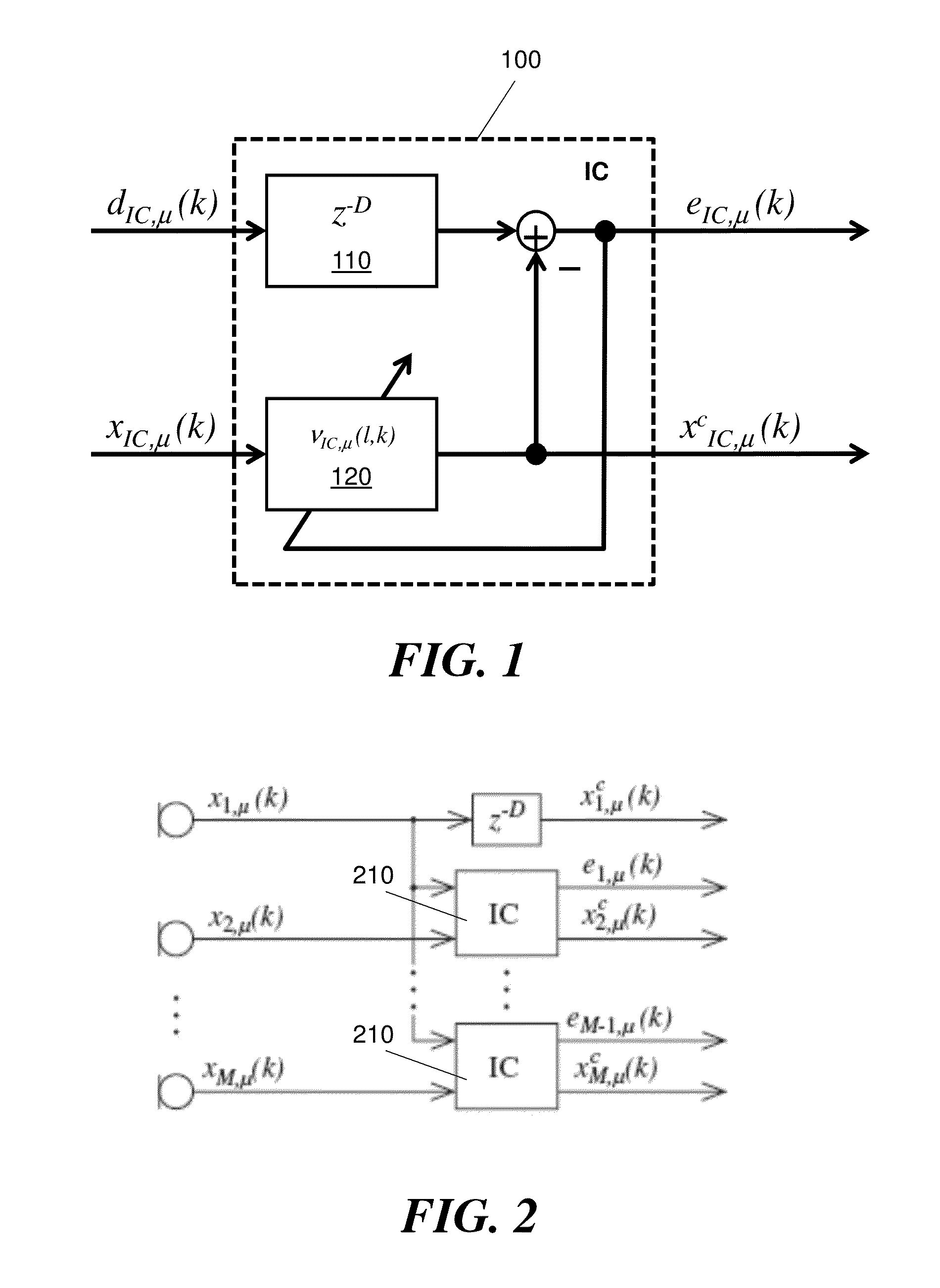
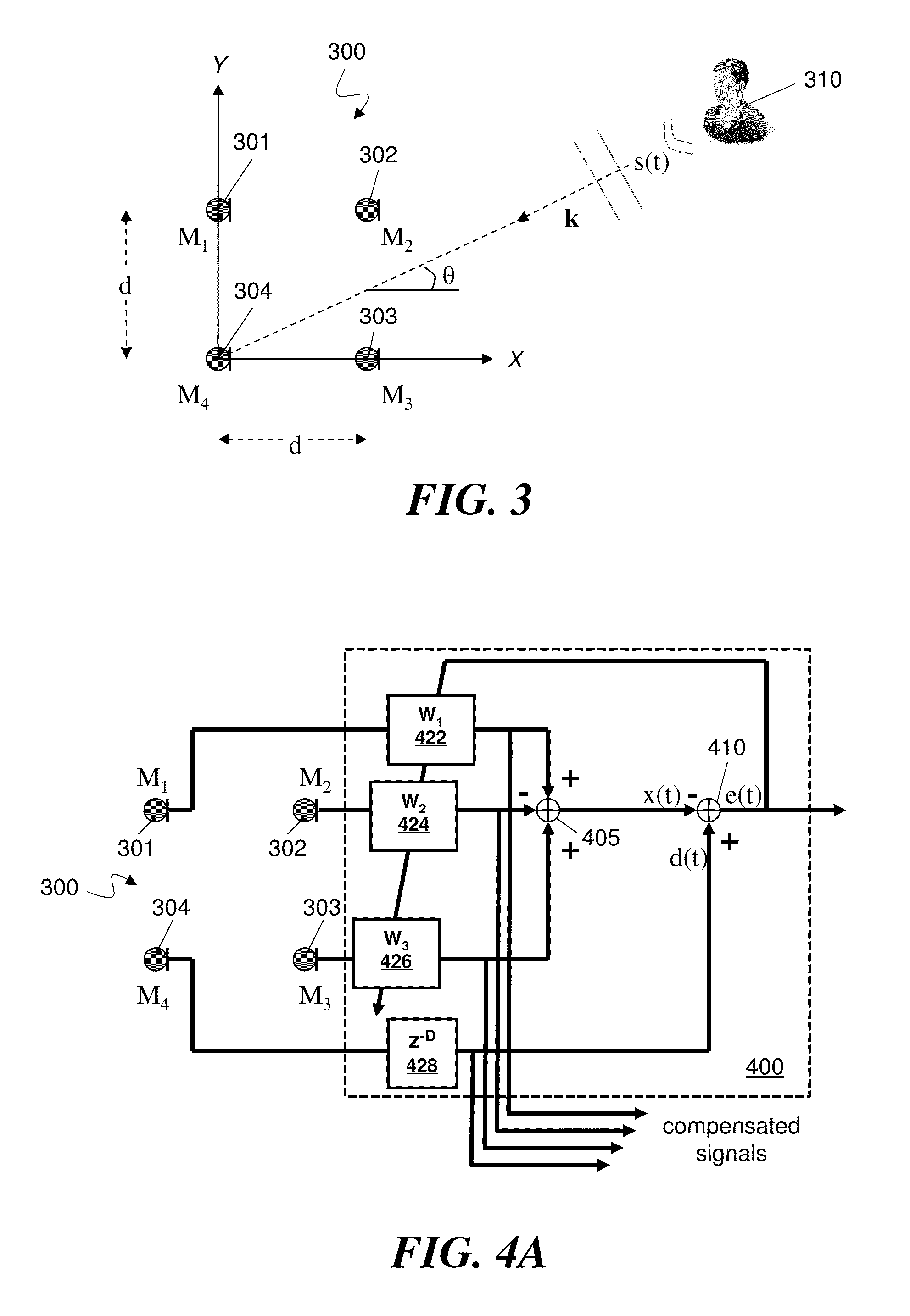
Patents
Literature
263 results about "Amplitude response" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
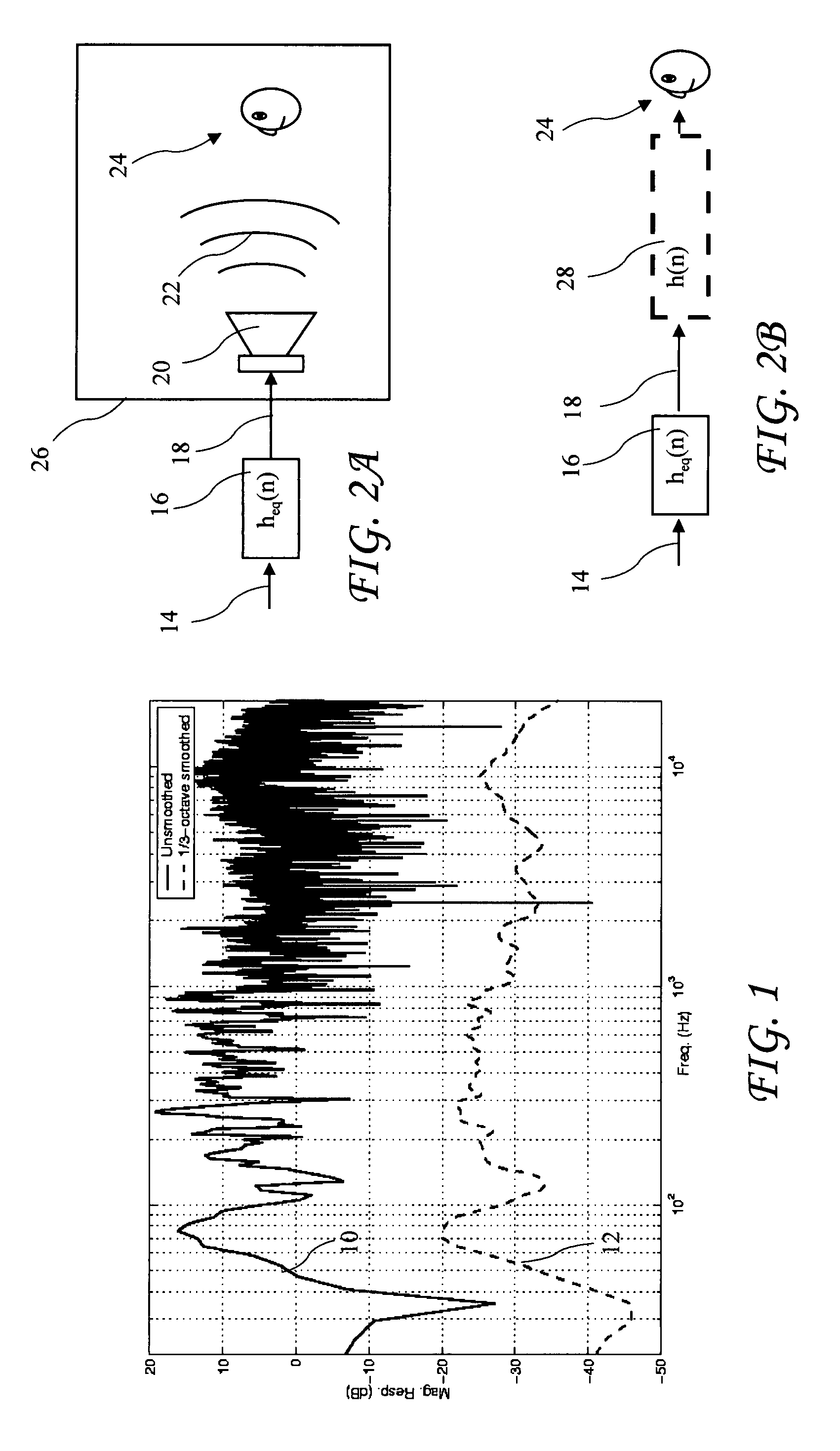
Amplitude response refers to the peak voltage (Volt) with respect to the average power of a signal at a particular operating frequency of interest is in fact the amplitude of the signal actually perceived in time domain. As said earlier, amplitude response and frequency response are inter-related by...
Compensating filters
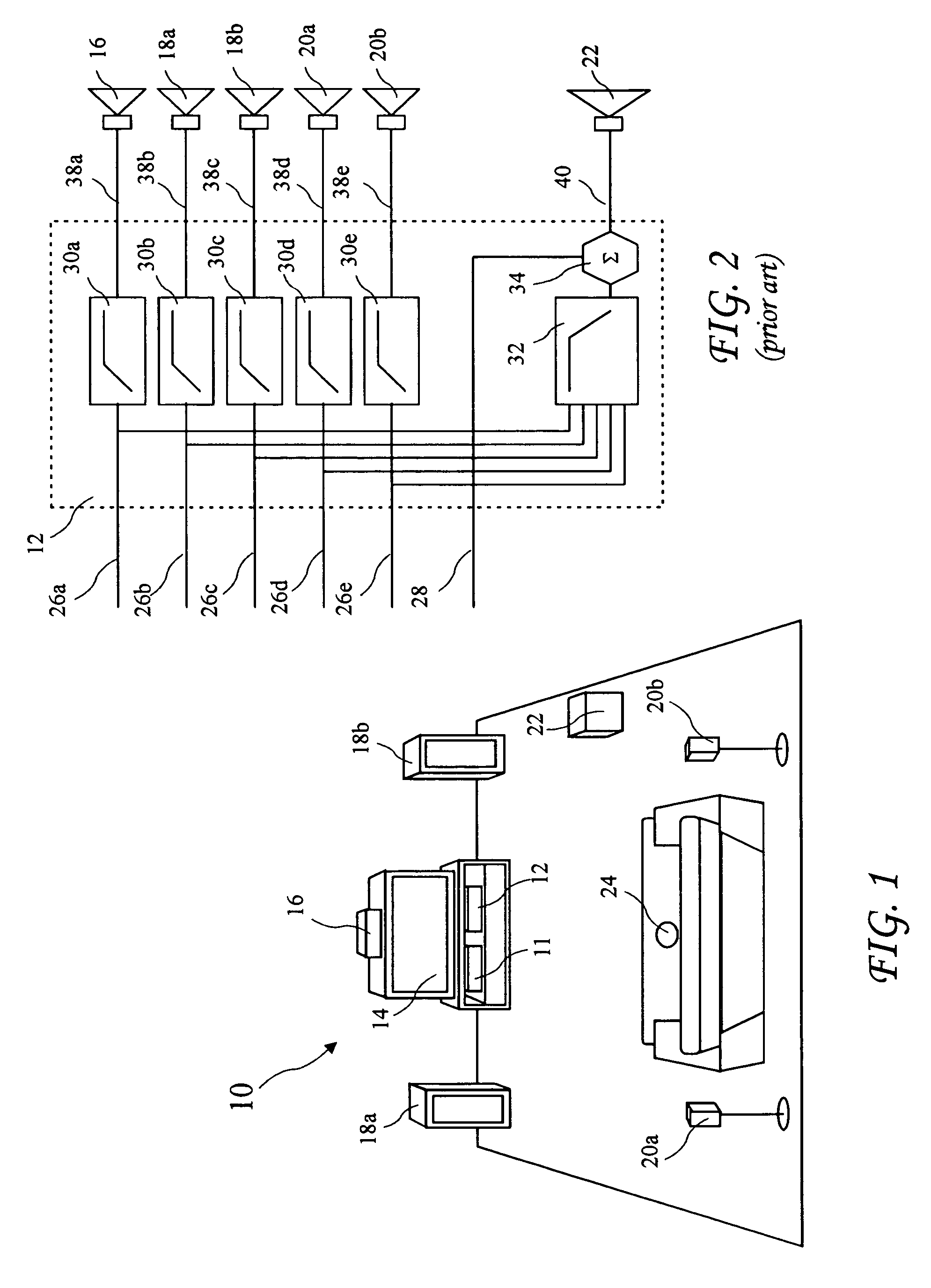
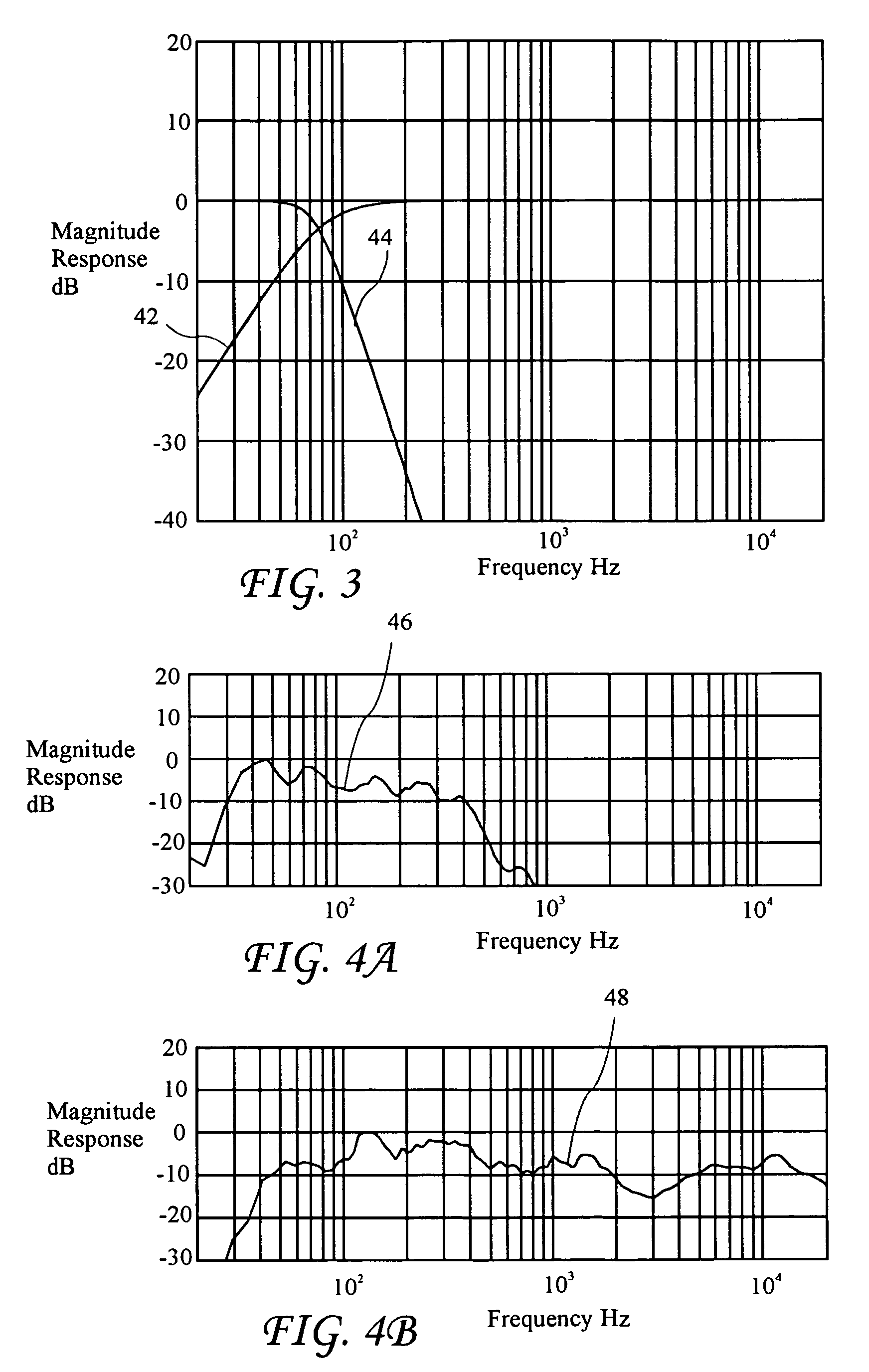
InactiveUS6760451B1Eliminate phase distortionAdaptive networkAutomatic tone/bandwidth controlDigital signal processingAmplitude response
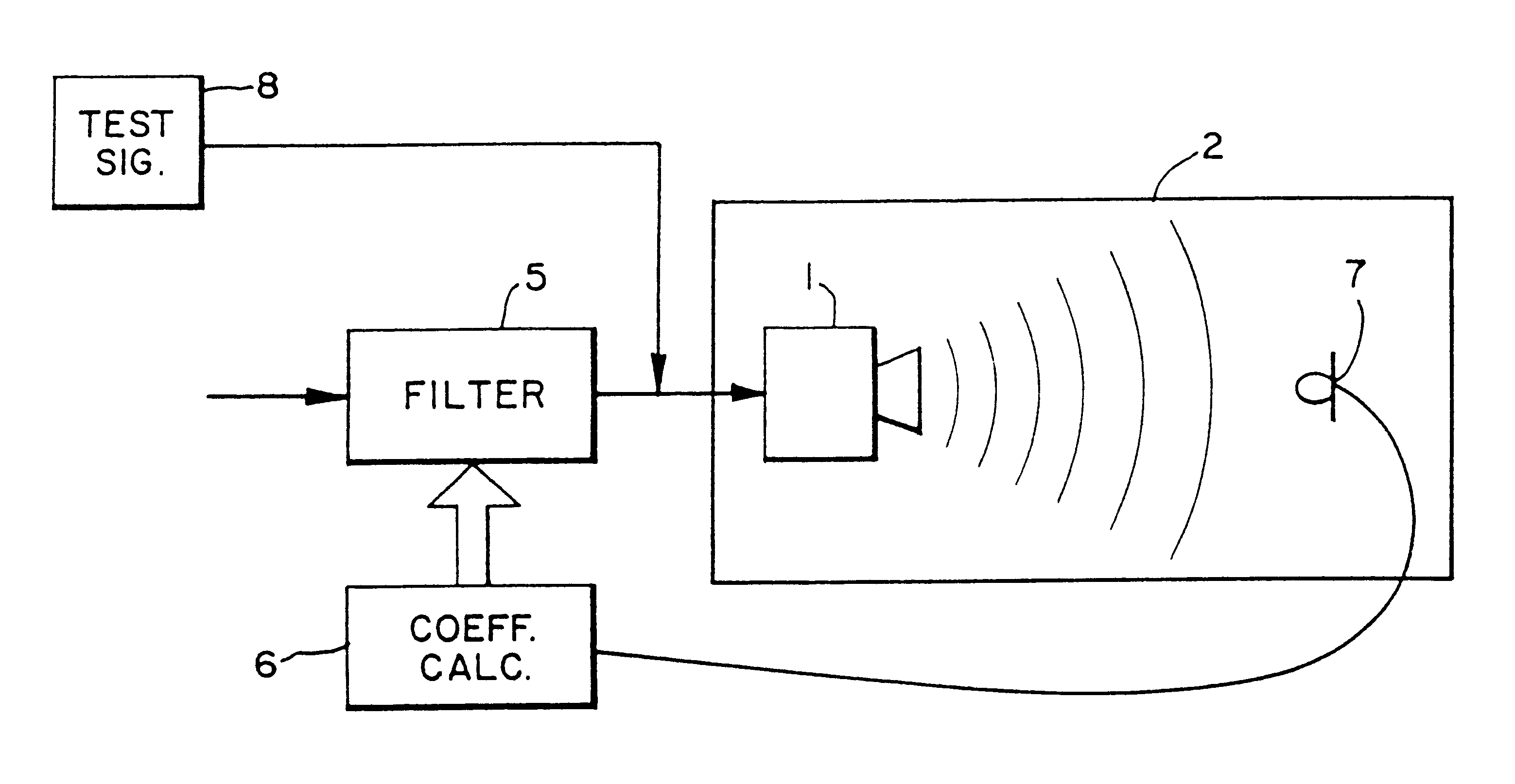
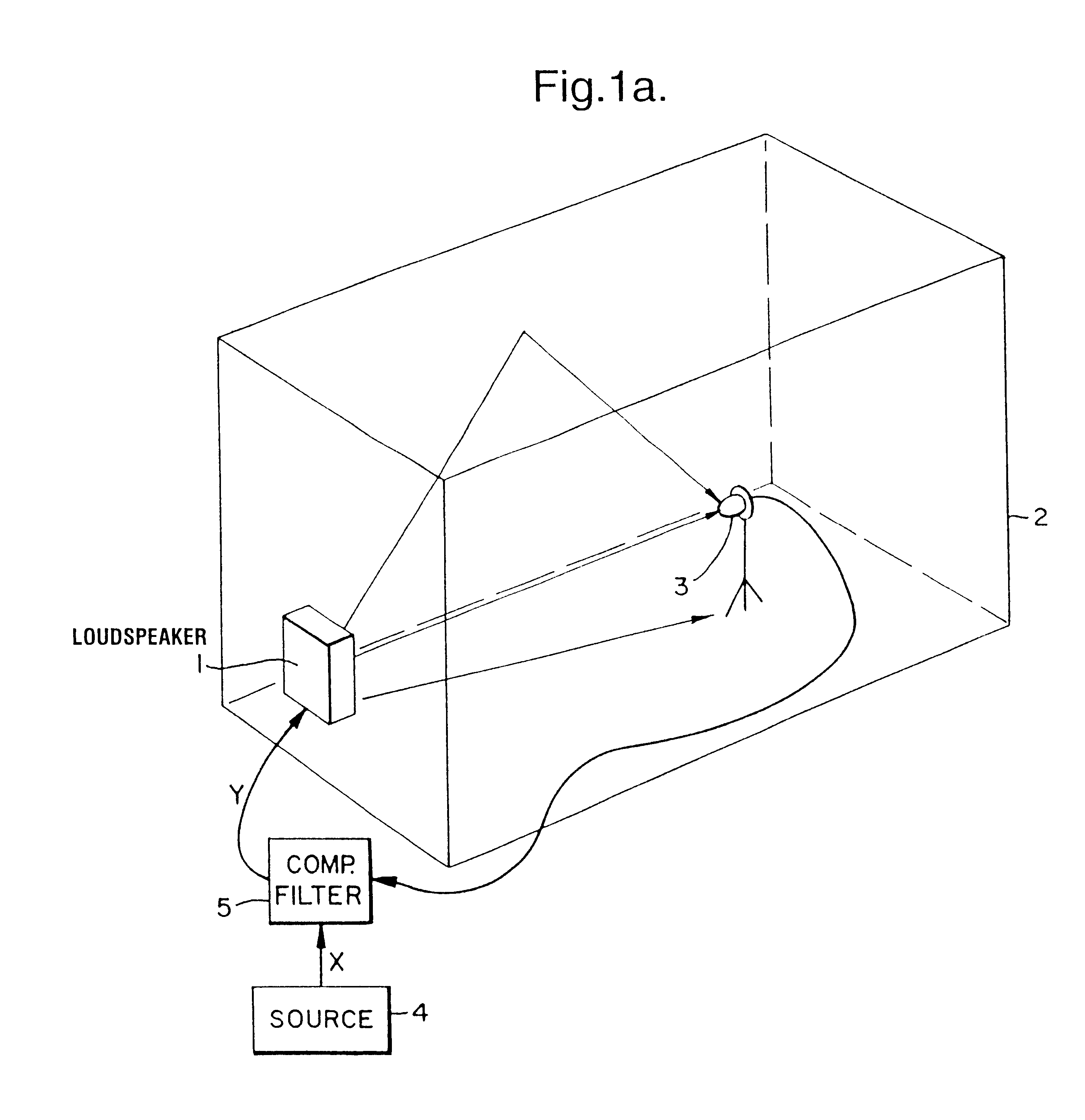
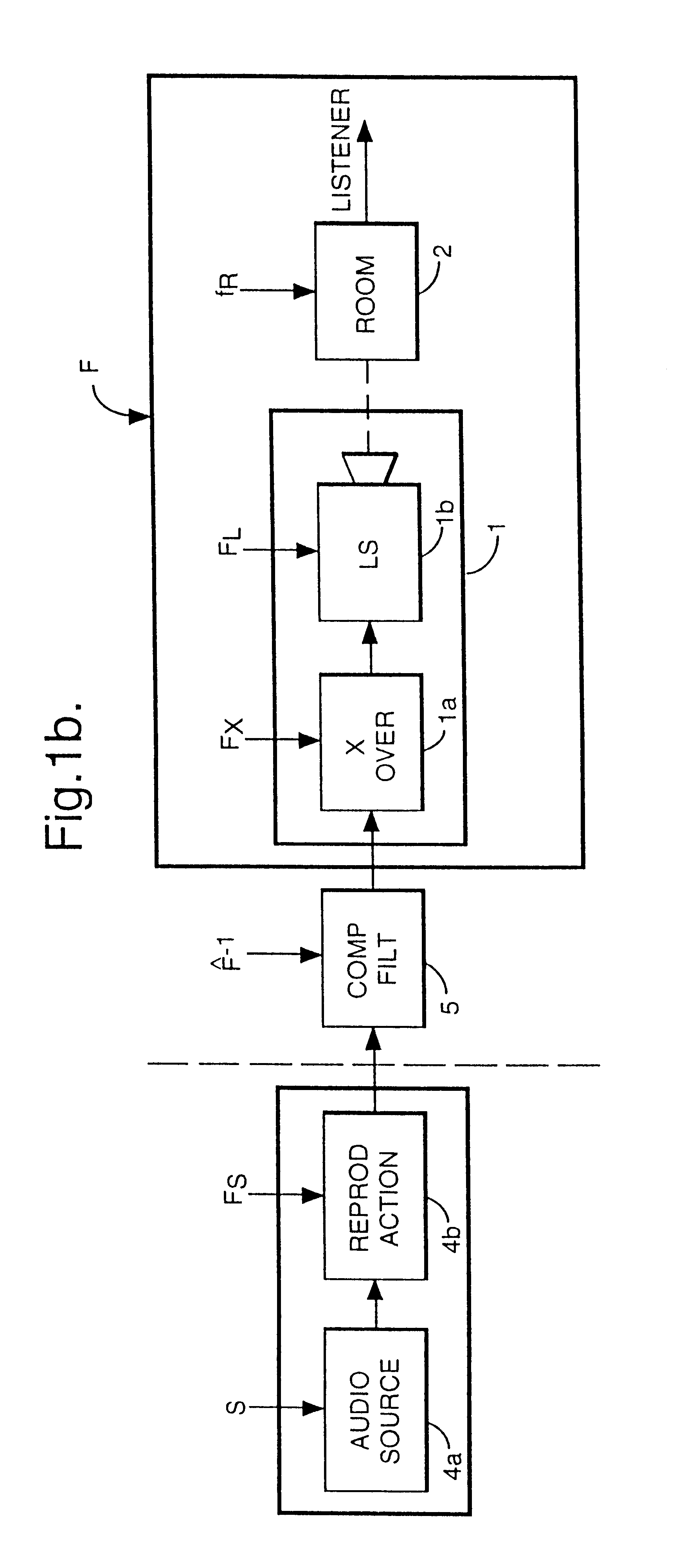
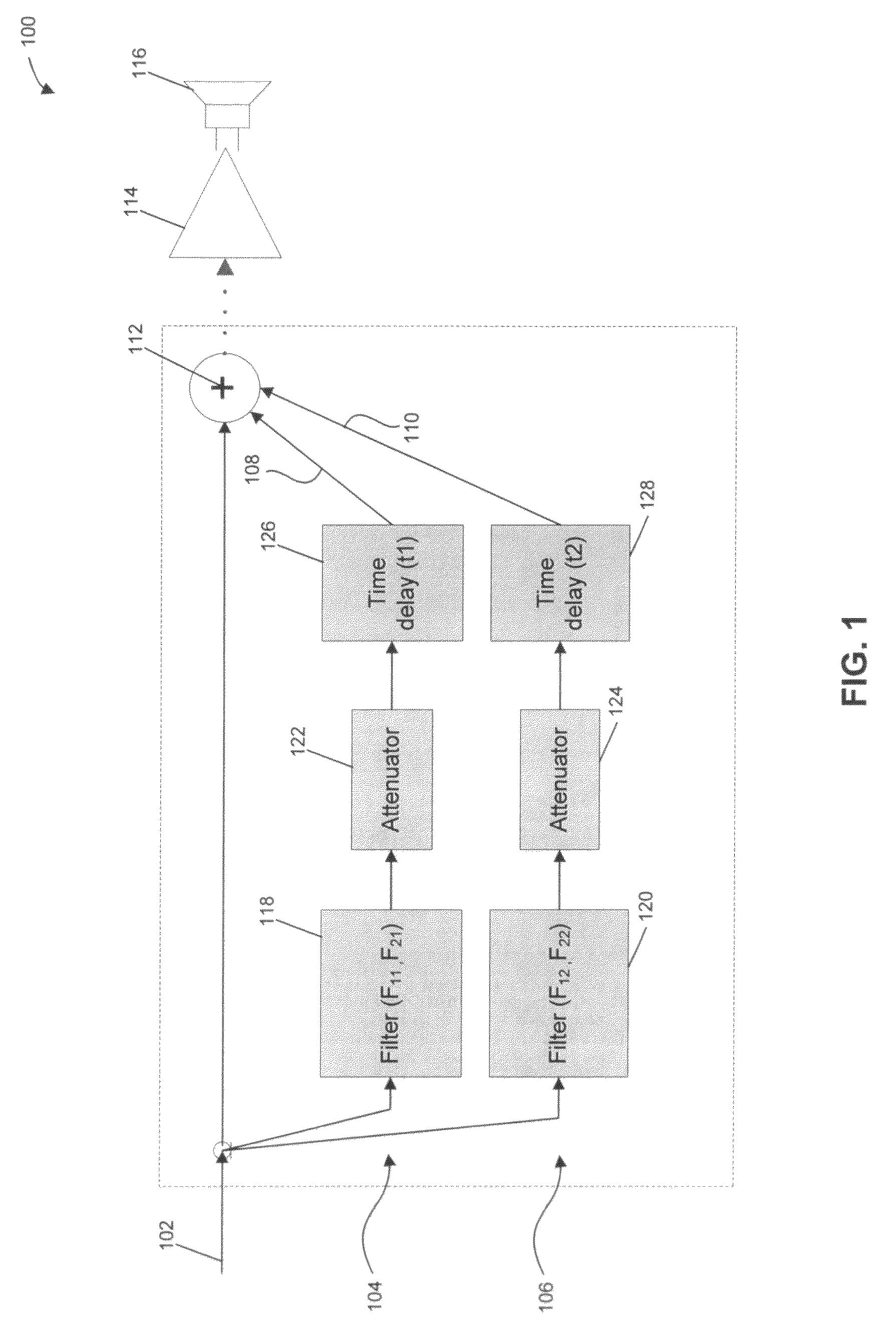
A prefilter (5) for an audio system comprising a loudspeaker (1) in a room (2), which corrects both amplitude and phase errors due to the loudspeaker (1) by a linear phase correction filter response and corrects the amplitude response of the room (2) whilst introducing the minimum possible amount of extra phase distortion by employing a minimum phase correction filter stage. A test signal generator (8) generates a signal comprising a periodic frequency sweep with a greater phase repetition period than the frequency repetition period. A microphone (7) positioned at various points in the room (2) measures the audio signal processed by the room (2) and loudspeaker (1), and a coefficient calculator (6) (e.g. a digital signal processor device) derives the signal response of the room and thereby a requisite minimum phase correction to be cascaded with the linear phase correction already calculated for the loudspeaker (1). Filter (5) may comprise the same digital signal processor as the coefficient calculator (6). Applications in high fidelity audio reproduction, and in car stereo reproduction.
