Patents
Literature
182 results about "Frequency separation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
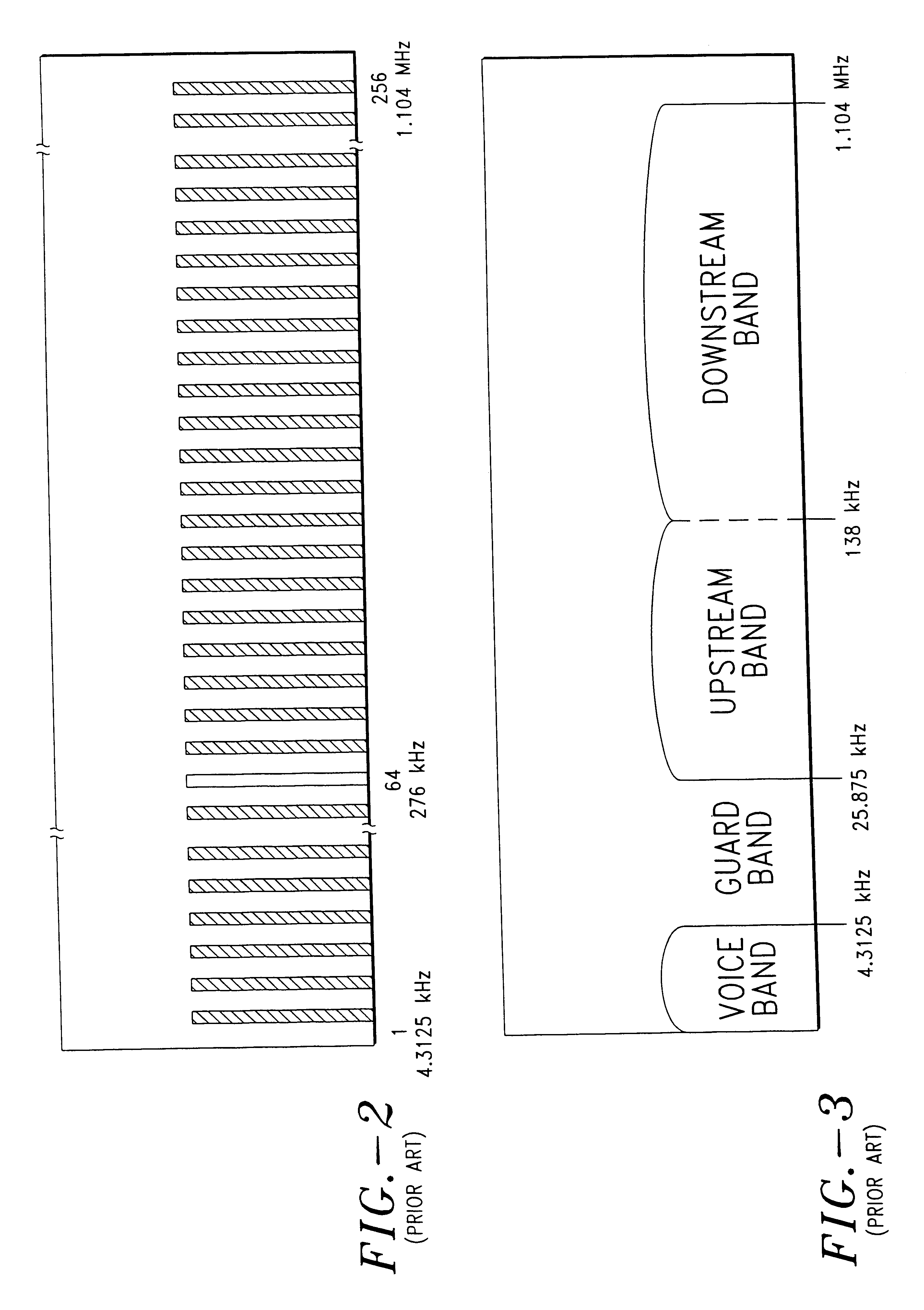
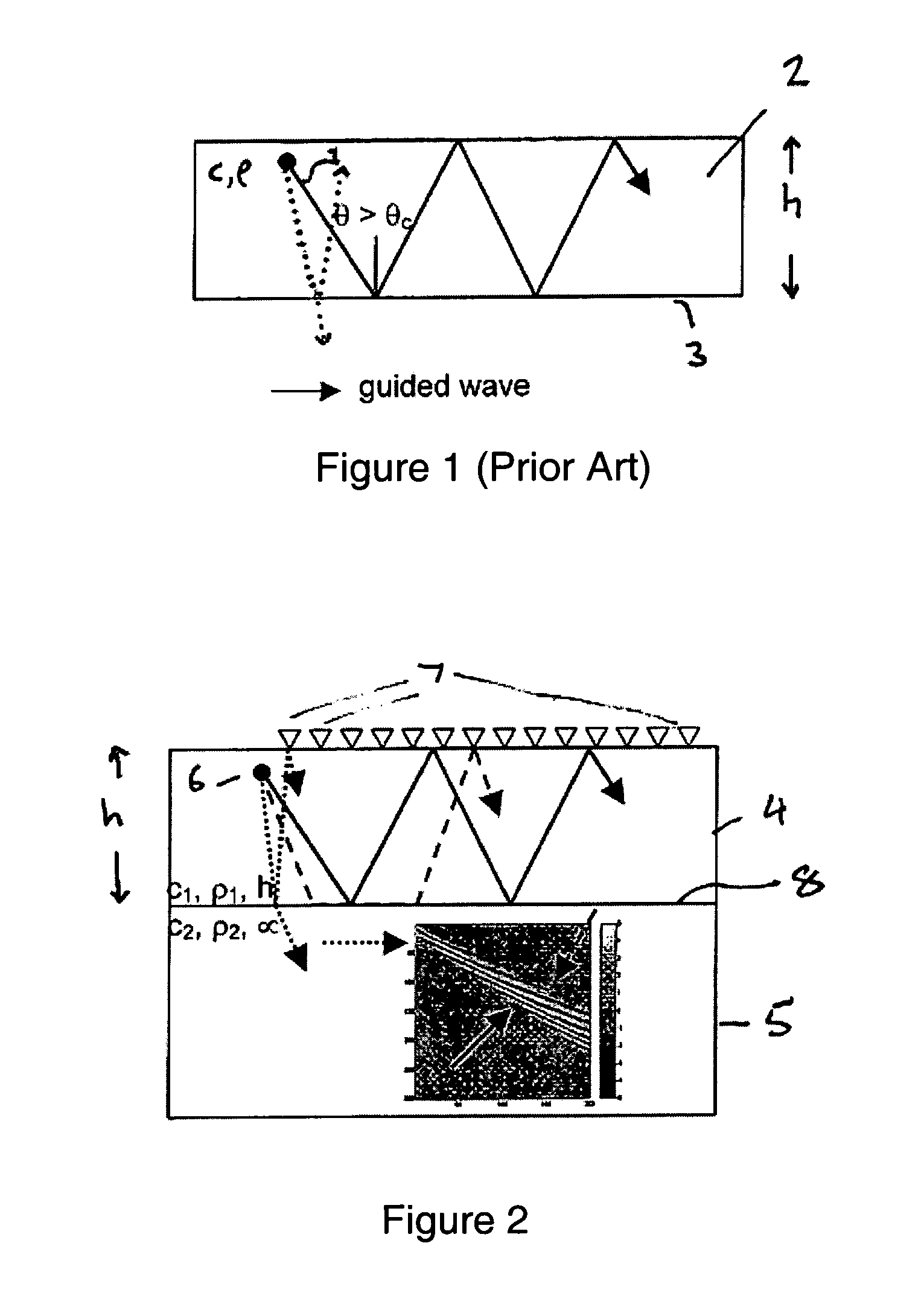
Frequency separation is a term used in Helio and Asteroseismology for the spacing in frequency between adjacent modes of oscillation having the same angular degree (l) but different radial order (n). For a Sun-like star the frequency can be further described using the 'large frequency spacing' between modes of different radial order (136 μHz in the Sun), and the 'small frequency spacing' between modes of even and odd angular degree within the same radial order (9.0 μHz in the Sun). The period corresponding to the large frequency spacing can be shown to be approximately the same as the time required for a sound wave to travel to the centre of the Sun and return, confirming the global nature of the oscillations seen.
Multiple access method and system
InactiveUS7010048B1Reduce decreaseLower Level RequirementsFrequency diversityWavelength-division multiplex systemsFiberPulse envelope
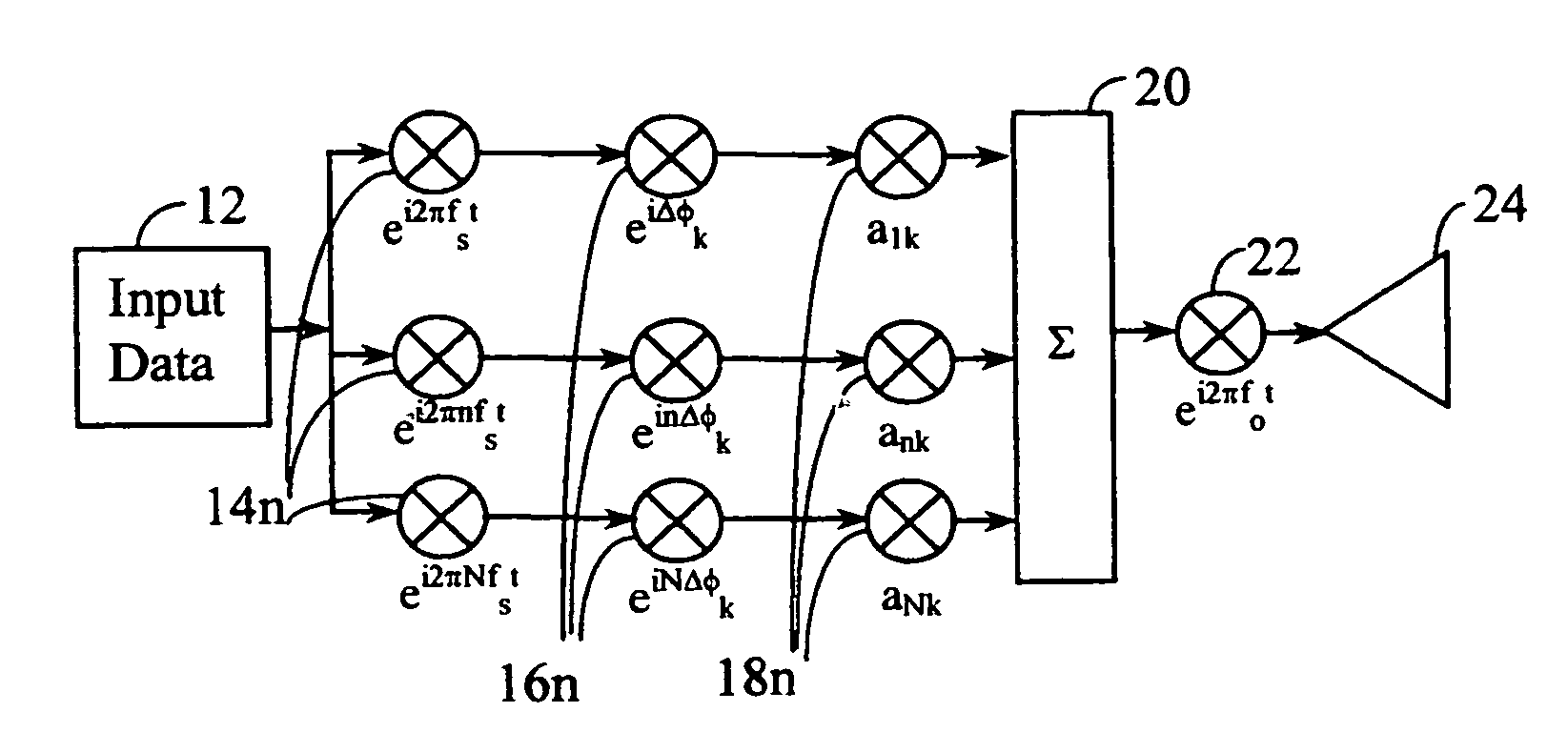
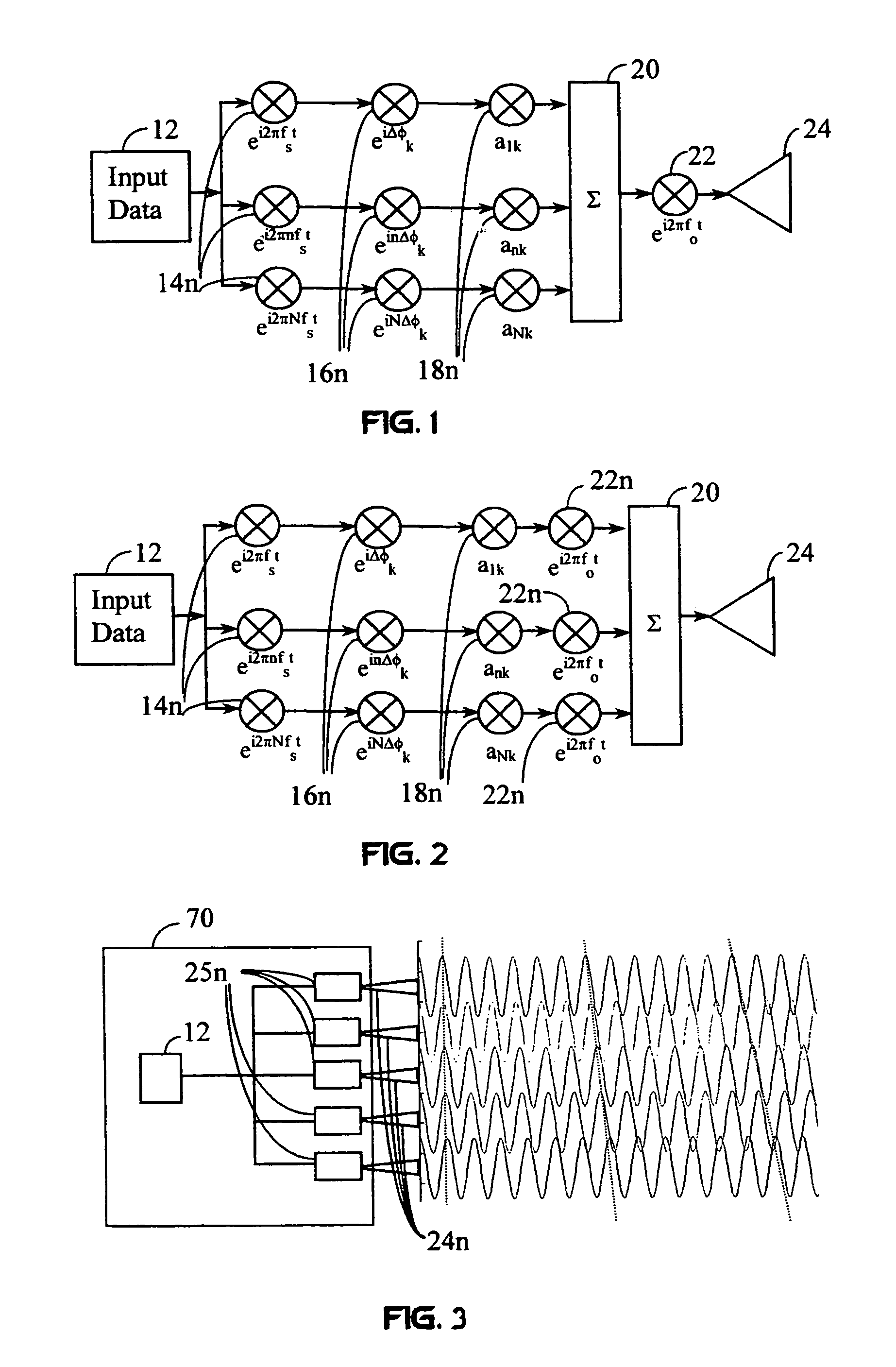
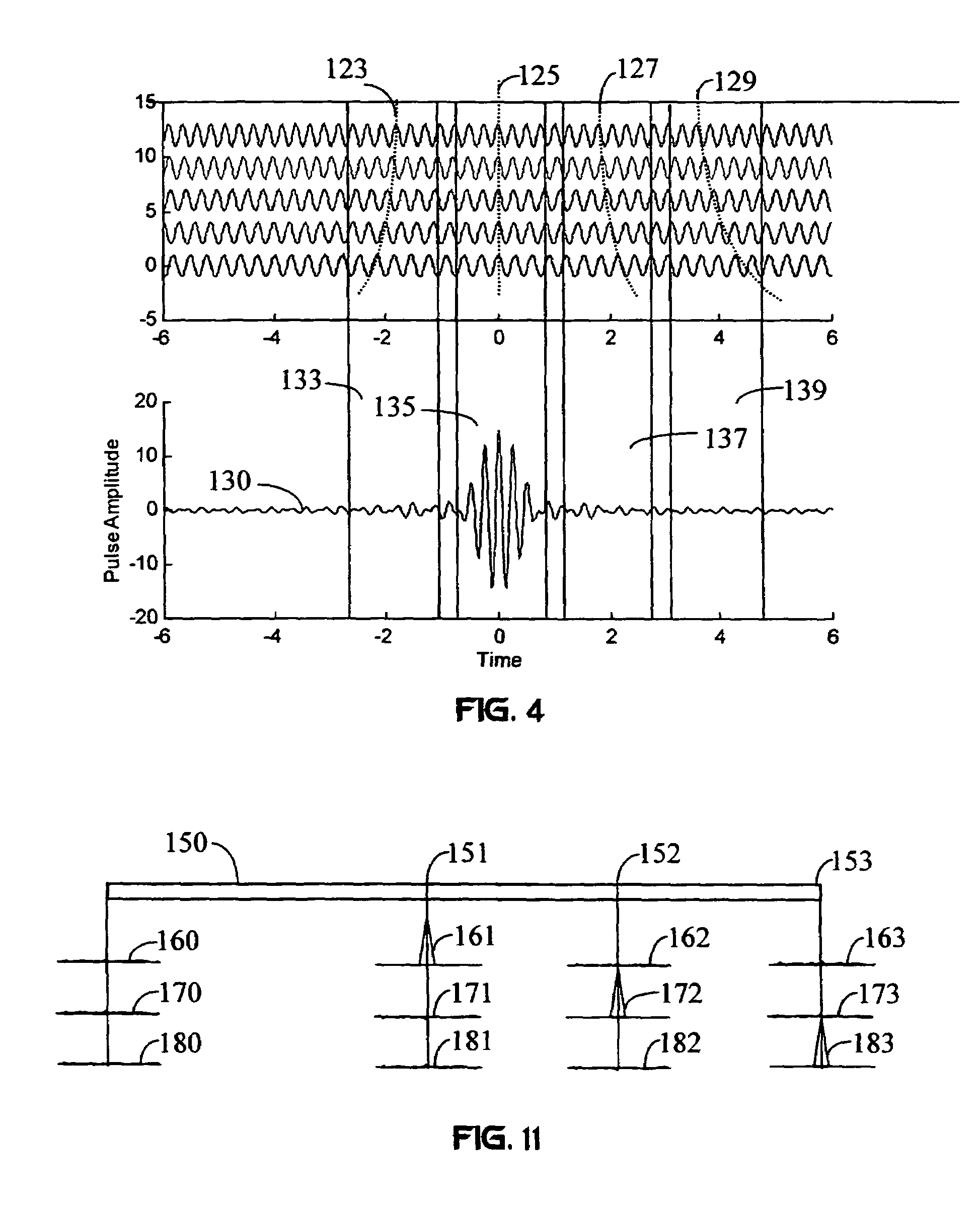
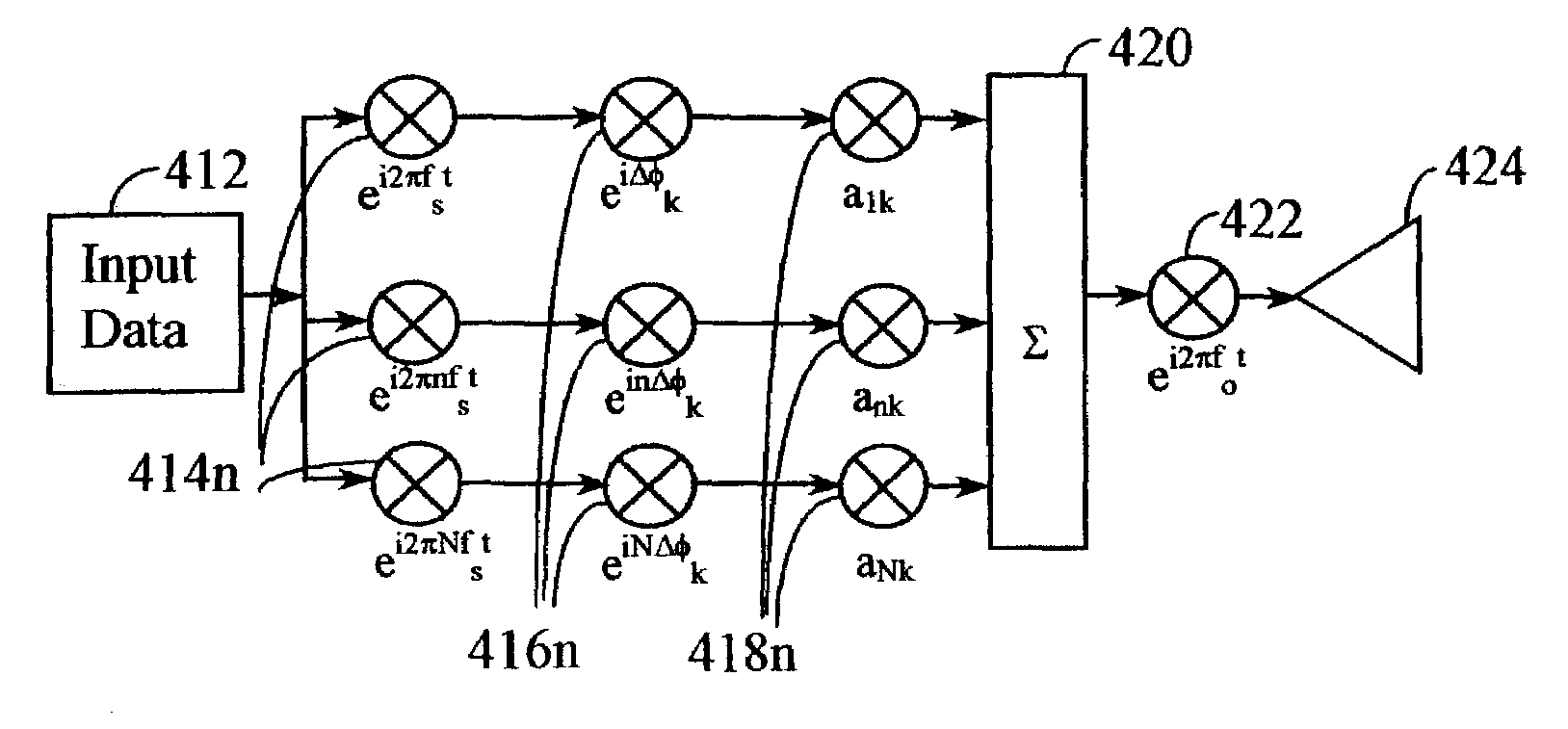
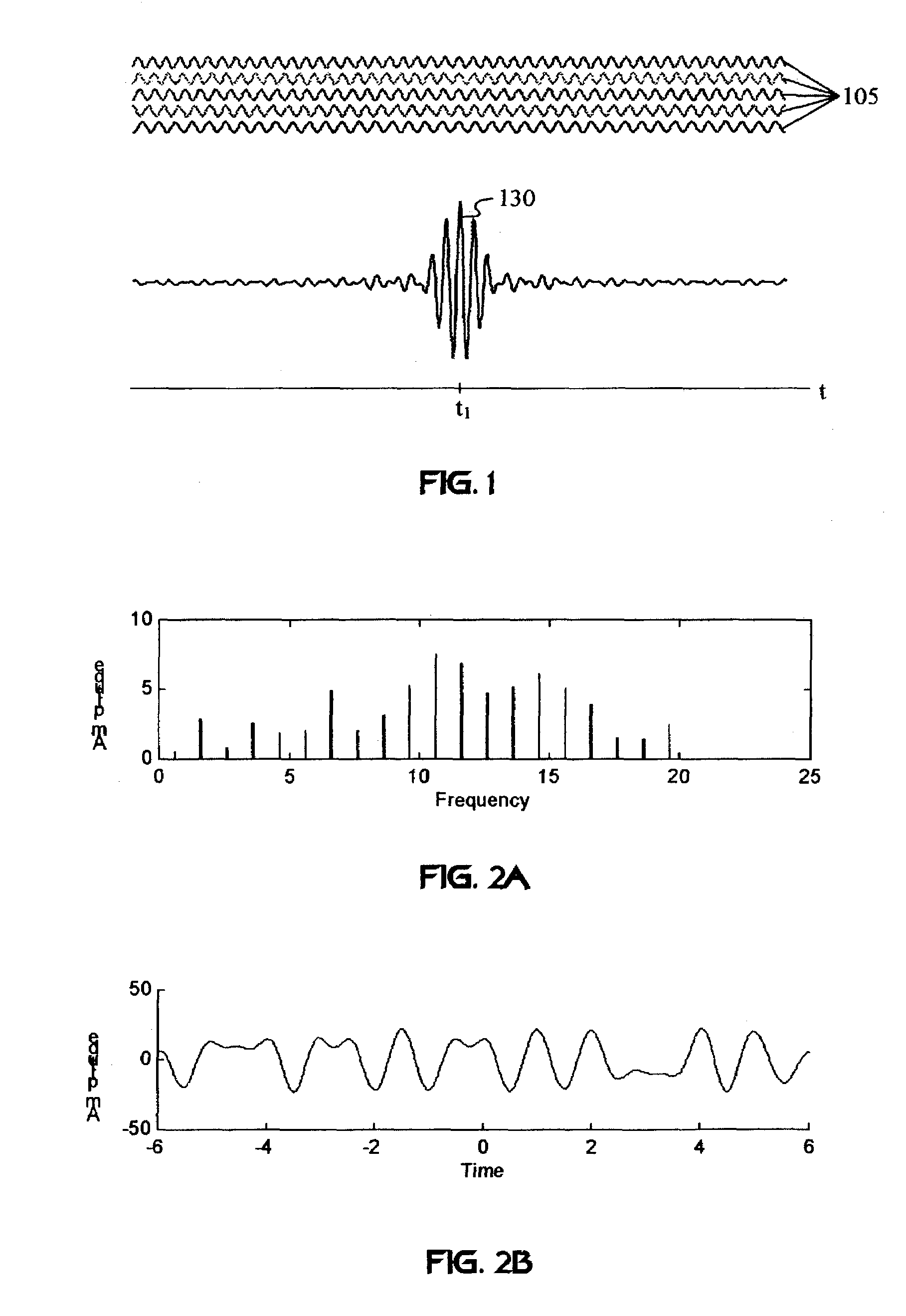
A wireless communication system transmits data on multiple carriers simultaneously to provide frequency diversity. Carrier interference causes a narrow pulse in the time domain when the relative phases of the multiple carriers are zero. Selection of the frequency separation and phases of the carriers controls the timing of the pulses. Both time division of the pulses and frequency division of the carriers achieves multiple access. Carrier interferometry is a basis from which other communication protocols can be derived. Frequency hopping and frequency shifting of the carriers does not change the pulse envelope if the relative frequency separation and phases between the carriers are preserved. Direct sequence CDMA signals are generated in the time domain by a predetermined selection of carrier amplitudes. Each pulse can be sampled in different phase spaces at different times. This enables communication in phase spaces that are not detectable by conventional receivers. The time-dependent phase relationship of the carriers provides automatic scanning of a beam pattern transmitted by an antenna array. In waveguide communications, the carrier frequencies and phase space may be matched to the chromatic dispersion of an optical fiber to increase the capacity of the fiber.
