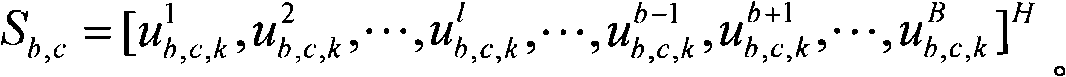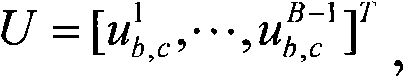Patents
Literature
46 results about "Orthogonal complement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In the mathematical fields of linear algebra and functional analysis, the orthogonal complement of a subspace W of a vector space V equipped with a bilinear form B is the set W⊥ of all vectors in V that are orthogonal to every vector in W. Informally, it is called the perp, short for perpendicular complement. It is a subspace of V.
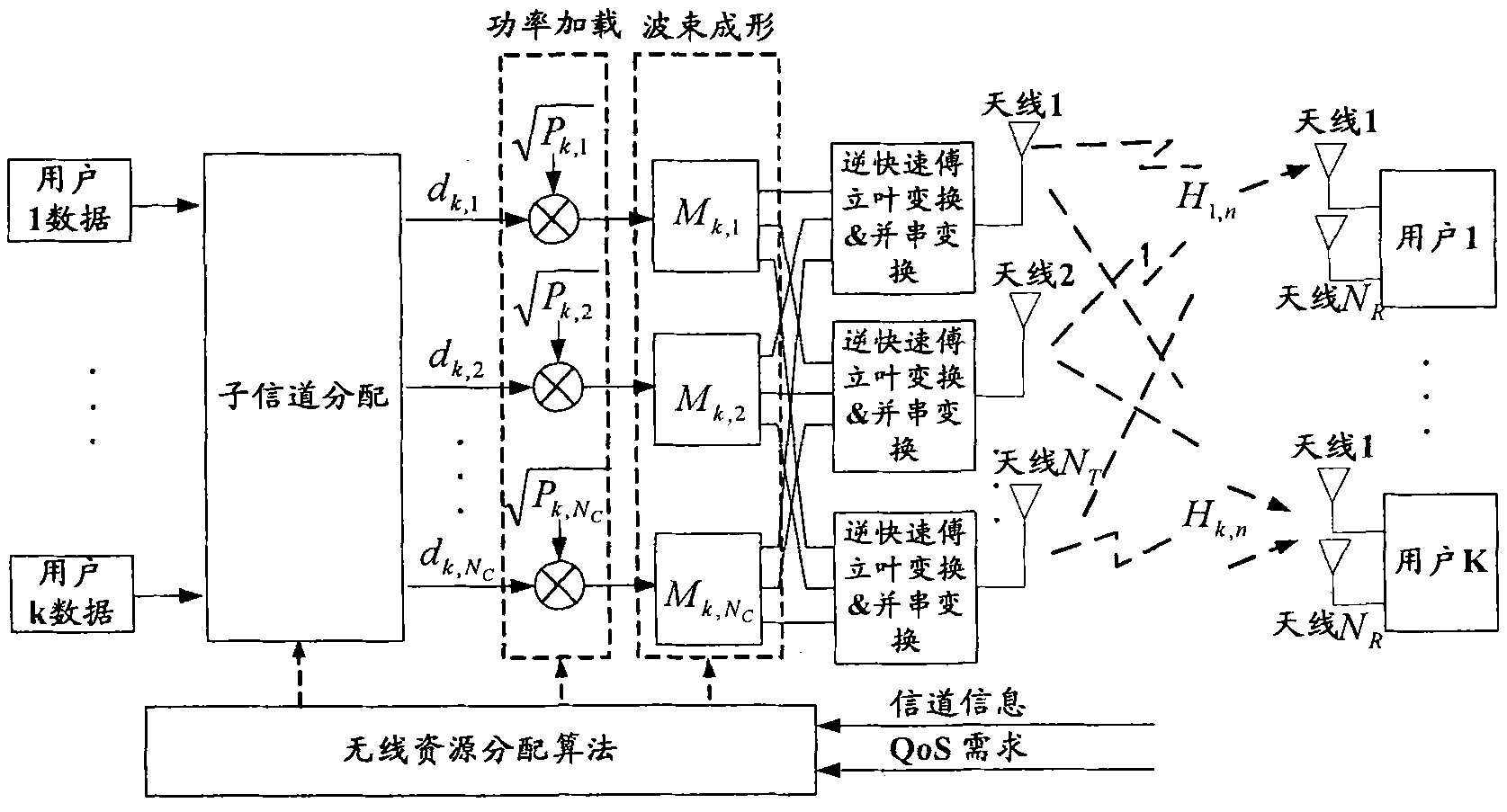
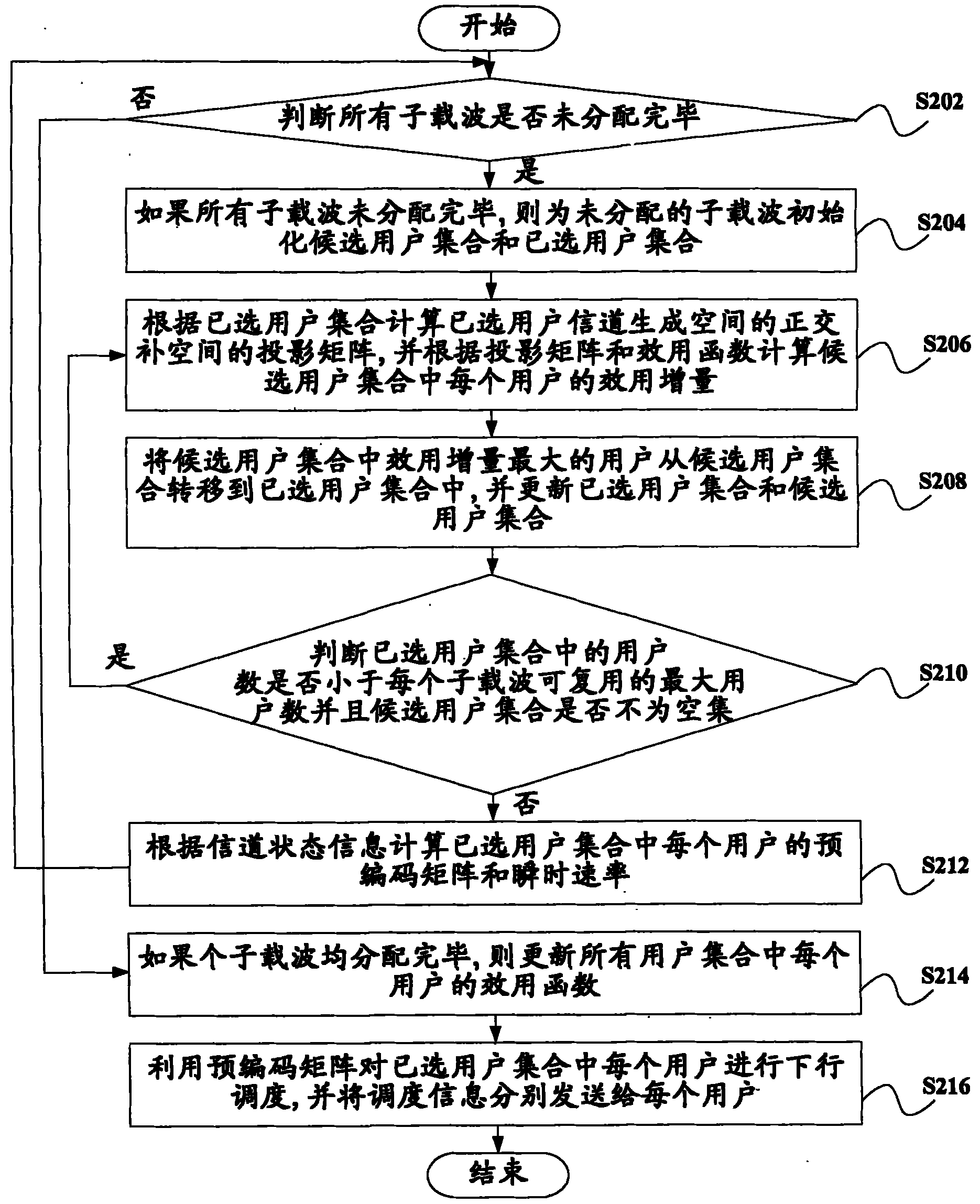
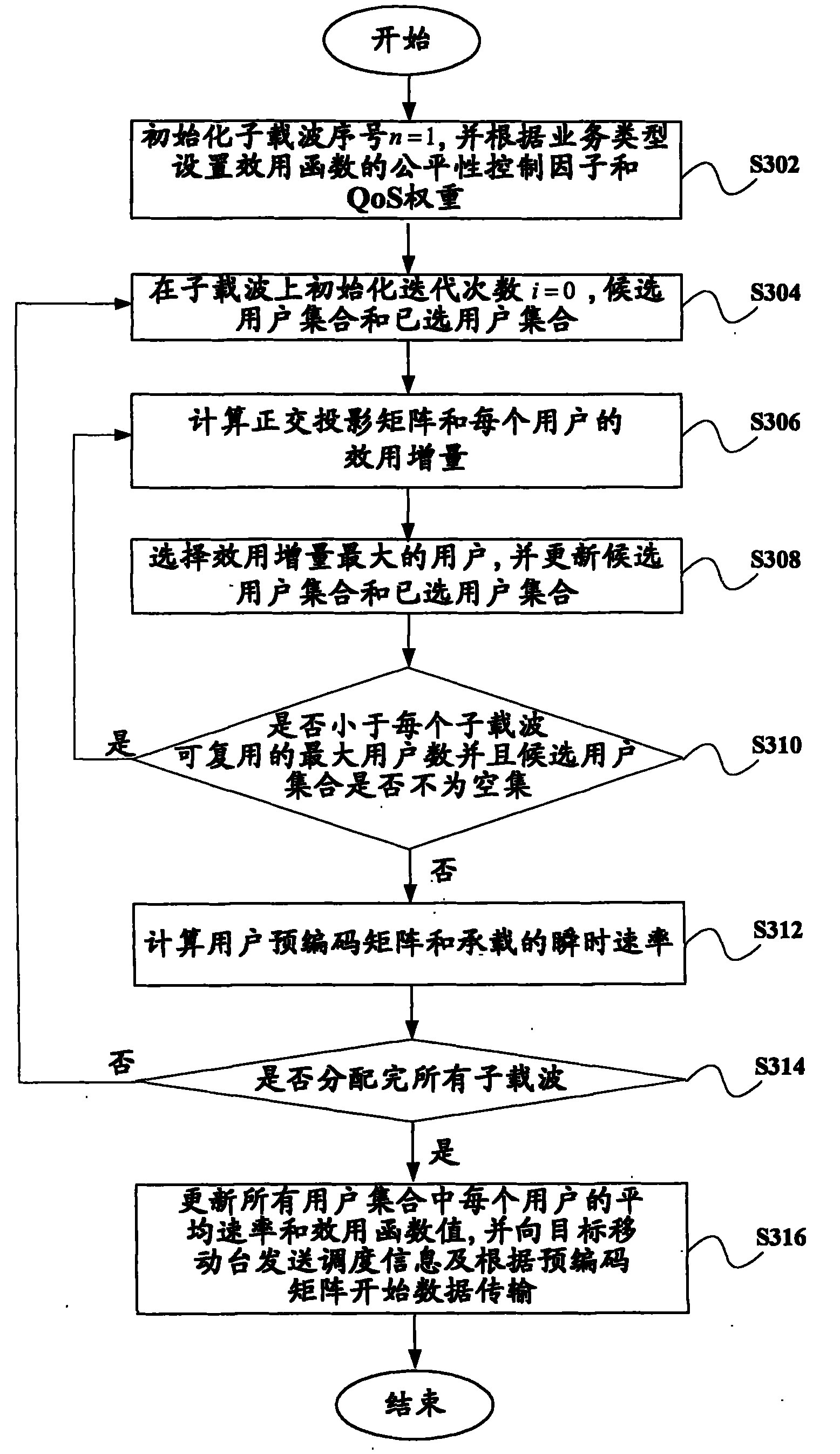
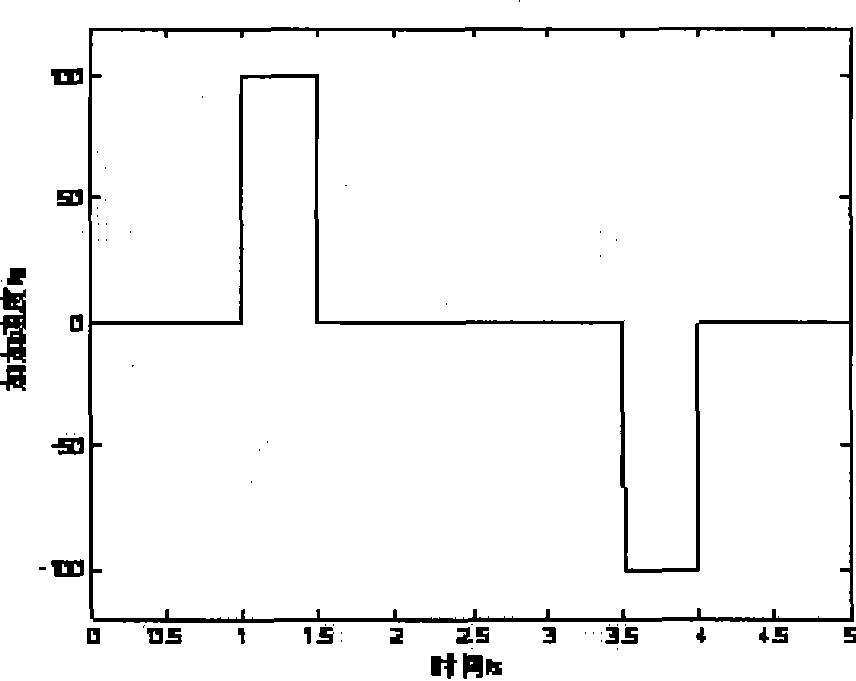
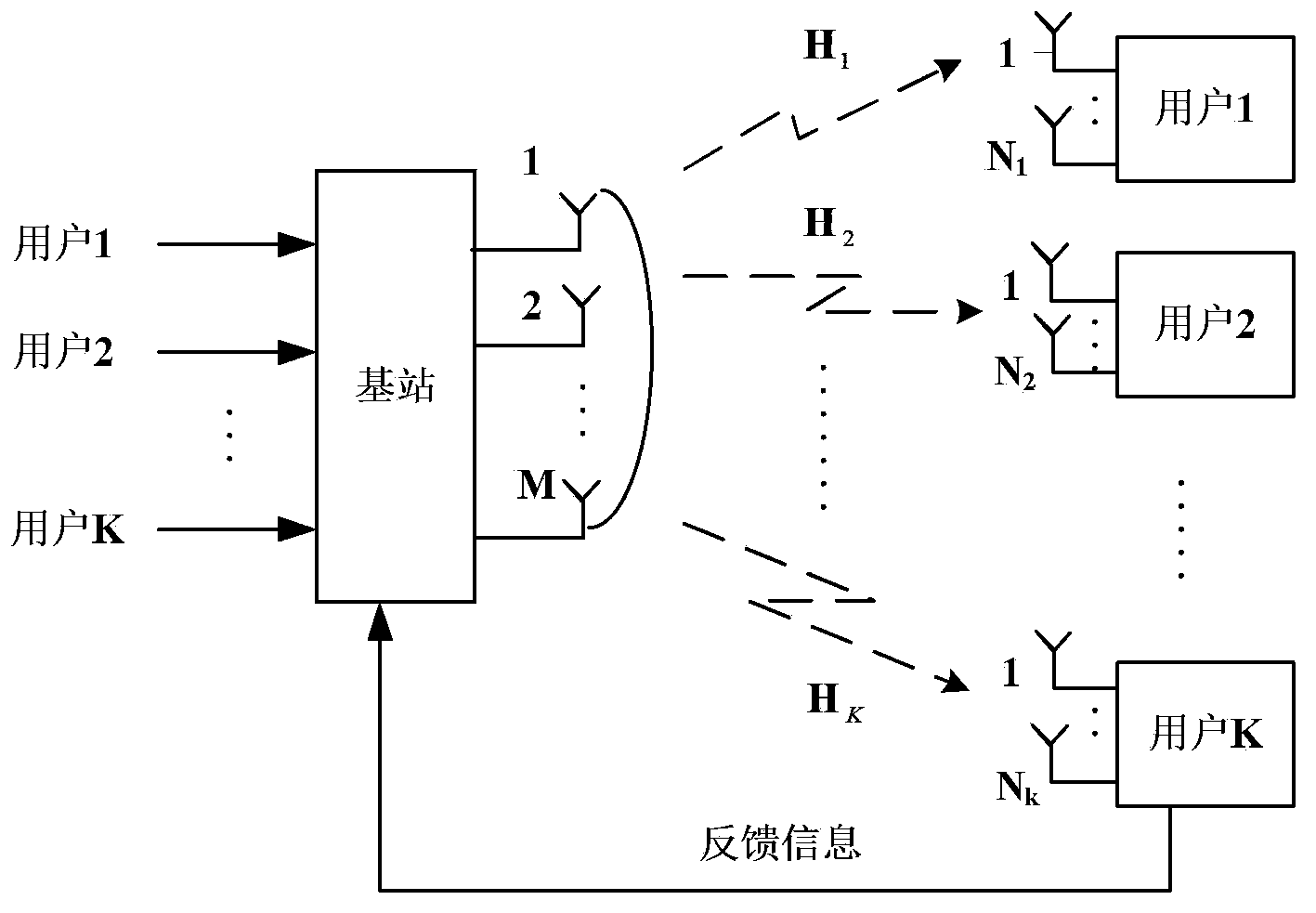
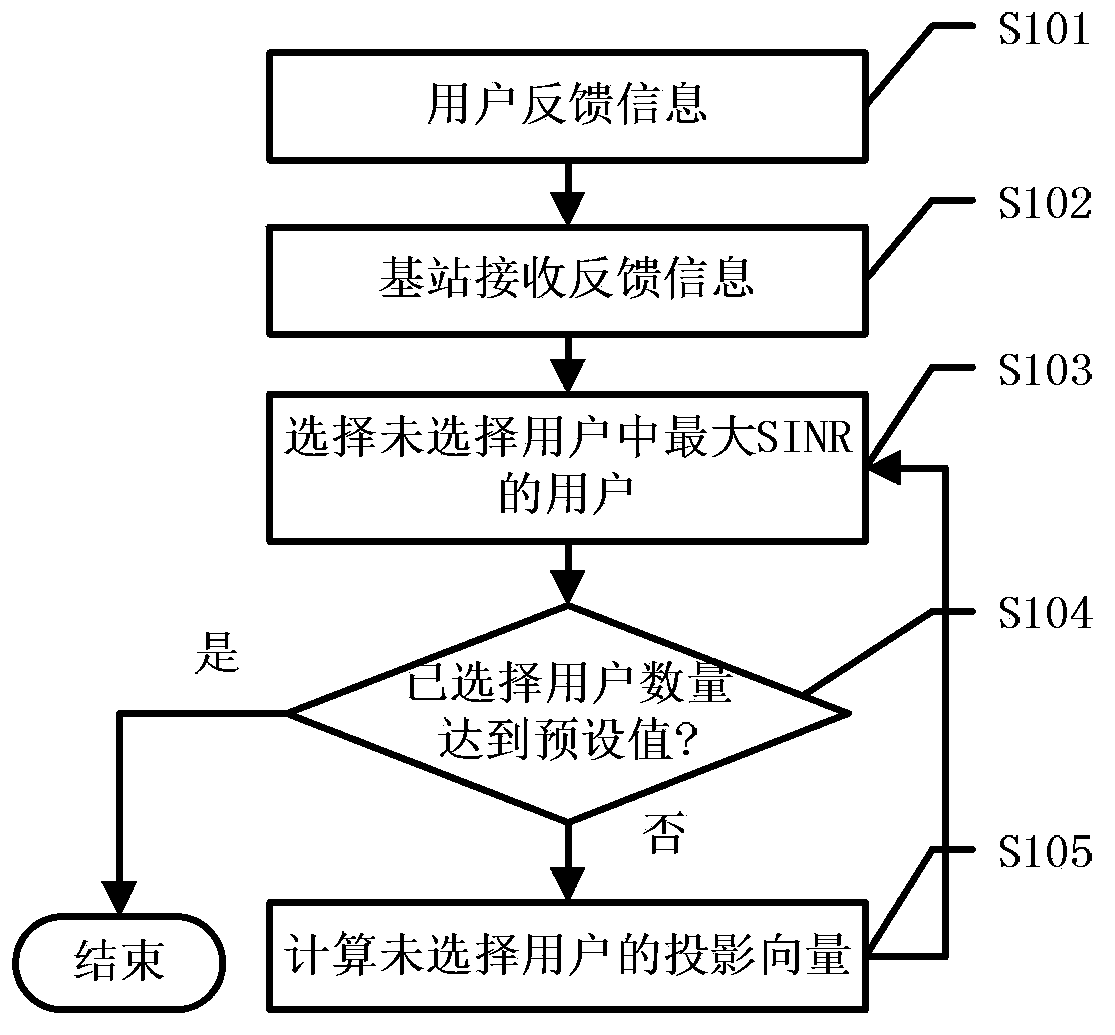
Downlink multiuser scheduling method, device and base station
InactiveCN101841916AMeet QoS requirementsImprove spectrum utilizationMulti-frequency code systemsWireless communicationHat matrixOrthogonal complement
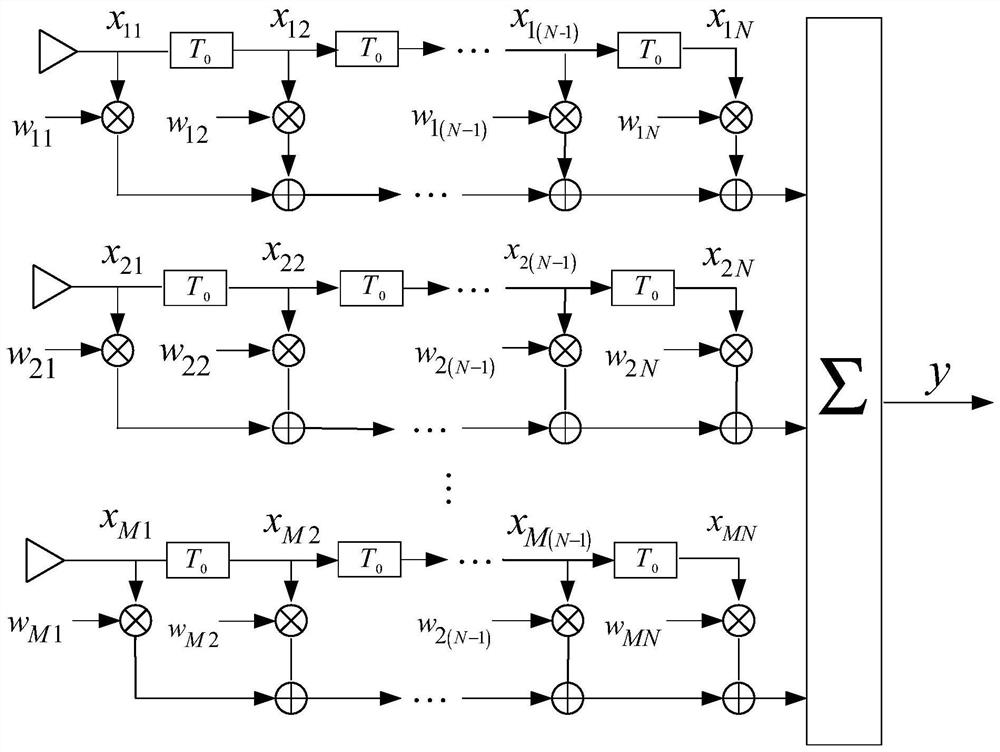
The invention discloses a downlink multiuser scheduling method, a device and a base station. The method comprises the following steps: judging whether NC subcarriers are allocated or not; if not, initializing a candidate user set and the selected user set for the unallocated subcarriers; calculating a projection matrix of an orthogonal complement space of a channel generation space of the selected user and the utility increment of each user in the candidate user set; transferring the user with maximum effective increment to the selected user set; judging whether the user number in the selected user set is less than the maximum number multiplexed by each subcarier or not and the candidate user set is not an empty set or not; if yes, returning to the step of calculating the projection matrix and otherwise calculating a precoding matrix and instantaneous speed of each user in the selected user set; updating a utility function of each user in all user sets K being from 1, 2 to k if the NC subcarriers are allocated; and downlink scheduling each user in the selected user set by using the precoding matrix.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
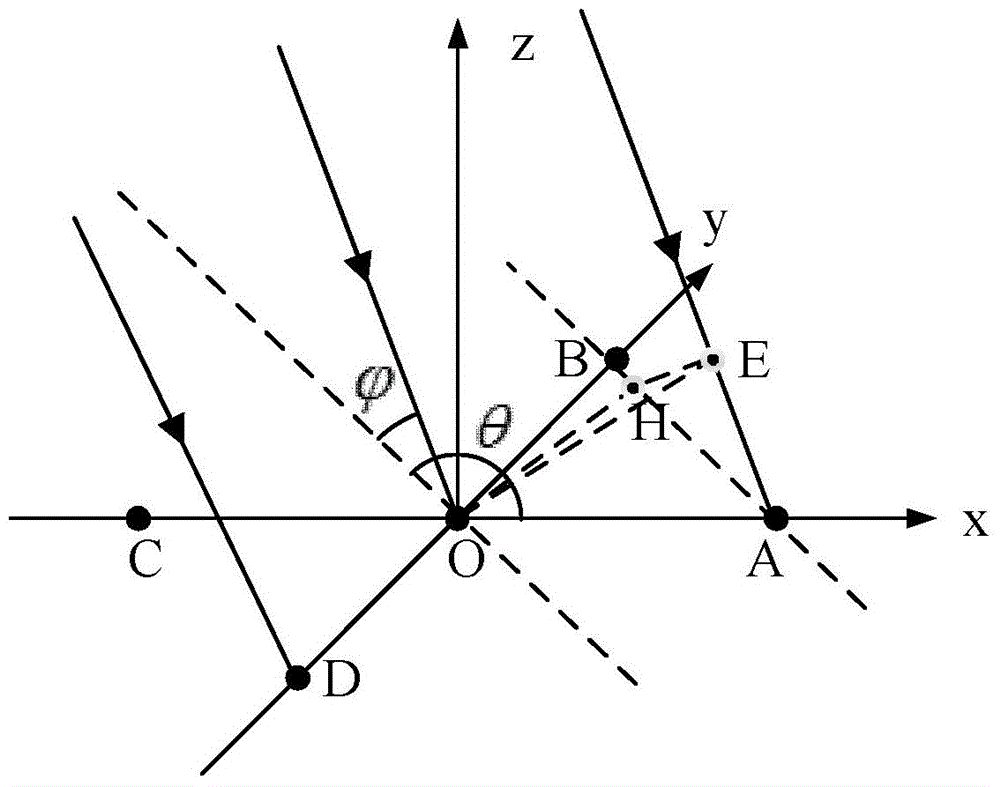
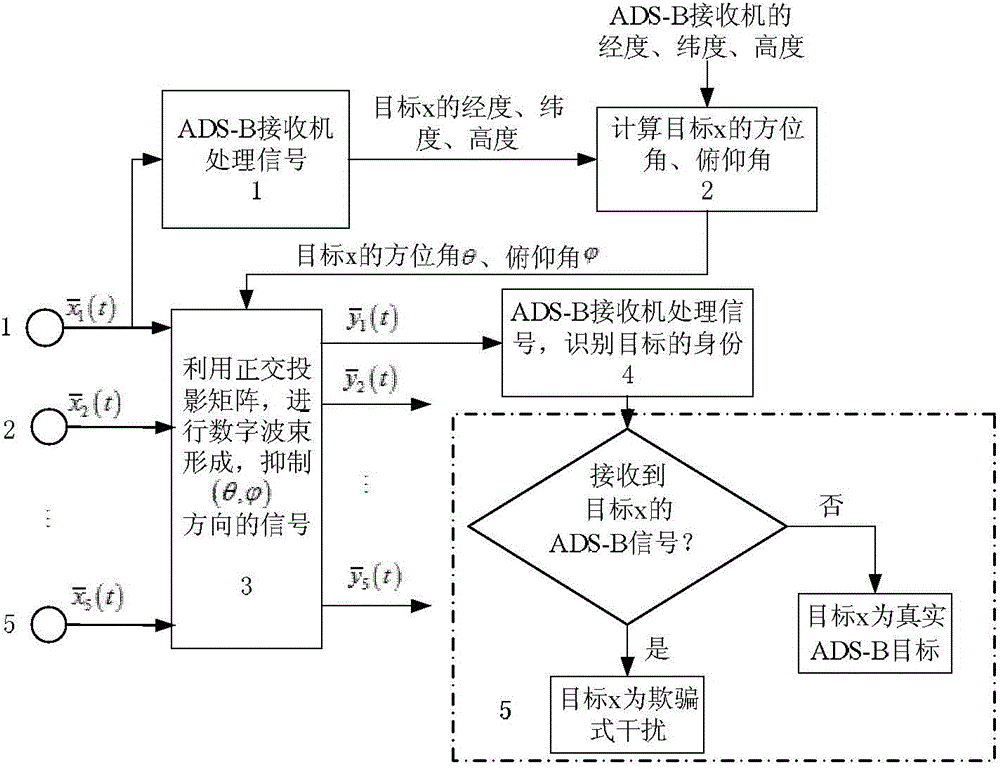
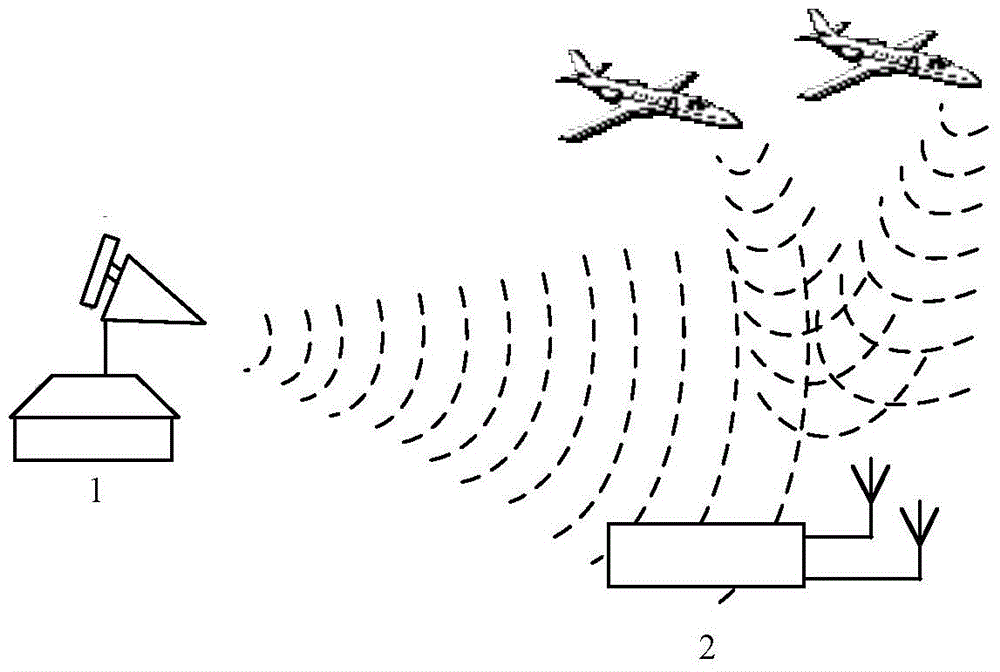
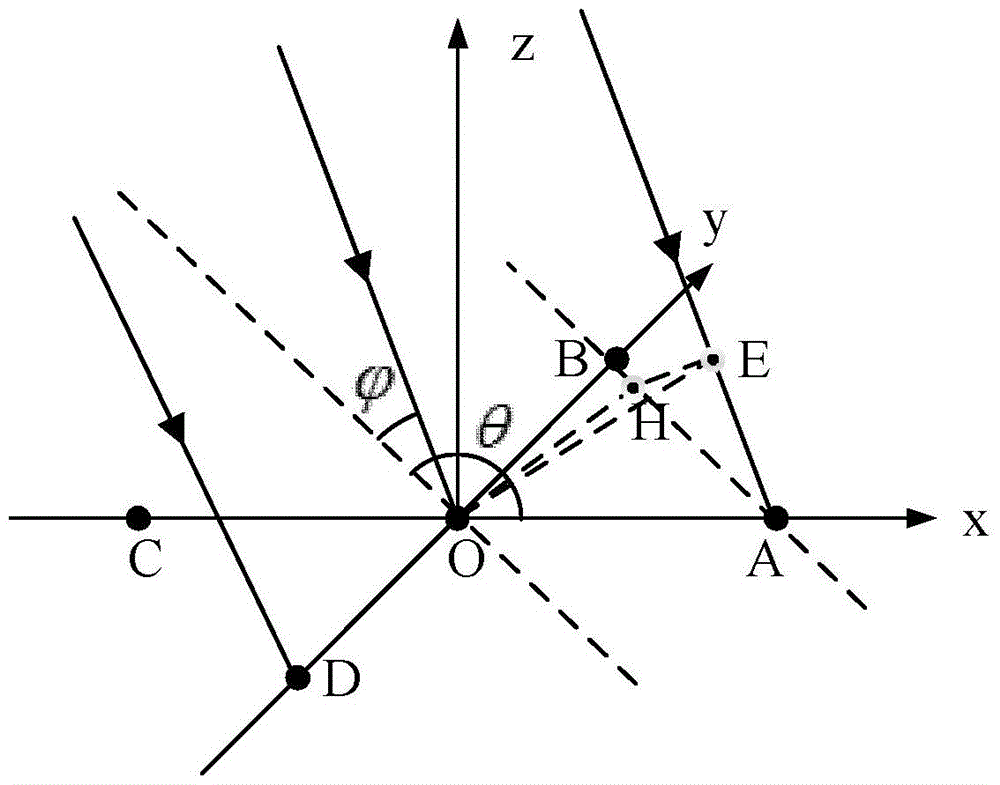
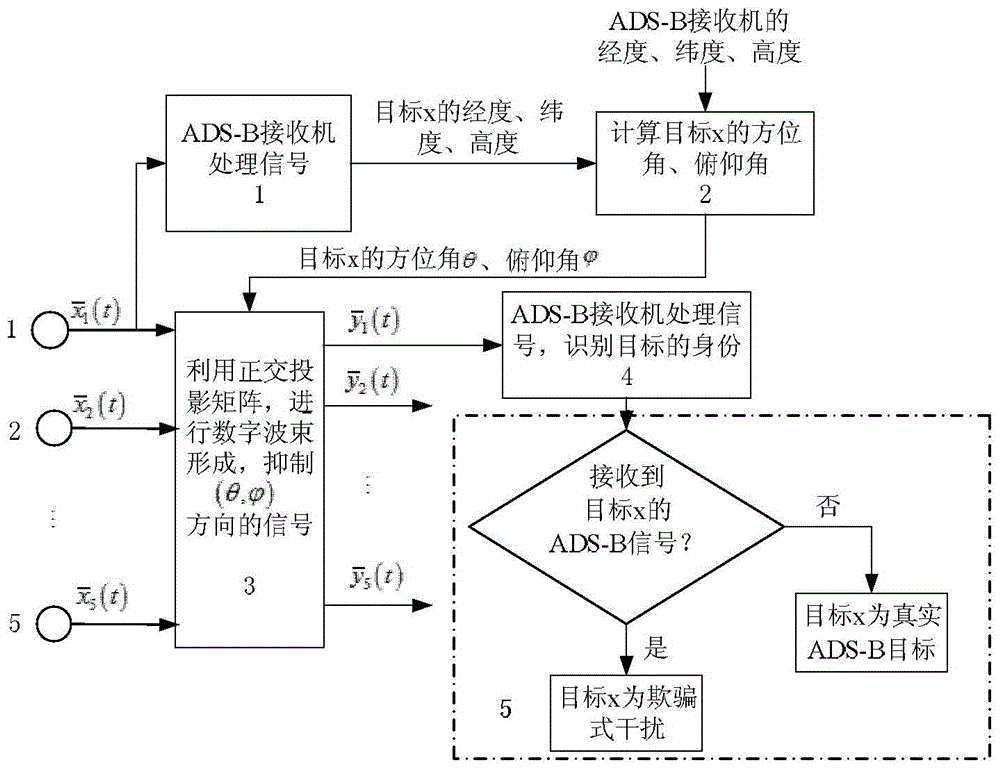
ADS-B deception jamming restraining method based on cross array
InactiveCN104360323AHigh resolutionDeceptive Jamming SuppressionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionOrthogonal complementArray element
The invention discloses an ADS-B deception jamming restraining method based on a cross array. The method includes: using an ADS-B receiving machine to analyze the target identity information and air position information received by a central array element of an antenna array; converting the target position information into the target azimuth angle and pitching angle further by the aid of the position of the receiving machine; projecting the received data to the orthogonal complement space of a target, and restraining the signals, with the coming direction of (theta, phi), in the data received by the antenna array; using the ADS-B receiving machine to process the data after orthogonal projection, and identifying the identify information of the target; judging the actual target and deception jamming according to a deception jamming judging algorithm, and the like. After jamming identification and restraining by the method, the ADS-B receiving machine can obtain real ADS-B signals through demodulation, deception jamming is restrained, and airspace monitoring is achieved.
