Patents
Literature
113 results about "Space-time adaptive processing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
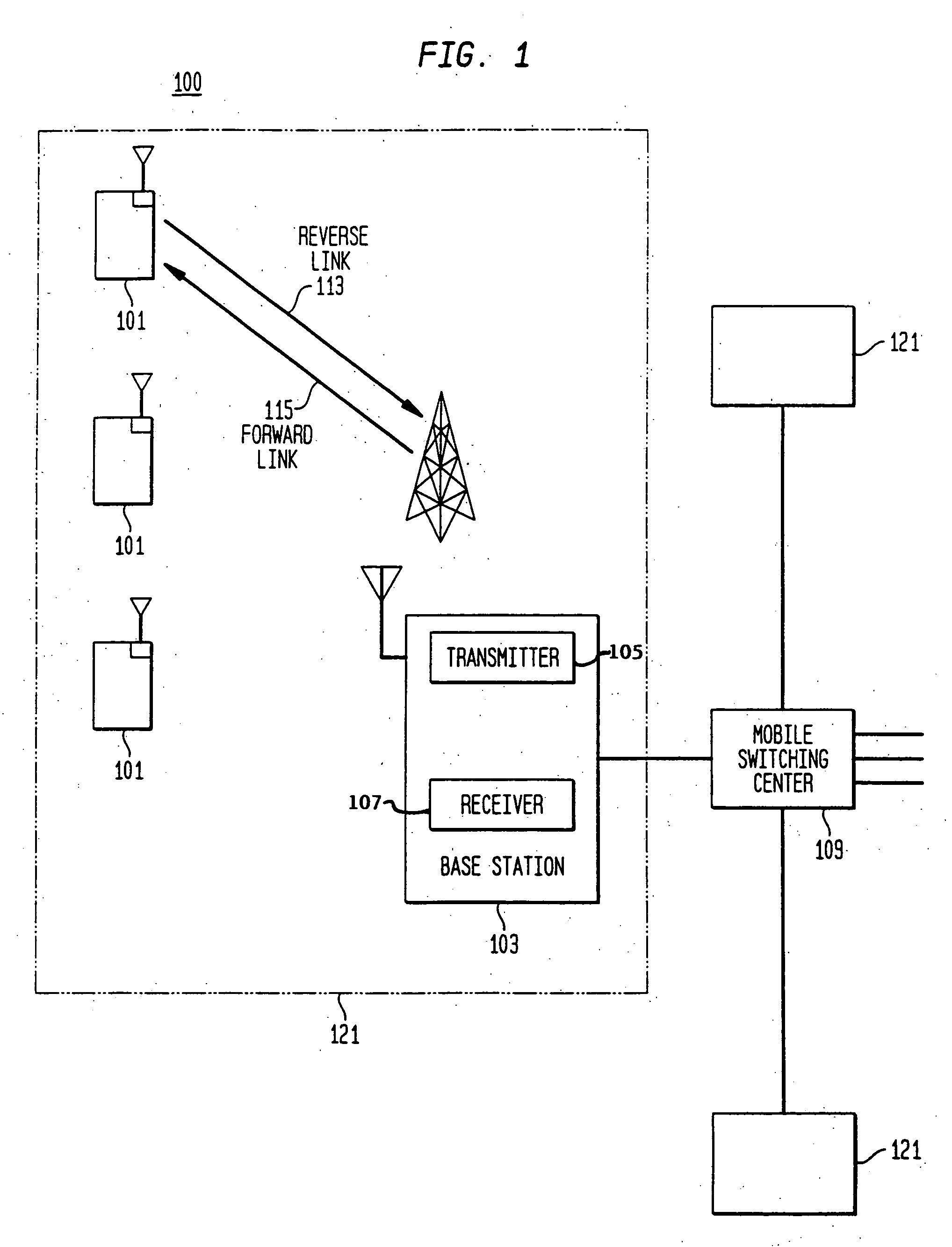
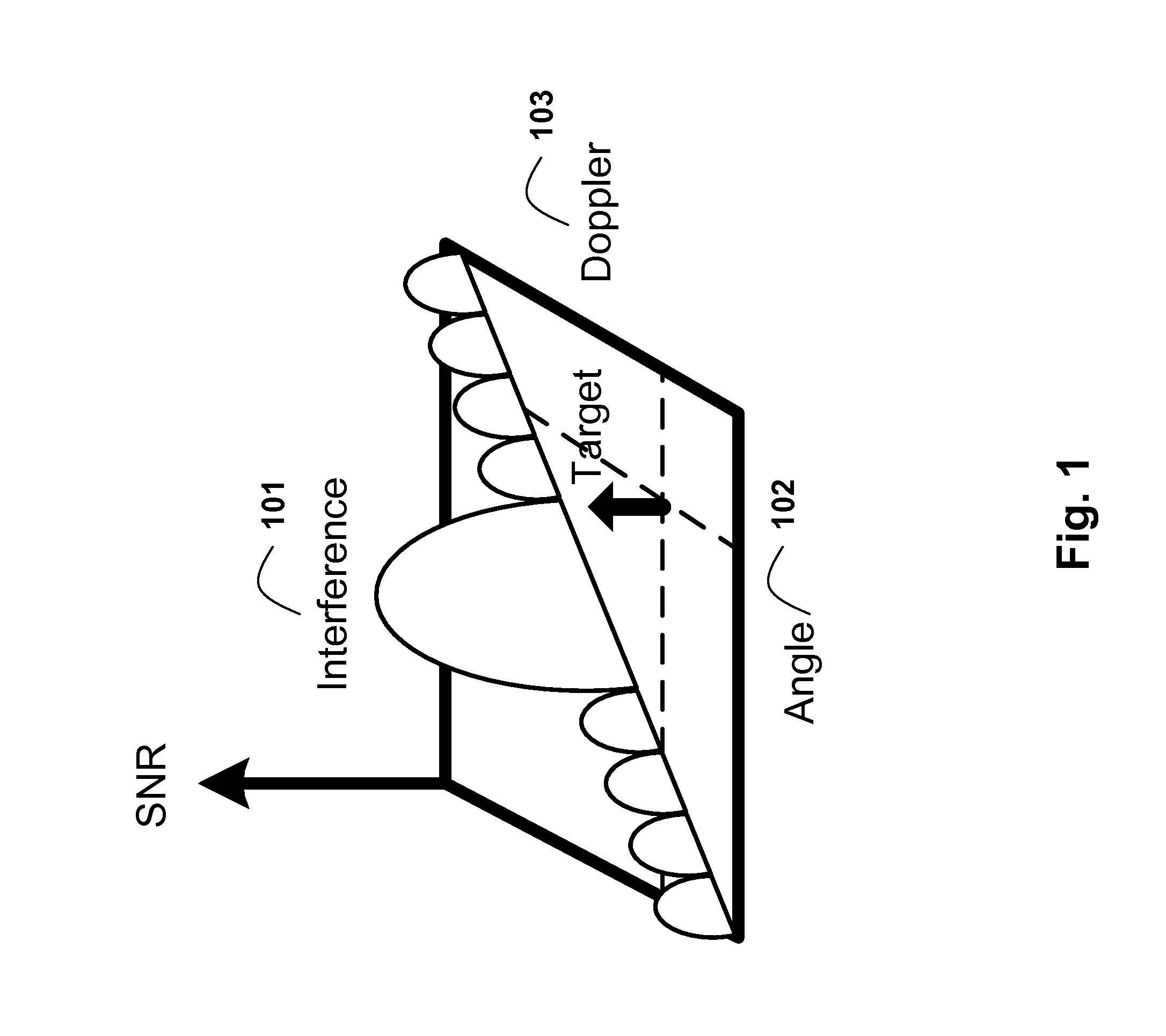
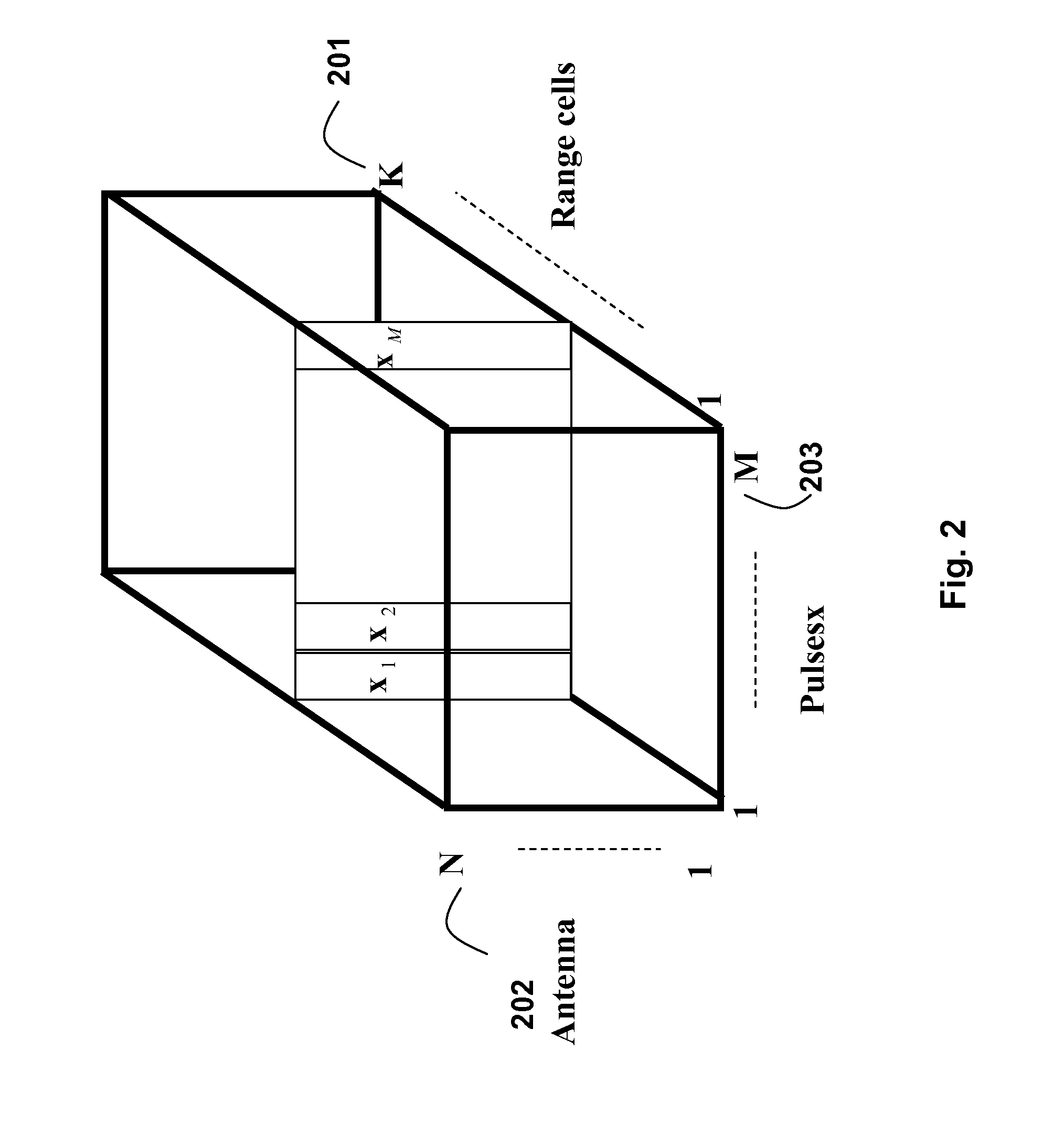
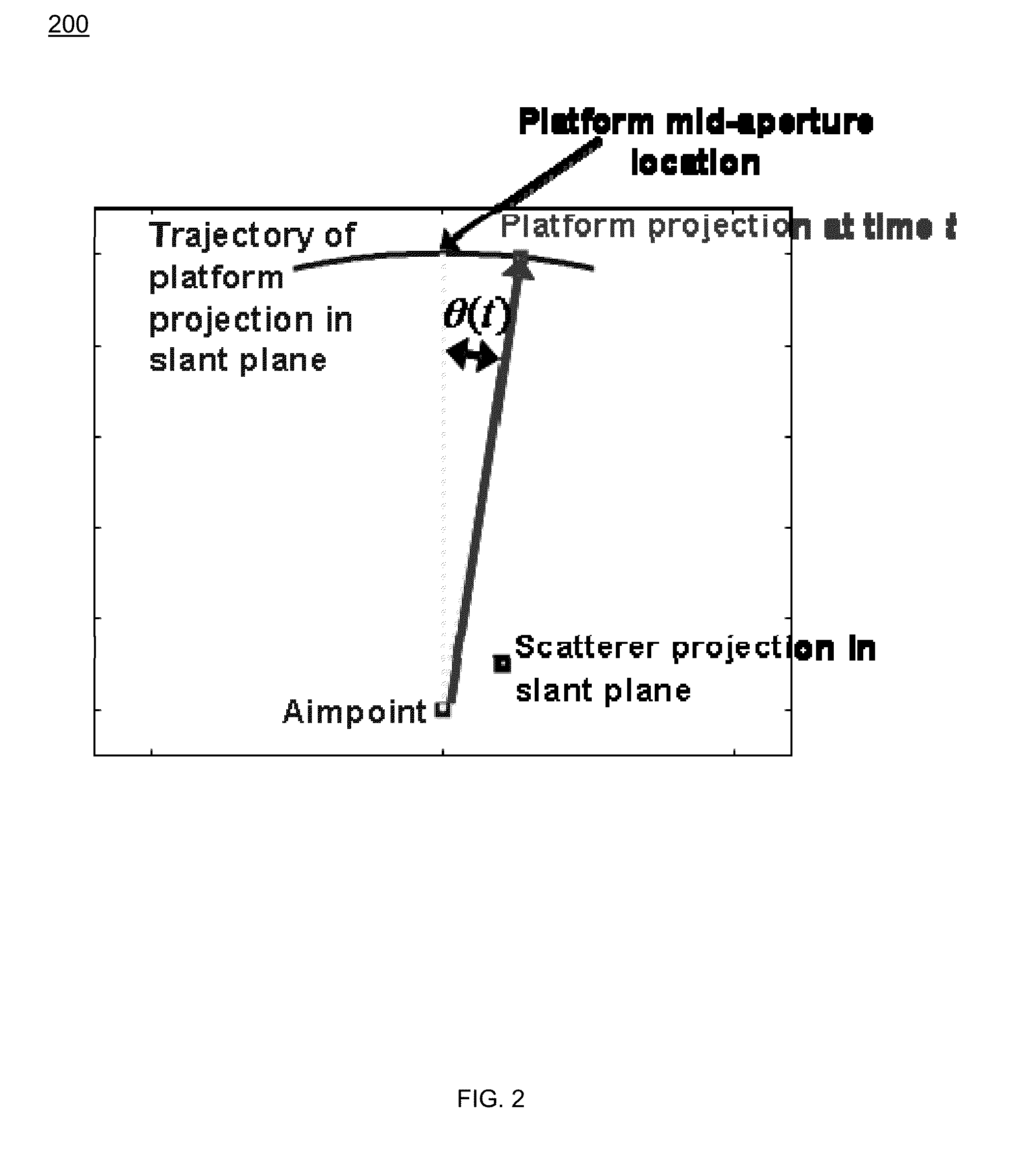
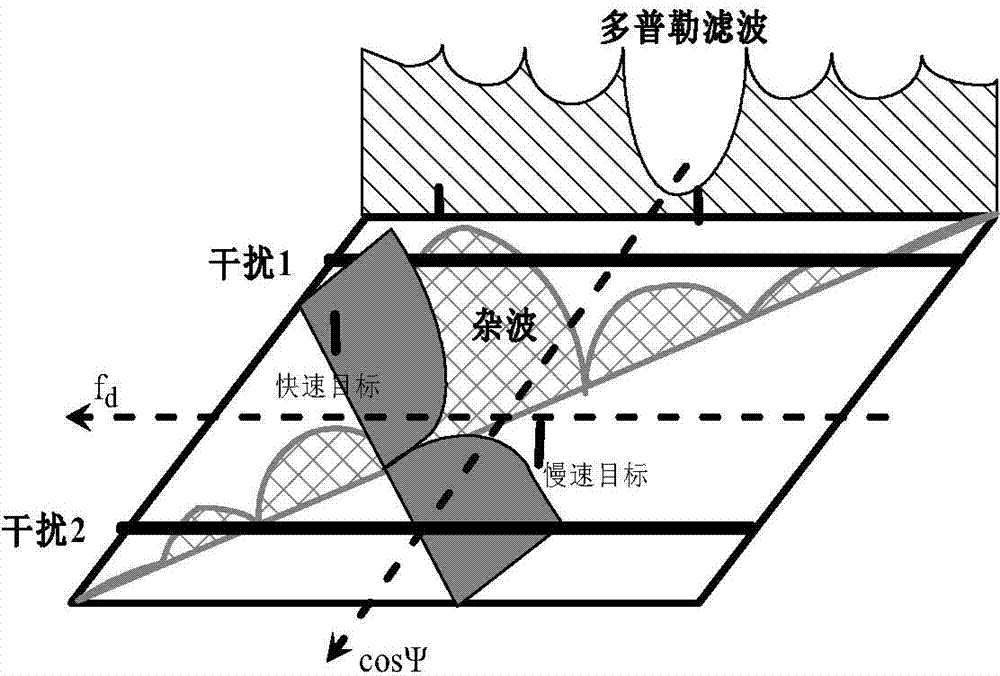
Space-time adaptive processing (STAP) is a signal processing technique most commonly used in radar systems. It involves adaptive array processing algorithms to aid in target detection. Radar signal processing benefits from STAP in areas where interference is a problem (i.e. ground clutter, jamming, etc.). Through careful application of STAP, it is possible to achieve order-of-magnitude sensitivity improvements in target detection.
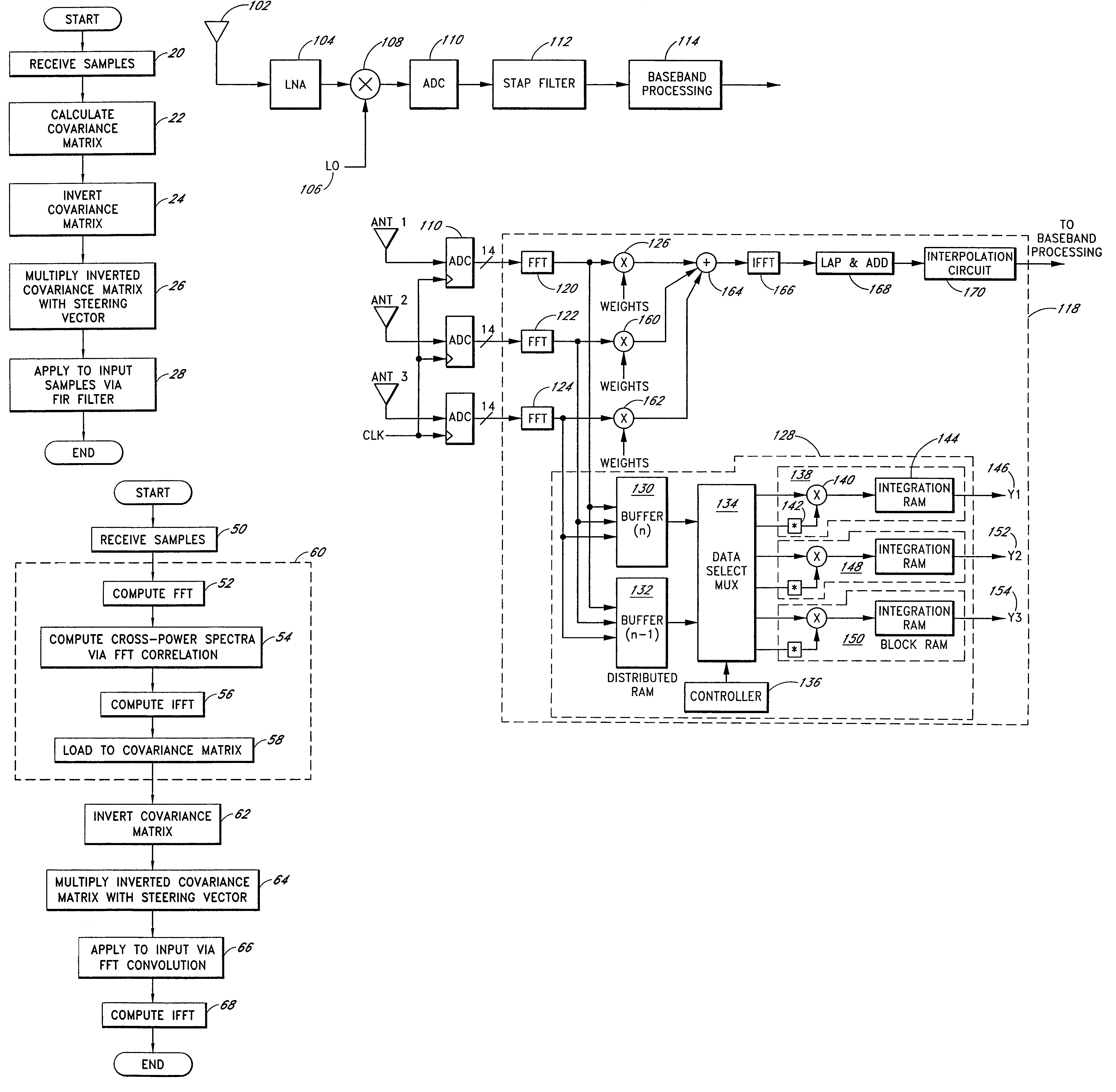
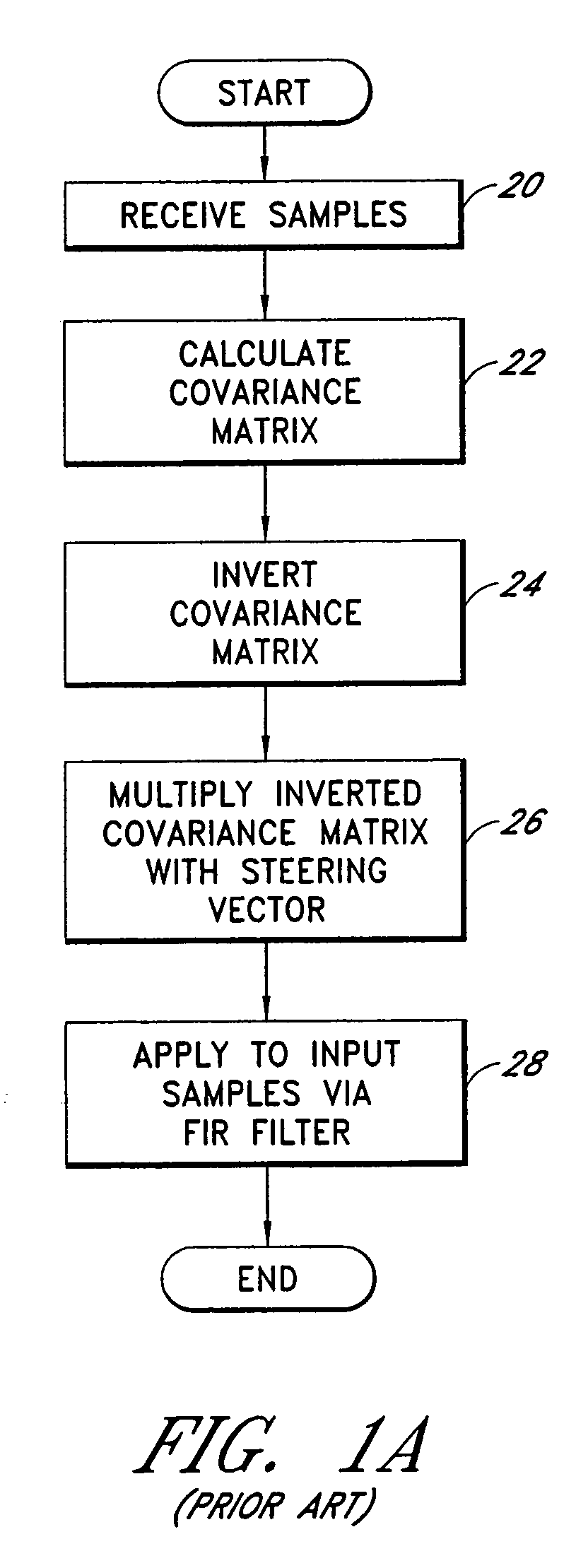
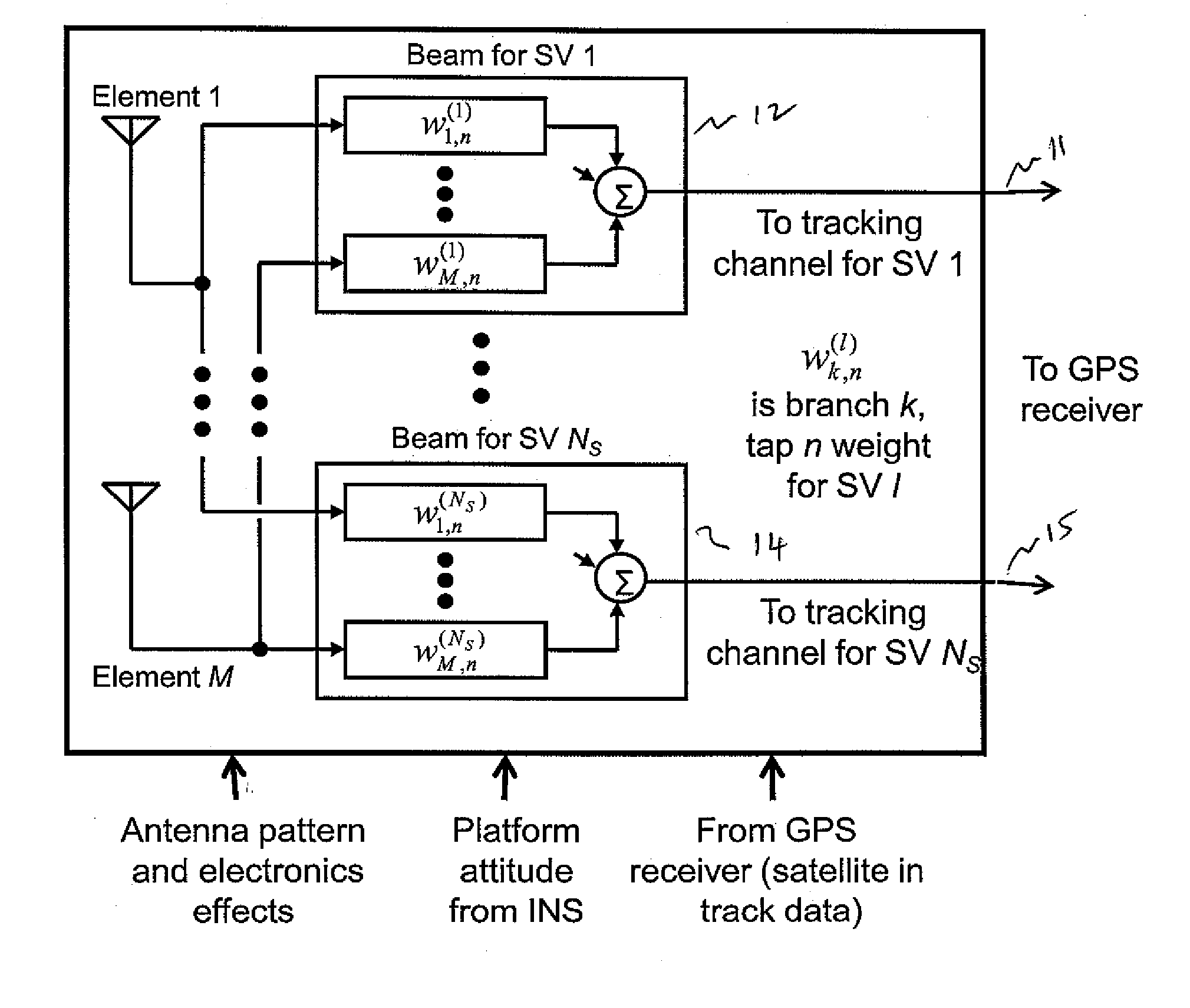
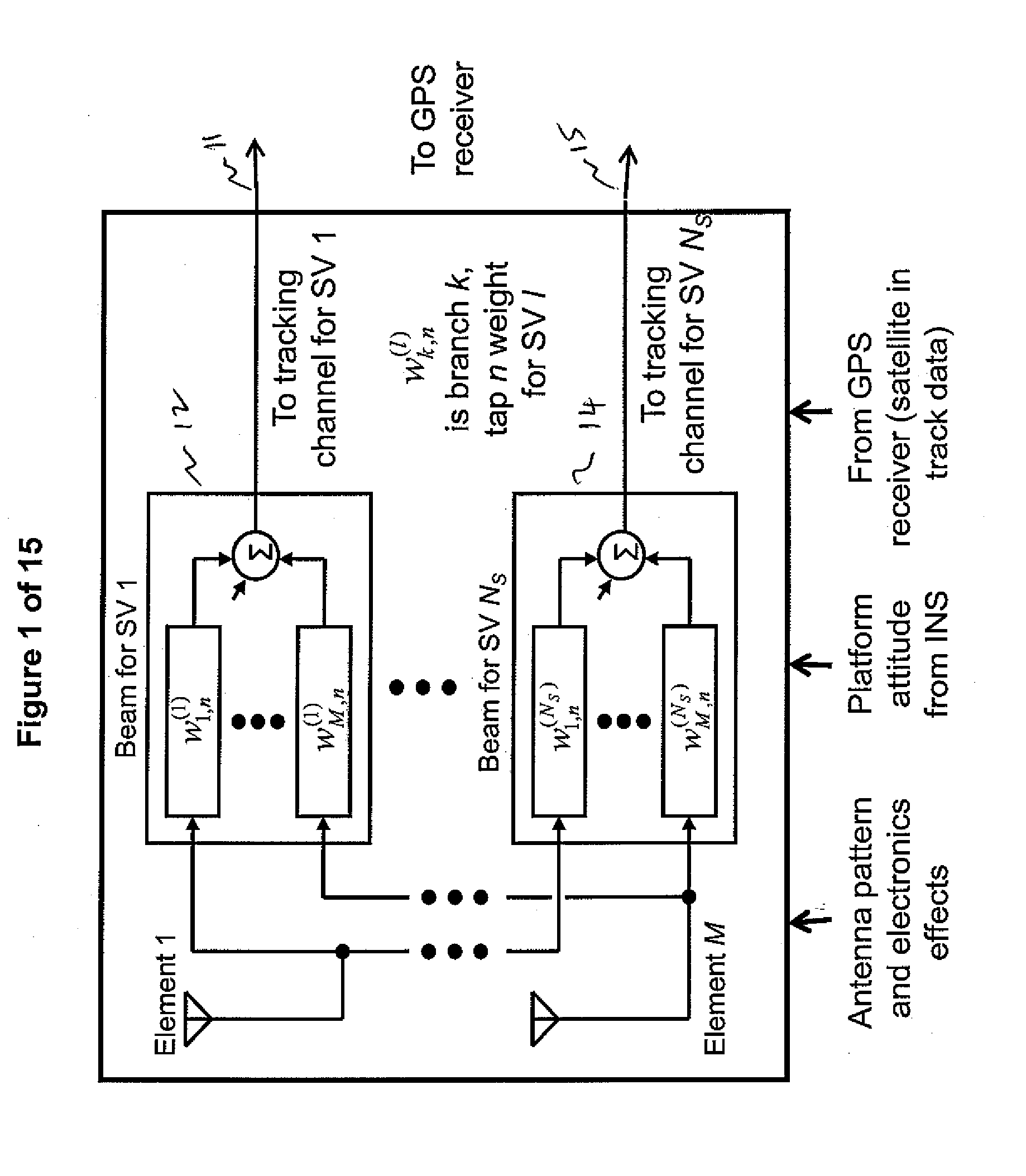
Efficient space-time adaptive processing (STAP) filter for global positioning system (GPS) receivers
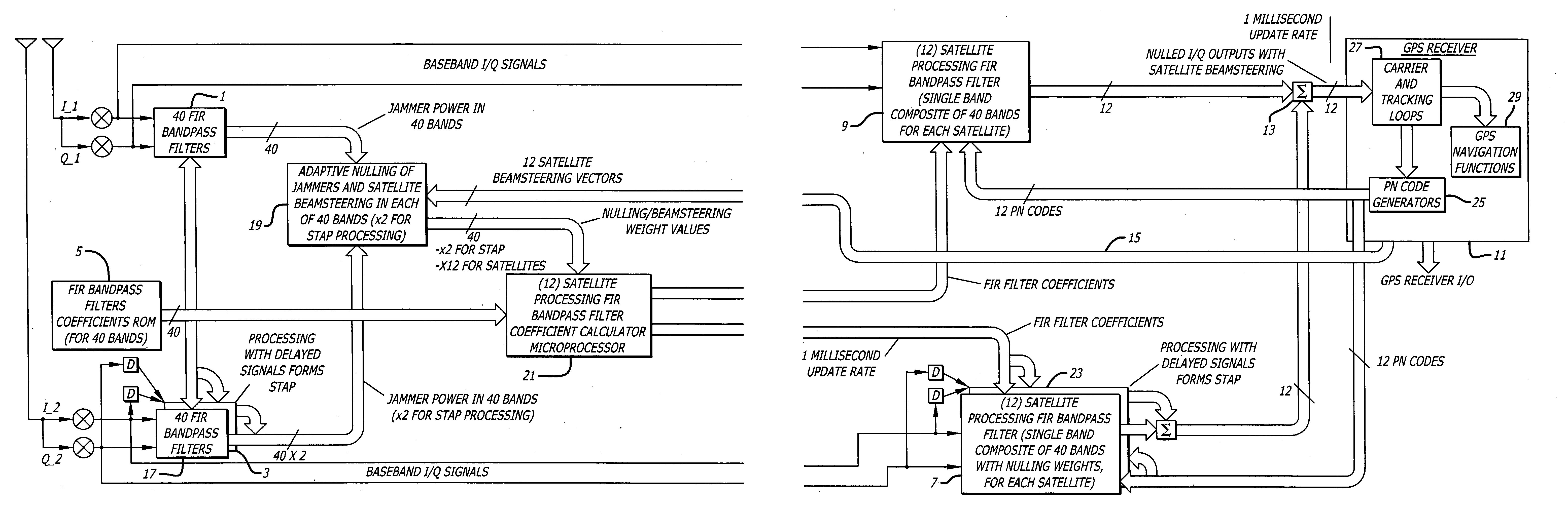
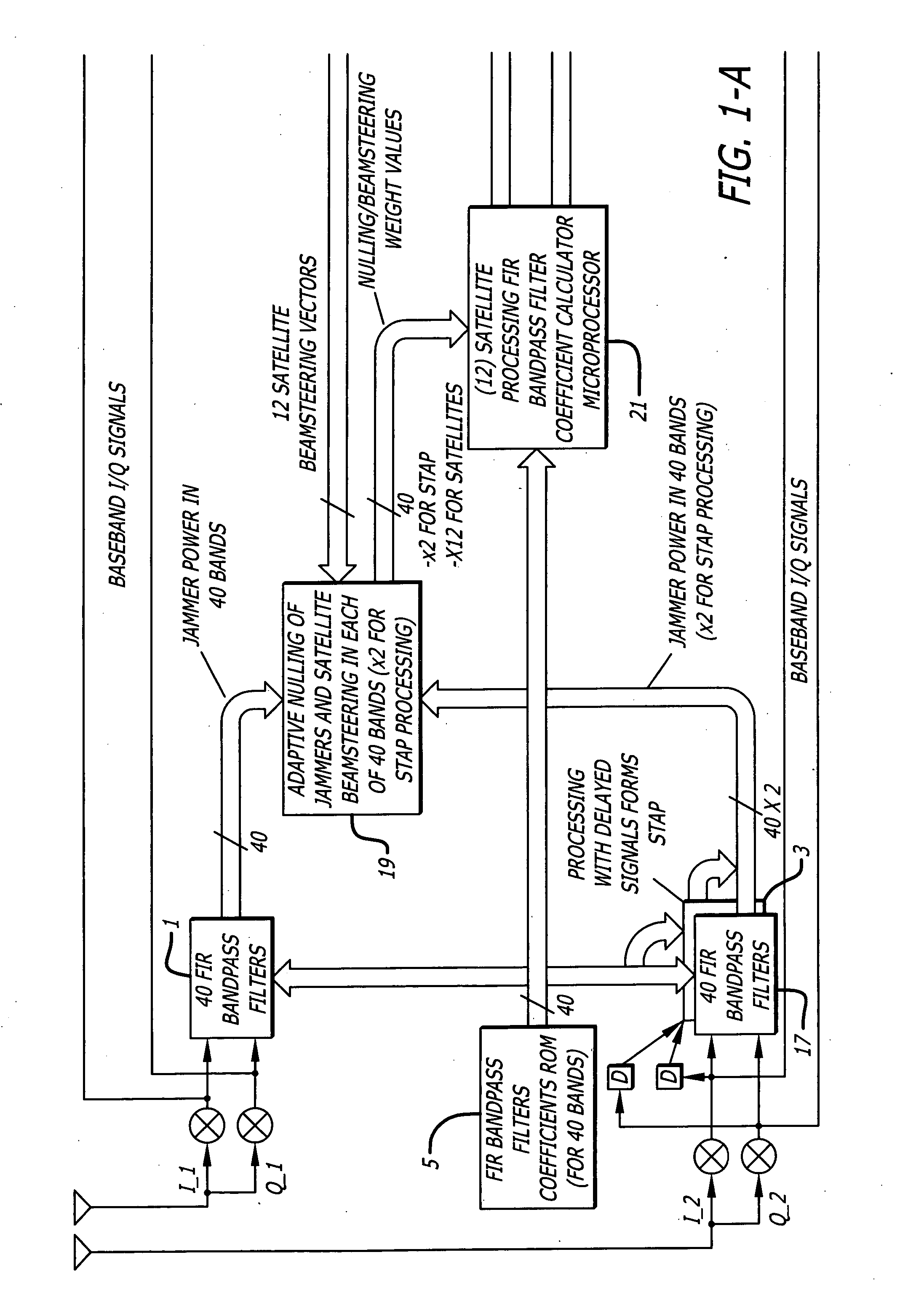
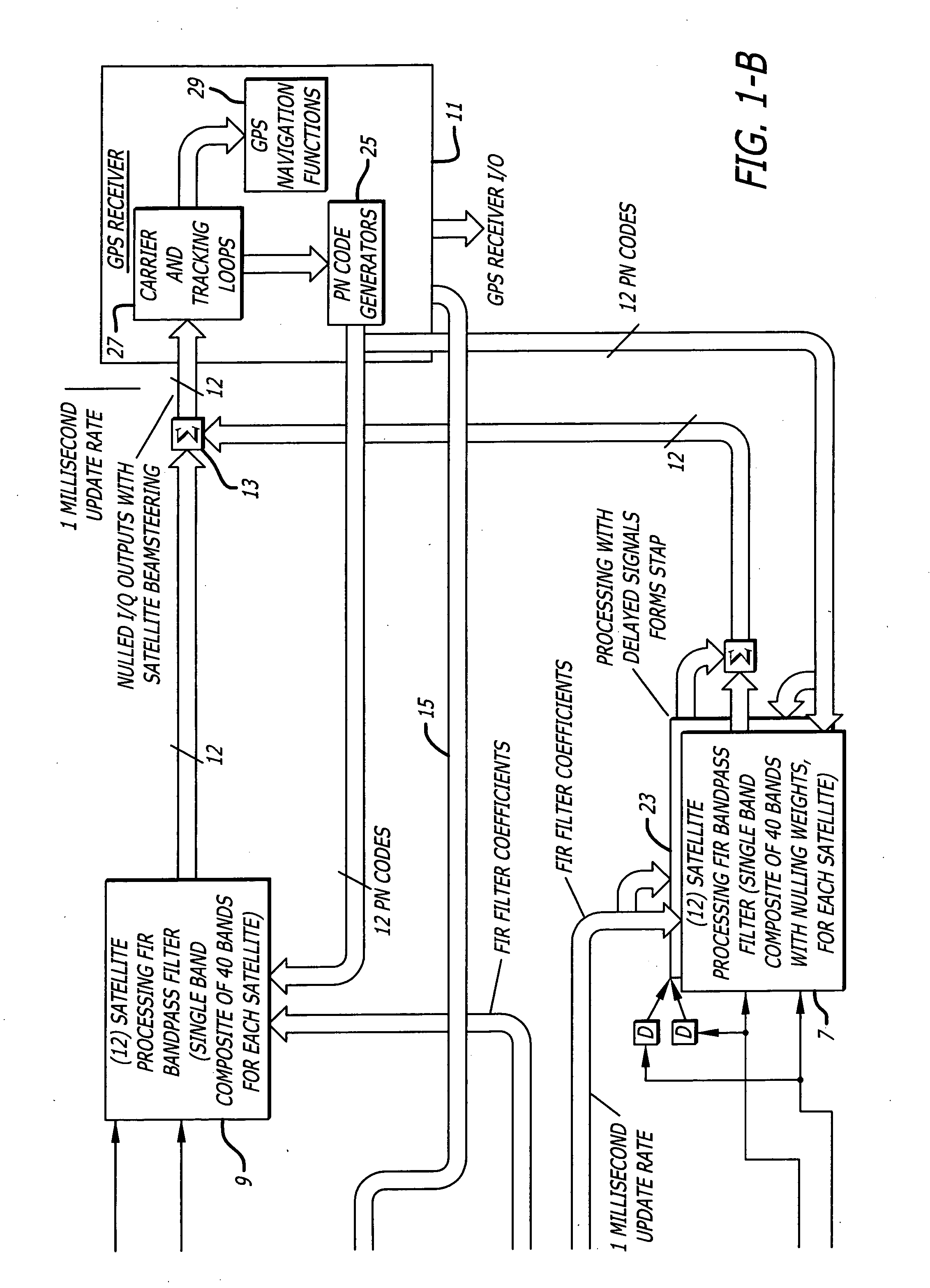
InactiveUS6952460B1Easy to trackEfficiently null a relatively large number of jammersBeacon systems using radio wavesCommunication jammingComputation complexityFourier transform on finite groups
