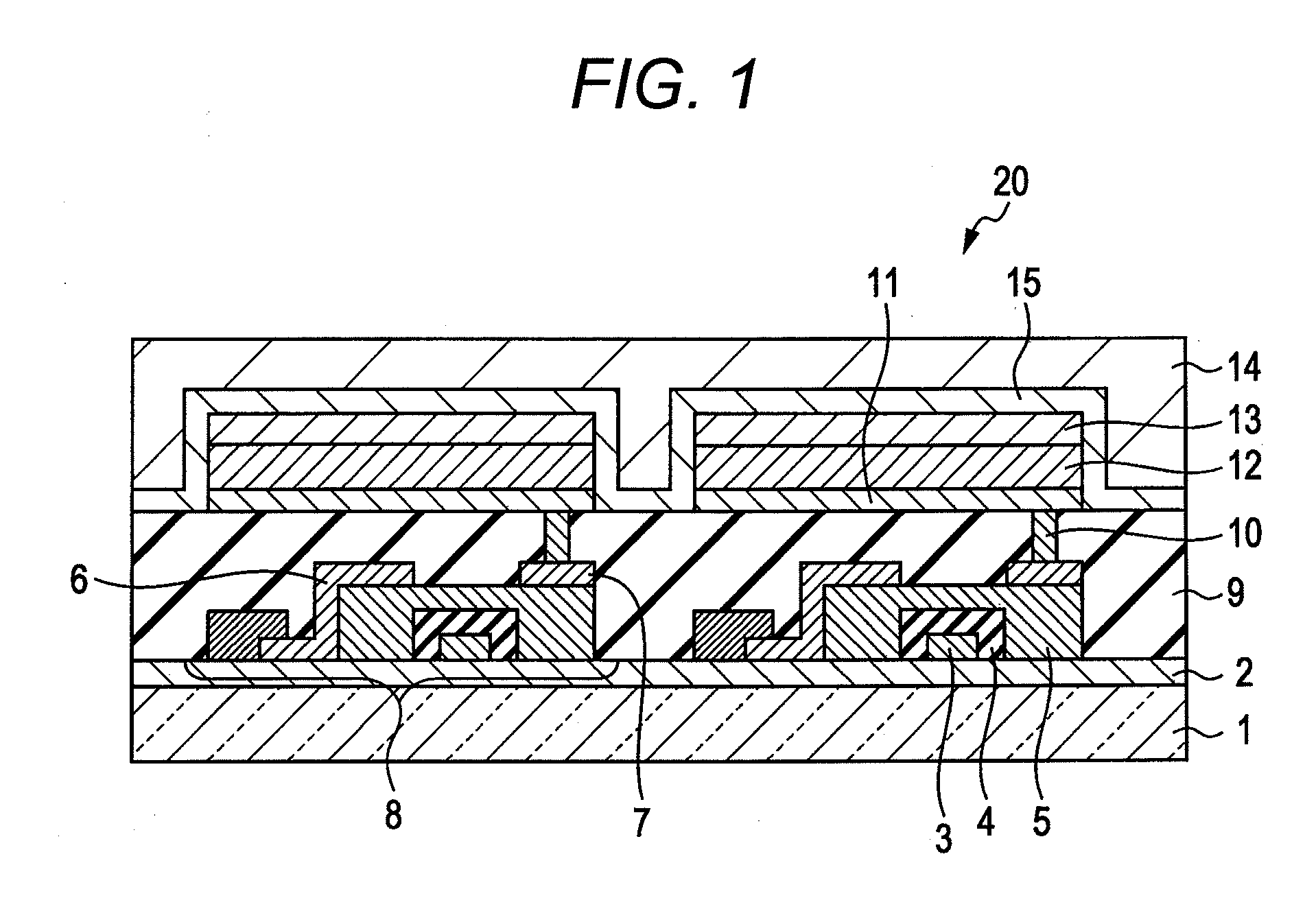
A piezoelectric element includes a pressure chamber member that has an opening 1 communicating with a nozzle, a vibrating plate that is disposed on the pressure chamber member so as to cover the opening 1, a lower electrode that is disposed on the vibrating plate, a piezoelectric body 5 that is disposed on the lower electrode, an upper electrode 6 that is disposed on the piezoelectric body 5 and in a region opposed to the opening 1, and a lead electrode 7 that is disposed on the piezoelectric body 5, that extends from the upper electrode 6, and that has a width smaller than that of the upper electrode 6. The piezoelectric body 5 includes a groove portion 12 that is disposed in a predetermined region along an edge portion 2a of the opening and an inactive region (piezoelectric inactive region 11) that is a region other than the groove portion 12, that is disposed along the edge portion 2a of the opening, and that does not substantially serve as a piezoelectric element. The lead electrode 7 is disposed in the piezoelectric inactive region 11.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Organic electroluminescence element
InactiveUS20090218935A1Improve external quantum efficiencyReduce the driving voltageDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsOrganic electroluminescenceOrganic compound
An organic electroluminescence element having at least one organic compound layer including a light-emitting layer, which is disposed between a pair of electrodes, wherein the light-emitting layer includes a light emitting material, a compound represented by the following formula (1) and a charge transporting material. An organic EL element that exhibits high light-emission efficiency and low driving voltage, and is excellent in drive durability is provided.
Owner:UDC IRELAND
Organic electroluminescent device and method for producing the same
ActiveUS20050287396A1Increase brightnessHigh luminous efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesArylHydrogen atom
An organic electroluminescent device and a method for producing the same, the organic electroluminescent device including a luminescent layer produced by a vapor-deposition method disposed between a pair of electrodes, the luminescent layer containing at least one host material and at least one metal complex including a partial structure represented by formula (I): wherein M represents a metal atom, R1, R2 and R4 to R8 each independently represent a hydrogen atom or a substituent, and R3 represents a group represented by formula (II), an alkoxy group or an aryloxy group: wherein R11 to R13 each independently represent a hydrogen atom or a substituent, provided that at least two of them each independently represent an alkyl group or an aryl group.
Owner:UDC IRELAND
Piezoelectric Actuator, Method of Driving Same, Liquid Ejection Apparatus and Piezoelectric Ultrasonic Osicllator
ActiveUS20110074888A1Efficiently obtainedImprove driving durabilityPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectricityHysteresis
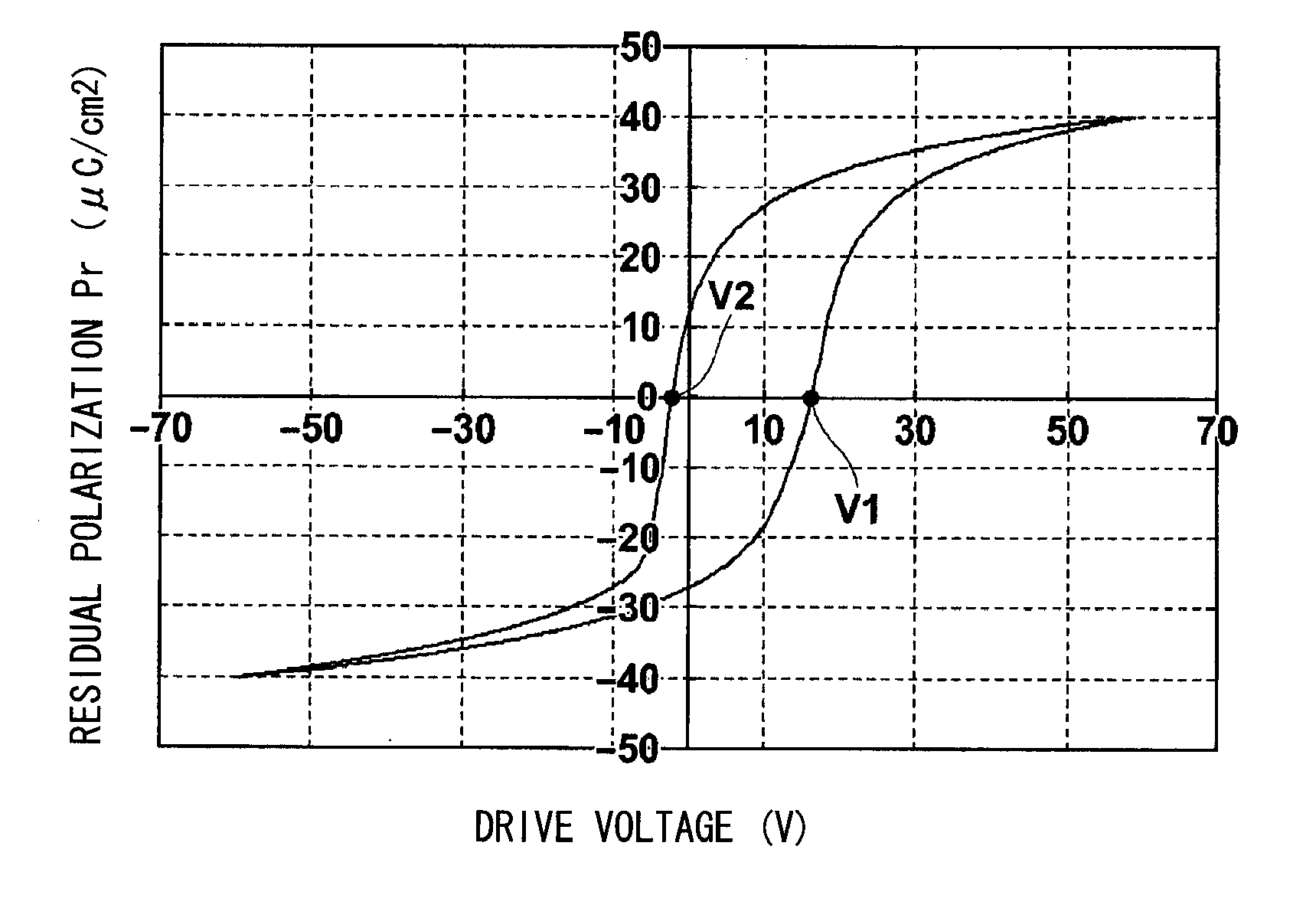
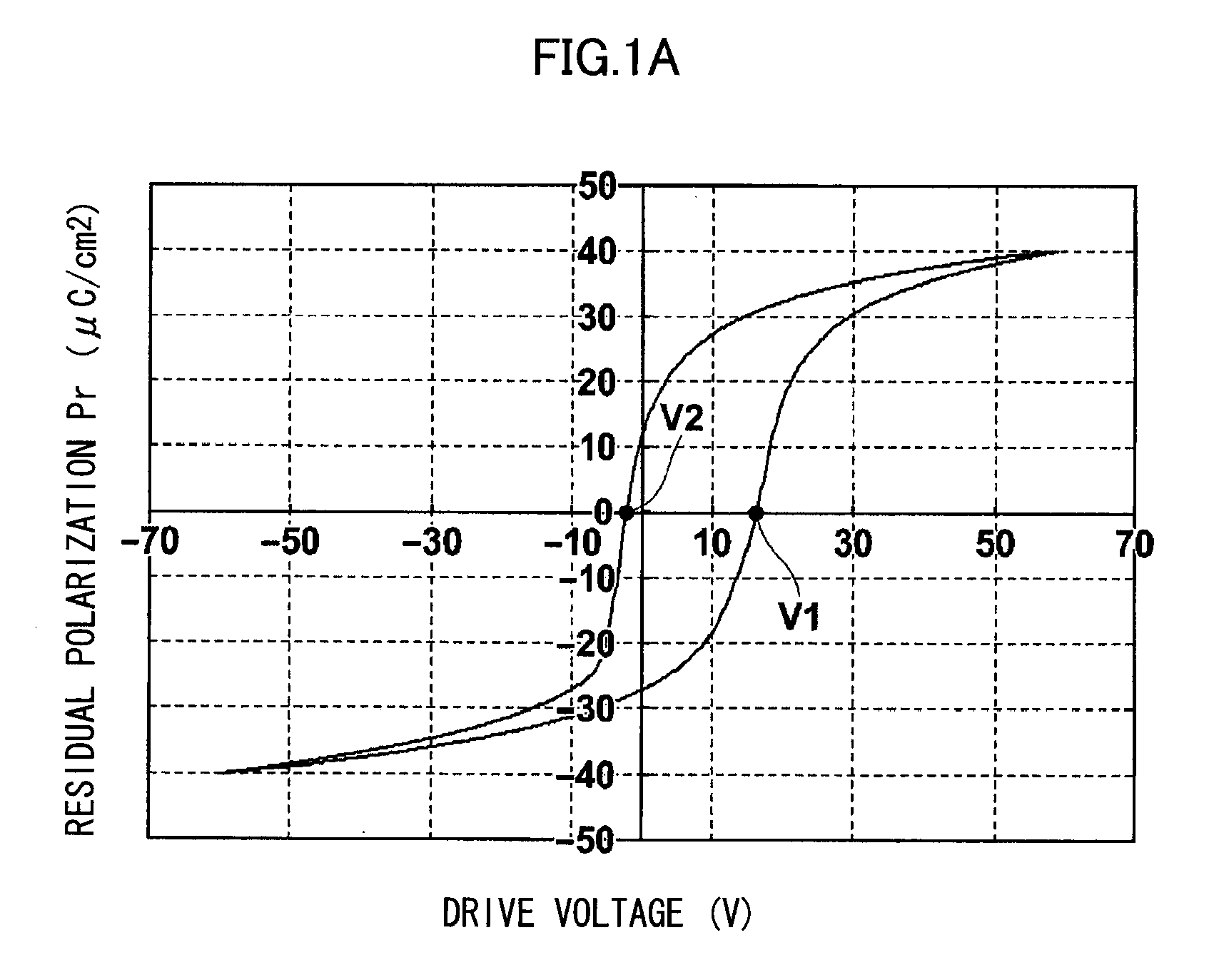
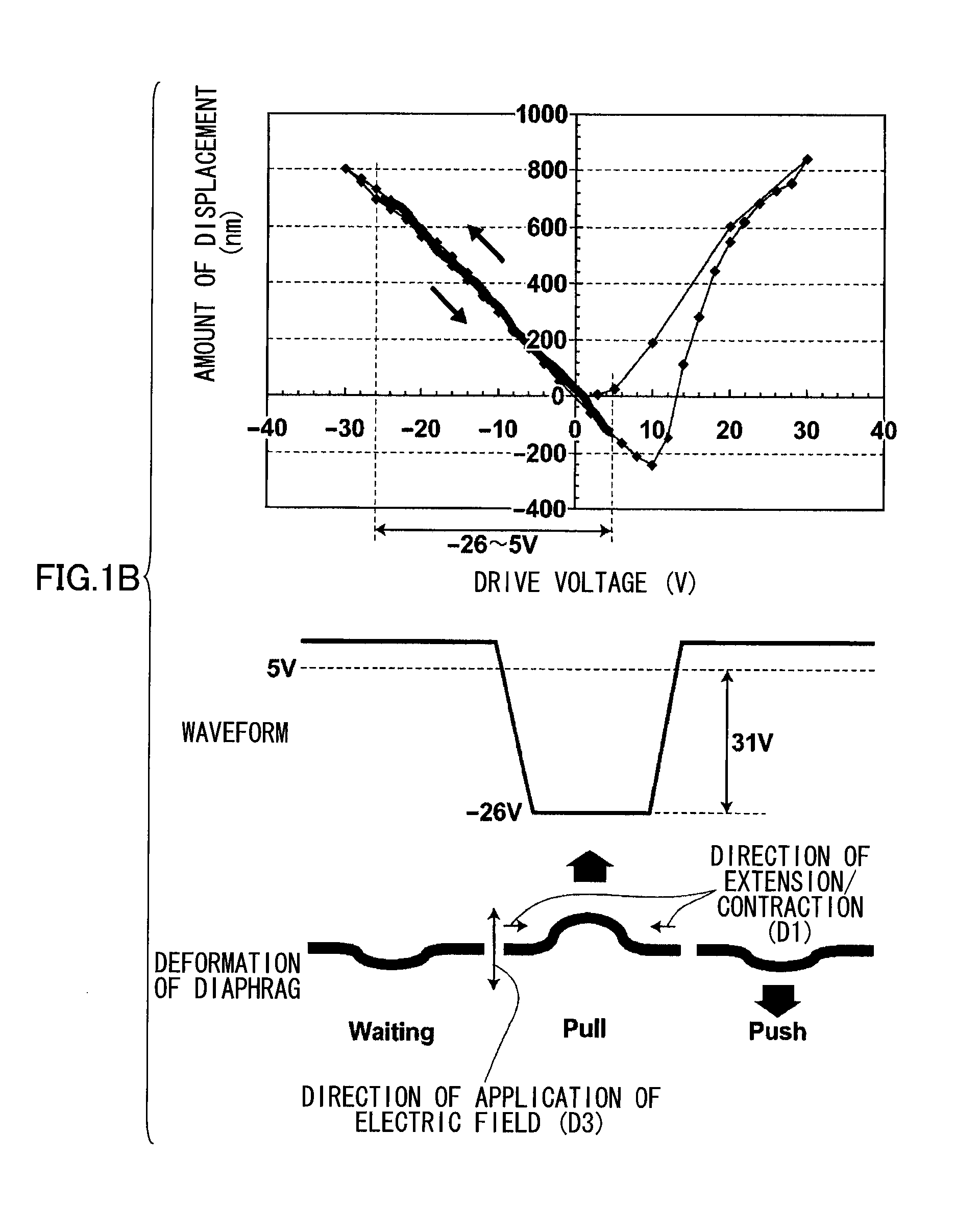
A method of driving a piezoelectric actuator including: a piezoelectric element containing a piezoelectric body having coercive field points on a negative field side and a positive field side respectively and having asymmetrical bipolar polarization—electric field hysteresis characteristics in which an absolute value of a coercive electric field on the negative field side and a coercive electric field value on the positive field side are mutually different, and a pair of electrodes for applying voltage to the piezoelectric body; and a diaphragm which externally transmits, as displacement, distortion produced in the piezoelectric body when the voltage is applied to the piezoelectric body, includes the step of driving the piezoelectric actuator between a positive drive voltage and a negative drive voltage in a range not exceeding the coercive electric field, from among the positive and negative coercive electric fields, which has the larger absolute value.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Columnar Structure Film and Method of Forming Same, Piezoelectric Element, Liquid Ejection Apparatus and Piezoelectric Ultrasonic Oscillator
