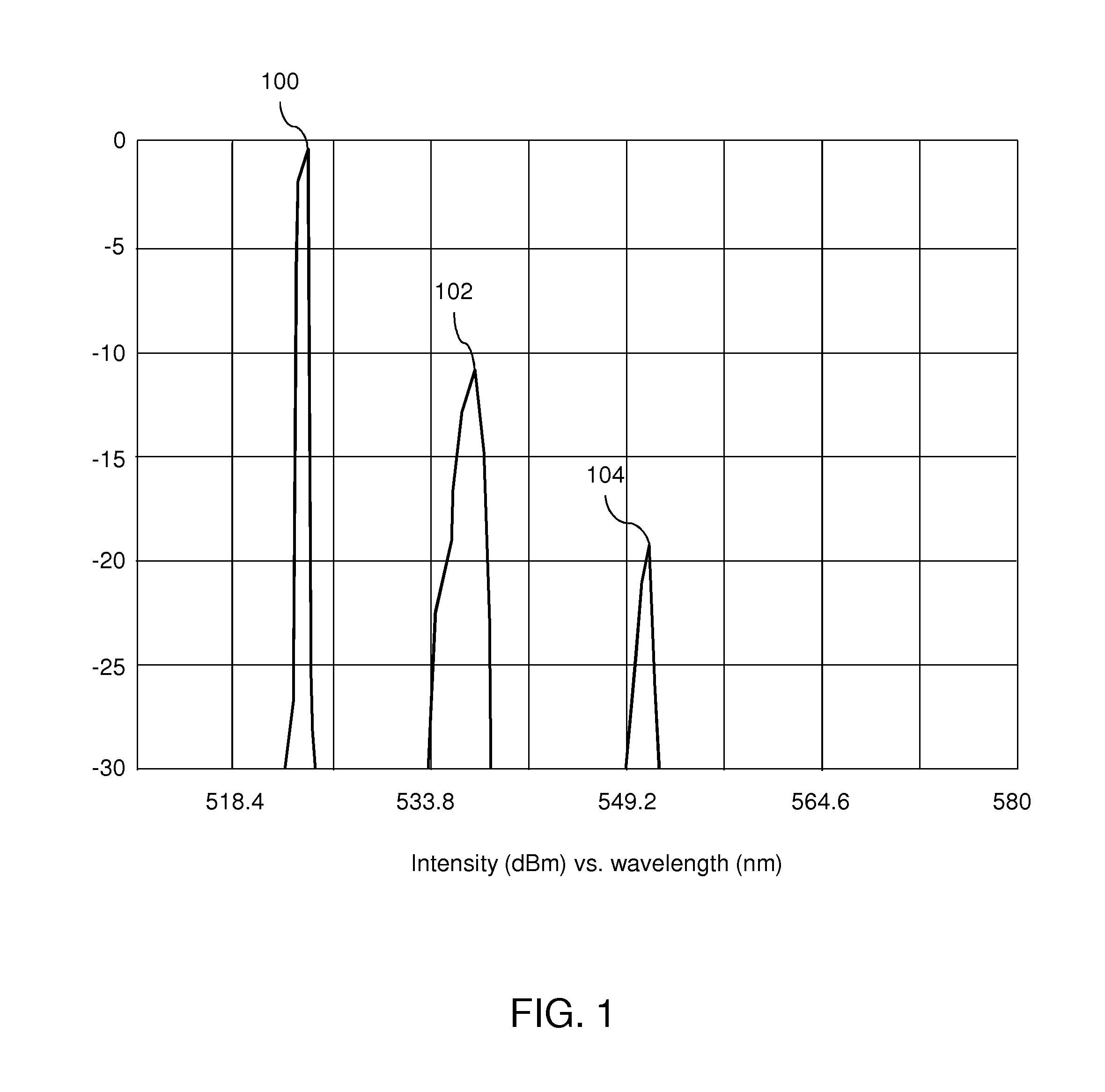
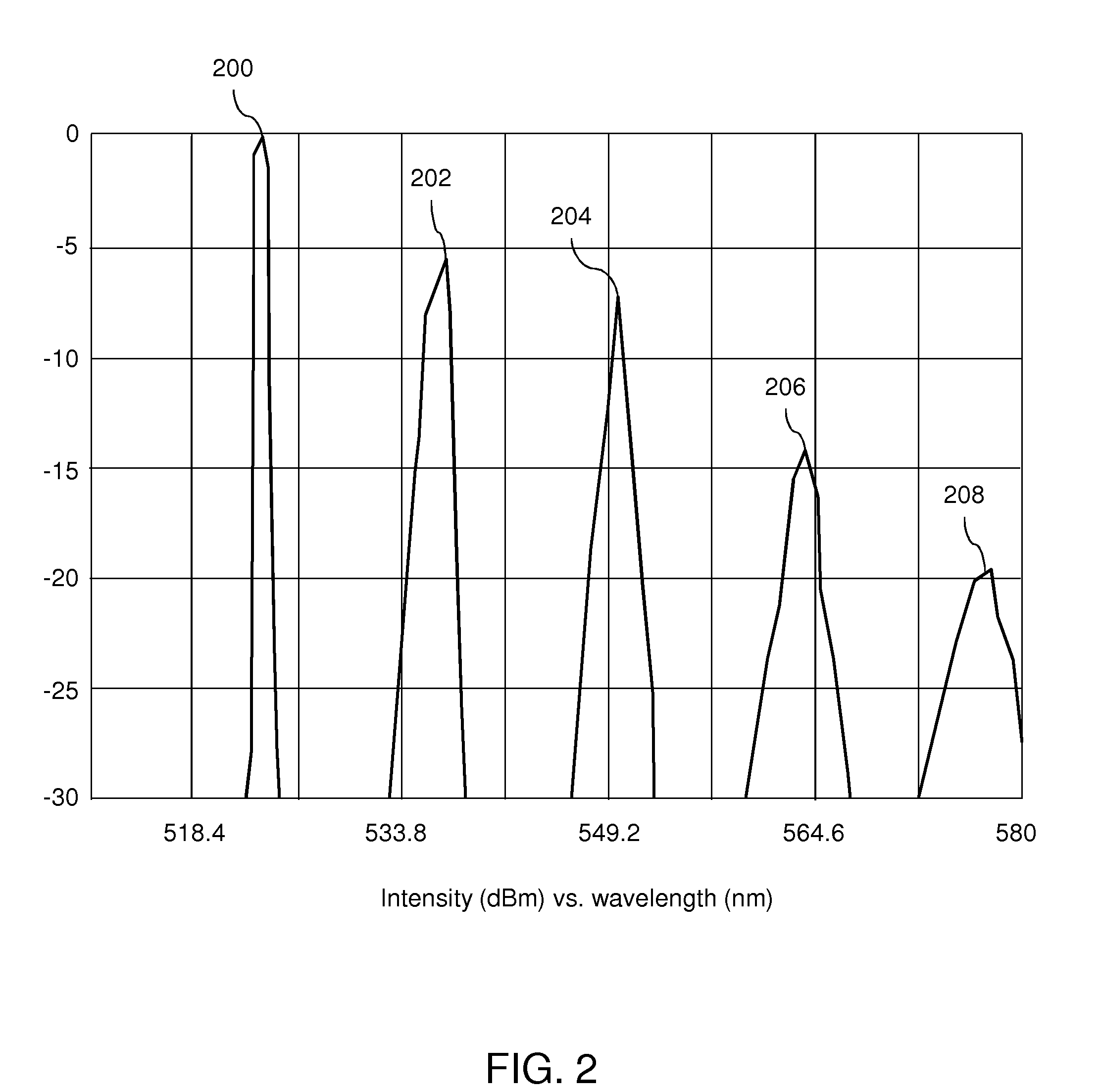
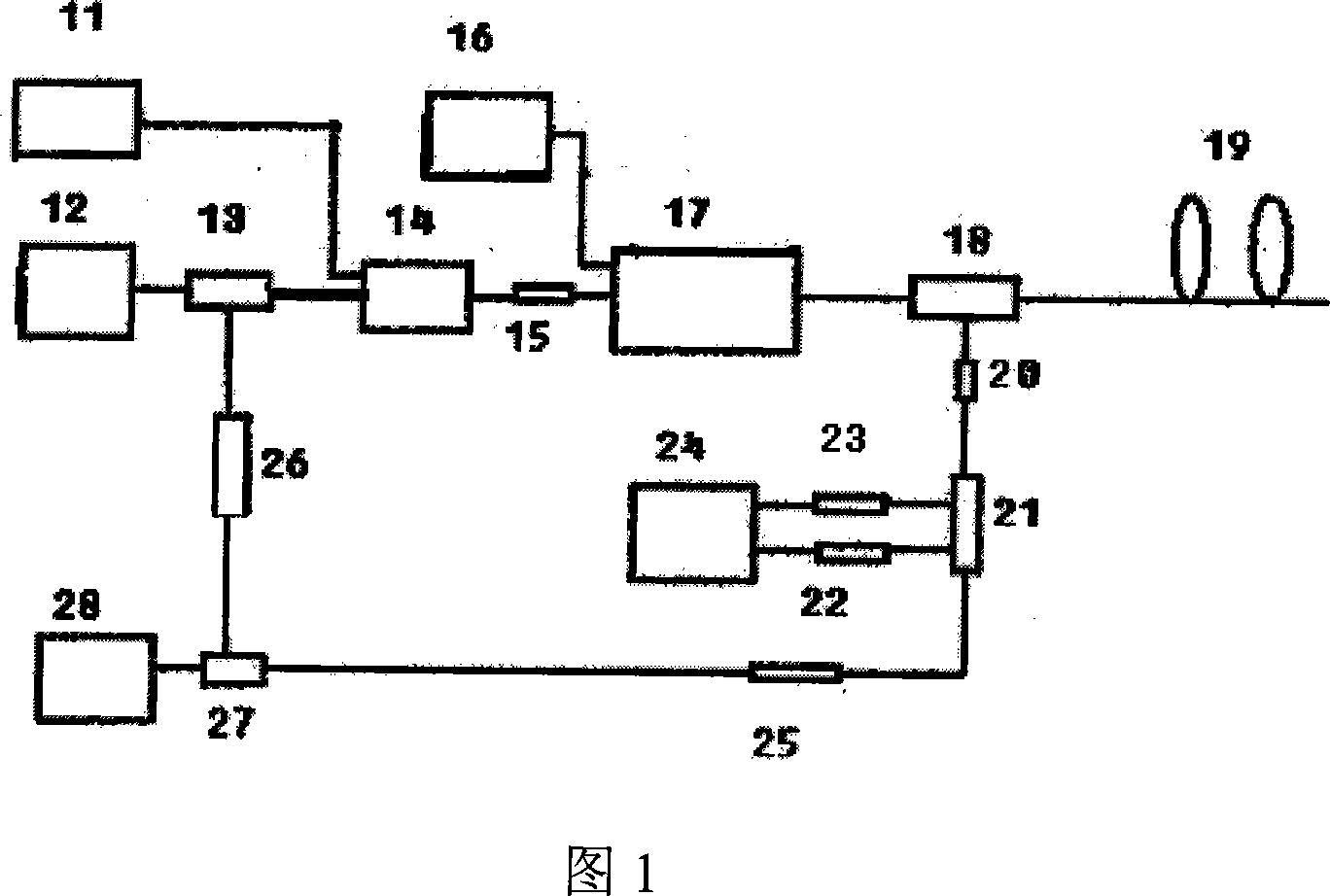
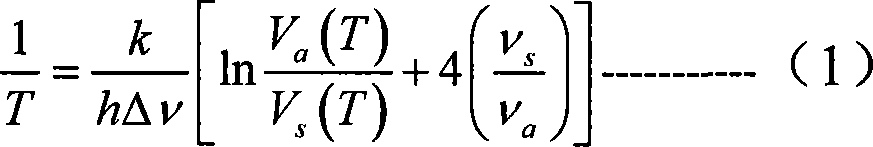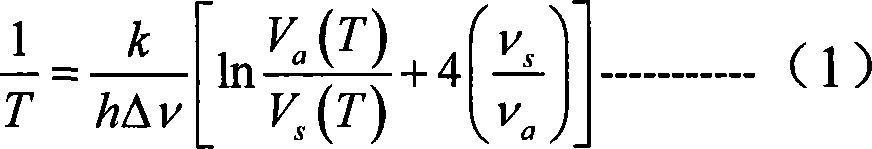Patents
Literature
441 results about "Stimulated raman" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Stimulated Raman spectroscopy, also referred to as stimulated raman scattering (SRS) is a form of spectroscopy employed in physics, chemistry, biology, and other fields. The basic mechanism resembles that of spontaneous Raman spectroscopy: a pump photon, of the angular frequency , which is absorbed by a molecule has some small probability of inducing some vibrational (or rotational) transition ...
