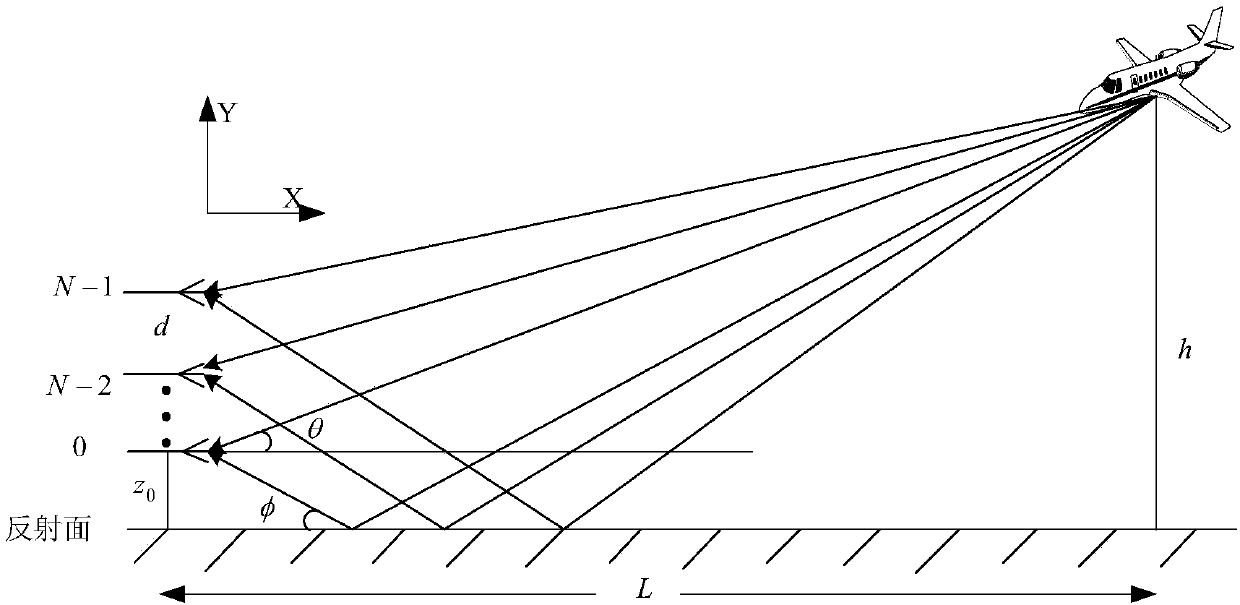
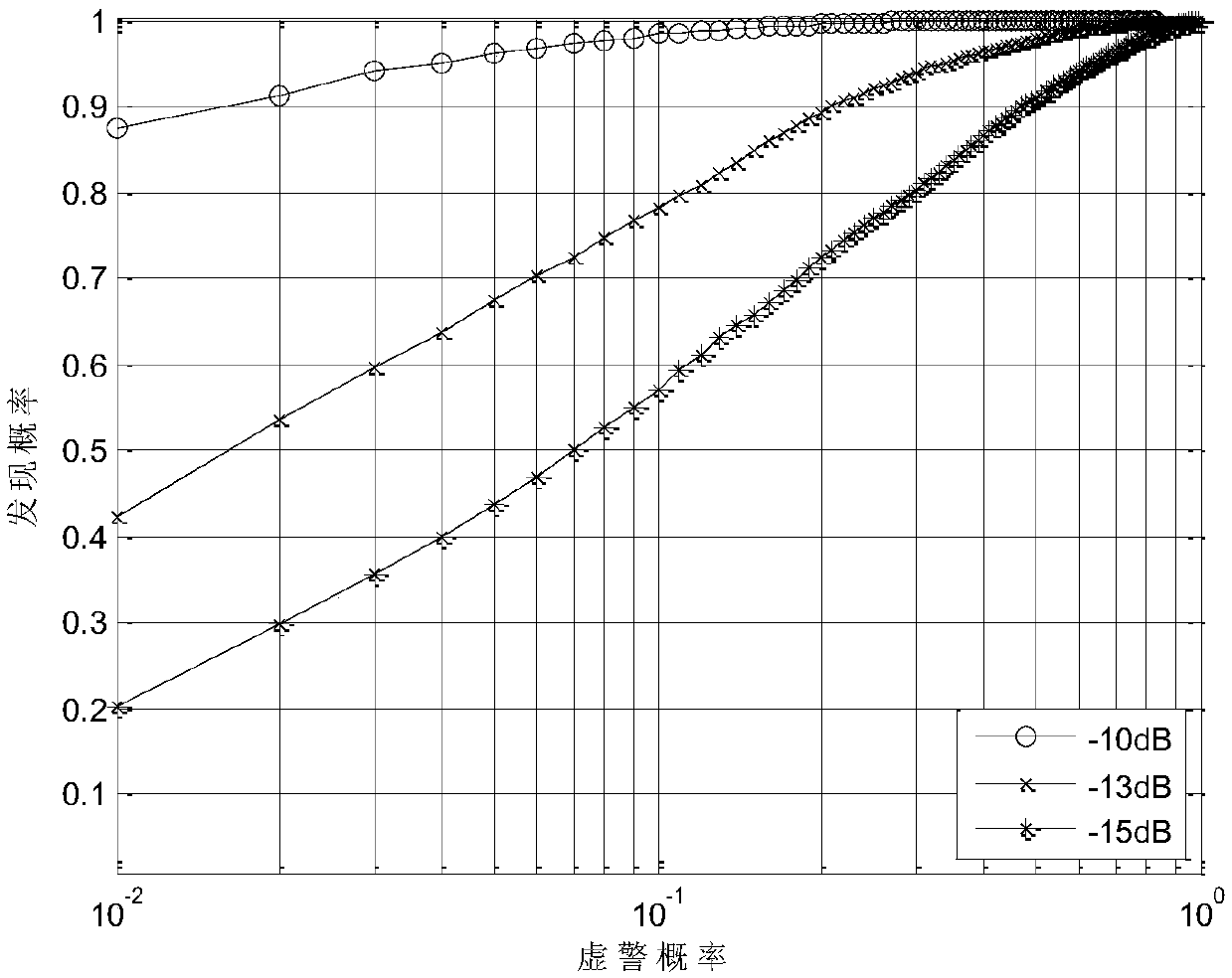
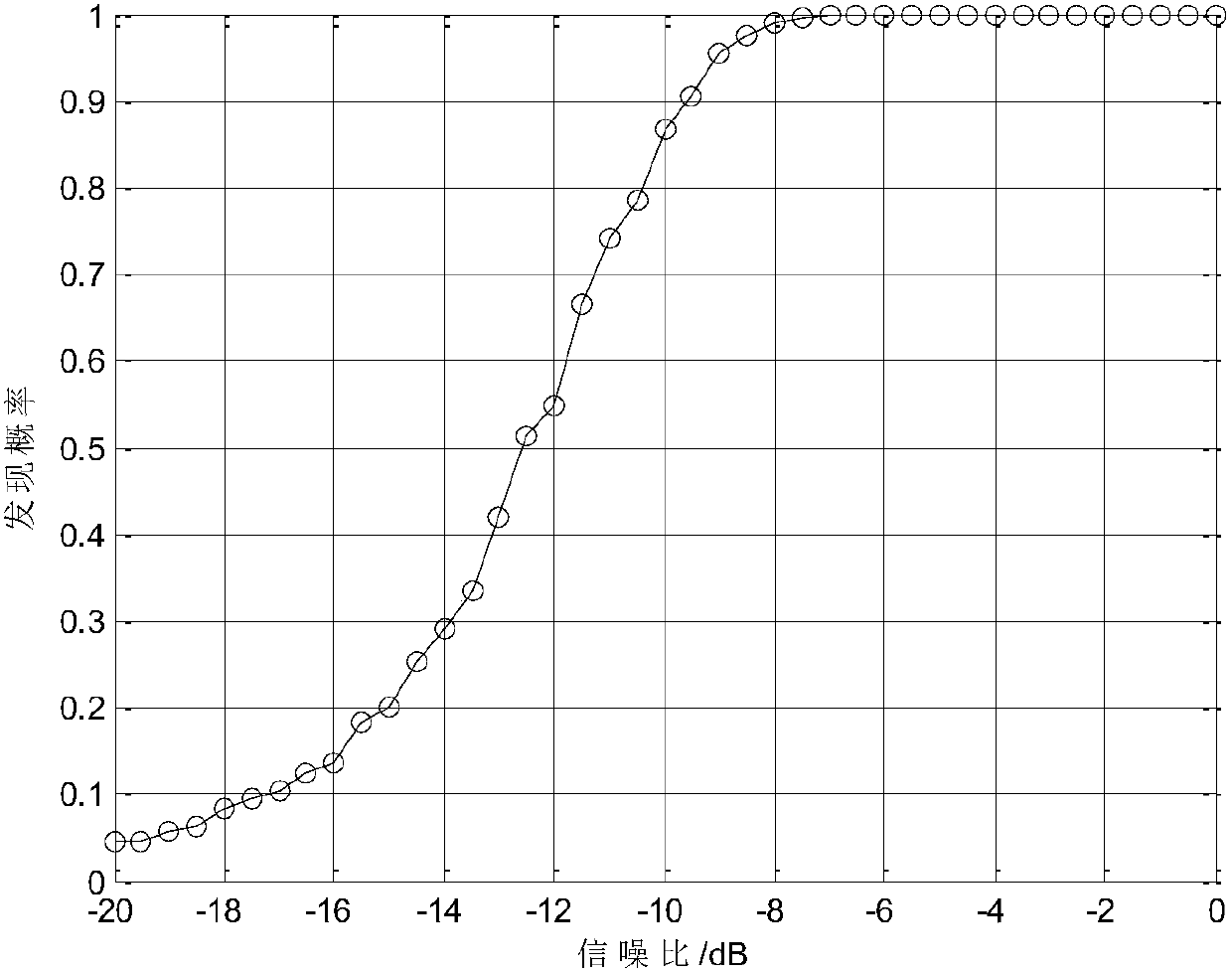
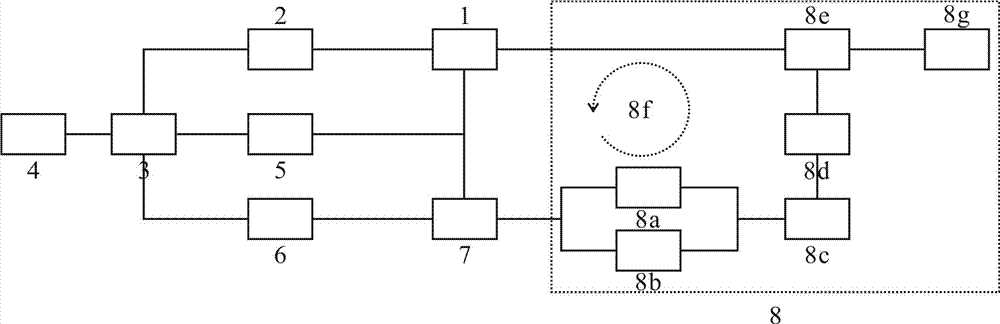
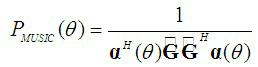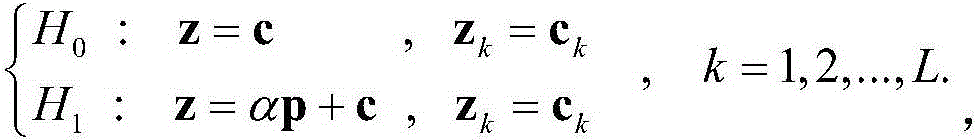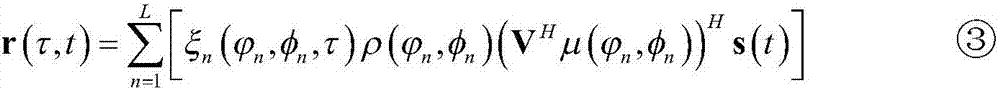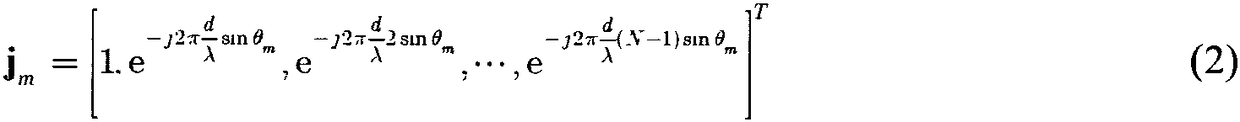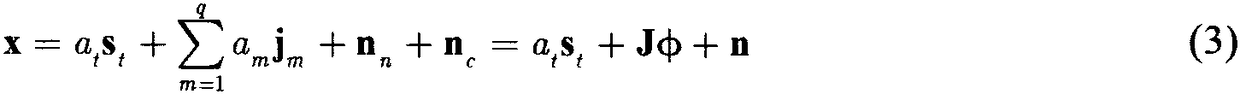Patents
Literature
143 results about "Generalized likelihood ratio" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
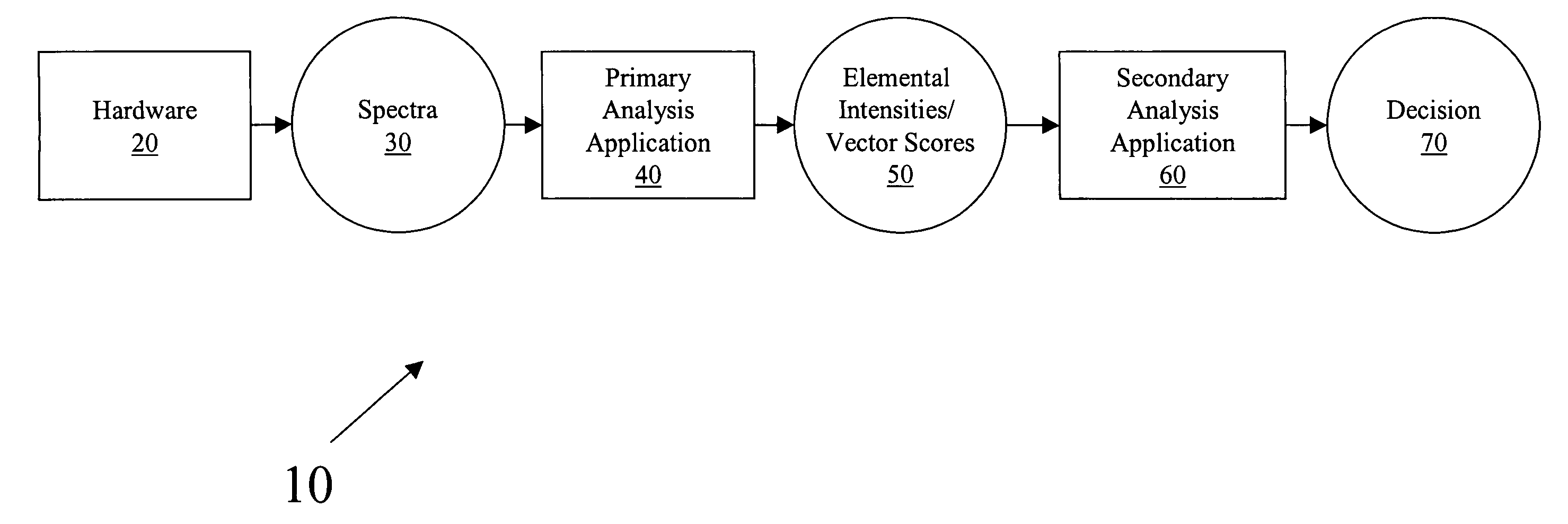
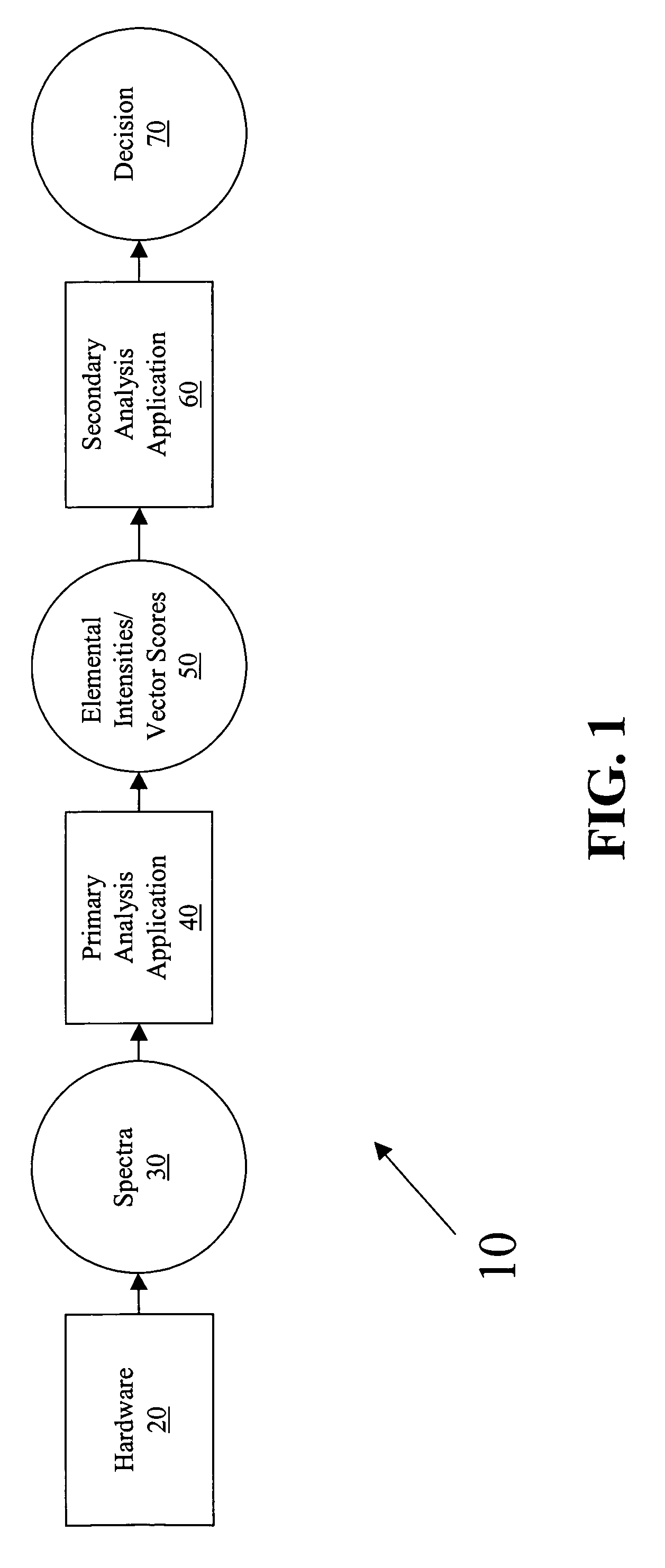
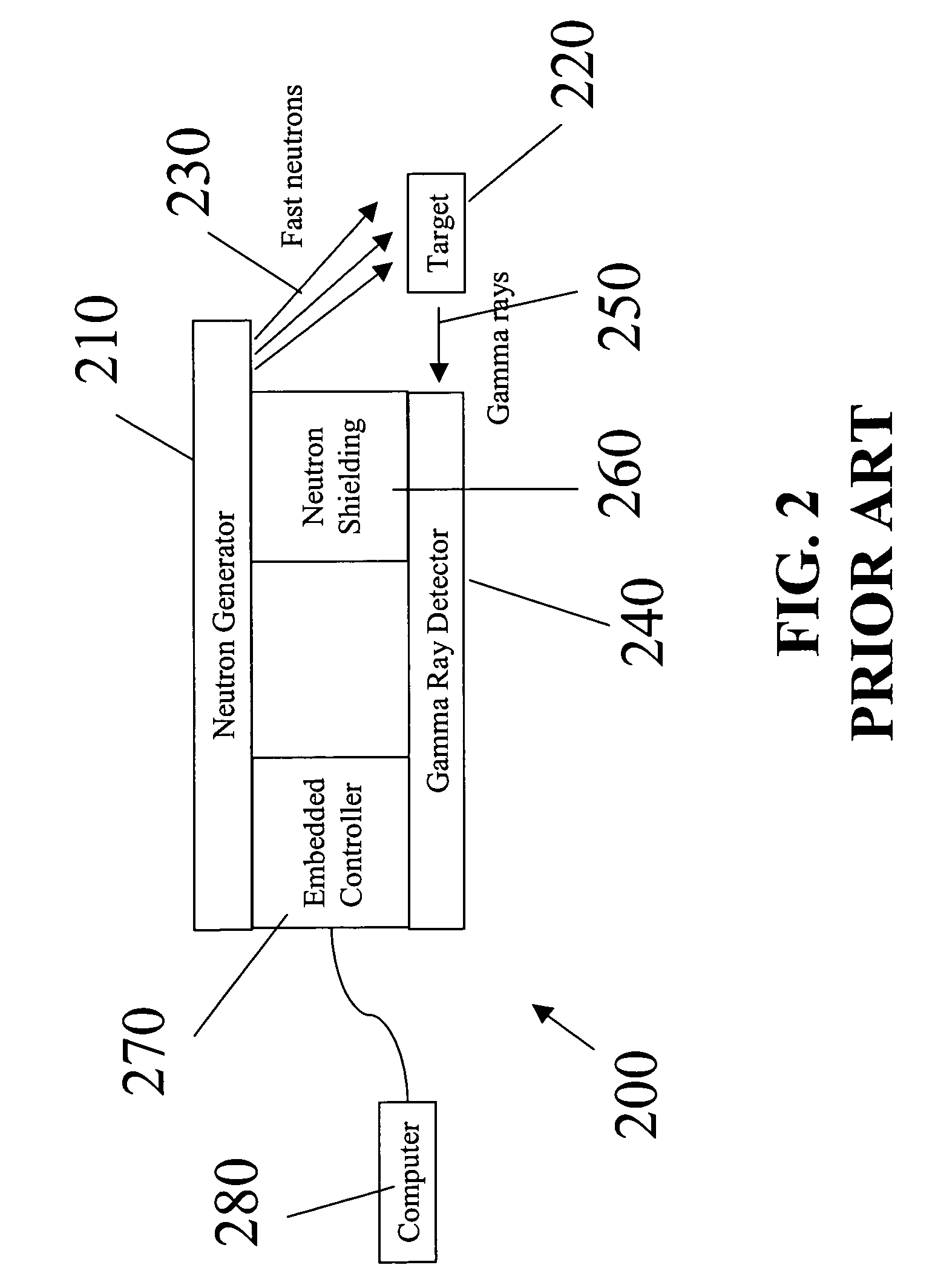
System and method for analyzing content data
InactiveUS7430479B1Less human interactionRapid dispositionConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsMaterial analysis by optical meansGeneralized likelihood ratioLeast squares
The system and method provide security and cargo handling personnel a versatile tool to rapidly check cargo for hidden radiological materials, explosives, drugs, and chemical weapons material. Gamma ray emission is stimulated by a pulsed neutron source. The gamma ray signature is used to classify the material. Passive gamma ray analysis can be used to detect and identify radiological material. The method of determining the contents of a target includes irradiating a target; detecting at least one spectrum emitted from the target; performing a primary analysis to extract a first set of indicators; and performing a secondary analysis to decide the contents of the target. The primary analysis utilizes either a least squares analysis or principal component analysis. The secondary analysis utilizes a generalized likelihood ratio test or support vector machines.