Owner:DEPARTMENT 13 INC
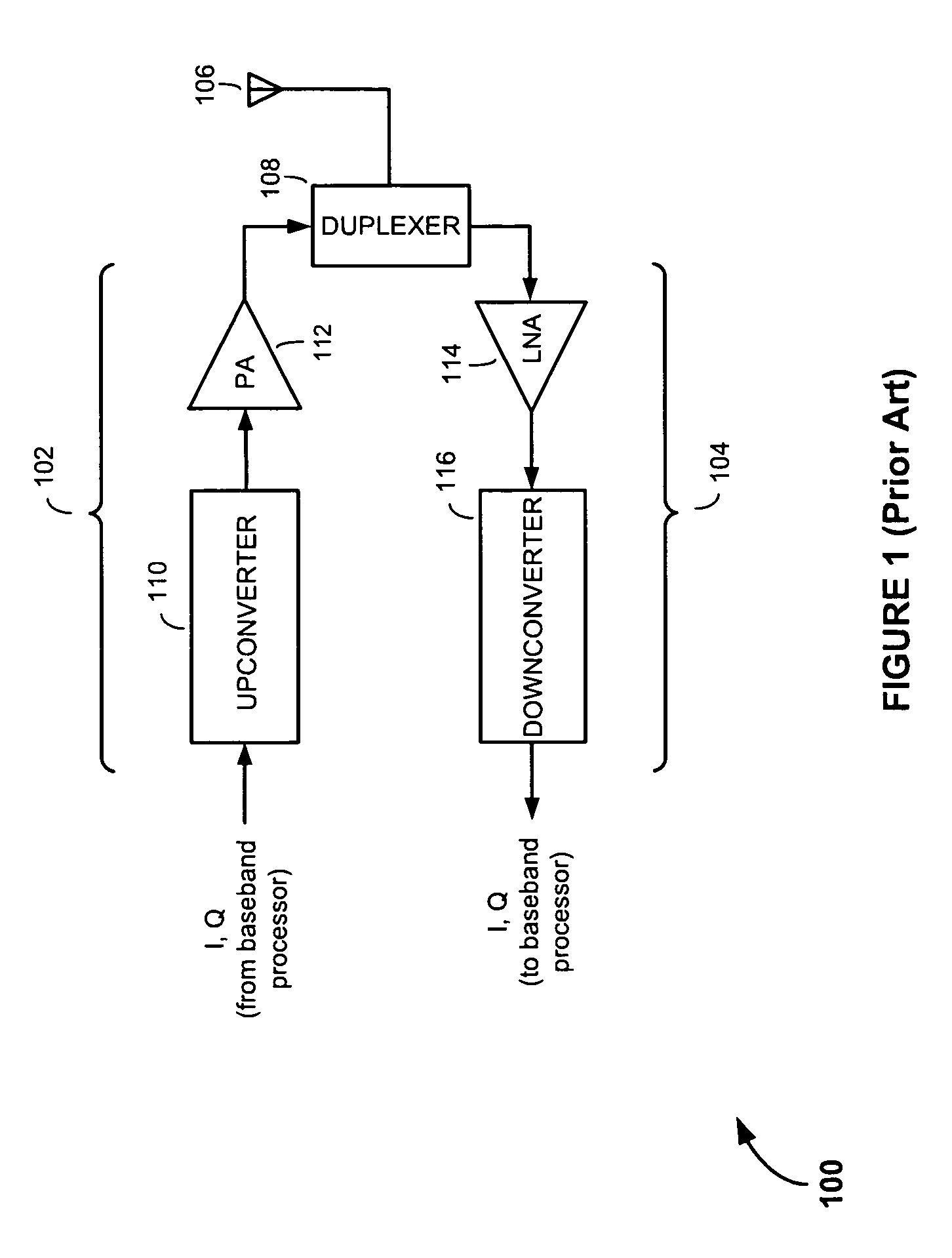
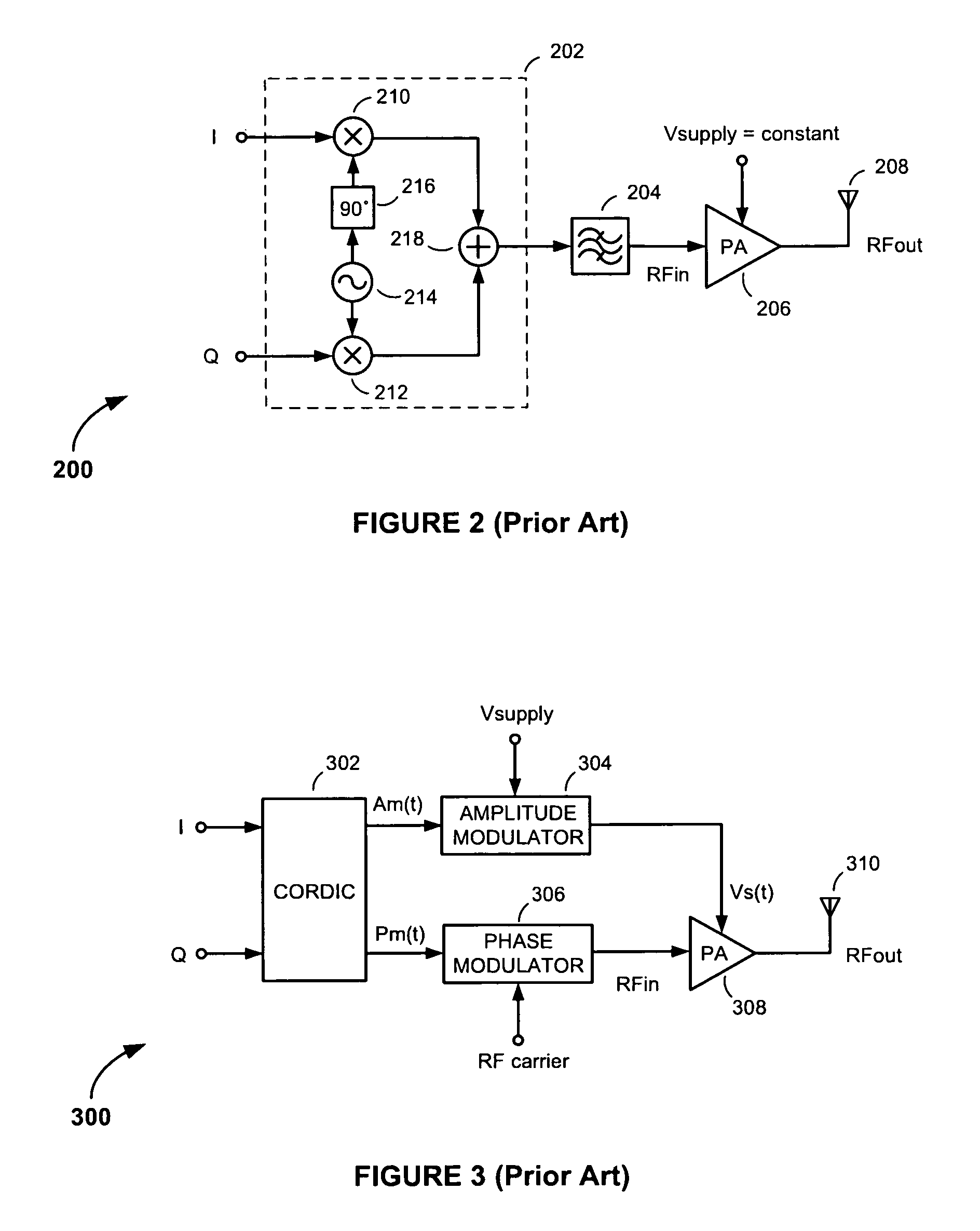
Multi-mode transmitter having adaptive operating mode control
ActiveUS8095093B2Improve power efficiencyPower efficiency and noiseResonant long antennasPower amplifiersPower efficientTransceiver
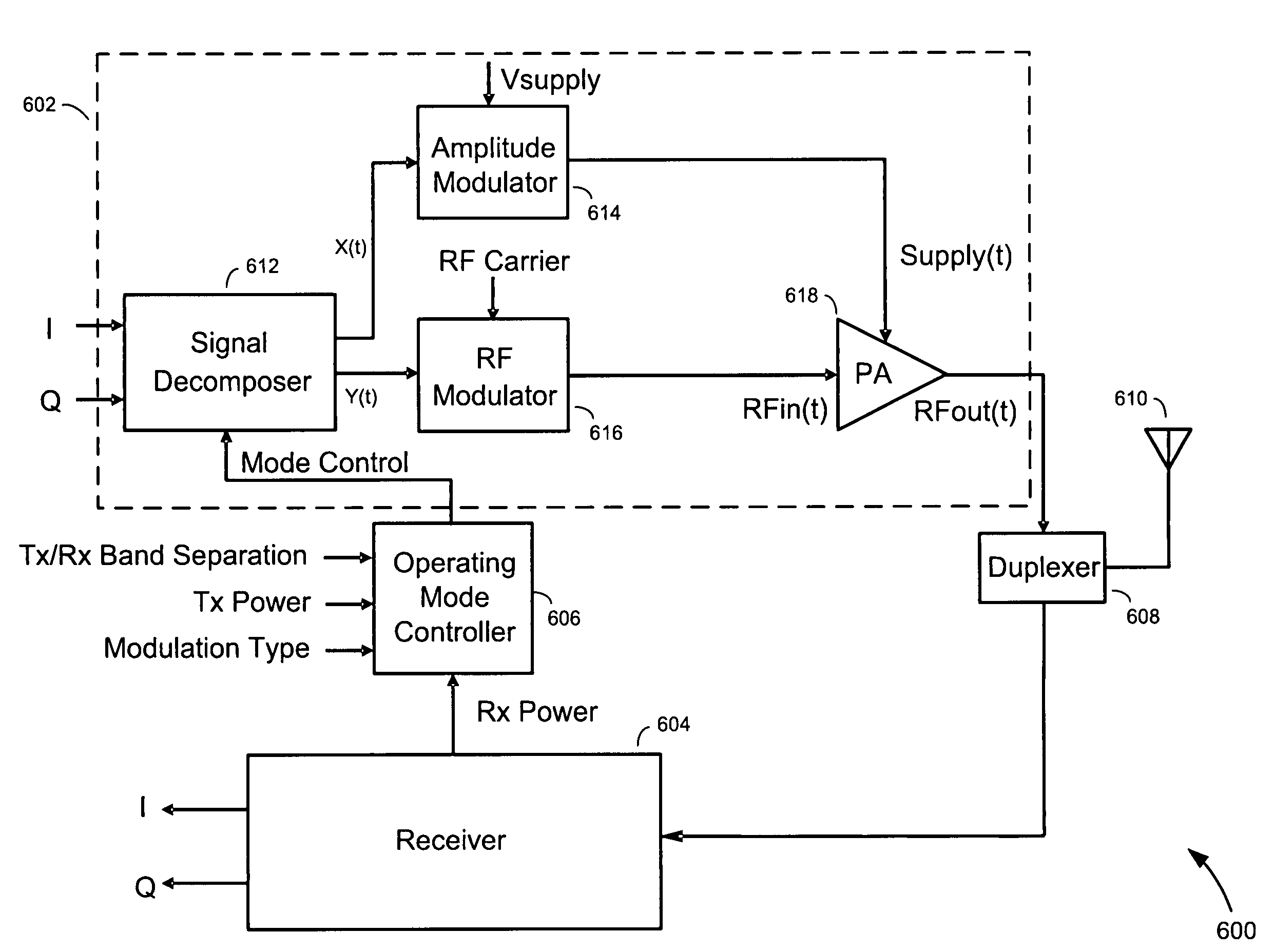
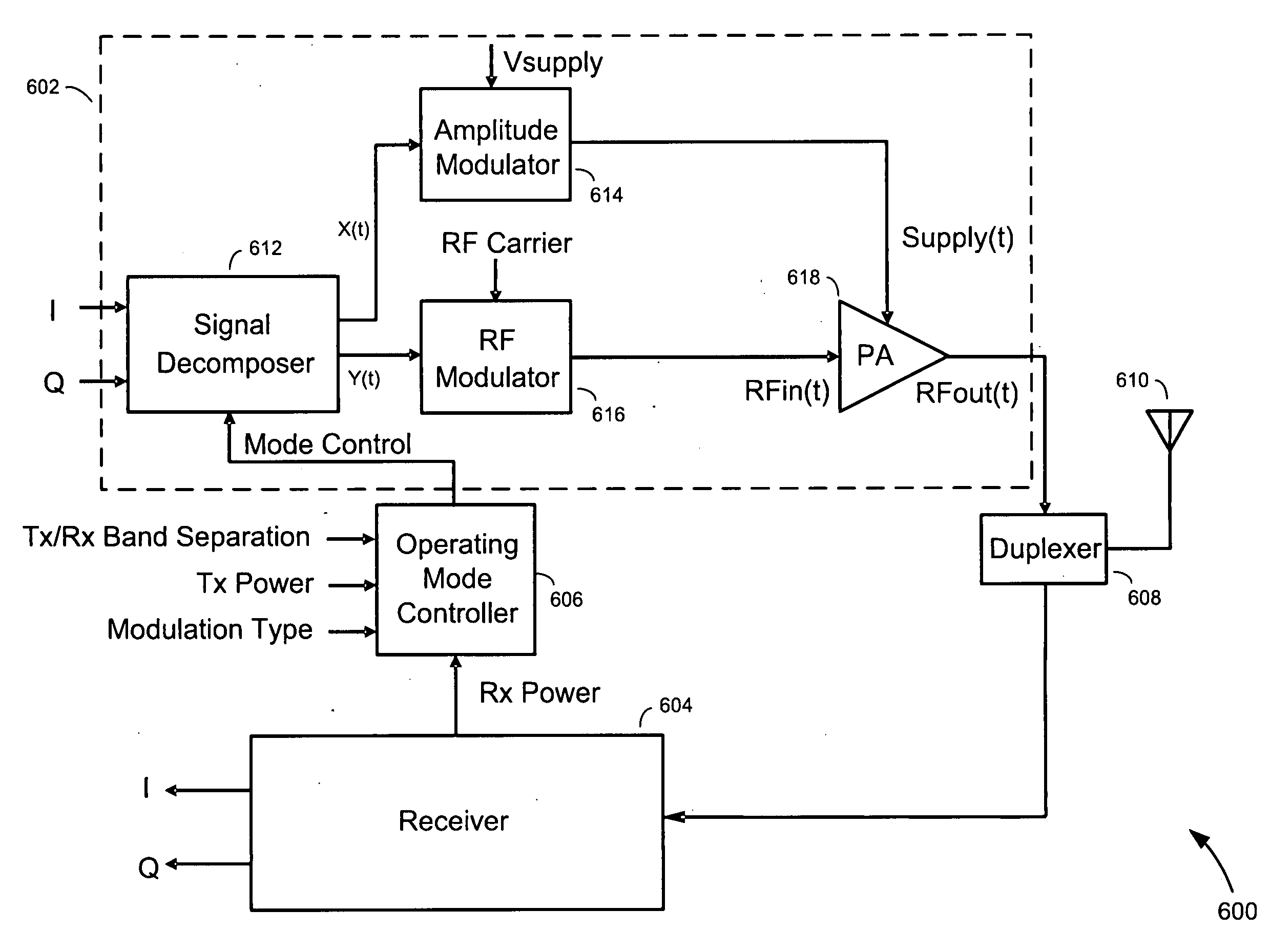
Methods and apparatus for transmitting communications signals that are both power efficient and effective at avoiding or reducing transmitter-generated receive band noise. An exemplary transceiver apparatus includes a multi-mode transmitter that is configurable to operate in a plurality of operating modes (e.g., a polar mode, a quadrature mode and a hybrid mode), a receiver, and an operating mode controller. The operating mode controller is configured to control which operating mode the transmitter is to operate, depending on one or more of a transmit (Tx) power, receive (Rx) power, the Tx power relative to the Rx power, a level of frequency separation between a Tx frequency band and a Rx frequency band (Tx / Rx band separation), and modulation type employed by the transmitter.
Owner:APPLE INC
Unified multi-carrier framework for multiple-access technologies
InactiveUS7406261B2Reduce the impactReduce transmit powerModulated-carrier systemsOptical multiplexTransmission protocolCarrier signal
A wireless communication system transmits data on multiple carriers simultaneously to provide frequency diversity. Orthogonality is provided by carrier interference, which causes a narrow pulse in the time domain corresponding to each transmitted data symbol. Selection of the frequency separation and phases of the carriers controls the timing of the pulses. Equivalently, pulse waveforms may be generated from an appropriate selection of polyphase sub-carrier codes. Time division of the pulses and frequency division of the carriers may be employed for multiple access. Received signals are processed by combining frequency-domain components corresponding to a desired user's allocated carriers. Individual data symbols are processed by providing polyphase decoding, matched filtering, or time-domain shifting the received carriers. Carrier Interferometry components may be used to build various signals corresponding to other transmission protocols.
Owner:DEPARTMENT 13 INC
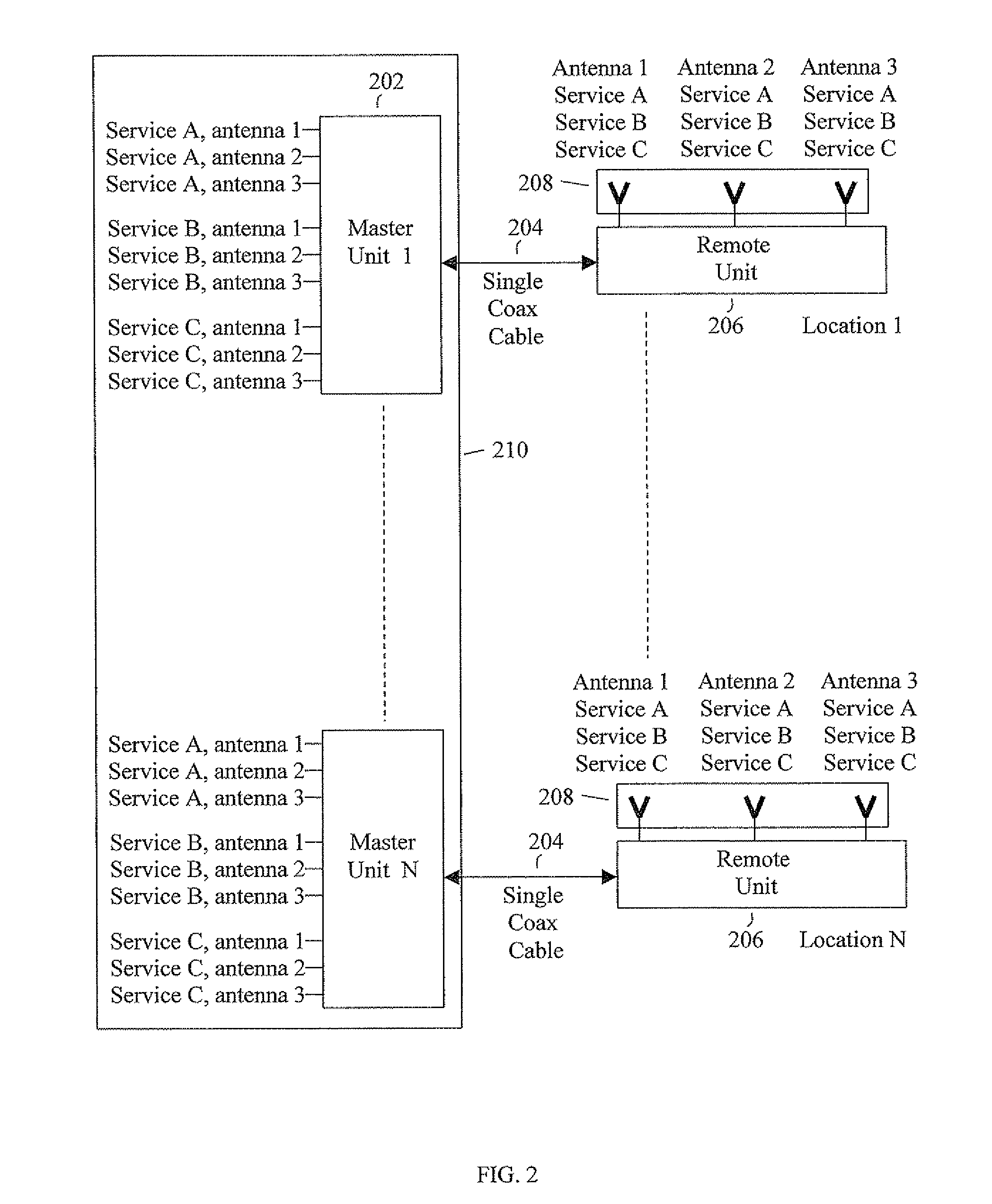
MIMO-adapted distributed antenna system
ActiveUS7483504B2Accurate reconstructionSite diversityModulated-carrier systemsCoaxial cableDistributed antenna system
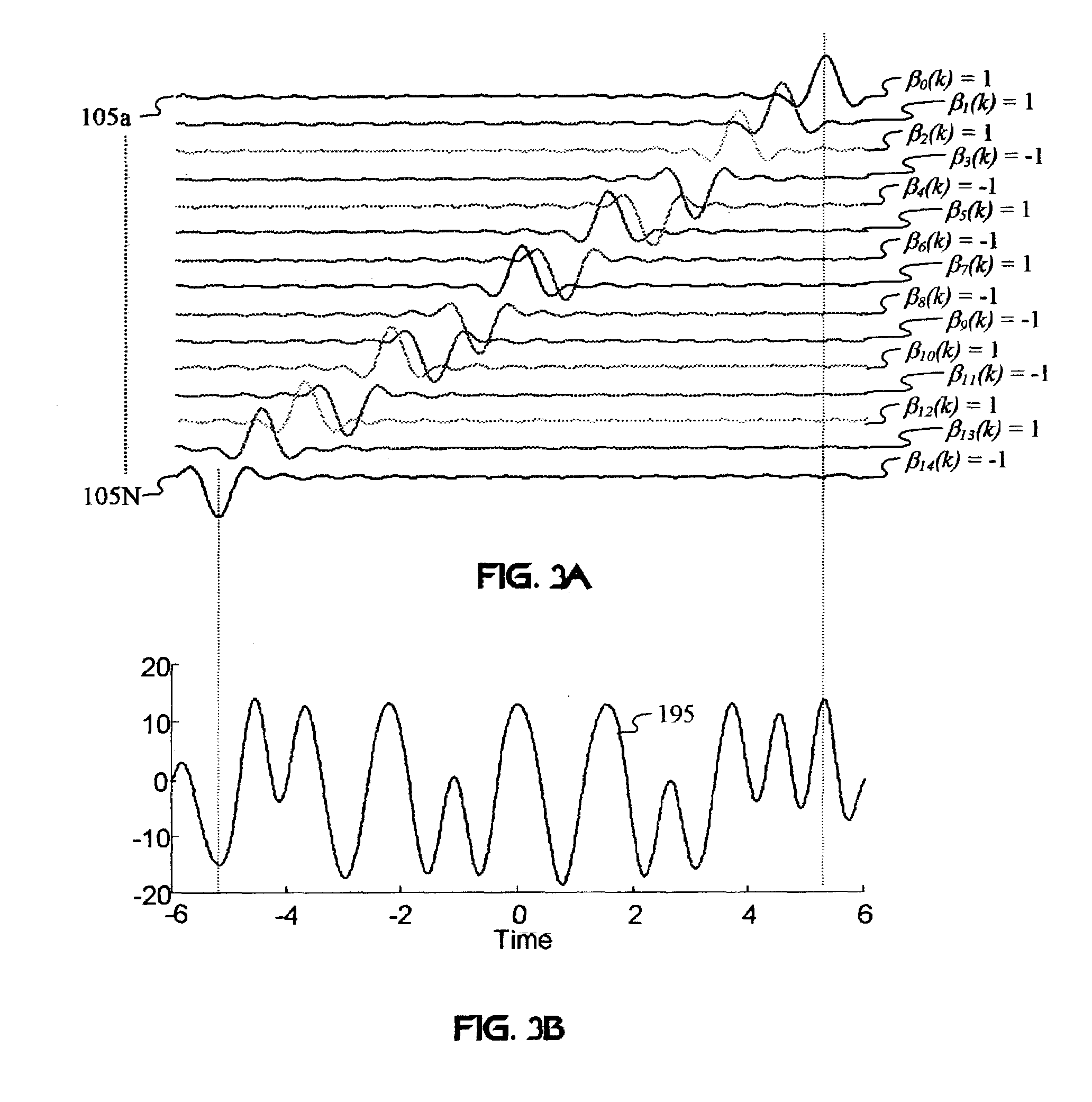
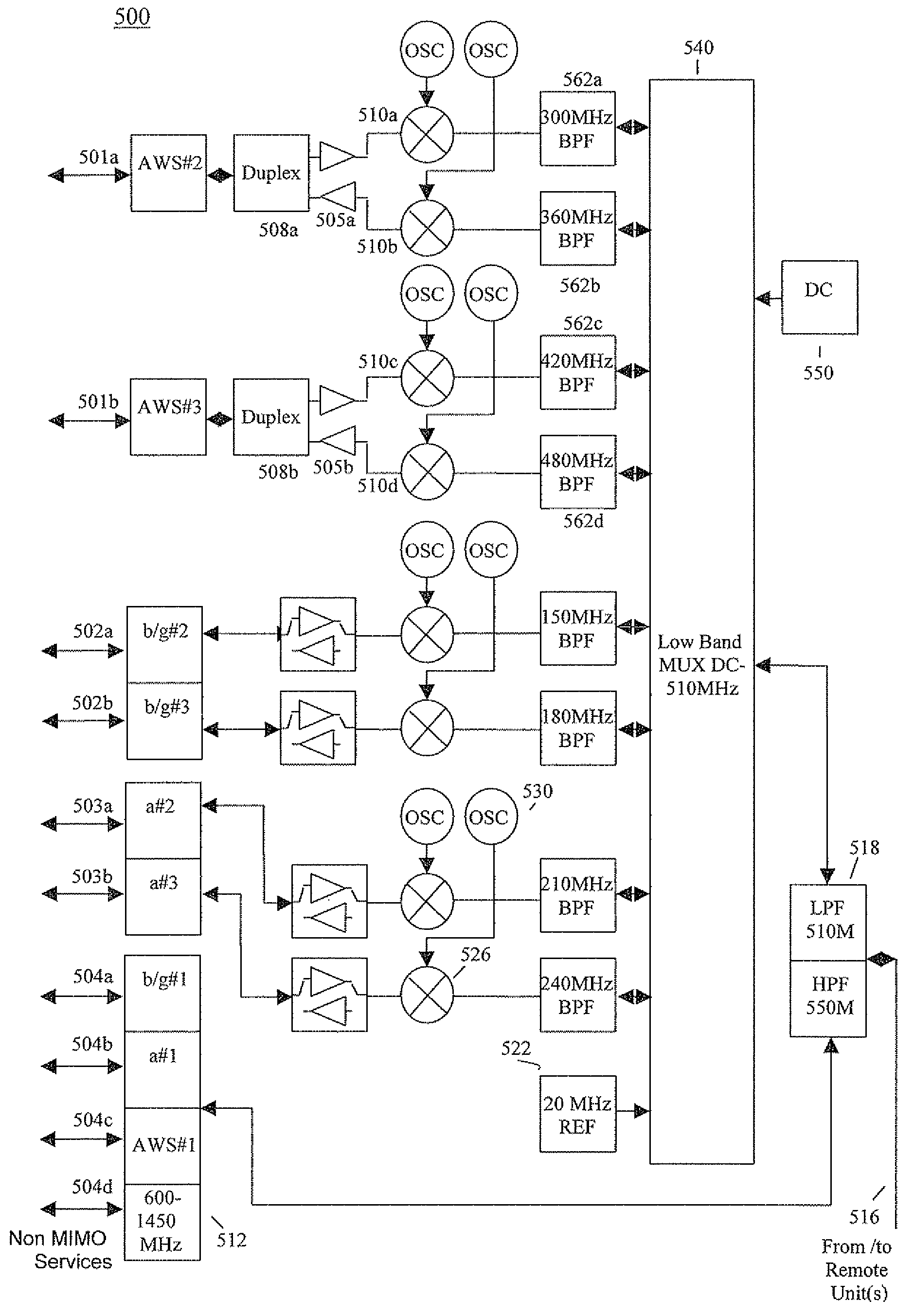
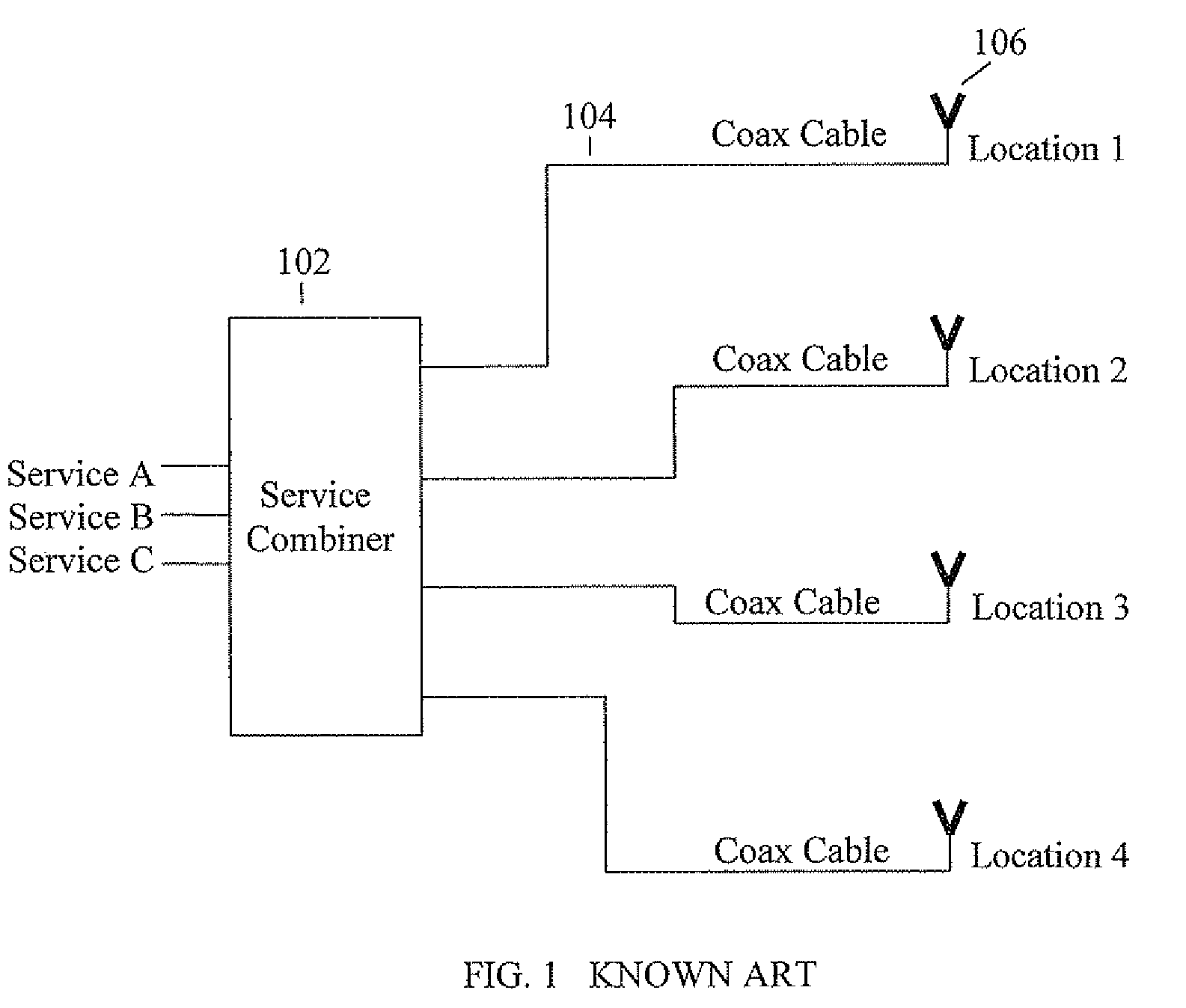
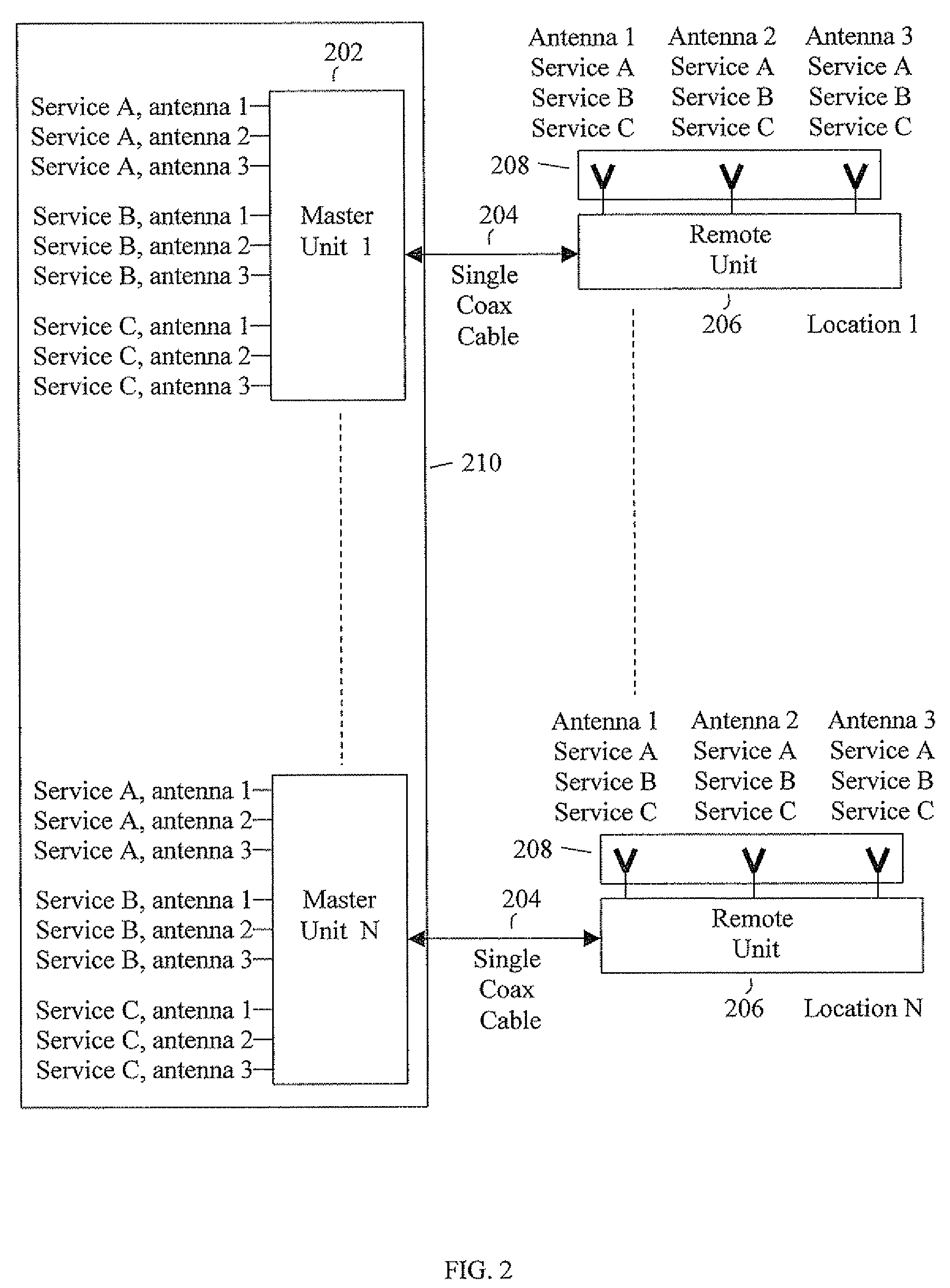
Methods and systems for carrying different signals required for MIMO communication using a single coaxial cable between two endpoints of a distributed antenna system (DAS) network. Original MIMO signals having the same frequency are frequency-separated at a first endpoint of the network. The frequency-separated signals are propagated together over the single coaxial cable and then reconstructed to their original frequency at a second endpoint of the network.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
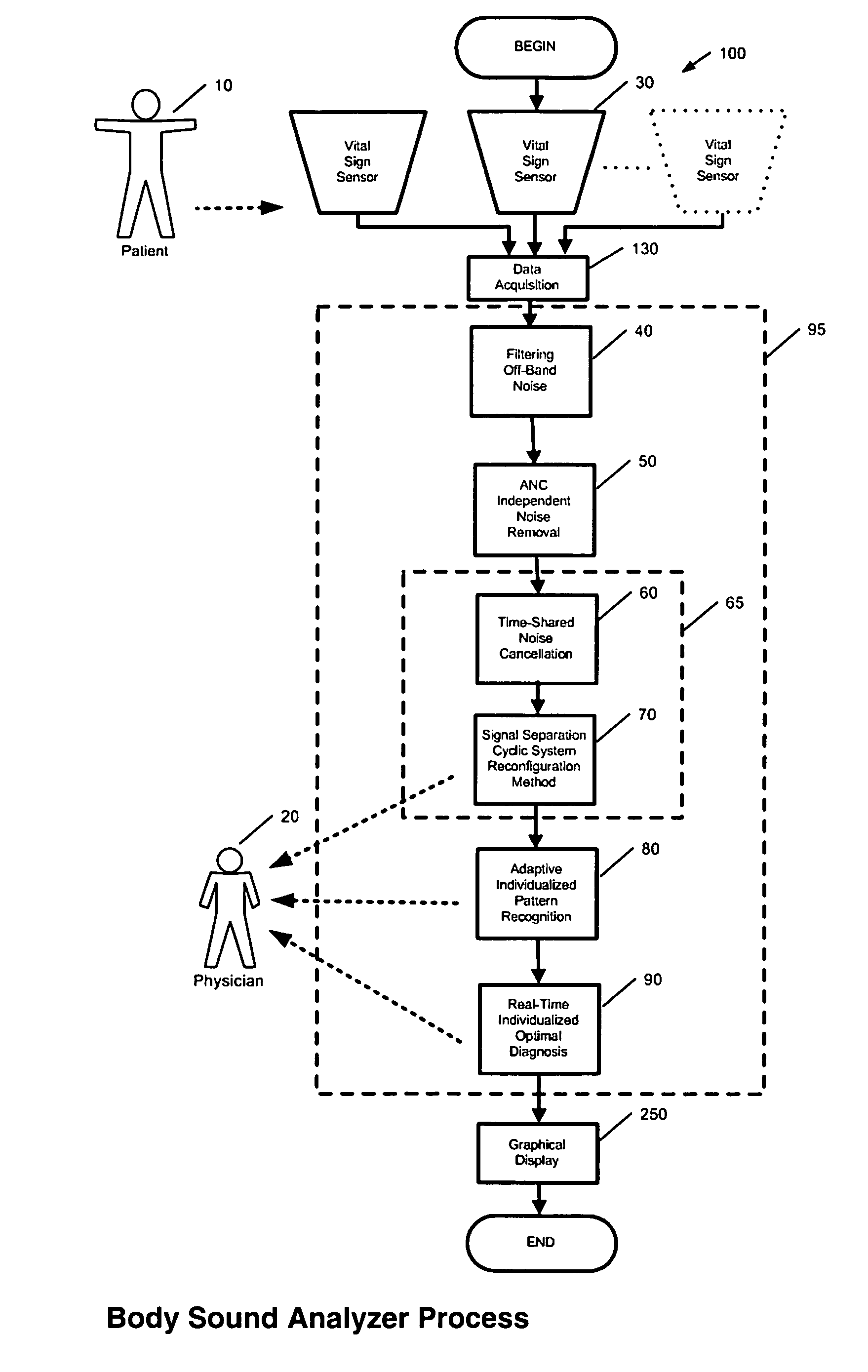
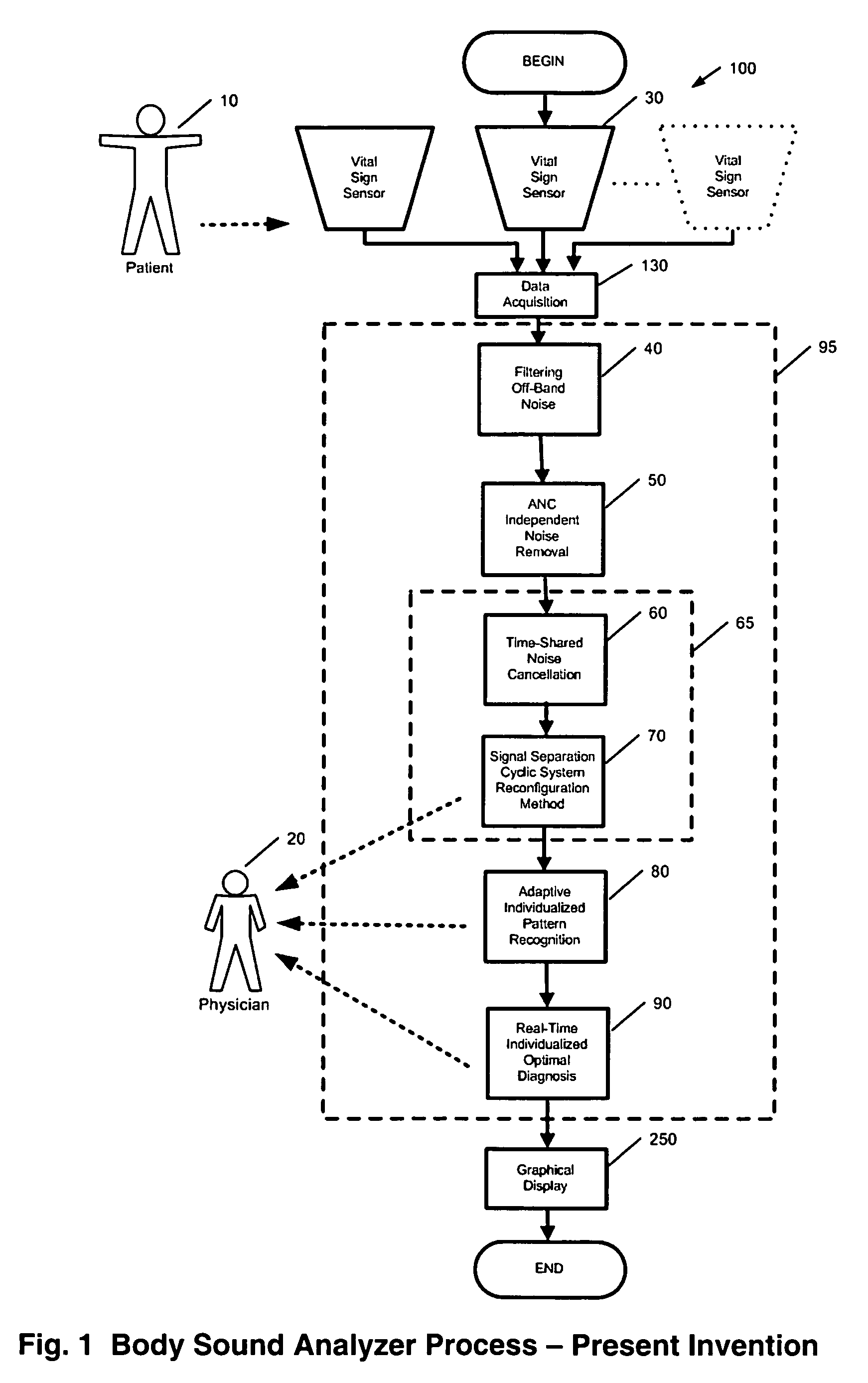
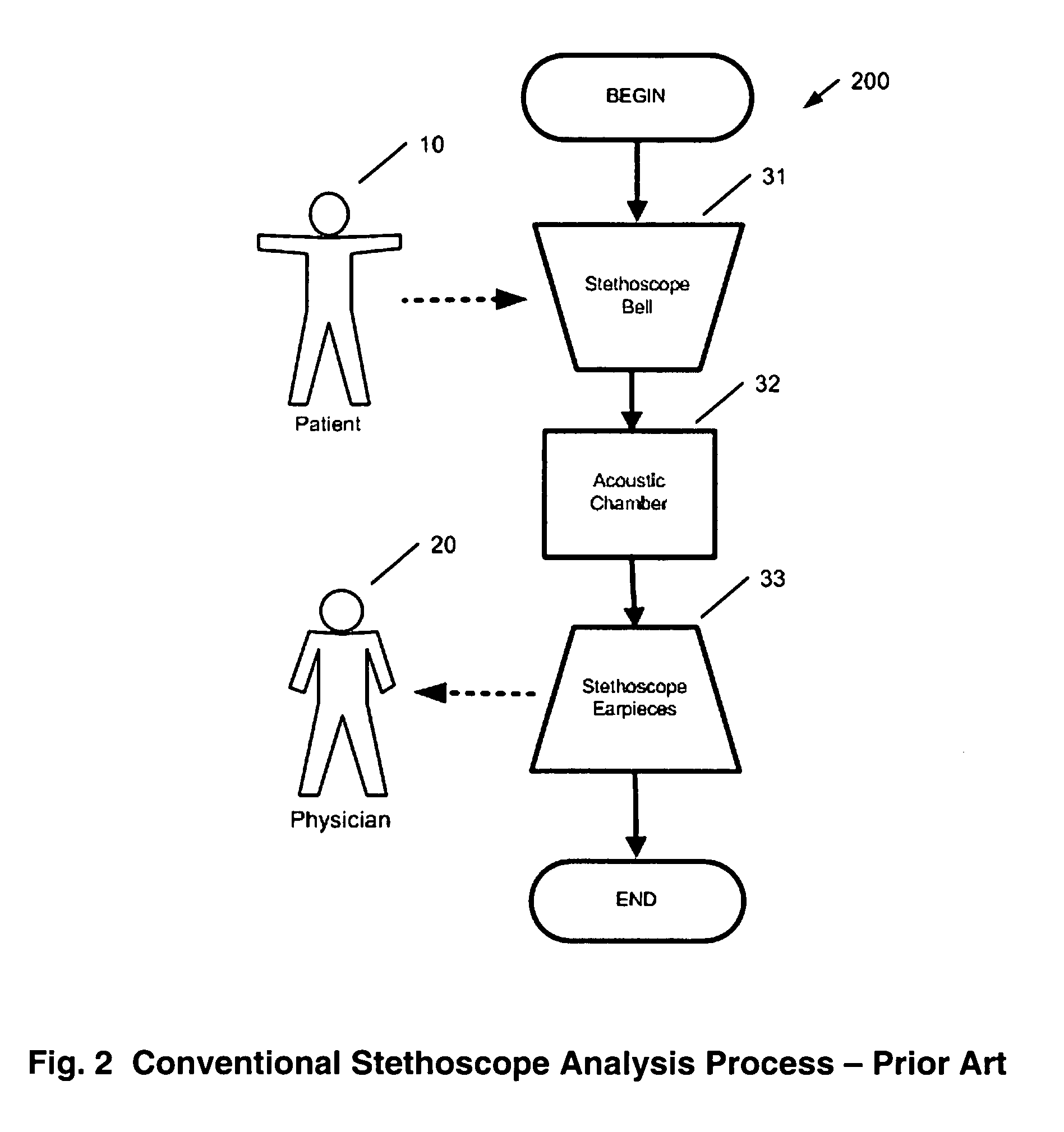
Method and system for continuous monitoring and diagnosis of body sounds
InactiveUS20060198533A1Reduce the impactQuality improvementStethoscopeTransmission noise suppressionContinuous measurementReal time analysis
