Patents
Literature
1017 results about "Base frequency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Base frequency is the standard frequency of your processor. So in that sense it still matters: the higher the base frequency, the faster your processor (when you consider same architectures, generation, etc.). That "actual" speed you mention, is in fact some sort of temporary system-induced overclock which we call...
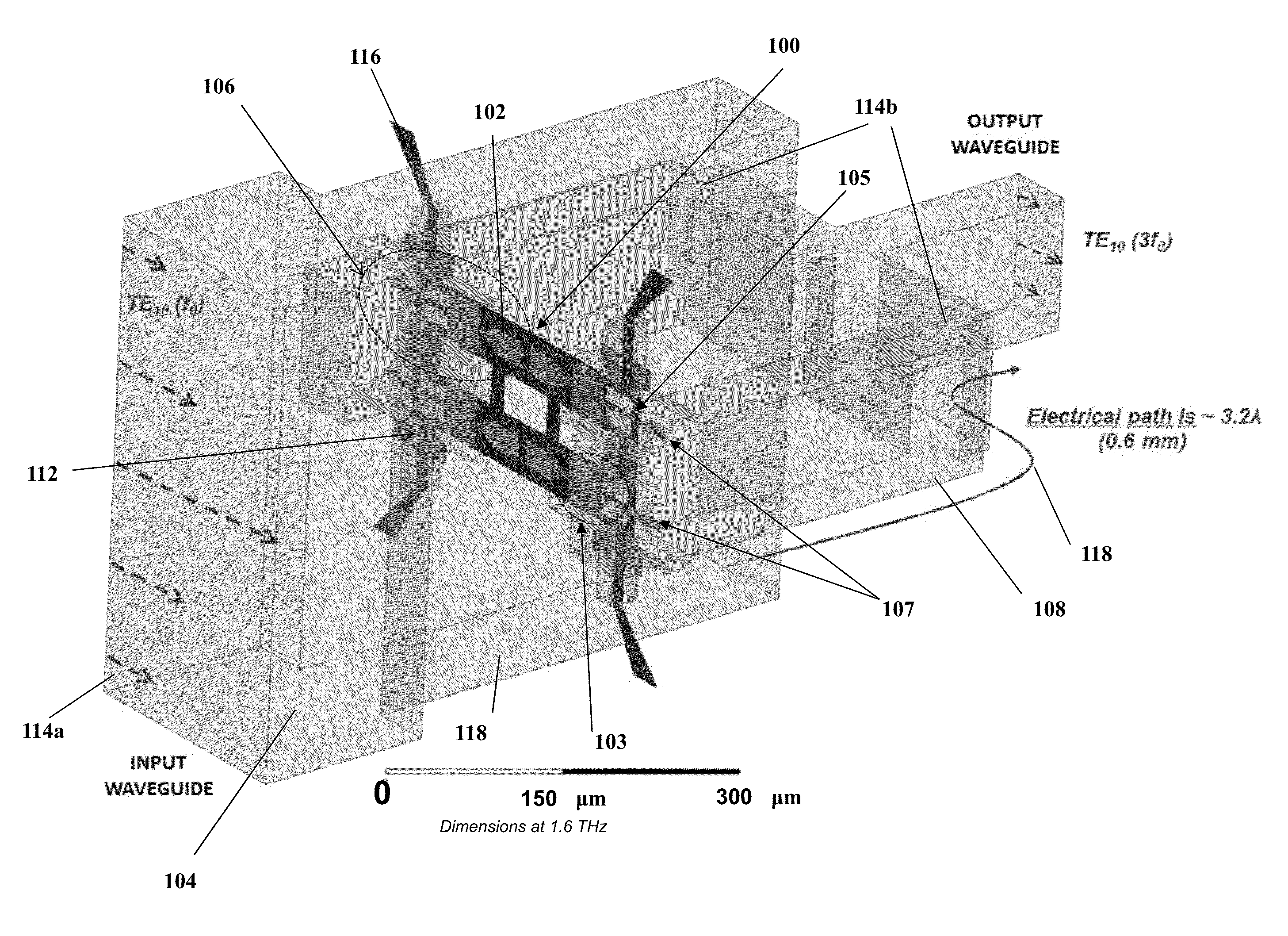
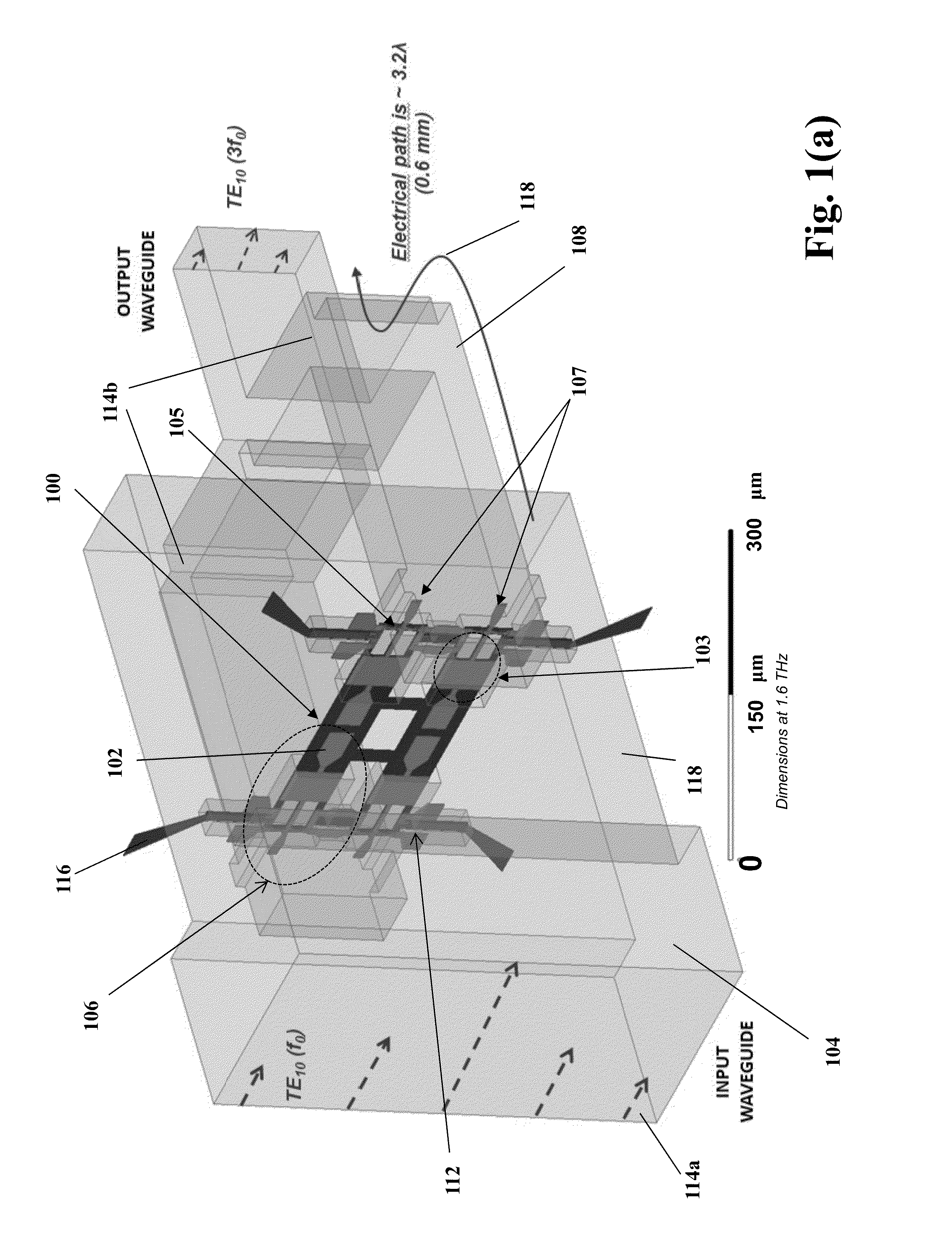
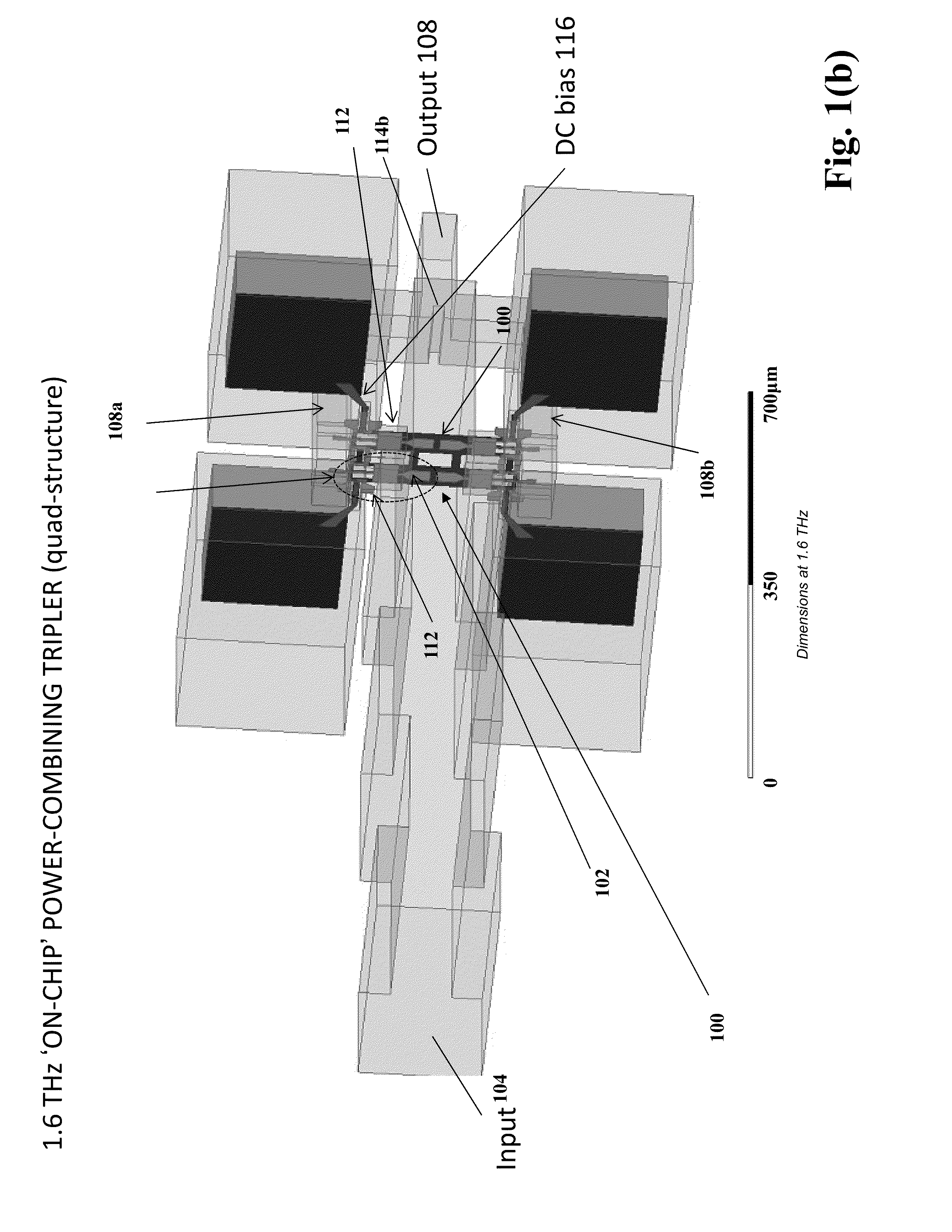
On-chip power-combining for high-power schottky diode based frequency multipliers
ActiveUS9143084B2Split evenlySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHarmonicFrequency multiplier
A novel MMIC on-chip power-combined frequency multiplier device and a method of fabricating the same, comprising two or more multiplying structures integrated on a single chip, wherein each of the integrated multiplying structures are electrically identical and each of the multiplying structures include one input antenna (E-probe) for receiving an input signal in the millimeter-wave, submillimeter-wave or terahertz frequency range inputted on the chip, a stripline based input matching network electrically connecting the input antennas to two or more Schottky diodes in a balanced configuration, two or more Schottky diodes that are used as nonlinear semiconductor devices to generate harmonics out of the input signal and produce the multiplied output signal, stripline based output matching networks for transmitting the output signal from the Schottky diodes to an output antenna, and an output antenna (E-probe) for transmitting the output signal off the chip into the output waveguide transmission line.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
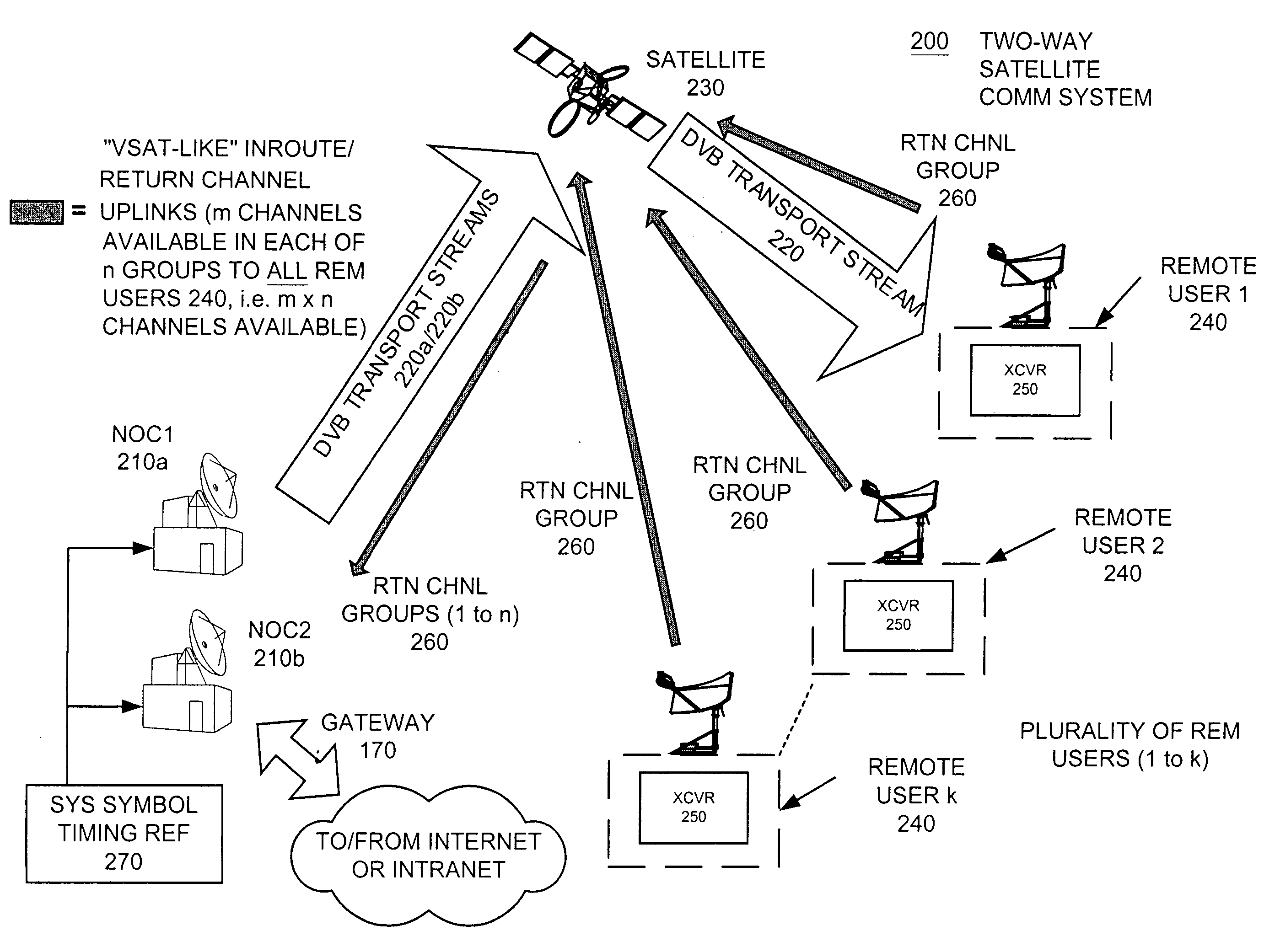
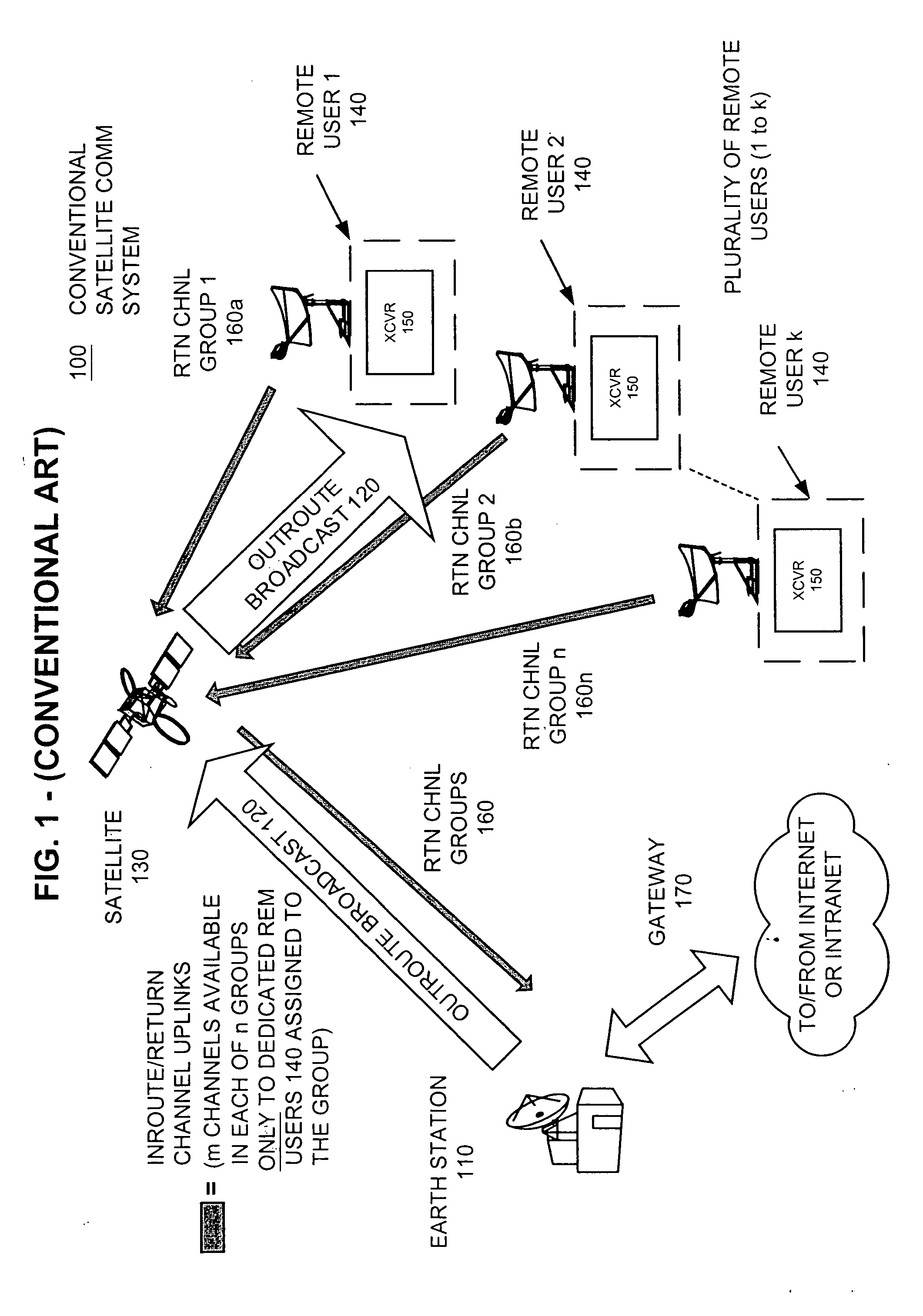
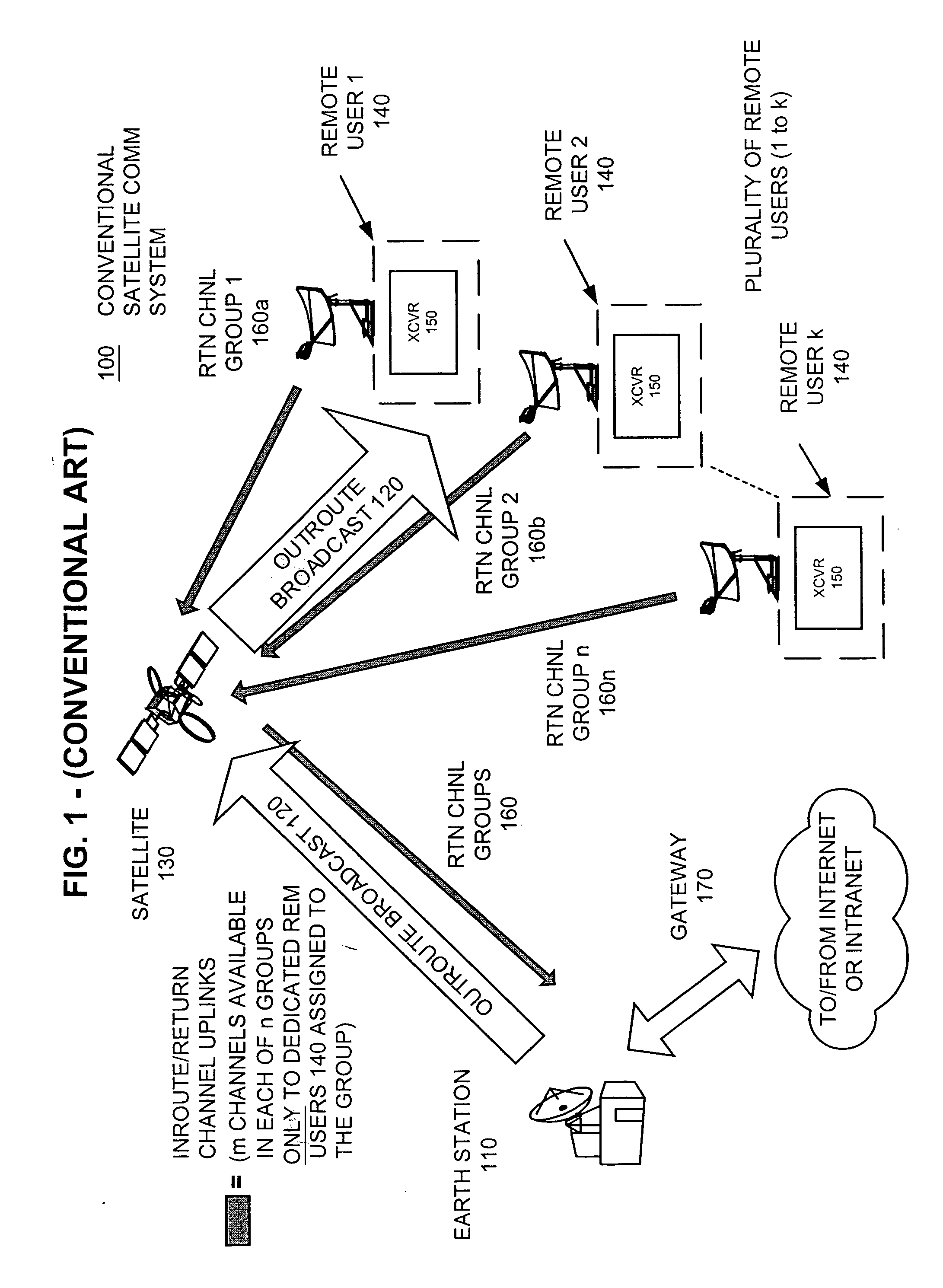
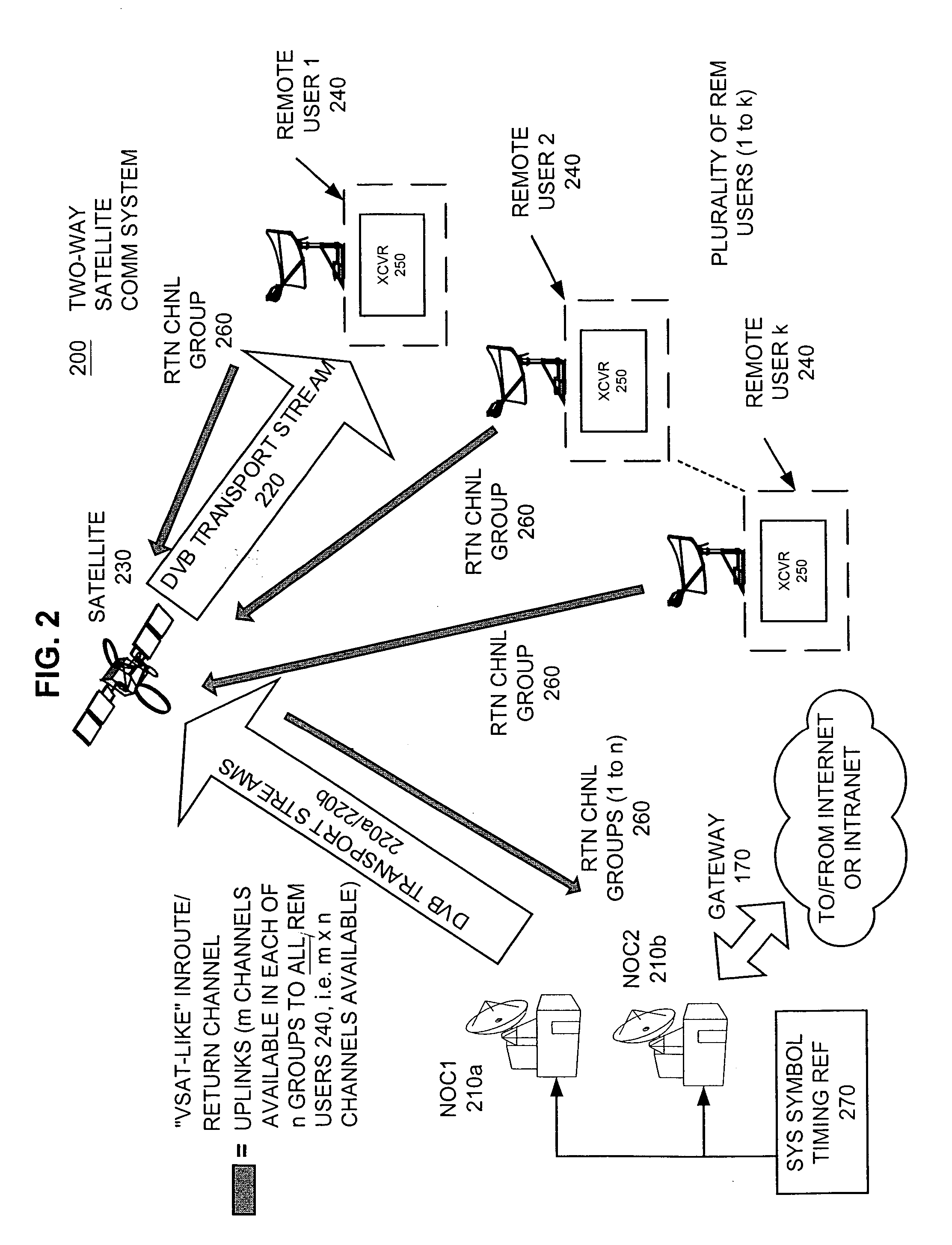
Apparatus and method for efficient TDMA bandwidth allocation for TCP/IP satellite-based networks
InactiveUS20050053033A1Balance traffic loadOptimize bandwidth allocationFrequency-division multiplex detailsAntenna supports/mountingsCommunications systemAloha
A communication system balances message traffic between return channel groups and within the groups, so that the user does not control the specific transmission frequency used. Uplink frequencies and bandwidths for the return channels are set by the system in a return channel control message in the broadcast signal so as to account for system and return channel group loading, and to account for user message backlogs. An initial transmission from a remote user may be made using an ALOHA-type burst signal that provides a message backlog to the control station, and is made on a frequency determined from a randomly weighted, load-based frequency selection process. The system, and not the individual users determine the frequency and channel allocations. For large backlogs or priority users, periodic bandwidth is provided. A method for balancing loads among and between groups of return channels in the communication system includes requesting return channel bandwidth in an uplink message from a remote user to a control station. The uplink message may include a both a backlog indicator and a bandwidth allocation request provided to a Network Operations Center (NOC) which can be used to set the return channel bandwidth and frequency for the remote uplink. A user message is transmitted on the designated return channel frequency using bandwidth allocated in accordance with the backlog indicator and a bandwidth allocation request so that traffic loads are maintained in balance between established return channel frequency groups, and within each return channel frequency group.