Owner:CRAVEN PETER GRAHAM +1
In-room acoustic magnitude response smoothing via summation of correction signals
A system and method are provided for smoothing the in-room acoustic magnitude response of an audio reproduction system. An in-room acoustic magnitude response analysis is performed to determine a room resonance induced peak associated with an audio signal. A replica of the audio signal is filtered at the room resonance induced peak. The filtered replica signal is added with the audio signal. Through this, smoothing of the room resonance induced peak may be achieved, such that a subjective impression of transient response and dynamics of the audio signal are preserved.
Owner:POLK AUDIO LLC +1
Non-invasive method and apparatus for cardiac pacemaker pacing parameter optimization and monitoring of cardiac dysfunction
InactiveUS20050043767A1Uniform peak amplitudeEasy to detectHeart stimulatorsCardiac dysfunctionAmplitude response
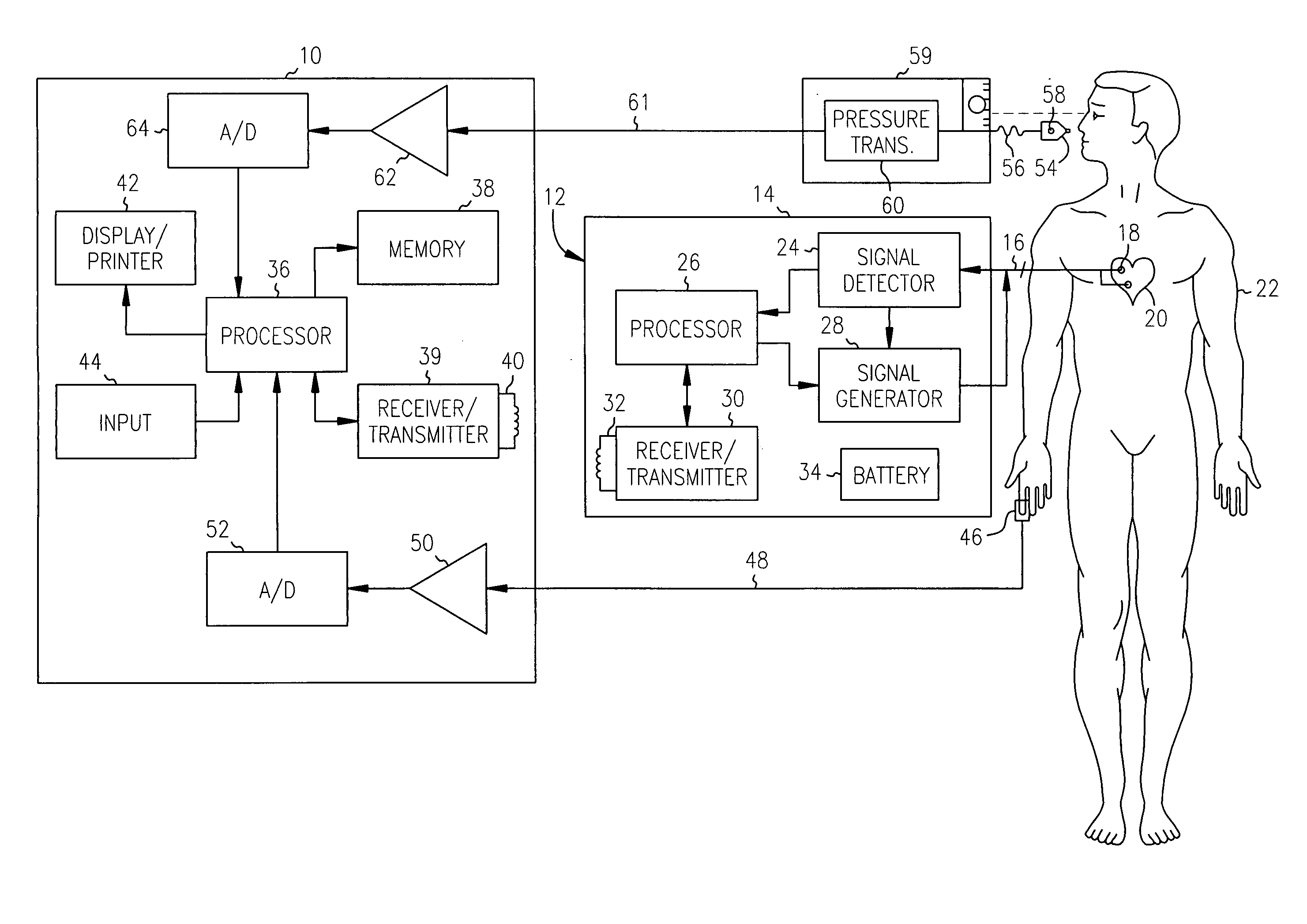
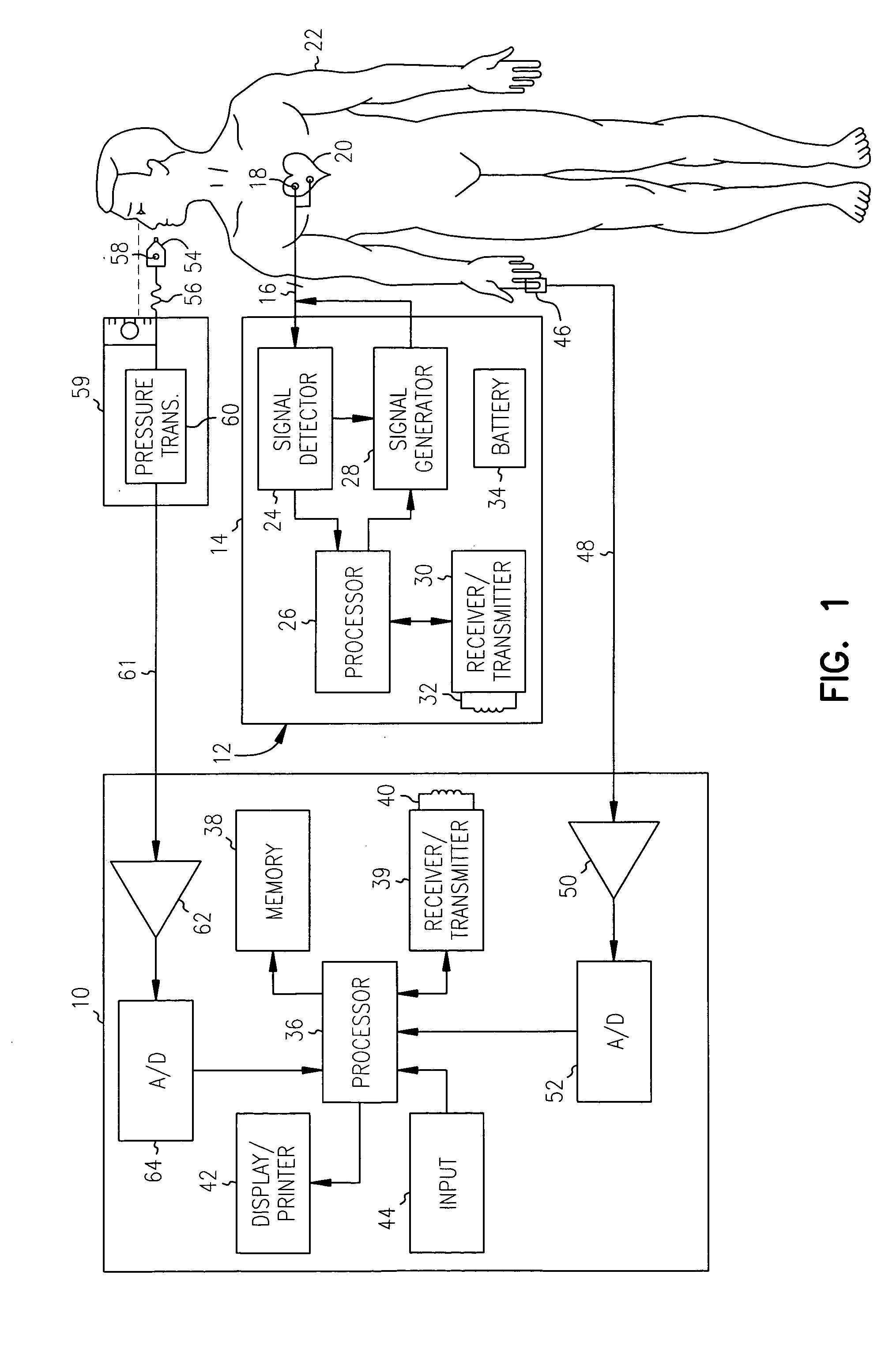
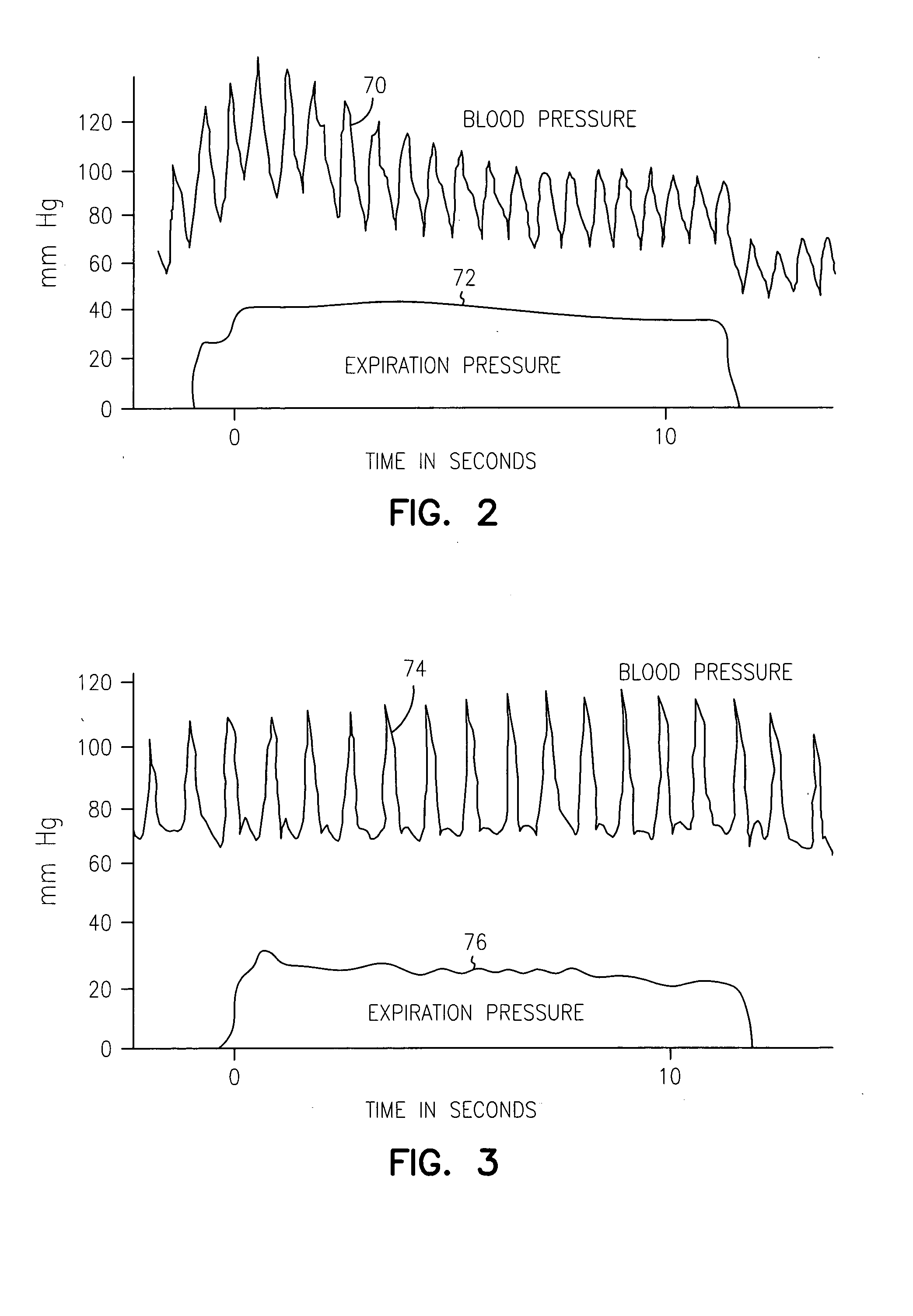
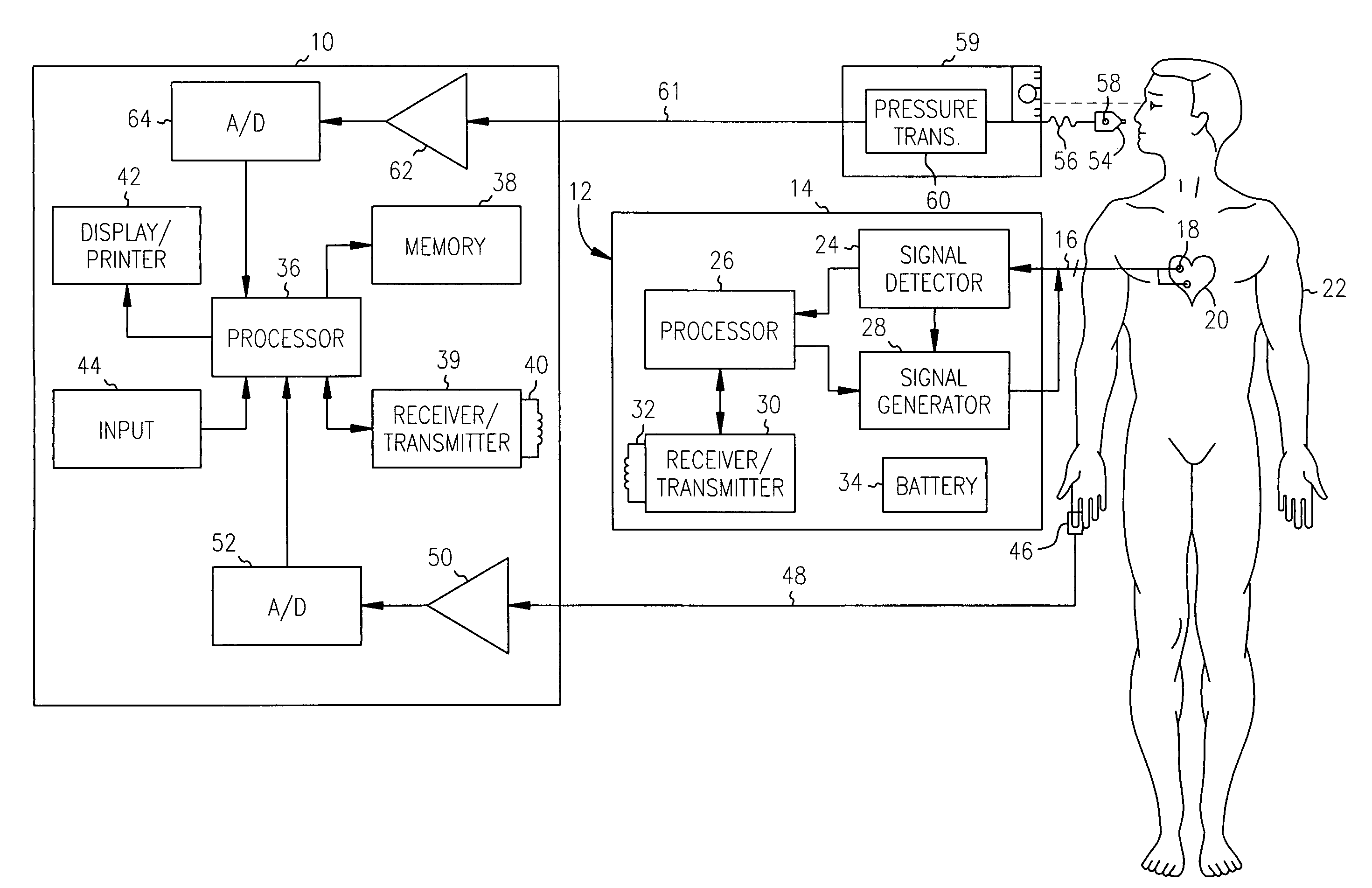
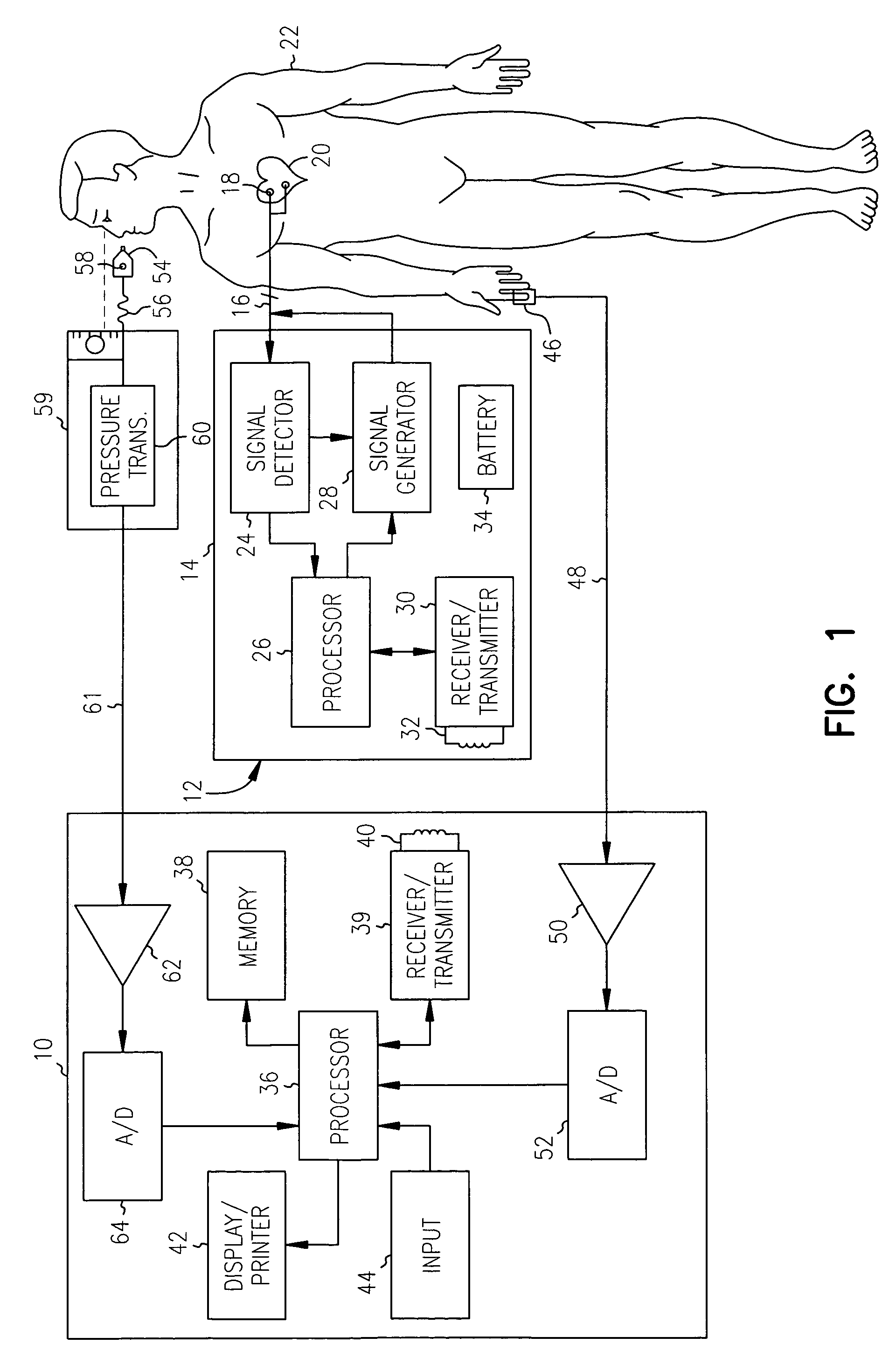
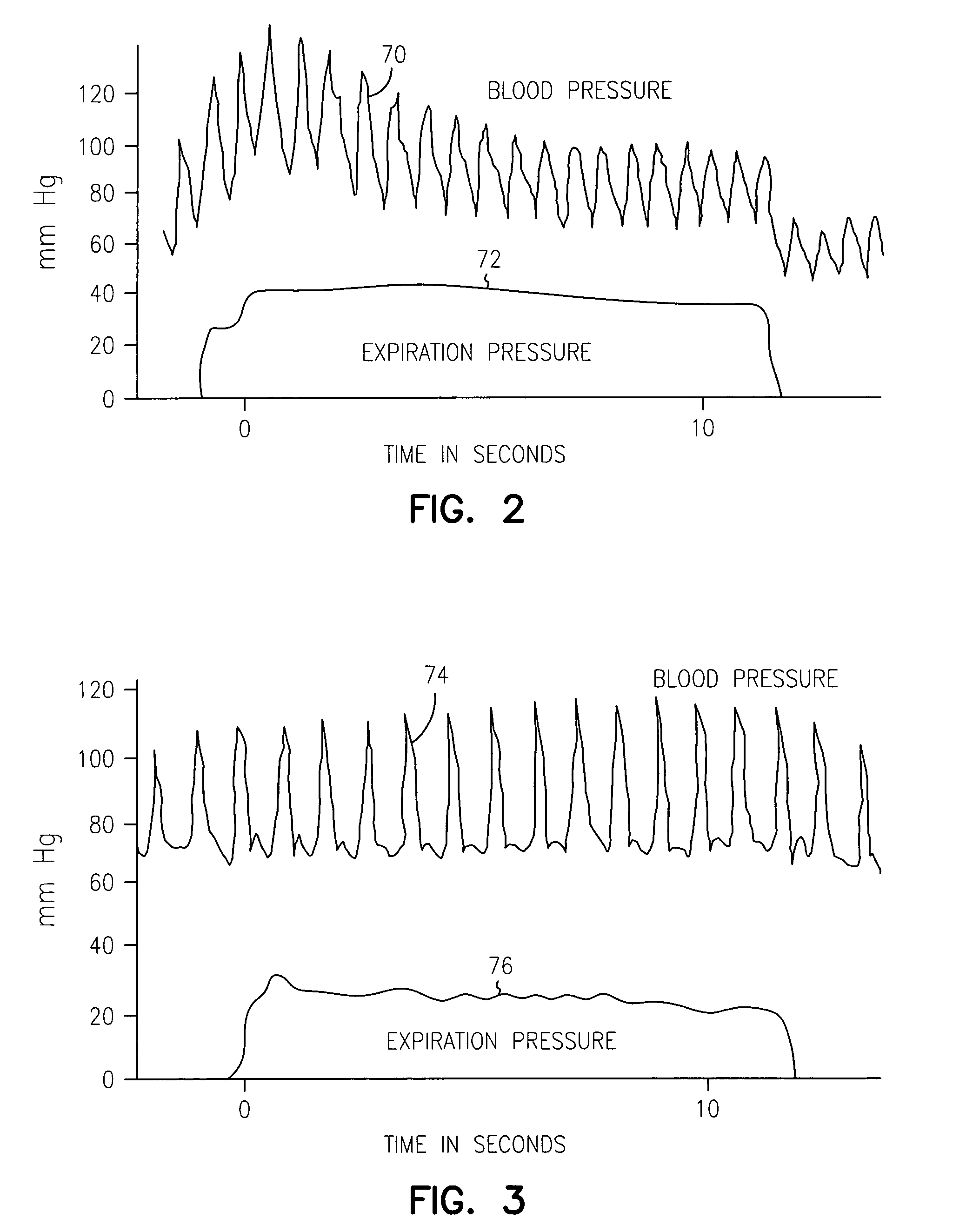
A plethysmogram signal is sensed from a patient and provided to a programmer device for monitoring the condition of the patient and for optimizing pacing parameters of a cardiac device implanted in the patient. The programmer device analyzes the plethysmogram signal for cardiac performance associated with different pacing parameters. The cardiac performance is indicated by, for example, a pulse amplitude response, a degree of pulsus alternans, or irregularity in the pressure pulses detected in an atrial fibrillation patient. The pacing parameters resulting in the best cardiac performance are selected as the optimum pacing parameters. In one embodiment, the programmer device monitors a Valsalva maneuver performed by a patient. Optimum pacing parameters are derived by analysis of the plethysmogram signals obtained during performance of the Valsalva maneuver while the patient is paced using different pacing parameters.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Non-invasive method and apparatus for cardiac pacemaker pacing parameter optimization and monitoring of cardiac dysfunction
A plethysmogram signal is sensed from a patient and provided to a programmer device for monitoring the condition of the patient and for optimizing pacing parameters of a cardiac device implanted in the patient. The programmer device analyzes the plethysmogram signal for cardiac performance associated with different pacing parameters. The cardiac performance is indicated by, for example, a pulse amplitude response, a degree of pulsus alternans, or irregularity in the pressure pulses detected in an atrial fibrillation patient. The pacing parameters resulting in the best cardiac performance are selected as the optimum pacing parameters. In one embodiment, the programmer device monitors a Valsalva maneuver performed by a patient. Optimum pacing parameters are derived by analysis of the plethysmogram signals obtained during performance of the Valsalva maneuver while the patient is paced using different pacing parameters.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
High speed noise tolerant multi-touch touch device and controller therefor
InactiveUS20110163992A1Reduce couplingReduce the amplitudeInput/output processes for data processingCapacitanceCapacitive coupling
A touch-sensitive device includes a touch panel, a drive unit, a sense unit, and a measurement unit. A touch applied to a node of the panel changes a capacitive coupling between two electrodes (a drive electrode and a sense electrode) of the touch panel. The drive unit delivers a drive signal, which may comprise one or more drive pulses, to the drive electrode. The sense unit couples to the sense electrode, and generates a response signal that includes a differentiated representation of the drive signal, which is then fed through a resistor. The amplitude of the response signal is responsive to the capacitive coupling between the electrodes, and is measured to provide an indication of a touch at the node.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Phase equalization for multi-channel loudspeaker-room responses
ActiveUS7720237B2Improved response controlMinimize phase incoherenceFrequency/directions obtaining arrangementsLine-transmissionAmplitude responseVocal tract
A system and method for minimizing the complex phase interaction between non-coincident subwoofer and satellite speakers for improved magnitude response control in a cross-over region. An all-pass filter is cascaded with bass-management filters in at least one filter channel, and preferably all-pass filters are cascaded in each satellite speaker channel. Pole angles and magnitudes for the all-pass filters are recursively calculated to minimize phase incoherence. A step of selecting an optimal cross-over frequency may be performed in conjunction with the all-pass filtering, and is preferably used to select an optimal cross-over frequency prior to determining all-pass filter coefficients.
