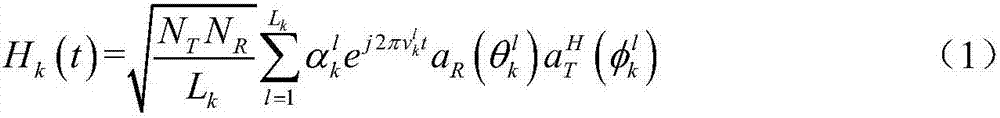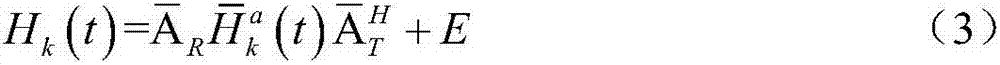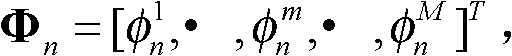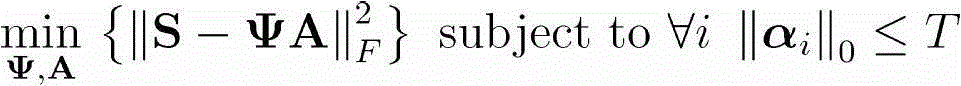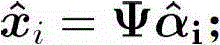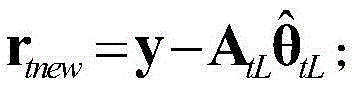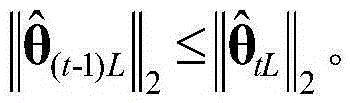Patents
Literature
361 results about "Matching pursuit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
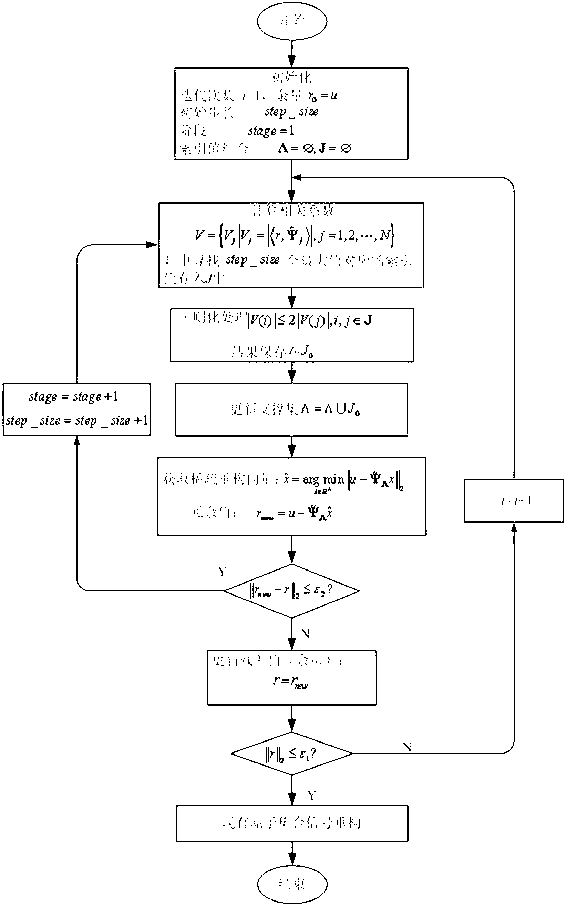
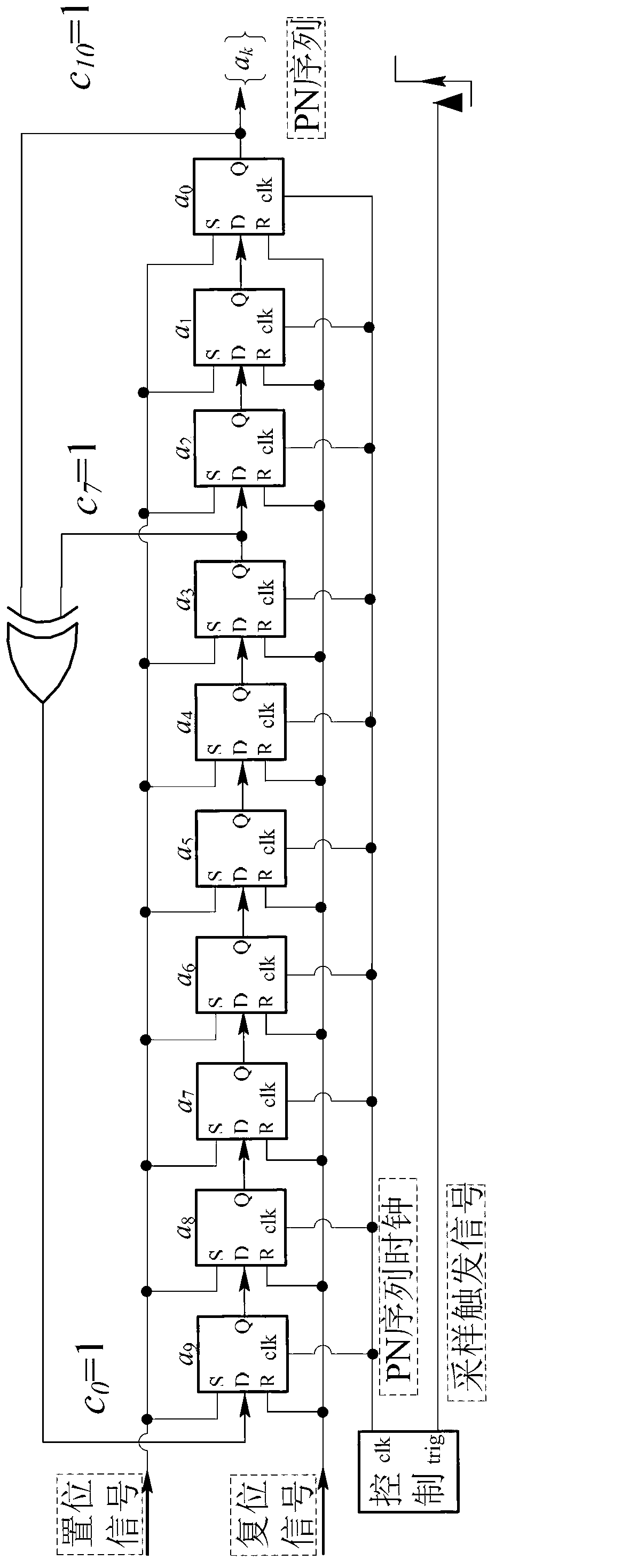
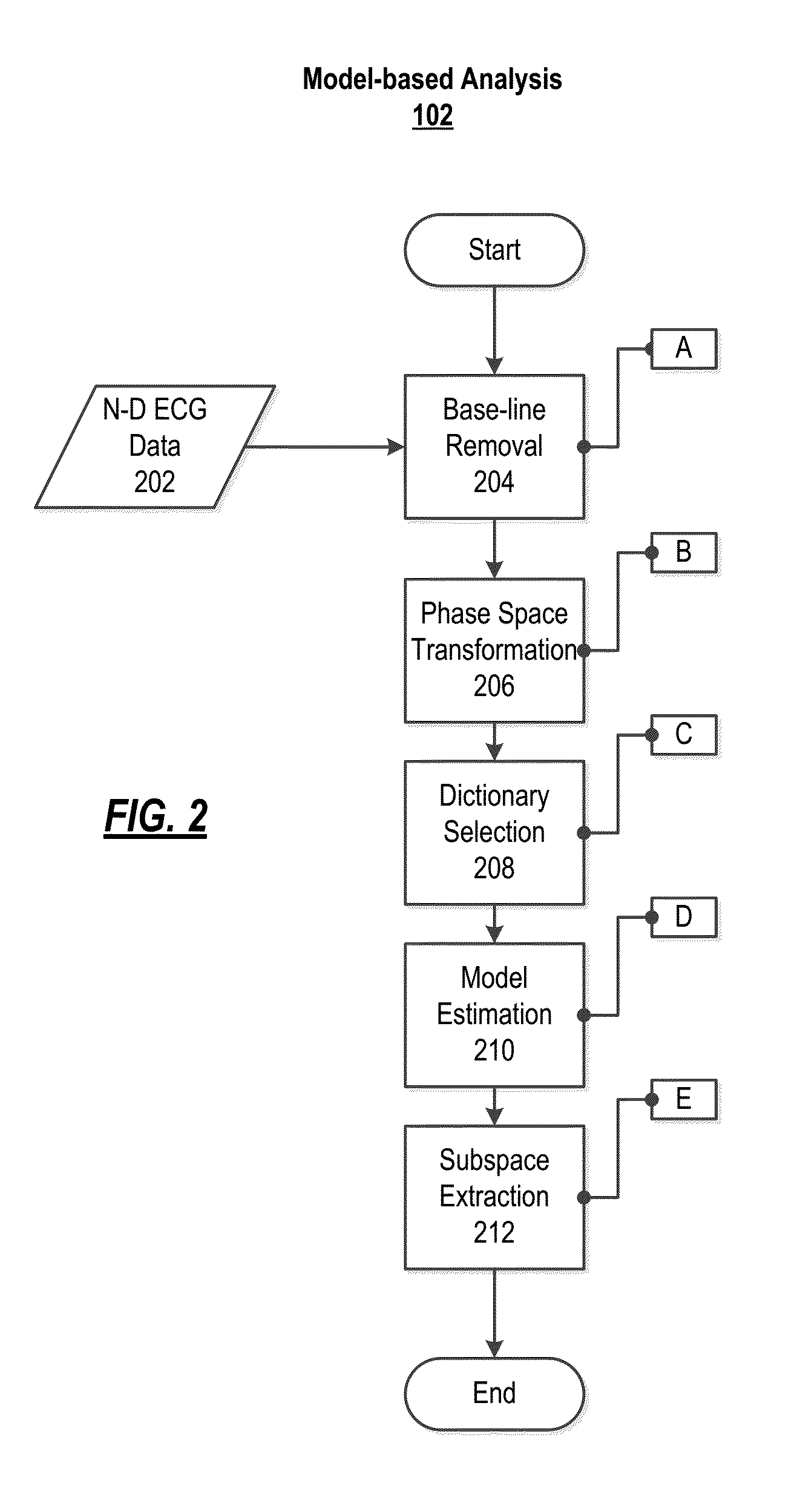
Matching pursuit (MP) is a sparse approximation algorithm which finds the "best matching" projections of multidimensional data onto the span of an over-complete (i.e., redundant) dictionary D. The basic idea is to approximately represent a signal f from Hilbert space H as a weighted sum of finitely many functions gγₙ (called atoms) taken from D. An approximation with N atoms has the form f(t)≈fN(t):=∑ₙ₌₁ᴺaₙgγₙ(t) where gγₙ is the γₙth column of the matrix D and aₙ is the scalar weighting factor (amplitude) for the atom gγₙ.
Dictionary generation method for video and image compression
InactiveUS7003039B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioImprove matchColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
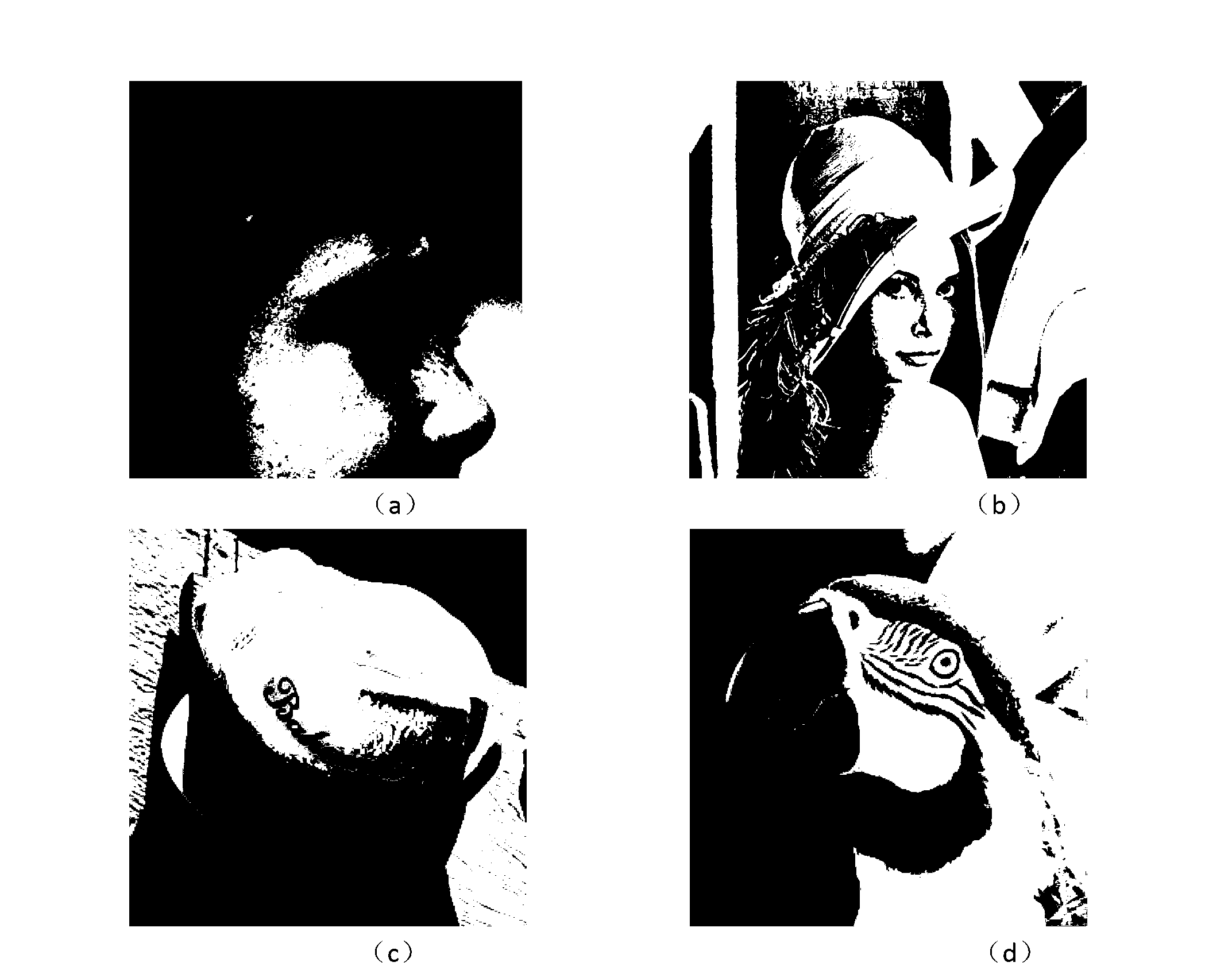
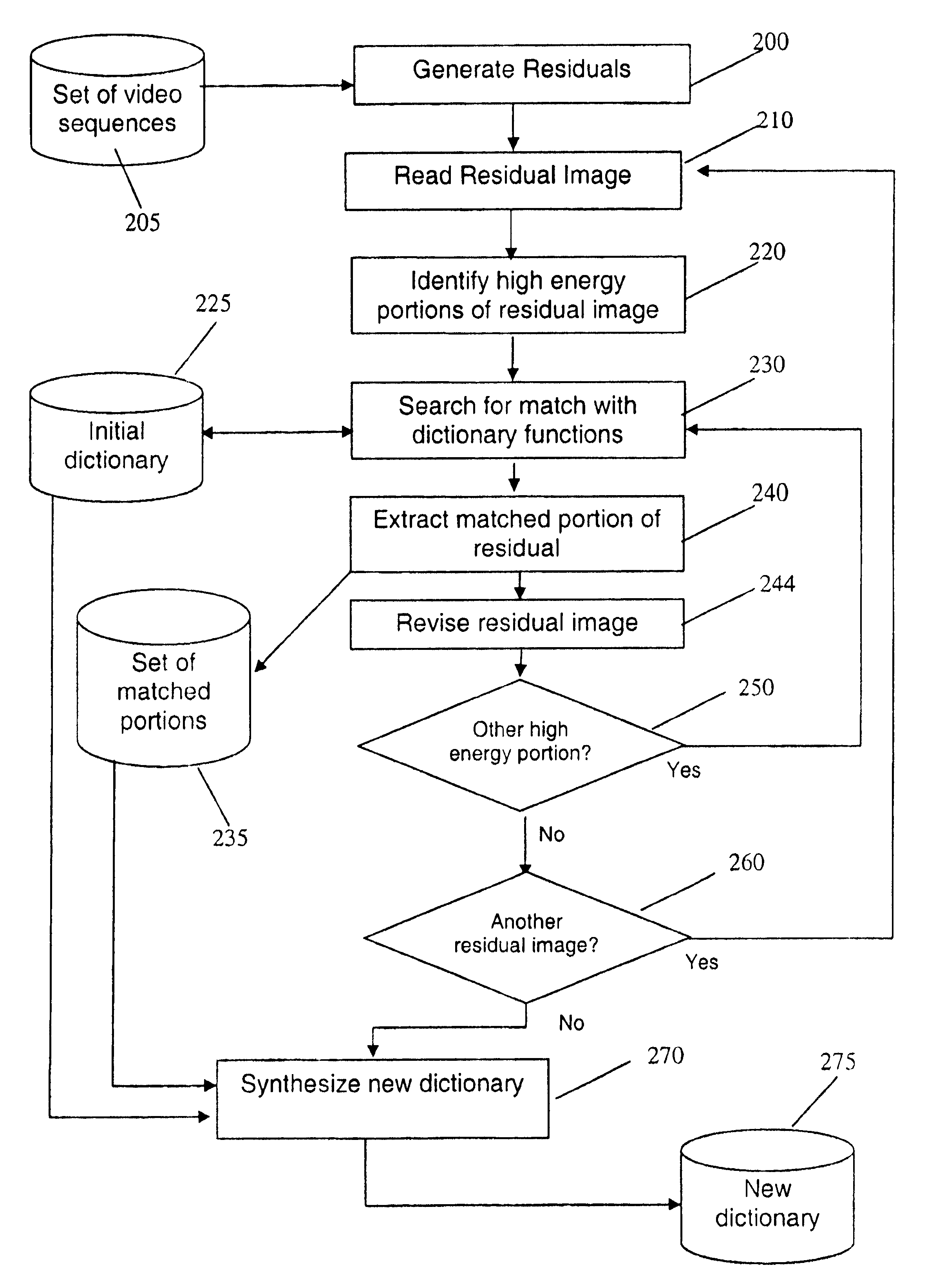
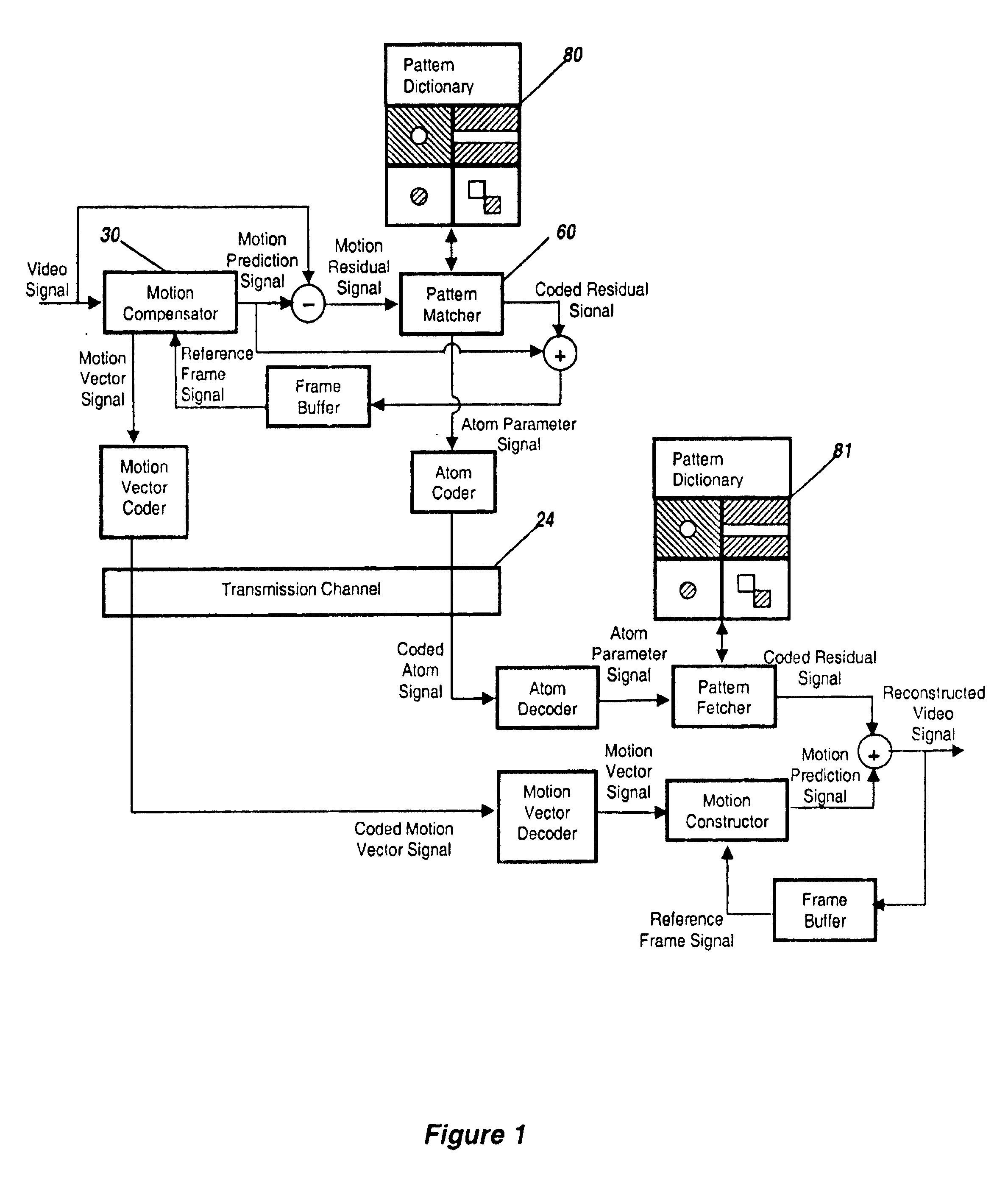
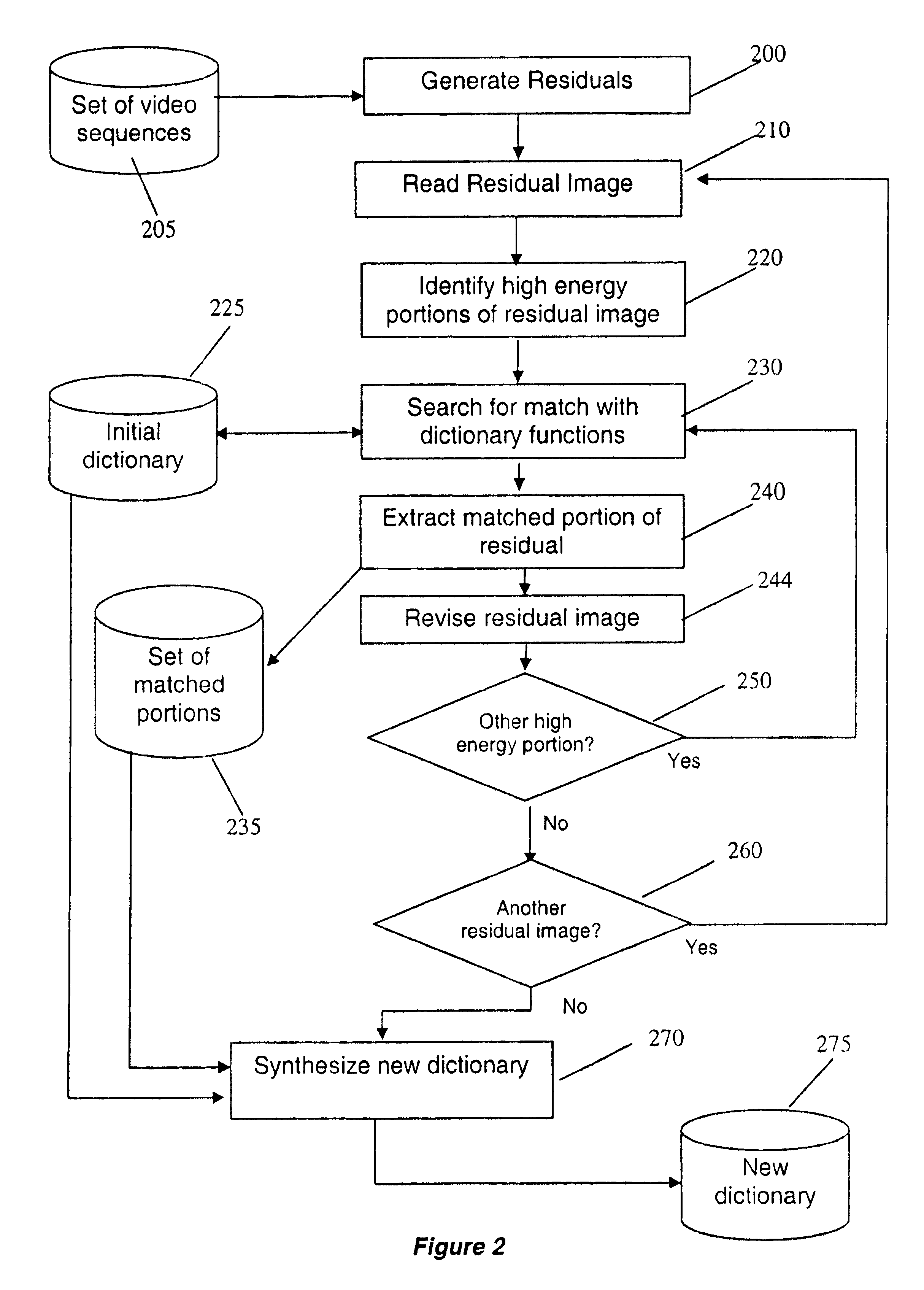
This invention relates to the creation of dictionary functions for the encoding of video signals using matching pursuit compression techniques. After an initial set of reference dictionary images is chosen, training video sequences are selected, and motion residuals are calculated. High energy portions of the residual images are extracted and stored when they match selection criteria with the reference dictionary. An energy threshold is used to limit the number of video signal “atoms” encoded for each frame, thus avoiding the encoding of noise. A new dictionary is then synthesized from the stored portions of the image residuals and the original reference dictionary. The process can then be repeated using the synthesized dictionary as the new reference dictionary. This achieves low bit rate signals with a higher signal-to-noise ratio than have been previously achieved.
