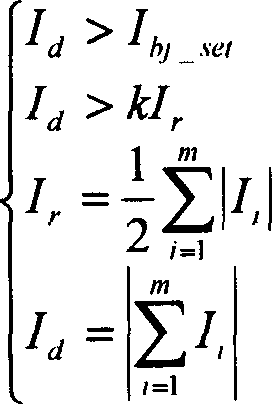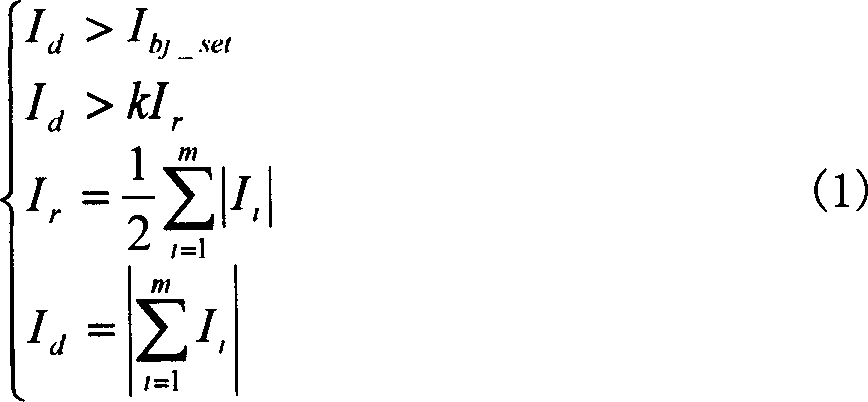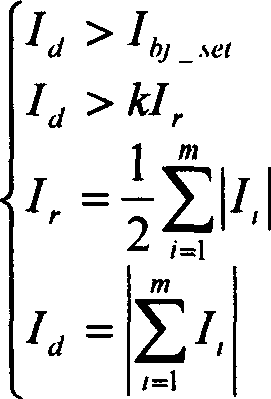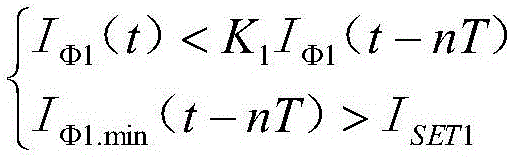Patents
Literature
235 results about "Locking differential" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
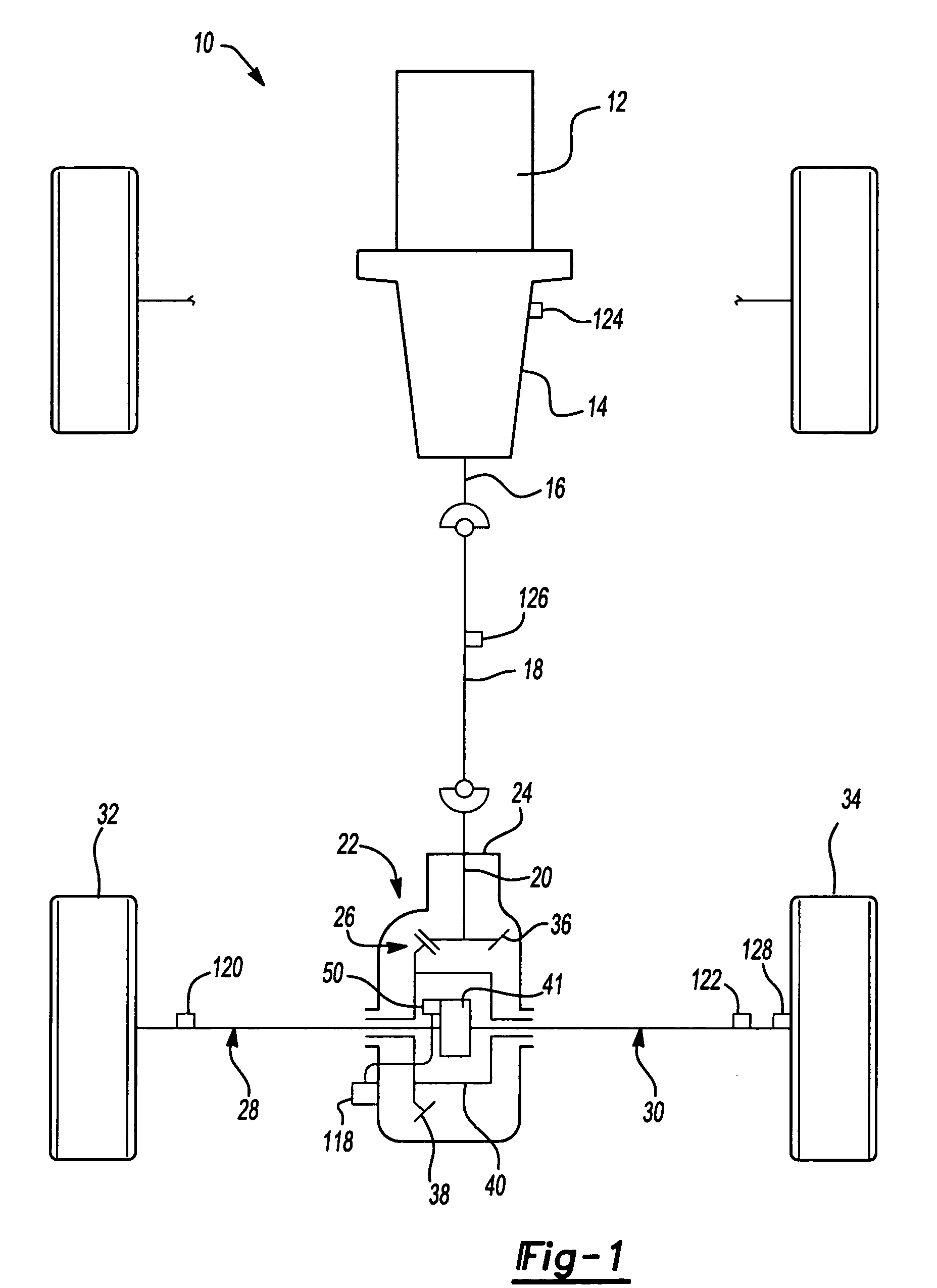
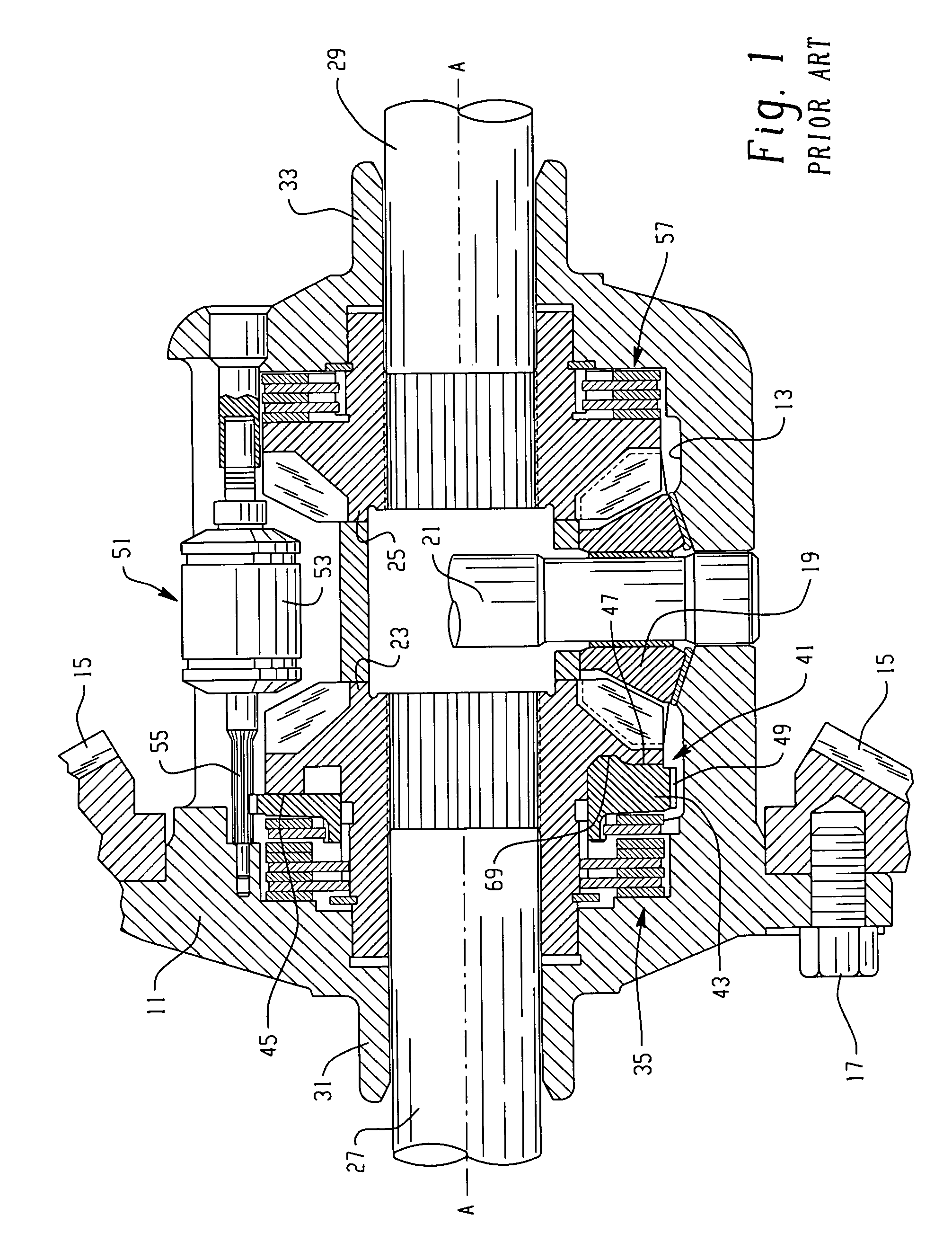
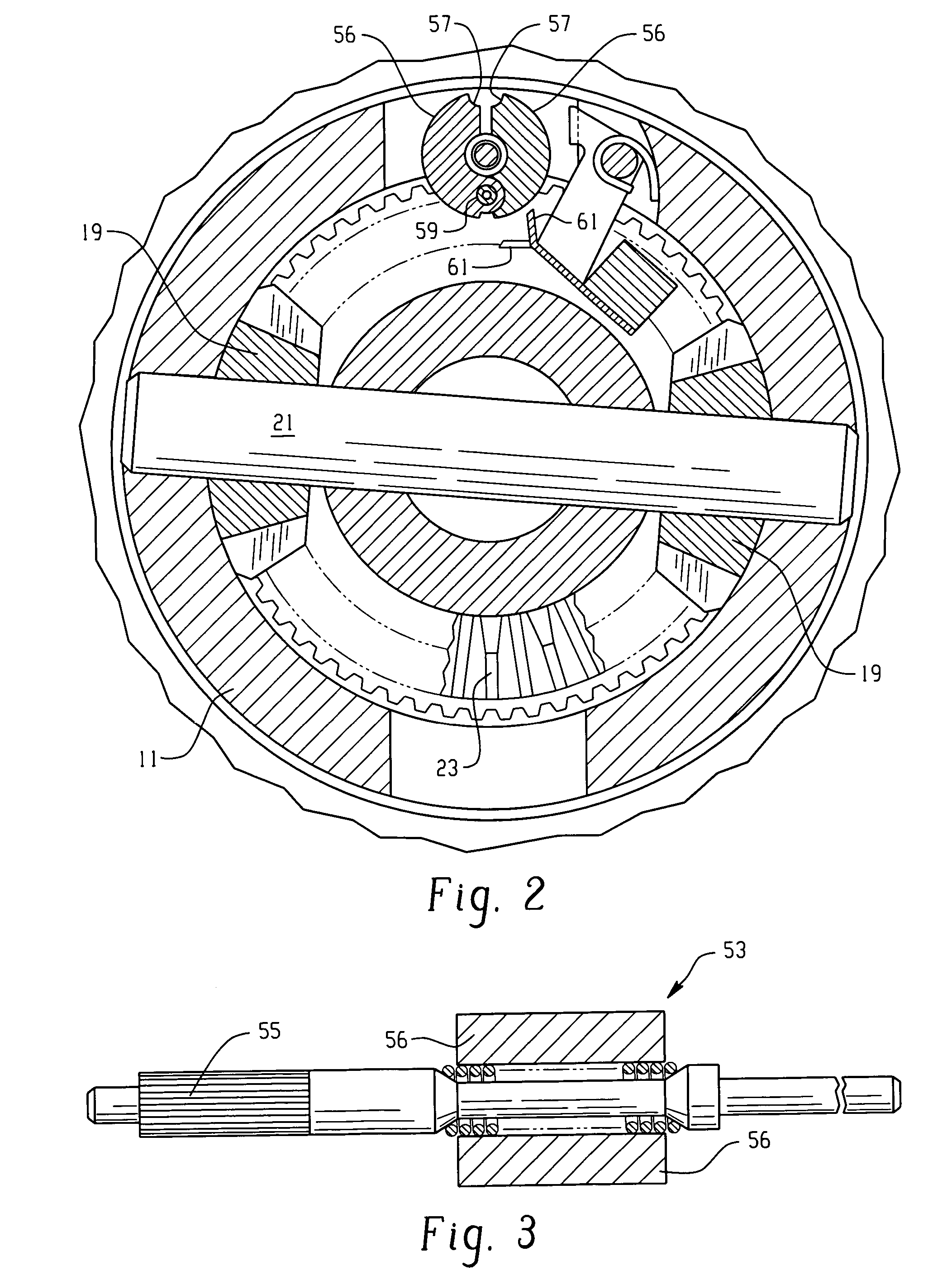
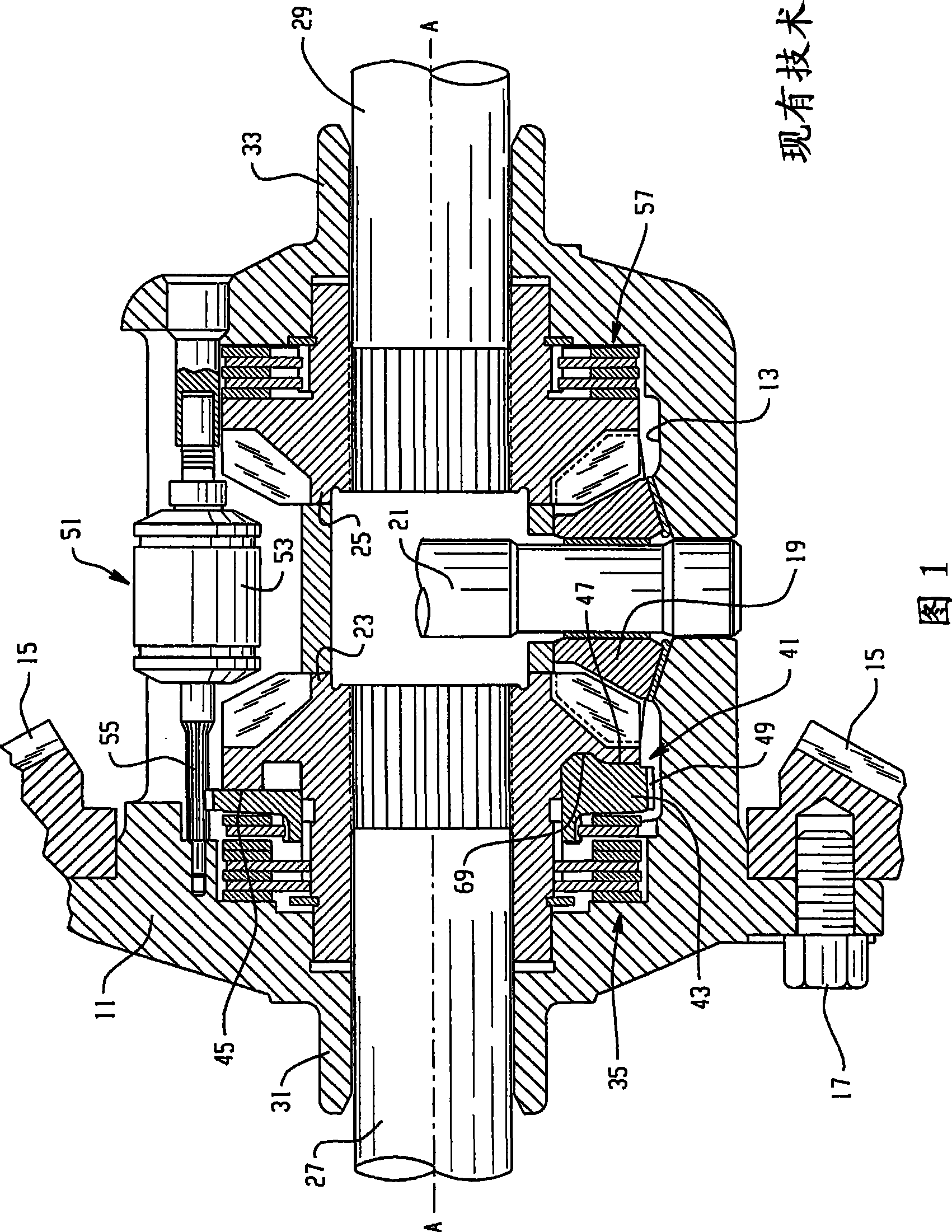
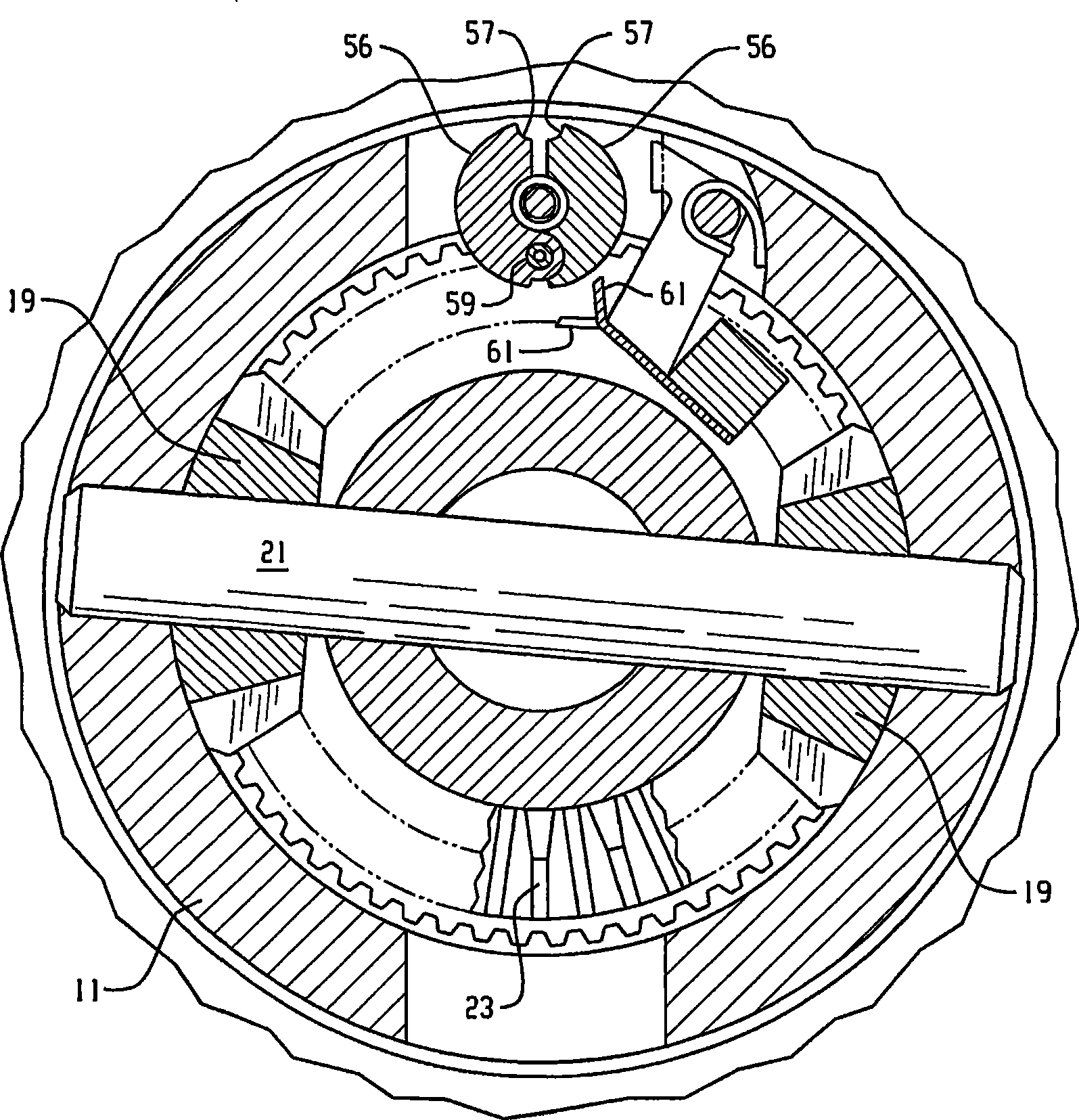
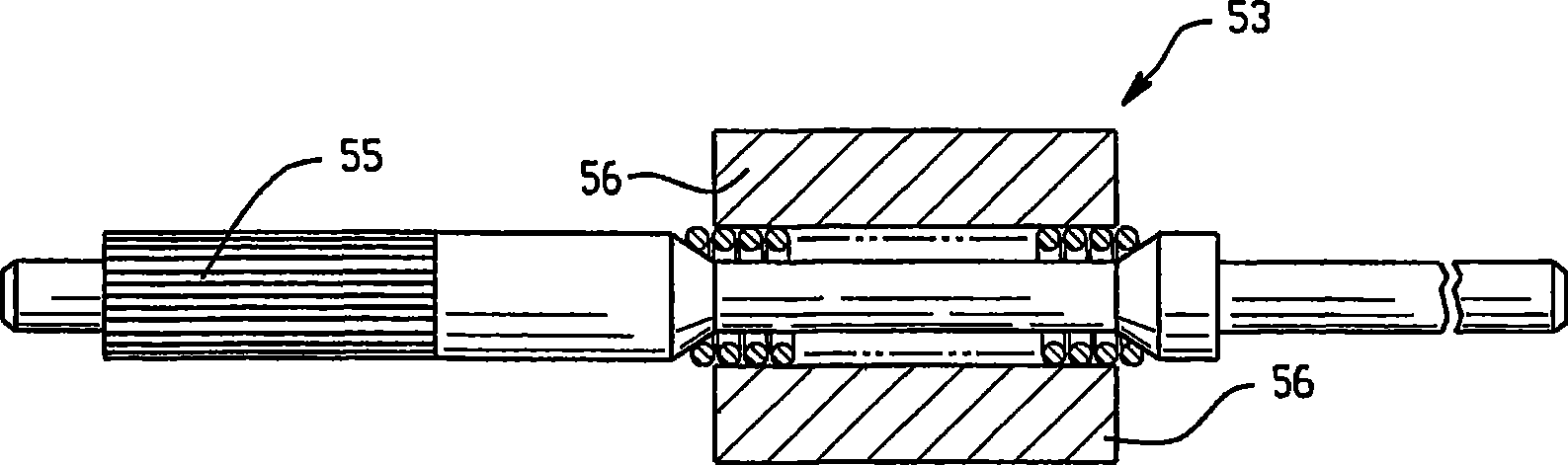
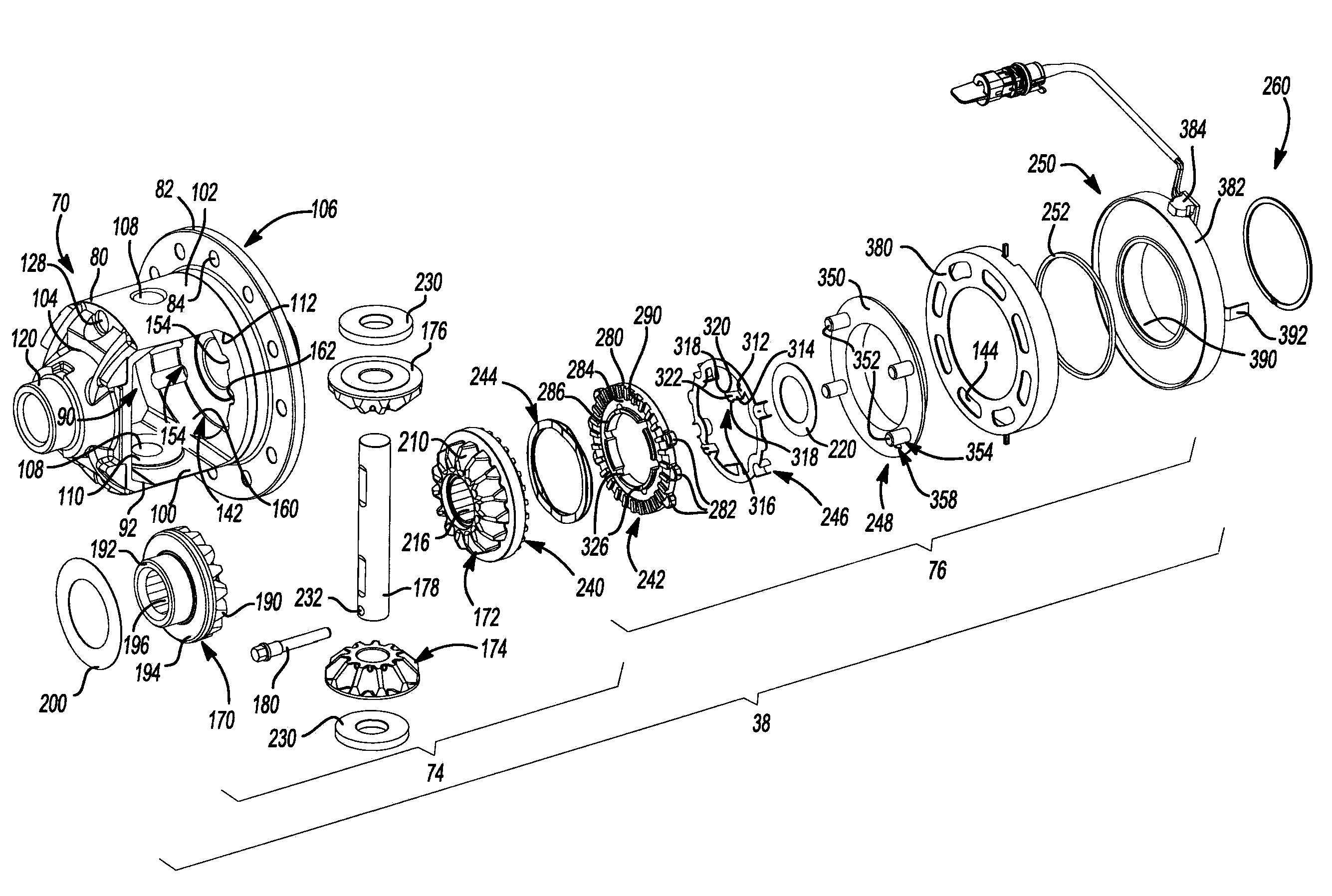
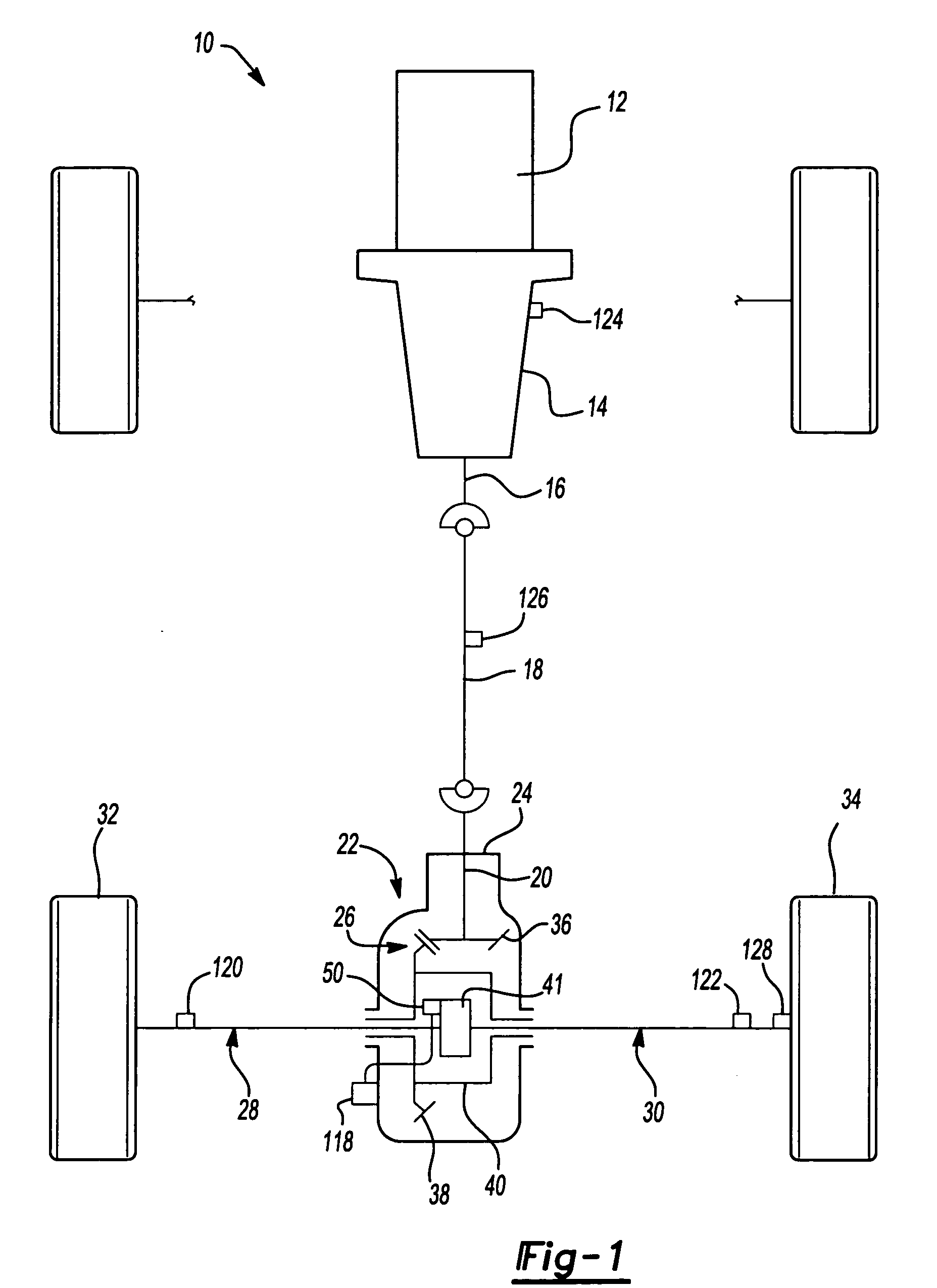
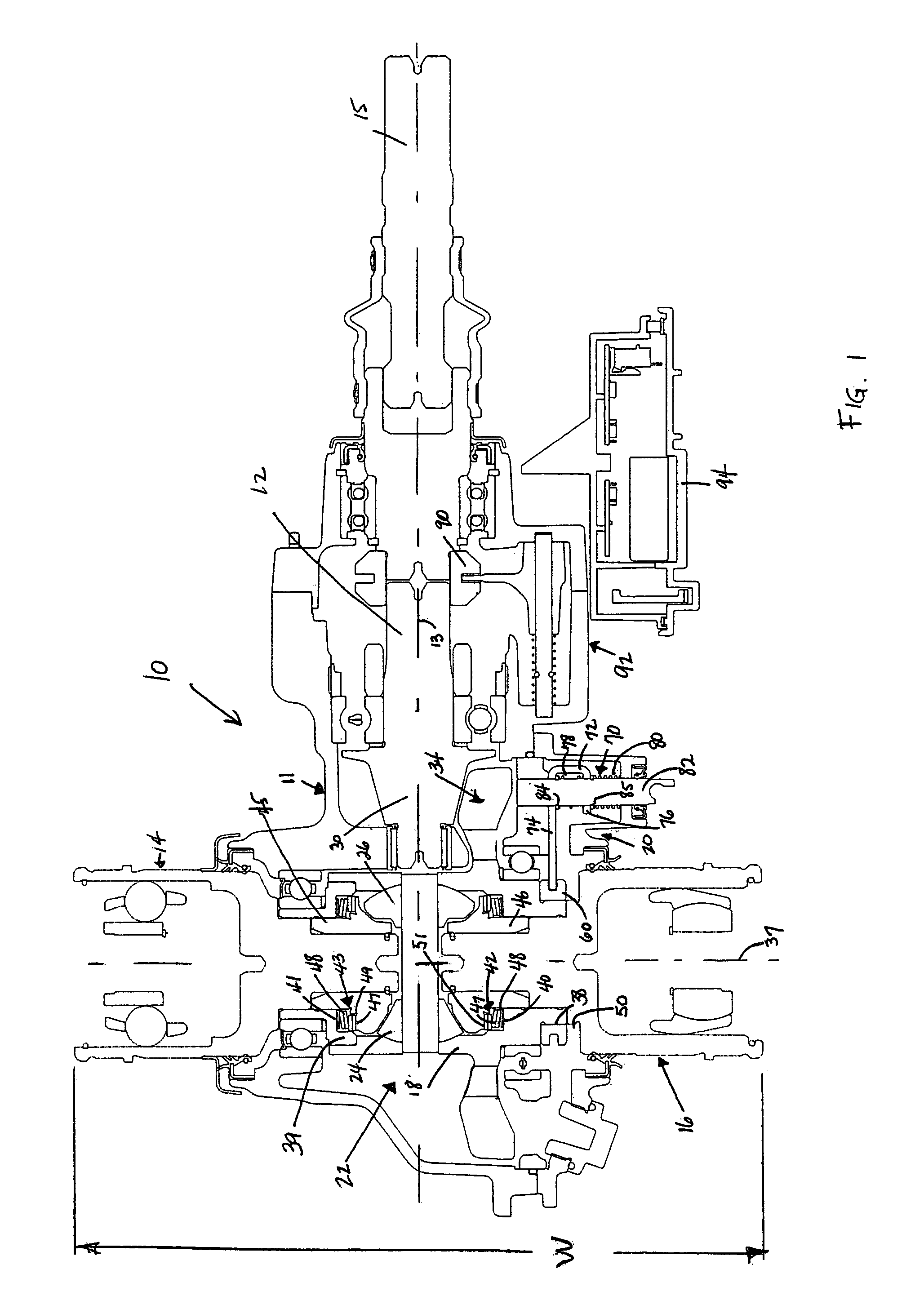
A locking differential is designed to overcome the chief limitation of a standard open differential by essentially "locking" both wheels on an axle together as if on a common shaft. This forces both wheels to turn in unison, regardless of the traction (or lack thereof) available to either wheel individually.
