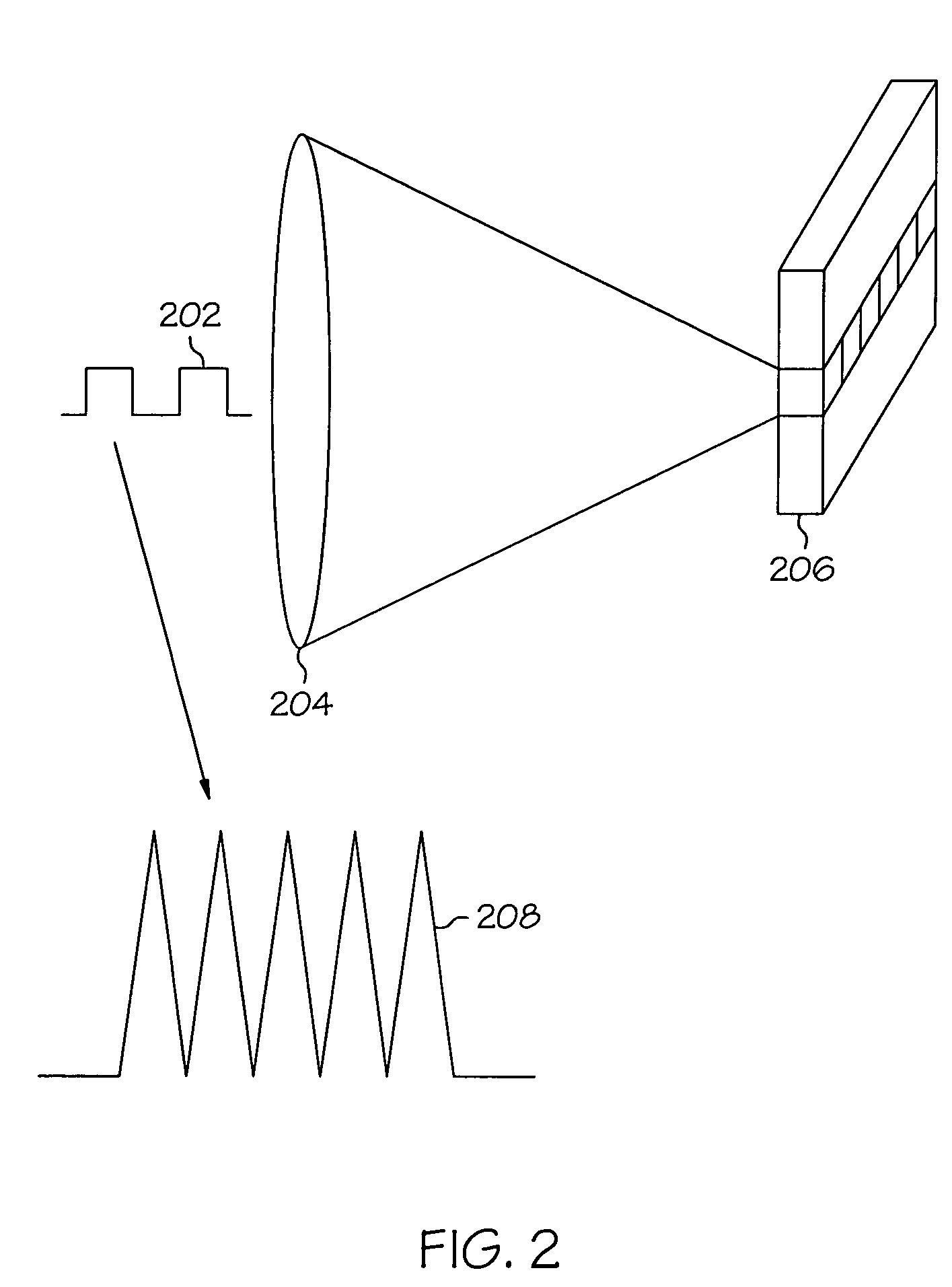
Patents
Literature
661 results about "Pulse repetition frequency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The pulse repetition frequency (PRF) is the number of pulses of a repeating signal in a specific time unit, normally measured in pulses per second. The term is used within a number of technical disciplines, notably radar.
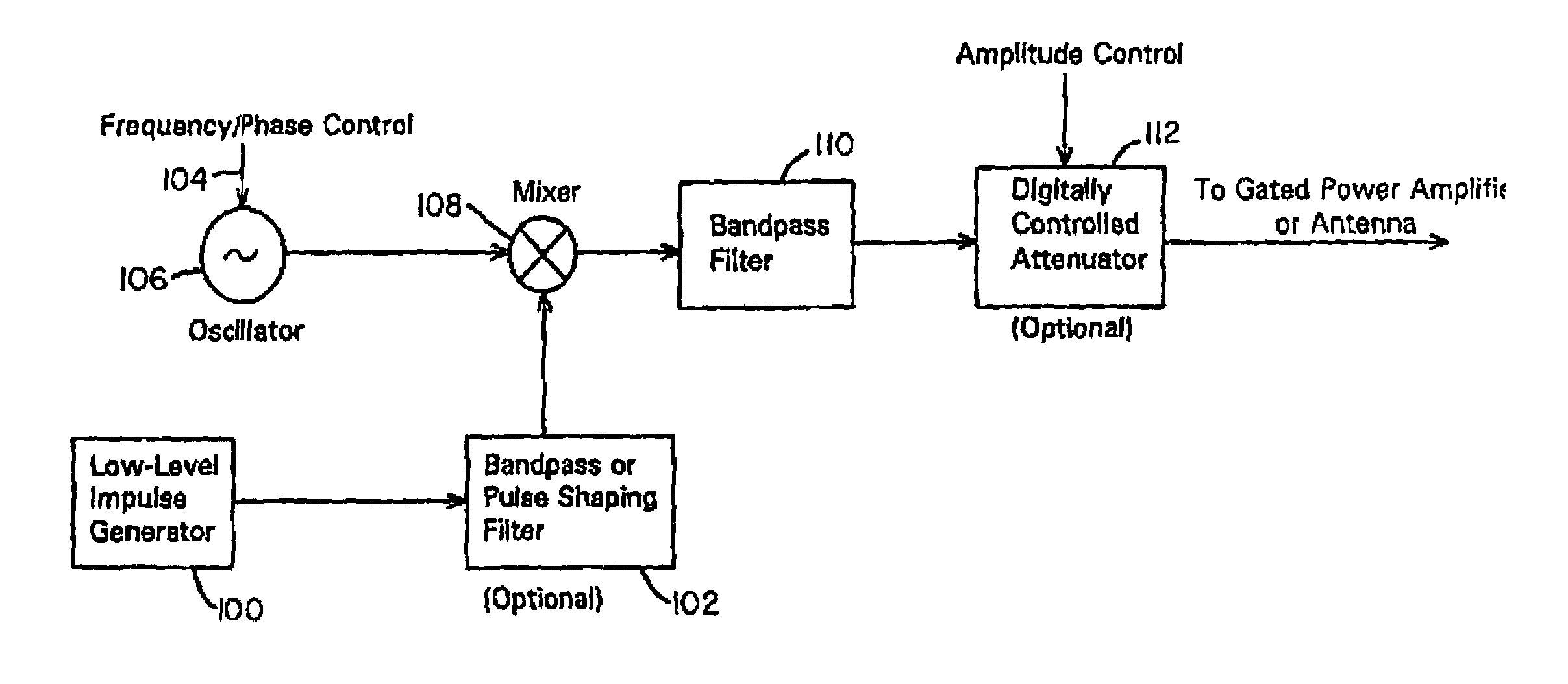
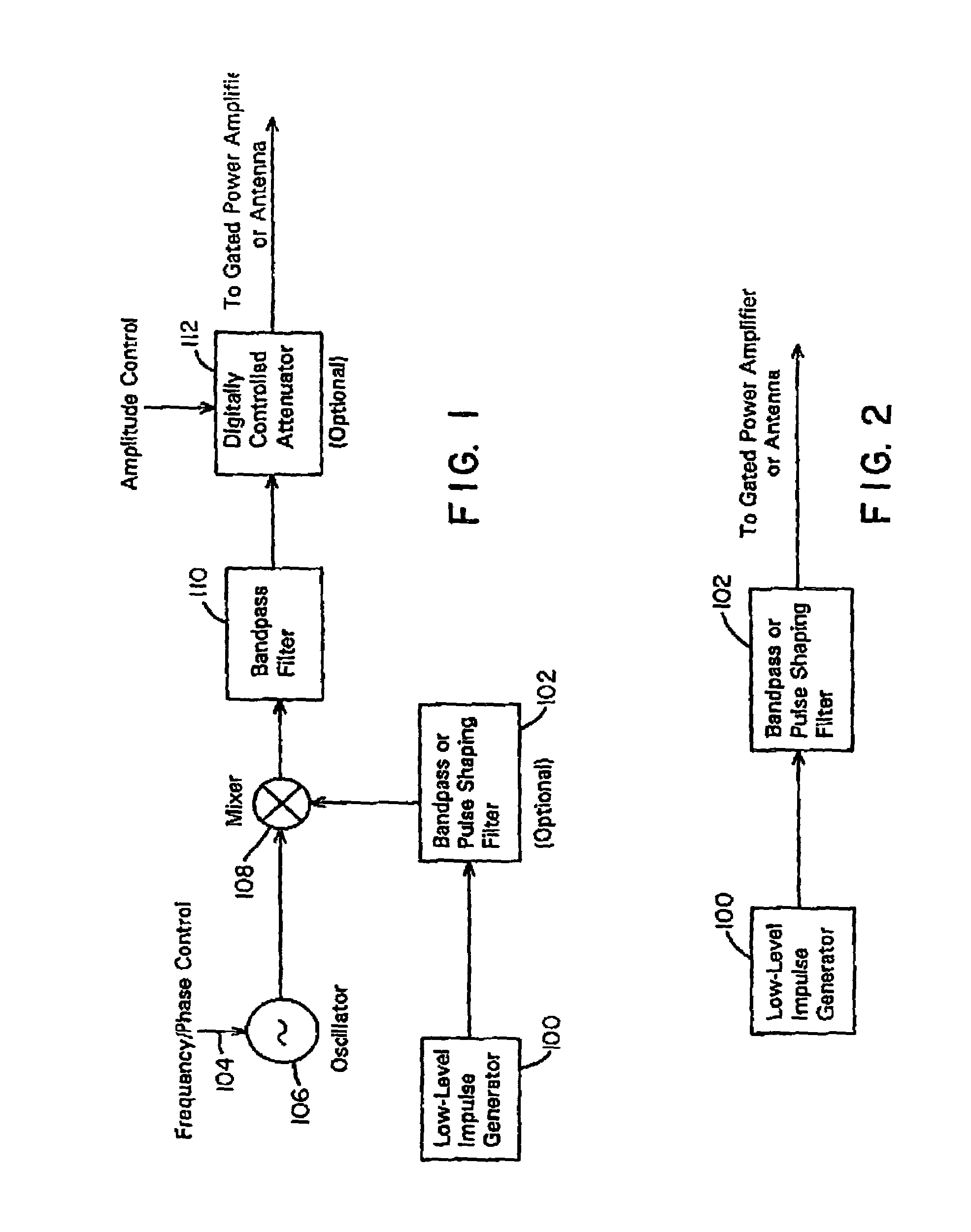
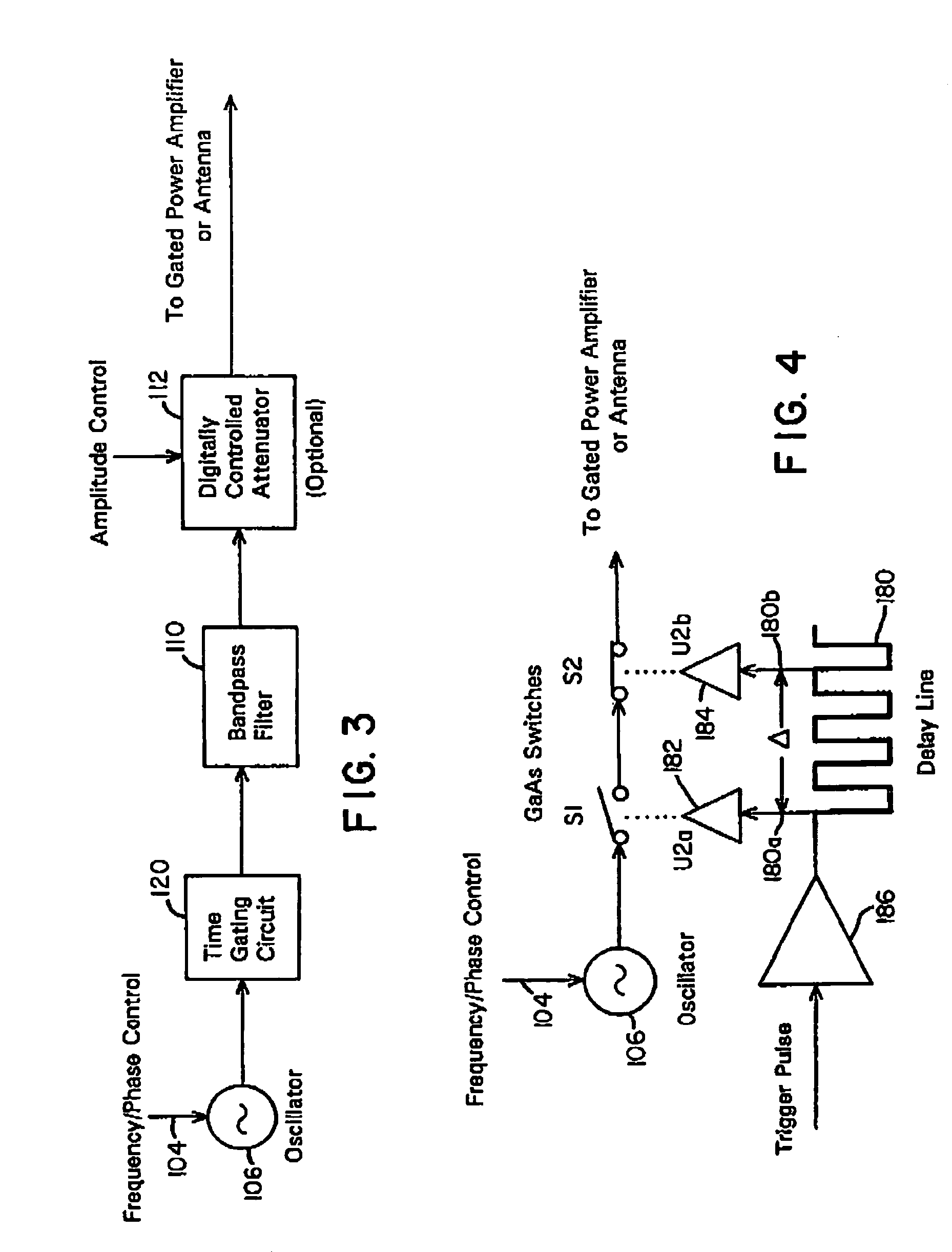
Waveform adaptive ultra-wideband transmitter
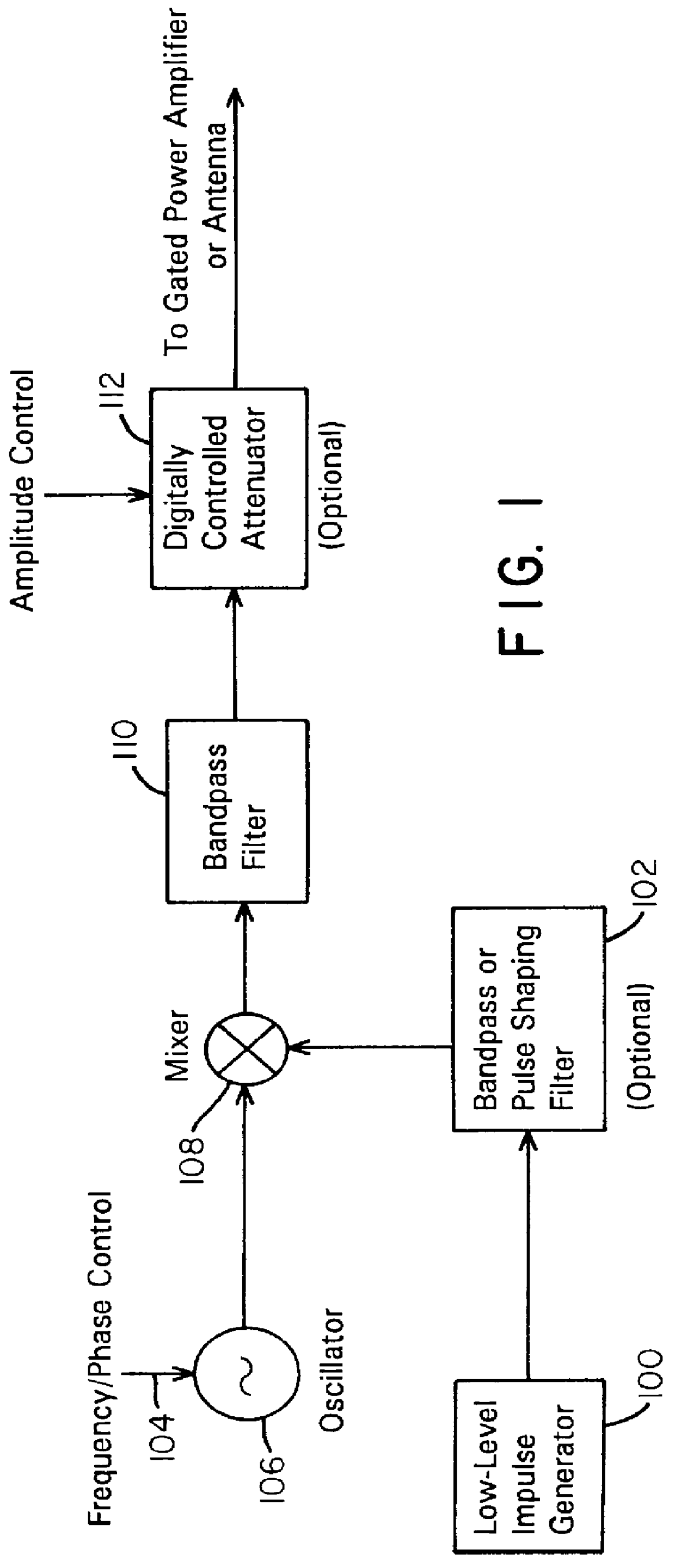
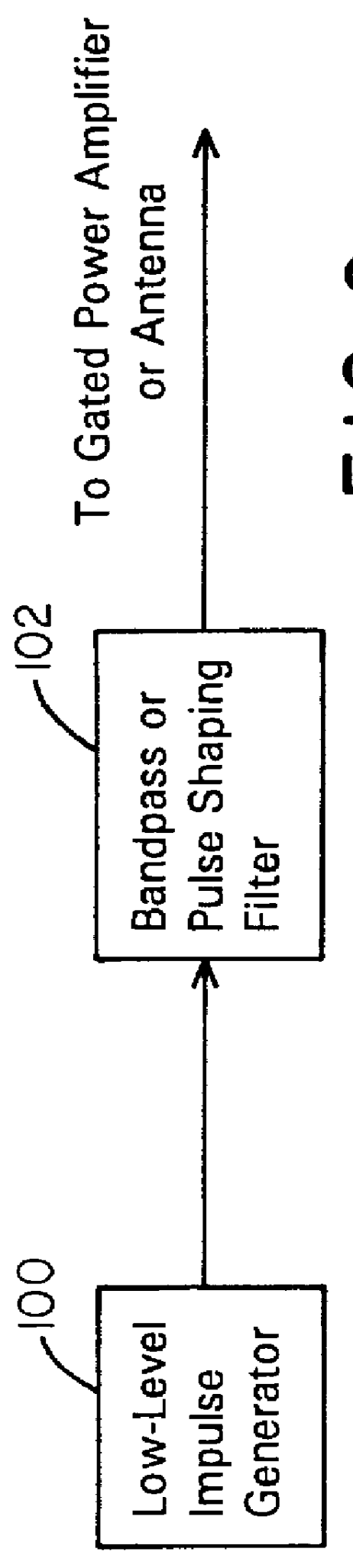
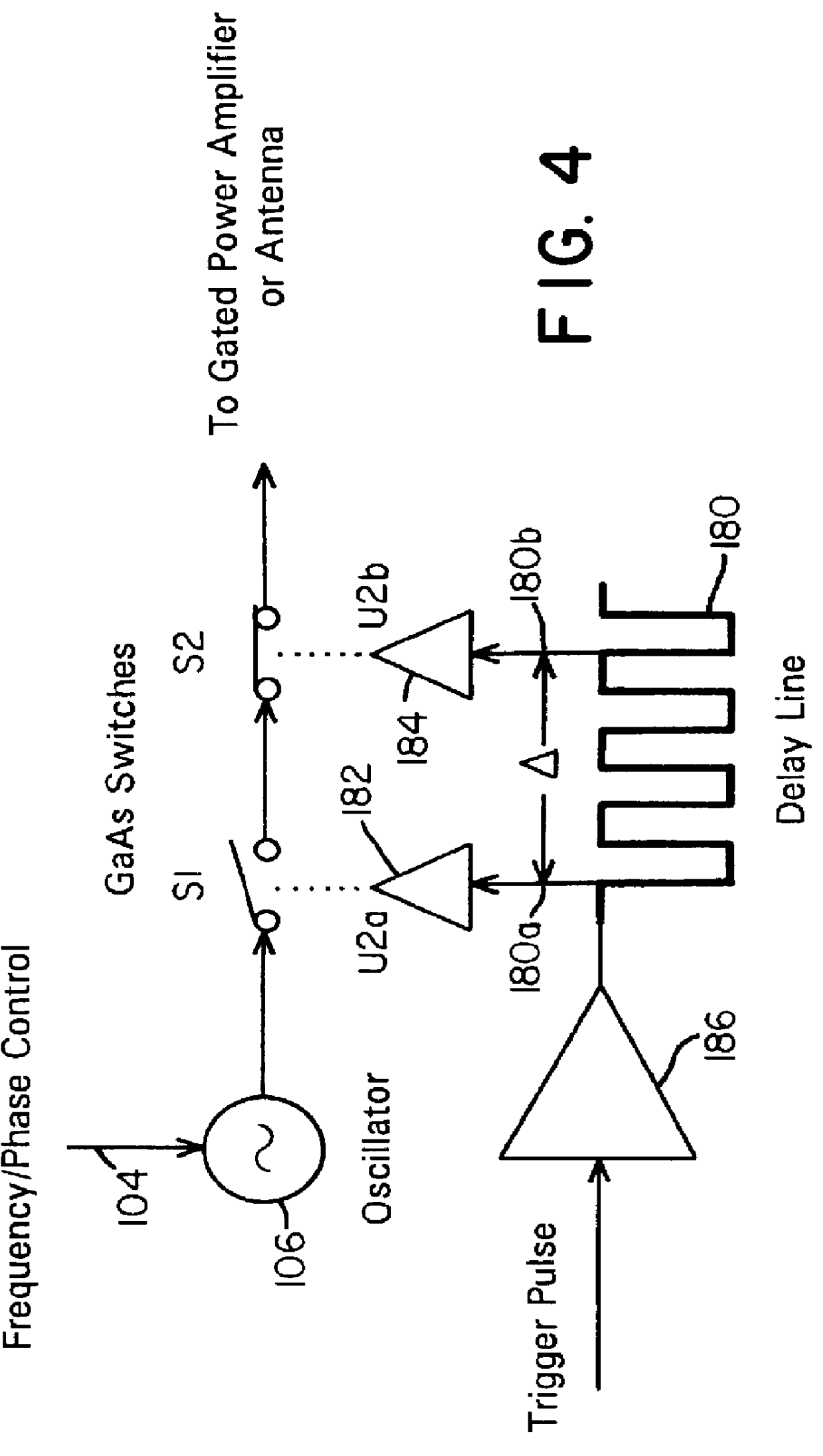
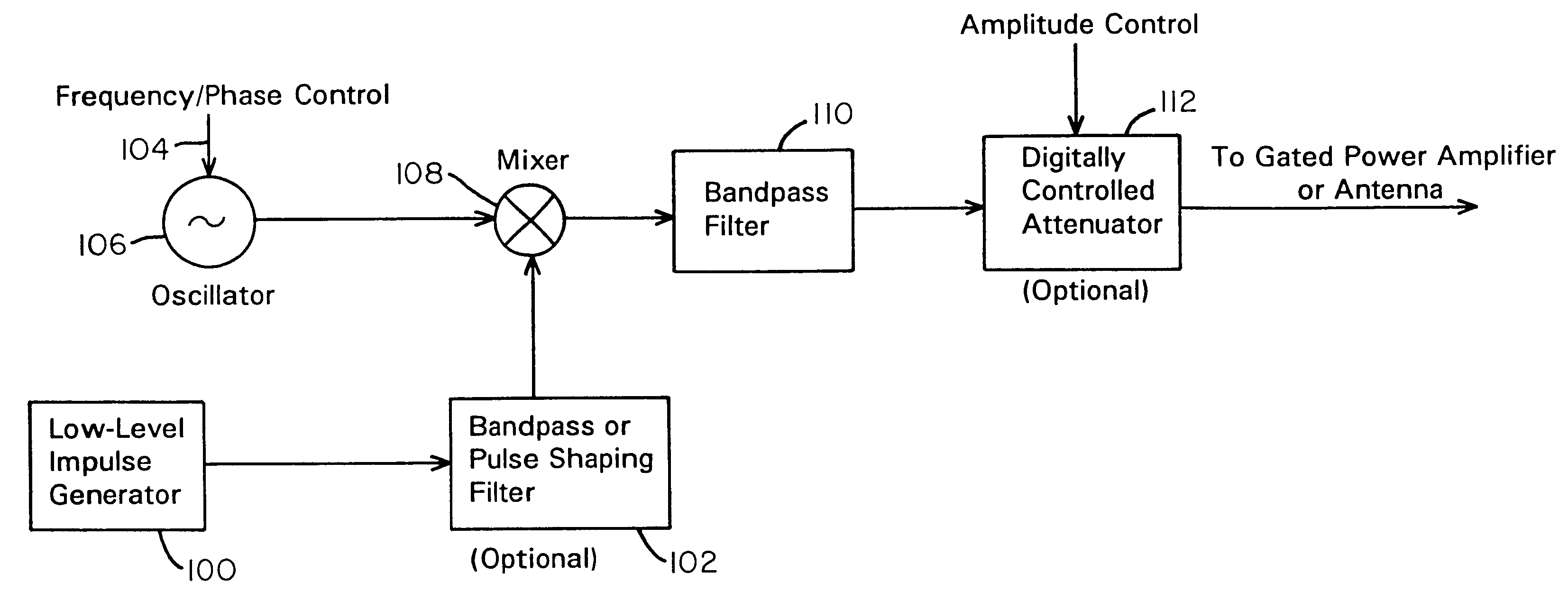
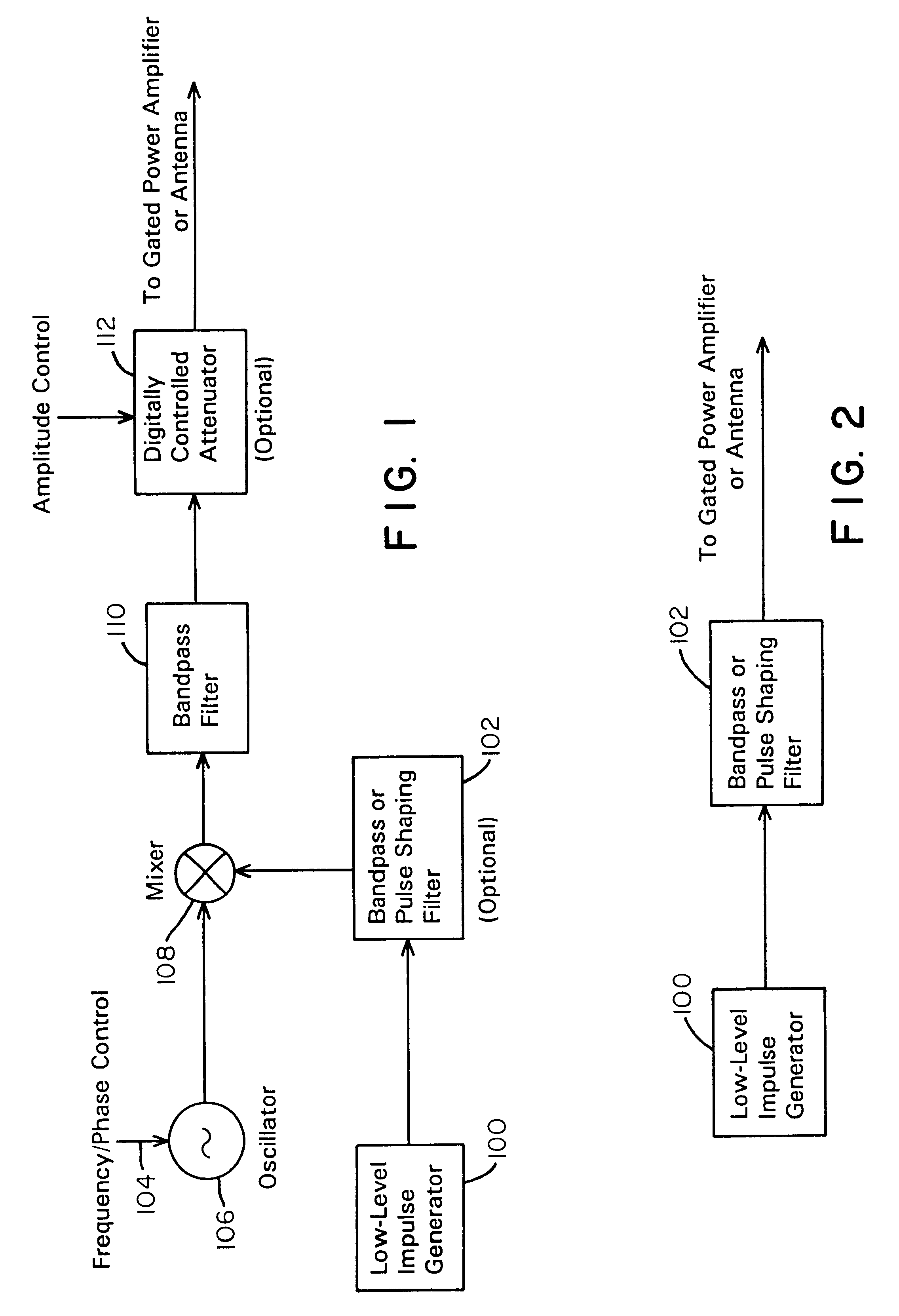
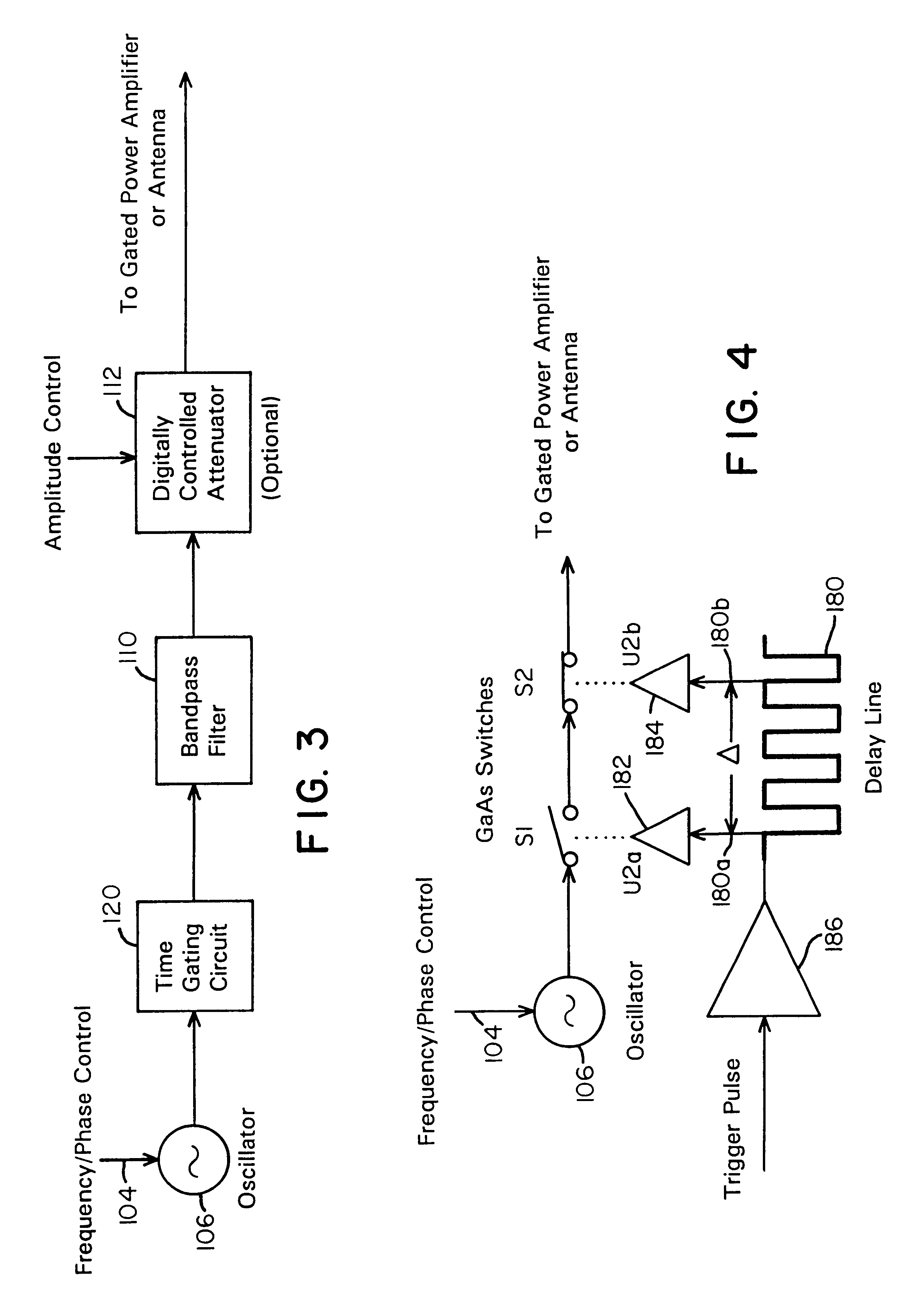
A waveform adaptive transmitter that conditions and / or modulates the phase, frequency, bandwidth, amplitude and / or attenuation of ultra-wideband (UWB) pulses. The transmitter confines or band-limits UWB signals within spectral limits for use in communication, positioning, and / or radar applications. One embodiment comprises a low-level UWB source (e.g., an impulse generator or time-gated oscillator (fixed or voltage-controlled)), a waveform adapter (e.g., digital or analog filter, pulse shaper, and / or voltage variable attenuator), a power amplifier, and an antenna to radiate a band-limited and / or modulated UWB or wideband signals. In a special case where the oscillator has zero frequency and outputs a DC bias, a low-level impulse generator impulse-excites a bandpass filter to produce an UWB signal having an adjustable center frequency and desired bandwidth based on a characteristic of the filter. In another embodiment, a low-level impulse signal is approximated by a time-gated continuous-wave oscillator to produce an extremely wide bandwidth pulse with deterministic center frequency and bandwidth characteristics. The UWB signal may be modulated to carry multi-megabit per second digital data, or may be used in object detection or for ranging applications. Activation of the power amplifier may be time-gated in cadence with the UWB source thereby to reduce inter-pulse power consumption. The UWB transmitter is capable of extremely high pulse repetition frequencies (PRFs) and data rates in the hundreds of megabits per second or more, frequency agility on a pulse-to-pulse basis allowing frequency hopping if desired, and extensibility from below HF to millimeter wave frequencies.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
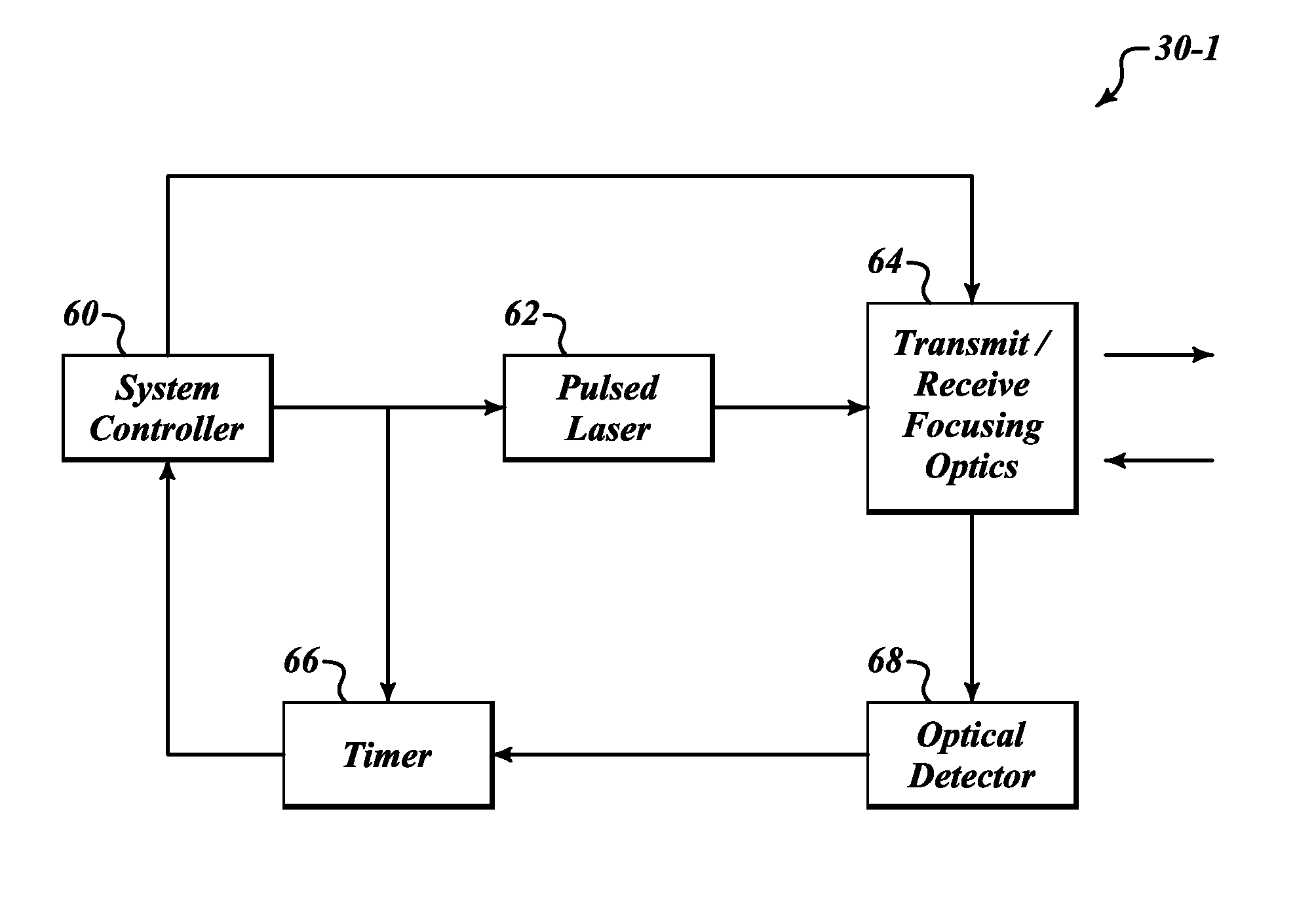
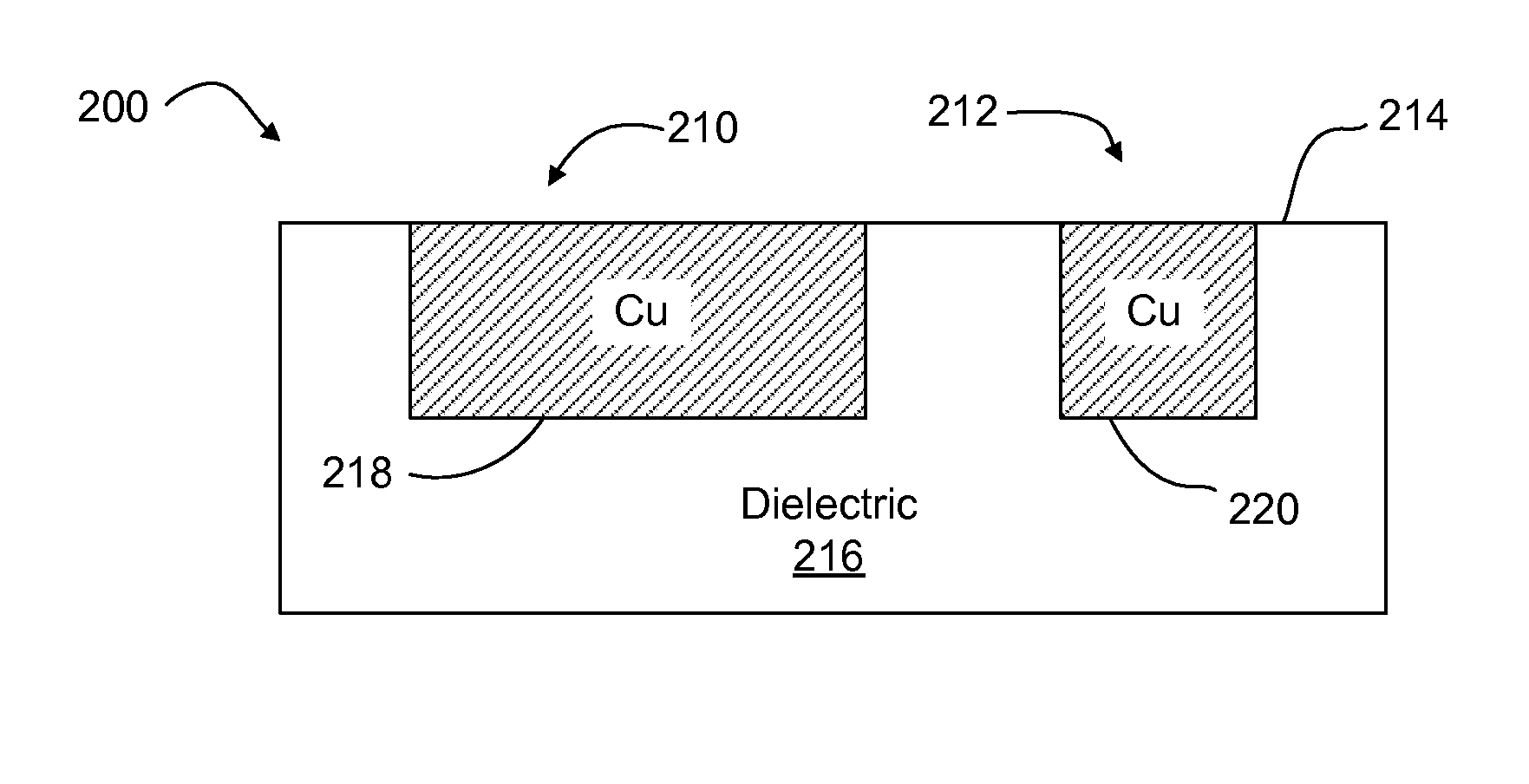
Systems and methods for safe laser imaging, detection and ranging (LIDAR) operation
InactiveUS20090273770A1Realize automatic adjustmentOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationLaser imagingField of view
A Laser Imaging, Detection and Ranging (LIDAR) system that automatically adjusts laser output so that no eye damage occurs to human targets. In one example, a component automatically measures range to targets in a field of view and determines the closest targets based on the measured range. A laser device outputs a laser beam and a controller adjusts one of pulse repetition frequency, power, or pulse duration of the laser device based on the measured range of the closest target in order to comply with a predefined eye safety model.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Ultra wideband data transmission system and method
InactiveUS6690741B1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsAngle modulationBandpass filteringExtensibility
A data-modulated ultra wideband transmitter that modulates the phase, frequency, bandwidth, amplitude and / or attenuation of ultra-wideband (UWB) pulses. The transmitter confines or band-limits UWB signals within spectral limits for use in communication, positioning, and / or radar applications. One embodiment comprises a low-level UWB source (e.g., an impulse generator or time-gated oscillator (fixed or voltage-controlled)), a waveform adapter (e.g., digital or analog filter, pulse shaper, and / or voltage variable attenuator), a power amplifier, and an antenna to radiate a band-limited and / or modulated UWB or wideband signals. In a special case where the oscillator has zero frequency and outputs a DC bias, a low-level impulse generator impulse-excites a bandpass filter to produce an UWB signal having an adjustable center frequency and desired bandwidth based on a characteristic of the filter. In another embodiment, a