Owner:TRU VIDEO CORP +1
Compressed sensing reconstructing method of sparse signal with unknown block sparsity
InactiveCN101908889AHigh probability of refactoringHigh precisionCode conversionReconstruction methodSignal compression
The invention relates to a compressed sensing reconstructing method of a sparse signal with the unknown block sparsity, belonging to the technical field of compressed sensing, in particular to a reconstruction method of a block sparse signal. The method comprises the steps of finding out one subset of a signal support set by initializing block sparsity k and iterating each block sparse signal, increasing the block sparsity while keeping iteration and finally finding out the support set of the whole source signal x so as to achieve the purpose of reconstructing the source signal x. The invention has high reconstruction precision by iterating and modifying the support set many times, and has high probability for reconstructing block sparse signals without the overmatching phenomenon compared with the traditional block sparsity matching and tracking and orthogonal matching and tracking method. The invention does not need the block sparsity as the priori knowledge and is particularly suitable for the reconstruction field of signals with unknown block sparsity.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Video encoding and decoding methods and corresponding devices
The invention relates to the field of video compression and, more specifically, to a video encoding method applied to an input sequence of frames in which each frame is subdivided into blocks of arbitrary size. This method comprises, for at least a part of the blocks of the current frame, the steps of: generating on a block basis motion-compensated frames obtained from each current original frame and a previous reconstructed frame; generating the said motion-compensated frames residual signals; using a matching pursuit algorithm for decomposing each of the generated residual signals into coded dictionary functions called atoms, the other blocks of the current frame being processed by means of other coding techniques; coding said atoms and the motion vectors determined during the motion compensation step, for generating an output coded bitstream; said method being such that any atom acts only on one block B at a time, said block-restriction leading to the fact that the reconstruction of a residual signal f is obtained from a dictionary that is composed of basis functions gγnæBrestricted to the block B corresponding to the indexing parameter γn, according to the following 2D spatial domain operation: gγnæB(i,j)=gγn(i,j) if pixel (i,j)εB; gγnæB(i,j)=0 otherwise (i.e. (i,j)∉B).
Owner:DYNAMIC DATA TECH LLC
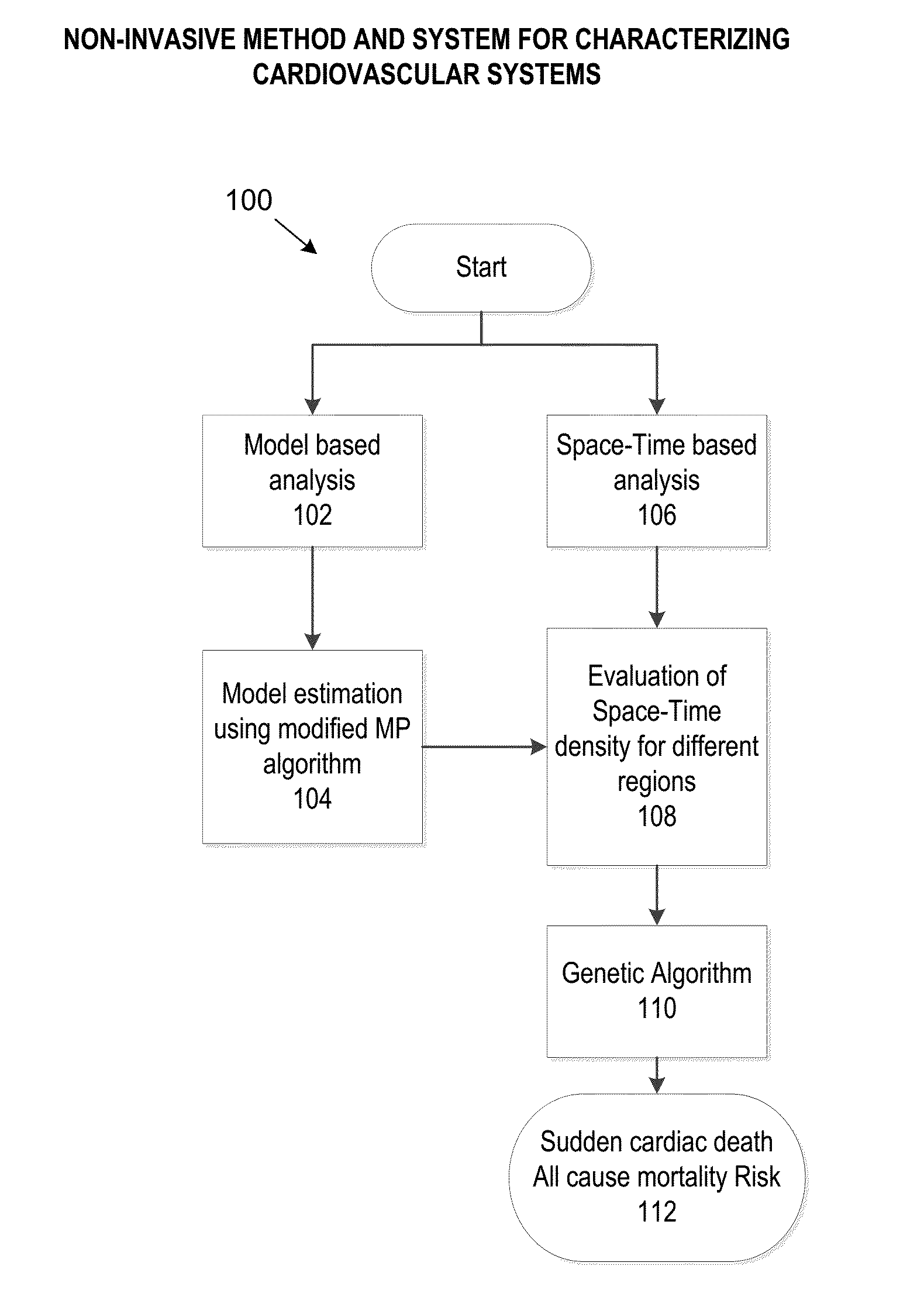
Non-invasive method and system for characterizing cardiovascular systems
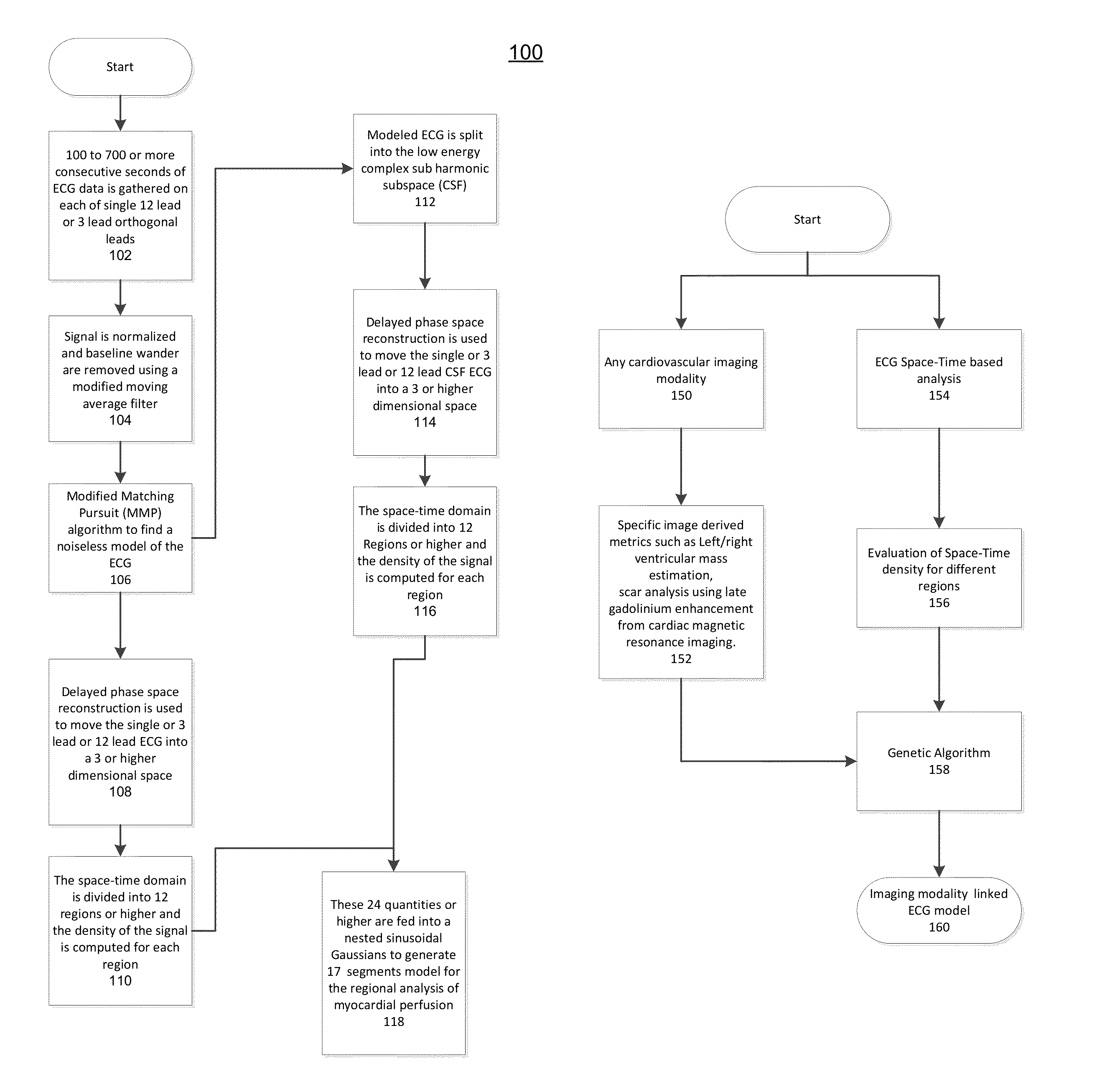
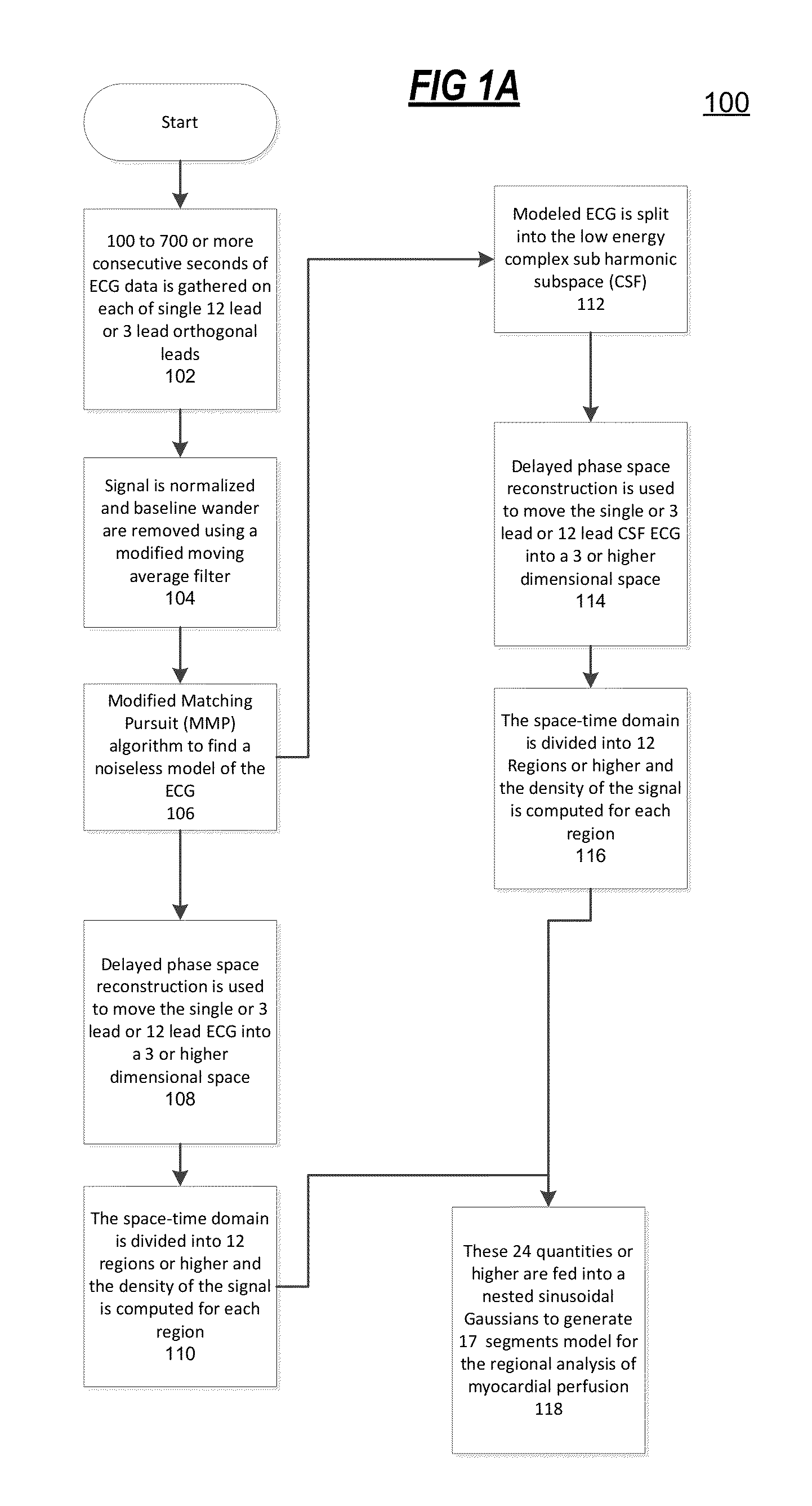
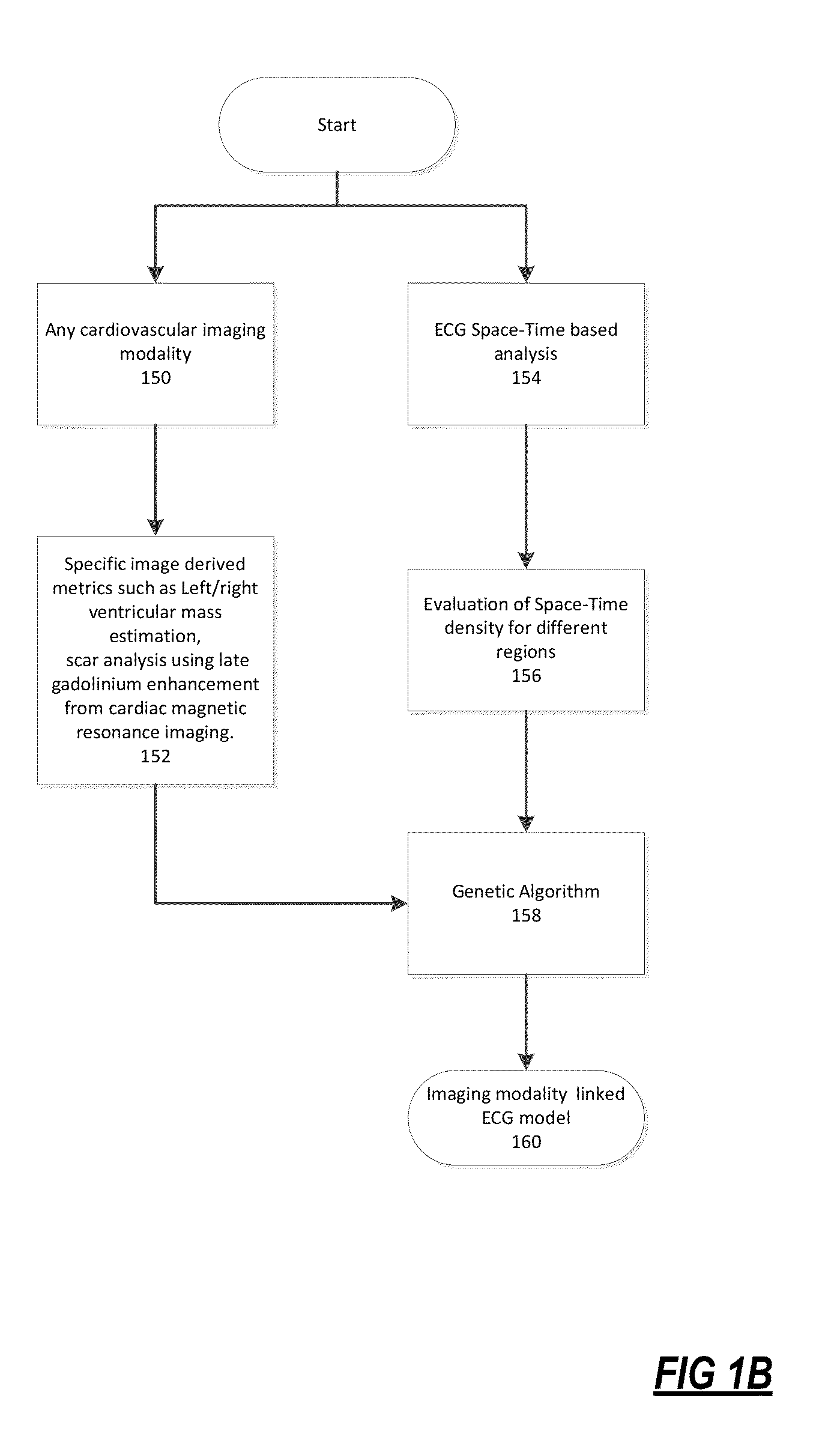
The present disclosure uses physiological data, ECG signals as an example, to evaluate cardiac structure and function in mammals. Two approaches are presented, e.g., a model-based analysis and a space-time analysis. The first method uses a modified Matching Pursuit (MMP) algorithm to find a noiseless model of the ECG data that is sparse and does not assume periodicity of the signal. After the model is derived, various metrics and subspaces are extracted to image and characterize cardiovascular tissues using complex-sub-harmonic-frequencies (CSF) quasi-periodic and other mathematical methods. In the second method, space-time domain is divided into a number of regions, the density of the ECG signal is computed in each region and inputted into a learning algorithm to image and characterize the tissues.