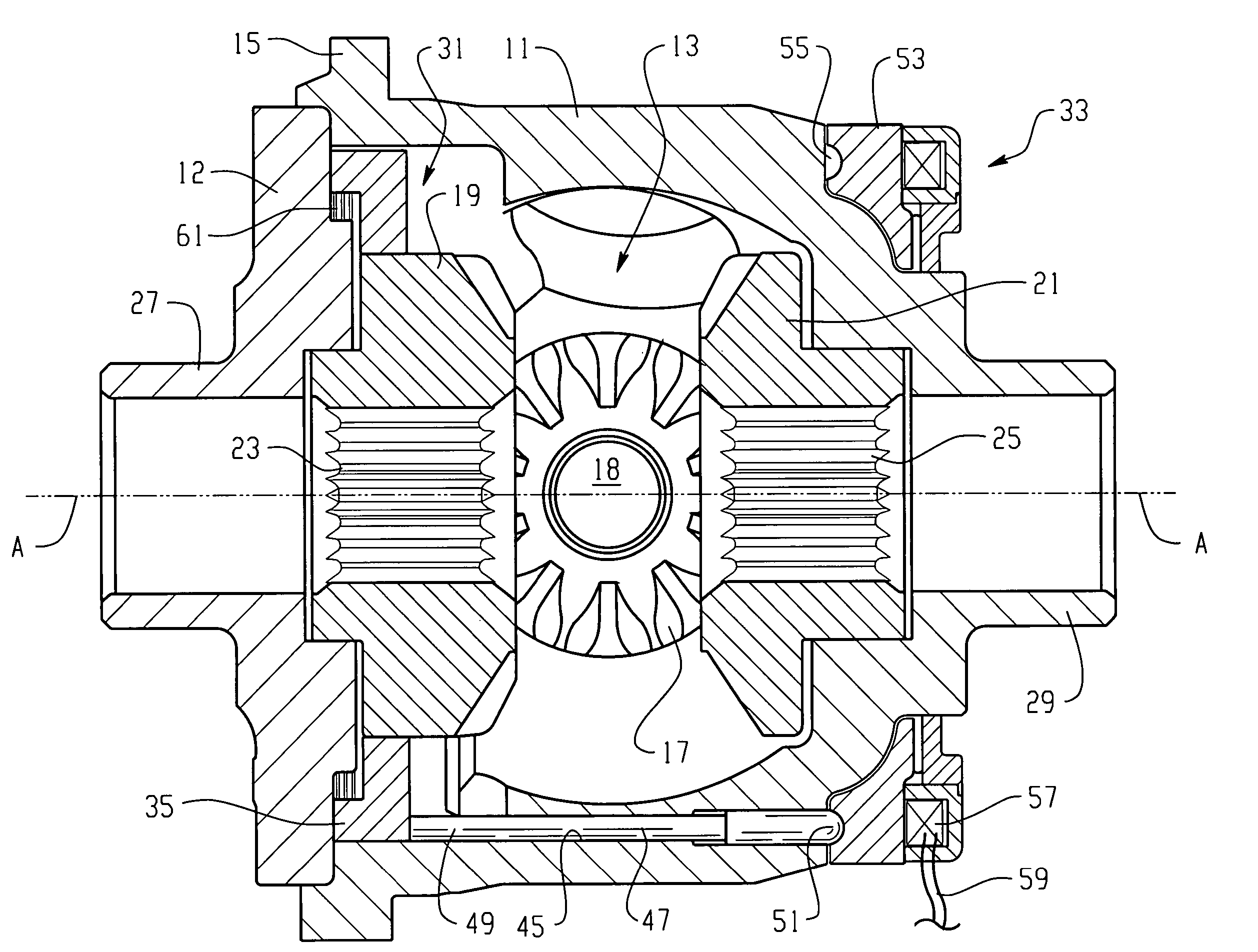
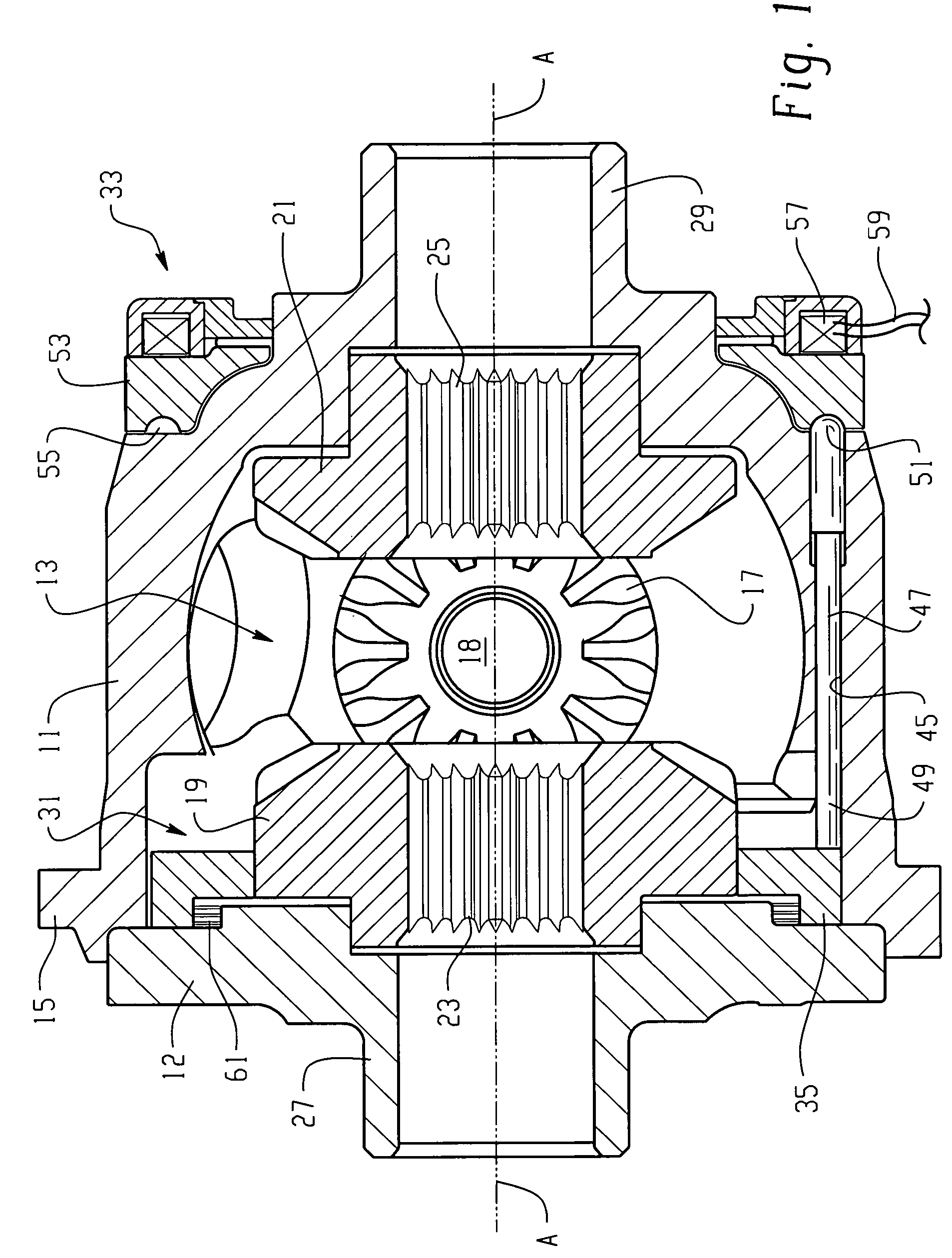
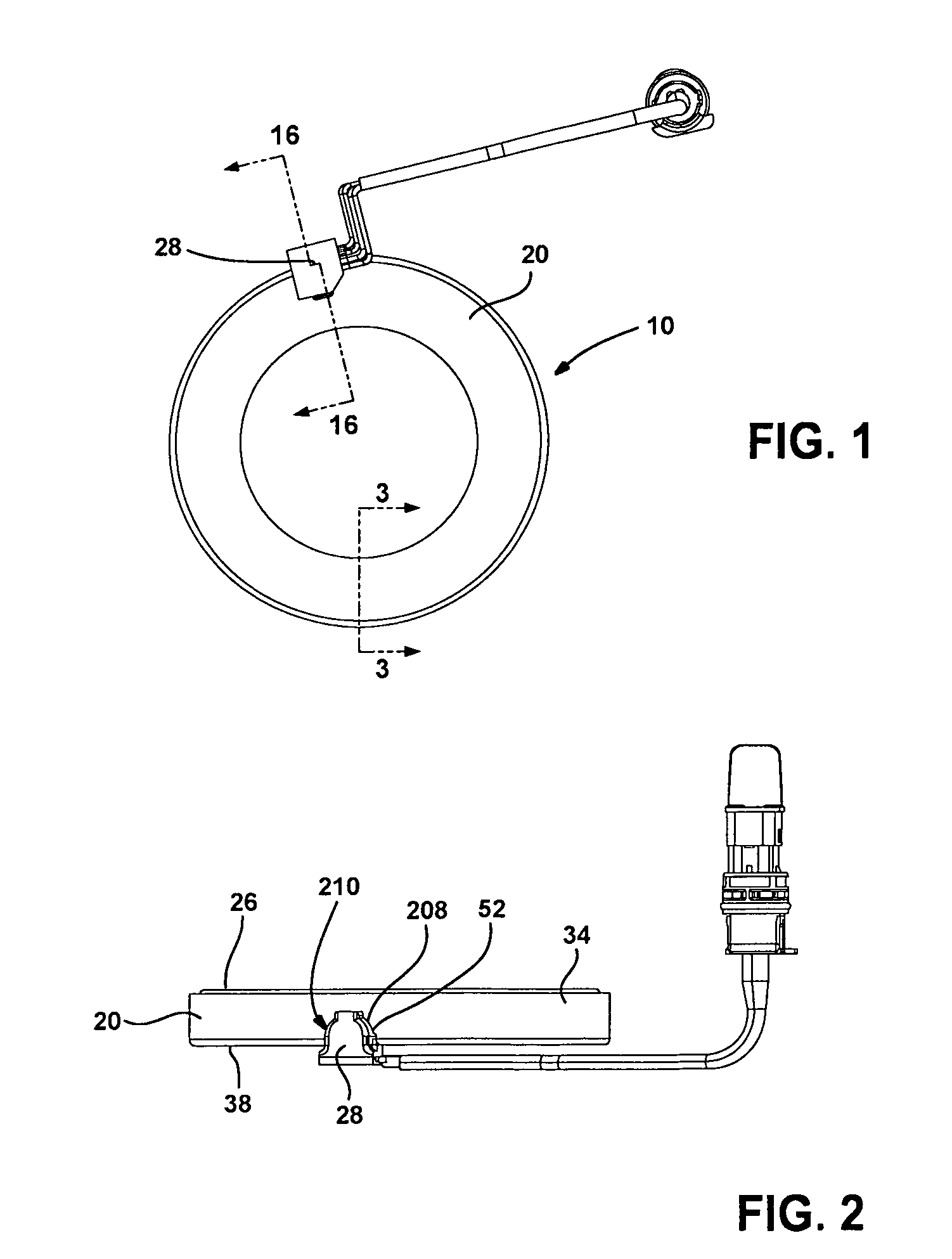
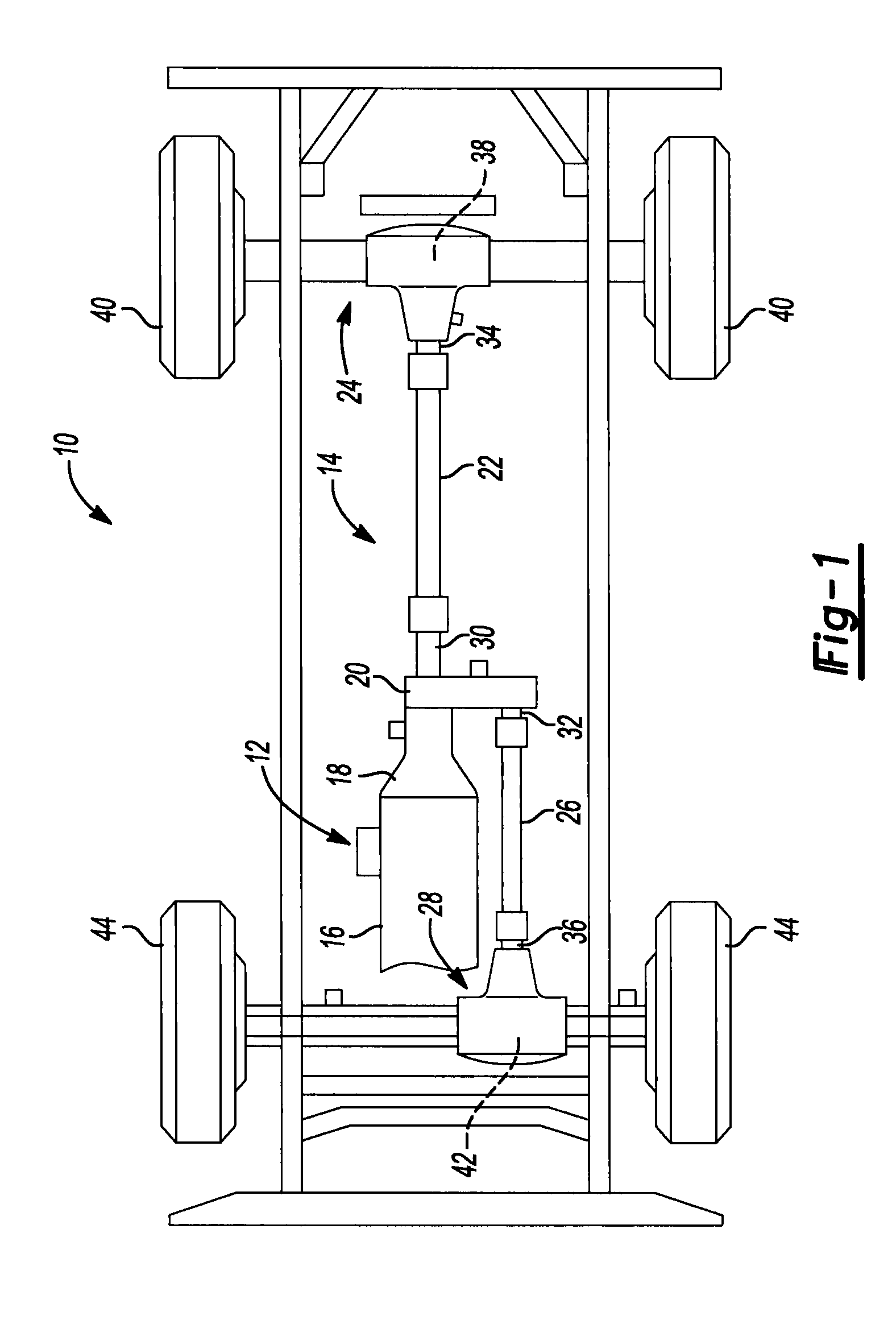
Automotive full locking differential
InactiveUS6269712B1Simple and effective and smooth in its operationMagnetically actuated clutchesDifferential gearingsCouplingEngineering
A full-locking differential drive mechanism, comprised of an input drive which is composed of a pair of opposed spaced drive races, each having an inner diameter, a coupling block disposed between the races for coupling them to drive together, output driven means comprising a pair of co-axially disposed coupler members, each having an outer diameter disposed within the drive races inner diameters, which produces a bi-directional roller clutch disposed between the inner diameters and the outer diameters and operative to couple the drive races to the coupler members enabling driving engagement therebetween.
Owner:ZENTMYER JOHN
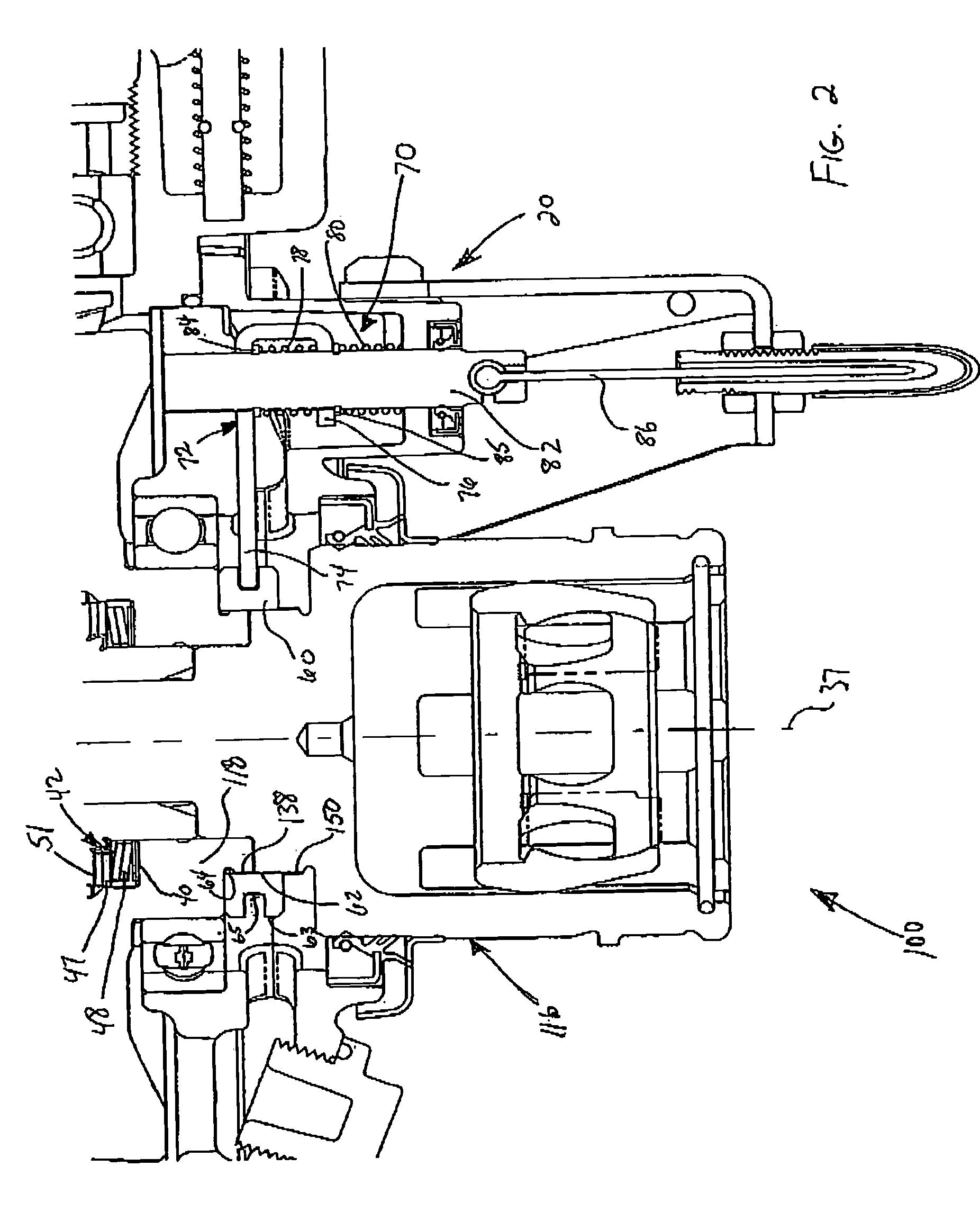
Dual ball ramp actuator for locking differential
A dual ball ramp actuator having a control ring acting with a pressure plates to supply an axial clutch clamping force to a differential clutch assembly where the ball ramp paths follow overlapping eccentric grooves that can be actuated in both the forward and reverse directions. The dual ramp feature doubles the effectiveness and sensitivity when compared to a single ramp system. The overlapping eccentric ball ramps increase (effectively double) the angular travel distance while reducing the ramp angle (in half). The forward and reverse feature provides clutch actuation in both the forward and reverse directions. The dual ramp, 3-piece sandwich construction permits the central control ring to roll up on two sets of balls on each side. This structure doubles the axial travel available to compress a disc pack and lock up the differential with the same ball ramp angle when compared to a single ramp system involving only two ramp plates.
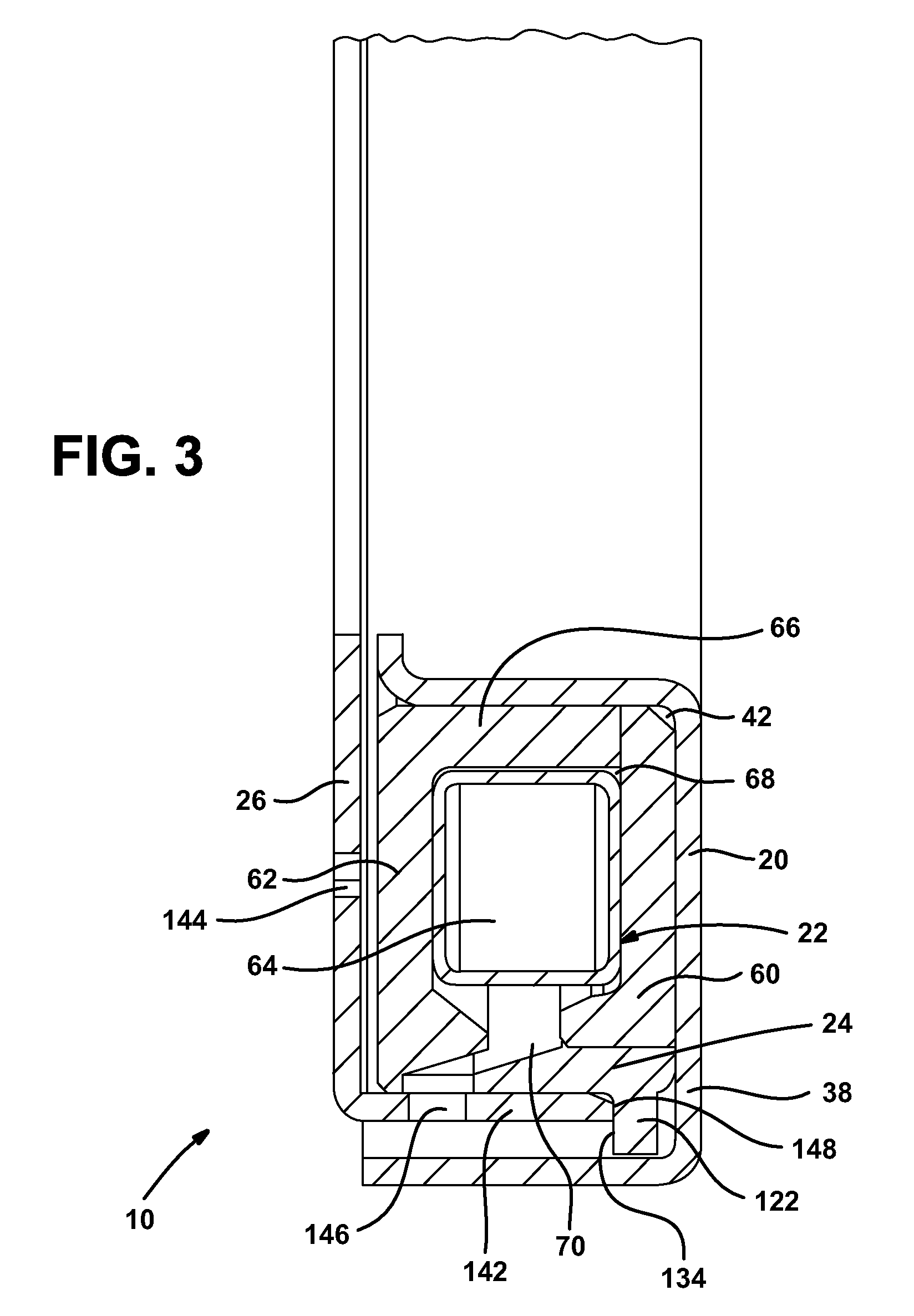
Owner:DANA AUTOMOTIVE SYST GRP LLC
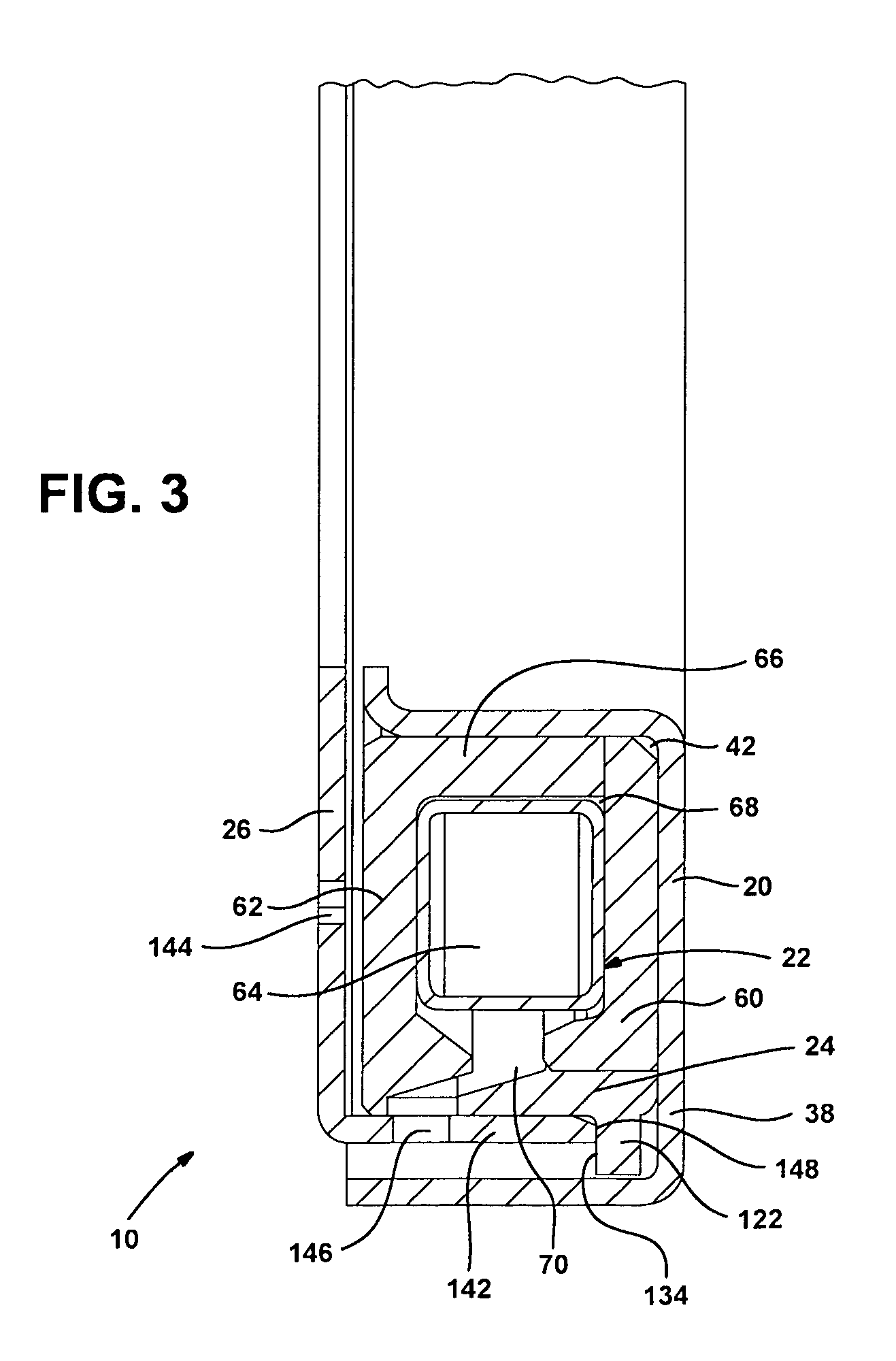
Electromagnetic locking differential assembly
InactiveUS6958030B2Mechanical actuated clutchesElectrodynamic brake systemsGear wheelElectromagnetic lock
Owner:AMERICAN AXLE & MFG
Electronically actuated locking differential
ActiveUS7264569B2Non-mechanical controlsDifferential gearingsMechanical engineeringLocking differential
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LTD
Locking differential with clutch activated by magnetorheological fluid
InactiveUS6428441B1Magnetically actuated clutchesFriction clutchesElectromagnetic couplingLimited-slip differential
A limited slip differential includes a friction clutch mechanism, an electromagnetic coupling, and a camming mechanism disposed between the friction clutch mechanism and the electromagnetic coupling. The camming mechanism converts shearing forces within the electromagnetic coupling to an axial force applied to engage the clutch mechanism. The camming mechanism includes annular discs having axially inclined ramps, and a roller bearing for movement along the ramps to provide for variable spacing between the annular discs, wherein increased spacing is used to apply the axial force.