ActiveUS20110037812A1Improve driving durabilityHigh maximum applied voltagePiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesIn planeGas phase
The columnar structure film is formed on a surface of a substrate by vapor phase epitaxy, and is constituted of a plurality of columnar bodies extending in directions non-parallel to the surface of the substrate. In the columnar structure film, a relationship GSmax>2.0 GSmin is satisfied, where GSmax and GSmin are respectively a maximum value and a minimum value of average diameters of the columnar bodies taken in planes perpendicular to a thickness direction of the columnar structure film.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Side part reinforcing layer and run-flat tire
InactiveCN101873942AImprove driving durabilityExcellent leak resistanceSpecial tyresPneumatic tyre reinforcementsPolymer sciencePolybutadiene
Provided is a run-flat tire having improved durability when punctured and showing increased running distance and speed. A side part reinforcing layer for a run-flat tire comprising a rubber composition obtained by compounding 0.1 to 50 parts by mass of a reinforcing material of poly(p-phenylene terephthalamide) with 100 parts by mass of a rubber component containing 20 to 80% by mass of natural rubber and / or polyisoprene rubber and 80 to 20% by mass of polybutadiene rubber, and the run-flat tire using the same.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
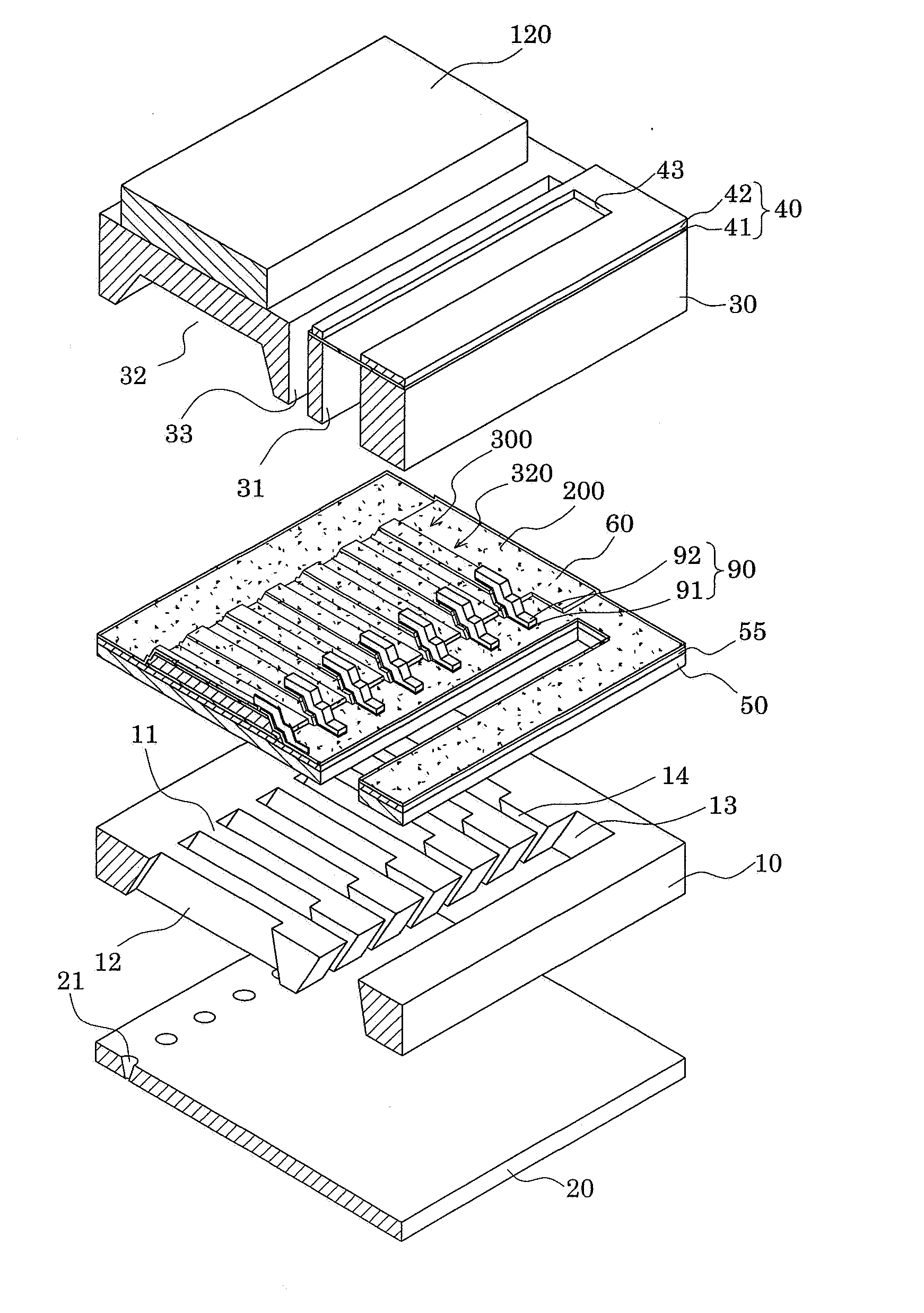
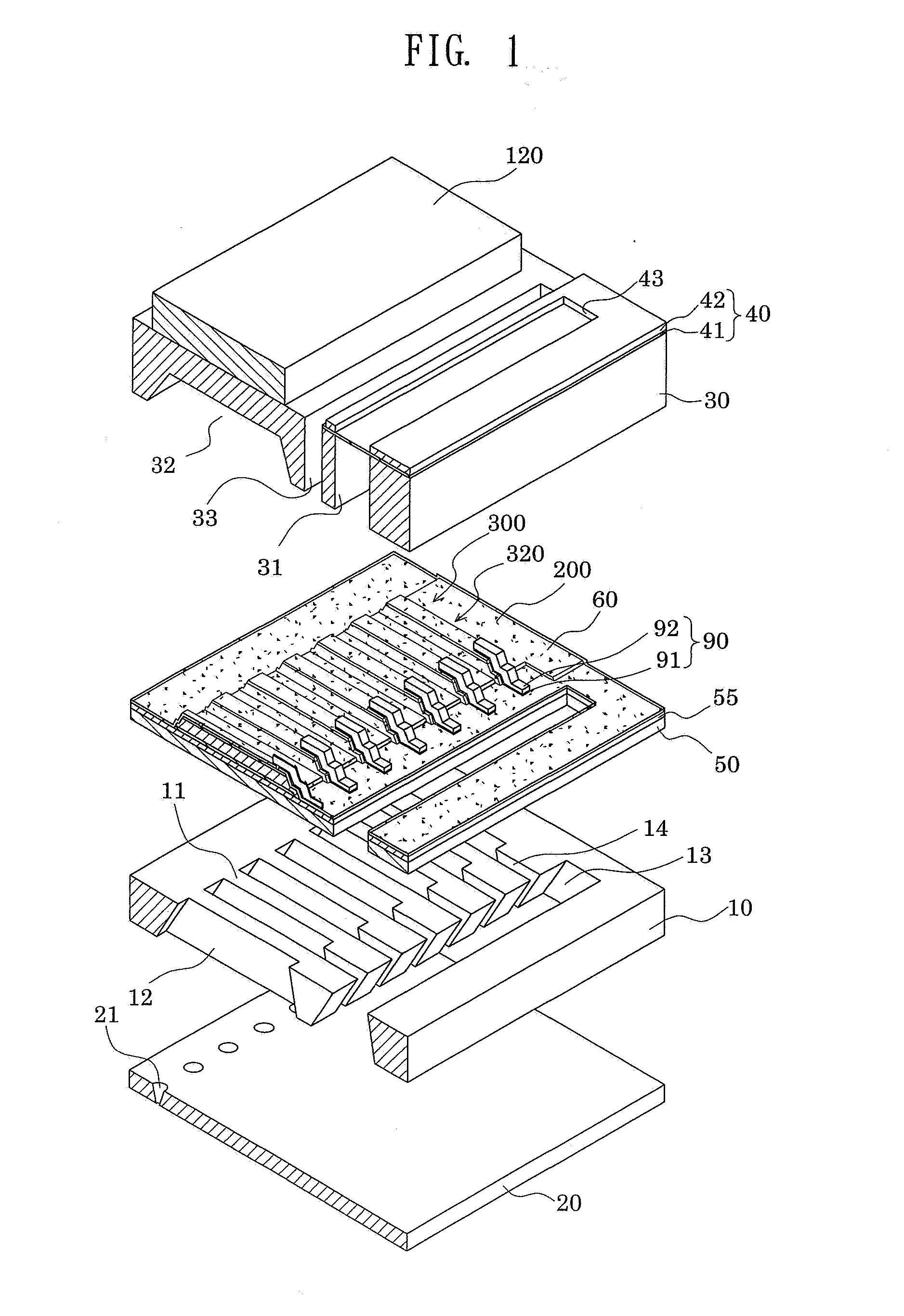
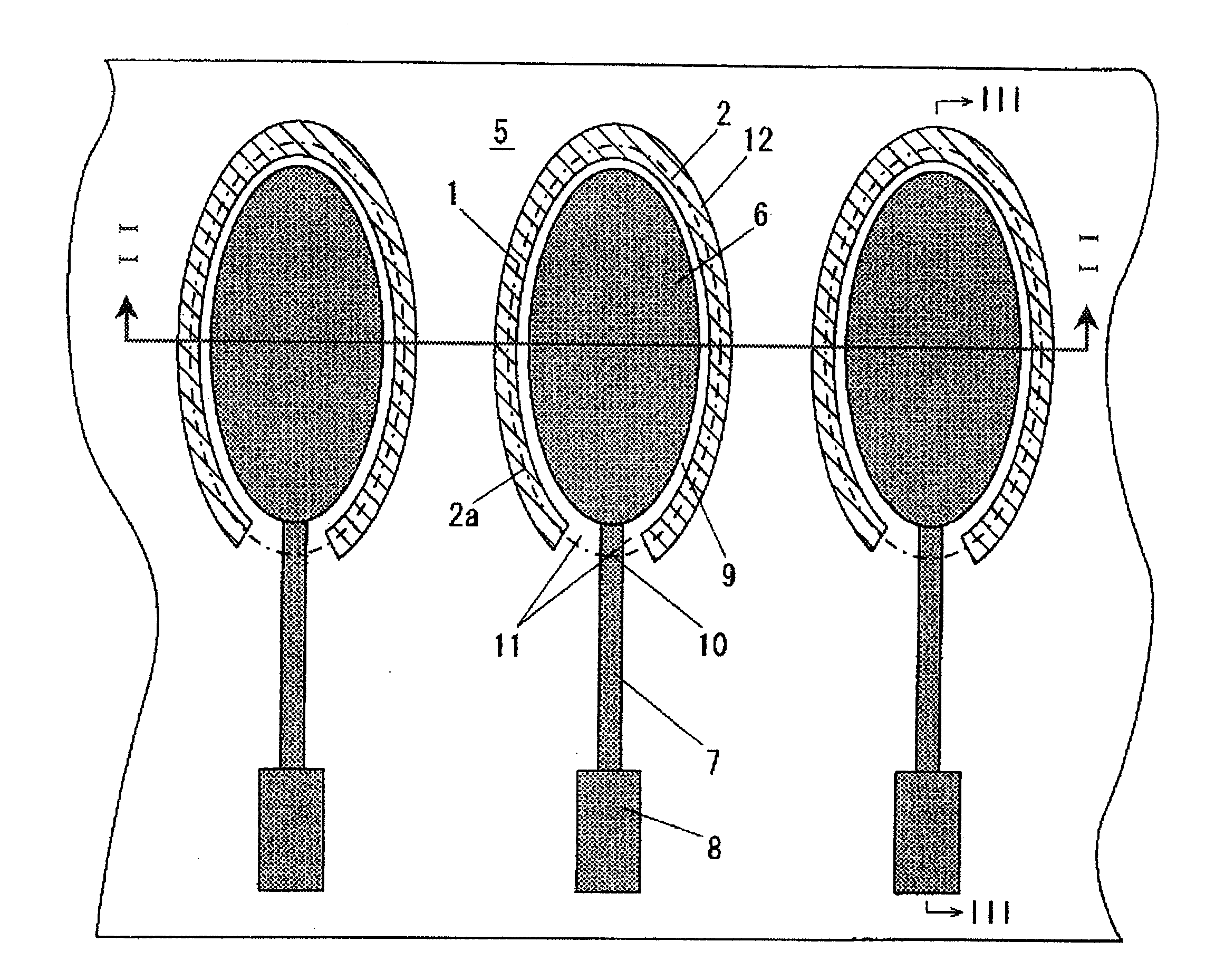
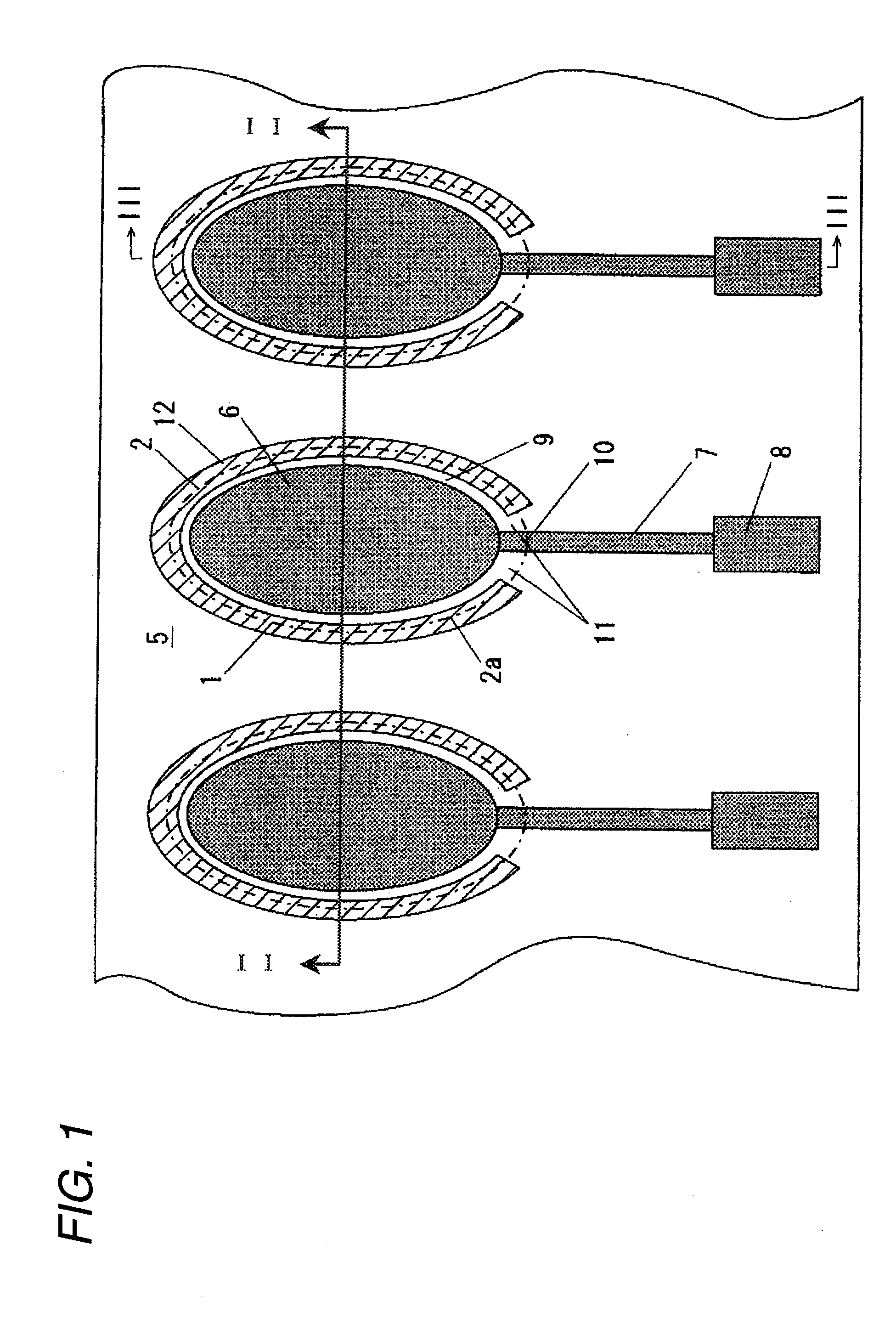
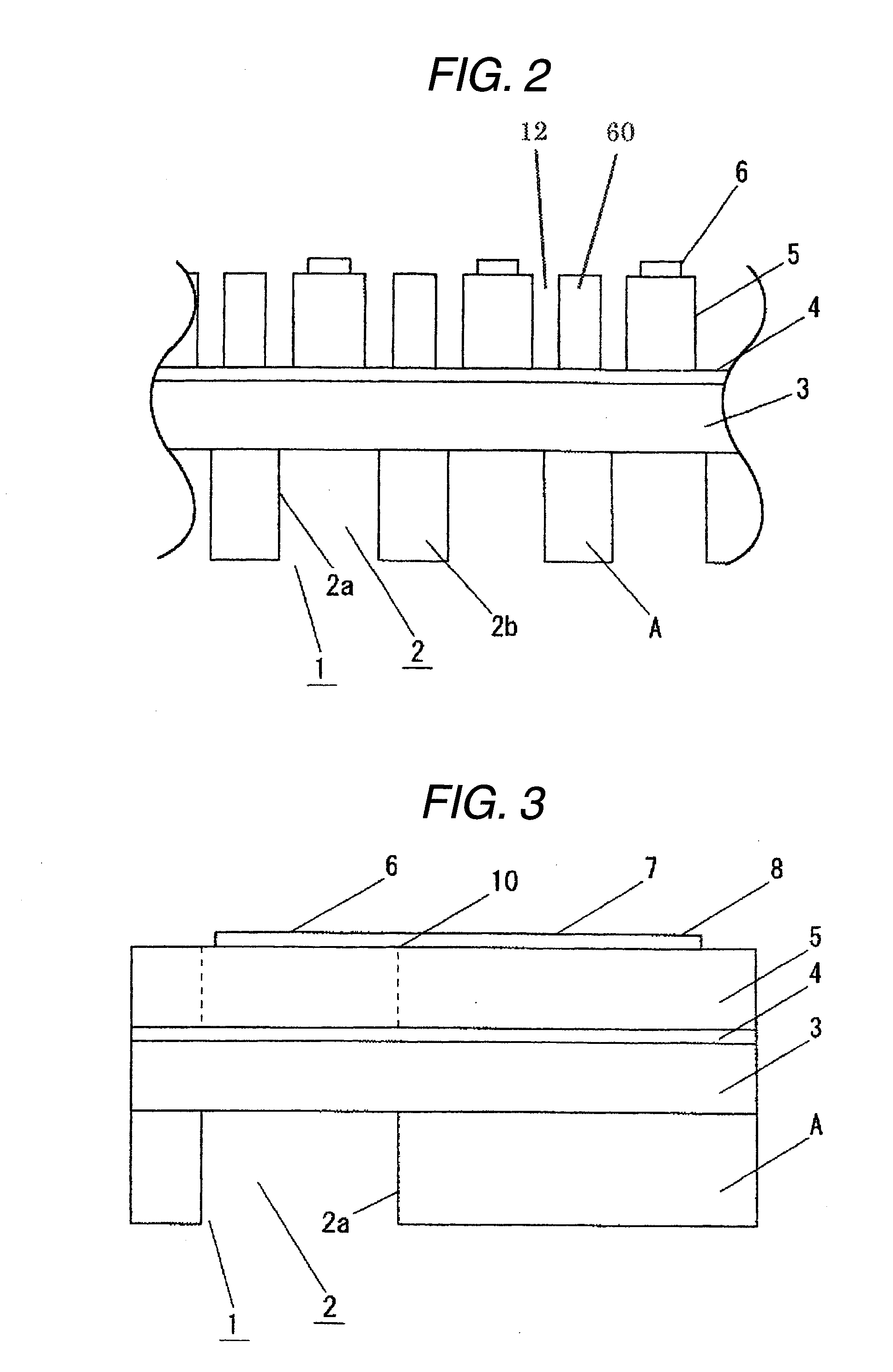
Liquid ejecting head, method of producing the same, and liquid ejecting apparatus
A liquid ejecting head includes a channel-forming substrate that communicates with nozzle orifices for ejecting a liquid and that includes a plurality of pressure-generating chambers separated by a plurality of partition walls and arranged in parallel in a direction in which a short side thereof extends; and pressure-generating elements that are provided on a surface of the channel-forming substrate, with a diaphragm therebetween, and that provide the pressure-generating chambers with a pressure change. In the liquid ejecting head, recesses that open to the side of the pressure-generating chambers are provided on areas of the diaphragm, the areas facing the pressure-generating chambers; opening edges of each of the recesses are disposed at the same positions as corners each defined by an inner surface of the corresponding partition wall, the inner surface defining a side surface of the pressure-generating chamber, and a surface of the partition wall that is joined to the diaphragm; and side surfaces of each of the recesses form inclined surfaces that are inclined so that the width of the recess at the bottom surface of the recess is smaller than the width of the recess at the opening edges of the recess.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Actuator device and liquid-jet head
ActiveUS20070284967A1Improve driving durabilityImproved liquid-ejecting characteristicInking apparatusPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesLiquid jetEngineering
An actuator device includes a plurality of piezoelectric elements formed on a surface of a substrate. Each piezoelectric element is configured of a piezoelectric layer, an upper electrode, and a lower electrode that is formed across the plurality of piezoelectric elements. The actuator device also includes a thin film portion provided to a region in the lower electrode between each adjacent two of the piezoelectric elements. The thin film portion has a thickness smaller than that of a region in the lower electrode provided to each piezoelectric element. The actuator device also includes a concave portion provided to the boundary portion between each thin film portion and the piezoelectric element adjacent thereto. In the actuator device, the inner surface and an edge of the opening, which is opposite to the adjacent piezoelectric element, of the concave portion are formed into curved surfaces.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Cone crusher