Owner:AUDYSSEY LABORATORIES
Frequency hopping spread spectrum passive acoustic wave identification device
InactiveUS7023323B1Fast readSubscribers indirect connectionRecord carriers used with machinesFrequency-hopping spread spectrumIntegrator
A system and method for interrogating a passive acoustic transponder, producing a transponder signal having characteristic set of signal perturbations in response to an interrogation signal, comprising a signal generator, producing an interrogation signal having a plurality of differing frequencies; a receiver, for receiving the transponder signal; a mixer, for mixing the transponder signal with a signal corresponding to the interrogation signal, to produce a mixed output; an integrator, integrating the mixed output to define an integrated phase-amplitude response of the received transponder signal; and an analyzer, receiving a plurality of integrated phase-amplitude responses corresponding to the plurality of differing frequencies, for determining the characteristic set of signal perturbations of the passive acoustic transponder.
Owner:X CYTE
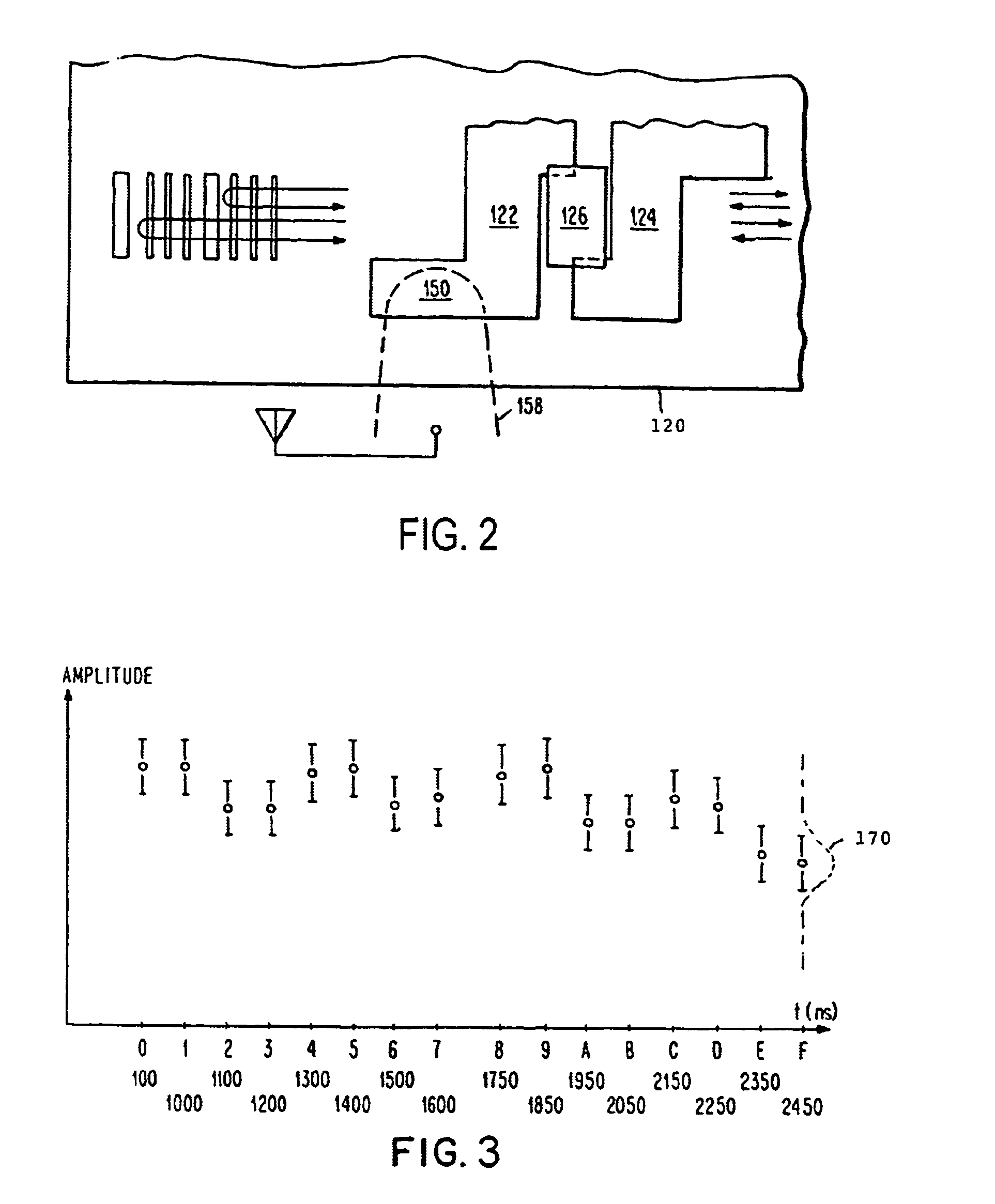
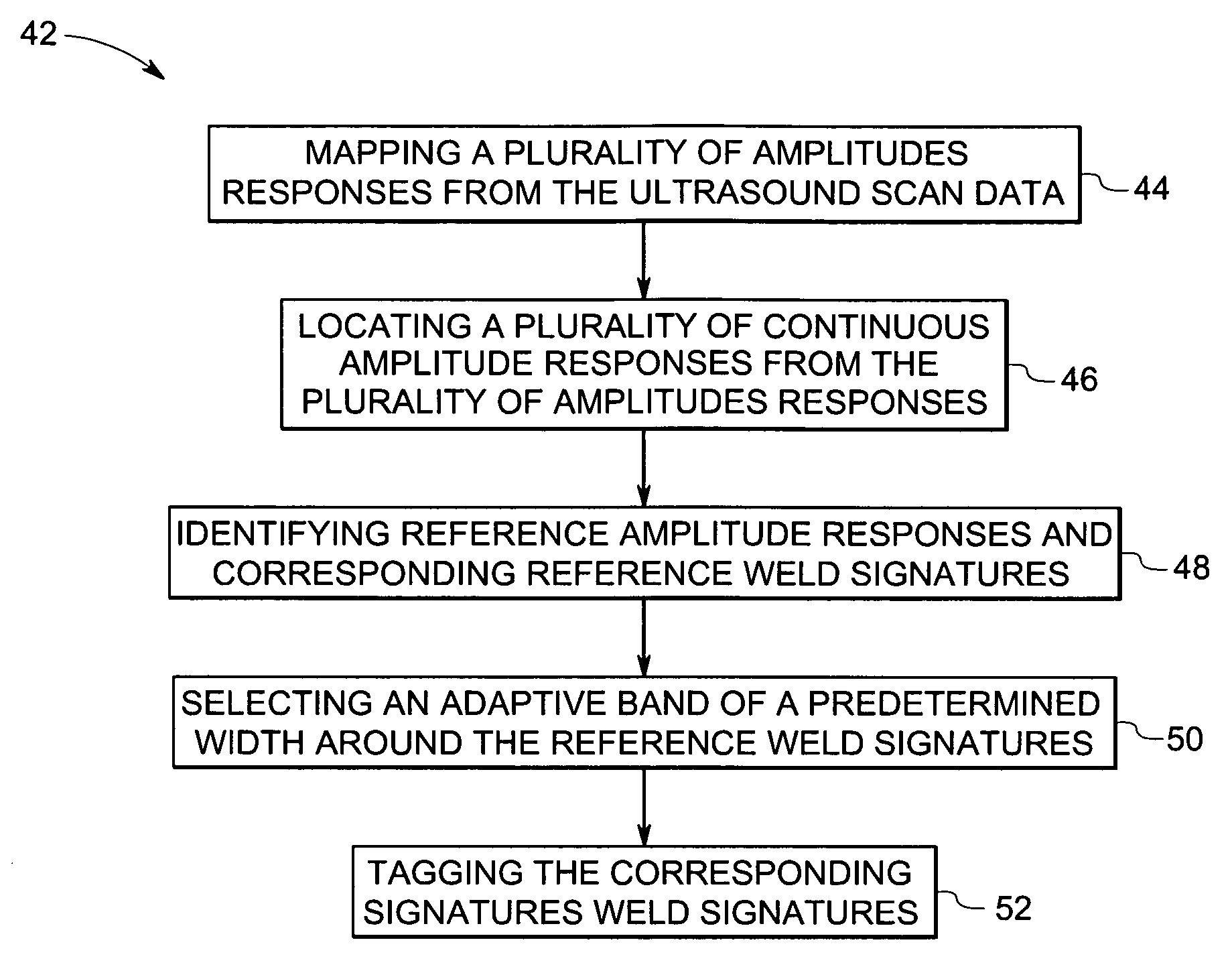
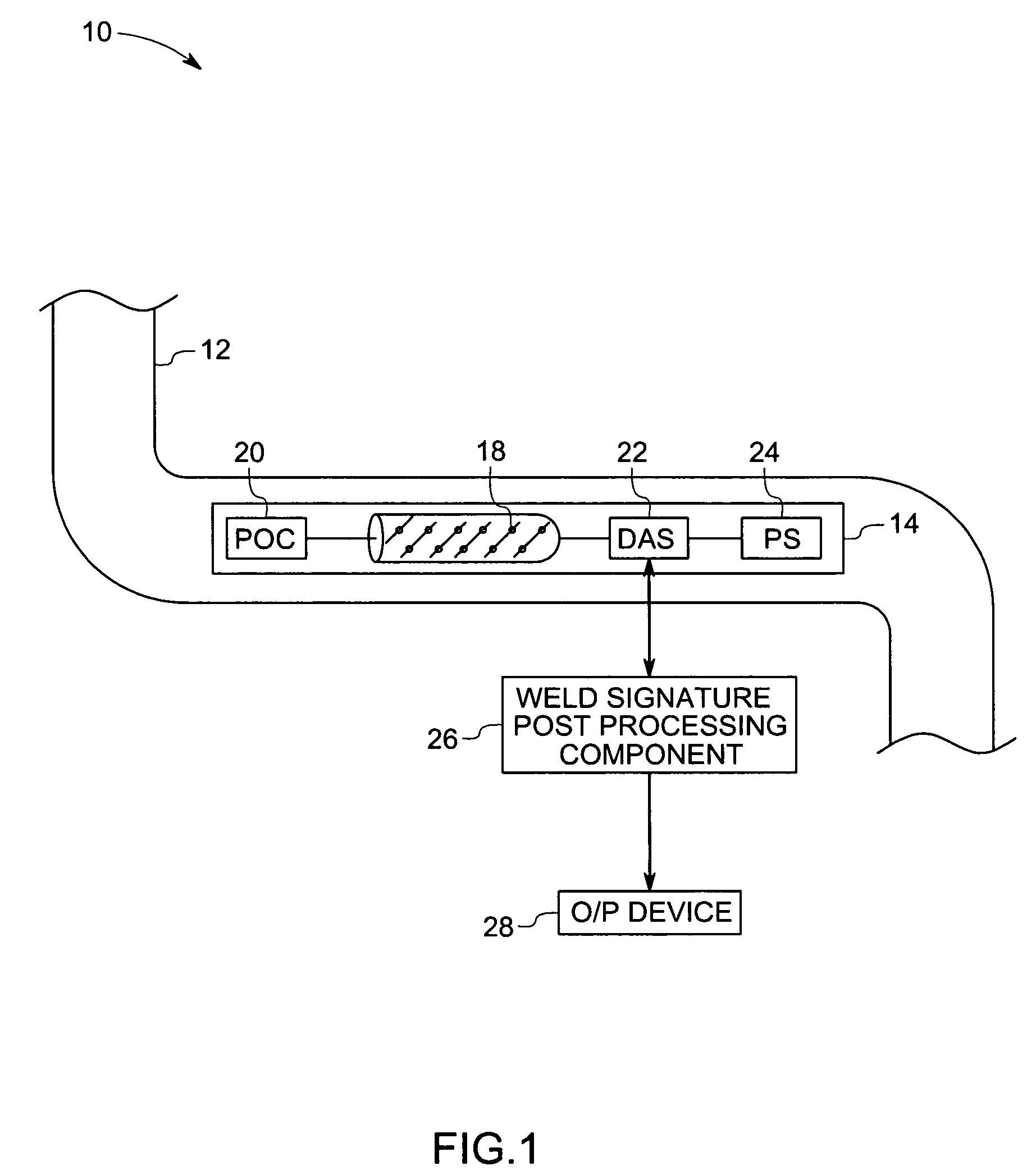
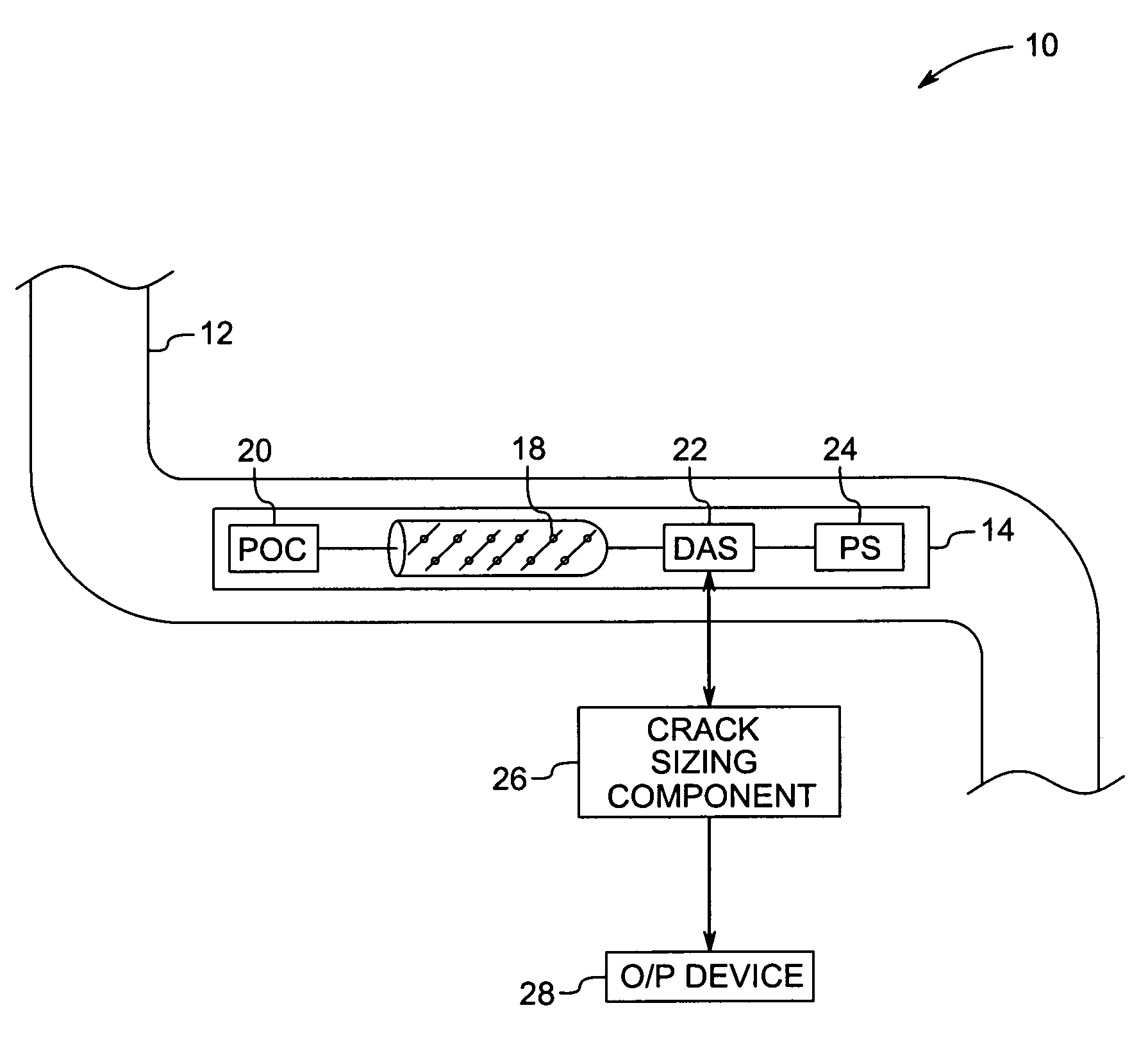
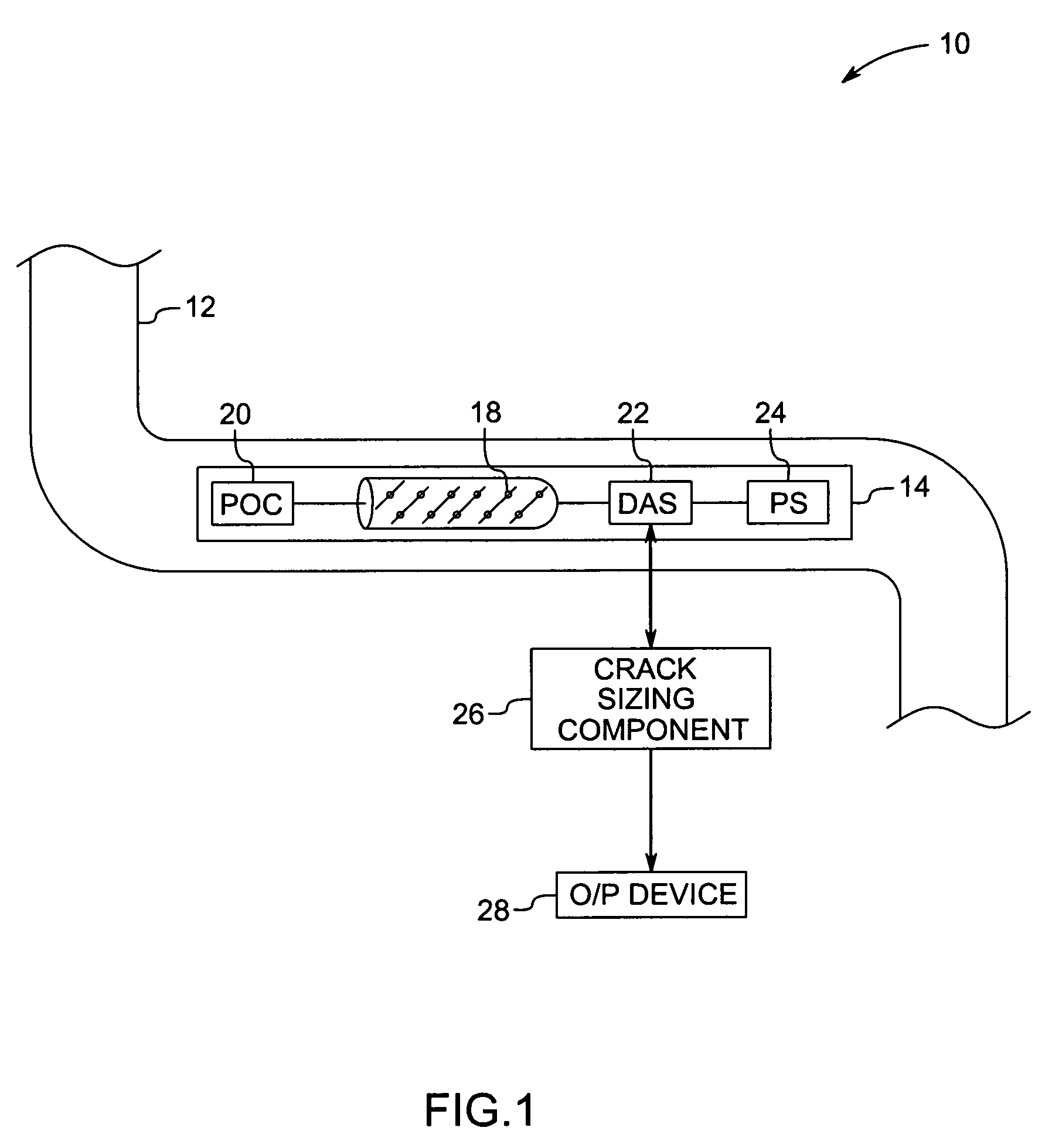
Method and system for inspecting flaws using ultrasound scan data
ActiveUS7234355B2Vibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSonificationAmplitude response
A method and system for detecting weld signatures from an ultrasound scan data obtained from scanning a pipeline is provided. The method includes a step for mapping multiple amplitude responses from the ultrasound scan data, each amplitude response being representative of a respective sensor signal. Continuous amplitude responses are located from the amplitude responses and corresponding signatures are identified for the continuous amplitude responses. The method also includes a step for tagging the corresponding signatures as weld signatures.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Speech separating apparatus, speech synthesizing apparatus, and voice quality conversion apparatus
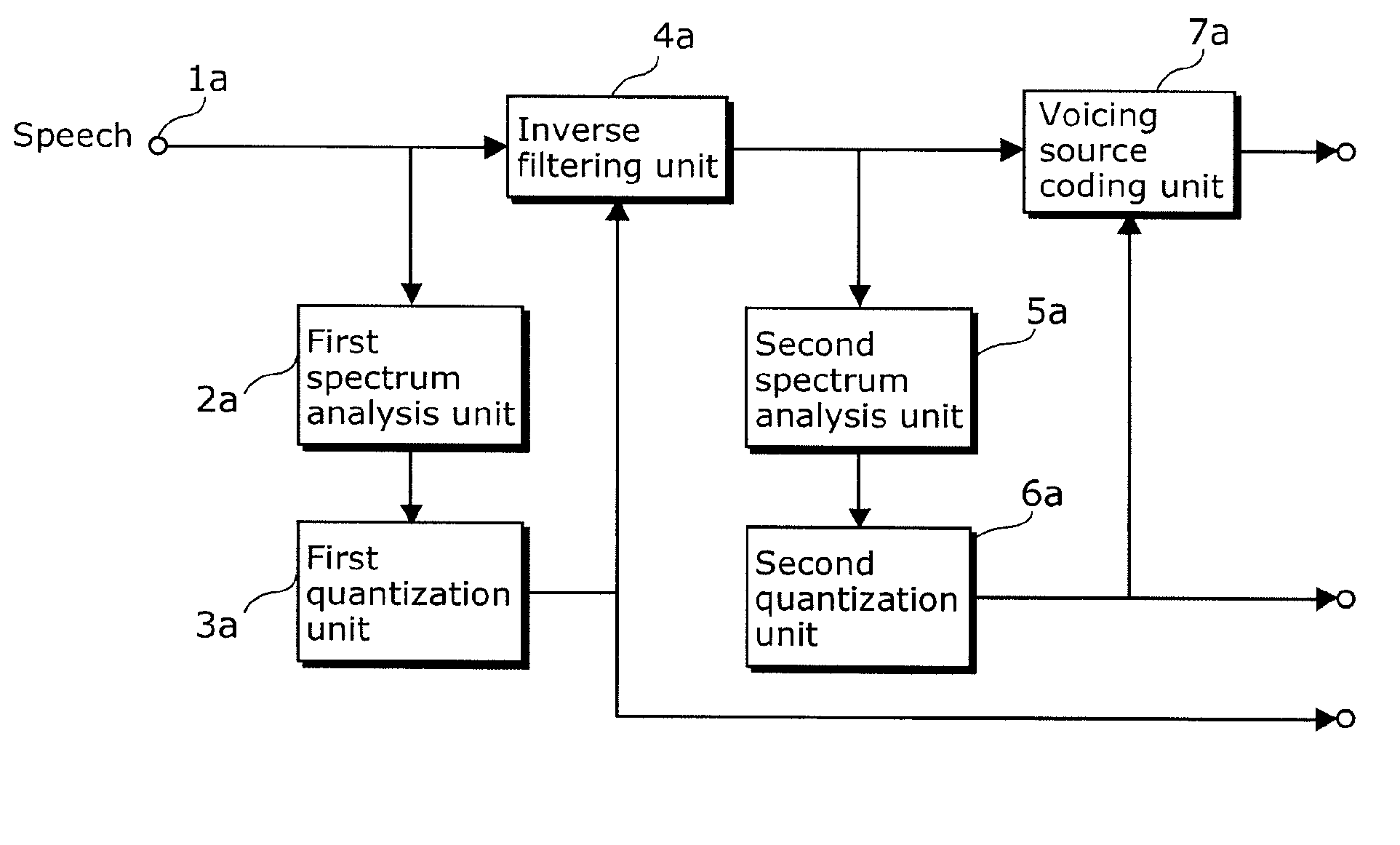
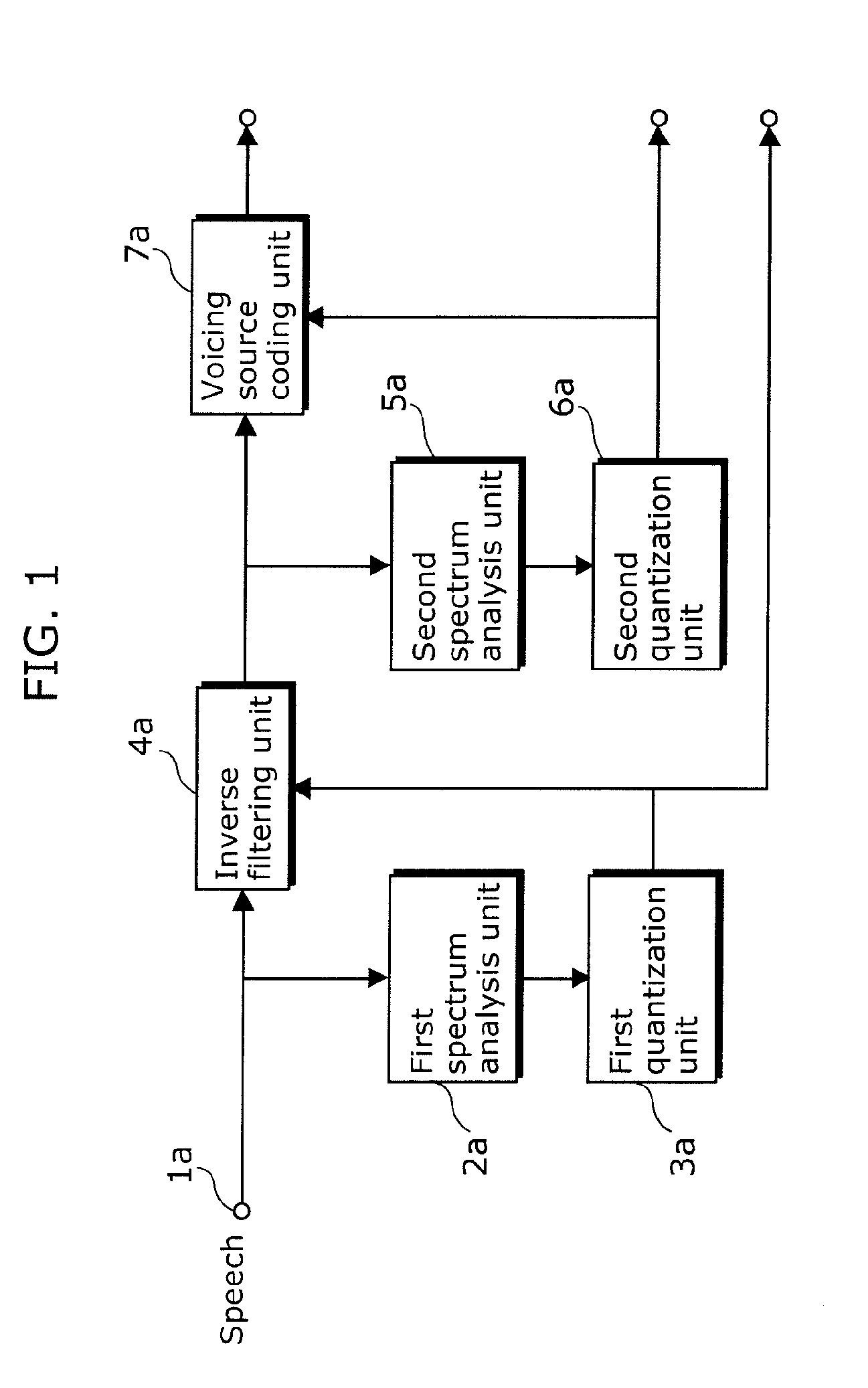
A speech separating apparatus includes: a PARCOR calculating unit (102) that extracts vocal tract information from an input speech signal; a filter smoothing unit (103) that smoothes, in a first time constant, the vocal tract information extracted by the PARCOR calculating unit (102); an inverse filtering unit (104) that calculates a filter coefficient of a filter having a frequency amplitude response characteristic inverse to the vocal tract information smoothed by the filter smoothing unit (103), so as to filter the input speech signal using the filter having the calculated filter coefficient; and a voicing source modeling unit (105) that cuts out, from the input speech signal filtered by the inverse filtering unit (104), a waveform included in a second time constant shorter than the first time constant, so as to calculate, for each waveform that is taken, voicing source information from the each waveform.
