Patents
Literature
633 results about "Dynamic storage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
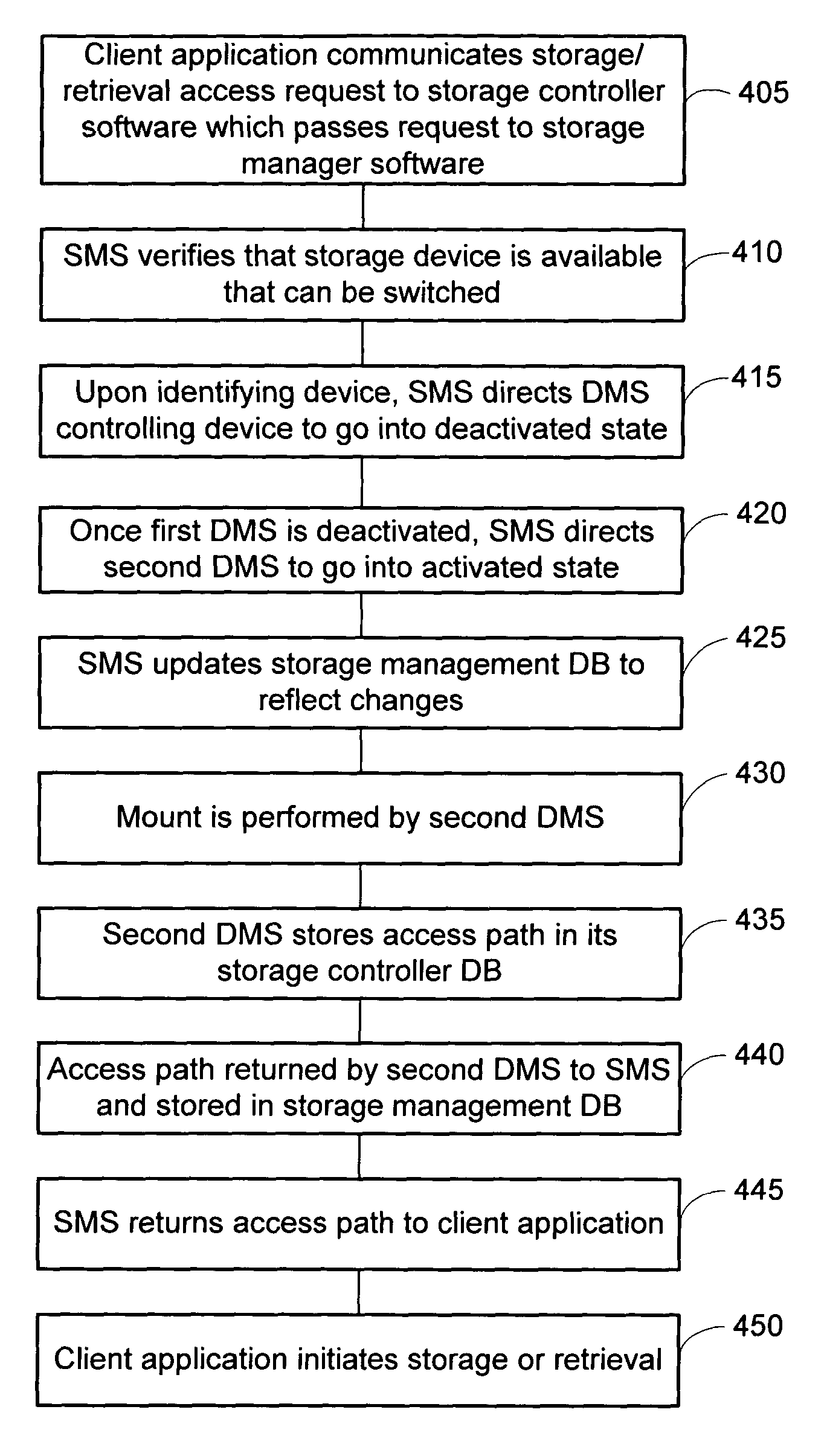
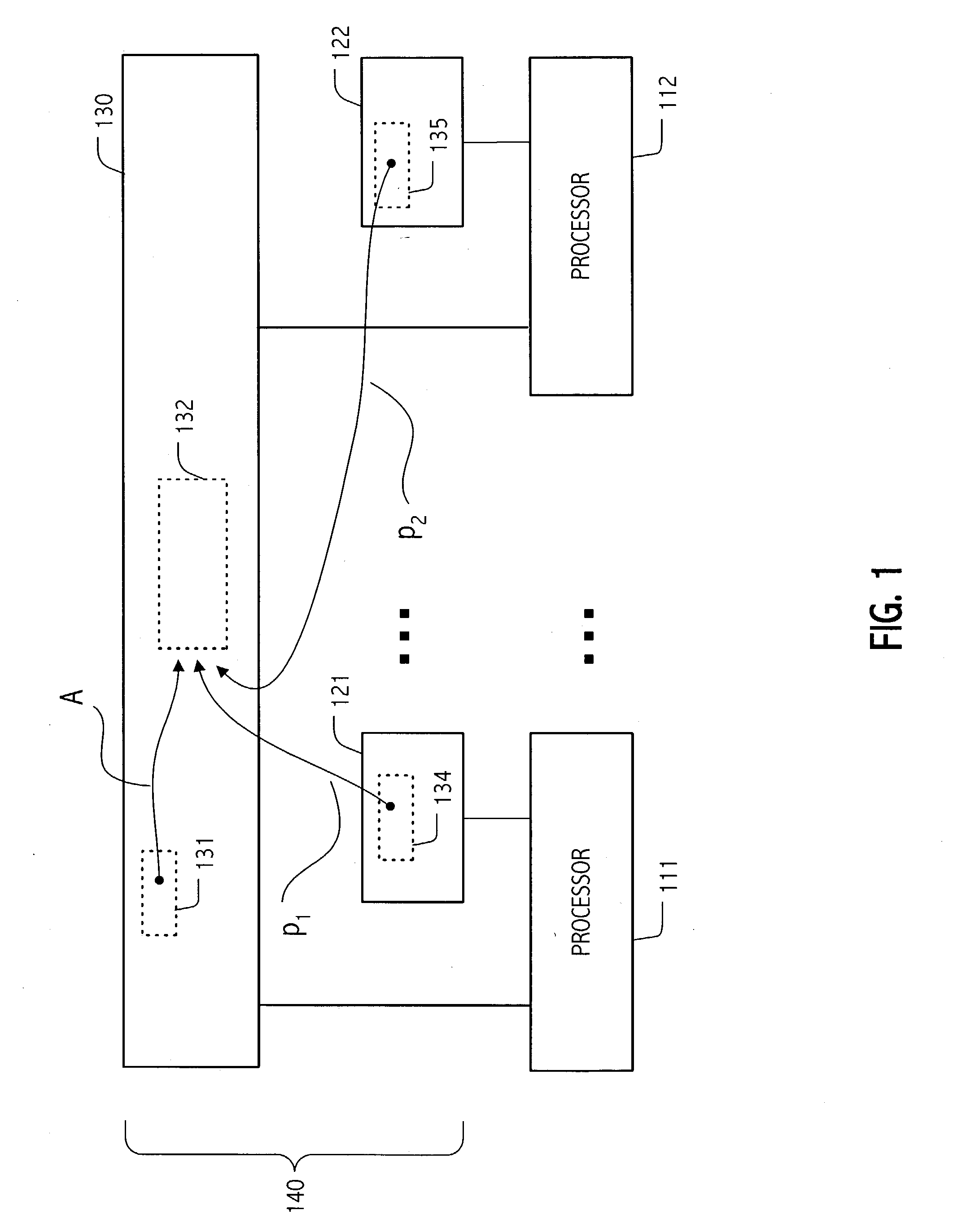
Dynamic storage device pooling in a computer system
ActiveUS7130970B2Not affectInput/output to record carriersMemory loss protectionDynamic storageComputerized system
A method for dynamically allocating control of a storage device, the method comprising receiving an access request from a first computer requesting access to a storage device; directing, based upon the access request, a first storage controller computer to assume an inactive state with respect to control of the storage device; and directing, based upon the access request, a second storage controller computer to assume an active state with respect to control of the storage device.
Owner:COMMVAULT SYST INC
Method and apparatus for managing server load
InactiveUS6922724B1Resource allocationMultiple digital computer combinationsBalancing networkTime information
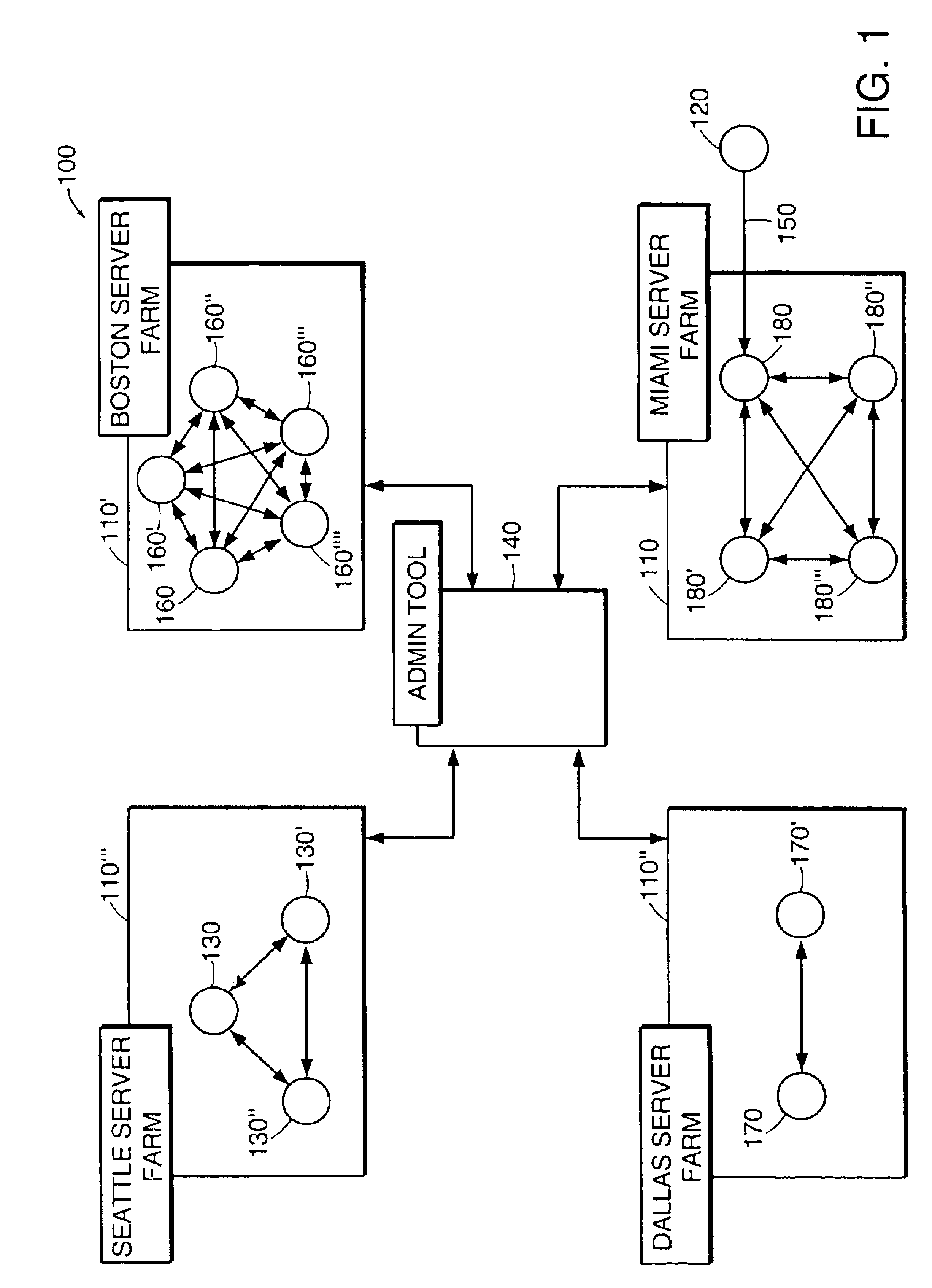
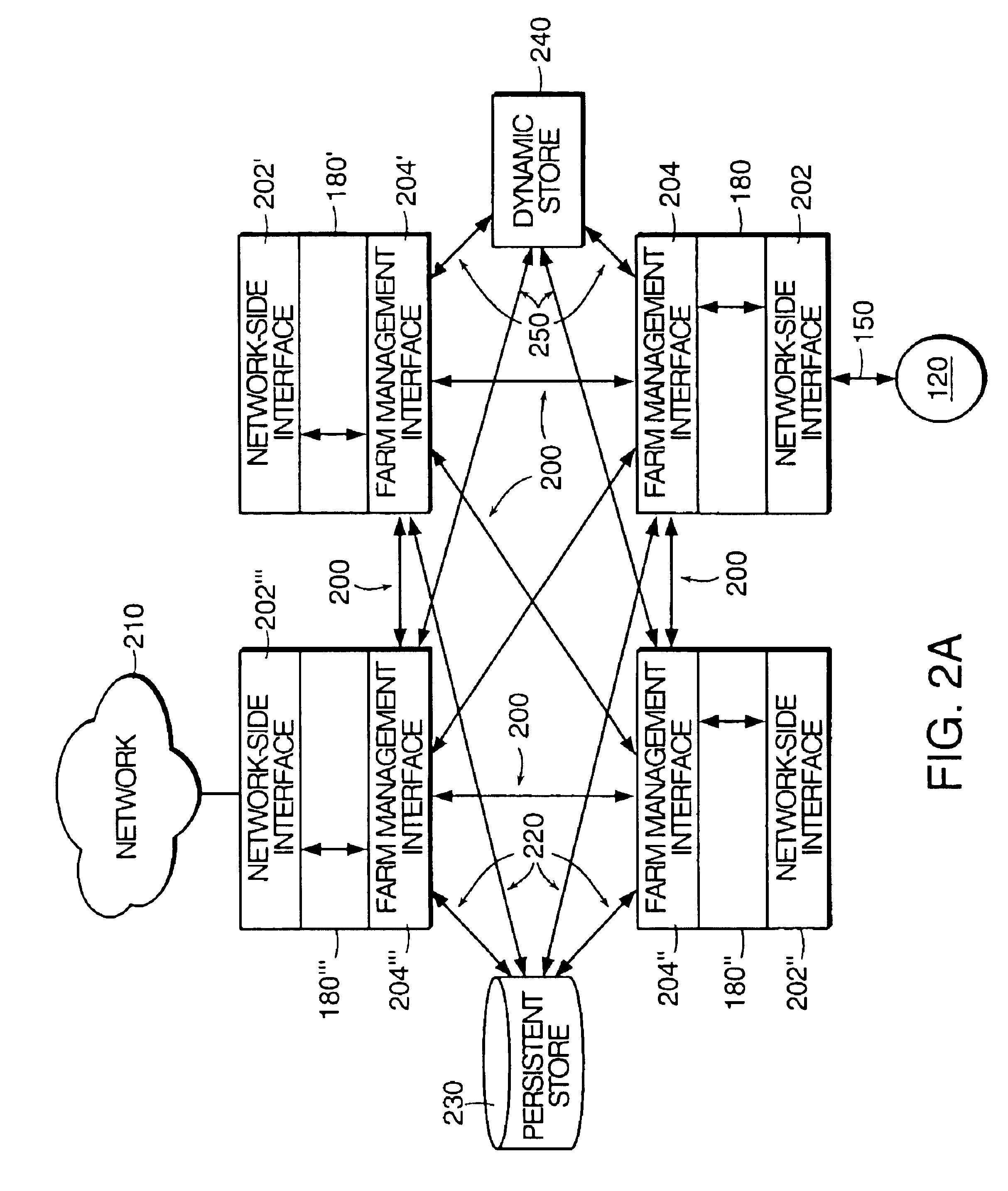
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for managing and balancing the load of each of the servers in the network. In one aspect, the invention relates to an apparatus for managing server load in a networked system of servers. The apparatus includes a dynamic store storing run-time information associated with a plurality of servers in a server farm. The apparatus also includes an event bus. The apparatus also includes a load management subsystem in communication with the dynamic store via the event bus. The load management subsystem receives a request from the event bus to identify a server and transmits a message to the event bus that includes an address of an identified server based on information from the dynamic store.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
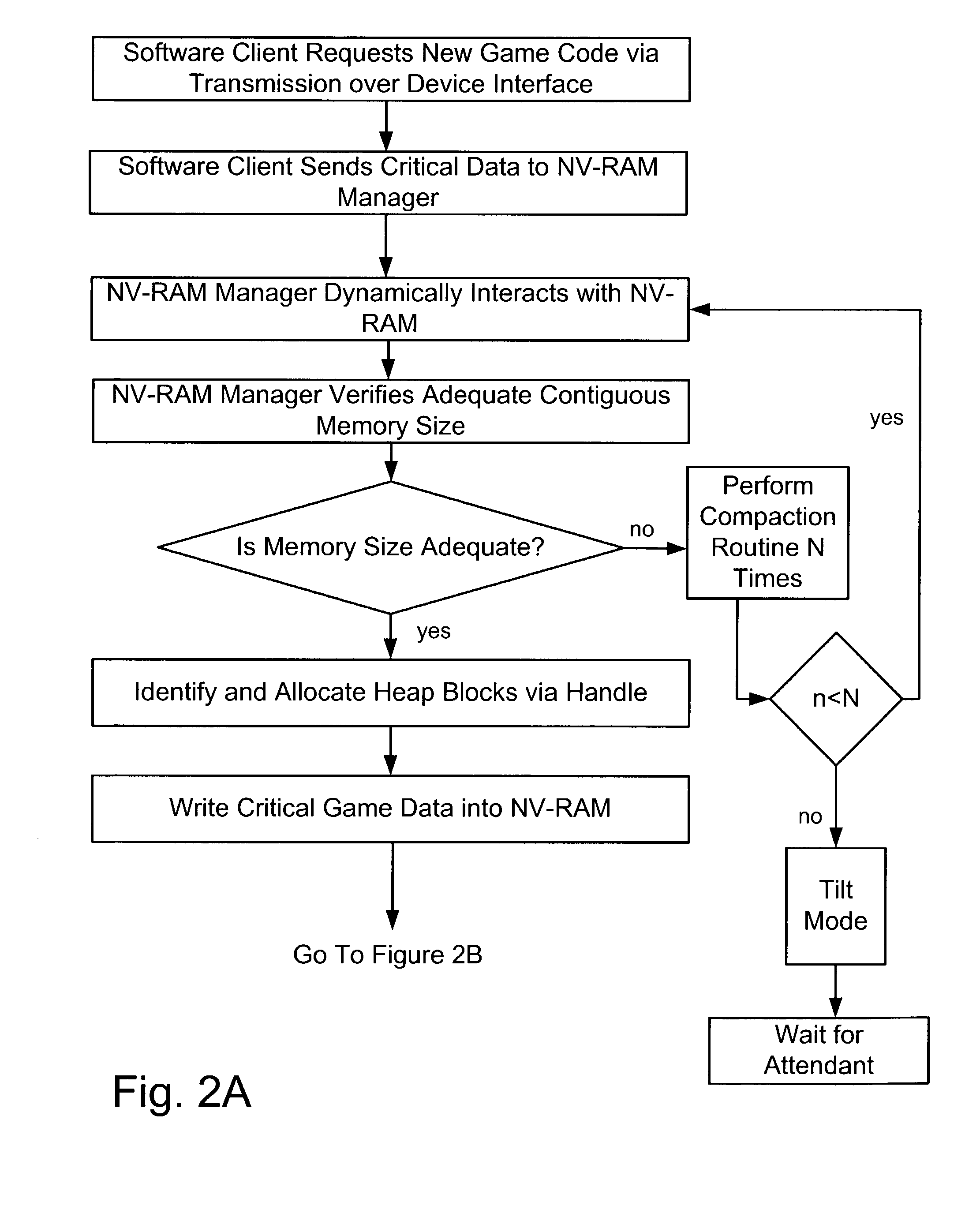
Dynamic NV-RAM
InactiveUS7111141B2Maximize useMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationParallel computingDynamic storage
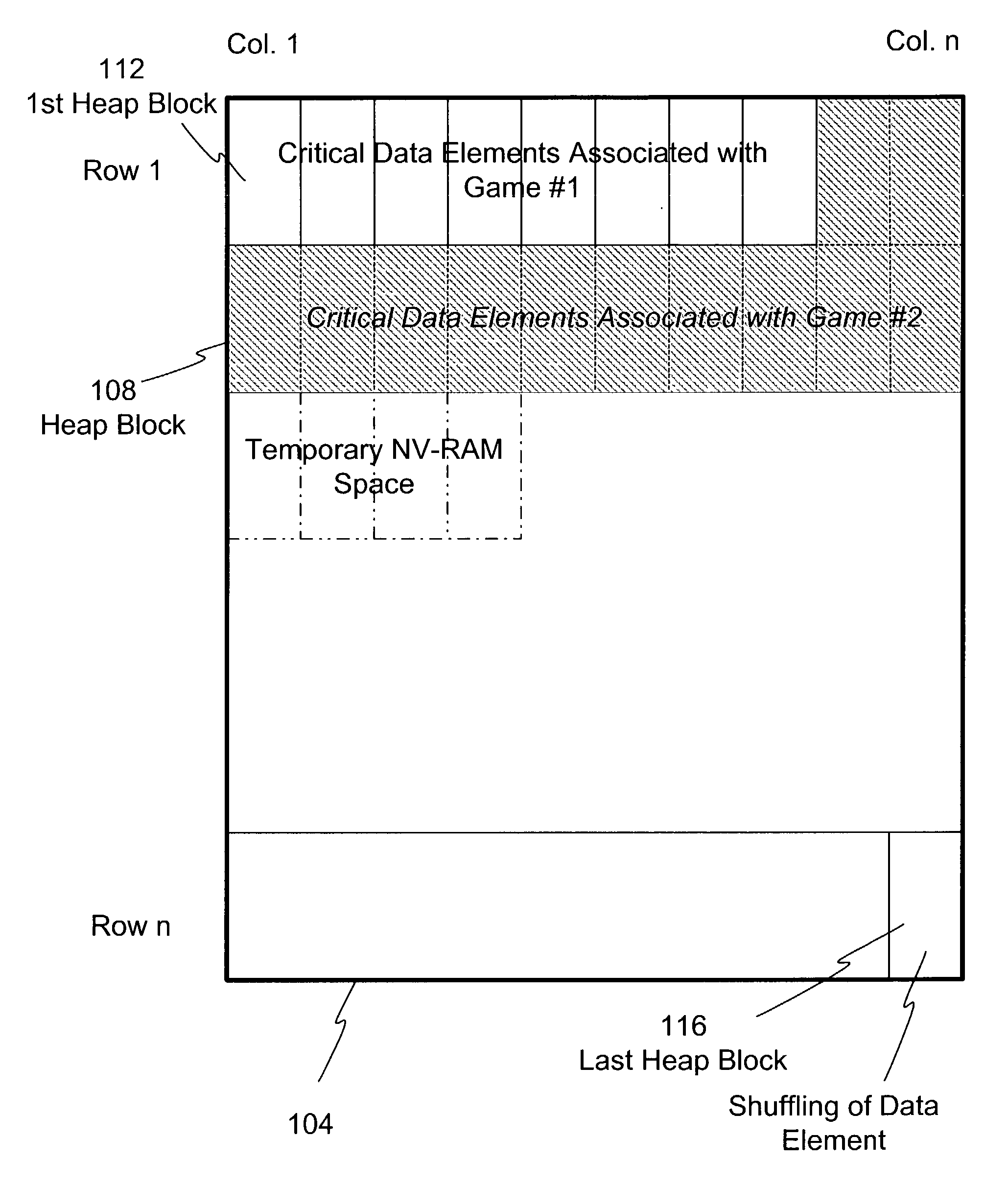
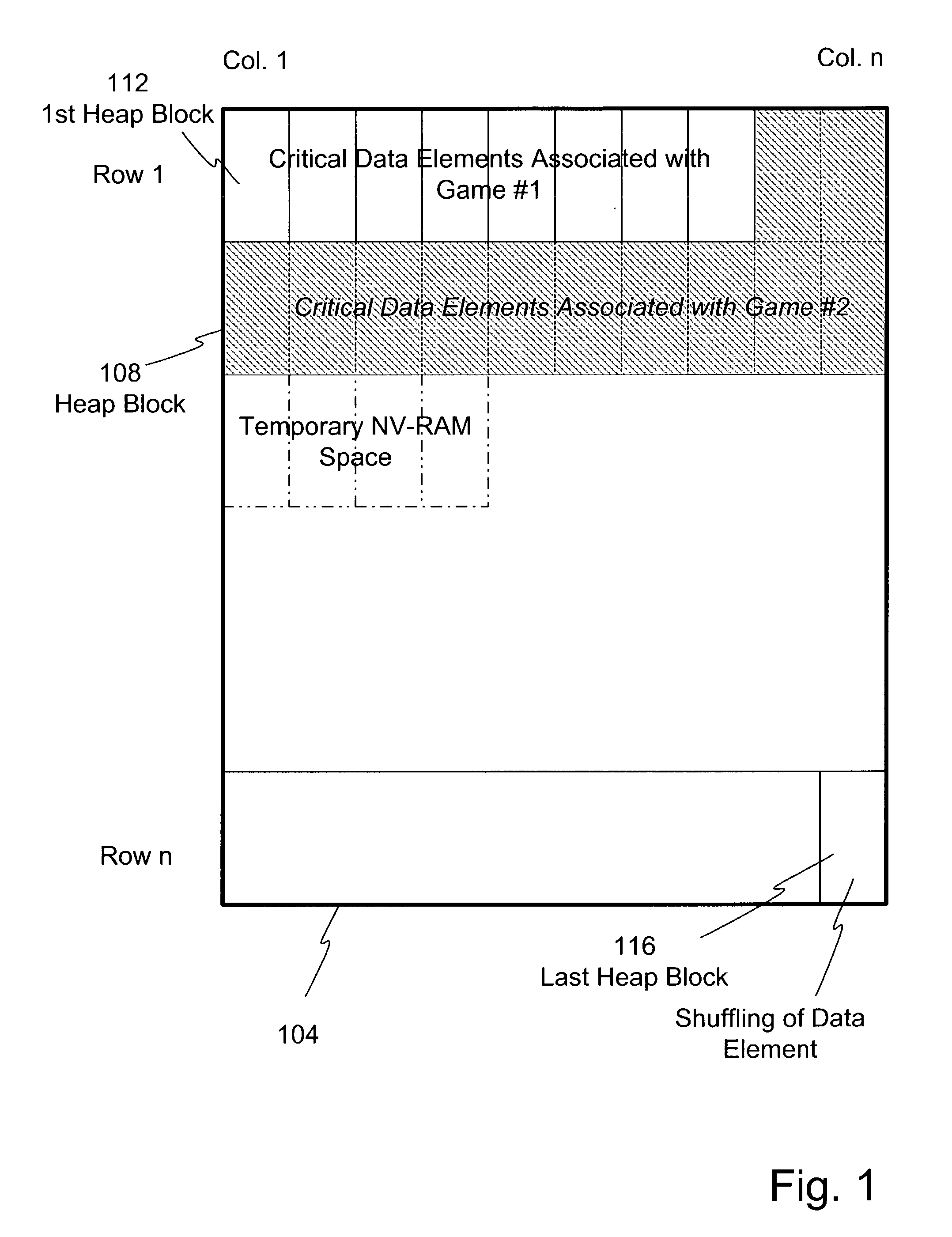
A method and apparatus of dynamically storing critical data of a gaming machine by allocating and deallocating memory space in a gaming machine is disclosed. One or more embodiments describe downloading or removing a new game to a gaming machine such that all existing critical data in NV-RAM memory is left intact. In one embodiment, the invention discloses a method and apparatus for dynamically allocating and deallocating memory space to accommodate either permanent or temporary storage in an NV-RAM. A method and apparatus is provided to monitor available memory space and dynamically resize the memory in NV-RAM. In one embodiment, a method is disclosed for performing an integrity check of the NV-RAM and determining whether a critical data error has occurred. In one or more embodiments, methods of compacting and shifting contents of an NV-RAM are described to consolidate available memory space or to prevent unauthorized access of NV-RAM memory.