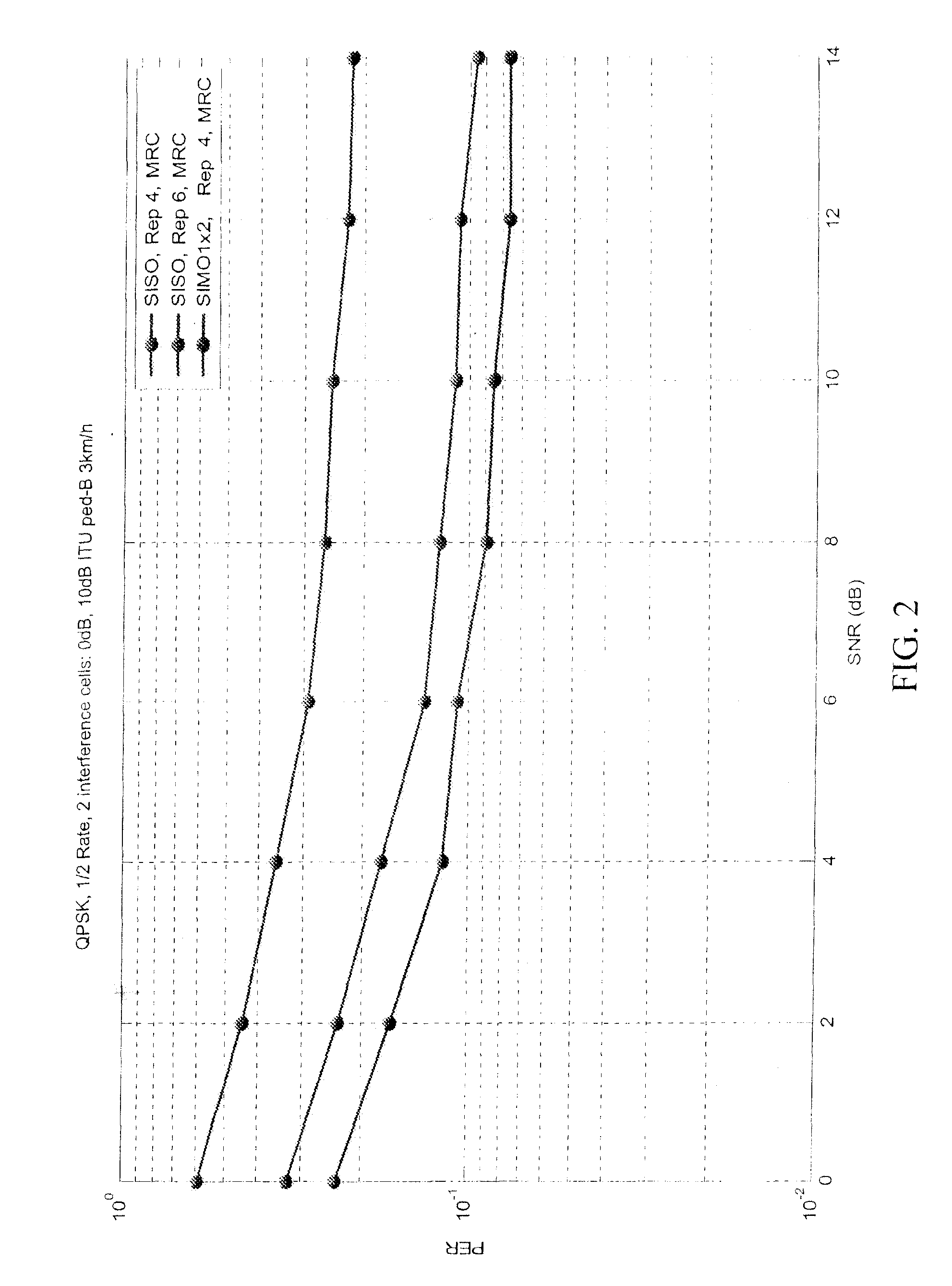
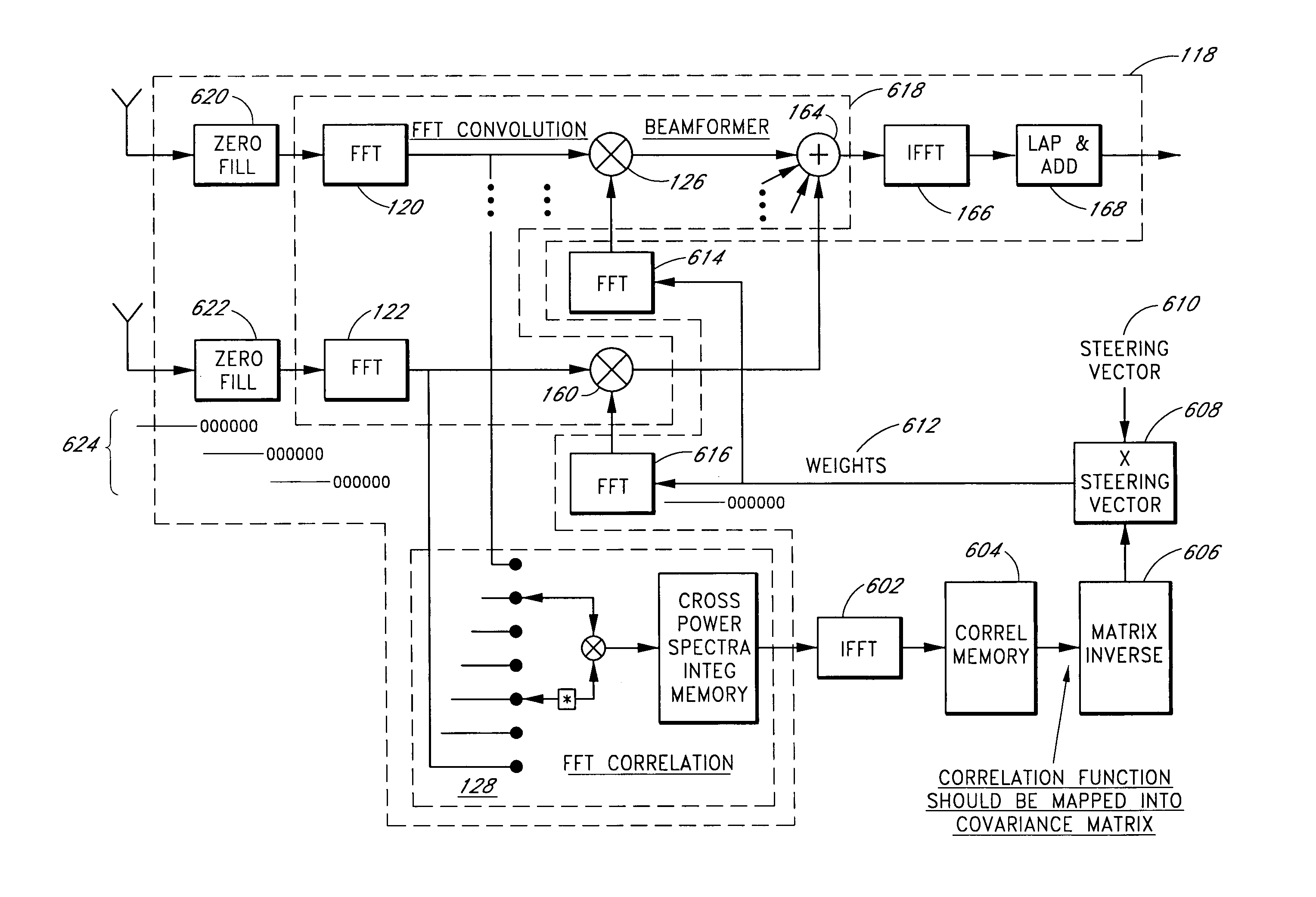
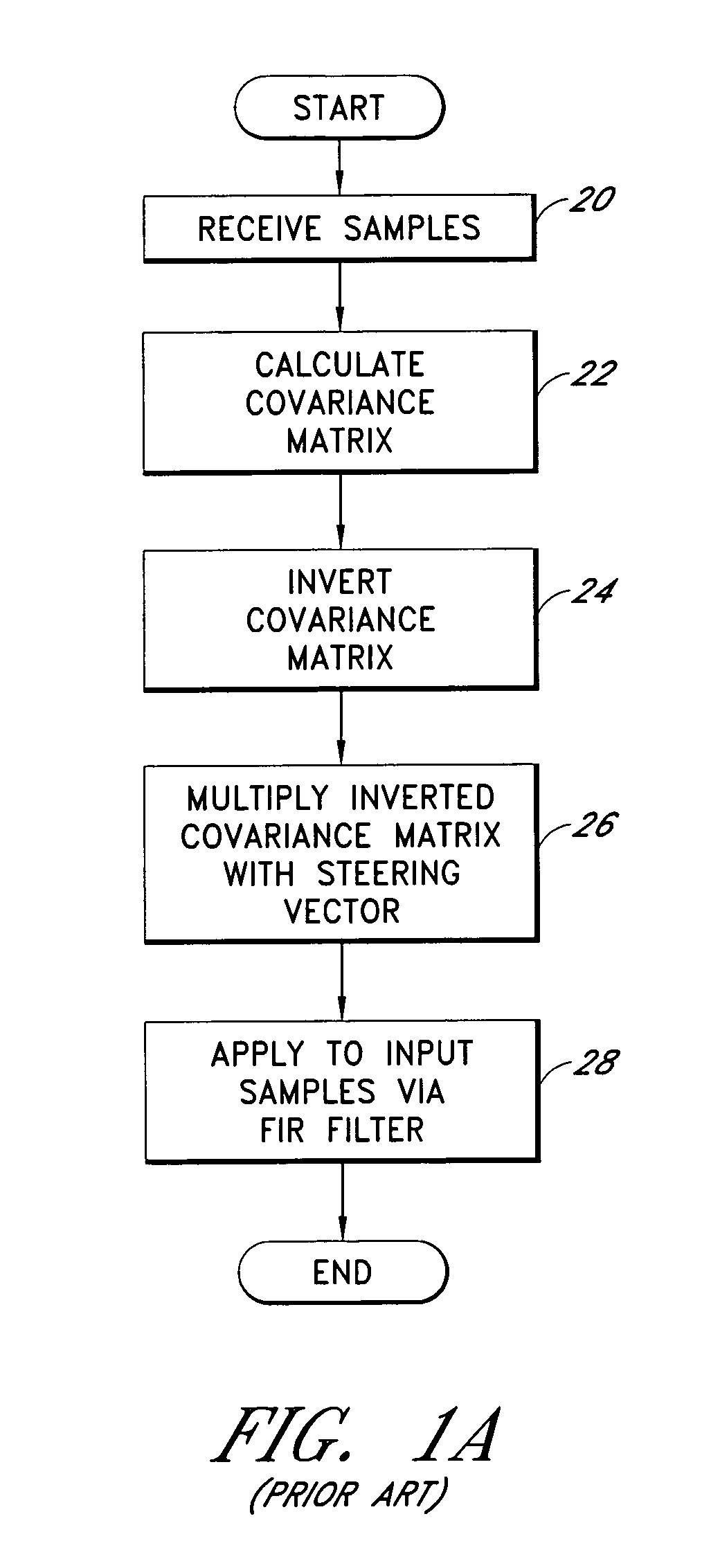
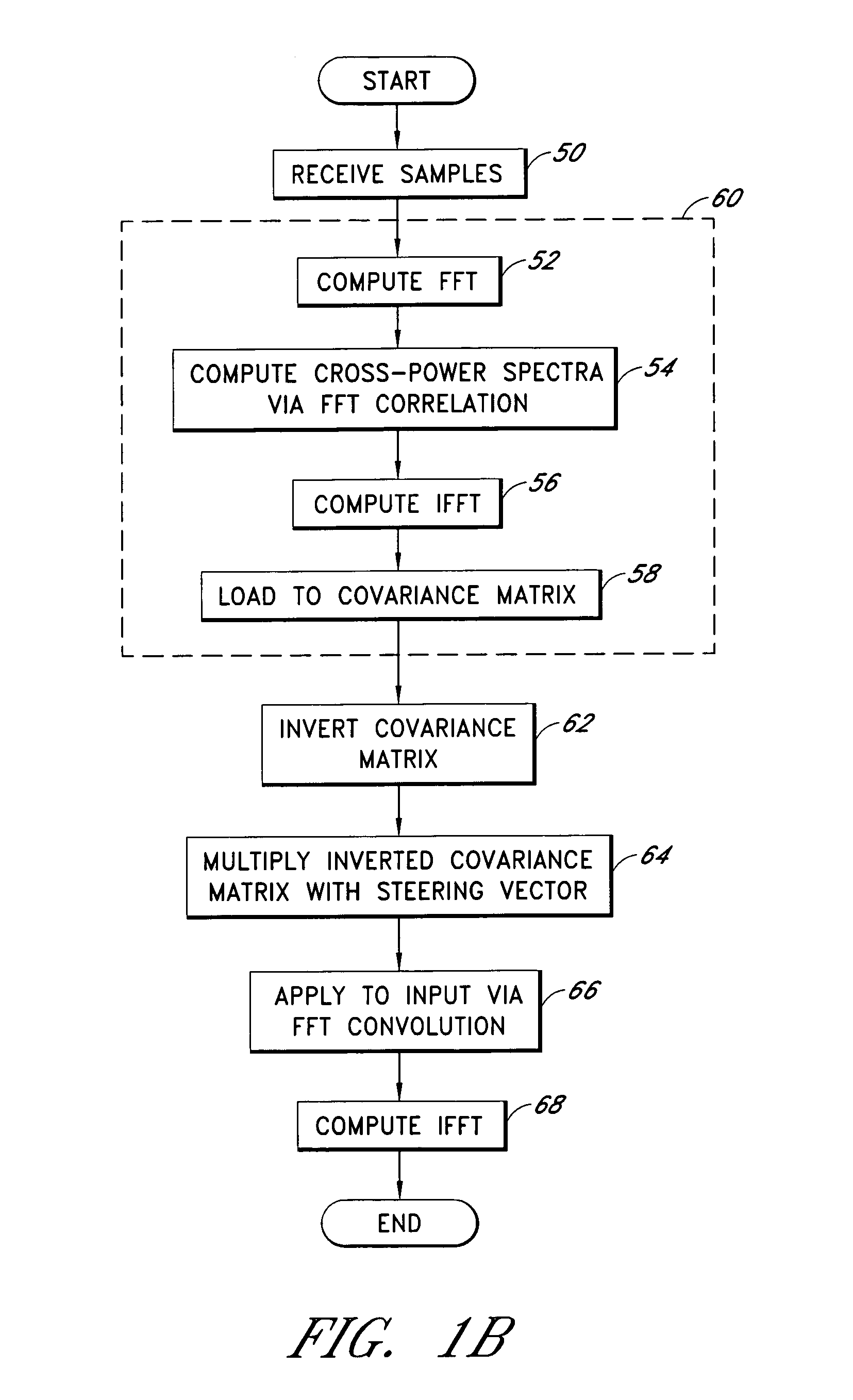
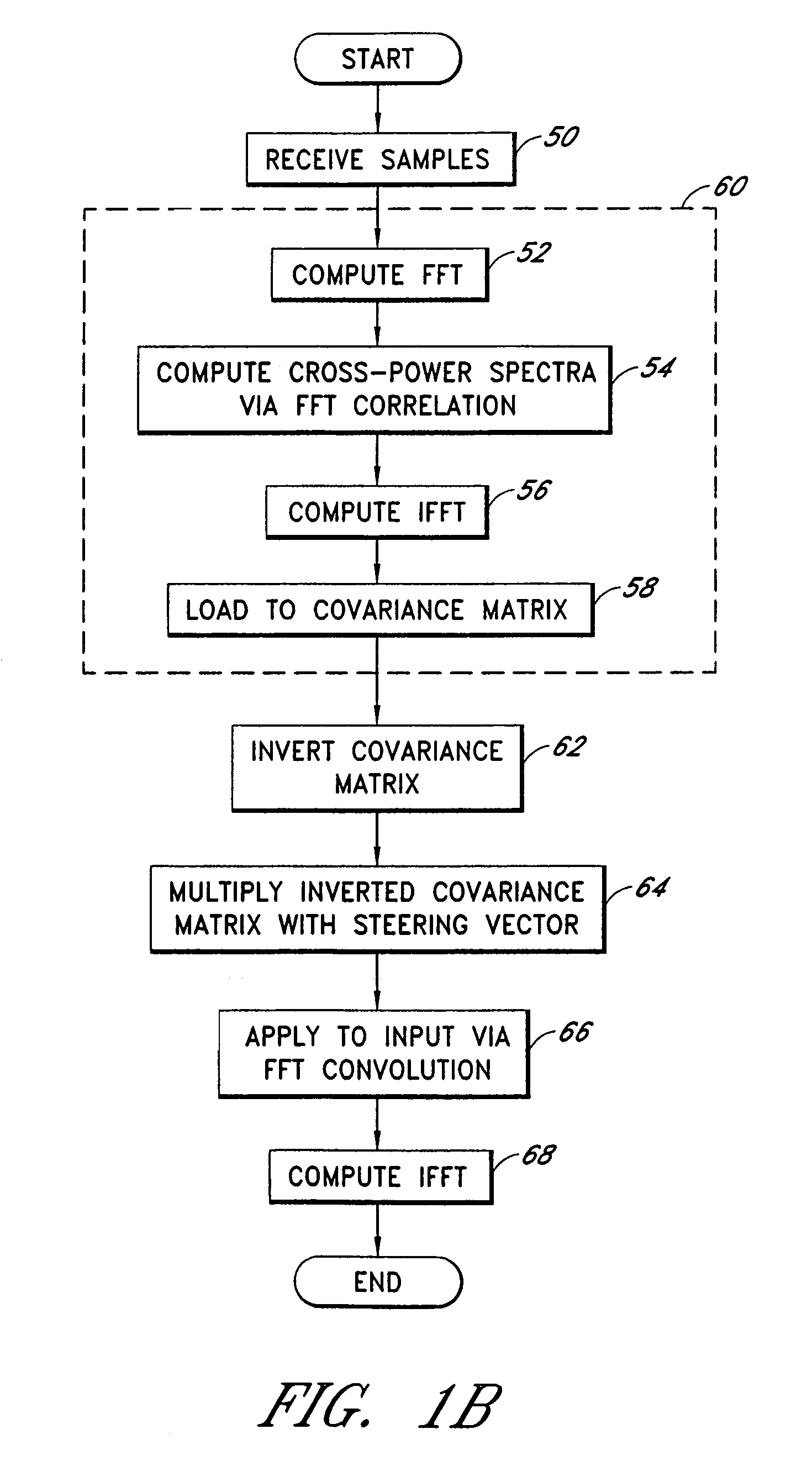
A system for efficiently filtering interfering signals in a front end of a GPS receiver is disclosed. Such interfering signals can emanate from friendly, as well as unfriendly, sources. One embodiment includes a GPS receiver with a space-time adaptive processing (STAP) filter. At least a portion of the interfering signals are removed by applying weights to the inputs. One embodiment adaptively calculates and applies the weights by Fourier Transform convolution and Fourier Transform correlation. The Fourier Transform can be computed via a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT). This approach advantageously reduces computational complexity to practical levels. Another embodiment utilizes redundancy in the covariance matrix to further reduce computational complexity. In another embodiment, an improved FFT and an improved Inverse FFT further reduce computational complexity and improve speed. Advantageously, embodiments can efficiently null a relatively large number of jammers at a relatively low cost and with relatively low operating power.
