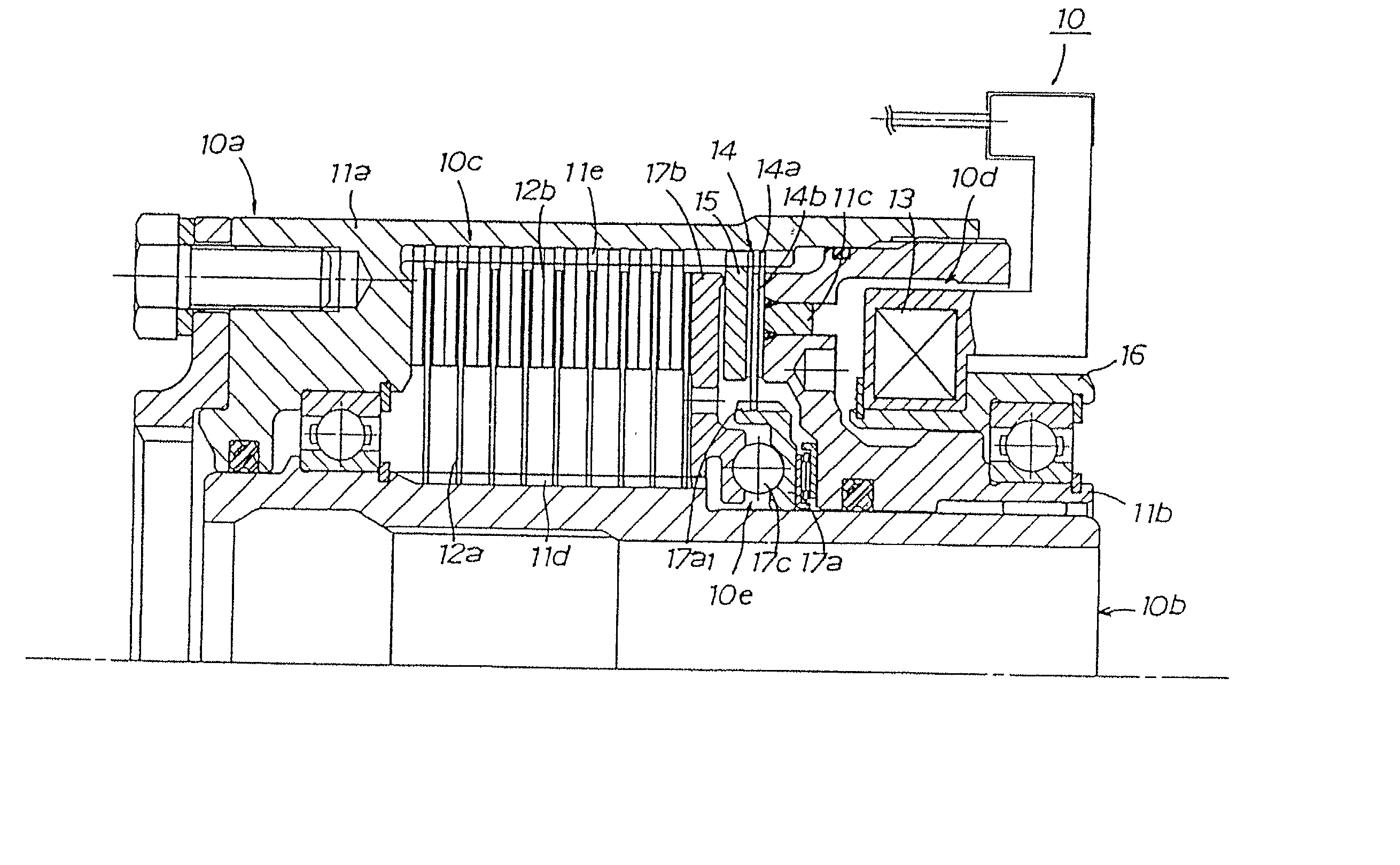
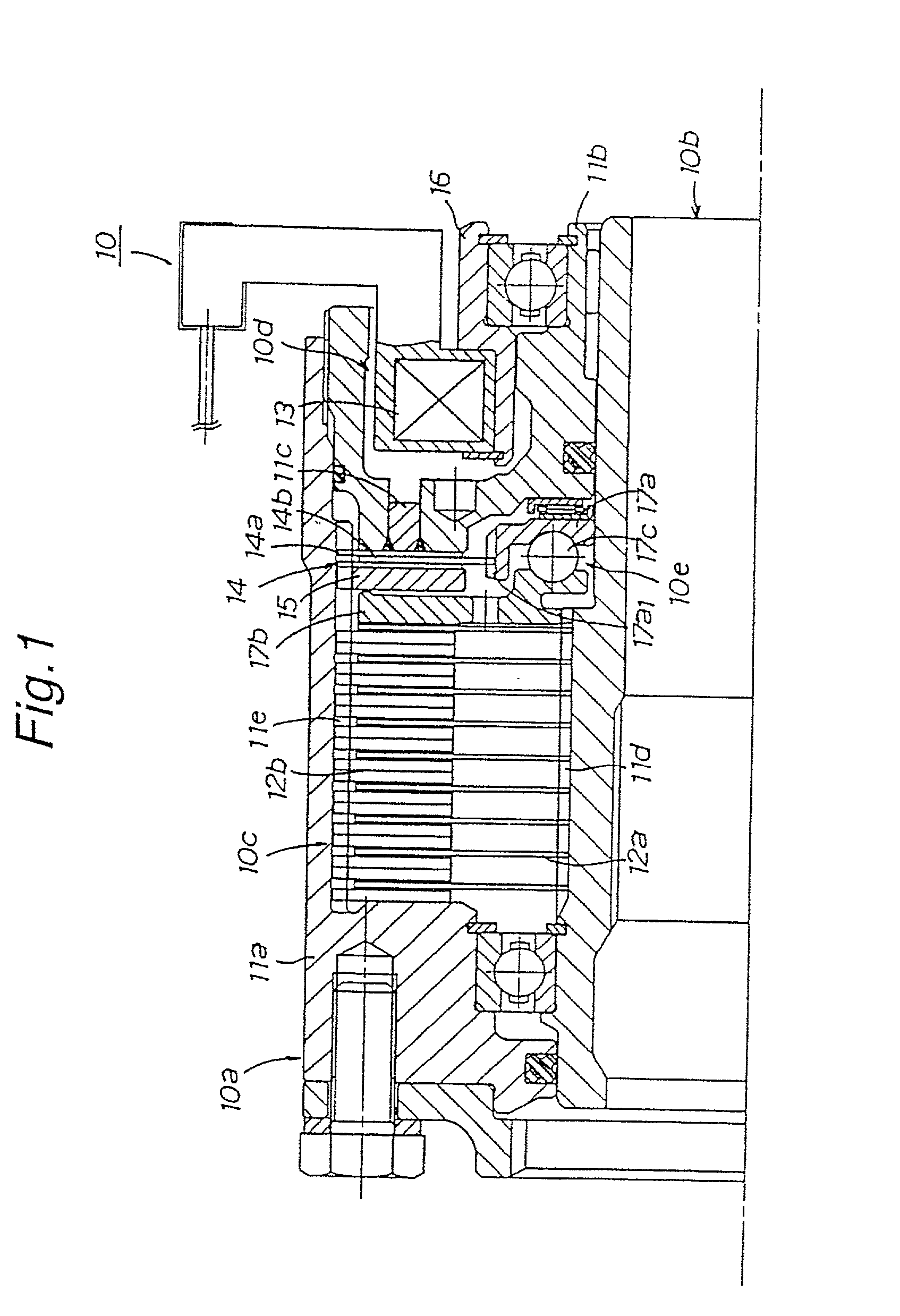
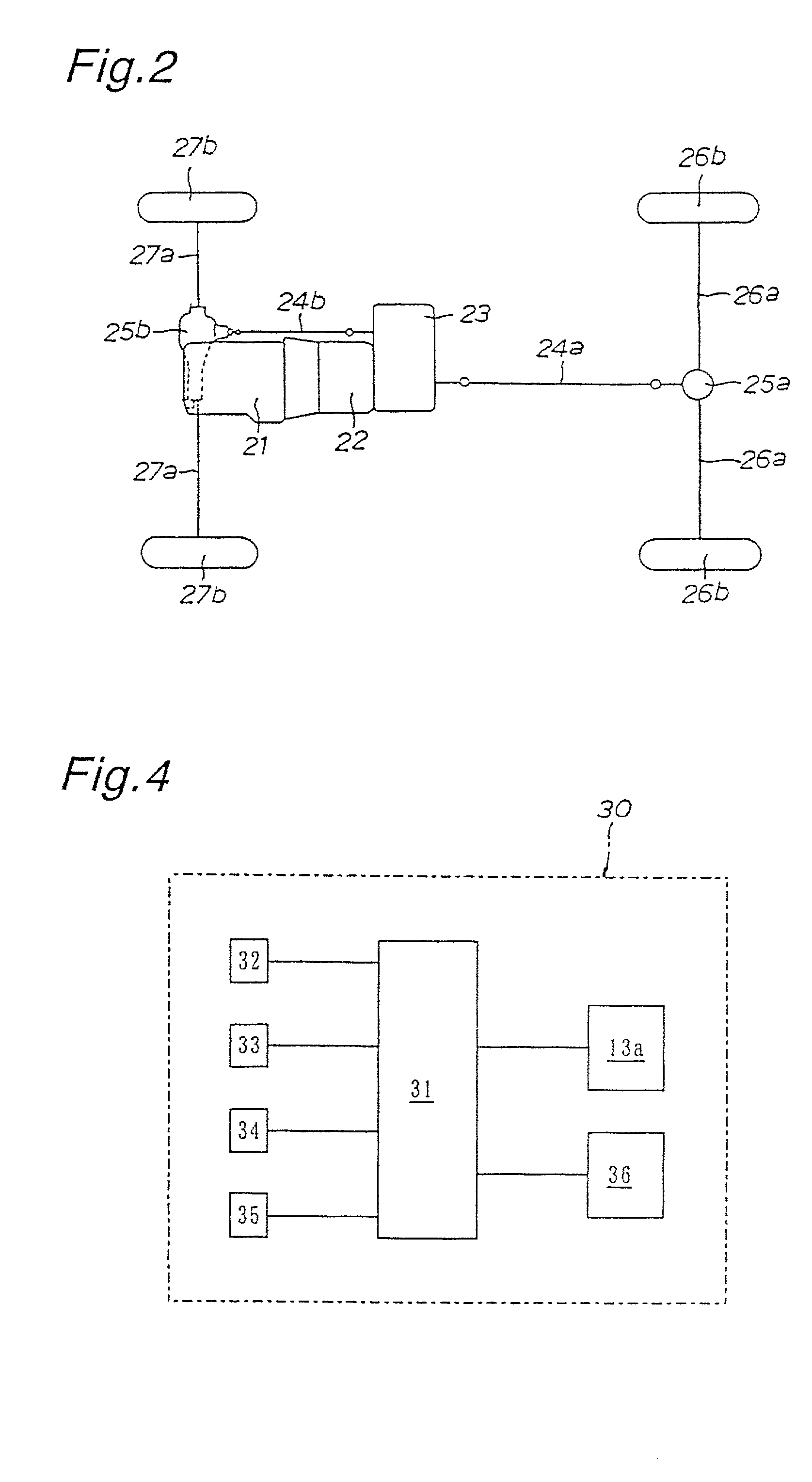
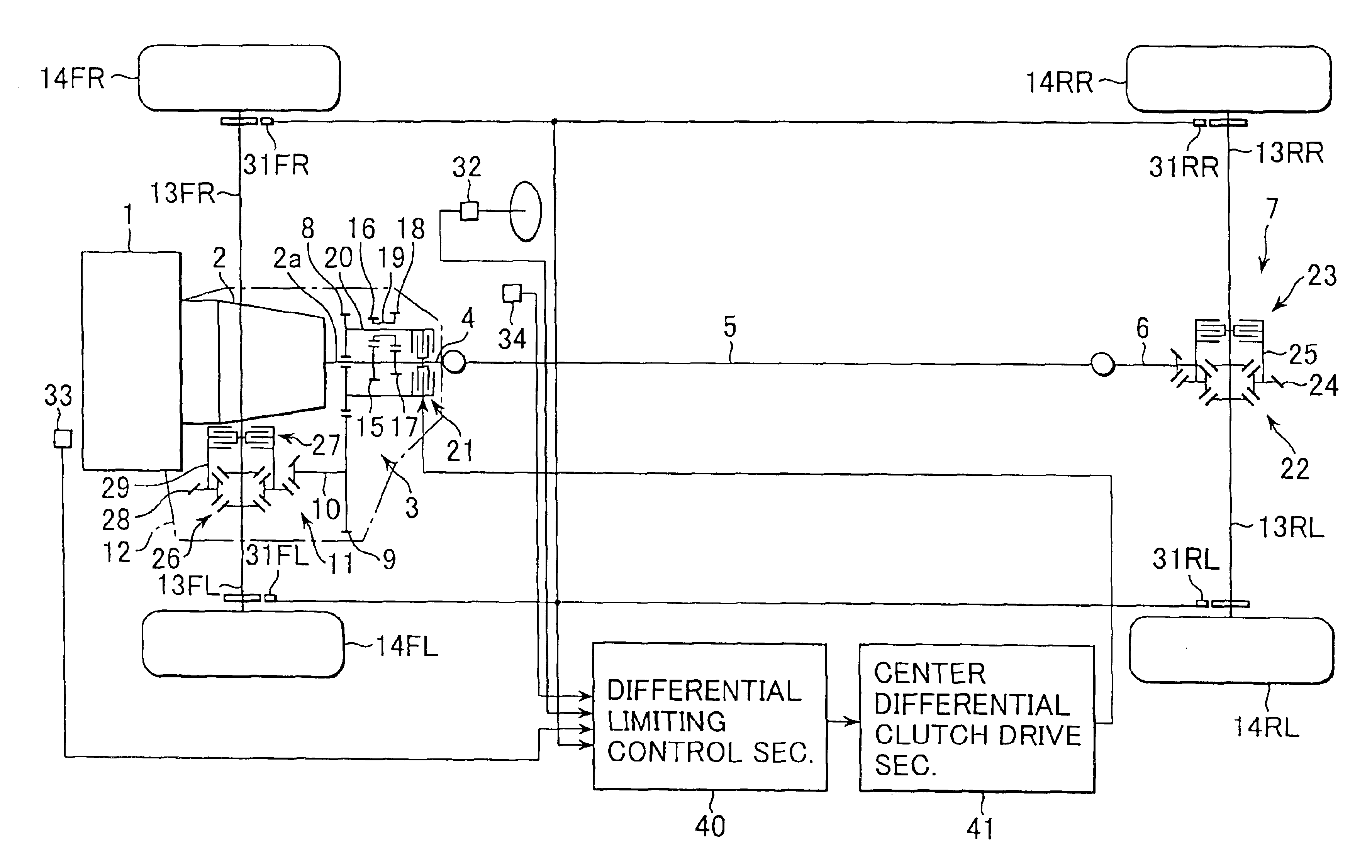
Patents
Literature
253 results about "Differential rotation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Differential rotation is seen when different parts of a rotating object move with different angular velocities (rates of rotation) at different latitudes and/or depths of the body and/or in time. This indicates that the object is not solid. In fluid objects, such as accretion disks, this leads to shearing. Galaxies and protostars usually show differential rotation; examples in the Solar System include the Sun, Jupiter and Saturn.
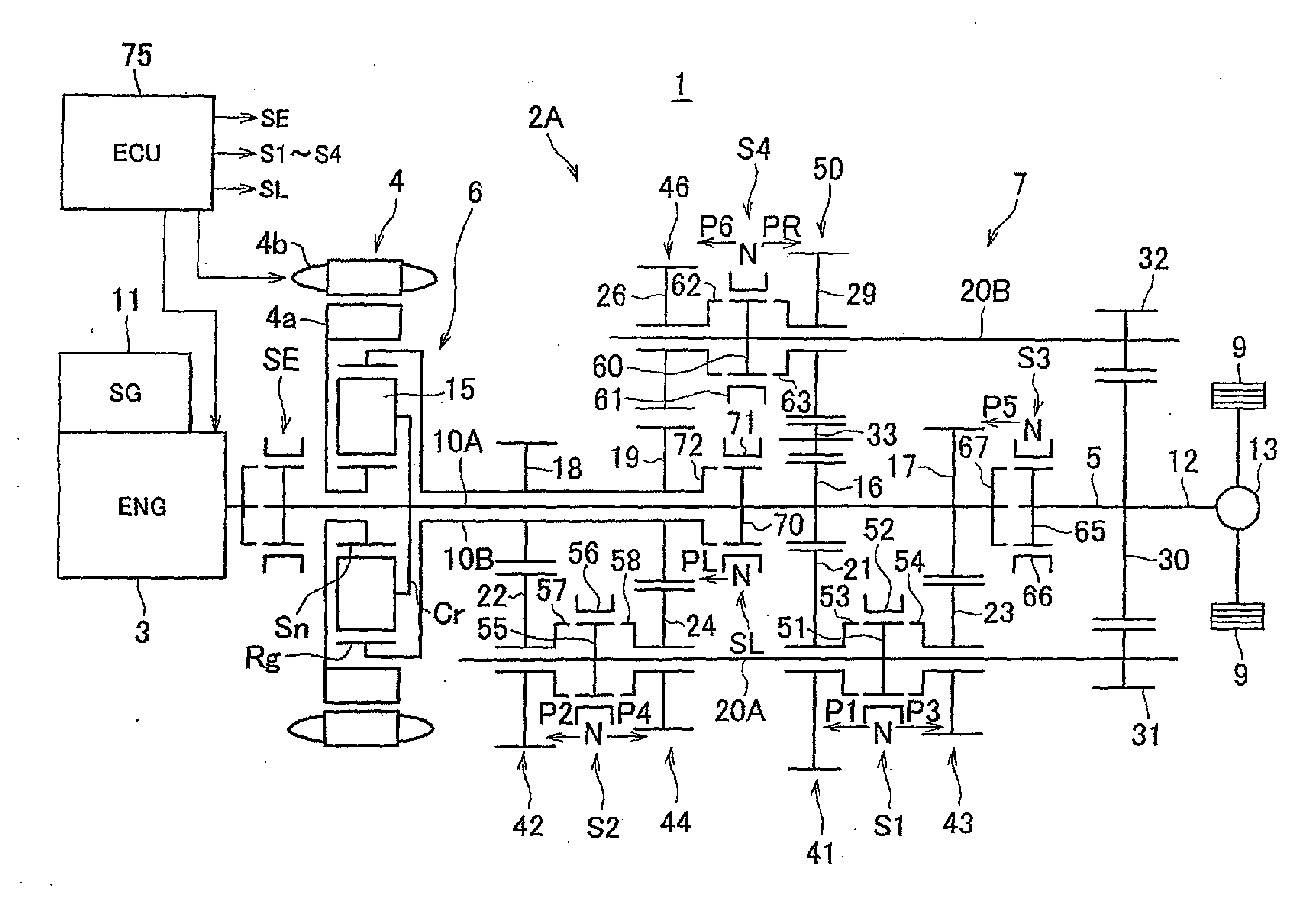
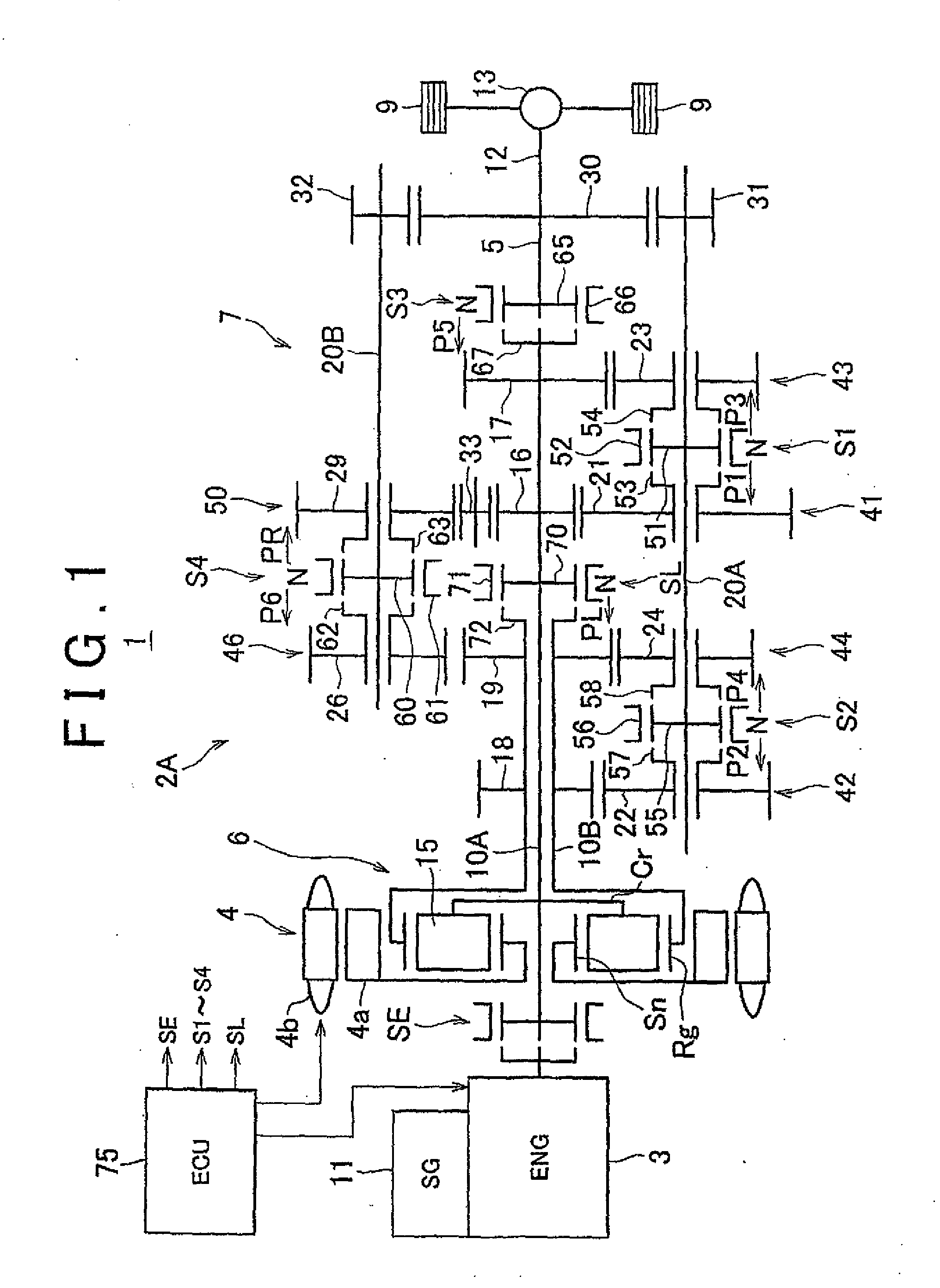
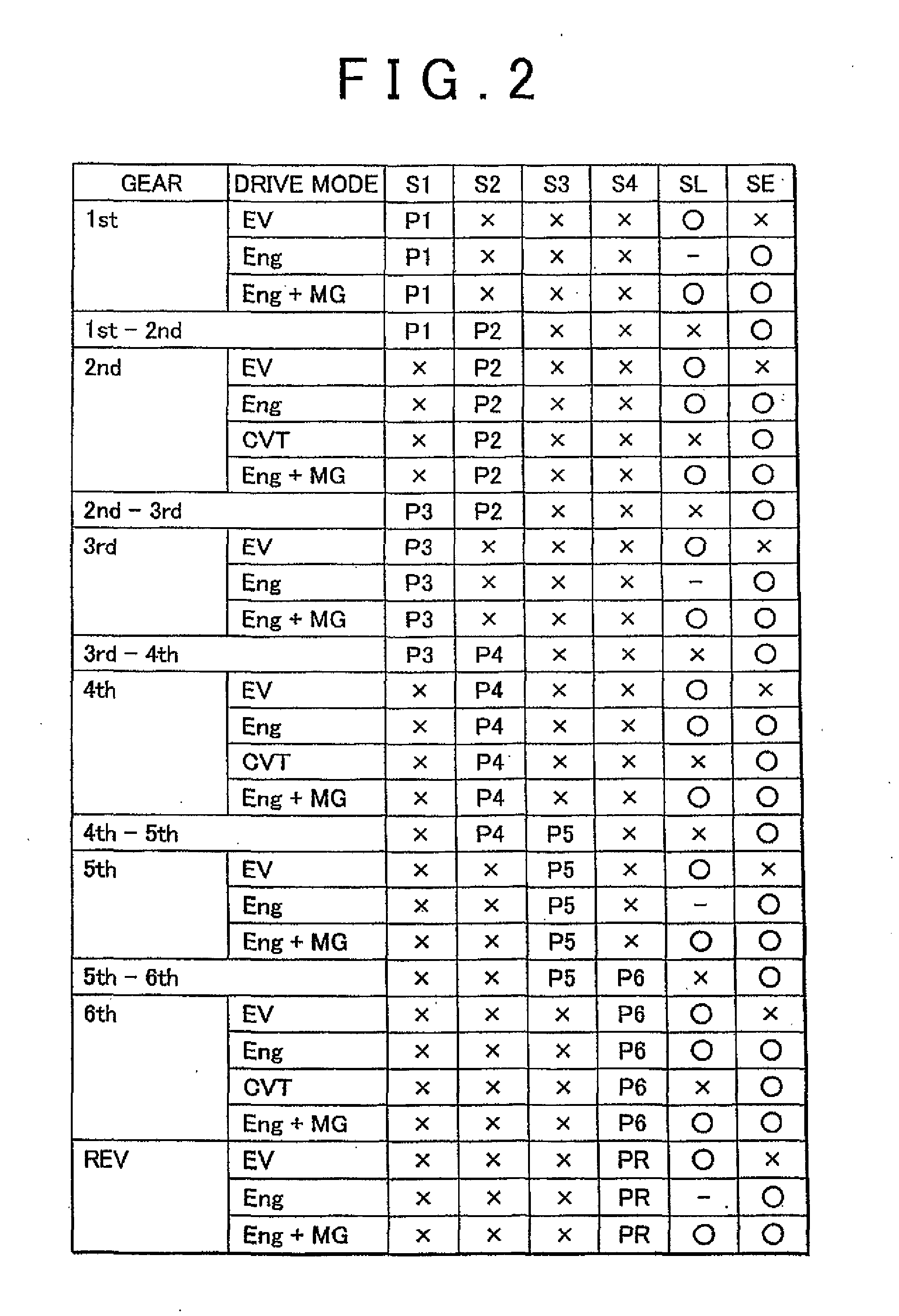
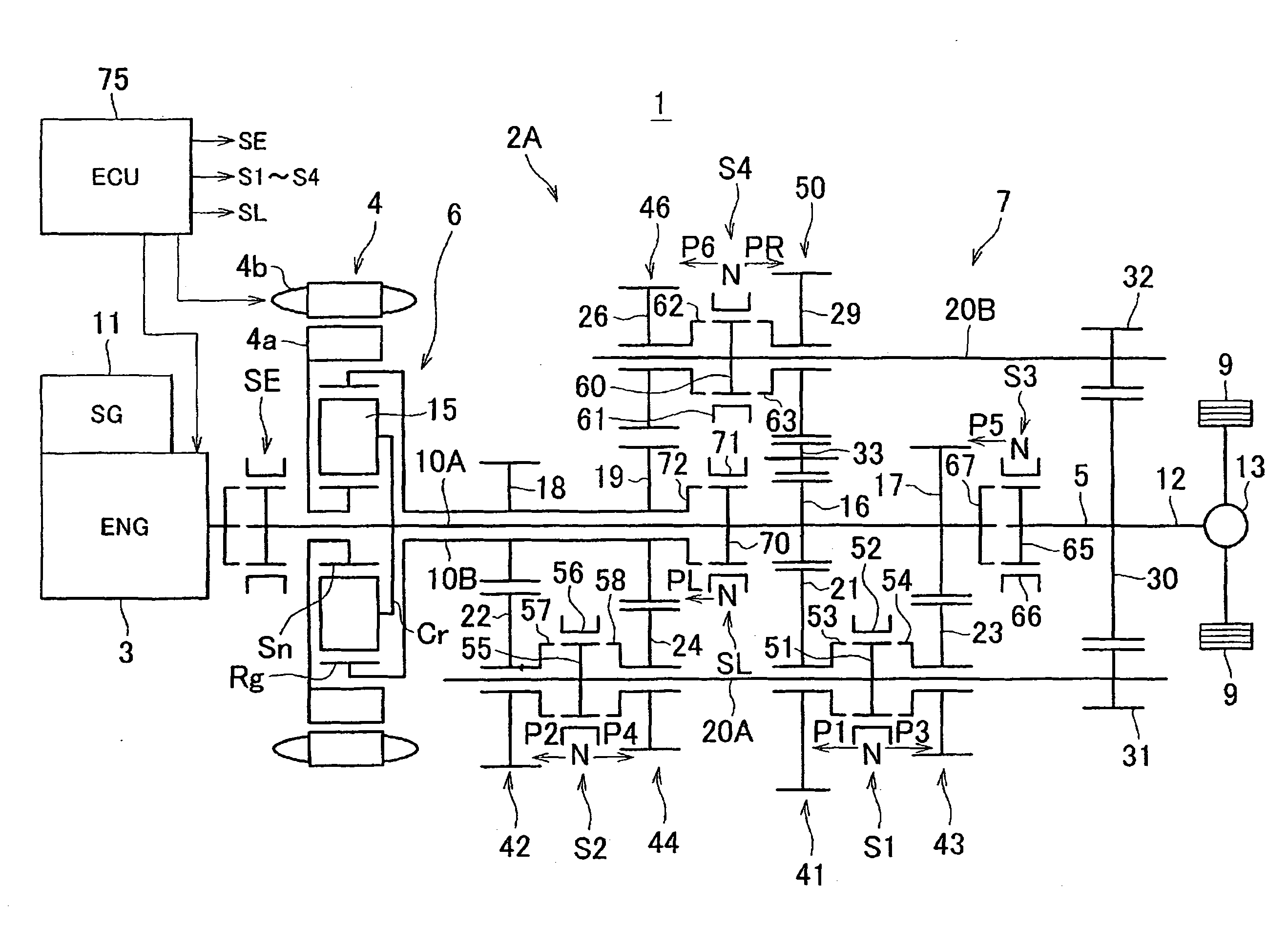
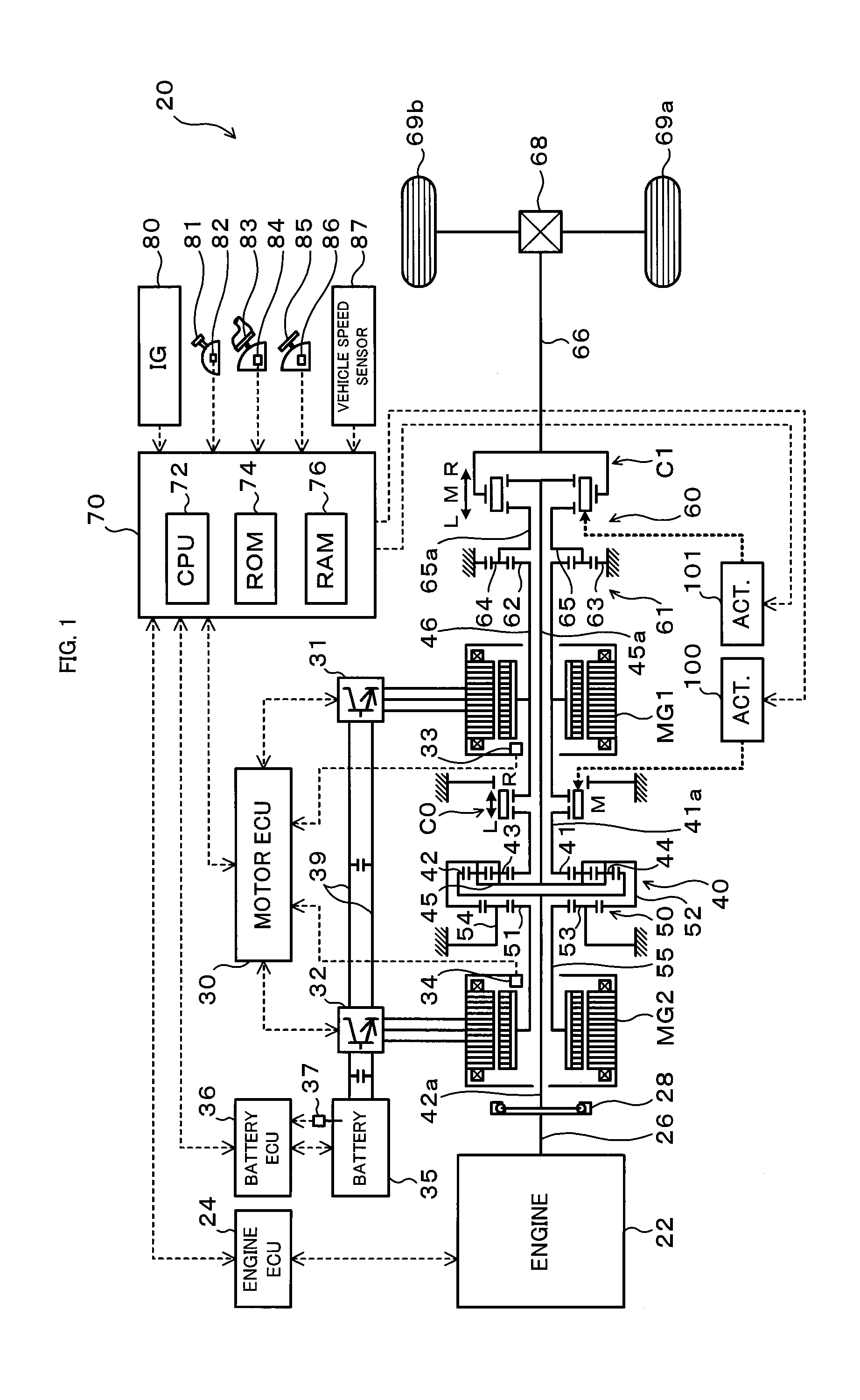
Vehicle drive system
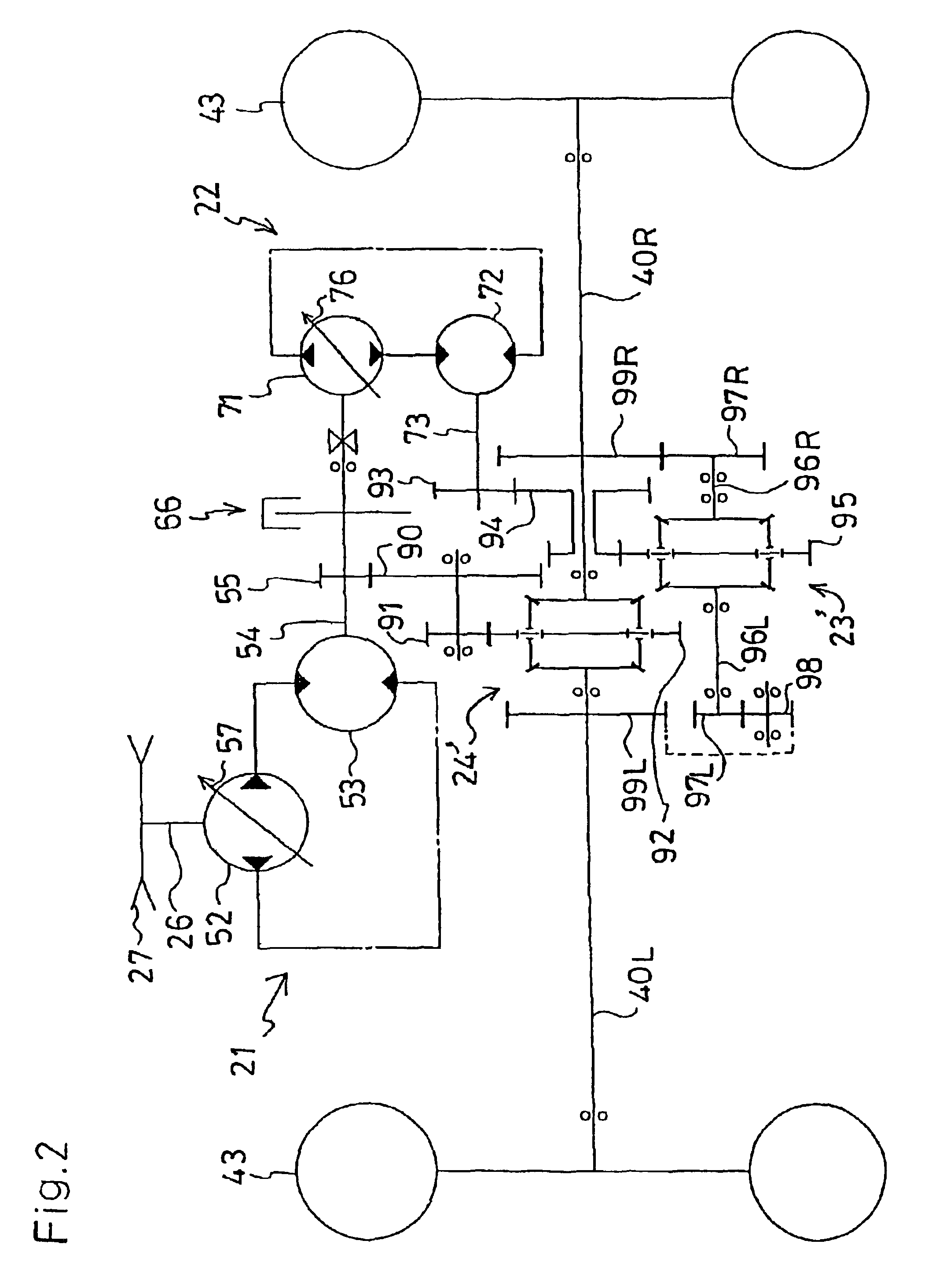
ActiveUS20110111910A1Reduce lossesGas pressure propulsion mountingToothed gearingsEngineeringGear train
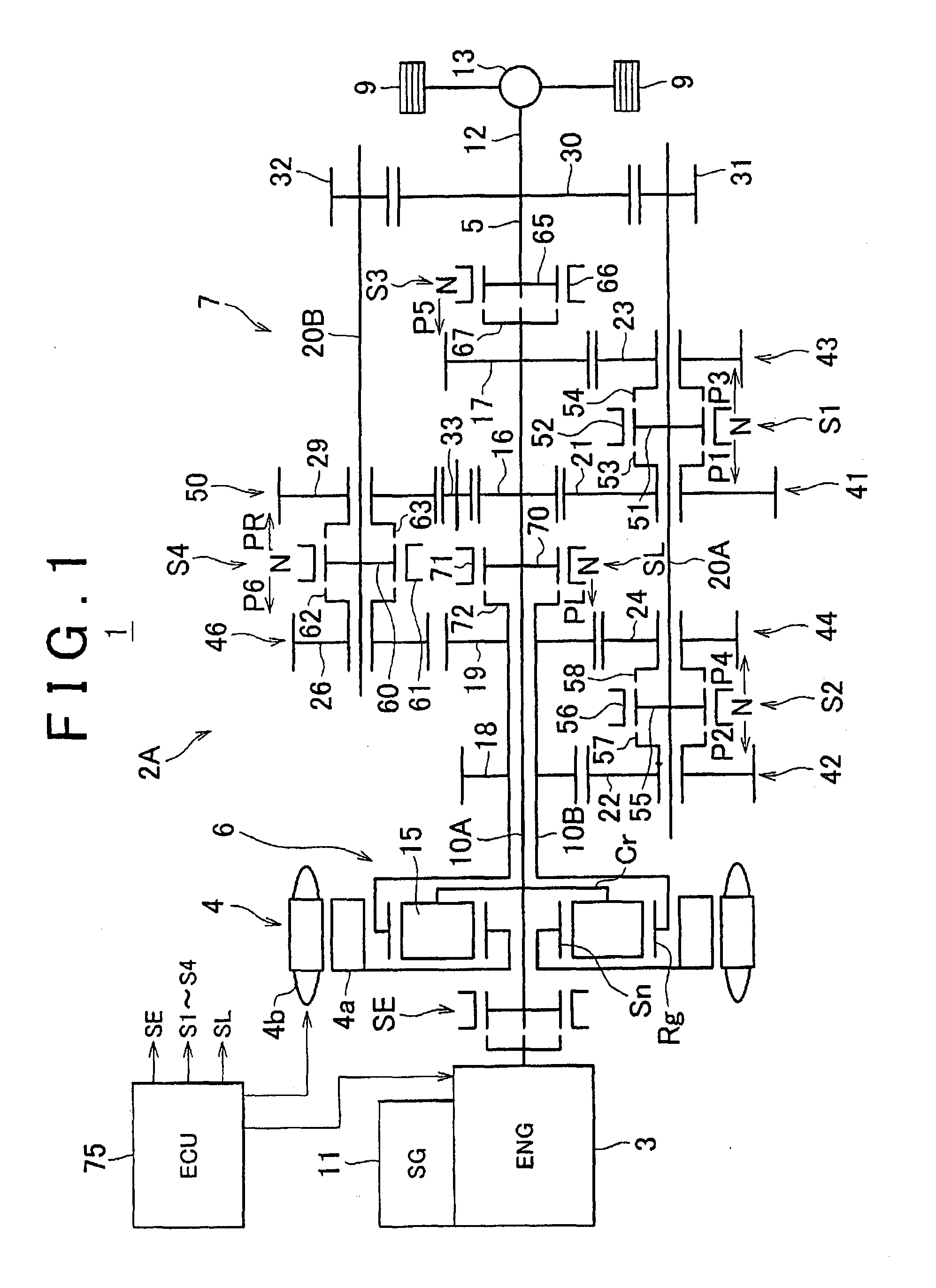
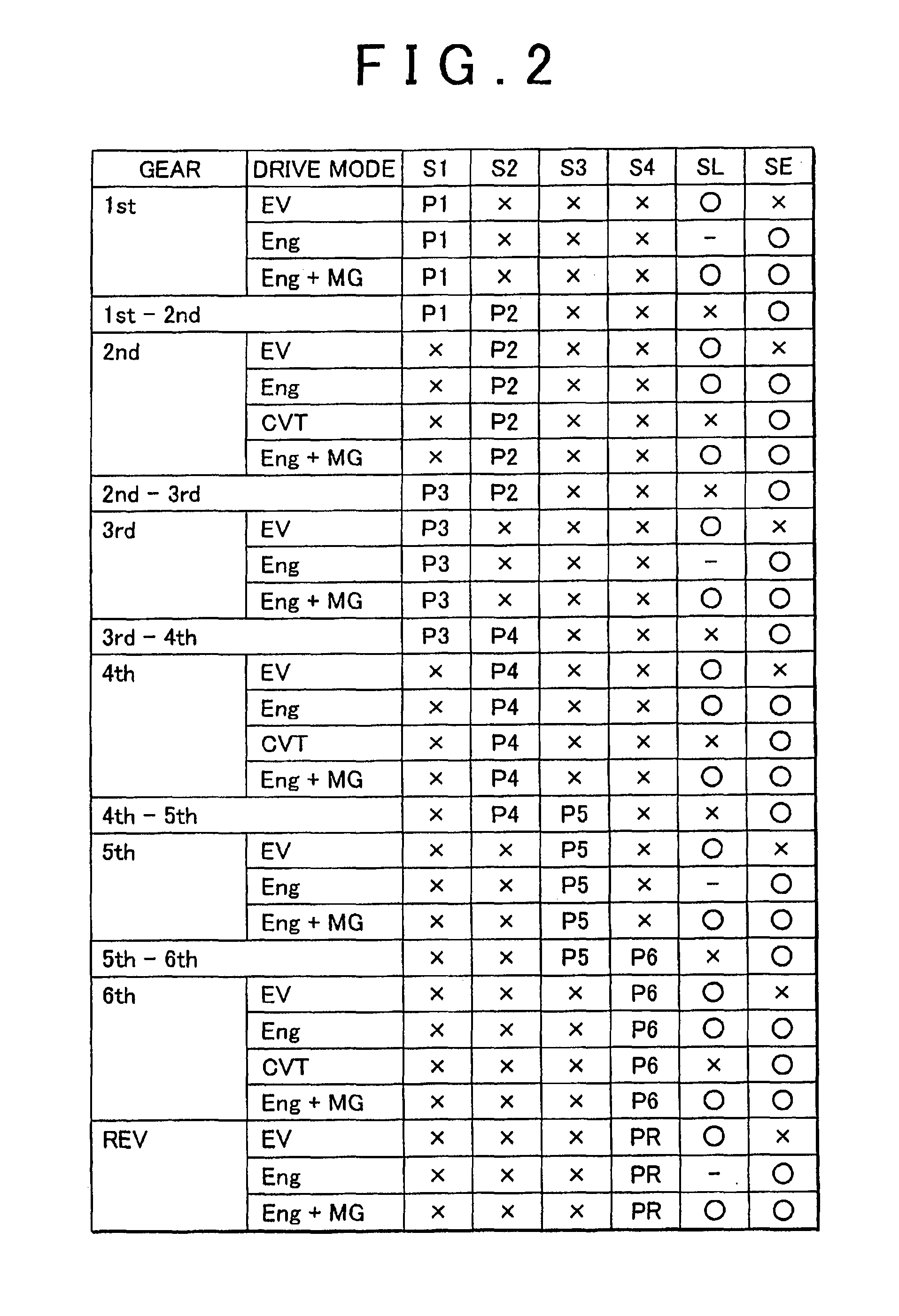
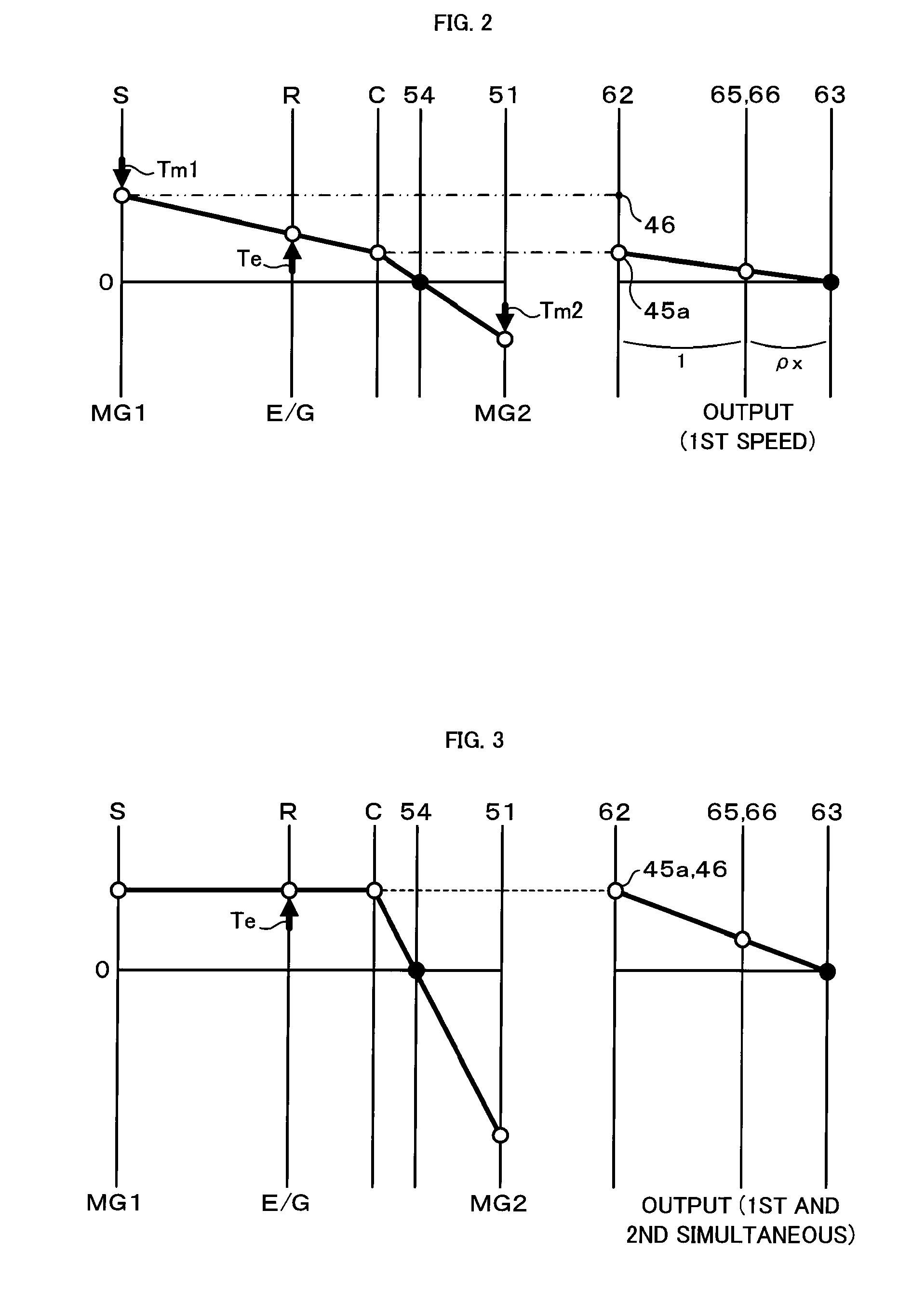
A drive system includes a transmission mechanism that establishes a plurality of gear positions comprising a first-speed through sixth-speed gear positions and a reverse-drive gear position, by switching among change gear trains and coupling a first driveshaft to an output member, and also includes a lock clutch that switches a power distribution mechanism between a locked state in which a ring gear and a carrier are coupled to each other and are inhibited from rotating in a differential fashion, and a released state in which the inhibition of the differential rotation is cancelled.