Owner:SOVEREIGN PEAK VENTURES LLC
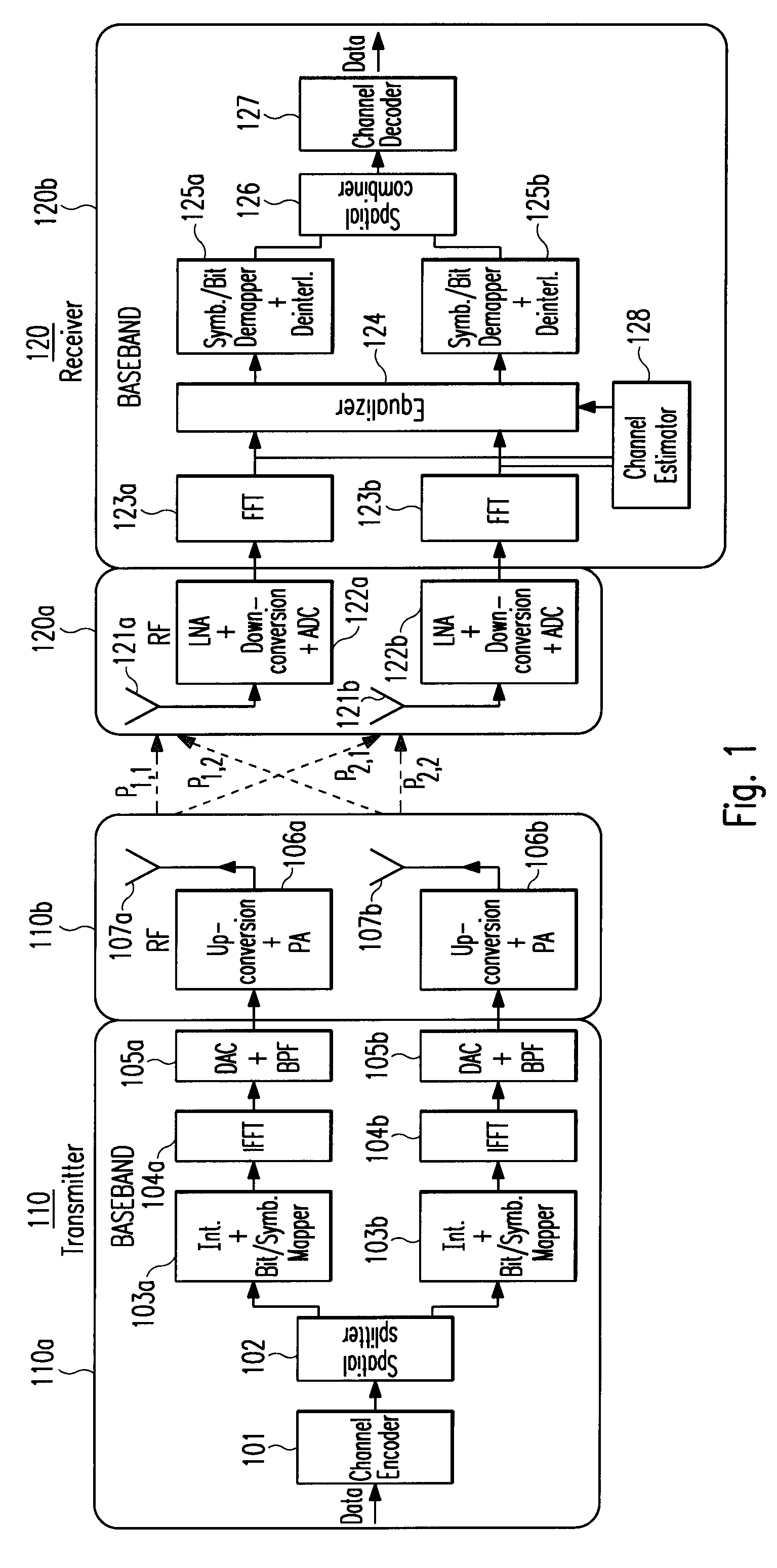
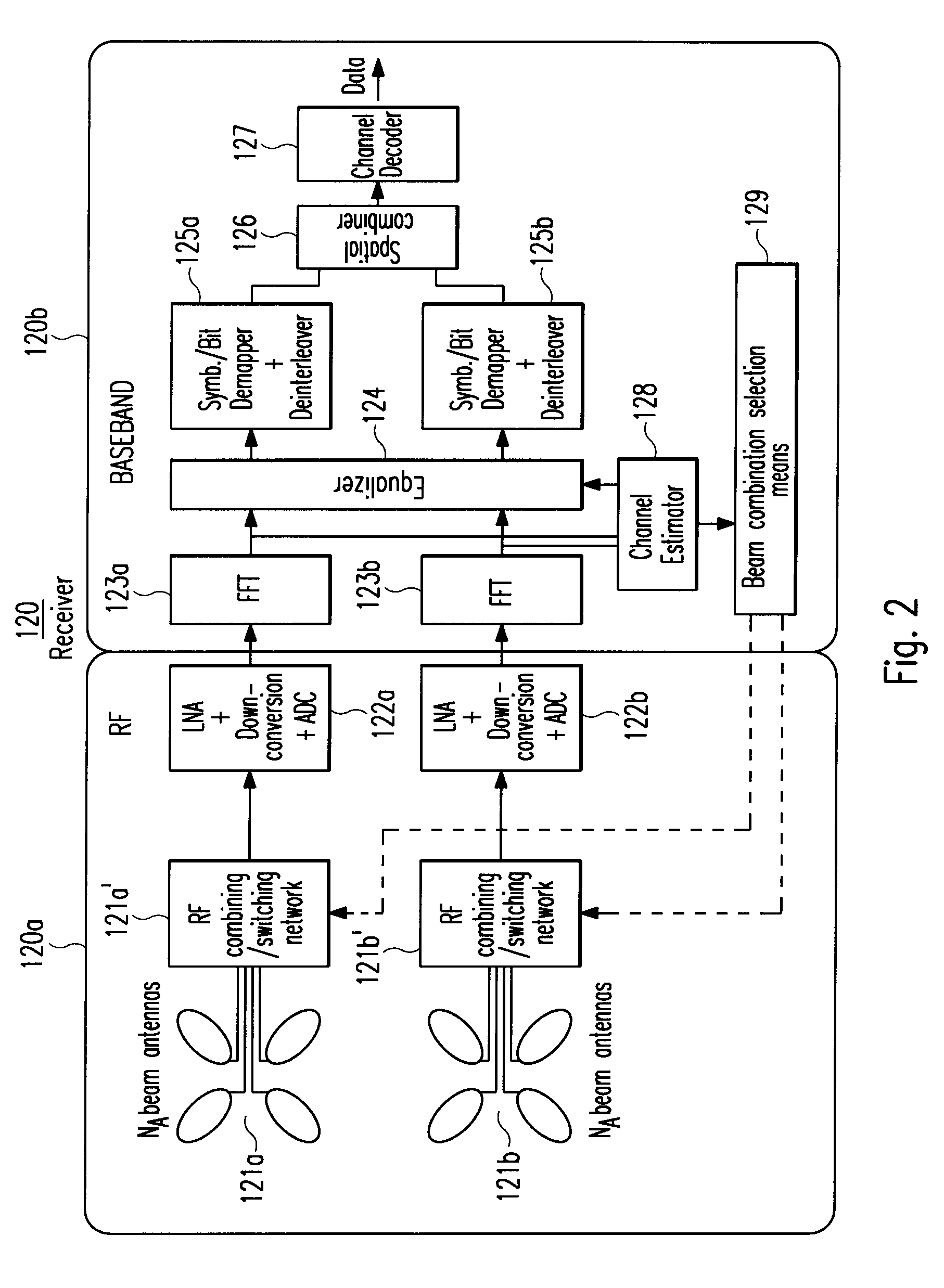
Multiple-input multiple-output spatial multiplexing system with dynamic antenna beam combination selection capability
ActiveUS20070230639A1Maximized ratioMinimizing correlation coefficientPolarisation/directional diversityMultiplex communicationAmplitude responseSignal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio
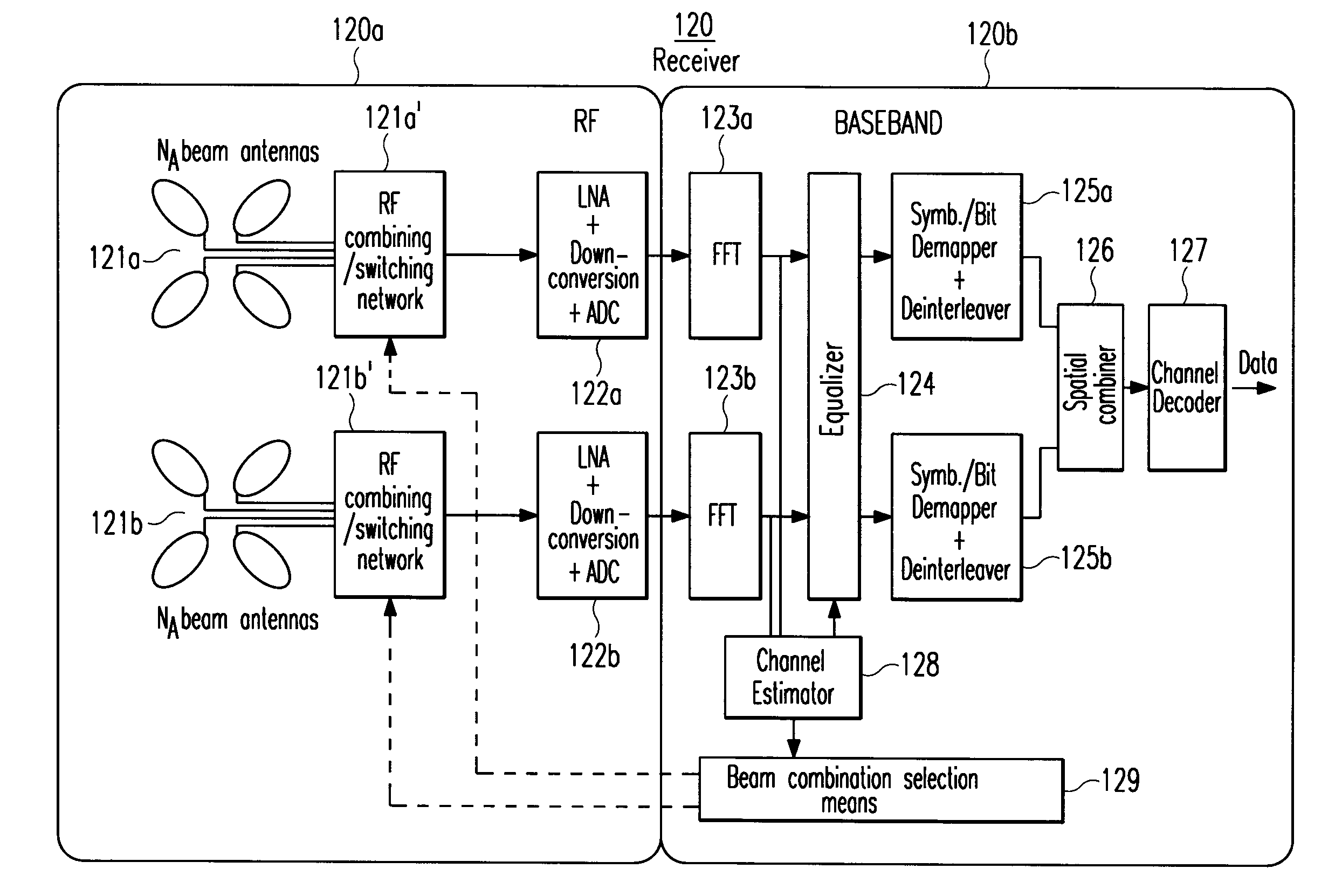
The present invention generally relates to the field of wireless communication systems. It particularly refers to a spatial diversity transmitter (110) and a spatial diversity receiver (120) in a wireless multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) spatial multiplexing system as well as a corresponding method for wirelessly transmitting and receiving modulated RF signals via multiple wireless signal propagation paths (Pl) of a multipath fading channel in a way that correlation between the MEMO channel components are reduced and / or the signal to interference plus noise ratio (SINR) is increased which hence result in an improved bit error rate (BER) or packet error rate (PER) performance of said wireless MIMO spatial multiplexing system. On the receiver side, for example, this is achieved by controlling at least one antenna switching and / or combining means (121a′+b′) to select a specific combination of different fixed beam antennas (121a+b) from each receiver-resident antenna array. According to the invention, said selection is based on estimated values of the channel impulse responses (hl(τl, t)) for said signal propagation paths (Pl). An antenna beam selection control means (129) is configured for selecting a specific antenna beam combination so as to maximize the average signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratios ( γl) of RF signals (rl(τl, t, φl)) received via said multiple wireless signal propagation paths (Pl) and / or to minimize the correlation coefficients (ρr<sub2>l1< / sub2>r<sub2>l2< / sub2>(t)) indicating the correlations of different pairs of these RF signals (rl1(τl1, t, φl1) and rl2(τl2, t, φl2)).Thereby, each fixed beam antenna (121a+b) of the receiver-resident antenna arrays has a distinct radiation pattern with a different beam center and / or beam width in the azimuth and / or elevation plane, wherein a superposition of all these radiation patterns may cover all possible azimuthal (φ) and / or elevational angles of arrival (θ) of an RF signal (s(t)).For compensating detected multipath fades in the channel amplitude response (|Hl(f, t)|) of at least one signal propagation path (Pl) between the spatial diversity transmitter (110) and the spatial diversity receiver (120), a receiver-resident channel estimation and / or equalization circuitry (124, 128) is applied.
Owner:SONY DEUT GMBH
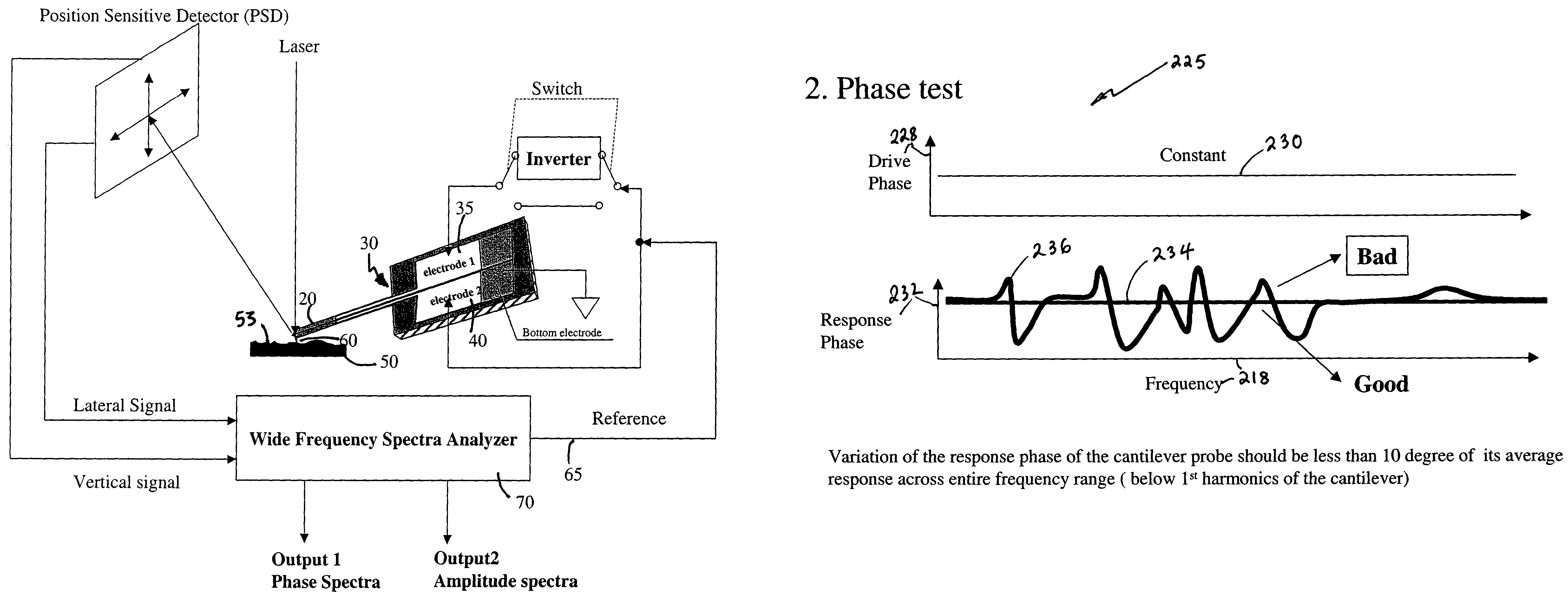
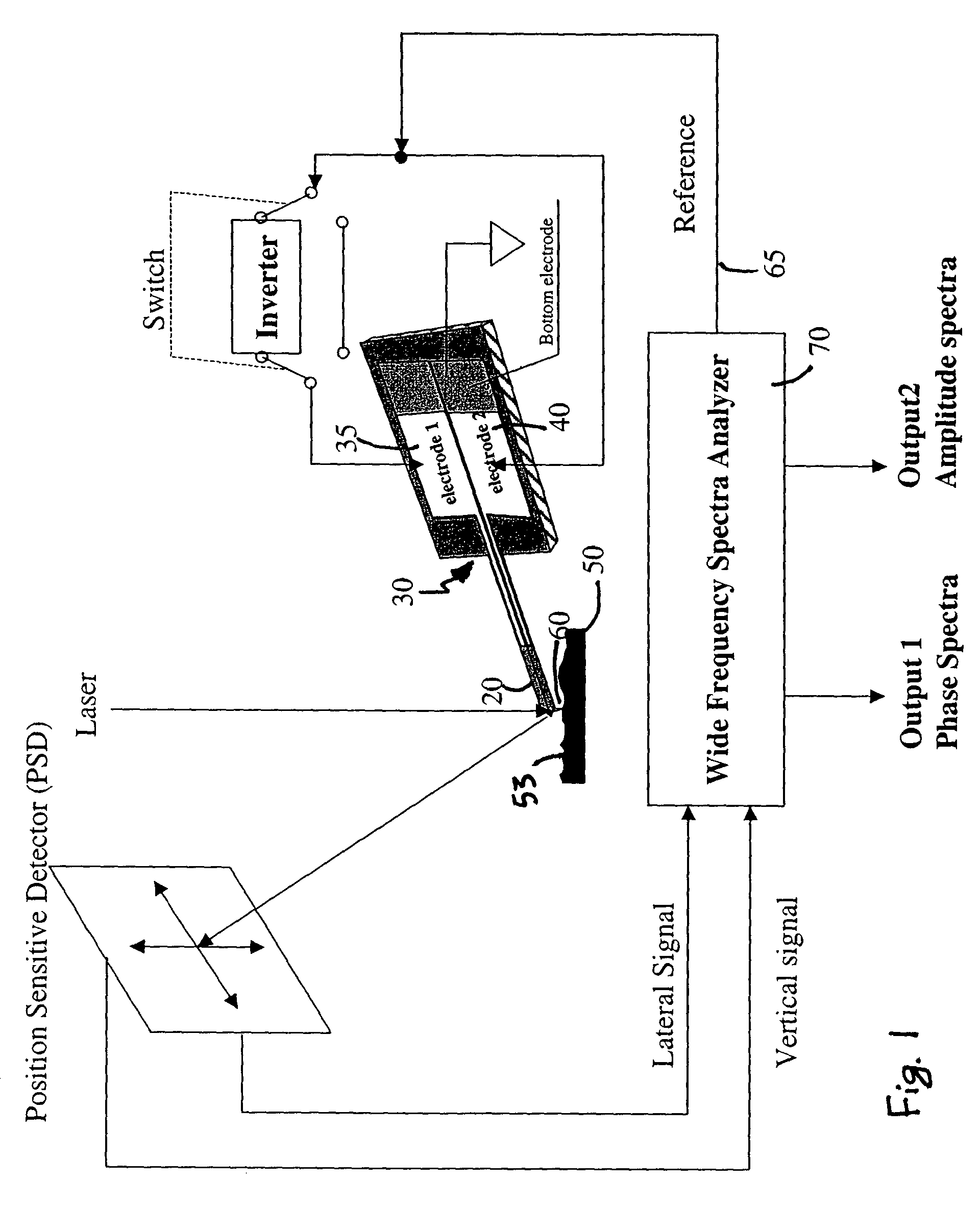
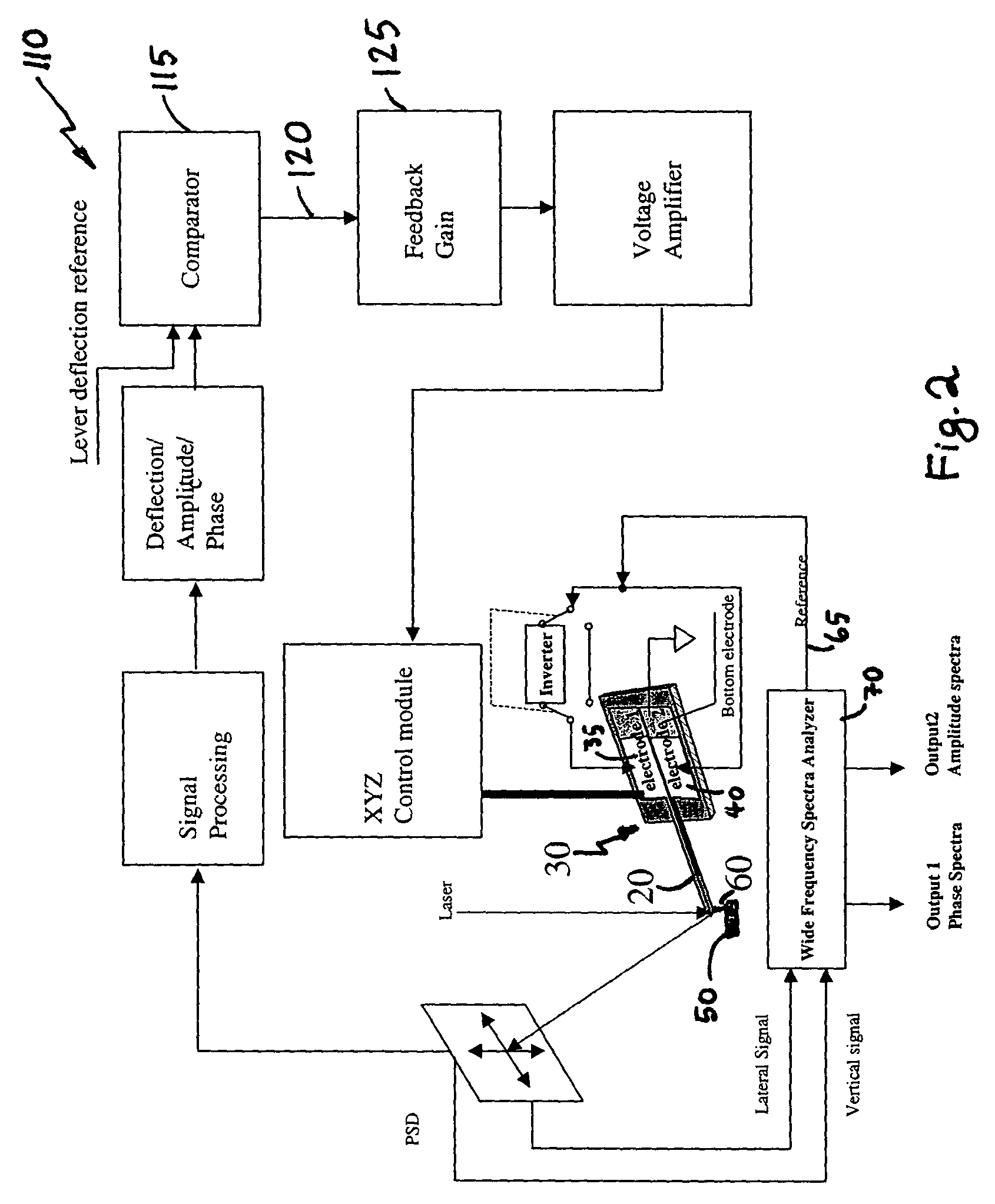
System for wide frequency dynamic nanomechanical analysis
ActiveUS7055378B2Easy to measureMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMeasurement/indication equipmentsAmplitude responseCantilever
Dynamic nanomechanical analysis of a sample is performed by using a cantilever probe that interacts with the sample using a force applied across a wide range of frequencies that includes frequencies greater than 300 Hz. The motion of the cantilever probe is detected in response to the applied force over the range of frequencies and analyzed over at least a portion of the wide range of frequencies to determine a mechanical response of the sample, preferably including quality factor and modulus of the sample. The analysis of the motion of the cantilever probe is preferably performed in terms of amplitude, phase, and frequency of both the probe and the sample and preferably, where the applied force is analyzed to determine both a real and an imaginary modulus of a mechanical response of the sample. Preferably, the force is applied so as to produce a minimum of phase and amplitude response variation in the absence of the sample. Furthermore the motion of the cantilever can be flexural or torsional and combinations thereof.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
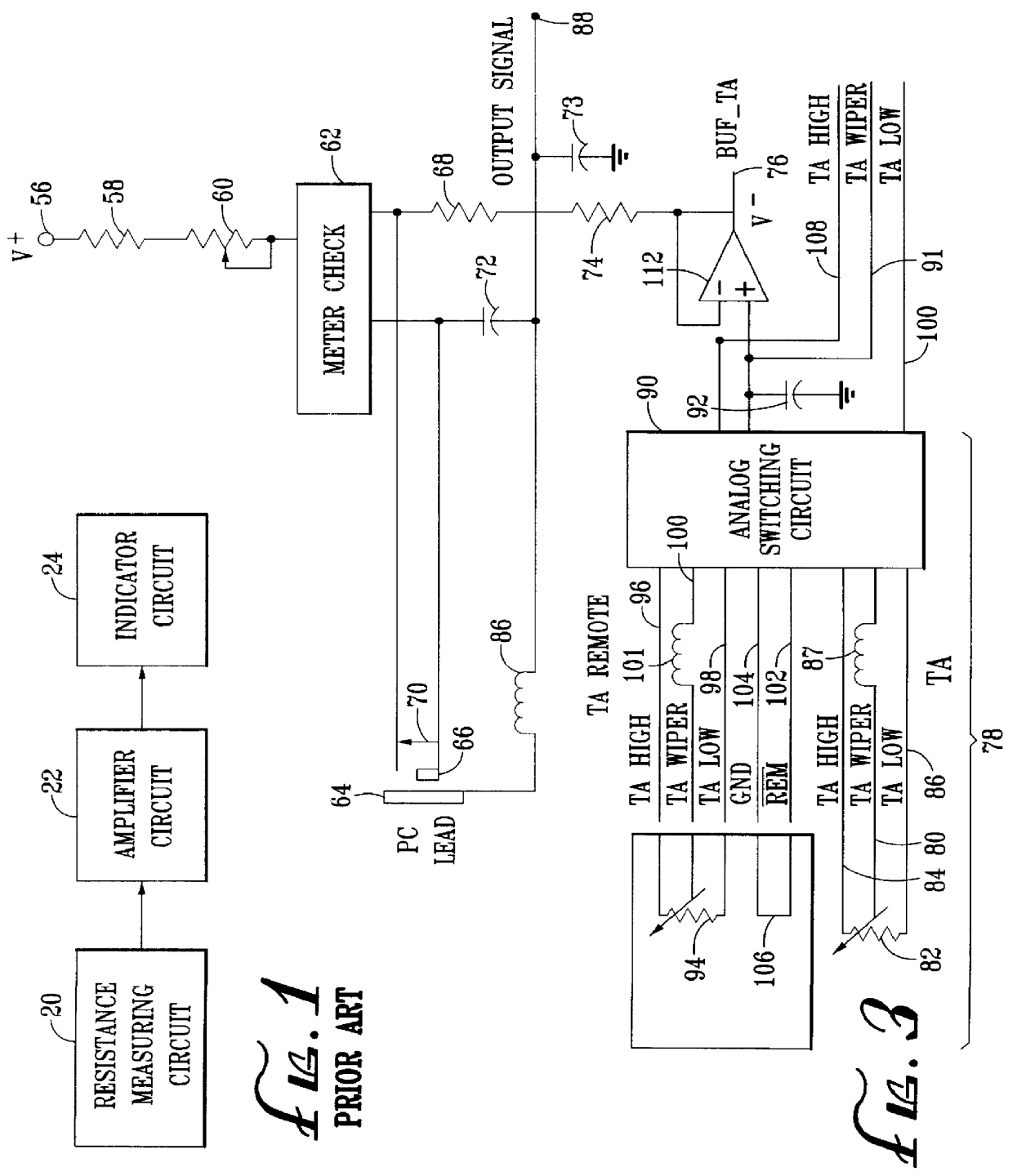
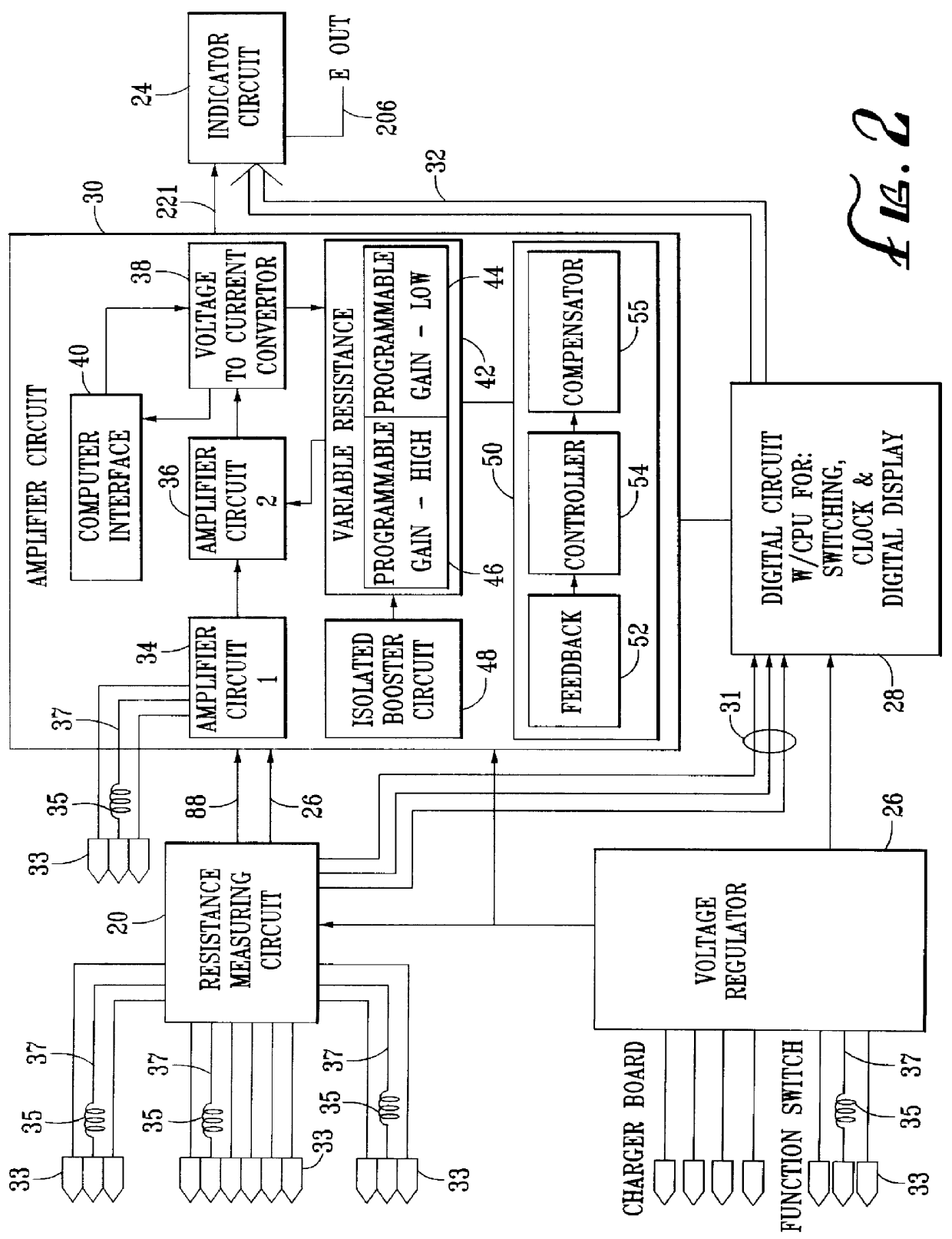
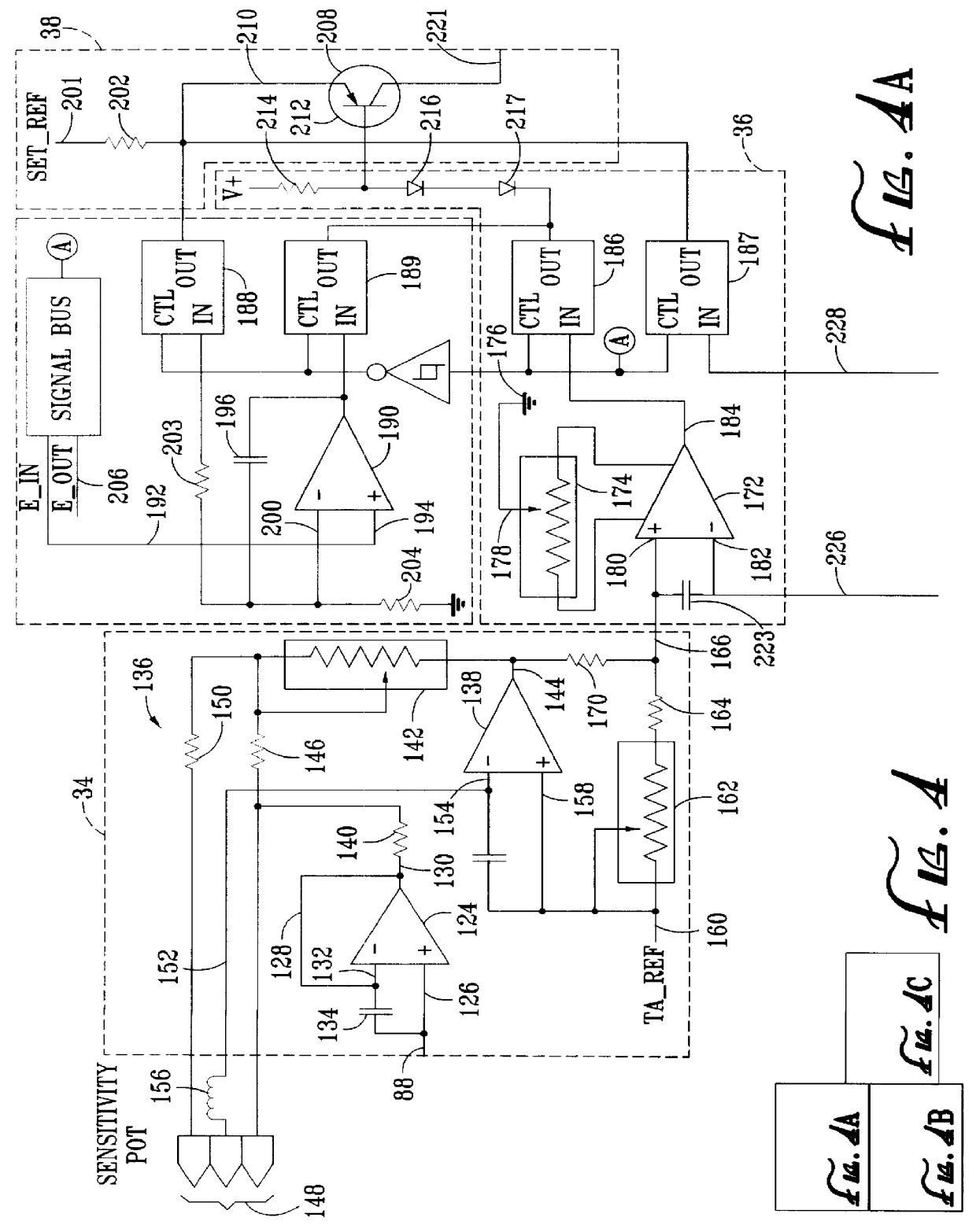
System for measuring and indicating changes in the resistance of a living body
InactiveUS6011992AMaintain sensitivityEliminate undesirable characteristic in measurement signalAntenna supports/mountingsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesElectrical resistance and conductanceAuto regulation
A system for measuring changes in the resistance of a living body includes a resistance measuring circuit, an amplifier circuit and an indicator circuit in which the amplifier circuit includes a calibration circuit to give a generally constant amplitude response to a given measured input. Radio frequency insulators are included to reduce noise in the system. The circuits are operated such that when an overall change in the resistance of a living body occurs, the resistance measuring circuit is adjusted to determine the overall resistance. To account for changes in sensitivity caused by the overall change in resistance, the gain of the amplifier circuit is automatically adjusted to thereby maintain a generally constant amplitude response.