Owner:HUGHES NETWORK SYST
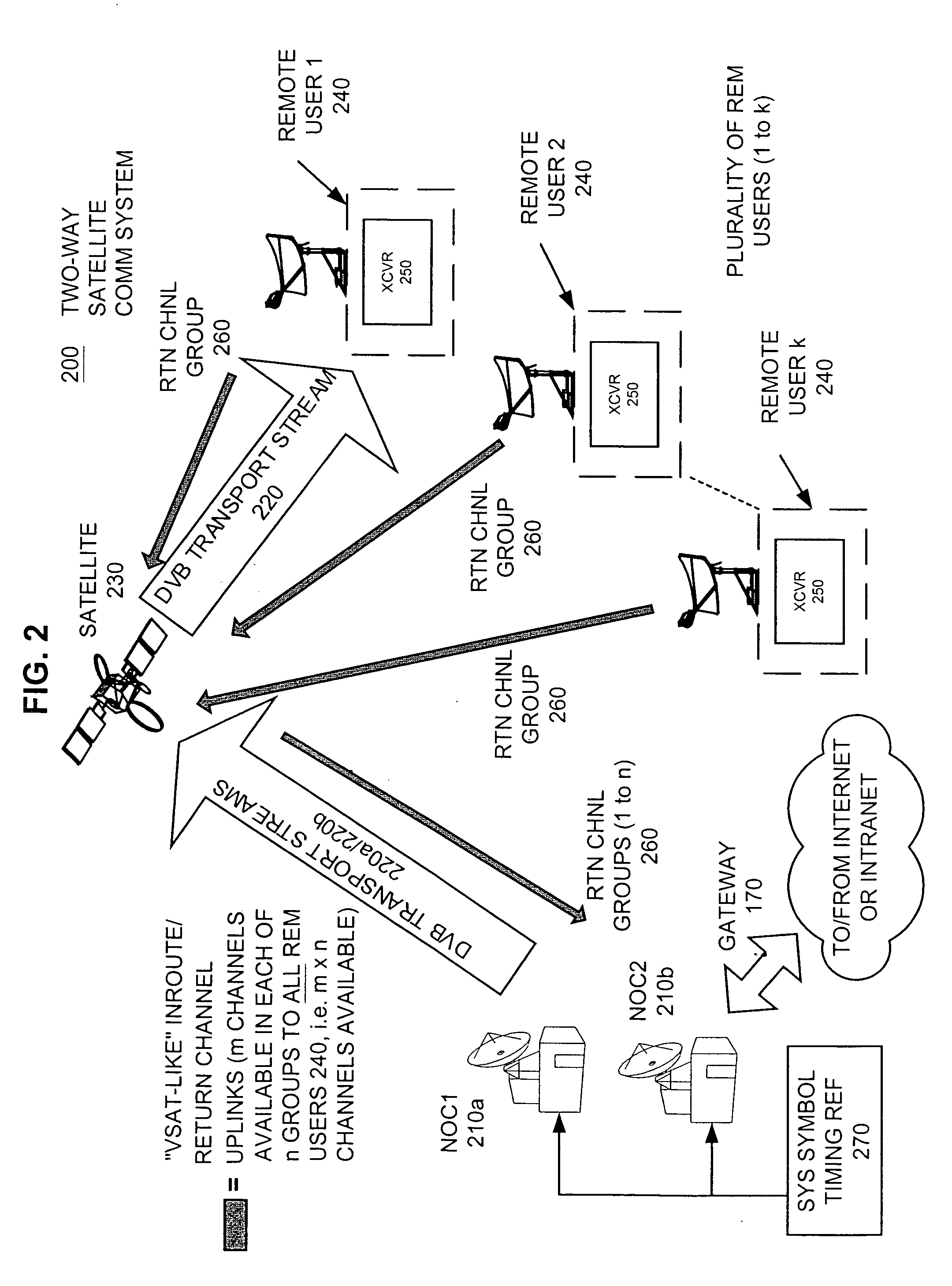
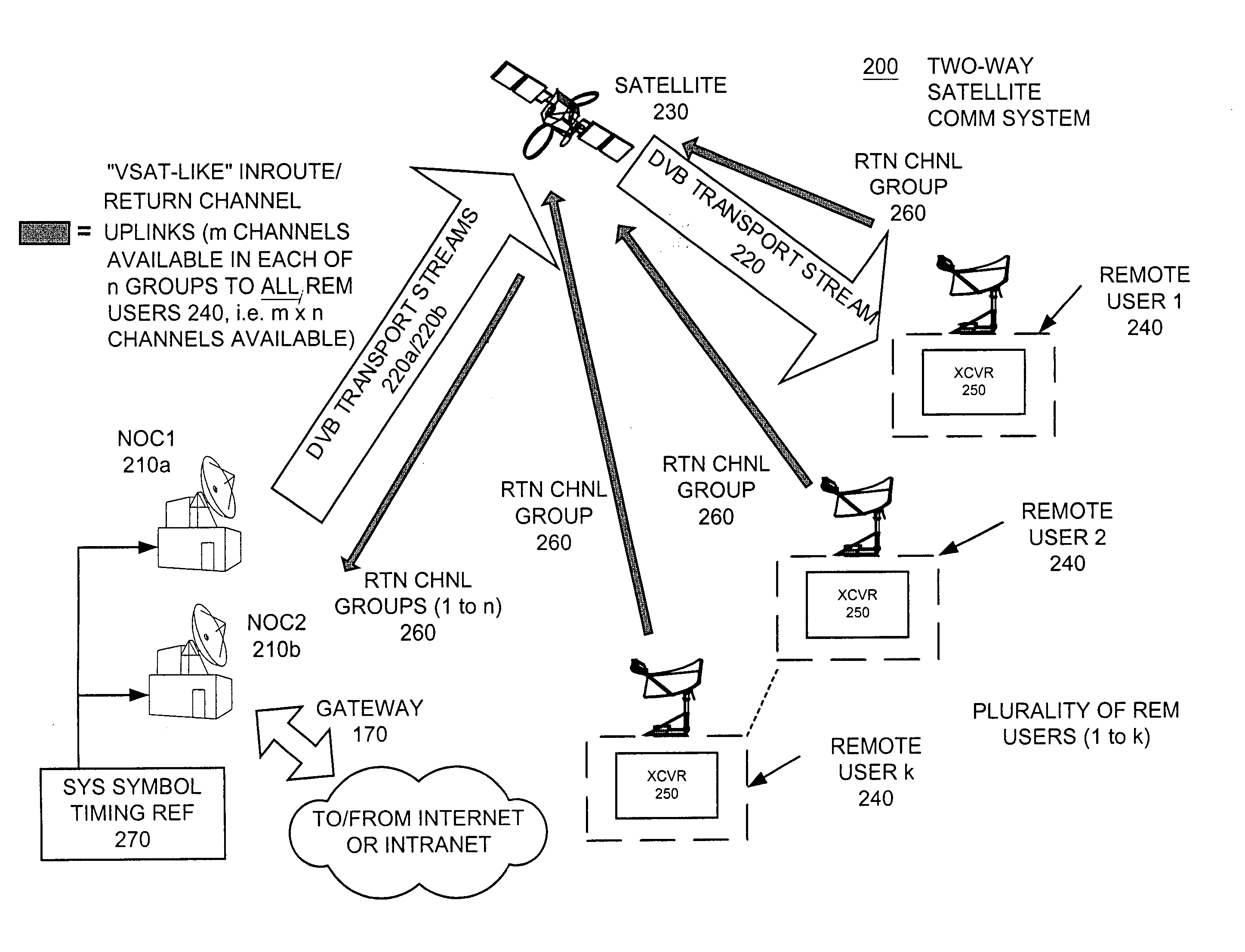
Apparatus and method for efficient TDMA bandwidth allocation for TCP/IP satellite-based networks
InactiveUS20050030932A1Optimized bandwidth allocation schemeBalance traffic loadError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemAloha
A communication system balances message traffic between return channel groups and within the groups, so that the user does not control the specific transmission frequency used. Uplink frequencies and bandwidths for the return channels are set by the system in a return channel control message in the broadcast signal so as to account for system and return channel group loading, and to account for user message backlogs. An initial transmission from a remote user may be made using an ALOHA-type burst signal that provides a message backlog to the control station, and is made on a frequency determined from a randomly weighted, load-based frequency selection process. The system, and not the individual users determine the frequency and channel allocations. For large backlogs or priority users, periodic bandwidth is provided. A method for balancing loads among and between groups of return channels in the communication system includes requesting return channel bandwidth in an uplink message from a remote user to a control station. The uplink message may include a both a backlog indicator and a bandwidth allocation request provided to a Network Operations Center (NOC) which can be used to set the return channel bandwidth and frequency for the remote uplink. A user message is transmitted on the designated return channel frequency using bandwidth allocated in accordance with the backlog indicator and a bandwidth allocation request so that traffic loads are maintained in balance between established return channel frequency groups, and within each return channel frequency group.
Owner:HUGHES NETWORK SYST
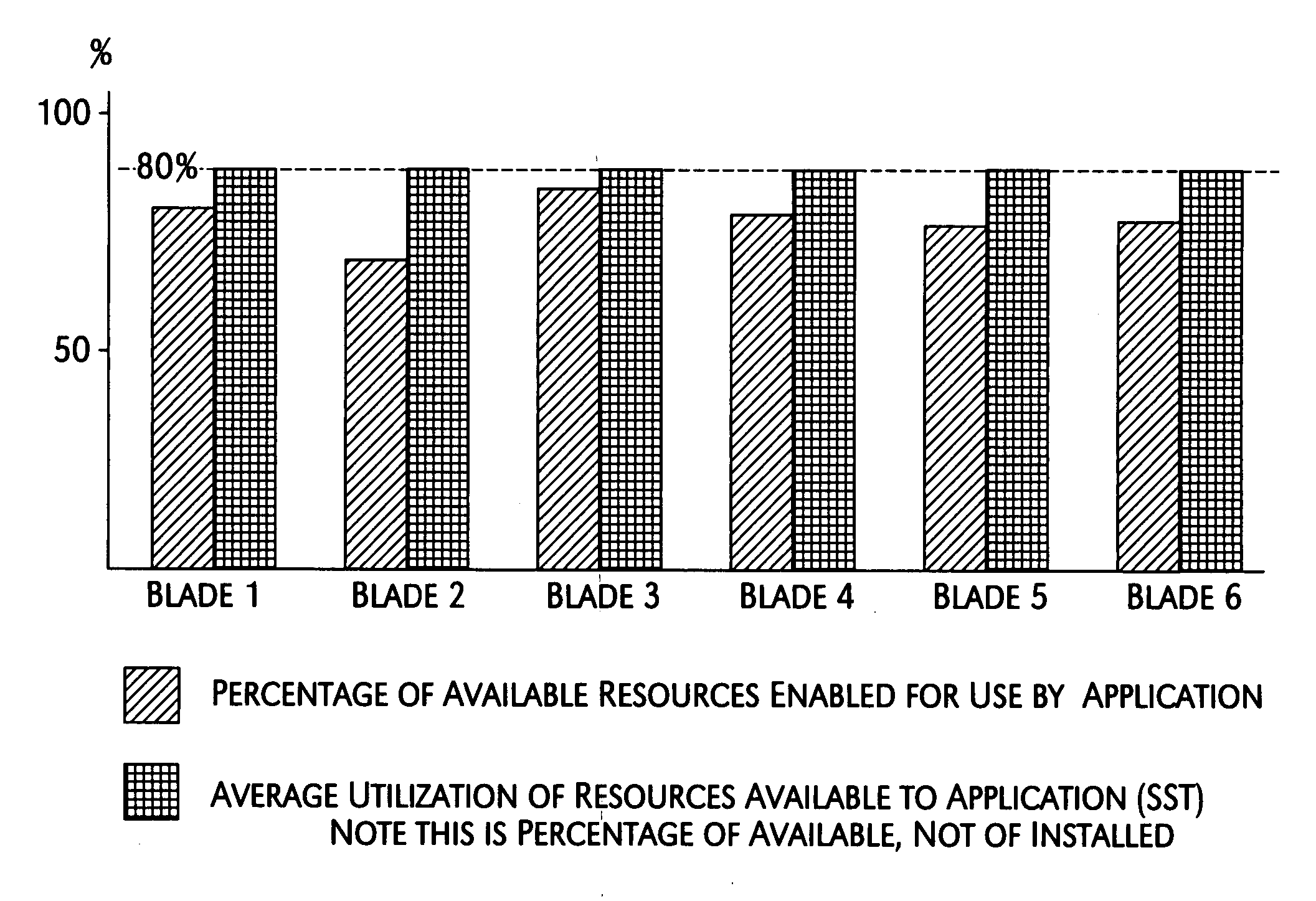
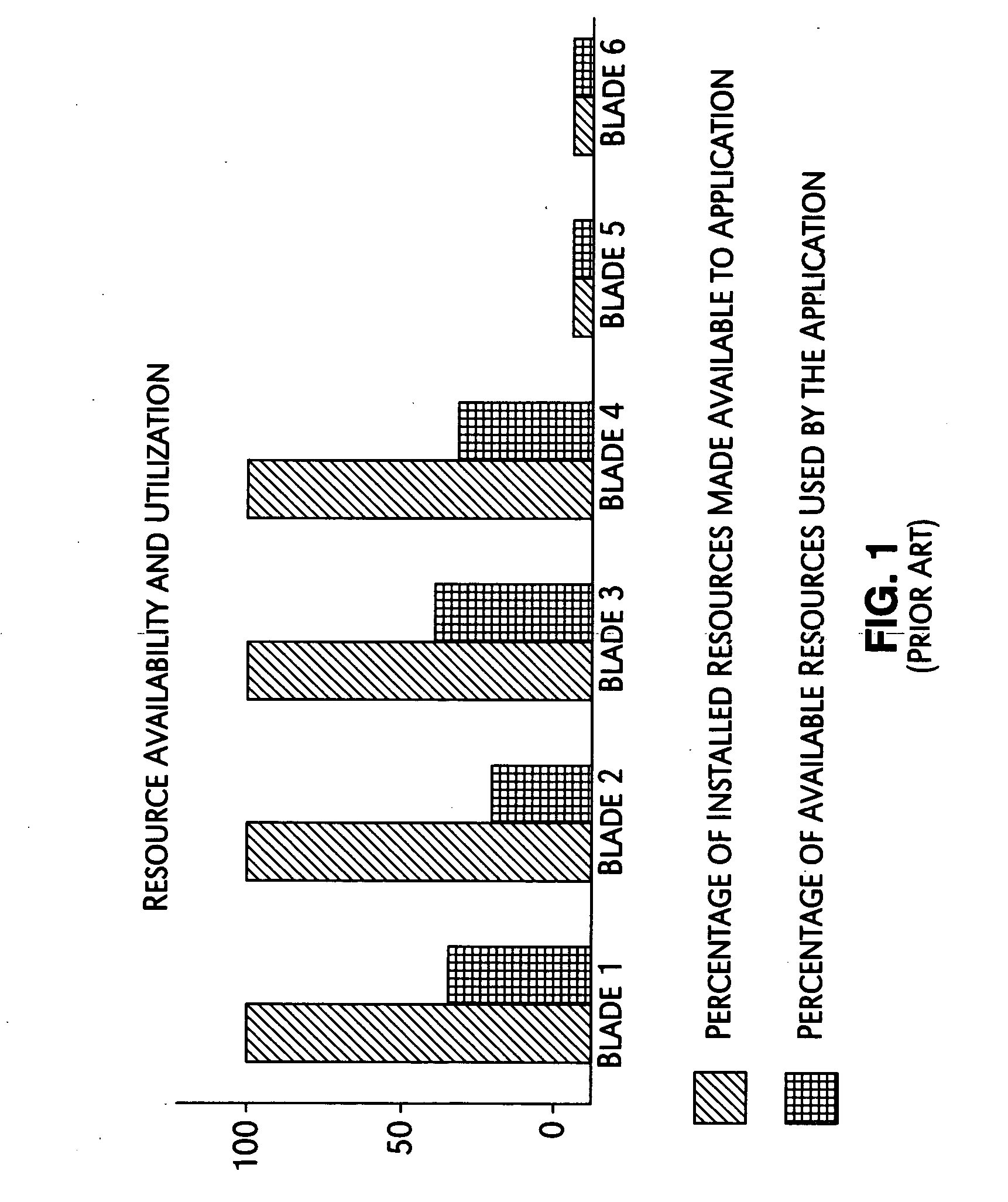
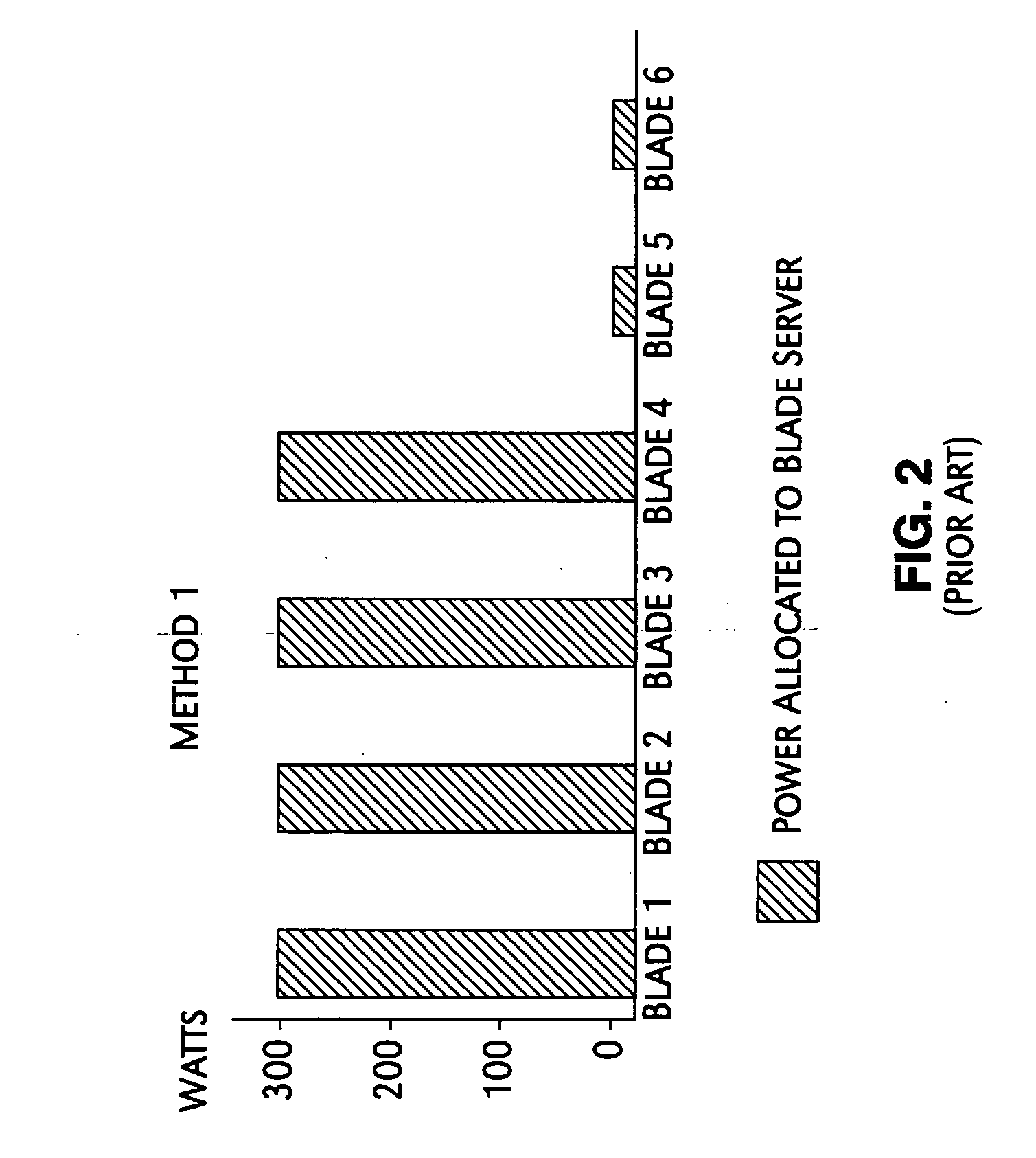
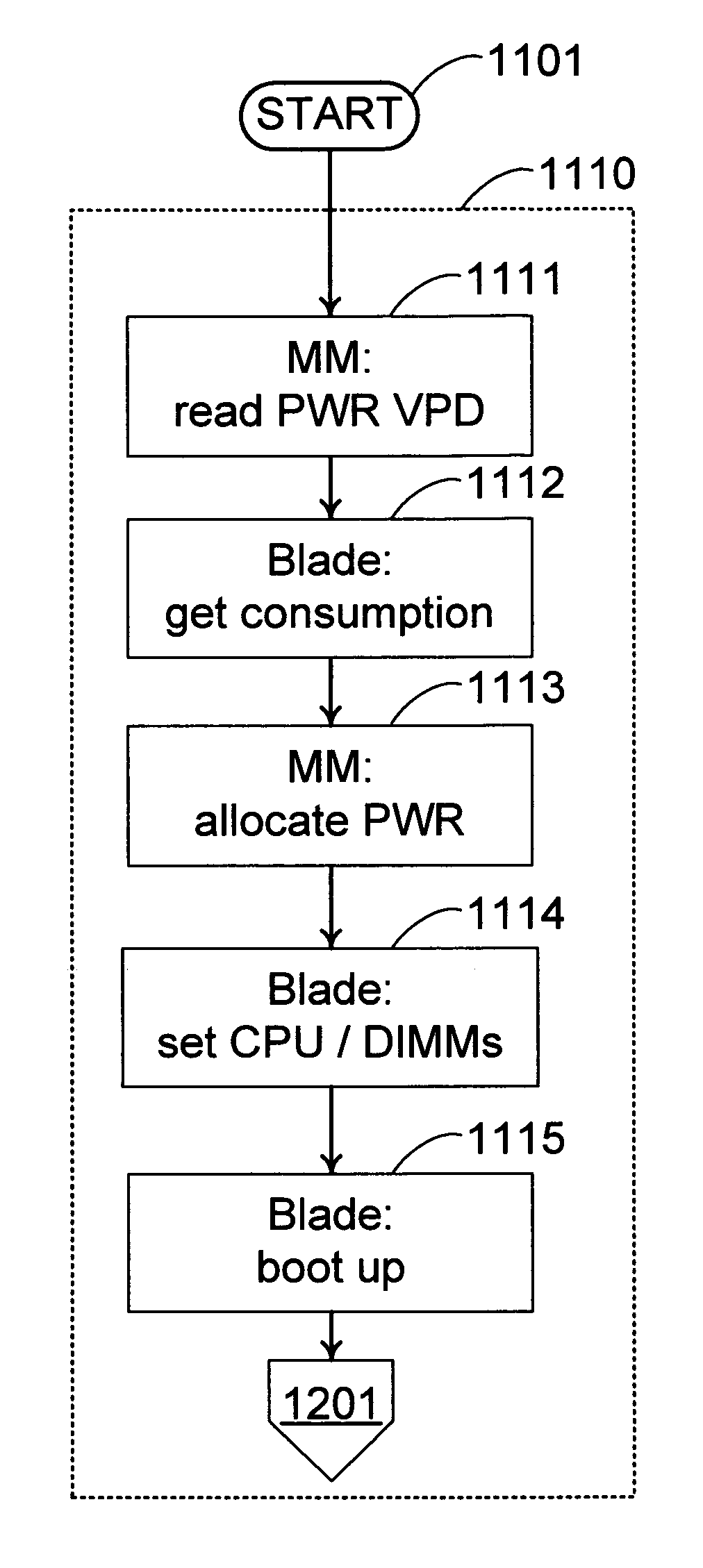
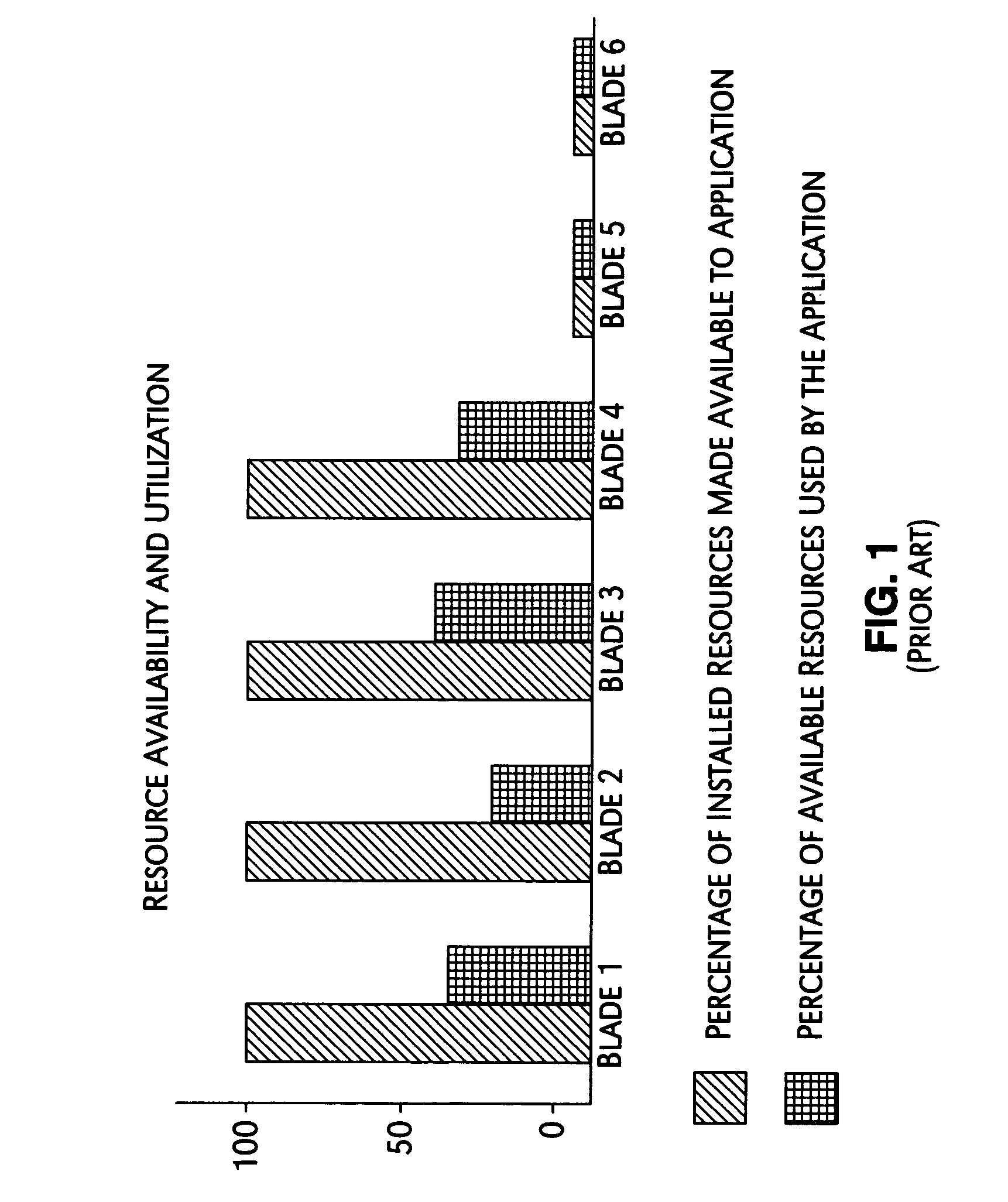
System and method for maximizing server utilization in a resource constrained environment
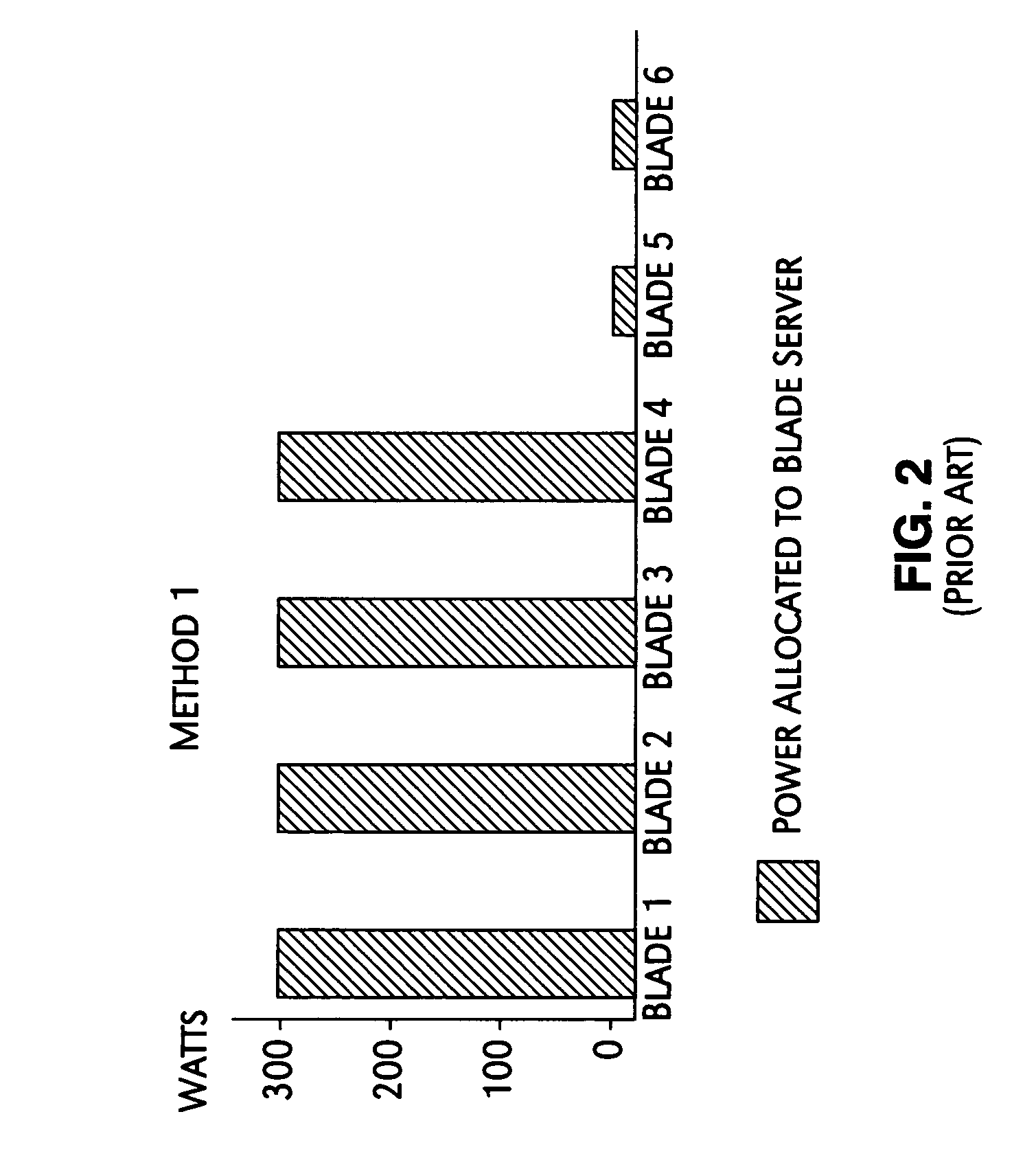
InactiveUS20070050644A1Control power consumptionReduce computing power requirementsEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementOperational systemBase frequency
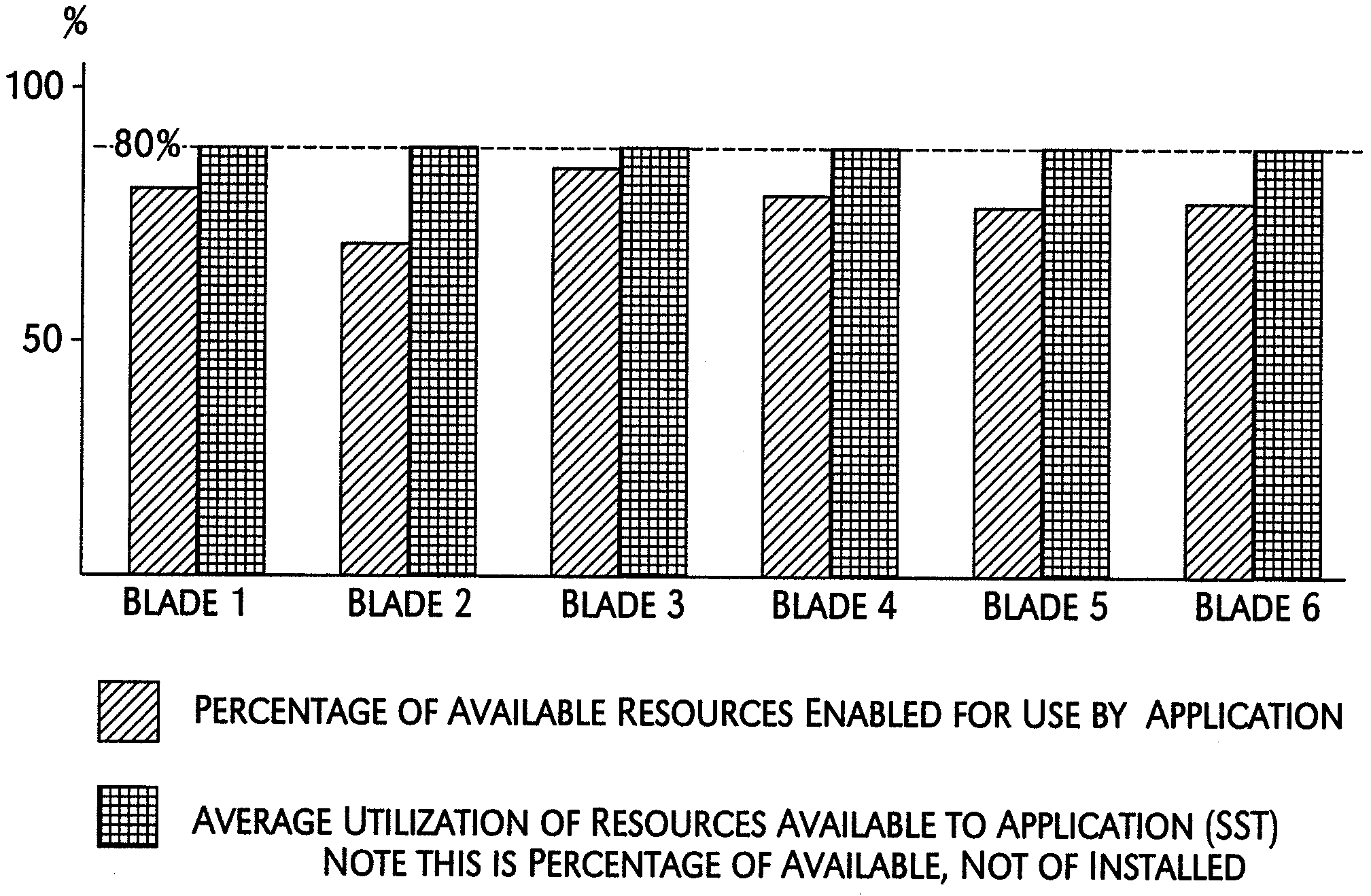
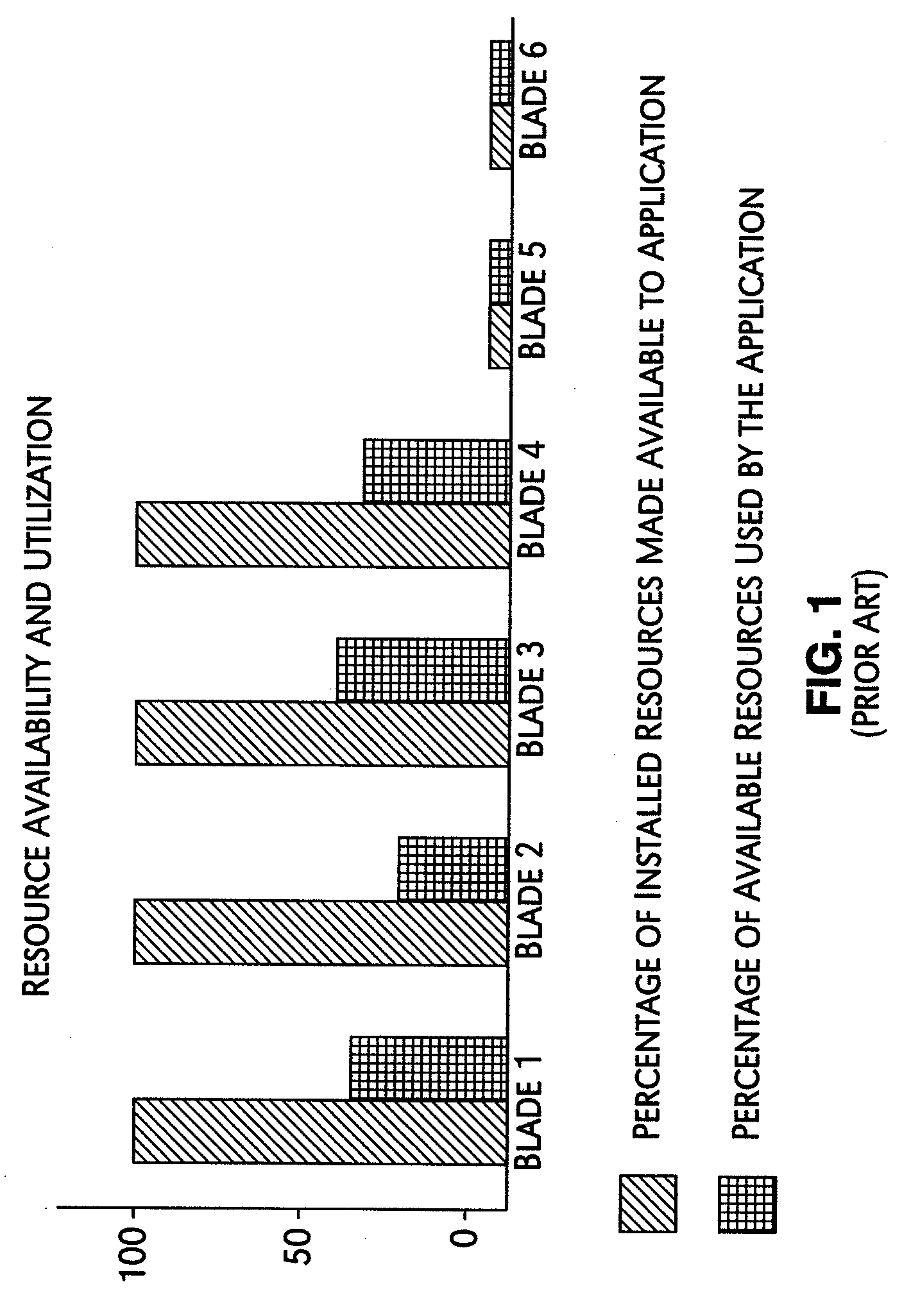
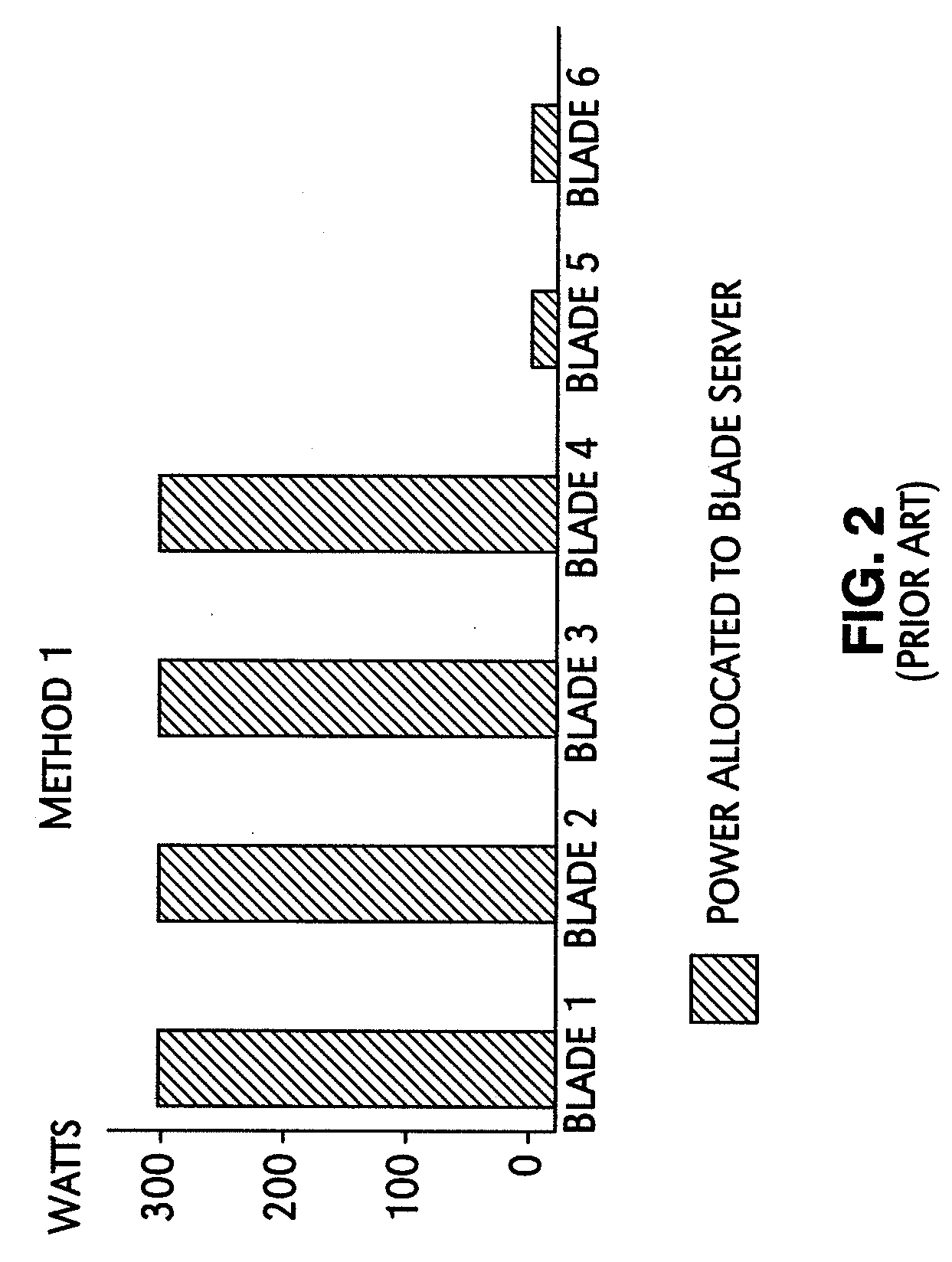
A mechanism for controlling the hardware resources on a blade server, and thereby limiting the power consumption of the blade server is disclosed. The enforceable hardware resources that are controlled include the base frequency of the central processing unit (CPU) as well as power to individual banks of physical memory, for example dual-inline memory modules (DIMMs). The hardware resources are tuned in dependence on actual server utilization such that applications running on the blade only have the allocated hardware resources available to them. Deactivated hardware resources are powered off and are so ‘hidden’ from the operating system when they are not required. In this manner, power consumption in the entire chassis can be managed such that all server blades can be powered on and operate at higher steady-state utilization. The utilization of the powered on resources in a blade center is also improved.