Owner:CIVIL AVIATION UNIV OF CHINA
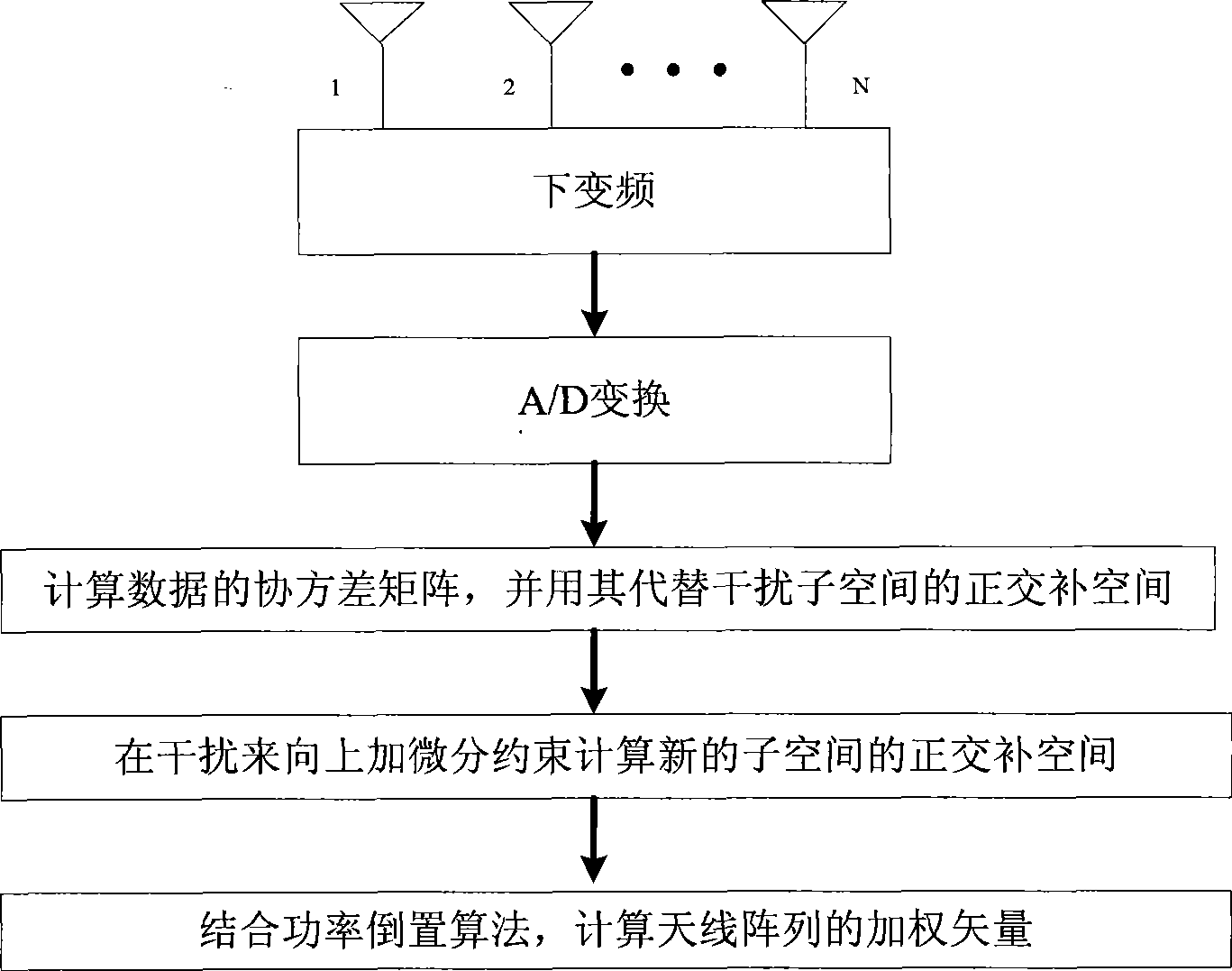
Trough widened interference suppression method of high-dynamic satellite navigation system
InactiveCN101482605AIncreased output signal stemIncreased output signal-to-interference ratioBeacon systems using radio wavesIntermediate frequencyArray element
The invention discloses a high dynamic satellite navigation system interference suppression method widening zero defect, the method comprises: respectively down-frequency conversing N ways of radio frequency signals received by the N (N>2) element aerial array into IF signals; respectively performing the A / D conversion for the IF signals in the N ways obtained by the down-frequency conversion; obtaining the orthogonal complement space of the interference subspace based on the relation between the interference power and the satellite signal and the noise power, by using the N ways IF digital signals obtained in the step 2; calculating the new orthogonal complement space of the subspace relating to the differentiation order, the array element position and the interference subspace based on the differential constraint principle; combining the new orthogonal complement space of the subspace and the power invert algorithm to calculate the weighting vector of the aerial array based on the wave packet zero defect width setting proportionality coefficient to be reached by using the obtained new orthogonal complement space of the subspace in the step4. The invention can enable the output signal inference ratio of the satellite navigation receiver under high dynamic environment to be obviously increased, and can reduce the mis-capturing rate of the satellite signal by the satellite navigation receiver under high dynamic environment.
Owner:CIVIL AVIATION UNIV OF CHINA
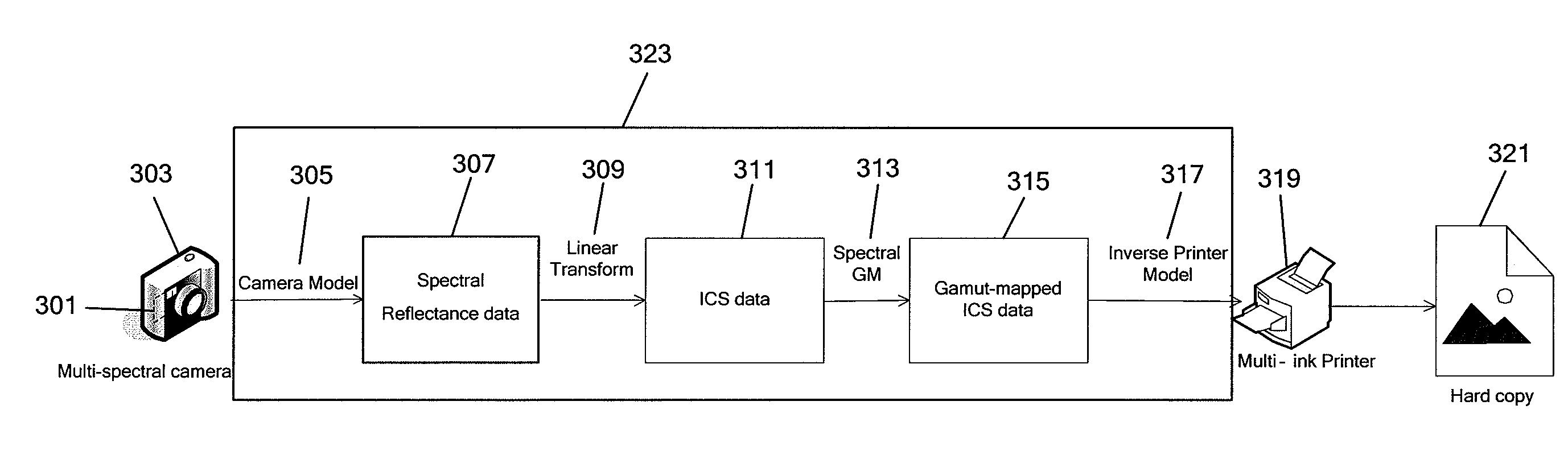
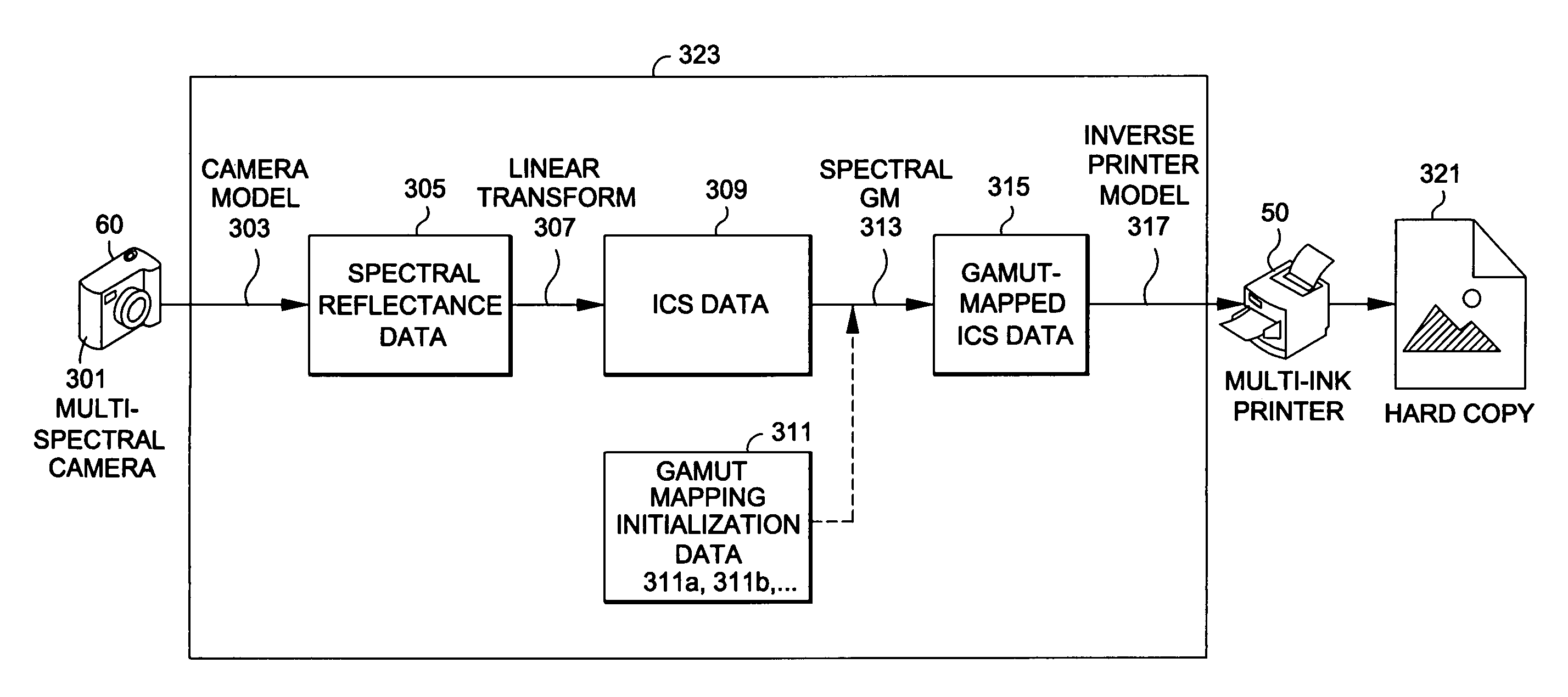
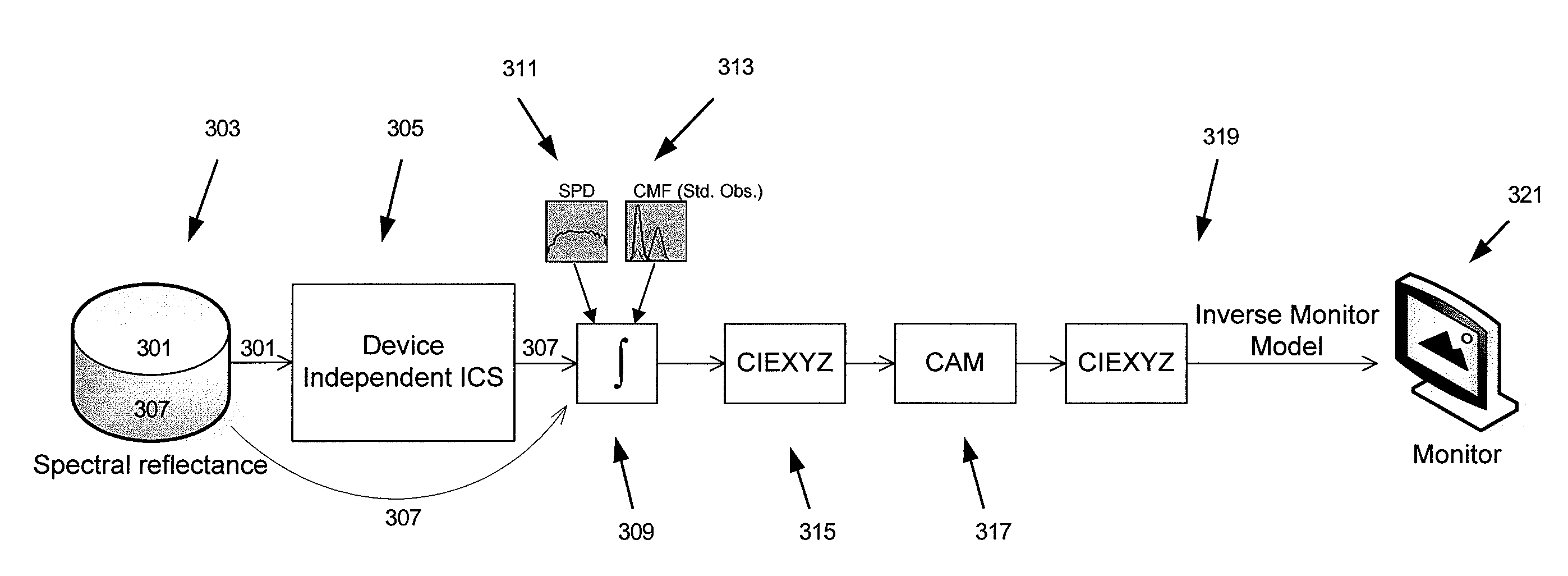
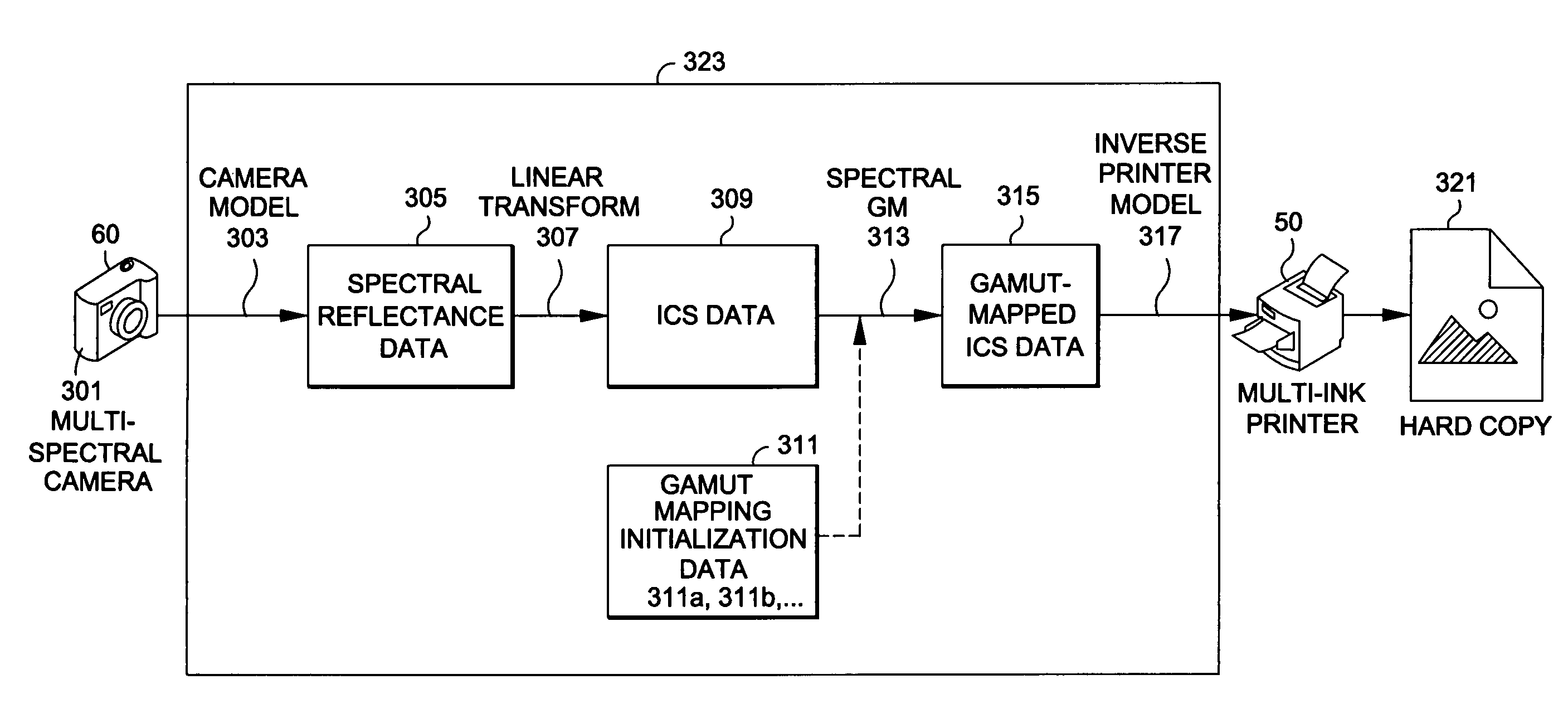
Generating a transformed interim connection space for spectral data
InactiveUS20090141970A1Simpler and efficientPotential benefitCharacter and pattern recognitionPictoral communicationOrthogonal complementLinearity
Generation of a transformed Interim Connection Space for spectral data is provided. A first Interim Connection Space for spectral data in a full spectral space is accessed. A first map, which characterizes a linear transformation from the full spectral space to a first color space, is accessed. A second map, which characterizes a linear transformation from the first Interim Connection Space to the first color space, is determined. The first Interim Connection Space is decomposed into orthogonal subspaces, the orthogonal subspaces including a first subspace that is a null space of the second map and a second subspace that is an orthogonal complement of the null space in the first Interim Connection Space. The transformed Interim Connection Space is generated based on the first subspace and the second subspace.
