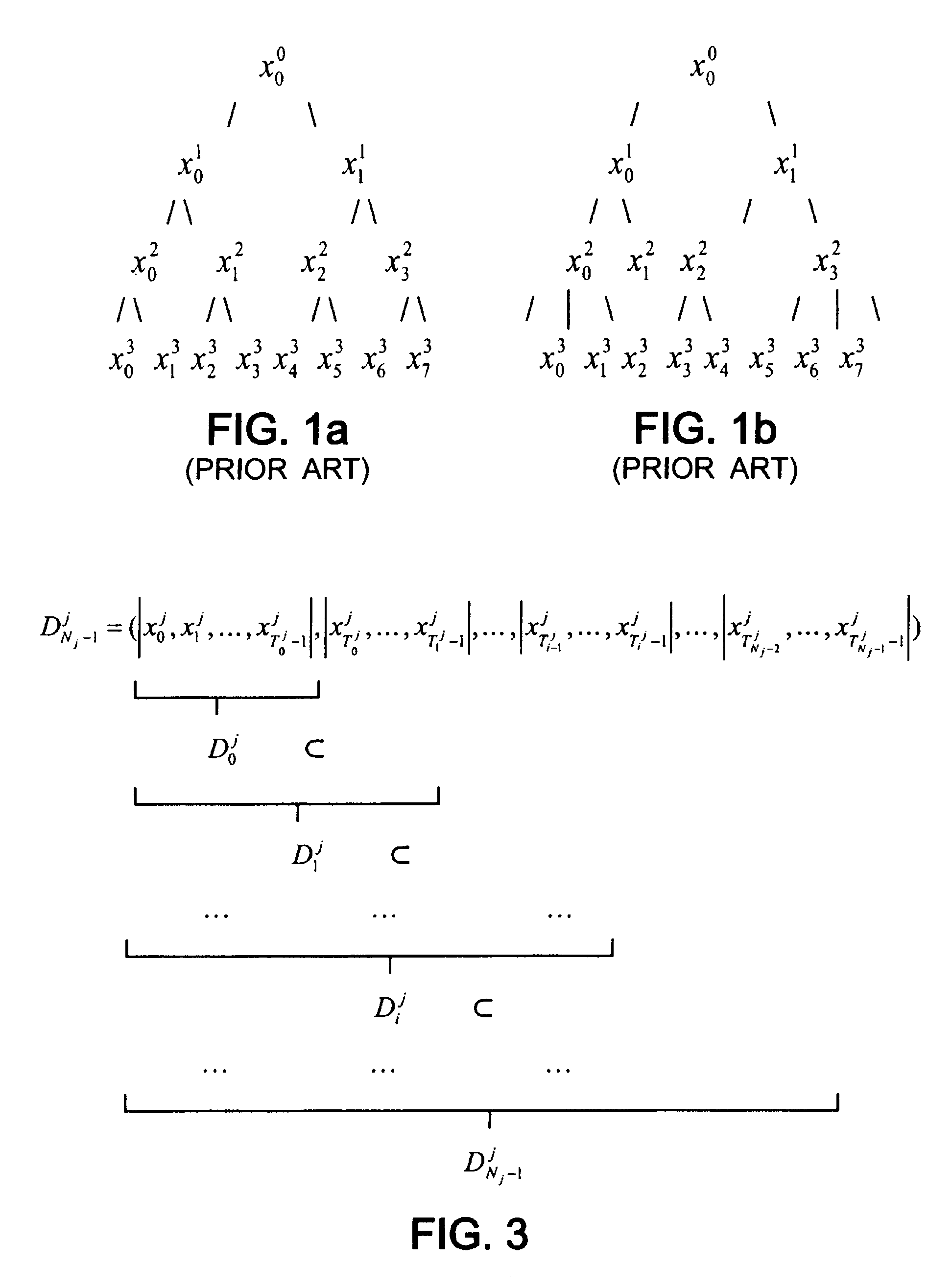Patents
Literature
192 results about "Variable resolution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
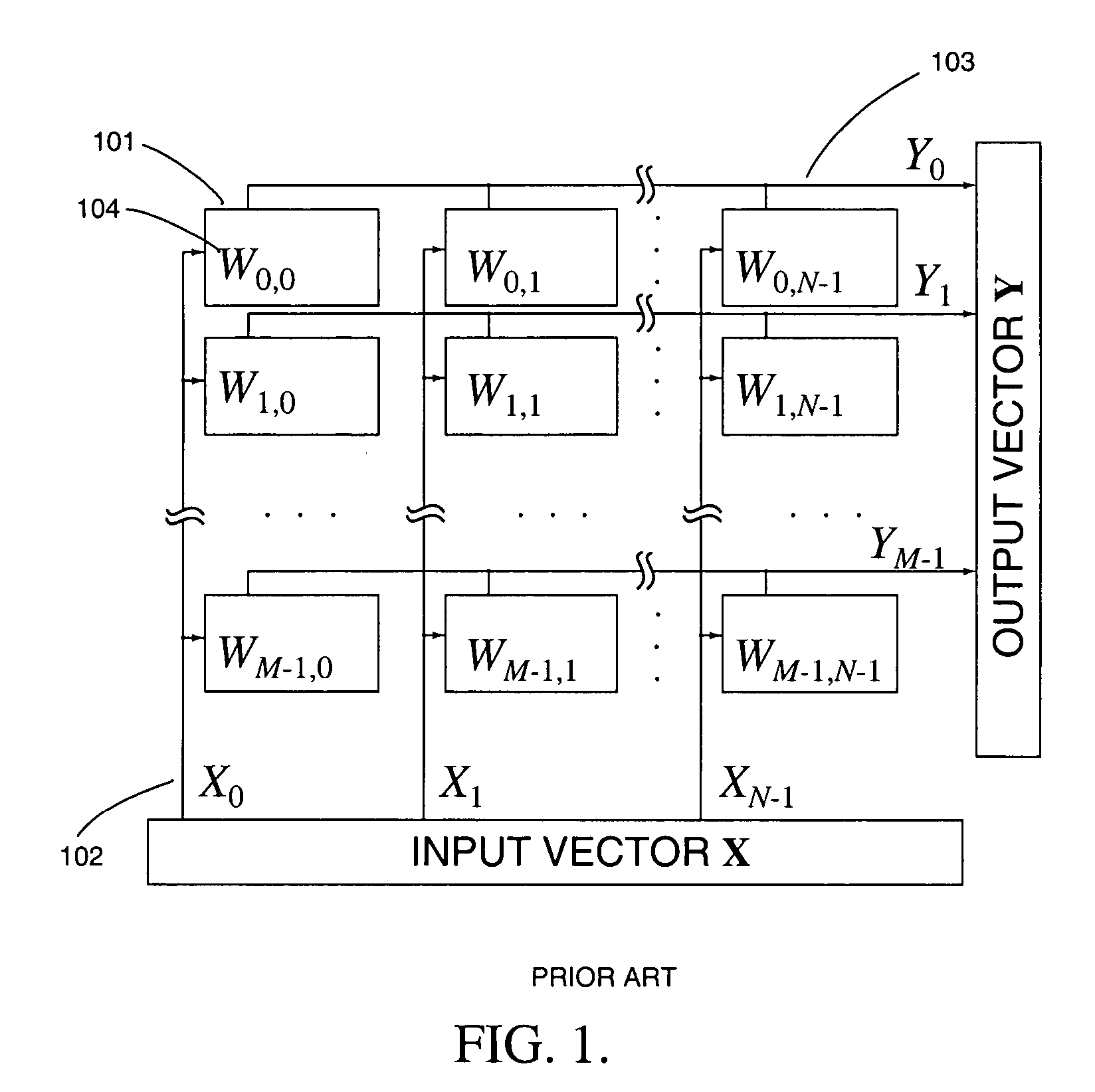
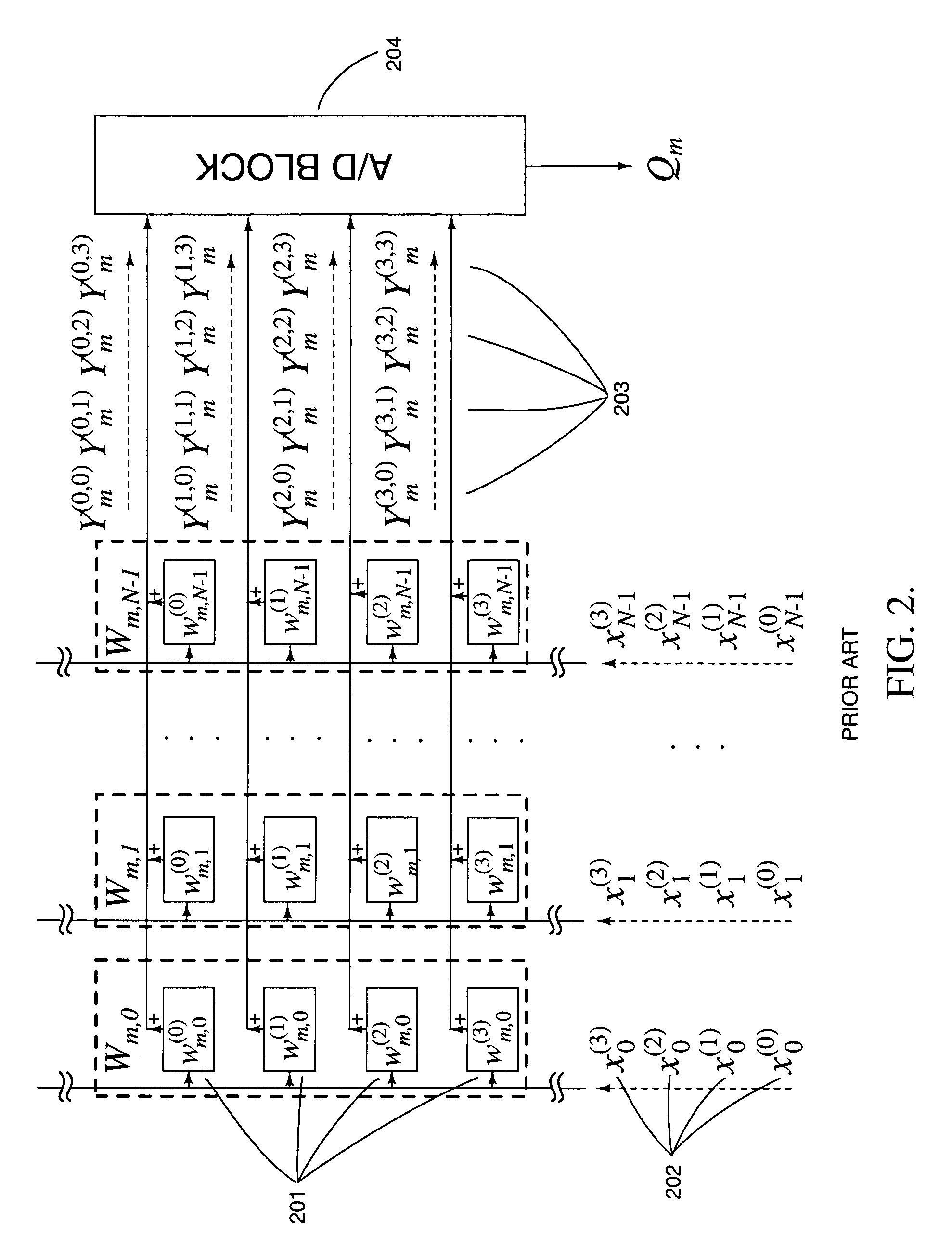
Variable resolution. This topic describes how variables are resolved both when you generate a plan and when you submit a job or a job stream. When you generate a plan, Tivoli® Workload Scheduler analyzes the variable tables in the order shown below for variable resolution: In the run cycle. In the job stream. In the workstation.
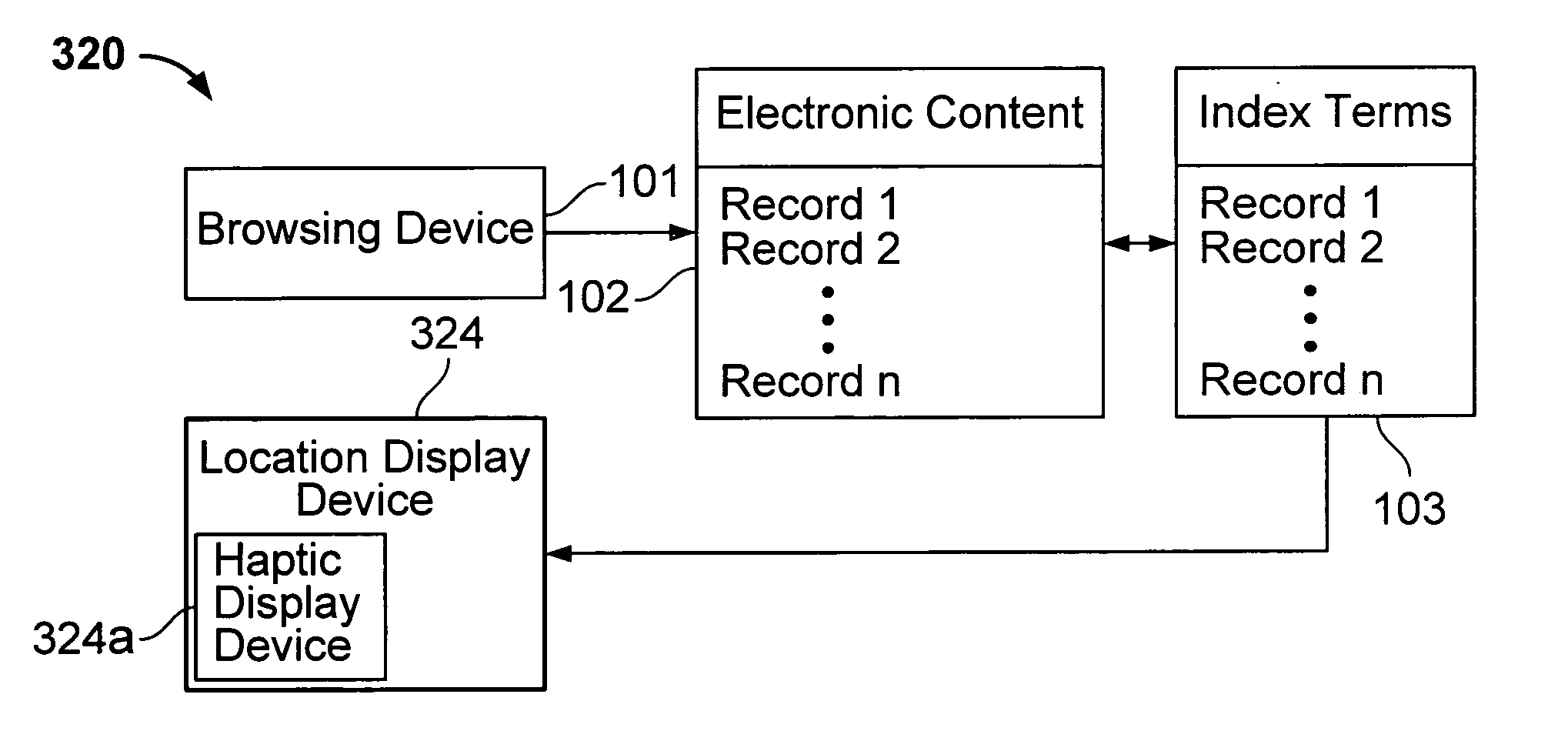
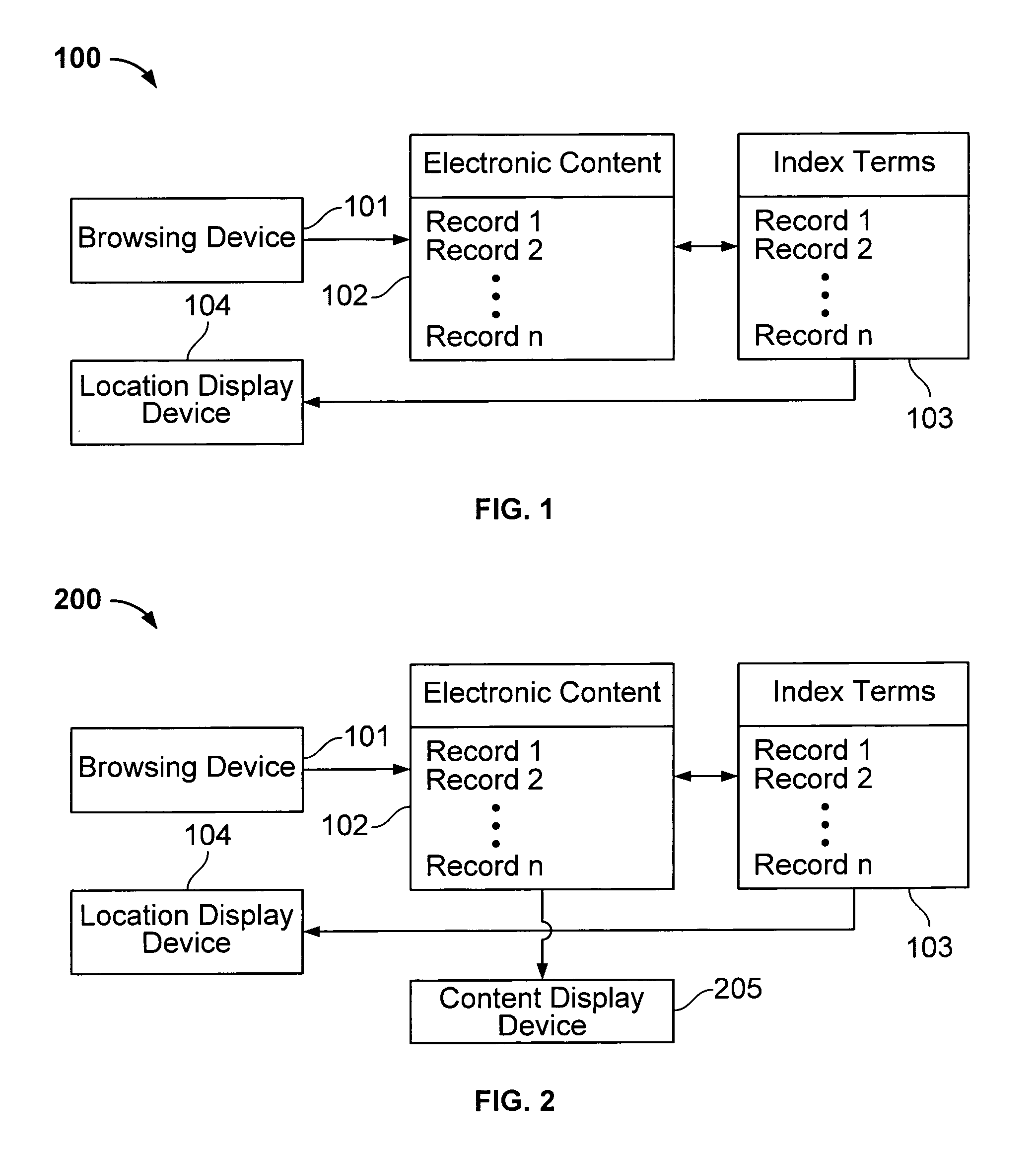
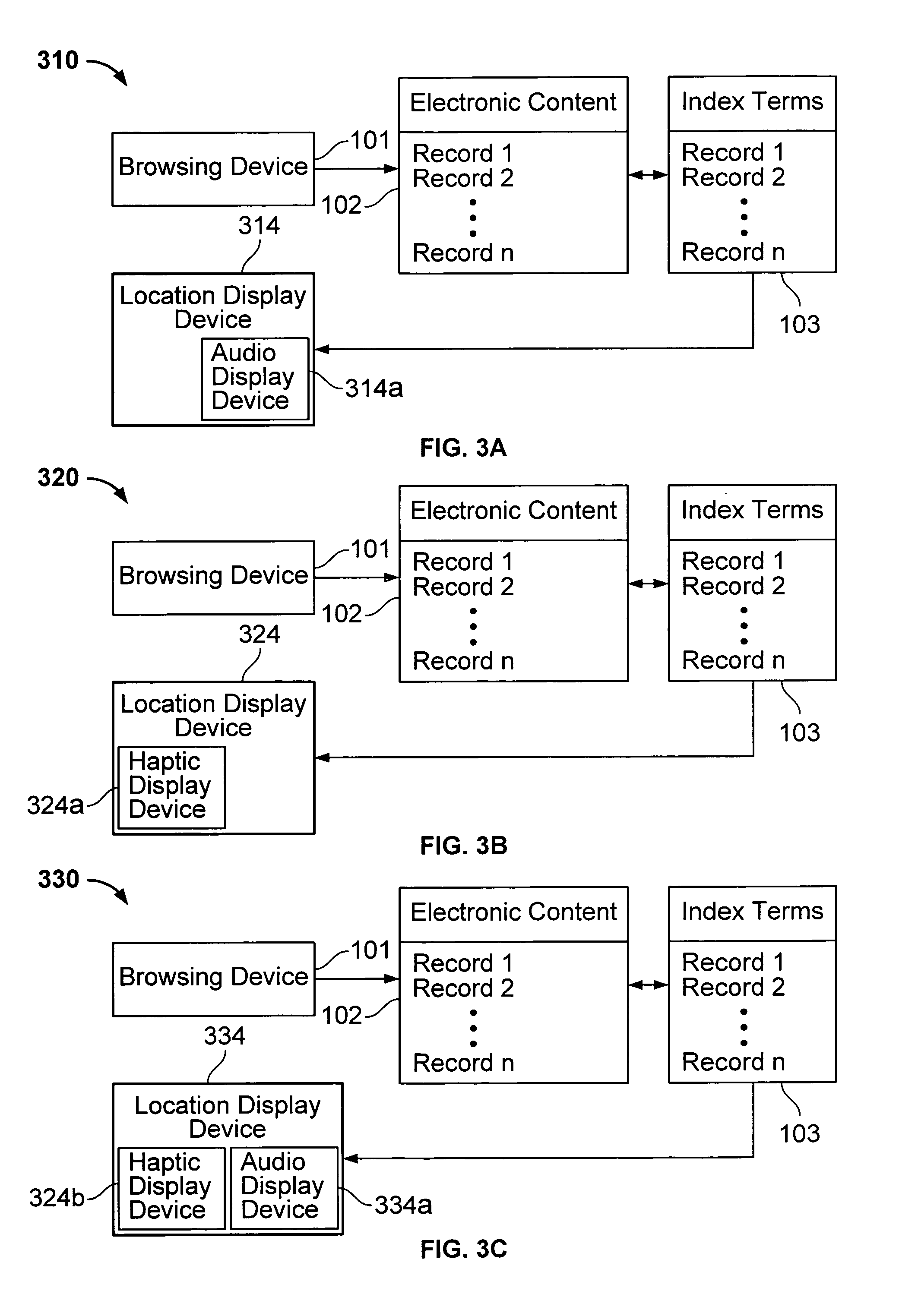
Interface including non-visual display for use in browsing an indexed collection of electronic content
InactiveUS7089292B1Facilitate indexingInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsImage resolutionVariable resolution
The invention facilitates browsing of an indexed collection of electronic content by displaying information identifying a current location within the collection of electronic content using a non-visual display (e.g., audio display and / or haptic display). The information identifying the current location can be displayed with variable resolution and the content of the display of the information identifying the current location can be dependent on the resolution. The invention can be used to browse any type of electronic content, including, for example, audio content, visual content, text content or some combination of such content. The invention can be used to browse electronic content that is indexed in any way, such as, for example, electronic content that is indexed (partly or entirely) alphabetically, numerically or by date.
Owner:VULCAN PATENTS
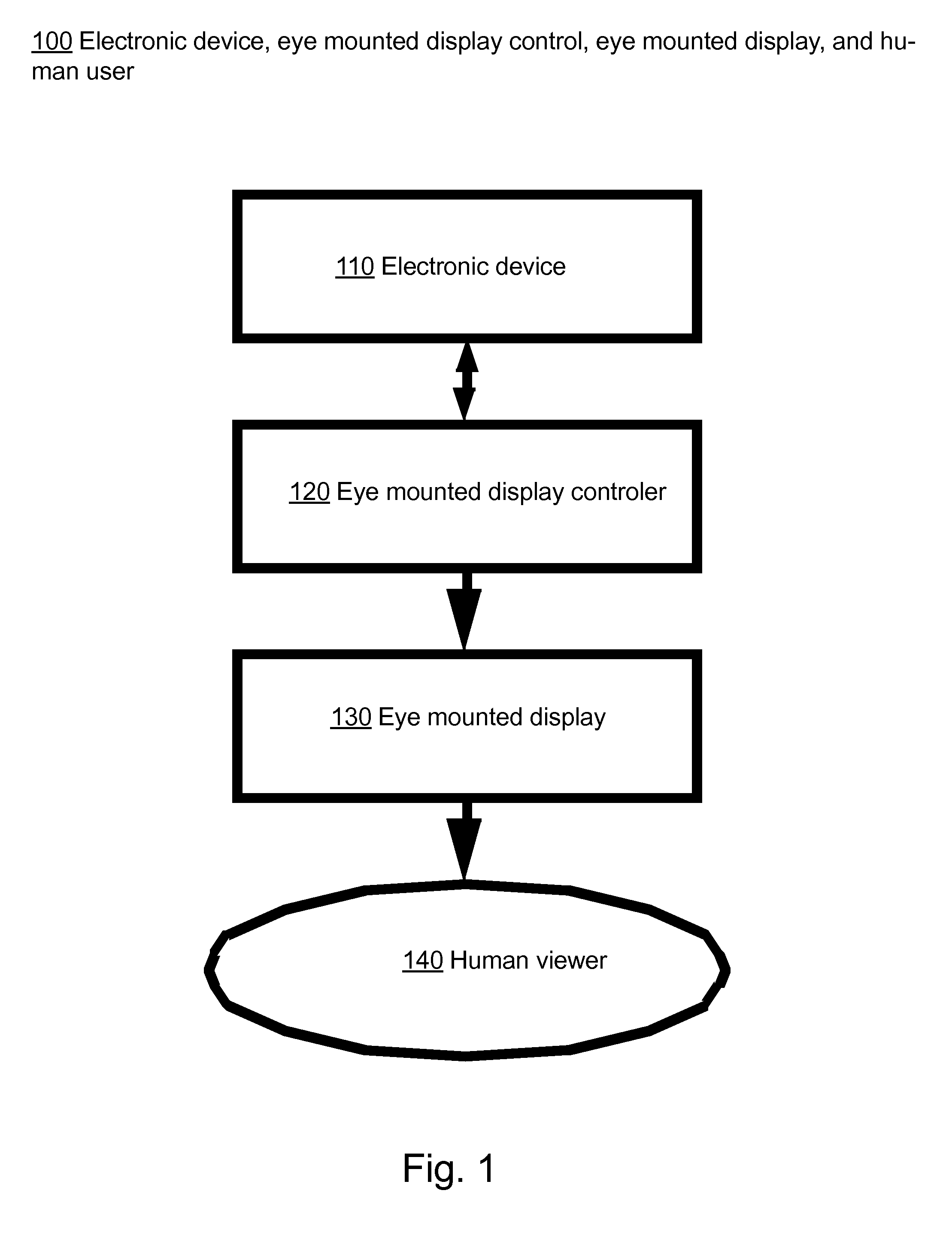
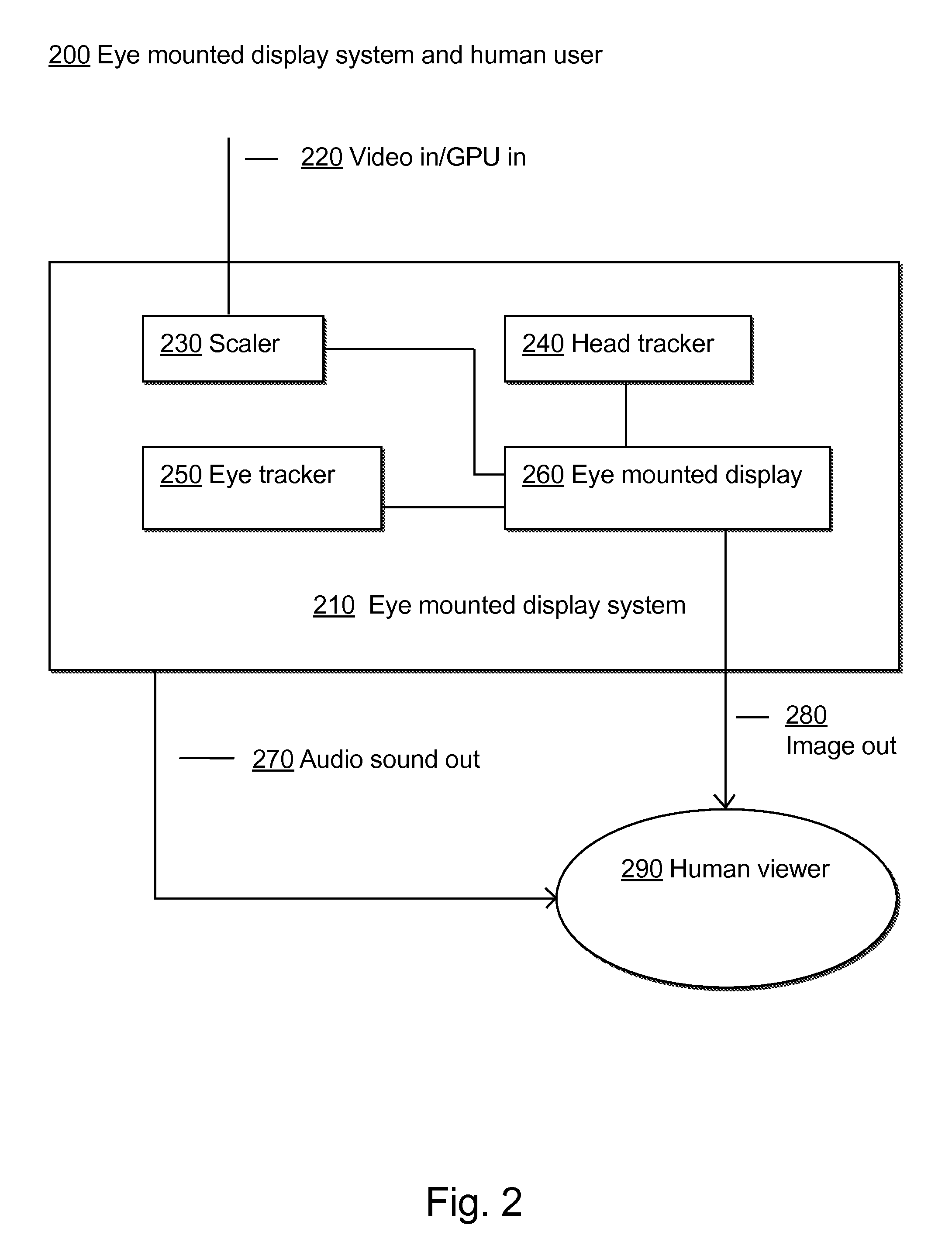
Variable Resolution Eye Mounted Displays
ActiveUS20150312560A1Reduce spherical aberrationOut of shapeInput/output for user-computer interactionPicture reproducers using projection devicesImage resolutionDisplay device
A display device (e.g., in a contact lens) is mounted on the eye. The eye mounted display contains multiple sub-displays, each of which projects light to different retinal positions within a portion of the retina corresponding to the sub-display. Additionally, a “locally uniform resolution” mapping may be used to model the variable resolution of the eye. Accordingly, various aspects of the display device may be based on the locally uniform resolution mapping. For example, the light emitted from the sub-displays may be based on the locally uniform resolution mapping.