Owner:IBM CORP
System for maximizing server utilization in a resource constrained environment
InactiveUS20090044036A1Control power consumptionReduce computing power requirementsEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementOperational systemBase frequency
A mechanism for controlling the hardware resources on a blade server, and thereby limiting the power consumption of the blade server is disclosed. The enforceable hardware resources that are controlled include the base frequency of the central processing unit (CPU) as well as power to individual banks of physical memory, for example dual-inline memory modules (DIMMs). The hardware resources are tuned in dependence on actual server utilization such that applications running on the blade only have the allocated hardware resources available to them. Deactivated hardware resources are powered off and are so ‘hidden’ from the operating system when they are not required. In this manner, power consumption in the entire chassis can be managed such that all server blades can be powered on and operate at higher steady-state utilization. The utilization of the powered on resources in a blade center is also improved.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
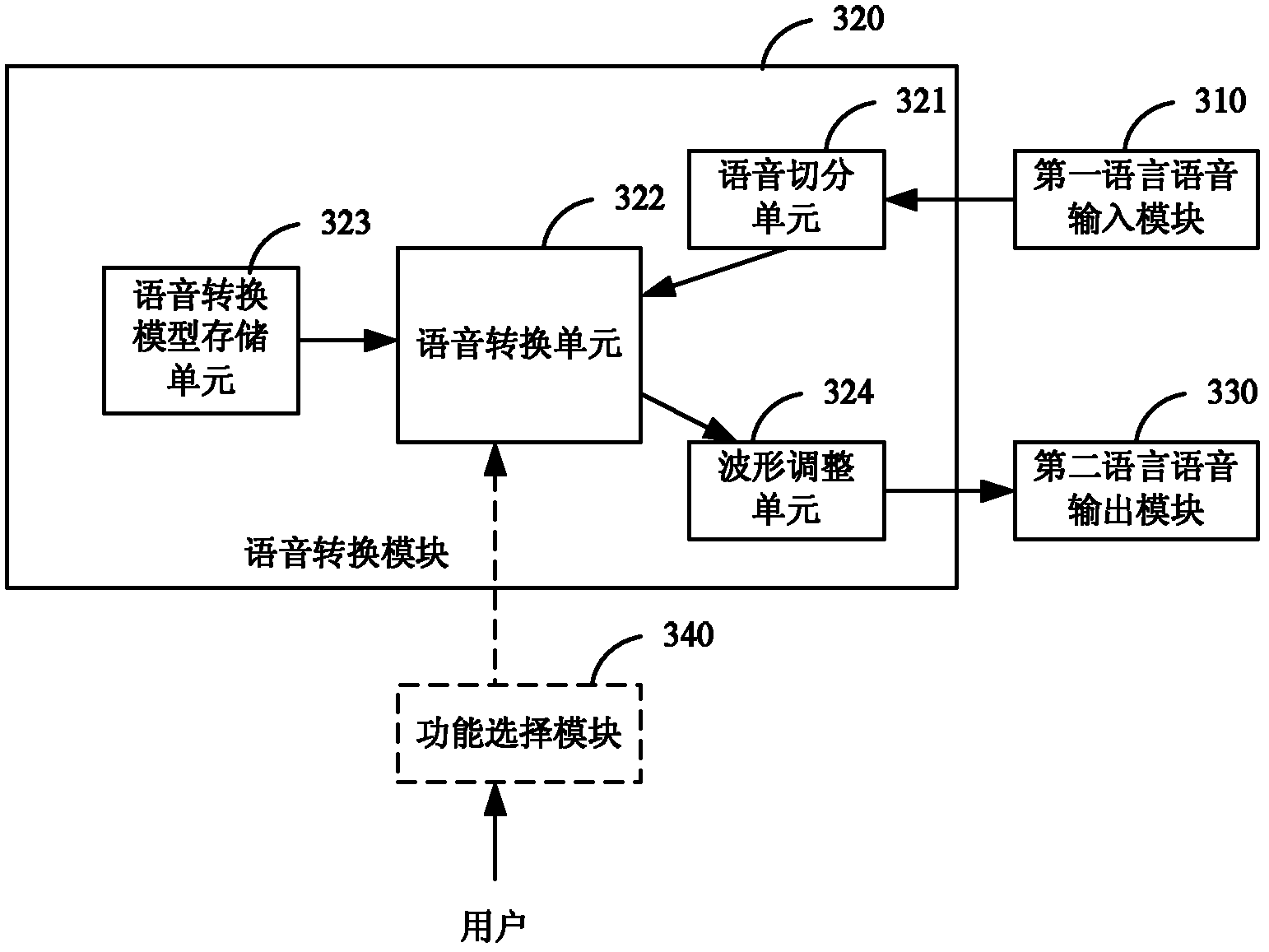
Method for building voice transformation model and method and system for voice transformation
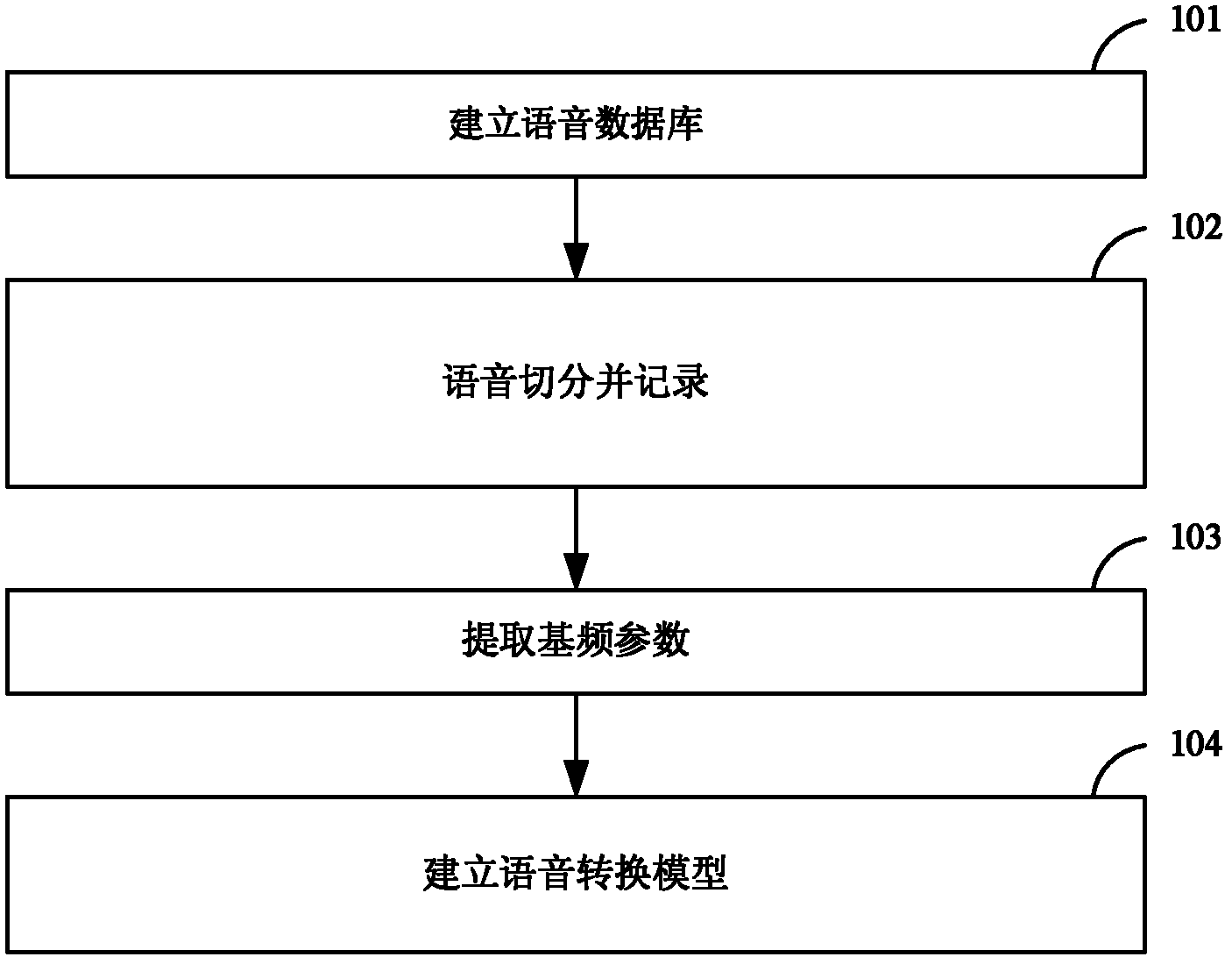
The invention discloses a method for building a voice transformation model and a method and device for achieving voice transformation between first language and second language. The method for transformation includes conducting voice segmentation on first language voice to be transformed to obtain at least one first language syllable, recording syllable duration parameter of each first language syllable and obtained by voice segmentation, extracting base frequency parameter of each first language syllable, determining base frequency parameter and syllable duration of each corresponding second language syllable according to the base frequency parameter and the syllable duration parameter of each first language syllable, adjusting voice waveform of the first corresponding language syllables by the base frequency parameter and the syllable duration according to each second language syllable to obtain voice waveform of each second language syllable and output the syllables. When the method is used for conducting voice transformation, voice quality of input voice and transformed output voice is basically consistent, and real-time transformation can be conducted.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Method for maximizing server utilization in a resource constrained environment
InactiveUS7461274B2Control power consumptionReduce computing power requirementsEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementOperational systemService utilization
A mechanism for controlling the hardware resources on a blade server, and thereby limiting the power consumption of the blade server is disclosed. The enforceable hardware resources that are controlled include the base frequency of the central processing unit (CPU) as well as power to individual banks of physical memory, for example dual-inline memory modules (DIMMs). The hardware resources are tuned in dependence on actual server utilization such that applications running on the blade only have the allocated hardware resources available to them. Deactivated hardware resources are powered off and are so ‘hidden’ from the operating system when they are not required. In this manner, power consumption in the entire chassis can be managed such that all server blades can be powered on and operate at higher steady-state utilization. The utilization of the powered on resources in a blade center is also improved.
Owner:IBM CORP
Speech synthetic method based on rhythm character
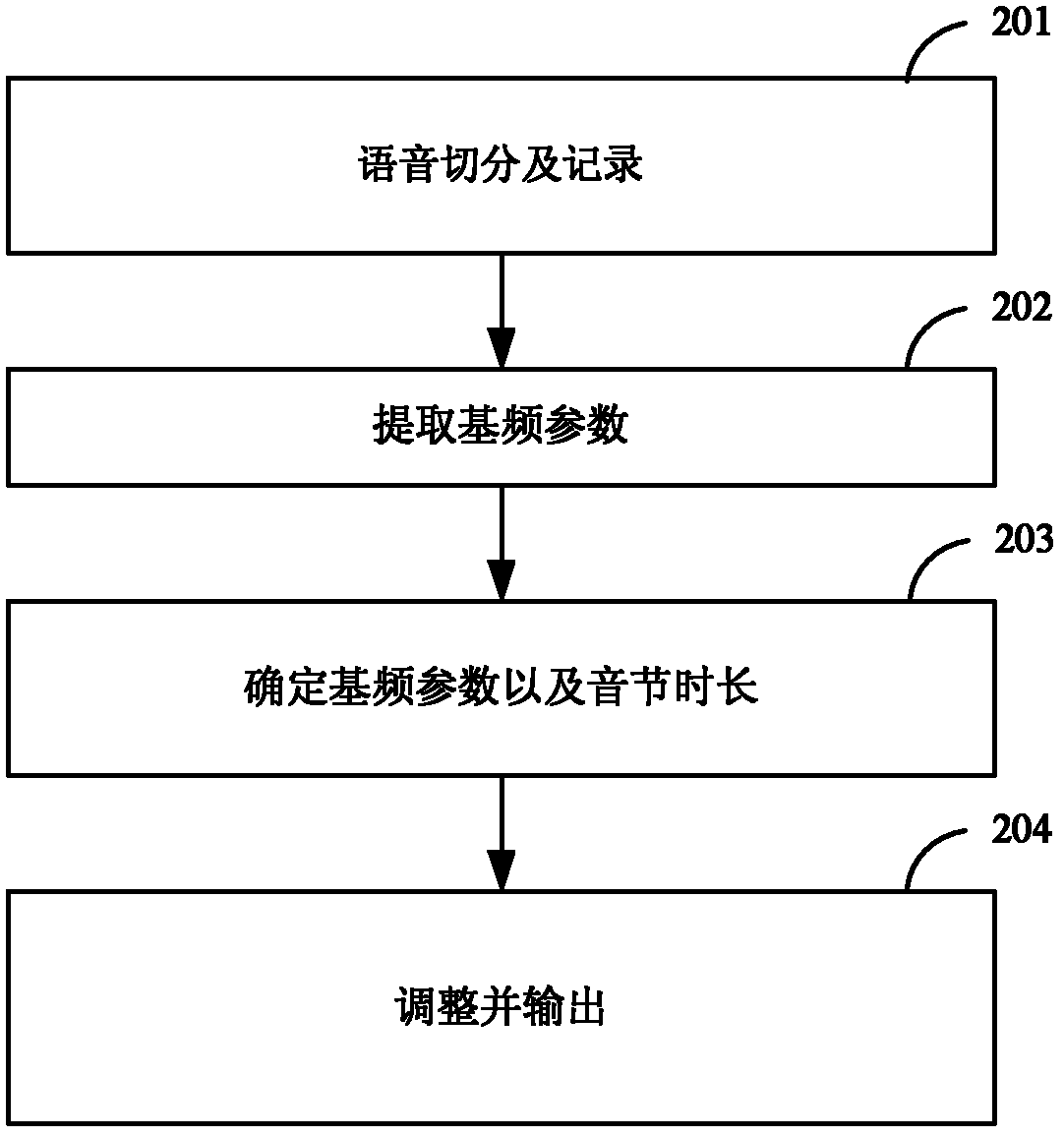
A method for synthesizing voice based on rhythm character includes text processing program formed by text standardizing step, rhythm structure analysis step and language treatment step, synthetic element selecting program formed by element confirming step, matching step, pasting-up step, optimizing and screening step; voice synthesization processing program formed by base frequency outline generating step of phrase unit, base frequency outline generating step of syllable unit and intonation superposing step.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV
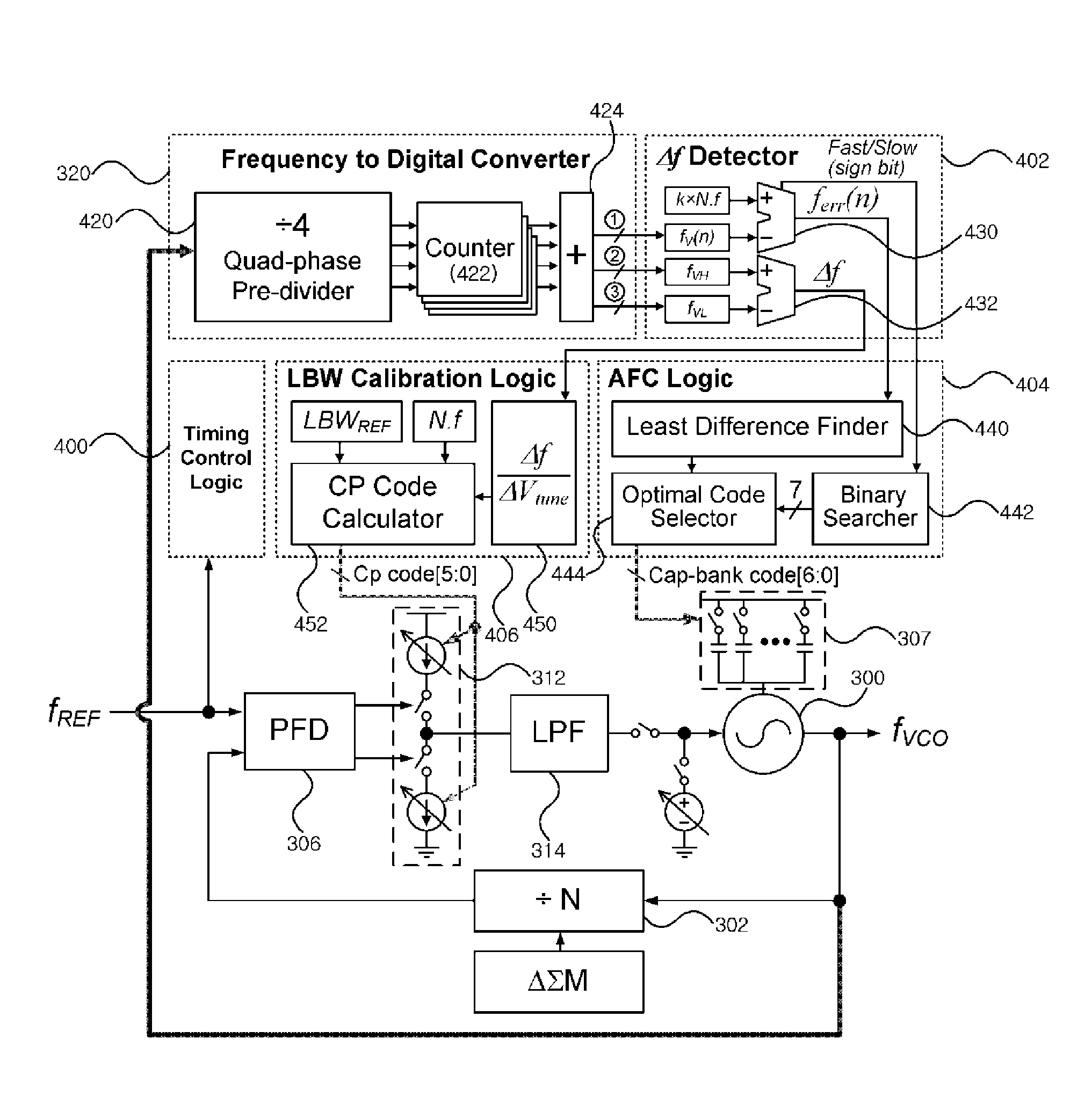
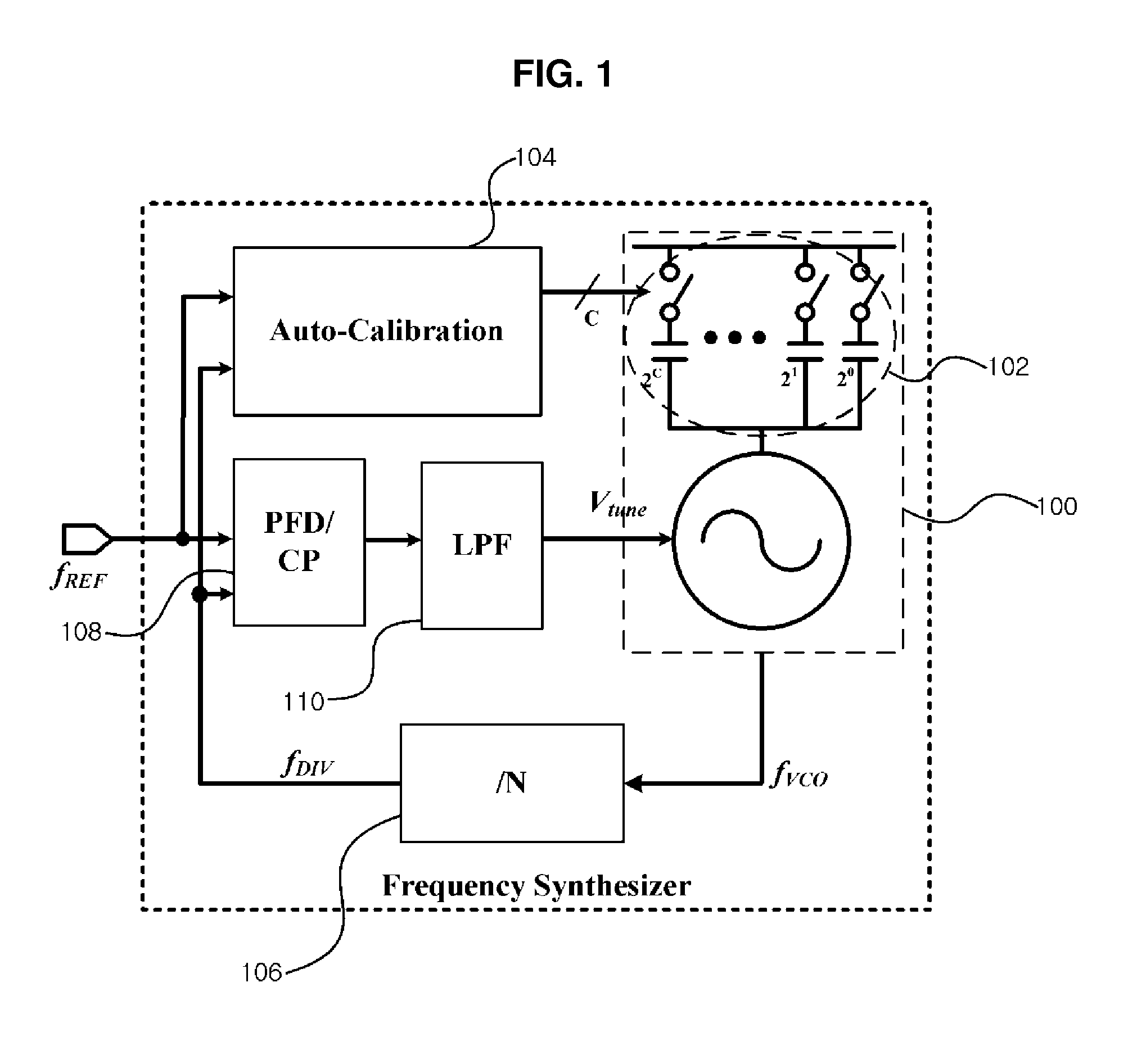
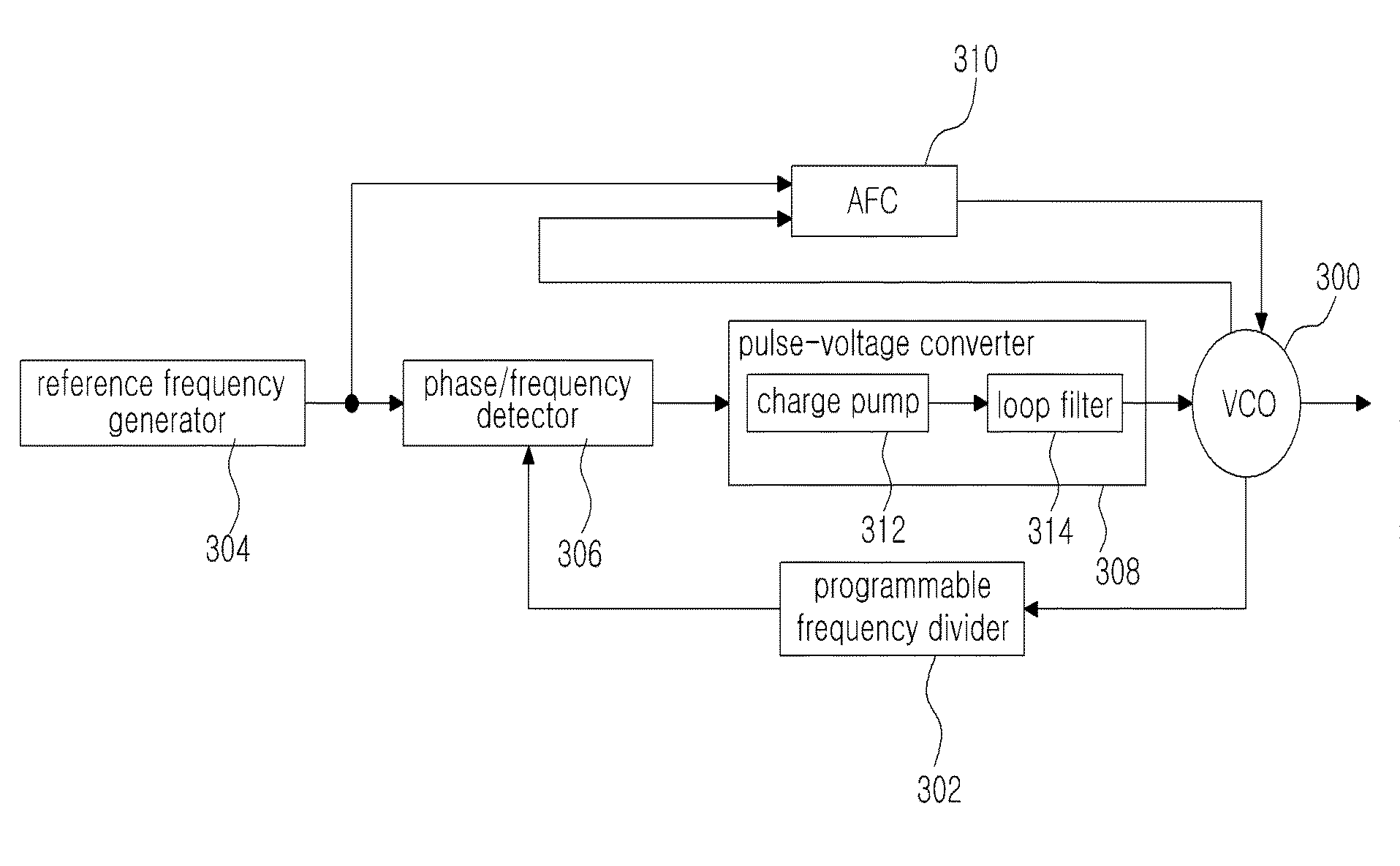
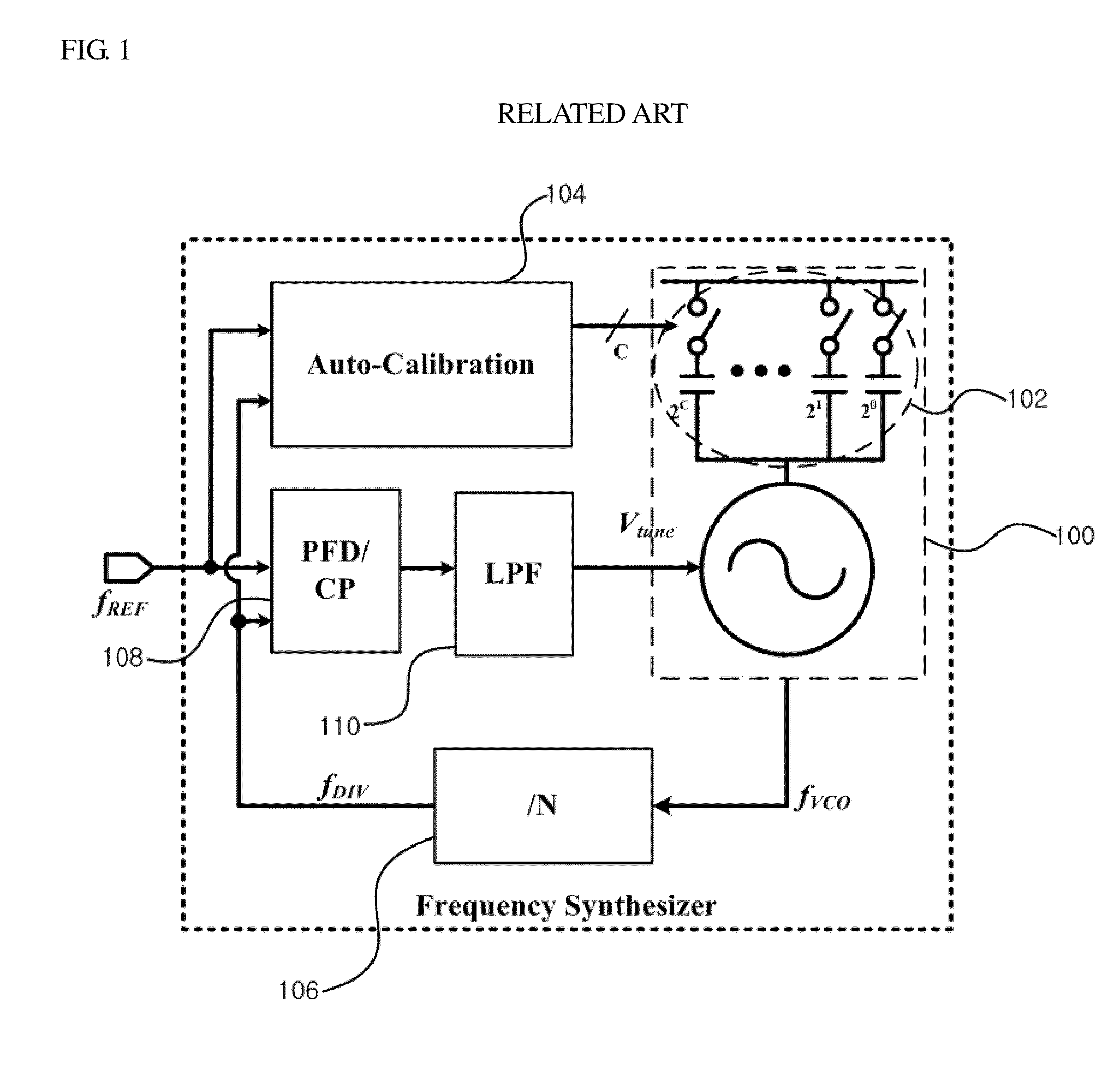
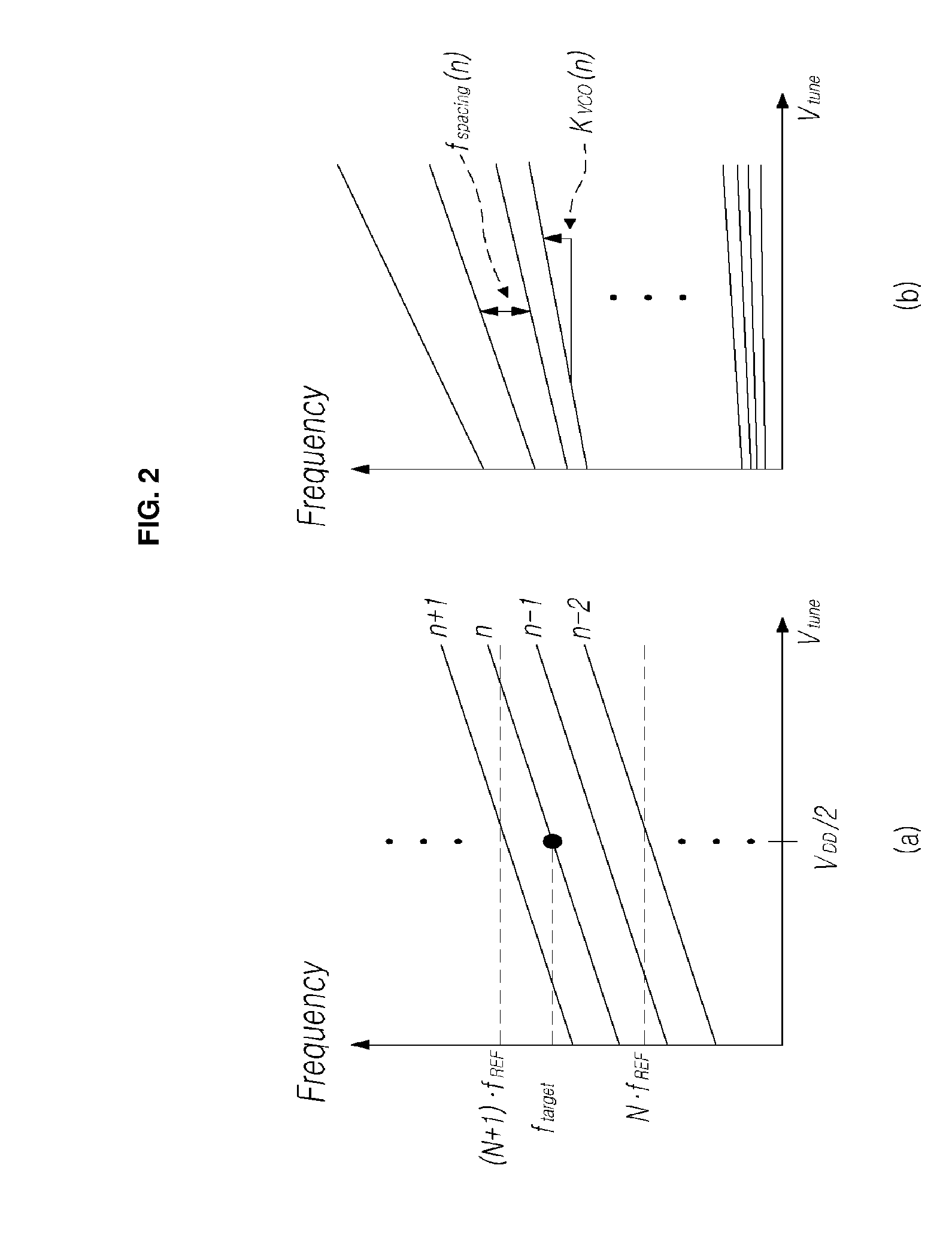
Frequency synthesizer and high-speed automatic calibration device therefor