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Vehicle height adjusting system
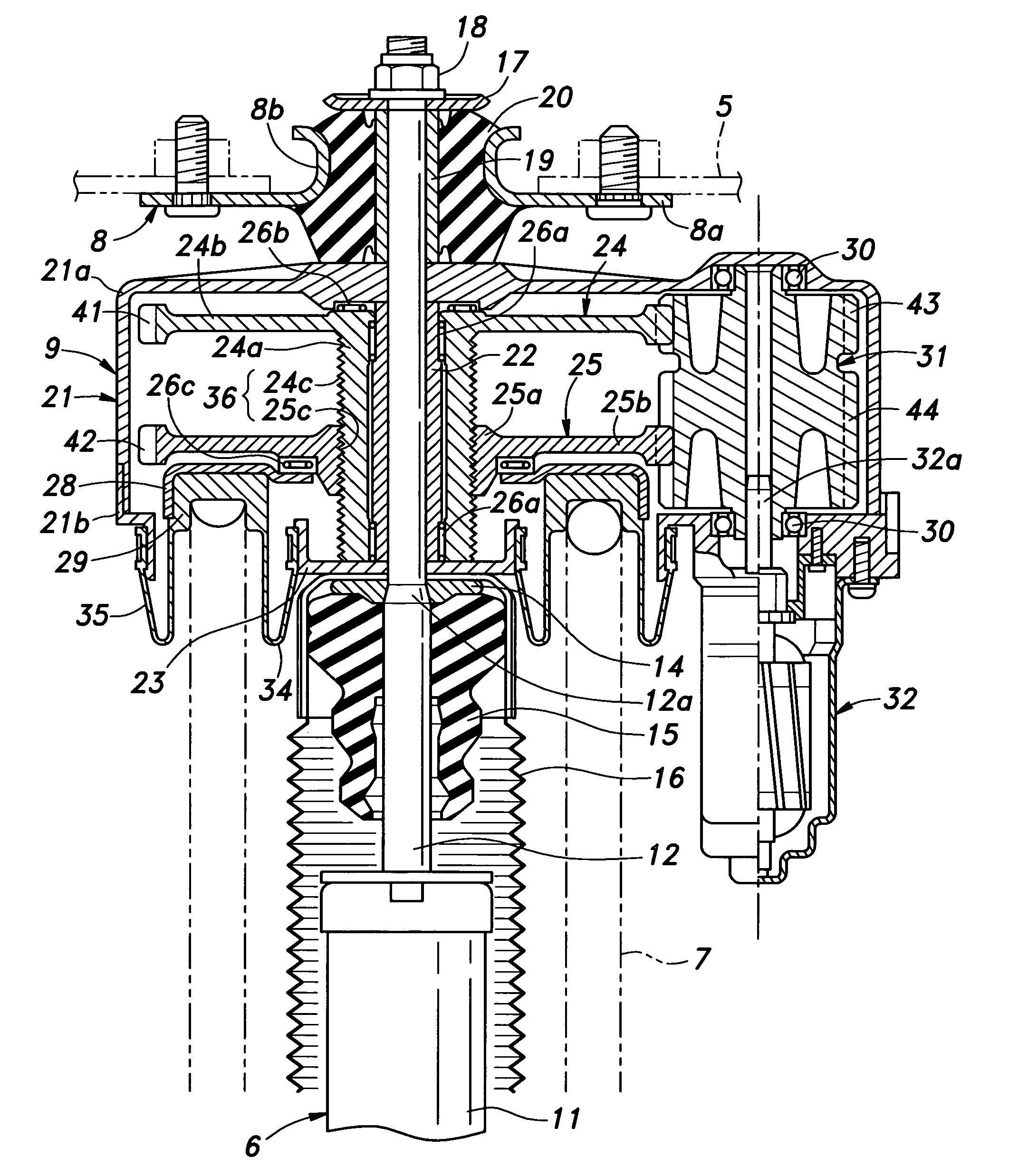
ActiveUS20070210539A1Stable supportCompact designVehicle cleaning apparatusToothed gearingsLinear motionDrive shaft
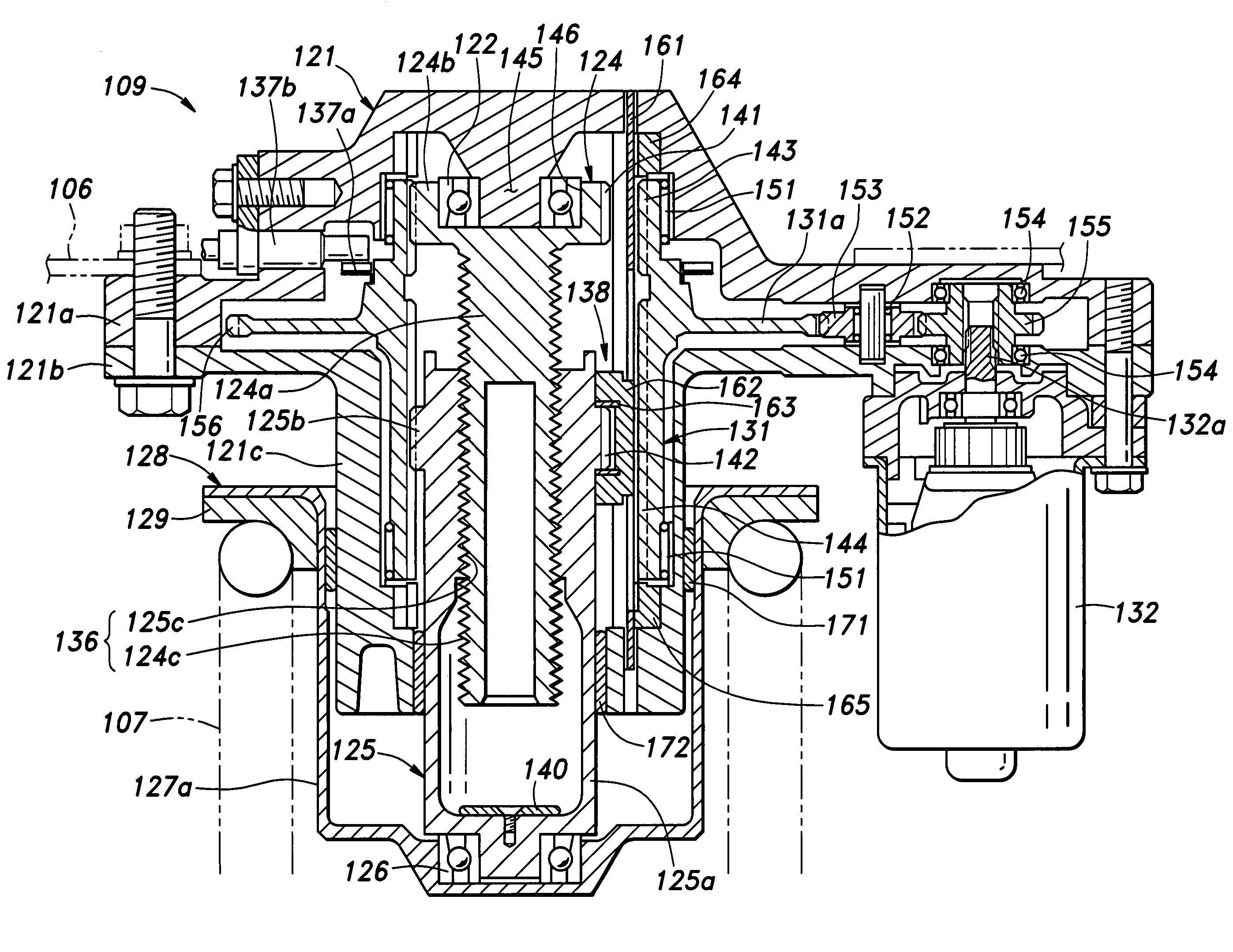
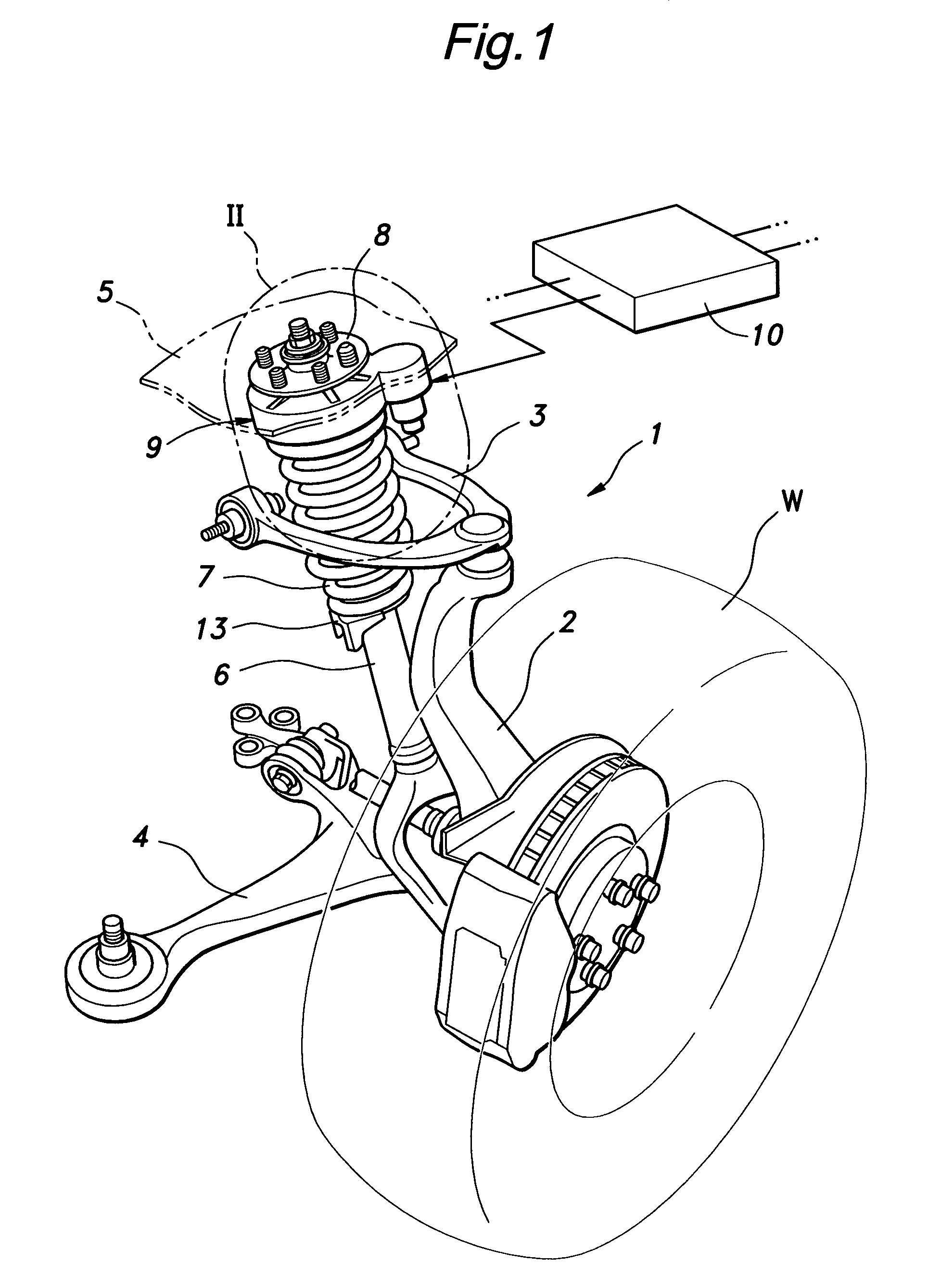
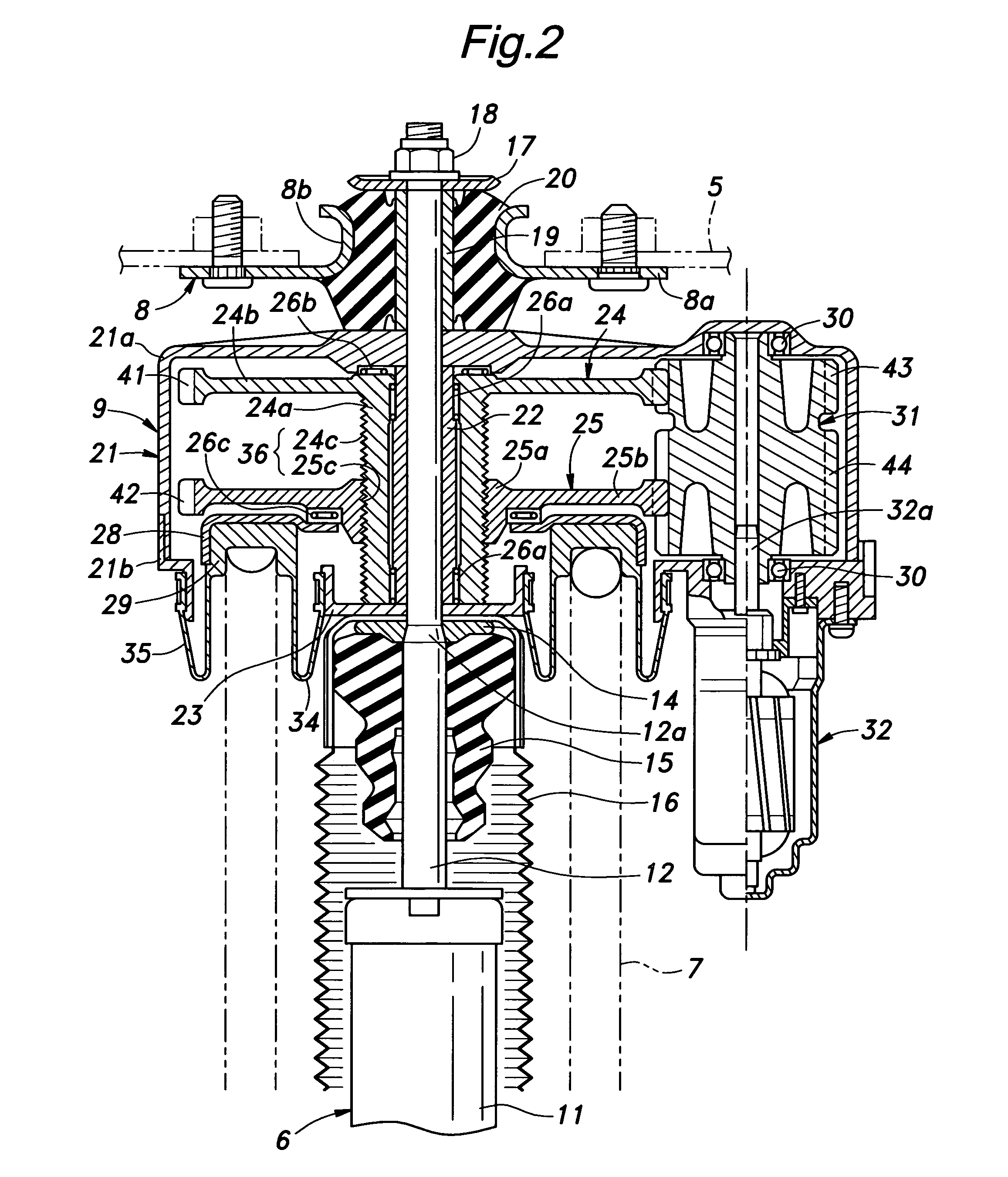
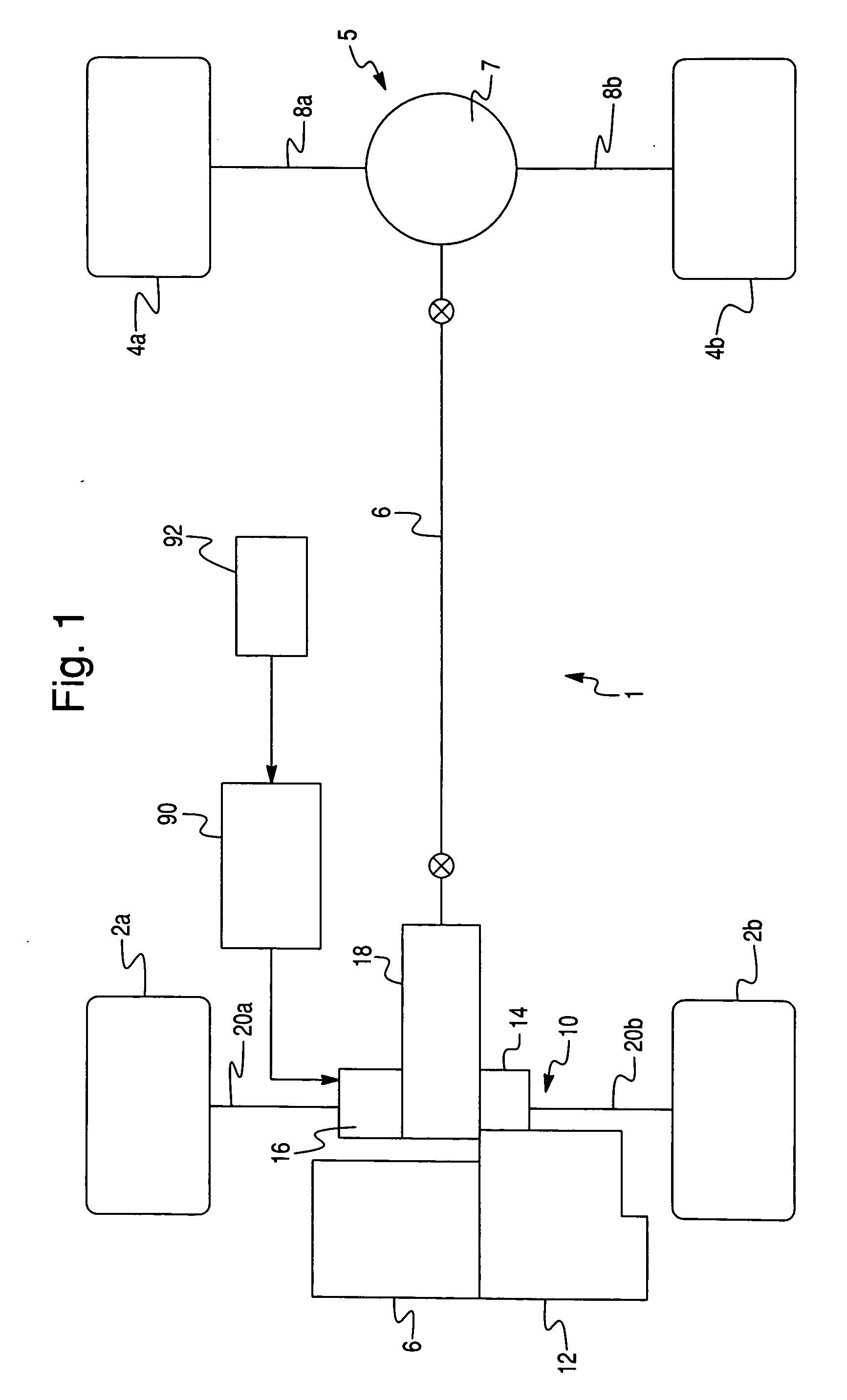
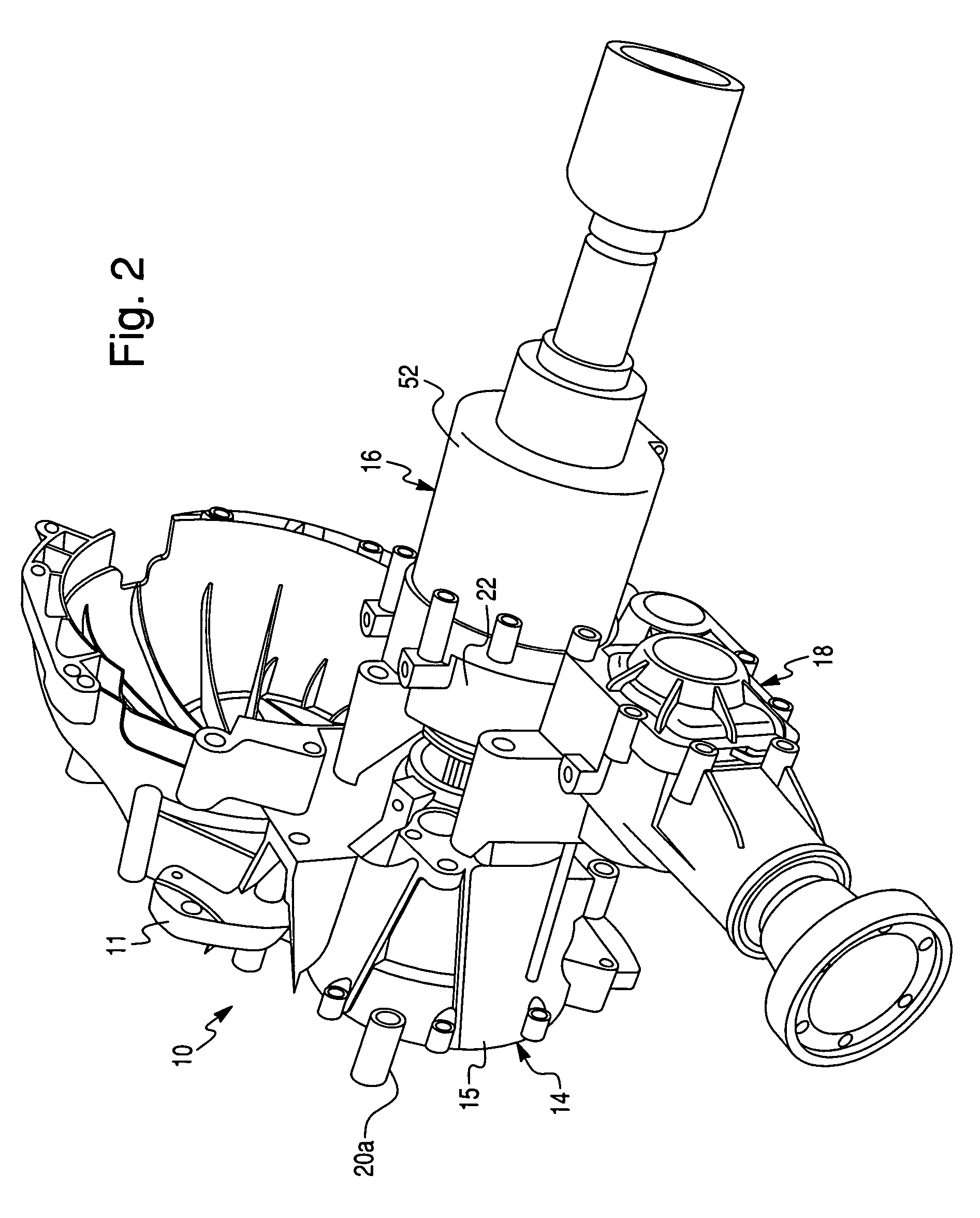
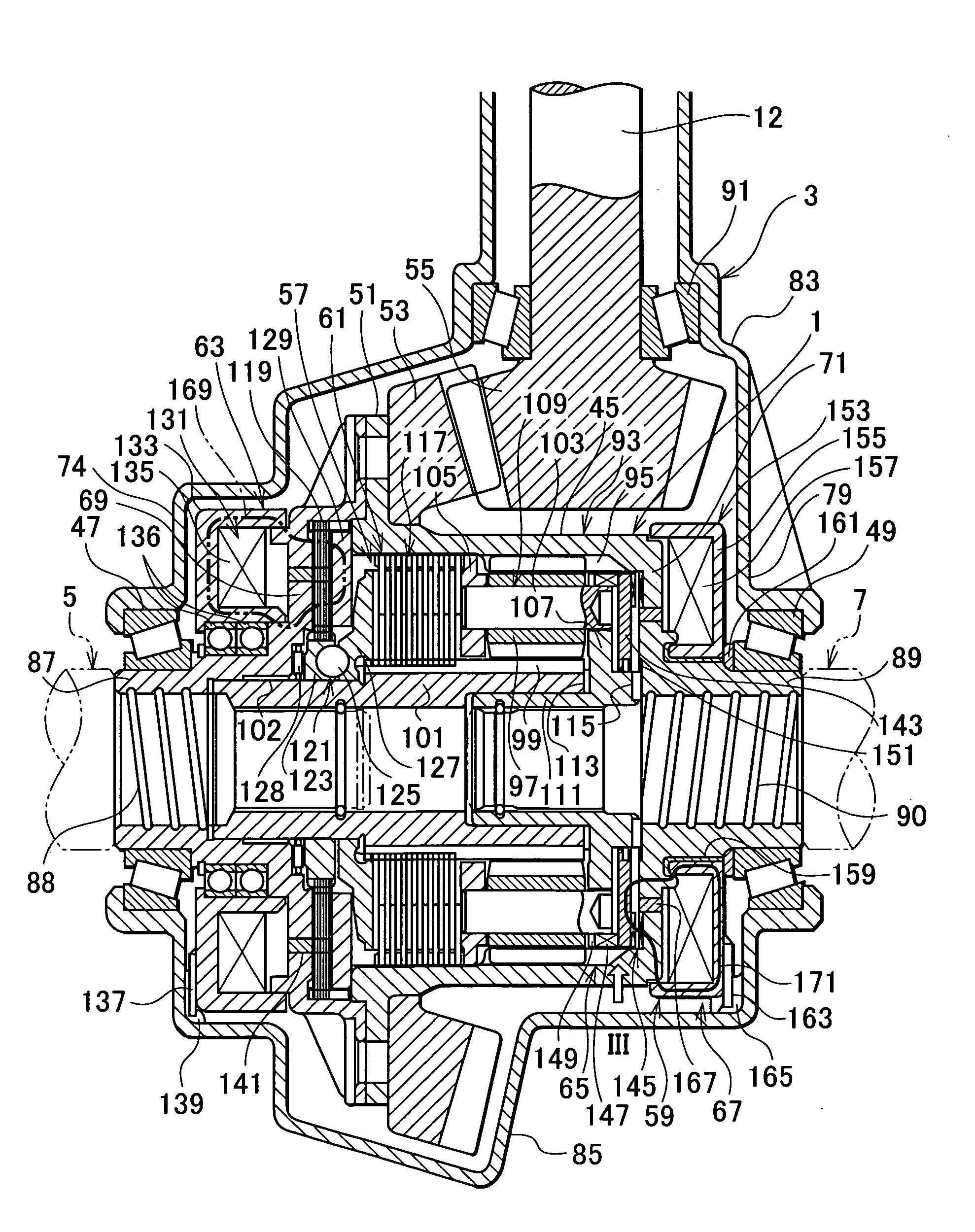
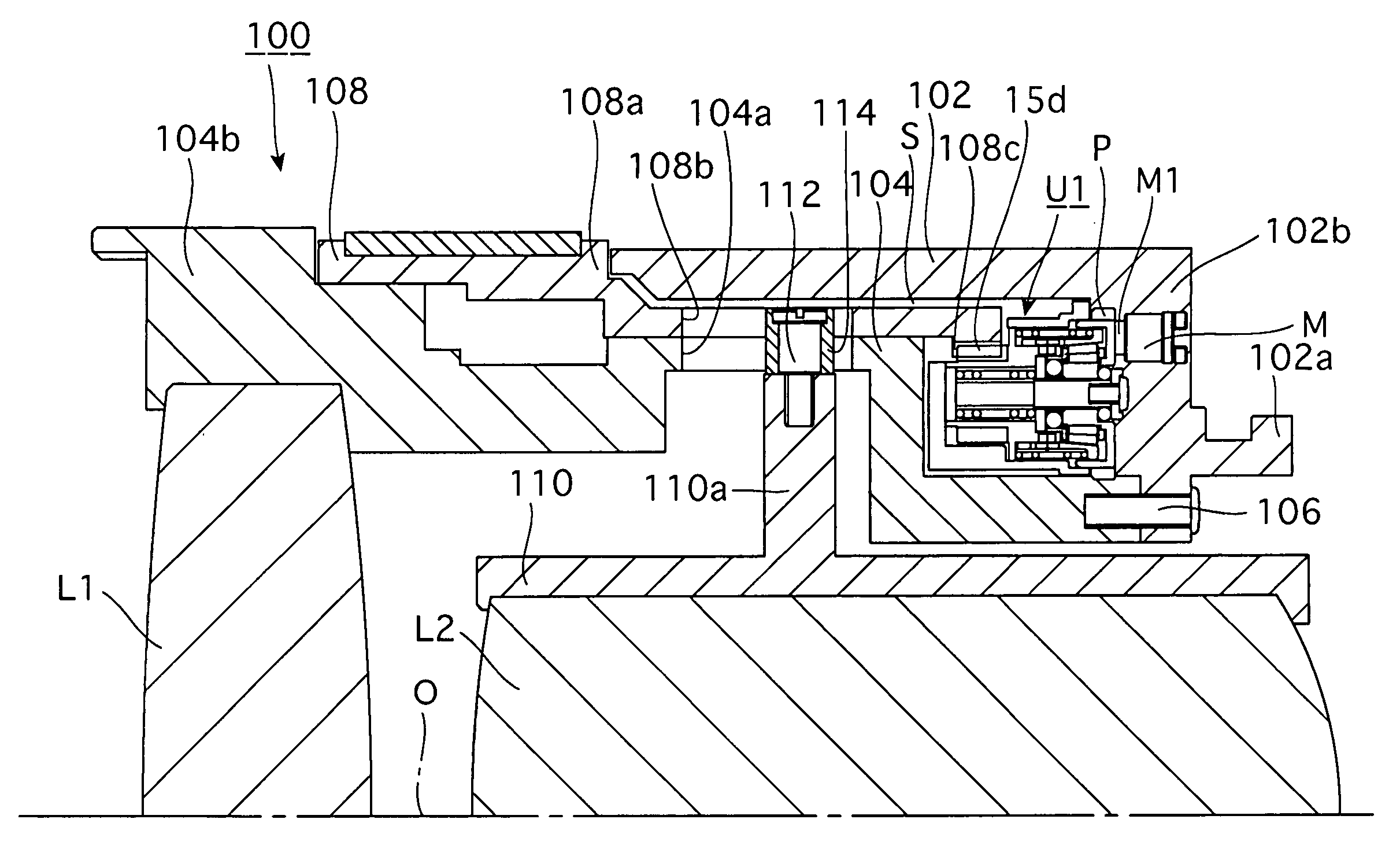
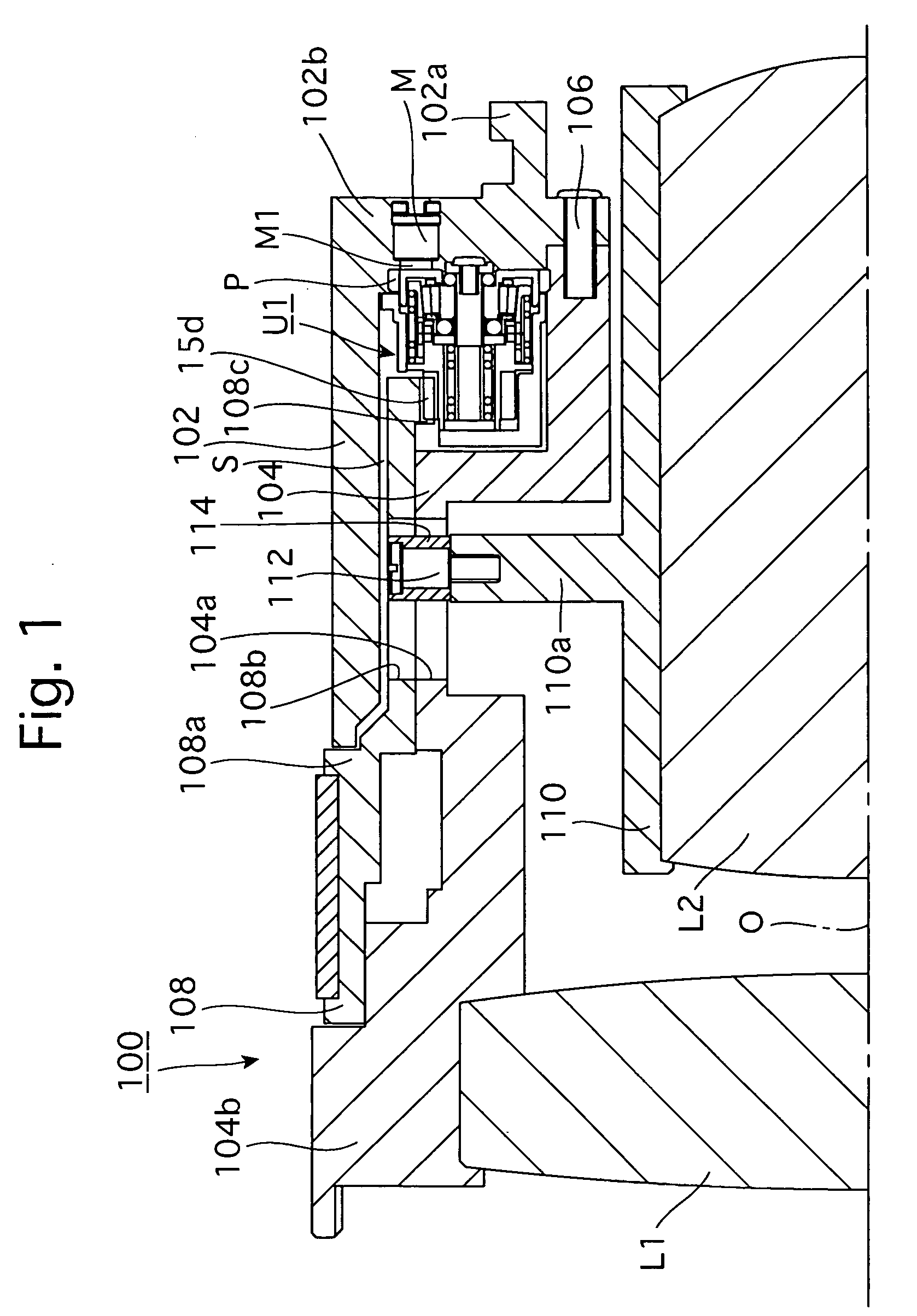
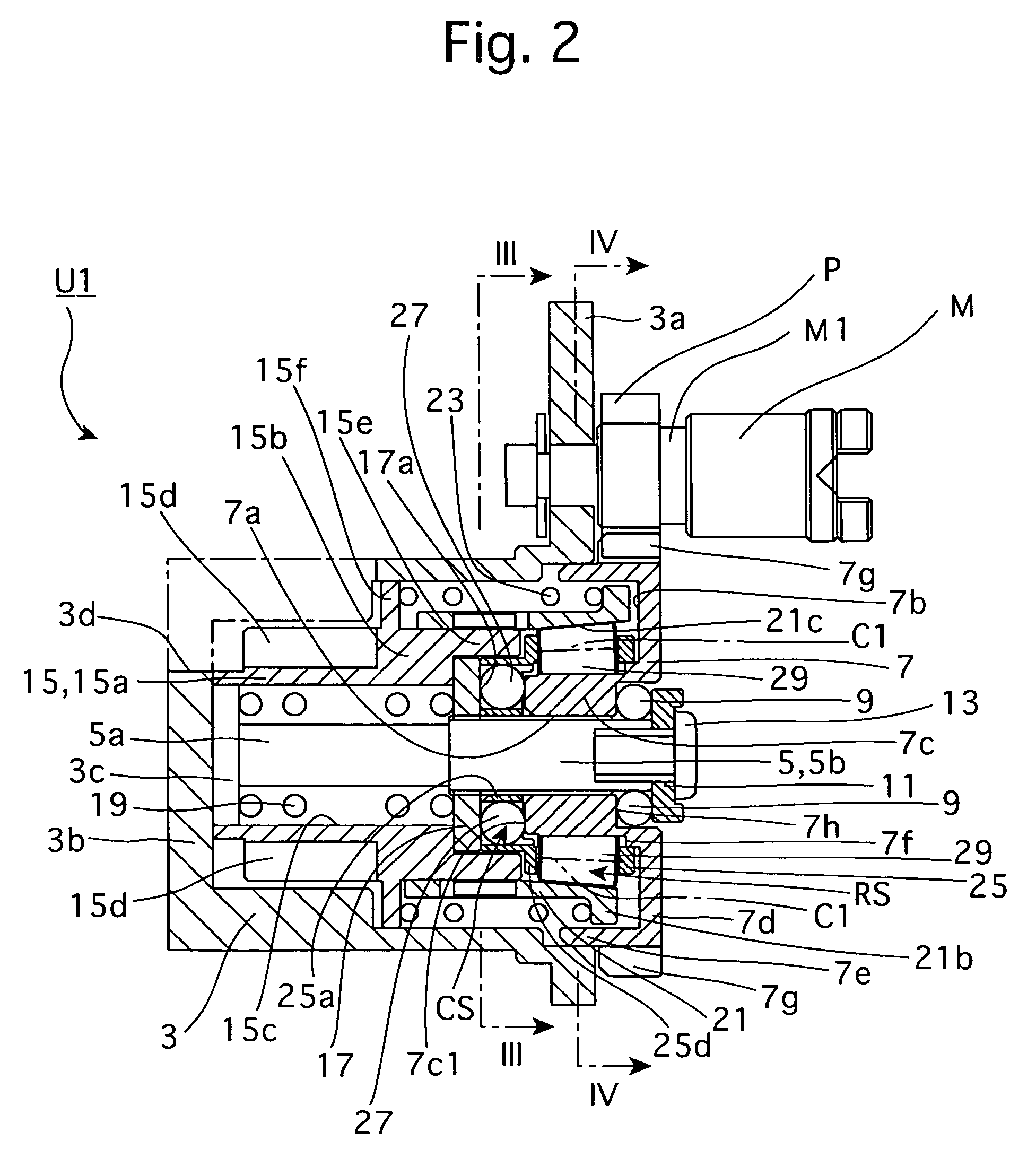
A first rotor (24; 124) and a second rotor (25; 125) are arranged in a coaxial and mutually rotatable relationship and are provided with a first driven gear (41; 141) and a second driven gear (42; 142), respectively. A drive shaft (31; 131) is also provided with a first drive gear (43; 143) and a second drive gear (44; 144) which are commonly connected to an output shaft of an electric motor (32; 132), and mesh with the first and second driven gears, respectively, at slightly different gear ratios. The first and second rotors are connected via a thread feed mechanism (36; 136) that converts a relative rotation between the first and second rotors into an axial linear movement between the first and second rotors that is used for changing a