Owner:LEIDOS
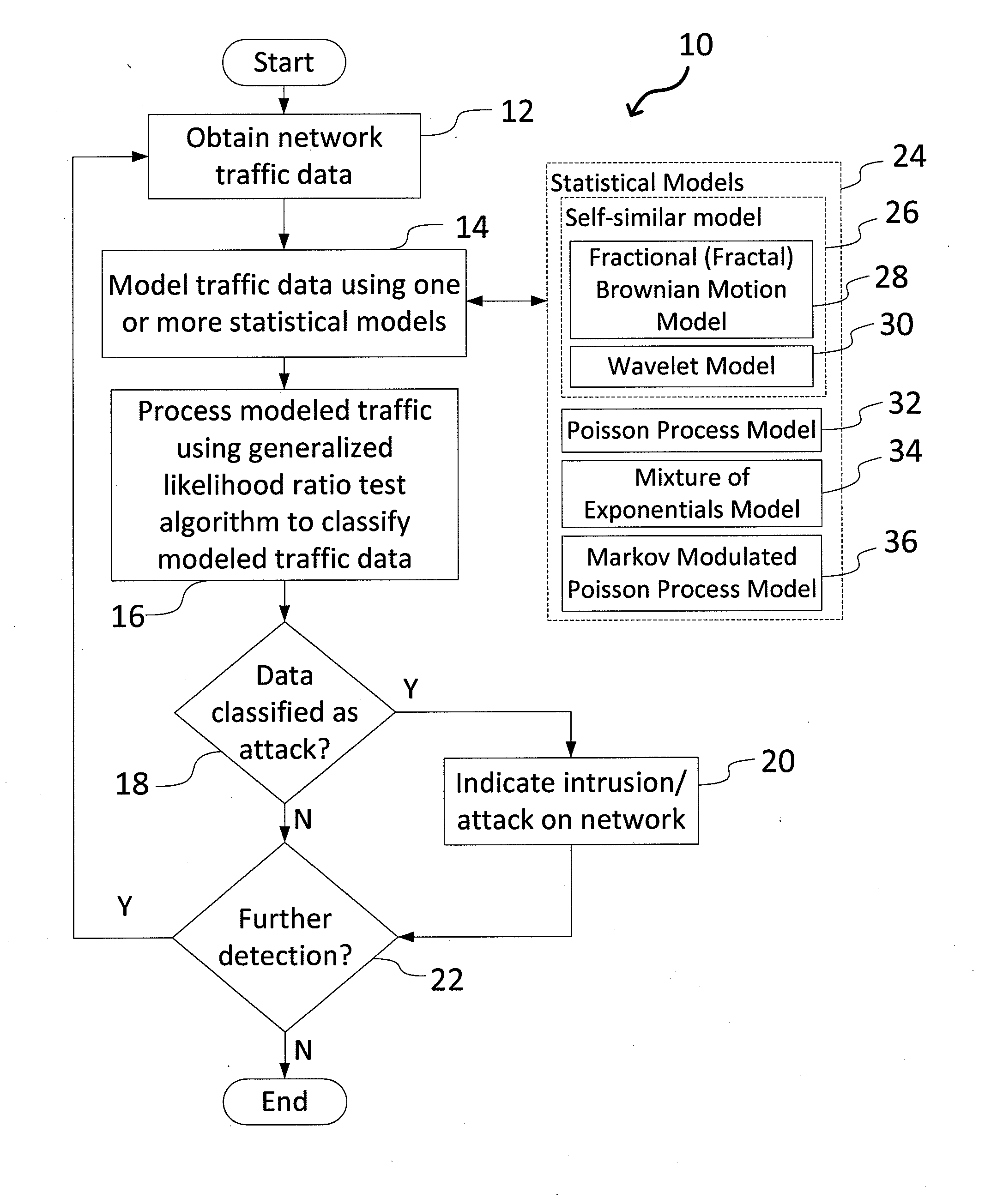
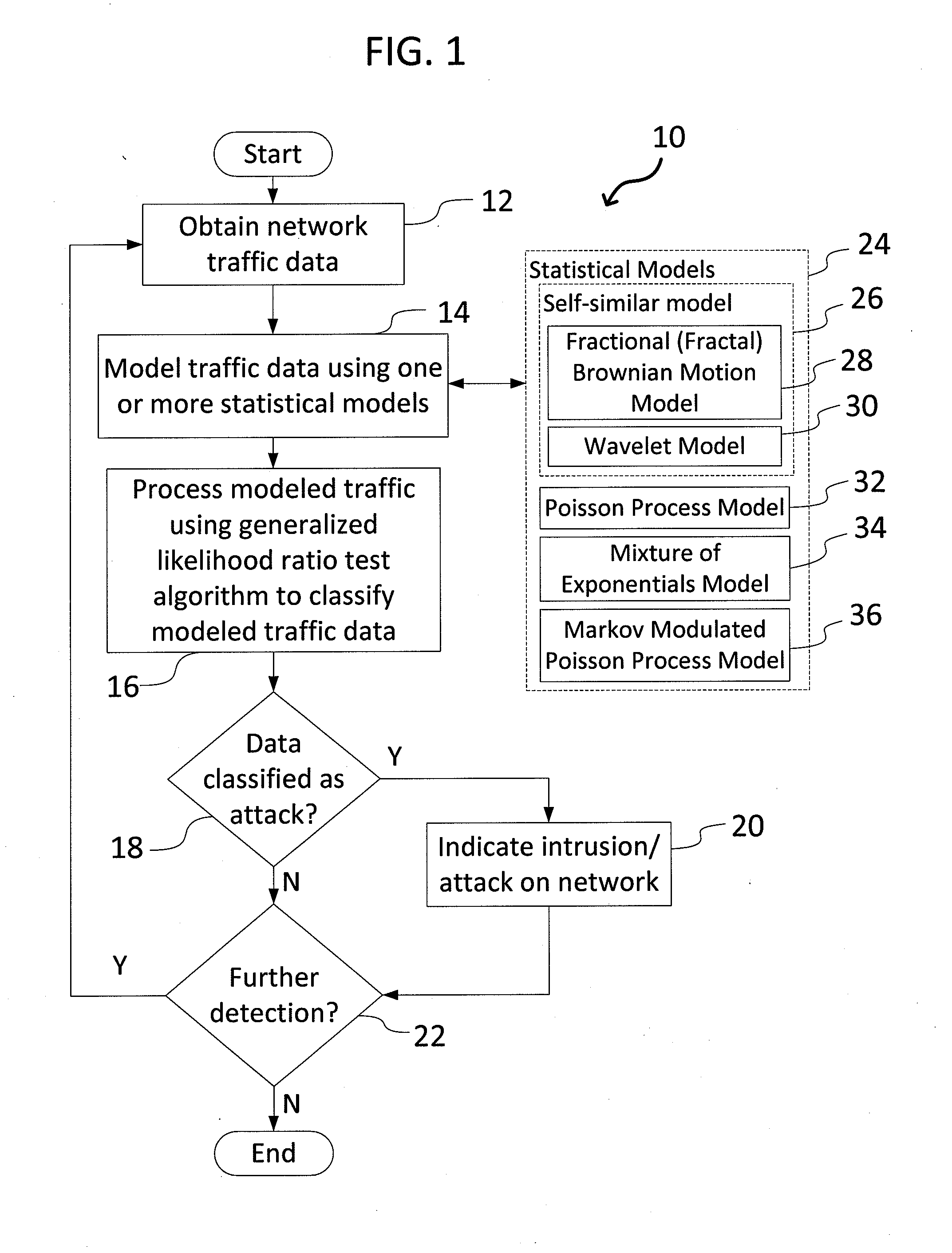
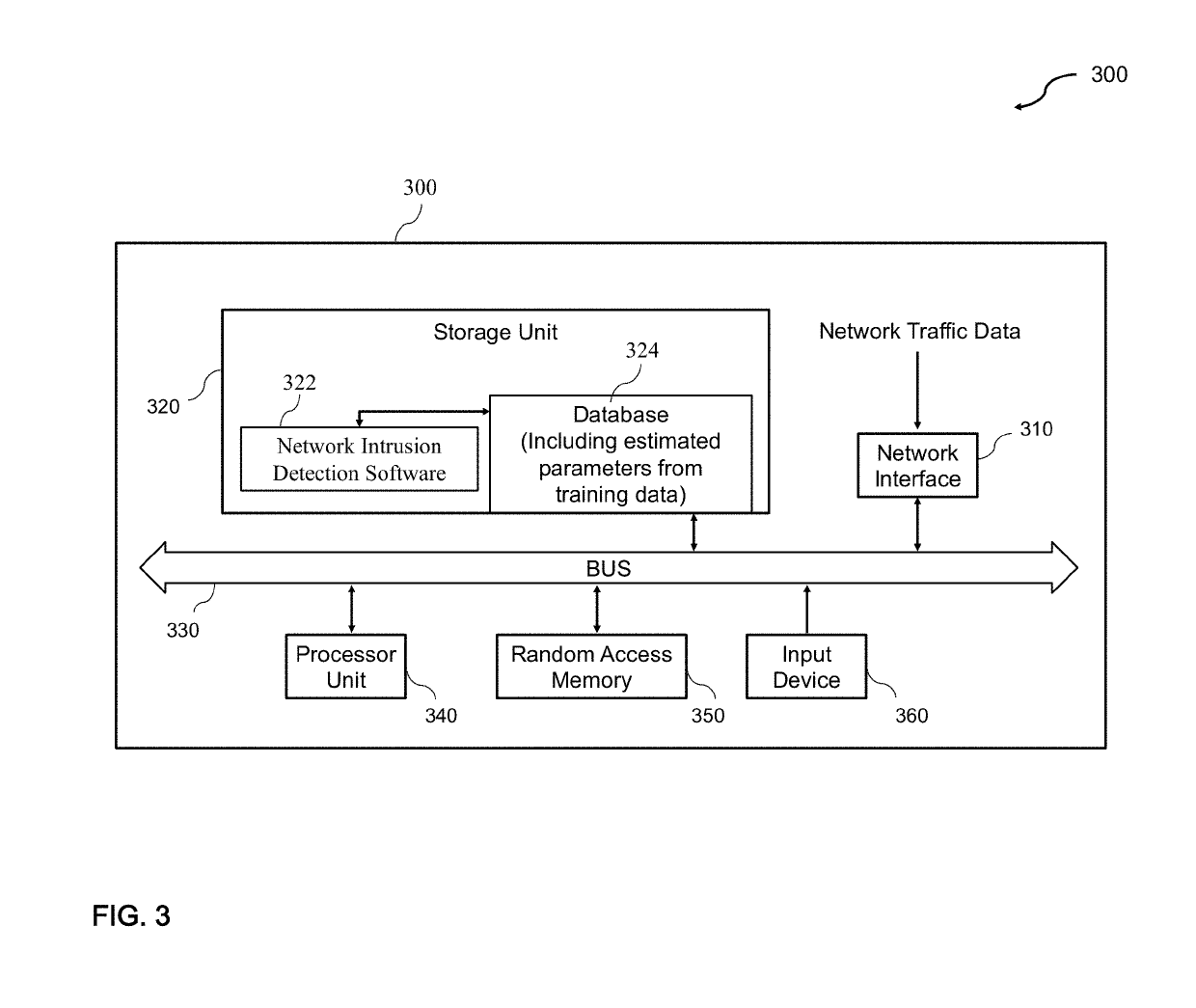
System and Method for Detecting Network Intrusions Using Statistical Models and a Generalized Likelihood Ratio Test
InactiveUS20140041032A1Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionInternet trafficTiered approach
A system and method for detecting network intrusions using one or more statistical models and a generalized likelihood ratio test (GLRT) is provided. The system includes a computer system and a network intrusion detection engine executed by the computer system. To detect network intrusions, the system receives network traffic data, computes a likelihood using one or more statistical models, such as an Markov-modulated Poisson process, and processes the traffic data using a GLRT. The statistical models are used to assess the likelihood of seeing a particular pattern of network traffic. The GLRT is used to classify a particular pattern as either indicative of an attack or not indicative of an attack. The system could apply one or more types of statistical models, such as in a flexible multi-tiered approach.
Owner:OPERA SOLUTIONS
Range-extended target adaptive detection method under inverse Gaussian texture complex Gaussian clutter
InactiveCN105425230AHigh precisionReduce false alarmsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionWideband radarHypothesis model
The present invention belongs to the technical field of radar target detection and discloses a range-extended target adaptive detection method under inverse Gaussian texture complex Gaussian clutter for the target detection under a wideband radar system. The method comprises a step of establishing the binary hypothesis model of radar target detection, a step of using a spherically invariant vector process model to construct an inverse Gaussian texture complex Gaussian clutter signal, a step of using a generalized likelihood ratio to obtain a range-extended target adaptive detector under the inverse Gaussian texture complex Gaussian clutter, a step of determining the detection threshold of the adaptive detector, a step of obtaining radar echo data and determining the detection statistic amount of the radar echo data according to the adaptive detector, and a step of judging whether the radar echo data has a range-extended target according to the detection statistic amount and the detection threshold, and if the detection statistic amount is larger than the detection threshold, determining that the radar echo data has the range-extended target, otherwise, determining that the radar echo data has no range-extended target.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
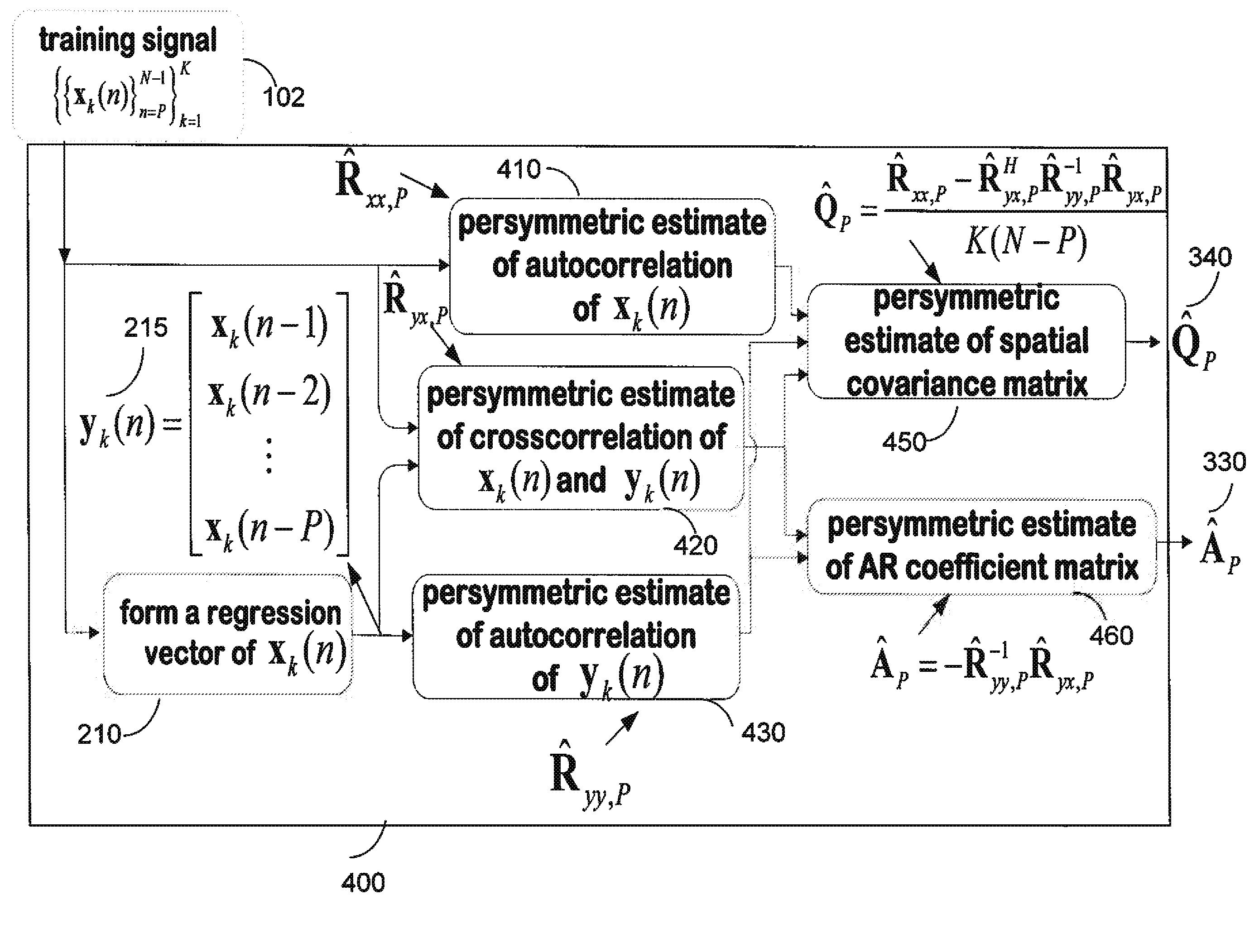
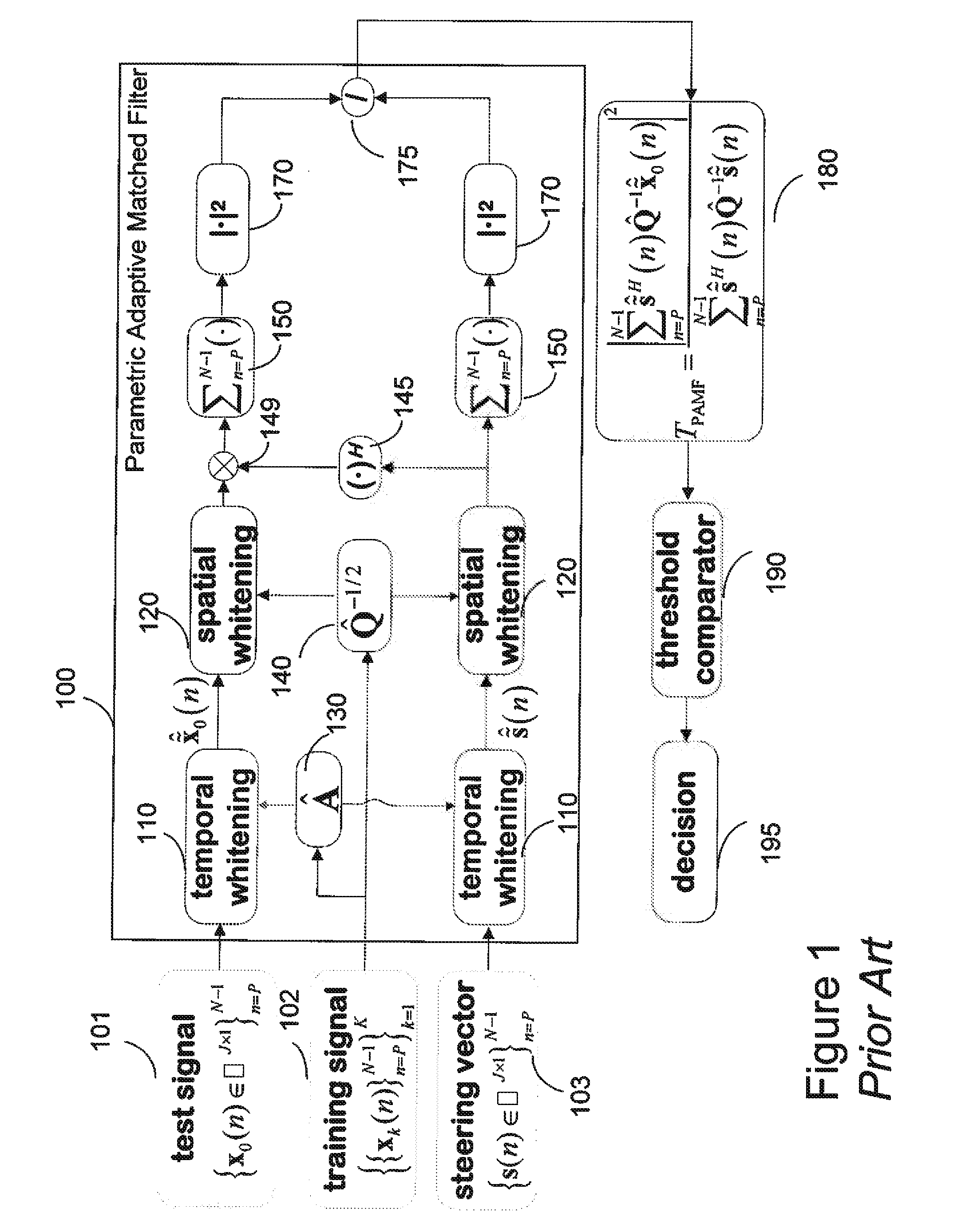
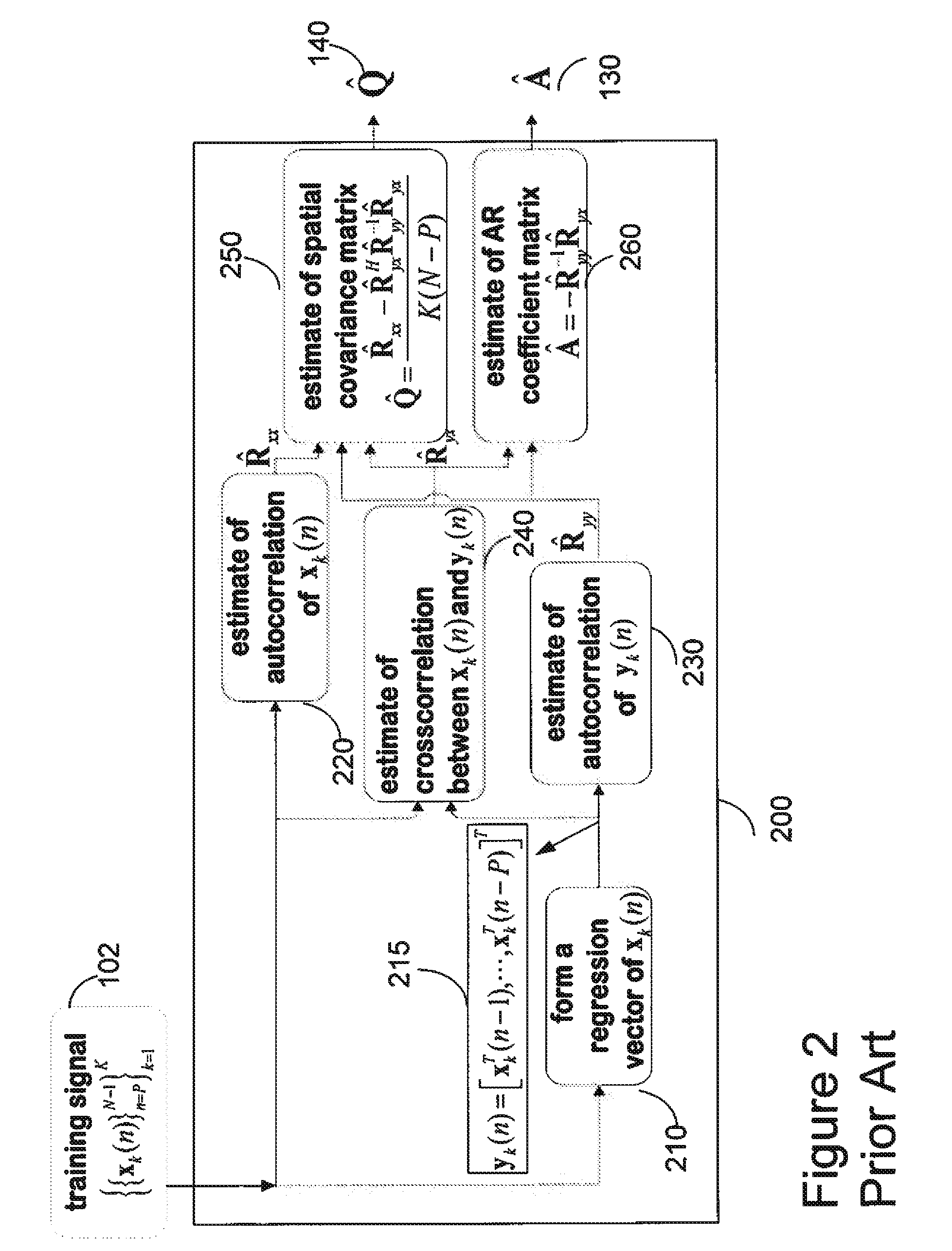
Persymmetric Parametric Adaptive Matched Filters for Detecting Targets Using Space-Time Adaptive Processing of Radar Signals
ActiveUS20120127027A1Radio wave reradiation/reflectionPattern recognitionSpace-time adaptive processing
A method provides space-time adaptive processing (STAP) for target detection using adaptive matched filters (AMF). A generalized likelihood ratio test (GLRT) is determined where spatial and temporal correlation matrices Q and A are assumed. Then, the correlation matrices A and Q are replaced with maximum likelihood (ML) estimates obtained only from training signals subject to a persymmetric constraint.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Method and system for communicating data symbols in a network
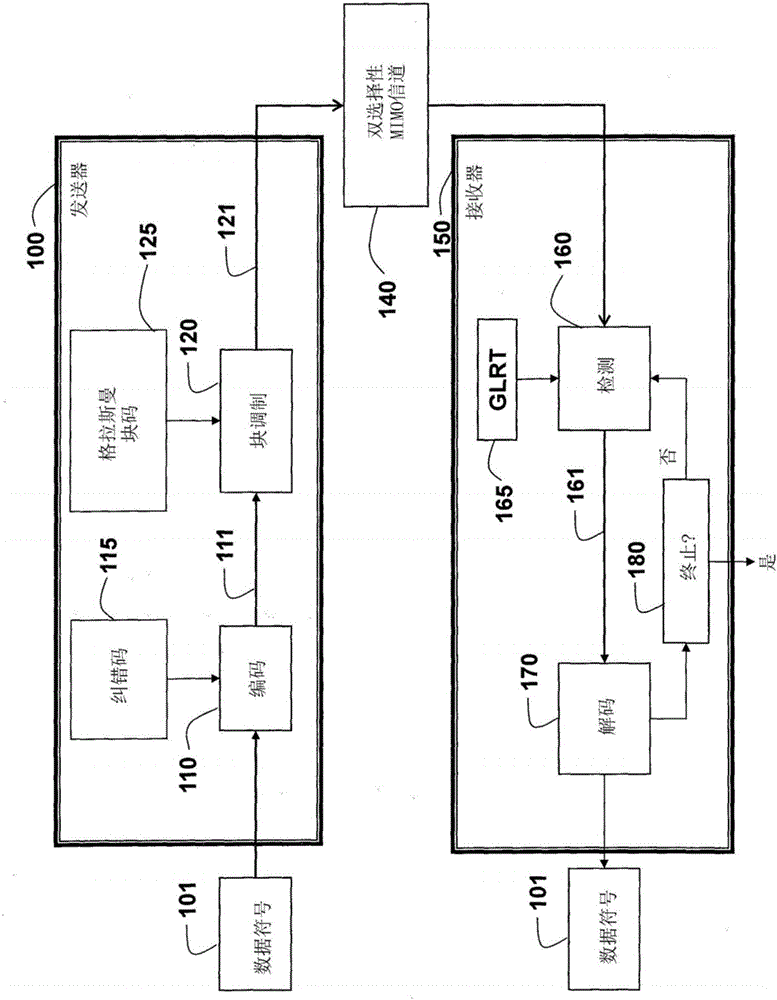
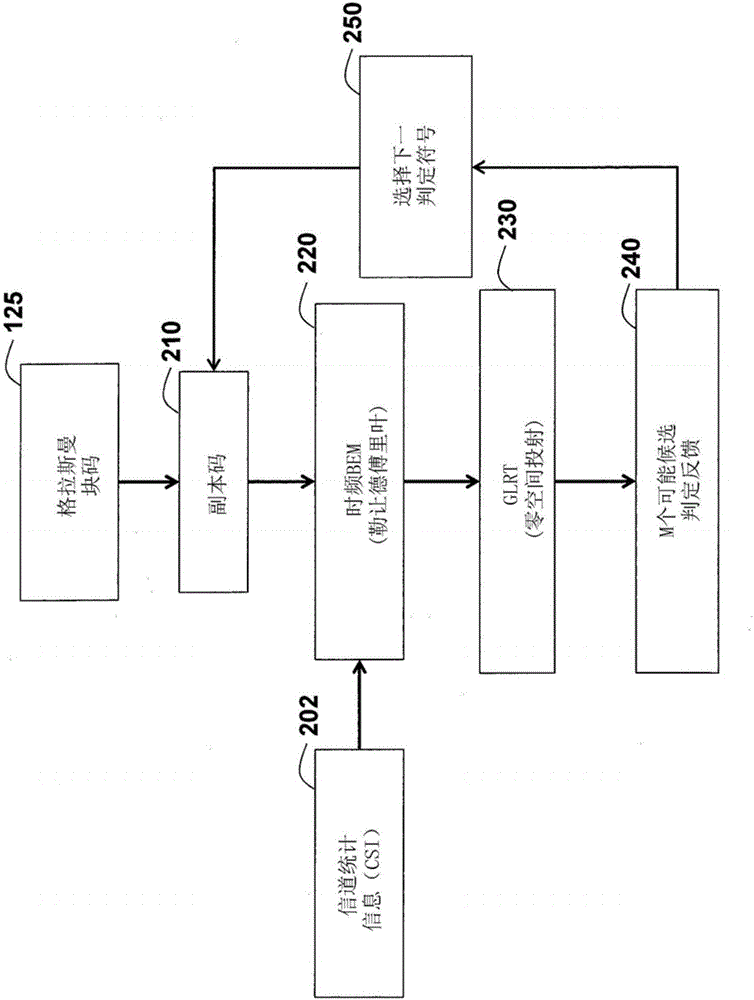
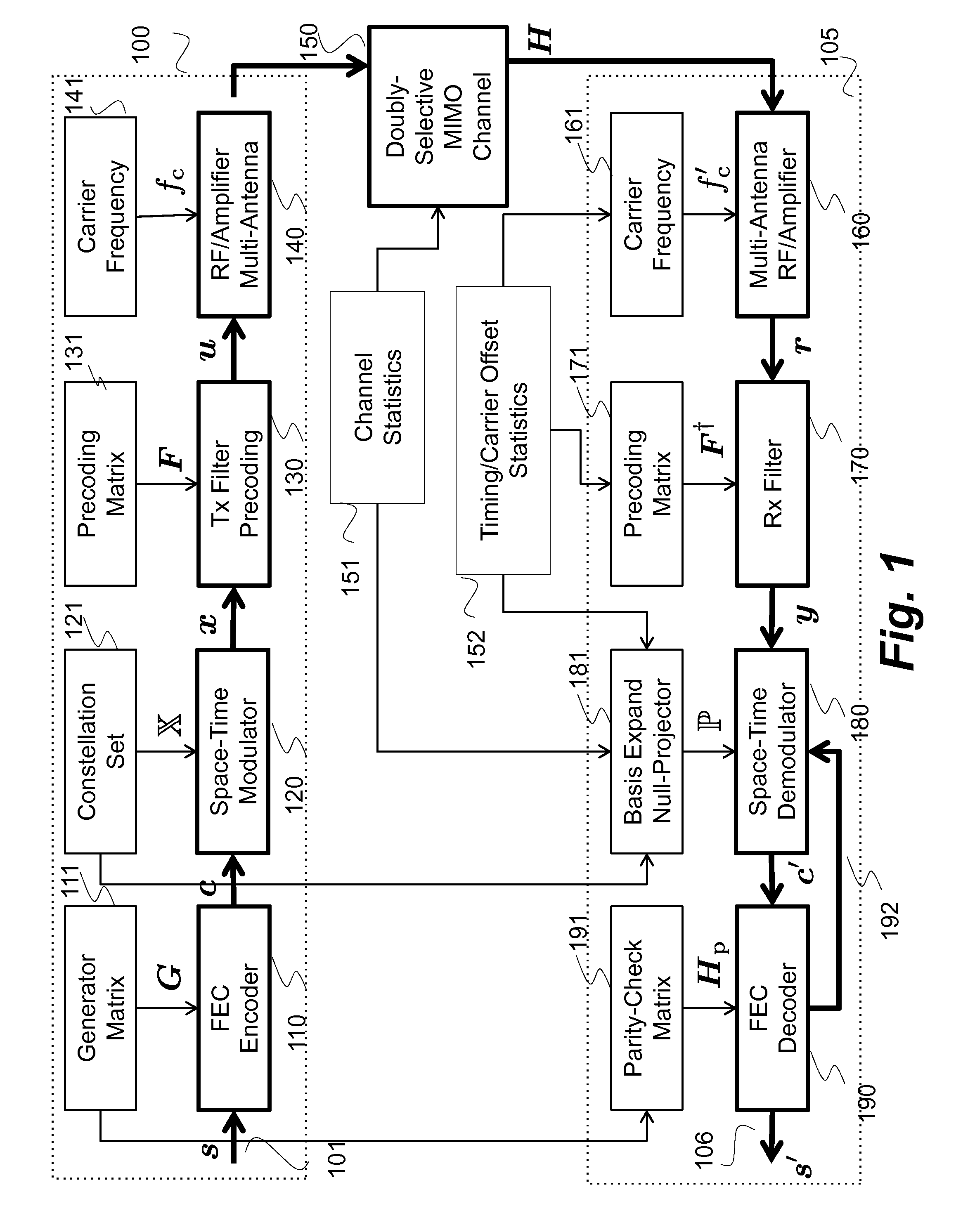
ActiveCN106105075AImprove performanceSuppress error propagationSpatial transmit diversityTransmitter/receiver shaping networksChannel statisticsParallel computing
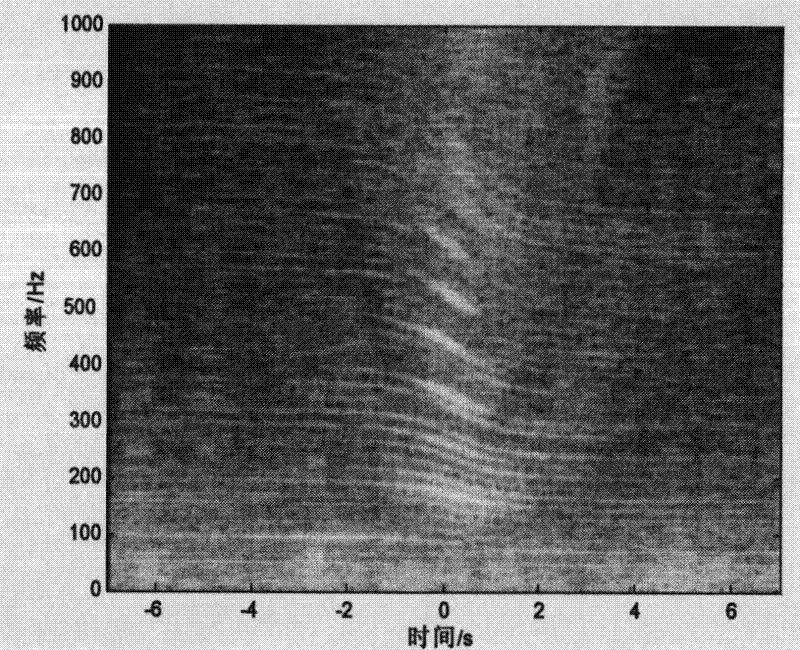
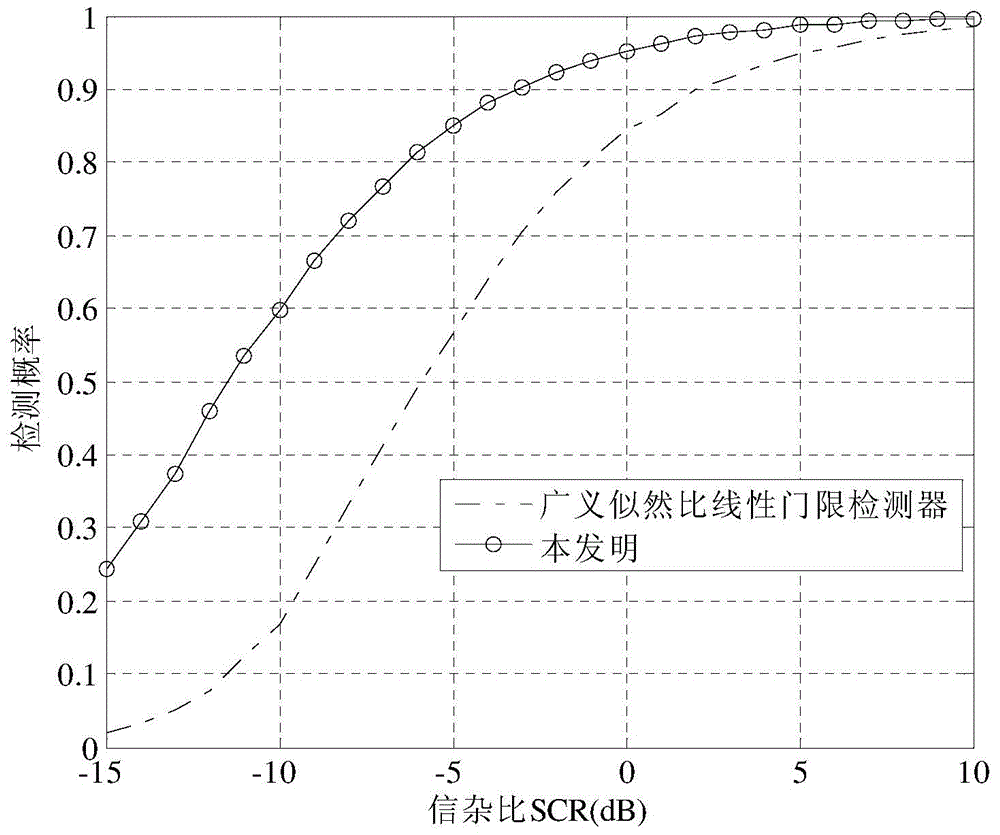
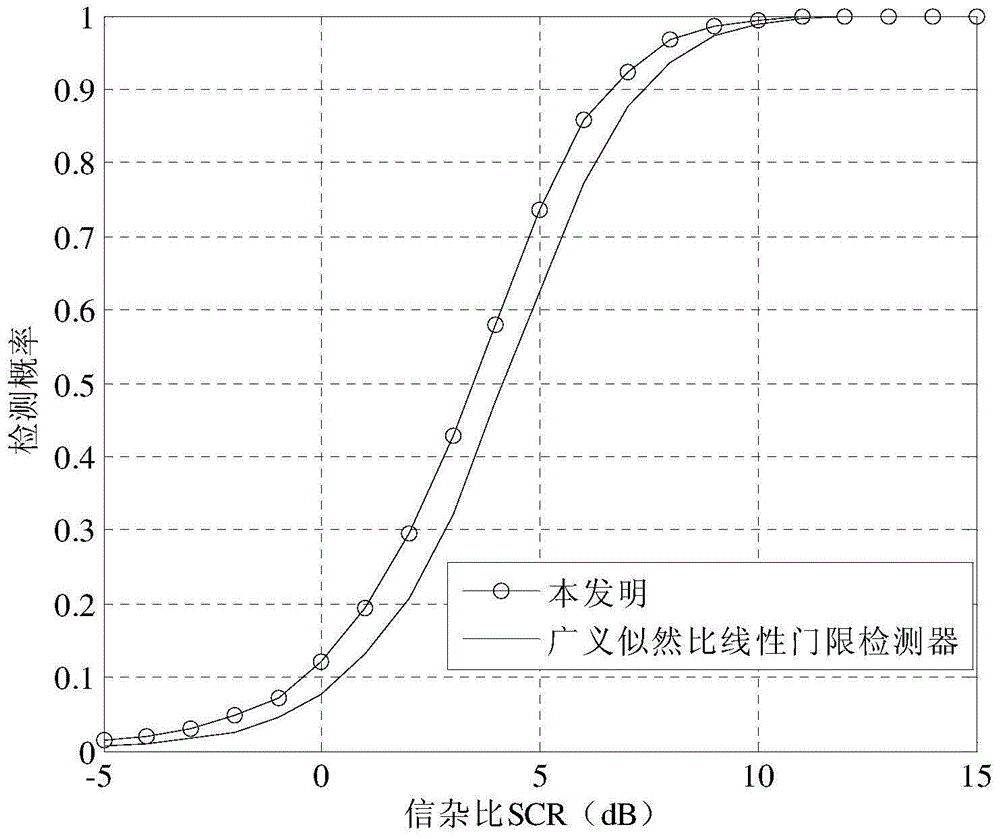
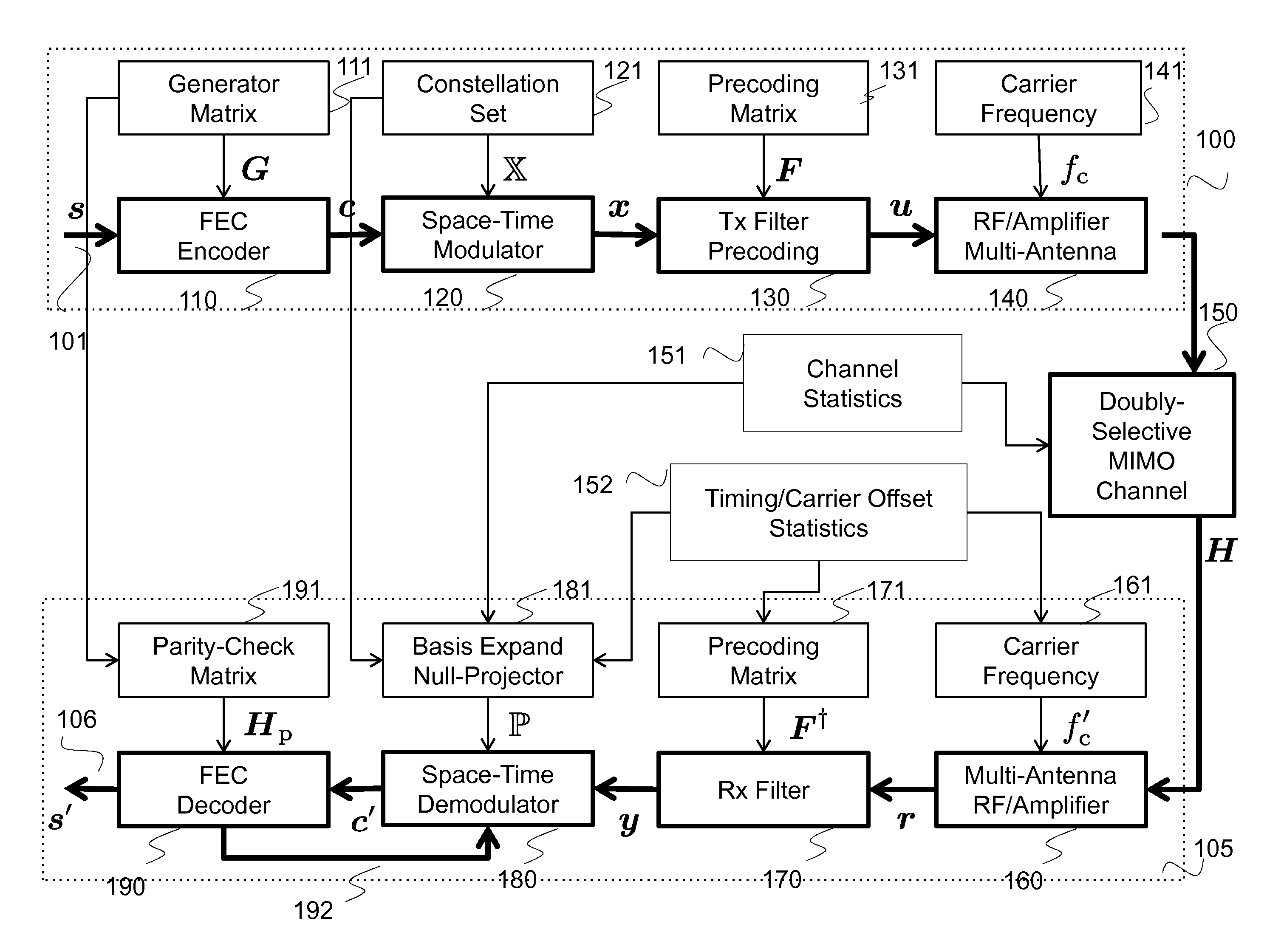
A method and system realize reliable wireless communications in non-coherent multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) doubly-selective channels. The method uses Grassmannian space-time-frequency block codes and an iterative generalized likelihood ratio test (GLRT) with a multi-dimensional basis expansion model (BEM), decision reordering, and a fixed number of surviving candidates. The computational complexity of a non-coherent MIMO equalizer becomes linear as a function of a code length and a size of a modulation alphabet. The codebook, the alphabet size, the bit labeling, and the block power are optimized using worst-case channel statistics or instantaneous channel states. The method can use soft-information feedback from error correction codes, such as low-density-parity-check codes to improve performance.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Non-invasive load monitoring method based on event detection
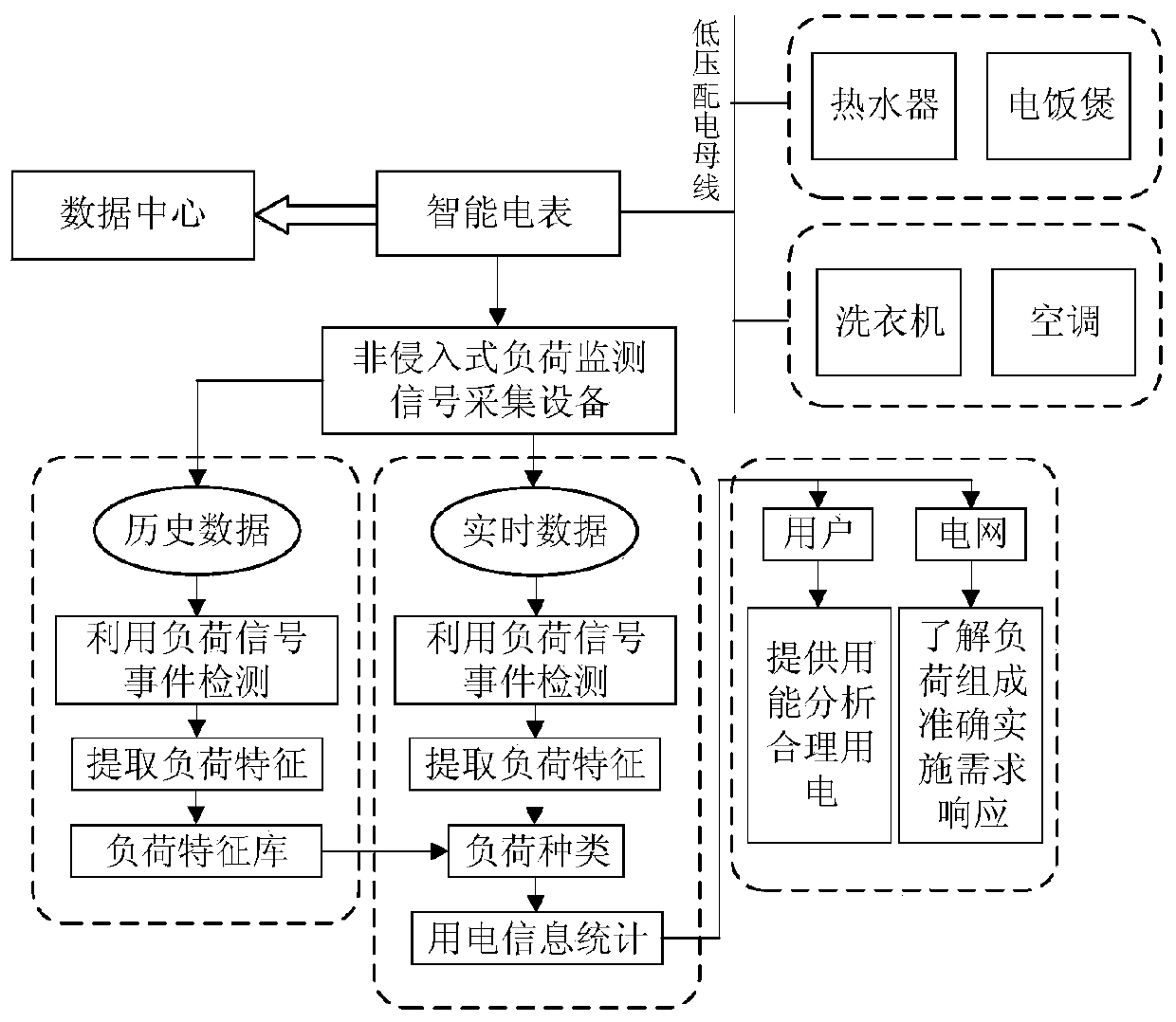
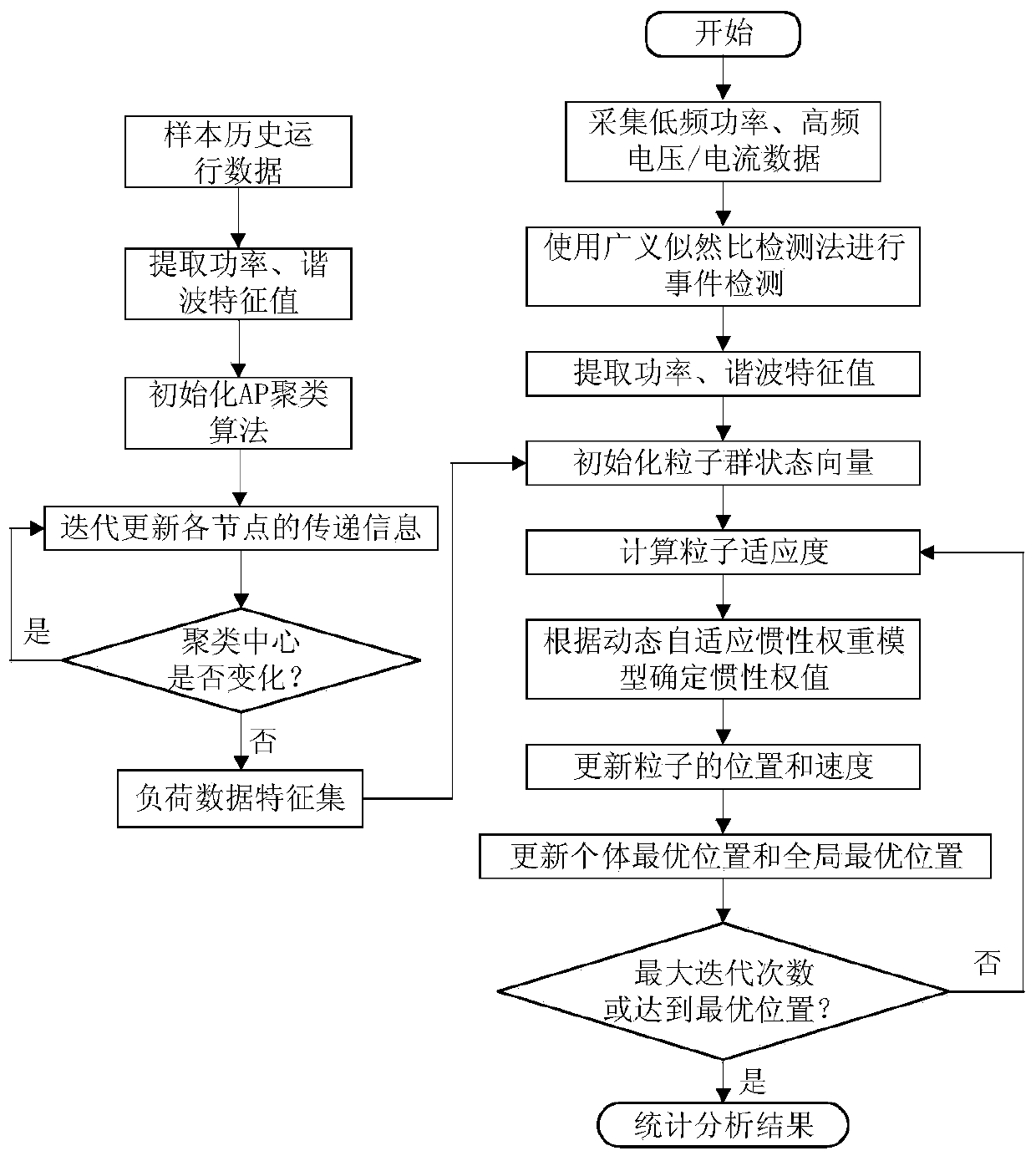
InactiveCN110954744AUnderstand the composition of the loadTo achieve the purpose of shaving peaks and filling valleysElectric devicesComplex mathematical operationsData setPower usage