InactiveUS8800904B2Improve driving durabilityReduce loadGrain treatmentsMetal working apparatusDrive shaftEngineering
Owner:SANDVIK INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AB
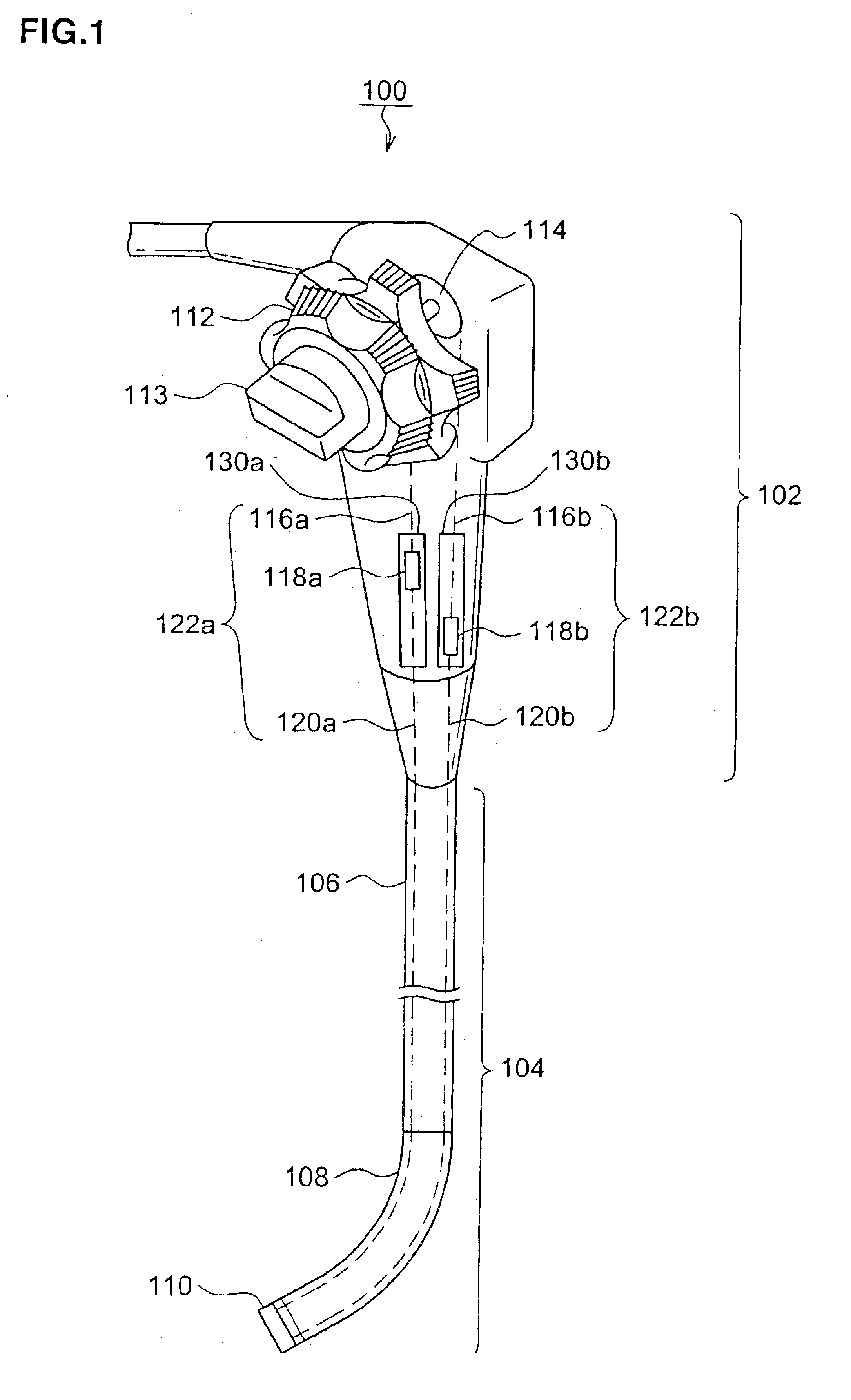
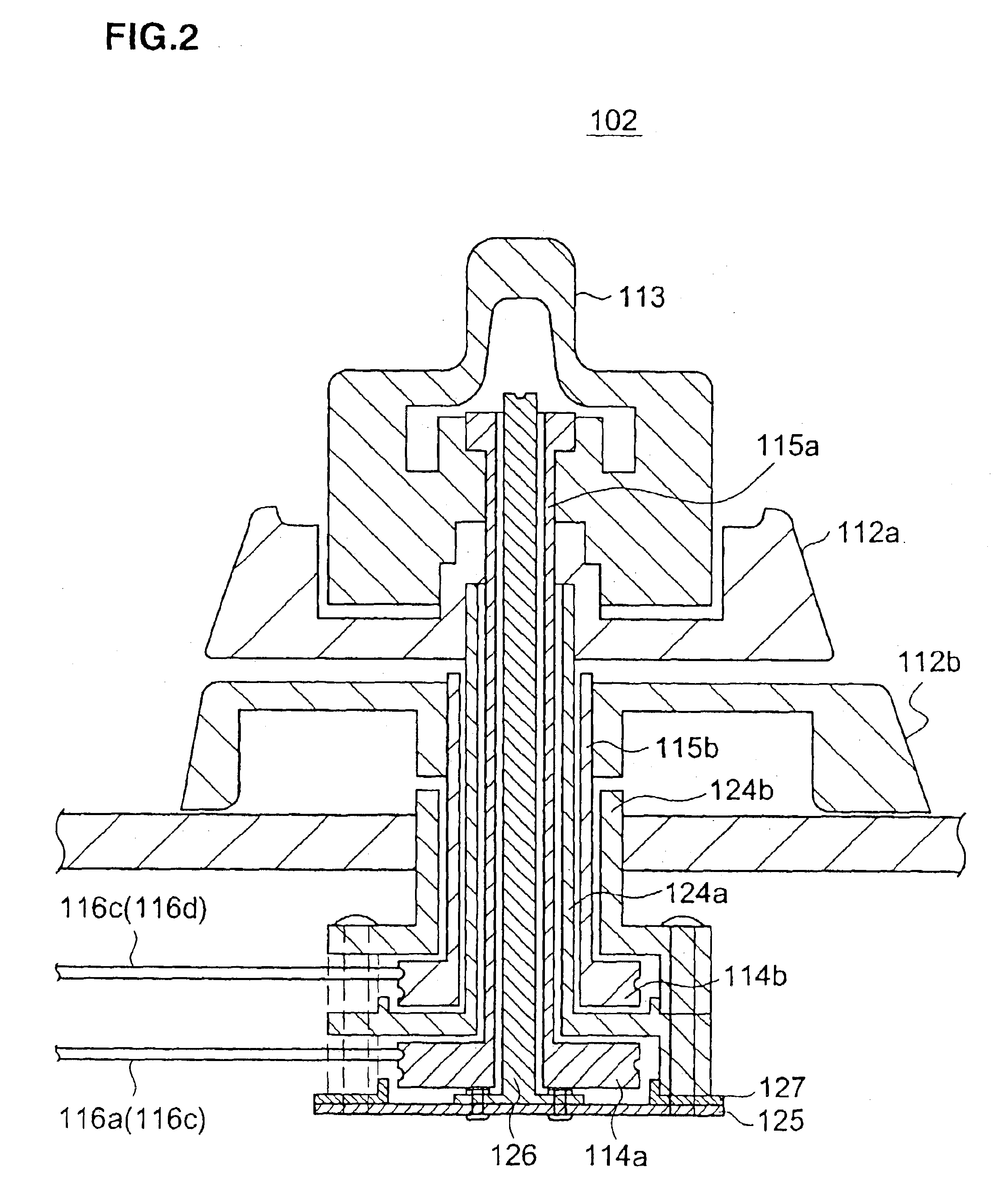
Bending control mechanism for endoscope
InactiveUS6905461B2Force is smallImprove controllabilitySurgeryEndoscopesConductor CoilControllability
Disclosed is a bending control mechanism for an endoscope according to the invention, which is characterized in that the bending control mechanism includes a bending portion provided in an insertion portion of the endoscope; a bending wire extended out from the bending portion in order to control the bending portion; a pulley as made operable in link with a bending control lever through the shaft portion of the pulley, the bending control lever being provided in the control portion of the endoscope; a driving wire winding groove as spirally formed on the outer peripheral surface of the pulley as well as in the peripheral direction of the pulley; a driving wire wound around the driving wire winding groove of the pulley; a connection member connecting the driving wire with the bending wire; and a guide member provided in the control portion and including a connection member slidably mounted thereon, wherein in the state where the most driving wire is would round the pulley, a relative position between the pulley and the guide member is determined such that the extending direction of the driving wire is substantially in parallel with the guide surface of the guide member. With the constitution of the above bending control mechanism, there is no need for any excess force to be used for winding up the driving wire round the pulley by using the bending control lever, and it become possible to control the bending portion with smaller force. Thus, controllability of the endoscope is improved and also, durability of the driving wire is improved.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
Piezoelectric film, piezoelectric device, liquid ejection apparatus, and method of producing piezoelectric film
InactiveUS20110215679A1Inhibition formationImprove driving durabilityPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSynthetic resin layered productsGas phaseDeposition process
A piezoelectric film is formed on a surface of a substrate by a vapor deposition process without generating grain boundaries which are substantially parallel to the surface of the substrate and are caused by lamination. A normal of a (100) plane of each of crystals constituting the piezoelectric film is inclined from a normal of the surface of the substrate by an angle of not smaller than 6° and not larger than 36°.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Organic light emitting device
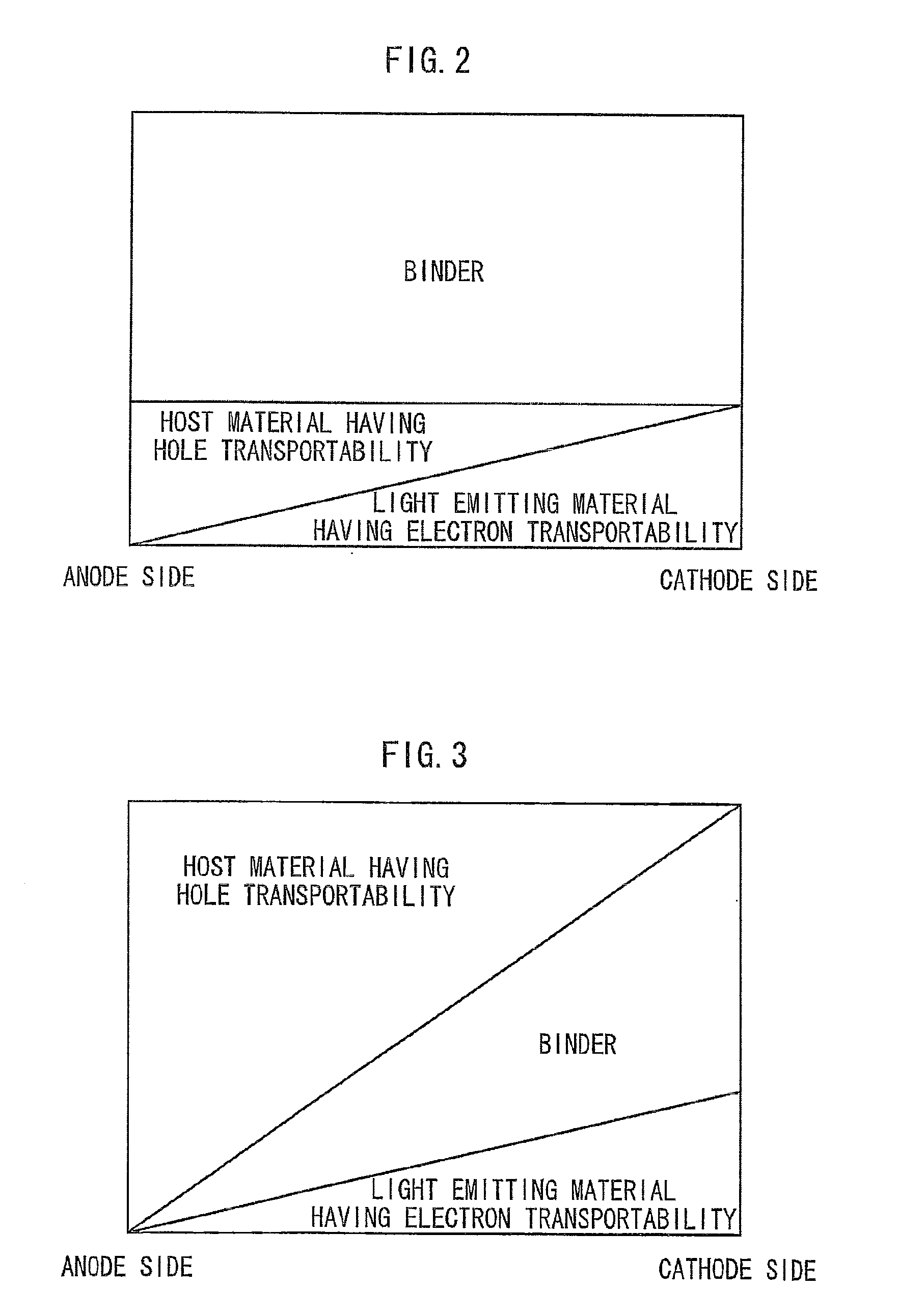
InactiveUS20070228948A1Improve driving durabilityLight extraction efficiency can be improvedDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsDopantTransport layer
An organic light emitting device has a light emitting layer and an electron injecting and transporting layer which are sandwiched between a pair of electrodes formed of an anode and a cathode. The electron injection dopant material is doped into an electron transporting material in such a manner that concentration of the dopant becomes low, high, and low in the regions of the electron injecting and transporting layer in the stated order from the light emitting layer side in the film thickness direction. Further, in the region brought into contact with the cathode of the electron injecting and transporting layer, the concentration of the dopant is preferably set high. The organic light emitting device improves drive durability and high light extraction efficiency.