Owner:TORQUE TRACTION TECH INC
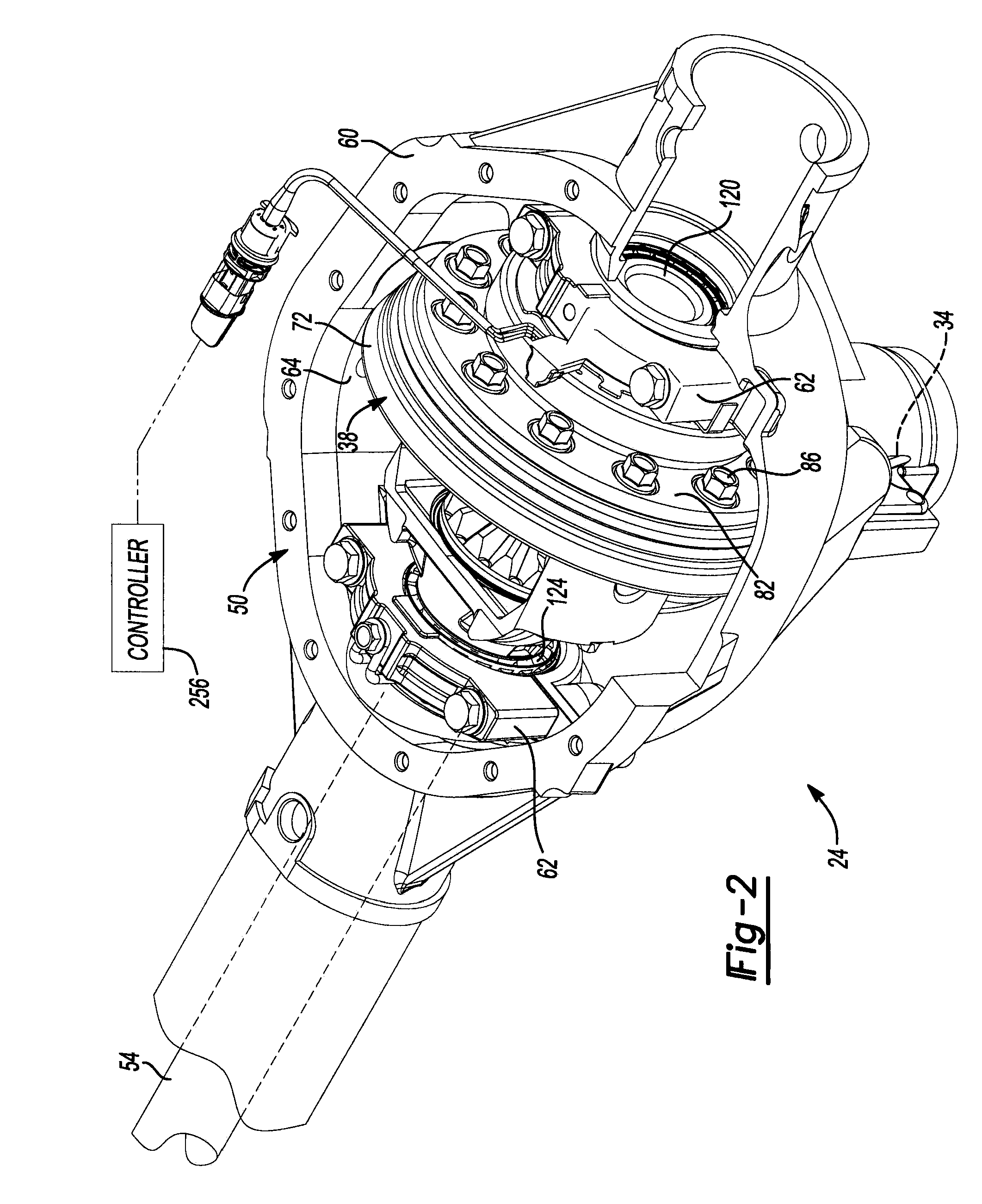
Axle assembly with electronic locking differential
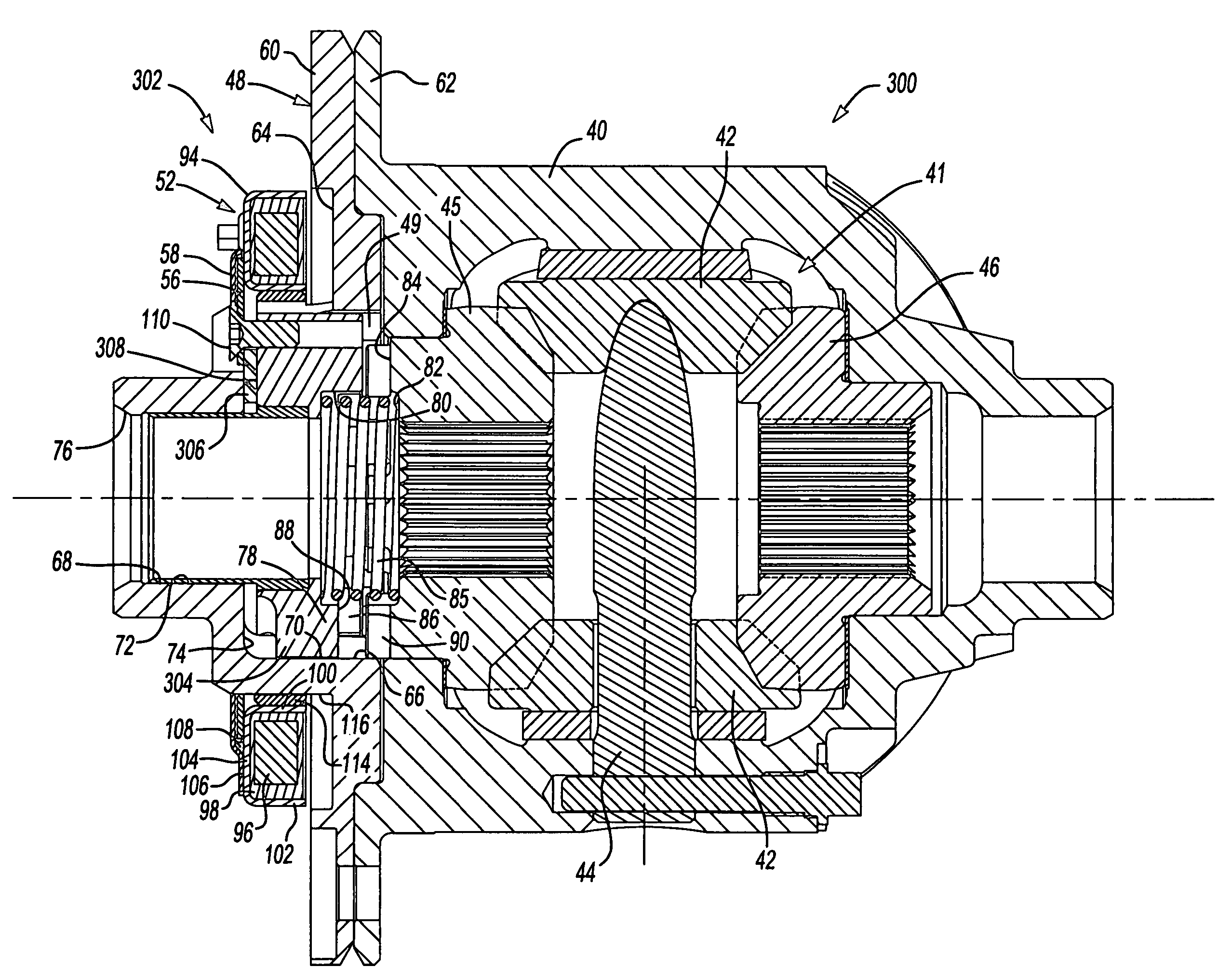
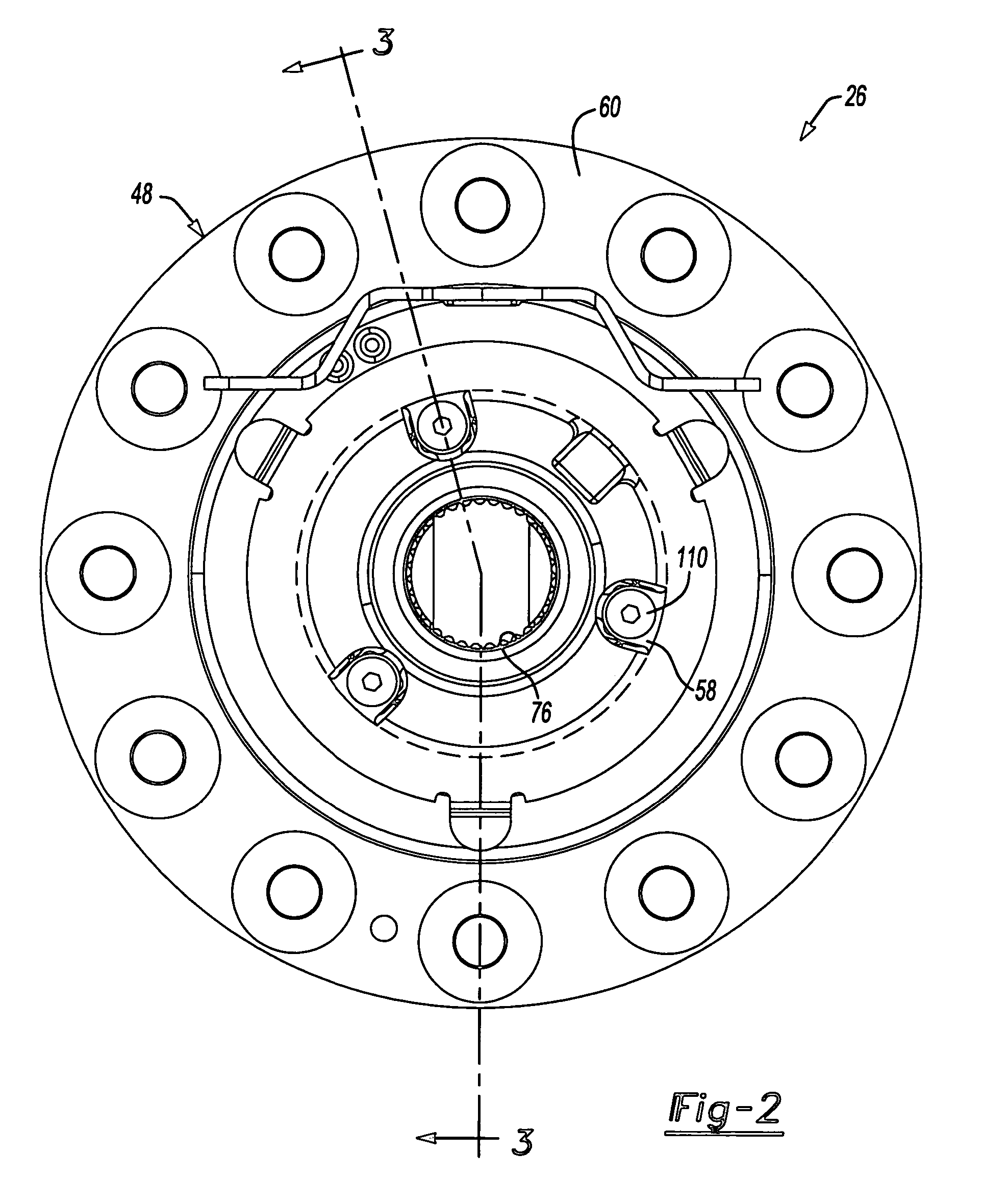
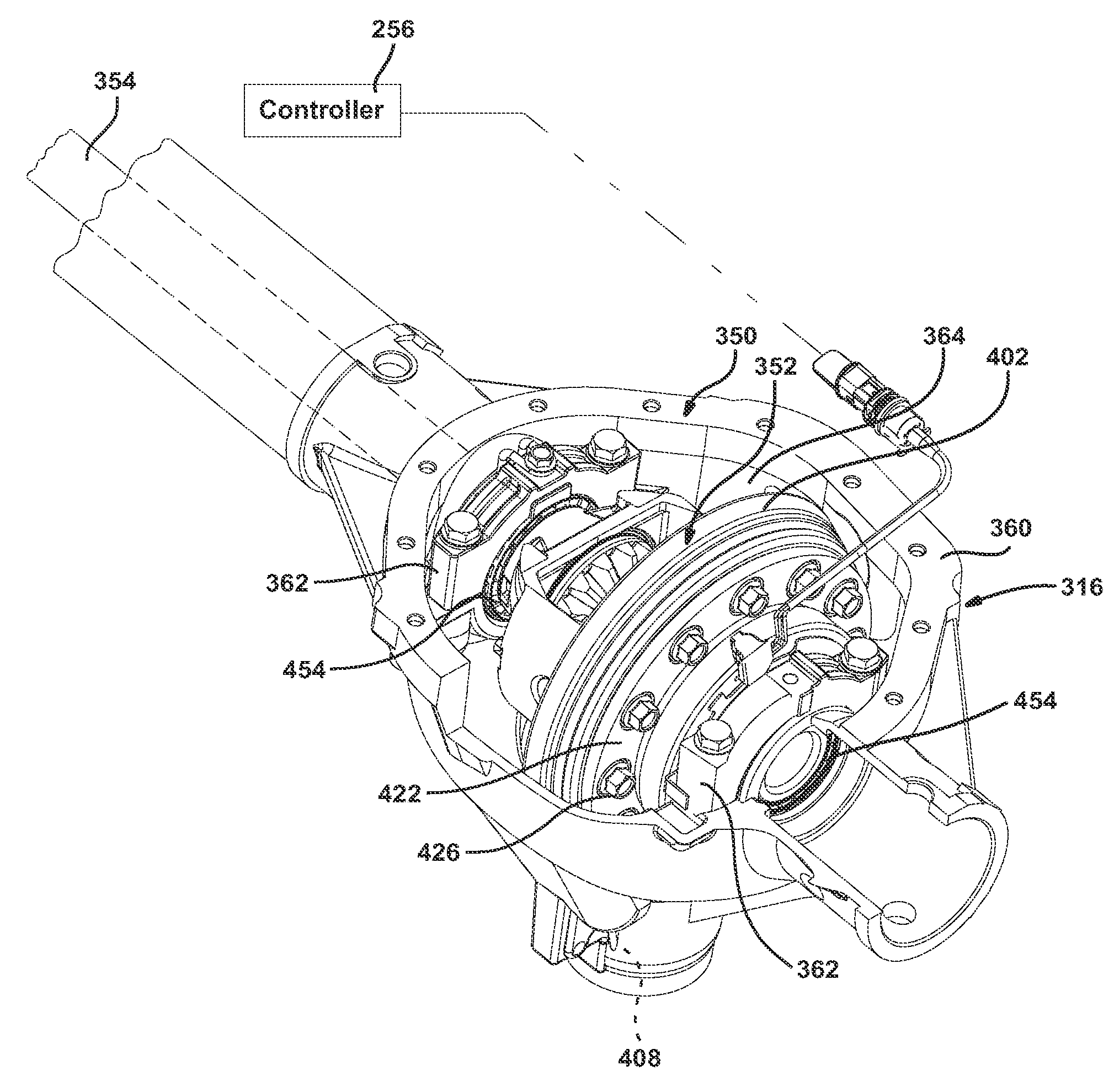
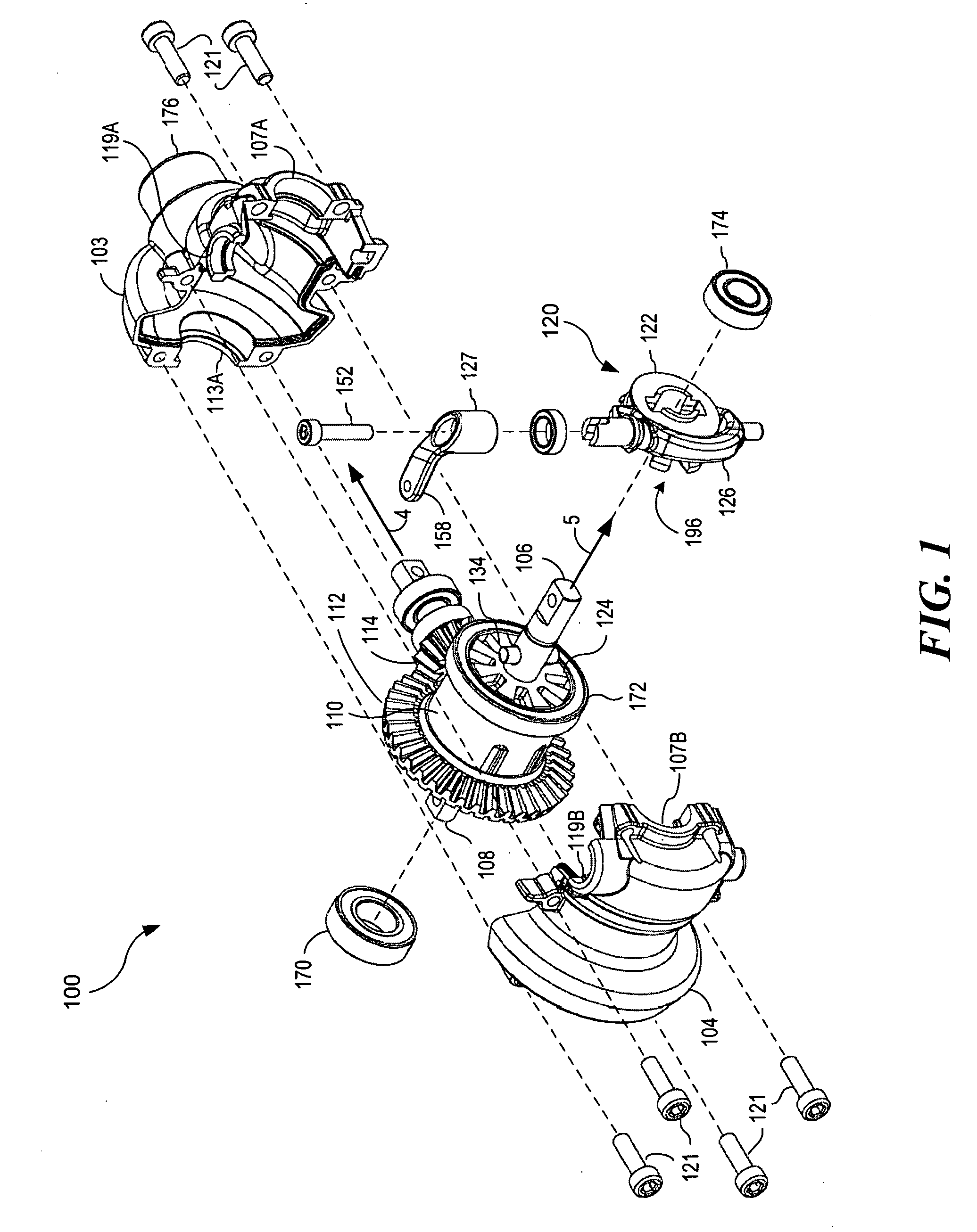
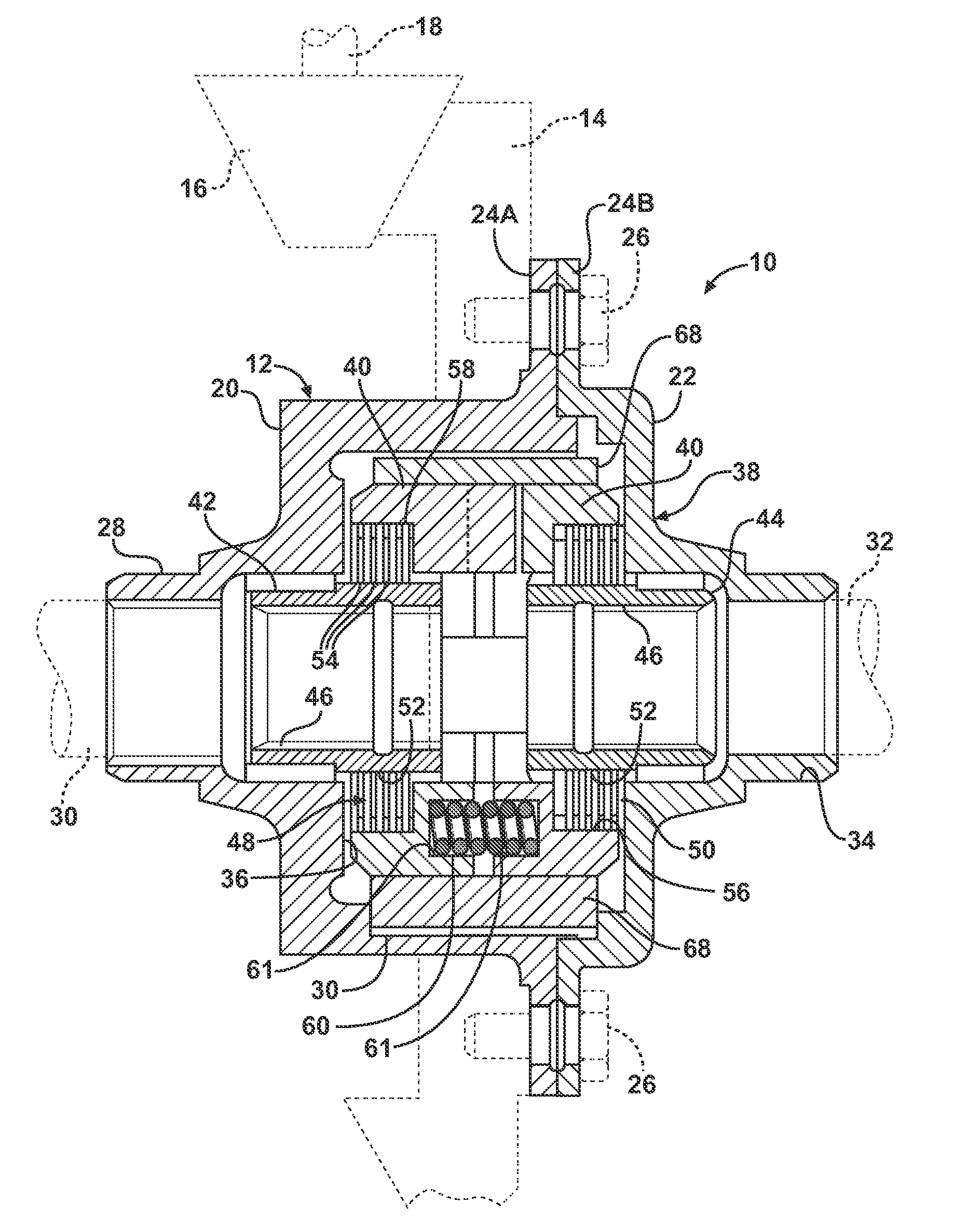
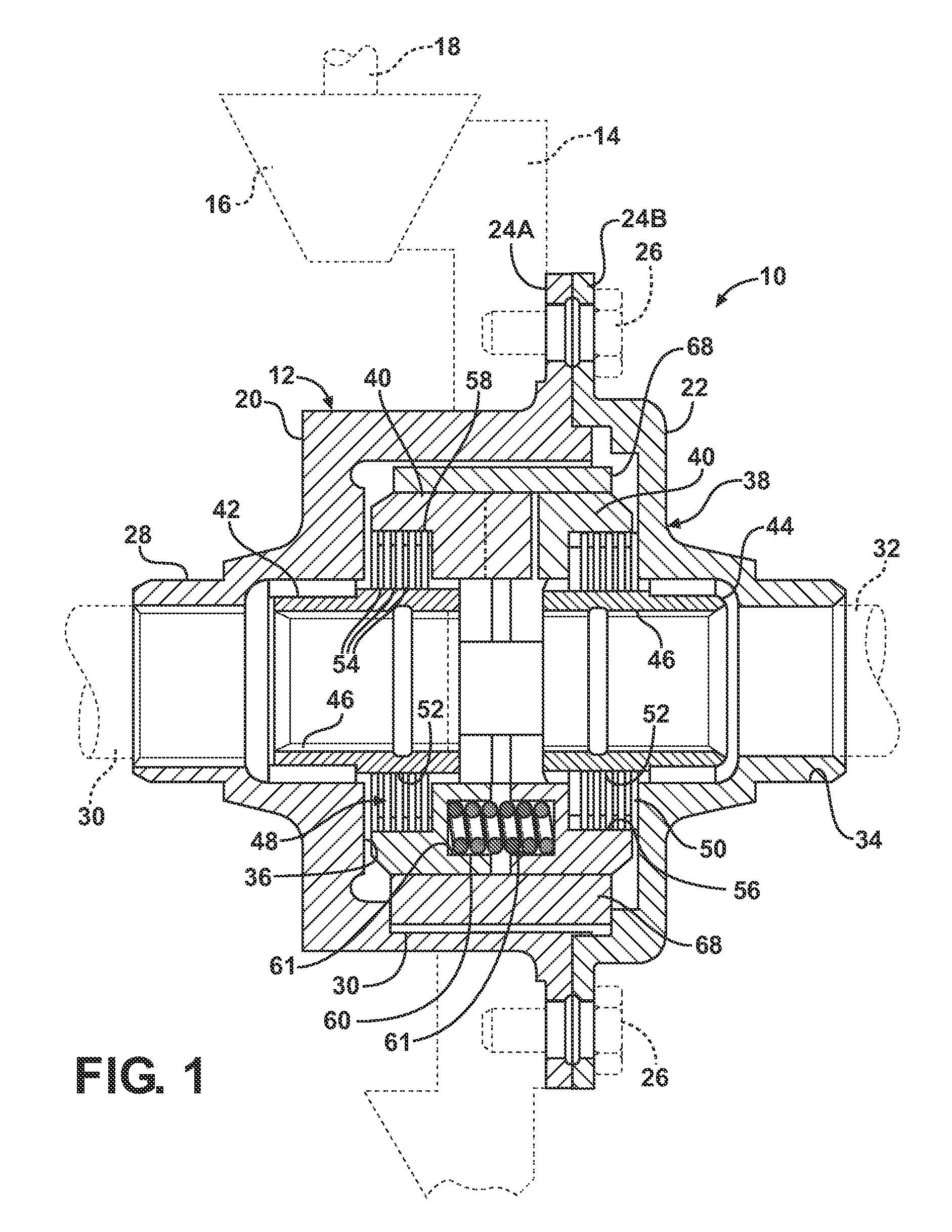
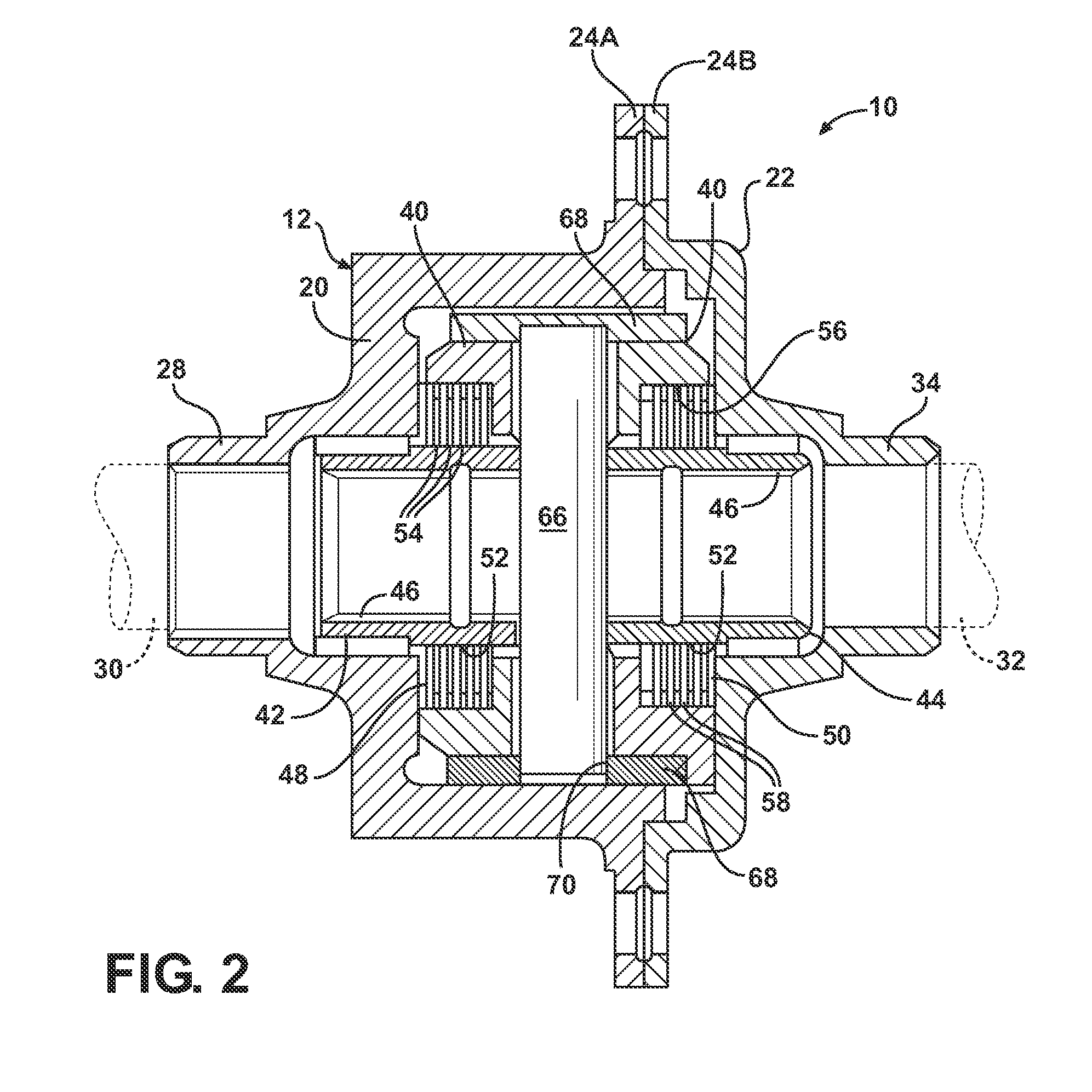
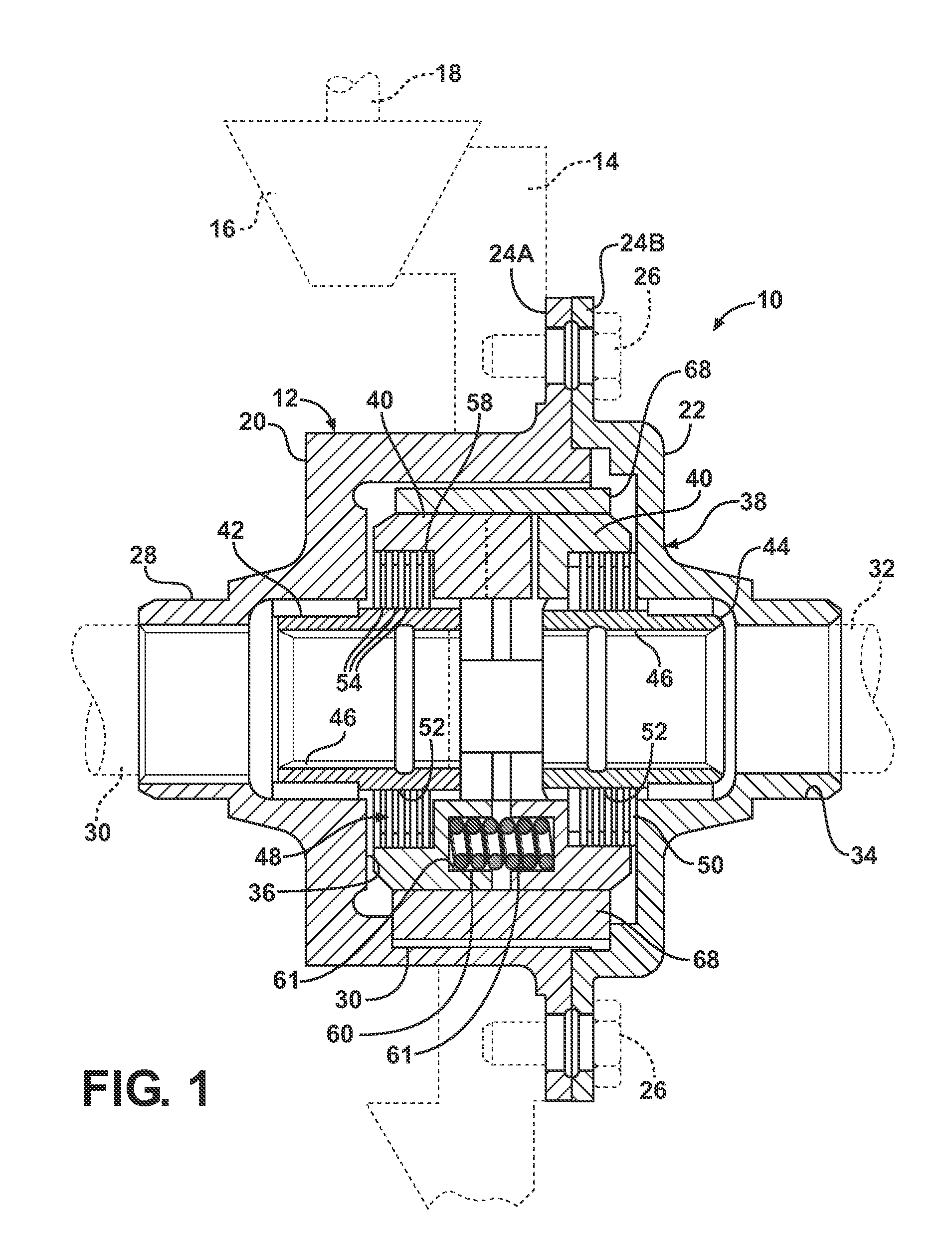
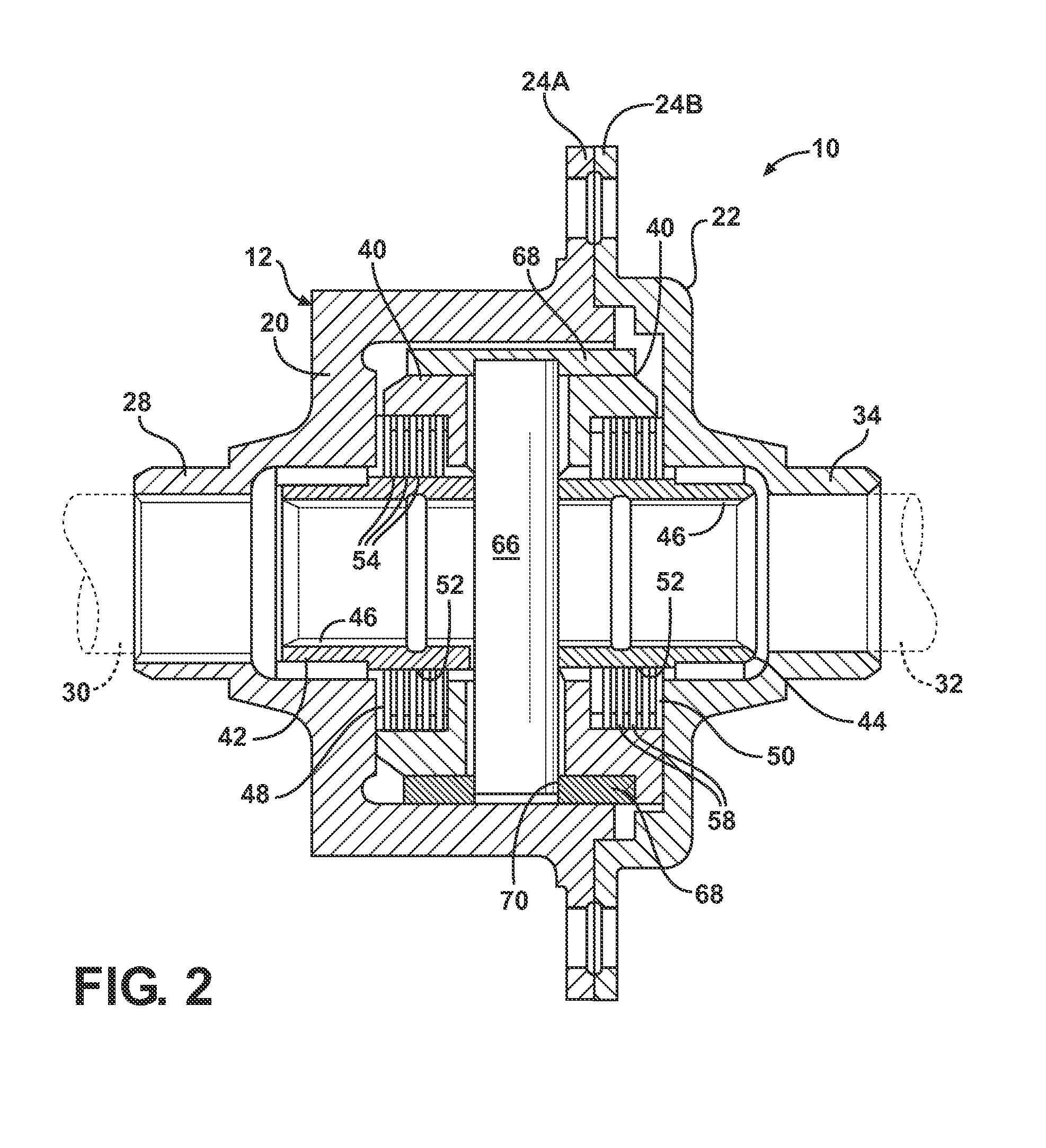
An axle assembly with an electric locking differential that can include a one-piece differential case and a locking device. The locking device includes a dog that is nonrotatably but axially slidably received into a pocket that is formed in an end of the differential case. An actuator is mounted on the differential case. Actuation of the actuator moves the dog into engagement with a second dog that is coupled to a side gear of the differential to thereby lock the side gear to the differential case.