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP
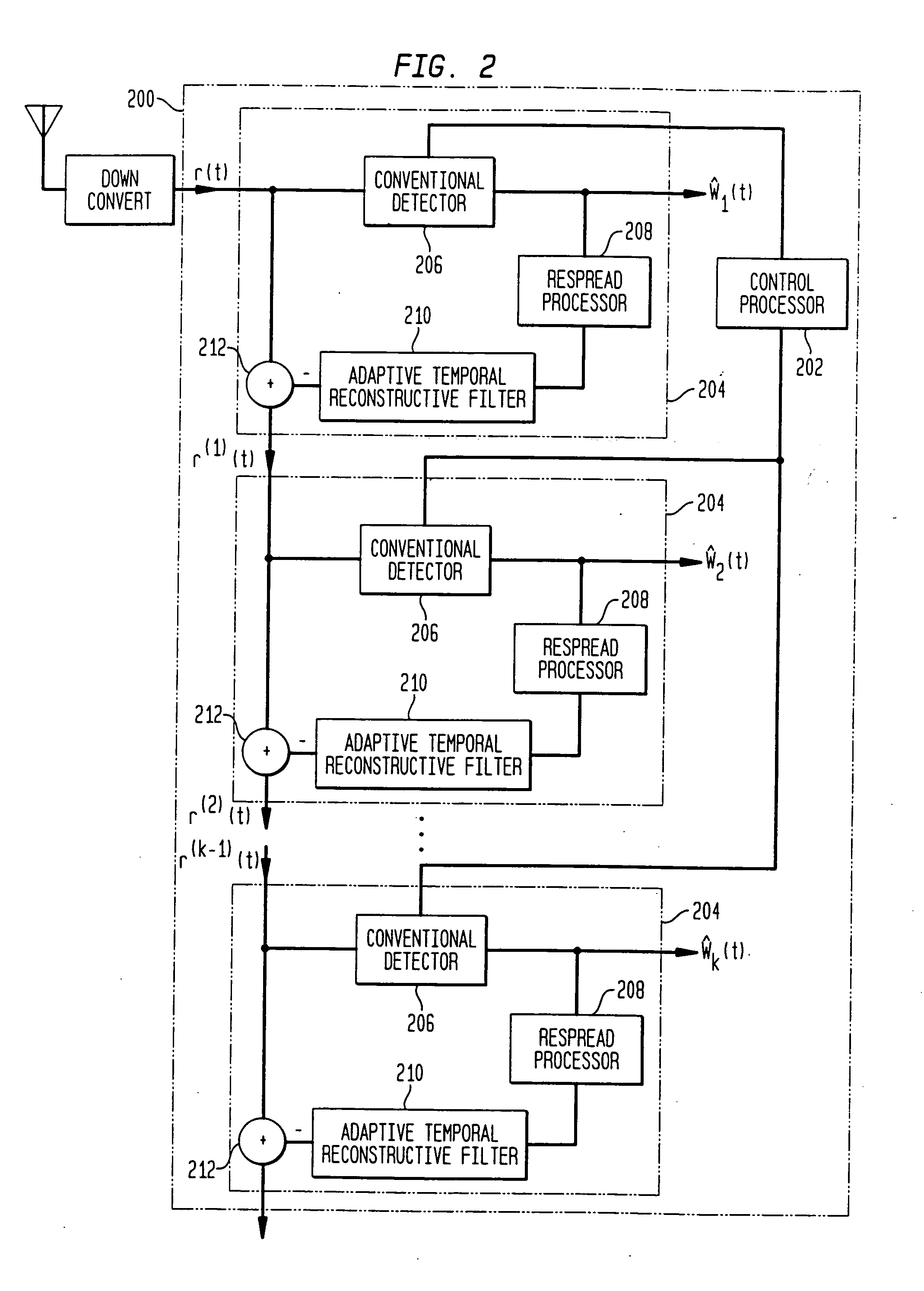
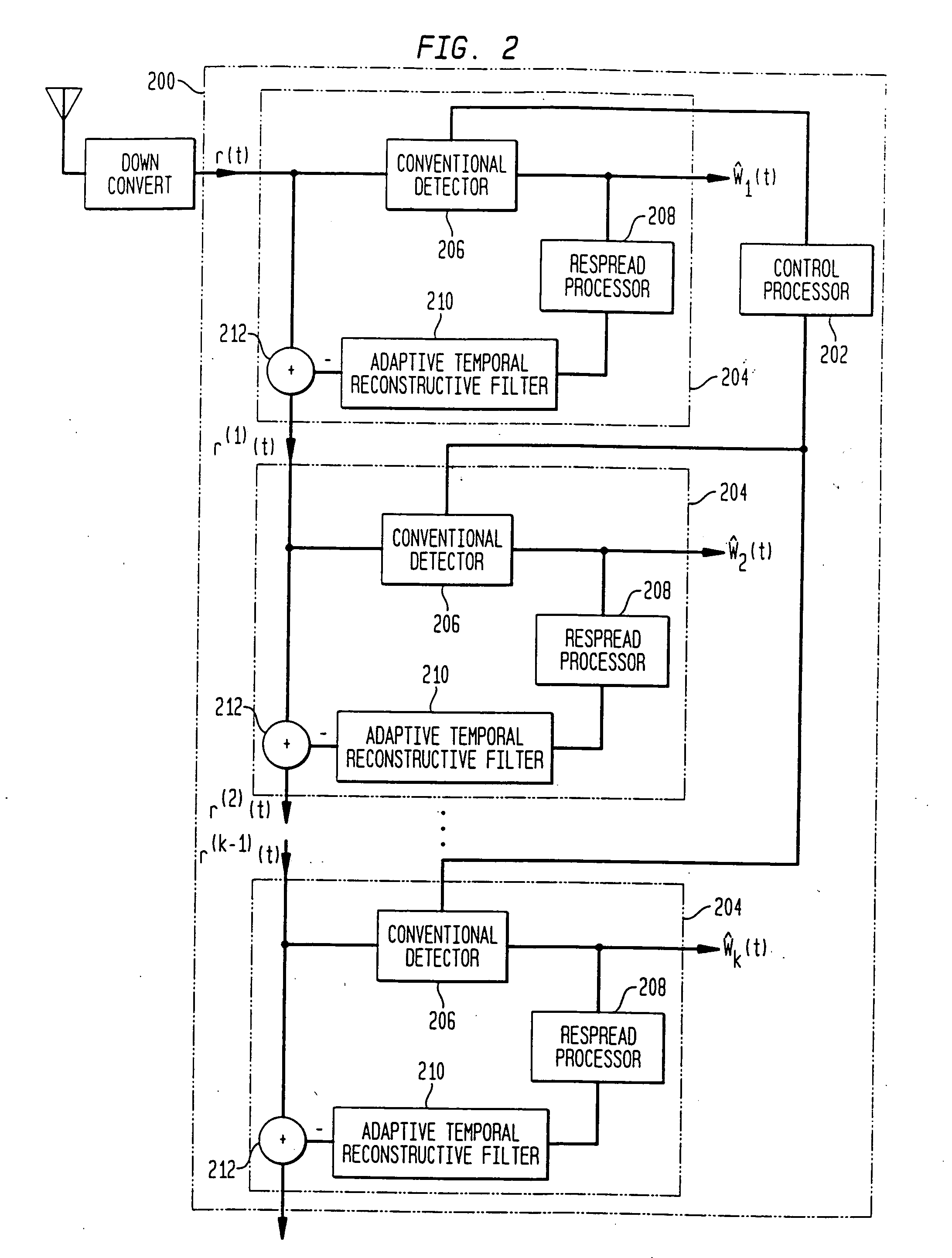
Combined adaptive spatio-temporal processing and multi-user detection for CDMA wireless systems
ActiveUS20050128985A1Reduce cancellationAccurate estimateRadio transmissionWireless commuication servicesEngineeringCo-channel interference
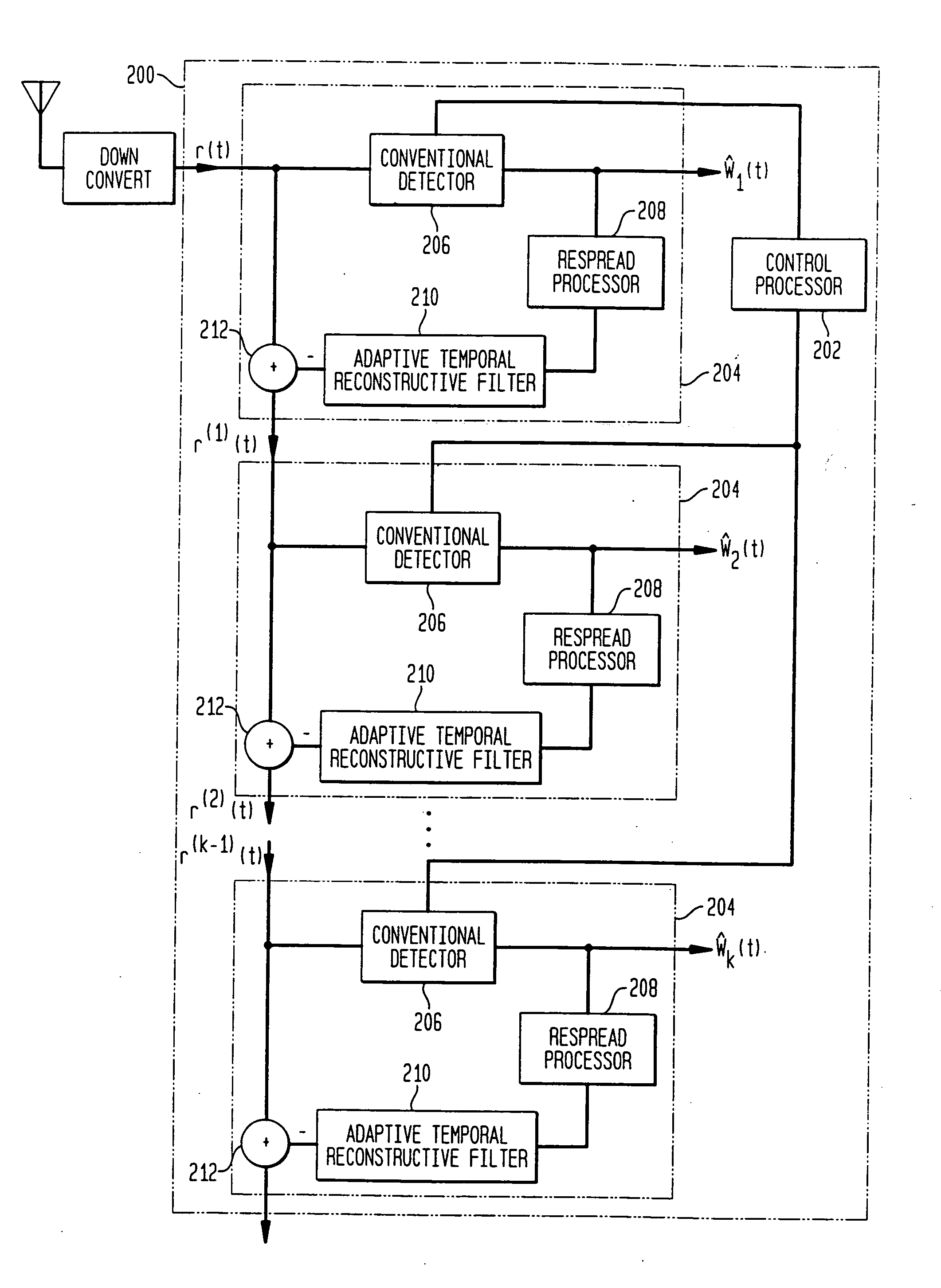
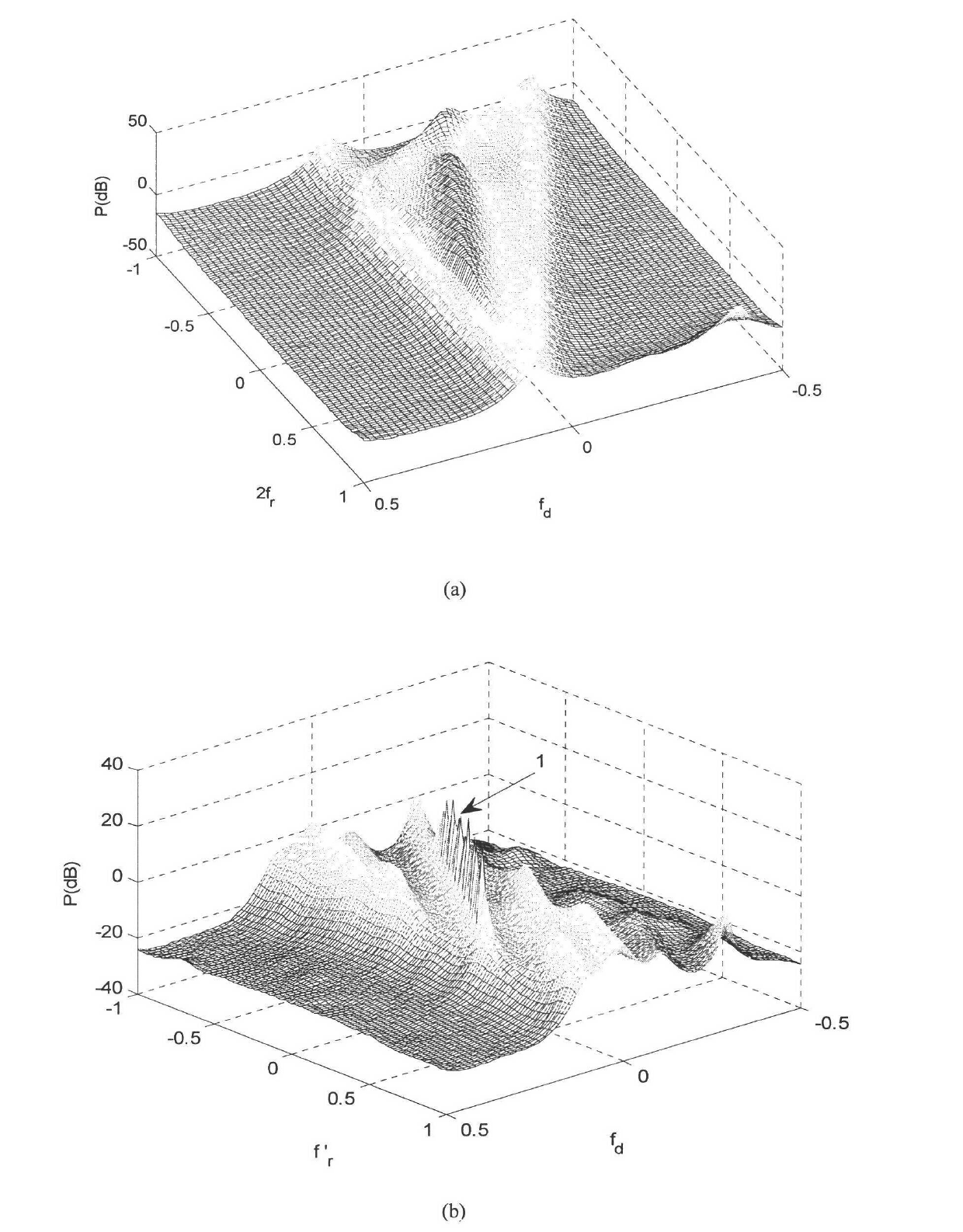
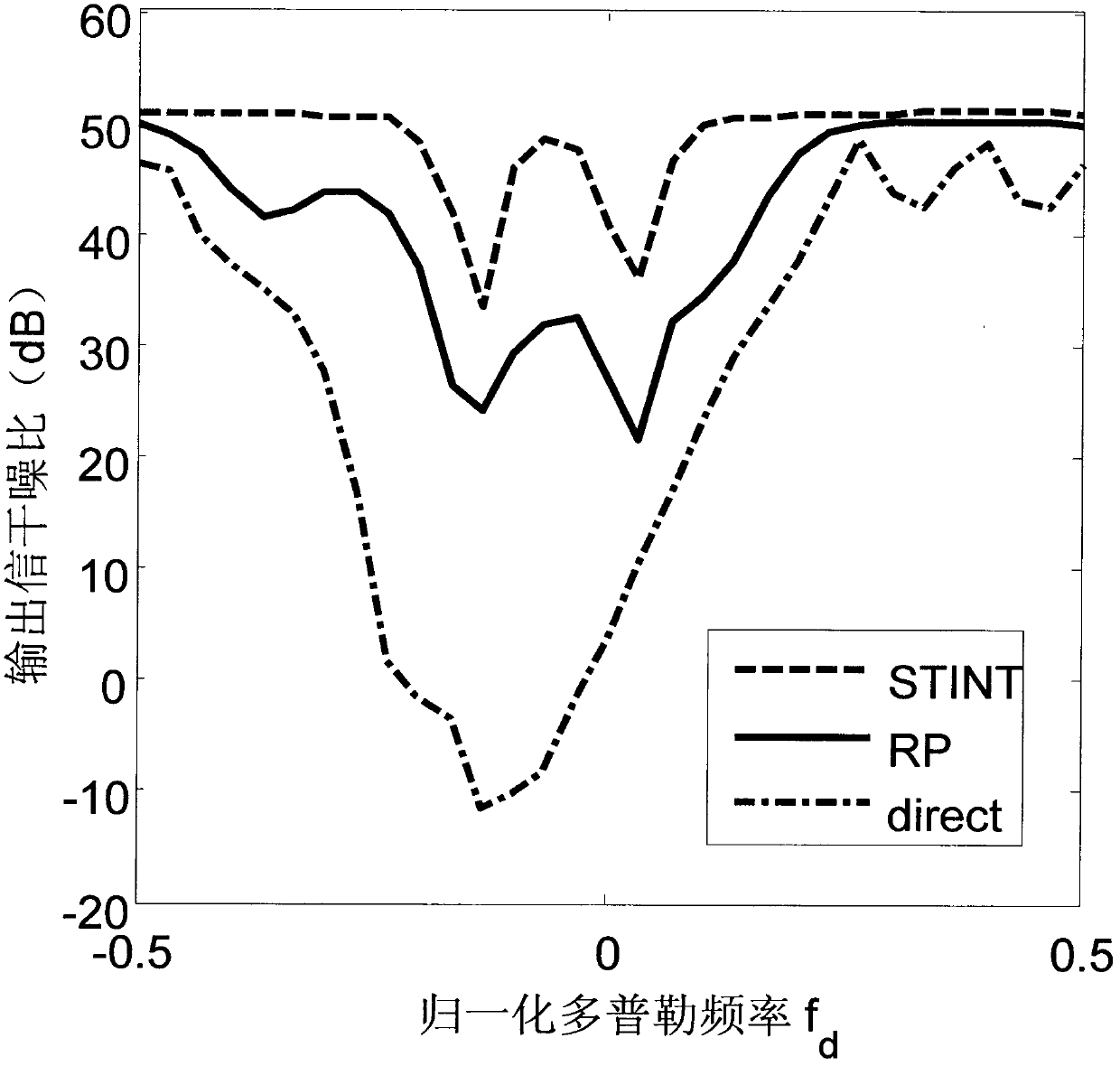
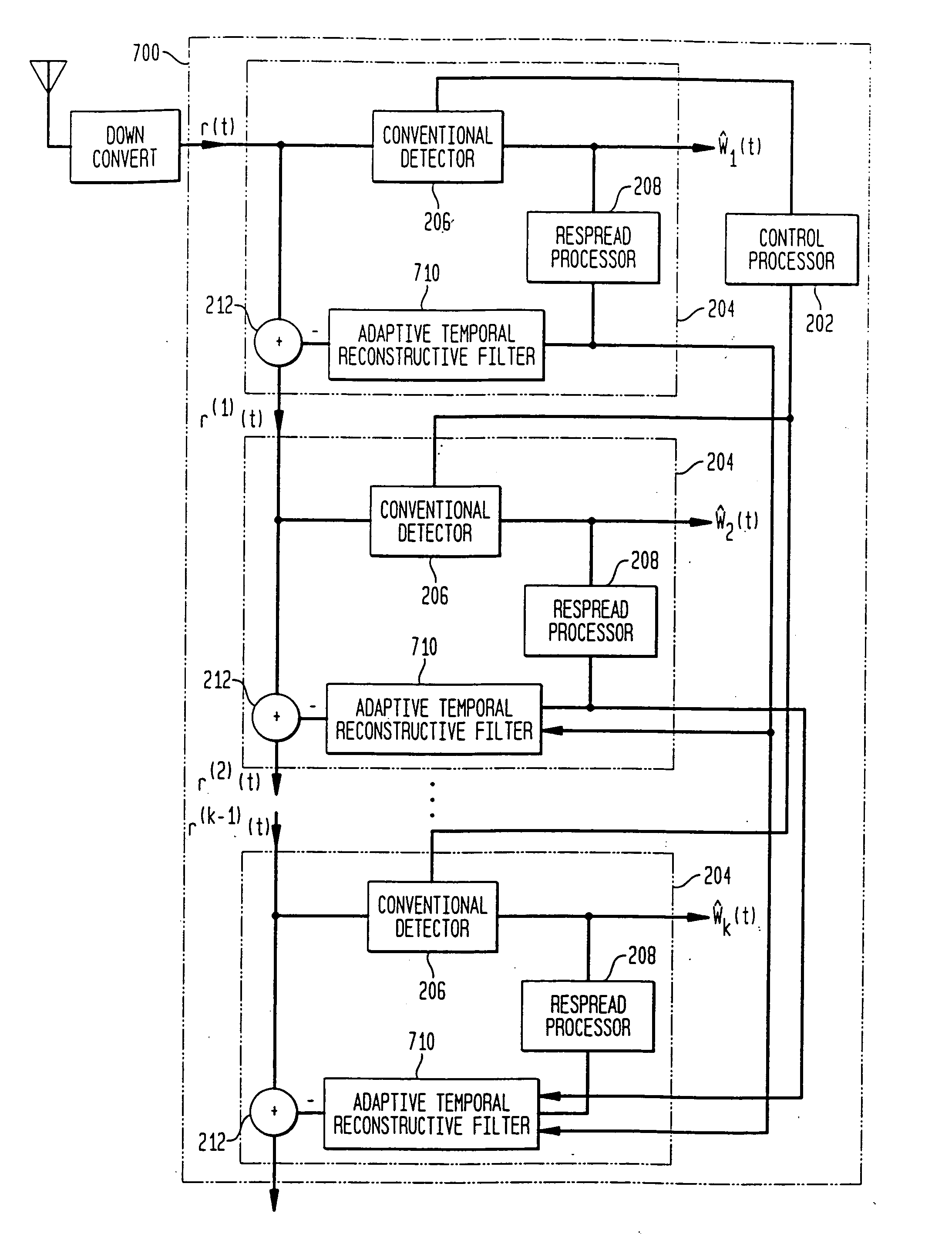
Methods and systems in a wireless receiver for enabling the reception of input signals at varied power levels in the presence of co-channel interference utilizing combinations of space-time adaptive processing (STAP), interference cancellation multi-user detection (MUD), and combined STAP / MUD techniques. In MUD, code, timing, and possibly channel information of multiple users are jointly used to better detect each individual user. The novel combination of adaptive signal reconstruction techniques with interference cancellation MUD techniques provides accurate temporal cancellation of interference with minimal interference residuals. Additional methods and systems extend adaptive signal reconstruction techniques to take Doppler spread into account. STAP techniques permit a wireless receiver to exploit multiple antenna elements to form beams in the direction of the desired signal and nulls in the direction of the interfering signals. The combined STAP-MUD methods and systems increase the probability of successful user detection by taking advantage of the benefits of each reception method. An additional method and system utilizes STAP techniques in the case where no pilot signal is available. This method compares the outputs of various hypothesized STAP solutions.