Owner:IGT
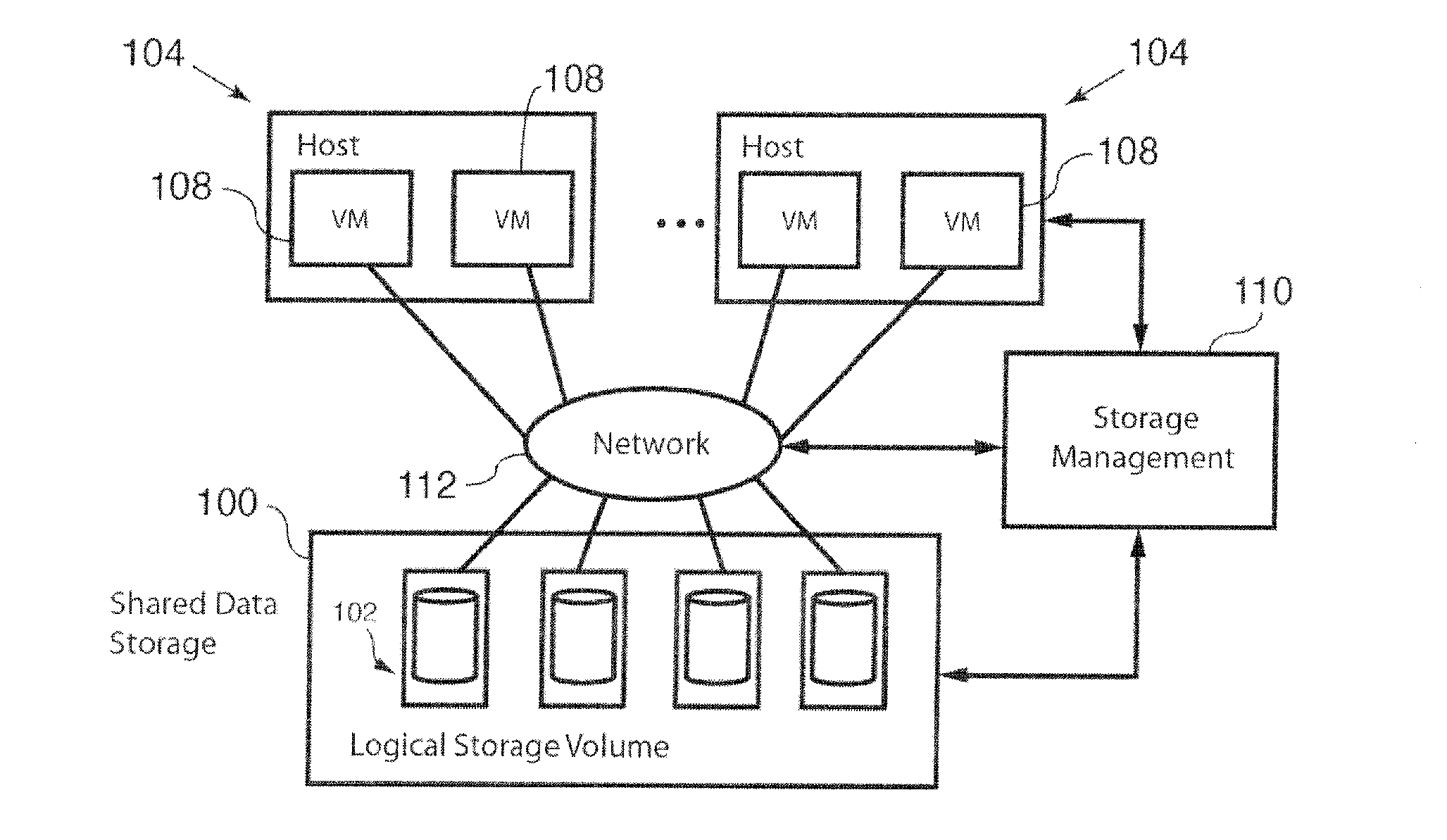
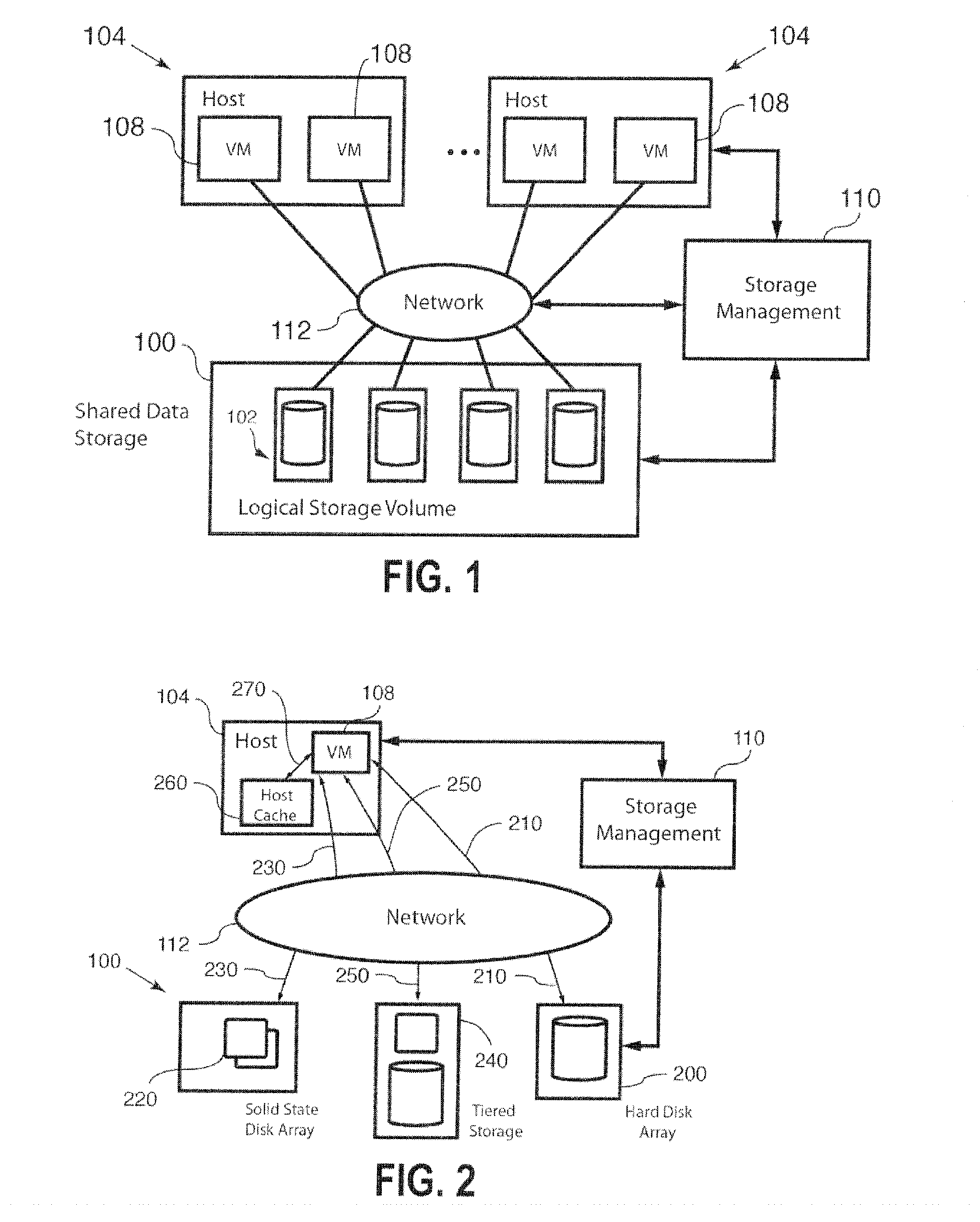
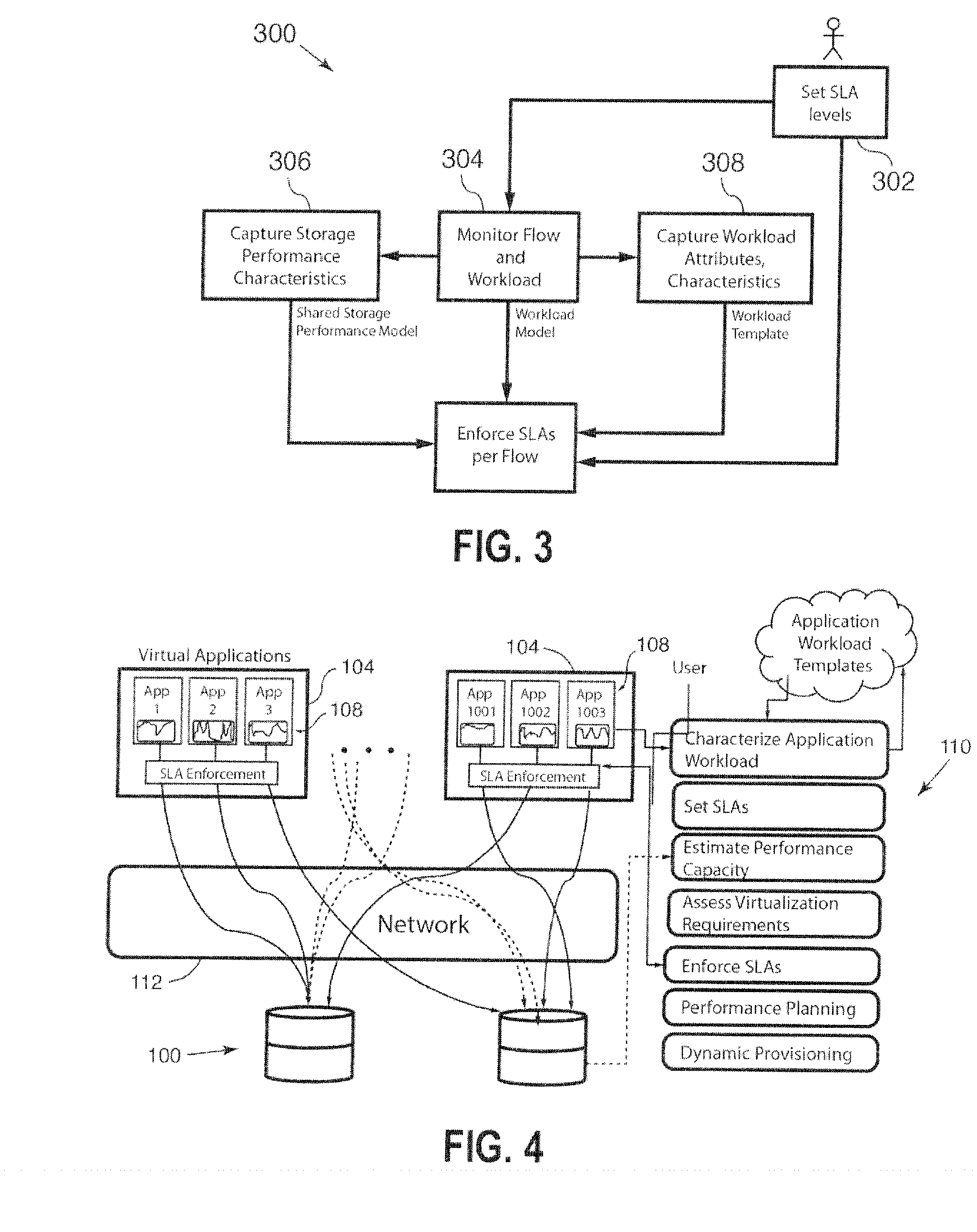
Systems and methods for provisioning of storage for virtualized applications
Methods and systems described herein implement an SLA-based dynamic provisioning of storage for virtualized applications or virtual machines (VMs) on shared storage. The shared storage can be located behind a storage area network (SAN) or on a virtual distributed storage system that aggregates storage across direct attached storage in the server or host, or behind the SAN or a WAN.
Owner:GUHA ALOKE
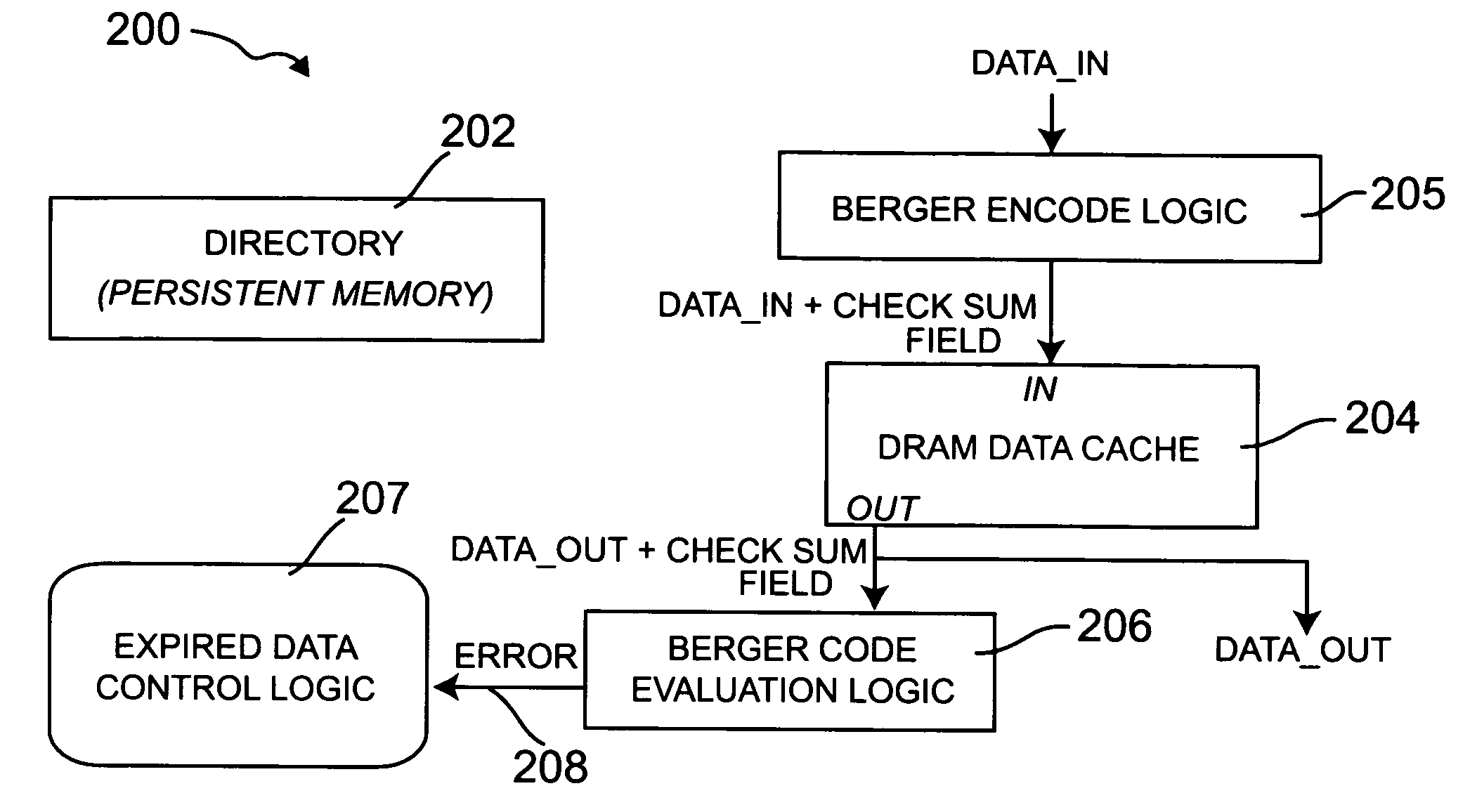
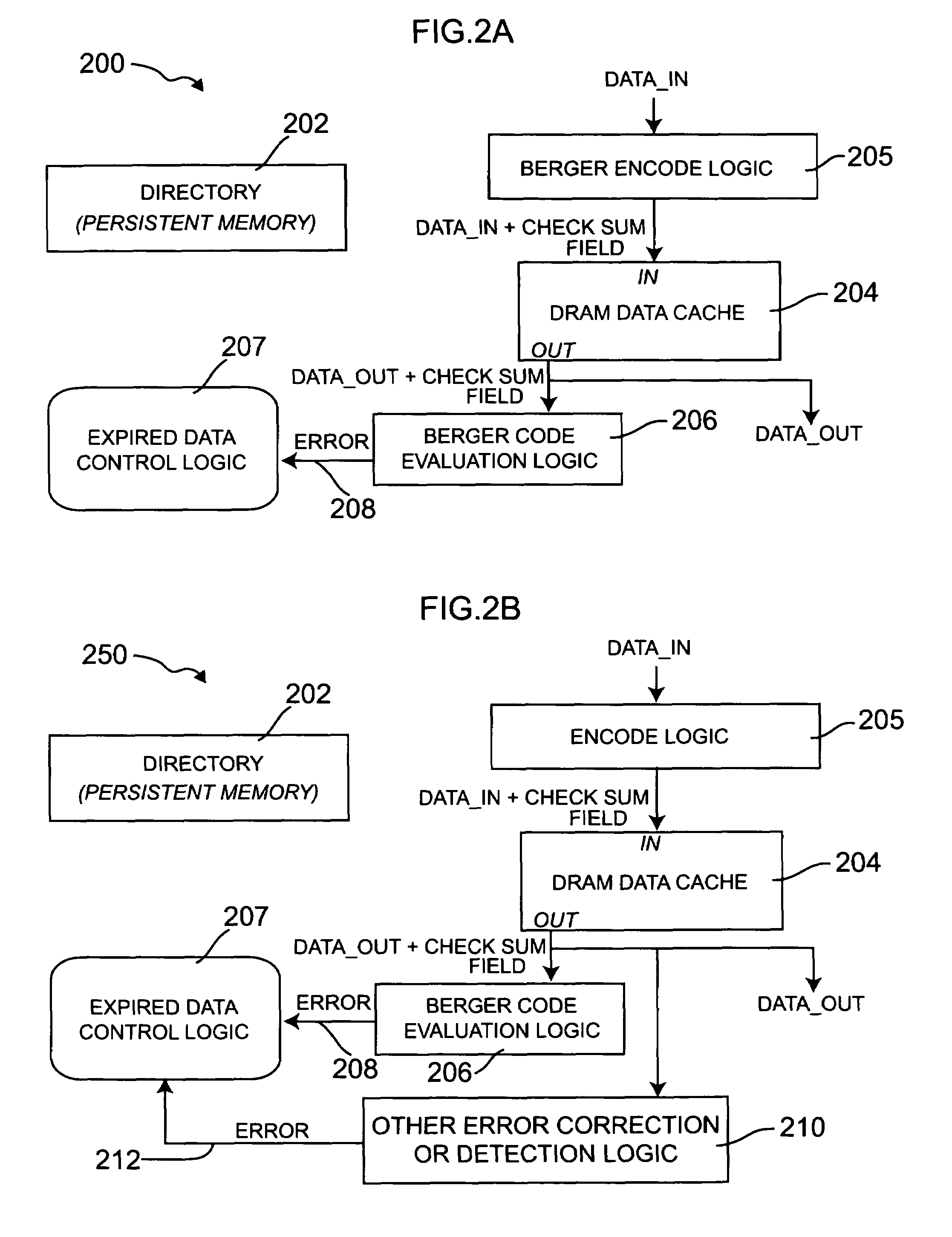
Dynamic memory architecture employing passive expiration of data
ActiveUS7290203B2Reduce manufacturing costUsed in environmentMemory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTDynamic storageEngineering
Apparatus for passively tracking expired data in a dynamic memory includes an error encoding circuit operative to receive an input data word and to generate an encoded data word which is stored in the dynamic memory. The apparatus further includes a decoding circuit operative to receive an encoded data word from the dynamic memory, to detect at least one or more unidirectional errors in the input data word read from the dynamic memory, and to generate an error signal when at least one error is detected, the error signal indicating that the input data word contains expired data. Control circuitry included in the apparatus is configured for initiating one or more actions in response to the error signal.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
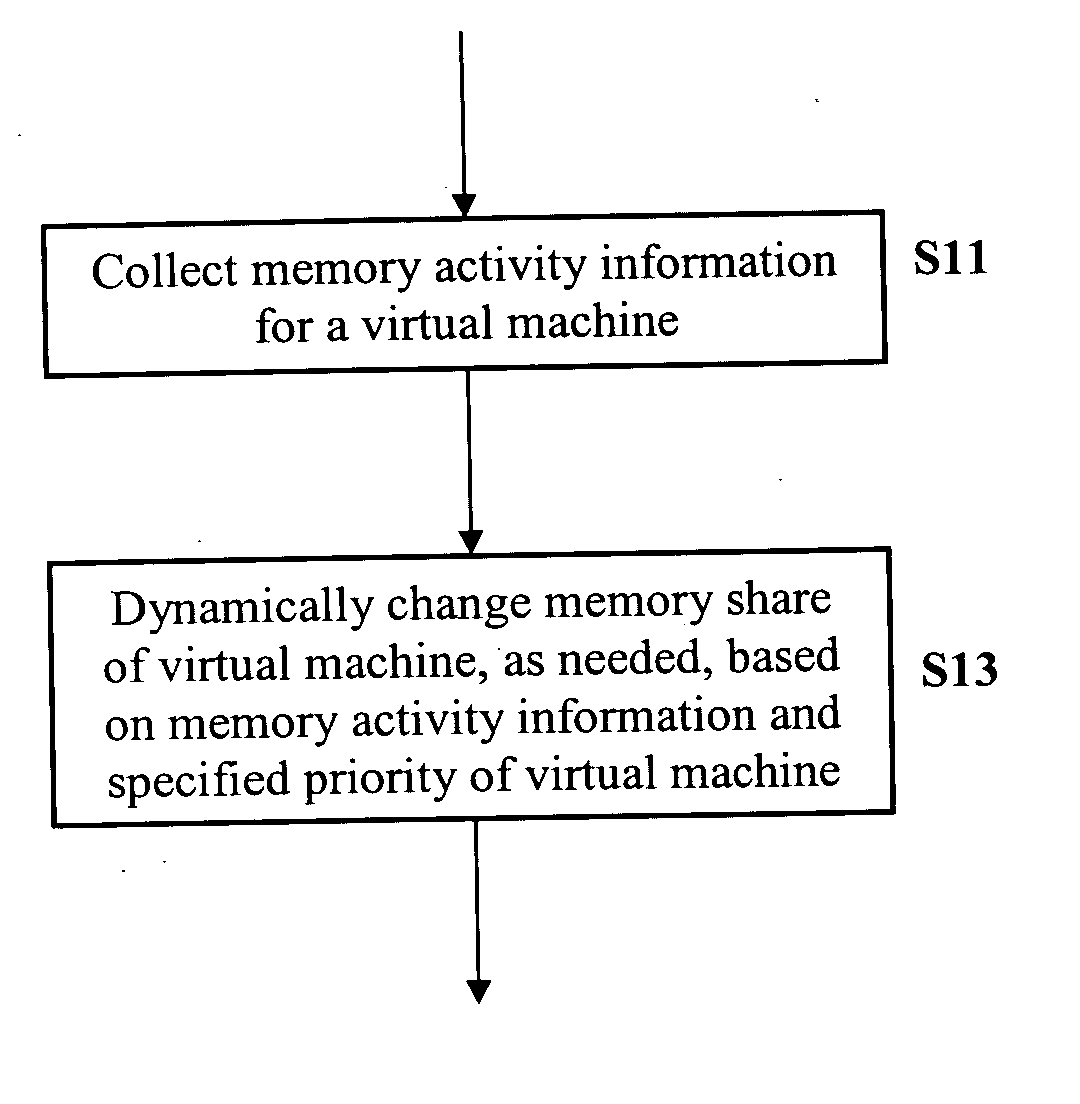
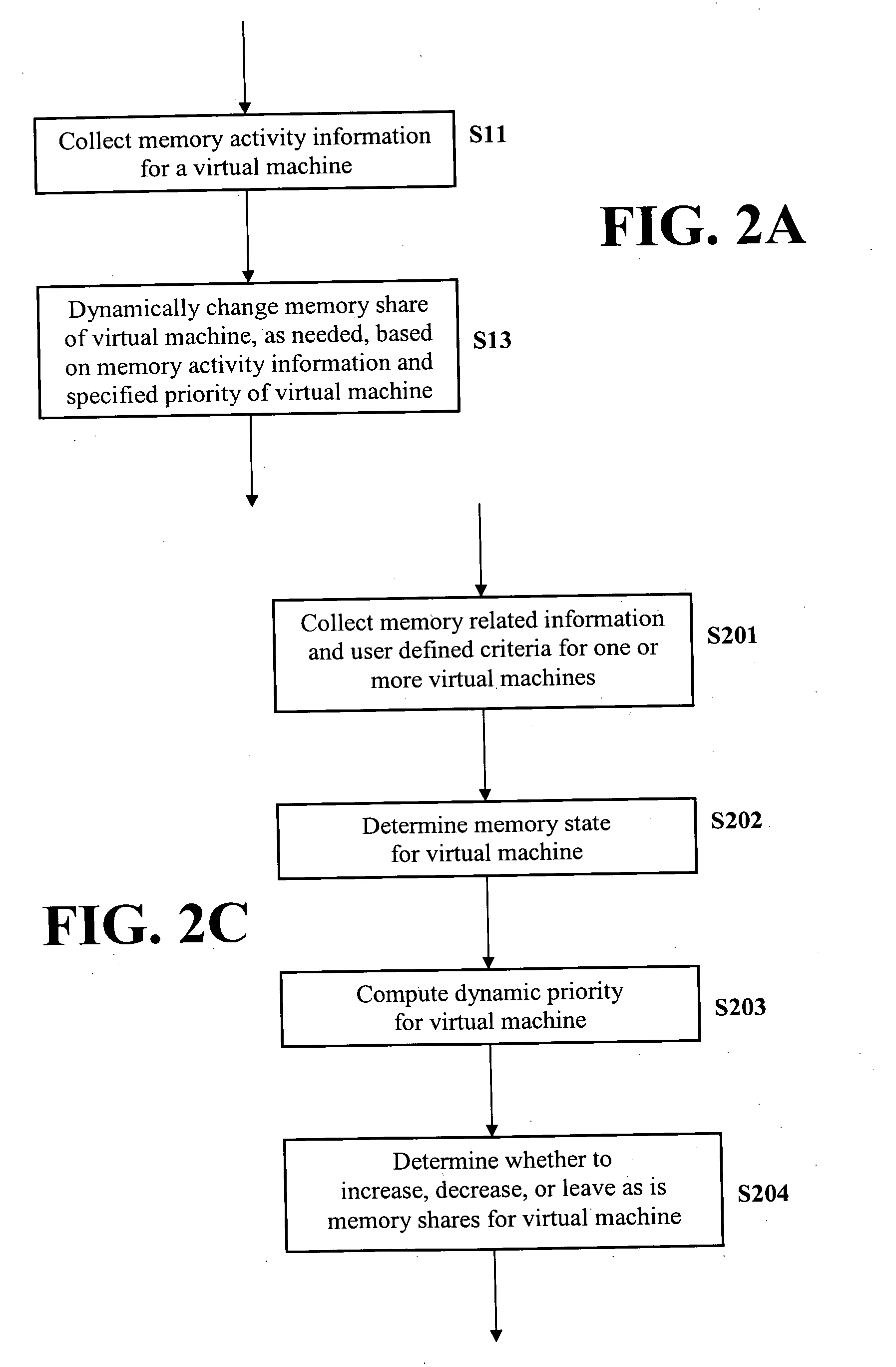
Method and apparatus for dynamic memory resource management
ActiveUS20050262505A1Increasing memory shareFreeing resource for useResource allocationDigital computer detailsDynamic storageResource management
A method and an apparatus for dynamic memory resource management are provided. Memory activity information is collected for a virtual machine. Additional memory shares are dynamically allocated to the virtual machine, as needed, based on the memory activity information for the virtual machine and based on a specified priority of the virtual machine in order to properly adjust the total physical memory used by the virtual machine.
