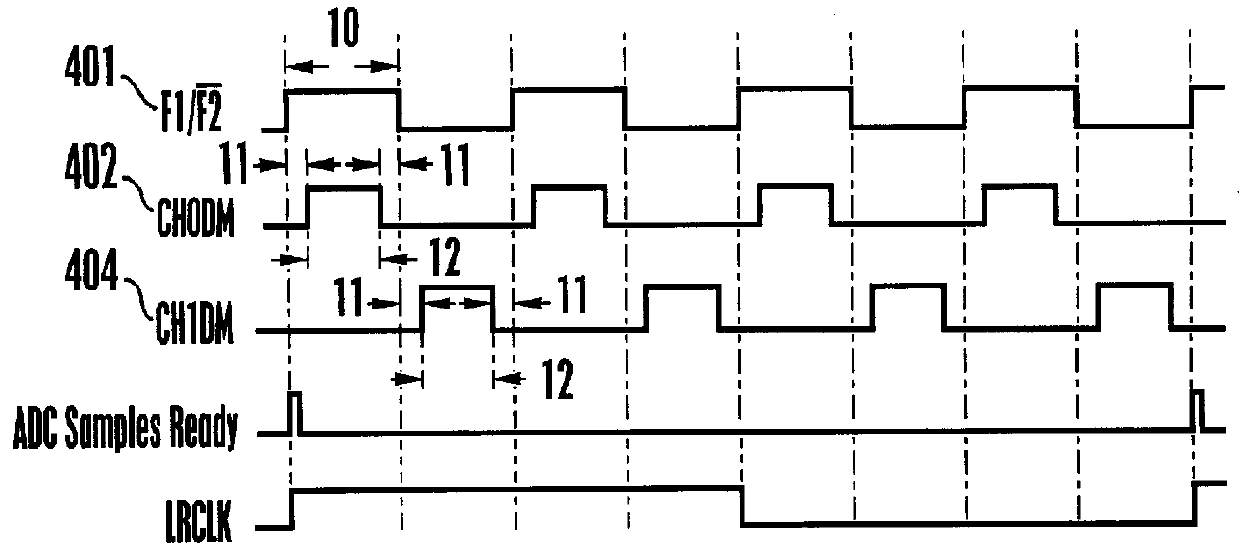
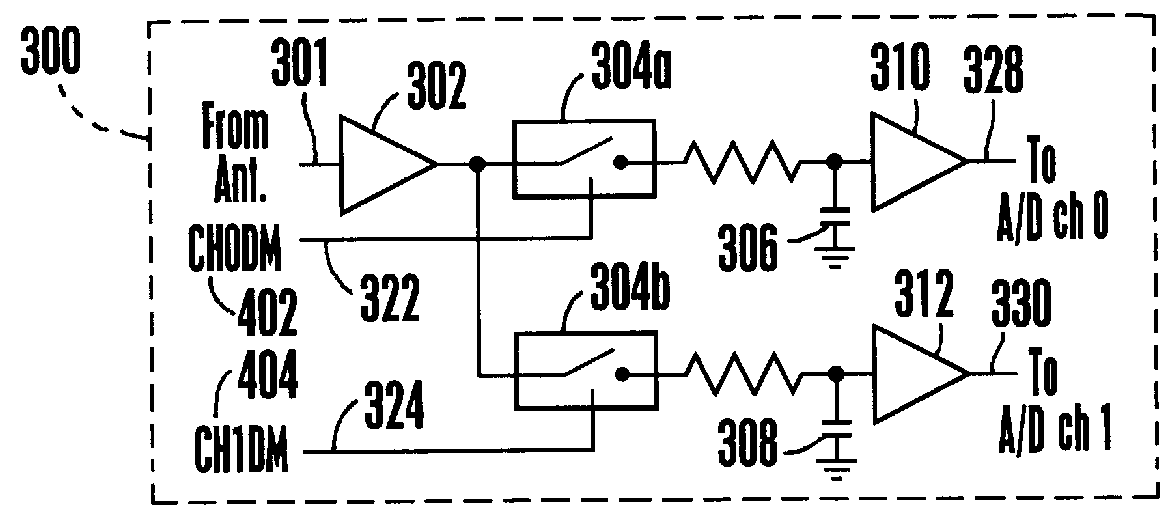
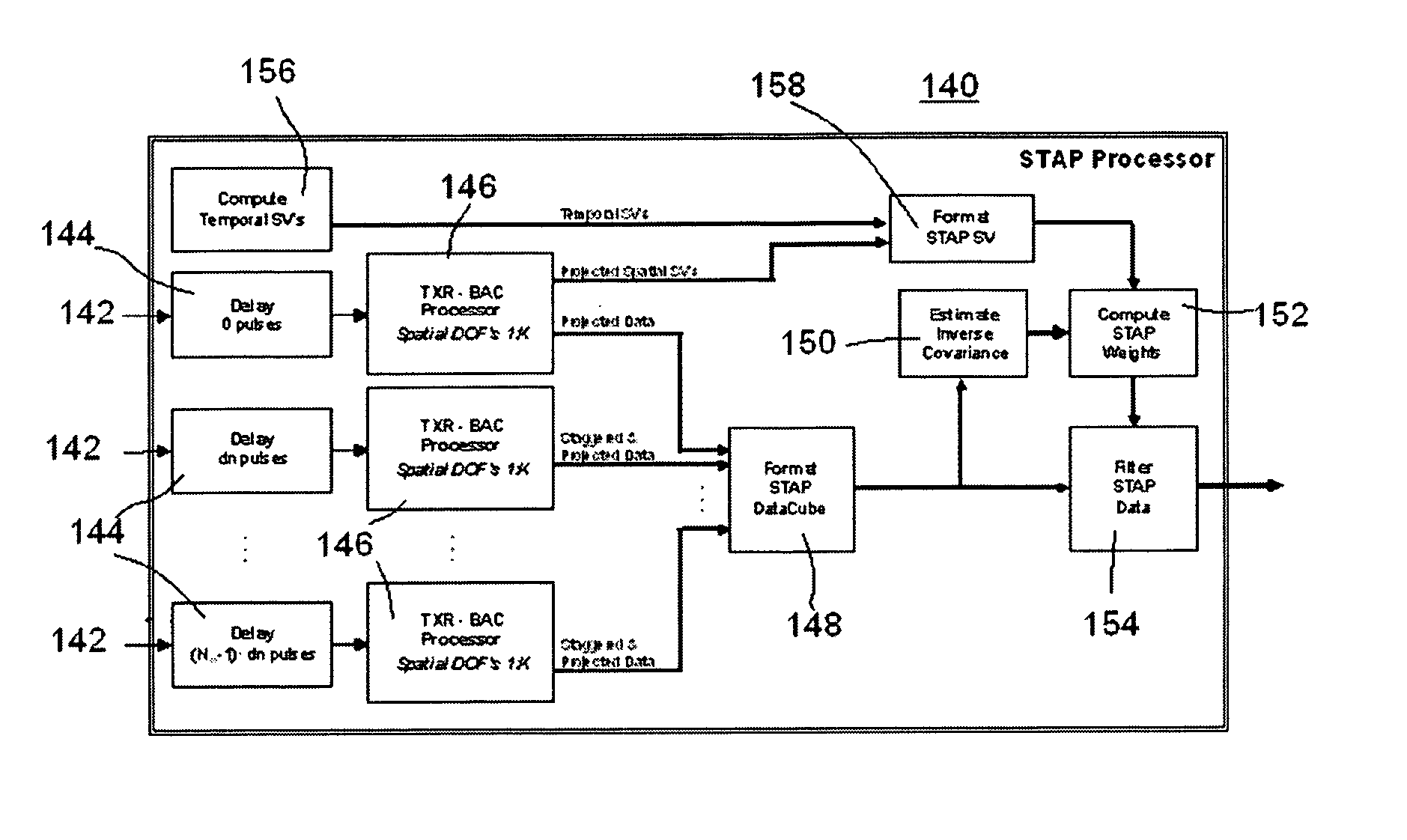
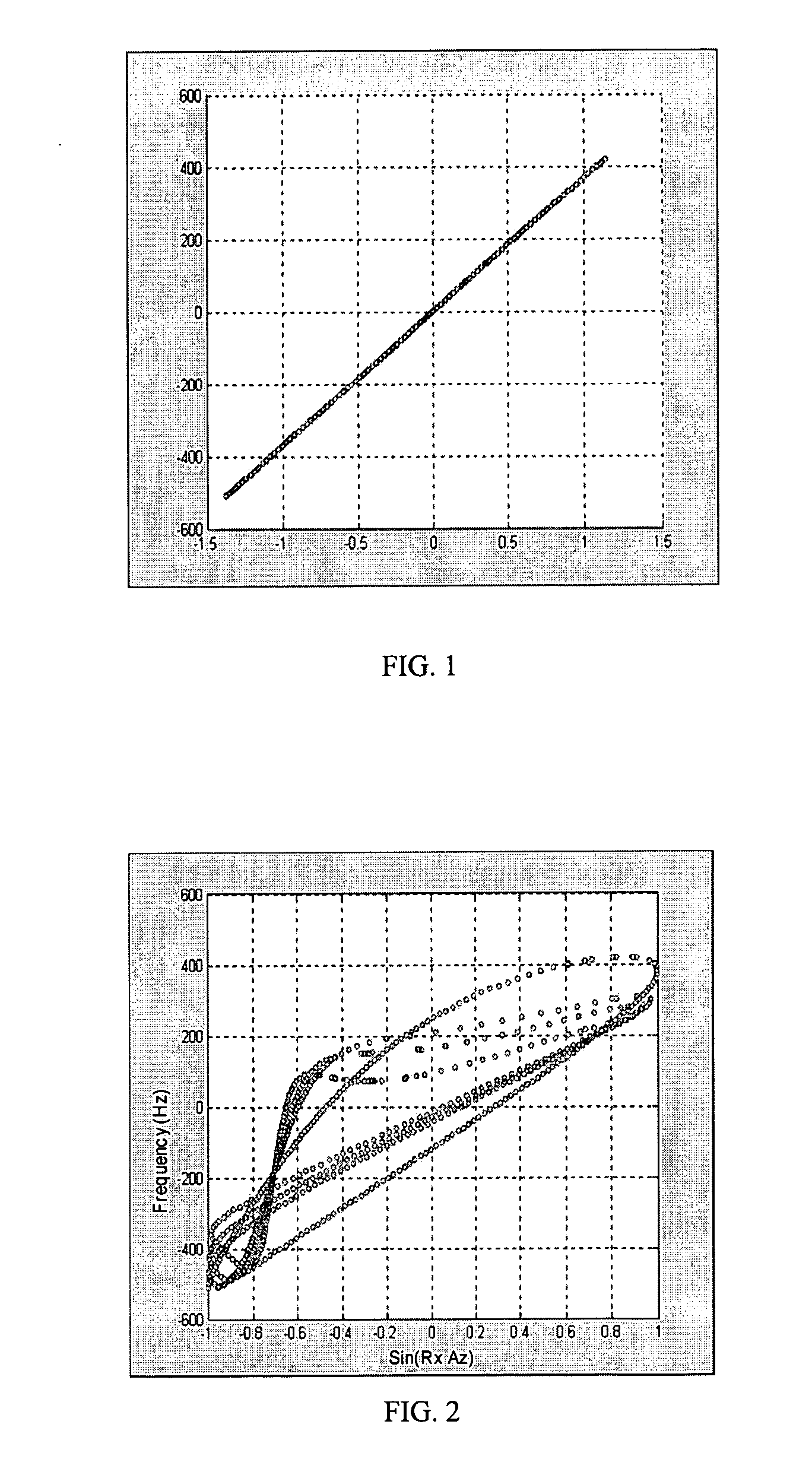
Patents
Literature
1043 results about "Clutter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
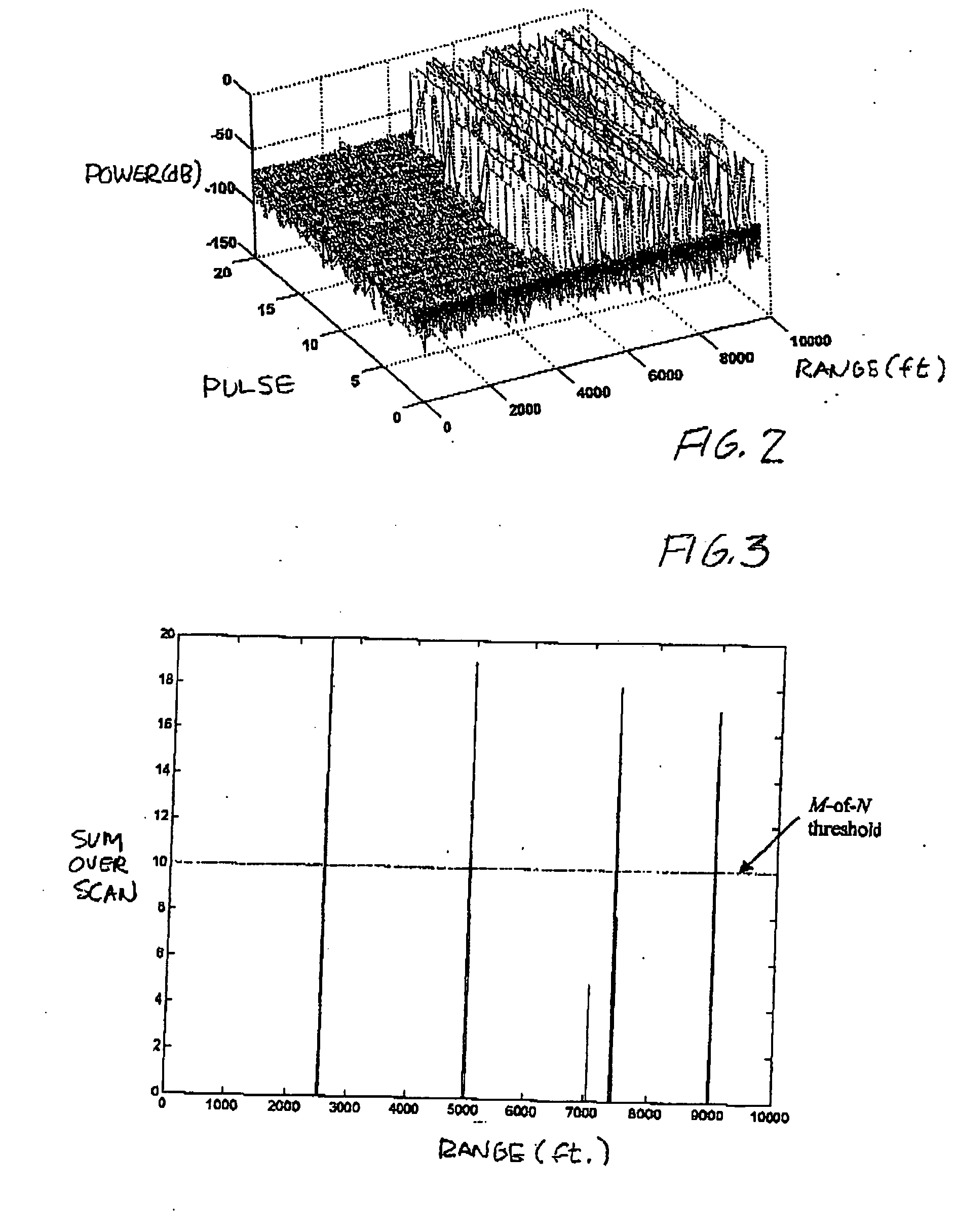
Clutter is a term used for unwanted echoes in electronic systems, particularly in reference to radars. Such echoes are typically returned from ground, sea, rain, animals/insects, chaff and atmospheric turbulences, and can cause serious performance issues with radar systems.
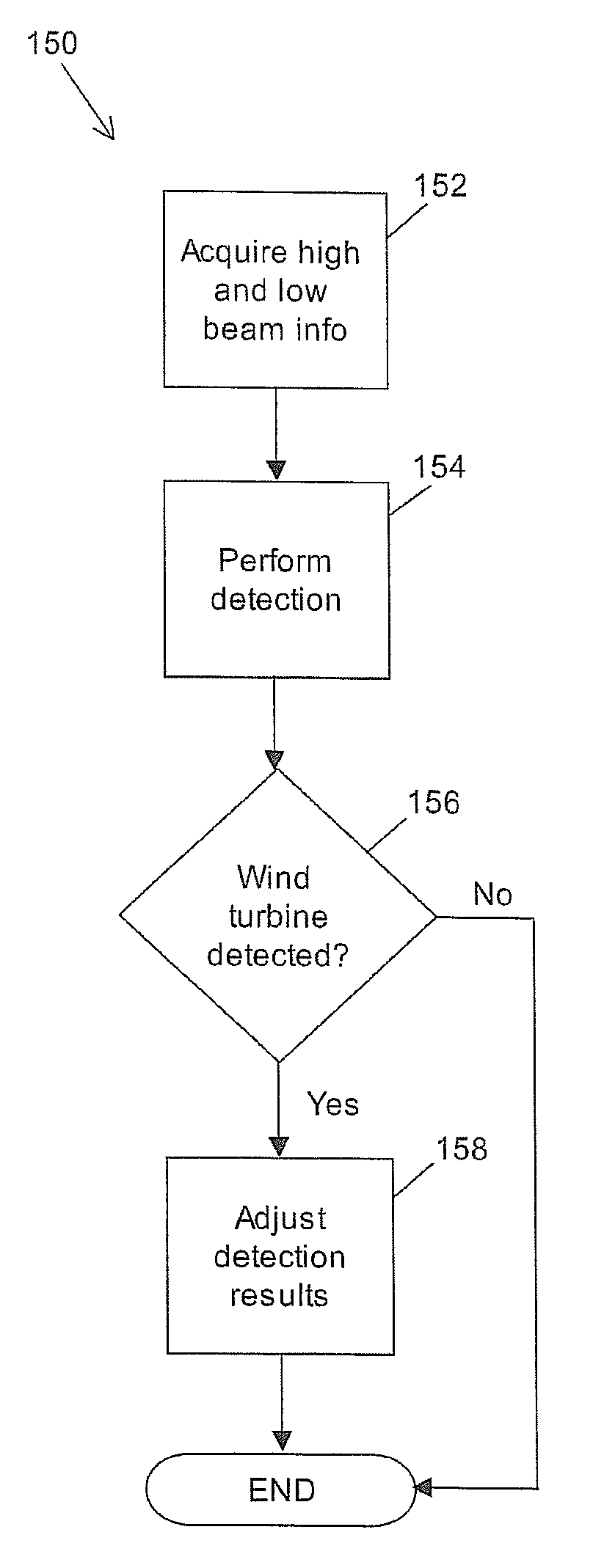
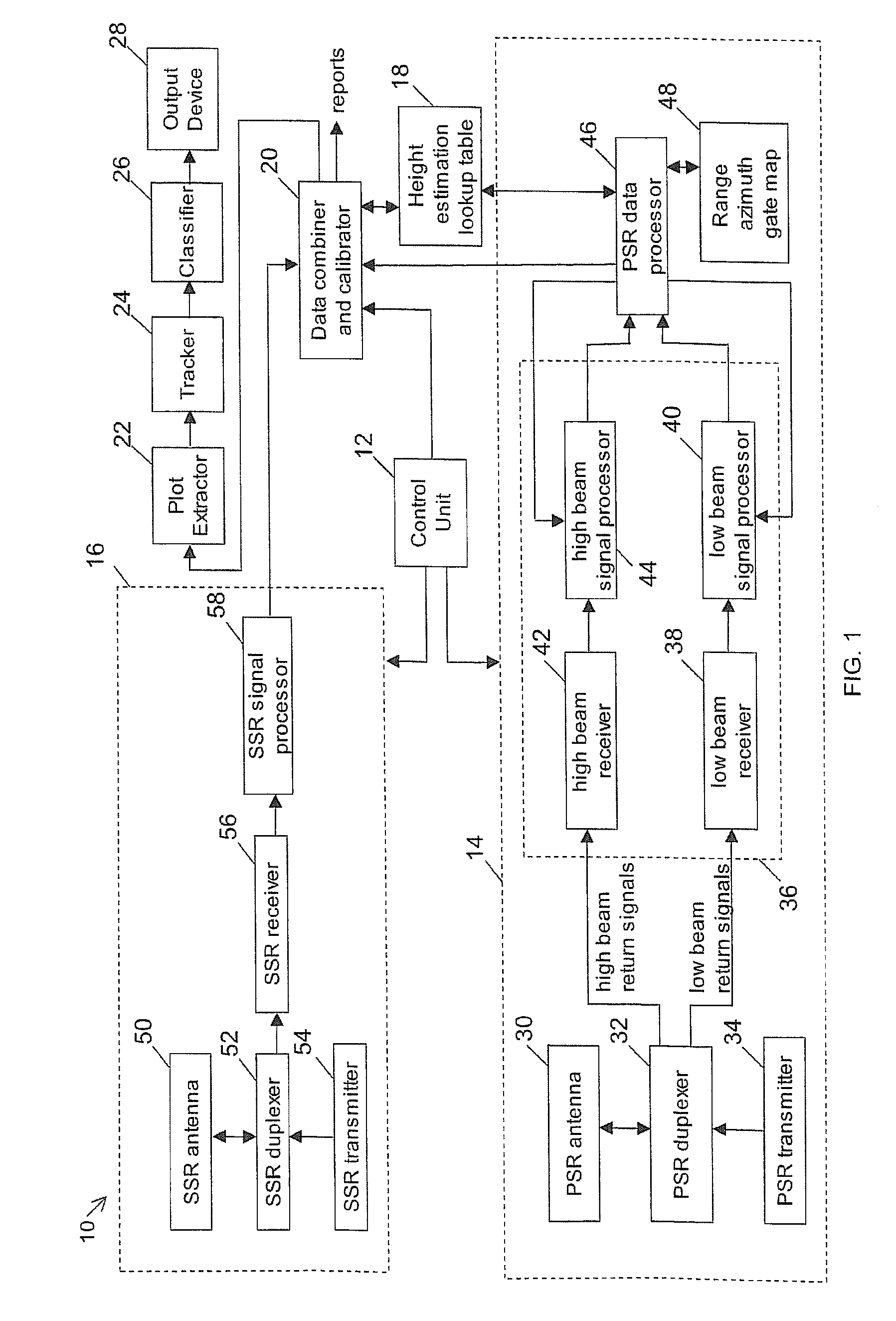
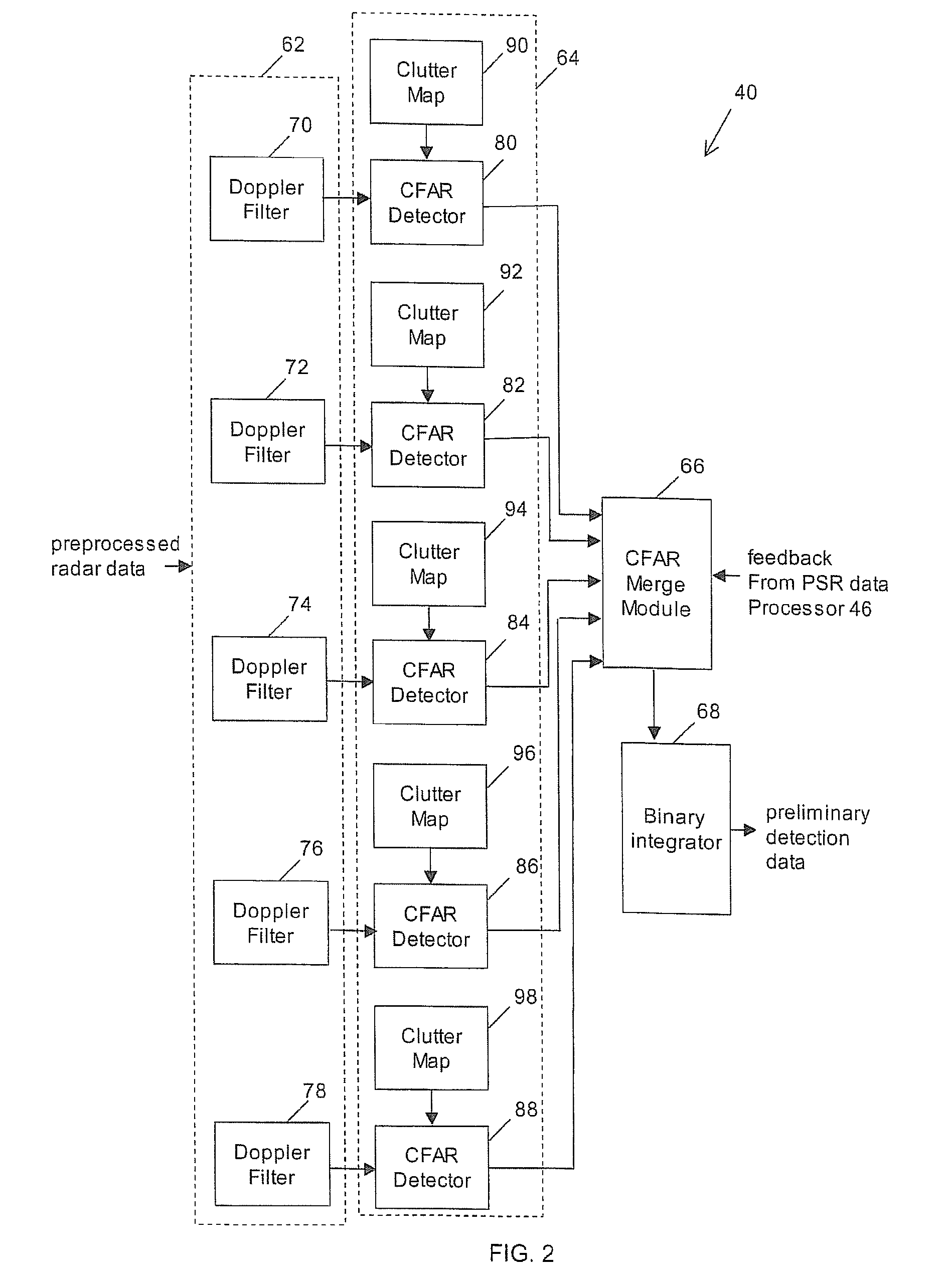
Dual beam radar system
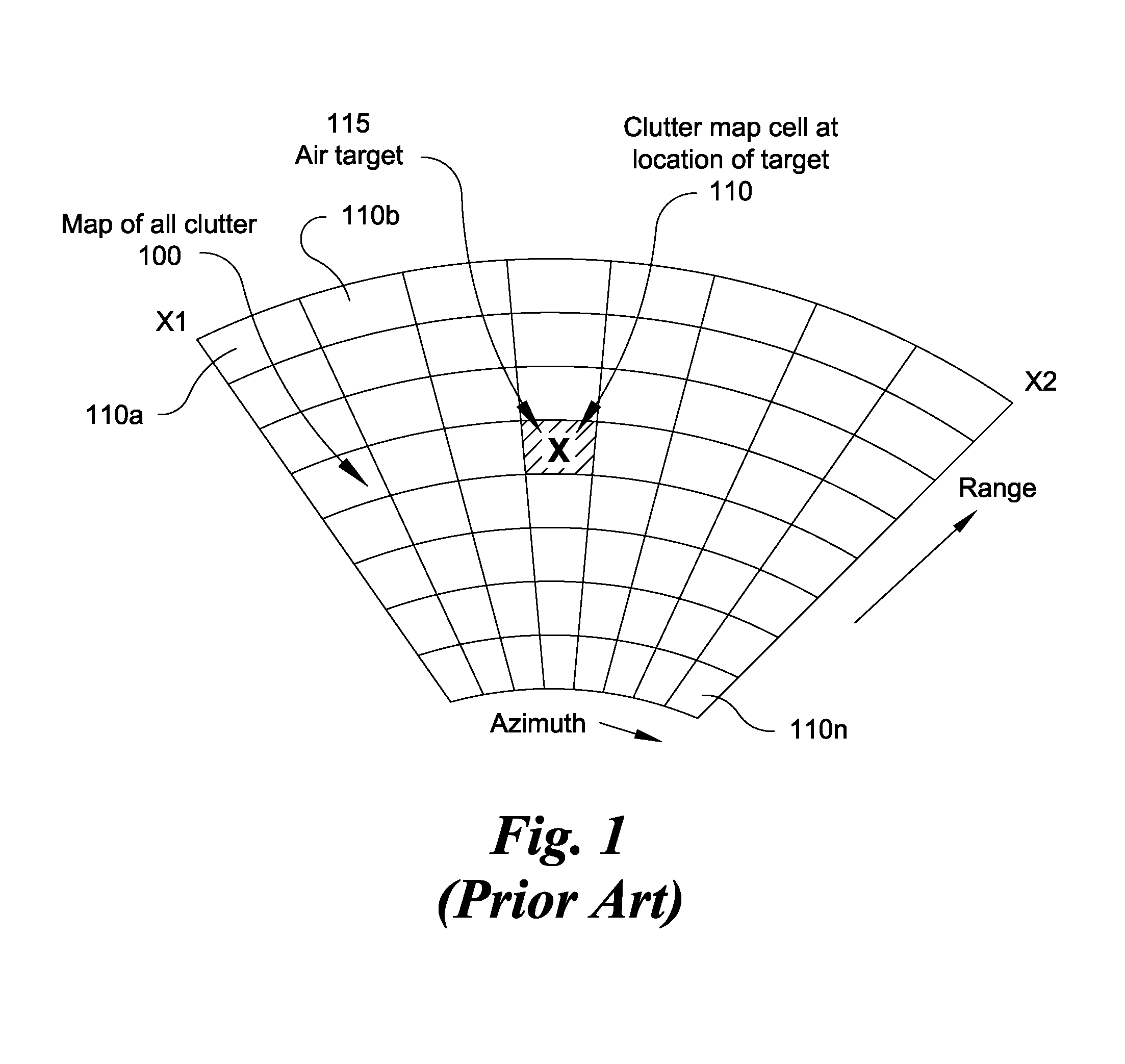
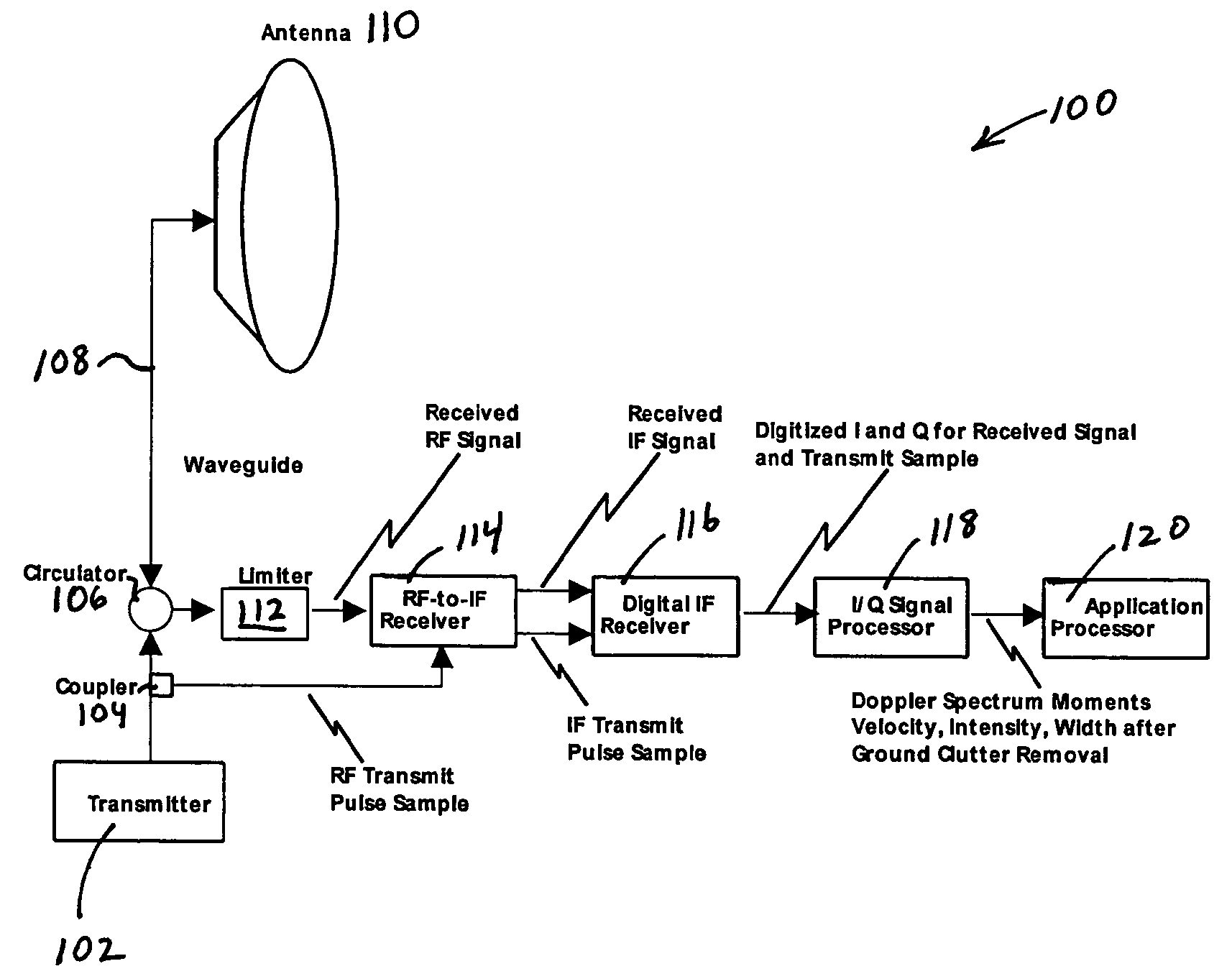
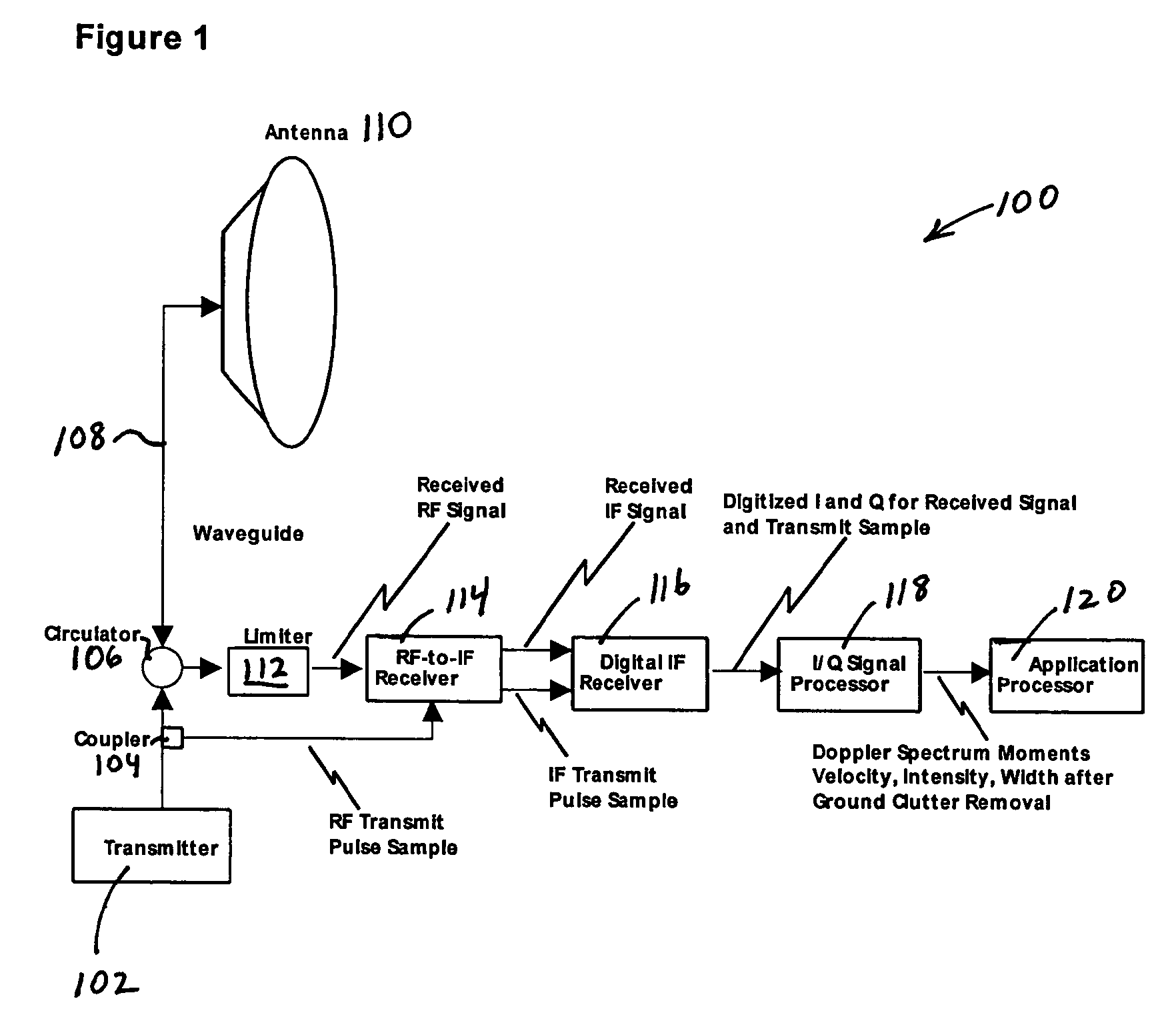
Various embodiments are described herein relating to a radar system and associated methods for detecting targets in the presence of certain types of clutter. The radar system generally comprises hardware operatively configured to obtain first and second sets of radar return signals concurrently, first circuitry operatively configured to detect targets in the first and second sets of radar return signals, and second circuitry operatively configured to identify detected targets due to clutter.
Owner:RAYTHEON CANADA LTD
Method and apparatus for rejecting rain clutter in a radar system
InactiveUS6127965ADue to rain clutter are dramatically reducedReduces false alarmsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPatch arrayRadar systems
A method and apparatus for detecting the presence of objects in a vehicle operator's blind spots. The apparatus comprises a side-facing Doppler radar system using continuous wave (CW) transmission with frequency modulation (FM) operation from a frequency modulation switching technique. The radar system determines the presence, range and closing rate of detected targets. The radar system detects targets even when operated in adverse weather conditions and will not generate false warnings due to rain clutter caused by wet roads and other wet surroundings. The radar system uses ranging techniques to reject false targets that are detected outside of a predetermined target detection zone. In accordance with the present invention, the radar system indicates that a target is detected if and only if any part of the target is within the detection zone and it: (1) remains in front of the antenna for at least TH1 seconds; (2) is at a range between Rangemin and Rangemax; and (3) is moving faster than Closing-Speedmin relative to the antenna. By rejecting targets that are closer than Rangemin feet to the antenna, false alarms due to rain clutter are dramatically reduced. Also, by rejecting targets that are further than Rangemax feet from the antenna, the radar system reduces false alarms caused by wet foliage and other wet "non-road" surroundings. In one embodiment, the radar system uses a patch array antenna oriented into a diamond-shape configuration to effectively create a natural linear amplitude taper that aids in rejecting clutter caused by wet road surfaces.