A method and system is invented for automated continuous monitoring and real-time analysis of body sounds. The system embodies a multi-sensor data acquisition system to measure body sounds continuously. The sound signal processing functions utilize a unique signal separation and noise removal methodology by which authentic body sounds can be extracted from cross-talk signals and in noisy environments, even when signals and noises may have similar frequency components or statistically dependent. This method and system combines traditional noise canceling methods with the unique advantages of rhythmic features in body sounds. By employing a multi-sensor system, the method and system perform cyclic system reconfiguration, time-shared blind identification and adaptive noise cancellation with recursion from cycle to cycle. Since no frequency separation or signal / noise independence is required, this invention can provide a robust and reliable capability of noise reduction, complementing the traditional methods. The invention further includes a novel method by which pattern recognition of groups of key parameters can be used to diagnosis physical conditions associated with body sounds, with confidence intervals on the diagnostic criterion to indicate accuracy of diagnosis.
Owner:WANG LE YI +1
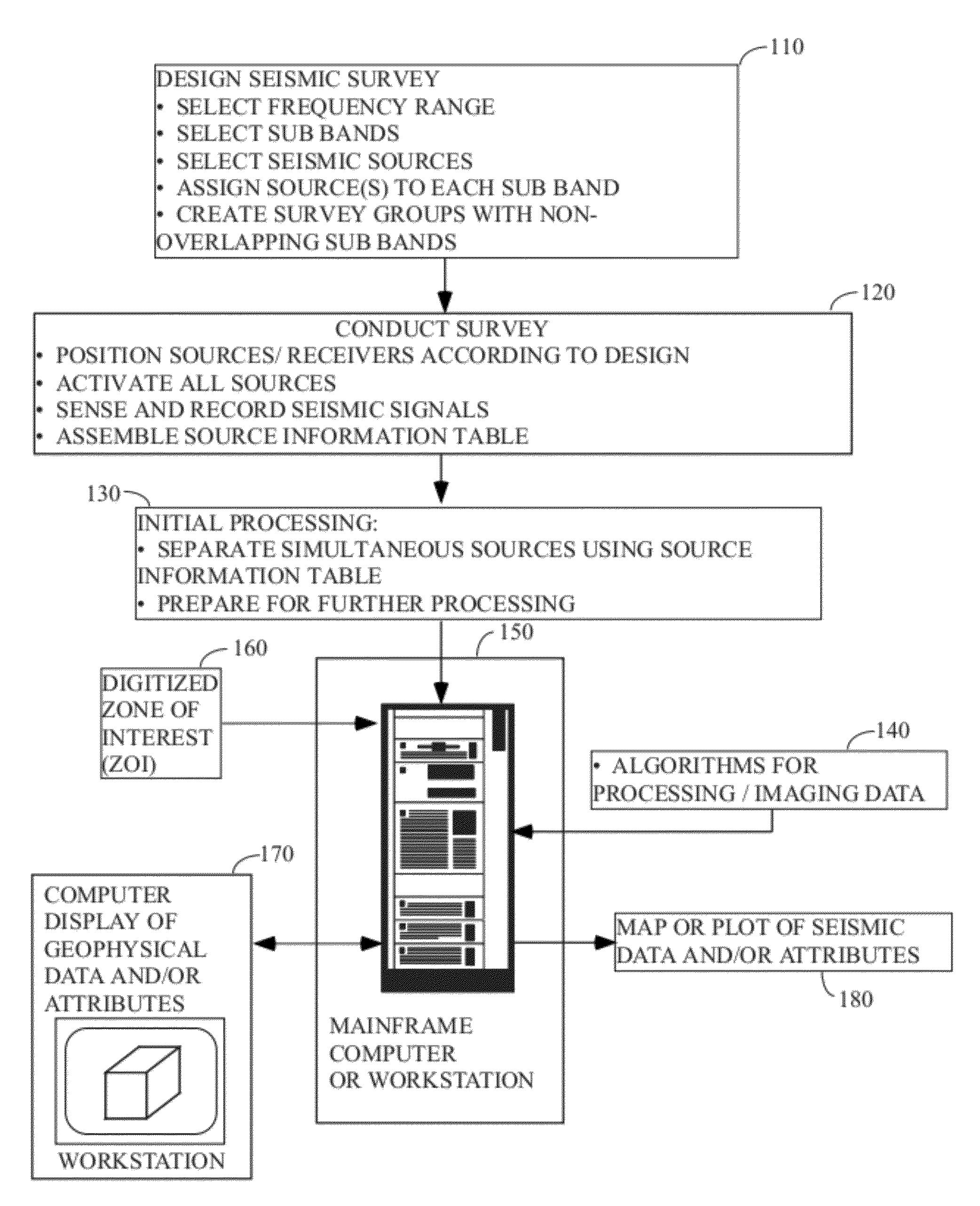
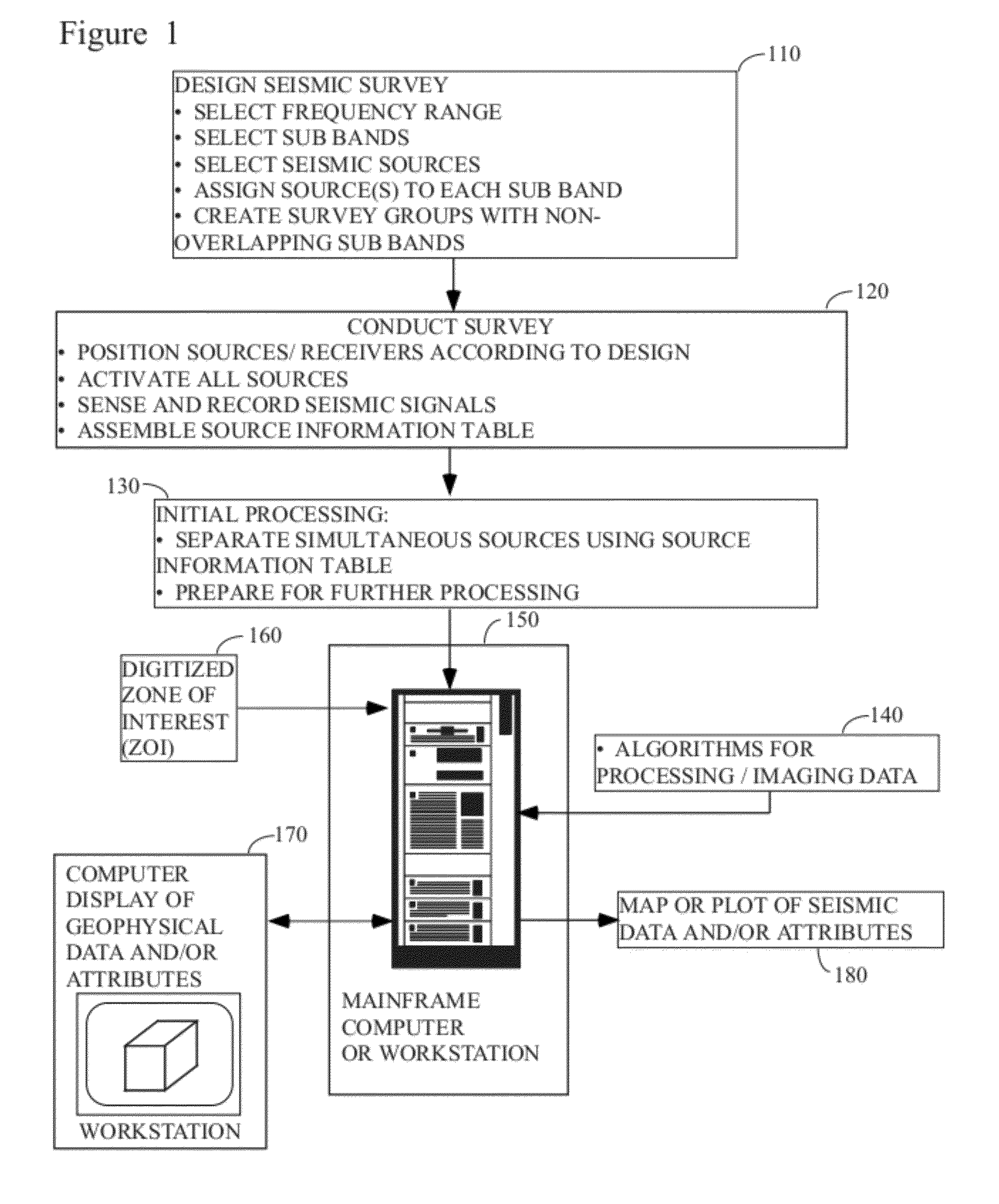
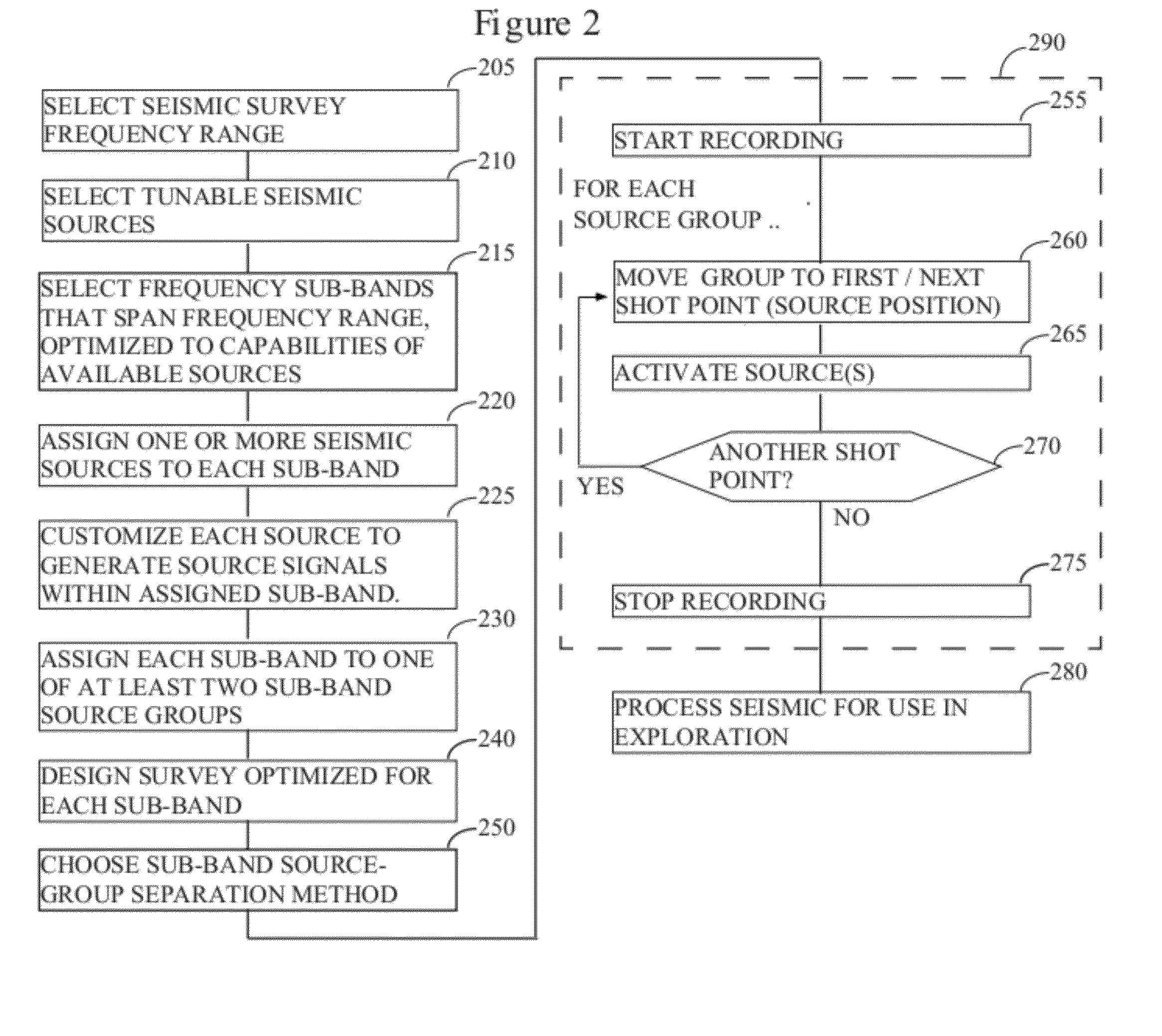
Distance- and frequency-separated swept-frequency seismic sources
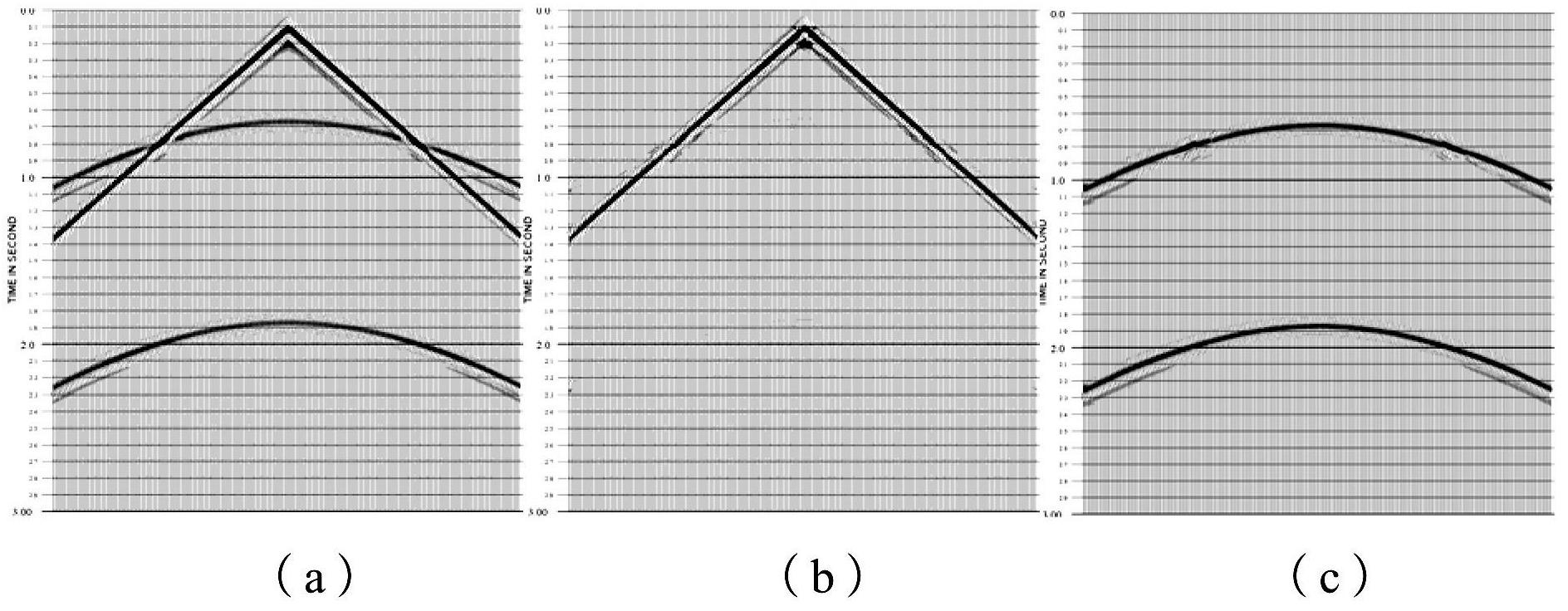
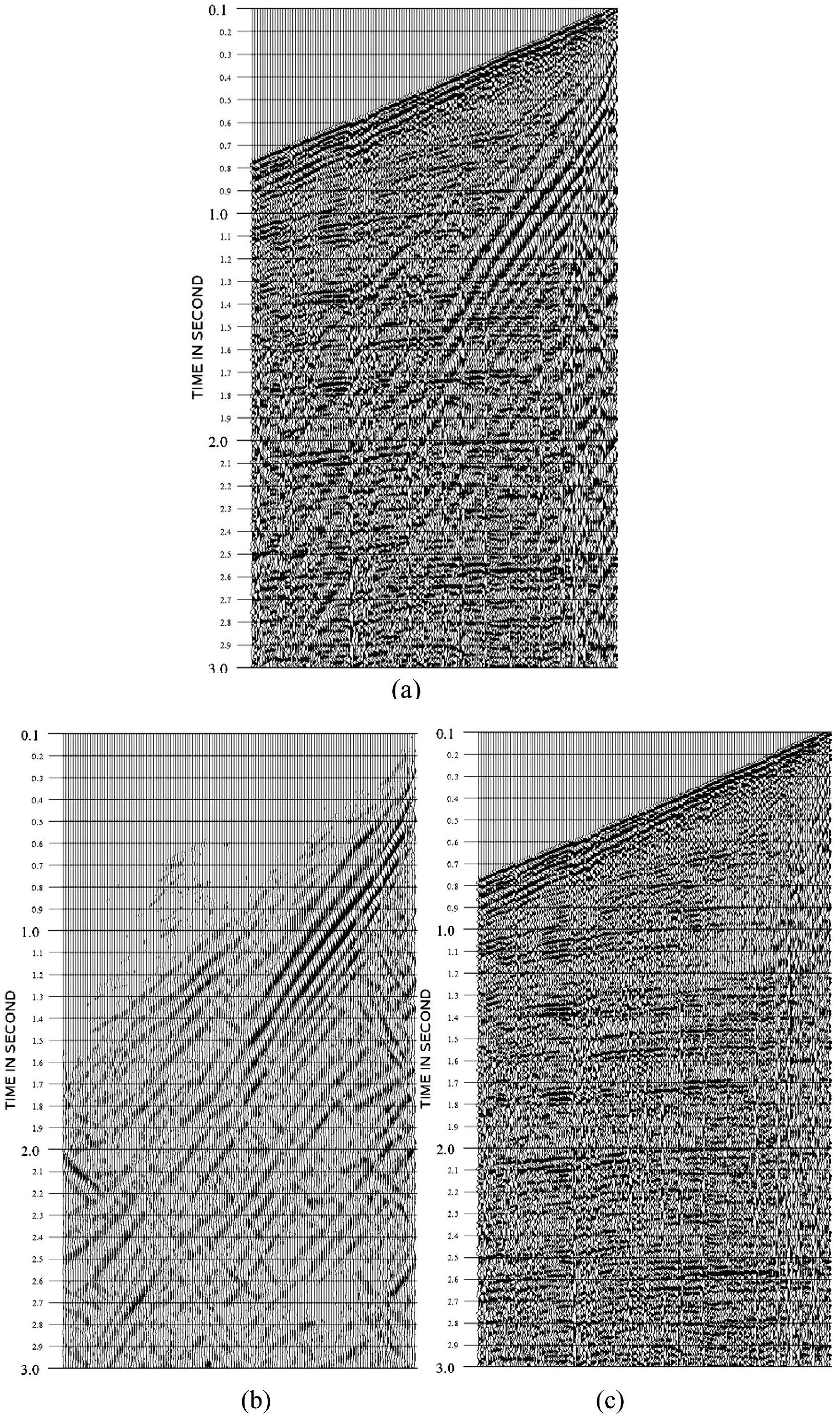
InactiveUS20120147699A1Enhance simultaneous source separationEasy to separateSeismic data acquisitionSeismic signal recordingBandpass filteringFrequency separation
There is provided a method of seismic acquisition that utilizes a bank of restricted-bandwidth swept-frequency sub-band sources as a seismic source. Each seismic source will cover a restricted sub-band of frequencies, with all the sources taken together covering the full frequency range. Adjacent frequency bands may partially overlap, but non-adjacent frequency bands should not. The sources may be divided into two or more groups, with no sources covering adjacent frequency bands being placed in the same group. The sources within a group can then be separated by bandpass filtering or by conventional simultaneous source-separation techniques. The source groups may be operated simultaneously but separated in space, and the individual sources themselves may each operate independently, on a sweep schedule customized for that particular source.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
System and method for extending the operating range and/or increasing the bandwidth of a communication link
InactiveUS6731678B1Transmission path divisionTelephonic communicationComputer hardwareTelecommunications link
A system and method for extending the operating range and / or increasing the bandwidth of a communication link. The communication link may consist of any two communication devices that are connected by two or more separate "band limited" communication paths for the transmission of information therebetween. In operation, the communication devices use a "frequency split scheme" to divide the information transmitted between the devices into two or more signals, each of which is transmitted over one of the communication paths. A "frequency foldback scheme" may also be used to shift the information from the higher frequencies to the lower frequencies of each respective signal, thereby taking advantage of the fact that more information can be carried in the lower frequencies. By using these schemes, it is possible to extend the operating range of the communication link and / or transmit a greater amount of information over the communication paths to thereby increase the bandwidth of the communication link.