The invention discloses a non-invasive load monitoring method based on event detection. The method comprises the steps of selecting an original measurement power signal in a public REDD data set for denoising processing, carrying out event detection on the processed data by using a generalized likelihood ratio detection method, and identifying a load switch and a state change time node by detecting an active or reactive power sequence of a load; switching a detected electric device into an event, extracting a steady-state current before and after switching, carrying out fast Fourier transformto extract current the harmonic characteristics, combining the active power, establishing a load characteristic library through an affinity propagation clustering algorithm, fitting the actual electric appliance data characteristics and a load characteristic set through a dynamic adaptive discrete particle swarm algorithm, and determining the operation state of the household electric appliance. According to the method, users can conveniently carry out household energy-saving management and make demand response measures for a power grid, the real-time bidirectional interaction of the intelligent power grid is realized, and the asset utilization rate and the energy utilization efficiency are effectively improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
A Spectrum Sensing Method Based on Signal Direction of Arrival Estimation
InactiveCN102291186AIncreased Spectrum OpportunitiesSpatial transmit diversityTransmission monitoringCognitive userFrequency spectrum
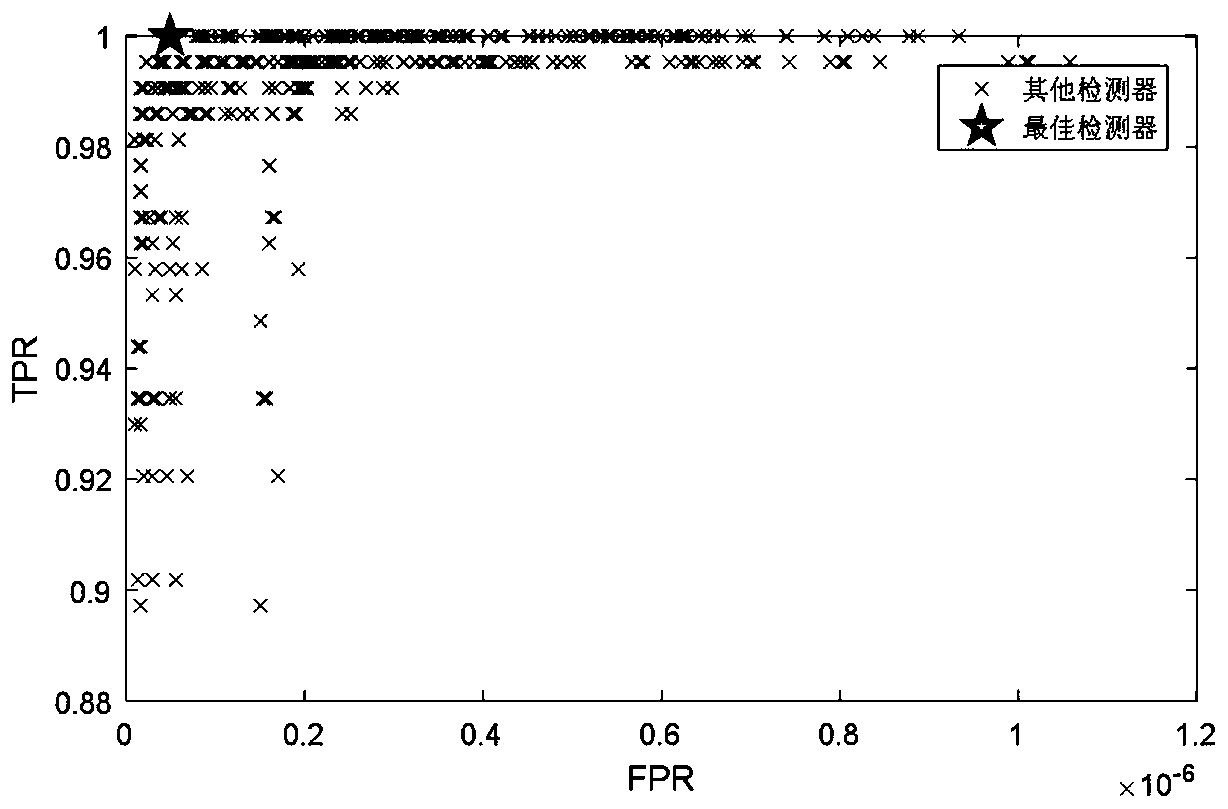
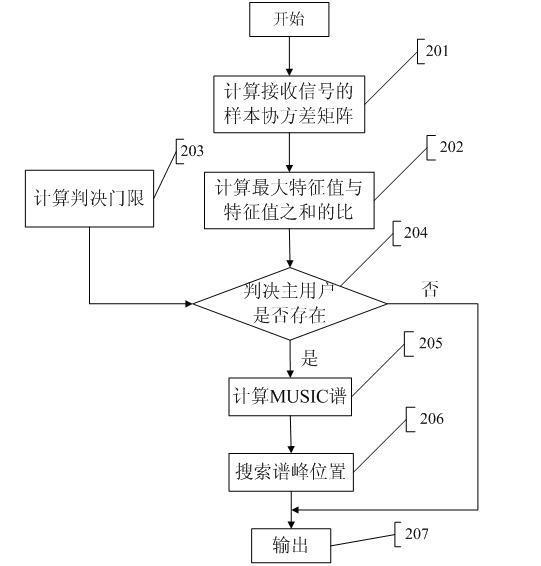
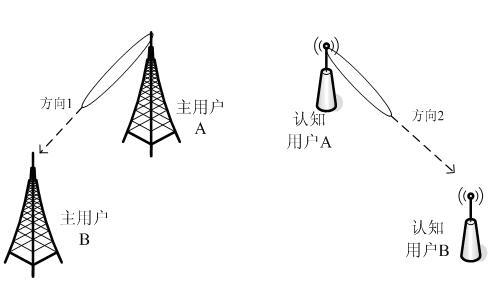
The invention discloses a frequency spectrum perceiving method based on the estimation of a signal arrival direction, which comprises the steps: in a cognitive radio system to which smart antenna technology is applied, the direction and the angle of signal transmission are used as a frequency spectrum opportunity, and a master user signal is subjected to two-step perception: firstly, the master user signal is detected by using a method based on a generalized likelihood ratio test, namely that the ratio of the maximum eigenvalue to the sum of the eigenvalues of a sample covariance matrix is used as test statistics; the test statistics are compared with a decision threshold which is set according to a given false alarm probability so as to decide whether the master user signal exists or not; if a master user does not exist, then the channel can be used, and if the master user exists, then a classical MUSIC (Multiple Signal Classification) algorithm is further used to estimate the arrival direction of the master user signal. A cognitive user can select other directions for communication, which do not cause disturbance to the master user, and the frequency spectrum perceiving method can effectively perceive time, frequency and the frequency spectrum vacancy of a space domain, perceive the frequency spectrum vacancy of an angle domain, and increase the frequency spectrum opportunity.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Main lobe deception jamming inhibition method based on frequency diversity MIMO radar
ActiveCN106154235AReduce processing complexityWave based measurement systemsSignal subspaceMain lobe
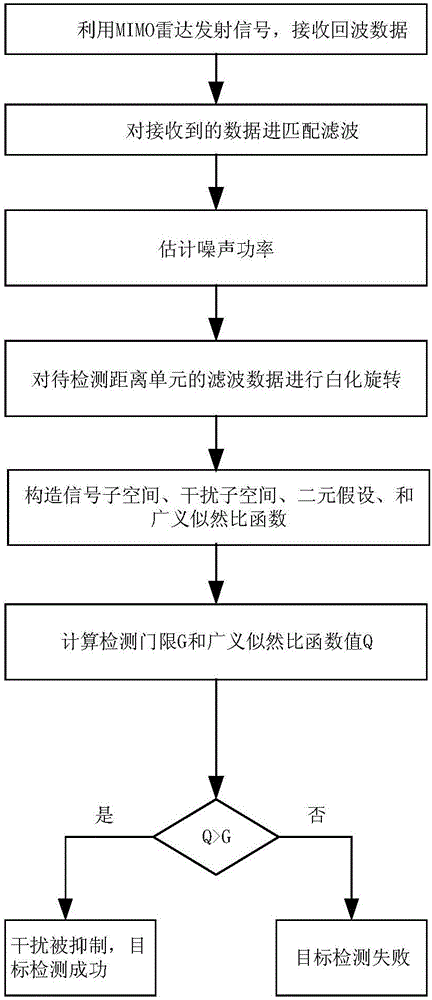
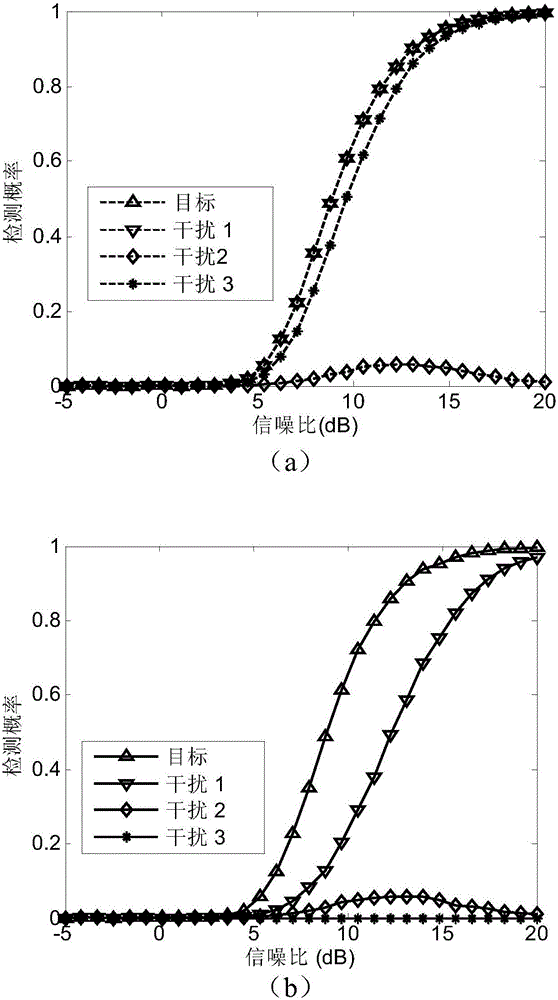
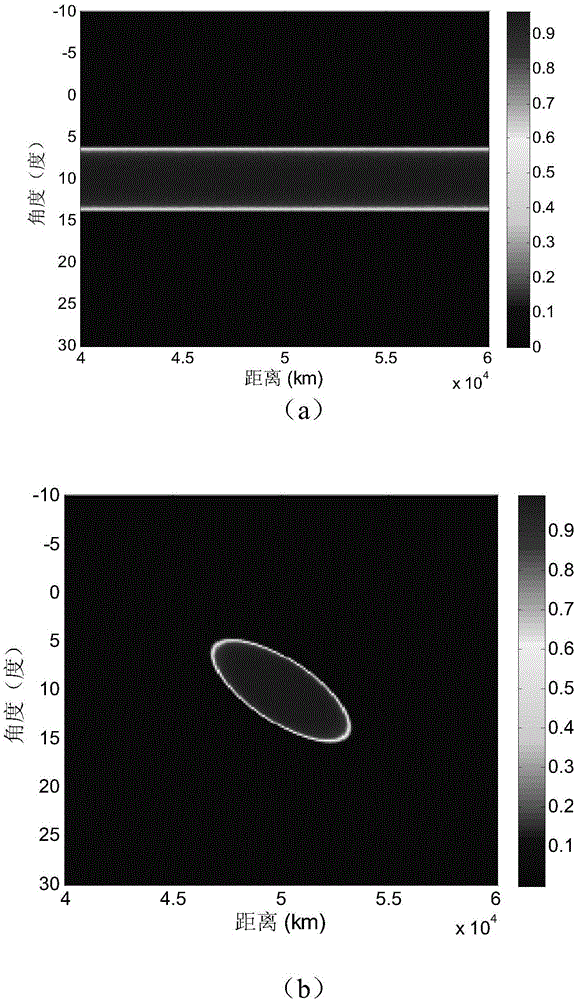
The invention discloses a main lobe deception jamming inhibition method based on frequency diversity MIMO radar, and mainly solves the problem that main lobe deception jamming can be inhibited only in an angle dimension in the prior art. The method of the invention includes the following steps of: 1, calculating echo data of an MIMO radar receiving array, and performing matched filtering on the echo data and obtaining data of distance units to be detected; 2, calculating a noise covariance matrix, and constructing a whitening rotary matrix according to the matrix and transmitting and receiving oriented vectors; 3, performing whitening rotation on the data of the distance units to be detected, and obtaining whitening rotary vectors; 4, constructing a signal subspace and a jamming subspace according to the whitening rotary matrix; 5, performing dualism hypothesis, and calculating a generalized likelihood ratio function value and a detection threshold according to the dualism hypothesis, the signal subspace, the jamming subspace and the whitening rotary vectors; and 6, comparing the generalized likelihood ratio function value with the detection threshold, and obtaining a detection result. The main lobe deception jamming inhibition method based on the frequency diversity MIMO radar can effectively inhibit the main lobe deception jamming and be used for target detection and tracking.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
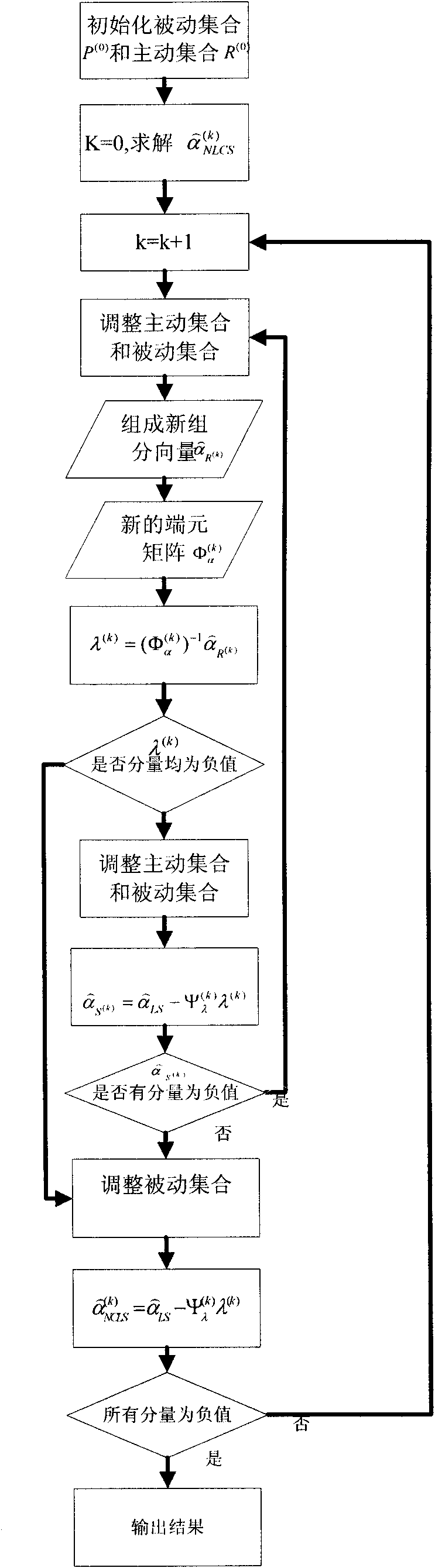
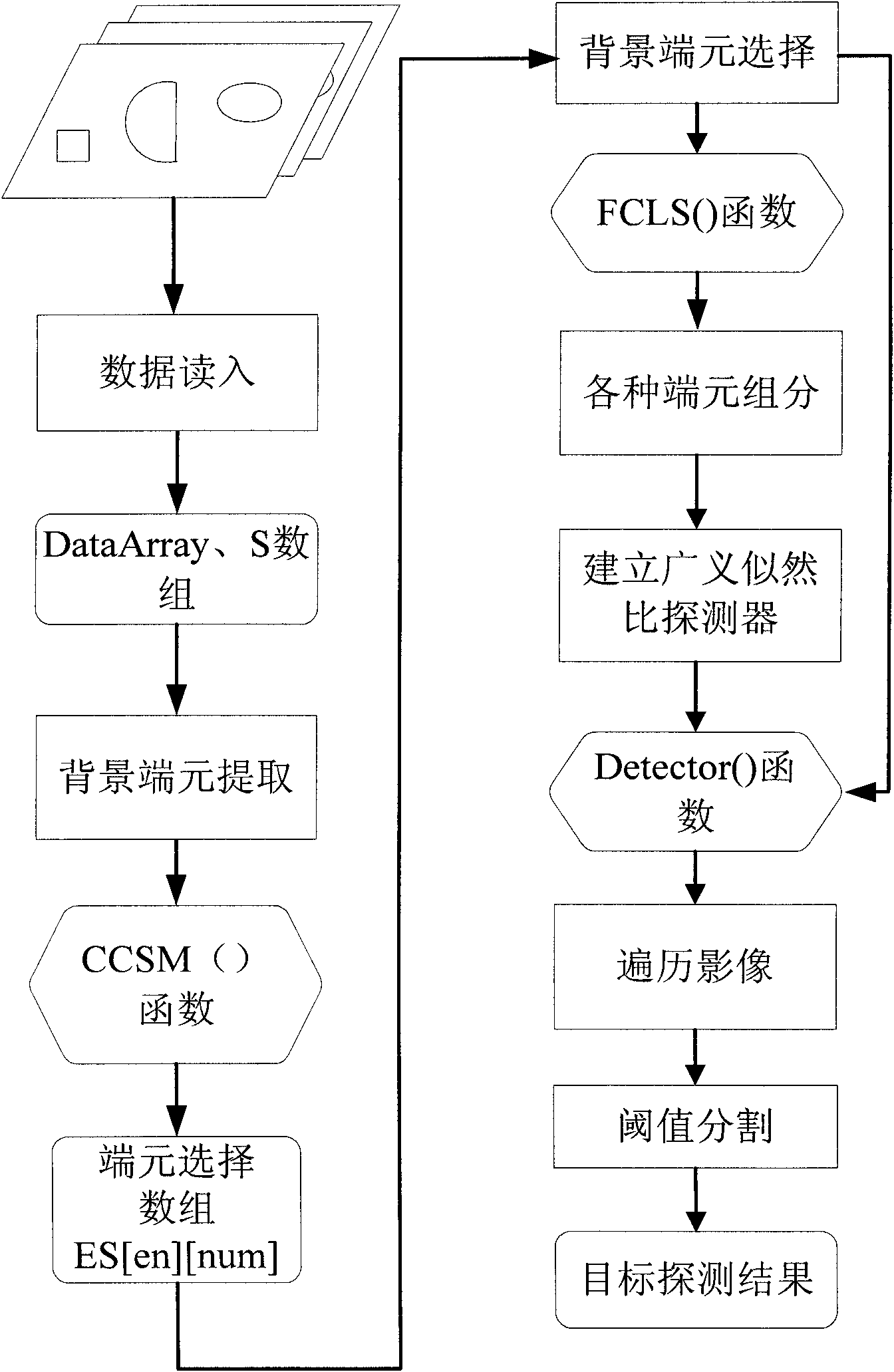
Hyperspectral remote sensing image target detecting method based on variable end members
InactiveCN101806898AReduce the impactImprove separabilityElectromagnetic wave reradiationPrior informationDecomposition
The invention discloses a hyperspectral remote sensing image target detecting method based on variable end members, comprising the following steps of: selecting a remote sensing image to be processed by target detection; acquiring prior information required for detection, wherein the prior information comprises spectral information of target end members and spectral information of background end members; traversing the remote sensing image to be detected by utilizing a cross correlation matching technique to determine the types of background end members in each pixel in the remote sensing image to be detected; carrying out spectral decomposition on the remote sensing image to be detected in a completely restricted least square way to acquire the component information of target end members and various background end members in each pixel in the remote sensing image to be detected; establishing a detector based on the GLRT (Generalized Likelihood Ratio Test); and traversing the remote sensing image to be detected by adopting the detector to acquire the detection function value of each pixel in the remote sensing image to be detected, thereby judging whether targets exist in each pixel in the remote sensing image to be detected or not. The method of the invention has the characteristics of strong structuration, high adaptability, self-organization and self-learning.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