Owner:CANON KK
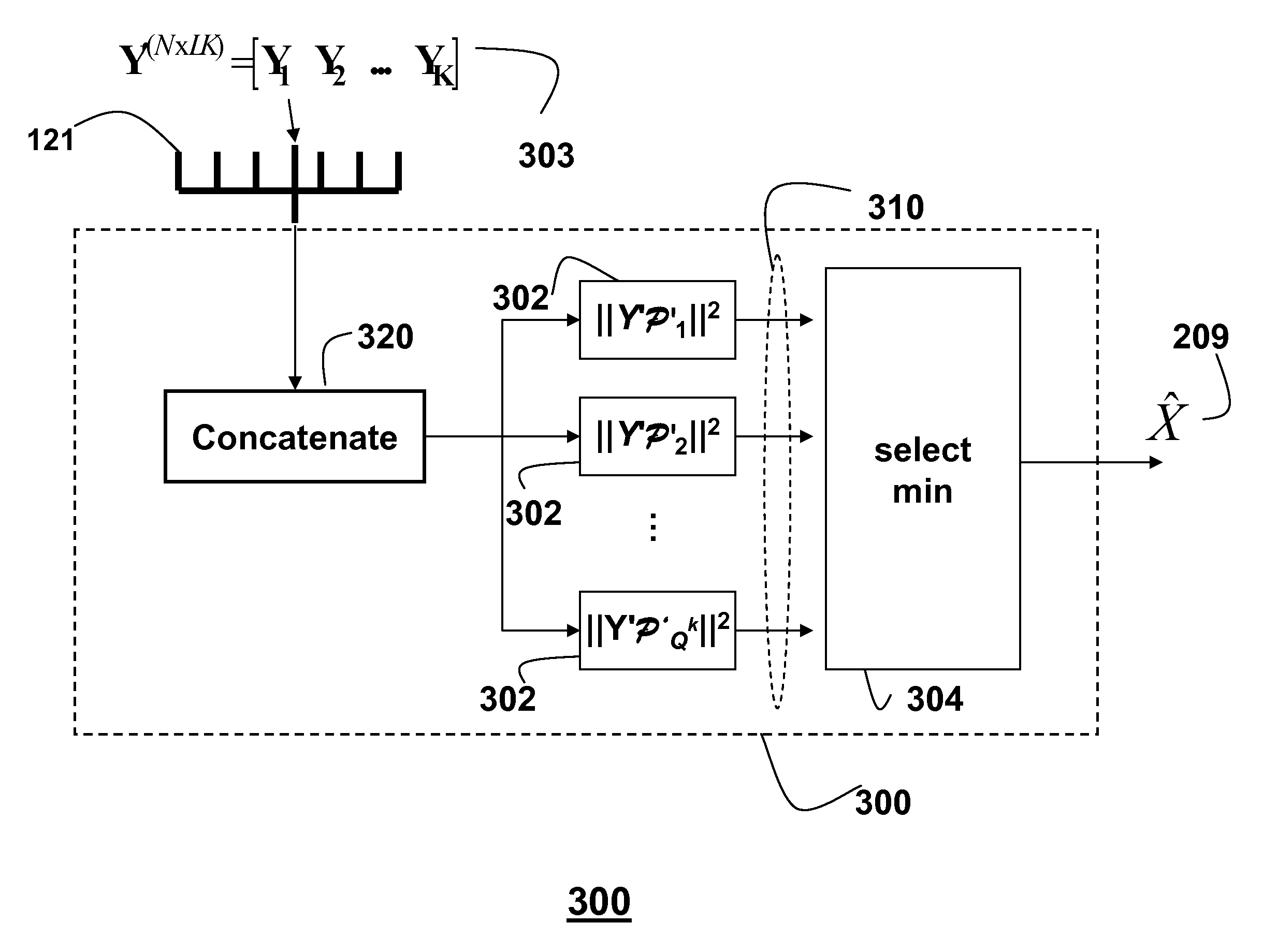
Method for decoding codewords transmitted over non-coherent channels in MIMO-OFDM networks using Grassmann codes and superblocks
ActiveUS8059747B1Easy to useOvercome changePolarisation/directional diversityCode conversionMulti inputMultiplexing
Codewords encoded using non-coherent codes and received at a receiver via non-coherent channels in a multi-input, multiple output (MIMO) network using orthogonal frequency demultiplexing (OFDM) are decode by concatenating multiple adjacent codewords of a received signal into a superblock at the receiver. A projector matrix based on a codebook is predetermining. Each codeword in the superblock is projected onto an orthogonal complement of a correspond transmitted codeword using the projector matrix to obtain a corresponding distance metric of a generalized likelihood ratio test (GLRT) codeword. A minimal distance metric is selected to obtain an estimate of the transmitted codeword corresponding to a transmitted signal.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
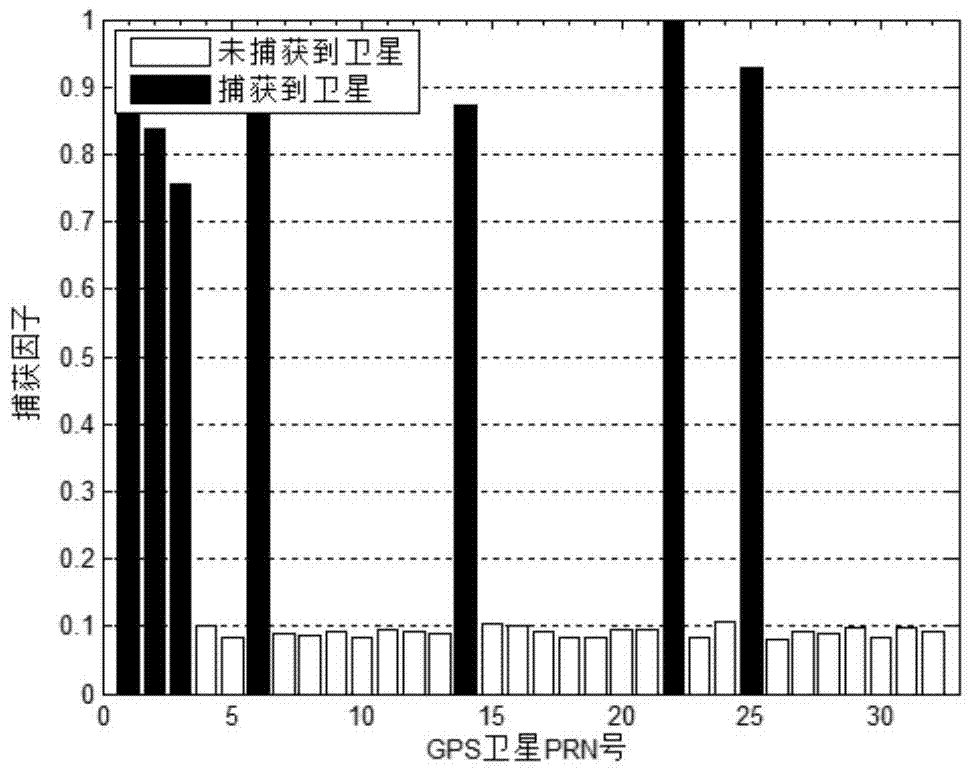
Self-coherent MUSIC algorithm-based global positioning system interference suppressing method
InactiveCN101776763AFulfill positioning requirementsImprove estimation accuracySatellite radio beaconingHat matrixImage resolution
Owner:CIVIL AVIATION UNIV OF CHINA
Multiclass satellite navigation interference suppression method based on solution expanding technology
The invention discloses a multiclass satellite navigation interference suppression method based on solution expanding technology. The method comprises the steps as follows: projecting the signal received by the array antenna to the interference orthogonal complement space for restraining the blanket jamming, calculating the solution expanding weight vector matrix for the projected data, judging whether the matrix is full rank for identifying the deception jamming. If having deception jamming, calculating the solution expanding weight vector dependency, identifying the number of deception interference source, the deception interference source comprises fake satellite signal and true satellite signal. Using the solution expanding weight vector of the deception jamming for forming the rectangular projection matrix of the deception jamming, having the projection restraining deception jamming on signal, using the weight vector of true satellite for forming multi-wave beam and obtaining the signal processing gain. The method can generate high gain multi-wave beam with suppress interference, transmitted deception jamming and generated type deception jamming resisting capability, the multi-wave beam forming capability is not limited by the array element, and there is no need to know the satellite signal and interference information.
Owner:CIVIL AVIATION UNIV OF CHINA
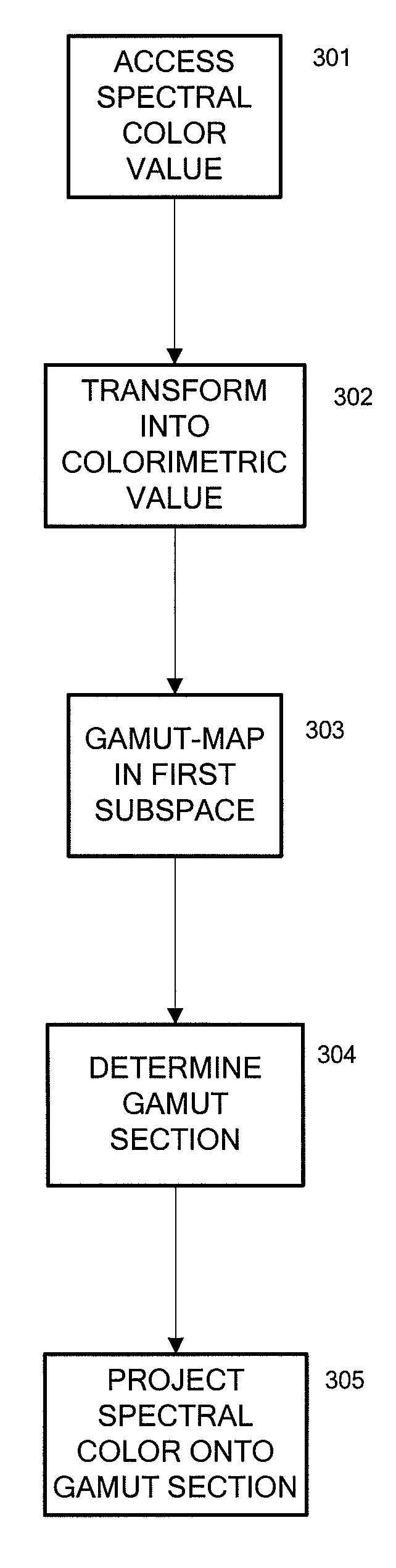
Gamut mapping in spectral space based on an objective function
InactiveUS20090185200A1Digitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsPattern recognitionGamut
Mapping spectral colors in an Interim Connection Space (ICS) of a full spectral space based on an objective function is provided. A spectral color value in the ICS is accessed, and a spectral gamut boundary of the destination gamut is accessed. The spectral color value is mapped into mapped spectral color value based on minimization of an objective function of coordinates of a first subspace of the ICS, by fixing coordinates of a second subspace of the ICS, subject to a constraint that a result is within the spectral gamut boundary. The first subspace is a null space of a transformation from the ICS to a color space, while the second subspace is an orthogonal complement of the first subspace in the ICS. The constraint is determined by a gamut section that is an intersection of the spectral gamut in the ICS and an affine subspace characterized by the fixed coordinates of the second subspace.
Owner:CANON KK
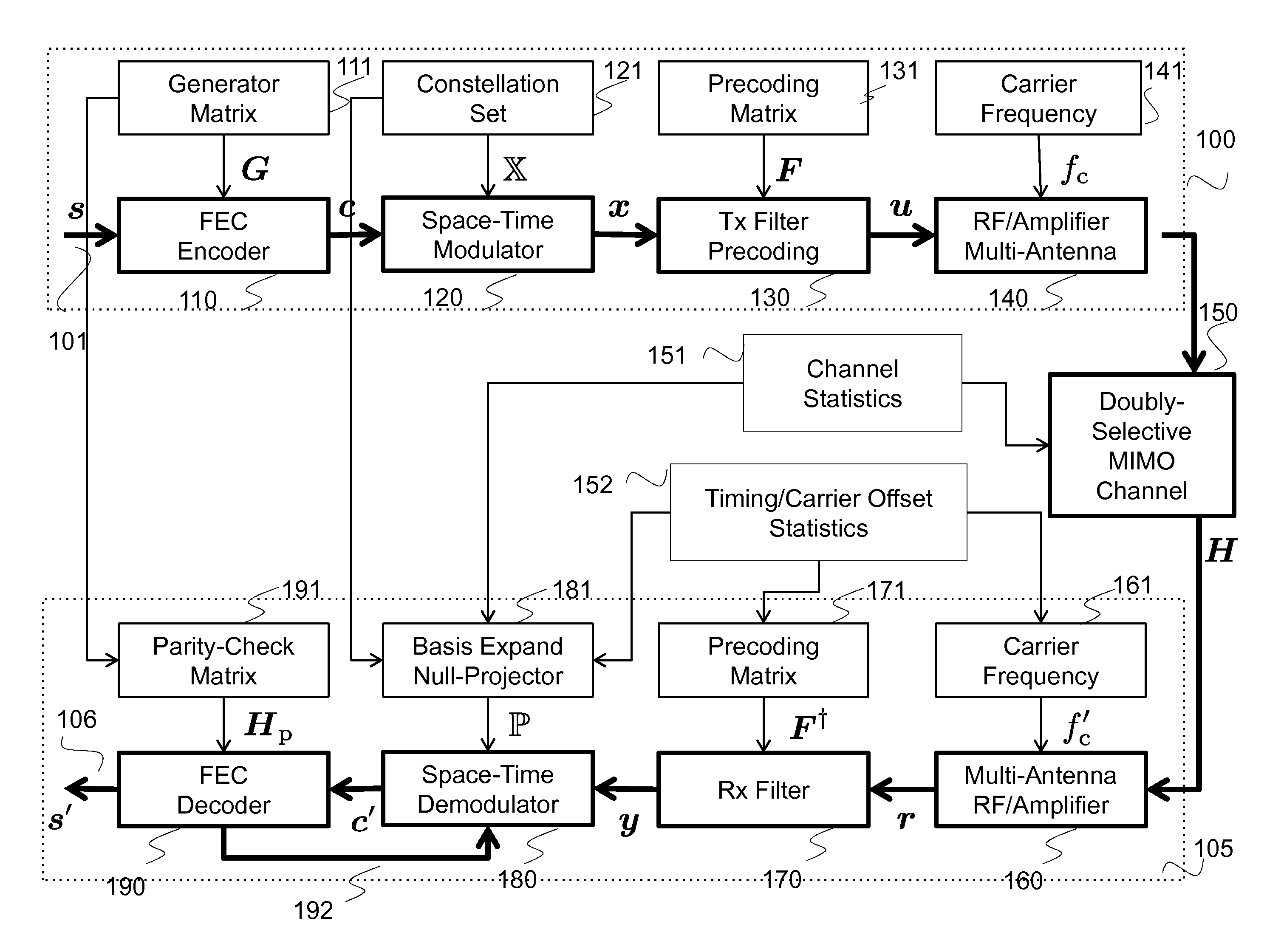
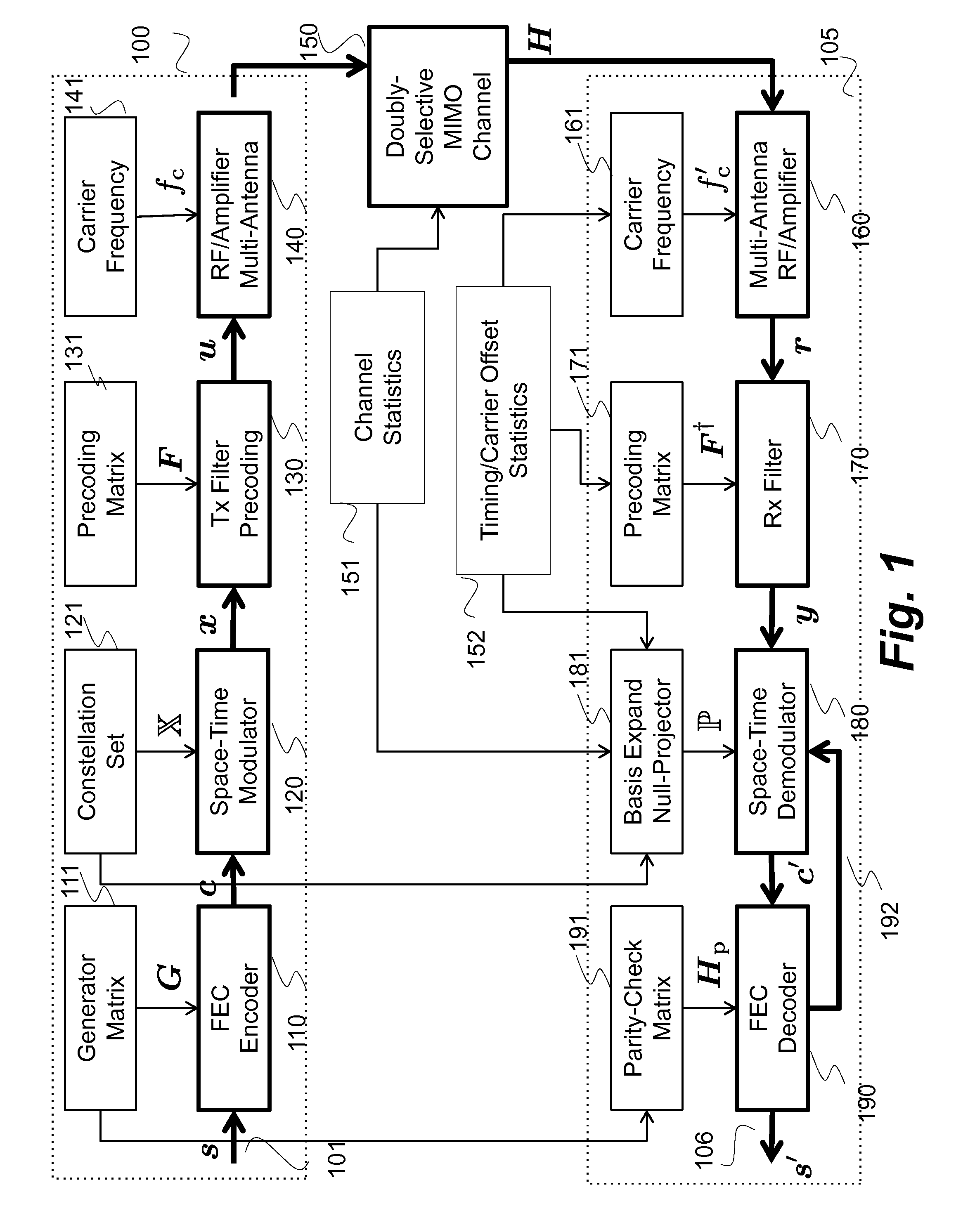
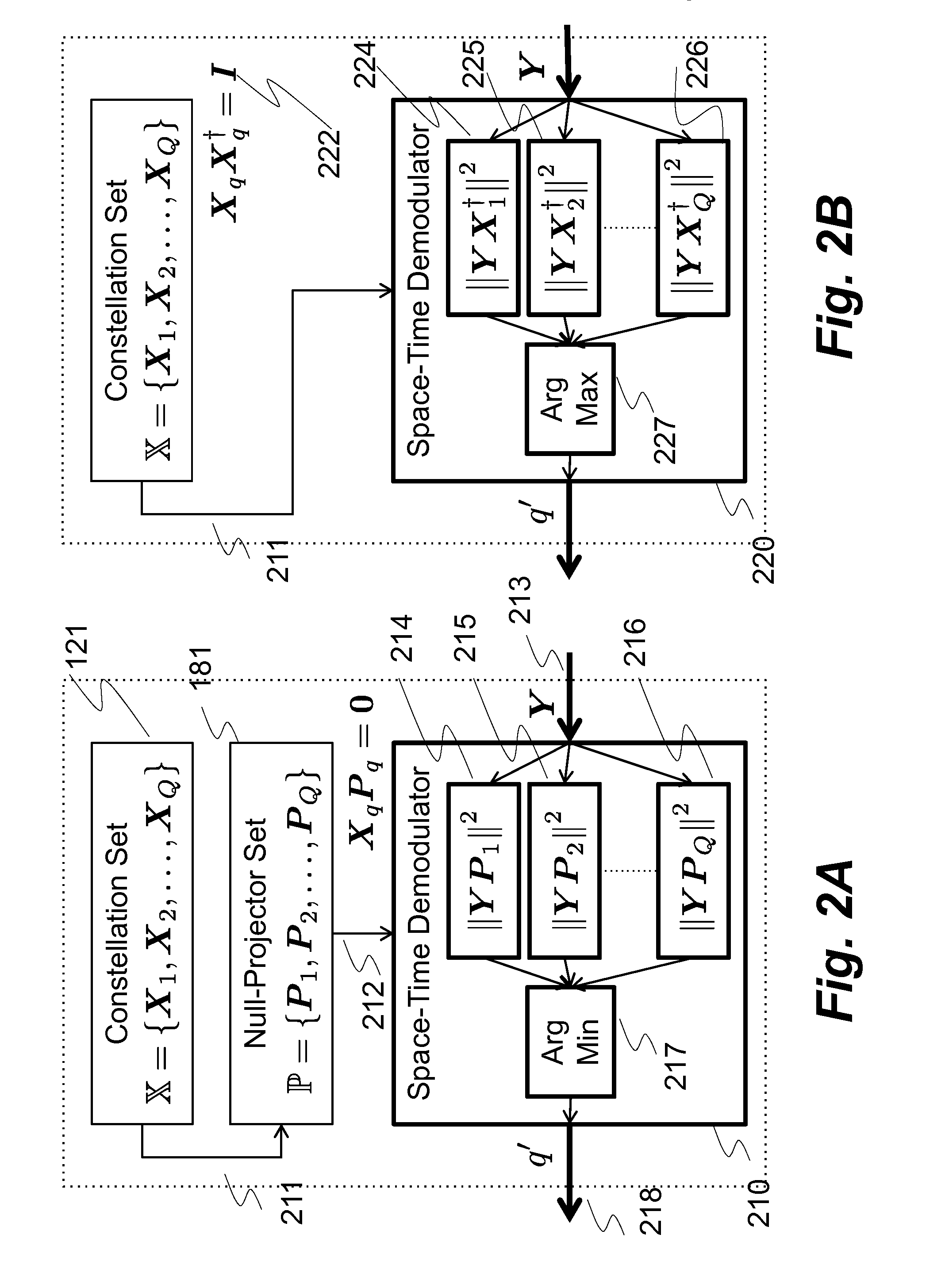
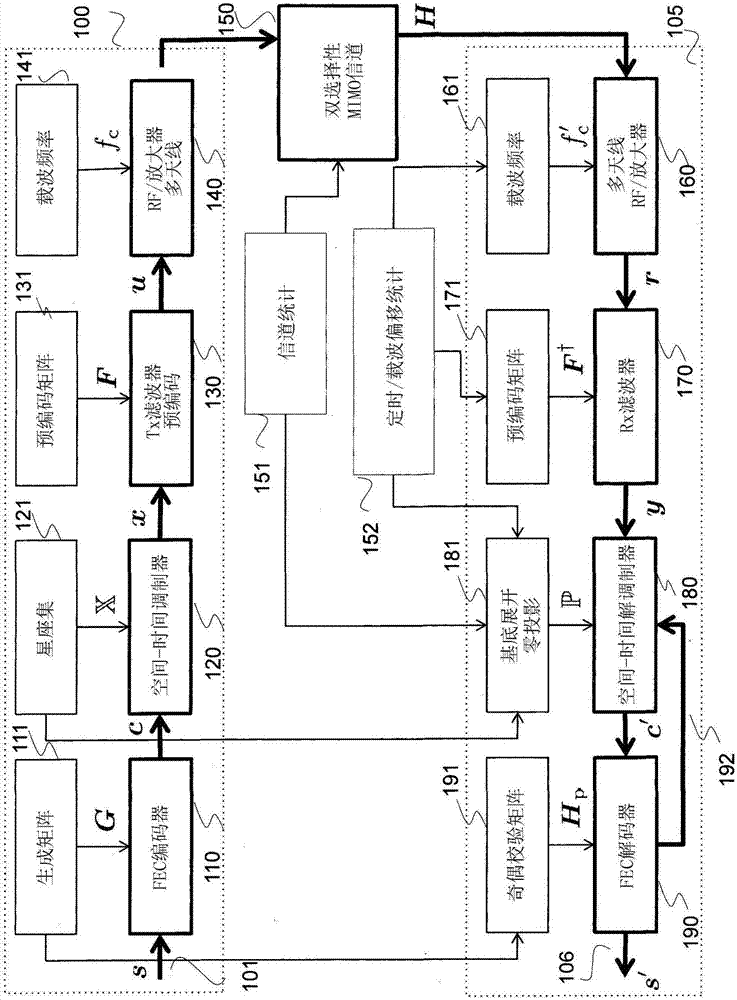
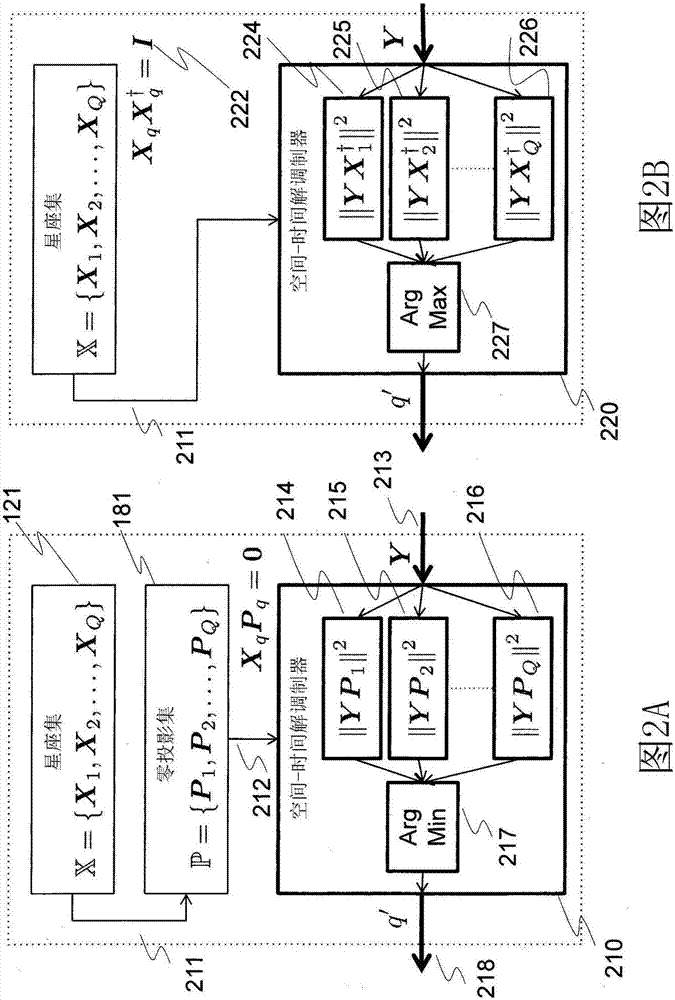
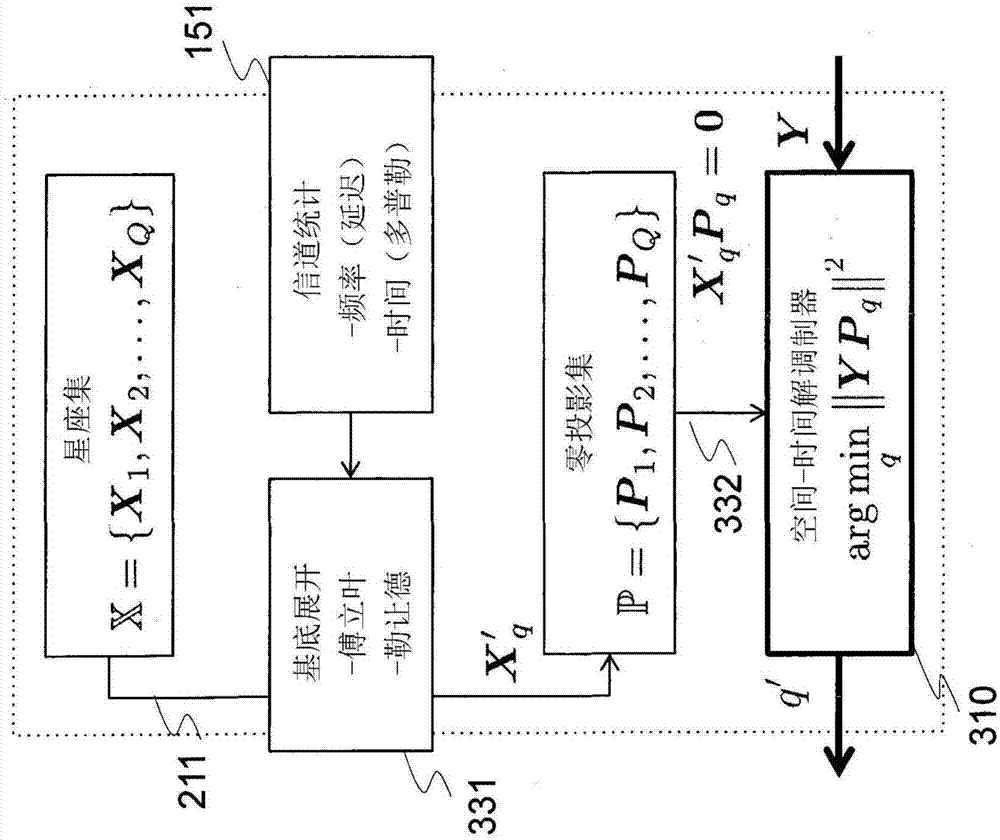
System and method for communicating data symbols via wireless doubly-selective channels
ActiveUS9264118B1Large toleranceSpatial transmit diversityCharacter and pattern recognitionTime domainMethod selection