Owner:SPRINT CORPORATION
System and method for enhanced interoperability between a plurality of communication devices
InactiveUS20050191964A1Avoid interferenceInterference minimizationHybrid switching systemsData switching by path configurationTime domainTransceiver
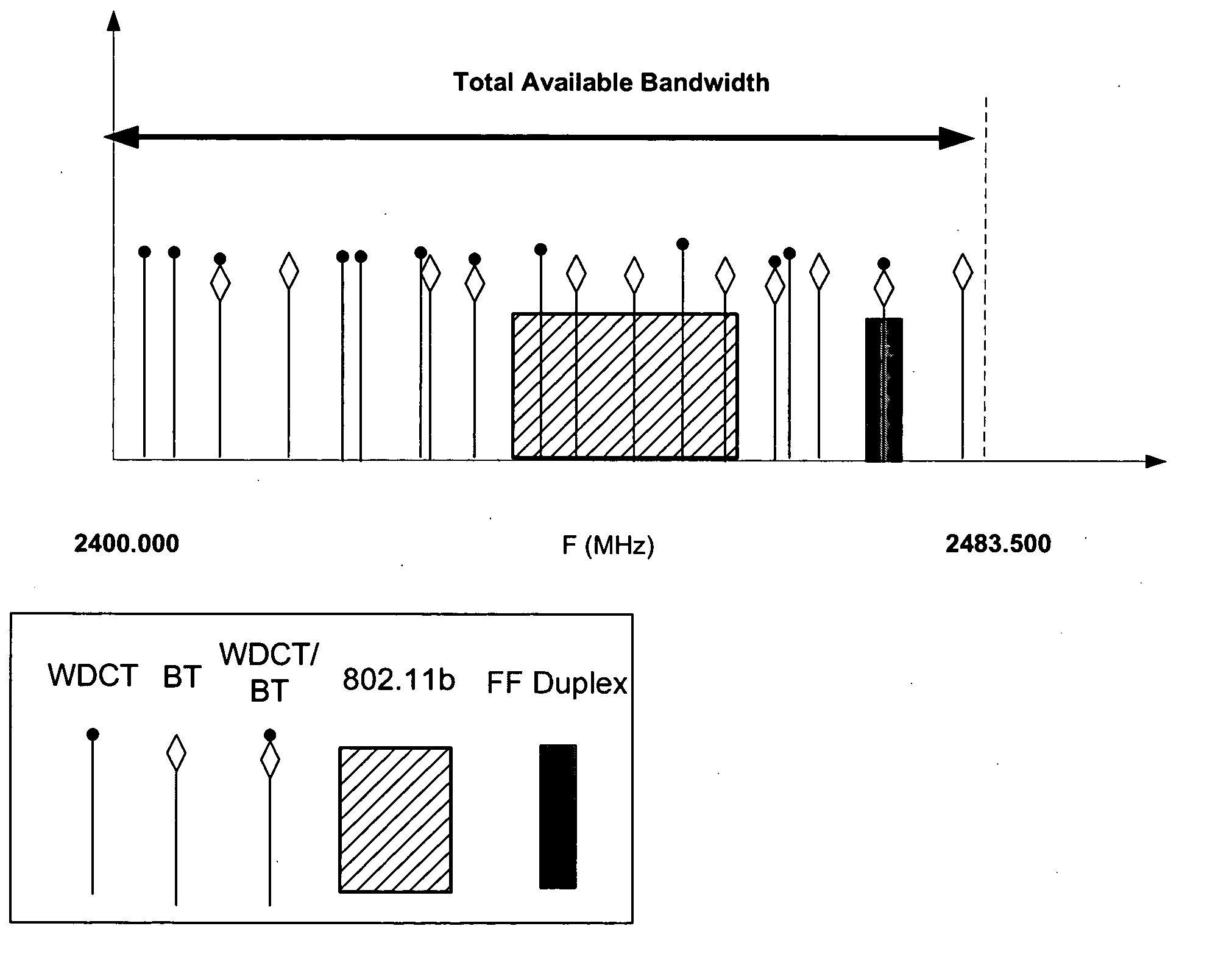
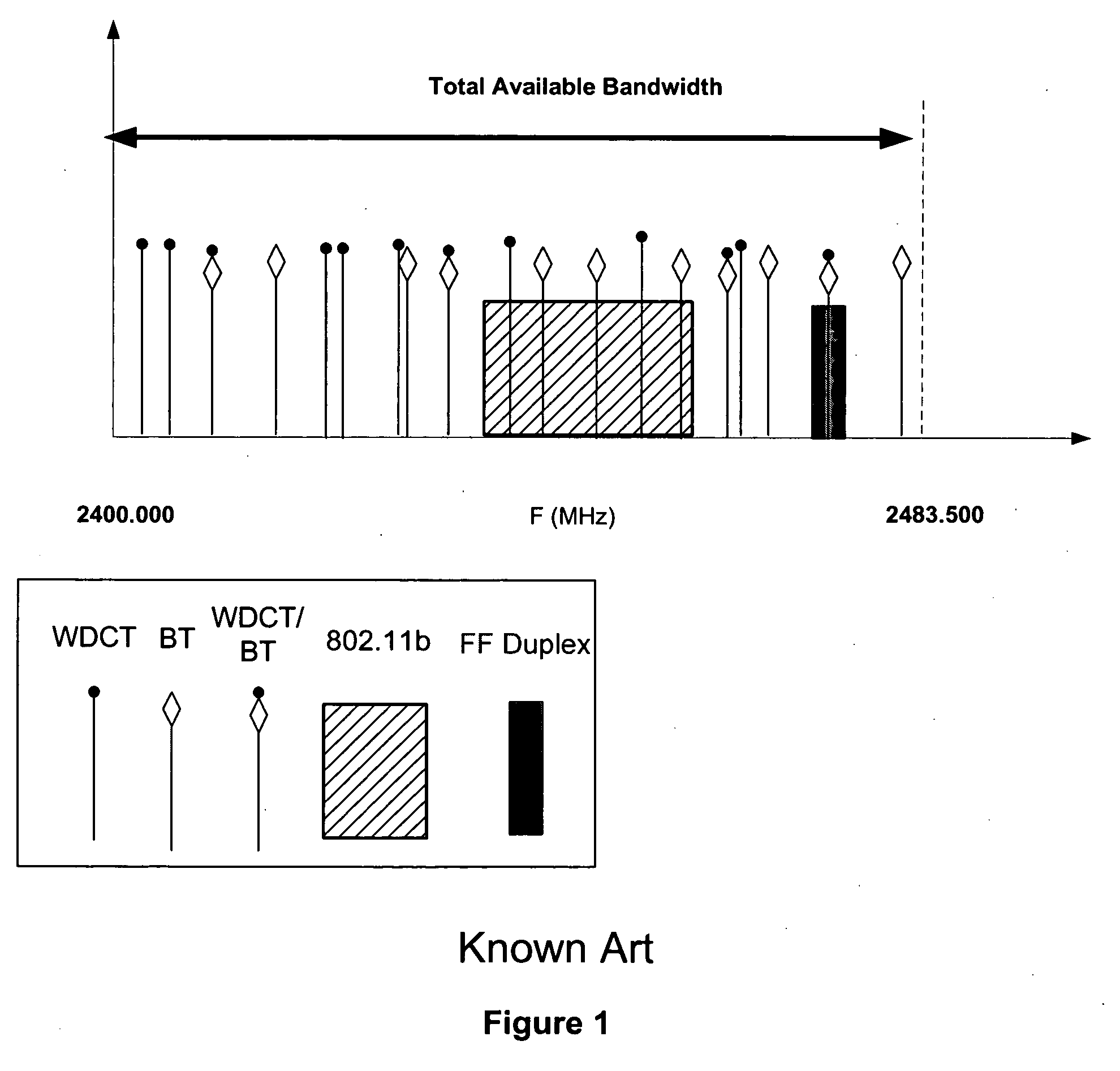
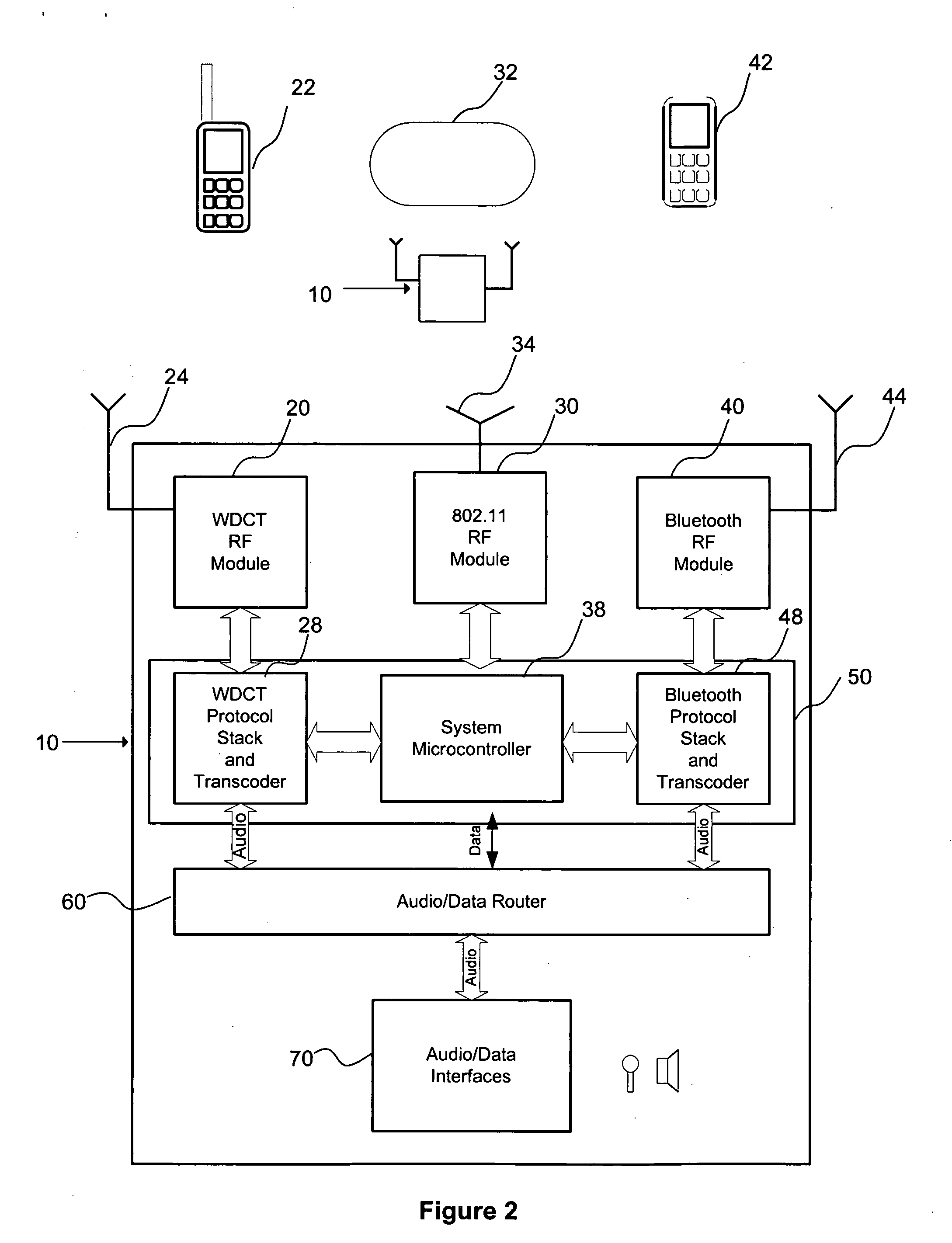
A system for allowing BT, WDCT, and 802.11 transceivers to operate in close proximity with a minimum of interference, is disclosed. In an exemplary embodiment, a method for avoiding interference between a first FHSS device and other RF devices using 802.11 or FHSS protocols is disclosed. The first FHSS device initially detects the presence of an interfering RF device (“interferer”), for example a device employing 802.11 protocol, and adjusts the frequency of channels used for operation of the first device accordingly to avoid overlap with the 802.11 band. In the presence of an additional interferer, for example, a second FHSS device emitting an interfering signal, the first FHSS device may segregate its operation channels to achieve maximum frequency separation from an 802.11 and second FHSS device. In addition, the first and third devices may also multiplex their transmit / receive timing to avoid interference in time domain. By avoiding interference in time domain, first and third device can occupy the same channels in the frequency band achieving further frequency separation from the 802.11 device.
Owner:VTECH TELECOMM
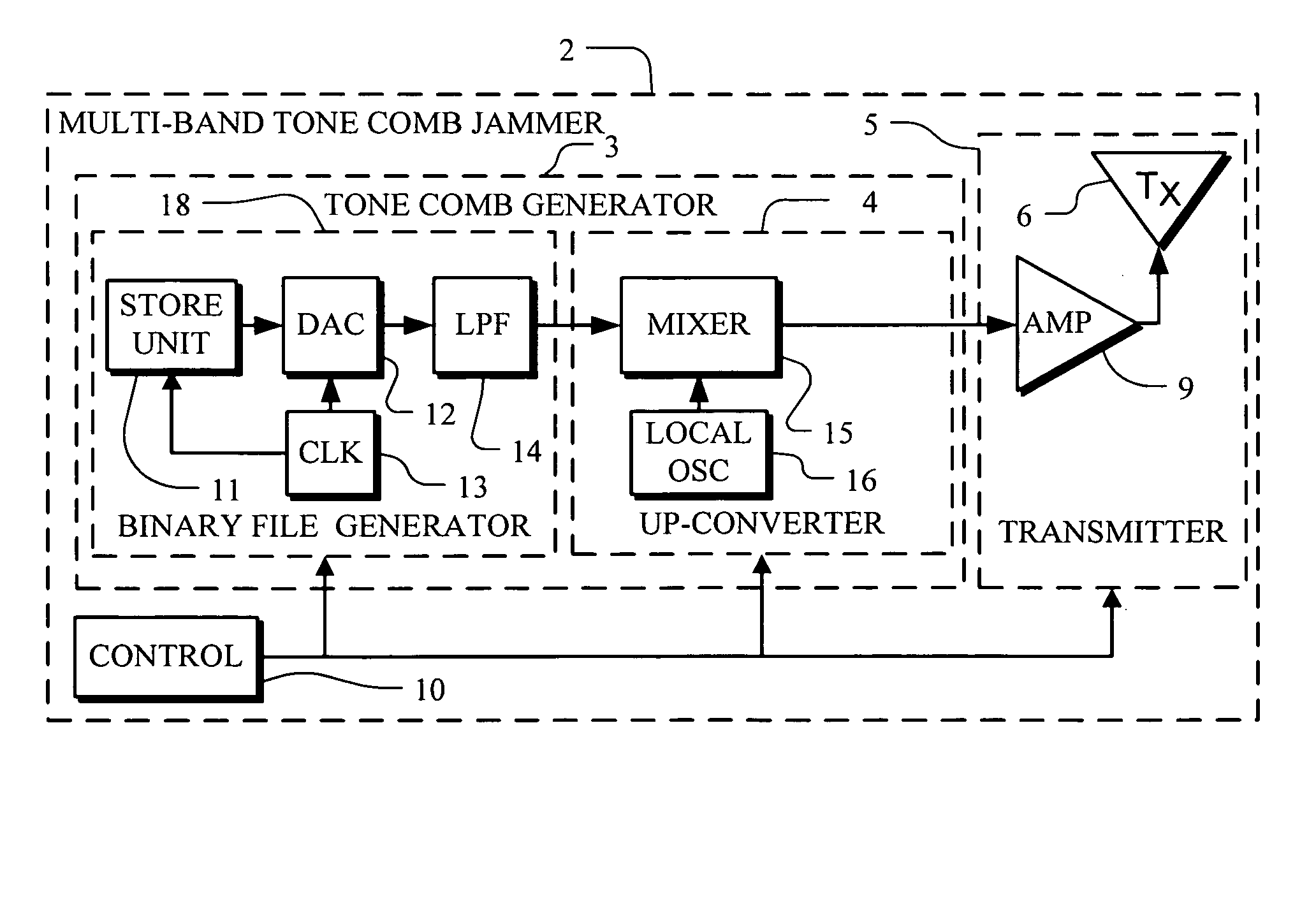
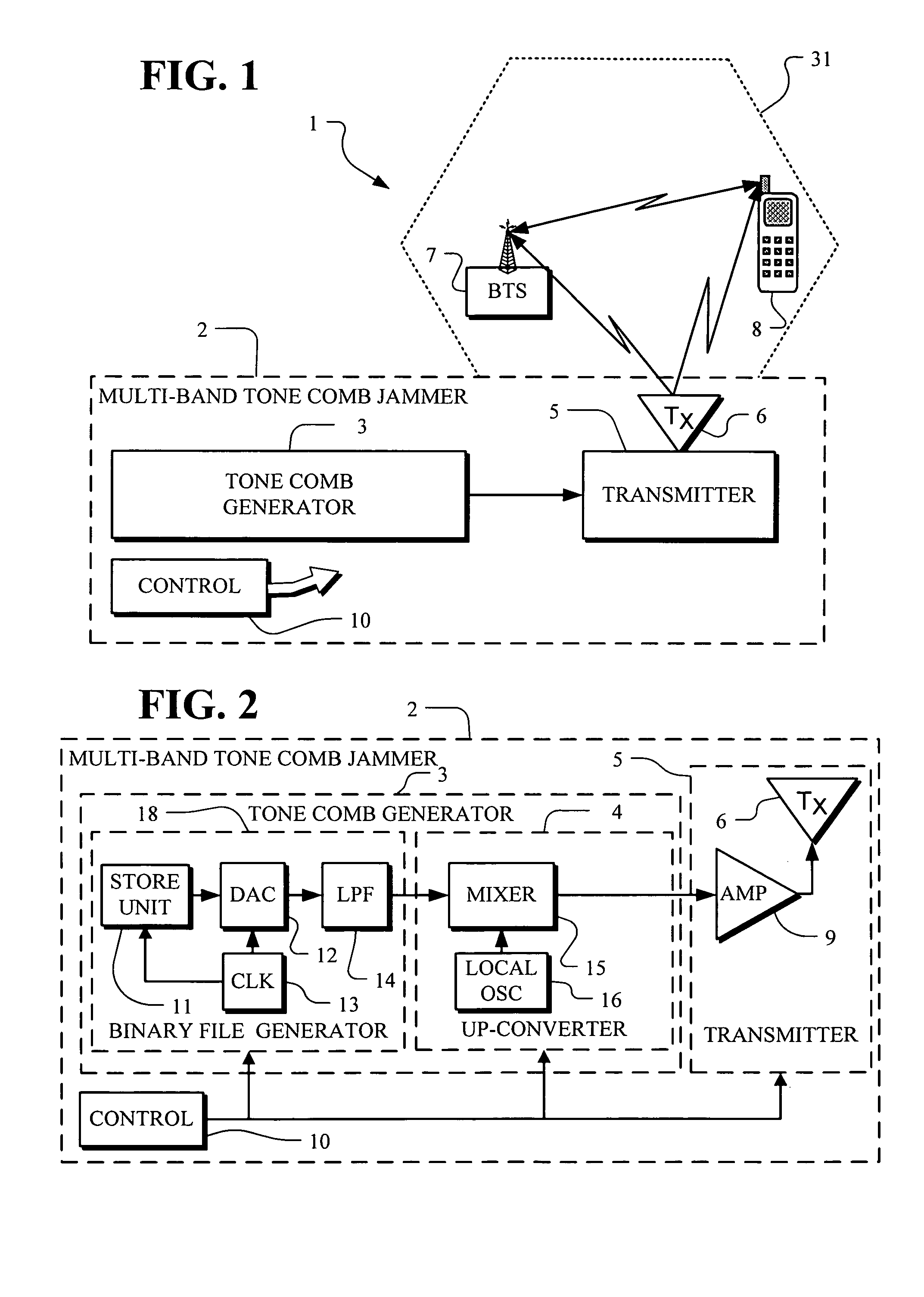
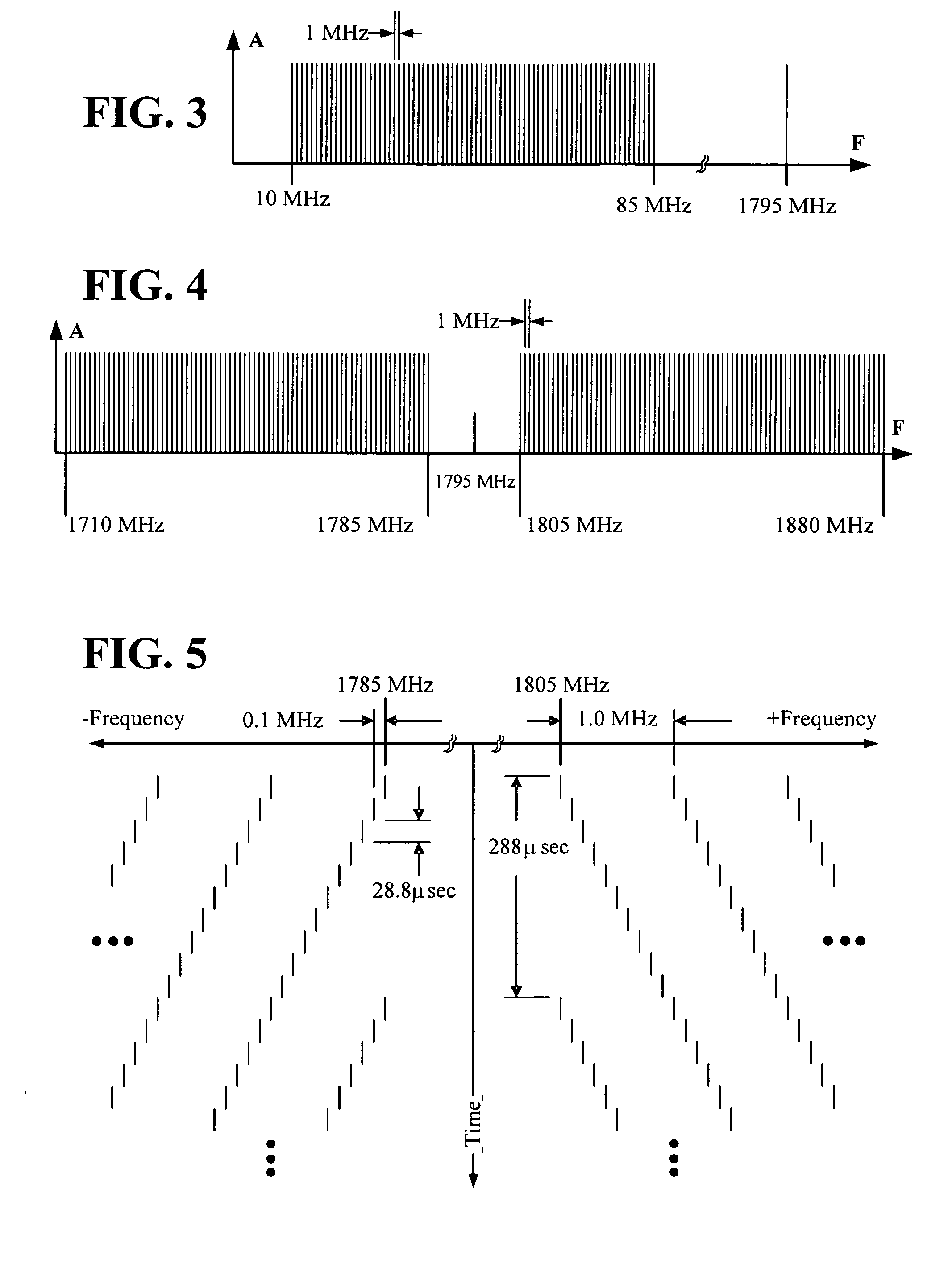
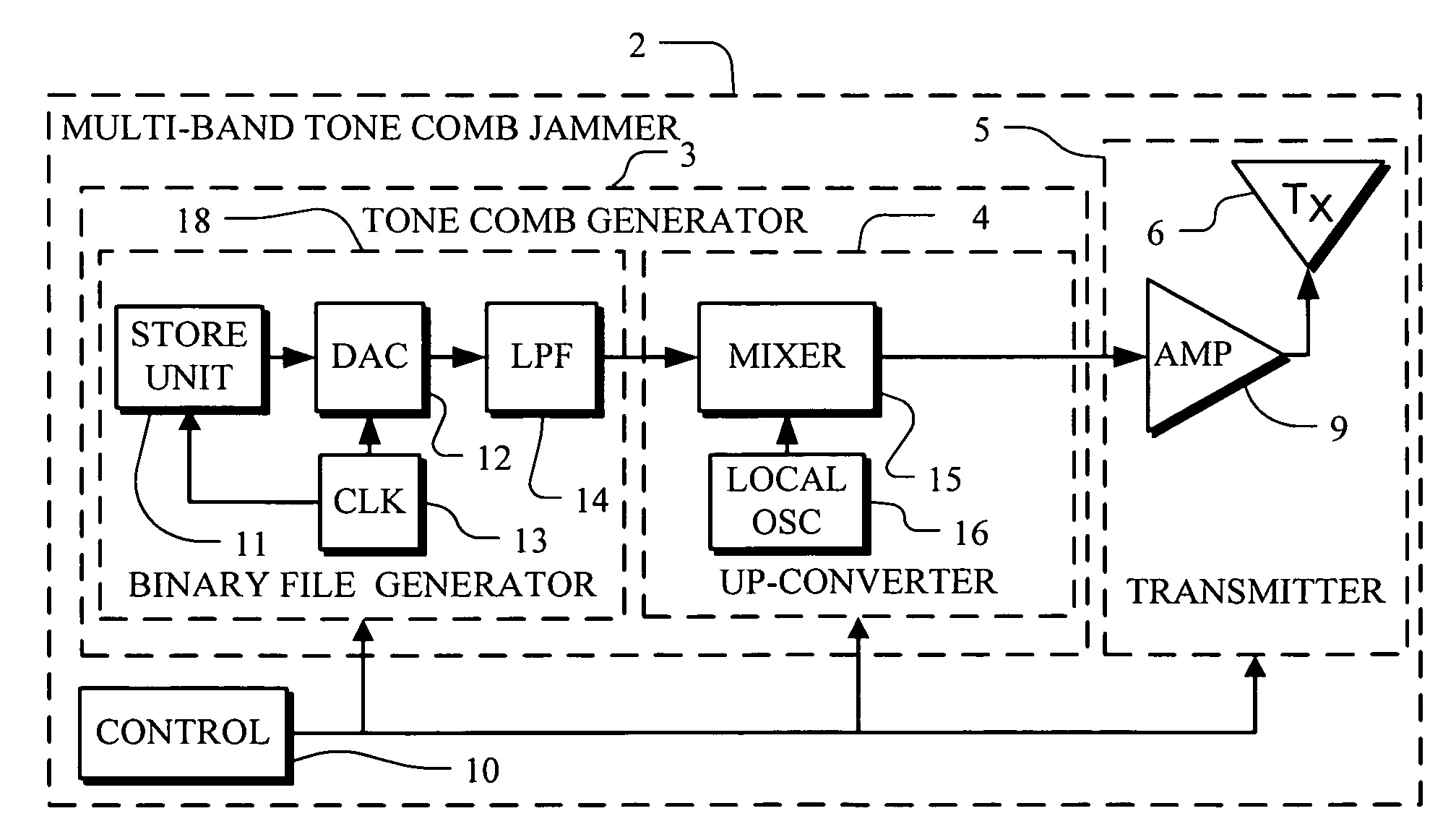
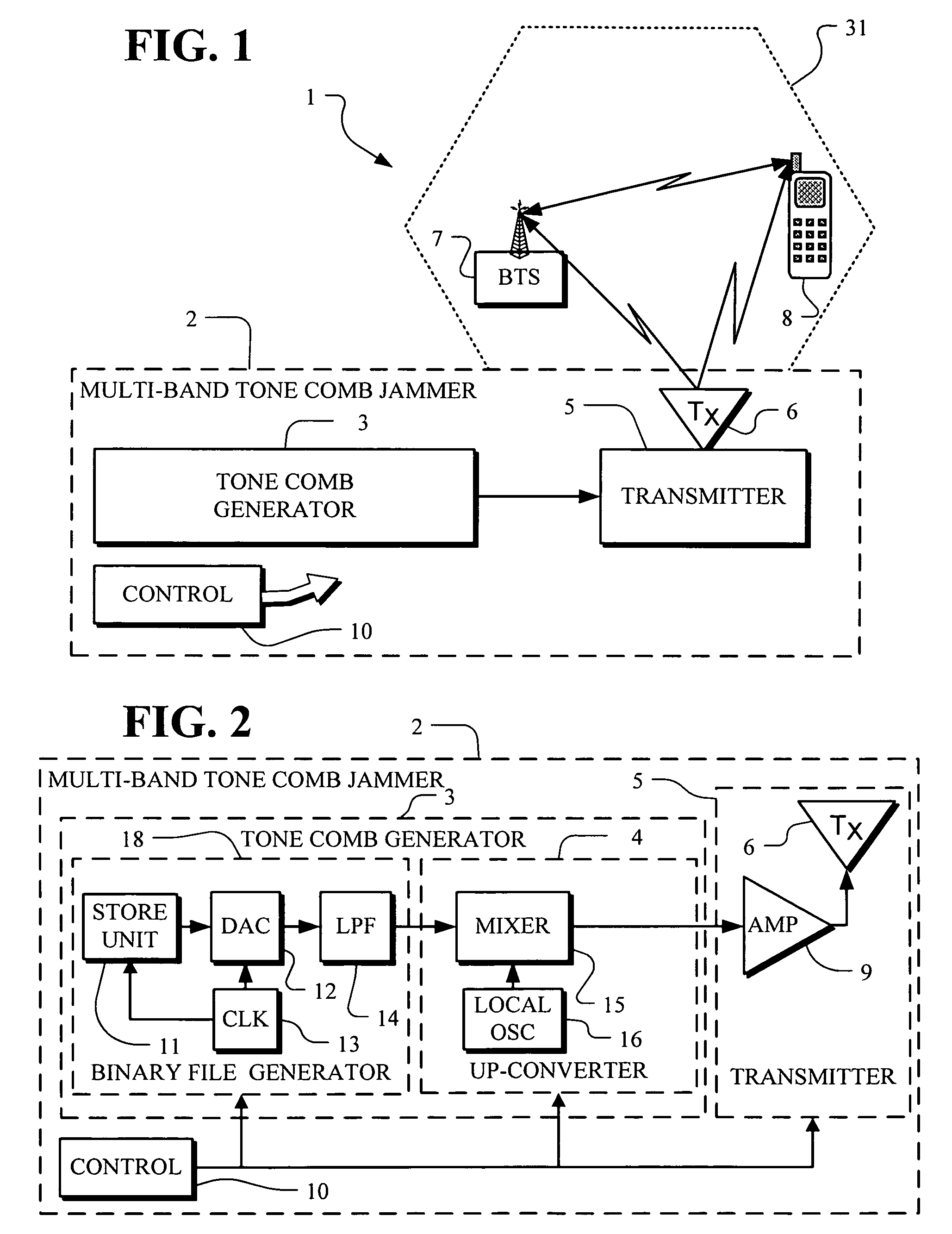
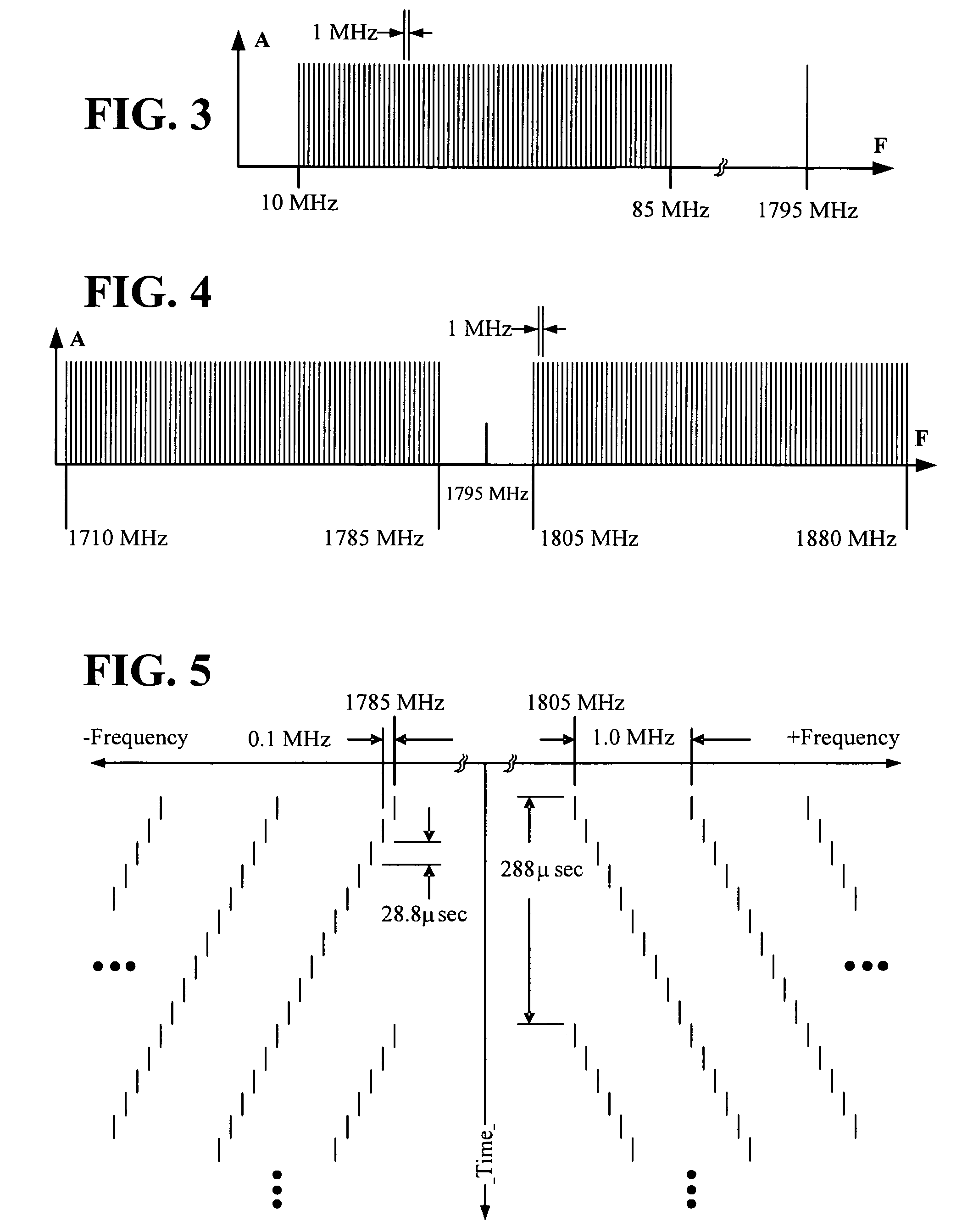
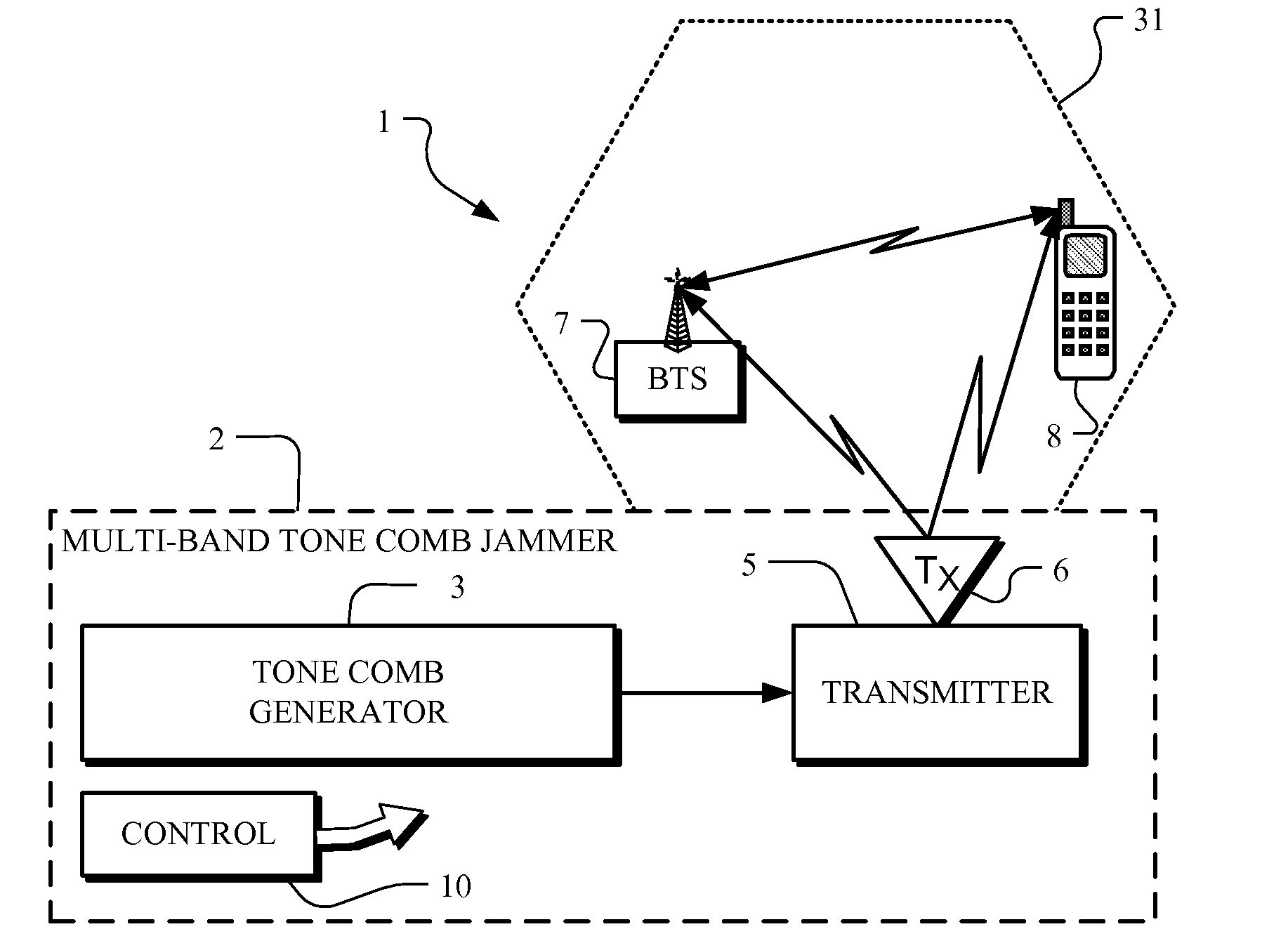
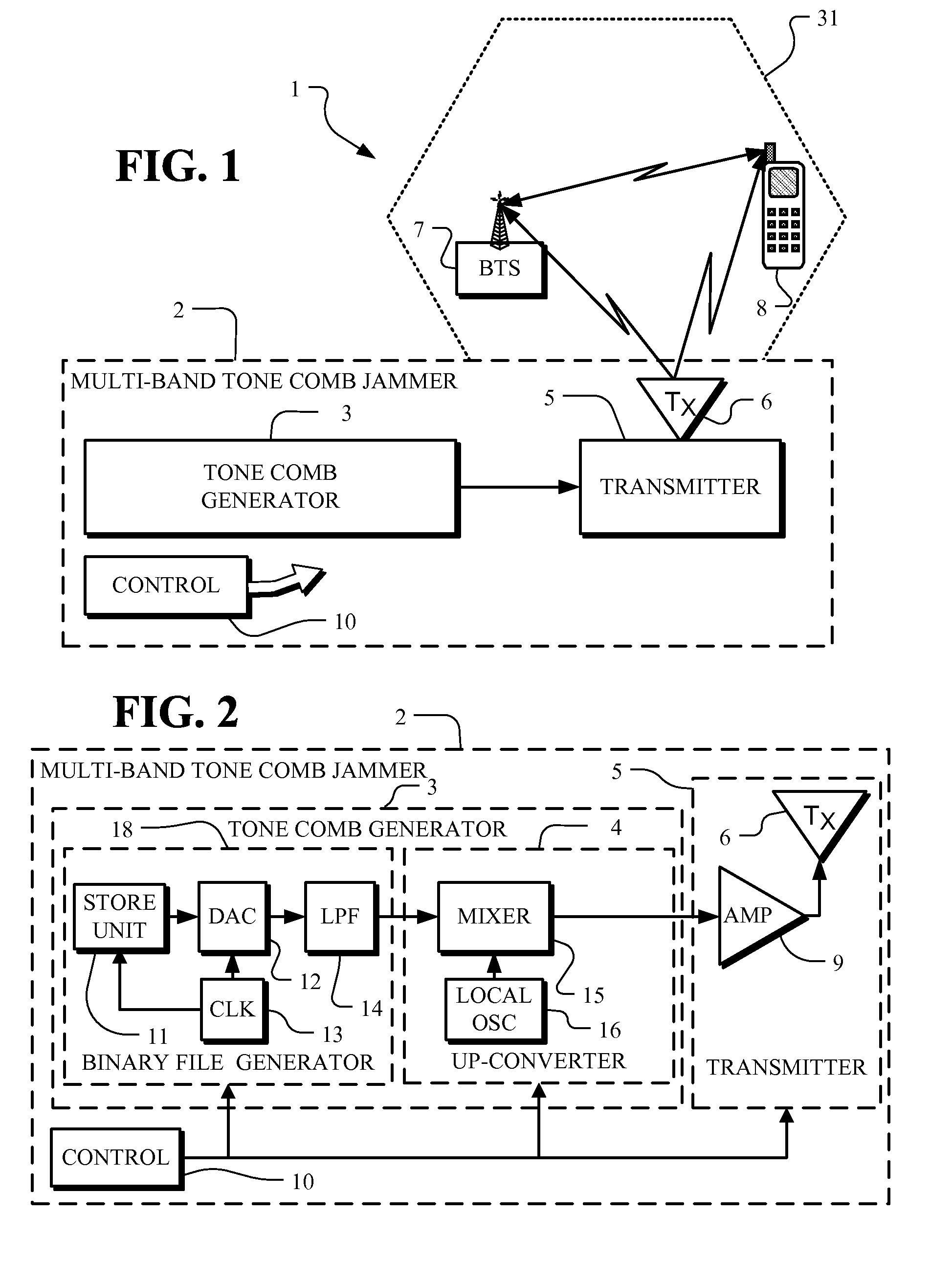
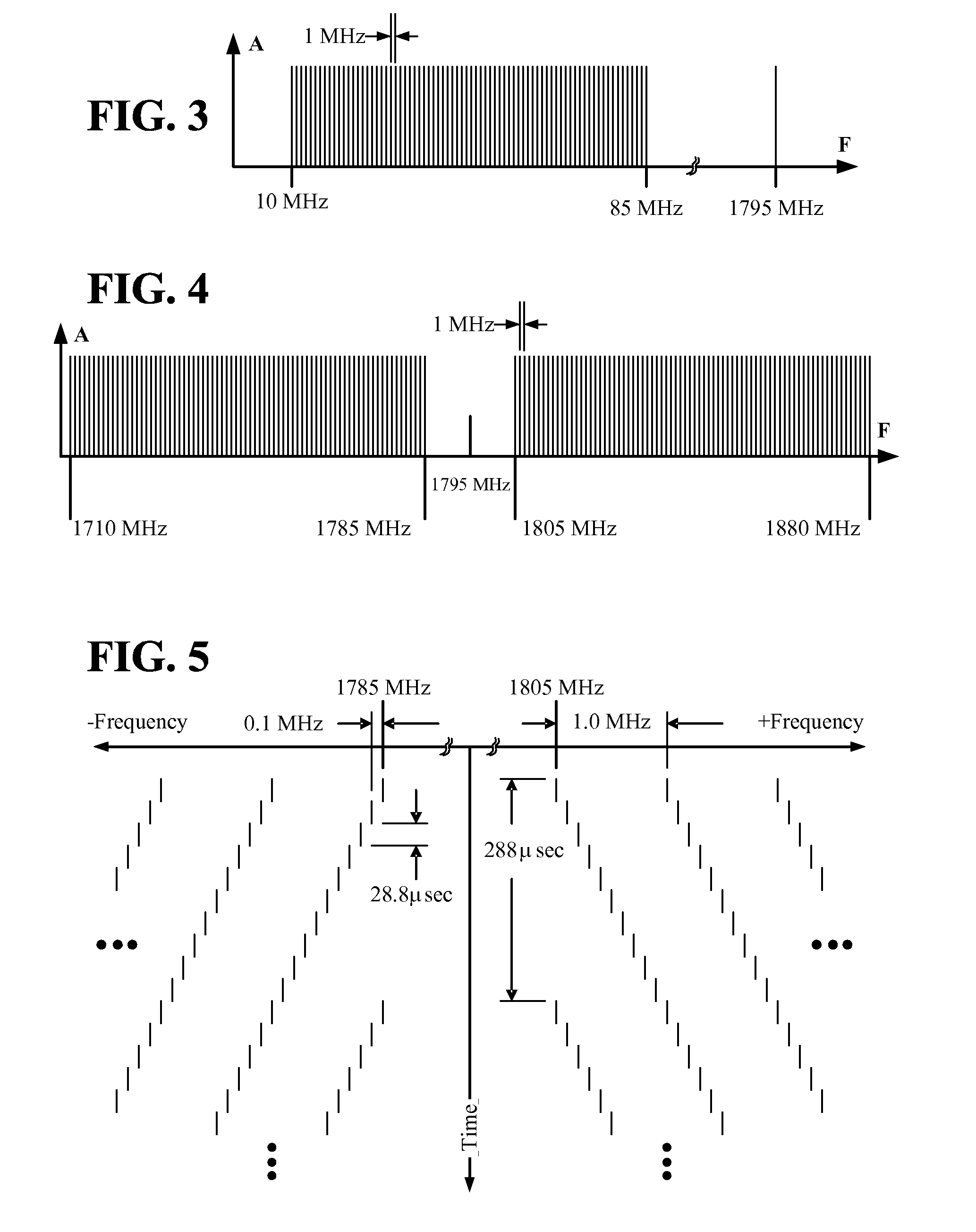
Multi-band jammer
InactiveUS20090237289A1Wave based measurement systemsCommunication jammingMulti bandCommunications system
A jammer for jamming communications in a communications system where the communications system operates with digital bursts having burst periods measured in time and occurring in a communication frequency band such as GSM having a transmit band and a receive band. The jammer includes a tone comb generator for providing repetitions of jamming signals for the communication frequency band where the jamming signals have jamming signal intervals providing frequency separation between the jamming signals. The jamming signals are generated with a dwell time substantially less than a burst period for the communications system. The jamming signals are generated concurrently for the transmit band and the receive band and are transmitted as RF jamming signals to jam communications for mobile stations.
Owner:AEROFLEX WICHITA
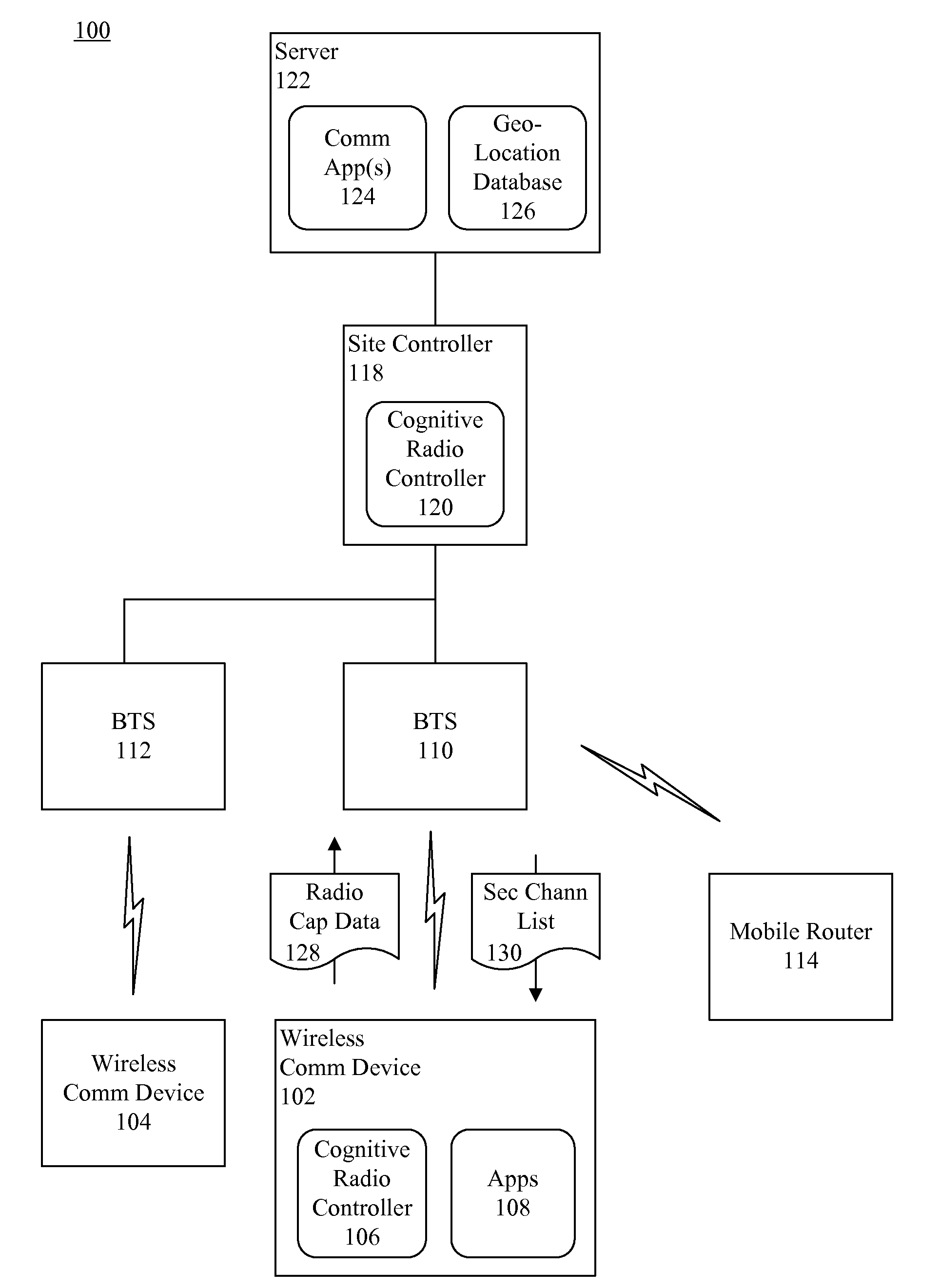
Dynamic spectrum allocation (DSA) in a communication network
ActiveUS20100248631A1Network traffic/resource managementTransmission monitoringFrequency spectrumTelecommunications
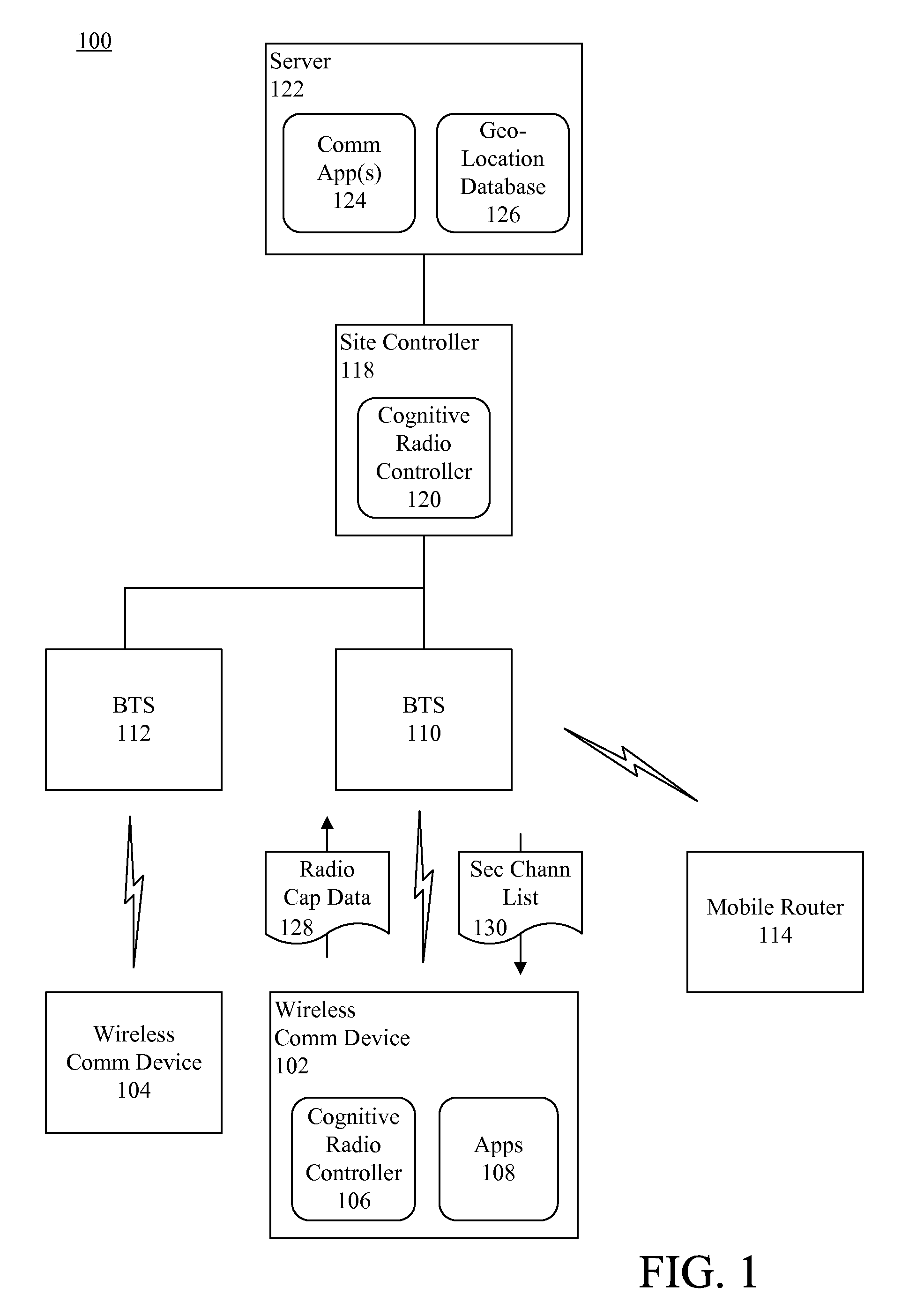
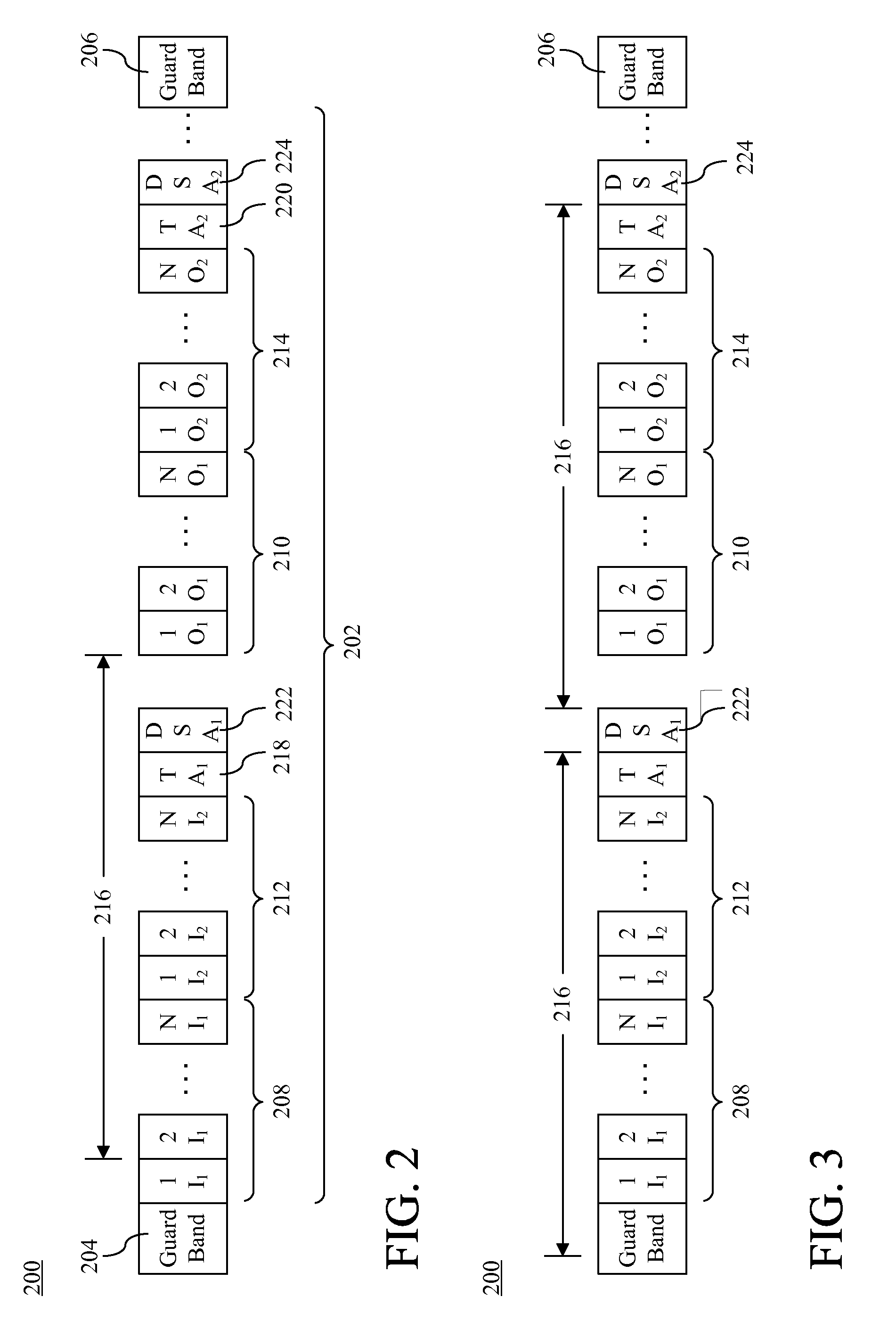
A method of dynamically allocating RF communication channels to a wireless communication device (102). A plurality of dynamic spectrum allocation (DSA) channels (222, 224) can be identified. The DSA channels can be channels that are available to a non-incumbent user to be used for RF communications. Based on at least one required channel parameter, a DSA channel can be selected as a first channel to allocate to the wireless communication device. At least a second channel can be selected to allocate to the wireless communication device based on a spectral relationship between the first channel and the second channel to ensure that the first and second channels are separated by at least a minimum required frequency separation (216).
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
Mimo-adapted distributed antenna system
ActiveUS20080192855A1Accurate reconstructionSite diversitySpatial transmit diversityCoaxial cableDistributed antenna system