Owner:BENDIX COMML VEHICLE SYST LLC
Method and apparatus for performing bistatic radar functions
InactiveUS20050237236A1Eliminate residual degree of freedomSmall sizeRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSpacetimeLinearization
A bistatic radar system having a transmitter that generates unique signals at spatially independent transmitter degrees of freedom and a receiver that filters the signal at each receiver degree of freedom into a group of signals identical in number to the number of transmitter degrees of freedom. The receiver formats the filtered signals into a 2-dimensional array of elements. The receiver rotates the array so that the new axes are aligned with the Doppler gradient. The data is then re-sampled and projected to linearize the clutter signal. The receiver may be integrated with a broad class of adaptive and non-adaptive clutter mitigation approaches such as electronic clutter tuning and projected bistatic space-time adaptive processing, or STAP.
Owner:BUDIC ROBERT D
Radar sensing of vehicle occupancy
ActiveUS20160200276A1Pedestrian/occupant safety arrangementDiagnostic recording/measuringRadar systemsAirbag
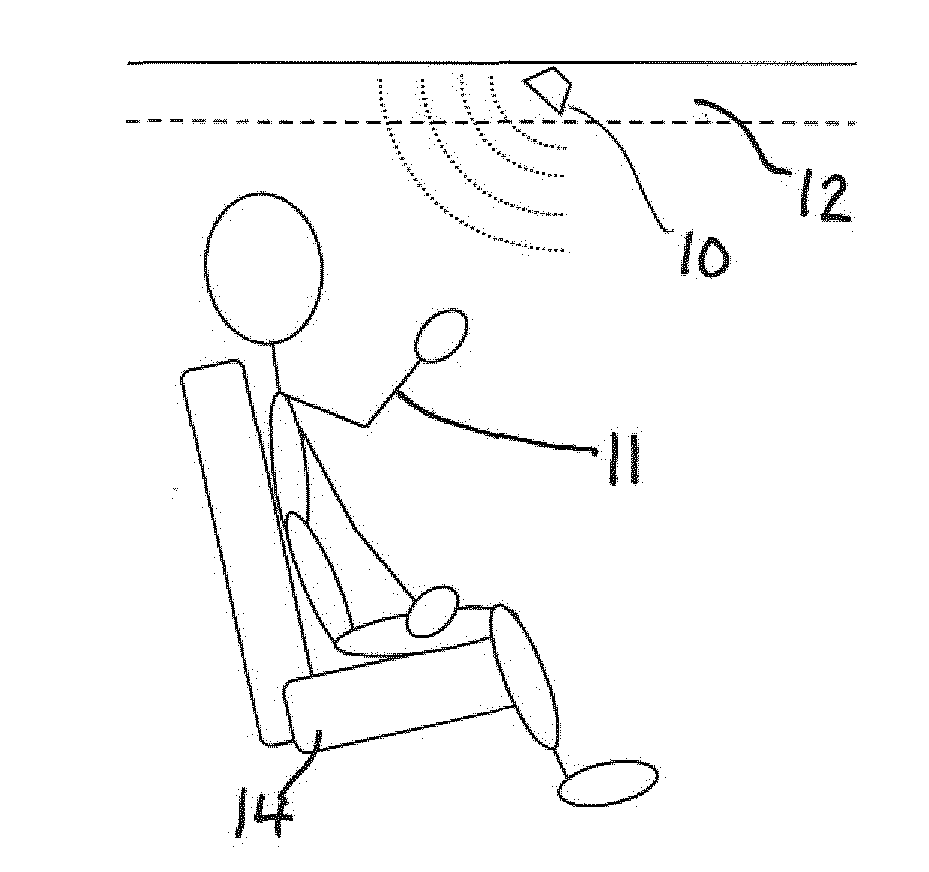
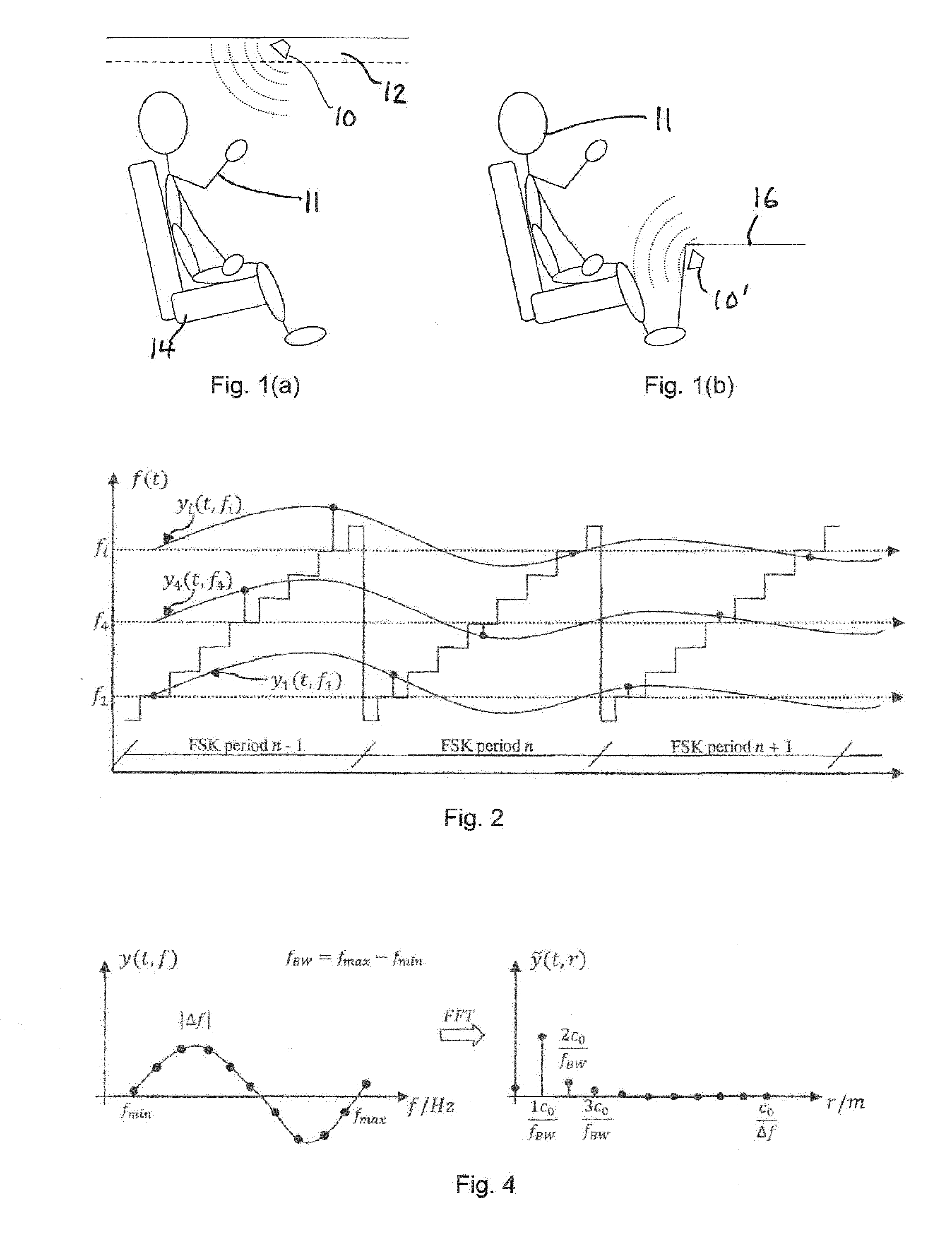
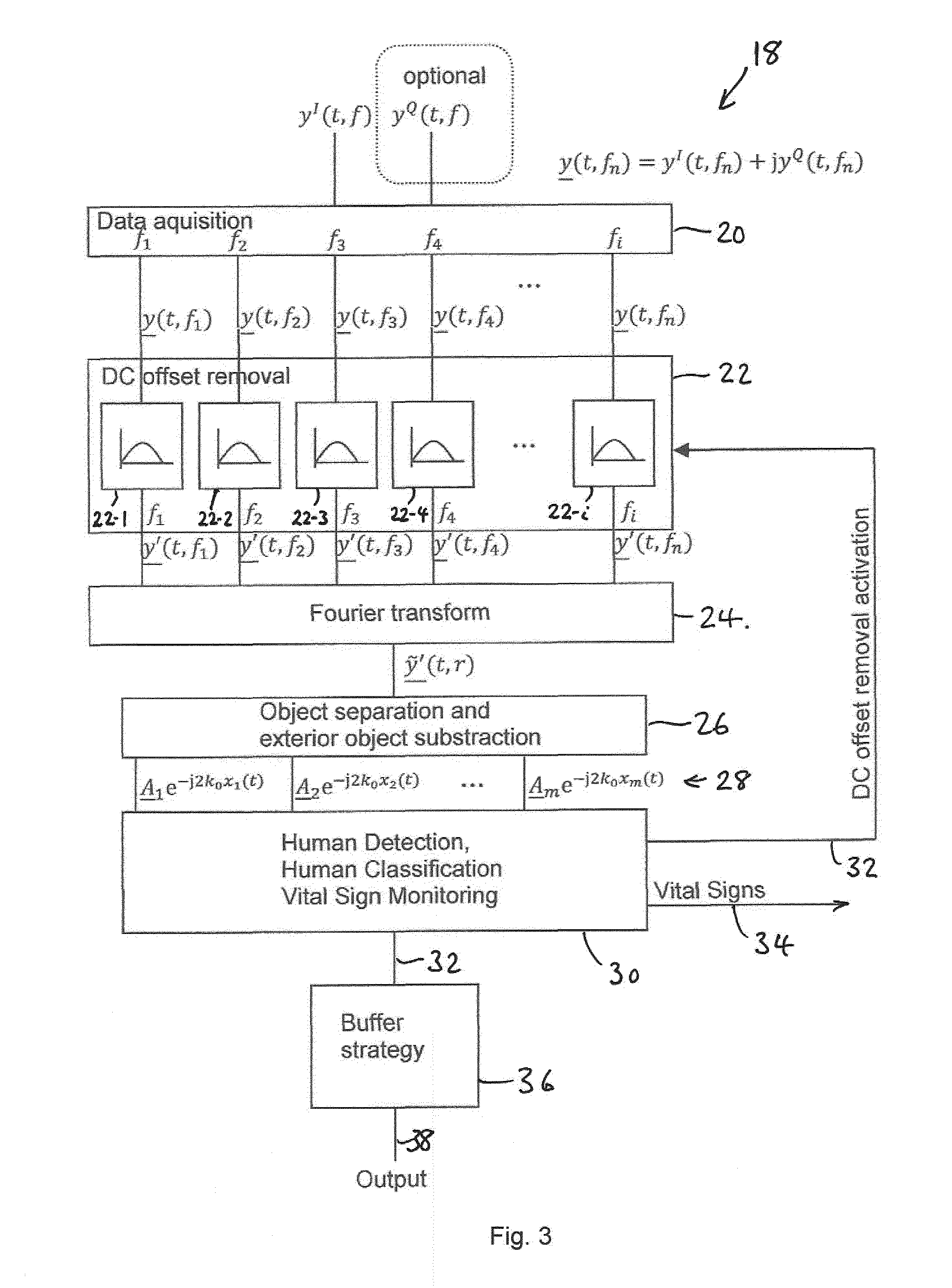
A method for sensing occupancy status within an automotive vehicle uses a radar sensor system, the radar sensor system comprising an antenna system, at least one sensor (10) and processing circuitry (18). The method comprises illuminating, using the antenna system, at least one occupiable position within the vehicle with continuous wave (CW signals), the CW signals being frequency modulated in time. At least one sensor signal (a) reflected as a result of the CW signals, is received using at least one sensor (10) the at least one sensor (10) defining a plurality of receive channels (1 . . . i), each channel having a different frequency (f1 . . . fi). Processing circuitry (18) is operable for applying, for each receive channel (1 . . . i), DC offset removal to the corresponding sensor signal (a) to generate a modified signal (b); and generating, based on the modified signals (b) one or more occupancy status signals (34, 38), the occupancy status signal indicating a property related to said at least one occupiable position. A system for carrying out the method is also disclosed. The techniques provide for in-vehicle occupant detection and classification (airbag suppression), for passenger presence detection and passenger's vital sign monitoring and for seat-belt reminder functionality (SBR). The radar system may consist of one or two (or four) outputs (I / Q) per channel. The received signal may be mixed down with a single channel demodulator or an I / Q demodulator into the baseband. An advanced signal processing including an auto calibration routine and clutter removal may be used to detect occupants and their vital sign (breathing and heart beat) and to determine their distance to the radar system.