low-level impulse signal is approximated by a time-gated continuous-wave oscillator to produce an extremely wide bandwidth pulse with deterministic center frequency and bandwidth characteristics. The UWB signal may be modulated to carry multi-megabit per second digital data, or may be used in object detection or for ranging applications. Activation of the power amplifier may be time-gated in cadence with the UWB source thereby to reduce inter-pulse power consumption. The UWB transmitter is capable of extremely high pulse repetition frequencies (PRFs) and data rates in the hundreds of megabits per second or more, frequency agility on a pulse-to-pulse basis allowing frequency hopping if desired, and extensibility from below HF to millimeter wave frequencies.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
Contrast agent imaging with destruction pulses in diagnostic medical ultrasound
InactiveUS6340348B1Increase the differenceImprove efficiencyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryEcg signalUltrasonography
The invention is directed to improvements in diagnostic medical ultrasound contrast agent imaging. In a preferred embodiment, high pulse repetition frequency (HPRF) destruction pulses are fired at a rate higher than necessary for receiving returning echoes. Pulse parameters can also be changed between the plurality of contrast agent-destroying pulses. Other preferred embodiments of the invention are directed to simultaneous transmission of multiple beams of destruction pulses. Destruction frames that consist of a plurality of destruction pulses can be triggered and swept over the entire region of tissue being imaged and at a variety of focal depths from the transmitter. The destruction frames are fired at some time triggered from a timer or some fixed part of a physiological signal, such as an ECG signal. Other preferred embodiments of the invention are directed to continuous low power imaging pulses alternating with destruction pulses triggered at a fixed point of a physiological signal, and a comparison of the received signals from imaging pulses fired before and after the destruction pulses. Alternatively, destruction pulses are triggered at a fixed point on a physiological signal different from the fixed point of a physiological signal used to trigger imaging pulses. In another embodiment, triggered destruction frames are used to enable a comparison of imaging frames in order to determine physiological functions, such as perfusion of blood in cardiac tissue. Finally, in another embodiment, destruction pulses are combined with subharmonic imaging.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Ultrashort laser pulse wafer scribing
InactiveUS20070272668A1Improve mechanical stressImprove thermal stressSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLight beamOptoelectronics
Systems and methods are provided for scribing wafers with short laser pulses so as to reduce the ablation threshold of target material. In a stack of material layers, a minimum laser ablation threshold based on laser pulse width is determined for each of the layers. The highest of the minimum laser ablation thresholds is selected and a beam of one or more laser pulses is generated having a fluence in a range between the selected laser ablation threshold and approximately ten times the selected laser ablation threshold. In one embodiment, a laser pulse width in a range of approximately 0.1 picosecond to approximately 1000 picoseconds is used. In addition, or in other embodiments, a high pulse repetition frequency is selected to increase the scribing speed. In one embodiment, the pulse repetition frequency is in a range between approximately 100 kHz and approximately 100 MHz.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
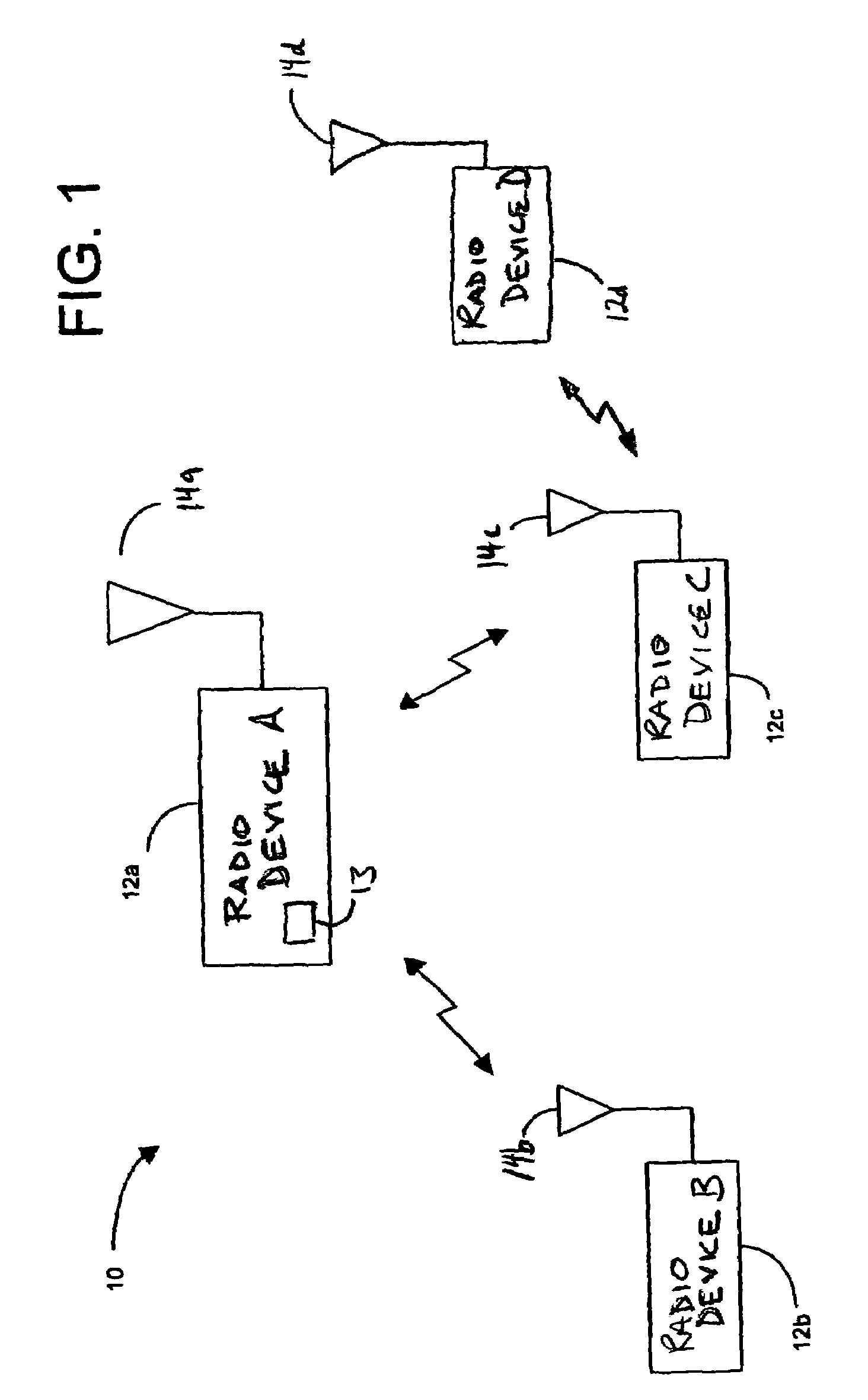
Wireless TDMA system and method for network communications
InactiveUS6970448B1Network traffic/resource managementInformation formatCommunications systemTransceiver
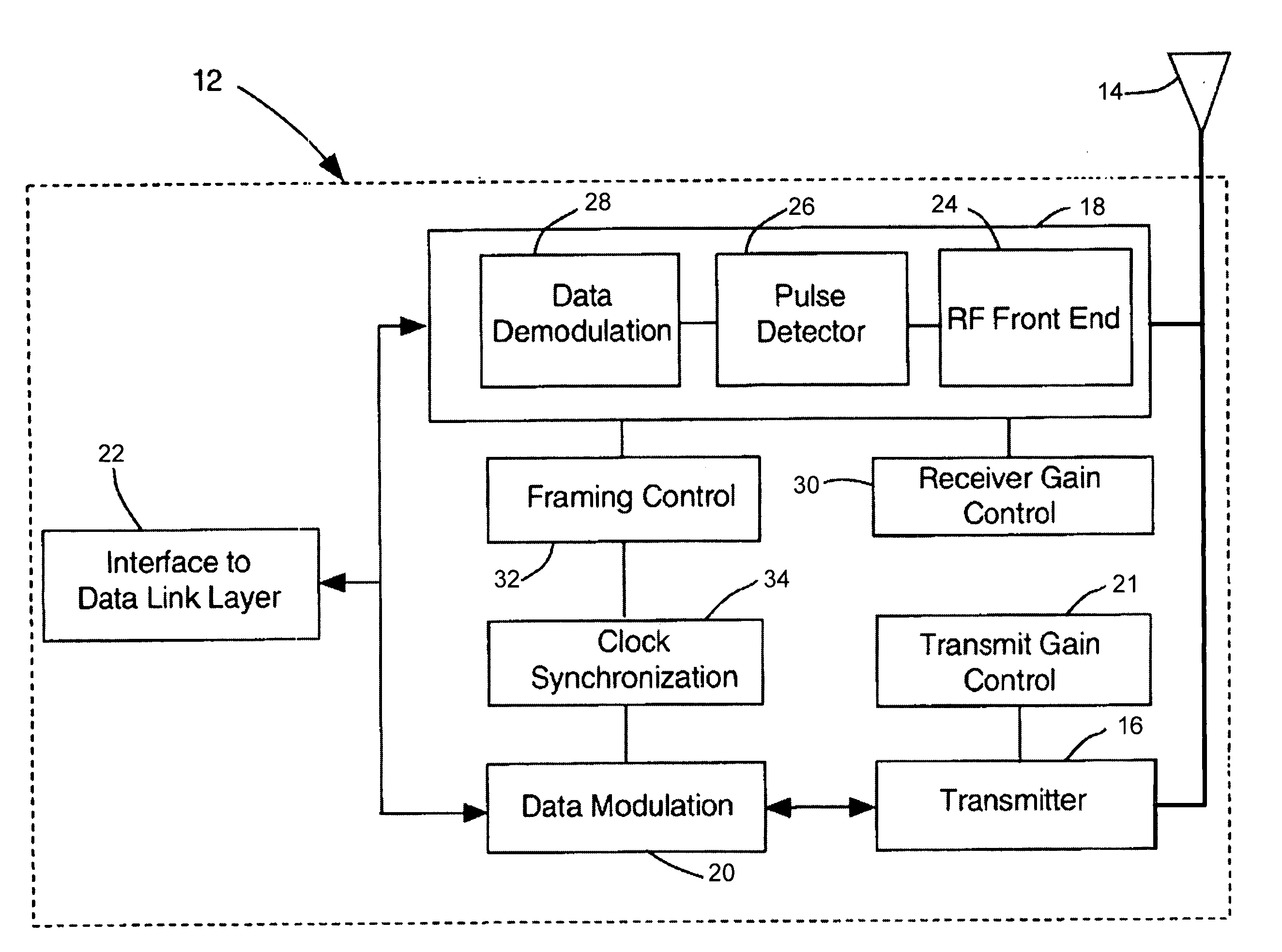
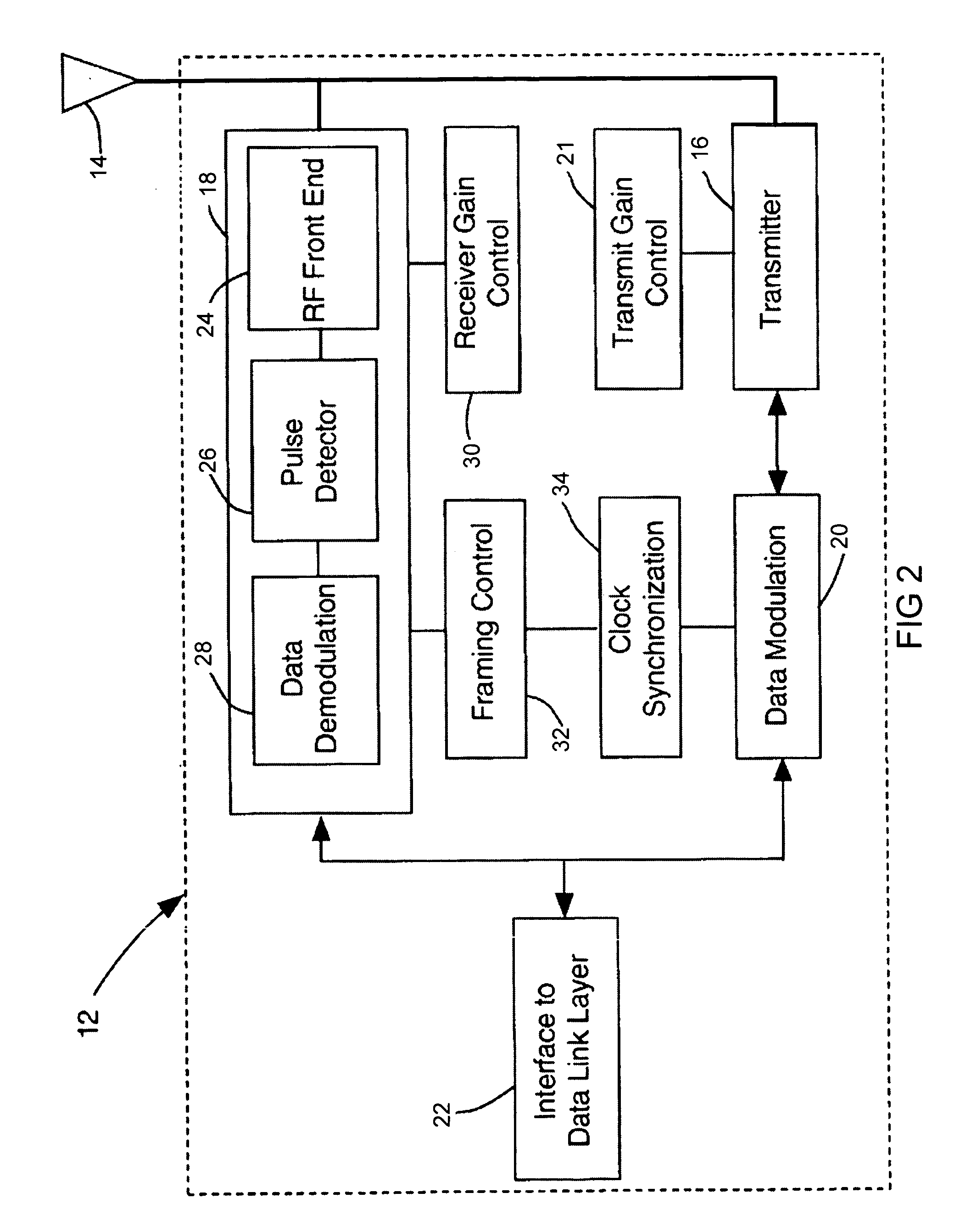