distance between a vehicle body part and a corresponding end of a suspension spring in a vehicle height adjusting system (9; 109). Owing to a differential rotation of a high gear ratio between the first and second rotors, a significant torque amplification is possible with a compact arrangement. The use of spur gears instead of a worm gear mechanism minimizes torque loss.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Multi-wheel vehicle
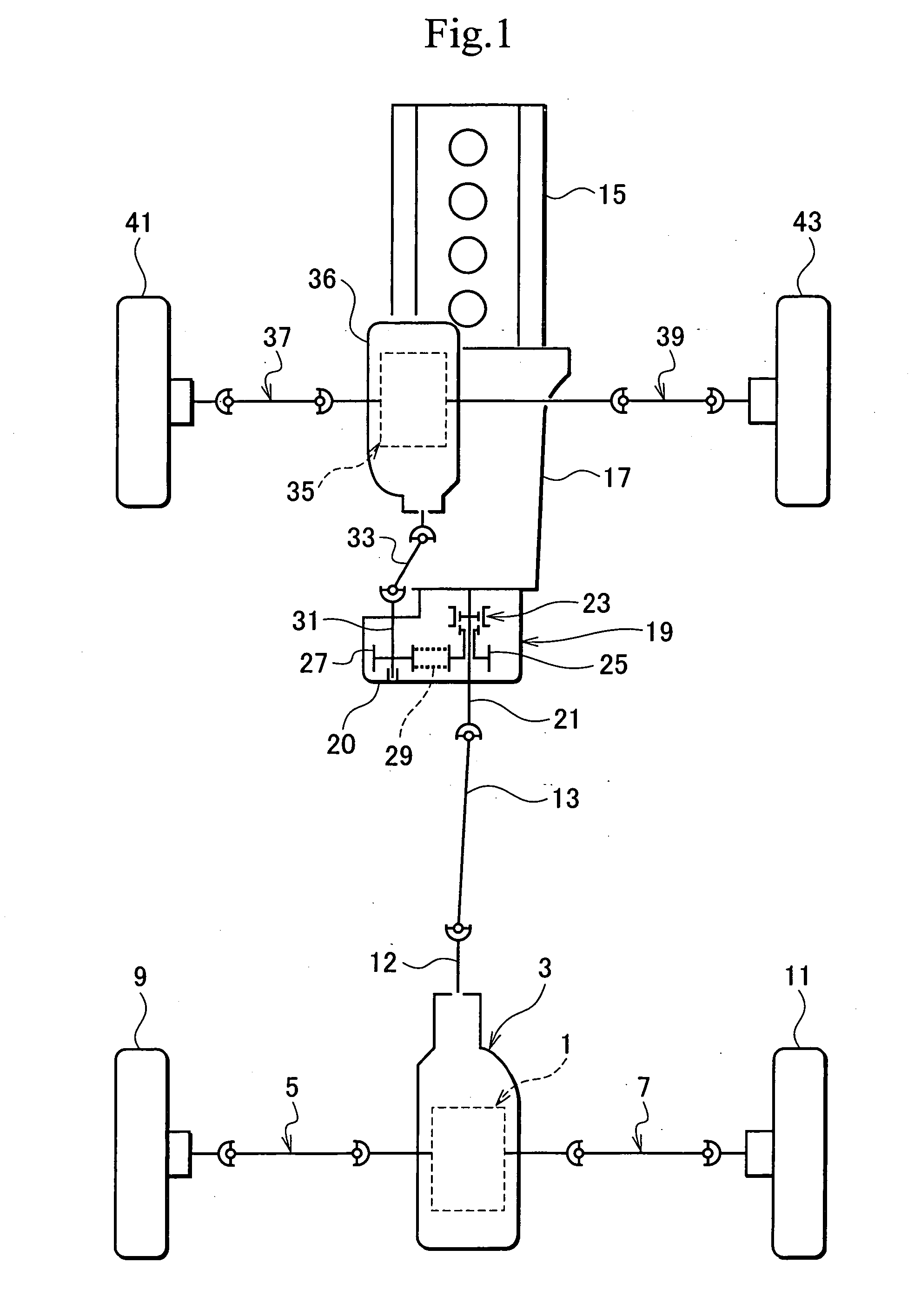
A vehicle comprises a steering operation device, a pair of running-driving wheels, which differentially drive when the steering operation device is manipulated, a pair of steerable running wheels interlocking with the steering operation device, and a steering mechanism interposed between the steering operation device and the pair of running-driving wheels. The steering mechanism includes a pair of drive gears interlocking with the steering operation device and a pair of follower gears interlocking with the respective steerable running wheels. The drive gears mesh with the respective follower gears so as to control lateral turning of the respective steerable running wheels. A gear radius of the drive gear may be greater than that of the follower gear meshing with it. A gear ratio between the mutually meshing drive and follower gears may be variable. The lateral turning centers of both the steerable running wheels may coincide with each other, and further coincide with a lateral turning center of the vehicle body caused by differential rotation of the running-driving wheels.