Owner:IEE INT ELECTRONICS & ENG SA
Moving target detection imaging method of dual-channel frequency modulation continuous wave SAR system
ActiveCN103744068AEfficient detectionAvoid splittingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPattern recognitionRadar systems
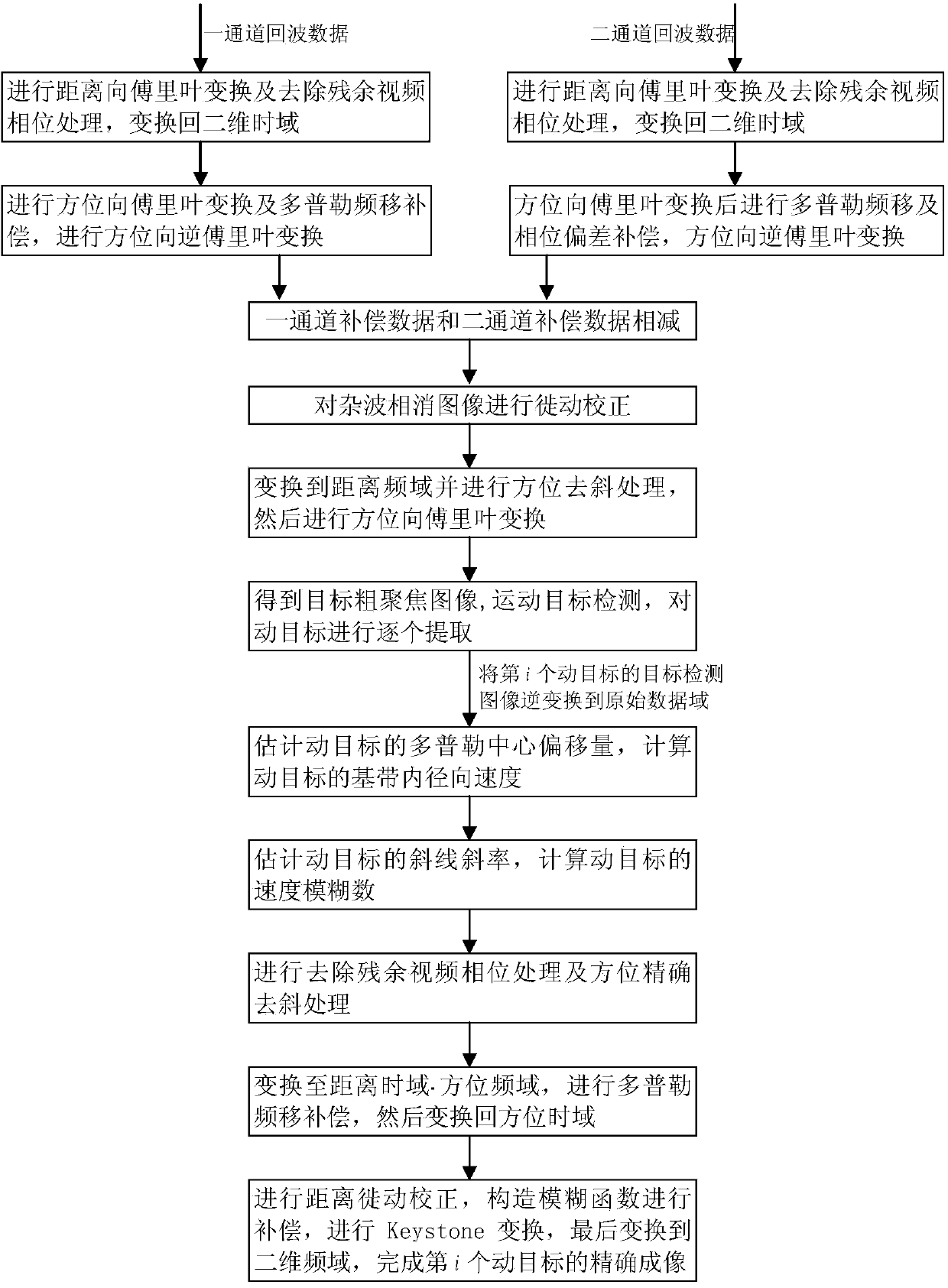
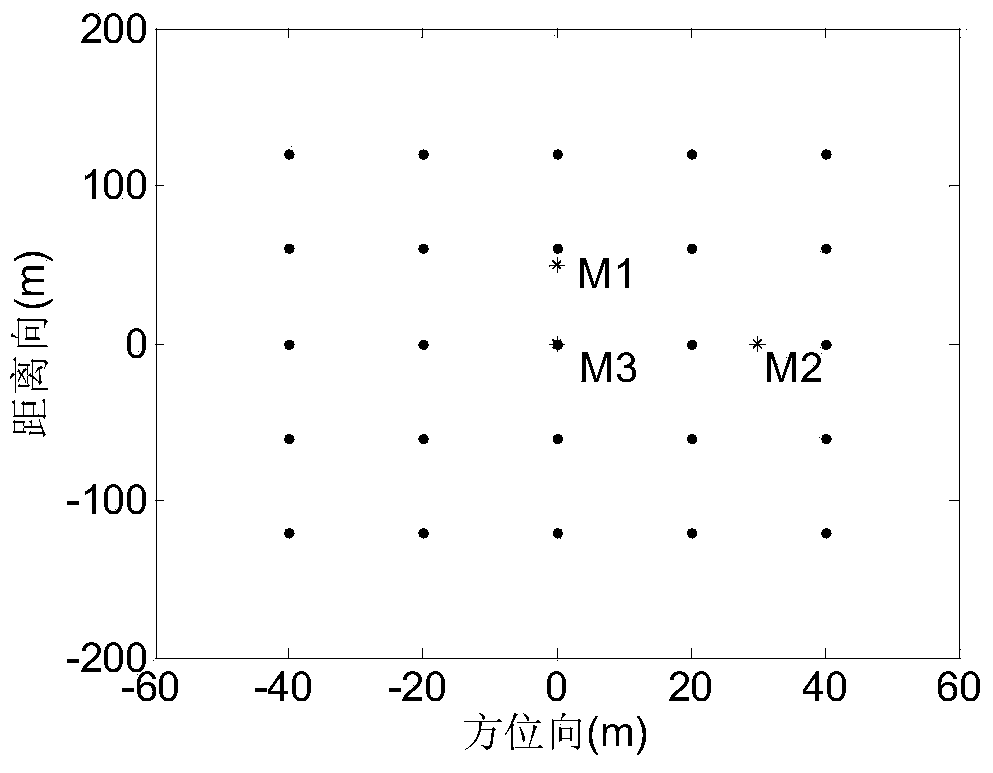
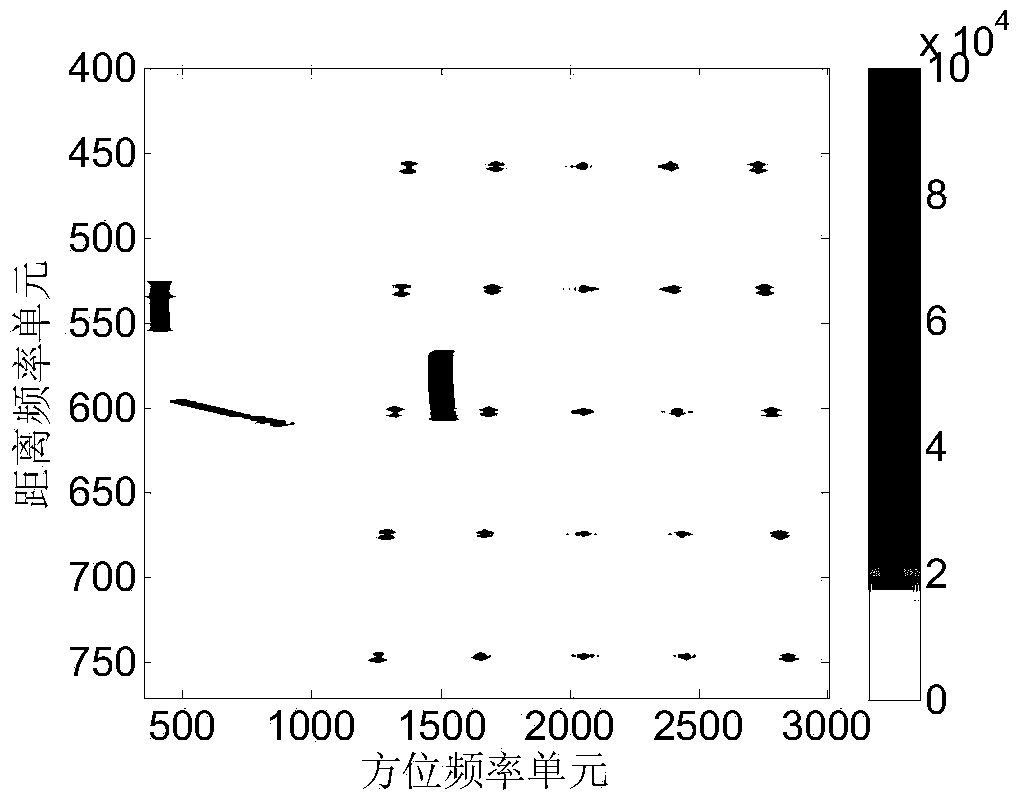
A moving target detection imaging method of a dual-channel frequency modulation continuous wave SAR system comprises the steps of recording echo data by a radar system, performing residual video phase removing processing on the echo data, performing Doppler frequency shift compensation on the data, performing phase deviation compensation on two-channel conversion data, and performing subtraction processing on the two-channel data; performing migration correction and direction dechirping processing on an image with clutter cancellation to realize the rough imaging of a target, and detecting the moving target and extracting one by one; performing inverse transformation on the extracted targets to an original data domain, estimating motion parameters to construct a precise direction dechirping function of the moving target, performing residual video phase removing processing, precise direction dechirping processing and distance migration correction, constructing a fuzzy function for compensation, and then performing Keystone transformation to finish the precise image of the moving target. The moving target detection imaging method solves the imaging problem of the fast moving target when motion parameters are unknown under the continuous wave system, so the signal-to-noise rate and the target detection probability are greatly improved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
System and method for detecting sea target by chaos optimizing radar
InactiveCN102147465AAchieving Chaotic Optimal Object DetectionFew samplesWave based measurement systemsSpecial data processing applicationsEnvironmental resource managementData pre-processing
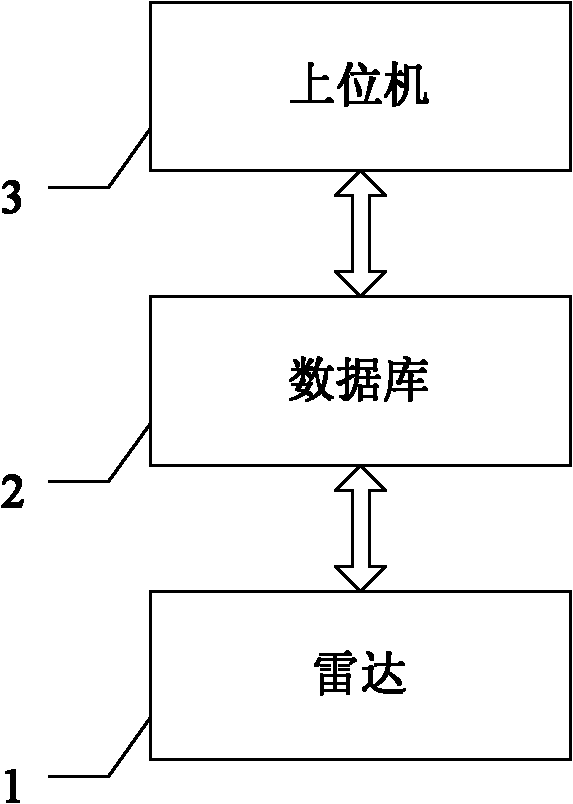
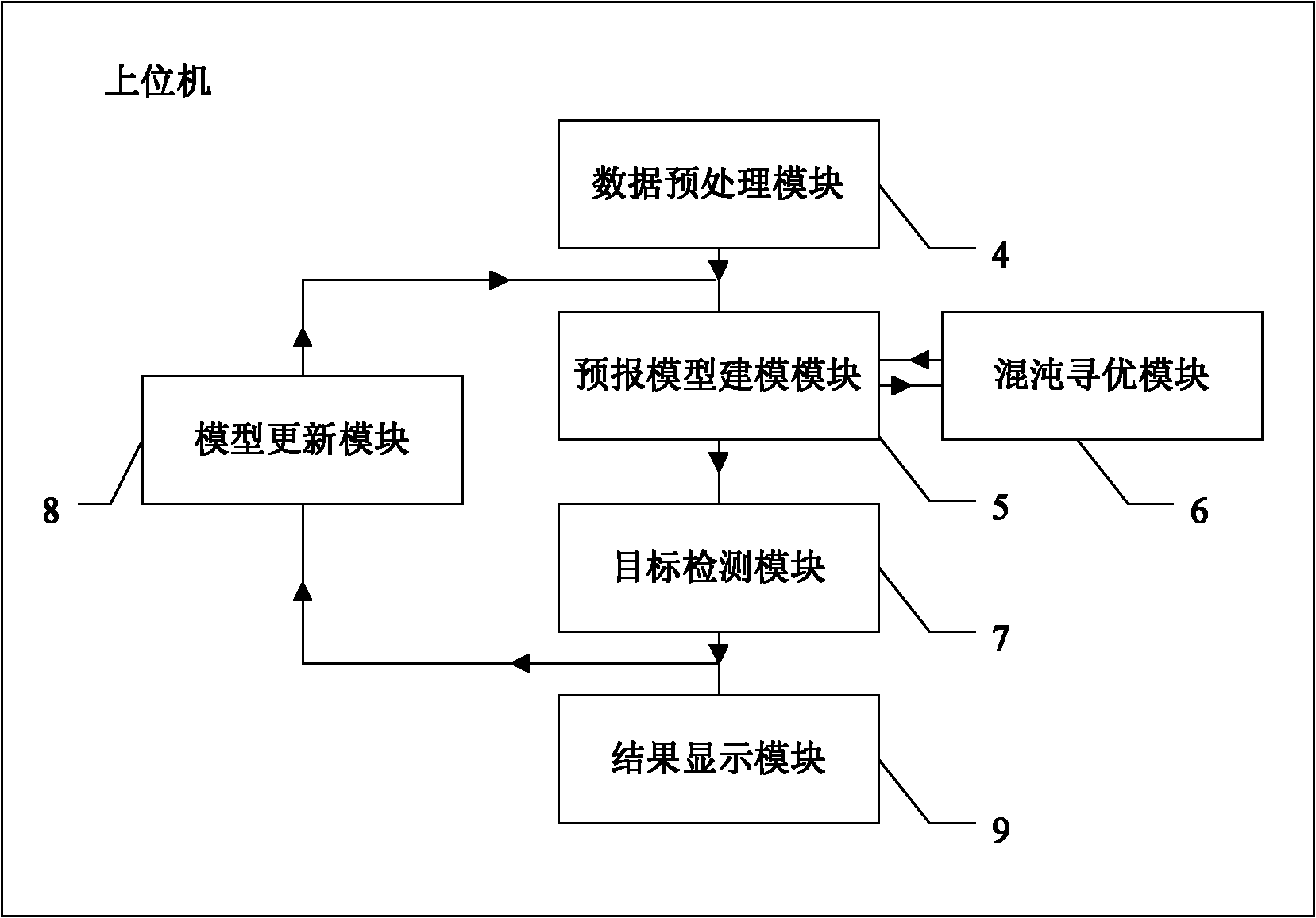
The invention discloses a system for detecting a sea target by a chaos optimizing radar, comprising a radar, a database and an upper computer, wherein the radar, the database and the upper computer are successively connected; the radar irradiates a detected sea area; radar sea clutter data are stored in the database; the upper computer comprises a data preprocessing module, a modeling module of a forecast model, a chaos optimization module, a sea clutter forecast model, a discriminative model updating module and a result displaying module. The invention also provides a method for detecting a sea target by a chaos optimizing radar. The invention provides the system and the method for detecting a sea target by a chaos optimizing radar, which have high precision and avoid the influence of the manual factor.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Doppler channel correlation two-stage dimension reduction method for onboard multiple input multiple output (MIMO) radar
InactiveCN103728606AFull rank reversibleFast convergenceWave based measurement systemsSmall sampleNavigation system
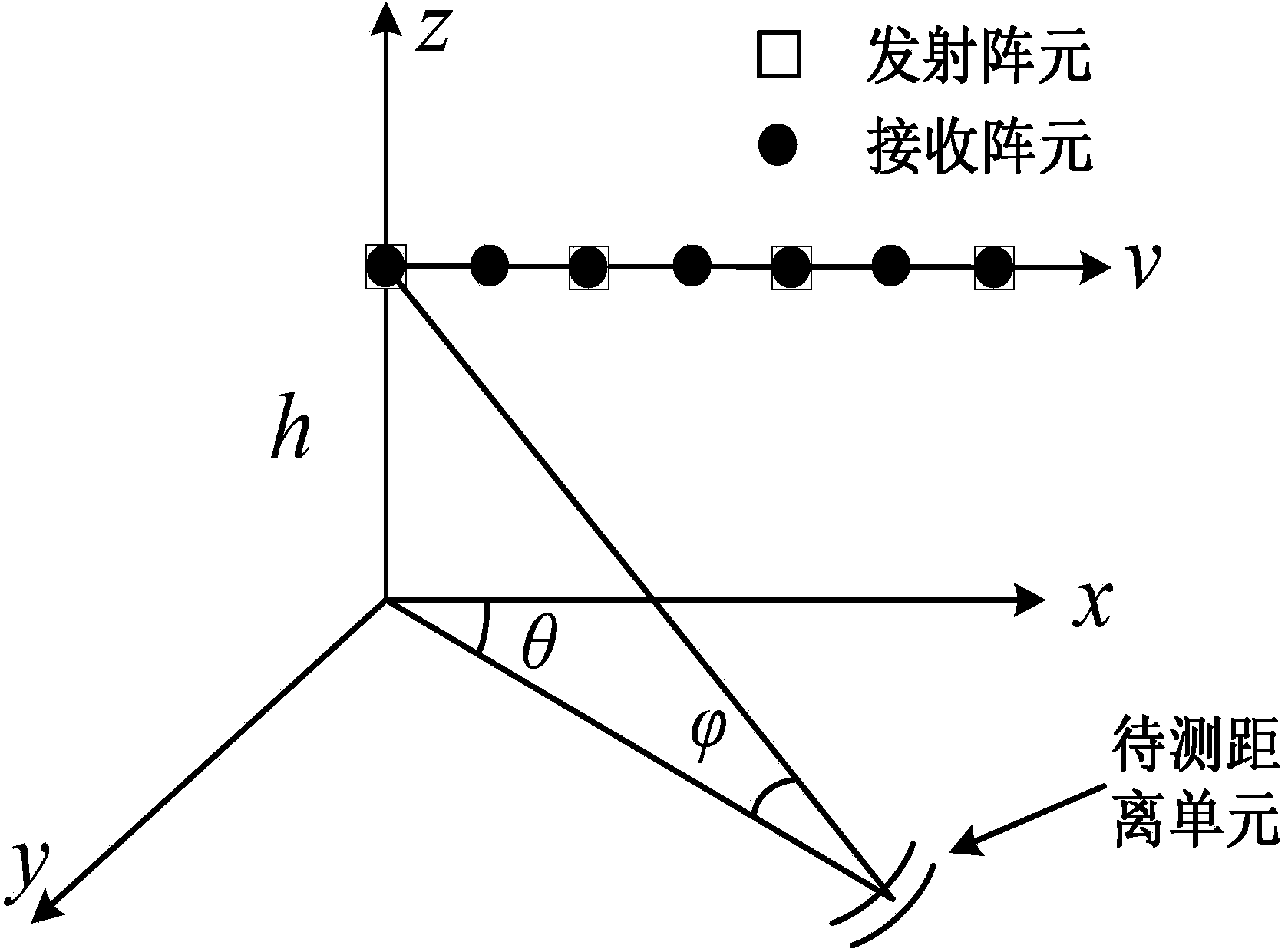
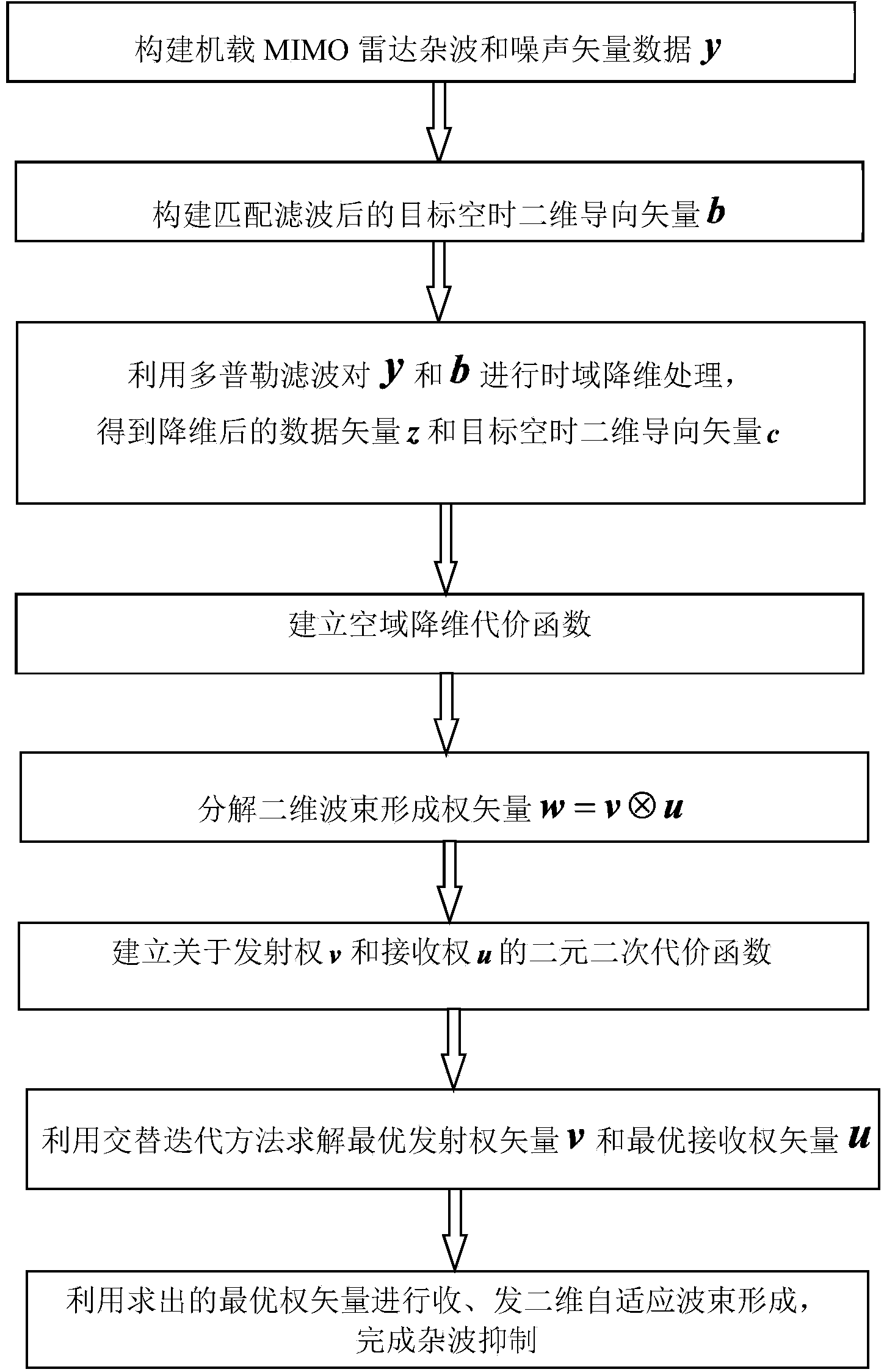
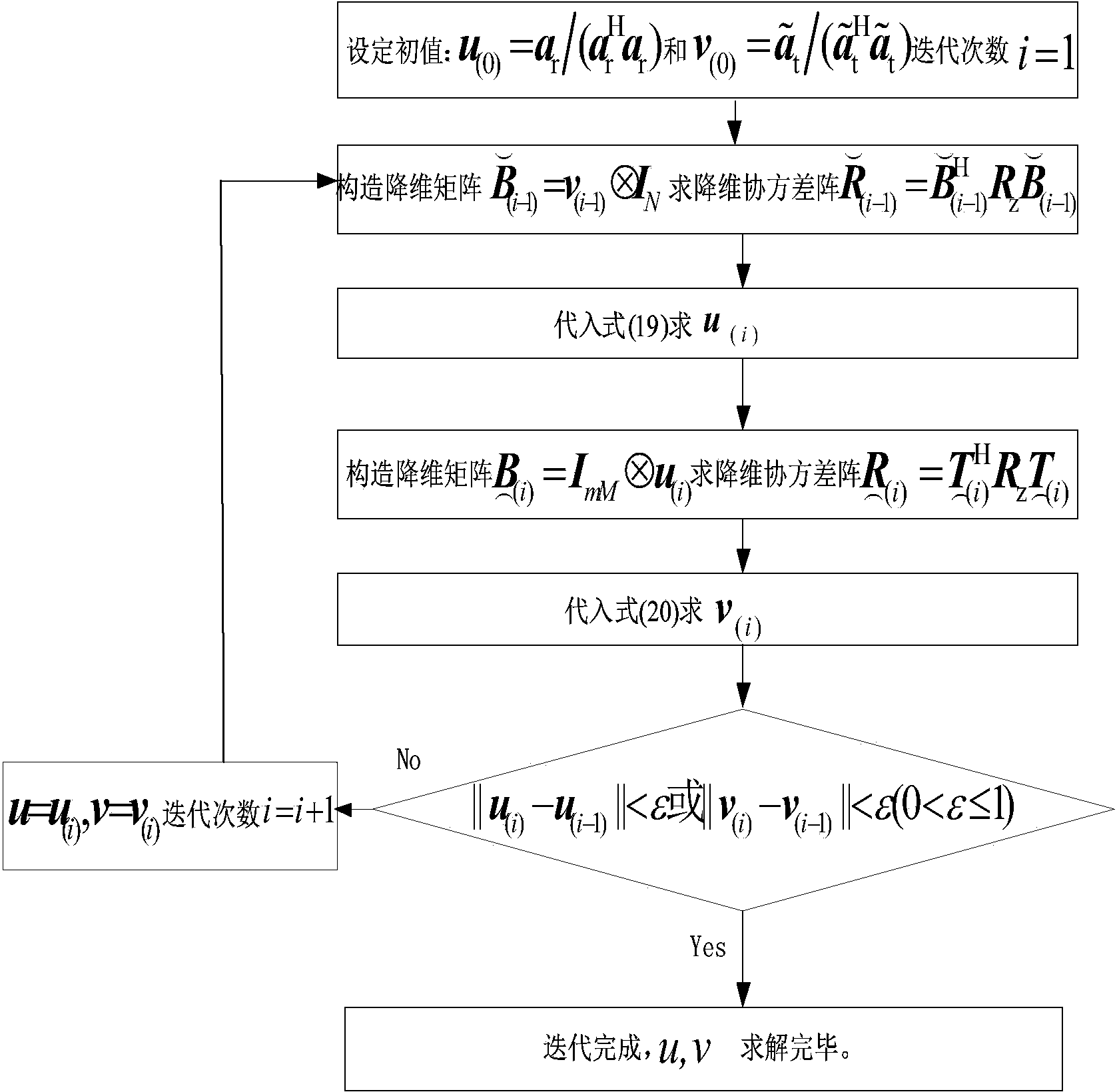
The invention discloses a Doppler channel correlation two-stage dimension reduction method for an onboard multiple input multiple output (MIMO) radar. The method includes constructing an onboard MIMO radar clutter signal model and a target space time two-dimensional guide vector; utilizing Doppler filtering to conduct time domain dimension reduction processing on the echo data; resolving weight vectors formed by a space domain transmitting-receiving two-dimensional wave beam into a Kronecker product of a receiving weight and a transmitting weight, building a dyadic and square cost function, utilizing alternative computation to calculate the optimal weight, utilizing the optimal weight to conduct receiving and transmitting two-dimensional self-adaptation wave beam forming and restraining clutter. By means of the method, the dimension of the obtained weight vectors is greatly reduced, optimum covariance matrix estimation can be obtained through less samples, and the clutter restraining performance is greatly improved under small samples. Meanwhile, high-dimensional sampling covariance matrix inversion is avoided, and the calculation quantity is greatly reduced. By means of clutter restraining, further target detection, target location and tracking and flight track forming are facilitated. The method is applied to various actual systems like navigation systems.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Clutter rejection in a passive radar receiver of OFDM signals
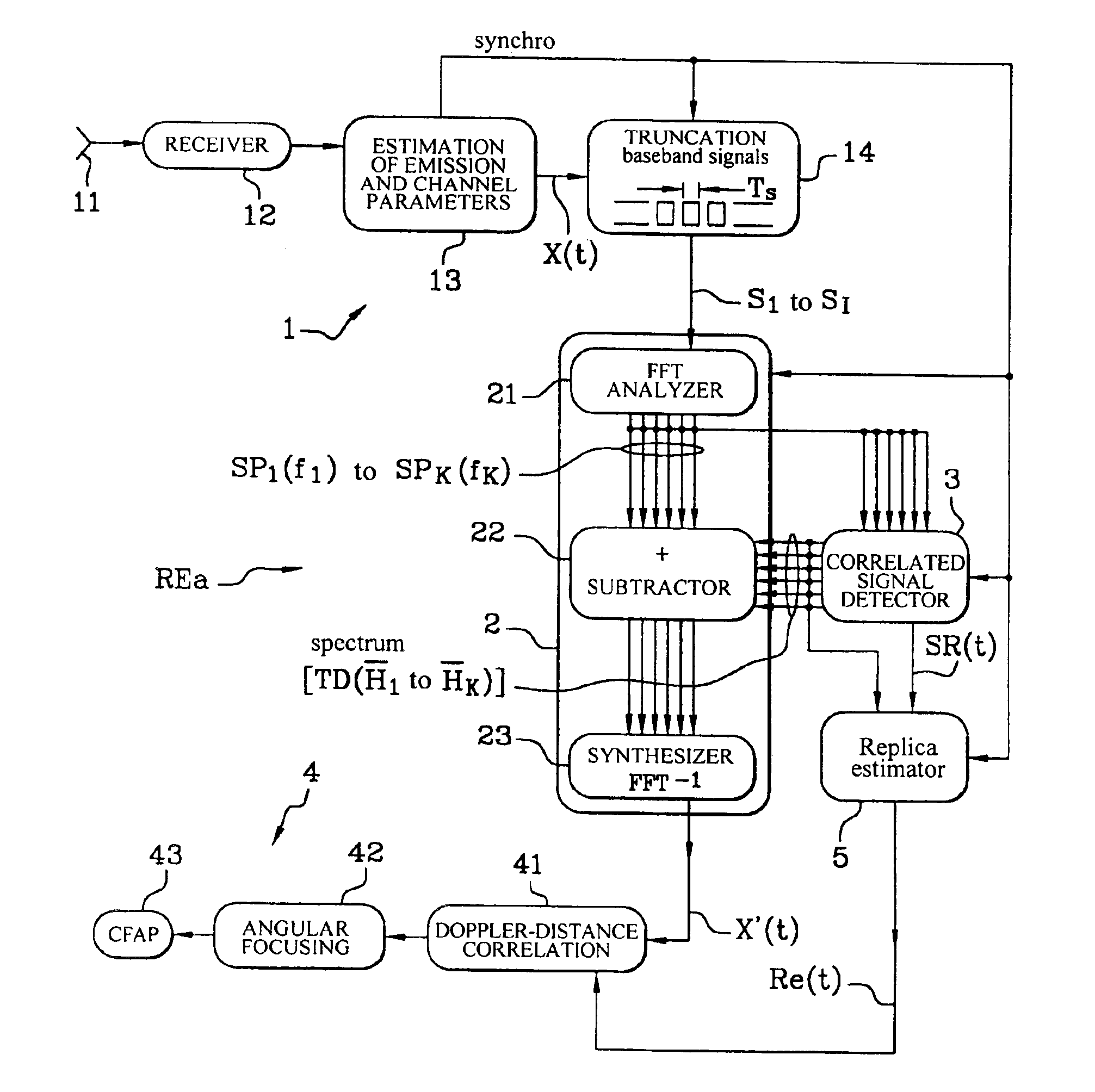
InactiveUS6924763B2Radio wave direction/deviation determination systemsOrthogonal multiplexPassive radarCovariance matrix
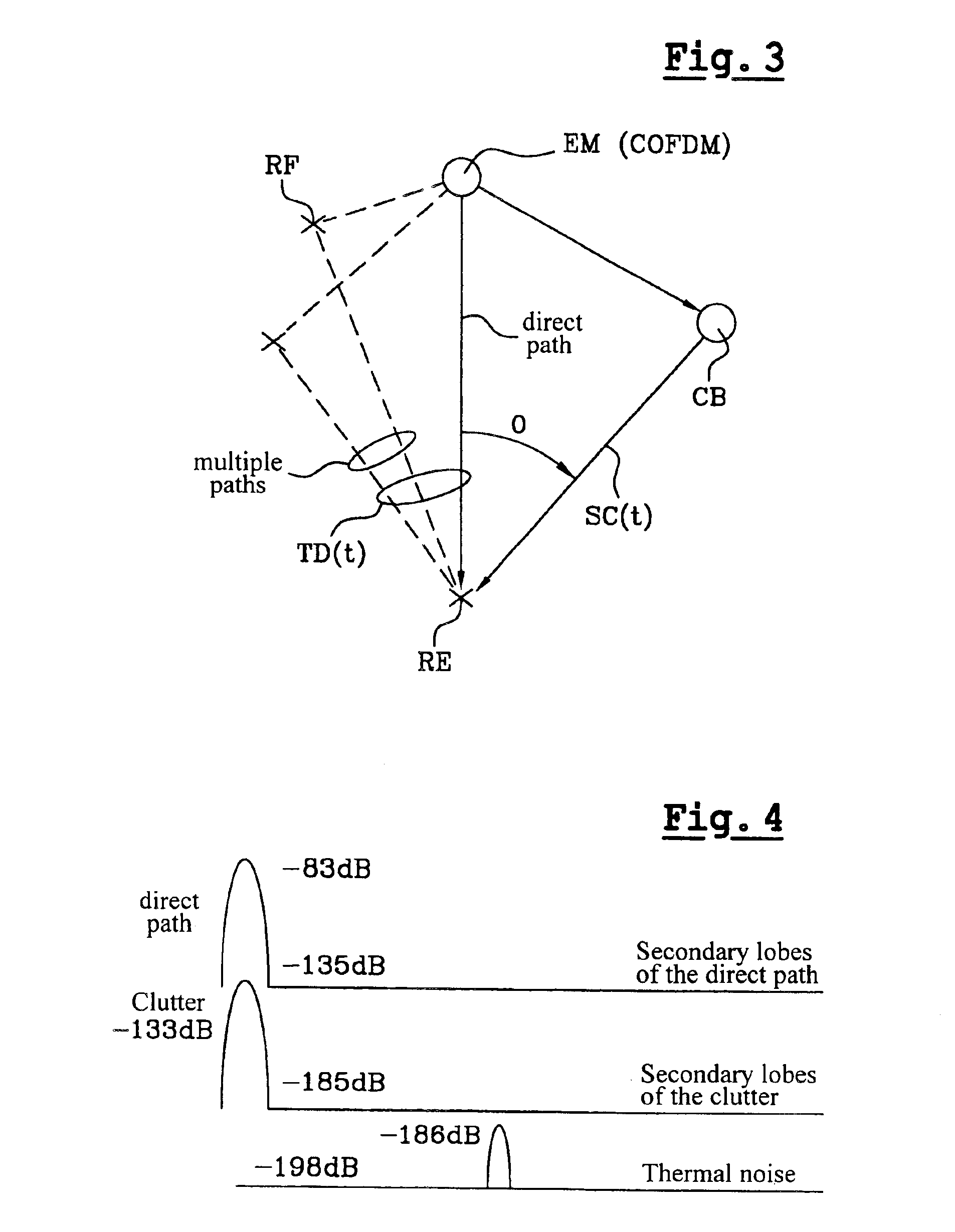
The invention concerns a passive radar receiver for a received orthogonal frequency division multiplex-type signal consisting of symbol frames each emitted on coded orthogonal carriers. After formatting the received signals into digital symbols (S1 S1), a filtering circuit (2) eliminates by subtraction or using a covariance matrix, in the symbol signal at least unwanted signals with null Doppler effect so as to apply a filtered signal (X′) including essentially signals backscattered by mobile targets to a Doppler-distance correlator (4).
