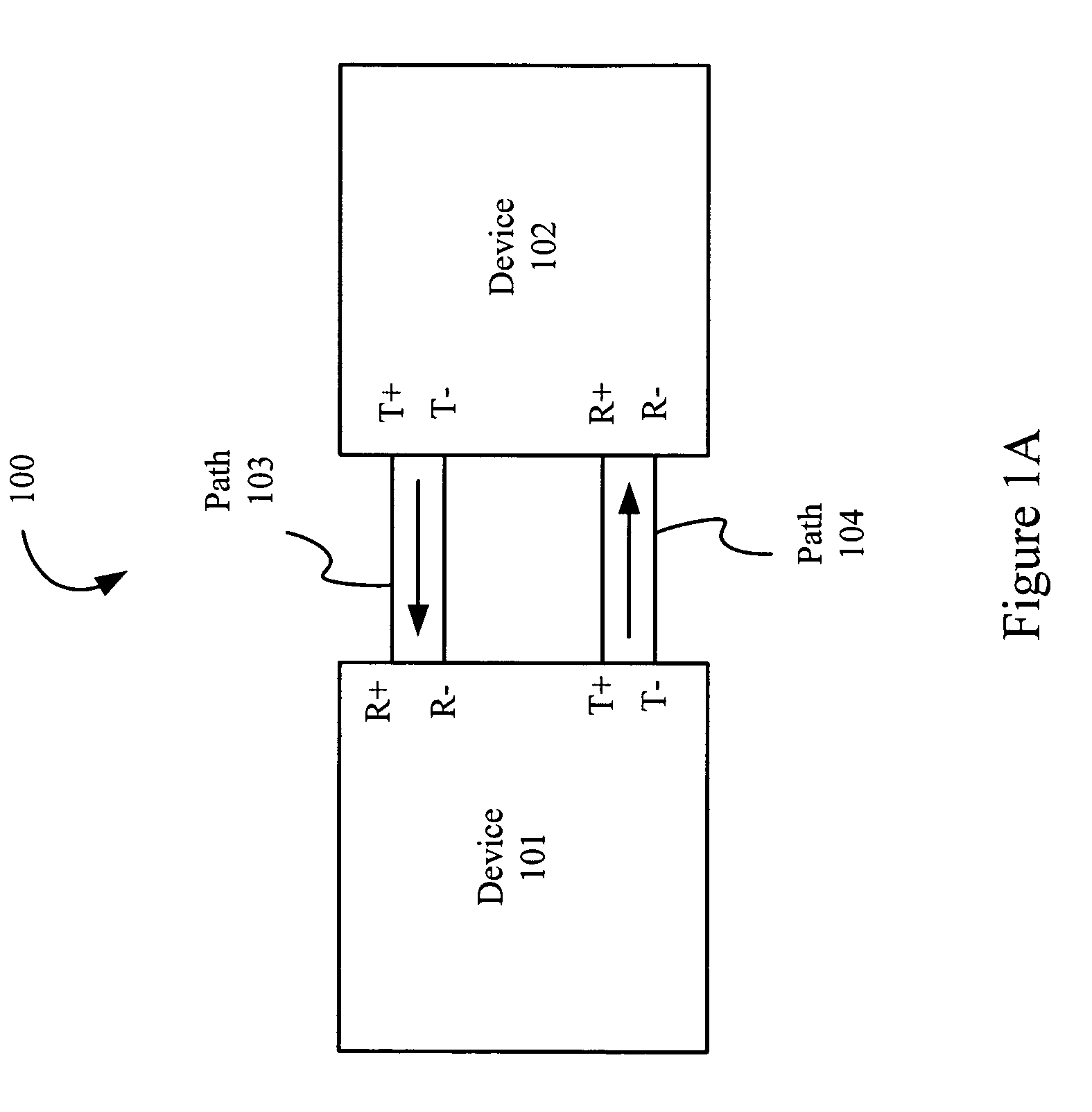
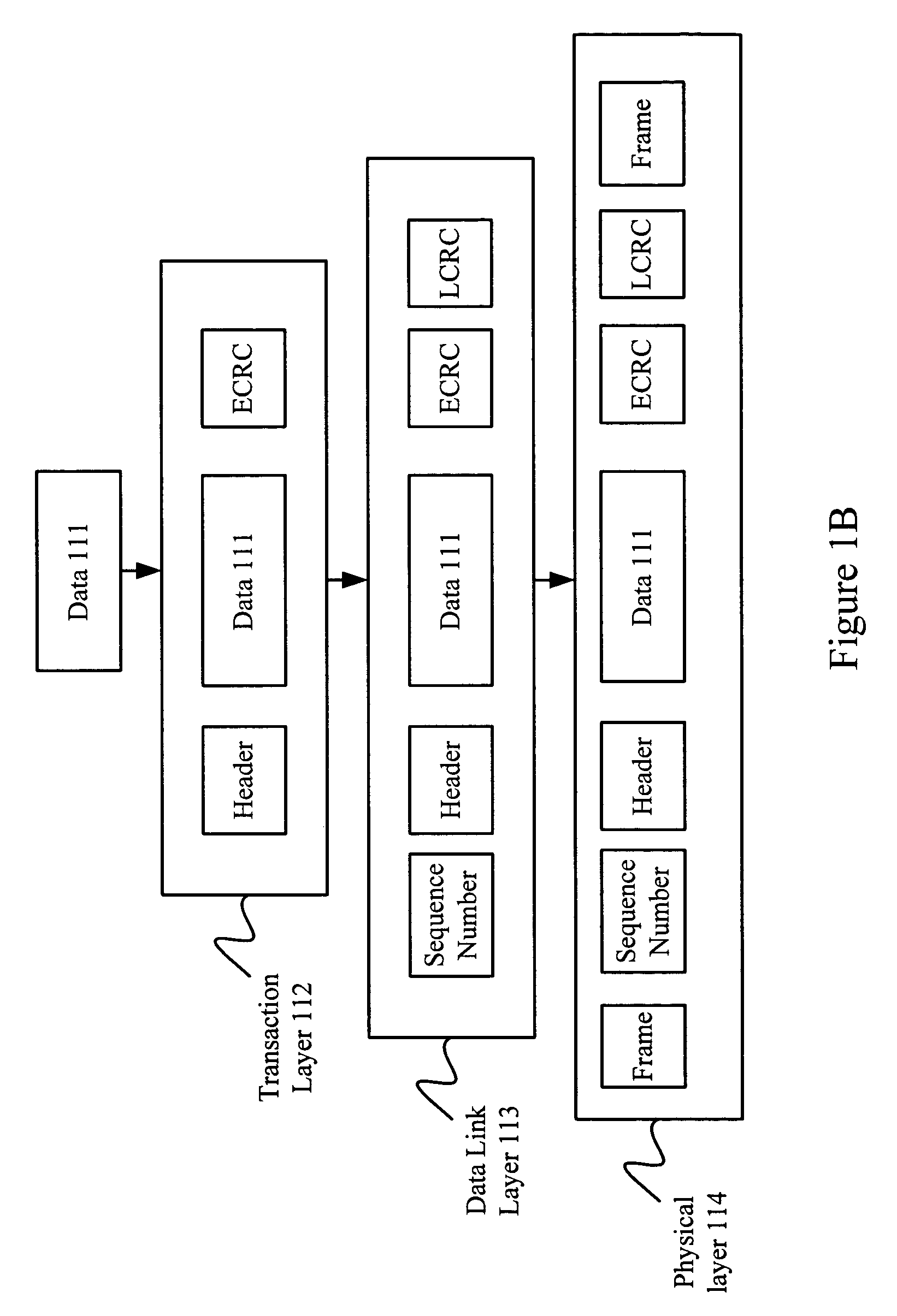
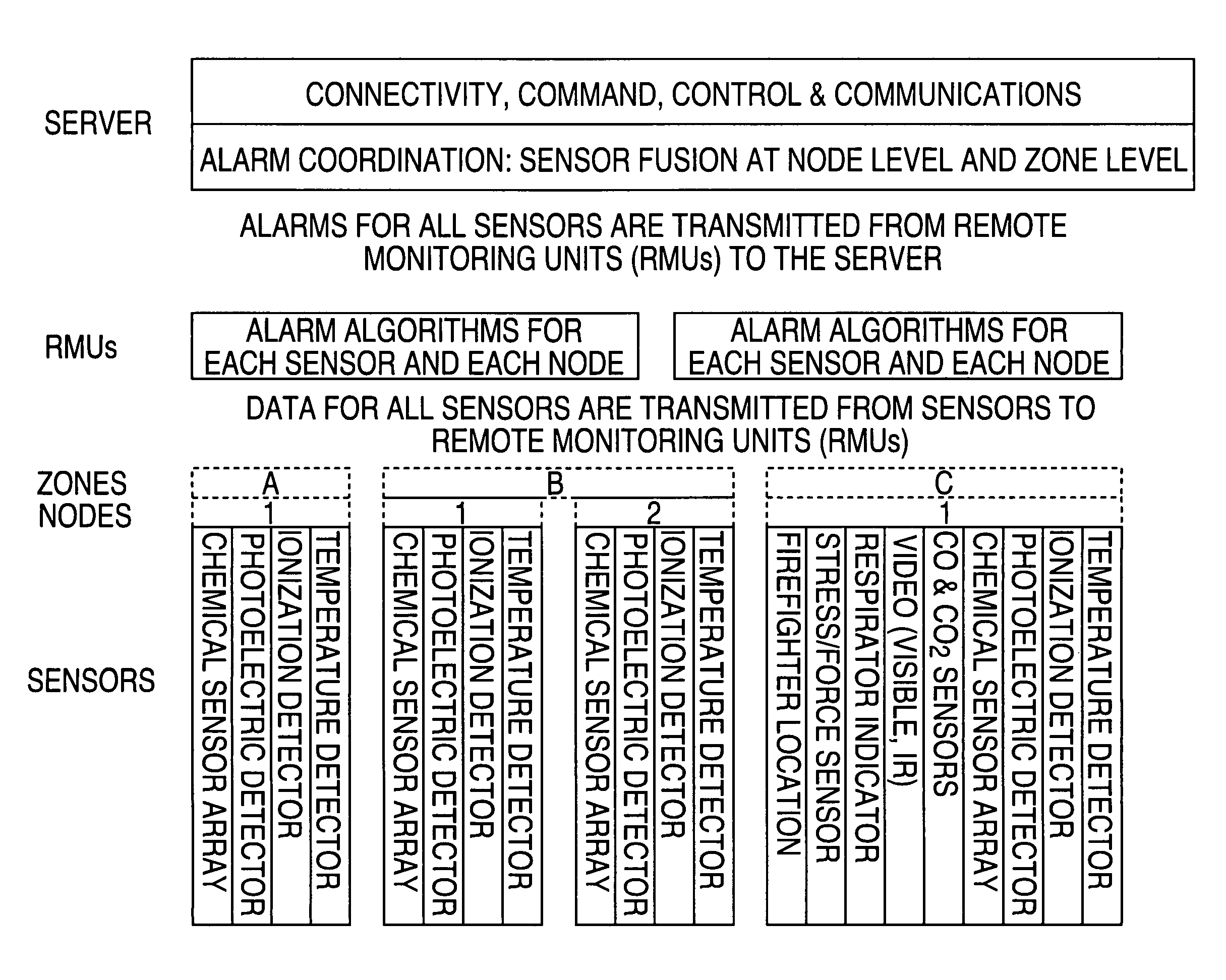
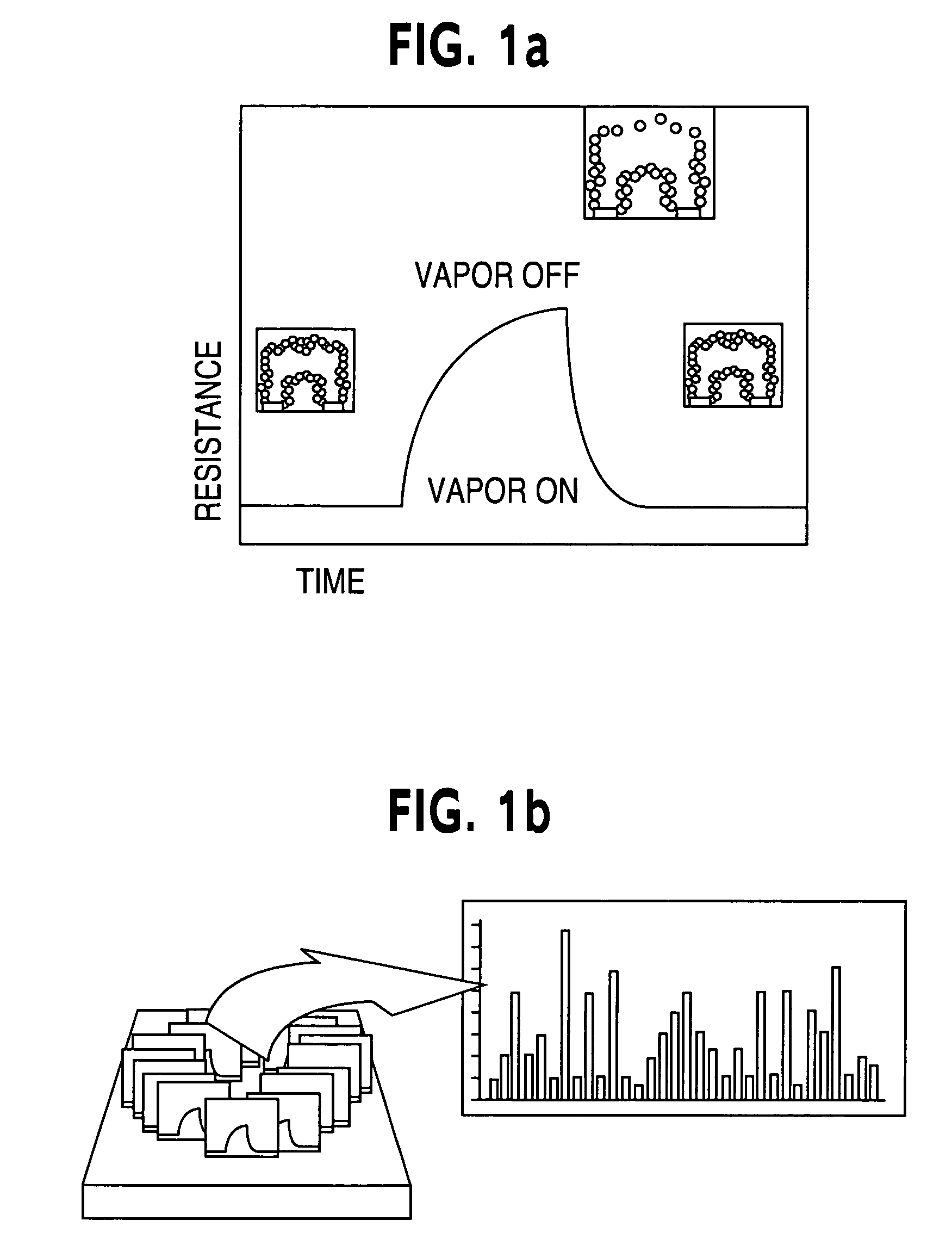
Patents
Literature
2910results about How to "Reduced Power Requirements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
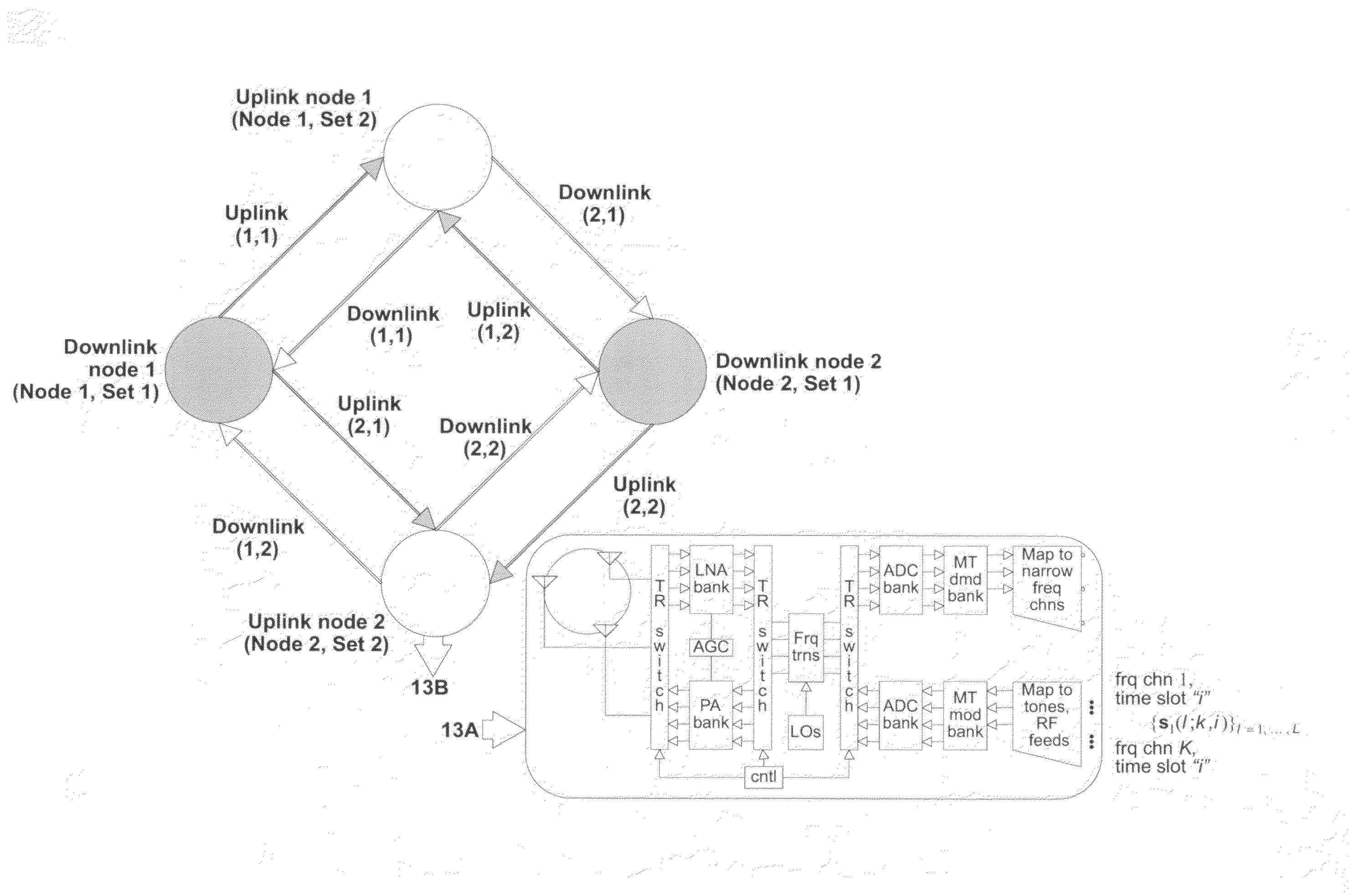
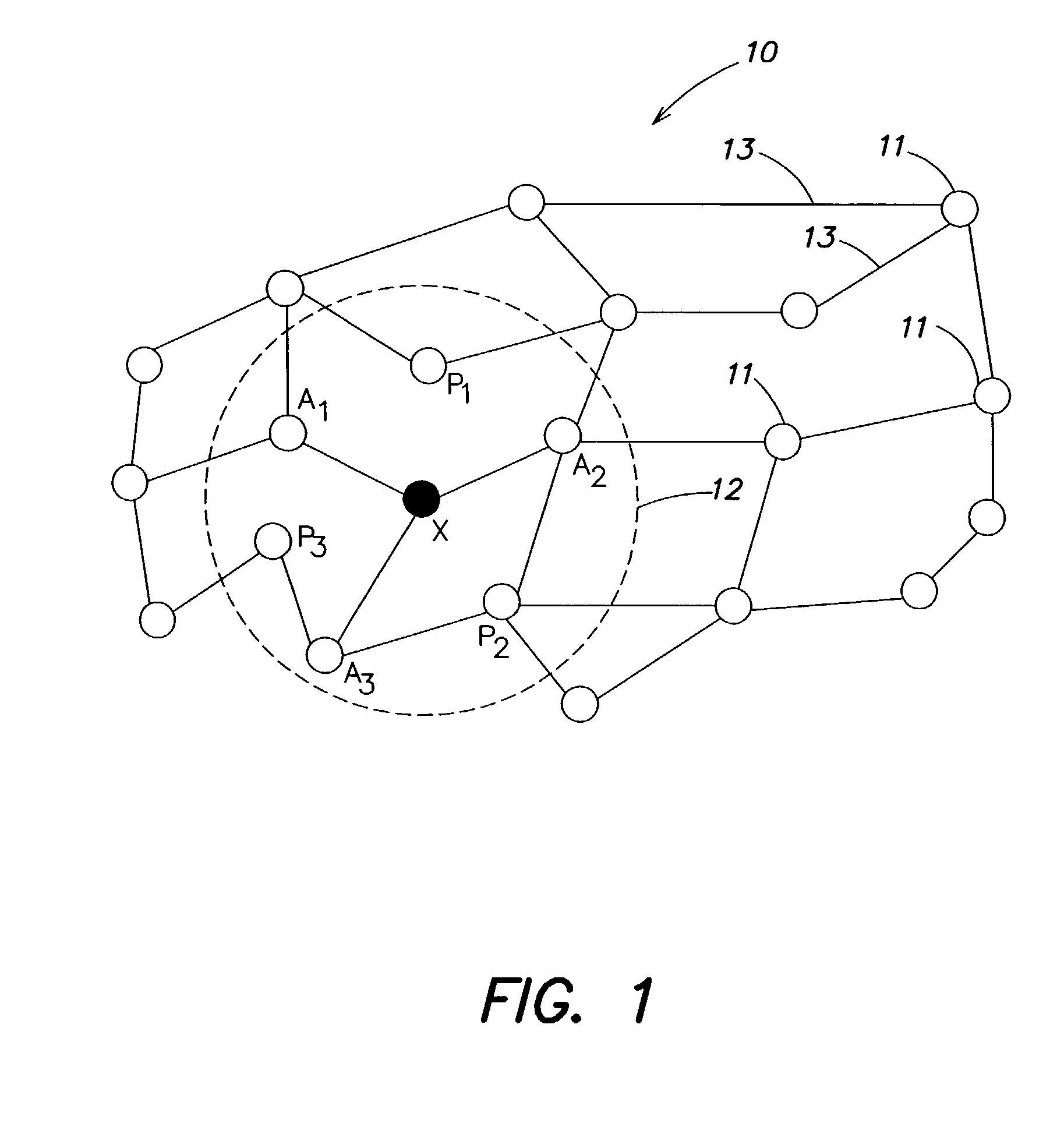
Method and apparatus for optimization of wireless multipoint electromagnetic communication networks
InactiveUS7248841B2Strong advantageReduced Power RequirementsPower managementSpatial transmit diversityGlobal optimizationRandom delay
Exploiting the substantive reciprocity of internode channel responses through dynamic, adaptive modification of receive and transmit weights, enables locally enabled global optimization of a multipoint, wireless electromagnetic communications network of communication nodes. Each diversity-channel-capable node uses computationally efficient exploitation of pilot tone data and diversity-adaptive signal processing of the weightings and the signal to further convey optimization and channel information which promote local and thereby network-global efficiency. The preferred embodiment performs complex digital signal manipulation that includes a linear combining and linear distribution of the transmit and receive weights, the generation of piloting signals containing origination and destination node information, as well as interference-avoiding pseudorandom delay timing, and both symbol and multitone encoding, to gain the benefit of substantive orthogonality at the physical level without requiring actual substantive orthogonality at the physical level.