Owner:CHURCH OF SPIRITUAL TECH
Nonlinear digital signal processor
InactiveUS20080080644A1Multiple-port networksAdaptive networkDigital signal processingPhase response
A digital signal processor (DSP) comprises an input terminal configured to receive an input, an adaptive nonlinear phase filter coupled to the input terminal, the adaptive nonlinear phase filter having a time-varying phase response, and an adaptive nonlinear amplitude filter coupled to the input terminal, the adaptive nonlinear amplitude filter having a time-varying amplitude response.A method of processing a signal comprises receiving the signal, sending the signal to an adaptive nonlinear phase filter, the adaptive nonlinear phase filter having a time-varying phase response, and sending the signal to an adaptive nonlinear amplitude filter, the adaptive nonlinear amplitude filter having a time-varying amplitude response.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and system for inspecting objects using ultrasound scan data
ActiveUS7299697B2Vibration measurement in solidsAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSonificationAmplitude response
A method and apparatus for estimating a depth of a crack from ultrasound scan data are provided. The method includes mapping multiple amplitude responses from the ultrasound scan data, each mapped amplitude response being representative of a signal from one of the sensors. The method further includes locating multiple linear responses among the mapped amplitude responses, each linear response being an indicator of a reflected signal from the crack. One or more sensor that corresponds to the linear responses from a given crack is identified. The depth of the crack is estimated using data from the identified sensors.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Sound tuning method
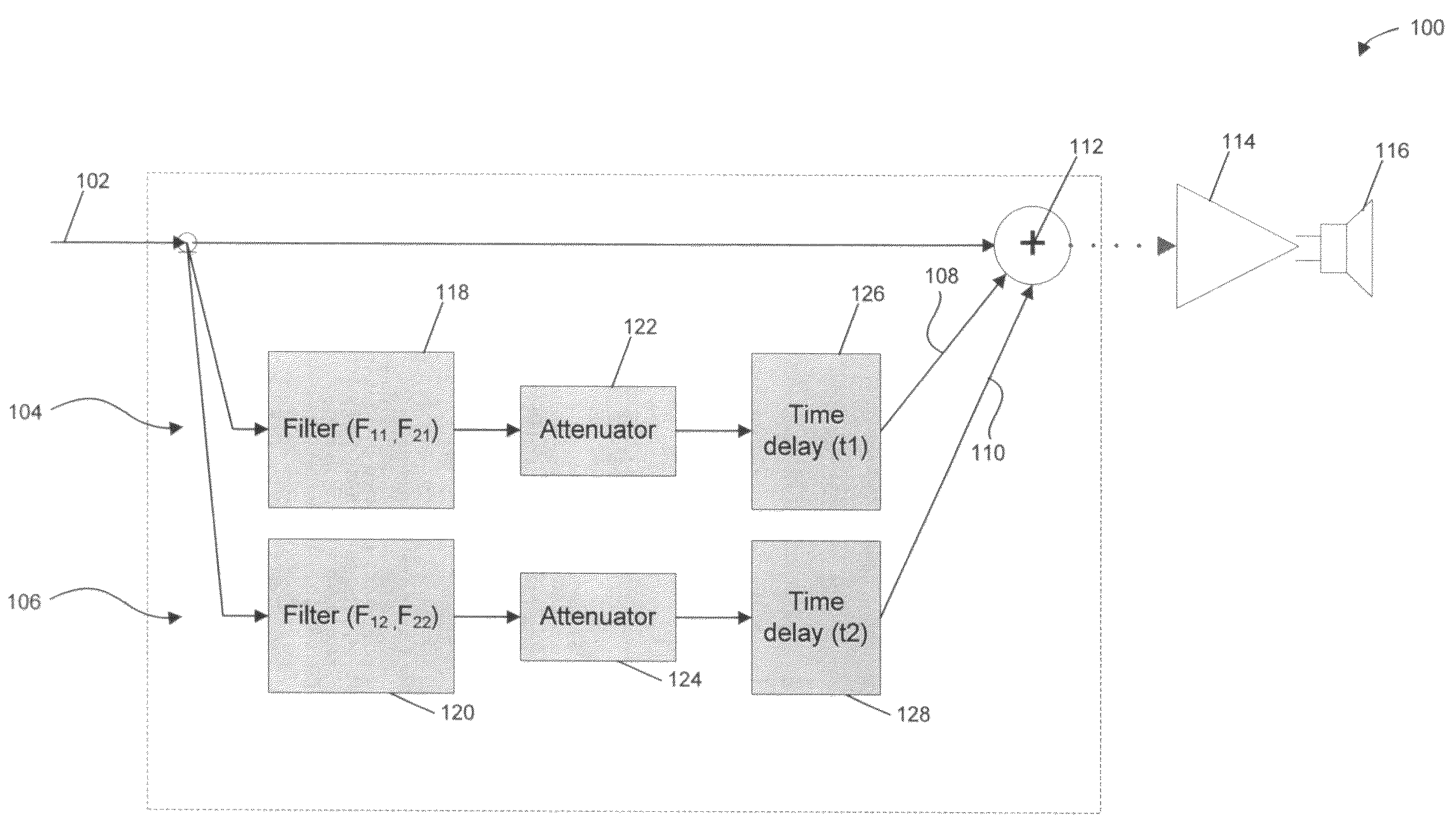
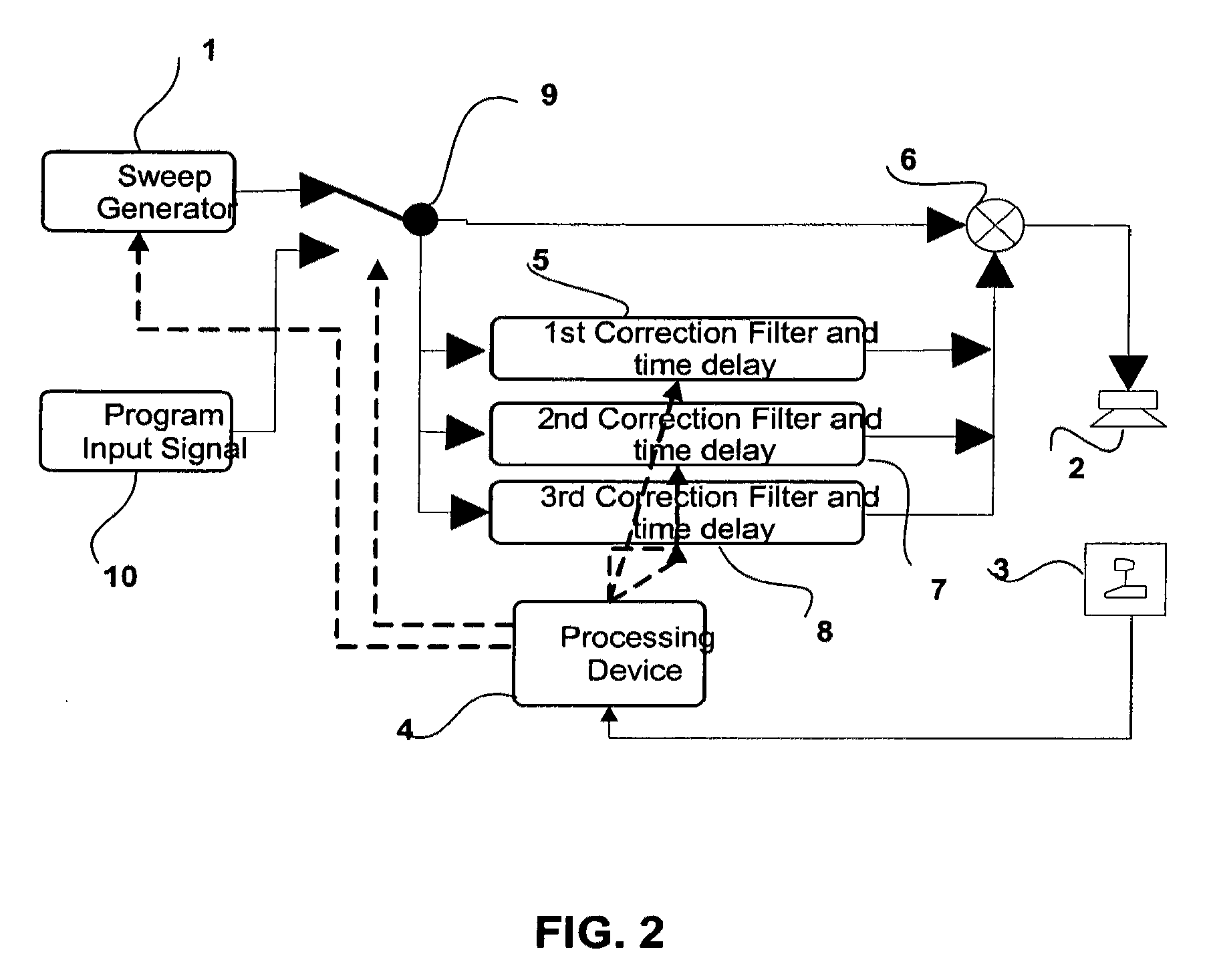
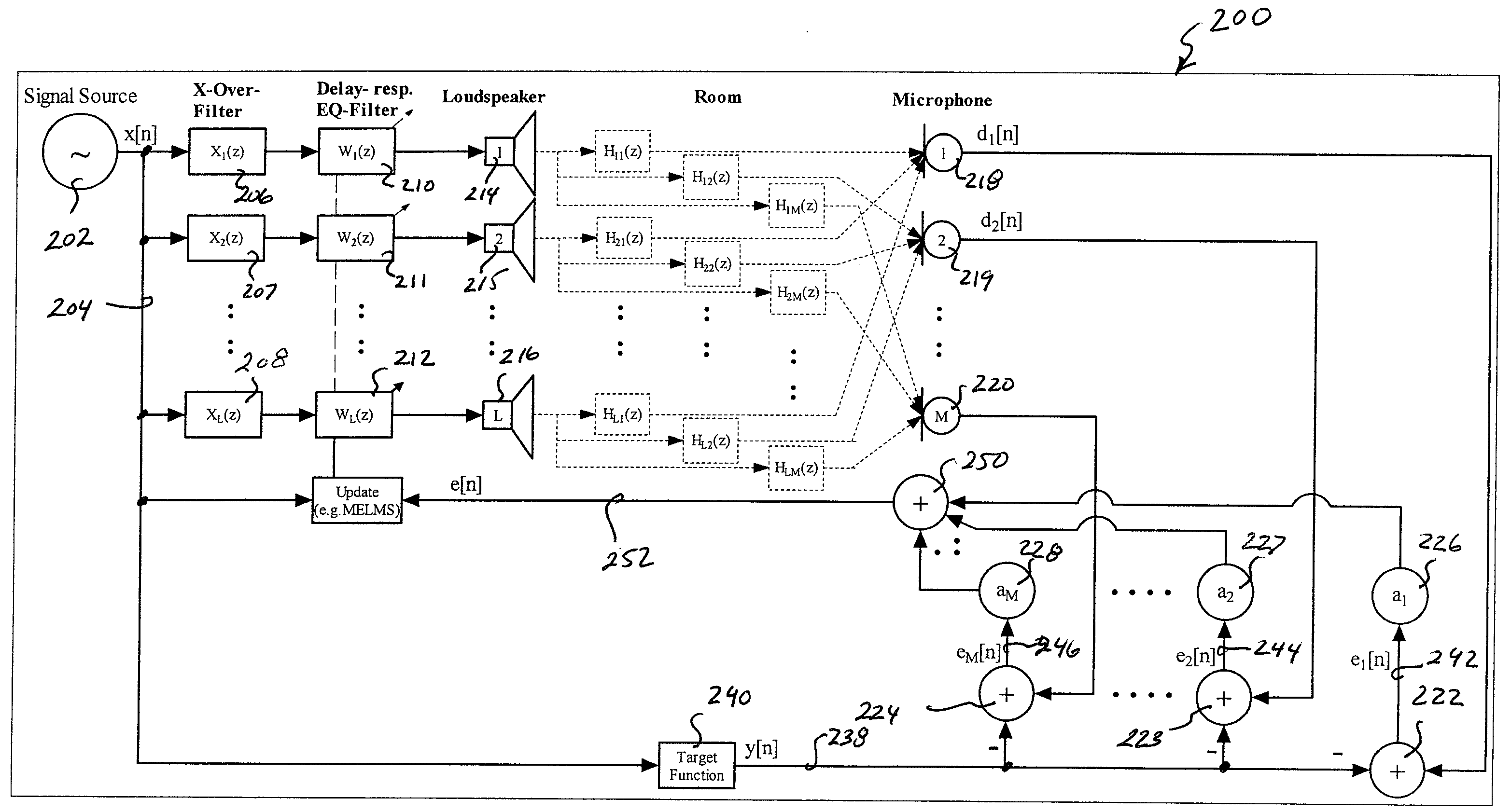
The invention relates to a method for automated tuning of a sound system, the sound system comprising delay lines, equalizing filters, and at least two loudspeakers, the method comprising the steps of reproducing a useful sound signal through the loudspeakers, measuring sound pressure values at least one location, providing a target transfer function for tuning the delay lines and the equalizing filters of the sound system, the target transfer function representing a desired transfer characteristics of the sound system, adjusting the delay of the delay lines, and adjusting amplitude responses of the equalizing filters such, that the actual transfer characteristics of the sound system approximates the target function.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
Sensor and method for remote detection of objects
InactiveUS6232879B1Reduce riskSimple designBurglar alarm by hand-portable articles removalElectric/magnetic detectionMetal alloyAmplitude response
A sensor for remote detection of objects (20), preferably for use in an article surveillance system, comprises a wireshaped element (22), which is arranged to be excited and detected electromagnetically. The wireshaped element (22) has a diameter less than 30 mum. The element is arranged to transmit an electromagnetic reply signal, the amplitude of which is modulated in response to an externally applied and time-varying magnetic field. According to a method of detecting the presence of an object (20) in a surveillance zone (10), the object is provided with at least one wireshaped element (22) of amorphous or nanocrystalline metal alloy with magnetic properties and with a diameter less than 30 mum. Electromagnetical signals are generated in the surveillance zone for exciting the wireshaped element. Furthermore, a time-varying magnetic modulating field is generated in the surveillance zone. Electromagnetic signals generated by the wireshaped element are received and analyzed with respect to a modulation in amplitude caused by the magnetic modulating field, so as to determine the presence of the element (and consequently the object) in the surveillance zone.
Owner:DEMODULATION
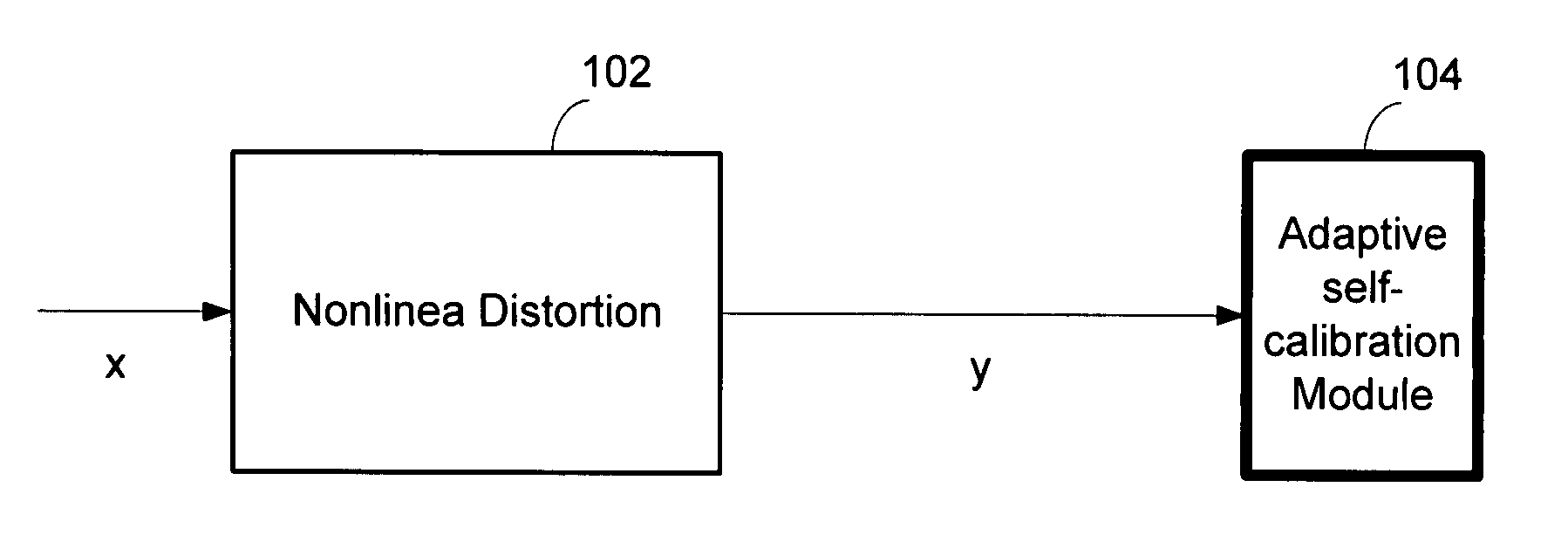
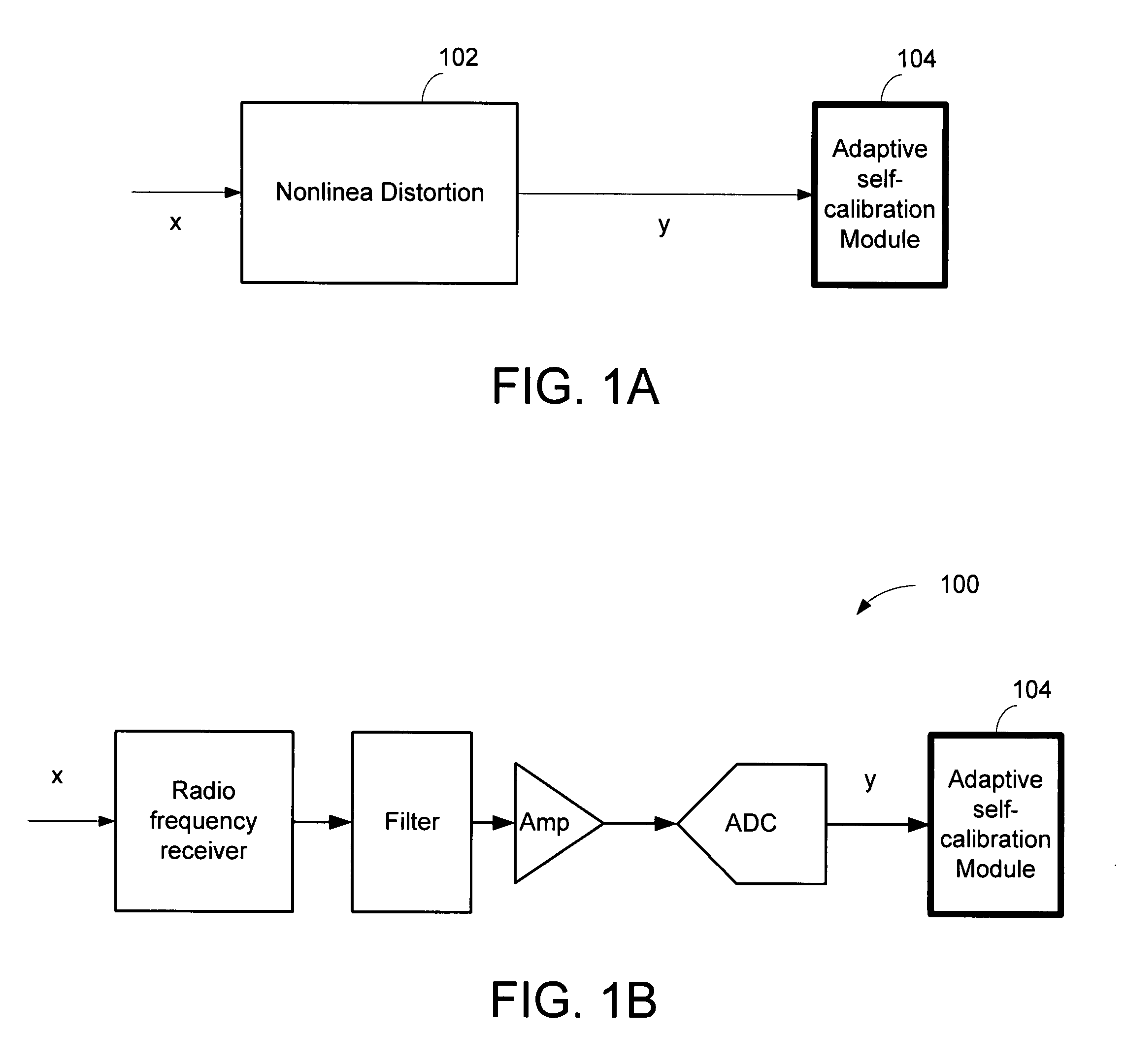
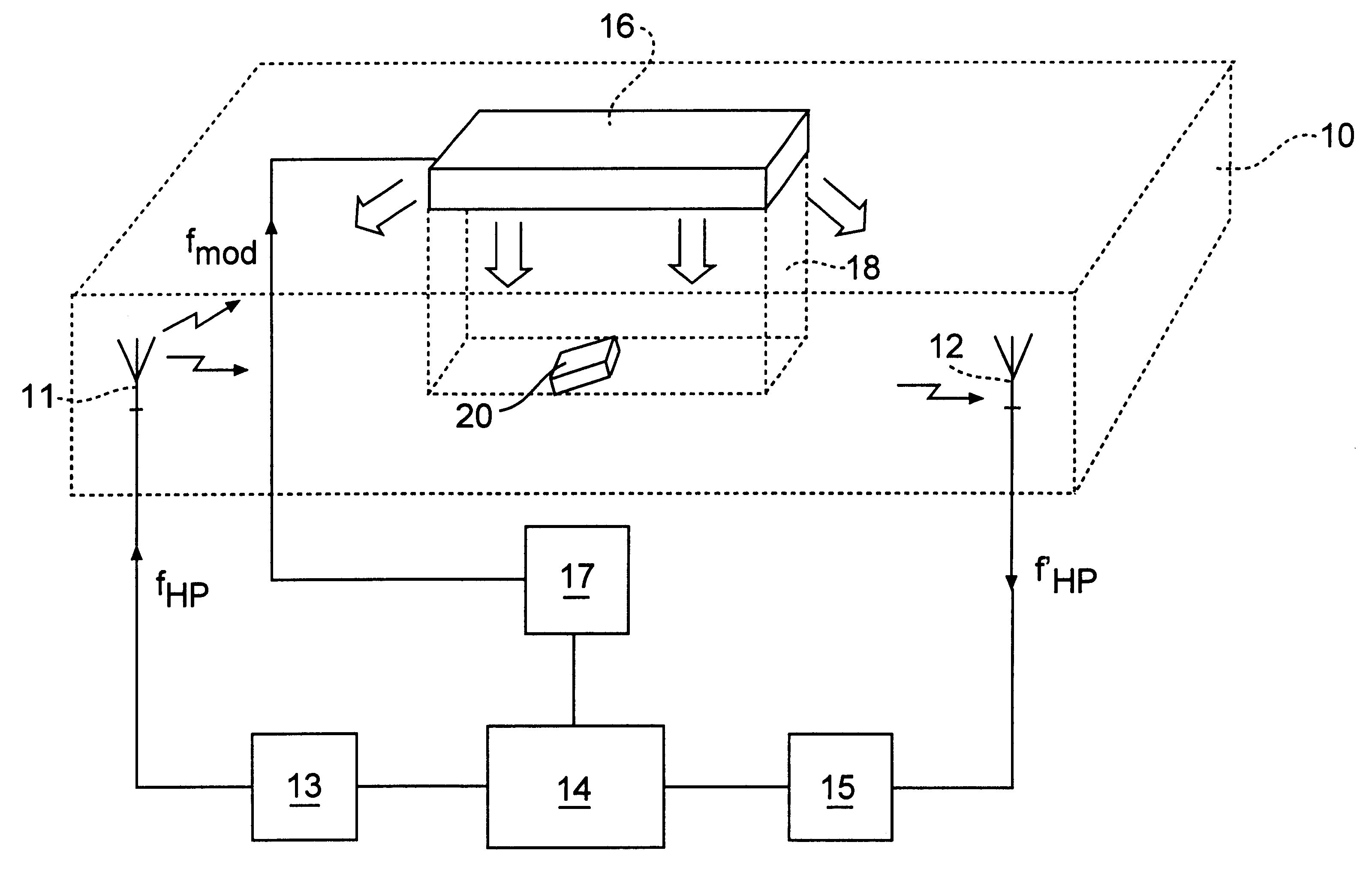
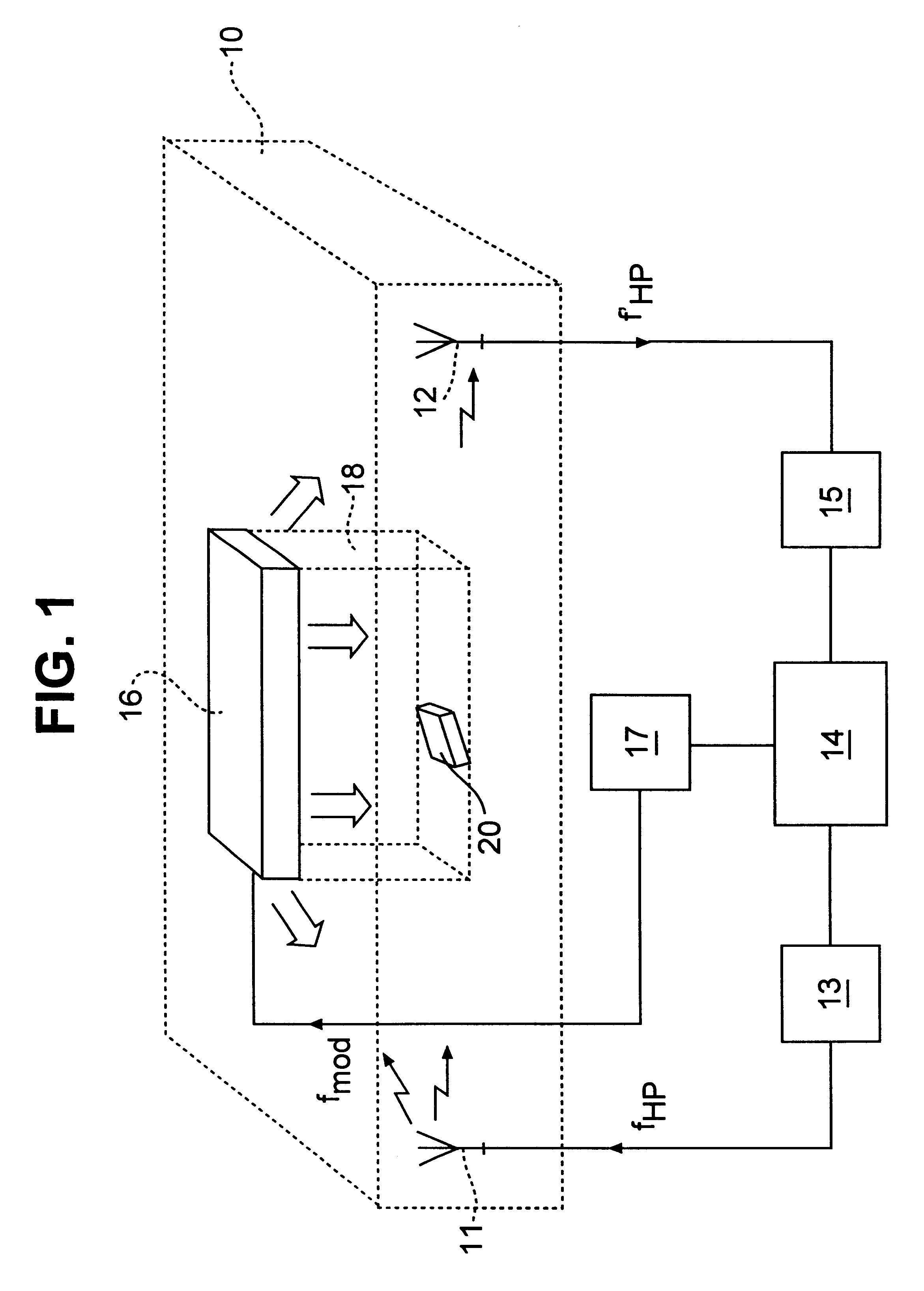