Owner:KANZAKI KOKYUKOKI MFG
Guided control of a transporter
A method for conducting the motion of a transporter under riderless conditions. The transporter has two laterally disposed primary wheels. In accordance with the method, an input is received via a user input disposed on the transporter and a control signal corresponding to the input received is generated. Then a torque is applied to the laterally disposed wheels so as propel the transporter on the basis of at least the control signal.The control signal may correspond to either a commanded torque or to a commanded transporter velocity. The torque may include coadded terms where the terms are, respectively, proportional to the control signal, to a counteracting artificial friction proportional to the common velocity of the wheels, and a term proportional to the differential rotation of the wheels to facilitate turning of the transporter.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
Vehicle height adjusting system
ActiveUS7922181B2Compact designDurable and reliable useVehicle cleaning apparatusToothed gearingsLinear motionDrive shaft
A first rotor (24; 124) and a second rotor (25; 125) are arranged in a coaxial and mutually rotatable relationship and are provided with a first driven gear (41; 141) and a second driven gear (42; 142), respectively. A drive shaft (31; 131) is also provided with a first drive gear (43; 143) and a second drive gear (44; 144) which are commonly connected to an output shaft of an electric motor (32; 132), and mesh with the first and second driven gears, respectively, at slightly different gear ratios. The first and second rotors are connected via a thread feed mechanism (36; 136) that converts a relative rotation between the first and second rotors into an axial linear movement between the first and second rotors that is used for changing a distance between a vehicle body part and a corresponding end of a suspension spring in a vehicle height adjusting system (9; 109). Owing to a differential rotation of a high gear ratio between the first and second rotors, a significant torque amplification is possible with a compact arrangement. The use of spur gears instead of a worm gear mechanism minimizes torque loss.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Transaxle unit with integrated power take-off unit and torque coupling device
InactiveUS20060283654A1Minimizes toolingMinimizes manufacturing expenseDifferential gearingsControl devicesHydraulic pumpVariable pressure
A transaxle unit comprises a differential assembly having a differential mechanism, a power take-off unit and a torque-coupling device for selectively restricting differential rotation of a differential mechanism. The torque-coupling device includes a friction clutch assembly for selectively frictionally engaging and disengaging a differential case and one of output axle shafts and a hydraulic clutch actuator. The hydraulic clutch actuator includes a hydraulic pump and a variable pressure relief valve assembly fluidly communicating with the hydraulic pump to selectively control a hydraulic pressure generated by the hydraulic pump. The variable pressure relief valve assembly comprises a valve closure member, a valve seat complementary to the valve closure member and an electro-magnetic actuator for engaging the valve closure member and generating a variable electro-magnetic force urging selectively vary a release pressure of the pressure relief valve assembly based on a magnitude of an electric current supplied to the electro-magnetic actuator.
Owner:DANA AUTOMOTIVE SYST GRP LLC
Differential unit
InactiveUS20060052207A1Small sizeWeight increaseDifferential gearingsControl devicesLocking mechanismEngineering
The invention provides a differential unit which can be arranged in compact as a whole, while a differential limit and a differential lock are appropriately executed. The differential unit is provided with a differential mechanism transmitting from a differential case (45) to a pair of axle shafts a rotational force while allowing a differential rotation, and is provided with a differential limiting mechanism (57) which can limit the differential rotation, and a differential lock mechanism (59) which can lock up the differential rotation. The differential limiting mechanism (57) is provided with a limiting actuator (63) for operation, the differential lock mechanism (59) is provided with a lock actuator (67) for operation, and the limiting actuator (63) and the lock actuator (67) are independently arranged in both sides of the differential case (45).
Owner:TOCHIGI FUJI IND CO LTD
Rotatively driving apparatus
ActiveUS20050187058A1Smooth rotationGood weight balanceElectric propulsion mountingToothed gearingsEngineeringControl theory
A rotatively driving apparatus includes: a differential rotation amplification mechanism for amplifying differential rotation between a rotating shaft and a drive pinion shaft which are relatively rotatable; a rotor interlockingly rotatable with a amplified differential rotation amplified; and a rotation controlling mechanism for controlling the rotation of the rotor. The rotation controlling mechanism includes a stator for constituting an electric motor together with the rotor, a variable resistor for absorbing electric energy generated by the electric motor by the rotation of the rotor, and a controller for controlling torque transmitted between the rotating shaft and the drive pinion shaft by adjusting the energy absorbed by the variable resistor. The differential rotation amplification mechanism and the rotor are disposed on an identical axis.
Owner:TOCHIGI FUJI IND CO LTD
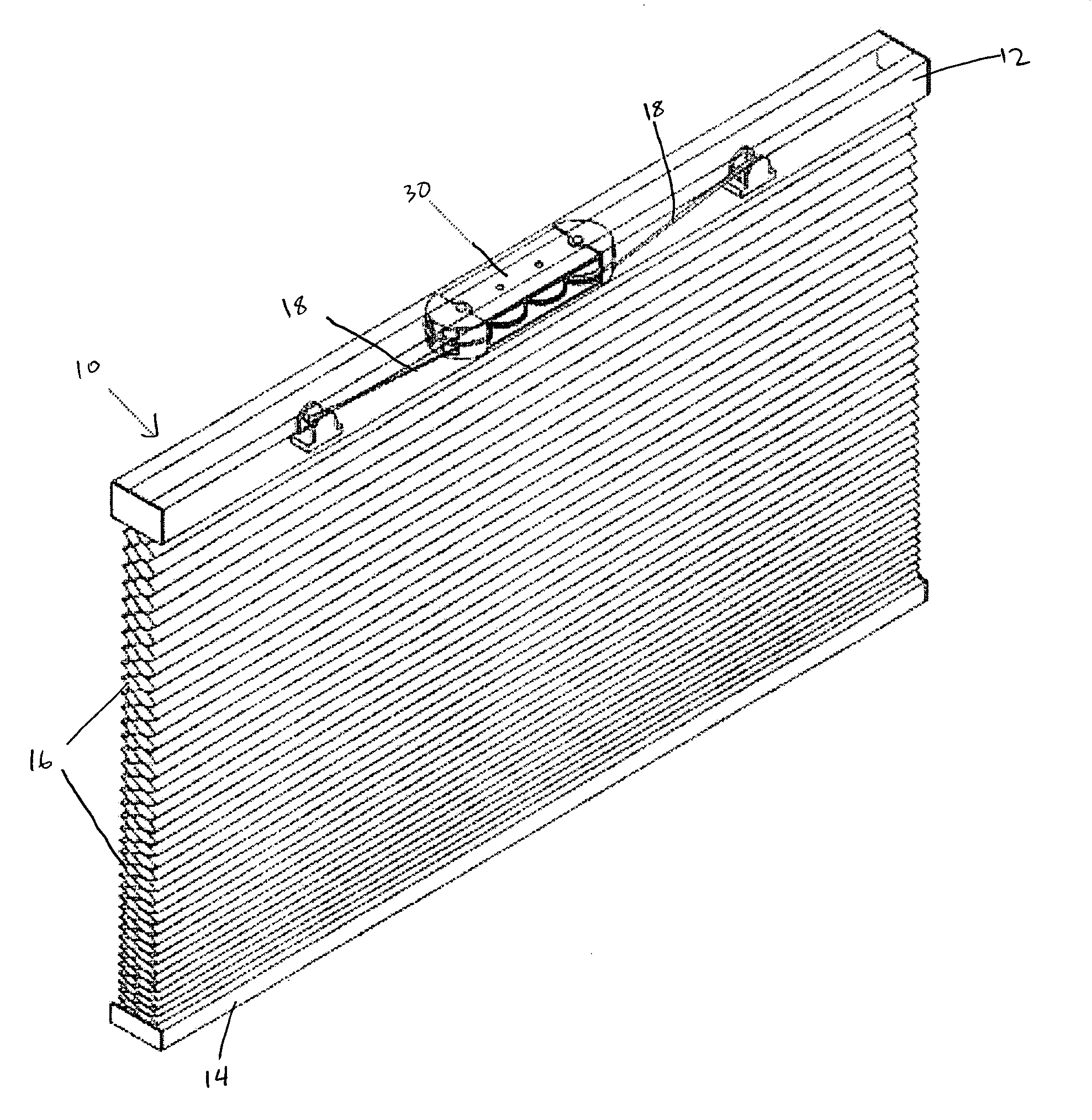
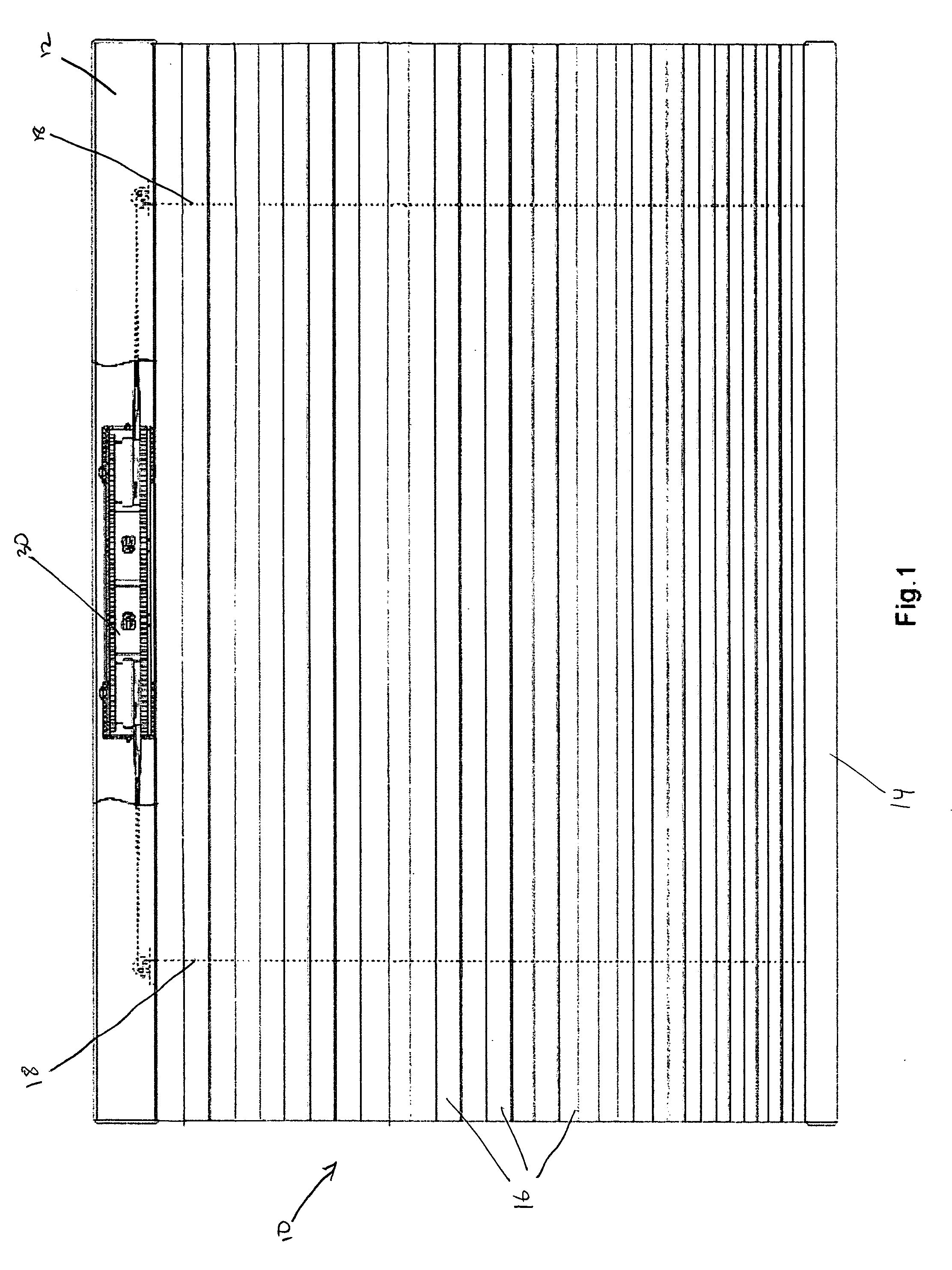
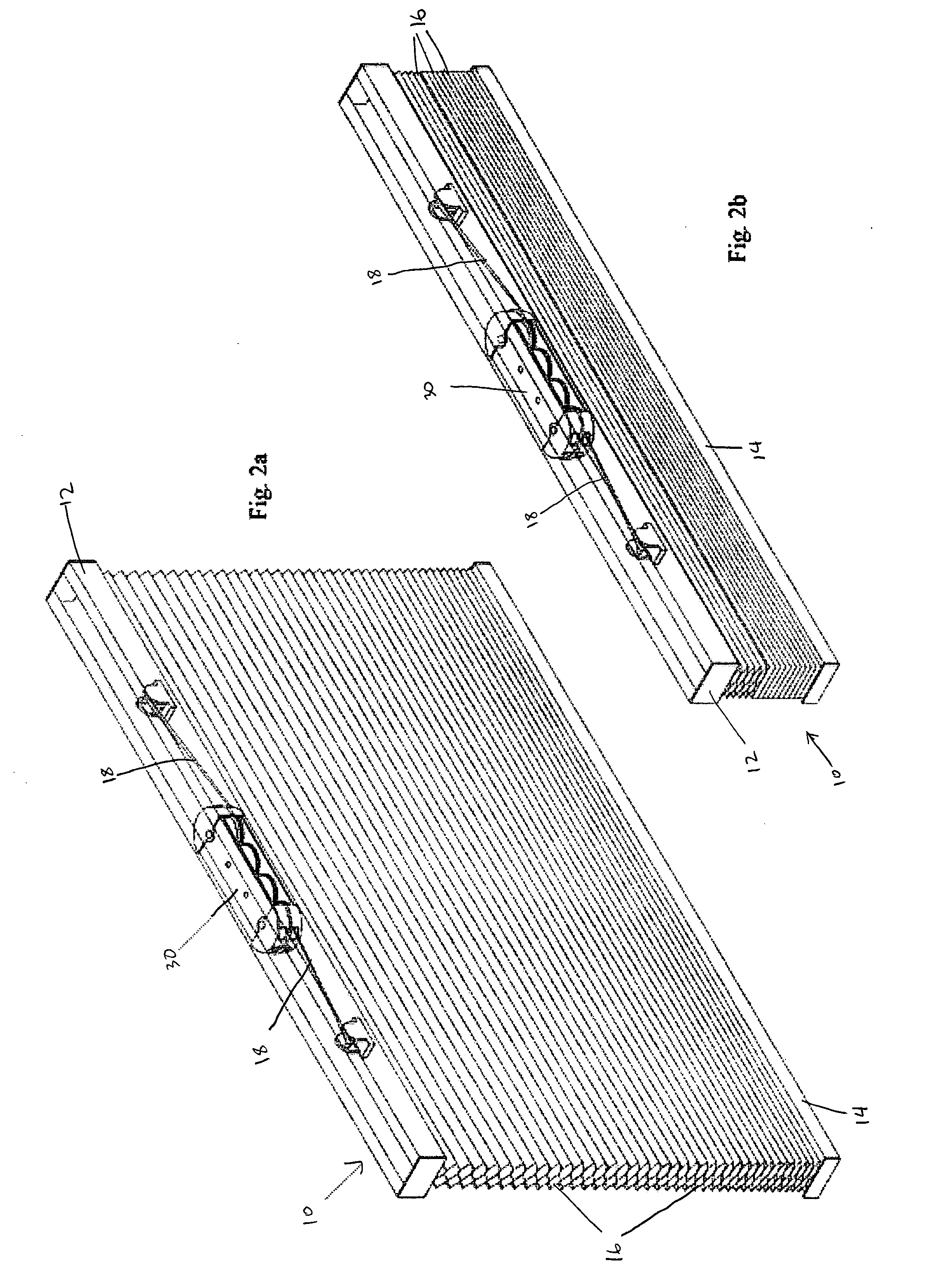
Cordless window covering
A cordless window covering having a differential suspension mechanism. The suspension mechanism is composed of a first rotary drum for winding and unwinding the suspension cord of a window covering and a second rotary drum housing a spring with one end connected to the second rotary drum and the other end of the spring connected to an axle. Rotation of the first rotary drum and at least one end of the spring are linked by a transmission system. In operation, the transmission system creates a differential rotation rate between the first rotary drum and the relative rotation rate of the two ends of the spring. In this manner, a greater length of cord can be deployed for with a shorter length of spring extension.
Owner:YU FU LAI +1
Vehicle drive system
A drive system includes a transmission mechanism that establishes a plurality of gear positions comprising a first-speed through sixth-speed gear positions and a reverse-drive gear position, by switching among change gear trains and coupling a first driveshaft to an output member, and also includes a lock clutch that switches a power distribution mechanism between a locked state in which a ring gear and a carrier are coupled to each other and are inhibited from rotating in a differential fashion, and a released state in which the inhibition of the differential rotation is cancelled.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