Owner:OFFICE NAT DETUD & DE RECH AEROSPATIALES
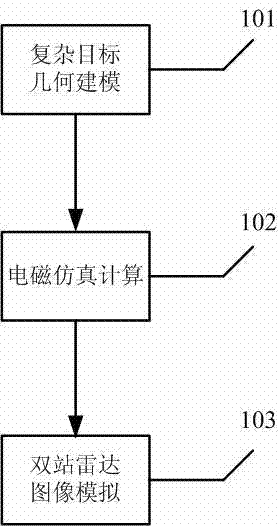
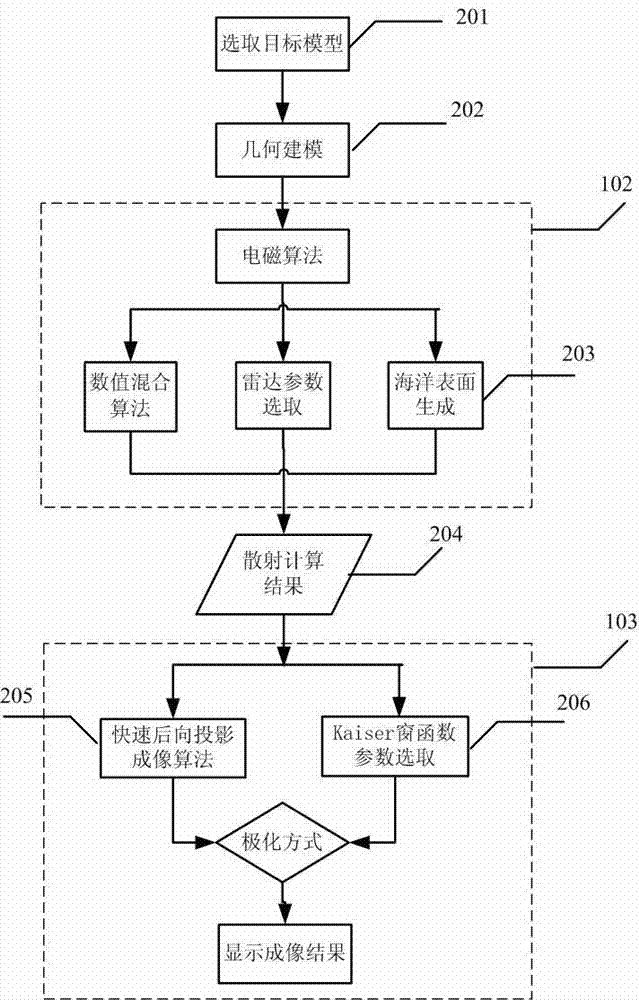
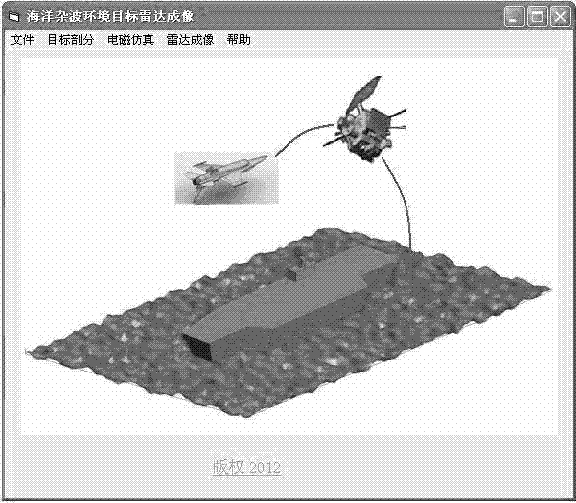
Radar imaging method of electrically large size target in ocean clutter environment
The invention relates to a radar imaging method of an electrically large size target in the ocean clutter environment. The radar imaging method is that the radar imaging of the electrically large size target in the ocean clutter environment is achieved by establishing a surface-box complex target scattering model in a multi-interference environment and adopting electromagnetic simulating calculation through a numerical and analytical hybrid algorithm and a rapid back projection imaging mode. The electrically large size in the radar imaging method means that the ratio of the physical dimension to the wavelength of the target is larger than ten. The working frequency range of a radar is generally in a high frequency area, for example, the L waveband frequency ranges from 1GHz to 2 GHz, and the S waveband frequency ranges from 2GHz to 4 GHz. Some military targets, such as fighters, invisible planes and aircraft carriers in the L waveband and the S waveband belong to the electrically large size. According to the radar imaging method, the radar imaging of the electrically large size target in the ocean clutter environment can be achieved by means of geometric modeling of complex targets, the electromagnetic simulating calculation, the rapid back projection imaging algorithm and Kaiser window edge filtering.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
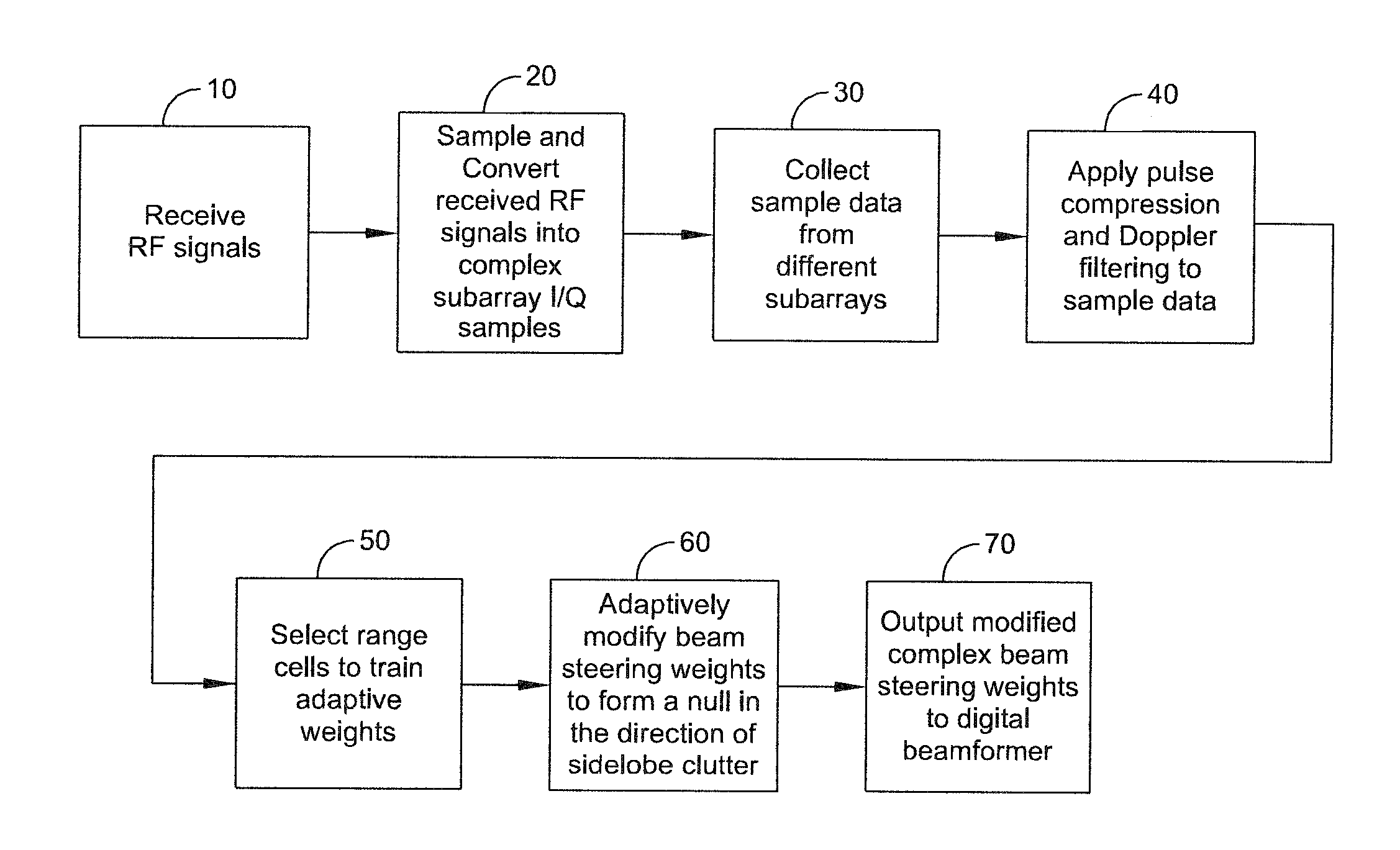
Method and system for adaptively cancelling clutter from the sidelobes of a ground-based radar
ActiveUS8947294B1Enhance clutter-to-noise ratioReduced sidelobe gainAntennasRadio wave reradiation/reflectionGround based radarHorizon
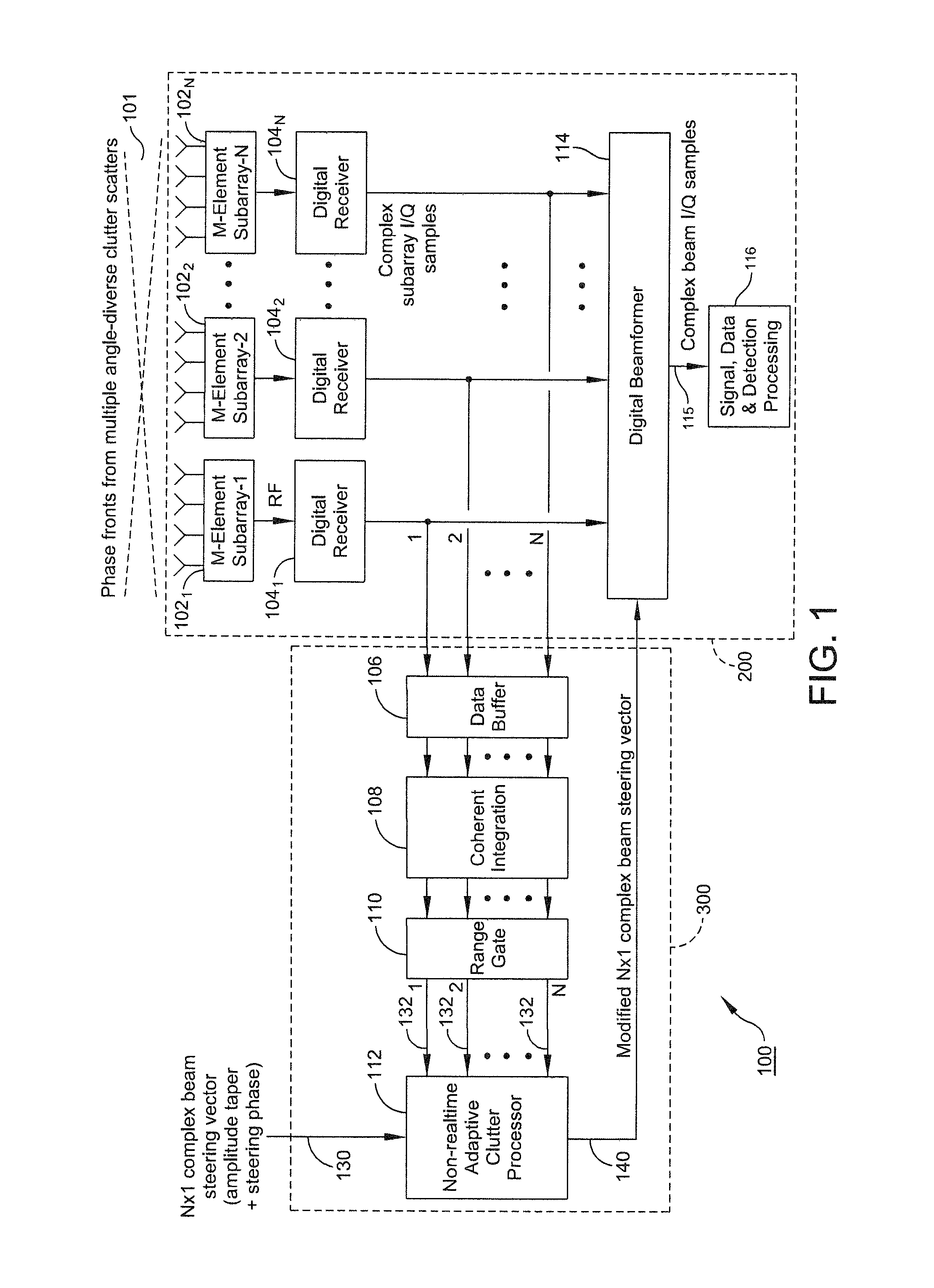
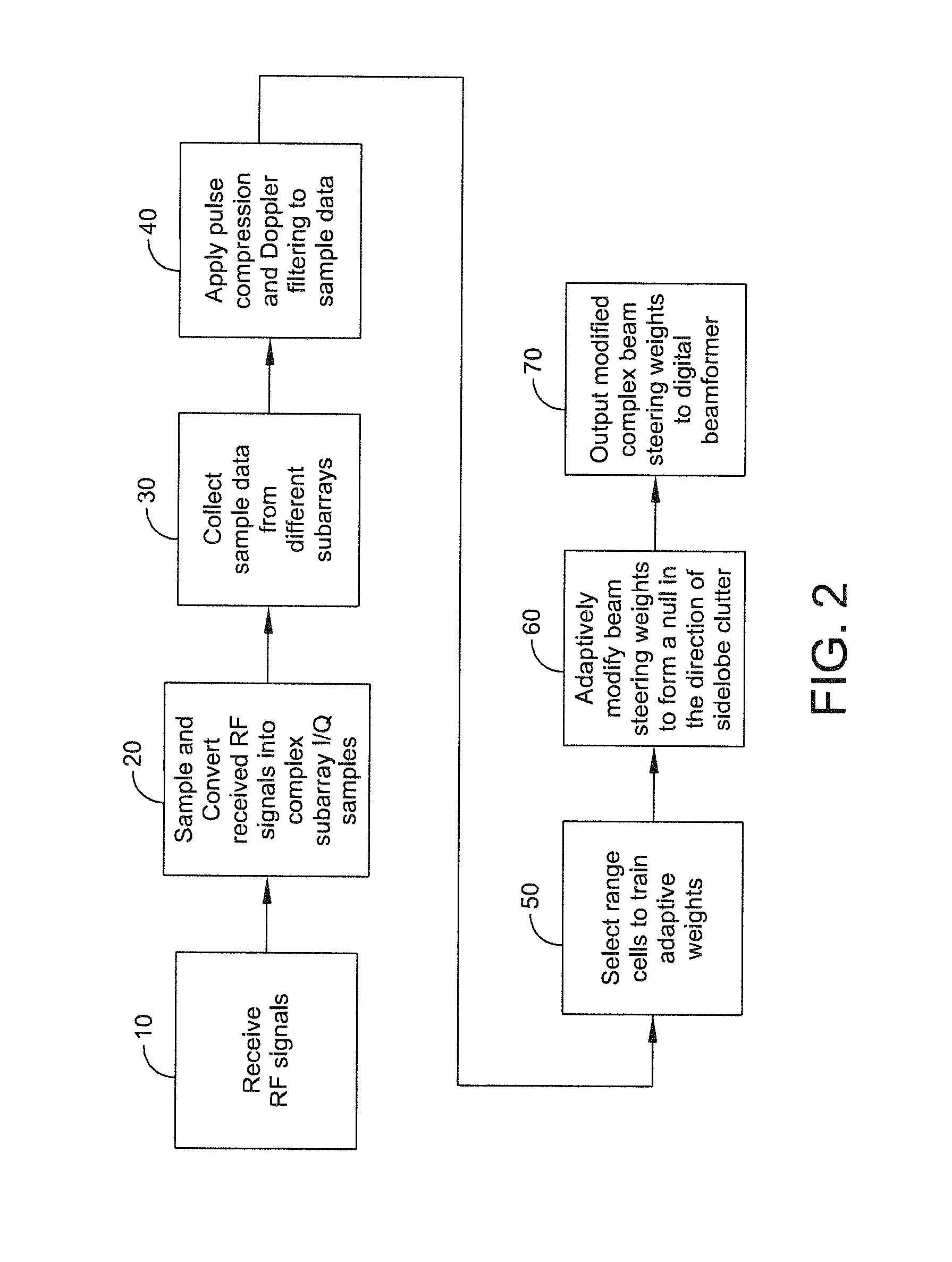
A system and method of providing to a beamformer a modified complex beam steering vector includes collecting subarray I / Q samples from a plurality of subarrays receiving clutter, performing coherent integration of the subarray I / Q samples to increase the CNR, adaptively modifying a complex beam steering vector to form a null in the direction of the received clutter, and outputting to a beamformer the modified complex beam steering vector. The beamformer receives complex I / Q data samples representing a radar signal containing near-horizon clutter and applies the modified beam steering vector to generate a beamformed signal having an elevated mainlobe and a spatial sidelobe null in the direction of the received clutter.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Marine navigation radar signal simulation method
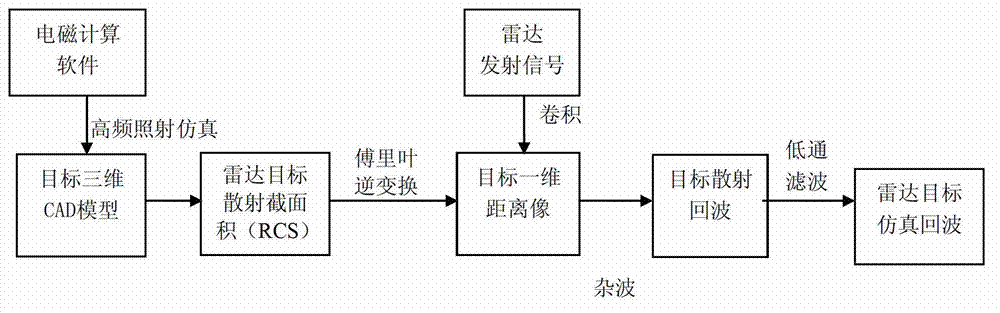
The invention belongs to the technical field of civil marine navigation, and relates to a marine navigation radar signal simulation method. A three-dimensional computer aided design (CAD) model of an offshore ship target is built by adopting computer aided design technology, predication is conducted to radar scattering sectional area of the target by high-frequency electromagnetic calculation software, the scattering area sectional area is processed so as to obtain a one-dimensional range image of the target, and convolution is conducted to radar transmitted wave form and the obtained one-dimensional range distance; Doppler frequency shift factors are introduced according to states of target motion; distance attenuation factors are introduced according to located position of the target; and low pass filtering is conducted so as to obtain marine navigation radar signal simulation echo through adding a sea clutter model. According to the marine navigation radar signal simulation method, a navigation radar ship target echo sample base which is high in similarity in various characteristic spaces with actual radar echo signals is provided, and radar echo signal sources are provided for teaching and training of navigation radars and seamen.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method and apparatus for radar surveillance and detection of sea targets
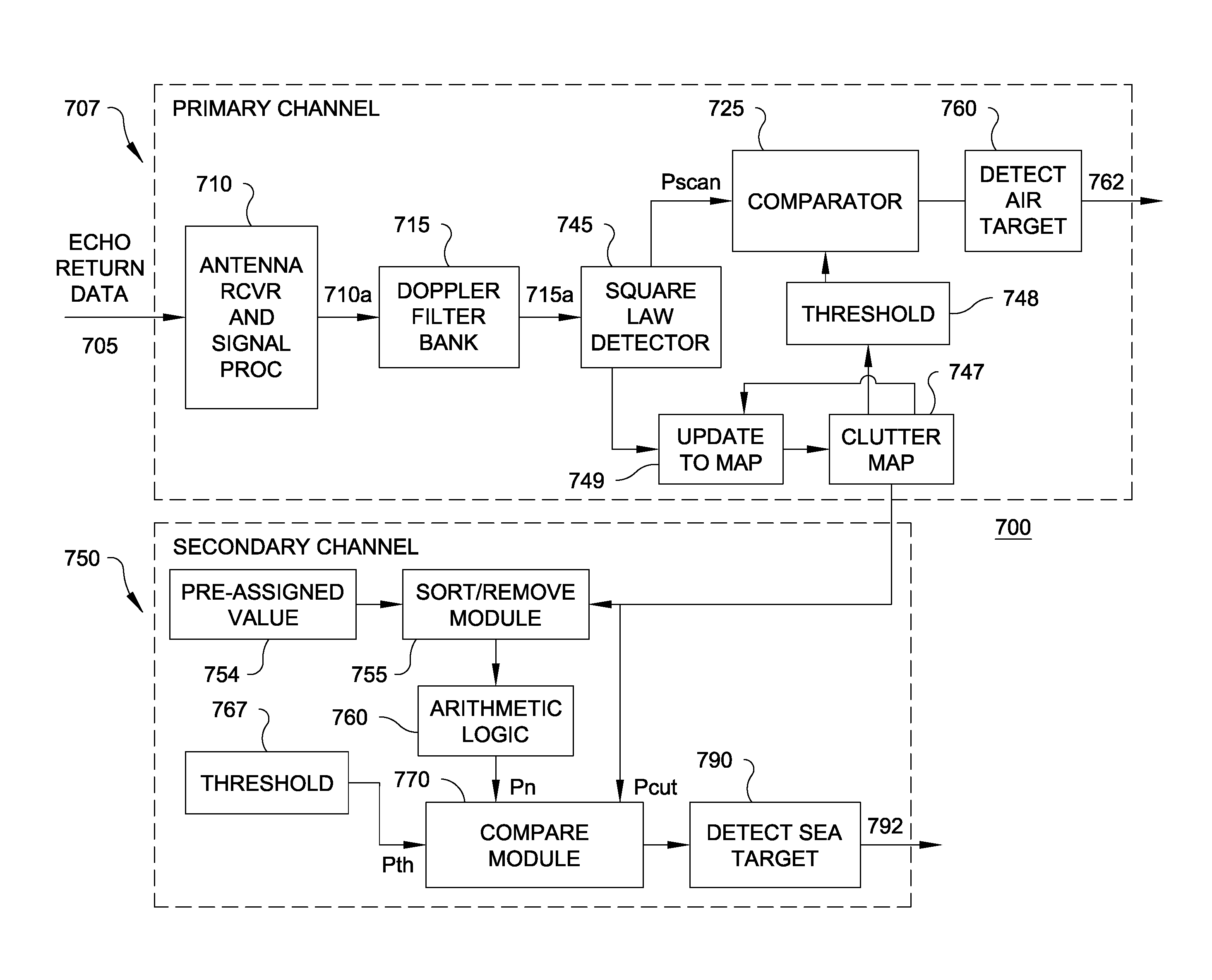
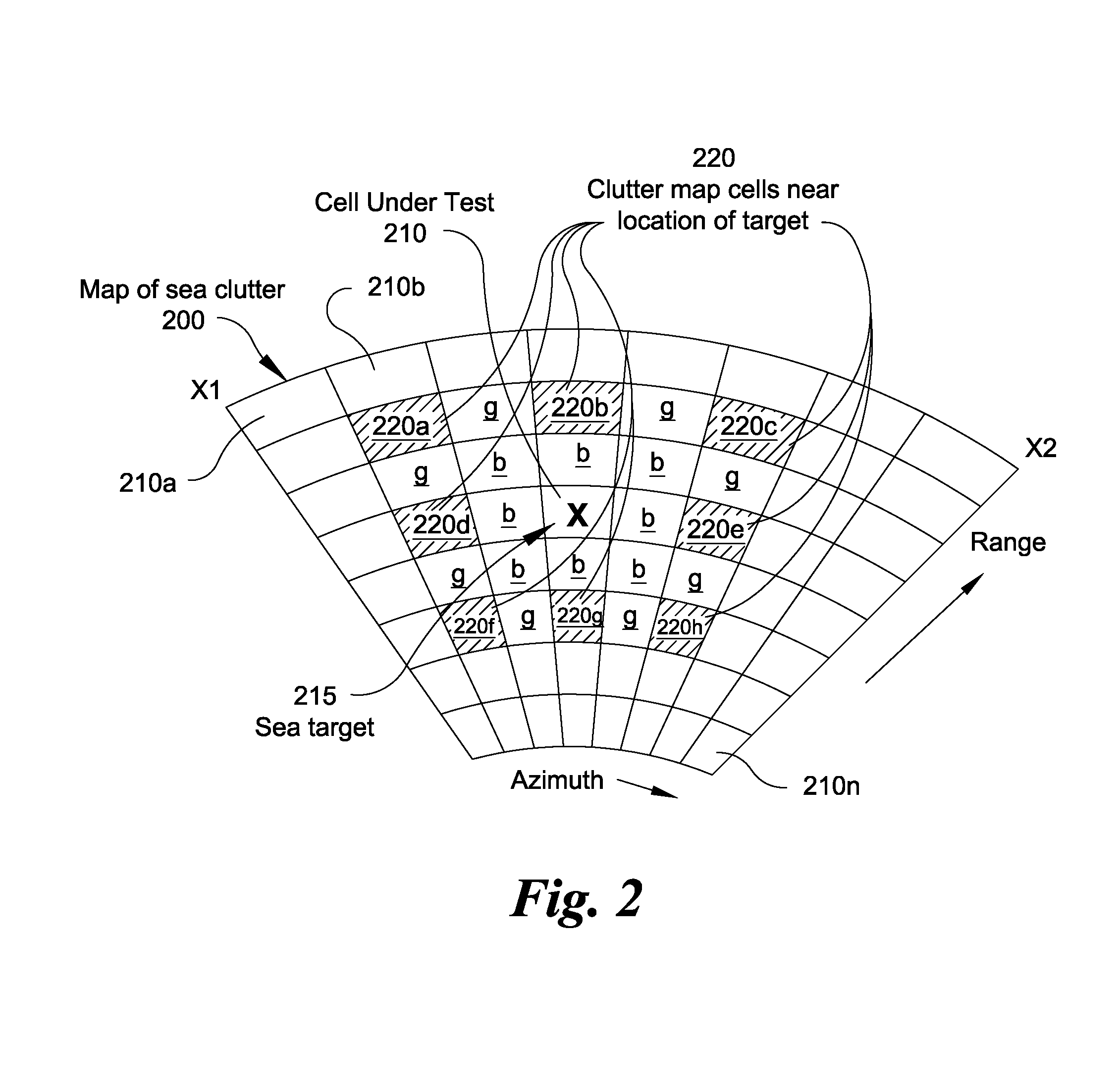
In a radar system using a radar clutter map comprising a plurality of range-azimuth cells containing parameter data values indicative of time averaged echo returns for affecting alarm threshold levels at range-azimuth locations scanned by the radar system antenna, a method for detecting comprising the steps of obtaining from the radar clutter map a first parameter data value associated with a given cell under test (CUT); determining a second parameter data value using parameter data values of other cells from the plurality of range-azimuth cells from the radar clutter map; comparing the first parameter data value associated with the CUT with the second parameter data value; and generating a signal indicative of a target detection when the first parameter data value exceeds the second parameter data value by a given threshold corresponding to a target false alarm rate.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
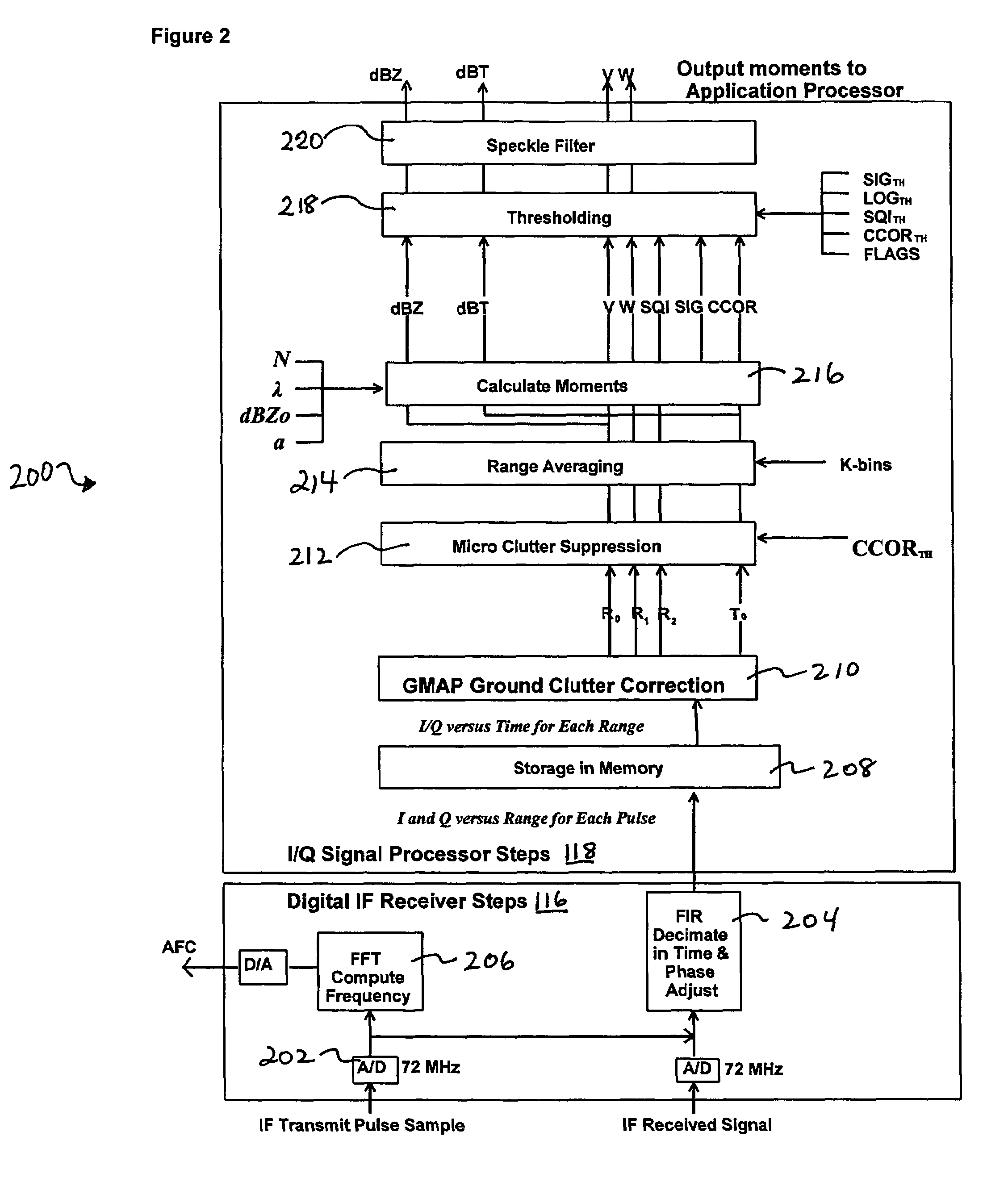
System and method for processing data in weather radar
ActiveUS7589666B2Reduce varianceICT adaptationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionWeather radarFrequency spectrum
Systems and methods that adapt to the weather and clutter in a weather radar signal and apply a frequency domain approach that uses a Gaussian clutter model to remove ground clutter over a variable number of spectral components that is dependent on the assumed clutter width, signal power, Nyquist interval and number of samples. A Gaussian weather model is used to iteratively interpolate over the components that have been removed, if any, thus restoring any overlapped weather spectrum with minimal bias caused by the clutter filter. The system uses a DFT approach. In one embodiment, the process is first performed with a Hamming window and then, based on the outcome, the Hamming results are kept or a portion of the process is repeated with a different window. Thus, proper windows are utilized to minimize the negative impact of more aggressive windows.