Owner:COMP ASSOC THINK INC
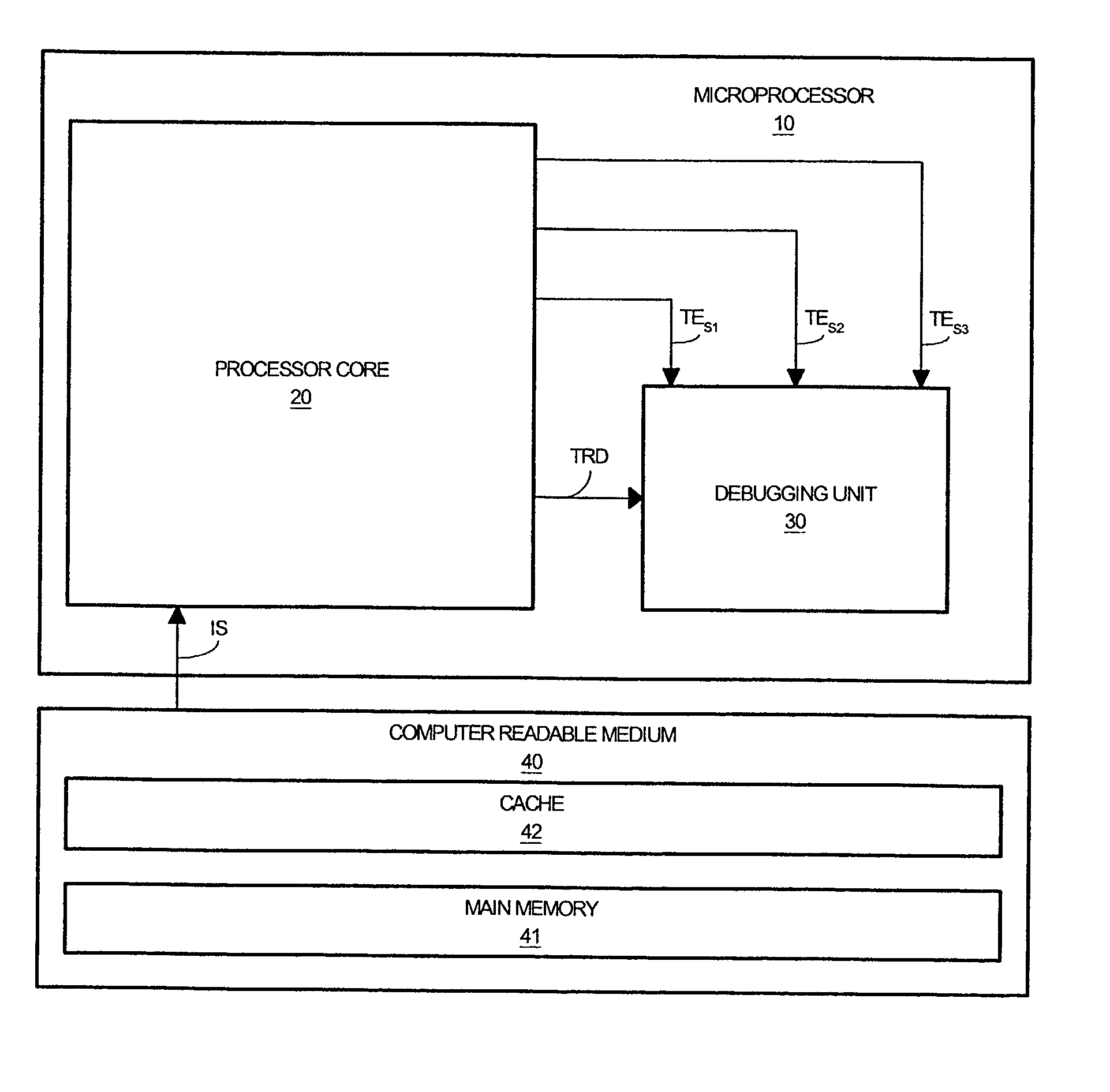
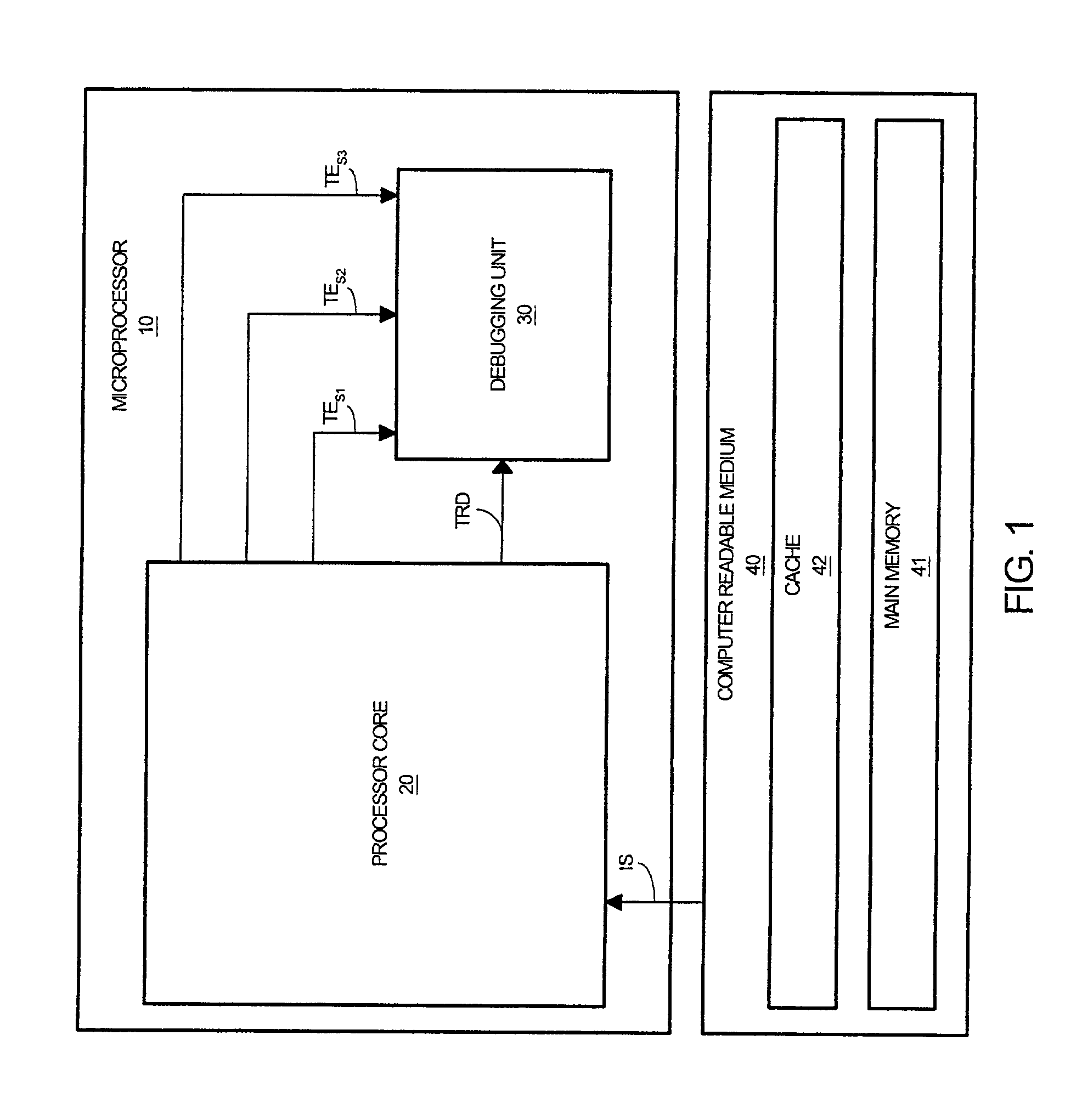
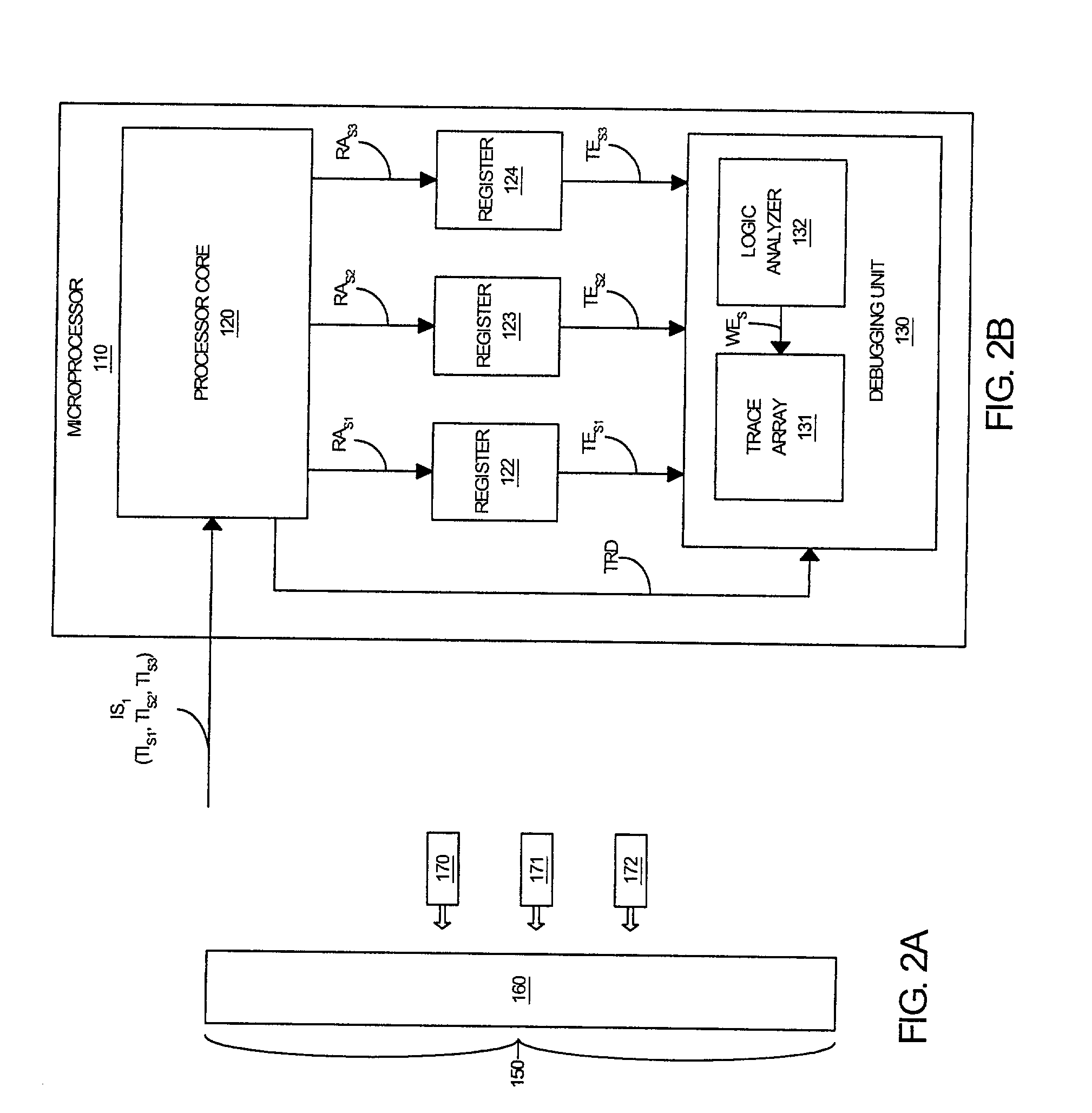
Method and system for triggering a debugging unit
InactiveUS20020129309A1Electronic circuit testingDigital computer detailsProcessing InstructionDynamic storage
A processor core for transitioning a debugging unit between a plurality of operating states in response to an instruction stream is disclosed. The processor core generates trace data as it processes operating signals of the instruction stream. The processor core provides a first trigger event signal to the debugging unit in response to a first trigger instruction signal within the instruction stream that is representative of a triggering instruction to transitions the debugging unit to a base operating state. The processor core provides a second trigger event signal to the debugging unit in response to a second trigger instruction signal within the instruction stream that is representative of a triggering instruction to dynamically store trace data within the memory component of the debugging unit. The processor core provides a third trigger event signal to the debugging unit in response to a third trigger instruction signal within the instruction stream that is representative of a triggering instruction to statically store trace data within the memory component of the debugging unit. Concurrently or alternatively, the processor core can provide one or more of the trigger event signals to the debugging unit as a function of a generated trigger data in response to additional operational instructions within the instruction stream.
Owner:IBM CORP
Quality of Service for Distribution of Content to Network Devices
ActiveUS20120173746A1Prevent excess lagQuality assuranceMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionQuality of serviceComputer compatibility
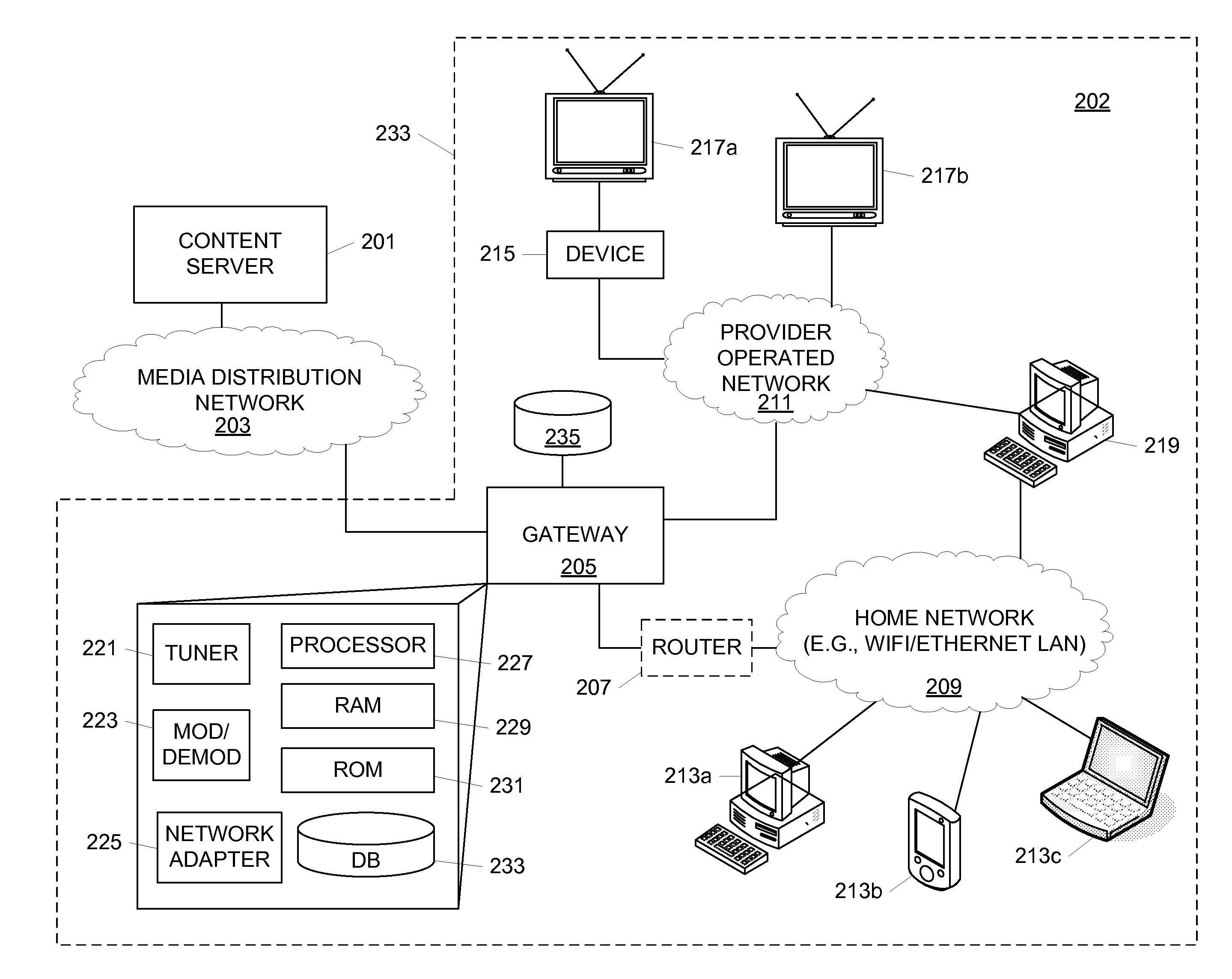
A gateway device configured to receive IP video content may select and use transmission methods that maintain a certain quality of service for delivering the content. A transmission method may be selected based on a network to which the client device is connected. The gateway device may select a network through which the content is to be delivered depending on a variety of factors including bandwidth availability, client compatibility, quality of service provided and the like. A gateway device may further be configured to convert multicast transmissions to unicast, to provide dynamic storage of content for pre-positioning and other purposes and / or to provide other functions.
Owner:COMCAST CABLE COMM LLC
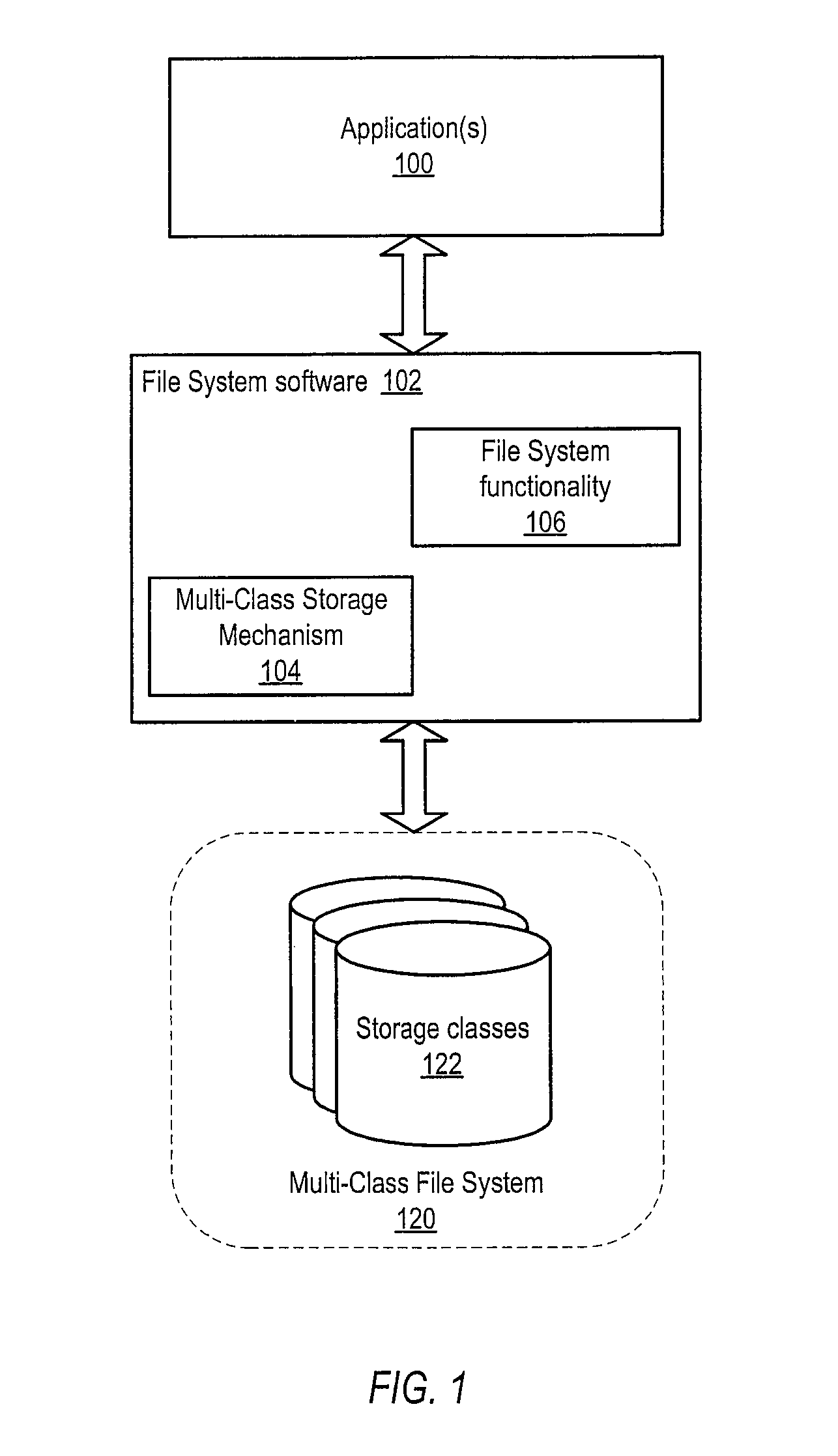
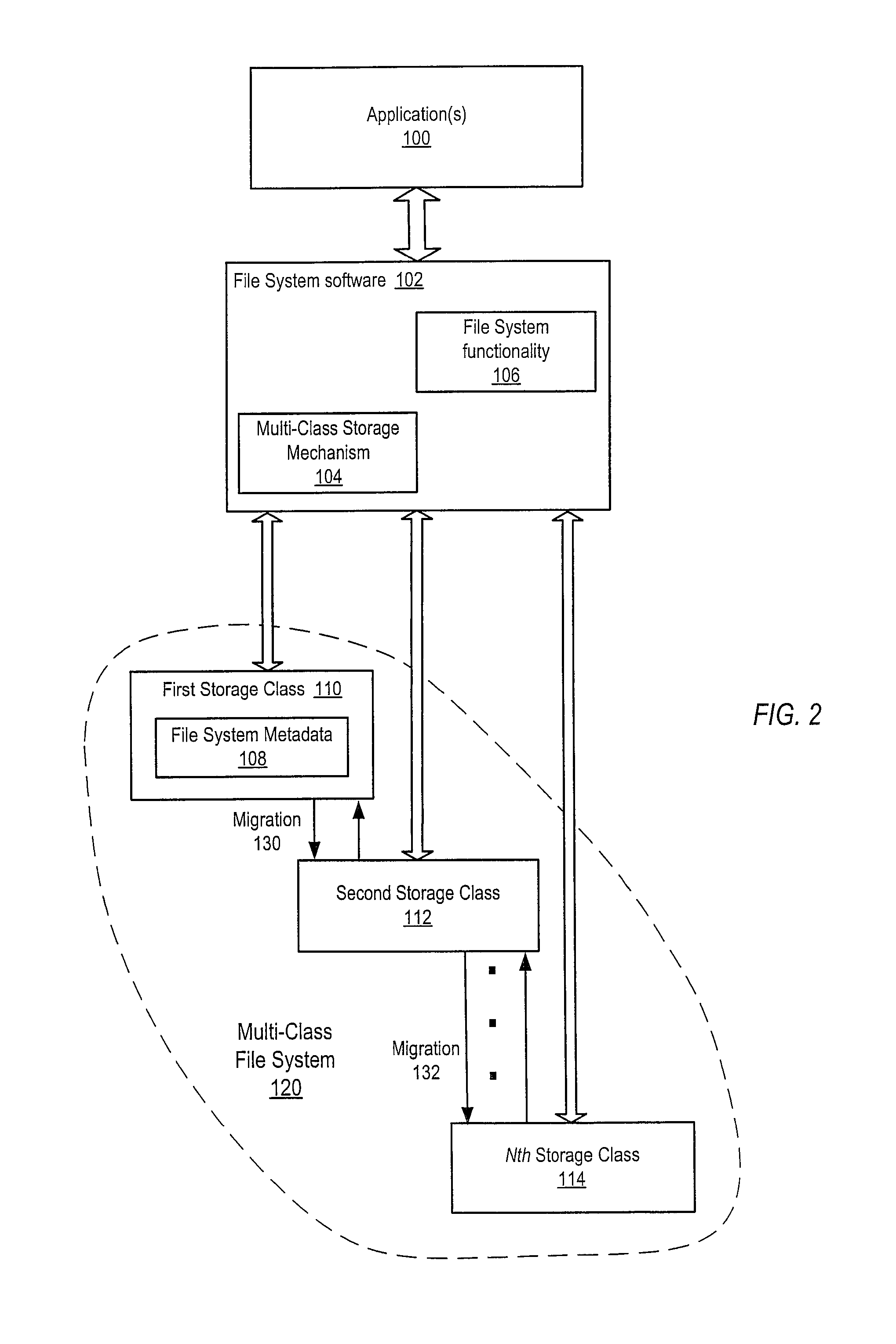
Dynamic storage mechanism
ActiveUS8280853B1Reduce storage costs without compromising performanceLess expensiveDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsTimestampTrace file
System and method for tracking statistics at the subfile level and transparently placing or migrating inactive or less active blocks of data to other storage devices. Embodiments may provide mechanisms to track statistics at the subfile level of files including, but not limited to, database files, and to transparently place or migrate inactive or less active blocks of data of the files from higher-performing, typically more expensive, storage to lower-performing, typically less expensive, storage, while placing or migrating active blocks of data of the files to higher-performing storage, based on the subfile-level statistics rather than on file-level timestamps. In some embodiments, knowledge of file structure (e.g., database file structure), for example knowledge of database partitions with header blocks and data blocks in databases using data partitioning, may be used to separate more active and less active blocks of data of files onto storage with different performance and / or other characteristics.
Owner:VERITAS TECH
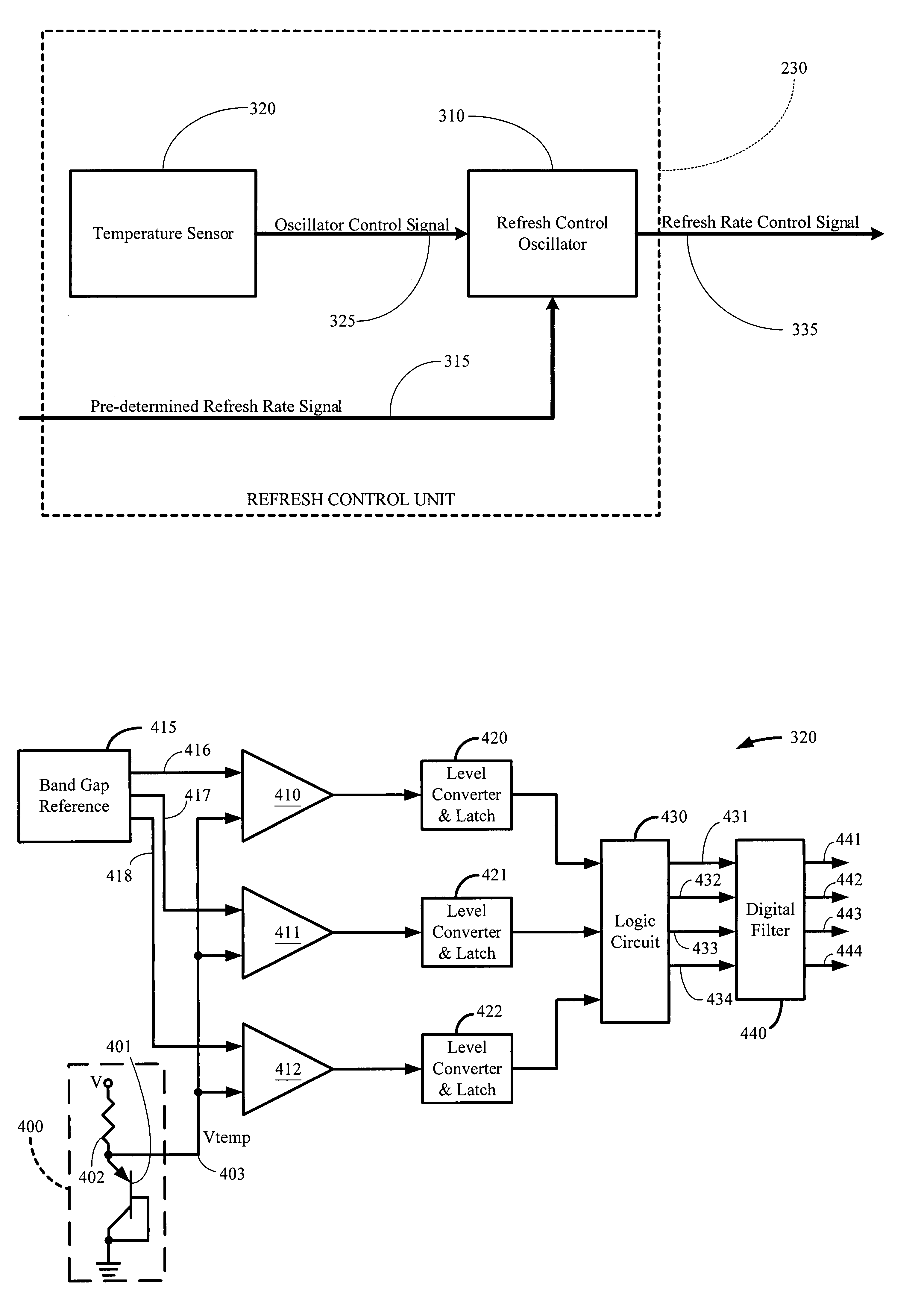
Method and apparatus for controlling refresh operations in a dynamic memory device
A method and apparatus are provided for controlling refresh operations of a dynamic memory device. The temperature of the dynamic memory device is detected. The detected temperature is then used to adjust a refresh rate of the dynamic memory device to compensate for increased leakage at higher temperatures and more closely tailor the timing of the refresh operations to the conditions of the dynamic memory device.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
Microactuated dimple for head suspensions
InactiveUS7256968B1Move preciselyTrack finding/aligningRecord information storageDynamic storageEngineering
A head suspension for supporting a head slider over a disk in a dynamic storage device and providing precise movement of the head slider relative to tracks on the disk. The head suspension includes a load beam, a flexure having a slider mounting region, and a dimple interface transmitting a load beam force to the slider mounting region. The head suspension further includes a microactuator mounted to the load beam. Movement of the microactuator is transmitted through the dimple interface by action of frictional forces at the dimple interface so as to cause movement of the slider mounting region transverse to tracks on the disk. A method of precisely moving a head slider supported by a head suspension includes providing and driving a microactuator configured to transmit movement of the microactuator to a slider mounting region through a dimple interface by action of frictional forces at the dimple interface.