The present invention describes a network communication system which includes a first slave transceiver configured to communicate a plurality of TDMA data packets at different data rates to a second slave transceiver. The second slave transceiver is also configured to communicate a plurality of TDMA data packets at different data rates to the first slave transceiver. A master transceiver manages data communications between the first slave transceiver and the second slave transceiver. Each transceiver includes a data modulation unit, a transmitter, an antenna, and a receiver. The data modulation unit is configured to generate a plurality of signals having variable pulse repetition frequencies and different modulation techniques. The transmitter is coupled to the data modulation unit and the transmitter is configured to generate a pulse stream according to the data modulation unit. The transmitting antenna is coupled to the transmitter and the transmitting antenna is configured to transmit a plurality of ultra wide band base band signals. The receiver is configured to detect and demodulate said ultra wide band base band signals operating at variable pulse repetition frequencies and having different modulation methods.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HOLDING 81 LLC
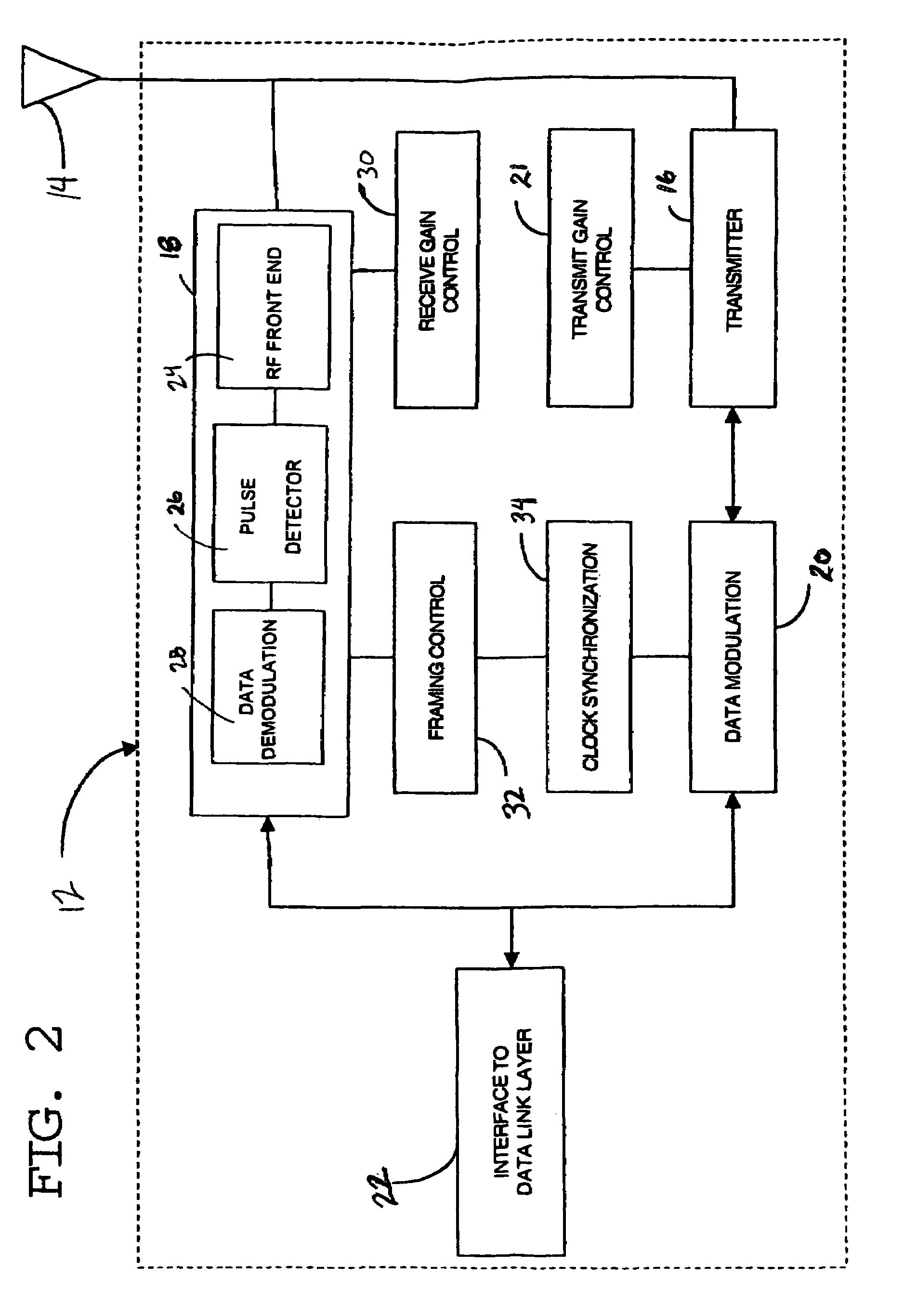
Ultra-wideband receiver and transmitter
InactiveUS7209523B1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsPulse demodulatorExtensibilityBandpass filtering
A waveform-adaptive ultra-wideband (UWB) transmitter and noise-tracking UWB receiver for use in communications, object detection and radar applications. In one embodiment, the output of an oscillator is gated by a low-level impulse generator either directly or through an optional filter. In a special case of that embodiment wherein the oscillator is zero frequency and outputs a DC bias, a low-level impulse generator impulse-excites a bandpass filter to produce an UWB signal having an adjustable center frequency and desired bandwidth based on a characteristic of the filter. In another embodiment, the low-level impulse signal is approximated by a time-gated continuous-wave oscillator to produce an extremely wide bandwidth pulse with deterministic center frequency and bandwidth characteristics. The low-level impulse signal can be generated digitally. The UWB signal may be modulated to carry data, or may be used in object detection or ranging applications. The power amplifier may be gated to provide a power-efficient UWB transmitter. The UWB transmitter exhibits well defined and controllable spectral characteristics. The UWB transmitter is capable of extremely high pulse repetition frequencies (PRFs) and data rates in the hundreds of megabits per second or more, frequency agility on a pulse-to-pulse basis allowing frequency hopping if desired, and extensibility from below HF to millimeter wave frequencies.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
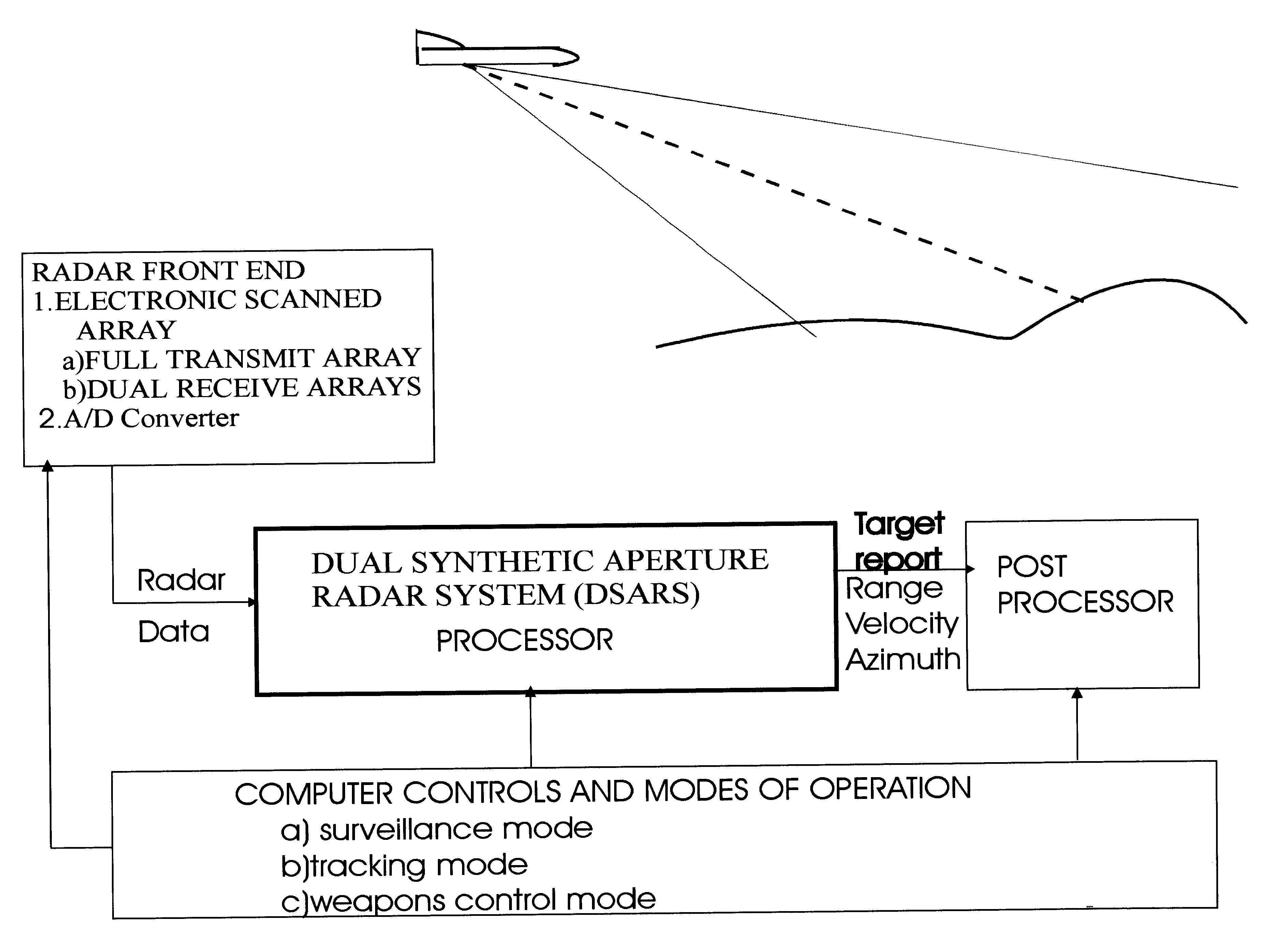
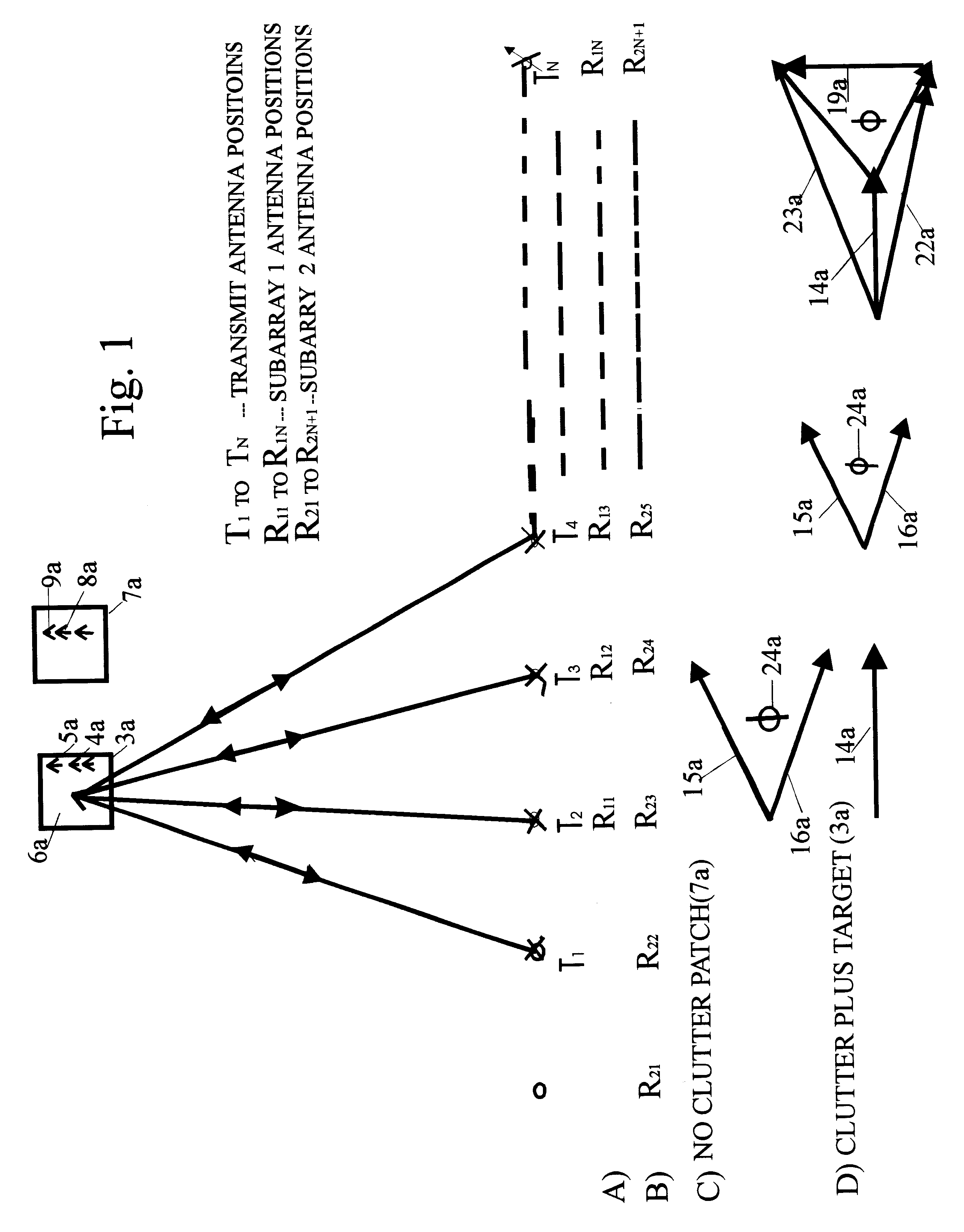
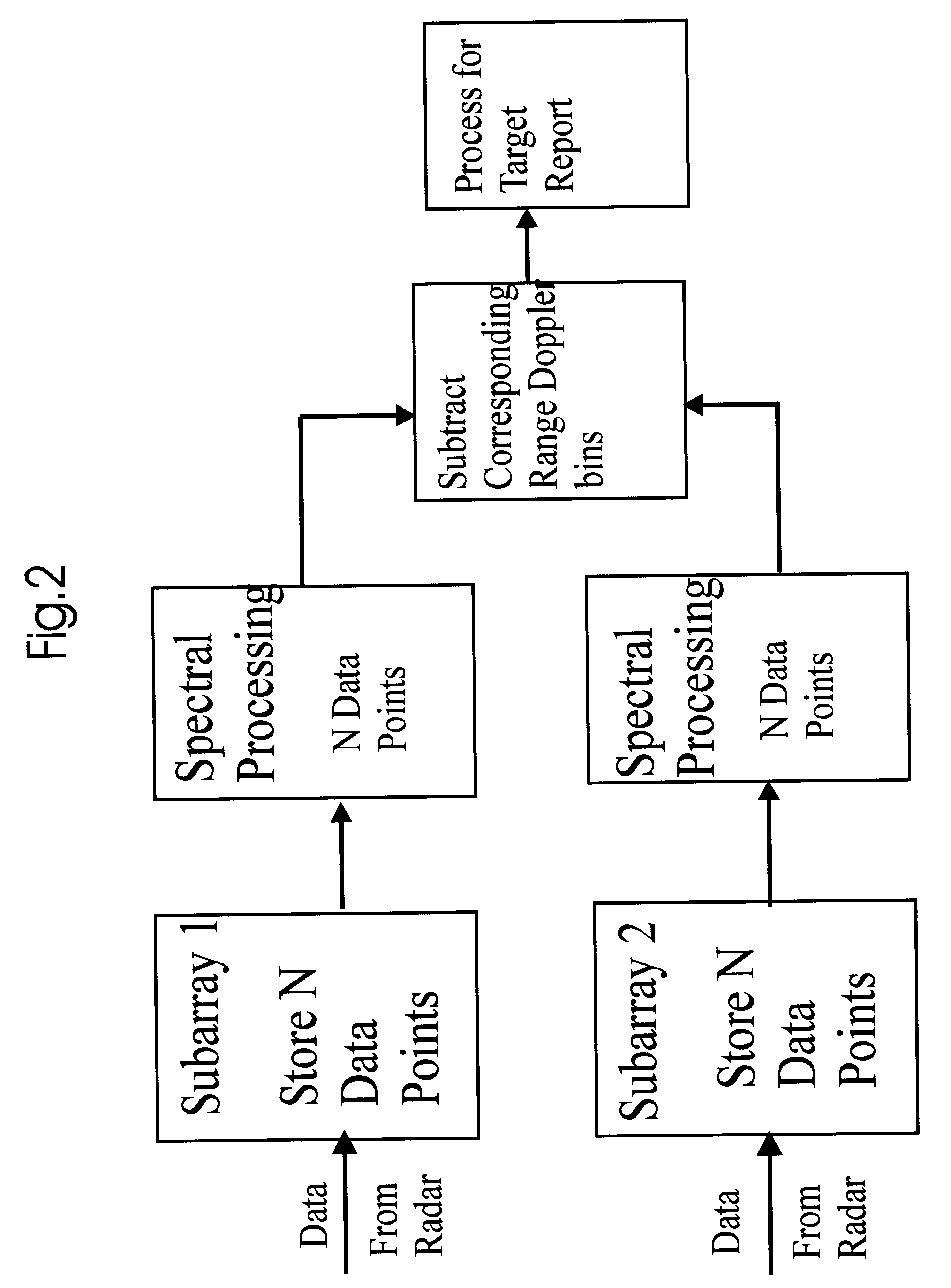
Dual synthetic aperture radar system
InactiveUS6633253B2Accurate angular positionAccurately radial velocityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFrequency spectrumControl system
The dual synthetic aperture array system processes returns from the receiving arrays. The two identical receiving arrays employing displaced phase center antenna techniques subtract the corresponding spectrally processed data to cancel clutter. It is further processed that a moving target is detected and its velocity, angular position and range is measured, in or out of the presence of clutter. There are many techniques presented in the disclosure. These techniques are basically independent but are related based on common set of fundamental set of mathematical equations, understanding of radar principles and the implementations involved. These many techniques may be employed singly and / or in combination depending on the application and accuracy required. They are supported by a system that includes, optimization of the number of apertures, pulse repetition frequencies, DPCA techniques to cancel clutter, adaptive techniques to cancel clutter, motion compensation, weighting function for clutter and target, and controlling the system in most optimum fashion to attain the objective of the disclosure.< / PTEXT>
Owner:CATALDO THOMAS J
Frequency Control of Despeckling
InactiveUS20130021586A1Speckle reductionProjectorsColor television detailsStimulate raman scatteringOptoelectronics
A method and apparatus that reduces laser speckle by using stimulated Raman scattering in an optical fiber. The pulse repetition frequency of the laser is adjusted to control aspects of the laser light such as color or despeckling. In DLP projection systems, an optical monitor may be used to send information to a bit sequence, and the bit sequence may control the pulse repetition frequency of the laser based on the optical monitor signal.
