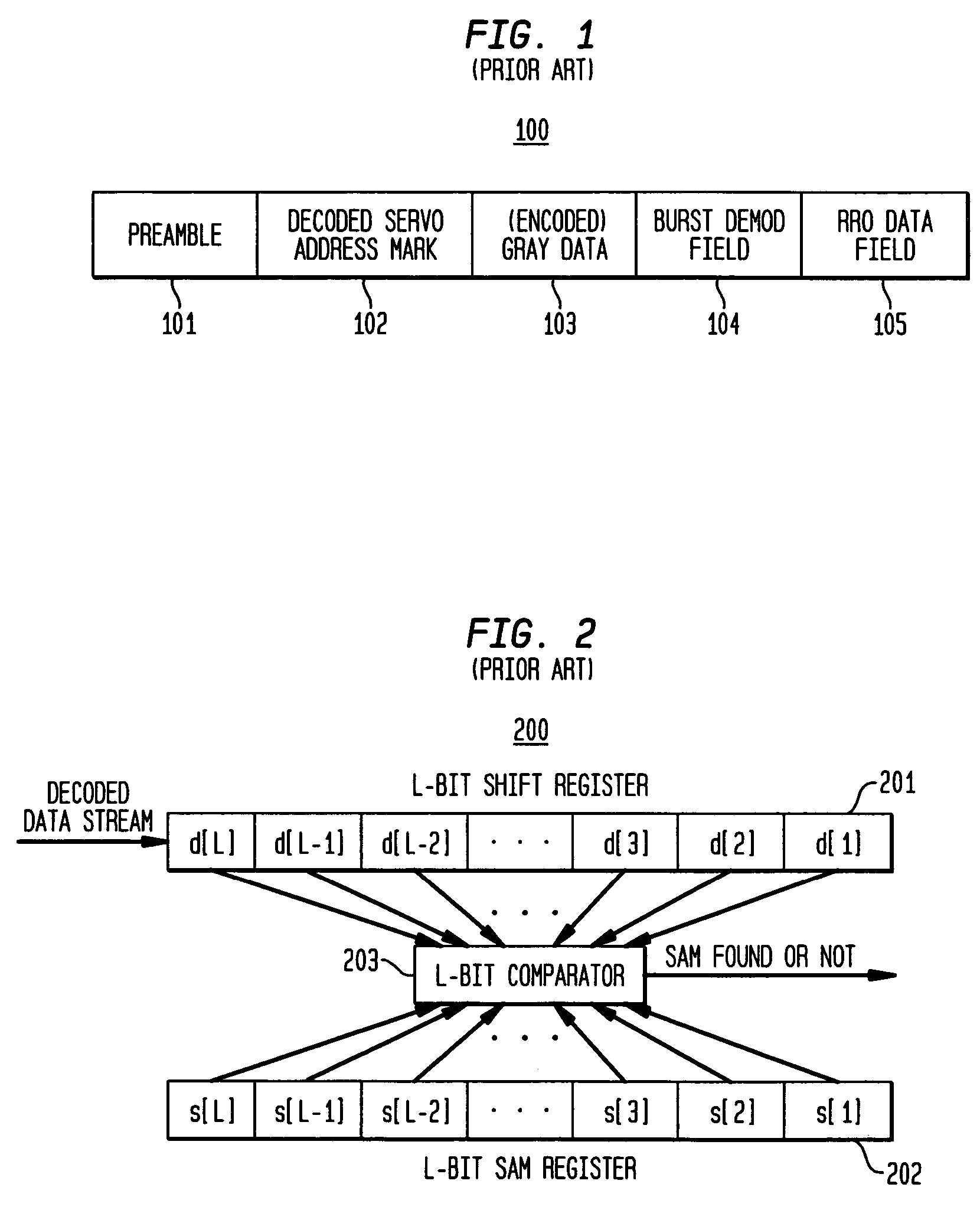
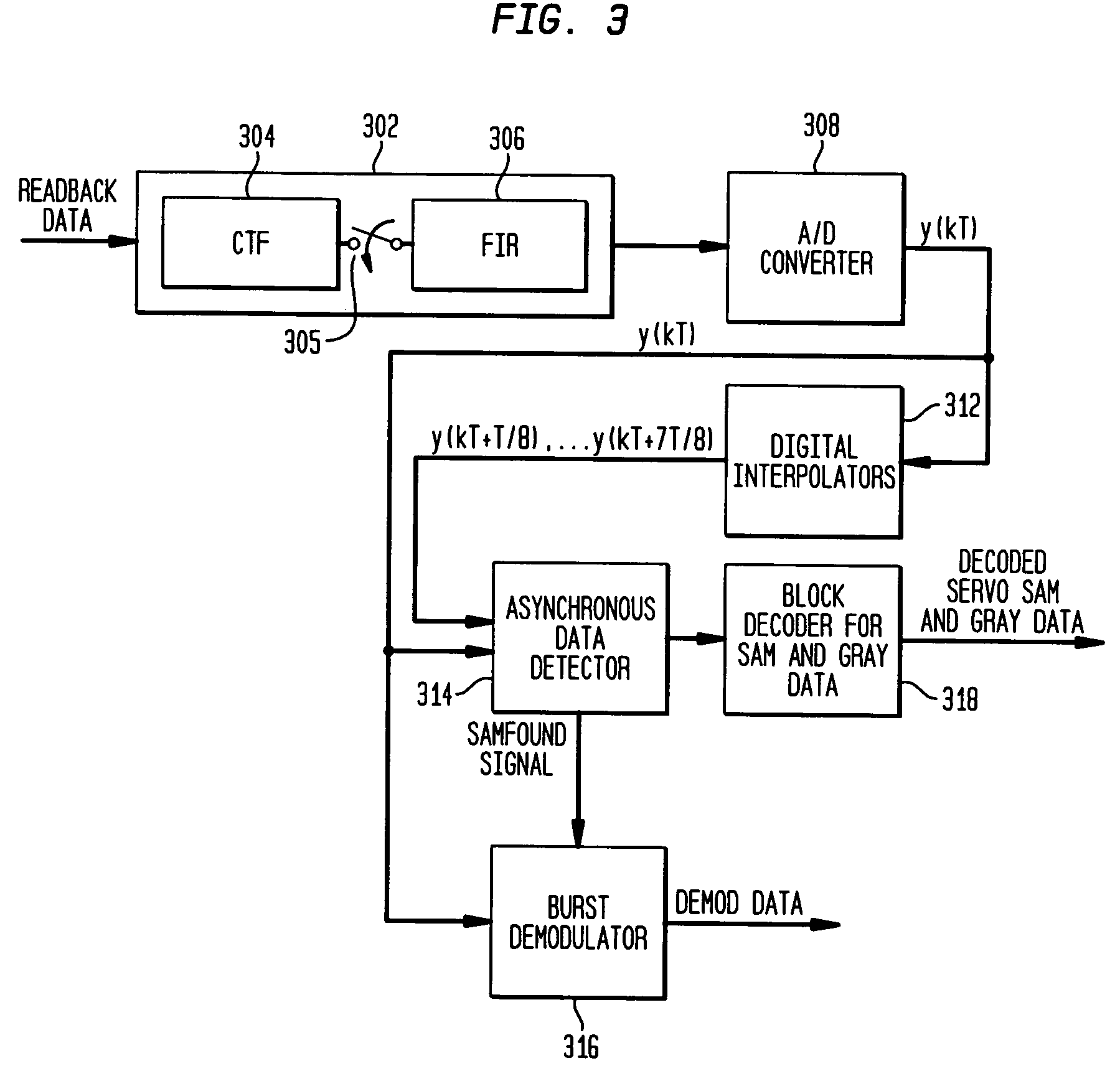
Patents
Literature
1153results about "Track finding/aligning" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
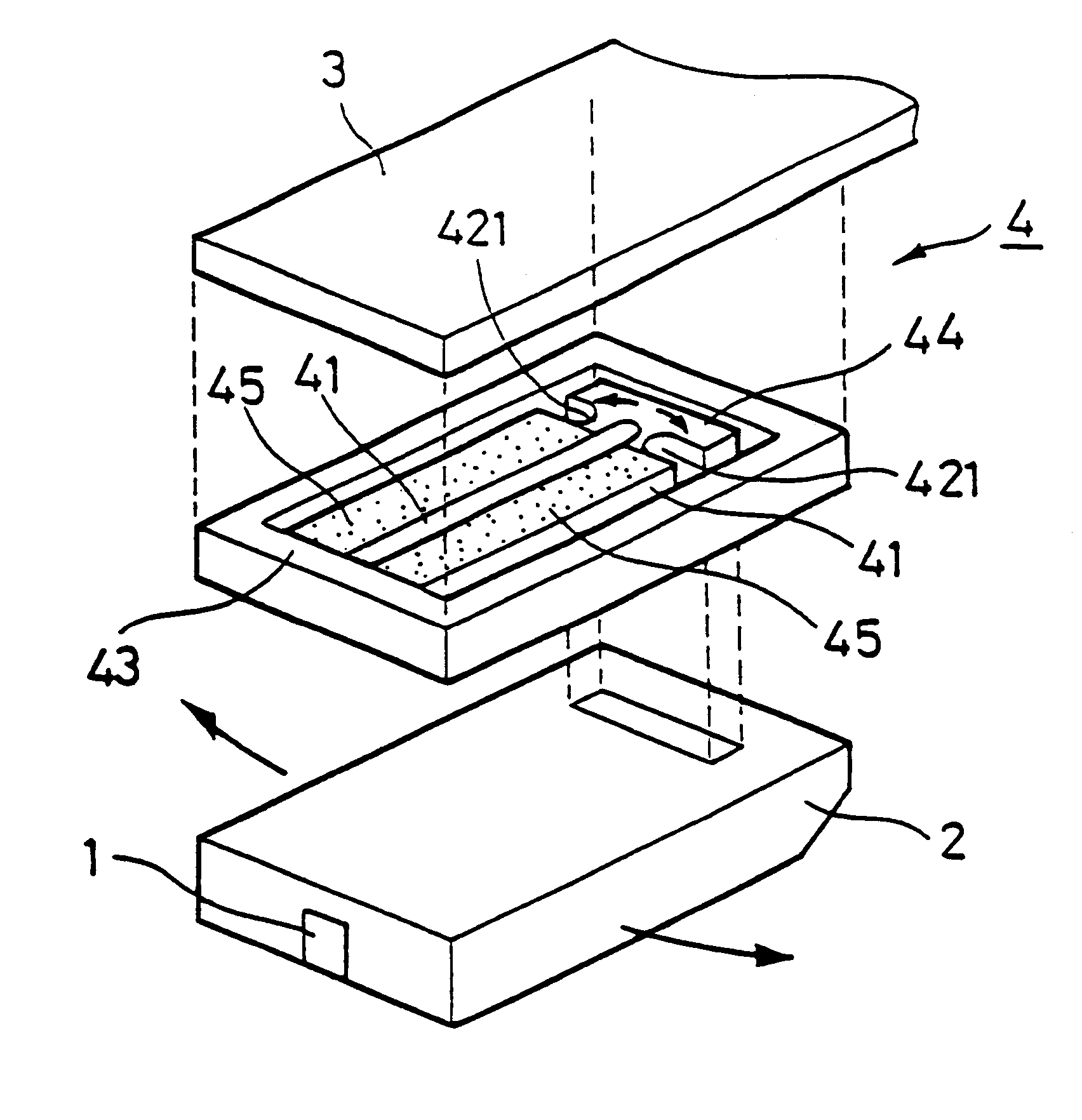
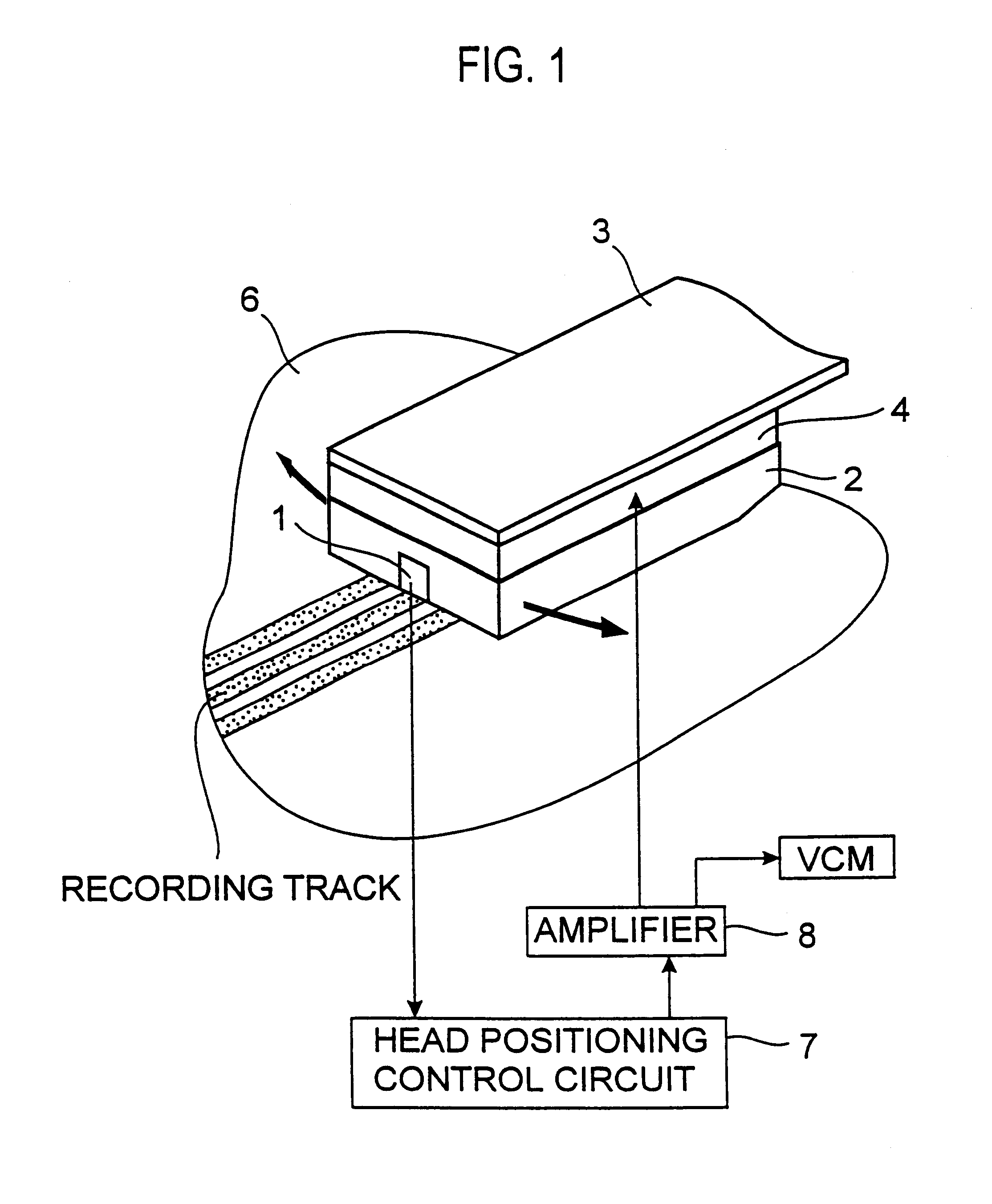
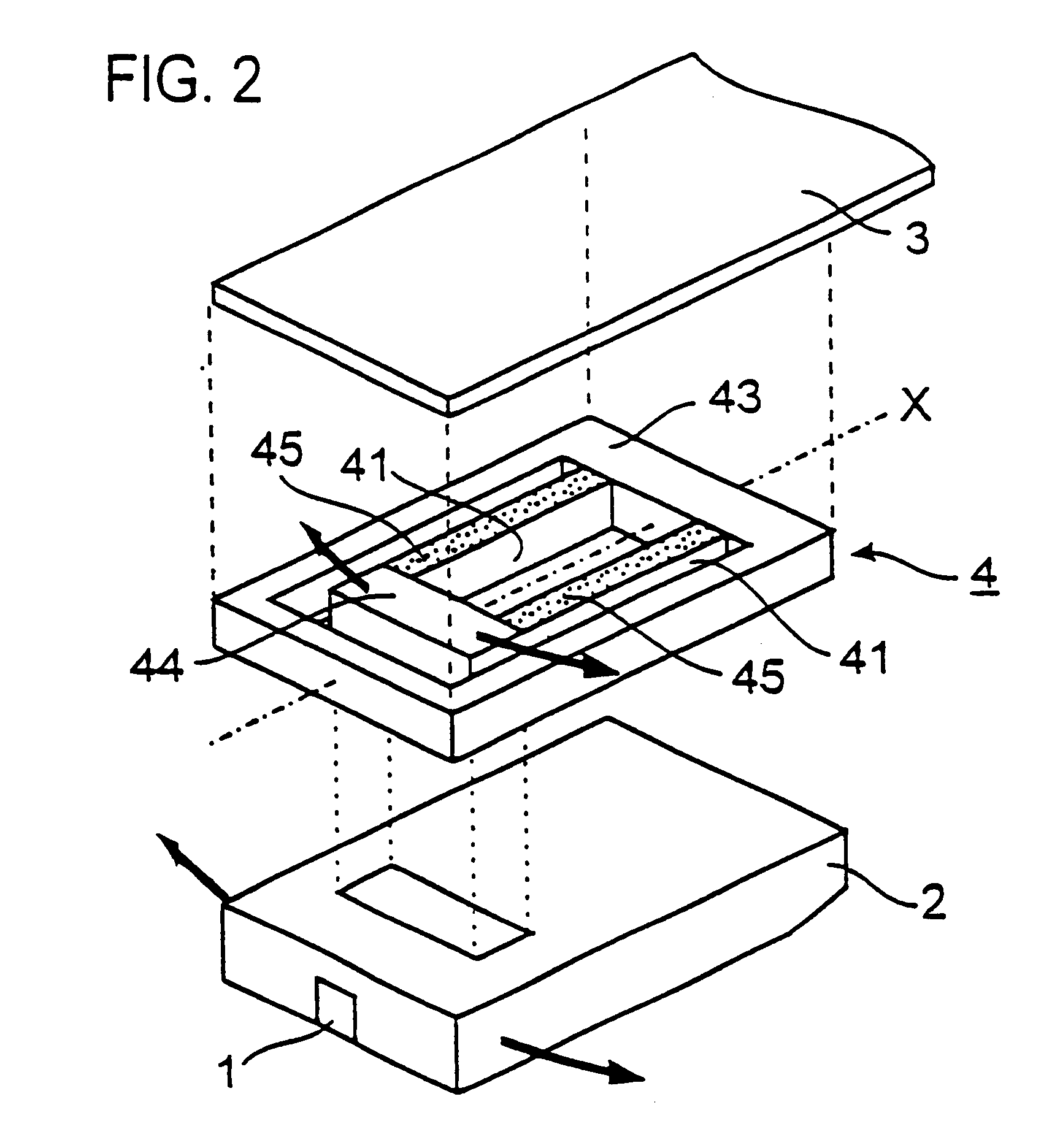
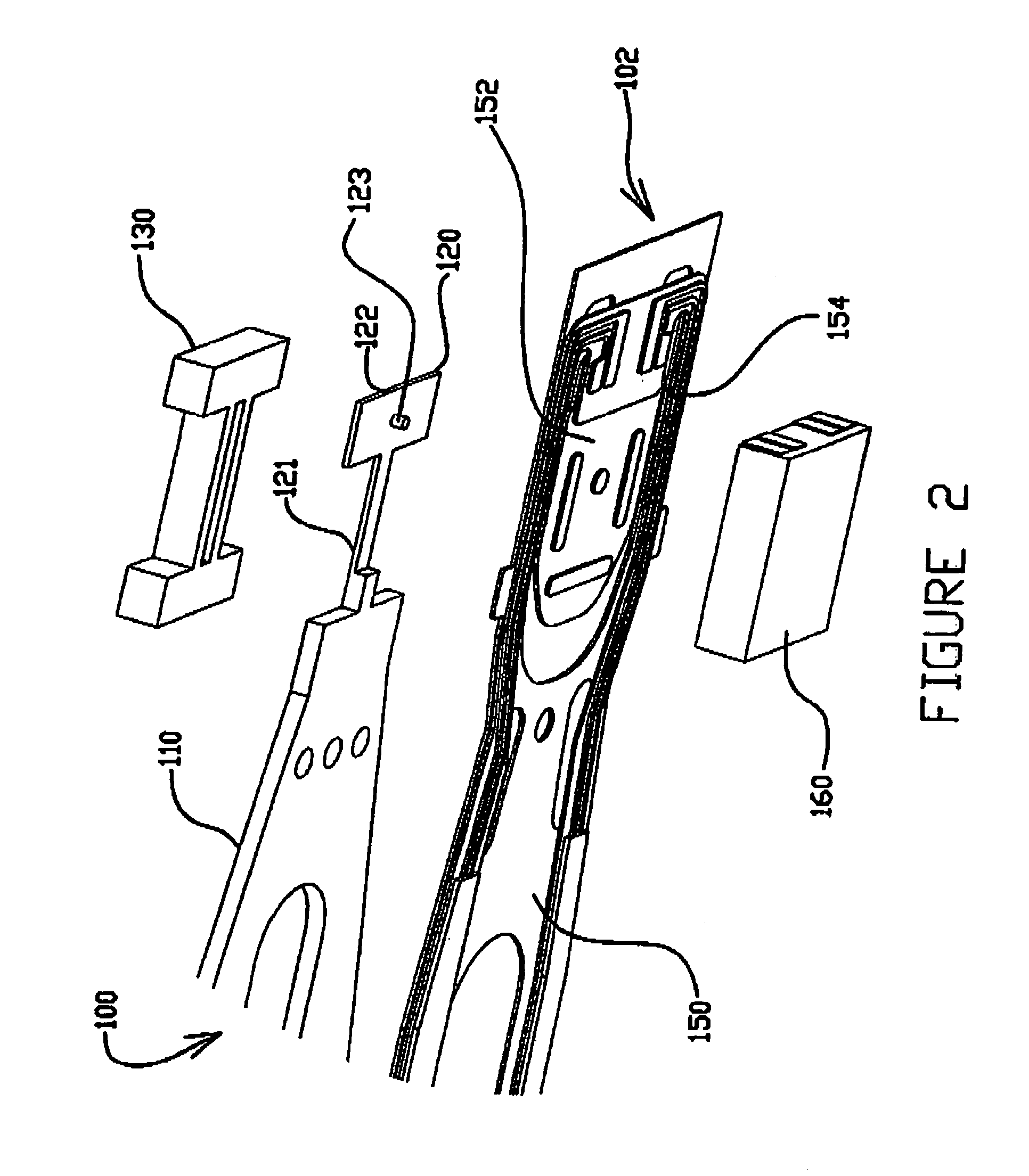
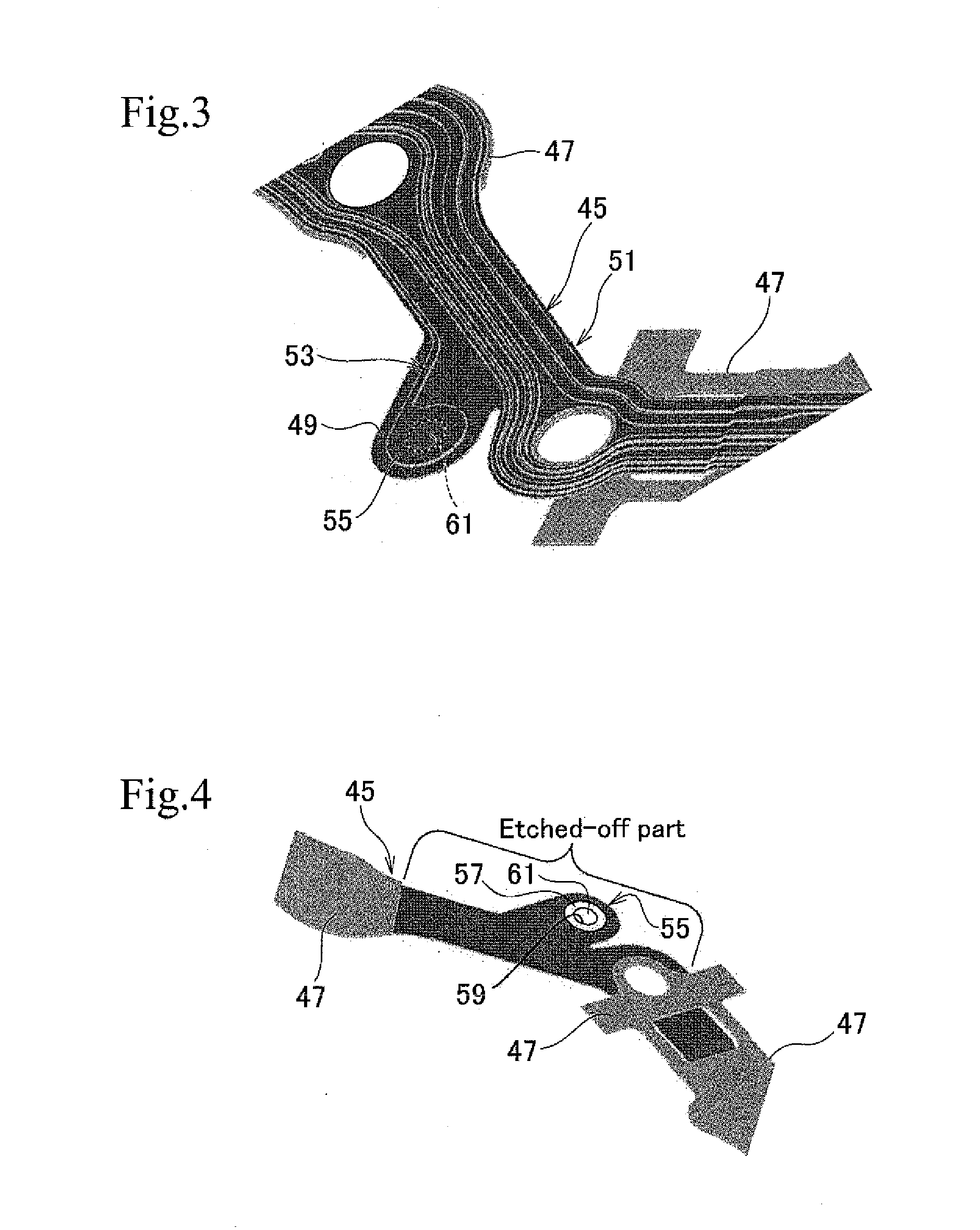
Read/write head including displacement generating means that elongates and contracts by inverse piezoelectric effect of electrostrictive effect
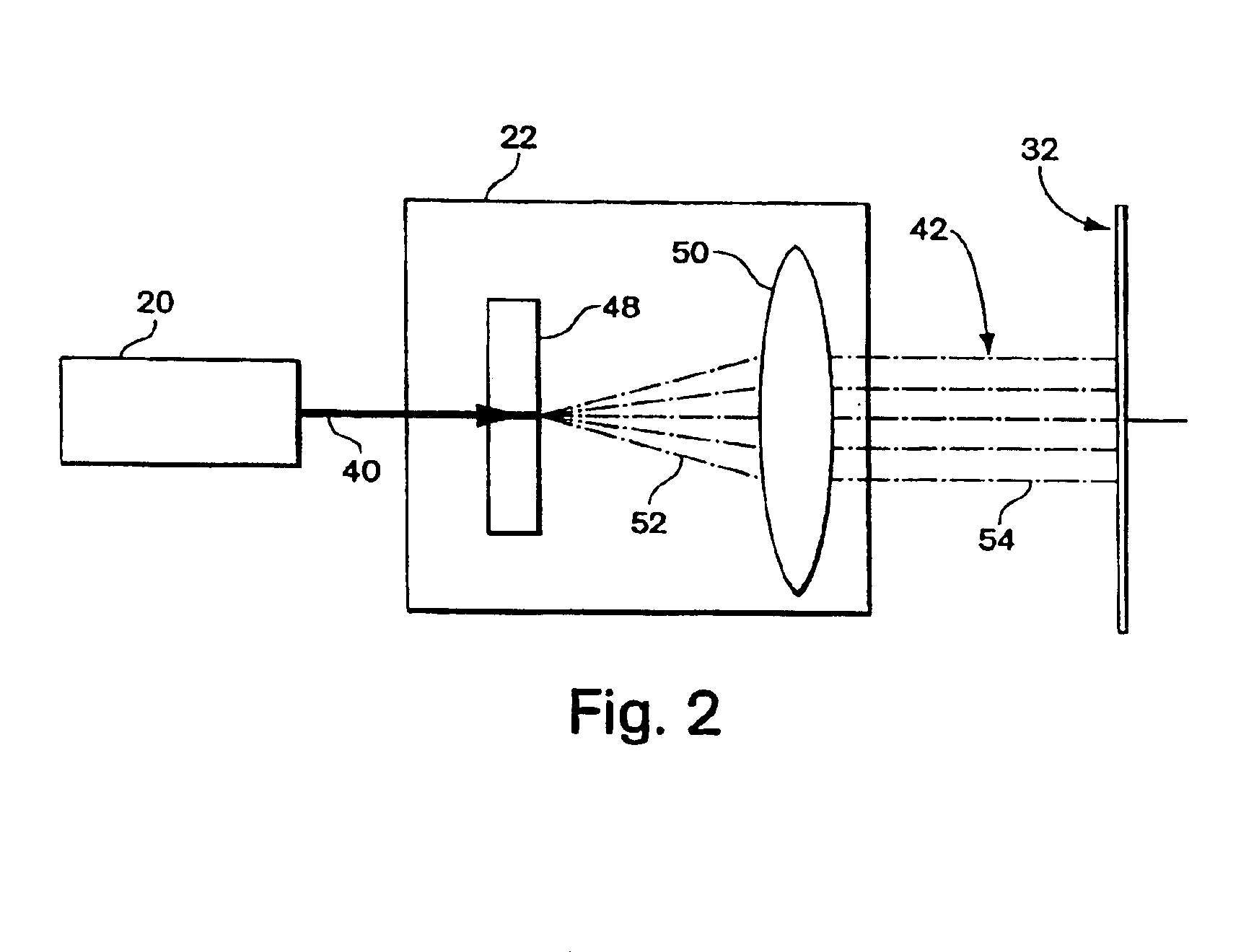
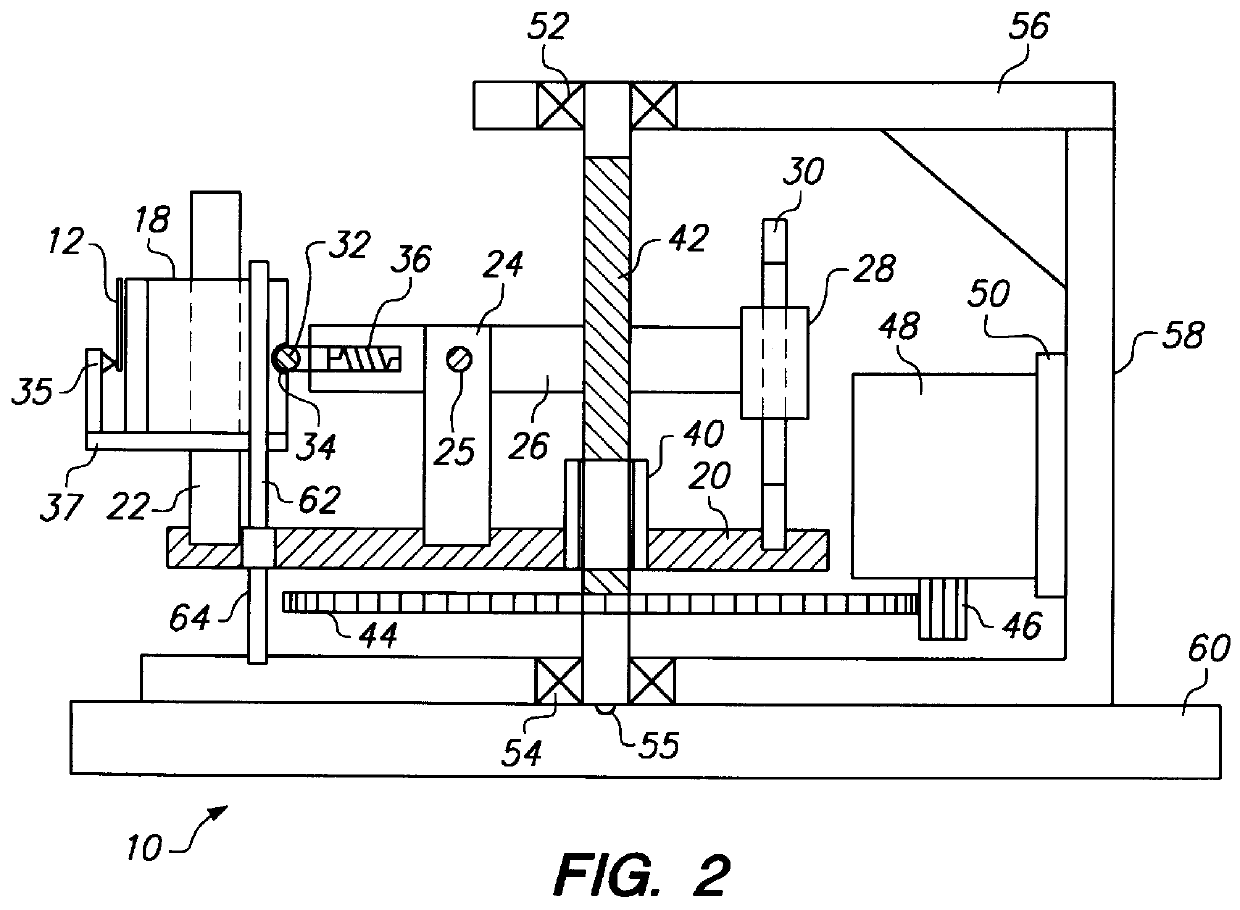
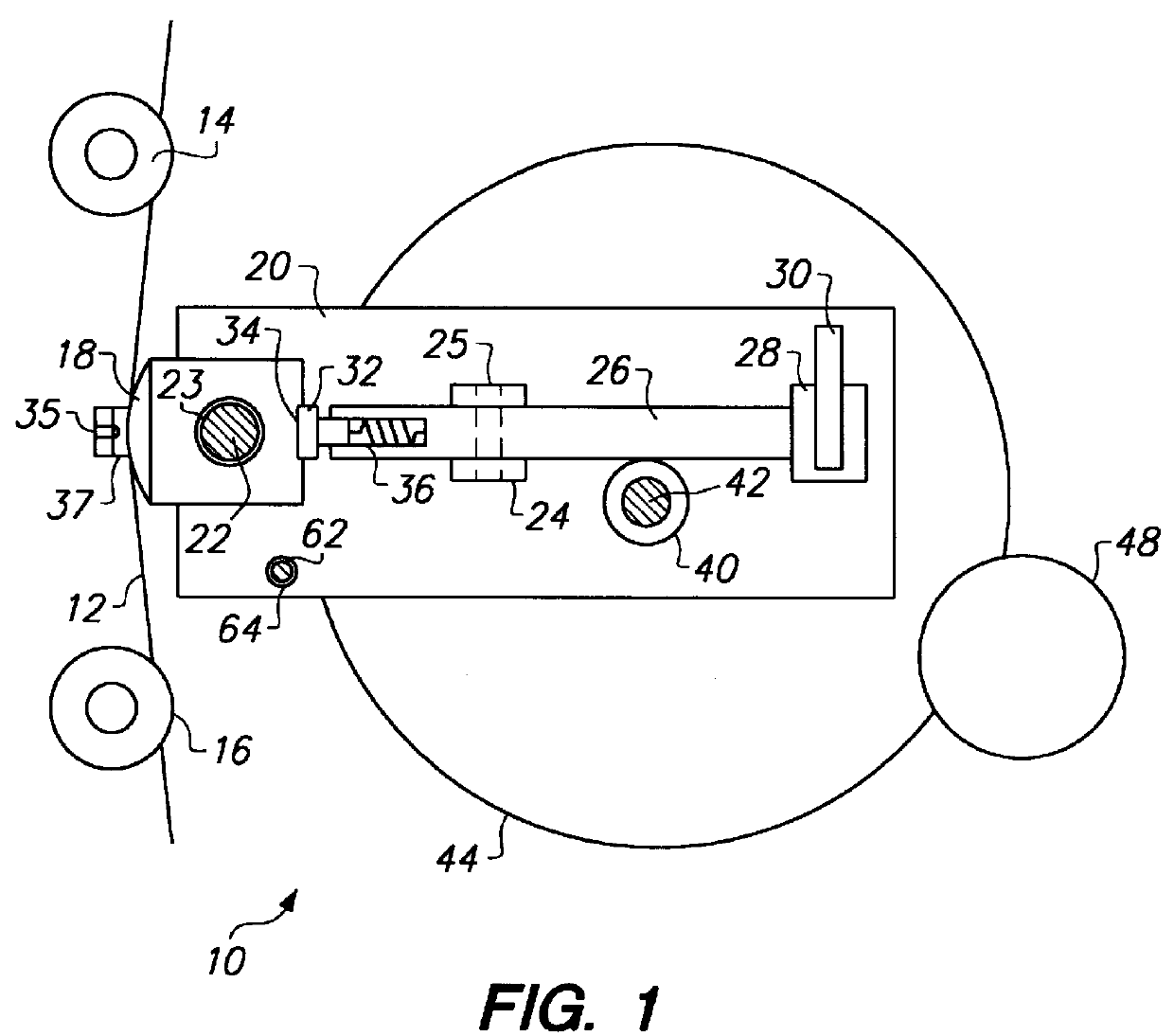
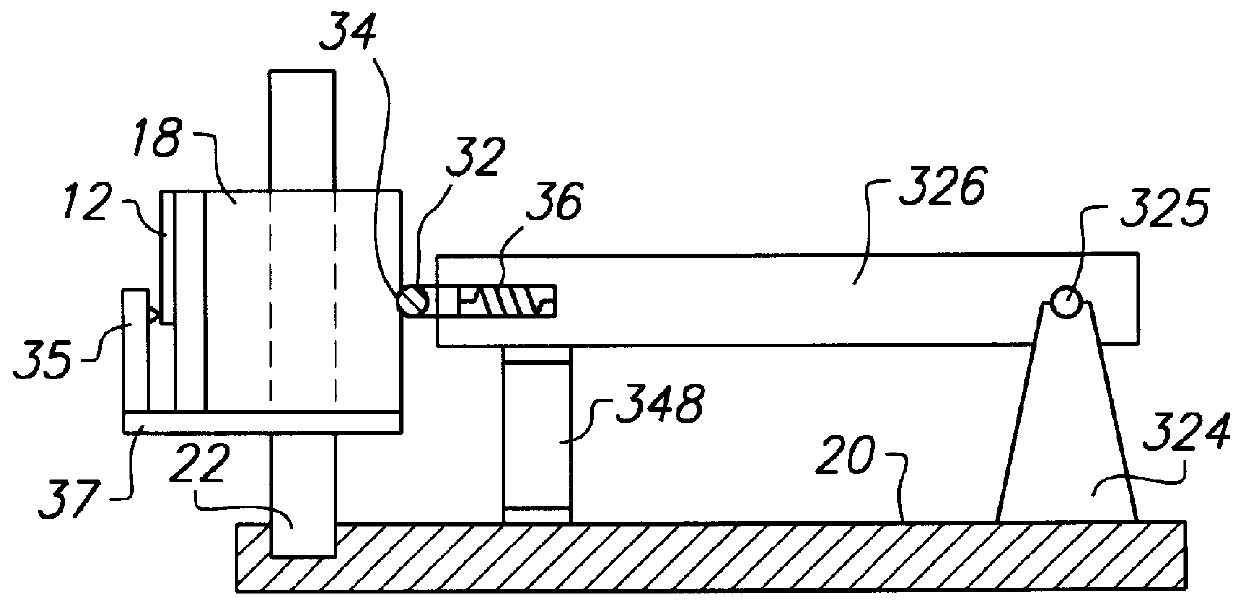
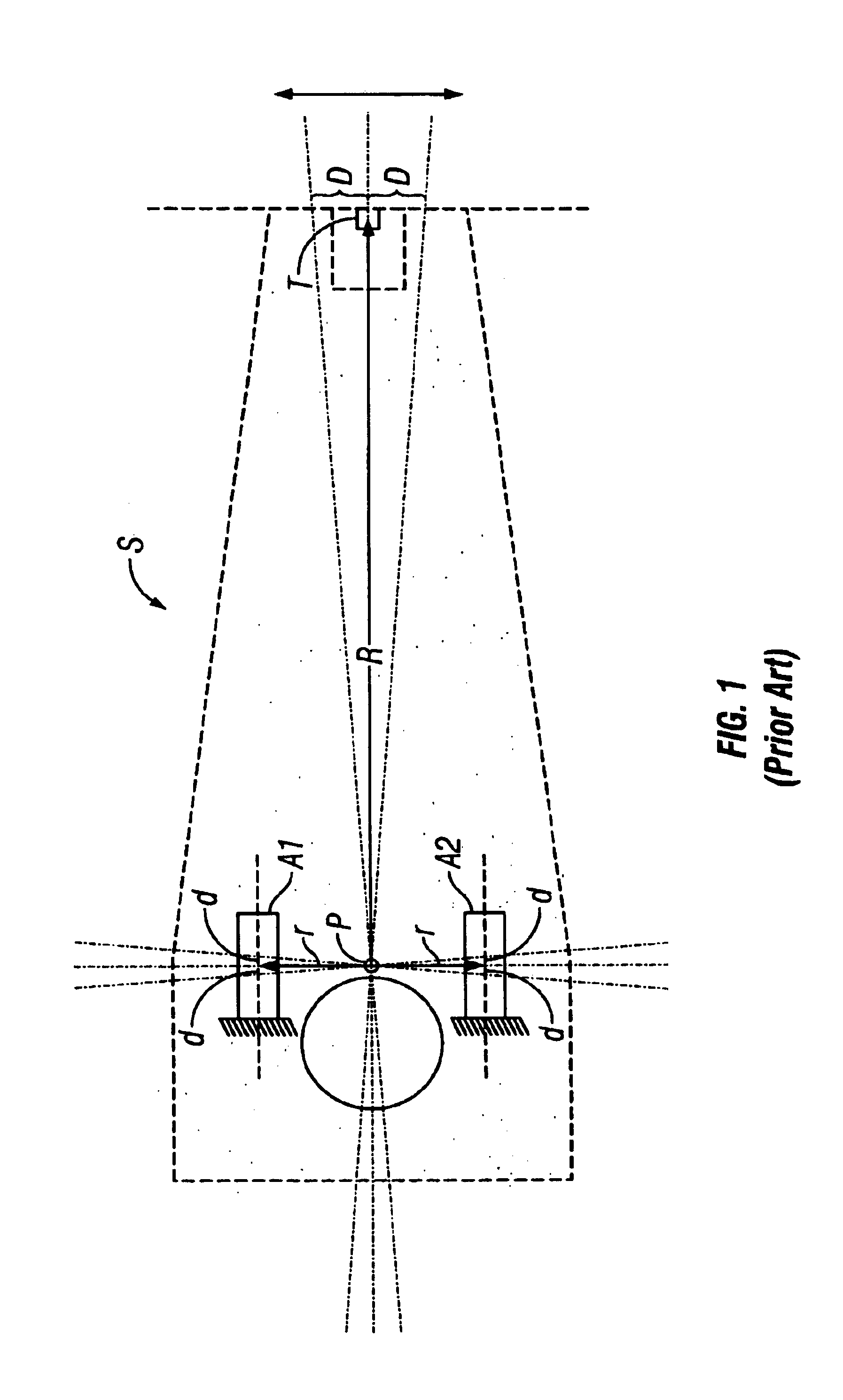
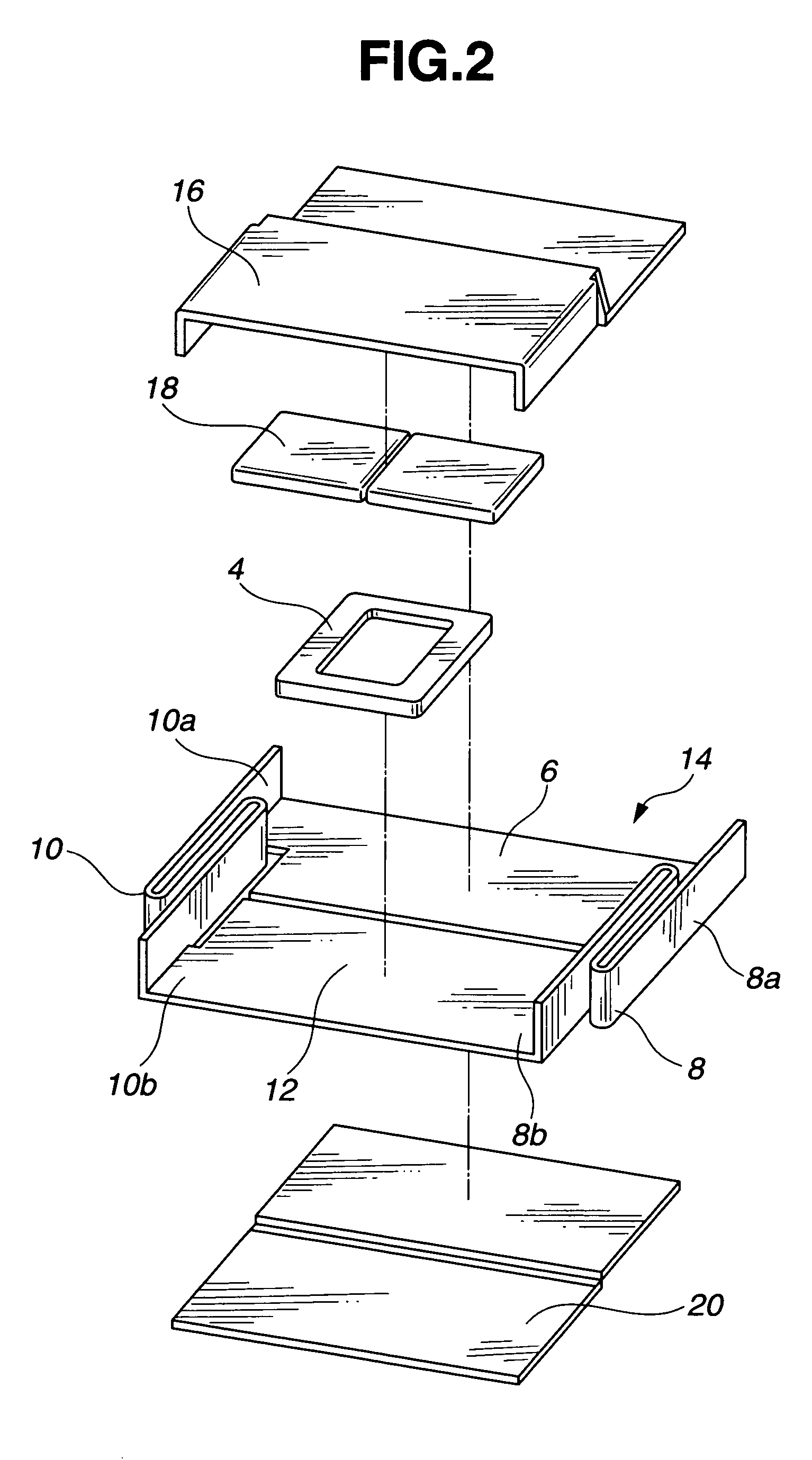
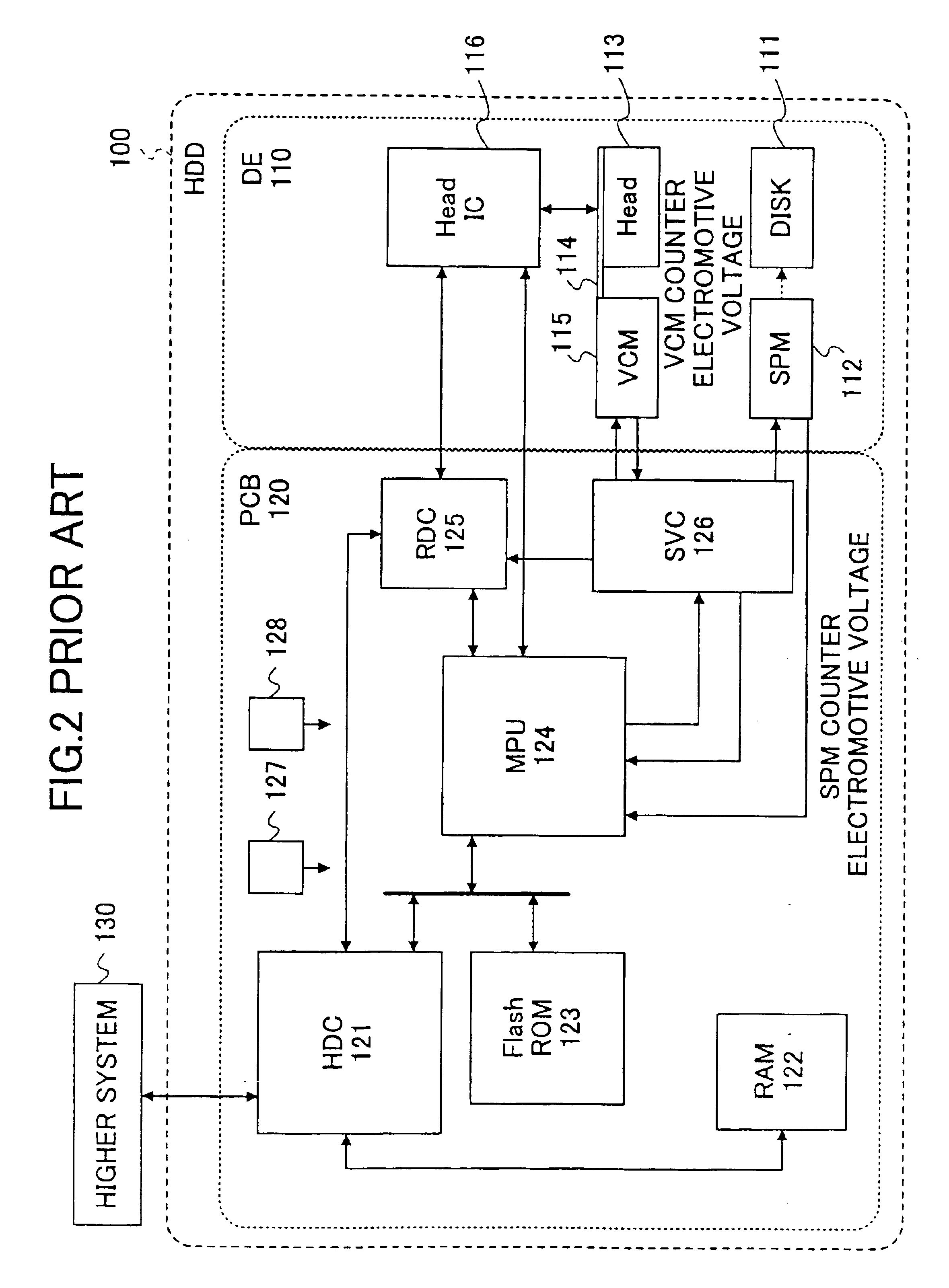
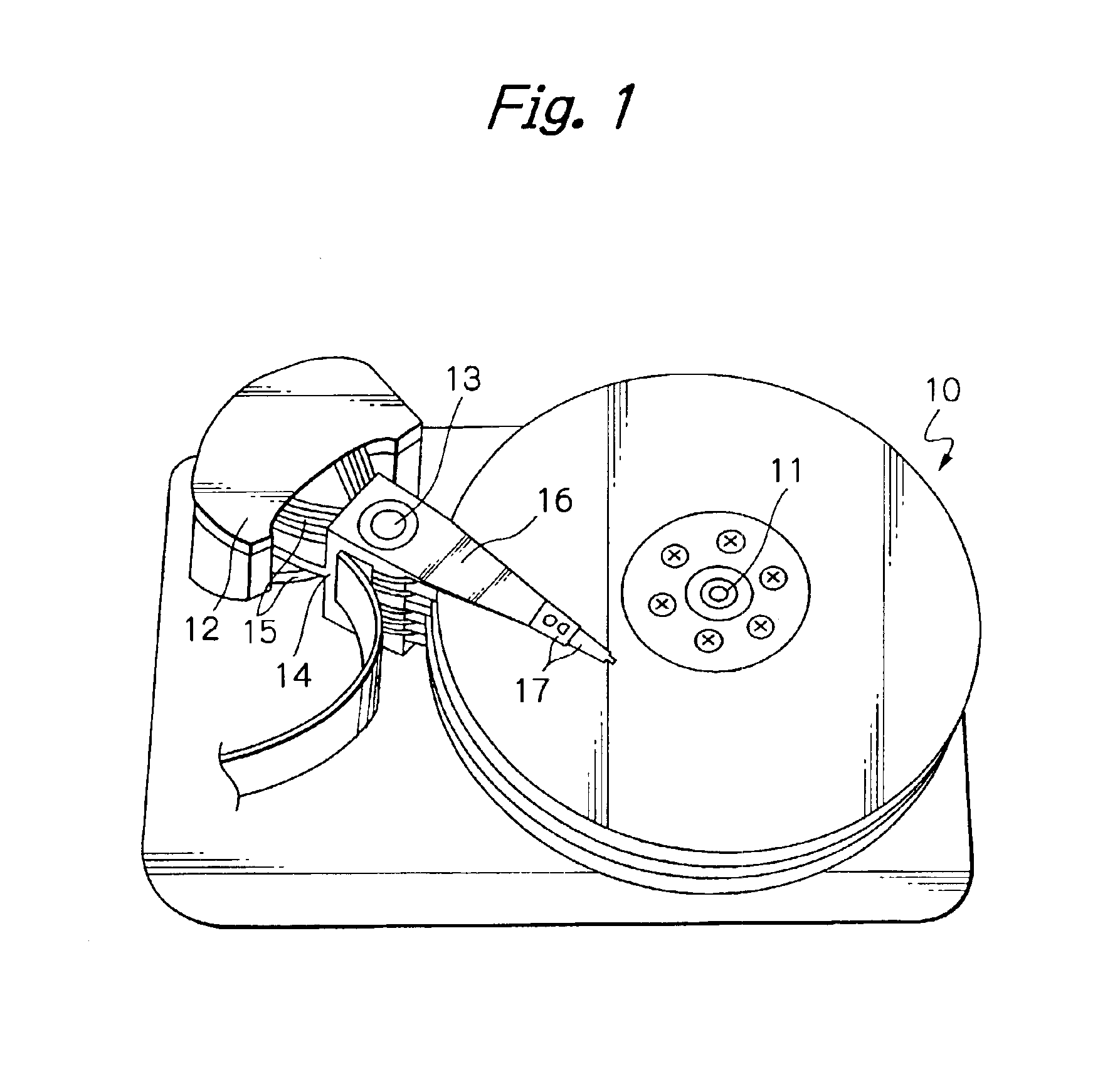
A read / write head includes a slider provided with an electromagnetic transducer element (or an optical module), an actuator, and a suspension. The actuator includes a fixed part, a movable part, and at least two beam members for coupling them together. The beam members have a displacement generating means that elongates and contracts by inverse piezoelectric effect or electrostrictive effect. The fixed part is fixed to the suspension, and the movable part is fixed to the slider. Upon the elongation and contraction of the displacement generator, the displacement generator deflects and the movable part displaces linearly, circularly or rotationally with respect to the fixed part, and the electromagnetic transducer element displaces in a linear or circular orbit, so that the electromagnetic transducer element intersects recording tracks. In the actuator, the fixed part, movable part and beam members are formed as an integrated single piece by providing a hole and / or a cutout in a sheet-like member constructed of a piezoelectric or electrostrictive material. The actuator of the structure illustrated is used for the positioning of a direction intersecting recording tracks. In this case, the total sum of voltages applied on the displacement generating means is controlled in such a manner that it is constant at any time, thereby controlling position fluctuations of the electromagnetic transducer element in the direction vertical to the recording medium surface.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
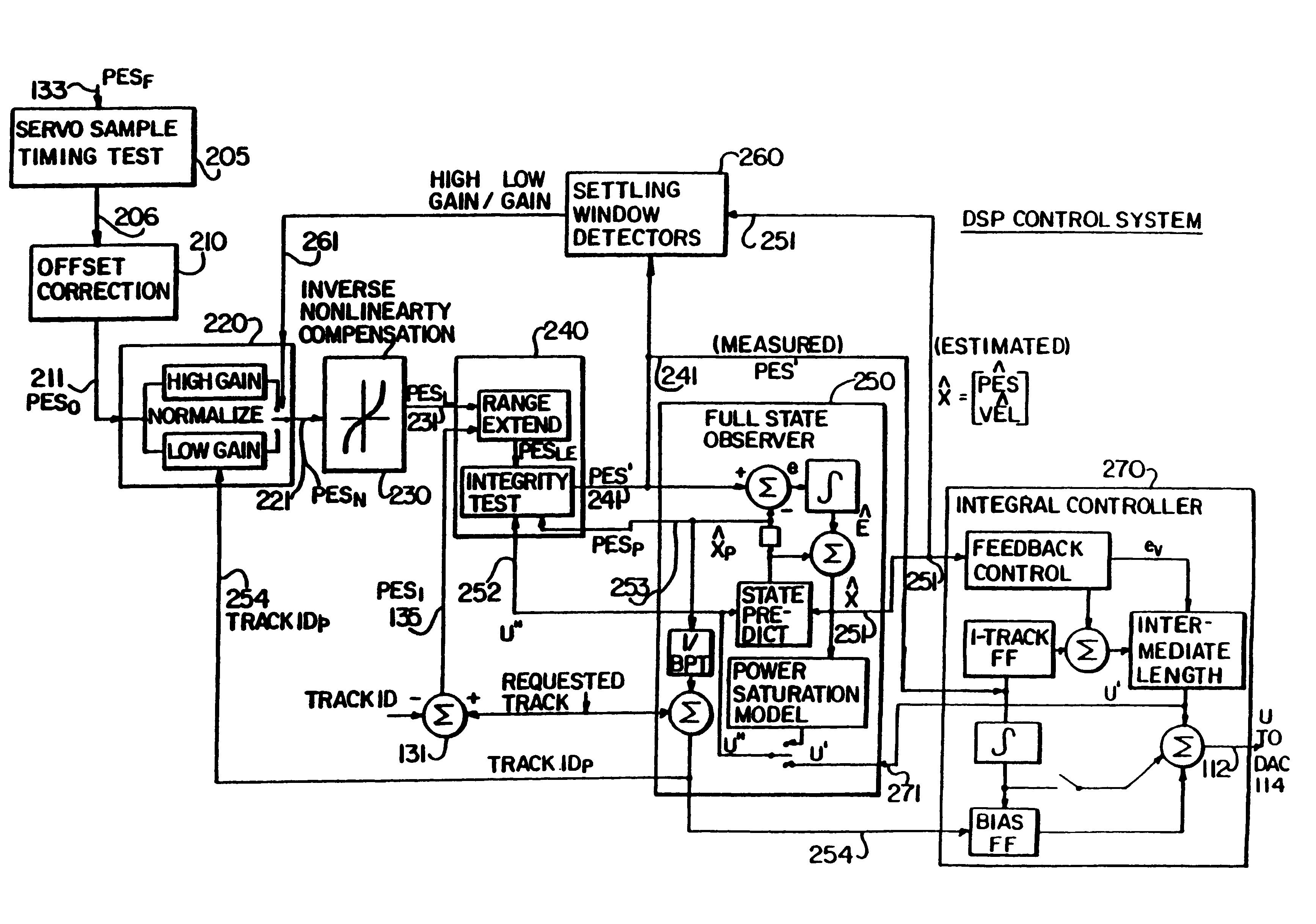
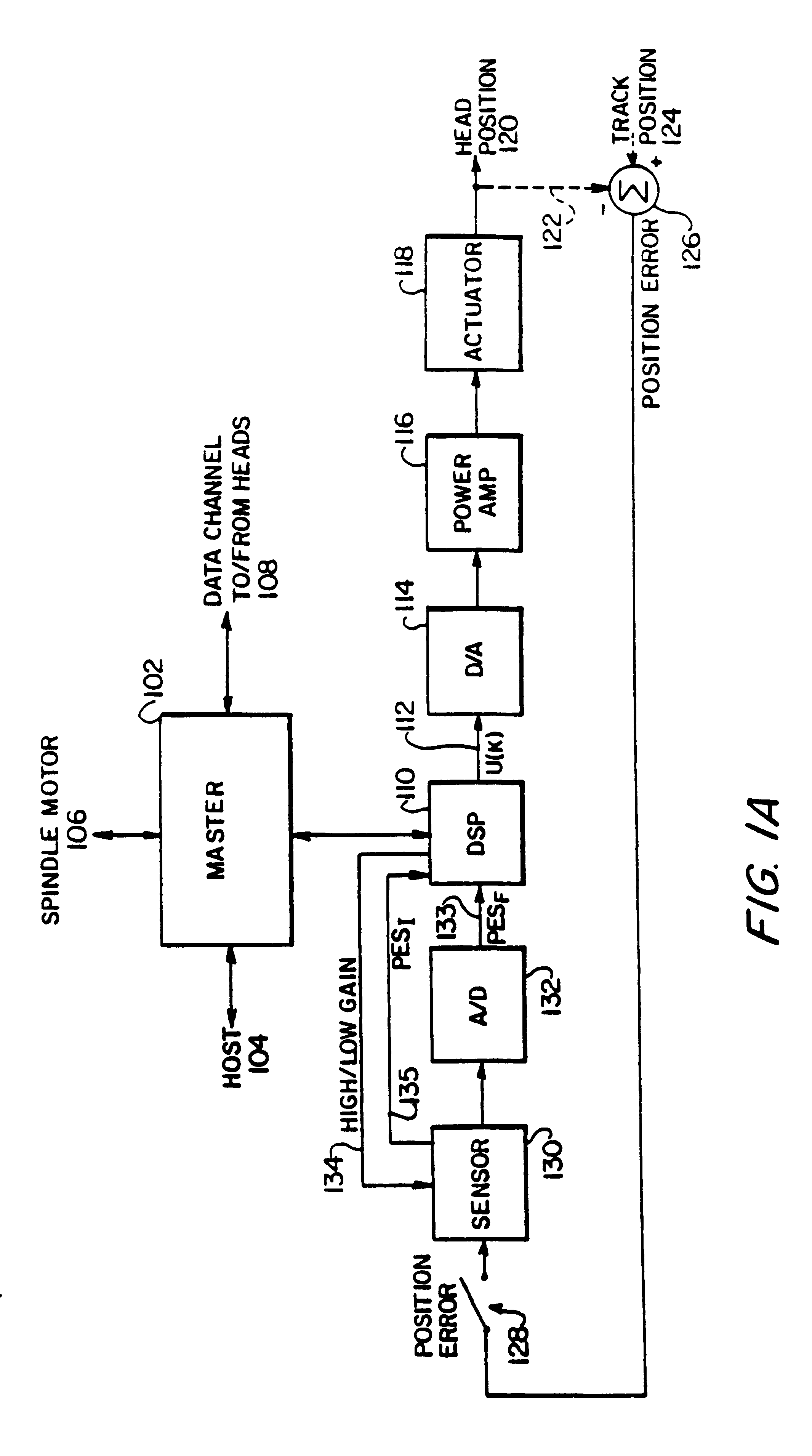
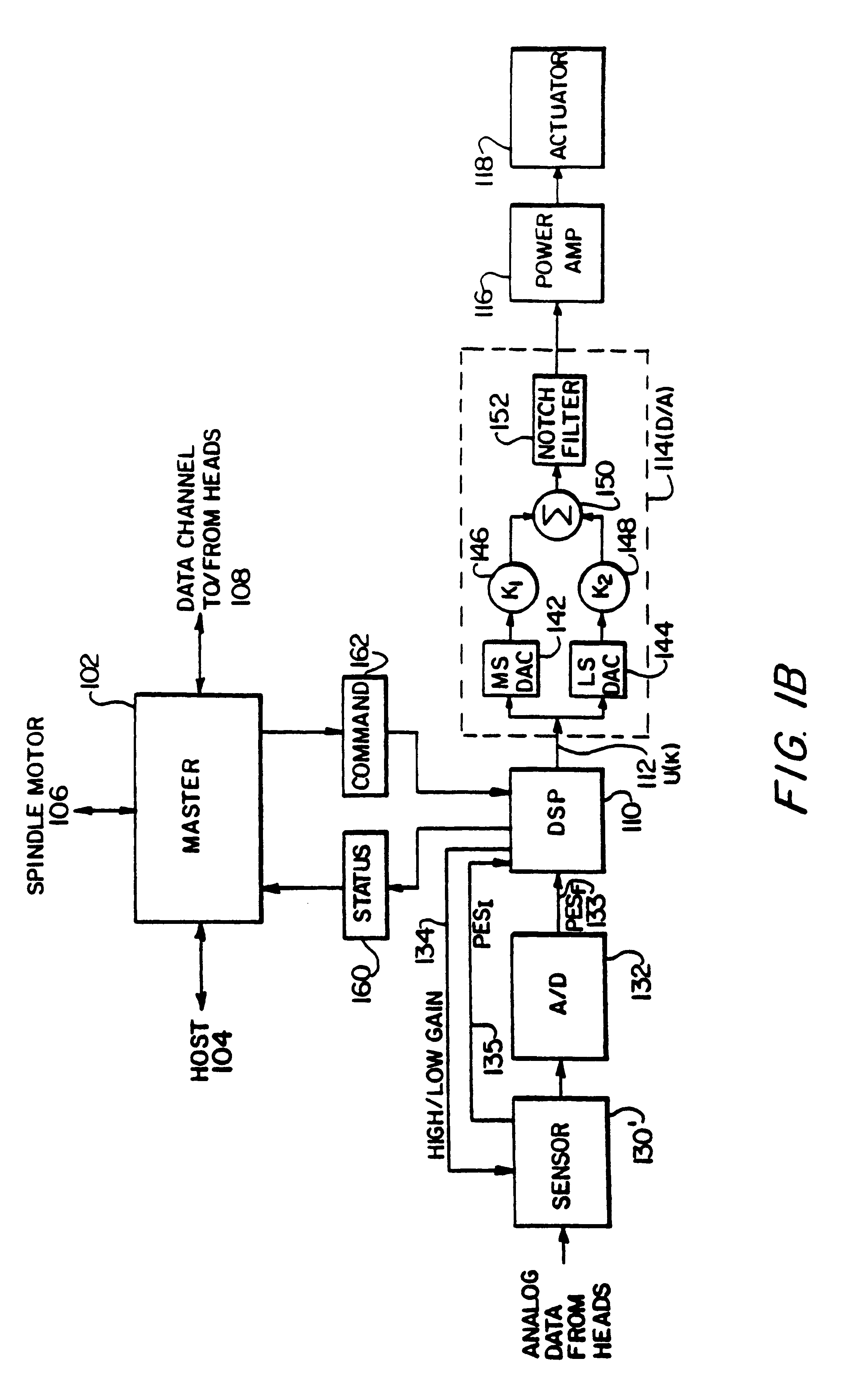
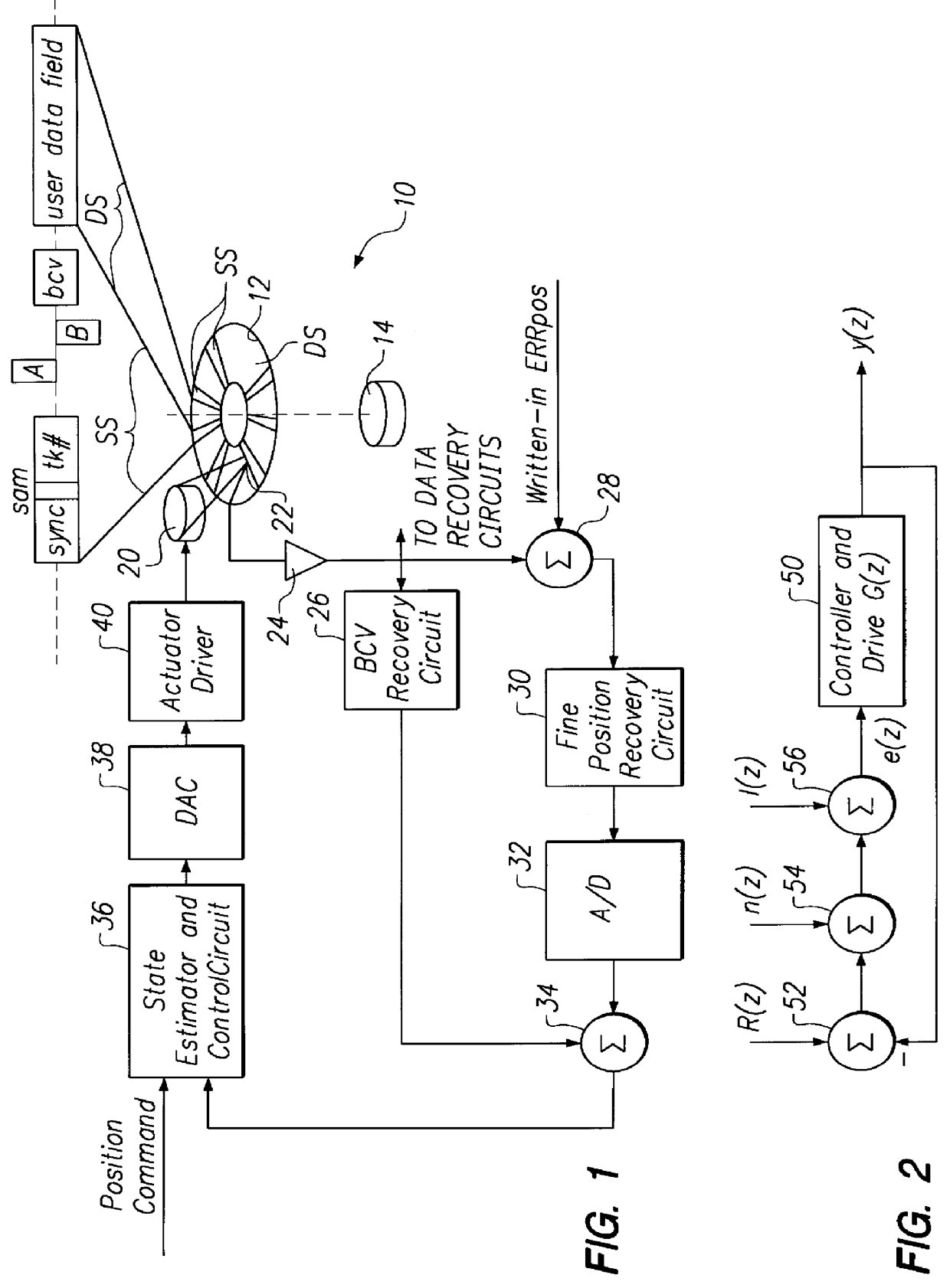
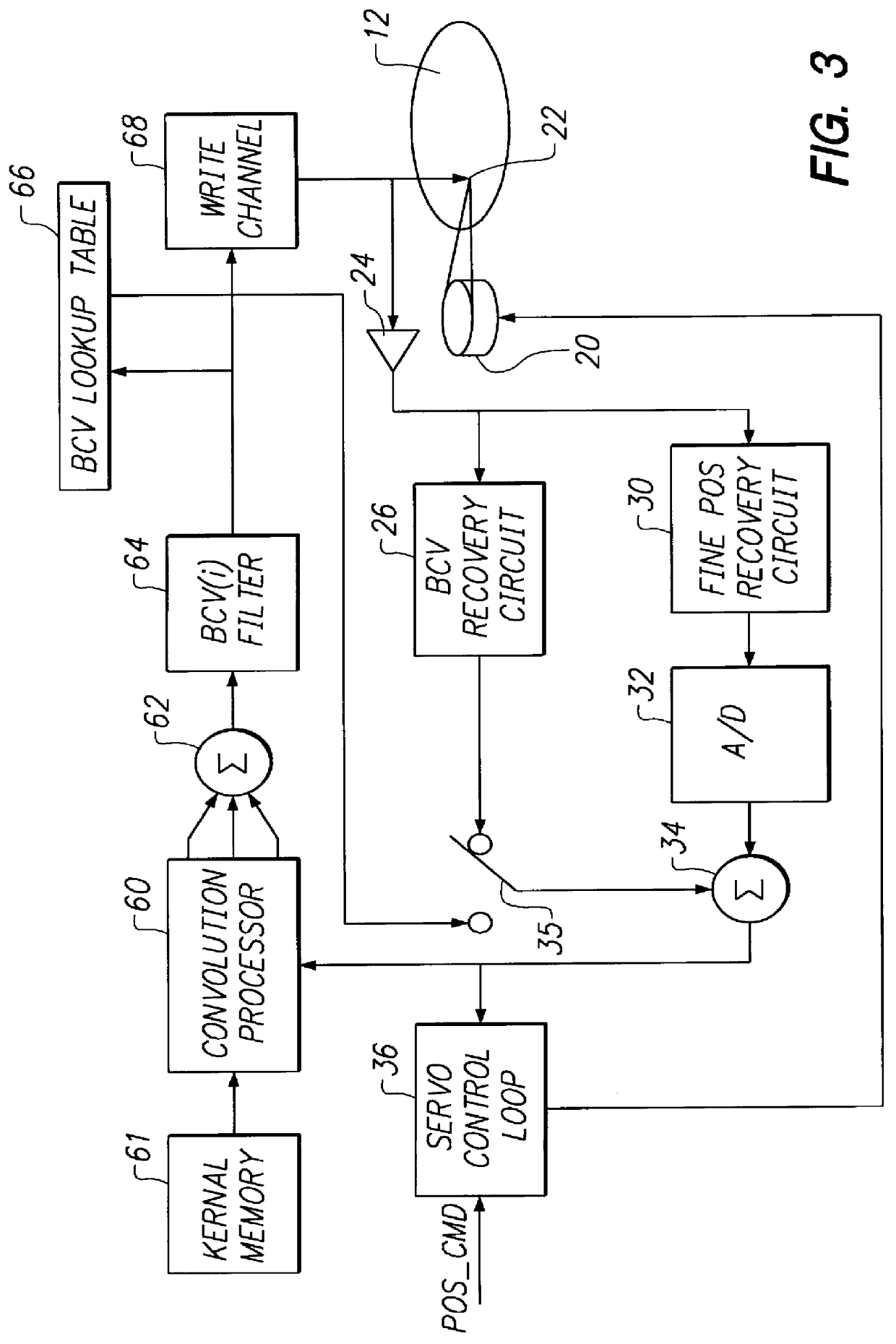
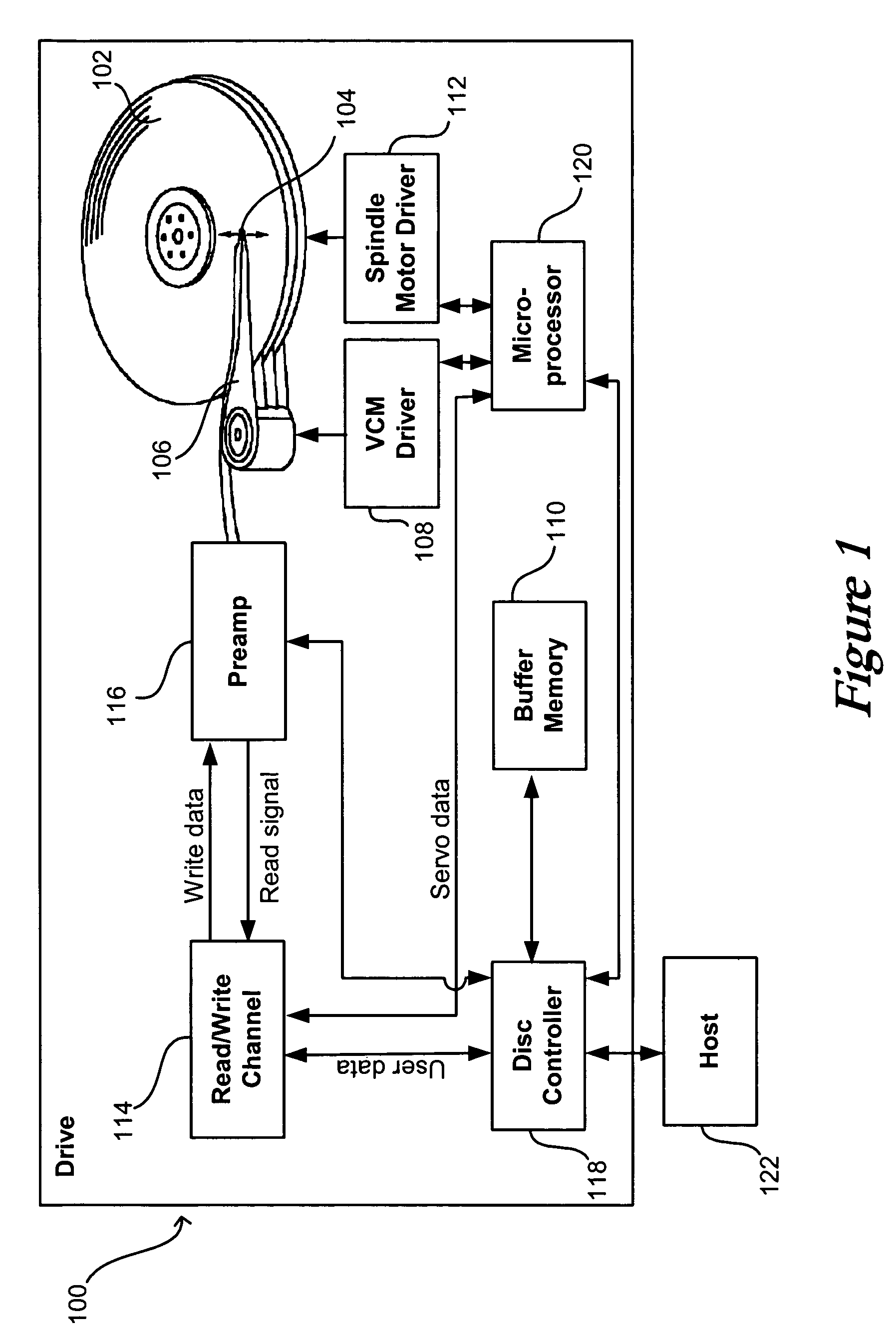
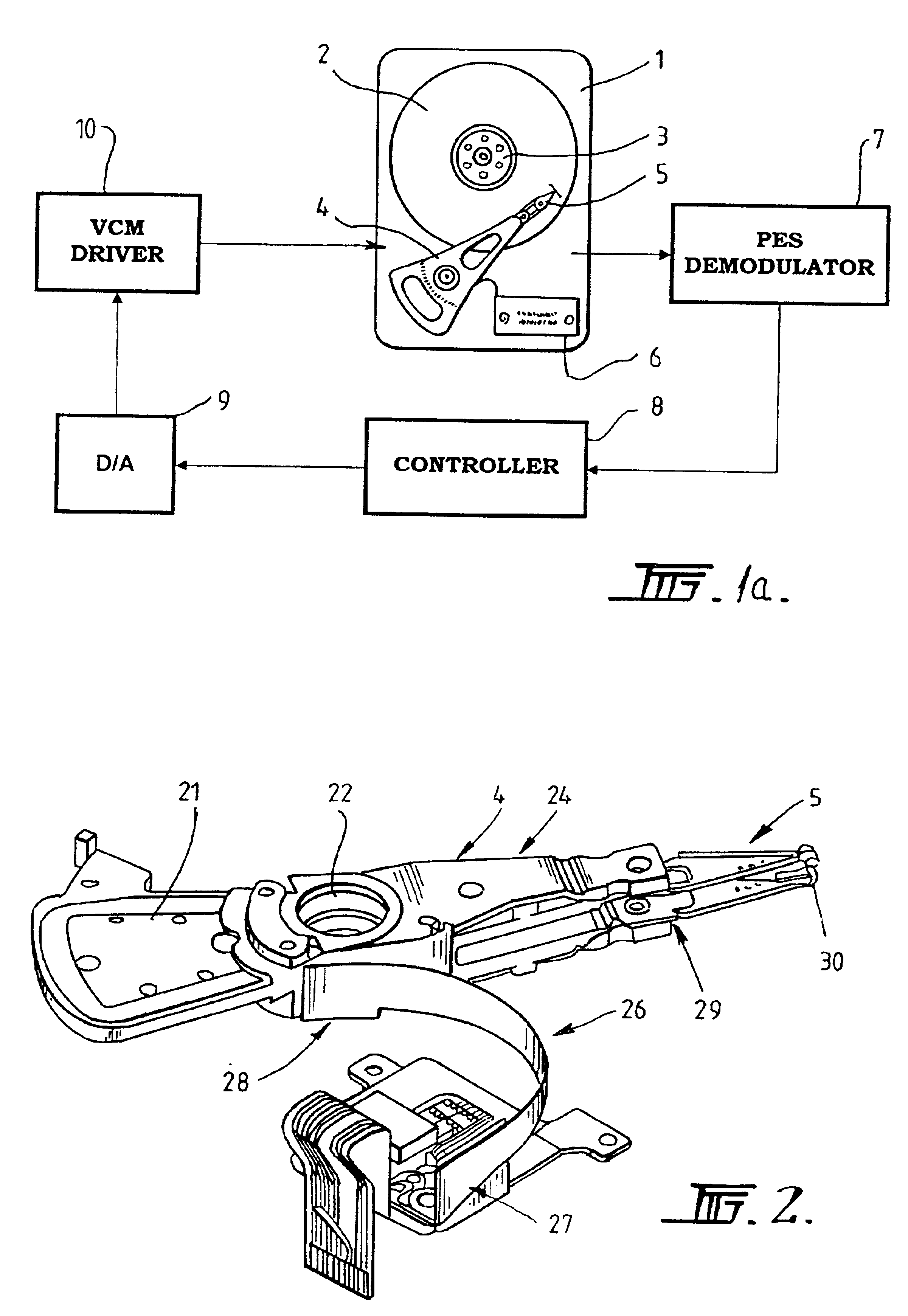