Owner:HUTCHINSON TECH
Value recycling facility for multithreaded computations
ActiveUS20030182462A1Data processing applicationsProgram synchronisationArray data structureDynamic storage
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Non-blocking memory management mechanism for supporting dynamic-sized data structures
ActiveUS20030174572A1Data processing applicationsProgram synchronisationDynamic storageApplication software
Solutions to a value recycling problem that we define herein facilitate implementations of computer programs that may execute as multithreaded computations in multiprocessor computers, as well as implementations of related shared data structures. Some exploitations of the techniques described herein allow non-blocking, shared data structures to be implemented using standard dynamic allocation mechanisms (such as malloc and free). Indeed, we present several exemplary realizations of dynamic-sized, non-blocking shared data structures that are not prevented from future memory reclamation by thread failures and which depend (in some implementations) only on widely-available hardware support for synchronization. Some exploitations of the techniques described herein allow non-blocking, indeed even lock-free or wait-free, implementations of dynamic storage allocation for shared data structures. A class of general solutions to value recycling is described in the context of an illustration we call the Repeat Offender Problem (ROP), including illustrative Application Program Interfaces (APIs) defined in terms of the ROP terminology. Furthermore, specific solutions, implementations and algorithm, including a Pass-The-Buck (PTB) implementation are described.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
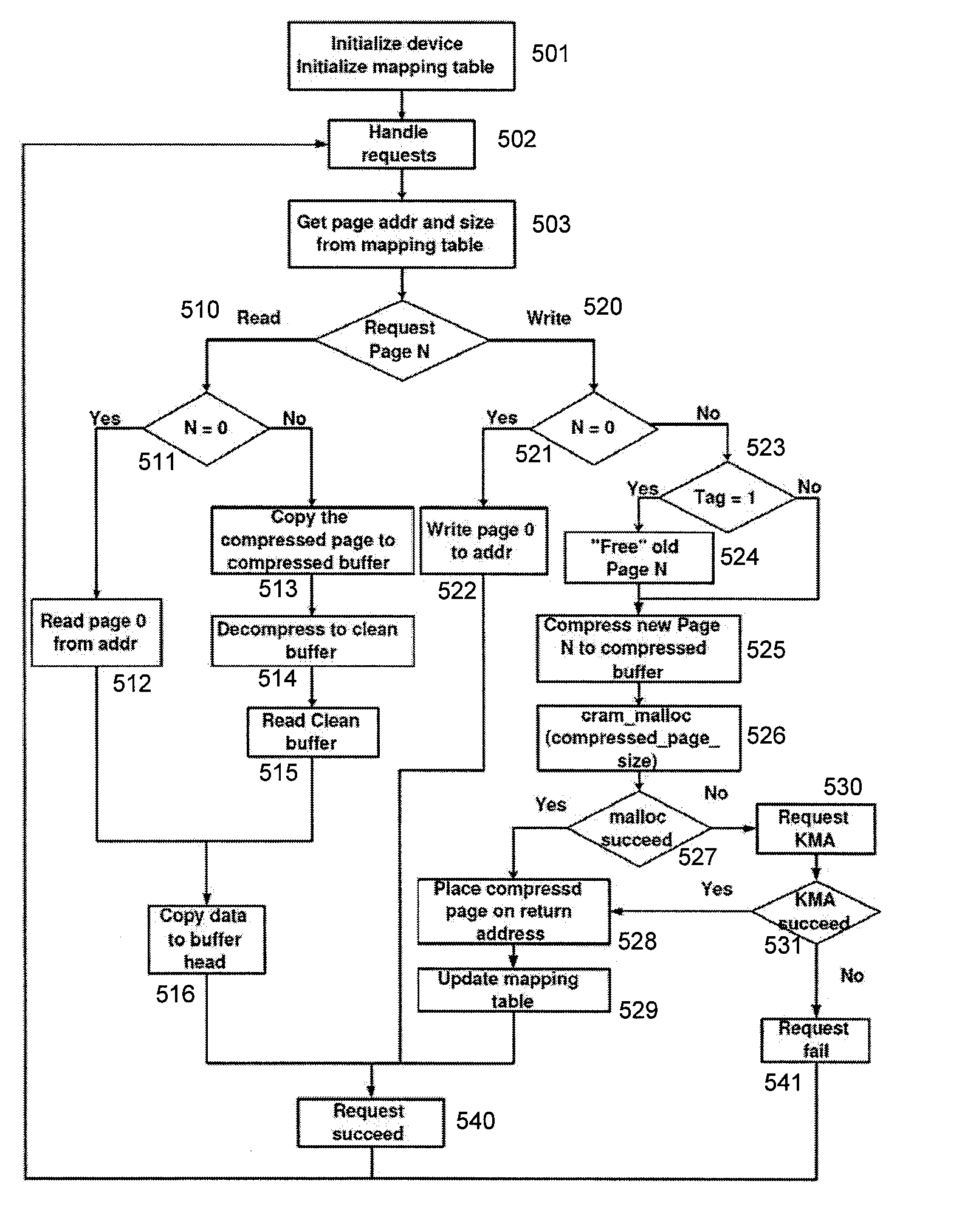
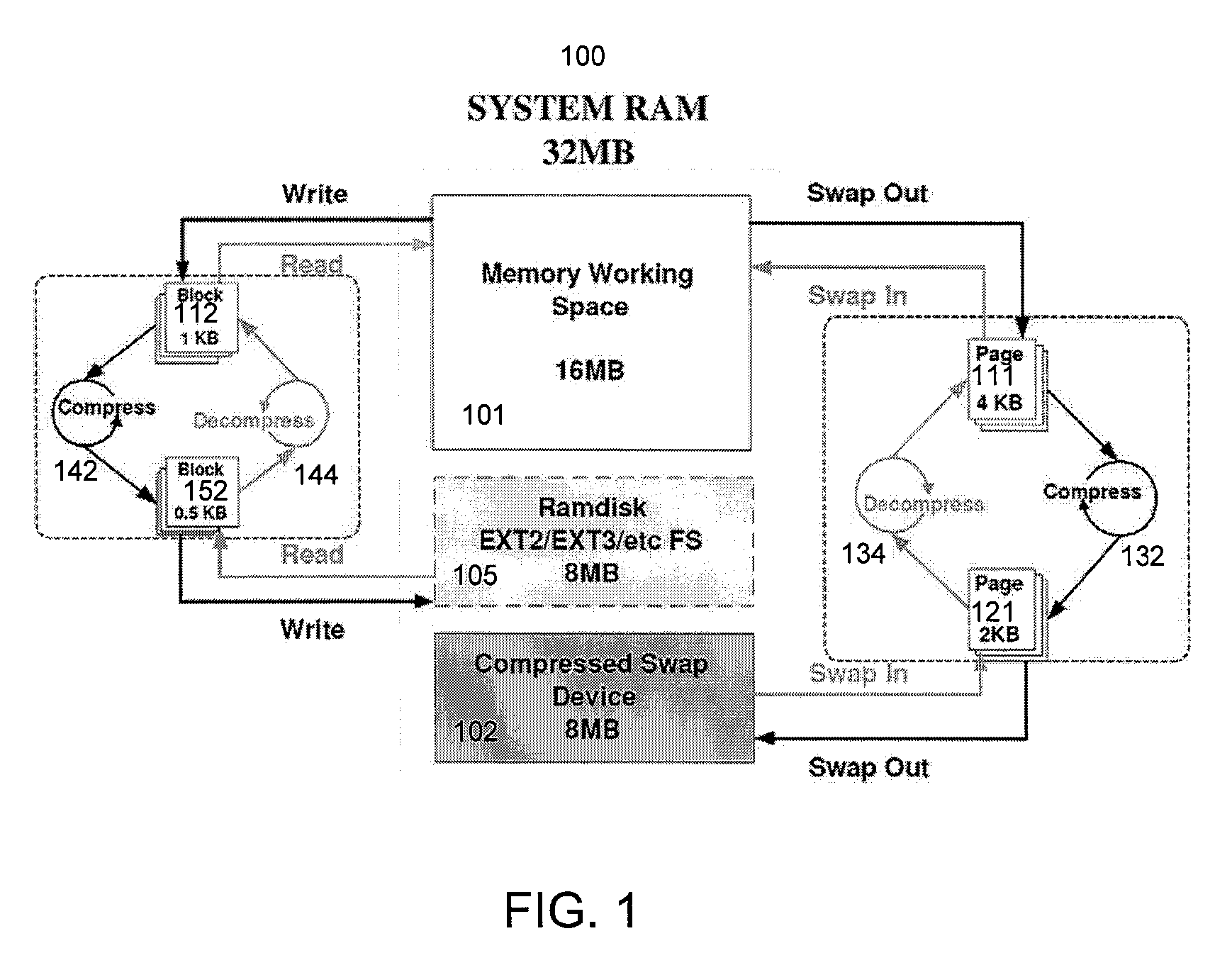
Operating System-Based Memory Compression for Embedded Systems
InactiveUS20070005911A1Avoid fragmentationMemory resourceMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationOperational systemData set
A dynamic memory compression architecture is disclosed which allows applications with working data sets exceeding the physical memory of an embedded system to still execute correctly. The dynamic memory compression architecture provides “on-the-fly” compression and decompression of the working data in a manner which is transparent to the user and which does not require special-purpose hardware. A new compression technique is also herein disclosed which is particularly advantageous when utilized with the above-mentioned dynamic memory compression architecture.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV +1
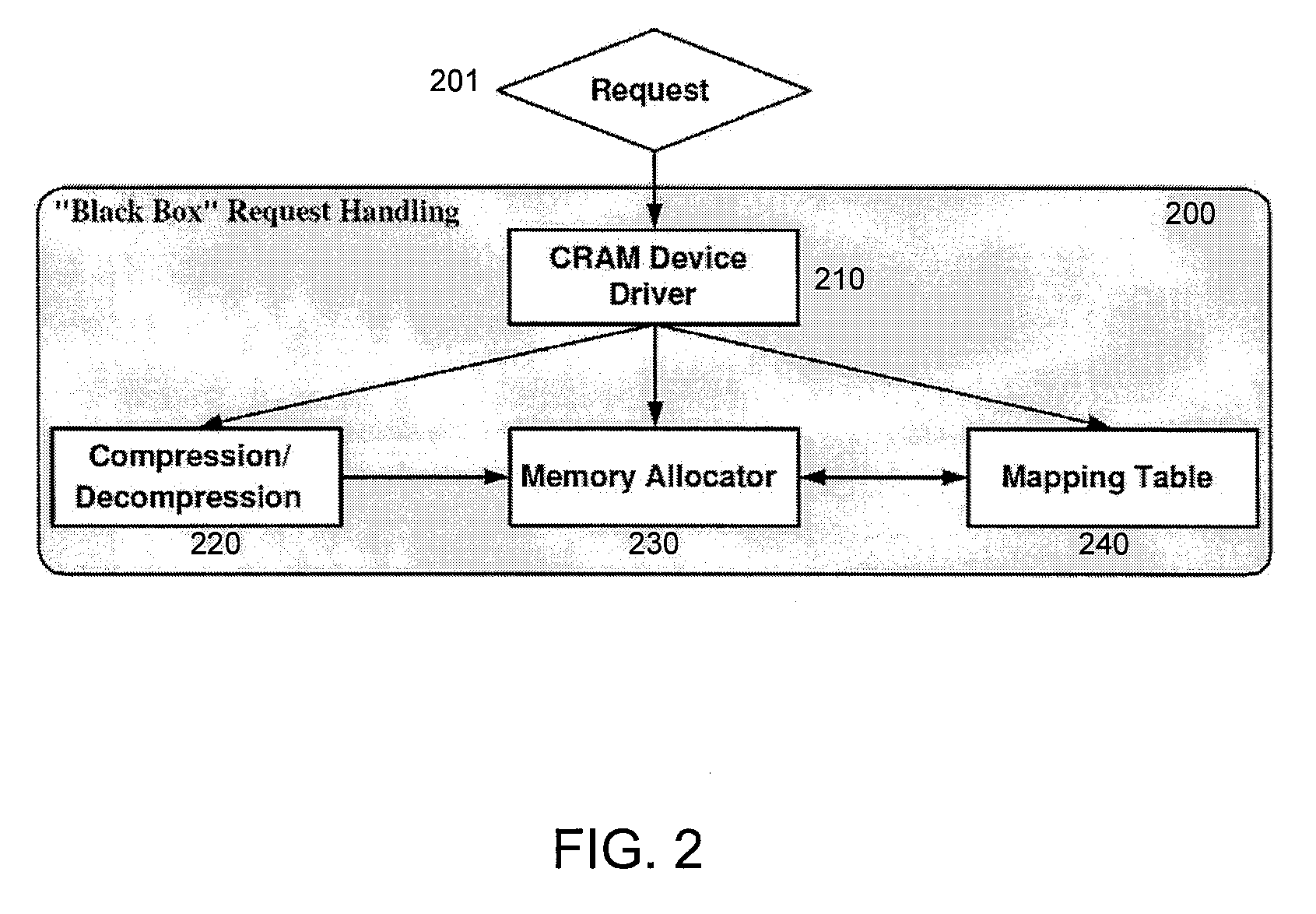
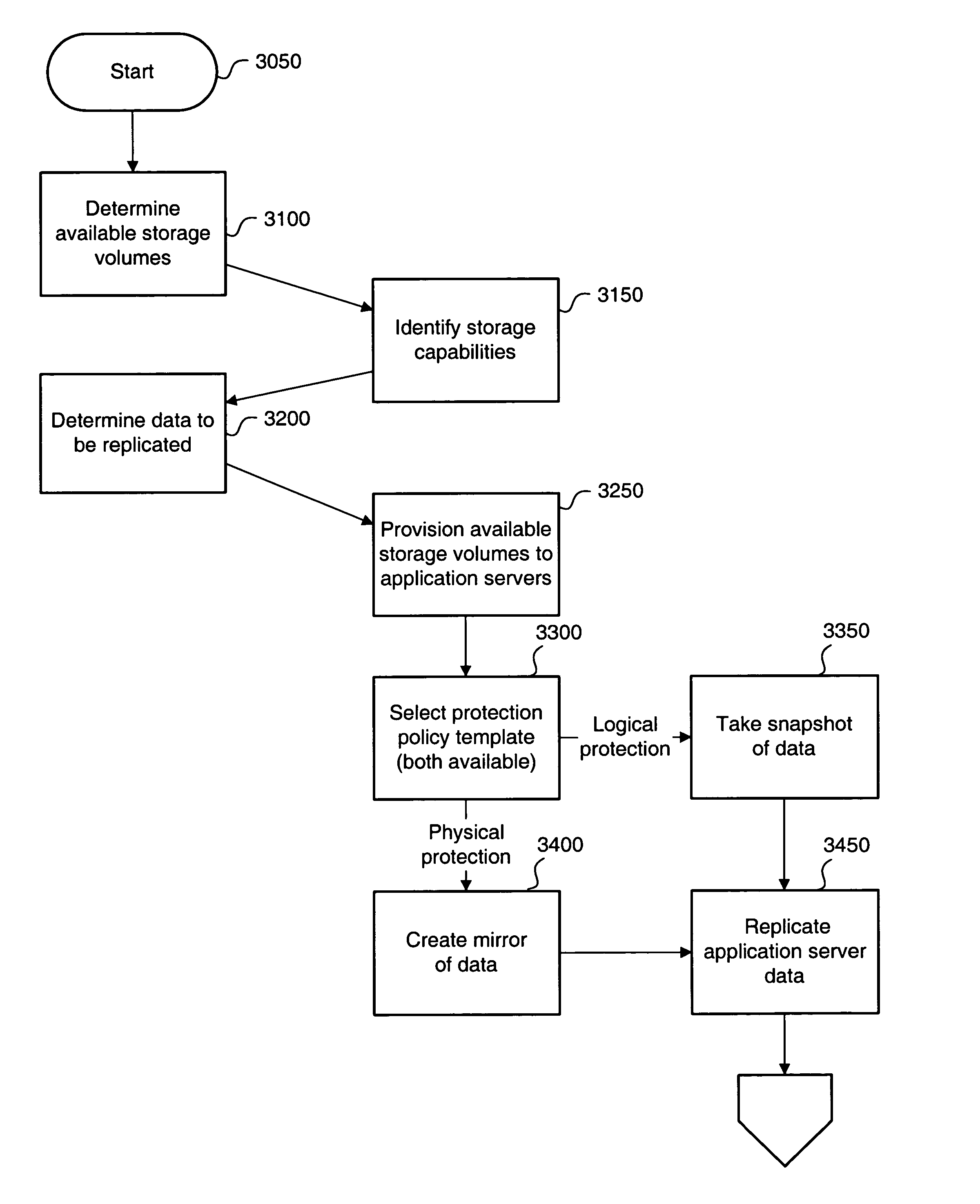
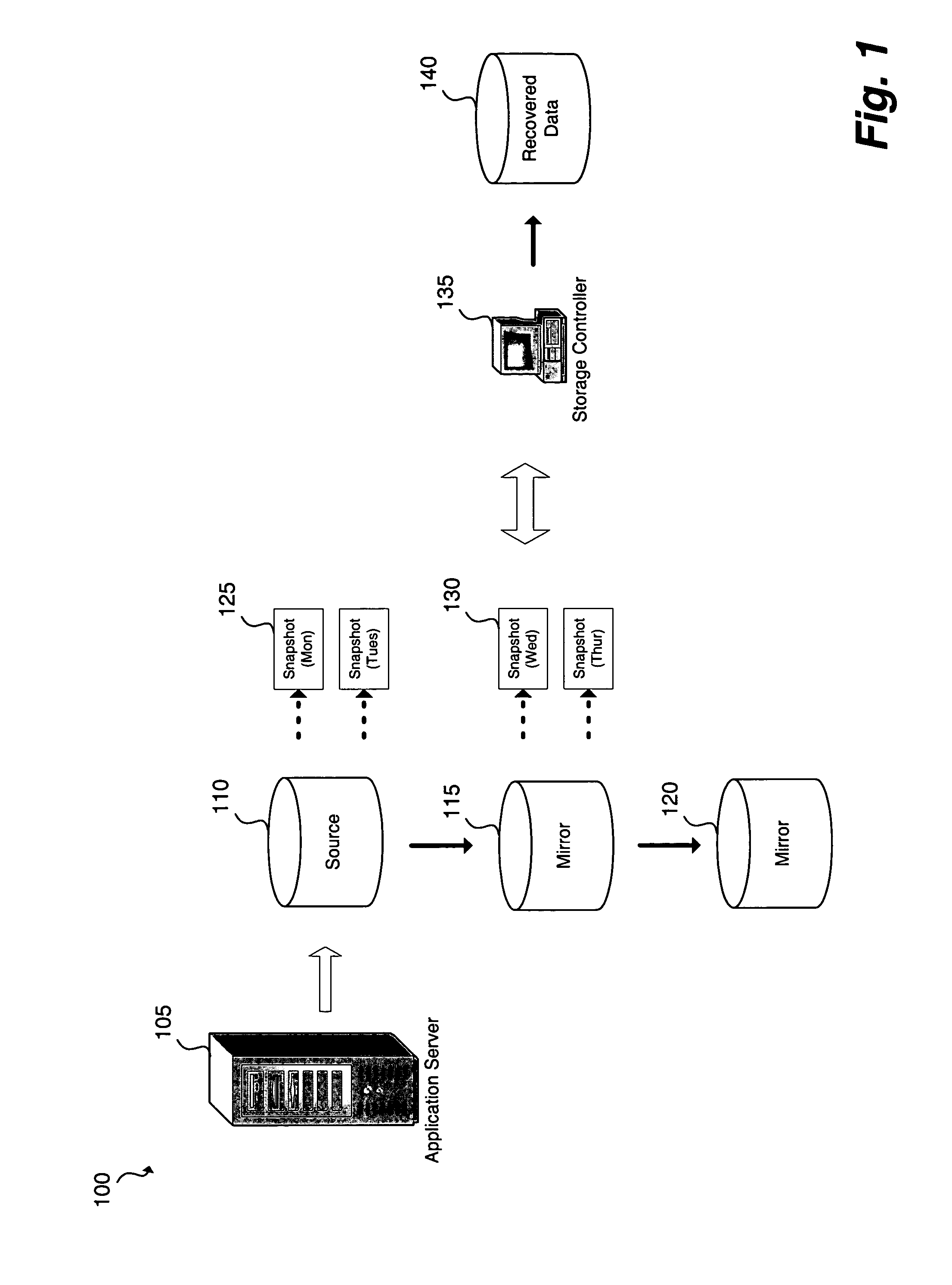
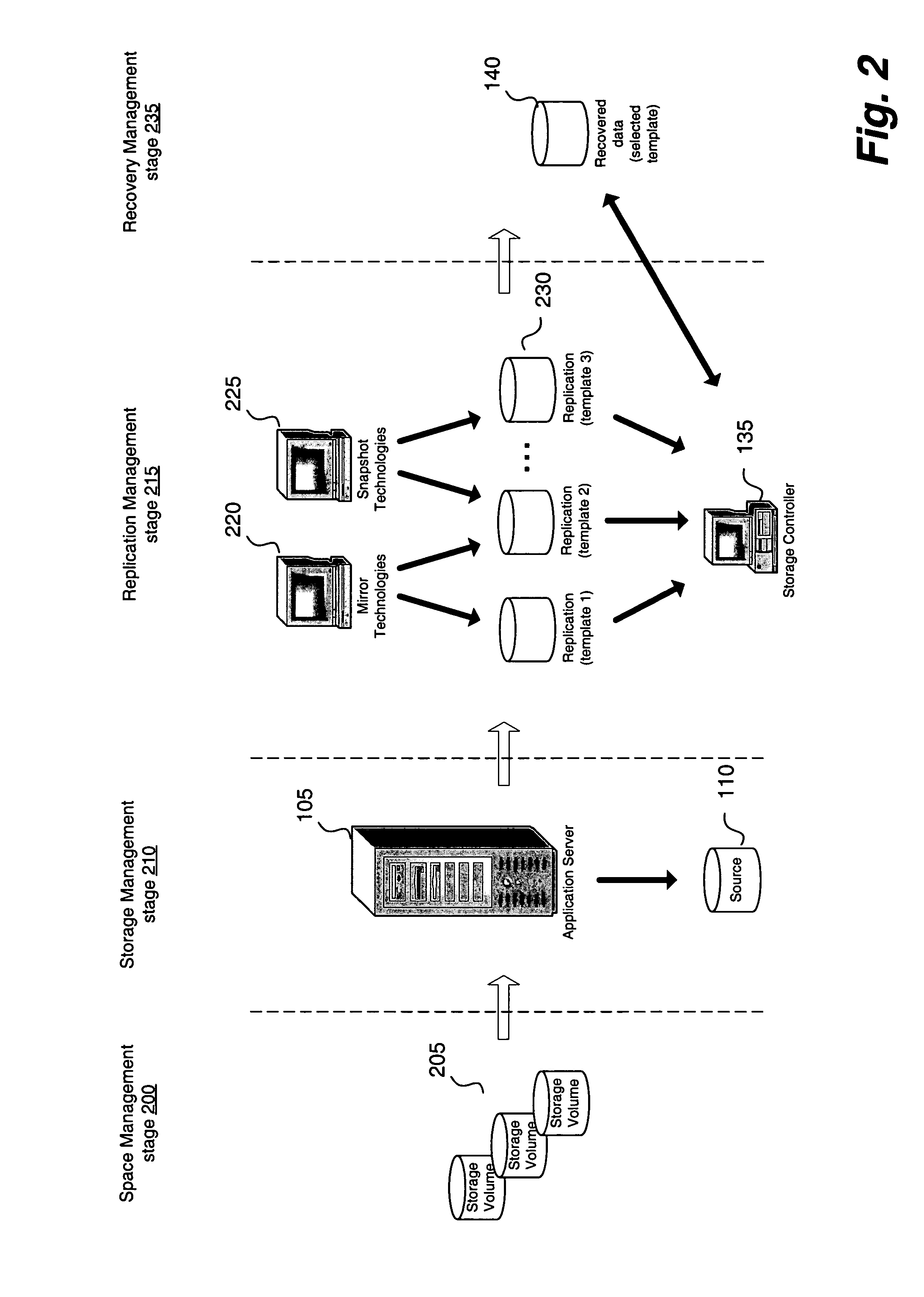
Method and apparatus for creating a storage pool by dynamically mapping replication schema to provisioned storage volumes
A method and apparatus for creating a dynamic storage pool for data recovery, is presented. The method may include determining amount of an available storage area, identifying storage capabilities of the available storage area, selecting a protection policy scheme for replication of an application server data based on the identified storage capabilities, provisioning a volume from the available storage area to the application server data, and replicating the application server data based on the selected protection policy scheme for storage to the available storage area.