Owner:PROJECTION VENTURES INC
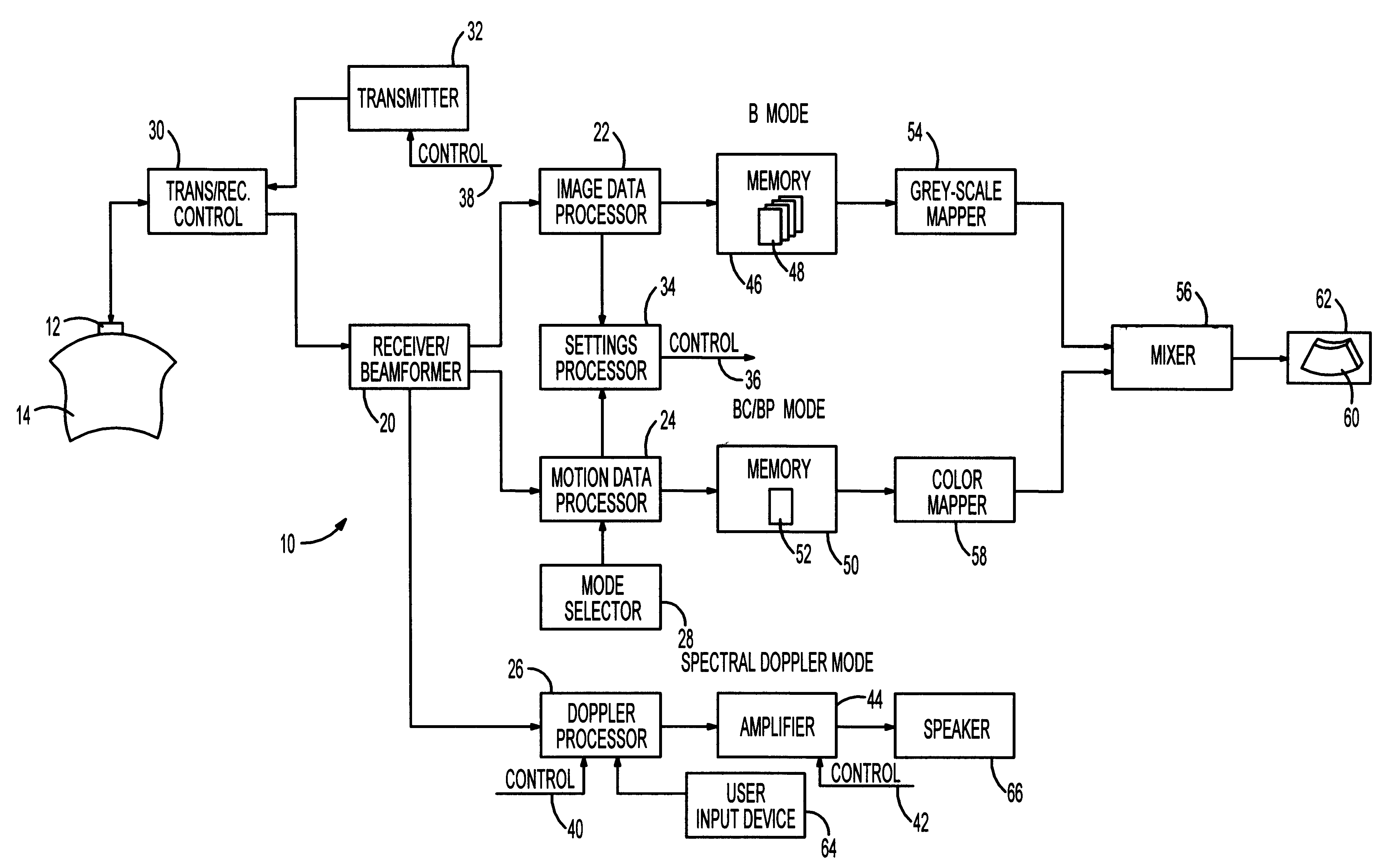
Method and system for pre-determining spectral doppler user parameters
InactiveUS6176830B1Blood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationFrequency spectrum
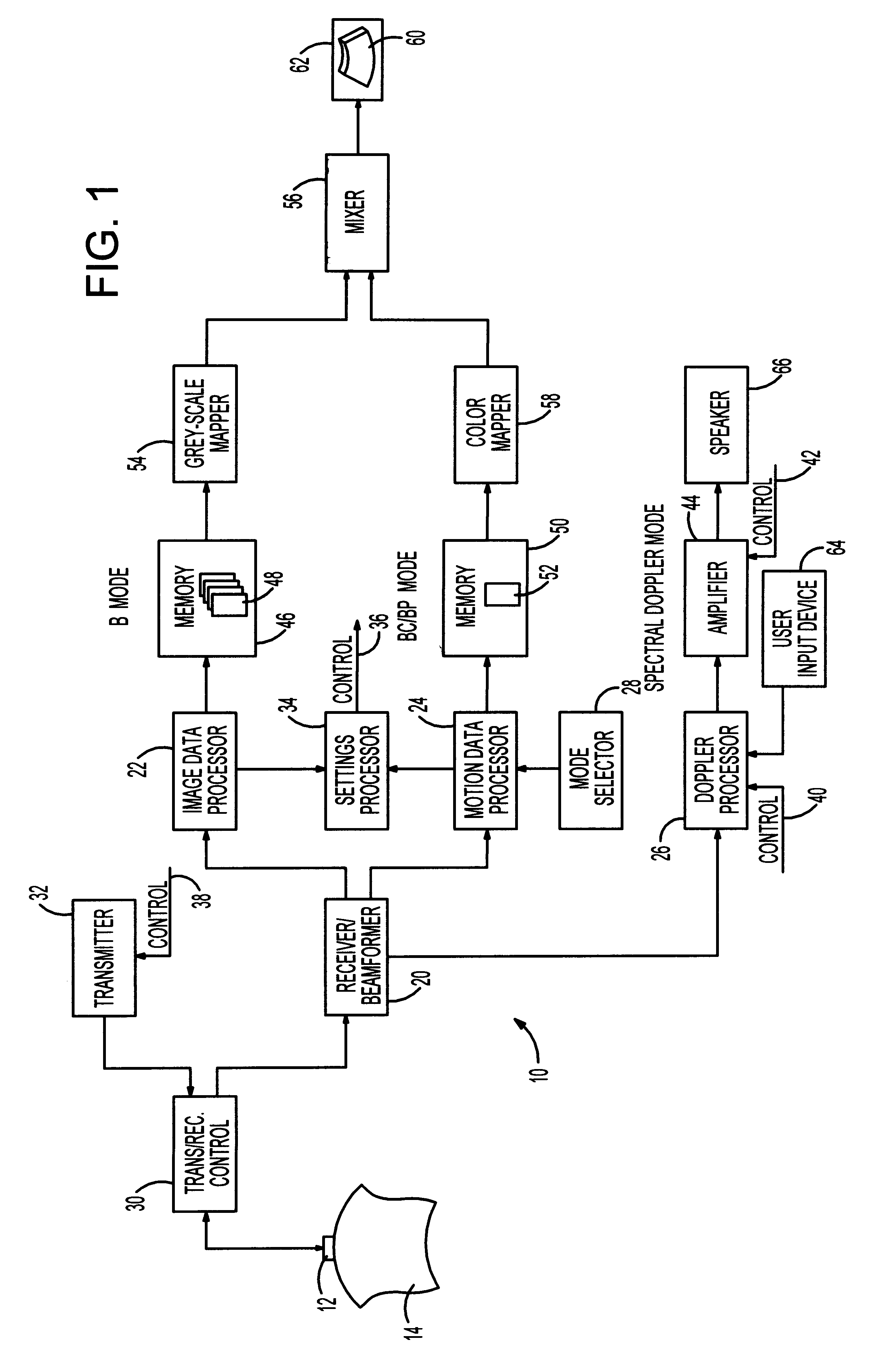
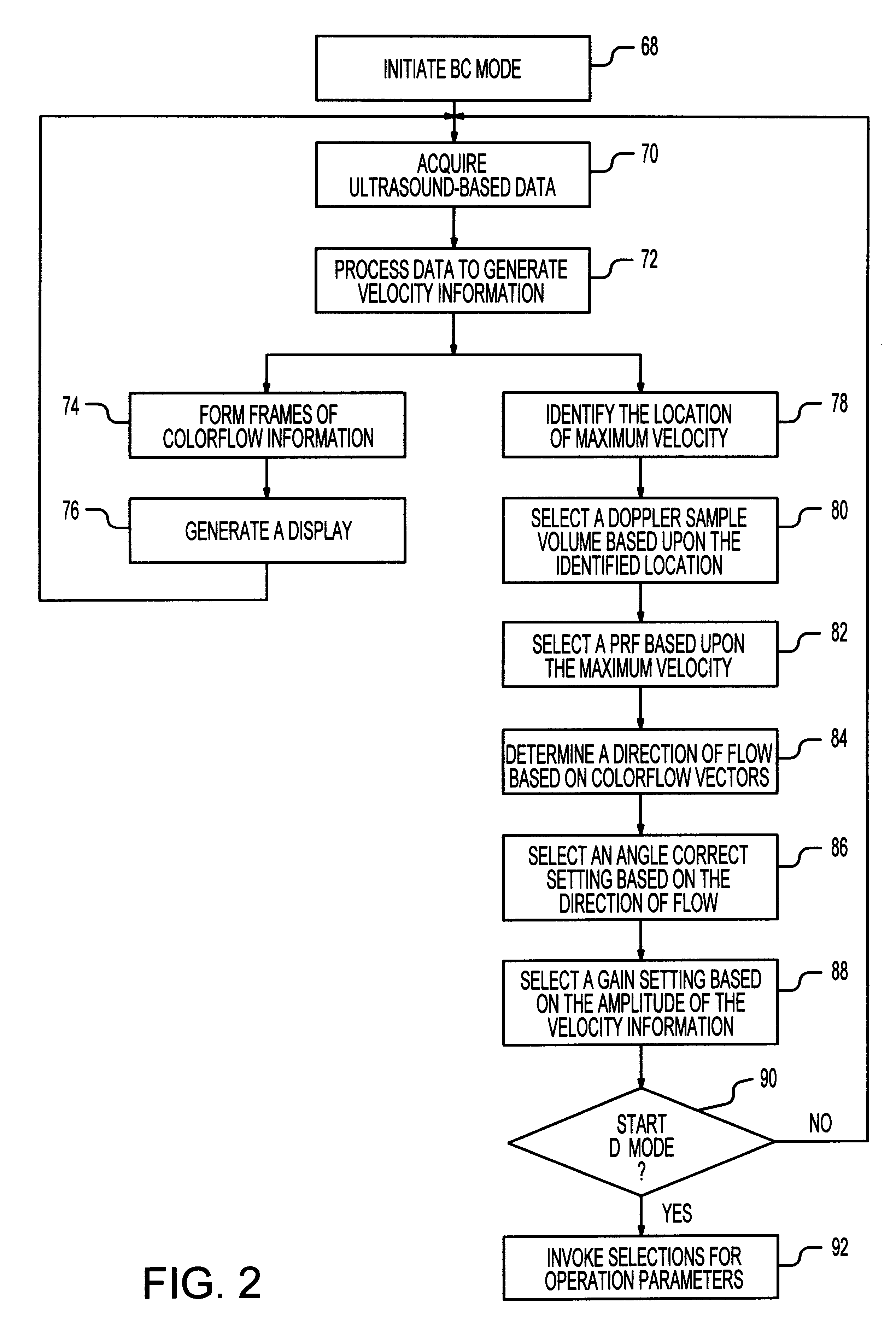
A method of initializing a spectral Doppler mode of operation for an ultrasonic system includes acquiring ultrasound-based data during a two-dimensional mode of operation for a particular examination session and includes automatically establishing settings for the Doppler mode operation parameters based upon the ultrasound-based data. That is, the ultrasound-based data is processed during the session to select spectral Doppler mode settings that are specific to the ongoing session. The session-specific settings are invoked when the system is switched to the spectral Doppler mode. If the two-dimensional mode is a colorflow mode, the Doppler sample volume can be based upon detecting the location of maximum velocity in the colorflow image, the angle correct setting can be based upon maximum velocities in colorflow vectors, the pulse repetition frequency setting can be based upon the maximum frequency shift detected in the colorflow data, and the gain setting can be based upon the amplitude of colorflow data. On the other hand, if the two-dimensional mode is a power mode, the Doppler sample volume is based upon detecting the region of the power mode image having the strongest signals, the angle correct setting can be based upon detecting the direction of flow, the Doppler pulse repetition frequency can be based upon a scale setting for the power mode data acquisition, and a gain setting can be based upon the amplitude of power mode data. Lastly, if the two-dimensional mode is the grey-scale imaging mode, the selection of a Doppler sample volume can be based upon identifying a dark region near the center of the grey-scale image, the angle correct setting can be based upon the orientation of the boundaries of the identified dark region, and the gain setting can be based upon the amplitude of image data.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Ultra wide band communication systems and methods
InactiveUS20050018762A1Easy to makeLow costEnergy efficient ICTMultiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsTransceiverTime division multiple access
Ultra wide band communication systems and methods are provided. In one embodiment, an ultra wide band communication system includes a first and a second communication device. A lowest common ultra wide band pulse repetition frequency is determined, and data is transmitted between the communication devices using the lowest common ultra wide band pulse repetition frequency. In another embodiment, a first and second slave transceiver communicate with a master transceiver using a time division multiple access frame, with the master transceiver providing transmission synchronization. This Abstract is provided for the sole purpose of complying with the Abstract requirement rules that allow a reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the disclosure contained herein. This Abstract is submitted with the explicit understanding that it will not be used to interpret or to limit the scope or the meaning of the claims.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HOLDING 81 LLC
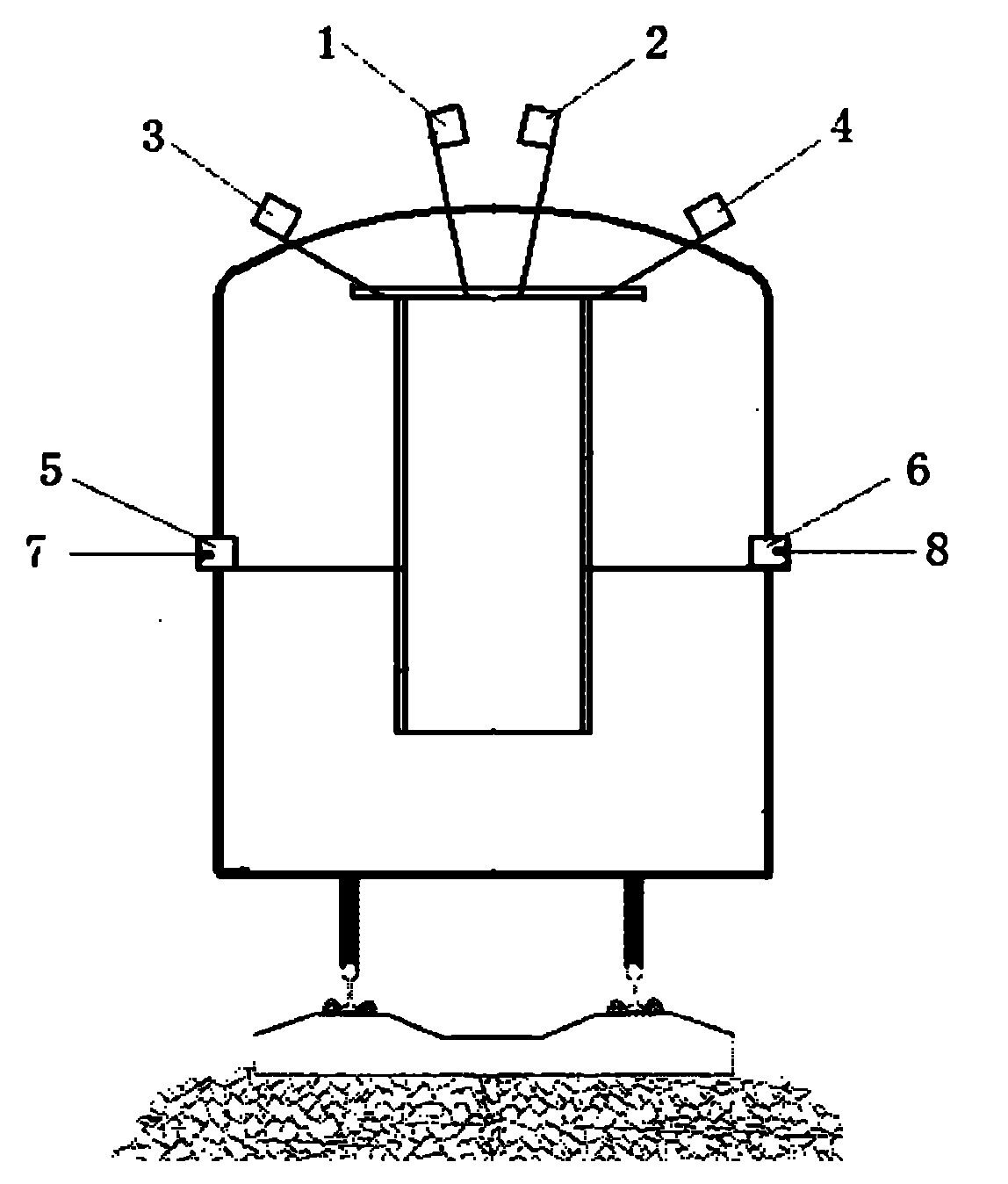
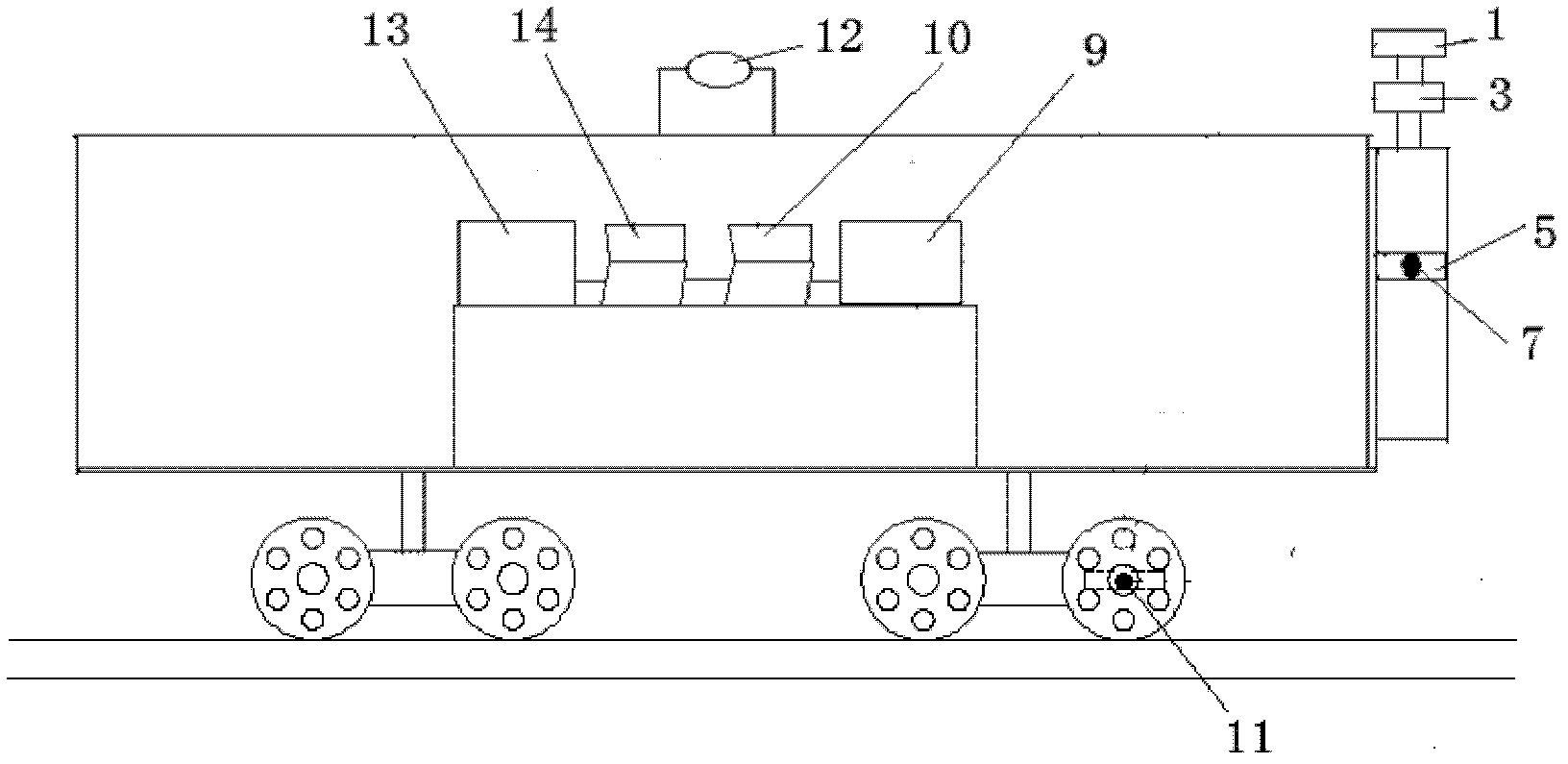
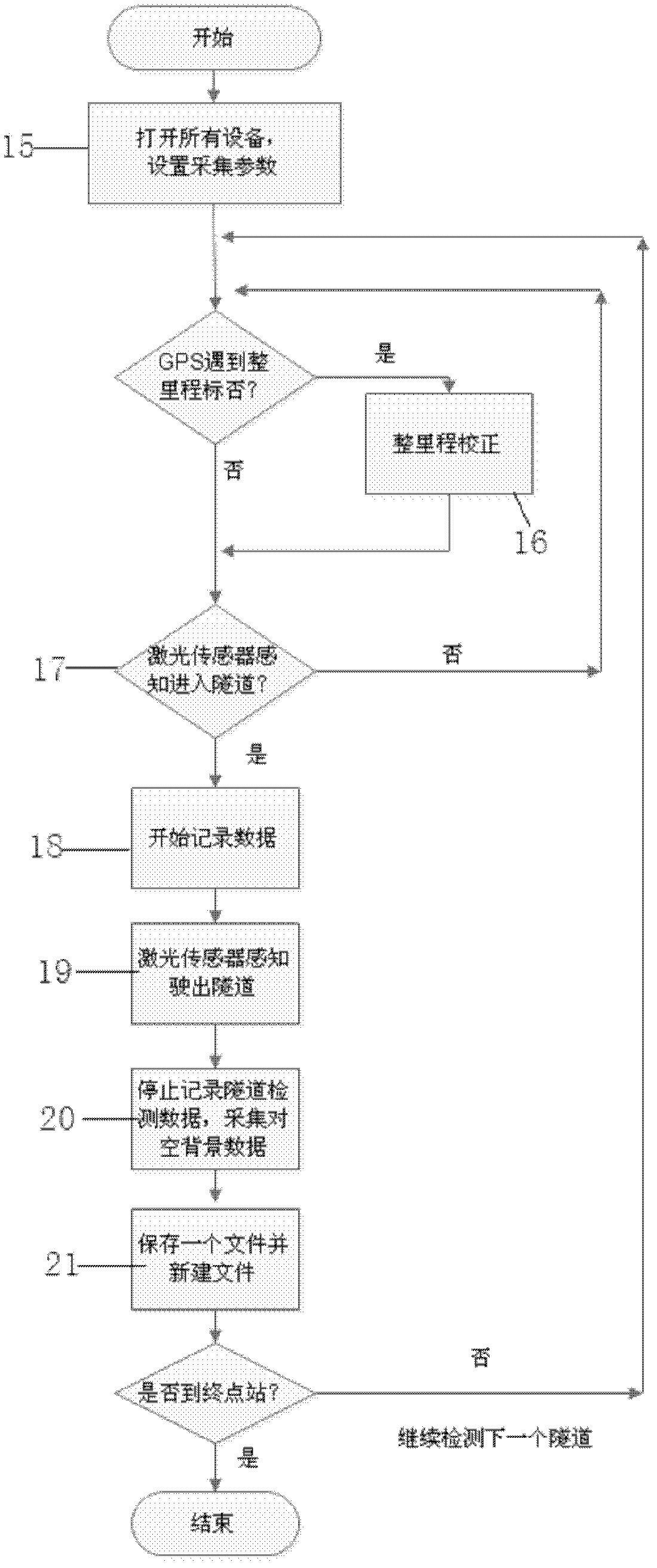
Full-face vehicular detection method for railway tunnel lining and device
ActiveCN102607477ARealize collection automationReduce data storageUsing wave/particle radiation meansMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionFace detectionRailway tunnel
A full-face vehicular detection method for a railway tunnel lining and a device aim to avoid collision of ground penetrating radar antennas with an overhead line system and a support of the overhead line system, the detection speed is a normal running speed of a train, the antennas in full-face detection are not interfered with each other, automatic positioning is realized during detection, only ground penetrating radar signals in a tunnel need to be acquired, and a penetrating radar signal processing and analyzing method in tunnel detection is modified. The vehicular device comprises a six-channel high-speed scanning penetrating radar, a positioning portion, a laser ranging portion and data acquisition and processing software. The pulse repetition frequency of the ground penetrating radar is 3MHz, the pulse repetition frequency of each channel is 500kHz, and the scanning rate is 976scan / s. The ground penetrating radar is provided with TEM (transverse electric and magnetic field) short-horn air coupled antennas, each group of antennas realizes a double-transmission and single-receiving function, and the center frequency of the antennas is 300MHz. The ground penetrating radar antennas are mounted outside passenger train connectors, radiation surfaces of the antennas respectively face to an arch crown, arch springing and side walls, and the full-face vehicular detection method and the device are used for automatically detecting to exam the railway tunnel lining.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Scanning Non-Scanning LIDAR