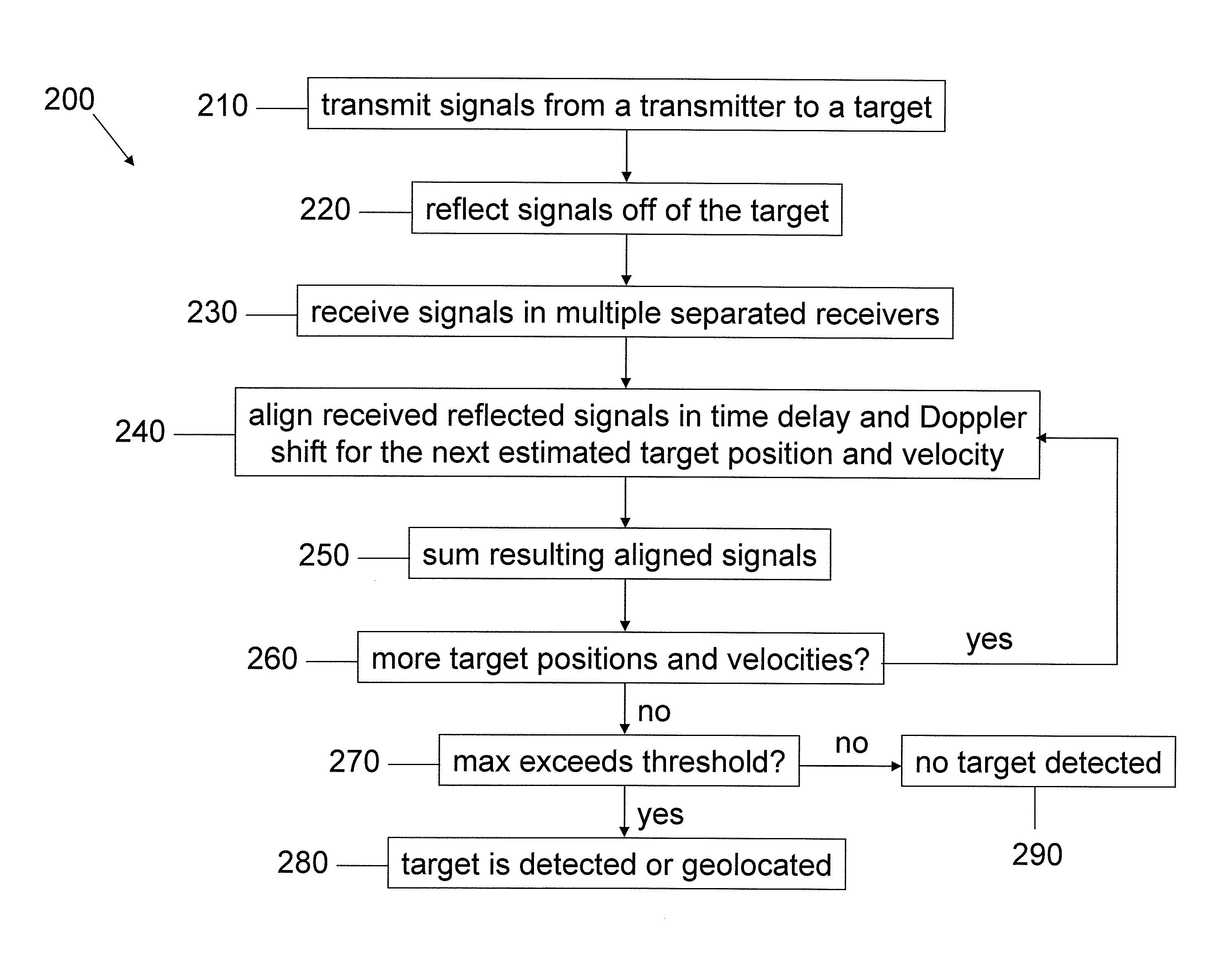
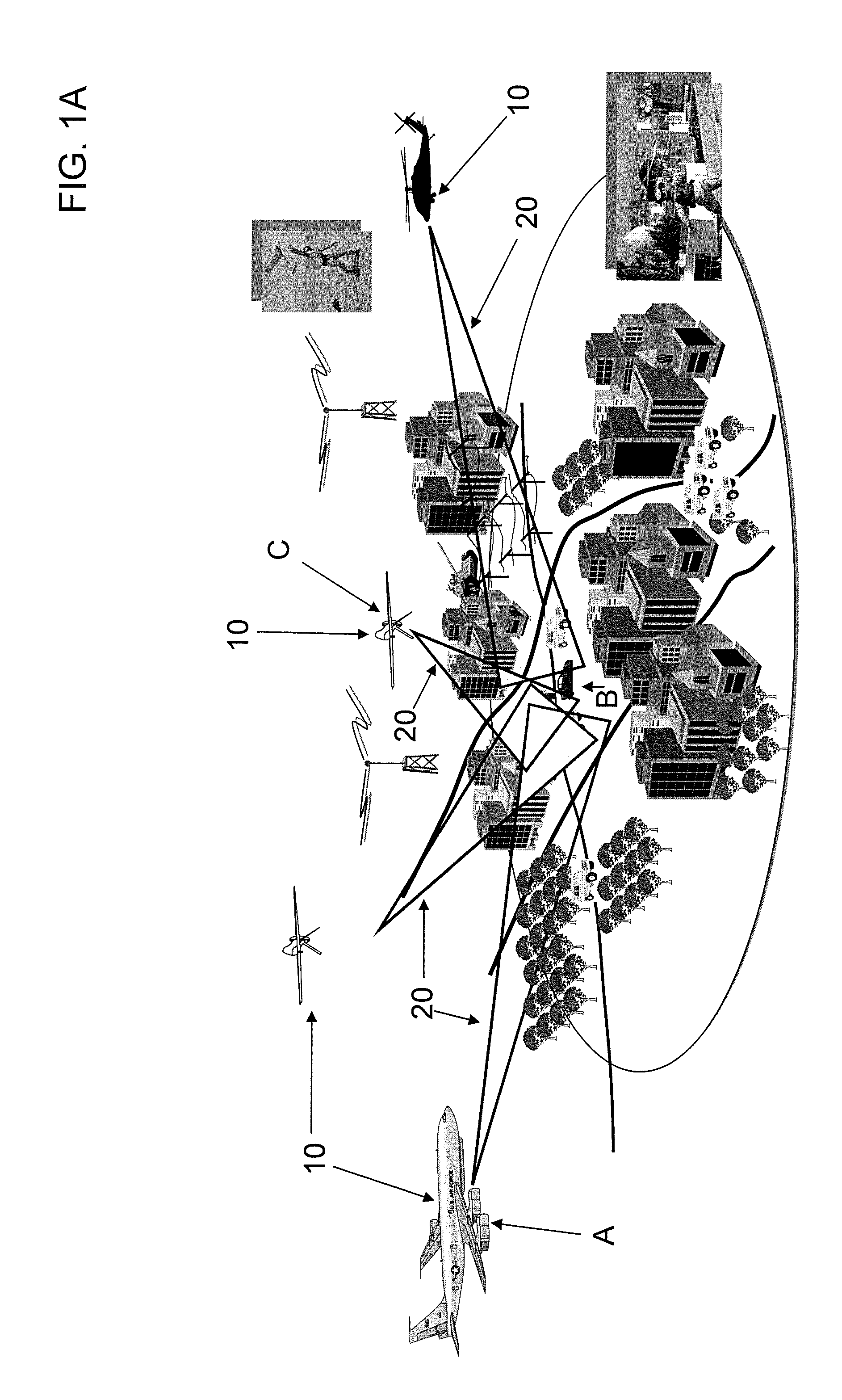
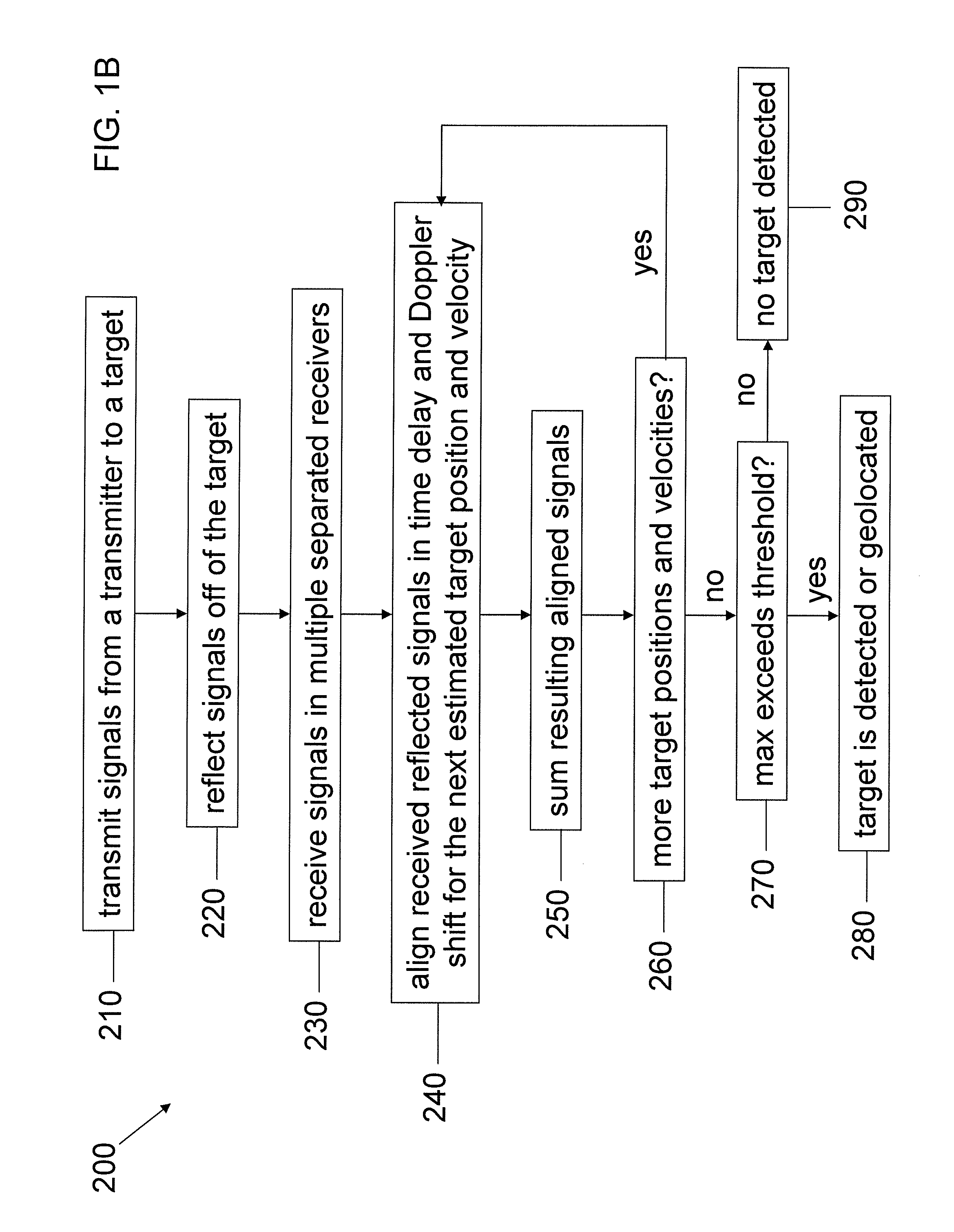
Multistatic target detection and geolocation
InactiveUS20120056772A1Improve detection accuracyImprove geolocation accuracyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTime delaysRadar
Aspects of this invention are directed to the substantially improved detection and geolocation accuracy of targets (stationary or moving) by using the coherent data received at multiple airborne sensors. Further aspects are directed to aligning the (unknown) time-delayed and Doppler-shifted signals received at the multiple sensors relative to an arbitrary reference sensor, which depend on the unknown target position. This results in the target position and velocity vectors being simultaneously estimated and the detection peak enhanced by obtaining near coherent gain. Still further aspects are directed to the coherent generalized likelihood ratio test (GLRT) and the minimum variance distortionless response (MVDR) statistic for multistatic radar systems, conditioned on estimation of certain parameters that render the system coherent. Analytical and computer simulation results are presented to show substantially enhanced detection and geolocation of moving targets in clutter.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
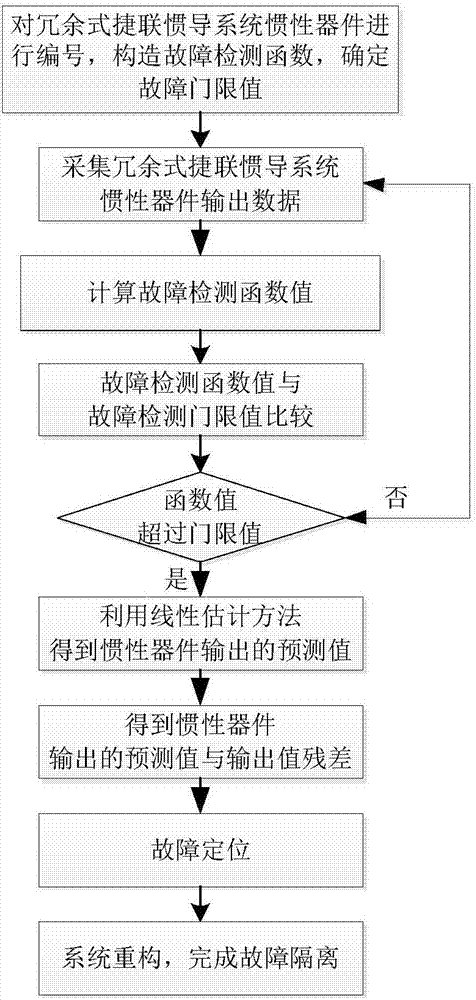
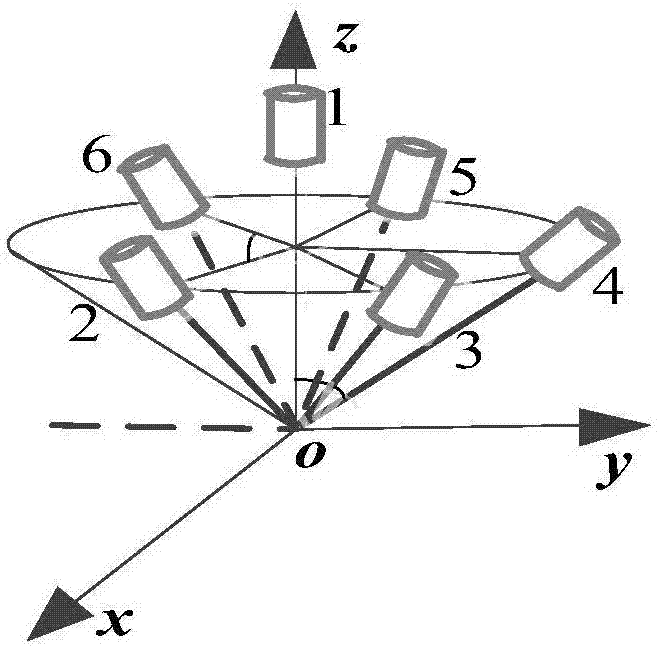
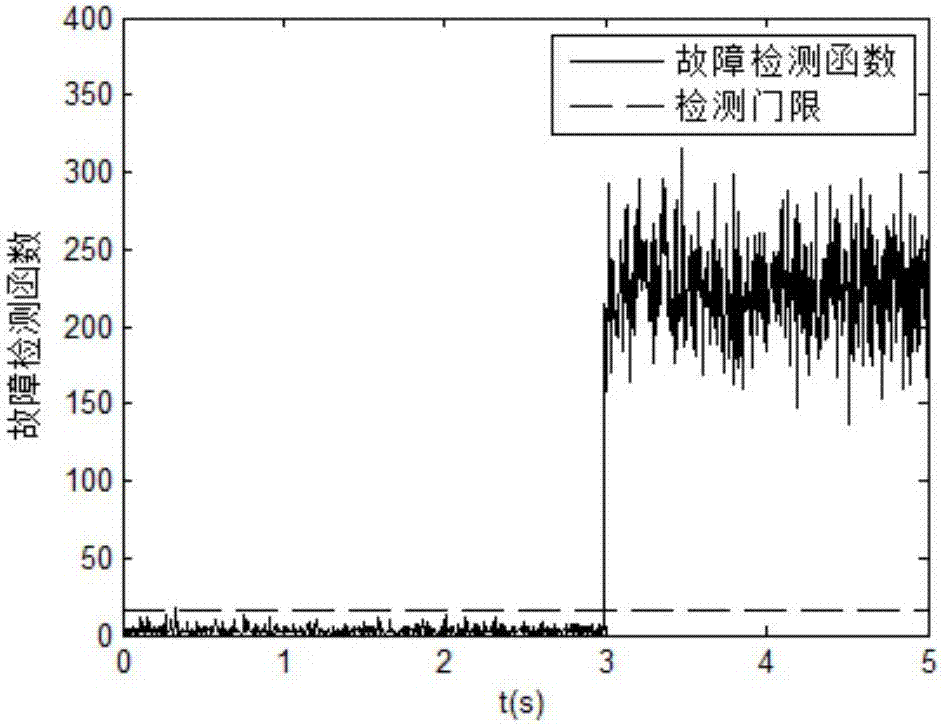
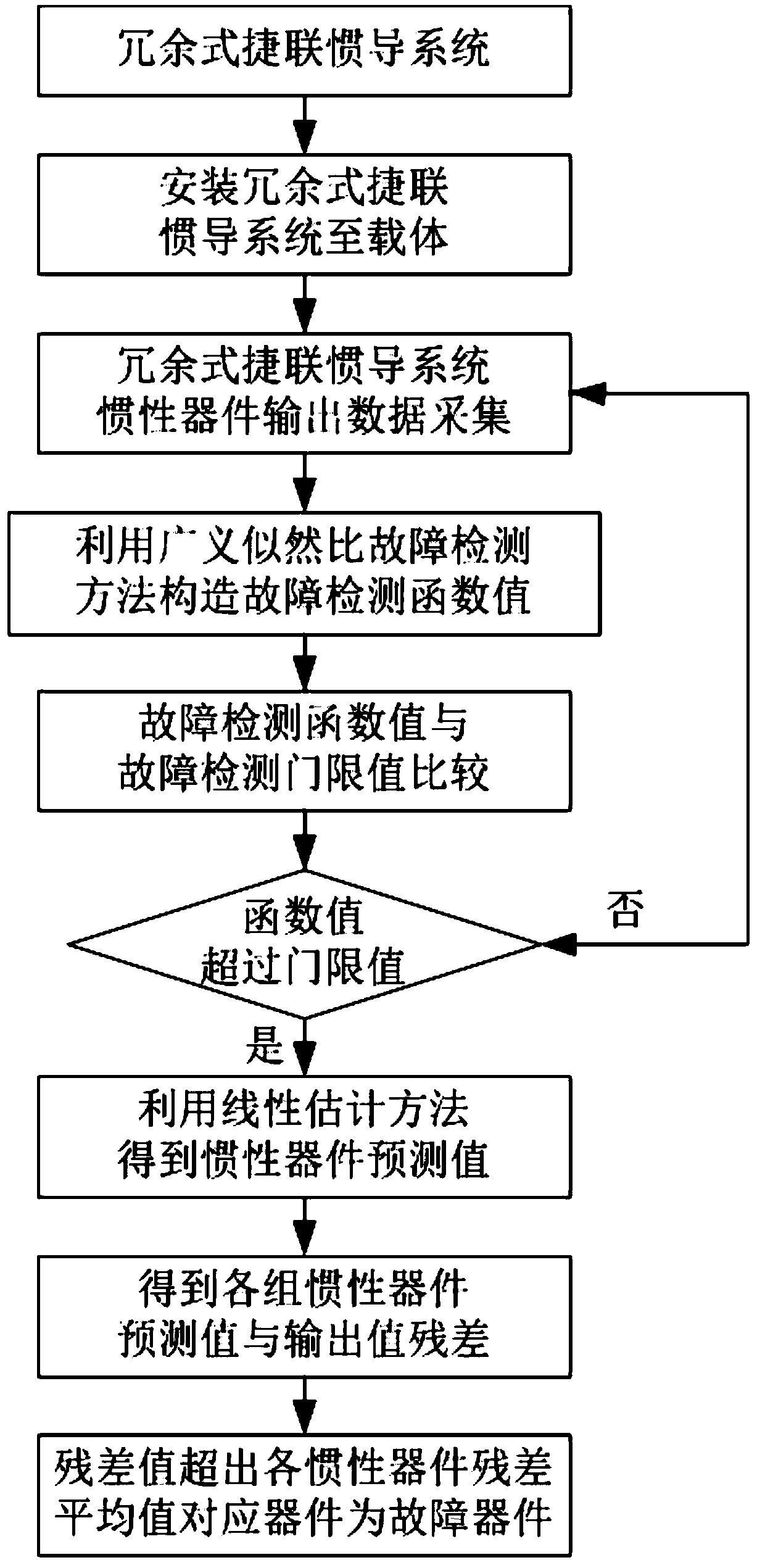
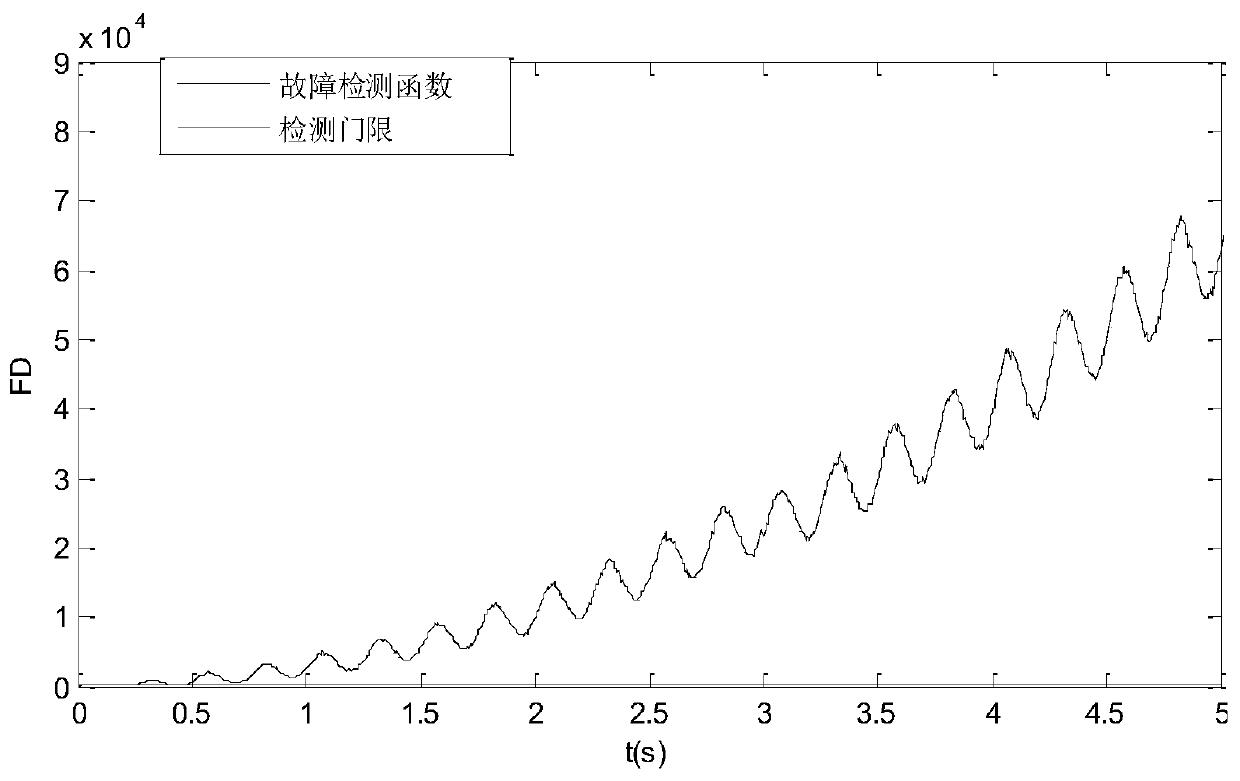
Multi-failure isolation method for redundant strapdown inertial navigation system
ActiveCN107421534AAccurate isolationQuick checkInstruments for comonautical navigationNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsComputer scienceInertial navigation system
The invention discloses a multi-failure isolation method for a redundant strapdown inertial navigation system. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring output data of inertial devices of the redundant inertial navigation system at first, performing failure detection by virtue of a generalized likelihood ratio method, estimating predicted values output by the inertial devices at failure moments by virtue of a linear estimation method when failures are detected to occur to the redundant strapdown inertial navigation system, finally comparing the predicted values of the inertial devices with output values to obtain difference values, locating the failing inertial devices, and isolating the failing inertial devices. According to the method, the generalized likelihood ratio method is combined with the linear estimation method, the characteristics of high sensitivity and convenience for implementation of the generalized likelihood ratio method and small calculated amount, high accuracy and the like of the linear estimation method are fully utilized, and the failing inertial devices are timely and accurately isolated when a plurality of inertial devices of the redundant strapdown inertial navigation system simultaneously fail, so that the reliability of the inertial navigation system is ensured.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Detection method for SMSP interference and C&I interference
ActiveCN105137396ASimple methodHigh accuracy of interference detectionWave based measurement systemsLikelihood-ratio testRadar signal detection
The invention discloses a detection method for SMSP interference and C&I interference, belonging to the radar signal detection technology field and particularly relating to the radar interference signal detection technology. The detection method disclosed by the invention comprises steps of utilizing a generalized likelihood ratio method to perform estimation on unknown amplitude parameters in an echo signal and an interference vector, respectively obtaining maximum likelihood estimation value, and bringing the unknown amplitude parameter and the interference vector maximum likelihood value into the generalized likelihood ratio detector to detect interference. The detection method for SMSP interference and C&I interference improves interference detection accuracy.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
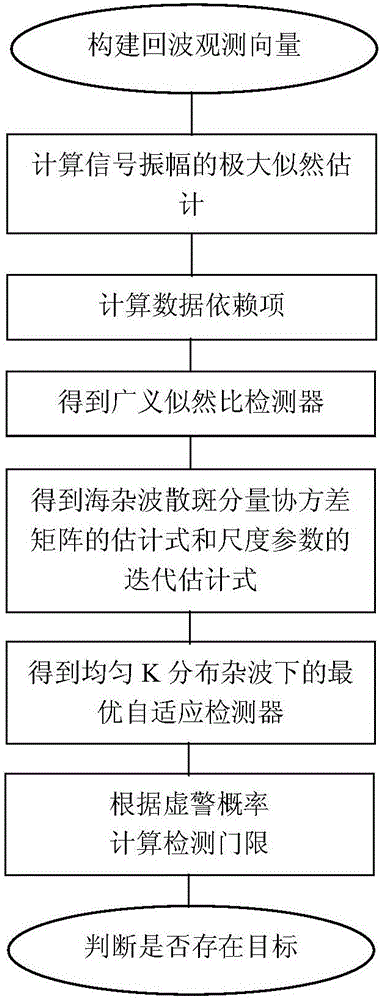
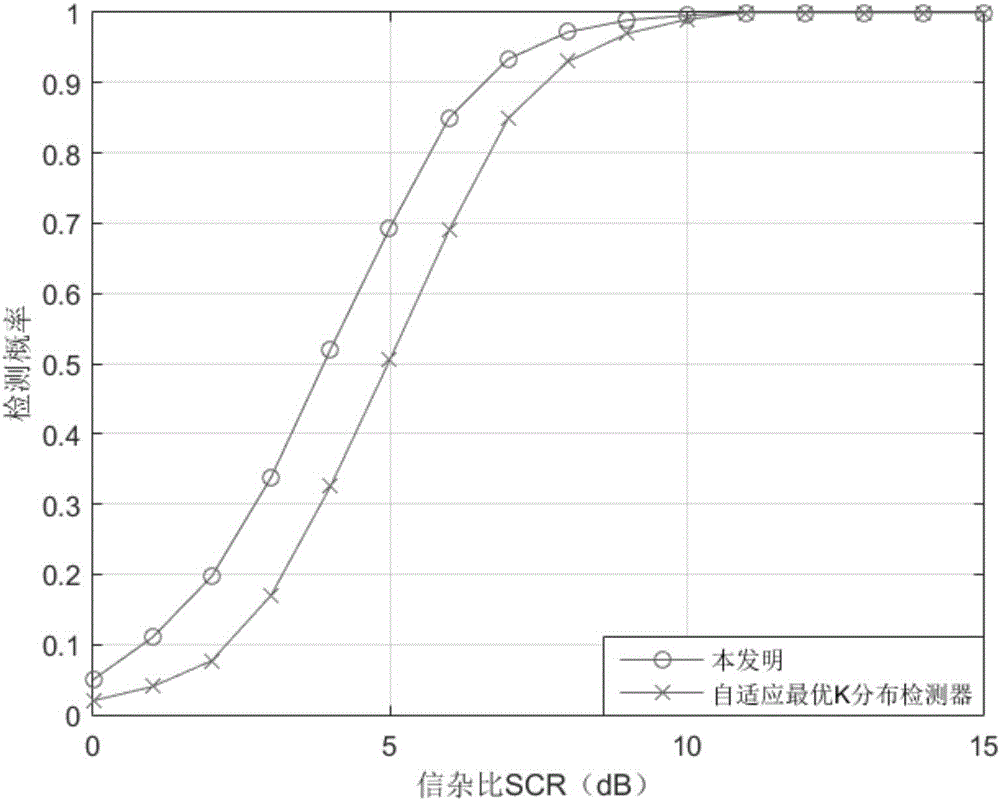
Optimal adaptive detection method under uniform K-distributed clutter
InactiveCN106483515AEasy to detectWave based measurement systemsSelf adaptiveGeneralized likelihood ratio
The invention discloses an optimal adaptive detection method under uniform K-distributed clutter. The method is implemented by the steps as follows: (1) building an observation vector of radar echo data; (2) calculating the estimated value of signal amplitude alpha<^>ML; (3) calculating data dependencies with use of the observation vector and alpha<^>ML; (4) getting a generalized likelihood ratio detector according to the Neyman-Pearson criterion; (5) getting the estimator M<^>SCM of a covariance matrix M of sea clutter speckle components and the iterative estimator beta of a scale parameter b through maximum likelihood estimation and sample covariance matrix estimation; (6) using M<^>SCM and beta to replace M and b in the generalized likelihood ratio detector respectively to get an adaptive optimal detector based on uniform K distribution; (7) calculating a detection threshold T; and (8) judging whether a target exists based on the detection threshold T. The target detection performance is improved. The method can be used in target detection under a sea clutter background.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
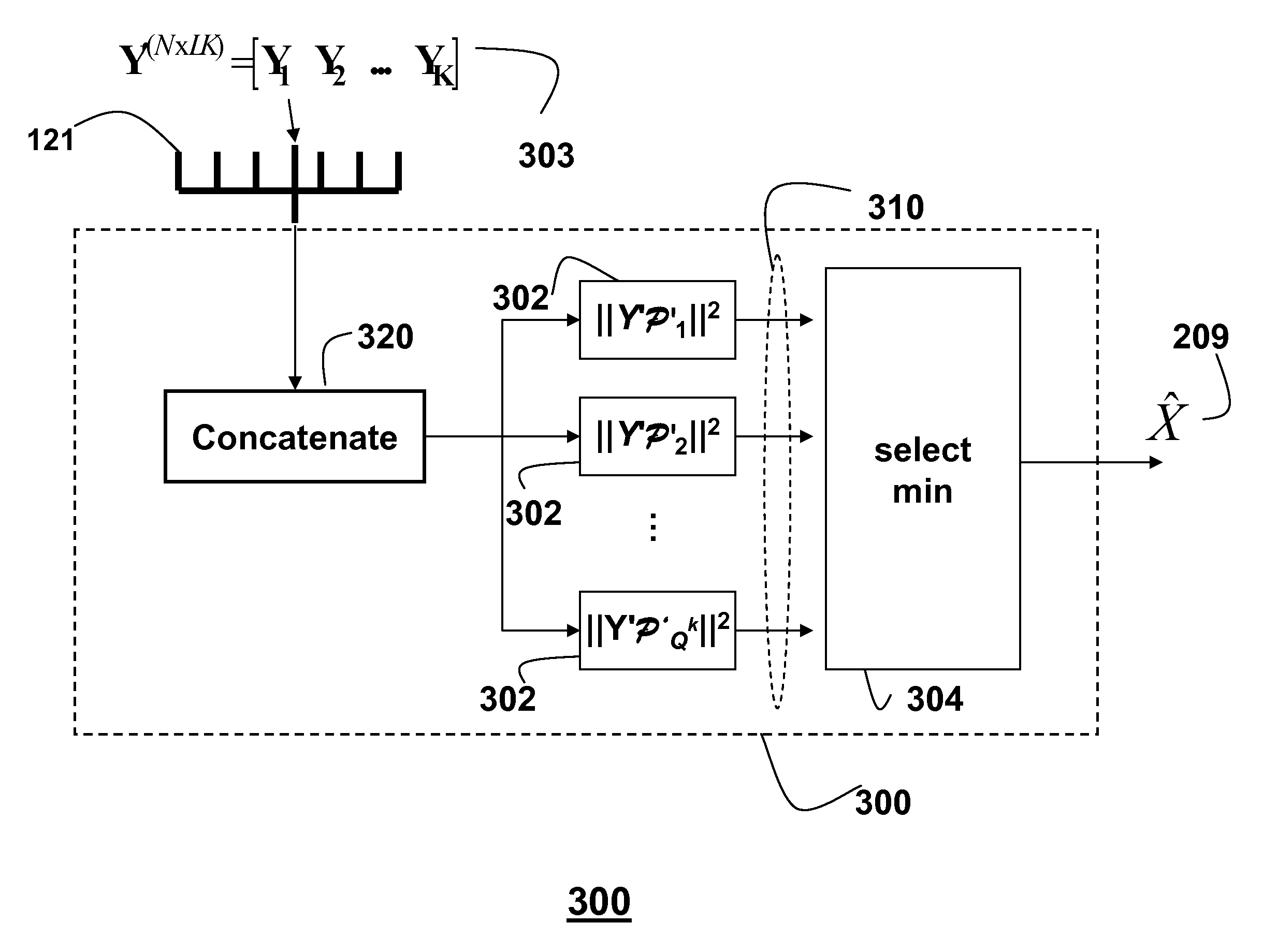