Owner:SOFTEK STORAGE SOLUTIONS CORP
Systems and methods for providing dynamic memory pre-fetch
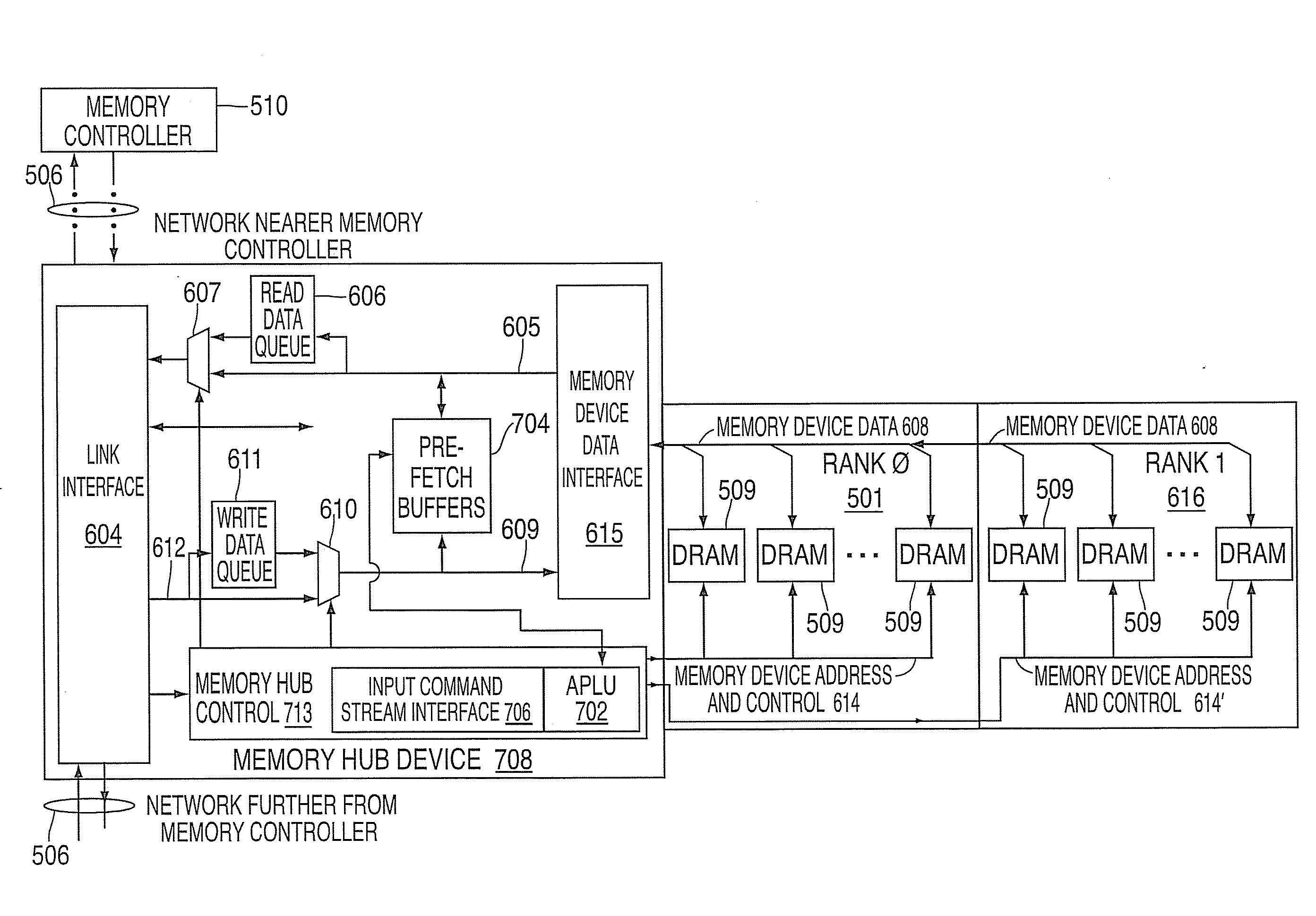
InactiveUS20080183903A1Memory systemsInput/output processes for data processingLogic cellDynamic storage
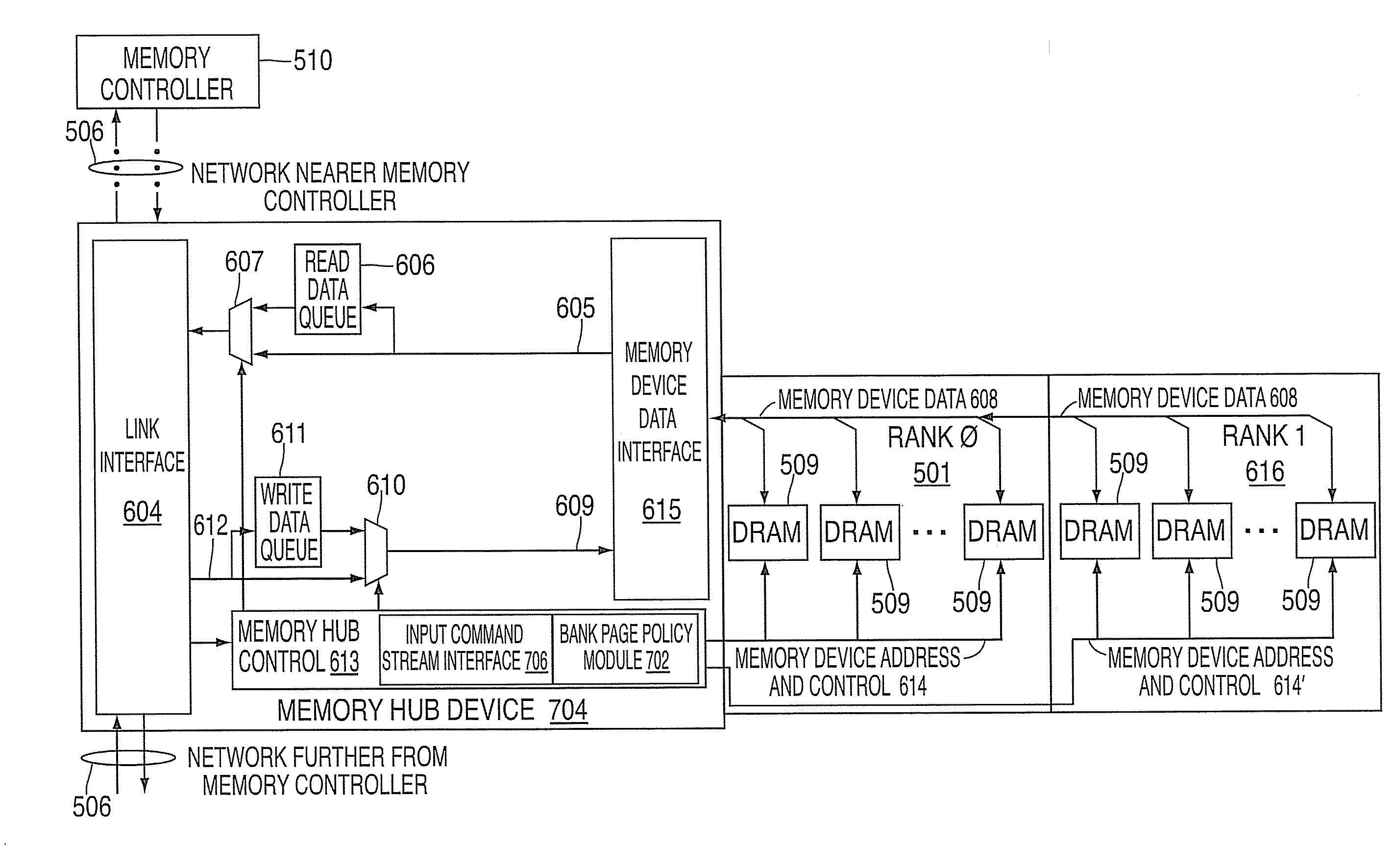
Systems and methods for providing dynamic memory pre-fetch. Embodiments include a hub device including an input command stream interface and an adaptive pre-fetch logical unit (APLU). The input command stream interface detects commands from a memory controller directed to one or more memory devices that are connected to the hub device. The APLU independently analyzes the commands to determine access patterns to the memory devices. The APLU also dynamically selects between enabling a pre-fetch function and disabling the pre-fetch function for the memory devices based on the results of the analysis.
Owner:IBM CORP
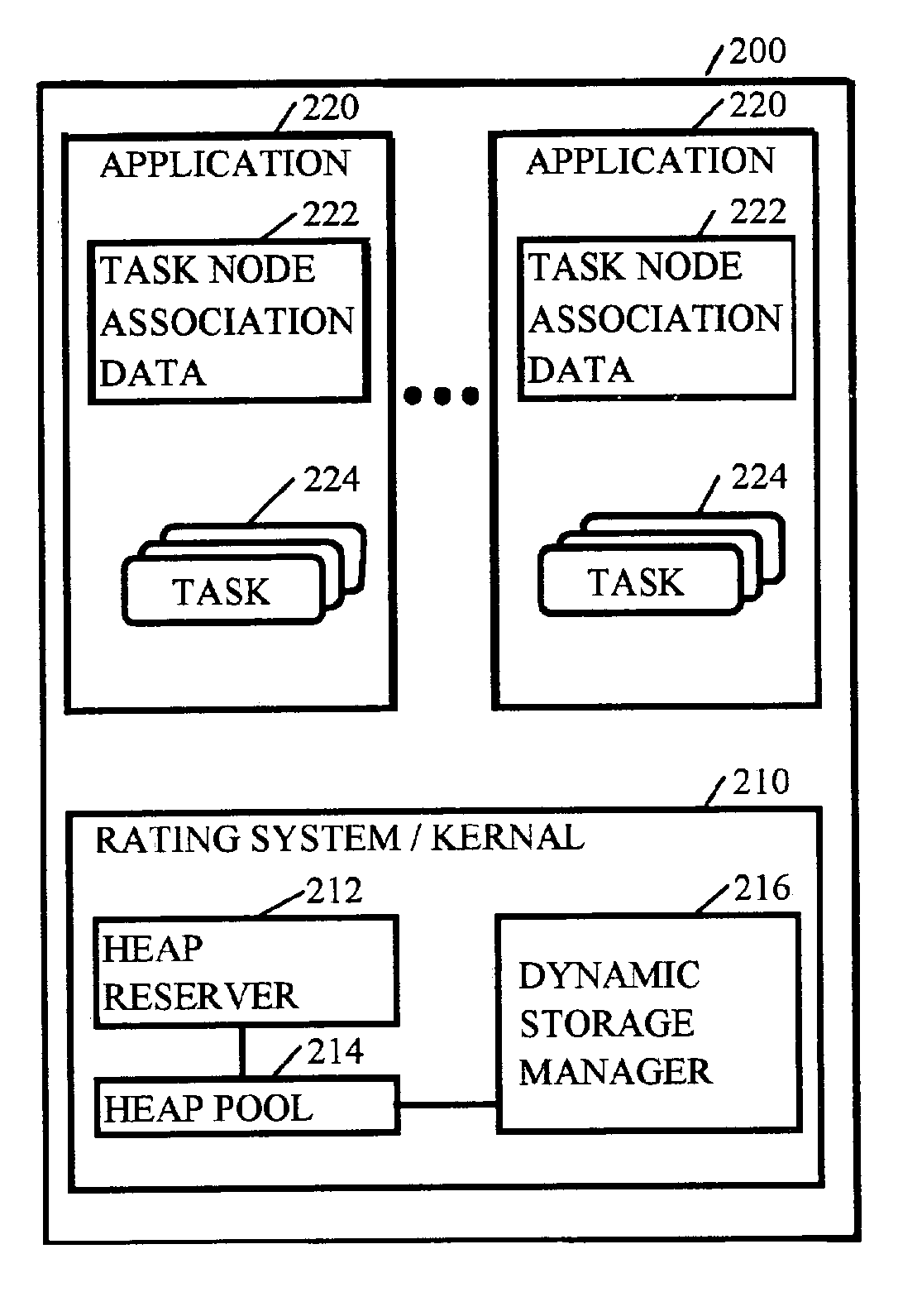
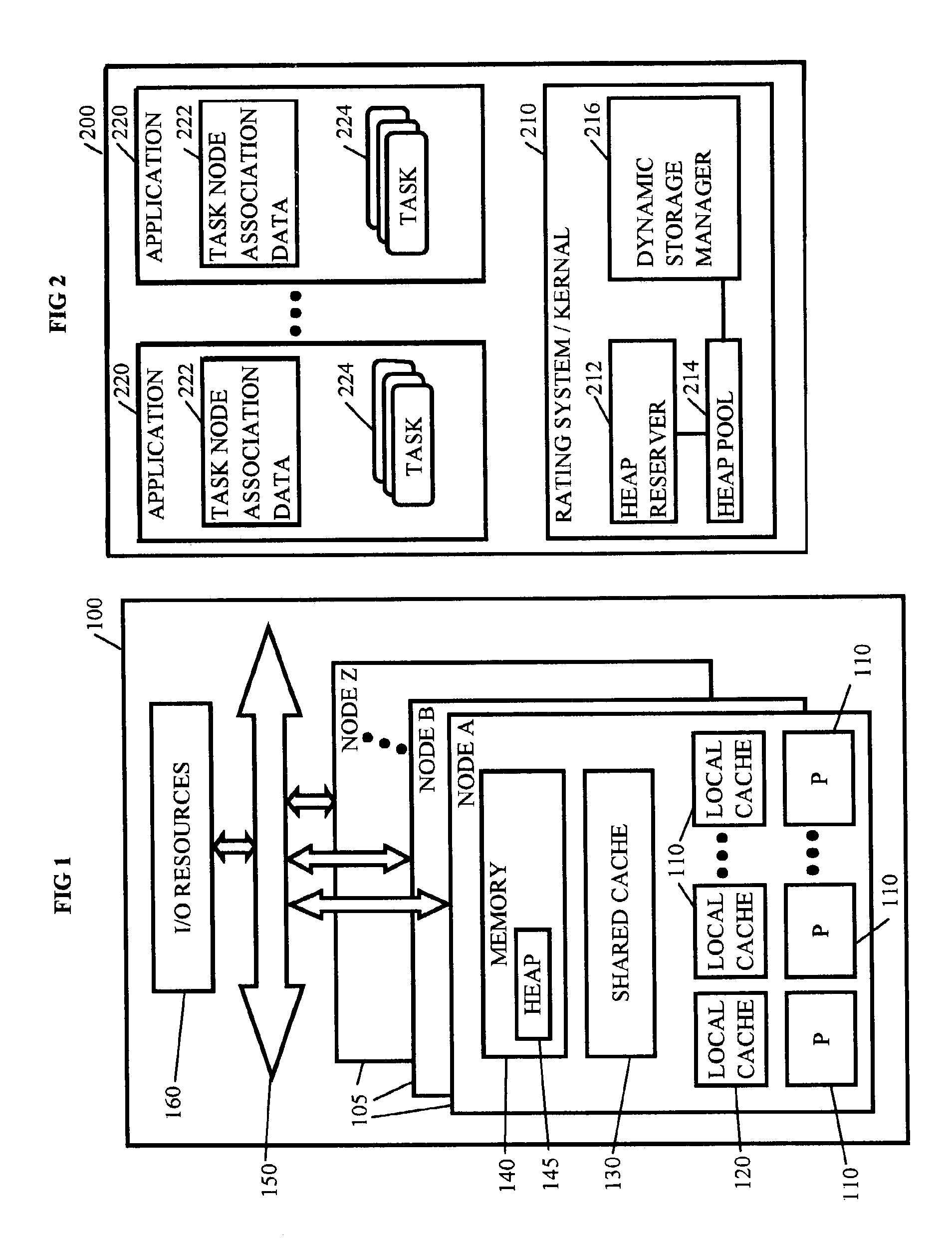
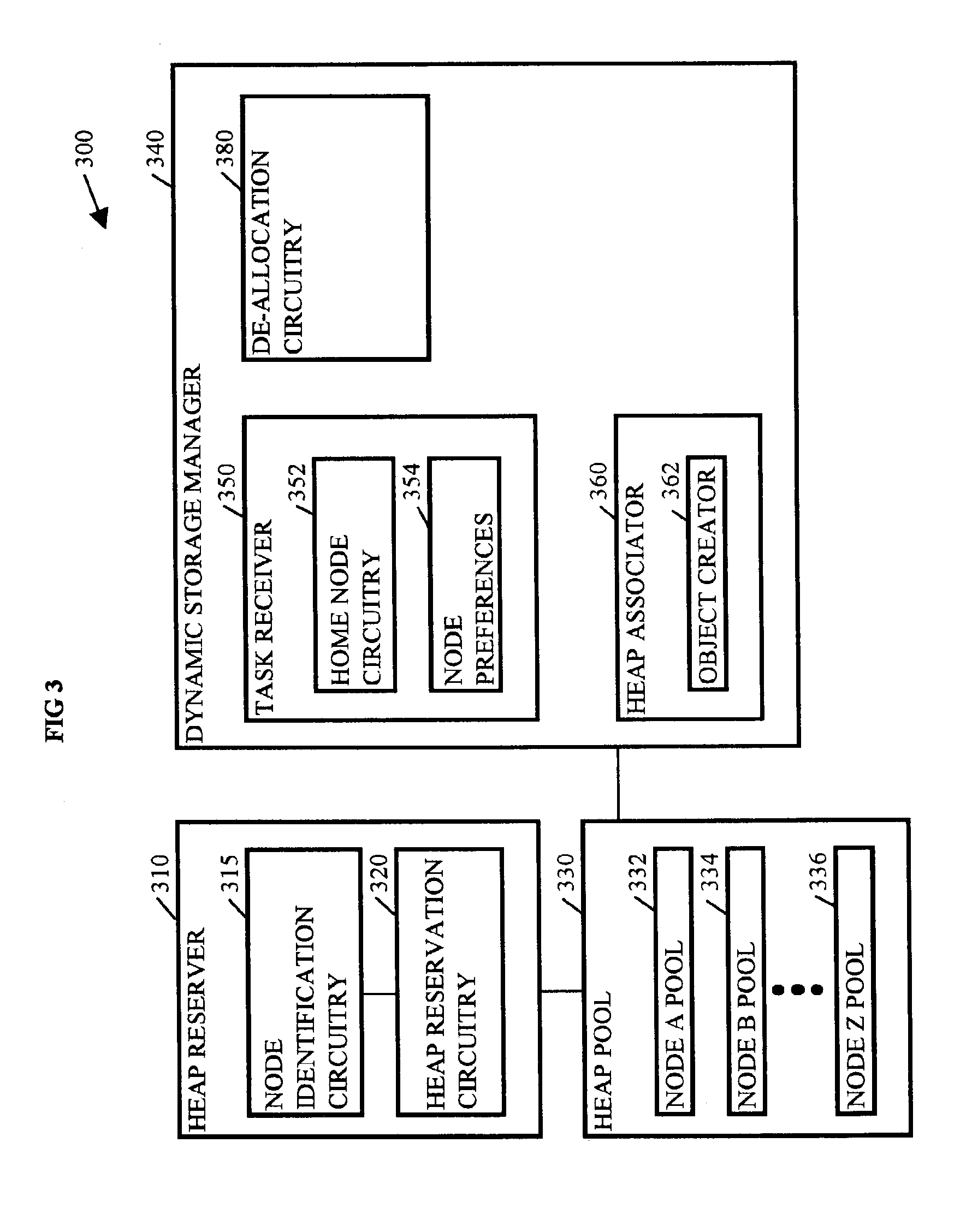
Methods, systems, and media for managing dynamic storage
Methods, systems, and media for managing dynamic memory are disclosed. Embodiments may disclose identifying nodes with having memory for dynamic storage, and reserving a portion of the memory from the identified nodes for a heap pool. After generating a heap pool, embodiments may allocate dynamic storage from the heap pool to tasks received that are associated with one of the identified nodes. More specifically, embodiments identify the node or home node associated with the task, the amount of dynamic storage requested by the task, and create a heap object in the node associated with the task to provide the requested dynamic storage. Some embodiments involve de-allocating the dynamic storage assigned to the task upon receipt of an indication that the task is complete and the dynamic storage is no longer needed for the task. Several of such embodiments return the de-allocated dynamic storage to the heap pool for reuse.
Owner:IBM CORP
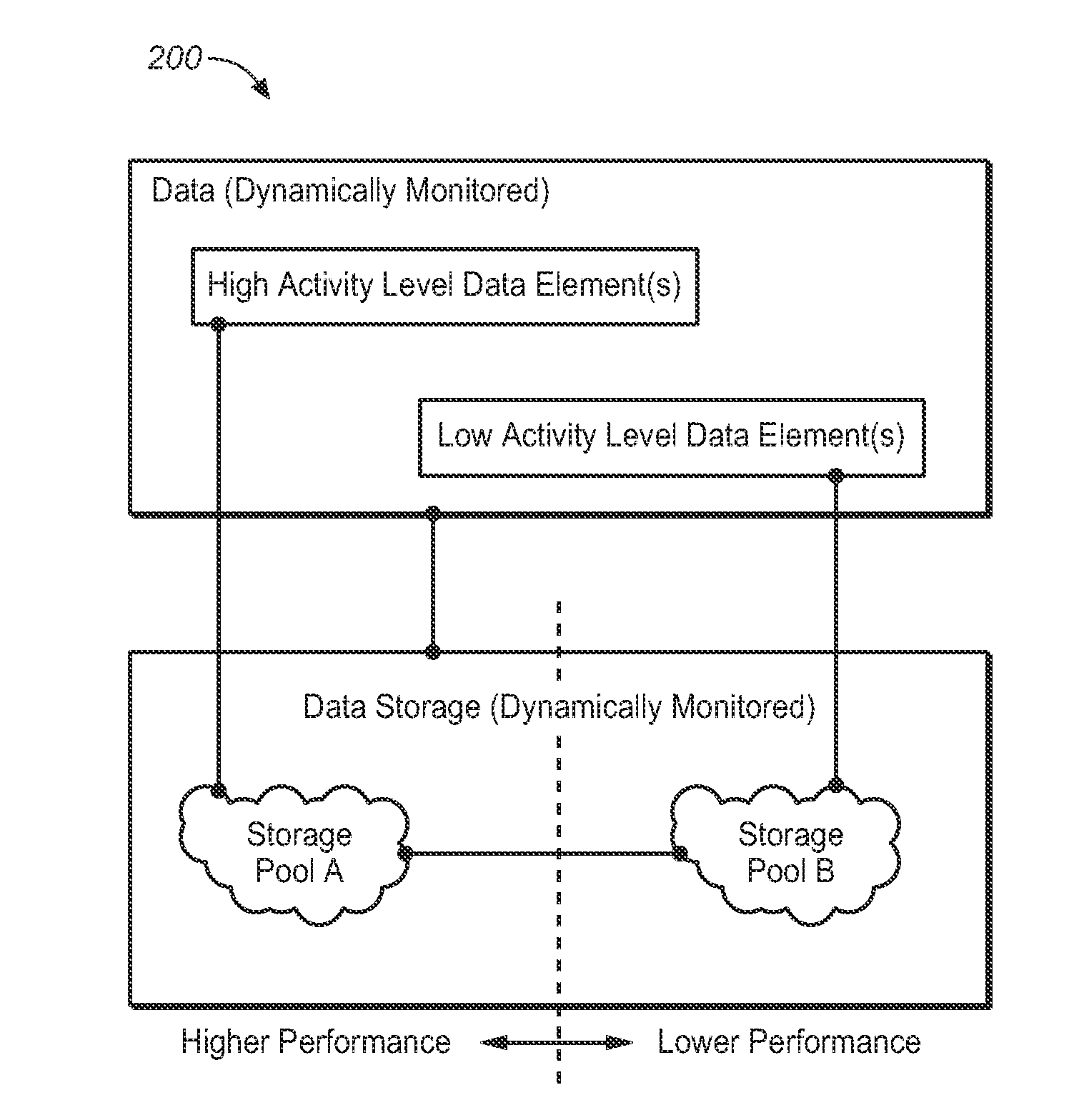
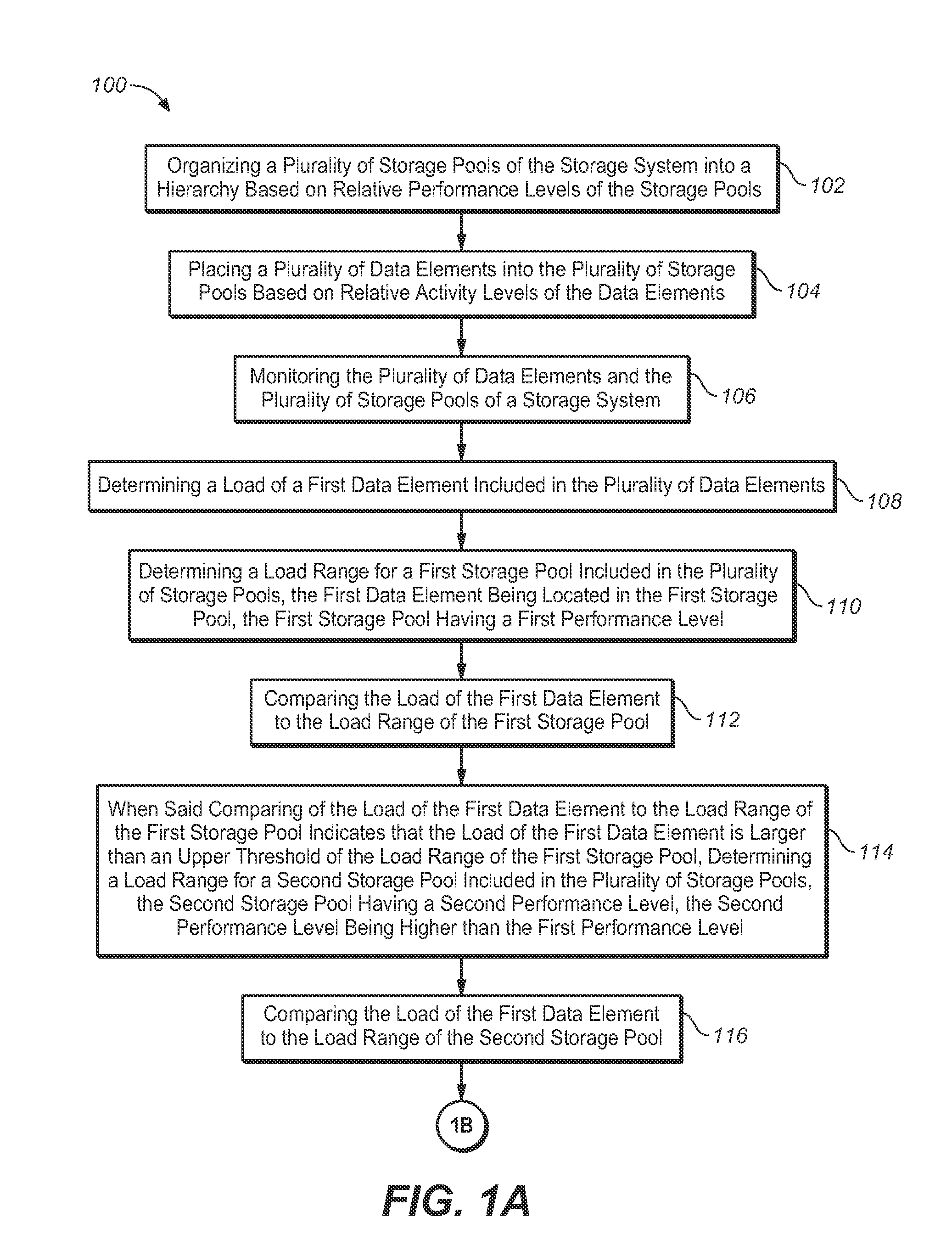
Method for placement of virtual volume hot-spots in storage pools using ongoing load measurements and ranking
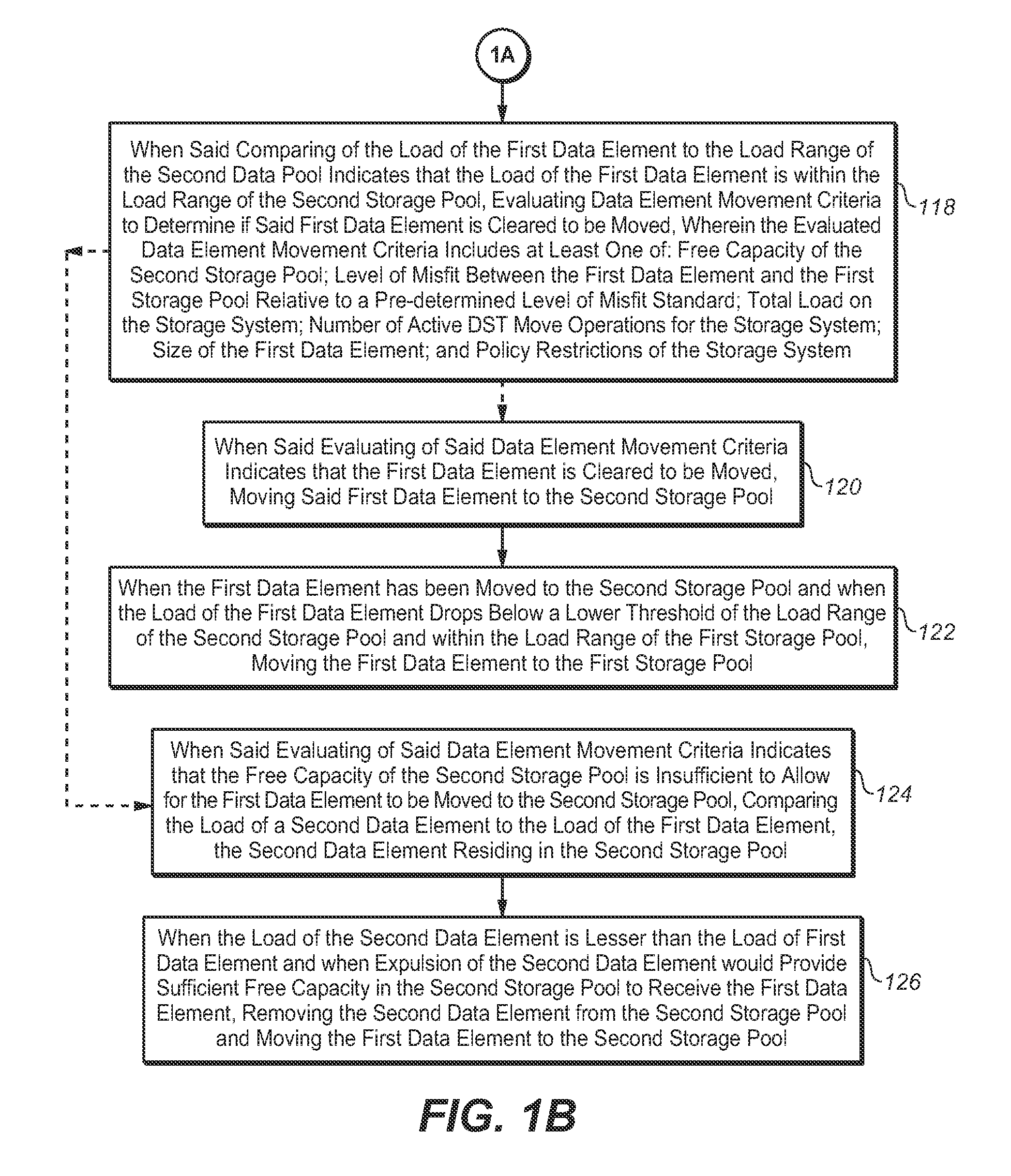
ActiveUS20110185120A1Heavy loadError detection/correctionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDynamic storageData element