ActiveUS8008956B1Reduce frequency calibration timeConstantPulse automatic controlOptimal controlLoop bandwidth
A frequency synthesizer and an automatic calibration device are disclosed. An automatic calibration device for a phase-locked loop based frequency synthesizer includes: a frequency-to-digital converter for converting a frequency of a signal outputted from a voltage controlled oscillator into a first digital value; a frequency difference detector for calculating a difference between the first digital value outputted from the frequency-to-digital converter and a second digital value corresponding to a target frequency; an automatic frequency calibration logic for selecting an optimal control code for a capacitor bank such that an output frequency of the voltage controlled oscillator is closer to the target frequency; and a loop bandwidth calibration logic for tuning a charge pump gain such that a loop bandwidth is kept constant in the optimal control code using the frequency-to-digital converter. Thus, the calibration speed can be increased, and the loop bandwidth can be kept constant within the output frequency range.
Owner:KWANGWOON UNIV IND ACADEMIC COLLABORATION FOUND
Inductively coupled stress/strain sensor
InactiveUS6912911B2Change relationshipForce measurement by measuring magnetic property varationWork measurementMagnetostrictionCouple stress
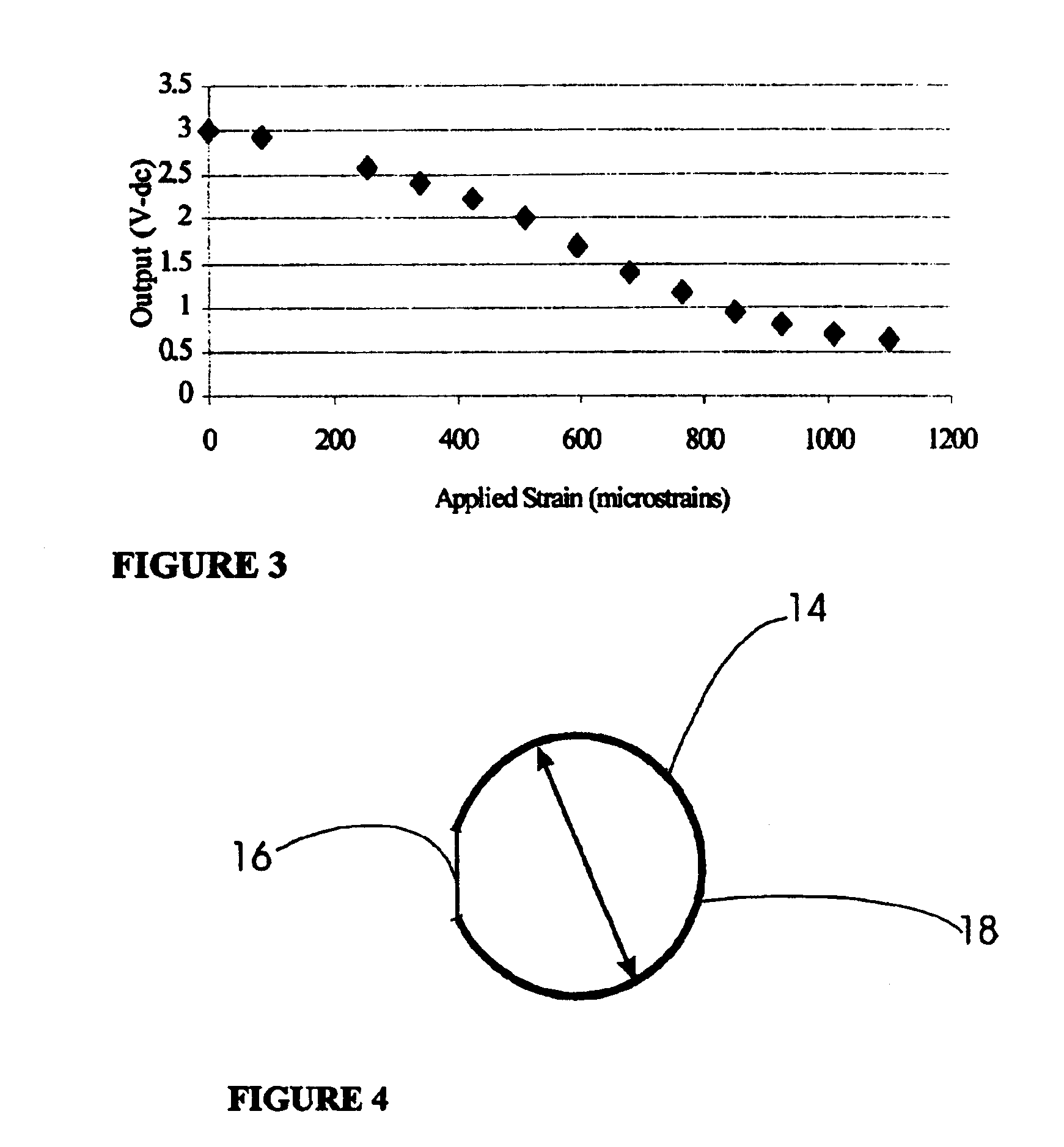
An improved method of sensing strain allows measurements of stress, torque, vibration and other loads imposed on a body without physical contact between the body / sensor and the monitoring equipment. An induction loop is at least partially comprised of a magnetostrictive material with a non-linear current-voltage relationship. An excitation device such as a coil is used to induce an AC response in the sensor. The non-linear response to the induced current is received by a sensing device such as a sensing coil, and the output thereof is filtered. The excitation device and sensing device are located in operative proximity to the sensor, but need not be in contact therewith, allowing easy measurement in small spaces, under harsh conditions, or of moving bodies such as drive shafts. The non-linear response of the sensor induces easily detectable harmonics of the base frequency of excitation. These harmonics may advantageously be measured as well.
Owner:SENSORTEX
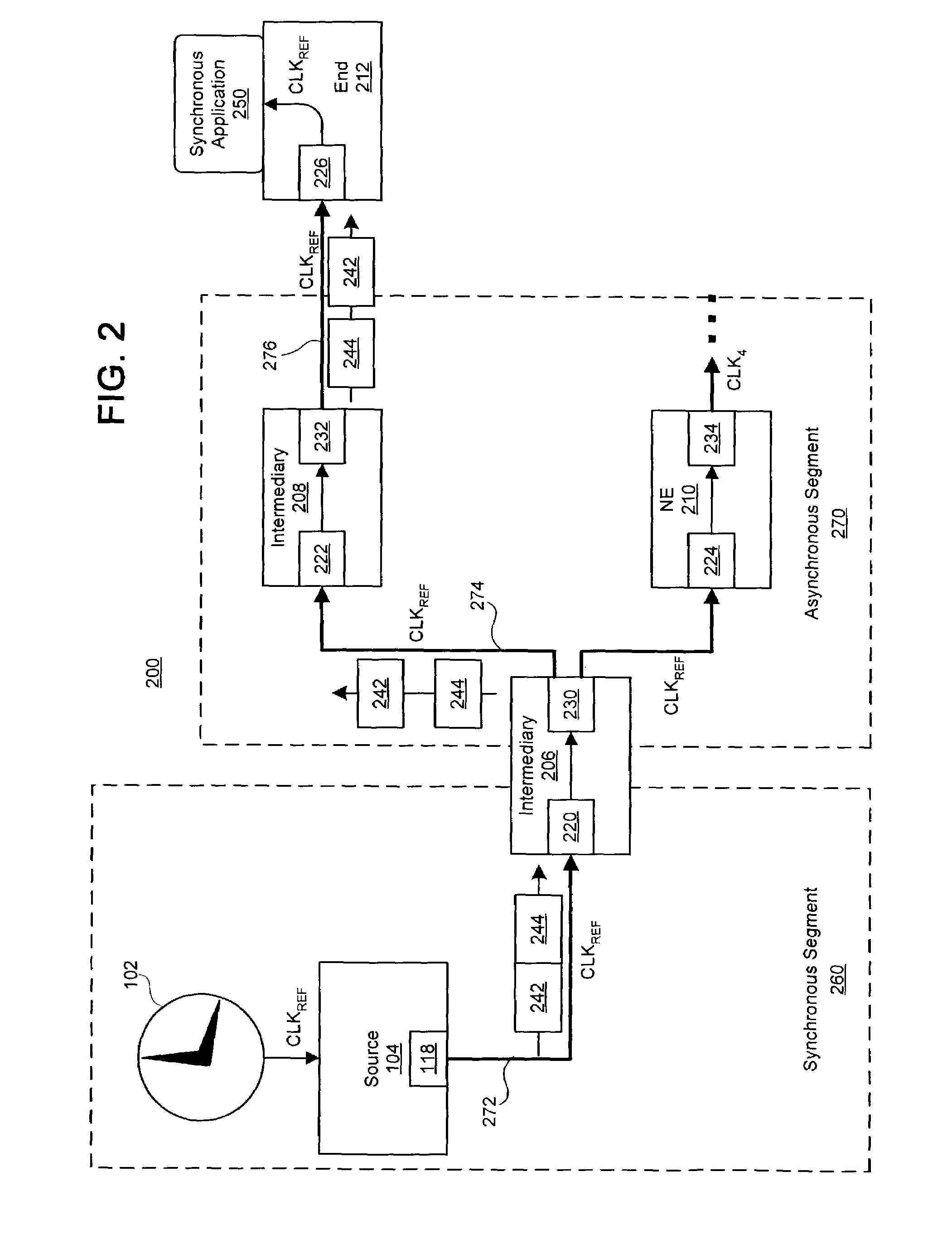
Method and system for link-based clock synchronization in asynchronous networks
InactiveUS7483450B1Guaranteed maximum utilizationTime-division multiplexSynchronising arrangementAsynchronous networkPhysical layer
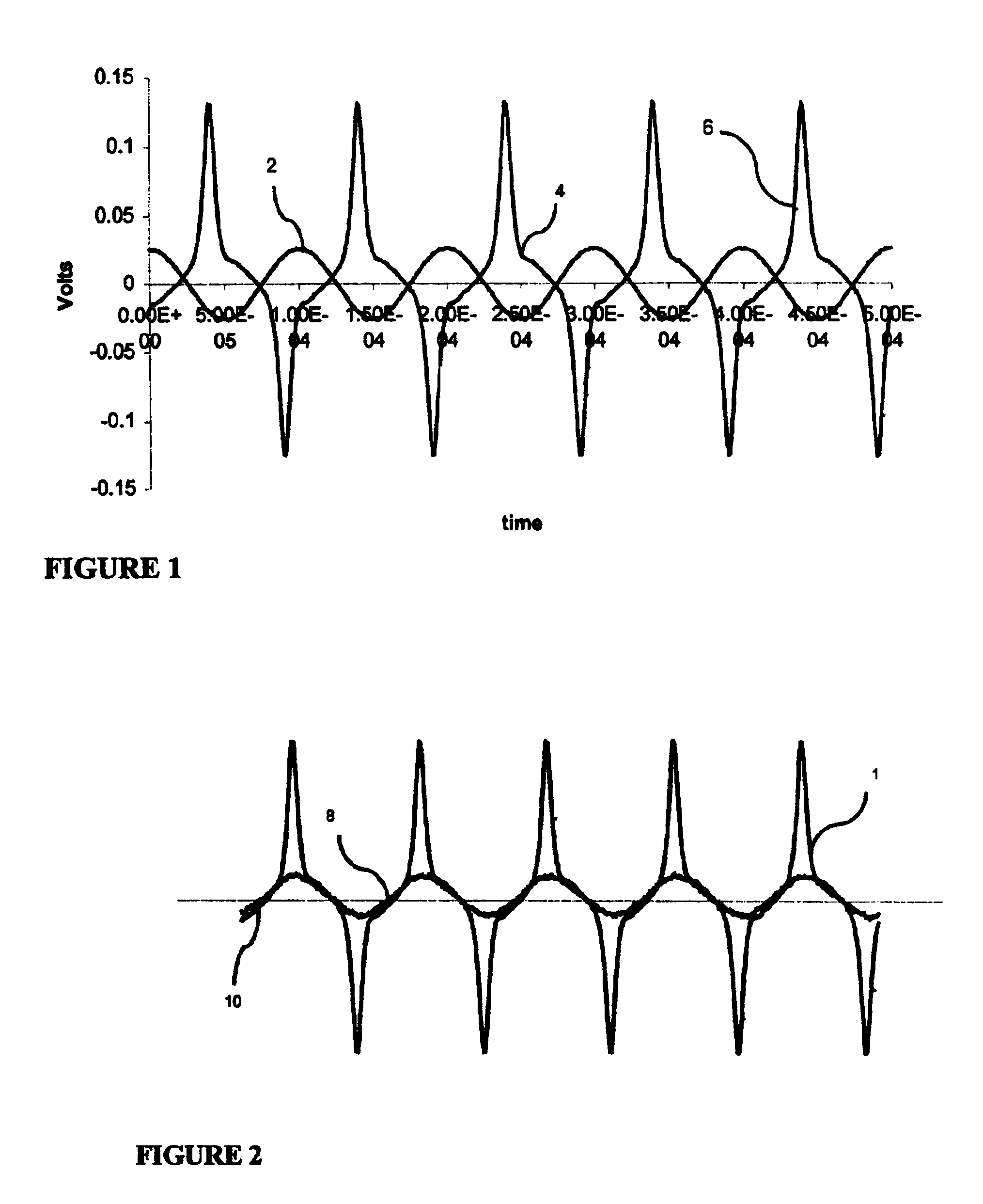
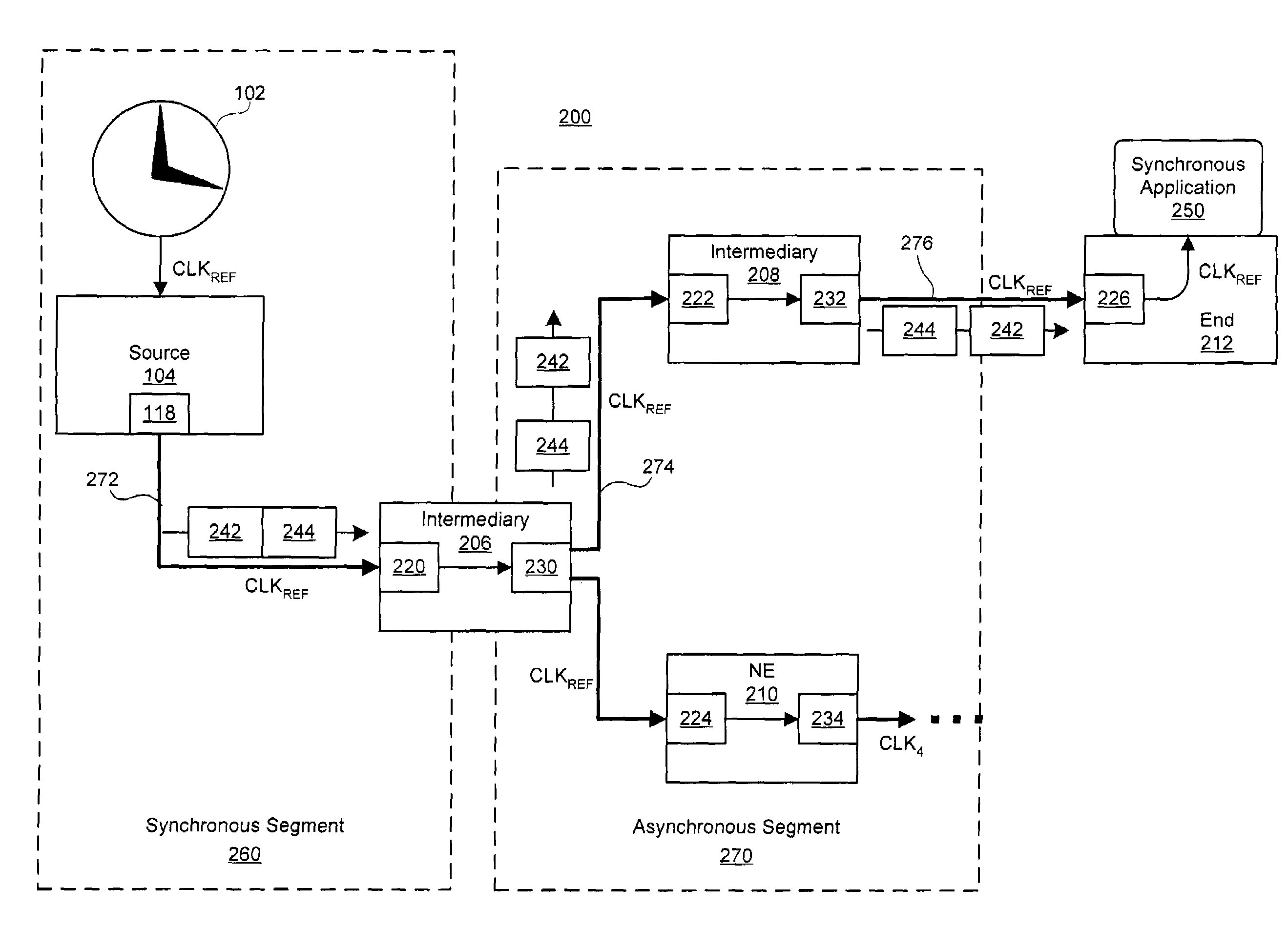
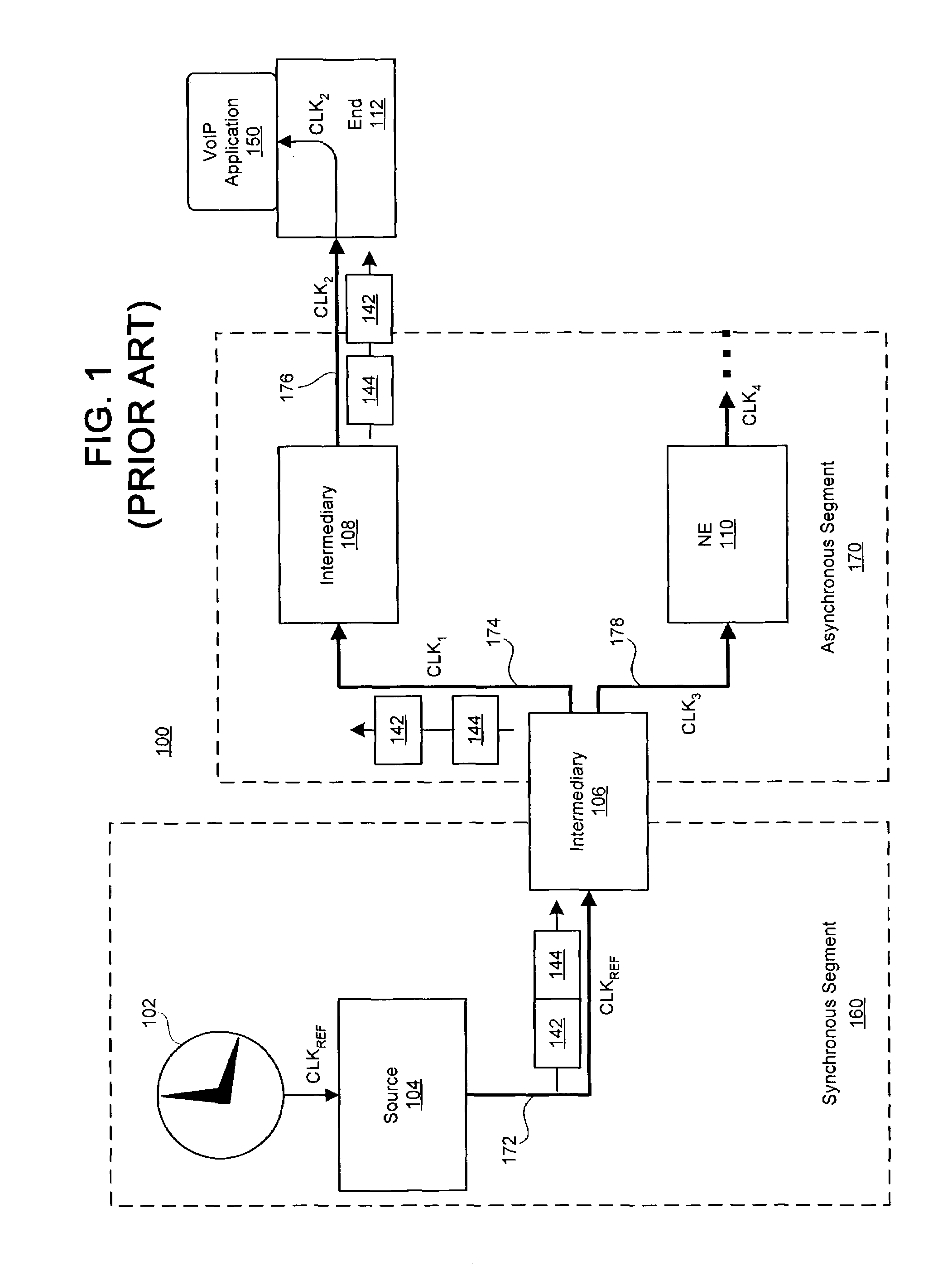
A system and method for clock synchronization in a network having one or more asynchronous data links is provided. A clock signal is propagated through, at the physical layer, a sequence of network devices linking a source network device to a destination network device of the network. Each asynchronous data link between the source network device and the destination network device is adapted to receive an incoming clock signal from the previous network device and then provide a clock signal synchronized to the received clock signal to the next network device of the sequence. At the same time, each network device of an asynchronous segment of the network can continue to transmit packets of data asynchronously. By locking the link-based frequency on a per link bases, the receiver clocks located at the edge of a network can be tied directly to a primary source located in the core network.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Laser based frequency standards and their applications
InactiveUS7809222B2Increase powerReduced Power RequirementsLaser detailsCoupling light guidesFiberMode locked fiber laser
Frequency standards based on mode-locked fiber lasers, fiber amplifiers and fiber-based ultra-broad bandwidth light sources, and applications of the same.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
System and method for frequency offsetting of information communicated in MIMO based wireless networks
InactiveUS20090117859A1Interference minimizationPolarisation/directional diversityFrequency diversityMulti inputCommunications system
A communications system includes a multiple-input / multiple-output architecture, which has a plurality of radio frequency chains. One of the plurality of radio frequency chains is configured to apply a first frequency offset to a base frequency of an output signal to generate a first transmitting frequency; and another of the plurality of radio frequency chains being configured to apply a second frequency offset to the base frequency to generate a second transmitting frequency.