Owner:TECTUS CORP
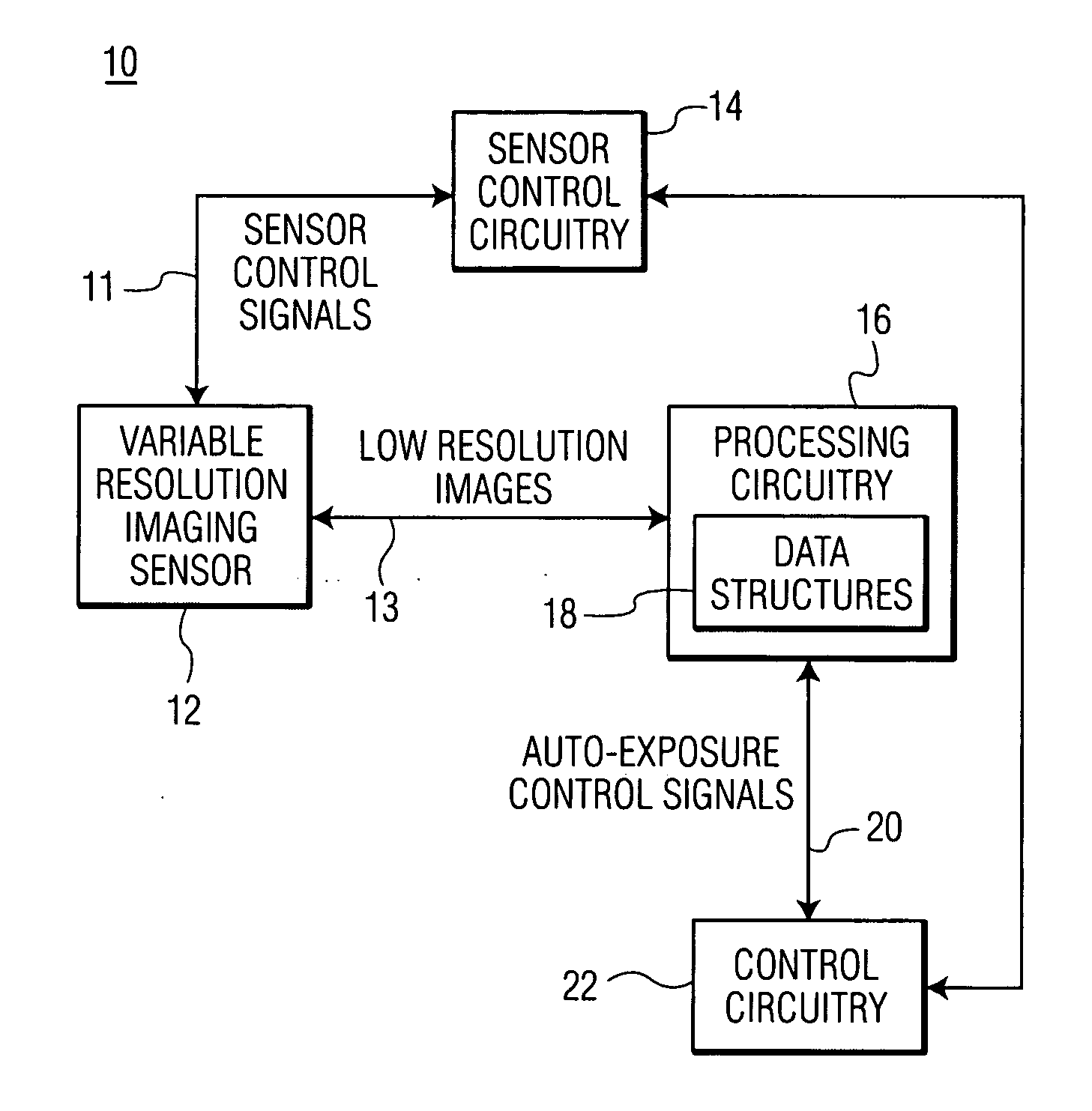
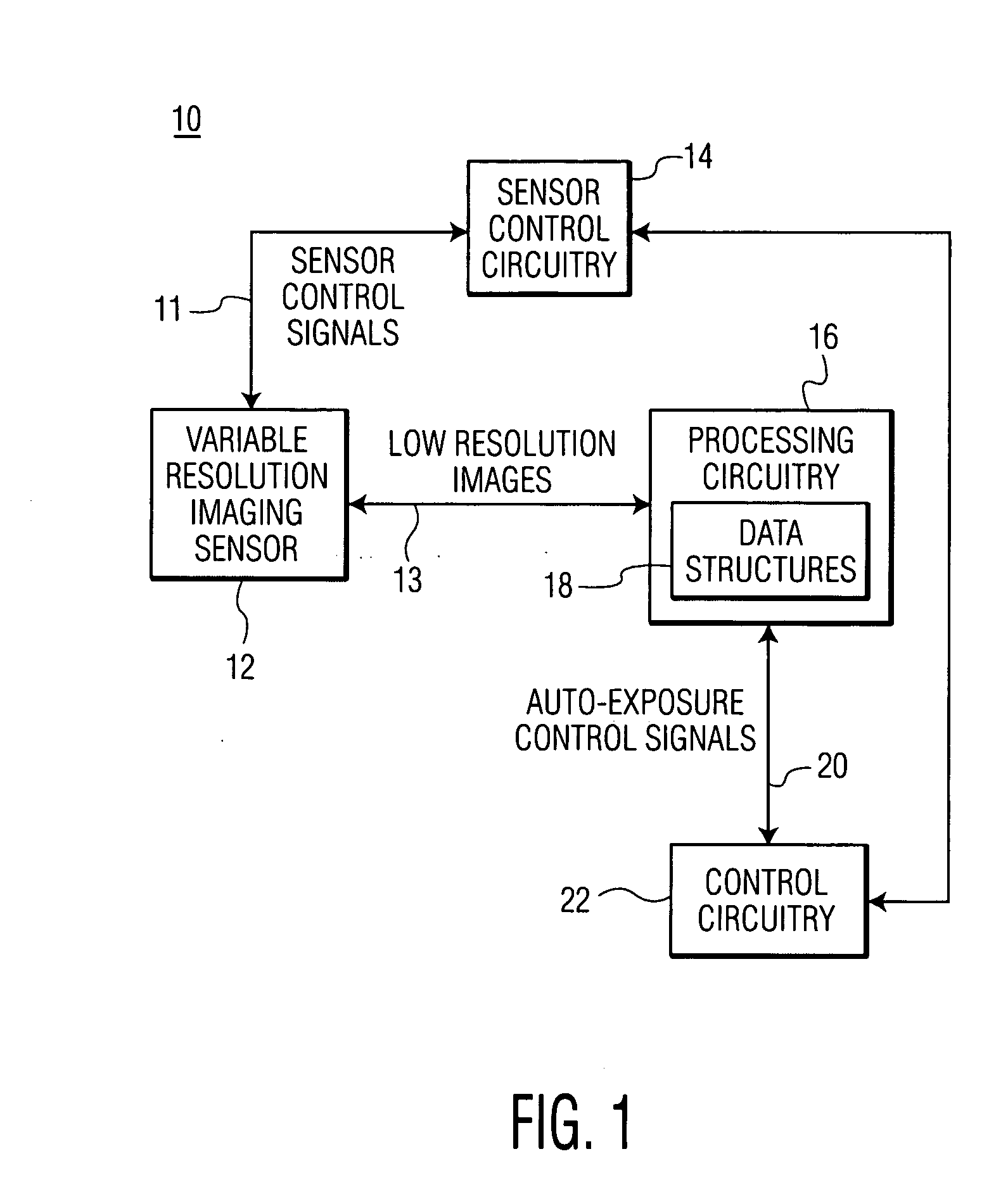
Optical code reading system and method using a variable resolution imaging sensor
InactiveUS20060011724A1Improve performanceLess timeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImage resolutionVariable resolution
An optical code reading system having an auto-exposure system for use with a variable resolution imaging sensor in which very low resolution images are used to determine exposure parameters is presented. The very low resolution images can be transferred much faster than high resolution images which results in a very fast auto-exposure system. The optical code reading system further includes an optical zoom system for zooming in and out of a target without the use of any moveable components. The optical zoom system makes use of a binning and / or subsampling feature of the imaging sensor for zooming in and out of the target. High-speed decoding methodologies are also presented for the optical code reading system. One decoding methodology utilizes low resolution images for performing high-speed decoding. Other methodologies utilize low resolution images and higher resolution images, if the optical code imaged by the low resolution images is not decoded successfully.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH INC
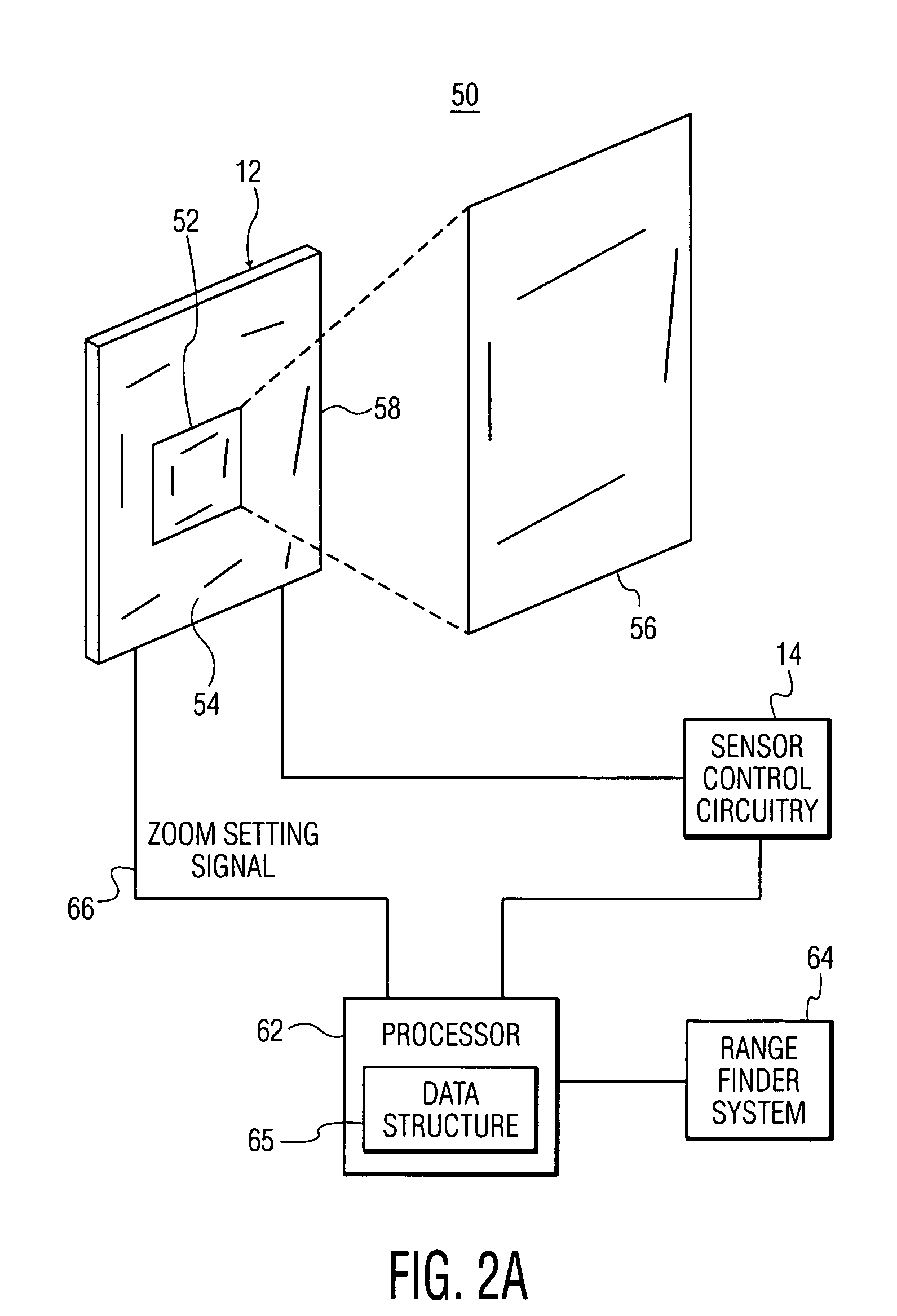
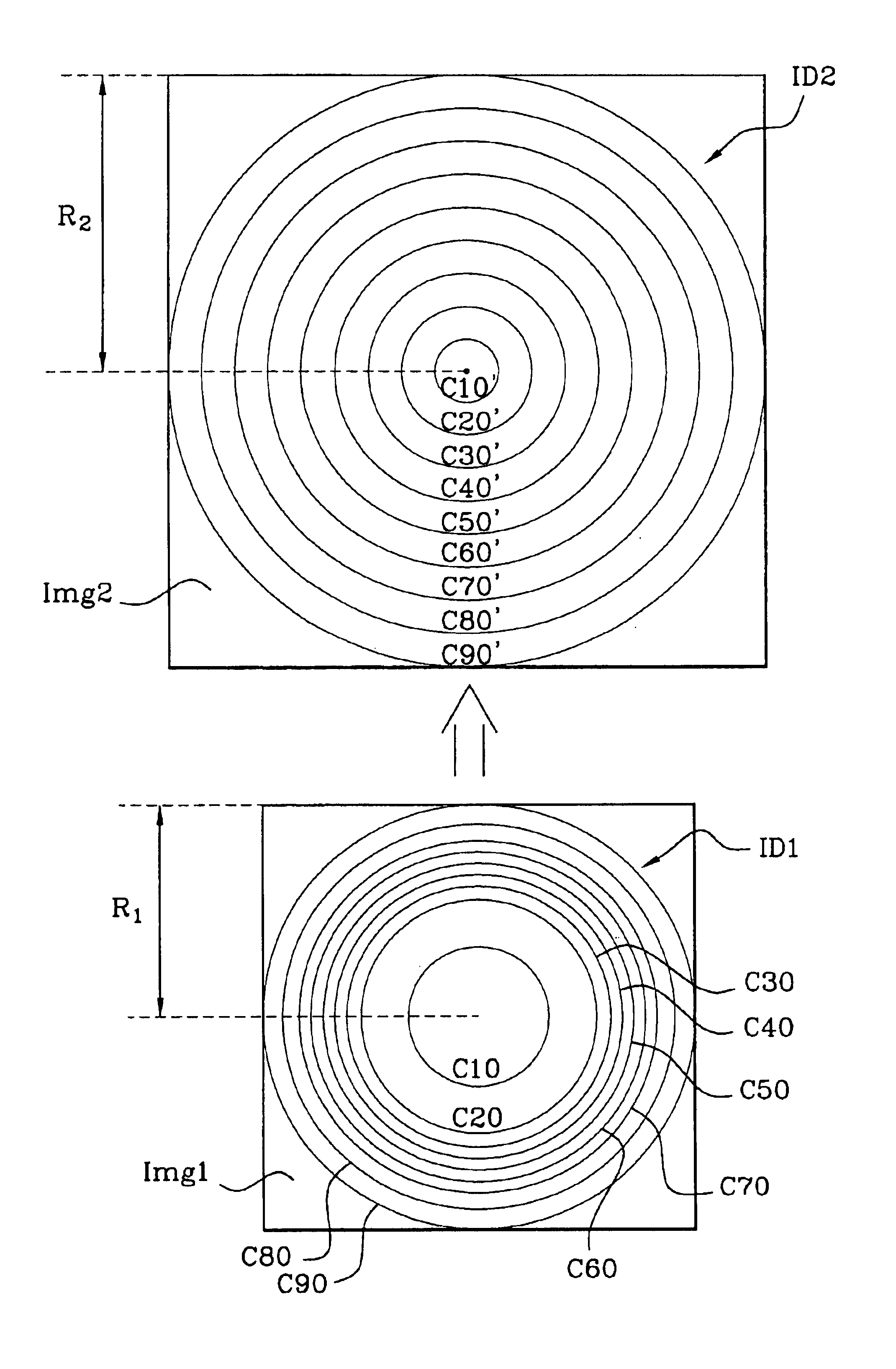
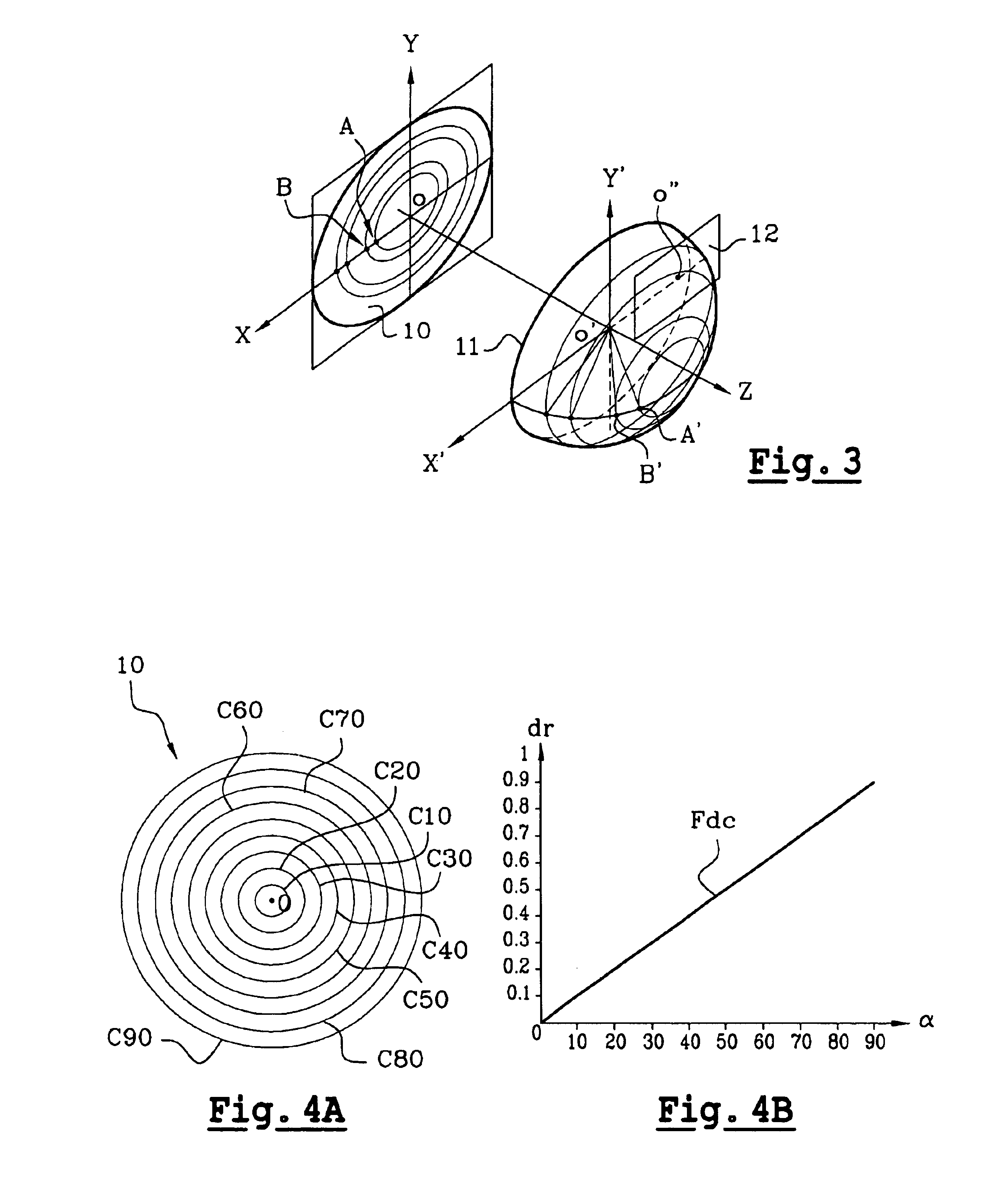
Method for capturing and displaying a variable resolution digital panoramic image
InactiveUS6844990B2Enhancement in definitionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsComputer graphics (images)Object point
A method for capturing a digital panoramic image includes projecting a panorama onto an image sensor by means of a panoramic objective lens. The panoramic objective lens has a distribution function of the image points that is not linear relative to the field angle of the object points of the panorama, such that at least one zone of the image obtained is expanded while at least another zone of the image is compressed. When a panoramic image obtained is then displayed, correcting the non-linearity of the initial image is required and is performed by means of a reciprocal function of the non-linear distribution function of the objective lens or by means of the non-linear distribution function.