Digital servo control system for use in disk drives
InactiveUS6347018B1Stable trackingSeek efficiencyTrack finding/aligningRecord information storagePretreatment methodControl theory
A digital servo control system for disk drives is an "embedded" system-one in which servo control information is embedded on the same disk surface as the user data. In contrast to known embedded-servo systems in which a space-consuming series of many dibit pairs is present, the present system provides only a single dibit pair in a fractional positional error (PESF) area. Thus, the disk drive's read head encounters only a single dibit pair per sample period (or per data sector), thus saving valuable disk space that may be used for user data. Various pre-processing methods may be provided so as to pre-process the measurement derived from the single dibit pair per sample period (or data sector), so as to compensate for non-ideal characteristics of the dibit measurement. The system thus provides an accurate and robust servo control system, while sacrificing a minimum amount of valuable disk space to the servo information field.
Owner:MAXTOR +1
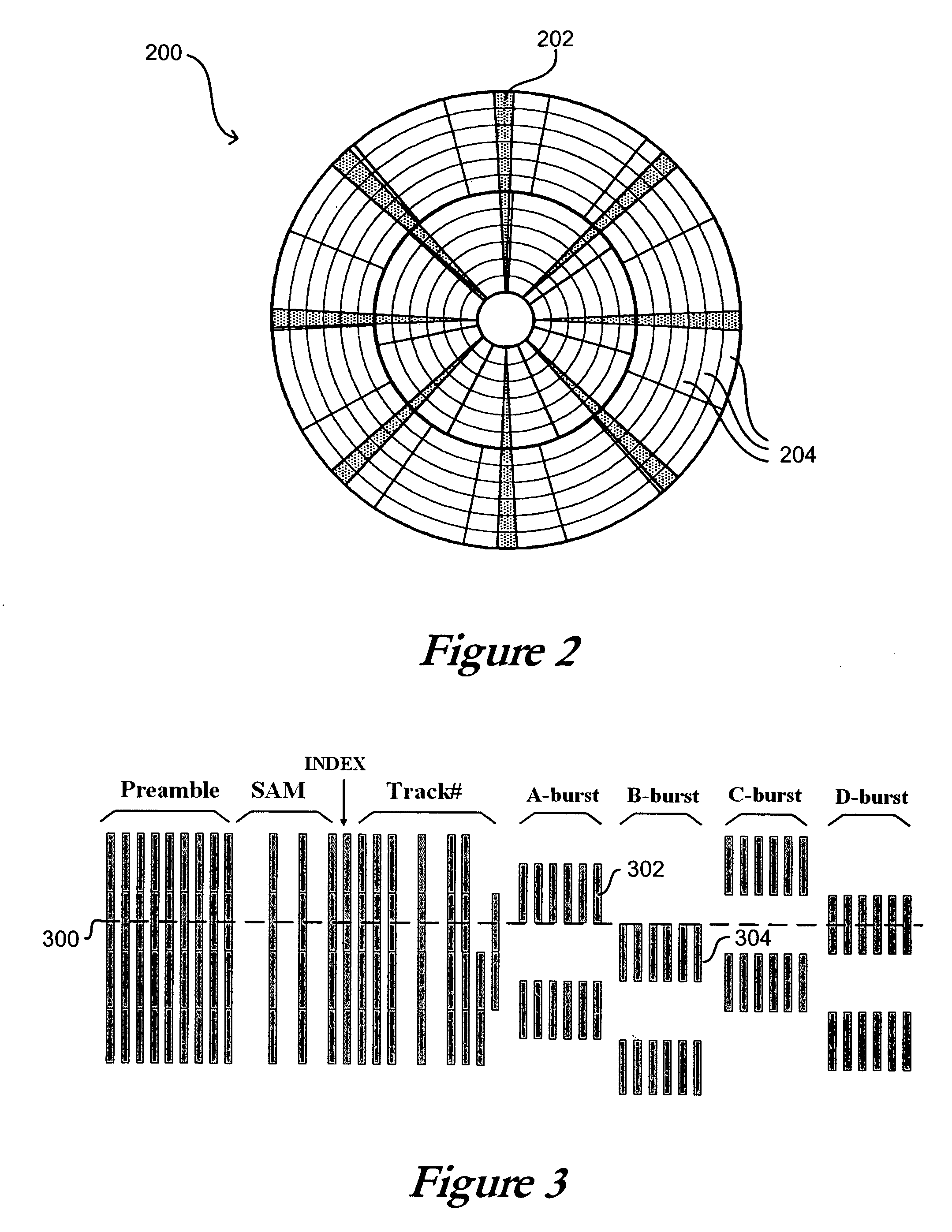
Method for forming a servo pattern on a magnetic tape
InactiveUS7029726B1Maintain alignmentTrack finding/aligningRadiation applicationsMagnetic tapeControl theory
The systems, methods and products of the invention include systems and methods for manufacturing servo tracks on a magnetic tape. In one aspect, the invention includes systems for manufacturing magnetic tapes having servo tracks thereon wherein the servo tracks are optically detectable and are capable of being processed by a servo control system for maintaining alignment of a magnetic recording head with the data tracks on the recording side of the magnetic tape. In one practice, the manufacturing systems described herein engrave the servo tracks onto the non-recording side of a magnetic tape by directing a laser beam at the non-recording side of the magnetic tape. In another practice, the manufacturing systems described herein engrave the servo tracks onto the magnetic side of a magnetic tape by directing a laser beam at the magnetic side of the magnetic tape. Such engraved patterns can act as optical servo tracks for maintaining alignment of the recording head with the data tracks on the magnetic tape.
Owner:QUANTUM CORP
Recording medium including patterned tracks and isolation regions
InactiveUS6977108B2Easy to manufactureIncrease speedTrack finding/aligningMagnetic materials for record carriersEngineeringRecording layer
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
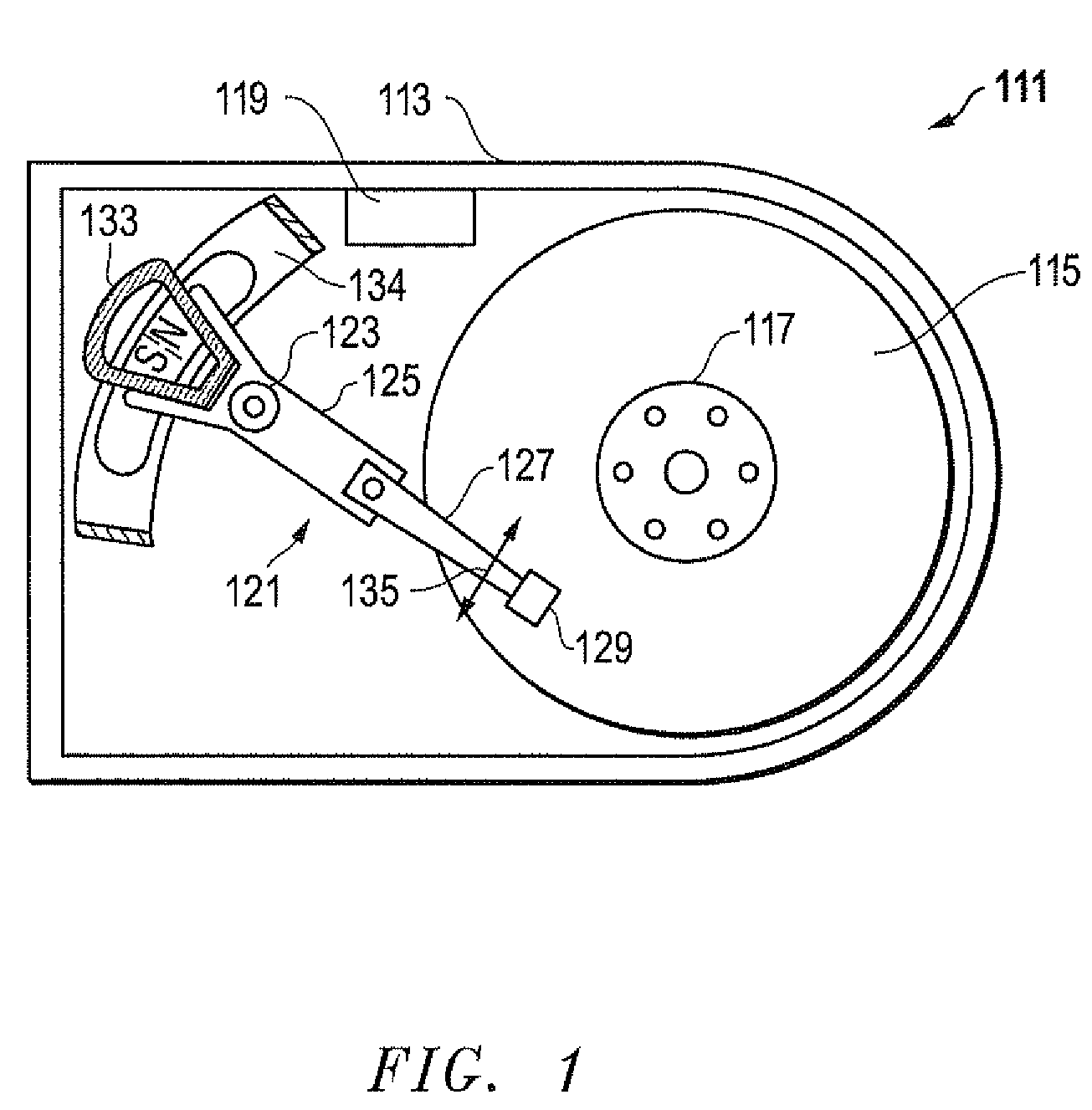
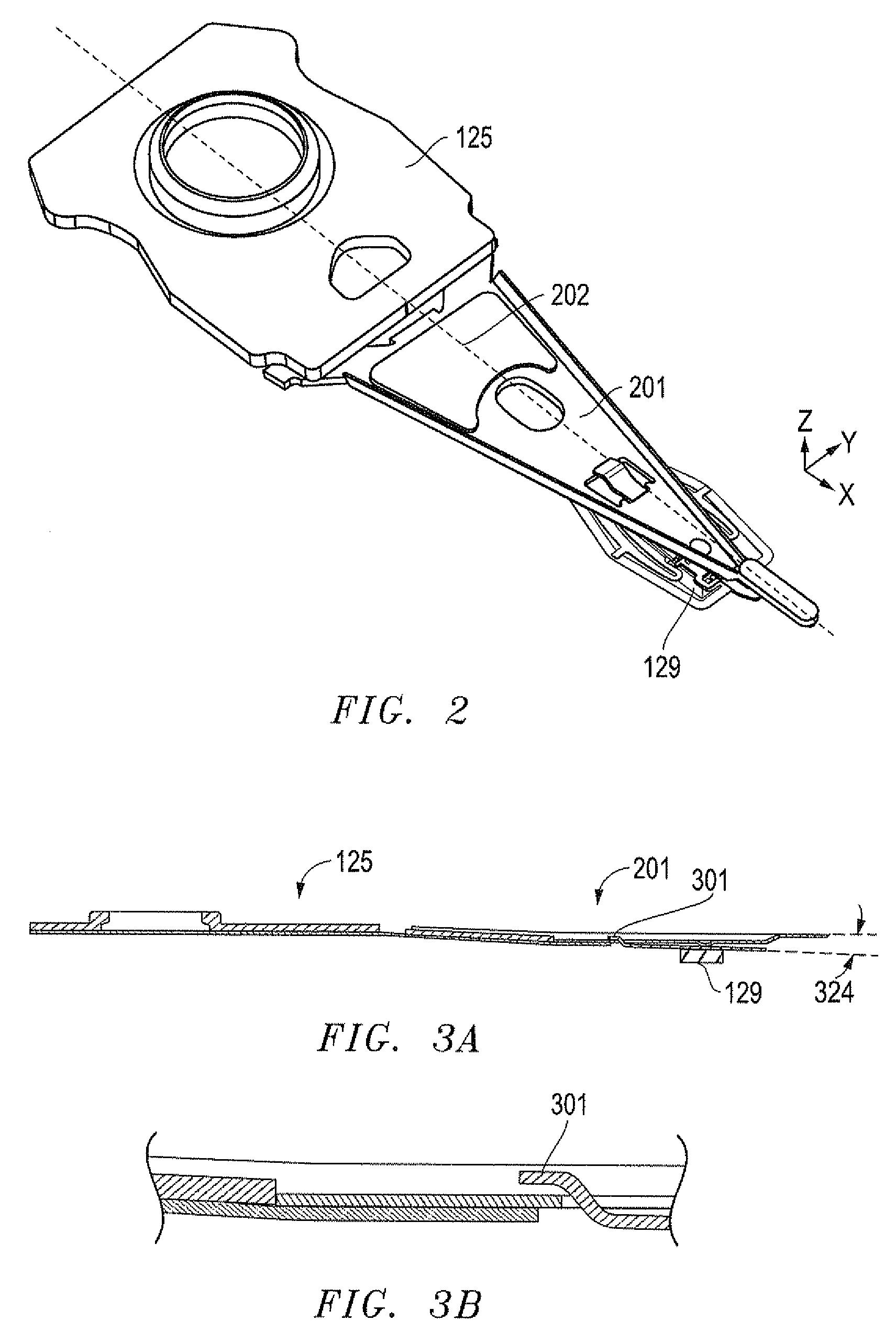