The present invention is directed to a method for providing data element placement in a storage system via a Dynamic Storage Tiering (DST) mechanism, such that improved system efficiency is promoted. For example, the DST mechanism may implement an algorithm for providing data element placement. The data elements (ex.—virtual volume hot-spots) may be placed into storage pools, such that usage of higher performing storage pools is maximized. Hot-spots may be detected by dynamically measuring load on LBA ranges. Performance of the storage pools may be measured on an ongoing basis. Further, the hot-spots may be ranked according to load, while storage pools may be ranked according to measured performance. If a hot-spot's load decreases, the hot-spot may be moved to a lower performing storage pool. If a hot-spot's load increases, the hot-spot may be moved to a higher performing storage pool.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Independently controlled, double gate nanowire memory cell with self-aligned contacts
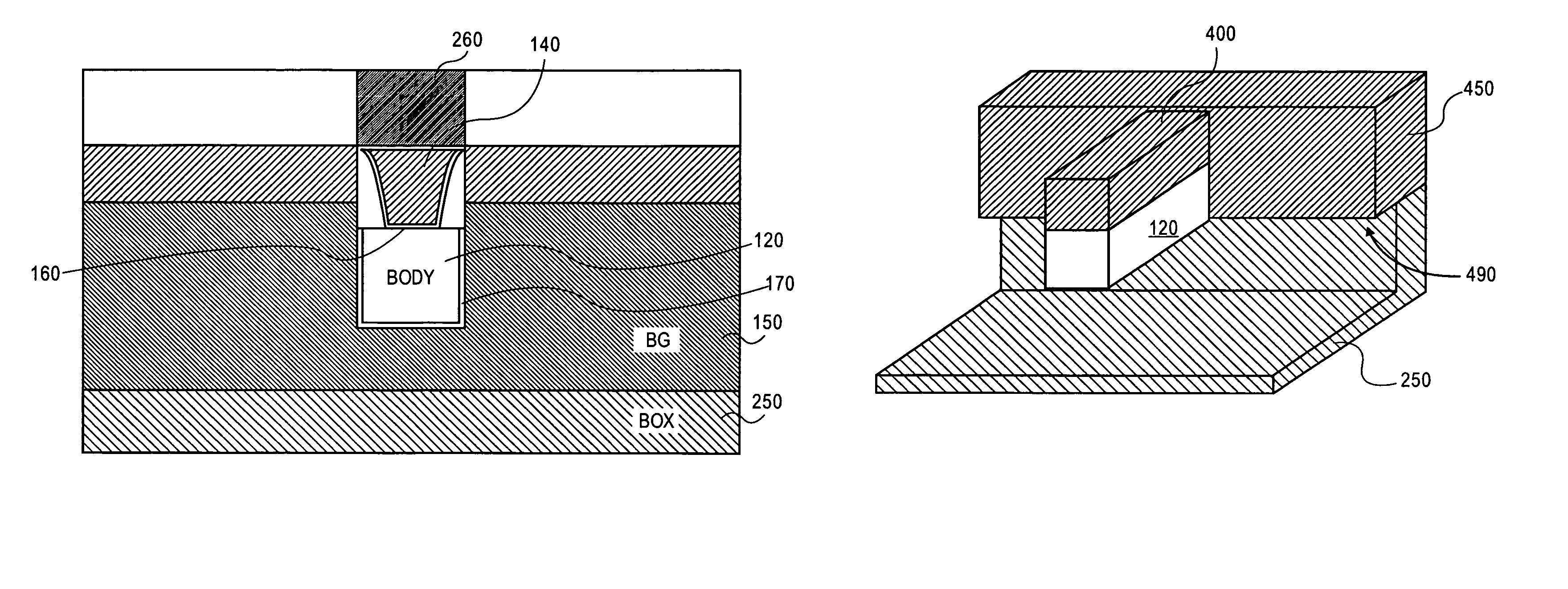
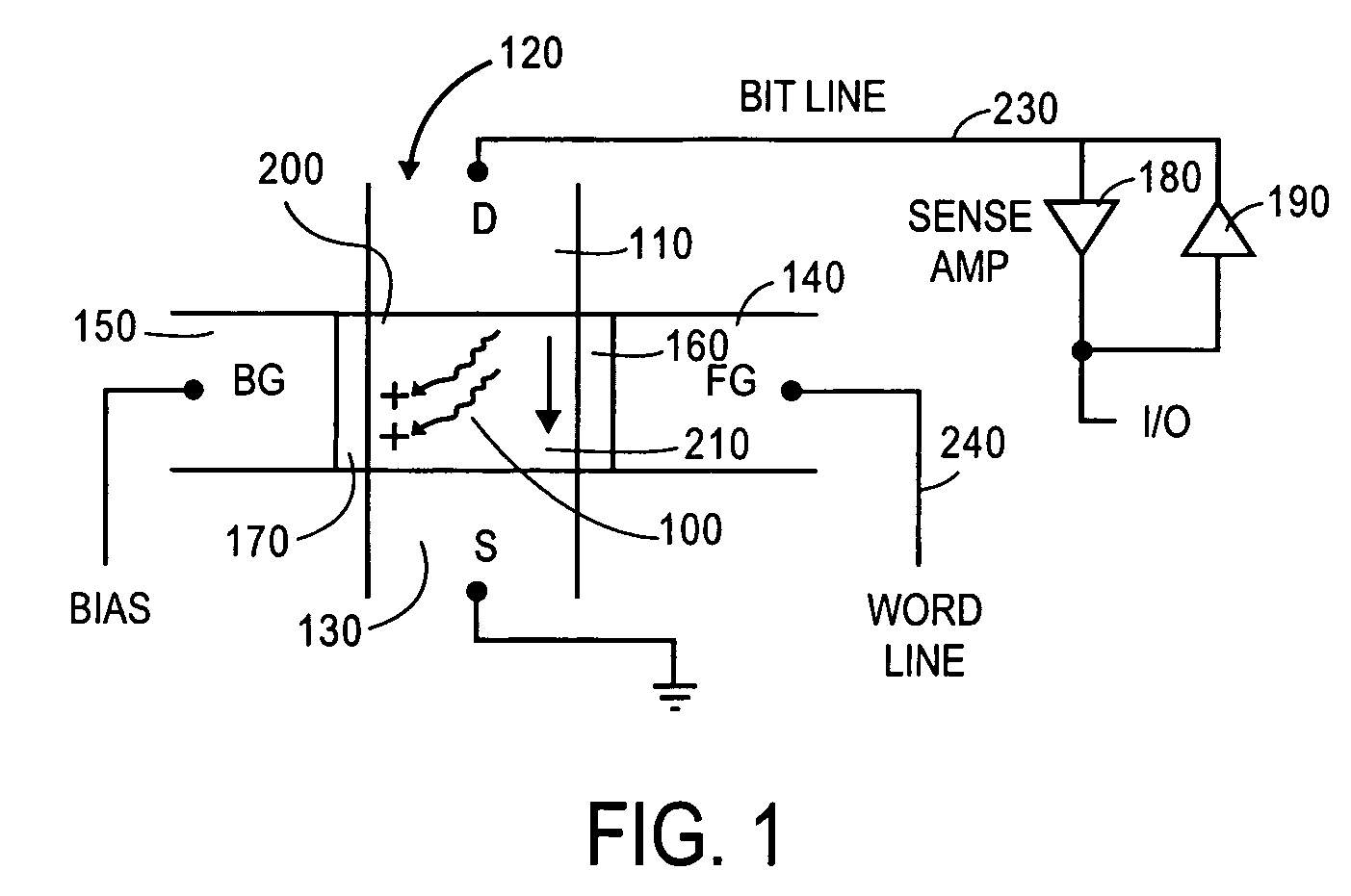
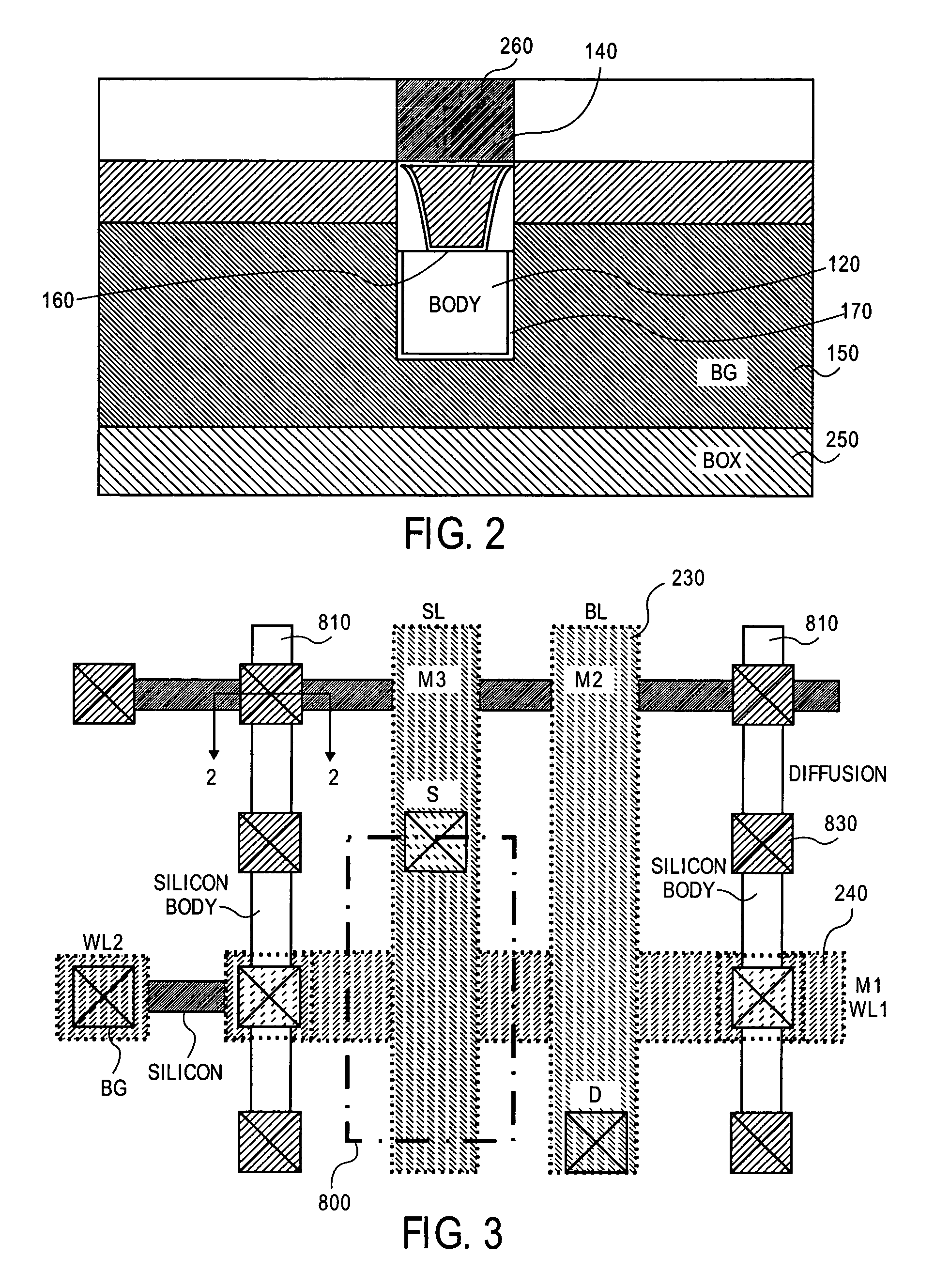
A doubled gate, dynamic storage device and method of fabrication are disclosed. A back (bias gate) surrounds three sides of a semiconductor body with a front gate disposed on the remaining surface. Two different gate insulators and gate materials may be used.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Dynamic information systems
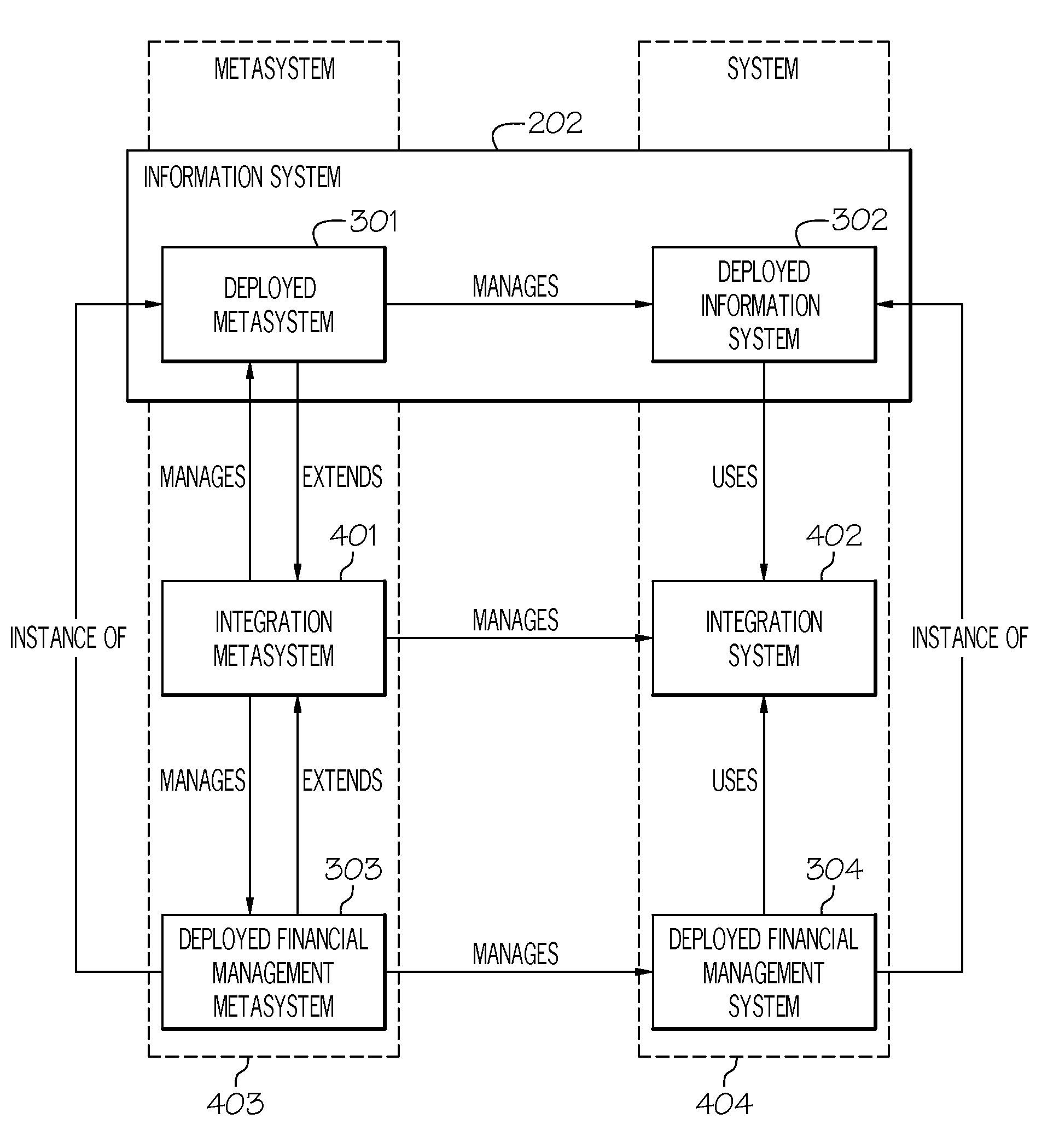
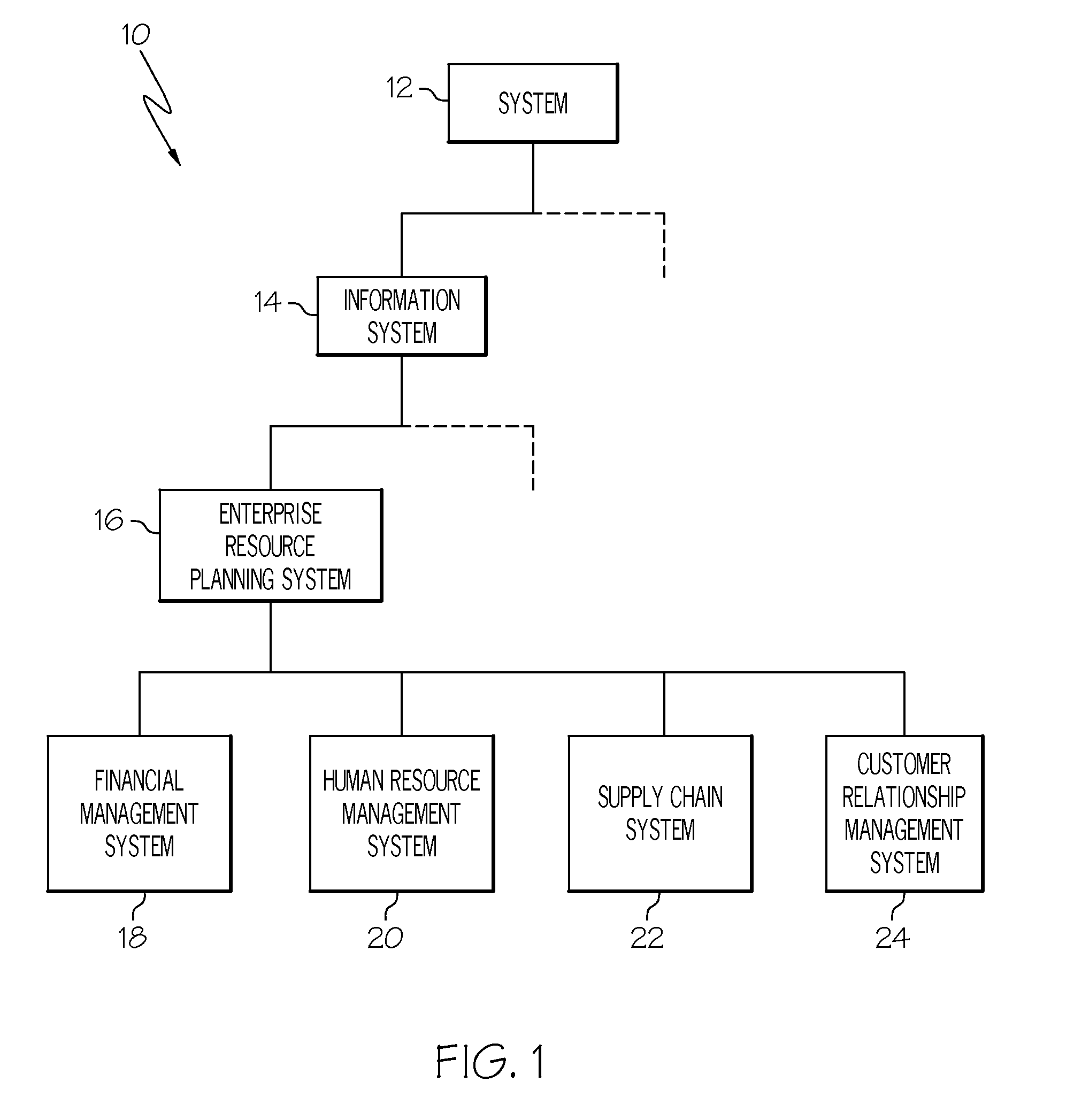
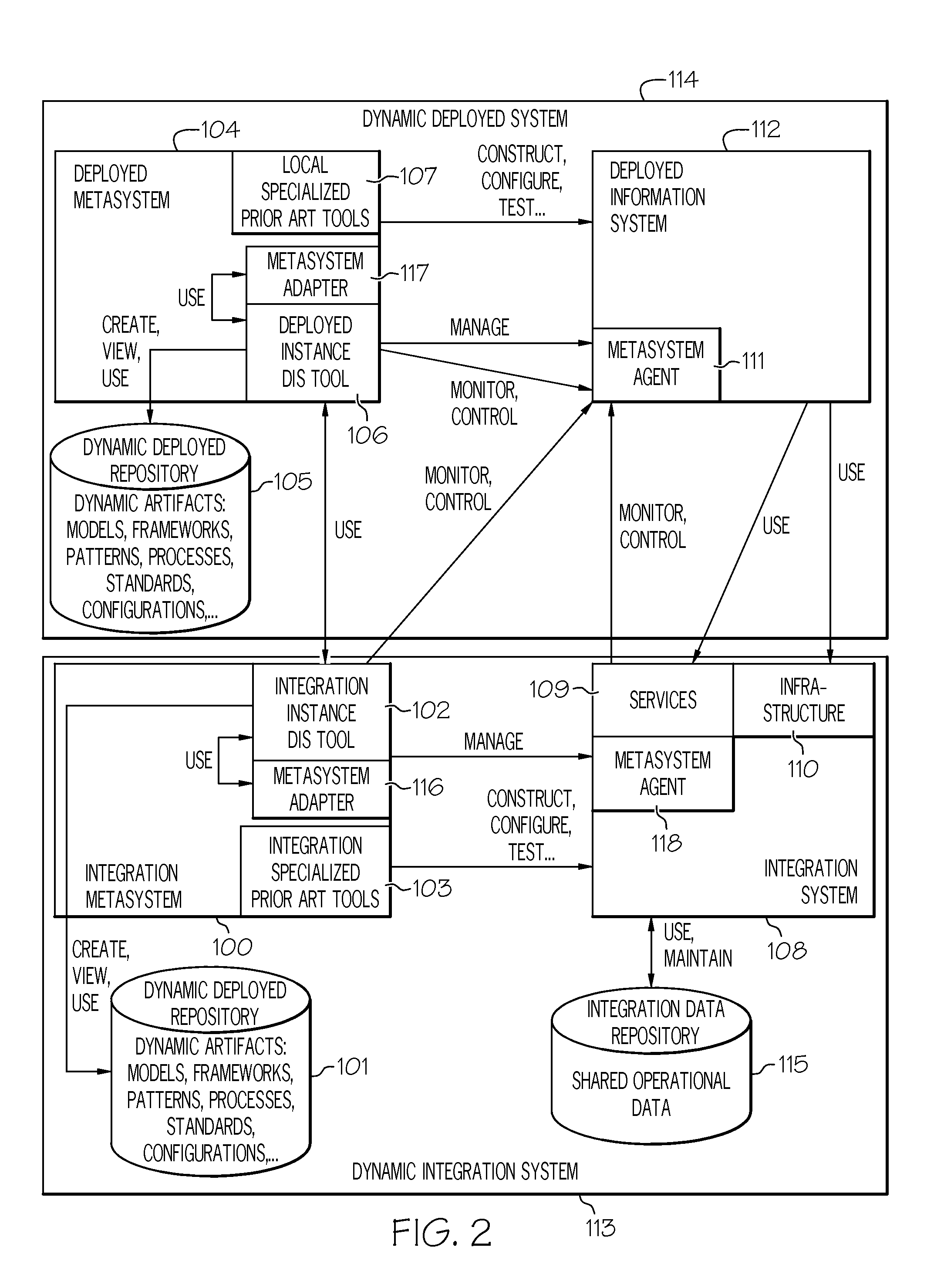
InactiveUS20100005122A1Database management systemsDigital computer detailsDynamic storageEnterprise architecture
This invention discloses the concept of a dynamic metasystem managing a dynamic system, achieved through the use of, and an environment (i.e., tools and ontologies) supporting dynamic artifacts. A system for generating a dynamic information system comprises a persistent dynamic repository of data and an integration metasystem. The repository forms an asymmetric navigational database, and the database includes an ontology model. The ontology model has an abstract model framework that supports creation and use of multi-dimensional and asymmetric abstract models of data, and views which define the content and form of presentation of that data using a computer. The integration metasystem includes components that describe components of shared infrastructure and services of an enterprise architecture, and a dynamic information system software tool generating artifacts representing information and views that define the presentation of data. The artifacts are provided to the ontology model, and have interfaces to the abstract model framework that permit creation, reading and modification of the contents of the asymmetric navigational database.