Owner:NYTELL SOFTWARE LLC
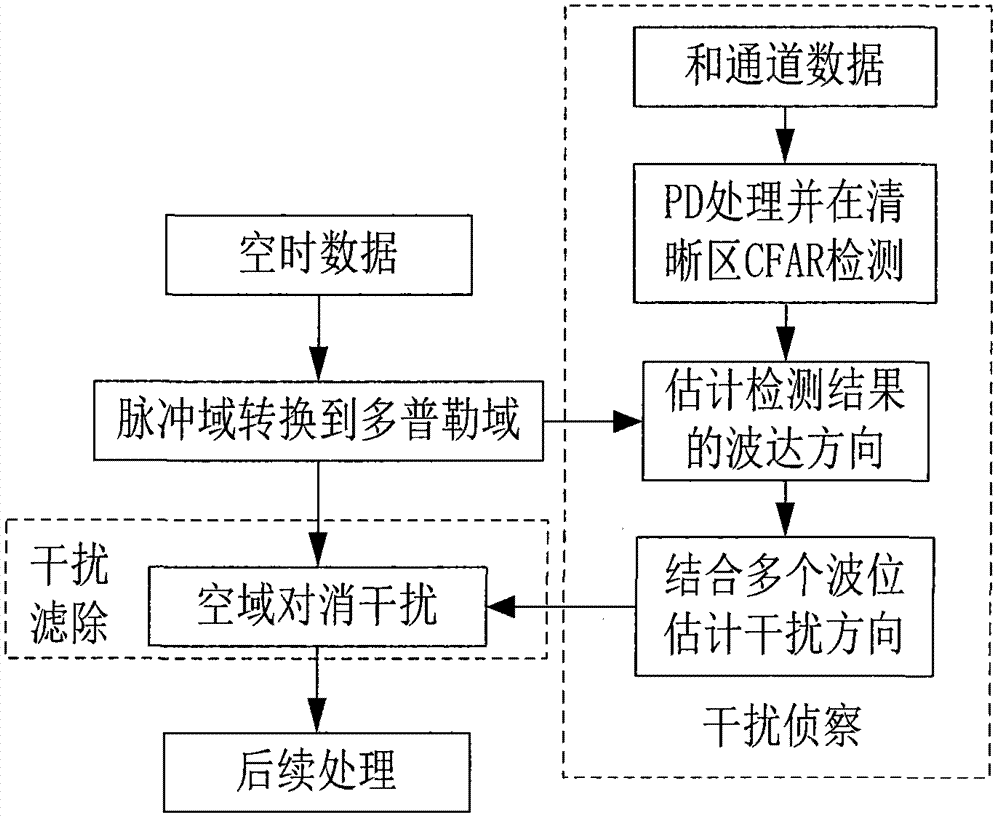
Method and system for resisting dense forwarding type defraud interference of airborne radar
ActiveCN103399303AImprove object detection performanceAddress issues that adversely affect performanceWave based measurement systemsFalse alarmCovariance matrix
The invention discloses a method and a system for resisting dense forwarding type defraud interference of an airborne radar, and the resistance of dense forwarding type defraud interference is realized through an interference scout module and an interference filter and elimination module. Interference scout is used for carrying out the PD (probability of defraud) treatment on data received by a radar; the CFAR (constant false alarm rate) detection is carried out on data in a clear area; a detection result direction of arrival is estimated; an interference direction of arrival is estimated with combination of the detection result of a plurality of wave positions. In the interference filter and elimination treatment, a sum beam pointing to the interference direction is formed according to an interference scout result; the sum beam pointing to the interference direction is used as an auxiliary passageway, an existing space passageway is used as a main passageway, the method of GSC (gain scheduling control) is adopted to filter and eliminate interference, and the channel covariance matrix of the interference is estimated according to an interference sample selected from the clear area. By adopting the method and the system, the difficult problem of inhibition on dense forwarding type defraud interference is solved, the dense forwarding type interference is fundamentally filtered and eliminated, false alarms caused by the dense forwarding type interference are reduced, adverse effects on a CRAR detection threshold and the STAP (space time adaptive processing) performance are eliminated, the detection performance of a radar target is improved, the system is simple and easy to realize, and an engineering application value is provided.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Sample-training-based non-stationary clutter suppression method of vehicle-mounted radar
InactiveCN103018727ASolve the problem of clutter distance dependenceImproved clutter suppression performanceWave based measurement systemsTime domainRadar
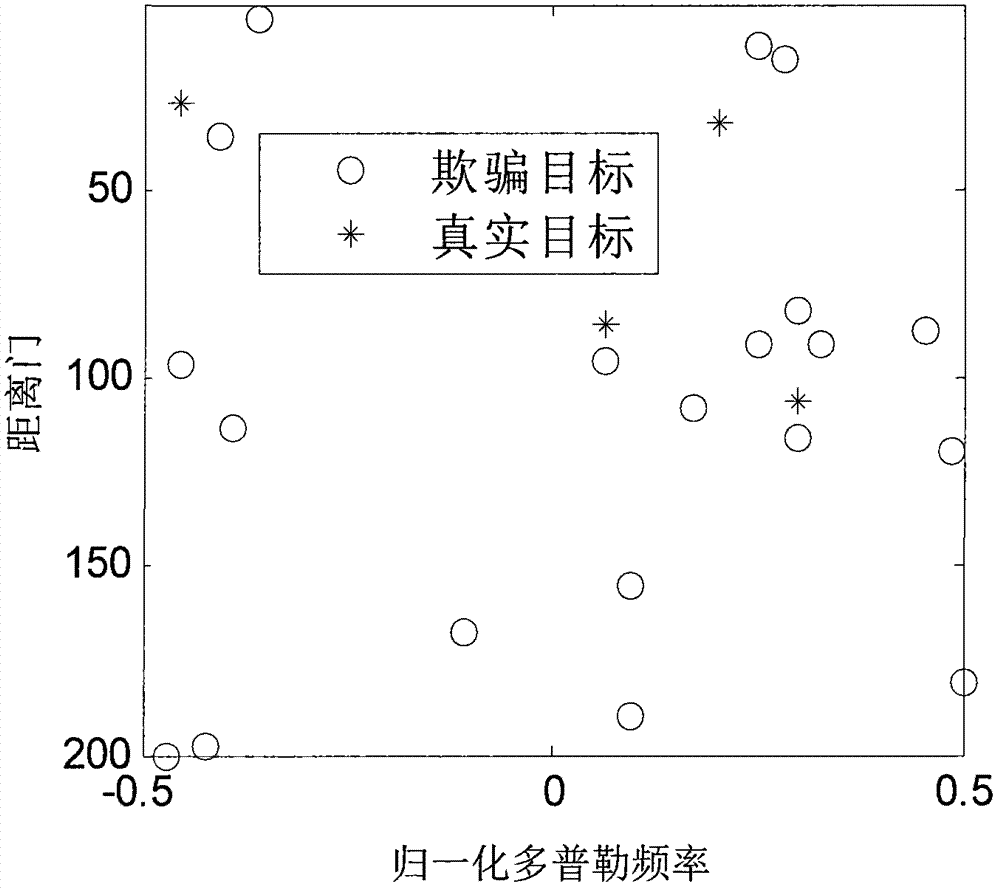
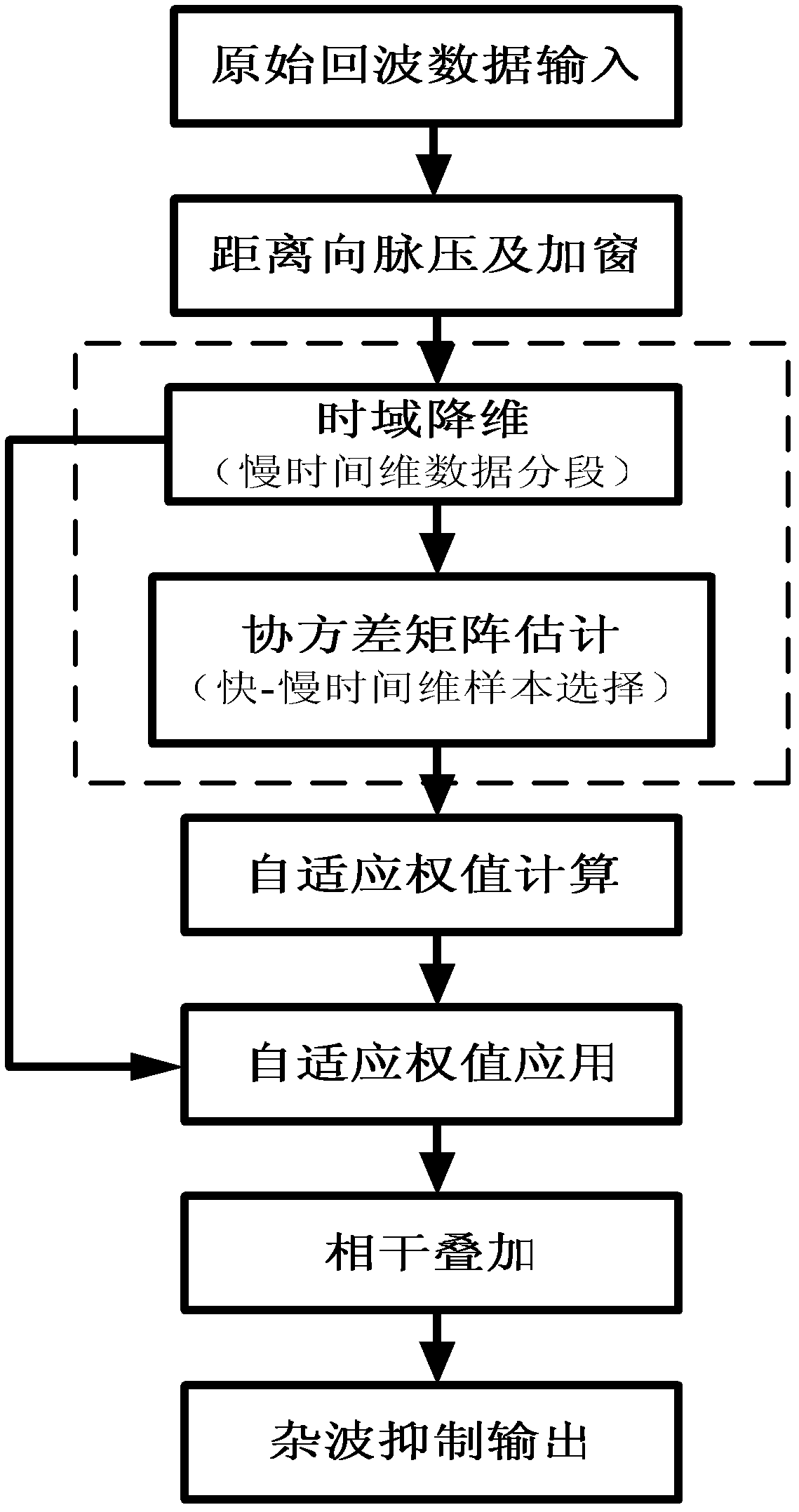
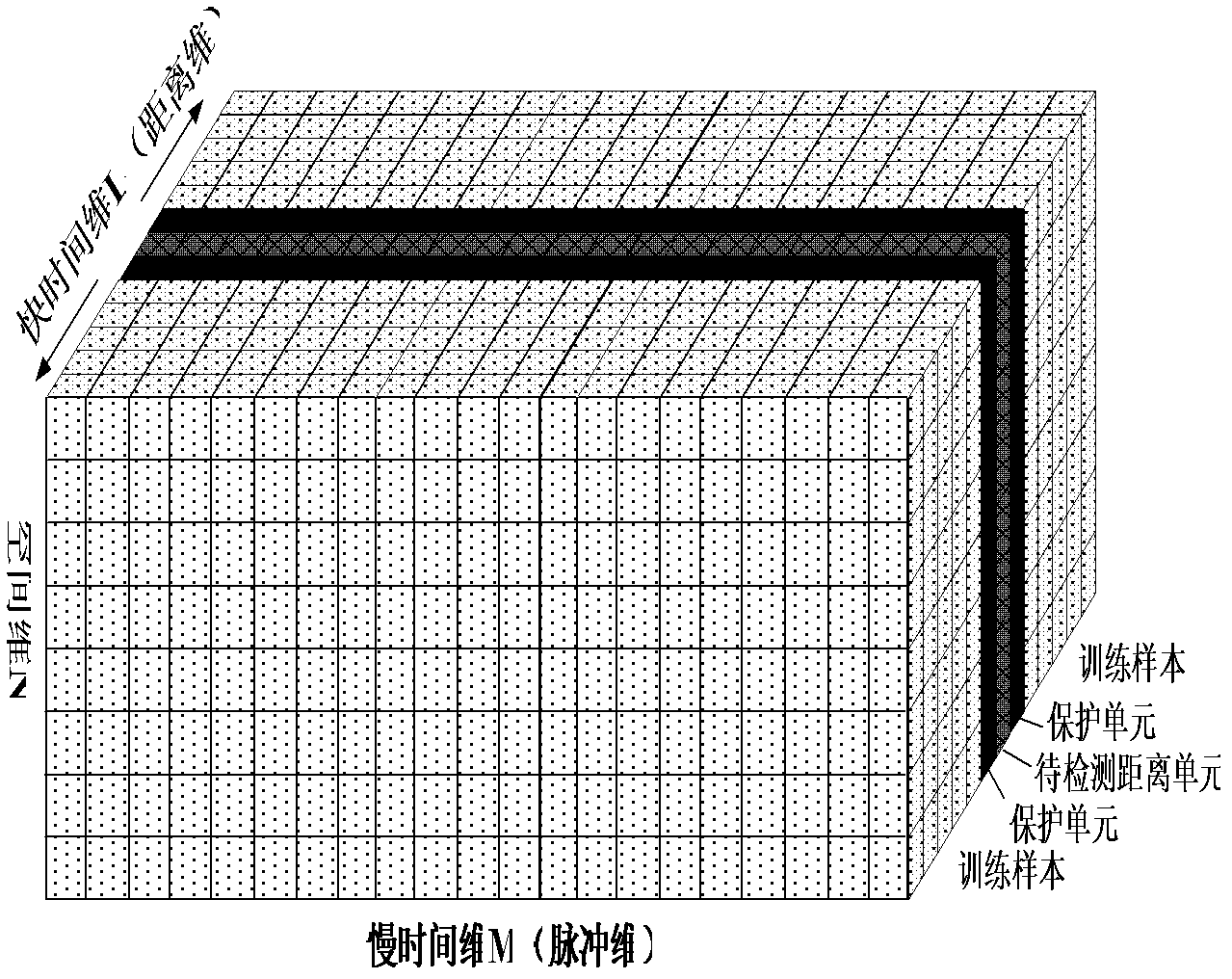
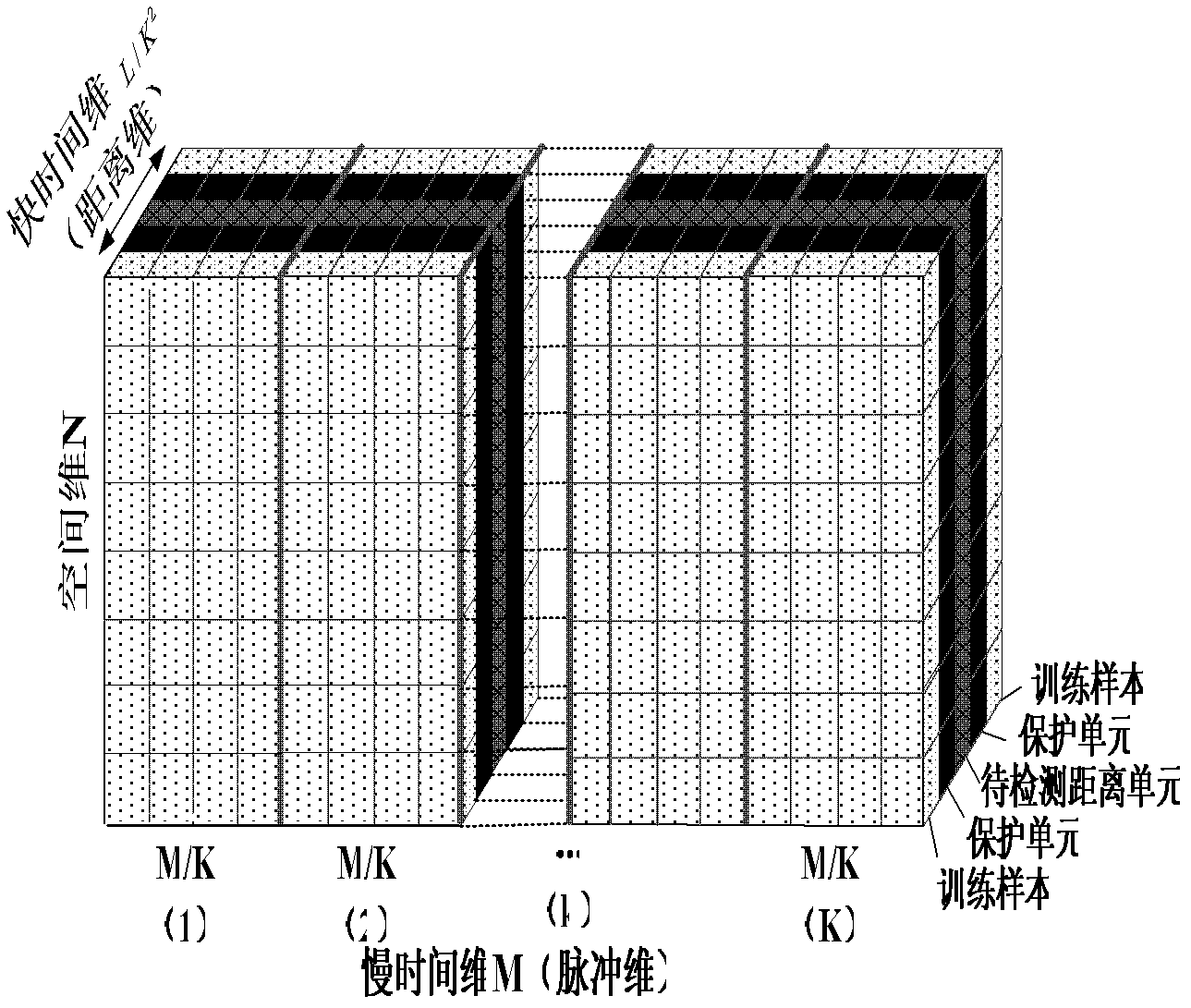
The invention discloses a sample-training-based non-stationary clutter suppression method of a vehicle-mounted radar, which relates to vehicle-mounted radar technology. The method comprises the steps of estimation of a clutter covariance matrix based on combined time-dimension sample training strategies, application of a self-adaptive weight, and coherence stack to output signals. The method specifically comprises the following steps of: inputting raw echo data; compressing and windowing pulses in a distance dimension; segmenting slow-time-dimension data; selecting quick-slow time dimension training samples; estimating the clutter covariance matrix; calculating and applying the self-adaptive weight; and carrying out coherence stack on the output signals. According to the method, the sample training strategies are changed under an STAP (space-time adaptive processing) time domain dimension reducing structure in light of the clutter range dependence of the vehicle-mounted radar, thus the estimation precision of the clutter covariance matrix can be effectively improved, and the clutter suppression performance of a main lobe is improved as well. The sample-training-based non-stationary clutter suppression method shows high robustness in engineering application, and is particularly applicable to detection on a slow moving object.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
System and method for dynamic weight processing
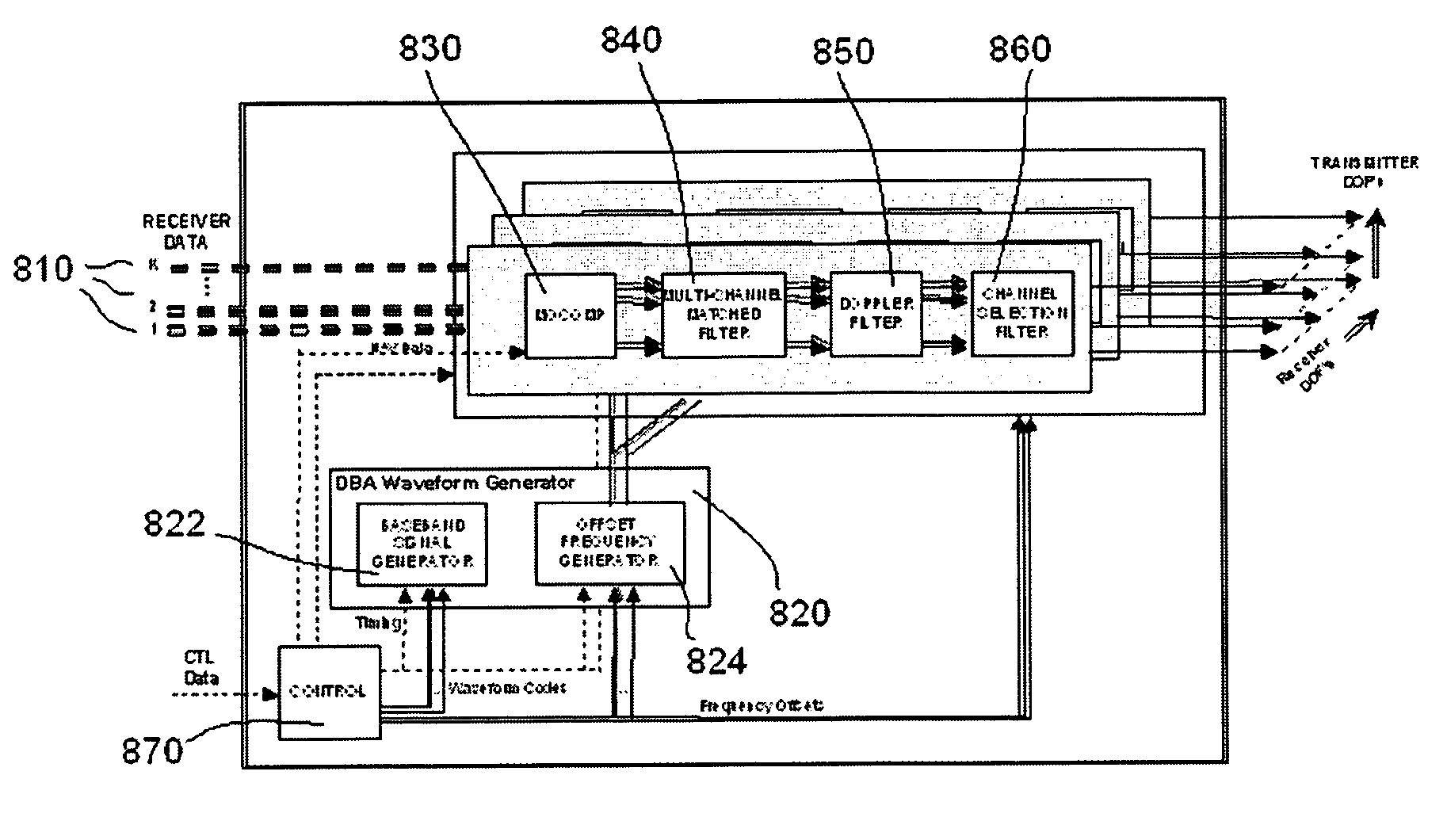
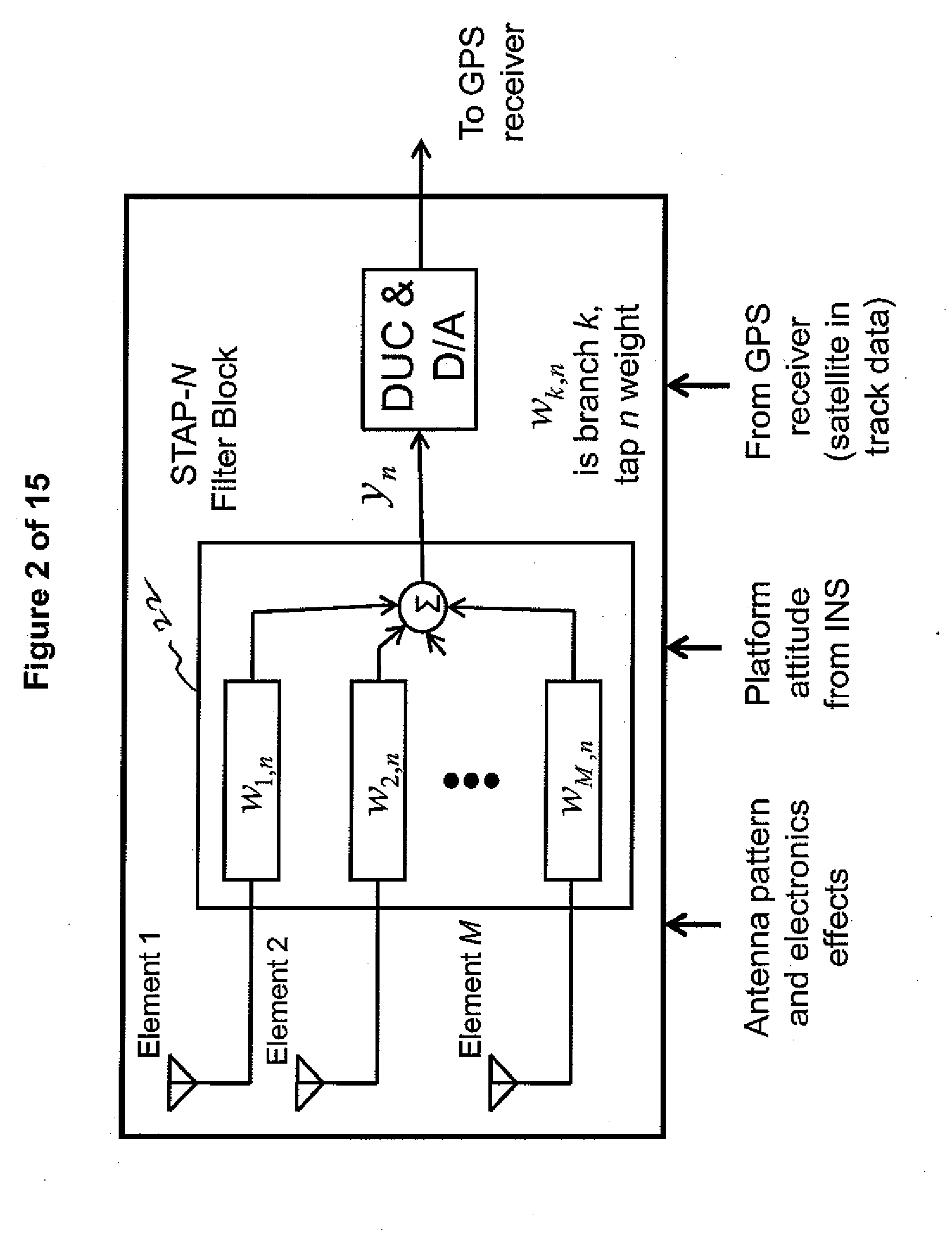
A dynamic weight generator. The inventive generator includes a first memory for storing a PN code; a second memory for storing a plurality of weights, the second memory being coupled to the first memory whereby data output by the first memory is used to address data stored in the second memory; and a correlator for multiplying an input signal by data output by the second memory. In the illustrative embodiment, the weights are finite impulse response filter correlation coefficients. The correlator includes two multipliers. The first of the multipliers is coupled to a source of an in-phase component of the input signal. The second of the multipliers is coupled to a source of a quadrature component of the input signal. The outputs of the multipliers are summed. In the illustrative application, the input signal is a GPS signal. For this application, the inventive teachings are implemented in a signal processing system adapted to receive a GPS signal and provide in-phase and quadrature signals in response thereto. The signal is filtered with a finite impulse response filter to provided weighted signals. The weighted signals are processed to generate nulling and beamsteering weights for the weighted signals. The weights may be used to equalize the received signals. In a more specific implementation, the received signals are partitioned into space frequency adaptive processing bands and space time adaptive processing is performed within the SFAP bands.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Clutter suppression method based on bistatic multiple-input and multiple-output radar
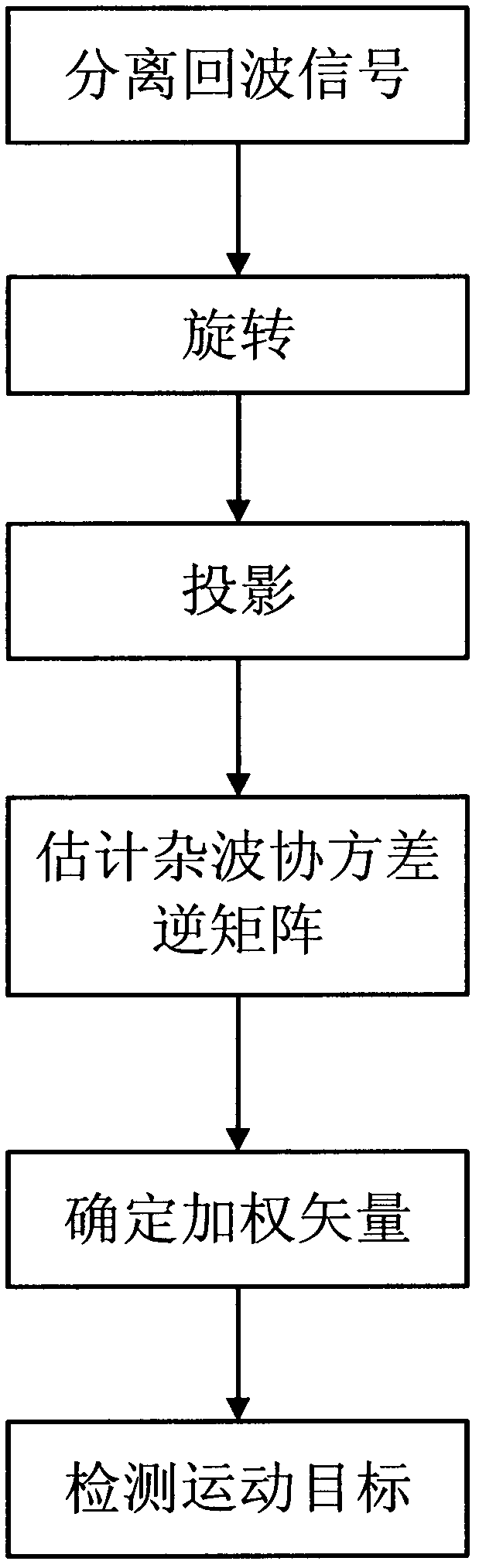
InactiveCN102520395AAccurate estimateSuppress clutterWave based measurement systemsRadarSpace-time adaptive processing