Methods and systems for carrying different signals required for MIMO communication using a single coaxial cable between two endpoints of a distributed antenna system (DAS) network. Original MIMO signals having the same frequency are frequency-separated at a first endpoint of the network. The frequency-separated signals are propagated together over the single coaxial cable and then reconstructed to their original frequency at a second endpoint of the network.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
Distance measurement method and device using ultrasonic waves
InactiveCN1997911ARaise differential gainHigh measurement accuracyAcoustic wave reradiationFrequency separationDistance measurement
Owner:李东活 +1
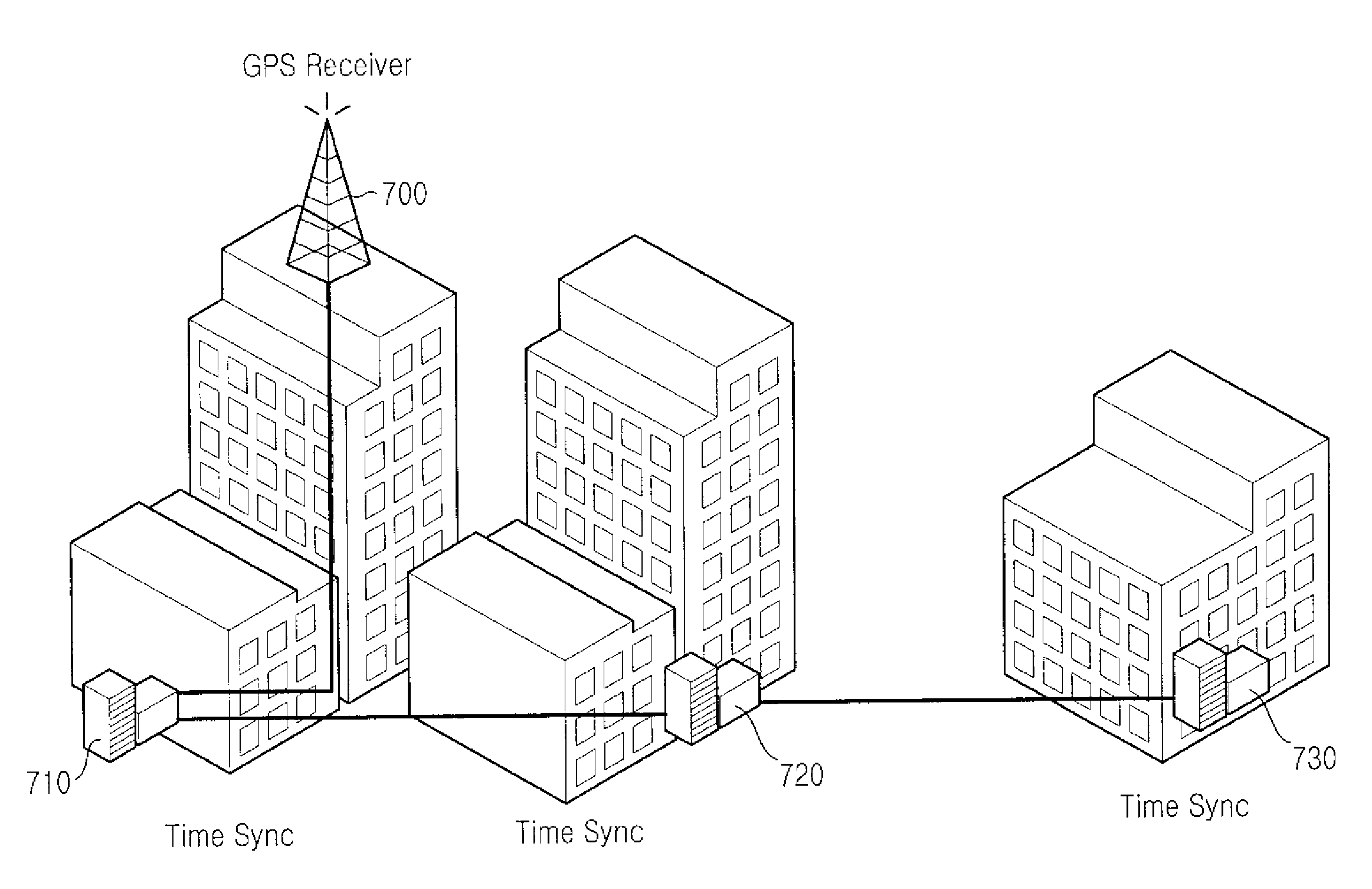
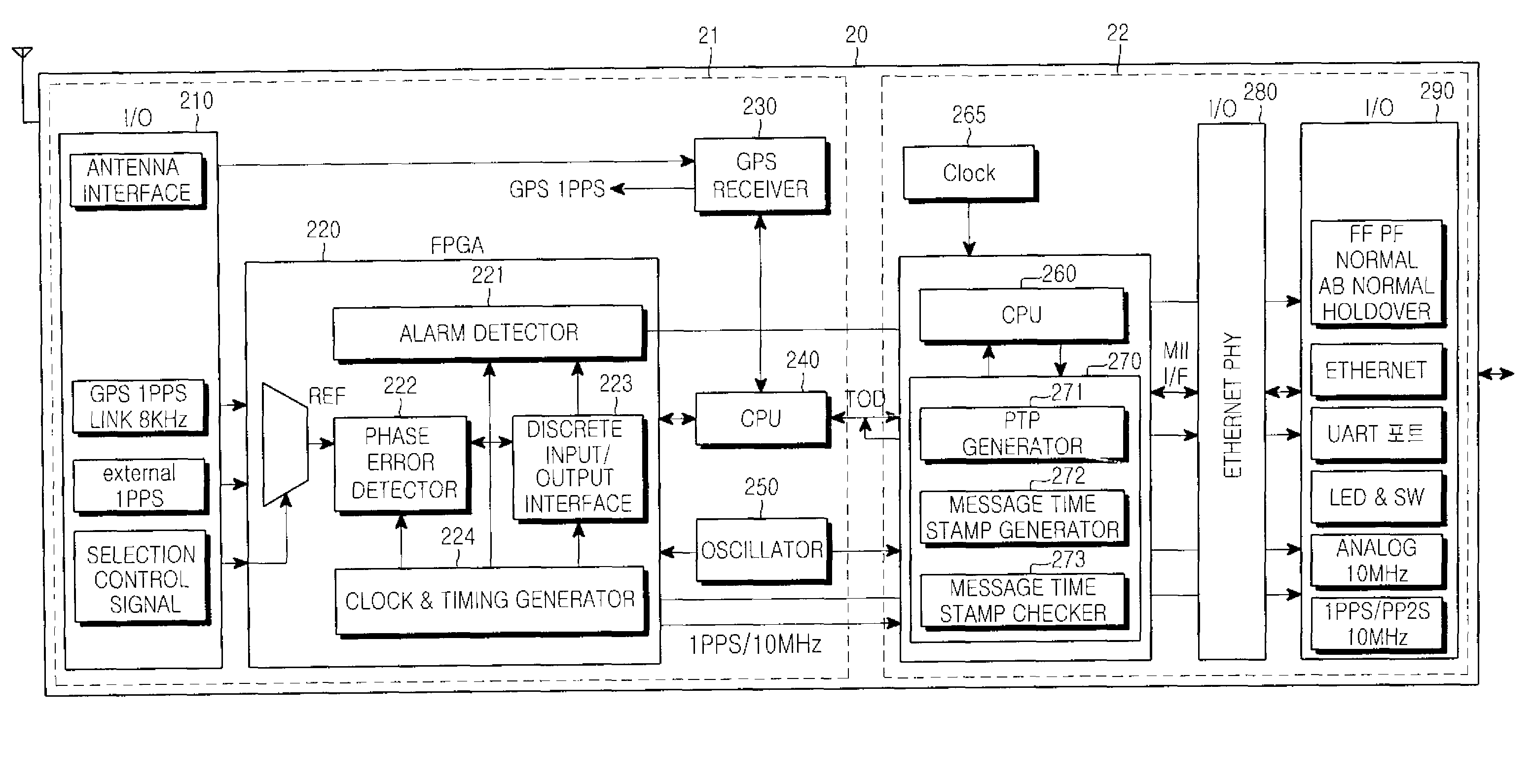
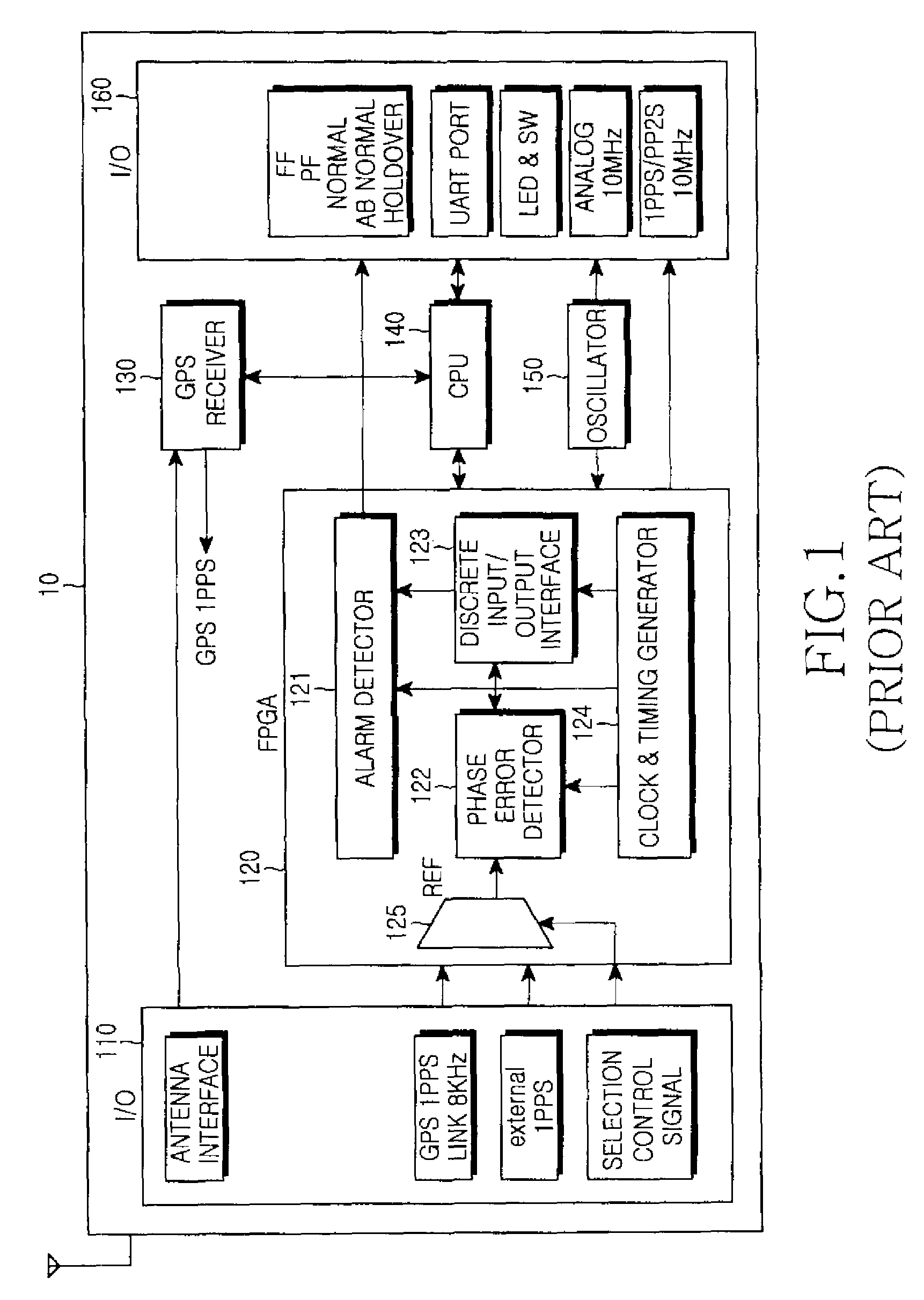
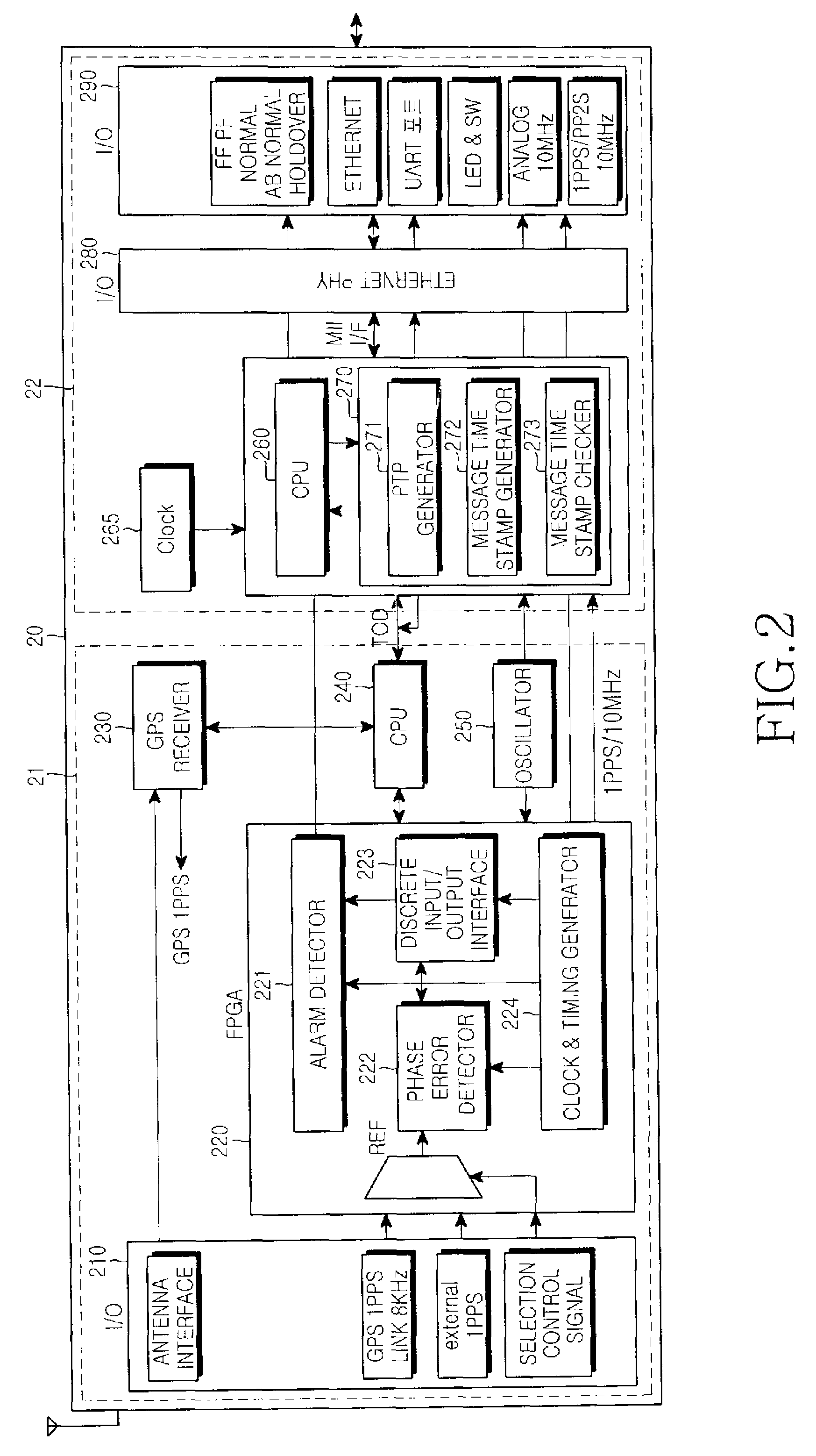
Apparatus and method for performing time synchronization using GPS information in communication system
InactiveUS20090168808A1Synchronisation information channelsTime-division multiplexTemporal informationCommunications system
Disclosed is an apparatus and a method for performing time synchronization by using Global Positioning System (GPS) information in a communication system. The apparatus comprises a grand-master node having a GPS receiver, for generating a synchronizing message required to synchronize time on slave nodes by using Time Of Day (TOD) information received from the GPS receiver and at least one slave node for receiving the synchronizing message required to synchronize time from the grand-master node or from another slave node, for carrying out time synchronization operation by using an Offset and Frequency Compensation Clock (OFCC) synchronization process supporting time offset and frequency separation compensation, and for generating a synchronizing message required to synchronize time on other slave nodes.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
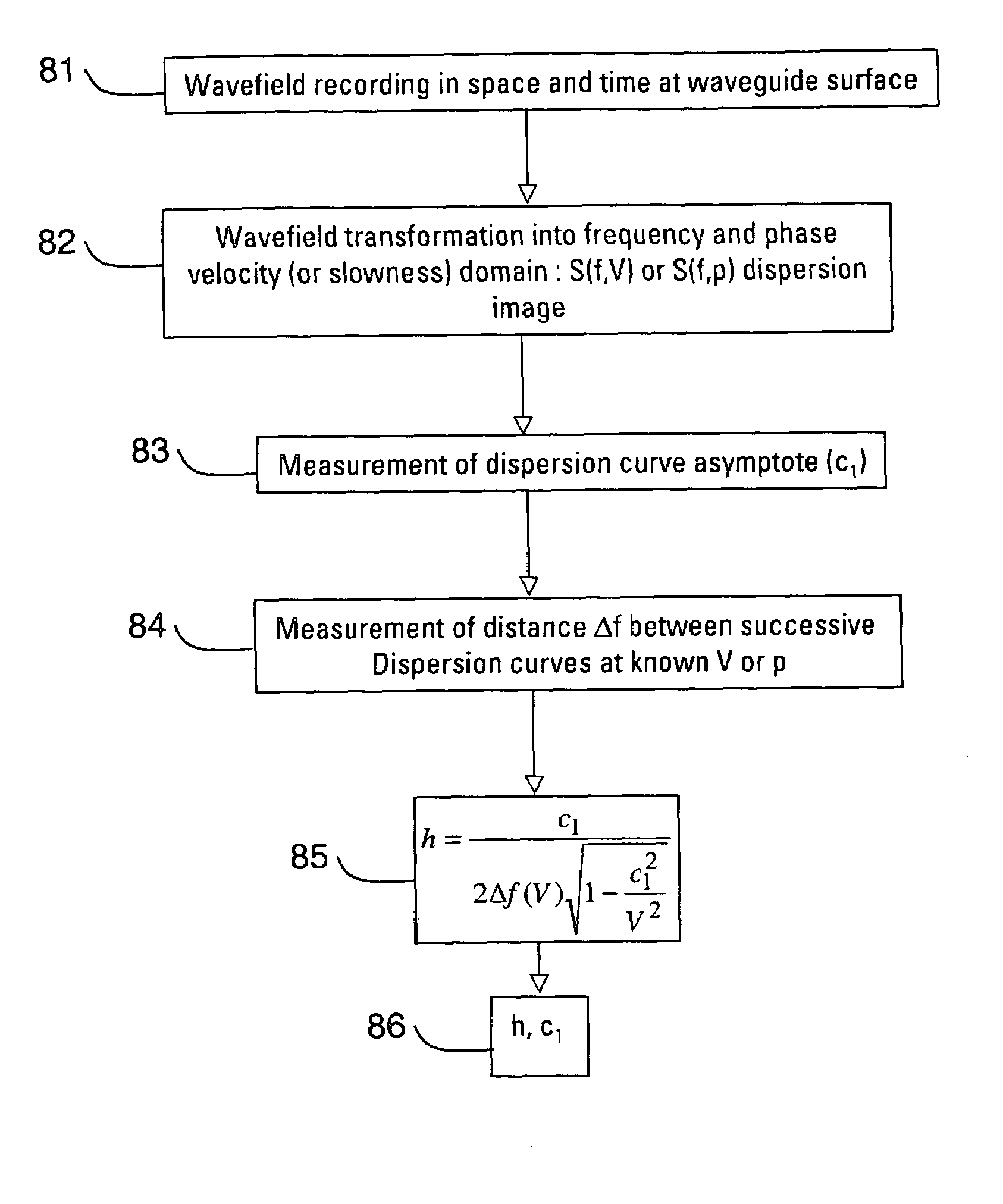
Determination of waveguide parameters
ActiveUS7110900B2Spectral/fourier analysisDigital variable/waveform displayDispersion curveClassical mechanics
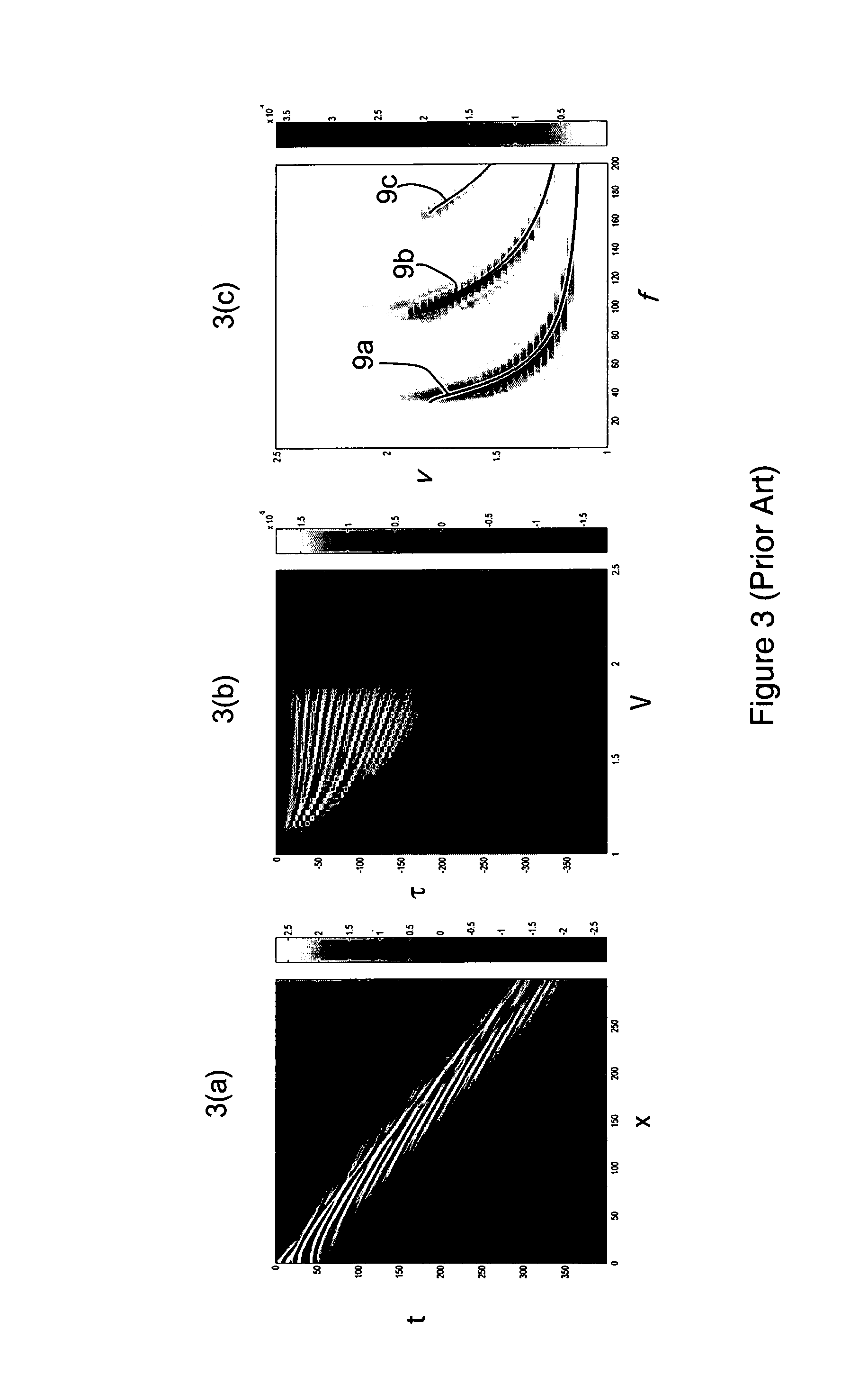
A method of determining at least one parameter of a waveguide (3) from wavefield data acquired from wave propagation in the waveguide including obtaining first and second dispersion curves (9a, 9b, 9c) in the frequency domain from the wavefield data. A frequency interval between the first dispersion curve and the second dispersion curve is found, and this is used in the determination of at least one parameter of the waveguide. The frequency separation Δƒ(V) between the first and second dispersion curves may be found at a particular value of the phase velocity V, and the thickness h of the waveguide can be found using:Δf(V)=c12h1-c12V2Here, c1 is the velocity of wave propagation in the waveguide. This may be found from the asymptotic velocity values of the dispersion curves.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
System and method for measuring a magnetic gradient field
ActiveUS10088535B1Improve signal-to-noise ratioEfficient detectionMagnetic property measurementsMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesMagnetic field gradientPhotodetector
A system and method is described to measure the magnetic field gradient using an optically pumped magnetometer configured as an intrinsic gradiometer. Atoms are prepared in a freely precessing coherent superposition of the magnetically sensitive hyperfine ground states in two or more physically separated locations. A probe laser beam is used to interrogate atoms in both locations. As the probe light beam passes through the coherent atoms, optical sidebands are self-generated at the ground state hyperfine frequency of the magnetically sensitive states. Each of the two sets of atoms produces distinct sidebands at a frequency separation proportional to the magnetic field experienced by each set of atoms. The probe light is captured using a photodetector. The self-generated probe optical sidebands interfere to produce a beat note whose frequency is proportional to the magnetic field gradient between the two sets of atoms. Measuring the frequency of the beat note therefore provides an accurate reading of the magnetic field gradient. An optical filter or a polarizer can be additionally used to remove the central frequency of the probe light, thus removing the noise produced by the residual probe beam.