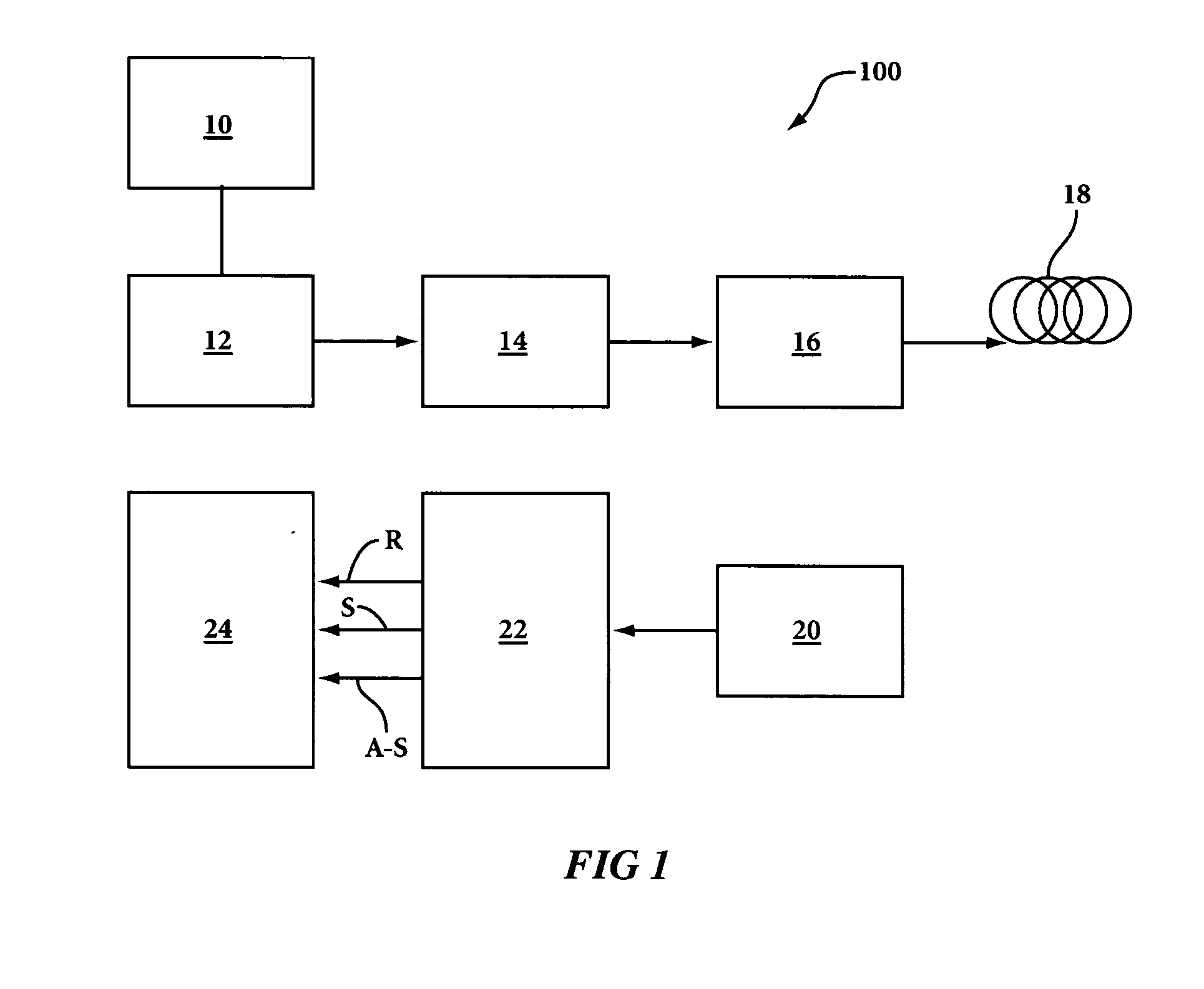
Optical Fiber Cable for Transmission of High Power Laser Energy Over Great Distances
ActiveUS20100215326A1Easy to transportIncrease powerGlass optical fibreDrill bitsHigh power lasersEngineering
There is provided a system and apparatus for the transmission of high power laser energy over great distances without substantial power loss and without the presence of stimulated Raman scattering. There is further provided systems and optical fiber cable configurations and optical fiber structures for the delivering high power laser energy over great distances to a tool or surface to perform an operation or work with the tool or upon the surface.
Owner:FORO ENERGY
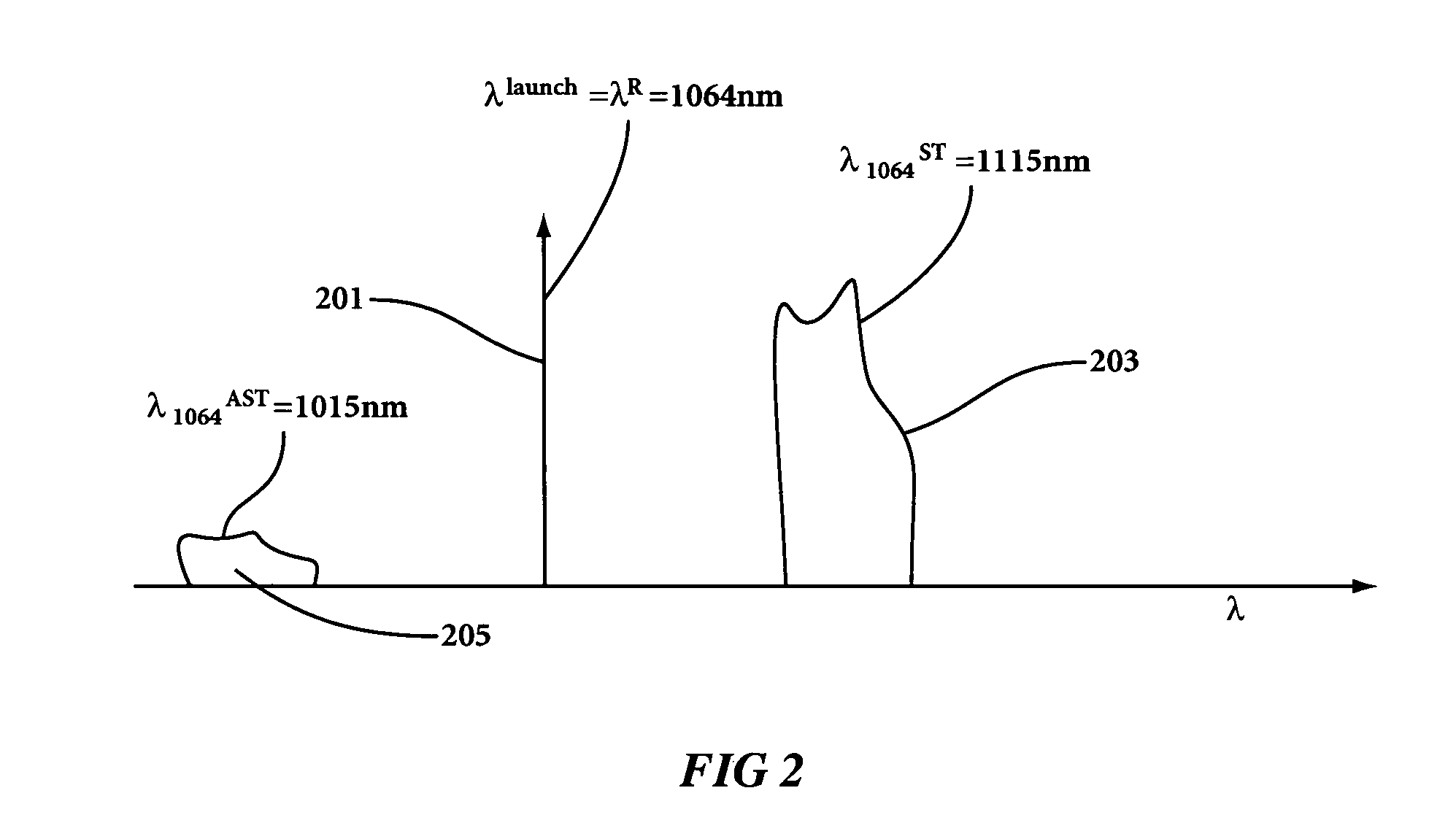
Frequency Control of Despeckling
InactiveUS20130021586A1Speckle reductionProjectorsColor television detailsStimulate raman scatteringOptoelectronics
A method and apparatus that reduces laser speckle by using stimulated Raman scattering in an optical fiber. The pulse repetition frequency of the laser is adjusted to control aspects of the laser light such as color or despeckling. In DLP projection systems, an optical monitor may be used to send information to a bit sequence, and the bit sequence may control the pulse repetition frequency of the laser based on the optical monitor signal.
Owner:PROJECTION VENTURES INC
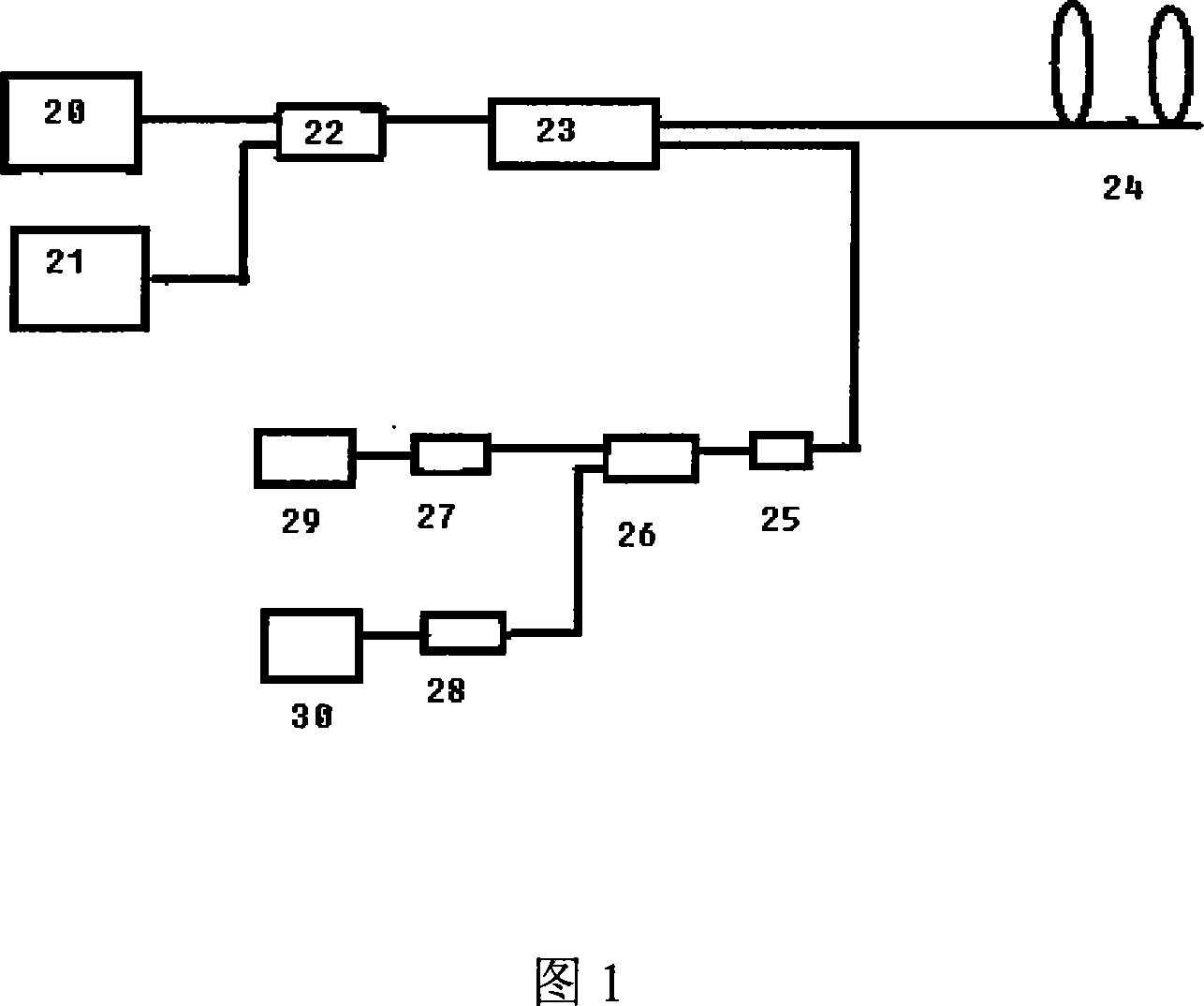
Ultra-remote distributed fiber raman and brillouin photons sensor
InactiveCN101162158AAvoid lossHigh strengthThermometers using physical/chemical changesUsing optical meansFiberPhotonic sensor
The invention discloses super-far distributed fiber Raman and Brillouin photon sensors; by using the stimulated Raman scattering effect of fiber, the self Raman scattering effect of fiber, the Brillouin scattering effect of fiber and the light time-field reflection principle, distributed fiber Raman photon temperature sensors, distributed fiber Brillouin photon strain sensors and distributed fiber Raman amplifier are integrated together. Fiber consumption is overcome by using the gain of amplifier, and strengths of self Raman scattering light and Brillouin scattering light in fiber is enhanced, the signal to noise ratio of the system of distributed fiber Raman photon sensor and distributed fiber Brillouin photon strain sensor is enhanced, meanwhile, the transmission distances of distributed fiber Raman photon sensor and distributed fiber Brillouin photon strain sensor are increased, finally, the temperature and stress measuring accuracy is enhanced.