Owner:COMCAST CABLE COMM LLC
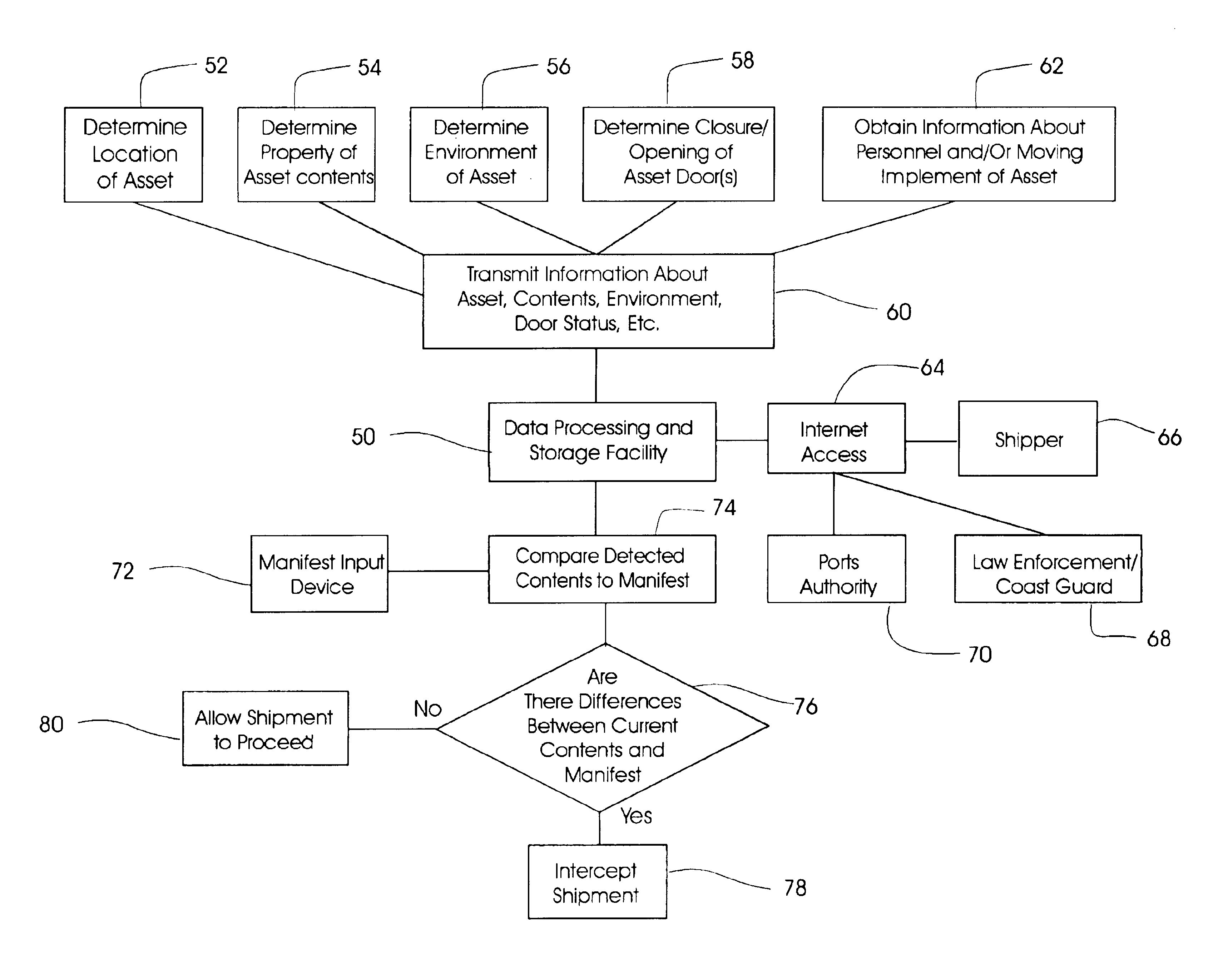
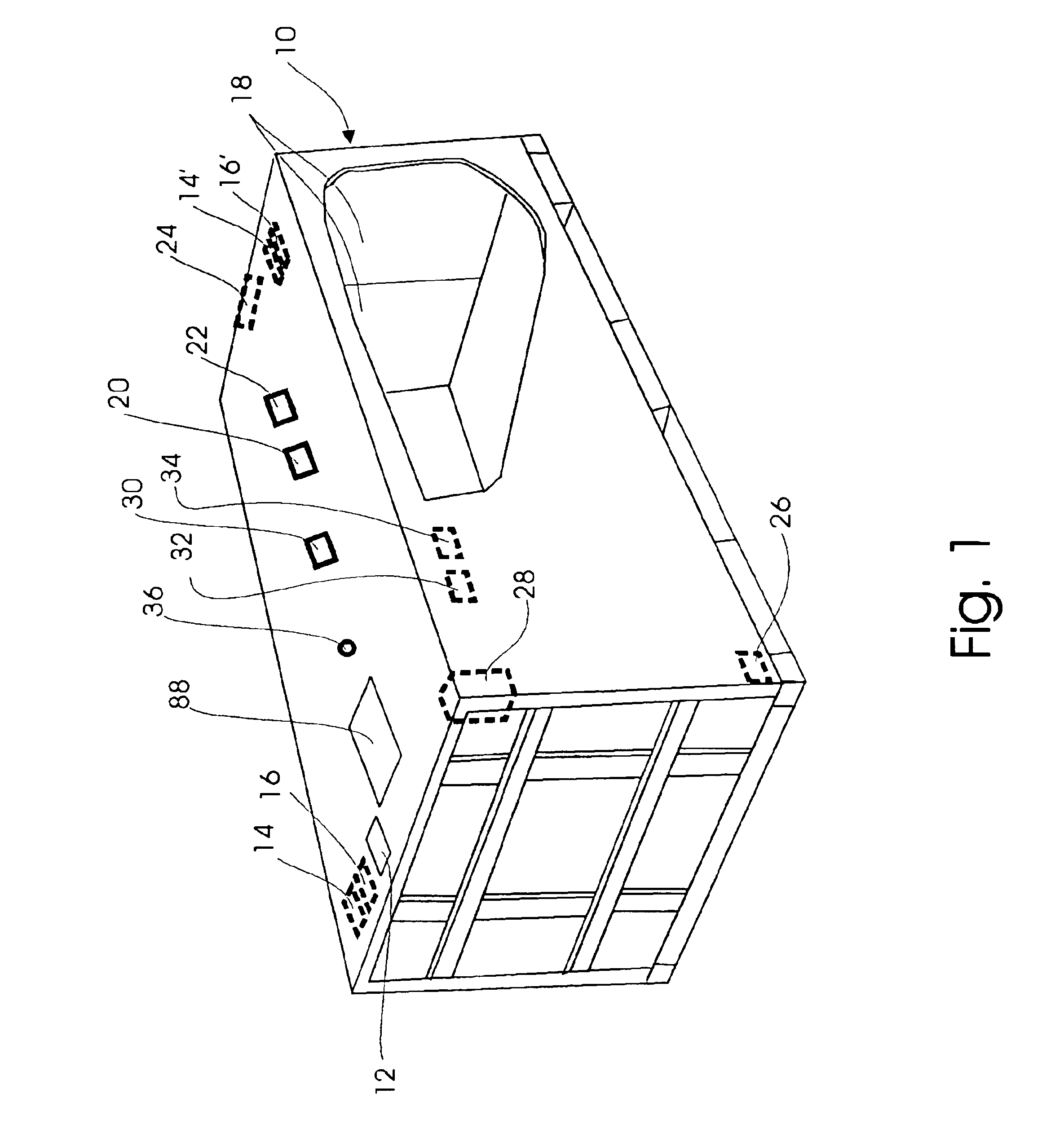
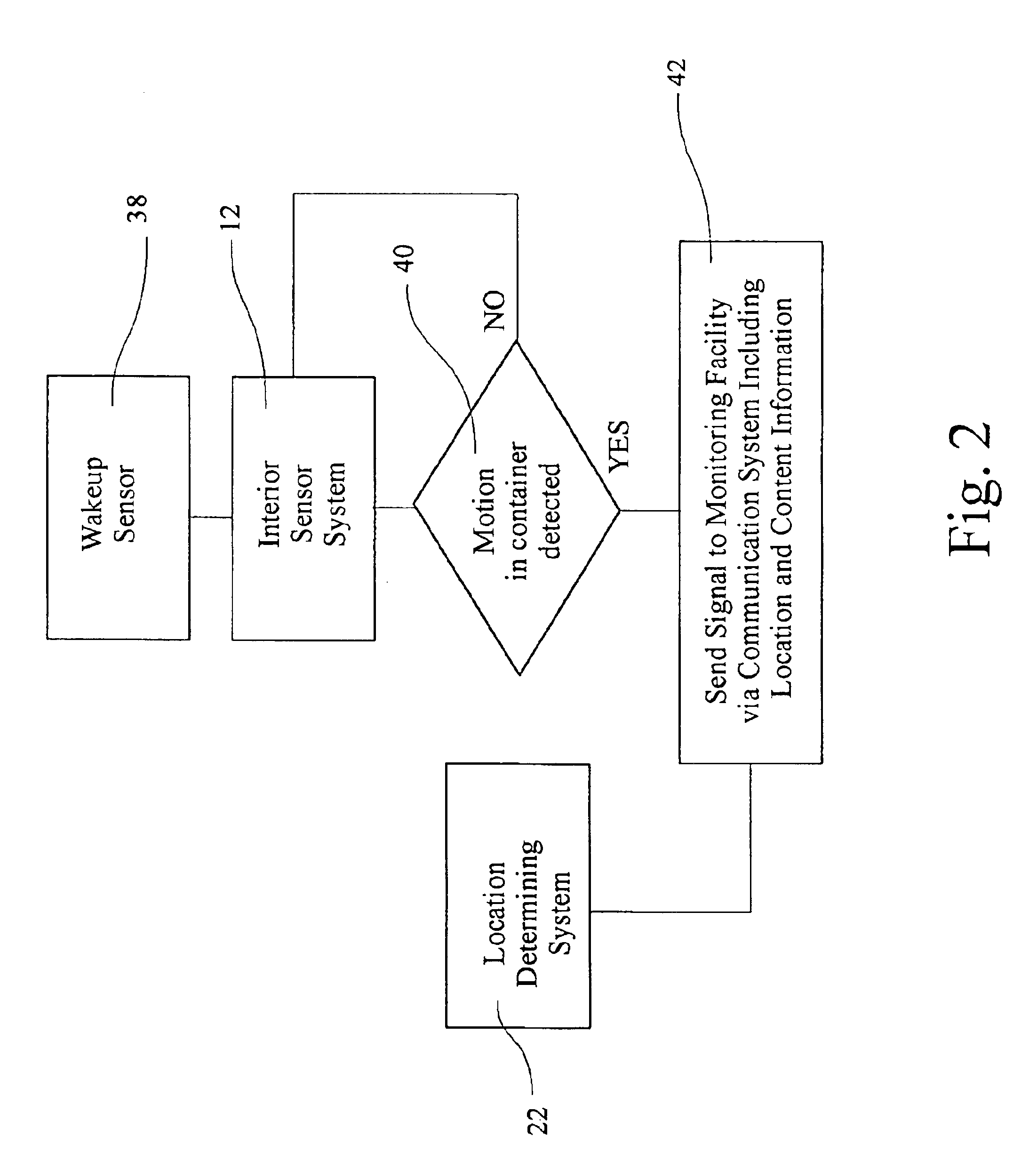
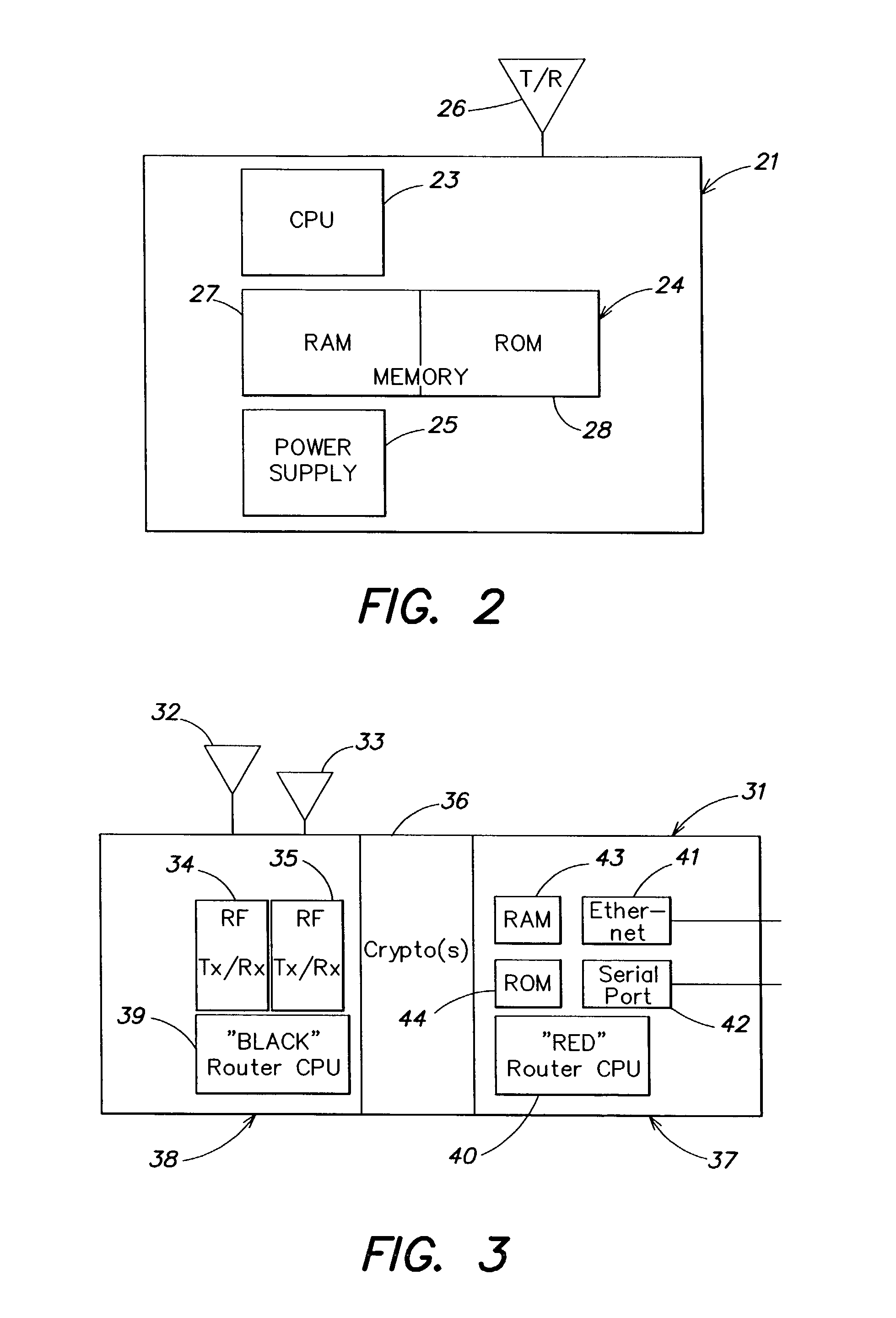
Low power remote asset monitoring
InactiveUS6919803B2Extended service lifeReduced Power RequirementsHand manipulated computer devicesDirection finders using radio wavesCommunications systemEngineering
Arrangement for monitoring an asset including an interior sensor system arranged on the asset to obtain information about contents in the interior of the asset, a location determining system arranged on the asset to monitor the location of the asset and a communication system arranged on the asset and coupled to the interior sensor system and the location determining system. The communication system operatively transmits the information about the contents in the interior of the asset and the location of the asset to a remote facility. The interior sensor system may include at least one wave transmitter arranged to transmit waves into the interior of the asset and at least one wave receiver arranged to receive waves from the interior of the asset. A processor may be provided to compare waves received by the wave receiver(s) at different times or analyze the waves received by the wave receiver(s).
Owner:INTELLIGENT TECH INT
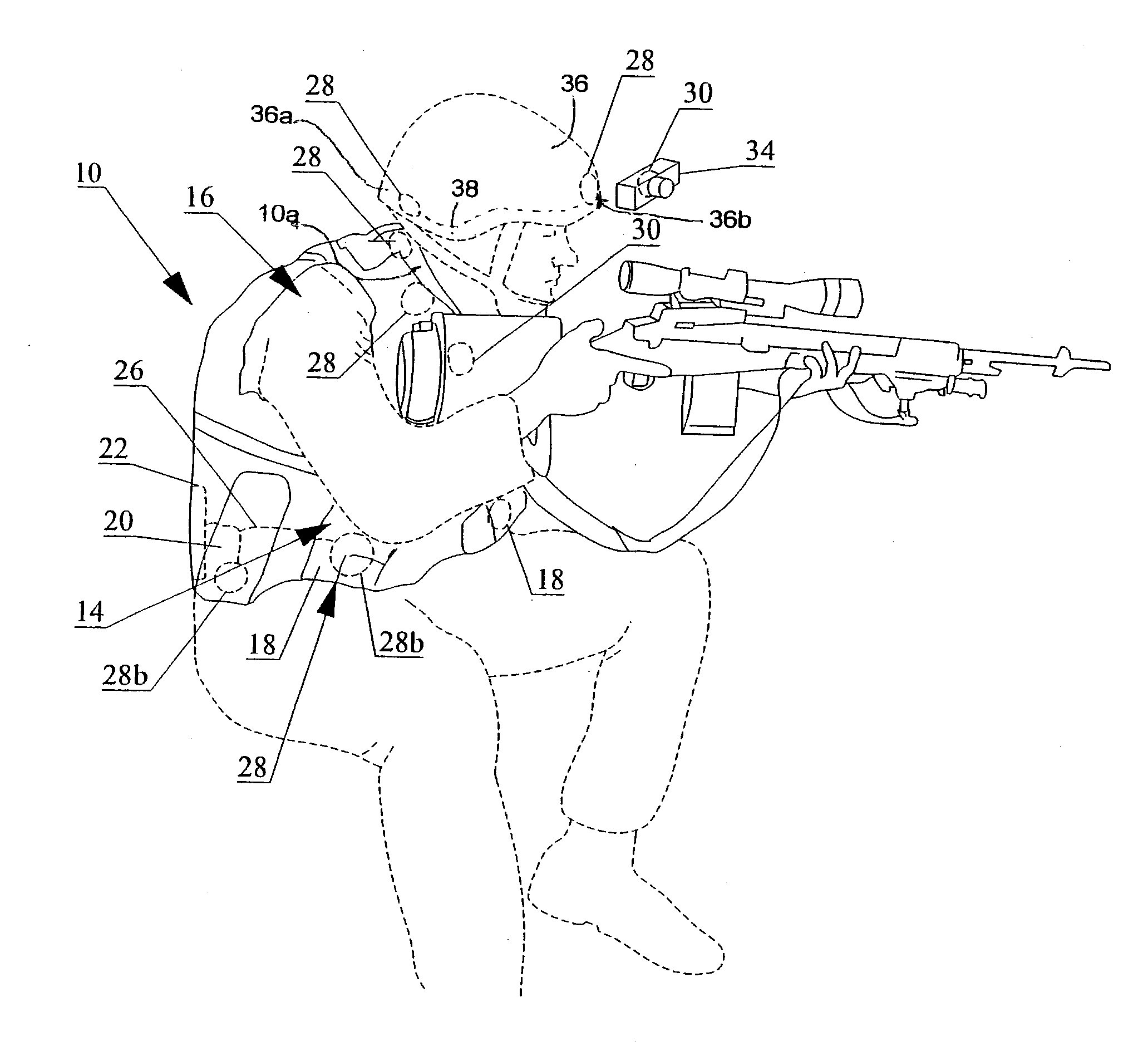
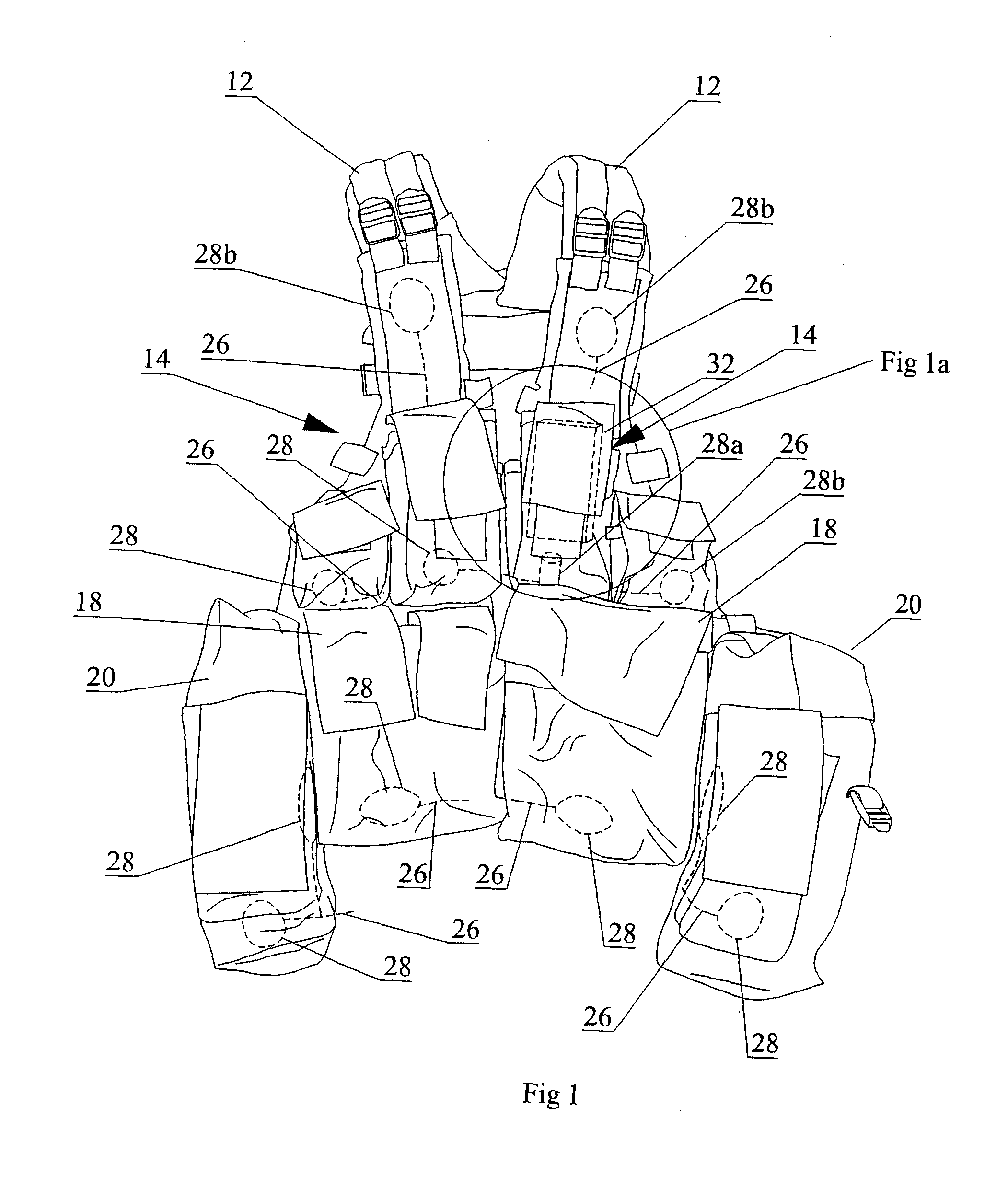
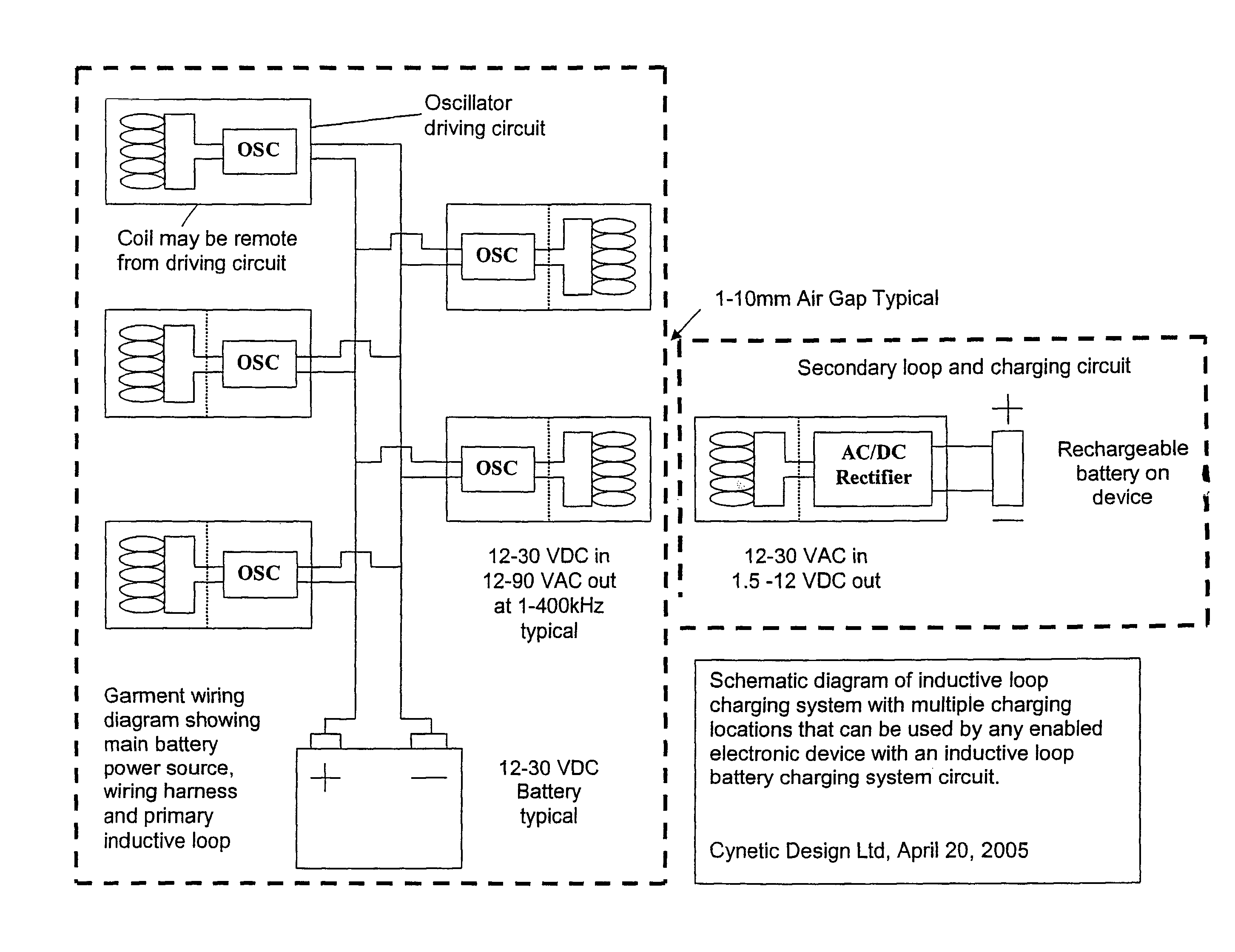
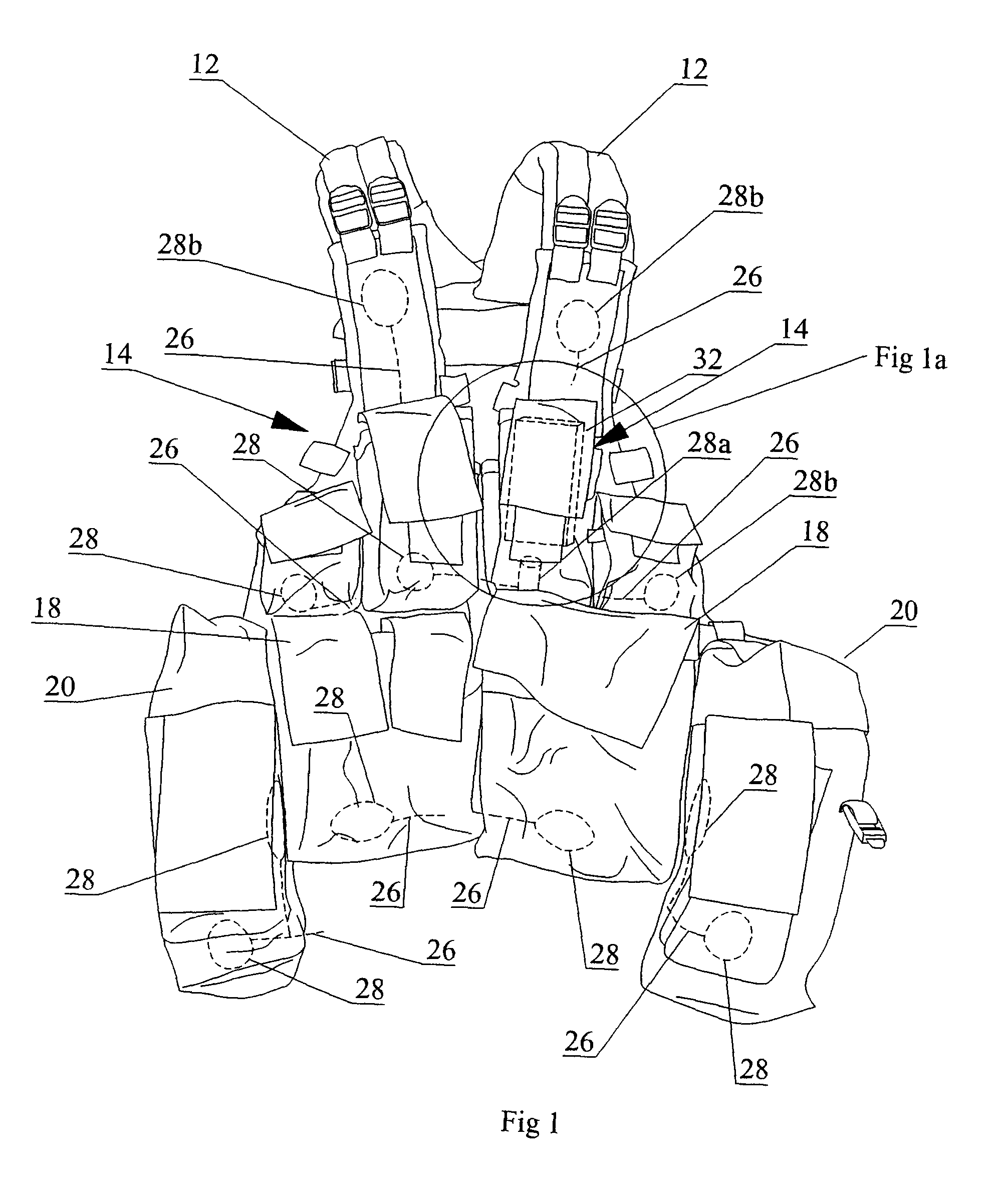
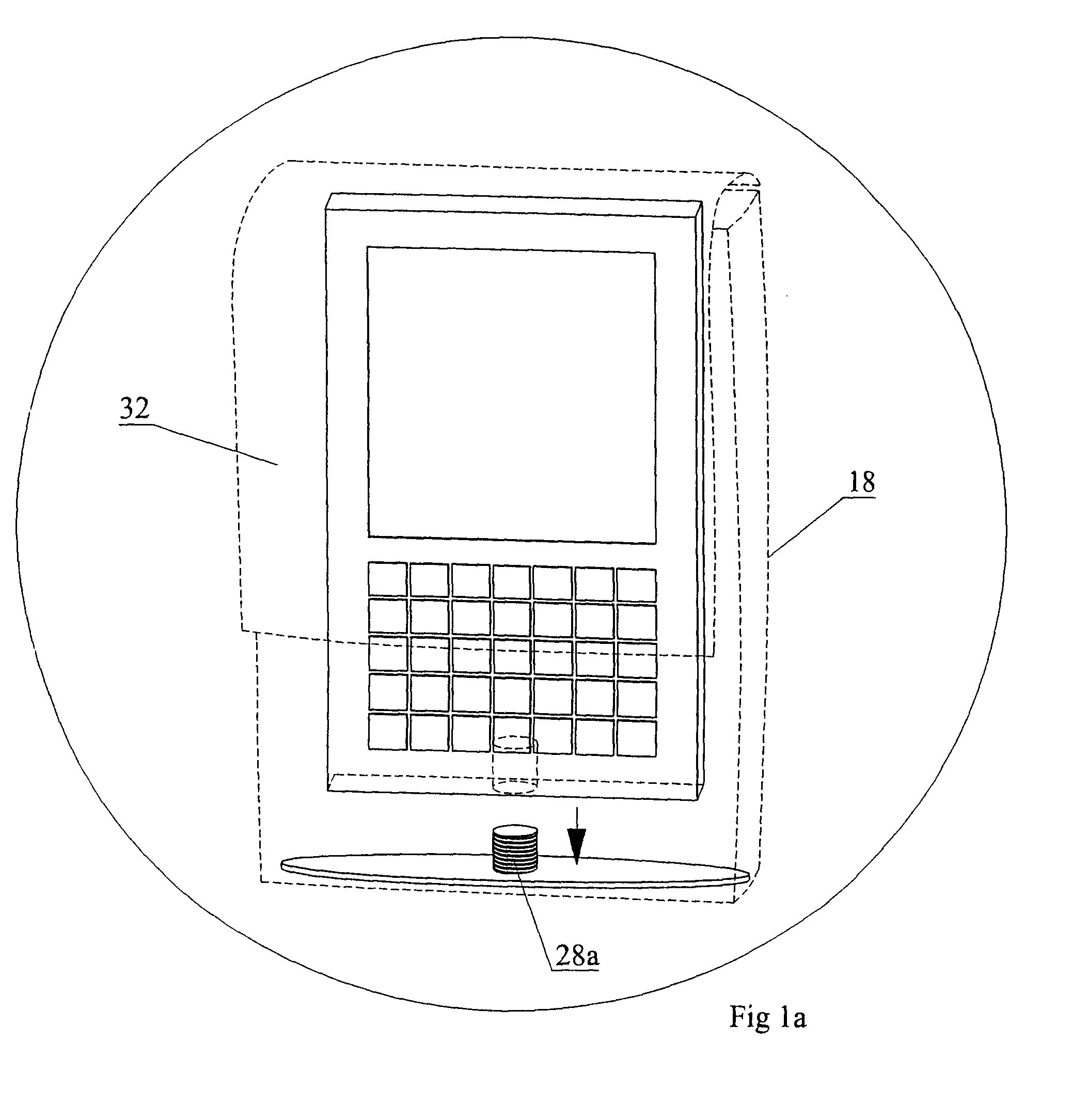
Contactless Battery Charging Apparel
InactiveUS20090218884A1Large battery powerReduce peripheral device power requirementDc network circuit arrangementsBatteries circuit arrangementsBattery chargeInductance
A sequential power transmission between a portable user-carried battery and first and second independent accessories. At least one primary inductive coupling coil is mounted on an article of apparel worn by the user, so as to place a primary coil adjacent a first intermediary inductive coupling coil on the first independent accessory. The energizing of the first intermediary coil energizes a second intermediary coil on the first independent accessory. The second intermediary coil, when energized, energizes a secondary coil on the second independent accessory for powering the use, including the charging of the batteries of that accessory.