Owner:QUSPIN
Frequency-shifted feedback cavity used as a phased array antenna controller and carrier interference multiple access spread-spectrum transmitter
InactiveUS20050232182A1Easy to adaptFrequency diversityWavelength-division multiplex systemsTime domainCarrier signal
An optical processor for controlling a phased antenna array uses a frequency-shifted feedback cavity (FSFC), which includes a traveling-wave cavity. The FSFC incrementally delays and incrementally frequency shifts optical signals circulating in the traveling-wave cavity. Optical signals coupled out of the FSFC are separated by frequency, hence by delay, and processed to control either or both transmit and receive beam-forming operations. The FSFC provides a receiver with multiple receive signals which have incremental values of frequency. Each frequency corresponds to an incremental time sampling of optical signals input into the FSFC. Transmit signals coupled out of the FSFC have frequency and phase relationships that result in short time-domain pulses when combined. Controlling modulation and frequency of the transmit signals achieves carrier interference multiple access, a new type of spread-spectrum communications.
Owner:DEPARTMENT 13 INC
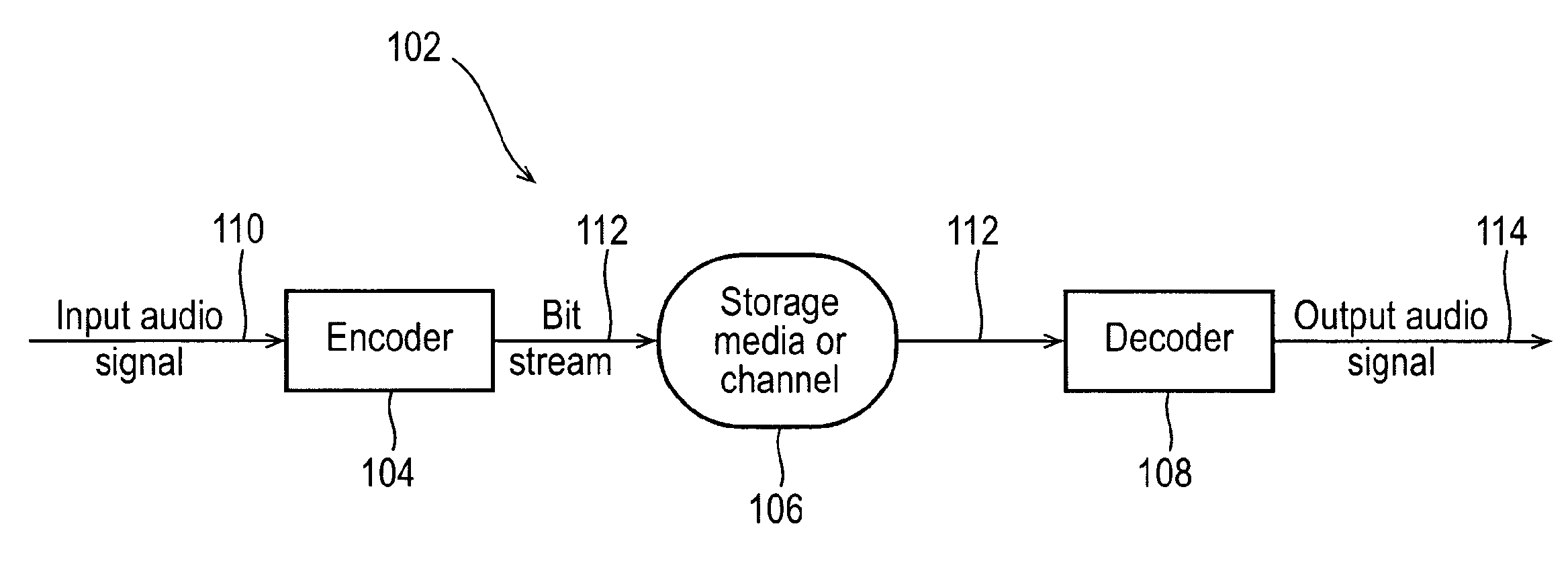
Encoder
An apparatus including at least one processor and at least one memory including computer program code the at least one memory and the computer program code configured to, with the at least one processor, cause the apparatus at least to select at least two single frequency components; generate an indicator, the indicator being configured to represent the at least two single frequency components and is configured to be dependent on the frequency separation between the two single frequency components.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Data separation in high density environments
InactiveUS20100277284A1Minimize timeIncrease power consumptionMultiplex system selection arrangementsMemory record carrier reading problemsHigh densityComputer science
Systems and methods for data separation, which may be employed to receive and process RFID tag data in RF signal environments where multiple RFID tags are tracked, localized and / or employed to transmit information. The disclosed systems and methods may be implemented for data separation in a high density aRFID environment using RFID tags in combination with spatial and / or frequency separation.
Owner:L 3 COMM INTEGRATED SYST
Method for transmitting a signal over a power line channel and power line communication modem
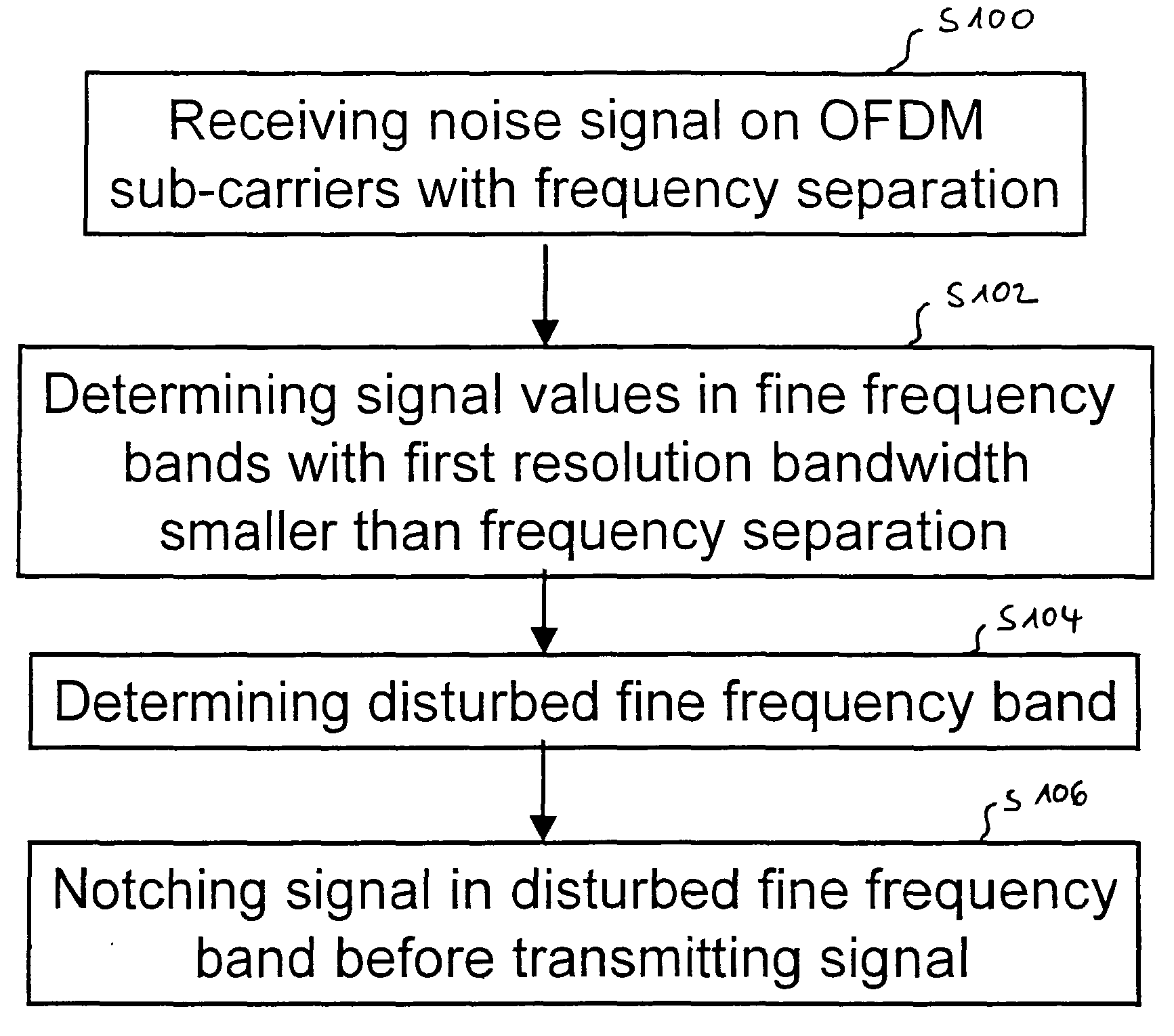
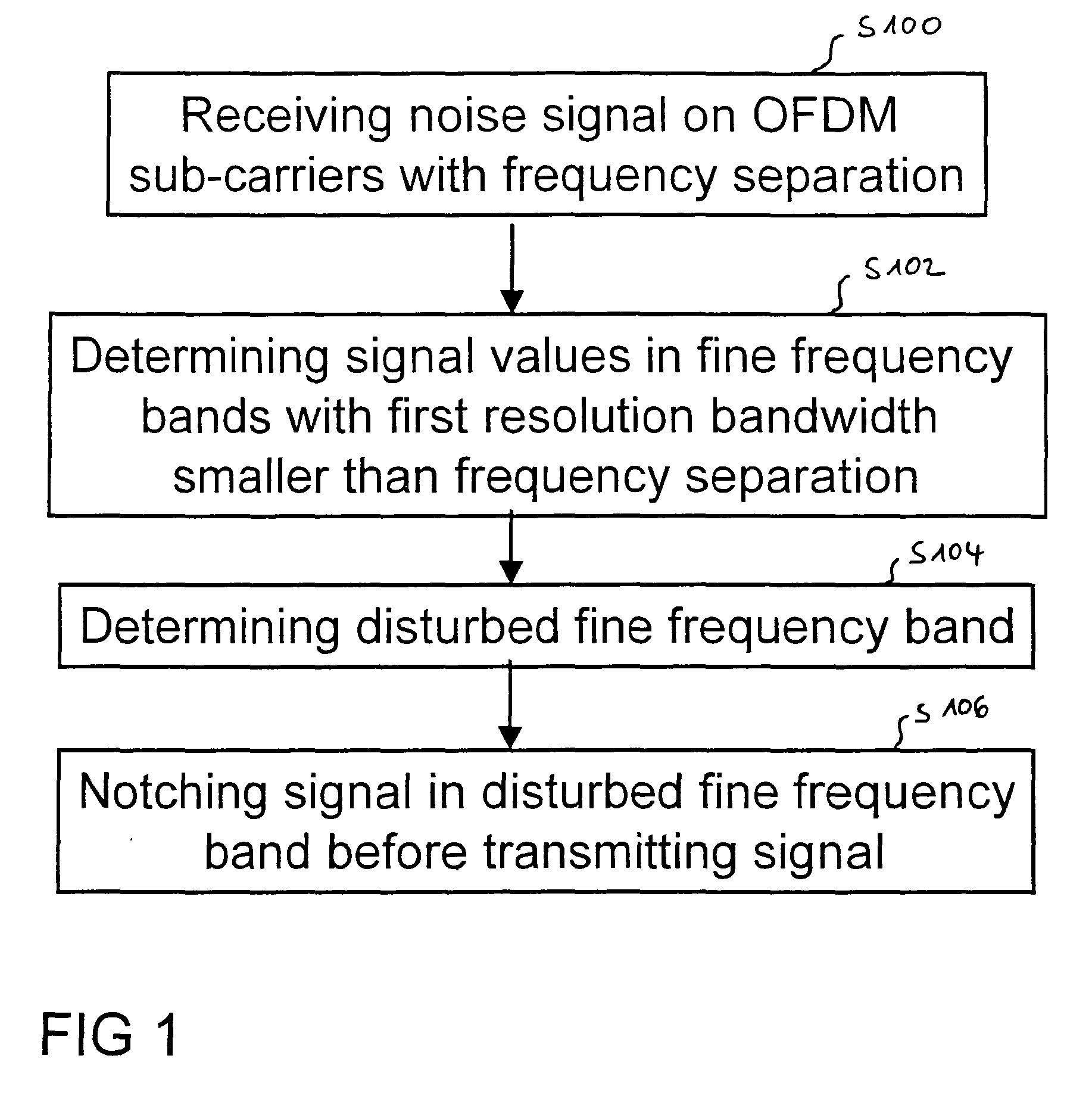
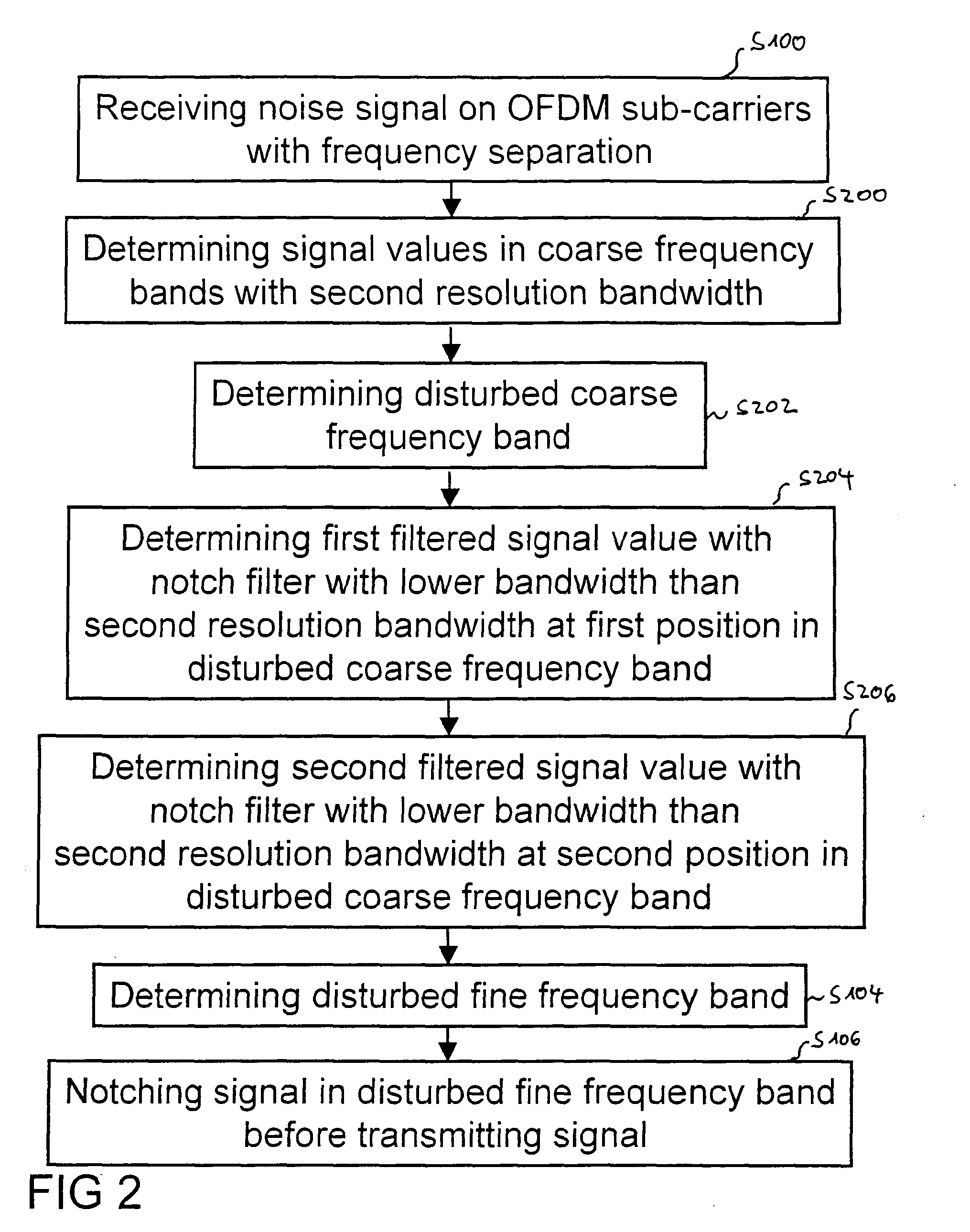
ActiveUS20100195744A1Transmission/receiving by adding signal to waveSystems with measurements/testing channelsModem deviceImage resolution
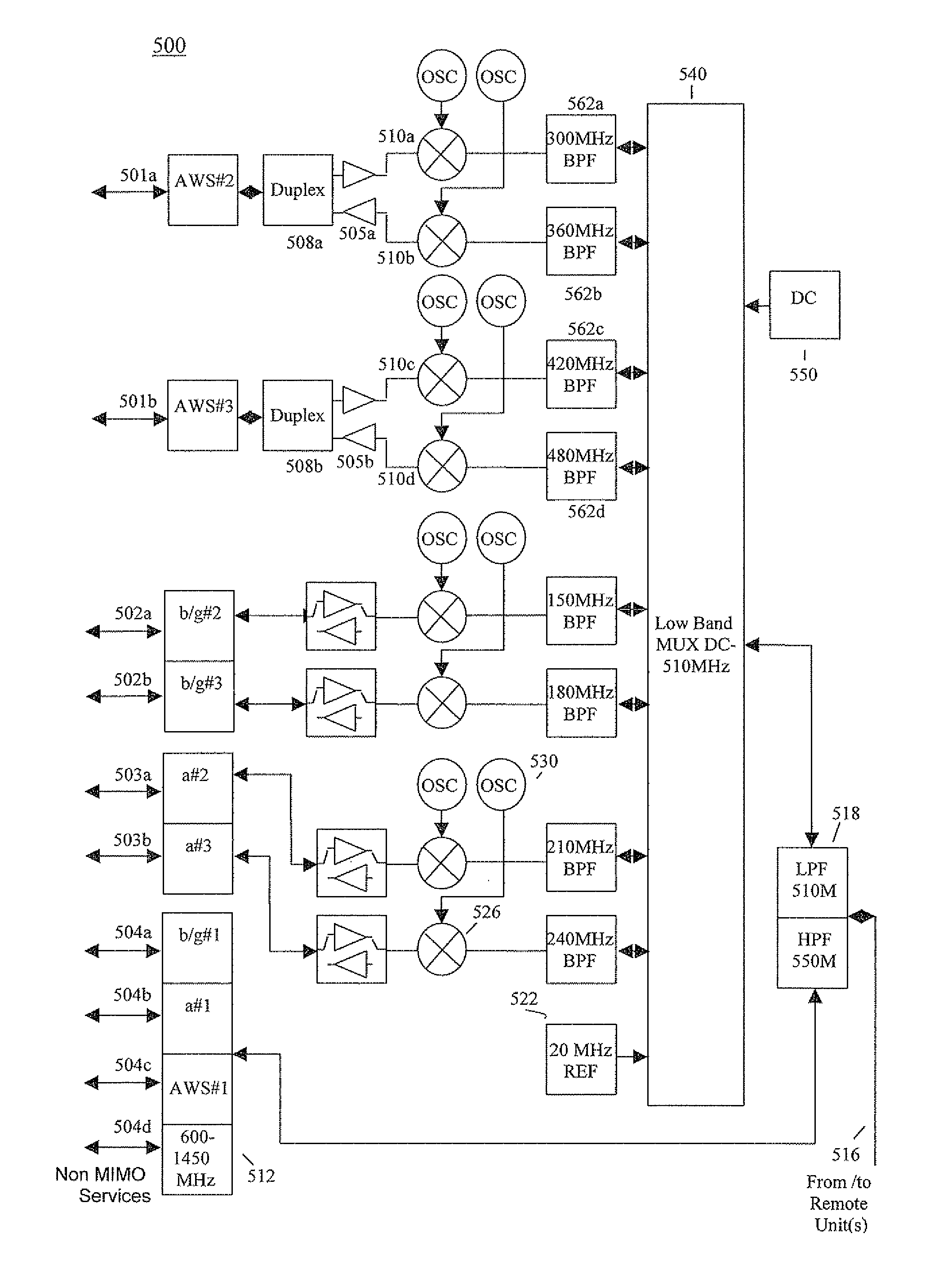
A method for transmitting a signal over a power line channel and a corresponding power line communication modem, wherein the signal is OFDM-modulated on a set of sub-carriers, the sub-carriers being separated by a frequency separation. The method includes receiving a noise signal via the power line channel, determining respective signal values of the received noise signal within a plurality of fine frequency bands with a first resolution bandwidth, wherein the first resolution bandwidth is smaller than the frequency separation, determining a first disturbed frequency band of the plurality of fine frequency bands based on the respective signal values, and notching the signal in the first disturbed frequency band before transmitting the signal.