Owner:ANALYTICS FOR LIFE
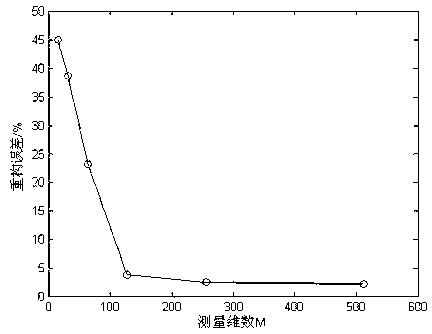
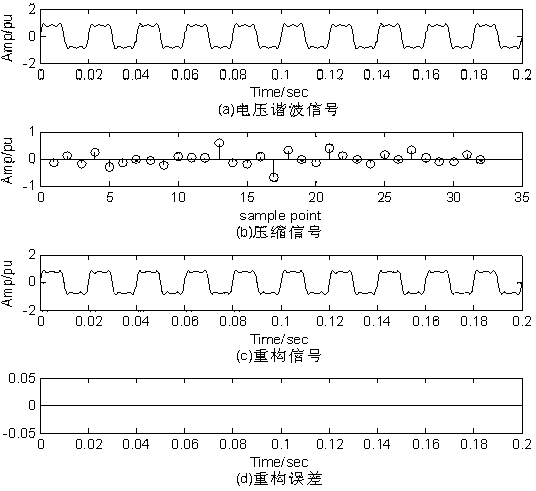
Self-adaptive reconstruction and uncompressing method for power quality data based on compressive sensing theory
The invention discloses a self-adaptive reconstruction and an uncompressing method for power quality data based on a compressive sensing theory. A power quality data compression process with concurrent sampling and compression is achieved through a random measurement matrix, compressive sensing thoughts are used to perform sparse decomposition on the power quality data, sparse signals are subjected to Gaussian measurement encoding, and a self-adaptive matching pursuit algorithm is applied to reconstruct signals. According to the self-adaptive reconstruction and the uncompressing method, the random measurement matrix is simple in structure and quick in operation, in no need of intermediate variable storage space and independent of power disturbance signal characteristics, and has universality; compared with greedy algorithms of an orthogonal matching pursuit and the like, known sparseness is not needed, self adaption and regularization processes are provided, the operation time is short, and accurate reconstruction can be achieved; and constraints of compression after sampling of traditional data compression methods are broken through, little sampling can recover original power quality signals well, and accordingly, requirements for hardware can be reduced, and the compression efficiency is improved.
Owner:镇江华飞检测技术有限公司
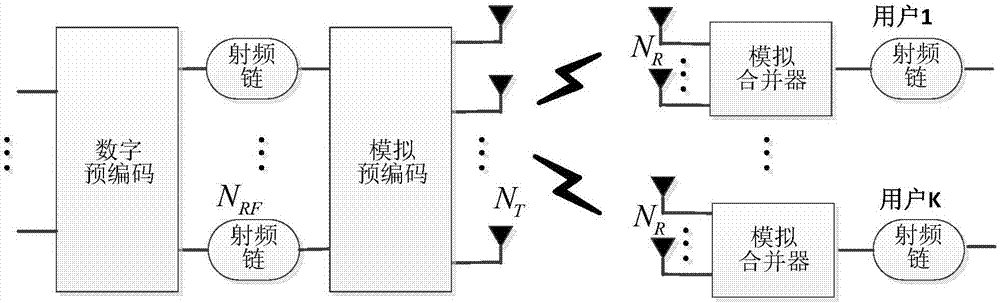
Time-varying channel estimation method for millimeter wave multi-user MIMO system
ActiveCN107018099AImprove accuracyImprove spectrum utilizationRadio transmissionChannel estimationEstimation methodsAngle of departure
The invention discloses a time-varying channel estimation method for a millimeter wave multi-user MIMO system. Based on the sparse characteristics of a millimeter wave channel in an angle domain, a channel estimation method based on compressed sensing is adopted. The method comprises the following steps: (1) modeling a time-varying millimeter wave channel; (2) quantitatively expressing the millimeter wave channel; (3) modeling a time-varying millimeter wave channel estimation problem as a compressed sensing mode; (4) recovering the estimated number of paths, angles of arrival and angles of departure by using a modified block orthogonal matching pursuit (R-BOMP) algorithm; (5) designing an analog precoding matrix and a digital precoding matrix based on the estimated number of paths and angles of arrival; (6) designing an analog merge vector based on the estimated number of paths and angles of departure; and (7) solving a millimeter wave channel matrix based on the number of paths, the angles of arrival and the angles of departure that are estimated as well as the analog precoding matrix, the digital precoding matrix and the analog merge vector that are designed. By adopting the time-varying channel estimation method disclosed by the invention, the accuracy and spectrum efficiency of the millimeter wave channel estimation can be improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
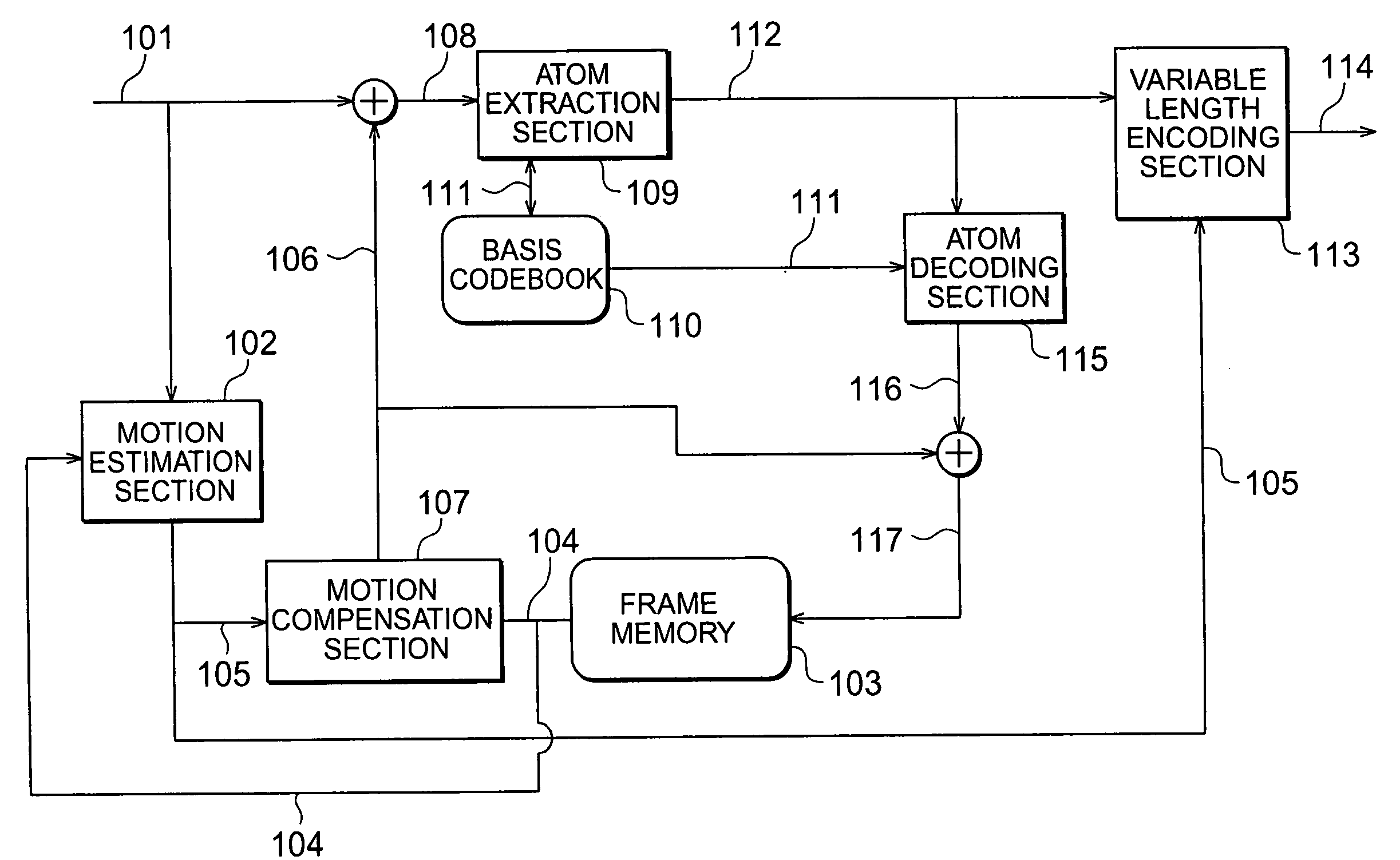
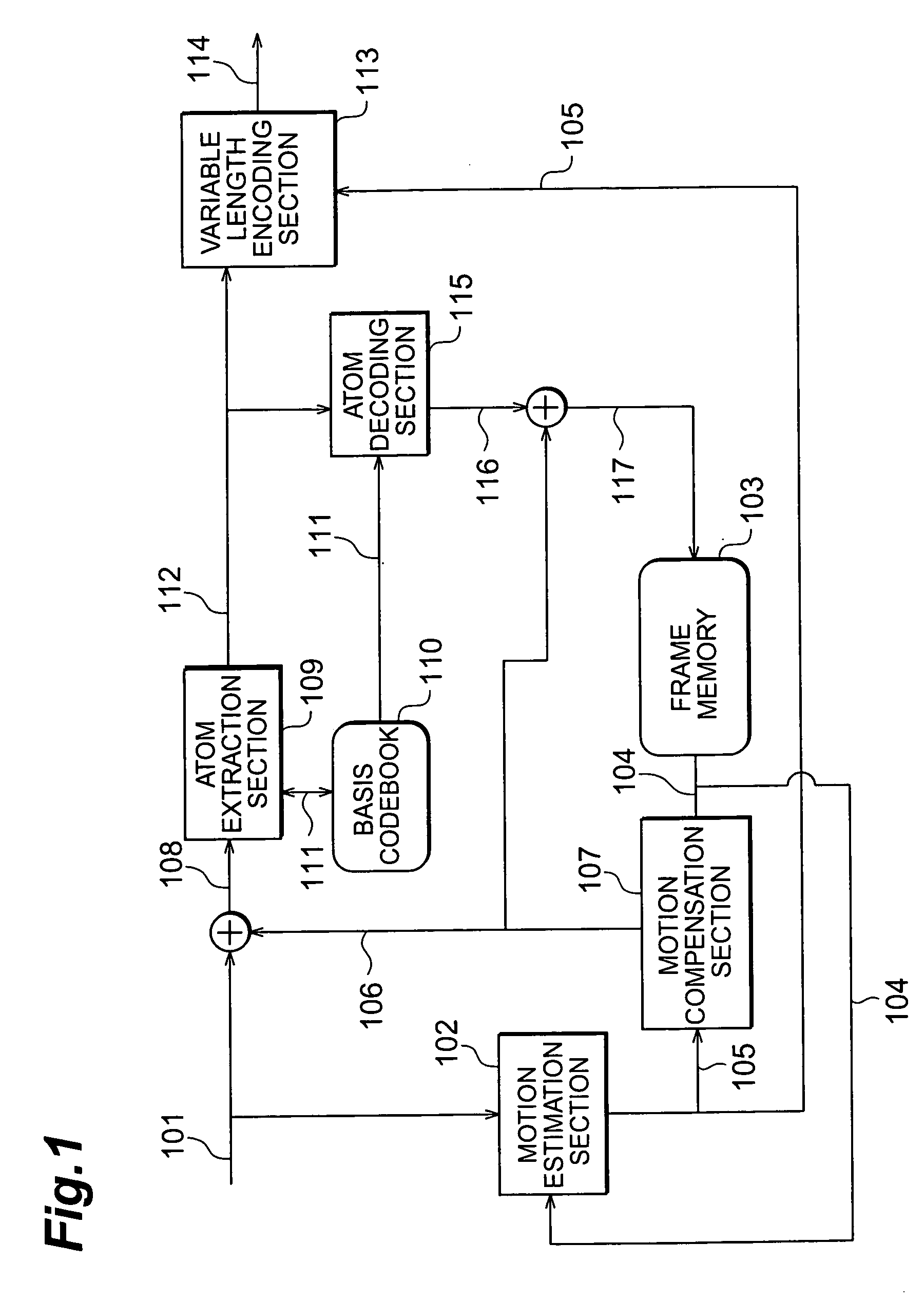
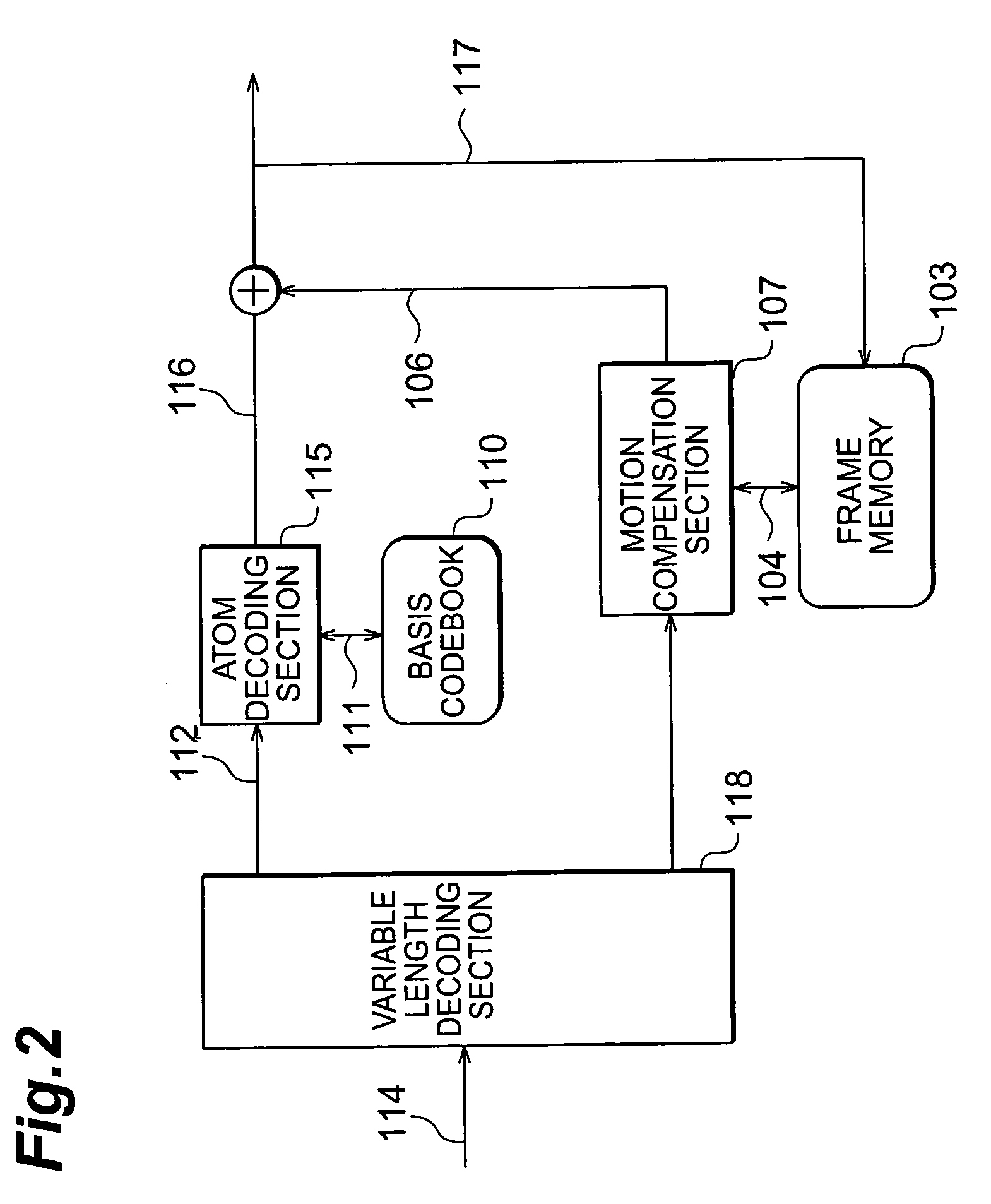
Image encoder, image decoder, image encoding method, and image decoding method
InactiveUS7292731B2Improve efficiencyImprove coding efficiencyPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningFrequency of occurrenceArithmetic coding
The image coding apparatus is constituted comprising an atom extraction section 109 for acquiring position data indicating the positions of atoms of prediction residual data in macroblocks, for each of the macroblocks; and a variable length encoding section 113 for determining the frequency of occurrence distribution of the position data in the macroblocks to be encoded, in accordance with the number of atoms of prediction residual data present in the macroblocks, and for performing arithmetic coding of the position data on the basis of the frequency of occurrence distribution thus determined. An improvement in the efficiency of the entropy coding of the atom parameters of Matching Pursuits coding is therefore feasible.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) tomography three-dimensional imaging method
InactiveCN102662171AImprove computing efficiencyHigh refactoring robustnessRadio wave reradiation/reflectionROMPSynthetic aperture sonar
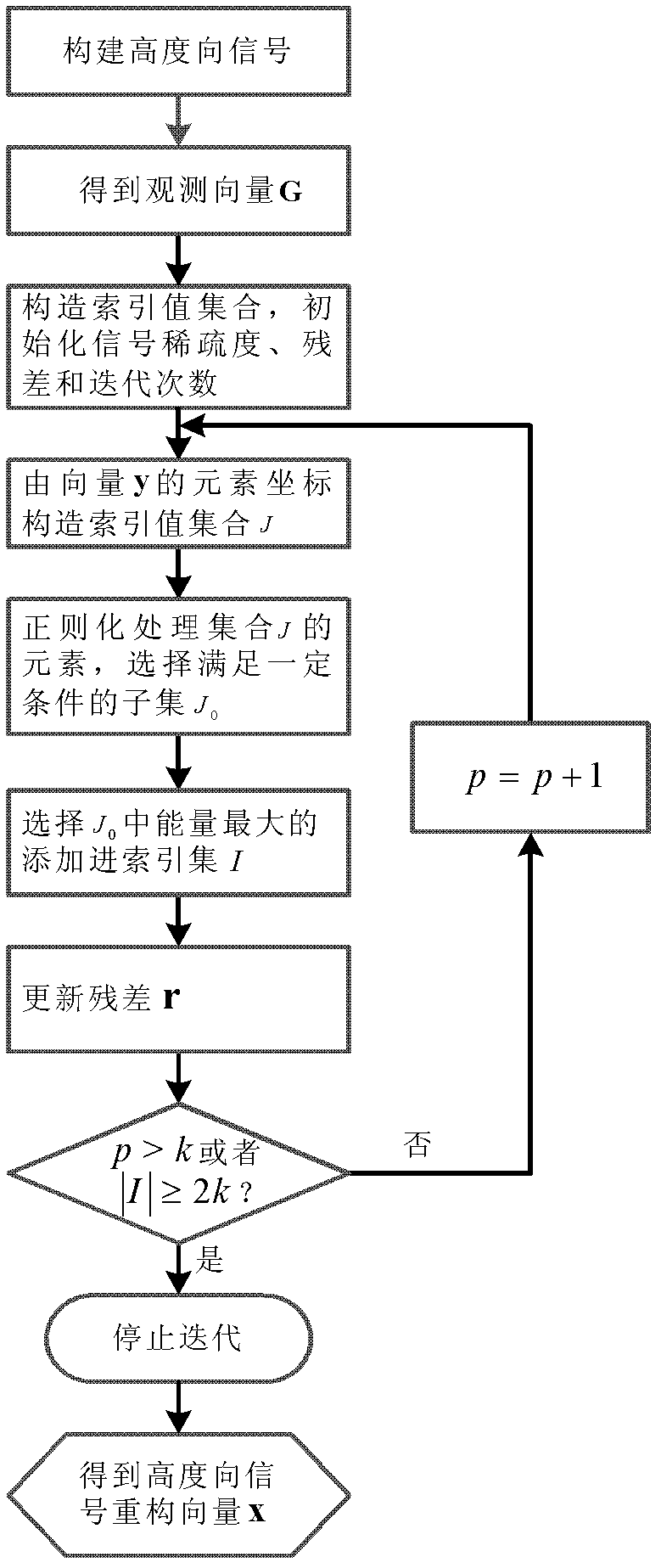
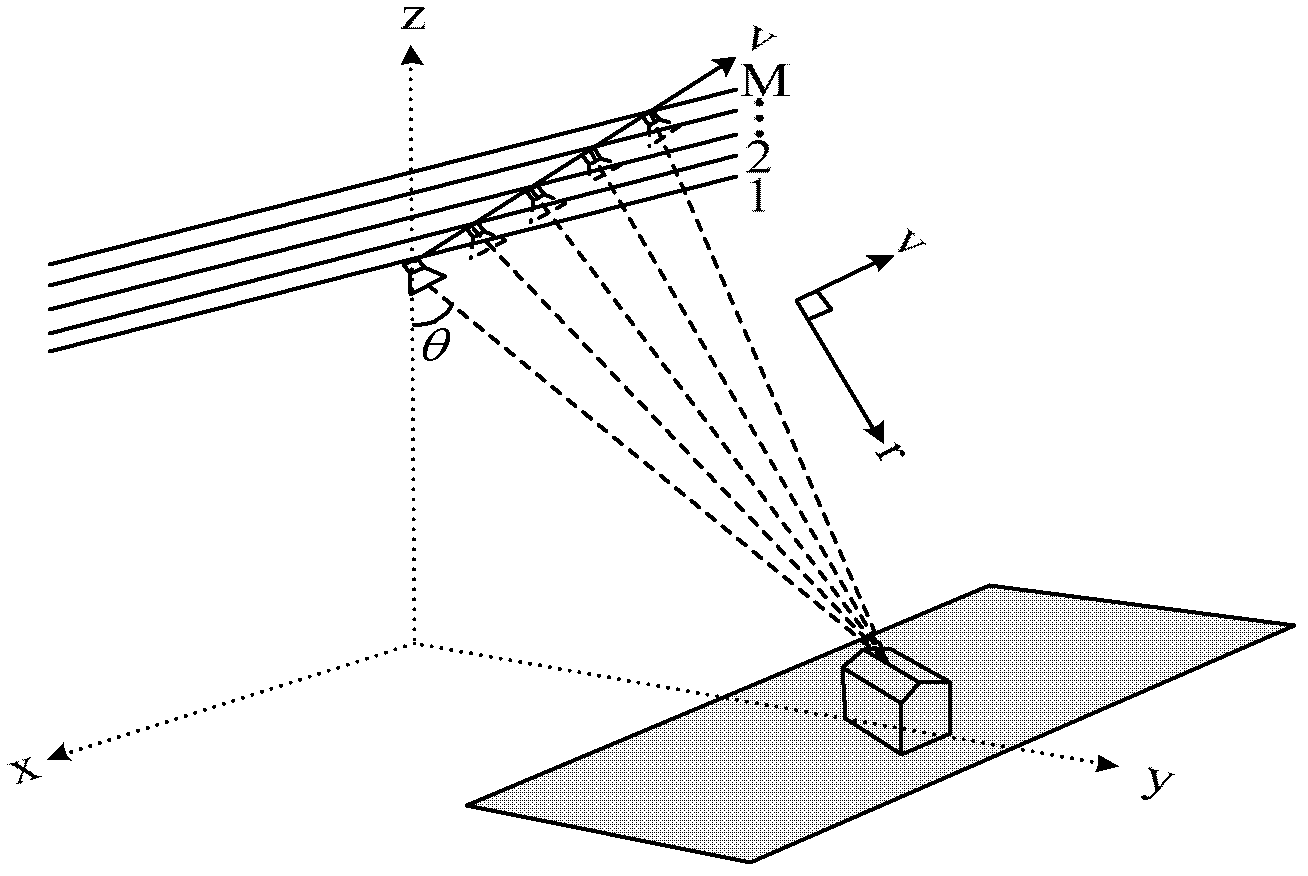
The invention discloses a synthetic aperture radar (SAR) tomography three-dimensional imaging method. According to the method, regularized orthogonal matching pursuit (ROMP) is combined with an SAR tomography three-dimensional imaging system, and height direction sparse signals are accurately reconstructed to realize height dimension focusing. When a measurement matrix strictly meets a restricted isometry property, any sparse signals can be accurately reconstructed by the method. By the imaging method, a sparse signal with the sparsity of k is subjected to iteration for k times to obtain a support set I of which the atomic number, namely absolute I is more than or equal to 2k, so that a height direction sparse signal is accurately reconstructed, the operation amount is small, and the operation efficiency is high; and moreover, observation vectors are sorted during iteration each time, the optimality of iteration is ensured and the reconstructing robustness is high.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Compressive-sensing-based sparse signal under-sampling method and implementation device
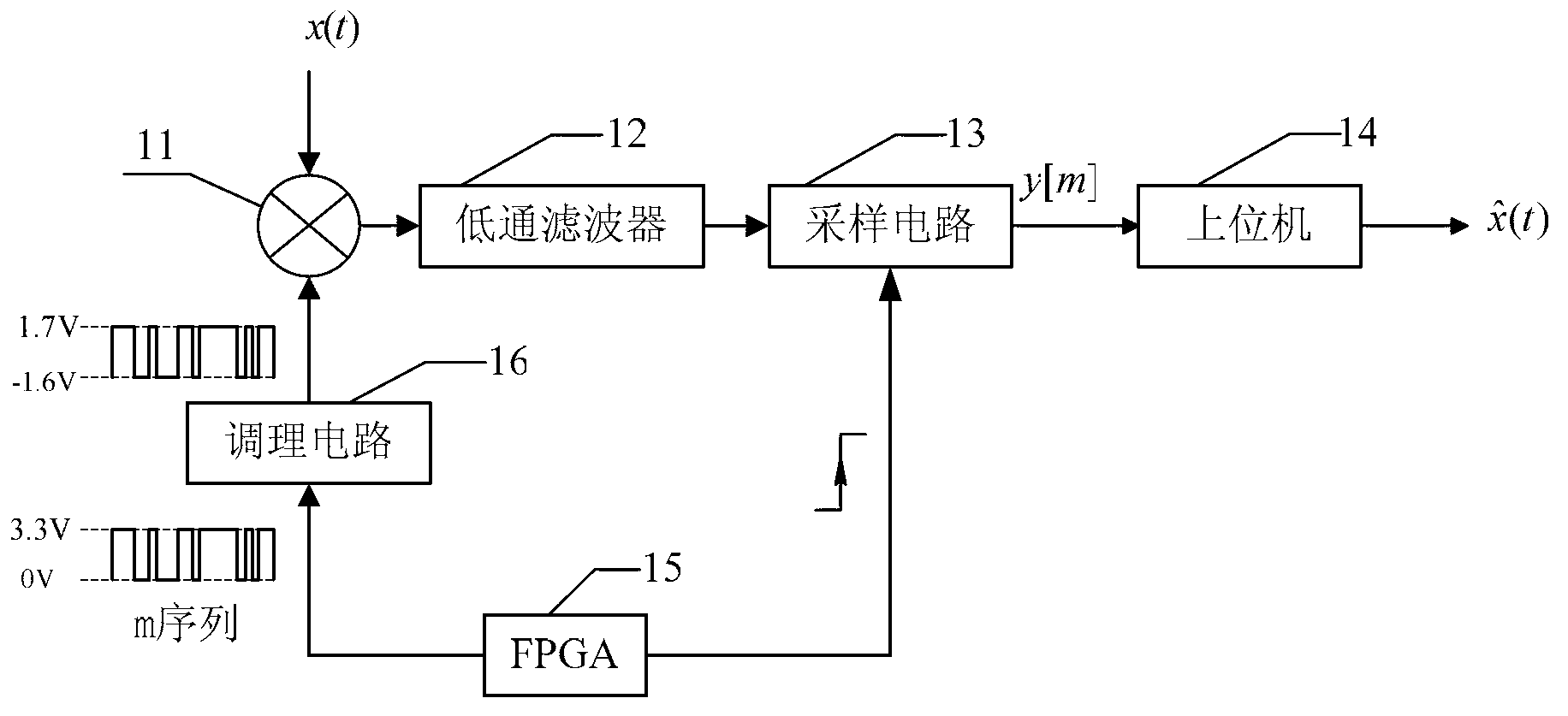
ActiveCN103178853ADownsamplingReduced rate requirementsAnalogue-digital convertersLow-pass filterSignal on