A method for decoding data symbols modulated with a corresponding codeword from a constellation set of codewords expands the constellation set of codewords with a set of basis functions to produce a basis-expanded constellation set and projects projecting a received modulated data symbol onto orthogonal complements of the basis expanded constellation set to obtain a set of distance metric of a generalized likelihood ratio test (GLRT) for each codeword of the constellation set. The set of basis functions includes a Fourier exponential basis function in a frequency domain, a Legendre polynomial basis function in a time domain, and a Fourier-Legendre product basis function in the frequency domain. The method selects a codeword corresponding to a minimal distance metric or a maximal correlation metric and decodes the data symbol from the received modulated data symbol using the codeword.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
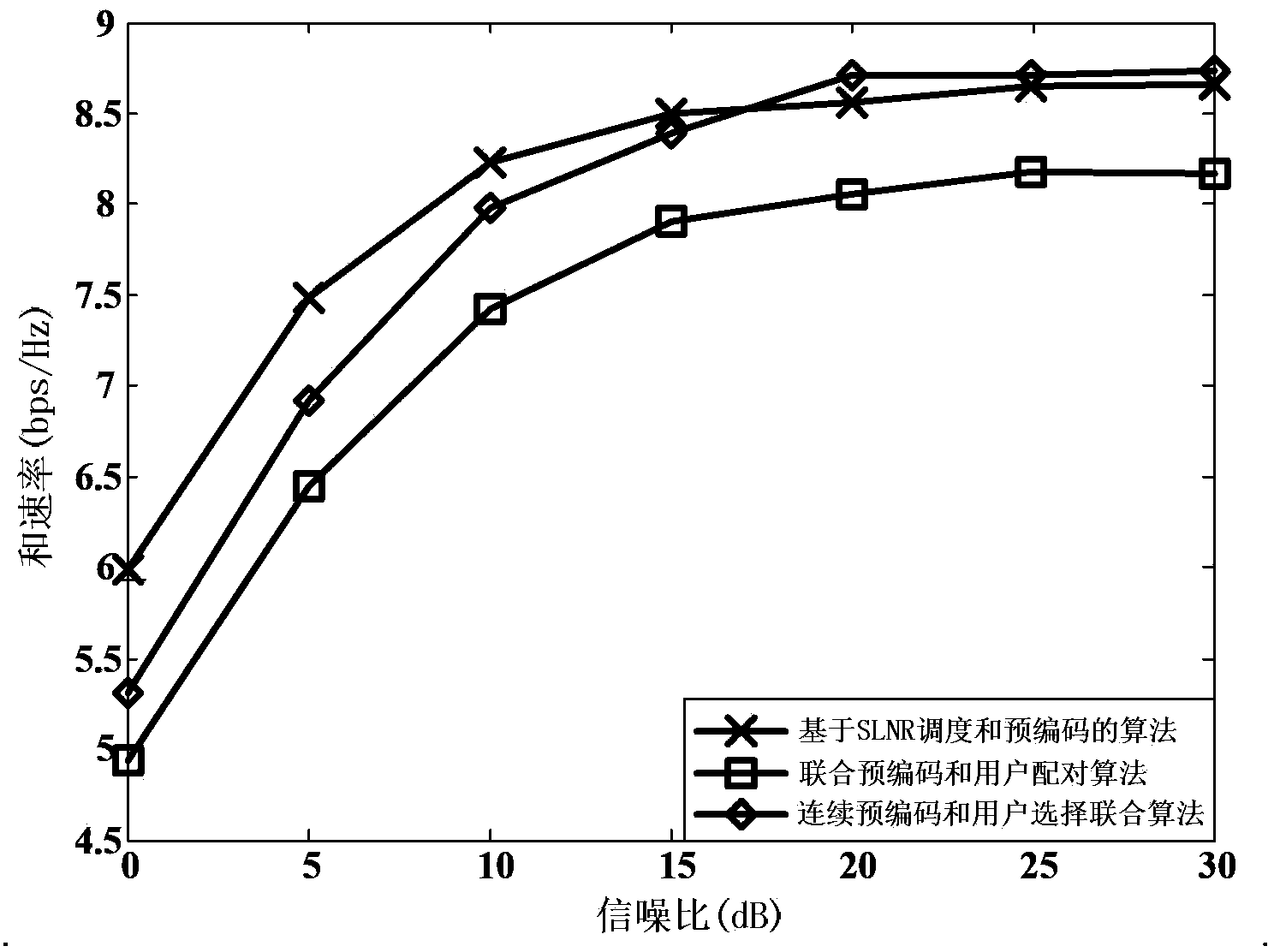
Continuous pre-coding and user selection united algorithm for multi-user MIMO (Multiple-Input Multiple-Output) broadcast channel
ActiveCN103384228ASuppress interferenceReduce complexitySpatial transmit diversityTransmitter/receiver shaping networksBroadcast channelsMulti user interference
The invention discloses a continuous pre-coding and user selection united algorithm for a multi-user MIMO (Multiple-Input Multiple-Output) broadcast channel. According to the continuous pre-coding and user selection united algorithm for the multi-user MIMO broadcast channel, a normalization projector vector of orthogonal complement space which is formed between all pre-coding vectors which do not select users and all pre-coding vectors which select users is served as a new pre-coding vector of users; user selection is performed according to a signal to interference plus noise ratio of every user; one user is selected at one time until a preset user number is achieved, and accordingly an optimal pre-coding vector of every user is achieved. Compared with the traditional method, the continuous pre-coding and user selection united algorithm for the multi-user MIMO broadcast channel has the advantages of being low in complexity, effectively suppressing multi-user interference, improving channel capacity and effectively improving system performance under the conditions that the number of users if large and the signal to interference plus noise ratio is large.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Generating a device independent interim connection space for spectral data
InactiveUS20090141322A1Wide applicabilityThe result is accurateTelevision system detailsDigitally marking record carriersComputer graphics (images)Orthogonal complement
Generation of an Interim Connection Space (ICS) of a full spectral space is provided. A space of illuminants is accessed, and the full spectral space is decomposed into a first subspace that is an orthogonal complement of a metameric black subspace for the space of illuminants. The Interim Connection Space is generated based on the first subspace. The generated ICS can be used, for example, for rendering an image on an additive color destination device. One image rendering workflow includes accessing color data of the image in an ICS, transforming the color data from the ICS into a device dependent color space of an additive color destination device, and rendering the transformed color data on the destination device.
Owner:CANON KK
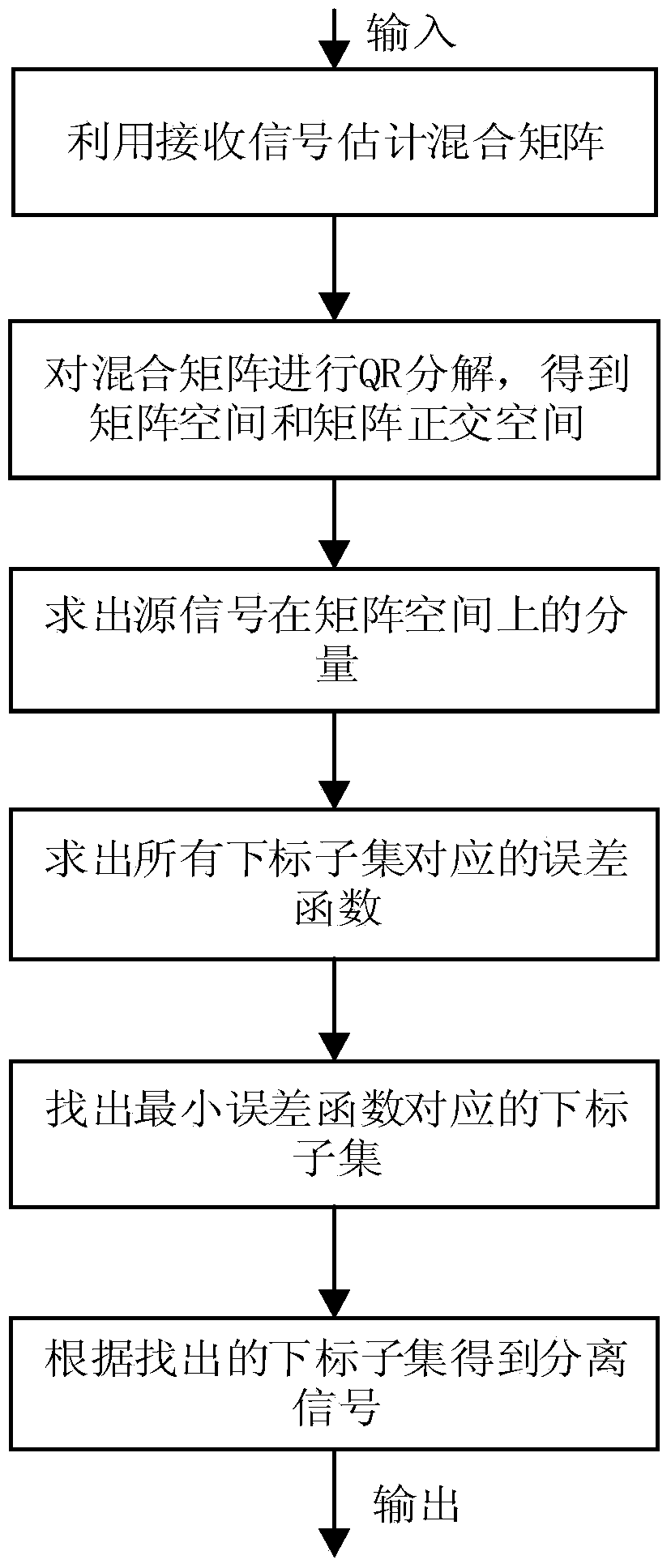
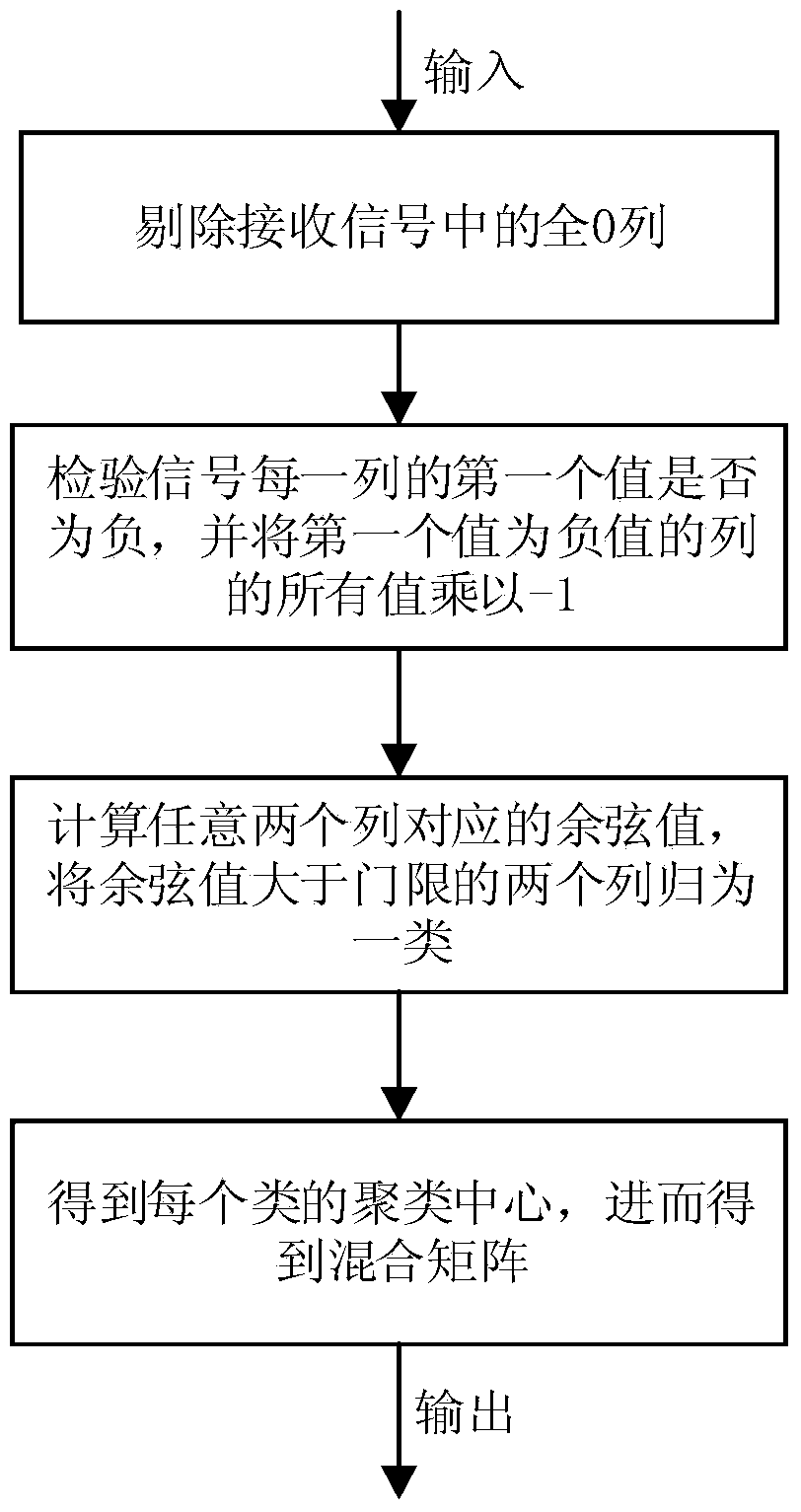
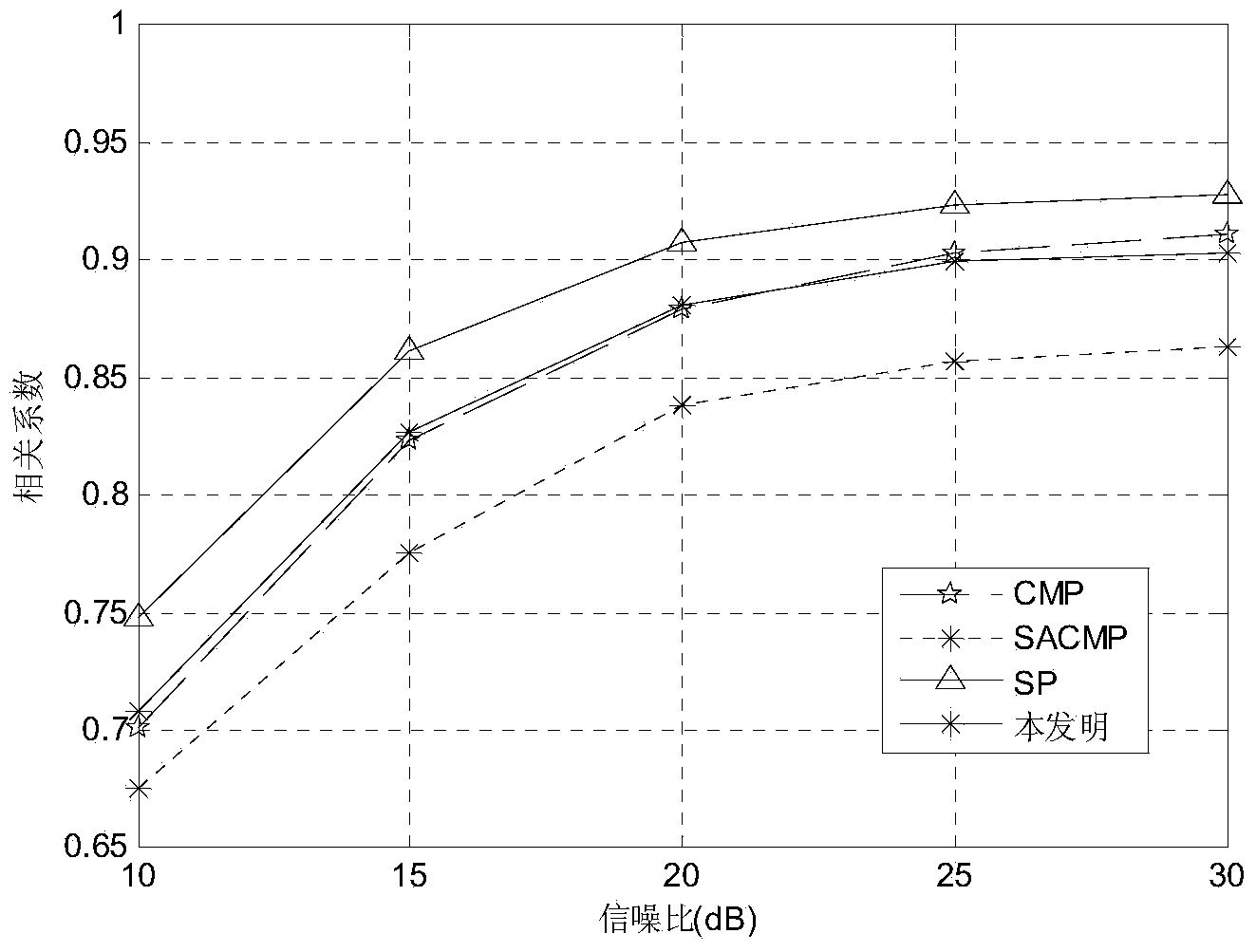
Underdetermined blind separation source signal recovery method based on SCMP (Subspace Complementary Matching Pursuit) algorithm
InactiveCN104392146AReduce complexityShorten the timeSpecial data processing applicationsQR decompositionMatrix space
The invention discloses an underdetermined blind separation source signal recovery method based on an SCMP (Subspace Complementary Matching Pursuit) algorithm, and mainly solves the problems of high complexity and low recovery precision in an existing underdetermined blind separation technology. The method comprises the following steps: 1, performing QR decomposition on transpose AT of a mixed matrix to obtain matrix space SA and corresponding orthogonal complement space described in the specification; 2, working out the component s1 of a source signal in the space SA by a received signal x(t); 3, searching the positions of N-M zero elements in the source signal s by an approximate l[0] norm process according to complementary properties of the source signal in the space SA and the space described in the specification; 4, working out other M elements by the complementary properties according to the searched positions of the N-M zero elements to obtain a recovery signal. The method is high in search speed and recovery precision and can be used in the fields of communication, signal processing and the like.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV +1