Pivoting lever cam guide tape head positioner
InactiveUS6075678AImprove mechanical rigidityHigh of resistance to vibrationTrack finding/aligningAlignment for track following on tapesLight beamEngineering
A fine lateral head positioner for a tape drive includes a frame mounted to a base of a tape transport. A tape head slides laterally along a head guide. A guide beam actuated by a fine position actuator applies limited transverse adjustments to the tape head relative to a tape transport path via a cam and cam-follower arrangement. A coarse positioner between the frame and the base provides coarse position adjustment of the tape head laterally among multiple sets of parallel tracks defined along a longitudinal direction of a magnetic tape moving along the tape transport path, and the guide beam provides fine position adjustment of the tape head enabling it to follow in real time a particular set of parallel tracks of the tape during each data writing or reading operation.
Owner:QUANTUM CORP
System, method and apparatus for flexure-integrated microactuator
ActiveUS8085508B2Overcome costsOvercomes manufacturabilityTrack finding/aligningRecord information storageHard disc driveTrack density
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
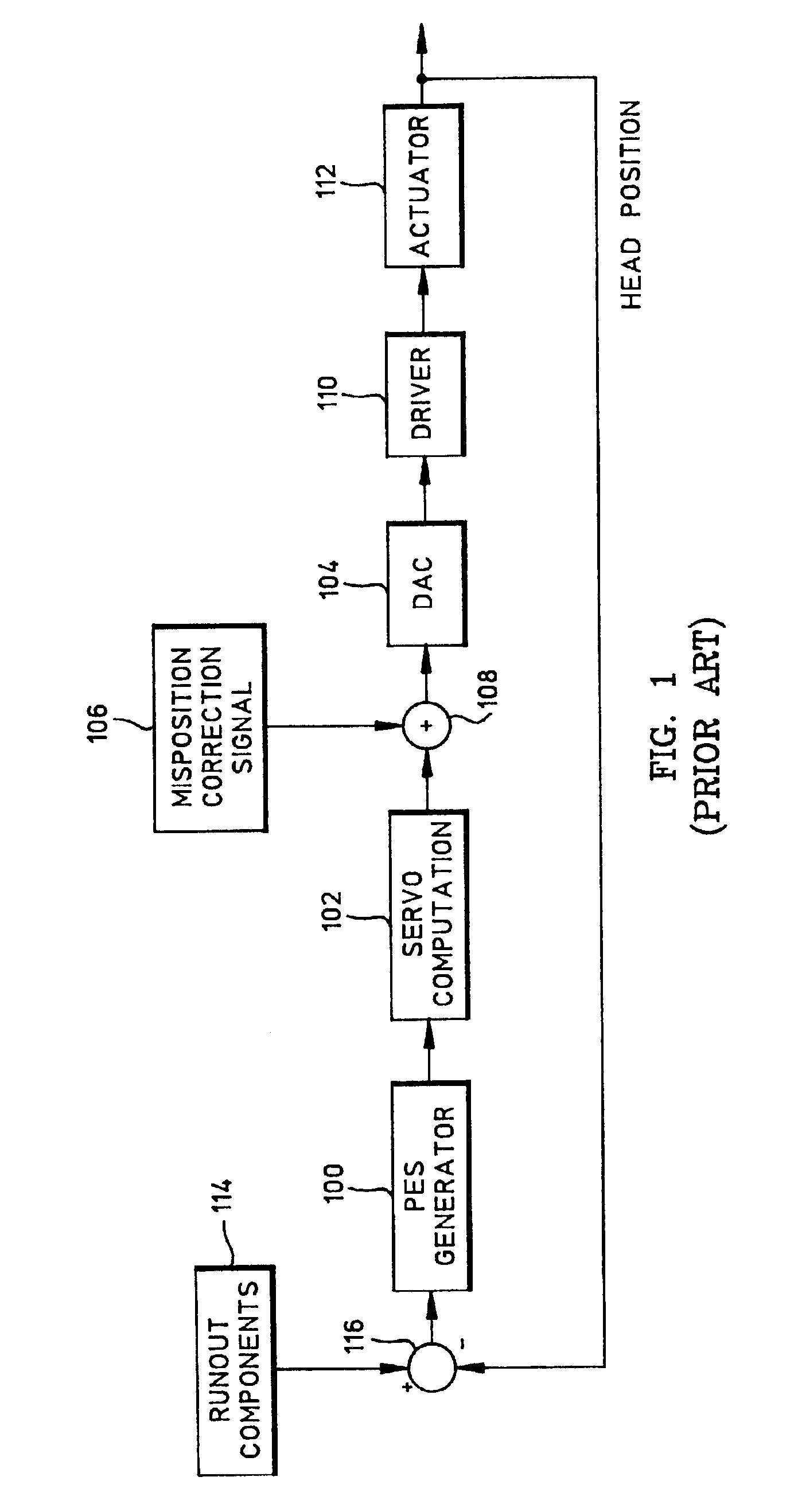
In-drive correction of servo pattern errors
InactiveUS6061200AImprove RRO correction valueTrack finding/aligningRecord information storageHard disc driveClosed loop
Embedded servo sectors within a data track of a hard disk drive including a rotating data storage disk and a closed loop rotary actuator structure for positioning a data transducer head relative to the data track are written by a method including the steps of positioning the rotary actuator structure relative to the data track with a laser-interferometer-based servo writer and writing a pattern of circumferentially sequential, radially offset fine position bursts within each servo sector with the data transducer head, this step including writing-in undetermined position errors within each pattern being written, moving the disk drive to a self scan environment away from the servo writer, operating the rotary actuator structure in closed loop for following the data track by reference to the servo burst pattern, extracting the undetermined position error from each pattern thereby to iteratively determine written-in position errors, generating burst correction values from the determined written-in position errors, and writing the burst correction values to the data track for later use by the closed loop rotary actuator structure during following of the data track to remove the written-in position errors.