The invention relates to a compressive-sensing-based sparse signal under-sampling method and an implementation device, which are used for lowering a sampling rate of frequency-domain sparse signals on the premise of guaranteeing the restoration effect of the signals. The method comprises the following steps of: generating a trigger signal and an m sequence by an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array), carrying out frequency mixing on the m sequence and the measured sparse signal after the m sequence is modulated, and carrying out filtering by a low pass filter; sampling the filtered signal and storing sampled data by a data sampling module after the data sampling module detects the triggering signal; and calculating a transfer function of a system and the m sequence corresponding to the sampled data when the signal is reconstructed, and then restoring the original signal by an OMP (Orthogonal Matching Pursuit) signal reconstructing algorithm. The compressive-sensing-based sparse signal under-sampling method and the implement device are suitable for the under-sampling of frequency-domain sparse analogue signals.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Power system sub-synchronous oscillation mode identification method
ActiveCN103208808ARealize modal identificationAccurate and effective extractionPower oscillations reduction/preventionElectric power systemTime complexity
The invention discloses a power system sub-synchronous oscillation mode identification method which is characterized in that time complexity of the matching pursuit search process is reduced by aid of a particle swarm optimization, sub-synchronous oscillation signals are subjected to atomic decomposition in an optimized matching pursuit method, and atomic parameters are converted to sub-synchronous oscillation mode parameters after the optimum atom is searched. The power system sub-synchronous oscillation mode identification method can accurately identify power system sub-synchronous oscillation mode parameters, has good time-frequency characteristic, is favorable for deeply analyzing power system sub-synchronous oscillation characteristic, accordingly effectively restrains oscillation, and ensures stable operation of a unit and a power system.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
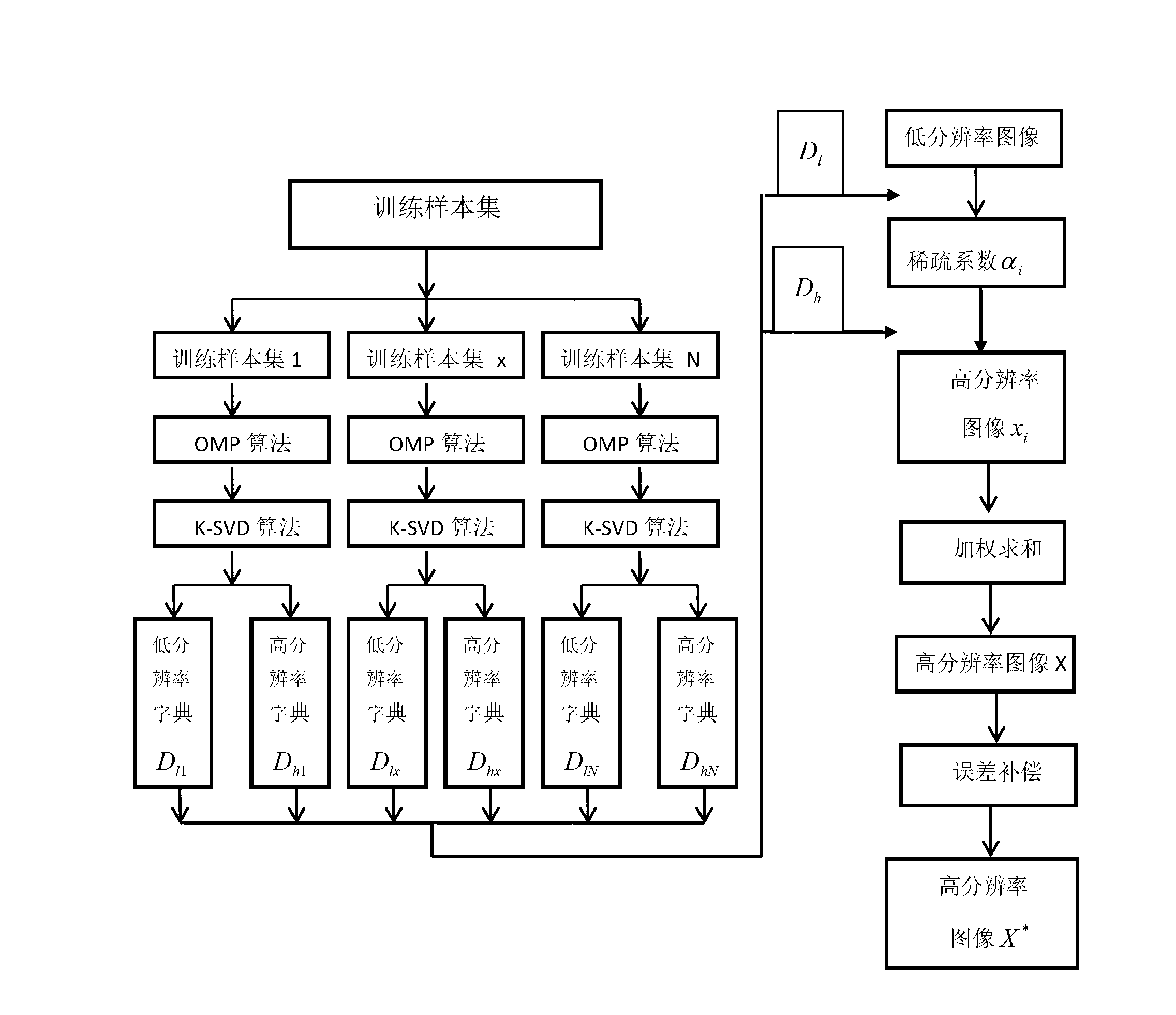
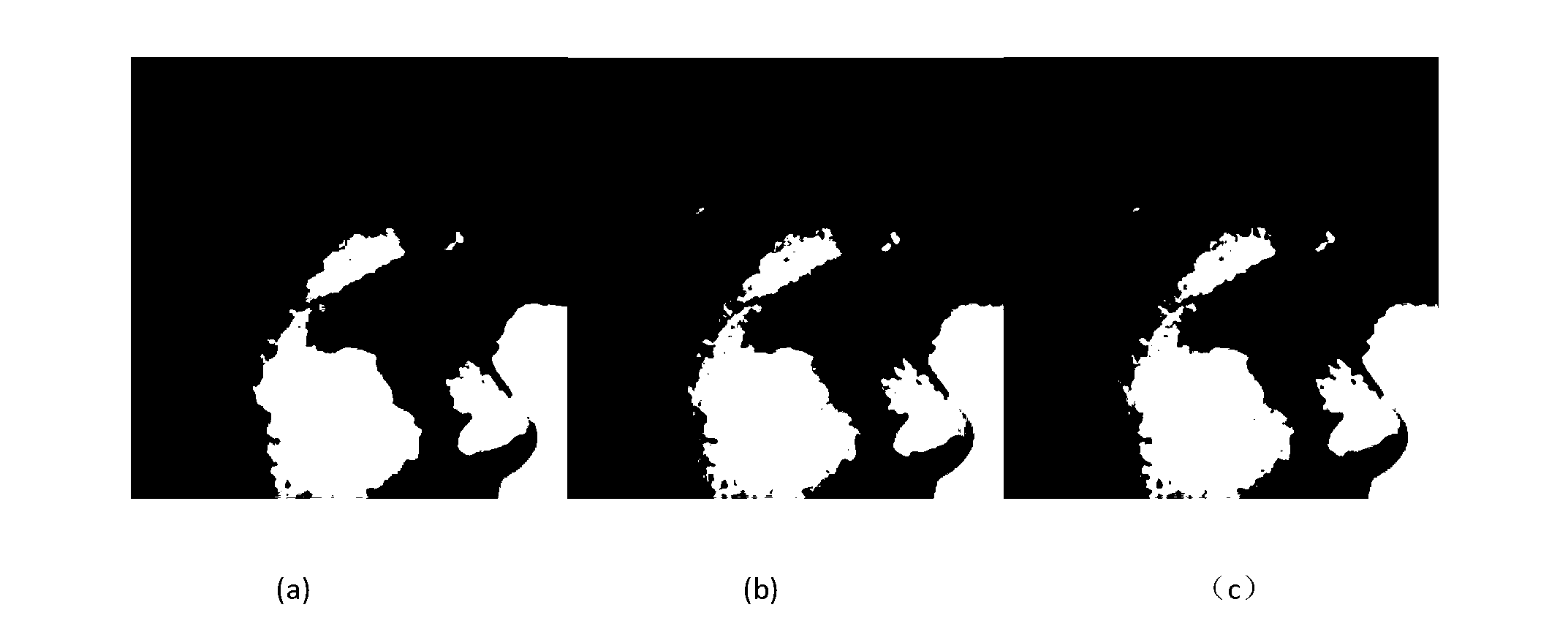
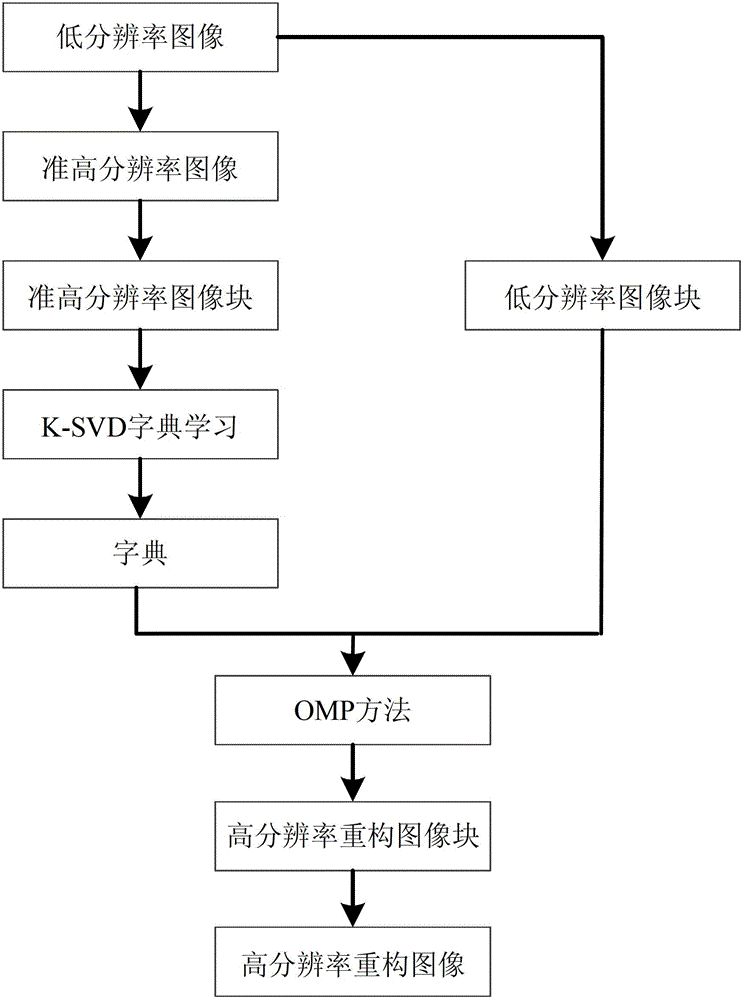
Image super-resolution reconstruction method based on dictionary learning and structure clustering
ActiveCN103077505ASufficient Information ComplementaryHigh resolution images are clearImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionImage resolutionK singular value decomposition
The invention discloses an image super-resolution reconstruction method based on dictionary learning and structure clustering, mainly solving the problem that a reconstructed image based on the prior art has a fuzzy surface and a serious marginal sawtooth phenomenon. The image super-resolution reconstruction method comprises the following implementation steps of: (1) acquiring training samples; (2) structurally clustering the training samples; (3) training by using OMP (Orthogonal Matching Pursuit) and K-SVD (K-Singular Value Decomposition) methods to obtain various dictionaries; (4) working out a sparse expression coefficient of an input low-resolution image block; (5) reestablishing a high-resolution image block by using a high-resolution dictionary and the spare coefficient; (6) performing weighting and summing on the high-resolution image block to obtain the high-resoluiton image block subjected to weighting and summing; (7) obtaining a high-resolution image according to the high-resolution image block; and (8) carrying out high-frequency information enhancement on the high-resolution image through error compensation to obtain a final result. A simulation experiment shows that the image super-resolution reconstruction method has the advantages of clear image surface and sharpened margin and can be used for image identification and target classification.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
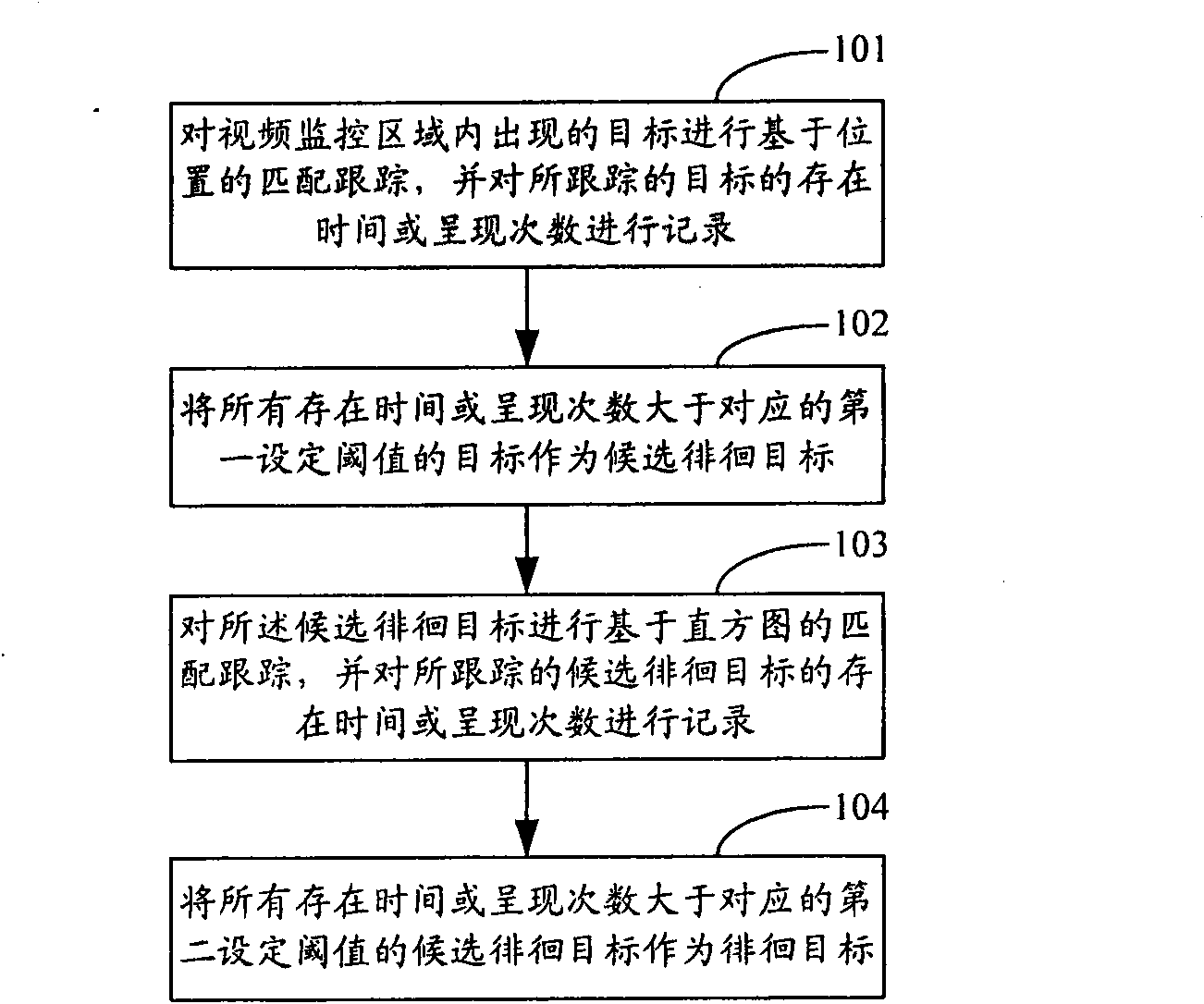
Loitering detecting method and loitering detecting system in video monitoring
ActiveCN101577006AAvoid judgment failureImprove accuracyImage analysisVideo monitoringMatching pursuit
The invention discloses a loitering detecting method in video monitoring, comprising the steps of: carrying out position-based matching pursuit on targets appearing in a video monitoring area, recording presence time or appearance times of the pursued targets, and taking the targets with the presence time or appearance times longer or more than a corresponding first set threshold as candidate loitering targets; carrying out histogram-based matching pursuit on the candidate loitering targets, recording presence time or appearance times of the pursued candidate loitering targets, and taking the target with the presence time or appearance times longer or more than a corresponding second set threshold as a loitering target. In addition, the invention also discloses a loitering detecting system in the video monitoring. The technical proposal disclosed by the invention can improve the accuracy of a detection result.
Owner:BEIJING VIMICRO ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE CHIP TECH CO LTD
Method and system for characterizing cardiovascular systems from single channel data
ActiveUS20150216426A1Cumbersome to executeBroaden applicationMedical simulationElectrocardiographyDiseaseCardiac defects
Methods to identify and risk stratify disease states, cardiac structural defects, functional cardiac deficiencies induced by teratogens and other toxic agents, pathological substrates, conduction delays and defects, and ejection fraction using single channel biological data obtained from the subject. A modified Matching Pursuit (MP) algorithm may be used to find a noiseless model of the data that is sparse and does not assume periodicity of the signal. After the model is derived, various metrics and subspaces are extracted to characterize the cardiac system. In another method, space-time domain is divided into a number of regions (which is largely determined by the signal length), the density of the signal is computed in each region and input to a learning algorithm to associate them to the desired cardiac dysfunction indicator target.
Owner:ANALYTICS FOR LIFE
Multiple observed value vector sparsity self-adaptive compressed sampling matching pursuit method
ActiveCN105281779AReduce refactoring timeHave the ability to correctCode conversionAdaptive compressionMean square