Owner:IMMERVISION INC
Position-tracking system
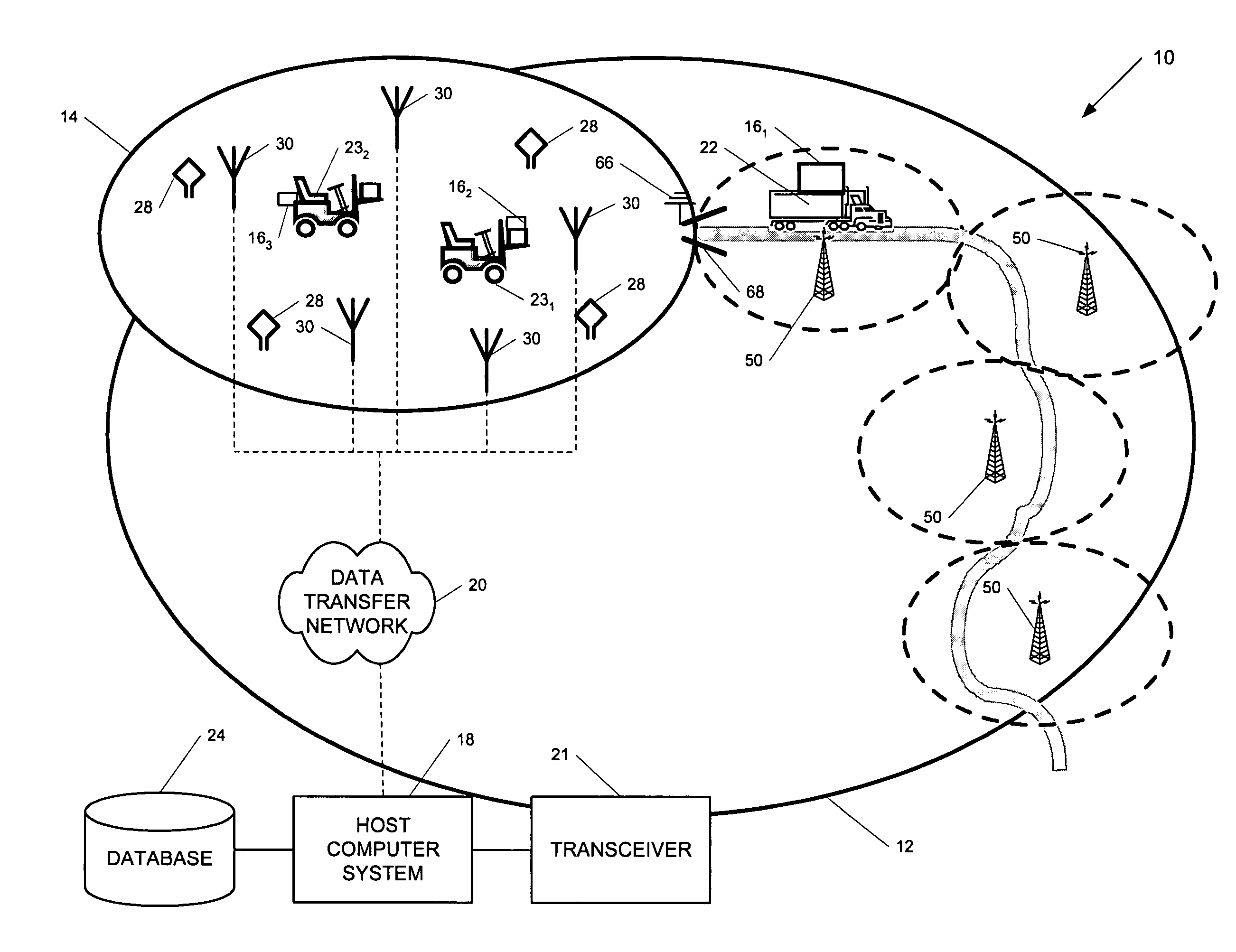
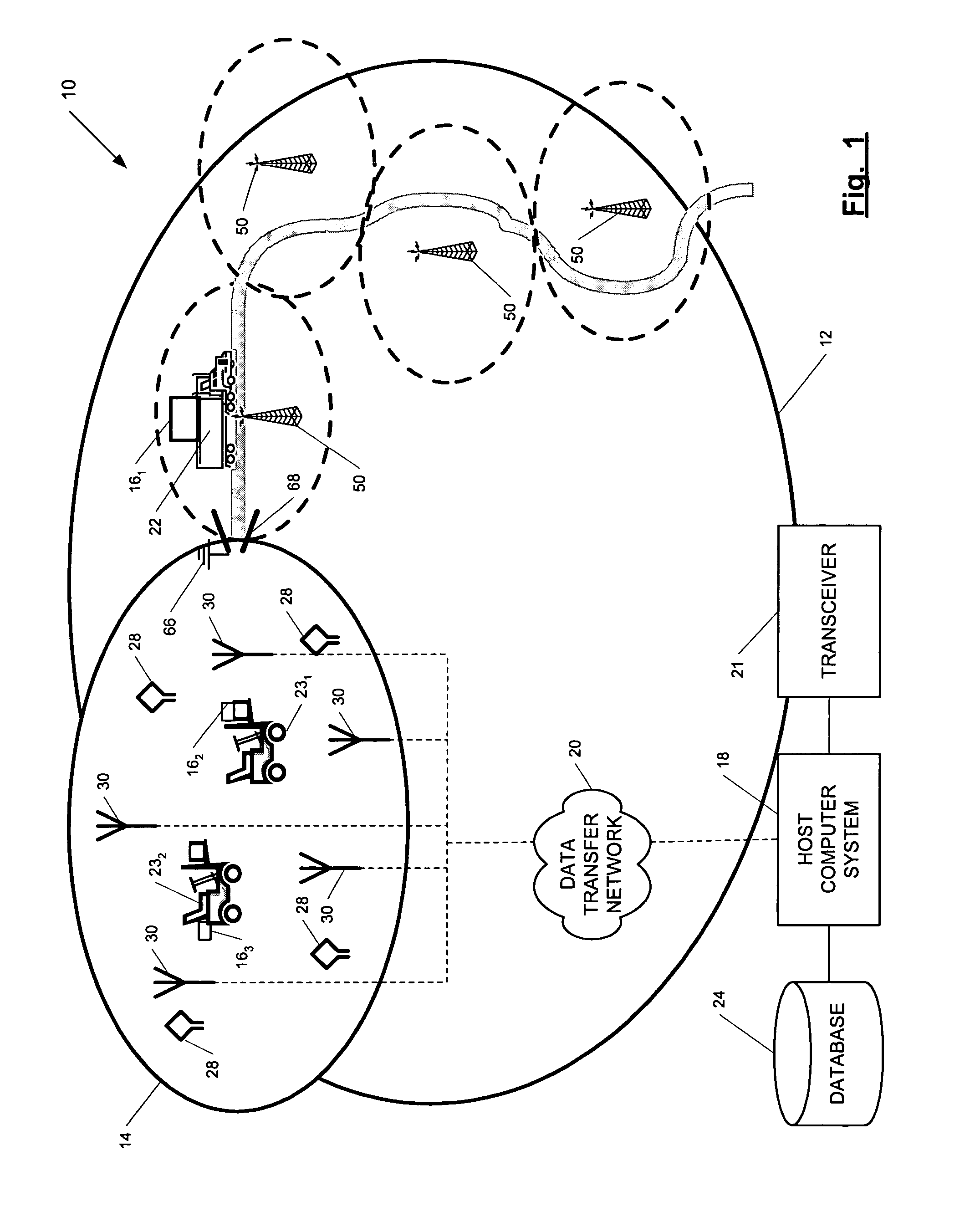
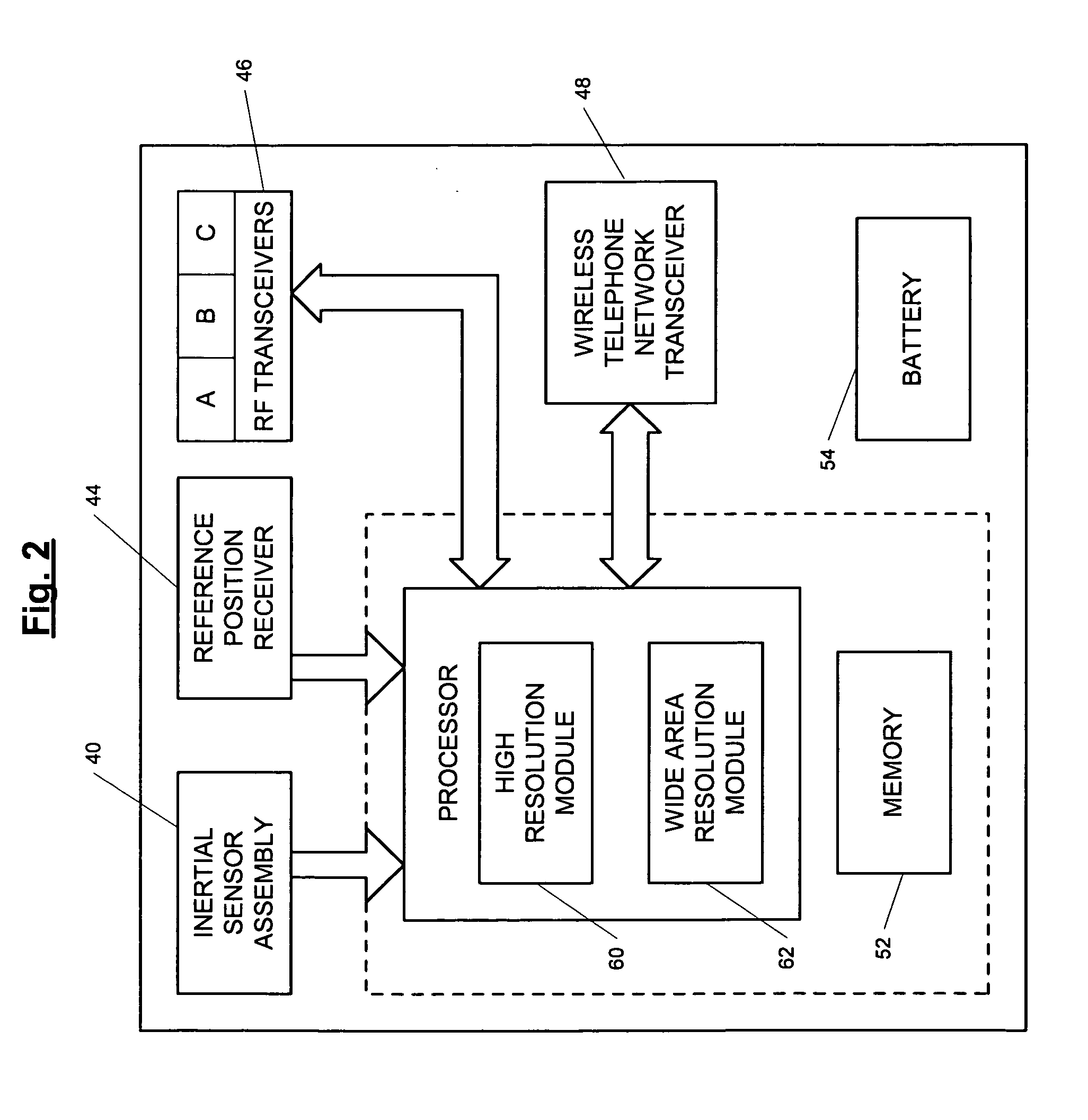
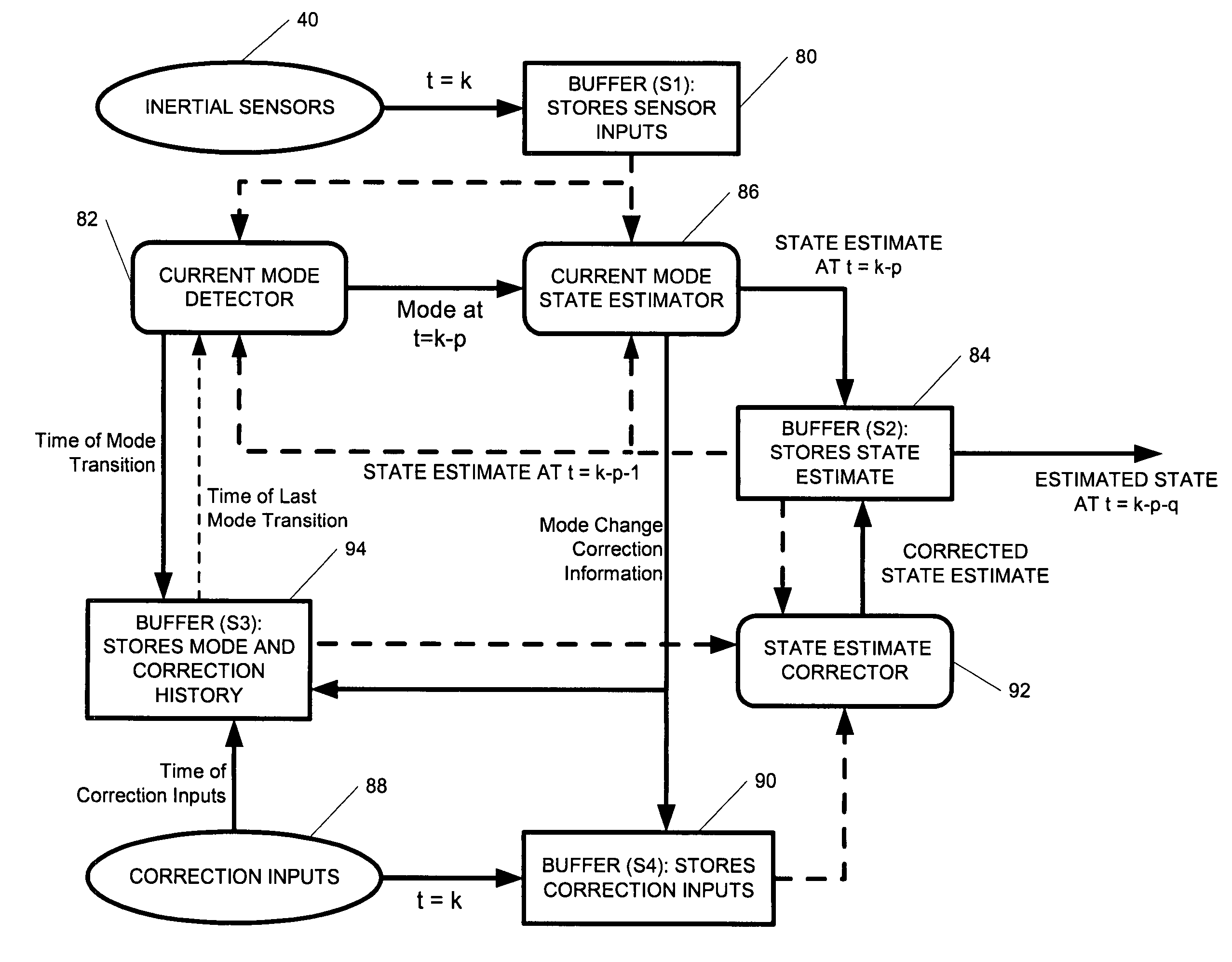
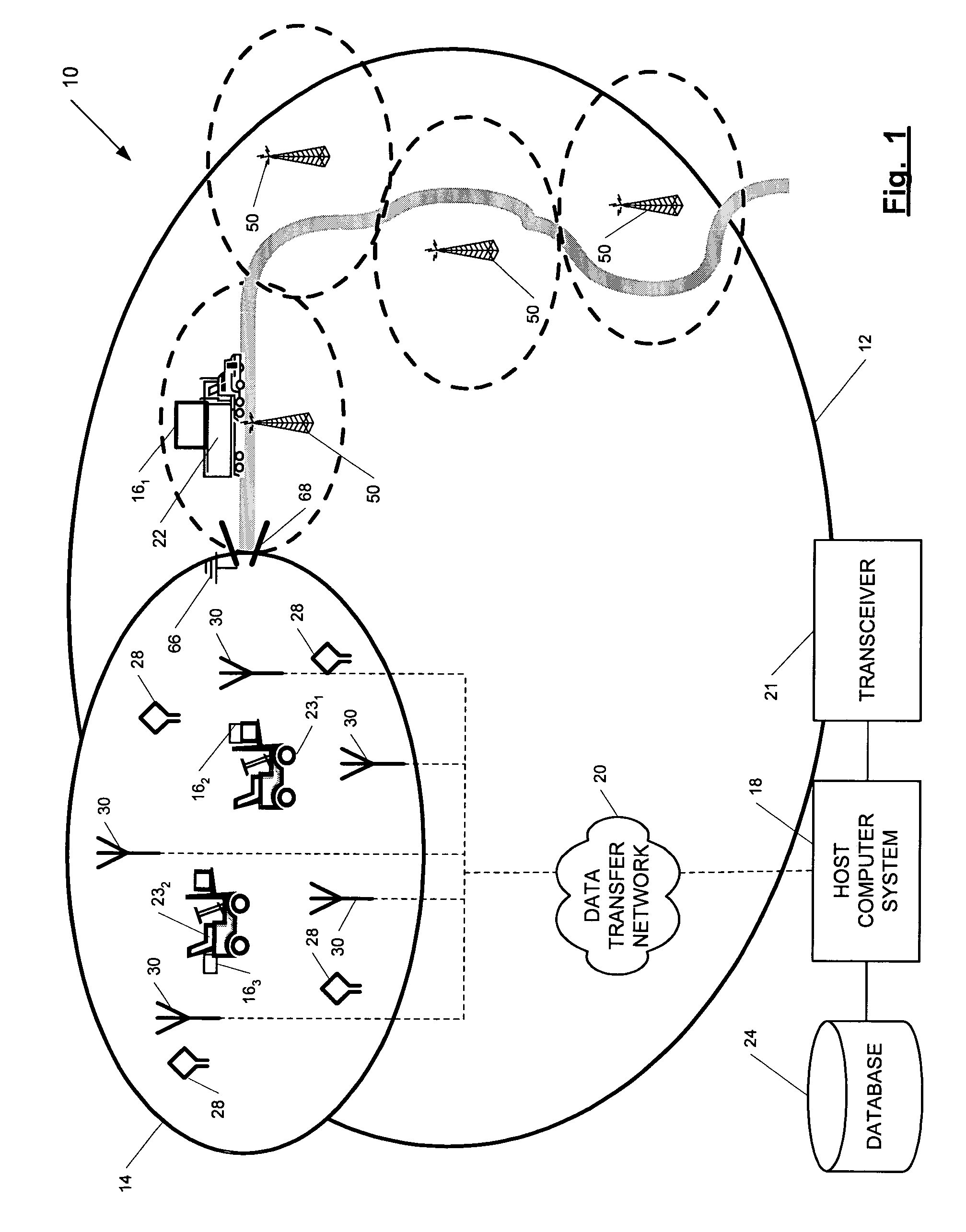
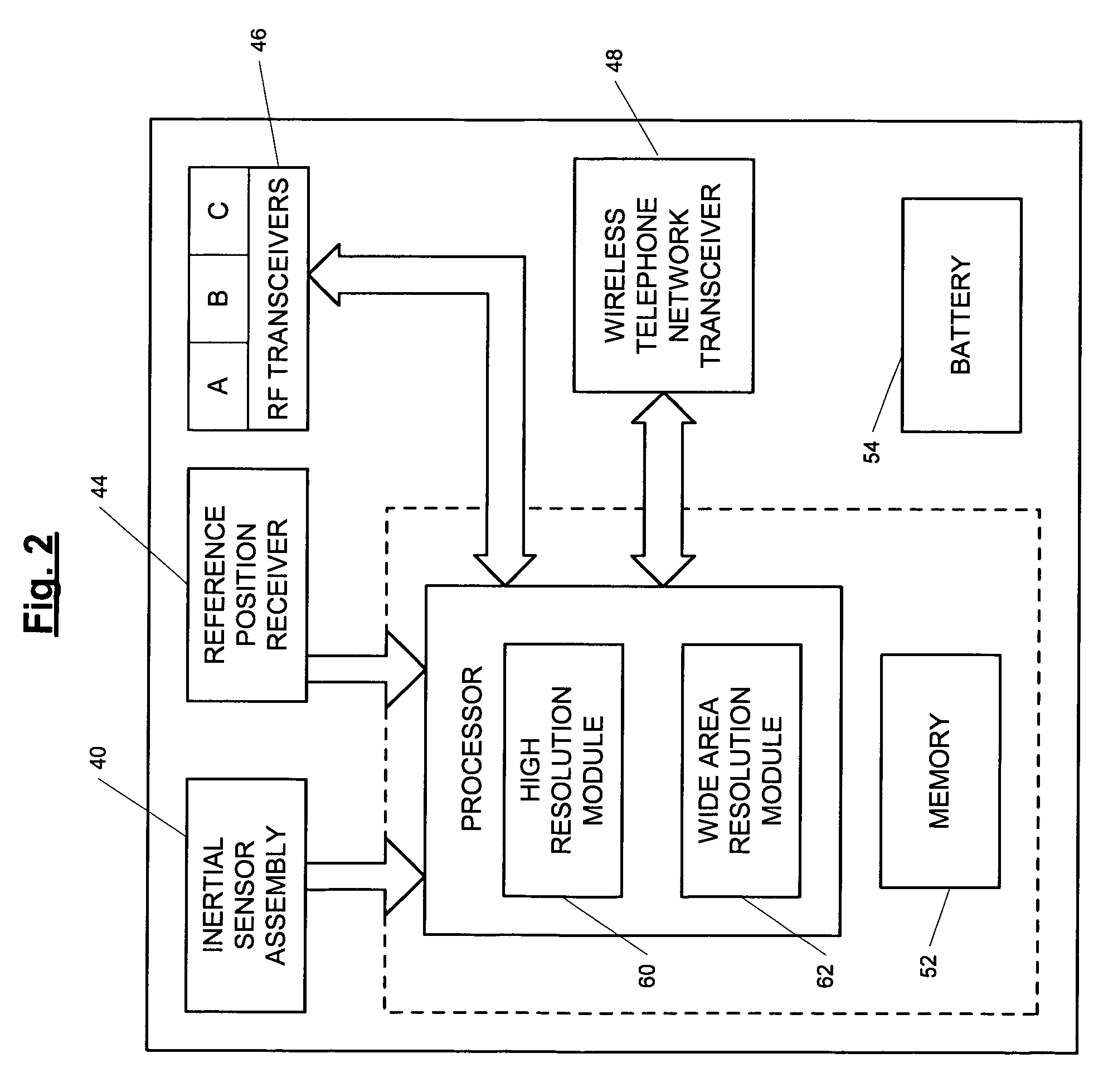
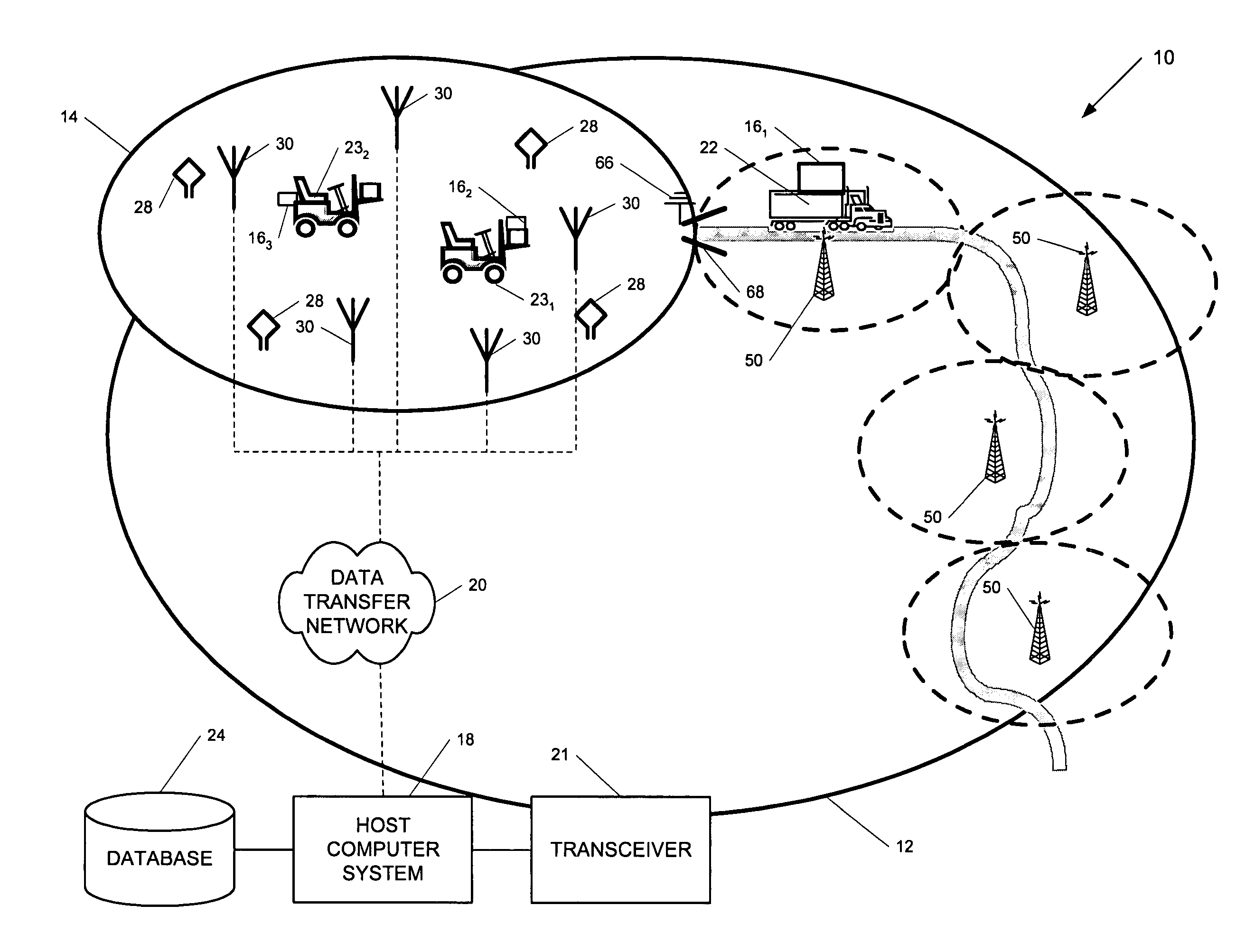
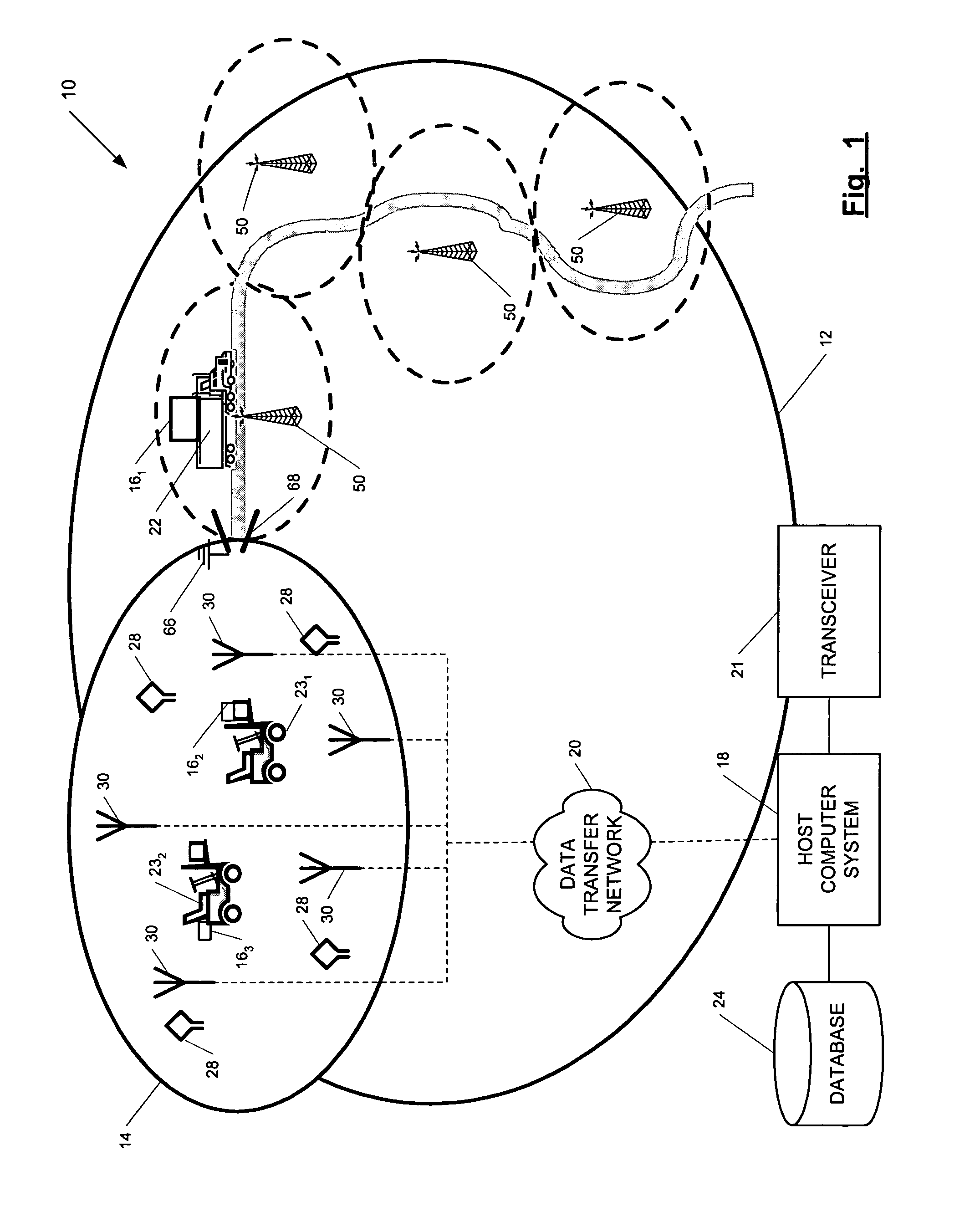
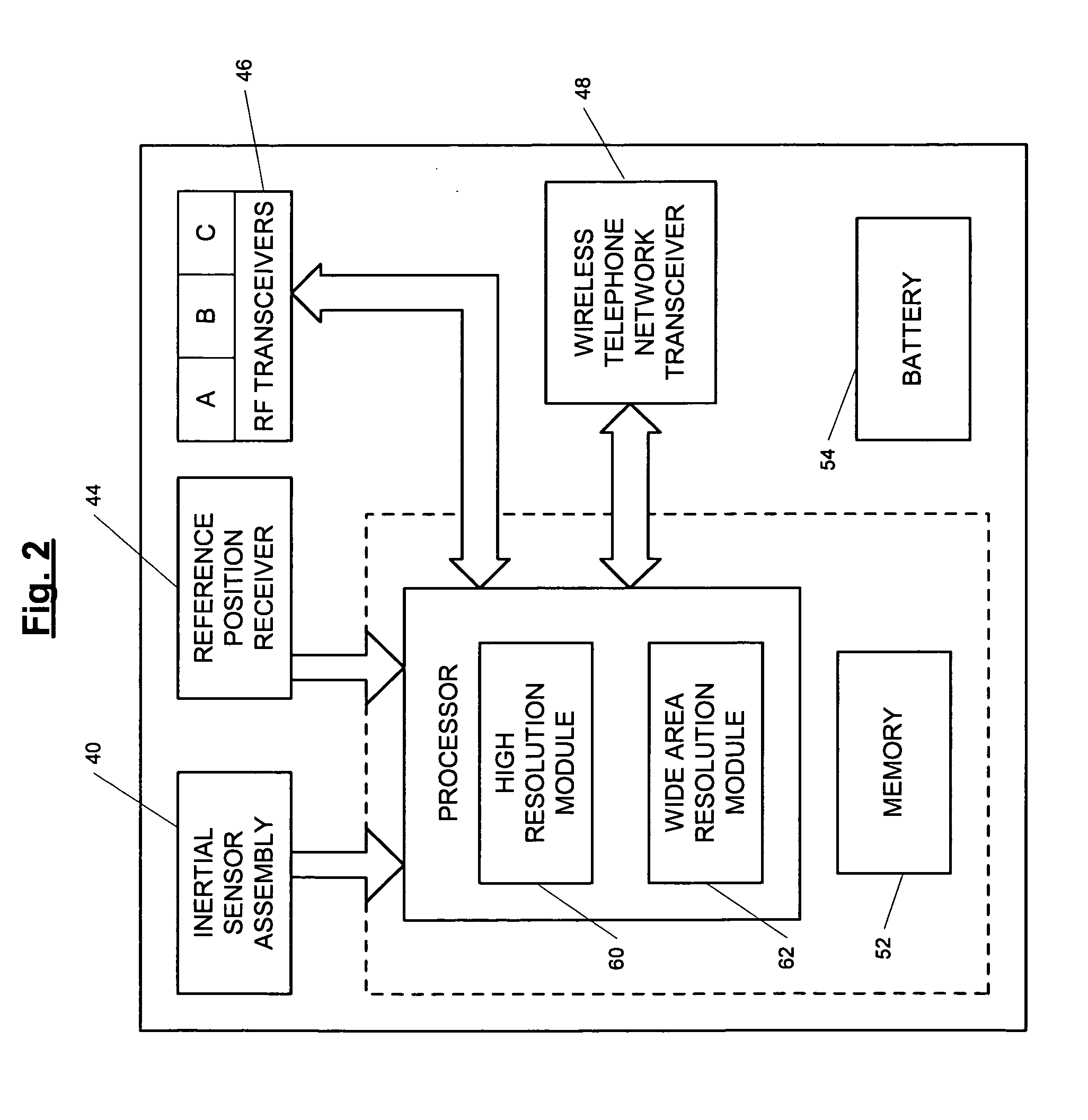
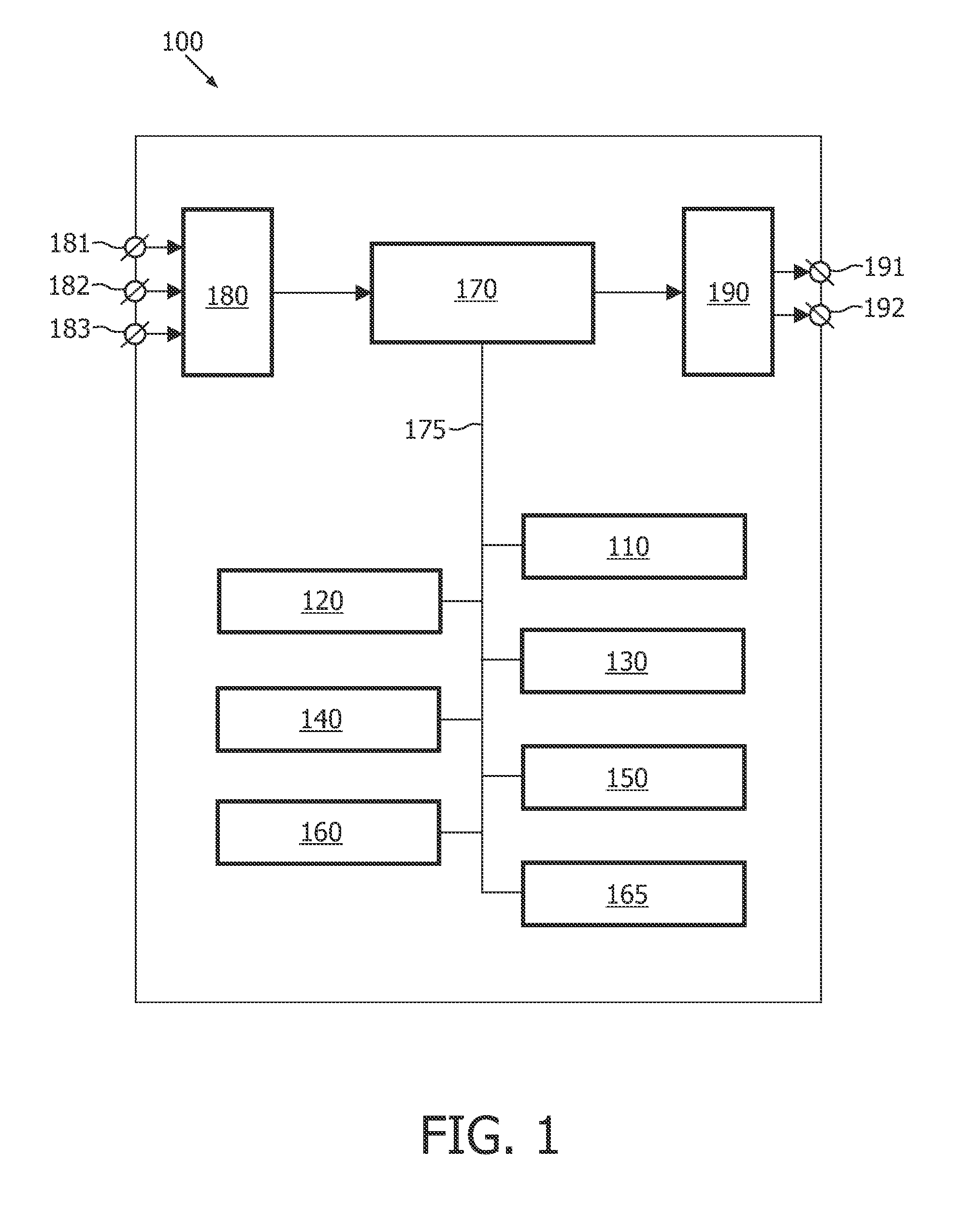
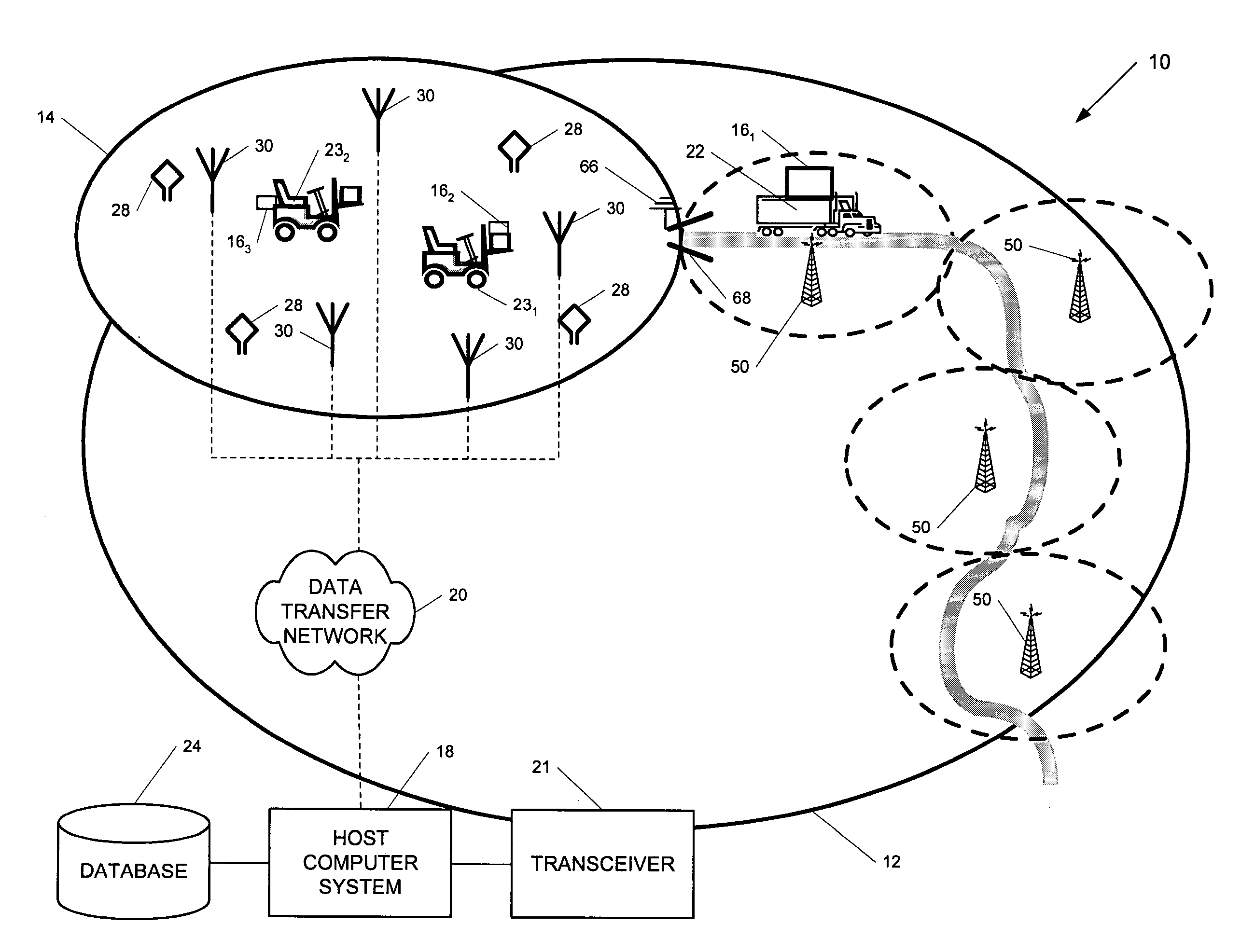
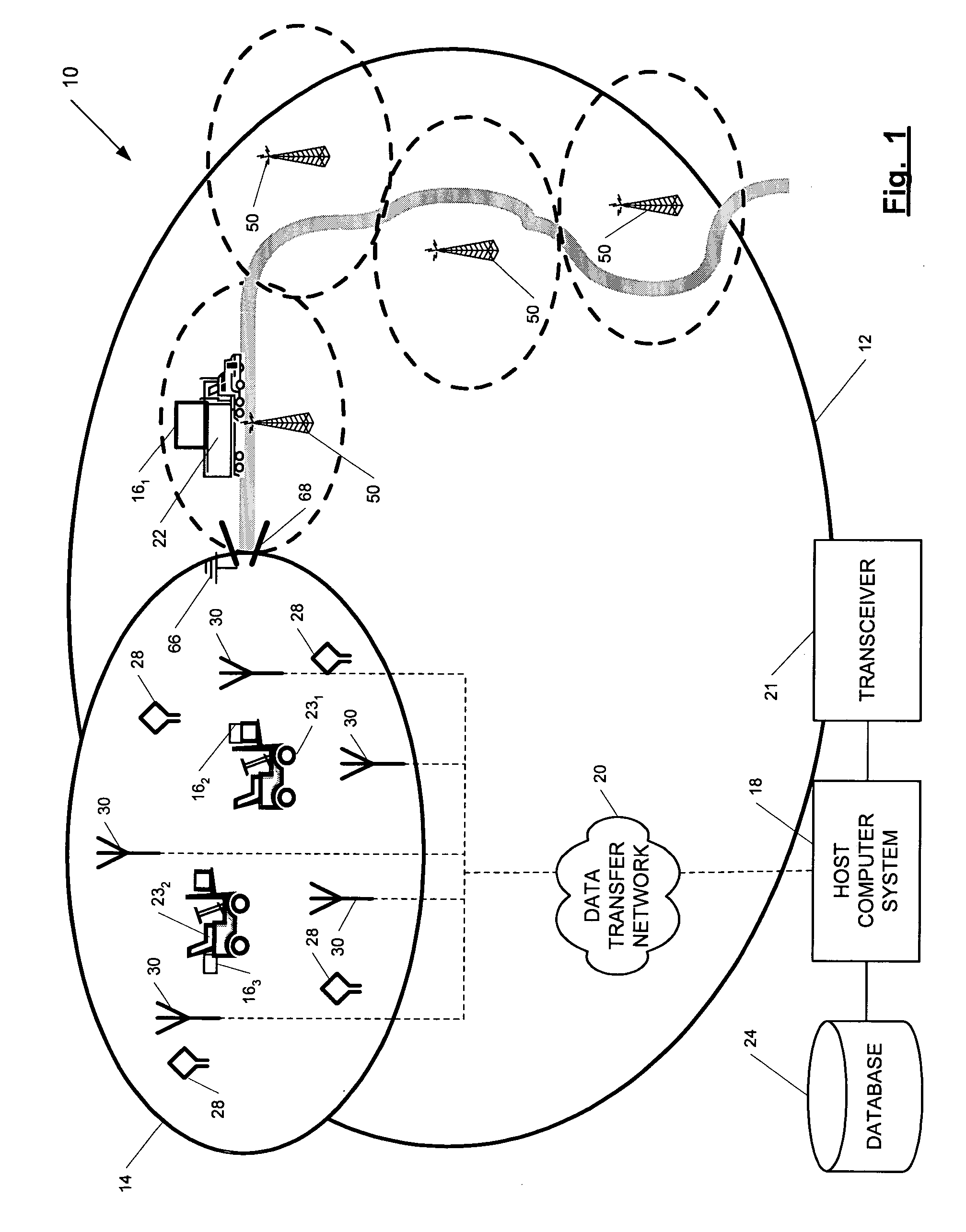
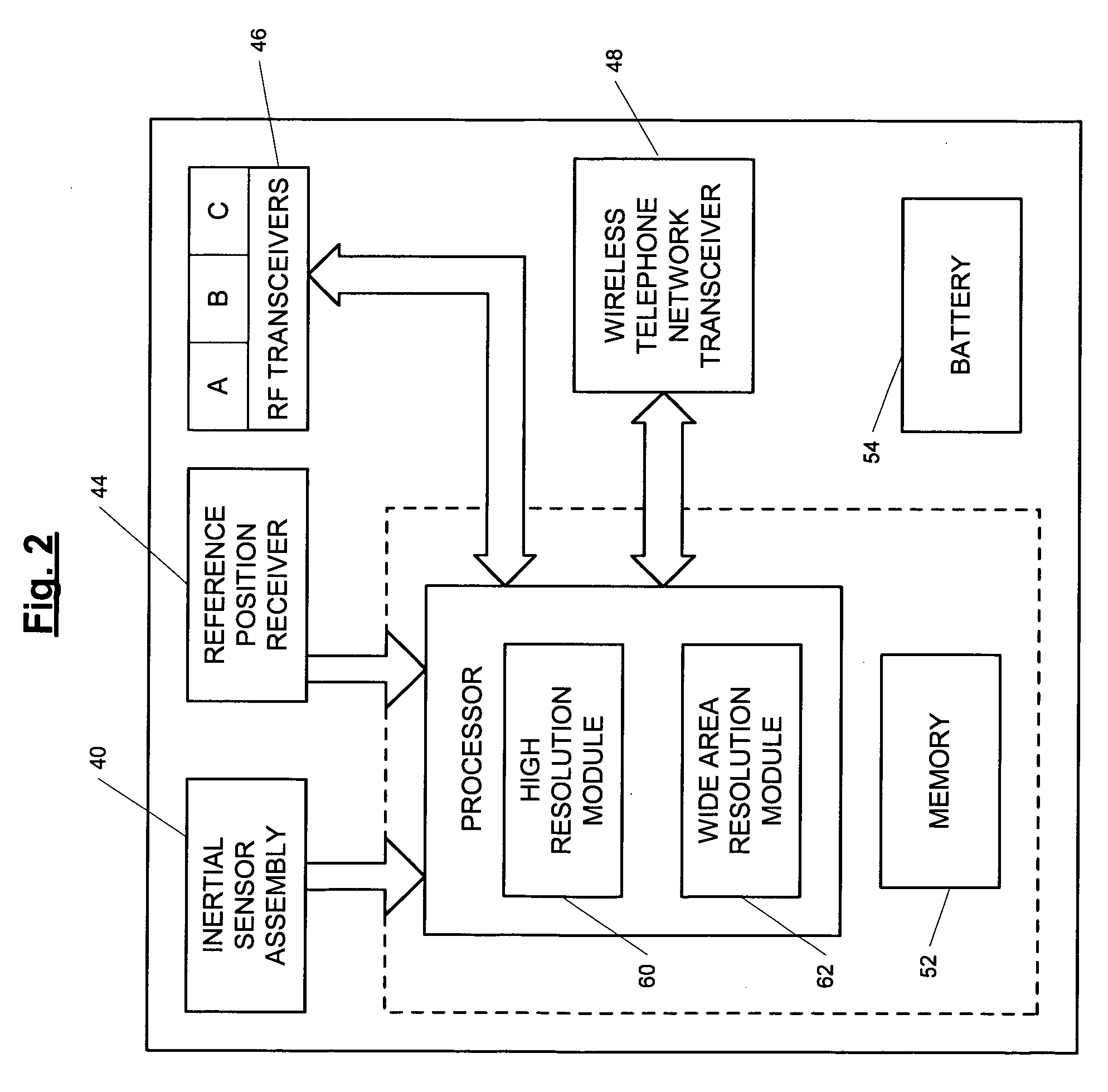
ActiveUS7236091B2High position resolutionImprove accuracyRoad vehicles traffic controlElectric/electromagnetic visible signallingObject basedTransceiver
A position-tracking system for tracking the position of an object is disclosed. According to various embodiments, the tracking system includes a tracking device that is connected to or otherwise affixed to the object to be tracked. The tracking device may include, among other things, an inertial sensor assembly, radio transceivers and a processor. The position tracking system may also include a host processing system that is in communication with the tracking device. The position tracking system may provide variable-resolution position information based on the environment in which the object is moving. In a “wide resolution” area, the system may compute a general position for the object based on a wireless telephone network Cell-ID / map correlation architecture. In a high-resolution area, greater position resolution may be realized from the combination of a wireless aiding system and inputs from the inertial sensors. In the high-resolution mode, the system may exploit distinct patterns of motion that can be identified as motion “signatures” that are characteristic of certain types of motion. Kinematic (or object movement) models may be constructed based on these motion signatures and the position tracking system may estimate the state of the object based on the kinematic model for the current mode of the object. Adaptive and cascaded Kalman filtering may be employed in the analysis to more accurately estimate the position and velocity of the object based on the motion pattern identified.
Owner:PINC SOLUTIONS
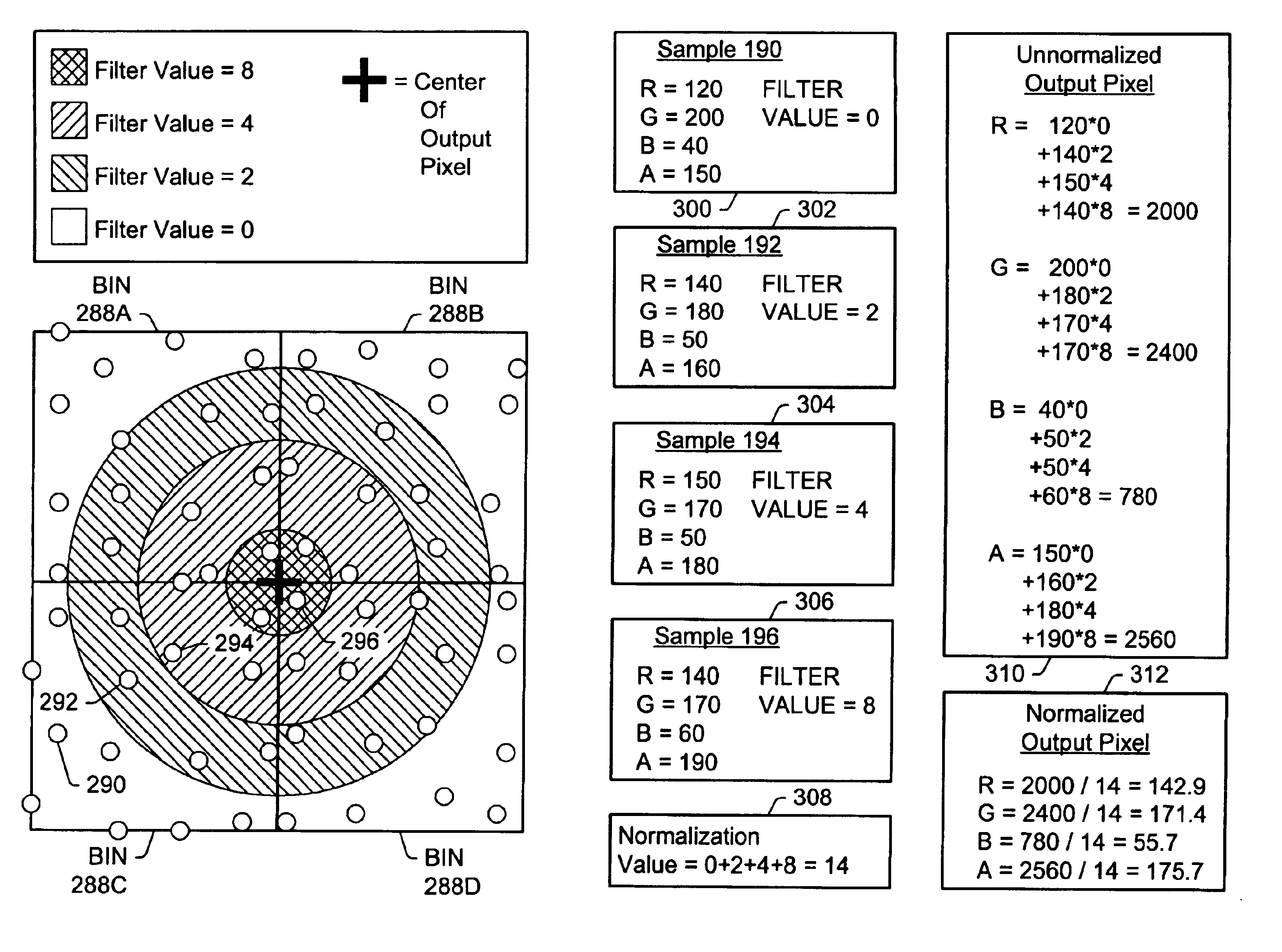
Graphics system with a variable-resolution sample buffer
A method and computer graphics system capable of super-sampling and performing real-time convolution are disclosed. In one embodiment, the computer graphics system may comprise a graphics processor, a sample buffer, and a sample-to-pixel calculation unit. The graphics processor may be configured to generate a plurality of samples. The sample buffer, which is coupled to the graphics processor, may be configured to store the samples. The sample-to-pixel calculation unit is programmable to select a variable number of stored samples from the sample buffer to filter into an output pixel. The sample-to-pixel calculation unit performs the filter process in real-time, and may use a number of different filter types in a single frame. The sample buffer may be super-sampled, and the samples may be positioned according to a regular grid, a perturbed regular grid, or a stochastic grid.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Position-tracking device for position-tracking system
ActiveUS7245215B2High position resolutionImprove accuracyInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlTransceiverObject based