Owner:CANON KK
Binaphthyl compound and organic light emitting element using the same
ActiveUS20090091252A1Improve luminous efficiencyIncreased durabilityDischarge tube luminescnet screensOrganic compound preparationOrganic compoundPhotochemistry
The present invention provides a novel binaphthyl compound and an organic light emitting element having a good light emitting efficiency and a high durability at a low driving voltage. An organic light emitting element including an anode and a cathode, and a layer including an organic compound sandwiched between the anode and the cathode, wherein one of the anode and the cathode is transparent or semi-transparent, and the layer including an organic compound includes at least one binaphthyl compound represented by the following general formula [I]:
Owner:CANON KK
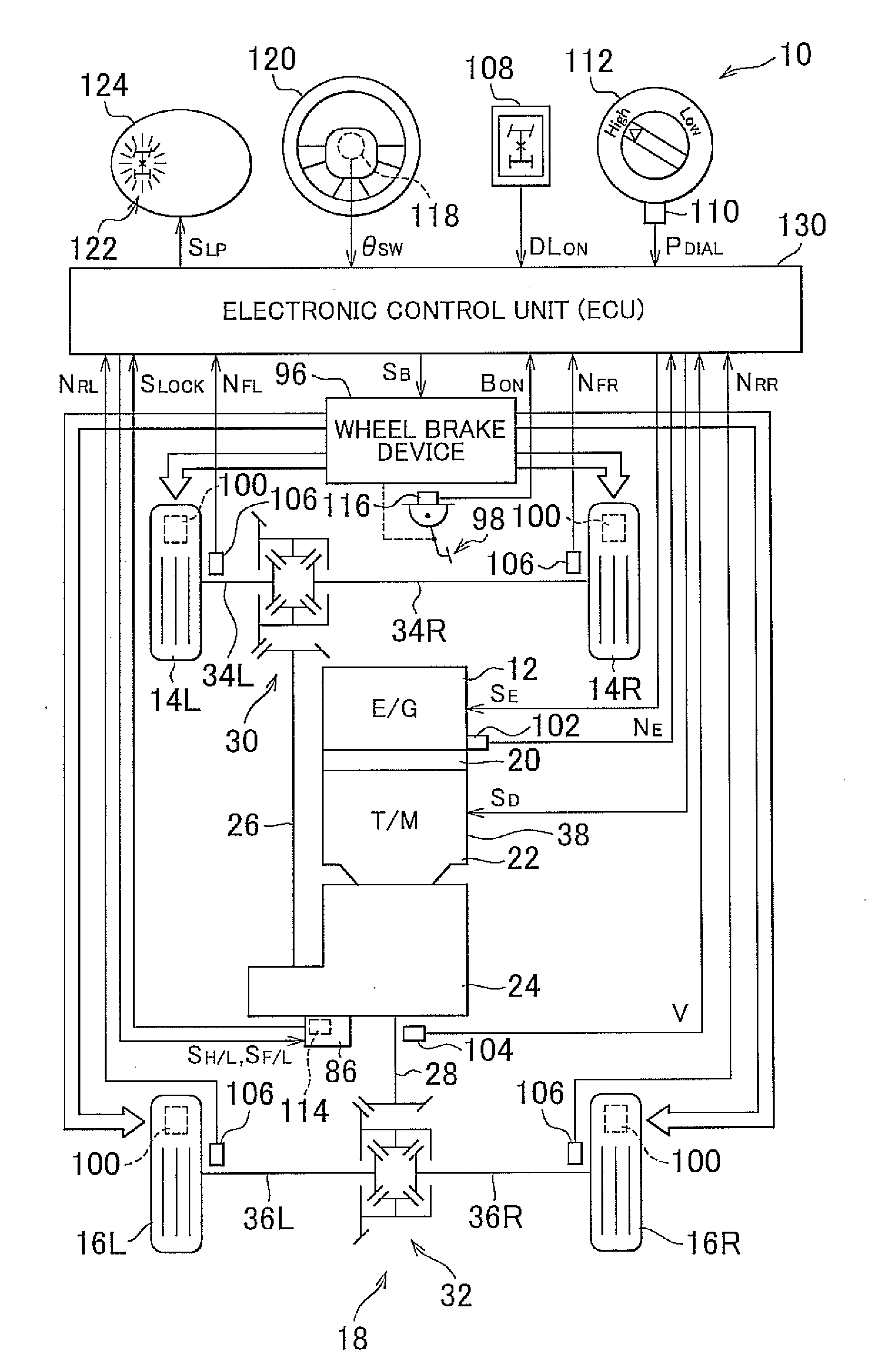
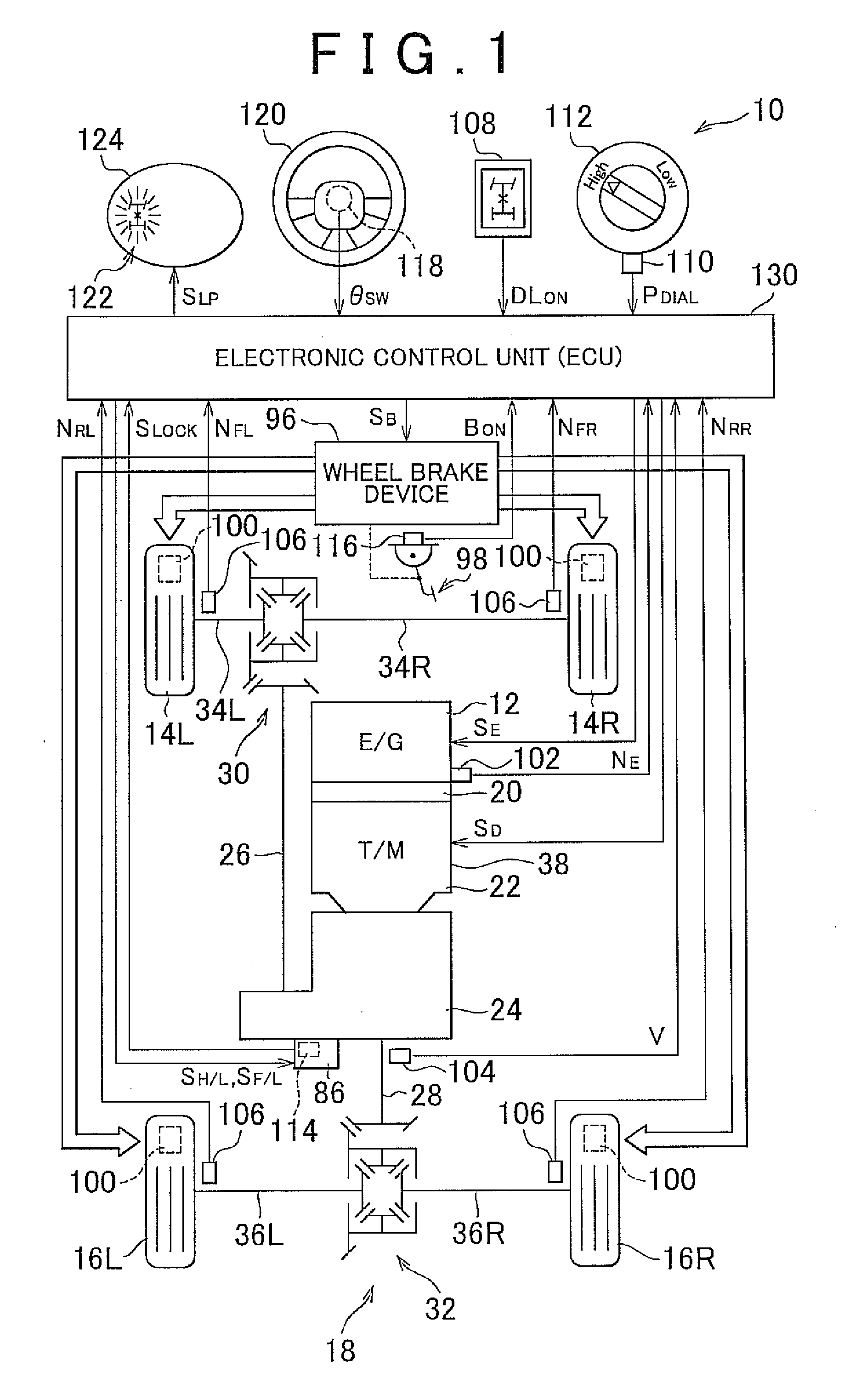
Control device and control method for four-wheel drive vehicle
InactiveUS20120010798A1Increased durabilityReduce torqueAnalogue computers for trafficComputations using stochastic pulse trainsArresting gearBrake force
In a control for a four-wheel drive vehicle that is able to travel in a non-differential mode in which differential rotation between front wheels and rear wheels is limited, it is determined whether a drive train is placed in a twisted state where a twisting torque resulting from a twist accumulated in the drive train is larger than or equal to a predetermined torque while the vehicle is cornering in the non-differential mode, and braking force is applied to the front wheels by a wheel brake device when it is determined that the drive train is placed in the twisted state.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Actuator device, liquid-jet head and liquid-jet apparatus
ActiveUS7841705B2High crystallinityImprove driving durabilityPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyInking apparatusLiquid jetActuator
Provided is an actuator device including piezoelectric elements which are displaceably provided on a substrate. Each piezoelectric element is formed of a lower electrode, a piezoelectric layer and an upper electrode. In the actuator device, longitudinal end portions of the upper electrode define longitudinal end portions of a piezoelectric active portion to be a substantial driver of the piezoelectric element. The lower electrode and the piezoelectric layer are provided continuously to the longitudinal outside of the piezoelectric active portion. Regions of the piezoelectric layer outside of the piezoelectric active portion are formed so that thin film portions may have a thin thickness.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
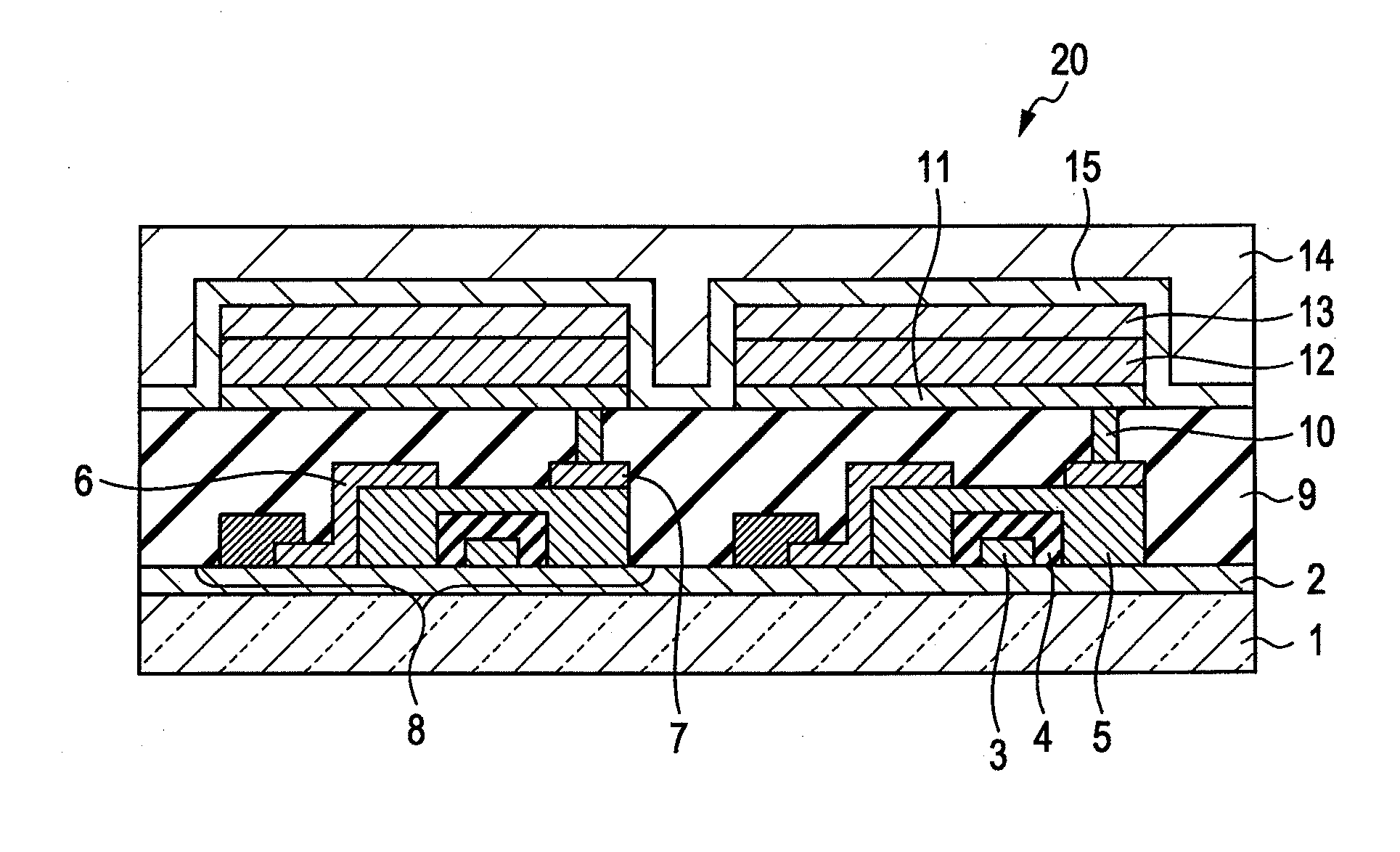
Organic electroluminescent device
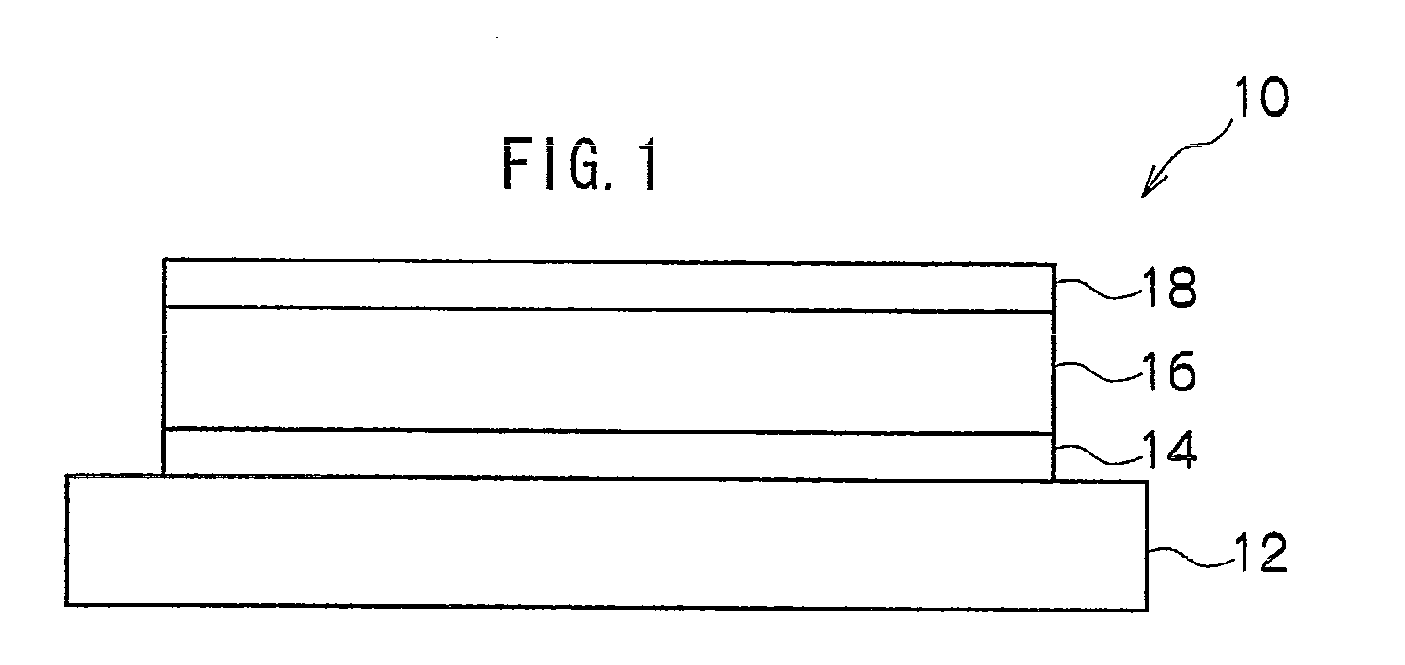
InactiveUS20100193776A1Reduce the driving voltageImprove driving durabilityElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesElectronic transmissionOrganic layer
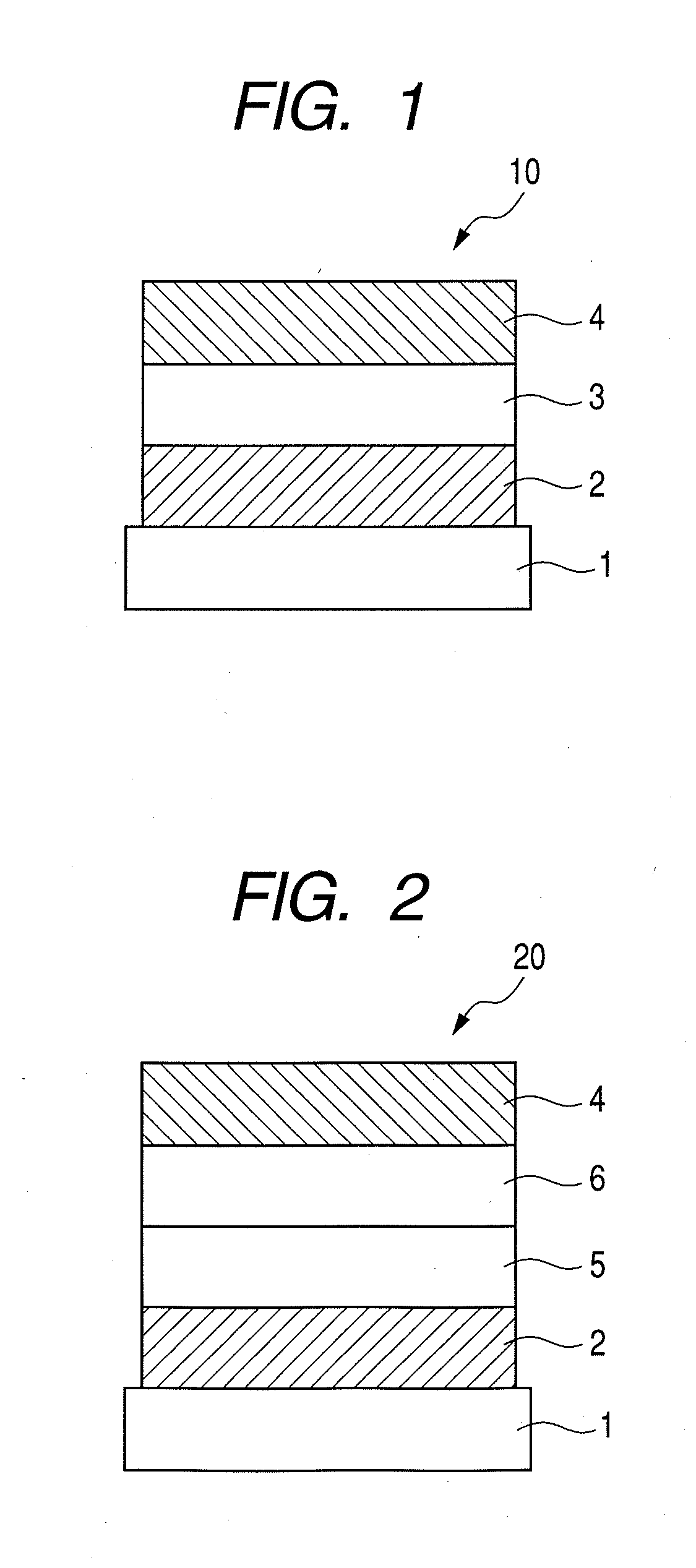
An organic electroluminescent device 10 has an anode 14, a cathode 18 disposed facing the anode, and an organic layer 16 that is sandwiched between the anode and the cathode and that includes at least a light emitting layer, wherein the light emitting layer includes a light emitting material having electron transportability, a host material having hole transportability and an electrically inert material, and the concentration of the light emitting material having electron transportability gradually decreases from the cathode side toward the anode side. Preferably, the concentration of the electrically inert material also gradually decreases from the cathode side toward the anode side.
Owner:UDC IRELAND
Piezoelectric element, liquid discharge head and liquid discharge apparatus
ActiveUS20130222482A1Large piezoelectric strainLittle effectInking apparatusPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesOptoelectronicsPerovskite
The piezoelectric element includes, on a substrate: a piezoelectric film; and a pair of electrodes provided in contact with the piezoelectric film; in which the piezoelectric film contains a perovskite-type metal oxide represented by the general formula (1) as a main component:Ax(ZnjTi(1-j))1(MgkTi(1-k))mMnO3 General Formula (1)wherein the perovskite-type metal oxide is uniaxially (111)-oriented in pseudo-cubic notation in a thickness direction, of the pair of electrodes, a lower electrode provided on the substrate side is a multilayer electrode including at least a first electrode layer in contact with the substrate and a second electrode layer in contact with the piezoelectric film, and the second electrode layer is a perovskite-type metal oxide electrode which is uniaxially (111)-oriented in pseudo-cubic notation in a thickness direction.