The invention discloses a multiple observed value vector sparsity self-adaptive compressed sampling matching pursuit method, which relates to the technical field of information and communication. The multiple observed value vector sparsity self-adaptive compressed sampling matching pursuit method is provided for solving the problem of recovering an original multiband signal from multiple observed value vectors with unknown sparsity after continuous-limited module conversion through sampling by a modulated broadband converter under an Xampling framework. The multiple observed value vector sparsity self-adaptive compressed sampling matching pursuit method comprises the steps of: conducting self-adaptive estimation on sparsity of a signal; updating the sparsity with a given step length factor through repeated iteration so that the sparsity gradually approaches the actual sparsity of the signal; correcting a support set through a backtracking thought and a minimum mean square criterion; stopping iteration until an residual error is less than a set threshold value; and finally reconstructing an original multiband signal through pseudo inverse operation by utilizing the obtained complete support set. The multiple observed value vector sparsity self-adaptive compressed sampling matching pursuit method can achieve the analog reconstruction of the multiband signal based on compressed sensing.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Compressive sensing theory-based Doppler ambiguity-resolution processing method
InactiveCN101975939AAvoid false value casesRemove restrictionsWave based measurement systemsObservational errorFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a compressive sensing theory-based Doppler ambiguity-resolution processing method, which comprises the following steps of: (1) performing non-uniform sampling on continuous echo pulses in a totally-coherent processing period by utilizing Q-fold pulse repetition frequency values; (2) designing the possible Doppler frequency range of a target, and ensuring the Q-fold pulse repetition frequency values do not have Doppler dead zones in the Doppler frequency range; (3) constructing a compressive sensing (CS) model by utilizing the time-domain under-sampling characteristics of sampled data in the totally-coherent processing period and the sparse characteristics of frequency spectrums of the target to be detected in the possible Doppler frequency range; and (4) resolving the CS model by utilizing an orthogonal matching pursuit (OMP) reconstruction algorithm to directly estimate the amplitude response of ambiguity-free Doppler spectrums. The method eliminates the restriction of the PRF multiplicity adopted by a radar system to the number of the targets to be detected, and simultaneously avoids the condition of false values caused by the influence of measurement errors in the conventional methods by taking the influence of noise on reconstruction results into account and performing de-noising operation when the CS model is resolved to estimate the amplitude response of the ambiguity-free Doppler spectrums by adopting the OMP reconstruction algorithm.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +1
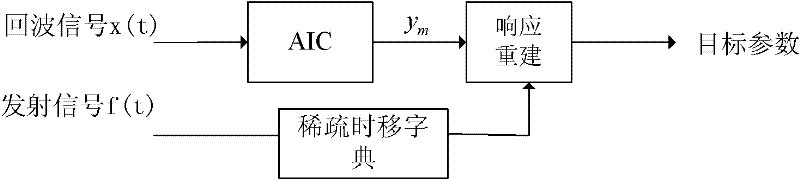
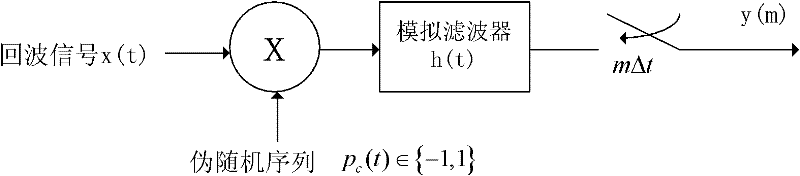
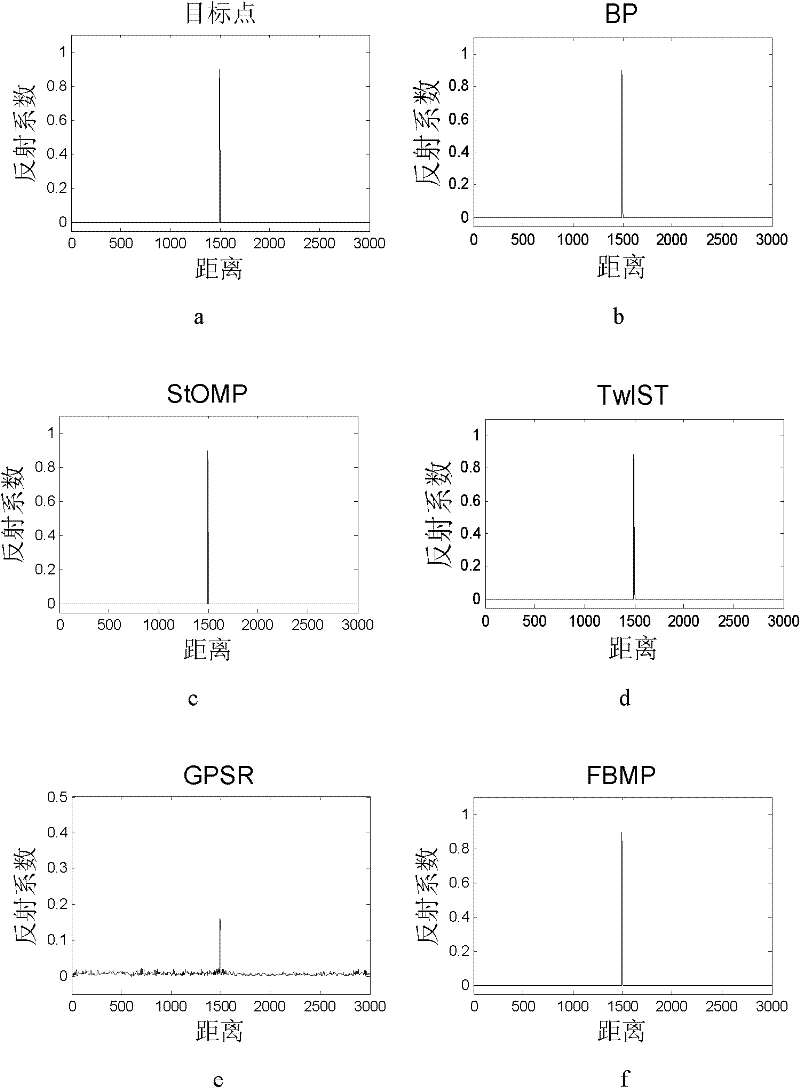
Radar Target Parameter Estimation Method Based on AIC Compressed Information Acquisition and FBMP
ActiveCN102288951AHigh precisionReduce time costWave based measurement systemsEstimation methodsRadar imaging
The invention discloses a radar target parameter estimation method based on AIC (automatic information center) compression information acquisition and FBMP (fast Bayesian matching pursuit), which mainly solves the problem that the existing compression sensing radar target parameter estimation method cannot simultaneously improve estimation precision and reduce time cost. The method comprises the implementation steps that low-dimension compression observation of radar echo signals is realized by AIC; a time shift sparse dictionary is designed on the basis of transmitted signals, so the radar echo signals can obtain sparse presentation on the time shift sparse dictionary; observation matrices needed in a compression sensing reconstruction theory are constructed according to AIC sampling sequences and the time shift sparse dictionary; sparse coefficient vectors of the radar echo signals are solved by a fast Bayesian matching pursuit FBMP algorithm so as to realize radar target parameterestimation. The invention has advantages that the number of non-zero coefficients in the sparse coefficient vectors of signals to be reconstructed is determined adaptively, the reconstruction precision can be improved when the time cost is reduced, and the method can be used for radar target recognition and radar imaging.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
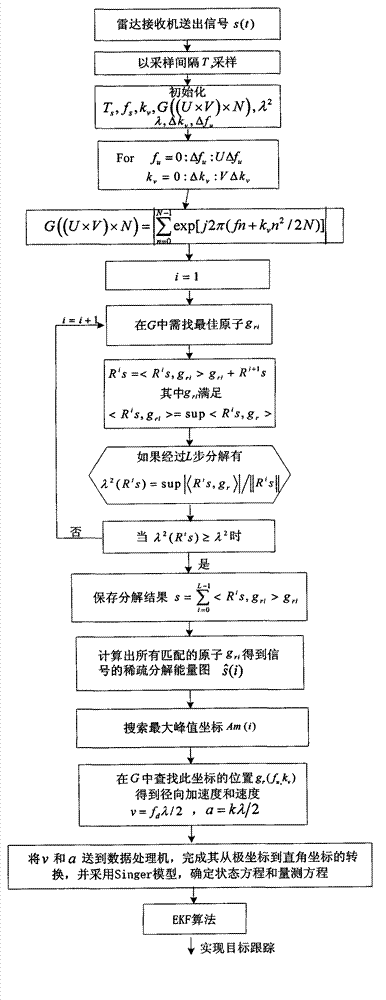
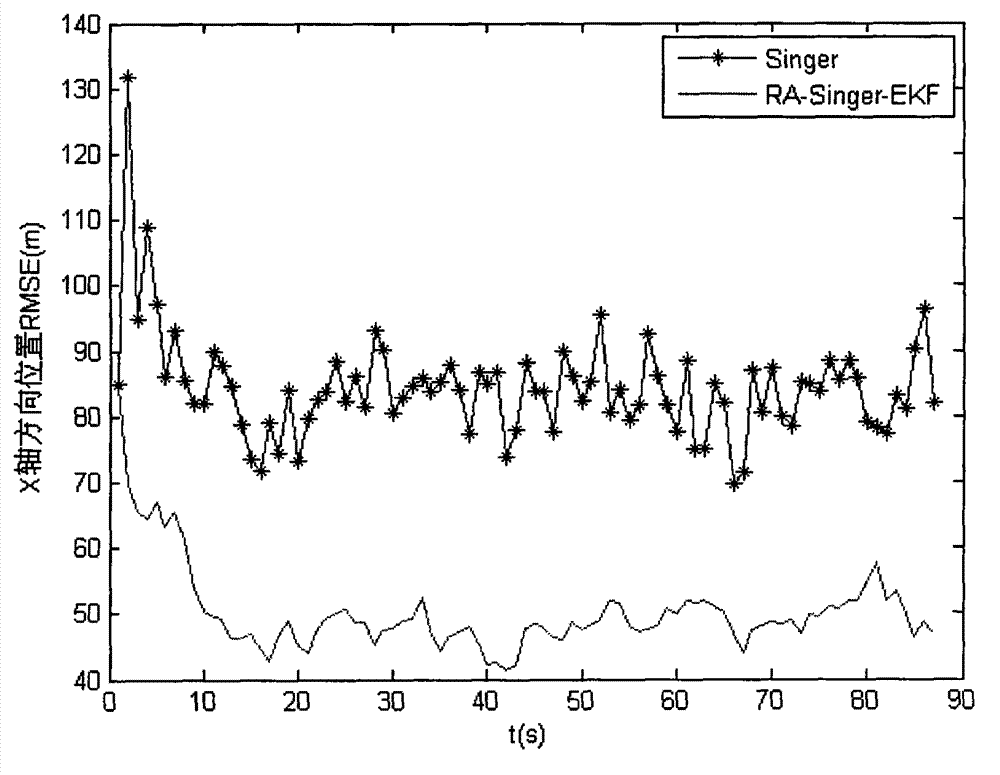
RA-Signer-EKF (Random Access-Singer-Extended Kalman Filter) maneuvering target tracking algorithm based on radial acceleration
InactiveCN103048658AImprove maneuvering target tracking accuracyImprove scalabilityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadarObject tracking algorithm
The invention discloses an RA-Singer-EKF (Random Access-Singer-Extended Kalman Filter) maneuvering target tracking algorithm based on radial acceleration, which belongs to the field of radar maneuvering target tracking. According to the method, the radial acceleration and radial speed information of a maneuvering target can be rapidly and accurately provided, and the tracking performance of a radar on the maneuvering target is improved effectively. The method comprises the following steps of: (I) sampling a radar receiving signal, and obtaining a target radial acceleration and a radial speed by using a matching pursuit (OMP (Operation Management Platform)) method; (II) performing coordinate conversion on the radial acceleration and the radial speed at a data processing stage, and introducing into a measuring equation and a state equation; and (III) realizing maneuvering target tracking by adopting a Singer model and an EKF algorithm. Due to the adoption of the RA-Singer-EKF maneuvering target tracking algorithm, the maneuvering situation of the target can be reflected accurately in real time, the target tracking accuracy is increased, the speed and acceleration estimation accuracies are improved, engineering implementation is easy, and a high engineering application value and a good popularization prospect are achieved.