A position-tracking system for tracking the position of an object is disclosed. According to various embodiments, the tracking system includes a tracking device that is connected to or otherwise affixed to the object to be tracked. The tracking device may include, among other things, an inertial sensor assembly, radio transceivers and a processor. The position tracking system may also include a host processing system that is in communication with the tracking device. The position tracking system may provide variable-resolution position information based on the environment in which the object is moving. In a “wide resolution” area, the system may compute a general position for the object based on a wireless telephone network Cell-ID / map correlation architecture. In a high-resolution area, greater position resolution may be realized from the combination of a wireless aiding system and inputs from the inertial sensors. In the high-resolution mode, the system may exploit distinct patterns of motion that can be identified as motion “signatures” that are characteristic of certain types of motion. Kinematic (or object movement) models may be constructed based on these motion signatures and the position tracking system may estimate the state of the object based on the kinematic model for the current mode of the object. Adaptive and cascaded Kalman filtering may be employed in the analysis to more accurately estimate the position and velocity of the object based on the motion pattern identified.
Owner:PINC SOLUTIONS
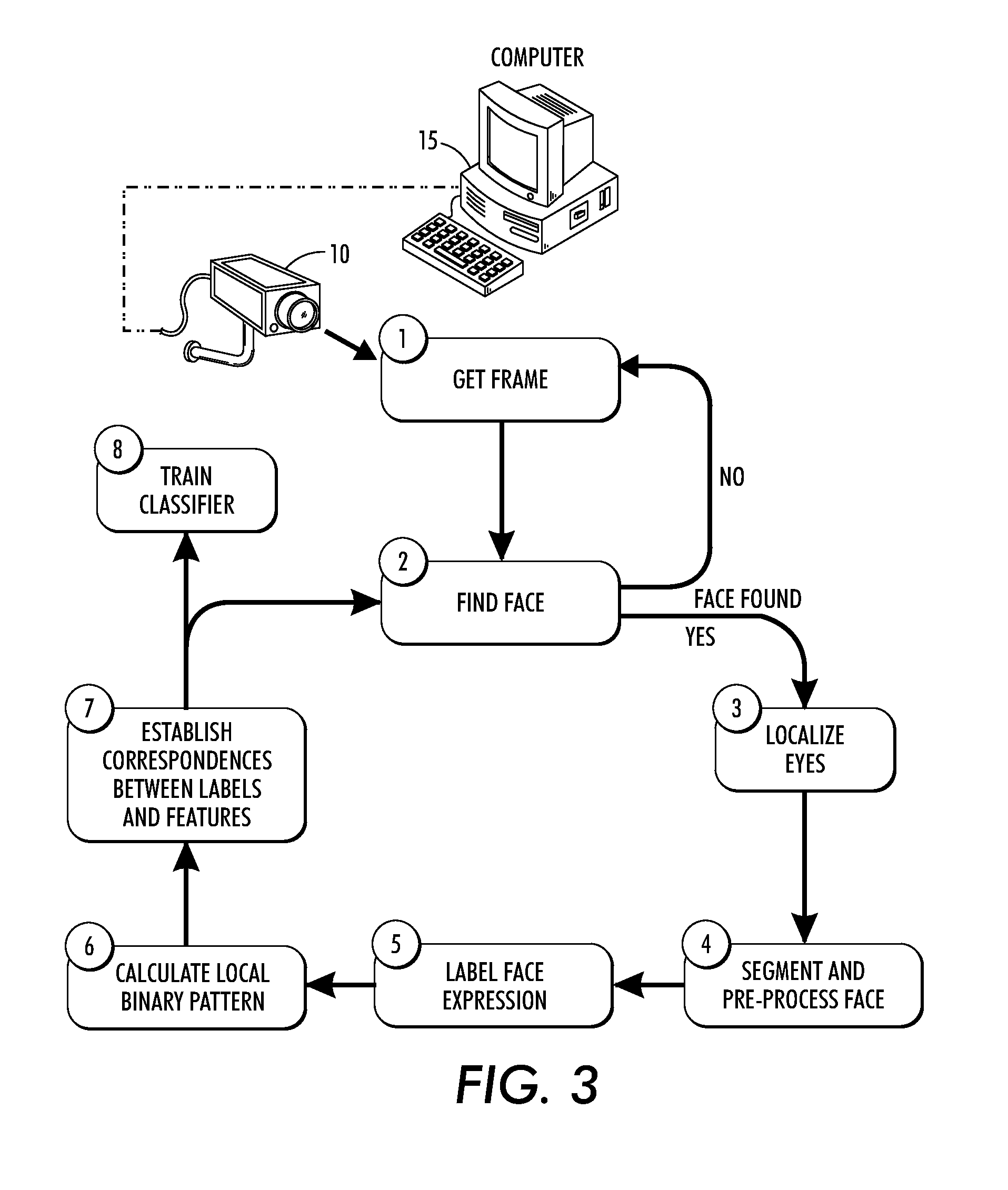
Method and system for automatically recognizing facial expressions via algorithmic periocular localization
ActiveUS20140063236A1Color television detailsClosed circuit television systemsVariable resolutionVideo sequence
This disclosure provides a method and system for automatically recognizing facial expressions at variable resolutions of video. According to one exemplary method, facial expressions are detected, extracted and classified from a video sequence based on an automatic localization of the periocular region associated with a detected and extracted face.
Owner:CONDUENT BUSINESS SERVICES LLC
Avionics device, systems and methods of display
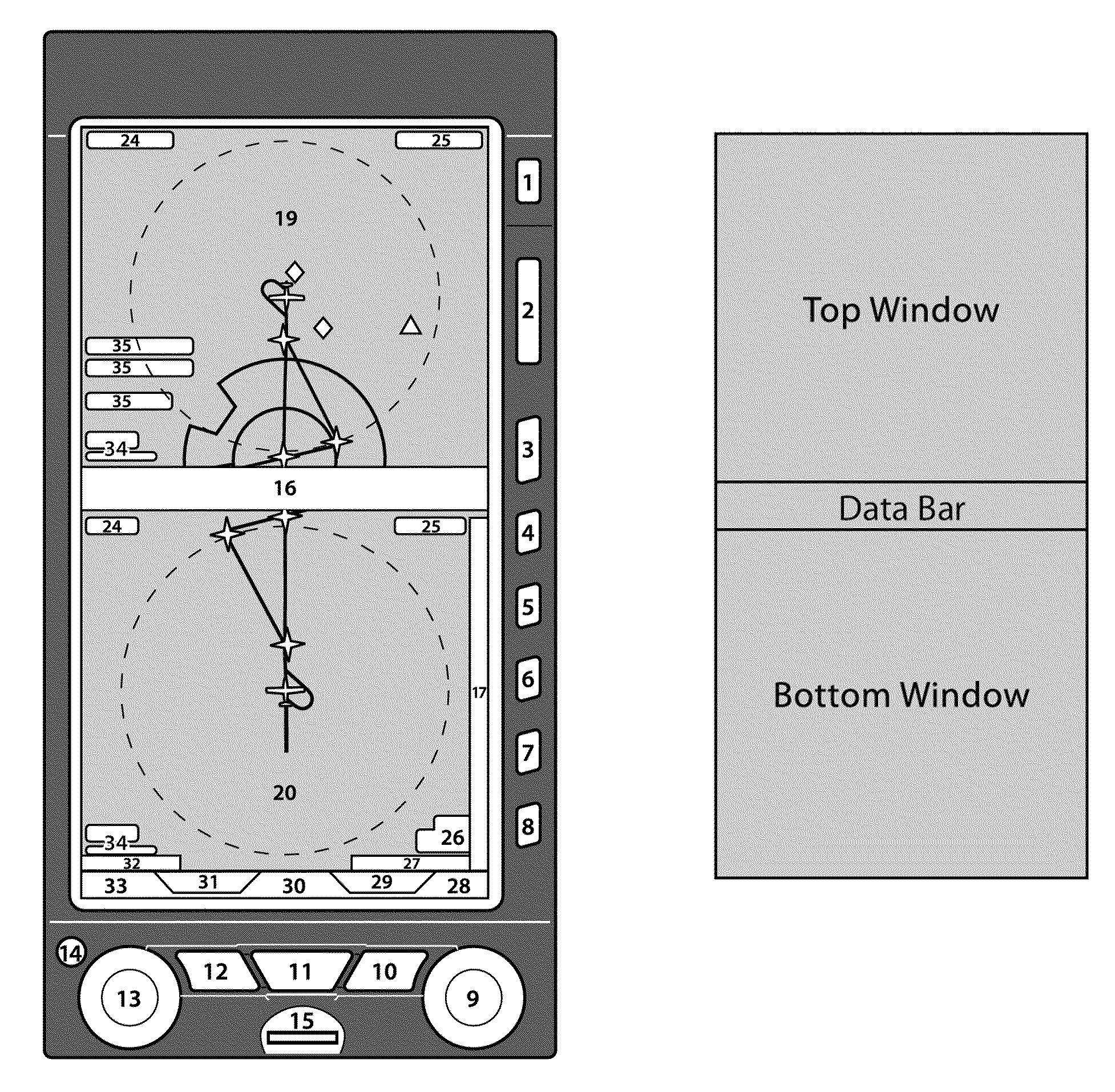
InactiveUS20120001773A1Eliminate needIncrease awarenessInput/output for user-computer interactionNavigation instrumentsAviationComputer graphics (images)
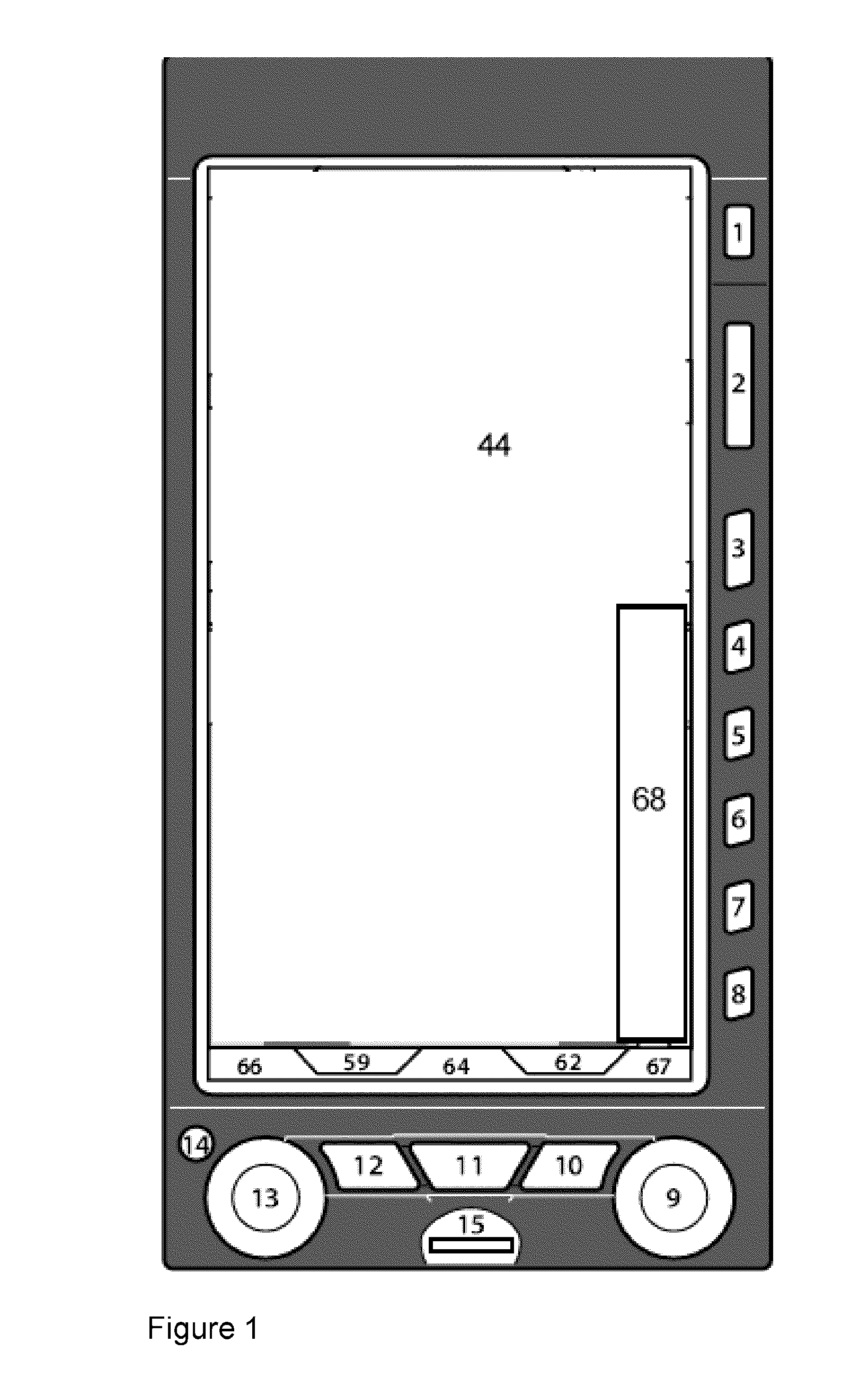
The present general inventive concept relates to methods and systems to select and display information on an avionics display screen. The systems and methods allow for the selection and display of information using knobs to highlight and select the desired information for display, eliminating the need for a cursor function. The systems and methods also provide for multiple pages and / or multiple windows or “tiles” within these pages and / or windows simultaneously on a single screen of a display, with each window, page, and / or tile being fully controlled independently when selected. The present general inventive concept also relates to systems and methods to provide multiple cues on an electronic display system altitude tape to a pilot in advance and impending approach to a predefined altitude. The present general inventive concept also relates to systems and methods to employ variable resolution topographical data based on display range for an avionics navigation display.