ActiveUS20130044309A1Optical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationOptoelectronicsVisual perception
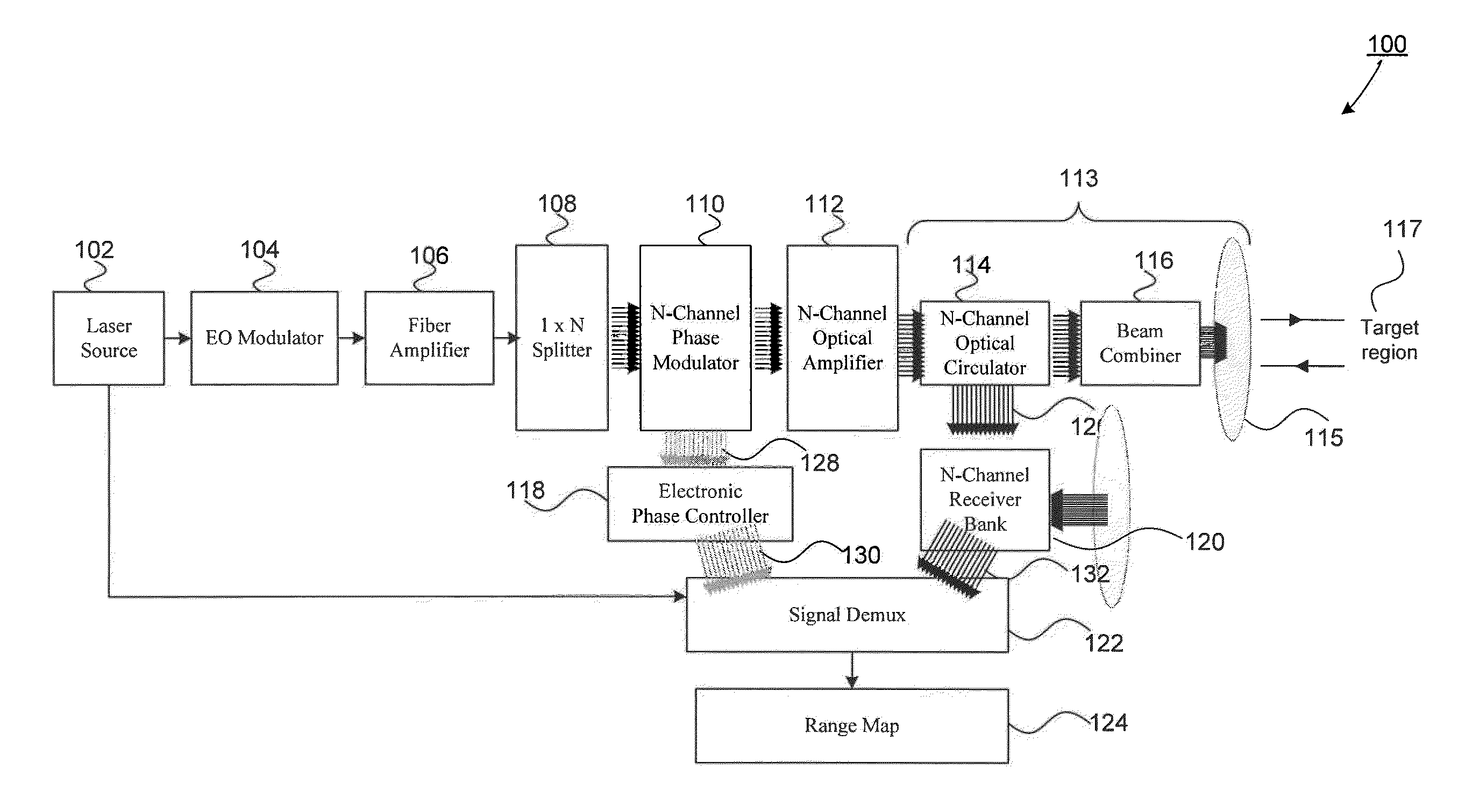
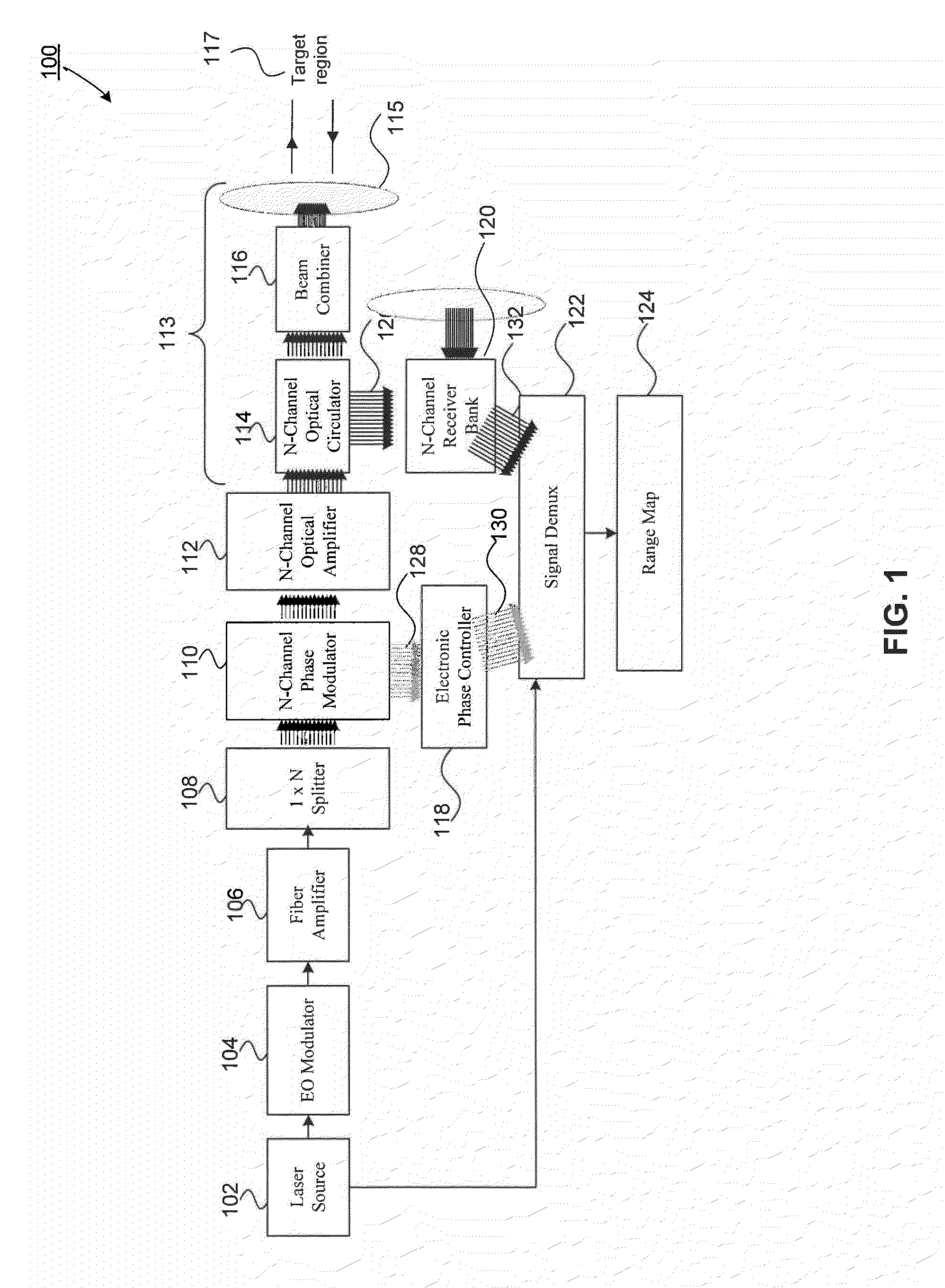
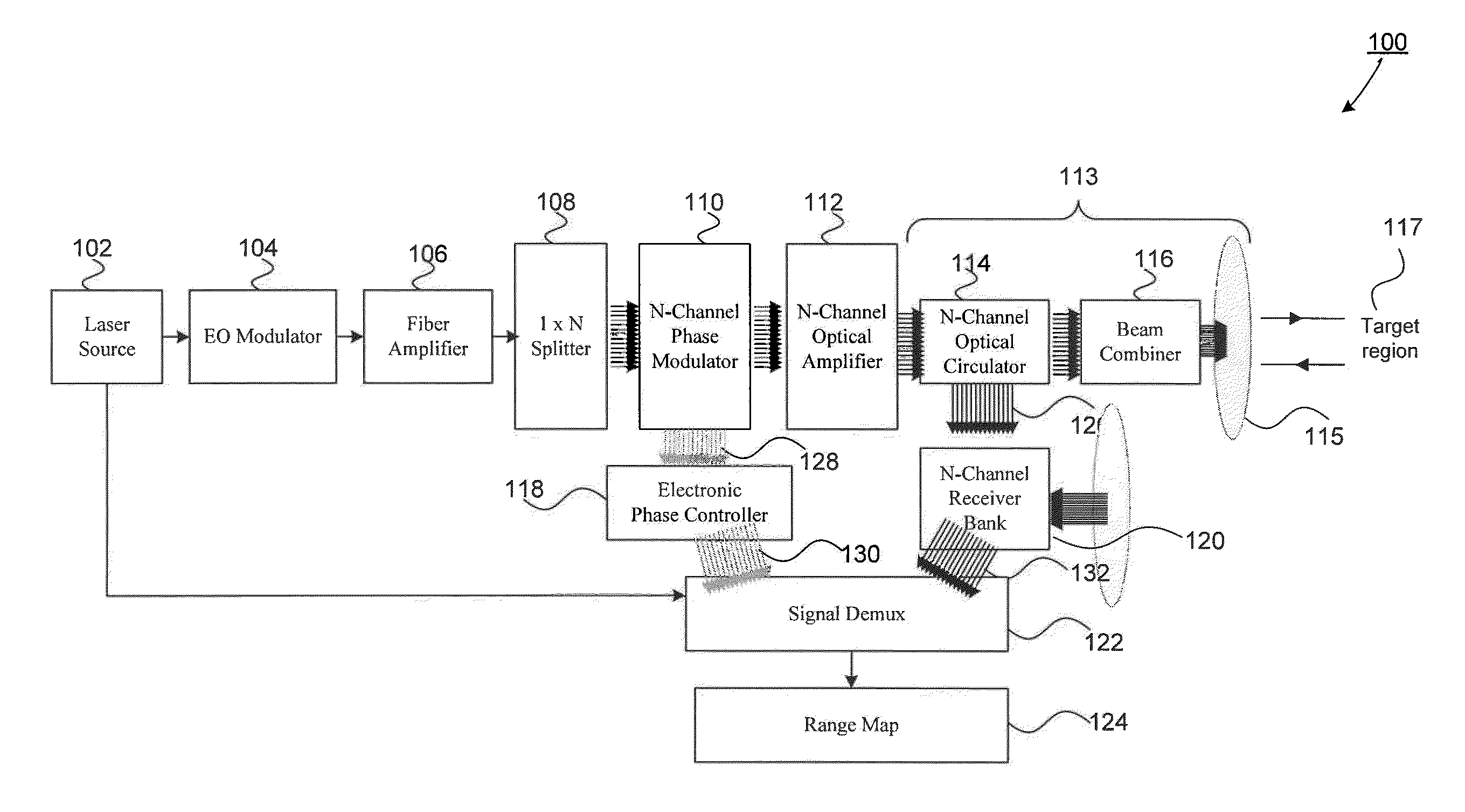
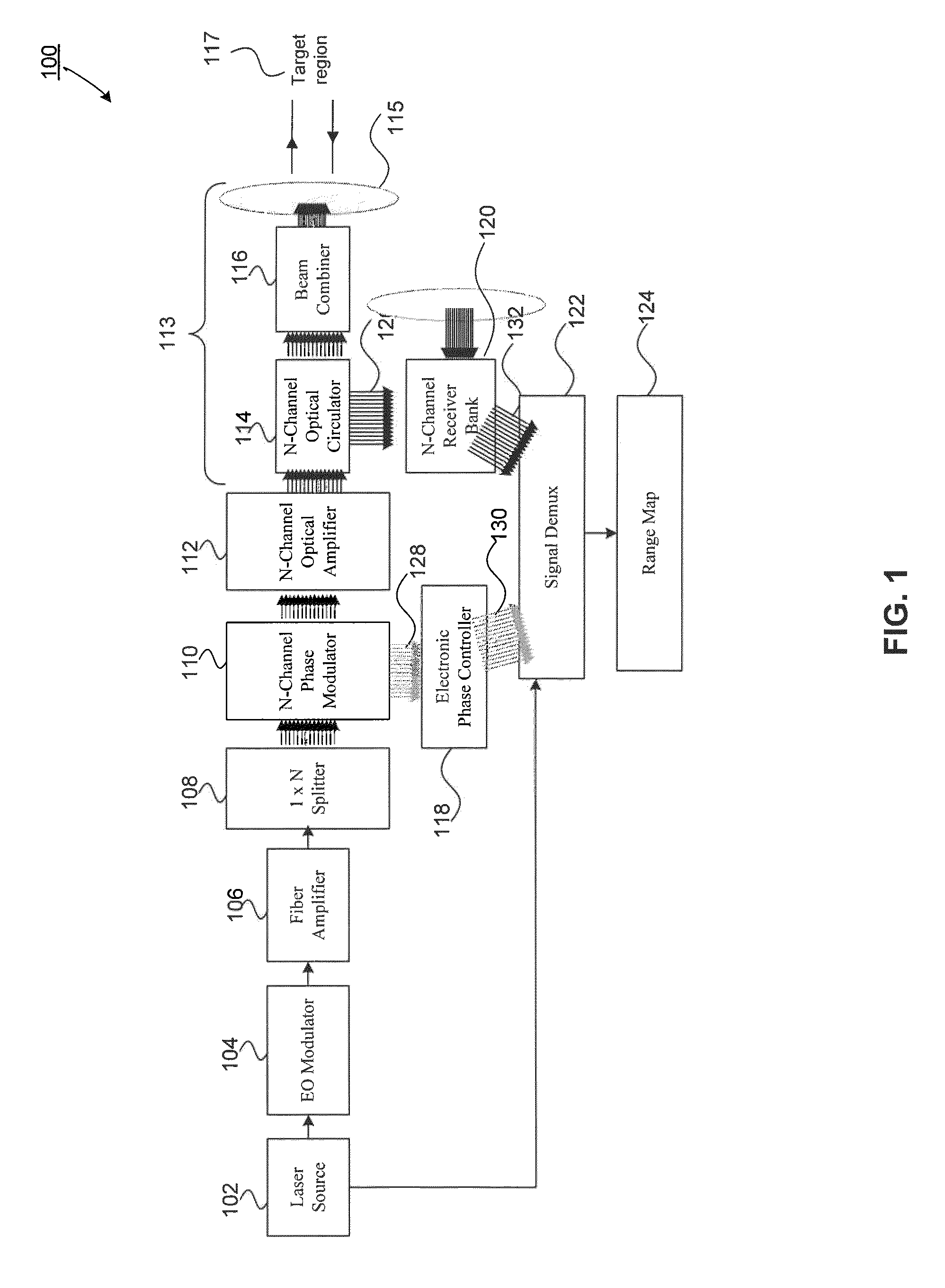
An all fiber optic laser based scanning system for real time terrain mapping under degraded visual conditions is disclosed. A laser output is modulated to achieve a desired pulse width and pulse repetition frequency (PRF) and the modulated signal is amplified. The amplified optical signals are split into N channels that correspond to N elements of an optically phased array that steers light by modulating the phase of light entering and exiting the optical system. By applying a linear phase shift across the beam's wave front, the light propagating along the system's optical axis is steered to an off-axis angle. A real time map of an underlying terrain is accomplished by sweeping the N channel array across the terrain while collecting range information from each scan grid.
Owner:RD2 LLC
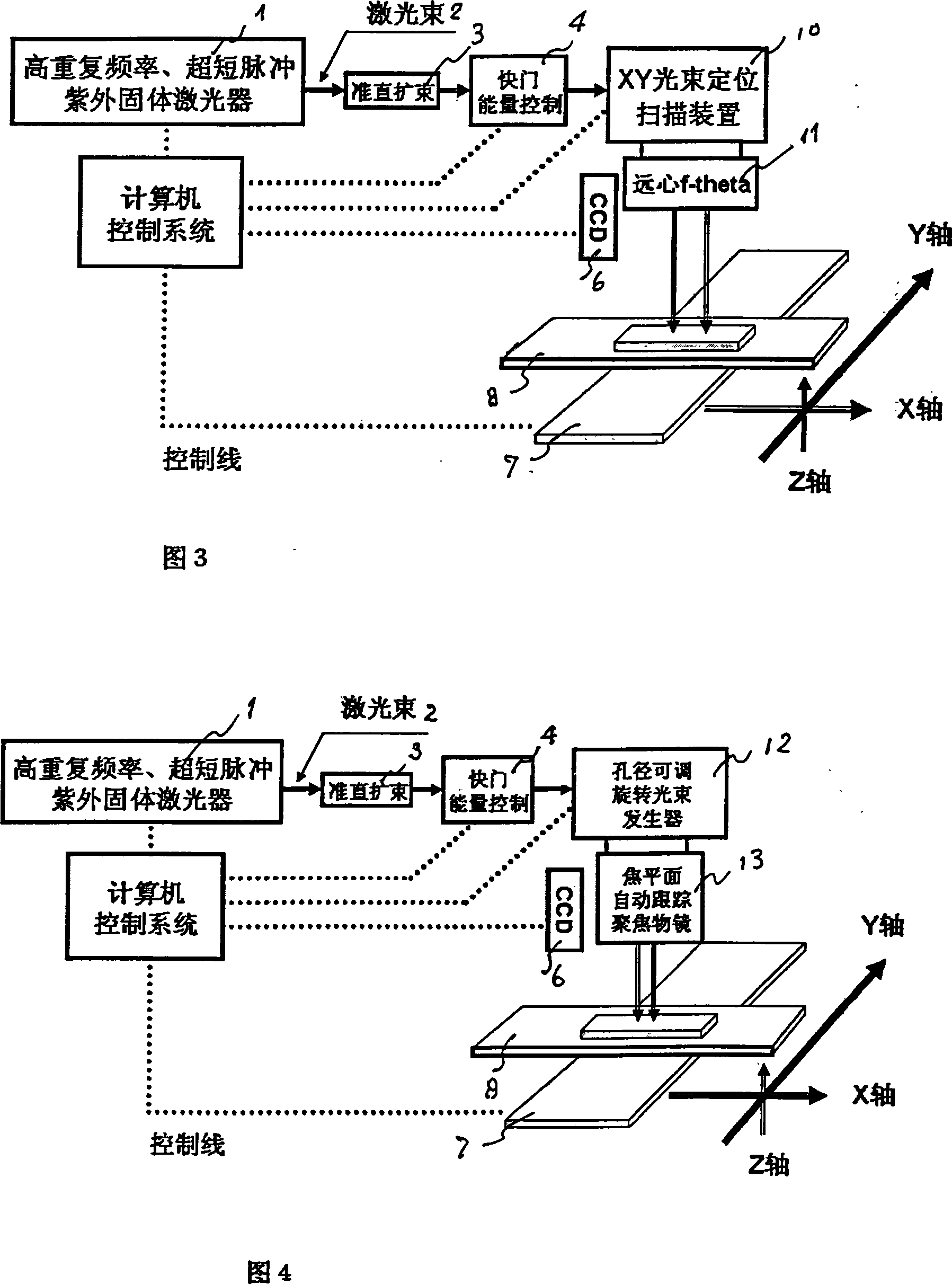
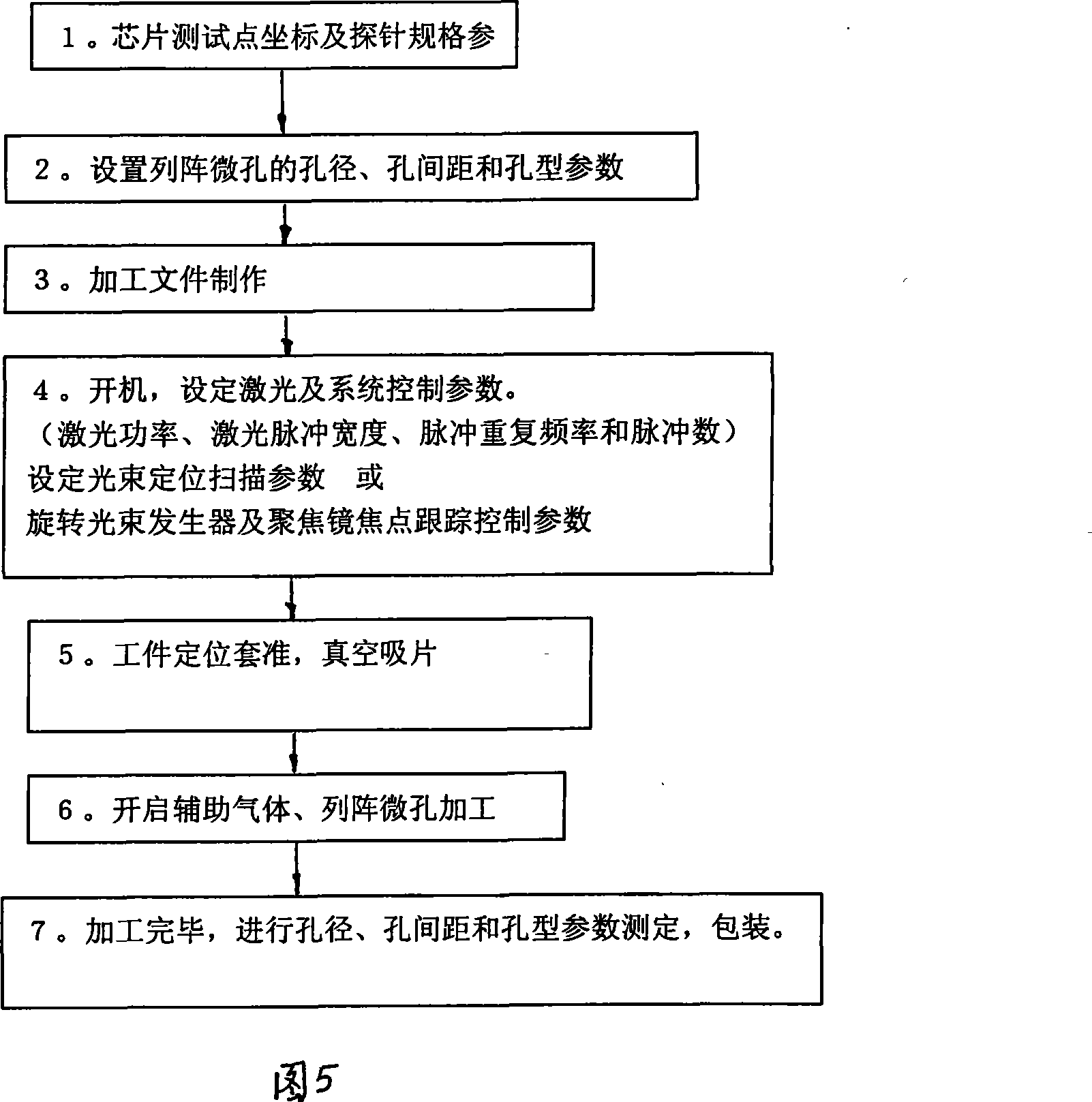
Laser array micro-pore forming device and method
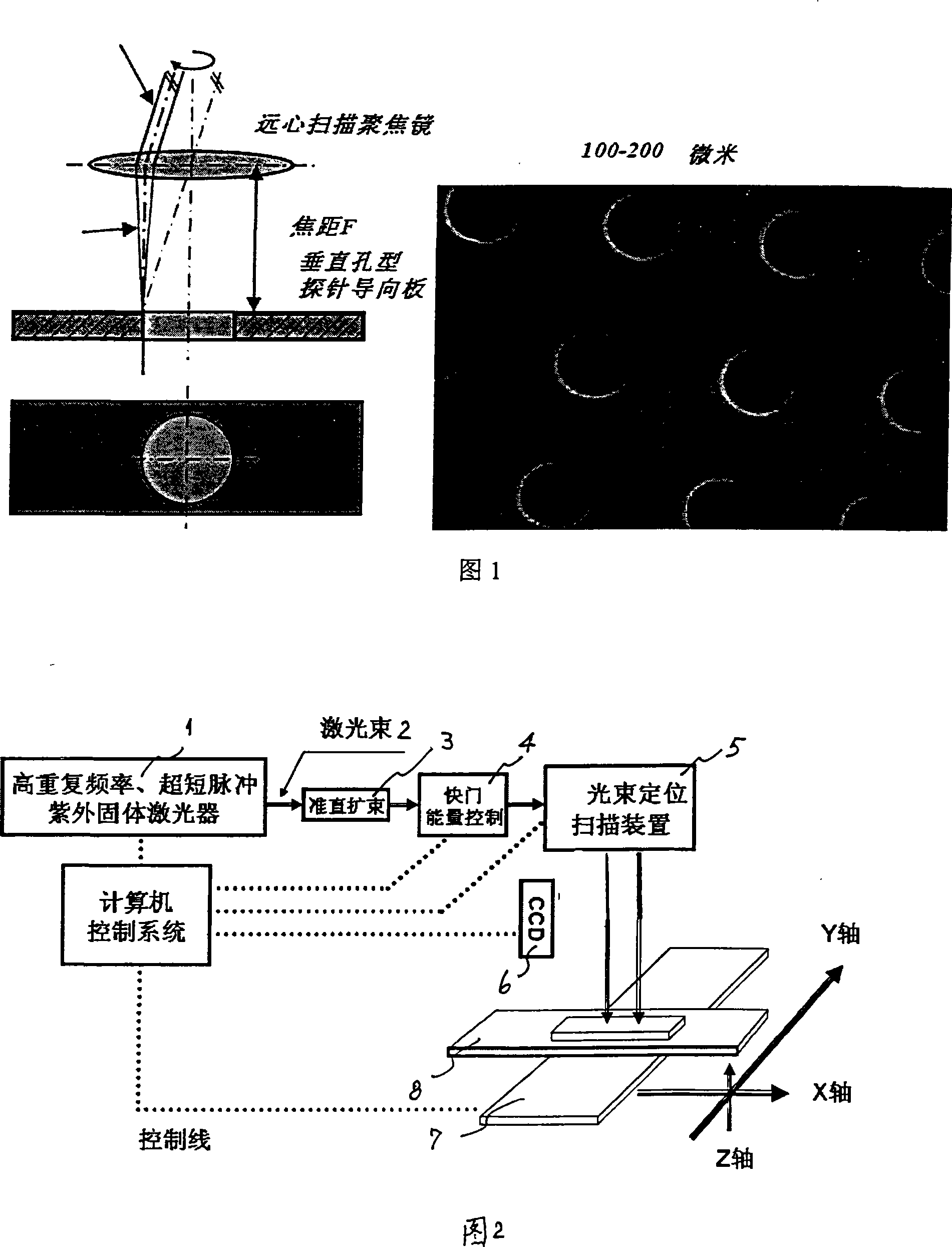
The invention discloses laser-array pore molding devices and a method. The steps of the invention includes that, firstly, pore diameter, pore distance and caliber parameter of a pore plate are set, and a processing file is produced, secondly, laser power, pulse width, pulse repetition frequency and pulse count are set, thirdly, the parameter of light beam location scanning is set, fourthly, work-pieces are located, a visual system is located, and vacuum negative pressure absorbs a probe guide plate, fifthly, pressure and flow capacity of opening assistant gas are set, the processing is started, finally, the pore diameter, the pore distance and the caliber parameter are measured after the finishing of the processing. The laser-array pore molding devices include an ultraviolet solid laser with high repetition rate and ultrashort pulse, a laser beam generator, a collimation beam-expanding device, a shutter, a light beam location scanning device, a CCD visual location system, an XYZ displacement working platform, and a vacuum negative pressure absorbing-sheet frame. The invention has the advantages that the disadvantages of low efficiency, easy damage of a 'punch', changeable pore diameter and the like which exit in the present mechanical punching manner are overcome, dynamic digital hologram is directly pressed on the surface of the material of noble metal commemorative coins, thereby ensuring the esthetics of the commemorative coins.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF LASER TECH
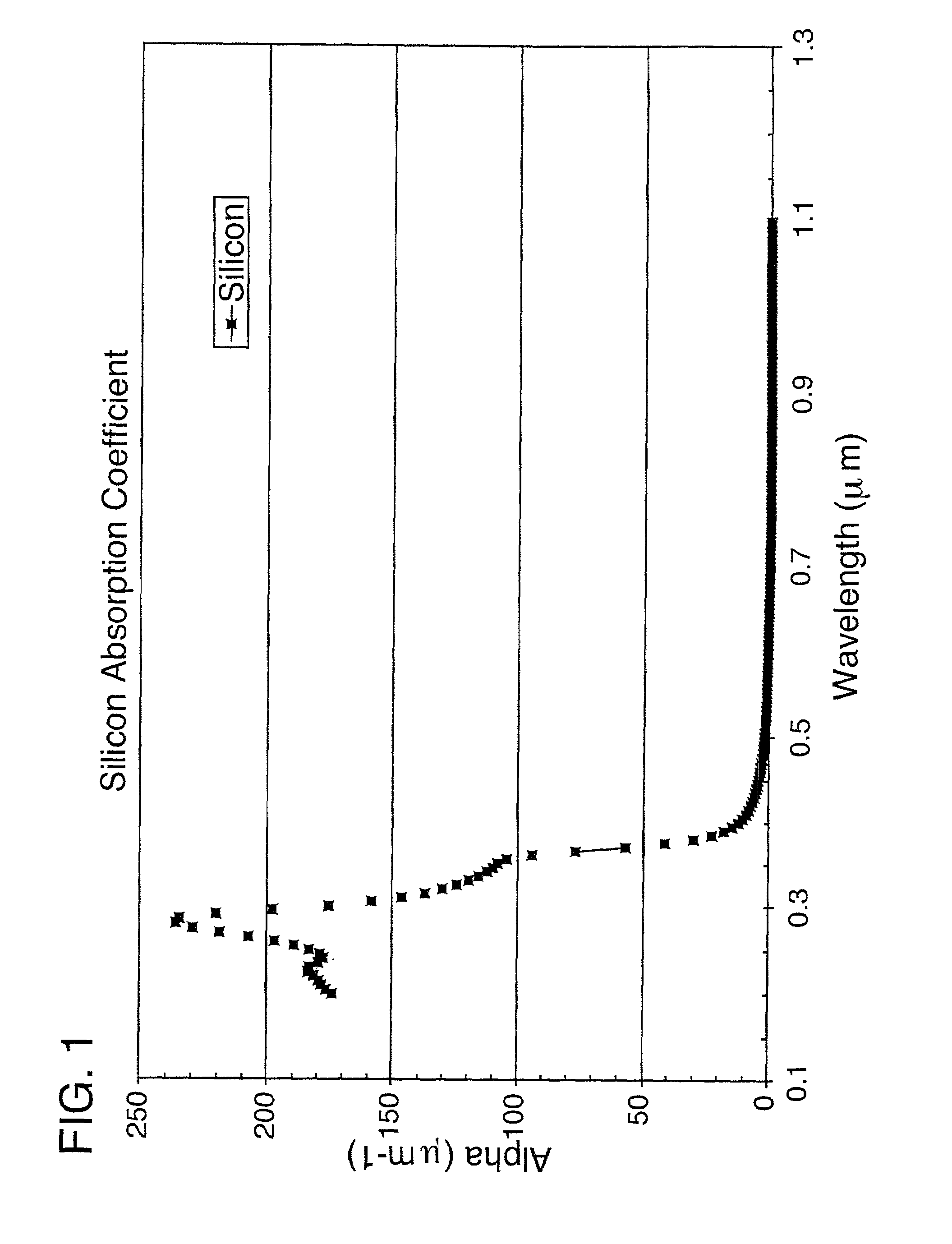
Ultraviolet laser ablative patterning of microstructures in semiconductors
InactiveUS7157038B2High aspect ratioGreat depth of focusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesUltravioletSingle crystal
Patterns with feature sizes of less than 50 microns are rapidly formed directly in semiconductors, particularly silicon, GaAs, indium phosphide, or single crystalline sapphire, using ultraviolet laser ablation. These patterns include very high aspect ratio cylindrical through-hole openings for integrated circuit connections; singulation of processed die contained on semiconductor wafers; and microtab cutting to separate microcircuit workpieces from a parent semiconductor wafer. Laser output pulses (32) from a diode-pumped, Q-switched frequency-tripled Nd:YAG, Nd:YVO4, or Nd:YLF is directed to the workpiece (12) with high speed precision using a compound beam positioner. The optical system produces a Gaussian spot size, or top hat beam profile, of about 10 microns. The pulse energy used for high-speed ablative processing of semiconductors using this focused spot size is greater than 200 μJ per pulse at pulse repetition frequencies greater than 5 kHz and preferably above 15 kHz. The laser pulsewidth measured at the full width half-maximum points is preferably less than 80 ns.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Scanning non-scanning LIDAR
An all fiber optic laser based scanning system for real time terrain mapping under degraded visual conditions is disclosed. A laser output is modulated to achieve a desired pulse width and pulse repetition frequency (PRF) and the modulated signal is amplified. The amplified optical signals are split into N channels that correspond to N elements of an optically phased array that steers light by modulating the phase of light entering and exiting the optical system. By applying a linear phase shift across the beam's wave front, the light propagating along the system's optical axis is steered to an off-axis angle. A real time map of an underlying terrain is accomplished by sweeping the N channel array across the terrain while collecting range information from each scan grid.