Owner:KYNDRYL INC
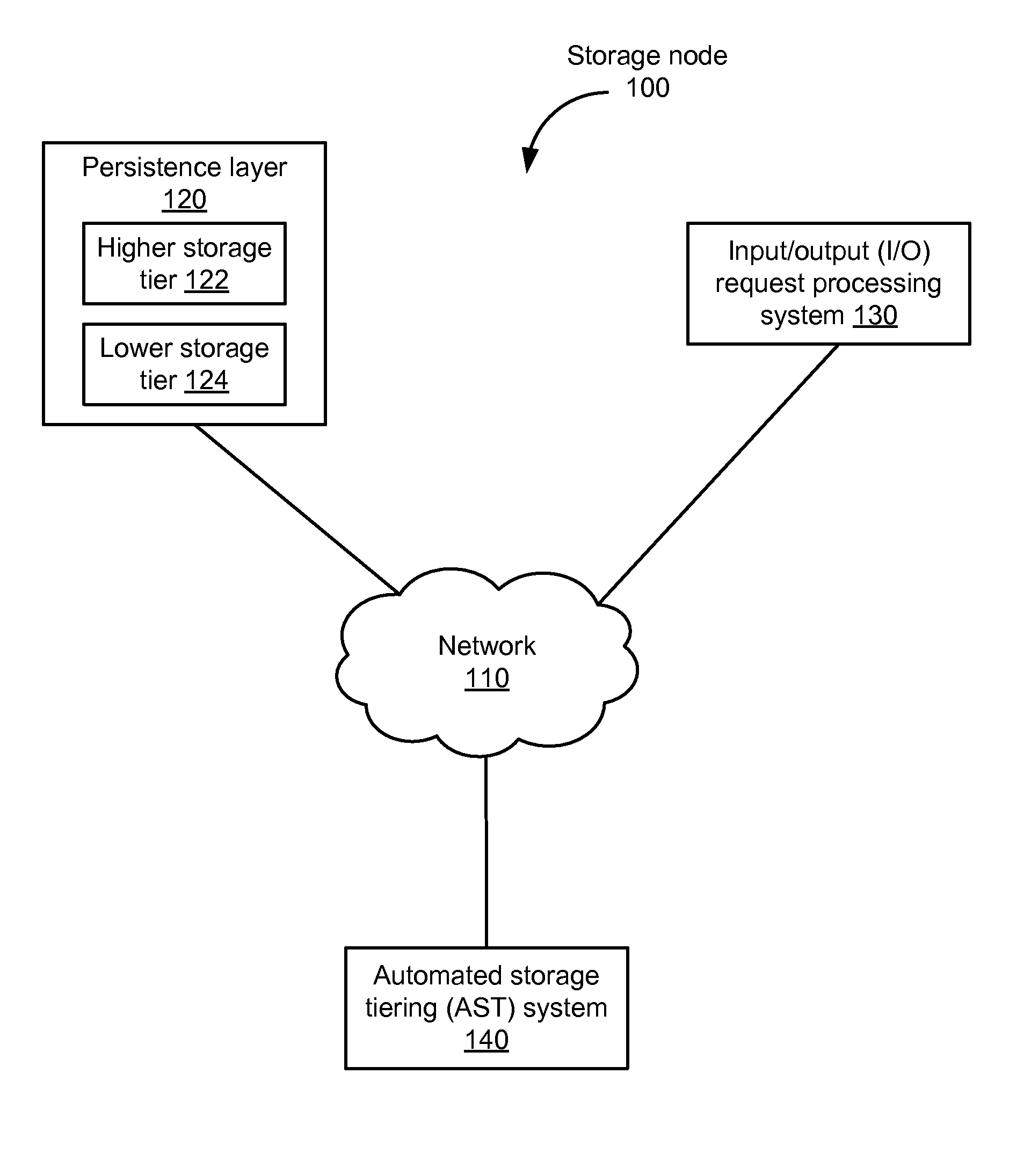
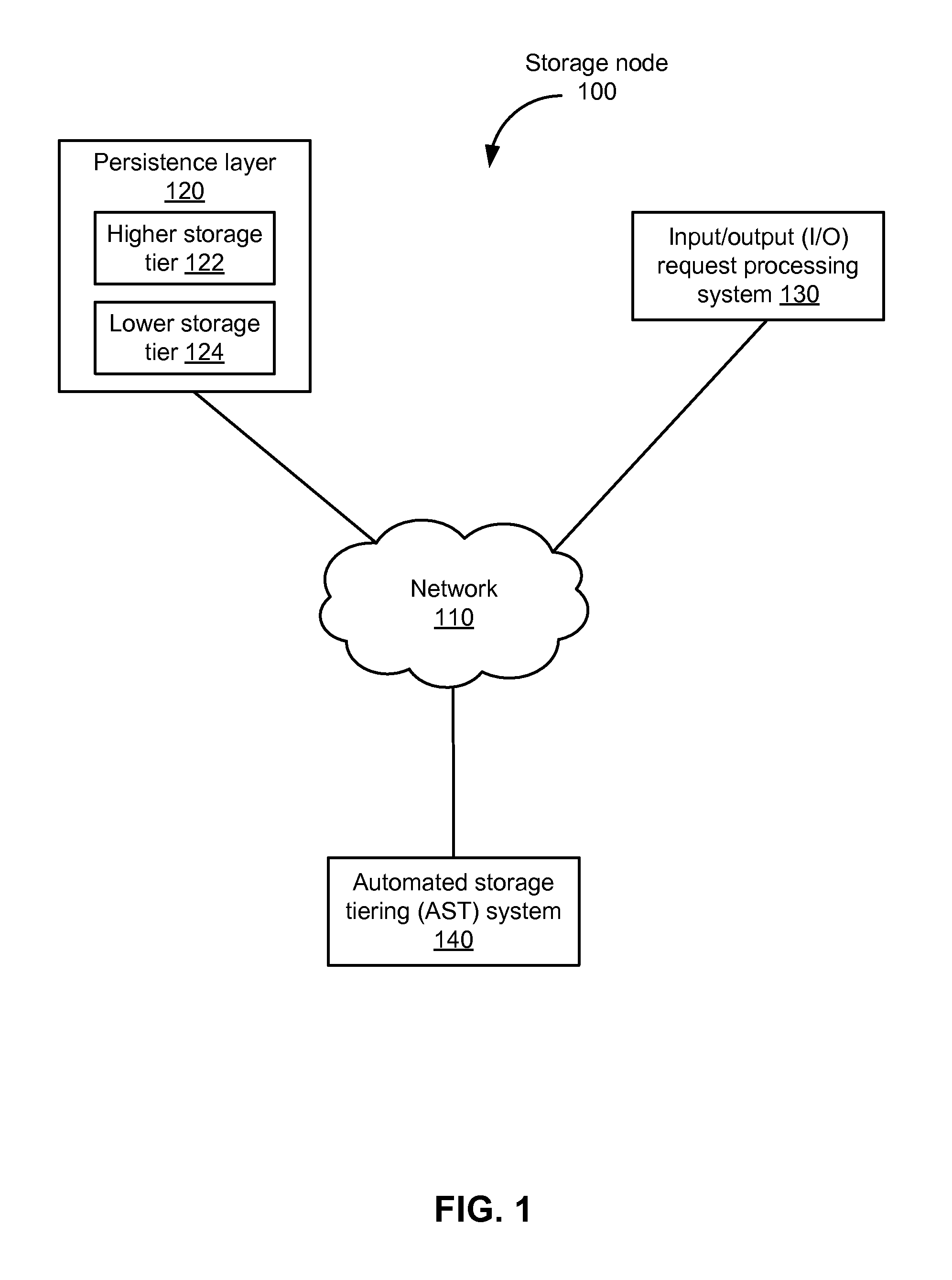
Dynamic Storage Tiering Based on Performance SLAs
ActiveUS20160231928A1Input/output to record carriersTransmissionService-level agreementDynamic storage
Data objects are stored on storage devices, taking into account service level agreements or other quality of service parameters. In one aspect, data objects grouped into storage volumes. In addition, the storage devices are classified into different level storage tiers, where higher level storage tiers have higher performance and lower level storage tiers have lower performance. Ranks for the data objects are calculated, based on both a data usage pattern for the data object (e.g., recency and frequency) and on quality of service (QOS) parameters for the storage volume containing the data object. Examples of QOS parameters include service level agreements, priority, minimum and maximum input / output operations per second. The data objects are then stored on storage devices, based on the data objects' ranks and the storage devices' storage tiers.
Owner:EBAY INC
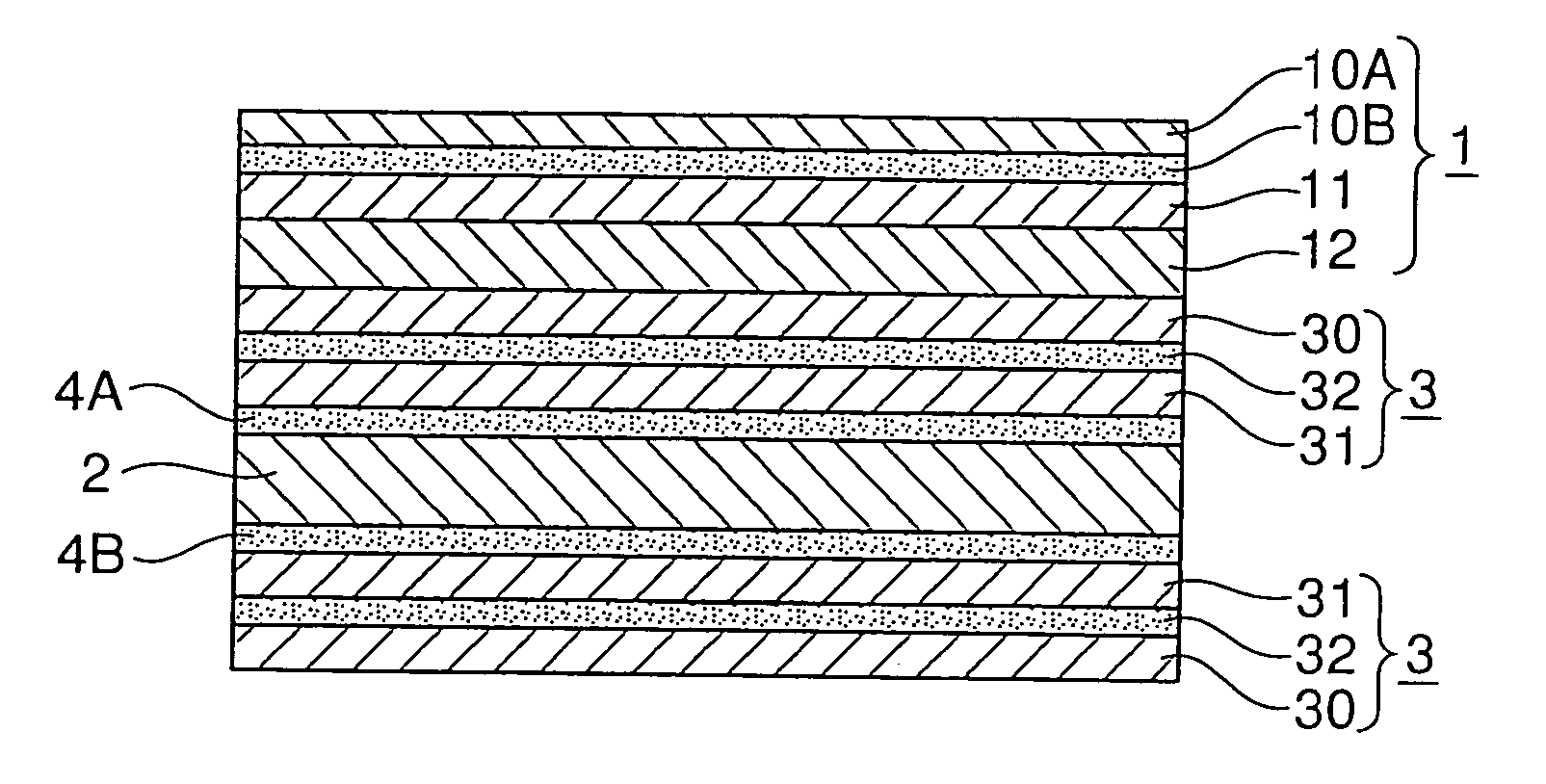
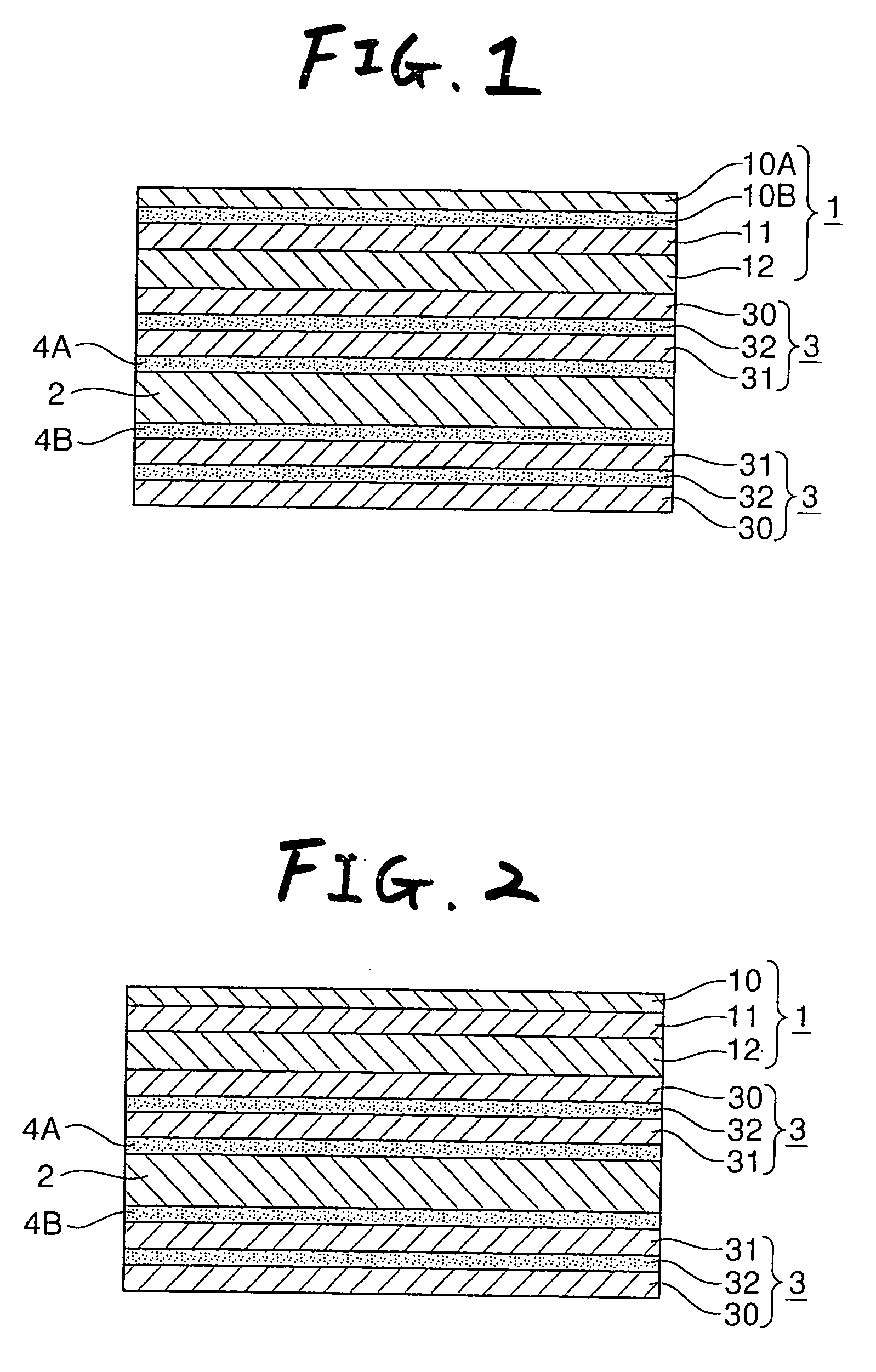
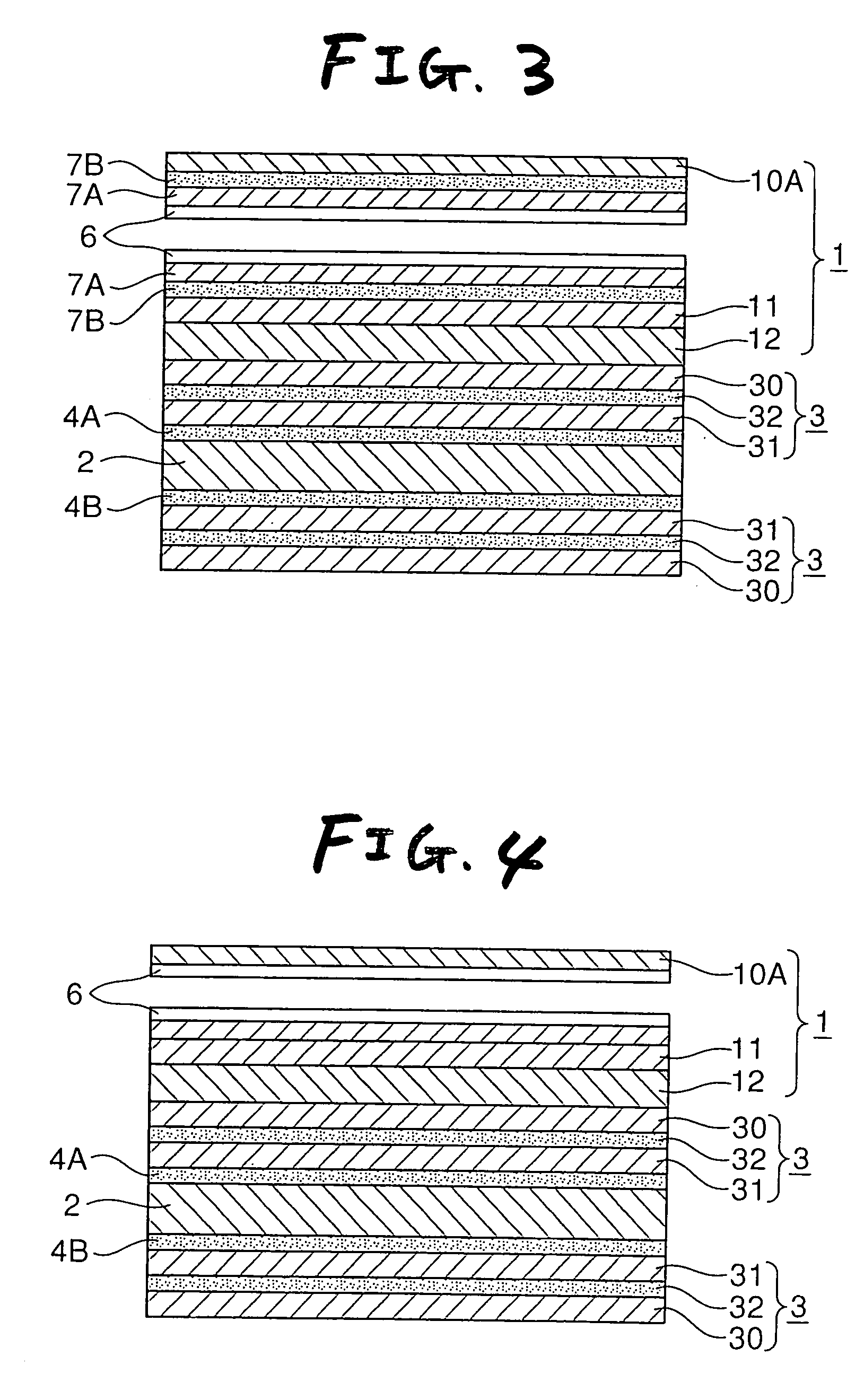
Transparent laminate, pen-input image display, and image display method
InactiveUS20050237307A1Reduce weightSmall sizeSynthetic resin layered productsCathode-ray tube indicatorsAdhesiveDisplay device
A surface-treated film, a transparent rigid layer and a transparent relaxing layer are laminated in this order to form a transparent laminate. Particularly, the transparent relaxing layer is made of an adhesive. The dynamic storage modulus G′ of the transparent rigid layer at 20° C. is not lower than 2×108 Pa. On the other hand, the dynamic storage modulus G′ of the transparent relaxing layer at 20° C. is not higher than 1×107 Pa. The transparent laminate is directly laminated onto a visual surface side (pen-input side) of a liquid crystal panel provided as an image display panel so that the transparent relaxing layer is placed inward. Thus, a pen-input image display device is produced.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
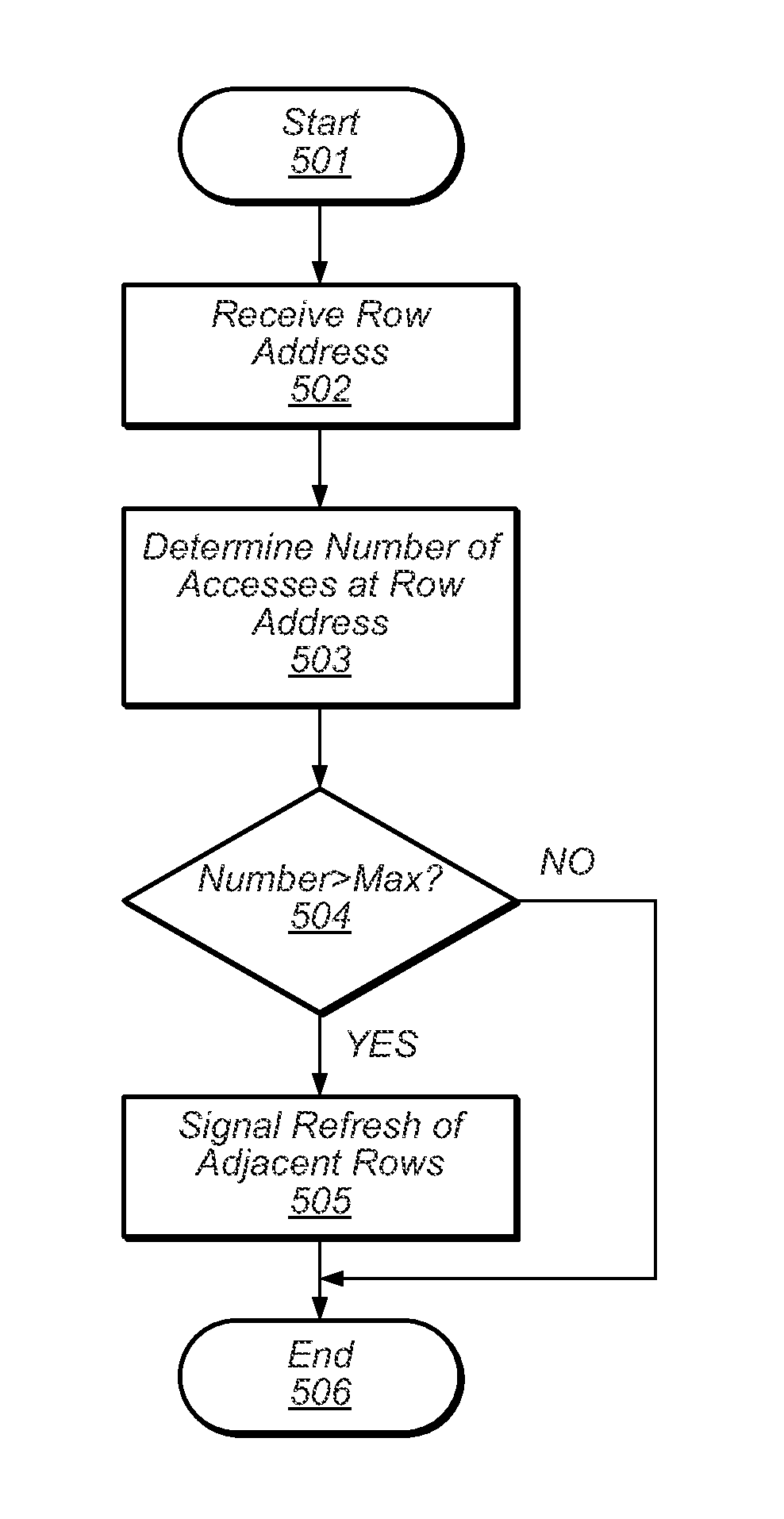
Detection of multiple accesses to a row address of a dynamic memory within a refresh period
Embodiments of a row address cache circuit are disclosed that may allow the determination the number of times a row address is used to access a dynamic memory. The row address cache circuit may include a memory, first and second pluralities of counters, and a control circuit. The control circuit may be configured to receive a row address and store the row address in an entry of the memory when the row address has not been previously stored. When the row address has been previously stored in an entry of the memory, the control circuit may be configured to change a value of a counter of the first plurality of counters corresponding the entry. The control circuit may be further configured to change a value of each counter of the second plurality of counters after a pre-determined time interval has elapsed, and initiate a refresh of the dynamic memory.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Systems and methods for providing a dynamic memory bank page policy
Systems and methods for providing a dynamic memory buffer bank policy. Embodiments include a hub device for selecting a bank page policy. The hub device includes an input command stream interface and a bank page policy module. The input command stream interface detects commands from a memory controller that are directed to one or more memory devices that are connected to the hub device. The bank page policy module independently analyzes the commands to determine access patterns to the memory devices and for dynamically selecting between an open bank page policy and a closed bank page policy for the memory devices based on the analysis.
Owner:IBM CORP
Dynamic Programmable Intelligent Search Memory
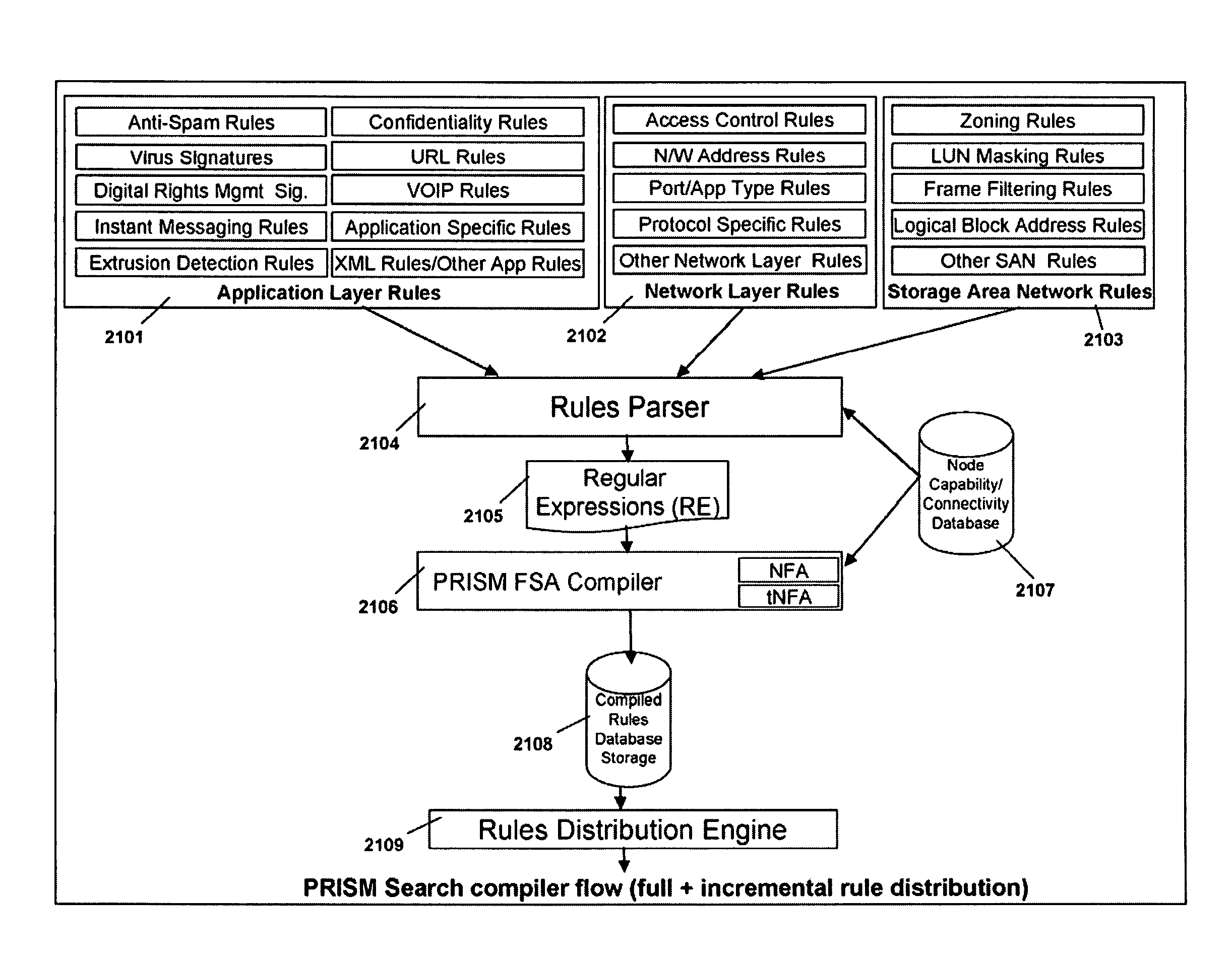
ActiveUS20080140991A1Reduce classification overheadEfficient and compact realizationDigital data information retrievalGeneral purpose stored program computerDynamic storageMemory circuits
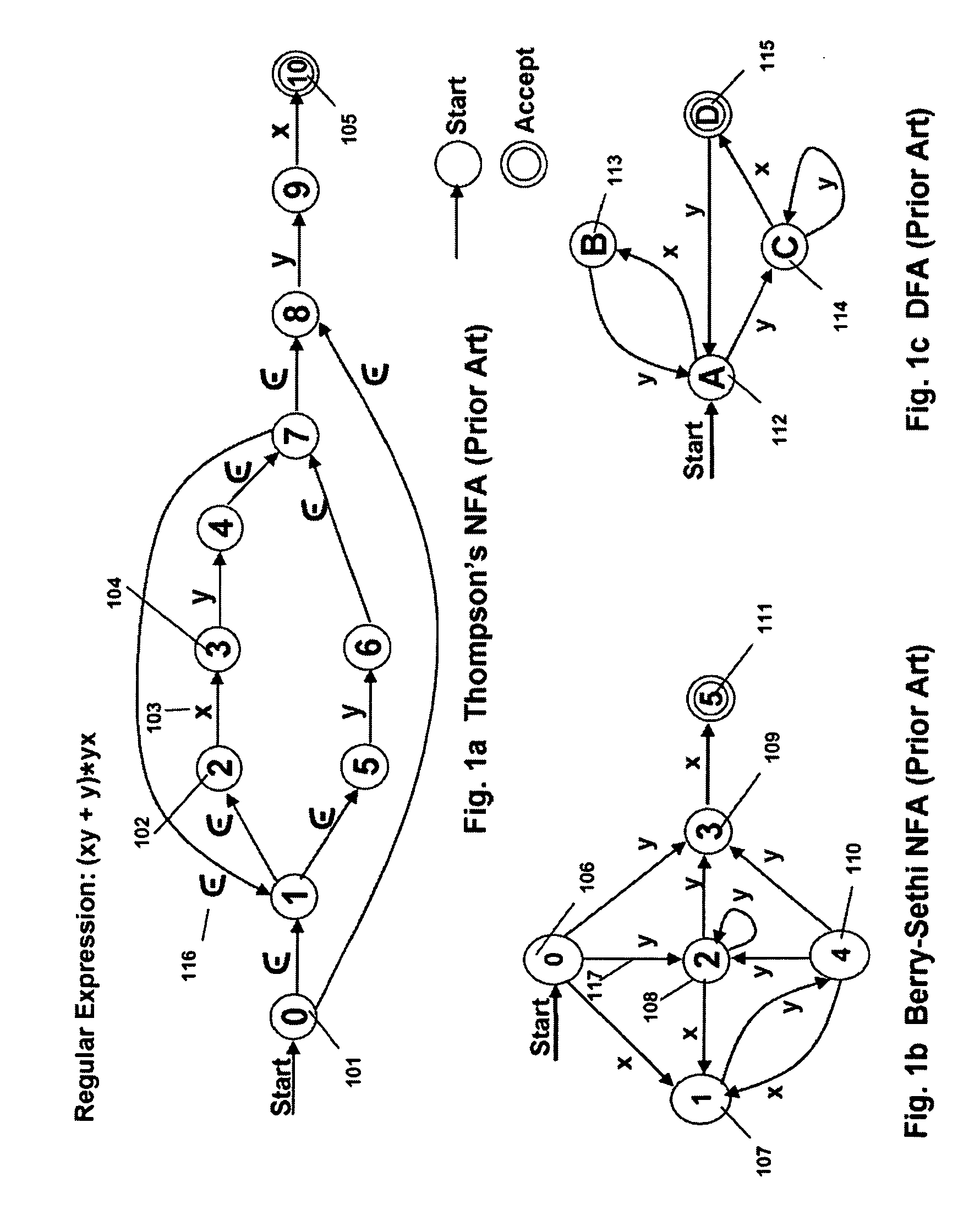
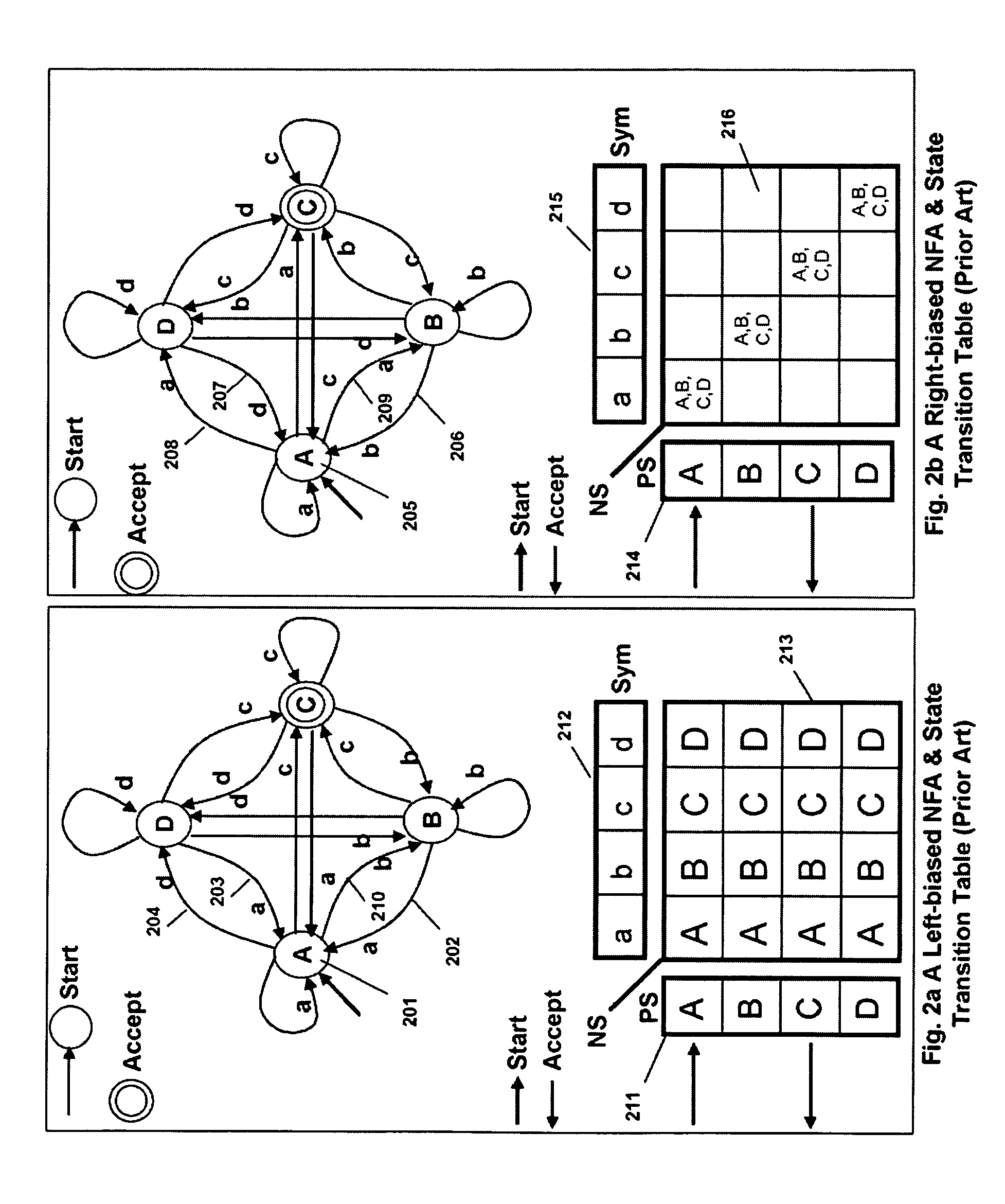
Memory architecture provides capabilities for high performance content search. The architecture creates an innovative memory derived using randomly accessible dynamic memory circuits that can be programmed with content search rules which are used by the memory to evaluate presented content for matching with the programmed rules. When the content being searched matches any of the rules programmed in the dynamic Programmable Intelligent Search Memory (PRISM) action(s) associated with the matched rule(s) are taken. Content search rules comprise of regular expressions which are converted to finite state automata and then programmed in dynamic PRISM for evaluating content with the search rules.