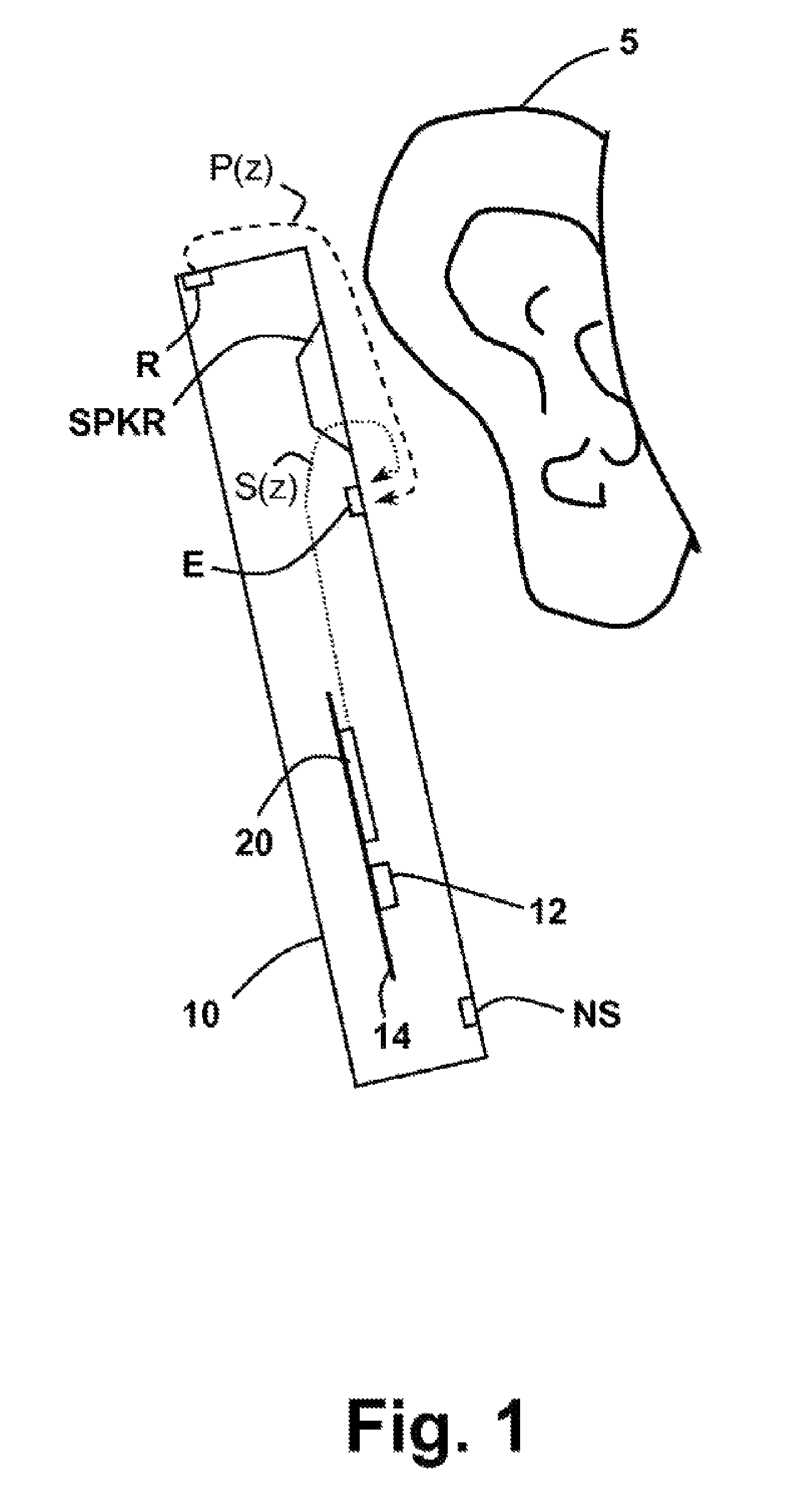
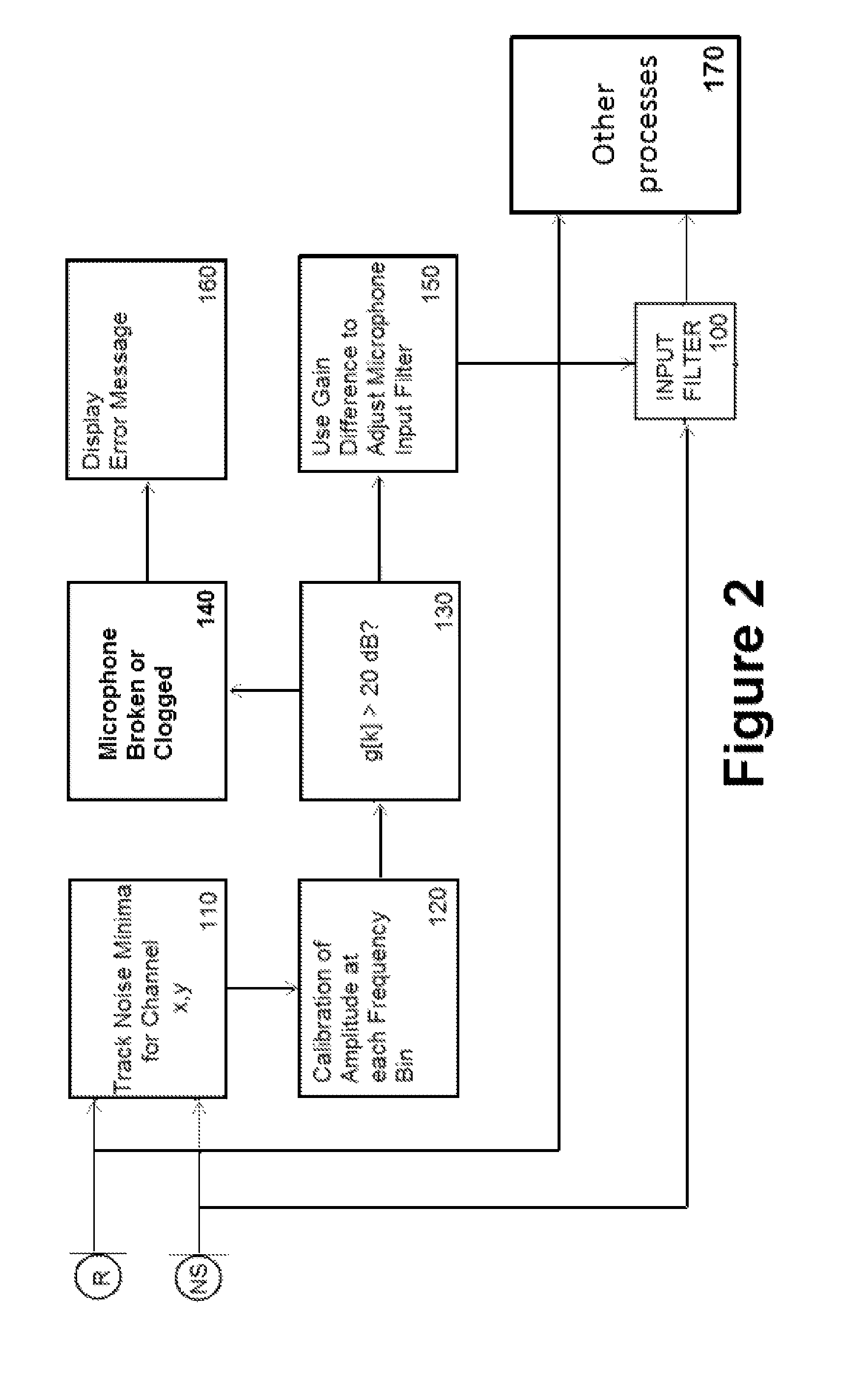
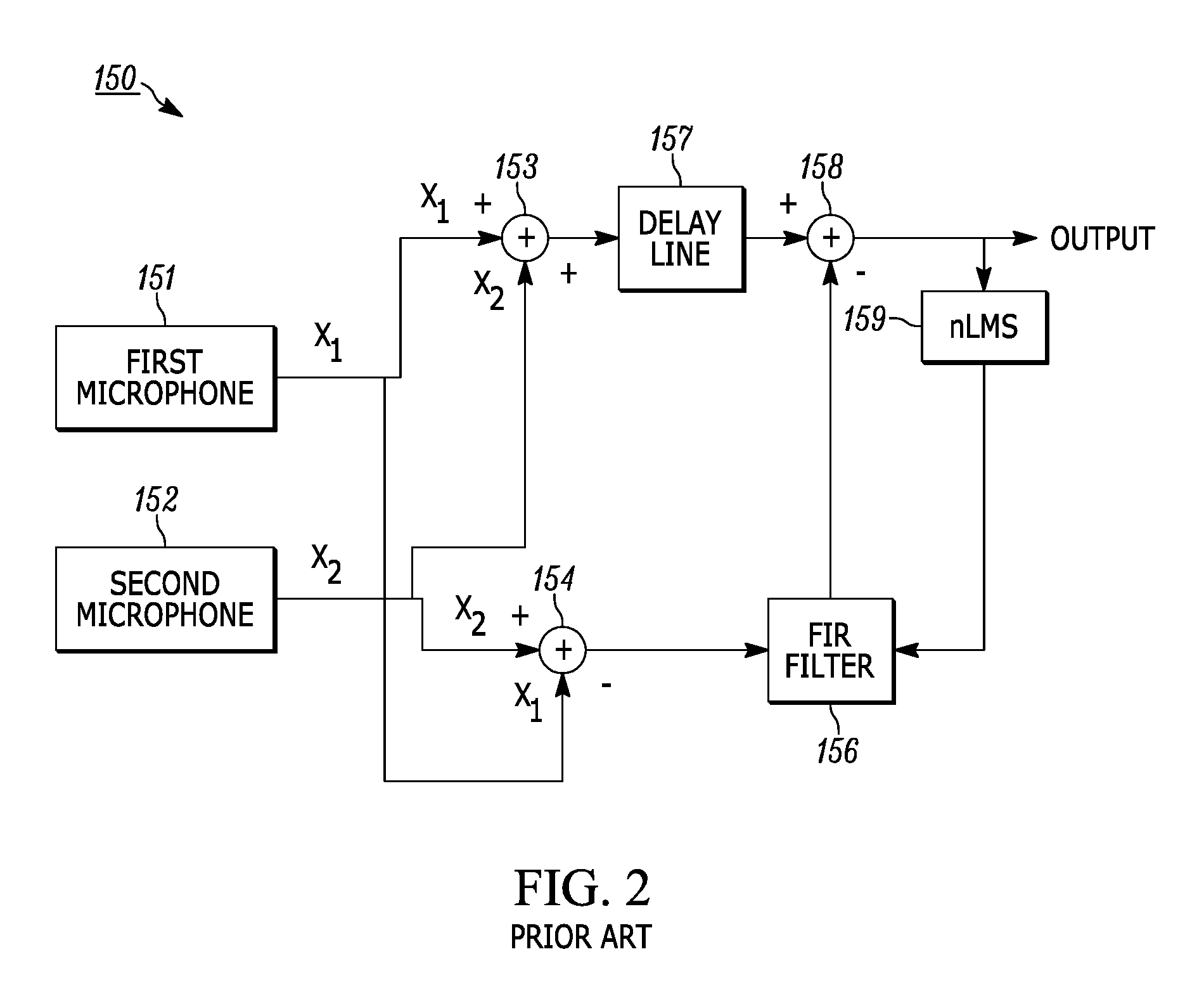
Dual-microphone frequency amplitude response self-calibration
ActiveUS9532139B1MicrophonesHearing device active noise cancellationAmplitude responseCellular telephone
A frequency domain method and system for online self-calibrating microphone frequency amplitude response based on noise floor (minima) tracking are disclosed. A cellular telephone or other system with dual microphones may self-calibrate itself on-the-fly. The system selects one of the microphones as a reference and calibrates the frequency response of the two microphones using the first microphone as a reference, so that they have a matched frequency amplitude response. To achieve this on-the-fly calibration, the system uses background noise for calibration purposes. The signal power spectra of the noise minima at the two microphones is used to calibrate the respective microphone frequency response. The system may then adapt the frequency amplitude responses of the two microphones so that the power spectral density from each microphone matches the other, and the system is then calibrated. This calibration could occur any time the device is receiving a noise minima and could be done continuously as the device is being used.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
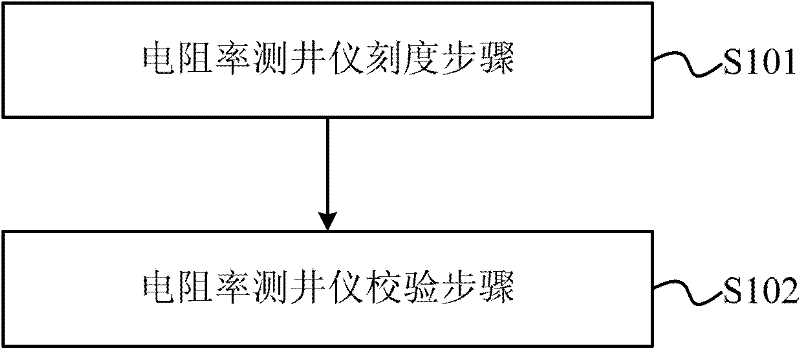
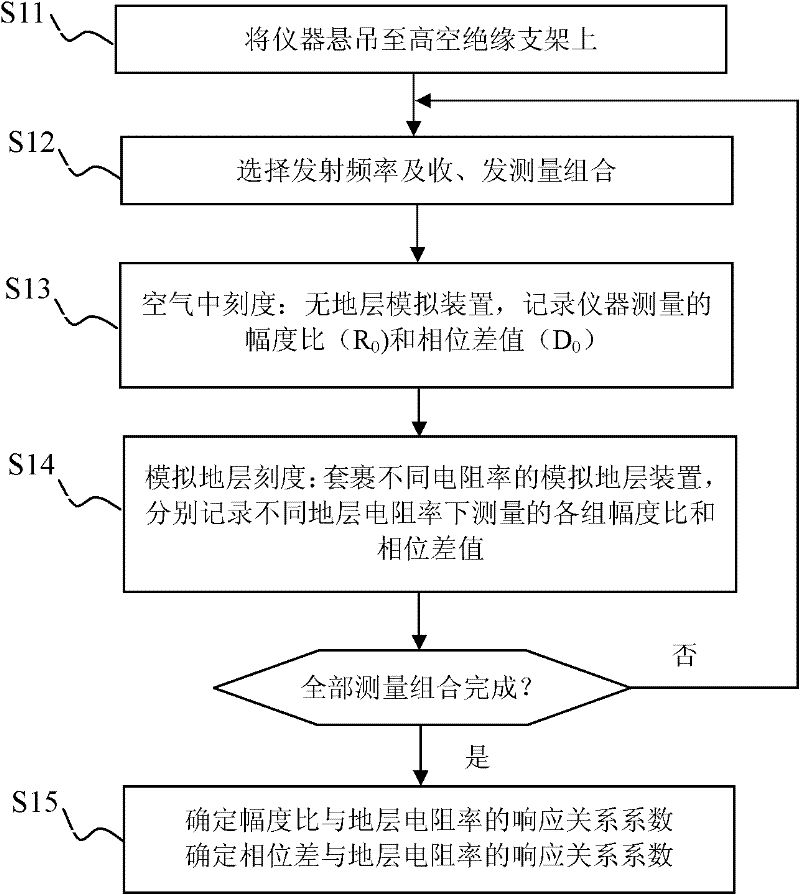
Method and device for checking scales of resistivity logging instrument
ActiveCN102565875AAccurate and reliable formation resistivity dataGeological measurementsPhase differenceAmplitude response
The invention discloses a method and device for checking scales of a resistivity logging instrument, and the method comprises a resistivity logging instrument calibrating step and a resistivity logging instrument checking step, wherein the resistivity logging instrument calibrating step is as follows: measuring the amplitude ratio R0 and the phase difference D0 of signals when the resistivity logging instrument is exposed in air, measuring the amplitude ratio Rn and the phase difference Dn of the signals when simulated formations with different resistivities are placed around the resistivity logging instrument, and confirming the amplitude ratio response function relationship and the phase difference response function relationship according to R0, D0, Rn and Dn; and the resistivity logging instrument checking step is as follows: measuring the amplitude ratio R and the phase difference D of the signals when a simulated formation with resistivity Rho is placed nearby the logging instrument, calculating the amplitude ratio resistivity and the phase difference resistivity as per R, D, the amplitude response function relationship and the phase difference response function relationship, and calculating difference values of the amplitude ratio resistivity and the phase difference resistivity with the resistivity Rho. If the difference values of the amplitude ratio resistivity and the phase difference resistivity with the resistivity Rho are both less than a preset measuring error of the instrument, the resistivity logging instrument passes through the checking.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
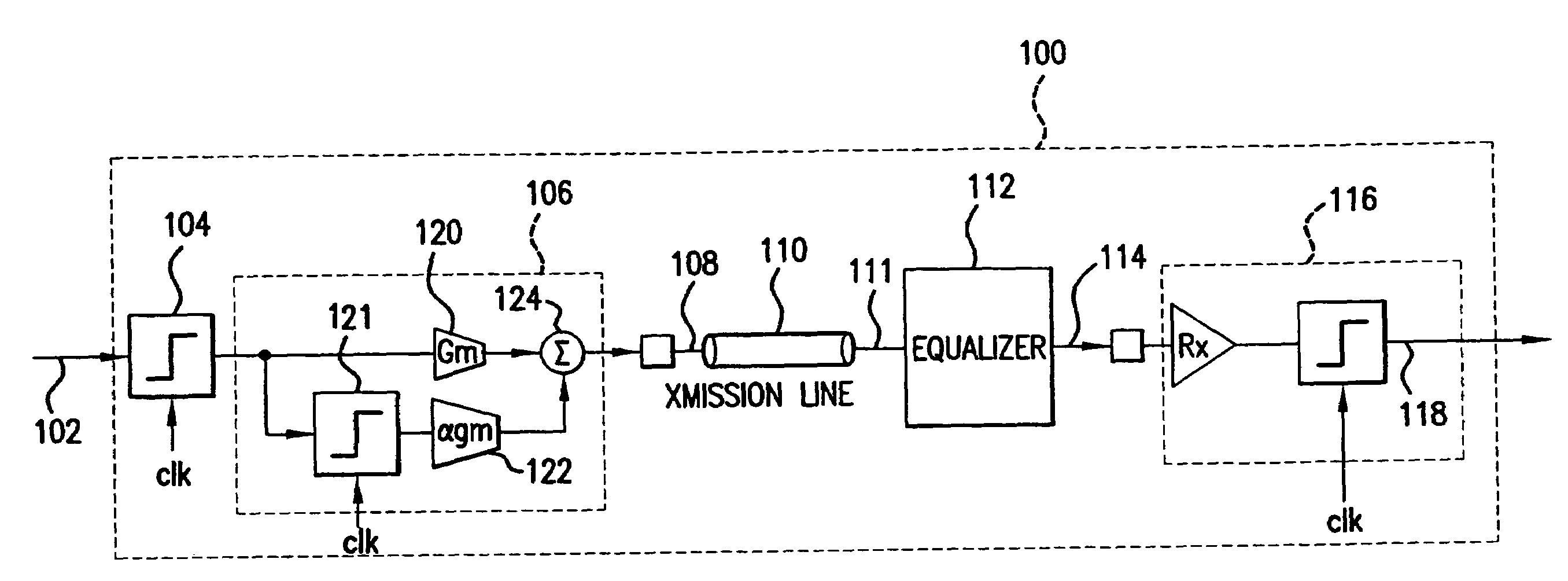
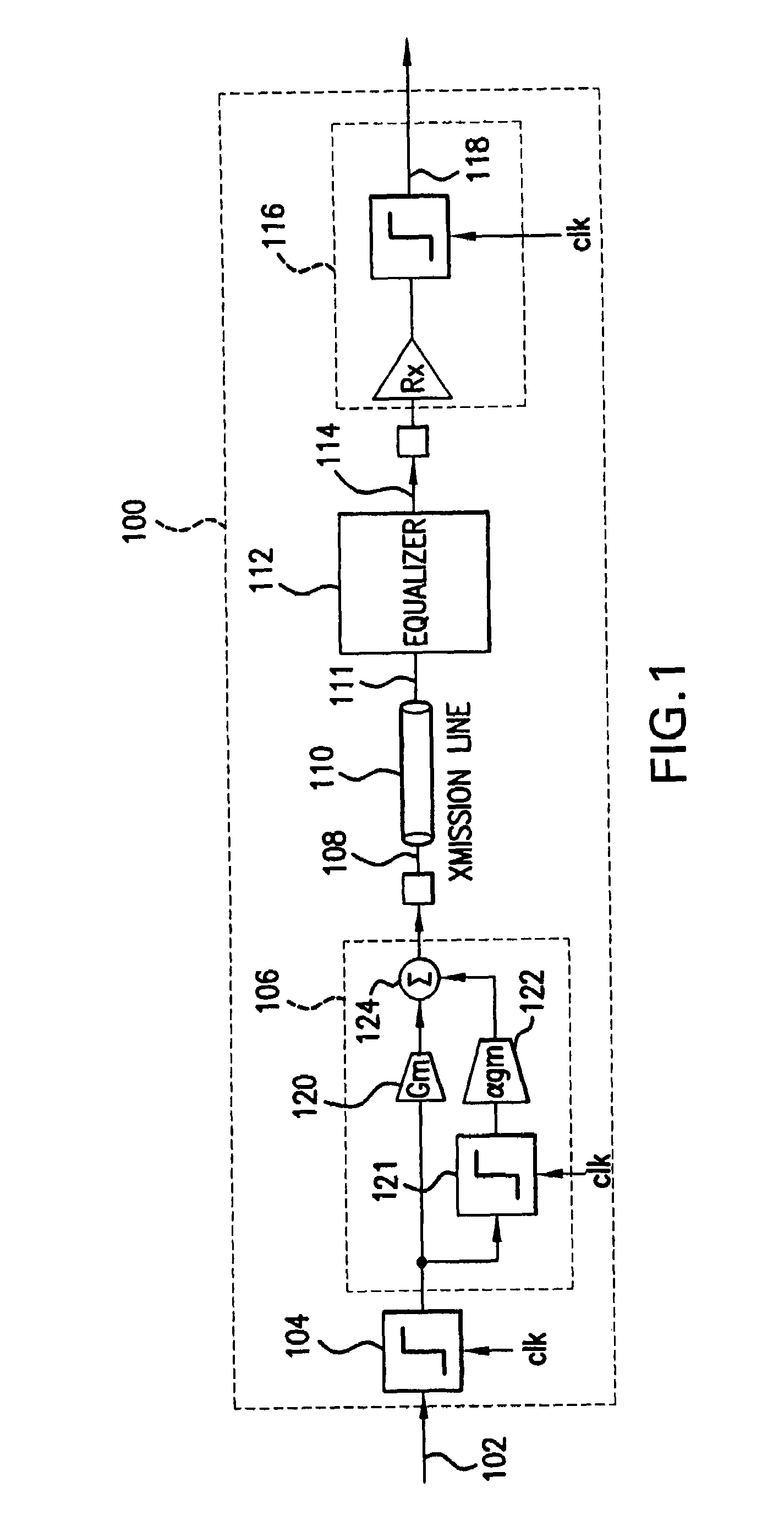
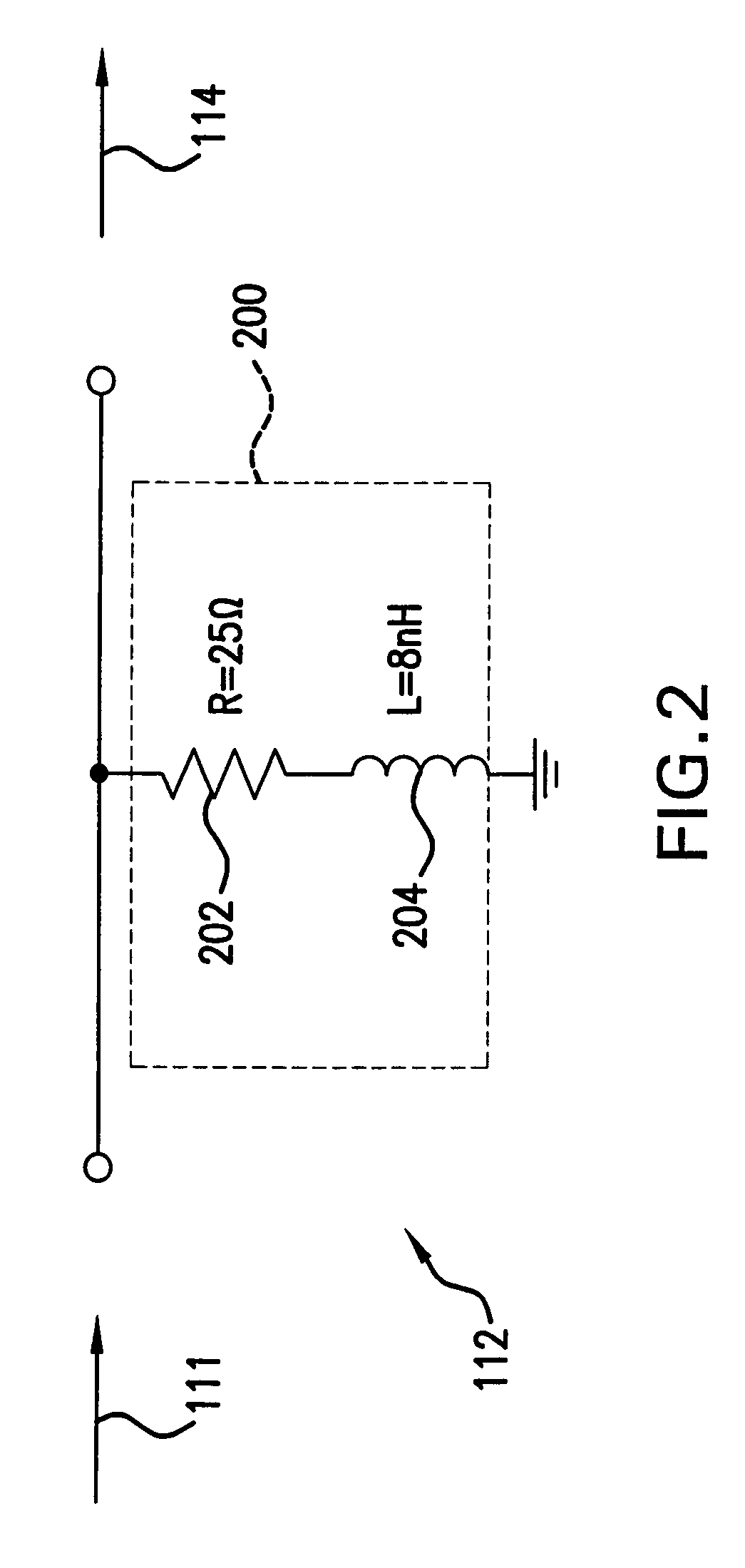
High speed data link with transmitter equalization and receiver equalization
ActiveUS7586987B2Improve bit error rateIncrease ratingsTransmission control/equlisationSecret communicationAmplitude responseEngineering
A high speed data link includes transmitter equalization and (passive) receiver equalization to compensate for frequency distortion of the data link. In one embodiment, the transmitter equalization is performed with a de-emphasis circuit. The transmitter de-emphasis circuit pre-distorts an input signal to compensate for at least some of the frequency distortion in the data caused by the transmission line. The (passive) receive equalization circuit further compensates for the frequency distortion at the output of the transmission line to flatten the amplitude response of the output signal, and thereby reduce inter-symbol interference, improve media reach and improve the bit error rate (BER).