Owner:SIGMET
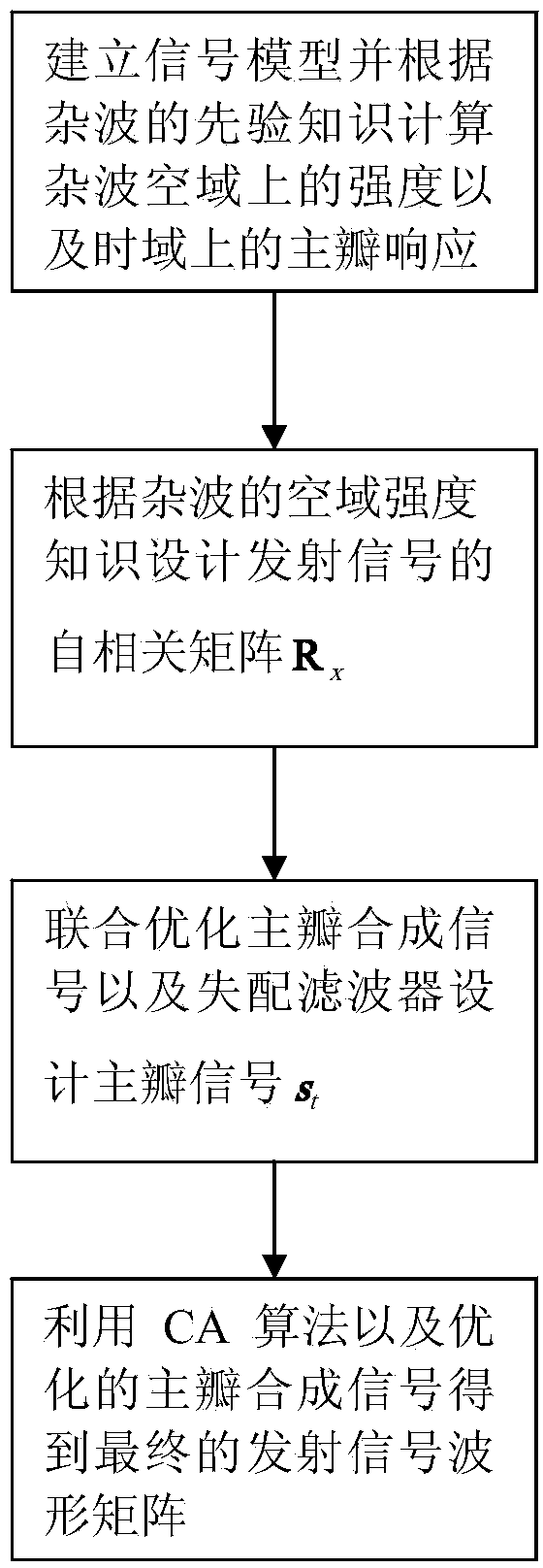
Method for hierarchically designing transmission waveforms of MIMI (multiple input multiple output) radar for detecting targets in clutter
ActiveCN103969633AAchieve inhibitionImprove the performance of detecting objectsWave based measurement systemsTime domainRadar
The invention belongs to the field of radar technologies, relates to designs for transmission waveforms of centralized MIMO (multiple input multiple output) radar, and discloses a method for hierarchically designing transmission waveforms of MIMO radar for detecting targets in clutter. The method includes steps of 1, building an MIMO radar signal model and acquiring the intensity of the clutter in a space domain and mainlobe response priori knowledge in a time domain; 2, designing autocorrelation matrixes Rx of transmission signals on the basis of intensity priori knowledge of the clutter in the space domain; 3, combining each optimal mainlobe synthesized signal (MSS) with a mismatched filter to suppress mainlob clutter signals; 4, designing transmission waveform matrixes under constant-modulus conditional constraints. The method has the advantages that the clutter suppression performance can be improved, and accordingly the radar can be used for detecting the targets in the heavy clutter.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
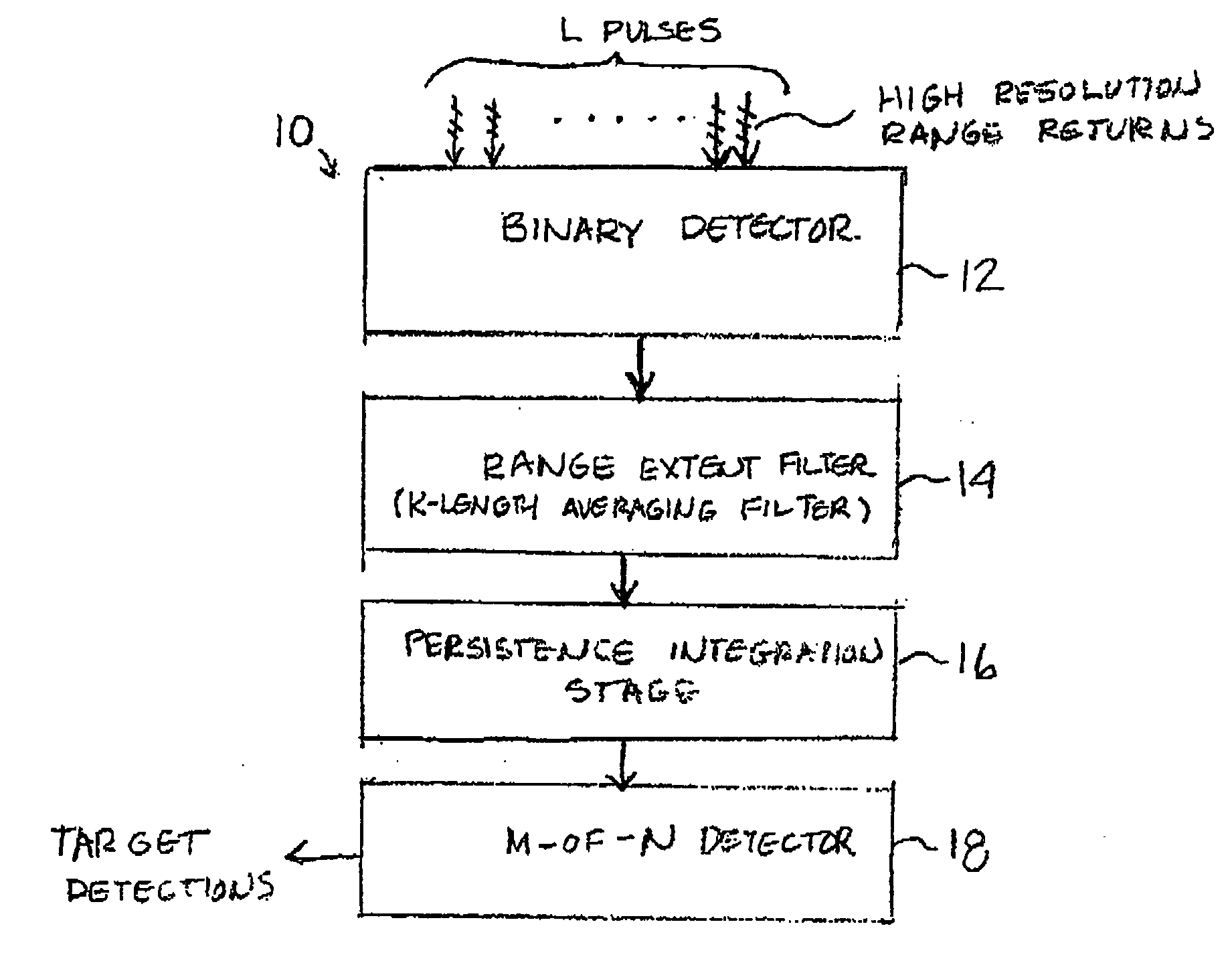
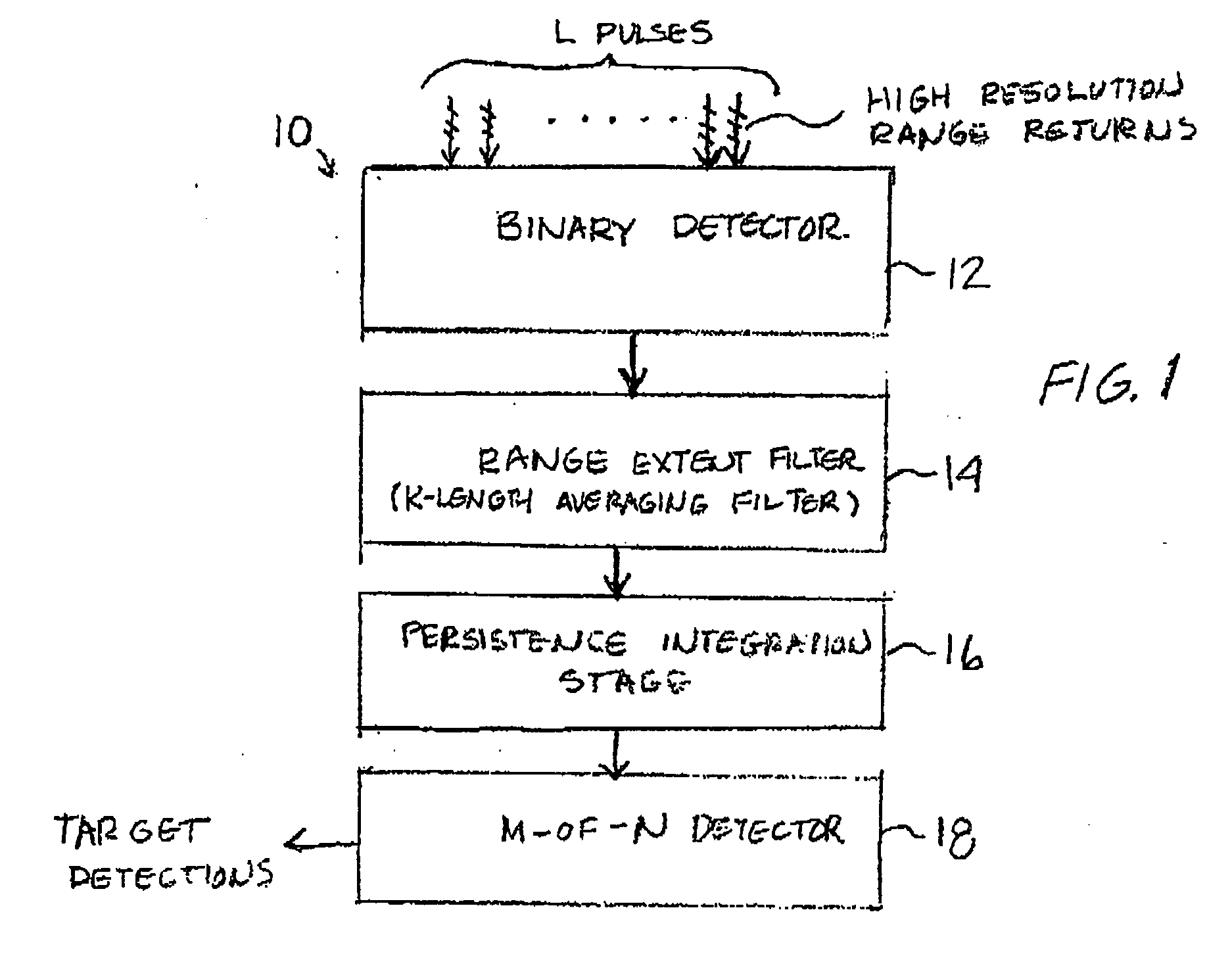
Method and apparatus for detecting slow-moving targets in high-resolution sea clutter
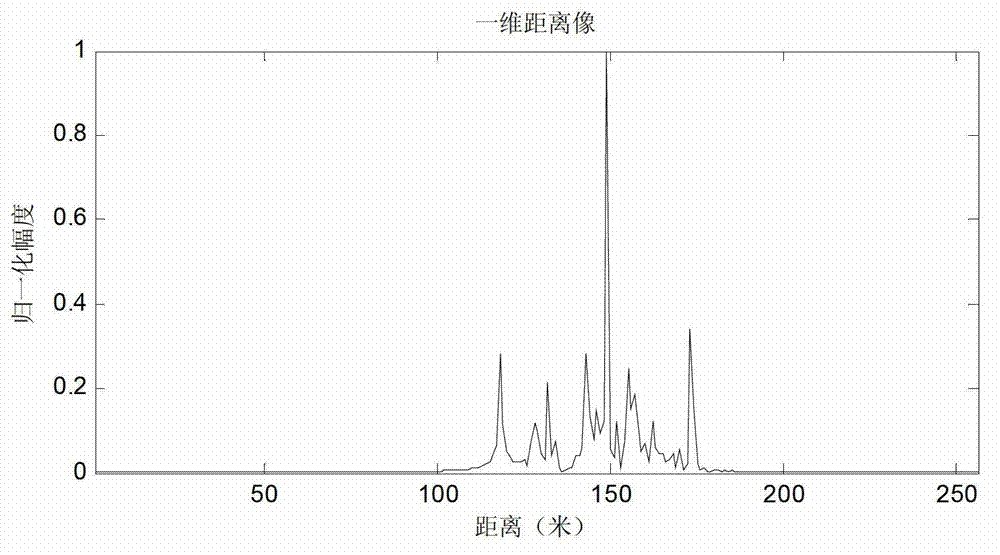
An apparatus for non-coherently detecting slow-moving targets in high resolution sea clutter includes a binary detector for converting high resolution radar returns, produced in response to a radar pulse scan of a plurality of identical pulses, into corresponding binary outputs based on a comparison of range cell magnitudes with a detector threshold. A range extent filter converts these binary outputs into an output indicating the presence or absence of a cluster of the returns that are closely spaced in range, while a third, persistence integration stage determines target range extent persistence over a predetermined time period. A detector stage declares detection of a target based on a comparison of the output of the third stage with a selected threshold.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Doppler information based method for tracking low-altitude low-speed small target through radar
ActiveCN105093215AImprove ranging accuracyImprove efficiency and qualityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPoint setLow altitude
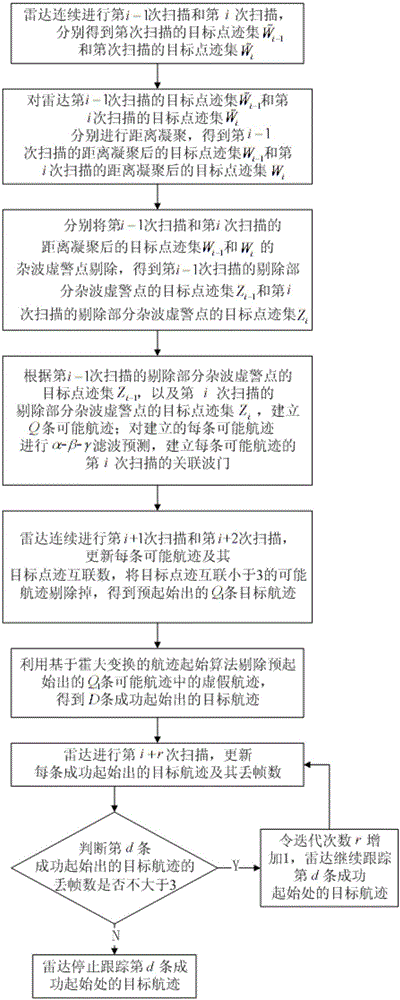
The invention discloses a Doppler information based method for tracking a low-altitude low-speed small target through a radar. The method comprises the following steps: 1), respectively carrying out distance clustering on target trace point sets generated when the radar performs scanning of an (i-1)th time and an i-th time, and respectively rejecting cluster false alarm points; 2), according to the target trace point sets with the cluster false alarm points being rejected after the scanning of the (i-1)th time and the i-th time, establishing Q possible tracks; and the radar continuously carrying out scanning of an (i+1)th time and an (i+2)th time, updating each possible track and a target trace point interconnection number, rejecting possible tracks whose target trace point interconnection numbers are smaller than 3, and then rejecting false tracks in the possible tracks so as to obtain D successfully starting target tracks; and 3), the radar carrying out scanning of an (i+r)th time, updating each successfully starting target track and its frame loss number, if the frame loss numbers of the successfully starting target tracks are not greater than 3, adding 1 to inertia frequency r, the radar continuously tracking the successfully starting target tracks, and otherwise, the radar stopping tracking the successfully starting target tracks.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Self-adaptive target detection method and device
InactiveCN106842194AAccurate descriptionAccurate Maritime Object DetectionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTarget signalGeolocation
The invention relates to the technical field of radar signal processing and provides a self-adaptive target detection method and device. The method includes performing area division on each frame of radar echo wave data of the same geographic location and obtaining amplitude data in radar echo wave data corresponding to different data frames of different areas; acquiring the mean value of the amplitude values in the radar echo wave data corresponding to a plurality of continuous data frames of each area and obtaining current threshold values of the radar echo wave data of different areas; fitting the current threshold values of the radar echo wave data of the different areas and taking the fitting result as background noise of the current radar echo wave data, and detecting a target signal from the current radar echo wave data. According to the invention, the current threshold values of the radar echo wave data are obtained through actual echo wave statistics and the threshold values are adjusted in a self-adaptive manner along with actual sea conditions. Therefore, accurate description of sea clutter features is realized and marine target detection is further realized accurately.
Owner:BEIJING HIGHLANDER DIGITAL TECH +1
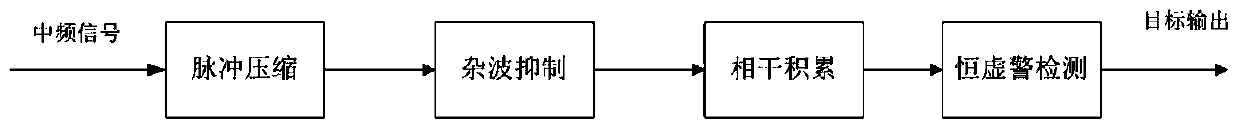
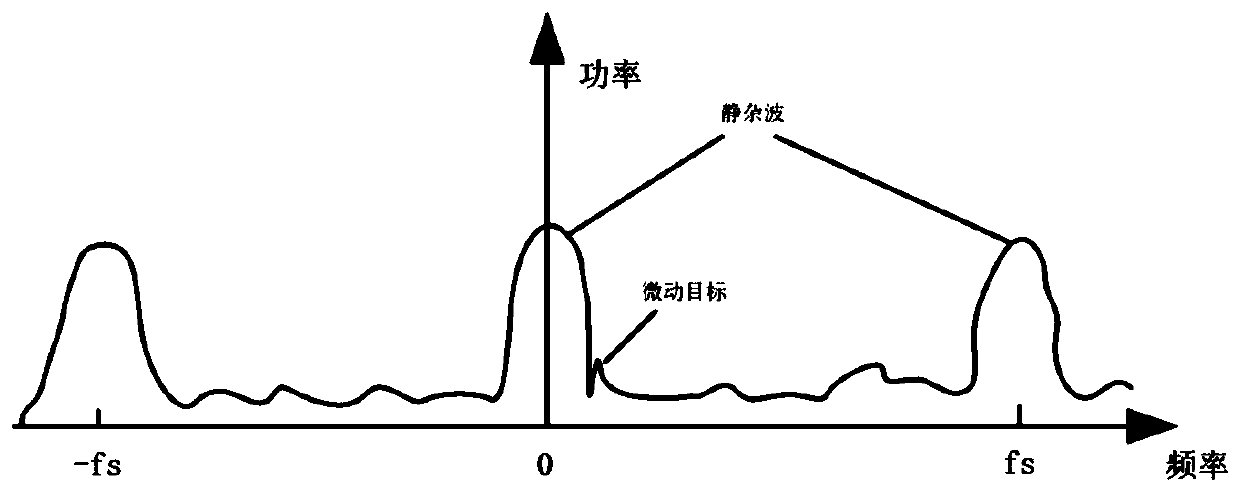
Method for detecting micro-motion target through-wall radar
InactiveCN110221288AImprove signal-to-noise ratioImprove detection rateRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Intermediate frequency
The invention discloses a method for detecting a micro-motion target of a through-wall radar, and belongs to the field of radar detection and the field of through-wall radar detection. The method fordetecting the micro-motion target of the through-wall radar comprises the following steps that collected intermediate frequency echo signal is subjected to pulse compression treatment; a narrowband filter is designed according to Doppler frequency shift characteristics of a micro-motion target and used for suppressing out-of-band clutter; the signal after clutter suppression treatment is subjectedtocoherent integration; the treated signal is subjected to constant false alarm detection; the pulse compression increases the signal-to-noise ratio and distance accuracy; the clutter suppression caneffectively suppress strong clutter behind the obstacle; according to the method for detecting the micro-motion target of the through-wall radar,on the basis of the analysis of the Doppler frequencyshift characteristics of the micro-motion target, and weak echo waves of the micro-motion target behind a wall are subjected to treatments such as targeted wave filtering, amplification, and extraction, and effective detection of the micro-motion target is achieved.