Owner:WEIHAI BEIYANG PHOTOELECTRIC INFORMATION TECH
Pulsed cascaded raman laser
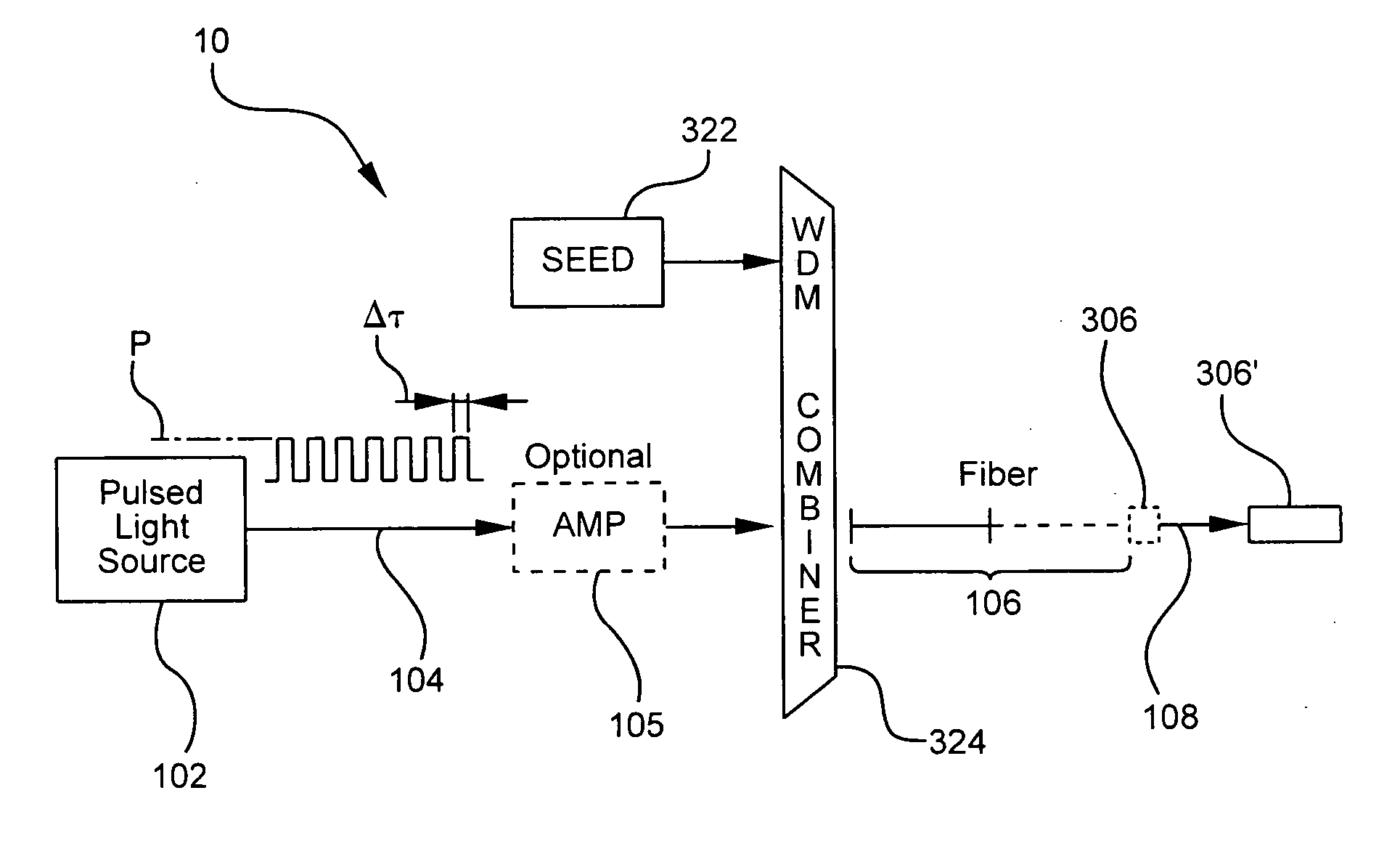
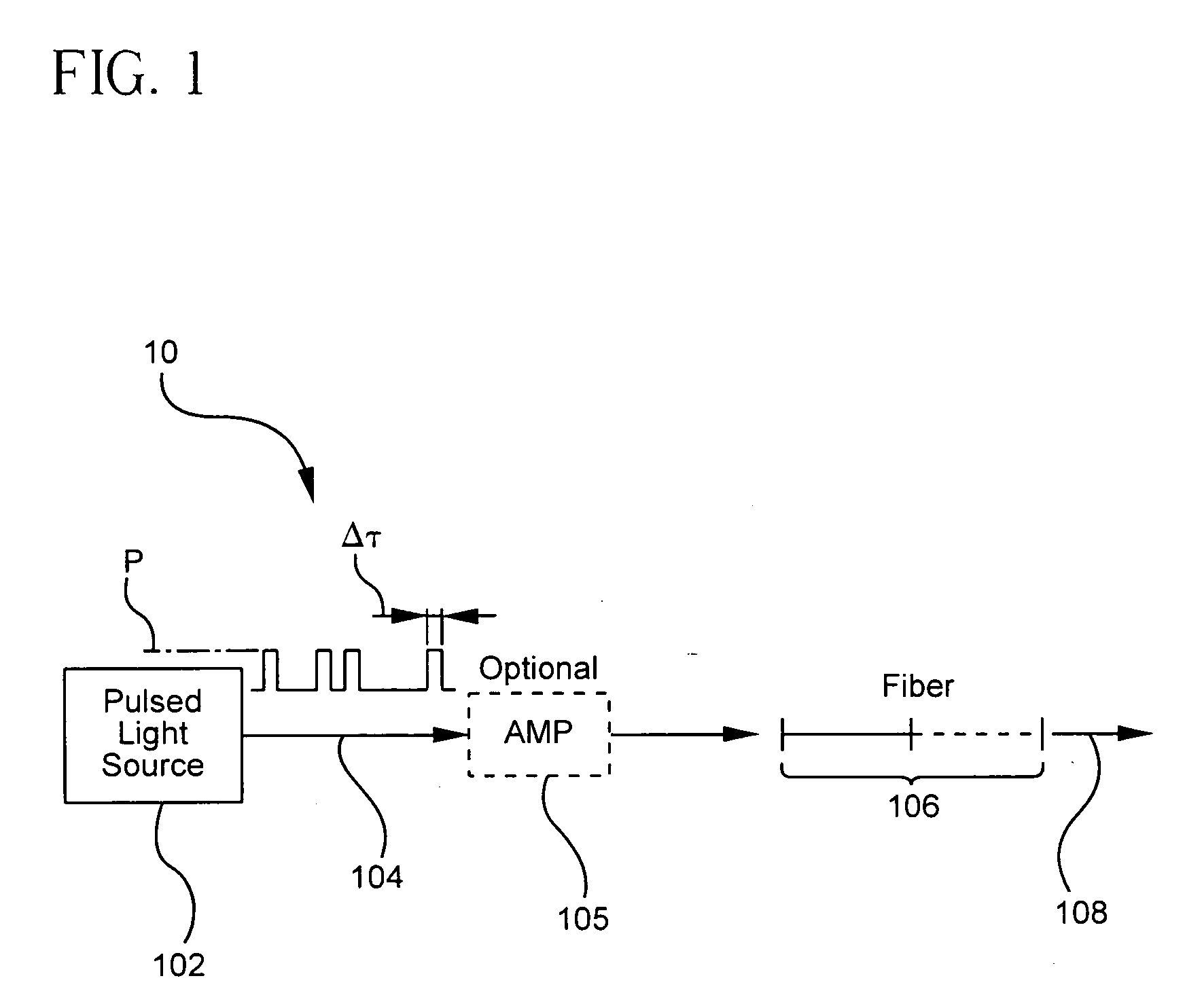
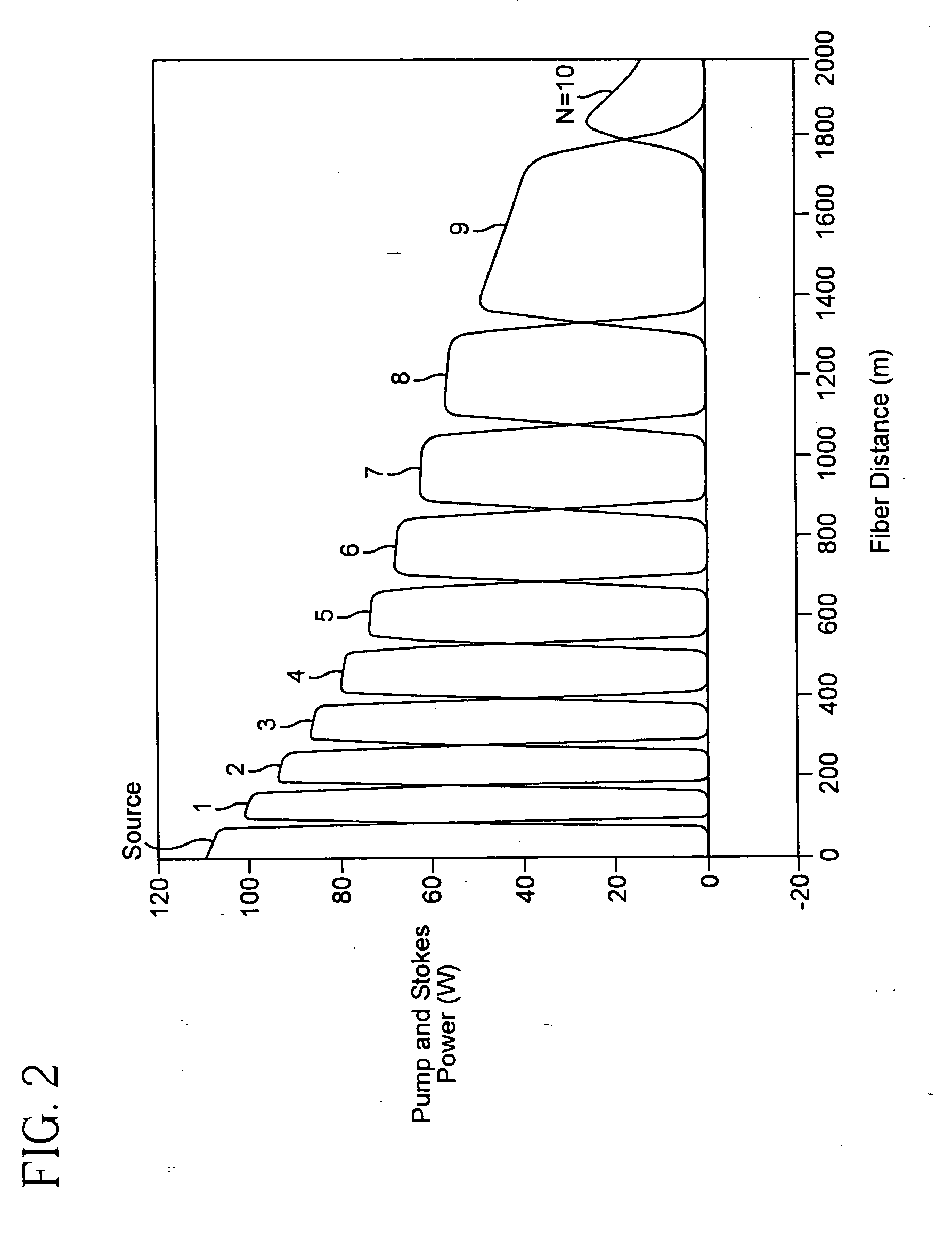
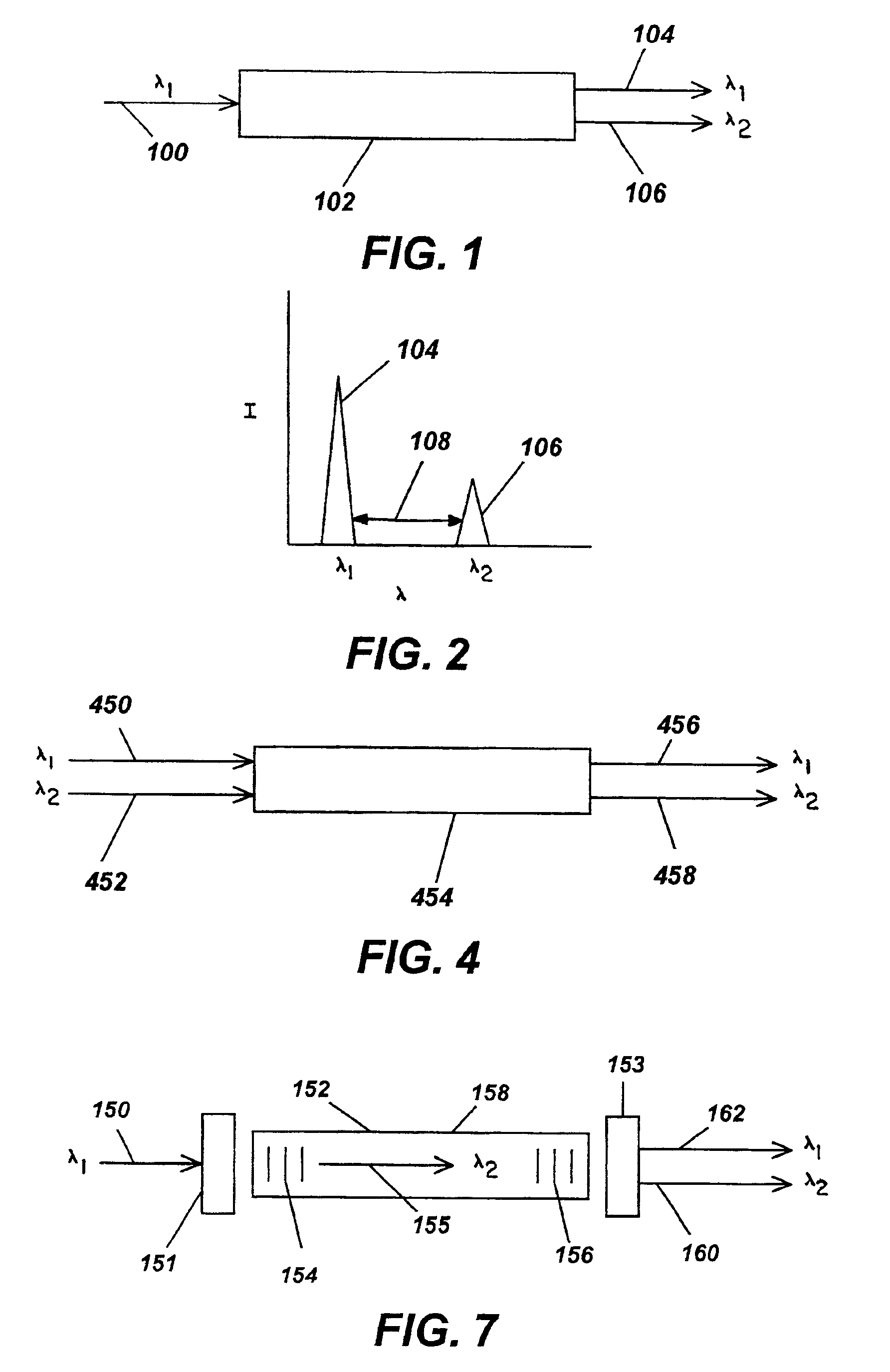
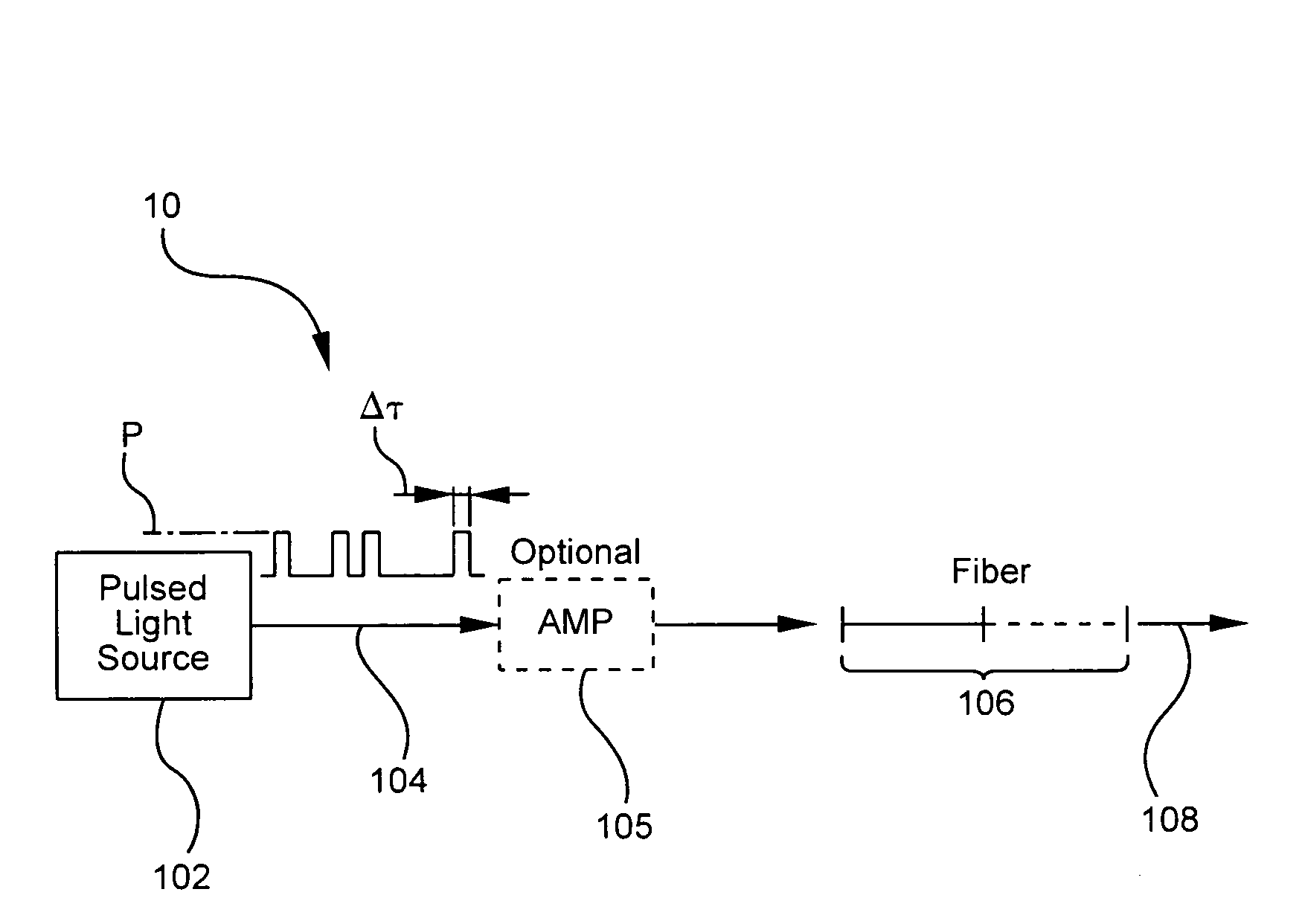
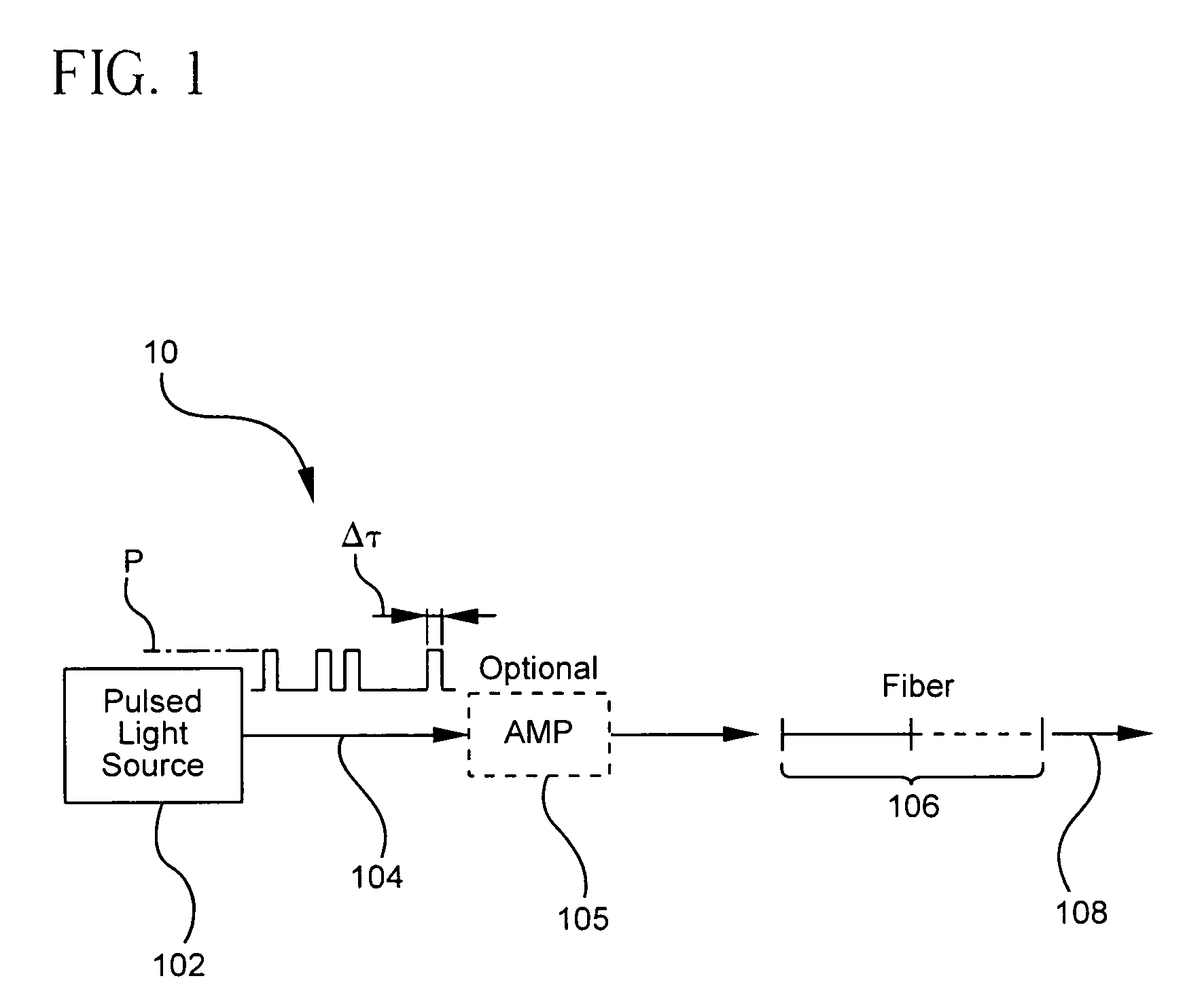
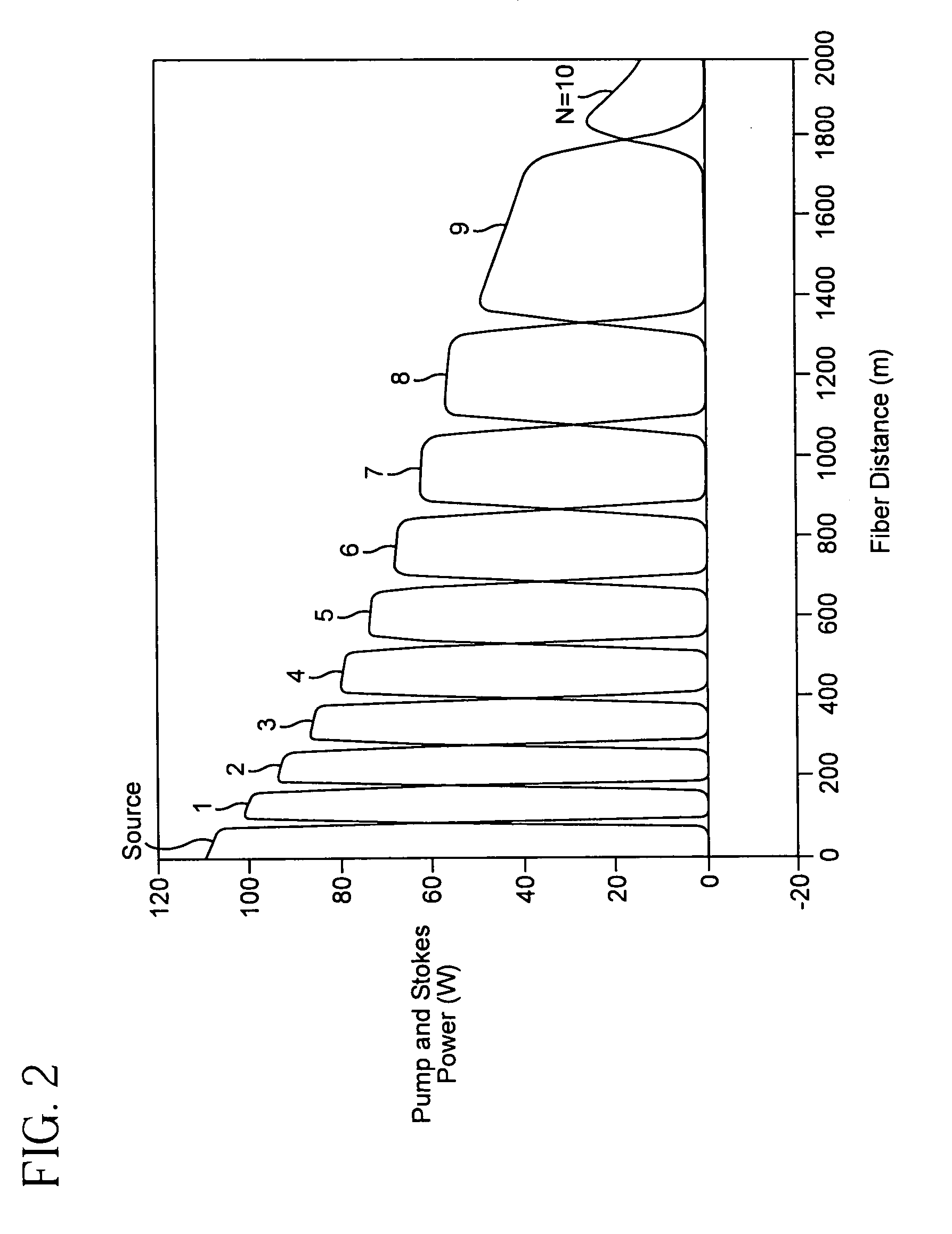
A pulsed cascaded Raman laser (10) includes a pulsed light source (102) for generating a pulsed light (104) having an optical spectrum centered at a source wavelength. A non-linear Raman conversion fiber (106) is coupled to the pulsed light source (102). The pulsed light (104) traverses the nonlinear Raman conversion fiber (106) and the source power at the source wavelength is converted to a power output of an output signal (108) having an output wavelength longer than the source wavelength by a cascaded Stimulated Raman Scattering process, such that most of the source power is converted to the power of the last Stokes order in a single pass through the non-linear Raman conversion fiber (106).