Owner:AMERICAN AXLE & MFG
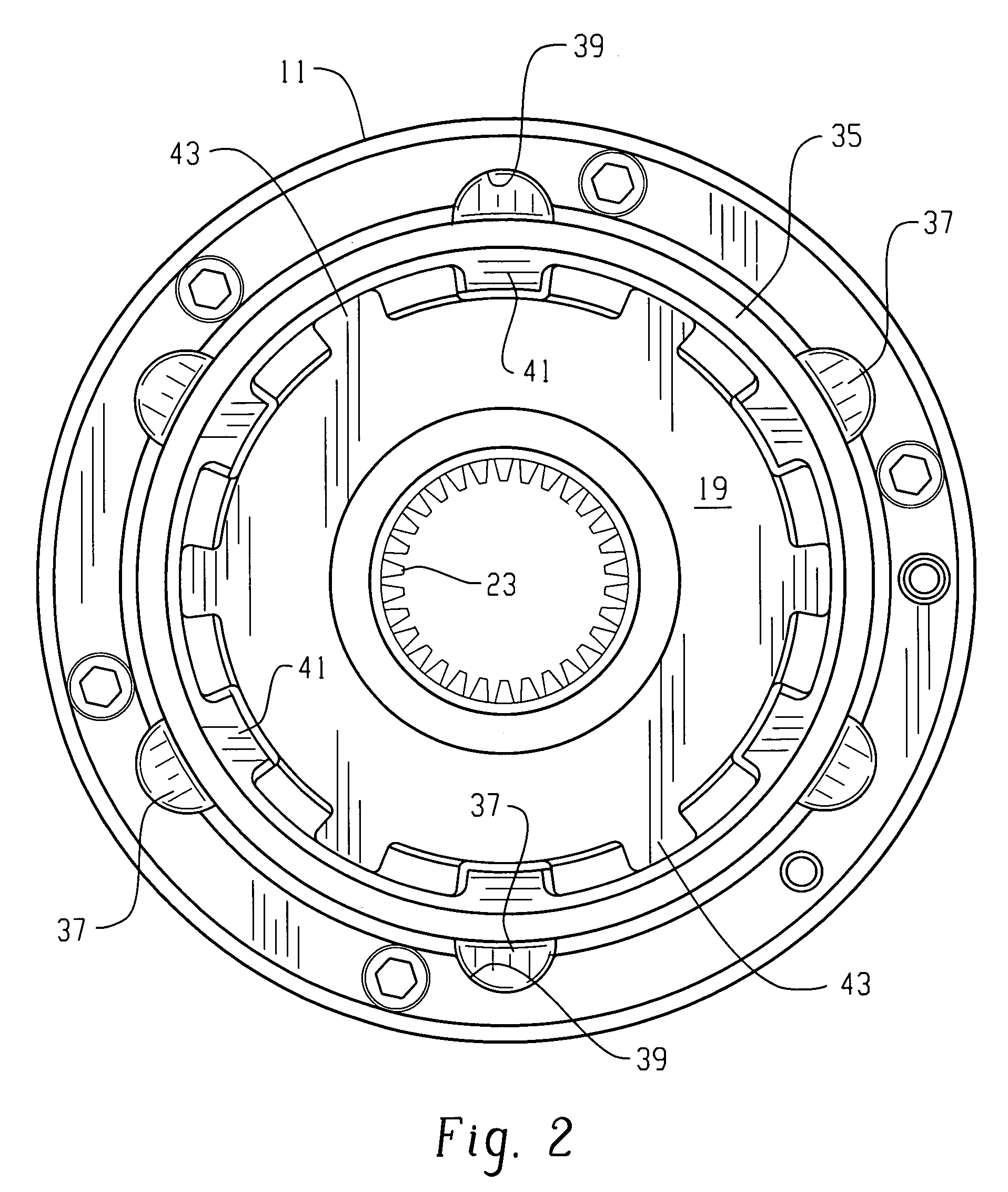
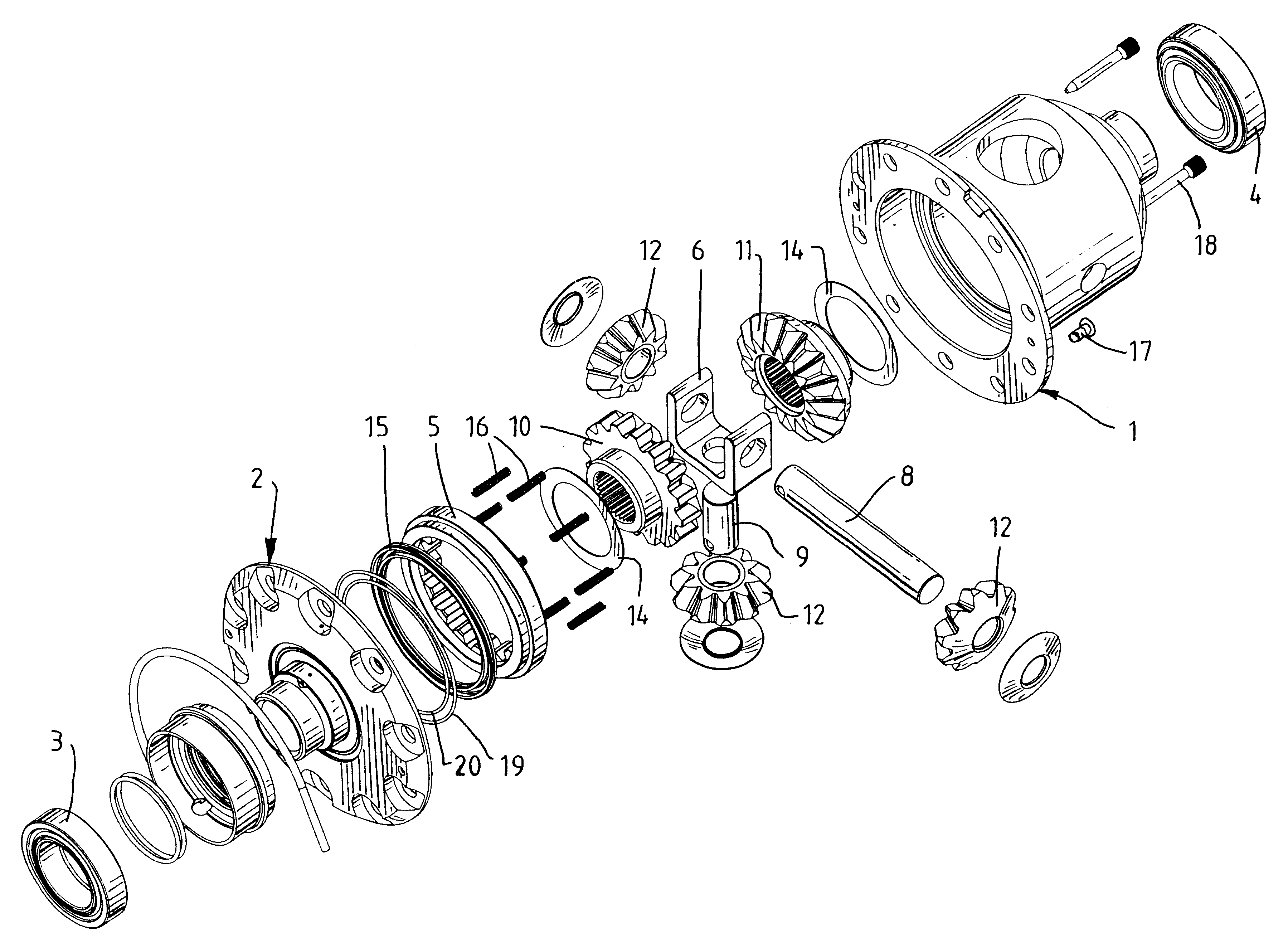
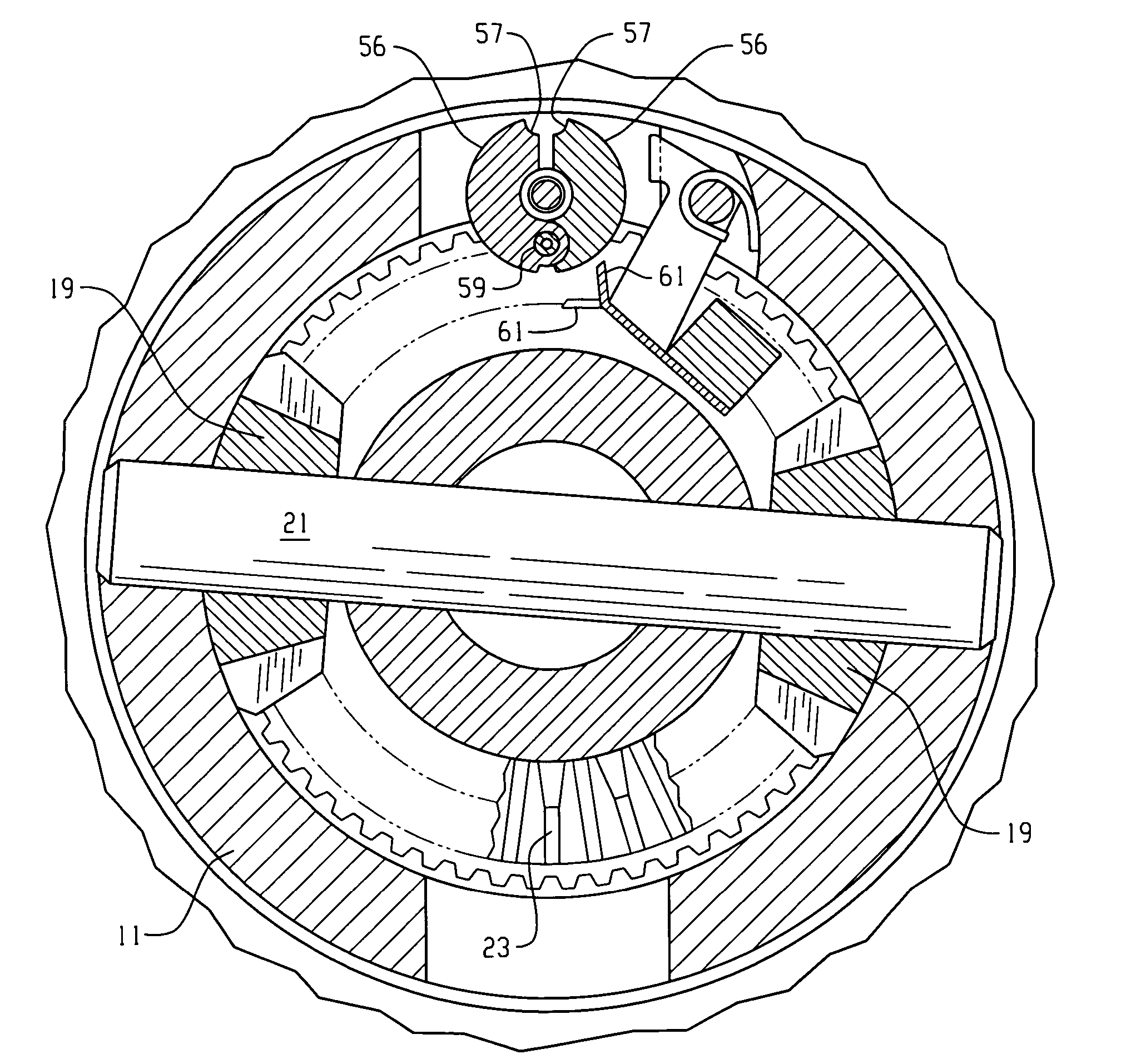
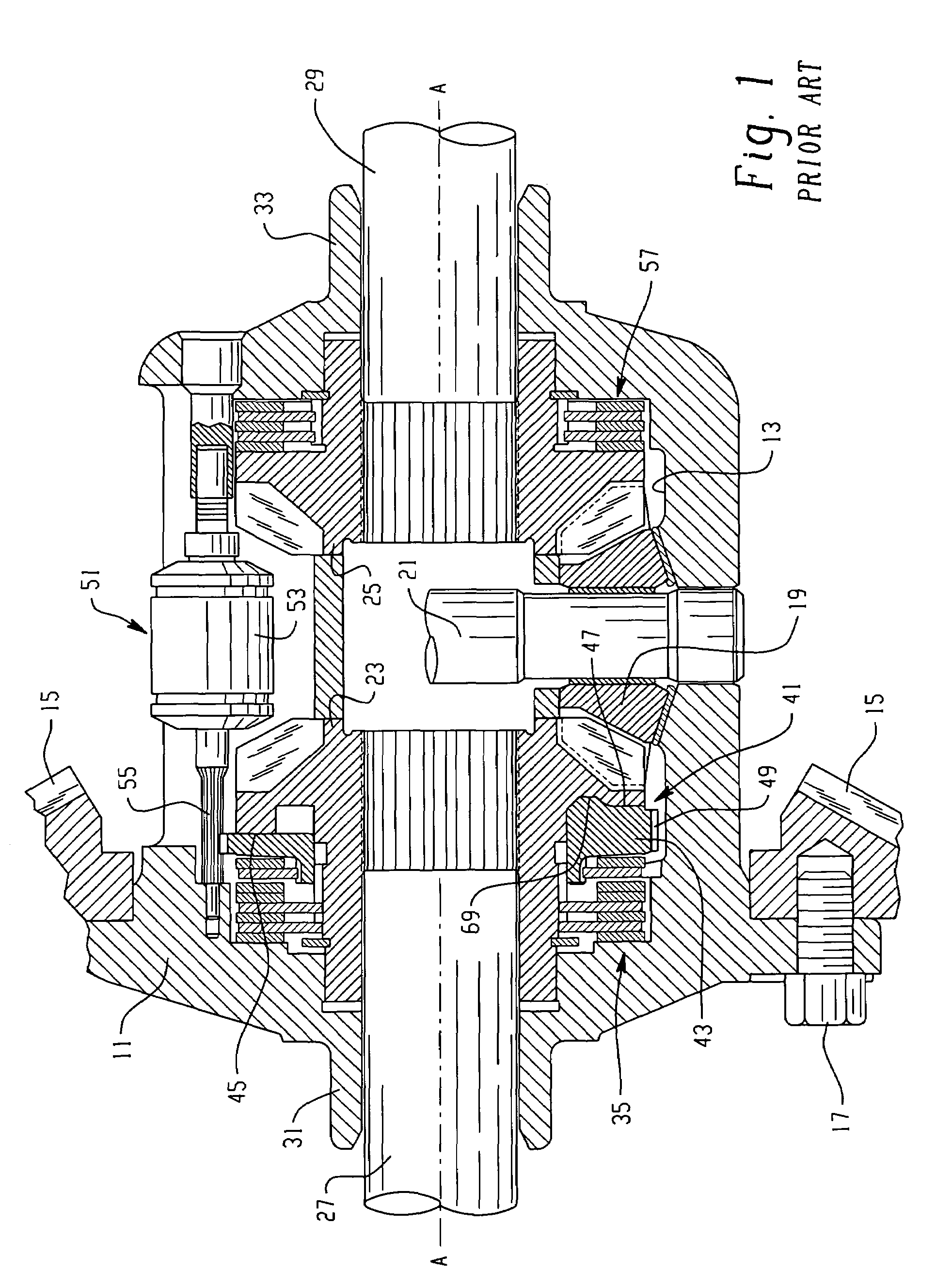
Locking differential with improved tooth meshing configuration
InactiveUS6394927B1Reduce the possibilityOptimizationTransmission elementsDifferential gearingsGear wheelEngineering
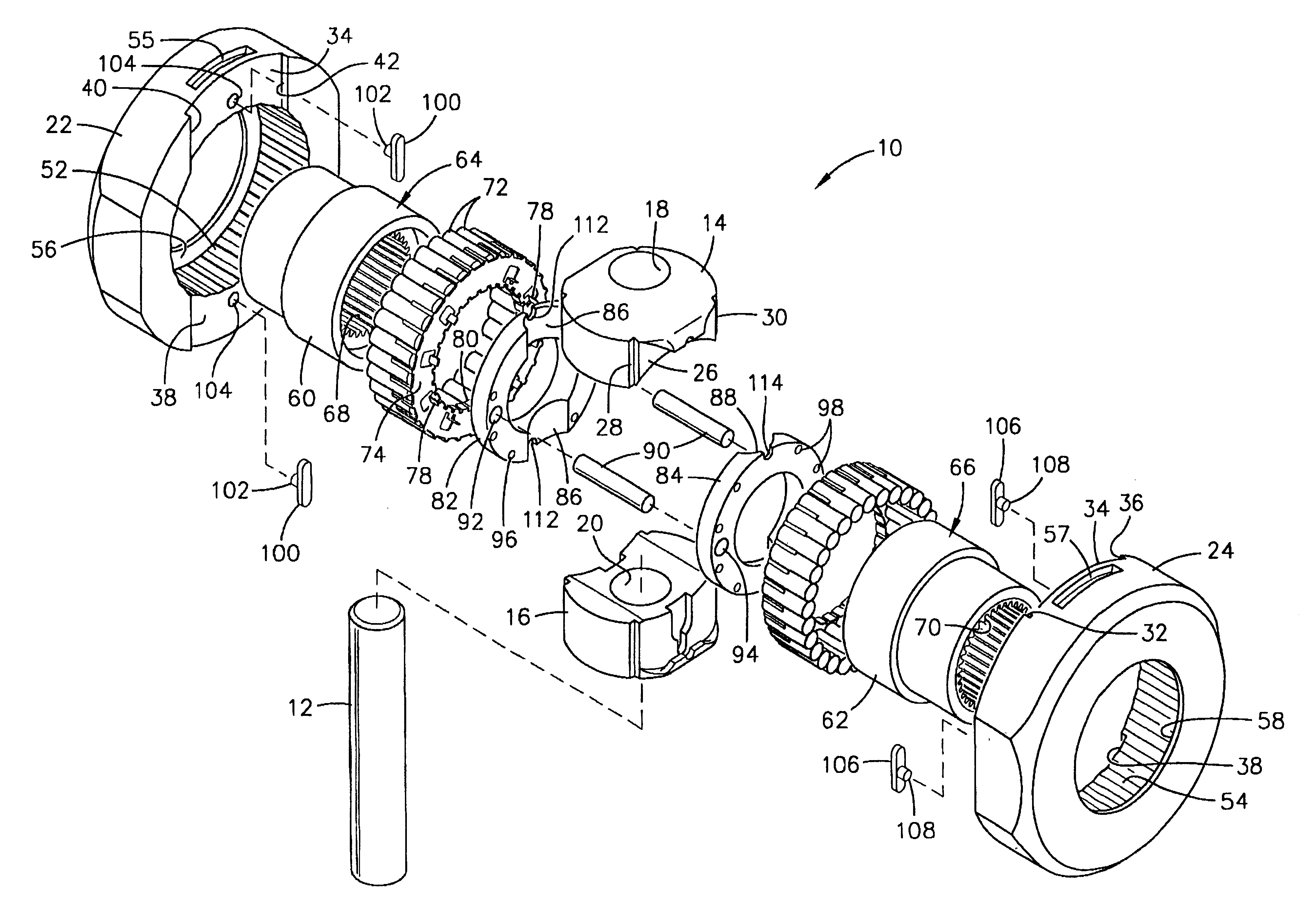
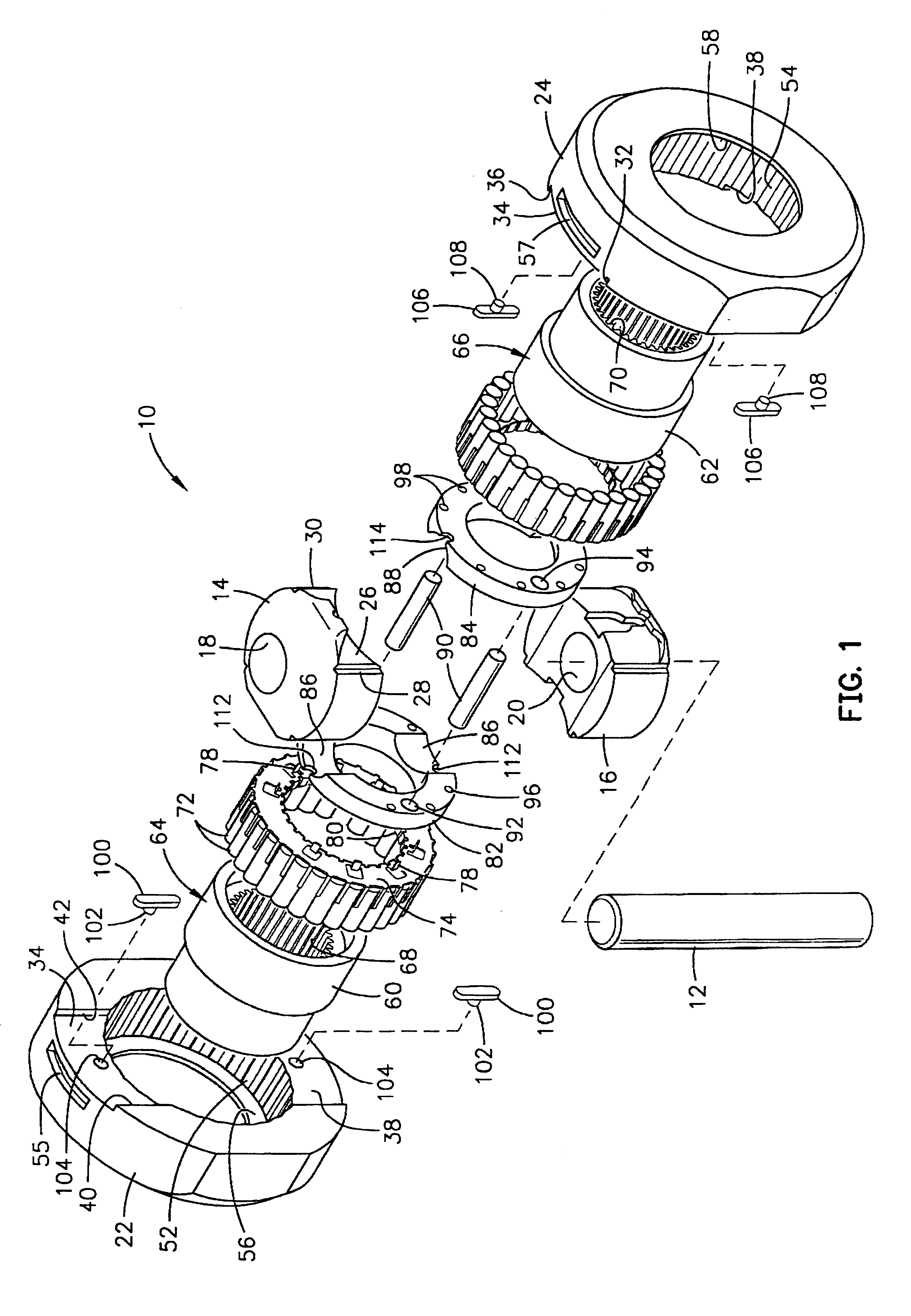
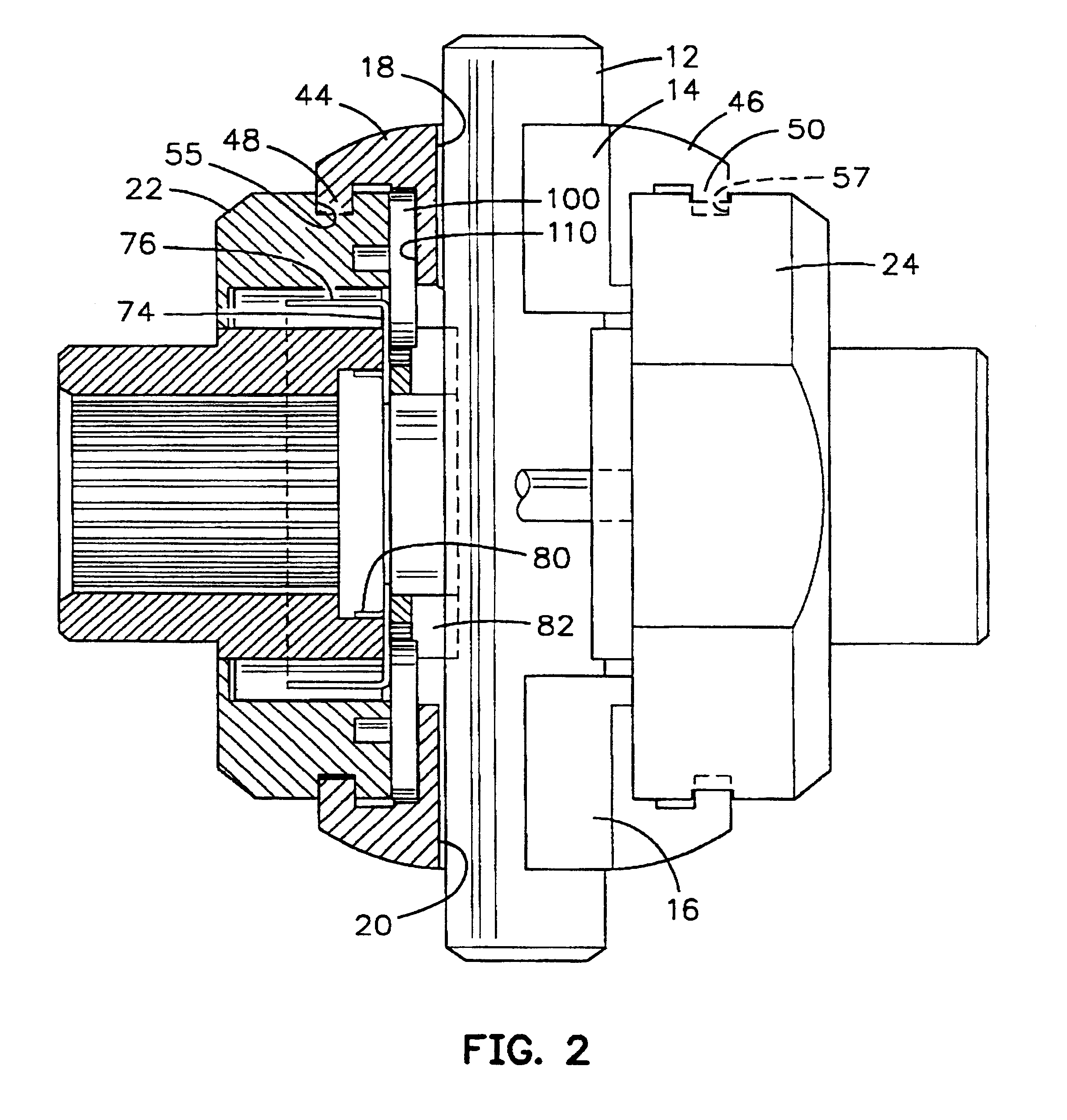
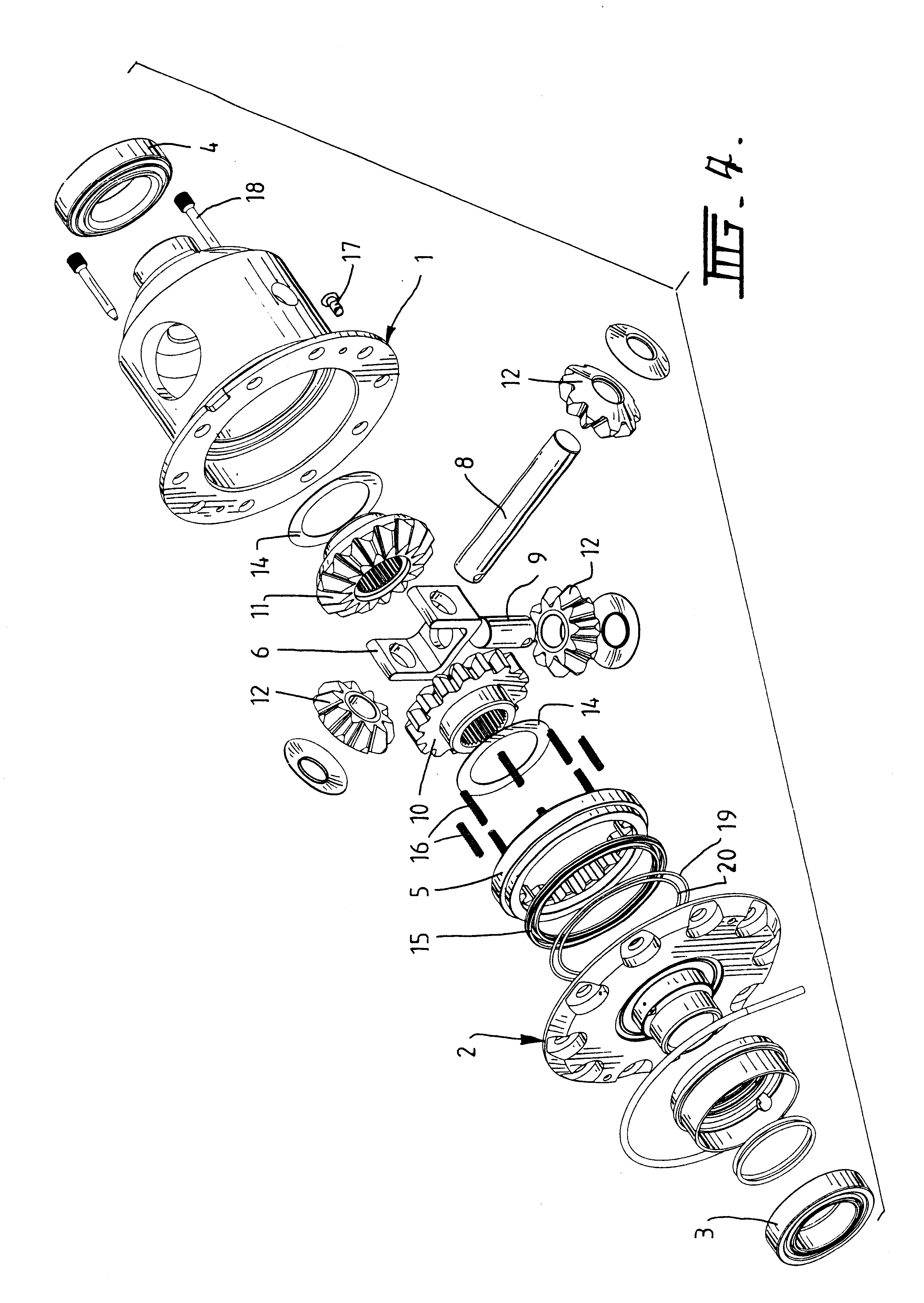
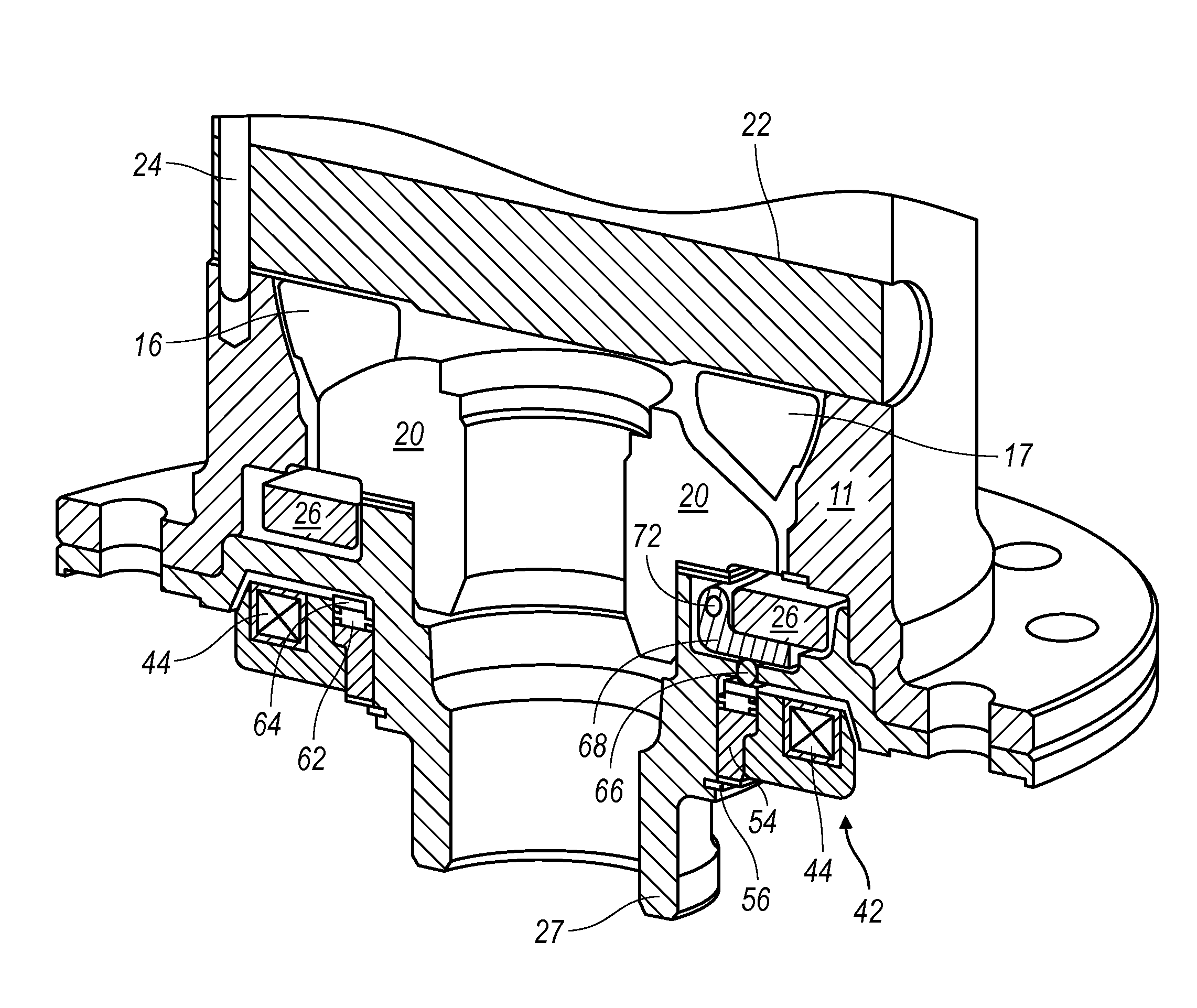
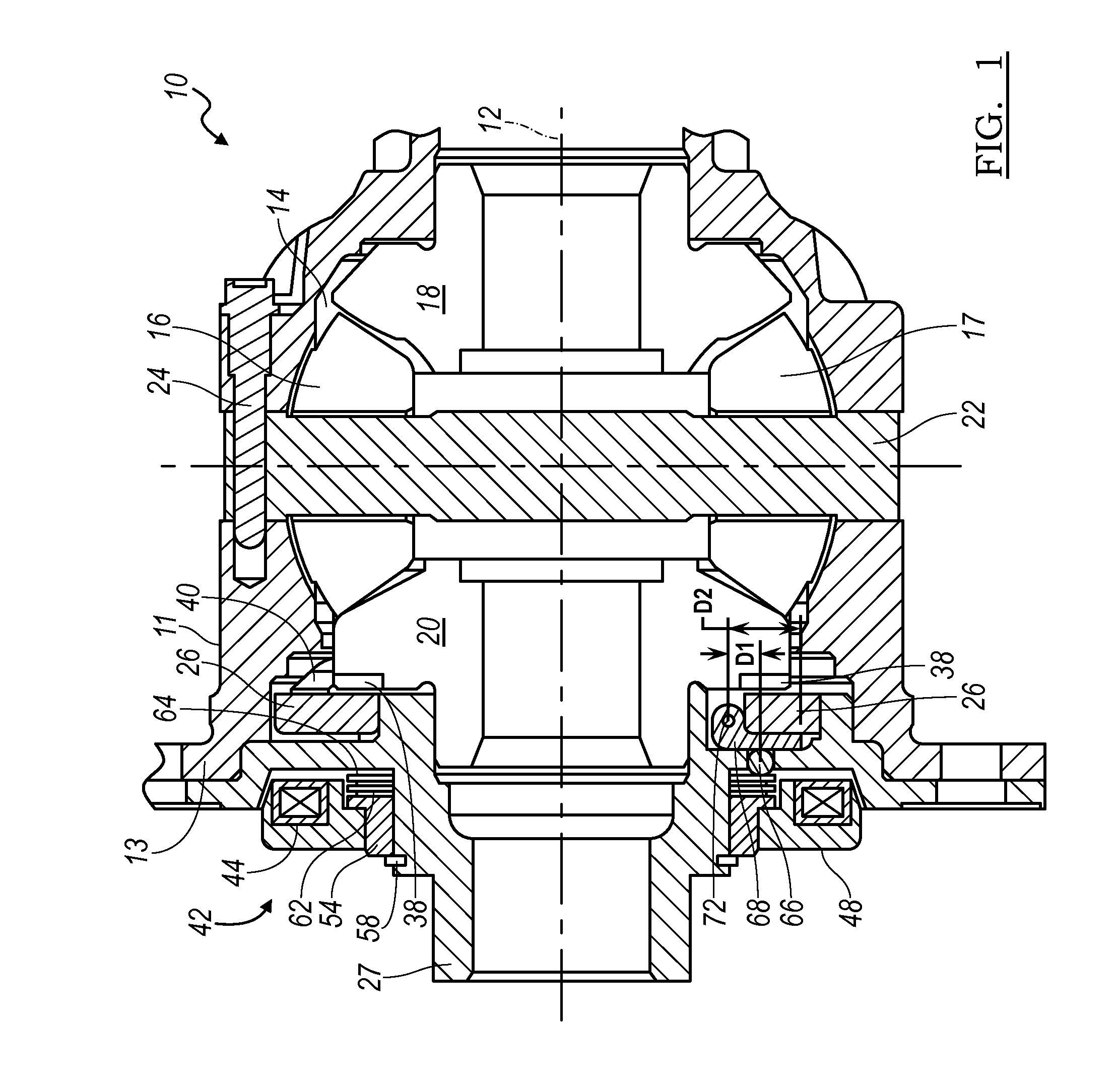
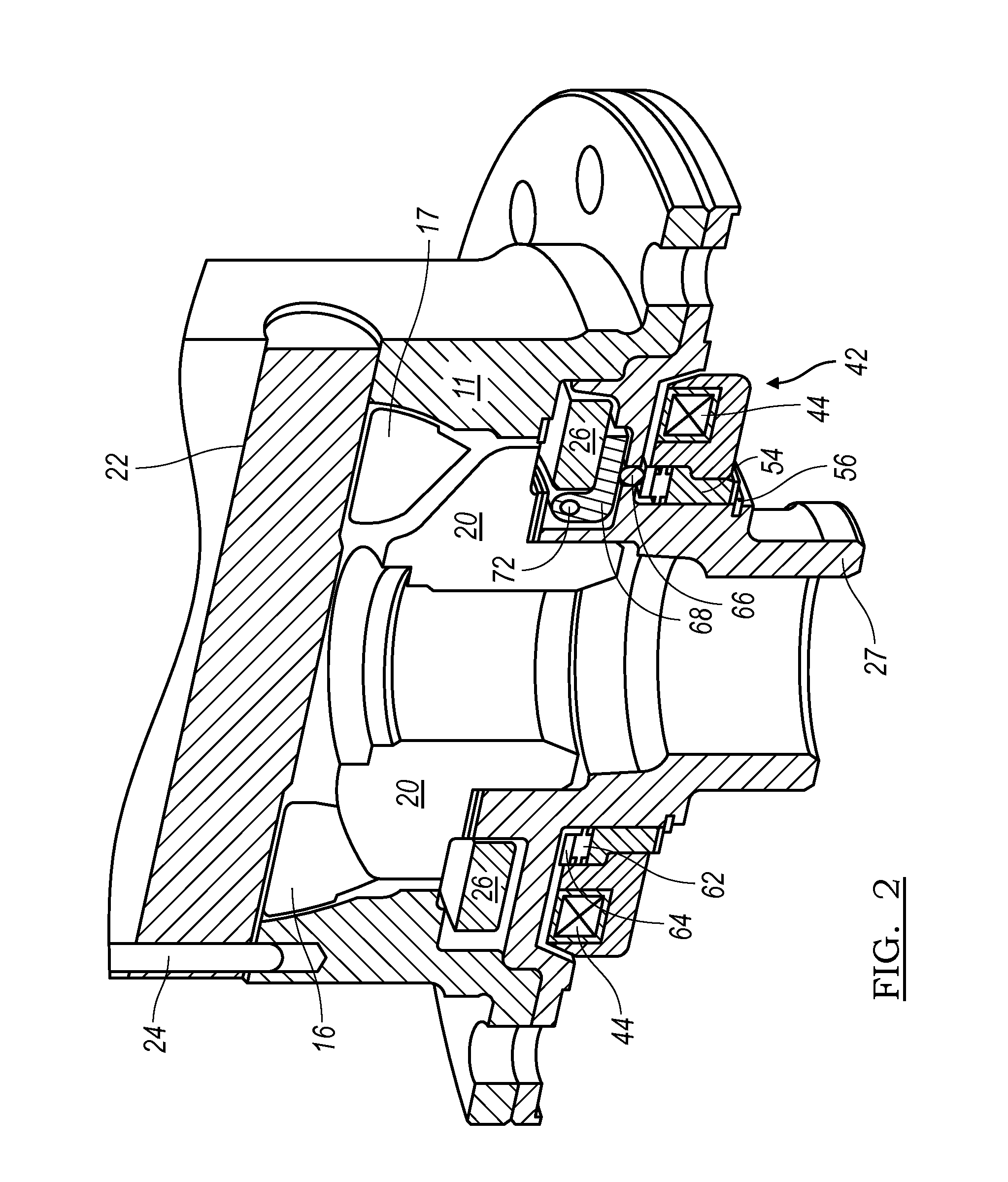
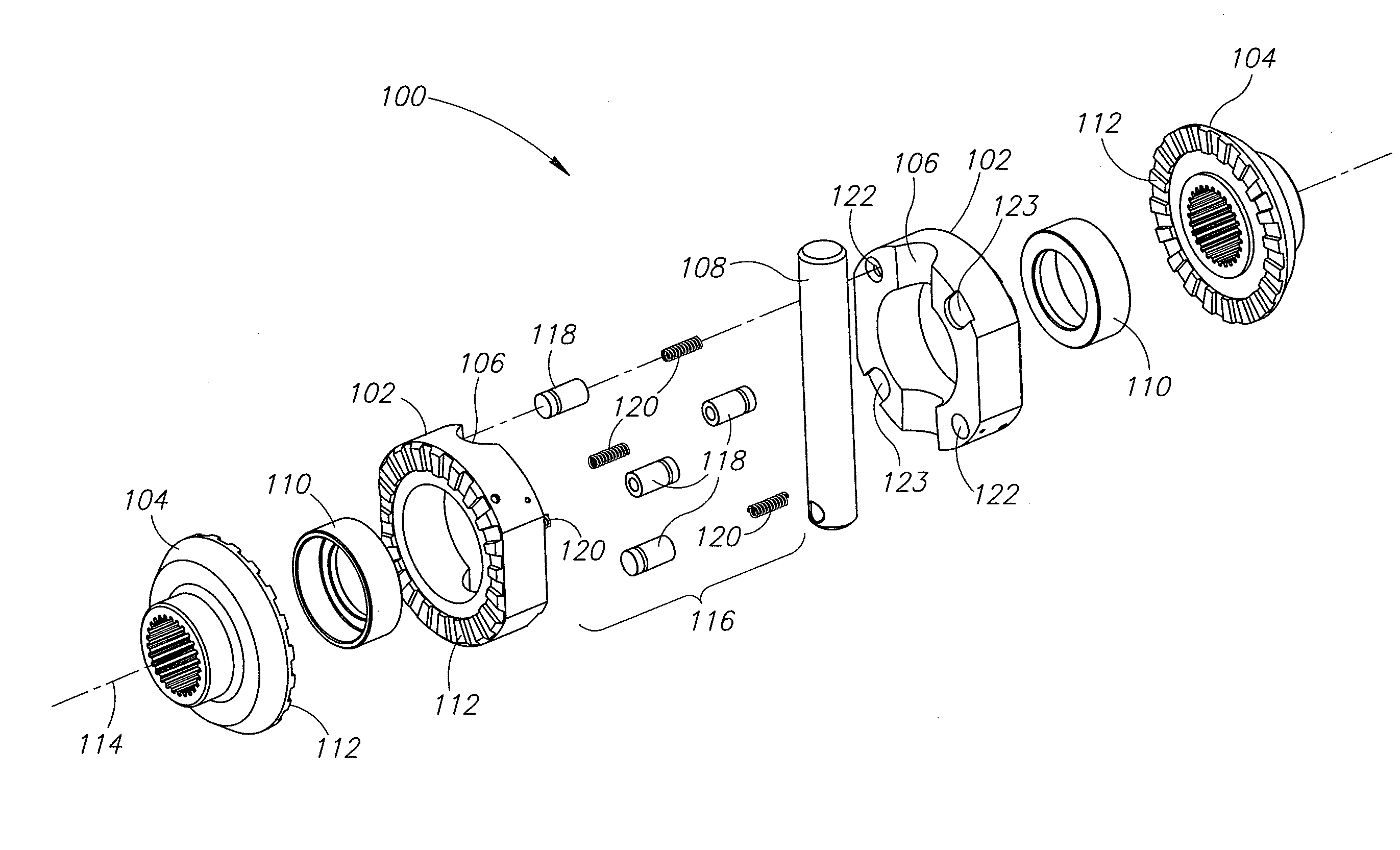
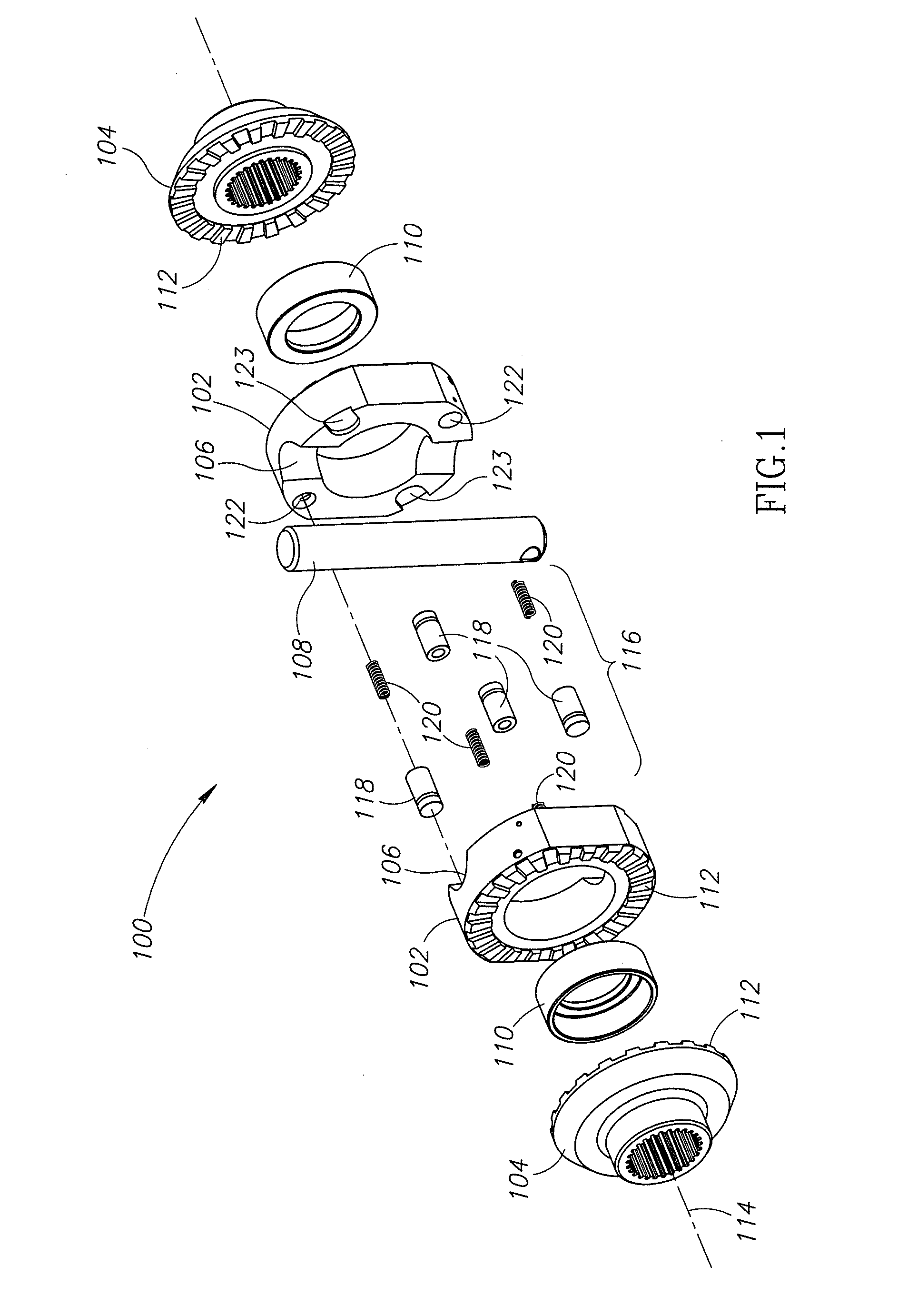
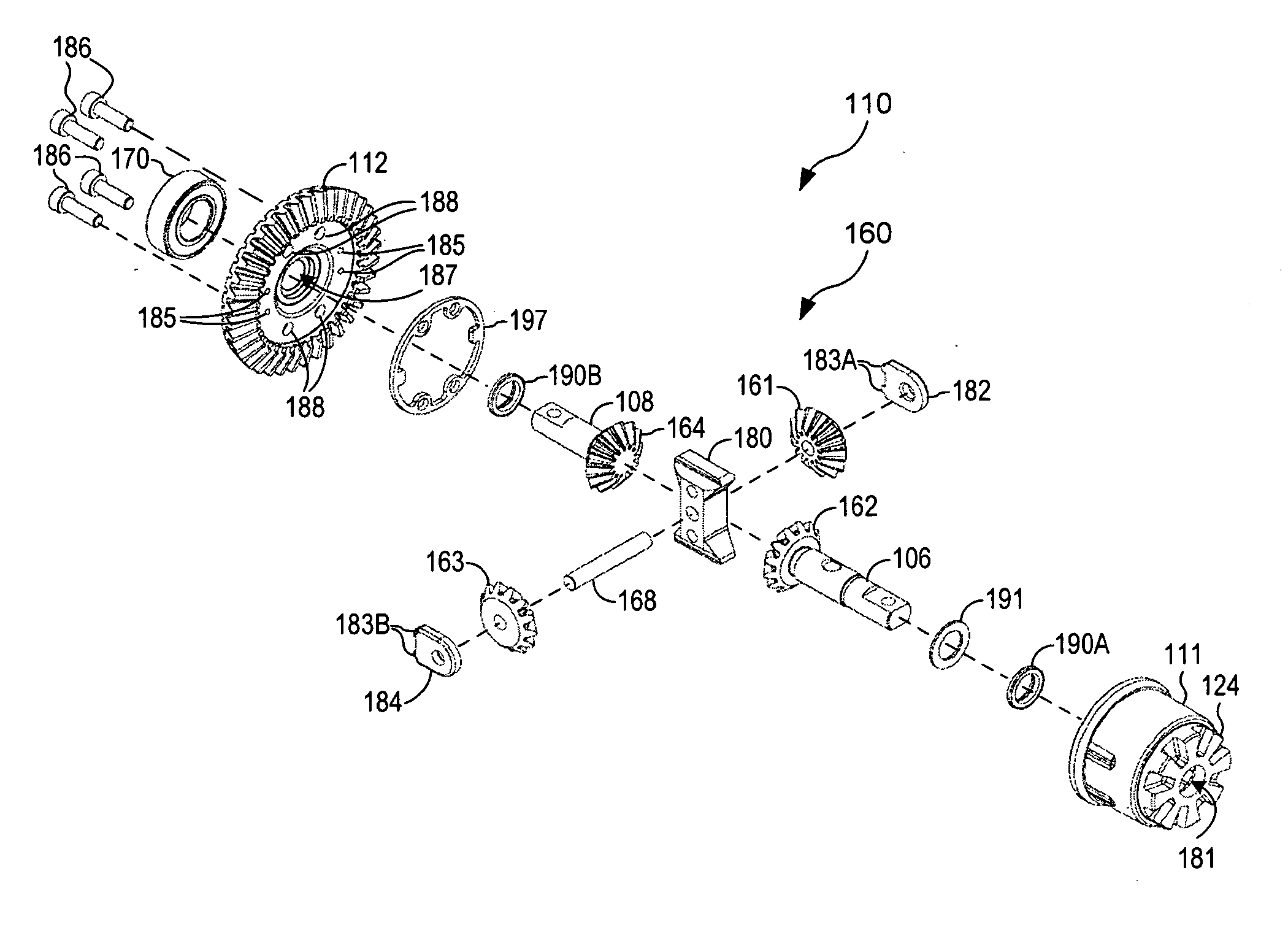
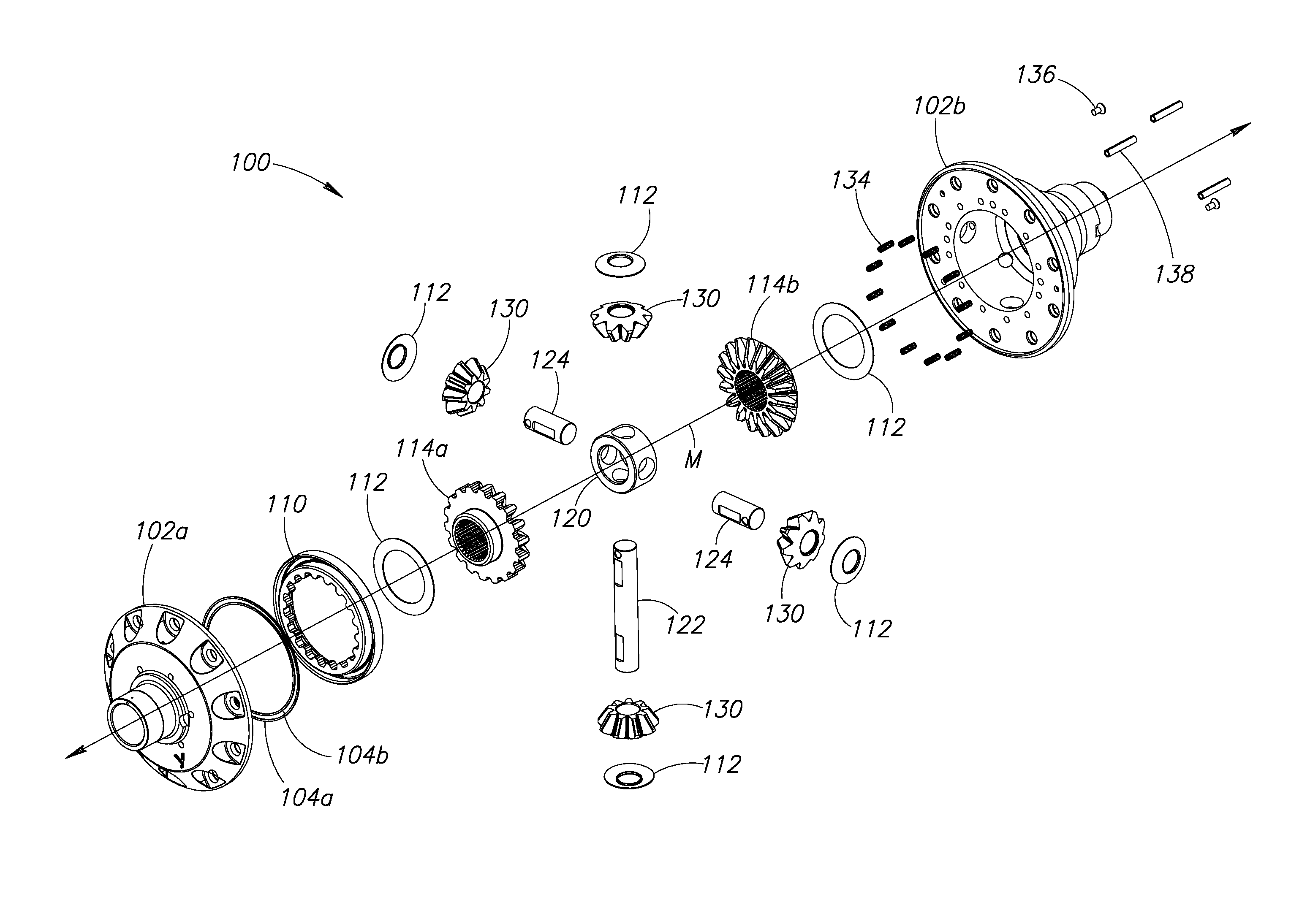
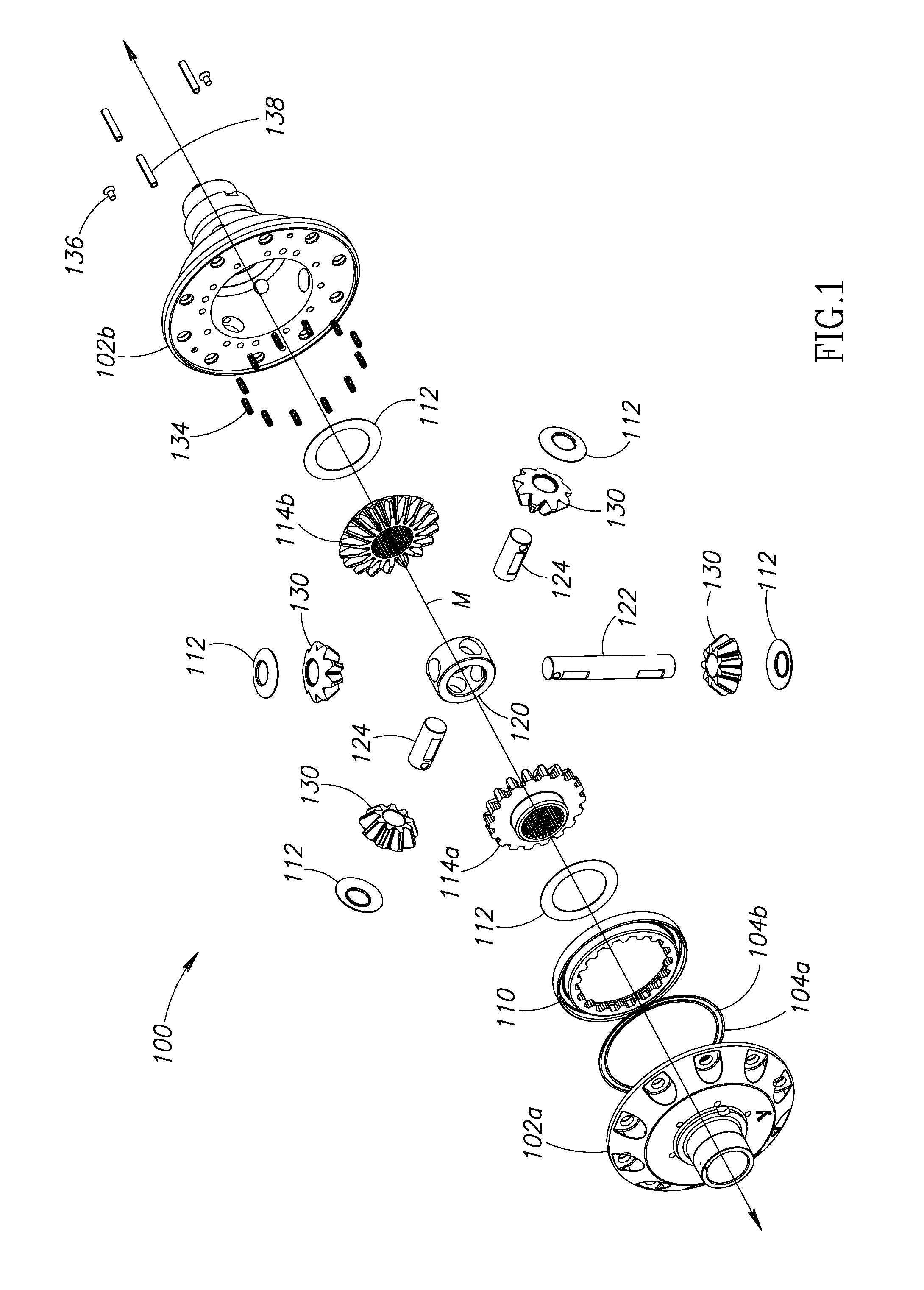
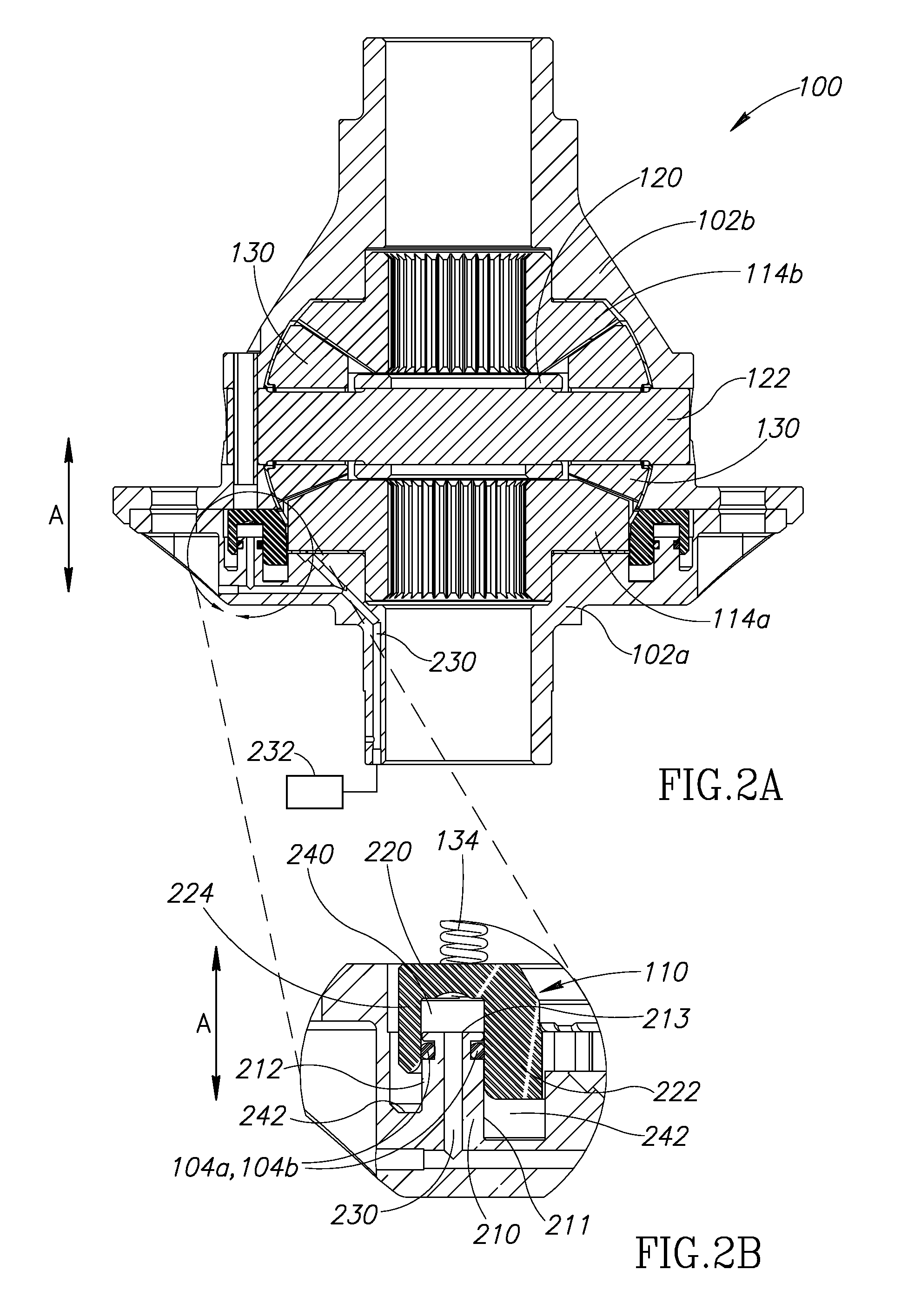
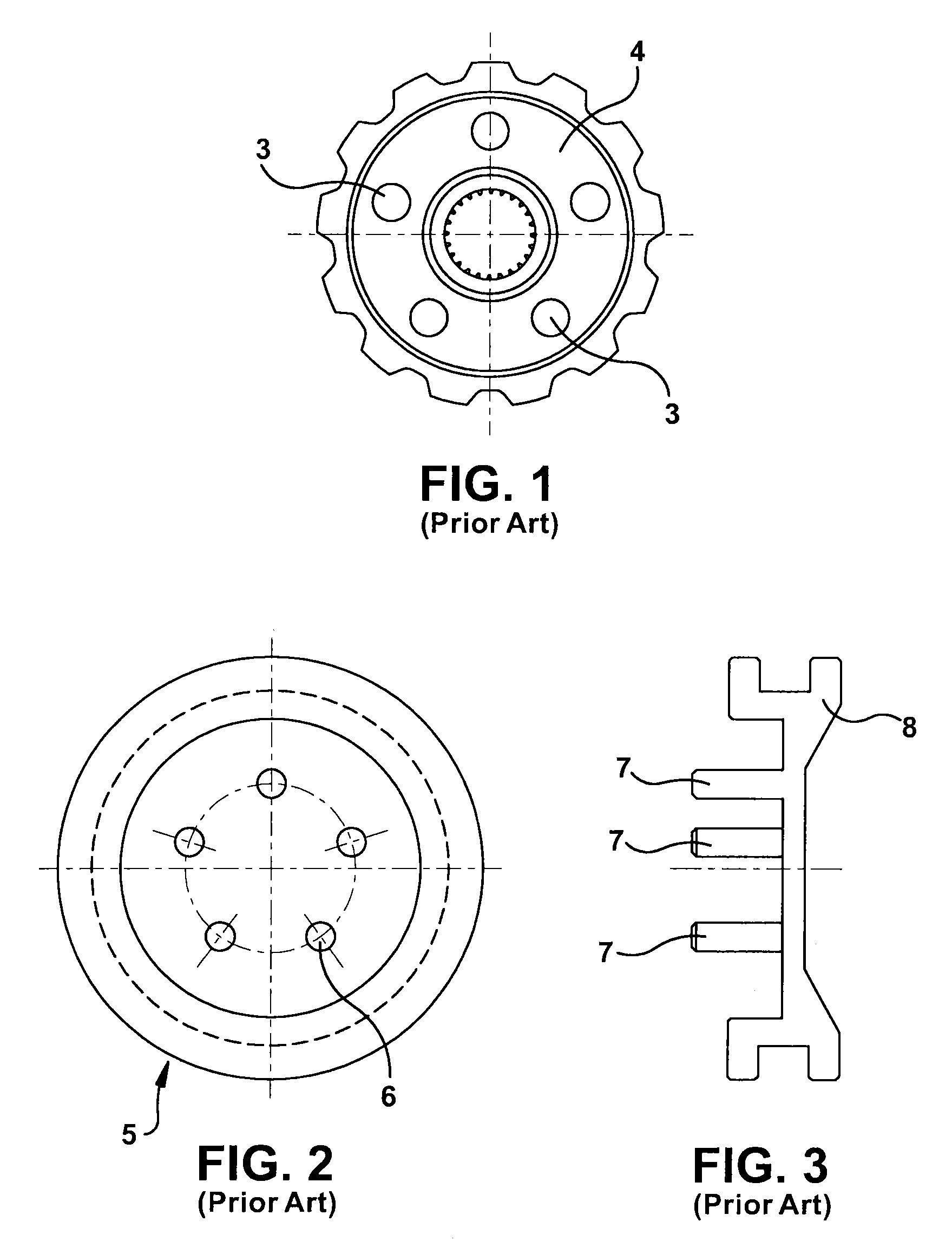
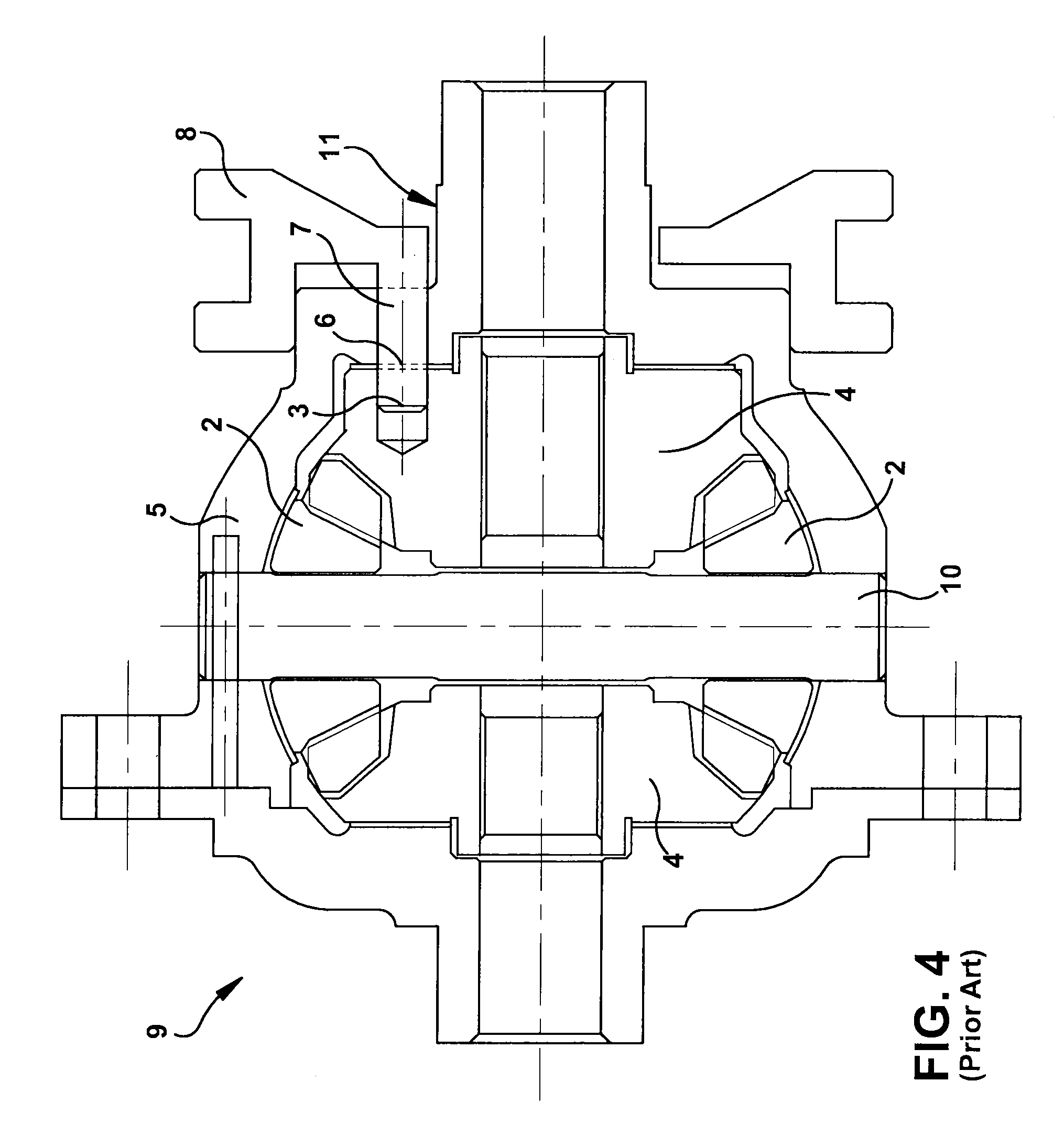
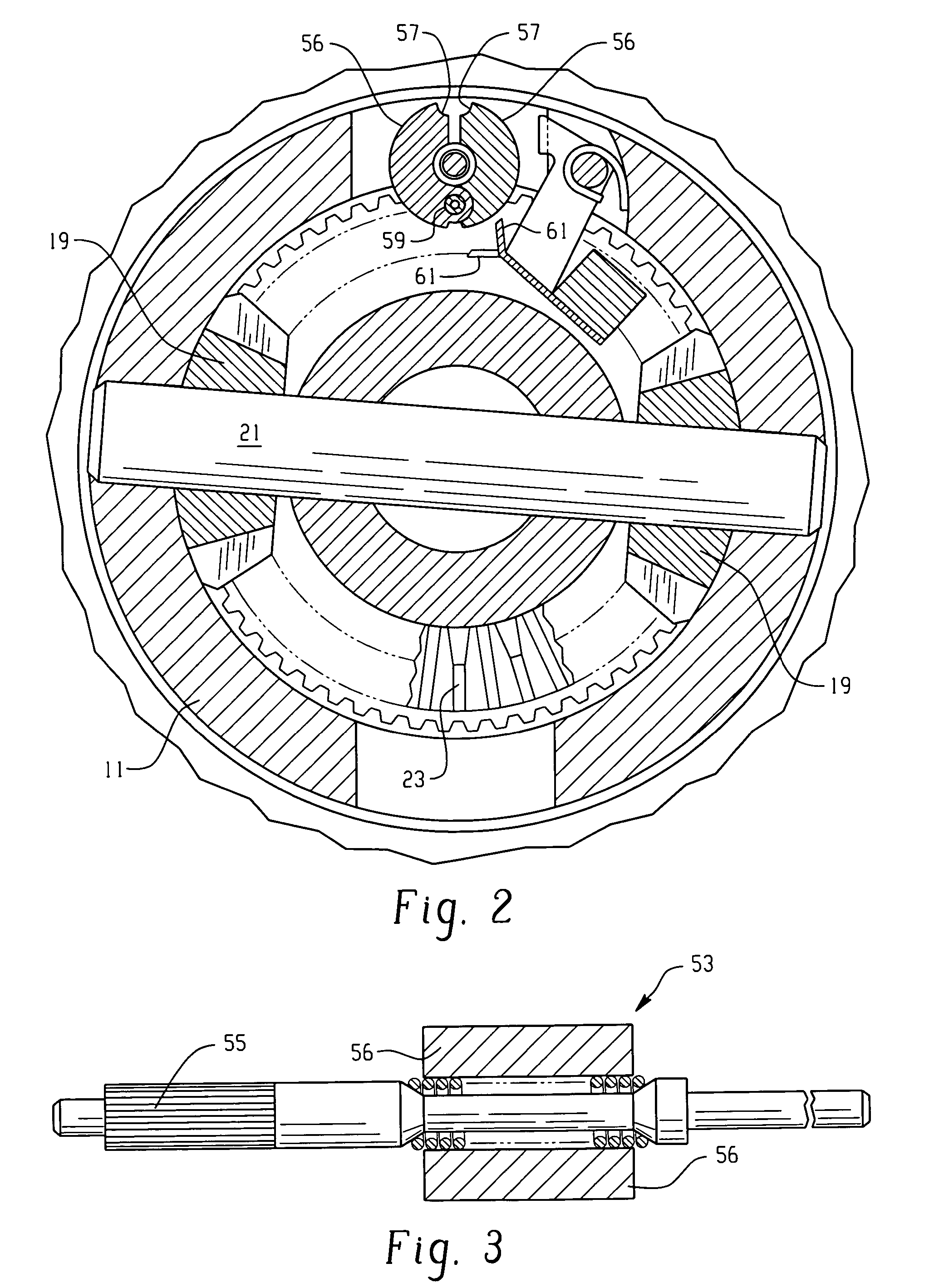
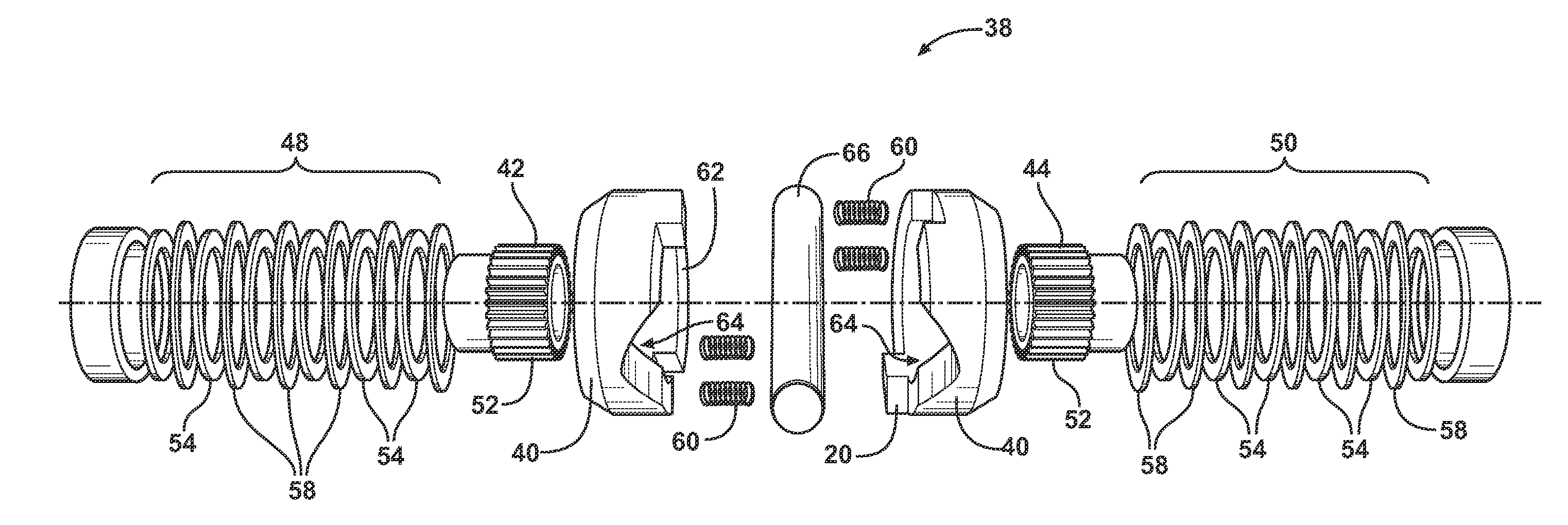
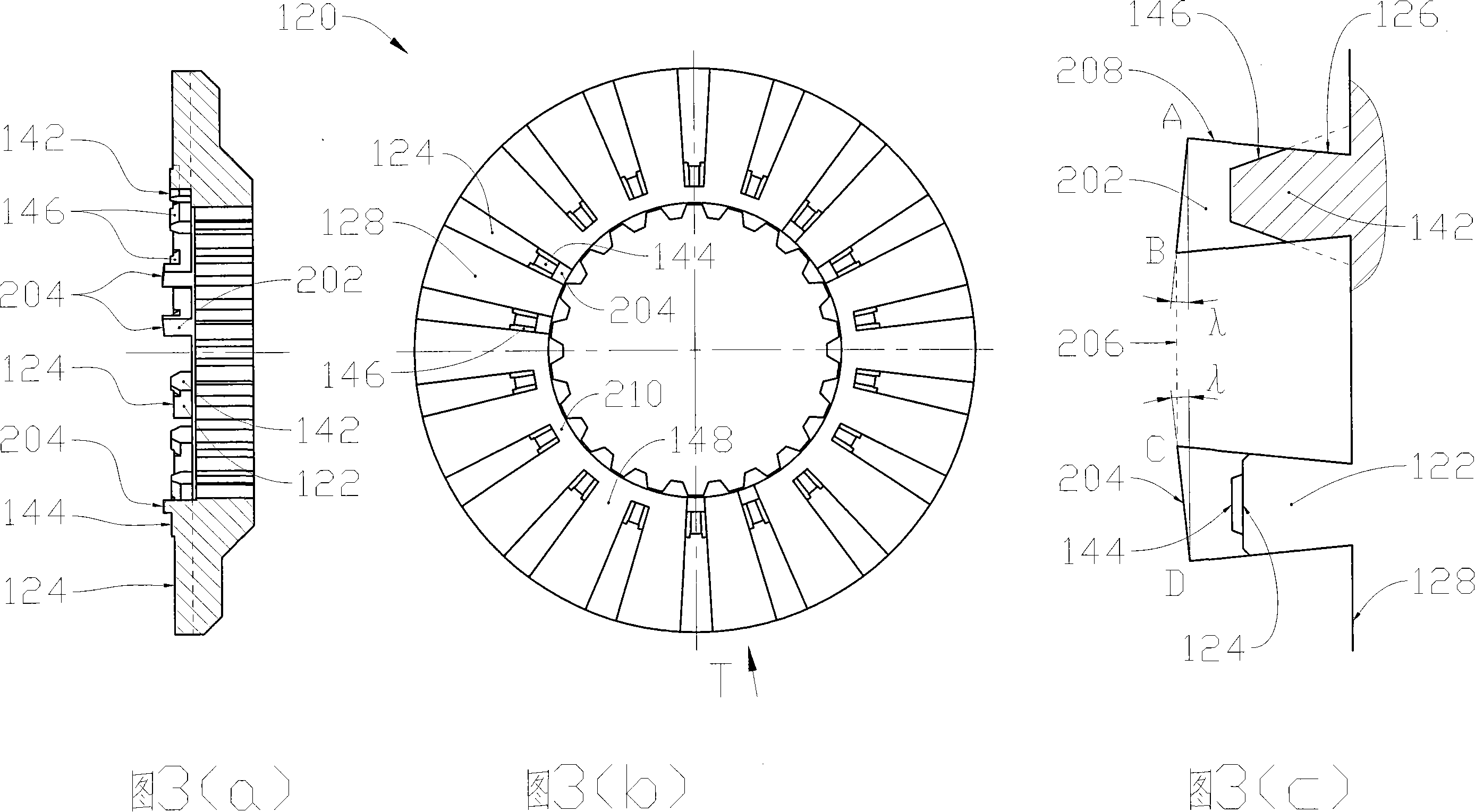
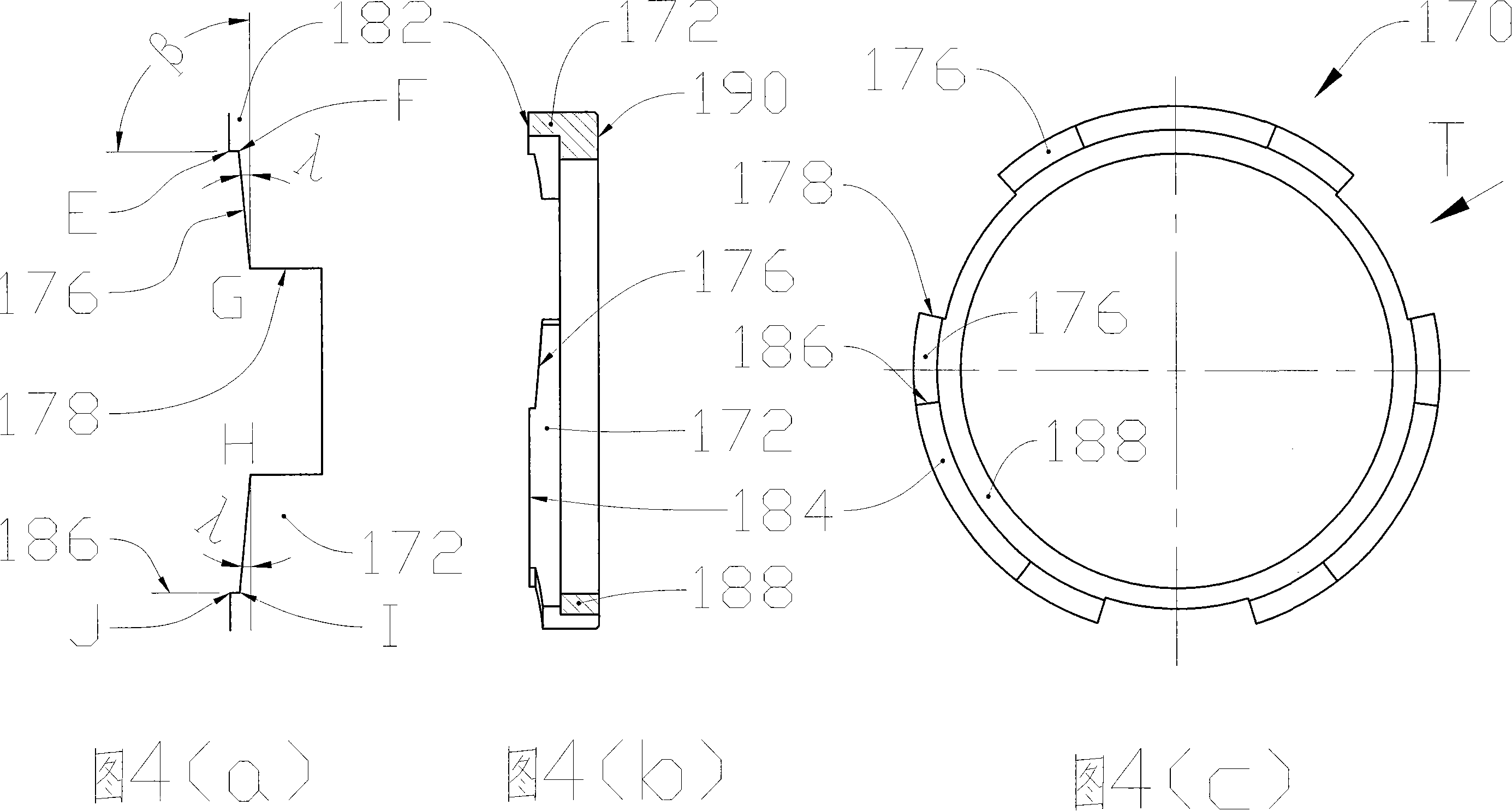