Owner:ERICSSON WIFI
High-frequency surgery generator
InactiveUS7238181B2Output voltageTotal current dropSurgical instruments for heatingHarmonicEngineering
A high-frequency generator for high-frequency surgery comprises a power generator for supplying high frequency energy at a base frequency. A standardizing factor is determined, with which an output variable from the power generator must be scaled in order to attain a given desired value. Furthermore, harmonics of the base frequency are determined from the output variable and scaled using this factor. By means of an input, the thus obtained signal now controls the output power of the generator. With this arrangement, a reliable first cut may be performed on various kinds of tissue without occurrence of any coagulation.
Owner:STORZ ENDOSKOP PROD GMBH
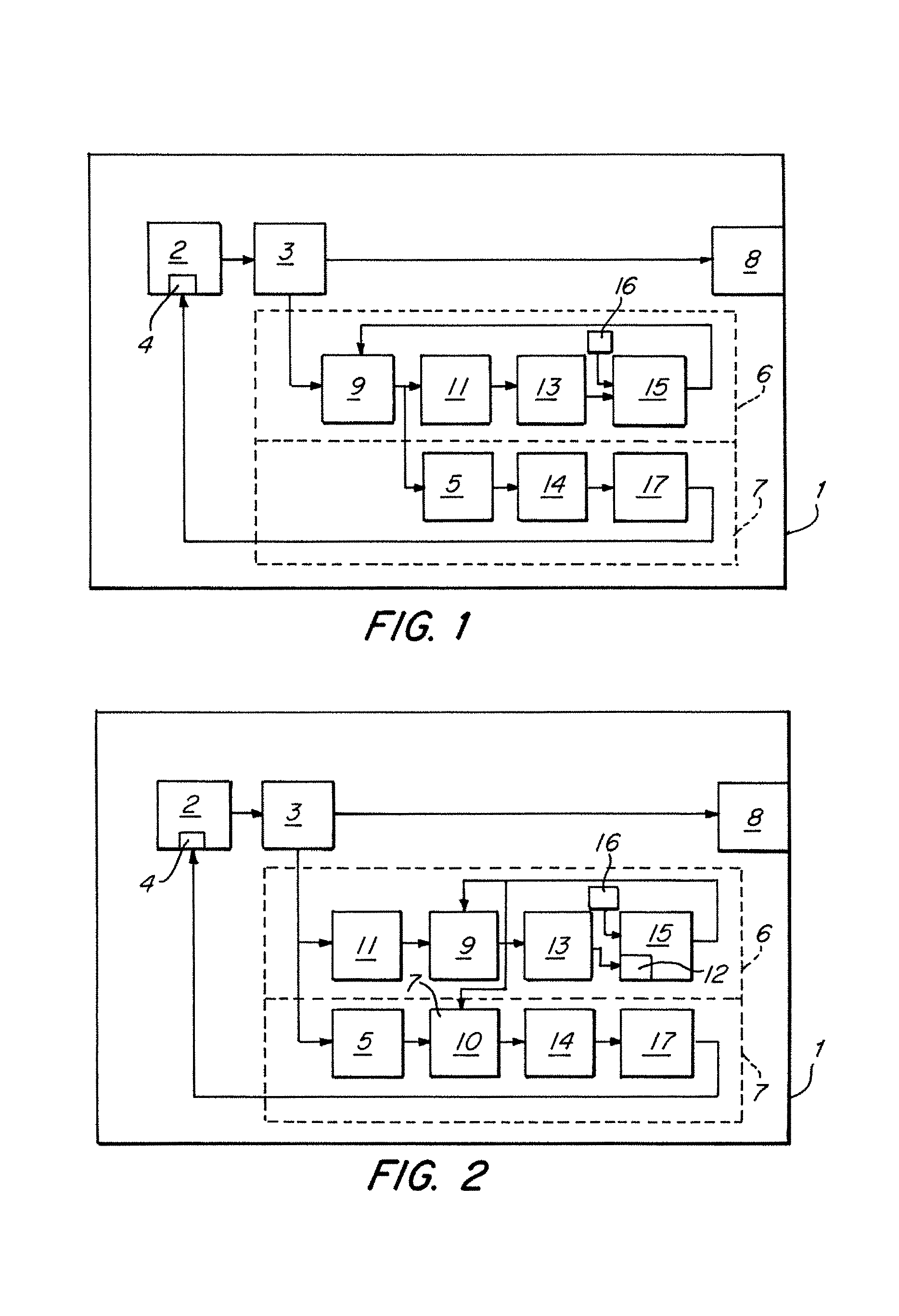
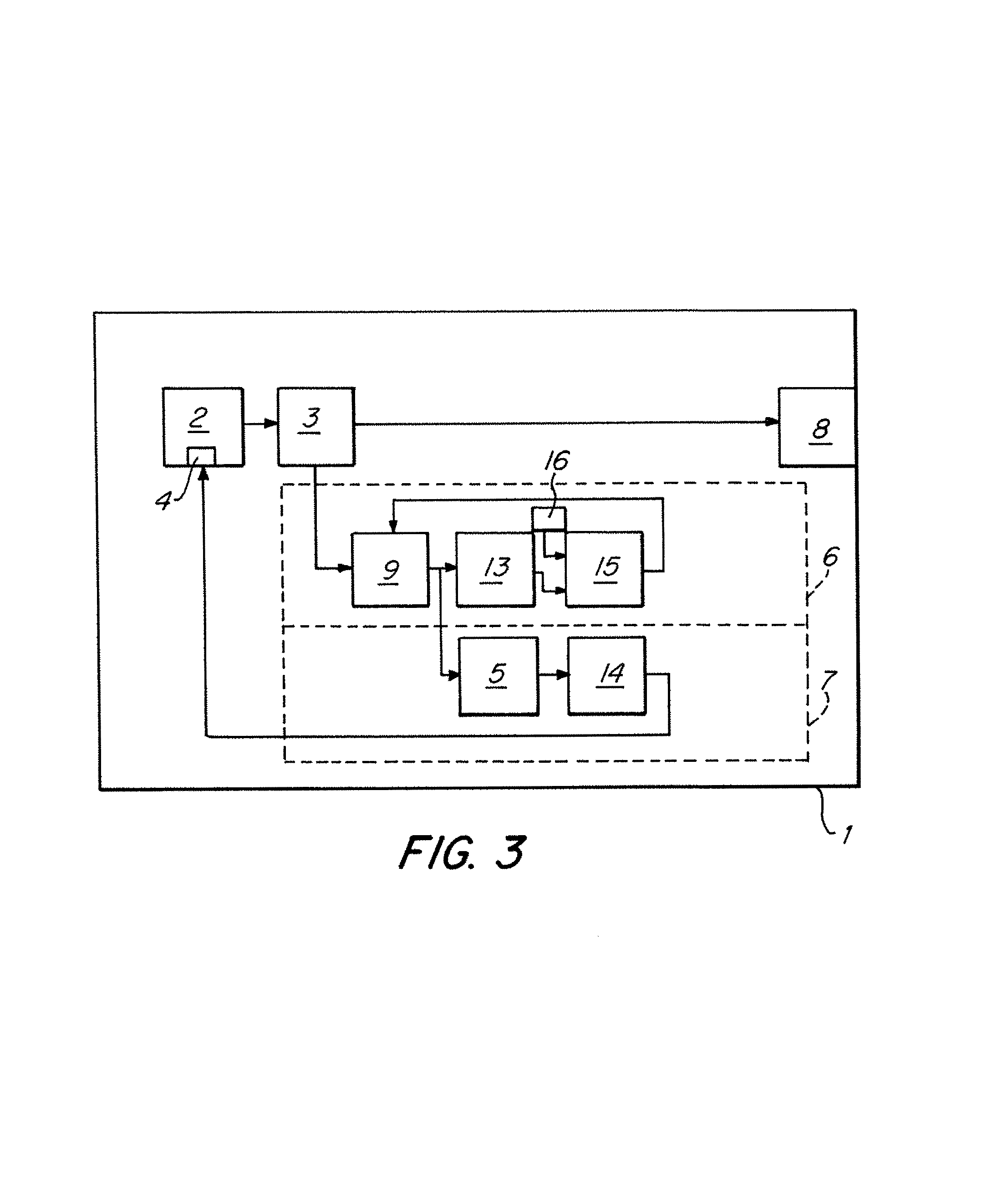
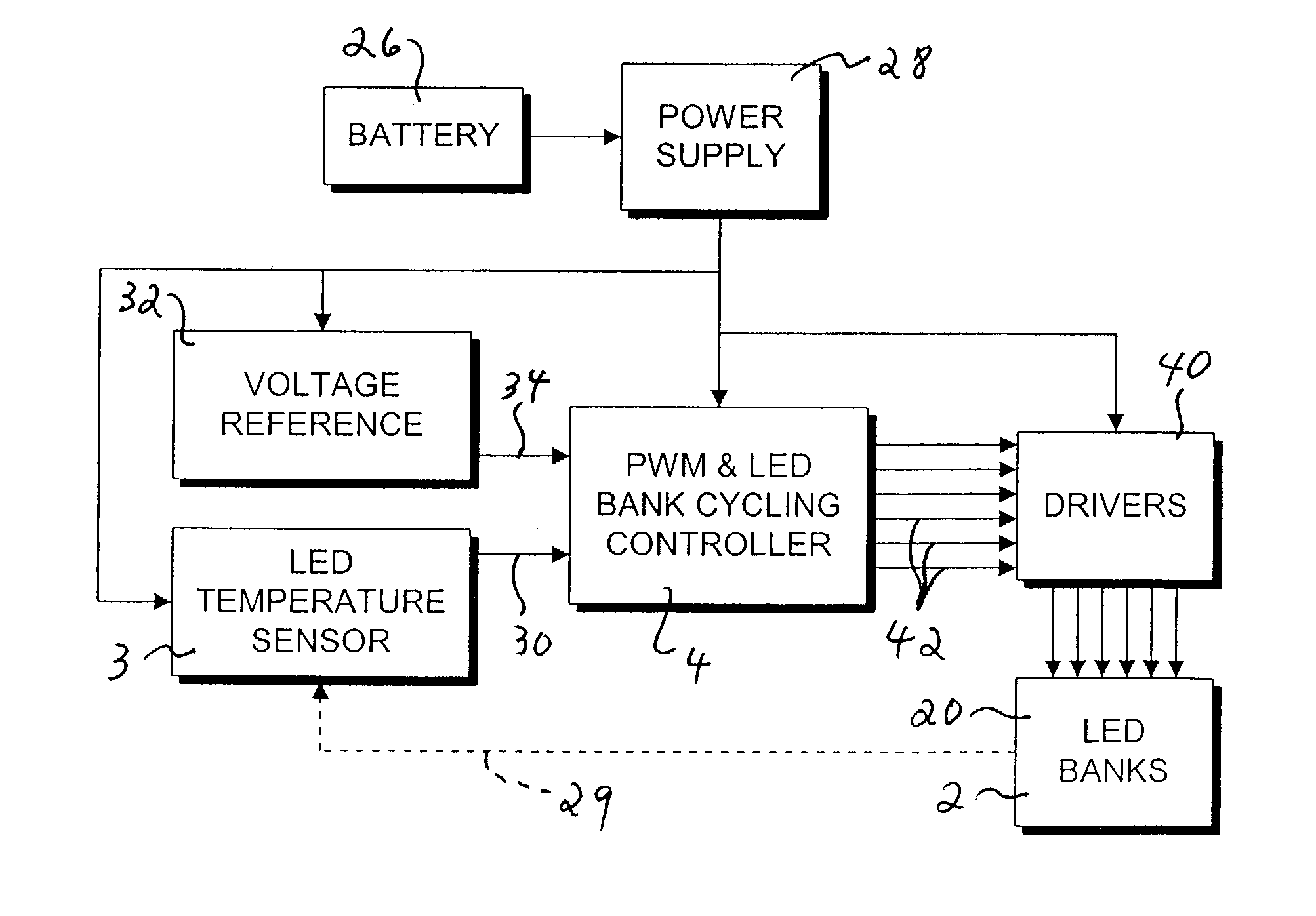
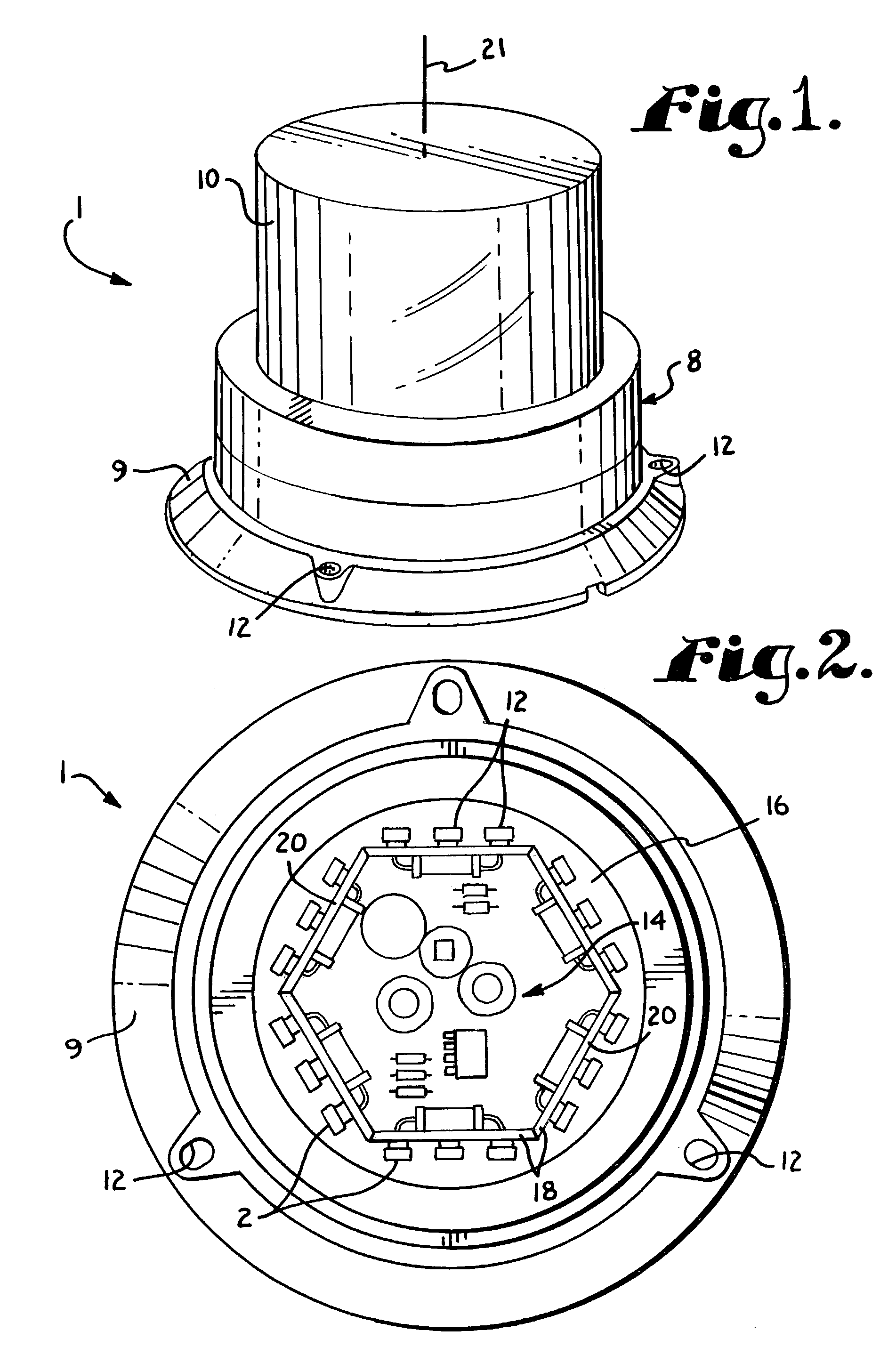
Temperature compensated warning light
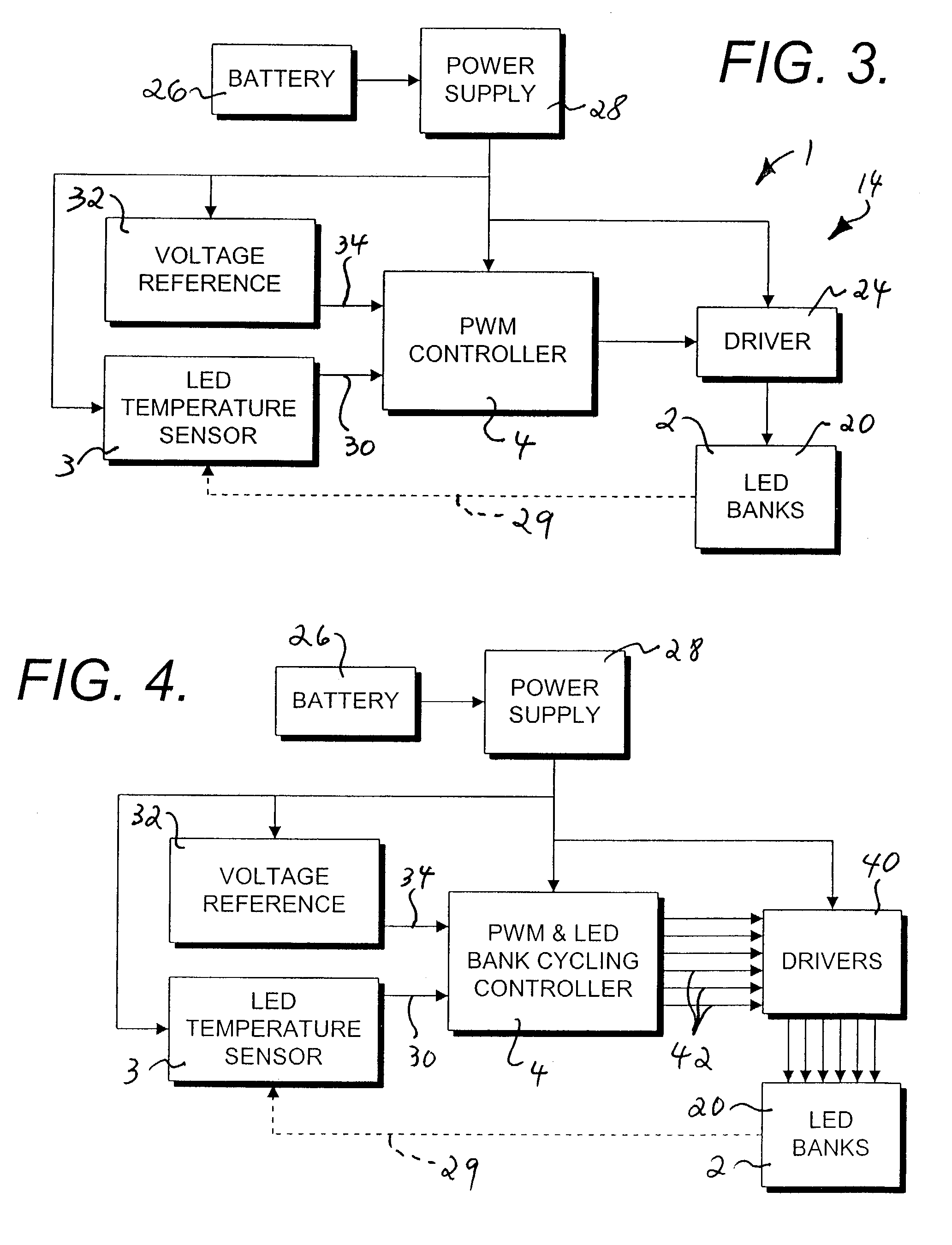
InactiveUS7091874B2Electrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesBase frequencyVoltage variation
A temperature compensated warning light includes banks of high output light emitting diodes (LED's), one or more drivers connecting the LED banks to a control processor, and a temperature sensor thermally coupled to the LED's to provide a temperature signal indicative of the temperature of the LED's to the processor. The processor pulse width modulates a base frequency signal to the LED's in such a manner as to maintain a constant brightness of the LED's as the temperature of the LED's varies. The processor also monitors supply voltage and further varies the pulse width of the base frequency signal to compensate for supply voltage variation. The base frequency signal is modulated by a flash signal to create desired flash patterns.
Owner:PETERSON MFG CO INC +1
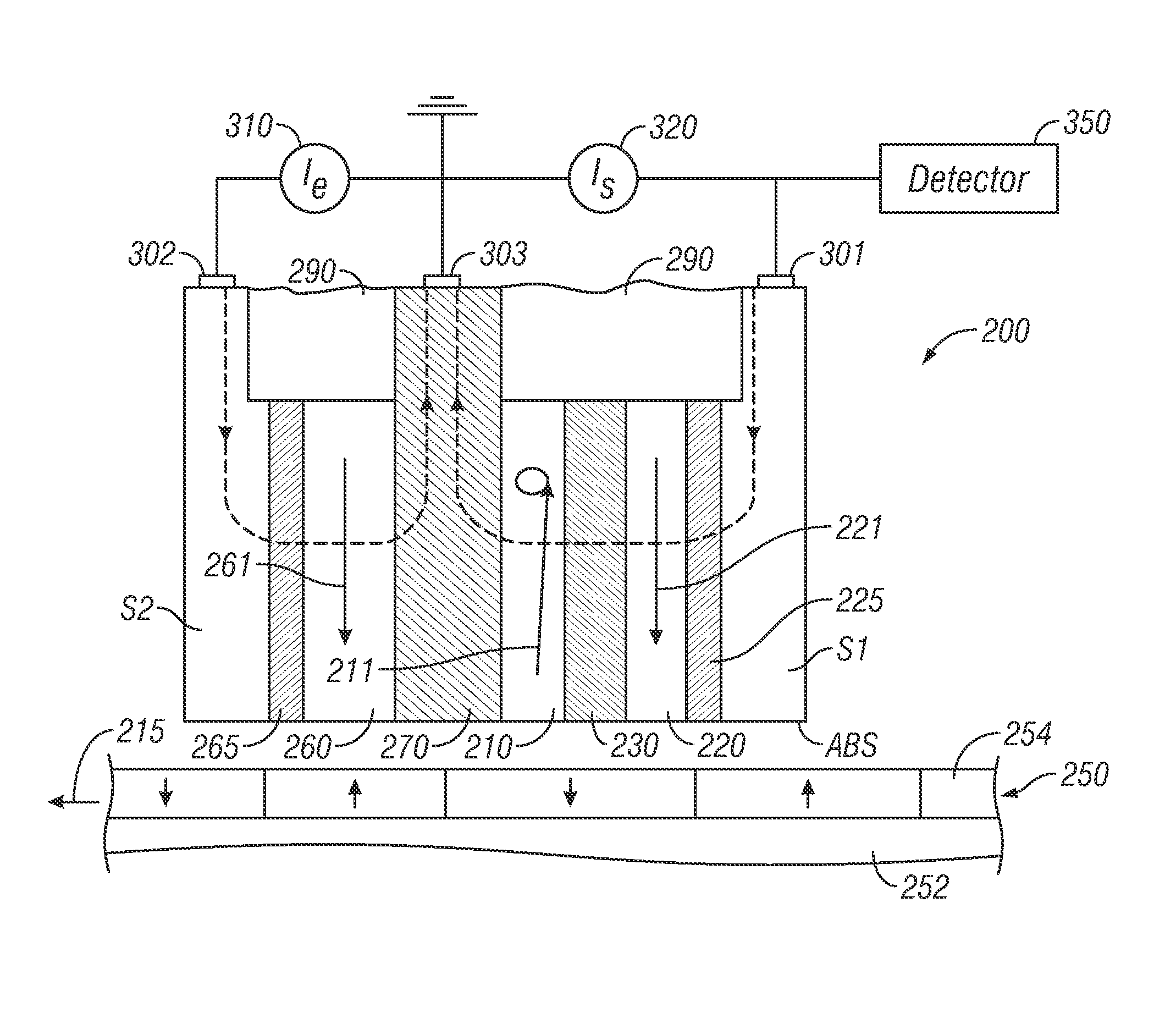
Three-terminal spin-torque oscillator (STO)
A spin-torque oscillator (STO) has a single free ferromagnetic layer that forms part of both a giant magnetoresistance (GMR) structure with a nonmagnetic conductive spacer layer and a tunneling magnetoresistance (TMR) structure with a tunnel barrier layer. The STO has three electrical terminals that connect to electrical circuitry that provides a spin-torque excitation current through the conductive spacer layer and a lesser sense current through the tunnel barrier layer. When the STO is used as a magnetic field sensor, the excitation current causes the magnetization of the free layer to oscillate at a fixed base frequency in the absence of an external magnetic field. A detector coupled to the sense current detects shifts in the free layer magnetization oscillation frequency from the base frequency in response to external magnetic fields.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
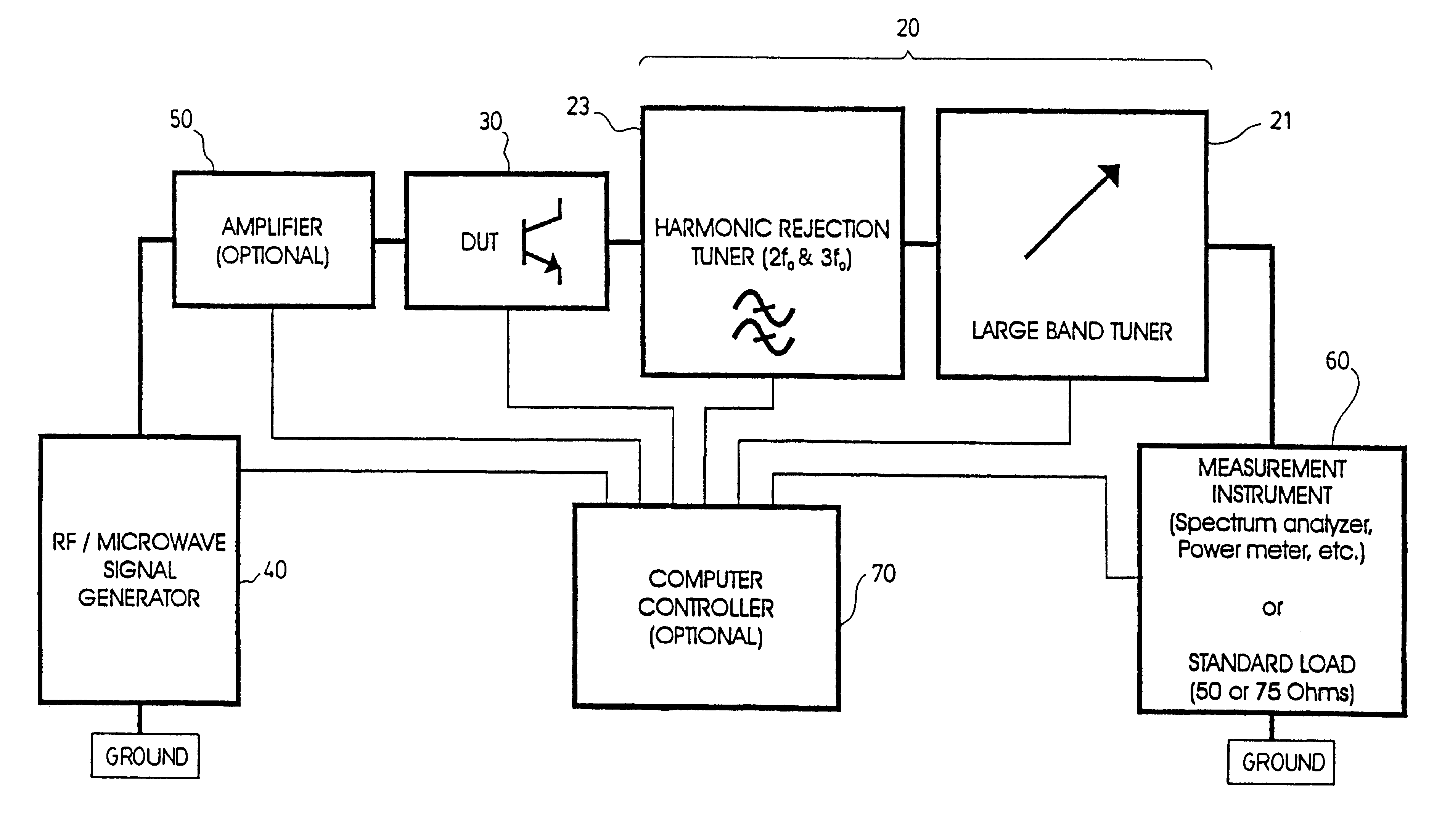
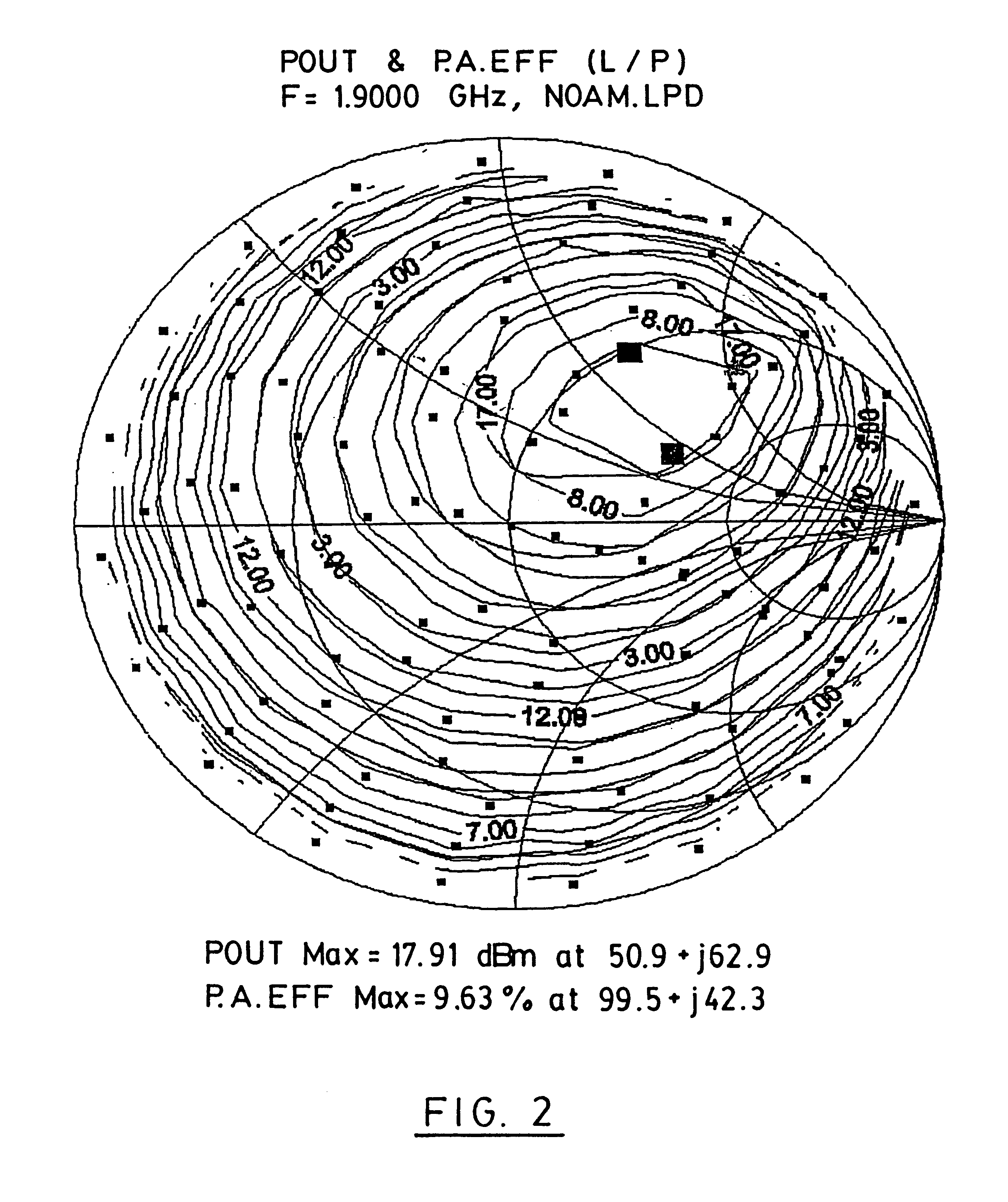
Harmonic rejection load pull tuner
The present invention discloses a harmonic rejection load pull tuner. The tuner of the invention has a large-band tuner having an input and an output, and a transmission line having a longitudinal axis. The transmission line has an input connected to the output of a DUT and an output connected to the input of the large-band tuner. In parallel with the transmission line is at least one stub, the at least one stub having a length adapted to reflect out an nth order harmonic of a base frequency, where n is an integer greater than 1. The tuner of the present invention can be used to perform input or output characterisation (or both) of a DUT, by selectively reflecting out at least one harmonic frequency of the base frequency. Consequently, the characterisation of the DUT is improved, since the effects of the harmonics are considerably reduced. The present invention also concerns a method for performing input or output characterisation.