Owner:ASPEN AVIONICS
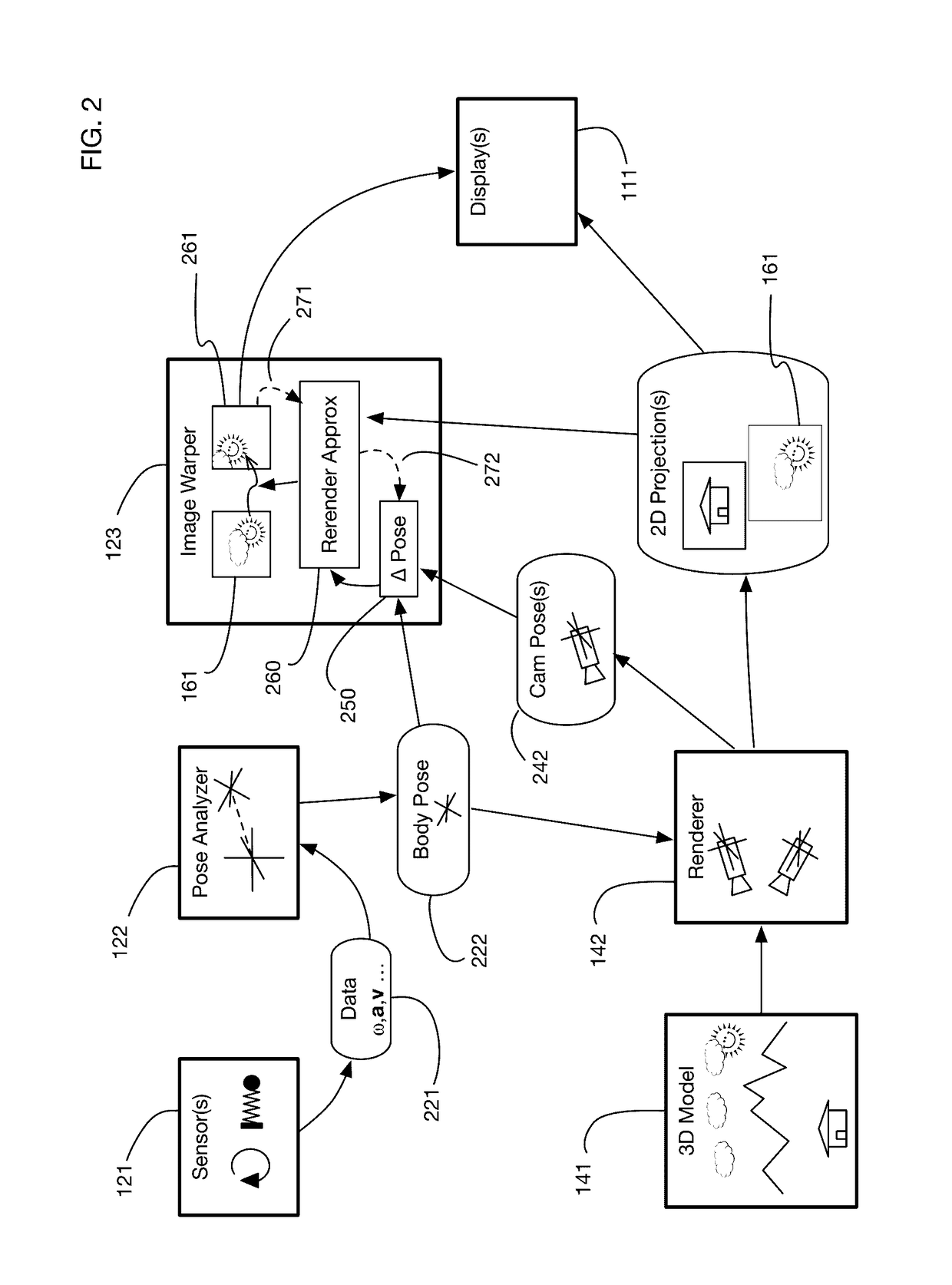
Variable resolution virtual reality display system
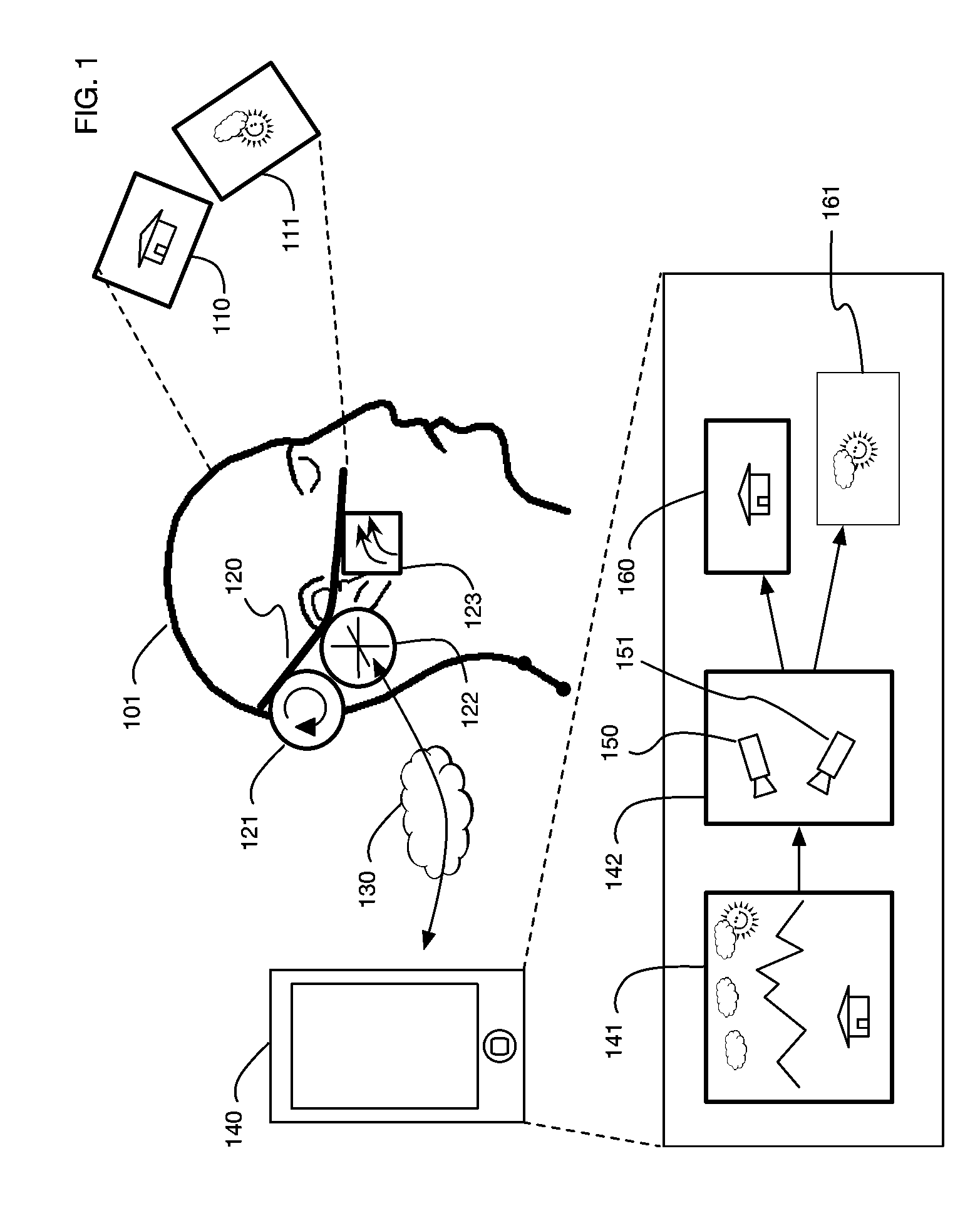
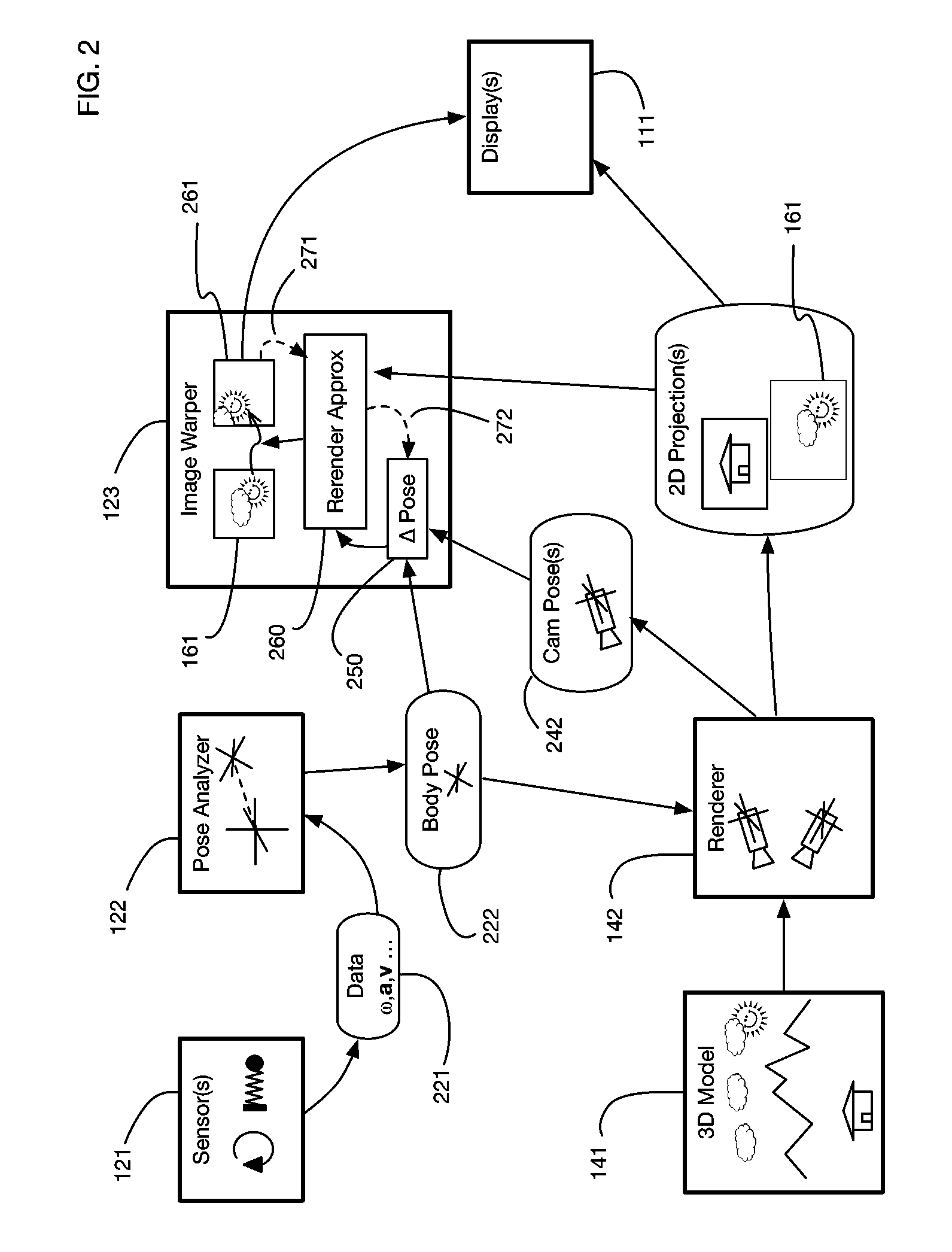
ActiveUS9607428B2Enhance the virtual reality experienceEfficient and rapid rerendering reduces latencyInput/output for user-computer interactionGeometric image transformationImage resolutionLevel of detail
Owner:LI ADAM
Method and device for projecting a panoramic image with a variable resolution
ActiveUS8016426B2Constant resolutionEasy to castProjectorsPanoramic photographyObservation pointProjection image
Embodiments include a method and apparatus for projecting a panoramic image, the method including steps of generating an image on an image generation surface, and then projecting the generated image on a projection surface to obtain a panoramic projected image, the points of the generated image being projected on the projection surface according to a non uniform distribution determined as a function of at least one parameter of a set comprising the shape of the generated image, the shape of the projection surface, and the position of an observation point of the projected image, in relation to the projection surface.
Owner:IMMERVISION INC
Position-tracing system
ActiveUS20060187028A1Improve accuracyHigh position resolutionInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlTransceiverObject based
A position-tracking system for tracking the position of an object is disclosed. According to various embodiments, the tracking system includes a tracking device that is connected to or otherwise affixed to the object to be tracked. The tracking device may include, among other things, an inertial sensor assembly, radio transceivers and a processor. The position tracking system may also include a host processing system that is in communication with the tracking device. The position tracking system may provide variable-resolution position information based on the environment in which the object is moving. In a “wide resolution” area, the system may compute a general position for the object based on a wireless telephone network Cell-ID / map correlation architecture. In a high-resolution area, greater position resolution may be realized from the combination of a wireless aiding system and inputs from the inertial sensors. In the high-resolution mode, the system may exploit distinct patterns of motion that can be identified as motion “signatures” that are characteristic of certain types of motion. Kinematic (or object movement) models may be constructed based on these motion signatures and the position tracking system may estimate the state of the object based on the kinematic model for the current mode of the object. Adaptive and cascaded Kalman filtering may be employed in the analysis to more accurately estimate the position and velocity of the object based on the motion pattern identified.
Owner:PINC SOLUTIONS
Variable resolution virtual reality display system
ActiveUS20170004648A1Enhance the virtual reality experienceEfficient and rapid rerendering reduces latencyInput/output for user-computer interactionGeometric image transformationImage resolutionLevel of detail
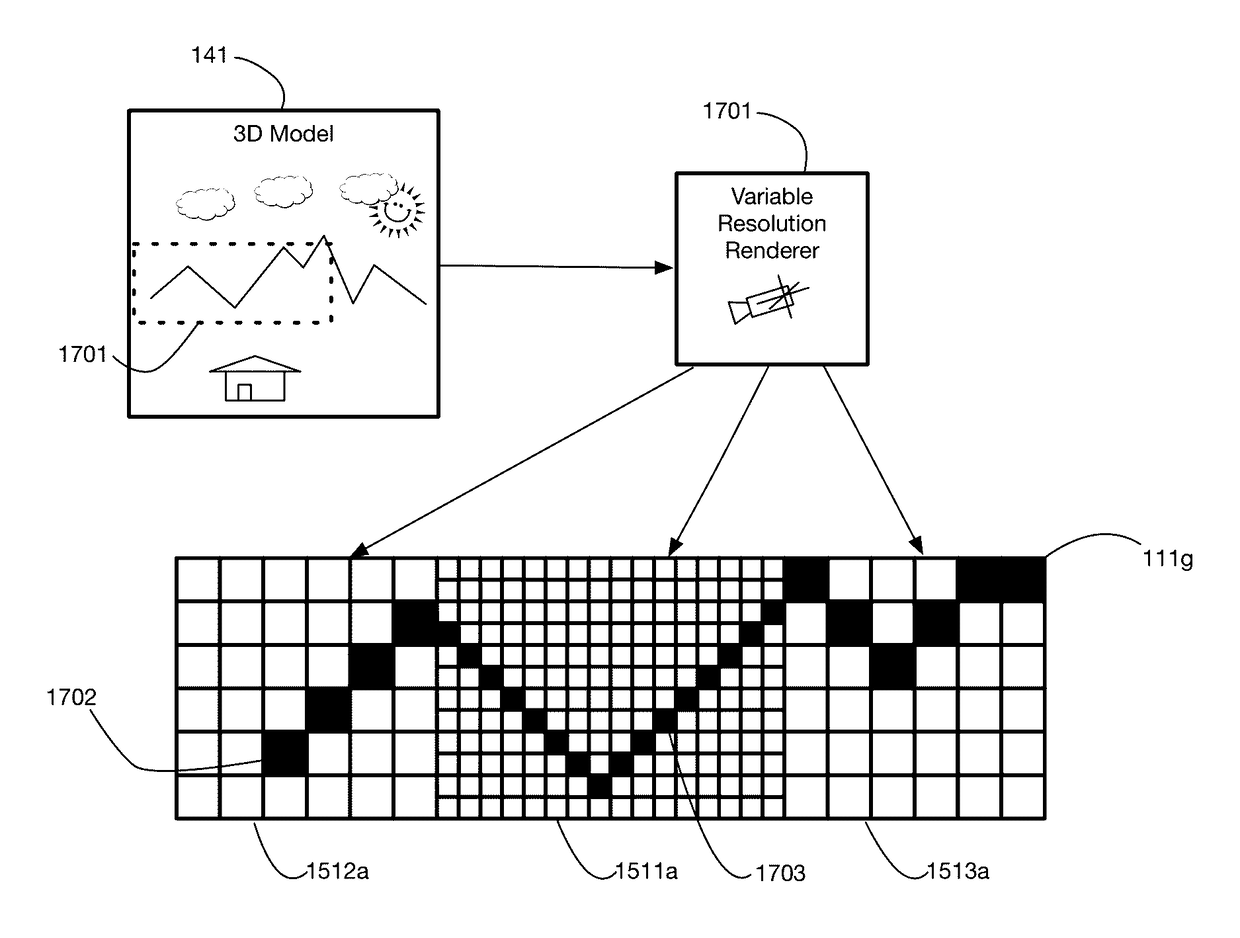
A virtual reality display system that renders images at different resolutions in different parts of a display. Reduces rendering latency by rendering at a lower resolution in selected regions, for example on the sides of a display where human vision has lower resolution than in the center. Pixels in low resolution regions are combined into grid elements, and rendering may generate grid element values rather than individual pixel values. Rendering may use ray casting, rasterization, or both. Variable resolution rendering may be combined with variable level of detail geometry models to further reduce rendering time. Selected objects may be designed as high resolution objects that are rendered at a high resolution even in low resolution display regions.
Owner:LI ADAM
Dimensional vector and variable resolution quantization
InactiveUS7680670B2Effective and economicalMemory storage required for the implementationSpeech analysisCode conversionImage resolutionTheoretical computer science
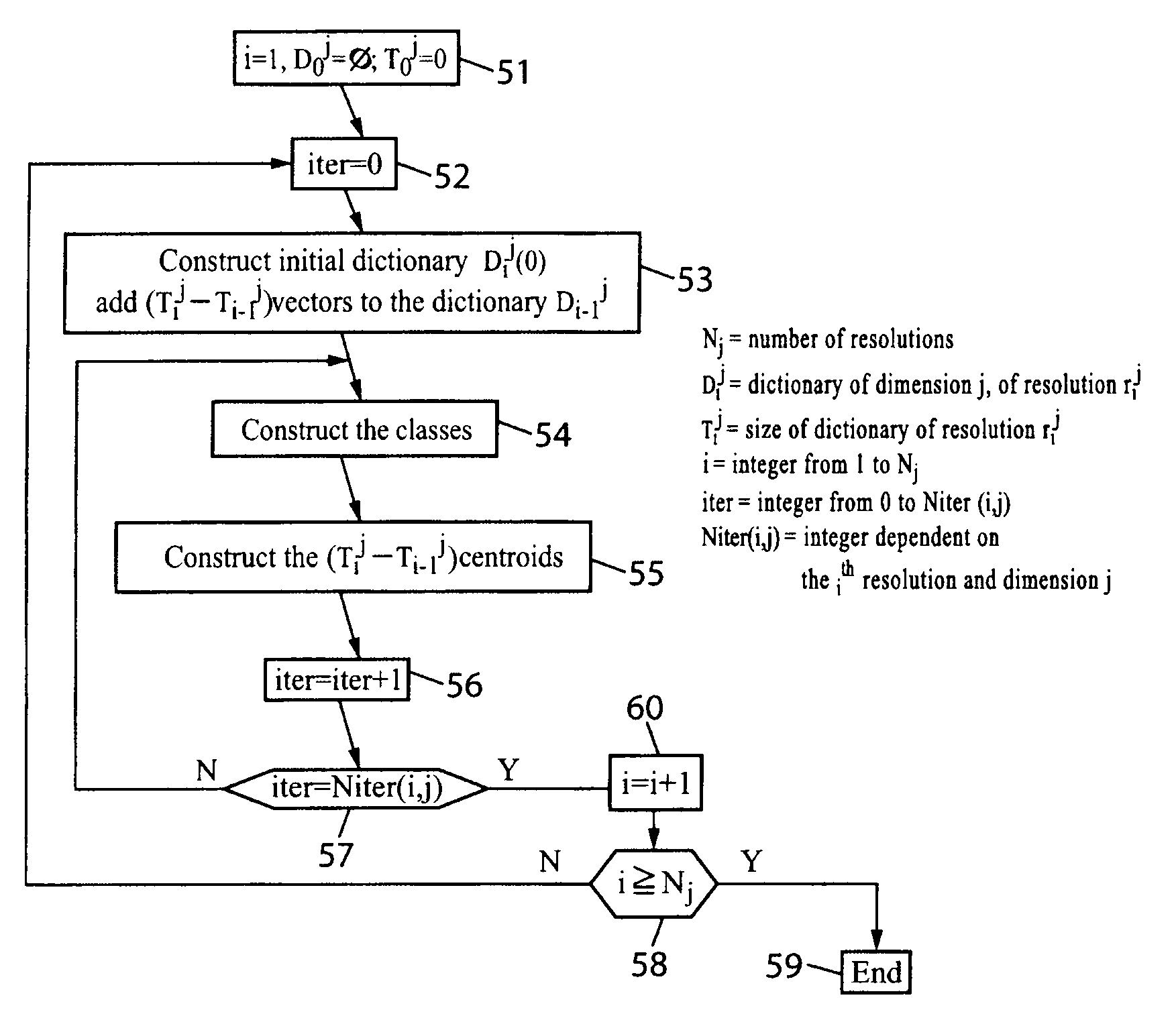
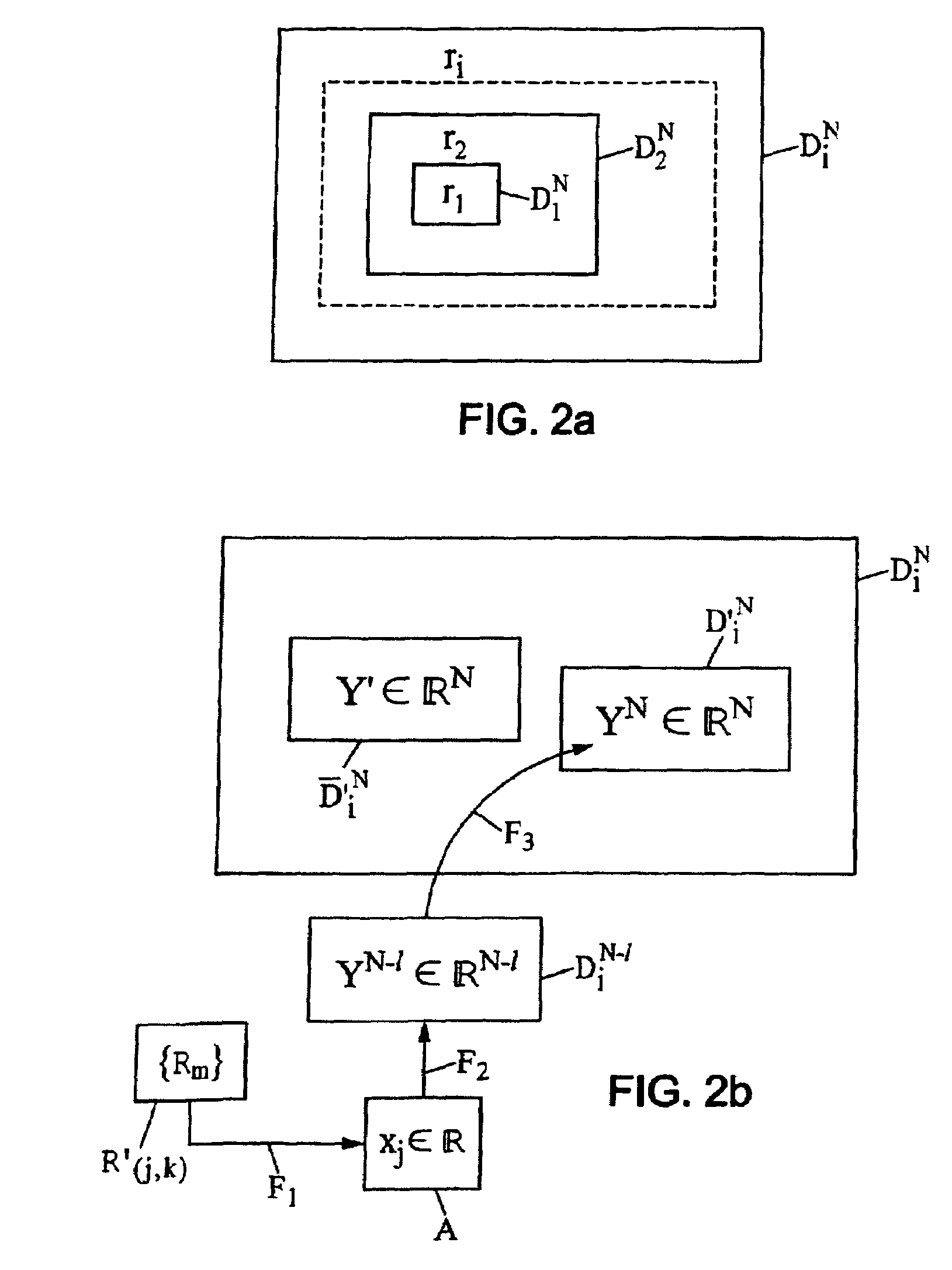
The invention relates to compression coding and / or decoding of digital signals, in particular by vector variable-rate quantisation defining a variable resolution. For this purpose an impulsion dictionary comprises: for a given dimension, increasing resolution dictionaries imbricated into each other and, for a given dimension, a union of: a totality (D′i<N>) of code-vectors produced, by inserting elements taken in a final set (A) into smaller dimension code-vectors according to a final set of predetermined insertion rules (F1) and a second totality of code-vectors (Y′) which are not obtainable by insertion into the smaller dimension code vectors according to said set of the insertion rules.