Owner:RD2 LLC
Quick high-flexibility manufacturing method for ceramic circuit board
ActiveCN103188877AImprove bindingImprove thermal conductivityPrinted circuit manufactureLaser beam welding apparatusChemical platingChemical reaction
A quick high-flexibility manufacturing method for a ceramic circuit board comprises the following steps: irradiating laser on the surface of a ceramic matrix, and controlling the energy density of the laser to reach above the fracture threshold of the chemical bond of the compound containing active ions, so that chemical reaction occurs on the surface of the ceramic matrix, an active substance is separated out to serve as a chemical plating catalytic source, and the active substrate generated by the reaction and the matrix form chemical metallurgical bonding, wherein different laser sources are selected aiming at different ceramic materials according to the chemical bond energy of the ceramic material components, and the laser energy is controlled to reach the ceramic modified threshold by controlling the average power of laser output, pulse repetition frequency, scanning speed, defocusing amount, space between scanning line and scanning times; and the ceramic matrix modified by the laser is placed into a chemical plating solution to perform plating to form a metal coating. The surface of the ceramic is modified by the laser, so that a metal conductive layer and the matrix form chemical metallurgical bonding, the bonding force of the circuit board is greatly increased, and the heat-conducting property and the electric property are improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN SUNSHINE LASER & ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
System for monitoring quality of optical signals having different bit rates
InactiveUS6396601B1Baseband system detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsSignal qualityTime segment
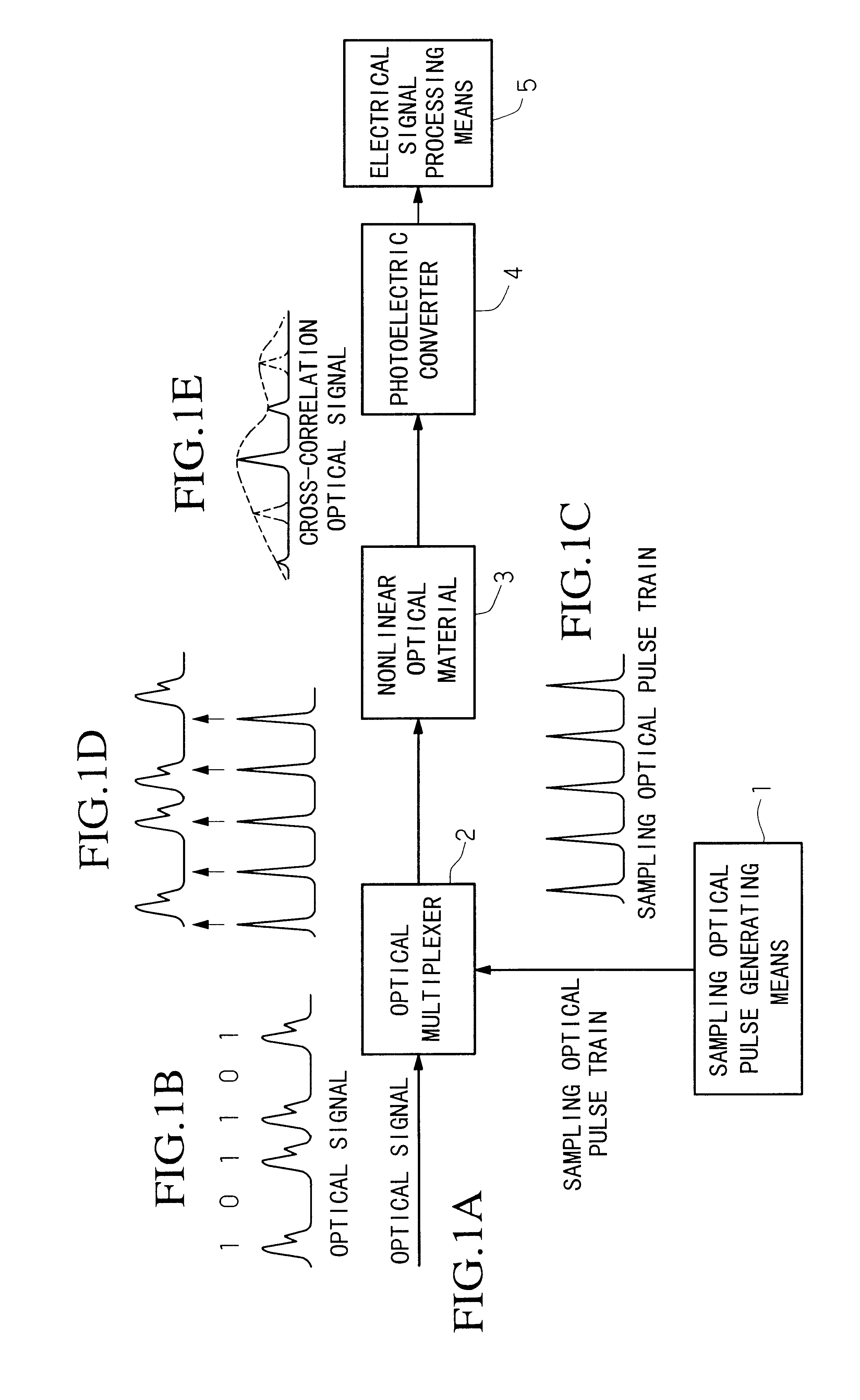
An optical signal quality monitoring system is provided, by which the quality of optical signals can be examined using a single monitoring system, not depending on the bit rate of each signal. In the system, an optical signal having a bit rate N.f0, that is, N times as much as basic clock frequency f0, is sampled by using a pulse repetition frequency f0 / n1-DELTAf or f0 / n1+DELTAf where n1 is a predetermined natural number and the pulse repetition frequency slightly differs from f0 / n1 by DELTAf, and an amplitude histogram of the optical signal is determined based on results of the sampling. Regarding the sampling points which constitute the histogram, a set of higher-level points and a set of lower-level points are extracted and a ratio of a difference between an average level of the set of higher-level points within a predetermined period and an average level of the set of lower-level points within a predetermined period, to the sum of standard deviations of both sets within each predetermined period is calculated as a coefficient of the S / N, and the quality of the optical signal is examined based on the coefficient. By performing optical sampling, quality of optical signals having bit rates of a few dozen Gbit / s or more can be monitored.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
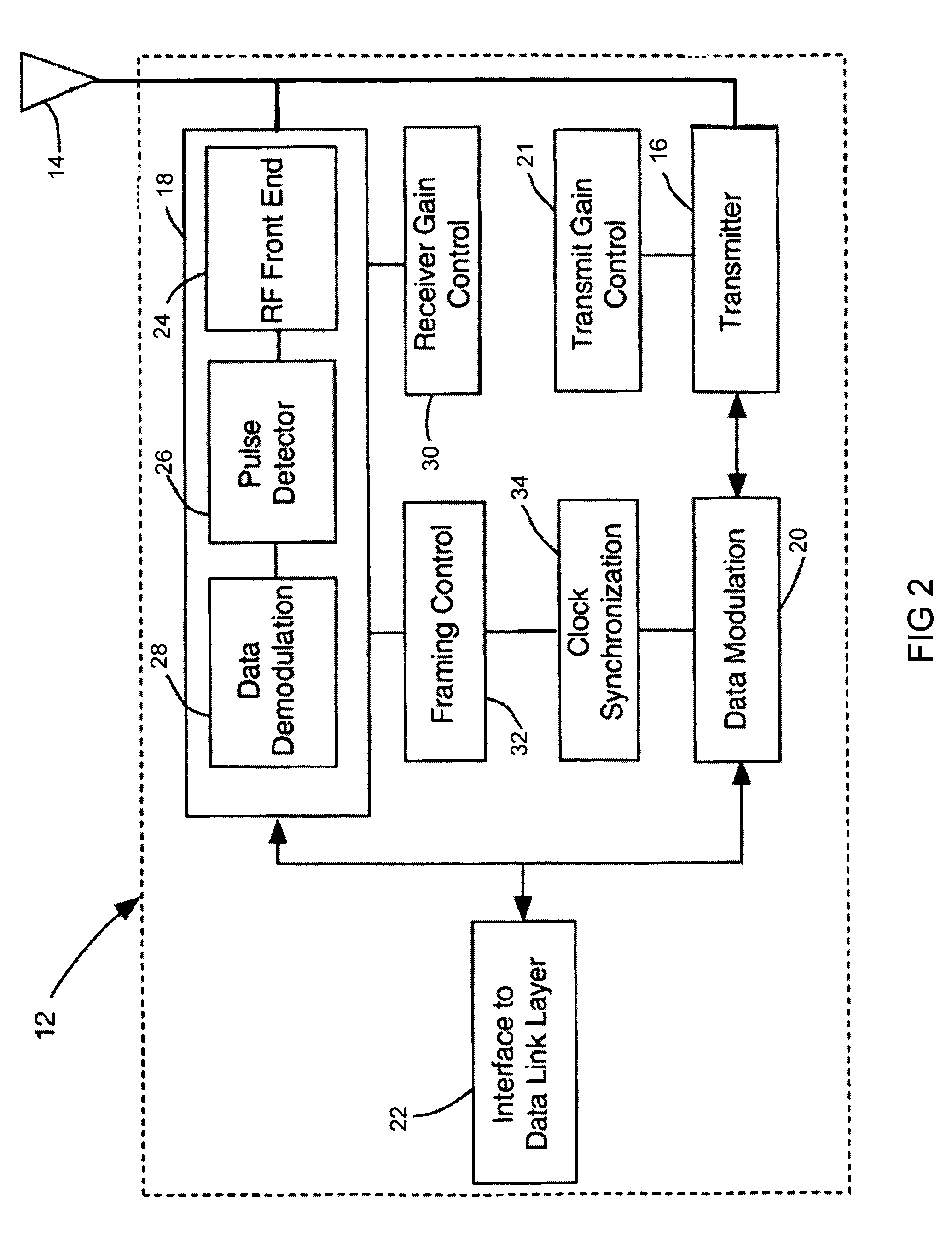
Ultra wide band base band receiver
InactiveUS7088795B1Easy to makeLow costEnergy efficient ICTMultiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsRF front endTransceiver
The present invention is a receiver having a radio frequency (RF) front end, a pulse detector operatively coupled to the RF front end, and a data recovery unit operatively coupled to the pulse detector. The data recovery unit is configured to receive spread spectrum RF signals having different pulse repetition frequencies and using different modulation techniques. The receiver may operate in conjunction with a transmitter as a transceiver. The receiver may also operate in a networked environment in which a network of transceiver node devices comprise a first slave transceiver having a receiver configured to receive spread spectrum signals, and a second slave transceiver configured to communicate with the first slave transceiver. Additionally, a master transceiver is in communication with the first slave transceiver and the second slave transceiver. The master transceiver is configured to manage data transmissions and synchronization between the first slave transceiver and the second slave transceiver.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HLDG 73
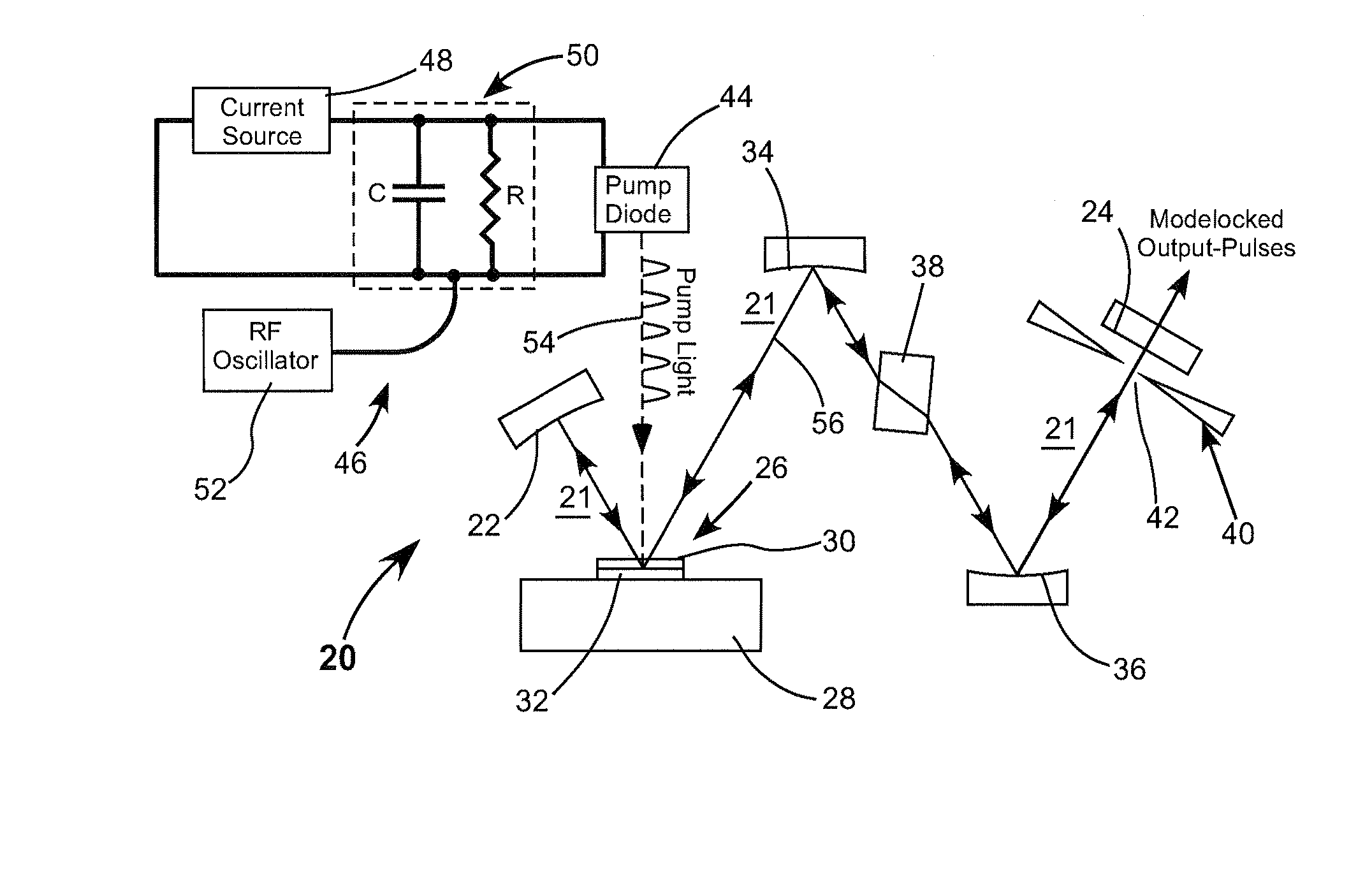
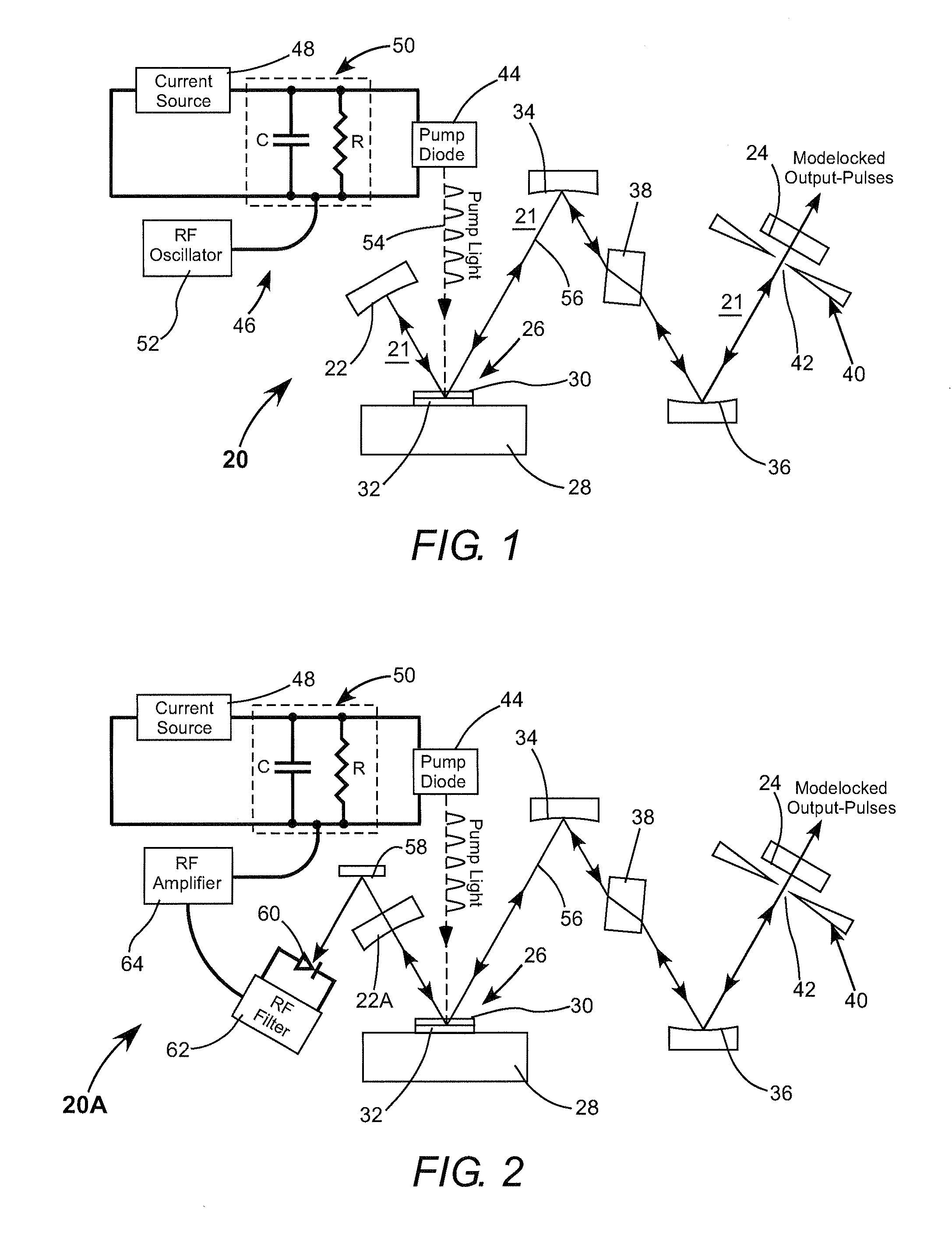
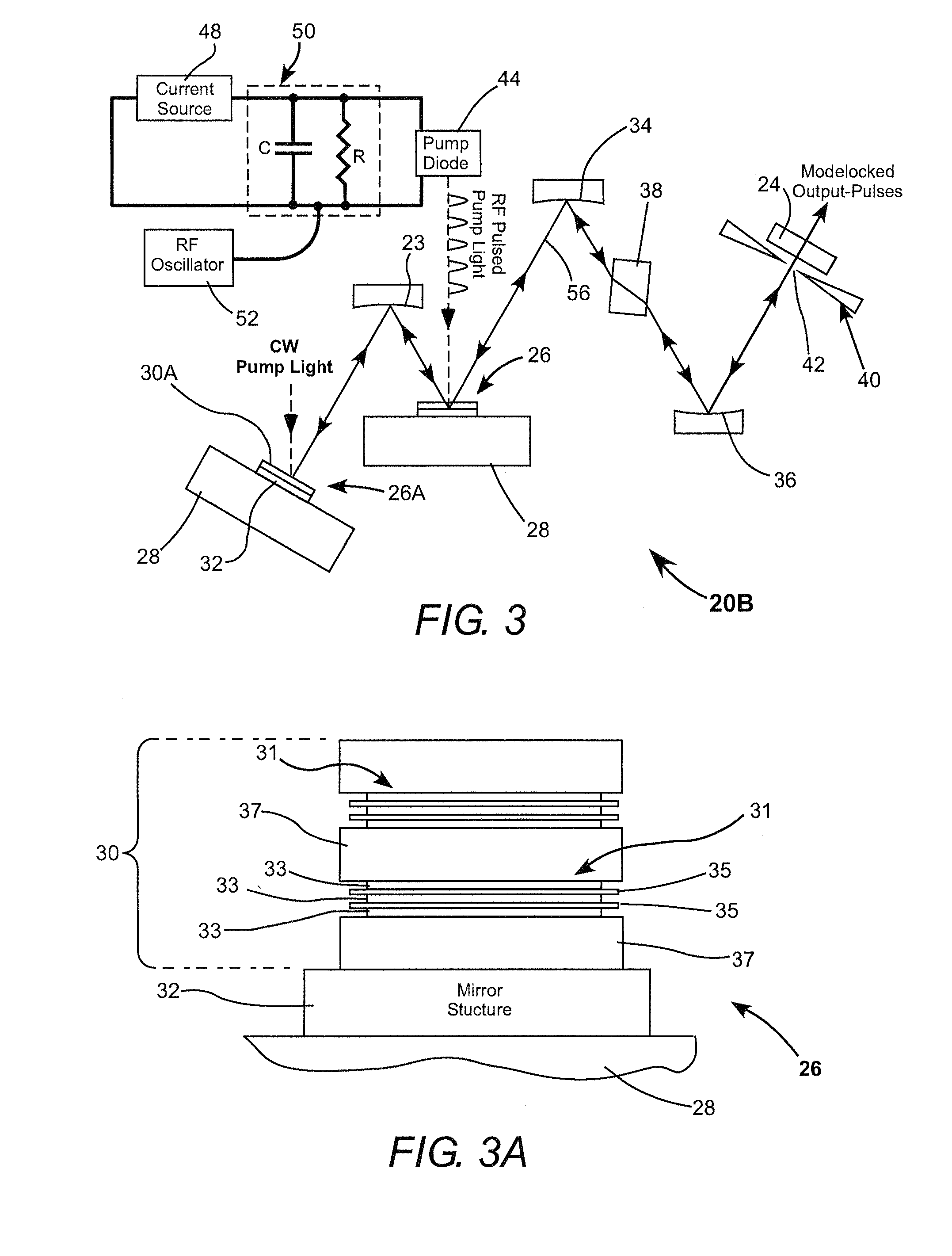
Mode-locked external-cavity surface-emitting semiconductor laser
A laser resonator includes an OPS gain-structure that is pumped with optical pulses repeatedly delivered at a pulse-repetition frequency corresponding to a resonant frequency of the laser resonator. The laser resonator additionally includes a passive mode-locking arrangement such that the resonator delivers mode-locked optical pulses. In one example the laser resonator further includes a CW optically pumped OPS gain-structure for increasing the power of the mode-locked pulses delivered from the resonator.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Effluent treatment combining solid/liquid separation and pulsed electric fields
The treatment of effluents in which a flow of the effluents is subjected to a pulsed electric field that modifies physicochemical and biologic characteristics of the medium, this modification being used during a solid / liquid separation operation, of the settlement or membrane filtration type. The solid / liquid separation operation and the application of a pulsed electric field are operations carried out at different locations along the effluent flow. The pulsed electric field has voltage value, current value, pulse repetition frequency, and voltage front shape characteristics chosen such that the required effluent treatment can be achieved as a function of the locations at which these membrane filtration operations are carried out and a pulsed electric field is applied.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Wide band RFID system with tag on flexible label
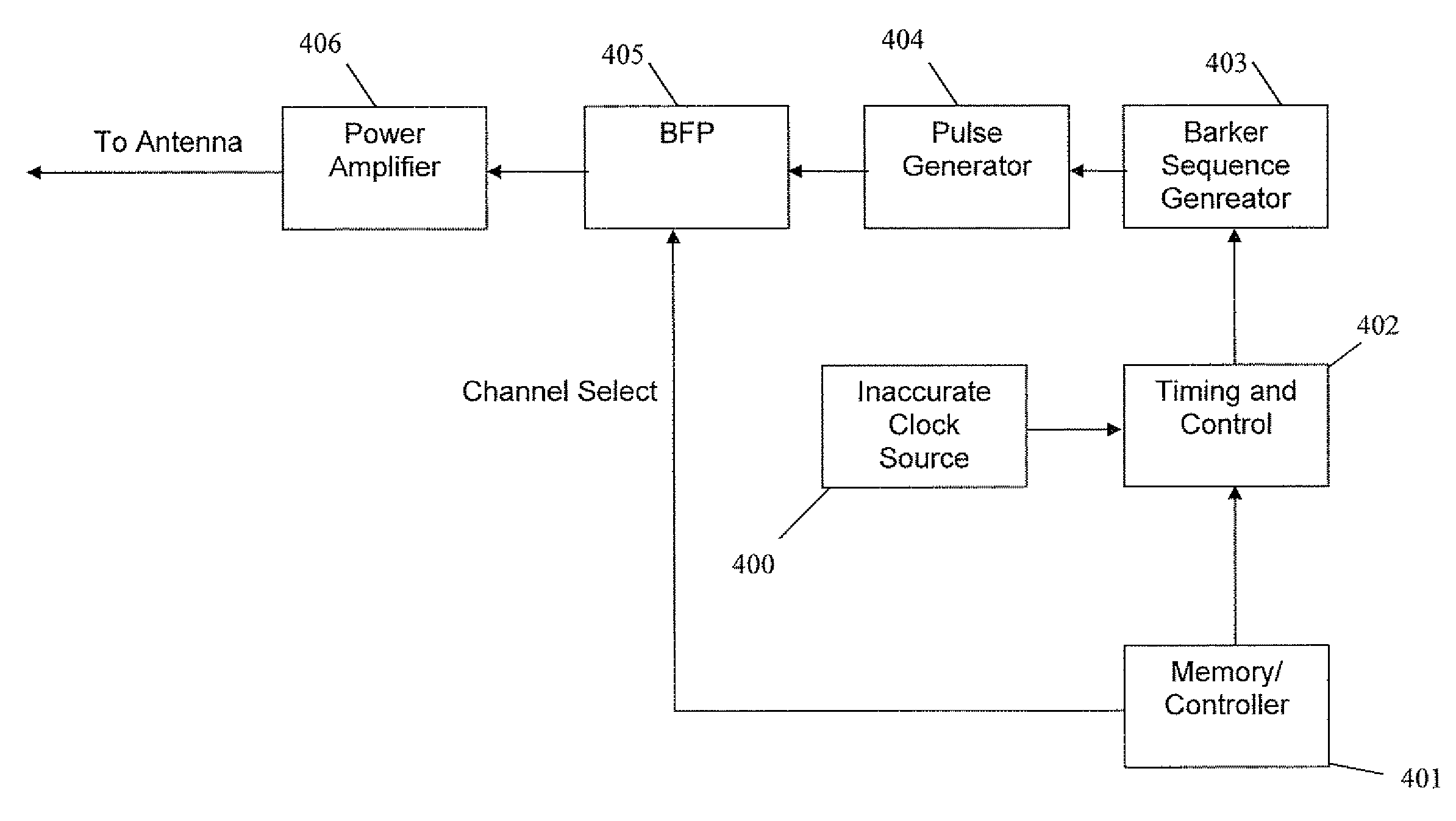
ActiveUS7504952B2Good synchronizationReduce power consumptionSubscribers indirect connectionRecord carriers used with machinesEngineeringWide band antenna
An active radio frequency identification (REID) tag implemented on a flat label. The tag includes a battery printed on the label, a flat wide-band antenna printed on the label and a wide band communication circuit implemented as a chip inlay inside the label. The circuit is attached to the battery and to the antenna. The combined thickness of the battery, the antenna and the circuit as printed on the flexible label is less than one millimeter. The battery, the antenna and the circuit are printed on the label so as to render substantial flexibility to the RFID tag. The circuit operates at a center frequency of at least one gigahertz and a bandwidth at least twenty percent of said center frequency or a bandwidth at least 500 Mhz. The tag typically includes an inaccurate clock source such as an RC circuit and does not include a crystal. Average power consumption of the battery is preferably reduced by operating the tag with a low duty ratio between an active and an inactive interval; and during the active interval transmitting in bursts while turning off parts of the tag between the bursts. The communications circuit performs timing measurements on incoming received waveforms and transmits transmit signals in response to the received waveforms with timing based on the timing measurements. The receiver circuitry locks on a repetition frequency of the incoming received waveforms, and based on the repetition frequency generates a pulse repetition frequency of the transmit signals.