Owner:MATSUSHITA KOTOBUKI ELECTRONICS IND LTD
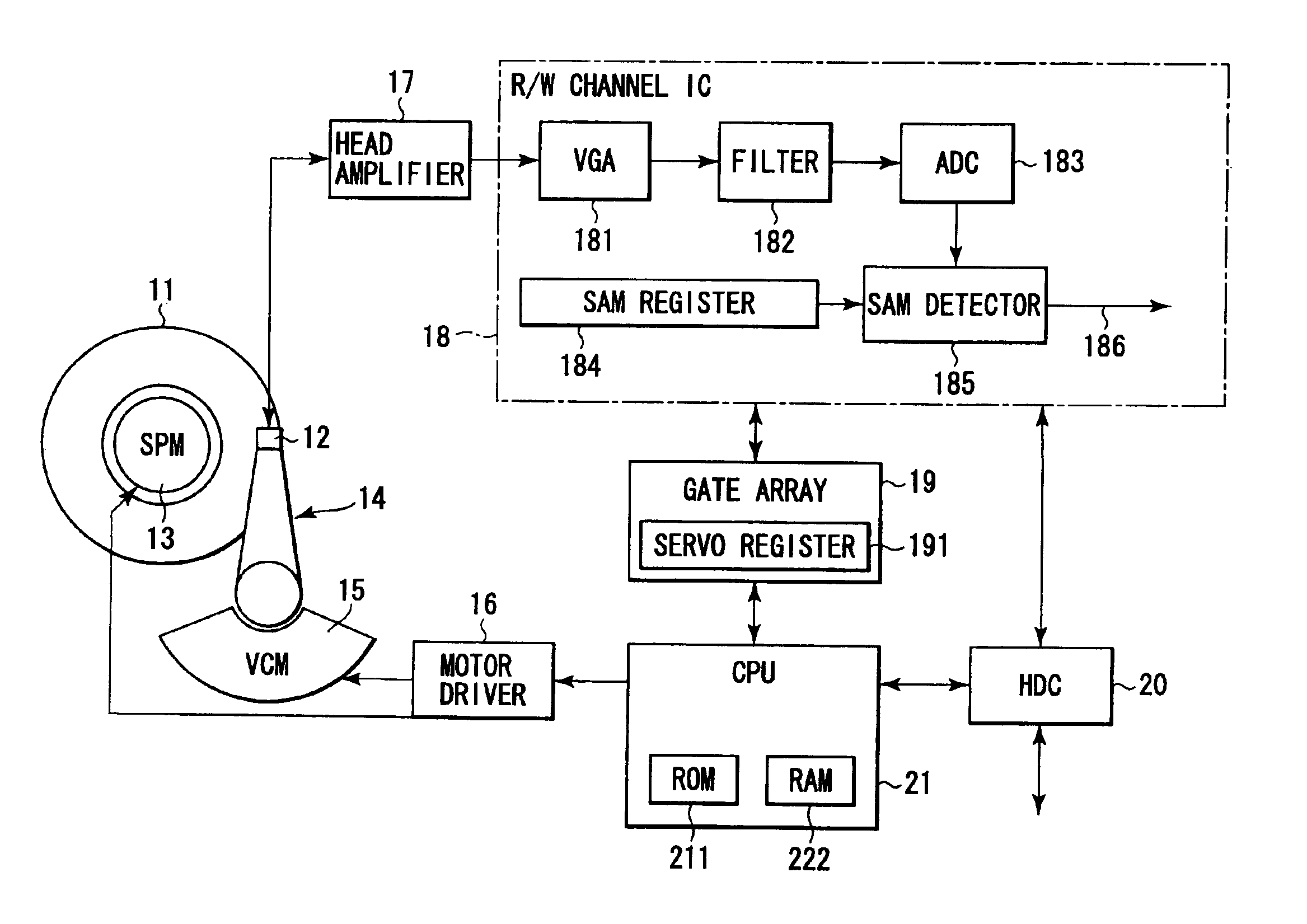
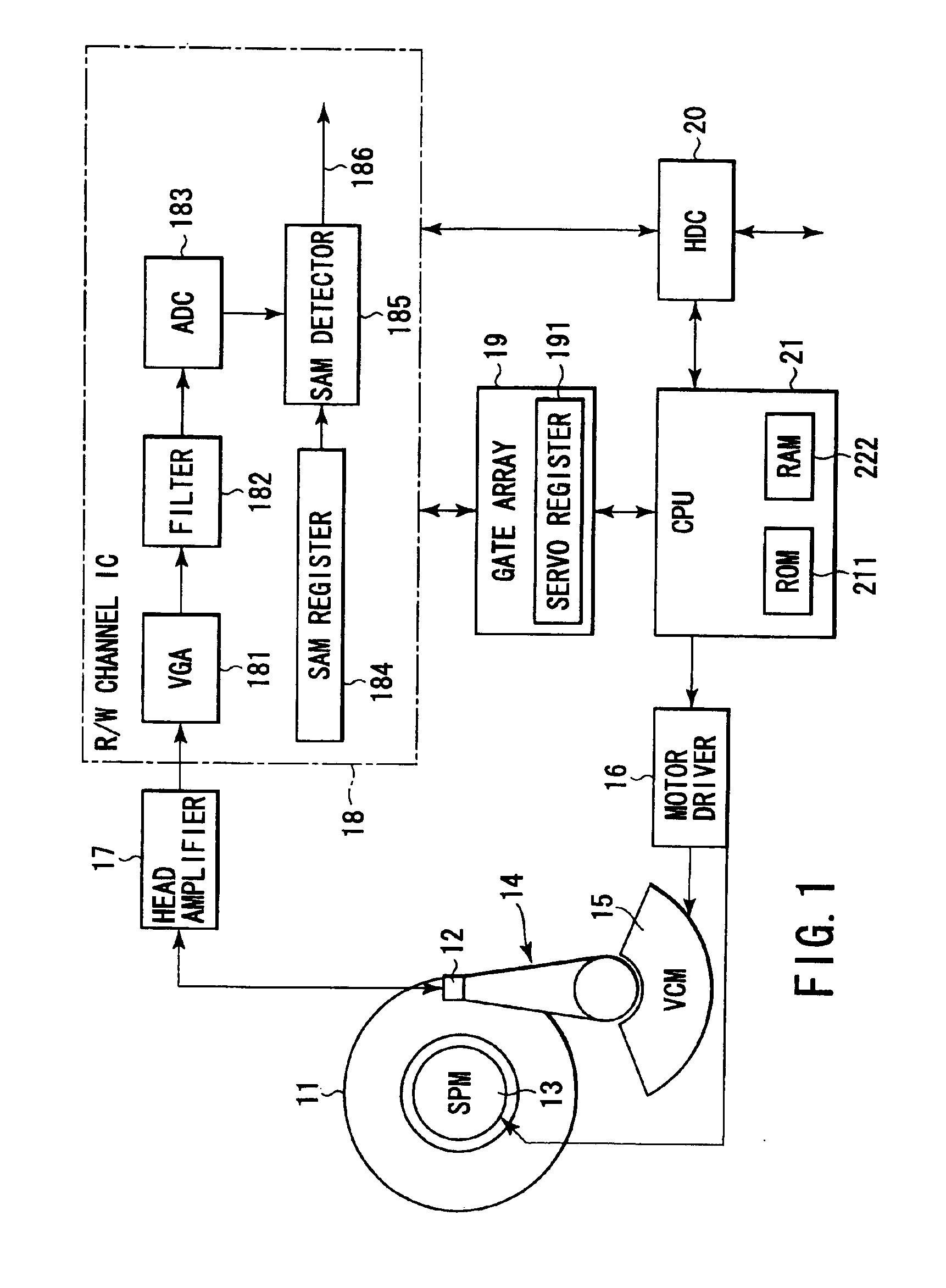
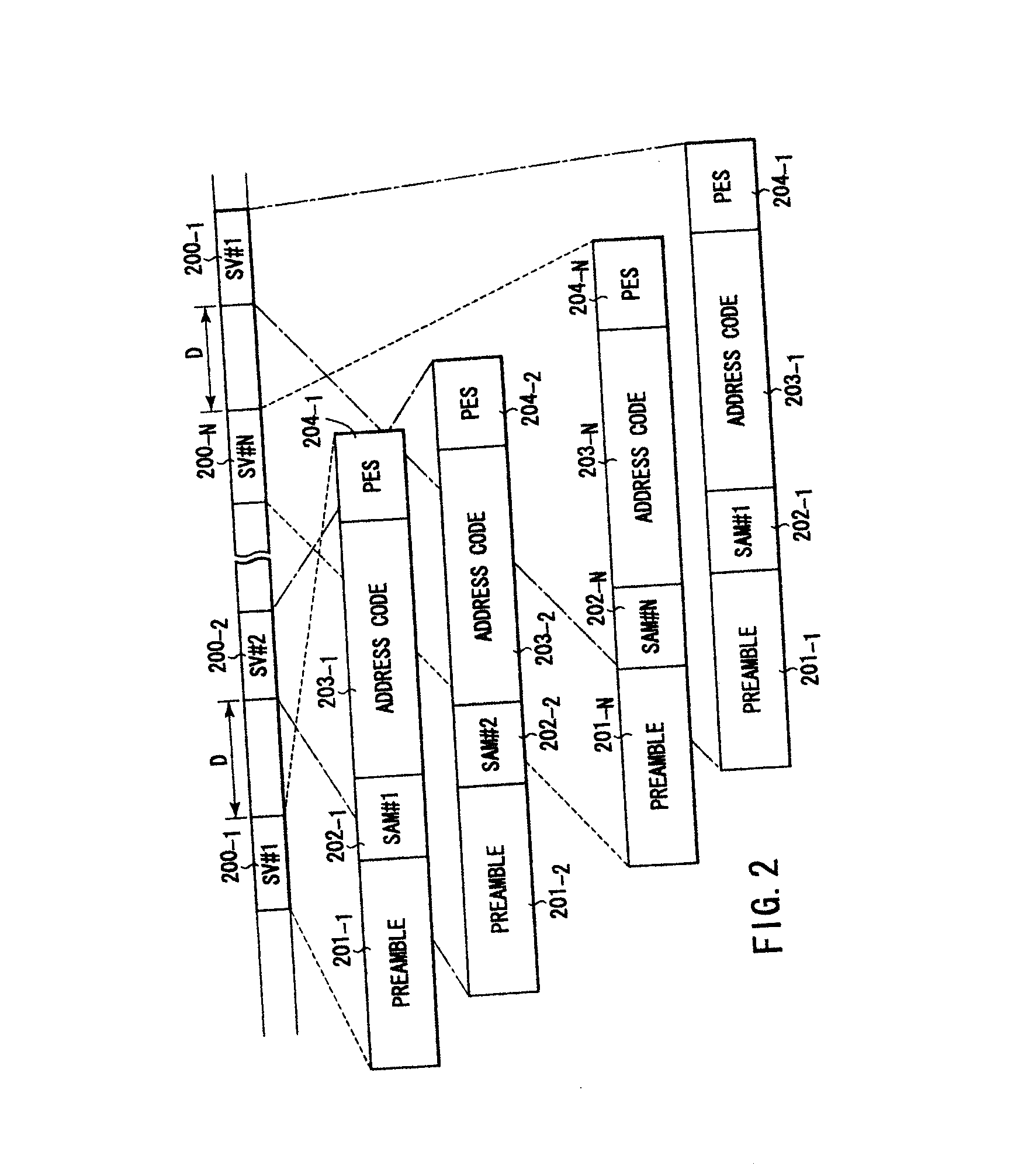
Disk drive and method of detecting servo address mark in the same
InactiveUS6876511B2Filamentary/web carriers operation controlTrack finding/aligningComputer sciencePosition shift
A detector detects, in read data, a servo address mark of a type indicated by a register. Every time a SAM is detected during a self servo process, a CPU carries out tracking control in accordance with corresponding servo data. The CPU causes a head to write a corresponding type of additional servo data item in a disk at a position offset from the position of servo data containing the detected SAM, by a predetermined distance in a circumferential direction of the disk. Every time sets of servo data, each consisting of various types of data items, are written in the disk, the head is moved by a predetermined pitch in a radial direction of the disk.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
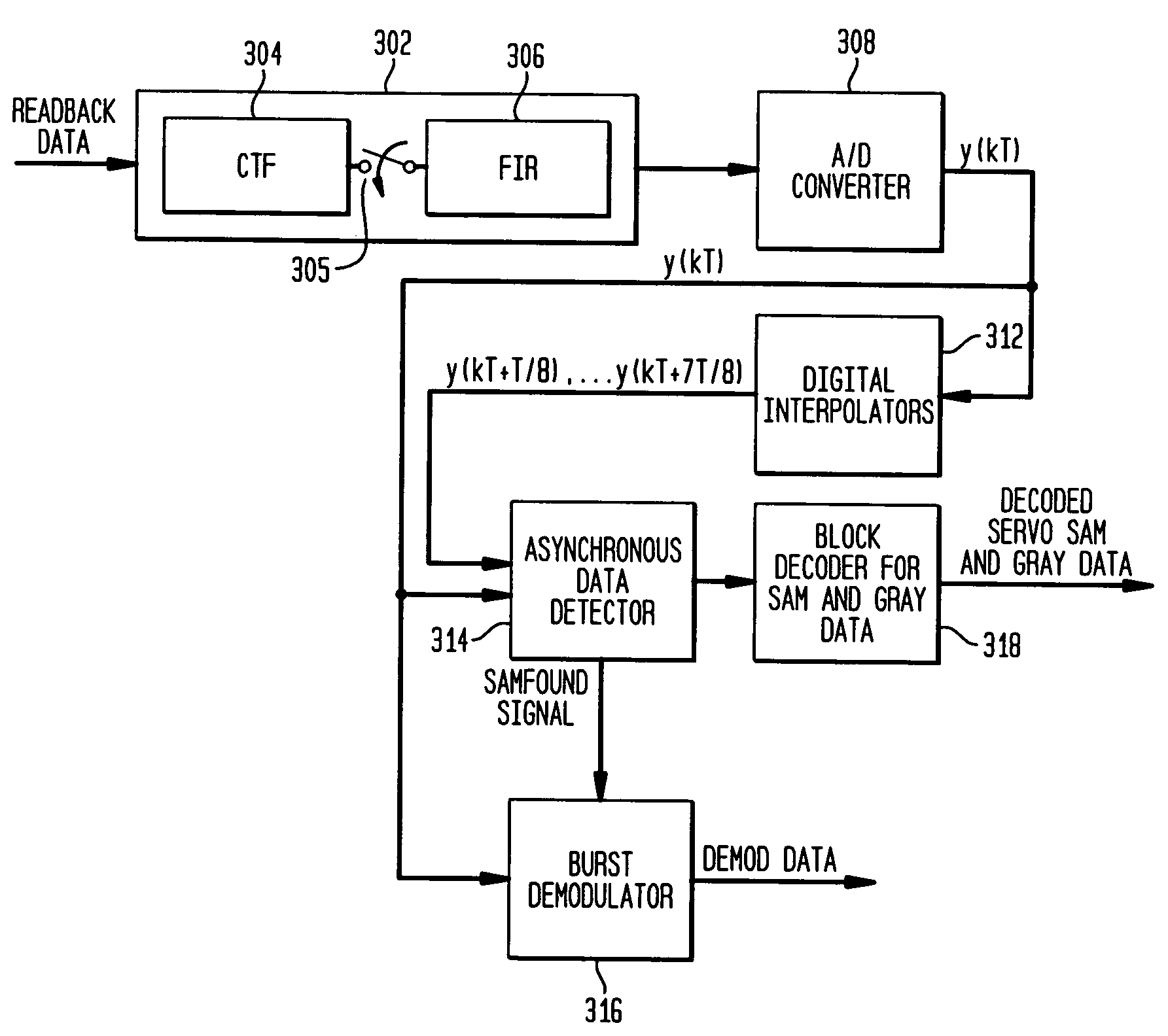
Synchronizing an asynchronously detected servo signal to synchronous servo demodulation
ActiveUS7167328B2Television system detailsModification of read/write signalsData recordingComputer science
A first set of data is detected in a signal having synchronous samples and interpolated samples, wherein the first set of data is detected asynchronously as corresponding to one of the samples. A time to transmit a data-found signal is determined based on an offset between the data-detected sample and one of the synchronous samples, and the data-found signal is transmitted at the determined time to enable the synchronous processing of the synchronous samples. In one implementation, the synchronous samples correspond to a readback signal read from a data recording channel, the first set of data corresponds to servo address mark (SAM) data in a servo sector in the readback signal, and the synchronous processing is demodulation of burst data in the servo sector.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
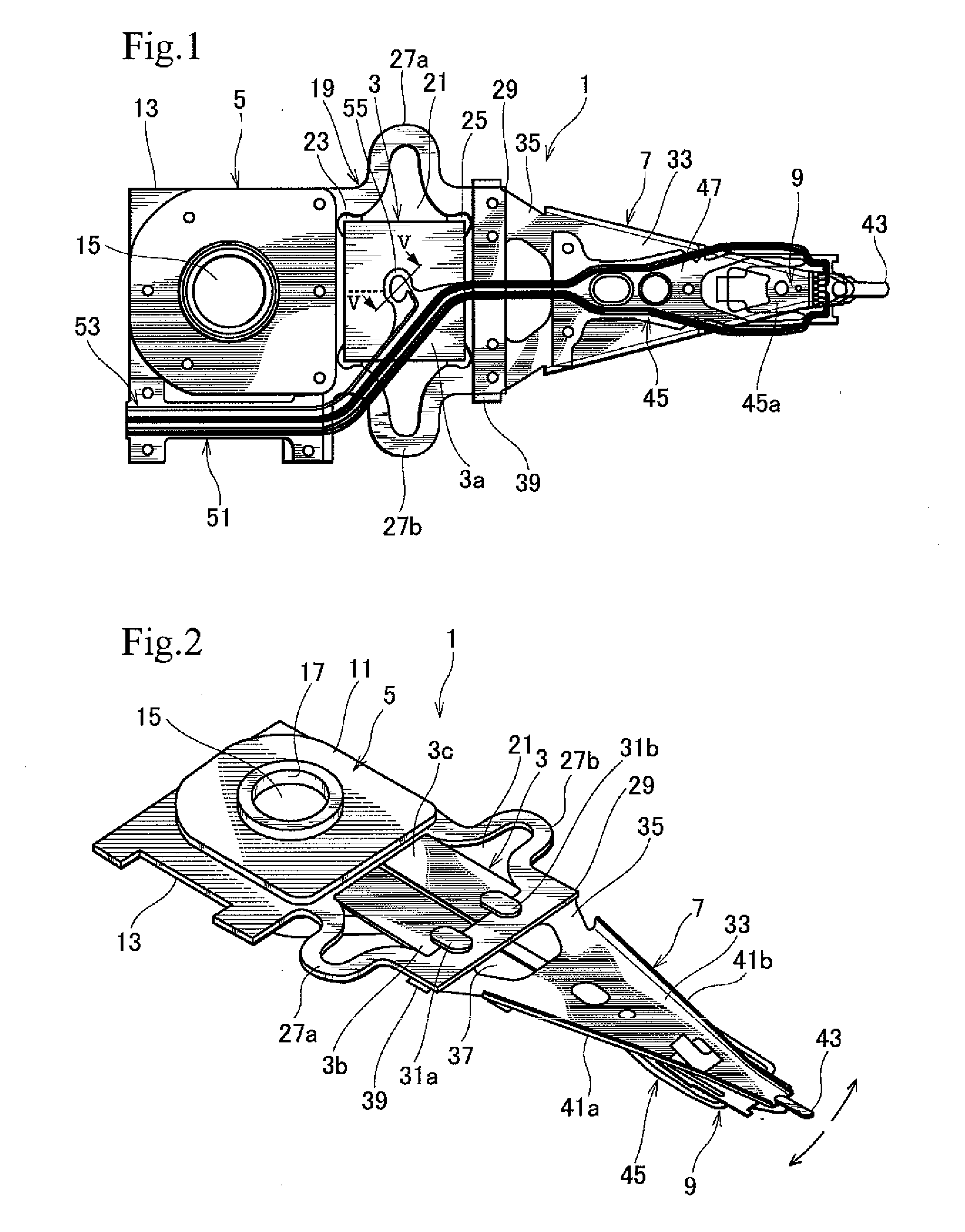
Microactuated dimple for head suspensions
InactiveUS7256968B1Move preciselyTrack finding/aligningRecord information storageDynamic storageEngineering
A head suspension for supporting a head slider over a disk in a dynamic storage device and providing precise movement of the head slider relative to tracks on the disk. The head suspension includes a load beam, a flexure having a slider mounting region, and a dimple interface transmitting a load beam force to the slider mounting region. The head suspension further includes a microactuator mounted to the load beam. Movement of the microactuator is transmitted through the dimple interface by action of frictional forces at the dimple interface so as to cause movement of the slider mounting region transverse to tracks on the disk. A method of precisely moving a head slider supported by a head suspension includes providing and driving a microactuator configured to transmit movement of the microactuator to a slider mounting region through a dimple interface by action of frictional forces at the dimple interface.
Owner:HUTCHINSON TECH
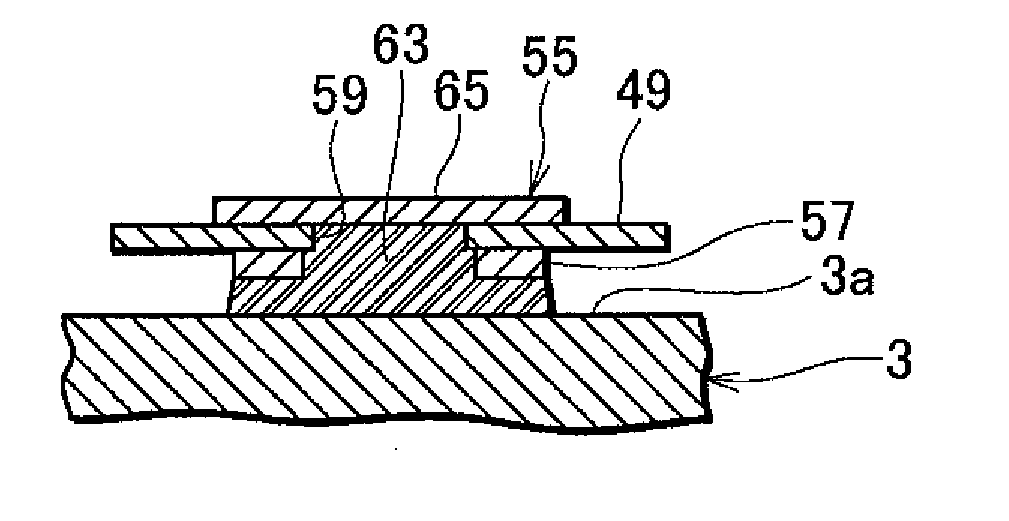
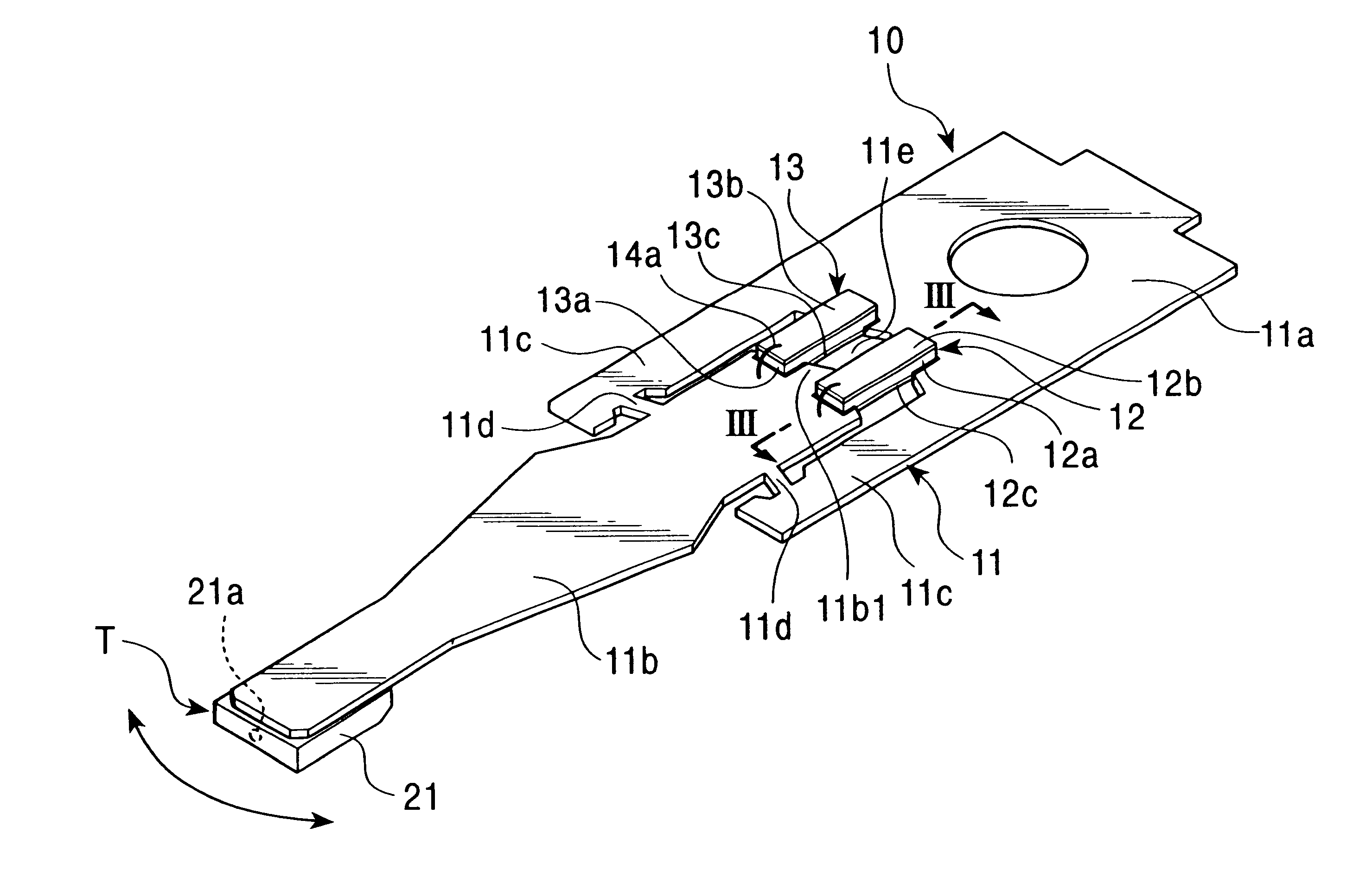
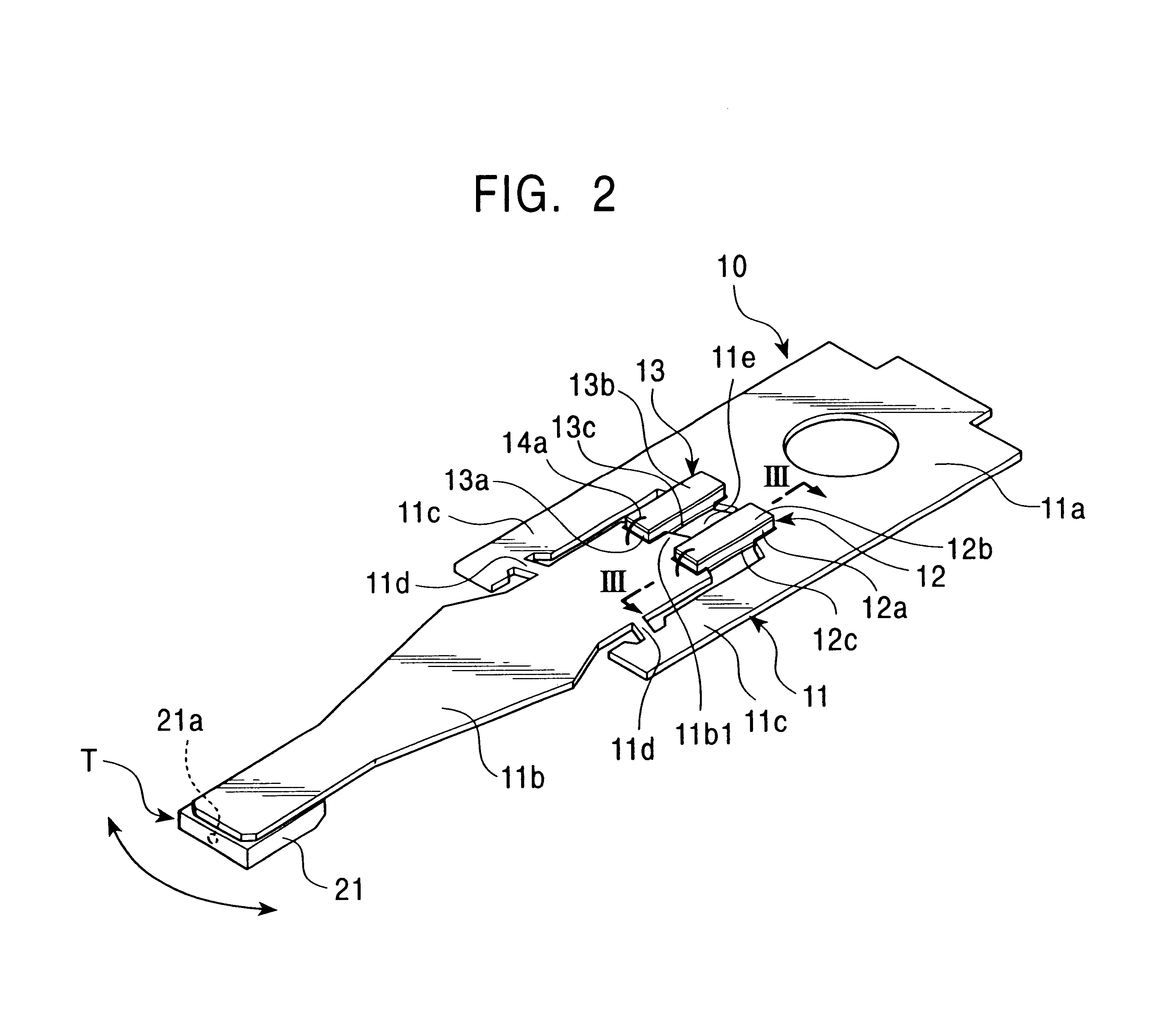
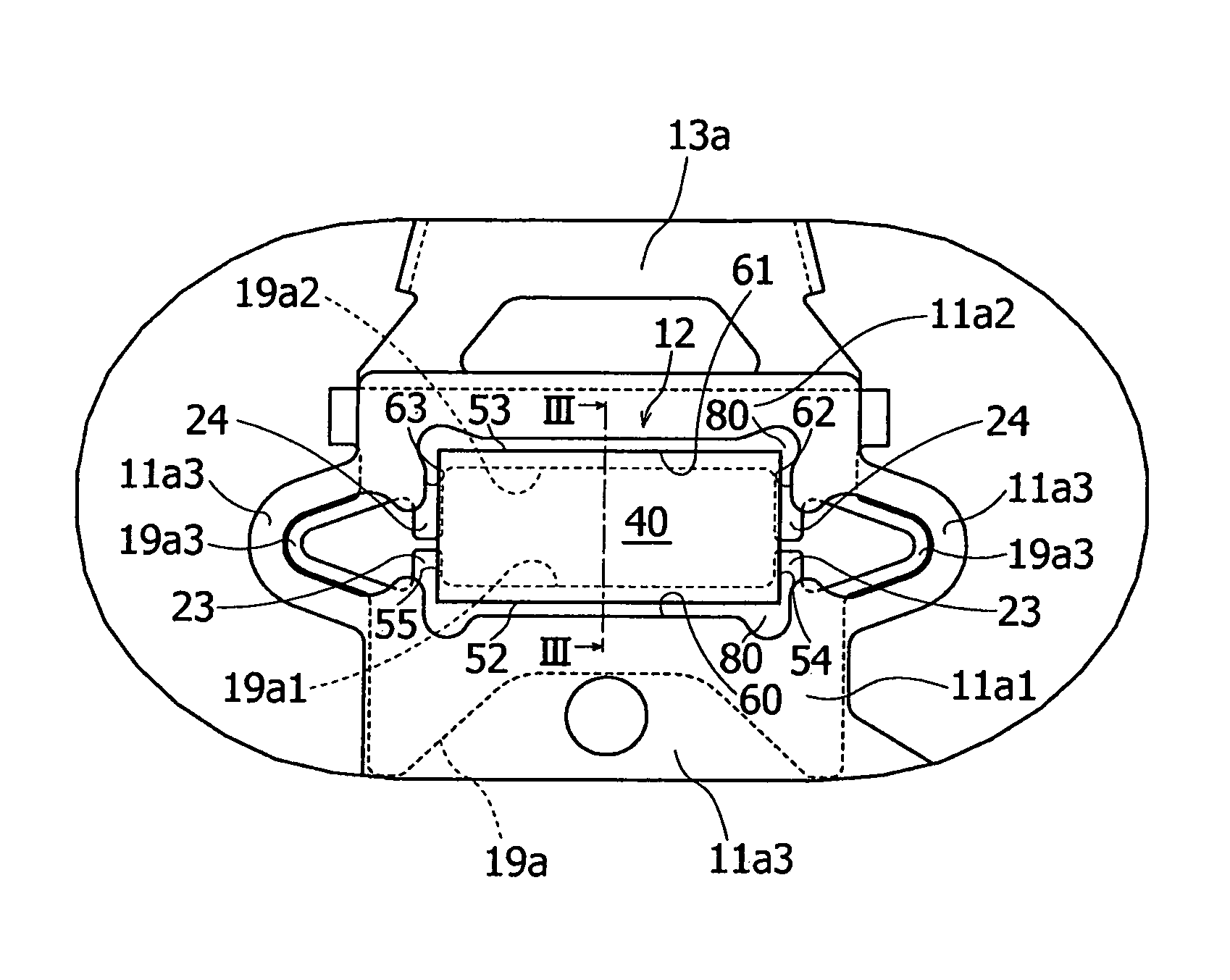
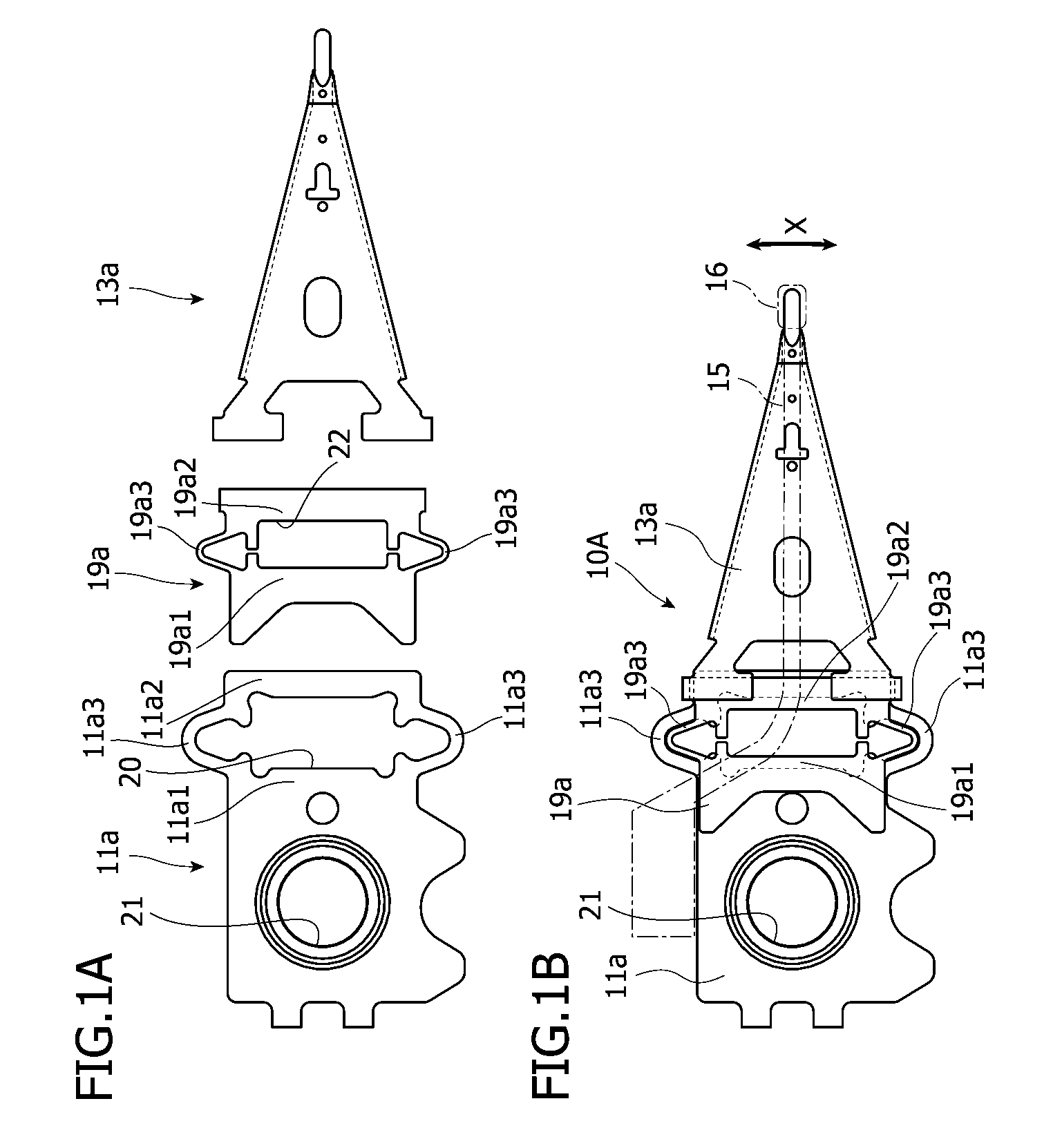
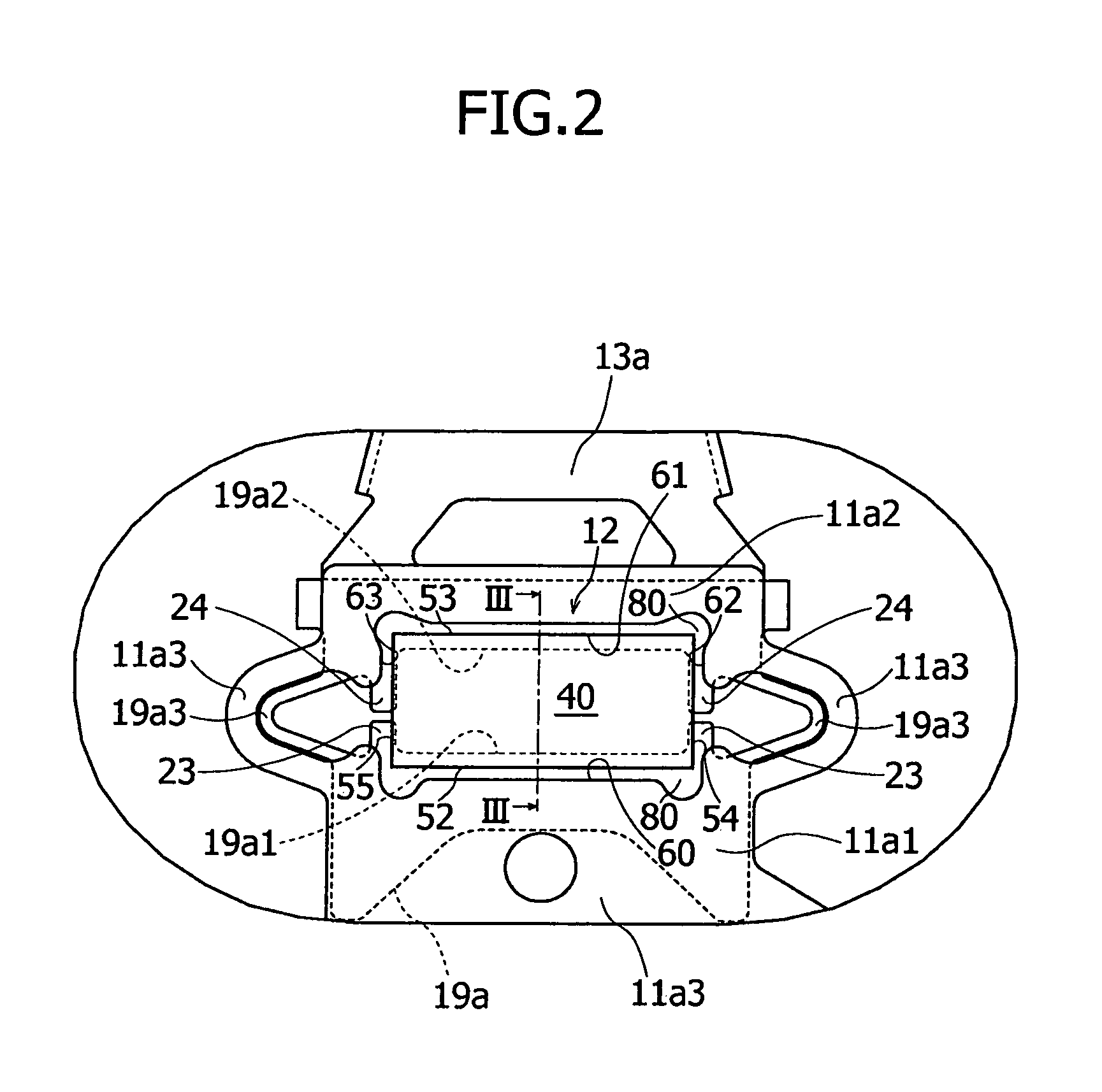
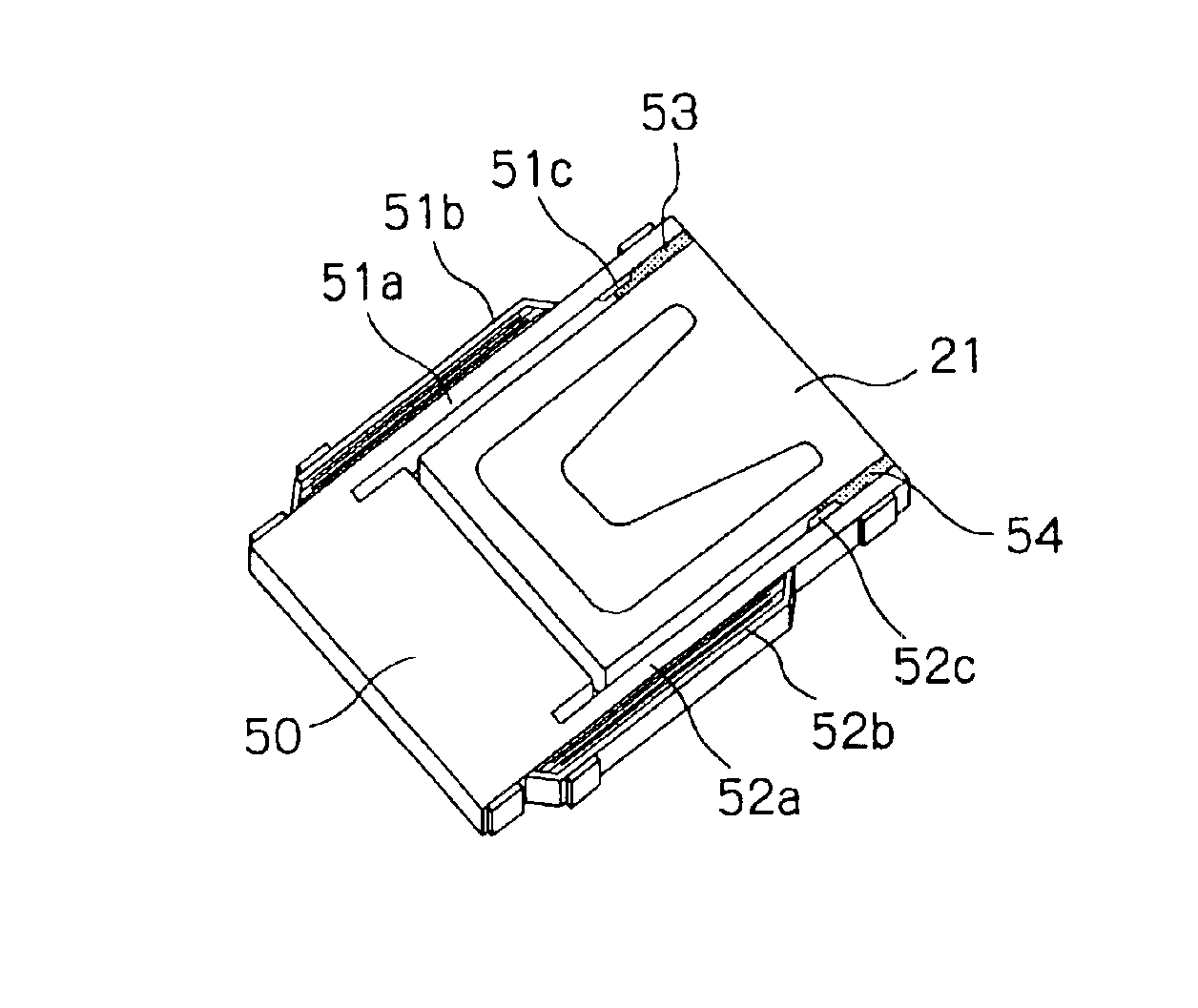
Magnetic head device having suspension with microactuator bonded thereto
The present invention provides a magnetic head device exhibiting a good bonded state of a piezoelectric element and a load beam, and excellent reliability. The magnetic head device includes a slider provided with a reproducing element for detecting a magnetic signal recorded on a recording medium, and a recording element for recording a magnetic signal on the recording medium, an elastic supporting member for supporting the slider, and piezoelectric elements mounted on the elastic supporting member, for distorting the elastic supporting member to change the position of the slider. The piezoelectric element and the elastic supporting member are bonded together with a photo-curing and thermosetting epoxy adhesive resin having a Young's modulus of 1 GPa or more at 25° C., and a glass transition temperature of 90° C. or more.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Method to achieve higher track density by allowing only one-sided track encroachment
InactiveUS7082007B2Reduced and minimized amountAccurate informationFilamentary/web carriers operation controlTrack finding/aligningTrack densityTransducer
A disc drive includes a transducer having a separate element for writing information and a separate element for reading information to and from the disc. In a disc drive designated to read and write long sequential records, the track misregistration budget is reduced to account for previously written tracks not being encroached on one side. An initial track is written. Subsequent tracks are written after a seek in one direction. The subsequent track is written so that the initially written track is overwritten to one side and leaves a track having a width substantially equal to the width of the read element. Records can be written into data bands of a selected number of tracks. A guard band is left between groups of data bands so that data on tracks in subsequent data bands are not overwritten.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Methods for variable multi-pass servowriting and self-servowriting
InactiveUS6999264B2Reduce the written runoutTrack finding/aligningRecord information storagePosition errorMultiple pass
The amount of position error written into a servo burst pattern can be reduced by using additional media revolutions to write the pattern. Where the edges of two servo bursts are used to define a position on the media, trimming the first burst and writing the second burst on separate revolutions will result in a different amount of position error being written into each burst. The end result will be a reduction in the overall error in position information. In order to further reduce the position error given by a burst pair, each burst also can be trimmed and / or written in multiple passes. This description is not intended to be a complete description of, or limit the scope of, the invention. Other features, aspects, and objects of the invention can be obtained from a review of the specification, the figures, and the claims.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
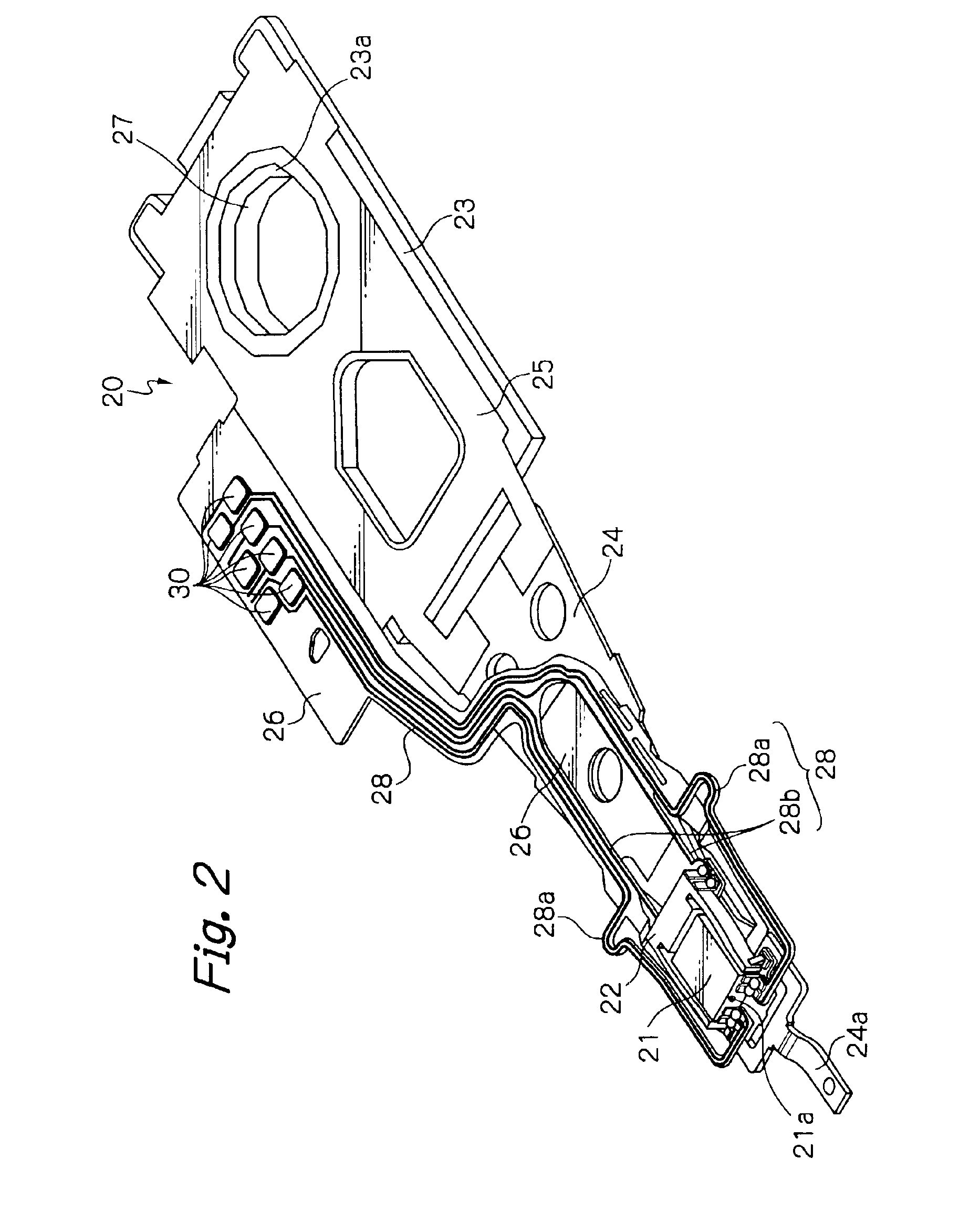
Electrical connection structure for piezoelectric element and head suspension
ActiveUS20110279929A1Reliable electrical connectionReliably movedElectrical connection between head and armTrack finding/aligningLaser processingSurface layer