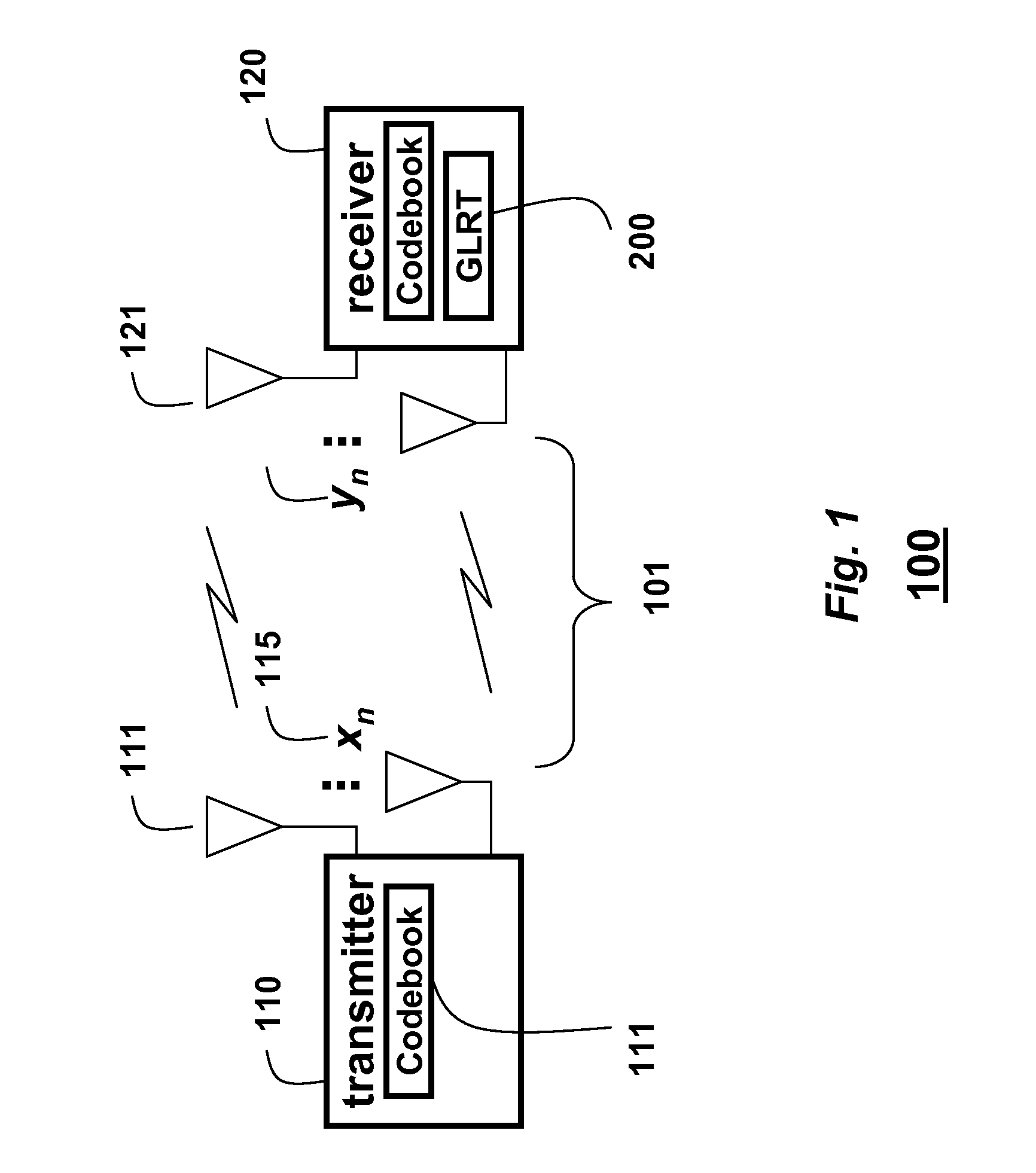
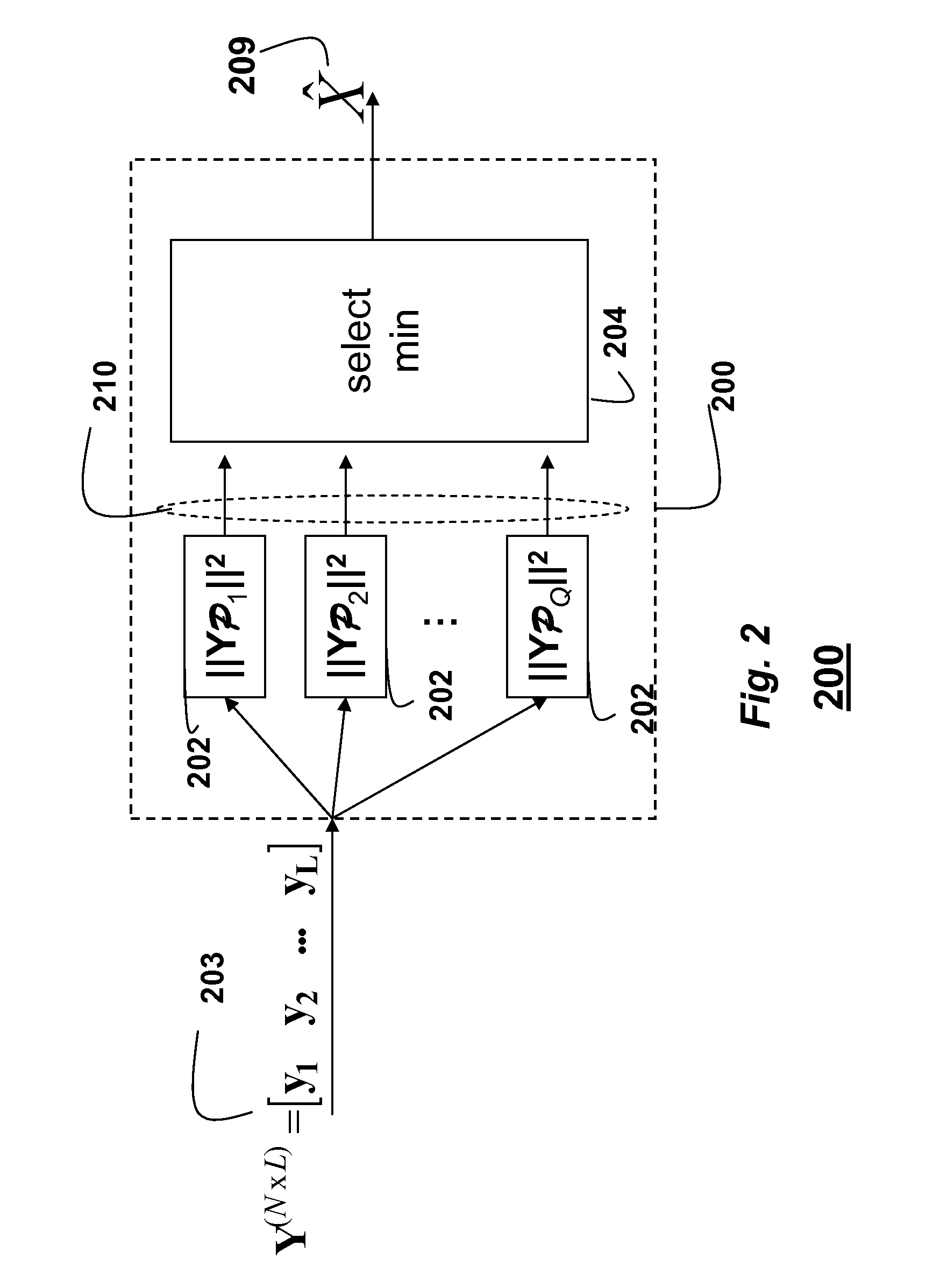
Method for decoding codewords transmitted over non-coherent channels in MIMO-OFDM networks using Grassmann codes and superblocks
ActiveUS8059747B1Easy to useOvercome changePolarisation/directional diversityCode conversionMulti inputMultiplexing
Codewords encoded using non-coherent codes and received at a receiver via non-coherent channels in a multi-input, multiple output (MIMO) network using orthogonal frequency demultiplexing (OFDM) are decode by concatenating multiple adjacent codewords of a received signal into a superblock at the receiver. A projector matrix based on a codebook is predetermining. Each codeword in the superblock is projected onto an orthogonal complement of a correspond transmitted codeword using the projector matrix to obtain a corresponding distance metric of a generalized likelihood ratio test (GLRT) codeword. A minimal distance metric is selected to obtain an estimate of the transmitted codeword corresponding to a transmitted signal.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
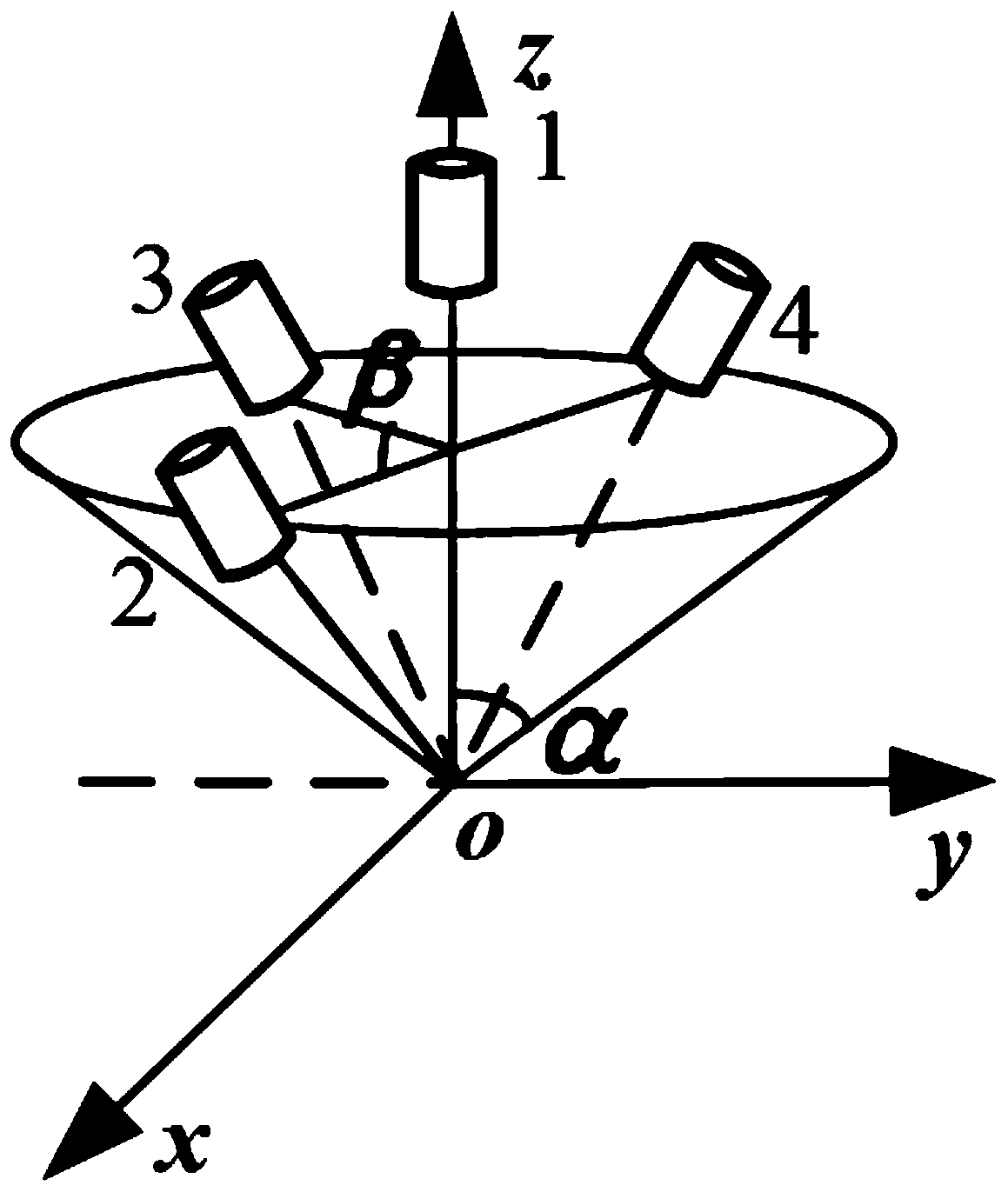
Four-gyro redundant strapdown inertial navigation system fault detection and isolation method in dynamic environment
InactiveCN110196049AEffective design combinationEffective isolationNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsFailure detection and isolationMarine navigation
The invention discloses a four-gyro redundant strapdown inertial navigation system fault detection and isolation method in a dynamic environment, which belongs to the technical field of strapdown inertial navigation systems. A redundant inertial navigation system inertial device is used to output data to build an inertial device error model, a fault detection and isolation method based on the combination of a generalized likelihood ratio, Kalman filter and linear estimation ideas is designed, and an inertial navigation system with hard fault is detected; and a linear estimation method is usedfor processing data, the prediction value of the inertial device at the fault moment is obtained, the difference between the prediction value of each group of inertial device and the output value is compared, and a fault inertial device is positioned and isolated. When hard fault happens to a single inertial device of the four-gyro redundant strapdown inertial navigation system in the dynamic environment, the reliability of the strapdown inertial navigation system is ensured.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
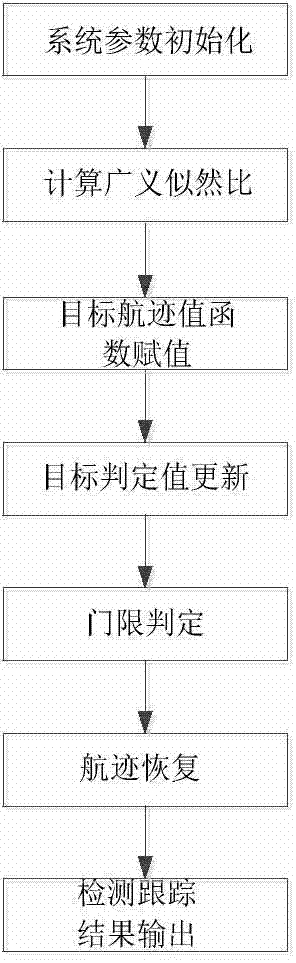
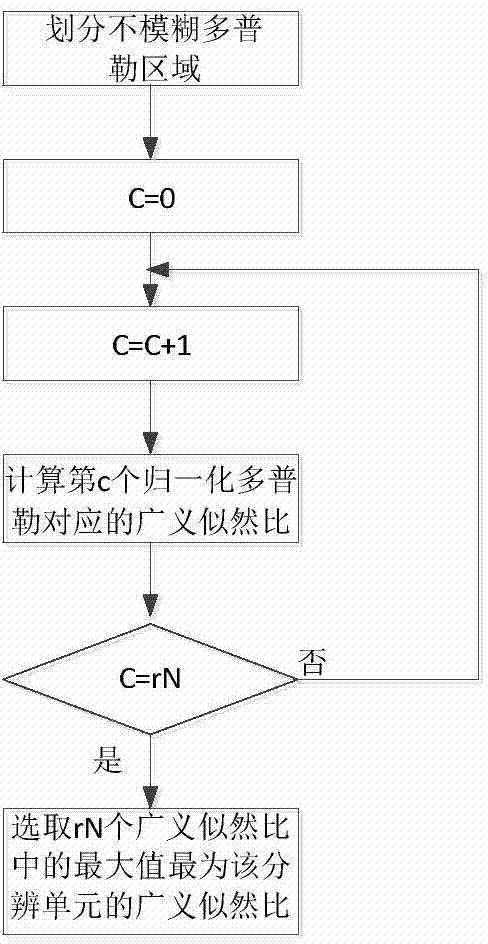
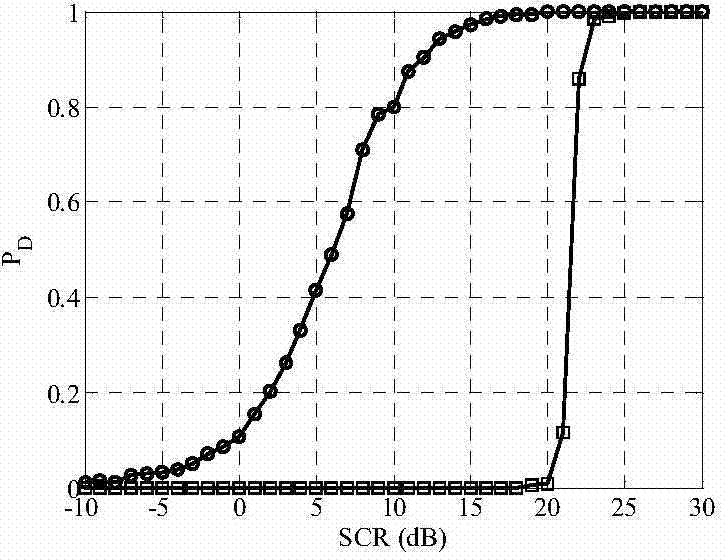
Dynamic programming tracking-before-detection method based on generalized likelihood ratios
ActiveCN104714225AImprove detection tracking performanceSpecial data processing applicationsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadarComputer science
The invention discloses a dynamic programming tracking-before-detection method based on generalized likelihood ratios, belongs to the technical field of radar target detection and tracking, and particularly relates to the technical field of weak target detection and tracking under a compound-gaussian clutter background. When radar echo data are received, the corresponding generalized likelihood ratios of all distance resolution units are computed, and the generalized likelihood ratios serve as target track value functions to be used for dynamic programming accumulation. Compared with a traditional dynamic programming tracking-before-detection method, by means of the dynamic programming tracking-before-detection method based on the generalized likelihood ratios, the difference of a target and clutter can be better reflected, and the weak target detection and tracking performance under the compound-gaussian clutter background can be improved; the generalized likelihood ratios are selected to serve as the target track value functions to be used for dynamic programming accumulation, and the weak target detection and tracking performance under the compound-gaussian clutter background can be improved effectively compared with the traditional dynamic programming tracking-before-detection method under the condition that the specific clutter amplitude distribution type, parameters and target statistical property are unknown.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Simulation method of MIMO radar target detection under non-Gaussian clutter environment
InactiveCN102520400ADetection performance dropsEasy to detectWave based measurement systemsRadarLikelihood-ratio test
The invention discloses a simulation method of MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) radar target detection under non-Gaussian clutter environment. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a target detection model based on the auxiliary data which is close to a detected unit and does not contain the target; substituting a likelihood function with a detection signal to get the detection statistic; under a condition that a non-Gaussian clutter covariance matrix is known, obtaining a theoretical MIMO radar target detector by using a generalized likelihood ratio test theory. Under a condition that the non-Gaussian clutter covariance matrix is unknown, an appropriate clutter covariance matrix is estimated based on the auxiliary data, and the generalized likelihood ratio is substituted by the estimated clutter covariance matrix, thus, a MIMO radar adaptive detector is proposed.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Radar target adaptive detection method based on linear fusion
ActiveCN106872958AEnhancing CFAR RobustnessImprove adaptabilityWave based measurement systemsPattern recognitionEstimation methods