Owner:CYNETIC DESIGNS
Ultrasonic Through-Wall Communication (UTWC) System
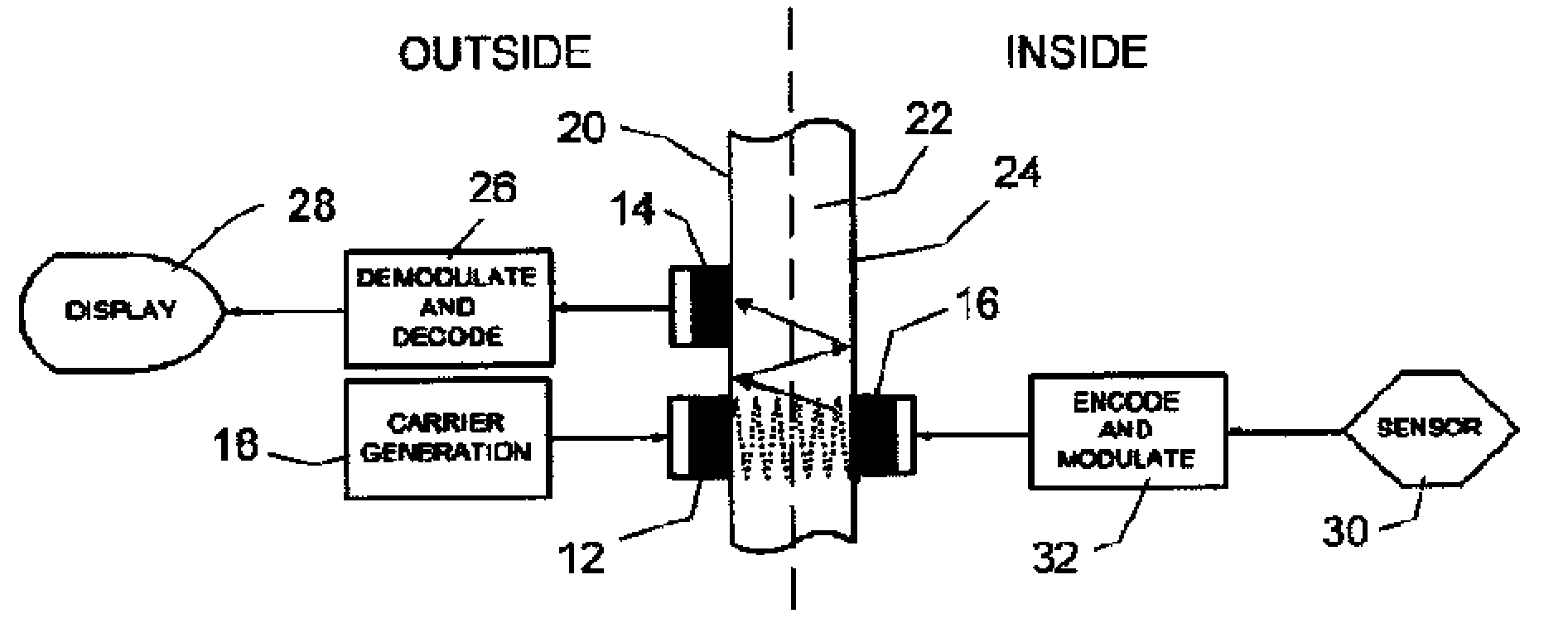
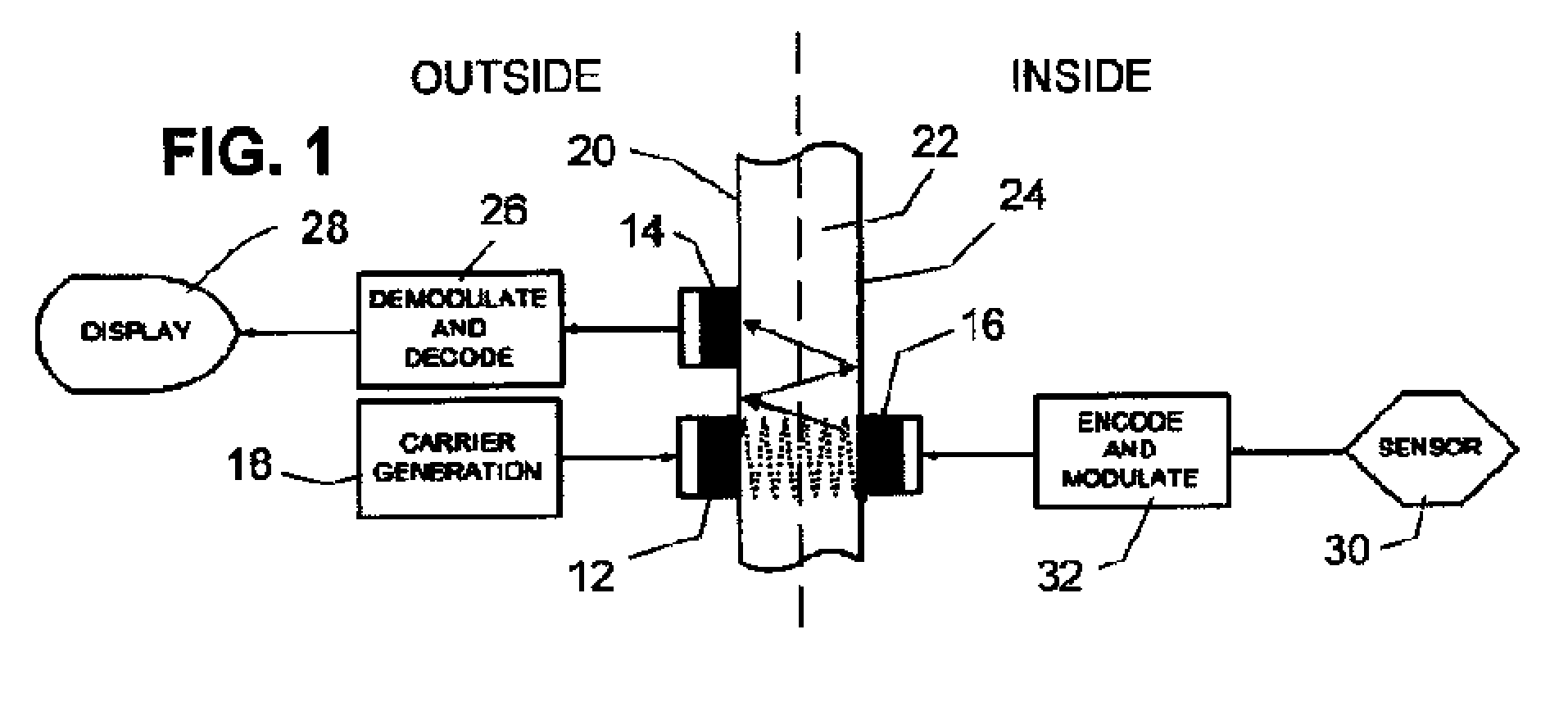
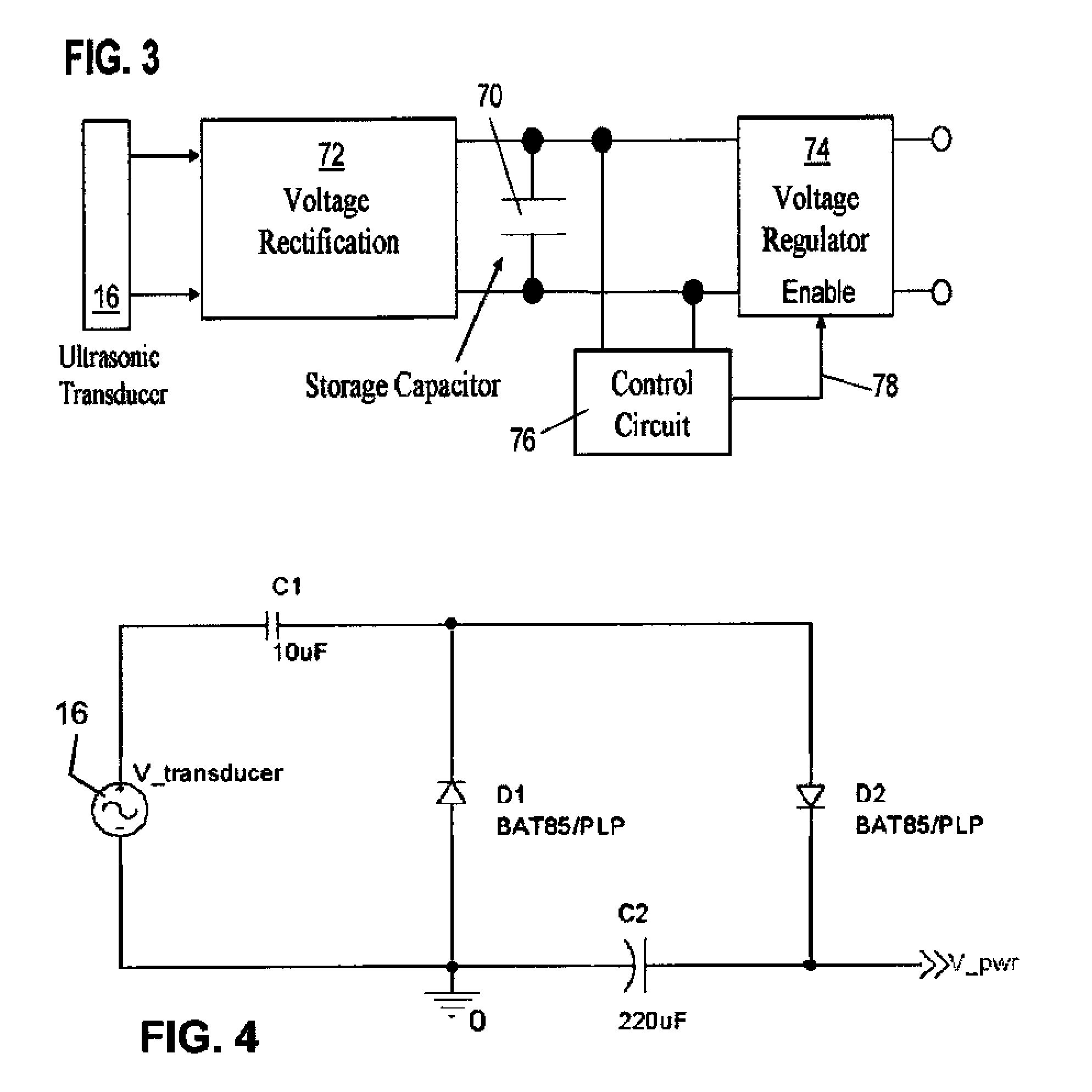
InactiveUS20100027379A1Reduced Power RequirementsMinimal complexityNon-electrical signal transmission systemsSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionUltrasonic sensorTransducer
Apparatus for communicating information across a solid wall has one or two outside ultrasonic transducers coupled to an outside surface of the wall and connected to a carrier generator for sending an ultrasonic carrier signal into the wall and for receiving an output information signal from the wall. One or two inside ultrasonic transducers are coupled to an inside surface of the wall and one of them introduces the output information signal into the wall. When there are two inside transducers inside the wall, one receives the carrier signal and the second transmits the carrier after it is modulated by the output information from the sensor. When there is one inside transducer, the output information from the sensor is transmitted by changing the reflected or returned signal from the inside transducer. A power harvesting circuit inside the wall harvests power from the carrier signal and uses it to power the sensor.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY +1
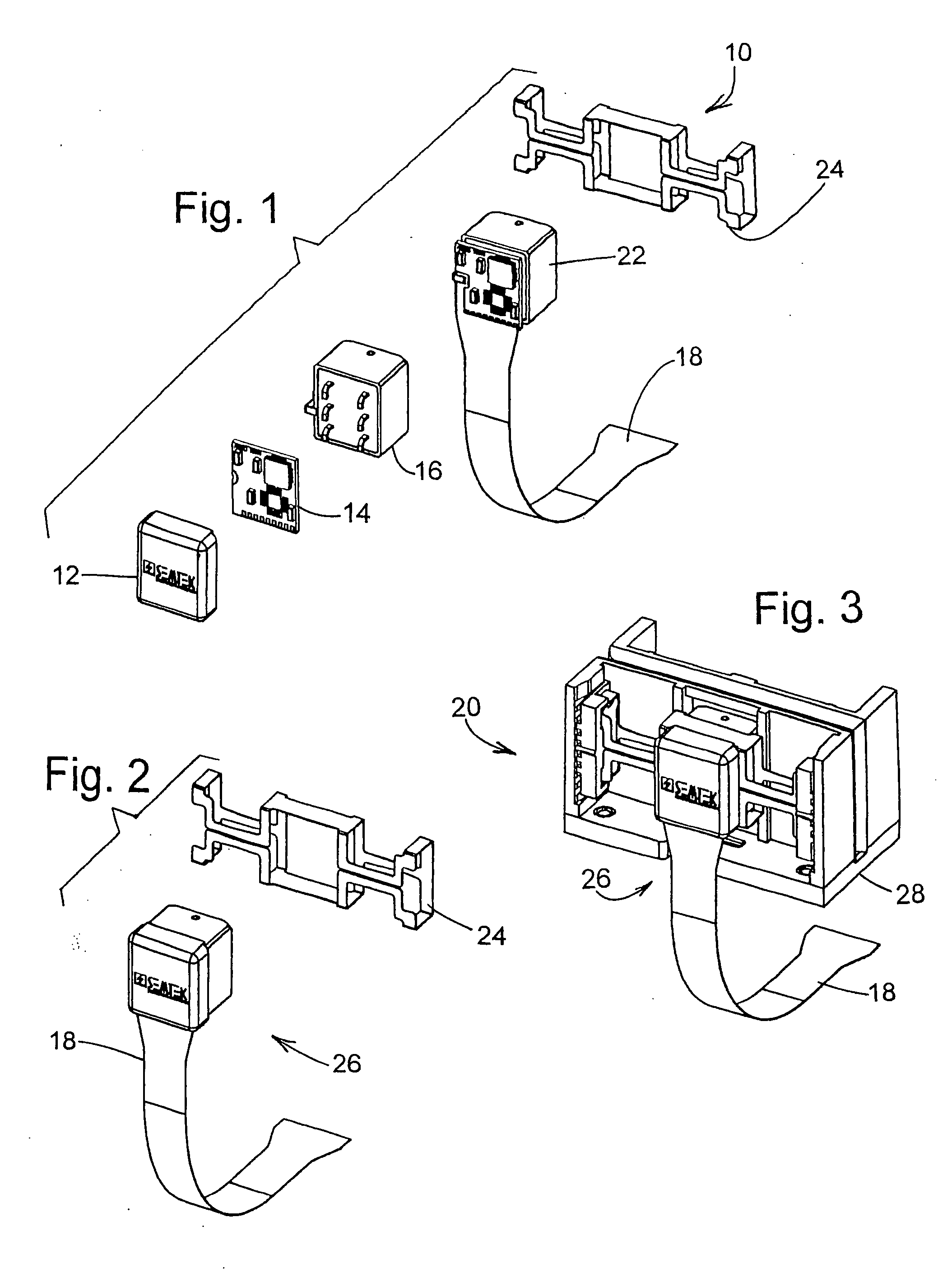
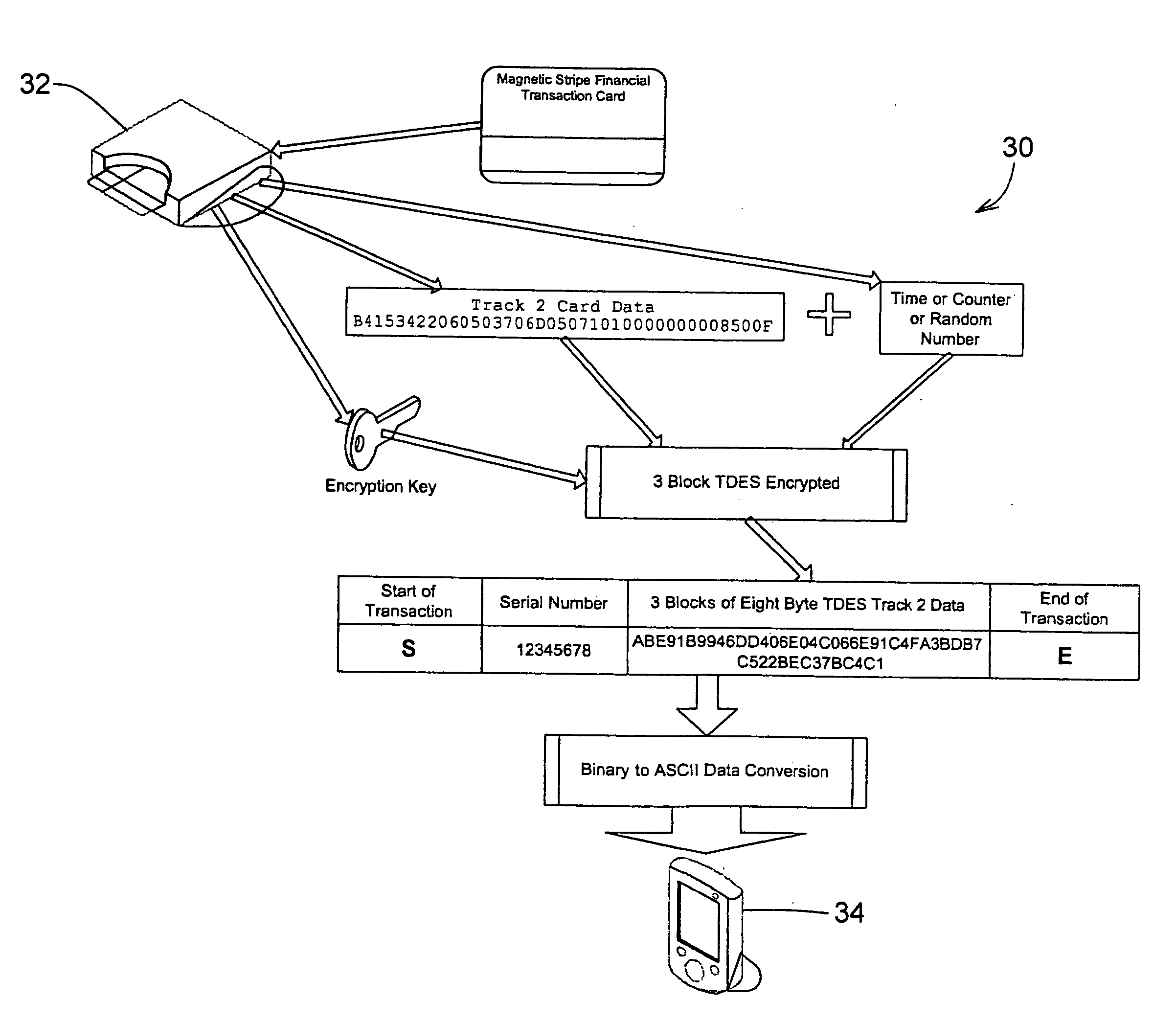
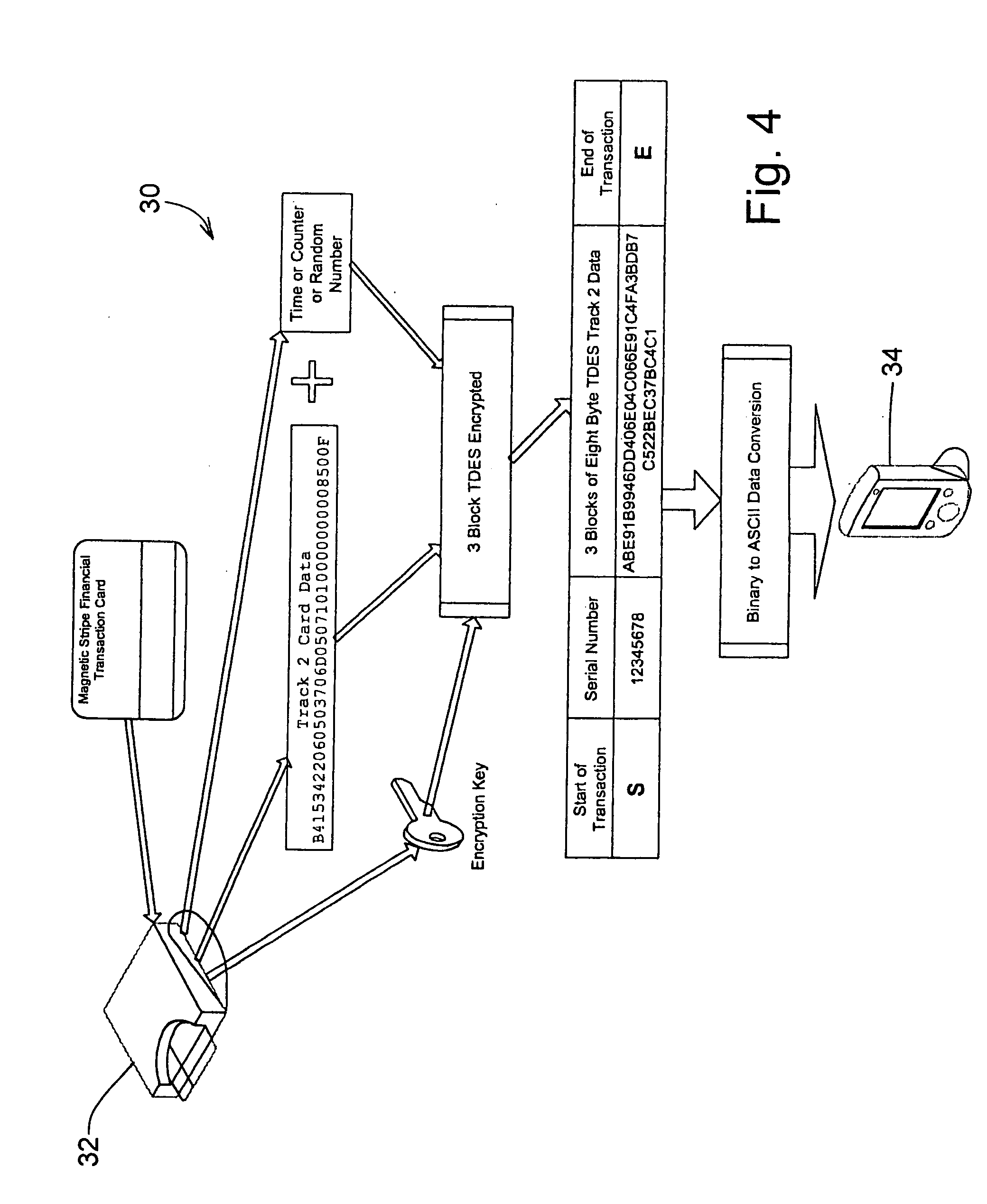
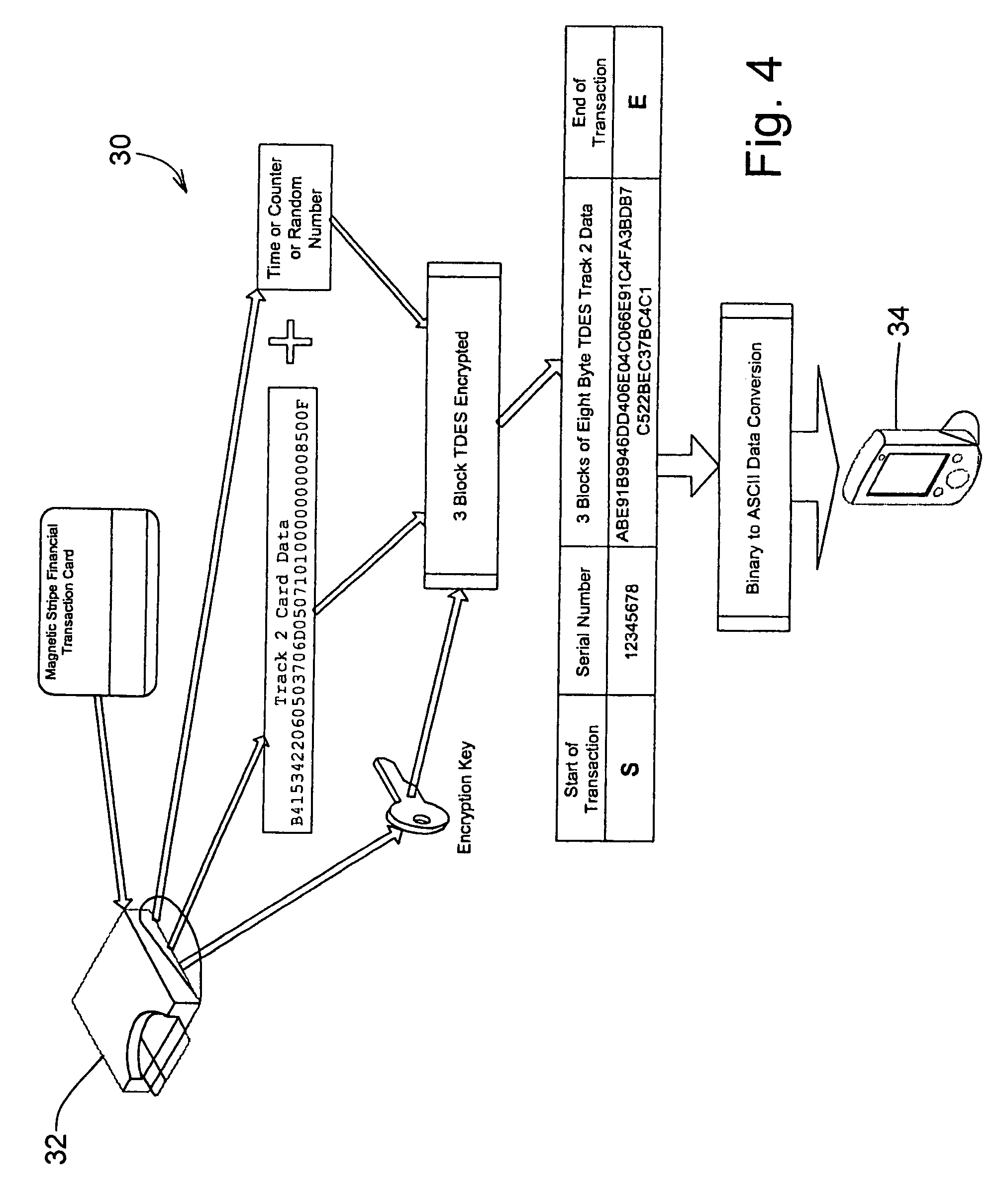
Magnetic stripe reader with power management control for attachment to a PDA device
InactiveUS20050247787A1Easy to operateIncrease powerVolume/mass flow measurementPower supply for data processingEngineeringField service
A magnetic stripe card manual swipe reader (MSR) unit capable of attaching to and communicating with a conventional personal digital assistant (PDA) from various manufacturers, using only the electrical power available as supplied by the PDA device, and capable of effective electrical power management and conservation operations. Additionally, this PDA attachable MSR unit is capable of recognizing multiple magnetic encoding formats and data record formats and converting said formats to a standardized output format, includes the capability of updating and adding new formats while in field service, and is readily allows verifying card data and encoding sensitive material prior to transmission to the PDA. These custom formats can then be used to fulfill current needs in age verification, law enforcement, security, and numerous other applications.