An electrical connection structure connects a piezoelectric element to a flexure with a conductive adhesive. An electrode surface is formed on the piezoelectric element, and a terminal surface is formed on the wiring member and is smoother than the electrode surface. A the gold plate layer is formed on the terminal surface and is connected to the electrode surface with the conductive adhesive. At least one recess is formed by laser processing on the conductive terminal surface layer. The electrical connection structure substantially equalizes the surface roughness of the terminal surface with the gold plate layer to that of the electrode surface, improves a bonding strength on the terminal surface nearly to that on the electrode surface, enhances the reliability of electrical connection between the electrode surface and the terminal surface, maintains electrical characteristics of the terminal surface, and prevents contamination around the terminal surface.
Owner:NHK SPRING CO LTD
Method for actively controlling the gram load on a disk drive suspension assembly
InactiveUS7082670B2Large range of motionOptimization rangePrinted circuit assemblingPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyElectricityControl system
A method and apparatus for actively controlling the gram load on a disk drive suspension assembly and to a disk drive using the present disk drive suspension assembly. The gram load can be actively changed by changing the applied voltage to one or more multi-layer piezoelectric actuators attached to the head suspension. The active gram control system allows the gram load to be changed on a non-permanent basis and to control the gram load to a much finer scale than can be accomplished using conventional techniques. By attaching the first and second ends of the piezoelectric actuator to discrete locations on the load beam, while the portion of the piezoelectric actuator between the first and second ends remains unattached to the load beam, a force non-parallel to the load beam can be applied to the head suspension.
Owner:HUTCHINSON TECH
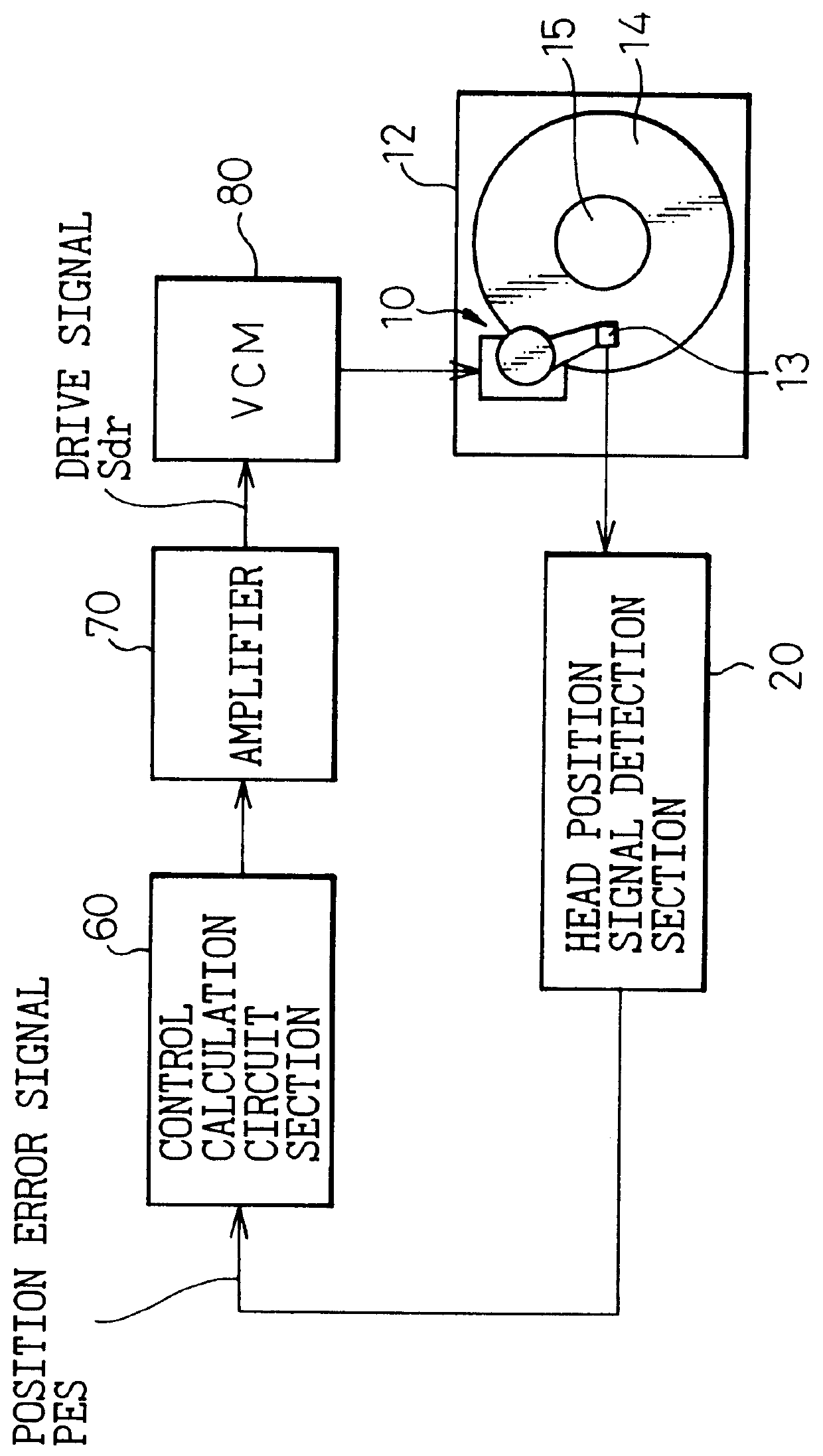
Head position control for a disk drive which performs recording about the rotational center even if the recorded servo information is eccentric
InactiveUS6128153AAverage power consumptionReduce power consumptionTrack finding/aligningRecord information storageCentre of rotationPosition control
Head position control is implemented in a disk drive for the case in which a disk is assembled into the disk drive after a precise track is recorded onto it using an external apparatus, which is capable of high-speed access even if there is eccentricity between a track defined by servo information and the center of rotation of the track. Two phase servo bursts consisting of servo information are recorded onto each of the servo information regions of a disk surface, in mutual alternation, the strength ratio between signals detected from these two phase servo bursts being used to determine to which side the head is displaced. By performing control so that this strength ratio is a prescribed value at each angular position, control is achieved so that the head moves along a circular path of rotation, even if there is eccentricity in the servo circular path defined by the recorded servo information with respect to the center of rotation.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Dual stage suspension with PZT actuators arranged to improve actuation in suspensions of short length
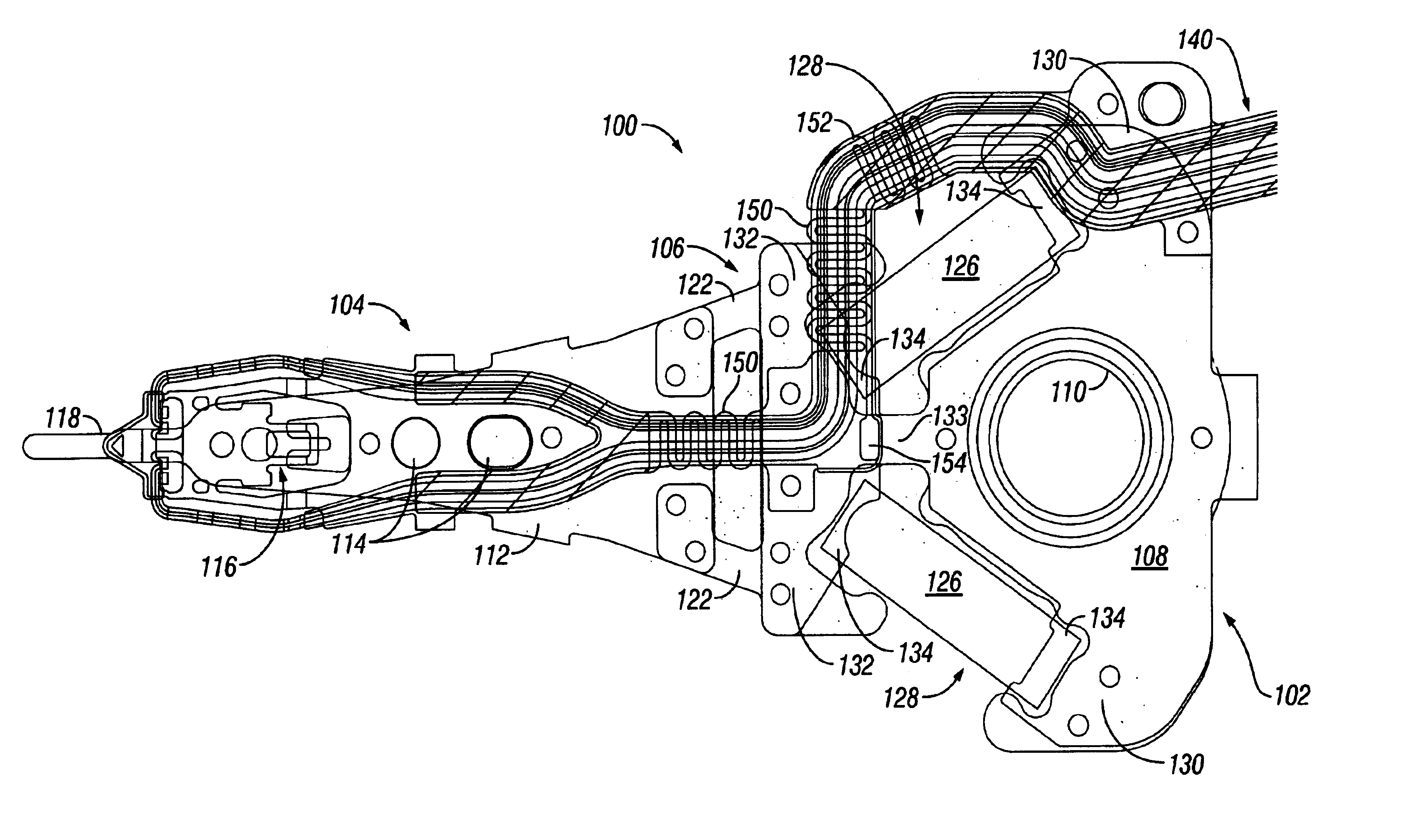
InactiveUS7023667B2Minimize impact of secondaryMinimize impactTrack finding/aligningElectrical connection between head and armDual stageEngineering
A suspension for a disk drive includes a mount plate adapted to mount to a primary actuator, a functional end portion adapted to carry a slider, and a hinge disposed between the mount plate and the functional end portion. A mounting configuration is provided on the mount plate for mounting the suspension to the primary actuator. A pair of secondary actuators are mounted in longitudinally overlapping relationship with the mounting configuration so as to minimize the impact of the secondary actuators on suspension length. The secondary actuators are operatively connected to the hinge for producing sway displacement of the slider.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Small-size direct-acting actuator
InactiveUS7355305B2Simple structureSmall sizeTrack finding/aligningRecord information storageEngineeringActuator
A direct-acting actuator is provided comprising a stator section (16), an attachment section (6) secured to the stator section, micro-beams (8, 10) extending from the attachment section, a rotor section (12) supported for swing motion by the micro-beams, a permanent magnet (18) disposed in the stator section, and a coil (4) disposed in the rotor section. Electric current is conducted through the coil in the magnetic field created by the permanent magnet for causing the micro-beams to be displaced for inducing swing motion of the rotor section. The actuator can be assembled to a small size, typically a width of 1-10 mm, a length of 1-10 mm, and a height of 0.1-5 mm.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Magnetic head device having suspension with microactuator bonded thereto
The present invention provides a magnetic head device exhibiting a good bonded state of a piezoelectric element and a load beam, and excellent reliability. The magnetic head device includes a slider provided with a reproducing element for detecting a magnetic signal recorded on a recording medium, and a recording element for recording a magnetic signal on the recording medium, an elastic supporting member for supporting the slider, and piezoelectric elements mounted on the elastic supporting member, for distorting the elastic supporting member to change the position of the slider. The piezoelectric element and the elastic supporting member are bonded together with a photo-curing and thermosetting epoxy adhesive resin having a Young's modulus of 1 GPa or more at 25° C., and a glass transition temperature of 90° C. or more.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
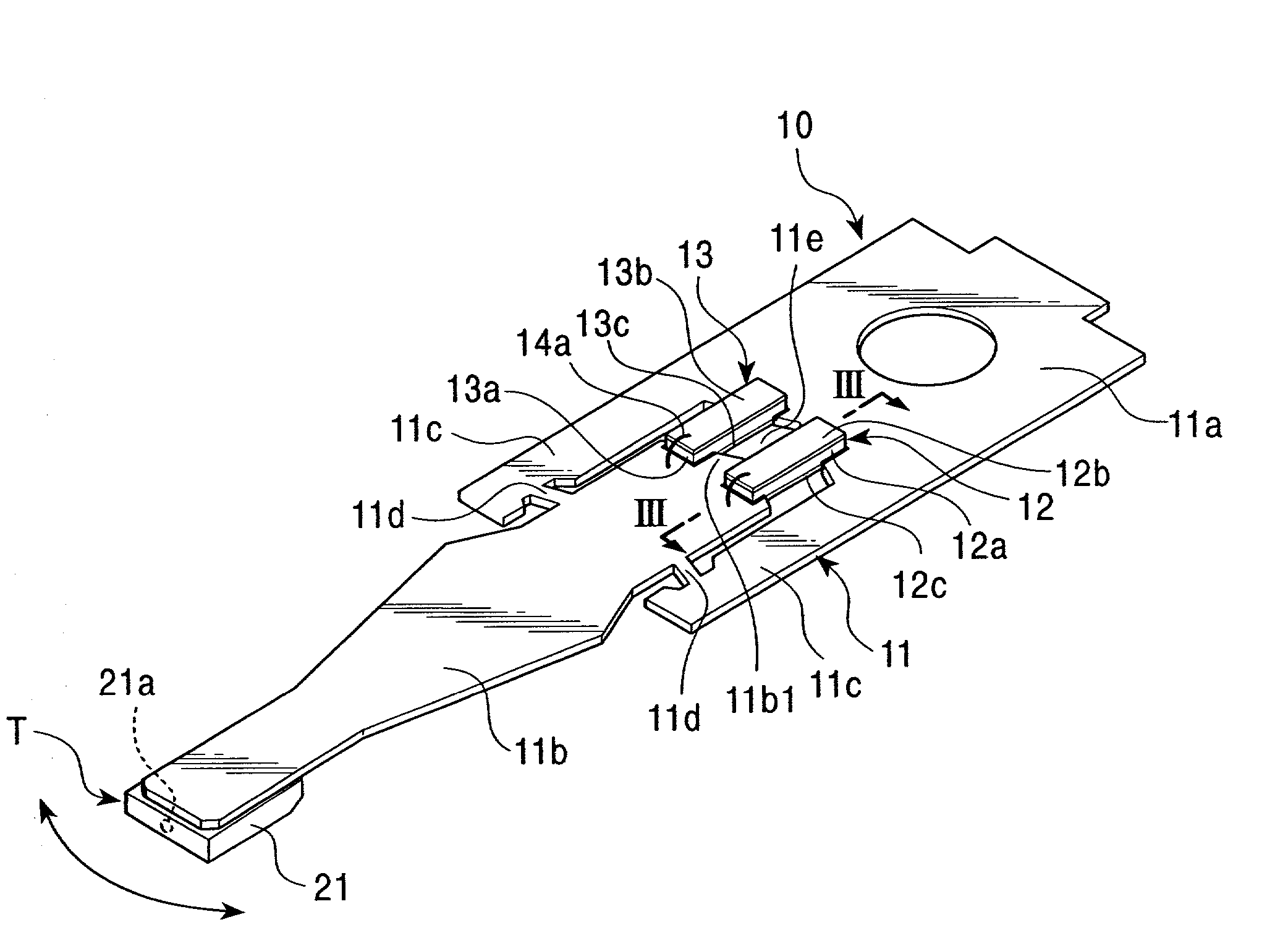
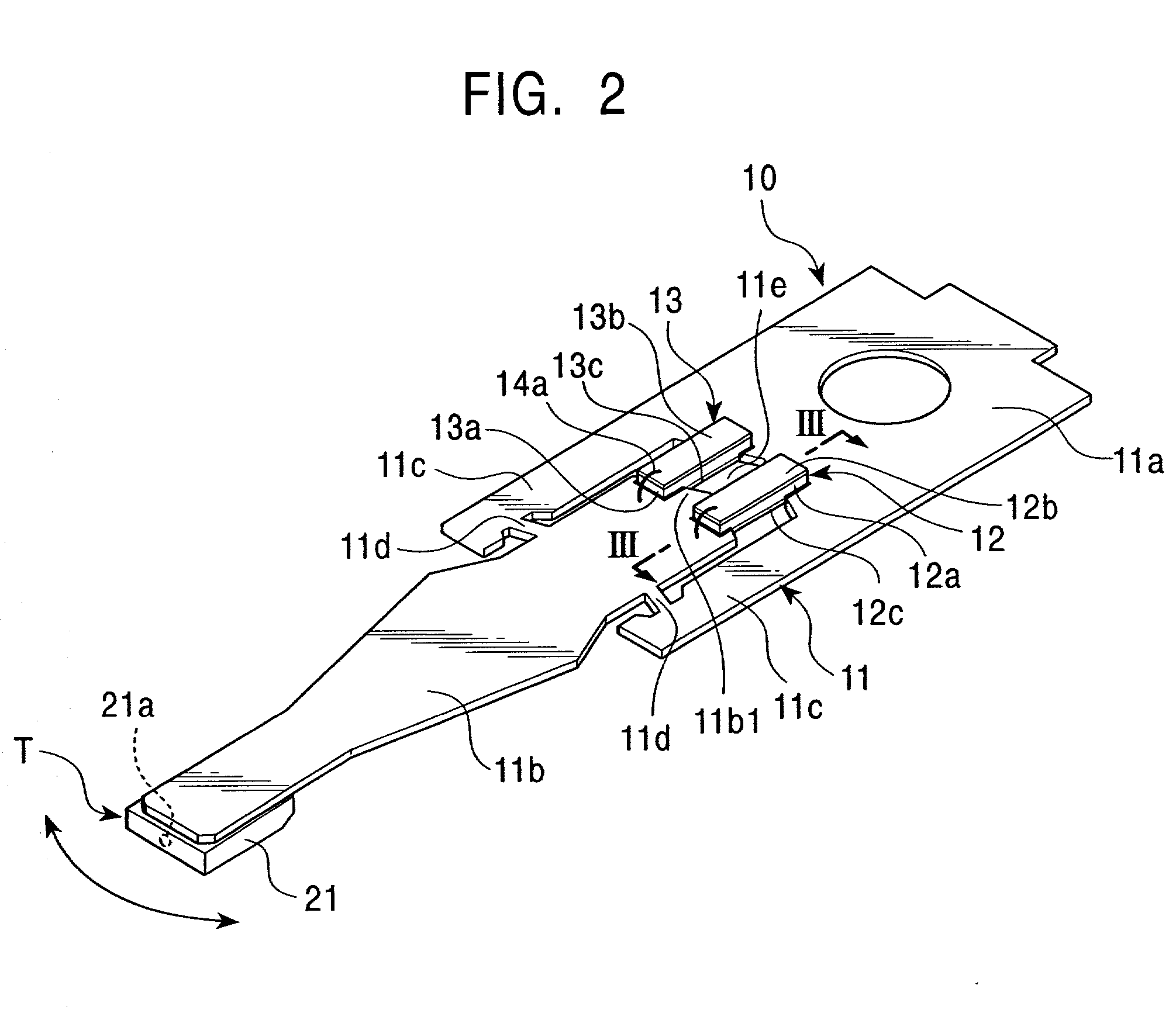
Electrode structure of piezoelectric element, method of forming electrode of piezoelectric element, piezoelectric actuator, and head suspension
ActiveUS20100195252A1Avoid shortingTrack finding/aligningPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric actuatorsMechanical engineering
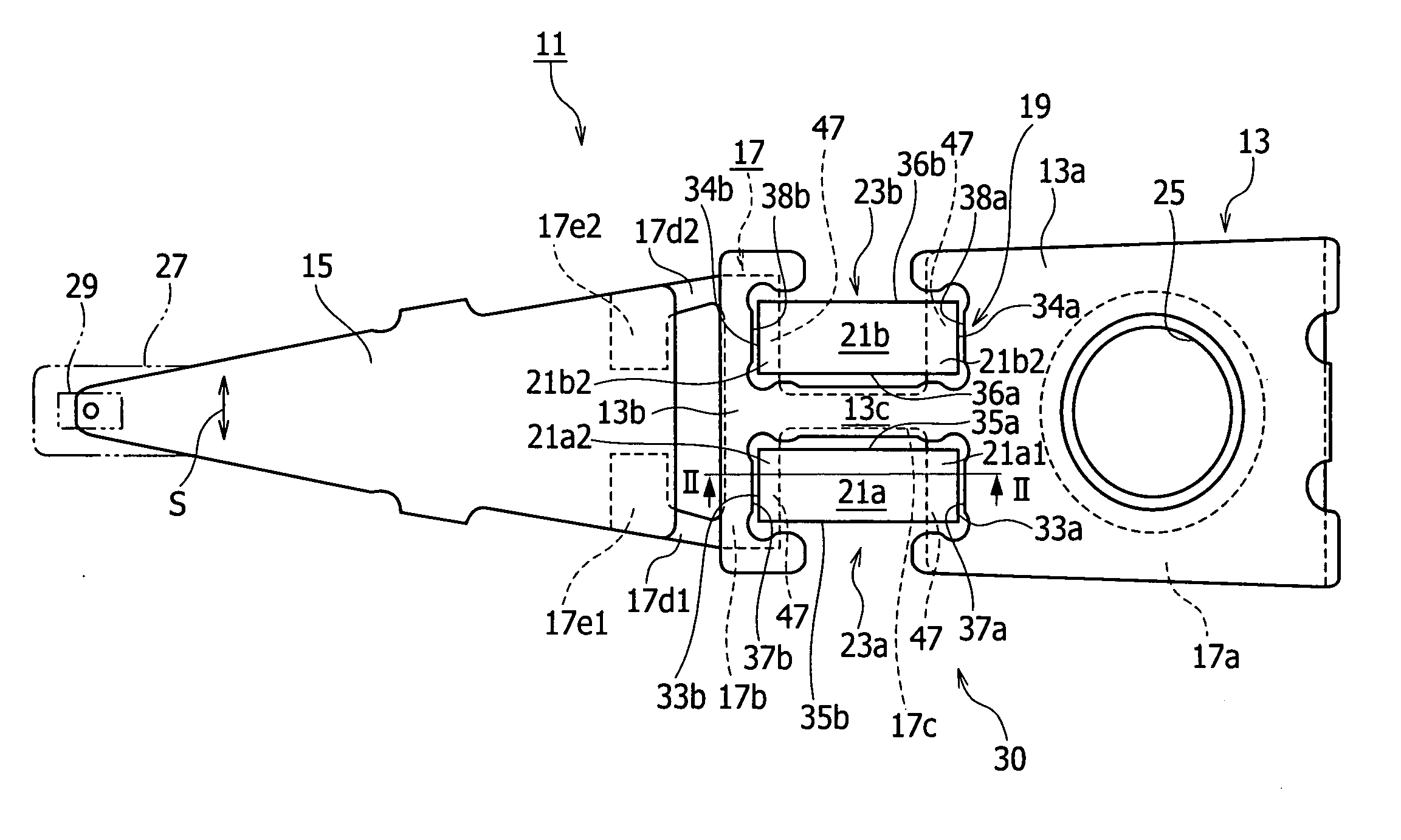
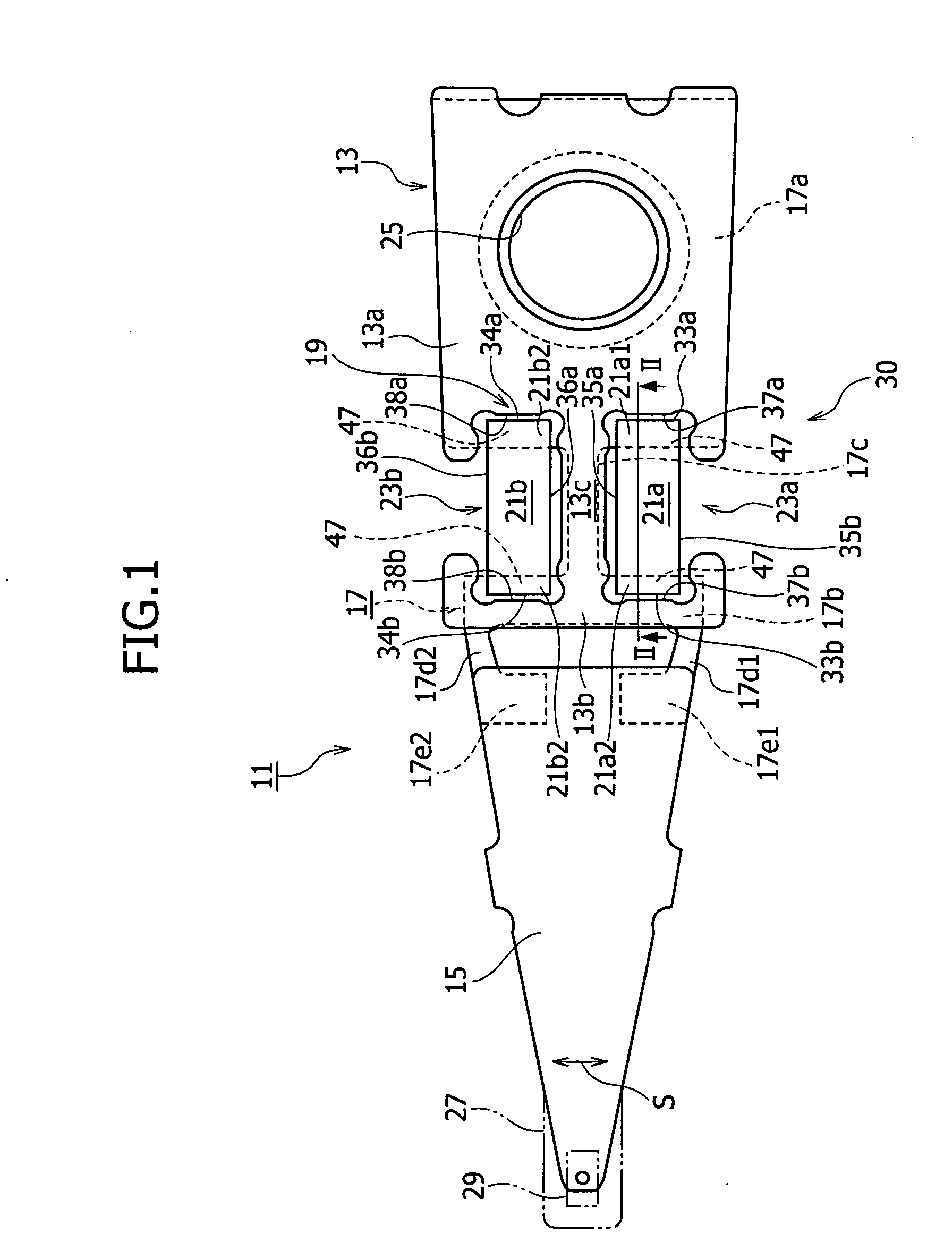
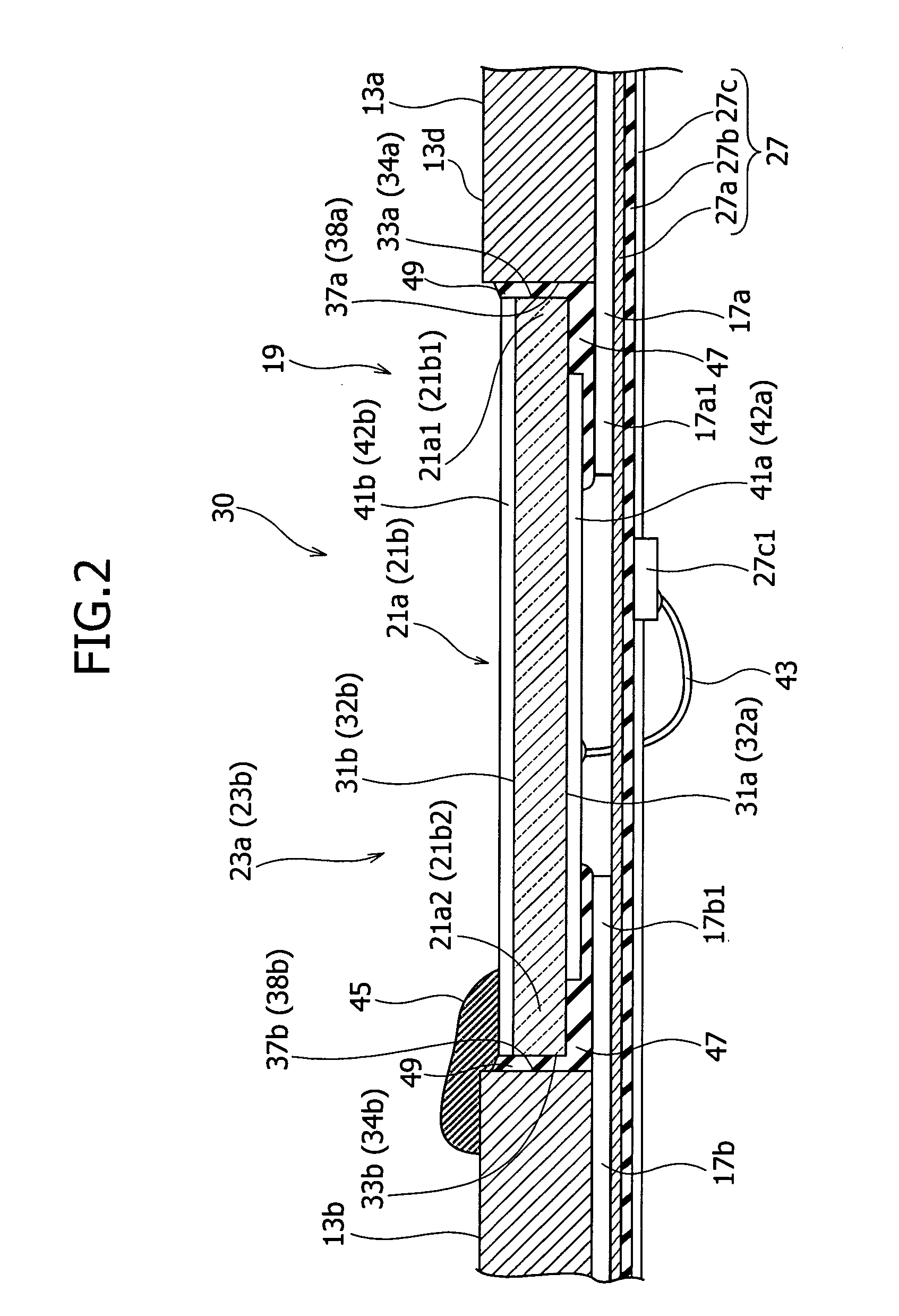
An electrode structure of a piezoelectric element is provided. The piezoelectric element 23a (23b) constitutes a piezoelectric actuator 19 attached to an attaching part 30 of an object, to minutely move a movable part 15 of the object relative to a base part 13 of the object according to deformation occurring on the piezoelectric element in response to a power applied state of the piezoelectric element. The electrode structure includes an electrode 41a formed on one of a pair of electrode forming faces 31a and 31b of the piezoelectric element on an inner side of a peripheral zone 31a1, the peripheral zone being defined along the periphery of the electrode forming face 31a on which the electrode is formed. The electrode structure also includes a non-electrode part 51 formed in the peripheral zone. Even if the peripheral zone 31a1 of the electrode forming face 31a having a short-circuit causing possibility touches the attaching part 30, no short circuit occurs.