Owner:CORNING INC
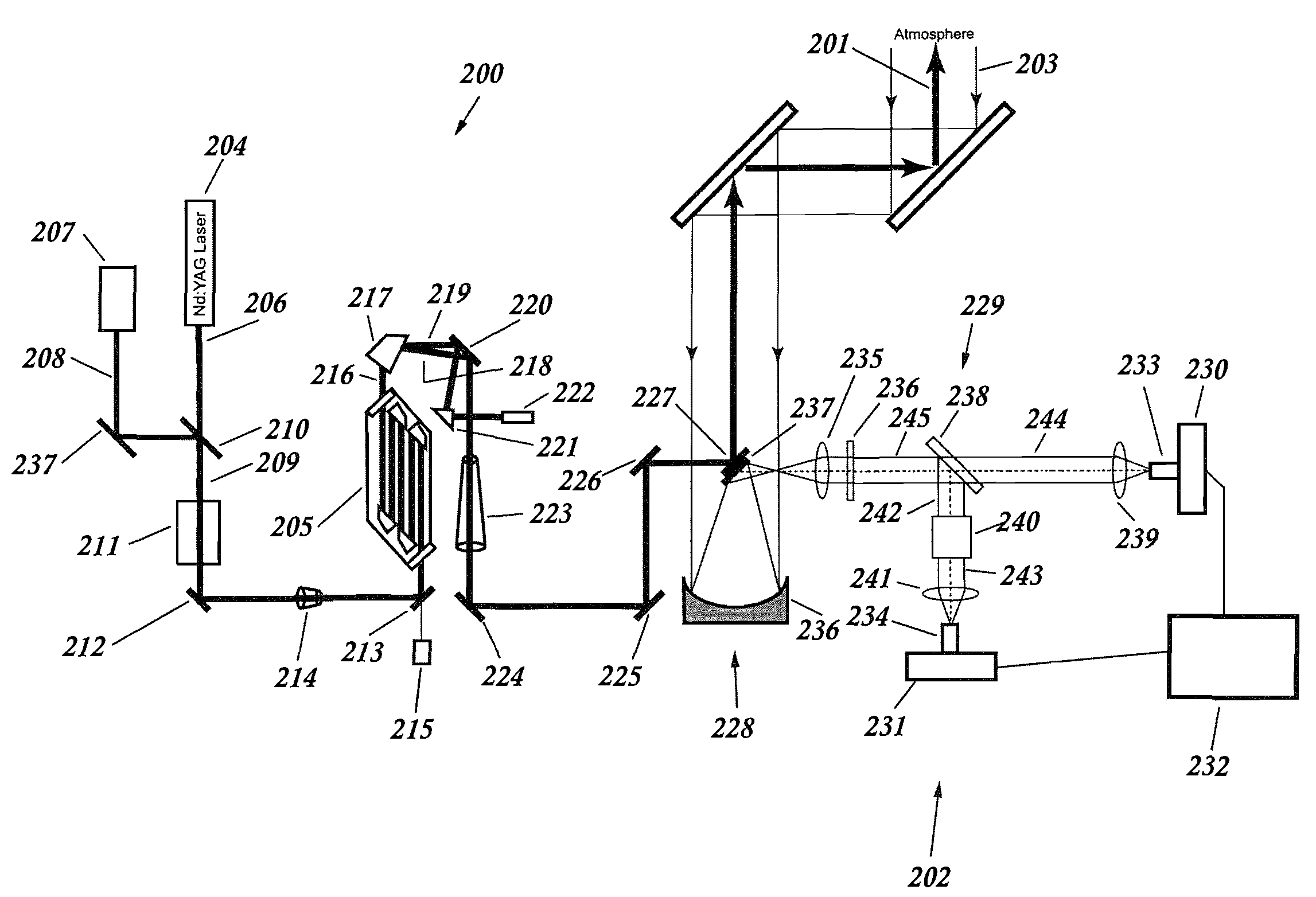
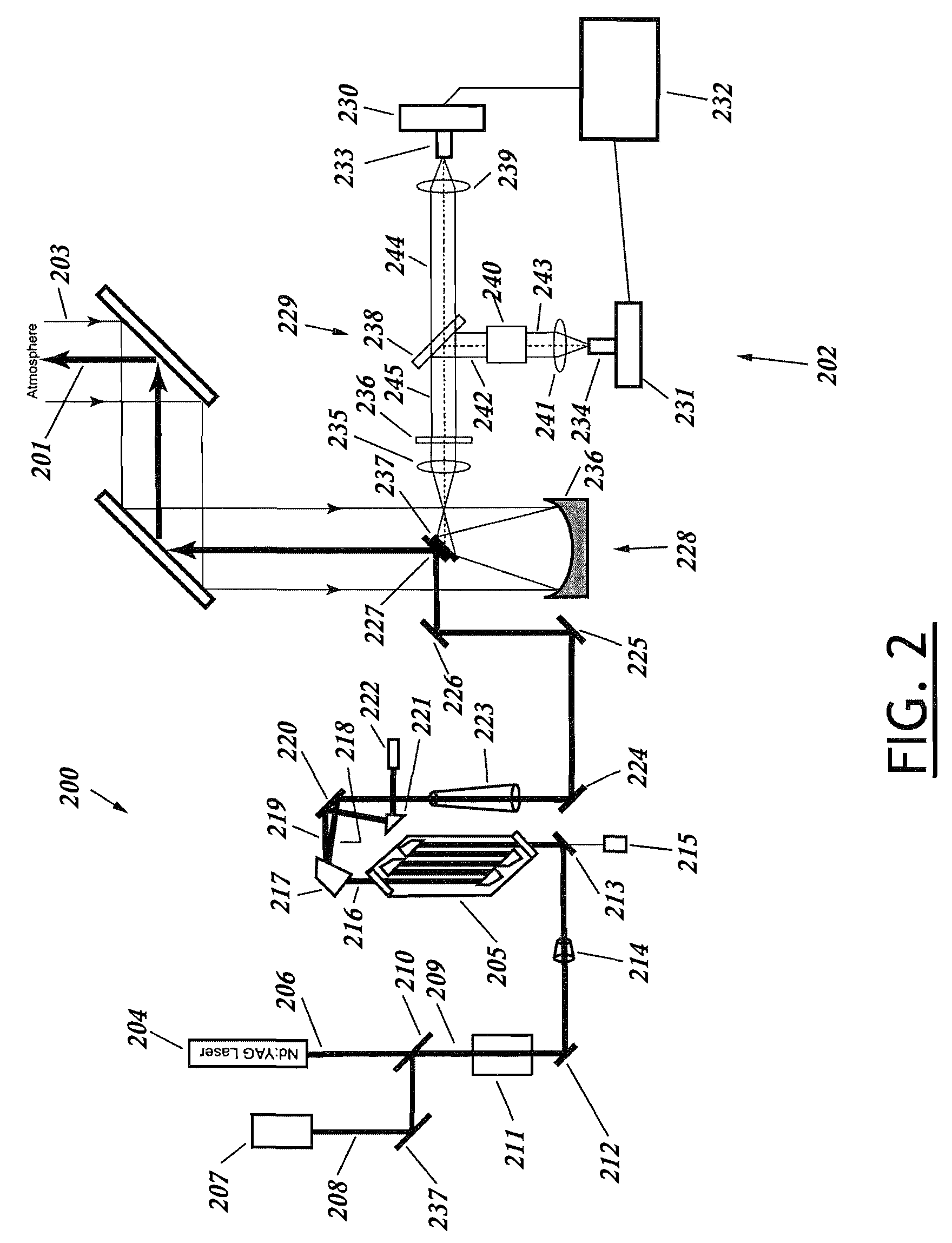
Lidar system for remote determination of calibrated, absolute aerosol backscatter coefficients
ActiveUS7656526B1Effort directedSafely and quickly and efficiently identifyRaman scatteringParticle size analysisBeam splitterAerosol backscatter
A lidar system capable of remotely identifying calibrated absolute aerosol backscatter coefficients of atmospheric aerosol particles by transmitting a beam of light and spectrally separating the intensity of Rayleigh and Mie backscattering is disclosed. The transmitter features high pulse energy to generate sufficient Rayleigh backscattering, enabling atmospheric scanning in a timely manner. The transmitter employs a seeded Nd:YAG laser and a seeded stimulated Raman scattering wavelength shifter to achieve narrow bandwidth, eye-safe laser pulses. The receiver employs a telescope, collimating lens, beam splitter, molecular absorption filter, focusing lenses, and avalanche photodiodes. Mie backscattering is blocked by the molecular absorption filter to provide a Rayleigh signal, which is used with knowledge of atmospheric density to calibrate the Mie signal. The system is intended for atmospheric research and aerosol monitoring applications where calibrated Mie scattering intensity is necessary to measure the optical depths of aerosol structures such as plumes, clouds, and layers.
Owner:UNIV FOR ATMOSPHERIC RES
Methods and systems for coherent raman scattering
InactiveUS20160178439A1Reduce repetition rateReduce background signalRaman/scattering spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryImage resolutionStimulate raman scattering
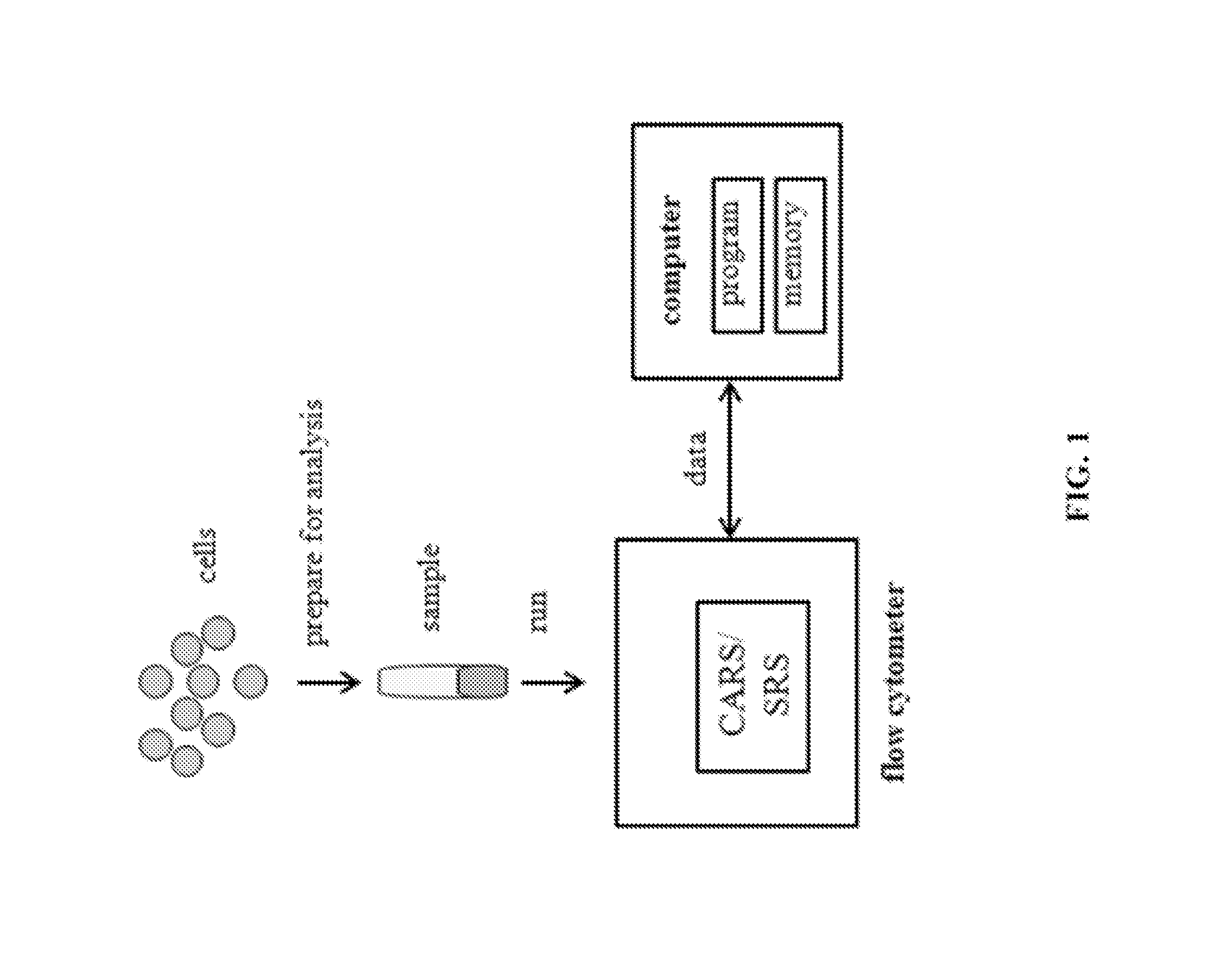
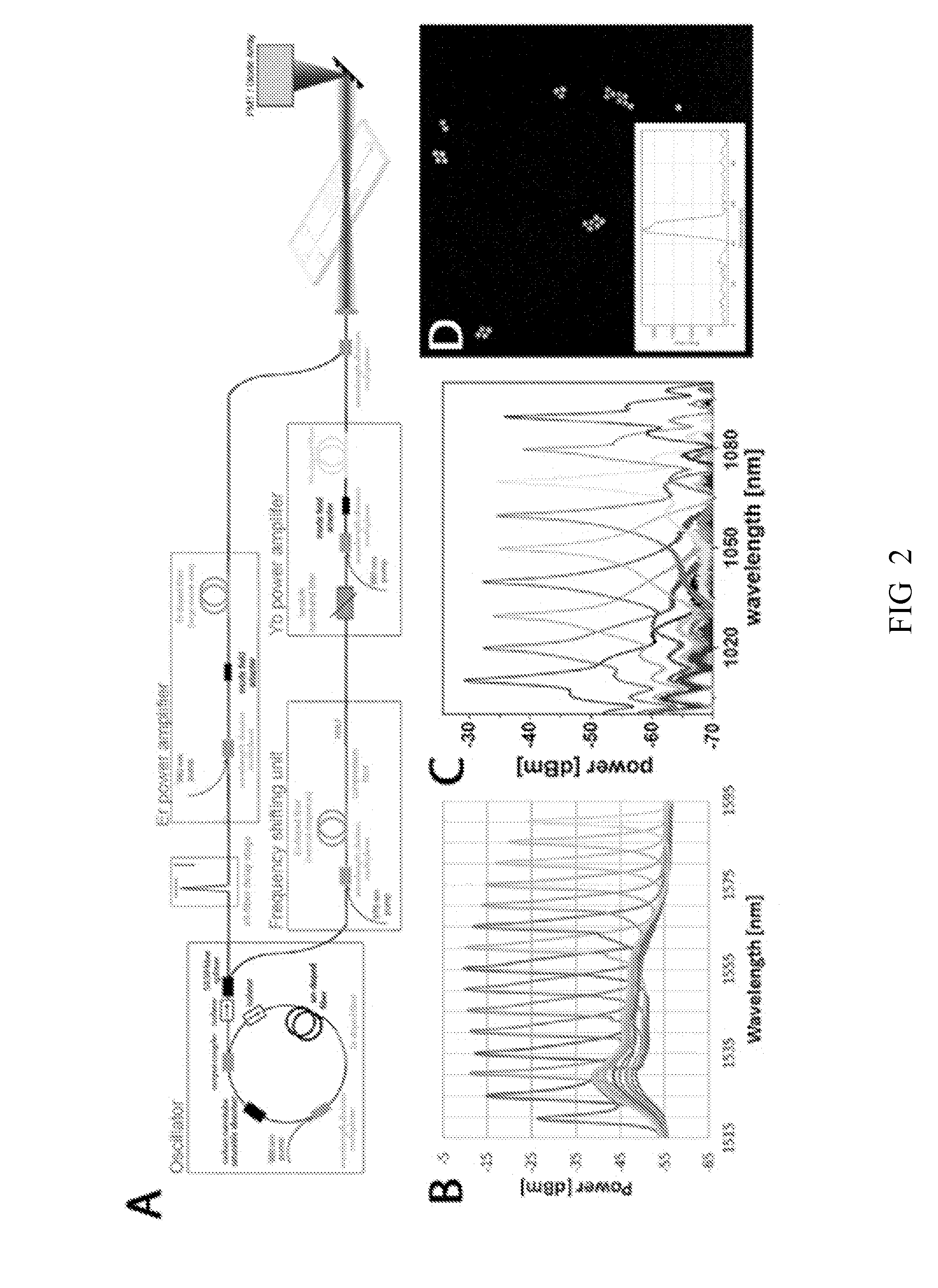
Systems and methods employing Coherent Raman Scattering (CRS), e.g., Coherent anti-Stokes Raman Spectroscopy (CARS) and / or Stimulated Raman Scattering (SRS) are provided. Systems and methods for performing flow cytometry, imaging and sensing using low-resolution CRS are also provided.