A locking differential including a differential carrier or housing 1 closed by a flange cap 2 engaging locking gear 2A, the housing 1 and flange cap 2 supporting side gears 10 and 11 which mesh with pinion gears 12 supported by cross shafts 8 and 9, the cross shafts engaging mounting holes in the housing 1, each pinion gear having an even number of teeth, and each side gear having a number of teeth which is a multiple of two where two pinions are at 180° to each other, three where three pinion gears are at 120° to each other, four where three or four pinion gears are at 90° to each other, or five where five pinions are at 72° to each other, the locking means further including a clutch gear 5 which slidably engages the locking gear 2A and the teeth on side gear 10 in the locked position, the cross shafts 8 and 9 being in a fixed relationship to the locking gear 2A.
Owner:ARB CORP LTD
Locking differential with electromagnetic actuator
A differential assembly includes a case, a pair of pinion gears, a pair of side gears and an electrically operable coupling including an electromagnet. The coupling selectively drivingly interconnects one of the side gears and the case. The electromagnet of the coupling is axially moveable within the case to selectively place the differential assembly in an open or a locked condition.
Owner:AMERICAN AXLE & MFG
Electronic Locking Differential
InactiveUS20120021862A1Low costReduce weightMechanical actuated clutchesMagnetically actuated clutchesElectronic differentialMechanical engineering
A differential mechanism includes a case, a gear rotatable about an axis, a lock ring held against rotation relative to the case, a lever contacting the lock ring, and an electromagnetic coil that is displaced axially when energized, pivoting the lever, engaging the lock ring with the side gear, and preventing the gear from rotating relative to the case.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
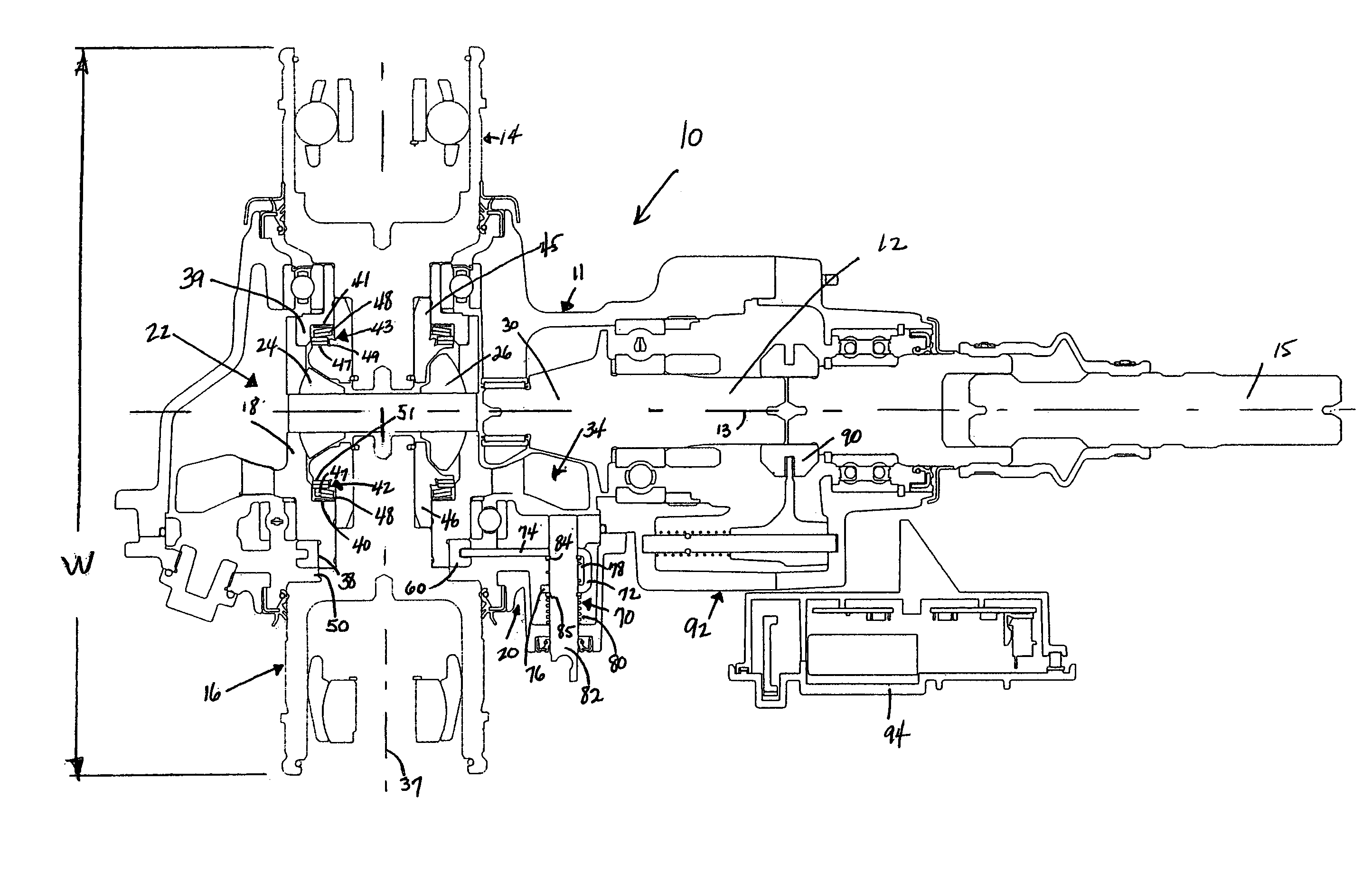
Two-speed gearbox with integrated differential
A gearbox assembly includes a housing which contains a differential gear set and a two-speed reduction gear set. A spider drives differential pinion gears nested between outer pinion gears. A first and a second clutch that can be engaged “on the fly” achieve the two-speed functionally of the gearbox assembly. Another gearbox assembly includes an on-demand locking differential with a differential clutch located between differential axle side gears to selectively lock the differential axle side gears together and thereby lock the axle shafts.