Owner:NAVAL AERONAUTICAL & ASTRONAUTICAL UNIV PLA
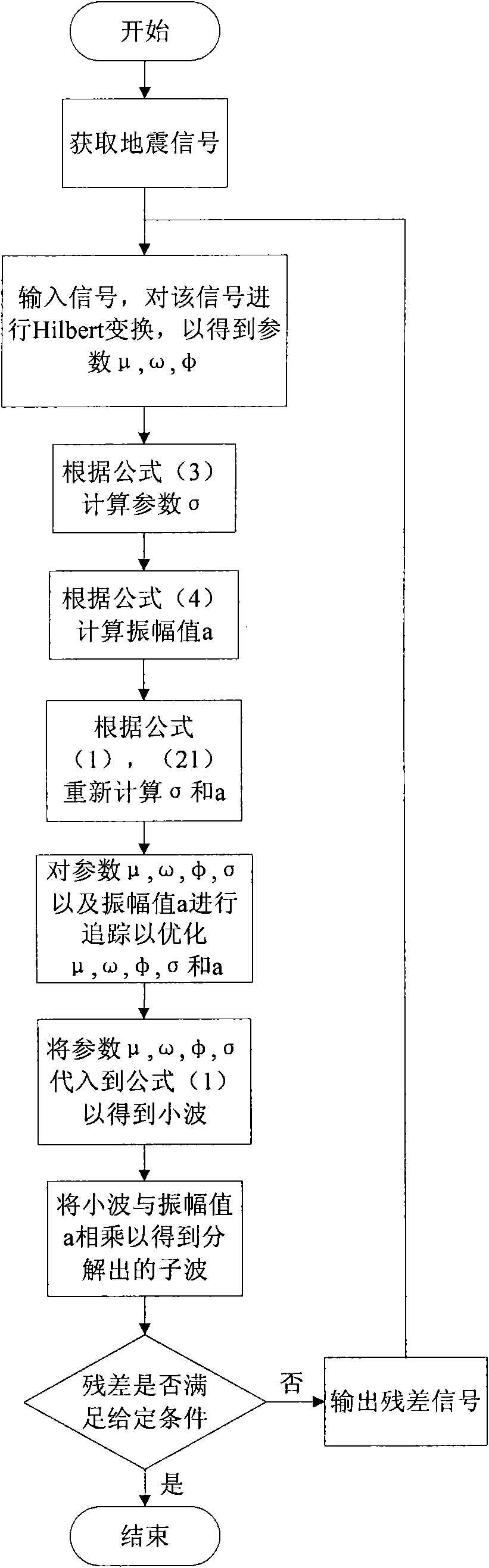
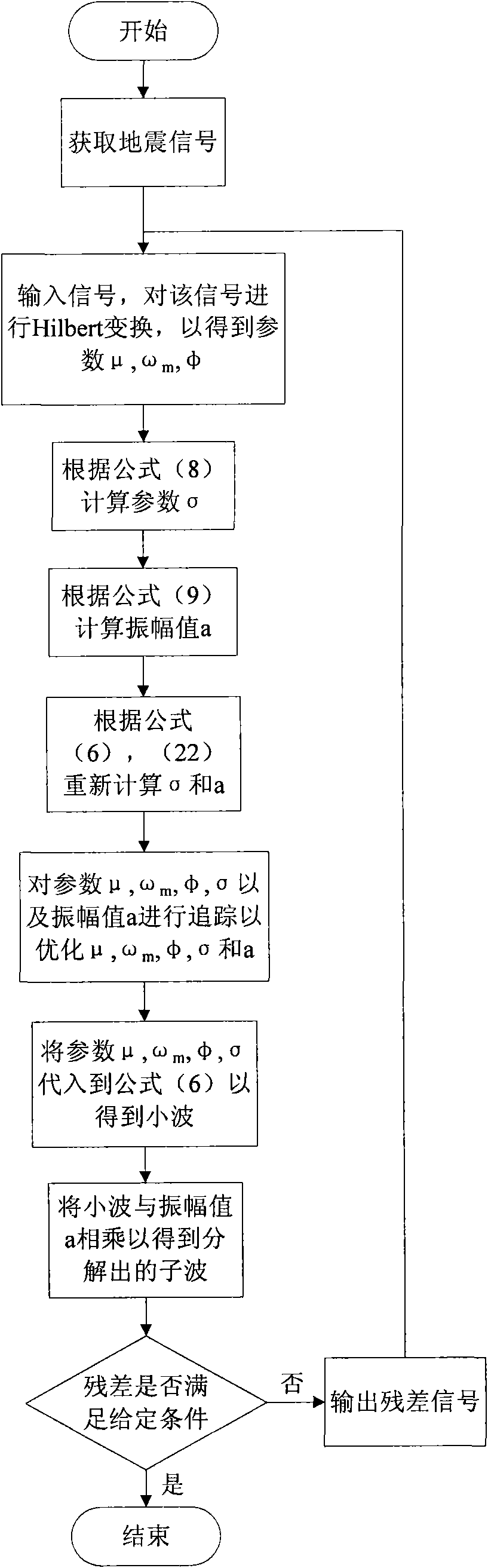
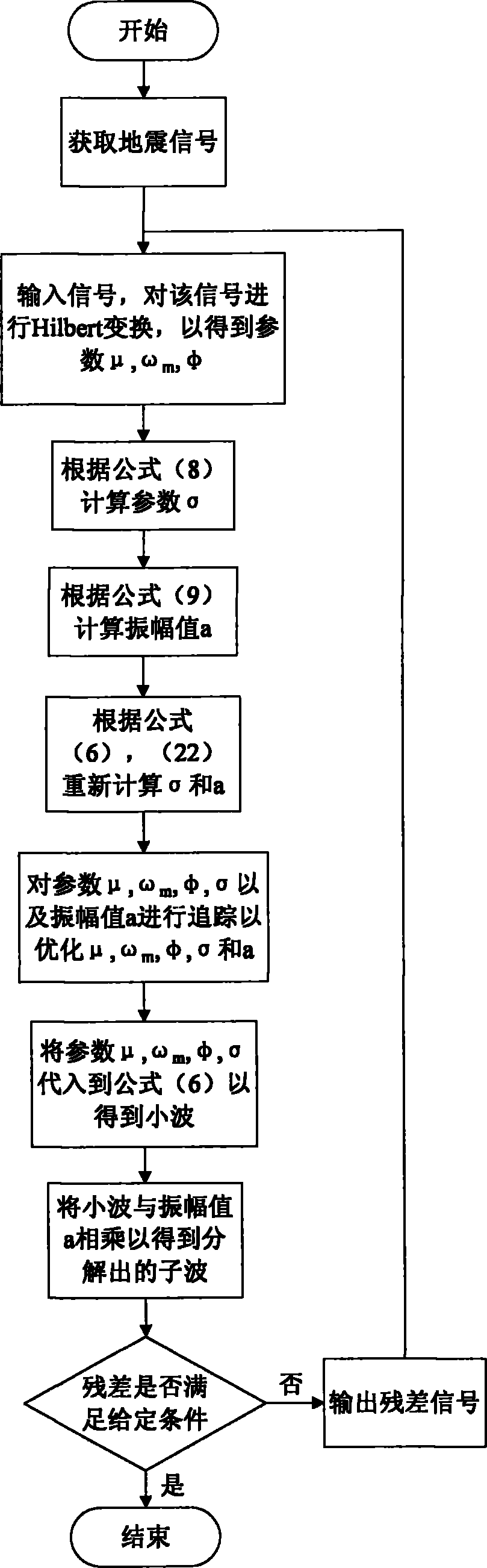
Seismic wave decomposition method
ActiveCN102116868AMatch Tracking Method ImprovementsSeismic signal processingDecompositionMatching pursuit
The invention relates to a seismic wave decomposition method which comprises the following steps: selecting a Gabor small wave or a Morlet small wave as a wavelet form; carrying out multiwavelet decomposition on an obtained seismic signal; calculating three parameters of the small wave, namely time shift u, center frequency Omega, phase shift Phi through the complex attribute of the seismic signal in each decomposition; calculating a time scale parameter Sigma according to the three parameters; estimating the amplitude Alpha of the small wave; and determining a final parameter through iteration and decomposing wavelets with different dominant frequencies. The seismic wave decomposition method improves the traditional matched tracking method and improves the calculation efficiency; and meanwhile, Sigma is self-adaptive and adjustable.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP
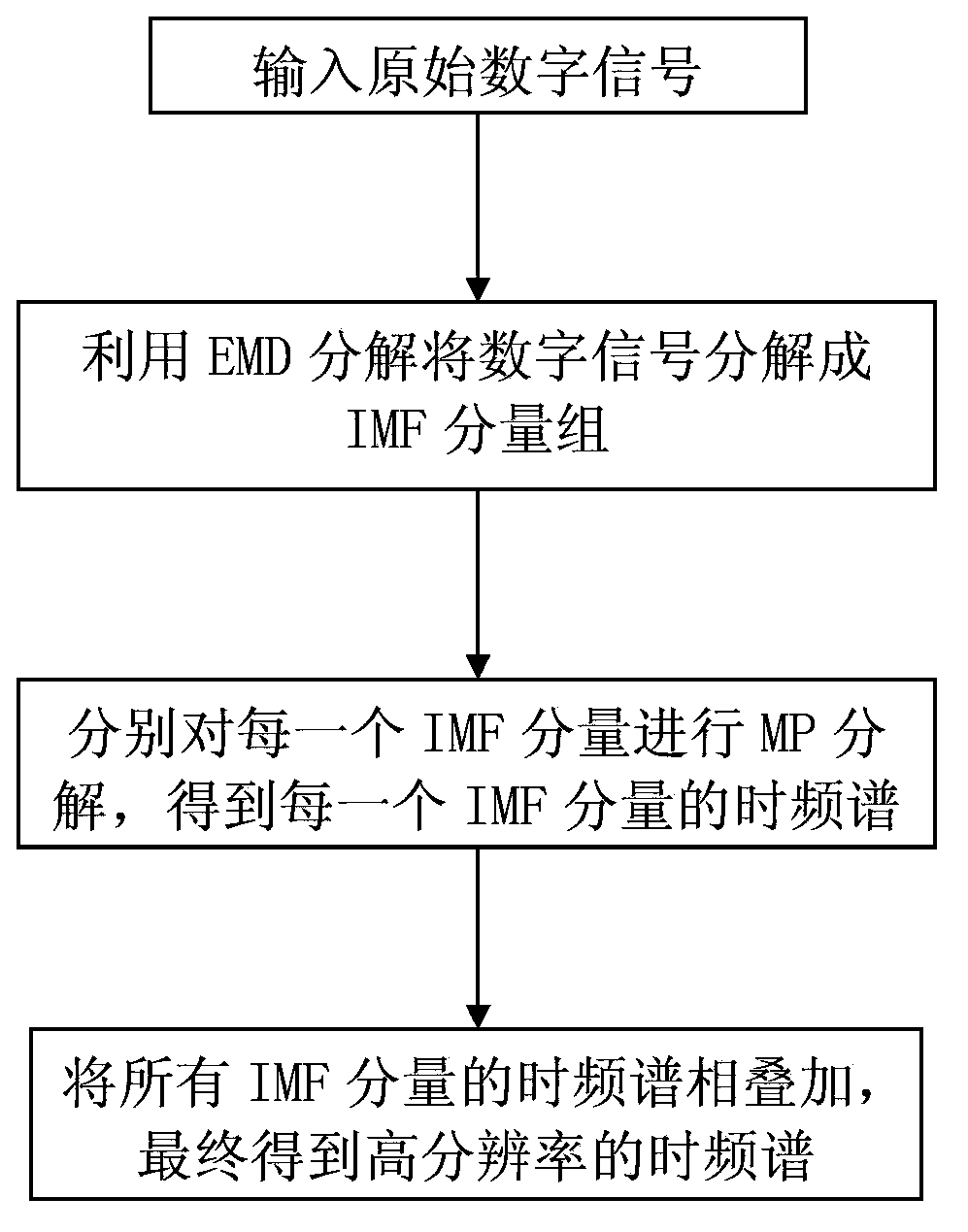
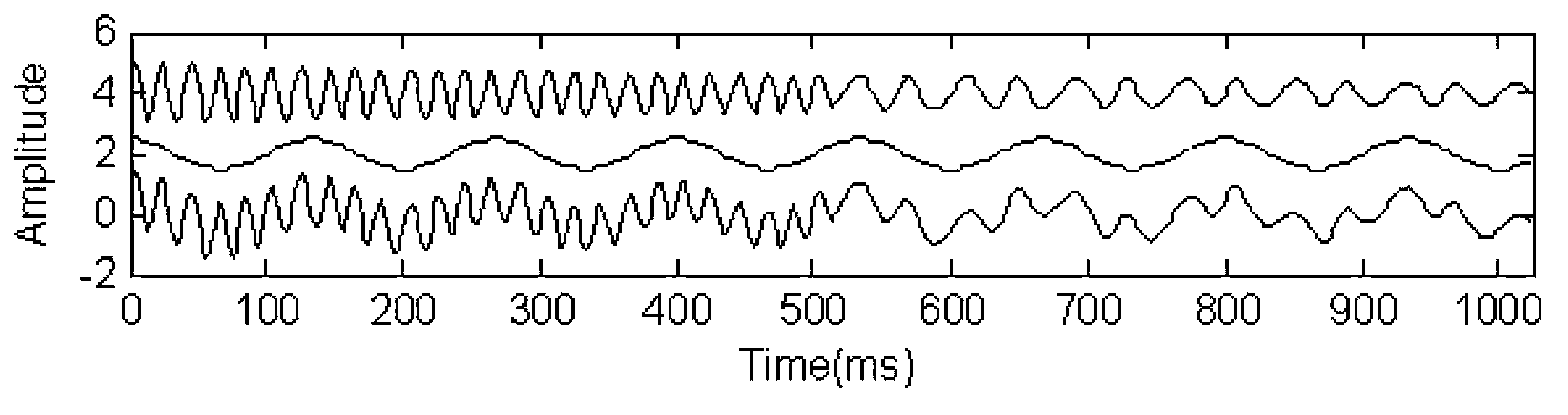
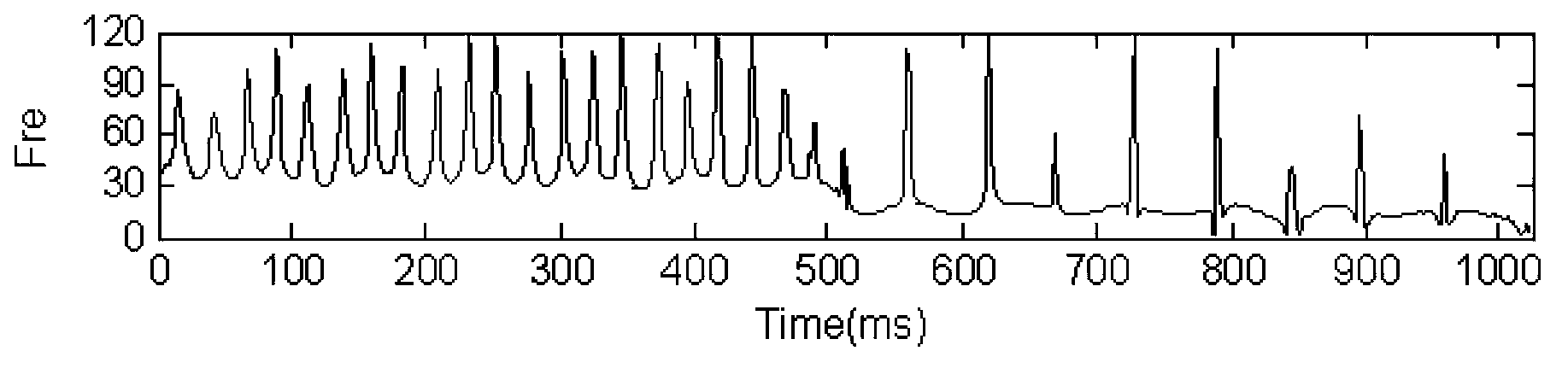
High-precision time-frequency analysis method
ActiveCN103675444AHigh resolutionAvoid matching inaccuraciesSpectral/fourier analysisDigital signal processingFrequency spectrum
The invention provides a high-precision time-frequency analysis method, and belongs to the field of digital signal processing. The method comprises the following steps of: (1)inputting original digital signals x(t), then carrying out empirical mode decomposition (EMD)to the original digital signals x(t), decomposing the original digital signals x(t) into sets of intrinsic mode function (IMF)components, namely ci(t) is the IMF component; (2) carrying out matching pursuit (MP)decomposition to each IMF component ci(t) respectively to obtain a time-frequency spectrum of each IMF component; and (3) carrying out mutual superposition to the time-frequency spectrum of each IMF component obtained in the step (2) to obtain the time-frequency spectrum of a high time-frequency resolution of the original digital signals x(t). The high-precision time-frequency analysis method disclosed by the invention avoids inaccuracy of time-frequency atoms when MP decomposition matching is implemented for composite signals directly, and MP decomposition is implemented for each IMF component, thereby being capable of obtaining the time-frequency spectrum with higher accuracy and time-frequency resolution and richer information.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
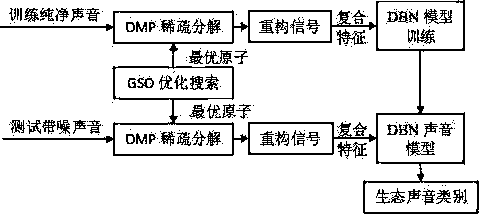
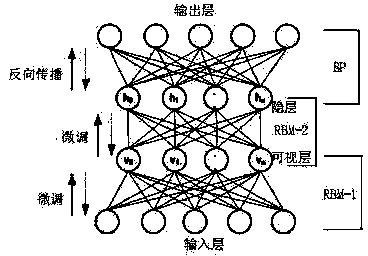
Ecological sound identification method on basis of rapid sparse decomposition and deep learning
InactiveCN103531199AImprove noise immunityReduce computational complexitySpeech recognitionDecompositionDynamic Bayesian network
The invention relates to an ecological sound identification method on the basis of rapid sparse decomposition and deep learning, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: S01, respectively carrying out OMP (Orthogonal Matching Pursuit) sparse decomposition on pure sound and test tape noise and correspondingly outputting reconstruction signals and OMP characteristics of the pure sound and the test tape noise; S02, respectively extracting composite characteristics comprising the OMP characteristics from the pure sound and the test tape noise; S03, carrying out DBN (Dynamic Bayesian Network) model training on the composite characteristics extracted from the reconstructed pure sound; and S04, carrying out DBN model classification on the composite characteristics extracted from the reconstructed test tape noise and the trained pure sound and outputting an ecological sound category which the test tape noise belongs to. The ecological sound identification method has a more obvious effect of improving noise resistance and robustness of a system.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
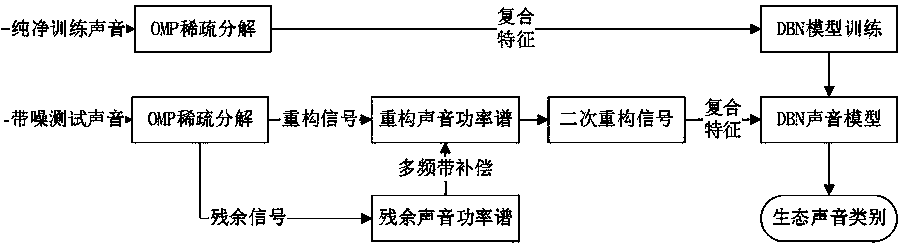
Ecological voice recognition method based on multiband signal reconstruction