Owner:VERIFONE INC
Heating system comprising semiconductor light sources
ActiveUS20160381732A1Improve homogeneityHeating system be improvedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor structureEngineering
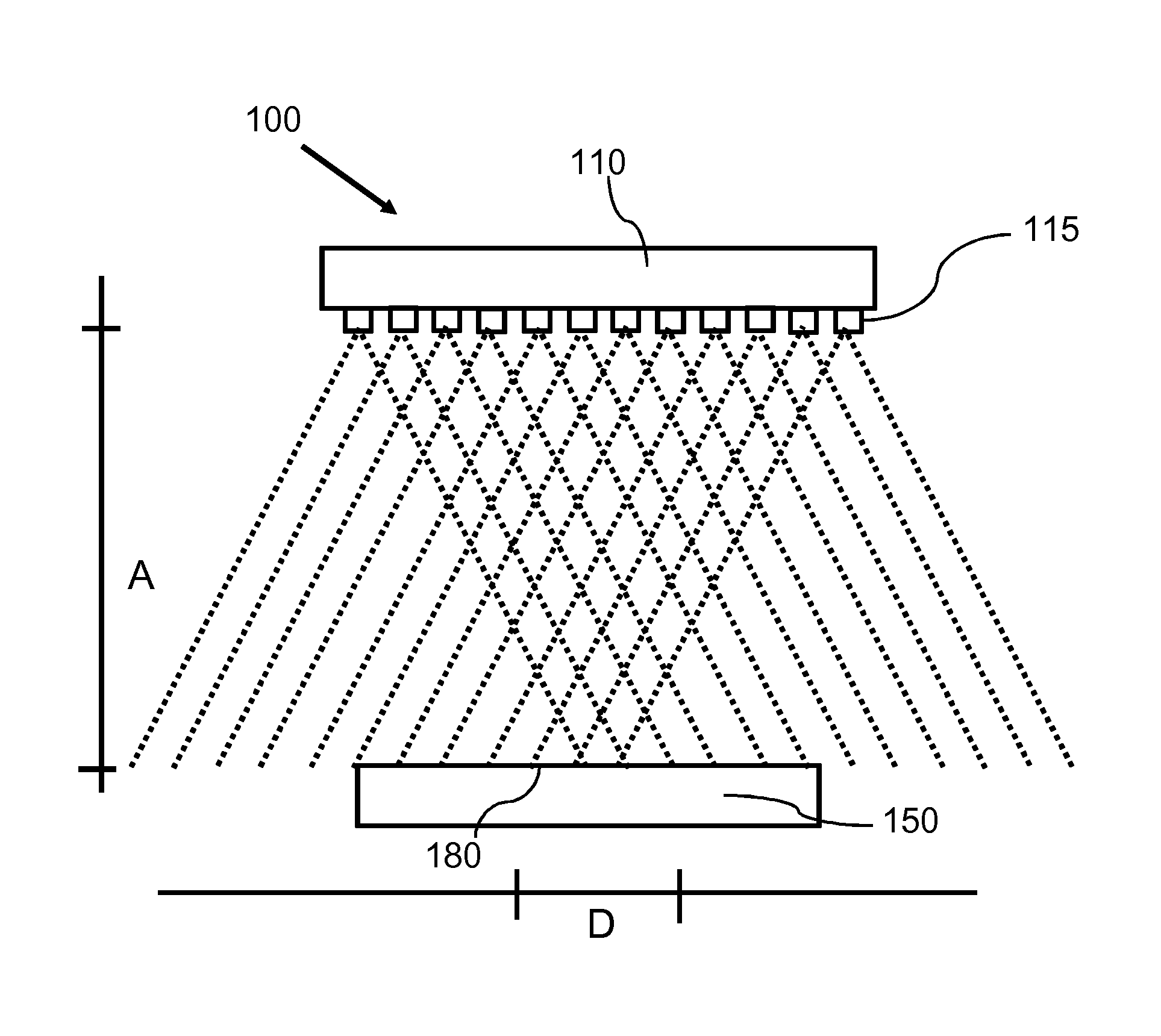
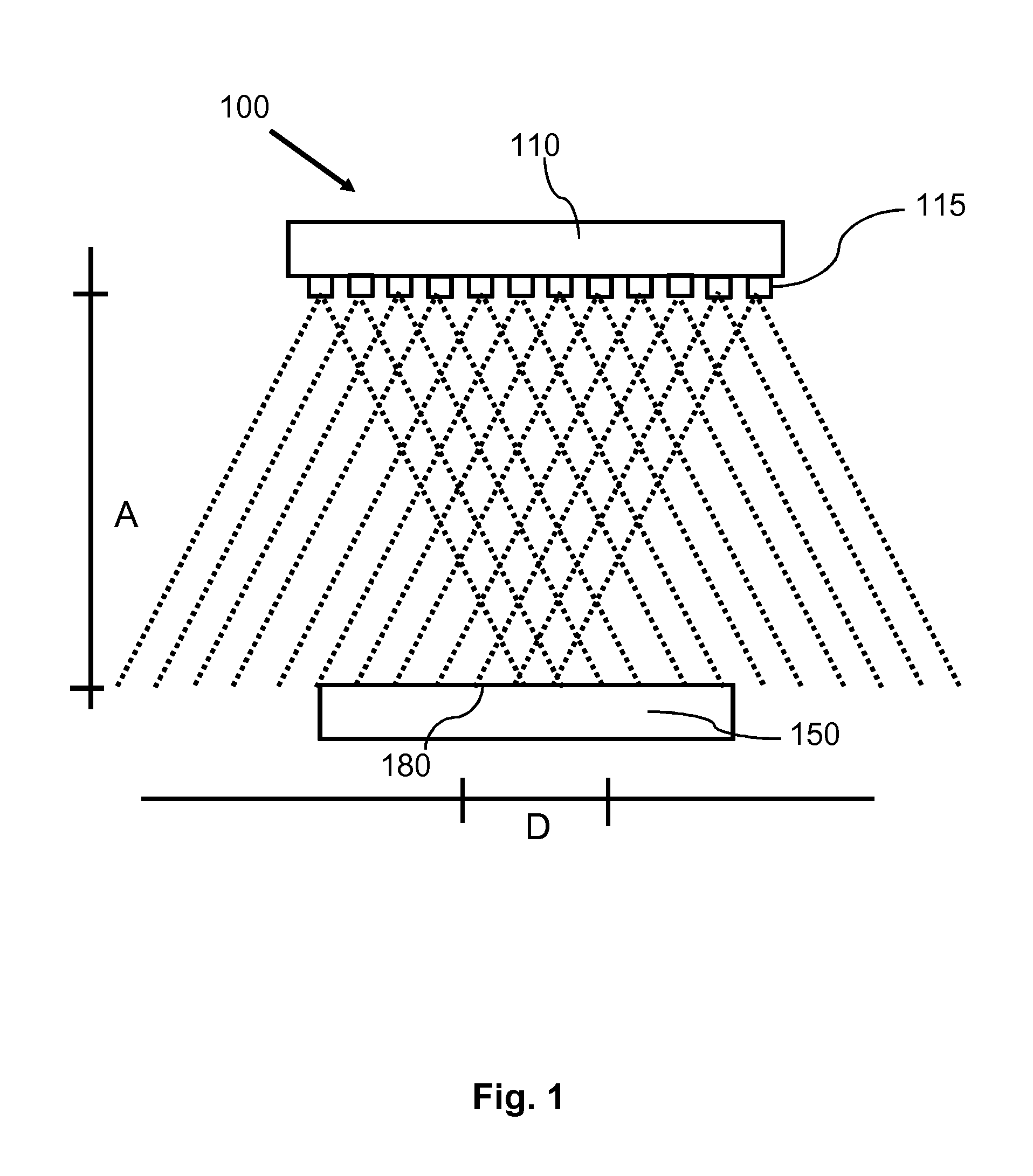
The invention describes a heating system (100) and a corresponding method of heating a heating surface (180) of an object (150, 950) to a processing temperature of at least 100° C., wherein the heating system (100) comprises semiconductor light sources (115), and wherein the heating system (100) is adapted to heat an area element of the heating surface (180) with at least 50 semiconductor light sources (115) at the same time. The heating system (100) may be part of a reactor for processing semiconductor structures. The light emitted by means of the semiconductor light sources (115) overlaps at the heating surface (180). Differences of the characteristic of one single semiconductor light source (115) may be blurred at the heating surface (180) such that a homogeneous temperature distribution across a processing surface of a, for example, wafer may be enabled.
Owner:TRUMPF PHOTONIC COMPONENTS GMBH
Multiple access method and system
InactiveUS7010048B1Reduce decreaseLower Level RequirementsFrequency diversityWavelength-division multiplex systemsFiberPulse envelope
A wireless communication system transmits data on multiple carriers simultaneously to provide frequency diversity. Carrier interference causes a narrow pulse in the time domain when the relative phases of the multiple carriers are zero. Selection of the frequency separation and phases of the carriers controls the timing of the pulses. Both time division of the pulses and frequency division of the carriers achieves multiple access. Carrier interferometry is a basis from which other communication protocols can be derived. Frequency hopping and frequency shifting of the carriers does not change the pulse envelope if the relative frequency separation and phases between the carriers are preserved. Direct sequence CDMA signals are generated in the time domain by a predetermined selection of carrier amplitudes. Each pulse can be sampled in different phase spaces at different times. This enables communication in phase spaces that are not detectable by conventional receivers. The time-dependent phase relationship of the carriers provides automatic scanning of a beam pattern transmitted by an antenna array. In waveguide communications, the carrier frequencies and phase space may be matched to the chromatic dispersion of an optical fiber to increase the capacity of the fiber.
Owner:DEPARTMENT 13 INC
Contactless battery charging apparel
InactiveUS7863859B2Reduced Power RequirementsReduce chargeDc network circuit arrangementsBatteries circuit arrangementsBattery chargeEngineering
A sequential power transmission between a portable user-carried battery and first and second independent accessories. At least one primary inductive coupling coil is mounted on an article of apparel worn by the user, so as to place a primary coil adjacent a first intermediary inductive coupling coil on the first independent accessory. The energizing of the first intermediary coil energizes a second intermediary coil on the first independent accessory. The second intermediary coil, when energized, energizes a secondary coil on the second independent accessory for powering the use, including the charging of the batteries of that accessory.
Owner:CYNETIC DESIGNS
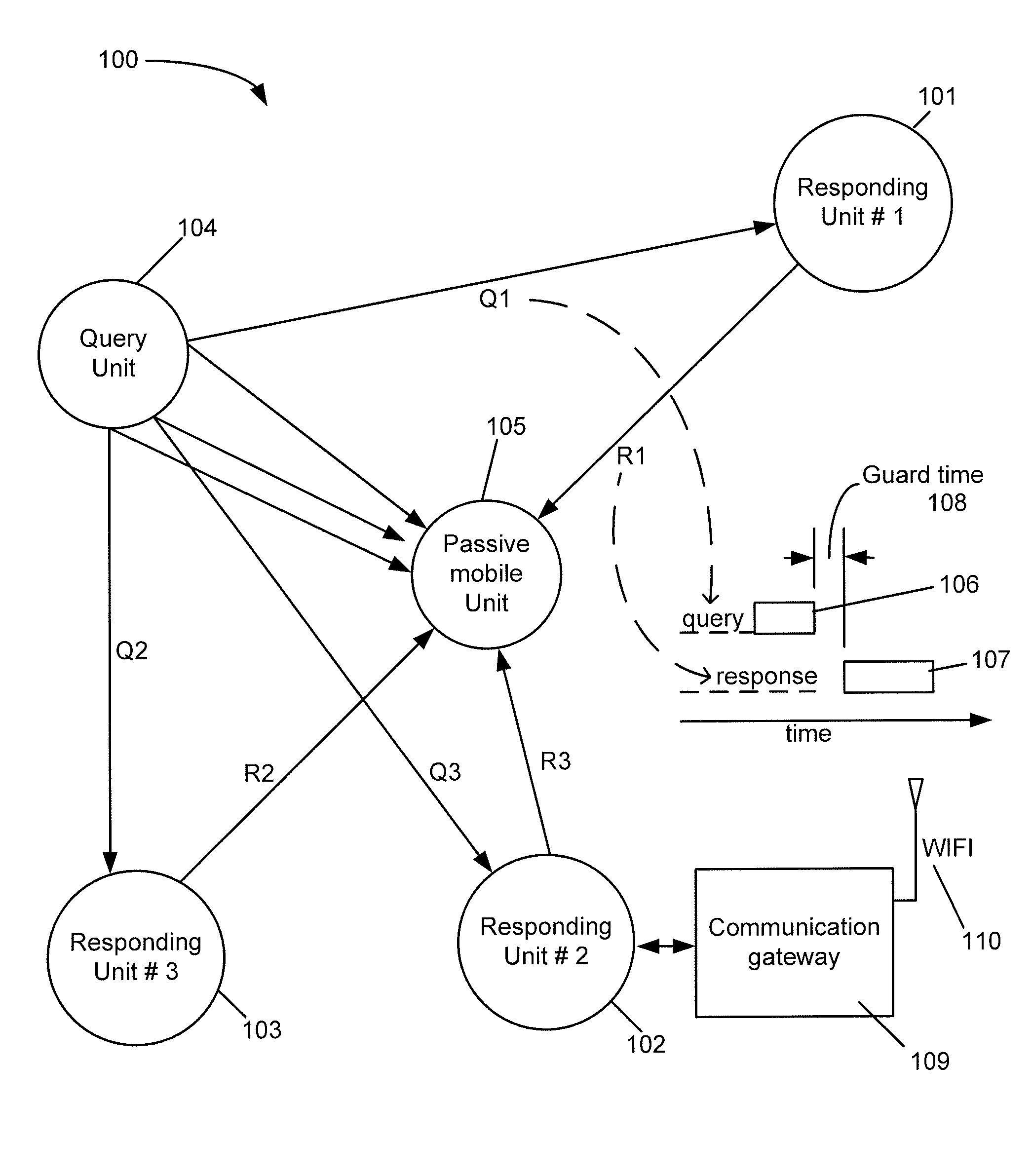
System and method for determination of position
InactiveUS20090149202A1Low costReduce requirementDigital computer detailsPosition fixationTime of arrivalGeographic area
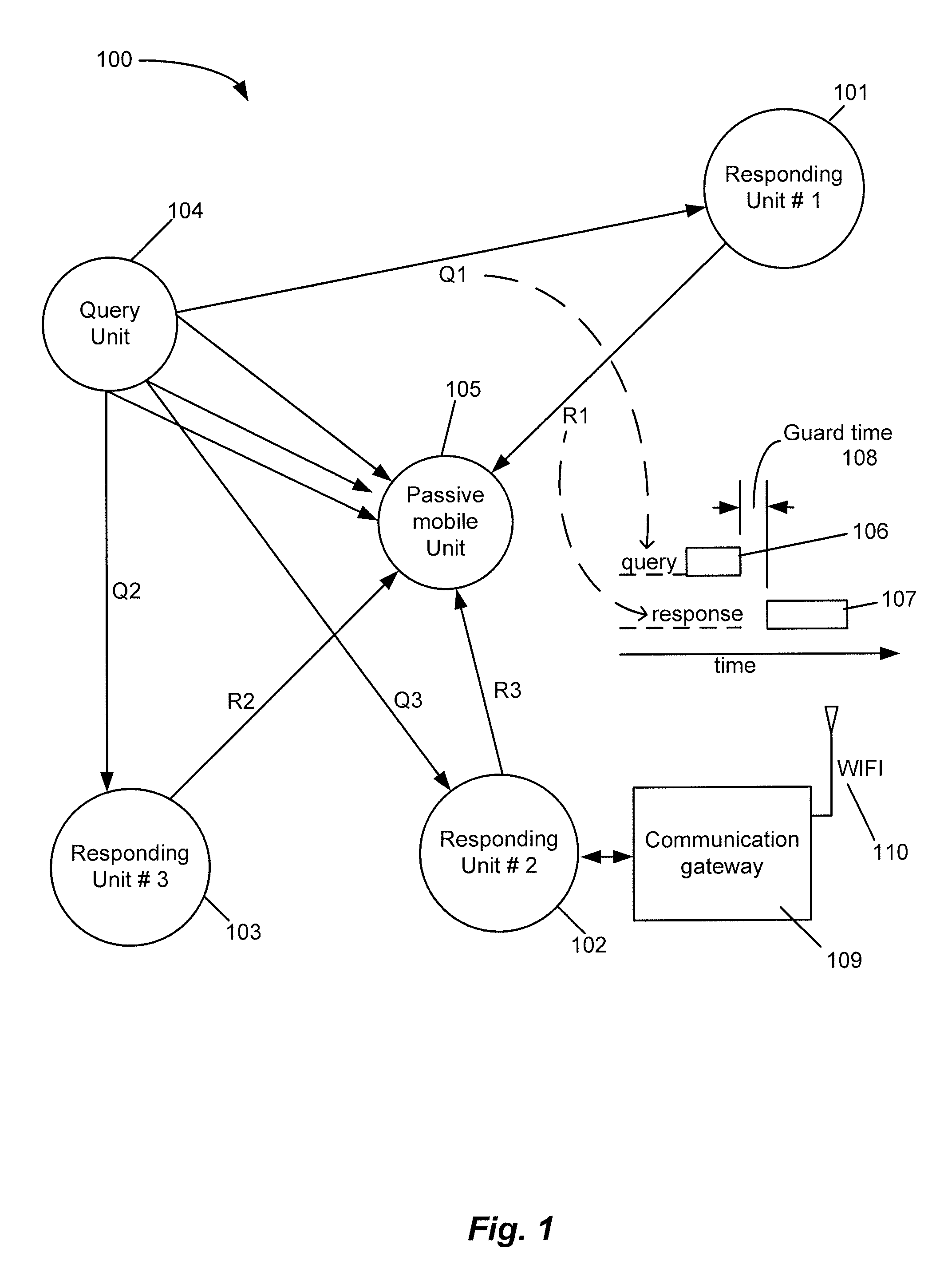
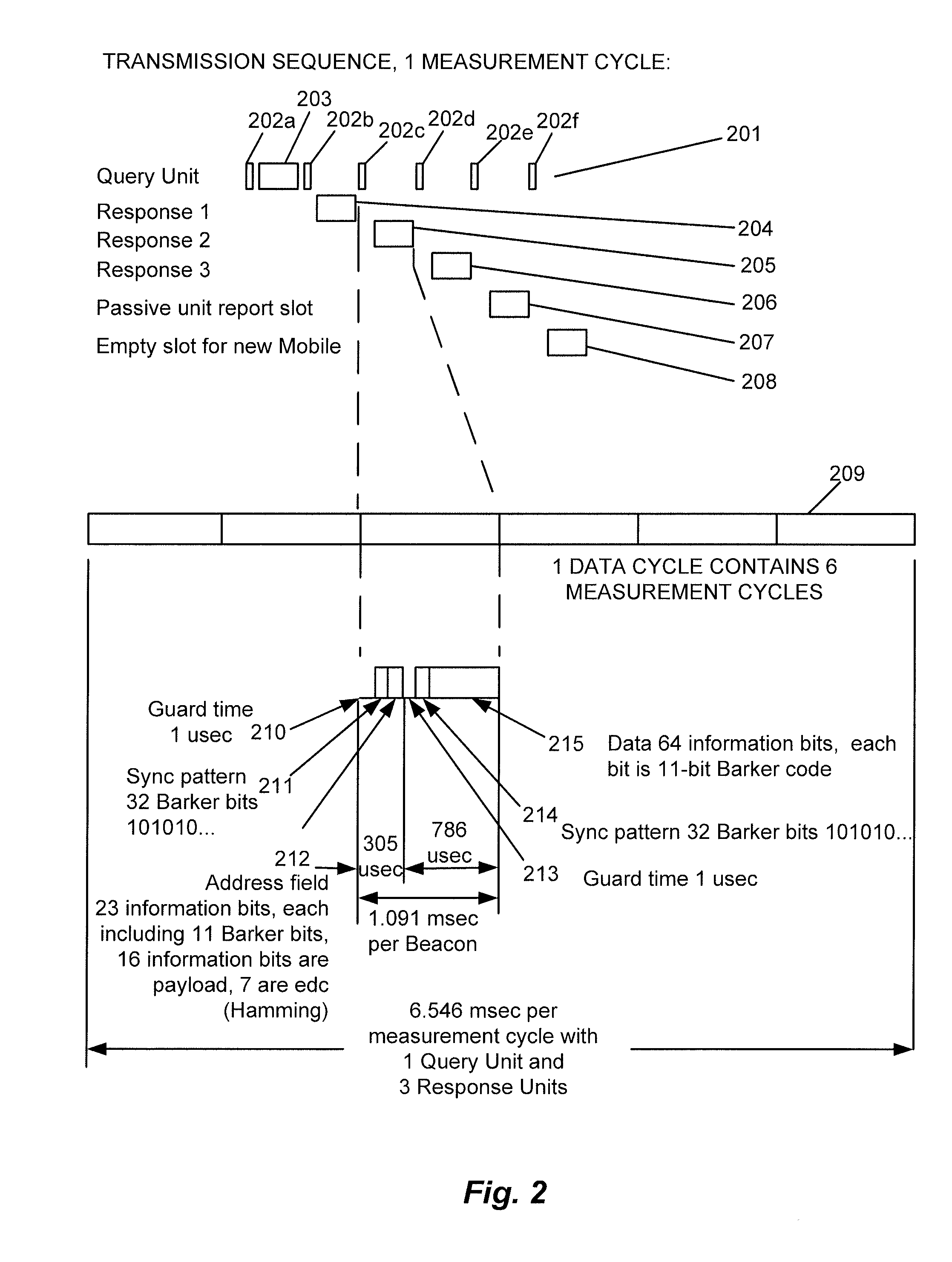
A system and method of determining and reporting on the position of a wireless device relative to a group of other wireless devices dispersed within a specified geographic area. The system includes at least one Query Unit, three or more Responding Units disposed at determinable locations within the specified geographic area, and one or more Mobile Units, which may correspond to additional Responding Units or units that function only as receivers. The Query Unit sequentially queries the Responding Units, and, responsive to the respective query messages, the Responding Units transmit corresponding response messages. One or more of the Mobile Units receive the query and response messages, and generate, for each query-response message pair, a set of time-difference-of-arrival (TDOA) measurements, which are used by the Mobile Units to determine their positions relative to the Responding Units. The Mobile Units record the times-of-arrival (TOAs) of the query message and the response messages at their respective receivers, and calculate the TDOAs based on the recorded TOAs. The TDOAs are then analyzed to determine the time differences due to the differences in lengths of the respective message propagation paths. The position of each Mobile Unit can then be computed using computation techniques typically employed in Long Range Navigation (LORAN) receivers, or any other suitable computation technique.