The invention discloses a clutter suppression method based on a bistatic multiple-input and multiple-output radar, which comprises the steps of: (1) separating echo signals; (2) rotating; (3) projecting; (4) estimating a clutter covariance inverse matrix; (5) detecting a weighted vector; and (6) detecting a moving target. The clutter suppression method based on the bistatic multiple-input and multiple-output radar can be suitable for conditions that a transmitter and a receiver of a bistatic radar move, and can eliminate the distance dependence of the bistatic radar. The clutter suppression method based on the bistatic multiple-input and multiple-output radar overcomes the defect of insufficient independent identical distribution training samples for space-time adaptive processing by adopting a rotary projection method for separated coordinates of all echo data, and has the advantages of sufficient independent identical distribution training samples, and capabilities of accurately evaluating clutter characteristics and forming a deep clutter notch in an actual main clutter area through space-time adaptive filtering as well as effectively suppressing clutters.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Parallel interference cancellation and minimum cost channel estimation
ActiveUS20050111414A1Minimize residualTiming errorRadio transmissionEngineeringCo-channel interference
Methods and systems in a wireless receiver for enabling the reception of input signals at varied power levels in the presence of co-channel interference utilizing combinations of space-time adaptive processing (STAP), interference cancellation multi-user detection (MUD), and combined STAP / MUD techniques. In MUD, code, timing, and possibly channel information of multiple users are jointly used to better detect each individual user. The novel combination of adaptive signal reconstruction techniques with interference cancellation MUD techniques provides accurate temporal cancellation of interference with minimal interference residuals. Additional methods and systems extend adaptive signal reconstruction techniques to take Doppler spread into account. STAP techniques permit a wireless receiver to exploit multiple antenna elements to form beams in the direction of the desired signal and nulls in the direction of the interfering signals. The combined STAP-MUD methods and systems increase the probability of successful user detection by taking advantage of the benefits of each reception method. An additional method and system utilizes STAP techniques in the case where no pilot signal is available. This method compares the outputs of various hypothesized STAP solutions.
Owner:NYTELL SOFTWARE LLC
Method and apparatus for performing bistatic radar functions
InactiveUS7038618B2Small sizeSuppress chaosRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadarSpace-time adaptive processing
Owner:BUDIC ROBERT D
Method for Suppressing Clutter in Space-Time Adaptive Processing Systems
ActiveUS20110187584A1Reduce complexityNear-optimal performanceRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSingular value decompositionData compression
A method surpresses clutter in a space-time adaptive processing system. The method achieves low-complexity computation via two steps. First, the method utilizes an improved fast approximated power iteration method to compress the data into a much smaller subspace. To further reduce the computational complexity, a progressive singular value decomposition (SVD) approach is employed to update the inverse of the covariance matrix of the compressed data. As a result, the proposed low-complexity STAP procedure can achieve near-optimal performance with order-of-magnitude computational complexity reduction as compared to the conventional STAP procedure.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Radar detection of endo-clutter high-value targets using tracker feedback
ActiveUS20160170019A1Efficient processingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSpace-time adaptive processingDegrees of freedom
A radar signal target detection and display system employs feedback to produce improved detection and tracking. Portions of the radar images for each antenna channel to search for the target of interest are defined using the track state to define the center of the search region and using the track covariance matrix to define the size of the region. Moving reference processing (MRP) is performed. MRP employs a search centered on the motion state derived from the detection sent to the tracker on the previous coherent processing interval (CPI). Space-time adaptive processing (STAP) is employed on each CPI using a unique set of adaptive degrees of freedom (DOFs) derived from pre-MRP and post-MRP complex radar image amplitudes for each antenna channel.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
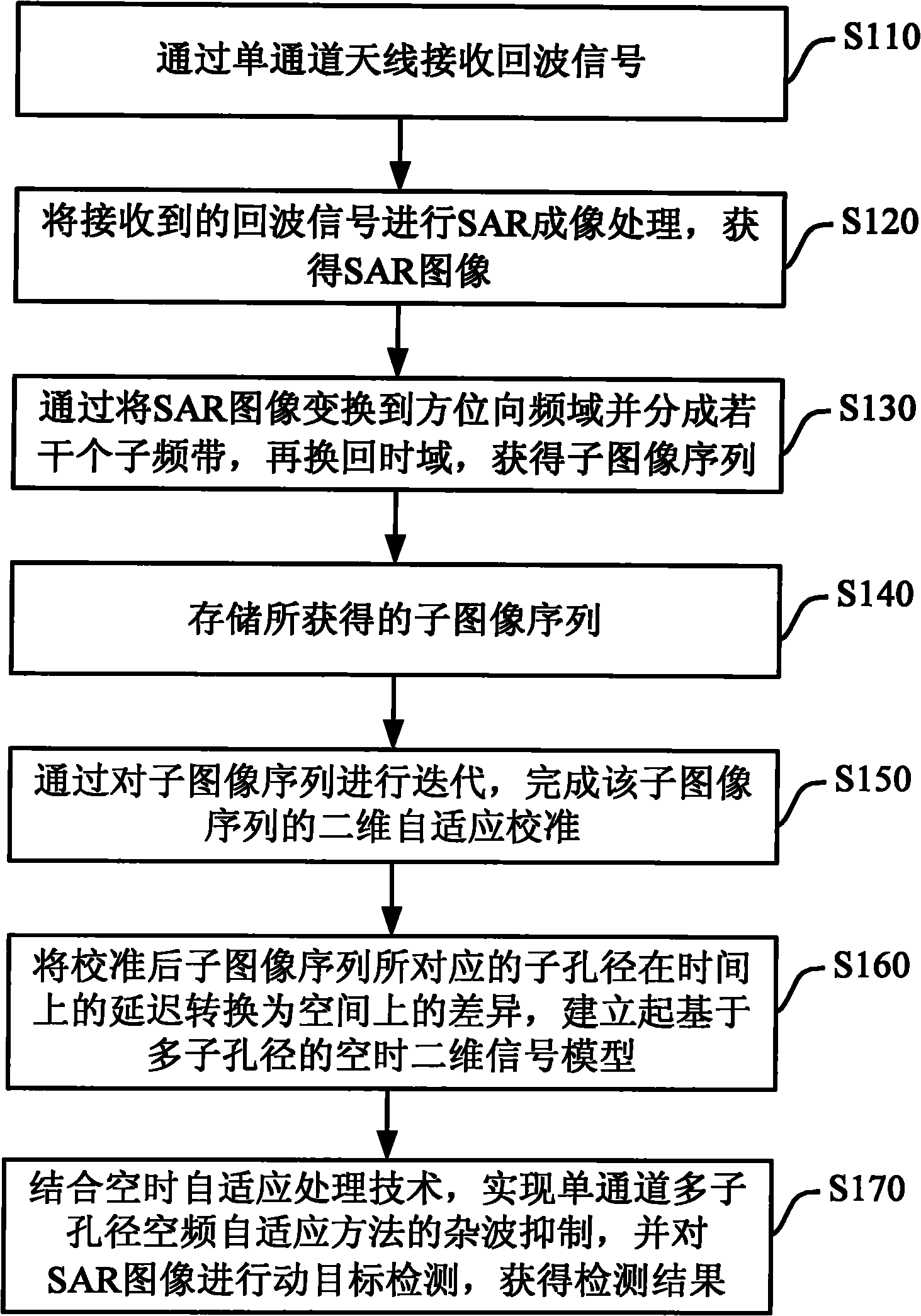
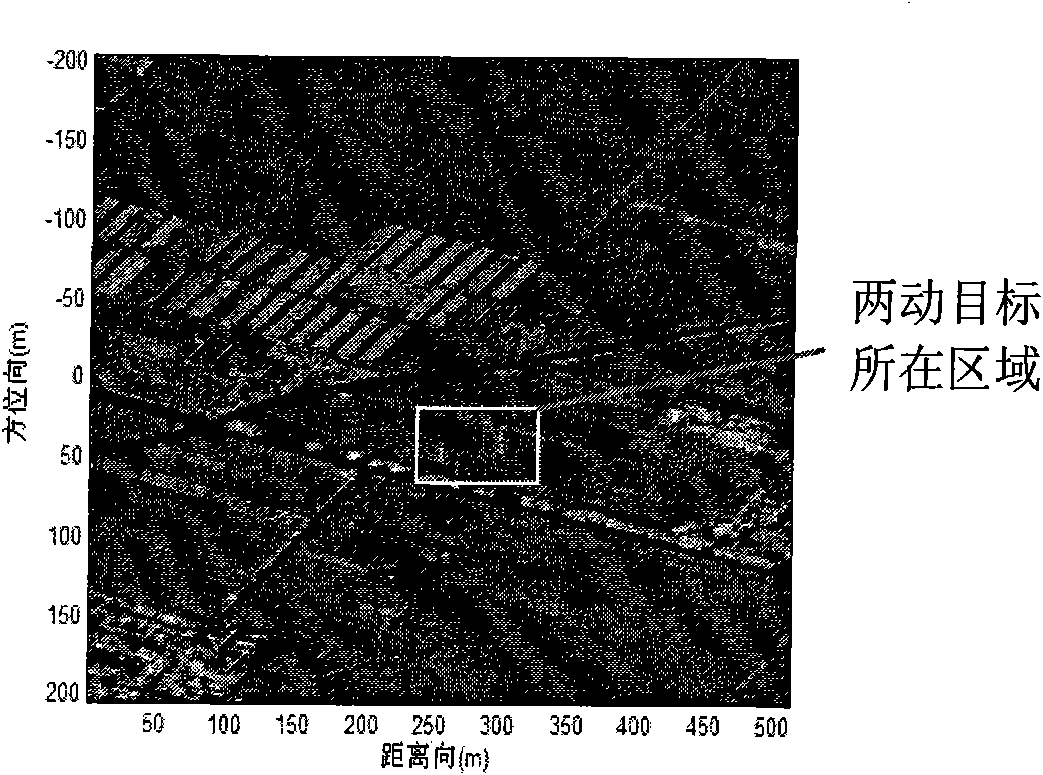
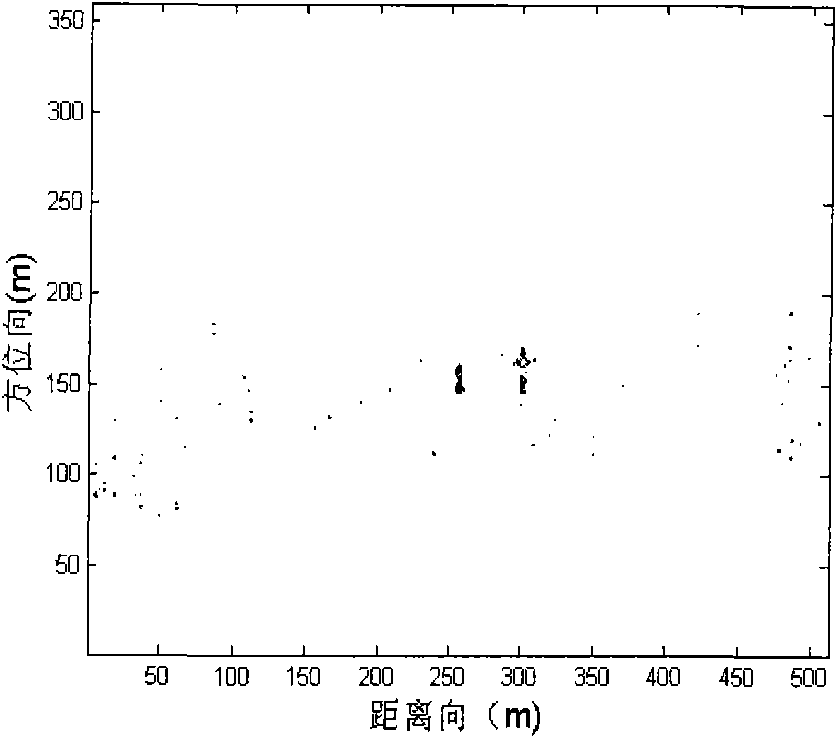
Moving target detection method based on multiple sub-apertures of single-channel SAR
InactiveCN101858976AEasy to detectImprove computing efficiencyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTime domainFrequency spectrum
The invention provides a moving target detection method based on multiple sub-apertures of a single-channel SAR, which belongs to the technical field of moving target detection. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring sub-apertures corresponding to sub-images based on division of an SAR image in azimuth spectrum, and correcting amplitude and phase errors of different sub-images in a two-dimensional adaptive method, thereby realizing rectification of the sub-apertures; acquiring space information of the sub-apertures in the azimuth direction through equalizing changes of the time delay of the sub-apertures corresponding to changes in the slope distance into location differences in different azimuth directions at one moment, and then obtaining the amount of space-time two-dimensional information in combination of pulse data accumulated by the sub-apertures in the time domain; and realizing clutter suppression and target detection through space-time adaptive processing algorithms based on the previous steps. The invention can overcome the defect that the single channel is insufficient in clutter suppression, and solves the problems of the multi-channel SAR such as large amount of operation, high complexity and the like. Therefore, the method can effectively realize the detection of the moving target, and can be applied in the moving target detection of the single-channel SAR image.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