Owner:TSIRONIS CHRISTOS +1
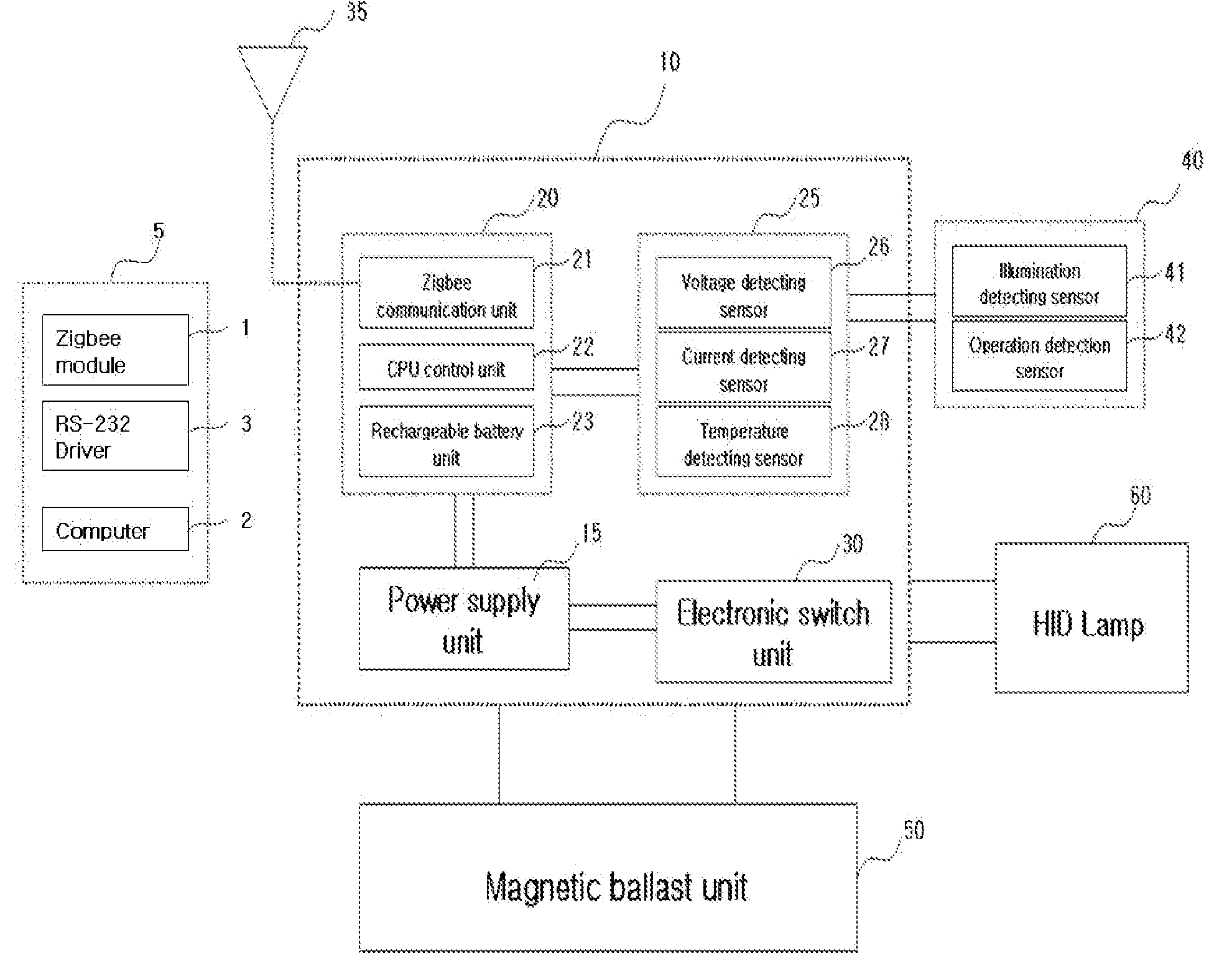
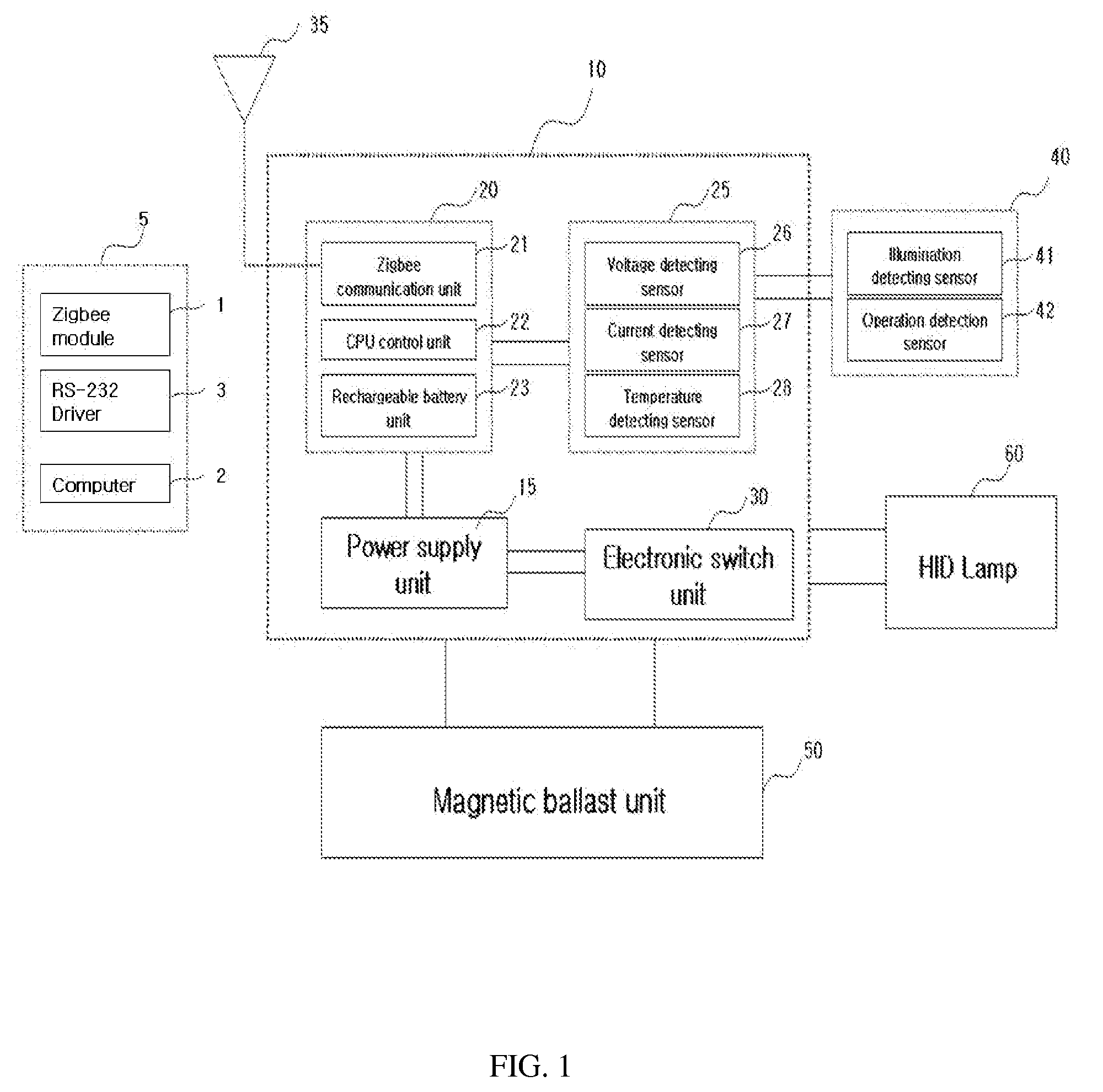
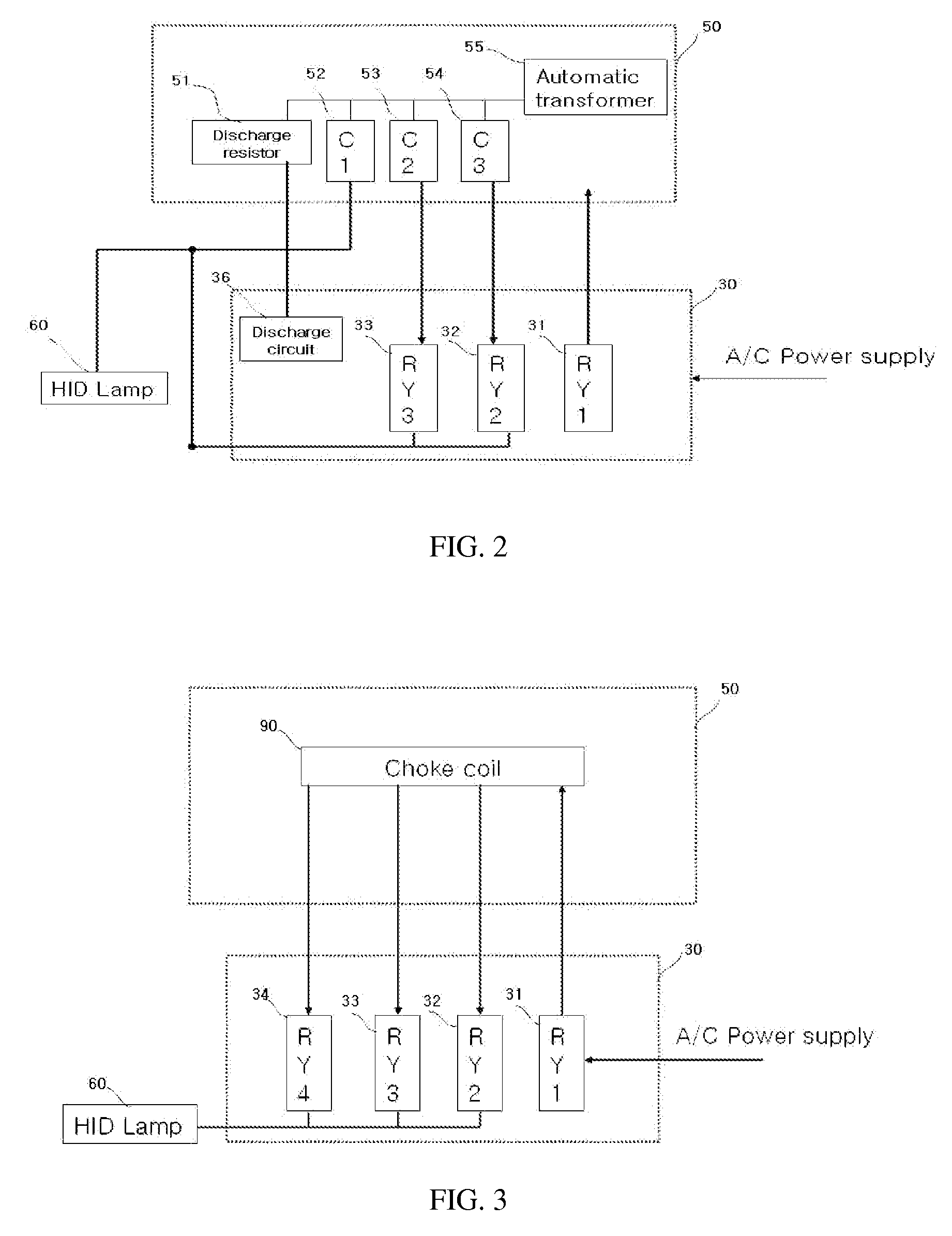
Ballast control system for hid lamp using zigbee
InactiveUS20080218317A1Easy to replaceEnergy efficient ICTLighting elementsControl systemElectronic switch
A control system for an HID lamp, which in one implementation includes a magnetic ballast control system for an HID lamp using Zigbee. A plurality of condensers or choke coils of different capacities is mounted on a magnetic ballast for the lamp, and an electronic switch unit controls illumination according to change of such capacities. RF transmitting / receiving means using a Zigbee-based frequency are employed to turn the HID on and off, and to control illumination through wireless remote communications, thereby achieving considerable energy savings. Operational states of the HID lamp and ballast can be bi-directionally controlled through the communication module, with failures of the HID lamp and ballast automatically detected and notified to users, thereby eliminating inconvenient confirmation processes. The magnetic ballast control system is useful in street lamps, tunnel lamps, factory lamps, warehouse lamps, landscape illuminations, and the like.
Owner:GRS CONSULTING
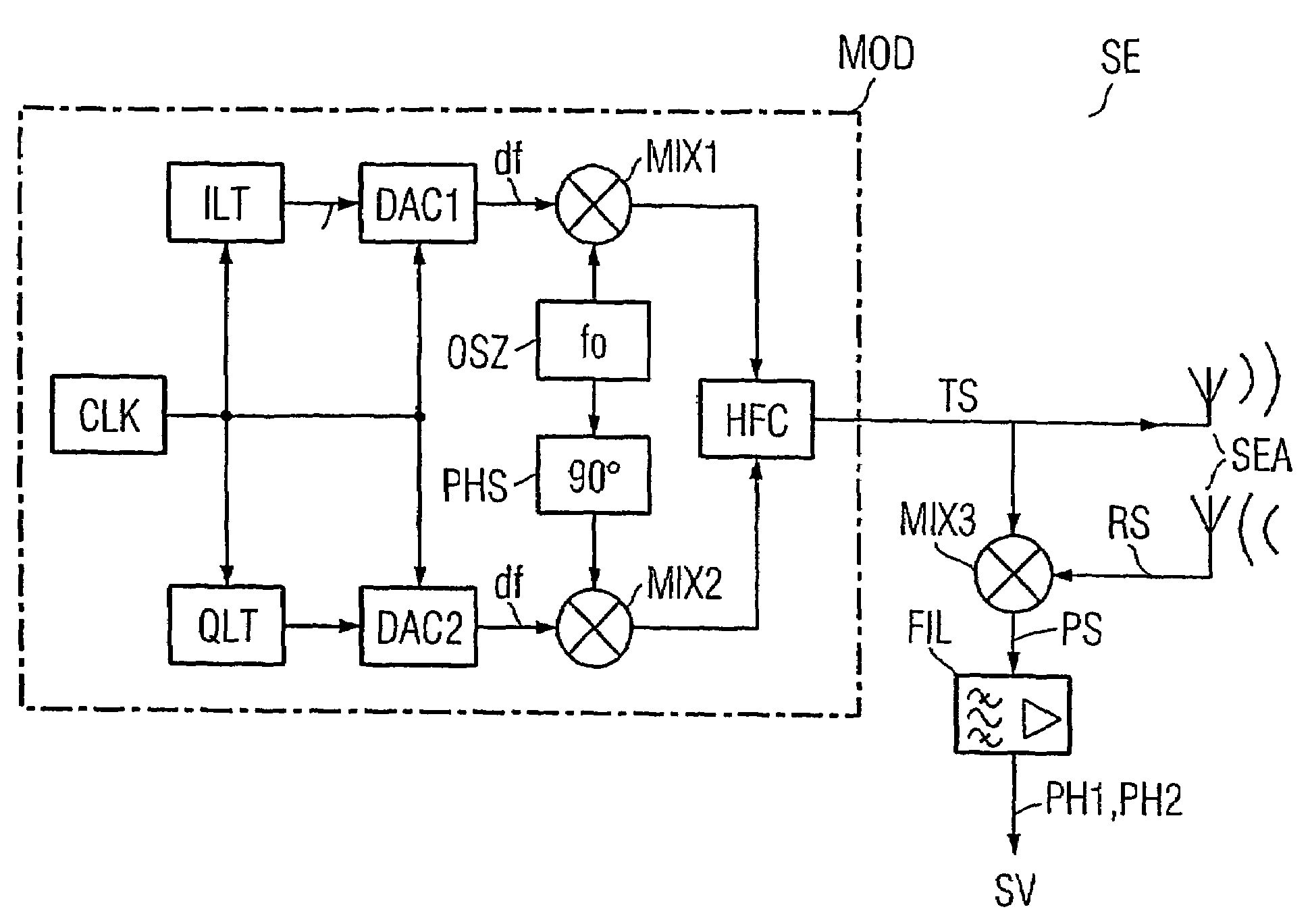
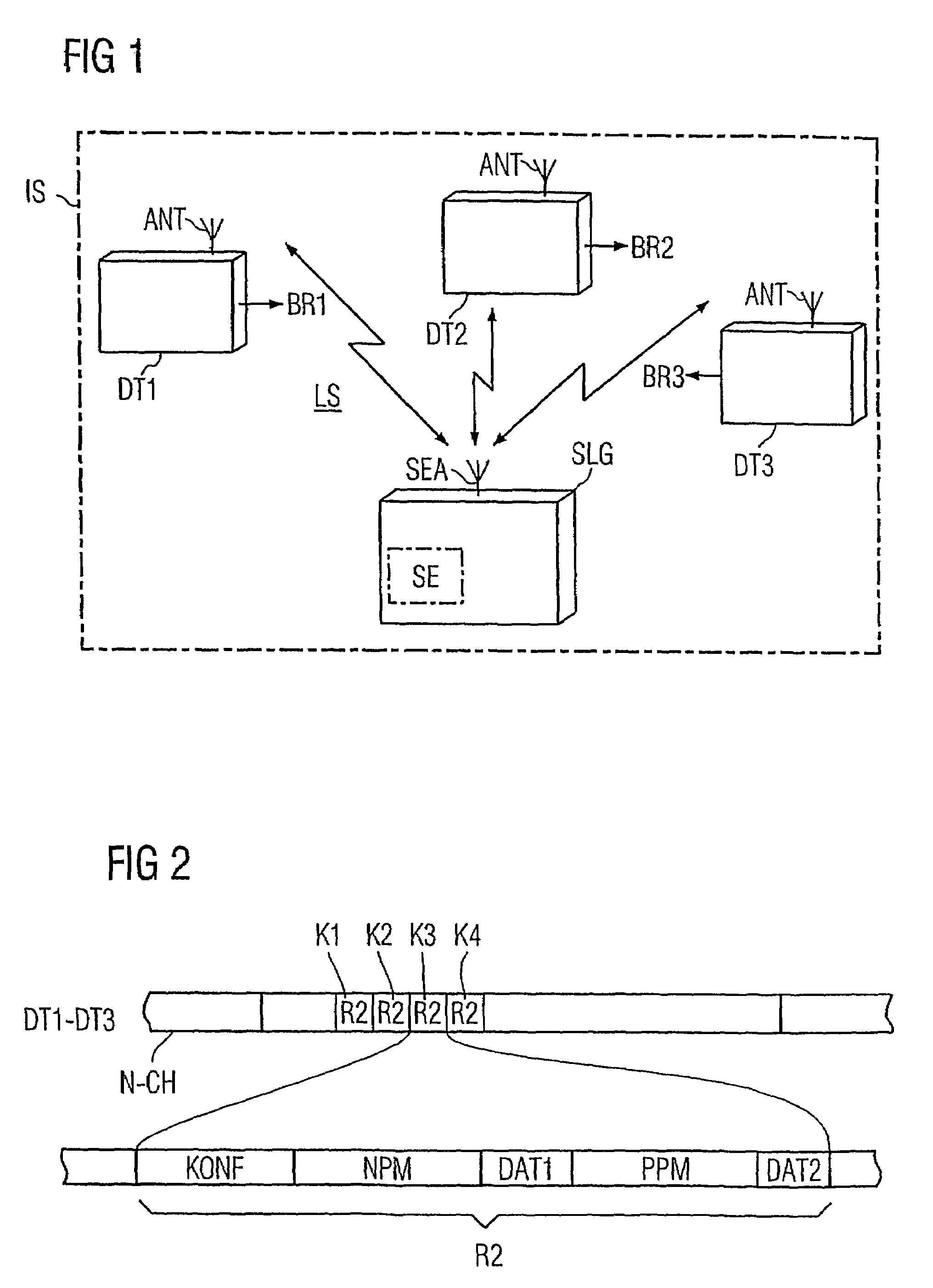
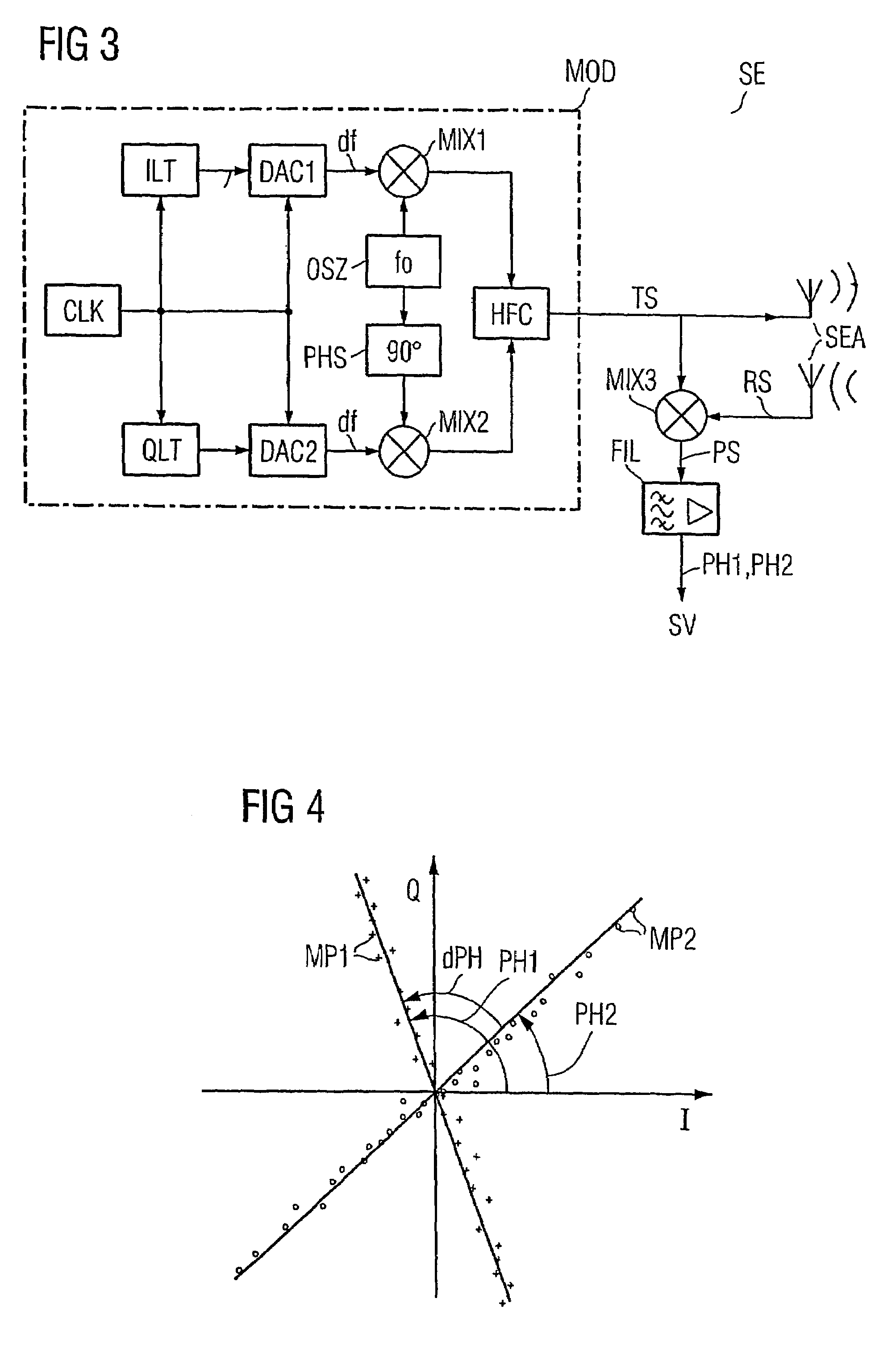
Method for determining the distance between a base station and a mobile object, in addition to a base station and identification system for a method of this type
InactiveUS7205931B2Measurement time is requiredEasy to measureRadio wave reradiation/reflectionQam modulationCarrier signal
A method for determining the distance between a base station (SLG) and a mobile object (DT1–DT3). A HF carrier frequency and an offset frequency (df) are predetermined for a QAM modulation. The HF carrier frequency is increased and decreased by the offset frequency in sequence over time in such a way that the HF carrier base frequencies (fo+df, fo−df) resulting in an HF carrier signal (TS) thus modulated exhibit an identical phase when the frequency is changed. The HF carrier signal is subsequently transmitted and simultaneously mixed (MIX) with an HF carrier signal (RS) that has been backscattered by the mobile object to obtain a carrier phase signal (PS). The corresponding carrier phase (PH1, PH2) for the two HF carrier base frequencies is determined in sequence over time. The difference (dPH) between these phases is used to calculate the distance between the base station and the respective mobile object.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
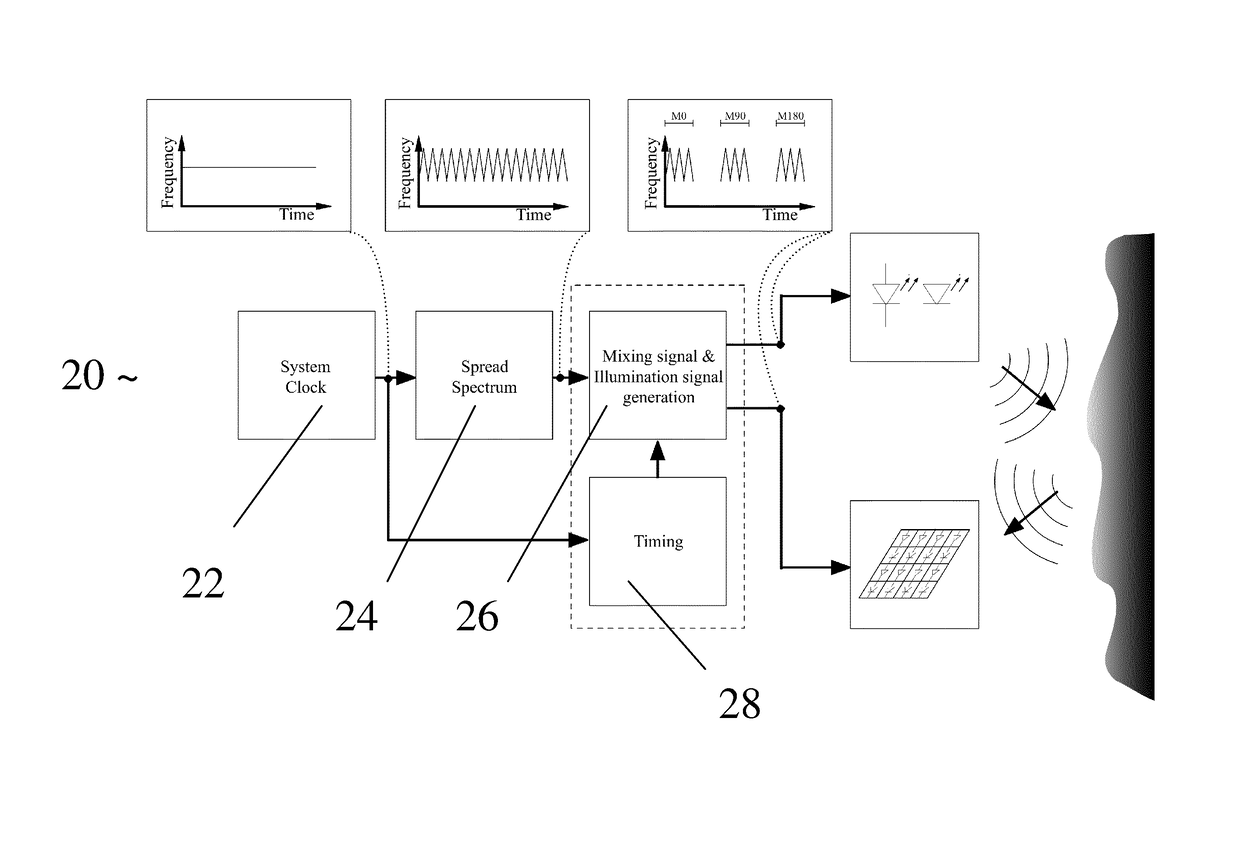
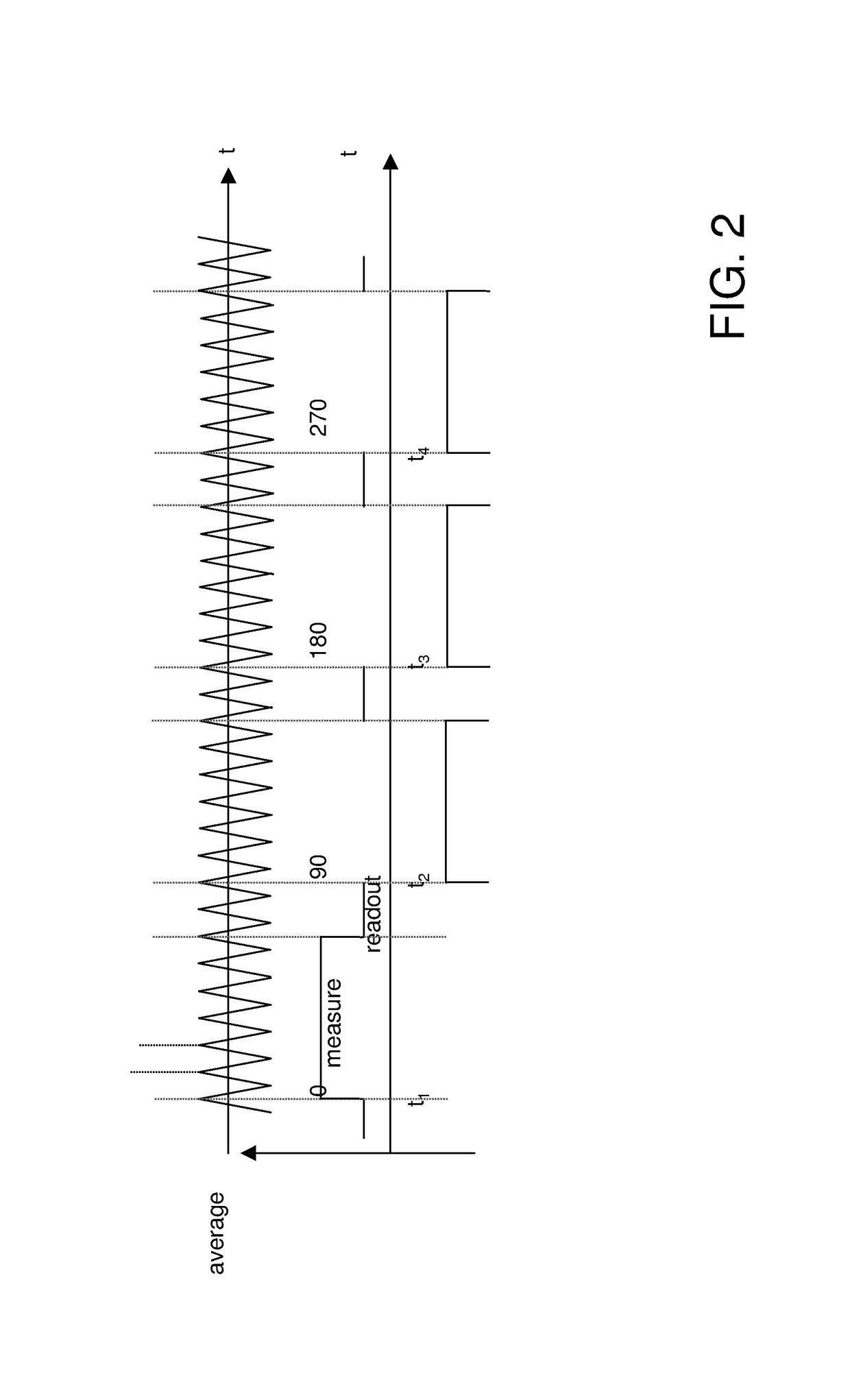
Method and time-of-flight camera for providing distance information
ActiveUS9599712B2Improve accuracyReduce electromagnetic interferenceOptical rangefindersTransmission noise suppressionOptoelectronicsTime-of-flight camera
The invention relates to a method for providing distance information of a scene with a time-of-flight camera (1), comprising the steps of emitting a modulated light pulse towards the scene, receiving reflections of the modulated light pulse from the scene, evaluating a time-of-flight information for the received reflections of the modulated light pulse, and deriving distance information from the time-of-flight information for the received reflections, whereby a spread spectrum signal is applied to a base frequency of the modulation of the light pulse, and the time-of-flight information is evaluated under consideration of the a spread spectrum signal applied to the base frequency of the modulation of the light pulse. The invention further relates to a time-of-flight camera (1) for providing distance information from a scene, whereby the time-of-flight camera (1) performs the above method.