Owner:CHANGZHOU NO 4 RADIO FACTORY
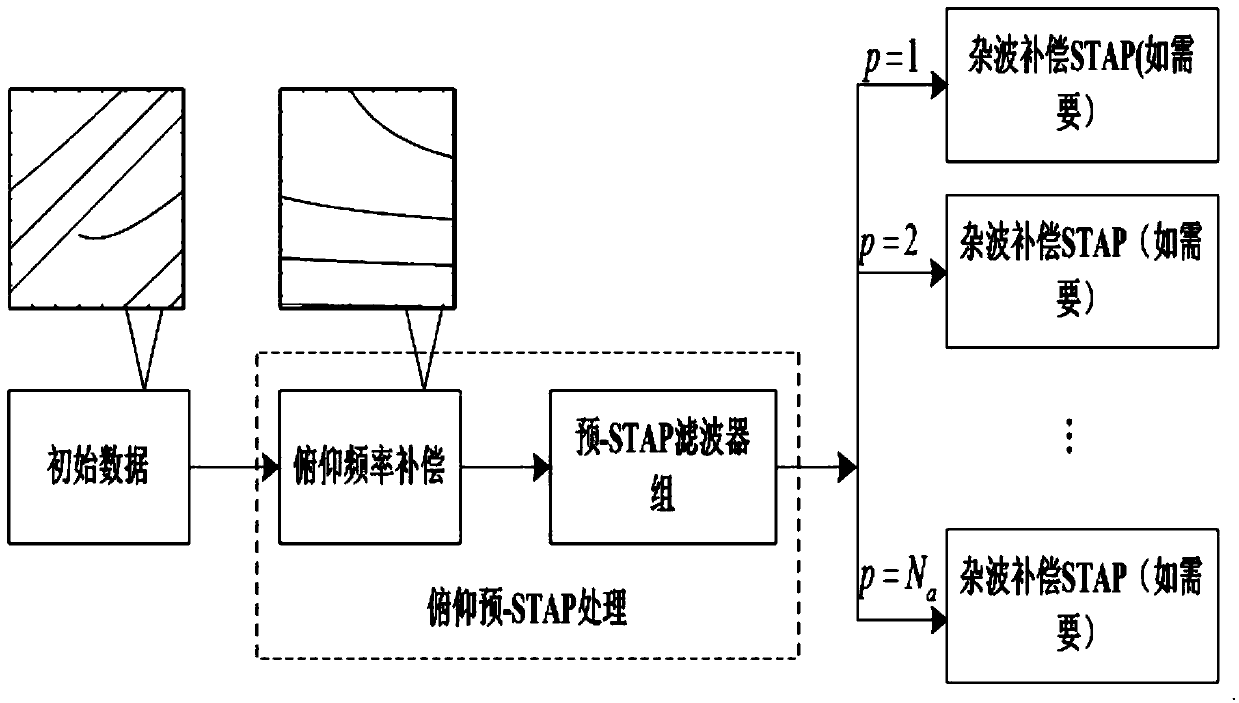
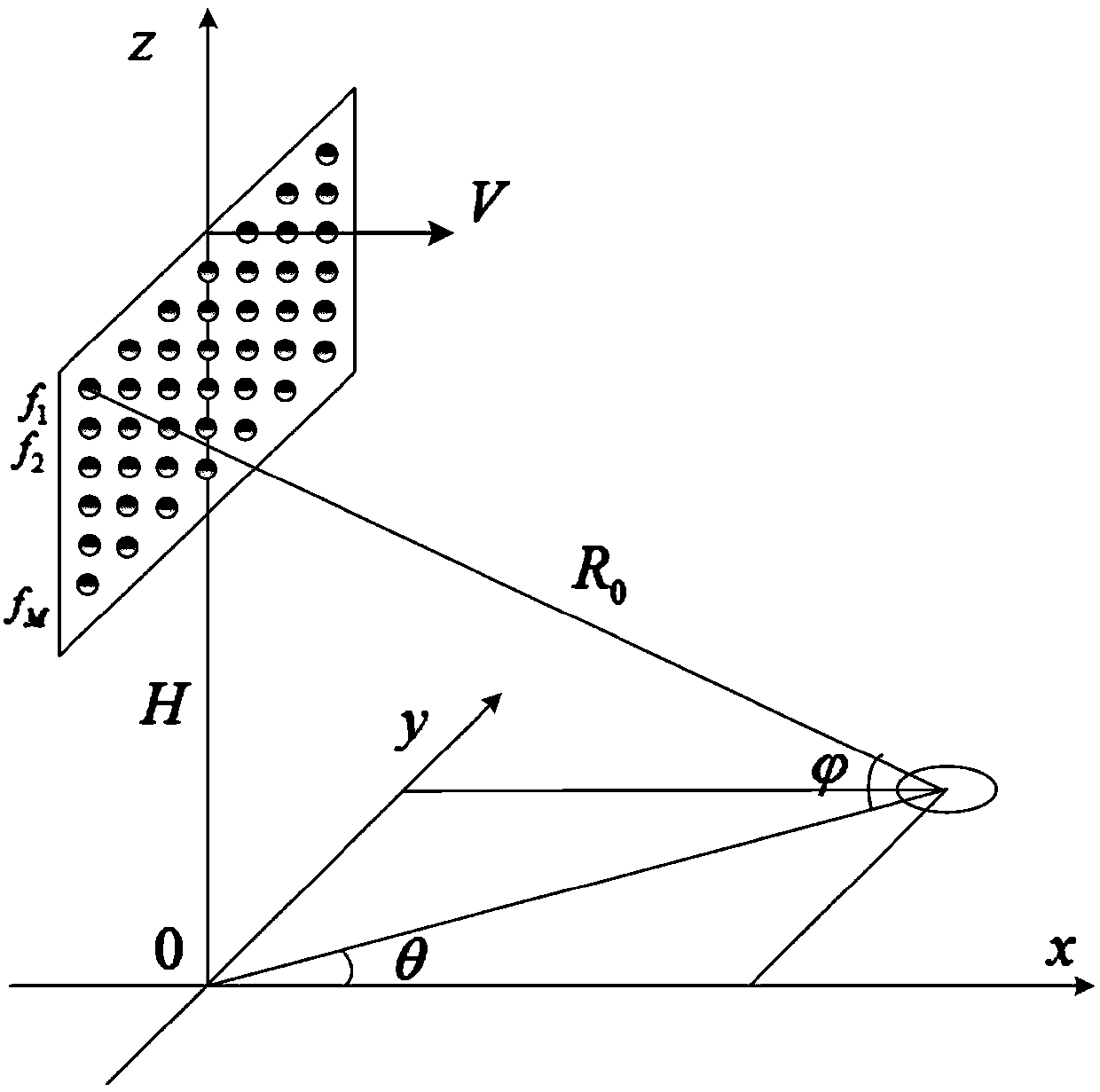
Distance blur clutter suppression method based on pitch frequency diversity STAP
ActiveCN104977571AImprove object detection performanceSuppression of non-uniform clutterWave based measurement systemsFrequency spectrumRange gate
The invention discloses a distance blur clutter suppression method based on pitch frequency diversity STAP. The method comprises the steps that down-conversion and matched filtering are sequentially carried out on a detected received signal to sequentially acquire the pitch-azimuth-time three-dimensional clutter snapshot model of each range gate, the pitch frequency expression of each range gate and the corresponding clutter compensation item; an appropriate clutter compensation item is used to separate distance blur clutters of different distance rings; due to the fact that pitch frequencies of different distance blur clutters are separated from each other, the distance blur clutter of each distance ring needs a filter with corresponding coefficients for filtering, and then all distance blur clutters are inhibited to solve the problem of distance blur; and finally, after the pitch distance blur clutters are separated, pitch frequency spectrum distribution and digital frequency periodicity are used to acquire the selection criteria of frequency increment. According to the invention, the freedom of a system and the operation complexity are not increased.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
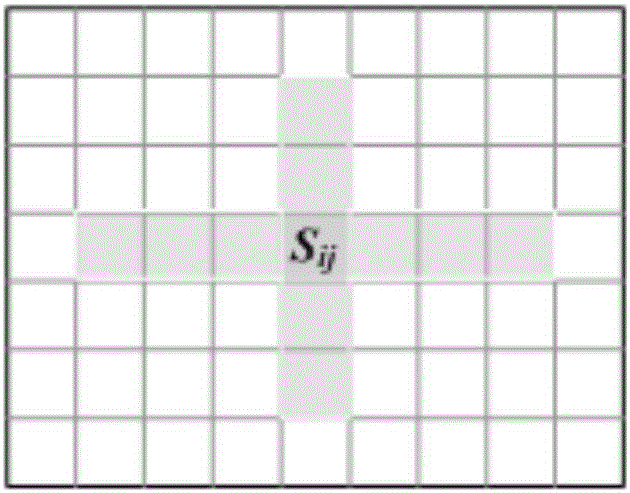
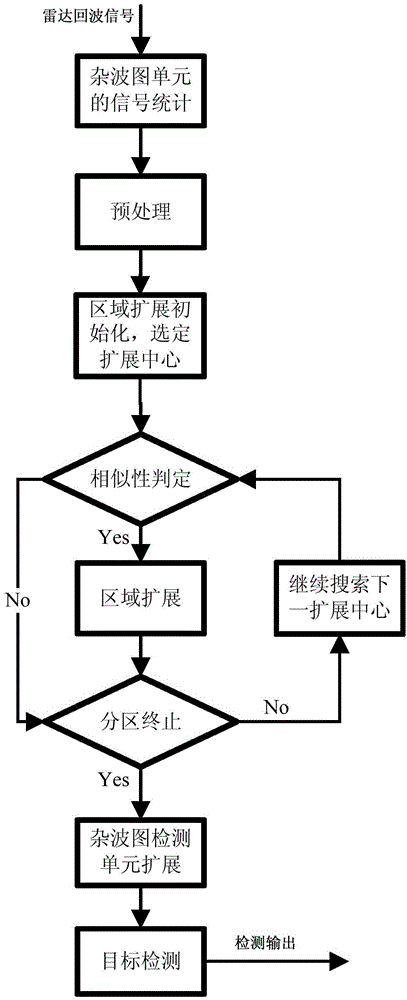
Clutter map partitioning method based on image processing
ActiveCN104360324AImprove connectivityFlexible by designWave based measurement systemsImaging processingRadar
The invention discloses a clutter map partitioning method based on imaging processing. The clutter map partitioning method includes steps of (1) calculating radar operating range and beam width and determining clutter map partitioning modes and resolution cells; (2) counting clutter signal strength in a clutter map unit and determining iteration coefficient; (3) subjecting clutter map data to median filtering and eliminating abnormal points having overlarge or too small estimated values by the median filtering; (4) partitioning a clutter map; (5) expanding a clutter map detecting unit, to be specific, simultaneously judging other eight units adjacent to one another in distance and direction when the clutter strength of the clutter unit is estimated, and finally subjecting the judgment results of the nine units to greatest selection processing as the final estimated value of the clutter scene; (6) detecting the clutter map, to be specific, expanding information by the clutter map detecting unit to form the clutter detecting threshold for radar target detection.
Owner:THE 28TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP
Infrared target detection method based on space-time cooperation framework
InactiveCN102496016AEfficient integrationEfficient removalCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural learning methodsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Nerve network
The invention relates to an infrared target detection method based on a space-time cooperation framework. The method comprises the following steps: 1. acquiring a background frame Bg and a current frame Ft of a video, combining the background frame Bg and the current frame Ft to carry out background clutter suppression and acquiring a background suppression graph Gt after the background clutter suppression is performed; 2. for the background suppression graph Gt obtained in the step 1, firstly establishing a space-time background model, and then carrying out target positioning aiming at space-time background model information after the model is established; 3. according to an imaging mechanism of the infrared target, analyzing a space difference of the infrared target and the surrounding background, using a fuzzy adaptive resonance nerve network to carry out local classification aiming at the target which is positioned in the step 2 and then extracting the infrared target. The method has the following advantages that: the method does not depend on any target shapes and motion information priori knowledge; the method is suitable for a complex outdoor scene; a signal to noise ratio can be increased; a target detection rate can be increased and a calculated amount can be reduced; false targets can be effectively removed and a false alarm rate can be reduced; the method is beneficial to follow-up target identification.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Real-time detection and separation method of multiple moving objects by through-the-wall radar
InactiveCN105137423AImprove work efficiencyEasy to separateRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadarSelf adaptive
The invention relates to a real-time detection and separation method of multiple moving objects by a through-the-wall radar. The method comprises: a complex background signal is rejected by using a clutter suppression algorithm based on an exponential smoothing filter and information of moving human objects can be kept rapidly and accurately; with an envelope detection algorithm based on Hilbert transform, all moving objects are arranged at different envelope peaks; and all moving objects can be separated at different areas rapidly according to an algorithm based on combination of a fixed threshold value and an adaptive threshold value. According to the invention, the method which is simple has the high execution efficiency and is suitable for detection on multiple moving human objects by a portable through-the-wall radar; a powerful guarantee can be provided for accurate positioning of all moving objects by the through-the-wall radar; and the working efficiency of the through-the-wall radar can be improved effectively.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
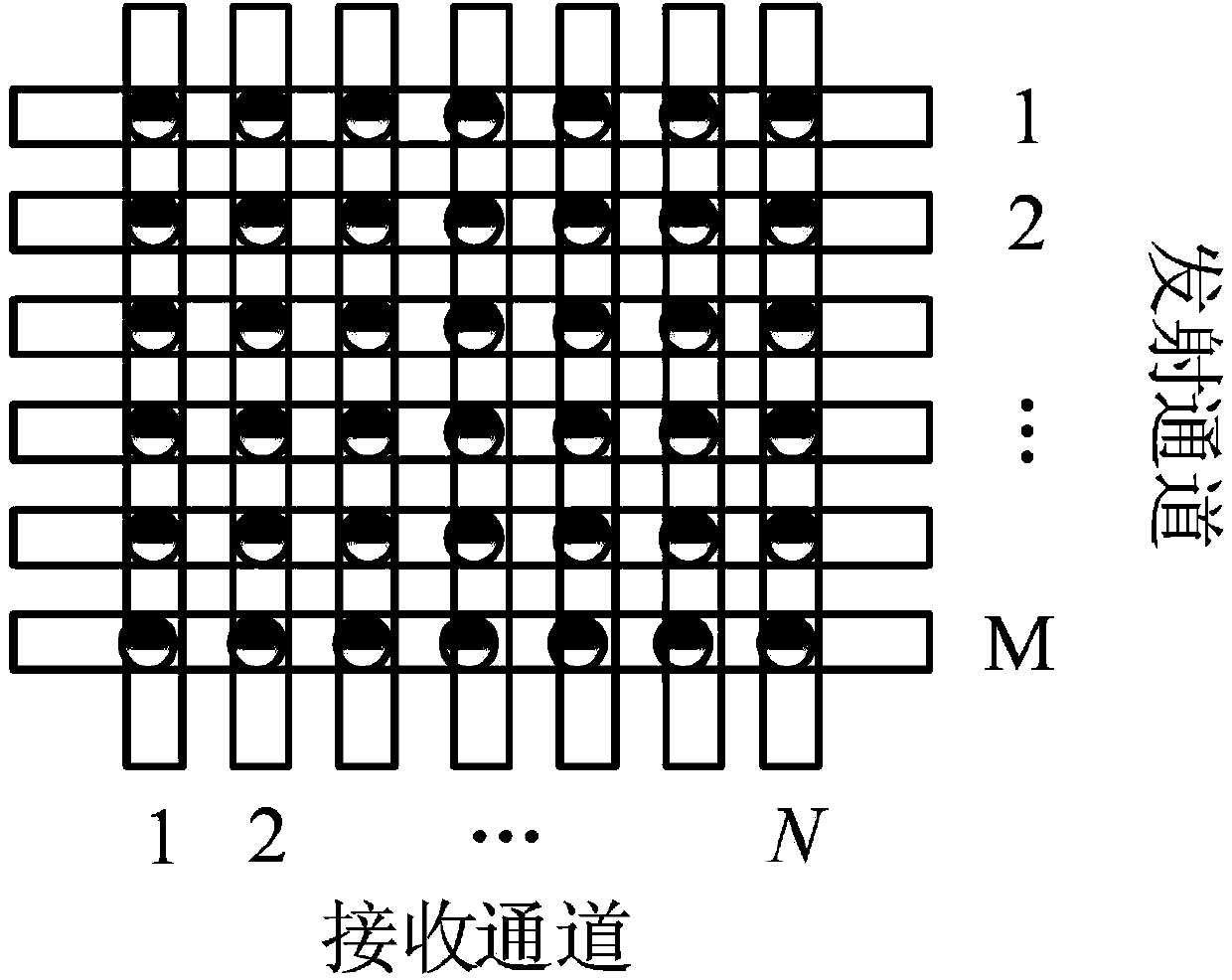
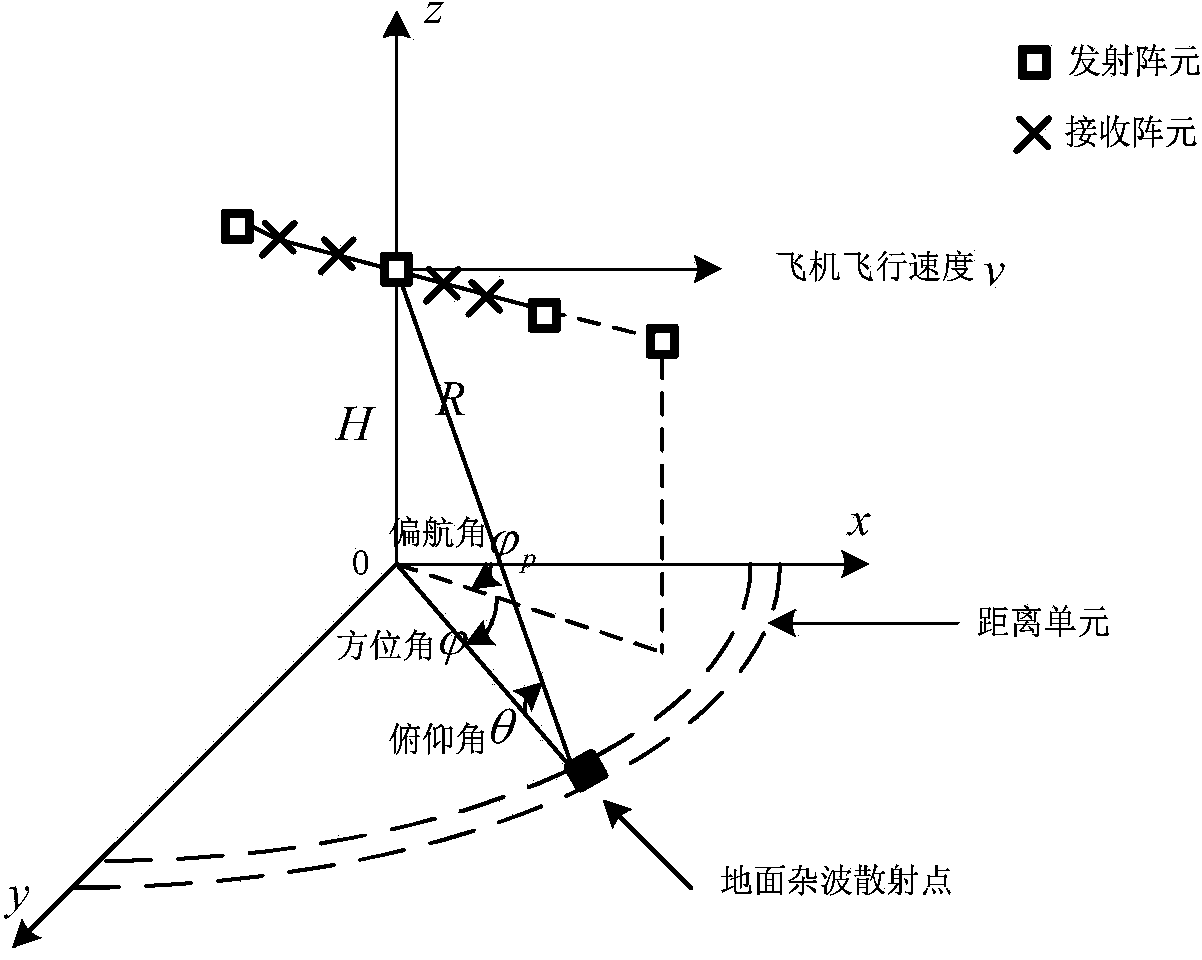
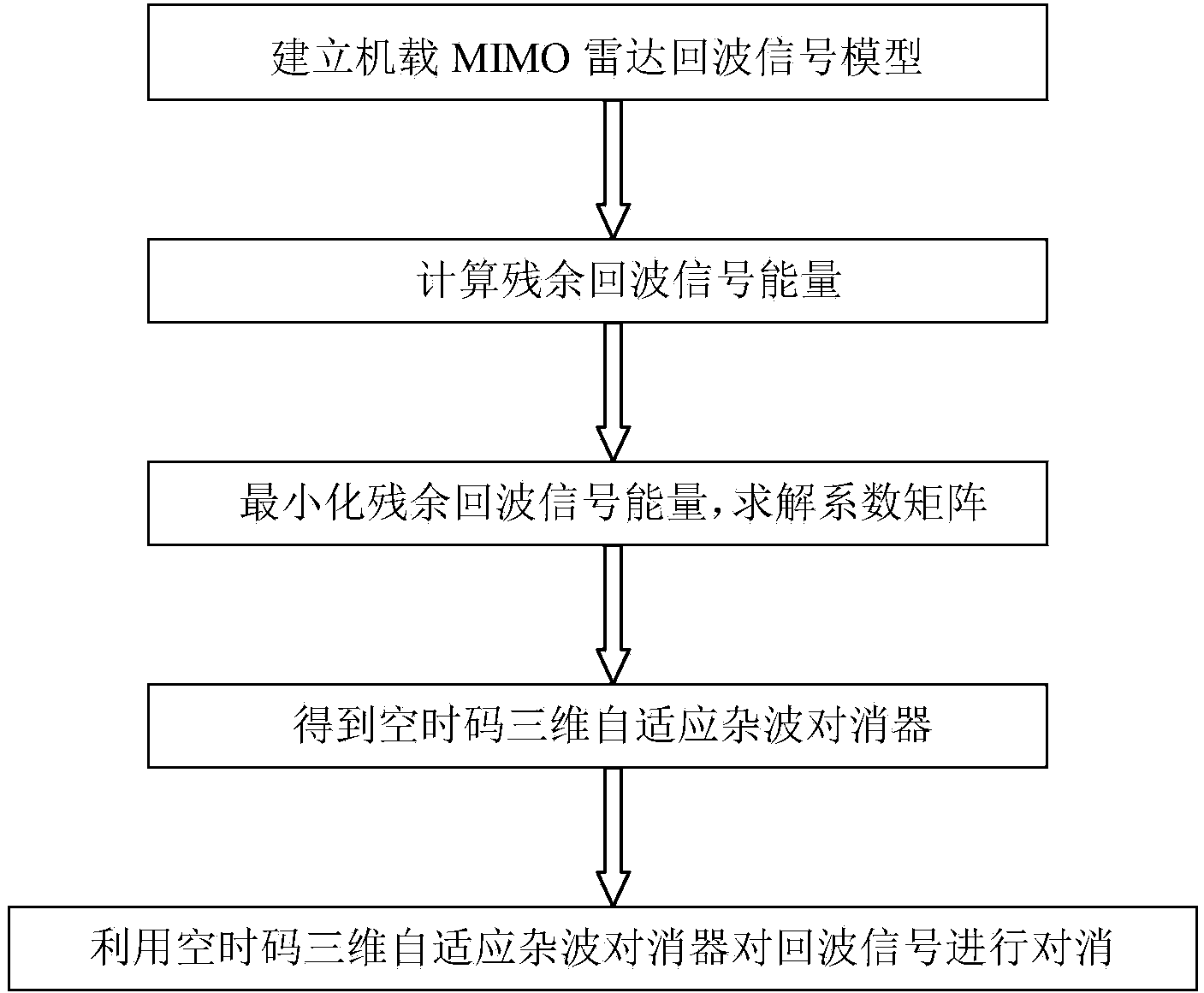
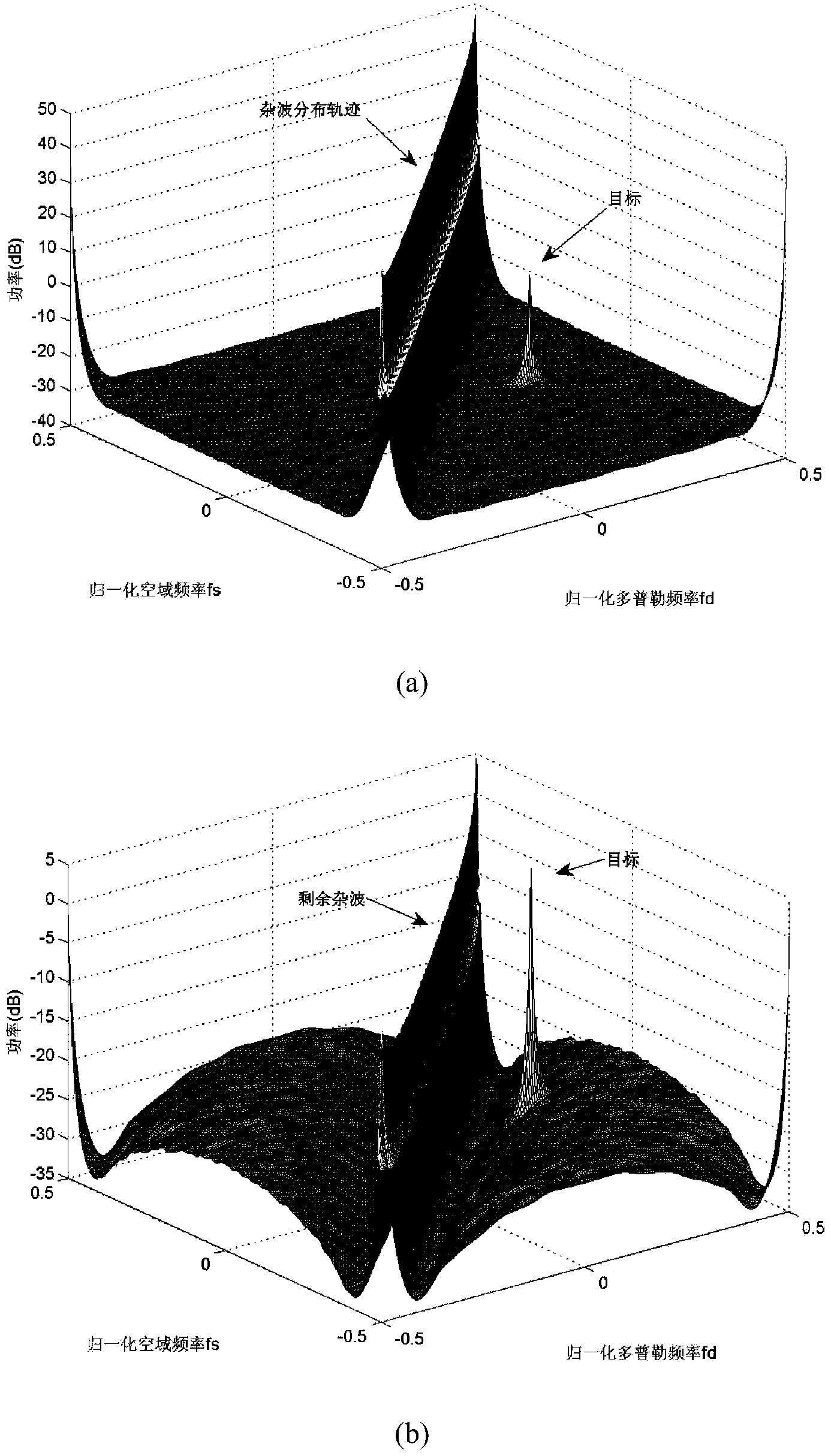
Space time code three-dimensional self-adaptation clutter cancelling method for onboard multiple input multiple output (MIMO) radar
InactiveCN103728607AReduced clutter degrees of freedomSmall amount of calculationWave based measurement systemsSimulationRadar signal processing
The invention discloses a space time code three-dimensional self-adaptation clutter cancelling method for onboard multiple input multiple output (MIMO) radar. The method includes first building an onboard MIMO radar echo signal model, calculating residue echo signal energy, minimizing the echo signal energy to obtain a self-adaptation clutter canceller coefficient compensation device, acquiring a space time code three-dimensional self-adaptation clutter canceller through sliding window arrangement, utilizing the canceller to cancel echo signals and cancelling most clutter through preprocessing of the space time code three-dimensional self-adaptation clutter canceller. The method is used before a common space time code processing method and a dimension reducing STAP method to conduct space time code three-dimensional canceling on the clutter in the onboard MIMO radar echo signals, the clutter can be effectively restrained in the first stage of radar signal processing, and detection performance of a moving target is improved. The method is applicable to both positive side looking radars and non-positive side looking radars, and has good moving target detection capability.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
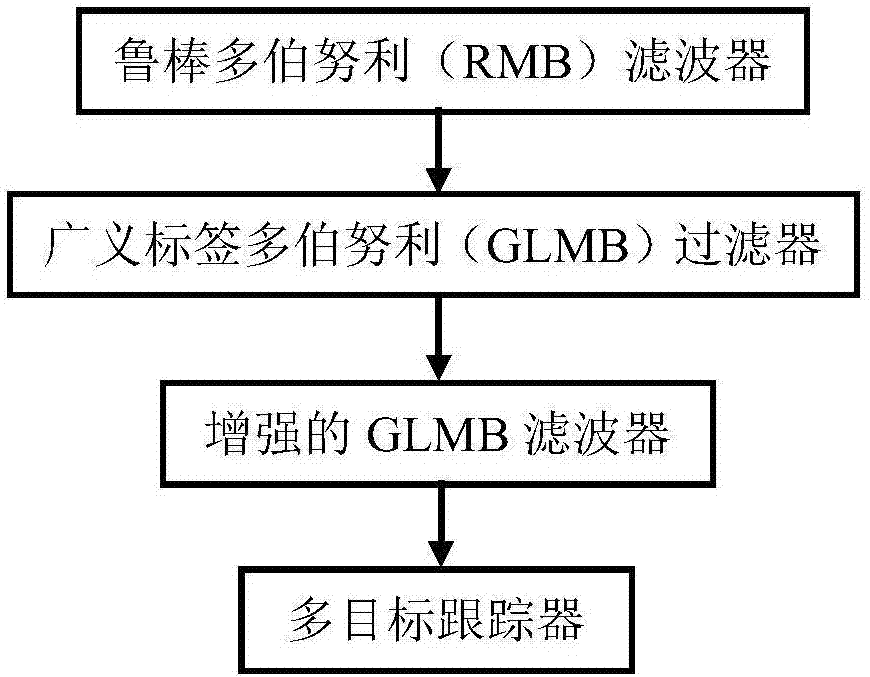
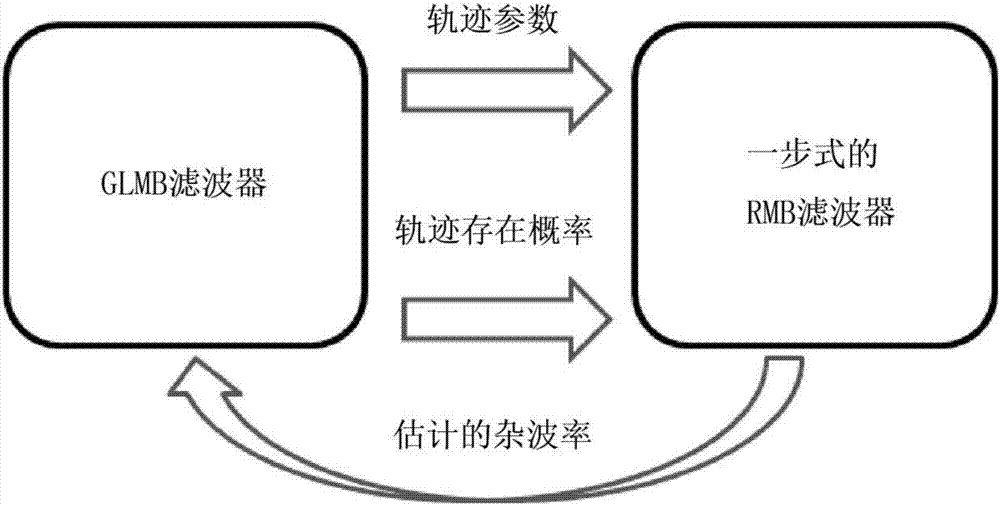
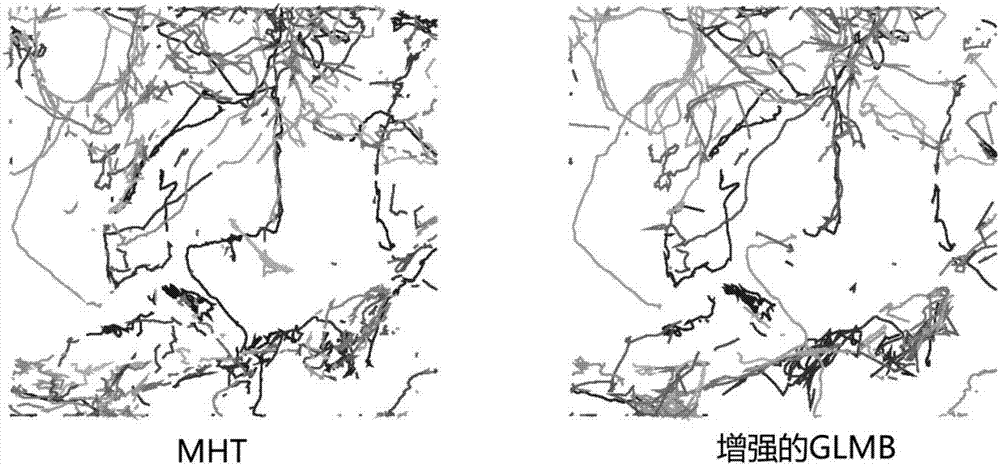
Multi-target tracking method based on random finite set filter coupling
The invention proposes a multi-target tracking method based on random finite set filter coupling, and the method comprises the contents: an RMB (robust multi-Bernoulli) filter, a GLMB (generalized label multi-Bernoulli) filter, an enhanced GLMB filter, and a multi-target tracker. The process comprises the steps: employing the GLMB filter as a main tracker under the condition of an unknown clutter rate so as to generate a track parameter; enabling the one-step RMB filer to modify the unknown clutter rate based on the provided track parameter and track existing probability; inputting the clutter rate estimated by the RMB filter into the GLMB filter, thereby achieving the robust online visual multi-target tracking. The method breaks the limit that different targets cannot be tracked and recognized during the filtering of the unknown clutter rate, and one multi-target tracker is designed for generating independent tracks. Moreover, the unknown clutter rate is estimated in operation, and the method can effectively adapt to a real scene, and achieves a robust multi-target tracking performance.