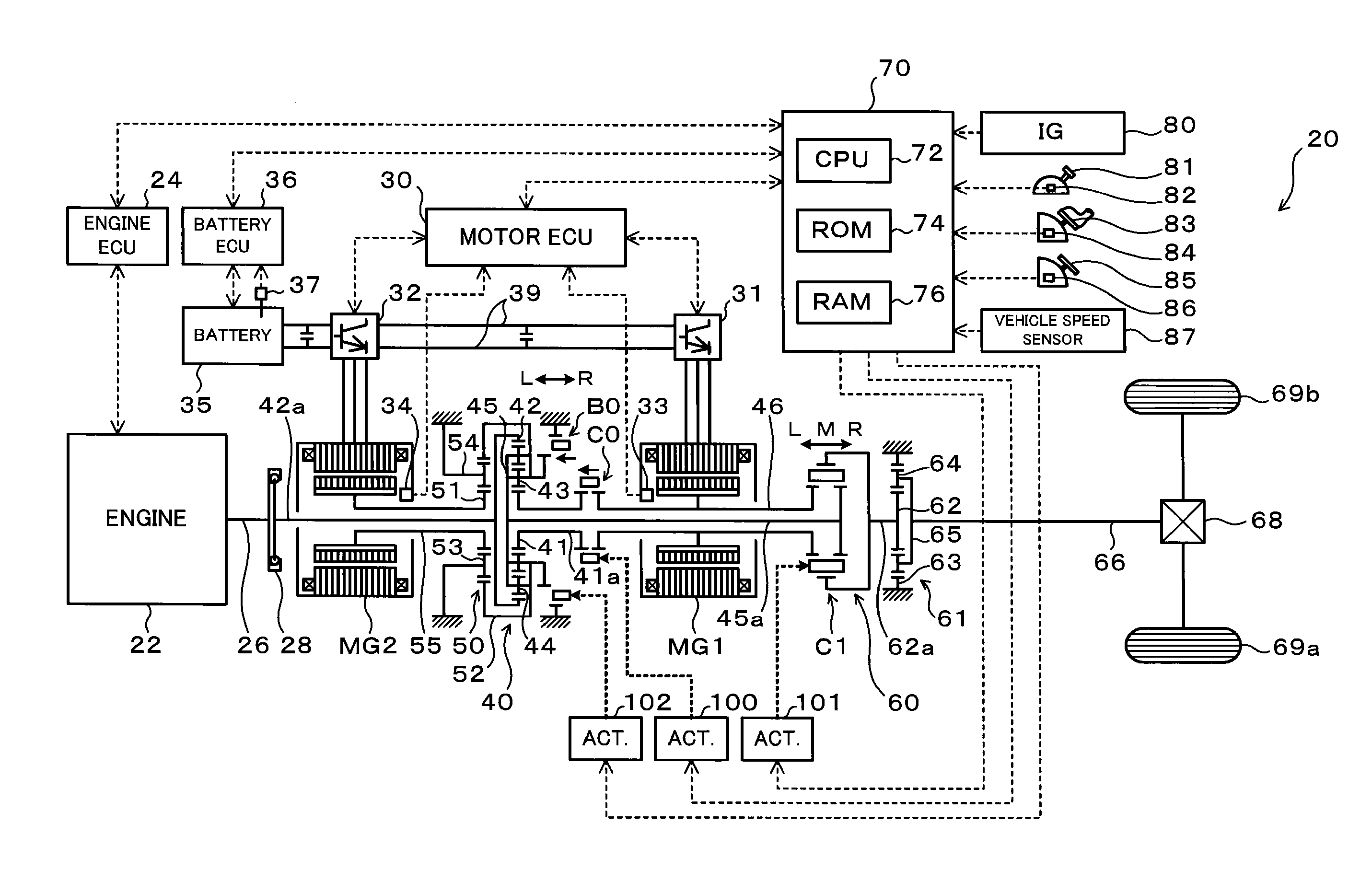
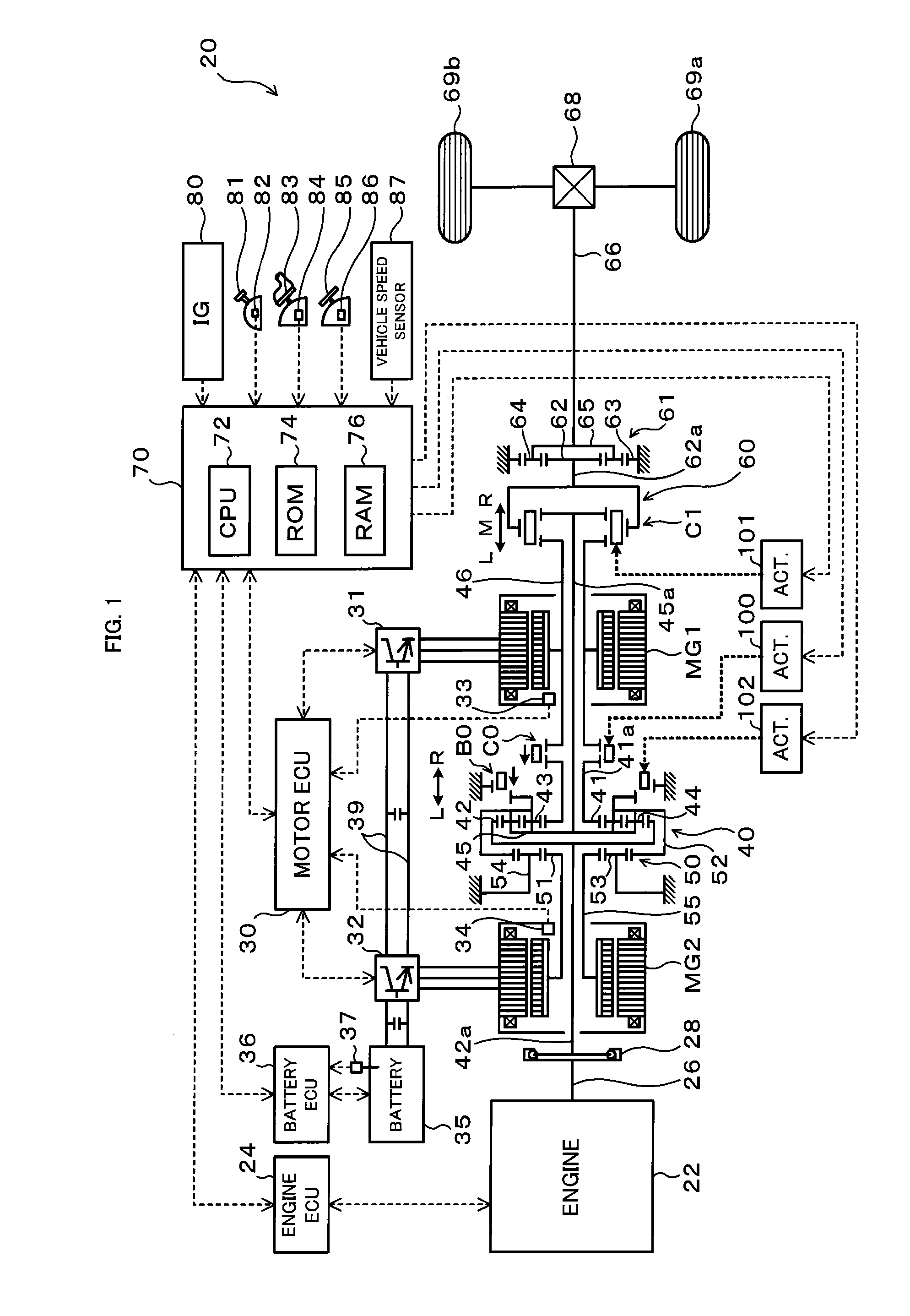
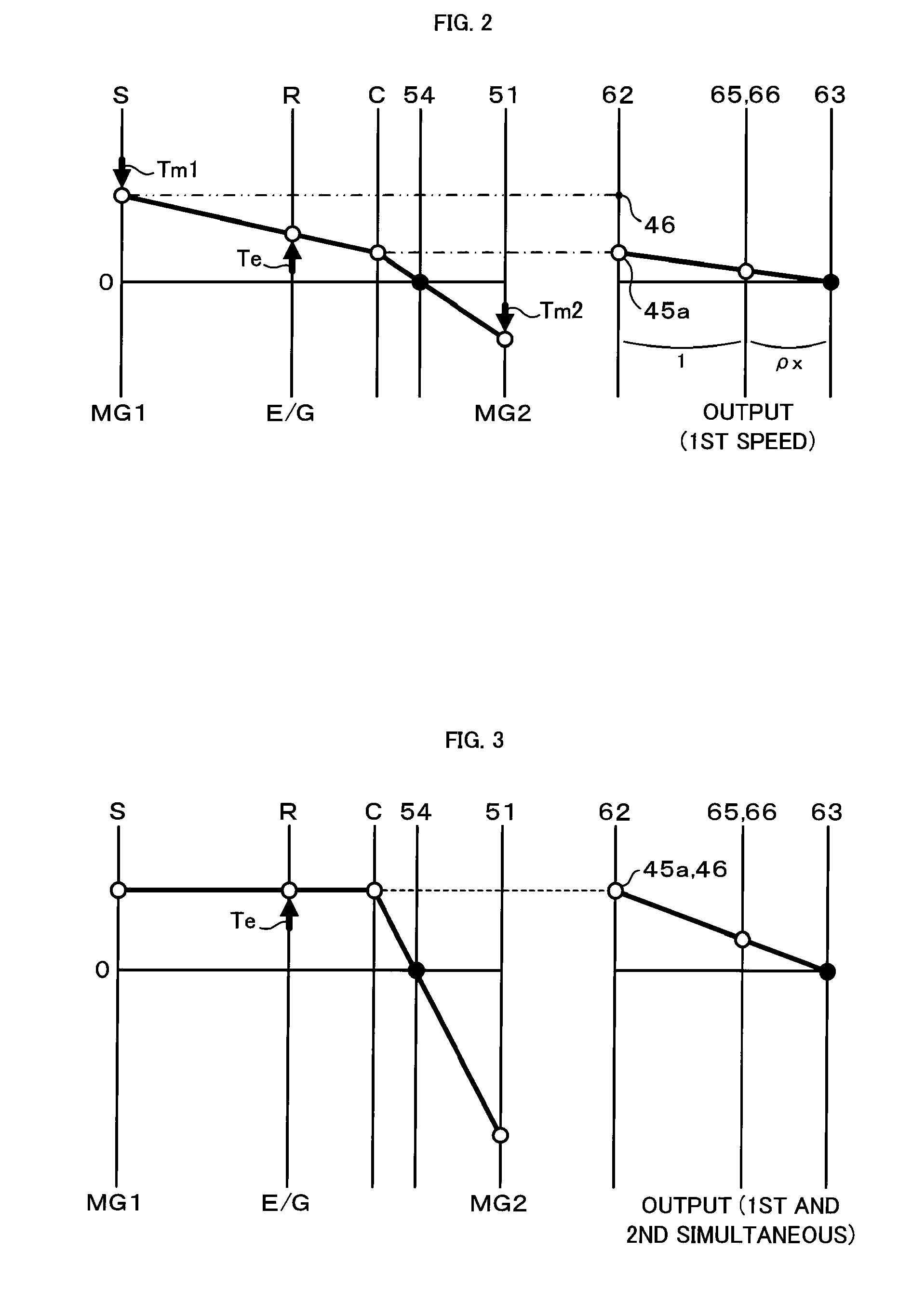
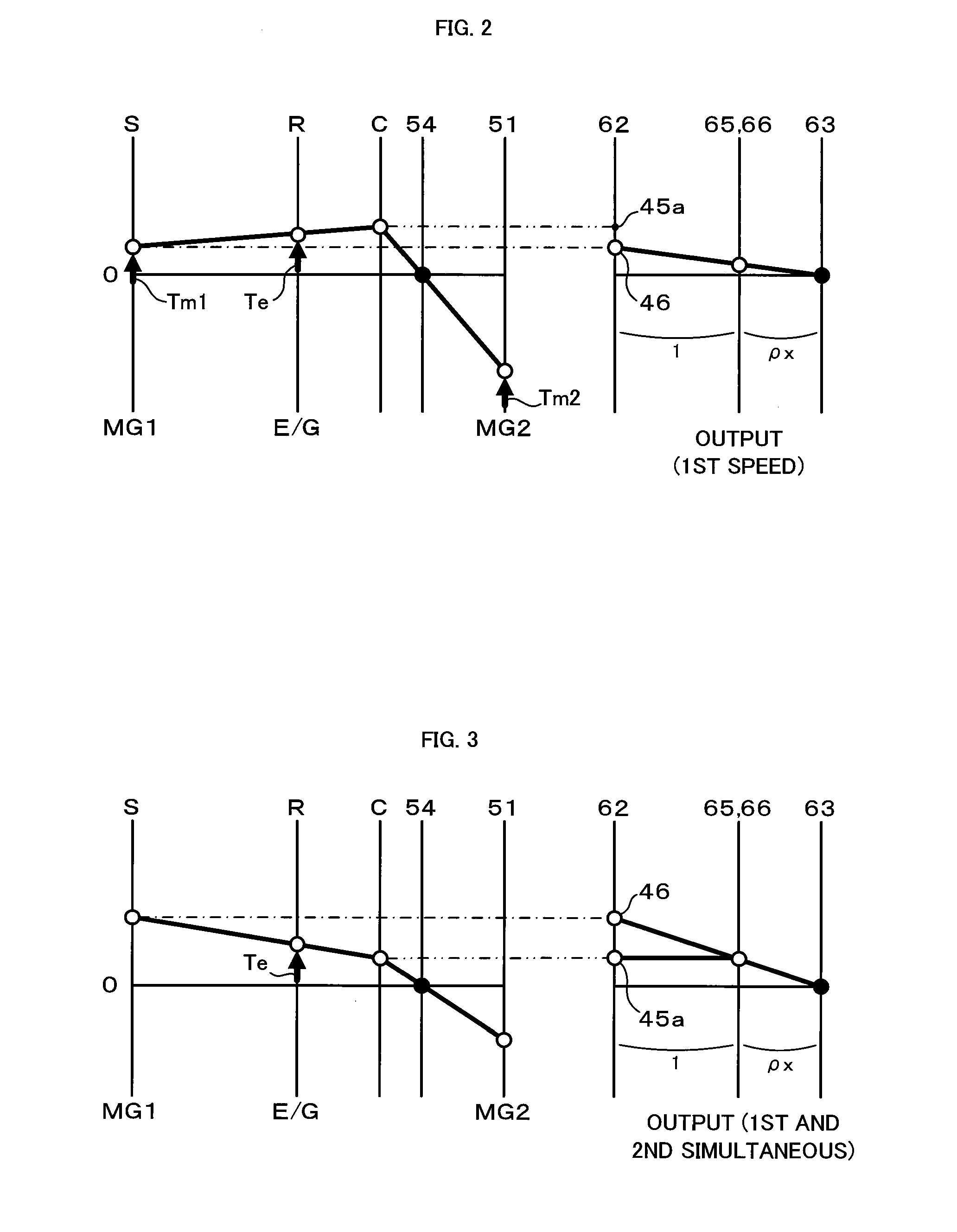
Power output apparatus and hybrid vehicle
InactiveUS20100012407A1Reduce power lossImprove productivityHybrid vehiclesTransmission elementsDrive shaftPinion
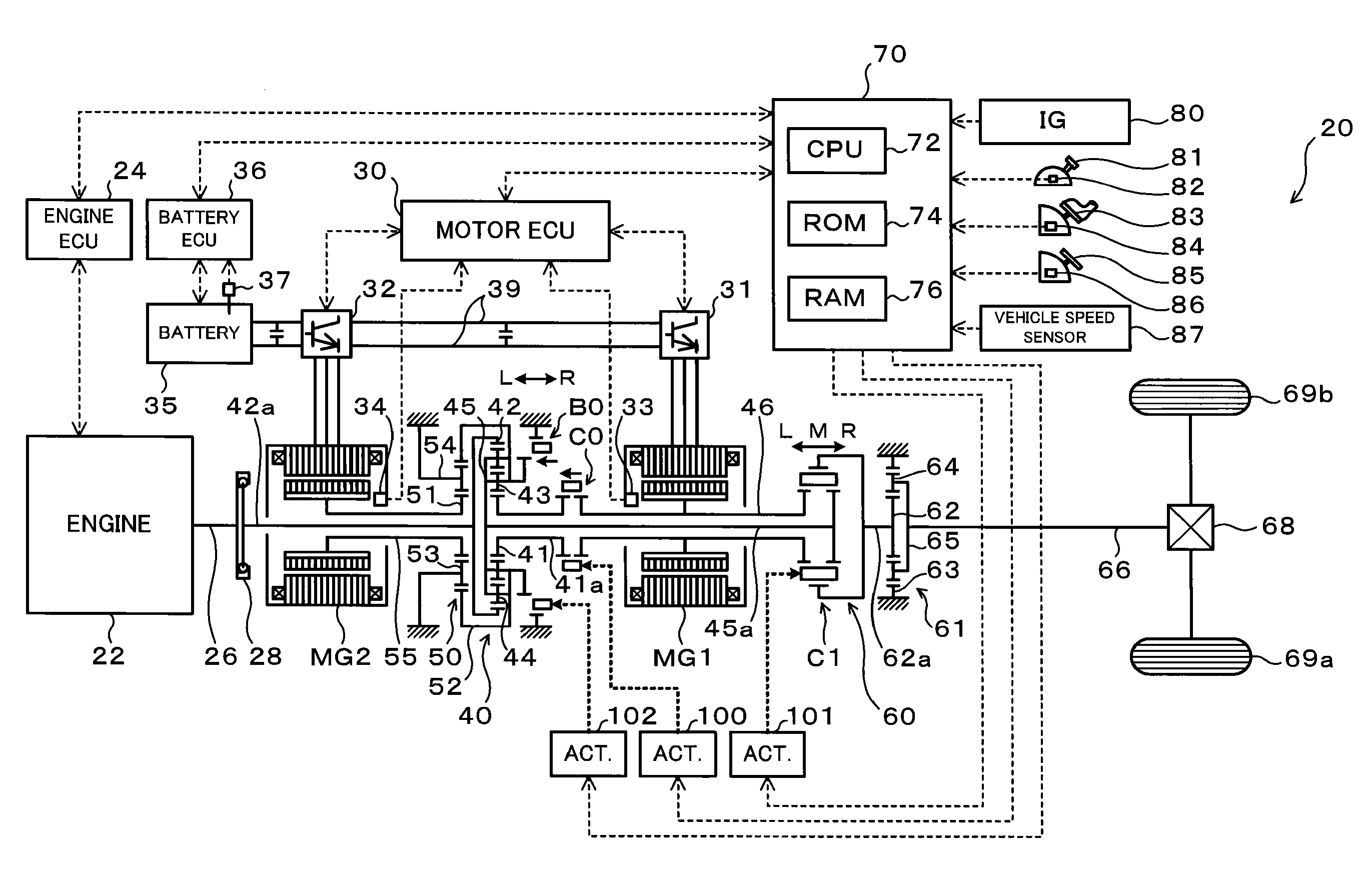
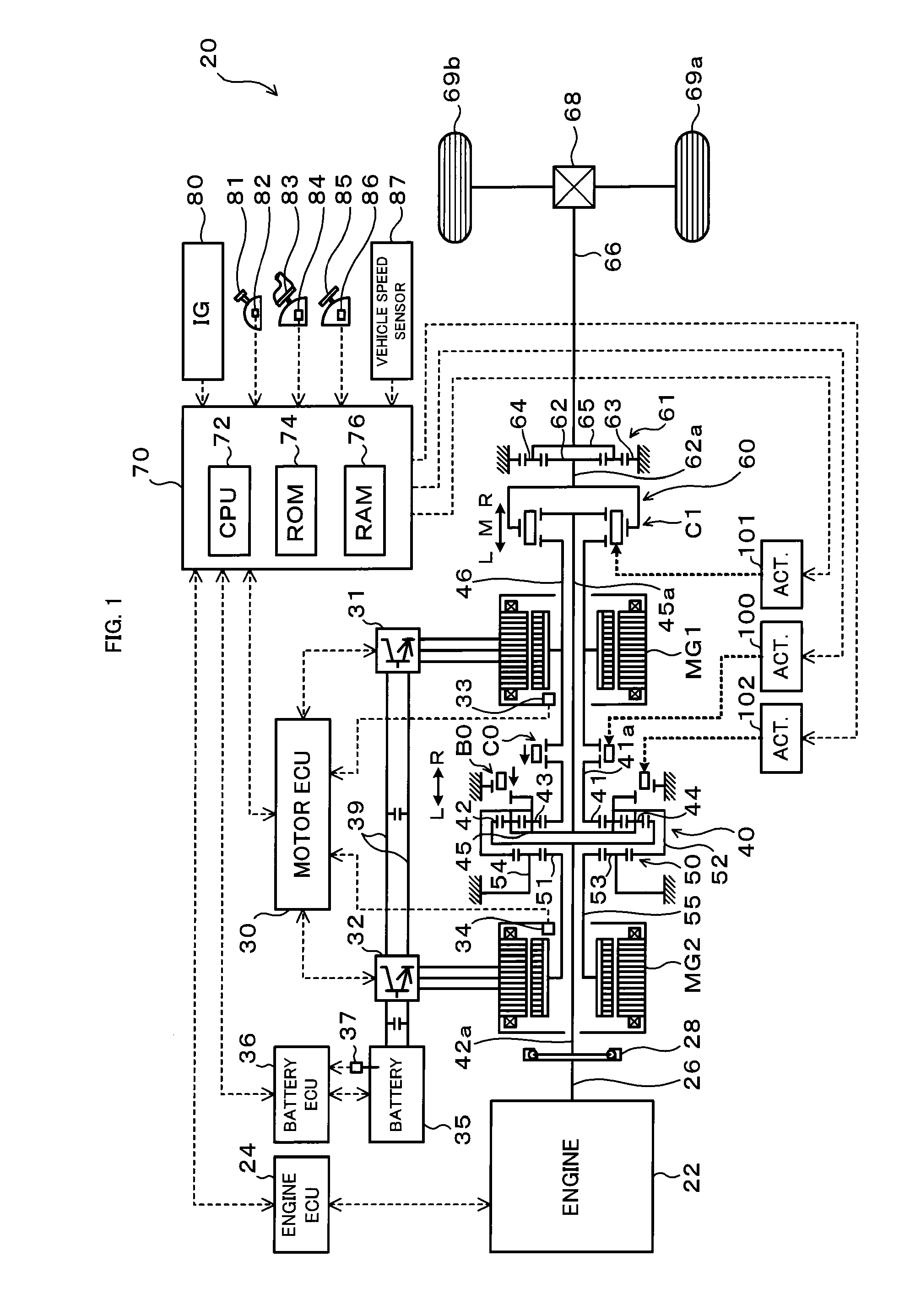
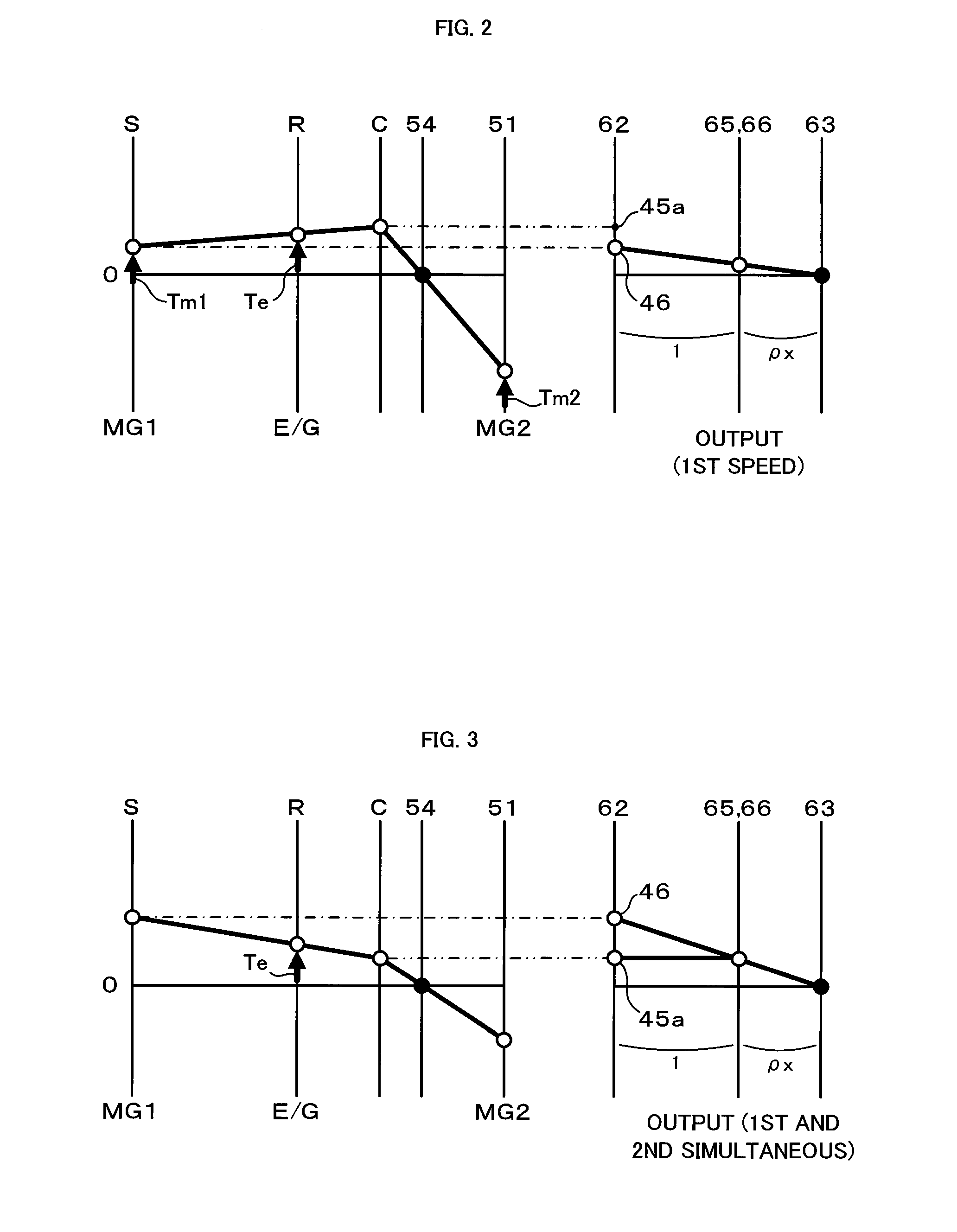
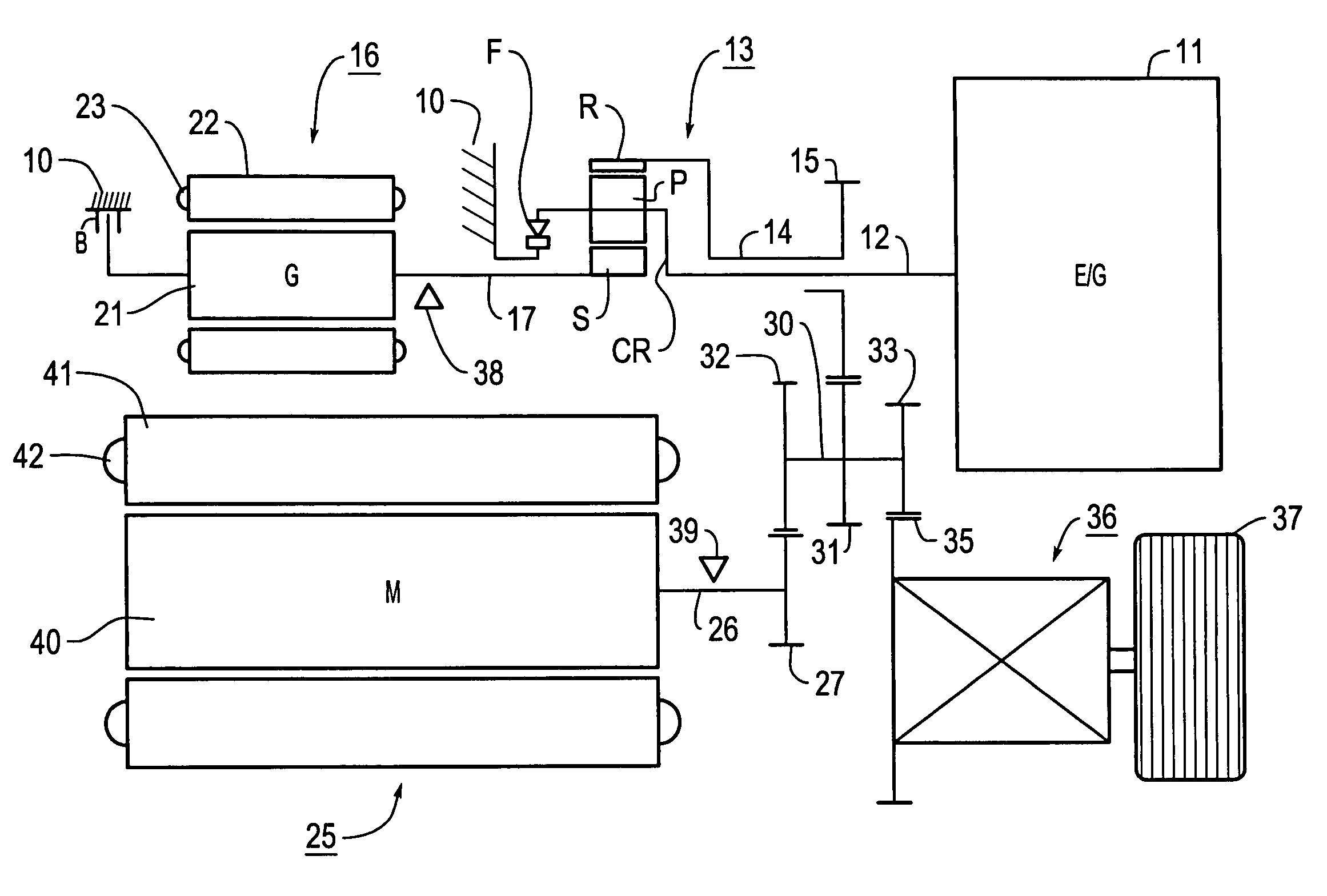
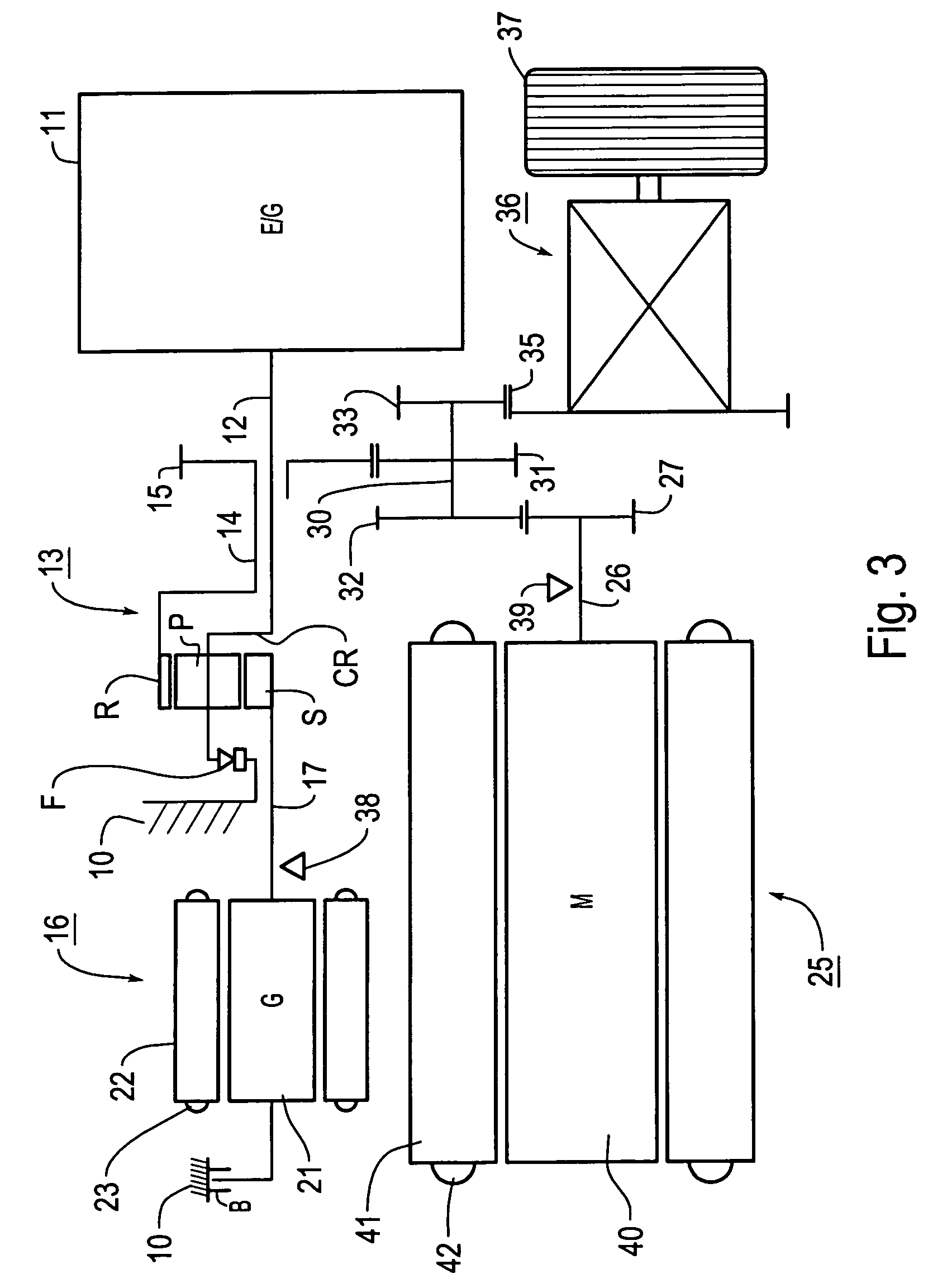
A hybrid vehicle includes an engine, motors, and a power distribution and integration mechanism that are coaxially arranged with respect to each other. The hybrid vehicle also includes a transmission including a transmission differential rotation mechanism that is a single pinion planetary gear mechanism having a sun gear, a ring gear, and a carrier that is connected to a drive shaft, and that is configured such that these three elements can differentially rotate with each other; and a clutch capable of selectively coupling one of or both of the carrier and the sun gear of the power distribution and integration mechanism with the sun gear of the transmission differential rotation mechanism.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
One-way rotational transfer mechanism, and a lens barrel incorporating the same
InactiveUS20050115358A1Simple structureHigh torqueYielding couplingProjector focusing arrangementTransfer mechanismControl theory
A one-way rotational transfer mechanism includes a rotary input shaft, a rotary output shaft, a clutch member, a differential rotating member, a circumferentially-uneven-width-space forming portion formed on the rotary input shaft, a torque transfer member, and an associating device. The torque transfer member wedges between the circumferentially-uneven-width-space forming portion and the clutch member while making the torque transfer member contact the clutch so that the rotary input shaft and the clutch member become integral upon rotation of the rotary input shaft. The associating device causes the clutch member to transfer torque thereof to the rotary output shaft, and the clutch member to release engagement of the rotary input shaft with the clutch member when the rotary output shaft is rotated so that a relative rotational torque greater than a predetermined torque determined by a shape of the associating device.
Owner:RICOH IMAGING COMPANY
Power output apparatus and hybrid vehicle
InactiveUS7938208B2Simple configurationImprove installabilityHybrid vehiclesTransmission elementsDrive shaftGear wheel
A hybrid vehicle includes an engine, motors, and a power distribution and integration mechanism that are coaxially arranged with respect to each other. The hybrid vehicle also includes a transmission including a transmission differential rotation mechanism that is a single pinion planetary gear mechanism having a sun gear, a ring gear, and a carrier that is connected to a drive shaft, and that is configured such that these three elements can differentially rotate with each other; and a clutch capable of selectively coupling one of or both of the carrier and the sun gear of the power distribution and integration mechanism with the sun gear of the transmission differential rotation mechanism.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Differential unit with limited slip differential mechanism
InactiveUS20060281599A1Simple structureEasy to assembleFriction clutchesDifferential gearingsDrive shaftLimited-slip differential
The differential unit with a limited slip differential mechanism of the present invention comprises a planetary gear mechanism for torque distribution of drive torque inputted to an input shaft from an engine between a front drive shaft and a rear drive shaft, and a multiple disc clutch for limiting differential rotation of the planetary gear mechanism, wherein, when a clutch plate receiving clutch engaging force applied to the multiple disc clutch is fixed to a side surface of a planetary carrier of the planetary gear mechanism, pins are formed on the ends of bolts for fixing the planetary carrier, and positioning and fixing is carried out by fitting the pins into check holes formed in the clutch plate.
Owner:SUBARU CORP
Power output apparatus and hybrid vehicle
InactiveUS8091661B2Simple configurationImprove installabilityRailway vehiclesTransmission elementsDrive shaftEngineering
A hybrid vehicle includes an engine, motors, and a power distribution and integration mechanism that are coaxially arranged with respect to each other. The hybrid vehicle also includes a transmission including a transmission differential rotation mechanism that has a sun gear as an input element connected to a sun gear which is a first element of the power distribution and integration mechanism, a ring gear as a fixing element, and a carrier as an output element, and that is configured such that these three elements can differentially rotate with each other; and a clutch as a coupling mechanism capable of selectively coupling the sun gear of the transmission differential rotation mechanism and the carrier which is the second element of the power distribution and integration mechanism with a drive shaft.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Hybrid vehicle drive control apparatus, hybrid vehicle drive control method, and program thereof
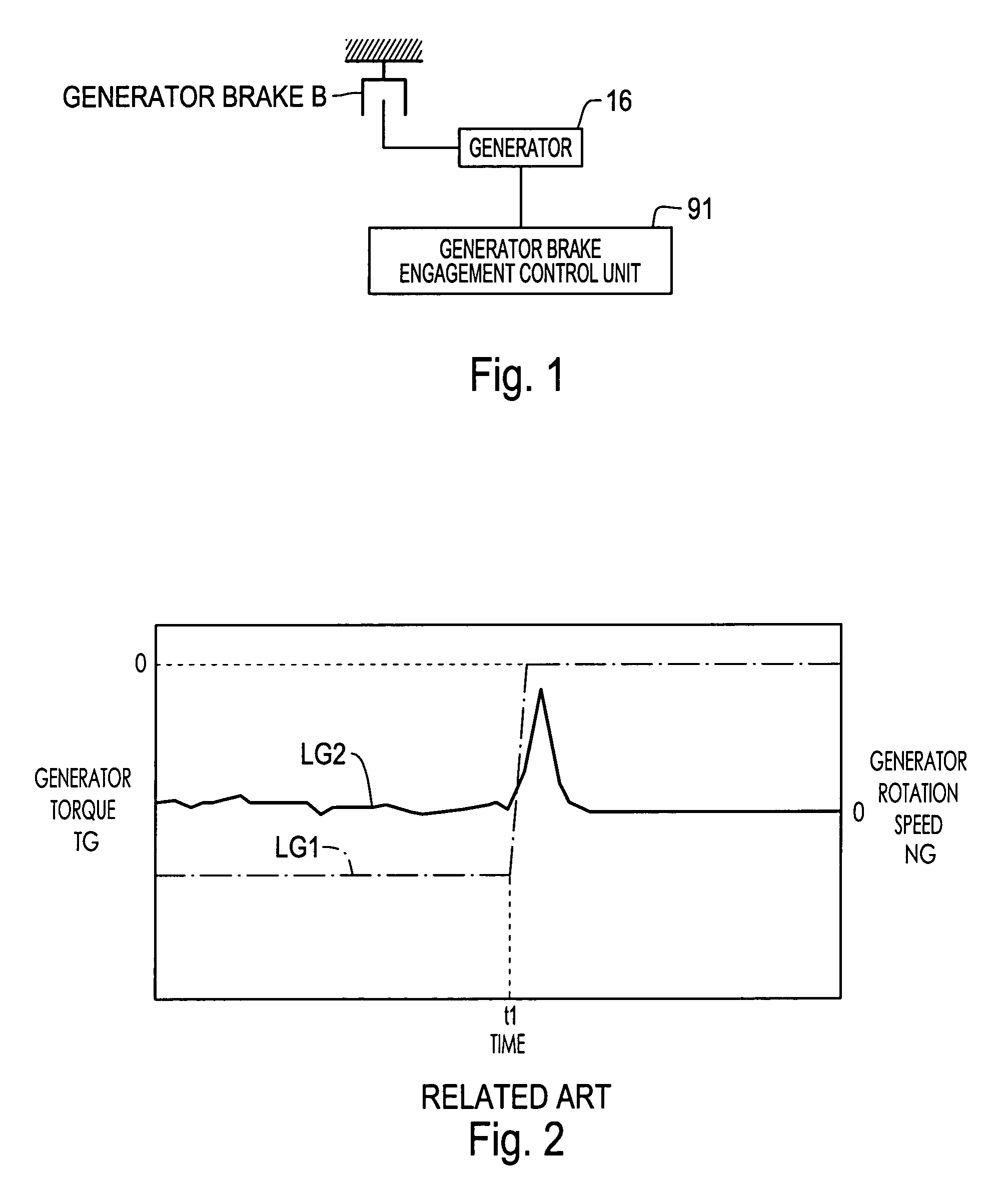
ActiveUS7100721B2Reduced service lifeInhibit productionHybrid vehiclesDigital data processing detailsHybrid vehicleElectric generator
A hybrid vehicle drive control apparatus including an electric generator mechanically connected to an engine so as to have a differential rotation with respect to the engine, a generator brake for mechanically stopping a rotation of the generator and a controller that gradually decreases a generator torque while engaging the generator brake.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
Gear selection assembly with nested differentially rotatable tube
InactiveUS7997159B2Shorten the axial lengthMechanical actuated clutchesToothed gearingsDrive shaftEngineering
The present invention broadly comprises a gear selector assembly including a tube with at least one engagement feature, arranged to be disposed within a drive shaft for a transmission, the transmission including at least one gear and the drive shaft including at least one gear actuation assembly; and a differential rotation element coupled with the tube and arranged to be coupled with the drive shaft so that the tube is differentially rotatable with respect to the drive shaft. The tube is arranged to differentially rotate such that the engagement feature engages the actuation assembly and the transmission engages a respective gear from the at least one gear. The assembly includes a means for displacing a portion of the differential rotation element such that the tube axially and rotationally displaces with respect to the drive shaft. The portion axially and rotationally engages with an interface element to controllably position the tube.