Owner:STEELE CHRISTIAN
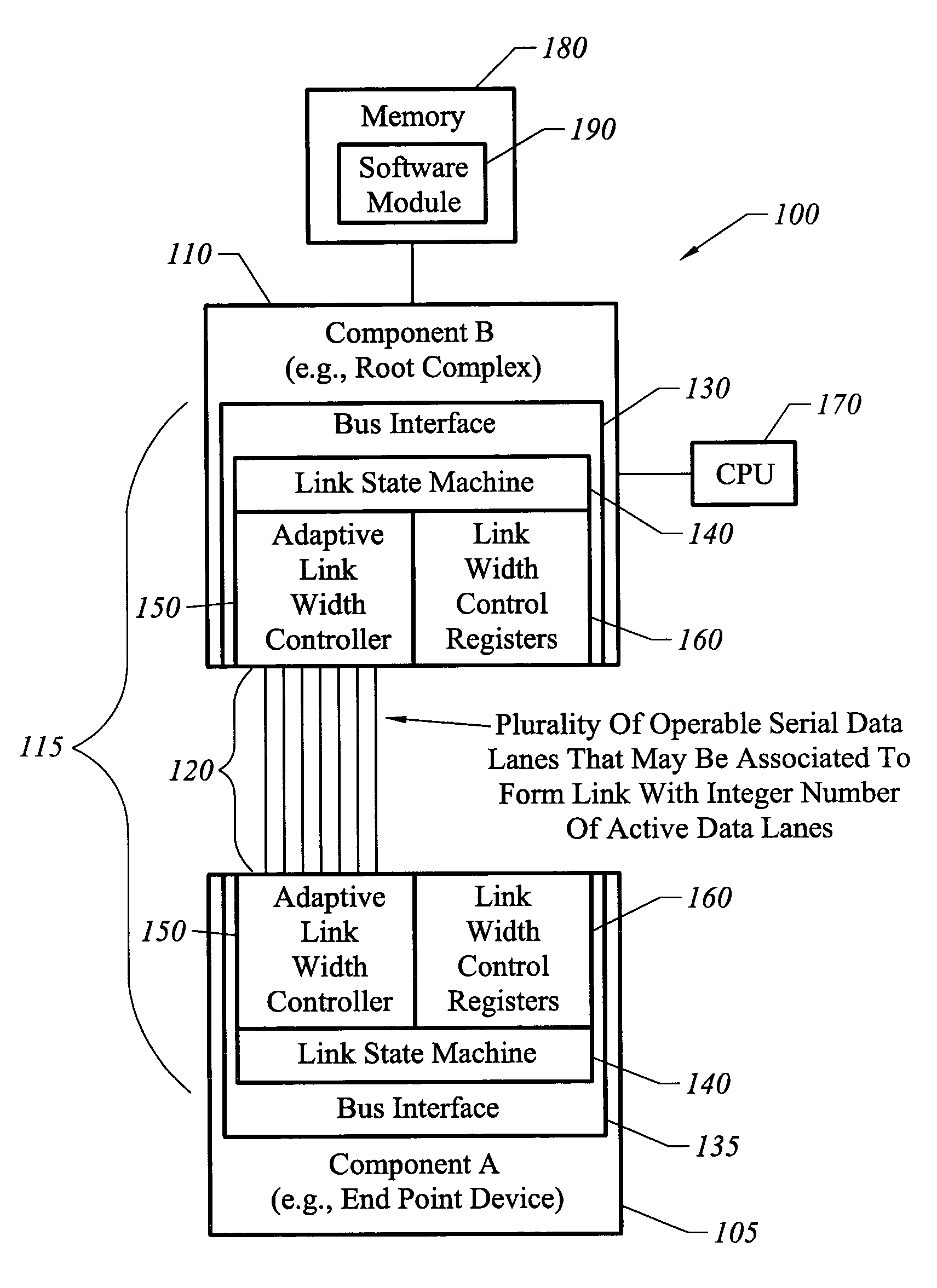
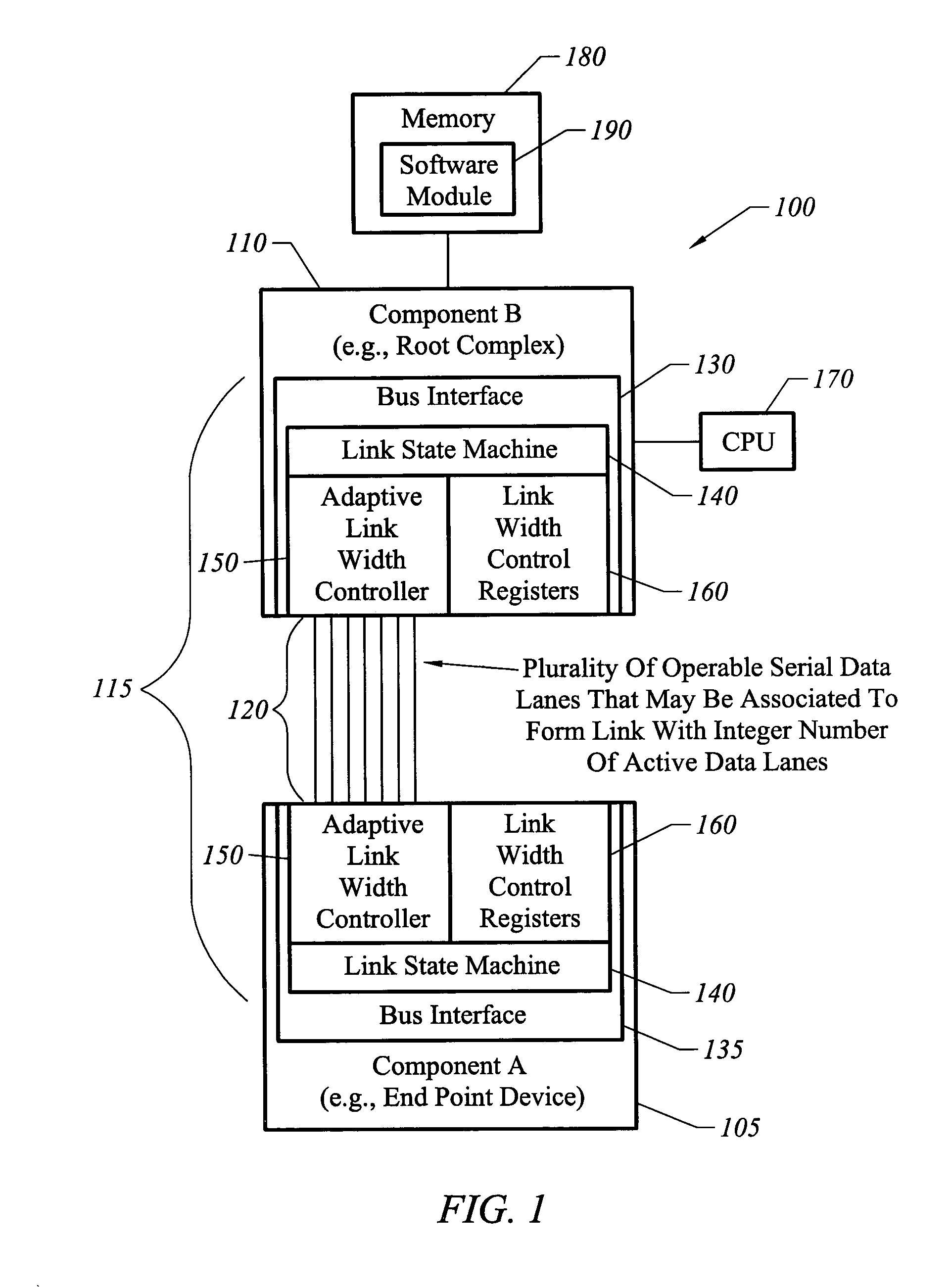
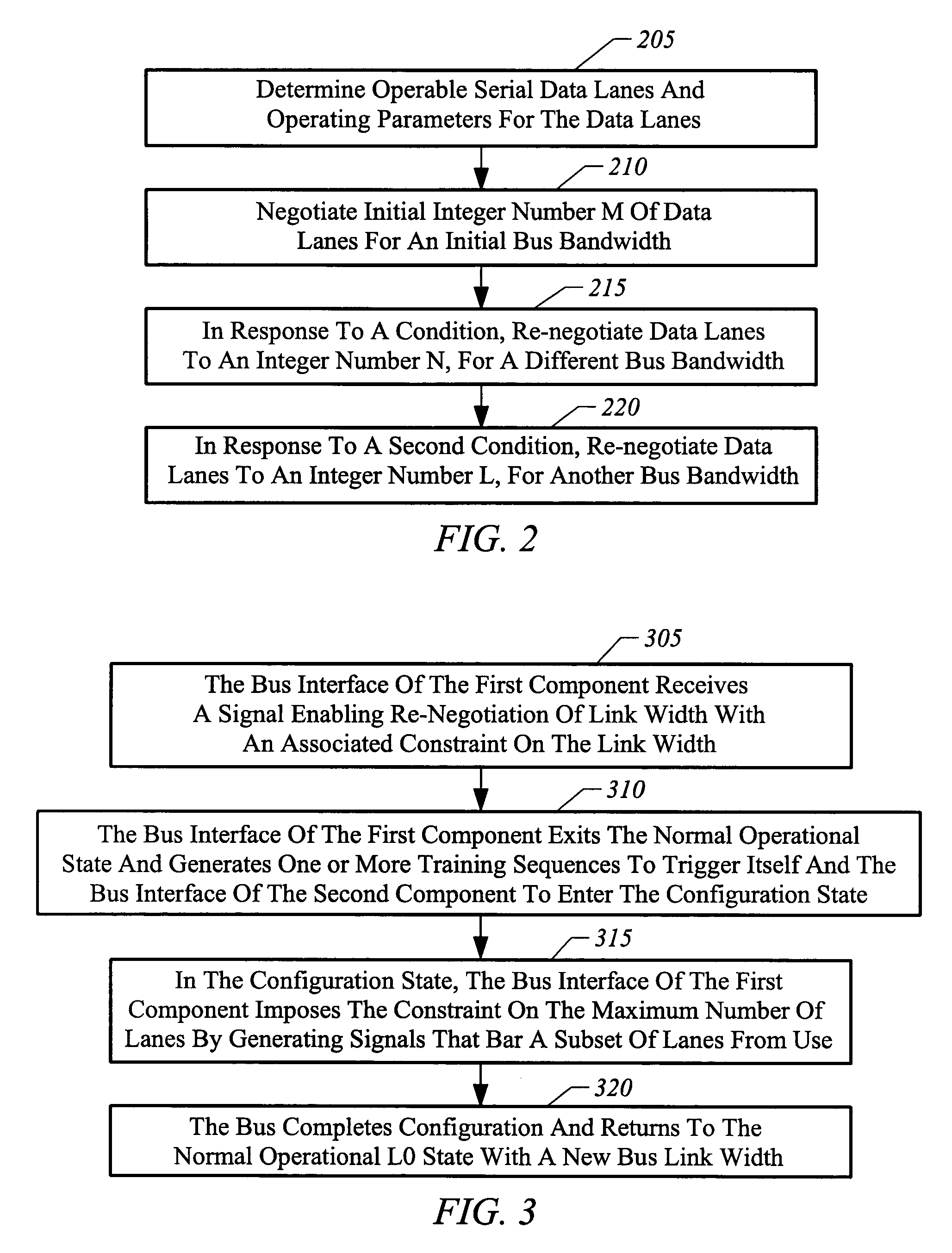
Apparatus, system, and method for bus link width optimization
ActiveUS7136953B1High bandwidthReducing bus power requirementEnergy efficient ICTStatic indicating devicesBus interfaceBandwidth requirement
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
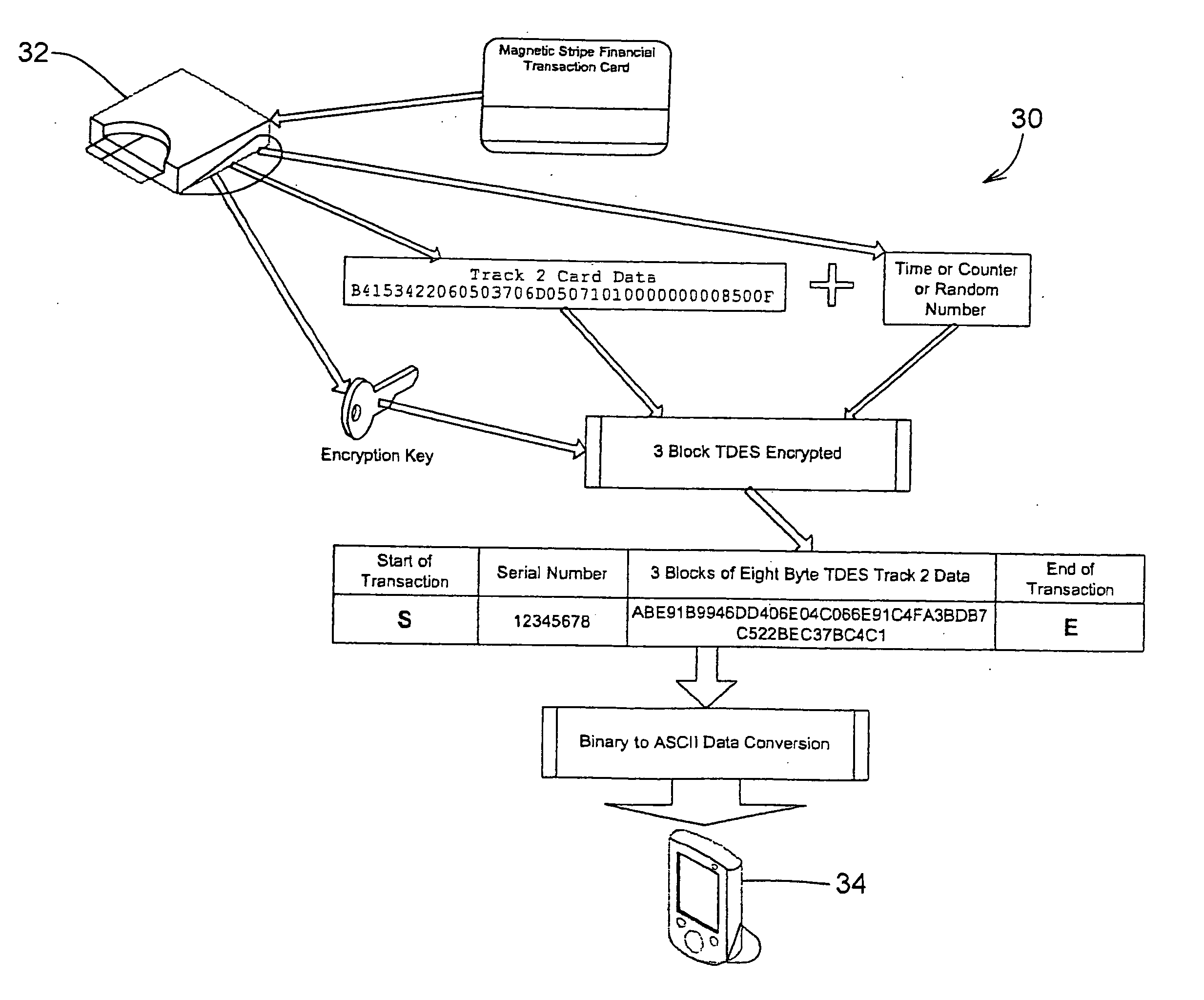
Transparently securing data for transmission on financial networks
ActiveUS20060049256A1Easy to operateIncrease powerAcutation objectsFinanceInformation processingSoftware system
A secure magnetic stripe card stripe reader (MSR) module and software system capable of encrypting the magnetic stripe data to CPI, SDP and CISP standards for use in point of sale (POS) and other applications requiring data security using non secure networks and computing devices. Additionally, when incorporated within an attachment for conventional personal digital assistant (PDA) or cell phone or stationary terminal, provides encrypted data from the magnetic head assembly providing compliance with Federal Information Processing Standards Publication Series FIPS 140 covering security and tampering standards. Moreover, this module and software system includes the capability of providing secure POS transactions to legacy transaction processing systems and POS terminals transparently to the existing infrastructure. Furthermore, this module and software system includes the capability of transparently providing detection of fraudulently copied magnetic stripe cards.
Owner:VERIFONE INC
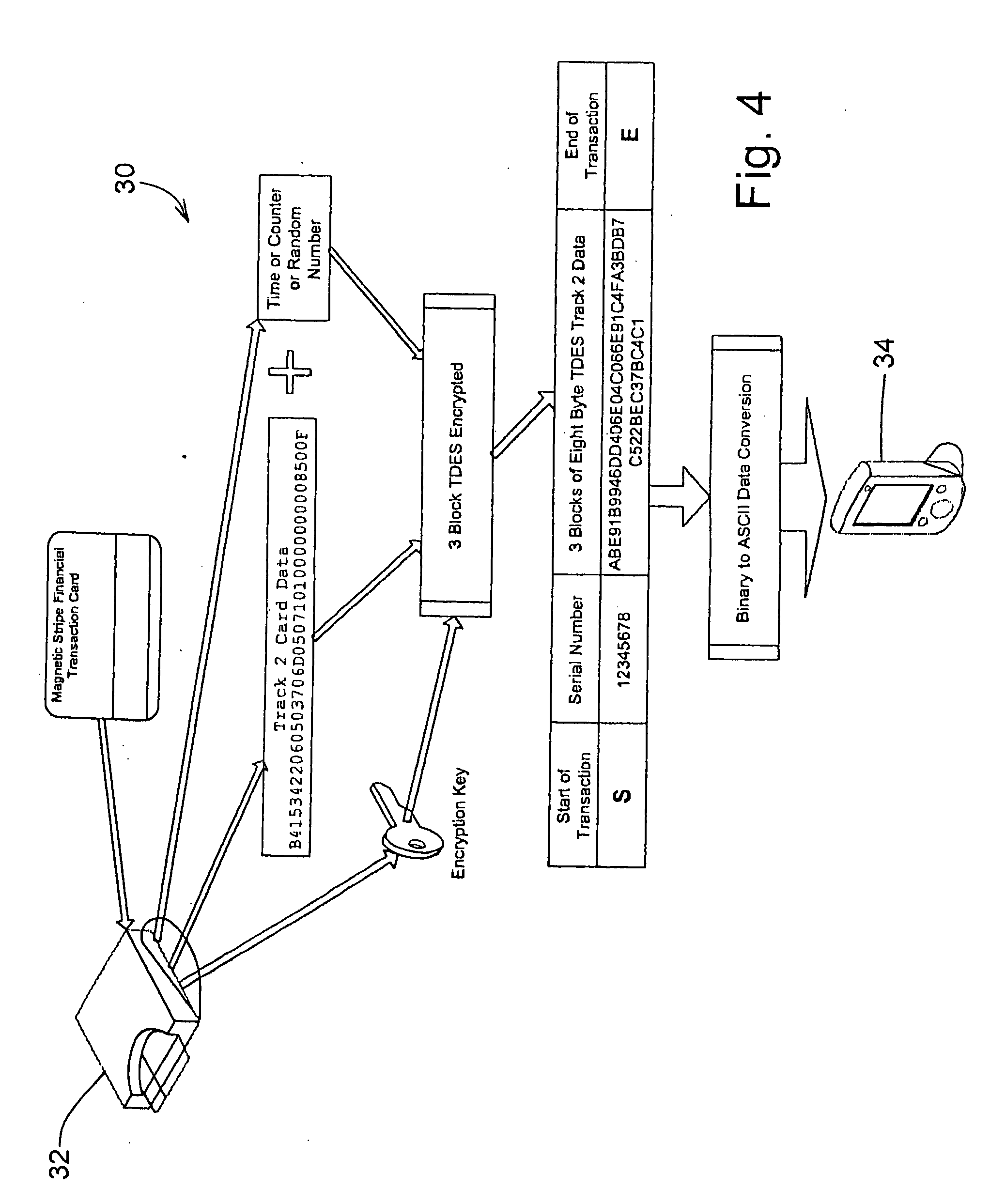
Secure magnetic stripe reader for handheld computing and method of using same
ActiveUS20060049255A1Support easily and efficientlyFunction increaseAcutation objectsFinanceInformation processingSoftware system
A secure magnetic stripe card stripe reader (MSR) module and software system capable of encrypting the magnetic stripe data to CISP standards for use in point of sale (POS) and other applications requiring data security using non secure networks and computing devices. Additionally, when incorporated within an attachment for conventional personal digital assistant (PDA) or cell phone or stationary terminal, provides encrypted data from the magnetic head assembly providing compliance with Federal Information Processing Standards Publication Series FIPS 140 covering security and tampering standards. Moreover, this module and software system includes the capability of providing secure POS transactions to legacy transaction processing systems transparently to the existing infrastructure. Furthermore, this module and software system includes the capability of transparently providing detection of fraudulently copied magnetic stripe cards.
Owner:VERIFONE INC
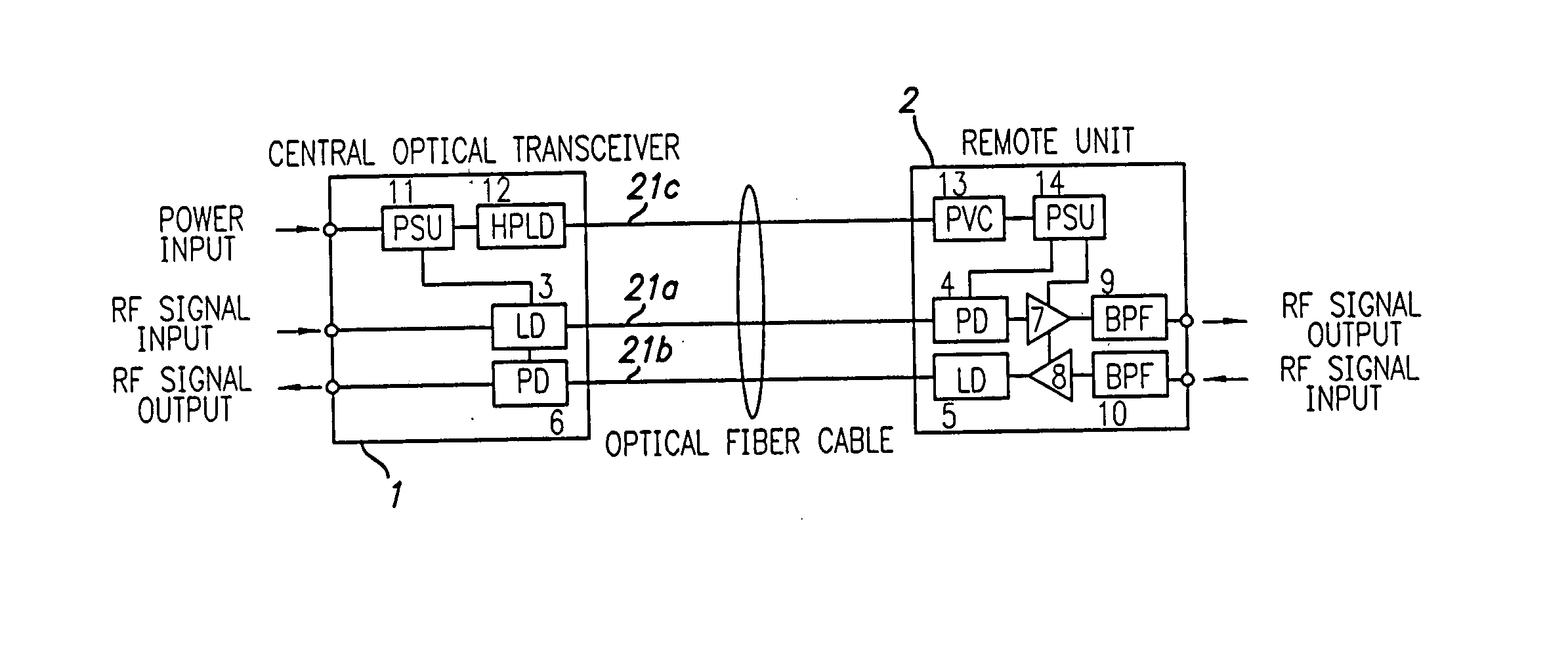
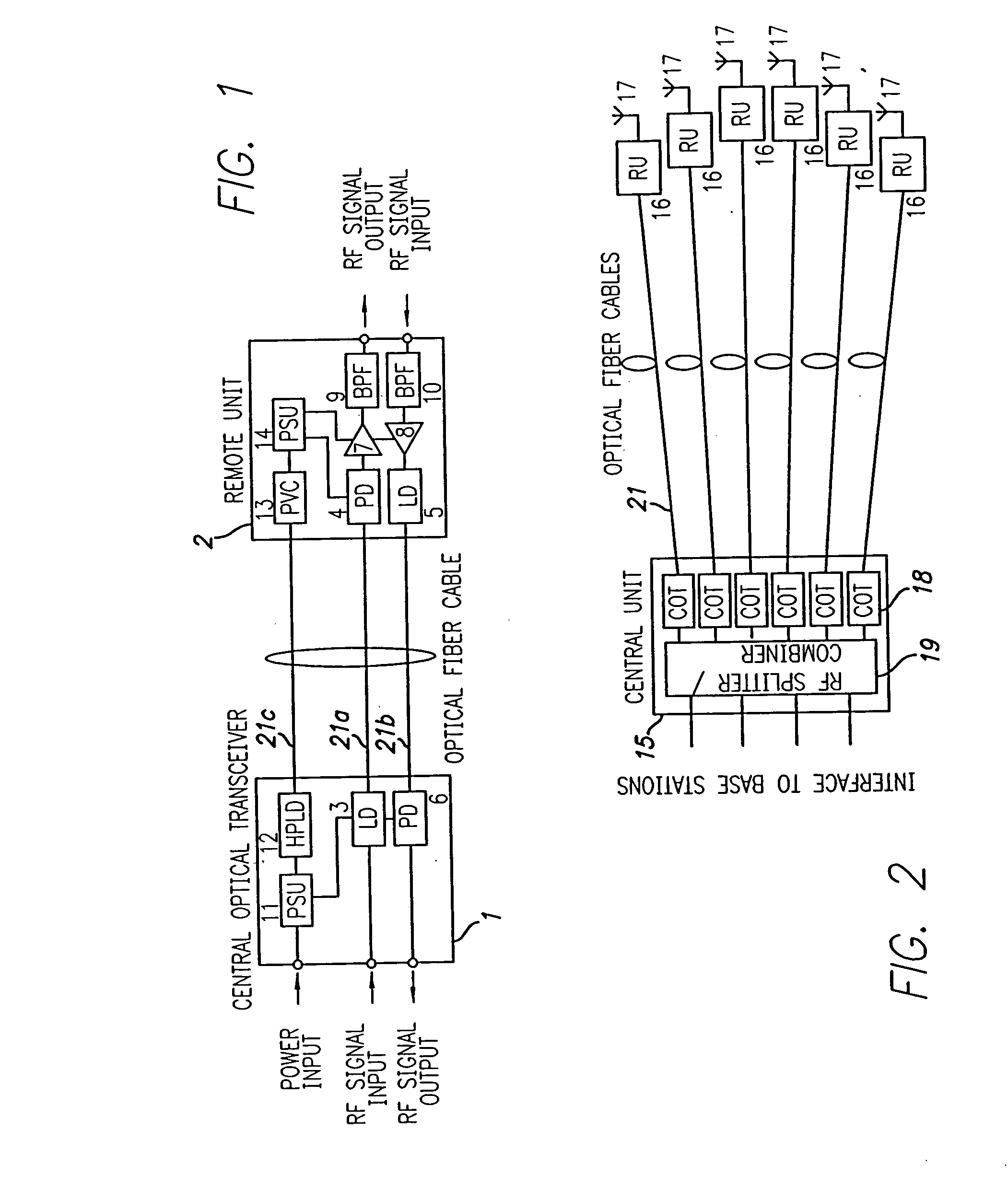
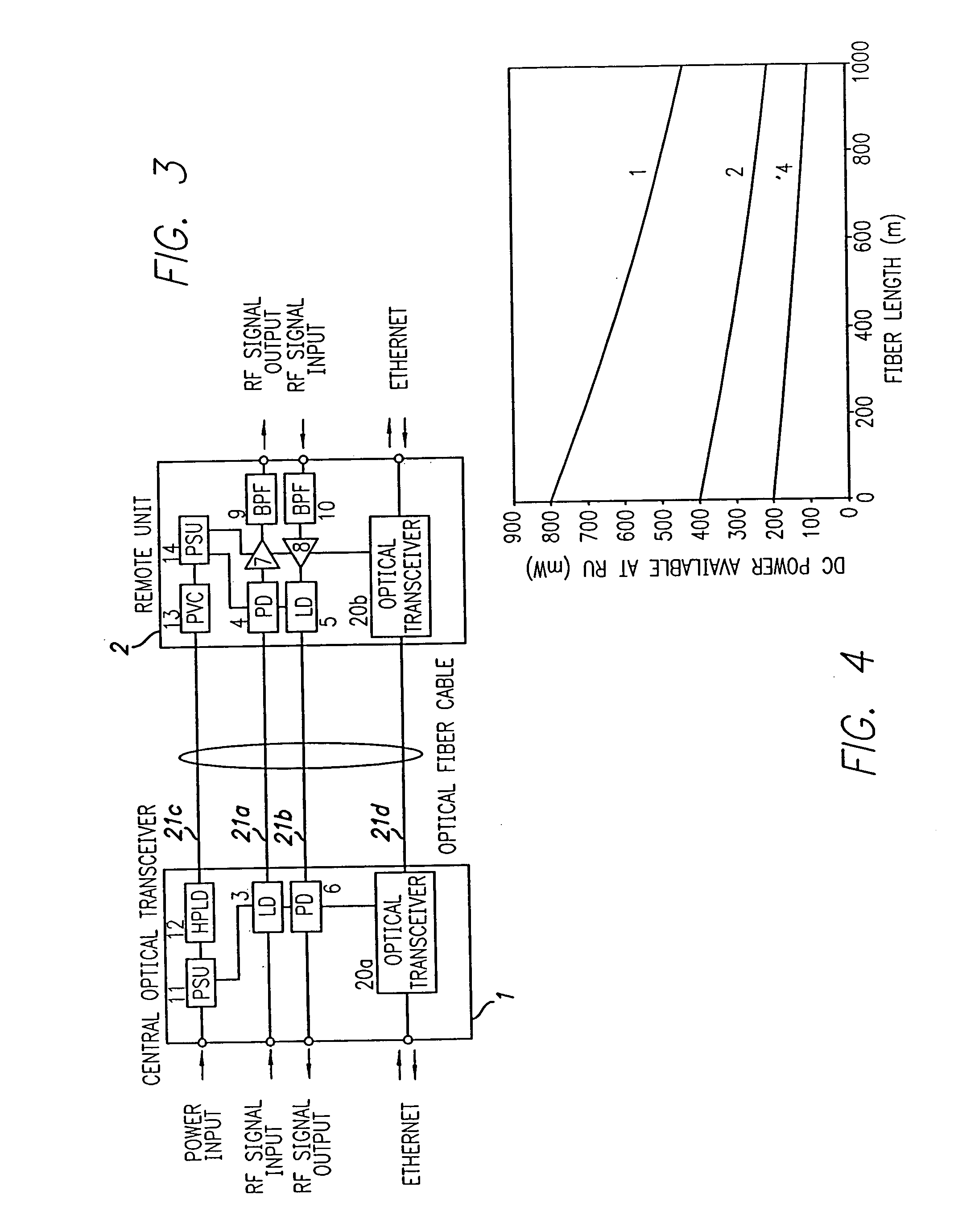
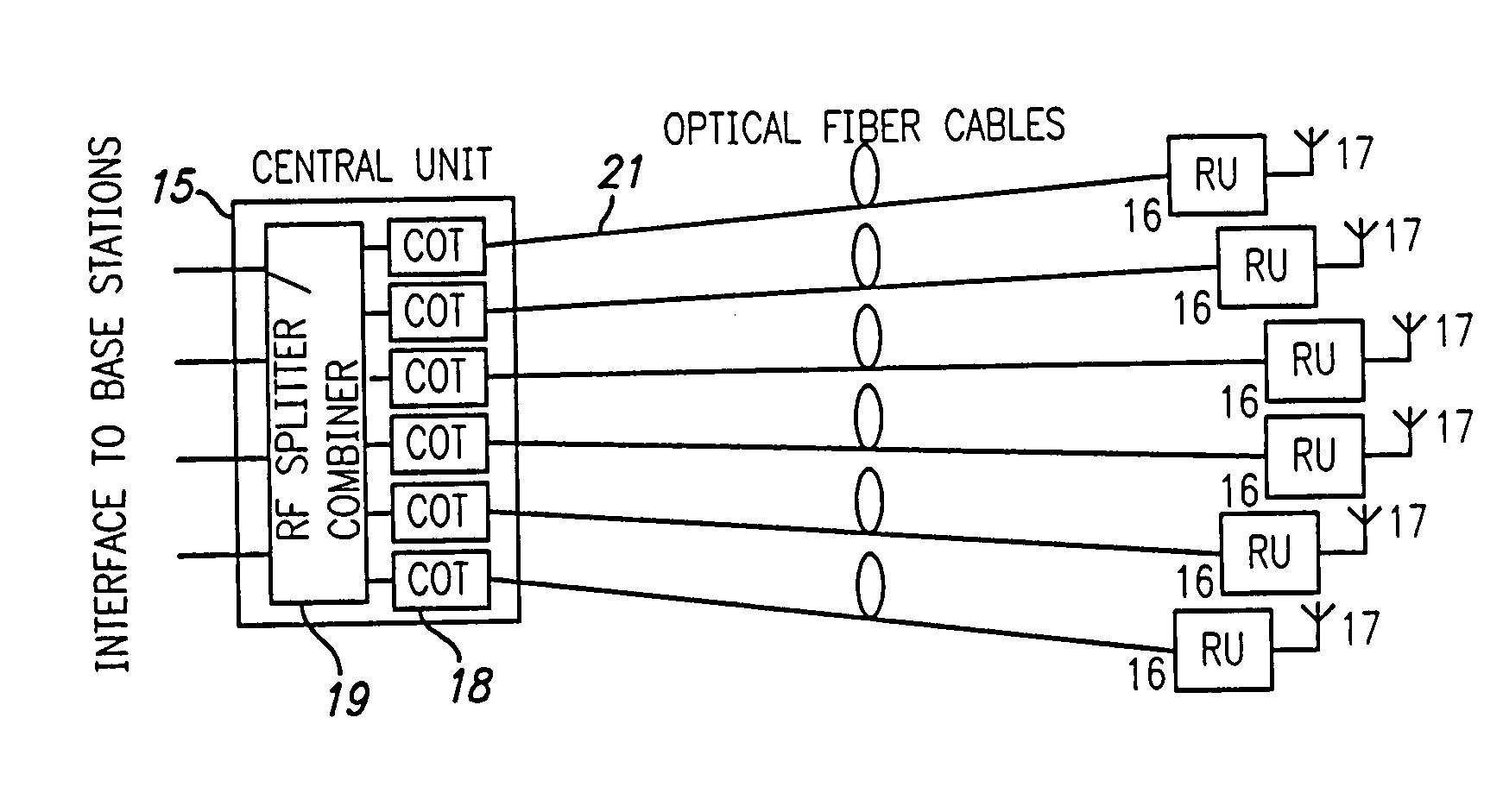
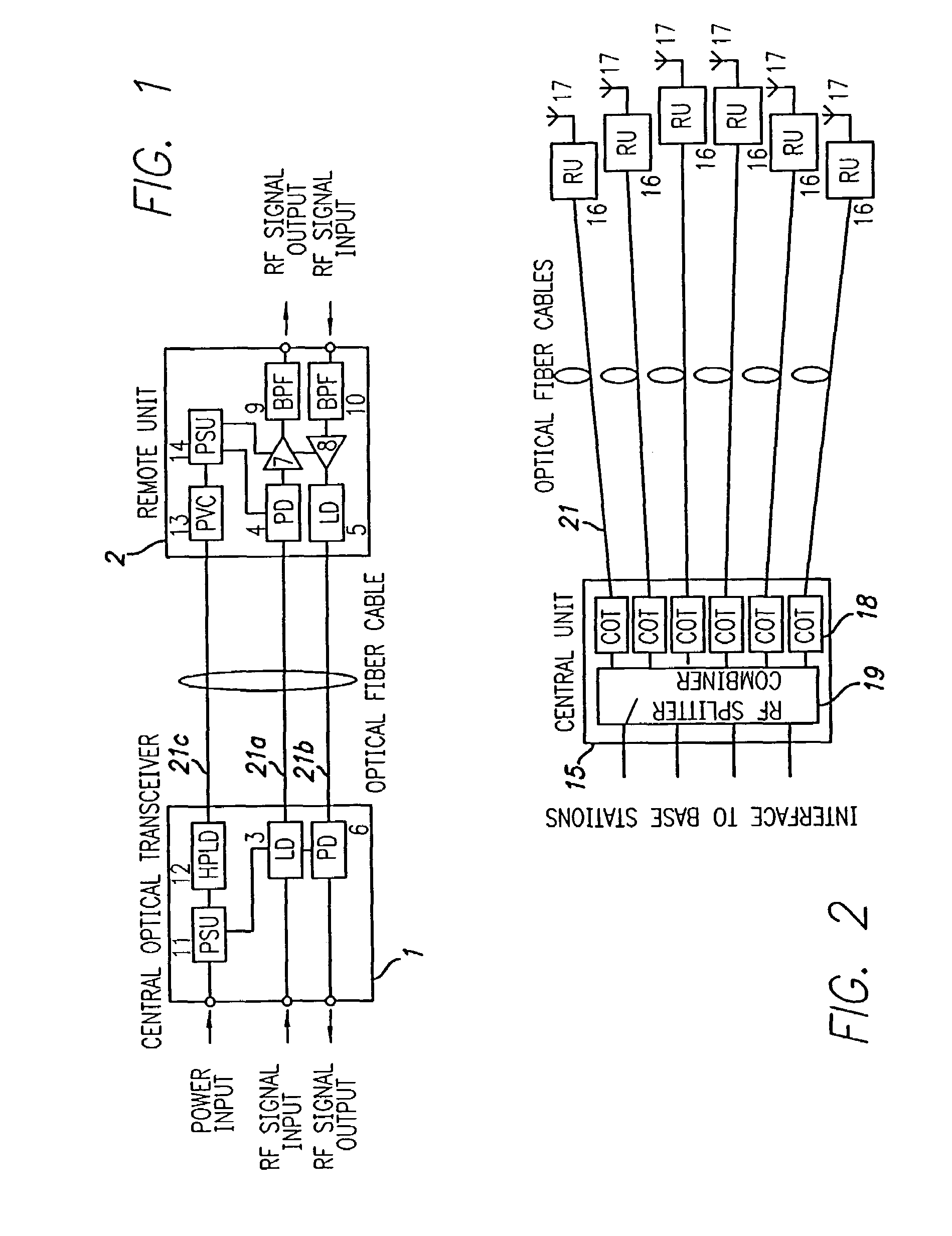
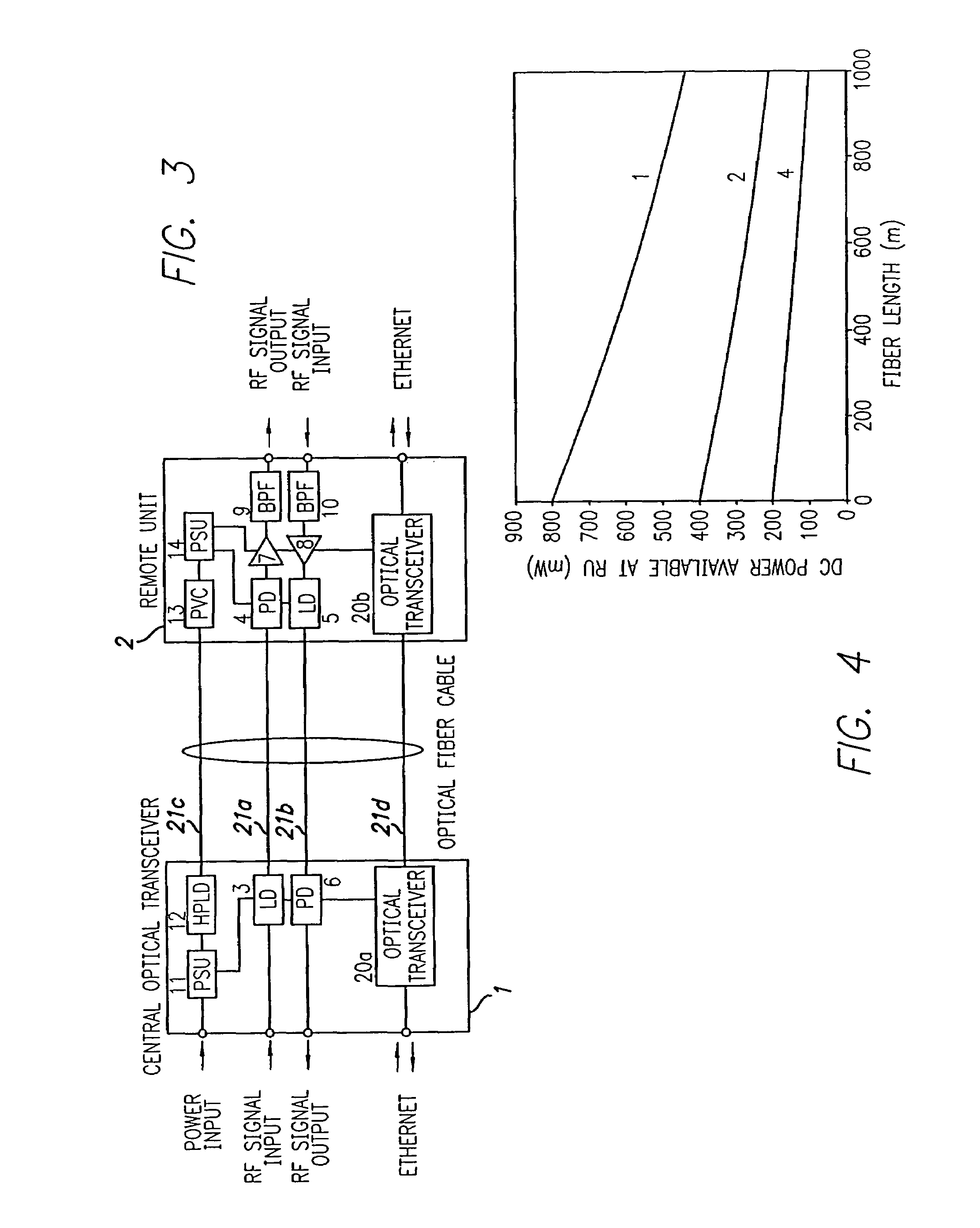
Optical fiber communications method and system without a remote electrical power supply
ActiveUS20050226625A1Reduce power consumptionReduced Power RequirementsElectromagnetic transmissionWireless communicationElectrical conductorOptical communication
The present invention allows remote antenna units for radio frequency signal transmission and receipt to operate without the requirement for remote electrical power supplies or for connecting cables that incorporate electrical conductors. According to an aspect of the present invention, an optical communications system employing radio frequency signals comprises a central unit; at least one remote unit having at least one optoelectronic transducer for converting optical data signals to radio frequency signals and converting radio signals to optical signals and at least one antenna to receive and send radio frequency signals; at least one optical fiber data link between the central unit and the remote unit for transmitting optical data signals therebetween; and at least one optical fiber power link between the central unit and the remote unit for providing electrical power at the remote unit.
Owner:NEXTG NETWORKS INC
Variable transmittance optical devices
ActiveUS20130278989A1Reduce solar heat gainReduce cooling loadAntiglare equipmentStatic indicating devicesThermal energyElectricity
A self-powered variable transmittance optical device, such as a smart window or other device, and associated method are provided. The device comprises one or more transparent substrates, with a switching material disposed thereon or therebetween. The switching material may be a hybrid photochromic / electrochromic material capable of transitioning from a first transmittance state to a second transmittance state with application of electricity, and from second state to first state due to another stimulus, such as UV radiation. Electrodes are coupled to the switching material for applying electricity. An electrical system provides for controllable application of the electricity, and may store energy. Energy is provided by an energy-harvesting power source such as a solar cell or other photovoltaic source, or array thereof, or another device for harvesting vibrational or thermal energy. Energy harvesting, energy storage capacity and / or switching material may be configured to provide at least a predetermined level of device operability.