Owner:SONY CORP
Disturbance attenuation in a precision servomechanism by a frequency-separated acceleration soft sensor
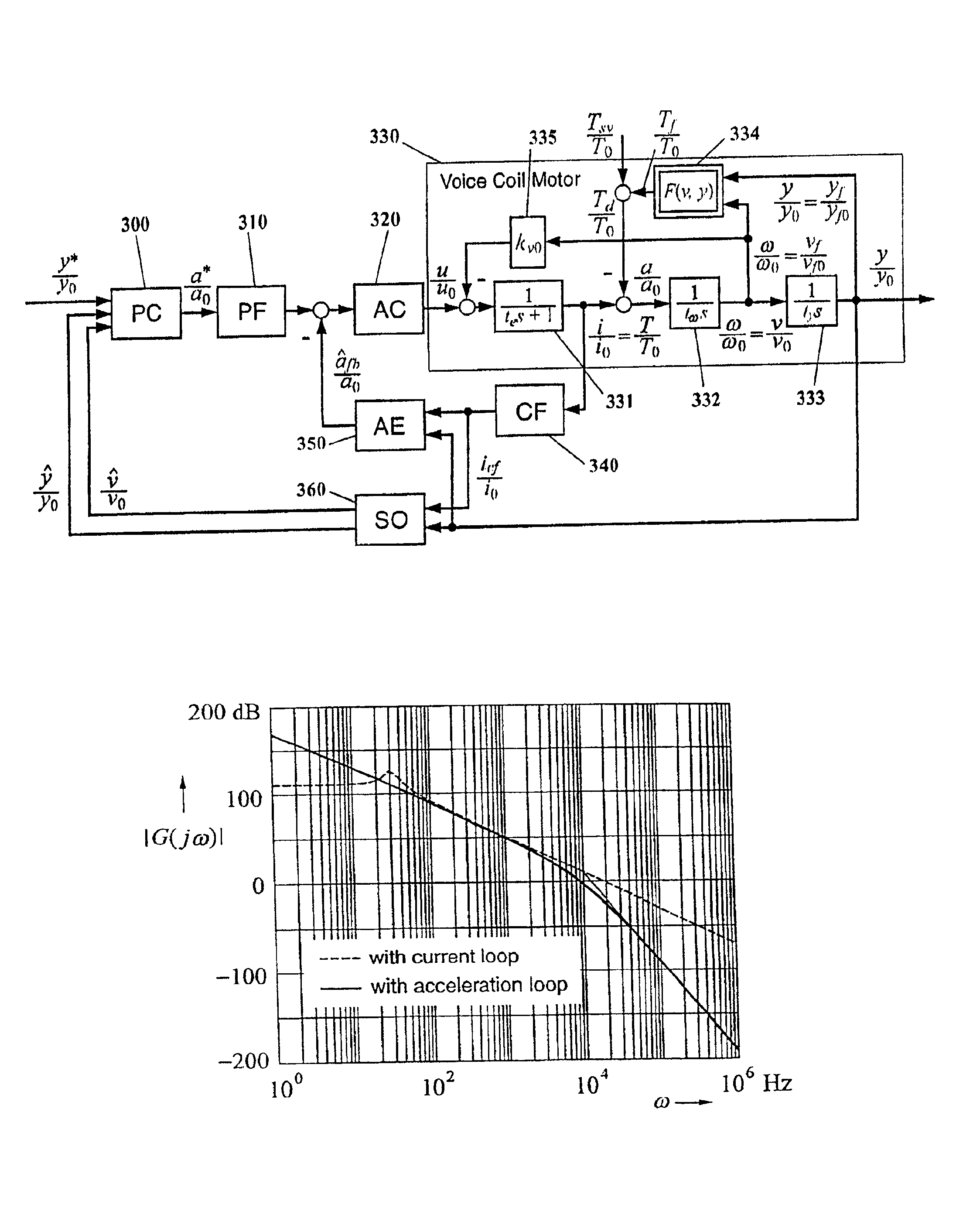
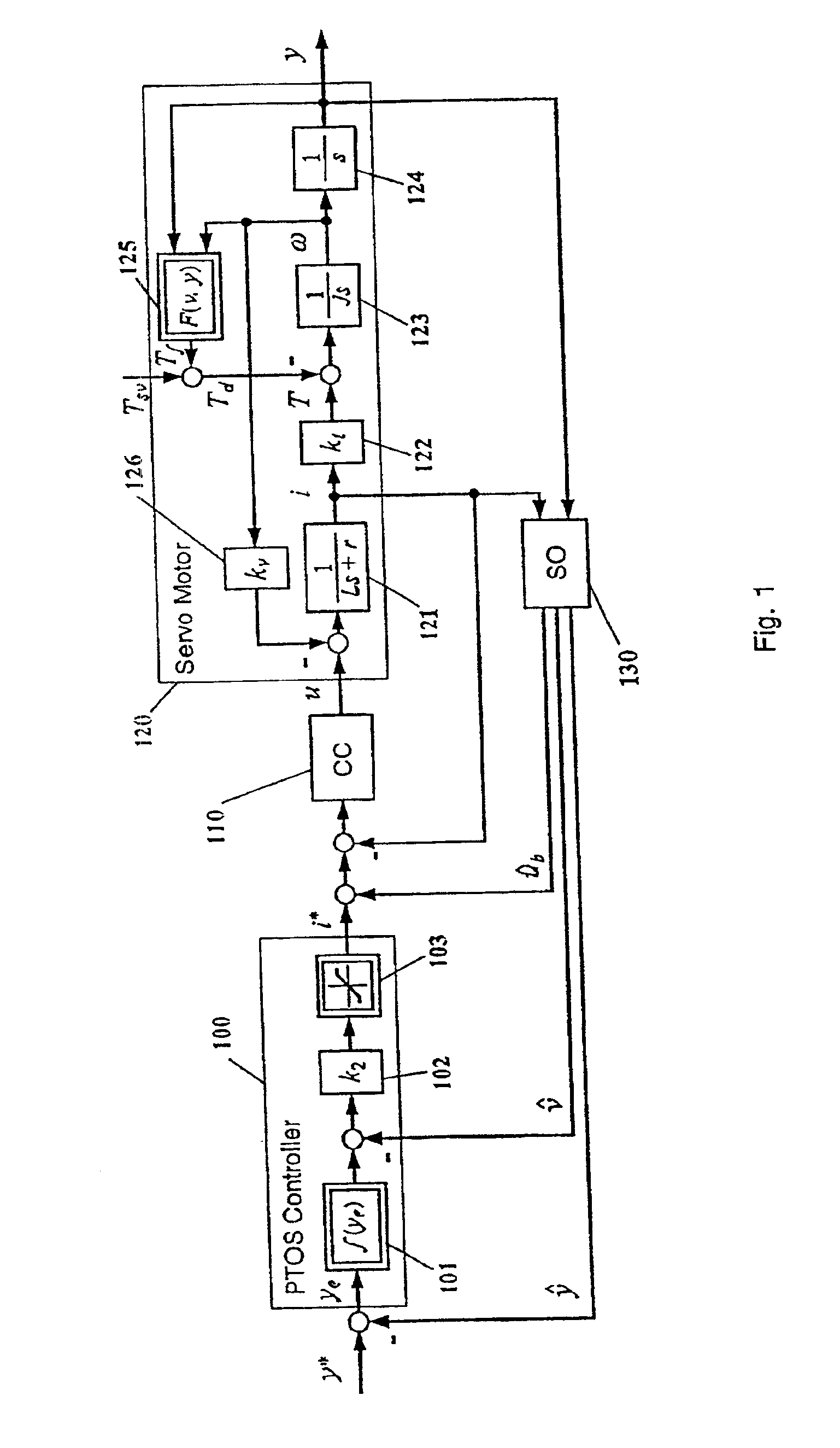
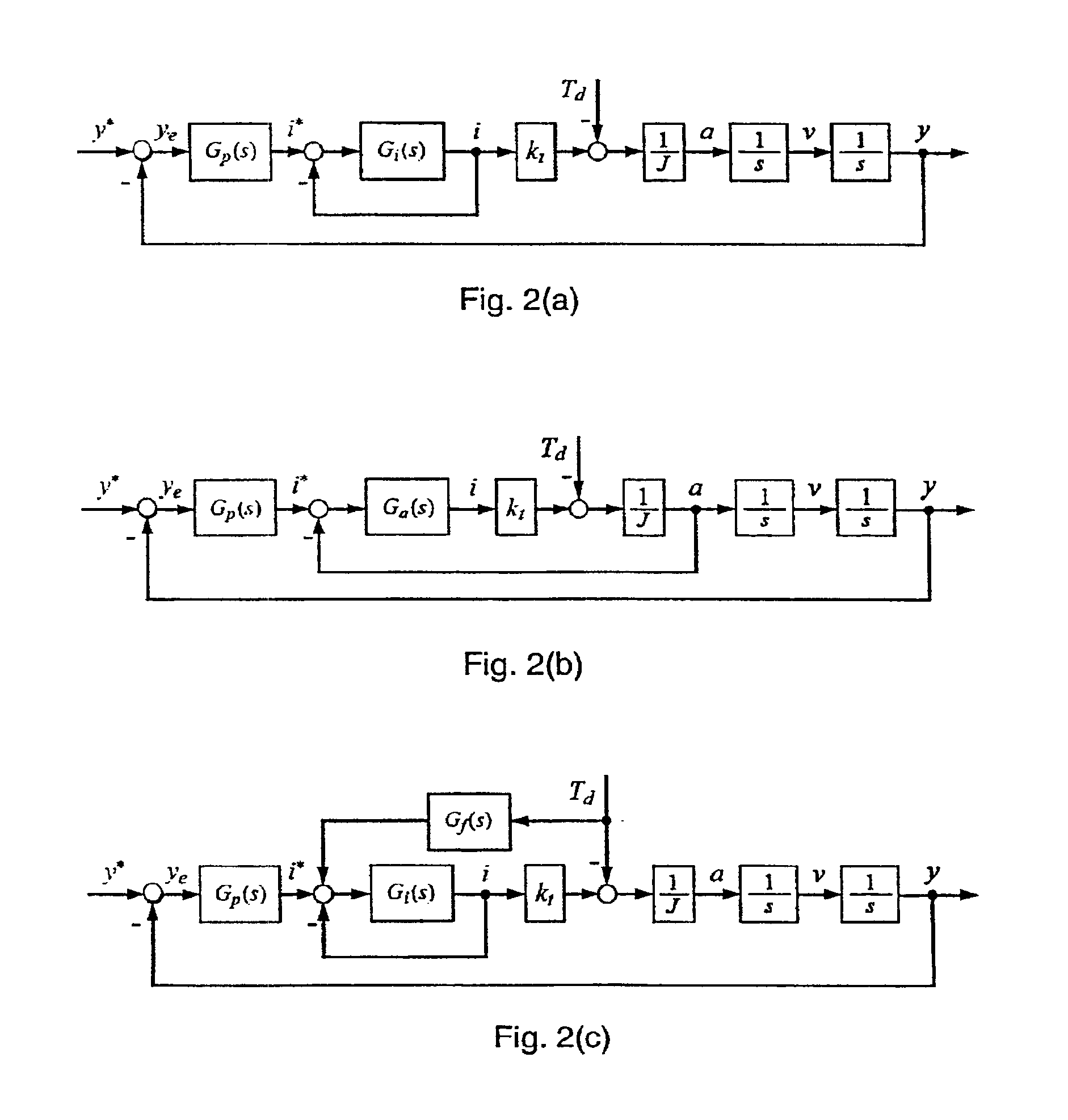
InactiveUS6876168B1Influence of disturbance can be reducedHigh positioning accuracyTrack finding/aligningComputer controlAccelerometerFeedback control
In servomechanisms, like for example used in disk drives, disturbances, for example, friction, shock and vibration, prevent the system positioning accuracy from further improvement. These disturbances occur in a relatively low-frequency range compared to the electrical dynamics. In the present invention, an acceleration feedback control loop using a frequency-separated acceleration soft sensor (350) replaces the conventionally used current control loop in the low frequency range, where the disturbances occur, so as to attenuate the influence of the disturbances enclosed in the loop. The current feedback continues to manage the electrical dynamics in the high-frequency range. Estimating the required acceleration signal by a soft sensor (350) eliminates the need for physical accelerometers, which reduce system reliability and increase system cost. The acceleration feedback control loop constructed with the obtained acceleration signal also makes the system more robust to the parameter inaccuracies and variations within the loop. This invention can be easily implemented with either software or hardware.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Multi-band jammer
InactiveUS7697885B2Wave based measurement systemsCommunication jammingMulti bandCommunications system
A jammer for jamming communications in a communications system where the communications system operates with digital bursts having burst periods measured in time and occurring in a communication frequency band such as GSM having a transmit band and a receive band. The jammer includes a tone comb generator for providing repetitions of jamming signals for the communication frequency band where the jamming signals have jamming signal intervals providing frequency separation between the jamming signals. The jamming signals are generated with a dwell time substantially less than a burst period for the communications system. The jamming signals are generated concurrently for the transmit band and the receive band and are transmitted as RF jamming signals to jam communications for mobile stations.
Owner:AEROFLEX WICHITA
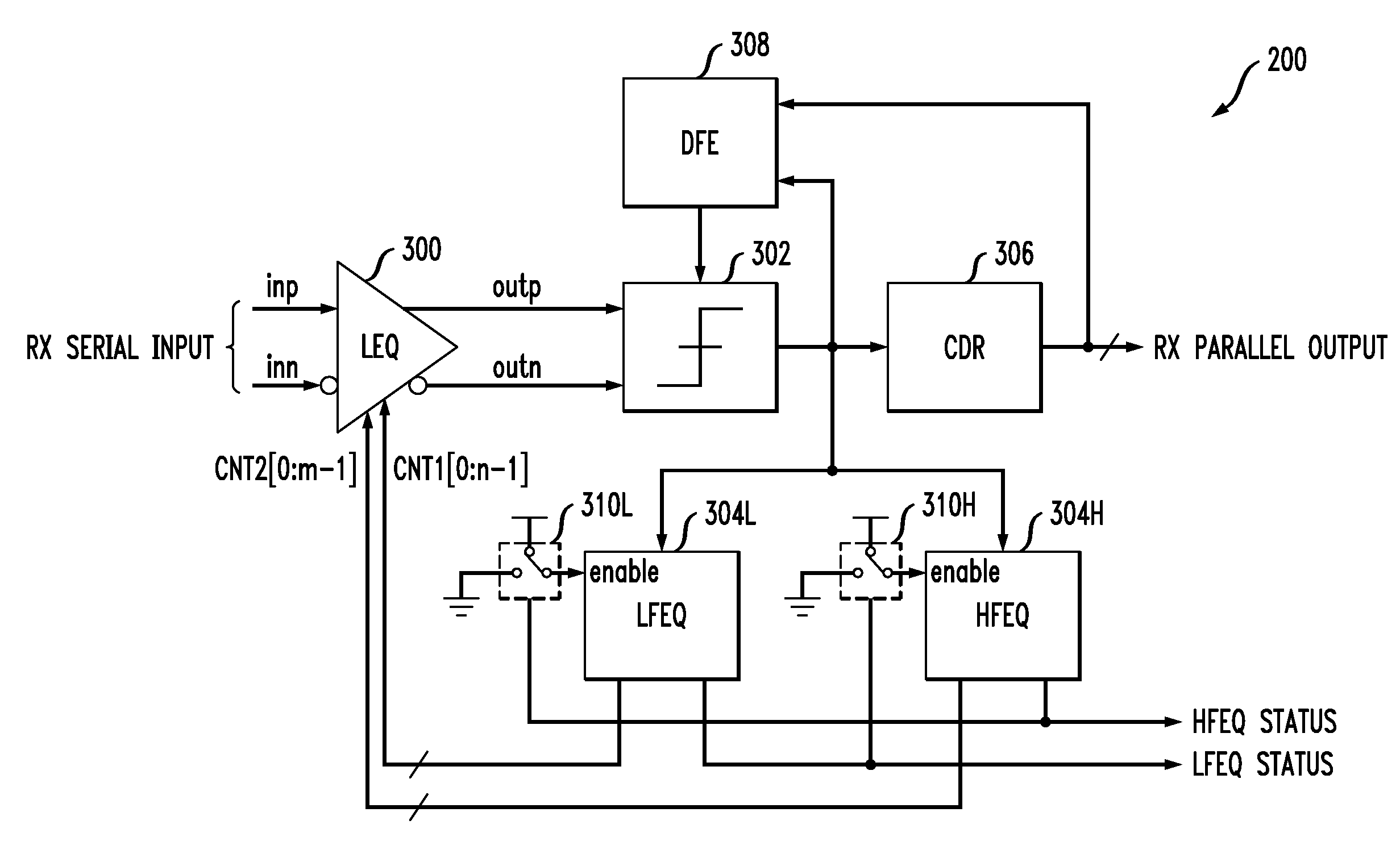
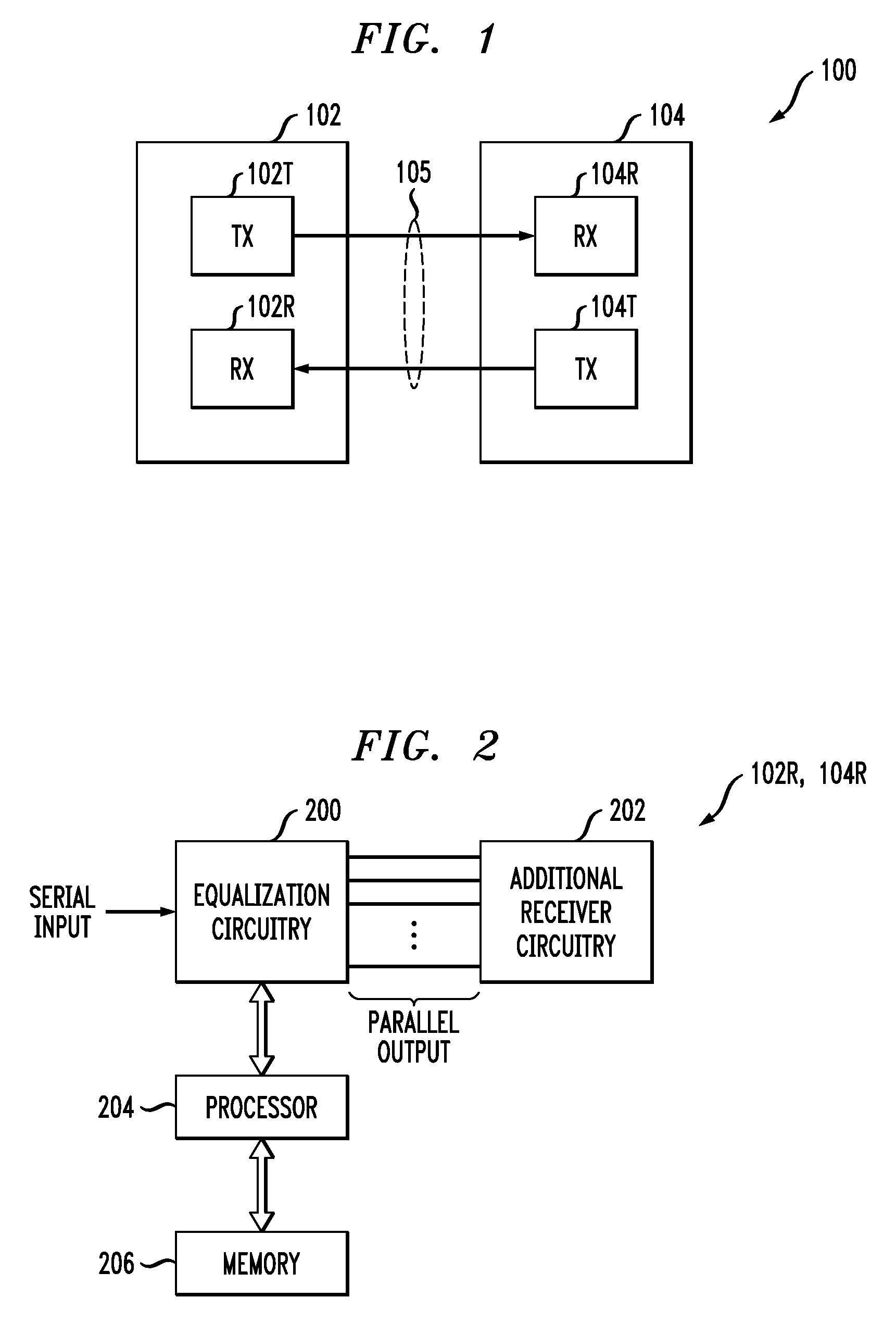
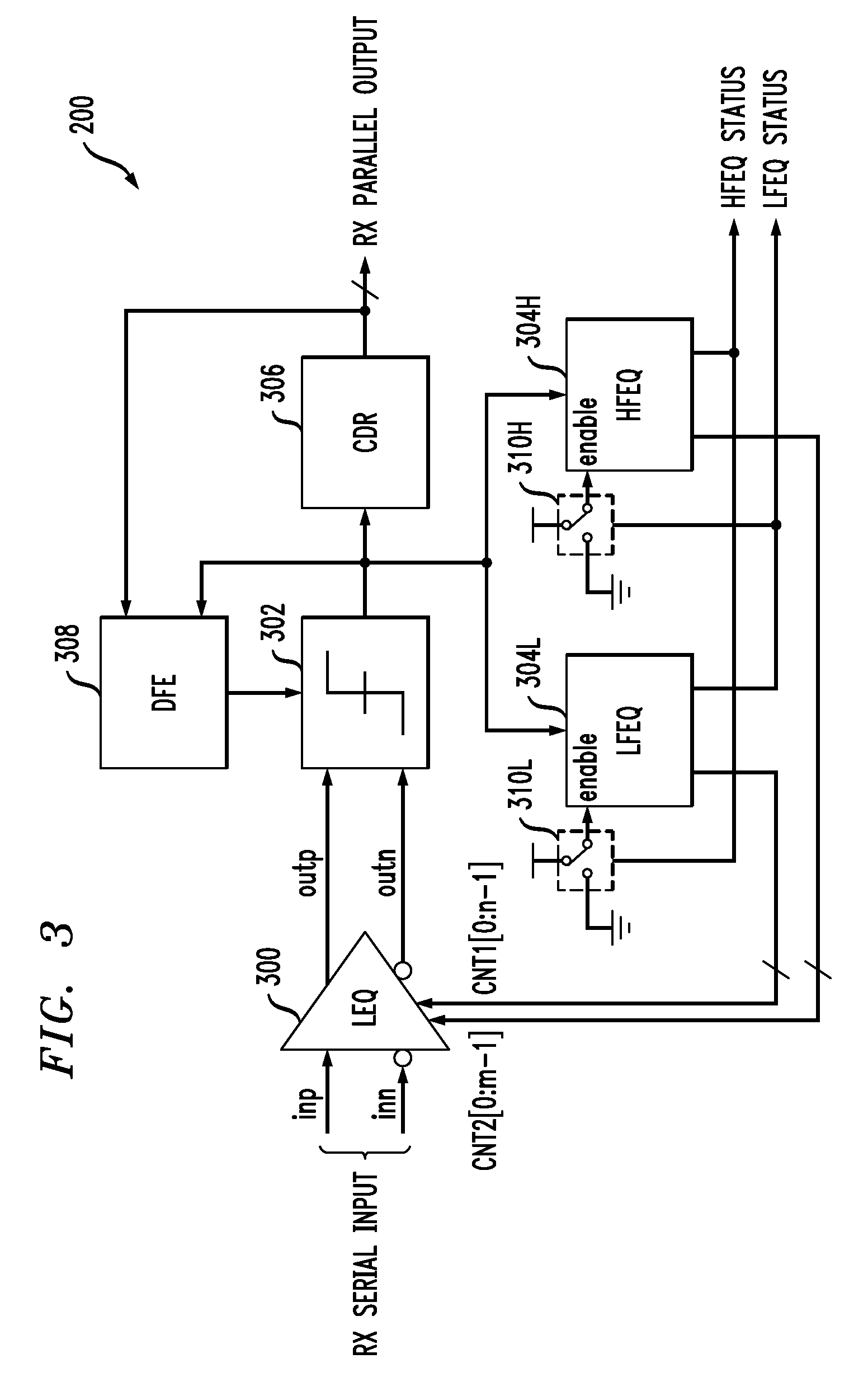
Multi-Band Gain Adaptation for Receiver Equalization Using Approximate Frequency Separation
InactiveUS20100290515A1Improved receiver equalizationLow costMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsMulti bandData stream
A receiver comprises equalization circuitry implementing at least first and second gain adaptation loops associated with respective first and second frequency bands. The equalization circuitry in one aspect is operative to identify a pattern in a portion of a received serial data stream, and to perform gain adaptation for the receiver utilizing a particular one of the gain adaptation loops responsive to the identified pattern. For example, the gain adaptation may be performed utilizing a low frequency gain adaptation loop if the detected pattern is of a first type generally associated with a low frequency band, and may be performed utilizing a high frequency gain adaptation loop if the detected pattern is of a second type generally associated with a high frequency band. In other aspects, the first and second gain adaptation loops may be activated in a particular serial order or in parallel.
Owner:LSI CORPORATION +1
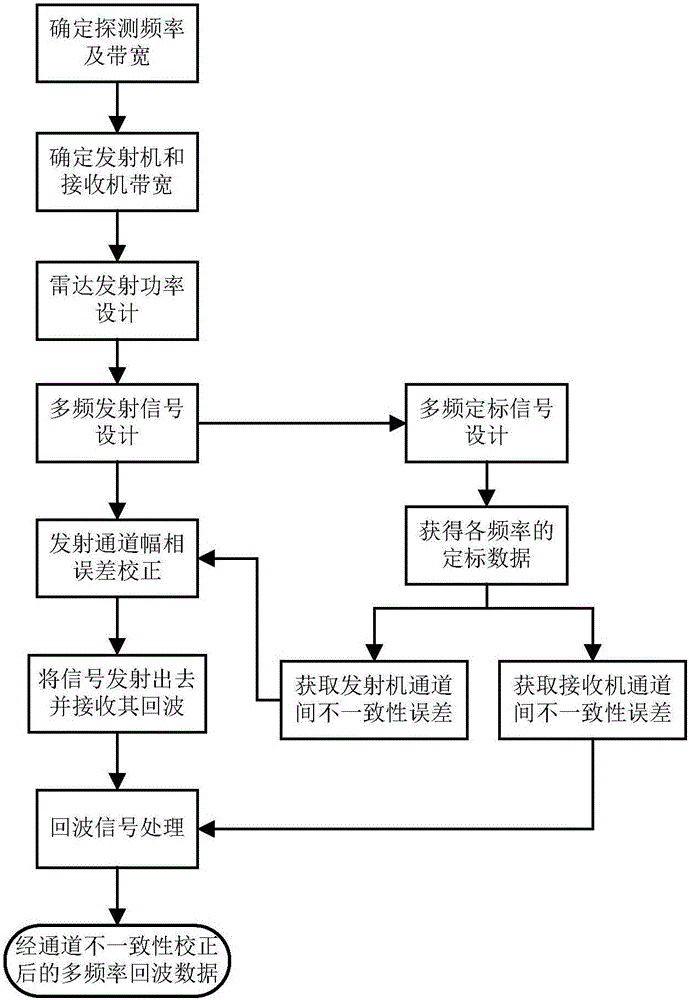
High-performance coherent high-frequency radar multi-frequency detection method
ActiveCN106226761AImprove performanceLow costRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPhase shiftedEmission channeling
The present invention provides a high-performance coherent high-frequency radar multi-frequency detection method. The method comprises the steps of 1) assigning the frequency values of a plurality of frequencies and an observation wave beam of each frequency, and according to the direction of the observation wave beam, determining the phase shift increment of each frequency to thereby design an emission signal of each channel of a radar emitter; designing a calibration signal, obtaining an inconsistency error between emission channels and an inconsistency error between reception channels, namely, an amplitude error and a phase error, by taking a first channel as the reference; utilizing the inconsistency error between the emission channels to carry out the amplitude compensation and the phase compensation on the emission signals to thereby correct the inconsistency between the emission channels; 2) using the emitter to filter and amplify the compensated emission signals, and then using an antenna to emit the signals out; then, using the antenna and a radar receiver to receive the echoes of the signals; 3) carrying out the frequency separation on the echo digital signals, and utilizing the inconsistency error between the emission channels obtained in the step 1 to compensate the amplitude and the phase to thereby obtain the radar echo data.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
Multi-mode transmitter having adaptive operating mode control
ActiveUS20100056068A1Improve power efficiencyPerformanceResonant long antennasPower amplifiersTransceiverPower efficient
Methods and apparatus for transmitting communications signals that are both power efficient and effective at avoiding or reducing transmitter-generated receive band noise. An exemplary transceiver apparatus includes a multi-mode transmitter that is configurable to operate in a plurality of operating modes (e.g., a polar mode, a quadrature mode and a hybrid mode), a receiver, and an operating mode controller. The operating mode controller is configured to control which operating mode the transmitter is to operate, depending on one or more of a transmit (Tx) power, receive (Rx) power, the Tx power relative to the Rx power, a level of frequency separation between a Tx frequency band and a Rx frequency band (Tx / Rx band separation), and modulation type employed by the transmitter.