Owner:INVENIO IMAGING
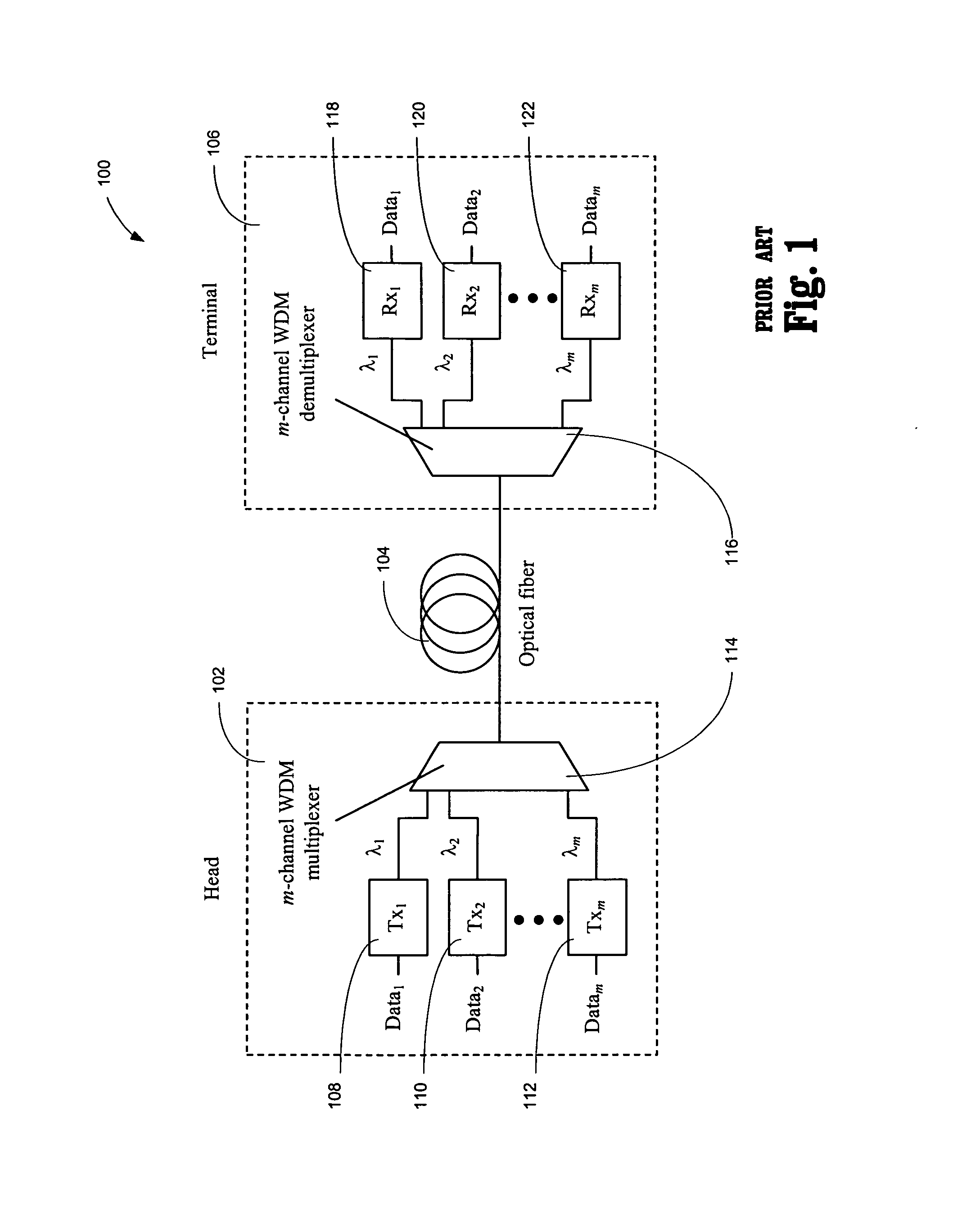
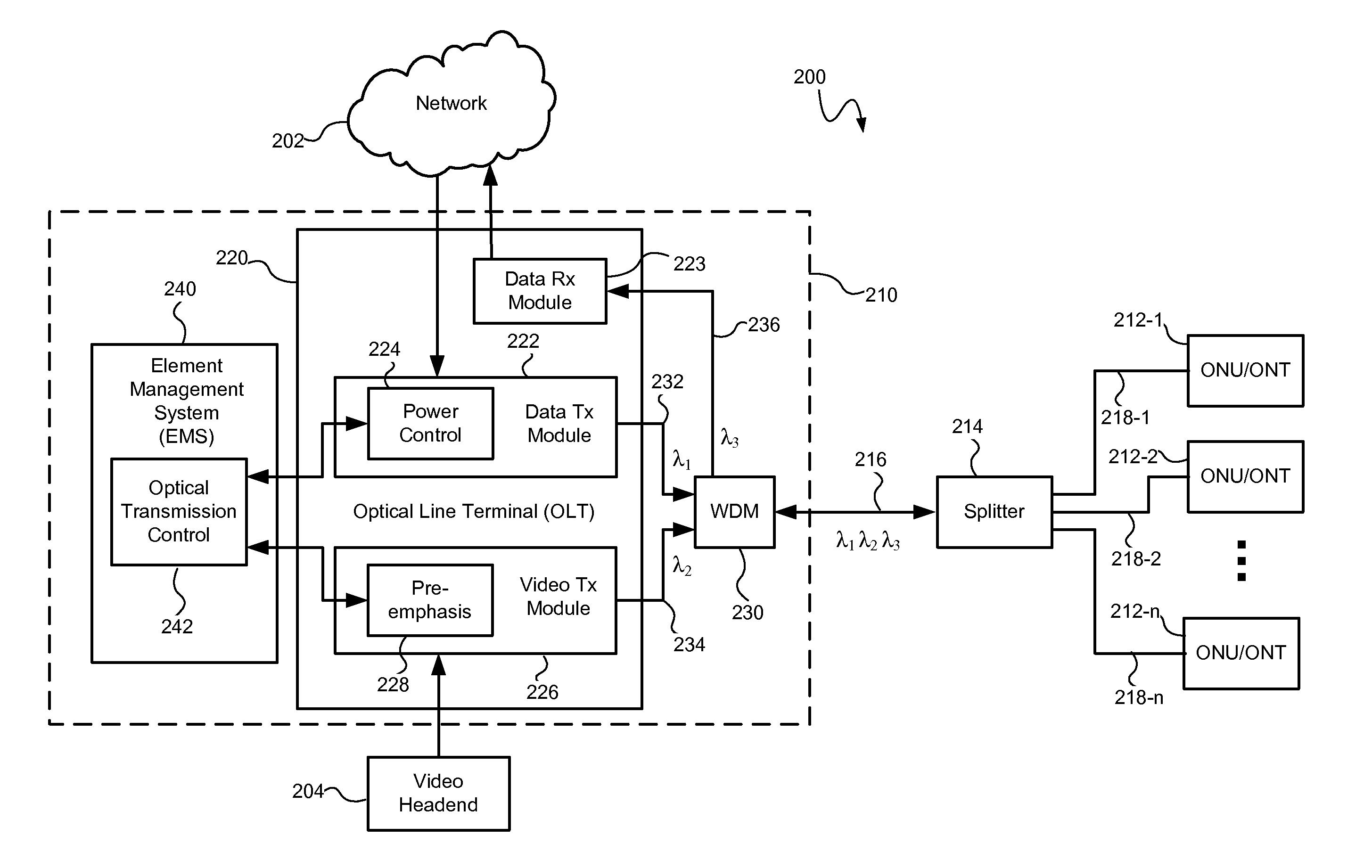
DWDM CATV return system with up-converters to prevent fiber crosstalk
InactiveUS20060165413A1Minimizing length of opticalReduce crosstalkOptical transmission adaptationsOptical multiplexFiberFrequency changer
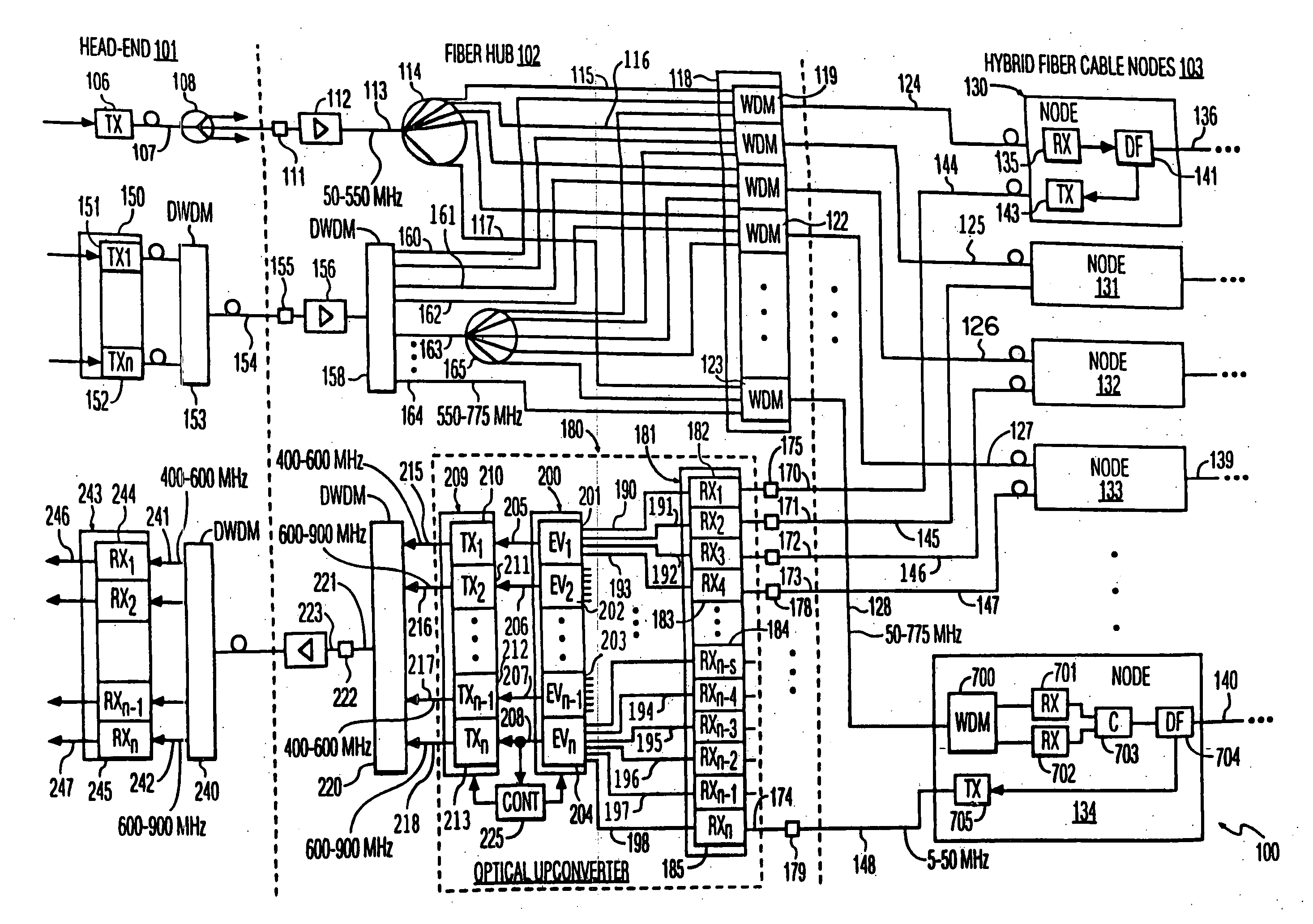
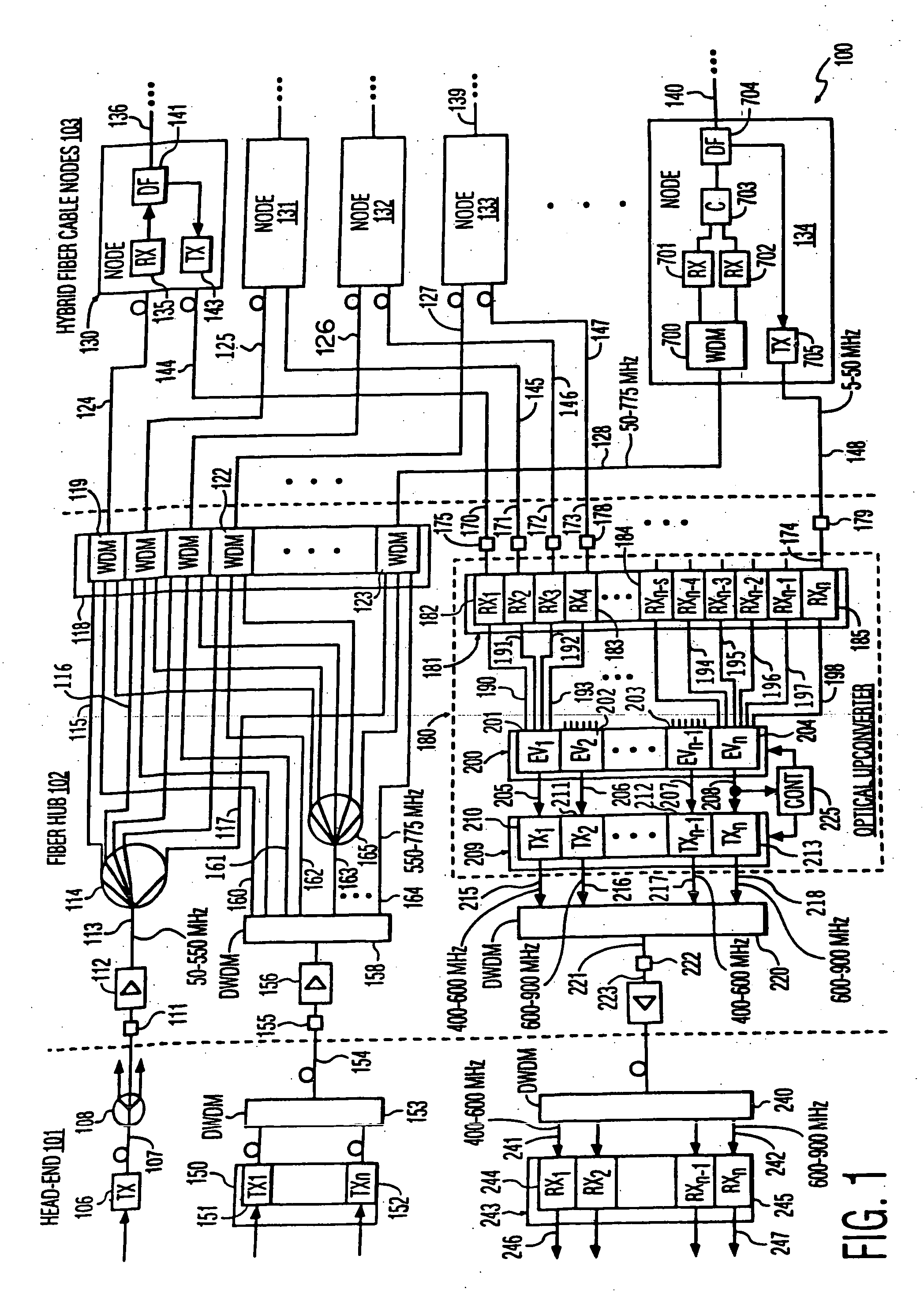
A hybrid fiber cable network includes multiple nodes, each of which receives a first multi-carrier return signal from multiple customers with carrier signals in a first frequency band. In a fiber-hub, one or more first multi-carrier signals are converted into a second multi-carrier signal with carrier signals in a second band. Each information signal modulates a different higher frequency carrier signal in the second signal. A multitude of second multi-carrier signals are converted into optical signals with different optical wavelengths, multiplexed onto an optical fiber, and transmitted to the head-end. The first frequency band is below 200 MHz, preferably from 5 to 50 MHz. The second frequency band is above 200 MHz, preferably between 300 and 1200 MHz to reduce crosstalk due to stimulated Raman scattering (SRS). Preferably, each second frequency band is no more than one octave wide, and more preferably, no more than one half an octave wide.