Owner:SOLUTIA CANADA INC
Multi-receiver communication system with distributed aperture antenna
InactiveUS20070176840A1Reduce distanceEqually distributedNear-field transmissionWeight reductionCommunications systemEngineering
A multi-user wireless communication system for use in an enclosed space includes a distributed aperture antenna having multiple apertures distributed along an outer shield of the antenna. The apertures allow radiated energy to leak from the antenna and form low-power, localized electric fields that can couple receivers to the antenna. The multiple electric fields ensure that the electric field strength is distributed evenly throughout the communication system. The low-power electric fields also reduce the likelihood of electric field leakage that may cause interference with other communication systems outside the enclosed space.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
Directional tactile feedback for haptic feedback interface devices
InactiveUS6864877B2Reduced Power RequirementsLow costInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsInertial massControl signal
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
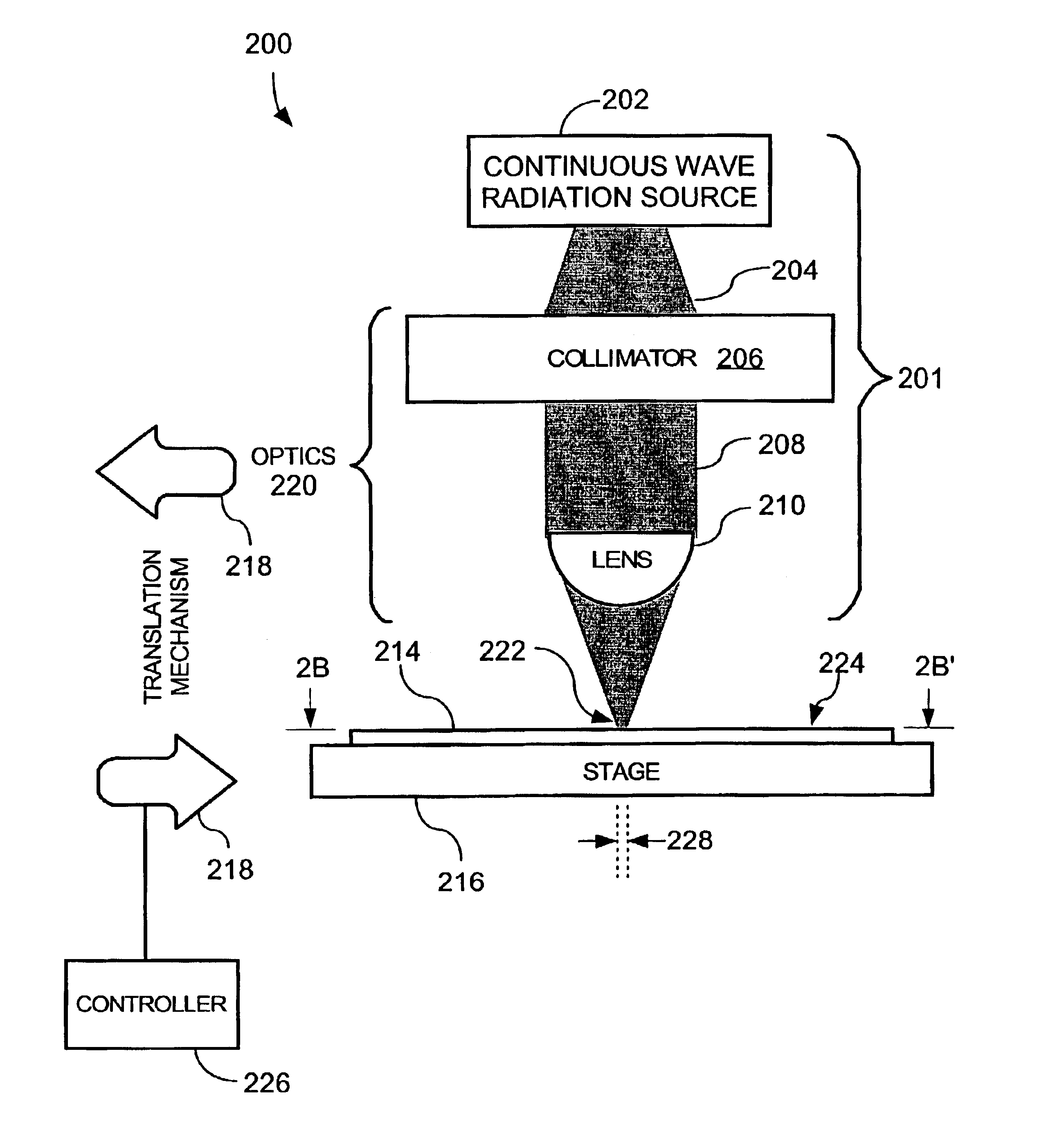
Thermal flux processing by scanning
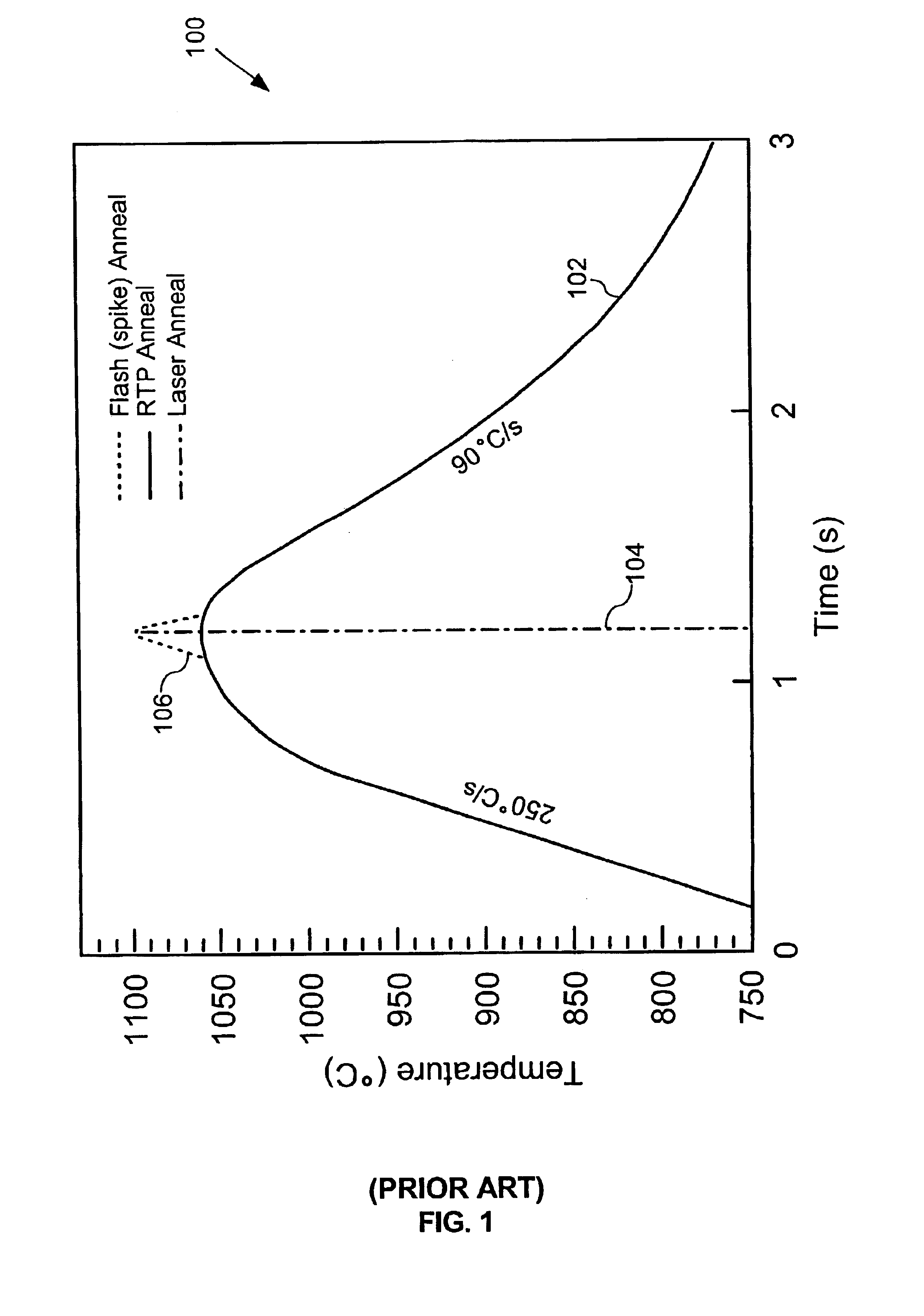
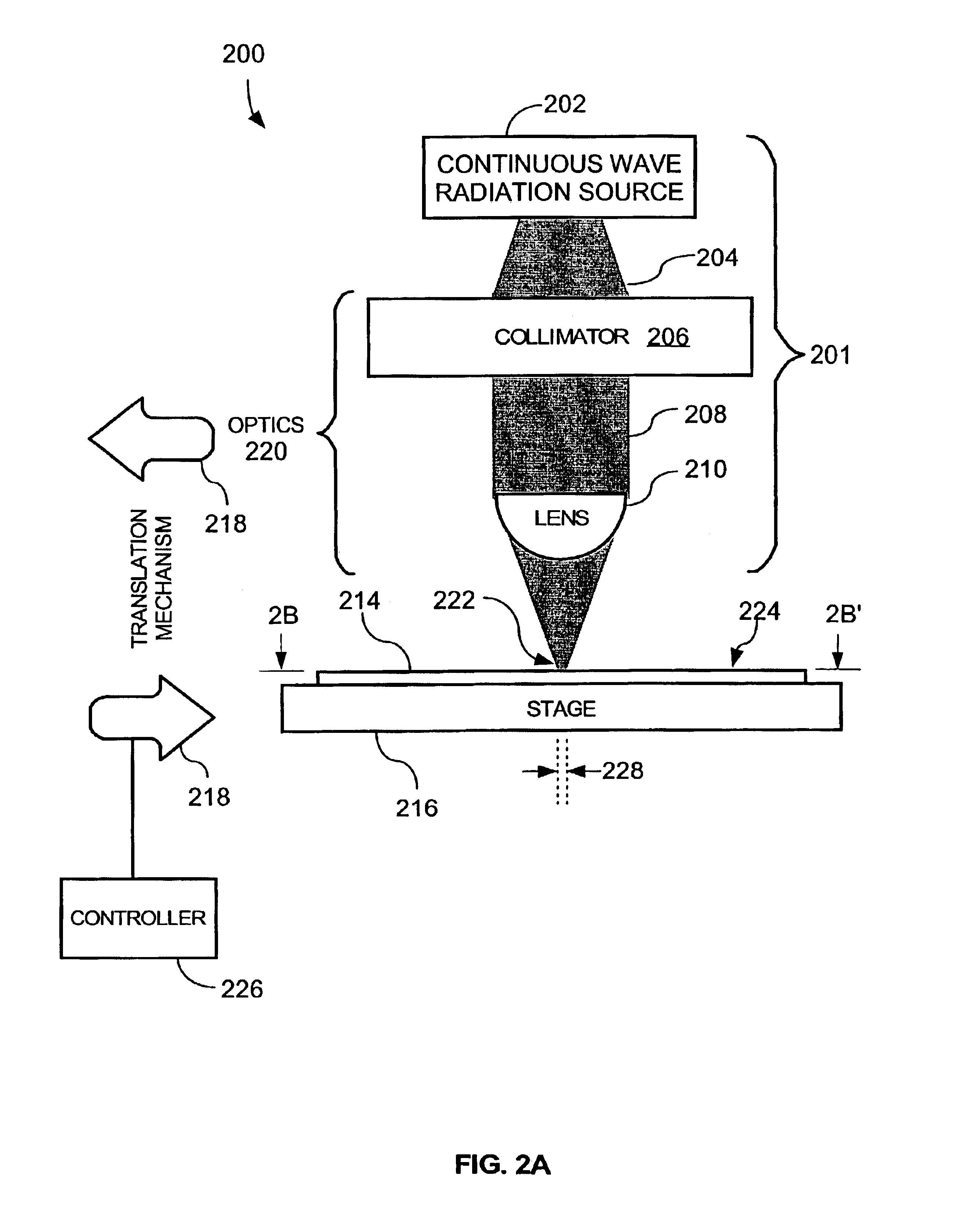
InactiveUS6987240B2Easy to controlReduced Power RequirementsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSolid state diffusion coatingHeat fluxComputerized system
The thermal processing device includes a stage, a continuous wave electromagnetic radiation source, a series of lenses, a translation mechanism, a detection module, and a computer system. The stage is configured to receive a substrate thereon. The continuous wave electromagnetic radiation source is disposed adjacent the stage, and is configured to emit continuous wave electromagnetic radiation along a path towards the substrate. The series of lenses is disposed between the continuous wave electromagnetic radiation source and the stage, and are configured to condense the continuous wave electromagnetic radiation into a line of continuous wave electromagnetic radiation on a surface of the substrate. The translation mechanism is configured to translate the stage and the line of continuous wave electromagnetic radiation relative to one another. The detection module is positioned within the path, and is configured to detect continuous wave electromagnetic radiation. The computer system is coupled to the detection module.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Secure magnetic stripe reader for handheld computing and method of using same
ActiveUS7309012B2Limited useful battery lifeLow costAcutation objectsFinanceInformation processingSoftware system
A secure magnetic stripe card stripe reader (MSR) module and software system capable of encrypting the magnetic stripe data to CISP standards for use in point of sale (POS) and other applications requiring data security using non secure networks and computing devices. Additionally, when incorporated within an attachment for conventional personal digital assistant (PDA) or cell phone or stationary terminal, provides encrypted data from the magnetic head assembly providing compliance with Federal Information Processing Standards Publication Series FIPS 140 covering security and tampering standards. Moreover, this module and software system includes the capability of providing secure POS transactions to legacy transaction processing systems transparently to the existing infrastructure. Furthermore, this module and software system includes the capability of transparently providing detection of fraudulently copied magnetic stripe cards.
Owner:VERIFONE INC
Magnetic strip reader with power management control for attachment to a PDA device
InactiveUS6944782B2Easy to optimizeEasy to doVolume/mass flow measurementPower supply for data processingEngineeringApplication software
A magnetic stripe card manual swipe reader (MSR) unit capable of attaching to and communicating with a conventional personal digital assistant (PDA) from various manufacturers, using only the electrical power available as supplied by the PDA device, and capable of effective electrical power management and conservation operations. Additionally, this PDA attachable MSR unit is capable of recognizing multiple magnetic encoding formats and data record formats and converting said formats to a standardized output format, includes the capability of updating and adding new formats while in field service, and is readily allows verifying card data and encoding sensitive material prior to transmission to the PDA. These custom formats can then be used to fulfill current needs in age verification, law enforcement, security, and numerous other applications.