Owner:NHK SPRING CO LTD
Active control system and method for reducing disk fluttering induced track misregistrations
InactiveUS6888694B2Easy to mergeNot affect stability of systemTrack finding/aligningRecord information storageVibration amplitudeVertical vibration
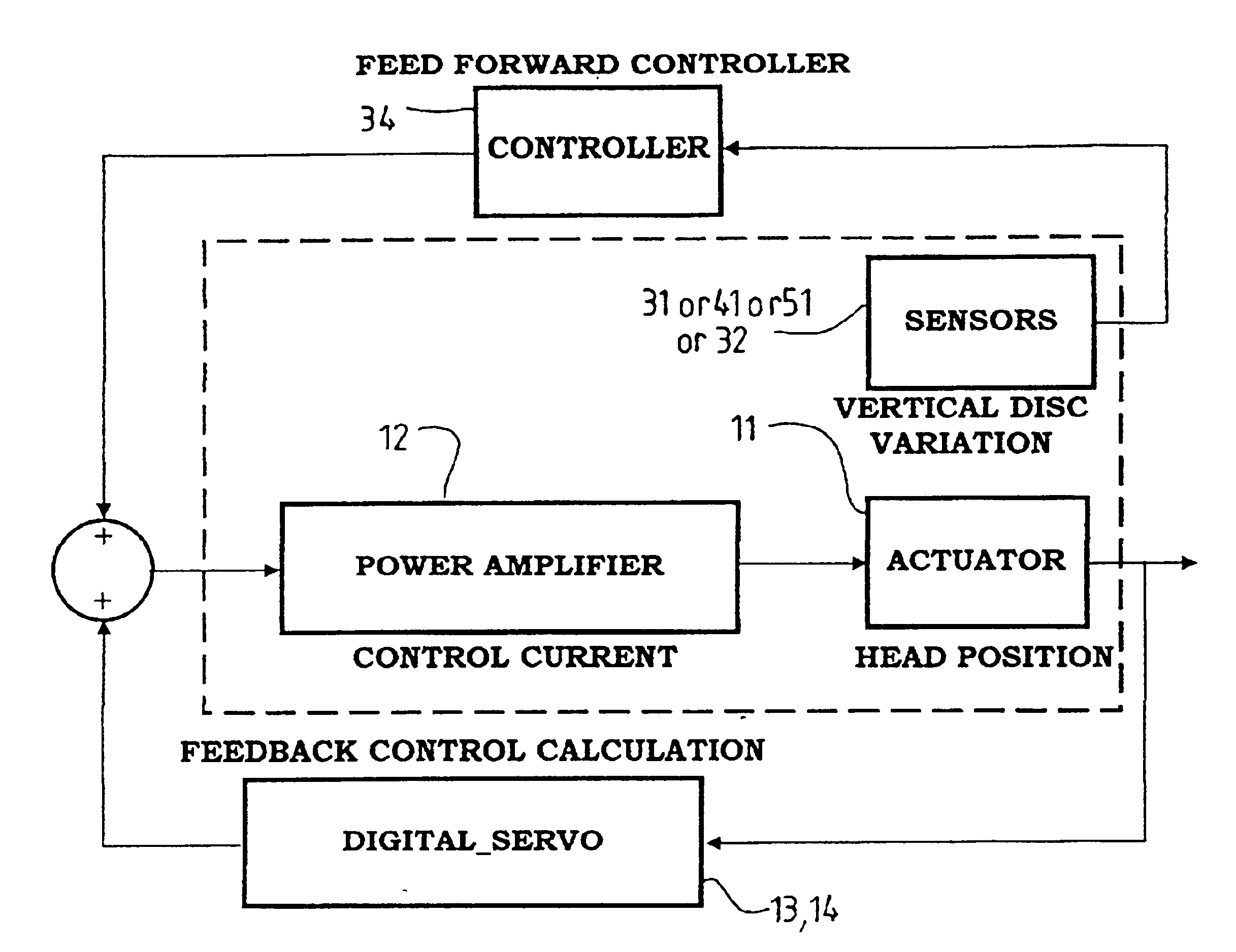
The present invention relates to controlling an actuator for positioning a read / write head in storage devices such as disk drives. More specifically, the invention relates to using a sensor to detect the disk vibration amplitude perpendicular to the disk surface, and using feed forward control to cancel or counteract the tendency of the read / write head to deviate off-track due to disk vibration. Various approaches are proposed to detect the disk vertical vibration.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
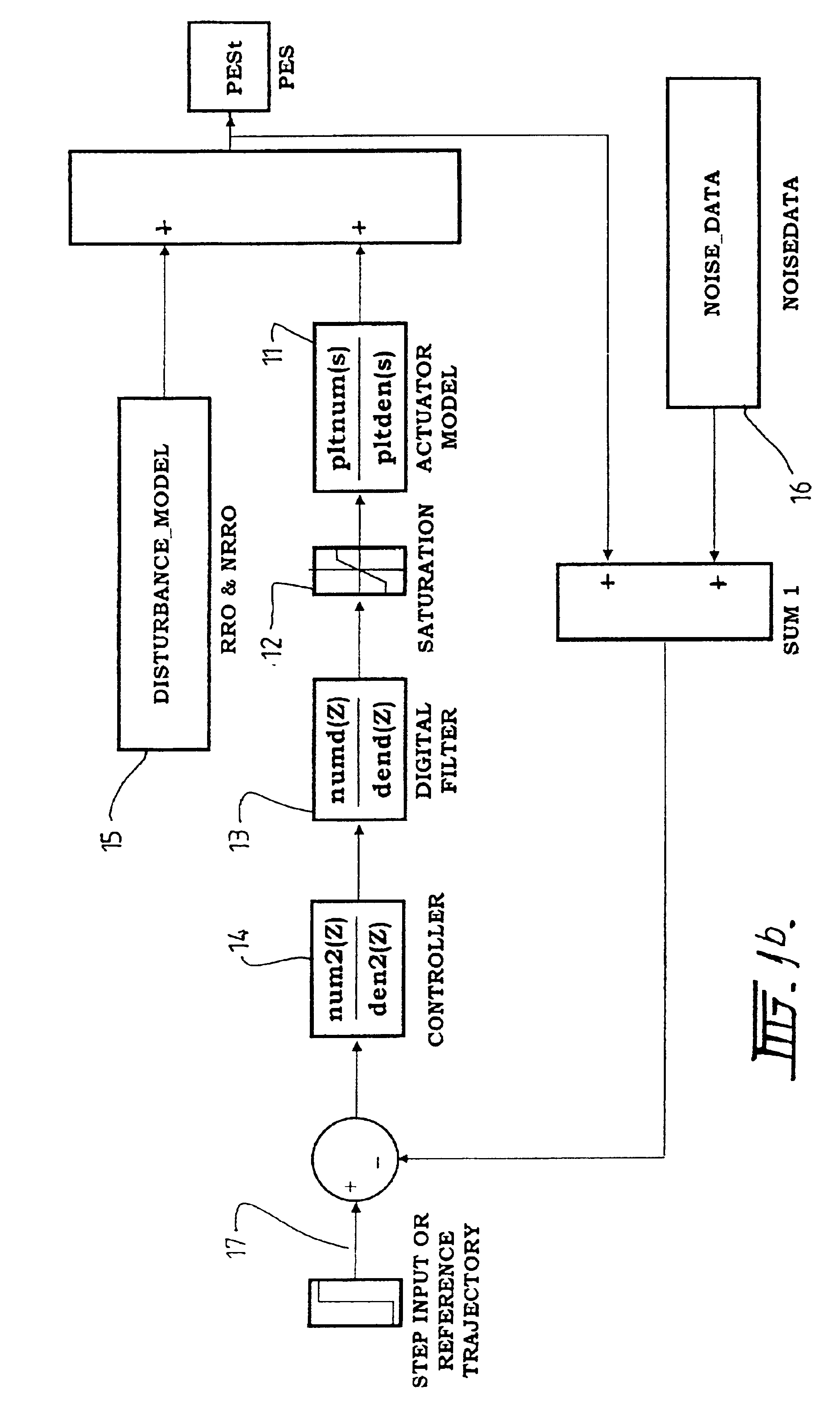
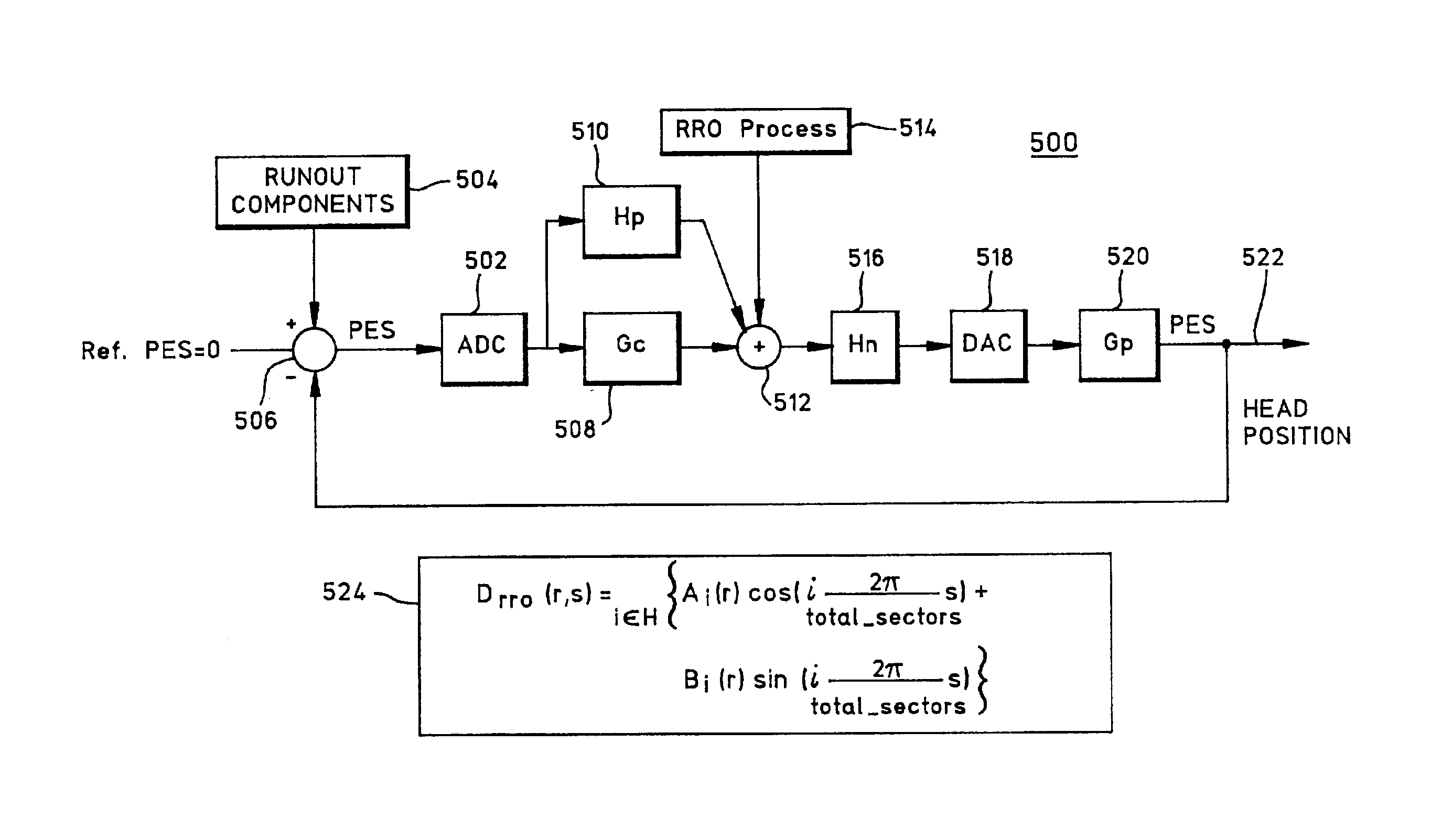
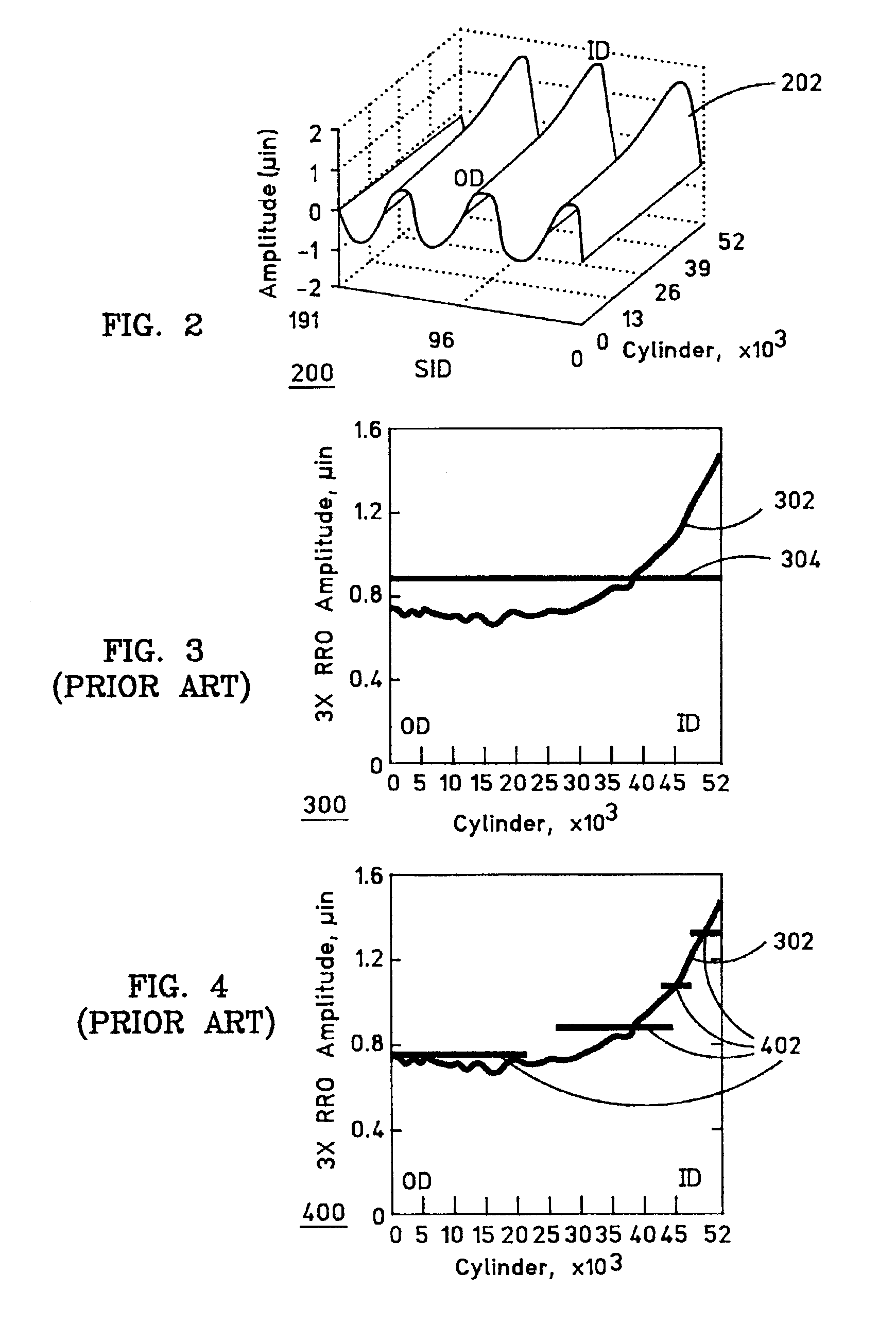
Repeatable runout (RRO) compensation methods and apparatus for data storage devices
InactiveUS6937424B2Reducing RRO errorAccurate compensationTrack finding/aligningAlignment for track following on tapesLeast squaresHarmonic
In one illustrative example, a method for use in reducing Repeatable Run Out (RRO) error in a data storage device involves obtaining an RRO measurement for each track of a limited number of N disk tracks; characterizing the RRO measurement for each track with real and imaginary values by performing a discrete Fourier transform (DFT) calculation on each RRO measurement; performing a least-squares fit on all of the real values to identify a first set of (n+1) coefficients of an nth-order polynomial function which is a function of disk track r and representable in the form Ai(r)=anrn+a(n−1)r(n−1)+ . . . +a1r+a0; and performing a least-squares fit on all of the imaginary values to identify a second set of (n+1) coefficients of an nth-order polynomial function which is a function of disk track r and representable in the form Bi(r)=bnrn+b(n−1)r(n−1)+ . . . +b1r+b0. RRO compensation is performed based on the relation DRRO(r, s)=Σi for all H {Ai(r)cos(i(s2π / total_sectors))+Bi(r)sin(i(s2π / total_sectors))} where DRRO is the estimated RRO error; r is a track number; s is a sector number at track number r; i is an RRO harmonic number; H is a set of harmonics to be compensated; and total_sectors is a total number of sectors along track number r. Advantageously, RRO variations across the disk can be accurately compensated for with use of a small amount of memory.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
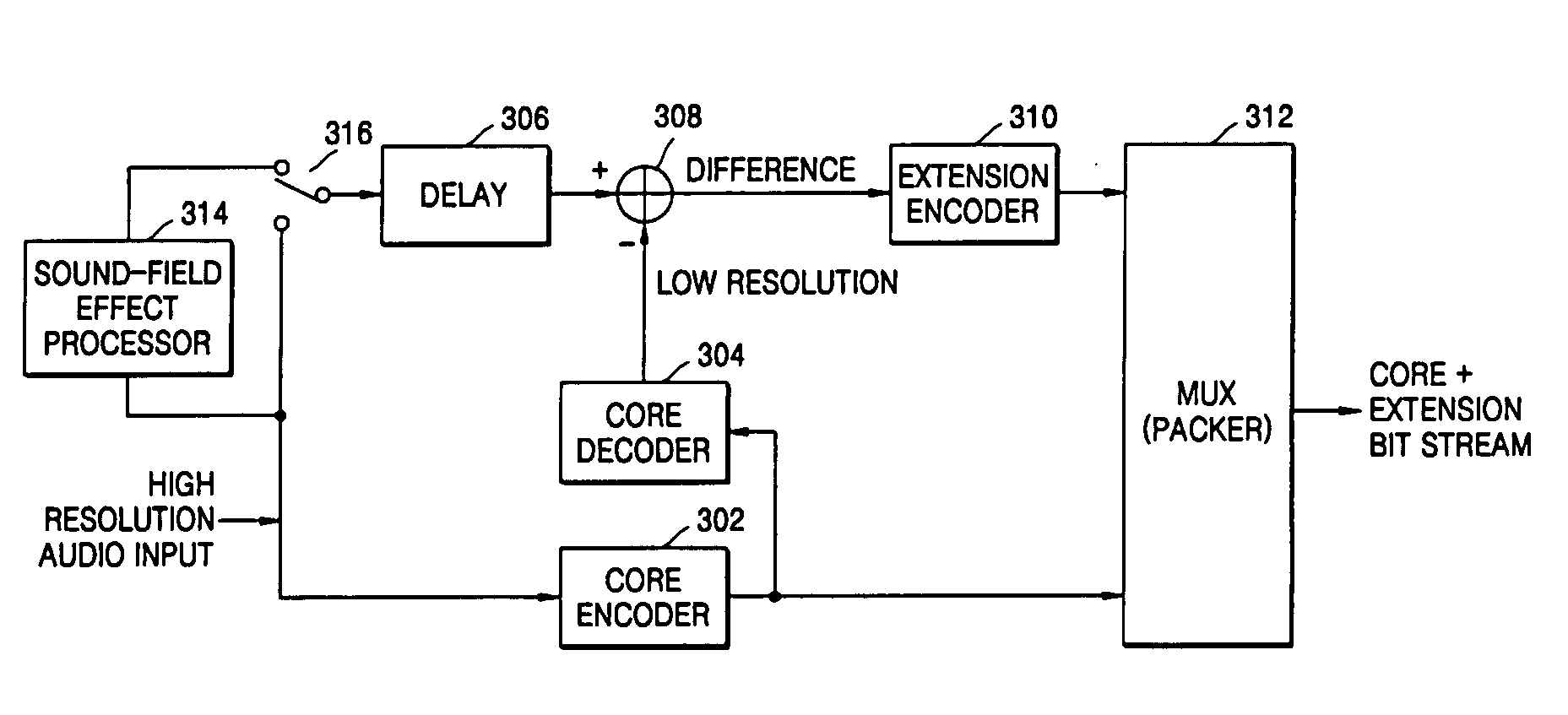
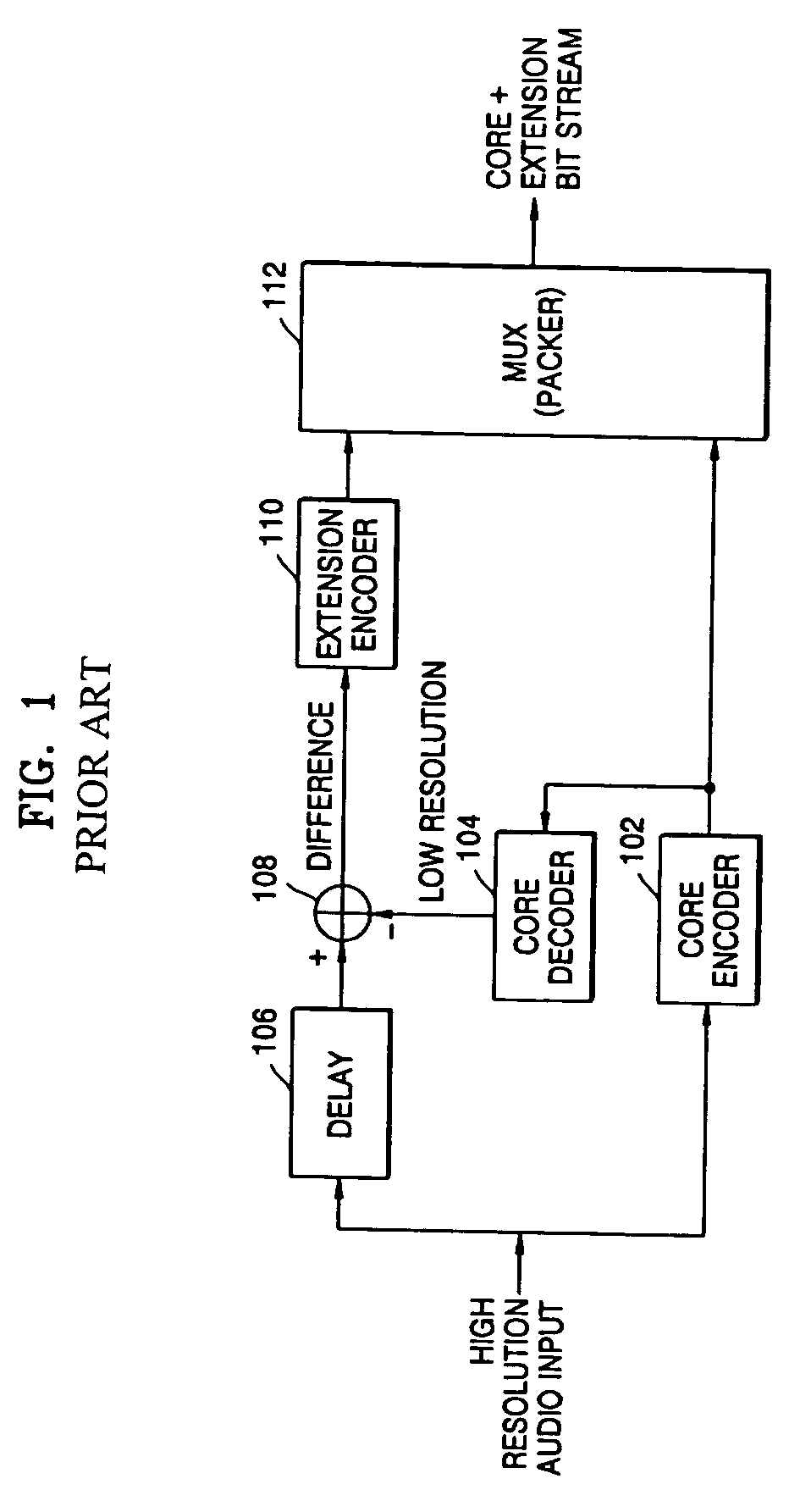
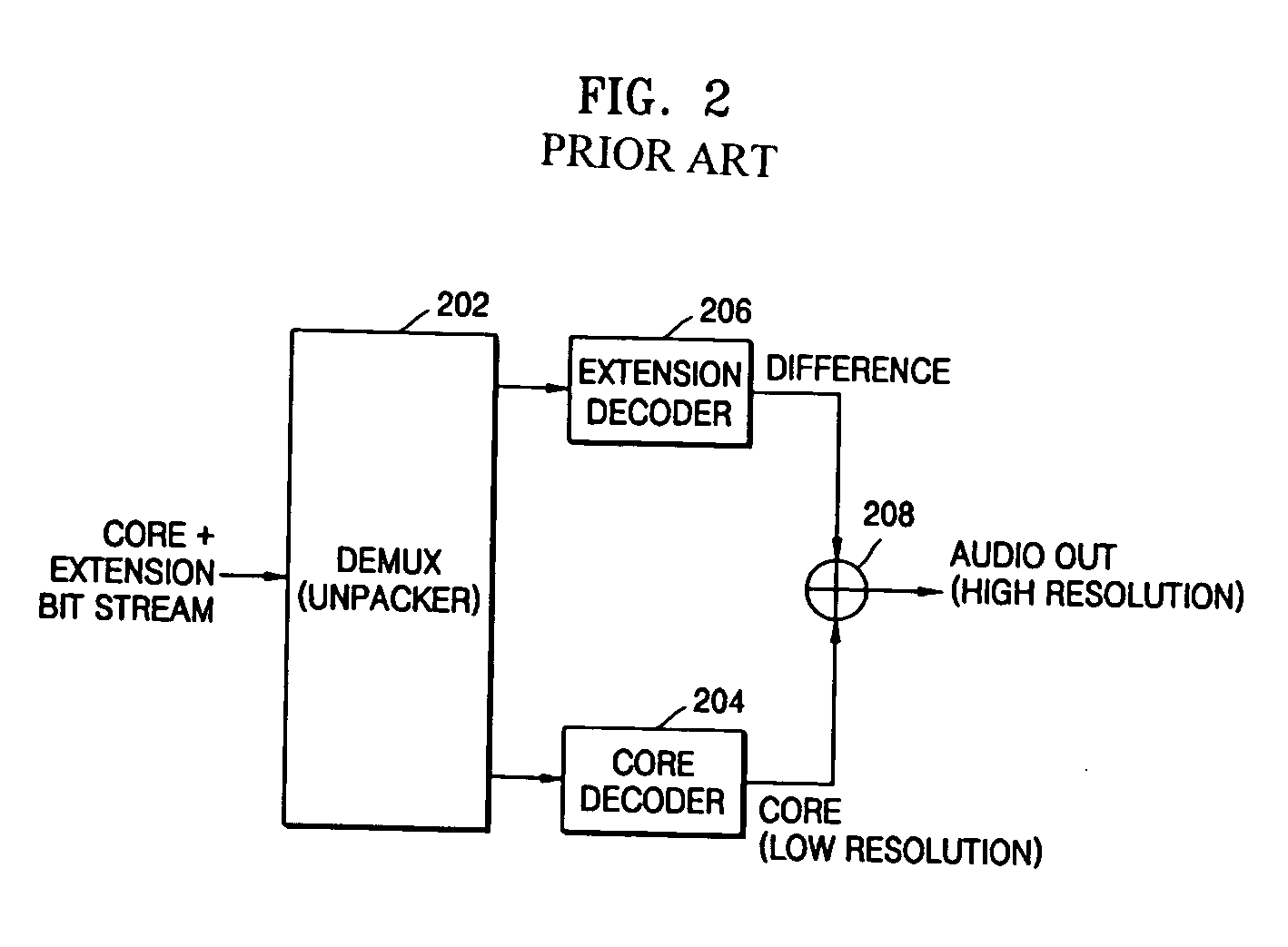
Audio signal encoding and decoding apparatus
An audio signal encoding and decoding apparatus capable of transmitting an audio signal or an audio signal together with a sound-field-effect-processed audio signal are provided. The audio signal encoding apparatus includes a core encoder to encode an input audio signal according to an audio signal encoding standard, a core decoder to decode the encoded audio signal output from the core encoder, a sound-field-effect processor to perform a sound-field-effect process on the input audio signal, a selector to selectively output the input audio signal or the sound-field-effect-processed audio signal output from the sound-field-effect processor, a subtraction unit to calculate a difference signal between the signals output from the core decoder and the selector, an extension encoder to encode the difference signal output from the subtraction unit according to an arbitrary encoding scheme and to output the extension encoded signal, and a multiplexer to multiplex the encoded audio signal output from the core encoder and the extension encoded signal output from the extension encoder into a composite encoded signal and to output the composite encoded signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