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
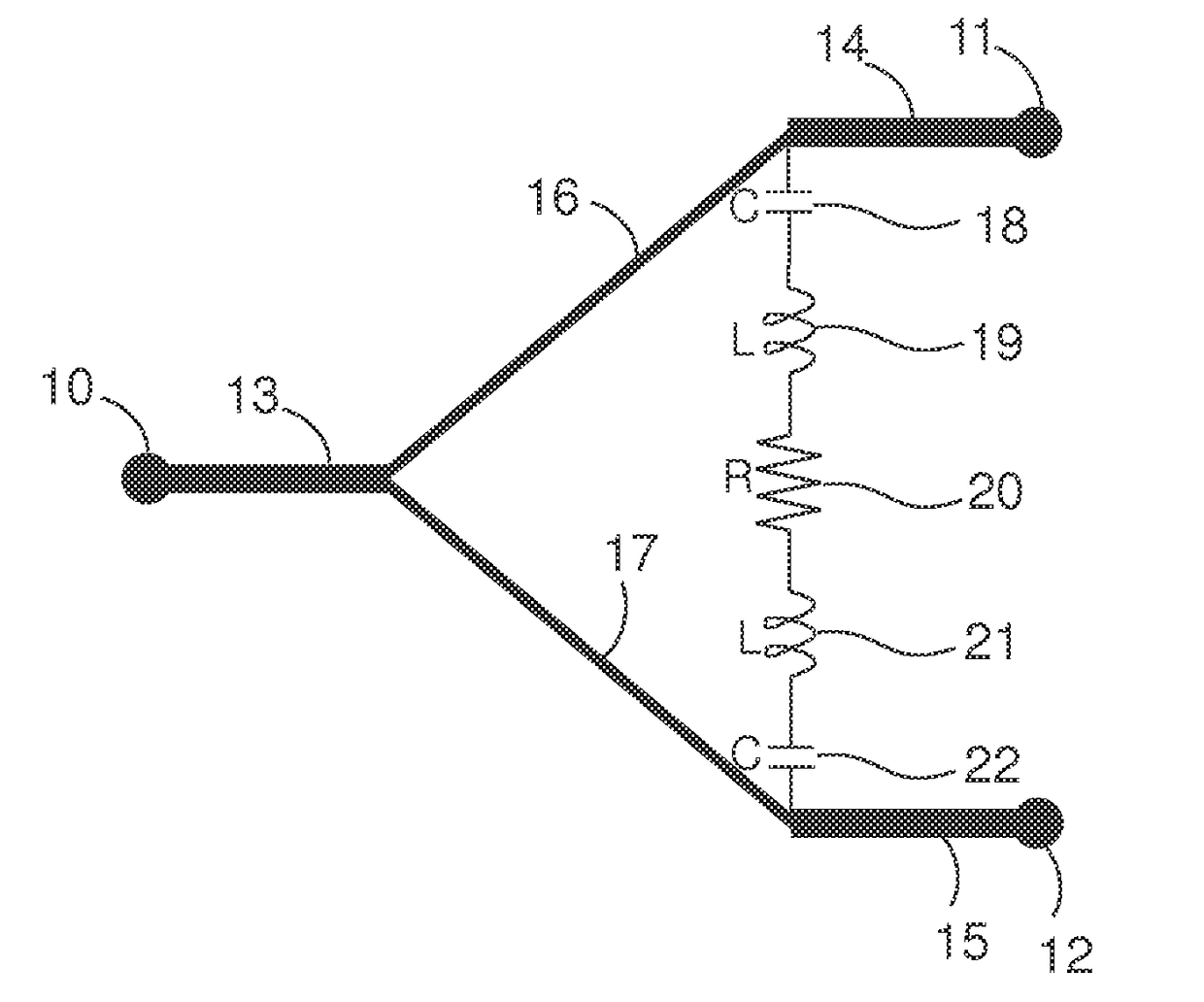
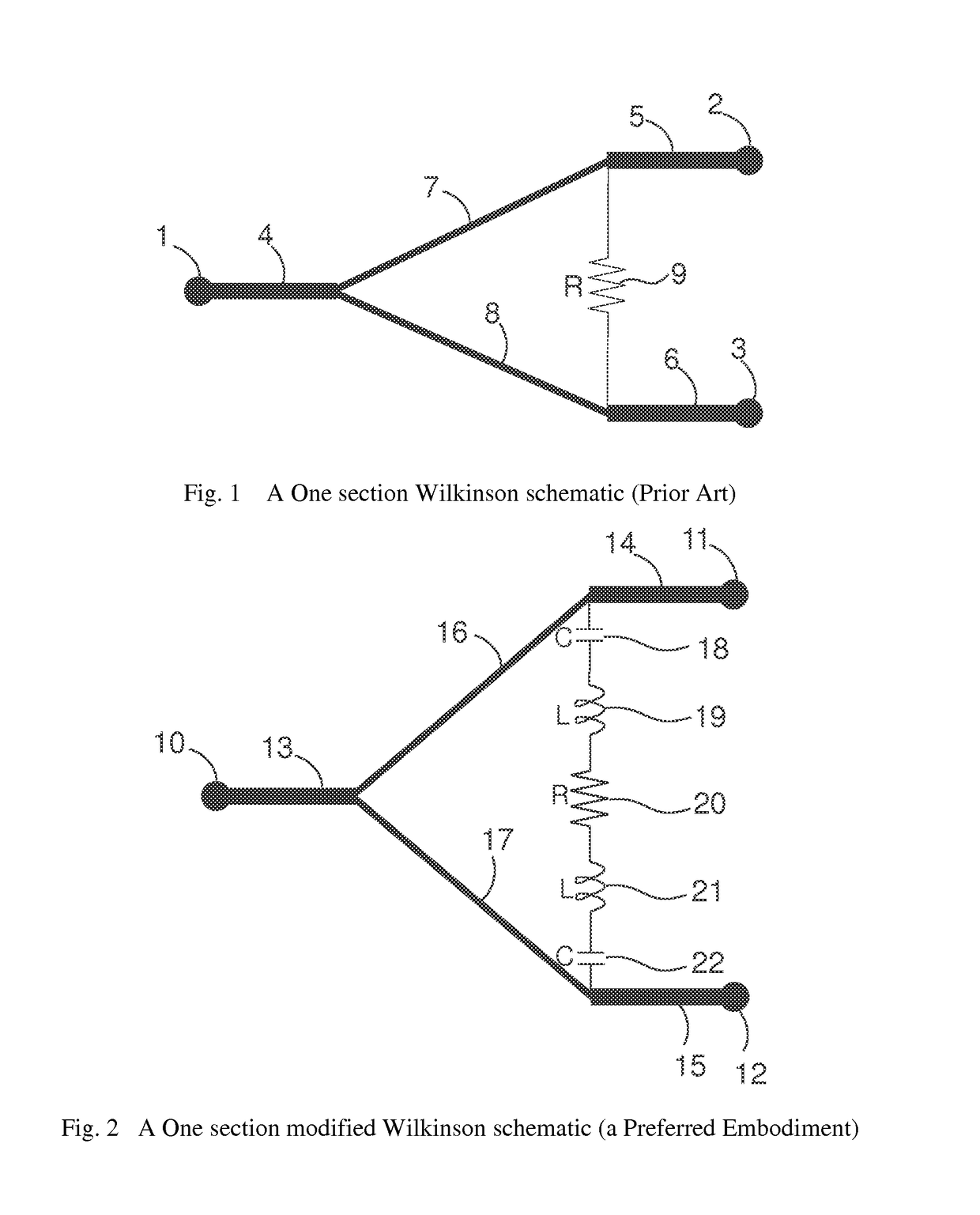
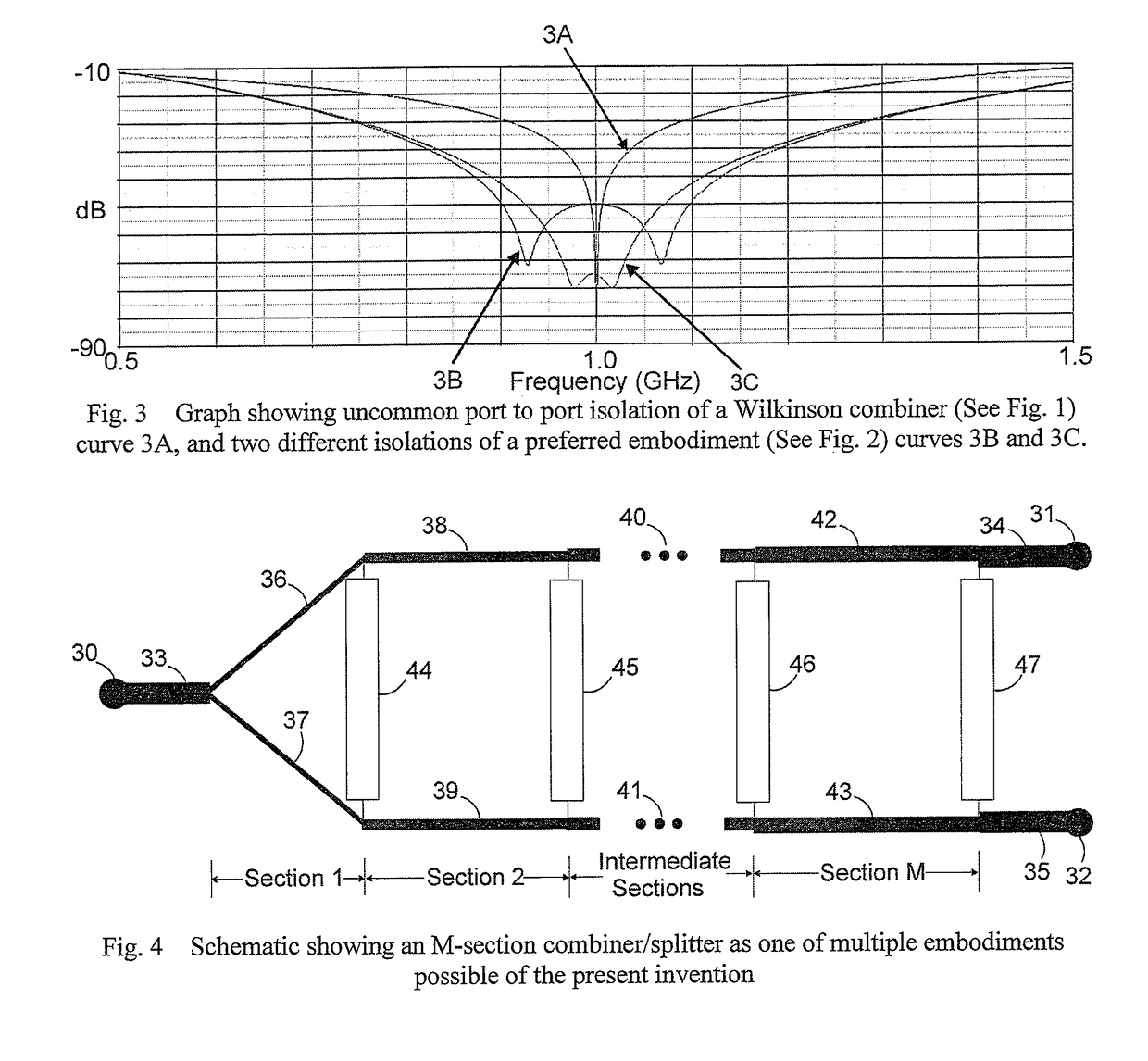
High isolation power combiner/splitter and coupler
A power combiner has at least two uncommon ports and at least one common port. Isolation between the uncommon ports over a broad band is achieved through a lossy band response circuit having a phase and amplitude response effective to compensate for changes in phase and amplitude between the uncommon ports with change in frequency of an input signal. The lossy band response circuit may have a resistance approximating a resistance effective to isolate the uncommon ports over a bandwidth at a center frequency. A coupler may likewise increase the band for which an input port is isolated from the isolated port by coupling a lossy circuit between the input port and isolated port. The lossy circuit may be embodied as a lossy band response circuit.
Owner:THORUP KARL L
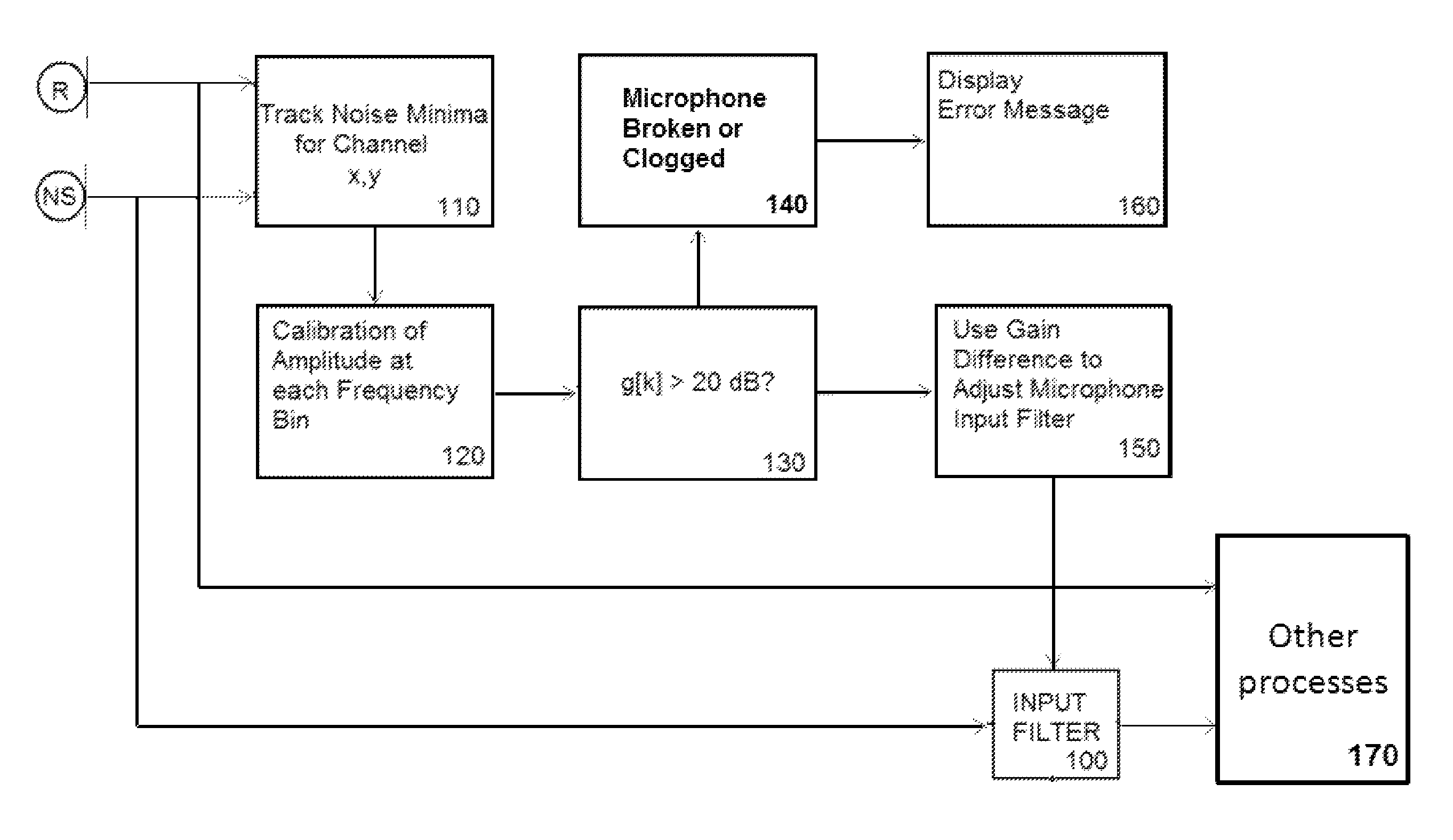
Adaptive self-calibration of small microphone array by soundfield approximation and frequency domain magnitude equalization
ActiveUS20130170666A1Long-term variationMicrophones signal combinationTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsAmplitude responseEngineering
Methods and apparatus for self-calibration of small-microphone arrays are described. In one embodiment, self-calibration is based upon a mathematical approximation for which a detected response by one microphone should approximately equal a combined response from plural microphones in the array. In a second embodiment, self-calibration is based upon matching gains in each of a plurality of Bark frequency bands, and applying the matched gains to frequency domain microphone signals such that the magnitude response of all the microphones in the array approximates an average magnitude response for the array. The methods and apparatus may be implemented in hearing aids or small audio devices and used to mitigate adverse aging and mechanical effects on acoustic performance of small-microphone arrays in these systems.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS ASIA PACIFIC PTE
Compressive sensing theory-based Doppler ambiguity-resolution processing method
InactiveCN101975939AAvoid false value casesRemove restrictionsWave based measurement systemsObservational errorFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a compressive sensing theory-based Doppler ambiguity-resolution processing method, which comprises the following steps of: (1) performing non-uniform sampling on continuous echo pulses in a totally-coherent processing period by utilizing Q-fold pulse repetition frequency values; (2) designing the possible Doppler frequency range of a target, and ensuring the Q-fold pulse repetition frequency values do not have Doppler dead zones in the Doppler frequency range; (3) constructing a compressive sensing (CS) model by utilizing the time-domain under-sampling characteristics of sampled data in the totally-coherent processing period and the sparse characteristics of frequency spectrums of the target to be detected in the possible Doppler frequency range; and (4) resolving the CS model by utilizing an orthogonal matching pursuit (OMP) reconstruction algorithm to directly estimate the amplitude response of ambiguity-free Doppler spectrums. The method eliminates the restriction of the PRF multiplicity adopted by a radar system to the number of the targets to be detected, and simultaneously avoids the condition of false values caused by the influence of measurement errors in the conventional methods by taking the influence of noise on reconstruction results into account and performing de-noising operation when the CS model is resolved to estimate the amplitude response of the ambiguity-free Doppler spectrums by adopting the OMP reconstruction algorithm.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +1
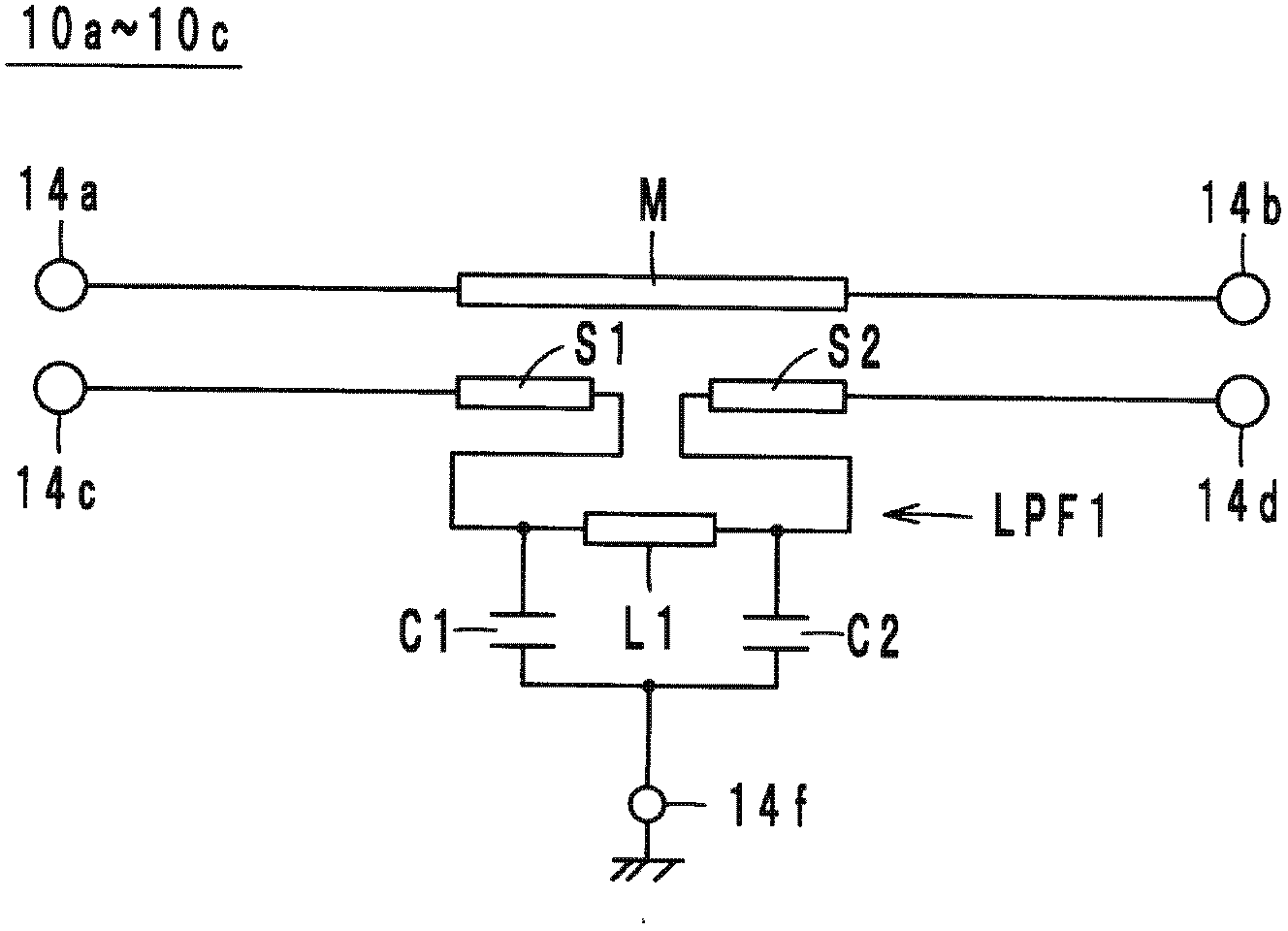
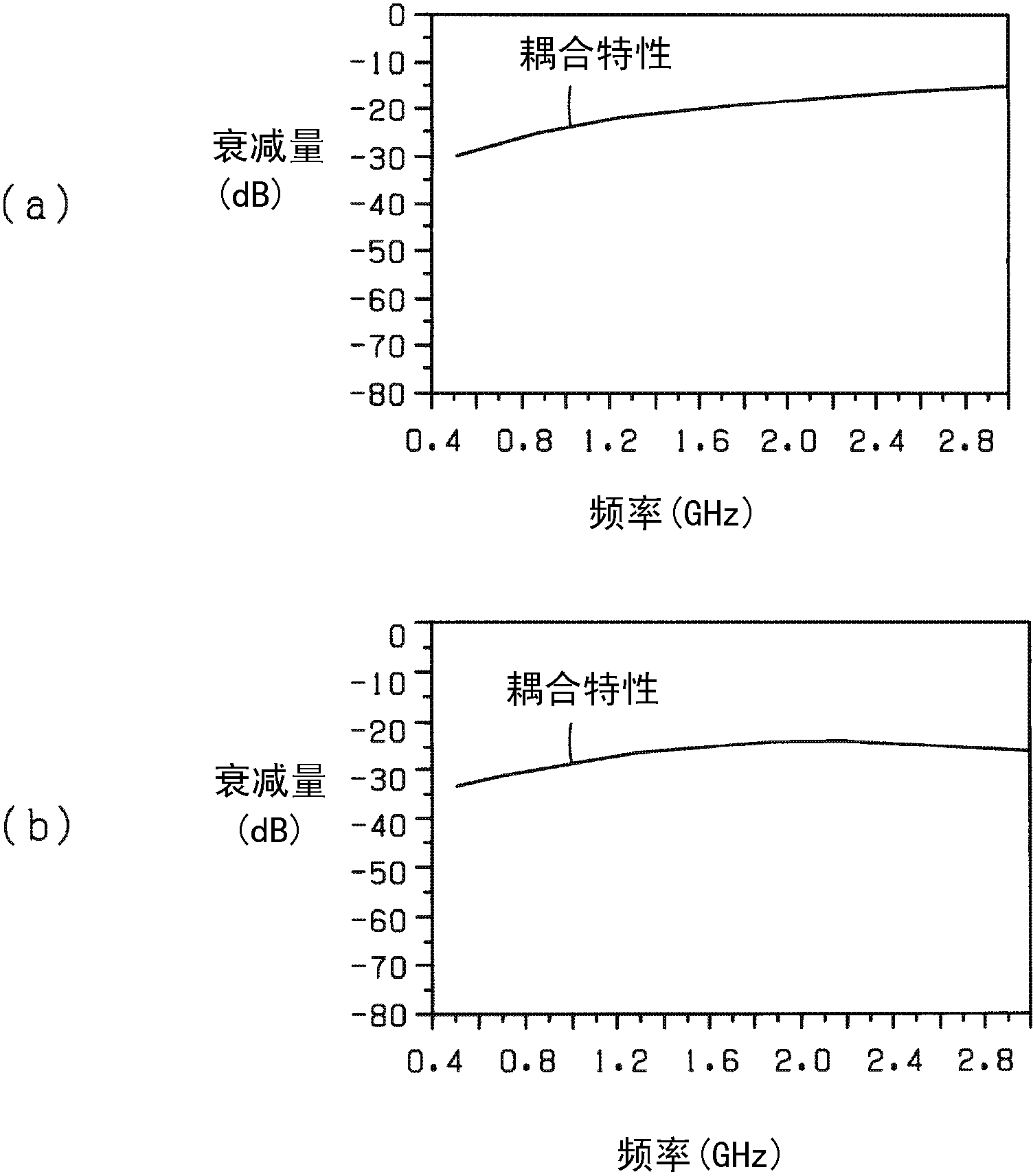
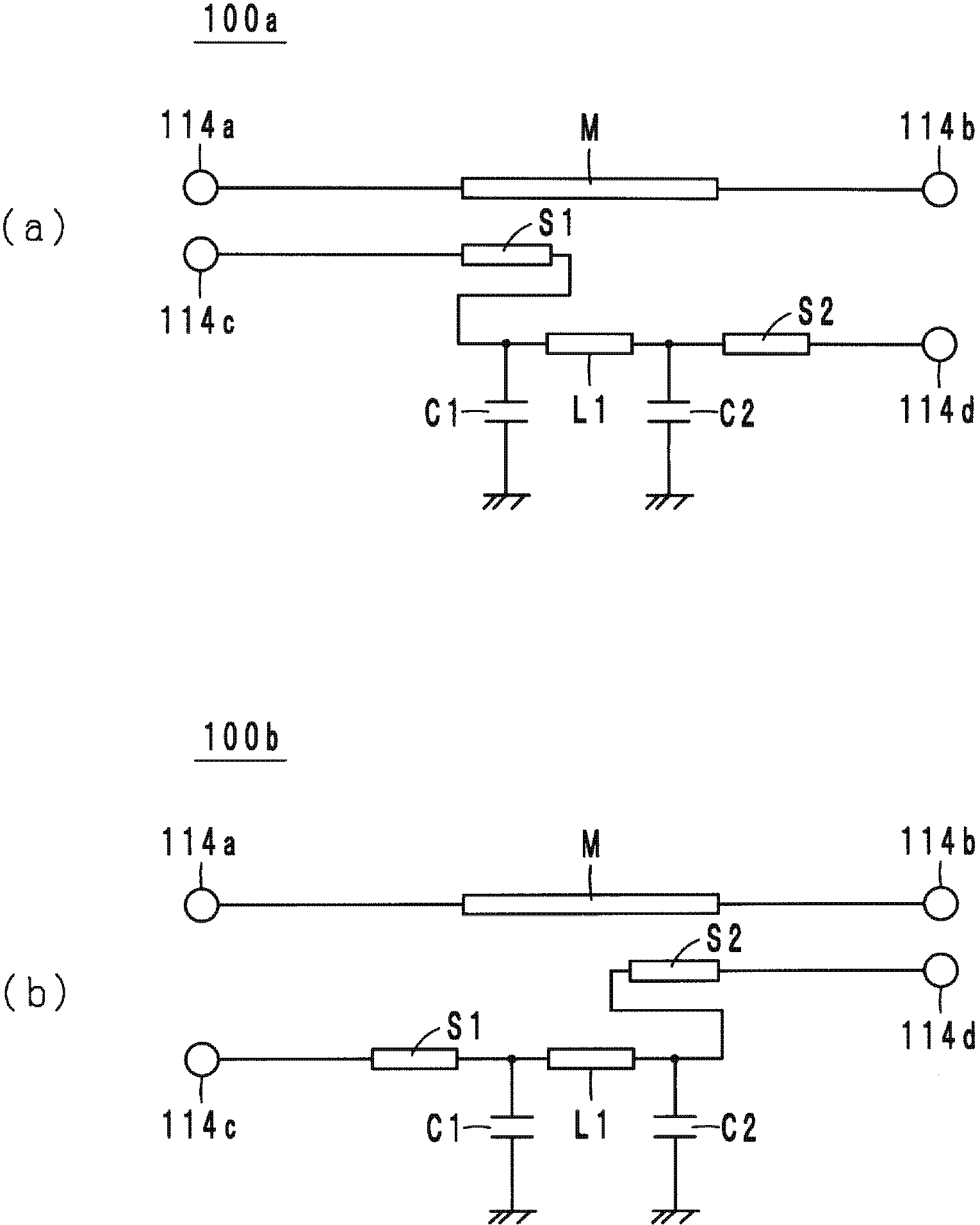
Directional coupler
ActiveCN102832435AFlat amplitude characteristicCoupling devicesElectromagnetic couplingPhase shifted
The invention relates to a directional coupler which can make amplitude response of coupling signals in the directional coupler close to flat, and the directional coupler (10a) is used in a predetermined frequency band. A main line (M) is connected between a first terminal (14a) and a second terminal (14b). A first sub line (S1) is connected to a third terminal (14c) and is electromagnetically coupled to the main line. A second sub line (S2) is connected to a fourth terminal (14d) and is electromagnetically coupled to the main line. A low pass filter (LPF1) is connected between the first sub line and the second sub line and causes a phase shift to be generated in a passing signal passing therethrough in such a manner that the phase shift monotonically increases within a range from about 0 to about 180 degrees with increasing frequency in the predetermined frequency band.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Dynamic time bending distance fault section locating method based on time sequence compression
ActiveCN108181547AReduce communication costsImprove robustnessFault location by conductor typesPrimary stationAmplitude response
The technical scheme of the invention is a dynamic time bending distance fault section locating method based on time sequence compression. The method comprises the steps: carrying out the preprocessing of the fault record data collected by a feed line terminal device, wherein the preprocessing operation comprises the extraction of the initial value and extreme values of the record data and the changes of the record data, and obtaining a new time sequence of the record data; transmitting the time sequence to a main station, solving the similarity of zero-mode currents of two adjacent feed lineterminal devices via a dynamic time bending distance algorithm through the main station, and determining a fault section. The beneficial effects of the invention are that the data size, compared withan original time sequence, is reduced by a half or more, thereby greatly reducing the communication cost; for a high-frequency signal, the dynamic time bending distance algorithm is stronger in synchronization error prevention capability and signal amplitude response capability than a correlated coefficient method; the method provided by the invention is higher in robustness, and does not need the strict time synchronization.