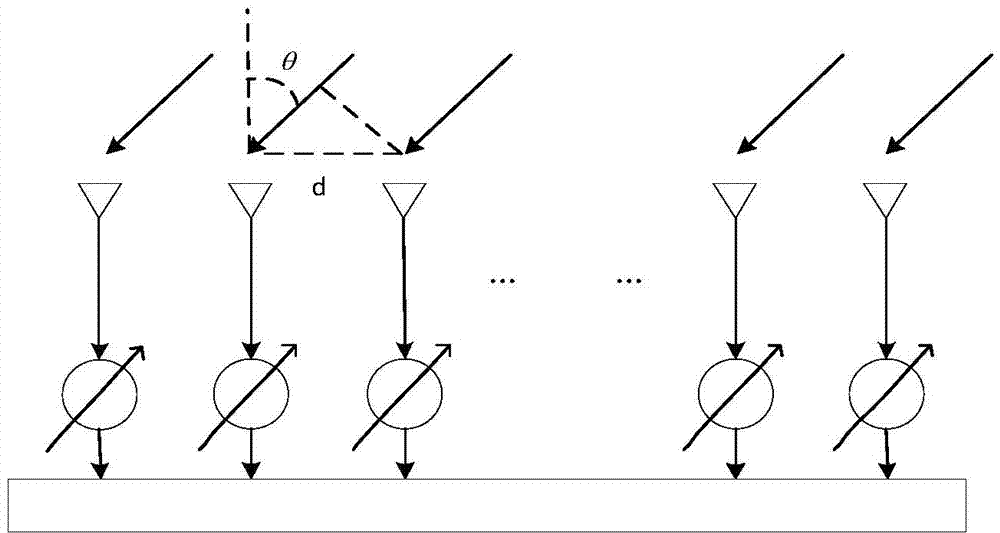
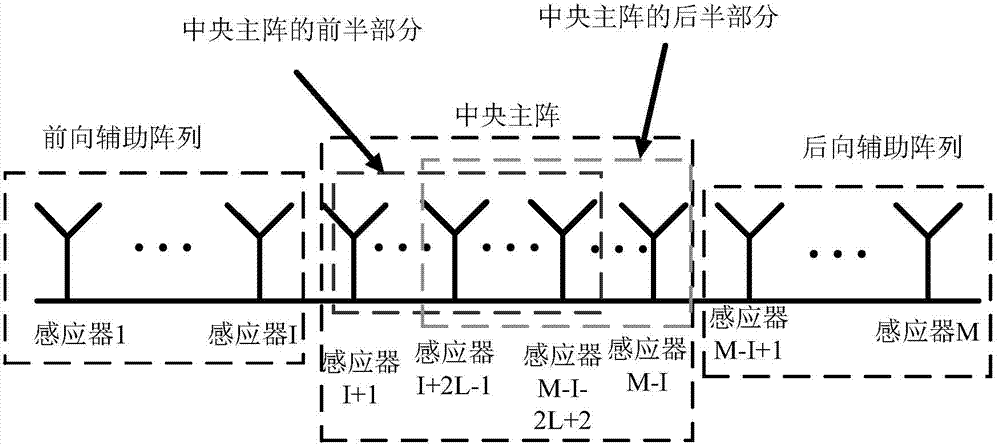
Robust estimation method of direction of arrival (DOA)
ActiveCN104330766AImprove estimation accuracyReduce complexityDirection findersSingular value decompositionEstimation methods
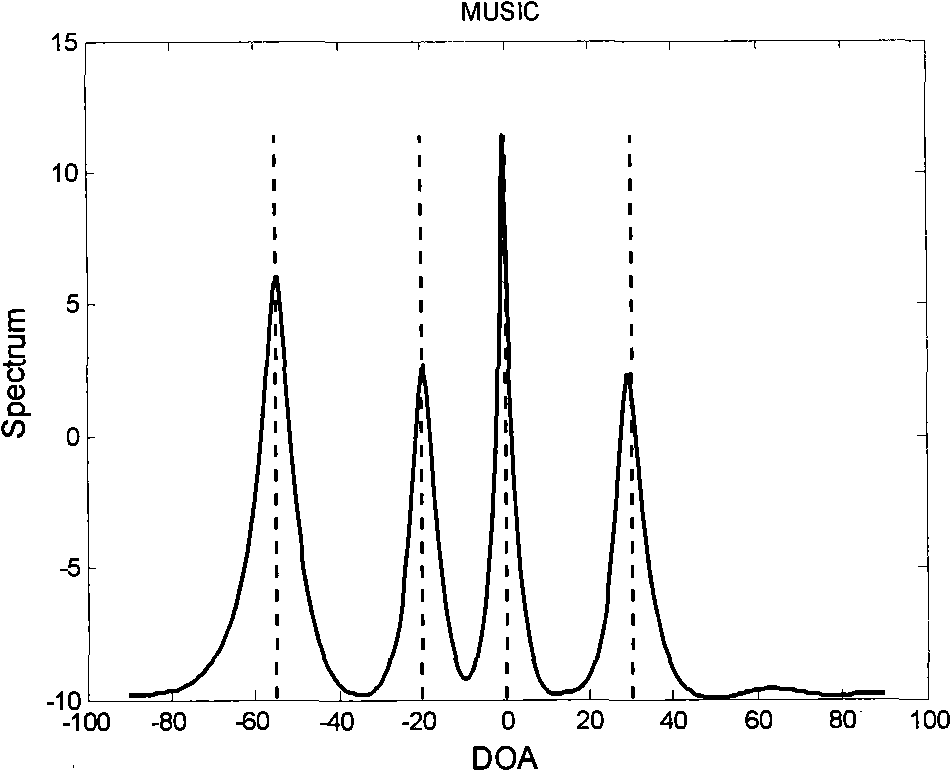
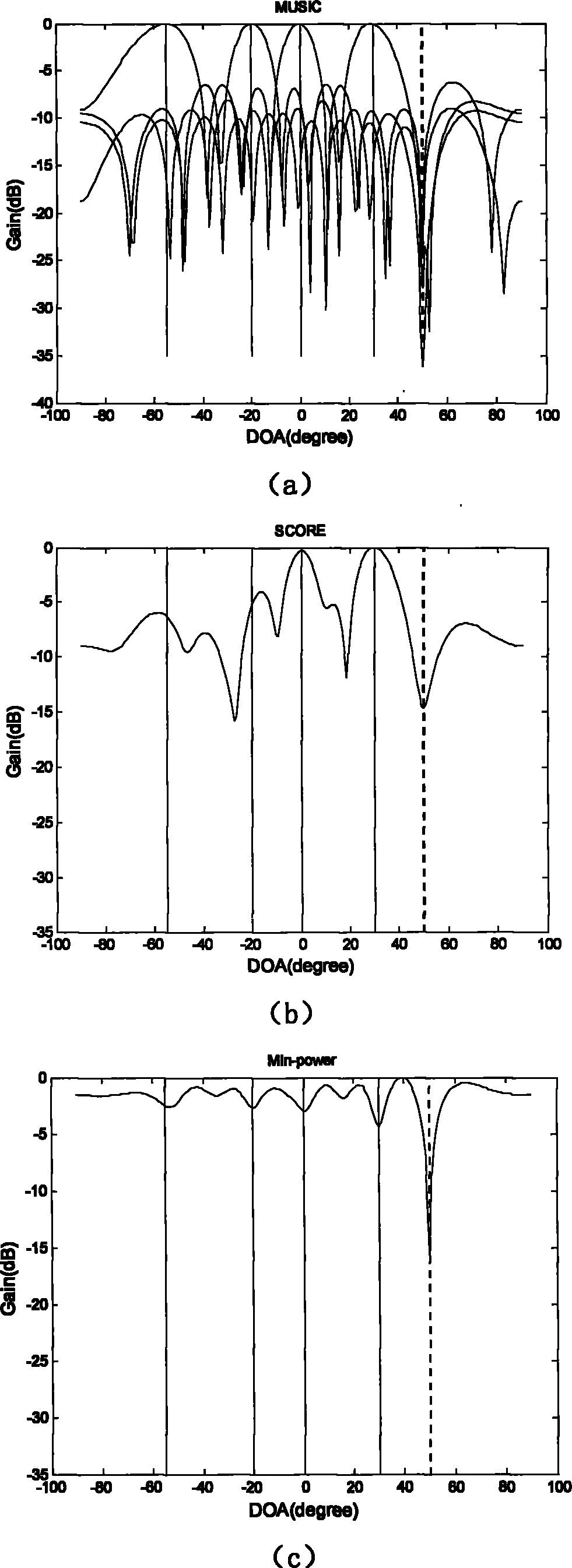
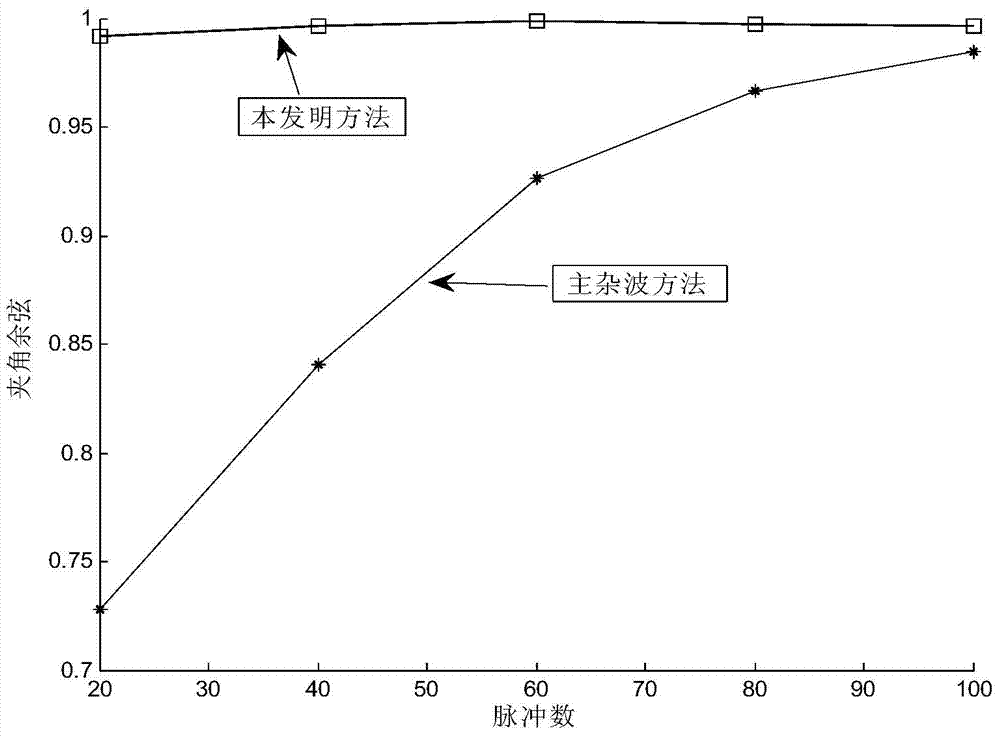
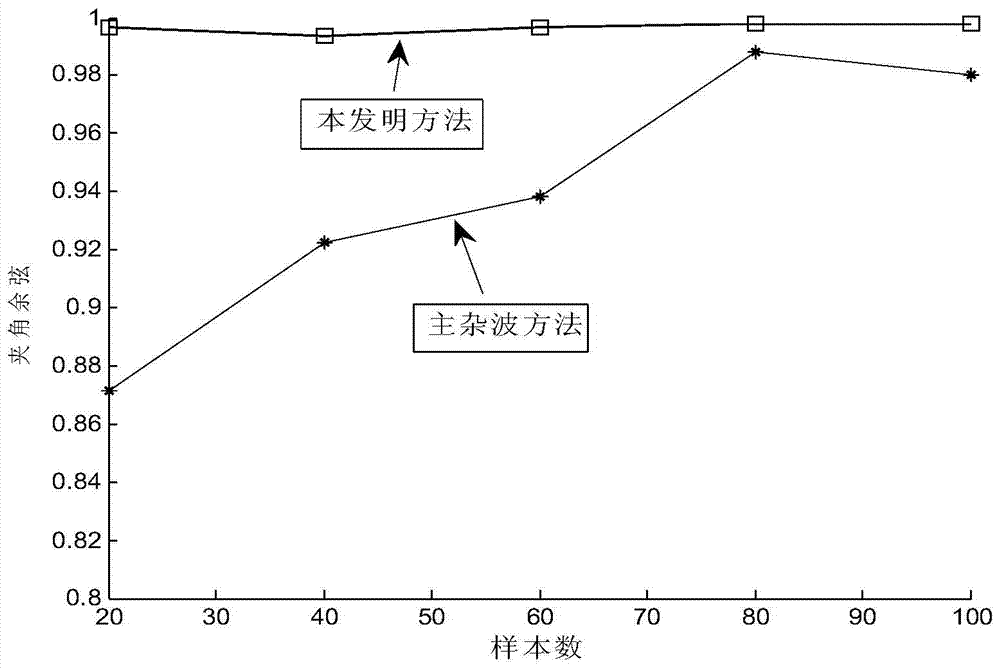
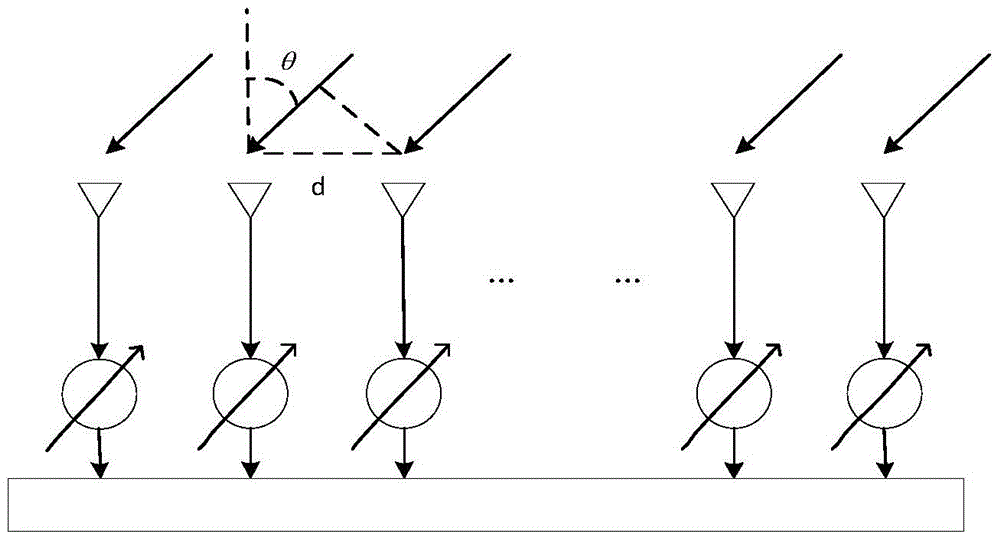
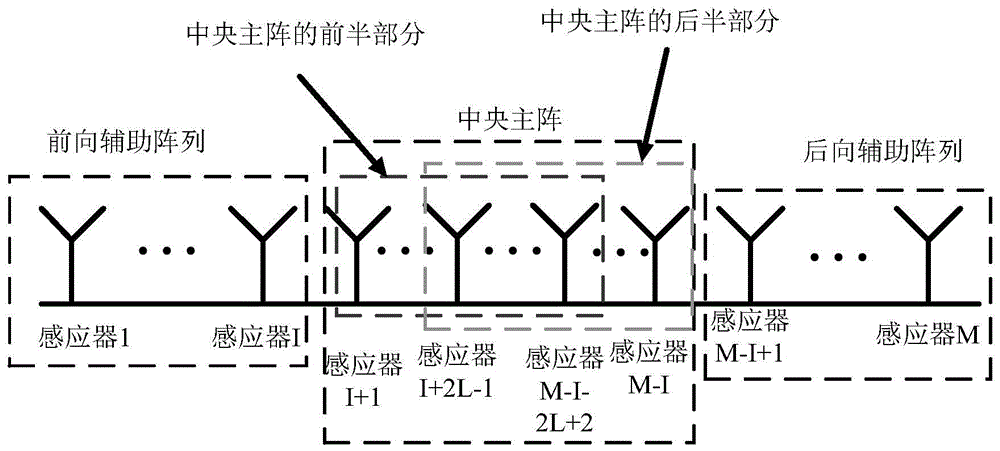
The invention discloses a robust estimation method of a direction of arrival (DOA), by which quite high estimation precision can be obtained. The method specifically comprises: sequentially dividing an equidistant linear array into three sub-arrays from the left to the right, i.e., a forward auxiliary array, a central main array and a backward auxiliary array respectively; dividing the central main array into a front half portion and a rear half portion according to a certain rule; then calculating a covariance matrix Rforward between the front half portion and the backward auxiliary array and a covariance matrix Rbackward between the rear half portion and the forward auxiliary array; performing singular value decomposition respectively on the Rforward and the Rbackforward, and extracting the orthogonal complement of the subspace of far-field signals received by the equidistant linear array from a singular value decomposition result; and establishing a DOA estimation operator by use of guiding vectors between the orthogonal complement and the front half portion and the rear half portion, performing search on the DOA estimation operator by use of a minimum parameter search method to obtain K minimum value points, and through the search, obtaining theta 1 to theta k of each minimum value point as k DOAs of the far-field signals.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Spectral gamut mapping based on a colorimetric gamut mapping
InactiveUS20090148040A1Simple methodDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsGamutOrthogonal complement
Mapping spectral colors in an Interim Connection Space (ICS) of a full spectral space based on a colorimetric gamut map in a color space is provided. A spectral color value in the ICS is accessed, and the spectral color value is transformed into a calorimetric color value in the color space. The calorimetric color value is mapped into mapped calorimetric color value in a first subspace of the ICS. Mapping the colorimetric color value includes gamut-mapping the calorimetric color value using the calorimetric gamut map, followed by identifying the color space with the first subspace. An intersection of a spectral gamut in the ICS and an affine subspace characterized by the mapped colorimetric color value is determined, and the spectral color value is projected onto the intersection. The first subspace is an orthogonal complement of a null space of a transformation from the ICS to the color space.
Owner:CANON KK
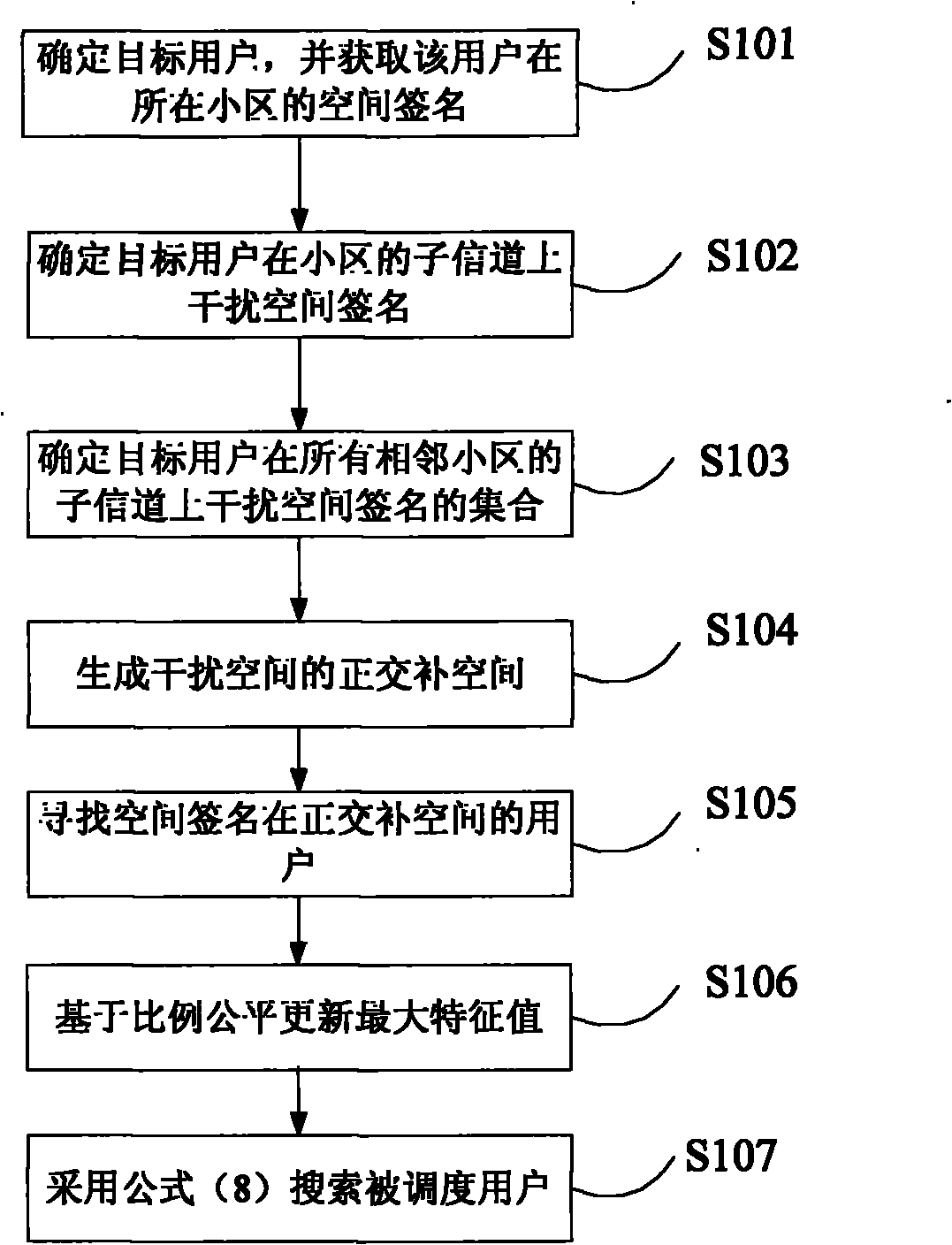
Interference coordination-based inter-cell user scheduling method
InactiveCN101965062ASuppress interferenceIncrease profitWireless communicationOrthogonal complementComputer science
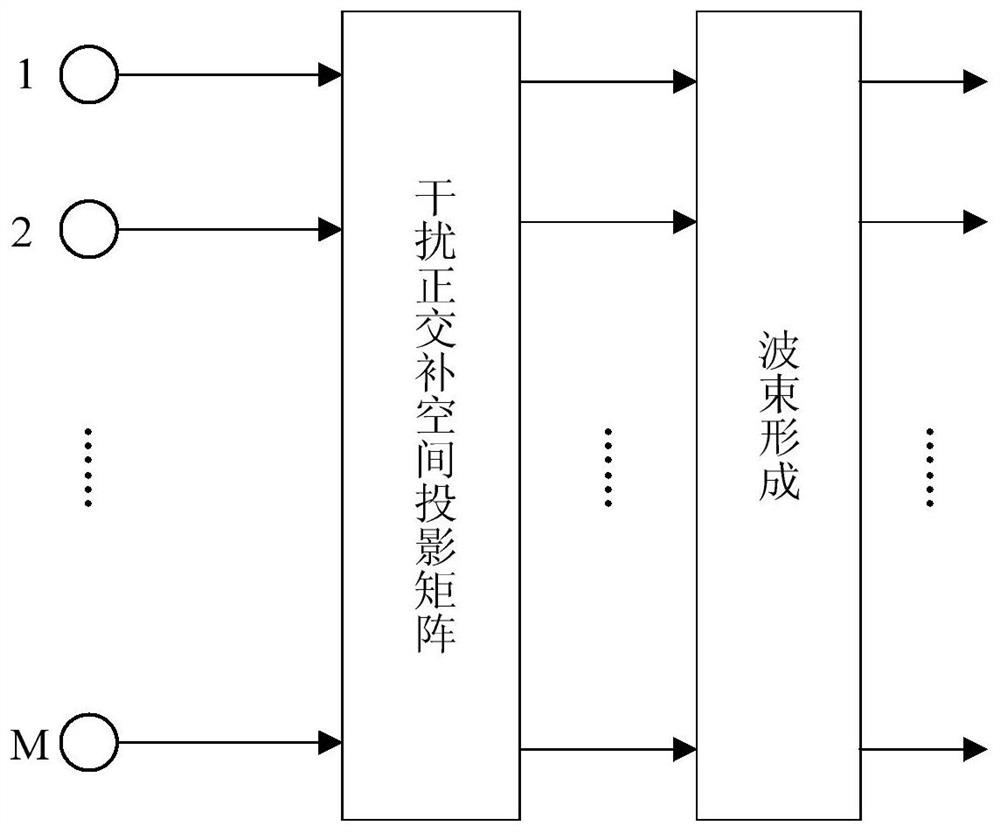
The invention discloses an interference coordination-based inter-cell user scheduling method. The method comprises the following steps of: determining a target user, and acquiring a space signature of the user in a cell where the user is located; generating an orthogonal complement space of an interface space; searching the user of the space signature in the orthogonal complement space; and searching a schedulable user. The interference coordination-based inter-cell multi-user scheduling method disclosed by the invention not only needs no base station exchange information, but also effectively inhibits inter-cell interferences and improves the utilization ratio of wireless channel resources.