Owner:CANON KK +2
Piezoelectric element, ink jet head, and ink jet recording device
ActiveUS7837305B2Improve efficiencyImprove driving durabilityInking apparatusPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesEngineeringLead electrode
A piezoelectric element includes a pressure chamber member that has an opening communicating with a nozzle, a vibrating plate that is disposed on the pressure chamber member so as to cover the opening, a lower electrode that is disposed on the vibrating plate, a piezoelectric body that is disposed on the lower electrode, an upper electrode that is disposed on the piezoelectric body and in a region opposed to the opening, and a lead electrode that is disposed on the piezoelectric body, that extends from the upper electrode, and that has a width smaller than that of the upper electrode. The piezoelectric body includes a groove portion that is disposed in a predetermined region along an edge portion of the opening and an inactive region (piezoelectric inactive region) that is a region other than the groove portion, that is disposed along the edge portion of the opening, and that does not substantially serve as a piezoelectric element. The lead electrode is disposed in the piezoelectric inactive region.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Organic Electroluminescent Device
InactiveUS20150303387A1Reduce voltageImprove driving durabilityElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesSimple Organic CompoundsHost material
A first aspect of the invention is an organic electroluminescent device that includes a plurality of organic compound layers between a pair of electrodes. The plurality of organic compound layers include a luminescent layer and two or more hole-transporting layers. The hole-transporting layers include a layer adjacent to the luminescent layer. The luminescent layer contains a host material and a luminescent material. The luminescent material is a metal complex containing a tri- or higher-dentate ligand. When the ionization potential of the luminescent layer is designated as Ip0, the ionization potential of the hole-transporting layer adjacent to the luminescent layer among the hole-transporting layers is designated as Ip1, and the ionization potential of the n-th hole-transporting layer from the luminescent layer among the hole-transporting layers is designated as Ipn, these values satisfy the relationship represented by the following formula (1). In formula (1) n is an integer of 2 or more.Ip0>Ip1>Ip2> . . . >Ipn-1>Ipn formula (1)
Owner:UDC IRELAND
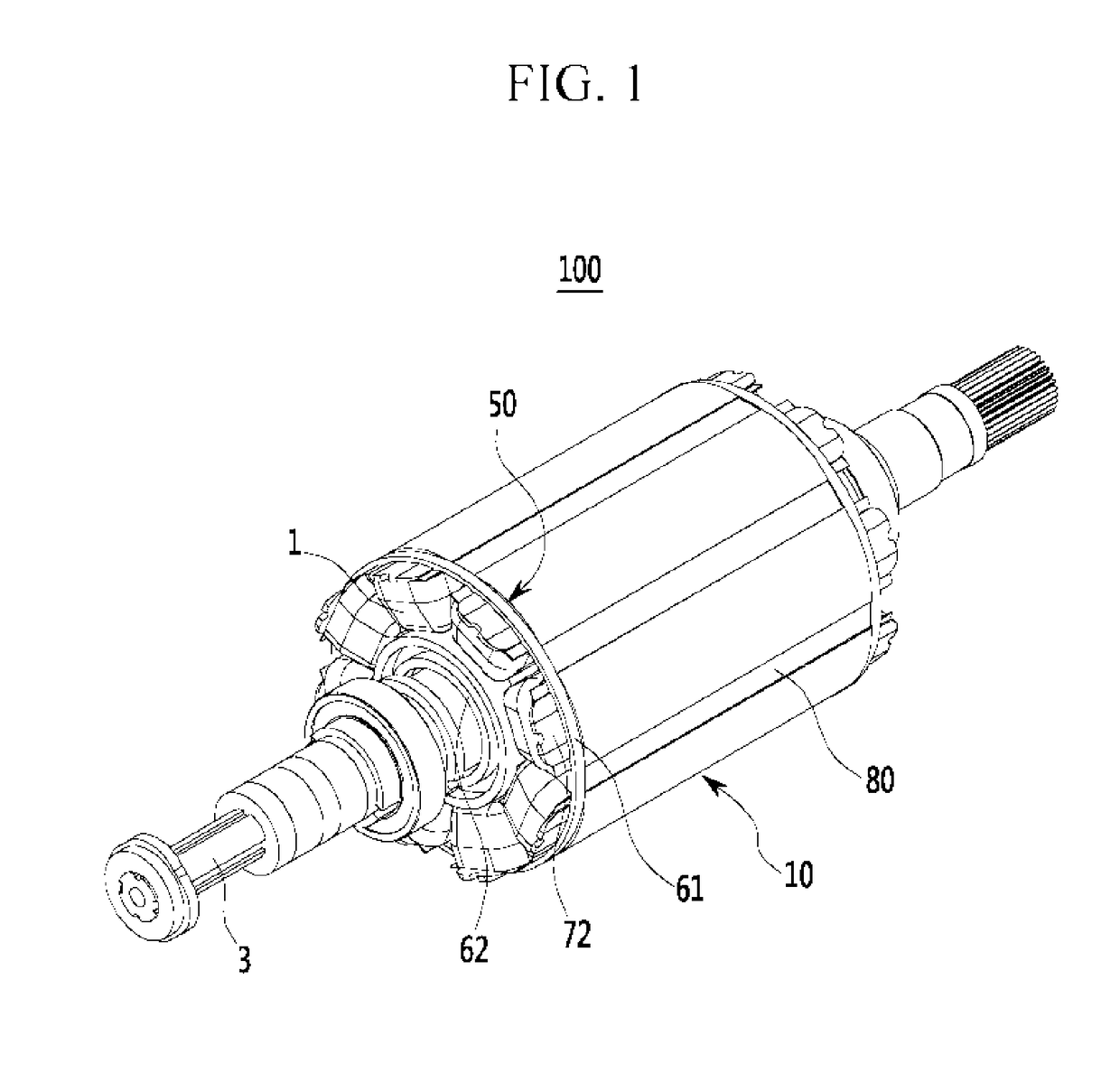
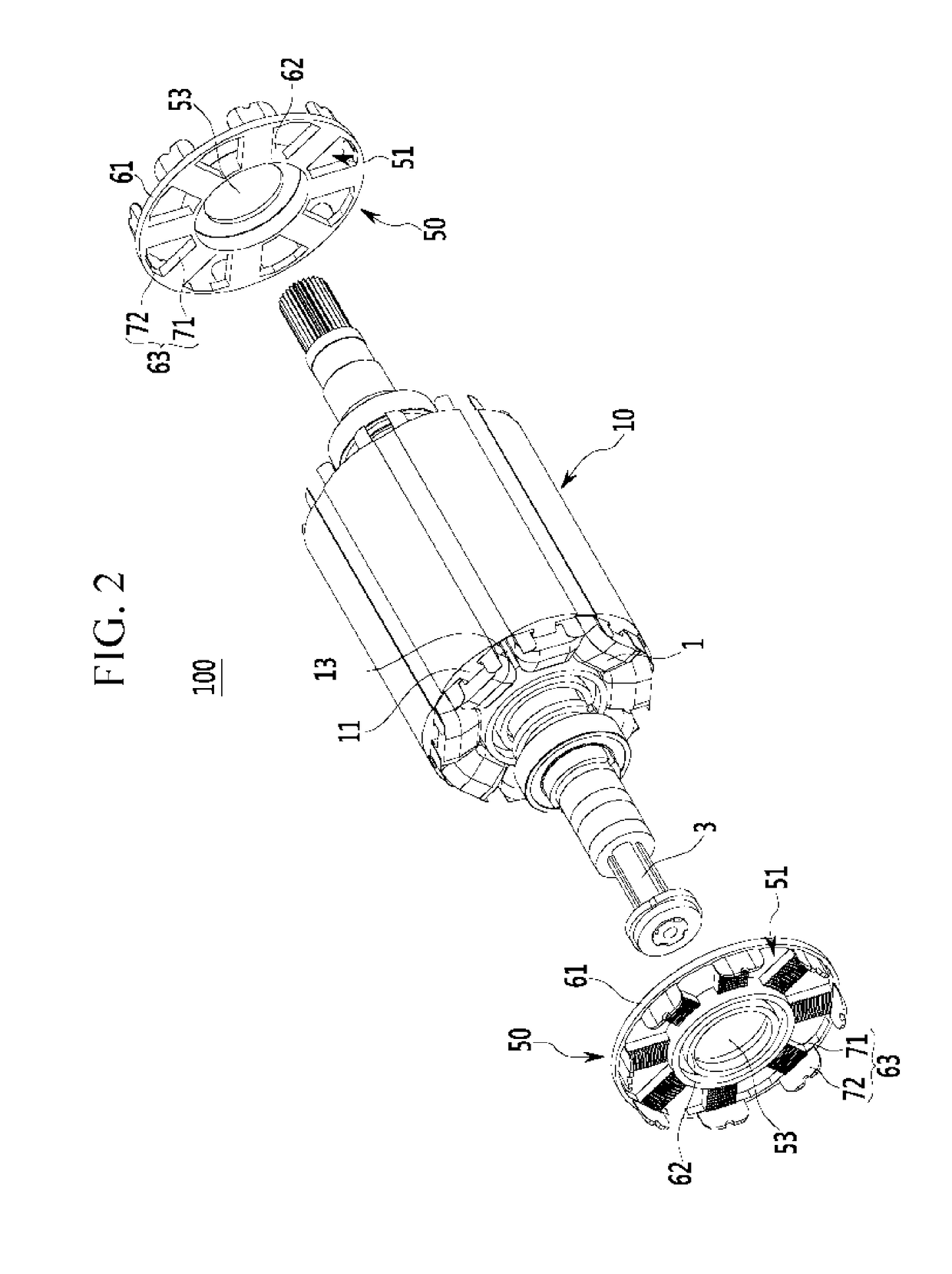
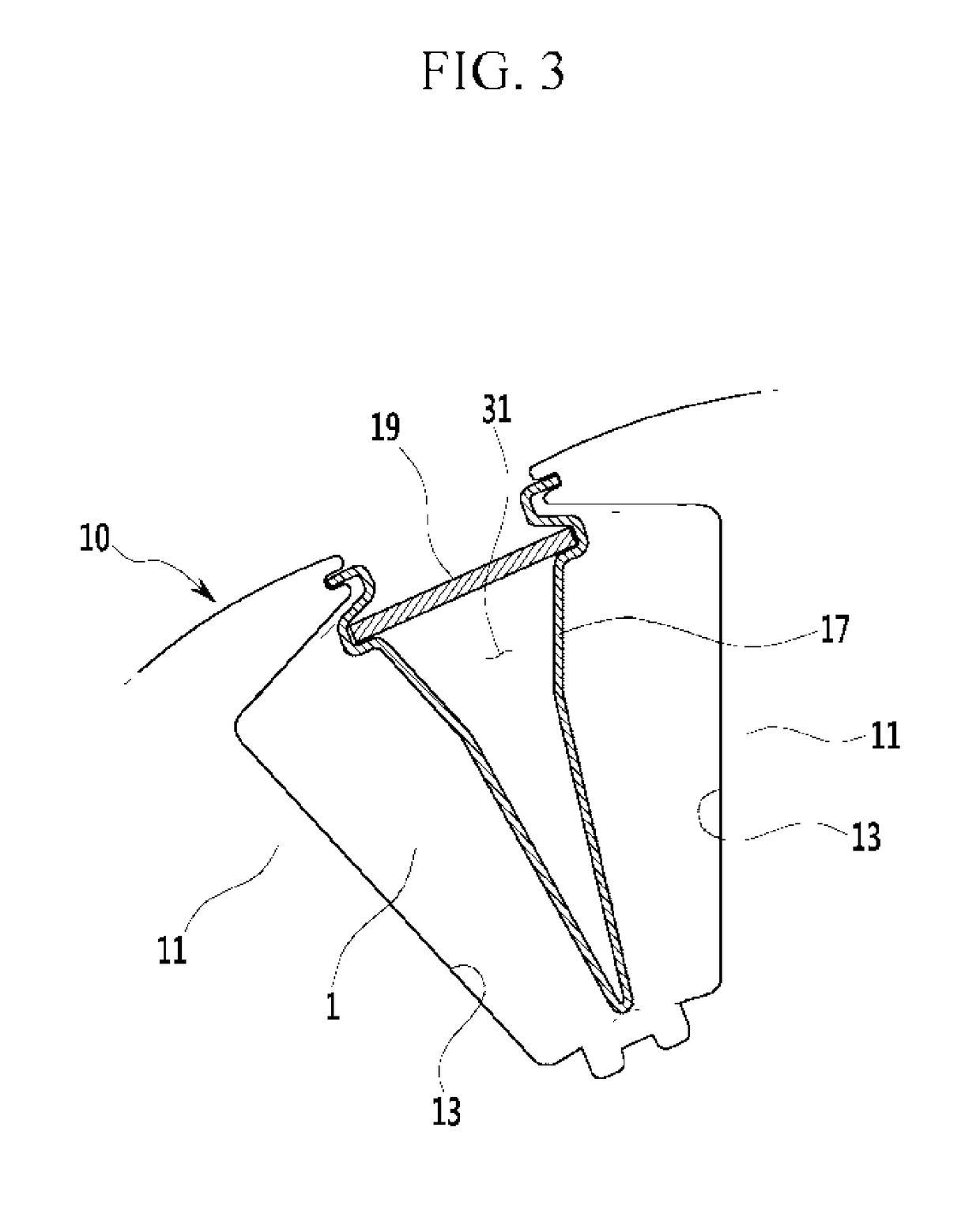
Rotor structure of wound rotor driving motor
ActiveUS10148145B2Efficient heatingEfficient dischargeWindings insulation shape/form/constructionMagnetic circuit rotating partsBobbinAir movement
A rotor of a wound rotor driving motor is provided. The rotor includes a rotor body that is rotatably installed with a predetermined air gap within a stator and in which a rotor coil is wound in a plurality of rotor teeth. A bobbin is fixed to the rotor body by the rotor coil disposed at opposing sides of an axial direction of the rotor body and supports the rotor coil. The rotor body forms a plurality of air movement passages that are opened to the exterior in an axial direction therein, and the bobbin forms a plurality of connection passage that are coupled to the air movement passages.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Indolophenoxazine compound and organic light emitting device using the same
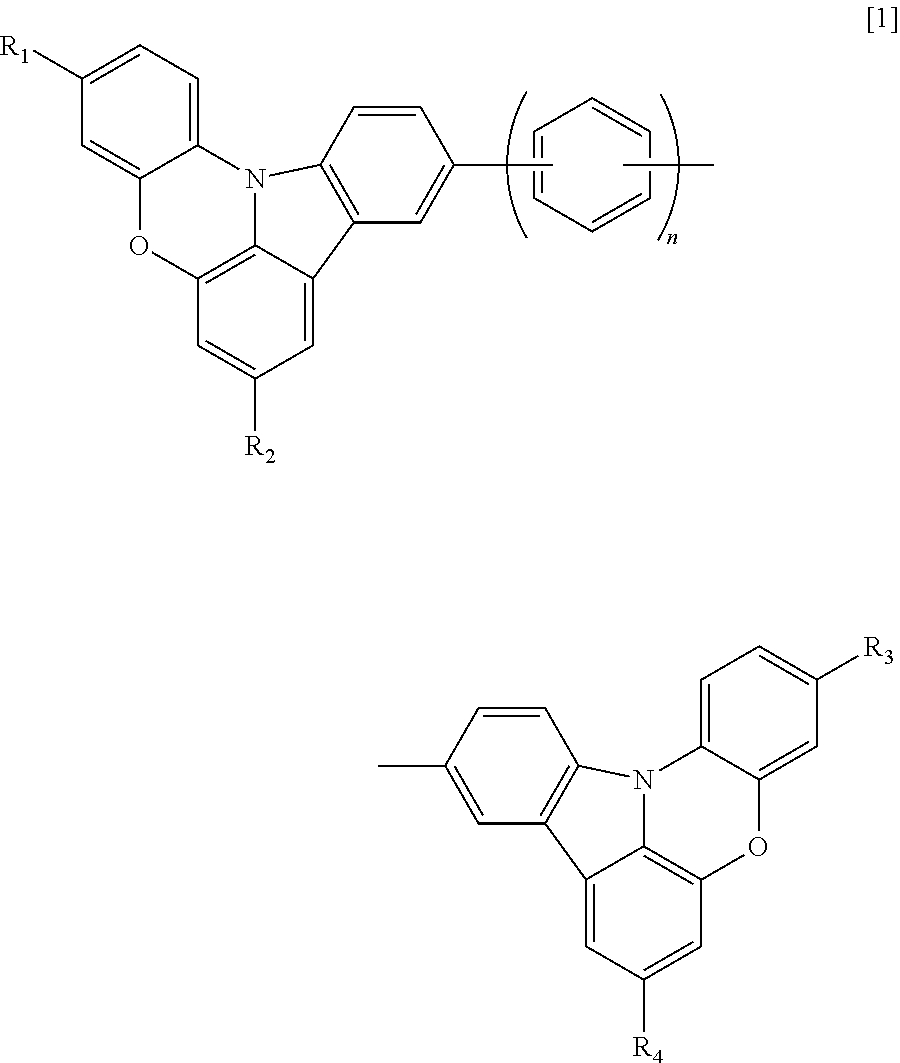
ActiveUS20130228770A1Good chemical stabilityImprove driving durabilityOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesSimple Organic CompoundsHydrogen atom
Provided is an organic light emitting device having high emission efficiency and excellent driving durability. The organic light emitting device includes an anode, a cathode, and an organic compound layer disposed between the anode and the cathode, in which the organic compound layer includes an indolophenoxazine compound represented by the following general formula [1]:(in the formula [1], R1 to R4 each represents one of a hydrogen atom and an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, and n represents an integer of 0 to 3).