Owner:SHENZHEN WEITESHI TECH
Method for supporting low-level flights
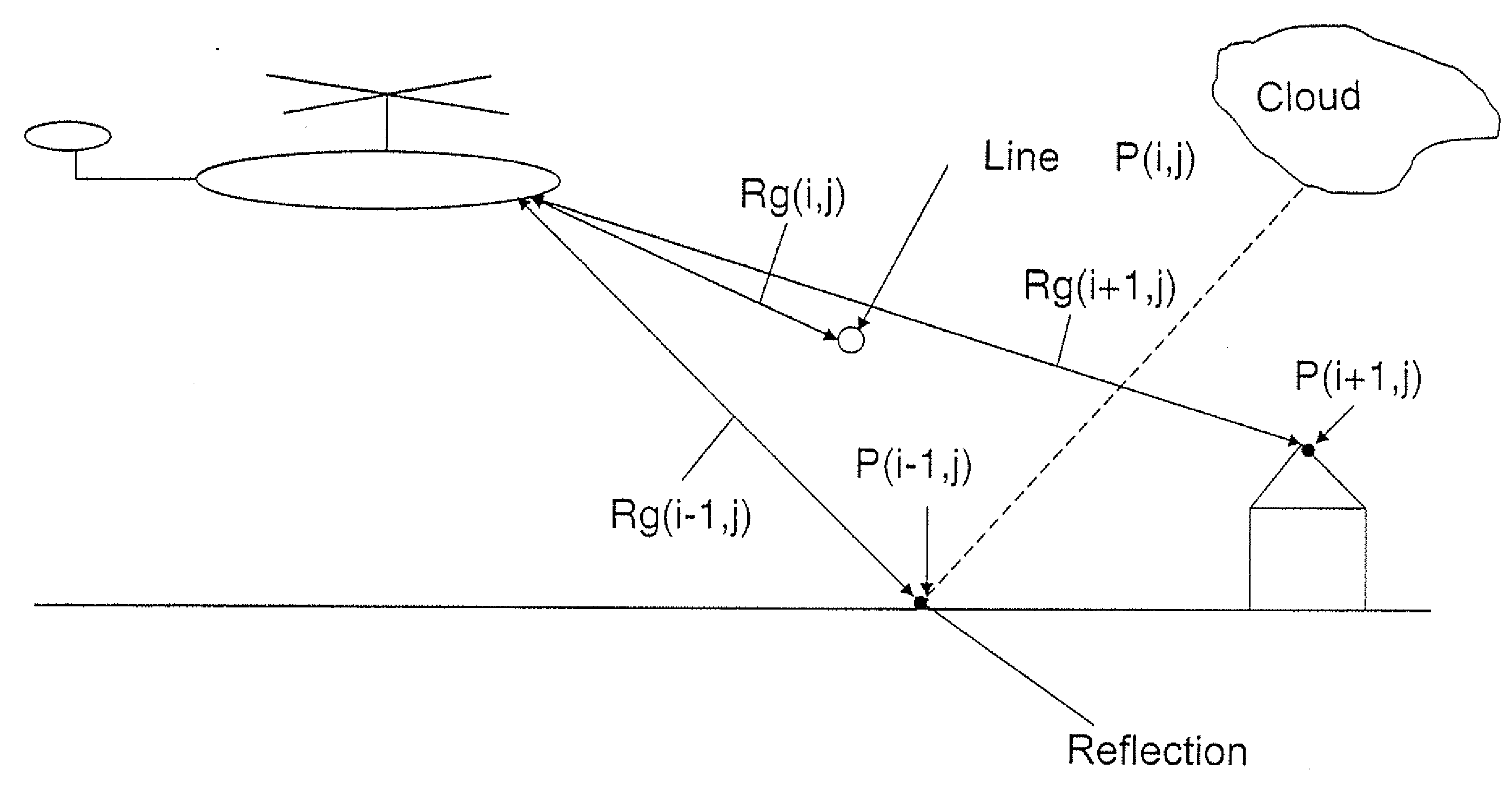
InactiveUS20070086657A1Reliably recognizeReliable methodDigital data processing detailsAnti-collision systemsTerrainSky
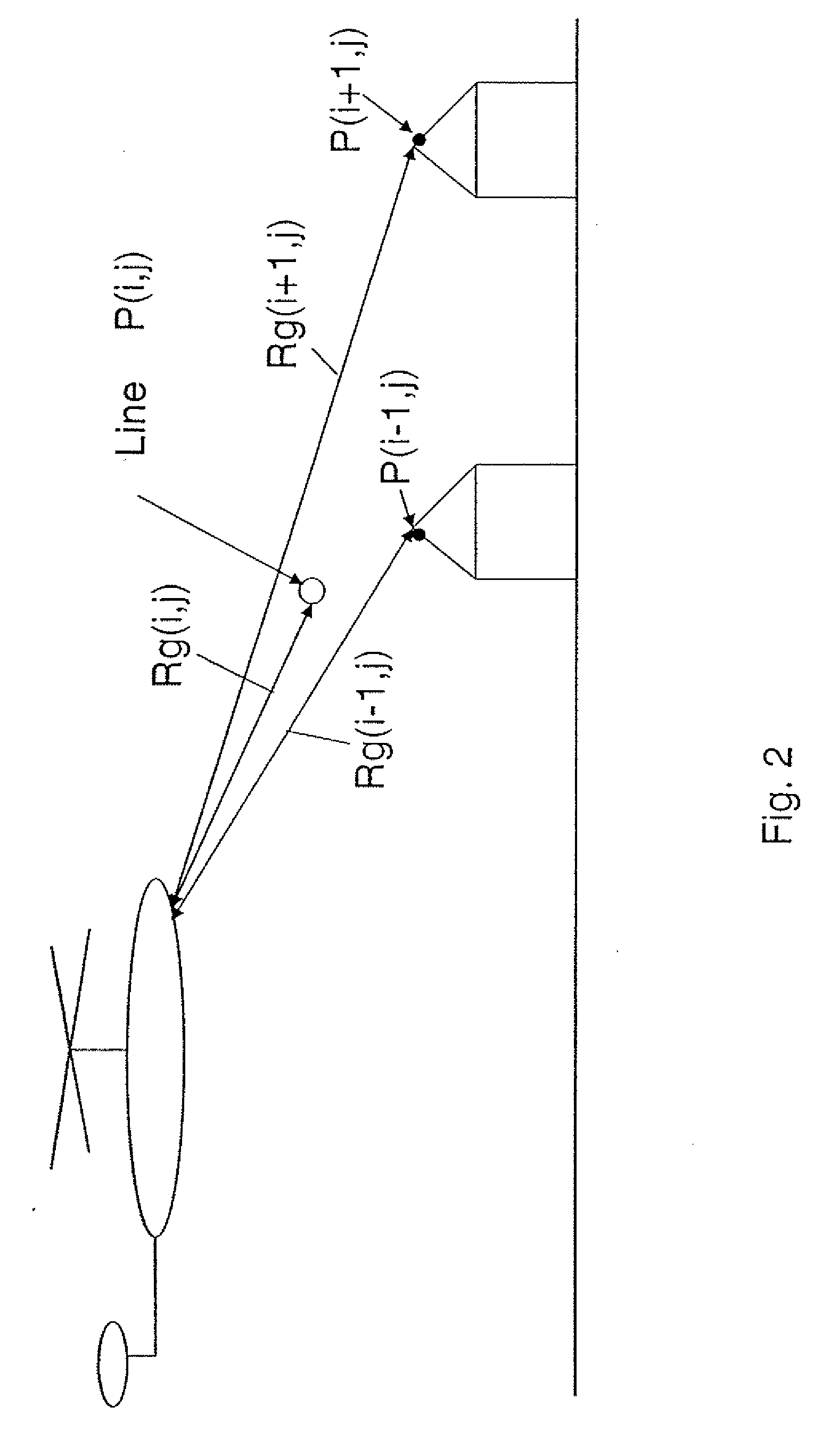
A method for supporting low-level aircraft flights in which a warning is provided for the pilot upon a reliable recognition of wire-like obstacles, even during extreme environmental influences, such as clutter, or even when such obstacles are seen against the sky. The method is performed upon the collection of information on the topography of the surrounding terrain by at least one sensor located on the aircraft, such information representing raw data, based upon which an image-like representation is calculated, such representation including a pixel quantity with pixels P(i, j) in columns j and lines i, which image-like representation is evaluated by calculating altitude values in a geodetic coordinate system using the flight condition from the aircraft, evaluating pixel quantity by comparing each pixel P(l, j) to threshold values or ranges of values, evaluating the image-like representation and highlighting each pixel as a picture element if any of various cases is present.
Owner:AIRBUS DEFENCE & SPACE
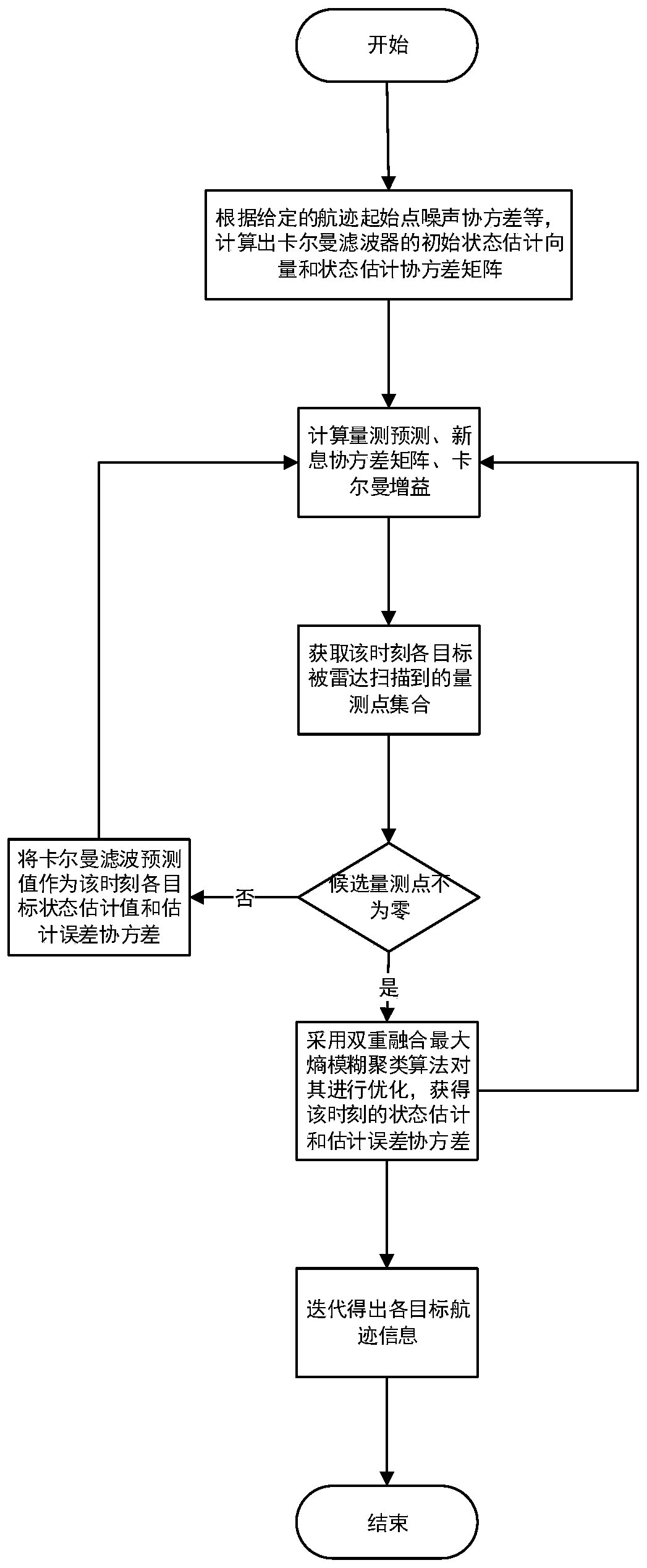
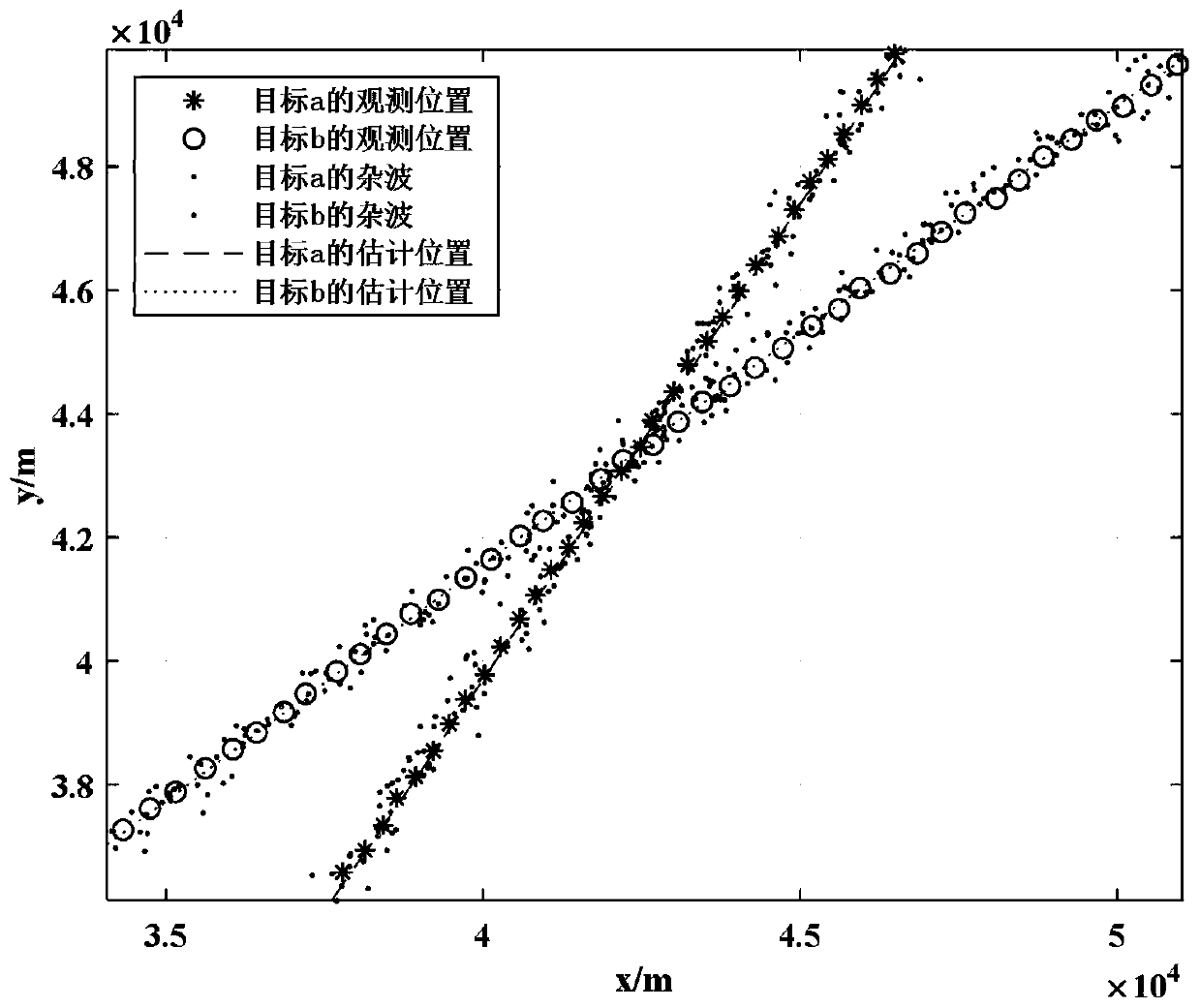
Target track optimization method based on dual-fusion maximum entropy fuzzy clustering JPDA
ActiveCN111007495AAvoid associationImprove the speed of associationInternal combustion piston enginesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionKaiman filterState prediction
The invention belongs to the technical field of radar. The invention relates to a flight path optimization method, in particular to a target track optimization method based on dual-fusion maximum entropy fuzzy clustering JPDA. The method comprises the following steps: (1) performing state prediction and updating by adopting a Kalman filter on the basis of a maximum entropy fuzzy clustering method,and performing preliminary screening on a target trace point set obtained at a moment k + 1according to an elliptical wave gate rule during scanning and tracking; (2) multiplying the measurement membership degree taking the wave gate center as the clustering center by the corresponding position of the wave gate membership degree taking the effective measurement data as the clustering center to obtain the bidirectional membership degree between each effective measurement and all the wave gate centers; and (3) analyzing clutter distribution and combining the bidirectional membership degree to obtain a final association probability, obtaining state estimation and estimation error covariance of the target according to a standard JPDA algorithm filtering program, and finally iterating trackingtrack information of the target. The method is high in tracking precision, and avoids complex correlation matrix splitting.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
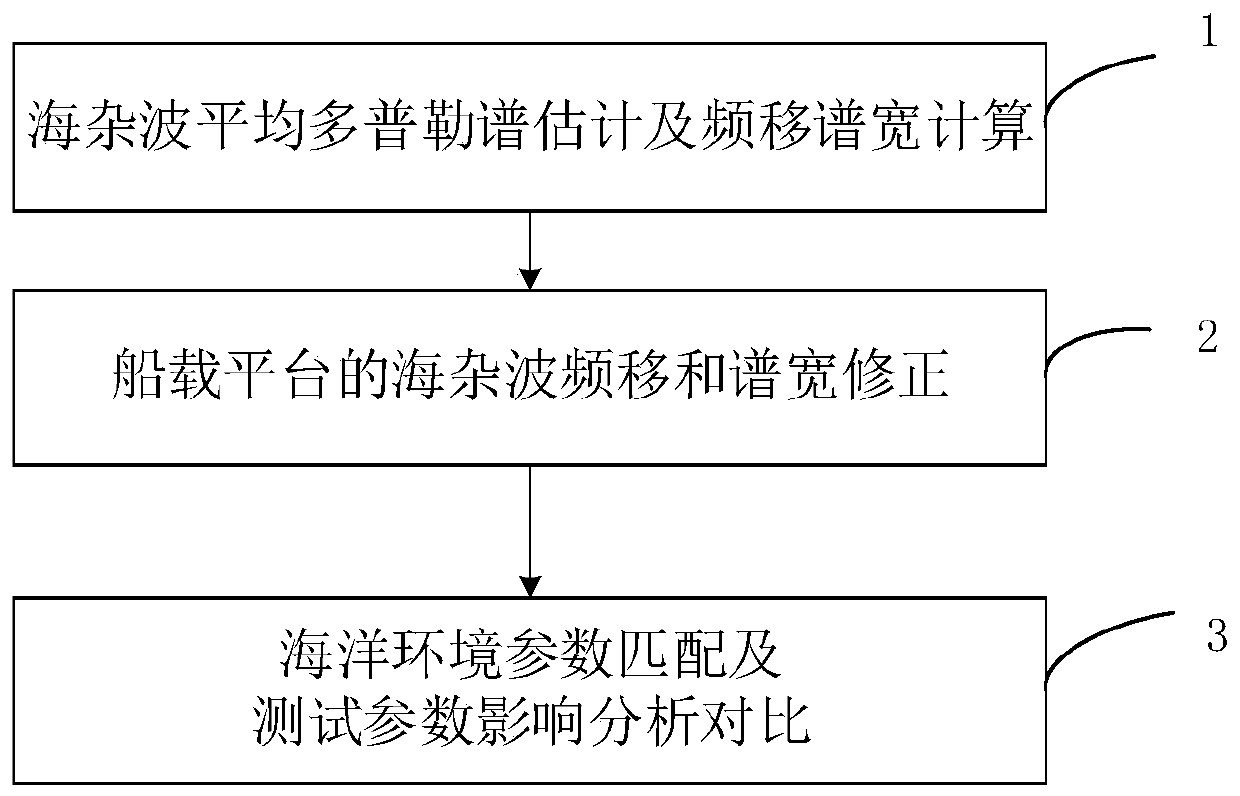
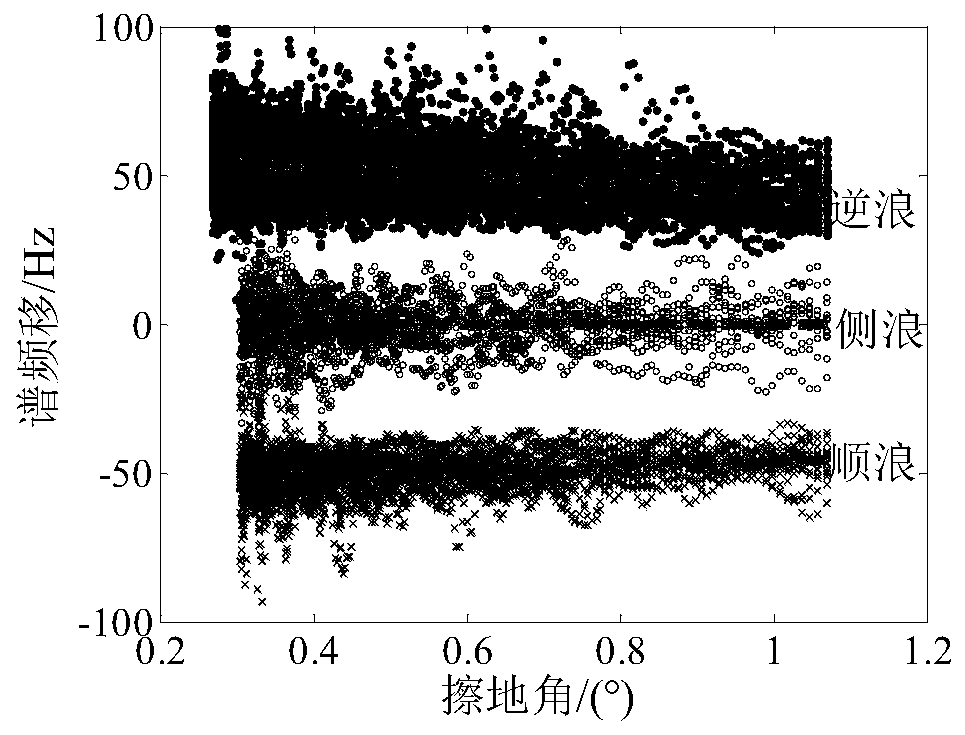
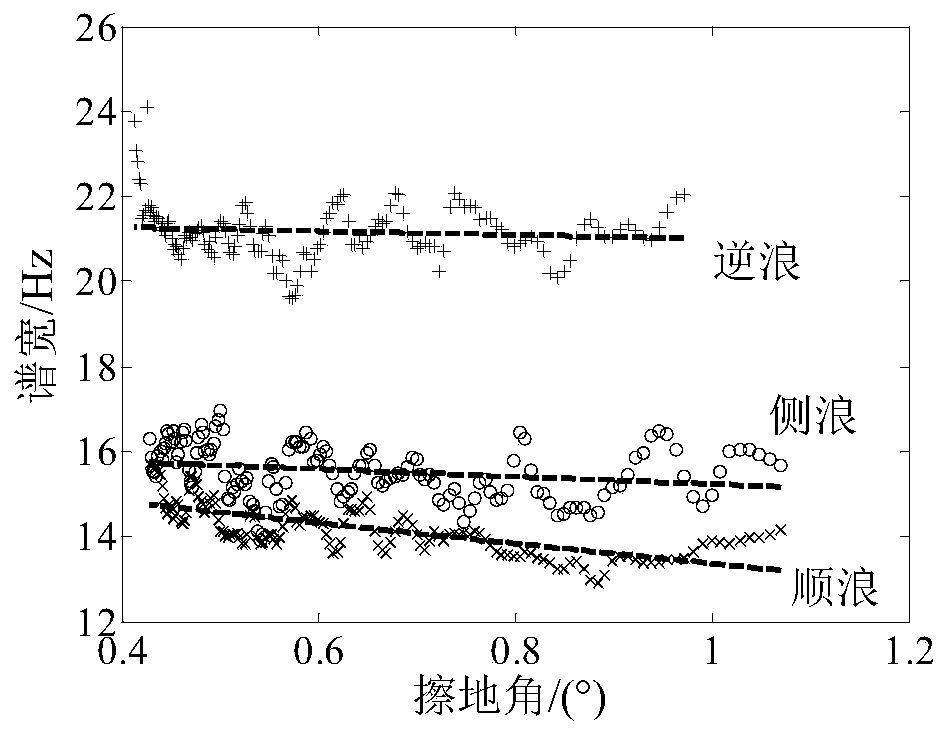
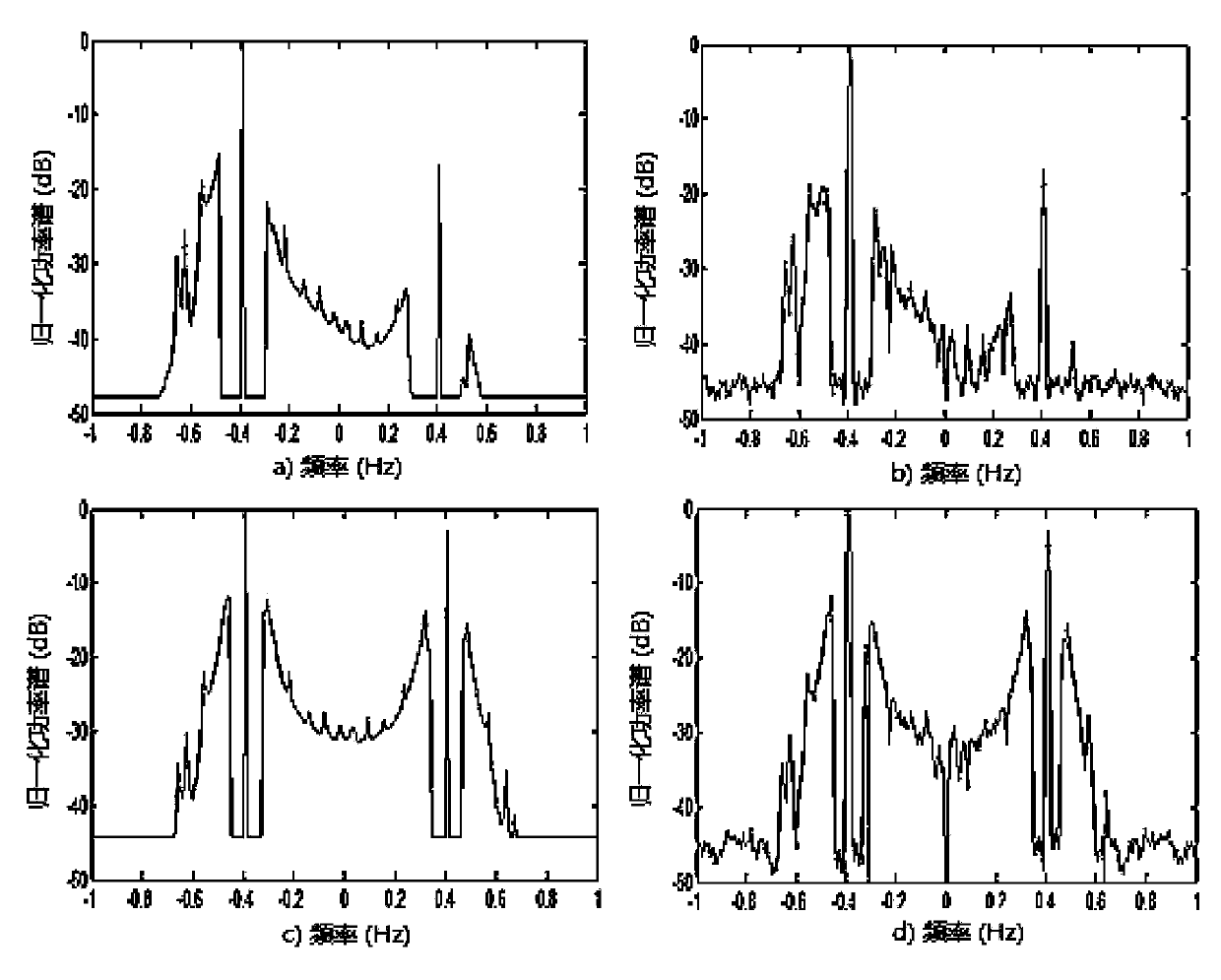
Sea clutter Doppler spectrum characteristic analysis and comparison method
ActiveCN110907907AEasy to analyzeAdd data sourceWave based measurement systemsSpectral widthAcoustics
The invention discloses a sea clutter Doppler spectrum characteristic analysis and comparison method. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, sea clutter average Doppler spectrum estimationand frequency shift spectrum width calculation; step 2, sea clutter frequency shift and spectral width correction of the shipborne platform; and step 3, marine environment parameter matching and testparameter influence analysis and comparison. Aiming at the phenomena of platform difference influence and complex and diverse test parameter conditions existing in sea clutter Doppler spectrum characteristic analysis and comparison of the same radar in multi-platform test, the invention provides the sea clutter Doppler spectrum characteristic analysis and comparison method. The influence caused bythe movement of the shipborne platform is corrected, and a certain analysis sequence and steps are designed according to the size difference of the influence of radar parameters and marine environment parameters, so that the Doppler spectrum characteristic difference of the same radar under various marine environment conditions tested by different platforms can be conveniently and quickly obtained.