Owner:ZTE CORP
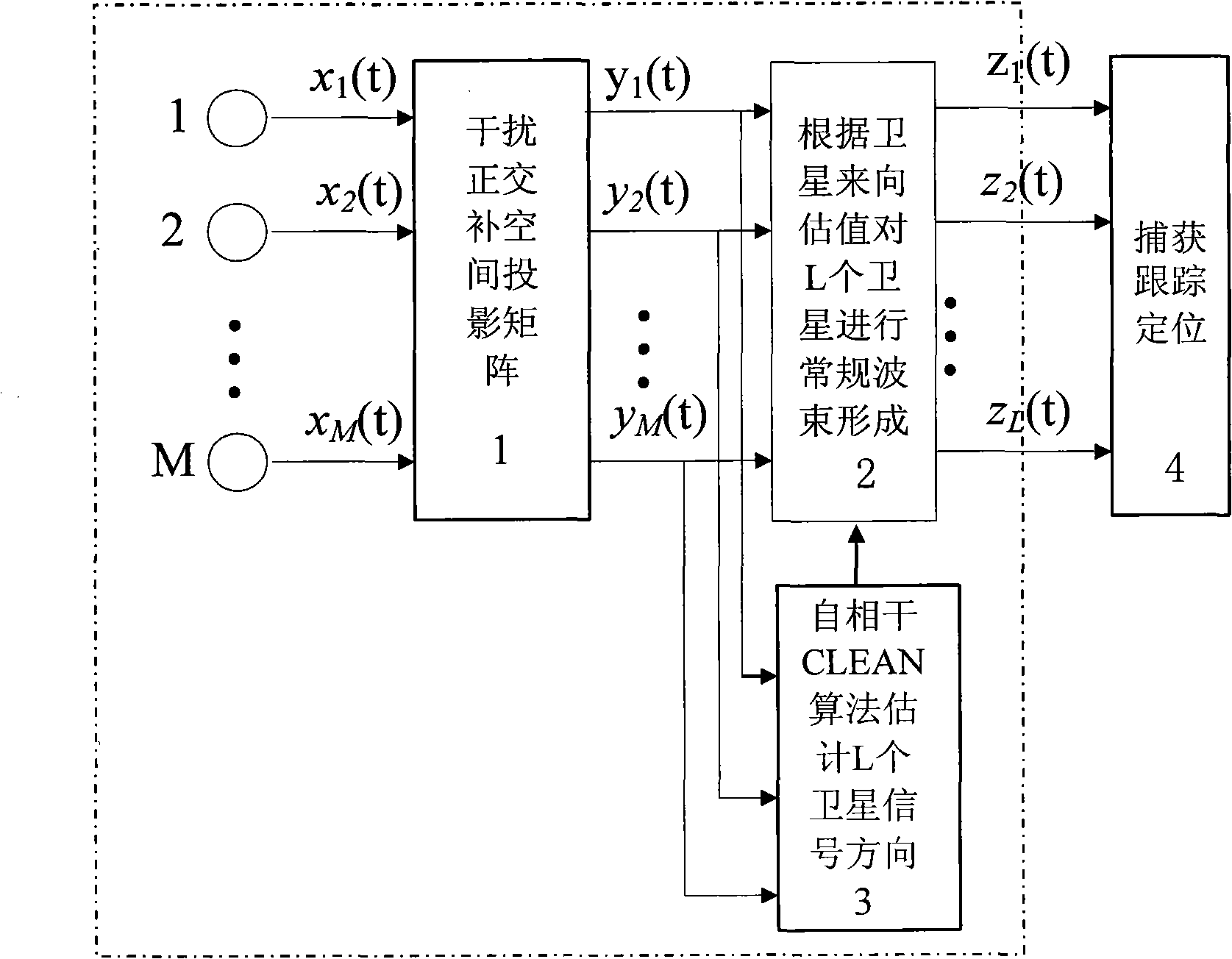
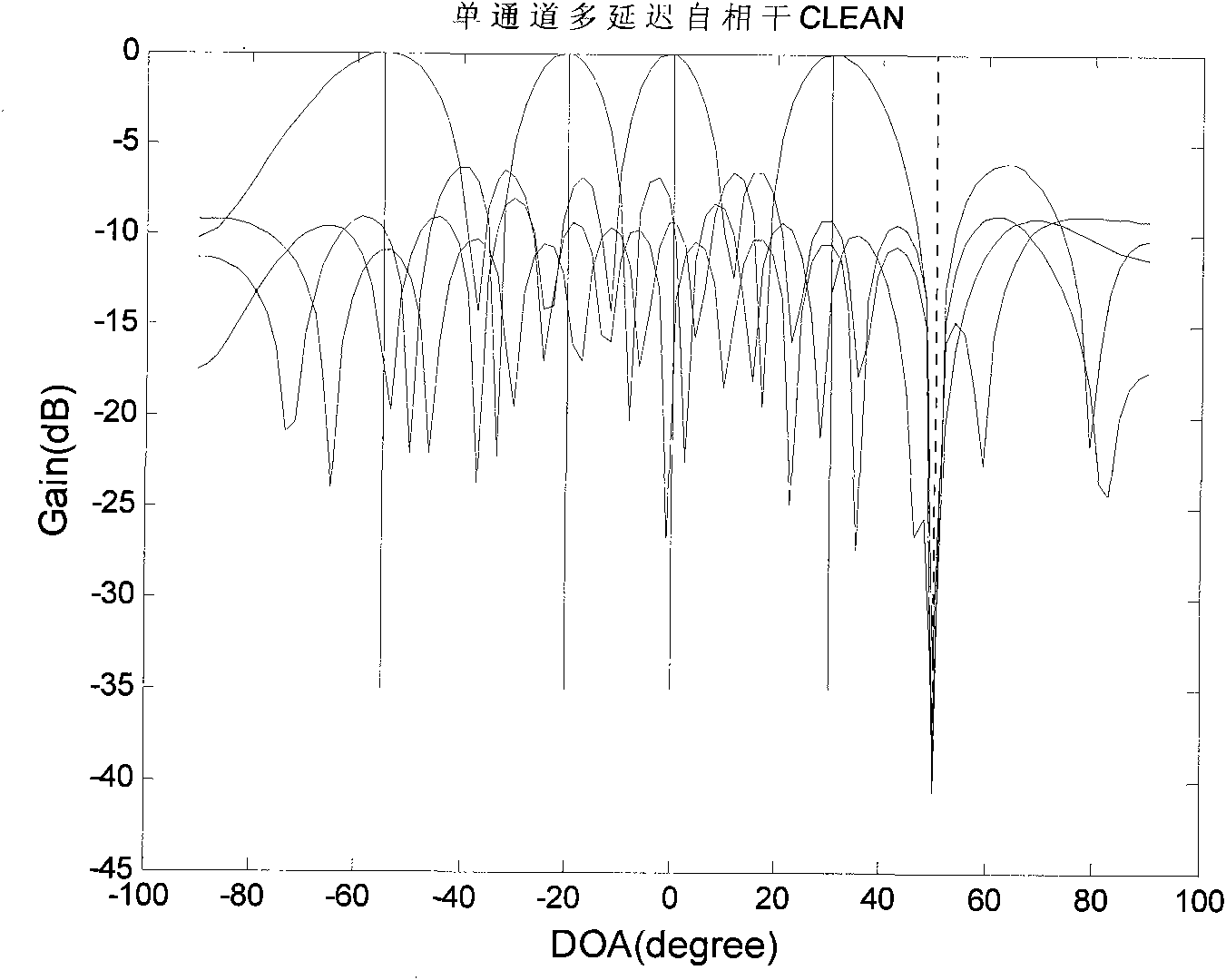
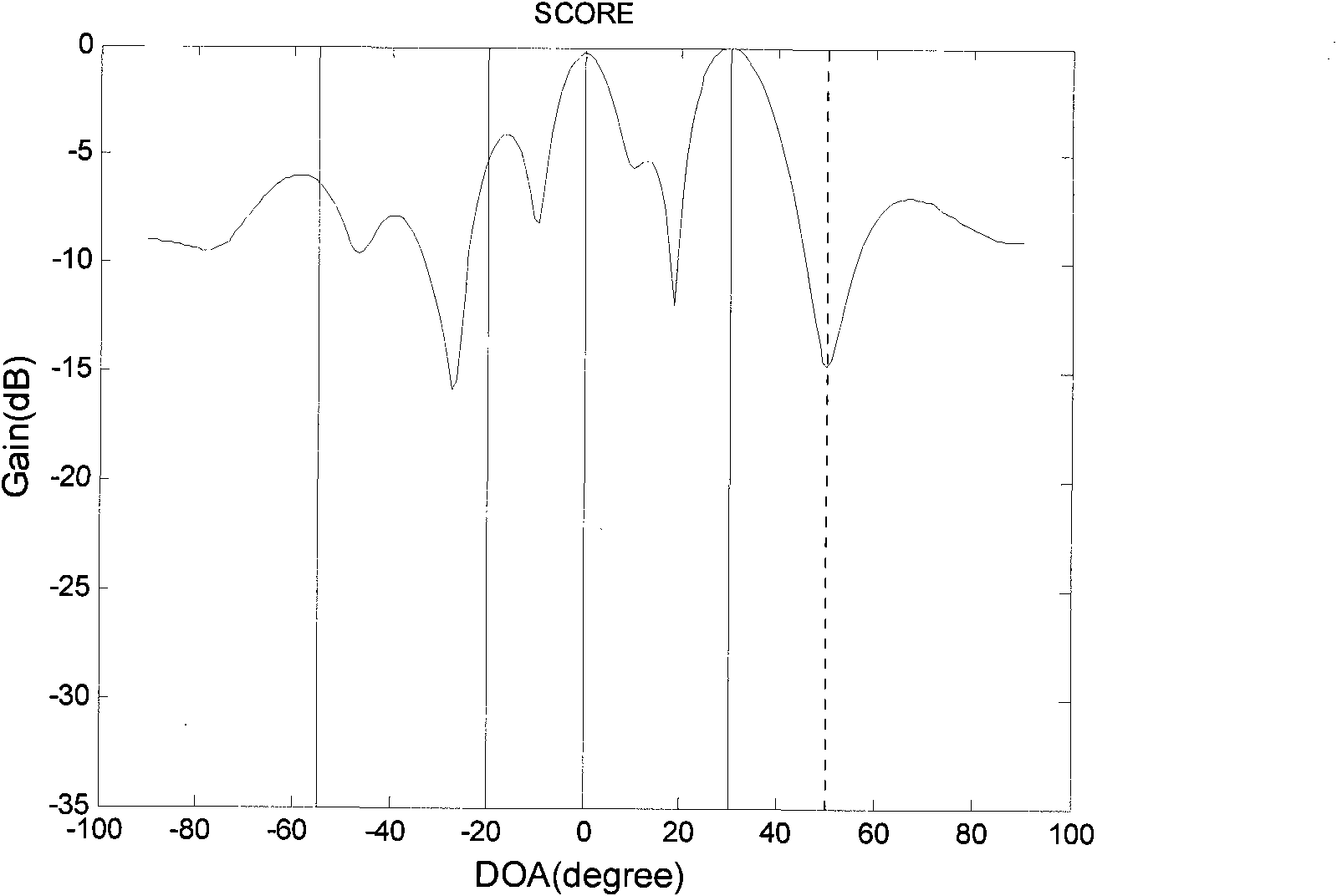
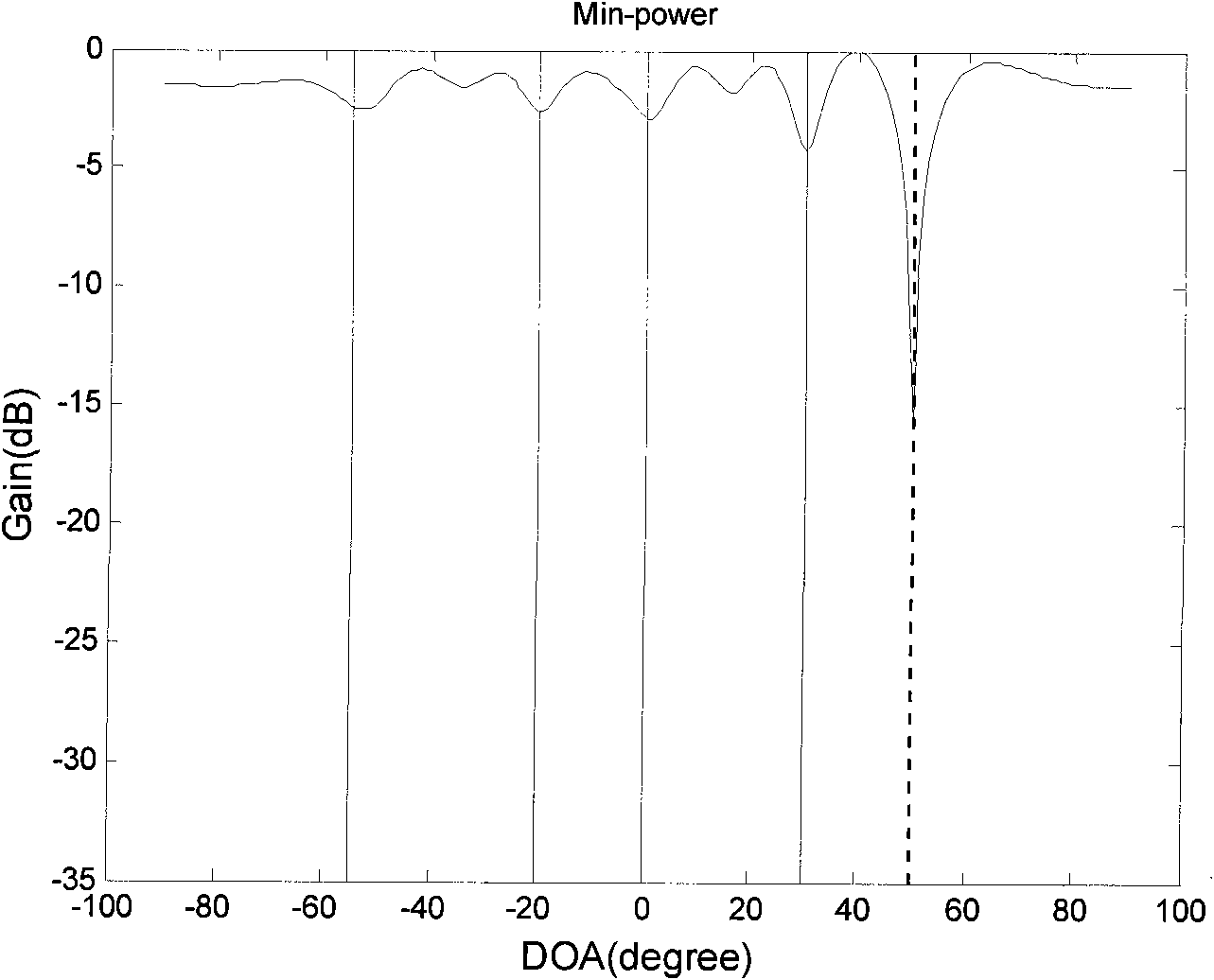
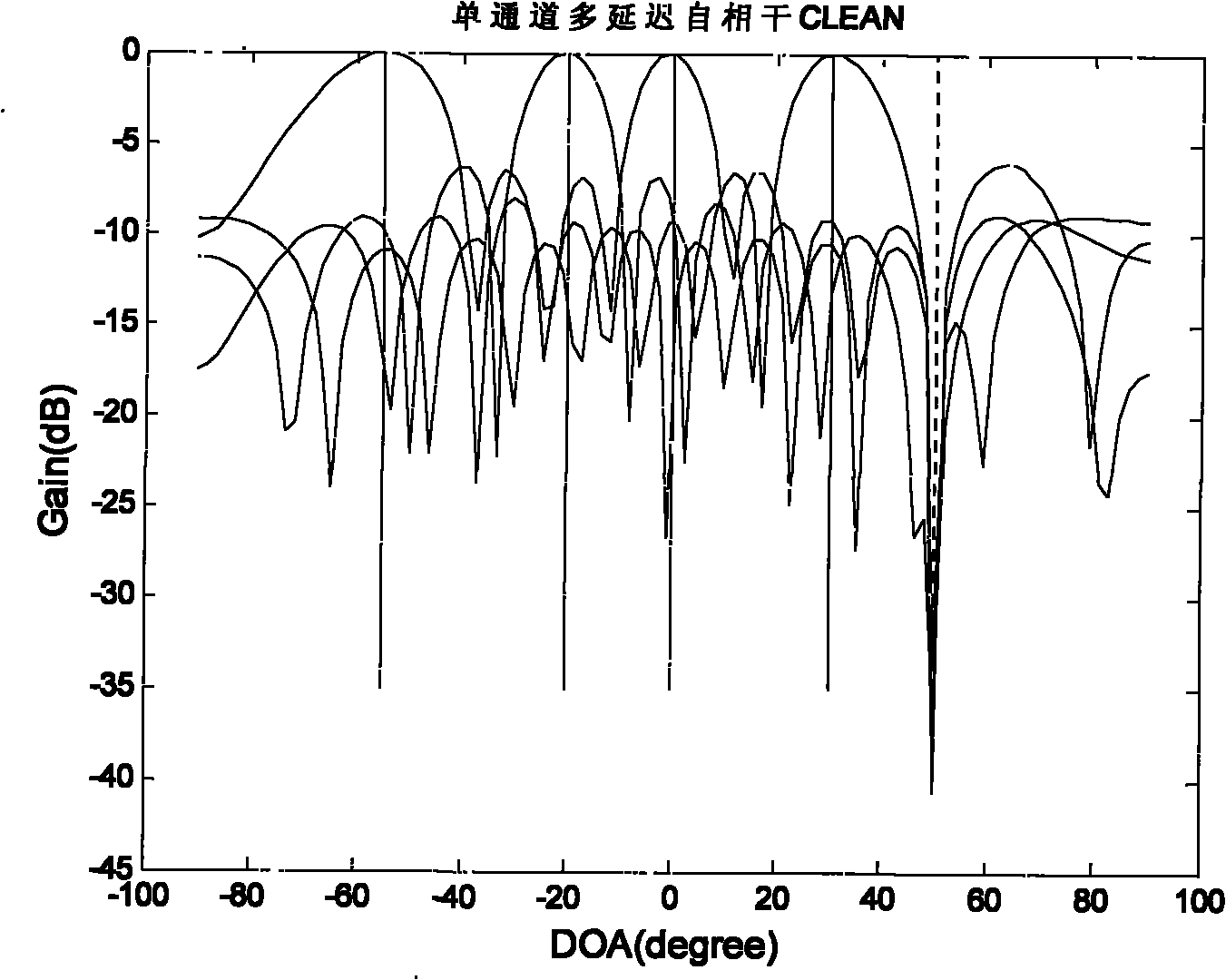
GPS (Global Positioning System) interference inhibition method based on single-channel multi-delay cross-correlation treatment
InactiveCN101788675AFulfill positioning requirementsGood estimateSatellite radio beaconingHat matrixUltrasound attenuation
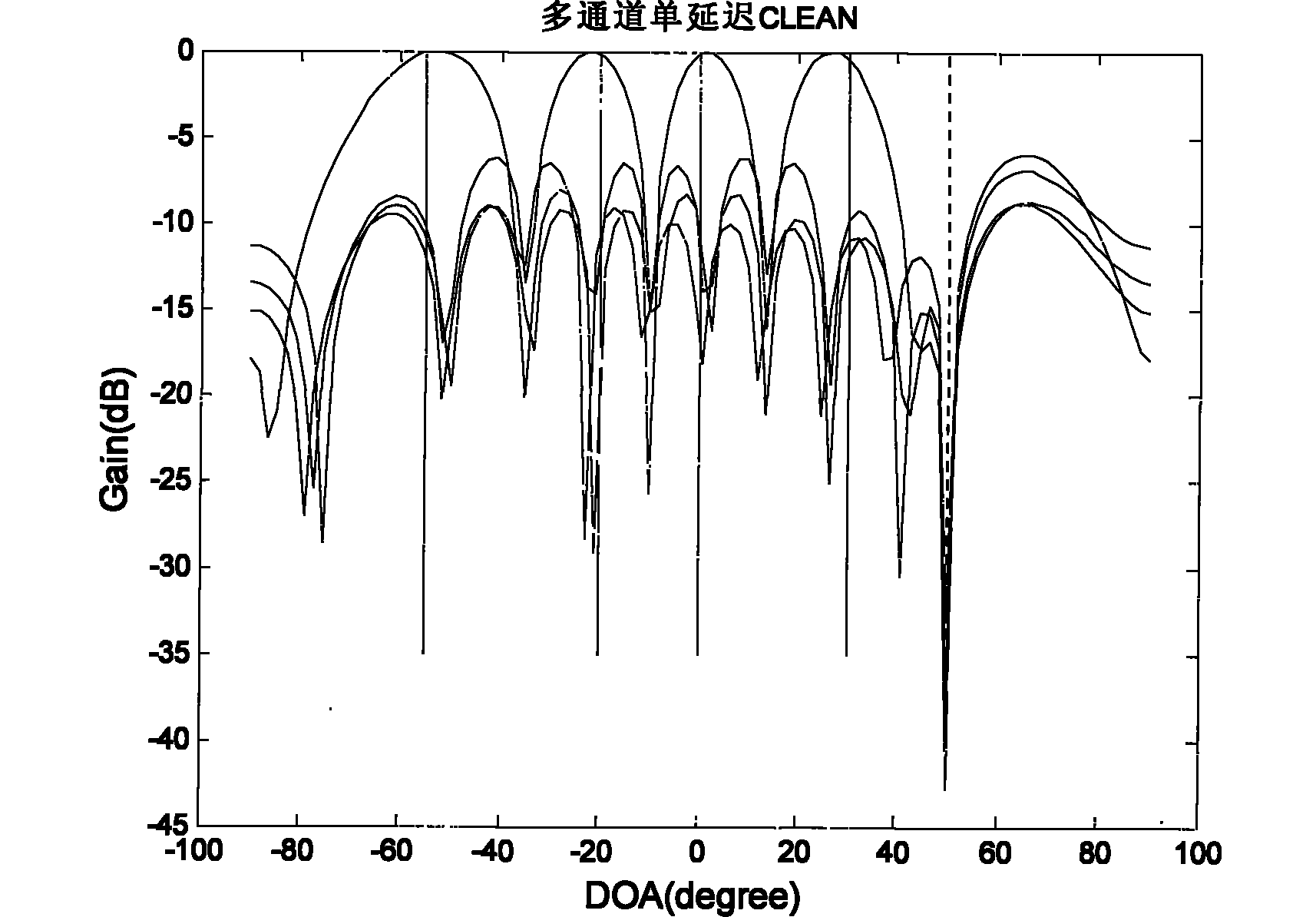
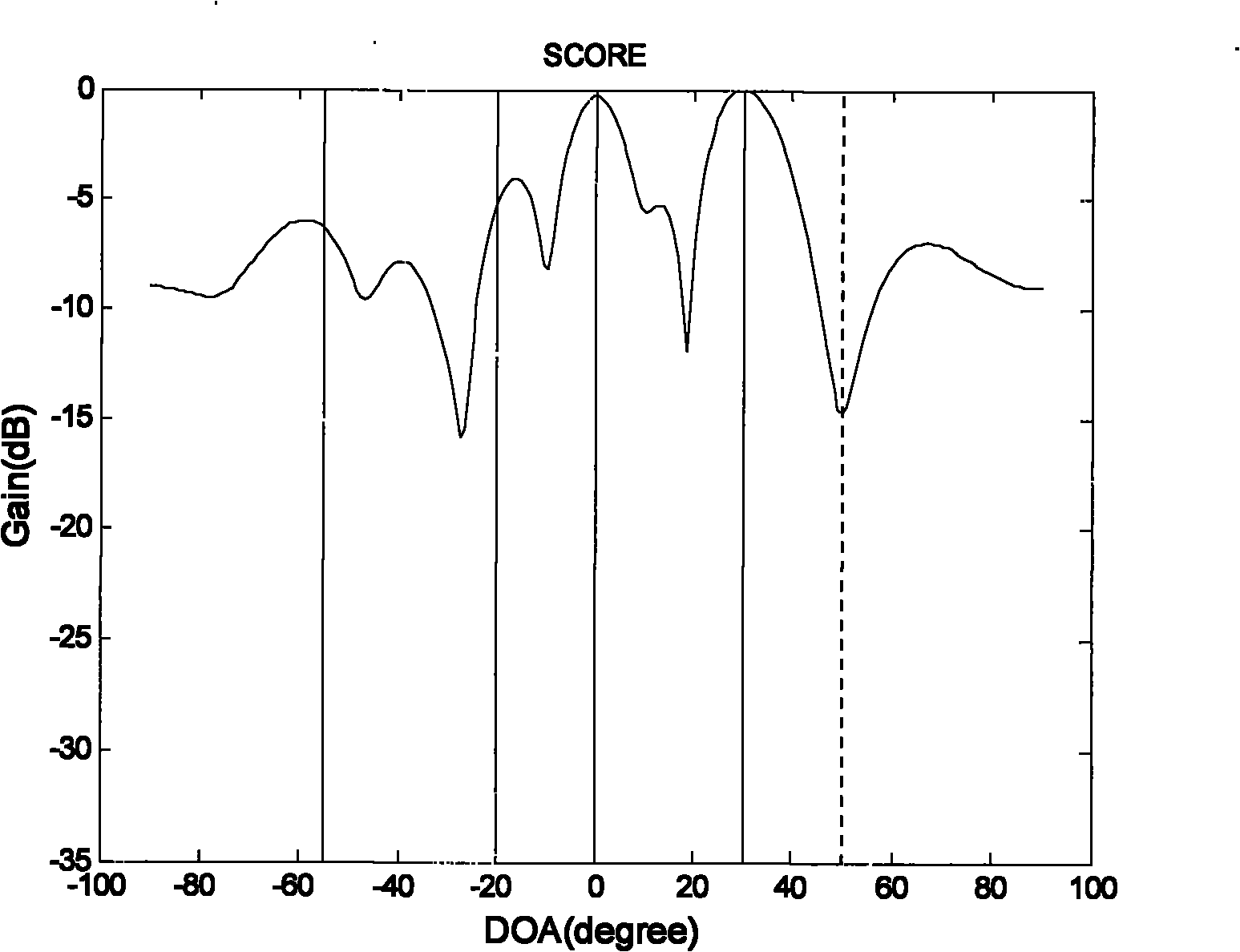
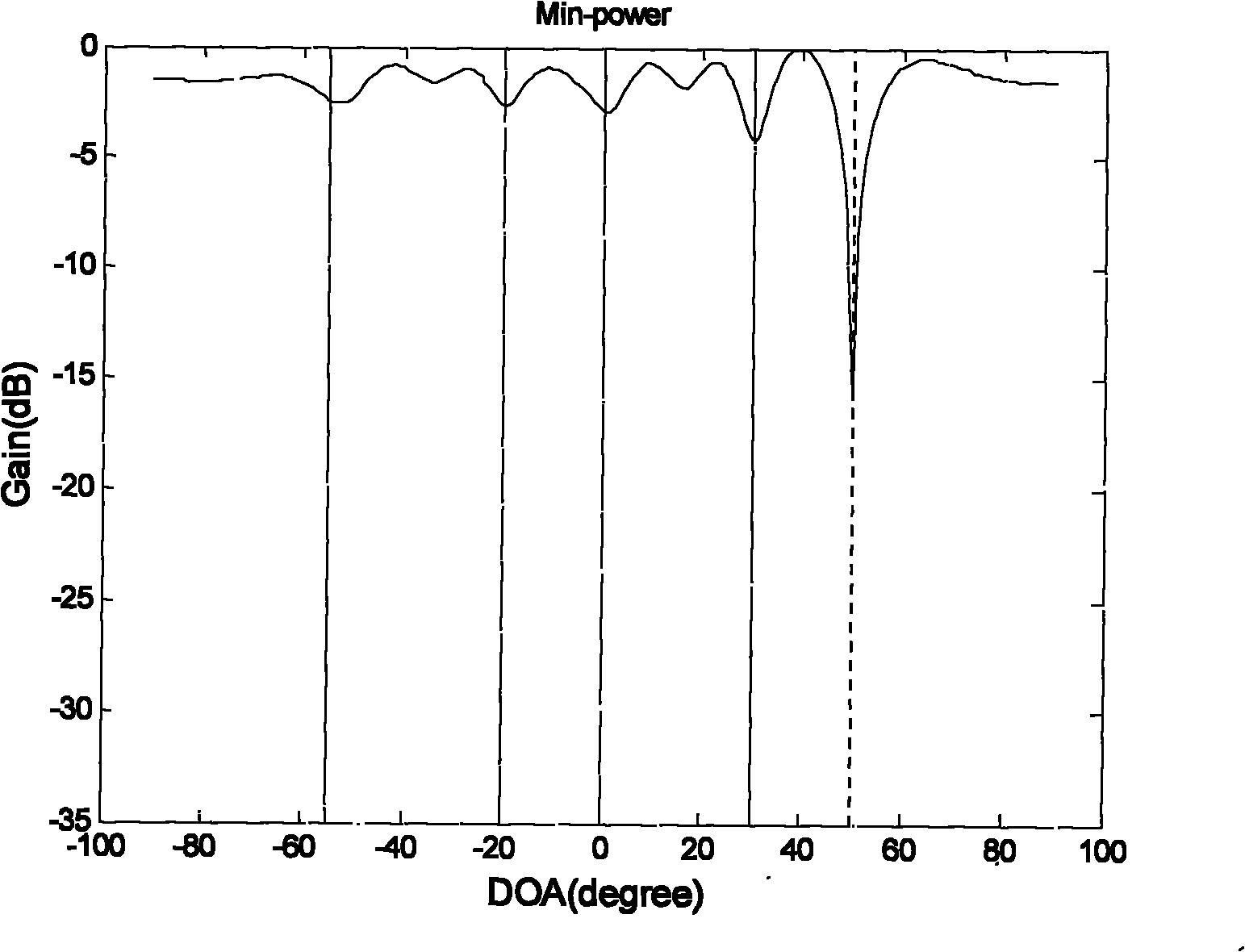
The invention provides a GPS (Global Positioning System) interference inhibition method based on single-channel multi-delay cross-correlation treatment, which is realized by combining subspace projection and a conventional wave beam forming technology. In the method, firstly, interference is inhibited by utilizing an interference orthogonal complement space projection matrix; and secondly, satellite signals are strengthened by utilizing the conventional wave beam forming technology, i.e. as for data after projection, the satellite signal direction is estimated by an autocorrelation CLEAN algorithm, and the estimated satellite signal direction is utilized to carry out conventional wave beam forming. The method comprises the following steps of projecting signals received by an array antennato an interference orthogonal complement space; as for a cross-correlation matrix of the projected single-channel multi-delay data and the projected array data, estimating the satellite signal direction by the autocorrelation CLEAN algorithm; and carrying out wave beam forming on the projected data by utilizing the estimated satellite signal direction. The invention realizes interference inhibition and ensures non attenuation of satellite signals by fully utilizing data information without needing an inertia navigation auxiliary unit and has the advantages of simple realization and higher estimation accuracy. The satellite signal direction is not limited by the array number.
Owner:CIVIL AVIATION UNIV OF CHINA
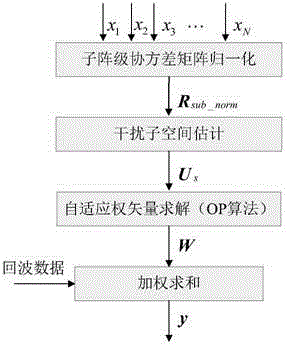
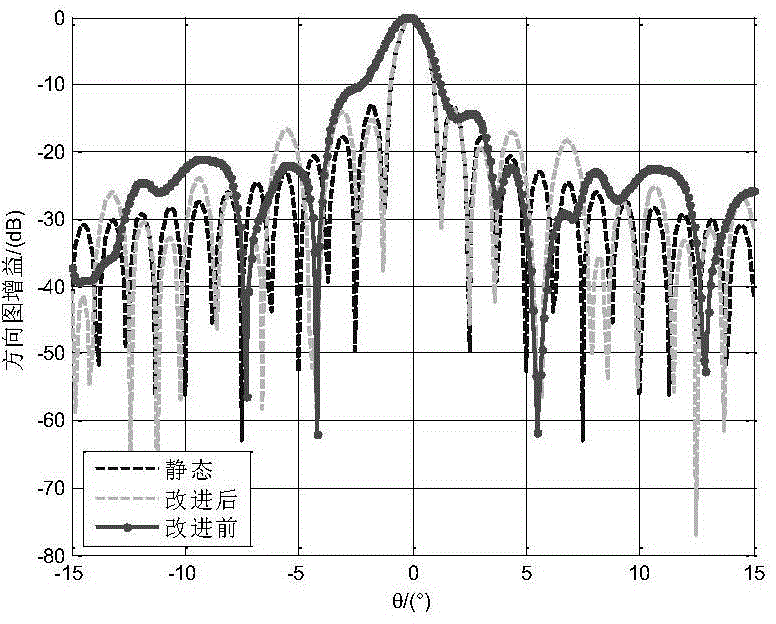
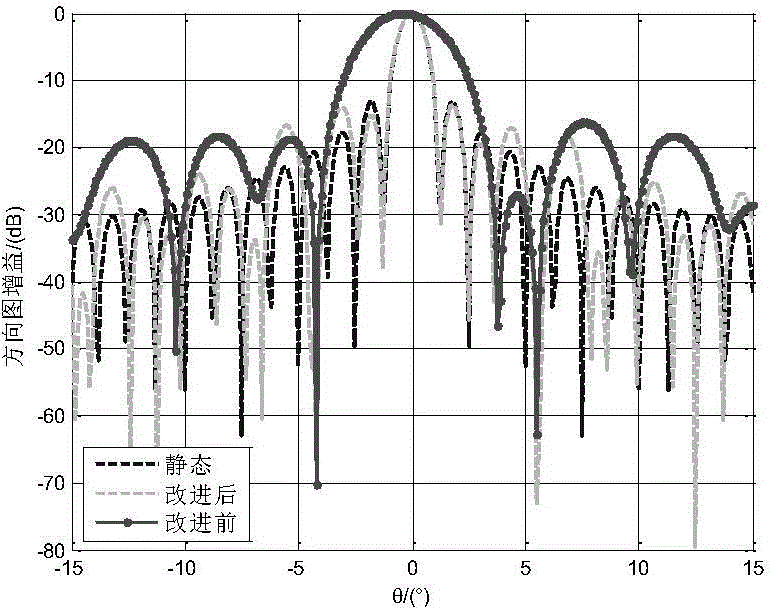
Submatrix-level orthogonal projection (OP) wave beam forming method based on covariance matrix normalization
ActiveCN104931937ALow Interference to Noise RatioLow sampling fast dry noise ratioWave based measurement systemsOrthogonal complementEngineering
The invention discloses a submatrix-level OP wave beam forming method based on covariance matrix normalization. The method can be used to effectively inhibit interference, make a main lobe of a self-adaptive directional diagram conformal, reduce side lobes the self-adaptive directional diagram and obtain higher output SINR and convergence speed. The method comprises that submatrix-level reception signals are normalized, and a corresponding normalized sampling covariance matrix is calculated; the amount of interference signal sources is estimated by utilizing the MDL criterion, and further an interference subspace is obtained; and finally, the static weight vector is projected to an orthogonal complement space of the interference subspace to obtain a self-adaptive weight vector.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
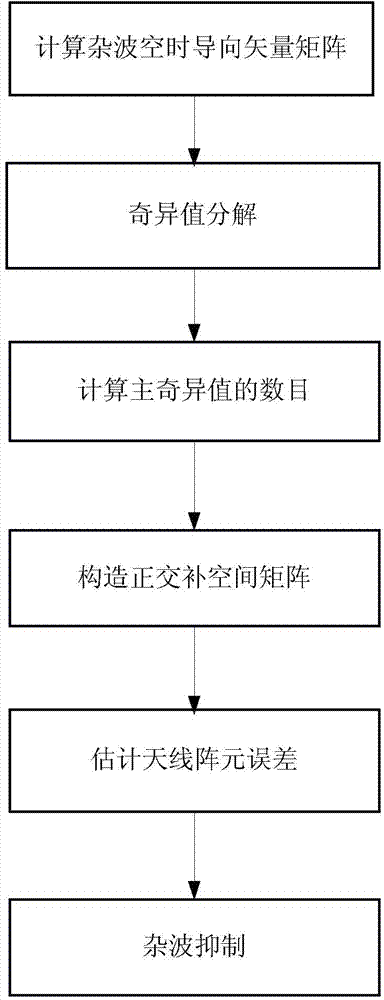
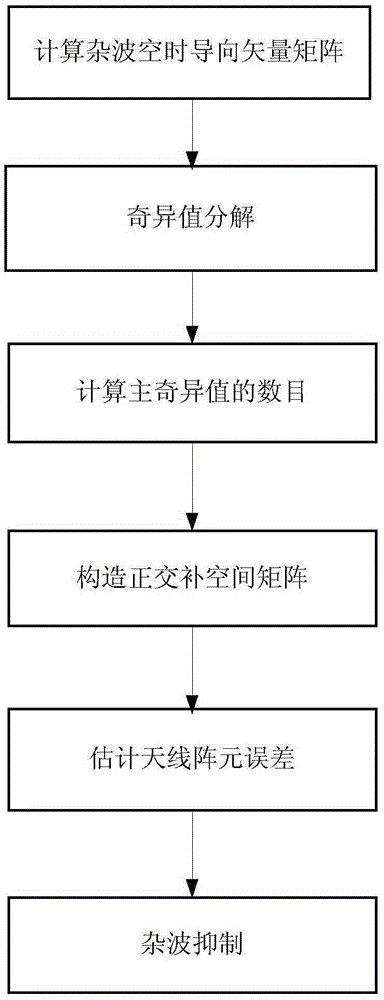
Array element error estimation method based on clutter subspace
InactiveCN103885042AHigh Error Estimation AccuracyOvercoming the problem of poor clutter suppression effectWave based measurement systemsSingular value decompositionPrior information
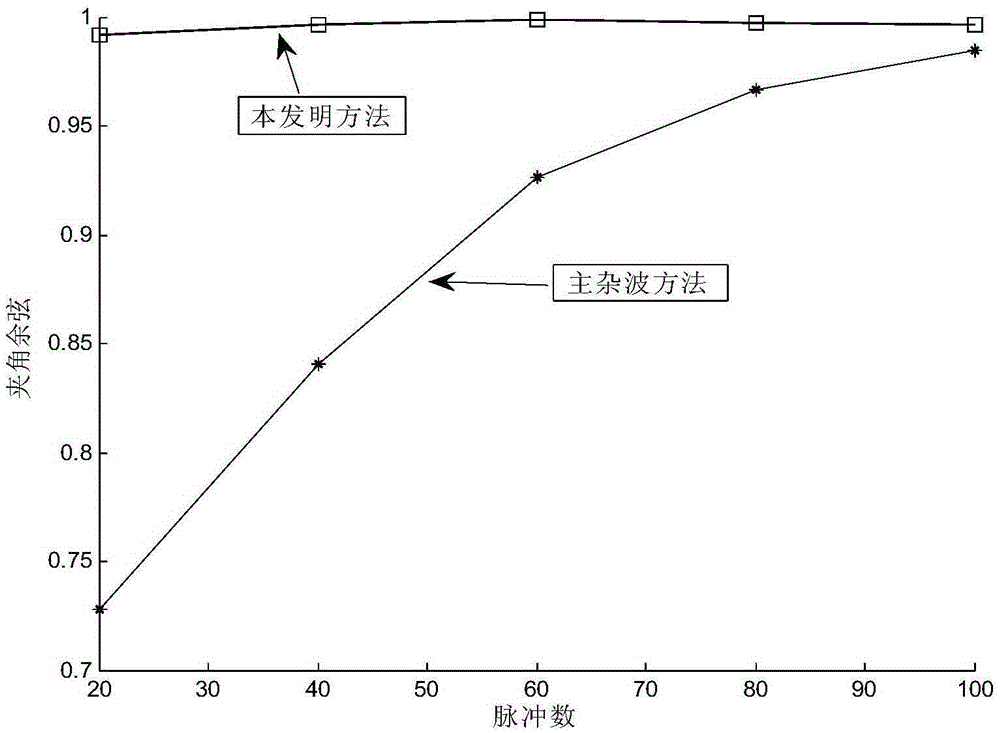
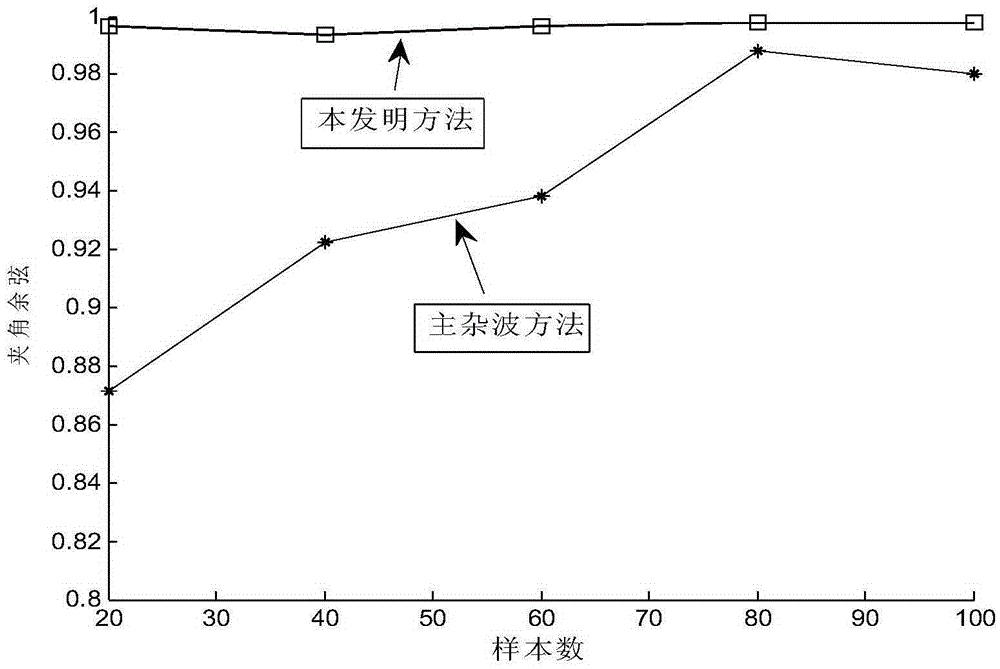
The invention discloses an array element error estimation method based on clutter subspace. The array element error estimation method based on clutter subspace includes the implementation steps that 1, radar prior information is utilized for calculating a clutter time-space steering vector matrix; 2, singular values of radar receiving data and the clutter time-space steering vector matrix are resolved; 3, the number of the main singular values is calculated; 4, a clutter orthogonal complement space matrix is built according to the obtained number of the main singular values; 5, antenna array element errors are estimated through the obtained clutter orthogonal complement space matrix and the orthogonality of a left singular vector corresponding to a largest singular value obtained by resolving the received data; 6, a clutter signal model is corrected according to the estimated antenna array element errors, and clutter is restrained. The good antenna array element error estimation performance can be obtained under the situation with few samples and few pulses, so that the array element error estimation method based on clutter subspace has the advantages of being high in error estimation accuracy and stable in estimation performance.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Gamut mapping in spectral space based on an objective function