Owner:INFOSIL INC
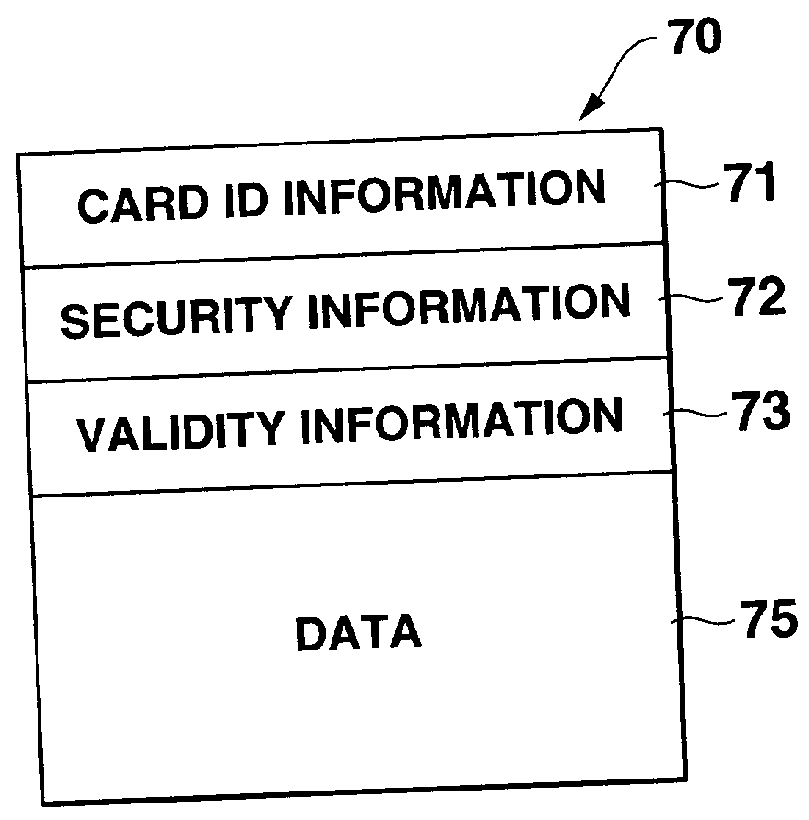
Data management systems
A data managing apparatus that manages various data such as contents in a simple storage / read controlling process, using a distributable recording medium. A card 10 has a first or static storage area IC7 adapted to be accessed in a first access method and having stored compressed high-quality music data and compressed high-quality image data, and a second or dynamic storage area CD2 adapted to be accessed in a second access method and having stored non-compressed high-quality music data and non-compressed high-quality image data. A portable player 10 or a household CD card reader 110' as a reproducer can retrieve and replay the high-quality music data and image data by referring to the compressed music data and image data stored in the IC7.
Owner:CASIO COMPUTER CO LTD
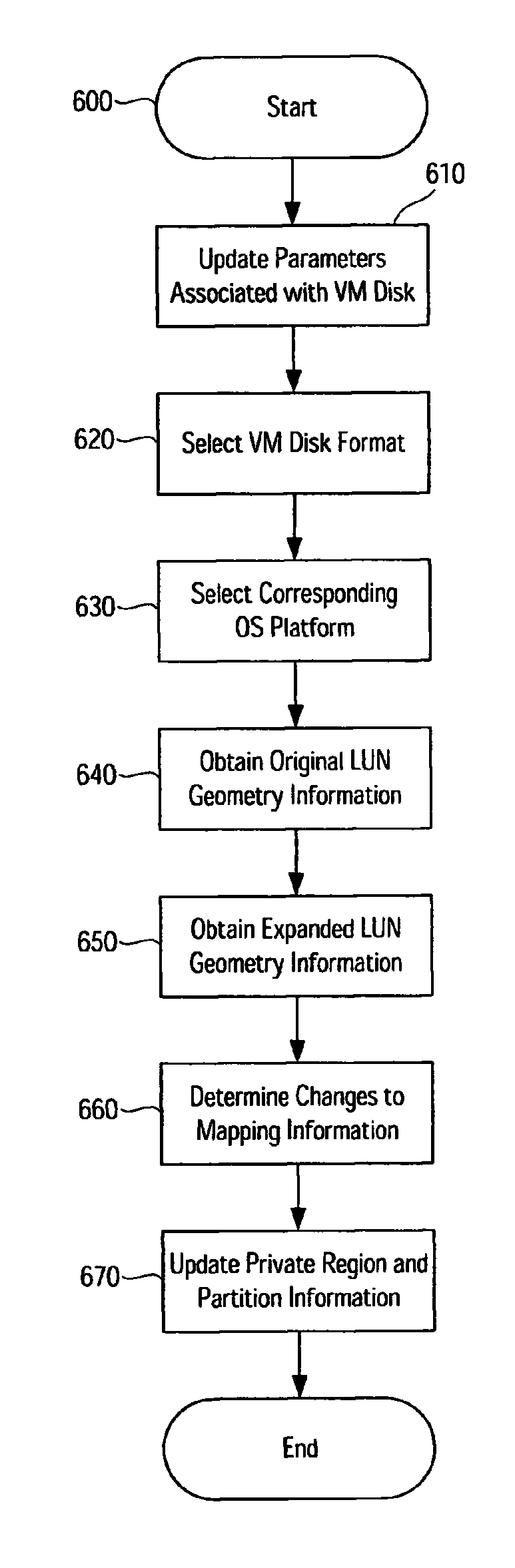
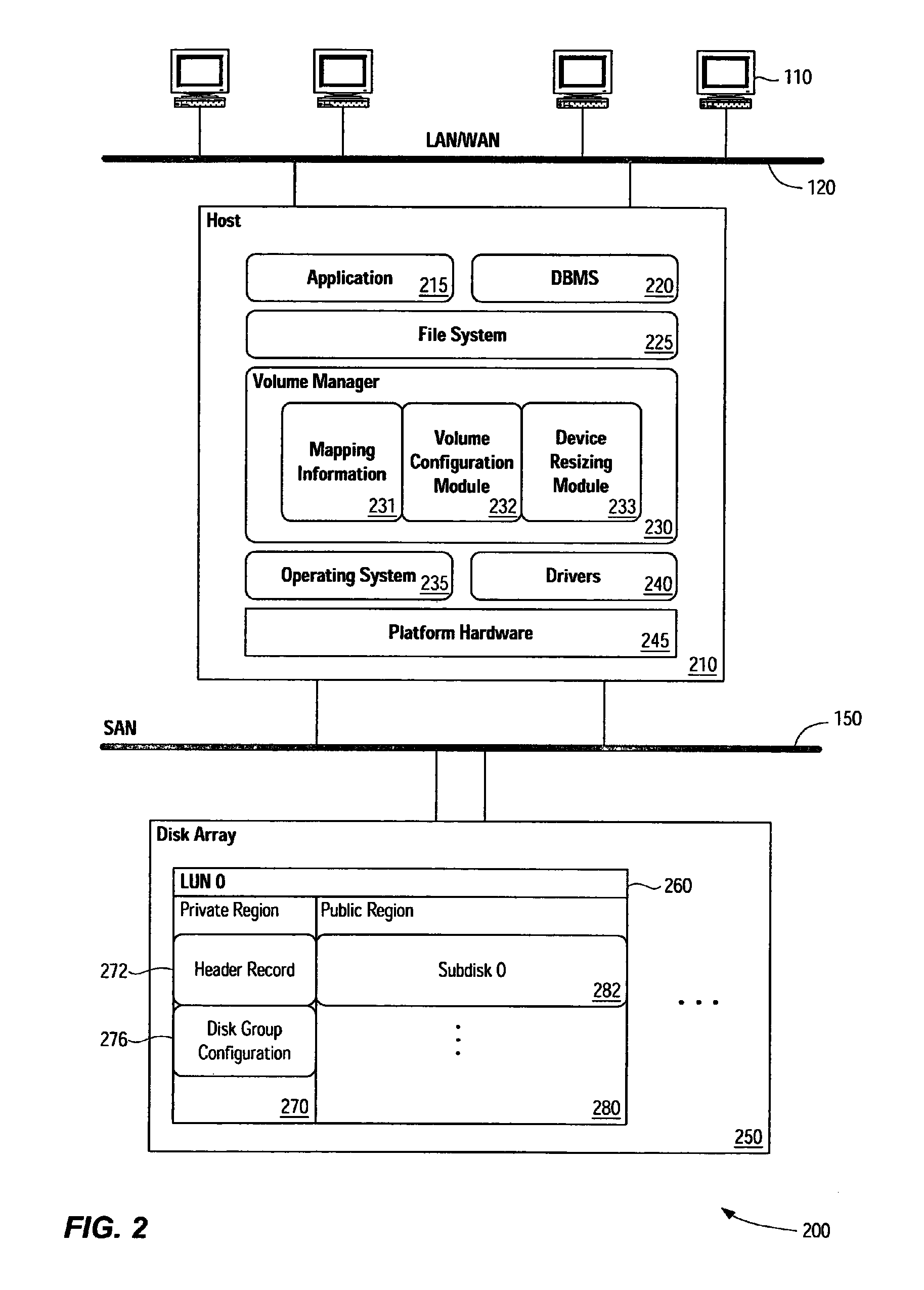
System and method for dynamic storage device expansion support in a storage virtualization environment
ActiveUS7921262B1Reduce stepsComputer security arrangementsMemory systemsOperational systemDynamic storage
It has been discovered that systems, methods, apparatus and software can accommodate the addition or removal of available physical storage (storage “expansion”) in a storage virtualization environment while virtual storage devices remain online and generally available to users. When a change to the available storage has occurred, new storage device geometry and configuration information reflecting the change is obtained and / or calculated. This new information is used to update mapping information used by virtualization software and / or to update information used by an operating system to manage storage devices. Such updating occurs while some or all of the virtual storage devices associated with the physical storage devices remain available to users. In some cases, I / O operations targeting a physical device are held, in a manner transparent to a user, while updating occurs.
Owner:SYMANTEC OPERATING CORP
Dynamic Storage Tiering In A Virtual Environment
ActiveUS20130159359A1Special data processing applicationsMemory systemsDynamic storageHybrid storage system
Various systems and methods for performing dynamic storage tiering in a virtual environment. For example, one method can involve identifying a location of a storage object within a virtual machine file, where the virtual machine file includes multiple storage objects. The method then involves detecting whether the storage object meets a criterion of a tiering policy. If the storage object meets the criterion, the storage object is moved from one tier of a multi-tier storage system to another tier of the multi-tier storage system.
Owner:VERITAS TECH
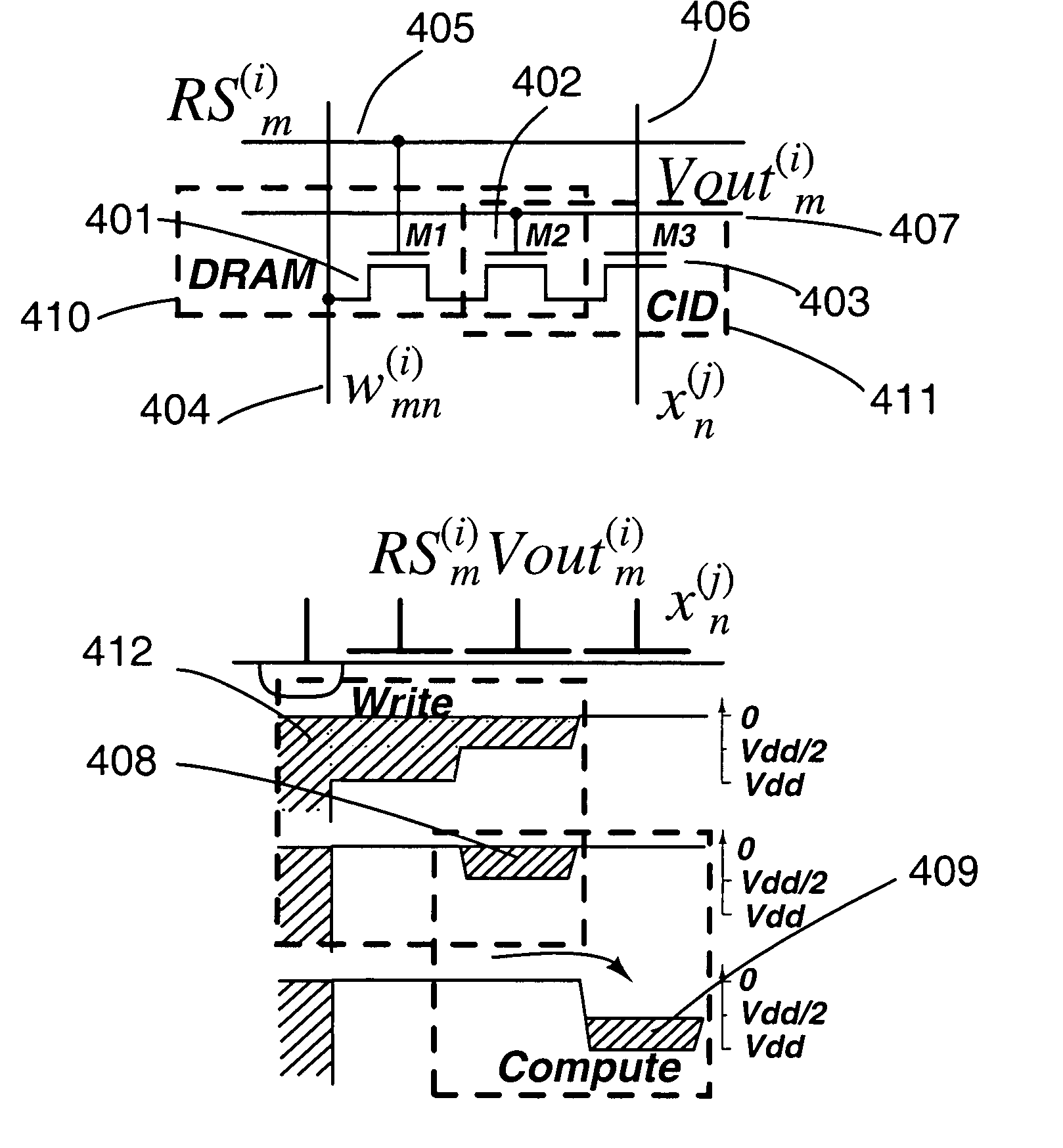
High-precision matrix-vector multiplication on a charge-mode array with embedded dynamic memory and stochastic method thereof
InactiveUS20050125477A1Efficient multiplicationIncrease cell densityComputation using non-contact making devicesPhysical realisationRandom methodReal time signal processing
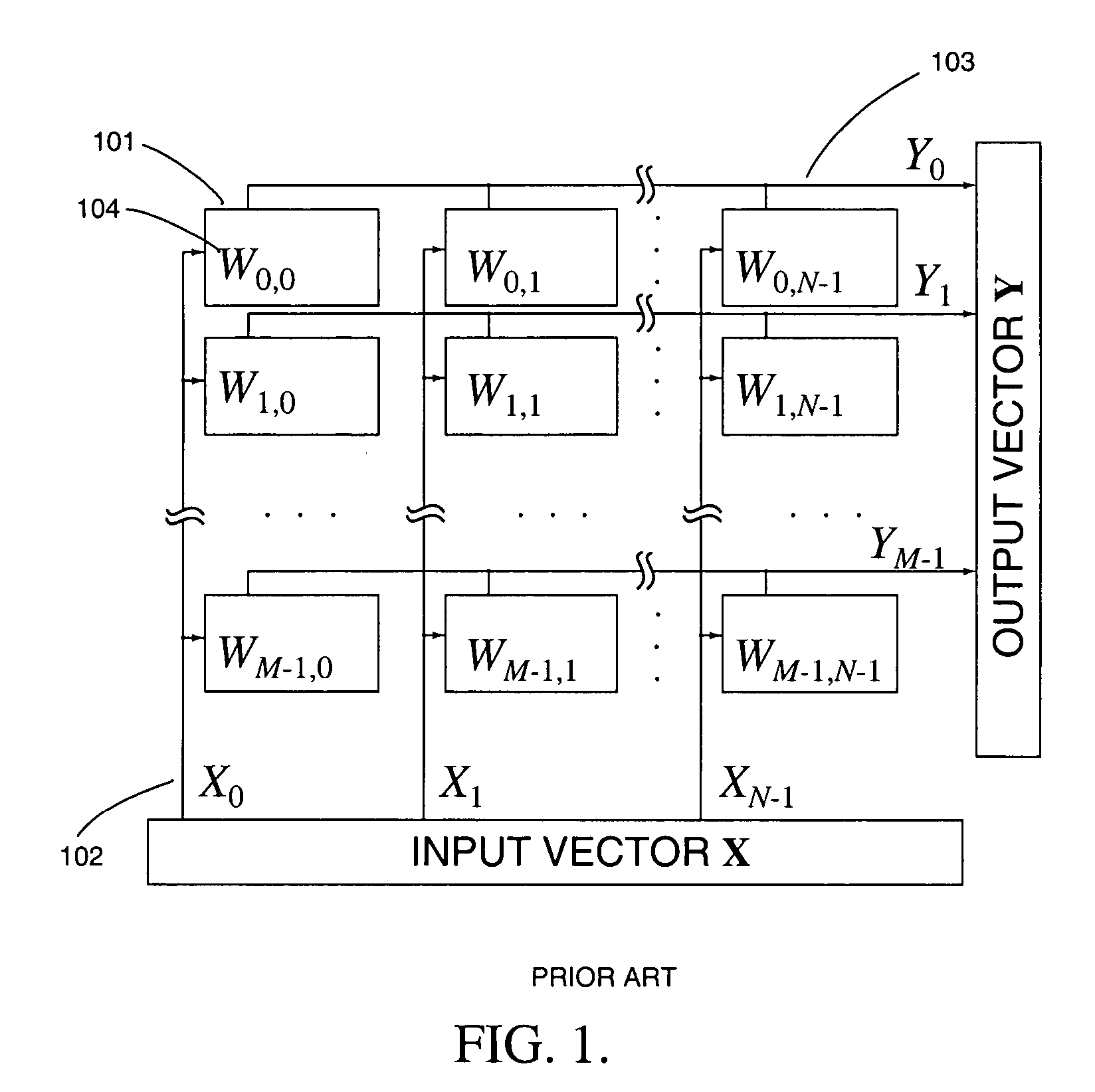
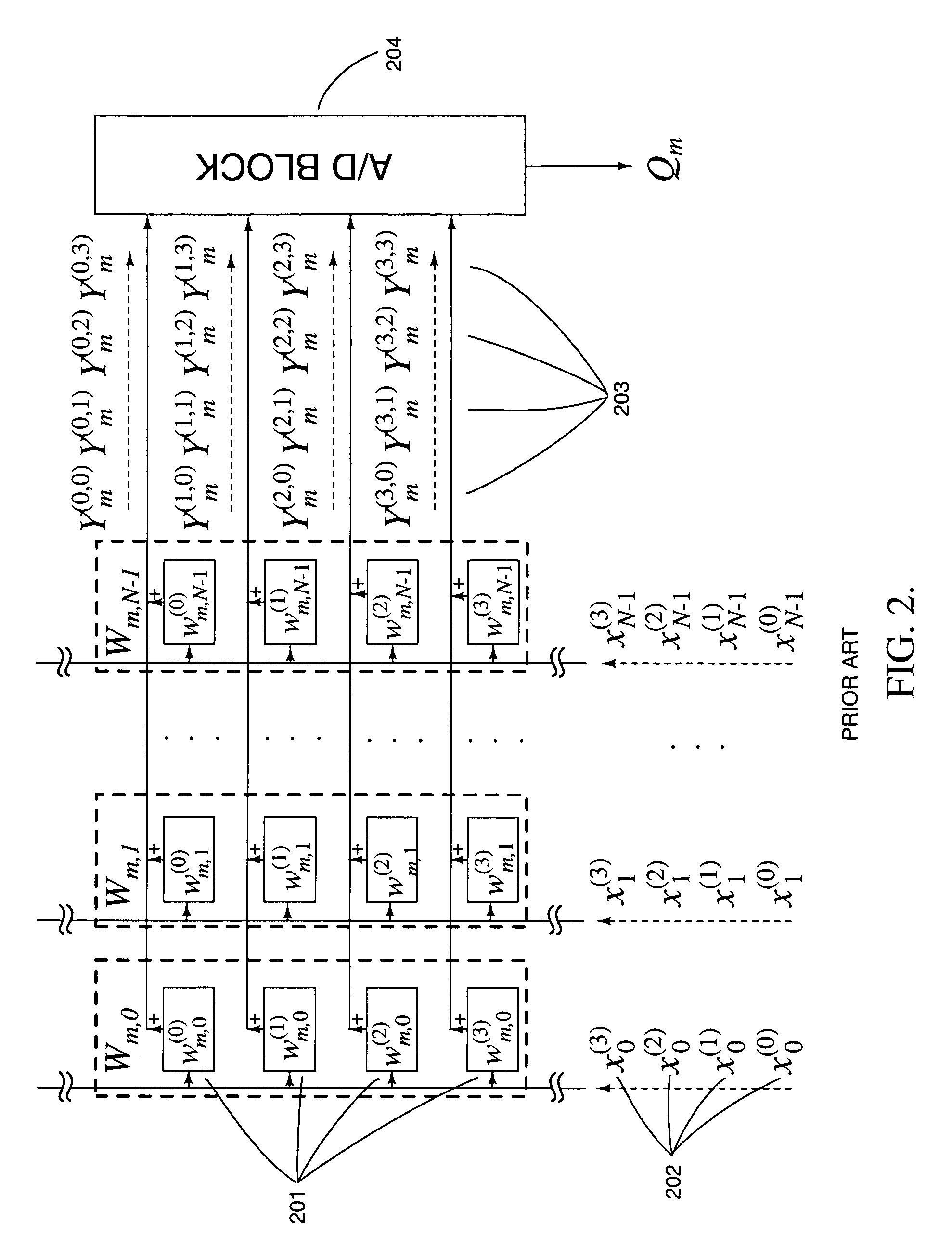
Analog computational arrays for matrix-vector multiplication offer very large integration density and throughput as, for instance, needed for real-time signal processing in video. Despite the success of adaptive algorithms and architectures in reducing the effect of analog component mismatch and noise on system performance, the precision and repeatability of analog VLSI computation under process and environmental variations is inadequate for some applications. Digital implementation offers absolute precision limited only by wordlength, but at the cost of significantly larger silicon area and power dissipation compared with dedicated, fine-grain parallel analog implementation. The present invention comprises a hybrid analog and digital technology for fast and accurate computing of a product of a long vector (thousands of dimensions) with a large matrix (thousands of rows and columns). At the core of the externally digital architecture is a high-density, low-power analog array performing binary-binary partial matrix-vector multiplication. Digital multiplication of variable resolution is obtained with bit-serial inputs and bit-parallel storage of matrix elements, by combining quantized outputs from one or more rows of cells over time. Full digital resolution is maintained even with low-resolution analog-to-digital conversion, owing to random statistics in the analog summation of binary products. A random modulation scheme produces near-Bernoulli statistics even for highly correlated inputs. The approach has been validated by electronic prototypes achieving computational efficiency (number of computations per unit time using unit power) and integration density (number of computations per unit time on a unit chip area) each a factor of 100 to 10,000 higher than that of existing signal processors making the invention highly suitable for inexpensive micropower implementations of high-data-rate real-time signal processors.
Owner:GENOV ROMAN A +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com