Owner:APPLE INC
Cell search process for wireless communication system
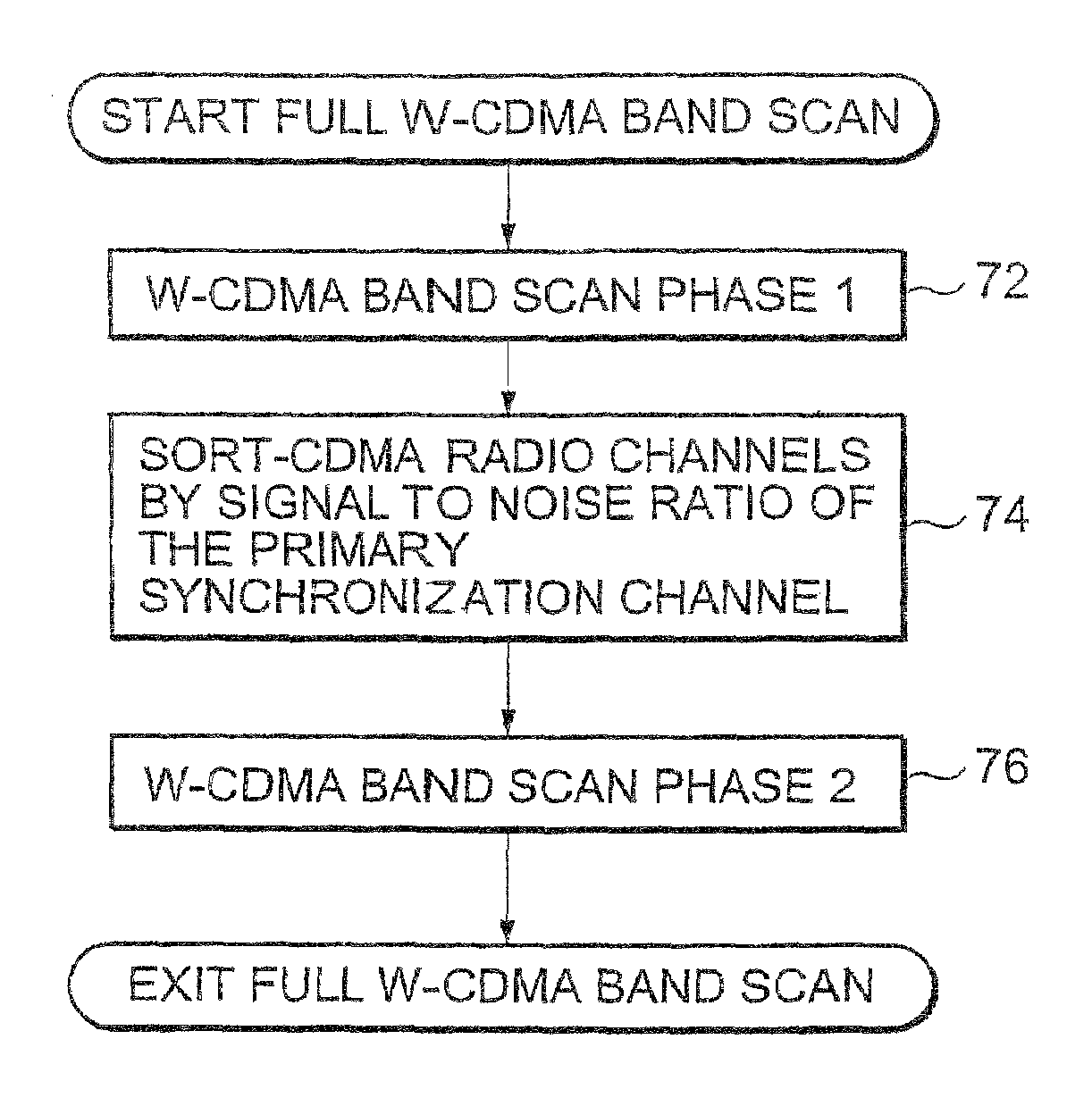
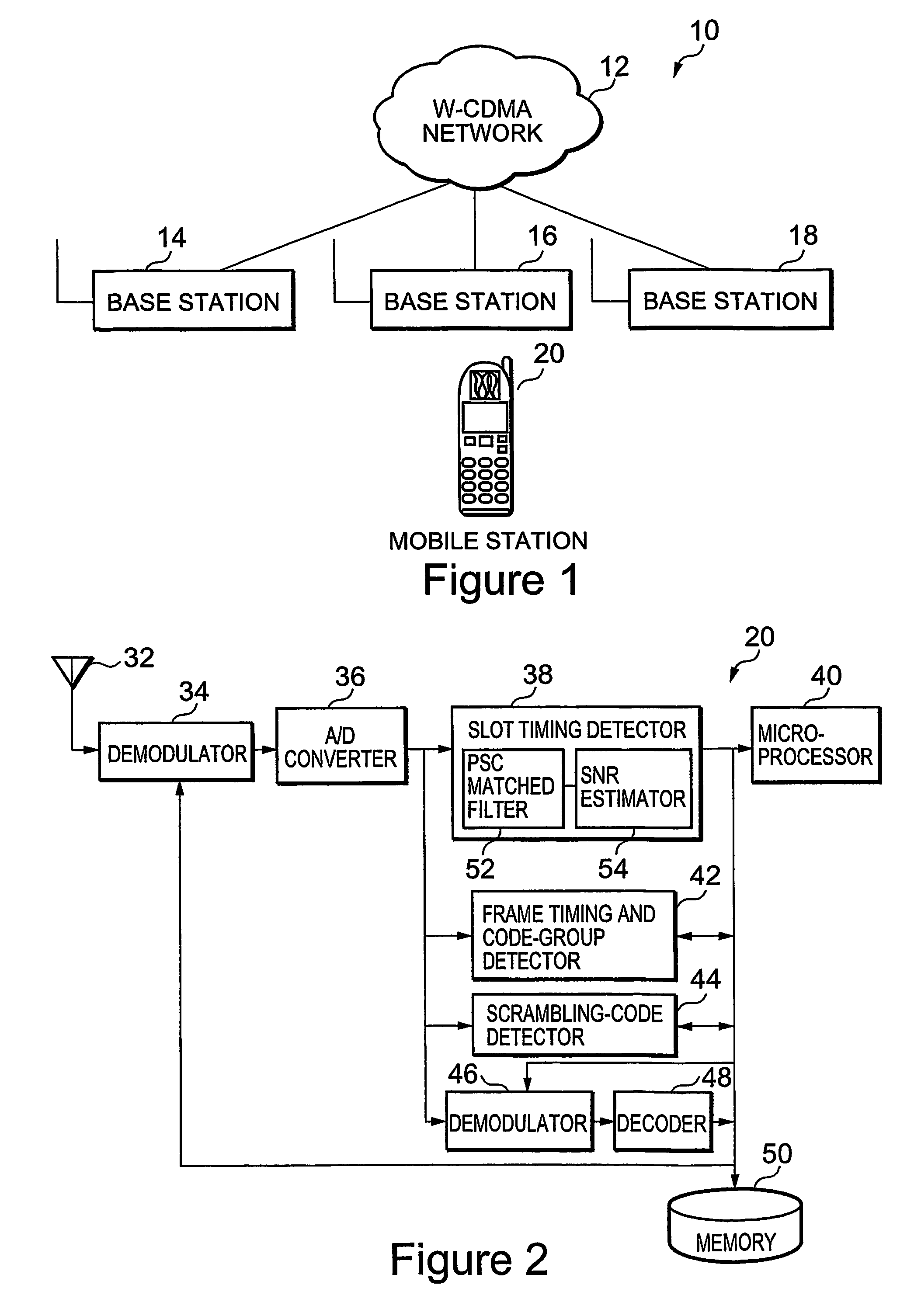
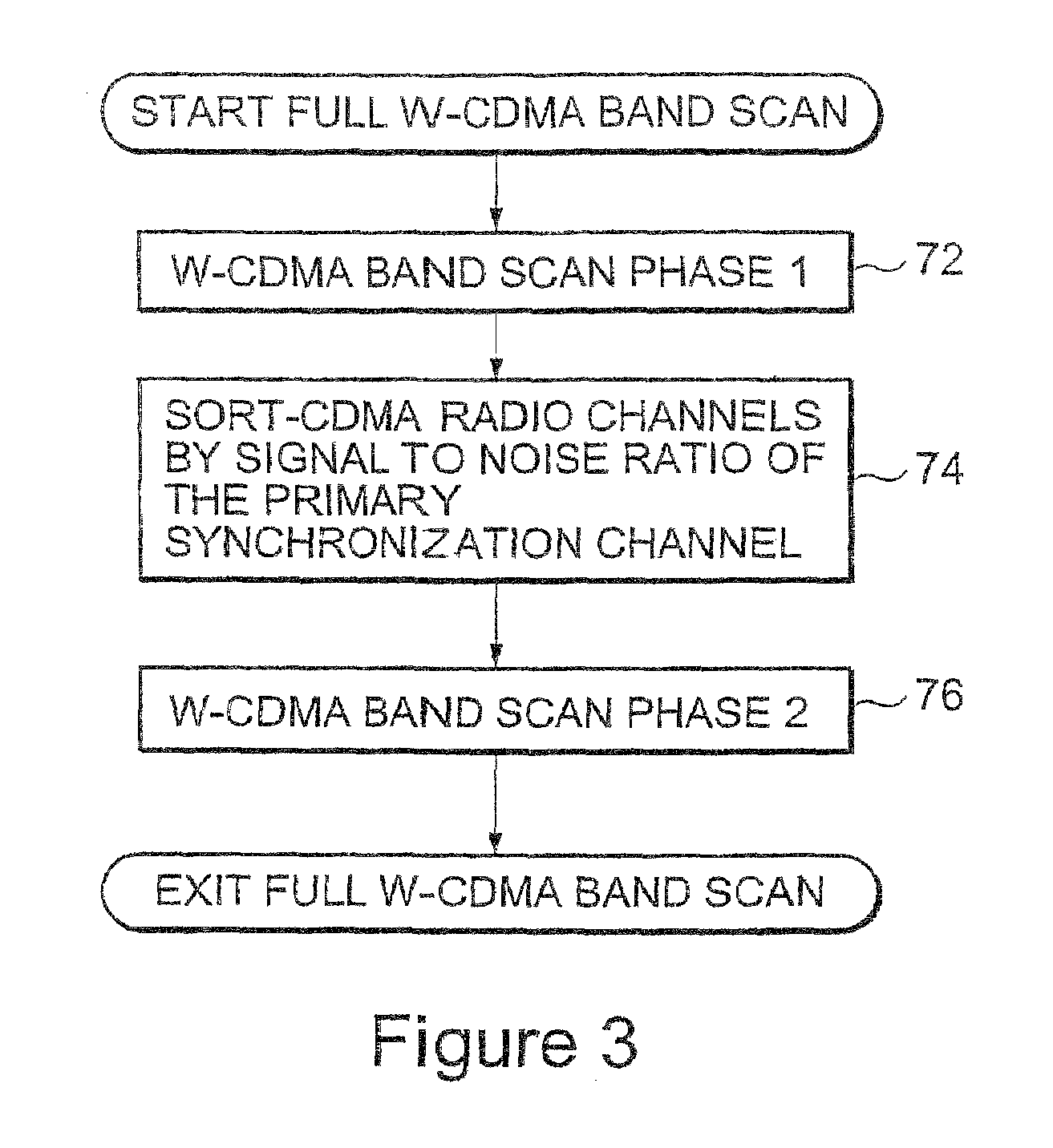
A method of cell search in a wireless communication systems having a plurality of base stations and a mobile station, each of the plurality of base stations serving a separate cell within a service area and transmitting a common primary synchronization code (PSC) in a primary synchronization channel within a slot of a radio frame, the method including the steps of: (a) scanning (72) through radio channels in scanning increments corresponding to a standard channel raster; (b) estimating (98) the PSC signal-to-noise ratio of each radio channel; (c) if a PSC signal-to-noise ratio is above a first predetermined threshold level (100), completing a cell search procedure including slot synchronization, frame synchronization and scrambling code detection steps for that radio channel; (d) if the cell search procedure is successfully completed (112) for the radio channel in step (c), increasing the scanning increments to the broadcast frequency separation between cells; (e) when all radio channels are scanned in step (d), sorting (74) the scanned radio channels in descending order by PSC signal-to-noise ratio; and (f) performing (76) the cell search procedure on each sorted radio channel in descending order.
Owner:LENOVO INNOVATIONS LTD HONG KONG
Regular linear interference suppressing method based on polynomial fitting
ActiveCN102681014AImprove processing qualitySeismic signal processingPattern recognitionApparent velocity
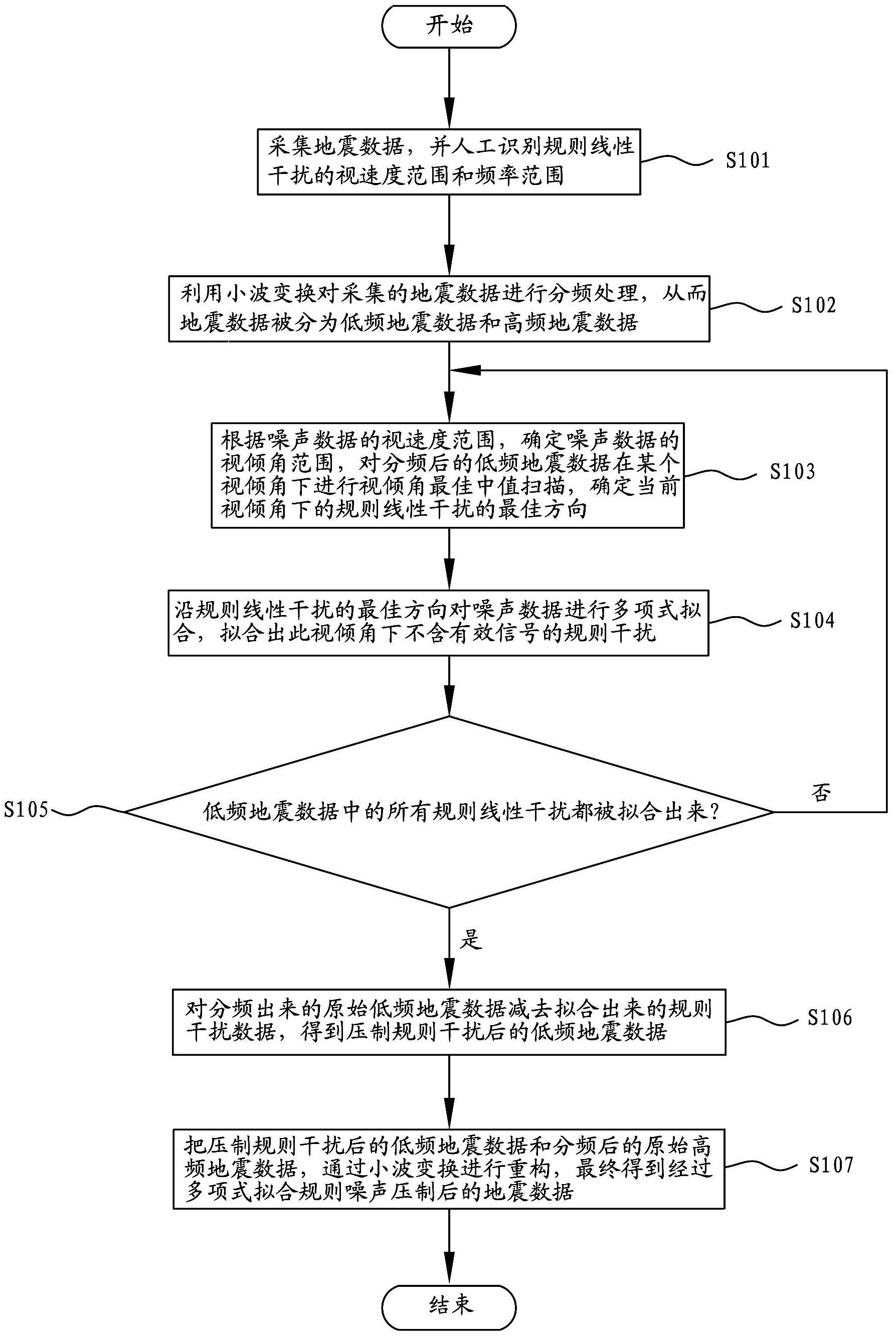
The invention provides a regular linear interference suppressing method based on polynomial fitting, comprising the following steps of: (a) artificially recognizing an apparent velocity range of regular linear interferences; (b) performing frequency separation processing on the acquired seismic data through wavelet transform, thereby obtaining low frequency data and high frequency data; (c) determining an apparent dip range of noise data according to the apparent velocity range of the noise data, performing optimal mid-value scanning of apparent dips, and determining the optimal direction of the regular linear interference at the current apparent dip; (d) performing polynomial fitting on the noise data in the optimal direction of the regular linear interference; (e) repeating the steps (c) and (d) until all regular linear interferences in the low frequency data are fitted out; (f) reducing the fitted regular interference data from the original low frequency data obtained through frequency separation, thereby obtaining low frequency data after the regular interference is suppressed; and (g) obtaining the seismic data after the noise is suppressed according to a polynomial fitting rule from the low frequency data after the regular interference is suppressed and the original high frequency data after frequency separation.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
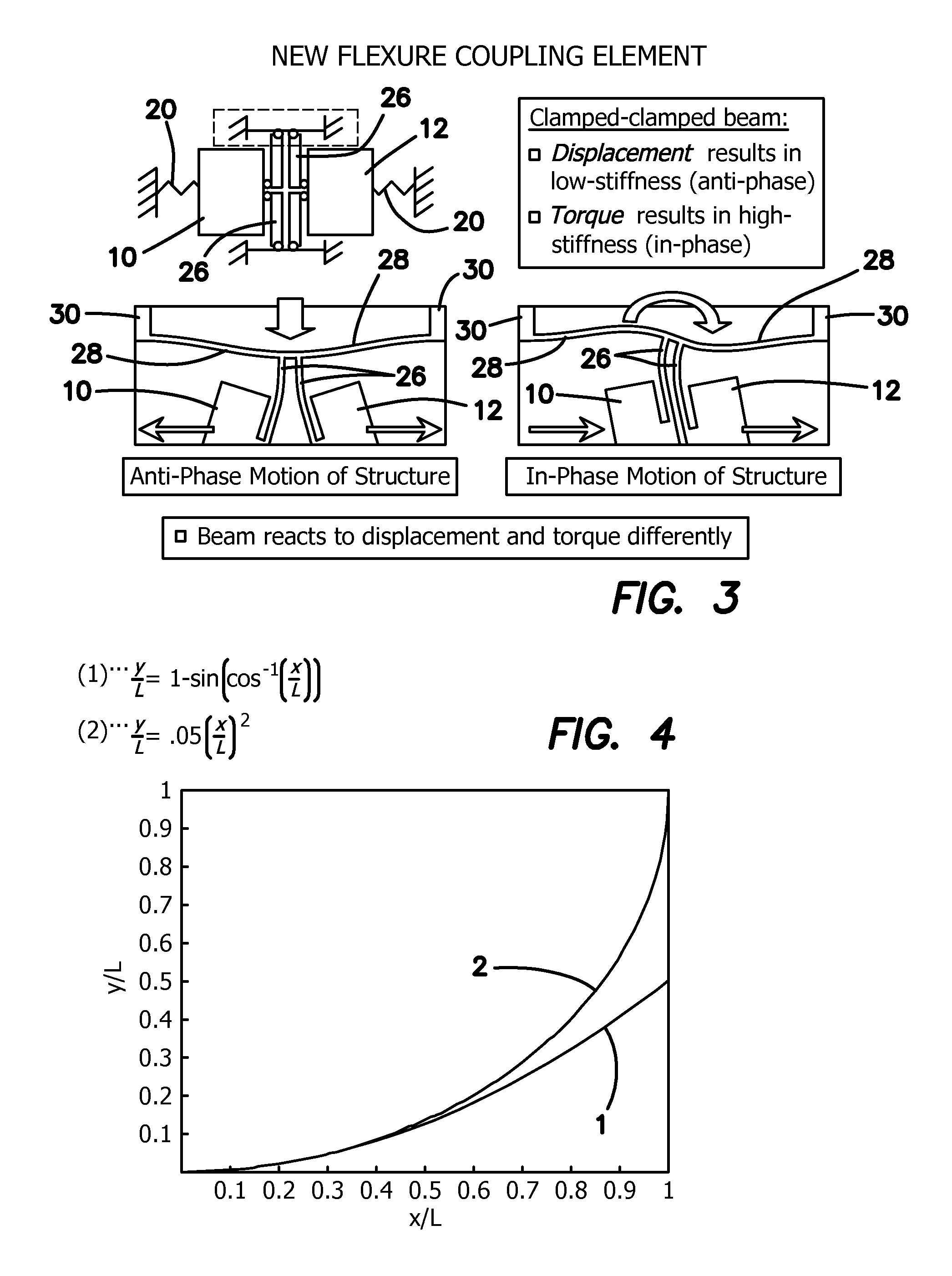
Lever mechanisms for anti-phase mode isolation in MEMS tuning-fork structures
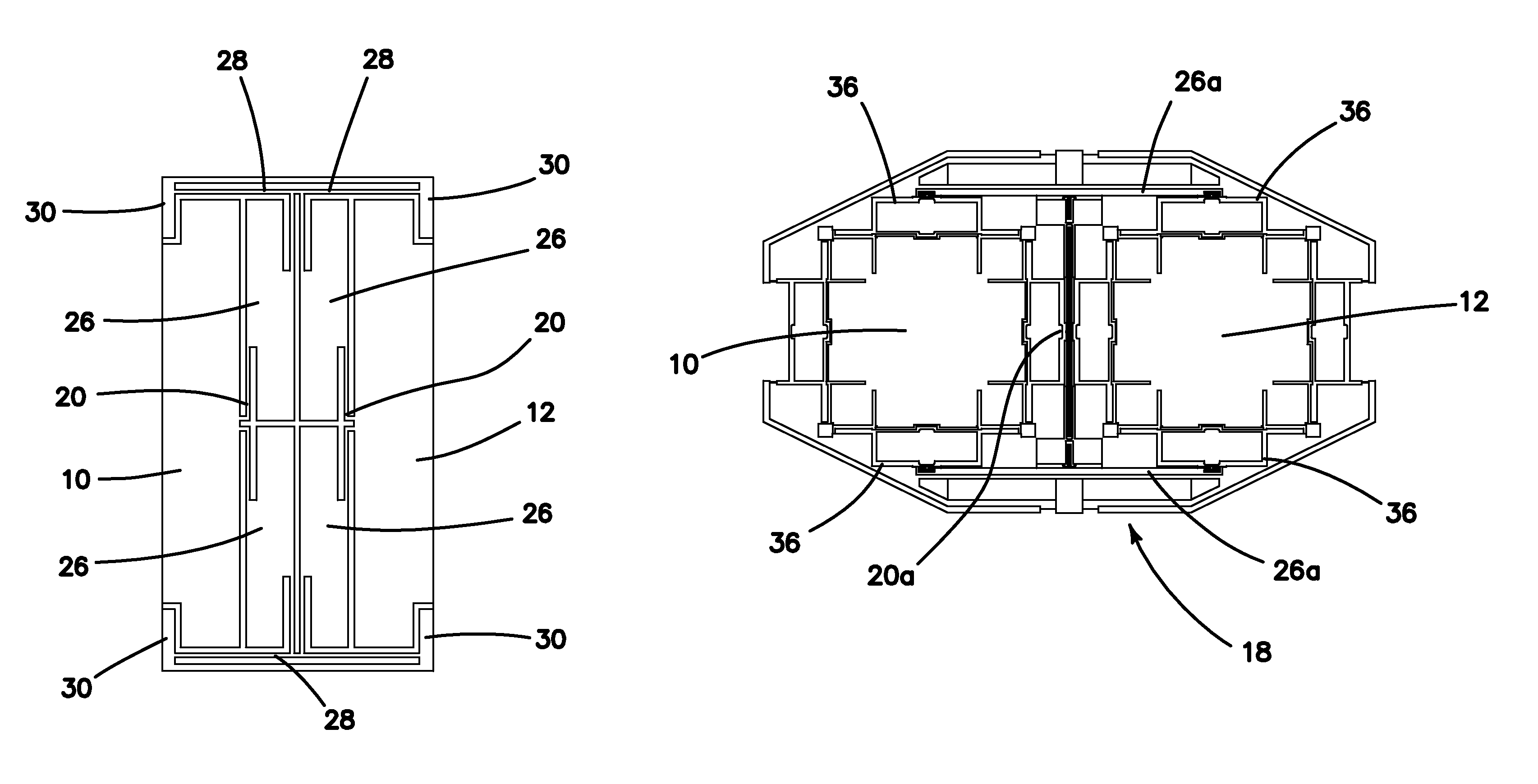
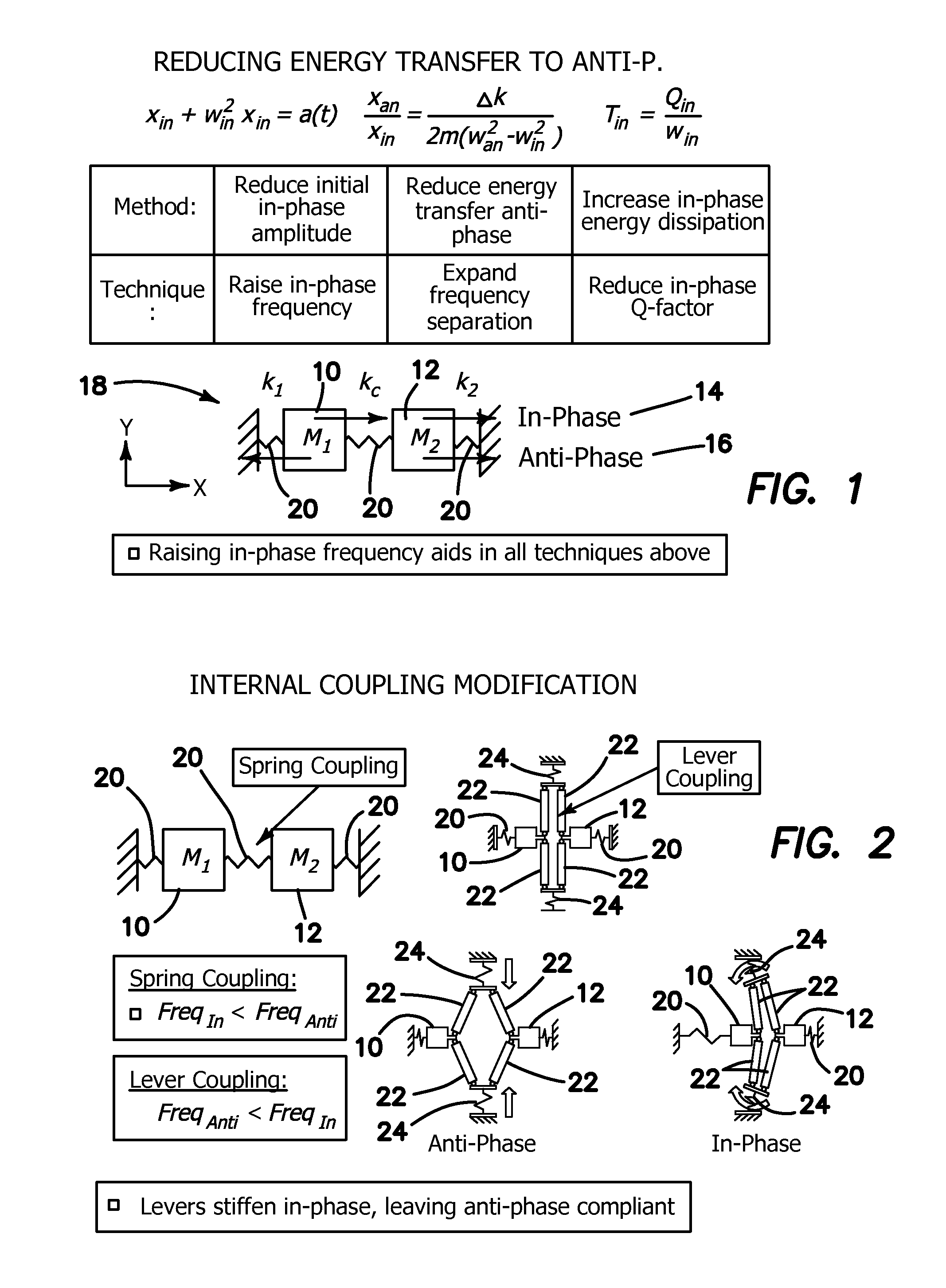
ActiveUS9217756B2Large frequency separationReduce energy transferImpedence networksAcceleration measurementTuning forkEnergy transfer
A MEMS resonator includes two resonating masses having an anti-phase and in-phase resonance mode, each mode having a resonance frequency, and an anti-phase resonance levering system coupled to the two resonating masses to stiffen and / or dampen the in-phase resonance mode while leaving the anti-phase resonance mode compliant. This effectively raises the in-phase resonance frequency above the anti-phase resonance frequency, and potentially creates a large frequency separation between the two resonance modes. This reduces the energy transfer between the two modes, allowing for robustness to external acceleration, because the in-phase mode is of a higher frequency. The anti-phase resonance levering system is disposed between the two resonating masses as an internal levering mechanism, or is disposed around the two resonating masses as an external levering mechanism.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
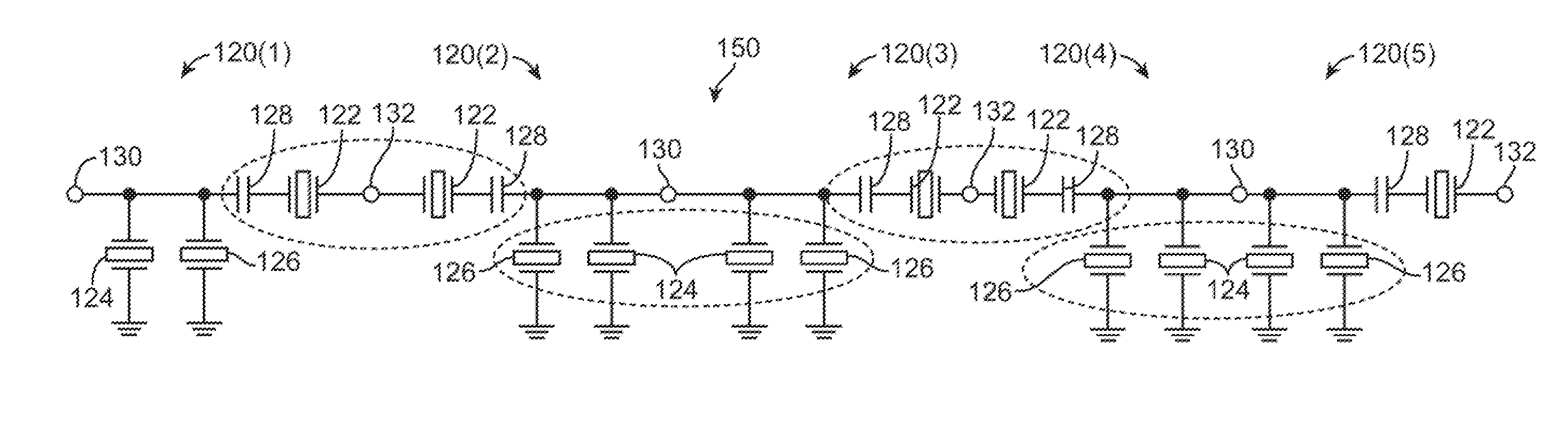
Microwave acoustic wave filters
An acoustic microwave filter comprises an input and an output, and a plurality of acoustic resonators coupled between the input and the output. The difference between the lowest resonant frequency and the highest resonant frequency of a plurality of resonators in the filter is at least 1.25 times the frequency separation of the resonator with the highest resonant frequency in the plurality of resonators. Another acoustic microwave filter comprises an input and an output, and a plurality of acoustic resonators coupled between the input and the output to form a passband. The frequency difference between a local minimum or a local maximum of a return loss magnitude of the acoustic microwave filter and the edge of the passband is at least once the frequency separation of the resonator with the highest resonant frequency.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Multi-band jammer including airborne systems
An airborne jammer for transport by an aircraft for jamming communications in a communications system where the communications system operates with digital bursts having burst periods measured in time and occurring in a communication frequency band such as GSM having a transmit band and a receive band. The jammer includes a tone comb generator for providing repetitions of jamming signals for the communication frequency band where the jamming signals have jamming signal intervals providing frequency separation between the jamming signals. The jamming signals are generated with a dwell time substantially less than a burst period for the communications system. The jamming signals are transmitted as RF jamming signals to jam communications for mobile stations.
Owner:AEROFLEX SYST GRP
Apparatus and method for performing time synchronization using GPS information in communication system
InactiveUS7876790B2Synchronisation information channelsTime-division multiplexTemporal informationCommunications system
Disclosed is an apparatus and a method for performing time synchronization by using Global Positioning System (GPS) information in a communication system. The apparatus comprises a grand-master node having a GPS receiver, for generating a synchronizing message required to synchronize time on slave nodes by using Time Of Day (TOD) information received from the GPS receiver and at least one slave node for receiving the synchronizing message required to synchronize time from the grand-master node or from another slave node, for carrying out time synchronization operation by using an Offset and Frequency Compensation Clock (OFCC) synchronization process supporting time offset and frequency separation compensation, and for generating a synchronizing message required to synchronize time on other slave nodes.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com