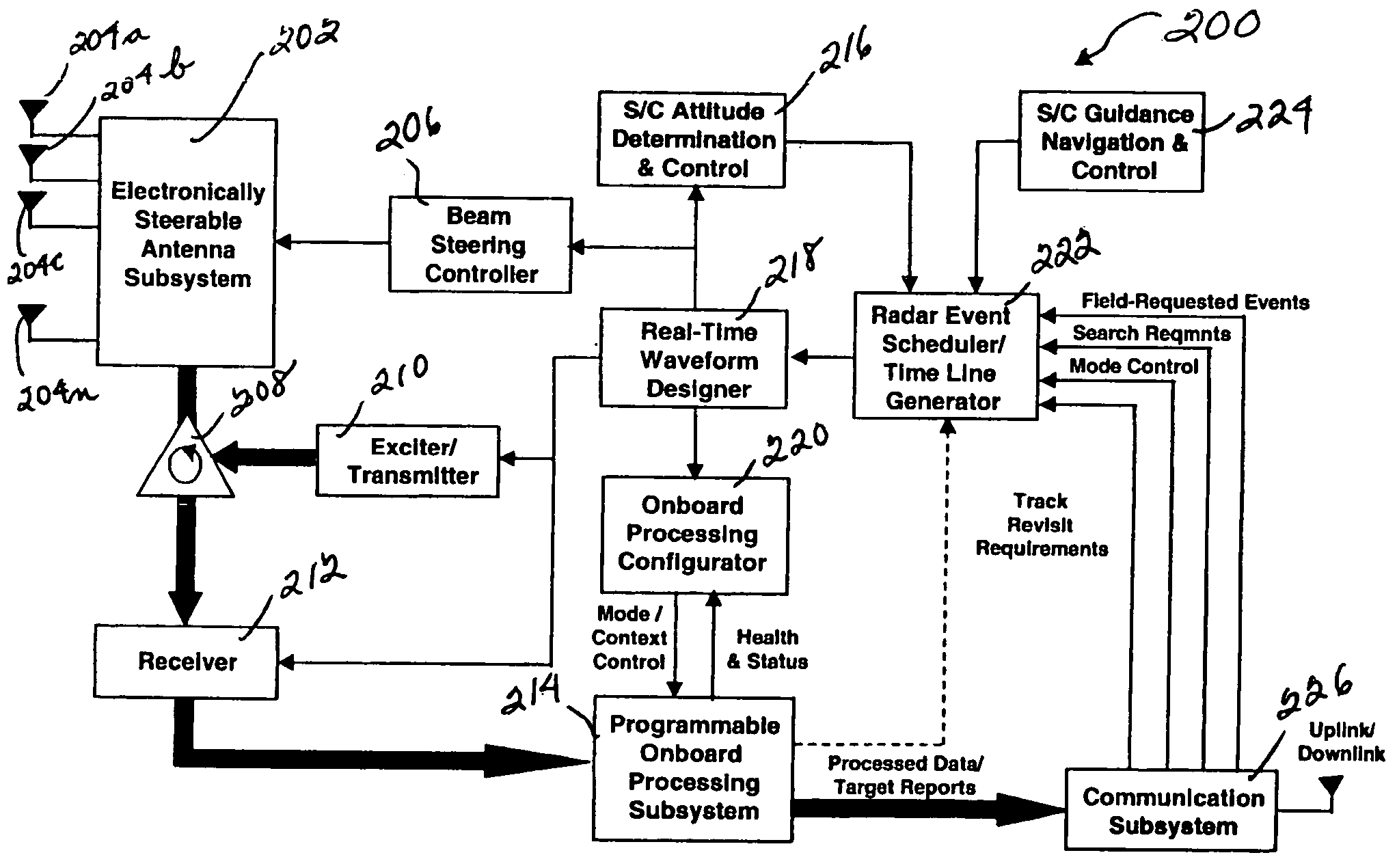
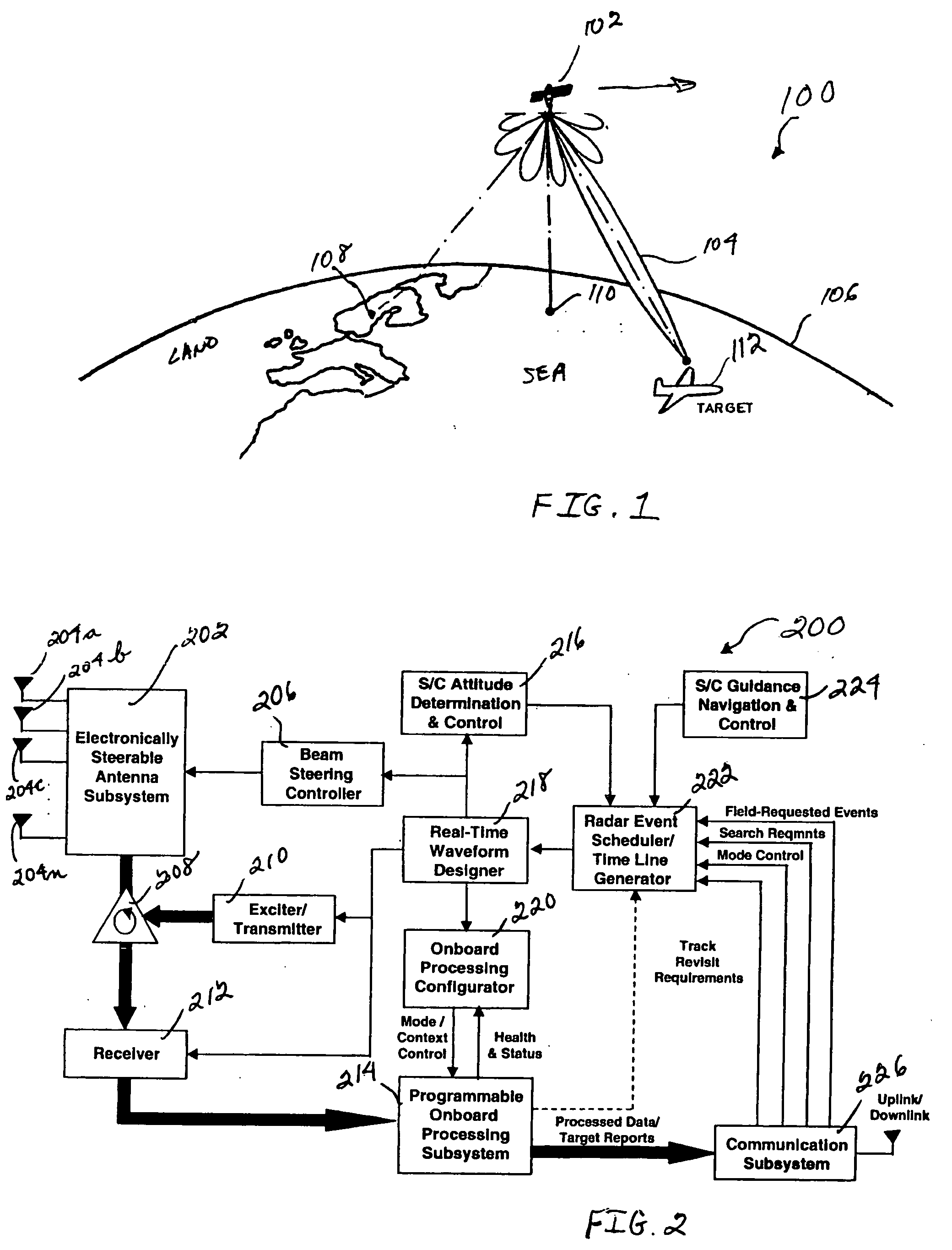
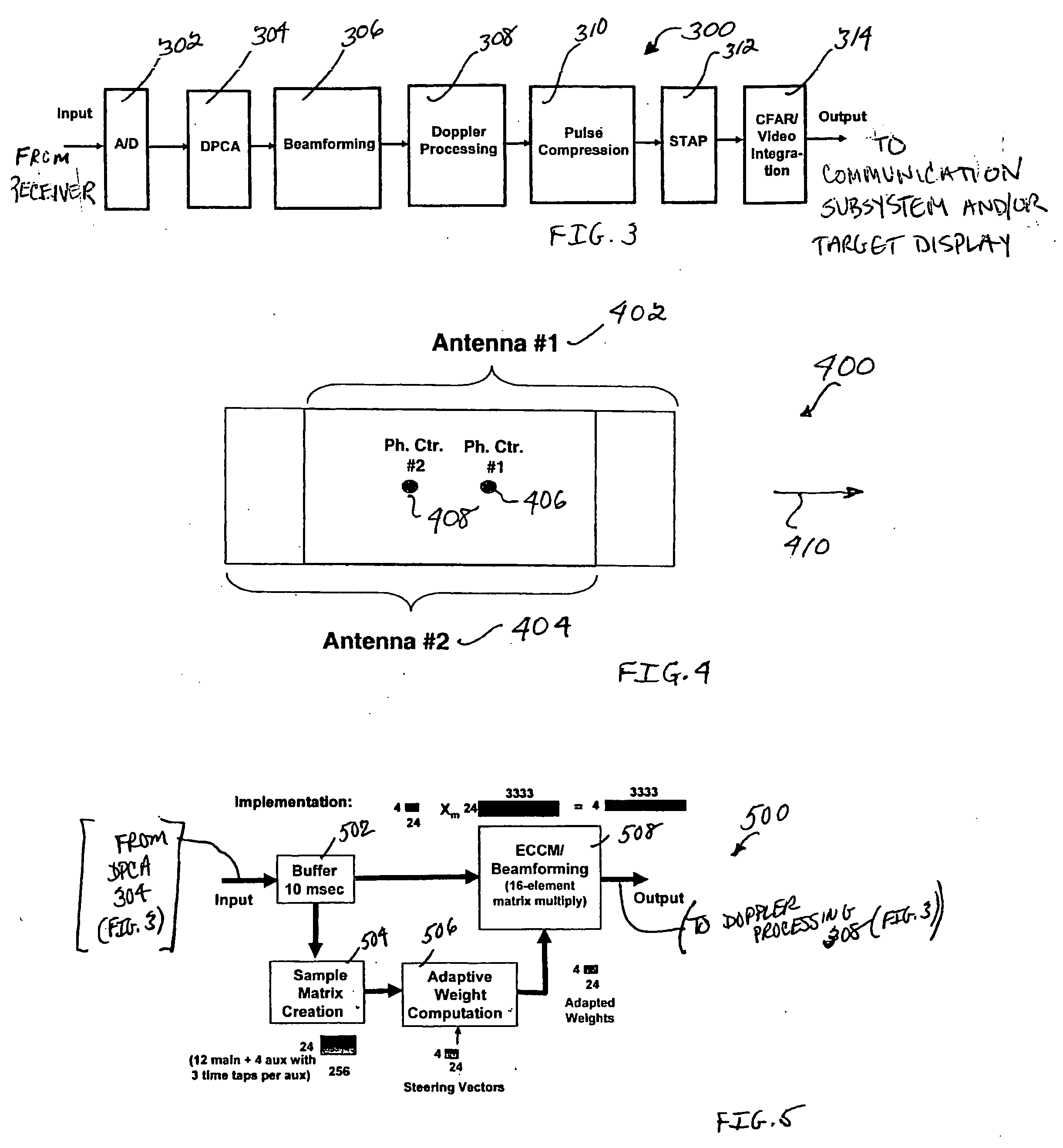
System and method for combining displaced phase center antenna and space-time adaptive processing techniques to enhance clutter suppression in radar on moving platforms
InactiveUS20060181451A1Easy to solveThe environment is moreRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsSpace-time adaptive processing
A system and method are disclosed for enhancing the suppression of clutter and target detection in a radar system located on a moving platform. For example, a radar system including an MTI subsystem is located on a moving platform (e.g., ship-borne, airborne or space-based radar system) with a DPCA processing unit located nearer to the front end of the radar receiver, and a STAP processing unit located nearer to the back end. The DPCA processing unit provides gross cancellation and suppression of the received clutter signals, and the STAP processing unit provides fine tuning for the clutter suppression process. In other words, the front end DPCA processing unit removes most of the rapidly varying clutter, which gives the back end STAP processing unit a more benign clutter environment to process. As such, using a DPCA processing unit on a space-based radar platform improves system performance, because the space-based platform is relatively stable and not subject to air turbulence or wave motion. Also, using a DPCA processing unit provides independence from clutter statistics, which is important because relatively little empirical clutter data is available from space-based radar platforms. Using a STAP processing unit for clutter suppression on the space-based radar platform provides fine tuning of the suppression process.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
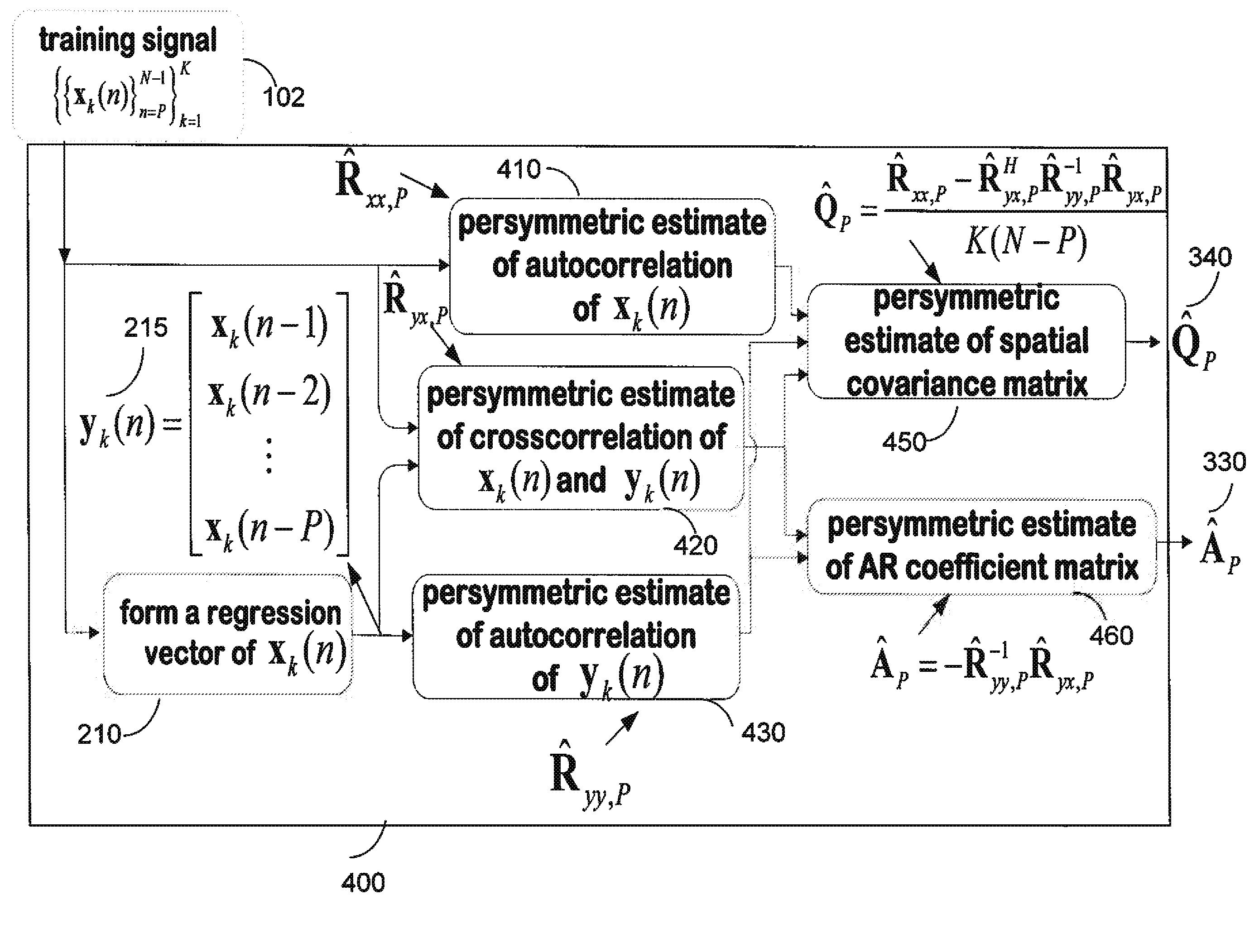
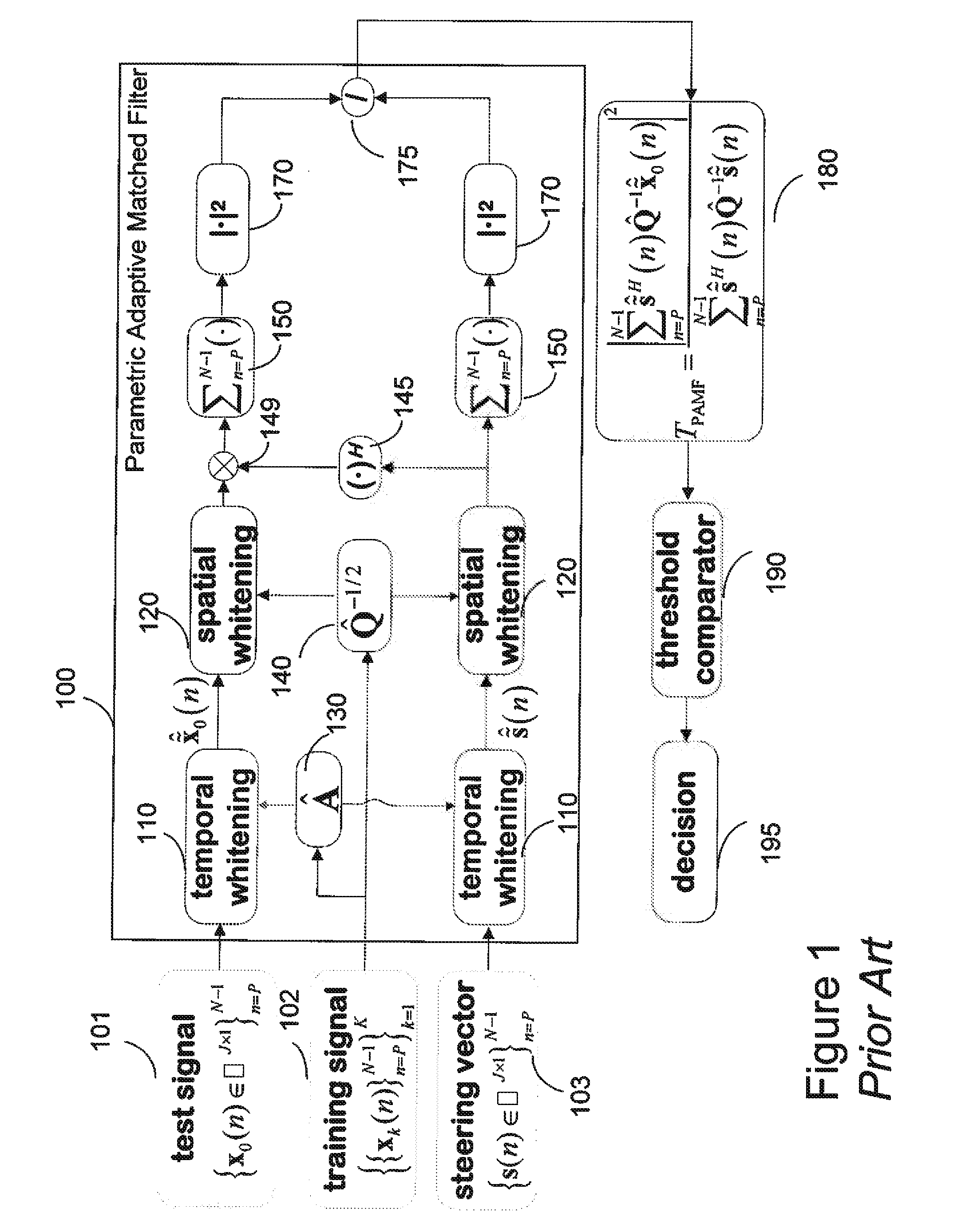
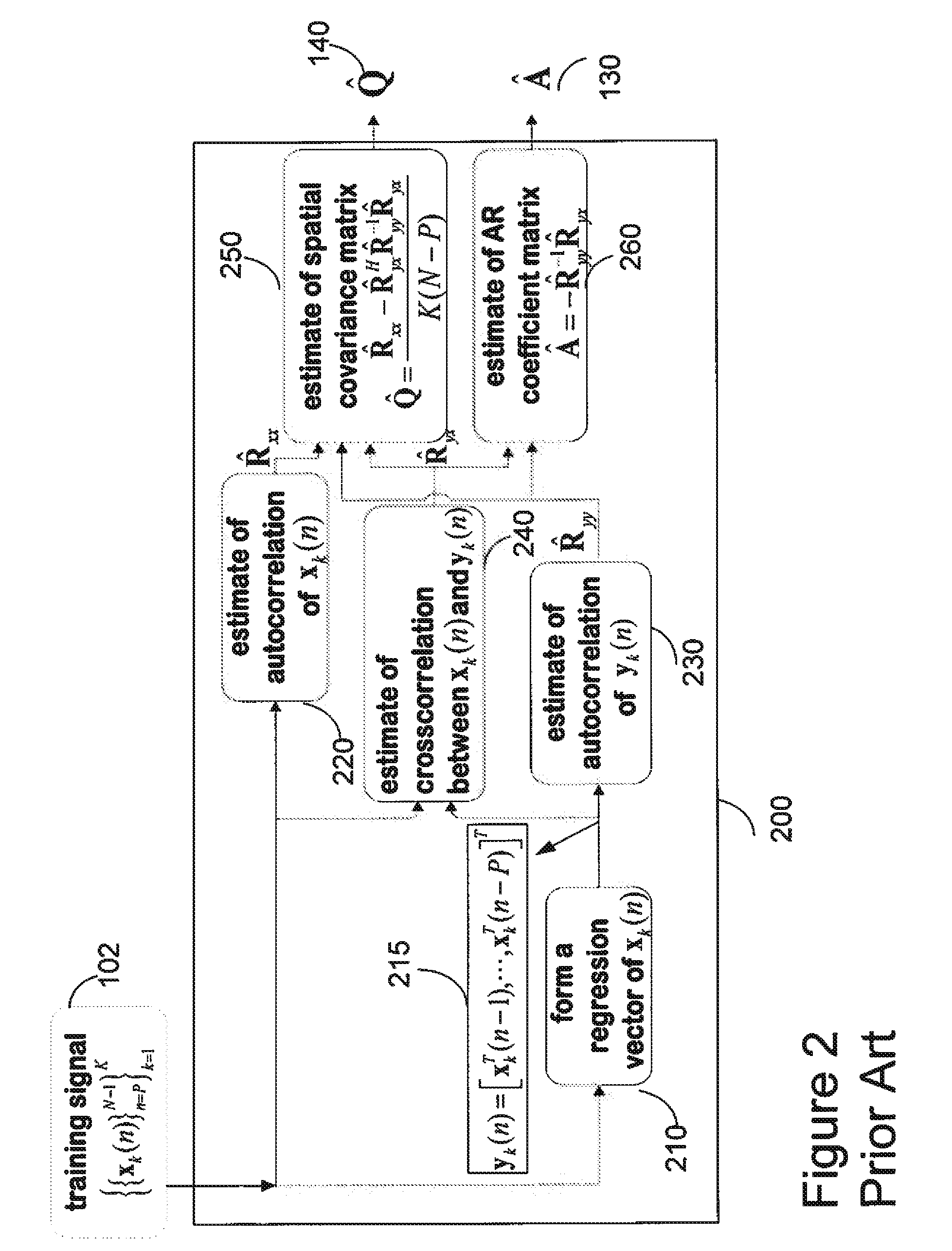
Persymmetric Parametric Adaptive Matched Filters for Detecting Targets Using Space-Time Adaptive Processing of Radar Signals
ActiveUS20120127027A1Radio wave reradiation/reflectionPattern recognitionSpace-time adaptive processing
A method provides space-time adaptive processing (STAP) for target detection using adaptive matched filters (AMF). A generalized likelihood ratio test (GLRT) is determined where spatial and temporal correlation matrices Q and A are assumed. Then, the correlation matrices A and Q are replaced with maximum likelihood (ML) estimates obtained only from training signals subject to a persymmetric constraint.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
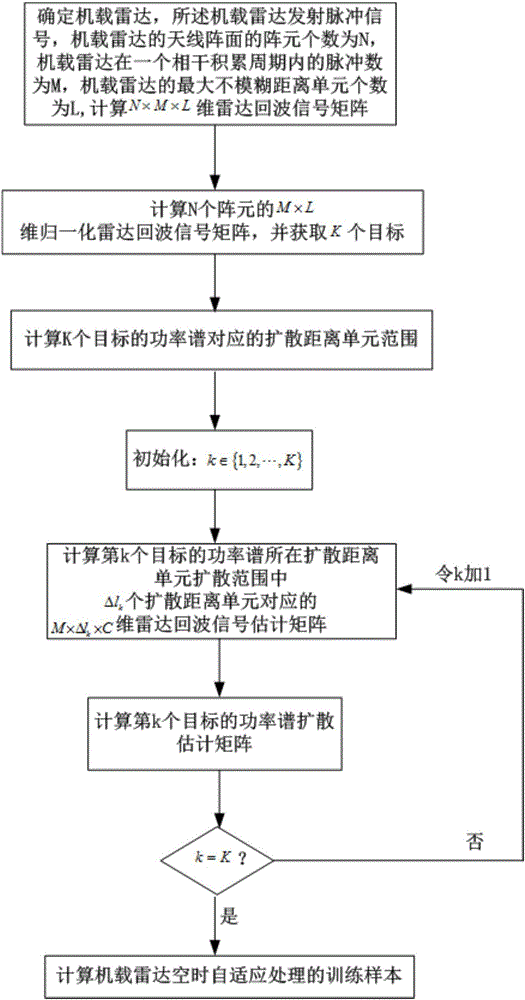
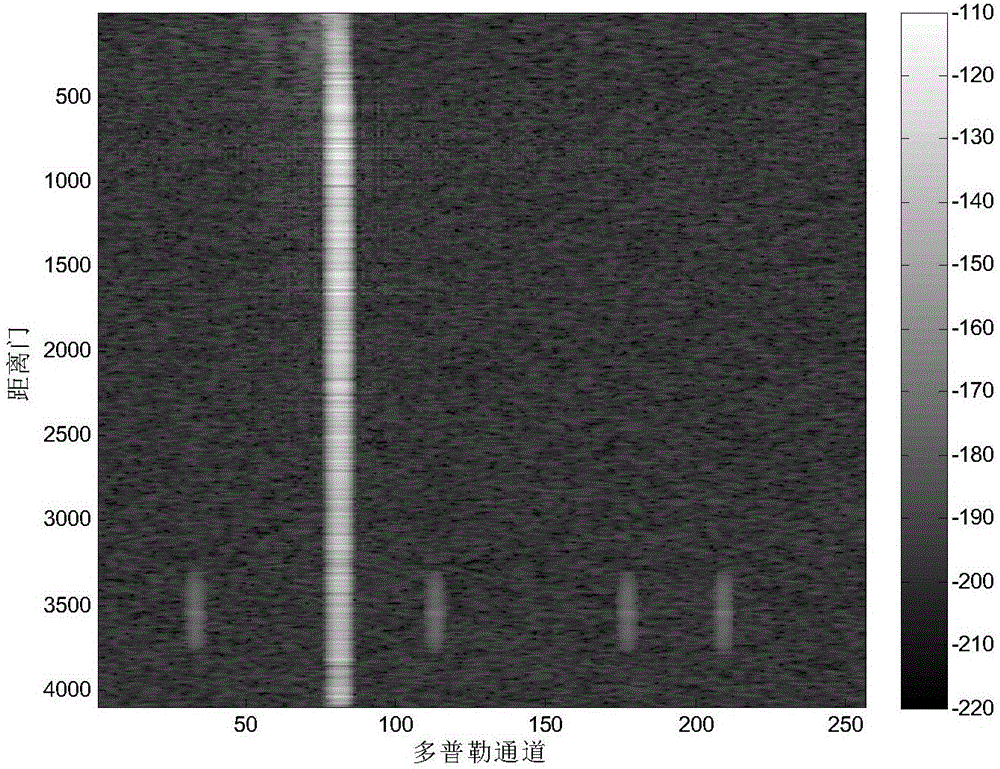
Time-space adaptive processing method based on radar amplitude and Doppler frequency estimation
The invention discloses a time-space adaptive processing method based on radar amplitude and Doppler frequency estimation. The approach is as follows: determining an airborne radar which emits pulse signals and receives radar echo signals in a detection scope, obtaining an N*M*L-dimensional radar echo signal matrix through calculation, calculating a D*L-dimensional radar echo signal matrix P of power values at D Doppler channels corresponding to L distance units in N array elements, obtaining K targets, accordingly, obtaining a diffusion distance unit scope corresponding to power spectra of the K targets, initializing K, calculating an M*delta1k*C-dimensional radar echo signal estimation matrix Tk corresponding to delta1K diffusion distance units in a diffusion matrix unit diffusion scope Lk of the power spectrum of the k-th target, accordingly, calculating a power spectrum diffusion estimation matrix Tk<^> of the k-th target, adding one to k until the power spectrum diffusion estimation matrix Tk<^> of the k-th target is obtained, and then according to a scope from the obtained power spectrum diffusion estimation matrix T1<^> of the first target to the power spectrum diffusion estimation matrix Tk<^> of the k-th target, calculating a training sample F for time-space adaptive processing of the airborne radar.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
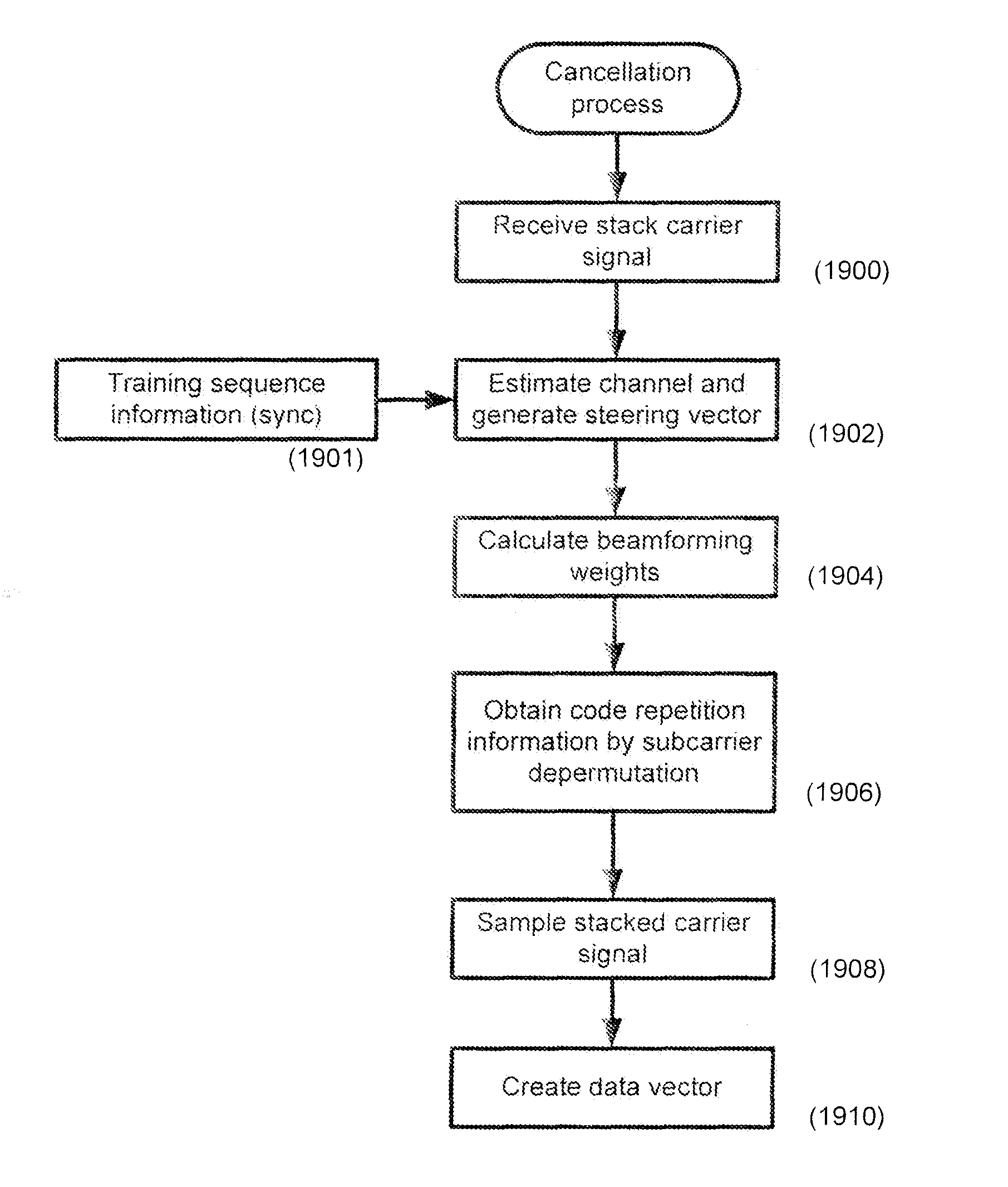
Systems and methods for channel based beamforming for stacked carrier multiple access
ActiveUS8300742B1Improve good performanceImprove system reliabilityLine-faulsts/interference reductionAmplitude demodulation detailsTime domainAccess method
Methods and systems that enhance interference cancellation are described. Samples are obtained from stacked carriers in a received signal and a data vector is created from the samples. Stacked carriers are selected using a steering vector received during synchronization of the receiver. The steering vector is calculated to obtain cancellation of interference from another receiver and is calculated based on time domain channel estimation. Specialized time domain training sequences and simple cross correlation are used to obtain a channel estimate for use in stacked carrier beamforming and / or for use in OFDM based spatial beamforming. State space or filter based modeled interpolators in the frequency domain or time domain to interpolation of the channels, or whitening matrix-filters over time or frequency are used for maintaining linear beamforming weights as a function of time or frequency. Space time adaptive processing facilitates beamforming of communications signals OFDM and 802.16 (WiMax) systems.