Owner:SOFTKINETIC SENSORS
Apparatus and Method for Monitoring A Device Having A Movable Part
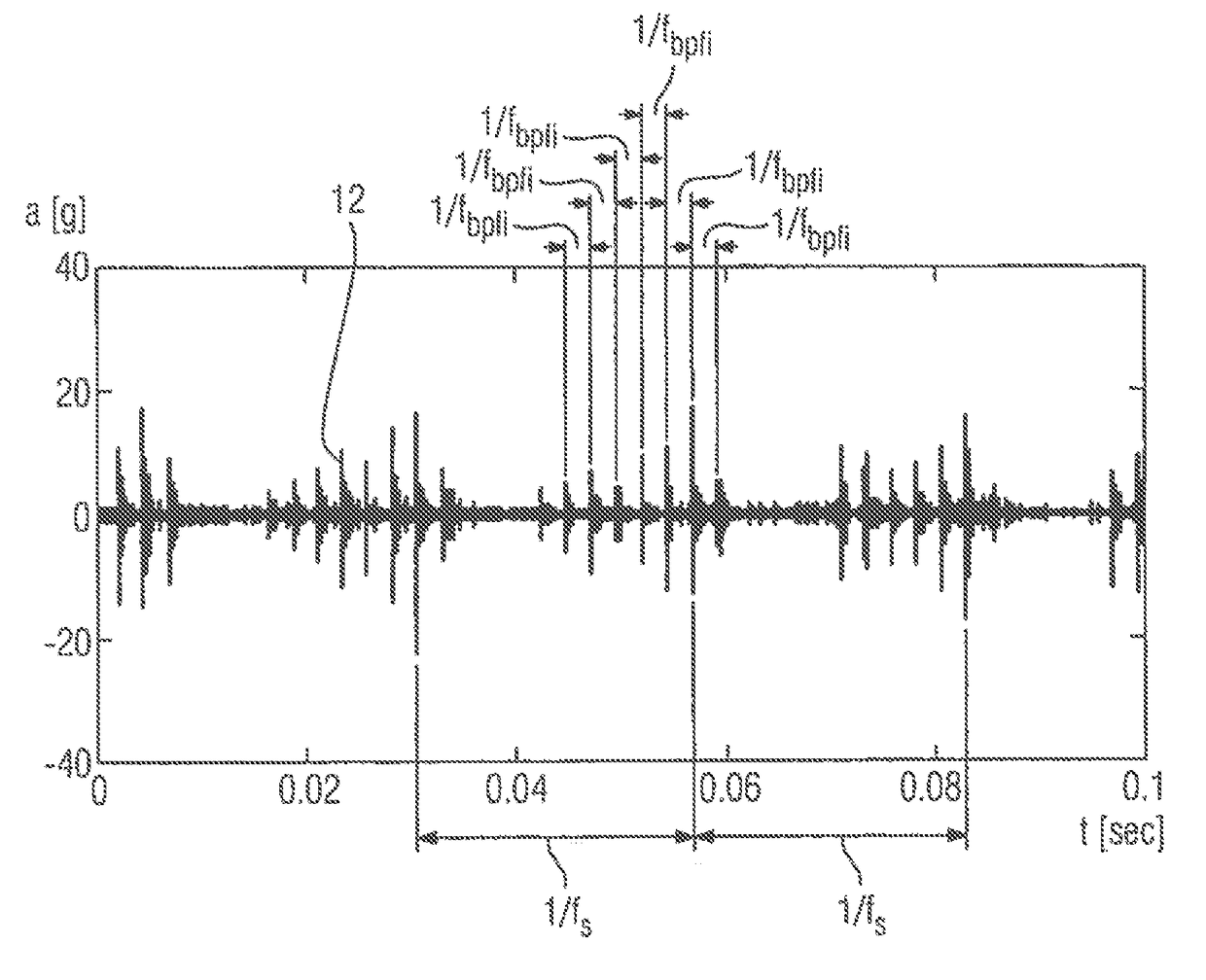
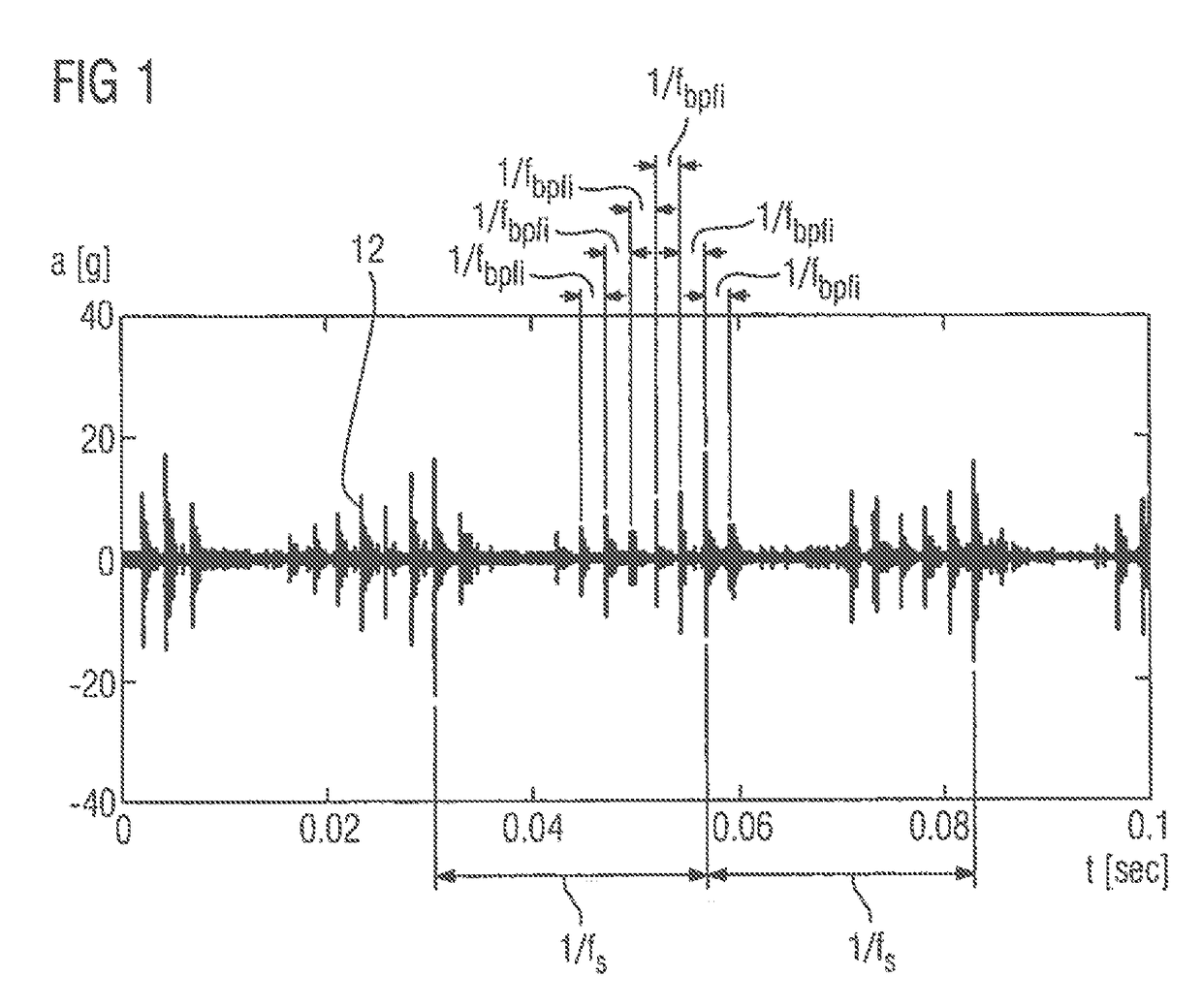
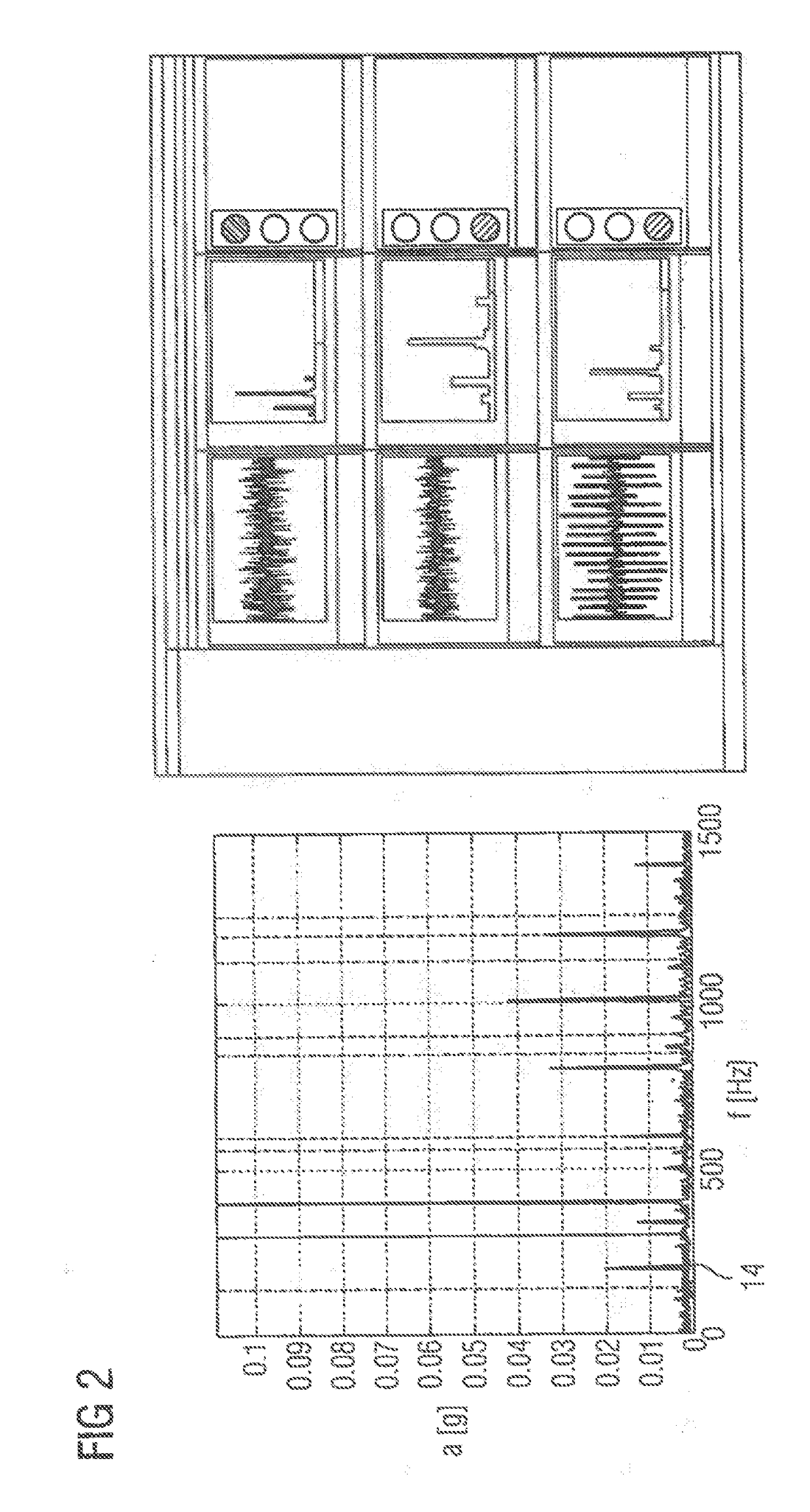
ActiveUS20170315516A1Accurate decisionEfficient use ofVibration measurement in solidsMachine part testingOne-class classificationEigen frequency
An apparatus for monitoring of a device including a moveable part, especially a rotating device, wherein the apparatus includes a control module which receives a measured vibration signal of the device provided by a sensor connected to the device, provides a spectrum of the measured vibration signal, pre-processes the spectrum to determine base frequencies and side frequencies, where the base frequencies are frequencies having peak powers corresponding to eigen frequencies of the device or faulty frequencies and the side frequencies correspond to other frequencies, where the control module additionally processes the base and side frequencies by applying separately a one-class classification on the base and side frequencies, combines the results of the one-class classifications to obtain a classification signal representing a confidence level, and outputs a decision support signal based on the classification signal, where the decision support signal indicates an error status of the monitored device.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
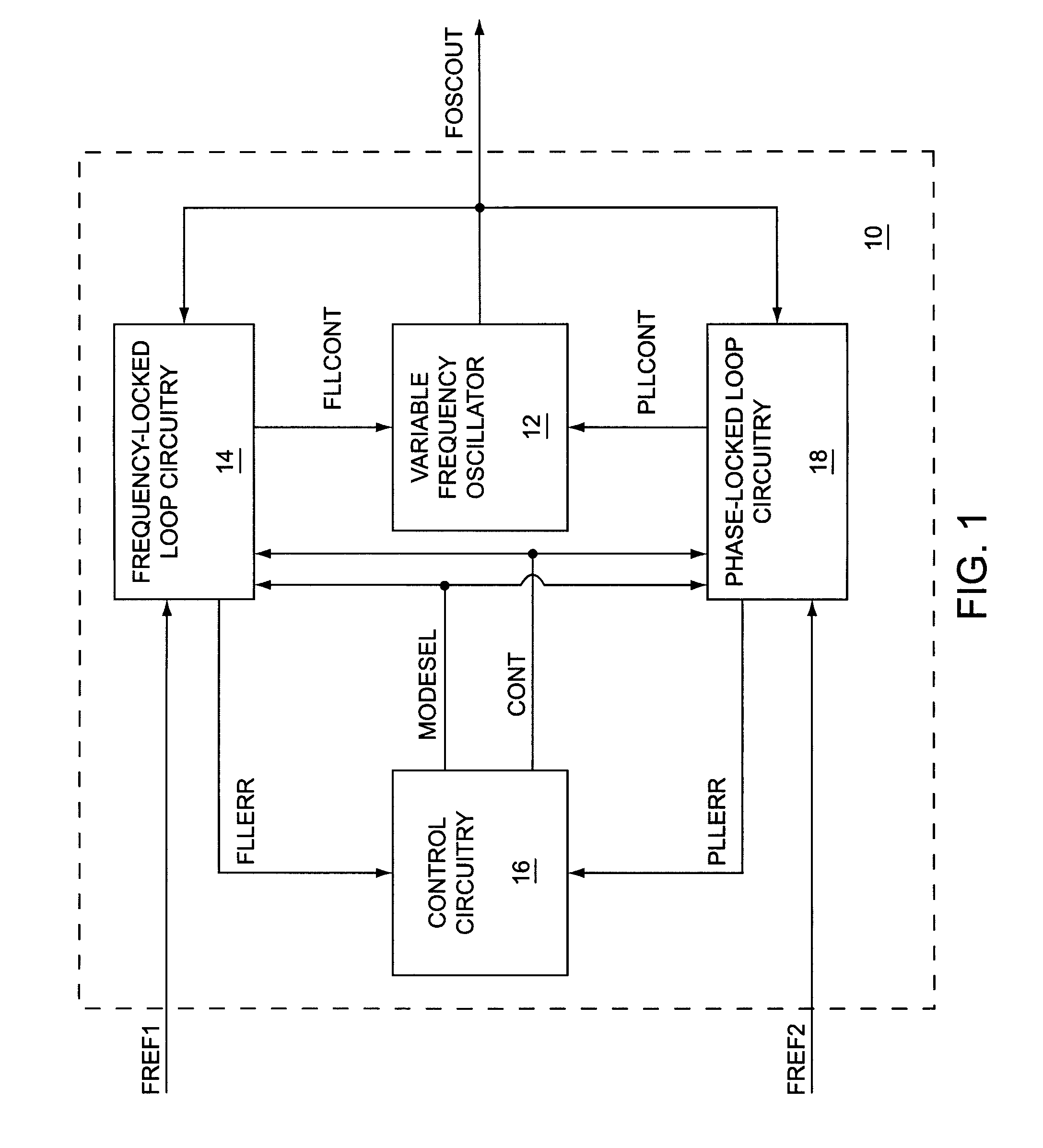
Frequency measurement based frequency locked loop synthesizer
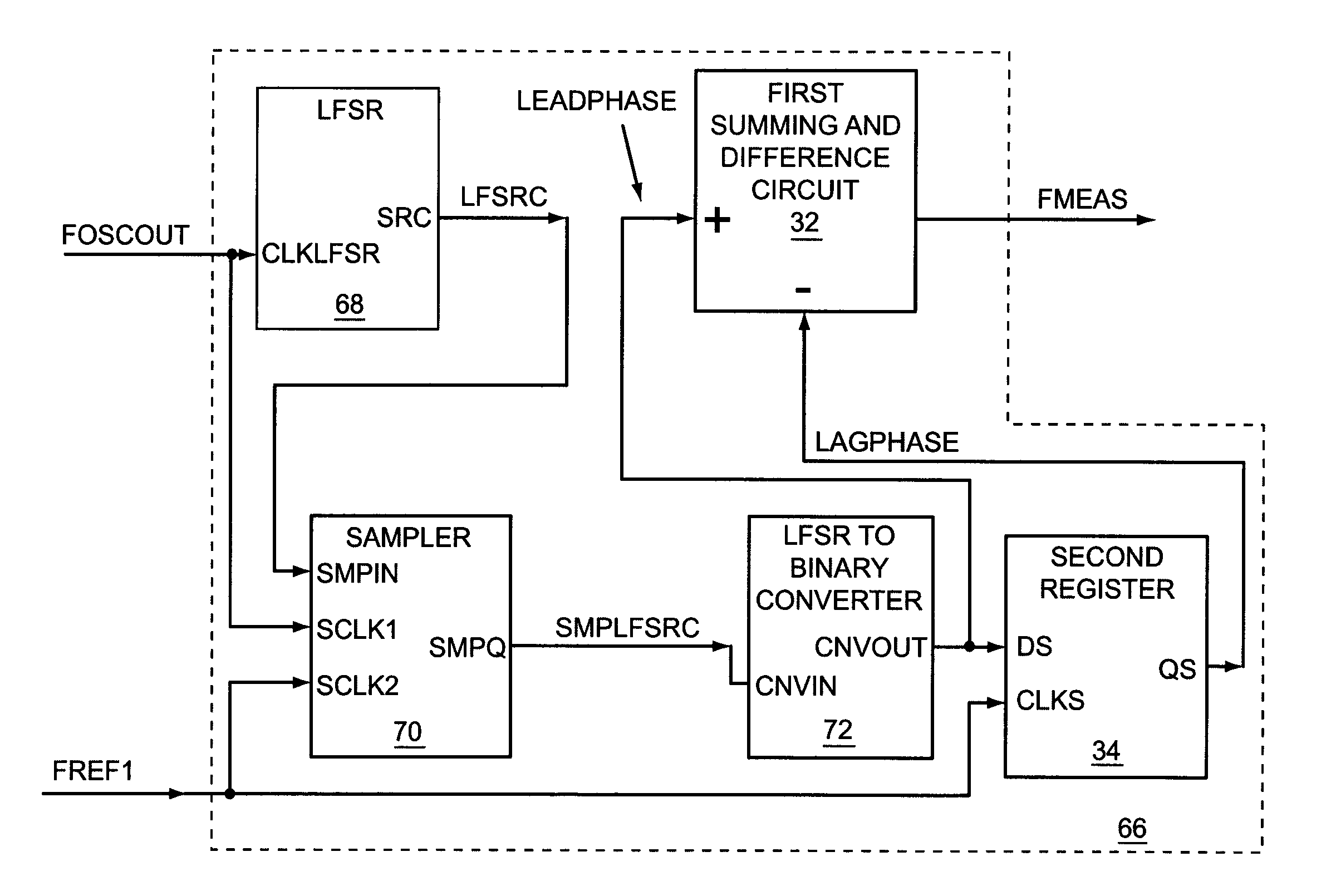
ActiveUS7750685B1Fast settling timeReduce frequencyMultiple input and output pulse circuitsPulse automatic controlFrequency measurementsEngineering
A first embodiment of the present invention relates to a frequency and phase locked loop (FPLL) synthesizer having a frequency-locked loop (FLL) operating mode and a phase-locked loop (PLL) operating mode. The FLL operating mode is used for rapid coarse tuning of the FPLL synthesizer and is followed by the PLL operating mode for fine tuning and stabilization of the frequency of an output signal from the FPLL synthesizer. A second embodiment of the present invention relates to a high resolution frequency measurement circuit that is capable of directly measuring the frequency of a high frequency signal to provide a high resolution frequency measurement using a lower frequency reference signal, and may include linear feedback shift register (LFSR) circuitry and LFSR-to-binary conversion circuitry. A third embodiment of the present invention relates to an FPLL having an FLL that includes the high resolution frequency measurement circuit.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Superposition coding based preamble designs for co-existing radio access technologies
Methods, systems, and devices are described for wireless communication at a device. A device may distinguish a preamble sent from a device configured for a first RAT (e.g., WLAN, Wi-Fi, etc.) from a preamble sent from a device configured for a second RAT (e.g., LTE, LTE-A, LTE-U, etc.). A wireless device associated with a second RAT may transmit a dual-use preamble over a contention-based frequency channel. The dual-use preamble may function as a valid preamble for a first RAT and may be received and decoded by devices associated with the first RAT in addition to devices associated with the second RAT. The dual-use preamble may also include a signature associated with the second RAT. The signature may be embedded with the preamble such that it minimizes interference with the valid preamble and be detected by devices associated with the second RAT.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
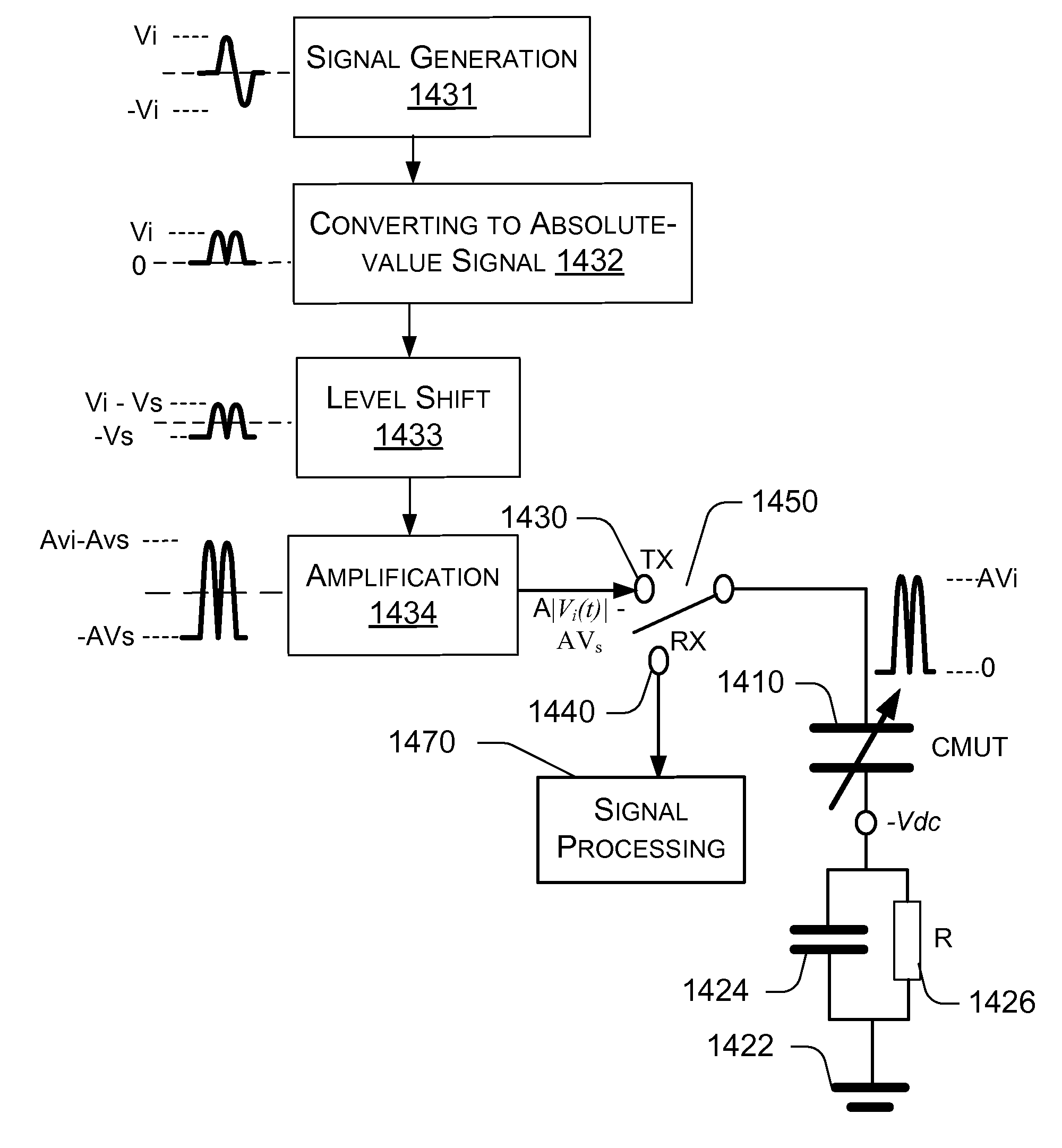
Signal Control in Micromachined Ultrasonic Transducer
ActiveUS20070228877A1Improve the level ofImprove performanceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesCapacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducersHarmonic
A capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers (cMUT) uses signal control methods to reduce harmonic distortion of the output signal. The method uses an AC transmission input signal characterized with a frequency ω and takes the second-order frequency component with frequency 2ω, rather than the first-order frequency component with the base frequency ω, as the desired output pressure signal. A frequency ω is preferably equal to ω0 / 2, where ω is the desired cMUT output frequency. Various examples of AC transmission input signals, in combination with or without a DC bias signal, that are suitable for producing a large second-order frequency component and small (ideally zero) first-order frequency component are disclosed.