Owner:CANON KK
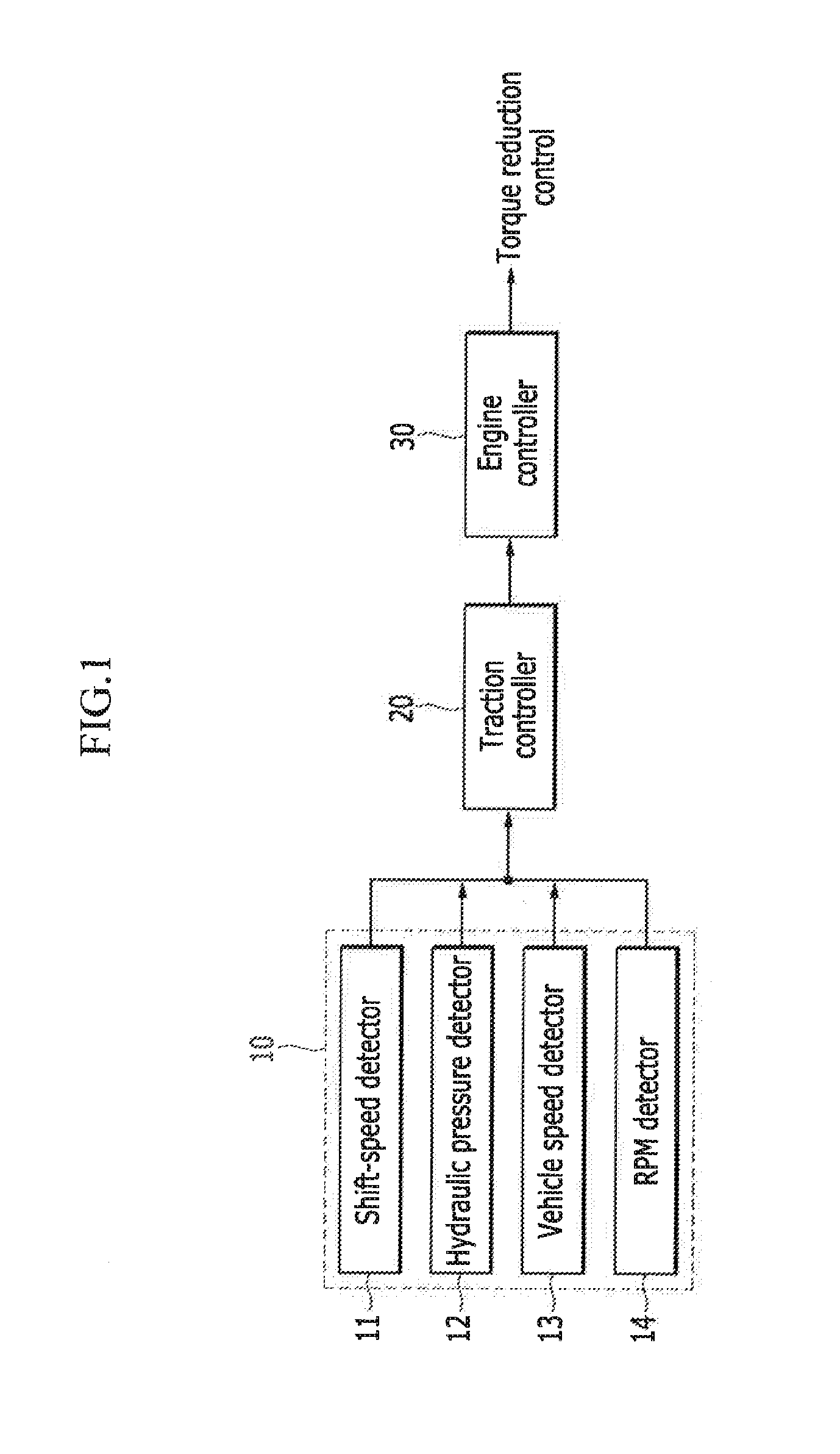
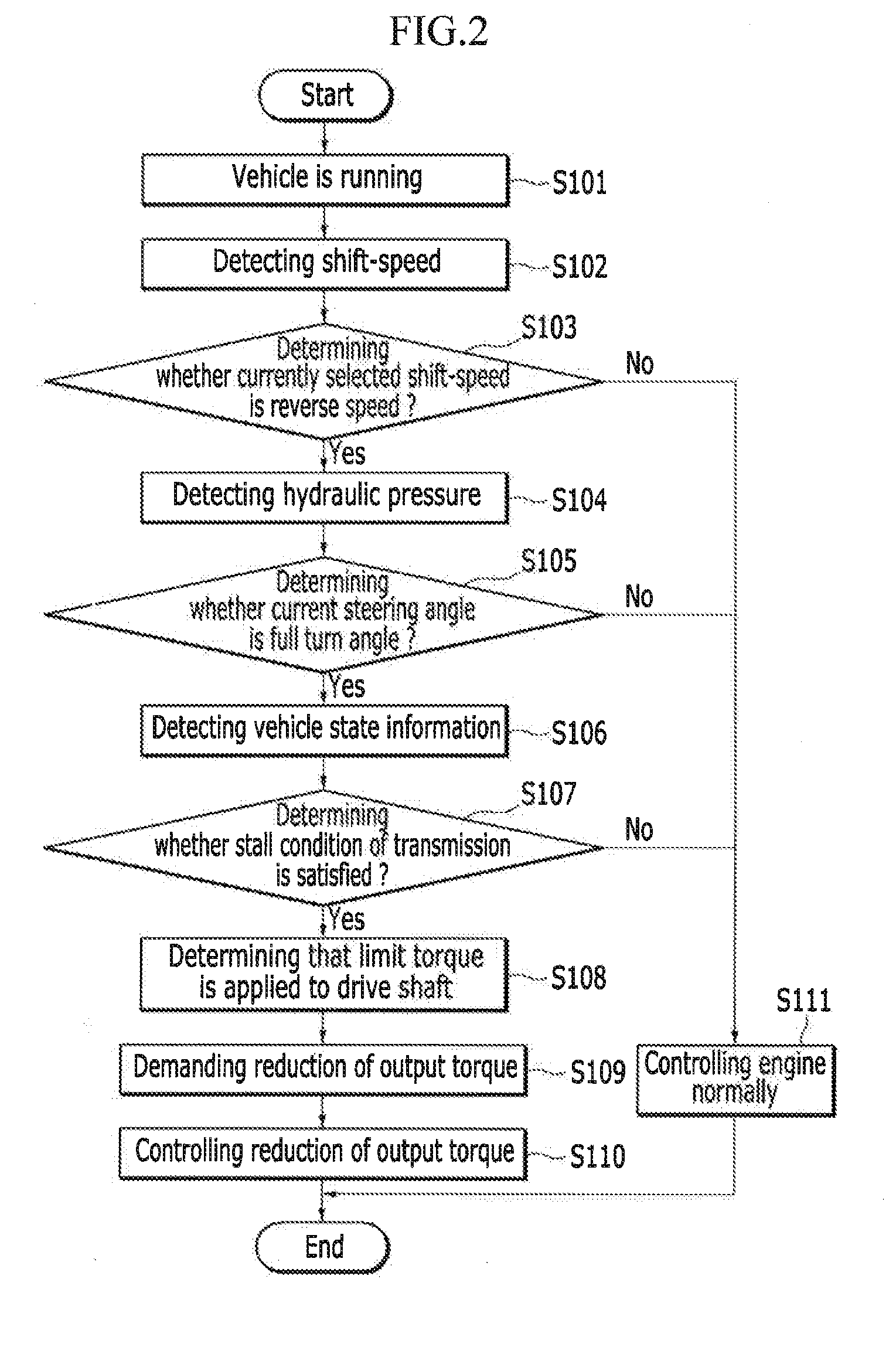
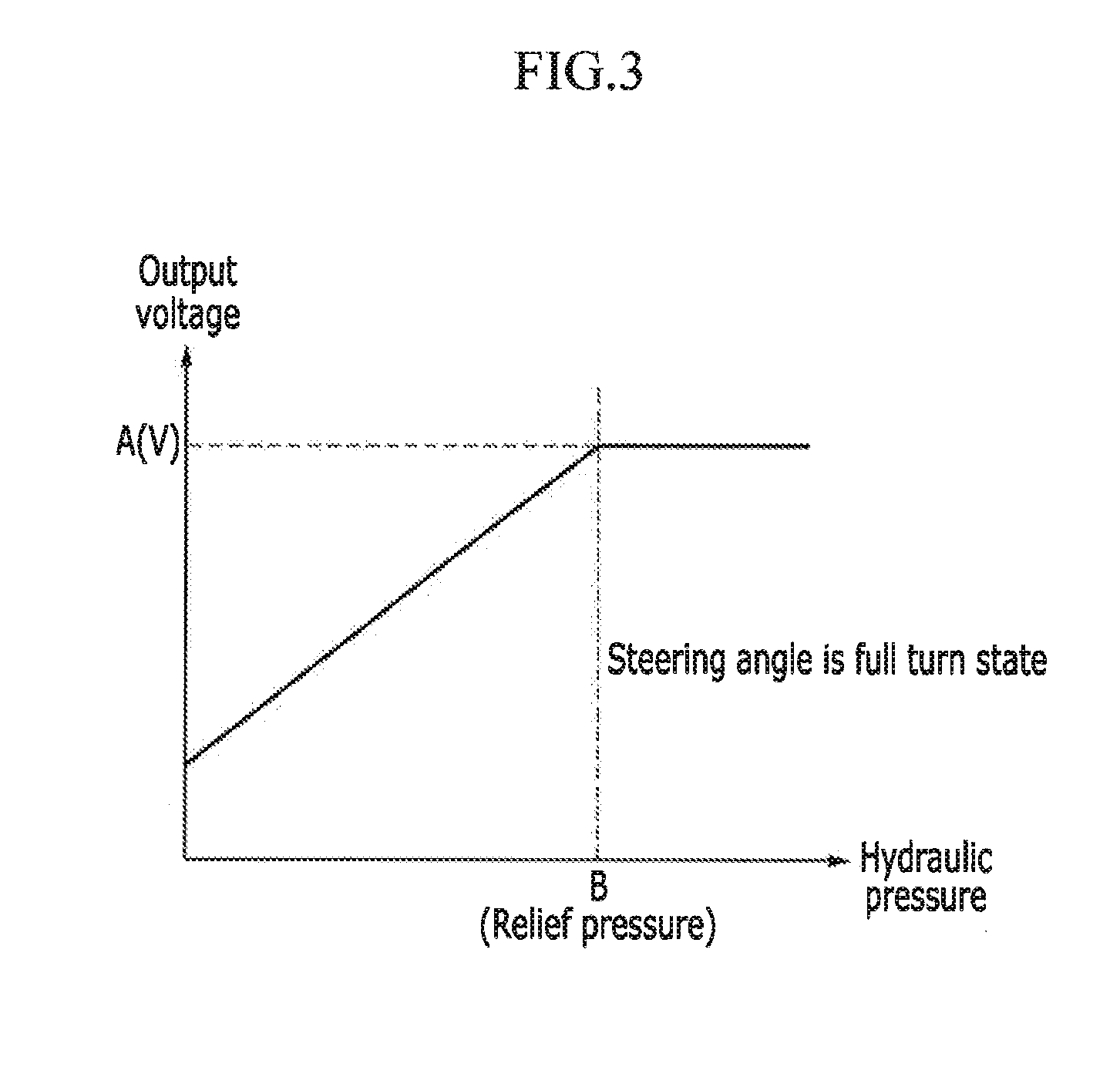
System and method for protecting drive shaft
InactiveUS20150149057A1Reduce output torqueImprove driving durabilityDigital data processing detailsAutomatic initiationsDrive shaftPower steering
A system and method for protecting a drive shaft that include a vehicle state detector configured to detect vehicle information including currently selected shift speed, hydraulic pressure signal detected by a hydraulic pressure detector mounted to a hydraulic pressure power steering assembly, vehicle speed, and engine RPM. In addition, a traction controller is configured to analyze the vehicle information delivered from the vehicle state detector and request reduction of torque when a predetermined condition is satisfied. An engine controller is configured to reduce output torque of an engine based on torque reduction requested by the traction controller to cause the torque applied to the drive shaft to be less than a limit torque.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
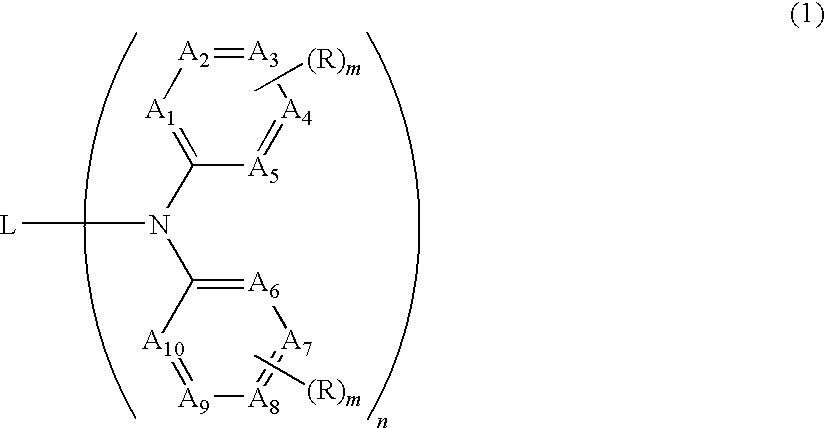
Organic electroluminescent device having specific diamine compound
ActiveUS8980441B2Improve efficiencyReduce the driving voltageDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsOrganic electroluminescenceDiamine
An organic electroluminescent device is provided and includes: a cathode; an anode; and a light-emitting layer between the cathode and the anode. The light-emitting layer includes a compound represented by formula (1).In formula (1), L represents a linking group; A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9, and A10 each independently represent a carbon atom or a nitrogen atom, provided that at least two of A1, A5, A6, and A10 each represent a carbon atom having R′; R′ represents a substituent having a carbon atom at a bonding position thereof; a plurality of Rs each independently represent a substituent; m represents an integer; and n represents an integer of 2 to 10.