Owner:DIRECTV LLC
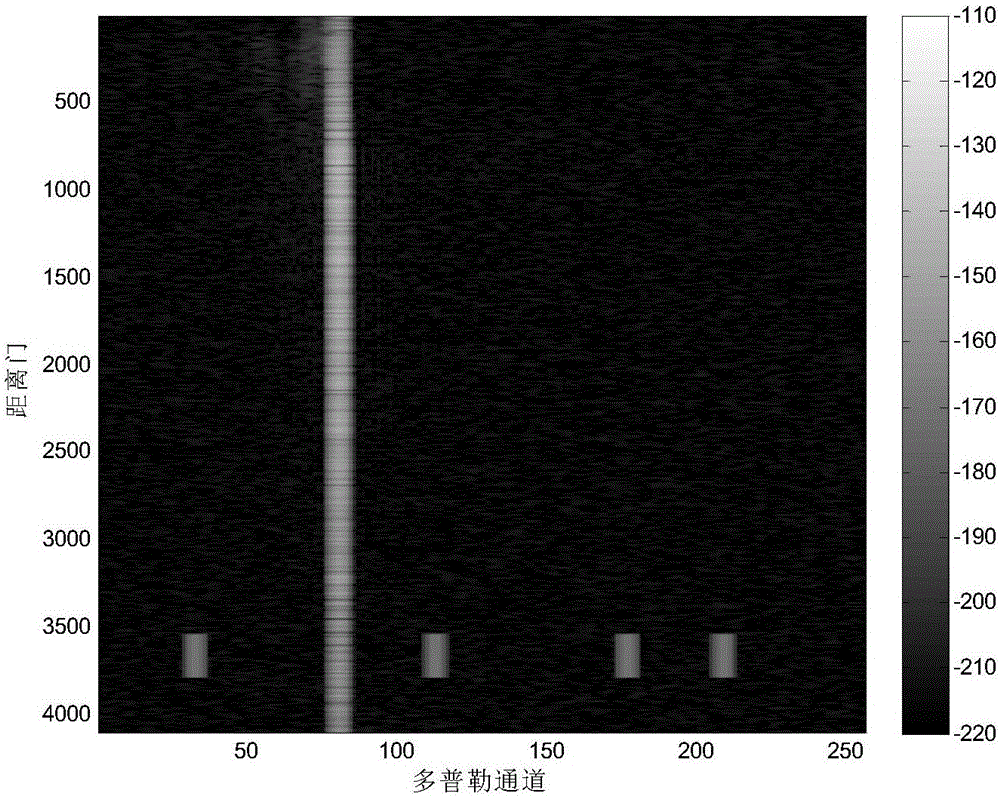
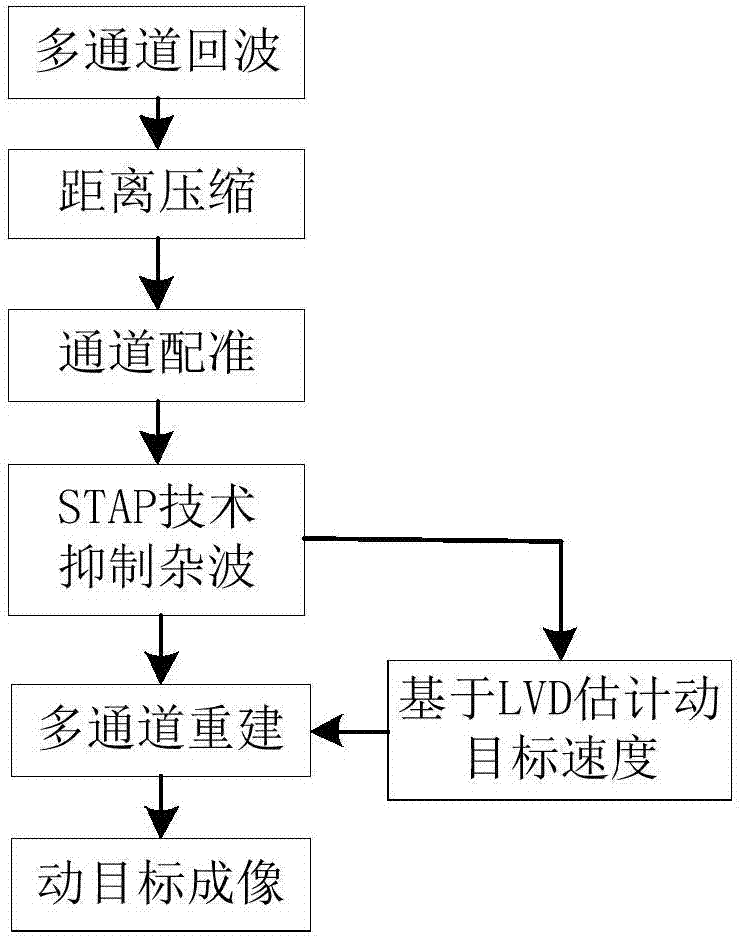
High-resolution wide-swath SAR moving target speed estimation and imaging method
ActiveCN107229048AFocusSuppress blurRadio wave reradiation/reflectionS distributionHigh resolution imaging
The invention discloses a high-resolution wide-swath SAR moving target speed estimation and imaging method. The method is characterized by, under a high-resolution wide-swath azimuth multichannel model, carrying out clutter suppression on data obtained after multichannel range compression by utilizing a space-time adaptive processing method; then, estimating distance and azimuth velocity of a moving target through a Lv's distribution method; suppressing azimuth ambiguity of the moving target by utilizing the distance velocity of the moving target; and finally, realizing high-resolution imaging through a back-projection algorithm (BP) and the distance and azimuth velocity of the moving target.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Noise suppression method based on inhomogeneous space solid array distributed SAR (Specific Absorption Rate)
InactiveCN101813765AEffective clutter suppressionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAdaptive filterSpace-time adaptive processing
The invention relates to a noise suppression method based on an inhomogeneous space solid array distributed SAR (Specific Absorption Rate), belonging to a noise suppression method and solving the problem that the traditional STAP (Space-Time Adaptive Processing) method is only suitable for noise suppression of a homogeneous linear array or homogeneous area array but not suitable for noise suppression of an inhomogeneous space array. The method comprises the steps of: firstly, establishing an inhomogeneous space solid array manifold; secondly, carrying out signal reconfiguration on the inhomogeneous space solid array manifold to obtain a homogeneous space solid array manifold; thirdly, computing and obtaining various dimensions of Doppler frequencies of noises according to the homogeneous space solid array manifold to obtain a noise model based on the homogeneous space solid array manifold; and fourthly, constructing full time space self-adaptive filter according to the noise model, various dimensions of Doppler frequencies and a full time space self-adaptive processing method. The invention overcomes the defects of the prior art, and can be used for noise suppression field in the SAR ground moving target detection technology.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
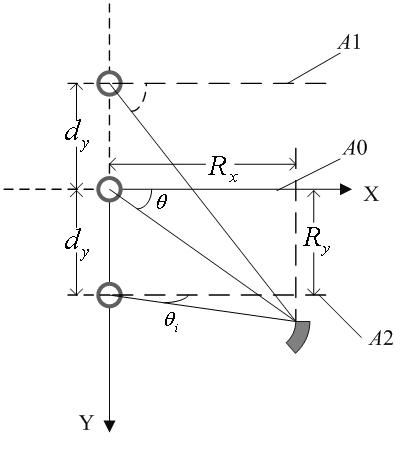
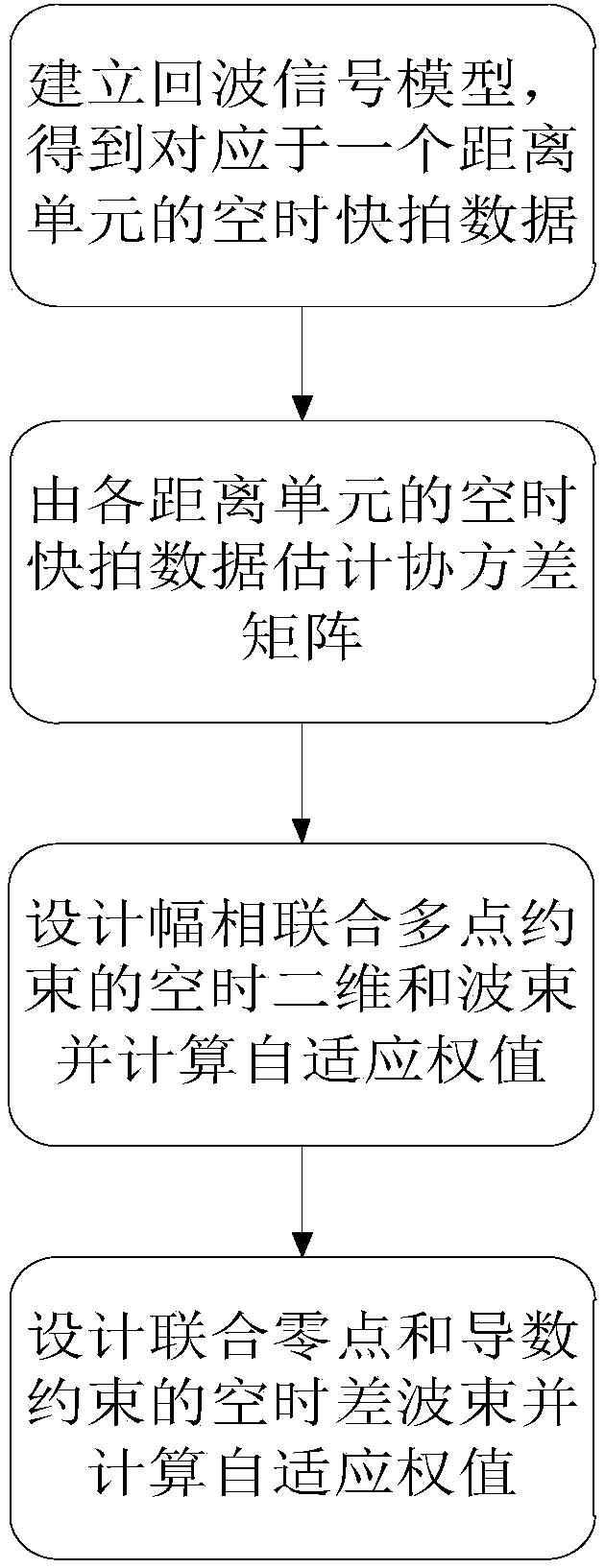
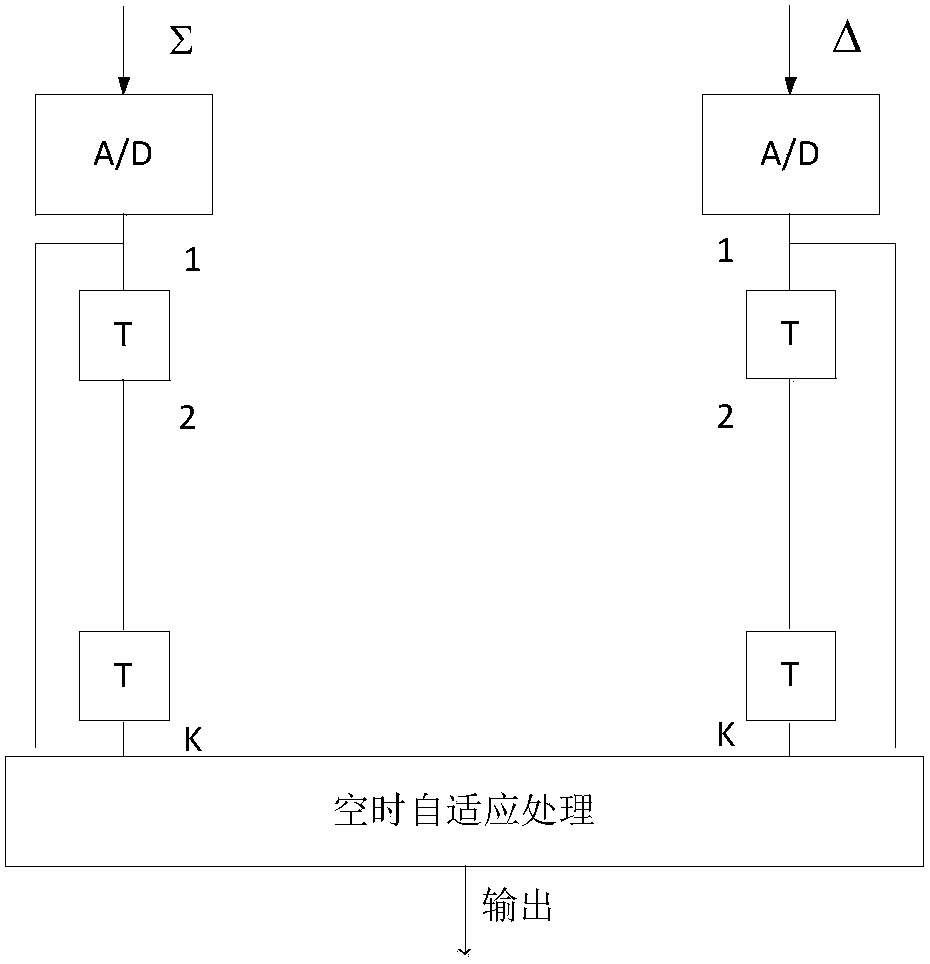
Robust adaptive clutter suppression method of sum and difference channel of missile-borne radar
The invention discloses a robust adaptive clutter suppression method of a sum and difference channel of a missile-borne radar. The problem that a traditional sum and difference system of the missile-borne radar may confront with severe loss of the object detection performance when object constraint is not determined and an object is polluted is solved. The method is realized by the steps that an echo signal model is established, and space-time snapshot data is obtained; the space-time snapshot data is used to estimate a covariance matrix; a space-time 2D sum beams of amplitude-phase combined multi-point constraint is designed; and a space-time difference beam combined with zero-point sum derivation constraint is designed. According to the method of the invention, the existing sum and difference channel of the missile-borne radar is used to output signals, spatial-domain and time-domain information is combined, and space-time adaptive processing is carried out via different types of constraints. Uncertainty of object pollution and object constraints is overcome, the robustness is high, the shape of a main lobe is maintained, either the object angle or Doppler parameter estimation ismore precise and robust, the method realizes a higher moving object detection performance, and the method is used in the field of missile-borne radars.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Bistatic radar localization dimension reduction clutter suppression method based on MIMO
InactiveCN103353591ALower requirementReal-time processingWave based measurement systemsComputation complexityOptimal weight
The invention discloses a bistatic radar localization dimension reduction clutter suppression method based on MIMO. By using a current bistatic MIMO radar distance dependence clutter suppression method, an operation amount is large and the number of needed independent identically distributed samples is high. By using the method of the invention, the above problems are mainly solved. Realization steps are characterized in that (1) a transmitted waveform is used to carry out matched filtering on echo data of the radar; (2) a localization dimension reduction matrix is constructed and dimension reduction processing is performed on the received data; (3) the data after the dimension reduction is used to estimate a clutter covariance matrix; (4) according to a space-time adaptive processing principle, an optimal weight vector is obtained; (5) the optimal weight is used to weight the data after the dimension reduction, the background clutter is suppressed and a target signal is detected. By using the method of the invention, there are the advantages that a computation complexity is low; a requirement to the number of the independent identically distributed samples is low and clutter suppression performance is good. The method can be used in bistatic radar ground target detection of the MIMO.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Bistatic radar multichannel combination dimension reduction clutter suppression method based on MIMO
InactiveCN103353592AReduce the number of requestsLower requirementWave based measurement systemsComputation complexityTarget signal
The invention discloses a bistatic radar multichannel combination dimension reduction clutter suppression method based on MIMO. By using a current bistatic MIMO radar distance dependence clutter suppression method, an operation amount is large and the number of needed independent identically distributed samples is high. By using the method of the invention, the above problems are mainly solved. Realization steps are characterized in that (1) a transmitted waveform is used to carry out matched filtering on echo data of the radar; (2) a multichannel combination dimension reduction matrix is constructed and dimension reduction processing is performed on the received data; (3) the data after the dimension reduction is used to estimate a clutter covariance matrix; (4) according to a space-time adaptive processing principle, an optimal weight vector is obtained; (5) the optimal weight is used to weight the data after the dimension reduction, the background clutter is suppressed and a target signal is detected. Compared to an existing full-dimension processing method, by using the method of the invention, there are the advantages that a computation complexity is low; a requirement to the number of the independent identically distributed samples is low and clutter suppression performance is good. The method can be used in bistatic radar ground target detection of the MIMO.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method and device for ground moving target indication based on InSAR (interferometric synthetic aperture radar) formation
InactiveCN104515980AImprove speed measurement accuracySuppress clutterRadio wave reradiation/reflectionInterferometric synthetic aperture radarInverse synthetic aperture radar
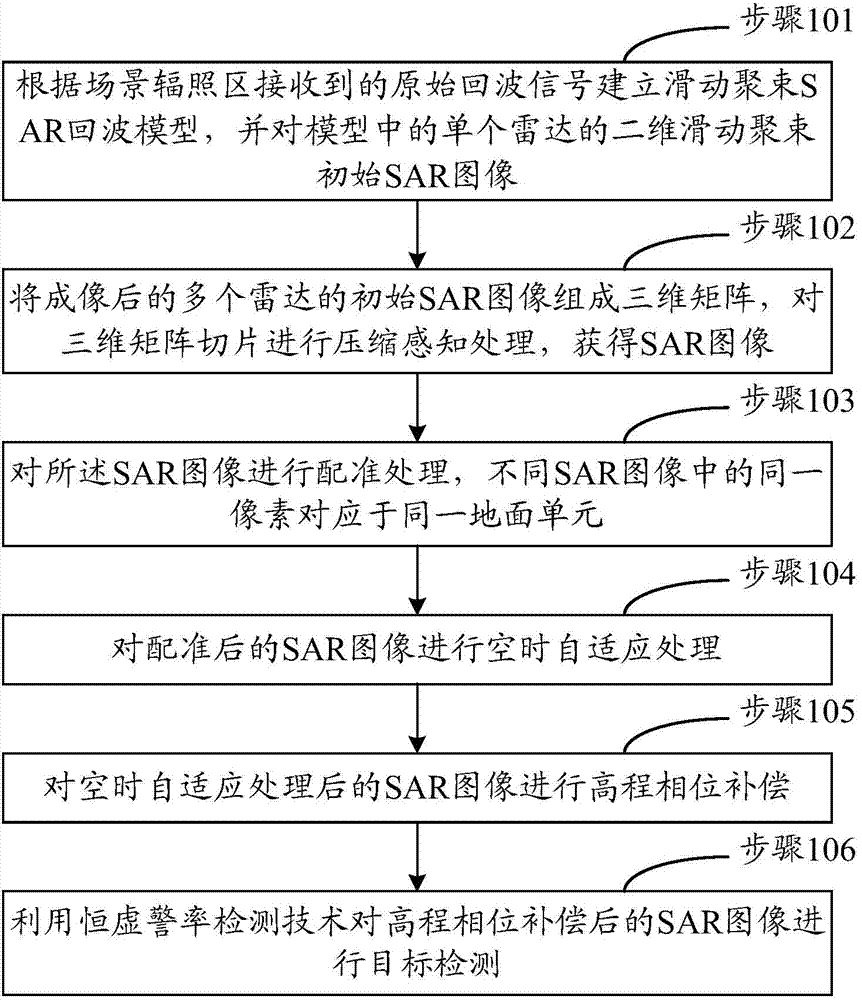
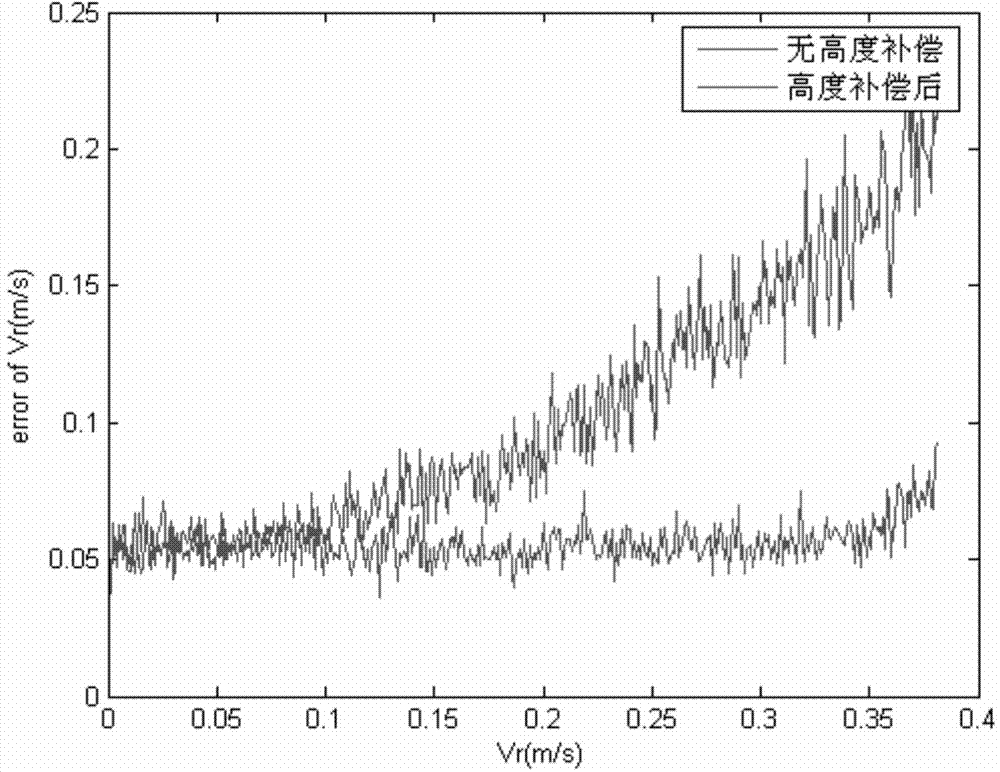
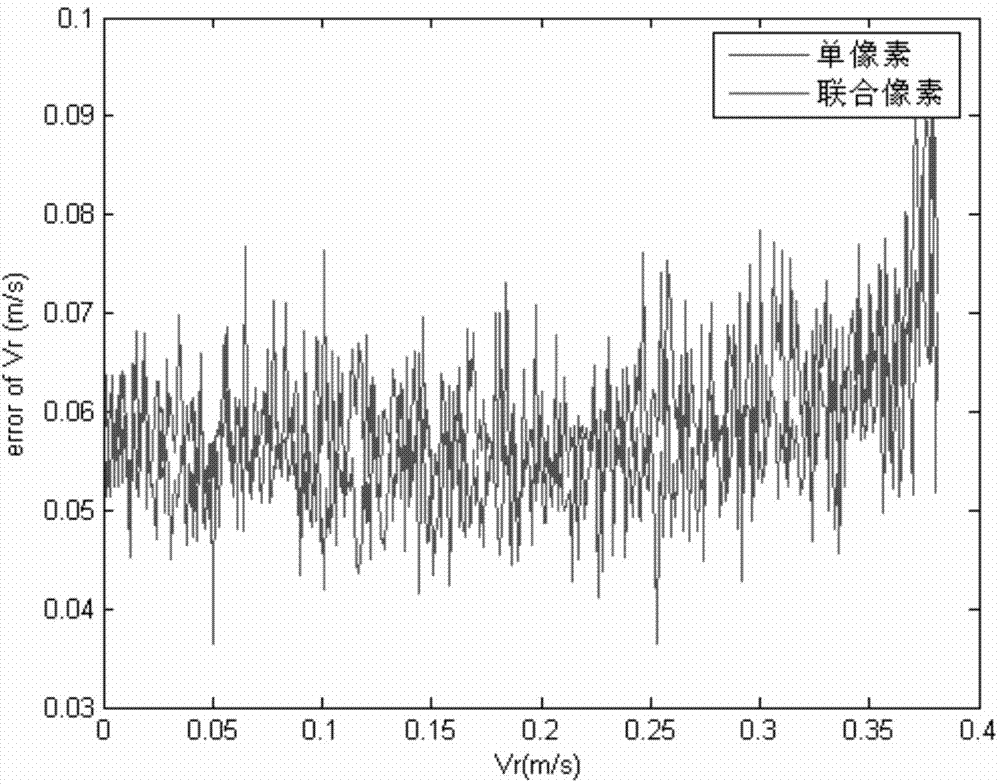
The invention discloses a method and a device for ground moving target indication based on InSAR (interferometric synthetic aperture radar) formation. The method includes: setting up a sliding spotlight SAR echo model according to original echo signals received in a scene irradiation region, and imaging each single radar two-dimensional sliding spotlight initial SAR image in the model; enabling the plurality of imaged radar initial SAR images to form a three-dimensional matrix, and subjecting sections of the three-dimensional matrix to compressed sensing treatment to acquire SAR images; subjecting the SAR images to registration, wherein same pixels in different SAR images correspond to a same ground unit; subjecting the registered SAR images to space-time adaptive processing; subjecting the SAR images to elevation phase compensation after space-time adaptive processing; subjecting the SAR images to target detection after elevation phase compensation by means of constant false alarm rate detection. By means of elevation phase compensation, measurement accuracy can be evidently improved, and measurement errors can be controlled about 0.05.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Efficient cascading space-time adaptive processing method based on passive detection
InactiveCN103760529ASuppress interferenceSuppress clutterWave based measurement systemsTime domainFast Fourier transform
The invention discloses an efficient cascading space-time adaptive processing method based on passive detection. Firstly, coherent integration is carried out on time domain pulses; secondly, weight of adaptive digital beam forming (ADBF) of a beam domain is calculated through high-frequency Doppler unit data only comprising interference information; thirdly, ADBF interference restraining is carried out on each Doppler unit; lastly, clutter is restrained through an adaptive double-delay canceller, and coherent integration is carried out on output signals of the self-adaptive double-delay canceller through weighting fast Fourier transform (FFT). By means of the efficient cascading space-time adaptive processing method, interference and clutter can be effectively restrained, the moving-target detection performance can be improved, and engineering implementation is easy because of small operand.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Inverse fast fourier transform (IFFT) with overlap and add
InactiveUS7197095B1Efficiently null a relatively large number of jammersReduced to practiceBeacon systems using radio wavesDigital computer detailsComputation complexitySpace-time adaptive processing
A system for efficiently filtering interfering signals in a front end of a GPS receiver is disclosed. Such interfering signals can emanate from friendly, as well as unfriendly, sources. One embodiment includes a GPS receiver with a space-time adaptive processing (STAP) filter. At least a portion of the interfering signals are removed by applying weights to the inputs. One embodiment adaptively calculates and applies the weights by Fourier Transform convolution and Fourier Transform correlation. The Fourier Transform can be computed via a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT). This approach advantageously reduces computational complexity to practical levels. Another embodiment utilizes redundancy in the covariance matrix to further reduce computational complexity. In another embodiment, an improved FFT and an improved Inverse FFT further reduce computational complexity and improve speed. Advantageously, embodiments can efficiently null a relatively large number of jammers at a relatively low cost and with relatively low operating power.