Owner:VERIFONE INC
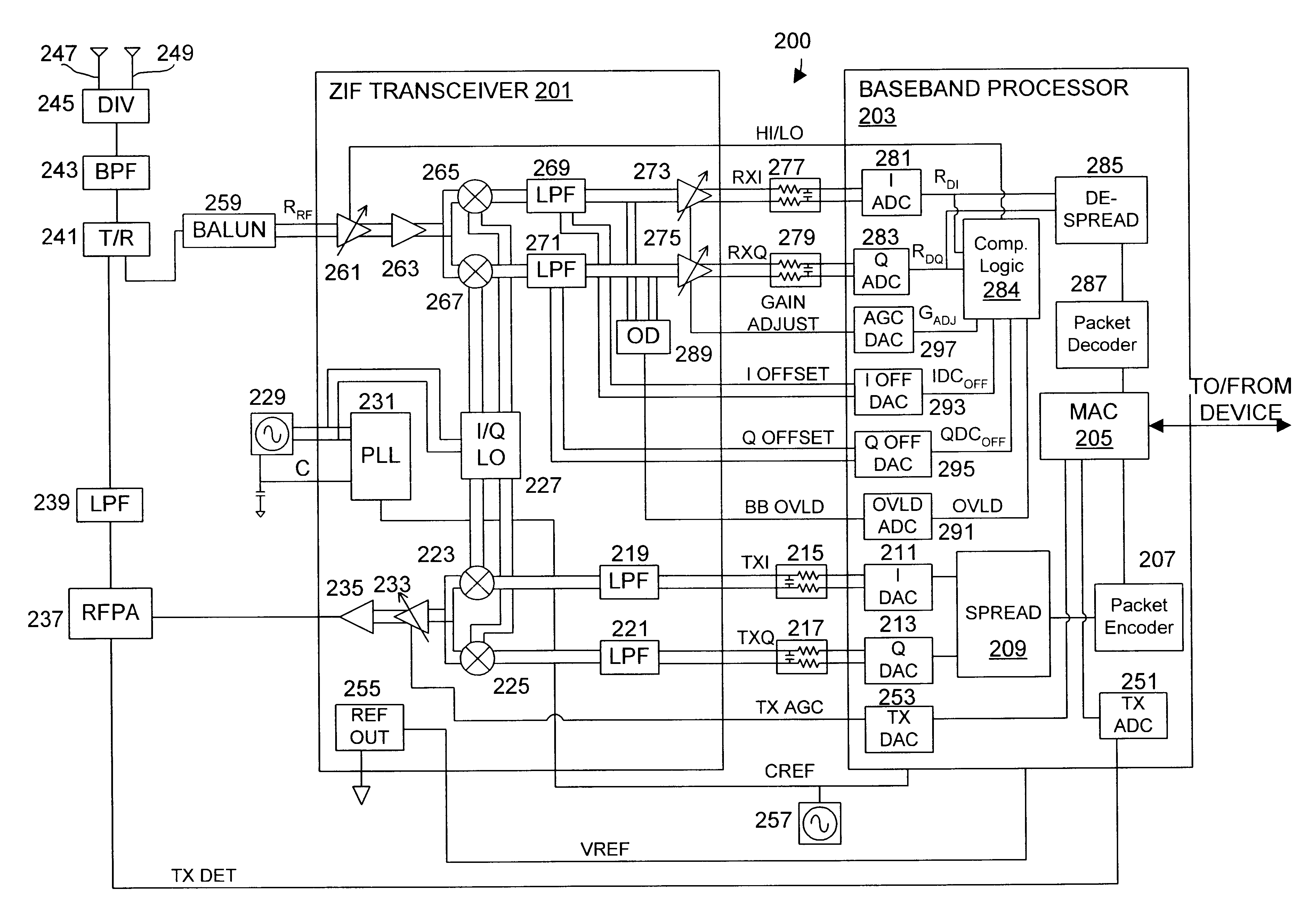
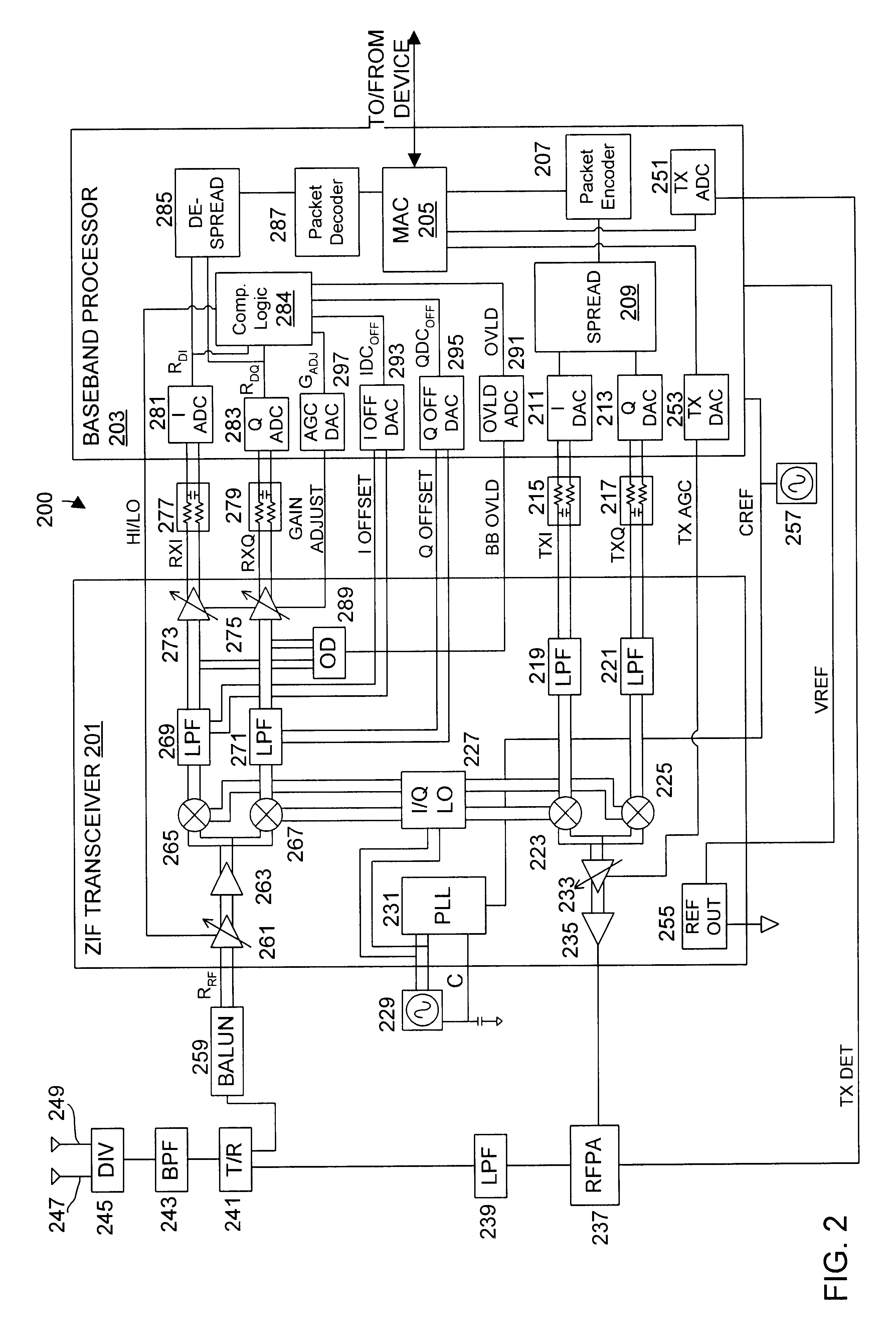
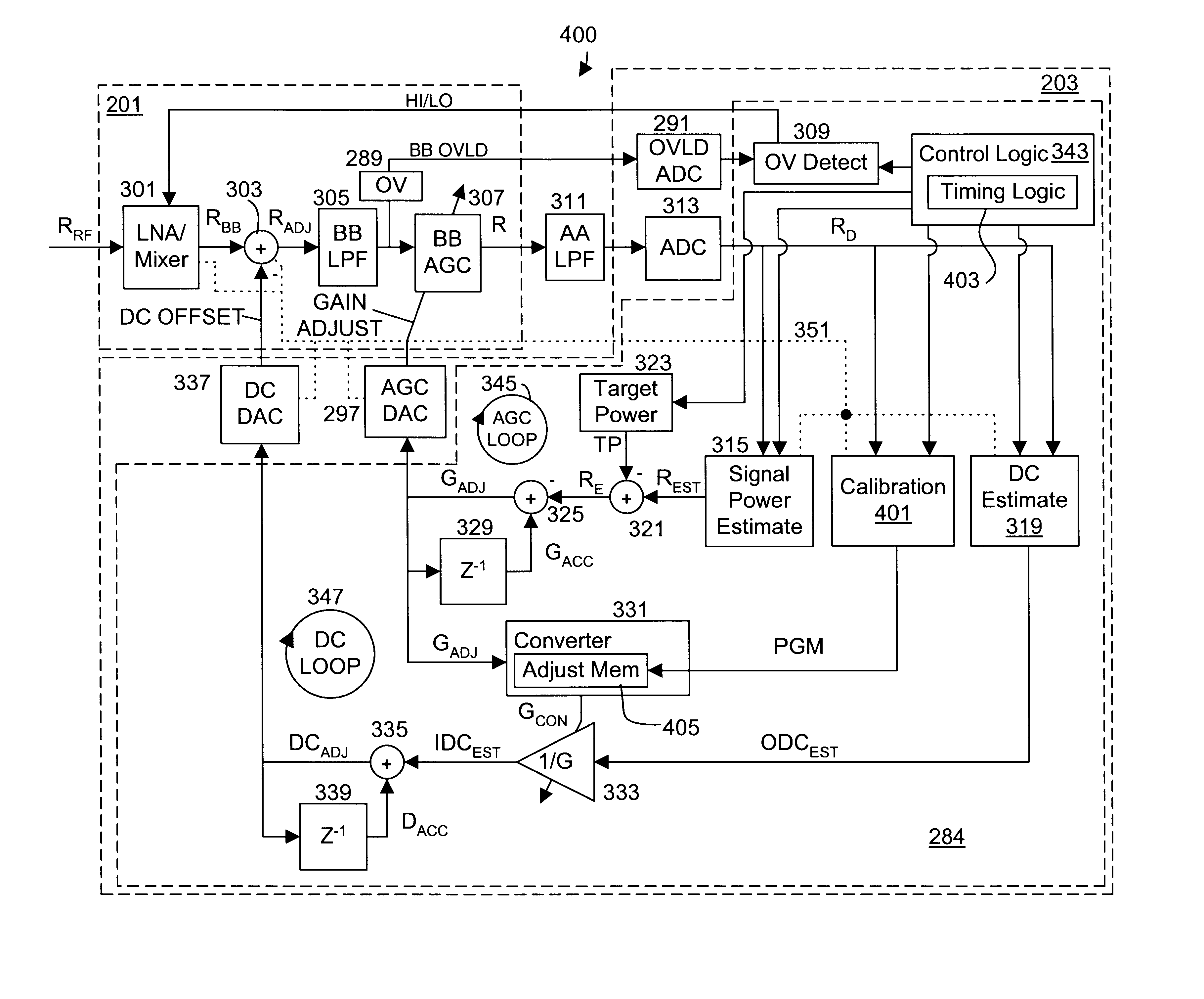
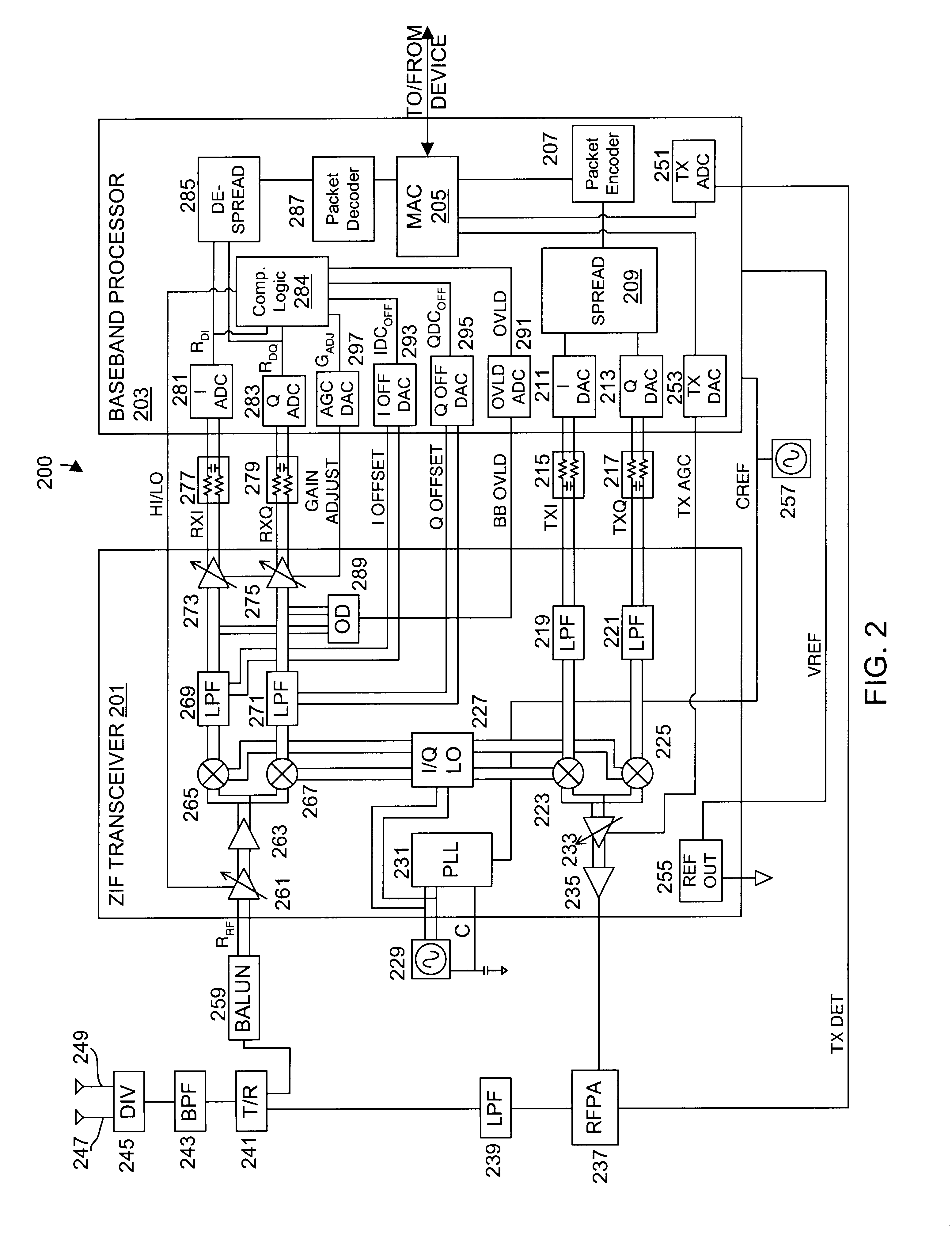
DC compensation system for a wireless communication device configured in a zero intermediate frequency architecture
InactiveUS6560448B1Low costMaximum performanceGain controlAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsTransceiverAudio power amplifier
A wireless communication device including a radio frequency (RF) circuit, a ZIF transceiver and a baseband processor. The ZIF transceiver includes an RF mixer circuit that converts the RF signal to a baseband input signal, a summing junction that subtracts a DC offset from the baseband input signal to provide an adjusted baseband input signal, and a baseband amplifier that receives the adjusted baseband input signal and that asserts an amplified input signal based on a gain adjust signal. The baseband processor includes gain control logic, DC control logic and a gain interface. The gain control logic receives the amplified input signal, estimates input signal power and asserts the gain adjust signal in an attempt to keep the input signal power at a target power level. The DC control logic estimates an amount of DC in the amplified input signal and provides the DC offset in an attempt to reduce DC in the amplified input signal. The gain interface converts gain levels between the gain control logic and the DC control logic. The RF signal may include in-phase (I) and quadrature (Q) portions, where the RF mixer circuit splits I and Q baseband input signals from the RF signal. Operation is substantially identical for both I and Q channels. The DC control logic operates to remove or otherwise eliminate DC from the received signal that is provided to decoders in the baseband processor.
Owner:M RED INC
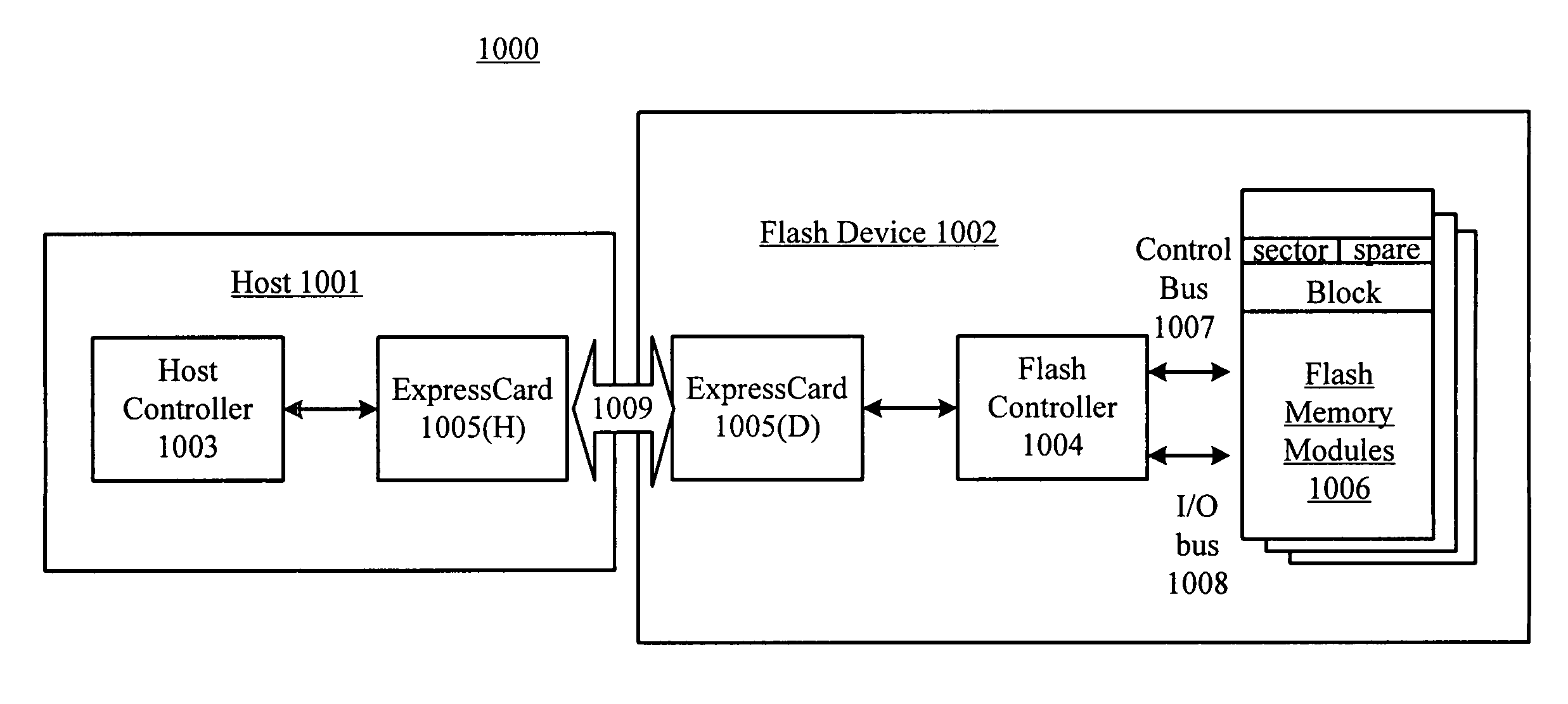
PCI express-compatible controller and interface for flash memory
InactiveUS7457897B1Improve performanceFacilitates optimal serviceabilityRead-only memoriesDigital storagePCI ExpressSystem bus
A PCI Express-compatible flash device can include one or more flash memory modules, a controller, and an ExpressCard interface. The controller can advantageously provide PCI Express functionality as well as flash memory operations, e.g. writing, reading, or erasing, using the ExpressCard interface. A PIO interface includes sending first and second memory request packets to the flash device. The first memory request packet includes a command word setting that prepares the flash device for the desired operation. The second memory request packet triggers the operation and includes a data payload, if needed. A DMA interface includes sending the second memory request from the flash device to the host, thereby triggering the host to release the system bus for the DMA operation.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
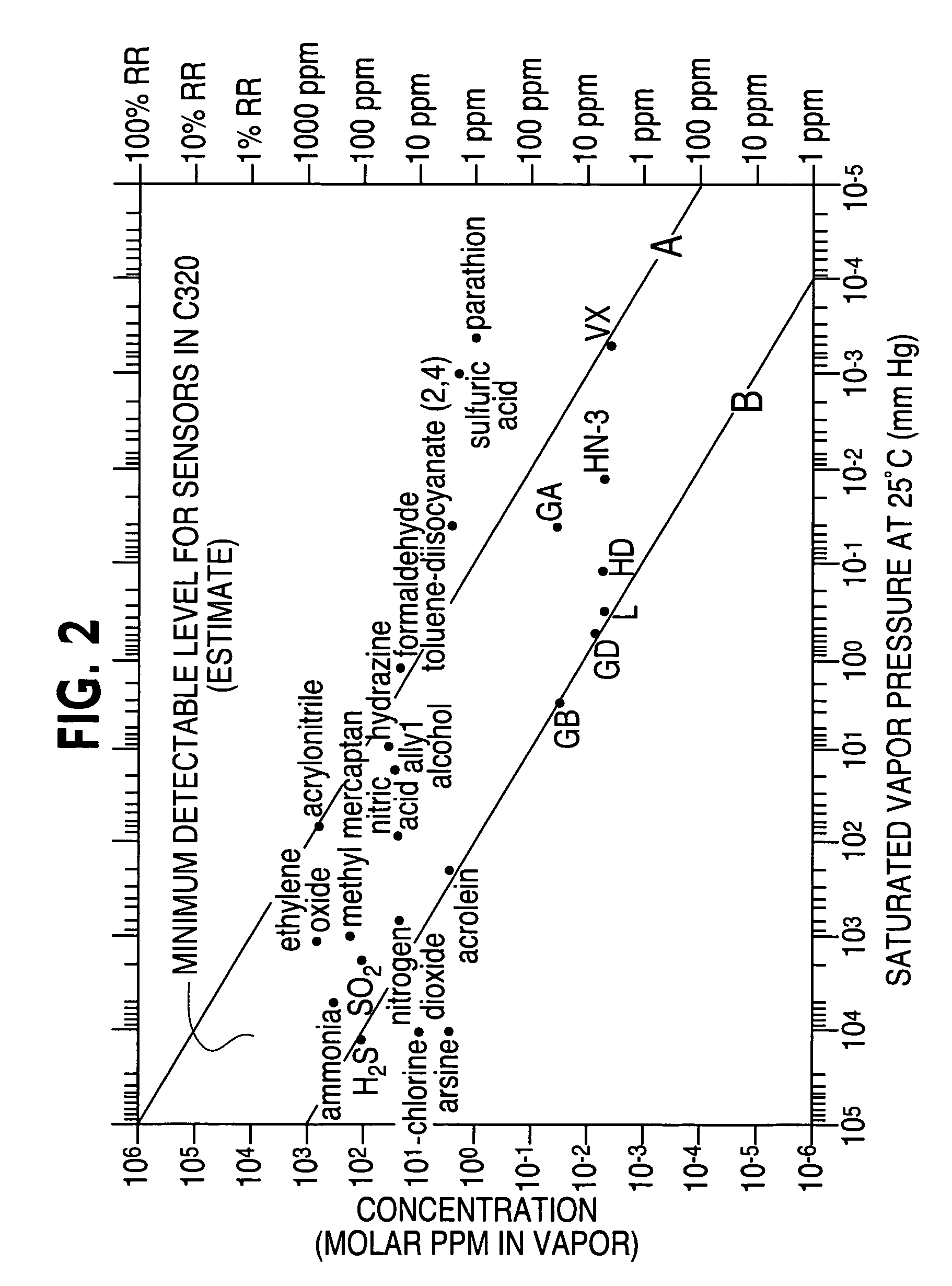
Chemical and biological agent sensor array detectors
Chemical and biological detector systems, devices and apparatus. Such devices may be portable and wearable, such as badges, that are analyte-general, rather than analyte-specific, and which provide an optimal way to notify and protect personnel against known and unknown airborne chemical and biological hazards. The devices of the present invention are advantageously low-cost, have low-power requirements, may be wearable and are designed to detect and alarm to a general chemical and biological threat. A sensor device of the present invention in one embodiment includes two or more sensor devices, a processing module coupled to each of the sensor devices and configured to process signals received from each of the two or more sensor devices to determine an environmental state; and a communication module that communicates information about the environmental state to a user.
Owner:SMITHS DETECTION
Laser based frequency standards and their applications
InactiveUS20070086713A1Minimize lossLow phase noiseLaser detailsCoupling light guidesFrequency standardLight source
Frequency standards based on mode-locked fiber lasers, fiber amplifiers and fiber-based ultra-broad bandwidth light sources, and applications of the same.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Computer rack heat extraction device
InactiveUS6412292B2More revenueExcessive coolingDucting arrangementsDigital data processing detailsAppliance componentEngineering
An air conditioning cooling apparatus and method which includes the steps of supplying cooling air generated from a cooling apparatus into an air passageway formed below a floor; guiding the cooling air within the air passageway into an equipment assembly disposed on the floor through an opening located in the floor; communicating the cooling air introduced into the equipment assembly into a plenum and introducing the air released from within the equipment into the plenum and communicating the released air through the cooling apparatus for cooling the released air. The method permits temperature differential between the air supplied to the air passageway and the air introduced into the plenum from the equipment assembly to be 45.degree. F. to substantially 40.degree. F. so as to reduce the power necessary for operating on the fan of the blowing apparatus. The equipment assembly utilizes an air flow control mechanism so as to substantially evenly distribute cooling air to the equipment.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LIMITED
Optical fiber communications method and system without a remote electrical power supply
ActiveUS7469105B2Reduce power consumptionReduced Power RequirementsElectromagnetic transmissionWireless communicationElectrical conductorEngineering
The present invention allows remote antenna units for radio frequency signal transmission and receipt to operate without the requirement for remote electrical power supplies or for connecting cables that incorporate electrical conductors. According to an aspect of the present invention, an optical communications system employing radio frequency signals comprises a central unit; at least one remote unit having at least one optoelectronic transducer for converting optical data signals to radio frequency signals and converting radio signals to optical signals and at least one antenna to receive and send radio frequency signals; at least one optical fiber data link between the central unit and the remote unit for transmitting optical data signals therebetween; and at least one optical fiber power link between the central unit and the remote unit for providing electrical power at the remote unit.
Owner:NEXTG NETWORKS INC
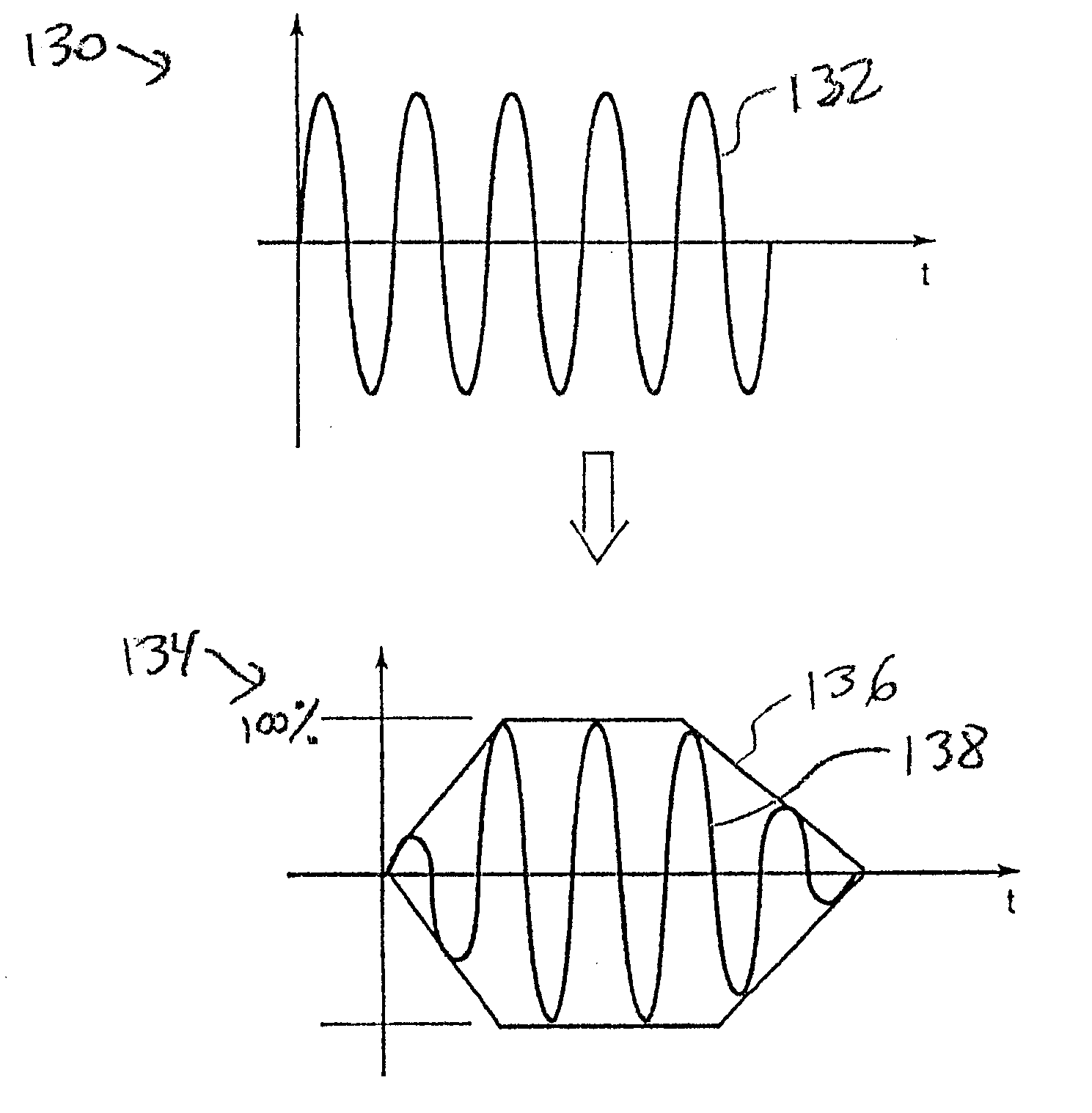
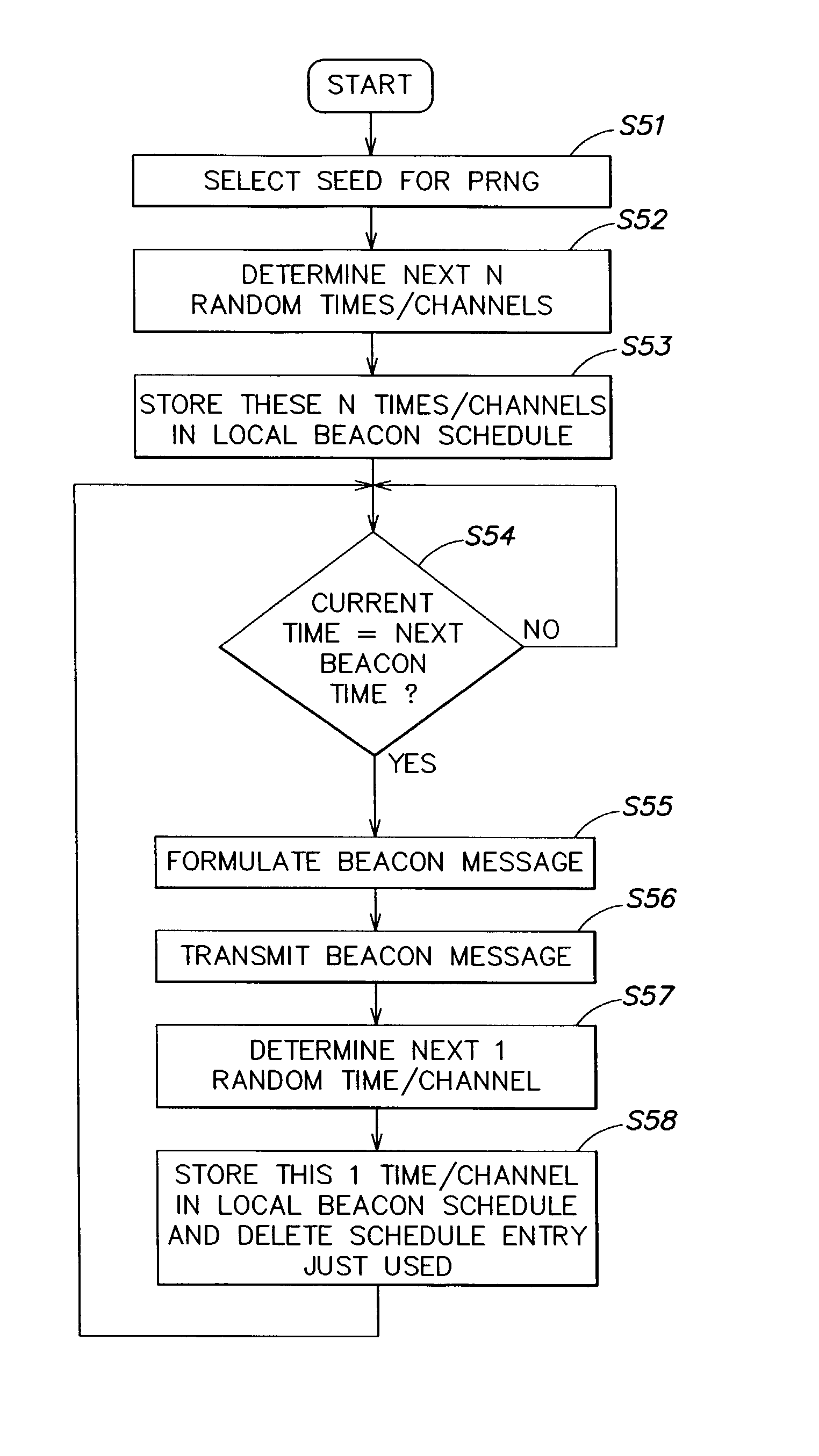
Method and apparatus for varying times/channels of broadcast beacons
Method and apparatus for varying the times and channels of broadcast beacons. The method and apparatus make it more difficult to monitor and / or disrupt such beacon transmissions. In one embodiment, pseudo-random times and pseudo-random channels are selected for transmitting the beacon messages. Preferably these times and channels are included in a beacon schedule which is transmitted with the beacon messages. In select embodiments, the beacon messages include schedules for both the transmitting node and other nodes, so that all of the nodes in the network may quickly learn the beacon schedules of the other nodes.