Owner:UDC IRELAND
Liquid jet head and a liquid jet apparatus
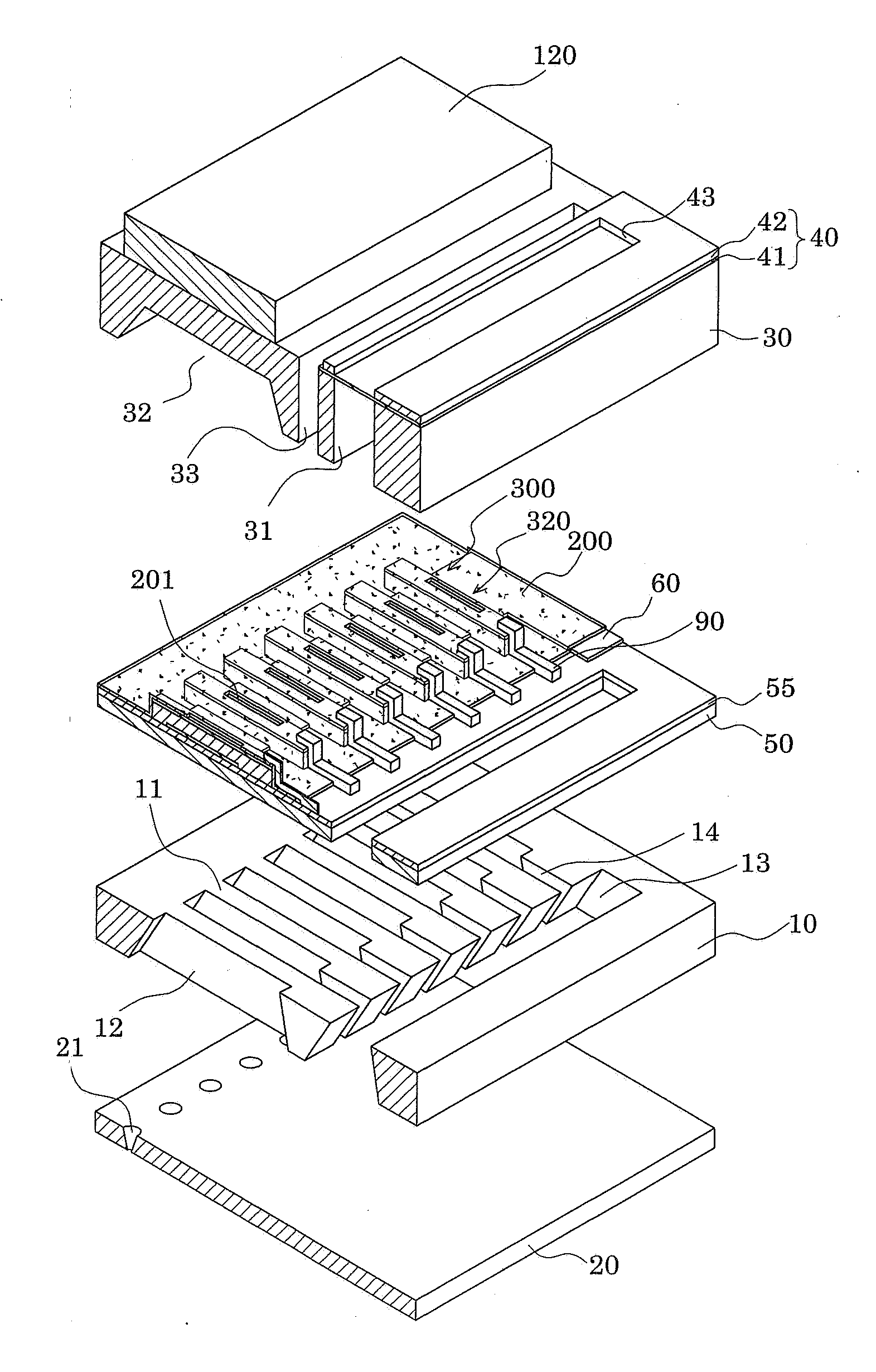
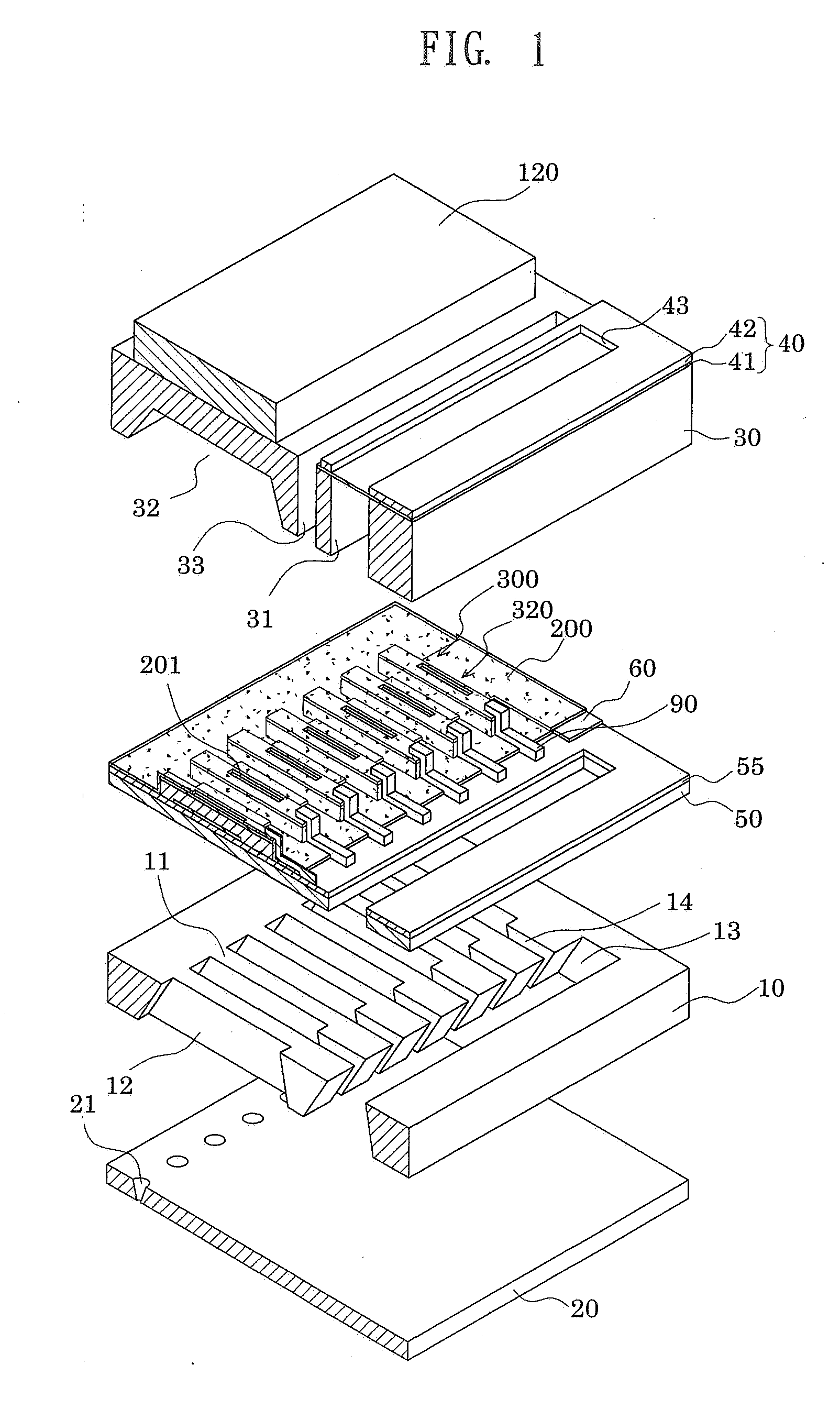
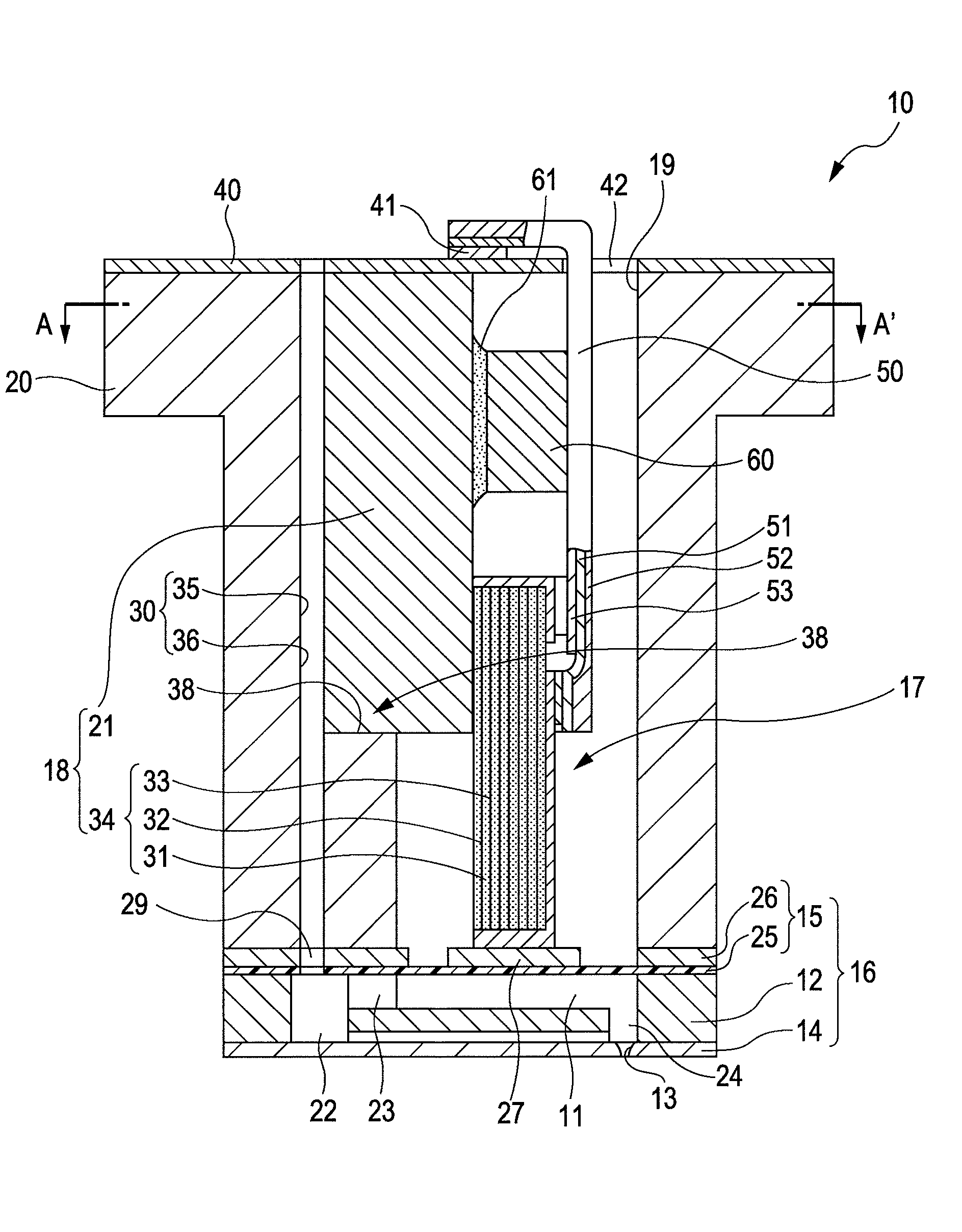
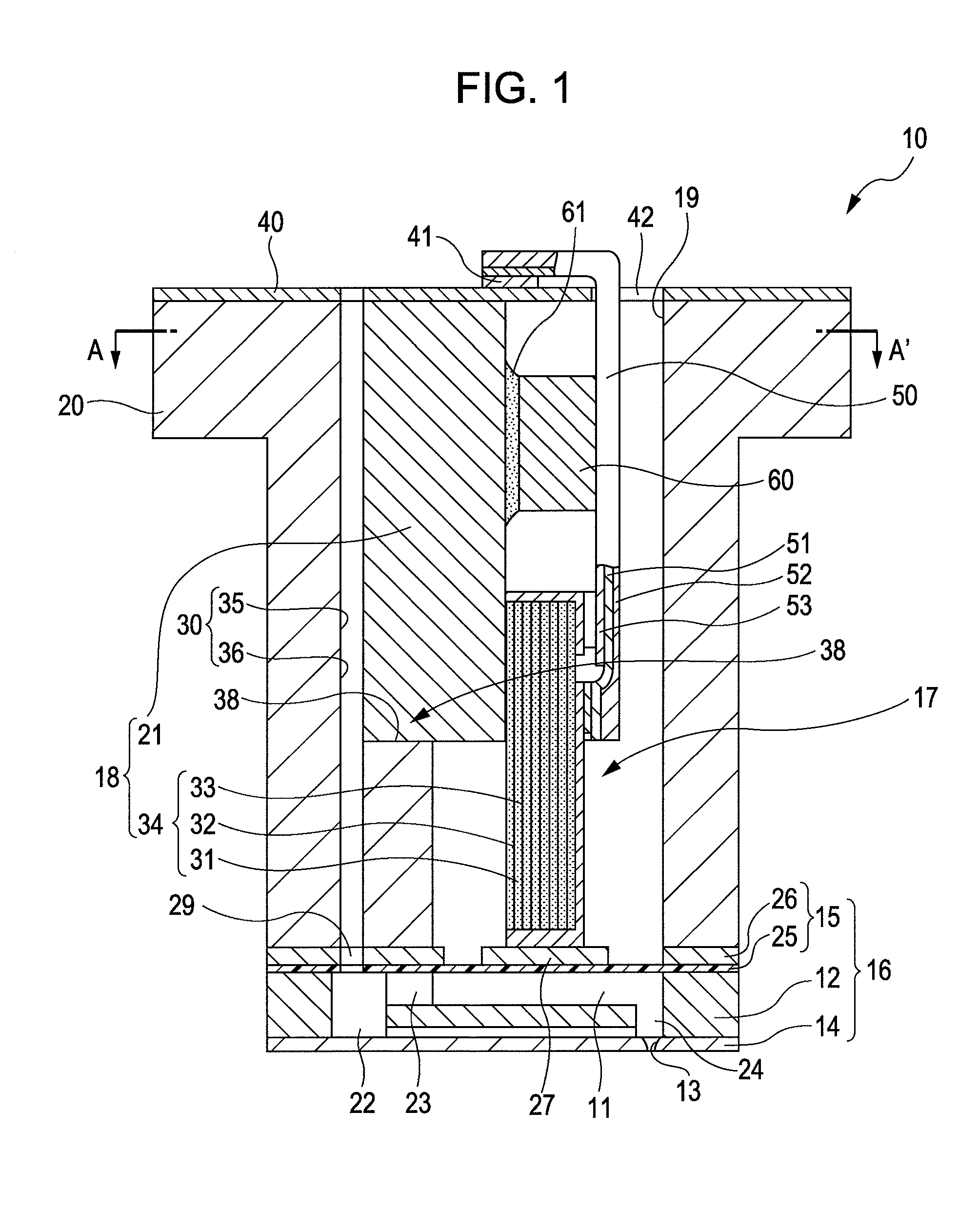
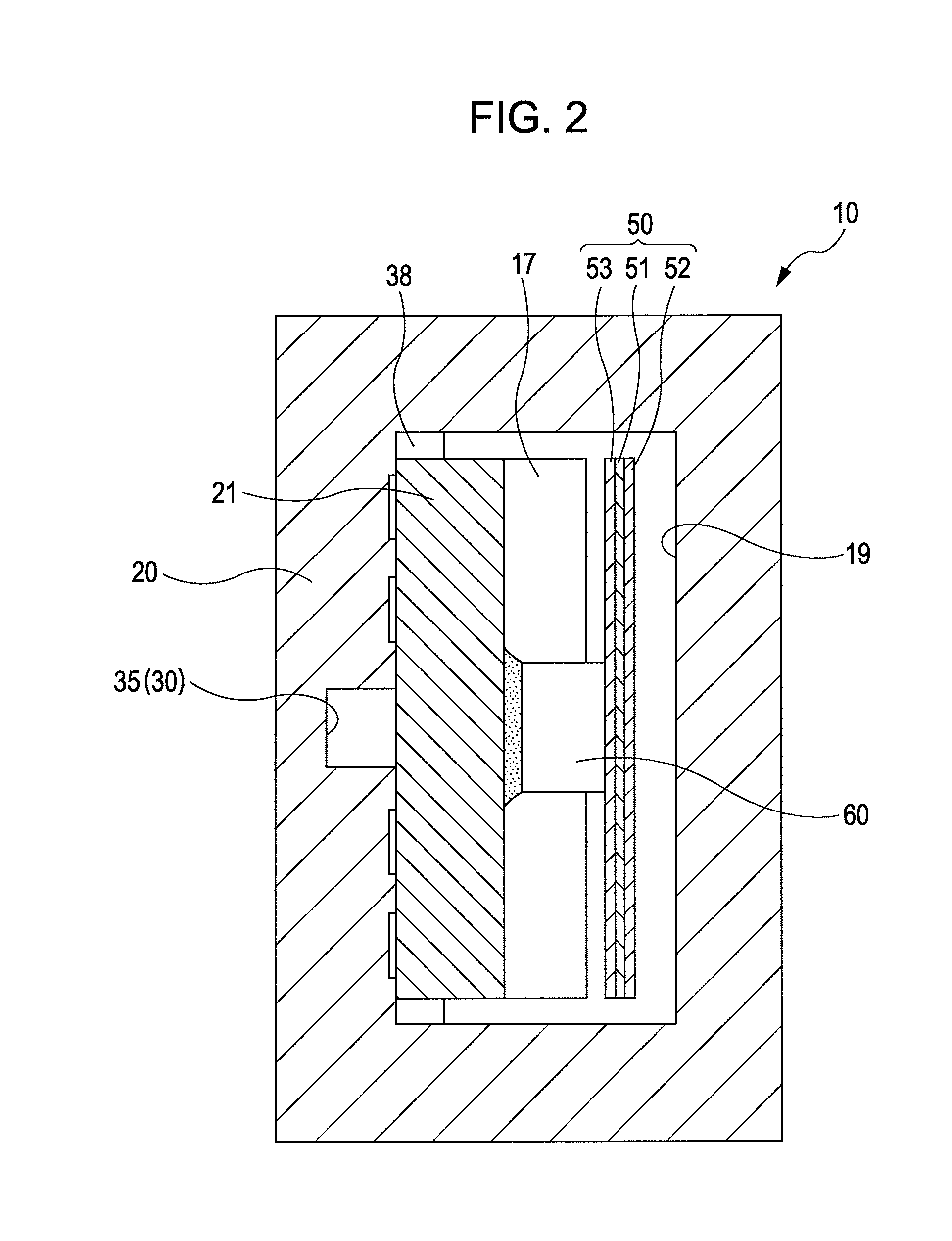
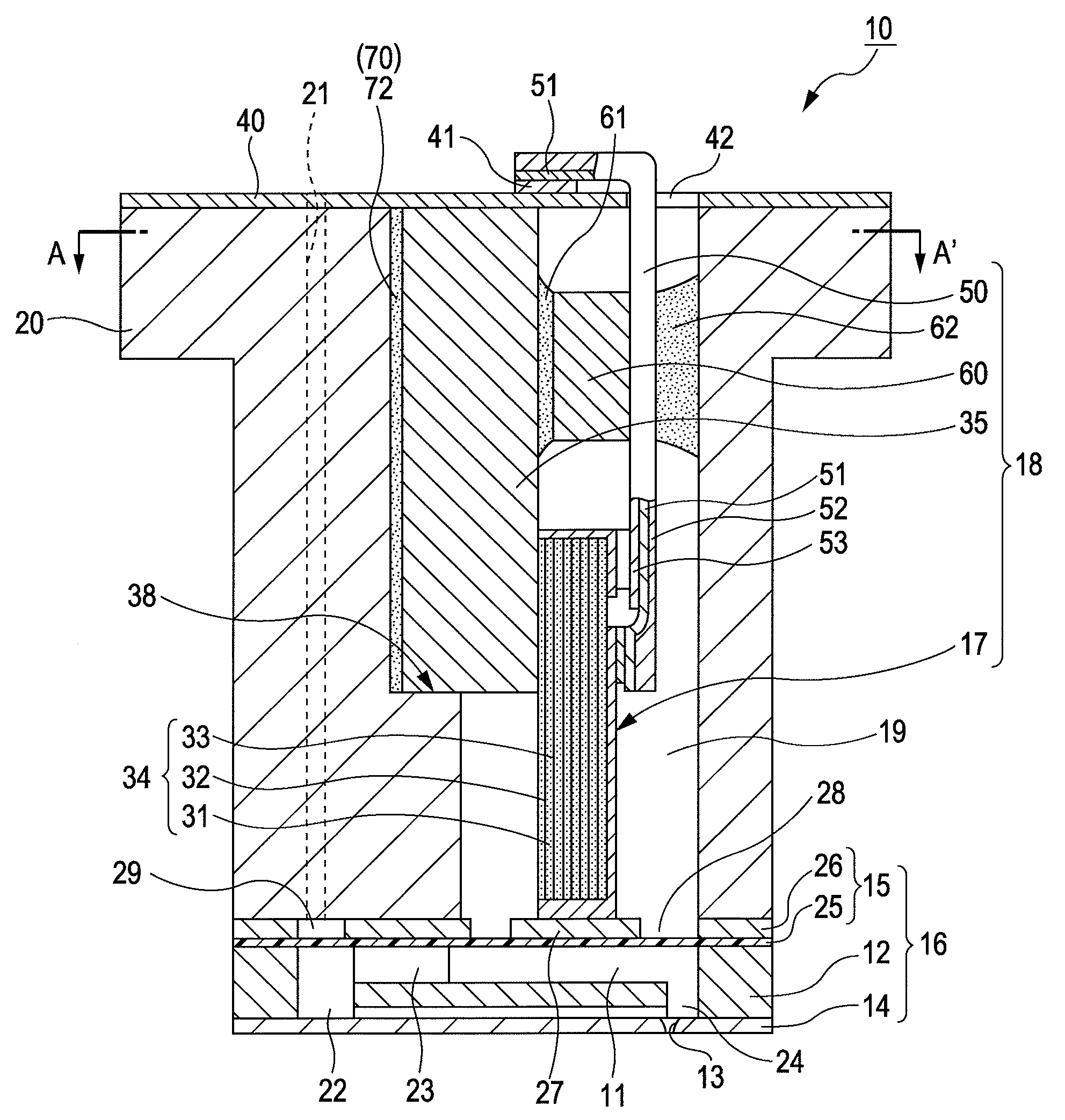
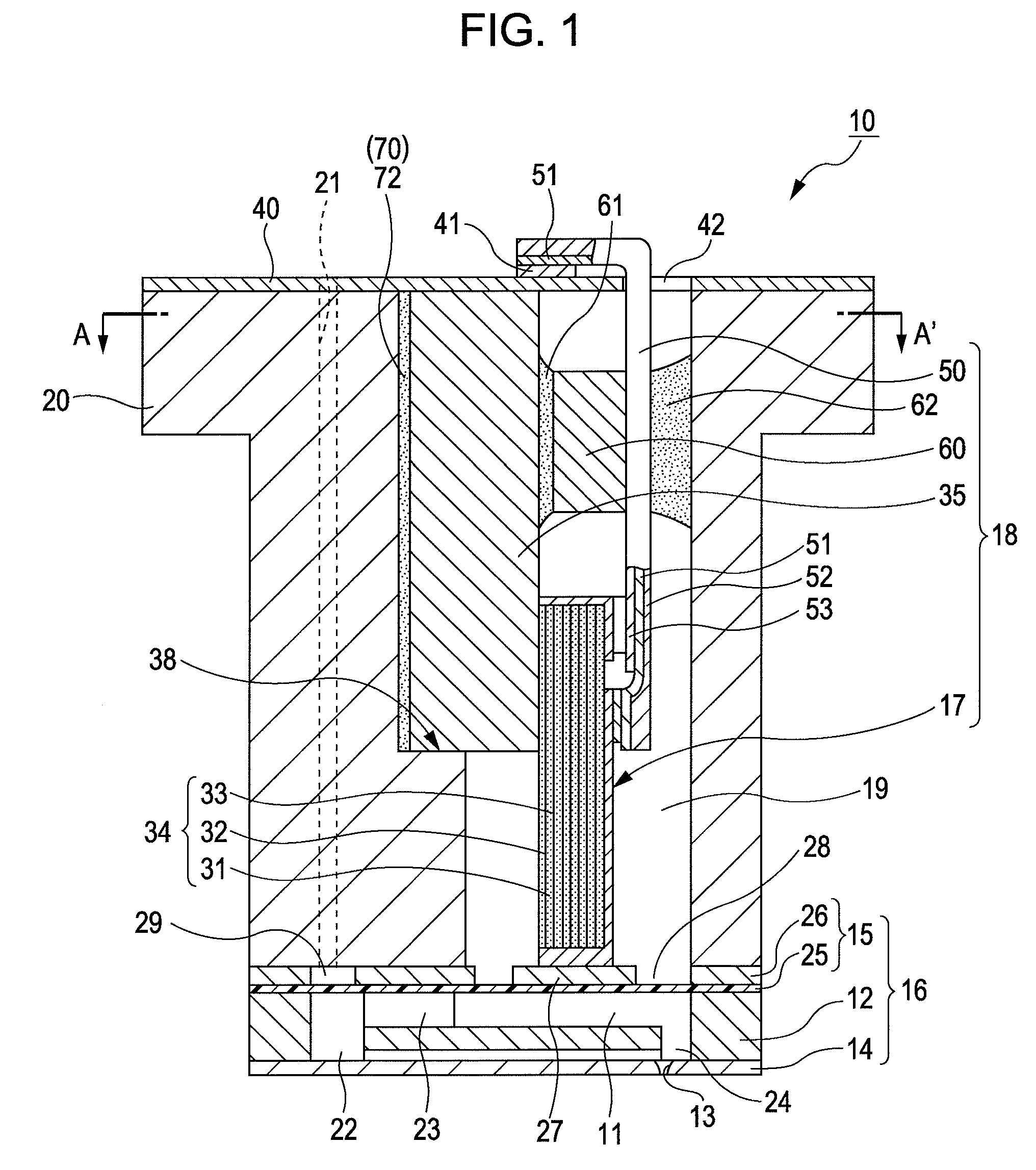
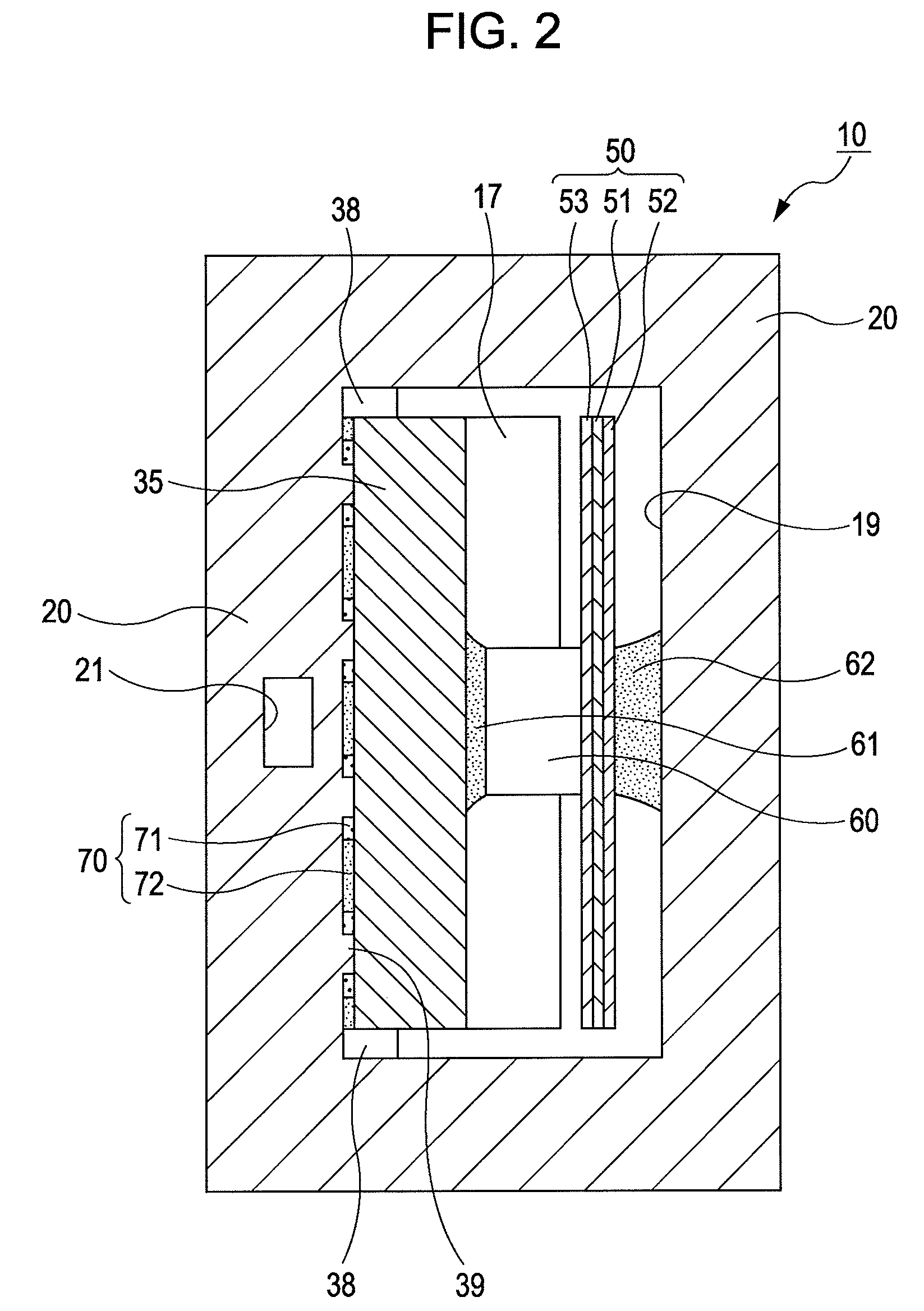
A liquid jet head includes: a pressure generation chamber 11 communicating with a nozzle opening 13 ejecting a liquid; a piezoelectric element 17 causing pressure change inside the pressure generation chamber 11; a case head 20 having an accommodation portion 19 accommodating the piezoelectric element 17; and a flexible printed board 50 having a driving circuit 60 mounted thereon and connected to the piezoelectric element 17 to drive the piezoelectric element 17. The accommodation portion 19 of the case head 20 is provided with a flow passage member 21 holding a base end portion of the piezoelectric element 17 and being connected to the driving circuit 60 in a thermally conductive manner, the case head 20 is provided with a liquid introduction passage 30 for supplying the liquid to the pressure generation chamber 11, and the flow passage member 21 partitions a part of at least a wall surface of the liquid introduction passage 30.