Mapping spectral colors in an Interim Connection Space (ICS) of a full spectral space based on an objective function is provided. A spectral color value in the ICS is accessed, and a spectral gamut boundary of the destination gamut is accessed. The spectral color value is mapped into mapped spectral color value based on minimization of an objective function of coordinates of a first subspace of the ICS, by fixing coordinates of a second subspace of the ICS, subject to a constraint that a result is within the spectral gamut boundary. The first subspace is a null space of a transformation from the ICS to a color space, while the second subspace is an orthogonal complement of the first subspace in the ICS. The constraint is determined by a gamut section that is an intersection of the spectral gamut in the ICS and an affine subspace characterized by the fixed coordinates of the second subspace.
Owner:CANON KK
Global position system (GPS) interference suppression method based on multichannel one-way delay mutual correlation processing
The invention relates to a global position system (GPS) interference suppression method based on multichannel one-way delay mutual correlation processing, which is realized by combining space projection and a conventional beam forming technology. Firstly, an interference orthogonal complement space projection array is utilized to restrain interference, and secondly, the conventional beam forming technology is utilized to enhance a satellite signal, i.e. an autocorrelation CLEAN algorithm is utilized for the data after projection to estimate the incoming direction of the satellite signal, and the estimated satellite signal direction is utilized to carry out conventional beam formation. The method comprises the following steps of: projecting the signals received by an array antenna to the interference orthogonal complement space; estimating the incoming direction of satellite signal by utilizing the autocorrelation CLEAN algorithm for the multichannel delay data after projection and thearray data after projection; and forming the beam for the data after projection by utilizing the estimated direction of the satellite direction. The invention ensures zero decrement of the satellite signal, does not need an inertial navigation auxiliary unit, is simple to realize, enables the main lobe of an array directional diagram to aim at each satellite signal and is suitable for any arrays,and in addition, the estimation of the satellite signal direction is not limited by the array element number.
Owner:CIVIL AVIATION UNIV OF CHINA
System and method for communicating data symbols via wireless doubly-selective channels
A method for decoding data symbols modulated with a corresponding codeword from a constellation set of codewords expands the constellation set of codewords with a set of basis functions to produce a basis-expanded constellation set and projects projecting a received modulated data symbol onto orthogonal complements of the basis expanded constellation set to obtain a set of distance metric of a generalized likelihood ratio test (GLRT) for each codeword of the constellation set. The set of basis functions includes a Fourier exponential basis function in a frequency domain, a Legendre polynomial basis function in a time domain, and a Fourier-Legendre product basis function in the frequency domain. The method selects a codeword corresponding to a minimal distance metric or a maximal correlation metric and decodes the data symbol from the received modulated data symbol using the codeword.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
GPS (Global Positioning System) interference inhibition method based on single-channel multi-delay cross-correlation treatment
InactiveCN101788675BFulfill positioning requirementsGood estimateSatellite radio beaconingHat matrixUltrasound attenuation
The invention provides a GPS (Global Positioning System) interference inhibition method based on single-channel multi-delay cross-correlation treatment, which is realized by combining subspace projection and a conventional wave beam forming technology. In the method, firstly, interference is inhibited by utilizing an interference orthogonal complement space projection matrix; and secondly, satellite signals are strengthened by utilizing the conventional wave beam forming technology, i.e. as for data after projection, the satellite signal direction is estimated by an autocorrelation CLEAN algorithm, and the estimated satellite signal direction is utilized to carry out conventional wave beam forming. The method comprises the following steps of projecting signals received by an array antennato an interference orthogonal complement space; as for a cross-correlation matrix of the projected single-channel multi-delay data and the projected array data, estimating the satellite signal direction by the autocorrelation CLEAN algorithm; and carrying out wave beam forming on the projected data by utilizing the estimated satellite signal direction. The invention realizes interference inhibition and ensures non attenuation of satellite signals by fully utilizing data information without needing an inertia navigation auxiliary unit and has the advantages of simple realization and higher estimation accuracy. The satellite signal direction is not limited by the array number.