Owner:FRANCE TELECOM SA
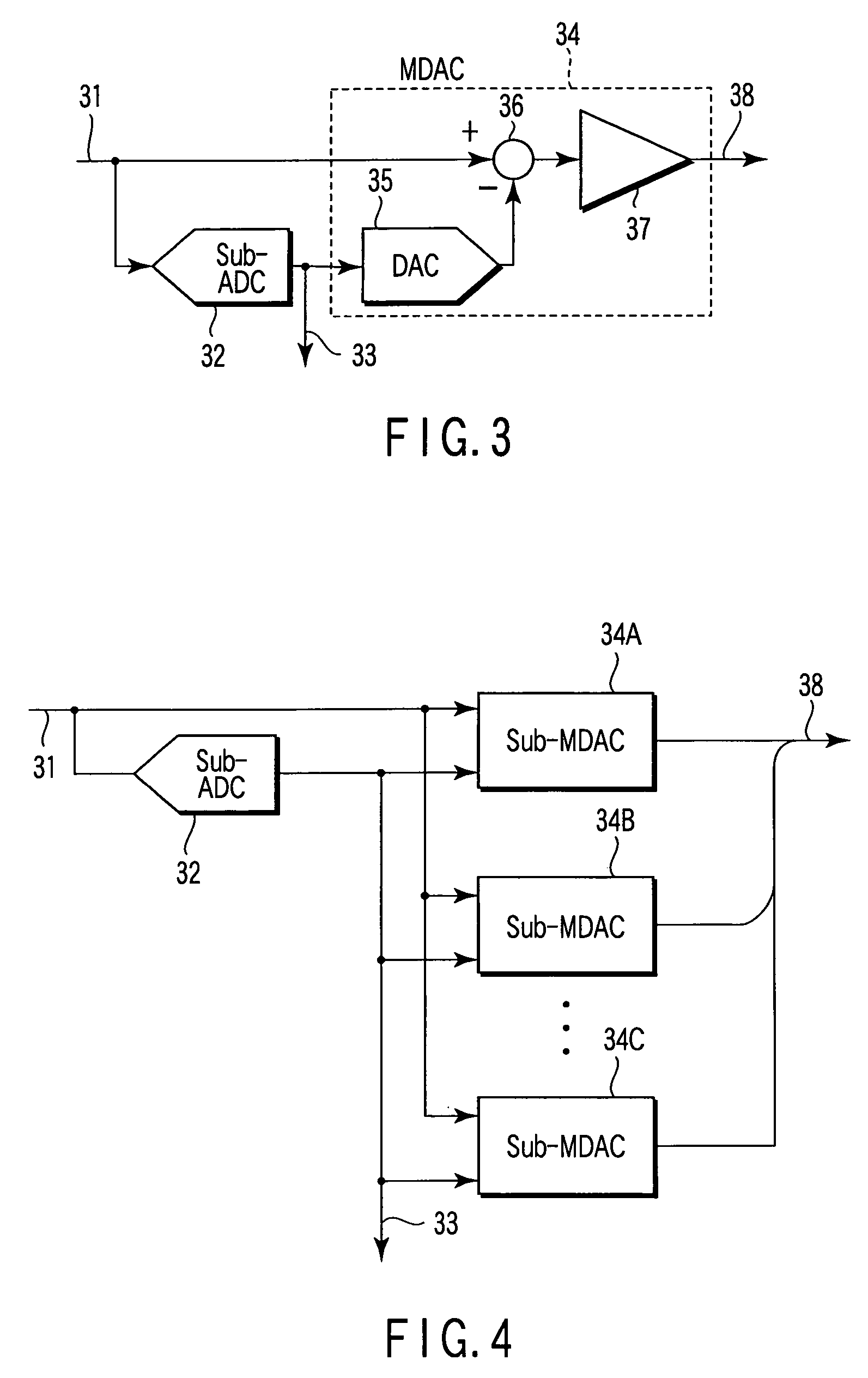
Analog-to digital converter and analog-to digital conversion apparatus
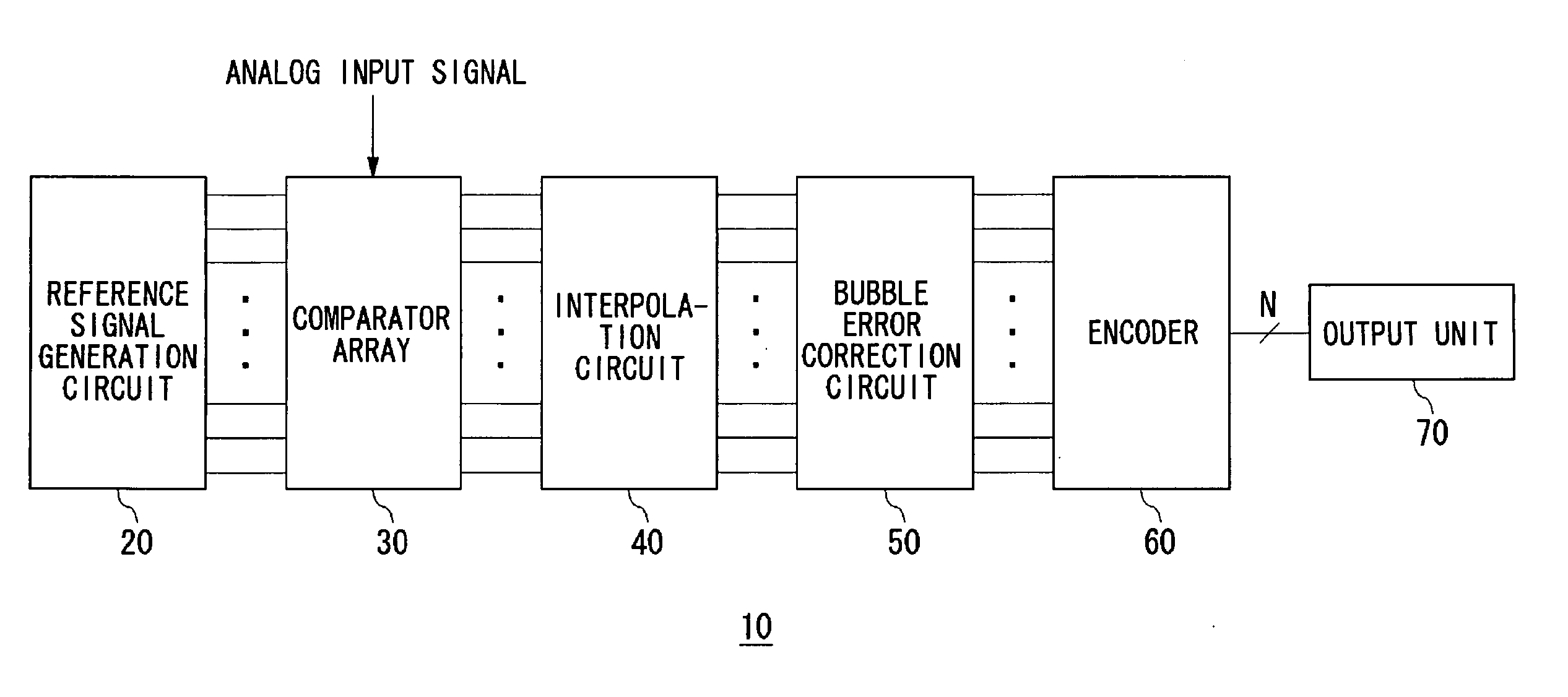
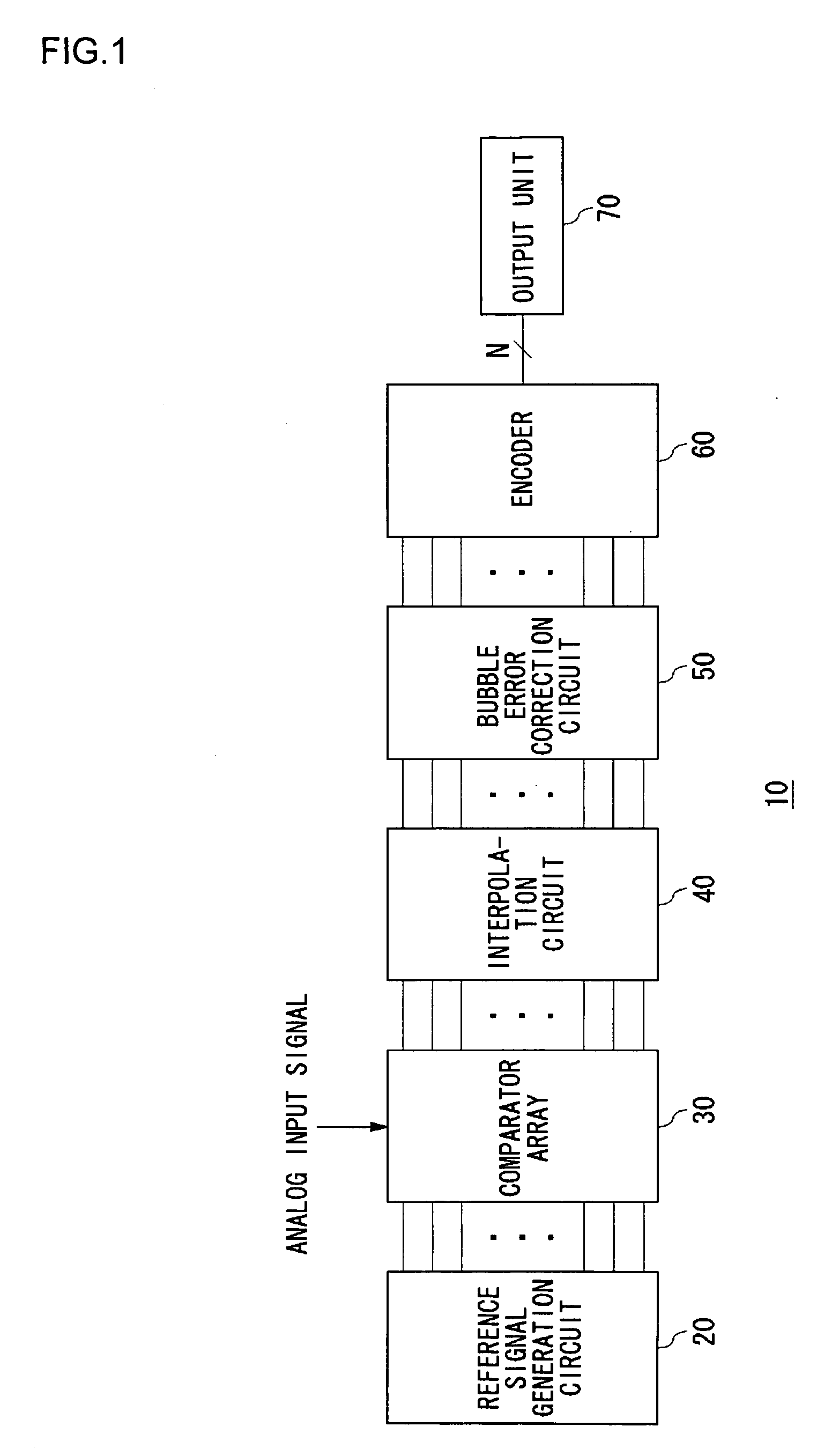
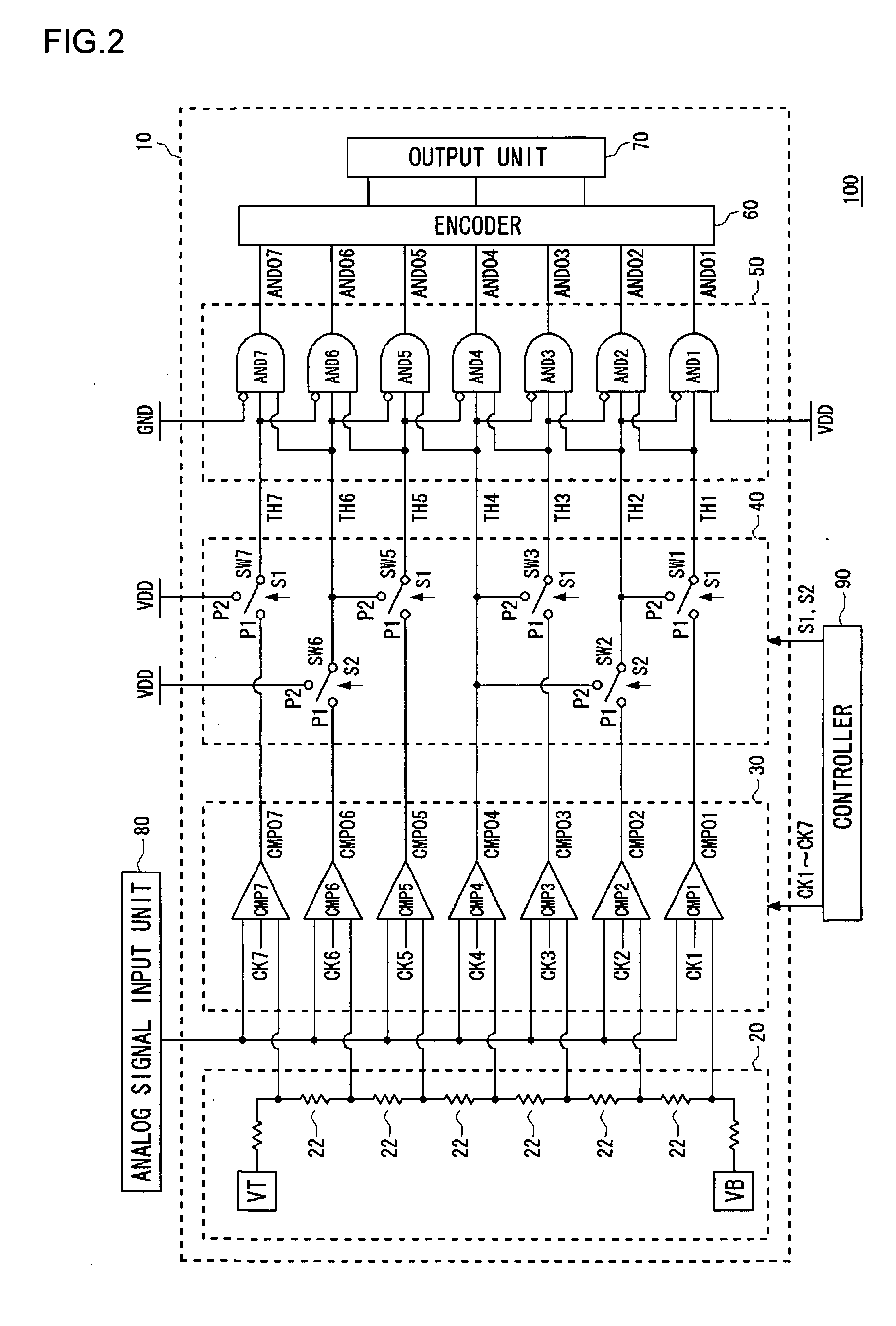
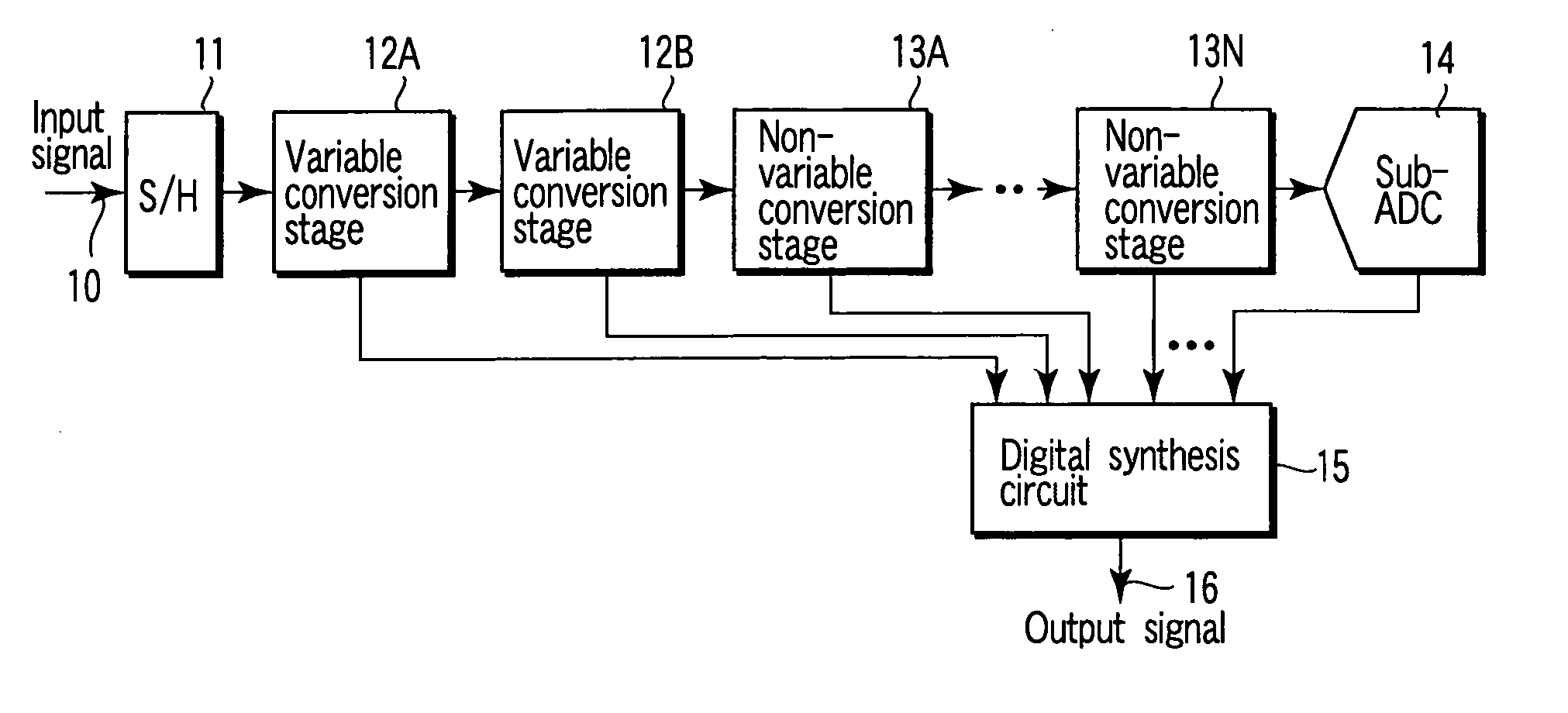
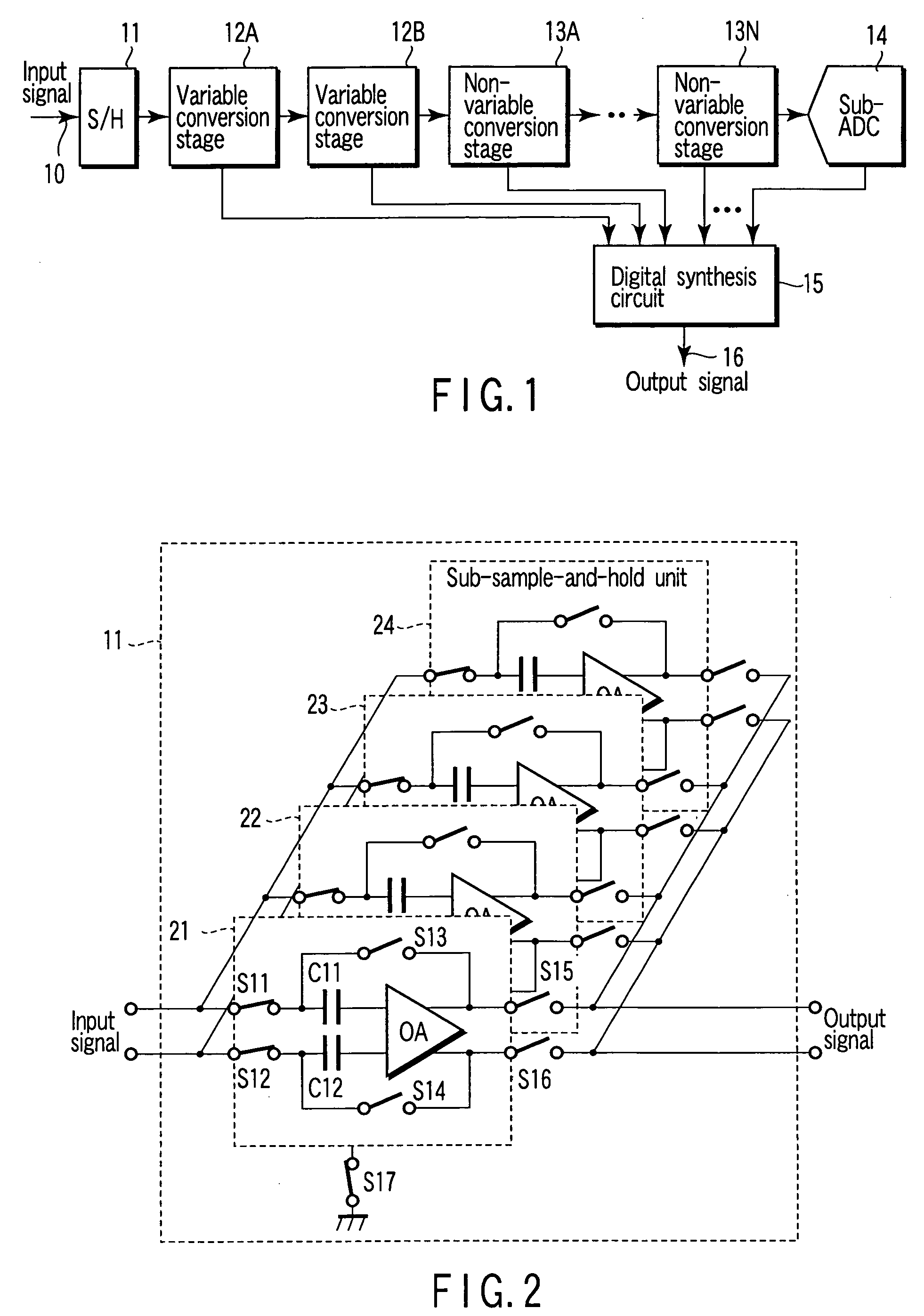
ActiveUS20060187105A1Variable resolutionReduce power consumptionPower saving provisionsElectric signal transmission systemsControl signalImage resolution
An analog-to-digital conversion apparatus which has a variable resolution and allows a reduction in power consumption. This apparatus comprises an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) of parallel type, a controller, and an interpolation circuit. The analog-to-digital converter has a plurality of comparators connected in parallel, each for comparing potentials of an analog input signal and a reference signal. The controller generates a control signal for controlling the resolution of the analog-to-digital converter. Specifically, the controller controls the number of comparators (CMP) to operate by means of the control signal, thereby determining the resolution. The interpolation circuit interpolates the output data of the comparators that are disabled depending on the resolution. The controller avoids simultaneous operation of two adjoining comparators when the analog-to-digital converter is operated at a resolution lower than its maximum resolution.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Variable-Resolution Processing of Frame-Based Data
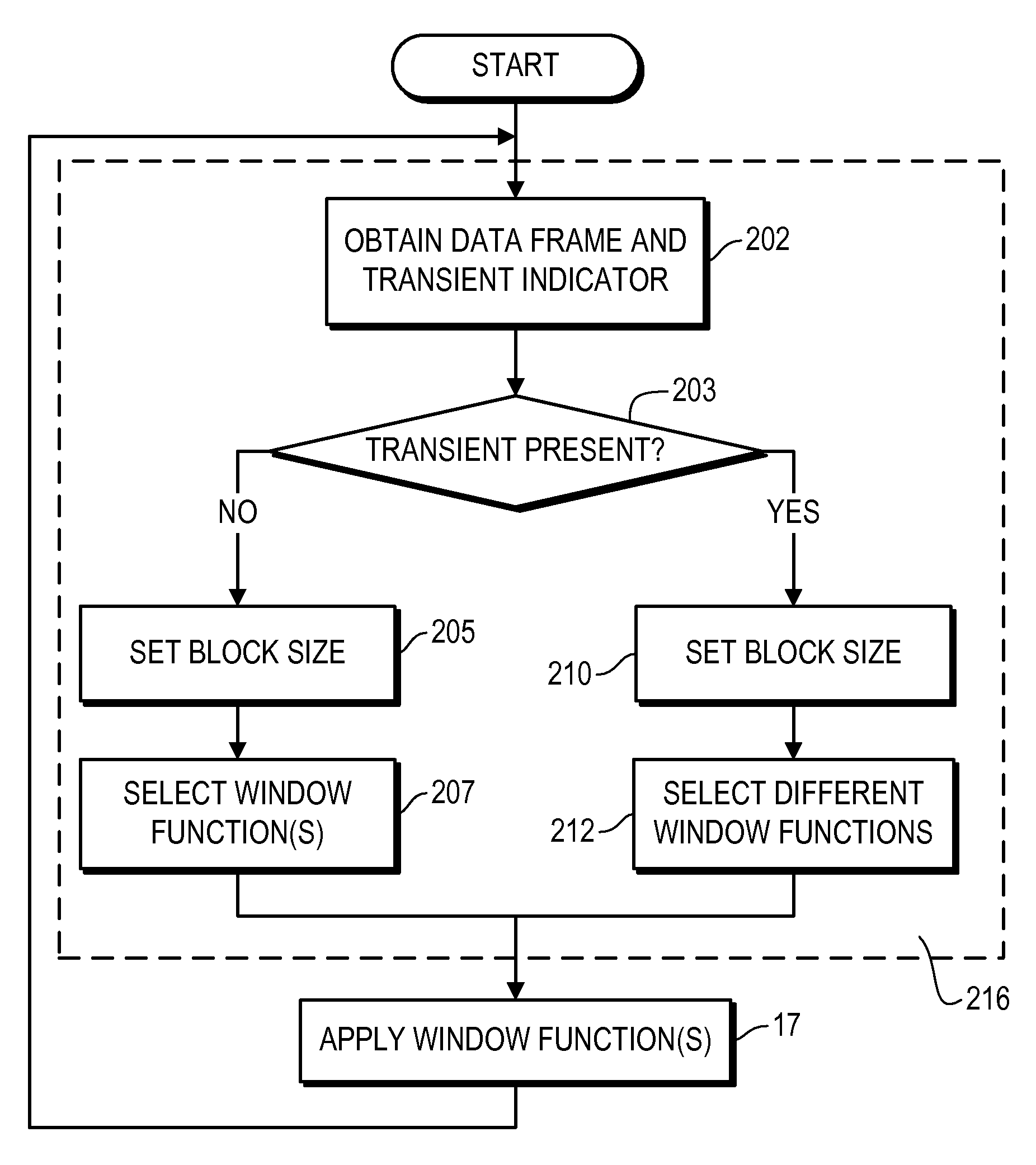
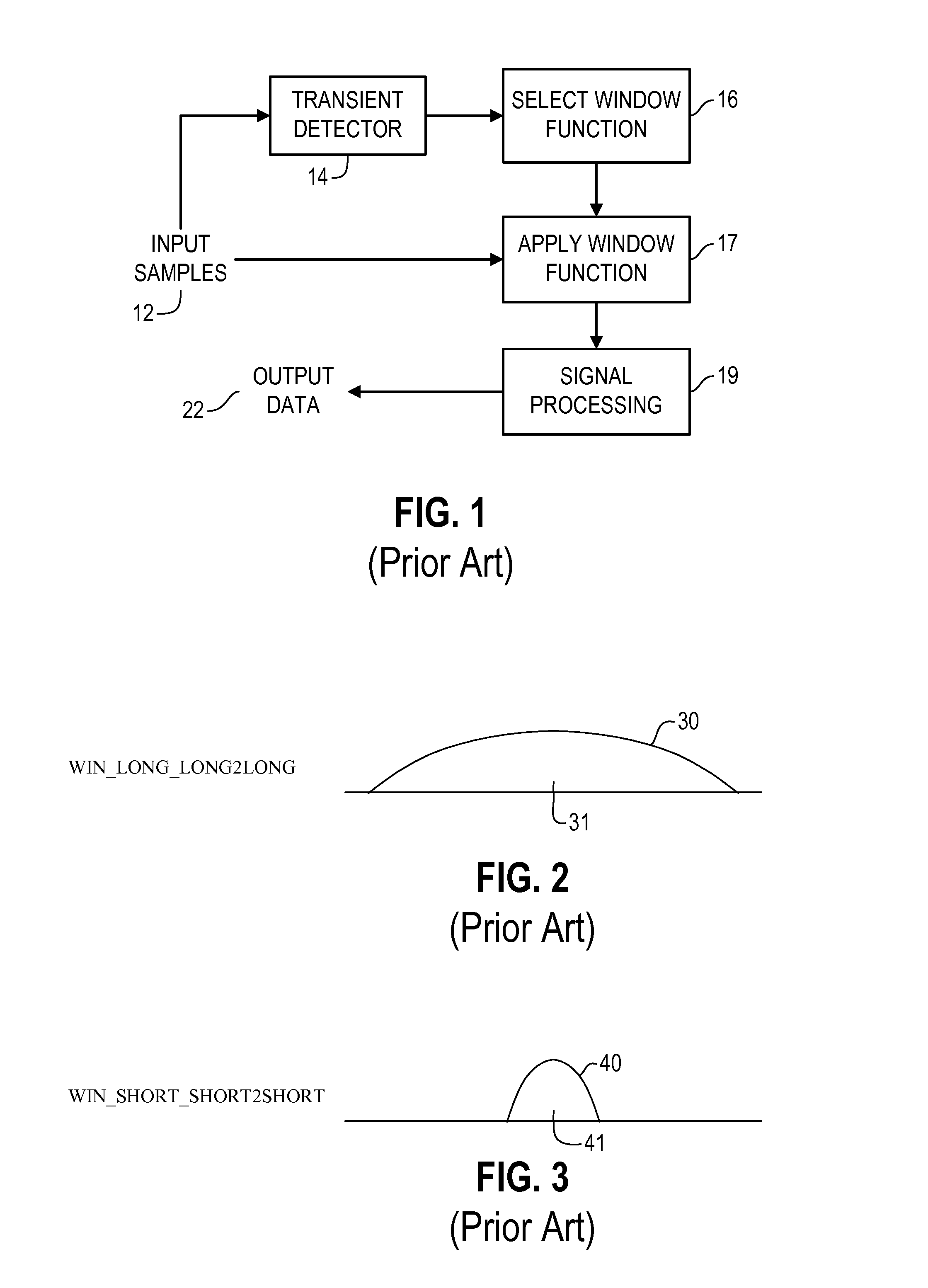
ActiveUS20080059202A1Without complicating processing structureHigh resolutionSpeech analysisCode conversionFrame basedVariable resolution
Provided are systems, methods and techniques for processing frame-based data. A frame of data, an indication that a transient occurs within the frame, and a location of the transient within the frame are obtained. Based on the indication of the transient, a block size is set for the frame, thereby effectively defining a plurality of equal-sized blocks within the frame. In addition, different window functions are selected for different ones of the plurality of equal-sized blocks based on the location of the transient, and the frame of data is processed by applying the selected window functions.
Owner:DIGITAL RISE TECH CO LTD
High-precision matrix-vector multiplication on a charge-mode array with embedded dynamic memory and stochastic method thereof
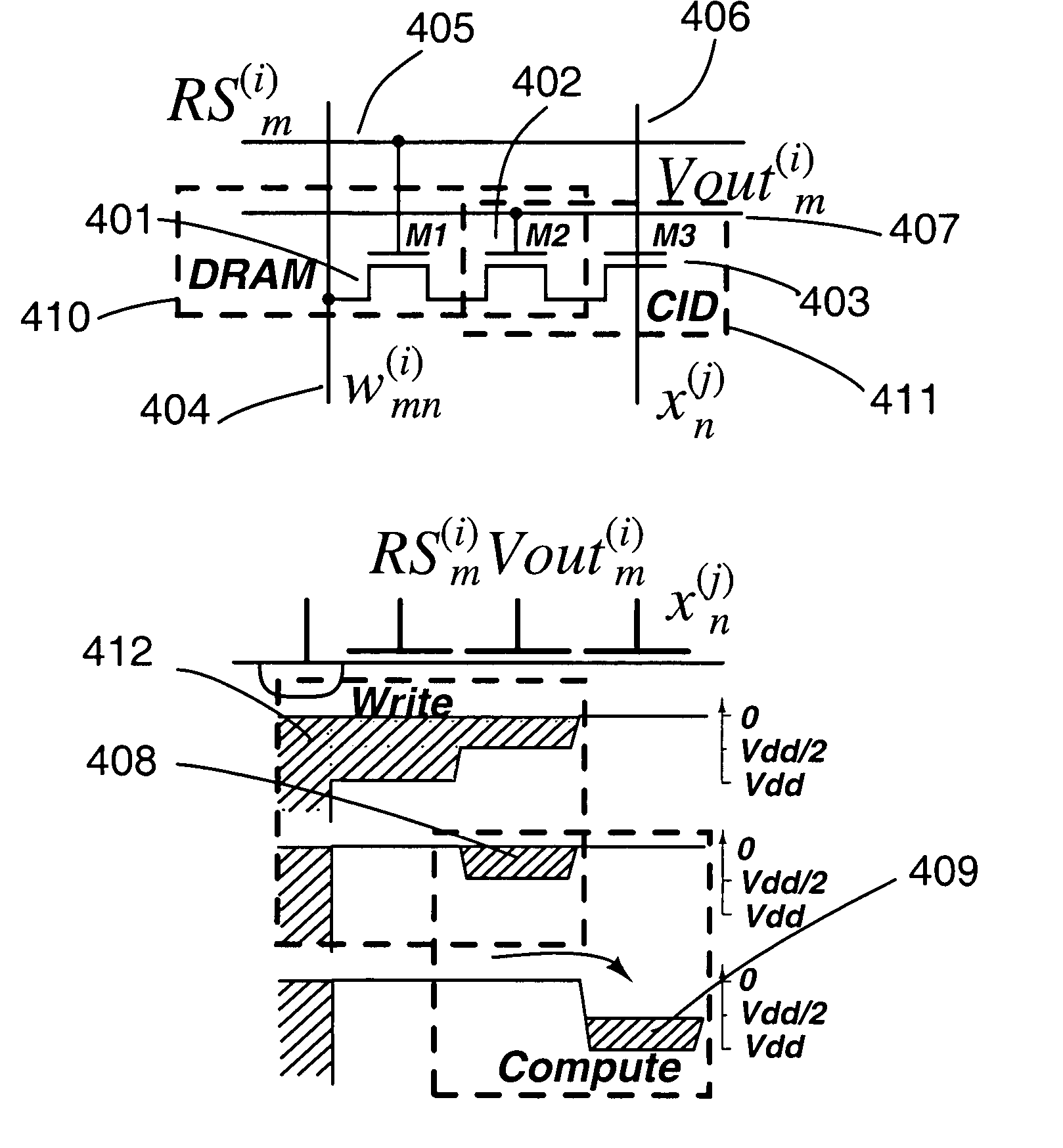
InactiveUS20050125477A1Efficient multiplicationIncrease cell densityComputation using non-contact making devicesPhysical realisationRandom methodReal time signal processing
Analog computational arrays for matrix-vector multiplication offer very large integration density and throughput as, for instance, needed for real-time signal processing in video. Despite the success of adaptive algorithms and architectures in reducing the effect of analog component mismatch and noise on system performance, the precision and repeatability of analog VLSI computation under process and environmental variations is inadequate for some applications. Digital implementation offers absolute precision limited only by wordlength, but at the cost of significantly larger silicon area and power dissipation compared with dedicated, fine-grain parallel analog implementation. The present invention comprises a hybrid analog and digital technology for fast and accurate computing of a product of a long vector (thousands of dimensions) with a large matrix (thousands of rows and columns). At the core of the externally digital architecture is a high-density, low-power analog array performing binary-binary partial matrix-vector multiplication. Digital multiplication of variable resolution is obtained with bit-serial inputs and bit-parallel storage of matrix elements, by combining quantized outputs from one or more rows of cells over time. Full digital resolution is maintained even with low-resolution analog-to-digital conversion, owing to random statistics in the analog summation of binary products. A random modulation scheme produces near-Bernoulli statistics even for highly correlated inputs. The approach has been validated by electronic prototypes achieving computational efficiency (number of computations per unit time using unit power) and integration density (number of computations per unit time on a unit chip area) each a factor of 100 to 10,000 higher than that of existing signal processors making the invention highly suitable for inexpensive micropower implementations of high-data-rate real-time signal processors.