Owner:SCHAEFFLER TECH AG & CO KG
Power output apparatus and hybrid vehicle
InactiveUS20090301800A1Simple configurationImprove installabilityRailway vehiclesTransmission elementsDrive shaftEngineering
A hybrid vehicle includes an engine, motors, and a power distribution and integration mechanism that are coaxially arranged with respect to each other. The hybrid vehicle also includes a transmission including a transmission differential rotation mechanism that has a sun gear as an input element connected to a sun gear which is a first element of the power distribution and integration mechanism, a ring gear as a fixing element, and a carrier as an output element, and that is configured such that these three elements can differentially rotate with each other; and a clutch as a coupling mechanism capable of selectively coupling the sun gear of the transmission differential rotation mechanism and the carrier which is the second element of the power distribution and integration mechanism with a drive shaft.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Gear selection assembly with nested differentially rotatable tube
ActiveUS20080098843A1Shorten the axial lengthManual control with multiple controlled membersMechanical actuated clutchesDrive shaftEngineering
The present invention broadly comprises a gear selector assembly including a tube with at least one engagement feature, arranged to be disposed within a drive shaft for a transmission, the transmission including at least one gear and the drive shaft including at least one gear actuation assembly; and a differential rotation element coupled with the tube and arranged to be coupled with the drive shaft so that the tube is differentially rotatable with respect to the drive shaft. The tube is arranged to differentially rotate such that the engagement feature engages the actuation assembly and the transmission engages a respective gear from the at least one gear. The assembly includes a means for displacing a portion of the differential rotation element such that the tube axially and rotationally displaces with respect to the drive shaft. The portion axially and rotationally engages with an interface element to controllably position the tube.
Owner:SCHAEFFLER TECH AG & CO KG
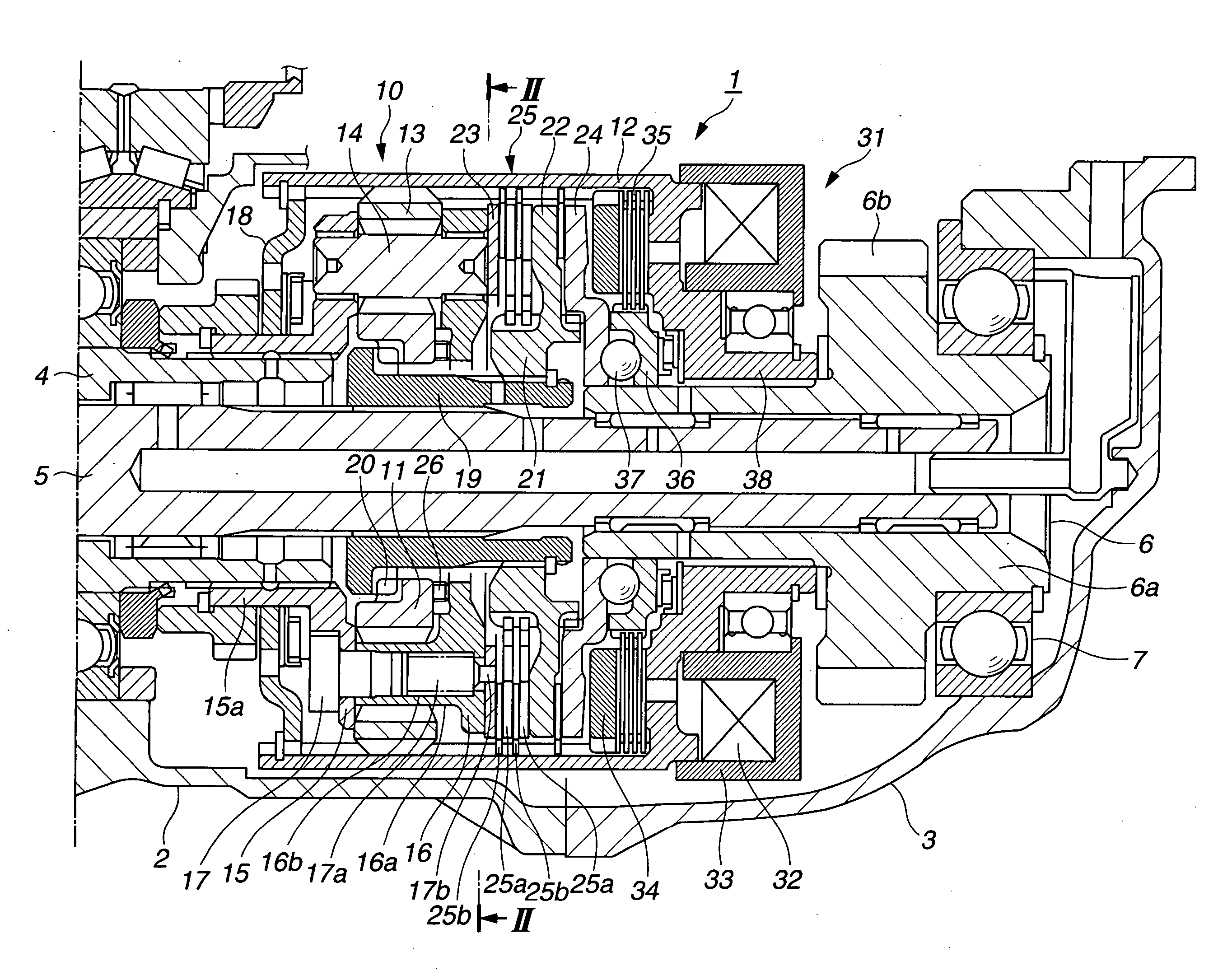
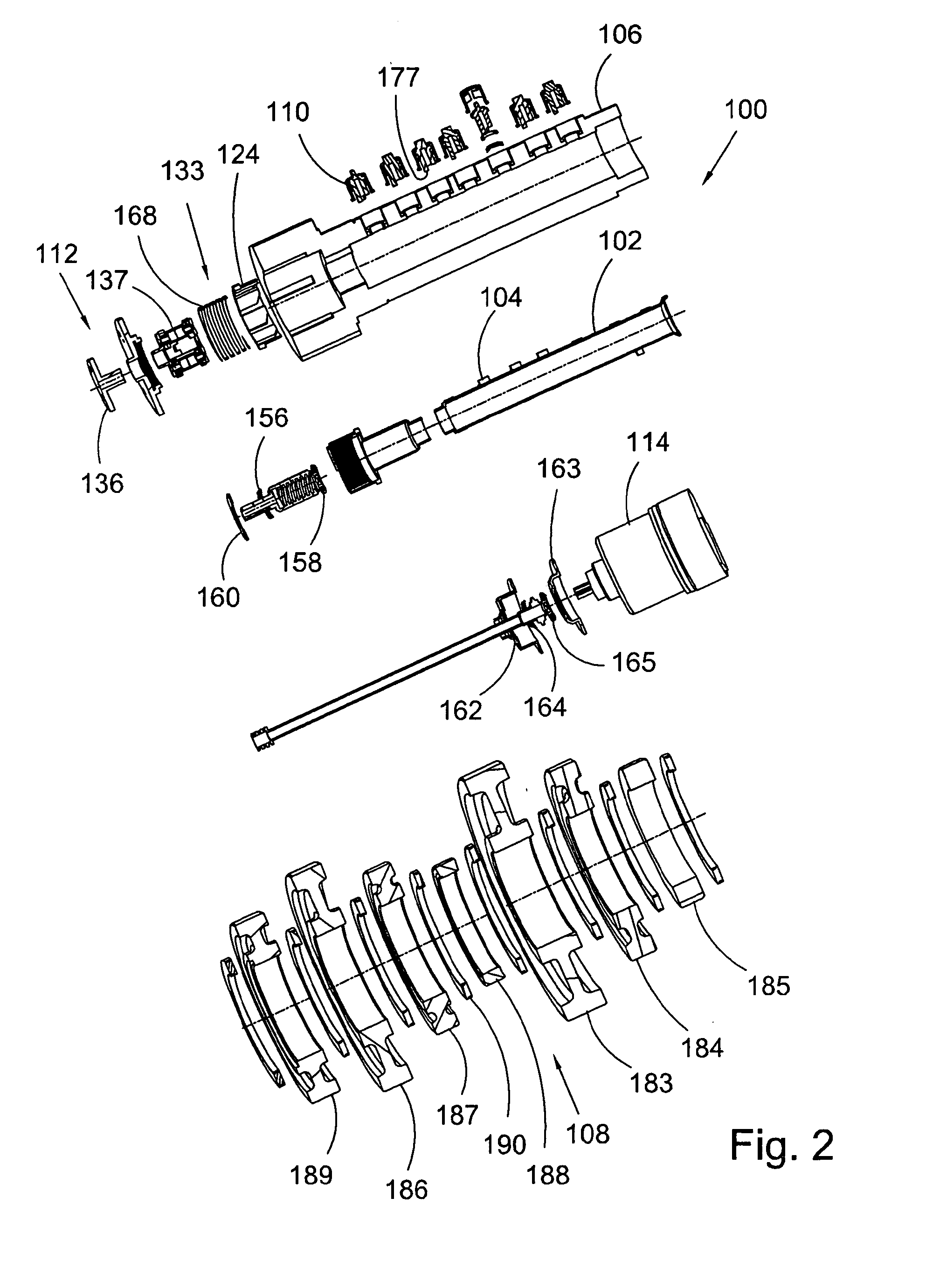
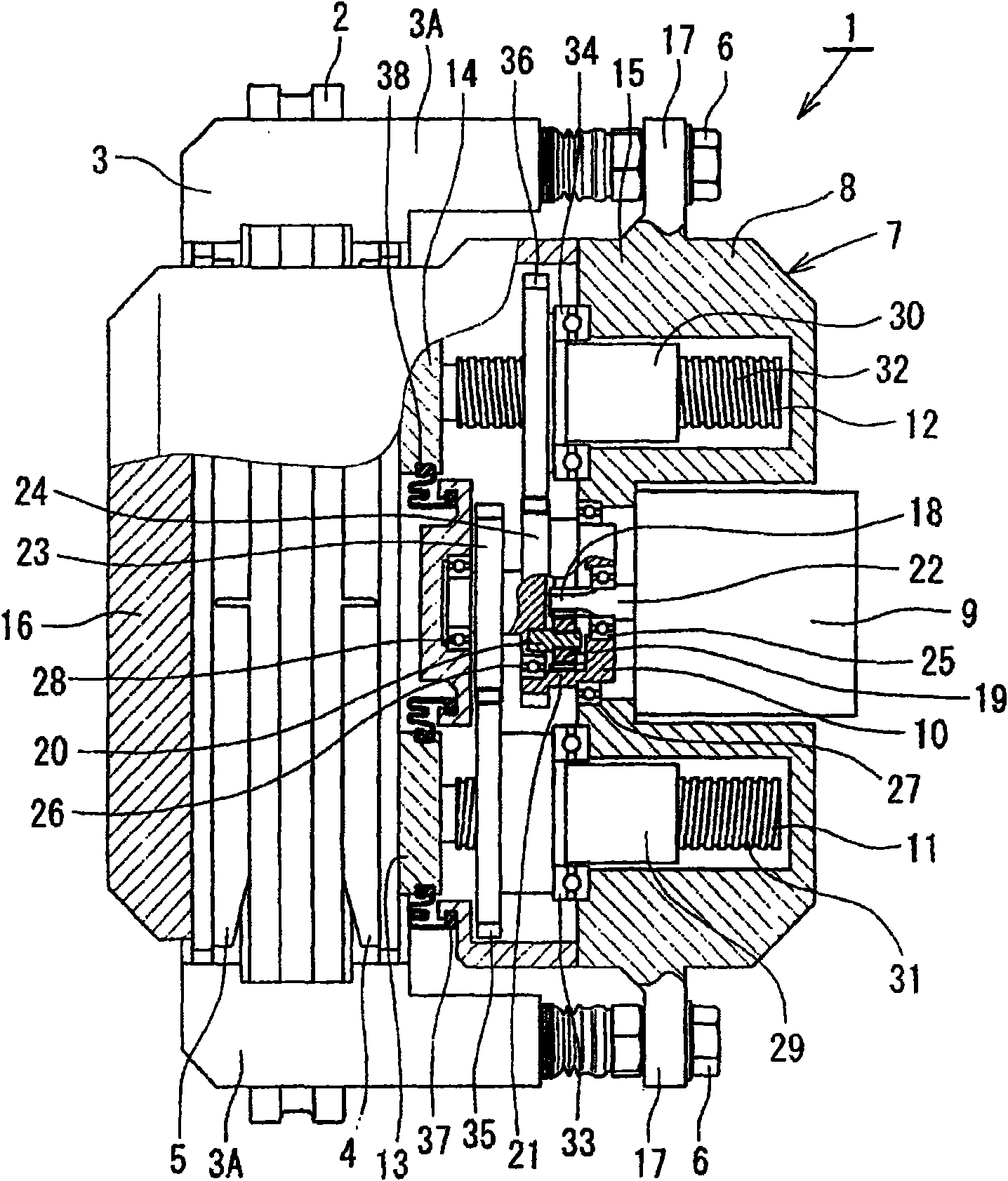
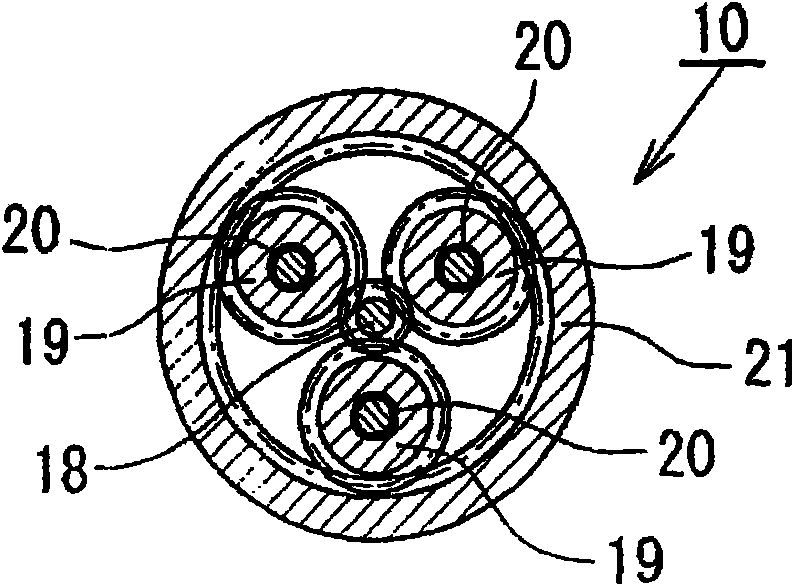
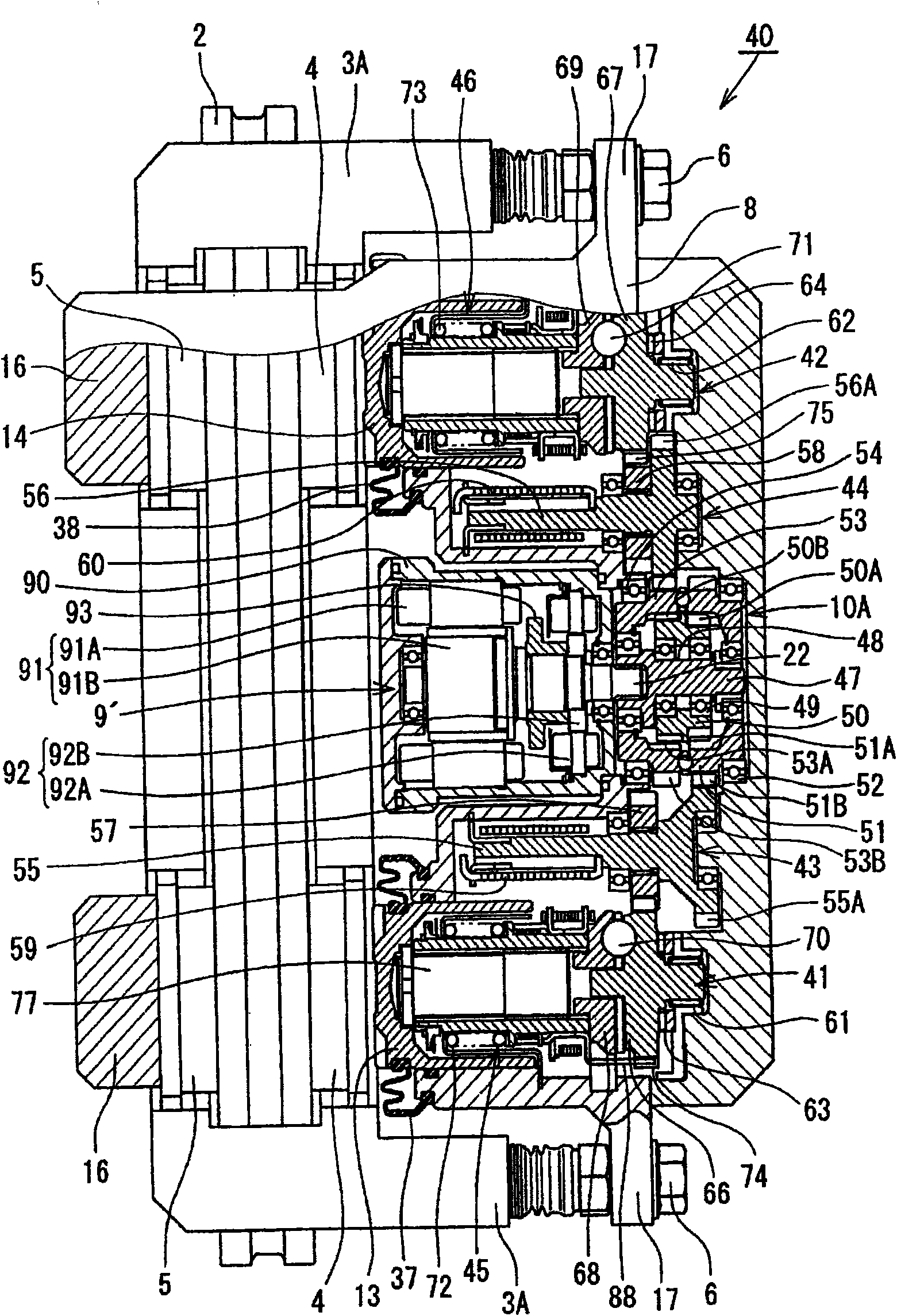
Electric disk brake
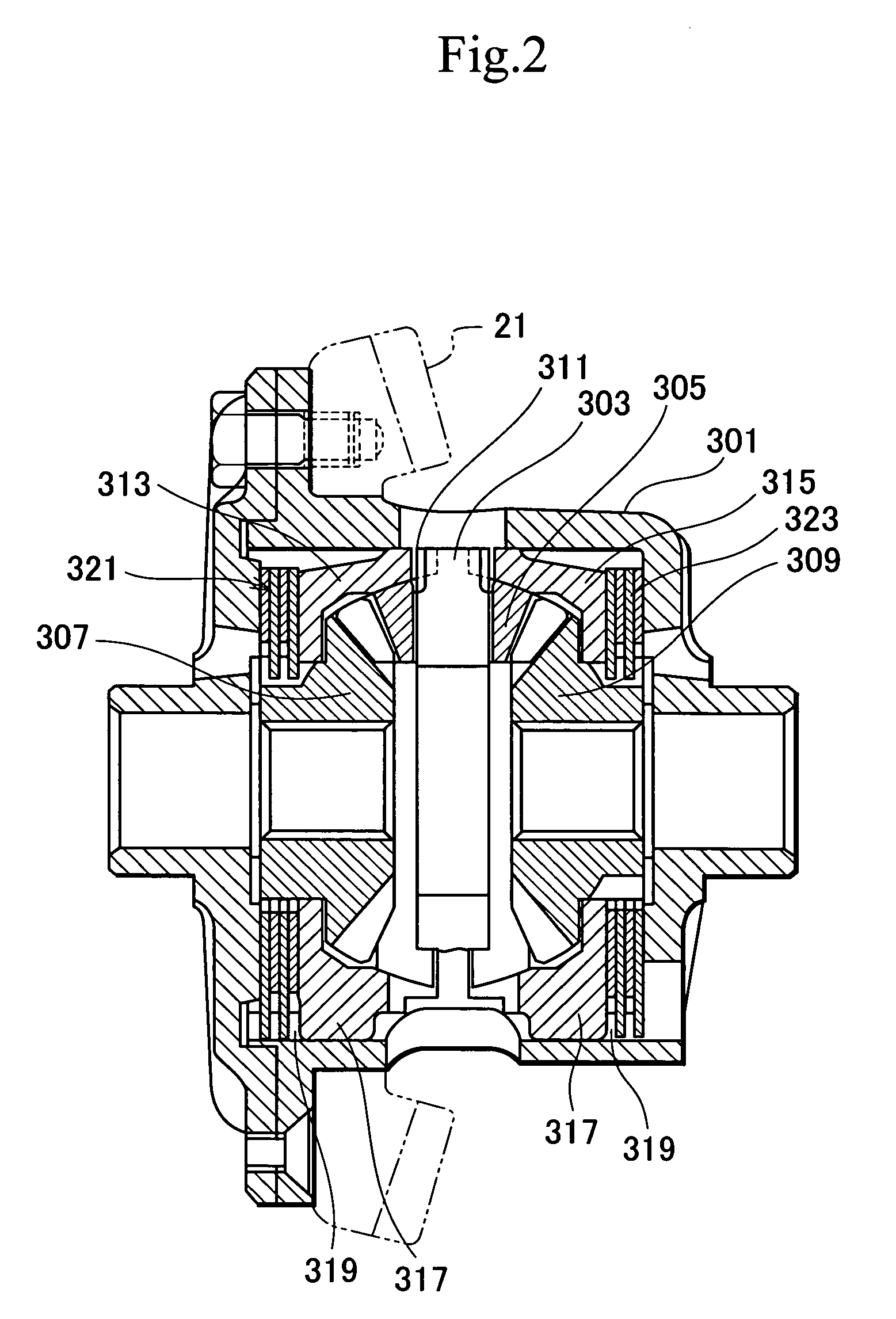
There is provided with an electric disk brake which is a small sized and is able to obtain large braking block pressure and run stably. The electric disk brake drives a sun gear of a reducing mechanism (10)(satellite gear mechanism) by an output shaft (22) of an electric motor / control unit (9), drives a ball screw mechanism (11) through a first output gear (23) by the rotation of a satellite gearrack (20), drives a ball screw mechanism (12) through a second output gear (24) by the rotation of a gear ring (21), and generates braking force by pressing braking blocks (4, 5) to a disk rotor. Theelectric disk brack can obtain double output by leading both the satellite gear rack (20) and the gear ring (21) of the satellite gear mechanism comparing with the condition that one of the satellitegear rack (20) and the gear ring (21) is fixed and the other is output, in addition, using differential rotation, even if one of driving ball screw mechanisms (11, 12) is stuck caused by fault, whichcan generate braking force.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Control device of automatic transmission, and control method of automatic transmission
ActiveUS20090062997A1Low calorific valuePrevent degradationClutchesDigital data processing detailsAutomatic transmissionOil pressure
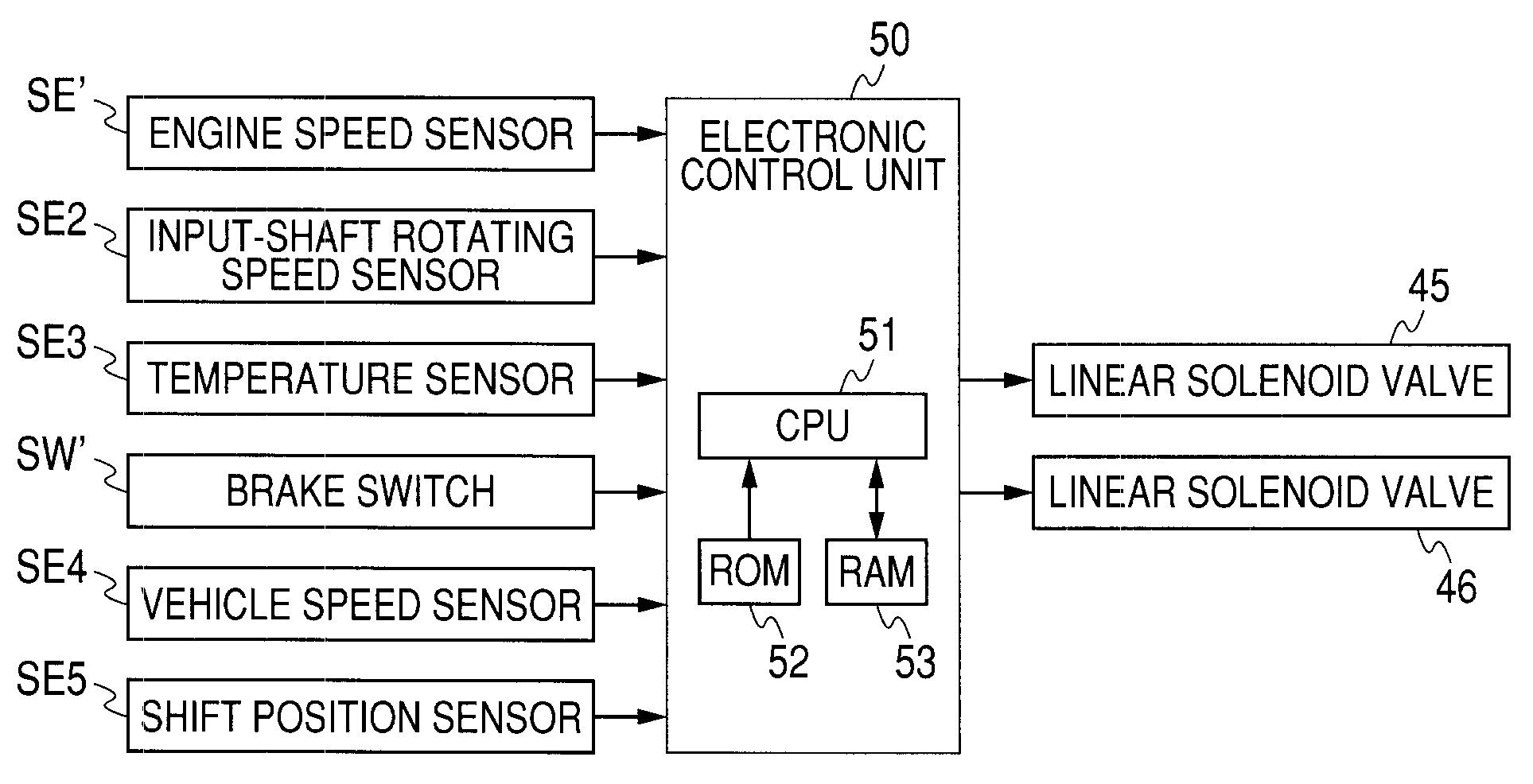
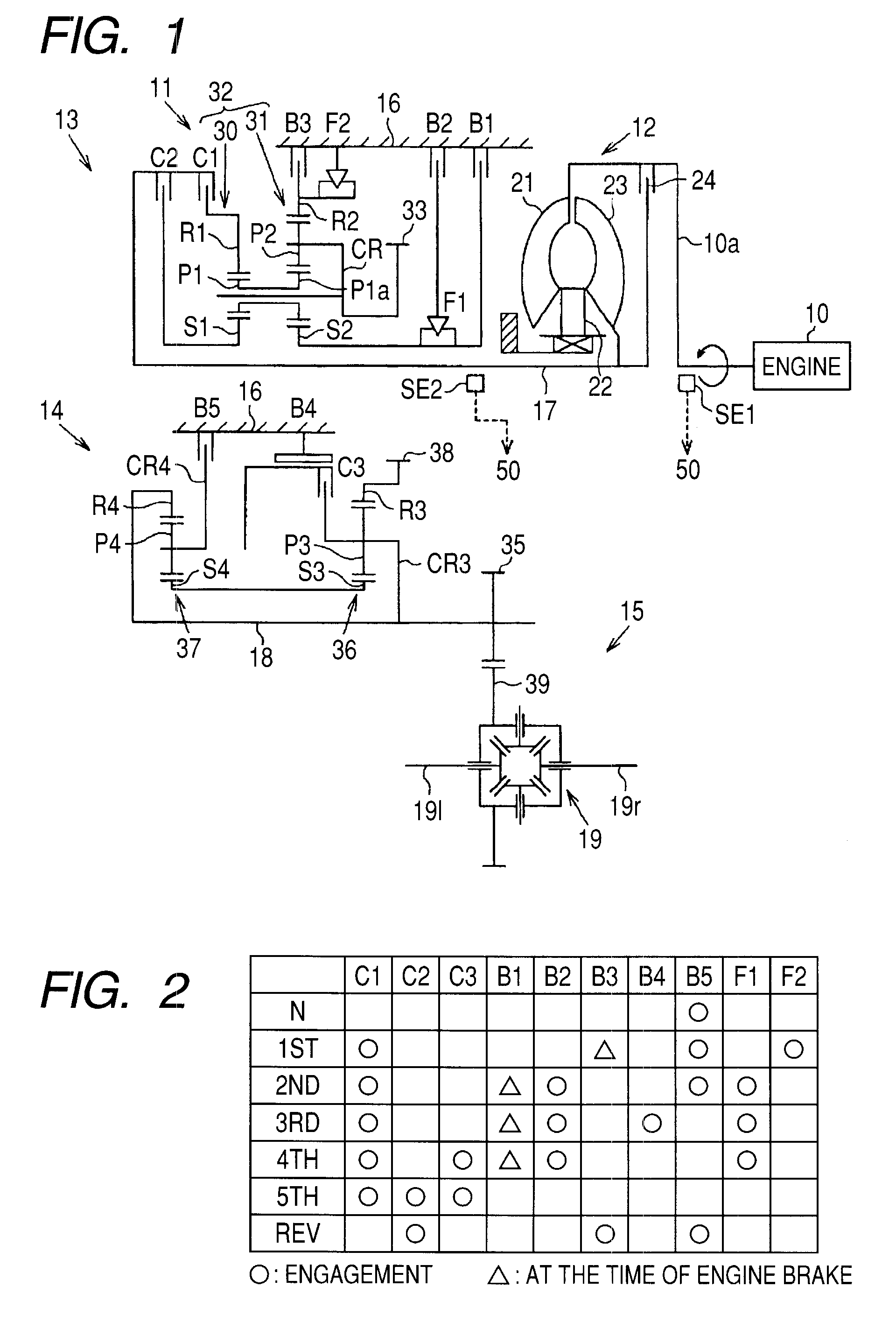
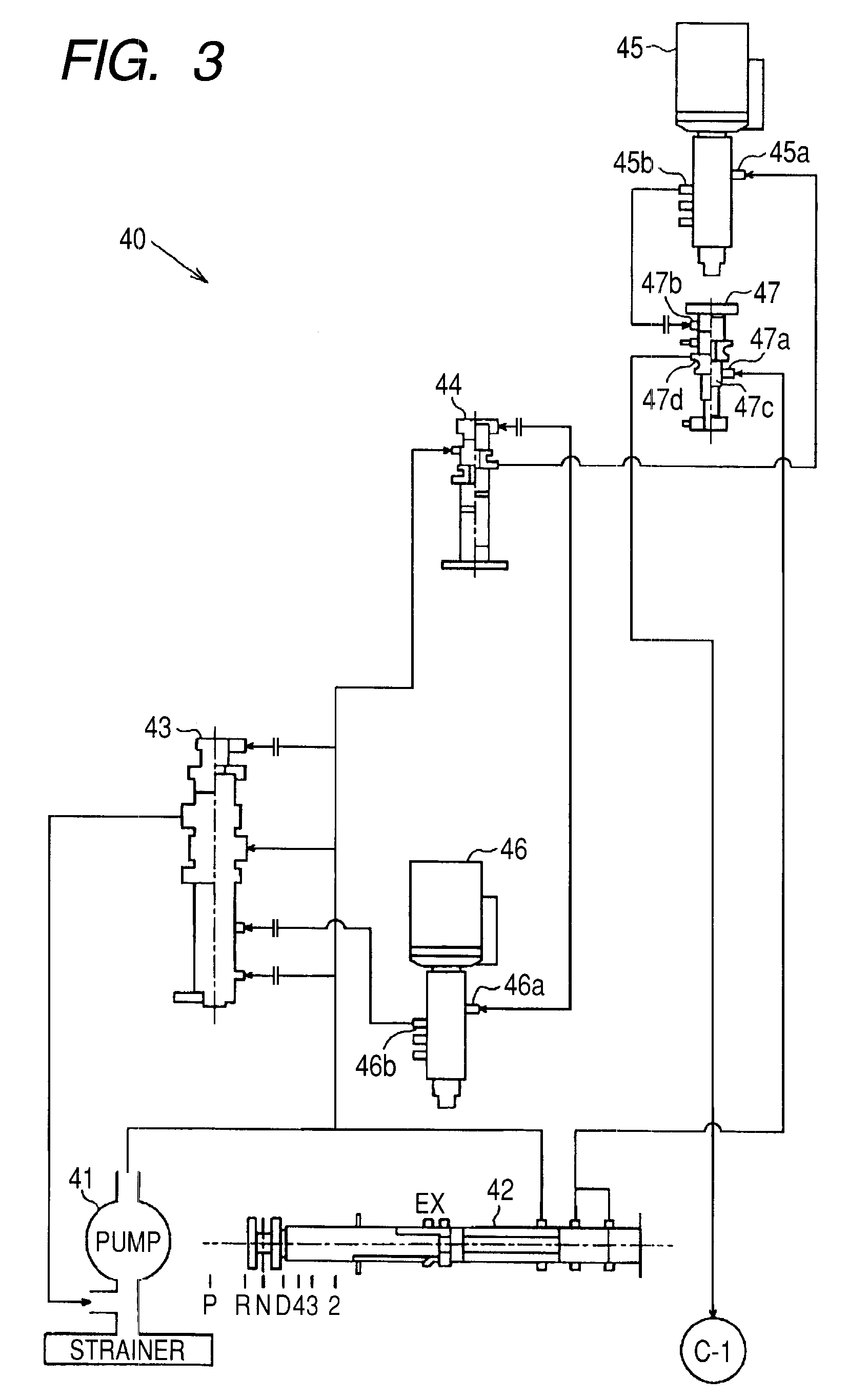
ECU executes in-neutral control in a case where a first clutch is brought into a half-engagement state on the basis of execution of neutral control. During the in-neutral control, ECU detects engine speed and input-shaft rotating speed, and detects differential rotation before an oil pressure change. Subsequently, in a case where the differential rotation before an oil pressure change detected by ECU has exceeded a first differential rotation threshold value, the operating oil pressure for a hydraulic servo is reduced by the first oil pressure.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
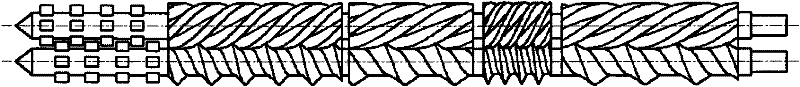
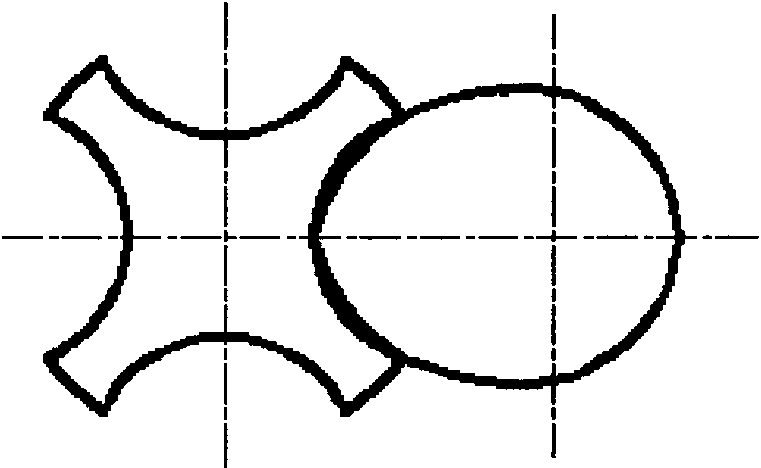
Exhaust-type differential double-screw extruder
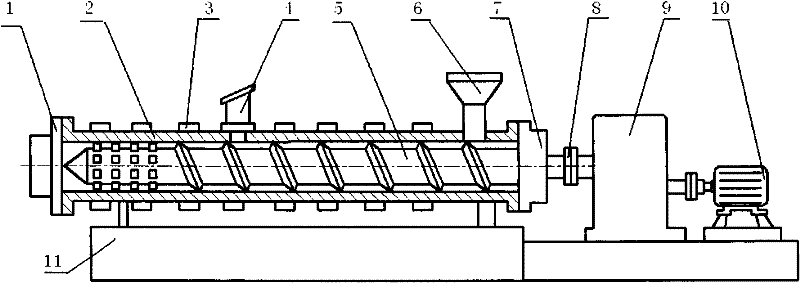