Owner:BROADBAND ROYALTY
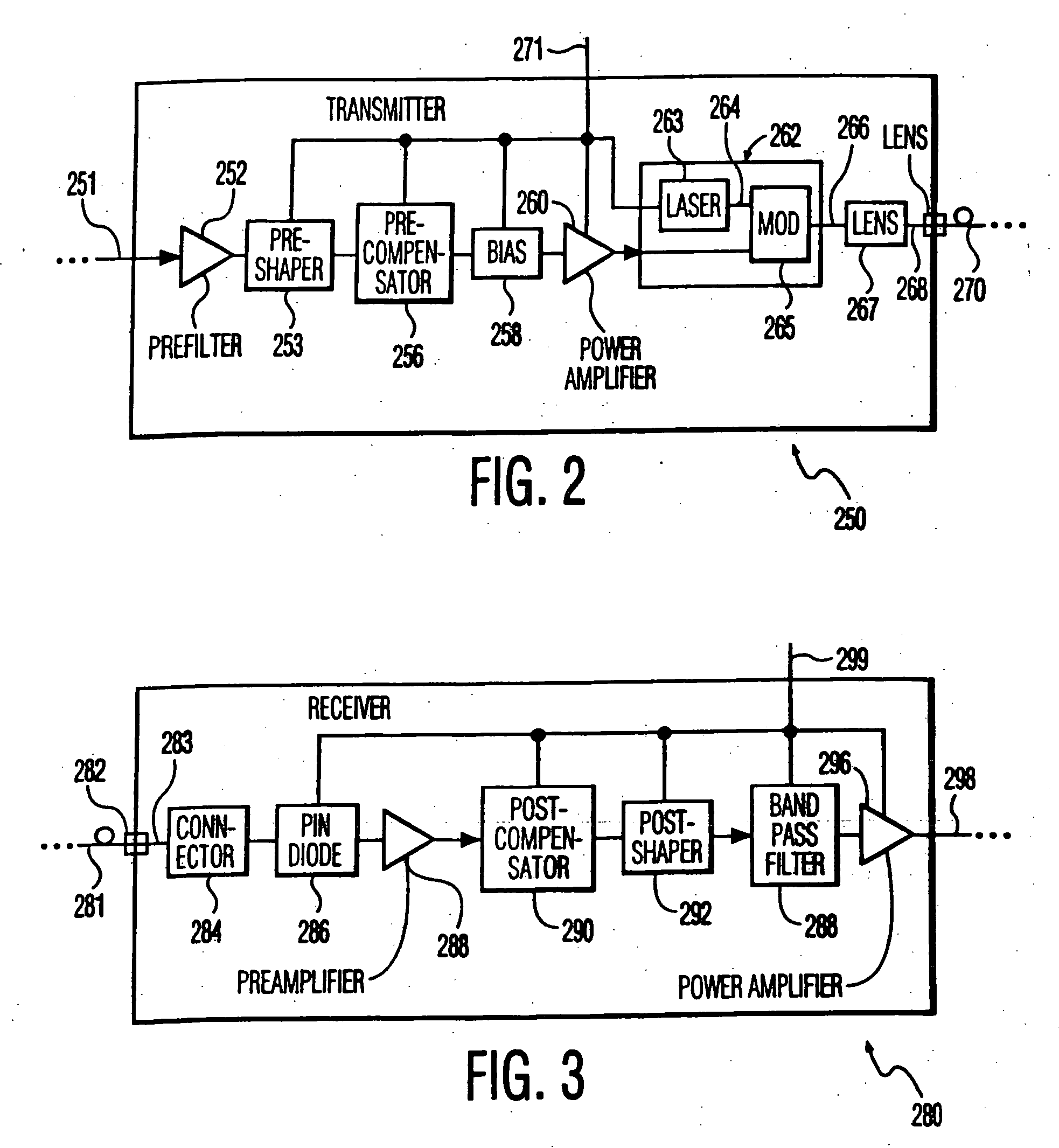
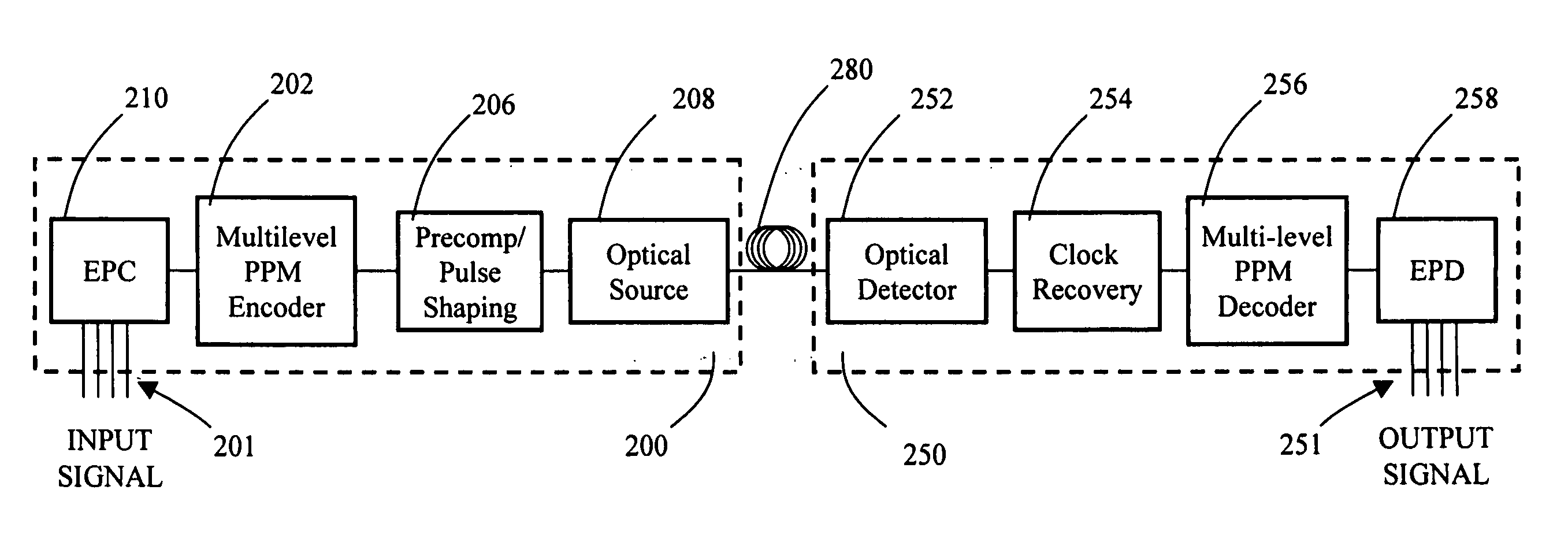
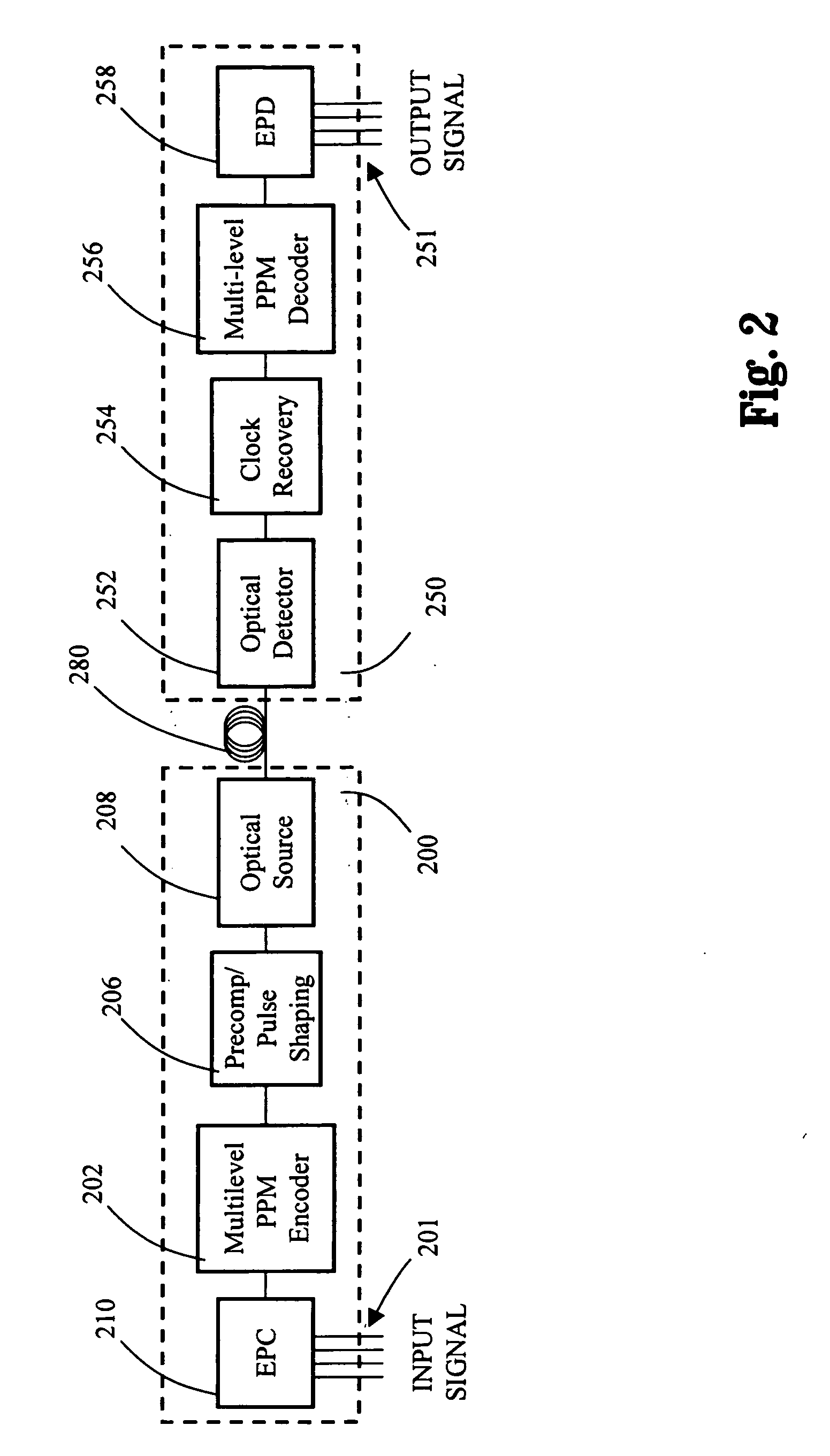
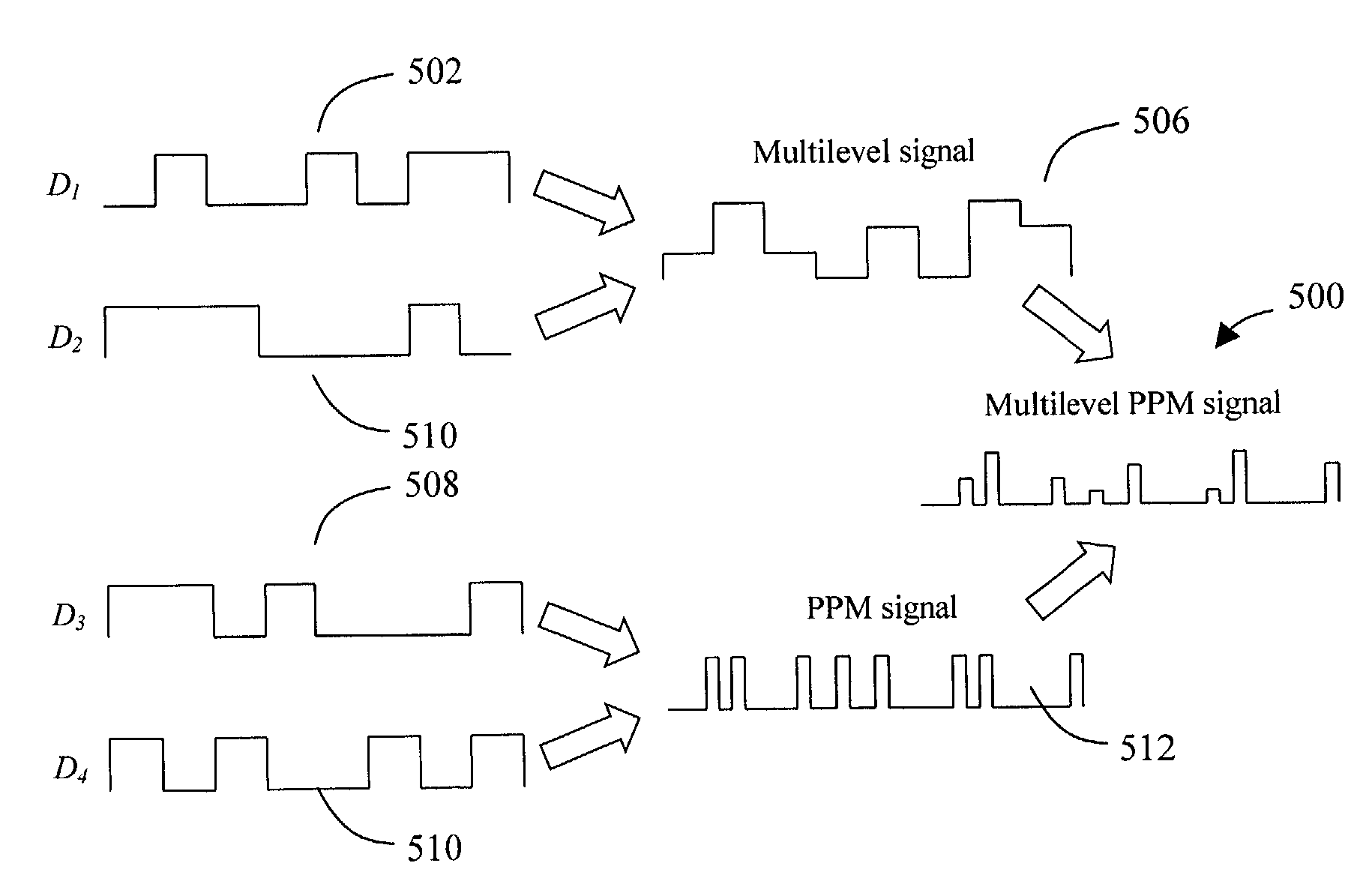
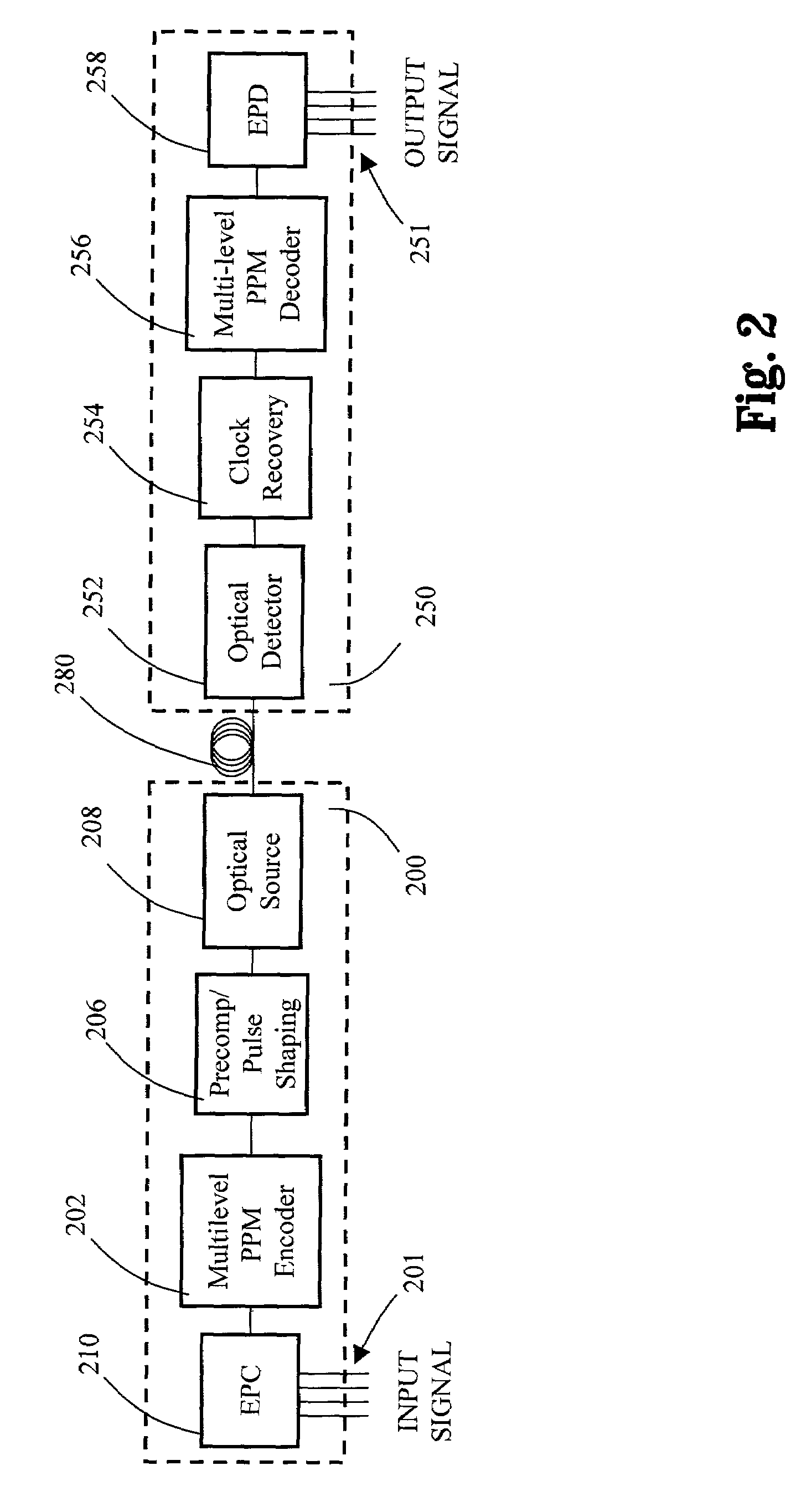
Multilevel pulse position modulation for efficient fiber optic communication
InactiveUS20070092265A1Increasing aggregate data rateReduce transmit powerModulated-carrier systemsElectromagnetic transmittersTransmitted powerStimulate raman scattering
Decreasing the average transmitted power in an optical fiber communication channel using multilevel amplitude modulation in conjunction with Pulse Position Modulation (PPM). This multilevel PPM method does not entail any tradeoff between decreased power per channel and channel bandwidth, enabling a lower