Owner:ARVINMERITOR TECH
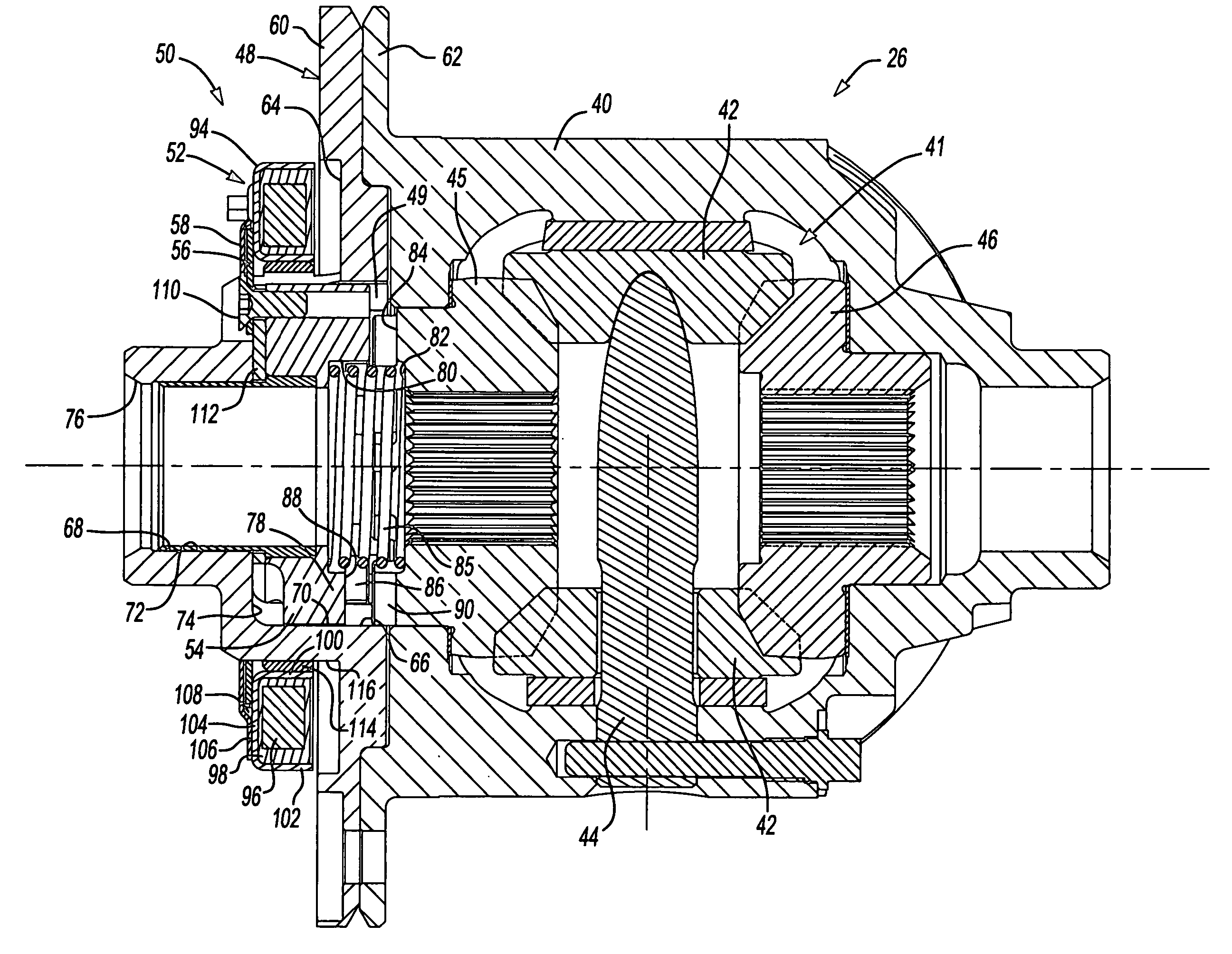
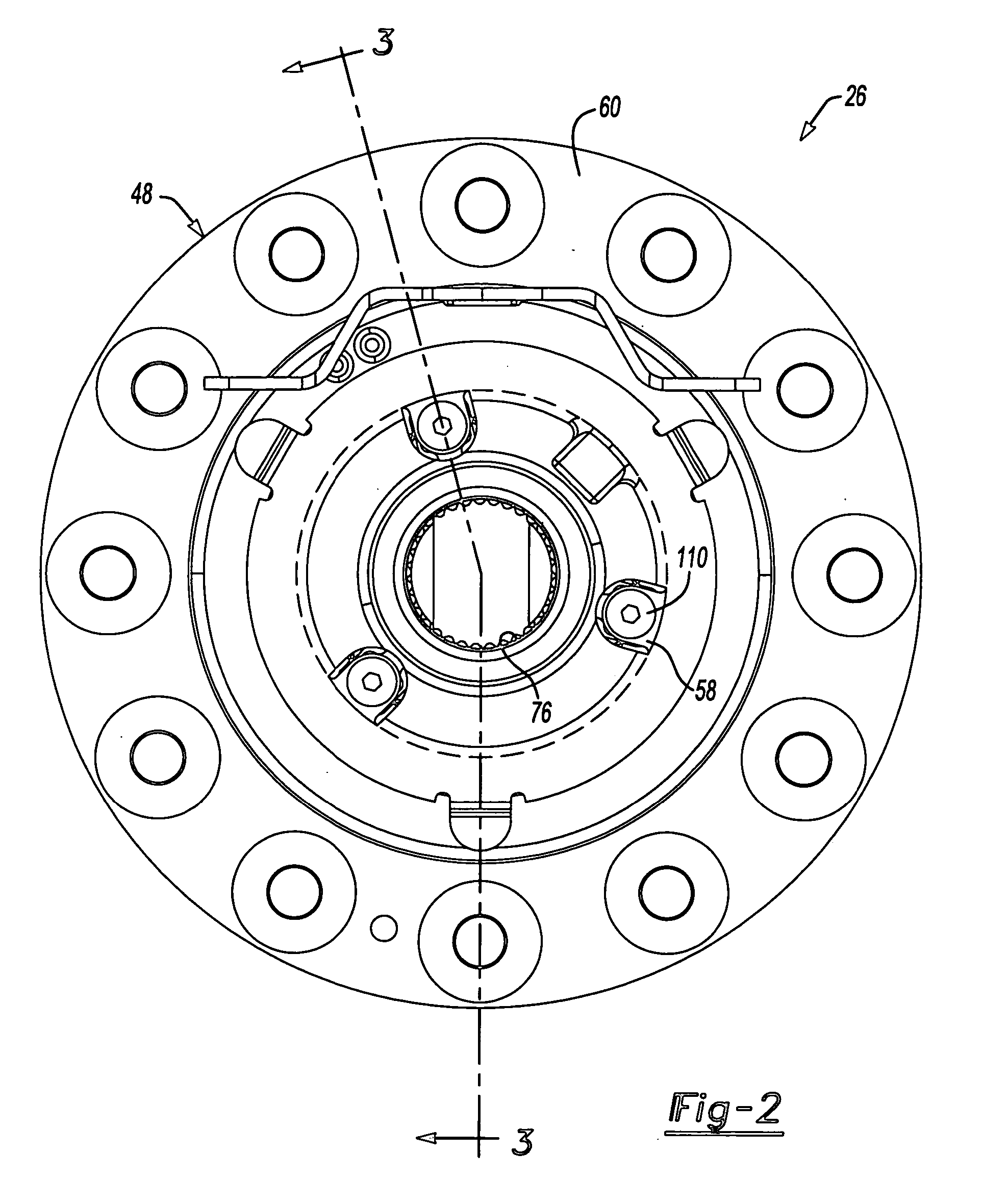
Locking differential including disengagement retaining means
A locking differential includes a pair of annular clutch members that are normally displaced apart to effect engagement between clutch teeth on the remote ends of the clutch members and corresponding gear teeth on the adjacent ends of a pair of side gears between which the clutch members are colinearly arranged. When one output shaft overruns the other by a predetermined amount, the clutch member associated with the overrunning output shaft is disengaged from its associated side gear. A retaining device retains the clutch members in the disengaged condition until the overrunning condition is terminated. In one embodiment, the retaining device is a cam arm and follower pin arrangement that is connected between the clutch members and operates in conjunction with a pair of friction rings. In a second embodiment, the retaining device comprises a pair of holdout rings that operate between the clutch members and the side gears.
Owner:EATON CORP
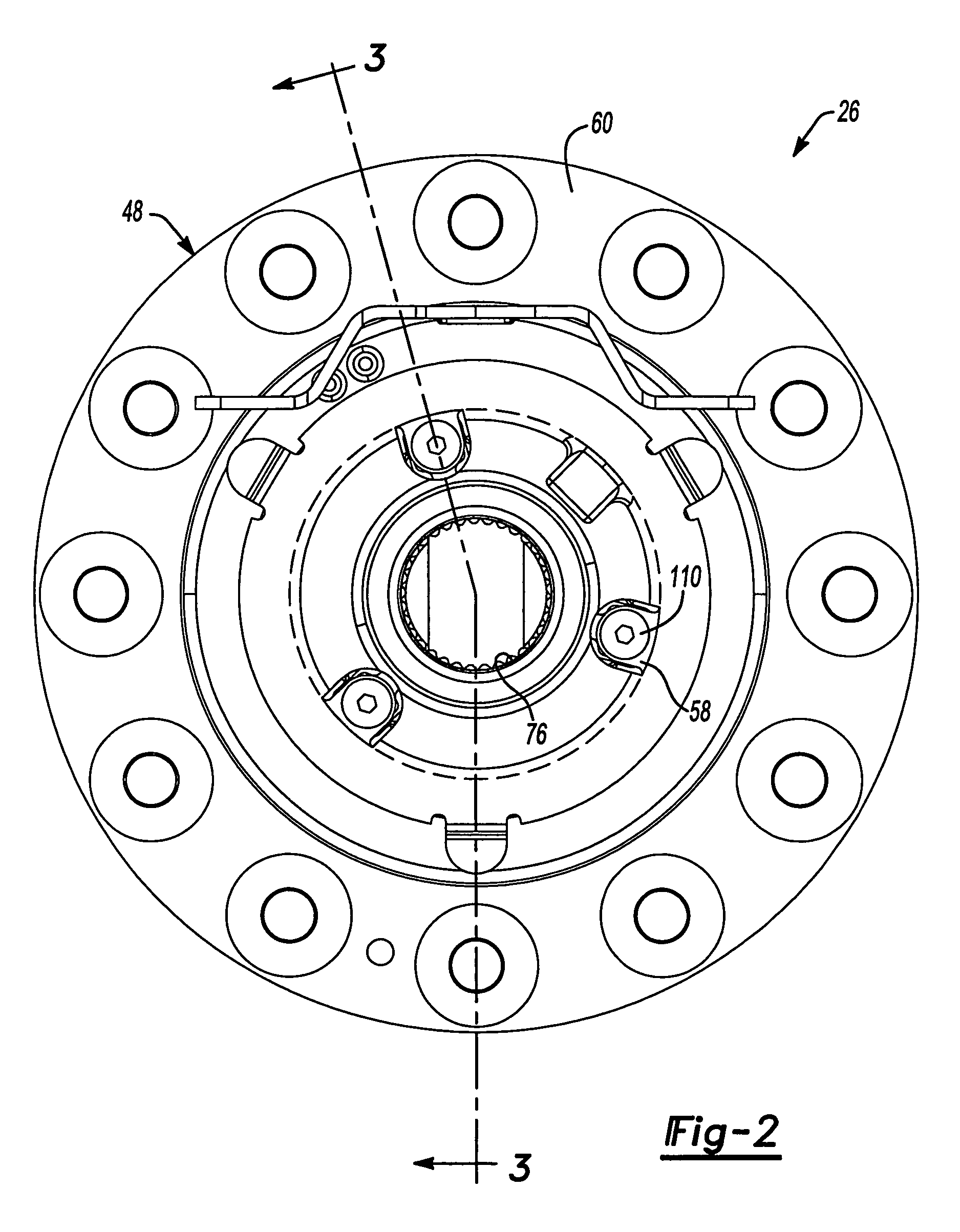
Locking Differential Assembly
An axle assembly with an electric locking differential that can include a one-piece differential case and a locking device. The locking device includes a dog that is nonrotatably but axially slidably received into a pocket that is formed in an end of the differential case. An actuator is mounted on the differential case. Actuation of the actuator moves the dog into engagement with a second dog that is coupled to a side gear of the differential to thereby lock the side gear to the differential case.
Owner:AMERICAN AXLE & MFG
Morphological gradient-based identification method for magnetizing inrush current of transformer
ActiveCN103050941ALower latencySmall amount of calculationCurrent/voltage measurementEmergency protective circuit arrangementsBase frequencyMathematical morphology
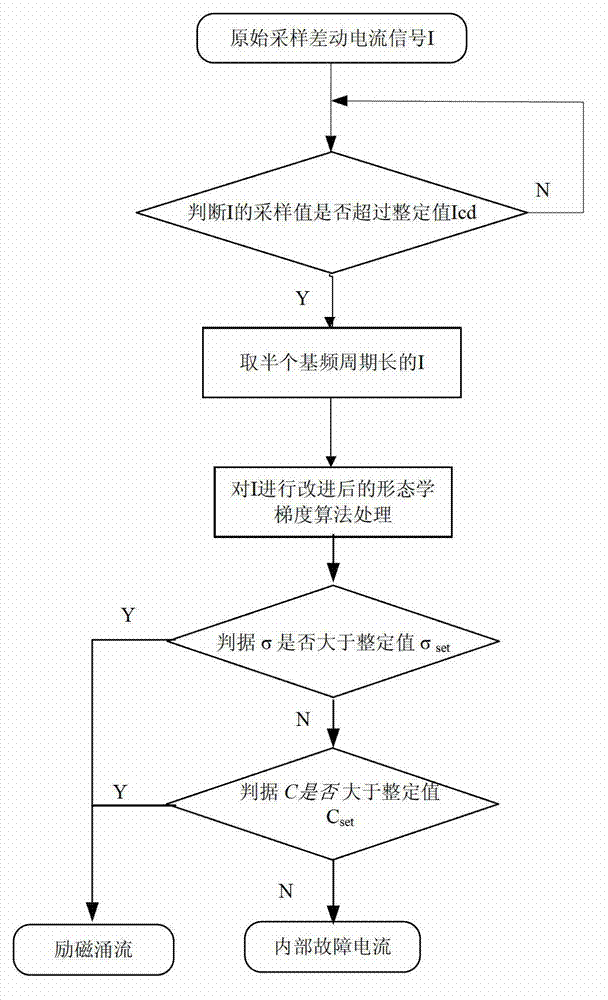
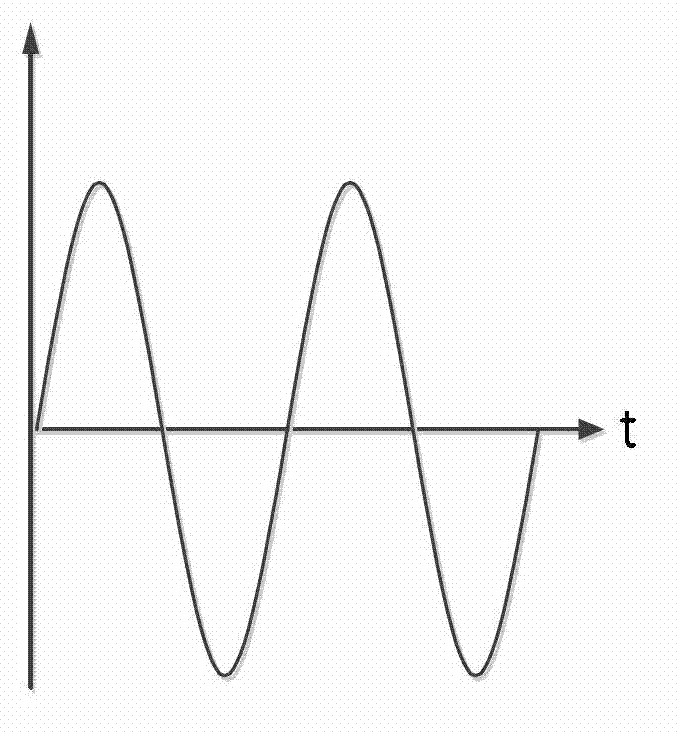
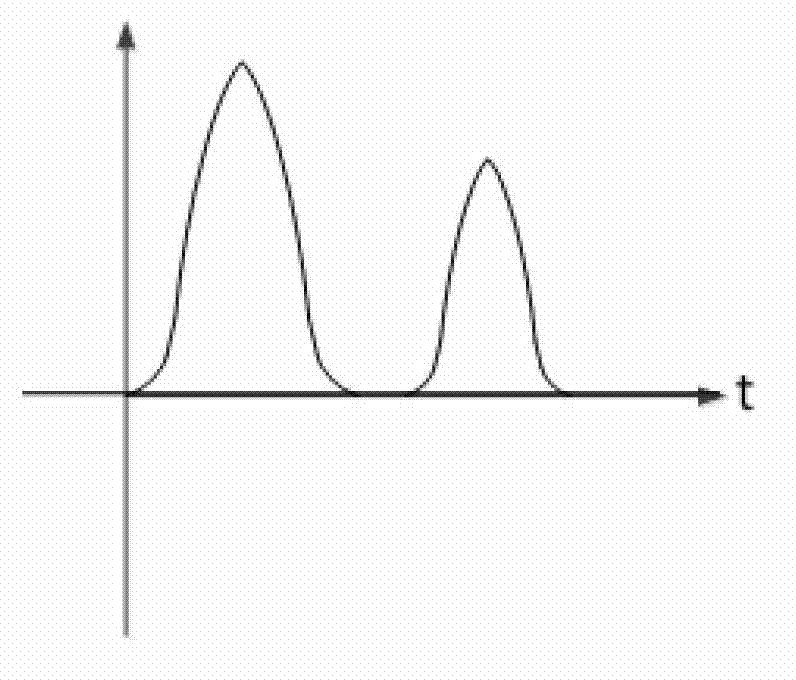
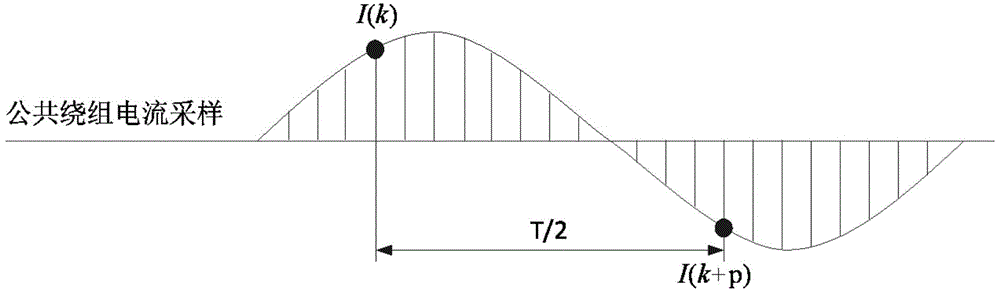
The invention discloses a morphological gradient-based identification method for the magnetizing inrush current of a transformer. The identification method comprises the following steps of: (1) acquiring a differential current signal I of current transformers arranged at two differential protection sides of the transformer; (2) sampling the differential current signal I; and (3) when the obtained differential current signal I exceeds a setting valve Icd of a differential-protection starting component, distinguishing the magnetizing inrush current. The step (3) specifically comprises the following steps of: (3-1) taking the differential current signal I of which a data window is a half of the length of a base frequency period to obtain a morphological gradient result of the I according to an improved mathematical morphology gradient algorithm; (3-2) introducing criterion sigma: determining that I is the magnetizing inrush current if sigma is greater than sigma set, and carrying out a step (3-3) otherwise; and (3-3) introducing criterion C: determining that I is the magnetizing inrush current if C is greater than C set, and determining that I is an inner fault signal otherwise. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of simple steps, small calculated quantity, short time delay, high reliability and the like, so that the magnetizing inrush current can be identified to realize the locking differential protection.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
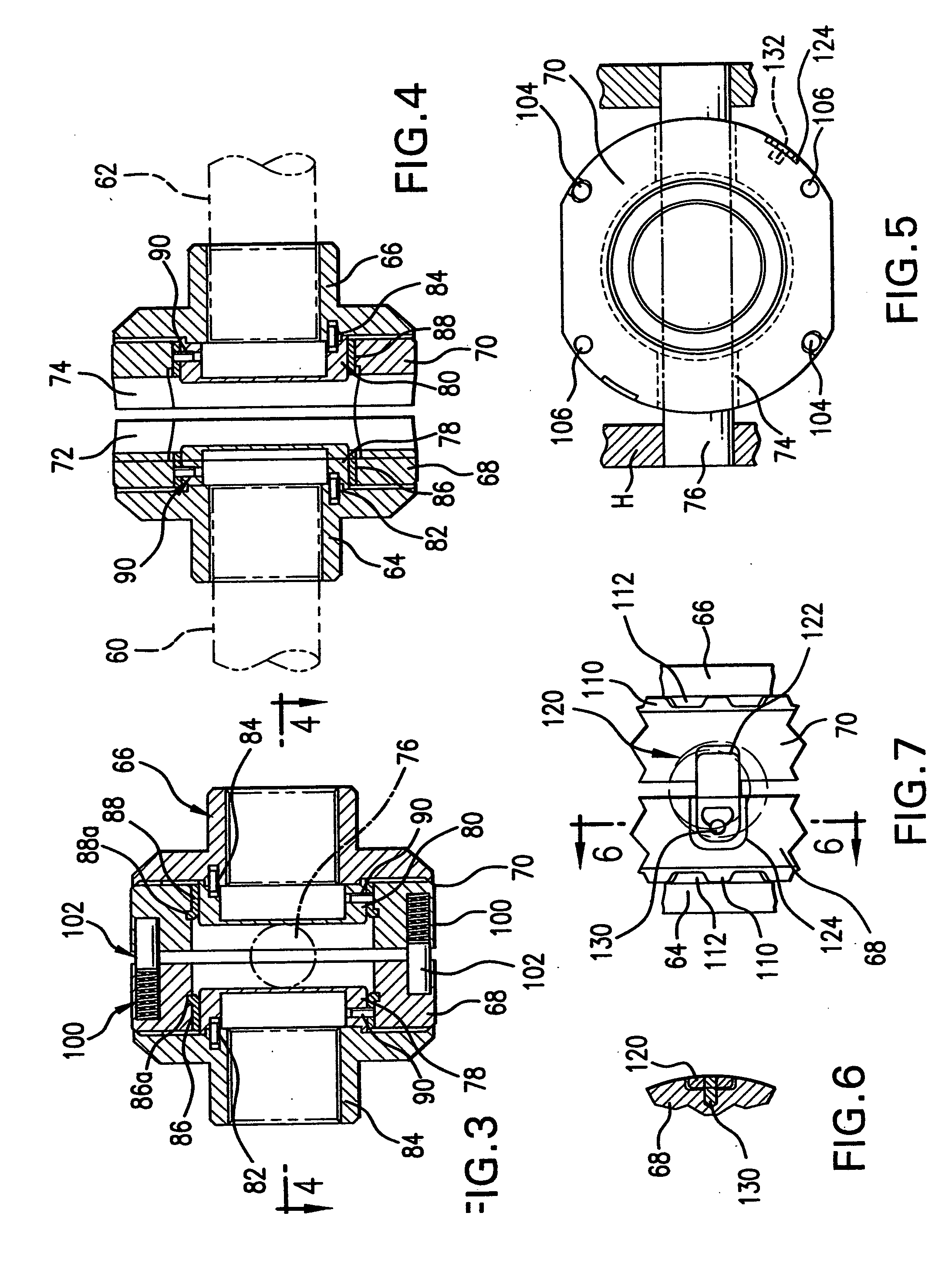
Locking differential with shear pin/spring assembly
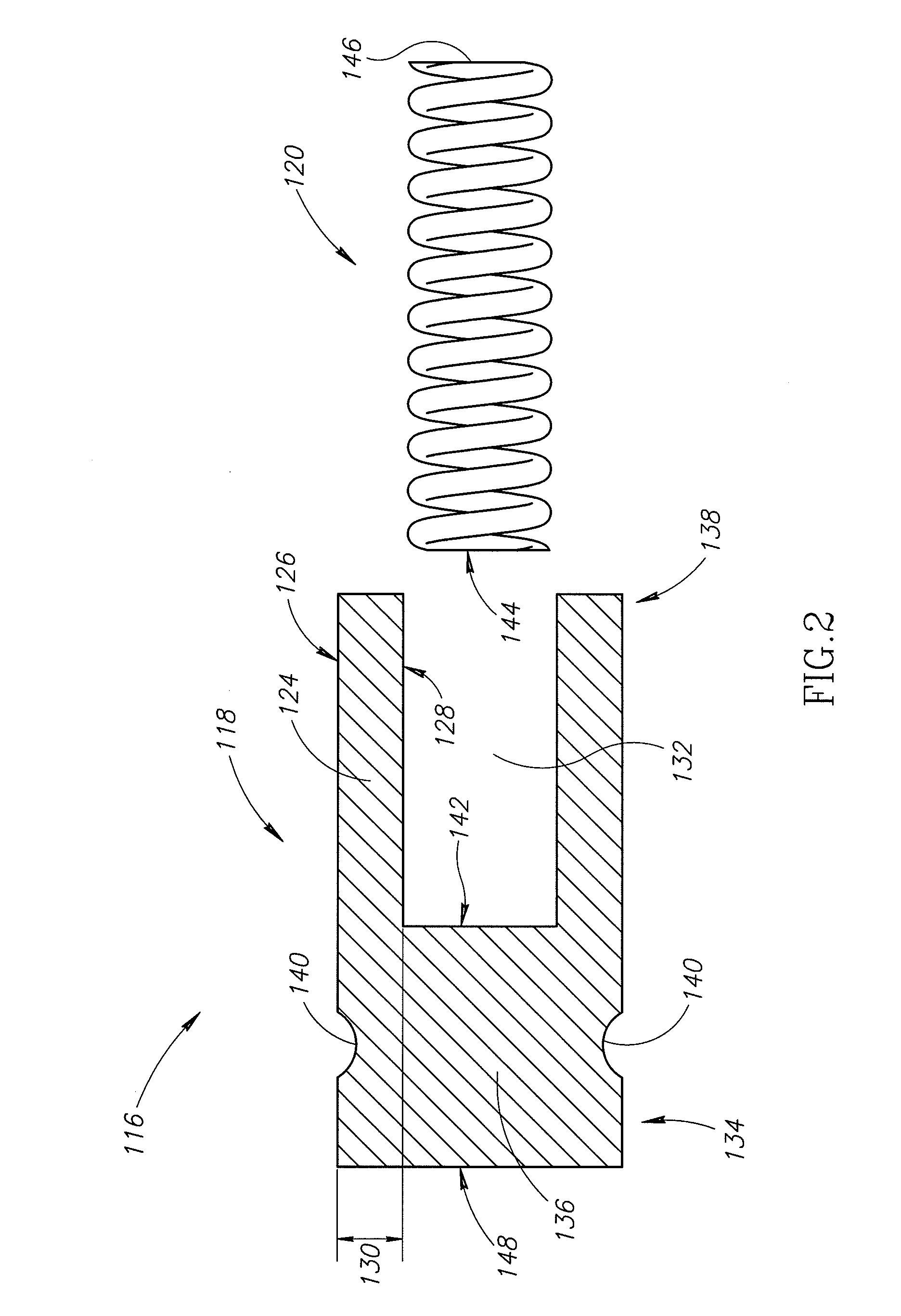
A clutch assembly for a locking differential includes driving clutch members engaged with driven clutch members in a preloaded configuration to provide a minimum amount of preload there between during low torque conditions. The driving clutch members are biased relative to each other with shear pin / spring assemblies located within bores of the driving clutch members. During assembly of the clutch assembly, the shear pin / spring assemblies may be positively locked down within the bores with a removable tool. In one embodiment, the removable tool is inserted into a small opening extending through the driving clutch member and the tool engages an annular groove on a shear pin of the shear pin / spring assembly. Further, the clutch assembly may include driving clutch members having drainage openings that may help prevent hydraulic lock during operation of the locking differential.
Owner:RING & PINION SERVICE
Locking differential assembly for a model vehicle
A locking differential assembly for use in a toy model vehicle. This is accomplished by mounting a locking clutch assembly on an output shaft of a differential gear carrier having an external face. The locking clutch assembly includes a slider member that may be configured to move along the output shaft to engage the external face to disable a differential action of the differential gear carrier.