InactiveCN103474066AImprove reconstruction accuracySuppress noiseSpeech recognitionPattern recognitionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention relates to an ecological voice recognition method based on multiband signal reconstruction. The ecological voice recognition method comprises the steps of: firstly, using OMP (Orthogonal Matching Pursuit) sparse decomposition as a first-stage reconstruction, and reserving a main body structure of foreground voice; secondly, allocating remained components decomposed in the former stage according to bands, and carrying out adaptive compensation on reconstruction signals according to the frequency distribution of the foreground voice and background noise to complete a second-stage reconstruction; finally, extracting compound noise-proof characteristics according to atom time-frequency information and frequency-domain information in a support set, and carrying out classification and recognition on ecologic voice by using a high-credibility network under different environments and signal to noise ratio conditions. According to the ecological voice recognition method, the noise can be inhibited by adopting two times of reconstruction, and the reconstruction precision of the foreground voice is improved; better noise robustness is achieved under a natural environment.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
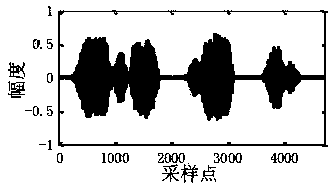
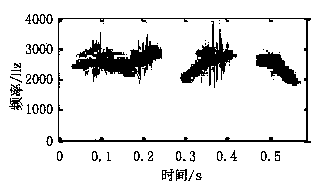
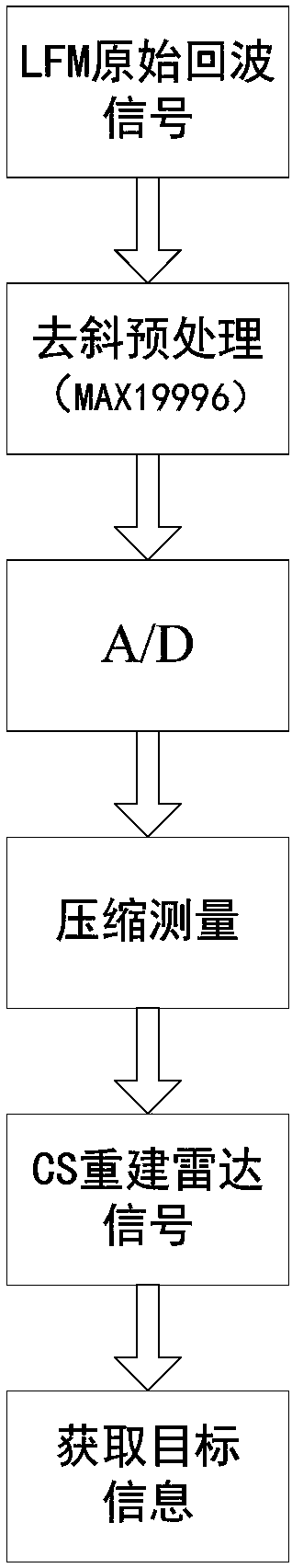
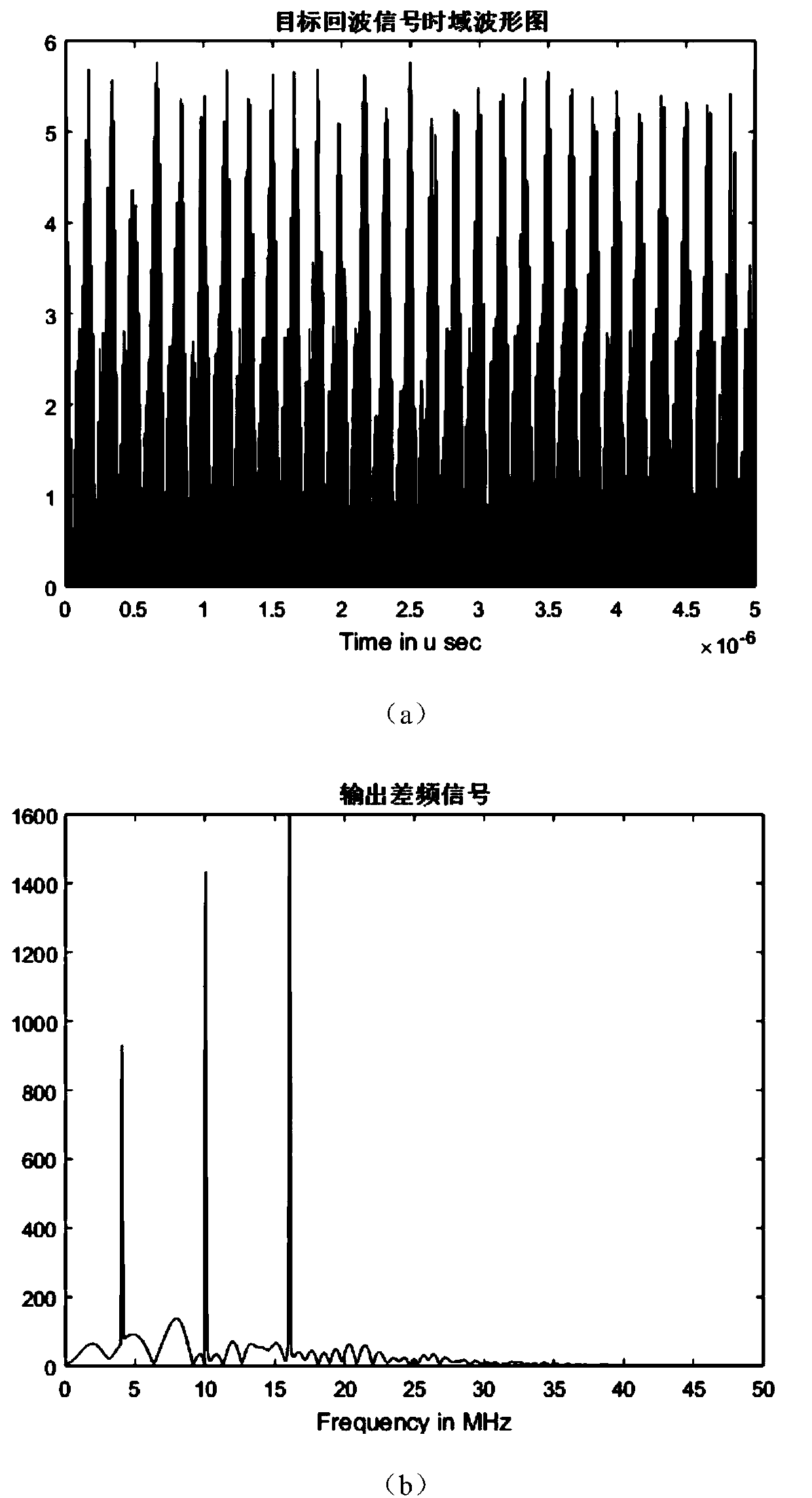
Linear frequency modulation radar signal processing method based on compressed sensing
ActiveCN107064883AEfficient acquisitionAchieve compressionWave based measurement systemsTime domainRadar observations
The invention discloses a linear frequency modulation radar signal processing method based on compressed sensing. The method comprises the steps of (1) emitting a linear frequency modulation signal to a radar and preprocessing an echo signal, which means that the deramping processing of the echo signal is carried out, a difference frequency signal is outputted, and a signal model of deramping processing is established in a time domain, (2) according to the sparsity of the difference frequency signal in a frequency domain, constructing a sparse conversion matrix, and establishing a sparse representation model of the radar echo signal, (3) constructing a measurement matrix, and realizing the projection transformation of a difference frequency sparse signal to a low dimensional space, and (4) using an orthogonal matching pursuit (OMP) algorithm, reconstructing a radar difference frequency signal, and efficiently obtaining target information. Accoding to the method, the compression of radar echo signal data can be fundamentally realized, the change of a sparse model according to a radar observation distance is not needed, finally the target information is obtained, and the method is suitable for the echo signal processing of an actual radar.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) radar sparse imaging algorithm based on hybrid matching pursuit algorithm
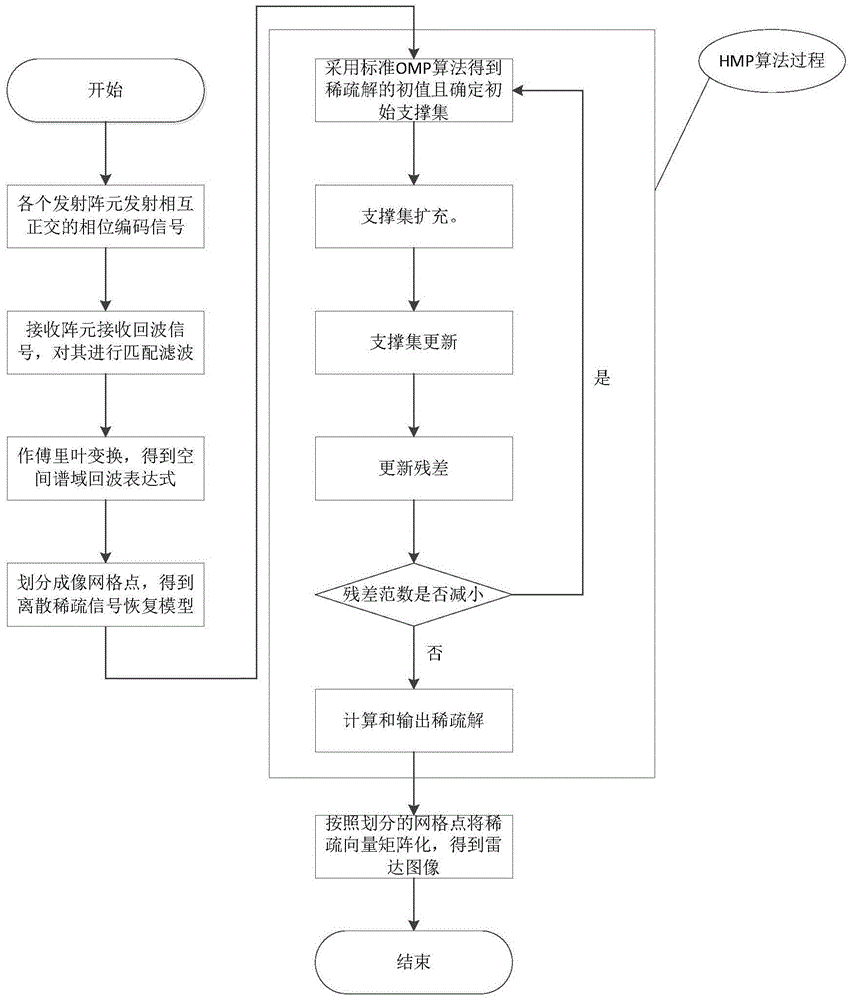
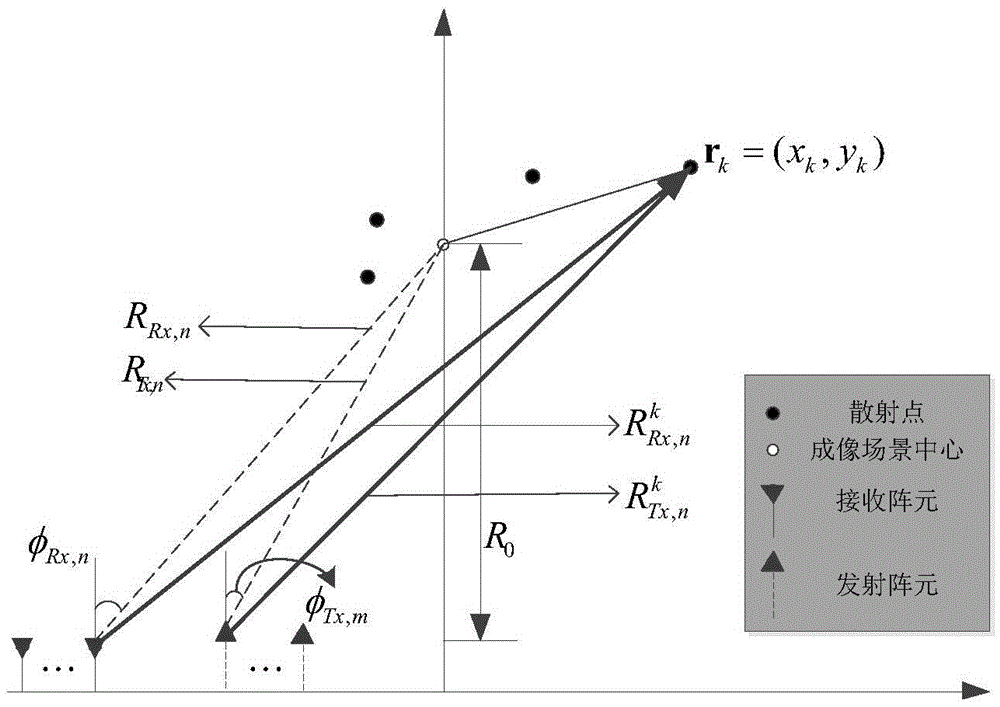
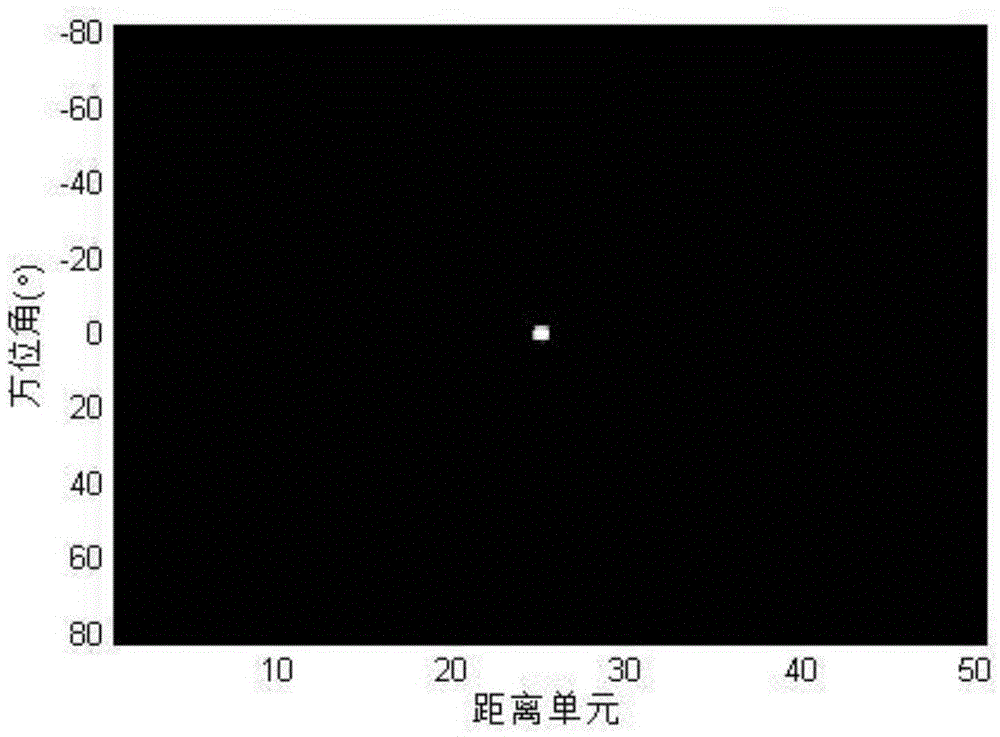
ActiveCN105652273AOvercoming resolutionOvercoming the disadvantage of high sidelobesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPhase CodeArray element
The invention belongs to the radar technology field and the signal processing field, and relates to application of a multiple input multiple output (MIMO) type system, in particular to an MIMO radar sparse imaging algorithm based on a hybrid matching pursuit algorithm. The MIMO radar sparse imaging algorithm comprises the steps that firstly, M emitting array elements emit orthometric phase-coded signals, and N receiving array elements receive the phase-coded signals; secondly, a matched filter of a receiver of each receiving array element conducts matched filtering on the received phase-coded signals; thirdly, fourier transform is conducted on the matched-filtered signals, and a spatial spectral domain echo expression is obtained. Index selection of each time in the HMP algorithm is realized through an OMP algorithm, orthogonality of base signal selection is guaranteed through the operation, and spatial surface elements which are very close to one another can be distinguished when fourier similar characteristics exist in a dictionary matrix; meanwhile, backtracking selection operation in the HMP algorithm is the same as that in an SP algorithm.