The invention discloses a radar target adaptive detection method based on linear fusion, which belongs to the field of radar signal processing. Aiming at non-Gaussian degree spatiotemporal variability of clutters in the actual environment, based on an adaptive match filter or a generalized likelihood ratio detection detector in the Gaussian background and adaptive normalized match filter in the non-Gaussian background, through simple and effective linear fusion rules, a suitable adaptive detector structure is designed by comprehensively adopting the optimal or sub-optimal clutter covariance matrix estimation method in the specific clutter background and rationally using clutter non-Gaussian feature information. The detector is simple in structure and has strong generalization ability. The detection performance of the detector, the amount of algorithm calculations and other needs are simultaneously taken into account. The constant false alarm rate robustness of the detector and the adaptability to the clutter environment are enhanced, and the radar target detection performance under unknown clutter environment is improved. The radar target adaptive detection method of the invention has popularization and application values.
Owner:NAVAL AVIATION UNIV
Multi-pass SAR coherent change detection method based on general likelihood ratio
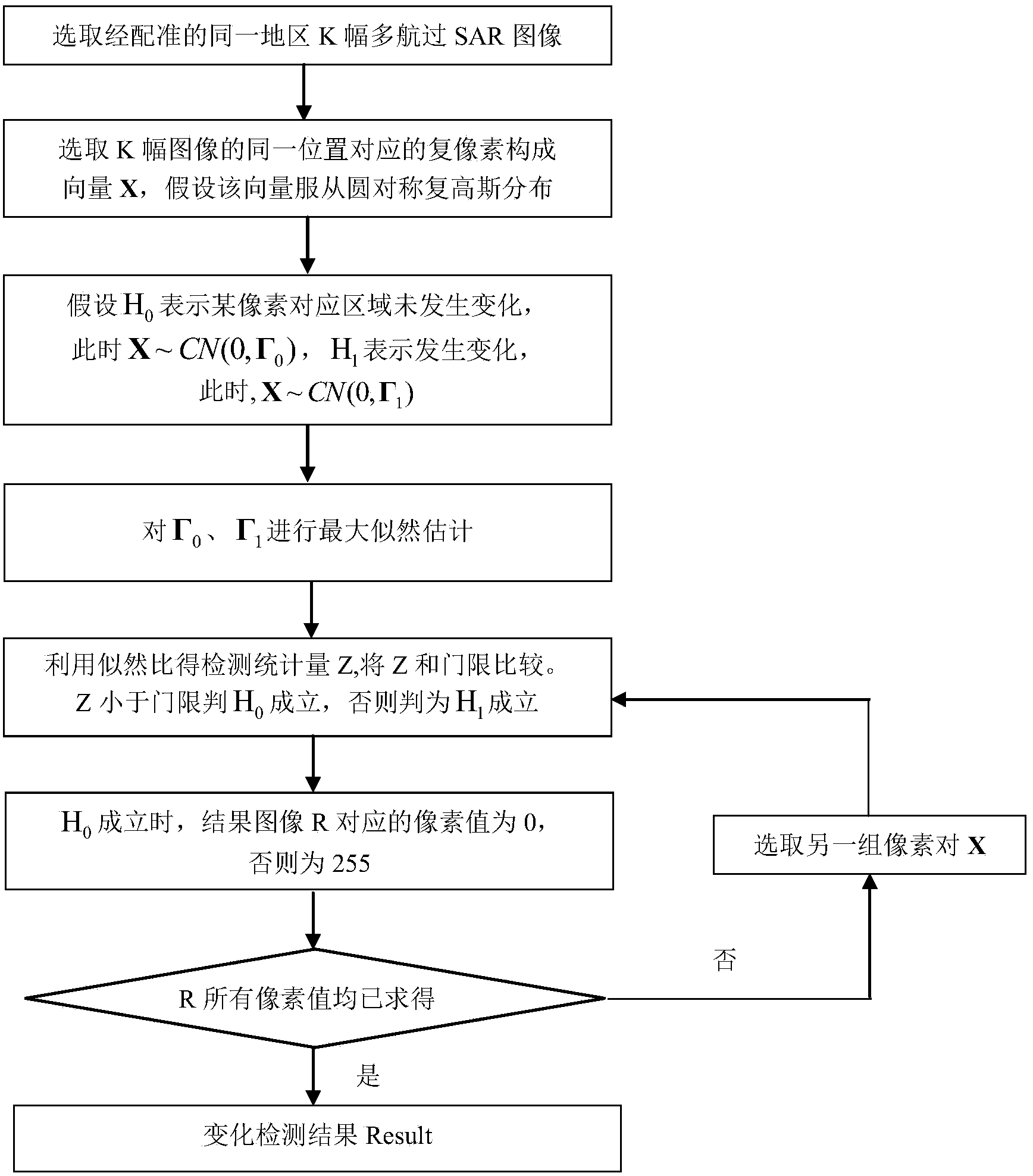
ActiveCN104166128AAchieve observationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionCoherent change detectionArea change
The invention discloses a multi-pass SAR coherent change detection method based on a general likelihood ratio. The multi-pass SAR coherent change detection method includes the steps that S1, multi-pass SAR image pairs are selected and recorded as {f1, f2,..,fk}; S2, multi-pass SAR image pixel pairs are selected; S3, maximum likelihood estimation is carried out on a covariance matrix; S4, likelihood ratio hypothesis testing is carried out; S5, the multi-pass SAR image pixel pairs are sequentially selected, and the step S4 is repeated to obtain a change detection result. The multi-pass SAR coherent change detection method assumes that complex pixels corresponding to an SAR imaging area changing in the multiple image collecting stage and complex pixels corresponding to the SAR imaging area not changing in the multiple image collecting stage follow different circular symmetry complex Gaussian distributions respectively, the covariance matrix of the circular symmetry complex Gaussian distributions in the assumption is estimated, then detection statistics is determined and compared with a threshold, whether the two assumptions succeed or not is checked, namely whether the imaging area changes or not is detected, the tiny changes can be detected, and the changing process can be observed.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method to transiently detect samples in atomic force microscopes
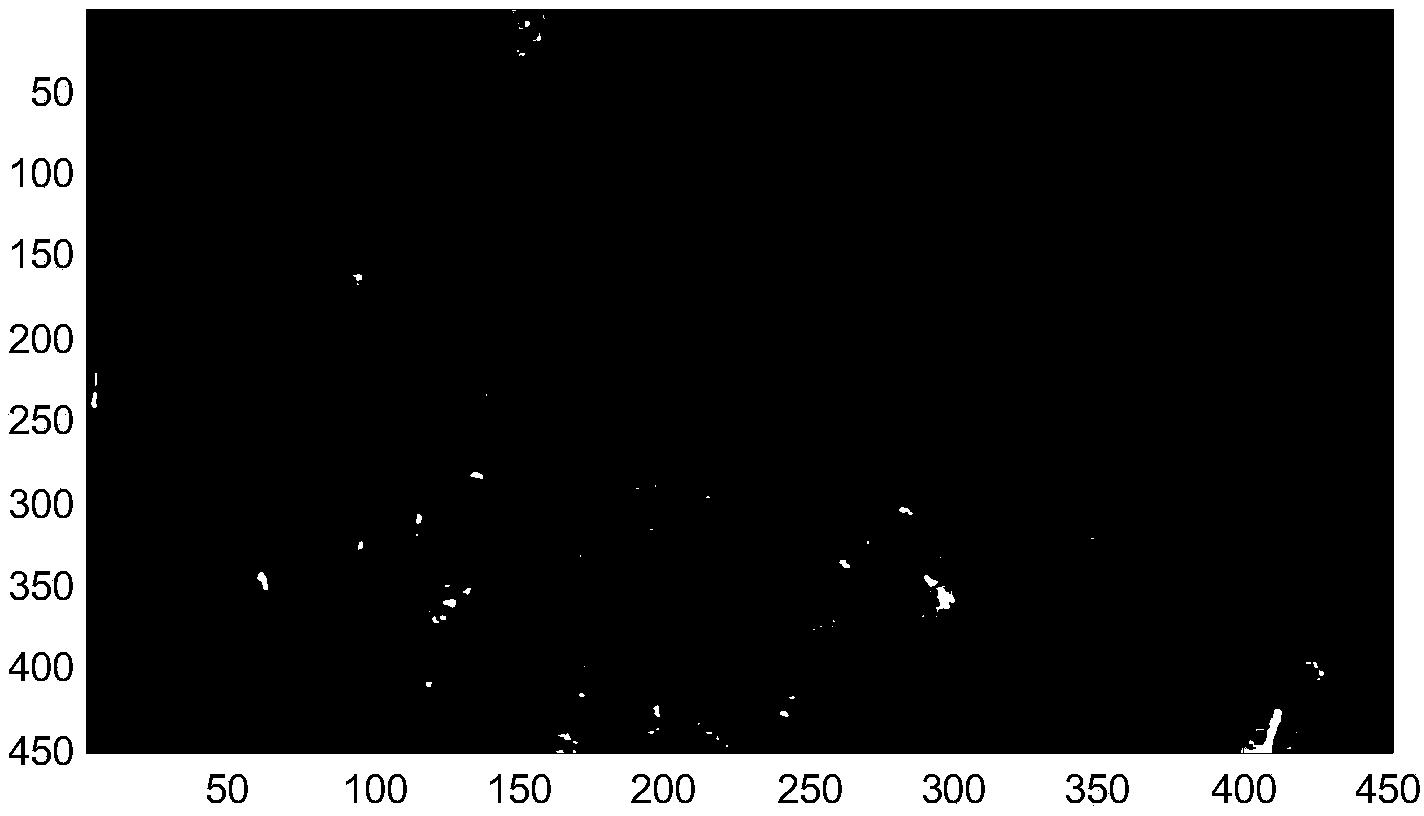
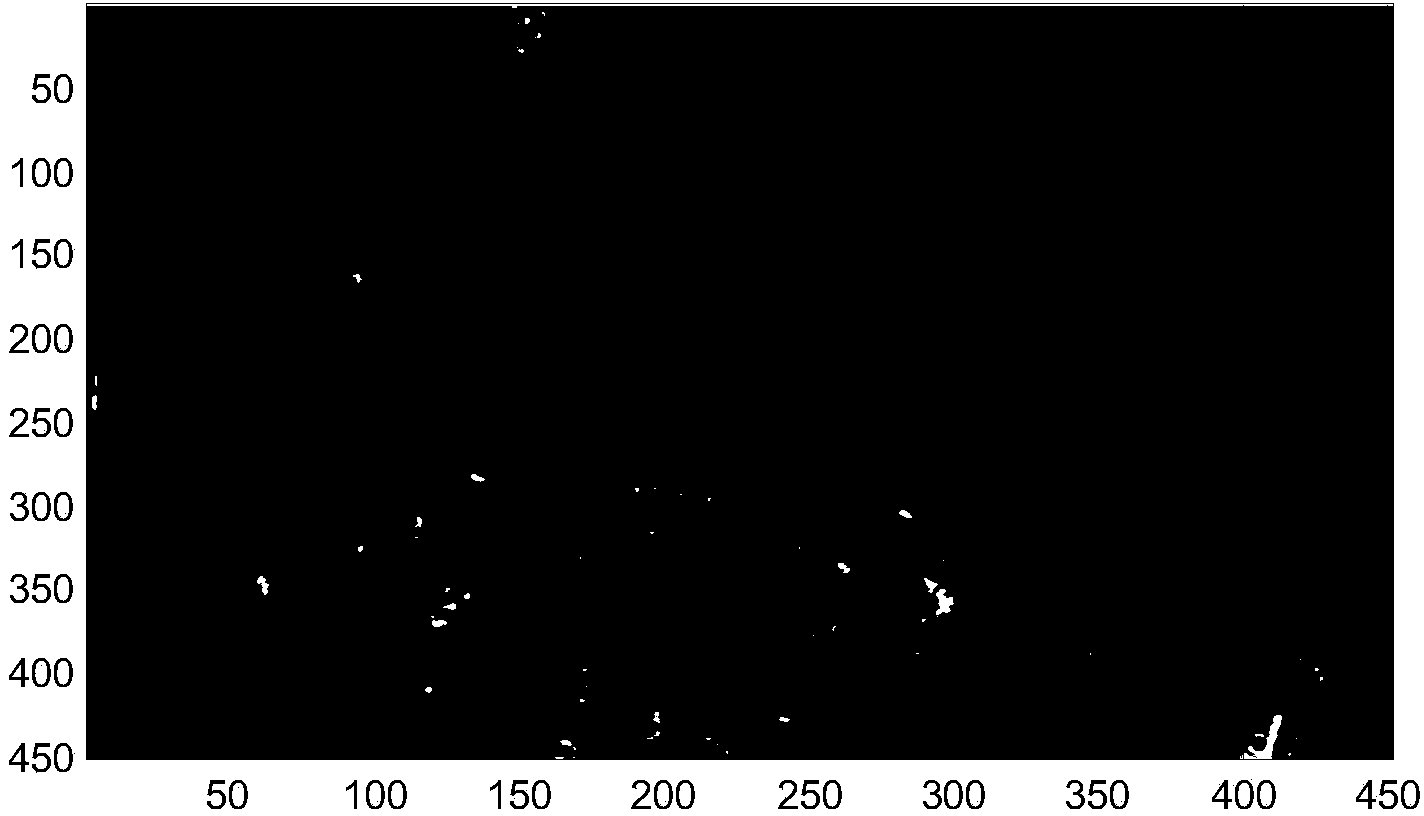
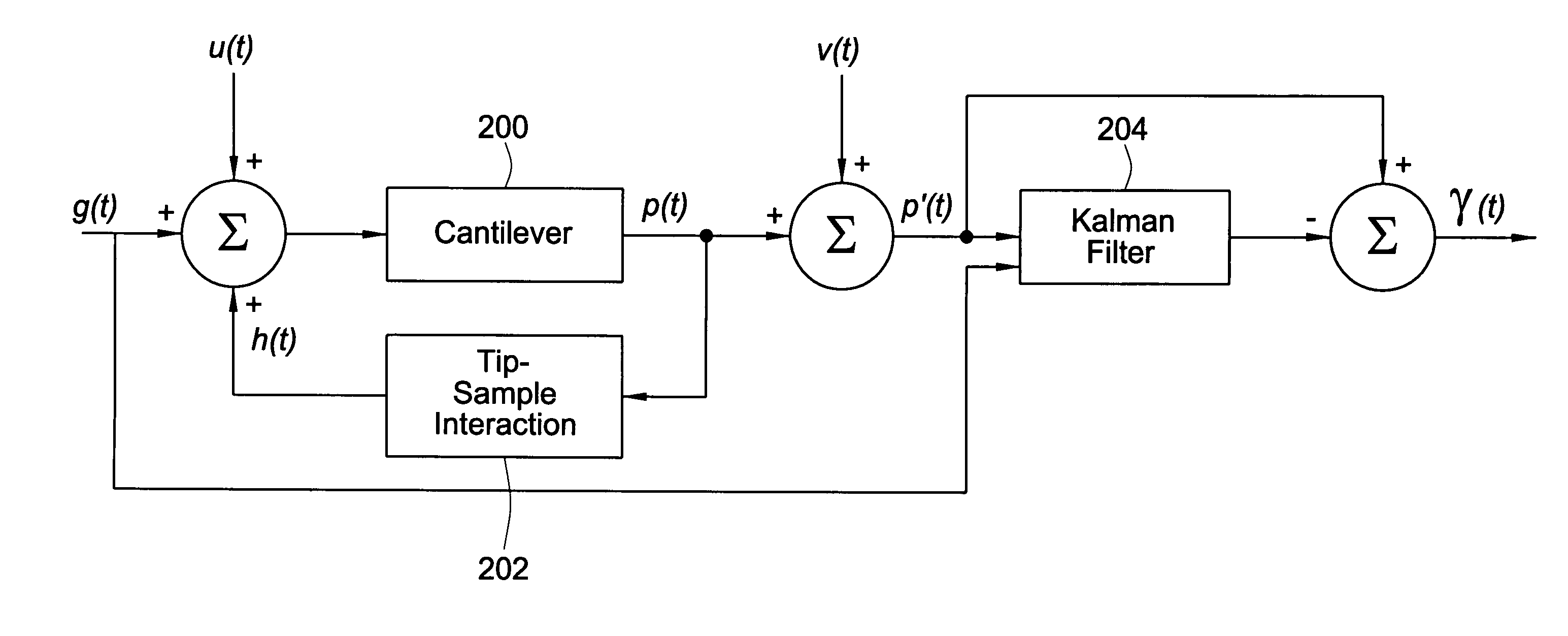
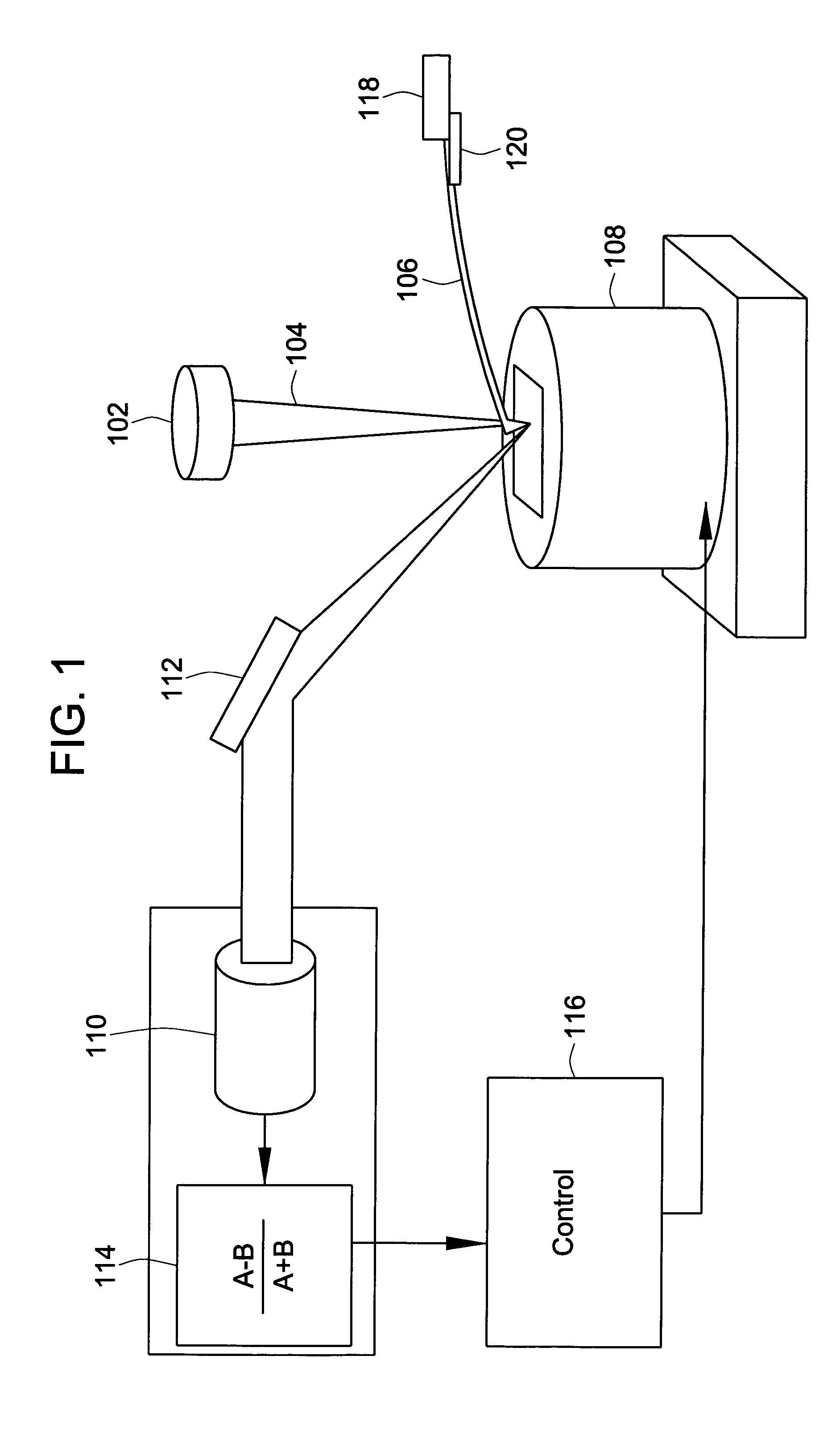
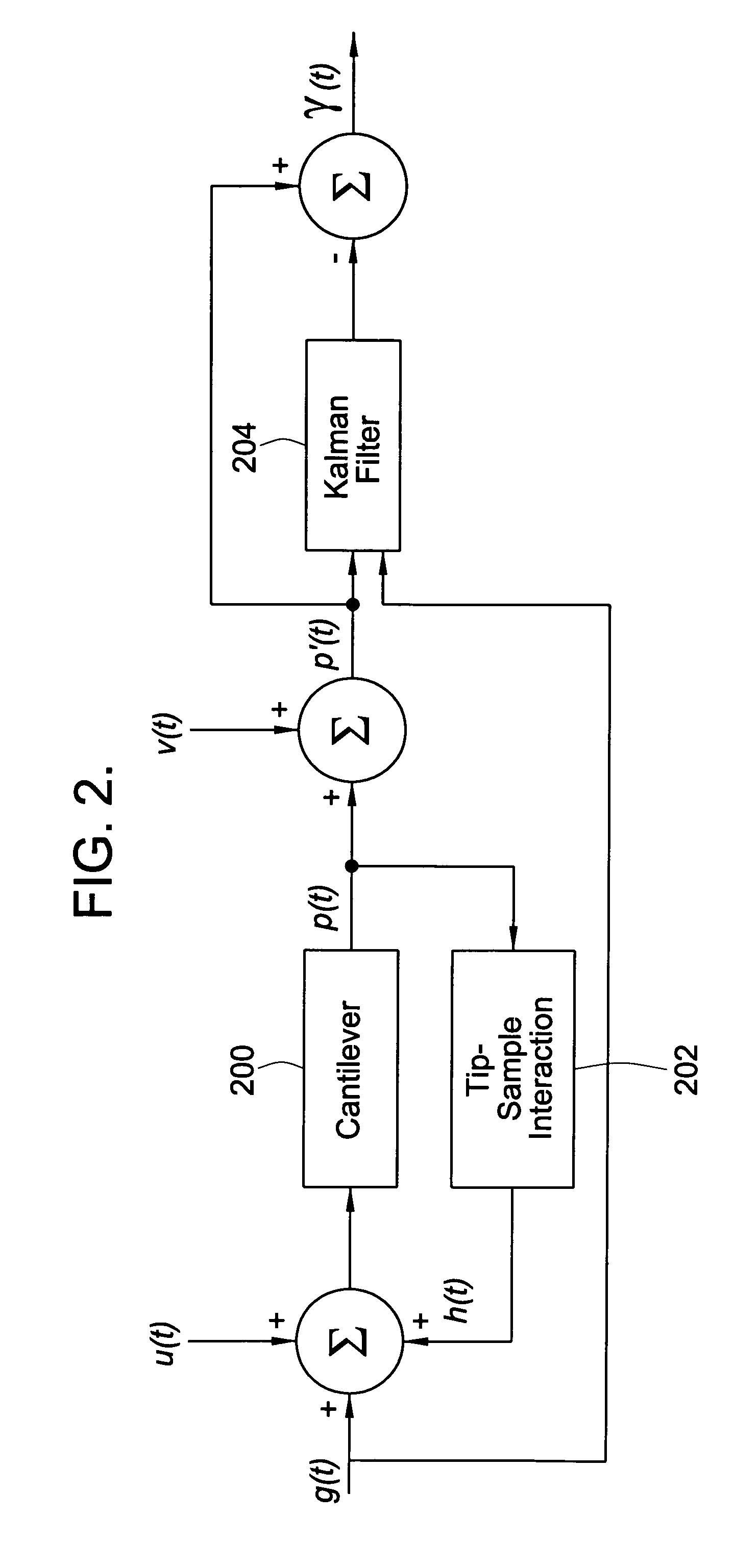
An approach to determine cantilever movement is presented. An observer based state estimation and statistical signal detection and estimation techniques are applied to Atomic Force Microscopes. A first mode approximation model of the cantilever is considered and a Kalman filter is designed to estimate the dynamic states. The tip-sample interaction is modeled as an impulsive force applied to the cantilever in order to detect the presence of sample. A generalized likelihood ratio test is performed to obtain the decision rule and the maximum likelihood estimation of the unknown arrival time of the sample profile and unknown magnitude of it. The use of the transient data results in sample detection at least ten times faster than using the steady state characteristics.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Detection method of sparse distance extension radar target in generalized Pareto clutter
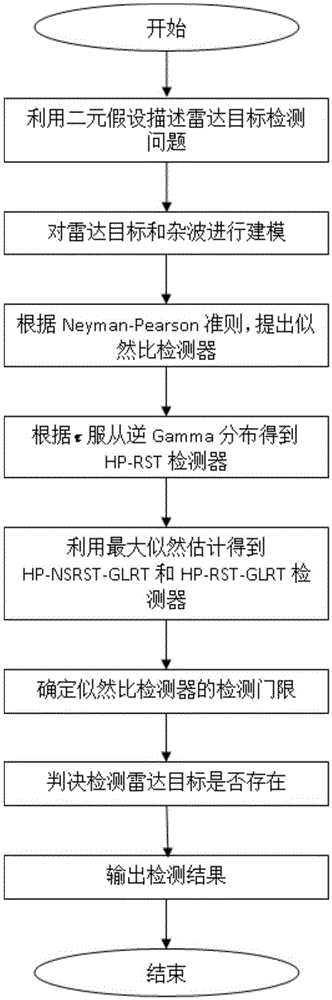
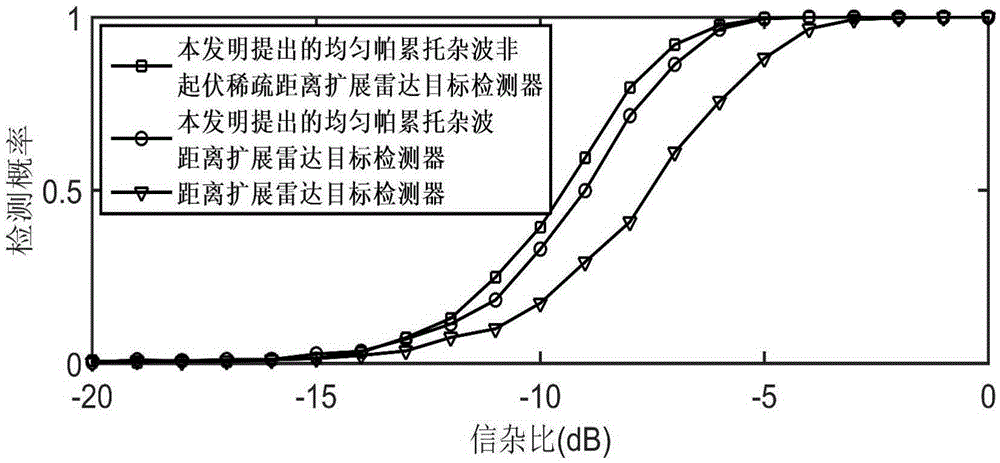
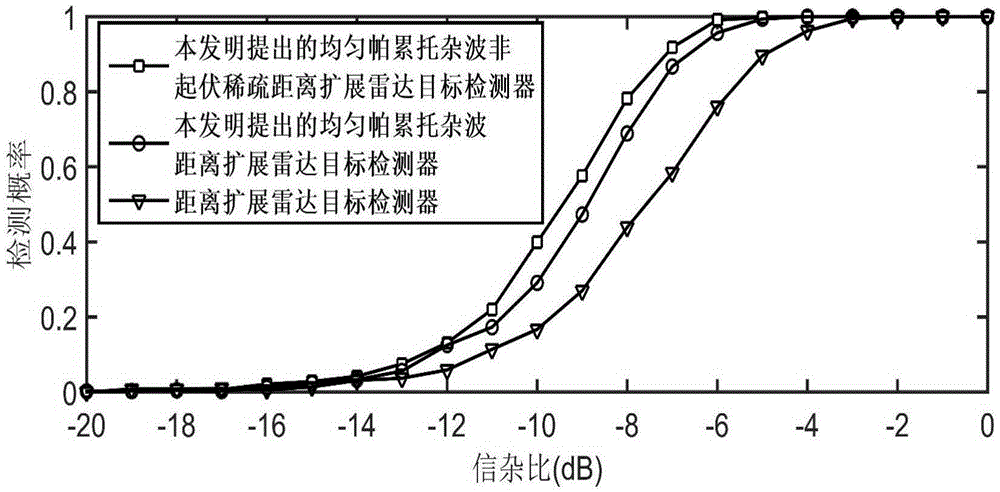
ActiveCN105425223AEasy to detectImprove estimation accuracyWave based measurement systemsHypothesisRadar
The present invention discloses a detection method of an adaptive sparse distance extension radar target in a generalized Pareto clutter background. The specific idea of the method is that: a binary hypothesis method is used to describe a radar target detection problem, the modeling is carried out on the above basis, sk and ck are obtained respectively, the likelihood detection statistical quantity of radar echo data is calculated according to sk and ck, thus a distance expension radar target detector of uniform Pareto clutter is obtained, then a maximum likelihood estimation method is utilized to obtain a generalized likelihood detector of a uniform Pareto clutter distance extension radar target and a generalized likelihood detector of a uniform Pareto clutter non-fluctuation sparse distance extension radar target, the false alarm probability PFA of the radar target is set, the detection threshold T of the likelihood detector is calculated and obtained, a distance unit in radar echo data is randomly selected as a detection unit, the detection statistical quantity ^ of the detection unit is calculated, and ^ and T are used to obtain the rardar target of each distance unit in the radar echo data.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Low-altitude target detection method for frequency diversity array radar
ActiveCN107607938ASuppression of SNR lossImprove target detection probabilityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionLikelihood-ratio testPhased array