The invention relates to an exhaust-type differential double-screw extruder, mainly comprising a feeder, a cylinder, screws, a machine head, a heating and cooling device, an exhaust outlet, a motor and a driving device, wherein one screw is a male rotor, and the other screw is a female rotor; at least one screw thread engaging region is arranged when the screws are combined, the screw socket number of the female rotor in the region is integral multiples of that of the male rotor, the rotating speeds of the female rotor and the male rotor are in inverse proportion to the screw socket number, and differential rotation and no interference during movement can be realized for the female rotor and the male rotor. At least one exhaust outlet is arranged on a material cylinder so as to remove moisture and other volatile components, and the screw configuration distribution meets the exhausting requirement. According to material processing requirements, screw thread sections or other forms with different leads and section shaped lines can be arranged on different sections of a charging section, a fusion section, an exhausting section and a metering section of the screws; when the screws are installed, besides at least one screw thread engaging region with differential rotation is ensured, the screws in different sections can be engaged and can be also unengaged so as to reinforce mixing or other functions. The extruder has favorable mixing, plasticizing and conveying capabilities and is suitable for processing and forming various granules, powder materials or even block materials, such as plastics, rubbers, food, explosives and the like.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
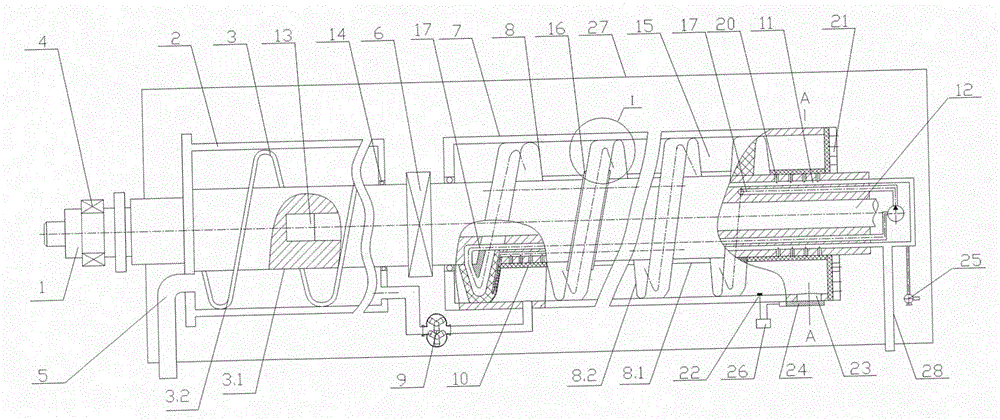
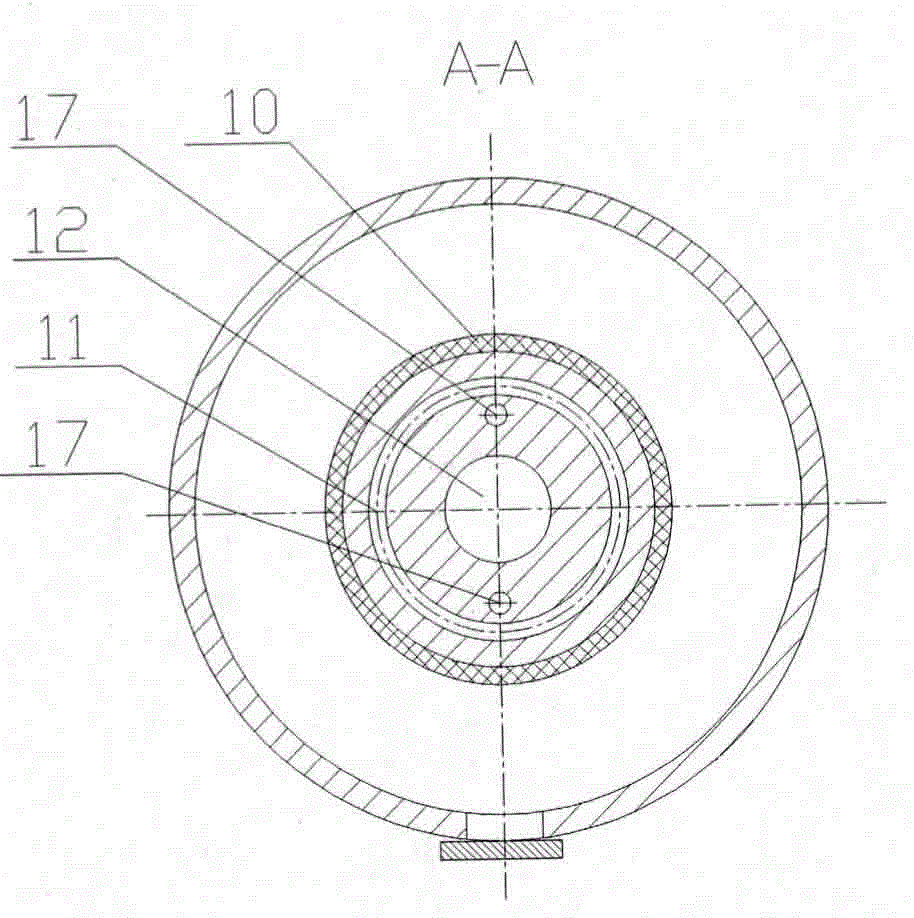
Centrifugation and pressure filtration double sludge dewatering method
InactiveCN104016565AReduce moisture contentGuaranteed uptimeSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningLiquid layerFiltration
The invention discloses a centrifugation and pressure filtration double sludge dewatering method. The method comprises the steps: sewage is conveyed into a first rotary drum (2) through a pipeline, the first rotary drum (2) and a spiral pusher (3) are in differential rotation, sludge is thrown to the internal wall of the first rotary drum (2) under the action of centrifugal force, so as to form a solid layer, and a liquid layer is formed at the inner side of the solid layer by water; the sludge treated by a front-section dewatering device is conveyed into a second rotary drum (7) of a rear-section dewatering device, a plurality of chambers are formed between a spiral press filter (8) and the second rotary drum (7), spiral pressure filtration blades (8.2) are made from elastic materials, high-pressure fluid is introduced into the spiral pressure filtration blades, so as to expand the spiral pressure filtration blades, and the expanded spiral press filter rotates and extrudes the sludge. According to the centrifugation and pressure filtration double sludge dewatering method, the front-section dewatering device is mainly used for filtering moisture out of the sewage by means of centrifugation, and the rear-section dewatering device is used for carrying out further treatment on the sewage by means of centrifugation and pressure filtration, so that continuous operation can be carried out, the production efficiency is high, and the moisture content is low after dewatering.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Driving device for vehicle
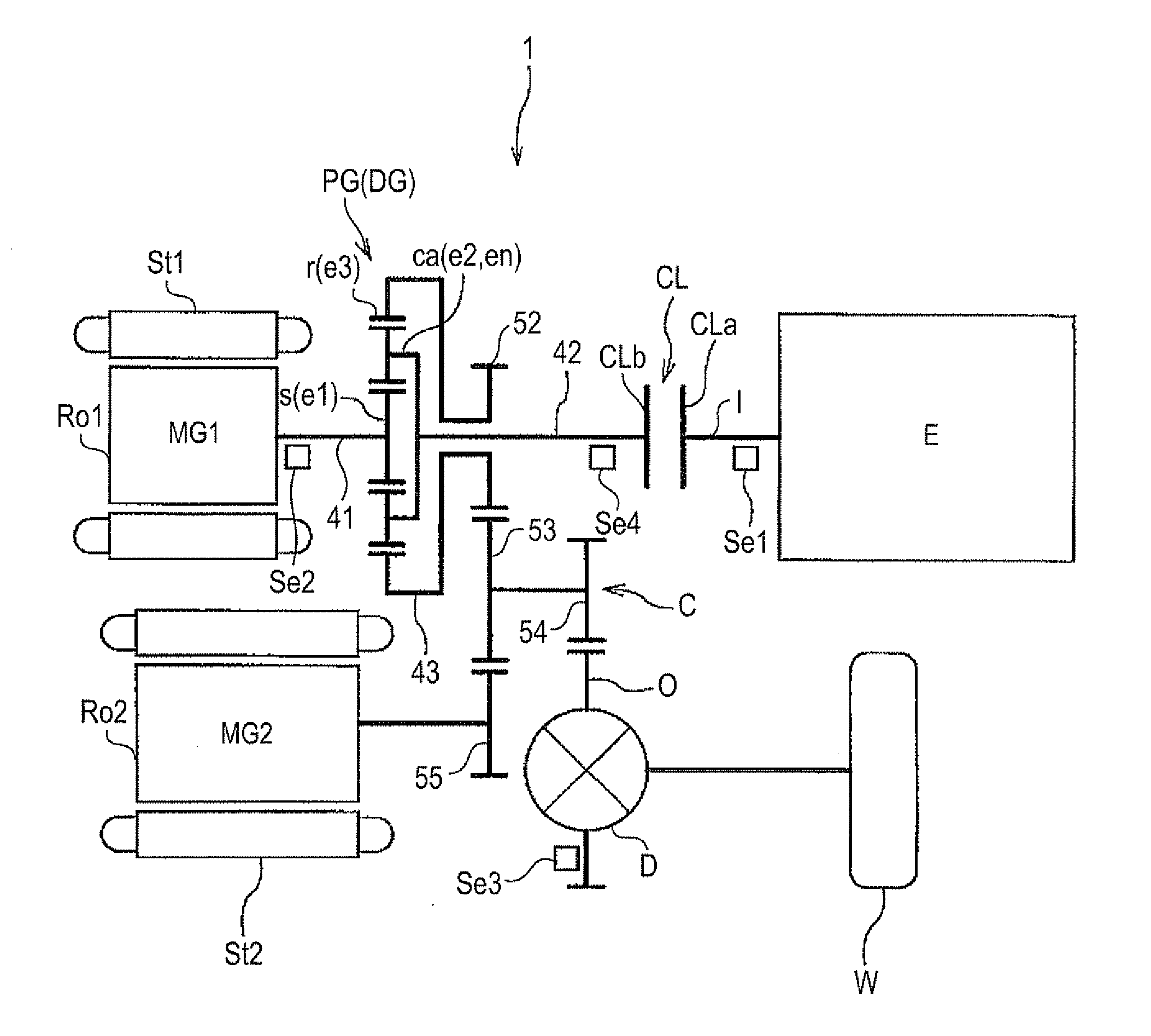
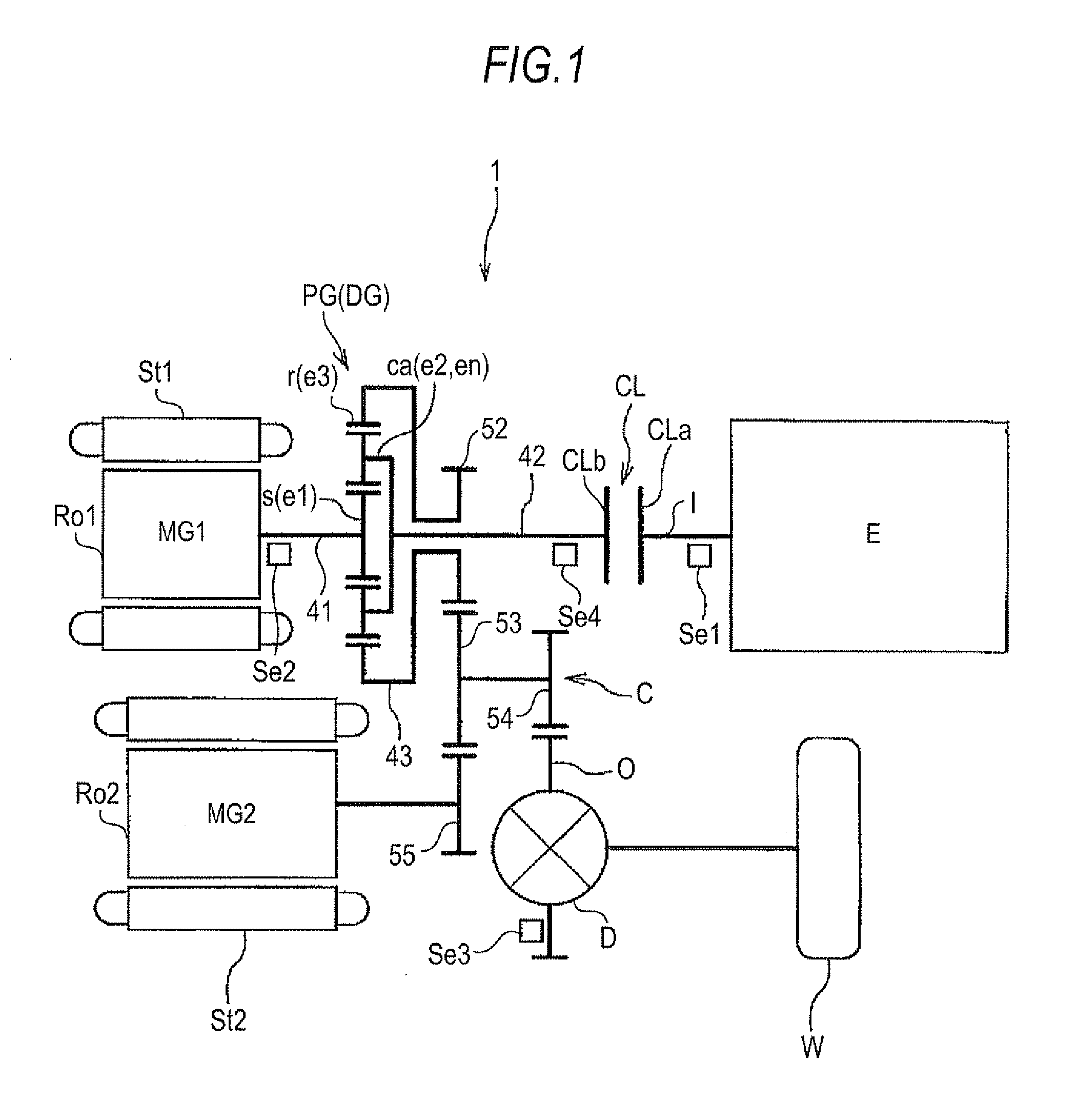
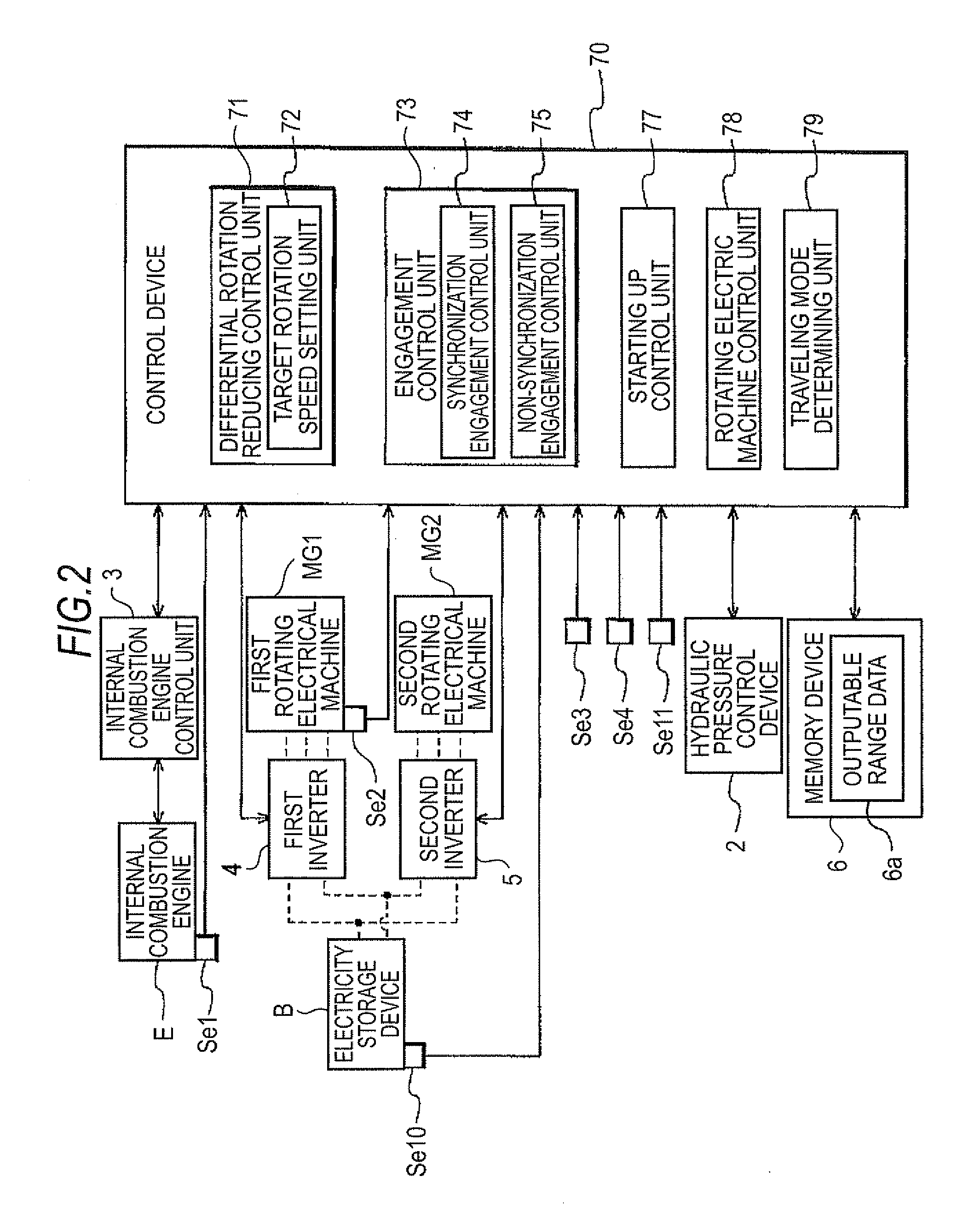
InactiveUS20120244992A1InhibitionReduction in an expected life spanPower operated startersInternal combustion piston enginesLower limitElectric machine
A driving device with an input member connected to an engine, an output member connected to wheels, first and second rotating electrical machines, a differential gear unit including at least three rotational elements, and a control device. The control device includes a differential rotation reducing control, an engagement control, and a start up control that changes the rotation speed of the first rotating electrical machine, which allows the internal combustion engine to have a rotation speed at which starting is possible, made as a target value, when in direct engagement. The differential rotation reducing control changes the rotation speed of the first rotating electrical machine with the upper limit and the lower limit of a starting torque output range, which is a rotation speed range in which the torque necessary for starting the internal combustion engine may be output by the first rotating electrical machine, made as limits.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
Apparatus for controlling driving force of vehicle
InactiveUS7562947B2Heat suppressionSuppressing wearingHybrid vehiclesDigital data processing detailsEngineeringElectric control
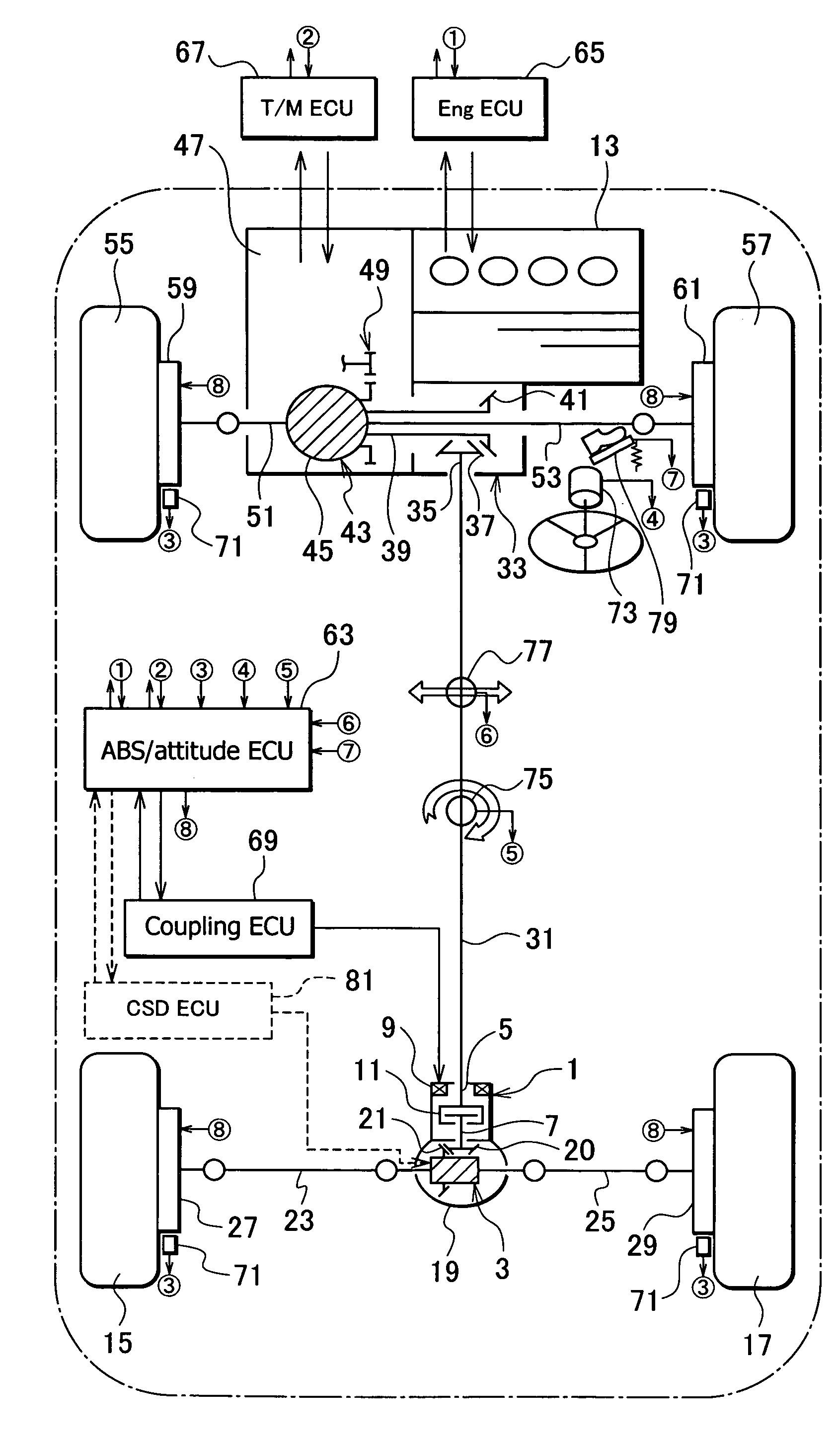
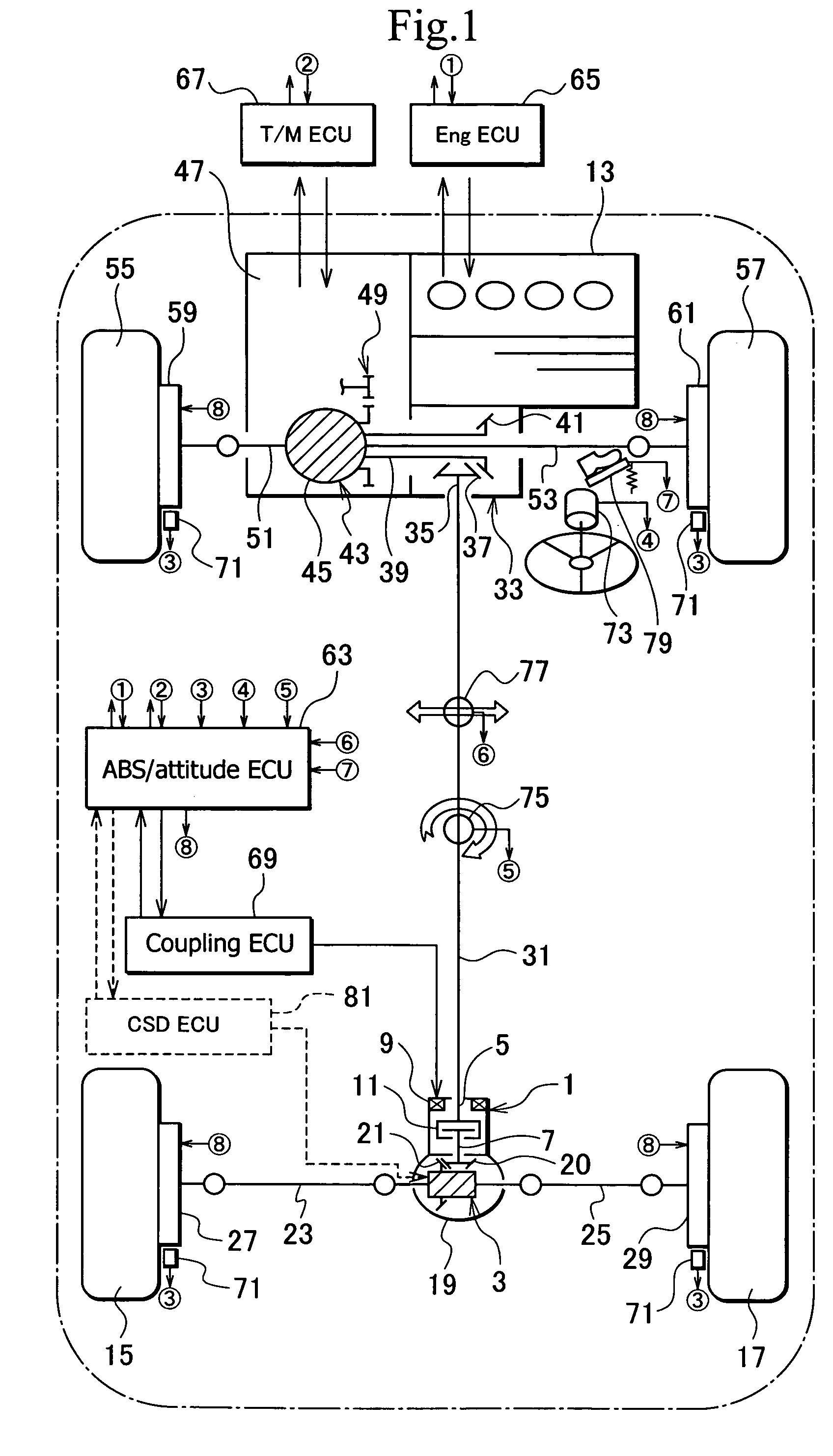
An apparatus for controlling the driving force of a vehicle is capable of using brakes to limit a differential operation, securing sufficient torque, and suppressing the heating and wearing of the brakes. In the vehicle, an engine generates torque to drive front wheels and / or rear wheels. A front differential allows differential rotation between the front wheels and transmits torque of the engine to the front wheels. A rear differential allows differential rotation between the rear wheels and transmits torque of the engine to the rear wheels. Disk brakes separately brake the front and rear wheels. An ABS / attitude electric control unit controls the disk brakes to limit differential rotation between the front wheels or between the rear wheels. At least one of the front and rear differentials is provided with a differential limiting mechanism.