Owner:江苏和正特种装备有限公司
Quick target identifying method and system based on compressed sensing
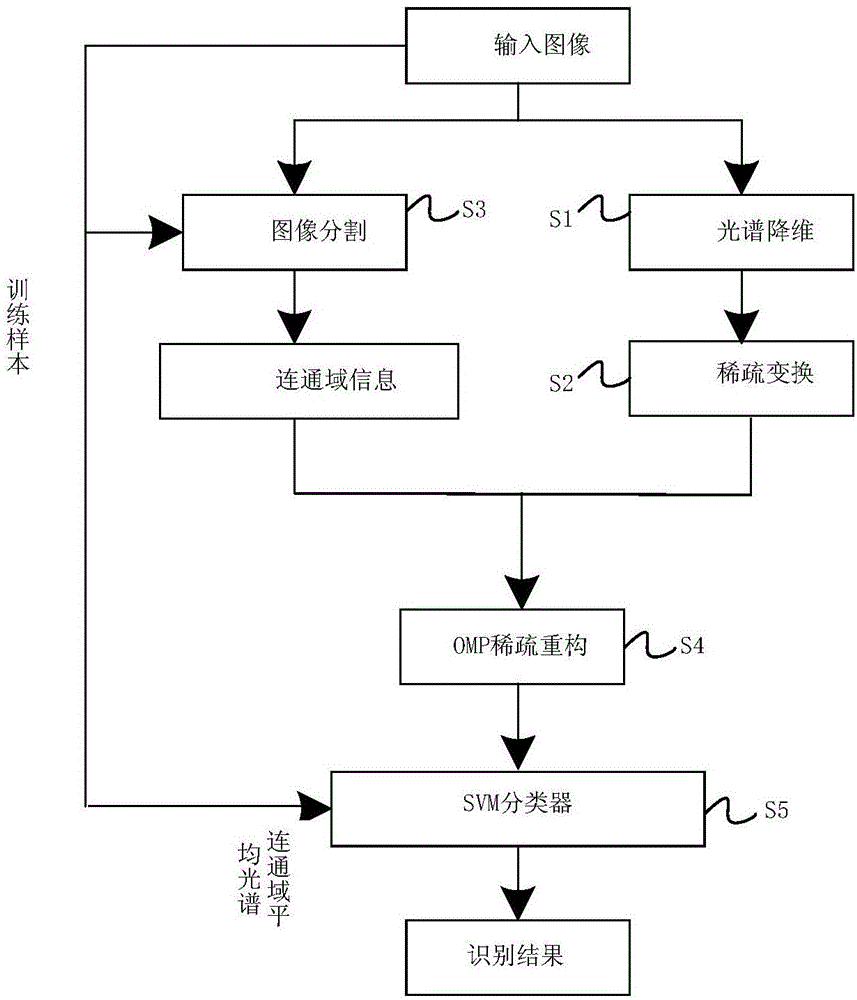
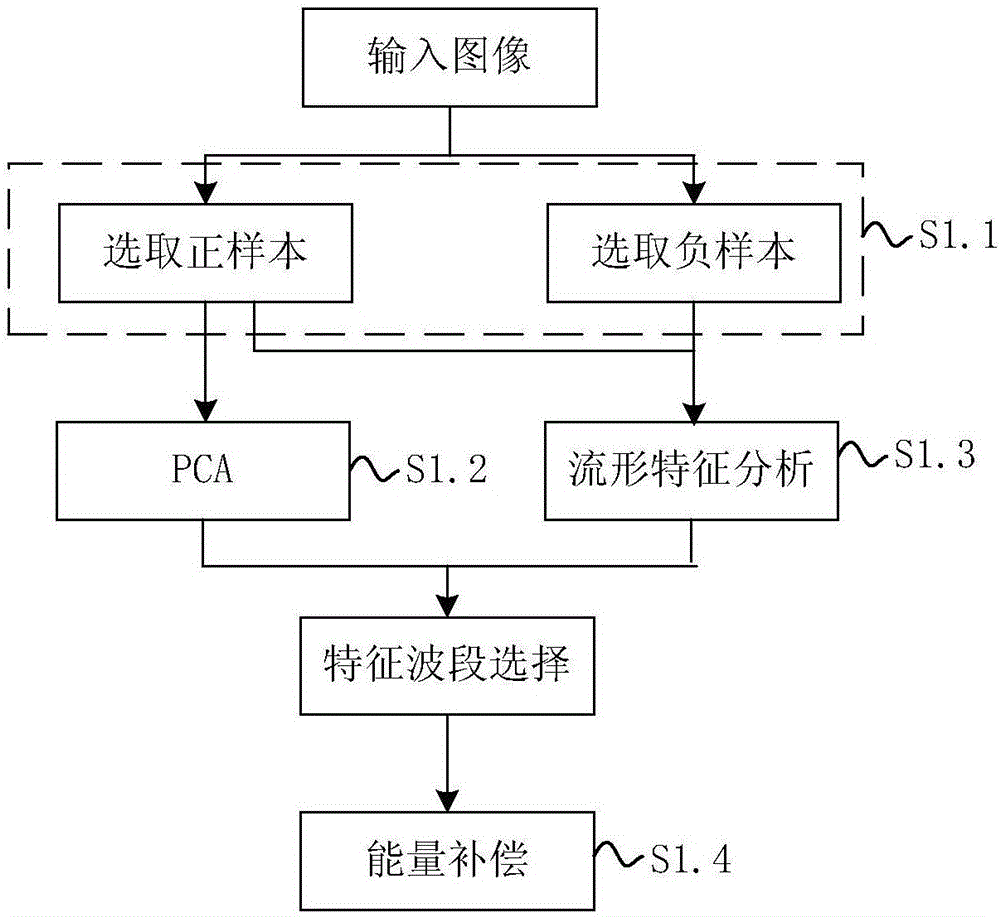
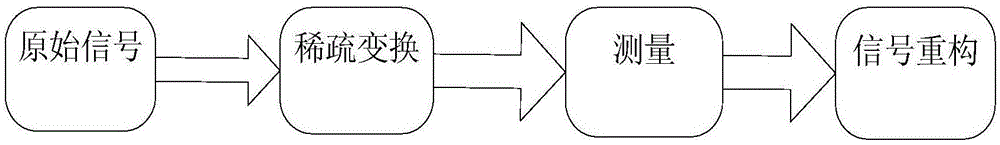
ActiveCN106557784AReduce the amount of post-calculationCapable of identifying objectsCharacter and pattern recognitionAnti jammingDimensionality reduction
The invention discloses a quick target identifying method and system based on compressed sensing. The method comprises steps of conducting spectrum dimensionality reduction via a spectrum selection method, sampling a target image and conducting spare transformation via a compressed sensing method, conducting compressed sensing reconstruction based on an orthogonal matching pursuit method, and identifying via an SVM classifier. Sampling and spare processing are conducted via the compressed sensing algorithm can reduce data post-calculation complexity, and can break through limitations of sampling frequency; spectrum selection and target identification algorithm are combined; with the high-spectral feature identification technology, unit target detection and multiple imaging detection can be combined; with the utilization of spectrum technology and imaging technology, the detection unit has a target identifying capacity, so target identifying rate can be improved; and target identifying time can be reduced and strong anti-jamming capability can be achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST
Single image super-resolution method based on identical scale structure self-similarity and compressed sensing
ActiveCN102750677AJoin precisionGuaranteed refactoring effectImage enhancementGeometric image transformationScale structureImage resolution
Disclosed is a single image super-resolution method based on identical scale structure self-similarity and compressed sensing. Firstly, the interpolation is performed for a low-resolution image and a quasi-high-resolution image is obtained; then, the quasi-high-resolution image is divided into quasi-high-resolution image blocks, vectors corresponding to the quasi-high-resolution image blocks serve as a training sample, a sample matrix is assembled, a K-SVD dictionary studying method is used for a solution and a dictionary is obtained; the low-resolution image is divided into low-resolution image blocks; by the aid of a down-sampling matrix, the dictionary and vectors corresponding to all low-resolution image blocks, an orthogonal matching pursuit (OMP) method is used for a solution, and vectors corresponding to high-resolution reconstruction image blocks; and finally, vectors corresponding to high-resolution reconstruction image blocks are assembled and a high-resolution reconstruction image is formed. According to the super-resolution method based on the identical scale structure self-similarity and the compressed sensing, additional information is added in the high-resolution reconstruction image through a compressed sensing frame, and the space resolution is improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Sparse matrix based compressed sensing processing method for hyperspectral remote sensing images
InactiveCN103024398AReduce sampling costsHigh gainTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationData classSource encoding
The invention belongs to the field of mobile communication source coding and discloses a sparse matrix based compressed sensing processing method for hyperspectral remote sensing images. The method includes the steps of wavelet transform, data type transform, quantization, sparse matrix compressed encoding, OMP (orthogonal matching pursuit) decoding, data type inverse transform, inverse quantization and wavelet inverse transform, and the eight steps are executed sequentially. The method can be used for processing two types of remote sensing images, wherein the remote sensing images of the first type are not subjected to geometric correction, and the remote sensing images of the second type are subjected to geometric correction. Data type transform and data type inverse transform are added to the whole processing method aiming at the remote sensing images of the second type. The method for processing the hyperspectral remote sensing images has the advantages of high image compression proportion, saving of memory and computation space and high image restoration quality.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Linear array SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) three-dimensional imaging method based on threshold gradient tracking algorithm
ActiveCN107037429AImproving Sparse Imaging PerformanceRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture sonarTotal blood
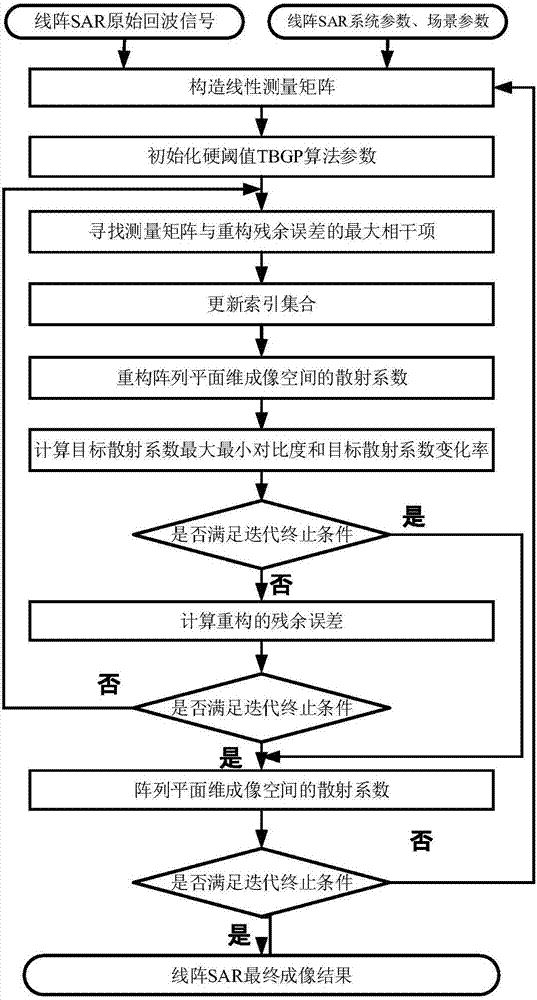
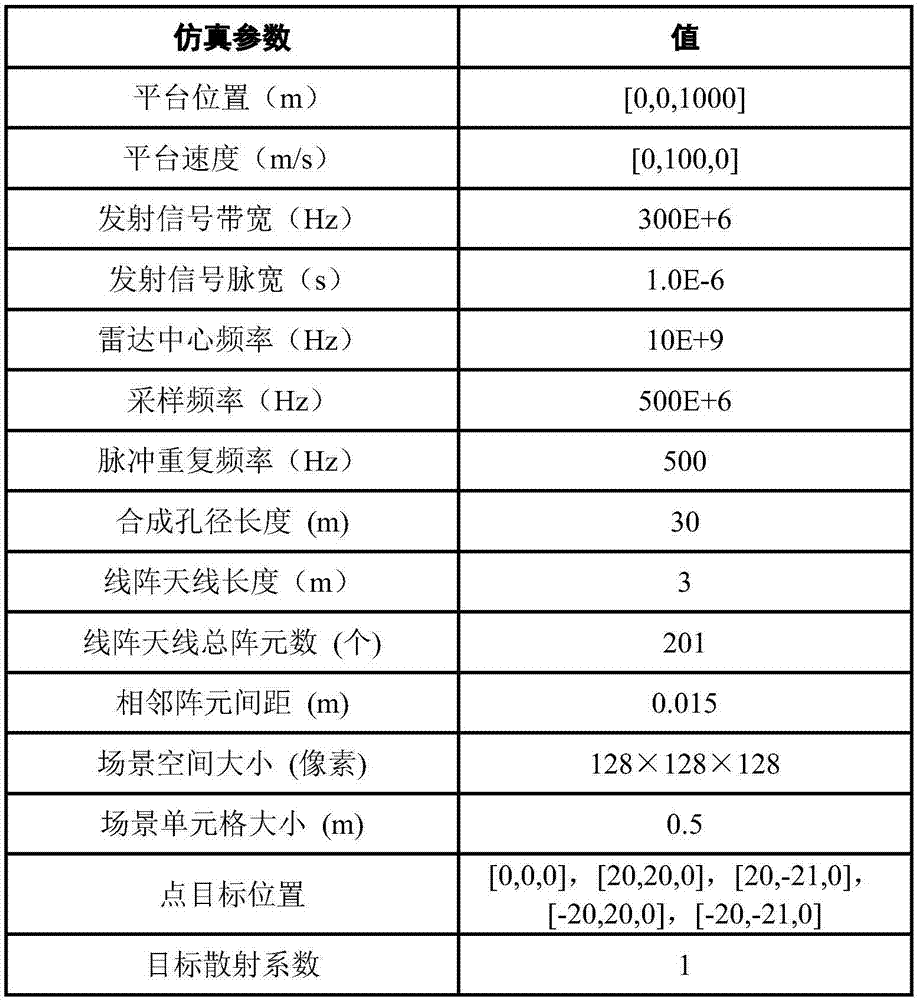
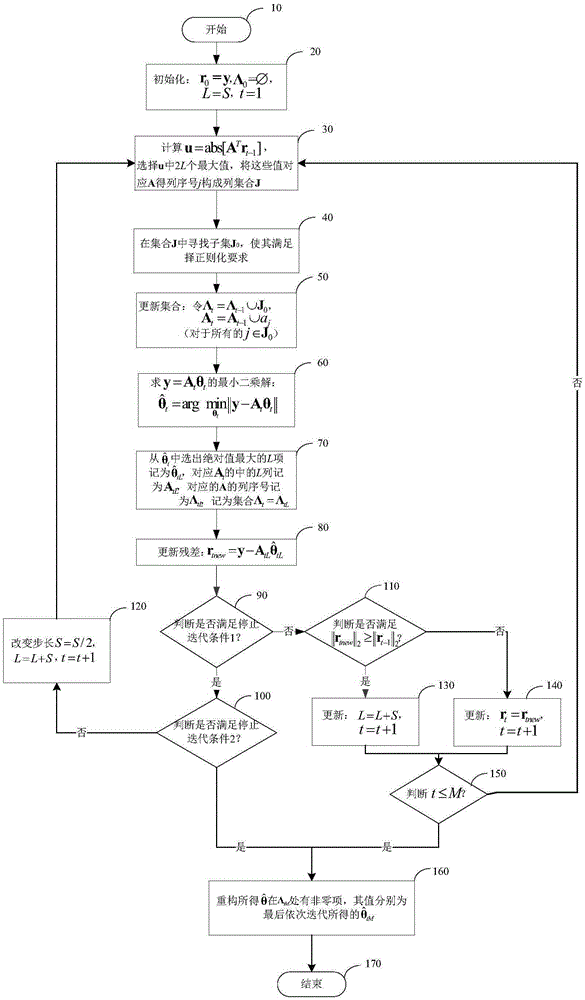
The invention provides a linear array SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) three-dimensional imaging method based on a threshold gradient tracking algorithm. The method comprises the steps of establishing a linear measurement model between linear array SAR original echo signals and a three-dimensional observation scene target scattering coefficient using a correlation among linear array SAR system parameters, motion platform parameters, space parameters of an observation scene target and original echo signals, and then reconstructing the observation scene target scattering coefficient using a TBGP (Total Blood Granulocyte Pool) method based on the signal linear measurement model. By using the contrast of maximum and minimum target scattering coefficients and the change rate of the target scattering coefficient as algorithm iteration termination conditions, the linear array SAR sparse imaging performance of a GP (Genetic Programming) algorithm under the condition that the sparsity of the observation scene is unknown is improved, the operation efficiency and the space storage efficiency are improved relative to an OMP (Orthogonal Matching Pursuit) algorithm, and the method can be applied in the fields of synthetic aperture radar imaging, earth remote sensing and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Variable step size regularized adaptive compressed sampling matching pursuit method
InactiveCN105281780AImprove refactoring effectIncrease the scope of applicationCode conversionAdaptive compressionReconstruction method
The invention provides a variable step size regularized adaptive compressed sampling matching pursuit method, specifically relates to a reconstruction method based on compressed sensing, and a solution aims at the prior two problems in the regularized orthogonal matching pursuit (ROMP) method. One of the problems is that the sparseness K is difficult to be obtained in reality, then the method provides that the adaptive idea of the sparse adaptive matching pursuit (SAMP) is applied in ROMP; the other problem is that once an atom which is selected in a support set will not able be deleted, then the method provides that the backtrack idea of the compressed sampling matching pursuit (CoSaMP) is applied in ROMP. In addition, the method adopts a stage orthogonal matching pursuit (StOMP) idea to set the threshold condition so as to stop the iteration, and the problem including lack of accuracy and over estimated caused by the fixed step size of the introduced SAMP is improved. The method provided by the invention greatly improves the reconstruction performance, estimated accuracy and application range of the reconstruction method based on the compressed sampling.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Compressed learning perception based SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) high-resolution image reconstruction method
ActiveCN102142139AReduce correlationQuality improvementImage enhancementSingular value decompositionPattern recognition
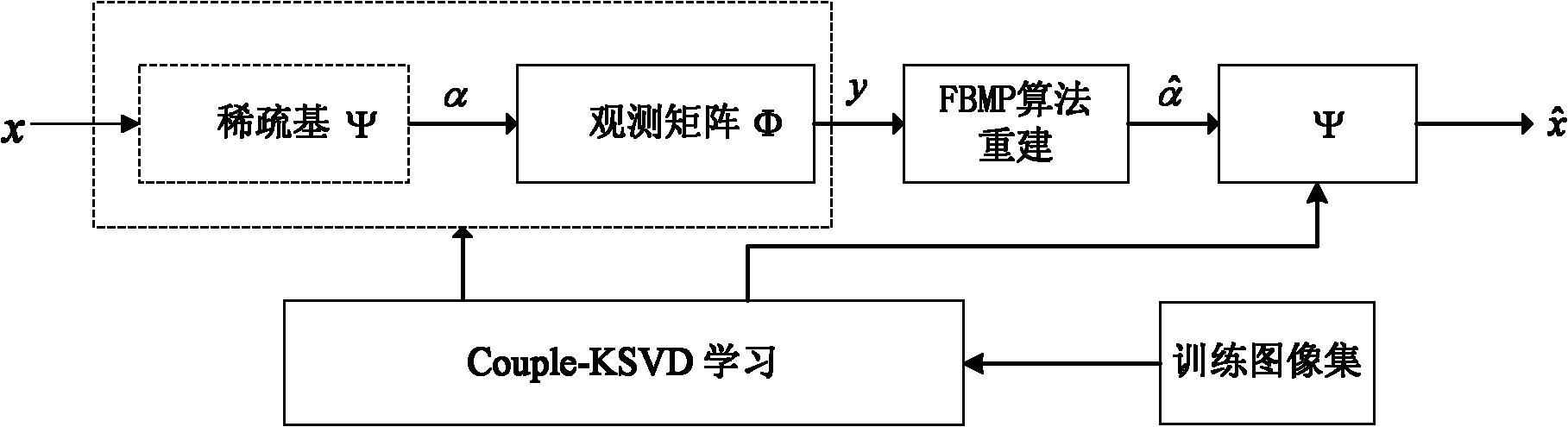
The invention discloses a compressed learning perception based SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) image high-resolution reconstruction method which is mainly used for solving the problem that the quality of a reconstructed image is reduced because a sparse base and an observation matrix cannot meet restricted isometry property (RIP) existing in the conventional method. The method comprises the following steps of: inputting a training sample set and a test image; learning a dictionary and the observation matrix by using a Couple-KSVD (Kernel Singular Value Decomposition) method to obtain a target training dictionary psi and a coupled observation matrix phi; finally reconstructing a small block of a high-resolution image by using a fast Bayesian matching pursuit FBMP algorithm; and repeating the operation on all small blocks of the image to acquire a final SAR high-resolution reconstructed image. By adopting the method, the reconstruction quality of various SAR high-resolution images can be improved at different sampling rates; and the method can be used for recovery and recognition of targets and objects in various SAR images.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
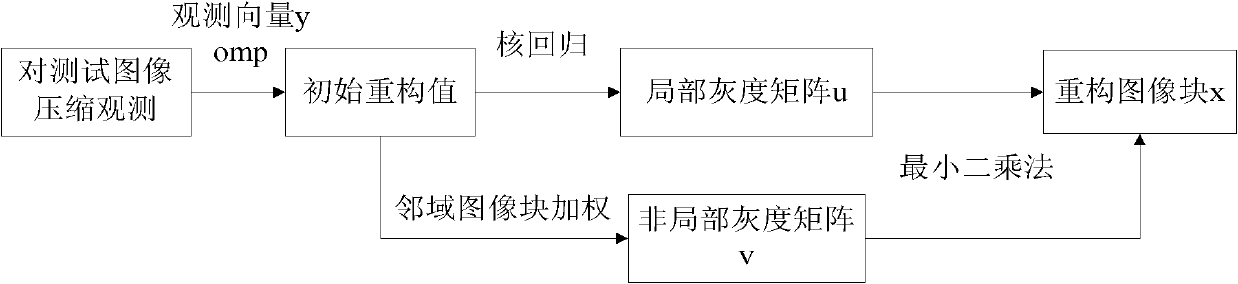
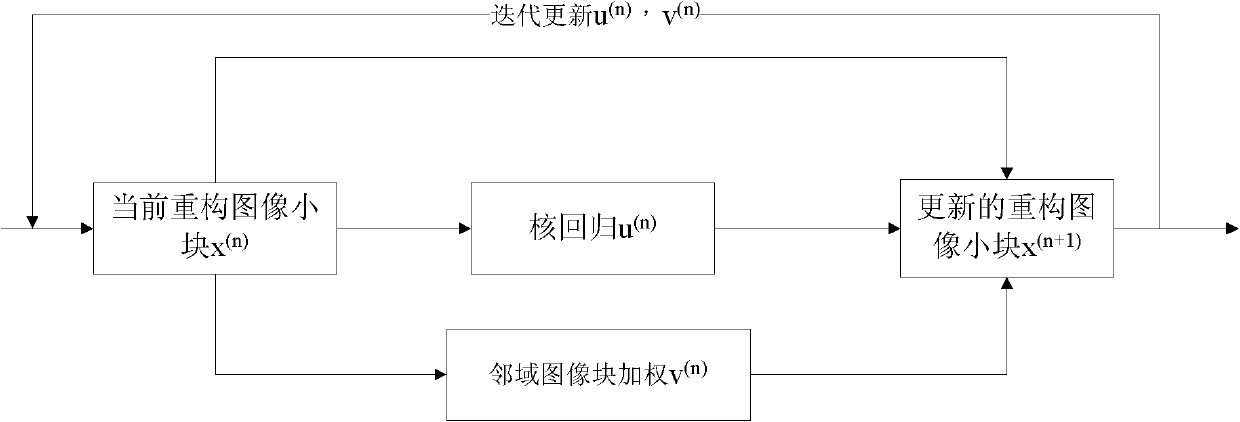
Kernel regression-based image compression sensing reconstruction method
ActiveCN102332153AImprove refactoring qualityQuality improvementImage enhancementPattern recognitionKernel regression
The invention discloses a kernel regression-based image compression sensing reconstruction method, which mainly solves the problem of reduced quality of a reconstructed image caused by mutually independent reconstruction of each image block and lack of considering linkage between the image blocks existing in the conventional method. The method comprises the following steps of: partitioning an input scene image; performing preliminary reconstruction on the image blocks by using an orthogonal matching pursuit (OMP) algorithm; then performing a kernel regression method on the image to obtain a local gray matrix of the image small blocks; weighing by using neighborhood image blocks to obtain a non-local gray matrix of the image small blocks; and finally, solving the final reconstruction imagesmall blocks through least square by using the local gray matrix and the non-local gray matrix of the image small blocks, and repeating the operation on all the image small blocks to obtain the finalreconstructed image. In the invention, both the reconstruction effects of various natural images and cartoon images can be improved under different sampling rates; and the method can be used for compressing high-resolution recovery or reconstruction of various low-resolution images under observation.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com