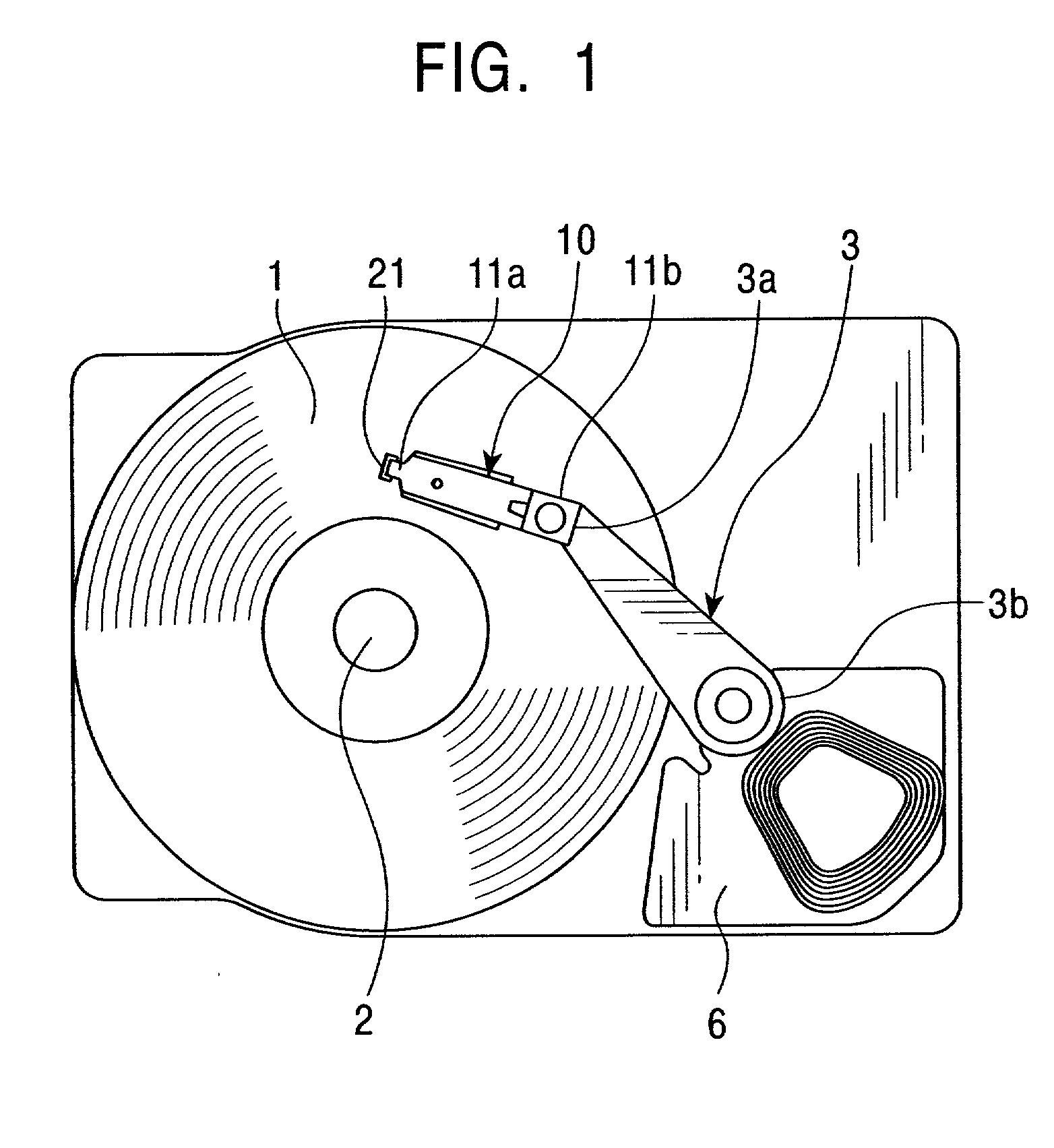
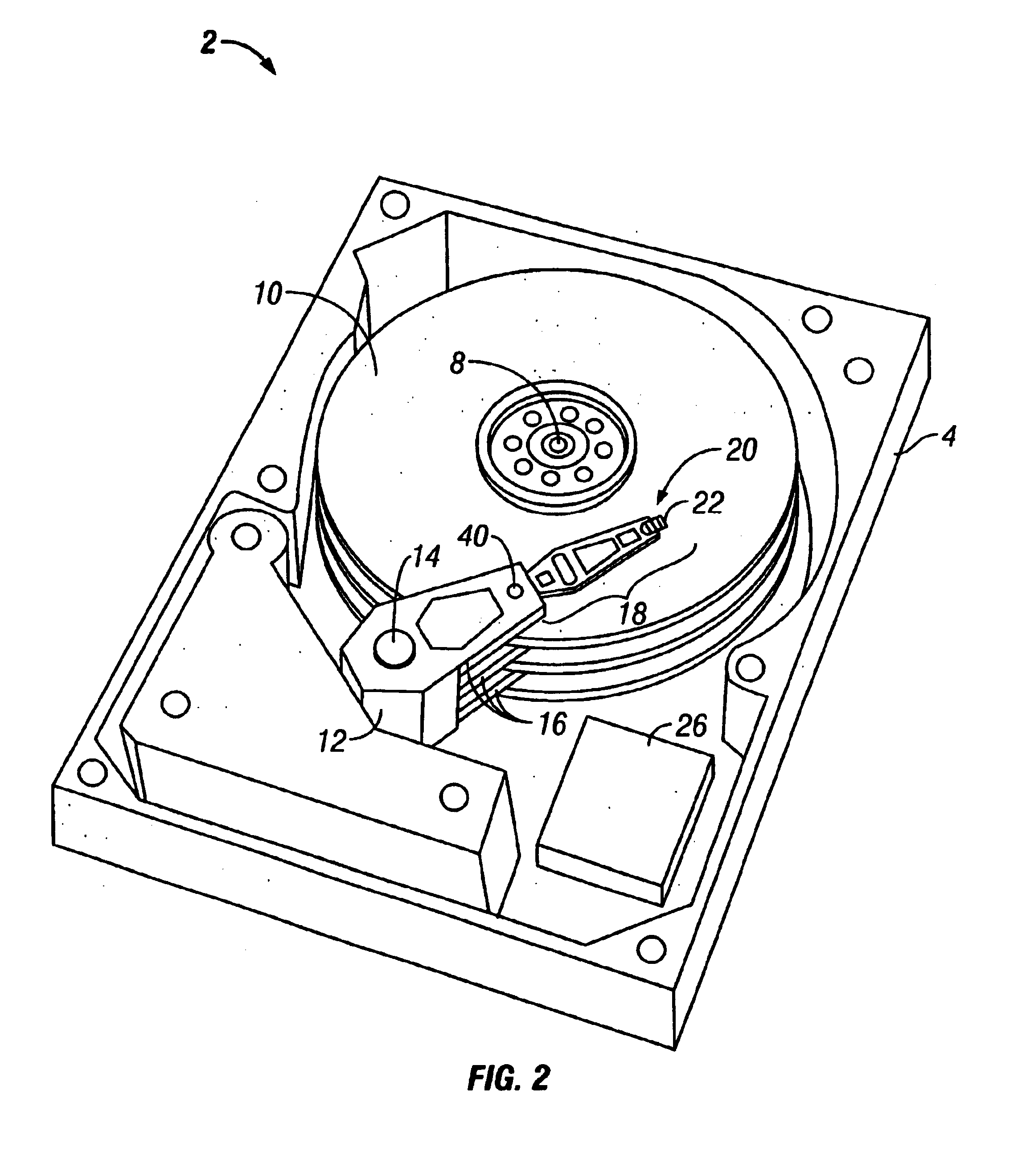
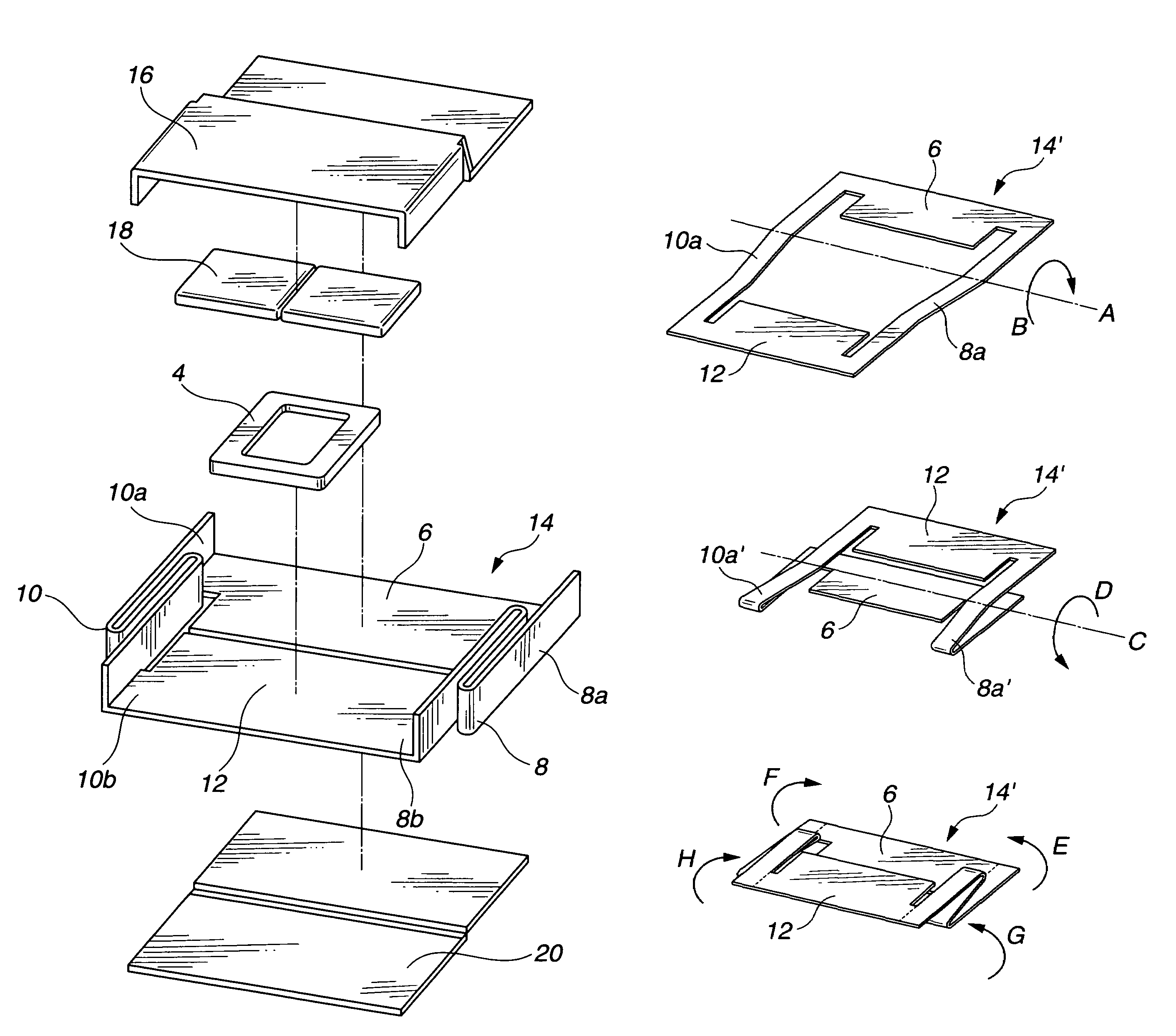
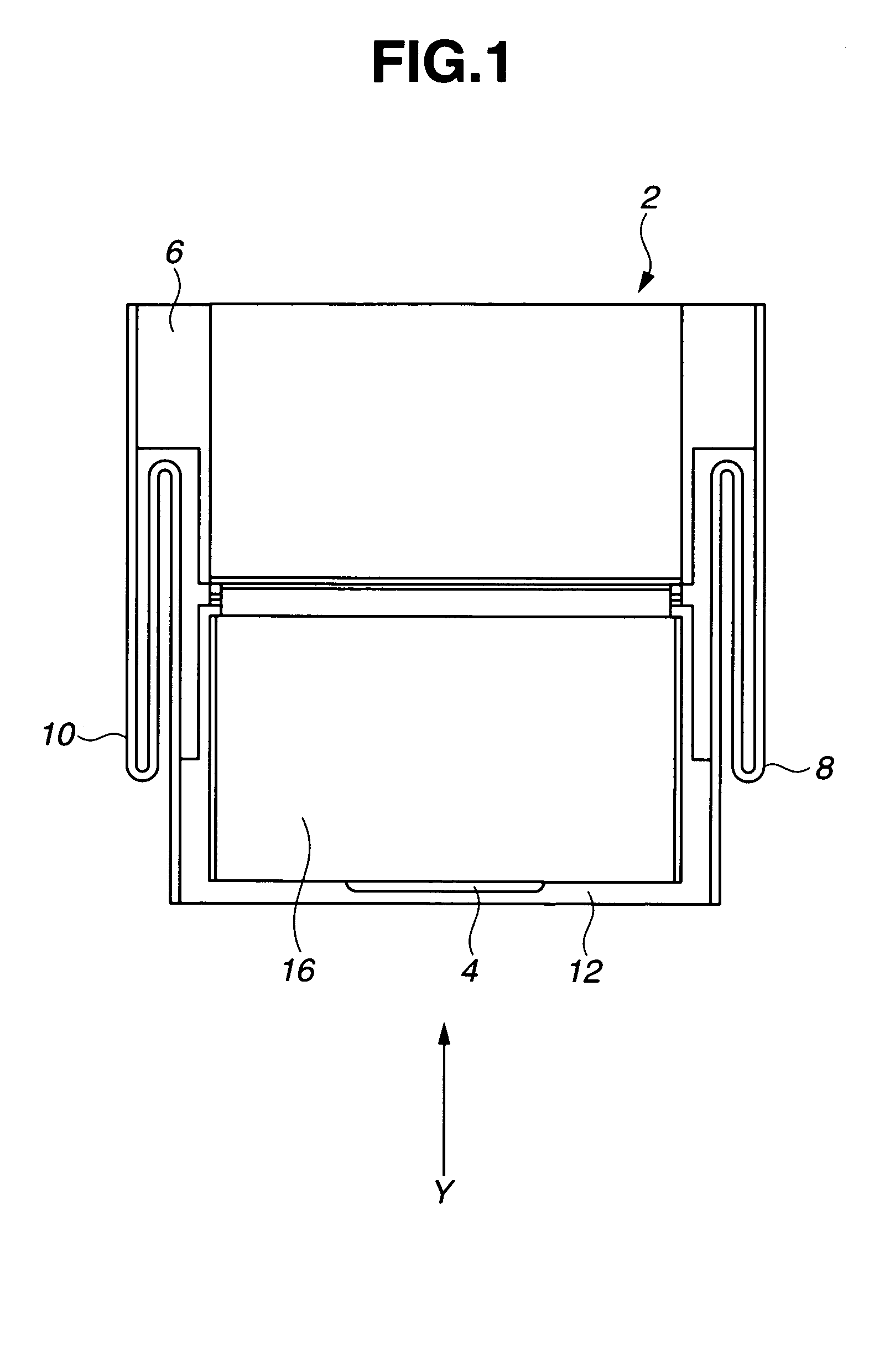
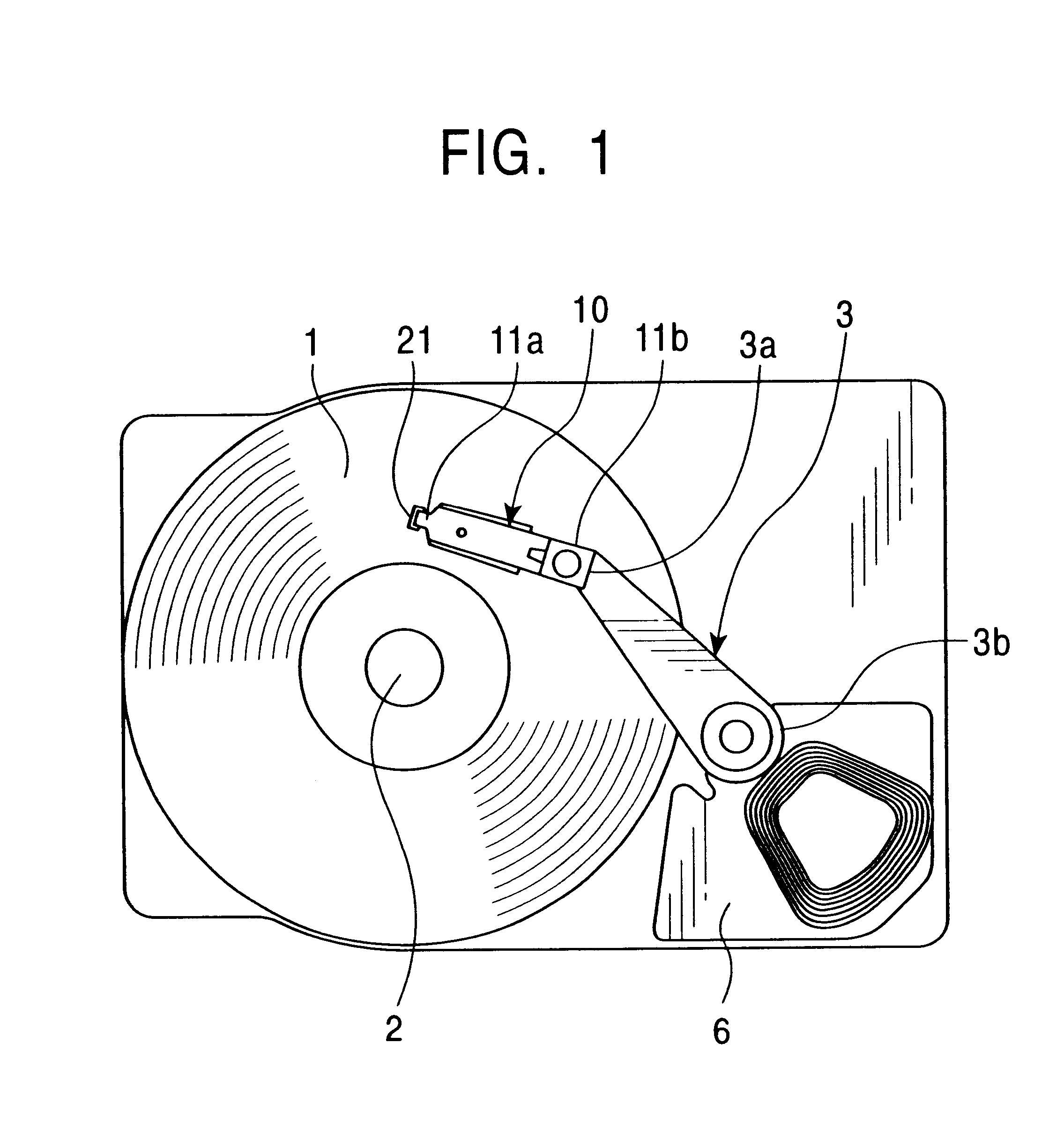
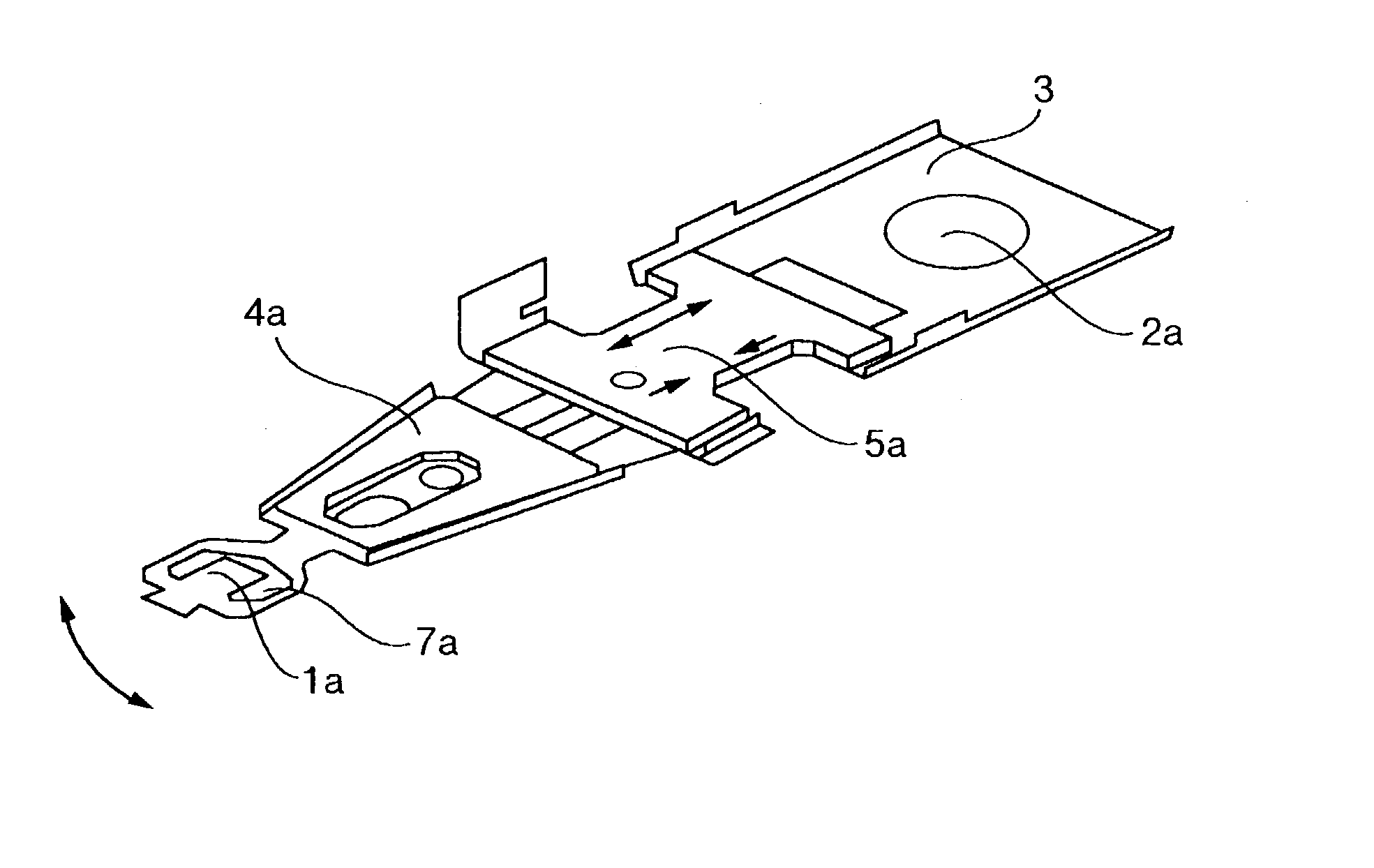
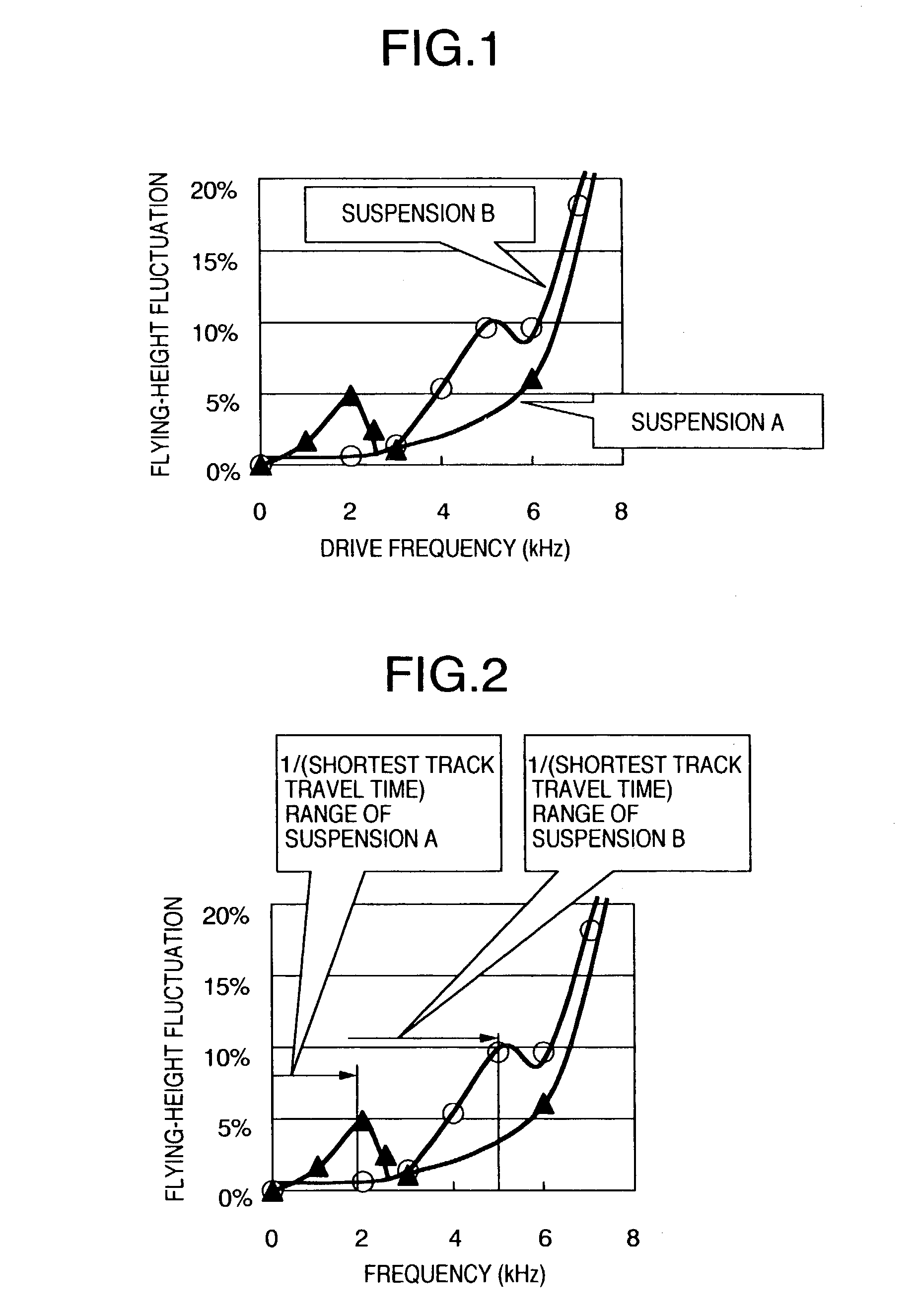
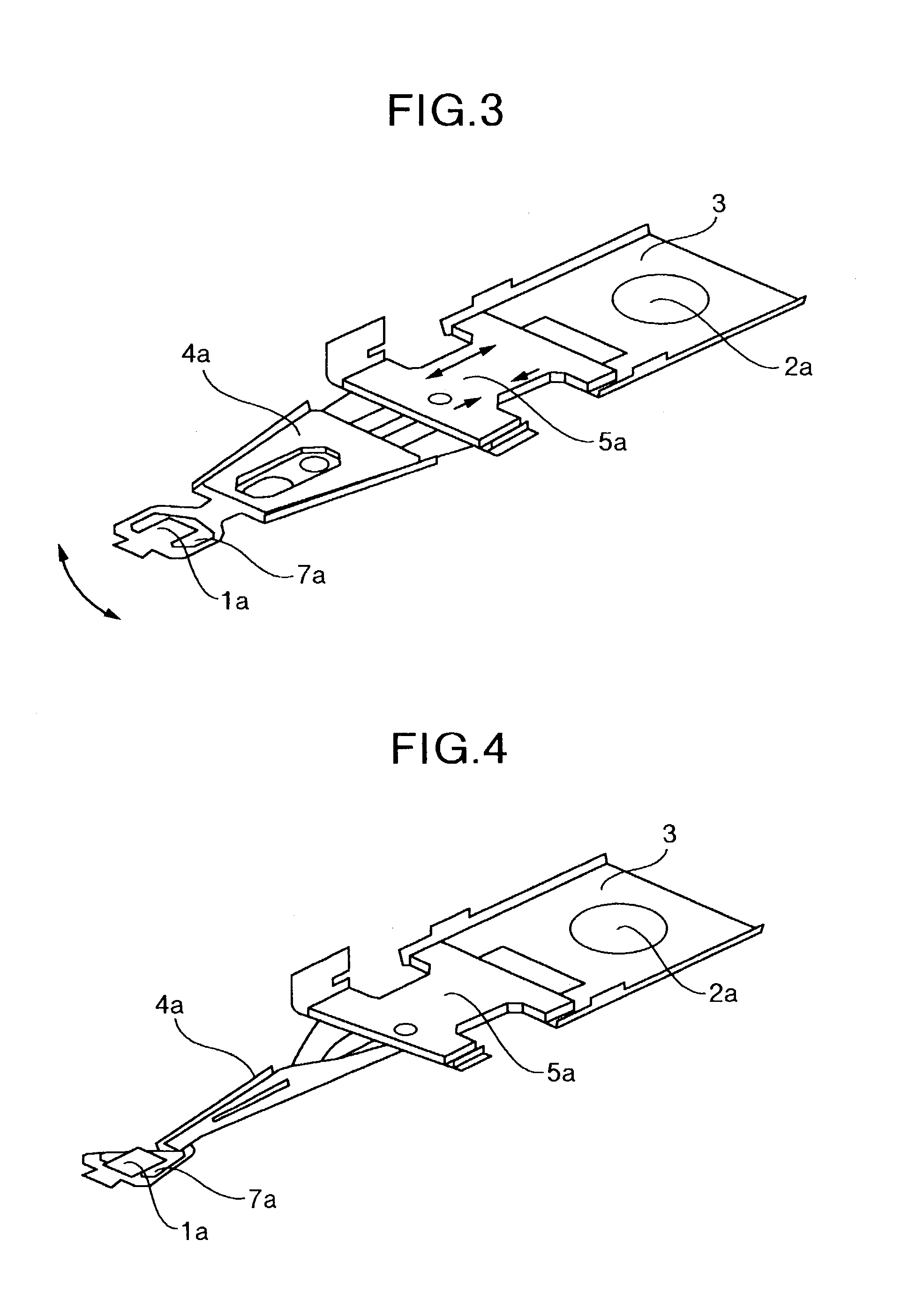
Disk drive
There is provided a magnetic disk drive in which a flying-height fluctuation produced by the operation of a fine actuator is decreased, the reliability is high, and recording density is high. For this purpose, the magnetic disk drive is configured as described below. The magnetic disk drive has a suspension including a base plate connected to a carriage, a load beam fitted with a slider, and a fine actuator which is provided on the base plate and finely moves the load beam. The configuration is such that the shortest track travel time using the fine actuator is larger than the inverse number of the local maximum of a flying-height fluctuation frequency of the suspension by the fine actuator. Also, the configuration is such that the shortest track travel time using the fine actuator is larger than the inverse number of the natural frequency of first torsion mode of the suspension by the fine actuator.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH JAPAN LTD +1
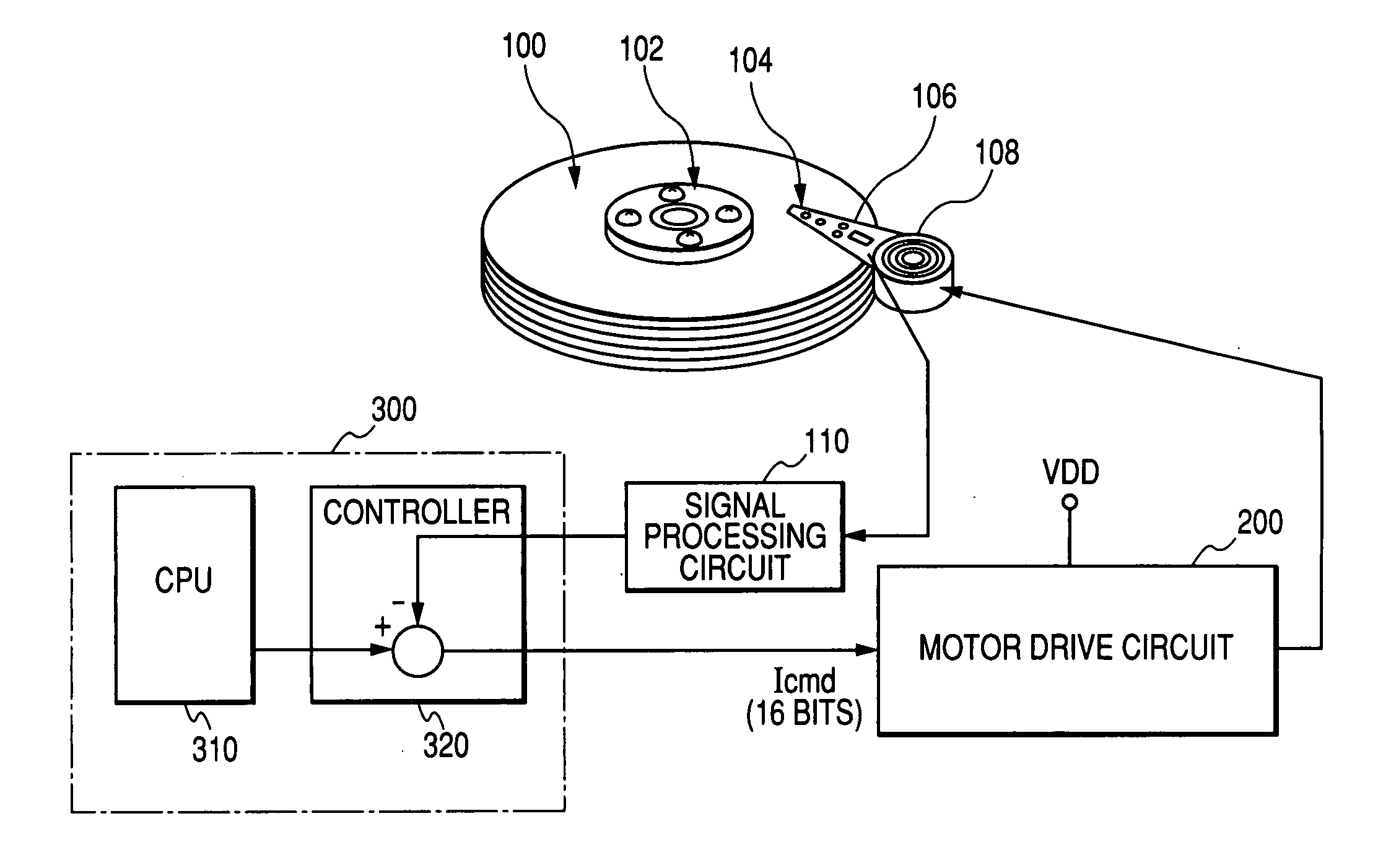
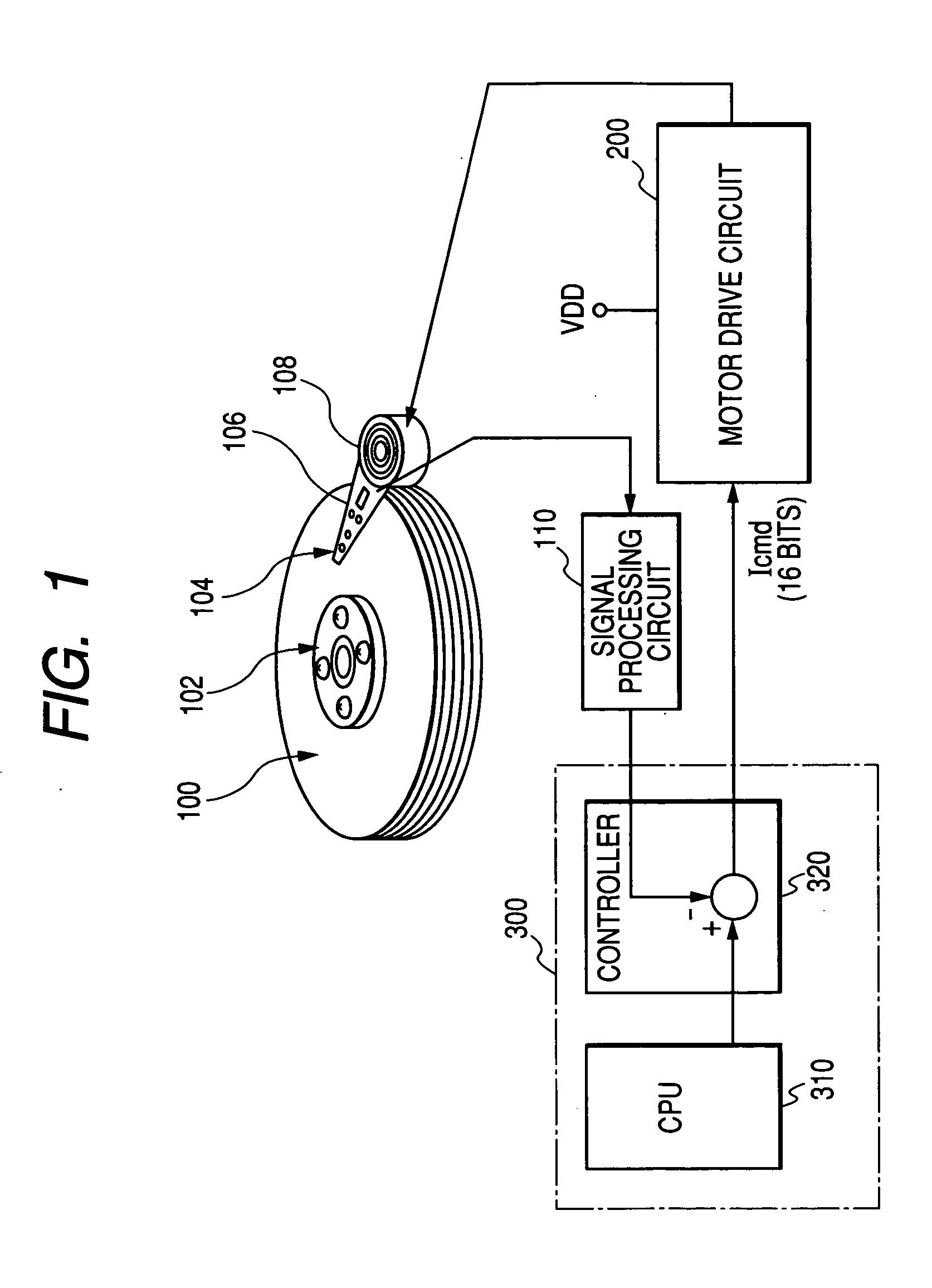
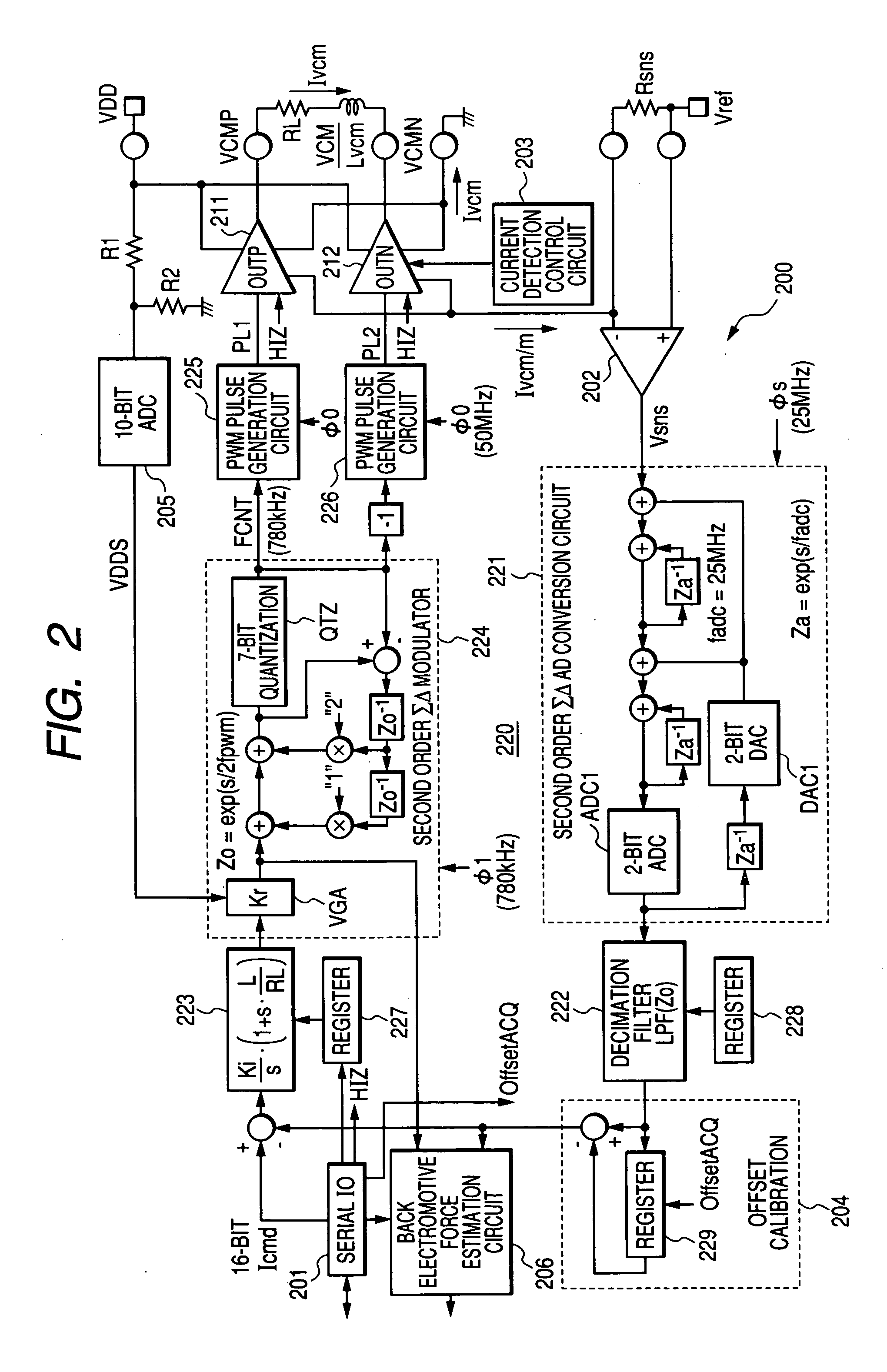
Motor drive semiconductor integrated circuit and magnetic disk storage apparatus
InactiveUS20050218853A1High precision driving controlAccurate detectionTrack finding/aligningAC motor controlHead movementsEngineering
The Invention provides a motor drive semiconductor integrated circuit for driving and controlling a voice coil motor that can conduct a seek operation, a track follow operation and a settling operation through PWM control, has desired control accuracy and can be produced by a CMOS process. In a voice coil motor drive circuit (200) for executing positioning control of a magnetic head by feedback-controlling a driving current of a voice coil motor (108) for moving a magnetic head (106) over a magnetic disk for reading information from a storage track on the magnetic disk driven for rotation while a read state of the magnetic head is being monitored, head movement control such as a seek operation, a track follow operation etc, of the magnetic head is executed by PWM driving on the basis of a command value from a controller.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
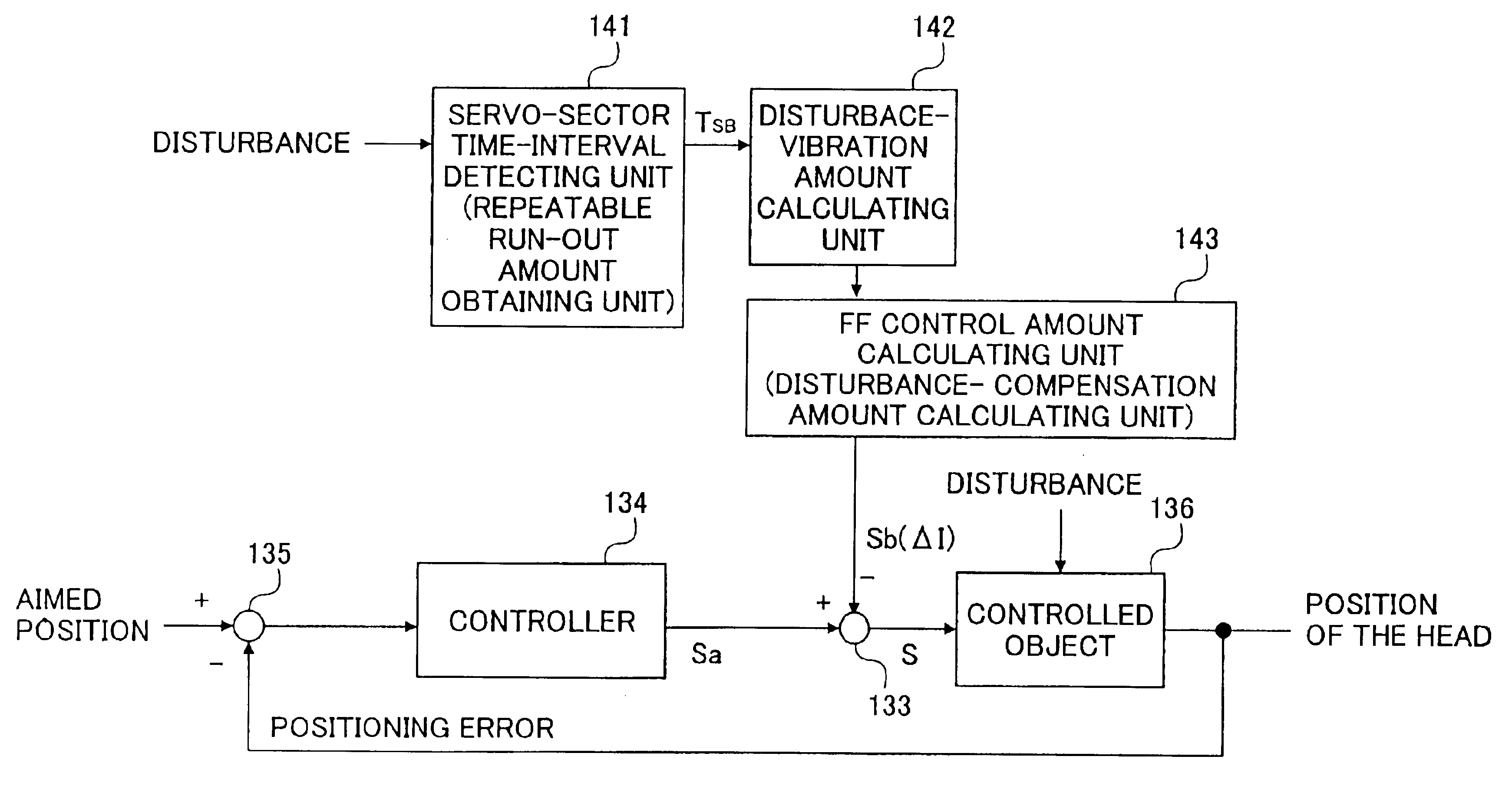
Disk device conducting a disturbance compensation based on a time-interval measurement in reading servo sectors recorded on a disk
Owner:TOSHIBA STORAGE DEVICE CORP
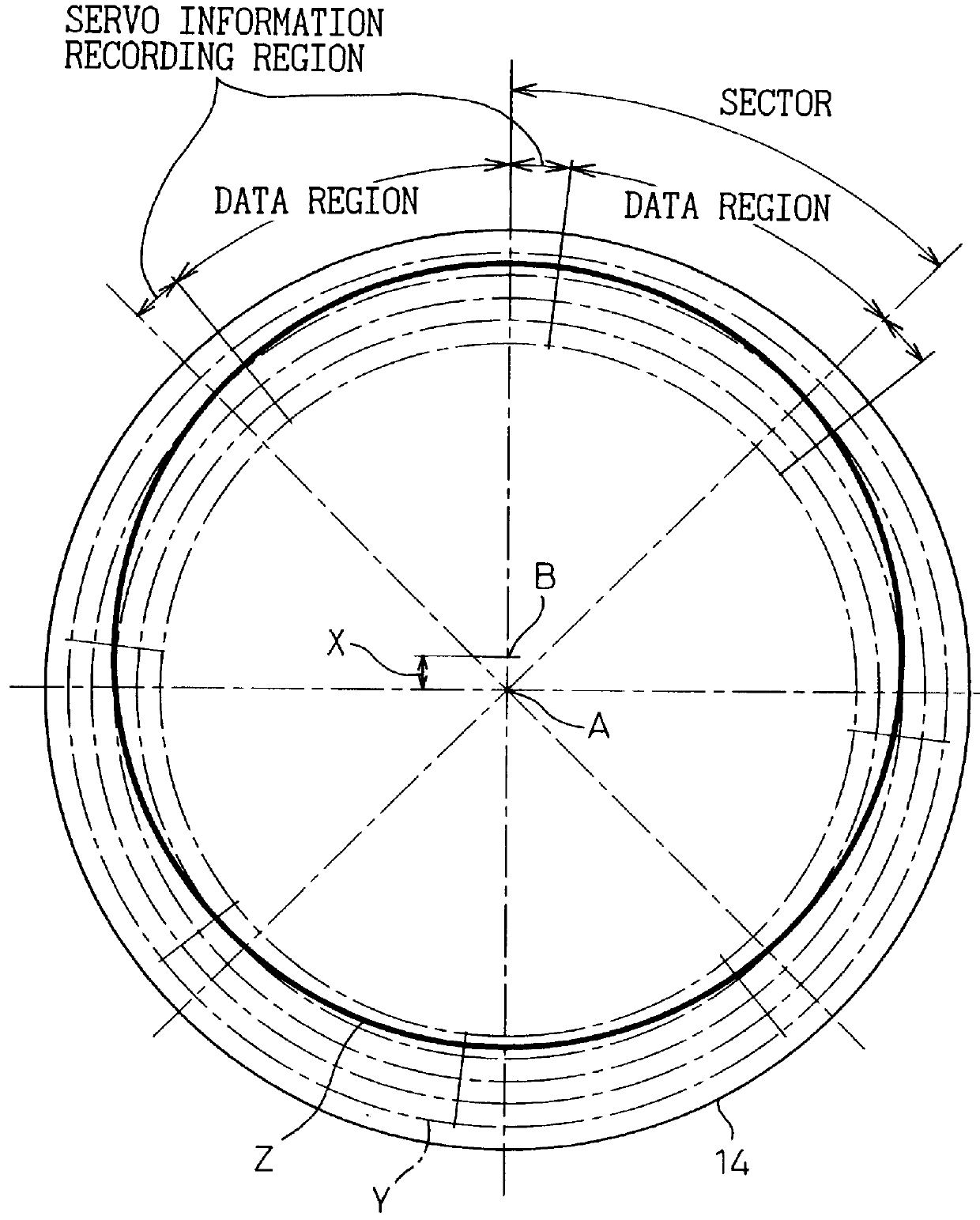
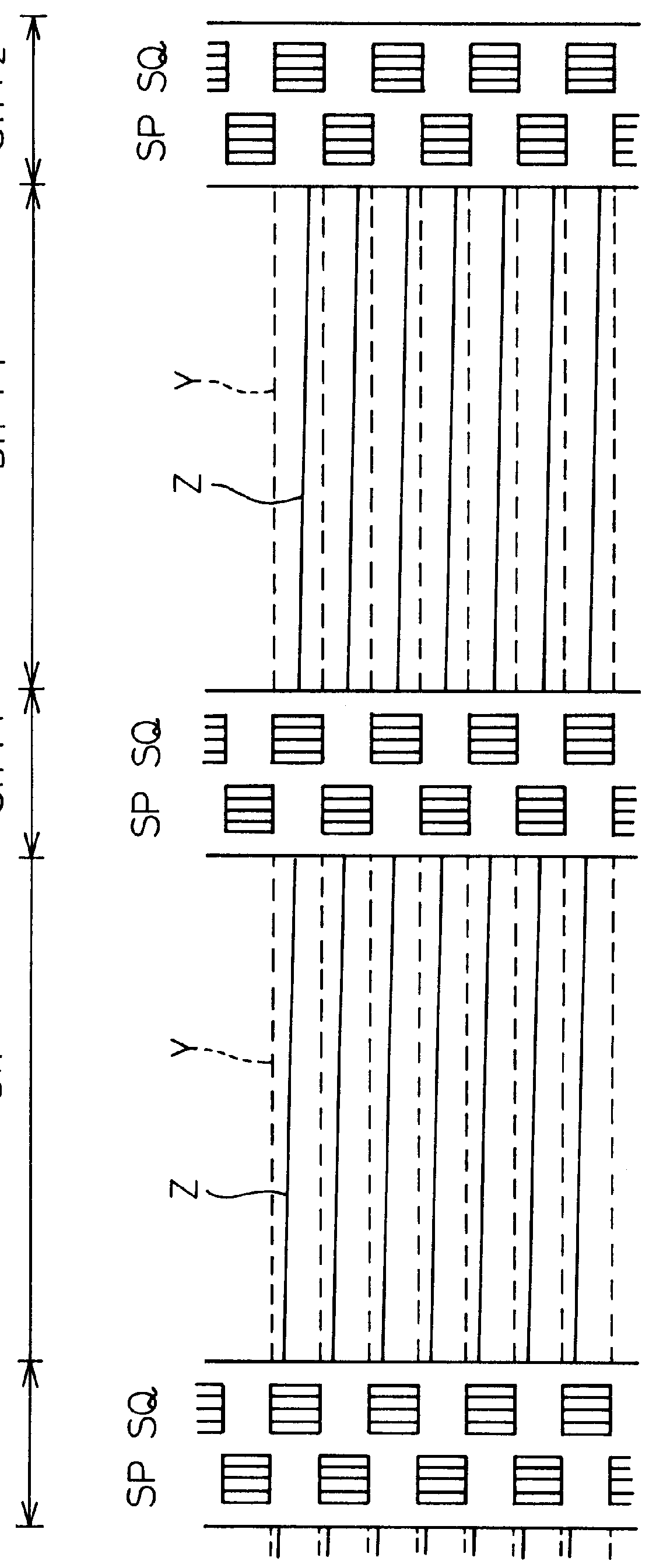
Disk device and disk medium, in which a plurality of servo cylinders formed concentrically from the inner diametrical portion to the outer diametrical portion of at least one disk are divided into predetermined areas
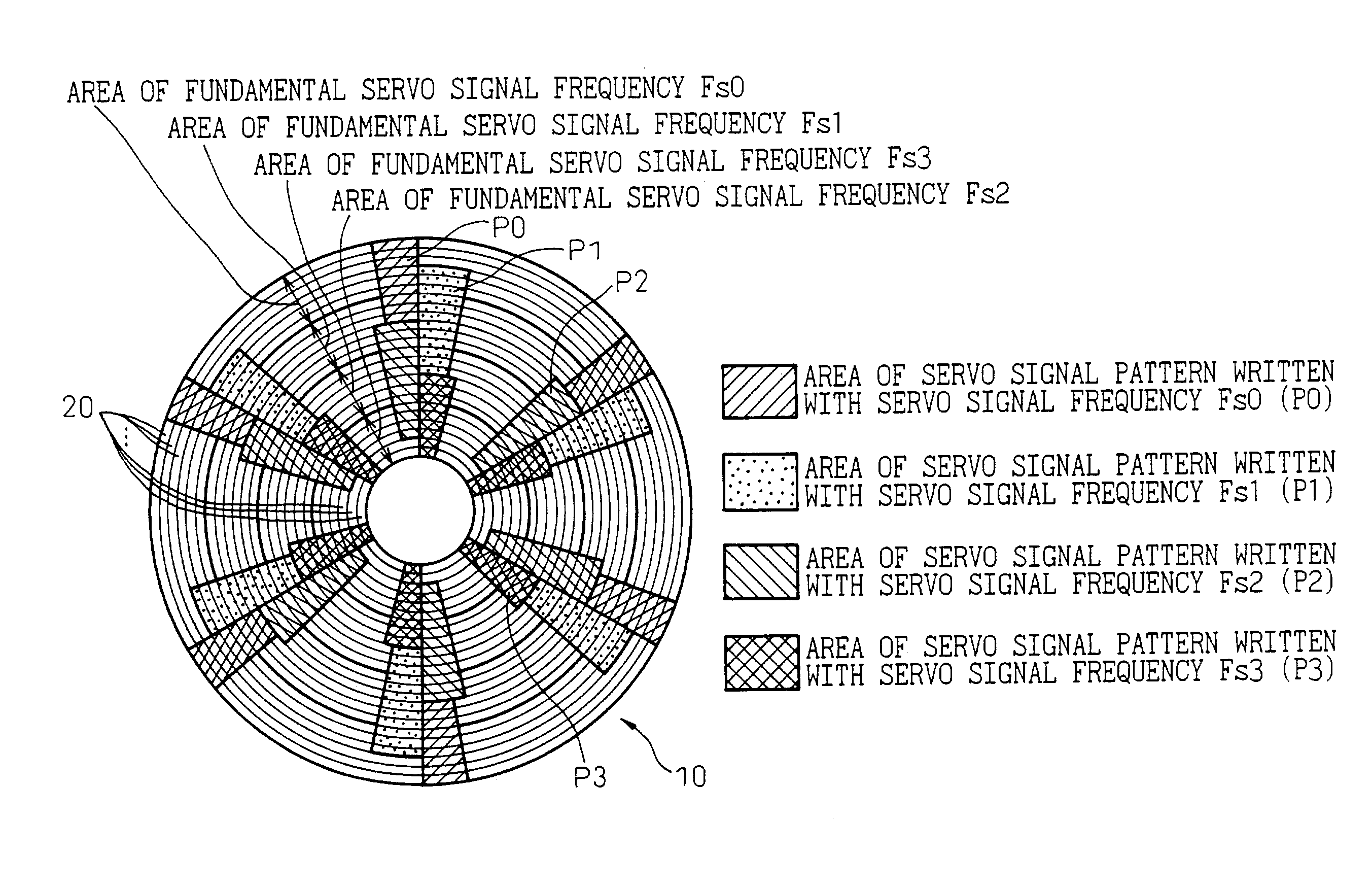
InactiveUS7012773B2Optimization rangeAccurate estimateTrack finding/aligningRecord information storageRecording densityControl theory