The invention discloses a low-altitude target detection method for a frequency diversity array radar, belonging to the field of phased array radar low-altitude target detection. According to the method, due to the scanning characteristics of an FDA radar, the beam direction of the radar is related to a radial distance and a frequency difference, by introducing a frequency difference between different transmitting elements, a signal-to-noise ratio loss brought by a multipath effect in a low-altitude target environment can be effectively suppressed. Then, a generalized likelihood ratio test (GLRT) method is used to derive an FDA radar low-altitude target detector, and a target detection probability can be effectively improved under a certain false alarm rate. Finally, through the design of sub modules of matrix multiplication, matrix determinant calculation the like, an FDA radar low-altitude target detector is realized in an FPGA hardware platform, and the real-time detection of the FDAradar low-altitude target detection is effectively improved. In summary, according to the method, in a low-altitude target environment, the scanning characteristics of the FDA radar can be used to effectively complete the detection of a low-altitude target, and the method has high practicability in modern warfare.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Obstacle avoidance radar method and device based on ultra-wideband cognitive CPPM signal
ActiveCN107121677ANot affectedStrong resistancePosition/course control in three dimensionsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionUltra-widebandSignal classification
According to the invention, an obstacle avoidance radar based on an ultra-wideband cognitive CPPM signal generates a number of wide band CPPM signals which are orthogonal to each other. The signals pass through a transmitting beamforming module to form radar transmitting signals, and the signals are transmitted by a rectangular electron scanning array antenna of a receiving / transmitting switch module. If another flight target carries out reflection, an echo signal is received by an electronic scanning array antenna to form a received signal, and the signal is collected by a signal acquisition module. A receiver matches a filter module to acquire the distance-doppler information of the target. The echo amplitude, the azimuth and the height information of the target are acquired through a two-dimensional multiple signal classification module. The information enters a Dirichlet process hybrid model clustering module for gather classification, and then different targets are distinguished through a generalized likelihood ratio detection module. The individual target information is sent into a variable point detection module to detect a mutational point in a target movement trajectory. According to the mutational point, the amplitude and the pulse width of the CPPM signals are redesigned, and the movement trajectory of an unmanned aerial vehicle is corrected to avoid collision with other flight targets.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
SAR image classification based on multi-feature and composite kernel
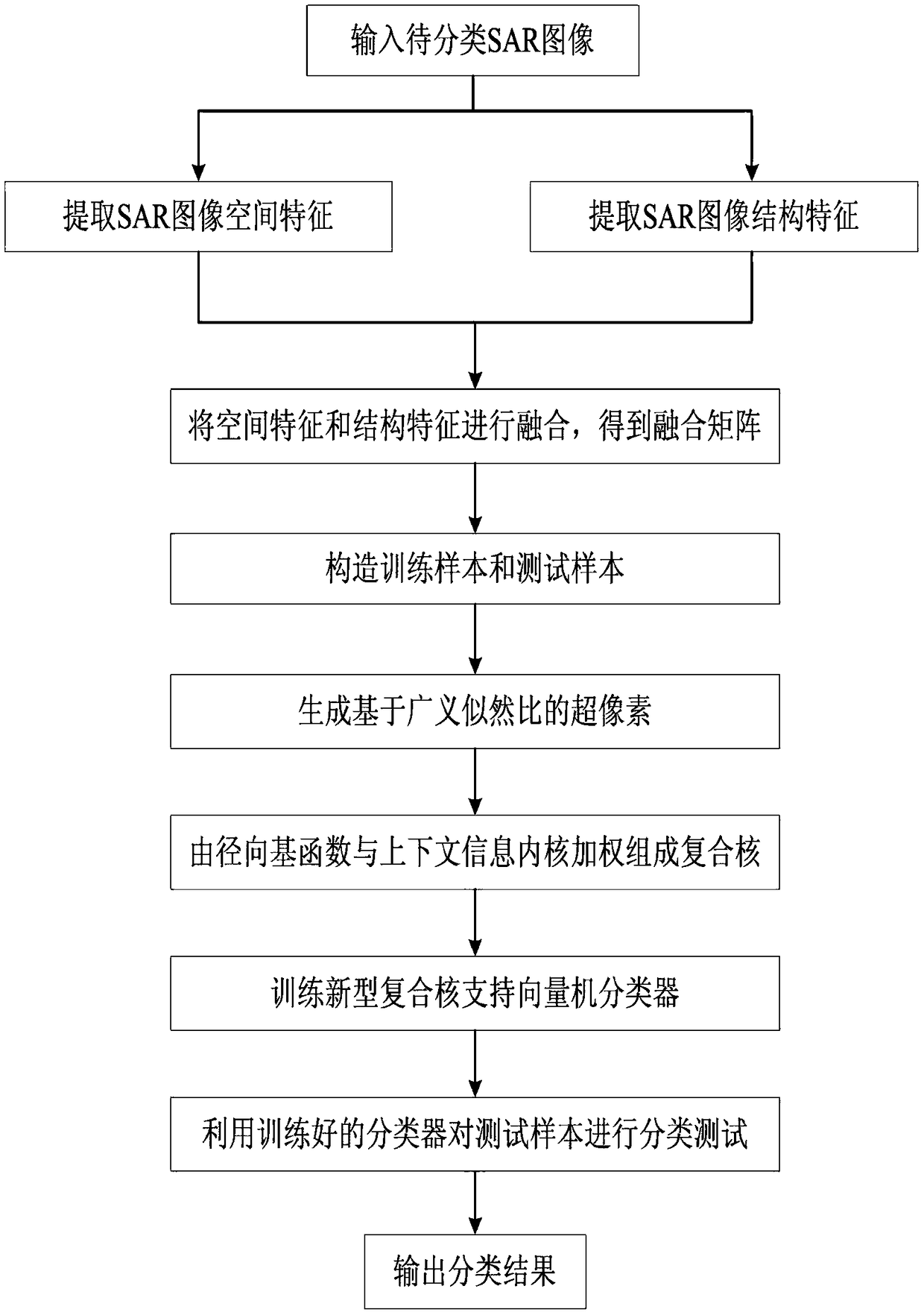
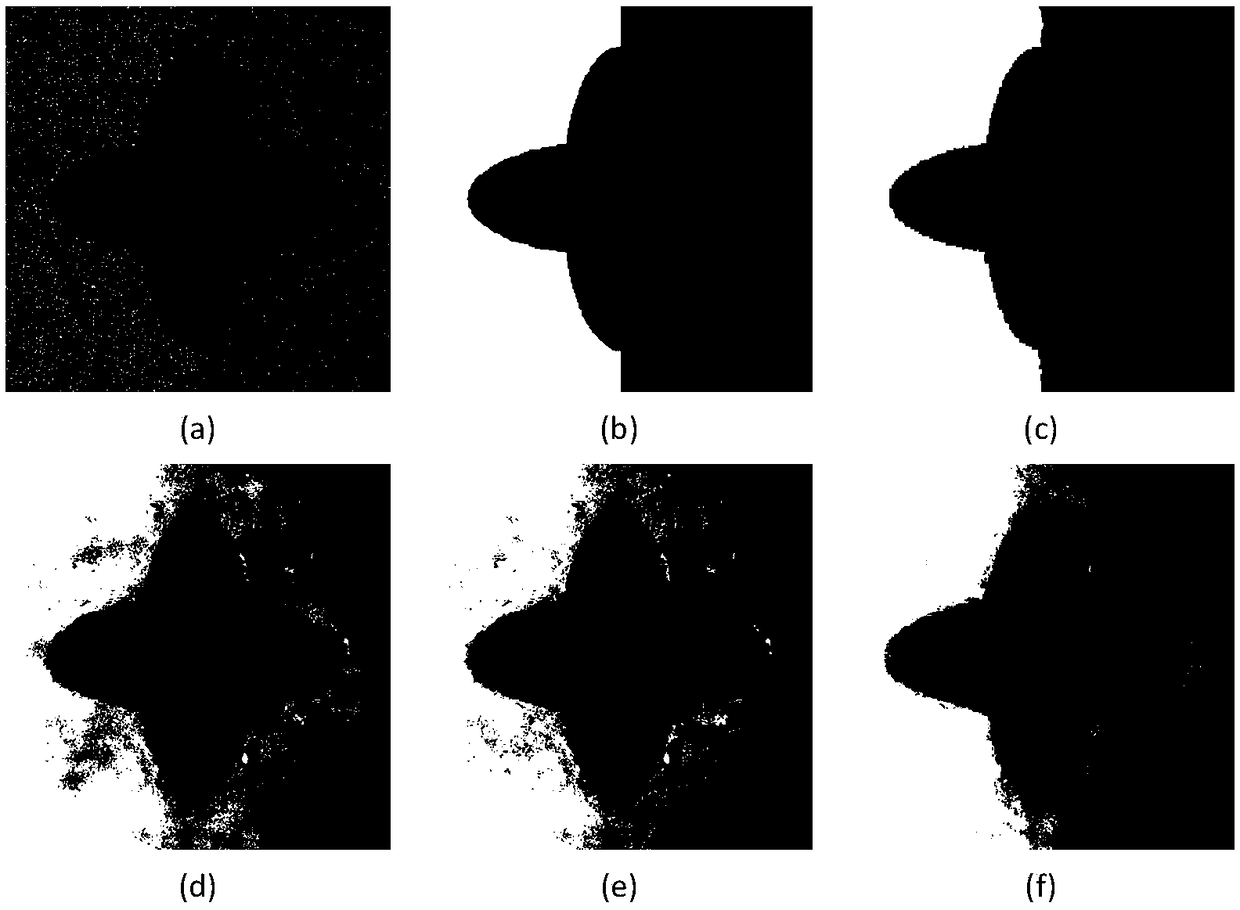
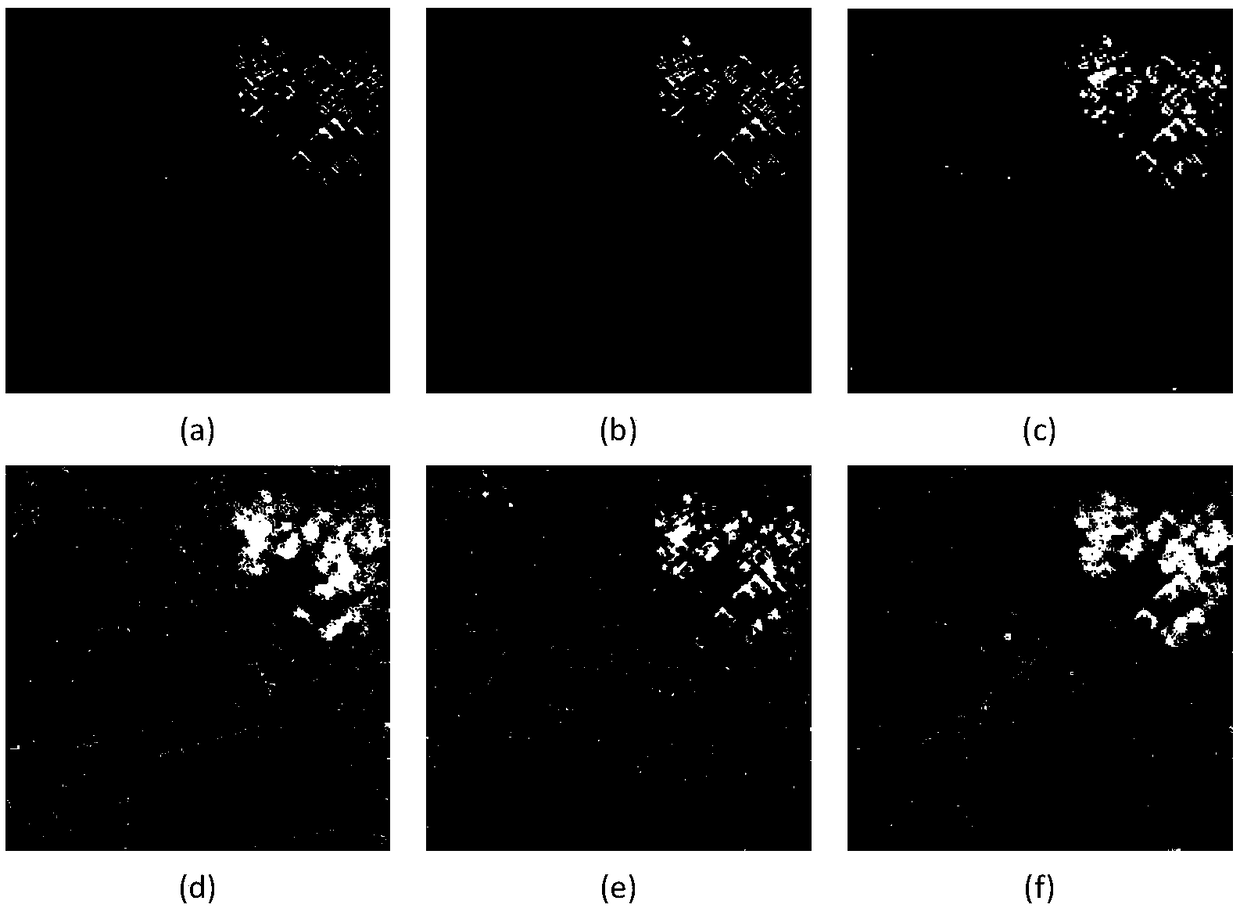
ActiveCN109344880AImprove classification accuracyImprove the problem of many misclassification pointsCharacter and pattern recognitionClassification methodsFeature fusion
A SAR image classification method based on multiple features and composite kernel comprises the following steps: 1, inputting an image; 2, extracting spatial features and structural feature by using gray level co-occurrence matrix and multi-level local pattern histogram; 3, fusing the extracted spatial features and the structural features to form a feature fusion matrix; 4, construct a training sample set and a test sample set; 5, generating the superpixel by using the generalized likelihood ratio and the like; 6. Weighing The traditional feature kernel provided by radial basis function and the context information kernel composed of super pixels into a composite kernel to form a new support vector machine. 7, performing classification; 8. Calculating Classification Precision. By using theinvention for classification, the influence of speckle noise can be effectively reduced, the accurate classification of the SAR image is realized, the classification precision is effectively improved,and the method can be used for target recognition and tracking of the SAR image.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Broadband radar target adaptive fusion detection method based on skew-symmetry structure
ActiveCN108919224AImprove estimation accuracyEasy to detectWave based measurement systemsRadar systemsRadar signal processing
The invention discloses a broadband radar target adaptive fusion detection method based on a skew-symmetry structure, belonging to the field of radar signal processing. Aiming at a broadband radar system for which auxiliary data is missing and a space symmetric linear array or a fixed coherent pulse recurrence interval is used, clutter background statistical characteristics are estimated through clutter covariance matrix skew-symmetry structured information in main data and the auxiliary data, target scattering point energy in all to-be-detected distance units is fused based on a one-step process generalized likelihood ratio detection criterion, the clutter information in the main data and the auxiliary data is used maximally, a broadband target skew-symmetry structured adaptive detector is designed, false alarm probability and detection probability analytical expression of the detector are derived, mathematical tool support is provided for detector threshold value setting and detection performance theoretical analysis, range spread target adaptive detection performance under an environment where the auxiliary data is missing is improved, and the method has a popularization and application value.