Owner:CIVIL AVIATION UNIV OF CHINA
Signal processing method and equipment
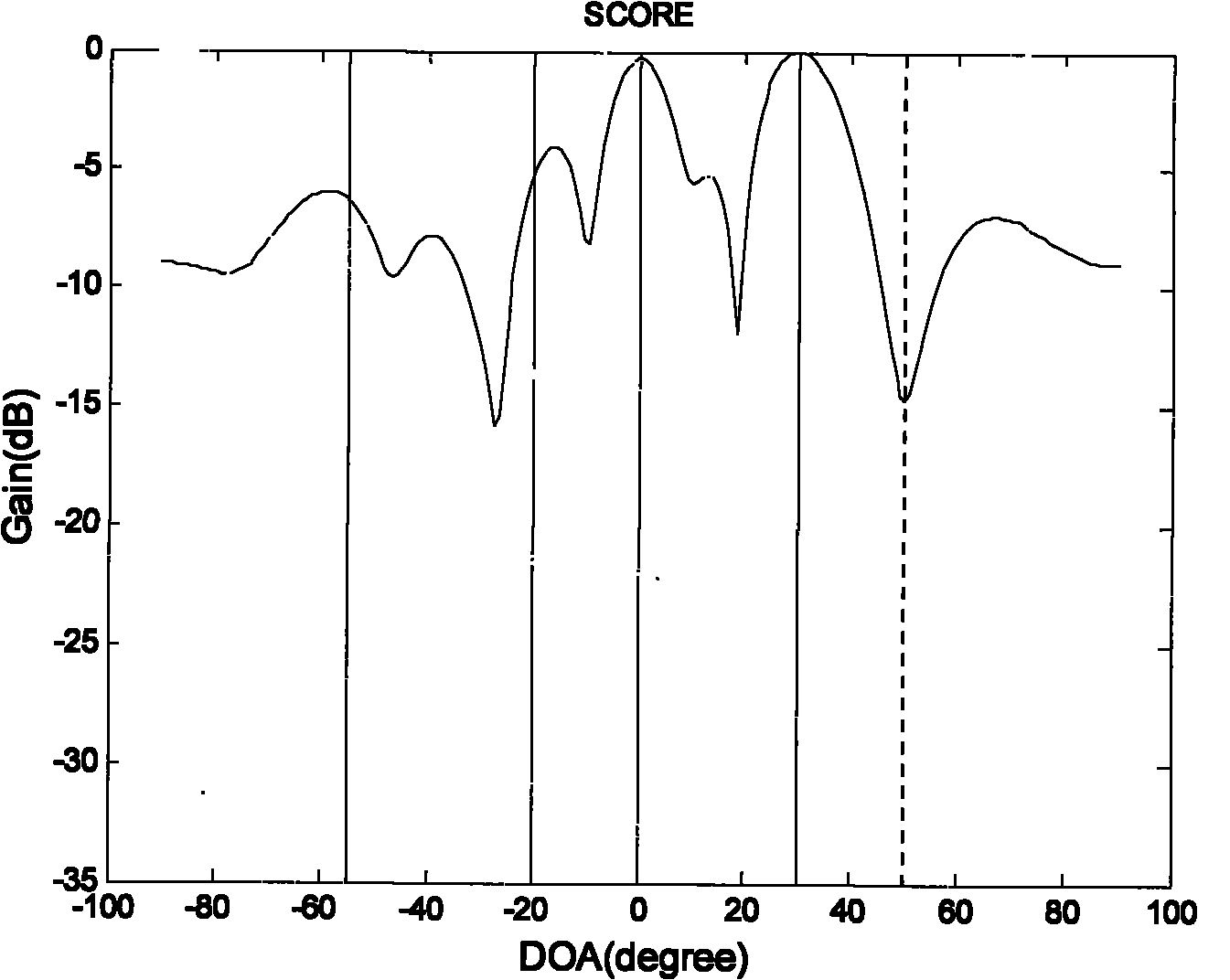
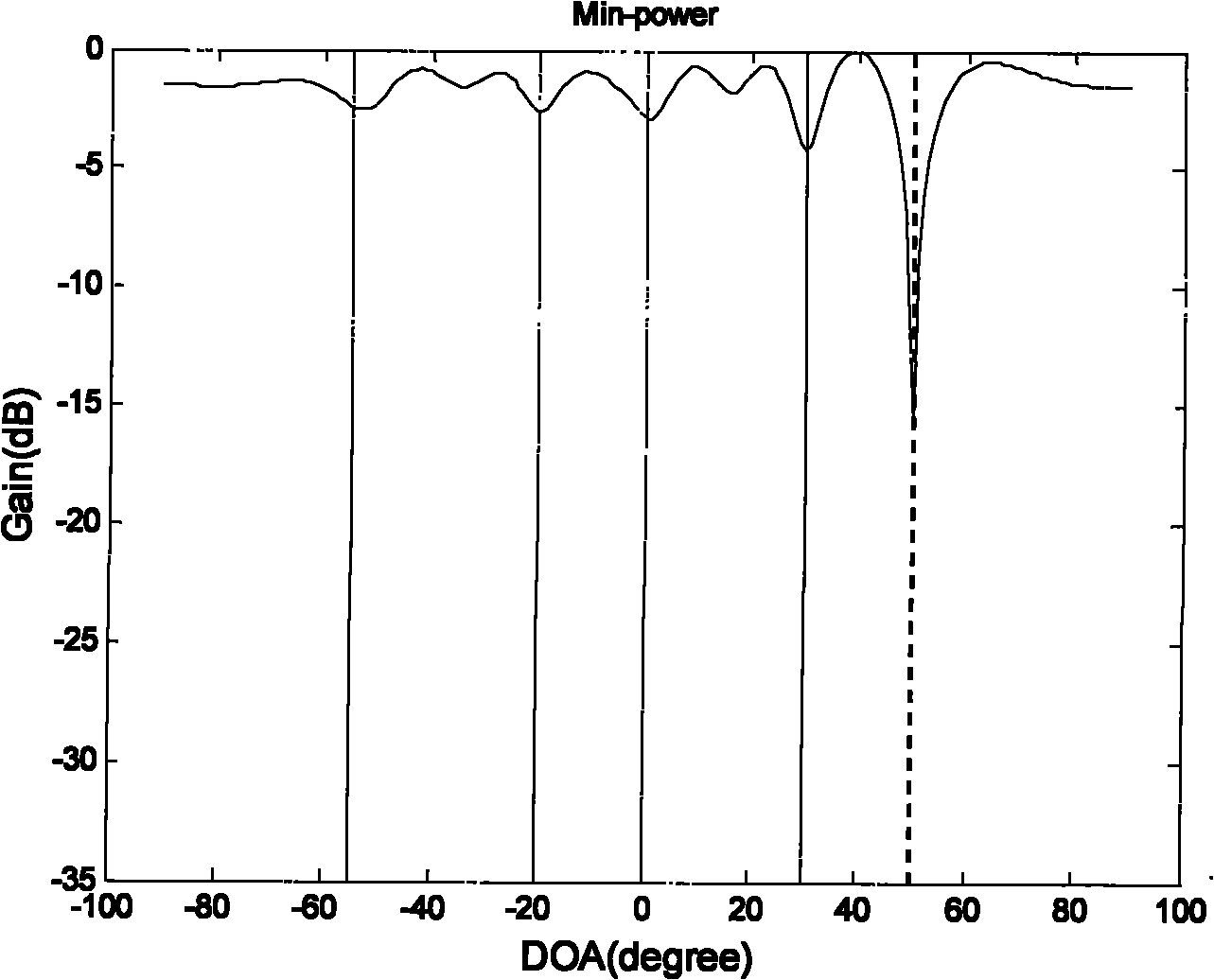
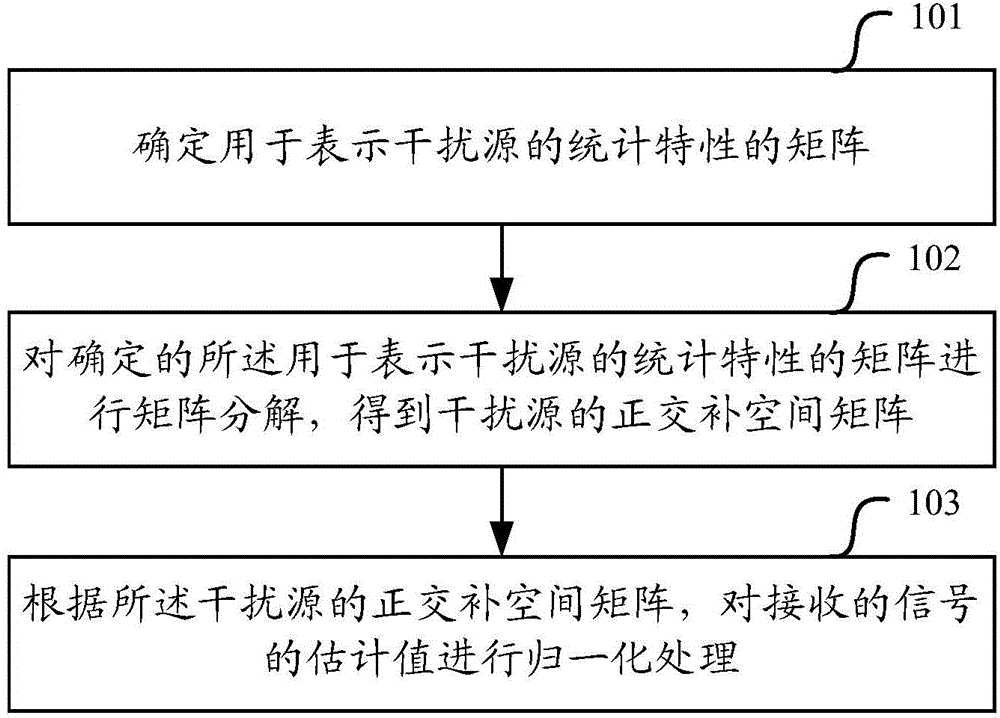
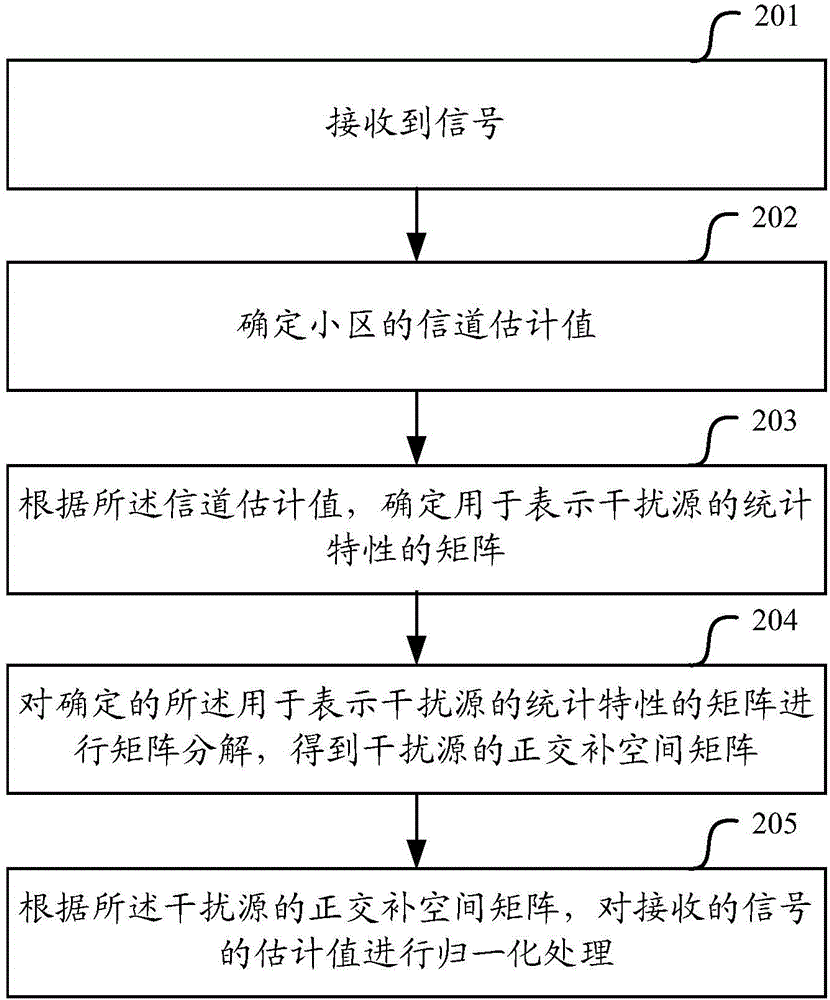
ActiveCN104836633AImprove SINRAdaptation strategy characterisationWireless communicationMatrix decompositionSystem capacity
The embodiment of the invention relates to the technical field of wireless communication, specially relates to a signal processing method and equipment, and is used to solve the problems that a current interference reduction scheme existing in the prior art cannot improve the system capacity and the signal-interference and noise ratio and cannot perform inhibition or coordination relative to a remote same-frequency cell. The method of the embodiment comprises determining a matrix for representing statistical characteristics of a reference source, performing matrix decomposition on the determined matrix for representing the statistical characteristics of the reference source to obtain an orthogonal complement space matrix, and performing normalized processing on an estimated value of a received signal according to the orthogonal complement space matrix of the reference source.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
A csmg beamforming method based on subspace projection
ActiveCN108415040BEasy to keepReduce computational complexitySatellite radio beaconingComputation complexityOrthogonal complement
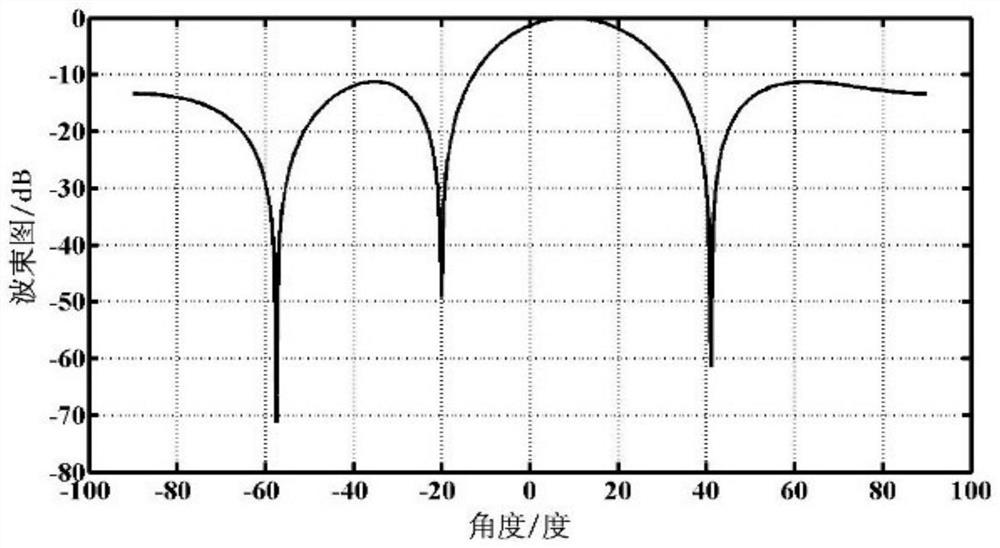
The invention provides a CSMG beamforming method based on subspace projection, and relates to the technical field of anti-jamming of navigation receivers. According to the satellite navigation signal and interference signal received by the navigation receiver, the method constructs the interference subspace and its orthogonal complement space, projects the space-time signal vector received by the antenna array into the subspace, and uses the sampling with strict minimum power The matrix gradient algorithm (CSMG) performs beamforming on the projected output signal in a fixed direction. The invention has a strictly constrained sampling matrix gradient algorithm, which has less computational complexity and faster convergence speed; the CSMG beamforming algorithm can form a deeper interference null, which can more effectively suppress interference signals, retain desired signals, and improve Output SINR.
Owner:SHENYANG AEROSPACE UNIVERSITY
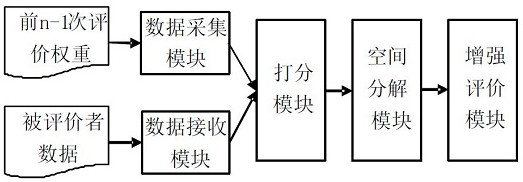
Multi-value chain collaborative evaluation system and method based on spatial decomposition enhancement
PendingCN114219381AImprove objectivityImprove the level ofResourcesComplex mathematical operationsOrthogonal complementData mining
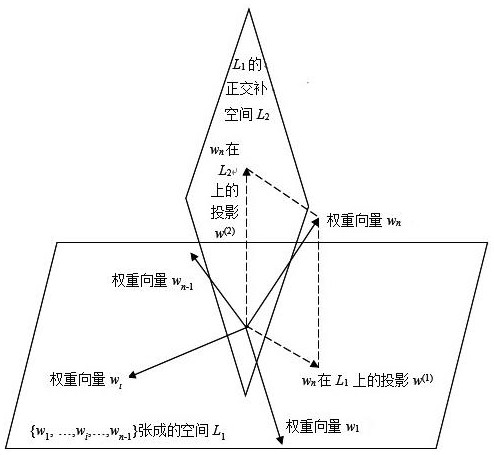
The invention discloses a multi-value chain collaborative evaluation system and method based on spatial decomposition enhancement, and aims at a scene in which an evaluated person participates in evaluation of a plurality of evaluation systems in sequence, under the condition of information asymmetry, according to sub-linear spaces formed by weight vectors in the first (n-1) evaluation systems and orthogonal complement spaces of the sub-linear spaces, projecting a weight vector vector sub-linear space and an orthogonal complement space of the nth evaluation system, performing linear decomposition on the projection of the sub-linear space by using a base formed by a maximum linear irrelevant group of a weight vector, quantitatively calculating an enhancement multiple, and enhancing the winner in the first n-1 evaluations, so as to partially realize the restoration of the hidden information, and the objectivity of the nth evaluation and the overall level of the winner are improved.
Owner:CHENGDU TECHCAL UNIV +4
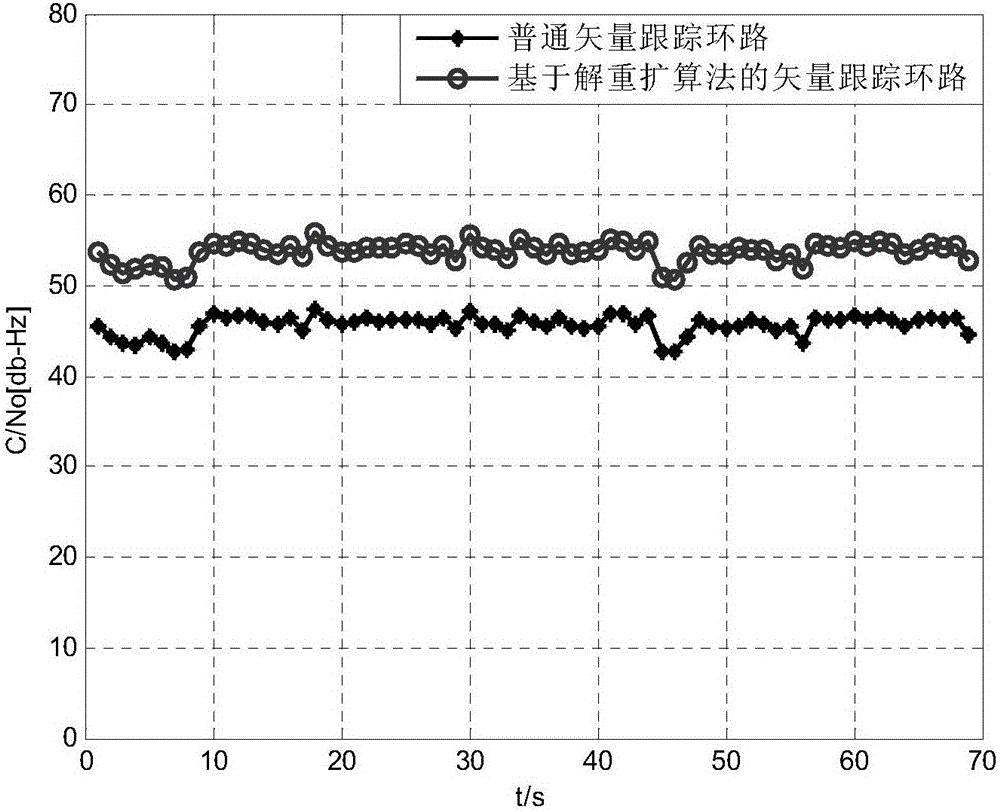
GNSS vector receiver anti-interference method based on despread respread algorithm
InactiveCN107179540APrecise positioningHigh gainSatellite radio beaconingDiscriminatorInterference resistance
The present invention provides a GNSS vector receiver anti-interference method based on the despread respread algorithm. The method comprises: performing projection of digital intermediate-frequency signals received by an array antenna to an interference orthogonal complement space, sending data after interference suppression into a receiver, giving out a receiver state vector and a tracking loop parameter initial value after the location solution is completed through a scalar tracking loop; performing predication of the receiver state vector and the tracking loop parameter, employing the predicated and obtained tracking loop parameter to construct reference signals, and performing coherent accumulation of the receiving signals and the reference signals to solve a weight vector; performing weighting of the receiving signals, and obtaining a correlated result after interference suppression; and sending a correlated result into a discriminator to perform updating and correction of the receiver state vector and the tracking loop parameter, etc. The GNSS vector receiver anti-interference method based on the despread respread algorithm can improve the location performance of a receiver while generating high gain, has the capabilities of suppression resistance and interference resistance, does not need to know satellite signals and interference direction information, is not sensitive to array manifold errors, and is good in robustness.
Owner:CIVIL AVIATION UNIV OF CHINA
Spectral gamut mapping based on a colorimetric gamut mapping
InactiveUS8009906B2Simple methodDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsGamutOrthogonal complement
Mapping spectral colors in an Interim Connection Space (ICS) of a full spectral space based on a colorimetric gamut map in a color space is provided. A spectral color value in the ICS is accessed, and the spectral color value is transformed into a calorimetric color value in the color space. The calorimetric color value is mapped into mapped calorimetric color value in a first subspace of the ICS. Mapping the colorimetric color value includes gamut-mapping the calorimetric color value using the calorimetric gamut map, followed by identifying the color space with the first subspace. An intersection of a spectral gamut in the ICS and an affine subspace characterized by the mapped colorimetric color value is determined, and the spectral color value is projected onto the intersection. The first subspace is an orthogonal complement of a null space of a transformation from the ICS to the color space.
Owner:CANON KK
Ads-b Deceptive Interference Suppression Method Based on Cross Array
InactiveCN104360323BHigh resolutionDeceptive Jamming SuppressionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionOrthogonal complementArray element
Owner:CIVIL AVIATION UNIV OF CHINA
Array Element Error Estimation Method Based on Clutter Subspace
InactiveCN103885042BHigh Error Estimation AccuracyOvercoming the problem of poor clutter suppression effectWave based measurement systemsSingular value decompositionPrior information
The invention discloses an array element error estimation method based on clutter subspace. The array element error estimation method based on clutter subspace includes the implementation steps that 1, radar prior information is utilized for calculating a clutter time-space steering vector matrix; 2, singular values of radar receiving data and the clutter time-space steering vector matrix are resolved; 3, the number of the main singular values is calculated; 4, a clutter orthogonal complement space matrix is built according to the obtained number of the main singular values; 5, antenna array element errors are estimated through the obtained clutter orthogonal complement space matrix and the orthogonality of a left singular vector corresponding to a largest singular value obtained by resolving the received data; 6, a clutter signal model is corrected according to the estimated antenna array element errors, and clutter is restrained. The good antenna array element error estimation performance can be obtained under the situation with few samples and few pulses, so that the array element error estimation method based on clutter subspace has the advantages of being high in error estimation accuracy and stable in estimation performance.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
A Robust Direction of Arrival Estimation Method
ActiveCN104330766BImprove estimation accuracyReduce complexityDirection findersSingular value decompositionEstimation methods
The invention discloses a robust estimation method of a direction of arrival (DOA), by which quite high estimation precision can be obtained. The method specifically comprises: sequentially dividing an equidistant linear array into three sub-arrays from the left to the right, i.e., a forward auxiliary array, a central main array and a backward auxiliary array respectively; dividing the central main array into a front half portion and a rear half portion according to a certain rule; then calculating a covariance matrix Rforward between the front half portion and the backward auxiliary array and a covariance matrix Rbackward between the rear half portion and the forward auxiliary array; performing singular value decomposition respectively on the Rforward and the Rbackforward, and extracting the orthogonal complement of the subspace of far-field signals received by the equidistant linear array from a singular value decomposition result; and establishing a DOA estimation operator by use of guiding vectors between the orthogonal complement and the front half portion and the rear half portion, performing search on the DOA estimation operator by use of a minimum parameter search method to obtain K minimum value points, and through the search, obtaining theta 1 to theta k of each minimum value point as k DOAs of the far-field signals.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com