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP
Space-time adaptive processing method for radar clutters based on prior knowledge
InactiveCN106483516AImprove robustnessWave based measurement systemsRadarSpace-time adaptive processing
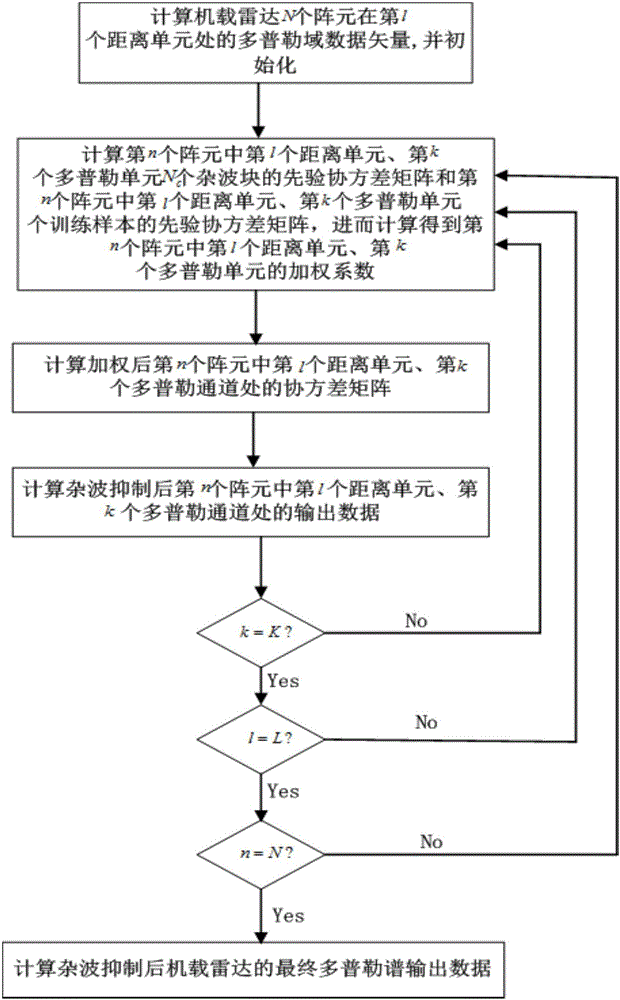
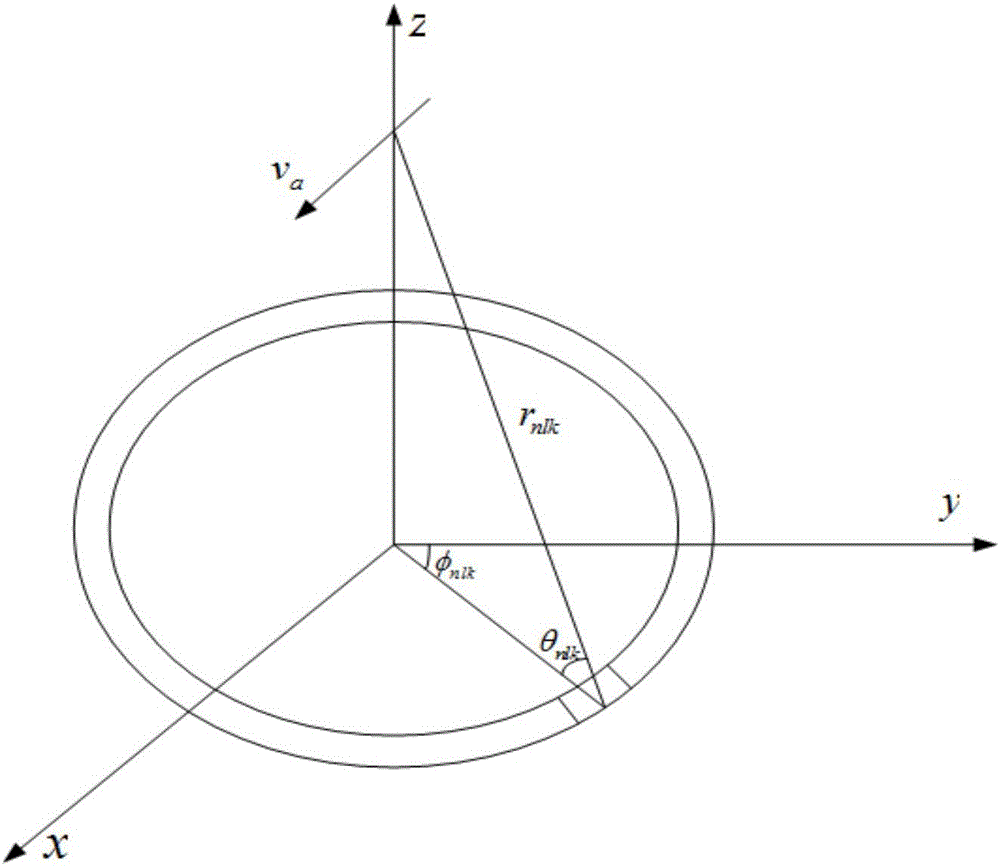
The invention discloses a space-time adaptive processing method for radar clutters based on prior knowledge. An airborne radar is determined, the airborne radar includes N array elements, each array element includes L distance units, each distance unit includes K coherent pulses, Doppler domain data vectors in the first distance units of the N array elements of the airborne radar are calculated, and the weighted coefficient alphanlk of the first distance unit in the nth array element and the kth Doppler unit, the Doppler domain data vectors znlk of the first distance unit in the nth array element in the (k-1)th, kth and (k+1)th Doppler channels, and a covariance matrix Rnlk of the first distance unit of the weighted nth array element in the kth Doppler channel are calculated successively; a space-time filter coefficient wnlk of the first distance unit in the nth array element and the kth Doppler channel is calculated, and output data ynlk of the first distance unit in the nth array element and the kth Doppler channel after clutter inhibition is calculated; and further, final Doppler-spectrum output data of the airborne radar after clutter inhibition is calculated.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Distortionless mean phase antijam nulling of GPS signals
ActiveUS20150226856A1Maximizes ratioOvercome disadvantagesSatellite radio beaconingComplete resolutionPhase distortion
System and method for mean phase compensation of code and carrier phase distortions induced by Space Time Adaptive Processing (STAP) filters used for removing interferences from received GPS signals. The phase distortion is mitigated (without the use of beamforming) using a single STAP filter for processing the GPS satellite channels in which appropriate bundling of constraints is applied to the filter weights. The complete solution can be contained in the antenna electronics with no required changes to the legacy GPS receiver.
Owner:MAYFLOWER COMM CO INC
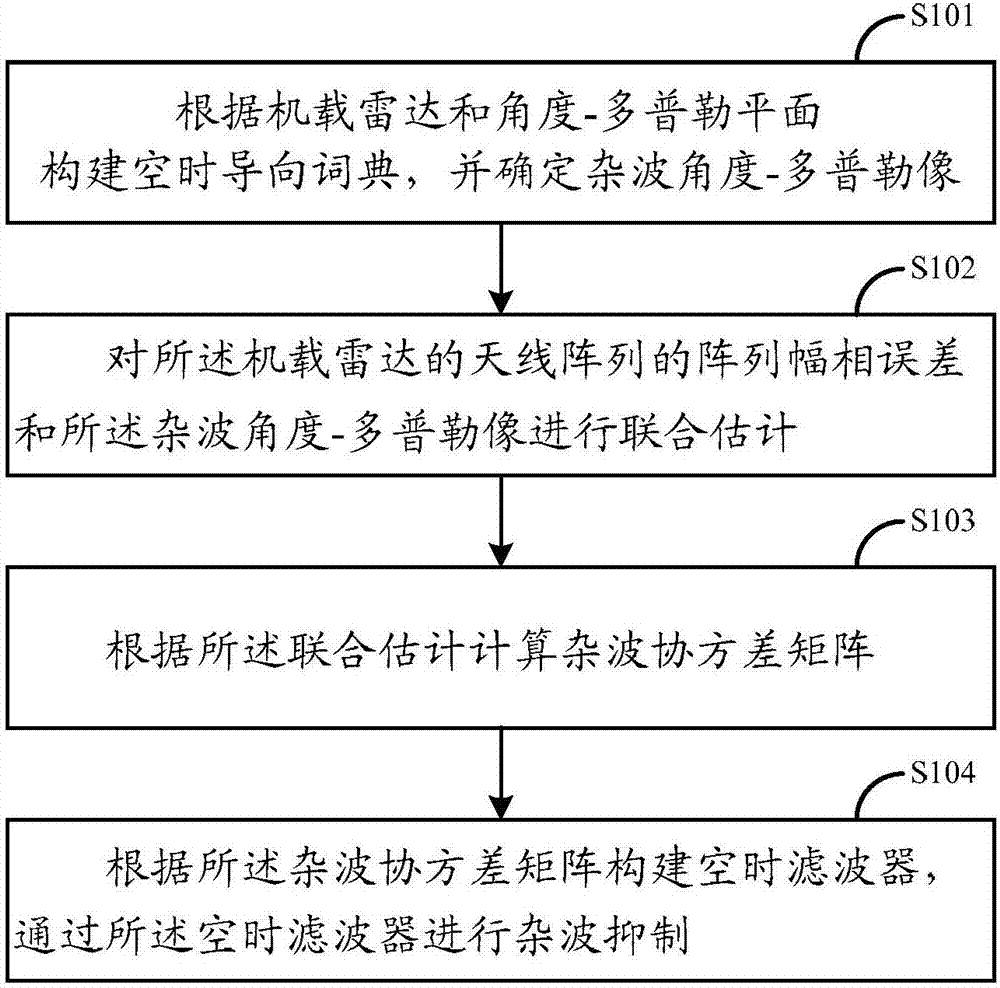
Knowledge-based sparse recovery space-time adaptive processing method and system
InactiveCN107544061AEnhanced inhibitory effectEasy to detectWave based measurement systemsRadar systemsSpace-time adaptive processing
The present invention is applicable to the field of radar signal processing, and provides a space-time adaptive processing method for sparse recovery based on knowledge, comprising: constructing a space-time guidance dictionary according to the airborne radar and angle-Doppler plane, and constructing a space-time guidance dictionary according to the space-time The guide dictionary determines the clutter angle-Doppler image; the array phase error of the antenna array of the airborne radar and the clutter angle-Doppler image are jointly estimated; according to the joint estimation, the clutter coordinate is calculated A variance matrix; constructing a space-time filter according to the clutter covariance matrix, and performing clutter suppression through the space-time filter. The embodiment of the present invention solves the problems of performance degradation and high computational complexity due to the presence of array errors faced by the sparse recovery STAP, and improves the clutter suppression level and target detection capability of the radar system.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Clutter suppression method based on knowledge-assisted sparse iterative covariance estimation
ActiveCN109116311AEasy to detectSolve the problem of non-uniform samplesWave based measurement systemsRadarSpace-time adaptive processing
The invention discloses a clutter suppression method based on knowledge-assisted sparse iterative covariance estimation, and solves the problem of poor clutter suppression performance of the conventional space-time adaptive processing technology because of non-uniformity of the clutter environment. The implementation steps are listed as follows: computing an airborne radar space-time steering vector matrix; determining an initial clutter power matrix and constructing an intermediate variable; computing a clutter power matrix in iteration by means of the intermediate variable; performing iteration to obtain the final clutter power matrix; determining a space-time covariance matrix constructed by the data of one unit to be detected and the corresponding weight; and traversing all the units to be detected so as to obtain the space-time adaptive processing result. The clutter covariance matrix is reconstructed by using the data of the units to be detected so as to avoid non-uniformity of the training samples, effectively suppress high ground clutters and improve the detection performance of the slow moving target; and the computational burden is low, the real-time performance is betterand engineering implementation is easy so that the clutter suppression method is suitable for the airborne radar to suppress the high ground clutters in the non-uniform environment and detect the slow ground moving target.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Space-time adaptive processing method based on co-prime pulse recurrence interval and apparatus thereof
ActiveCN106338723AImplement object detectionImprove reusabilityWave based measurement systemsInterference resistanceSpace-time adaptive processing
The invention is suitable for the radar signal processing and array signal processing technology field and provides a space-time adaptive processing method based on a co-prime pulse recurrence interval and an apparatus thereof. The method comprises the following steps of step S1, receiving pulses emitted by using a co-prime way and using time delay among the received pulses to construct a virtual pulse Ps; step S2, according to the constructed virtual pulse, constructing a virtual snapshot xv; step S3, using the constructed virtual snapshot to estimate a covariance matrix RCPRI-SMI of clutters and noises; and step S4, using the acquired covariance matrix to design a space-time filter so as to carry out clutter suppression. By using the method and the apparatus of the invention, a distance and doppler ambiguity can be solved to some extent, a capability of electronic interference resistance can be increased and simultaneously flexibility of a system can be increased too.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
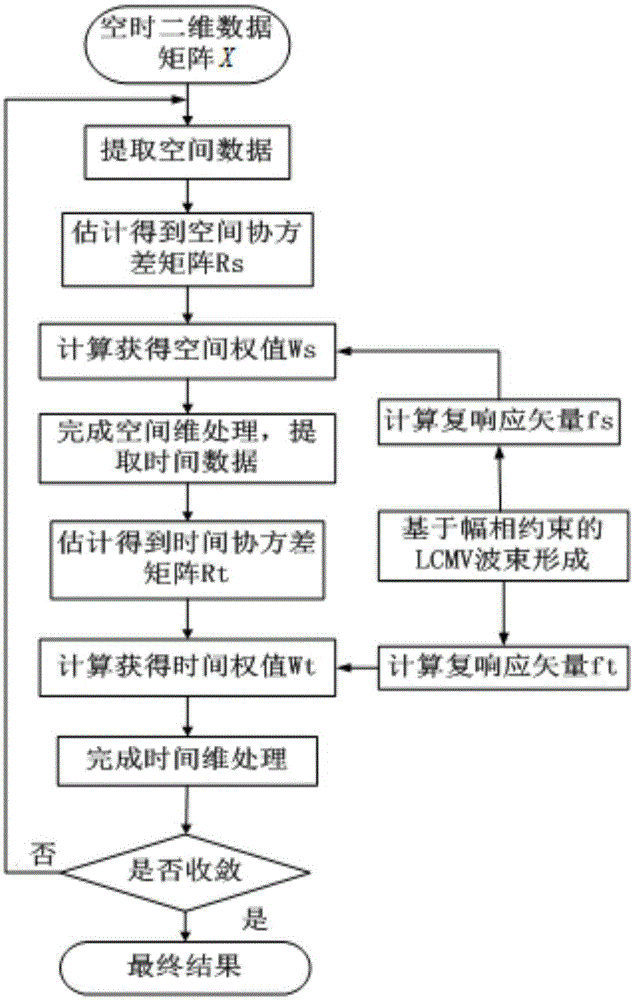
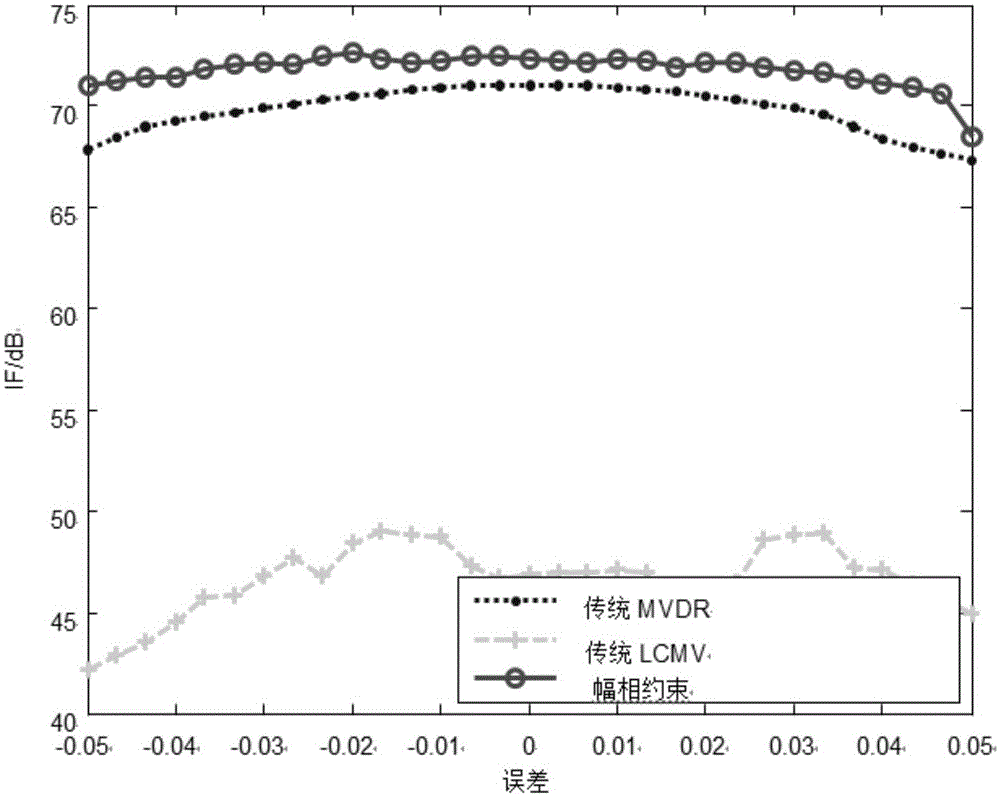
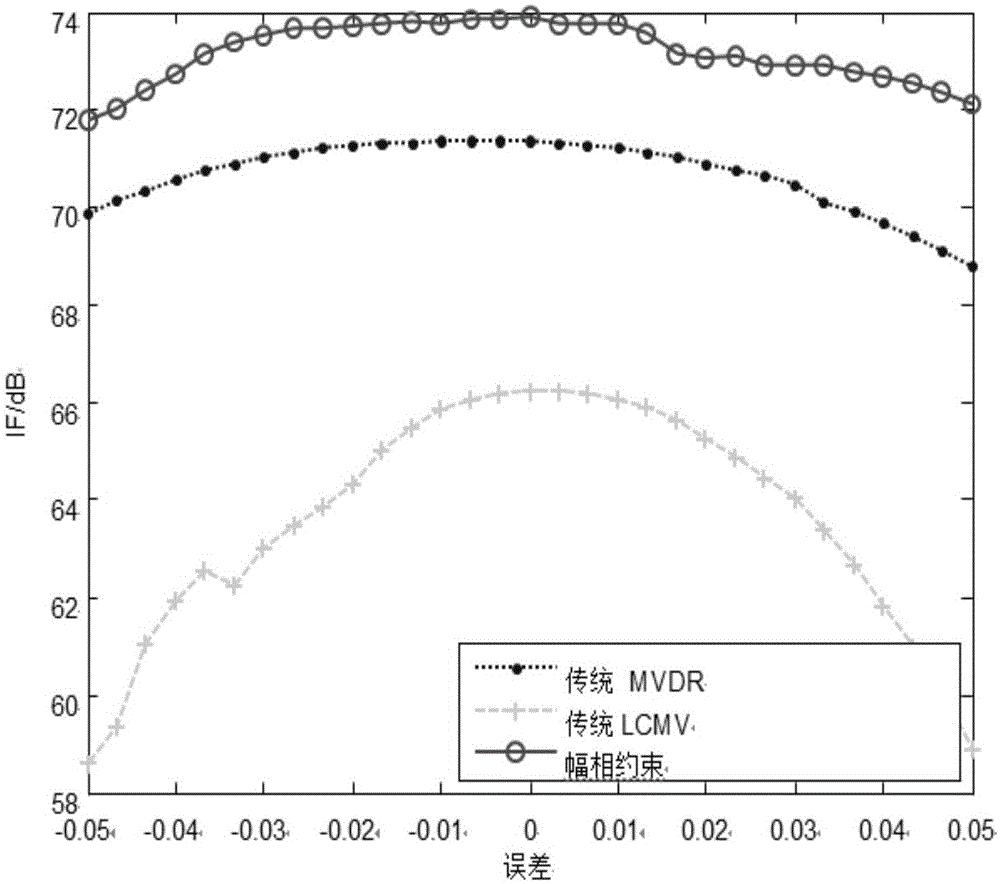
Target signal robust space-time adaptive processing method based on amplitude and phase constraints
ActiveCN105137409AImprove robustnessImprove performanceWave based measurement systemsComplex responseRadar
The invention discloses a radar target signal robust space-time adaptive processing method based on amplitude and phase constraints. The method comprises steps: target signals are set to be a radar space-time data matrix, a first space-time adaptive weight matrix for the radar space-time data matrix is obtained, and an optimality condition equation is further obtained; then, according to the optimality condition equation, a second space-time adaptive weight matrix for the radar space-time data matrix is calculated, and an amplitude and phase constraint-based linear constrained minimum variance beam former complex response vector is built; and after an amplitude and phase constraint-based beam former space-time adaptive weight matrix is obtained through calculation, an amplitude and phase constraint-based beam former unconstrained cost function is obtained through calculation, a robust time covariance matrix and a robust space covariance matrix are calculated respectively, a robust correction space steering vector and a robust correction time steering vector are calculated respectively, a robust correction space-time steering vector is further obtained, and a final target signal through space-time processing is obtained through calculation finally.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
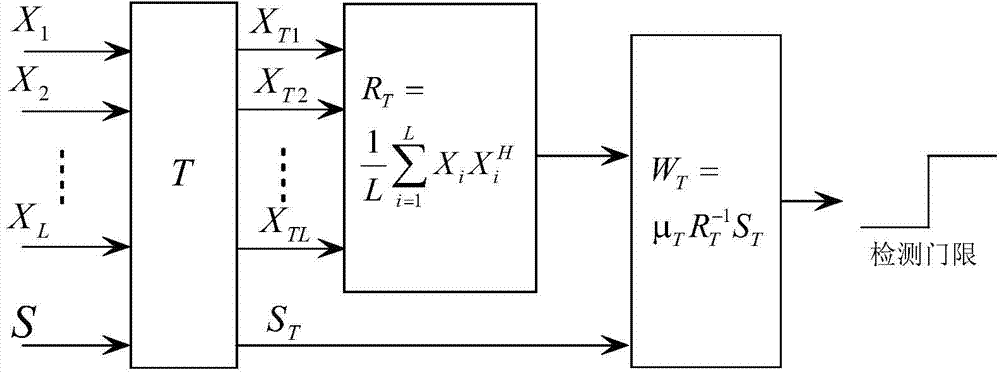
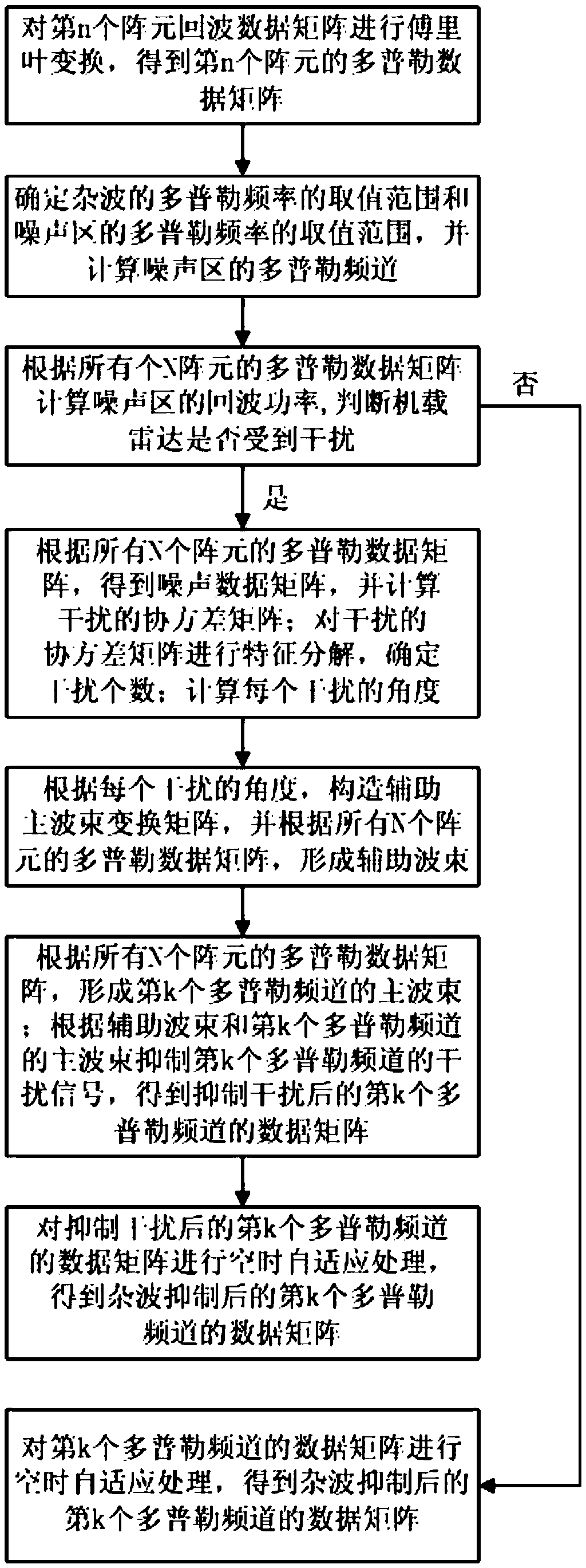
Method for inhibiting active suppressing jamming to airborne radar under clutter background
ActiveCN105510887AReduce dimensionalityImprove object detection performanceWave based measurement systemsSpace-time adaptive processingCovariance matrix
The invention discloses a method for inhibiting active suppressing jamming to airborne radar under a clutter background. The method includes the following steps: (1) performing a Fourier transform on the nth array element echo data matrix; (2) determining a value range of Doppler frequencies of a clutter and a noise zone, and calculating a Doppler channel and echo power of the noise zone; and (3) if phased array radar is jammed, calculating a covariance matrix of the jamming, performing characteristic decomposition on the covariance matrix, determining the jamming number, and calculating an angle of each jamming; forming an assistant wave beam and a main wave beam of the kth Doppler channel, inhibiting an jamming signal of the kth Doppler channel, obtaining the data matrix of the kth Doppler channel after the jamming is inhibited, then performing space-time adaptive processing on the data matrix, and obtaining the data matrix of the kth Doppler channel after the clutter is inhibited; if the phased array radar is not jammed, performing the space-time adaptive processing on the data matrix of the kth Doppler channel, and obtaining the data matrix of the kth Doppler channel after the clutter is inhibited.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com