Owner:GENOV ROMAN A +1
Mute detection method based on speech characteristic to jude
InactiveCN1835073AImprove classification effectImprove robustnessSpeech analysisSupport vector machineFrequency spectrum
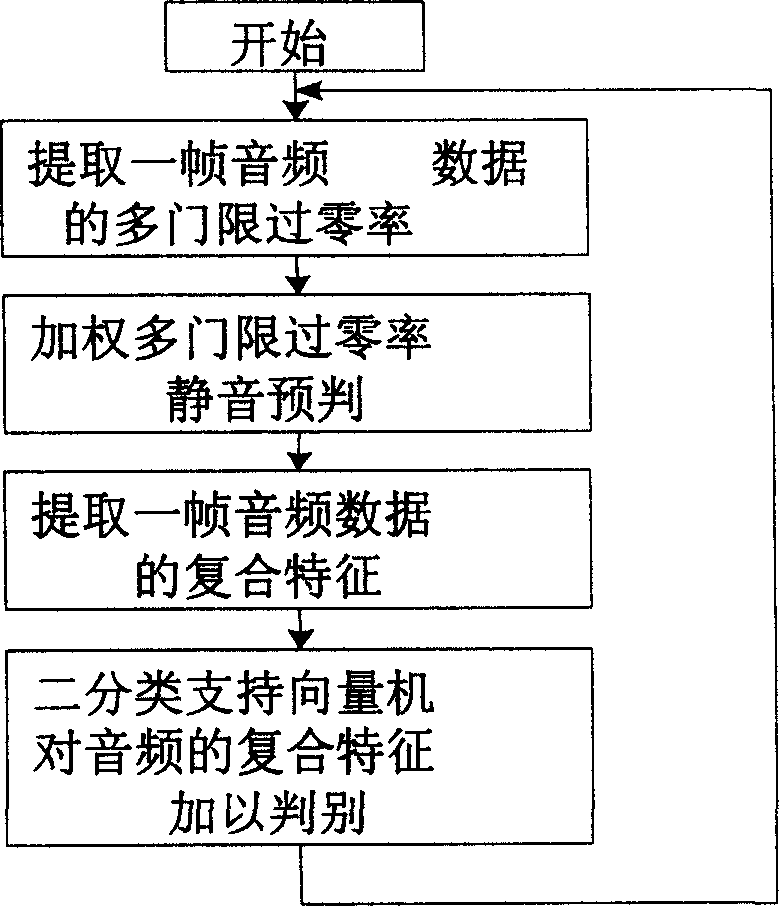
The invention discloses a voice characteristic identification-based silence detecting method, firstly extracting multi-threshold overzero rate of an audio data frame; pre-identify silence by weighting the multi-threshold overzero rate to identify obvious silence; extracting composite characteristic of an audio data frame, where the composite characteristic comprises overzero rate, short-time energy value, and variable resolution frequency spectrum-based Mel scale revere spectrum coefficient; using dichotomy support vector machine to identify the composite character of the audio frequency, one class normal voice and the other class silence. And the invention can raise success rate of silence detection and can identify some special voices, able to be widely applied to network voice talking, especially voice chatting and video meeting.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
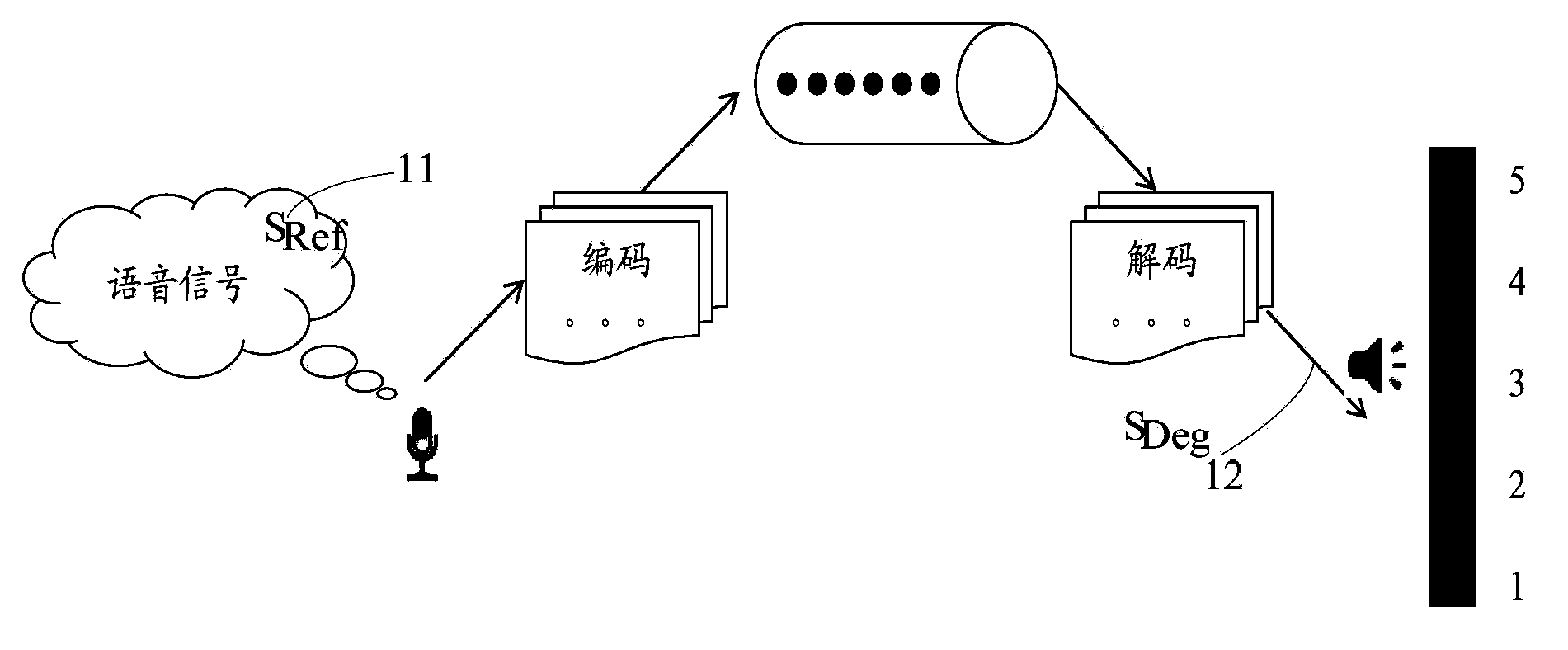
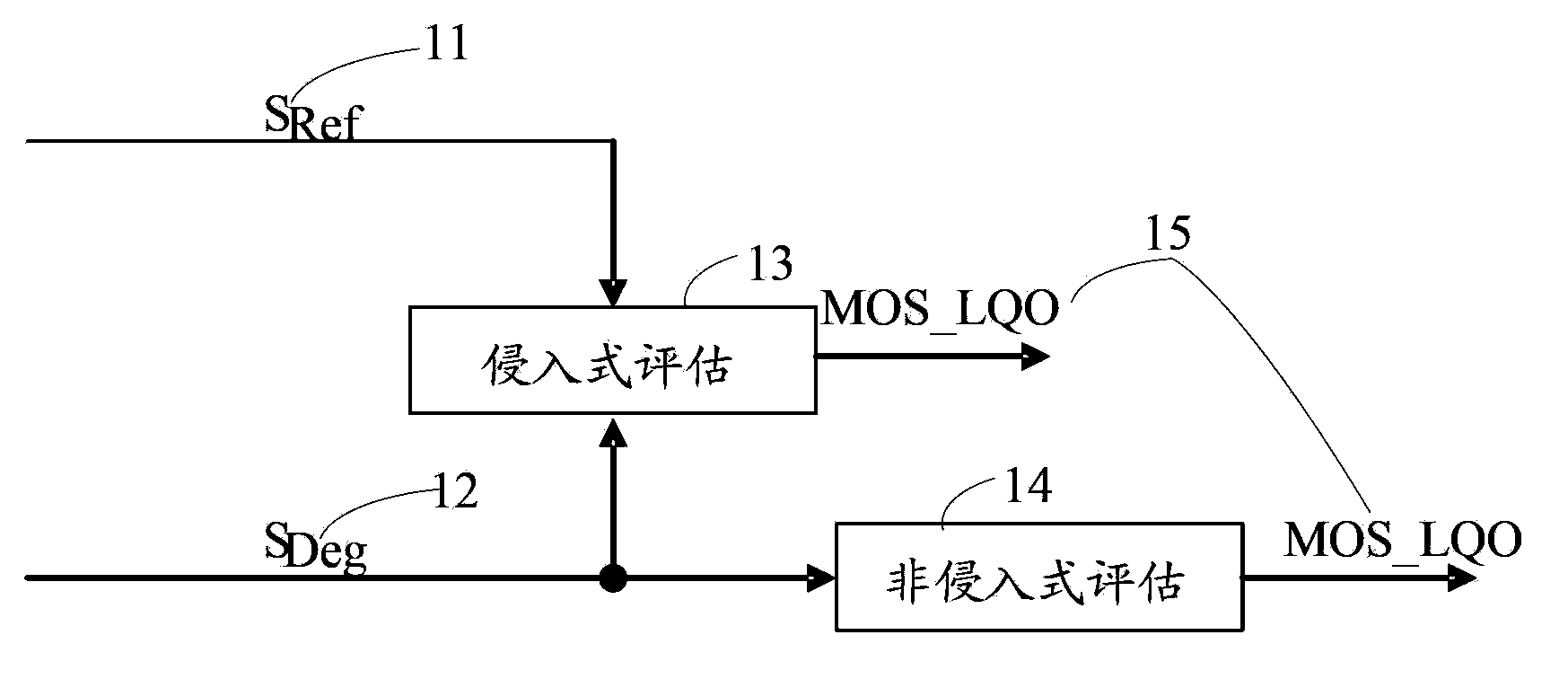
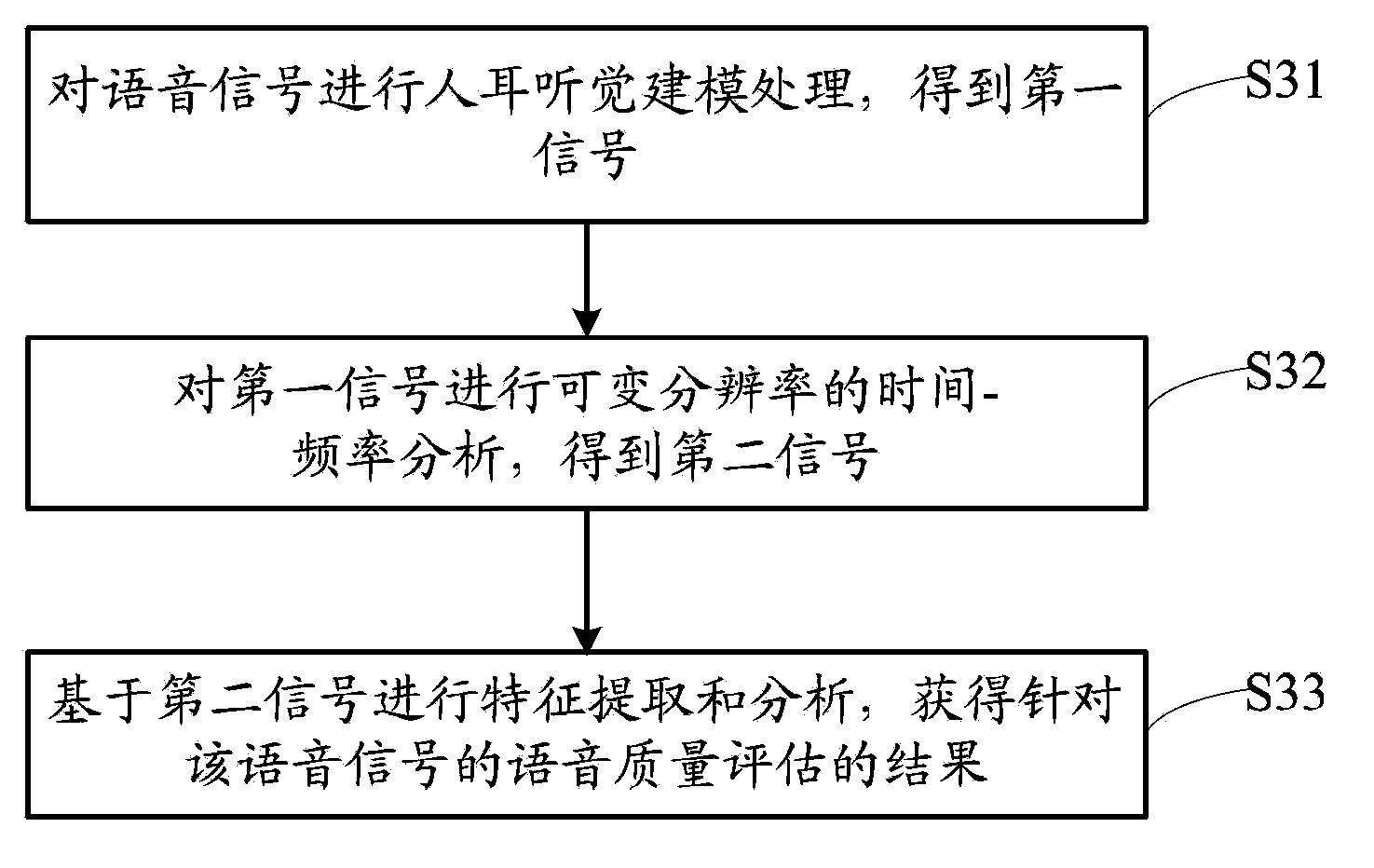
Voice quality evaluation method and device
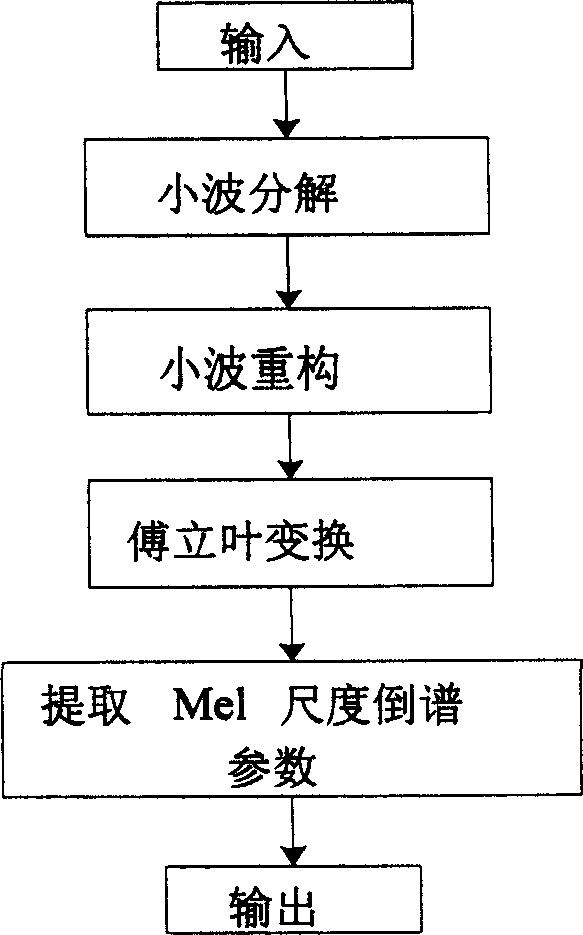
The invention relates to a voice quality evaluation method which includes the steps of conducting human ear auditory sense modeling processing on voice signals to obtain first signals, conducting resolution-ratio-variable time-frequency analysis on the first signals to obtain second signals, and conducting feature extraction and analysis based on the second signals to obtain voice quality evaluation results for the voice signals. According to the technical scheme, the problem that the accuracy of the voice quality evaluation is not high is solved; human ear auditory sense modeling processing is carried out, the signals to be detected are converted into time-frequency signals capable of showing the variable resolution ratio, the time-frequency signals with the variable resolution ratio are further analyzed, features corresponding to the signals are extracted, further analysis is carried out, and therefore the high-accuracy voice quality evaluation results are finally obtained.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Variable resolution model based image segmentation
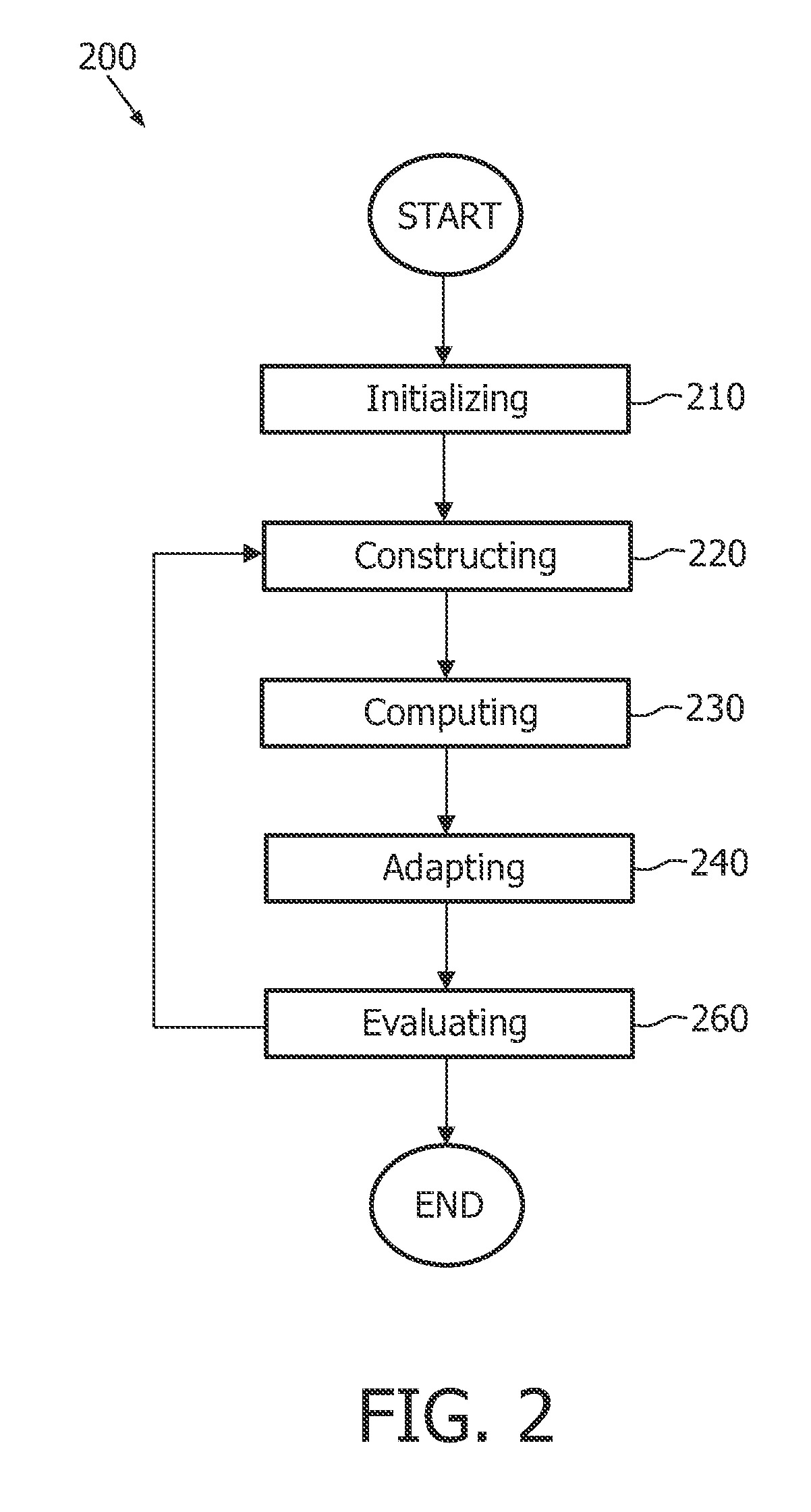
InactiveUS20090202150A1Effectively controlling smoothness of the computed model surface representedIncrease computational costImage enhancementImage analysisCoarse meshData set
The invention relates to system (100) for segmenting an image dataset based on a deformable model for modeling an object in the image dataset, utilizing a coarse mesh for adapting to the image dataset and a fine mesh for extracting detailed information from the image dataset, the system comprising an initialization unit (110) for initializing the coarse mesh in an image dataset space, a construction unit (120) for constructing the fine mesh in the image dataset space based on the initialized coarse mesh, a computation unit (130) for computing an internal force field on the coarse mesh and an external force field on the coarse mesh, wherein the external force is computed based on the constructed fine mesh and the scalar field of intensities, and an adaptation unit (140) for adapting the coarse mesh to the object in the image dataset, using the computed internal force field and the computed external force field, thereby segmenting the image dataset. Since only the coarse mesh is adapted to the image dataset, keeping the modeled object surface smooth does not require a smoothing of the surface over large neighboring areas, and therefore the adaptation of the coarse mesh is much faster than the adaptation of the fine mesh. Advantageously, the proposed technique can be easily integrated into existing frameworks of model-based image segmentation.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Position-tracking device for position-tracking system
ActiveUS20060176174A1Improve accuracyHigh position resolutionInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlTransceiverObject based
A position-tracking system for tracking the position of an object is disclosed. According to various embodiments, the tracking system includes a tracking device that is connected to or otherwise affixed to the object to be tracked. The tracking device may include, among other things, an inertial sensor assembly, radio transceivers and a processor. The position tracking system may also include a host processing system that is in communication with the tracking device. The position tracking system may provide variable-resolution position information based on the environment in which the object is moving. In a “wide resolution” area, the system may compute a general position for the object based on a wireless telephone network Cell-ID / map correlation architecture. In a high-resolution area, greater position resolution may be realized from the combination of a wireless aiding system and inputs from the inertial sensors. In the high-resolution mode, the system may exploit distinct patterns of motion that can be identified as motion “signatures” that are characteristic of certain types of motion. Kinematic (or object movement) models may be constructed based on these motion signatures and the position tracking system may estimate the state of the object based on the kinematic model for the current mode of the object. Adaptive and cascaded Kalman filtering may be employed in the analysis to more accurately estimate the position and velocity of the object based on the motion pattern identified.
Owner:PINC SOLUTIONS
Variable resolution A/D converter
InactiveUS7313380B2Reduce power consumptionVariable resolutionElectric signal transmission systemsReconfigurable analogue/digital convertersBuck converterImage resolution
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method and apparatus for high speed digitized exposure
A light modulation and exposure system comprising: a light source; a light sensitive media; a two-dimensional light modulator containing a plurality of rows of light valves; means of imaging light source onto light modulator and light modulator onto light sensitive material; means of generating relative motion between image of light modulator and light sensitive material; means of shifting into the first of rows the data to be imaged onto light sensitive material and means of editing data from the first row to subsequent rows of modulator at a rate keeping the image of individual data pattern substantially stationary relative to light sensitive material until data transferred to the selected final rows; this sequence continuing until all data to be imaged has passed through light modulator. The two-dimensional light modulator may be oriented at a rotation relative to the direction of motion of the light sensitive media in a manner conducive to achieving variable resolution levels and half-tone generation.
Owner:KUBOTA MASANORI
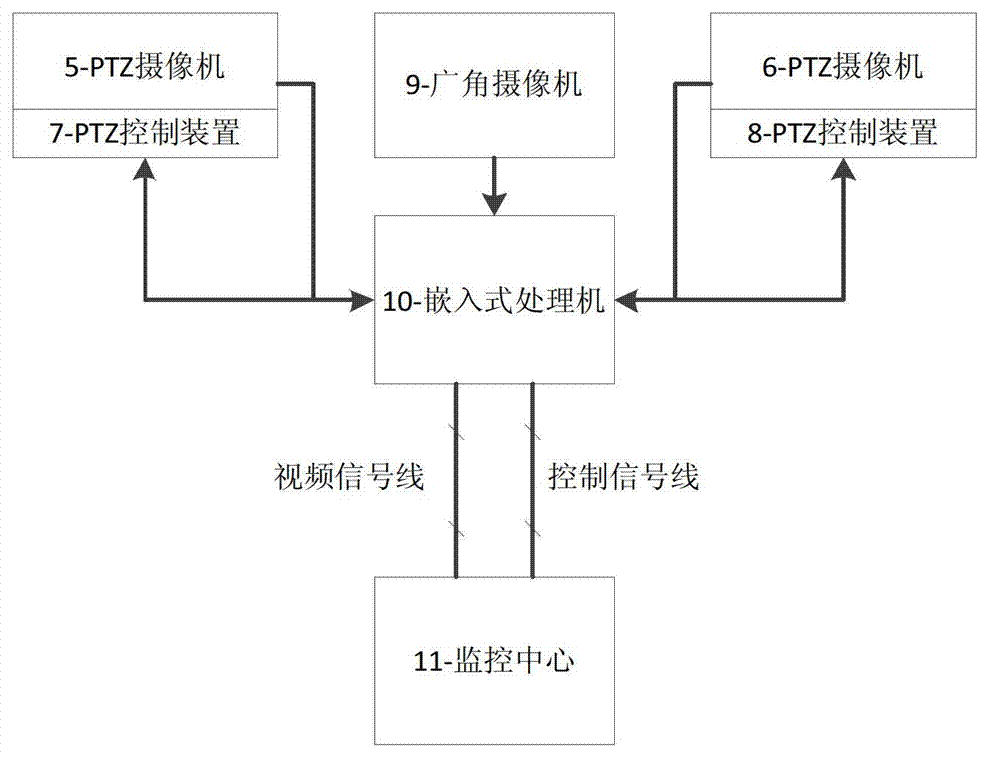
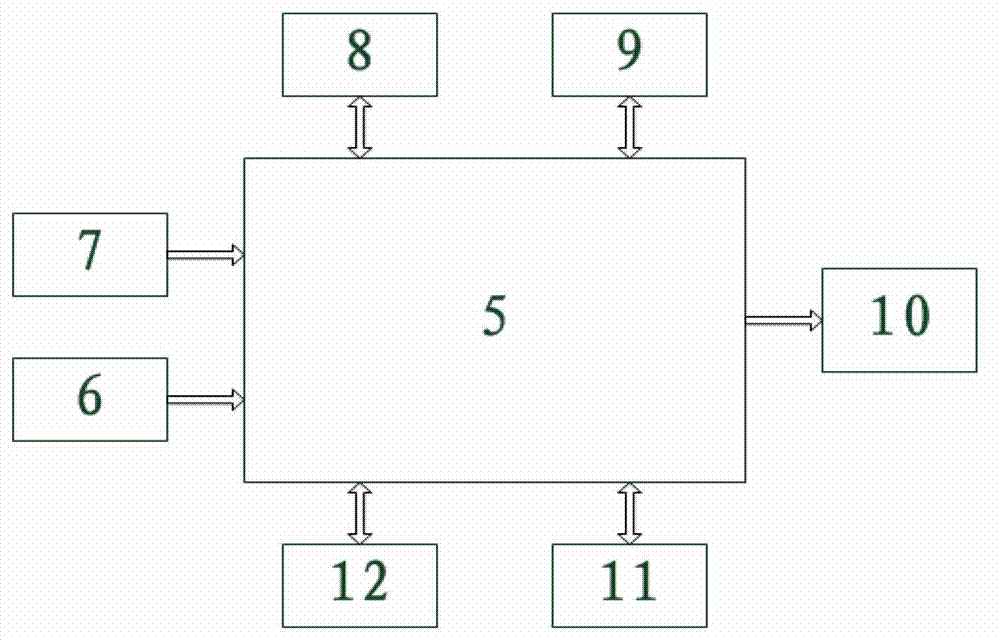
Eagle eye-imitated intelligent visual sensing node and work method thereof
InactiveCN103051887AIncrease profitEasy to customizeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsVariable resolutionVision sensor
The invention relates to an eagle eye-imitated intelligent visual sensing node which comprises a wide-angled camera, two PTZ cameras, an embedded type processor and a PTZ controller, wherein the wide-angled camera and the two PTZ cameras are positioned on a hardware platform, the wide-angled camera is arranged in the middle and fixed in position, the two PTZ cameras are arranged at two sides, the wide-angled camera and the two PTZ cameras are connected with the embedded type processor by signal wires, an acquired image is processed by the embedded type processor, the embedded type processor is used for controlling the PTZ cameras by the PTZ controller, and the two PTZ cameras can be adjusted under the control of the embedded type processor. After the eagle eye-imitated intelligent visual sensing node and a work method of the eagle eye-imitated intelligent visual sensing node are adopted, a visual range can be expanded to reach about 180 degrees, a suspicious target can be conveniently detected and positioned in a glancing way within a large range in a manner of variable resolution, and the target can be elaborately analyzed and recognized with high resolution.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
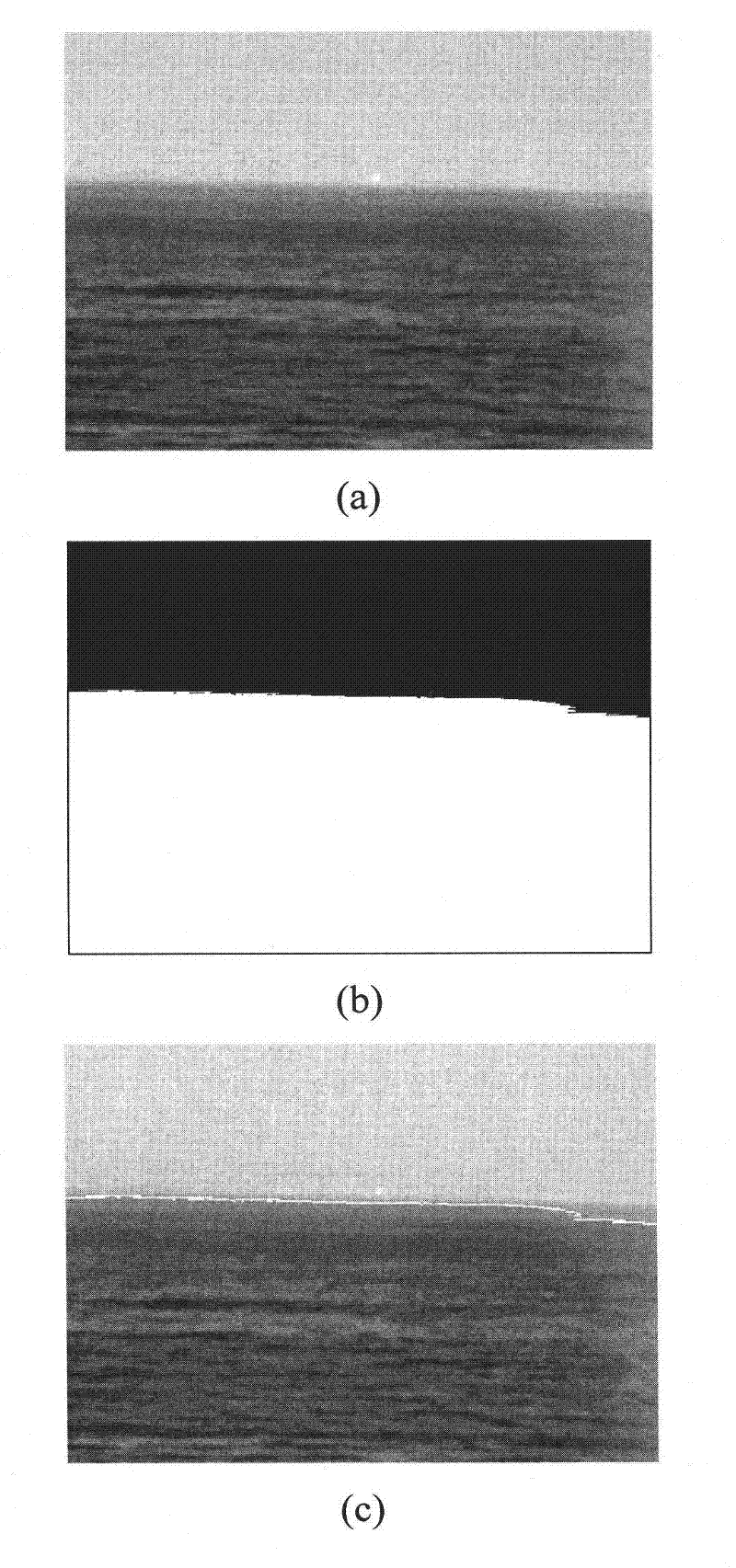
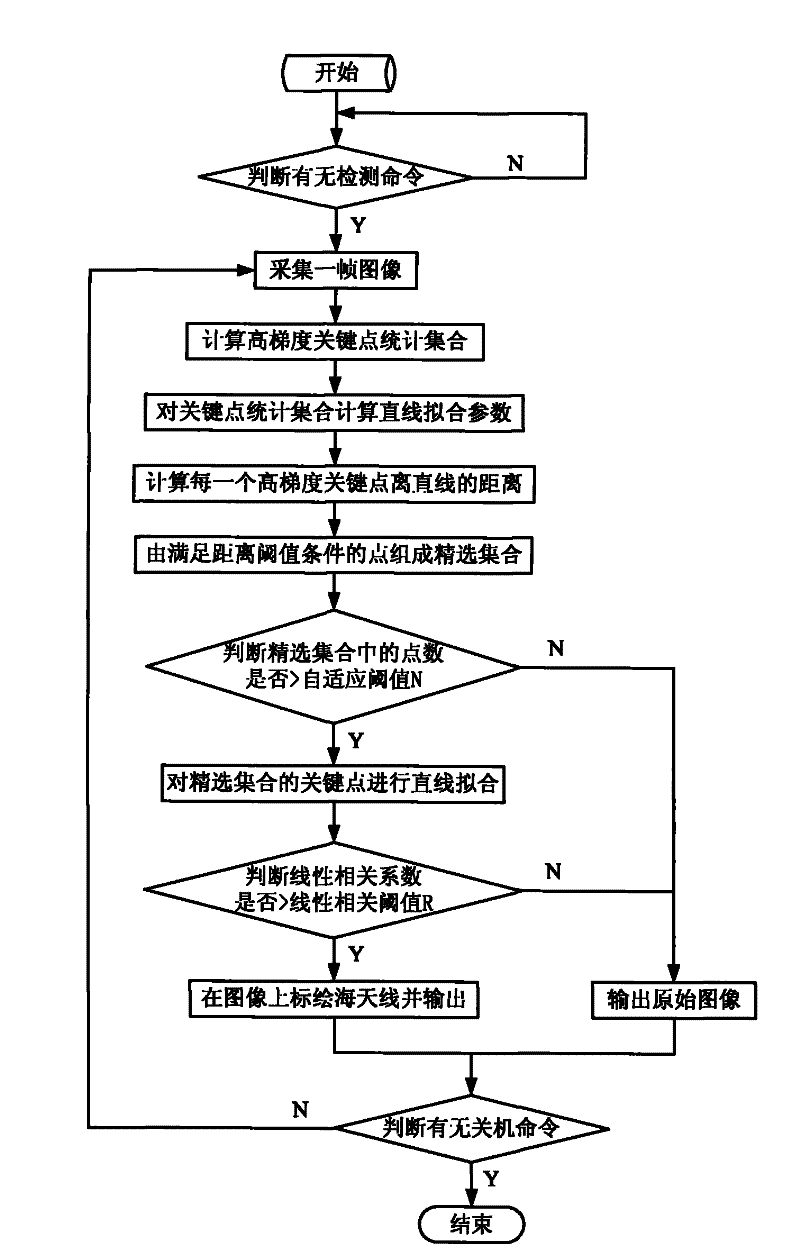
Sea antenna detection method based on high gradient key points
ActiveCN102279973AHigh precisionImprove real-time performanceImage analysisLinear correlationCrucial point
The invention discloses a sea-sky-line detection method based on high gradient key points, and the method is suitable for ocean ship object identification and positioning devices. The method is characterized in that: based on a high efficiency attention mechanism of visual information, obtaining a statistical set of high gradient key points of an image column through employing a recursion optimization algorithm and a variable resolution sampling technique, subjecting the statistical set to least squares straight line fitting, rejecting outliers which do no satisfy a distance threshold condition in the statistical set and obtaining a selected set of the high gradient key points, subjecting the selected set to least squares straight line fitting, determining a selected set of the high gradient key points which satisfies an adaptive quantity threshold and a linear correlation threshold simultaneously as sea-sky-line. A problem of effective, accurate and real-time detection of sea-sky-line in a complex sea surface environment is solved by the sea-sky-line detection method based on high gradient key points, and the method has the characteristics of strong anti-interference capability and high calculating efficiency.