Owner:KOLO MEDICAL (SUZHOU) CO LTD
Modular generation method for multi-waveform radar signal
InactiveCN102073032AVersatileImprove compatibilityWave based measurement systemsData acquisitionEngineering
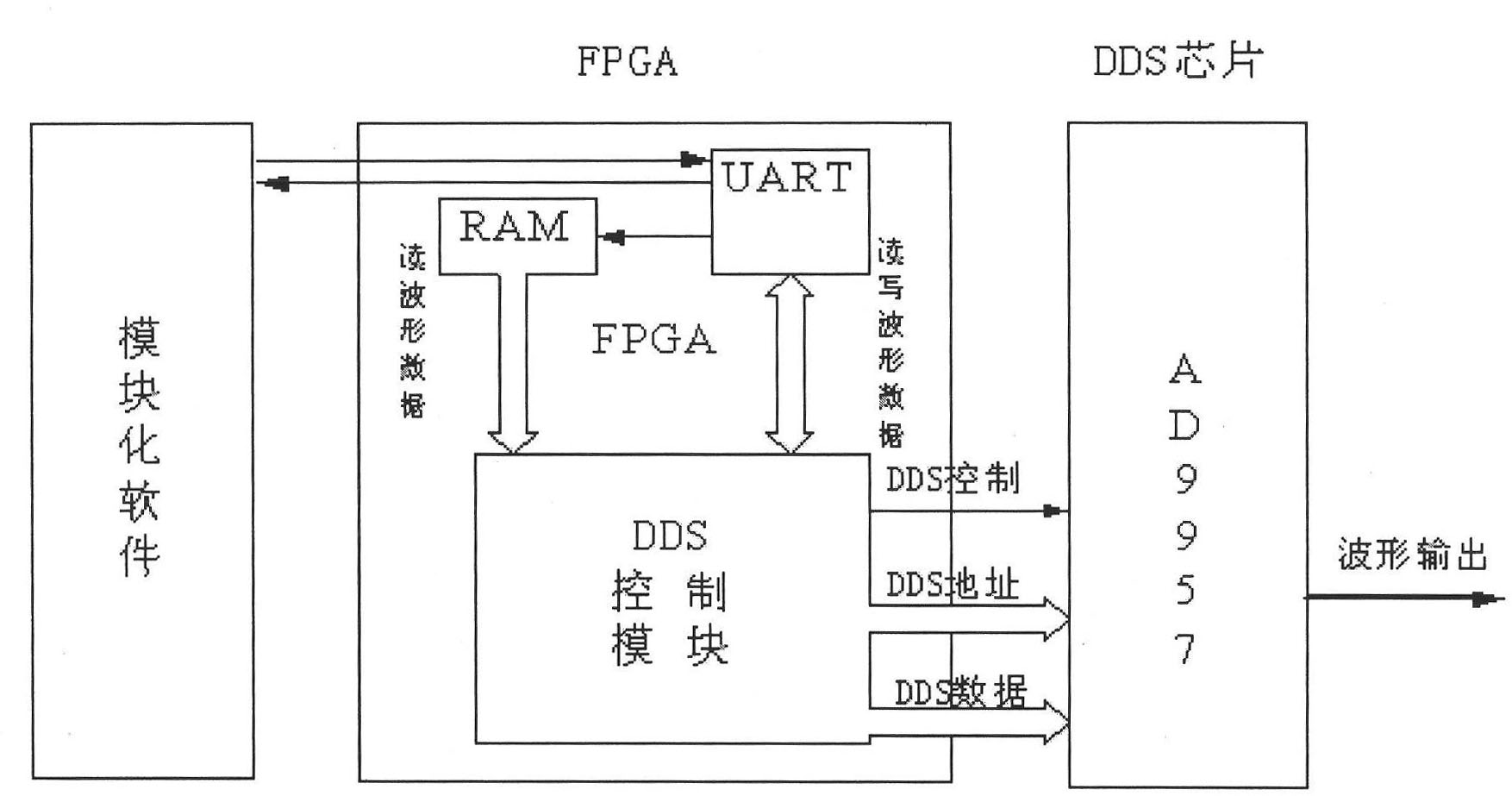
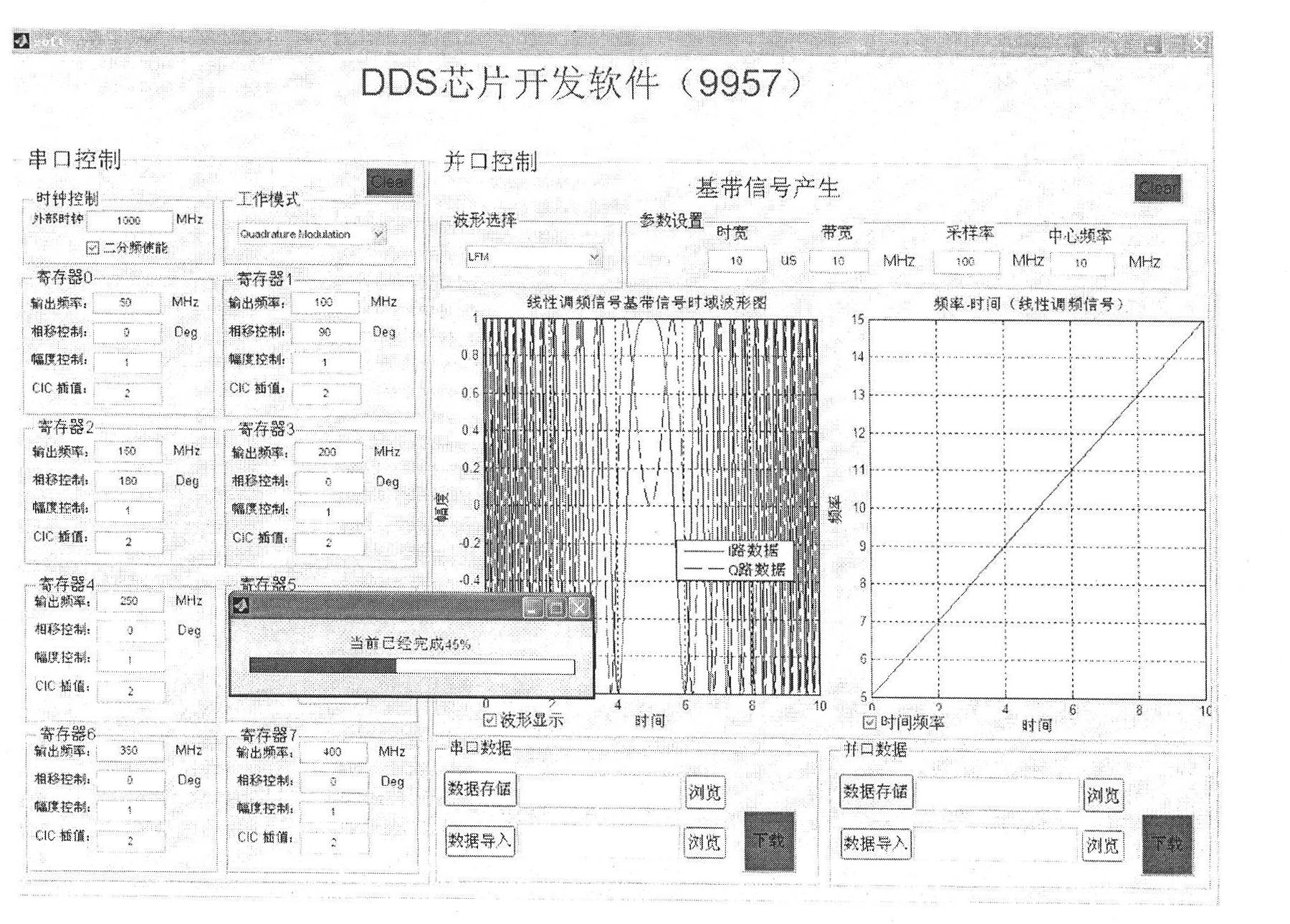
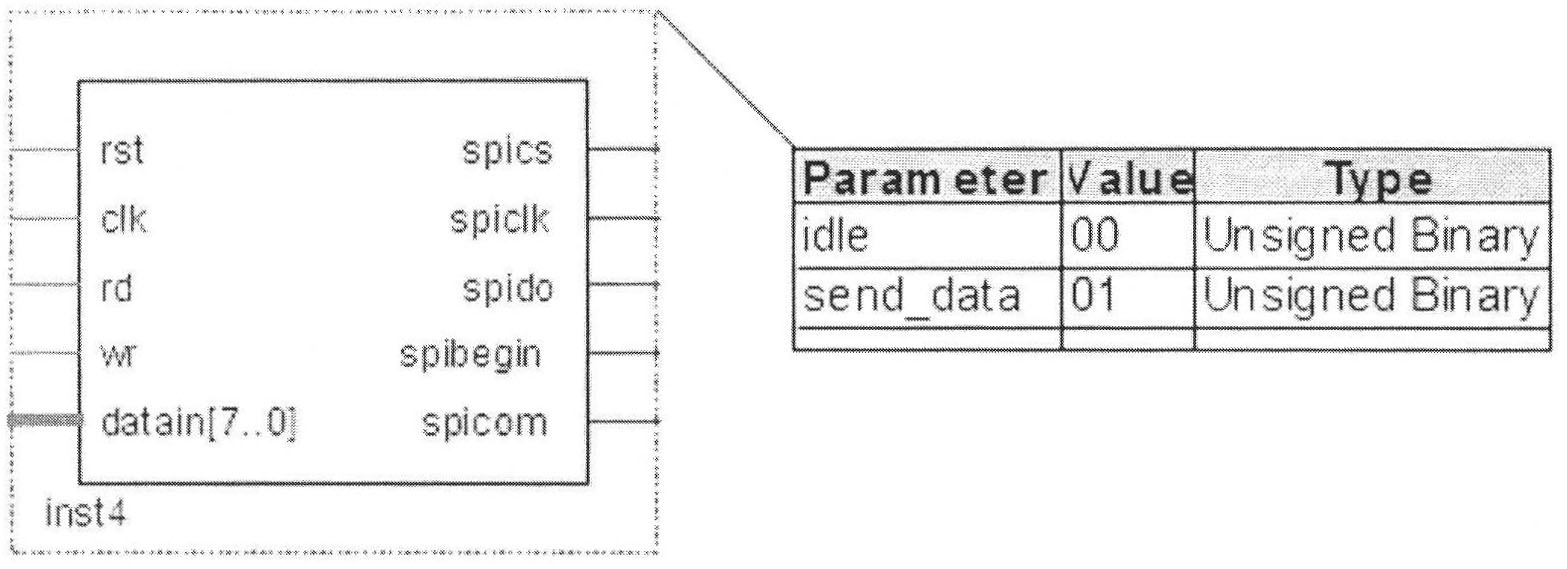
The invention relates to a modular generation method for a multi-waveform radar signal, which belongs to the technical field of radar frequency synthesis and is applied to the design of a direct digital frequency synthesis (DDS)-based frequency synthesizer. A multi-waveform radar signal module consists of modular software, a field programmable gate array (FPGA) and DDS chips. The modular software comprises a man-machine interactive interface and a modular serial port timing module, wherein the man-machine interactive interface performs relevant operation and storage of control parameters and waveform data of the DDS chips and performs data communication with the FPGA; and the modular serial port timing module generates modular serial port control timing which is suitable for the DDS series chips and completes data acquisition and updating by computer communication. The FPGA is provided with a random-access memory (RAM), a universal asynchronous receiver / transmitter (UART) and a DDS control module, and realizes the functions of data communication with a computer and the storage of the control parameters and waveform data of the DDS chips and DDS chip control. The DDS chips output various signals set by the parameters under the control of the FPGA. The modular software developed by the method configures different DDS chips, so various radar signals of point frequency, linear frequency modulation, nonlinear frequency modulation and phase encoding can be generated, and the software supports on-line programming and the real-time updating of the control parameters and waveform data of the DDS chips.
Owner:中国兵器工业第二〇六研究所
Dual band transceiver architecture for wireless communication
ActiveUS7313368B2Reduce interferenceReduce the numberSubstation equipmentTransmissionFrequency synthesizerEngineering
The present invention relates to a dual band transceiver architecture for wireless communication. A high frequency integrated circuit is used for converting down the received multi-mode frequency signal, and then a decoding circuit for base frequency will perform the processes of up-sampling and emitting a signal so as to transmit / receive the dual band signal by using a single frequency synthesizer.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Micro-strip rectangular double annular circular-seam resonator-based frequency selectivity surface structure
InactiveCN102074777AAchieving Omnidirectional ResponseSmall sizeWaveguide type devicesEngineeringBase frequency
The invention discloses a micro-strip rectangular double annular circular-seam resonator-based frequency selectivity surface structure, which comprises a micro-strip rectangular double annular circular-seam resonator unit and a medium substrate, wherein a micro-strip rectangular double annular circular-seam resonator is arranged on one side or both sides of the medium substrate or clamped betweenmedium layers, and is provided with circular seams in different directions. In a working process, electromagnetic waves in different directions enter the frequency selectivity surface structure. The structure has the advantages of small size, adjustable resonance frequency, capability of realizing omnidirectional response to electromagnetic waves and the like.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Digital spread spectrum circuitry
InactiveUS7010014B1Increased frequency rangeIncrease flexibilityPulse automatic controlSingle output arrangementsElectromagnetic radiationBase frequency
The frequency of a skew clock signal is dithered around a base frequency, thereby enabling this clock signal to comply with FCC requirements for electromagnetic emissions within a specified window. Delay is introduced such that the clock signals exhibits slightly different frequencies in successive periods. For example, the frequency of a 100 MHz clock signal can be adjusted to have frequencies of approximately 98, 98.5, 99, 99.5, 100, 100.5, 101, 101.5, and 102 MHz during different periods. Because the frequencies are spread in 0.5 MHz increments, only three frequencies are included in any 1 MHz window. As a result, ⅔ of the energy of the clock signal is not included when determining whether the clock signal meets the FCC electromagnetic emission requirements. By spreading the frequencies above and below the base frequency in a regular manner, the average frequency of the clock signal becomes equal to the base frequency.
Owner:XILINX INC
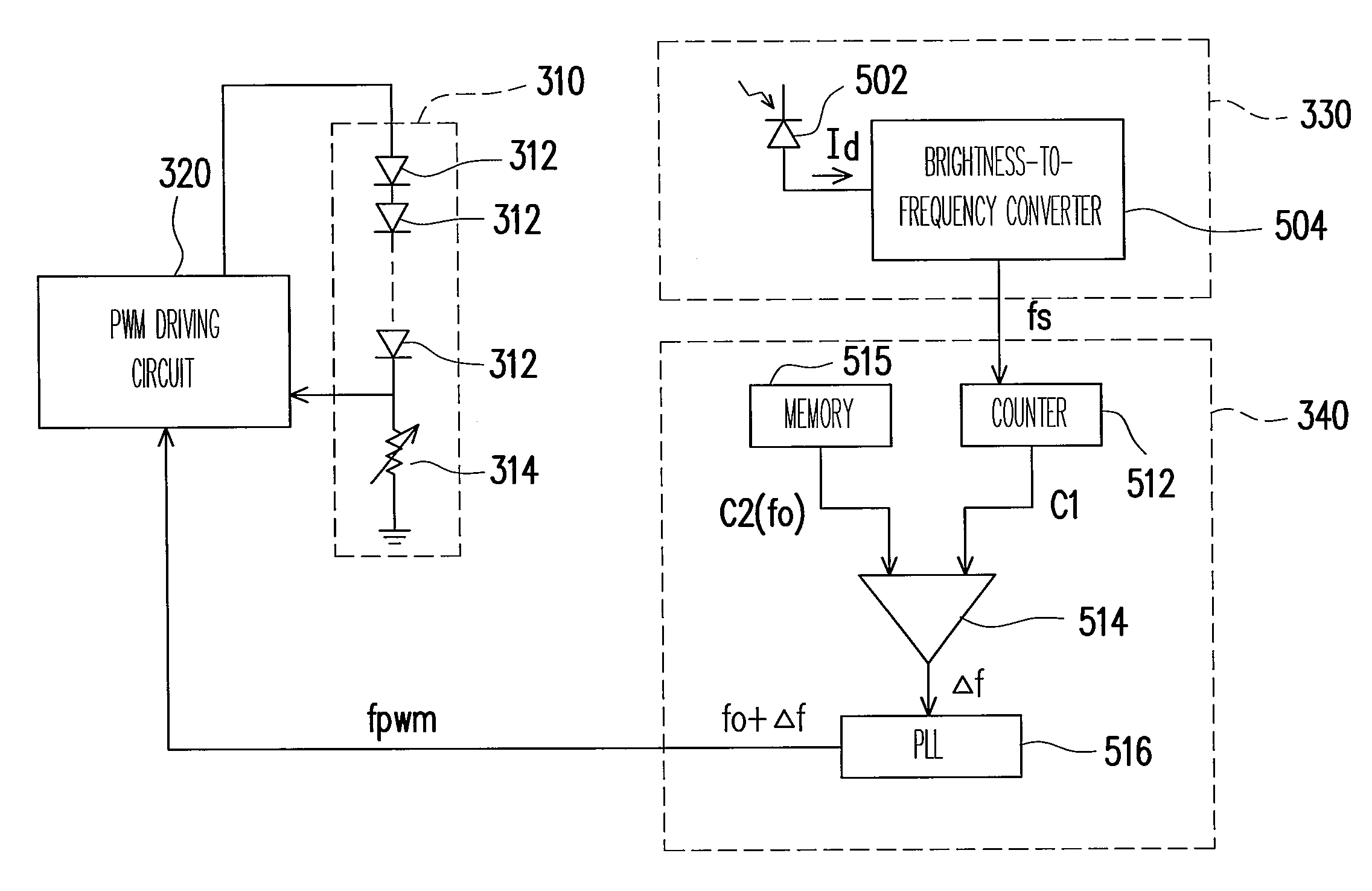
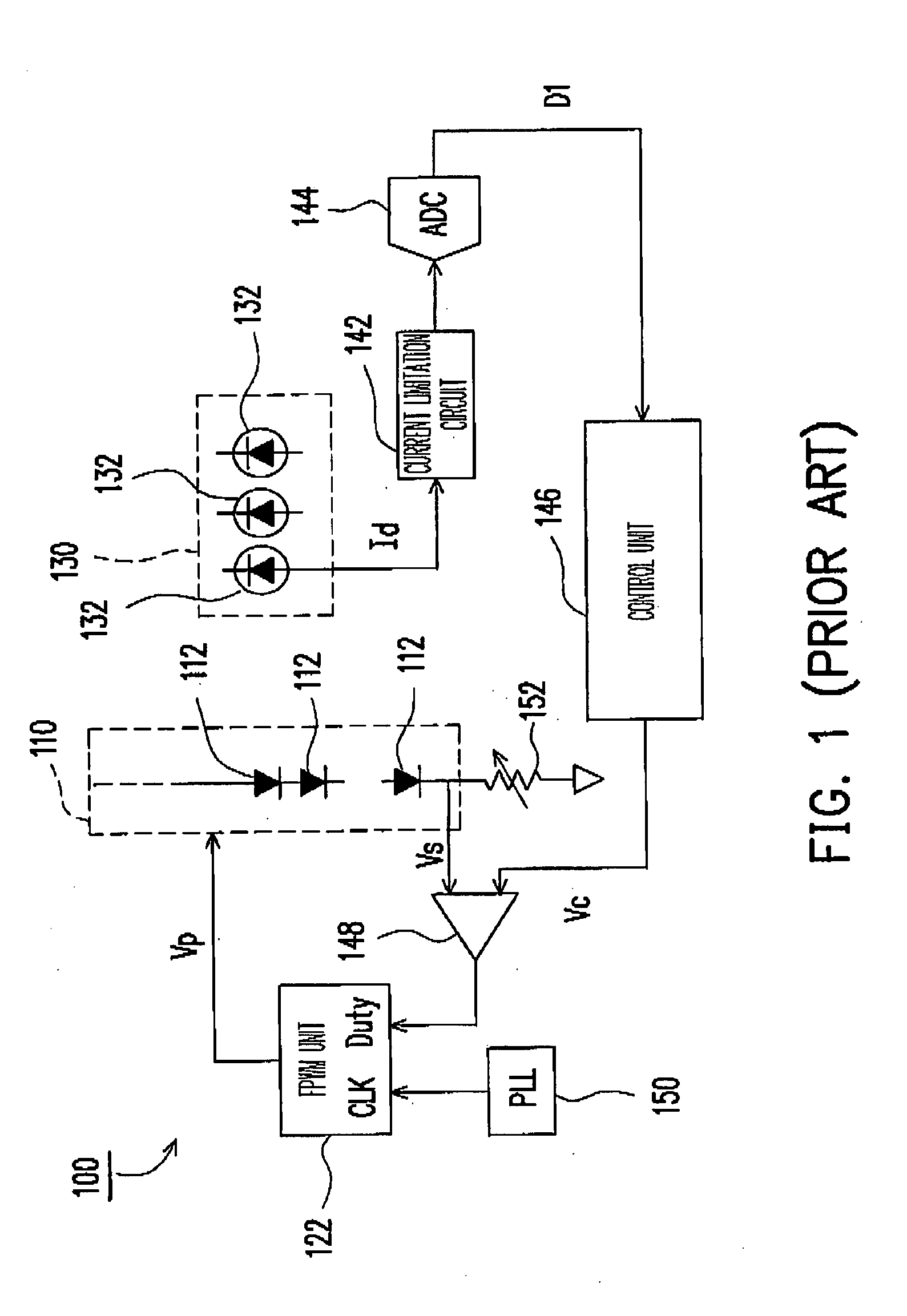
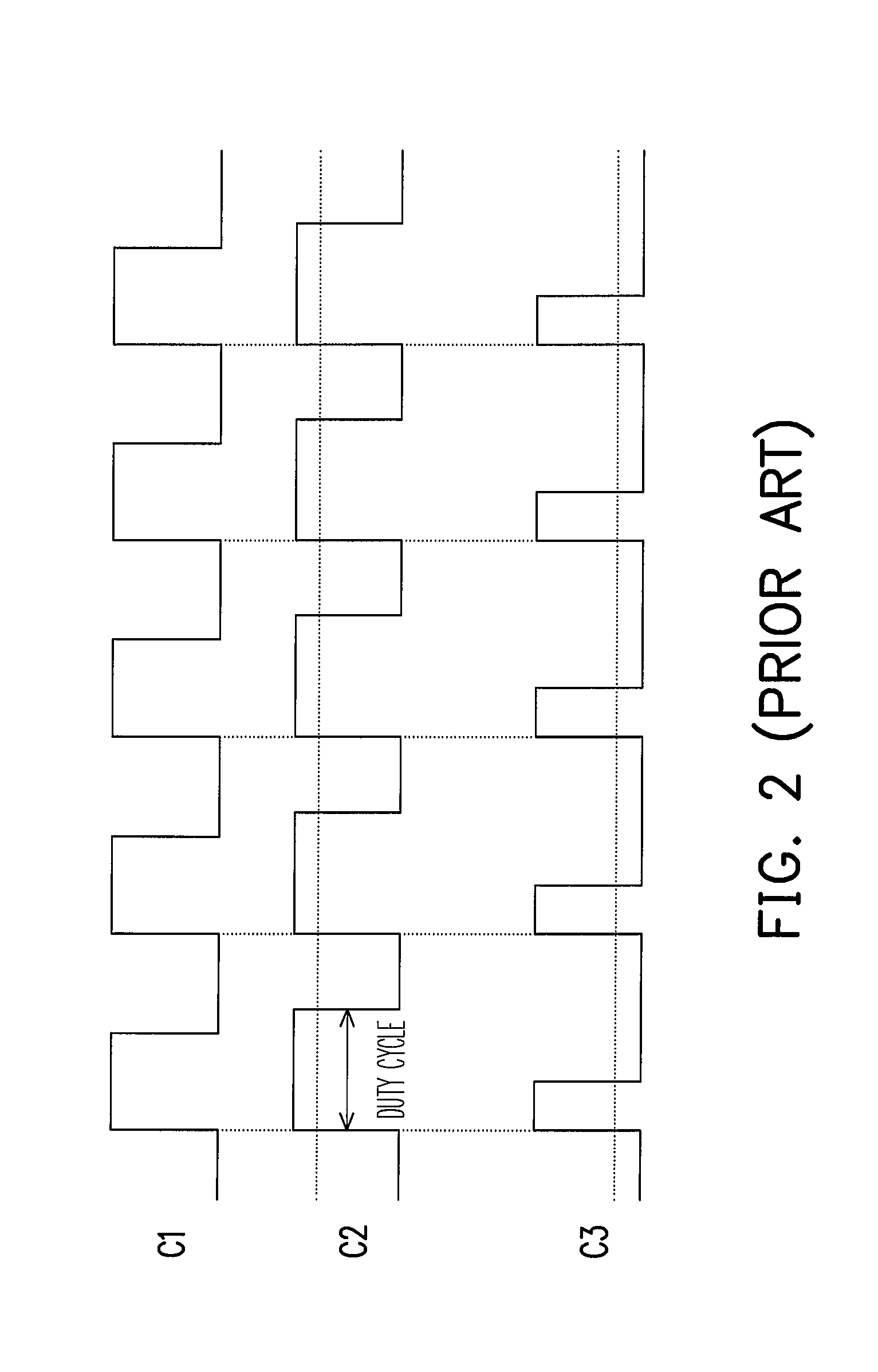
Backlight device and method for controlling light source brightness thereof
InactiveUS20070257869A1Low costLimited brightnessElectrical apparatusStatic indicating devicesControl signalOptoelectronics
A backlight device includes a light source module having a plurality of light sources, a detecting circuit, a control unit, and a pulse width modulation (PWM) driving circuit. The detecting circuit is used for detecting the brightness of the light source module and generating a detecting signal to the control unit, such that the control unit outputs a control signal according to the detecting signal. In addition, the PWM driving circuit is used for generating a PWM signal for driving the light source module. In the present invention, the PWM driving circuit adjusts the base frequency of the PWM signal according to the control signal without adjusting the duty cycle of the PWM signal, so as to control the brightness of the light sources.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
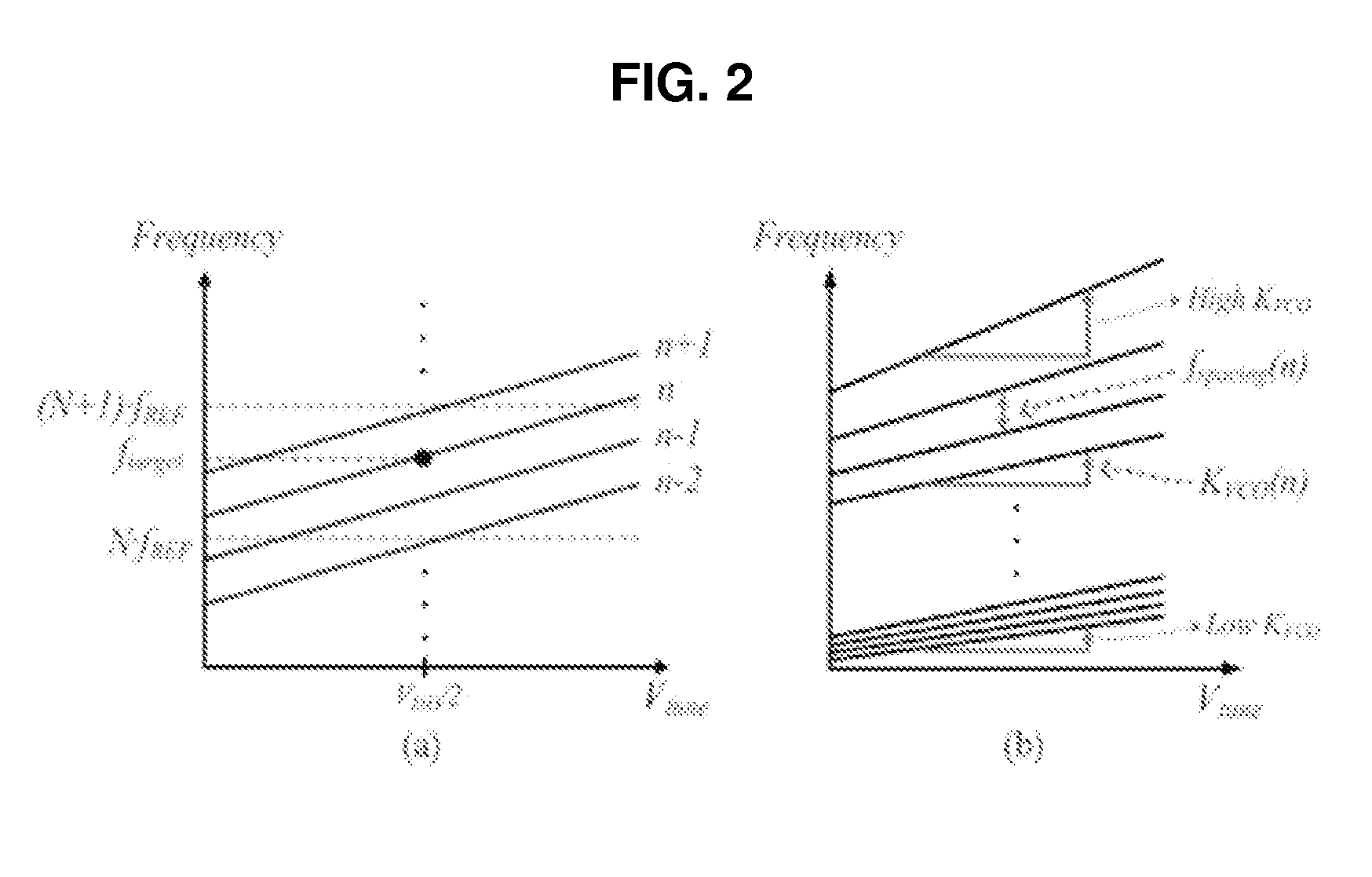
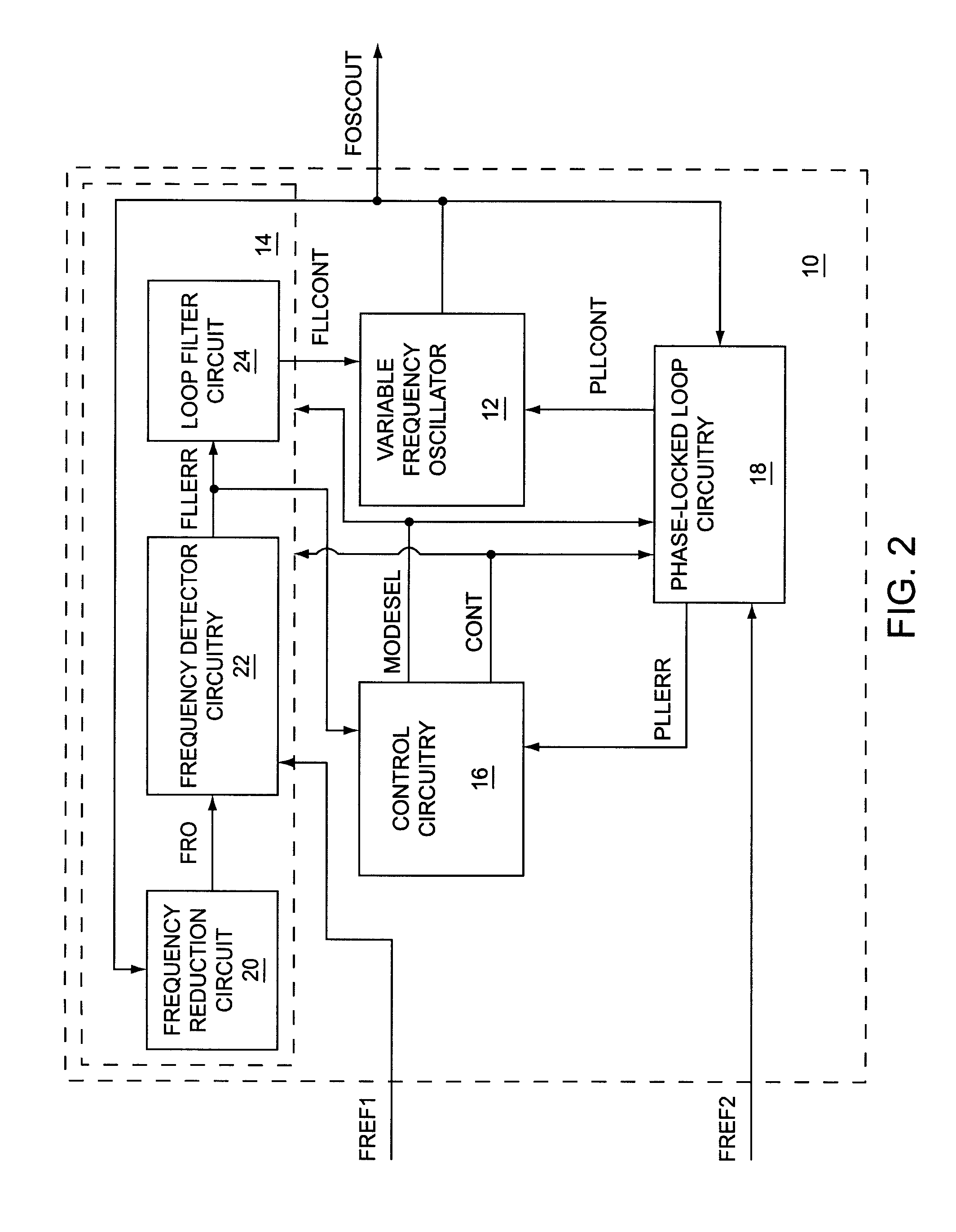
Automatic frequency calibration apparatus and method for a phase-locked loop based frequency synthesizer
ActiveUS20100213984A1Improve the speed of calibrationAccurate CalibrationPulse automatic controlOscillations generatorsImage resolutionFinite-state machine
An automatic frequency calibration apparatus and a method thereof for a phase-locked loop based frequency synthesizer are disclosed. The apparatus includes a frequency-to-digital converter configured to convert a frequency of a VCO output signal to a first digital value, a target value setting section configured to provide a second digital value corresponding to a target frequency, and a finite state machine configured to calibrate the frequency of the VCO output signal by using the difference of the first digital value and the second digital value. Accordingly, the calibration speed and a frequency resolution of the automatic frequency calibration apparatus in a frequency synthesizer may be enhanced.
Owner:KWANGWOON UNIV IND ACADEMIC COLLABORATION FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com