Owner:ZHUHAI XJ ELECTRIC +1
Methods and apparatuses for performing null steering of adaptive microphone array
ActiveUS9479885B1Reduce distractionsMicrophonesSignal processingAmplitude responseAngular orientation
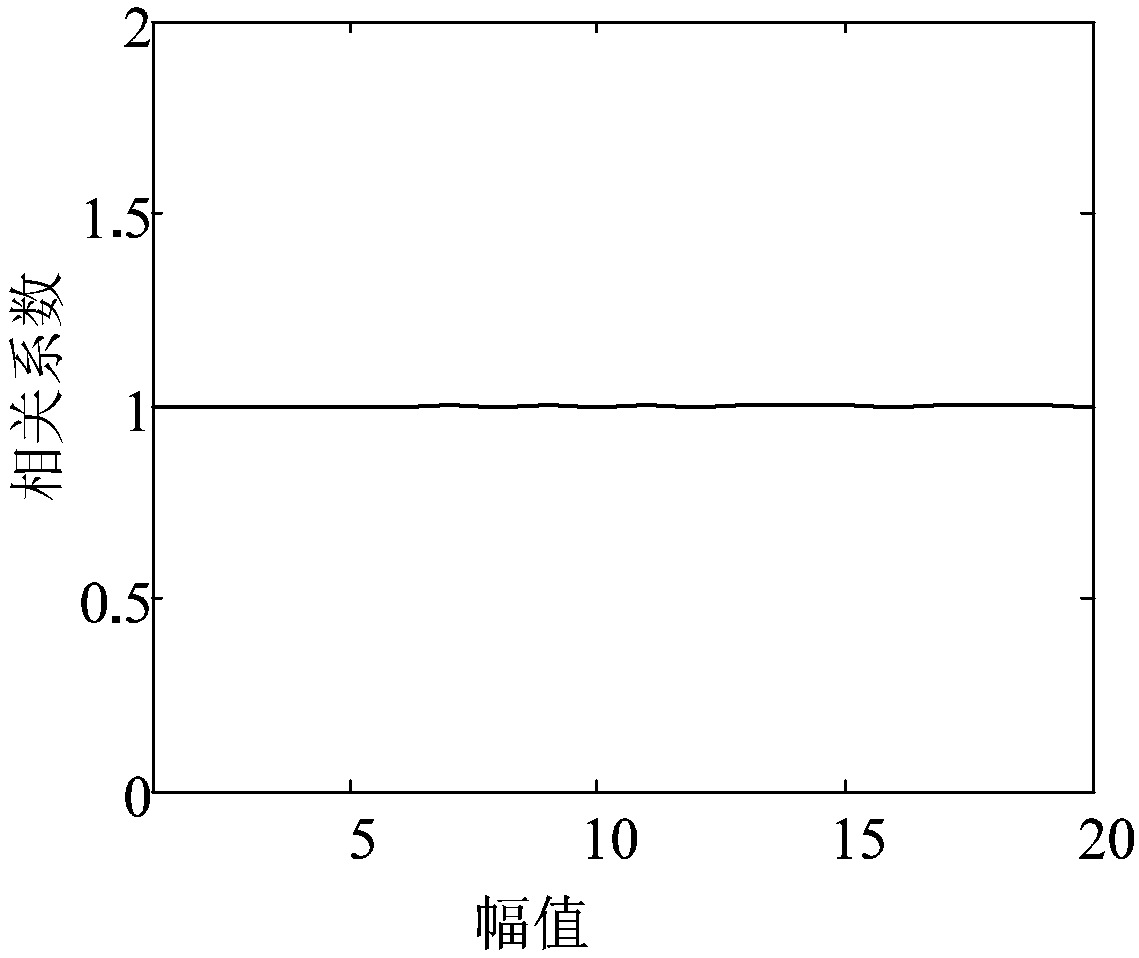
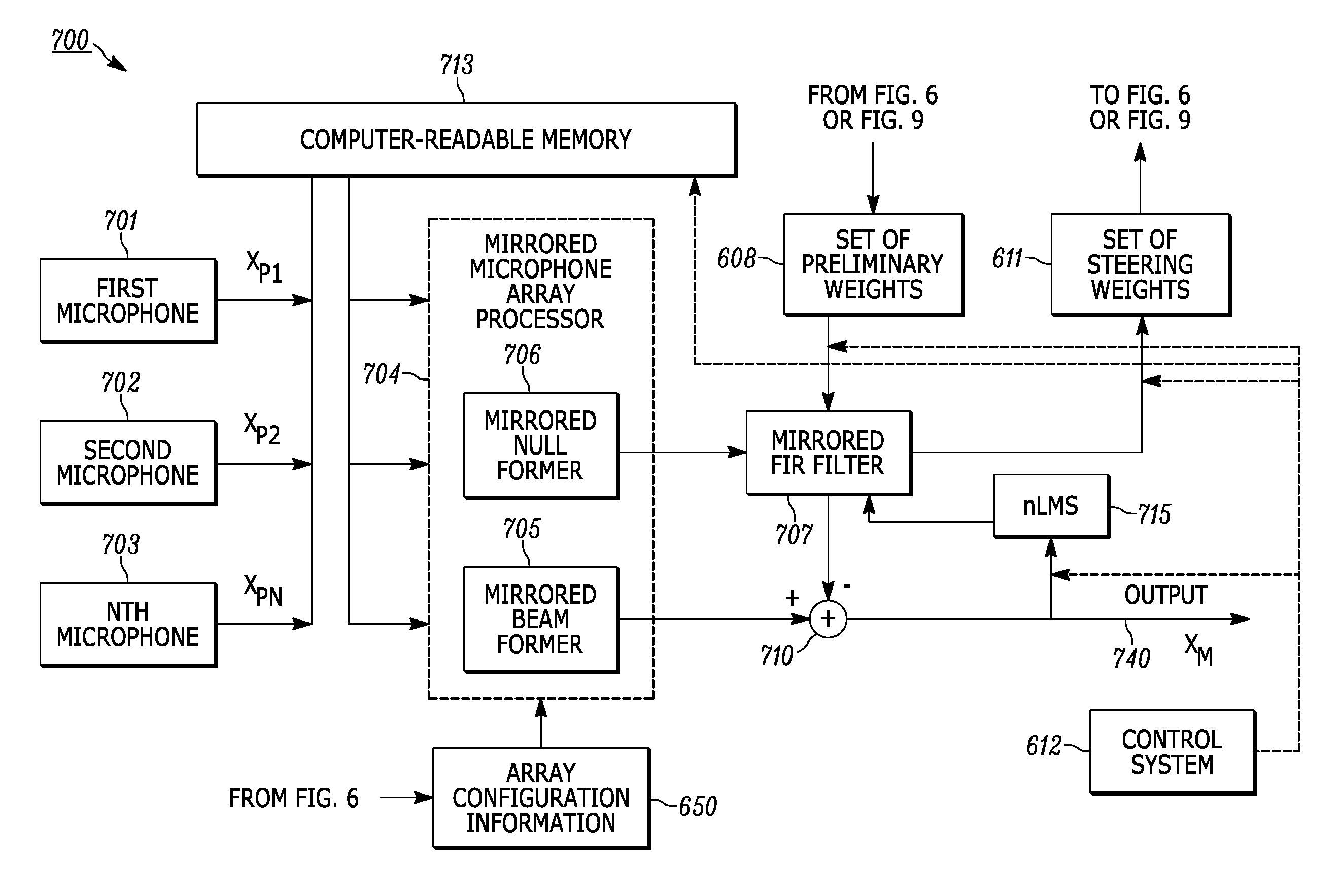
Configuring an adaptive microphone array to gather signals from a main lobe of the array, and configuring the array to reduce side interference gathered from sources that are not situated within the main lobe. A memory stores test signals gathered by the array at a plurality of predetermined angular bearings with reference to the array in an anechoic chamber. Signals gathered in real time are processed to provide a preliminary output and preliminary weights. The test signals are retrieved from memory. The preliminary weights are applied to the test signals to provide null steering weights. The null steering weights and the preliminary output are processed to reduce or minimize the amplitude response of the array at the angular orientation.
Owner:MOTOROLA MOBILITY LLC
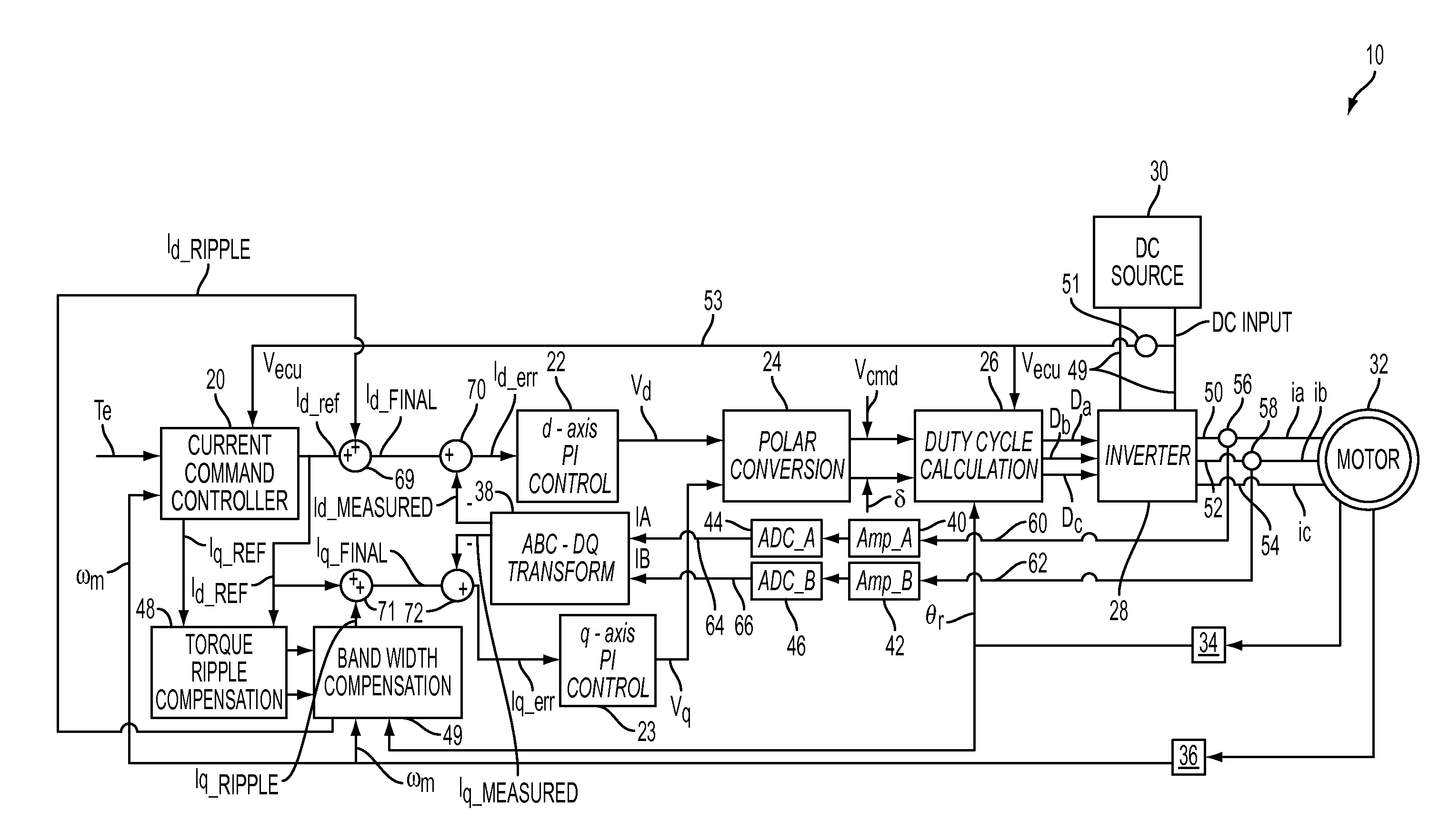
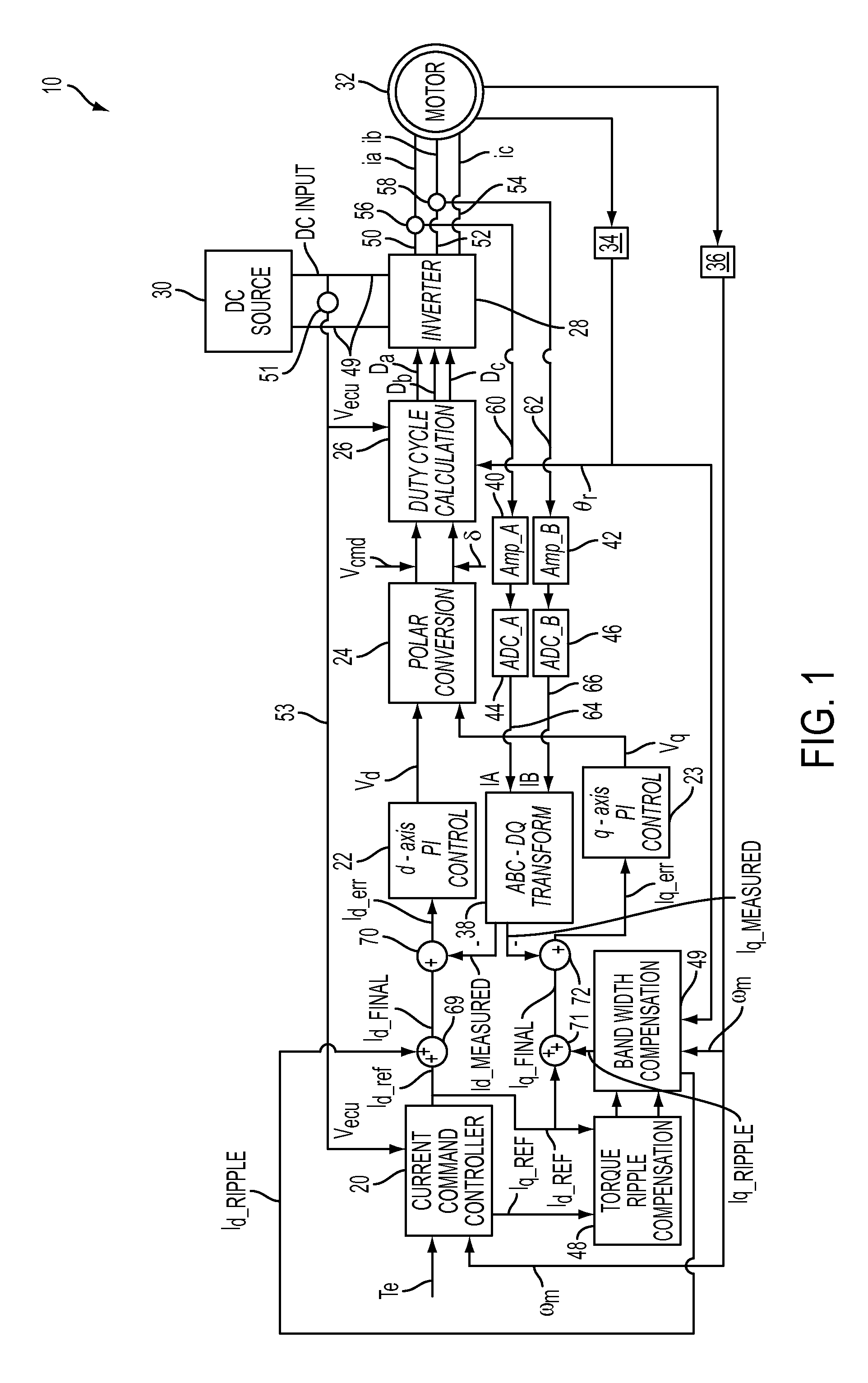
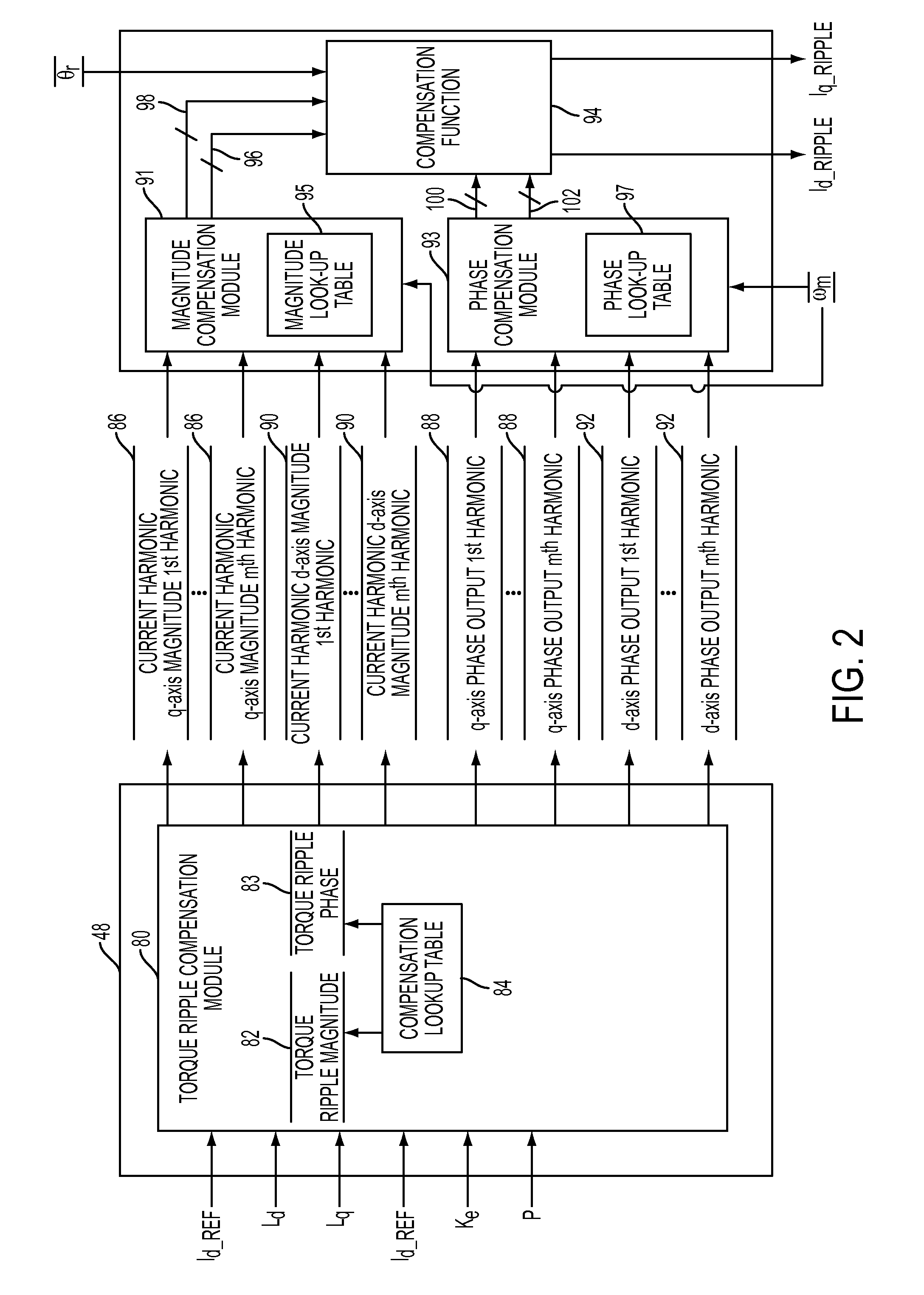
Motor control system having bandwith compensation
ActiveUS20140265962A1Torque ripple controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersAmplitude responseControl system
A motor control system for determining a ripple compensating current is provided. The motor control system includes a motor having a plurality of motor harmonics and a motor frequency, and a bandwidth compensation controller that is in communication with the motor. The bandwidth compensation controller is configured to determine a magnitude response compensation value and a phase compensation value for each of the plurality of motor harmonics. The magnitude response compensation value and the phase compensation value are both based on the motor frequency. The bandwidth compensation controller is configured to determine the ripple compensating current based on the magnitude response compensation value and the phase compensation value.
Owner:STEERING SOLUTIONS IP HLDG
High speed multi-touch touch device and controller therefor
ActiveUS9417739B2Reduce couplingReduce the amplitudeInput/output processes for data processingCapacitanceCapacitive coupling
A touch-sensitive device includes a touch panel, a drive unit, a sense unit, and a measurement unit. A touch applied to a node of the panel changes a capacitive coupling between two electrodes (a drive electrode and a sense electrode) of the touch panel. The drive unit delivers a drive signal, which may comprise one or more drive pulses, to the drive electrode. The sense unit couples to the sense electrode, and generates a response signal that includes a differentiated representation of the drive signal. The amplitude of the response signal is responsive to the capacitive coupling between the electrodes, and is measured to provide an indication of a touch at the node.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
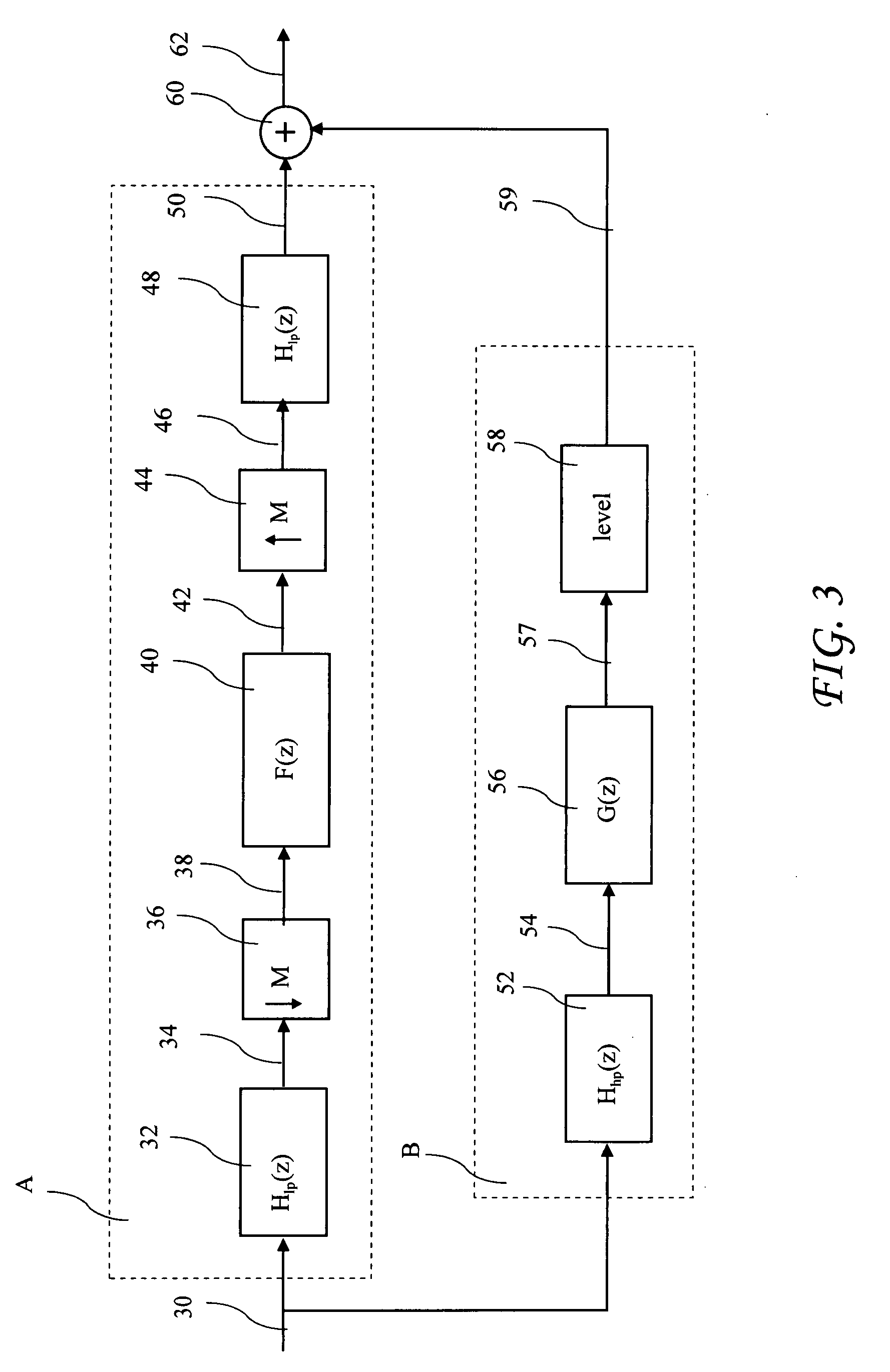
Combined multirate-based and fir-based filtering technique for room acoustic equalization
ActiveUS20080279318A1Improve equalization performanceReduce computational complexityPublic address systemsFrequency response correctionFinite impulse responseComputation complexity
A combined multirate-based Finite Impulse Response (FIR) filter equalization technique combines a low-order FIR equalization filter operating at a lower rate for equalization of a loudspeaker-room response at low frequencies, and a complementary low-order minimum-phase FIR equalization filter operating at a higher rate for equalization of the loudspeaker-room response at higher frequencies. The design of two complementary band filters for separately performing low and high frequency equalization, keeps the system delay at a minimum while maintaining excellent equalization performance. Splicing between the two equalization filters, for maintaining a flat magnitude response in the transition region of the two complementary filters, is done automatically through level adjustment of one equalization filter relative to the other. The present invention achieves excellent equalization at low filter orders and hence reduced computational complexity.
Owner:AUDYSSEY LABORATORIES
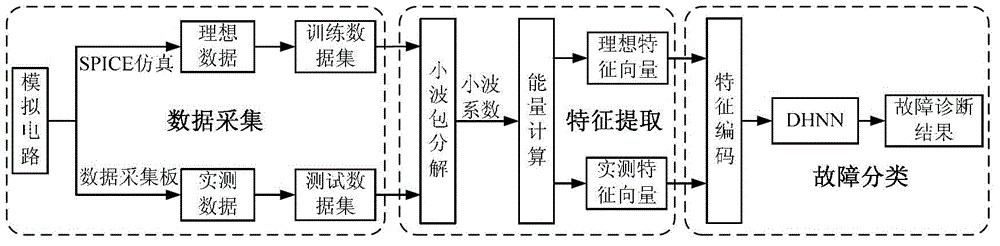
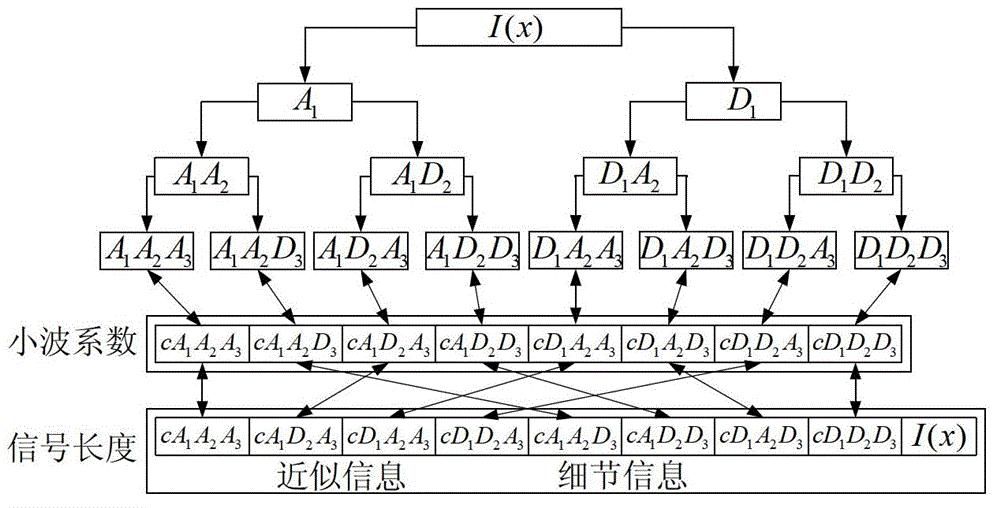
Analog circuit fault diagnosis method based on wavelet packet analysis and Hopfield network
InactiveCN102749573ADescribe the fault characteristicsFast and accurate fault classificationAnalog circuit testingHopfield networkData set
The invention provides an analog circuit fault diagnosis method based on wavelet packet analysis and the Hopfield network. The method includes data obtaining, feature extraction and fault classification, wherein data obtaining includes performing data sampling for output response of an analog circuit respectively through simulation program with integrated circuit emphasis (SPICE) simulation and a data collection plate connected at a practical circuit terminal so as to obtain an ideal output response data set and an actually-measured output response data set; feature extraction includes performing wavelet packet decomposition with ideal circuit output response and actually-measured output response respectively serving as a training data set and a test data set, and leading energy values obtained by decomposed wavelet coefficient through energy calculating to form feature vectors of corresponding faults; and fault classification includes leading the feature vectors of all samples to be subjected to Hopfield coding and then submitting the coded feature vectors to the Hopfield network to achieve accurate and fast fault classification. The analog circuit fault diagnosis method is good in fault feature pretreatment effect aiming at hard faults with weak amplitude response and soft faults with large amplitude response, and the newly defined energy function and the newly defined coding rule are remarkable in influence on fault diagnosis accuracy of the analog circuit.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Method and system for Gaussian filter modification for improved modulation characteristics in Bluetooth RF transmitters
InactiveUS20060088123A1Improve modulation characteristicsMultiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsLower limitAmplitude response
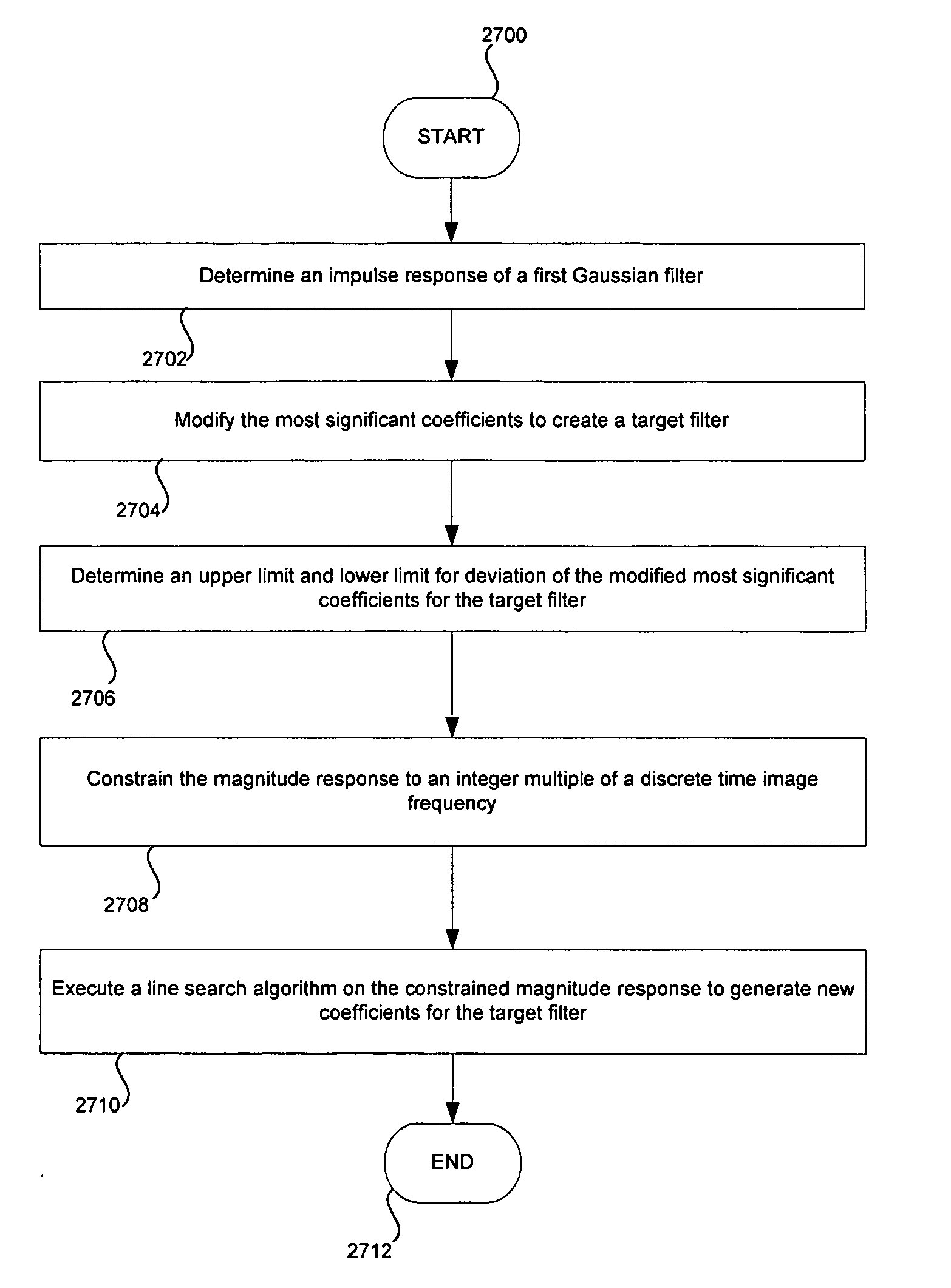
Certain aspects of the invention may comprise determining an impulse response of a first Gaussian filter based on a filter length and an oversampling ratio (OSR). The most significant coefficients of the first Gaussian filter may be modified to create a target filter. An upper limit and a lower limit for deviation of the modified most significant coefficients for the target filter may be determined. A magnitude response for the target filter may be constrained based on at least a selected corner frequency, which is related to the OSR. A line search algorithm may be executed on the constrained magnitude response to generate new coefficients for the target filter.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com