Owner:CHINA NORTH IND NO 205 RES INST
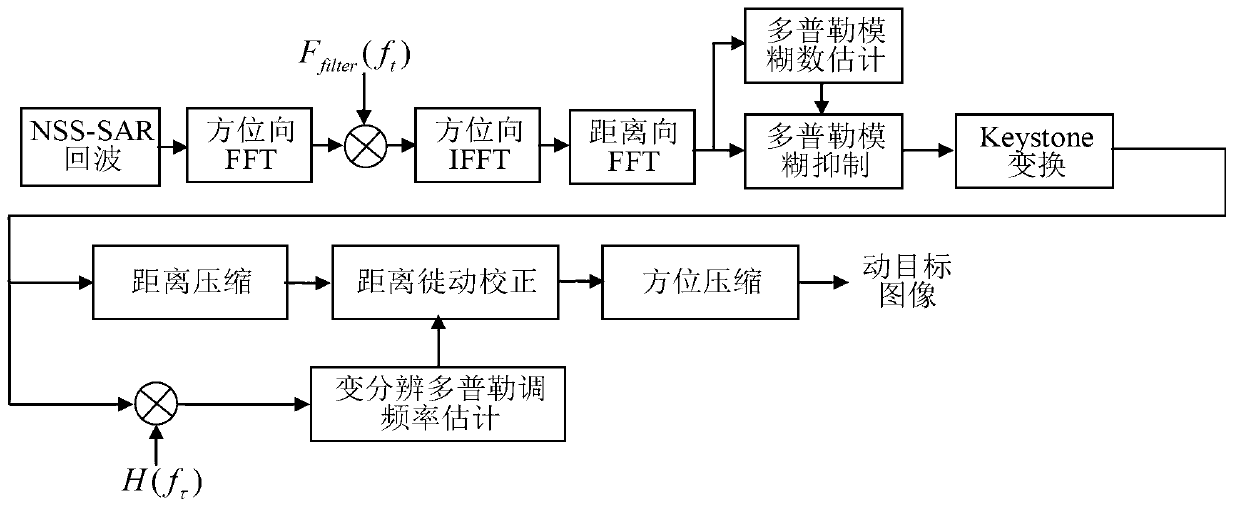
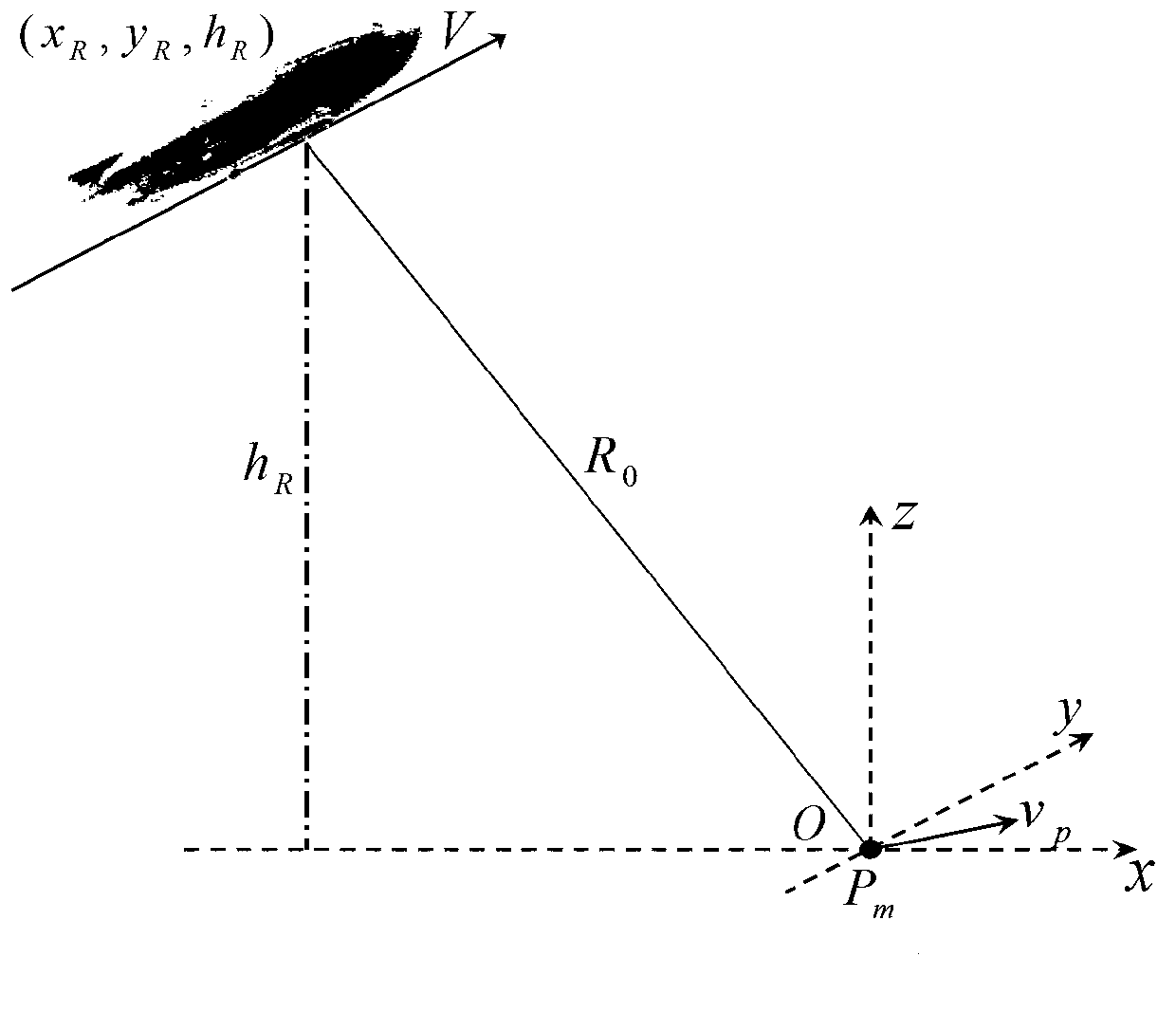
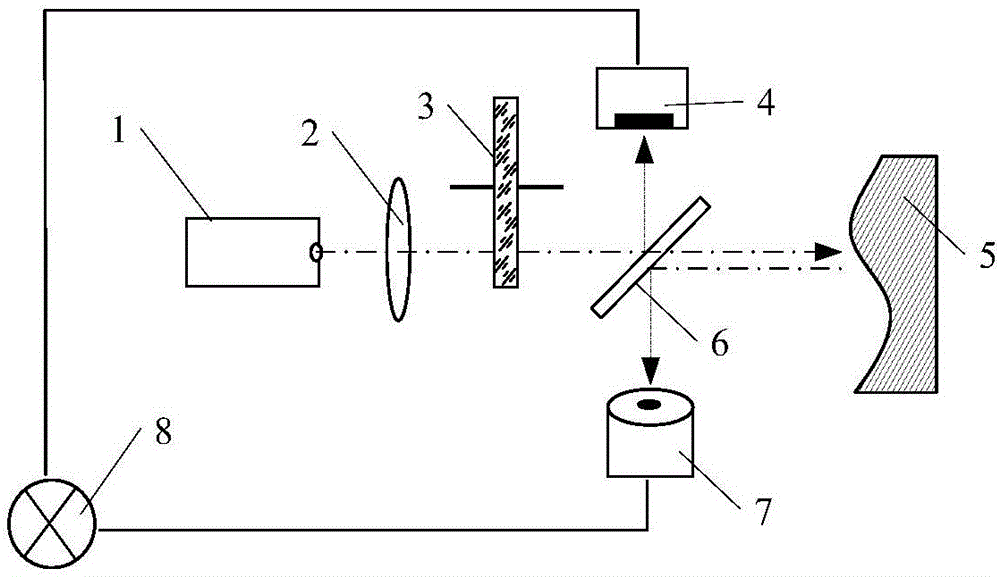
Moving target detection method and imaging method for near space slow platform SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar)
ActiveCN103278820ASolve the problem of difficult separation of dynamic and static clutterSolve the difficult problem of moving target echo distance migration correctionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture sonarEstimation methods
The invention discloses a moving target detection method and an imaging method for a near space slow platform SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar). In the detection method disclosed by the invention, the characteristics of low platform speed and smaller ground static clutter Doppler broadening of the near space slow platform SAR are utilized, and separation of a moving target from static clutter is realized by designing a Doppler filter in a Doppler domain, so that the problem of difficulty in separating dynamic and static clutters of the SAR in moving target imaging is solved. According to the imaging method disclosed by the invention, moving target echo is extracted after separation of dynamic and static clutters and moving target detection, one-order keystone conversion is combined with a variable-resolution Doppler frequency modulation estimation method, and range walk correction is completed under the condition that the speed of the moving target is unknown, so that the problem of difficulty in range walk correction of the moving target echo is solved. The methods have the advantages that rapid moving targes can be detected and imaged; and the methods are suitable for detecting and imaging slow moving targets.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method for variable resolution and error control in spoken language understanding
ActiveUS7962339B2Error minimizationLow cost-errorsSpeech recognitionSpeech synthesisSpoken languageAlgorithm
A method for variable resolution and error control in spoken language understanding (SLU) allows arranging the categories of the SLU into a hierarchy of different levels of specificity. The pre-determined hierarchy is used to identify different types of errors such as high-cost errors and low-cost errors and trade, if necessary, high cost errors for low cost errors.
Owner:VERINT AMERICAS +1
Ghost imaging method and ghost imaging system based on bionic vision mechanism
ActiveCN106646512AHigh resolution imagingFast imagingElectromagnetic wave reradiationHigh resolution imagingDetector array
The invention relates to a ghost imaging method and a ghost imaging system based on a bionic vision mechanism, and belongs to the photoelectric imaging field. A laser source, a collimating lens, a rotary frosted glass, and a spectroscope are respectively disposed on the same optical path sequentially. The laser source, the collimating lens, and the rotary frosted glass are used to generate parallel pseu-dothermal light required by the ghost imaging. The spectroscope is used to divide the pseu-dothermal light into two optical paths, and reflection light is a reference arm optical path, and transmission light is a detection arm optical path. The light intensity distribution of the reference arm optical path is received by a bionic detector array, and pseu-dothermal light source two-dimensional light intensity distribution information is completed. After the light of the detection arm is irradiated on a target, the light is reflected, and then the light is reflected by the spectroscope, and the reflection light total light intensity is received by a barrel detector, and the target reflection light total light intensity information acquisition is completed. A related arithmetic unit is used for the operation of the information acquired by the bionic detector array and the barrel detector. The bionic variable resolution detector array is adopted, and large visual field, high resolution imaging and fast imaging are realized at the same time.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
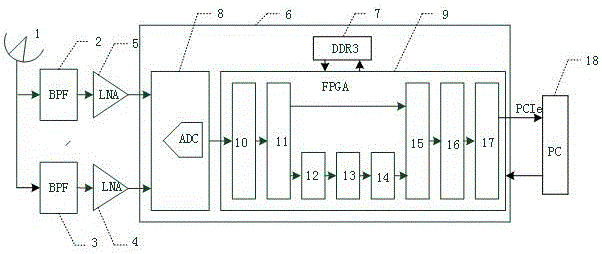
Solar radio burst variable resolution spectrum device based on high speed AD acquisition card and method thereof
The invention discloses a solar radio burst spectrum device based on a high speed AD acquisition card to analyze and study solar radio burst at different time and frequency resolutions. The system comprises a parabolic antenna, a low noise amplifier, the high-speed AD acquisition card, a computer, a high-speed solid state hard disk, c language processing software, FPGA internal threshold judgment software, Matlab processing software and labview processing software. The device amplifies a solar radio signal and sends the signal to the FPGA in AD conversion digital quantity. The sum of the power spectrum is acquired. When the sum is greater than a set threshold value, solar radio burst occurs, and the system intensively collects data. When the sum is less than the threshold value, solar radio burst does not occur, and the system sparsely collects data. The data are uploaded to a computer through a PCIe interface and are stored in the solid-state hard disk. At night, FFT operation of different length is carried out on the stored data to acquire a solar radio burst intensity graph at different time and frequency resolutions.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
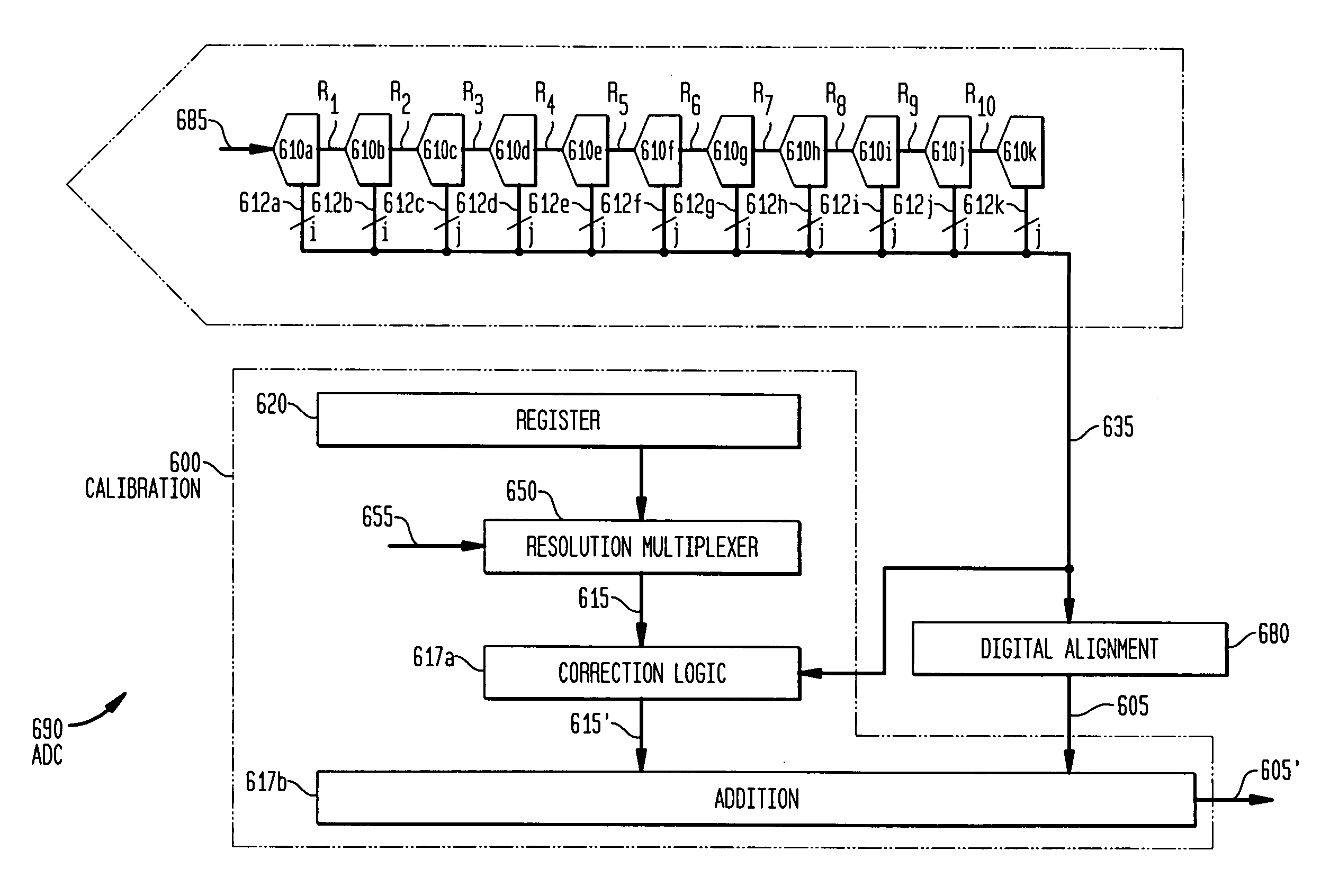
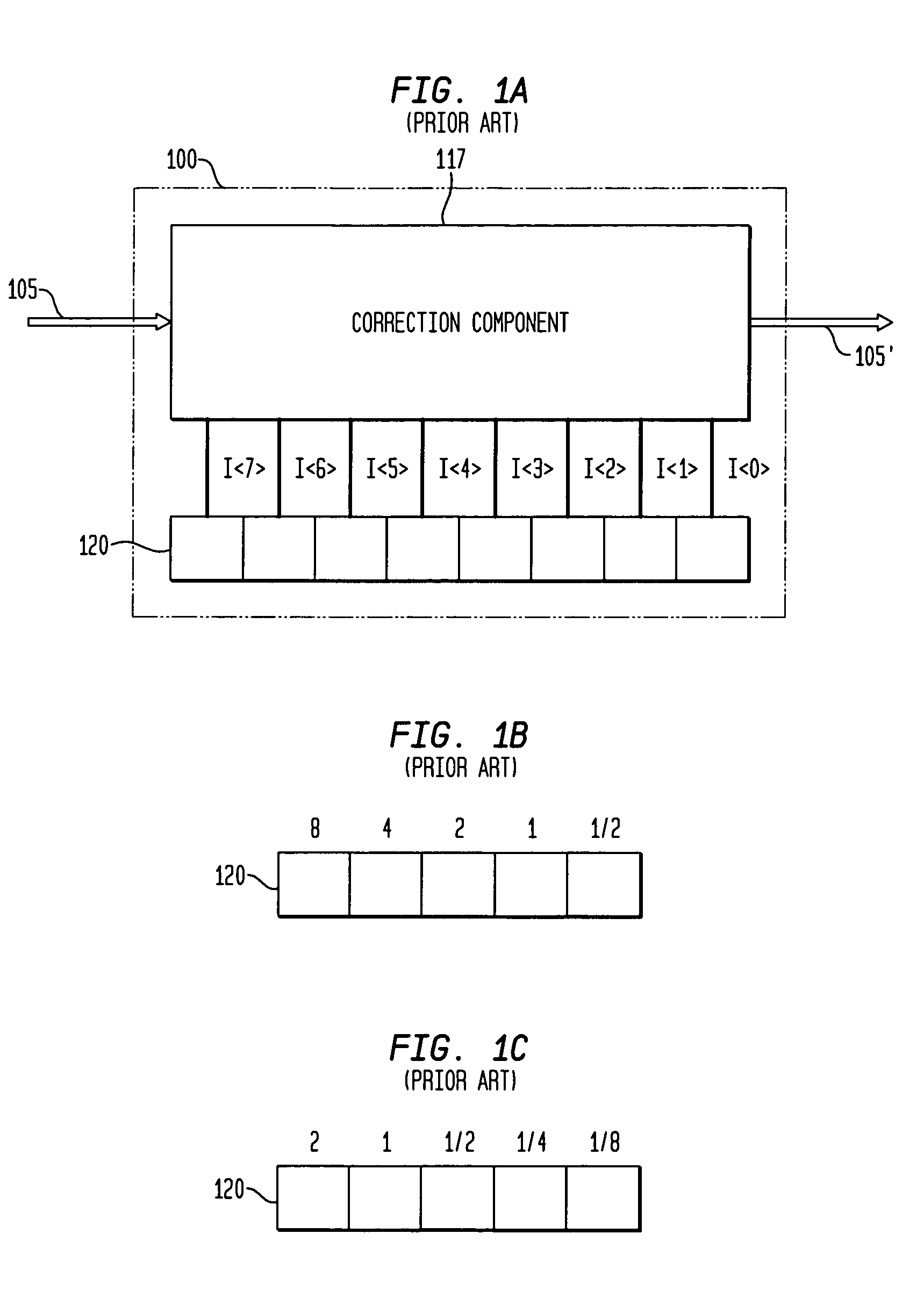
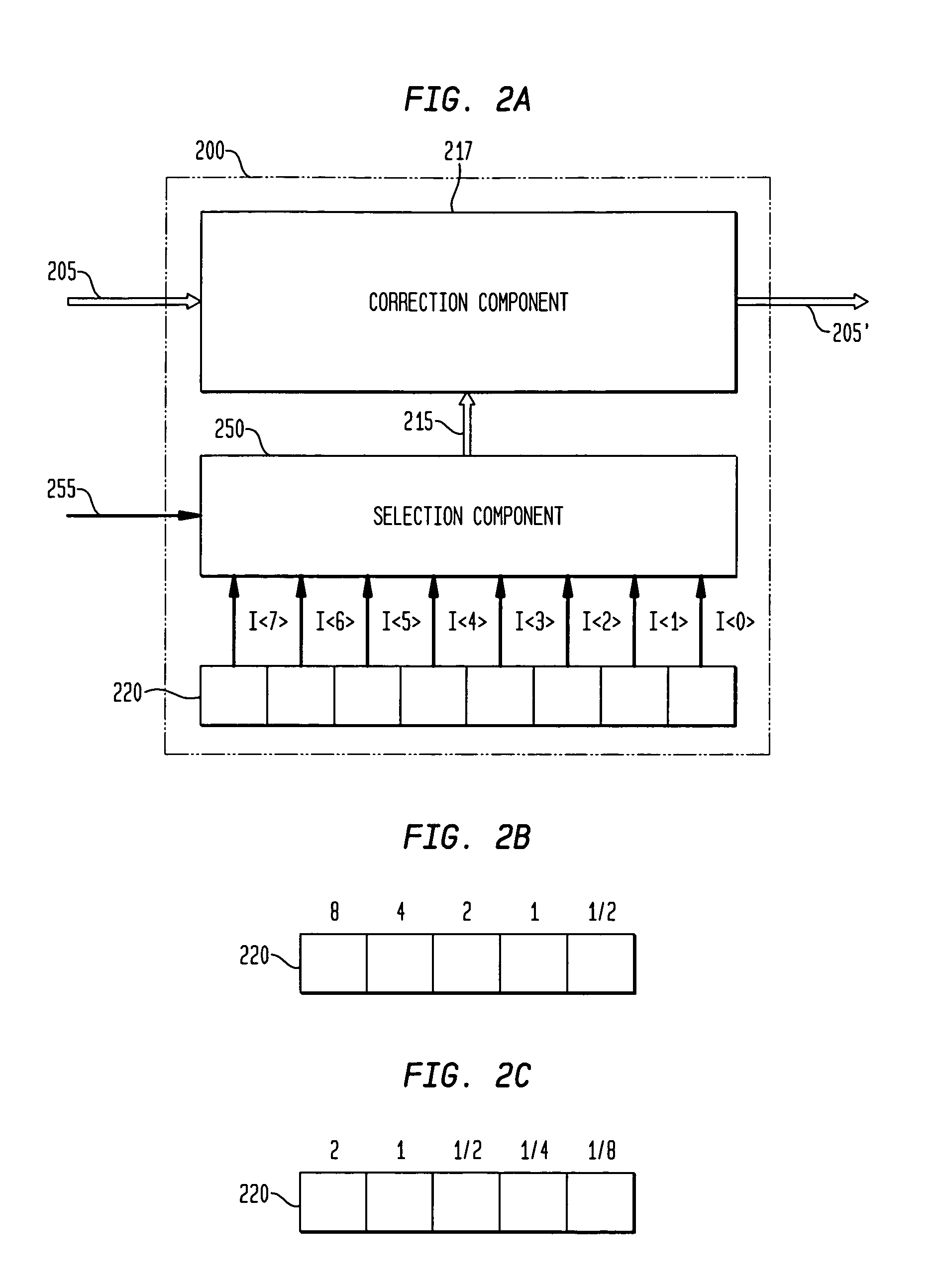
Variable resolution digital calibration
ActiveUS6975950B2Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsImage resolutionMultiplexer
Methods and apparatus for calibrating one or more signals of an electronic device are provided. Calibration coefficients are stored in a memory, such as a fuse bank, to be applied to correct the one or more signals. A selection multiplexer is provided, the selection multiplexer capable of assigning one of a number of bit weight configurations to the calibration coefficients to set a desired range and resolution for calibration information applied to the one or more signals of the electronic device.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com