Owner:中国电波传播研究所
Method and system for identifying marine oil spill object by marine radar
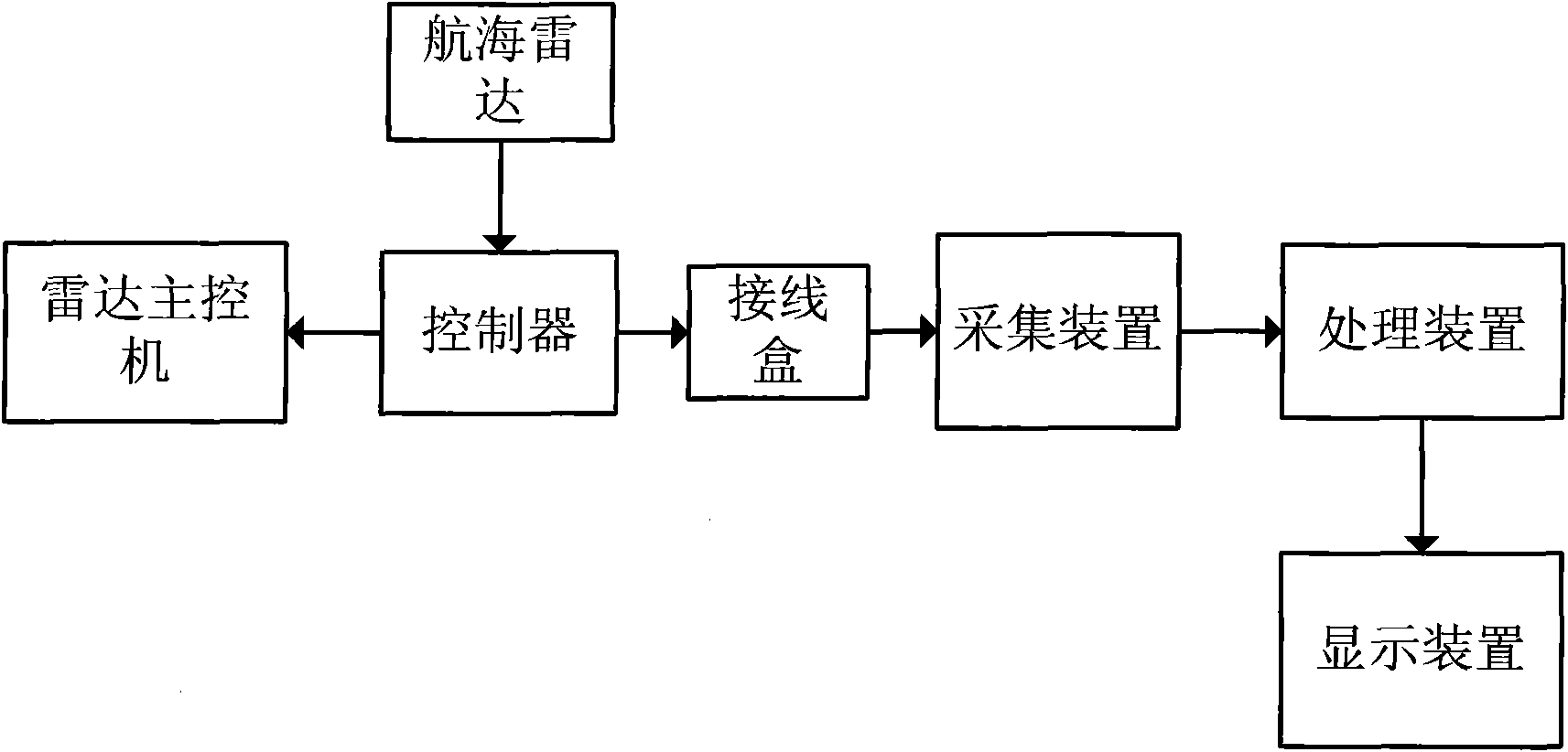
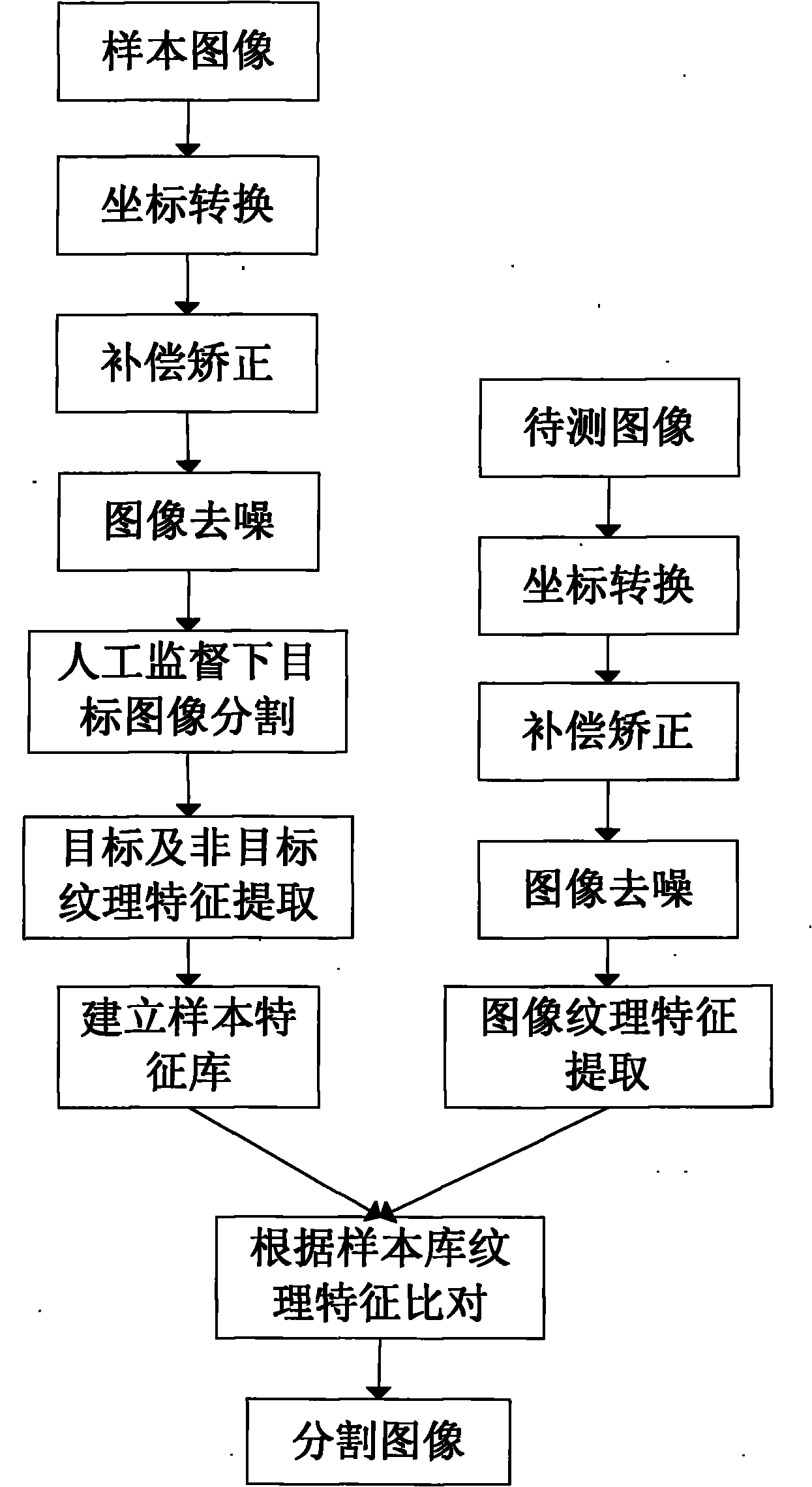
ActiveCN101915910AReduce extractionEasy extractionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSea wavesDisplay device
The invention discloses a method and system for identifying a marine oil spill object by a marine radar. The method of the invention comprises the following steps: A, converting output image signals from radar projection into Descartes projection; B, correcting images and compensating motion; C, processing the radar images corrected in the step B by a Gamma filtering method, reserving marginal information and simultaneously filtering high-frequency noise of the radar images; D, detecting a strong signal area in the images, according to the distribution of signal strength in the images, determining the saturated state strength as the strength threshold of the signal area, and directly deleting the signal data exceeding the strength threshold; and E, carrying out image segmentation by a gray level co-occurrence matrix method to abstract the marine oil spill object. The system comprises a radar main controller, a marine radar controller, a junction box, an acquisition device, a processing device and a display device. The invention utilizes the noise wave information such as ocean wave and the like to obtain a small object, identifies the oil spill object by a texture algorithm, and can better abstract the marine oil spill object.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Space-time adaptive processing method for radar clutters based on prior knowledge
InactiveCN106483516AImprove robustnessWave based measurement systemsRadarSpace-time adaptive processing
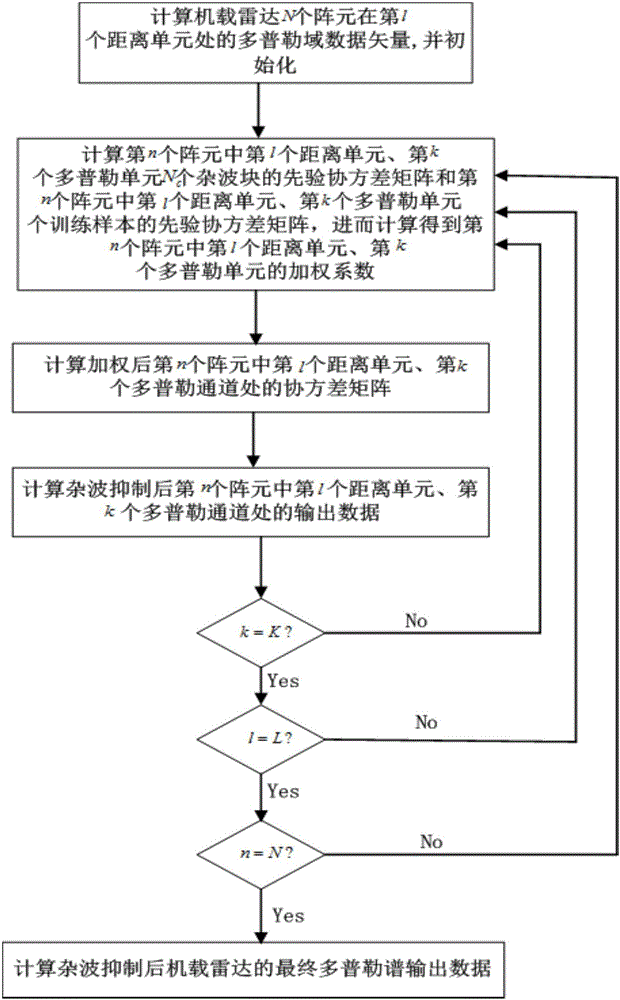
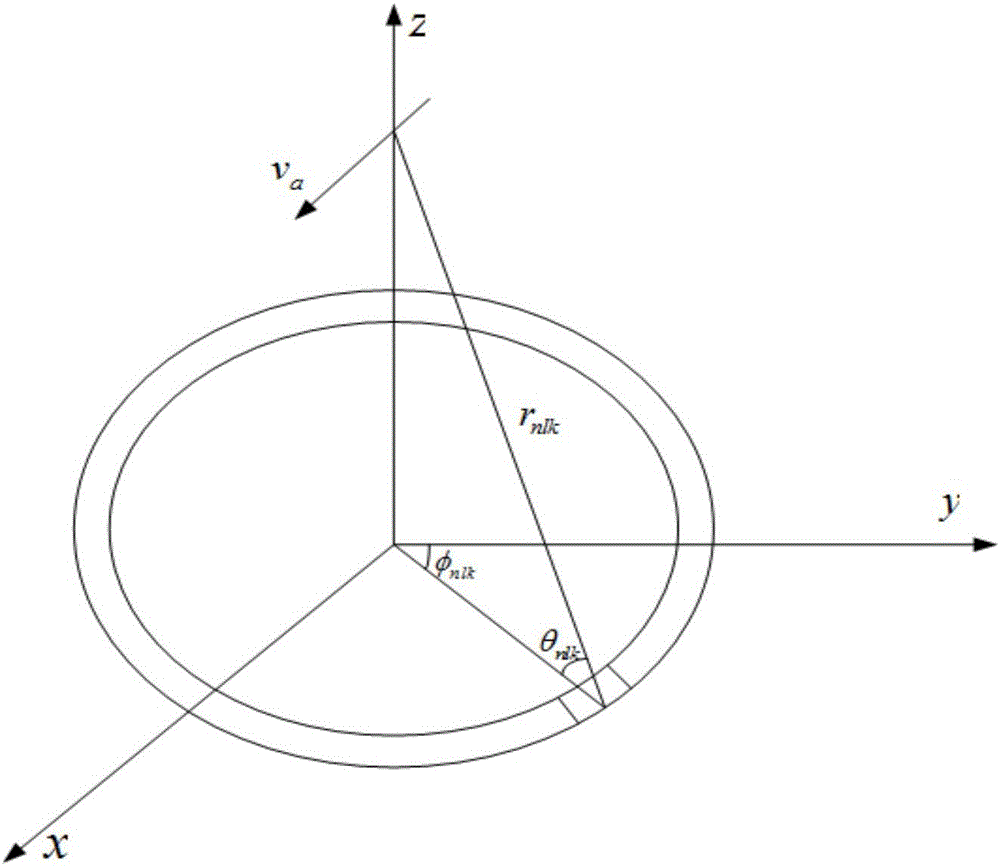
The invention discloses a space-time adaptive processing method for radar clutters based on prior knowledge. An airborne radar is determined, the airborne radar includes N array elements, each array element includes L distance units, each distance unit includes K coherent pulses, Doppler domain data vectors in the first distance units of the N array elements of the airborne radar are calculated, and the weighted coefficient alphanlk of the first distance unit in the nth array element and the kth Doppler unit, the Doppler domain data vectors znlk of the first distance unit in the nth array element in the (k-1)th, kth and (k+1)th Doppler channels, and a covariance matrix Rnlk of the first distance unit of the weighted nth array element in the kth Doppler channel are calculated successively; a space-time filter coefficient wnlk of the first distance unit in the nth array element and the kth Doppler channel is calculated, and output data ynlk of the first distance unit in the nth array element and the kth Doppler channel after clutter inhibition is calculated; and further, final Doppler-spectrum output data of the airborne radar after clutter inhibition is calculated.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
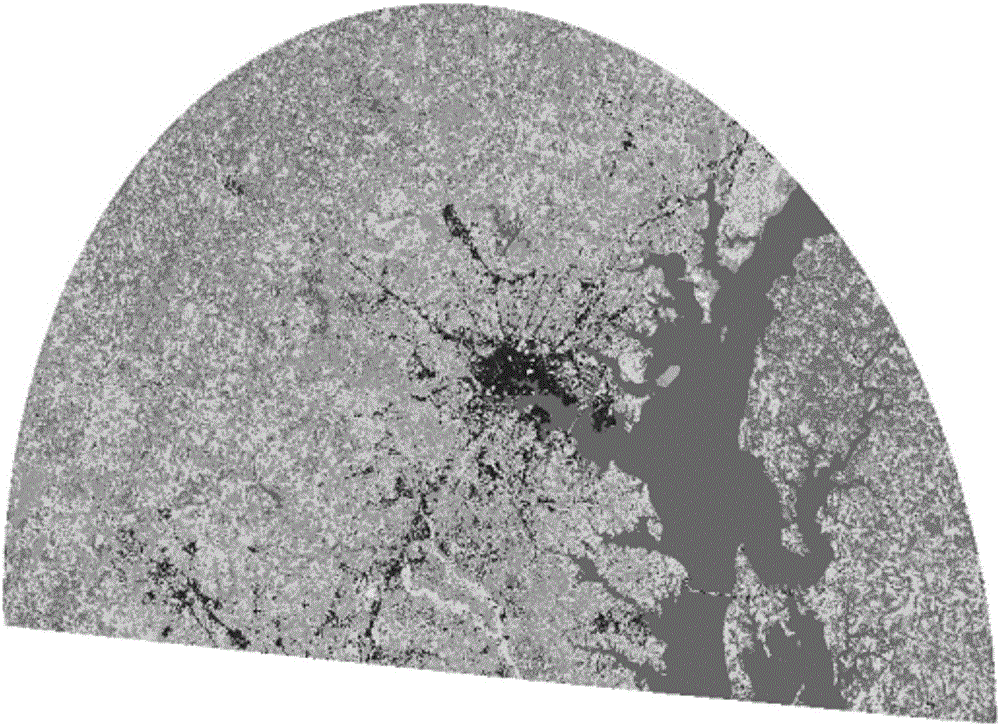
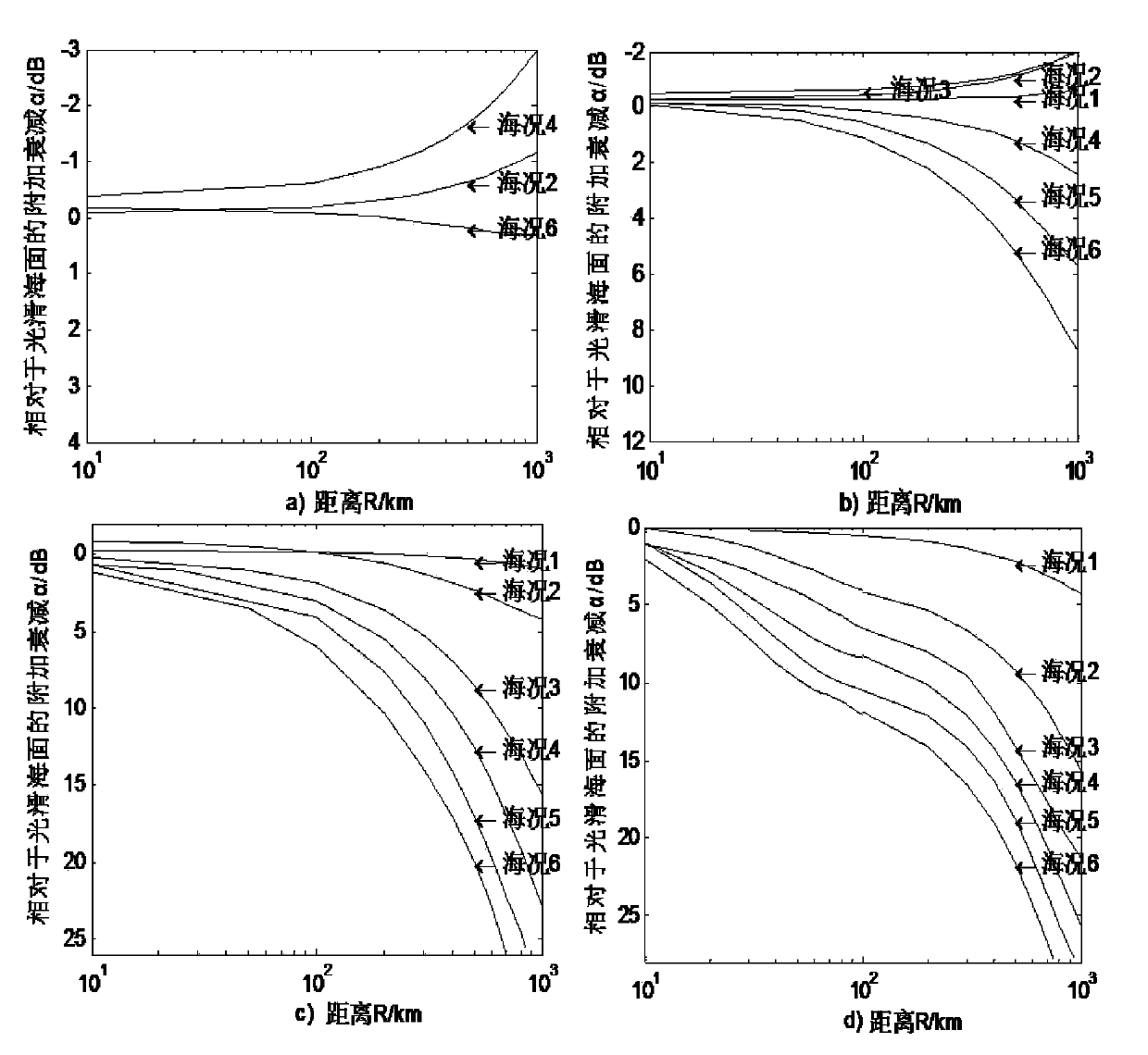
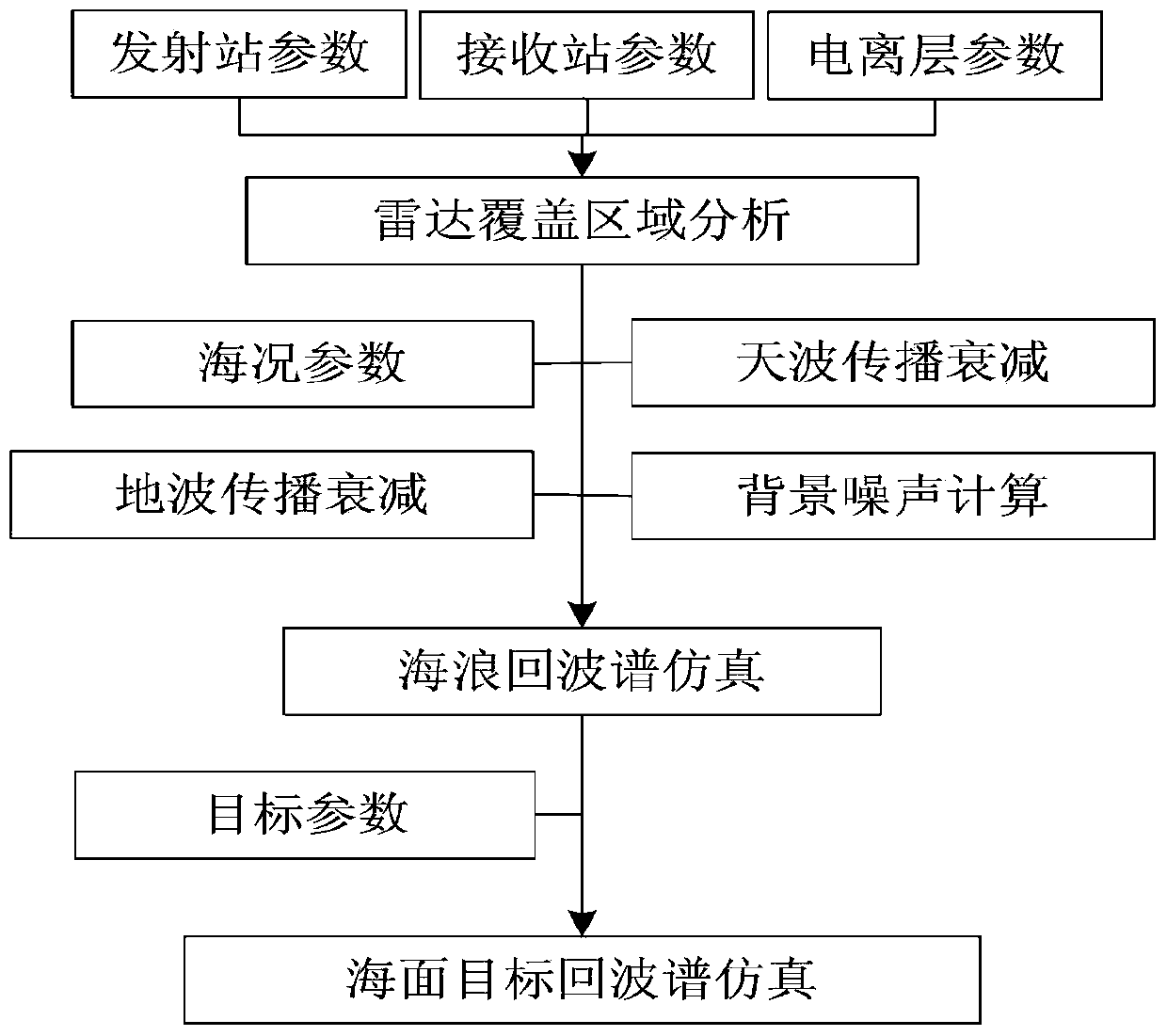
Sky wave and ground wave hybrid radar echo spectrum simulating method
The invention discloses a sky wave and ground wave hybrid radar echo spectrum simulating method. The method comprises the following steps of calculation on positioning of an object of a sky wave and ground wave radar, calculation on transmission attenuation, simulation on a radar echo spectrum under the background of noise and simulation on a radar echo spectrum under the background of sea clutter. A complete process of a sky wave and ground wave hybrid radar is completely shown from an objective positioning model; in the complete process, a sky wave radar transmits high-frequency electromagnetic waves, a ground wave receiving station receives sea echo and also receives noise, attenuation and clutter in the process, and the final echo spectrum shows that the radar with the novel system can detect a given object on a certain sea surface really; and the detection performance of the radar in the type is analyzed, and a certain reference is provided for later research on a novel processing algorithm and construction of a guiding position.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com