Owner:NAVAL AVIATION UNIV
Multichannel radar interference inhibition and then target detection method during coexistence of clutter and interference
ActiveCN109444820AImplement object detectionHas constant false alarm (CFAR) characteristicsWave based measurement systemsSingular value decompositionConstant false alarm rate
The invention discloses a multichannel radar interference inhibition and then target detection method during coexistence of clutter and interference. Interference inhibition, clutter inhibition and CFAR (constant false alarm rate) detection area realized on the basis of the idea of multichannel adaptive detection. The number and direction of interference are obtained by means of reconnaissance pulses in a rest period of a radar, singular value decomposition is carried out on an interference guiding matrix, and an interference inhibition matrix is constructed; the interference inhibition matrixis used to carry out interference inhibition on to-be-detected data and a training sample, the dimension of data is reduced, and requirement for the number of training samples during subsequent adaptive detection is lowered; according to a generalized likelihood ratio criterion, the to-be-detected data and training sample after interference inhibition are combined to detect design of a detector;and a detection threshold is determined according to statistical characteristic of the detector and the false alarm rate set by the system, and compared with a detection statistic quantity of the detector, if the detection statistic quantity is greater than the threshold, it is determined that there is a target, and otherwise, it is determined that there is no target. Thus, interference inhibition, clutter inhibition and CFAR detection can be realized at the same, time, and work is normal when the number of training samples is lower than the number of system channels.
Owner:AIR FORCE EARLY WARNING ACADEMY
A Spectrum Tracking Method for Faint Targets Based on Dynamic Programming
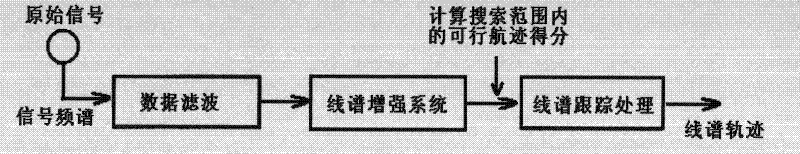
InactiveCN102279399AImprove identification sensitivityEnhanced ability to handle non-Gaussian noiseAcoustic wave reradiationFrequency spectrumInterconnection
The invention relates to a dim target frequency spectrum tracking method based on dynamic programming. In the method, data association and track detection are completed on a dim target submerged in background noise in a frequency spectrum tracking form. The method comprises the following steps of: determining a line spectrum searching range, calculating all feasible track scores in a line spectrum searching region in a line spectrum distribution form, determining a highest score state as an optimal line spectrum track for the termination of the state, and recovering a line spectrum track by forwardly tracking a state value obtained at each processing stage; and finishing data interconnection and track detection in a single optimizing process by using a dynamically-programmed line spectrumtracking method, so that the identification sensitivity of a target frequency spectrum is enhanced and the detection and tracking of a dim signal are further completed. A score function in practical work is in an additive form, and the score value of a state transition path is calculated by accumulating transition scores. During working, a line spectrum score function is combined with a generalized likelihood ratio, so that the nongaussian noise processing capability is enhanced.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Coherent detection method under complex Gaussian model based on inverse gamma texture
ActiveCN105093196AEasy to detectWave based measurement systemsLikelihood-ratio testDetection threshold
The invention belongs to the radar target detection technology field and discloses a coherent detection method under a complex Gaussian model based on an inverse gamma texture. By using the method, adaptive detection of a target under an uniform sea clutter background can be realized and detection performance is increased. The method comprises the following steps that a radar emits a pulse signal through a radar transmitter and receives an echo signal through a radar receiver; according to echo data, an observation vector of a detection unit and an observation vector of a reference unit are constructed; according to the observation vector of the detection unit and the observation vector of the reference unit in the echo data, a generalized likelihood ratio detector is constructed; a parameter in the generalized likelihood ratio detector is estimated so as to obtain an optimal coherent detector; according to a preset false alarm probability, a detection threshold is calculated; according to the detection threshold, the optimal coherent detector is used to detect a target.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
System and method for communicating data symbols via wireless doubly-selective channels
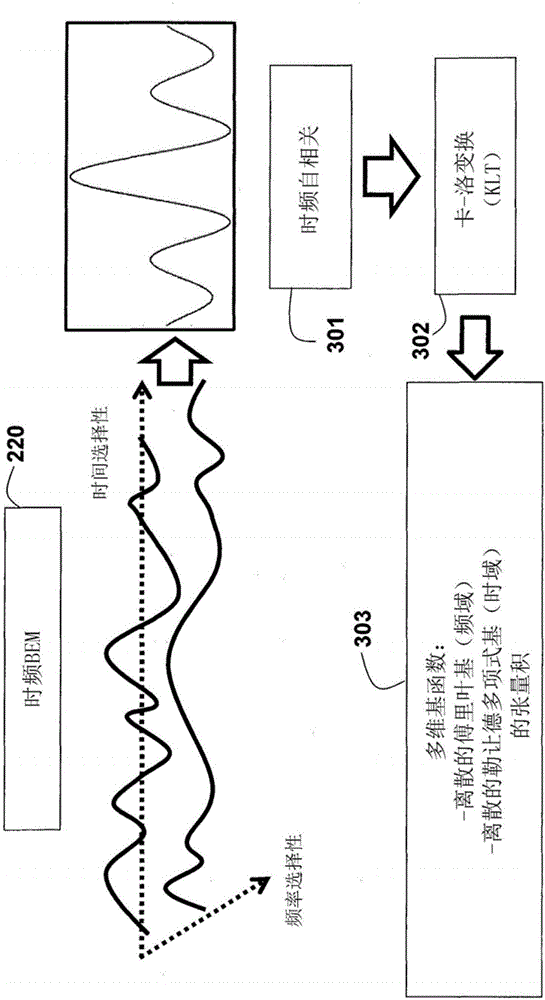
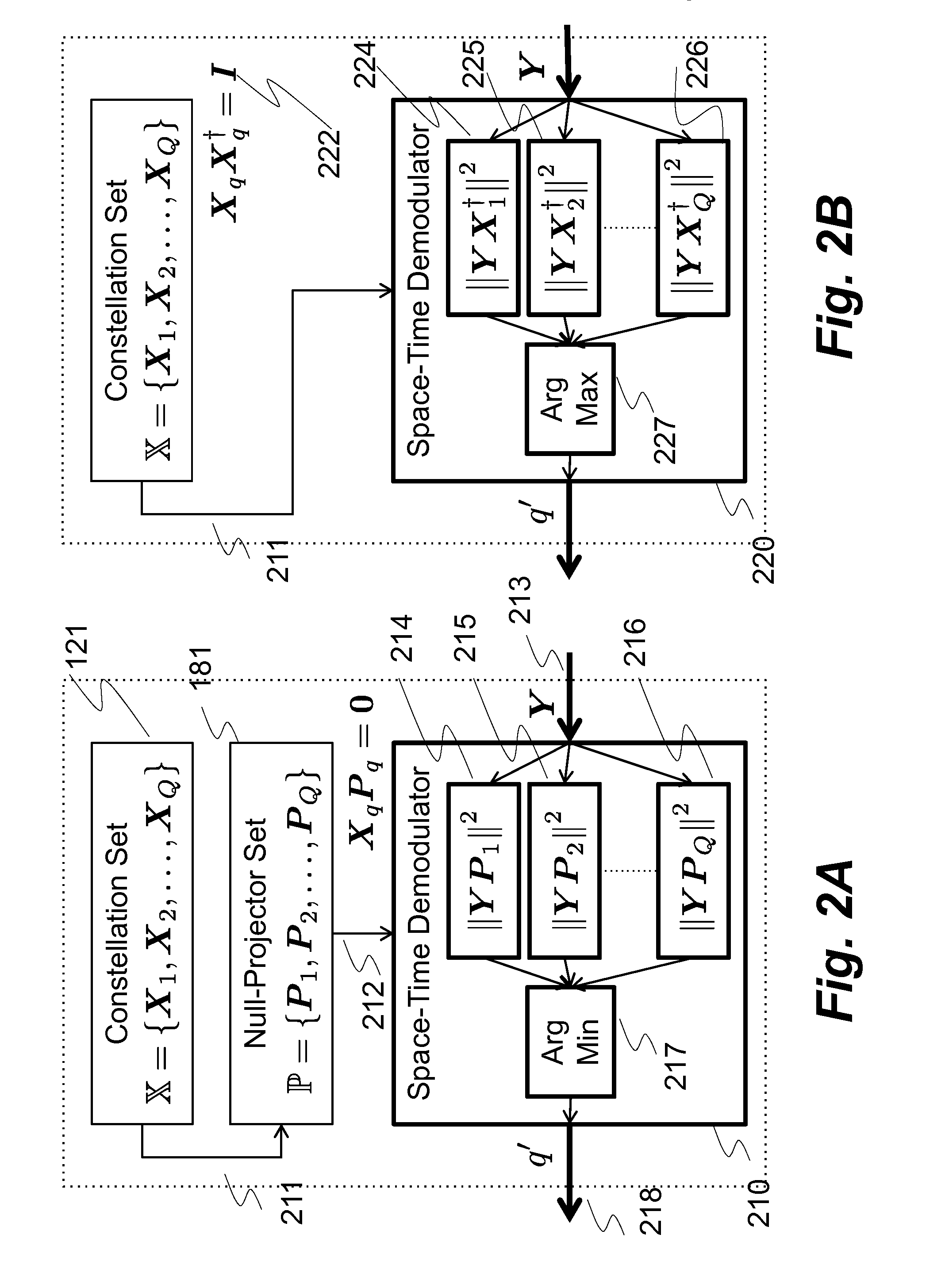
ActiveUS9264118B1Large toleranceSpatial transmit diversityCharacter and pattern recognitionTime domainMethod selection
A method for decoding data symbols modulated with a corresponding codeword from a constellation set of codewords expands the constellation set of codewords with a set of basis functions to produce a basis-expanded constellation set and projects projecting a received modulated data symbol onto orthogonal complements of the basis expanded constellation set to obtain a set of distance metric of a generalized likelihood ratio test (GLRT) for each codeword of the constellation set. The set of basis functions includes a Fourier exponential basis function in a frequency domain, a Legendre polynomial basis function in a time domain, and a Fourier-Legendre product basis function in the frequency domain. The method selects a codeword corresponding to a minimal distance metric or a maximal correlation metric and decodes the data symbol from the received modulated data symbol using the codeword.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
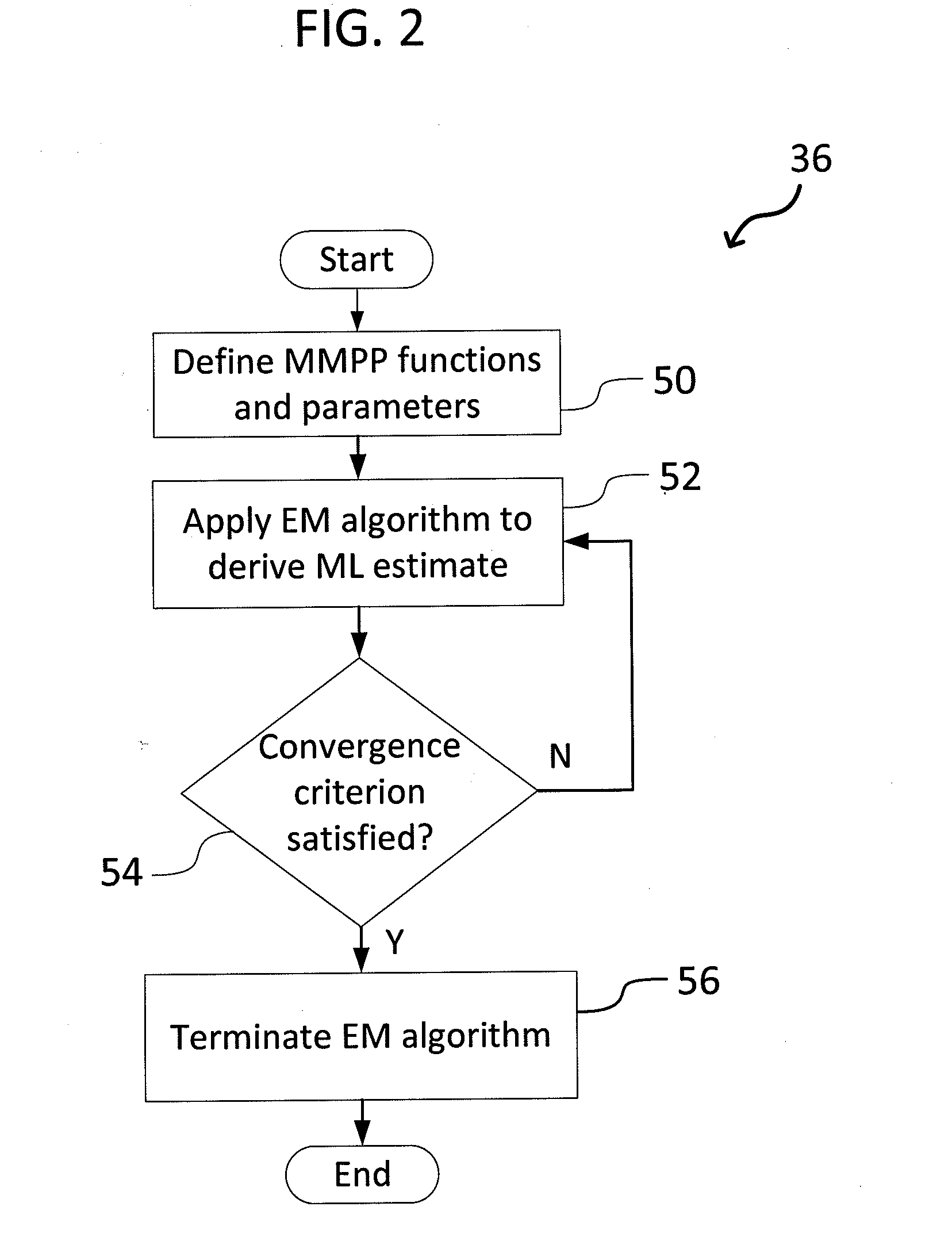
Generalized likelihood ratio test (GLRT) based network intrusion detection system in wavelet domain
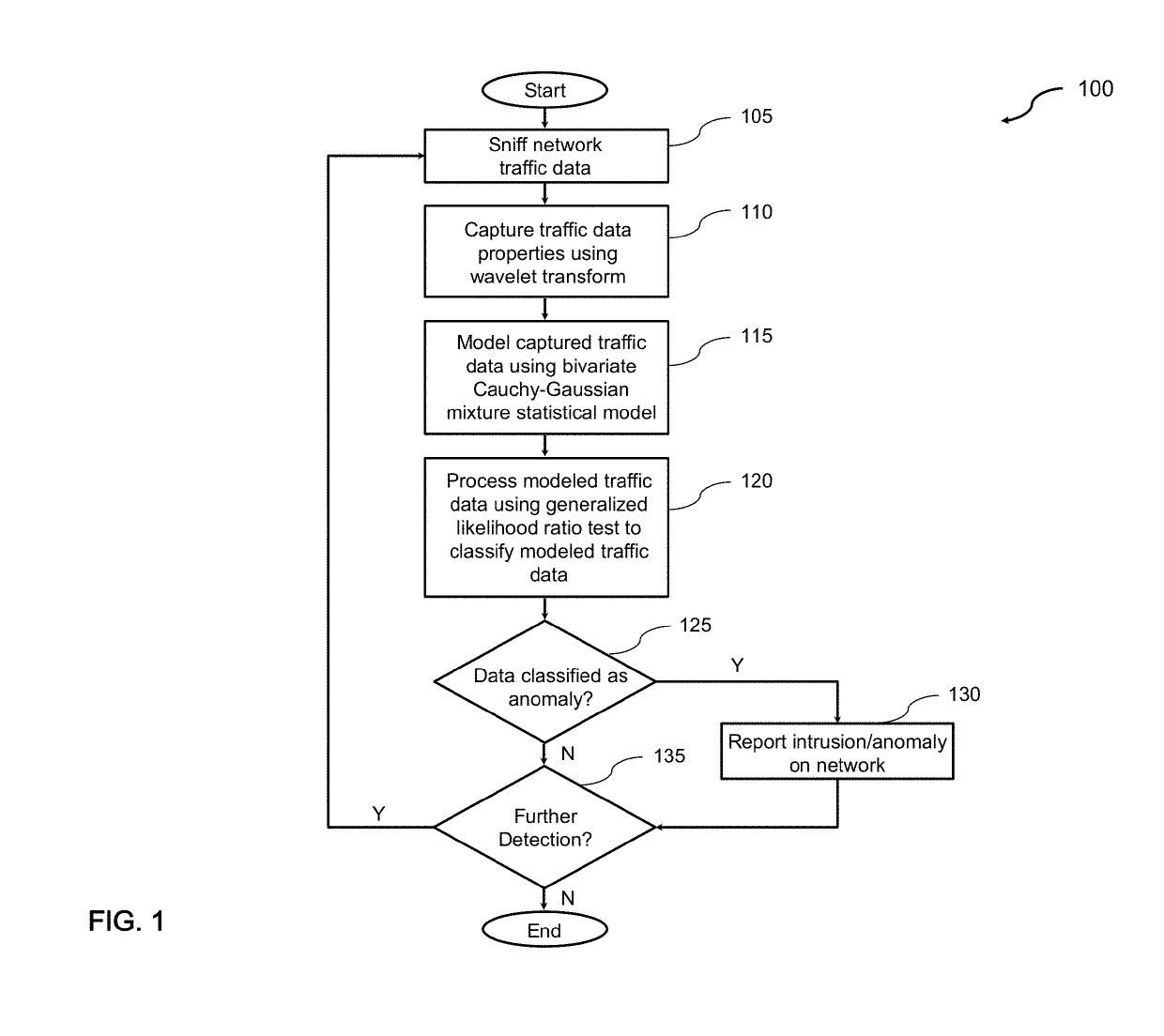
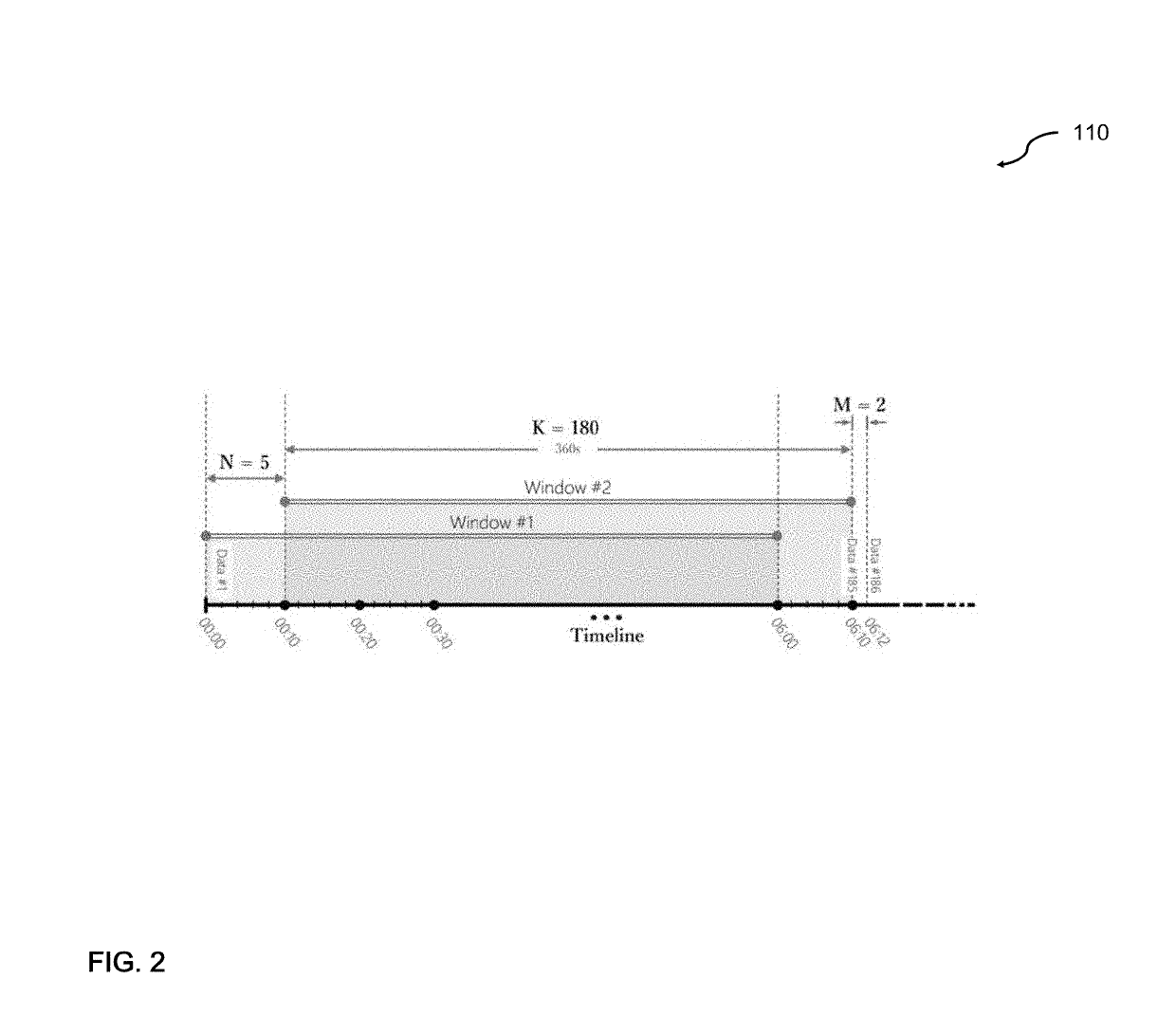
ActiveUS20190158522A1Improve accuracyIncrease analytical tractabilityMathematical modelsComputer security arrangementsFast algorithmLikelihood-ratio test
An improved system and method for detecting network anomalies comprises, in one implementation, a computer device and a network anomaly detector module executed by the computer device arranged to electronically sniff network traffic data in an aggregate level using a windowing approach. The windowing approach is configured to view the network traffic data through a plurality of time windows each of which represents a sequence of a feature including packet per second or flow per second. The network anomaly detector module is configured to execute a wavelet transform for capturing properties of the network traffic data, such as long-range dependence and self-similarity. The wavelet transform is a multiresolution transform, and can be configured to decompose and simplify statistics of the network traffic data into a simplified and fast algorithm. The network anomaly detector module is also configured to execute a bivariate Cauchy-Gaussian mixture (BCGM) statistical model for processing and modeling the network traffic data in the wavelet domain. The BCGM statistical model is an approximation of α-stable model, and offers a closed-form expression for probability density function to increase accuracy and analytical tractability, and to facilitate parameter estimations when compared to the α-stable model. Finally, the network anomaly detector module is further configured to execute a generalized likelihood ratio test for detecting the network anomalies.
Owner:AMIRMAZLAGHANI MARYAM +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com