A disk device and a disk medium are disclosed in which a plurality of servo cylinders on the surface of at least one disk are divided into several areas, and a different servo signal frequency is set and recorded for each of the areas. The servo cylinders are divided into predetermined areas, and a different servo signal frequency for each of the areas is set so that the recording density of the servo signal recorded in the disk can be set so as to allow the servo signal demodulation characteristic to be included in a relatively superior range. In the disk device, the boundary between the area of a first servo signal frequency and the area of a second servo signal frequency adjoining the first servo signal frequency area is preferably formed with an area in which a servo signal pattern written with the first servo signal frequency and a servo signal pattern written with the second servo signal frequency are arranged on the same servo cylinders.
Owner:TOSHIBA STORAGE DEVICE CORP
Head suspension including integral piezoelectric element electrode support member
ActiveUS8331061B2Simple manufacturing processImprove assembly accuracyTrack finding/aligningArm with actuatorsMechanical engineeringElectrode
Owner:NHK SPRING CO LTD
Precise positioning actuator for head element, head gimbal assembly with the actuator and disk drive apparatus with the head gimbal assembly
InactiveUS6934127B2Improve seismic performanceStable and reliable adhesionTrack finding/aligningRecord information storageEngineeringActuator
A precise positioning actuator for precisely positioning at least one head element is provided with a base and a pair of movable arms capable of displacing in response to a drive signal applied to the actuator. The pair of movable arms extend from the base for catching a head slider with at least one head element in a space between the pair of movable arms. Each of the pair of movable arms includes an arm member made of an elastic sintered ceramic and having substantially the same cross sectional shape from a root thereof to a top end thereof, a piezoelectric element formed on a side surface of the arm member and a protrusion additionally formed on an inside surface of the arm member near its top end section. The protrusion has tapered surfaces. Side surfaces of the head slider are adhered to the inside surfaces of the arm members at the protrusions and within regions between the protrusions and top ends of the arm members.
Owner:SAE MAGNETICS (HK) LTD
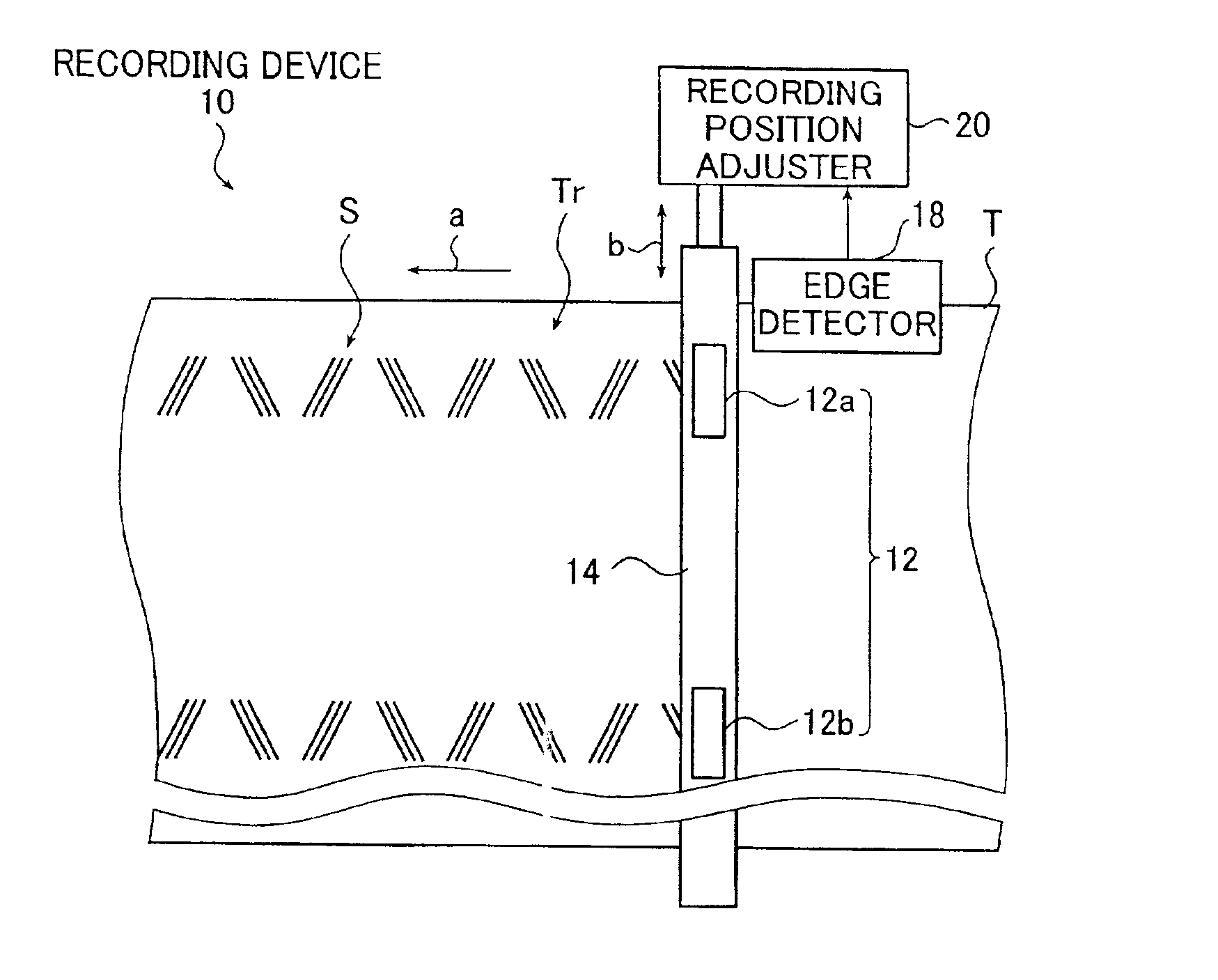
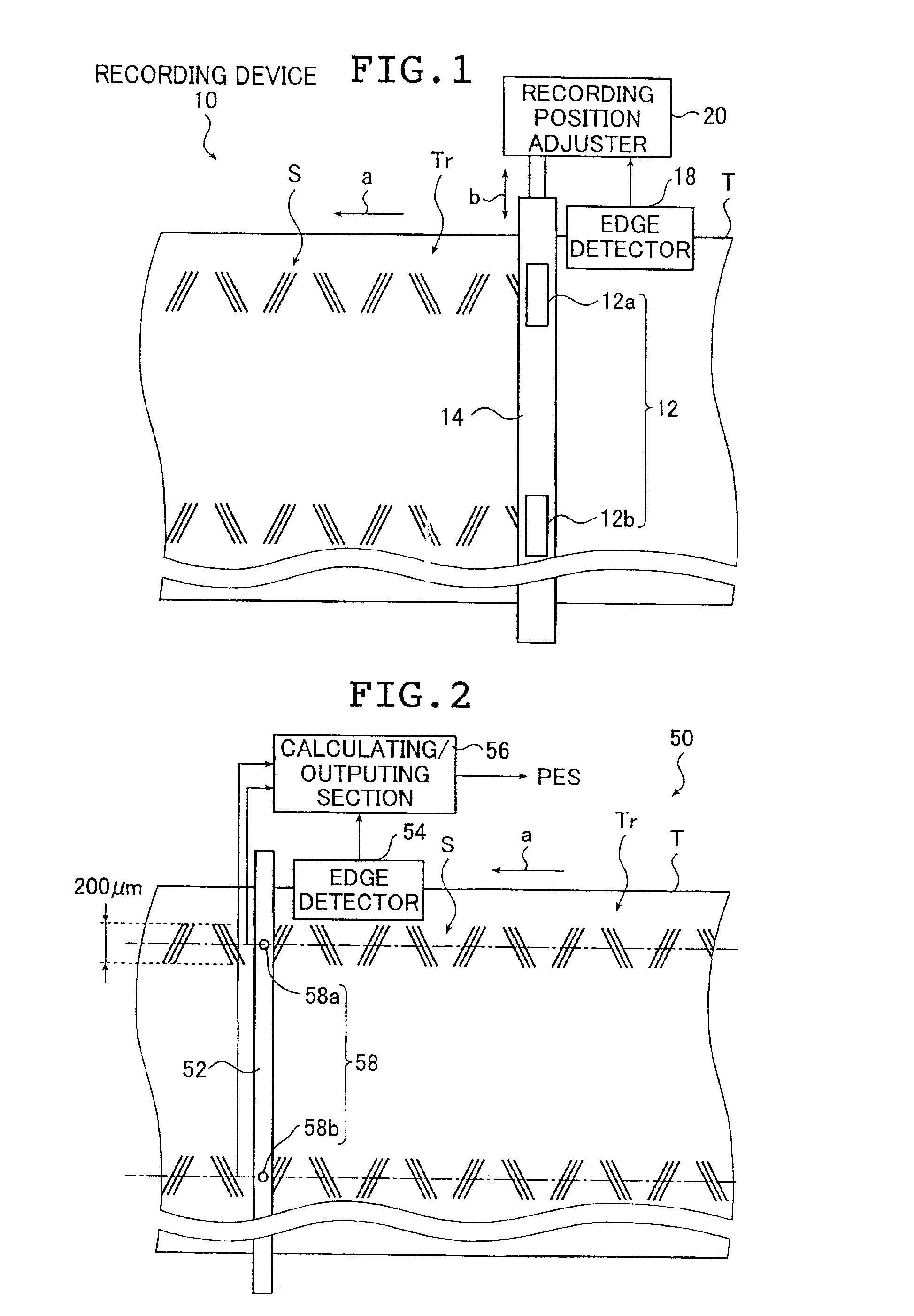
Servo signal recording device and servo signal verifying device using edge detection
InactiveUS6865050B2Accurate verificationAppropriately evaluatedTrack finding/aligningAlignment for track following on tapesMagnetic tapeControl theory
The servo signal recording device records a servo signal onto a magnetic tape. The device includes a transporting unit for transporting the magnetic tape along its lengthwise direction, a recording unit for recording the servo signal onto the transported magnetic tape, a detecting unit for detecting an edge of the magnetic tape at a time when the servo signal is recorded and an adjusting unit for adjusting a recording position of the servo signal along a crosswise direction of the magnetic tape in accordance with a detection result of the edge of the magnetic tape by the detecting unit. The servo signal verifying device verifies a servo signal recorded onto a magnetic tape. The device includes a reproducing unit for reproducing the servo signal, a detecting unit for detecting an edge of the magnetic tape at a time when the reproducing unit reproduces the servo signal and a calculating unit for calculating a verification result of the servo signal recorded onto the magnetic tape using a reproduction result of the servo signal and a detection result of the edge.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com