Owner:TRAXXAS
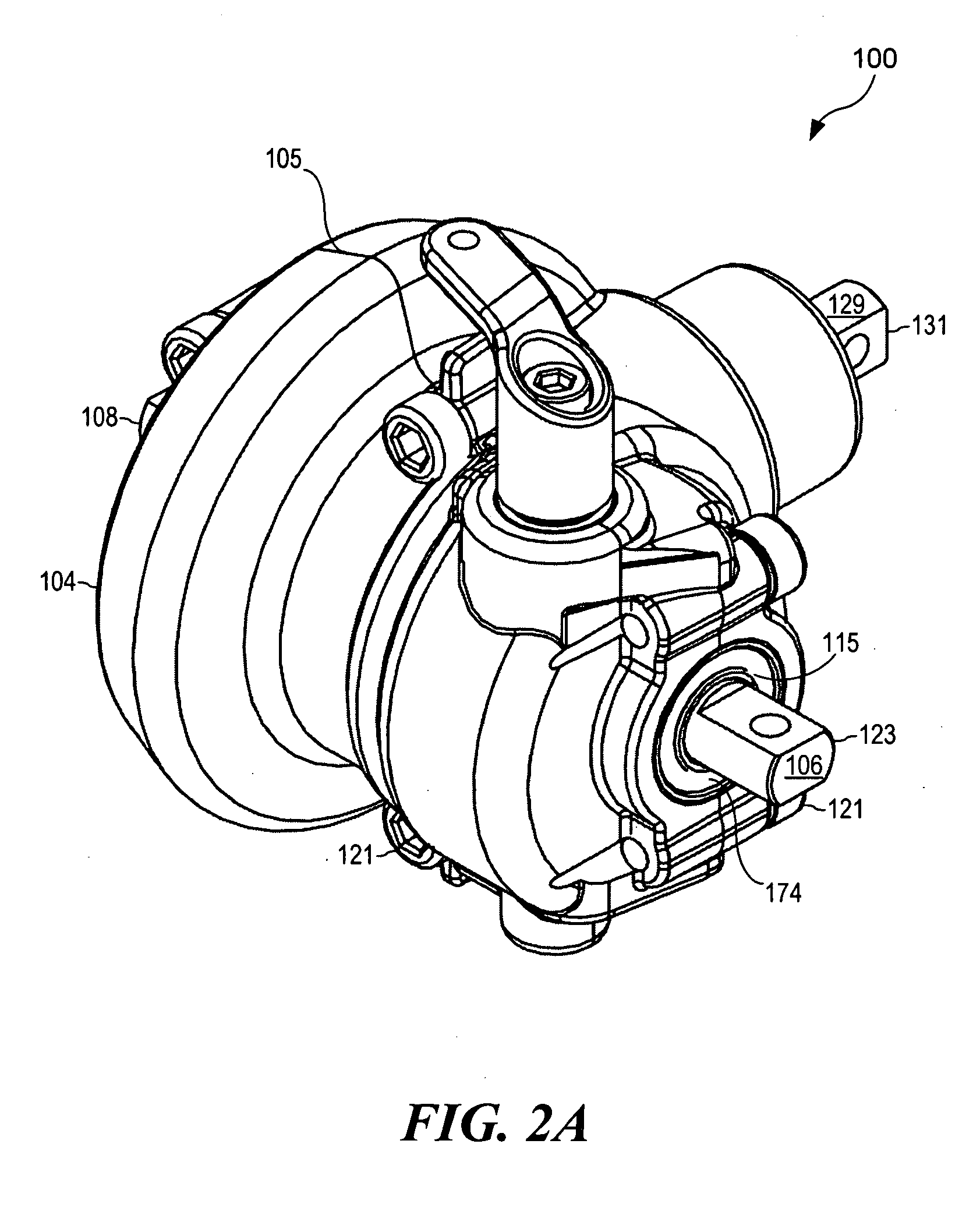
Mechanical locking differential lockout mechanism
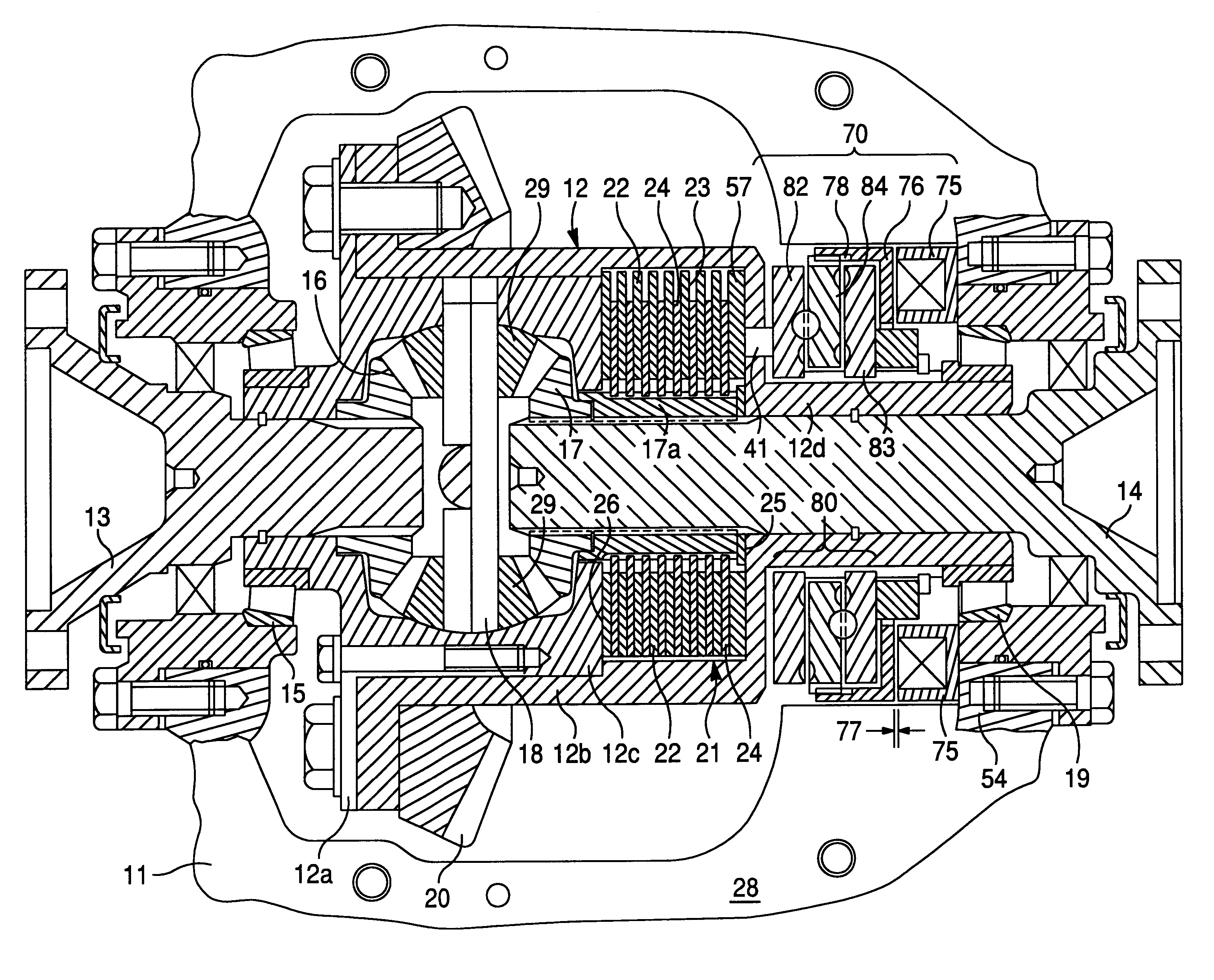
An improved differential gear mechanism is characterized by a lockout mechanism (129) operably associated with a latch member (119) that cooperates with a flyweight mechanism (53) to retard differentiating action in the differential gear mechanism. The lockout mechanism (129) includes a lockout member (131) positionable, in response to an input signal, in a normal condition and a lockout condition. In the normal condition, the lockout member (131) permits the latch member (119) to move freely between a locking position and an unlocking position. In the lockout condition, the lockout member (131) prevents the latch member (119) from moving into the locking position.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LTD
Mechanical locking differential lockout mechanism
An improved differential gear mechanism is characterized by a lockout mechanism ( 63, 90, 129) operably associated with a flyweight mechanism ( 53 ) or latch member (119) cooperating with the flyweight mechanism (53) to block differential action of differential gear mechanism.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LTD
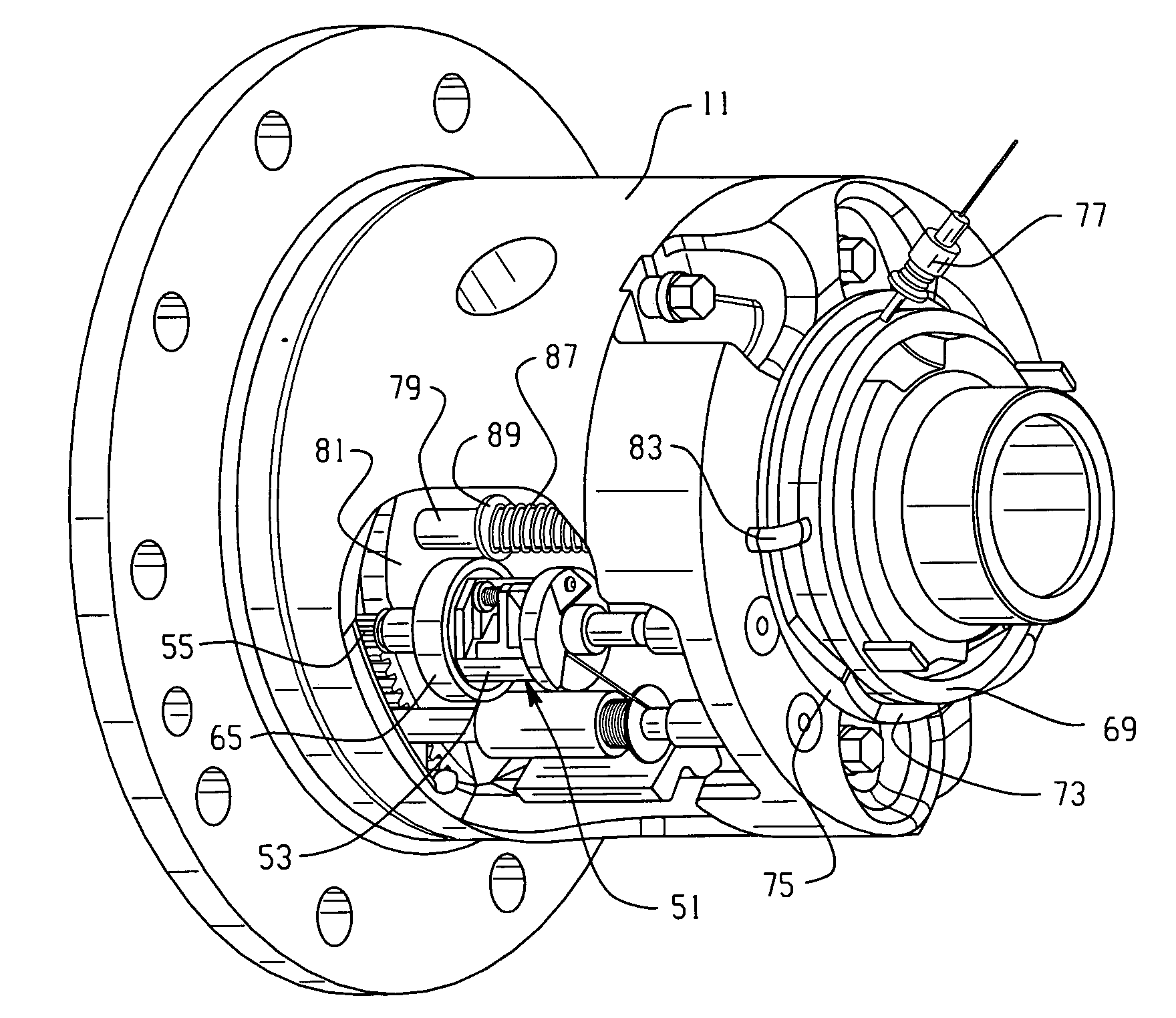
Electronic locking differential with direct locking state detection system
ActiveUS7744500B2Mechanical actuated clutchesMagnetically actuated clutchesLocking mechanismElectronic differential
An axle assembly with an electronic locking differential that employs a locking mechanism having components that are fixed to one another along an axis such that they co-translate with one another when the actuator that effects the locking and unlocking of the differential is operated.
Owner:AMERICAN AXLE & MFG
Transformer differential protection difference stream and differential protection instantaneous TA abnormal state identification protecting method
ActiveCN1545179ASolve the problem of differential protection misoperationEmergency protective circuit arrangementsPhase differenceExcitation current
Owner:NR ELECTRIC CO LTD
Locking differential assembly
A locking differential having a movable locking ring that can selectively engage a gear of the differential to lock or unlock the differential is disclosed. The locking ring is moved by a pressure source, such as a pneumatic pressure source, and a spring. The locking ring engages a fixed annular ring in the case of the differential. Two O-rings create a seal between sides of the fixed annular ring and arms of the locking differential.
Owner:RING & PINION SERVICE
Transformer differential protection method and device based on current transformer disconnection
ActiveCN106684824APrevent malfunctionAvoid the phenomenon of differential protection refusalEmergency protective circuit arrangementsCurrent transformerElectrical and Electronics engineering
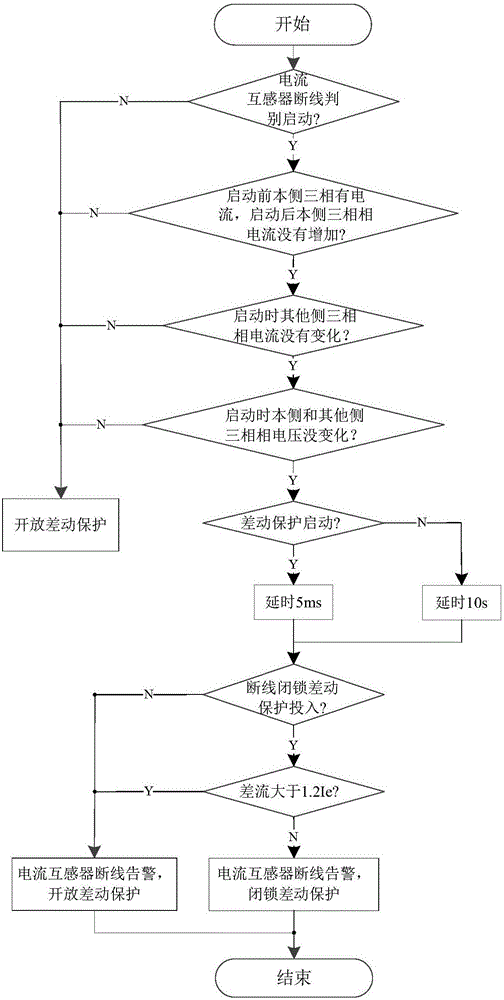
The invention relates to a transformer differential protection method and device based on a current transformer disconnection. The transformer differential protection method comprises the steps of judging whether a current transformer disconnects; if the current transformer disconnects, judging whether differential protection is started; if the differential protection is started, instantaneously determining that the current transformer disconnects, or otherwise, delaying to determine that the current transformer disconnects; after determining that the current transformer disconnects, judging whether disconnection locking differential protection is used; if the disconnection locking differential protection is not used, alarming the current transformer disconnection and opening the differential protection, and if the disconnection locking differential protection is used, judging whether a differential current is greater than a set value; if the differential current is greater than the set value, alarming the current transformer disconnection and opening the differential protection; and if the differential current is not greater than the set value, alarming and locking the differential protection. The transformer differential protection method and device related by the invention can reliably detect whether the current transformer disconnects; and the problems that the differential protection is likely to be mistakenly operated after the current transformer disconnects, and the differential protection refuses operation when a failure reoccurs are effectively solved.
Owner:XUJI GRP +3
Pin retention and assembly system for locking differential
A pin retention and assembly system that is used with vehicles, such as, off-road vehicles is provided. The pin retention and assembly system has modular locking pins engaging a collar positionable about a bearing journal of a differential housing. Channels are formed in the bearing journal for receiving the locking pins. The channels aid in maximizing the size of the bearing journal. The locking pins engage the collar to lock the differential housing. In an embodiment, the locking pins and locking apertures in the differential housing are orientated asymmetrically causing the number of locking pins to be independent to the apertures in the side gear.
Owner:METALDYNE LLC
Differential protection method for extra-high voltage transformer
InactiveCN104319736AMove quicklyImprove reliabilityEmergency protective circuit arrangementsElectric power systemHarmonic
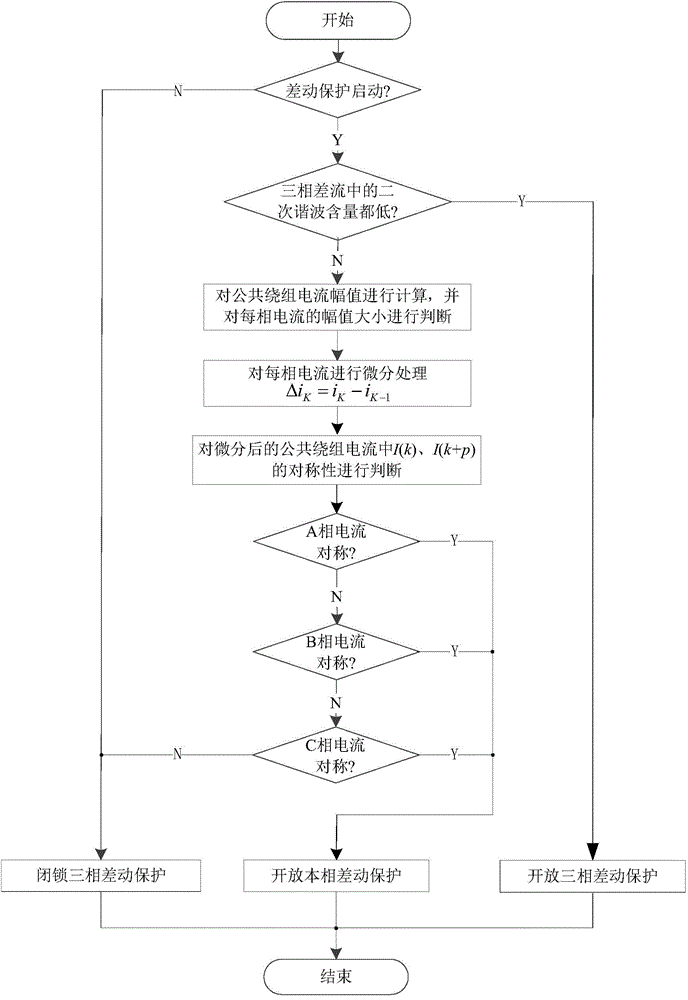
The invention relates to a differential protection method for an extra-high voltage transformer, and belongs to the technical field of power system relay protection. The differential protection method includes: firstly locking differential protection that has not been started, then judging harmonic content of a difference stream which has been started the differential protection, and if harmonic contents of three-phase difference streams are all low, directly opening three-phase differential protection; otherwise, judging that current amplitude of each phase of a common winding is more than a no-flow threshold, judging symmetry of the current more than the no-flow threshold, and only opening differential protection of the phase which meets the requirement of symmetry. No-load and no-load faults of the transformer are identified through comparing symmetry of current waveforms of the common winding of the extra-high voltage transformer, so that the differential protection does not operates mistakenly when in a normal no-load test and acts quickly when a faulty transformer is in the no-load test, and reliability of a protection device is improved.
Owner:XUJI GRP +2
Helical tooth limited slip differential with automatic locking function
ActiveCN103807405APrevent slidingSafe drivingDifferential gearingsControl devicesLimited-slip differentialGear wheel
The invention relates to a helical tooth limited slip differential with an automatic locking function, which comprises a shell. A left half axle gear and a right half axle gear are laterally symmetrically arranged in the shell; the left half axle gear and the right half axle gear are respectively meshed with planetary gears; the shell is provided with a locking device. The helical tooth limited slip differential with the automatic locking function, which is disclosed by the invention, makes up the defect that a locking differential is equivalent to a common open differential under the nonlimiting condition and cannot limit sliding of wheels. A helical tooth limited slip functional part of the helical tooth limited slip differential can automatically work, does not need to be artificially interfered and transfers the torque in real time, can well inhibit the wheels from sliding on ice and snow, muddy, sloppy and gravel pavements and ensures that a vehicle safely runs. The differential also has a function of locking the wheels in the limit state that the wheels at one side of the vehicle are suspended in the air and completely lose the adhesive force.
Owner:TANGSHAN AIT GEAR BOX
Locking differential with electromagnetic actuator
A differential assembly includes a case, a pair of pinion gears, a pair of side gears and an electrically operable coupling including an electromagnet. The coupling selectively drivingly interconnects one of the side gears and the case. The electromagnet of the coupling is axially moveable within the case to selectively place the differential assembly in an open or a locked condition.
Owner:AMERICAN AXLE & MFG
Recreational vehicle locking differential
InactiveUS7018317B2Facilitates variable allocation of powerDifferential gearingsControl devicesRecreationFree rotation
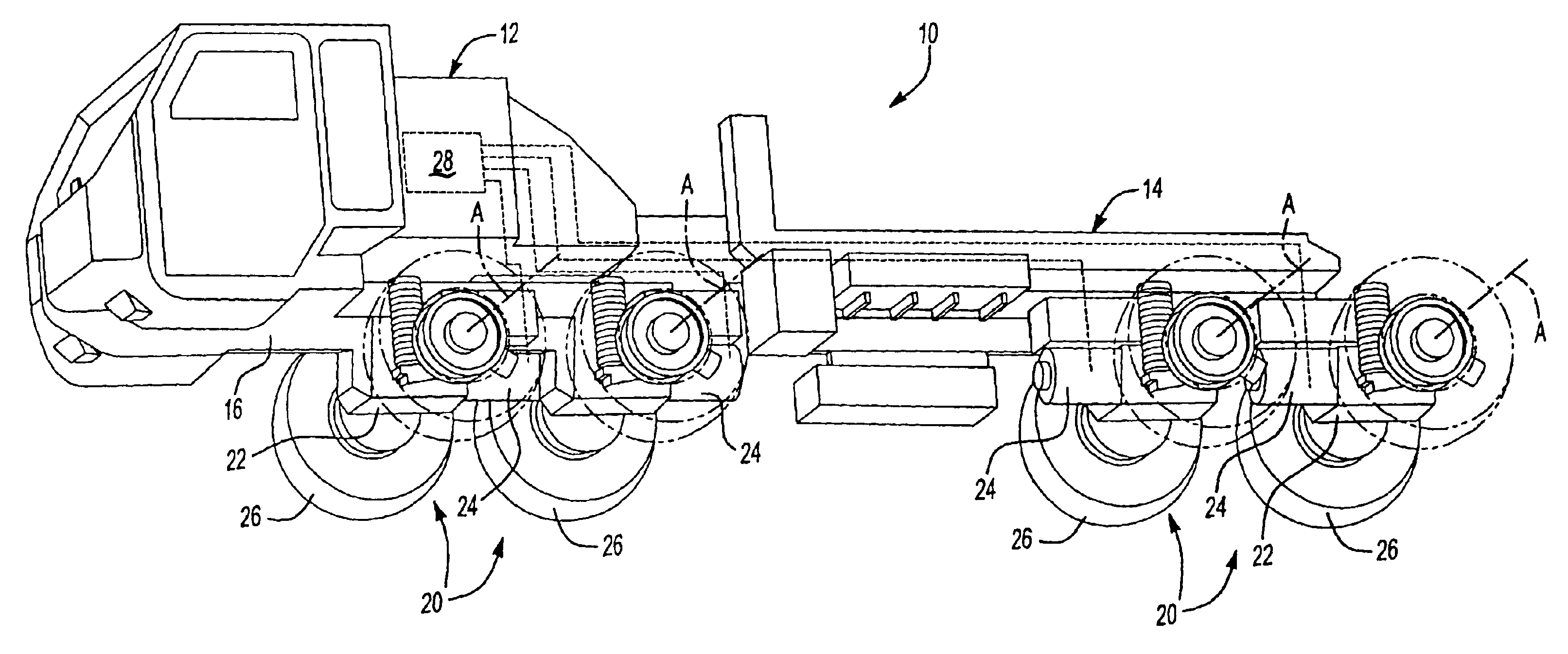
The present invention relates to a transmission for a recreation vehicle, such as an all-terrain vehicle that includes a locking assembly for locking a differential joint in the front- or rear-end portion of the transmission. A vehicle having both front and rear differentials may include separate locking assemblies for each differential to lock and unlock the differentials for various combinations of power allocation to wheels of the vehicle. A differential joint according to the invention may include a ring gear and spider gears that drive a universal joint coupled to wheels of the vehicle. A coupler of the locking assembly includes an inner surface configured to engage outer surfaces of the ring gear and the universal joint, and an outer surface configured to be engaged by an actuator. The actuator adjusts the coupler between a locked position wherein the ring gear and the universal joint are locked together, and an unlocked position wherein the universal joint is free to rotate relative to each other. The coupler preferably has a relatively thin width so as to minimize a track width of the vehicle.
Owner:ARCTIC CAT
Mechanical locking differential lockout mechanism
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LTD
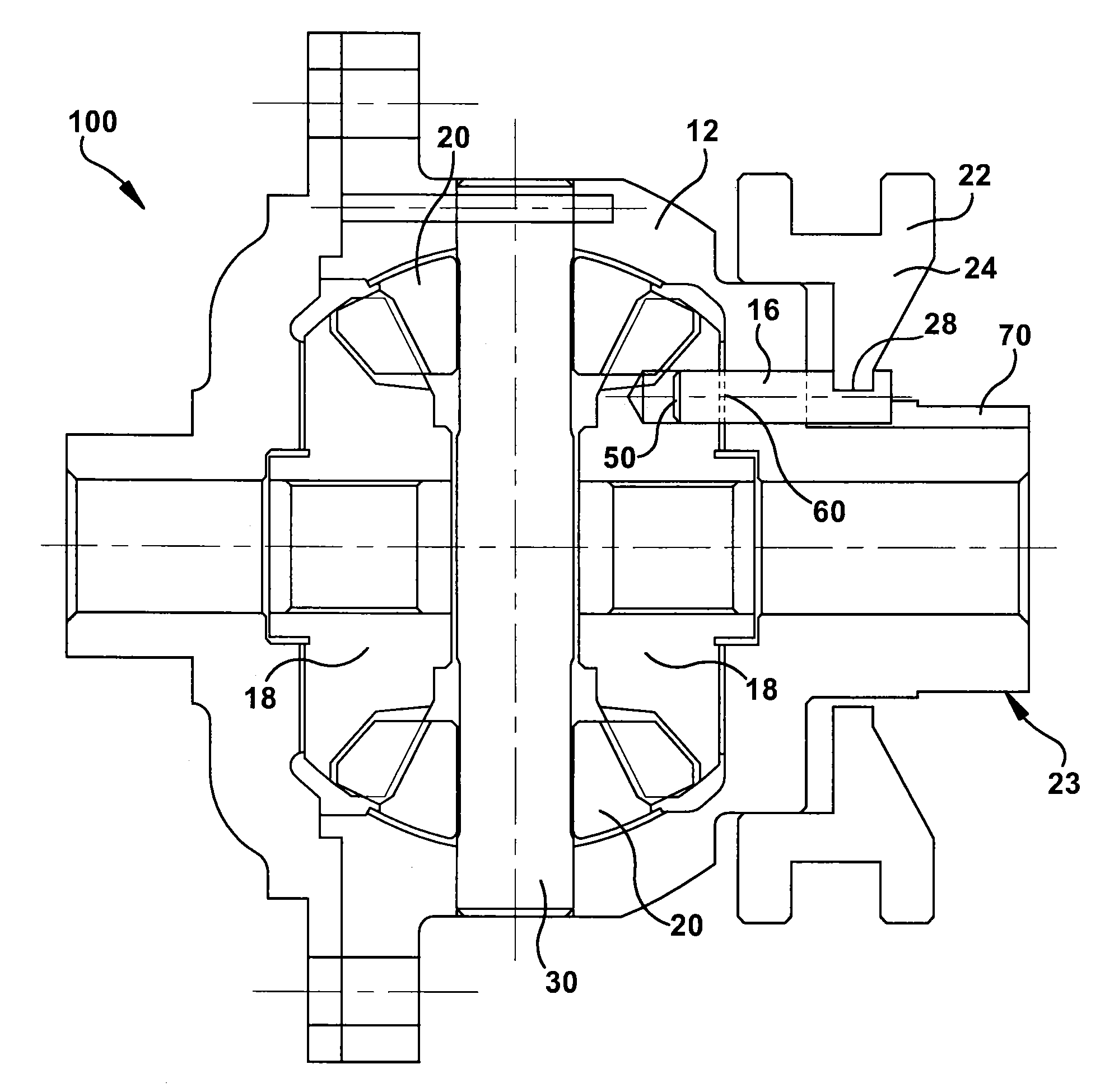
Locking differential having improved torque capacity
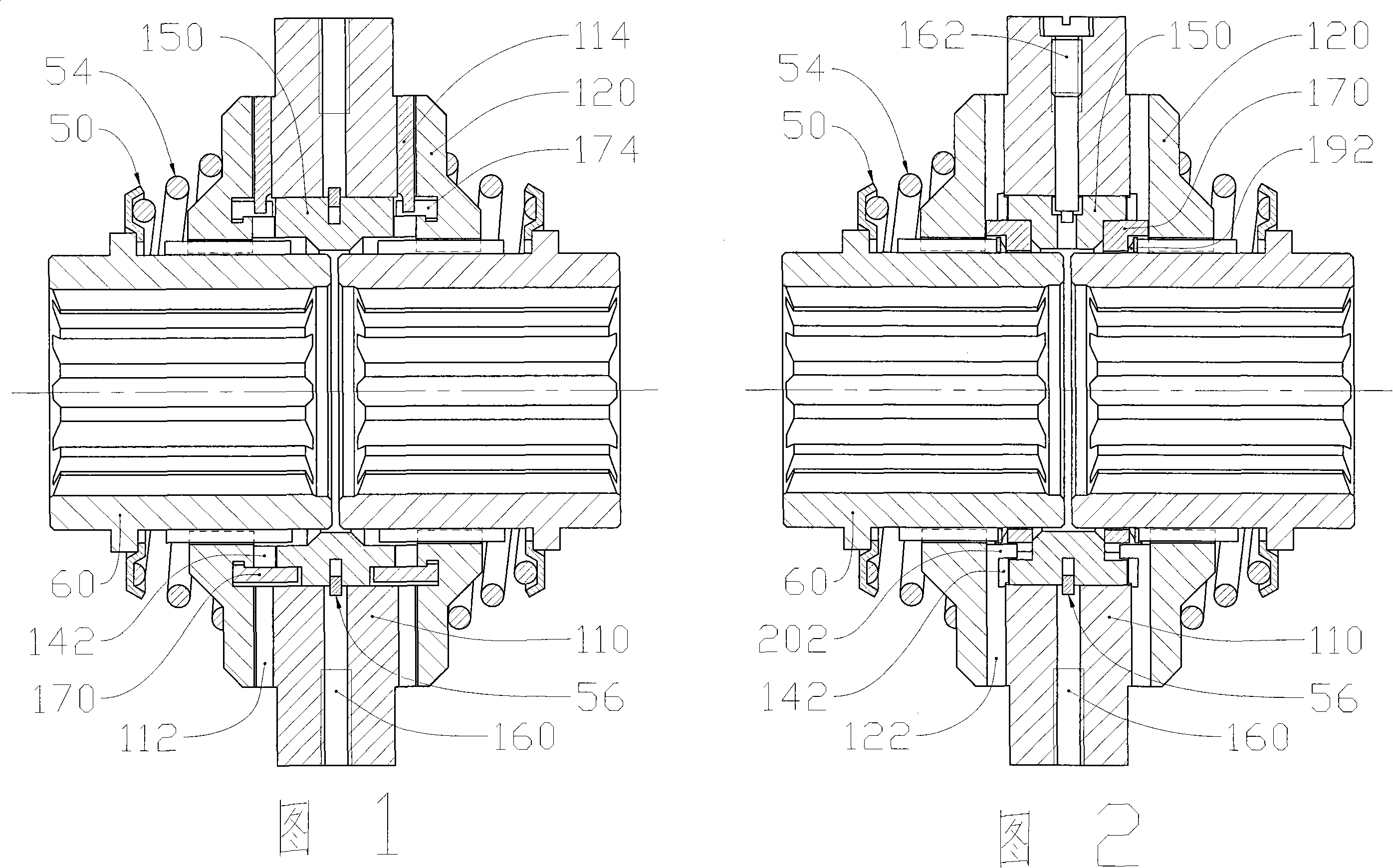
ActiveUS8146458B2Reduce edge stressIncreased torque densityDifferential gearingsControl devicesEngineeringLateral extension
A locking differential for an automotive vehicle including a housing and a differential mechanism supported in the housing. The differential mechanism includes a pair of clutch members disposed in spaced axial relationship with respect to each other wherein each clutch member includes a groove disposed in an opposed inwardly directing face that is adapted to receive a cross pin. Each of the grooves includes a working surface extending laterally relative to each other. Each of the working surfaces defines a screw involute surface such that the cross pin contacts the working surface along a line extending in the direction of the cross pin in the event of differential rotation of an axle half shaft relative to the housing. Alternatively, each of the working surfaces defines a slightly convex surface in one plane such that the cross pin contacts the working surface at a point defined thereon. In another embodiment, the working surface defines a slightly convex surface in two planes such that the cross pin contacts the working surface at a point defined thereon.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LTD
Differential having improved torque capacity and torque density
ActiveUS20110021306A1Lower resistanceGuaranteed uptimeDifferential gearingsControl devicesTorque densityLocking differential
A locking differential for an automotive vehicle including a housing and a differential mechanism supported in the housing. The differential mechanism includes a pair of clutch members where each of the clutch members presents an inwardly directed face. Each face includes a groove disposed in spacing relationship with respect to the other. A cross pin is received in the grooves and is operatively connected for rotation with the housing. The clutch members are axially moveable within the housing so that they may engage respective clutch members coupled to a pair of axle half shafts. Each of the grooves in the clutch members defines a first predetermined radius of curvature. The cross pin defines a second radius of curvature wherein the first radius of curvature of the groove is greater than the second radius of curvature of the cross pin such that contact between the cross pin and the groove defines a line extending along the axis of the cross pin.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LTD
Basic mode jaw self locking speed differential gear
InactiveCN101118005ACircumferential degrees of freedom constantEliminate impact wearDifferential gearingsControl devicesSelf limitingSelf locking
The present invention relates to a basic jaw type self-locking differential, which has the characteristics of no collision, high reliability, and long service life. The present invention is characterized in that a force transmission tooth and separating teeth and an accessory blocking tooth which are positioned on driven rings are connected as a whole; a self-limiting type blocking embedding mechanism is embedded by two embedding mechanisms of a force transmission embedding mechanism and a separation embedding mechanism under the differential condition, and axially positioned in the two mechanisms and radially positioned in the two mechanisms, between the two mechanisms or outside the two mechanisms, a lift angle of both sides blocking the working surface is formed to enough ensure the friction self-locking collided on the both sides and the stability of the blocking operating condition, in order that the lift angle has the capabilities that the adaptive axle base changes and the abrasion is automatically compensated, and the slipping mode of no collision is unvaryingly maintained between the separating teeth in the operating condition, two processes of the self-separating block process and the embedding return process are absolutely reliable, and has no relation to the stability of the spring parameter compacted by the driven rings, hence the problem that the driven rings on the both sides are synchronously separated is not a problem any longer. The processing of the differential is obviously improved, the difficulty of the assembly is largely reduced, and the performance, the service life, and the interchangeability, etc. are remarkably improved.
Owner:洪涛
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com