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Liquid jet head, a liquid jet apparatus and a method for manufacturing a liquid jet head
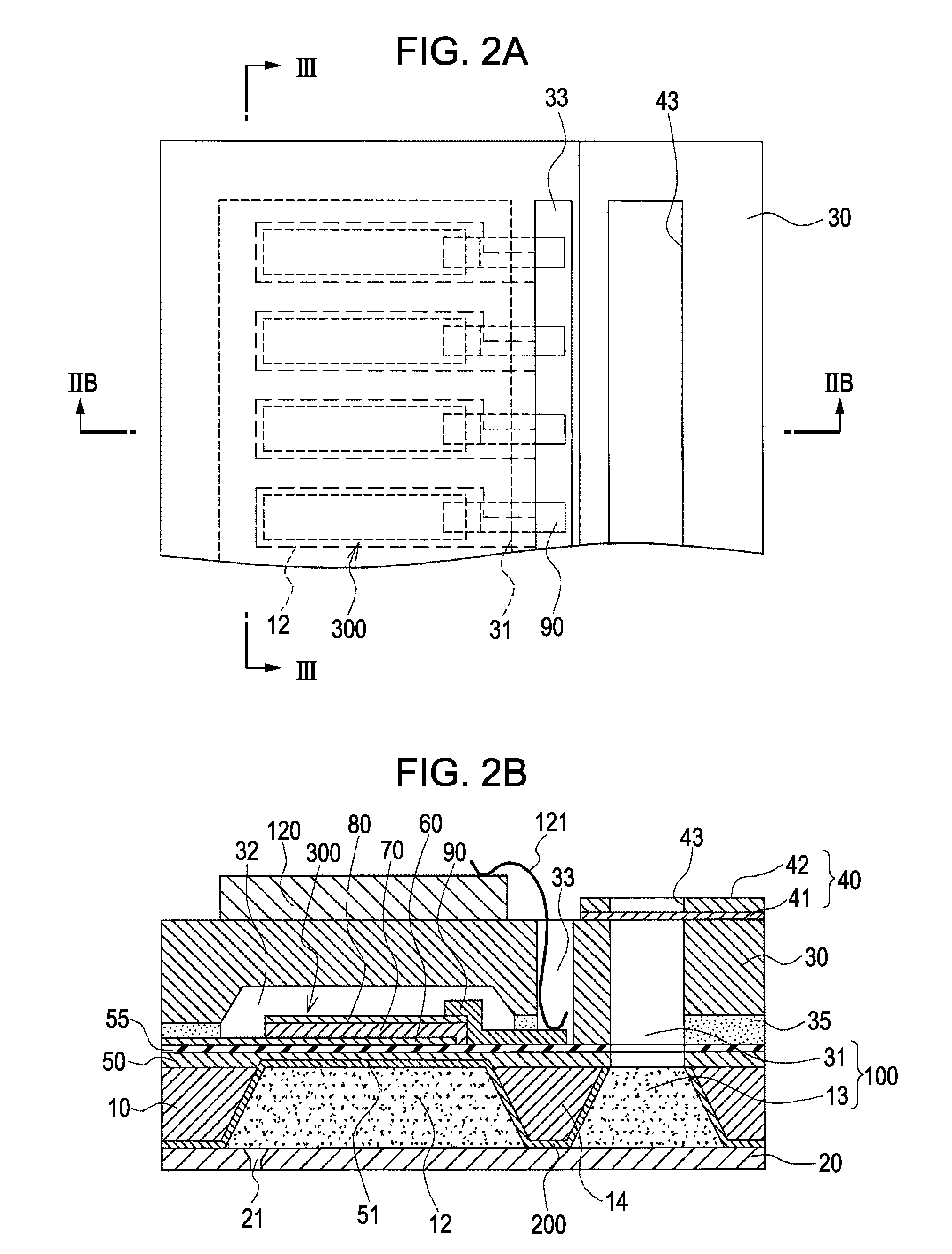
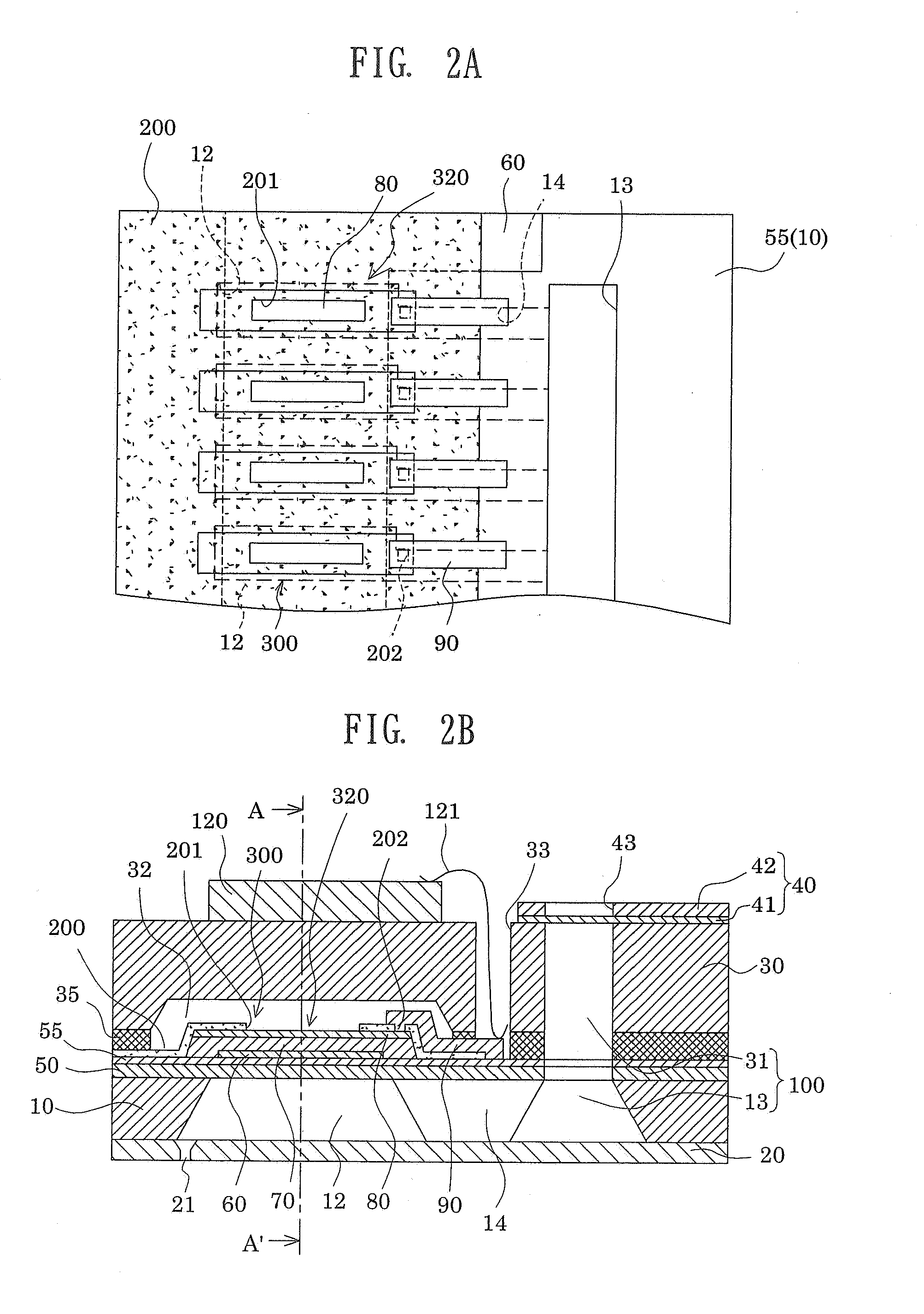
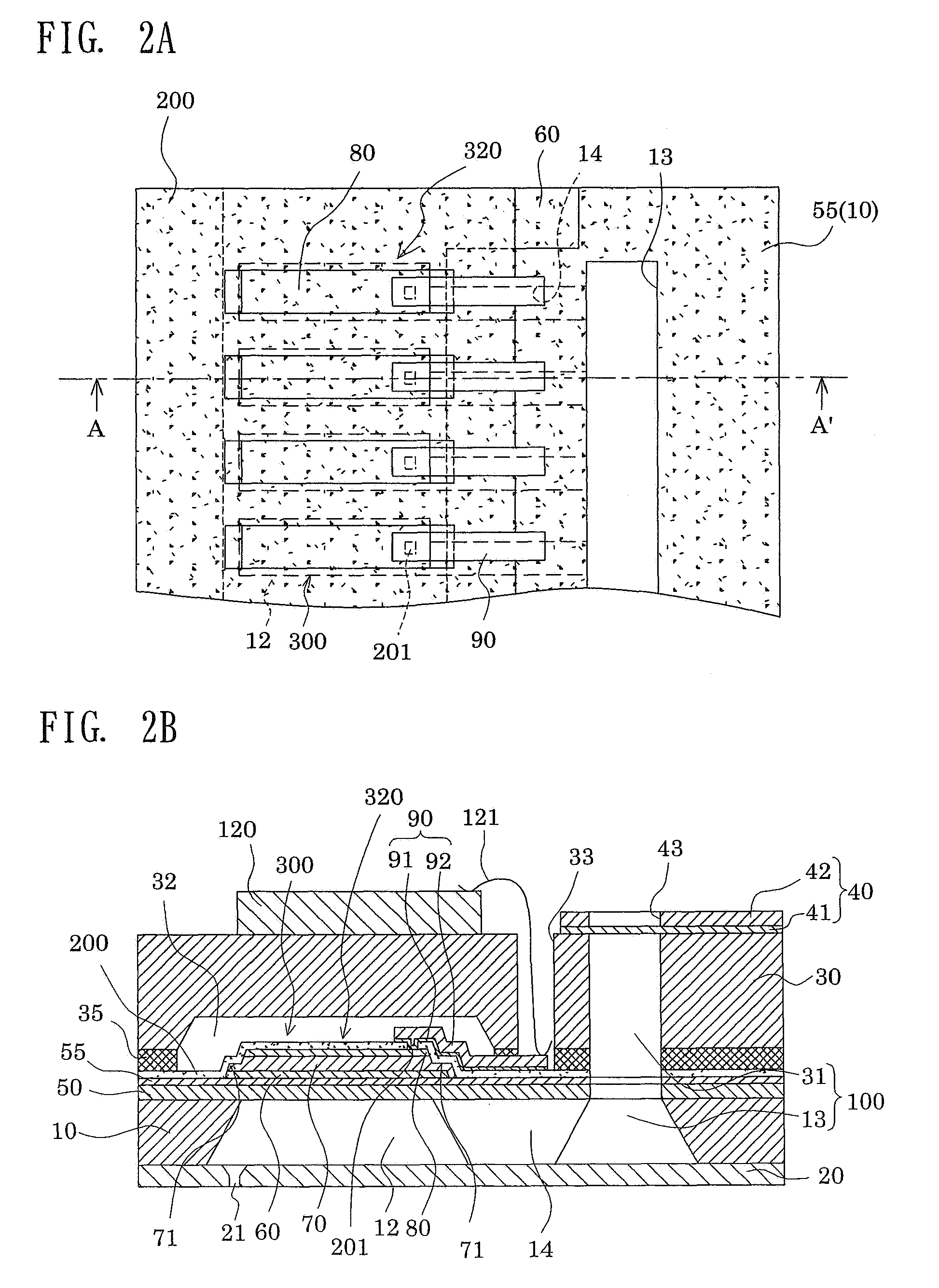
ActiveUS20090185013A1Effective coolingImprove driving durabilityOther printing apparatusLiquid jetPressure generation
An ink jet recording head 10 is provided which includes: piezoelectric elements 17 as a pressure generation unit that causes pressure change in pressure generation chambers 11 which are communicated with nozzle openings 13 that eject liquid; a driving circuit 60 as a driving unit that generates a driving signal for driving the pressure generation unit; a case head 20 that accommodates therein the driving unit; and a thermally conductor 35 that is in contact with the driving unit and the case head 20, in which the thermally conductor 35 and the case head 20 are fixed to each other via an thermally conductive adhesive layer 72 as a thermally conductive layer.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com