Owner:SANDLINKS
Time correlation of ultrafast laser pulses
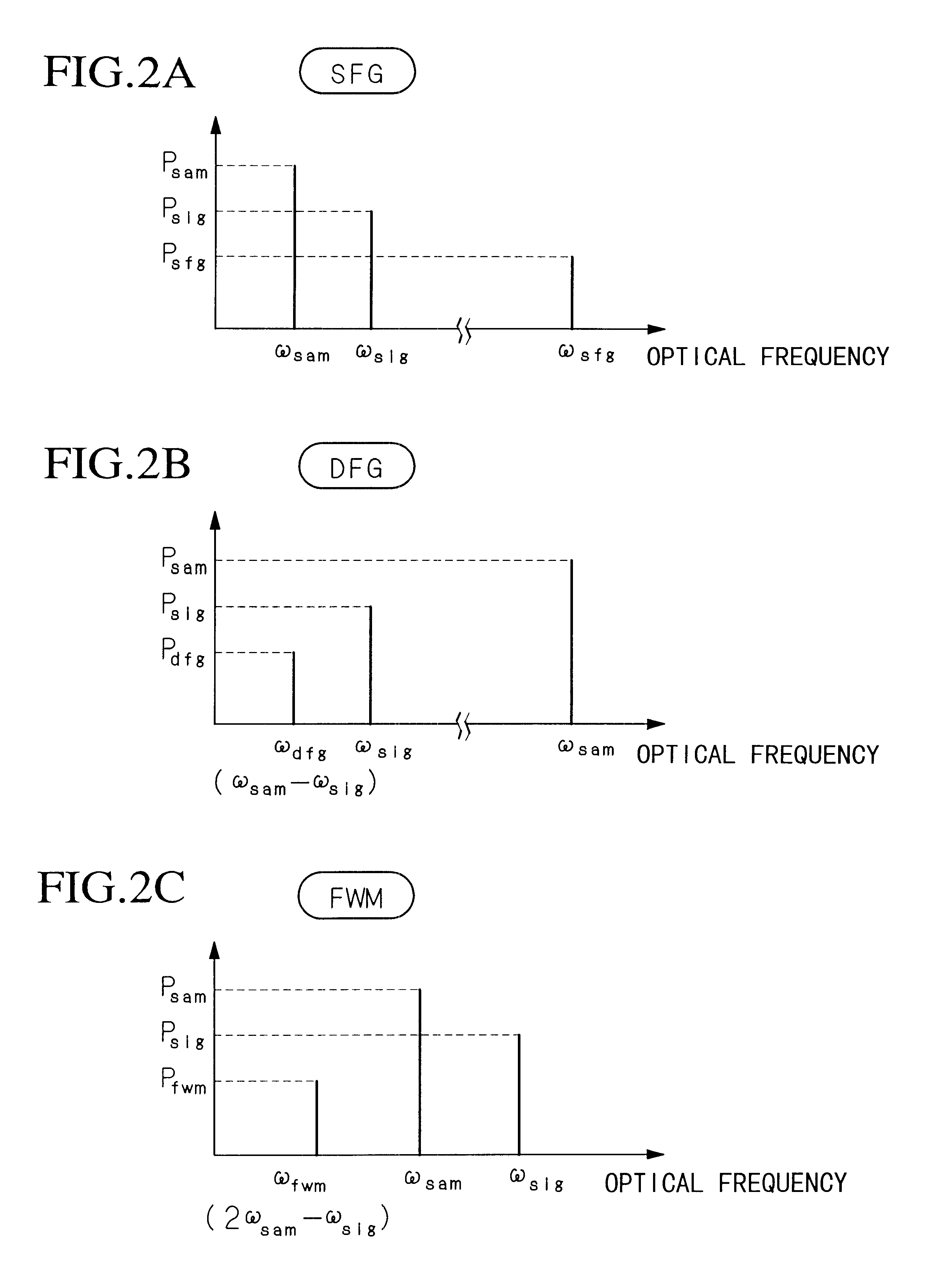
Time-correlation methods for determining pulse characteristics from a modelocked ultrafast laser include a cross-correlation method and an auto-correlation method. In the cross-correlation method, pulses from the laser and pulses from another modelocked laser are incident on a two-photon detector that responds when the pulses overlap in time. The lasers are synchronized to the same frequency and the phase difference between pulses from the two lasers is varied to vary the temporal pulse overlap while recording the detector response. Pulse characteristics are determined from recorded data representing the detector response as a function of phase difference. In the auto-correlation method, pulses from one laser are divided into two components. One component follows a fixed delay path before being temporally overlapped at the detector with another component that has not been delayed. The temporal overlap is varied by varying the pulse repetition frequency. Pulse characteristics are determined from recorded data representing the detector response as a function of phase difference.
Owner:COHERENT INC
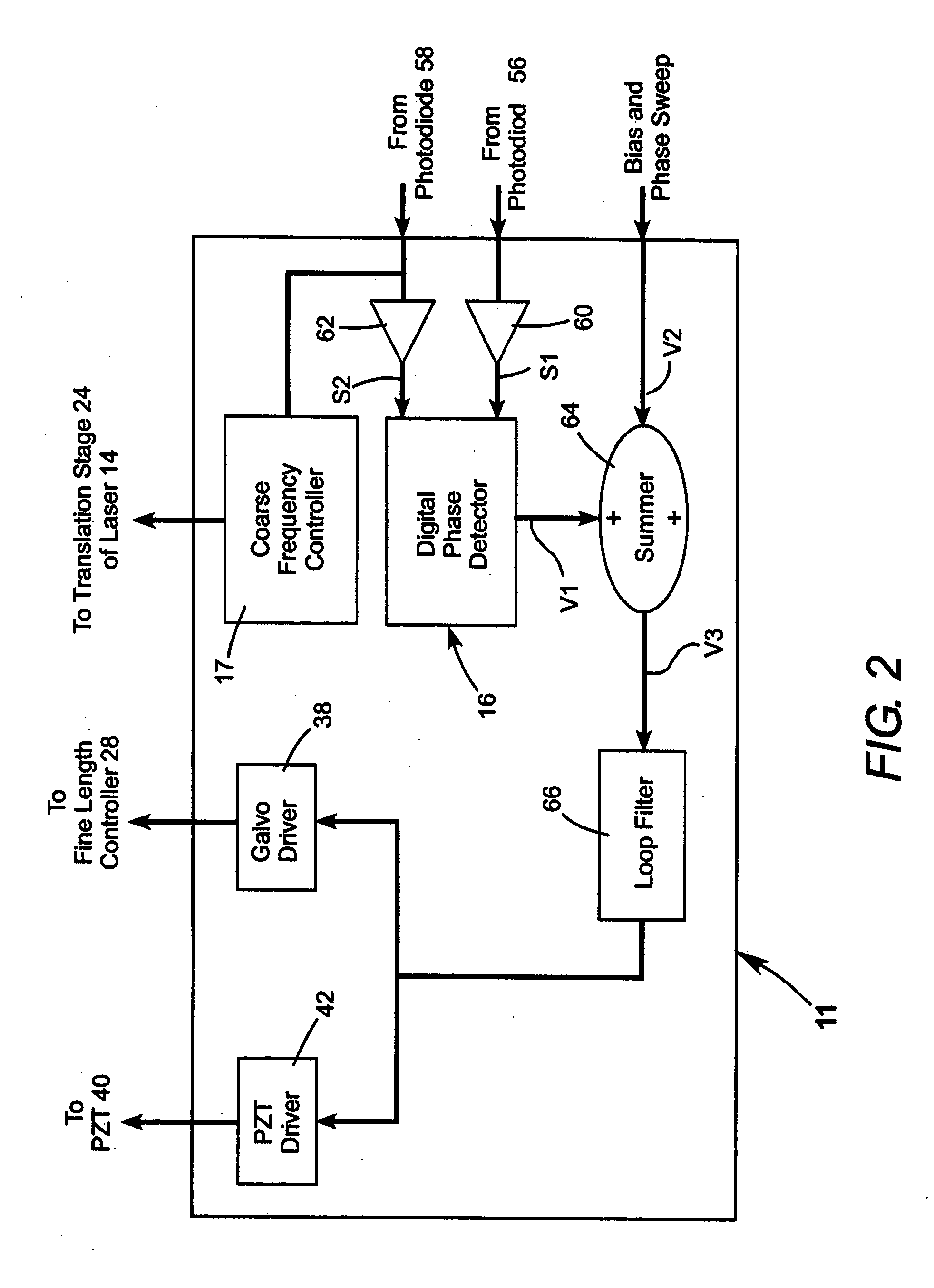
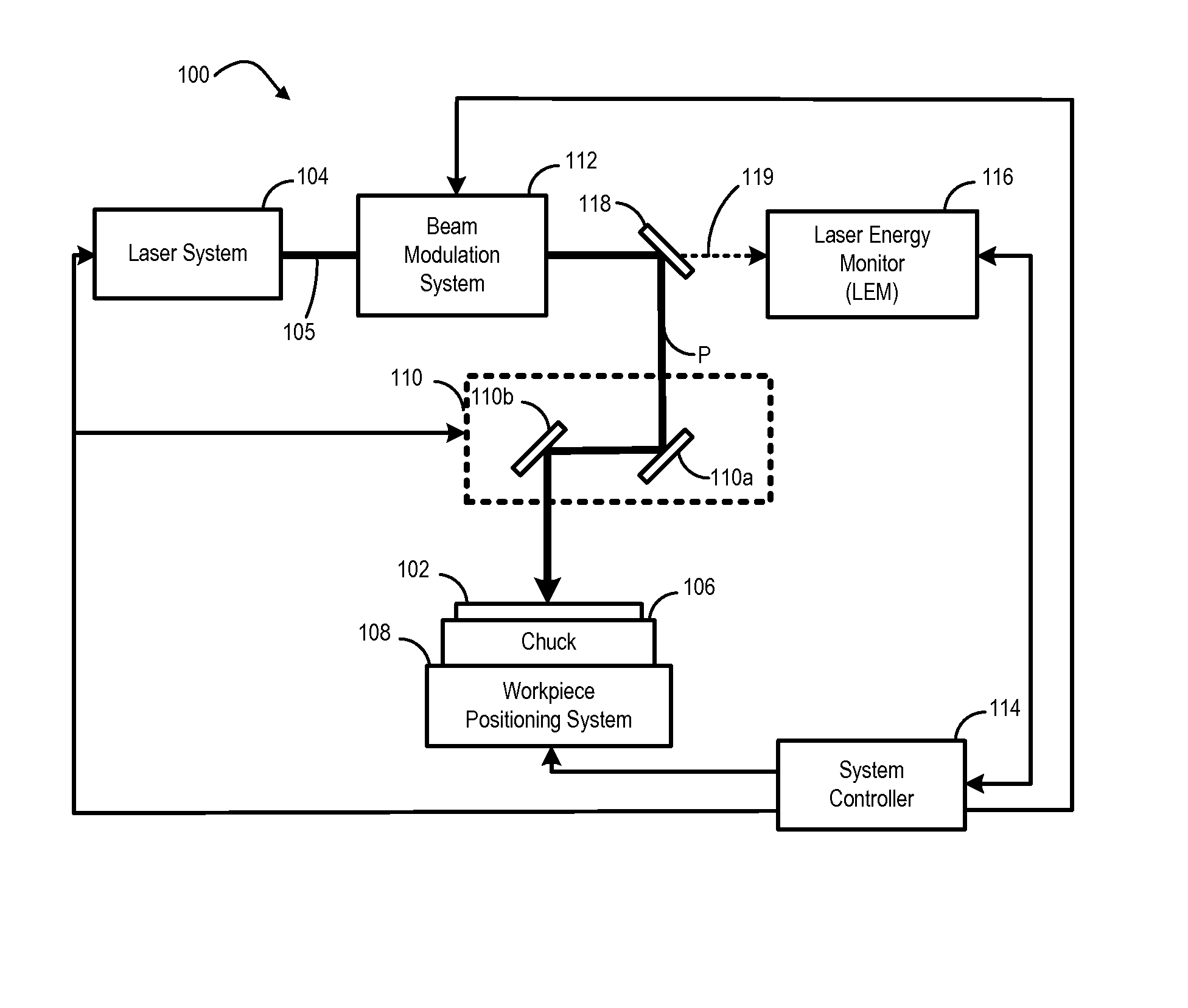
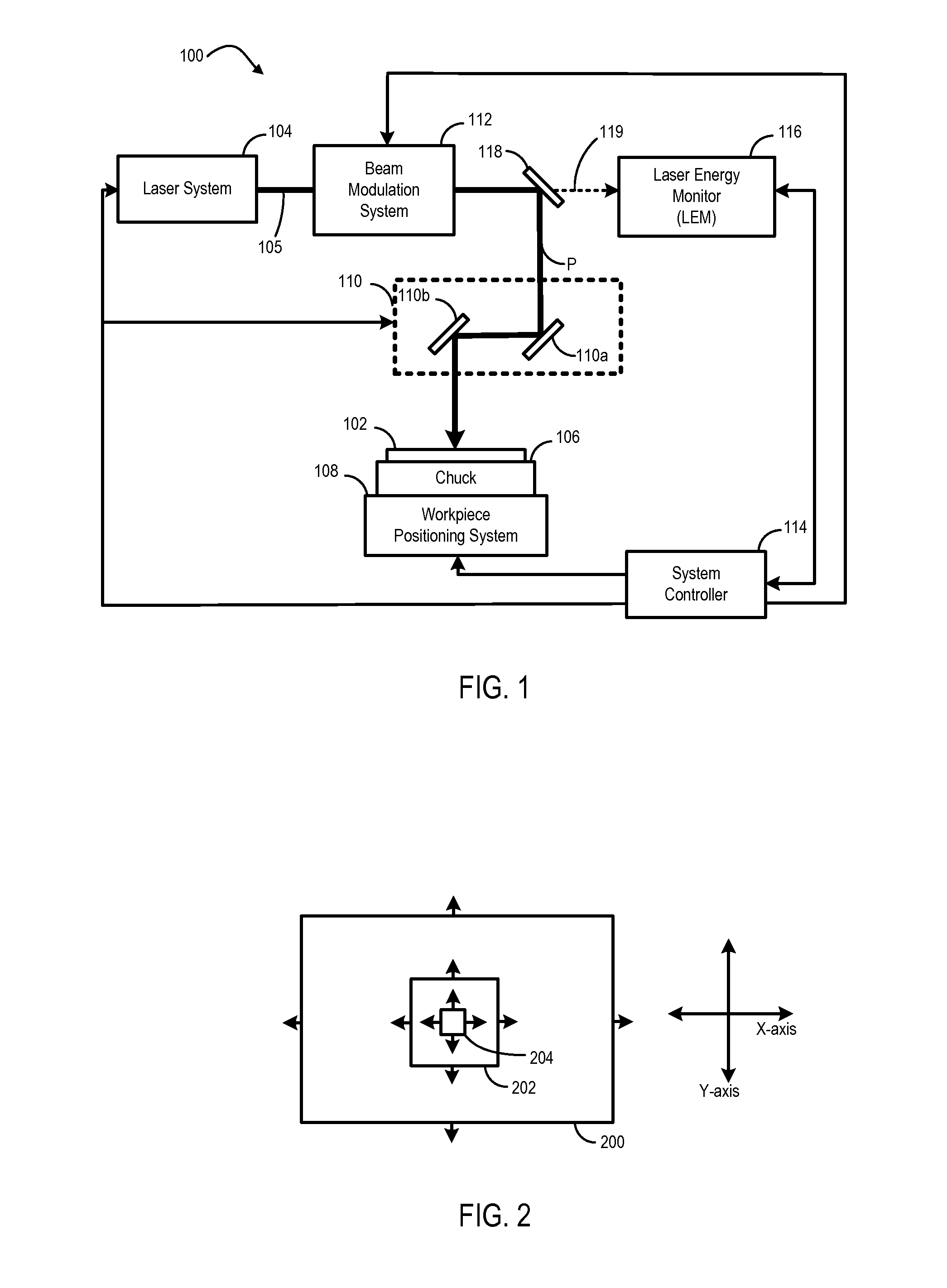
Laser pulse energy control systems and methods
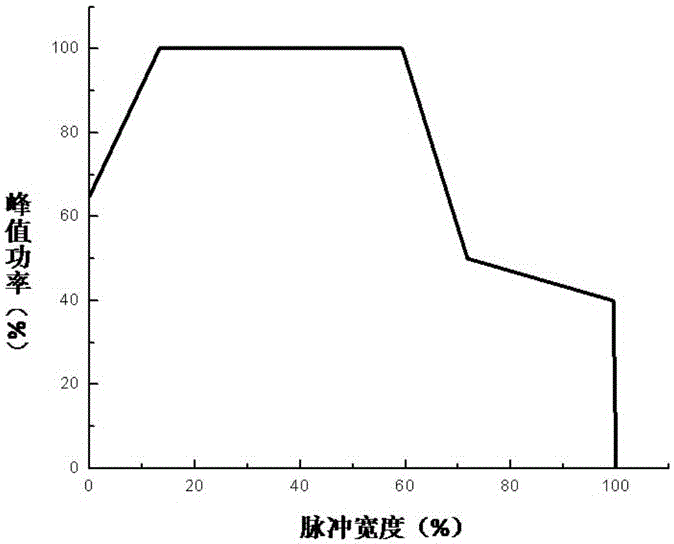
Systems and methods provide laser pulse energy control and / or monitoring. An example laser processing apparatus includes a laser system to generate a beam of laser pulses and a pulse energy control system to adjust the pulse energy of each laser pulse in the beam on a pulse-by-pulse basis. The pulse energy control system includes an open loop feedforward control path that selects a pulse energy transmission value for each laser pulse based on a calibrated transmission curve that maps laser pulse energy as a function of pulse repetition frequency. A laser energy monitor measures the laser pulse energy of each laser pulse in the beam of laser pulses. A power control loop may further adjust the pulse energy of one or more laser pulses in the beam of laser pulses based on feedback from the laser energy monitor.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
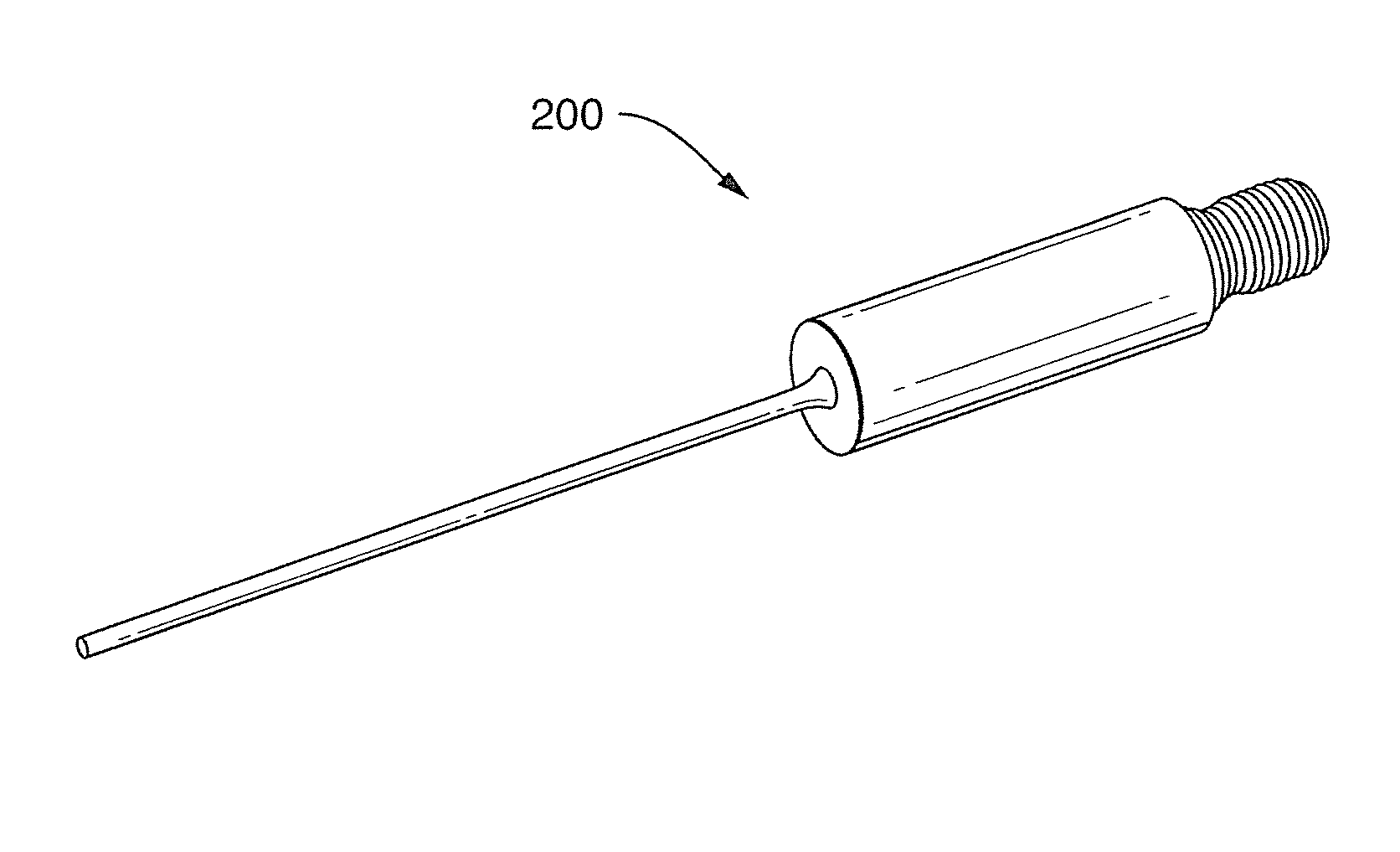
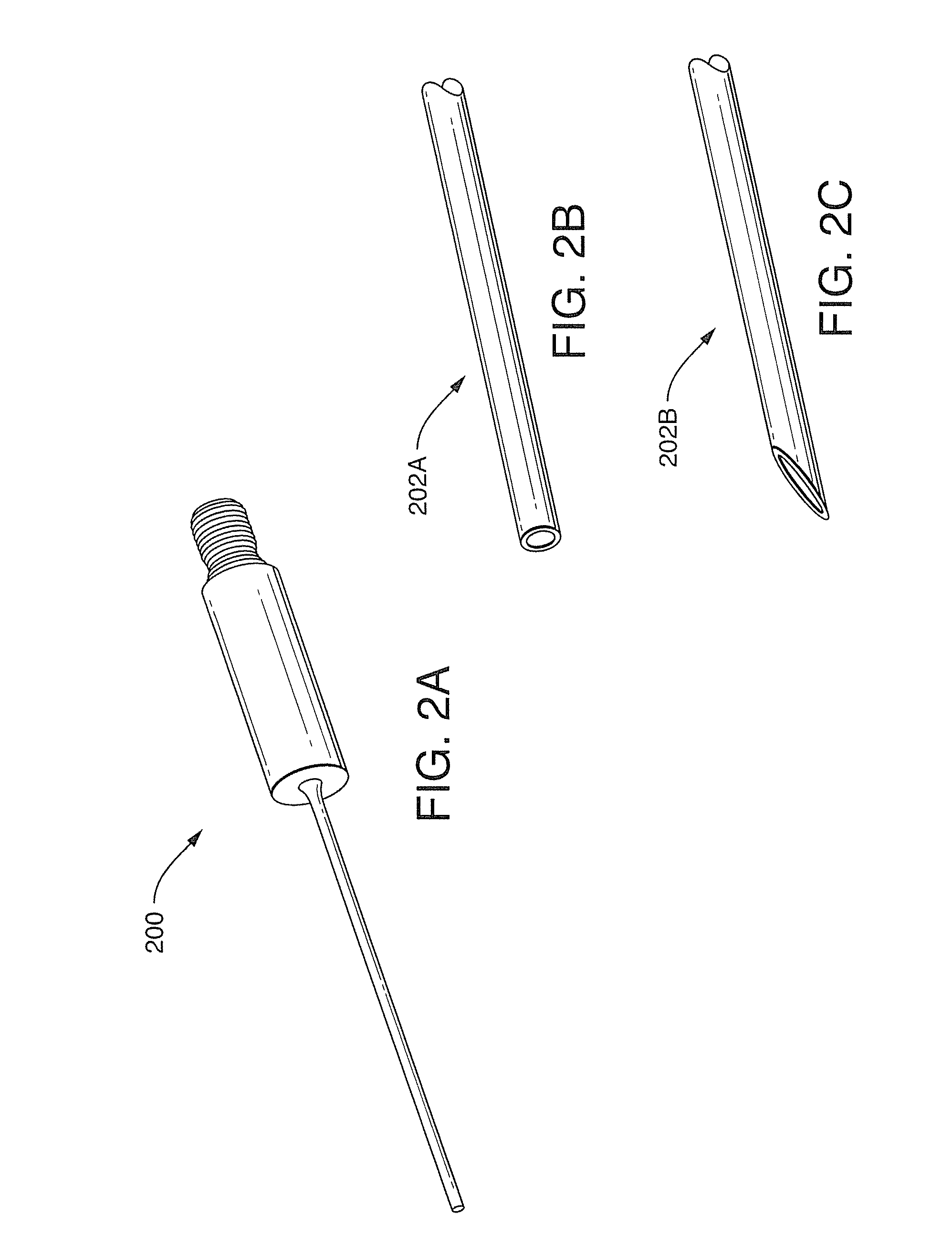
Thrombolysis In Retinal Vessels With Ultrasound
InactiveUS20080262512A1Reduce riskHigh resolutionImage enhancementLaser surgeryVenous occlusionBlood vessel
Systems and methods are described providing for the use of ultrasound energy to effect the dislodging of one or more blood clots inside blood vessels. Such clots can include those inside retinal vessels, especially in patients with central retinal vein occlusion. Embodiments of the present disclosure may be used for any retinal arterial or venous occlusion. In exemplary embodiments, a small probe can be inserted into the eye of a patient and placed over the retinal vessels. Acoustic streaming created by the probe can be directed to an area or region including targeted blood vessels, resulting in increased flow in one or more retinal veins and facilitating or effecting mechanical dislodging of one or more blood clots in the targets blood vessels. Exemplary embodiments can utilize ultrasonic energy produced at a frequency of approximately 44 MHz to 46 MHz with pulse repetition frequencies of approximately 100 Hz to 100 kHz.