Owner:RAYTHEON BBN TECH CORP
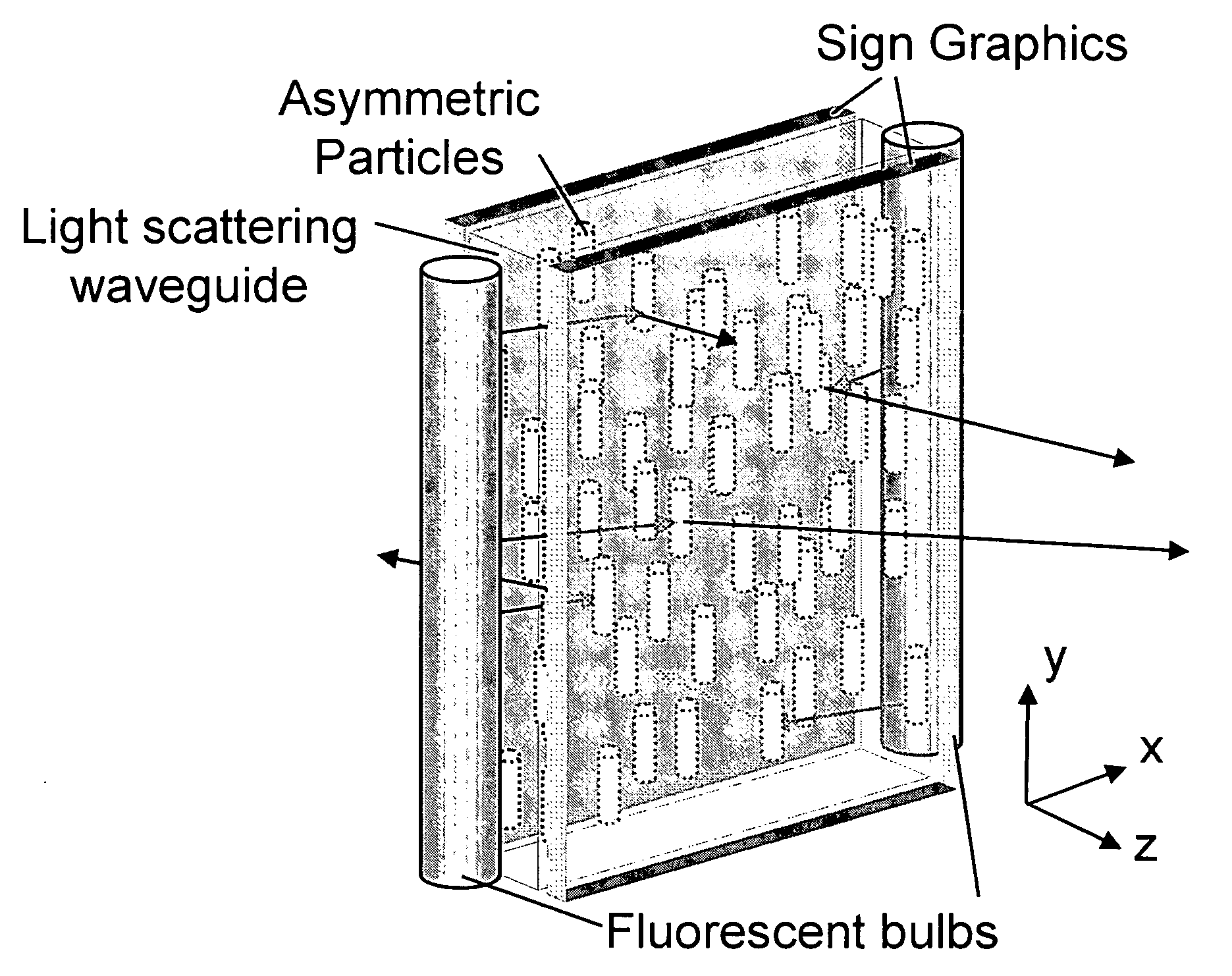
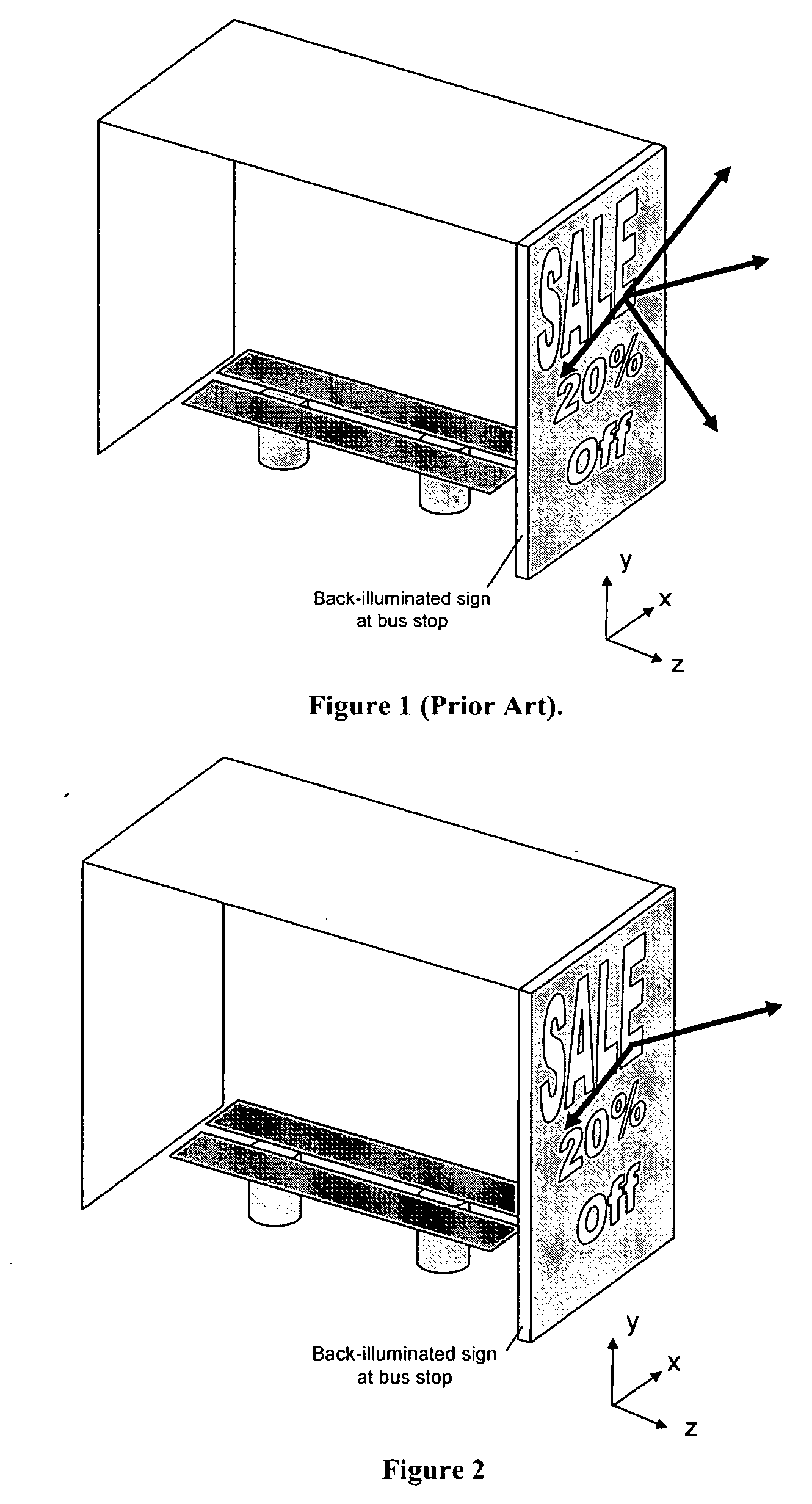
Enhanced electroluminescent sign
InactiveUS20060215958A1Signs improvedEfficiently directsCoupling light guidesIlluminated signsElectricityLightness
An enhanced electroluminescent sign containing a volumetric, anisotropic scattering element to control the angular spread of light from the sign and the spatial luminance uniformity of the sign. The anisotropic scattering element contains one or more regions of asymmetrically-shaped light scattering particles. The angular spread of light leaving a sign from a light emitting source can be efficiently controlled by using a thin, low cost, volumetric, anisotropic scattering elements to angularly and spatially distribute light, permitting the reduction in number of light sources, a reduction in power requirements, or a more tailored viewing angle.
Owner:FUSION OPTIX
Calibrated DC compensation system for a wireless communication device configured in a zero intermediate frequency architecture
InactiveUS6735422B1Low costMaximum performancePulse automatic controlGain controlTransceiverAudio power amplifier
A calibrated DC compensation system for a wireless communication device configured in a zero intermediate frequency (ZIF) architecture. The device includes a ZIF transceiver and a baseband processor, which further includes a calibrator that periodically performs a calibration procedure. The baseband processor includes gain control logic, DC control logic, a gain converter and the calibrator. The gain converter converts gain between the gain control logic and the DC control logic. The calibrator programs the gain converter with values determined during the calibration procedure. The gain converter may be a lookup table that stores gain conversion values based on measured gain of a baseband gain amplifier of the ZIF transceiver. The gain control logic may further include a gain adjust limiter that limits change of a gain adjust signal during operation based on a maximum limit or on one or more gain change limits. A second lookup table stores a plurality of DC adjust values, which are added during operation to further reduce DC offset. The calibration procedure includes sampling an output signal for each gain step of the baseband amplifier at two predetermined range values and corresponding DC offsets using successive approximation. The data is used to calculate gain, DC offset and DC differential values, which are used to determine the conversion values programmed into the lookup tables or the gain adjust limiter.
Owner:M RED INC
White light-emitting device with improved doping
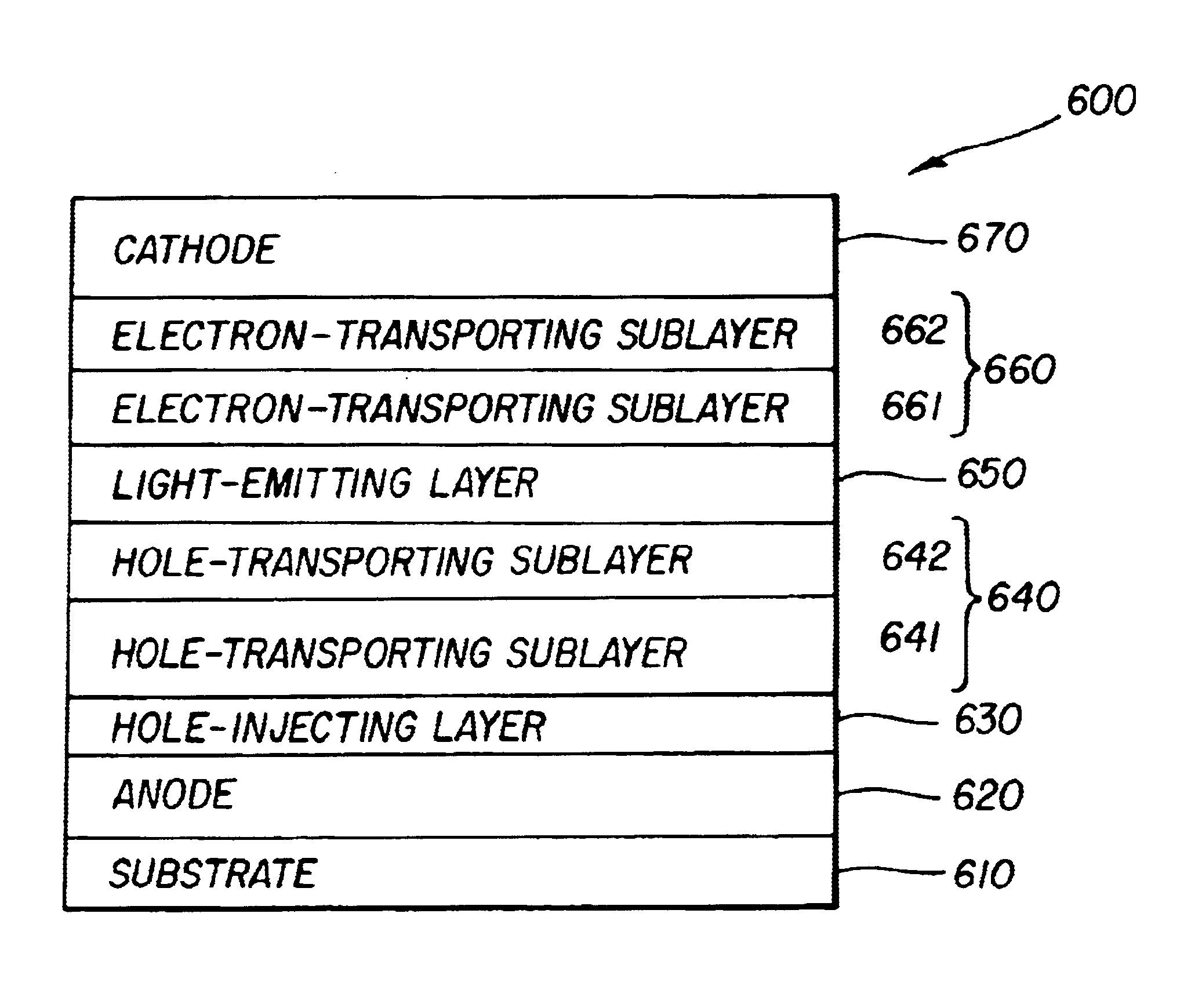
InactiveUS6875524B2High strengthReduced Power RequirementsDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesLiquid crystal light valveDisplay device
Organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) that produce white light include an anode, a hole-transporting layer disposed over the anode, a blue light-emitting layer disposed over the hole-transporting layer, an electron-transporting layer disposed over the blue light-emitting layer, and a cathode disposed over the electron-transporting layer. The hole-transporting layer is doped with both a yellow-emitting and a red-emitting dopant. When used together with red, green, and blue color filters, the OLEDs produce red, green, and blue light with good color quality and high efficiency. Also disclosed are multicolor display devices utilizing the OLEDs together with color filters or together with both color filters and liquid-crystal light valves.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
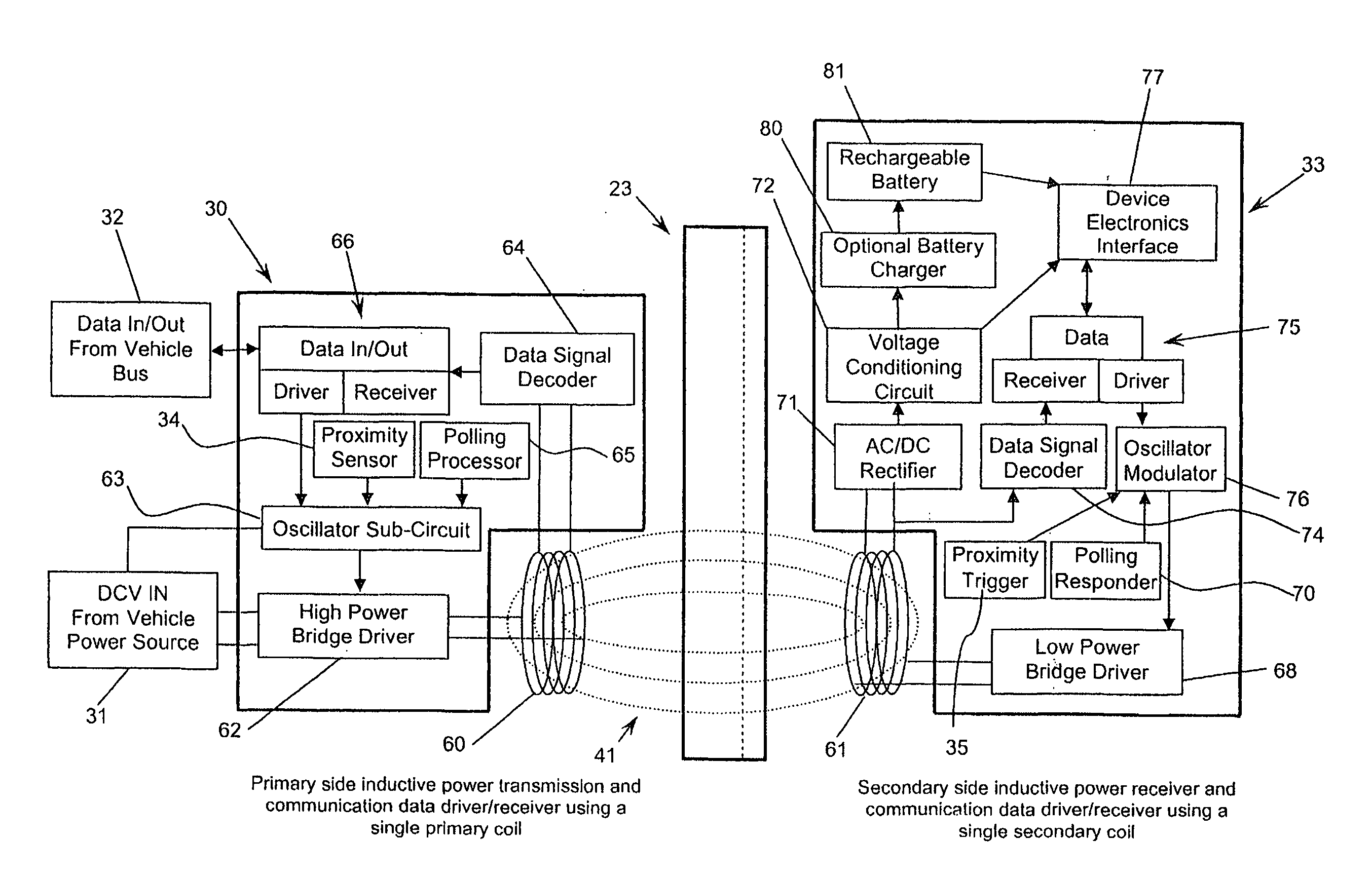
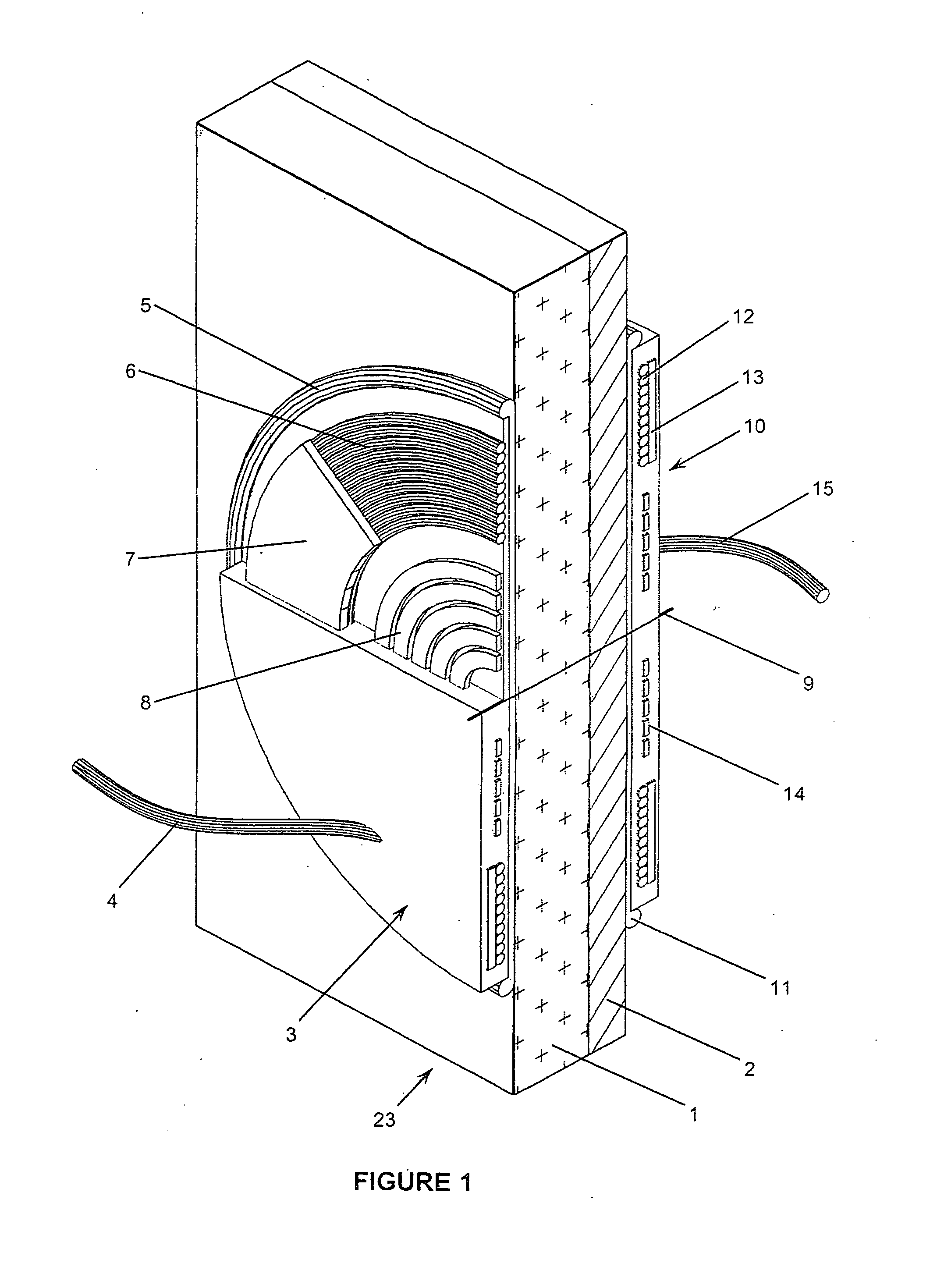
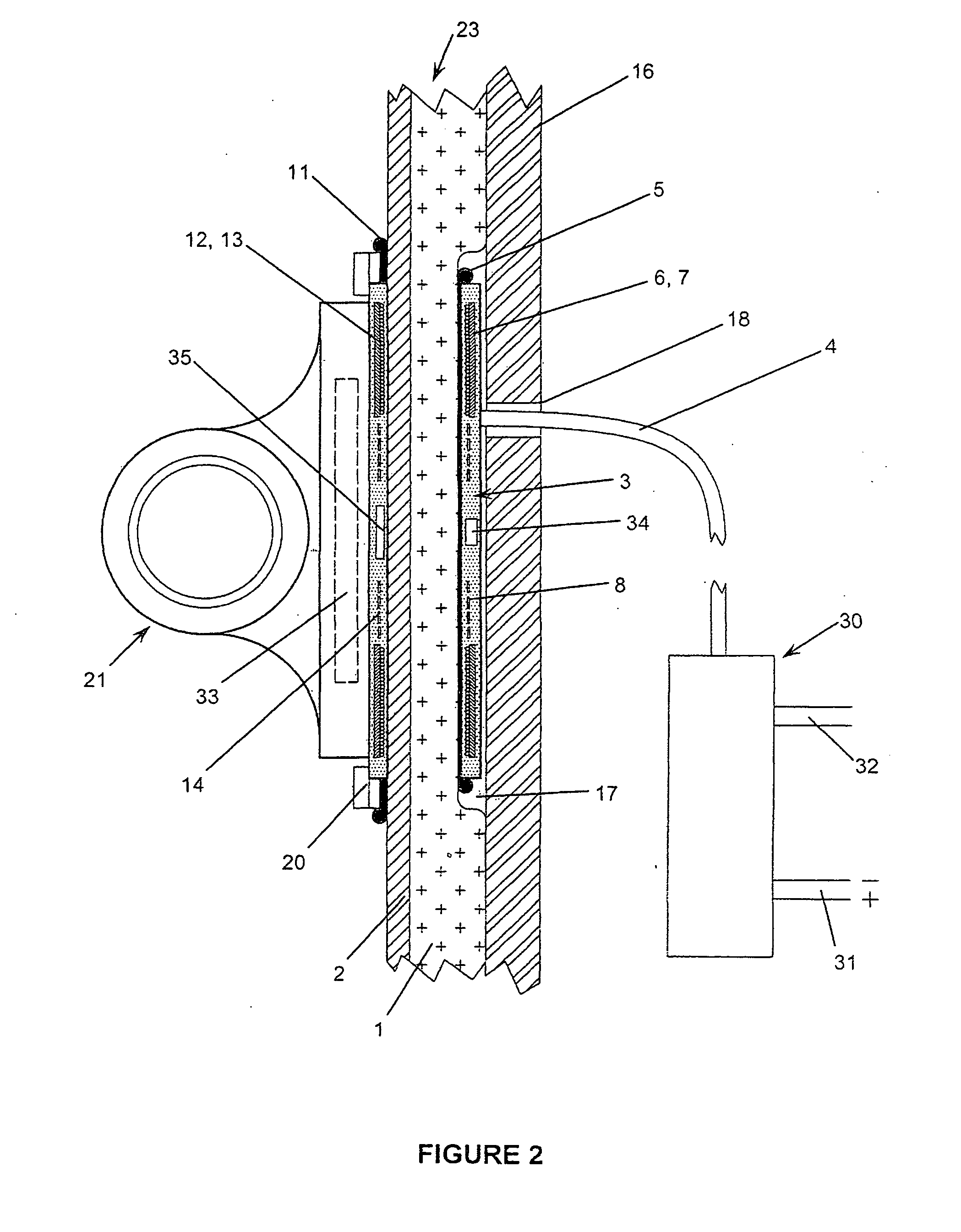
Inductive transmission of power and data through ceramic armor panels
ActiveUS20120032632A1Decreasing its survivabilityCompromising their effectivenessCircuit authenticationElectromagnetic wave systemElectrical devicesData transmission
A system for the inductive transmission of power and data through large caliber ballistic appliqué composite armor panels mountable to military vehicle includes a large caliber ballistic appliqué composite armor panel and a quick-release base mounted to the outer face of the panel and a primary coil mounted to the inner face of the panel so as to be opposite to and aligned with the base; and, a portable electrical device having a secondary coil mounted in its base end, and wherein the armor thickness is no greater than substantially the range of 30 to 50 percent of the diameter of the secondary coil. The base end of the portable electrical device is adapted to releasably mount onto the quick release base for power transfer to the electrical device and for data transfer between the primary coil and the secondary coil by inductive coupling between the primary and secondary coils.
Owner:CYNETIC DESIGNS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com