Owner:GKN DRIVELINE TORQUE TECHNOLOGY KK
Damper
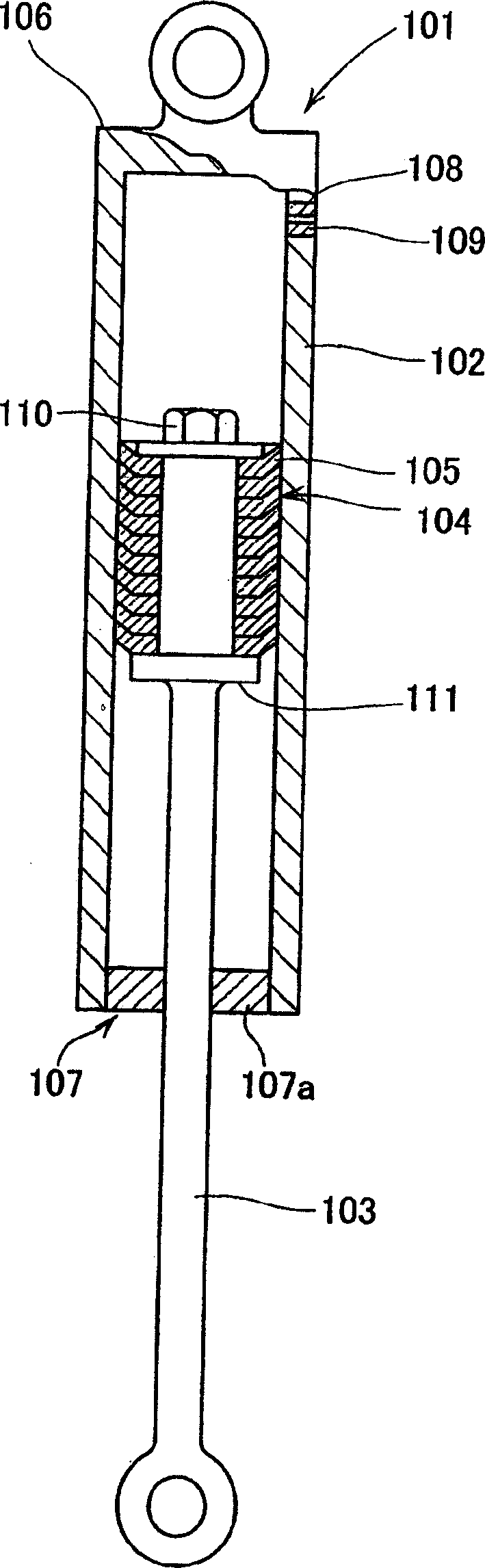
A damping device for use in industrial machinery and tools comprising a housing ( 102, 602 ) and a flange member ( 104, 604 ) arranged in the housing, wherein at least portions of the flange member apart from the center thereof are composed of an elastic material and inclined with respect to the axial direction or the radial direction of the rotational axis and the flange member is so designed that the peripheral face thereof is brought into contact with the inner wall of the housing. This device can generate a damping force which may be drastically changed depending on the operating directions and thus permits stable damping. In the direct acting type one, the flange member ( 104 ) is tapered on the corresponding both faces towards the periphery thereof, it never requires the formation of any space for allowing any deformation on the largely deformed side, the device can thus be miniaturized in the axial direction and permits the reduction of the weight thereof and it can operate even in response to motions having a fine amplitude to thus show excellent damping characteristics. In the rotary type one, the flange member ( 604 ) comprises an engaging member capable of being engaged with a shaft body ( 603 ) and is provided with projected or convex portions ( 604 a) on its outer periphery. The projected portions are inclined towards the radial direction of the rotating shaft to thus efficiently show their excellent differential rotation-damping characteristics and the damping characteristics may arbitrarily be controlled. These damping devices can be used as dampers for suspensions of bicycles, rotary dampers applied to chairs and dampers for opening and closing doors.
Owner:FUKOKU CO LTD
Power transfer device
A power transfer device including a main clutch, a cam mechanism and an electromagnetic pilot clutch mechanism coaxially assembled within a cylindrical space between an external cylindrical rotary member and an internal rotary member, wherein an electromagnetic coil of the pilot clutch mechanism is applied with an electric current to produce pilot torque, the cam mechanism is applied with the pilot torque to produce thrust force in an axial direction, and the main clutch is engaged by the thrust force applied from the cam mechanism to effect drive connection between the rotary members. In the power transfer device, residual thrust force of the cam mechanism is electrically or mechanically decreased at an instance when differential rotation of the rotary members is reversed.
Owner:TOYODA MASCH WORKS LTD
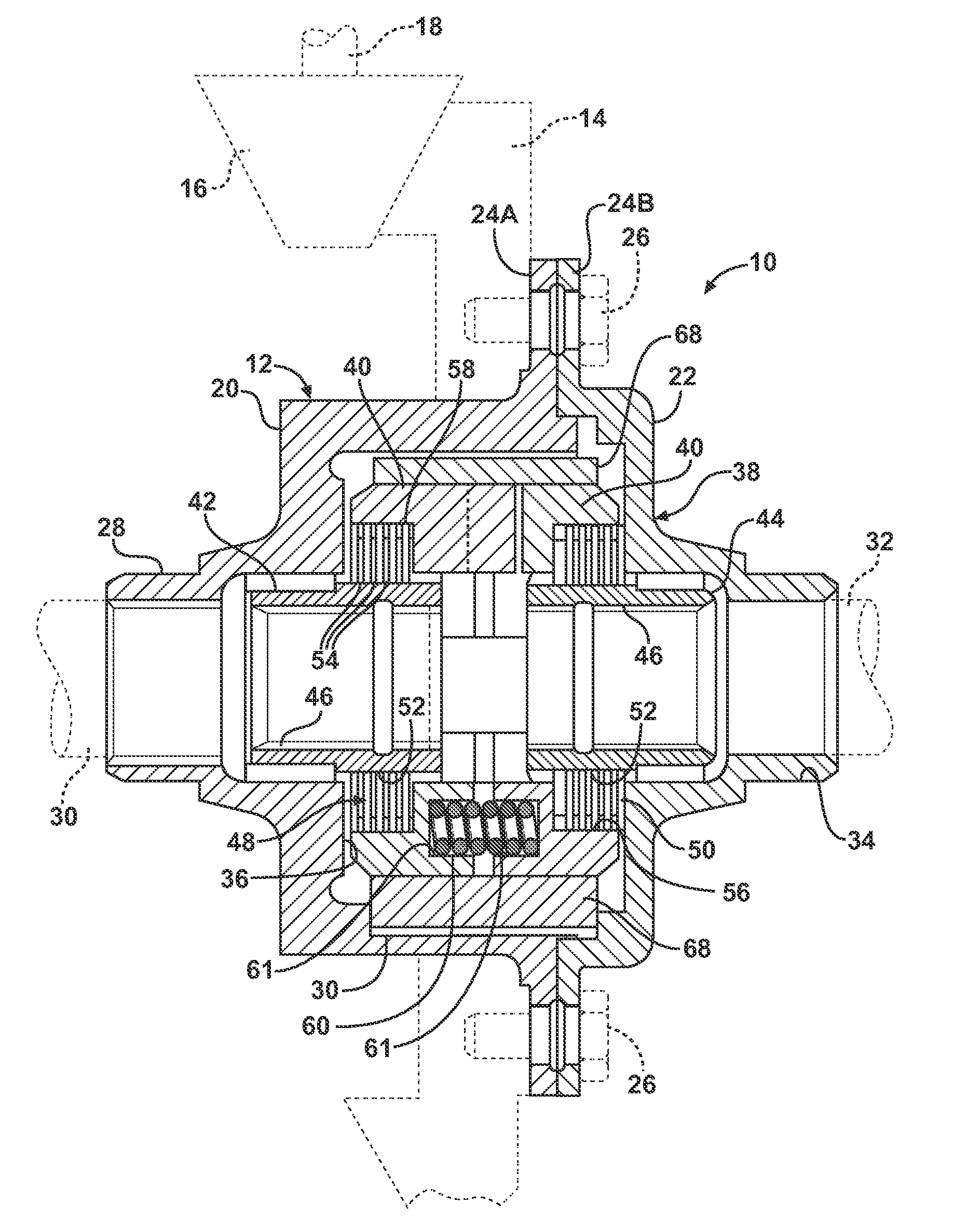
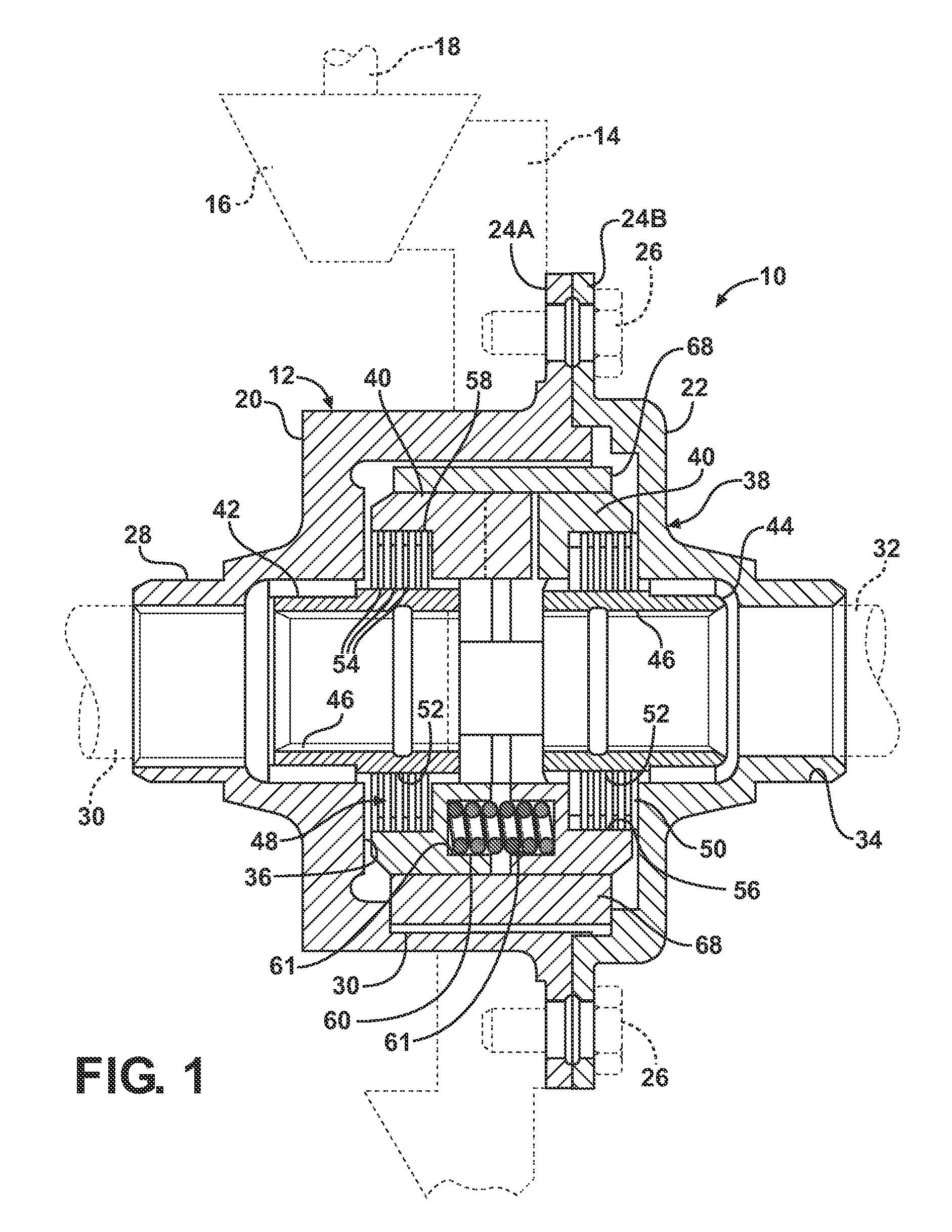
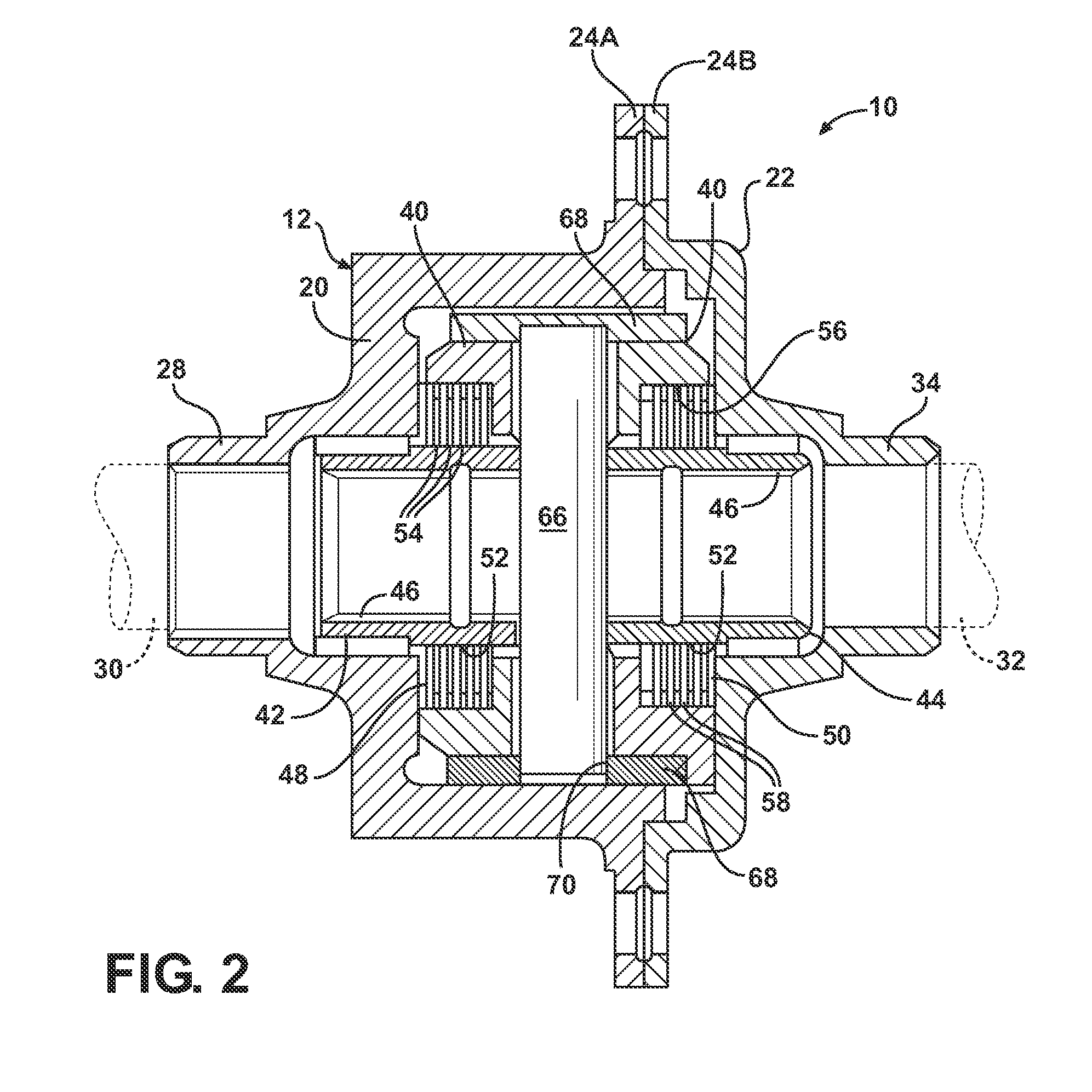
Locking differential having improved torque capacity
ActiveUS8146458B2Reduce edge stressIncreased torque densityDifferential gearingsControl devicesEngineeringLateral extension
A locking differential for an automotive vehicle including a housing and a differential mechanism supported in the housing. The differential mechanism includes a pair of clutch members disposed in spaced axial relationship with respect to each other wherein each clutch member includes a groove disposed in an opposed inwardly directing face that is adapted to receive a cross pin. Each of the grooves includes a working surface extending laterally relative to each other. Each of the working surfaces defines a screw involute surface such that the cross pin contacts the working surface along a line extending in the direction of the cross pin in the event of differential rotation of an axle half shaft relative to the housing. Alternatively, each of the working surfaces defines a slightly convex surface in one plane such that the cross pin contacts the working surface at a point defined thereon. In another embodiment, the working surface defines a slightly convex surface in two planes such that the cross pin contacts the working surface at a point defined thereon.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LTD
Power transfer device
A power transfer device including a main clutch, a cam mechanism and an electromagnetic pilot clutch mechanism coaxially assembled within a cylindrical space between an external cylindrical rotary member and an internal rotary member, wherein an electromagnetic coil of the pilot clutch mechanism is applied with an electric current to produce pilot torque, the cam mechanism is applied with the pilot torque to produce thrust force in an axial direction, and the main clutch is engaged by the thrust force applied from the cam mechanism to effect drive connection between the rotary members. In the power transfer device, residual thrust force of the cam mechanism is electrically or mechanically decreased at an instance when differential rotation of the rotary members is reversed.
Owner:TOYODA MASCH WORKS LTD
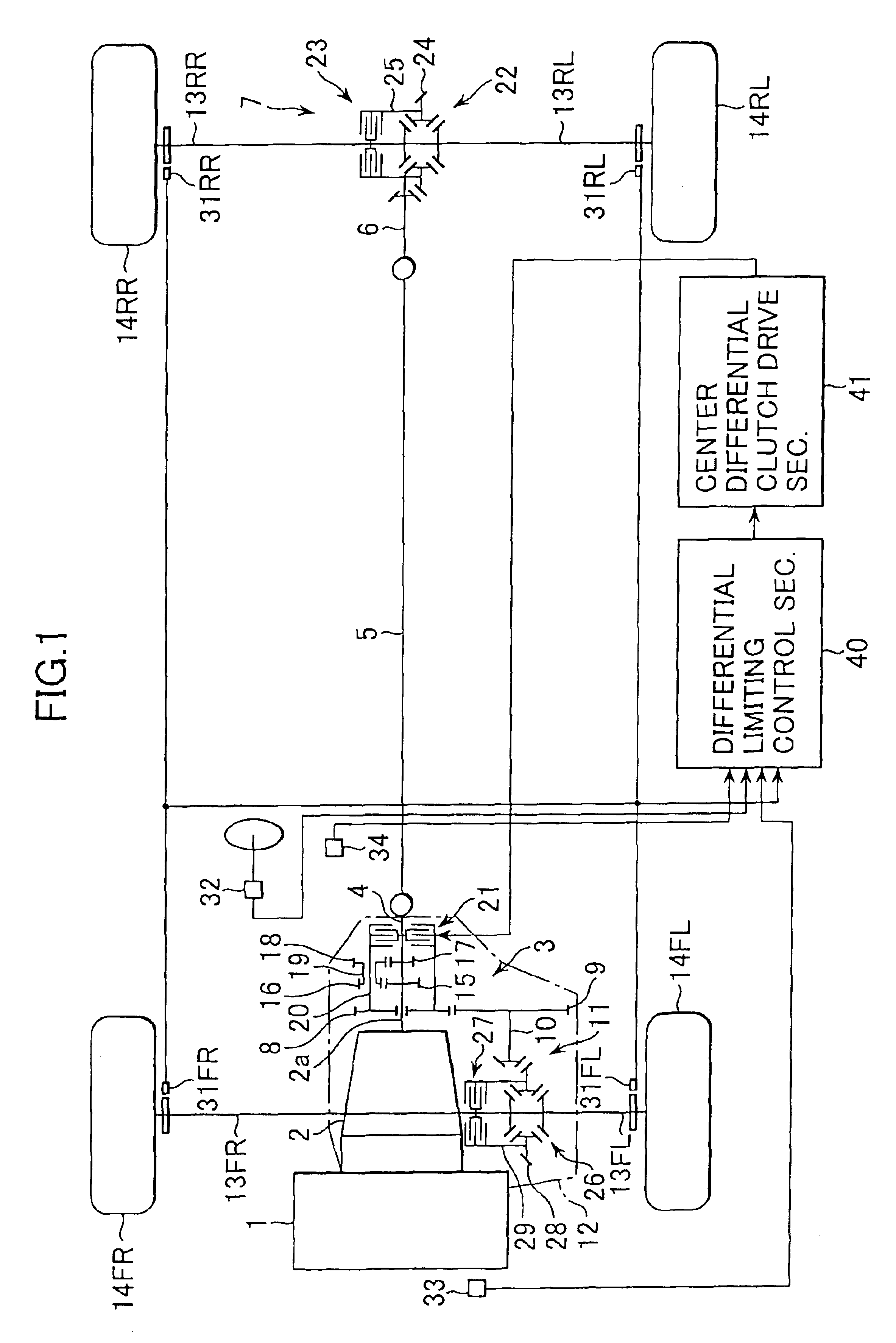
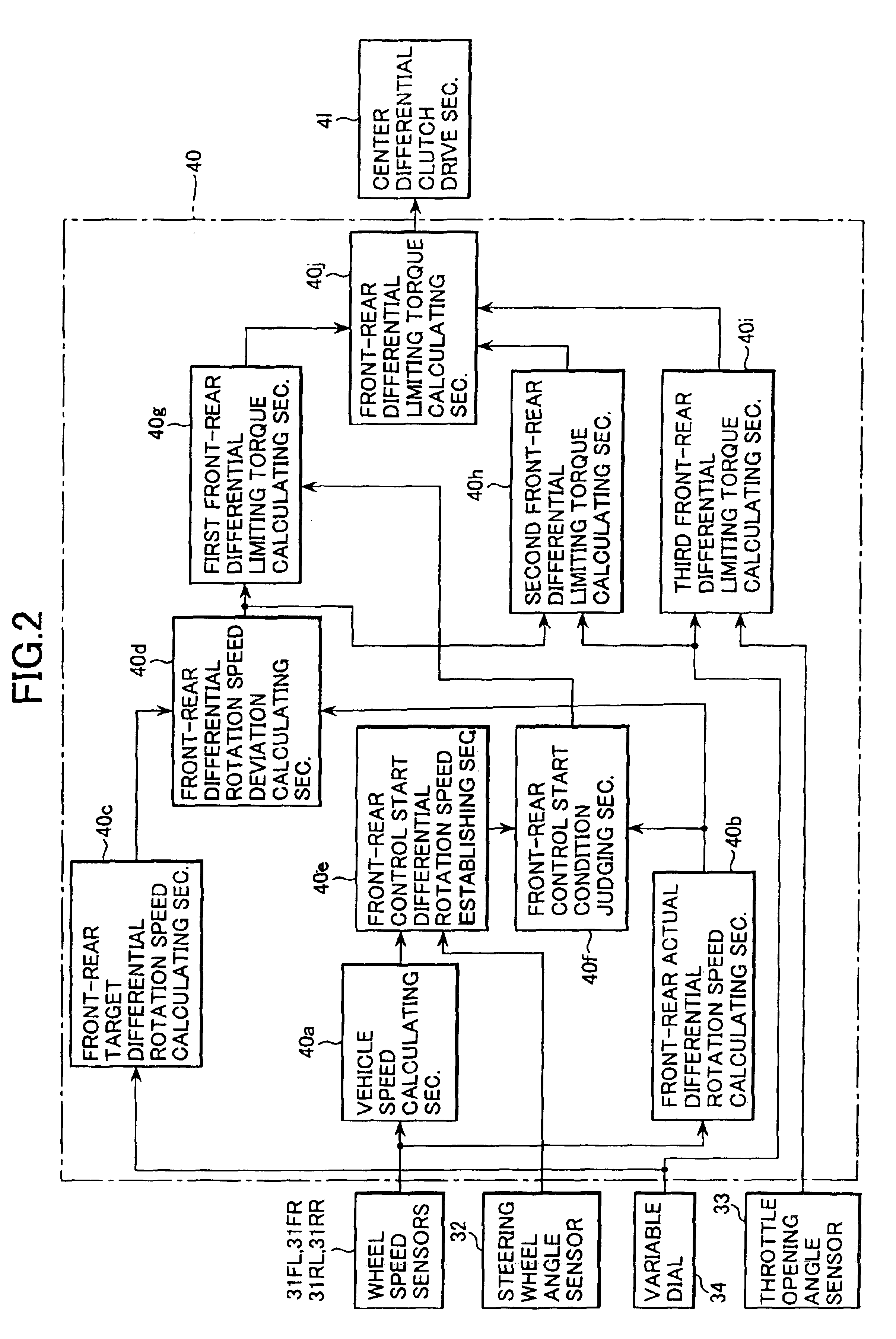
Power distribution control apparatus and control method
InactiveUS6878085B2Improve mobilityDigital data processing detailsToothed gearingsDistribution controlDrive shaft
In a differential limiting torque control section, a target differential rotation speed between front and rear drive shafts is established according to a dial position inputted by a driver of a variable dial. Further, an actual differential rotation speed between front and rear drive shafts is calculated and a deviation between the target differential rotation speed and the actual differential rotation speed is calculated. Based on the deviation, a first differential limiting torque and based on a dial position of a variable dial a second differential limiting torque are calculated. Further, a third differential limiting torque is calculated based on the dial position and a throttle opening angle. A final differential limiting torque between front and rear drive shafts is obtained by summing up these first, second and third differential limiting torques.
Owner:SUBARU CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com