Owner:DOHENY EYE INST
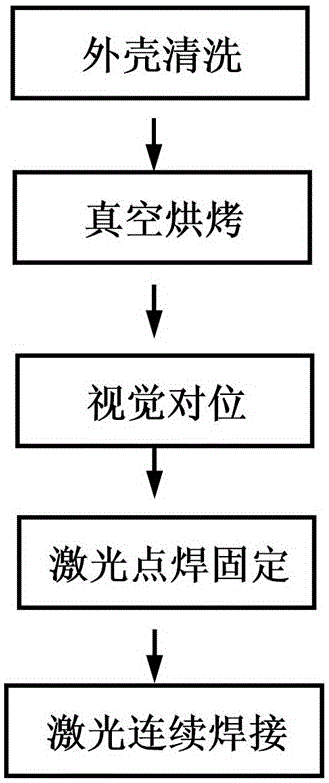
Laser seal welding technique for 3A21 aluminum alloy casing
ActiveCN105081573ASmall heat affected zoneSmall thermal deformationWelding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusWeld seamSpot welding
The invention discloses a laser seal welding technique for a 3A21 aluminum alloy casing. The laser seal welding technique comprises the following steps of visual alignment, laser spot welding location and laser seal welding. The technological parameters of the laser seal welding are that the laser pulse peak power is 3000W-3500W, the impulse waveform is preheating thermal-insulation wave, the pulse width is 4ms-8ms, the pulse repetition frequency is 10Hz-20Hz, the welding speed is 108mm / min-180mm / min, and the defocusing amount is -1mm to -2mm. The laser seal welding technique for the 3A21 aluminum alloy casing can effectively remove cracks and air holes on welding seams of laser welding of the 3A21 aluminum alloy casing. The sealed 3A21 aluminum alloy casing has the beneficial effects of being attractive in welding seam appearance, high in air tightness, high in reliability, high in efficiency and low in cost.
Owner:48TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP
Laser direct ablation with picosecond laser pulses at high pulse repetition frequencies
ActiveUS8648277B2Efficient processingSufficient pulse overlapSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPrinted circuitsPicosecond laserPicosecond laser pulse
Laser direct ablation (LDA) produces patterns cut into a dielectric layer for the formation of electrically conductive traces with controlled signal propagation characteristics. LDA processing includes selecting a dose fluence for removing a desired depth of material along a scribe line on a surface of a workpiece, selecting a temporal pulsewidth for each laser pulse in a series of laser pulses, and selecting a pulse repetition frequency for the series of laser pulse. The pulse repetition frequency is based at least in part on the selected temporal pulsewidth to maintain the selected dose fluence along the scribe line. The selected pulse repetition frequency provides a predetermined minimum overlap of laser spots along the scribe line. The LDA process further includes generating a laser beam including the series of laser pulses according to the selected dose fluence, temporal pulsewidth, and pulse repetition frequency.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Compressive sensing theory-based Doppler ambiguity-resolution processing method
InactiveCN101975939AAvoid false value casesRemove restrictionsWave based measurement systemsObservational errorFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a compressive sensing theory-based Doppler ambiguity-resolution processing method, which comprises the following steps of: (1) performing non-uniform sampling on continuous echo pulses in a totally-coherent processing period by utilizing Q-fold pulse repetition frequency values; (2) designing the possible Doppler frequency range of a target, and ensuring the Q-fold pulse repetition frequency values do not have Doppler dead zones in the Doppler frequency range; (3) constructing a compressive sensing (CS) model by utilizing the time-domain under-sampling characteristics of sampled data in the totally-coherent processing period and the sparse characteristics of frequency spectrums of the target to be detected in the possible Doppler frequency range; and (4) resolving the CS model by utilizing an orthogonal matching pursuit (OMP) reconstruction algorithm to directly estimate the amplitude response of ambiguity-free Doppler spectrums. The method eliminates the restriction of the PRF multiplicity adopted by a radar system to the number of the targets to be detected, and simultaneously avoids the condition of false values caused by the influence of measurement errors in the conventional methods by taking the influence of noise on reconstruction results into account and performing de-noising operation when the CS model is resolved to estimate the amplitude response of the ambiguity-free Doppler spectrums by adopting the OMP reconstruction algorithm.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +1
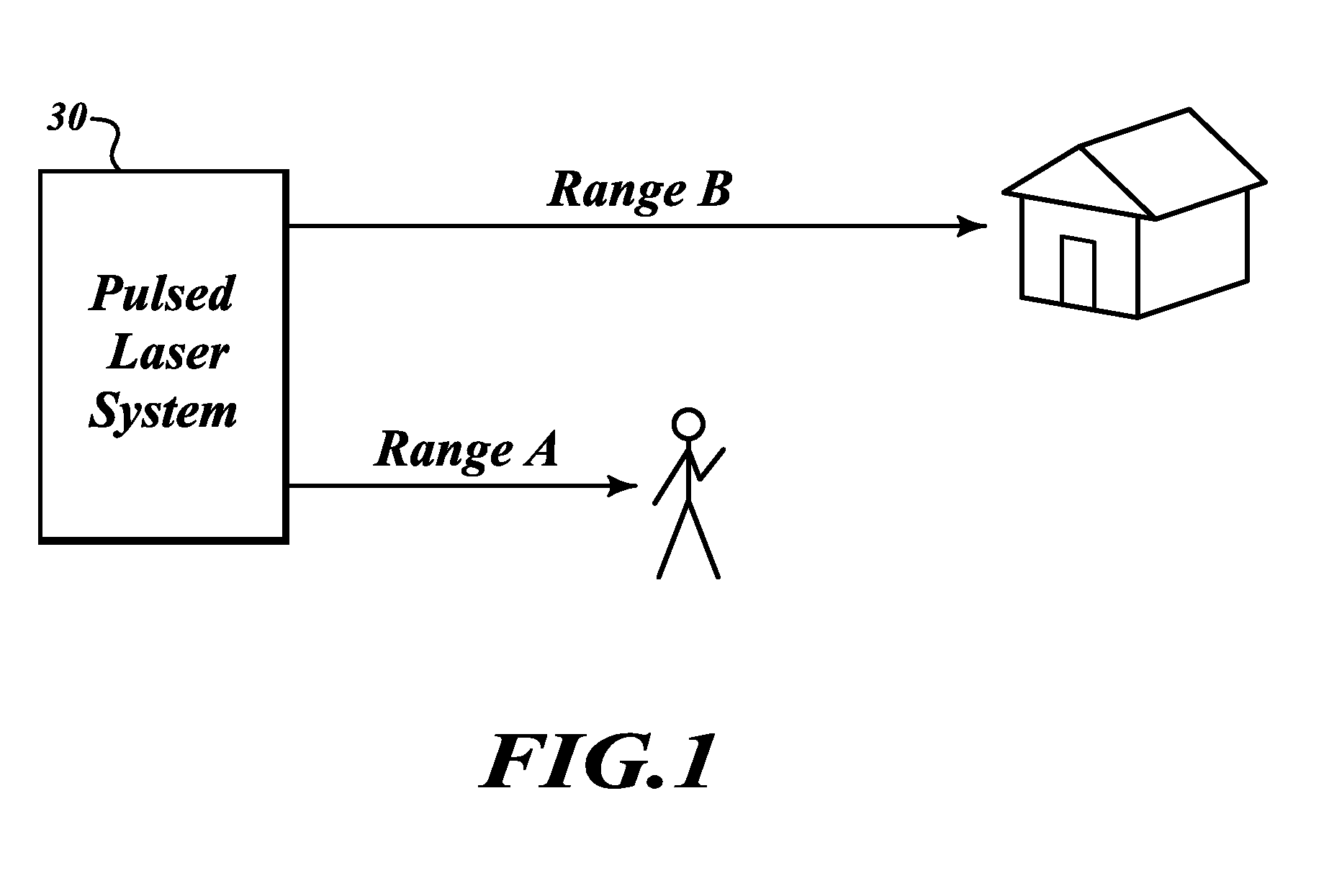
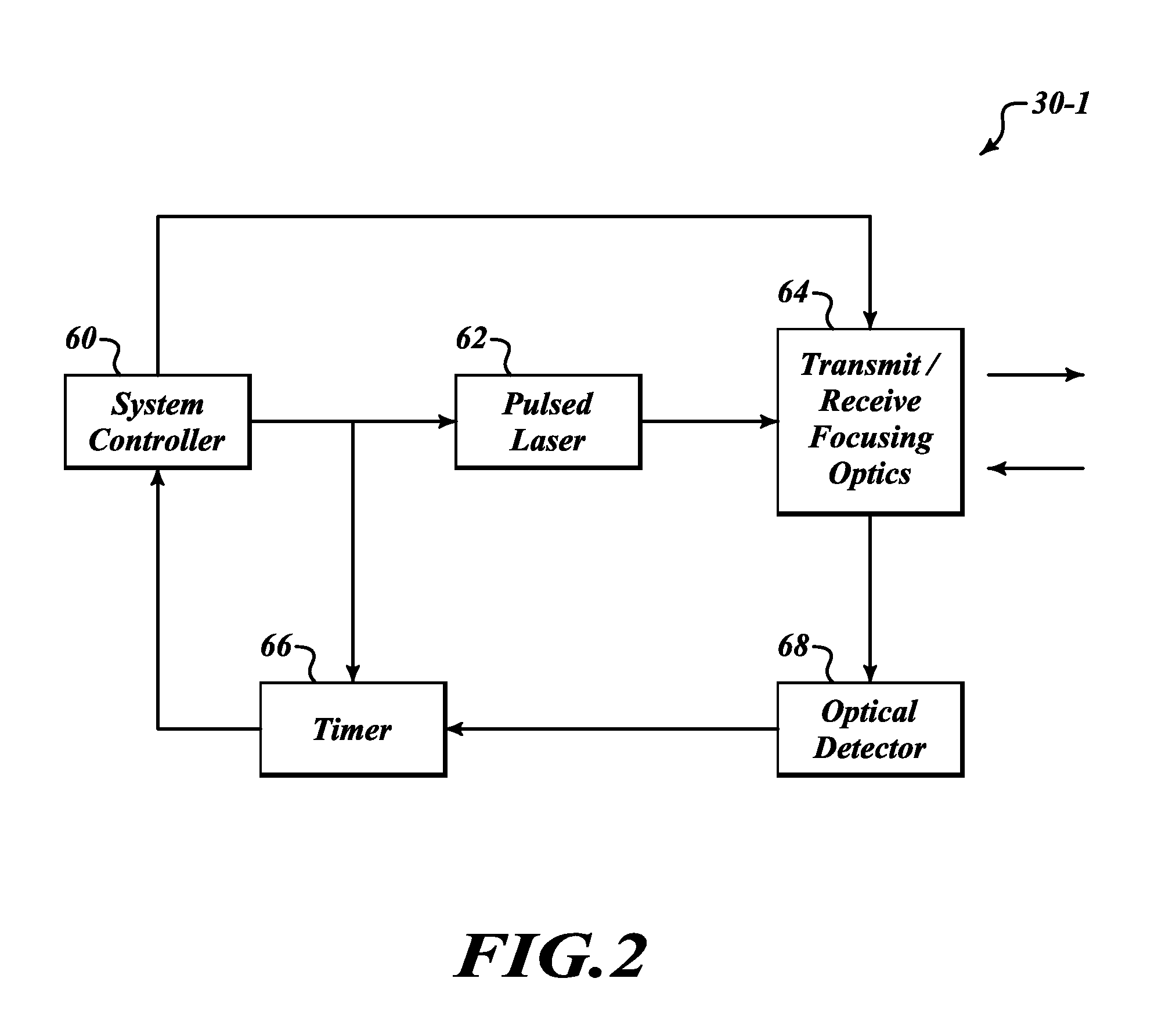
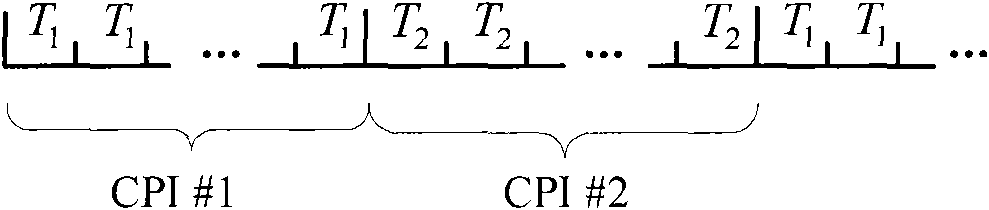
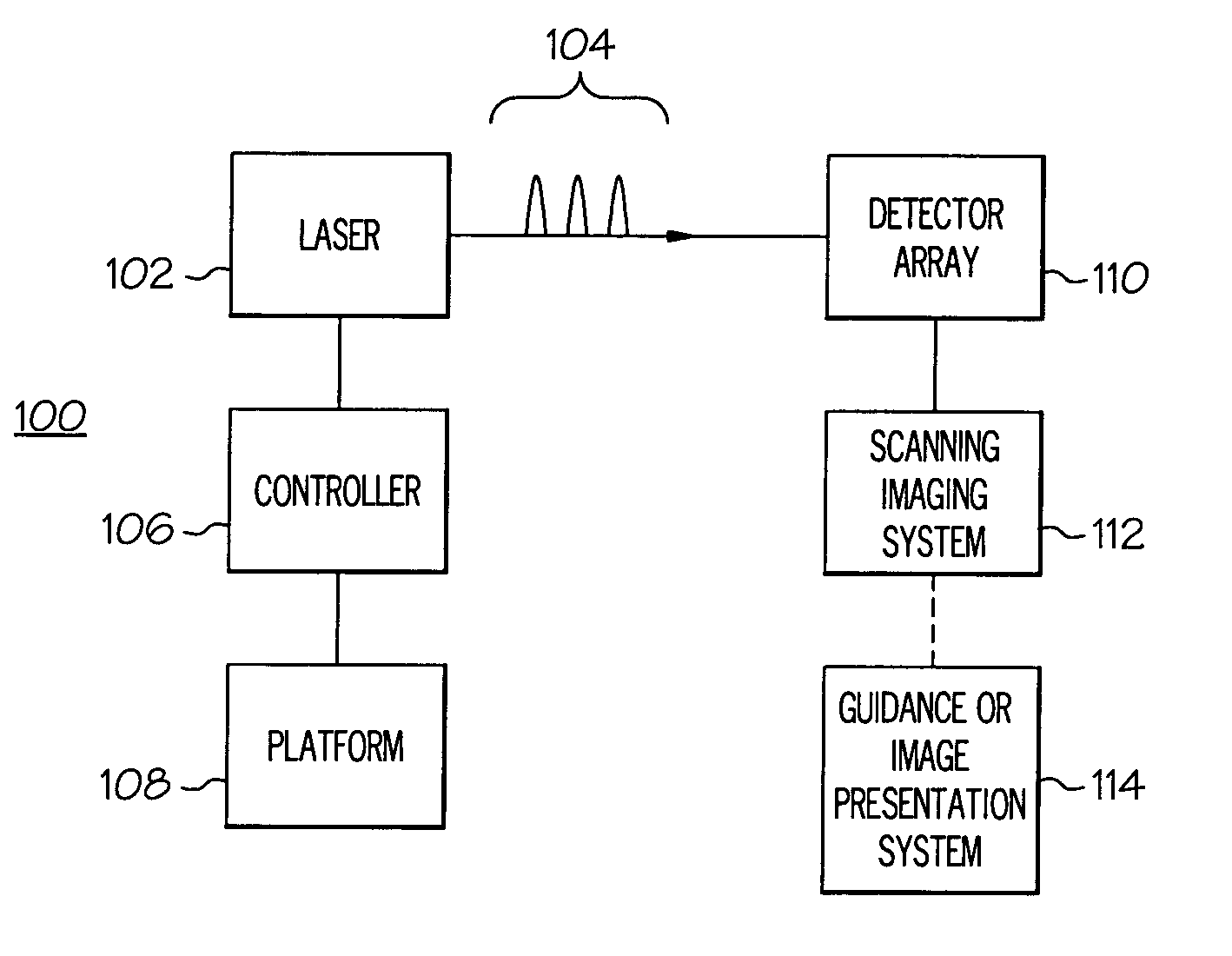
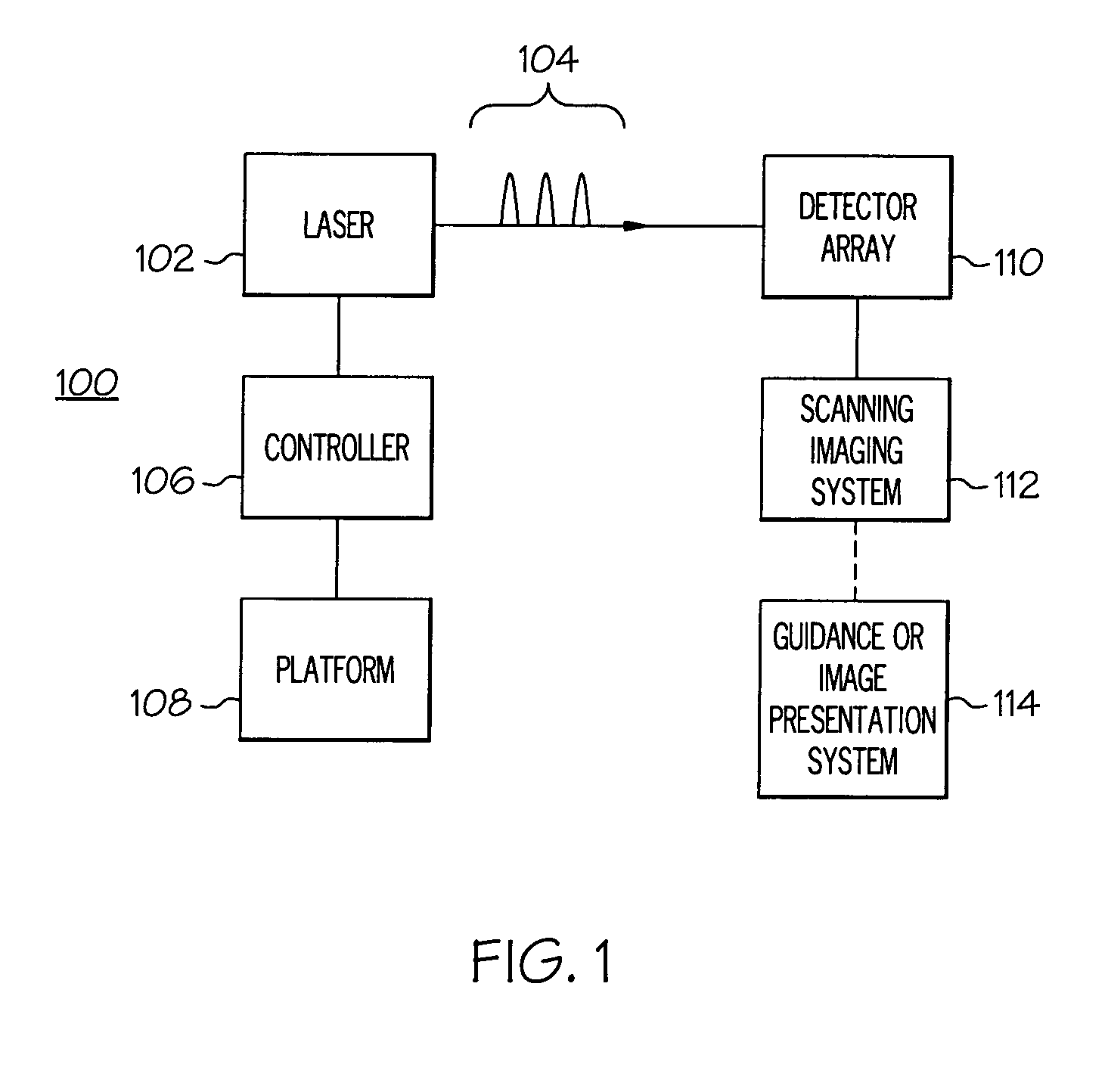
System and processes for causing the simultaneity of events including controlling a pulse repetition frequency of a pulsed laser for disabling a scanning imaging system
ActiveUS20050224706A1Wave based measurement systemsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsSimultaneityPulse repetition frequency
A system and processes for causing the simultaneity of events from two or more families of events are described. A repetition rate and modulus of each one the first families of events is determined. A second family of events has a controlled repetition rate that optimizes the simultaneity of a number of events of the second family with a corresponding number of events from the first family within a desired time period. The first families of events can be occurrences of scanning an image of a target across a detector element of a scanning imaging system. The modulus can be a number of lines per frame of the scanning imaging system. Laser pulses having a pulse repetition rate can be events from the second family of events. A system and processes may disable one or more scanning imaging systems by controlling a pulse repetition frequency of a laser output.
Owner:TEXTRON INNOVATIONS
Ground terahertz radar system for detecting cloud
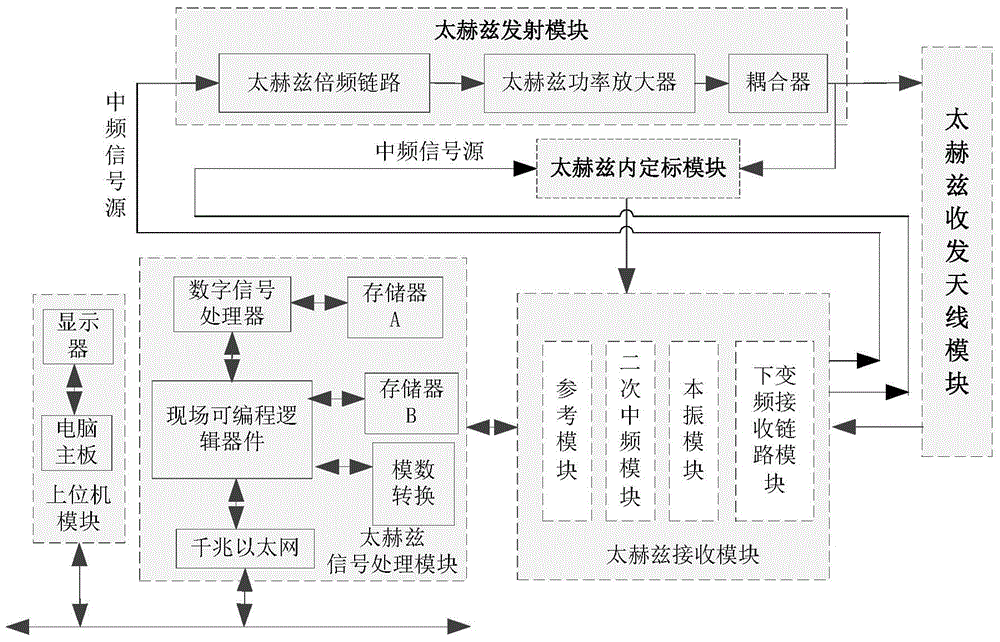
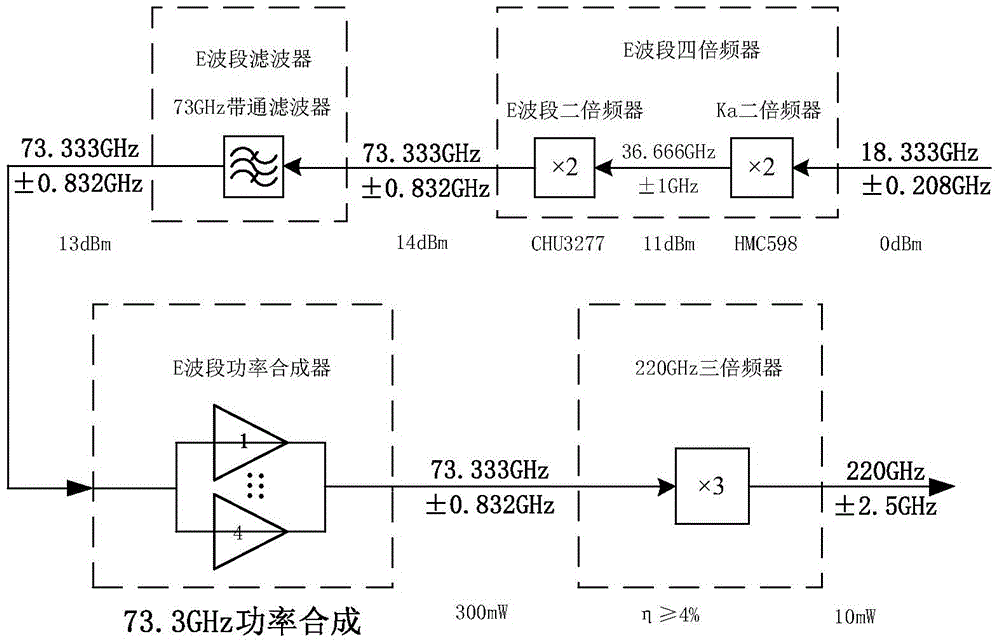
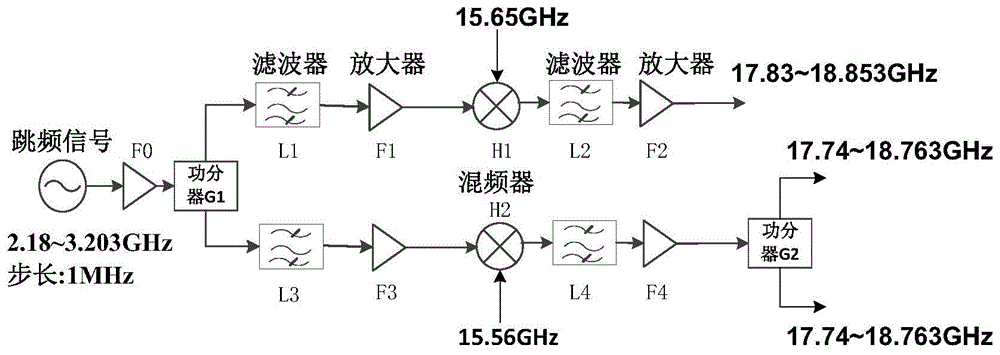
ActiveCN104569980AGet sizeGet shapeRadio wave reradiation/reflectionICT adaptationIce waterRadar systems
The invention discloses a ground terahertz radar system for detecting a cloud. The system comprises a terahertz transmitting module, a terahertz receiving module, a terahertz transmitting-and-receiving antenna module, a terahertz signal processing module and an upper computer module; the center frequency of a terahertz signal transmitted by the terahertz transmitting module is 220 GHz, the work bandwidth is 5 GHz, the transmitting power is 200 mW, the pulse width is adjustable ranging from 100ns to 3mus and the adjusted step length is 100ns, and the pulse repletion frequency is adjustable ranging from 1KHz to 10KHz and the adjusted step length is 1KHz. Compared with a laser radar and a millimeter wave radar, the ground terahertz radar system for detecting the cloud utilizes a set of parameters applicable to the cloud detection and is capable of penetrating into a thin cloud and an extremely thin cloud to carry out the three-dimensional structure detection for the cloud, and therefore not only a macrostructure such as the cloud thickness, the cloud height, the number of cloud layers, the vertical section variance of the cloud can be obtained, but also a microstructure such as the size, the shape, and the ice water content of a cloud particle can be obtained.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com