average transmitted power compared to On / Off Keying (OOK) with no reduction in aggregate data rate. Therefore, multilevel PPM can be used in high-speed Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexed (DWDM) systems where the maximum number of channels is traditionally limited by nonlinear effects such as self-phase modulation (SPM), cross-phase modulation (XPM), four-wave mixing (FWM), stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS), and stimulated Raman scattering (SRS). This modulation technique can enable an increased number of channels in DWDM systems, thereby increasing aggregate data rates within those systems.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
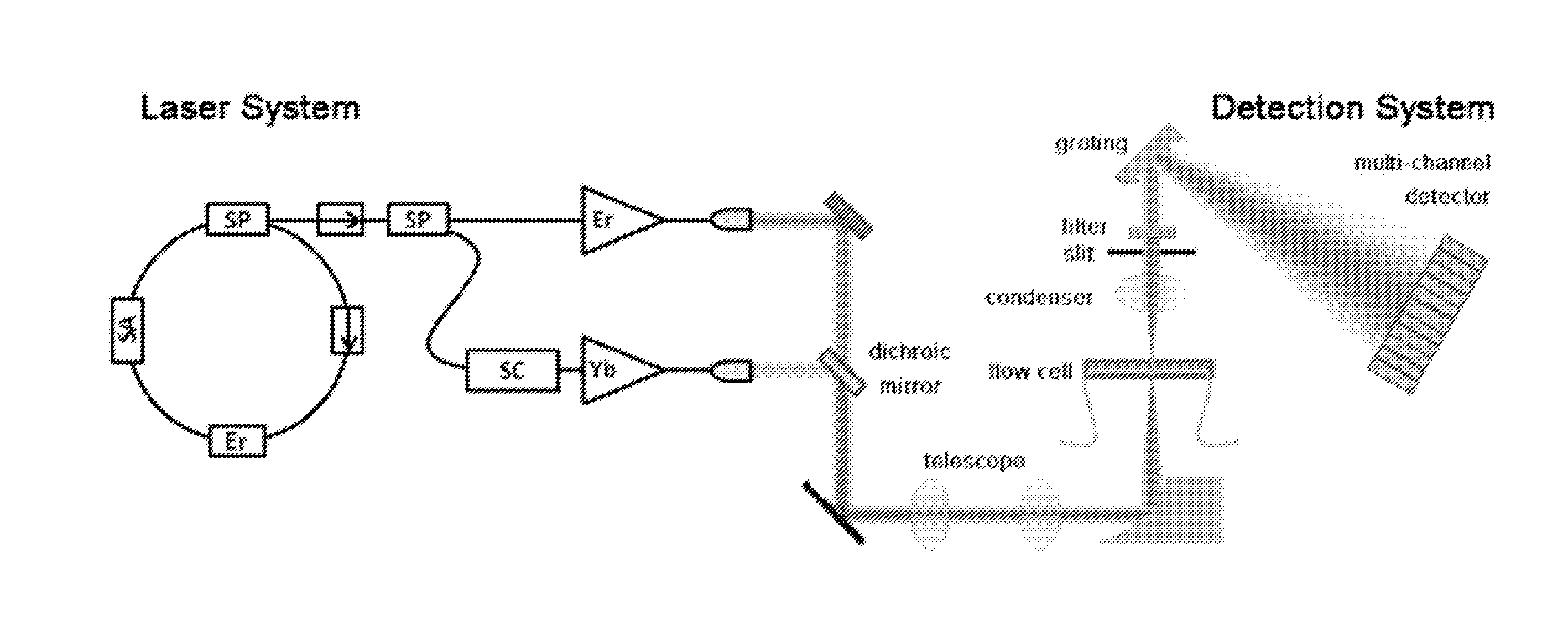
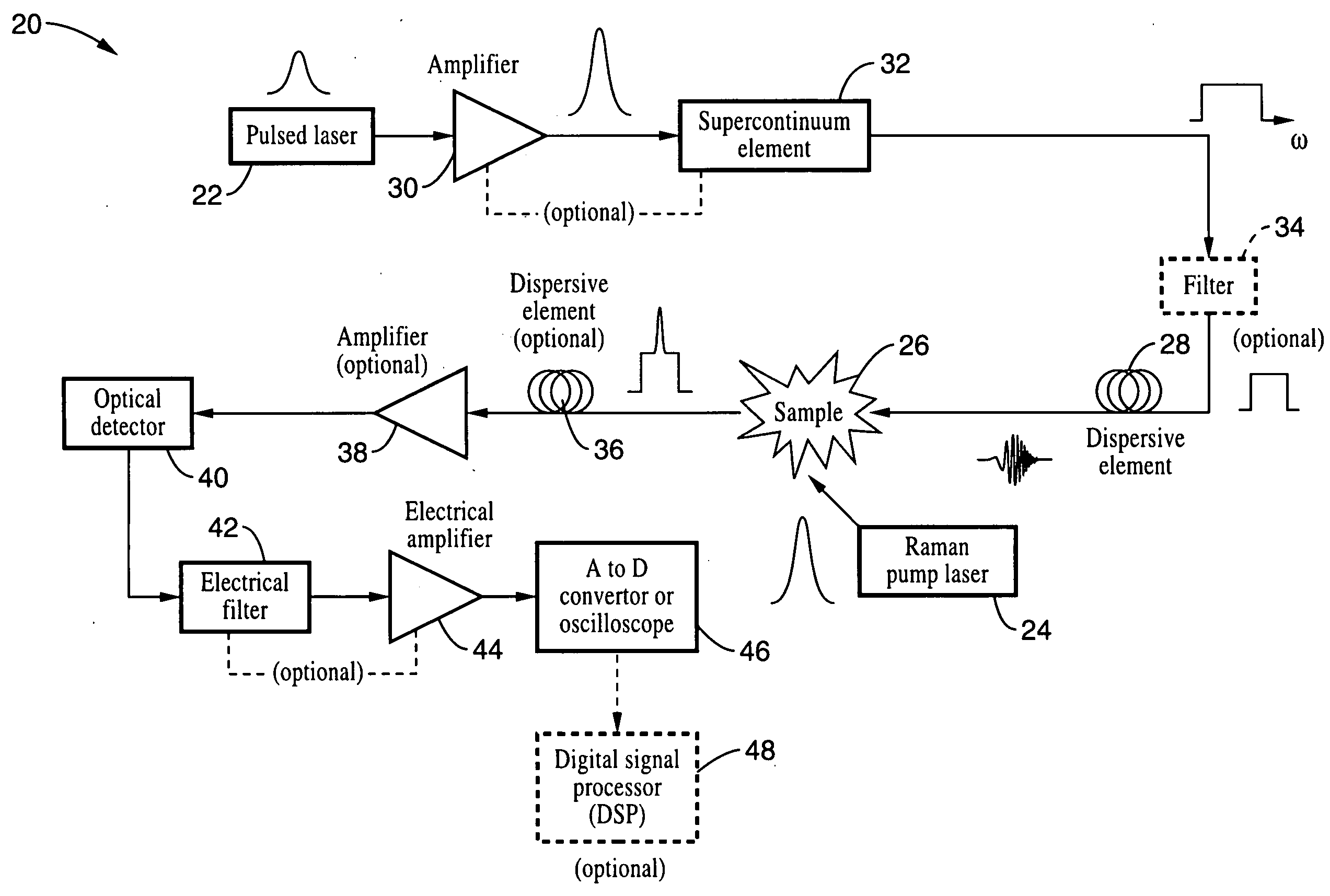
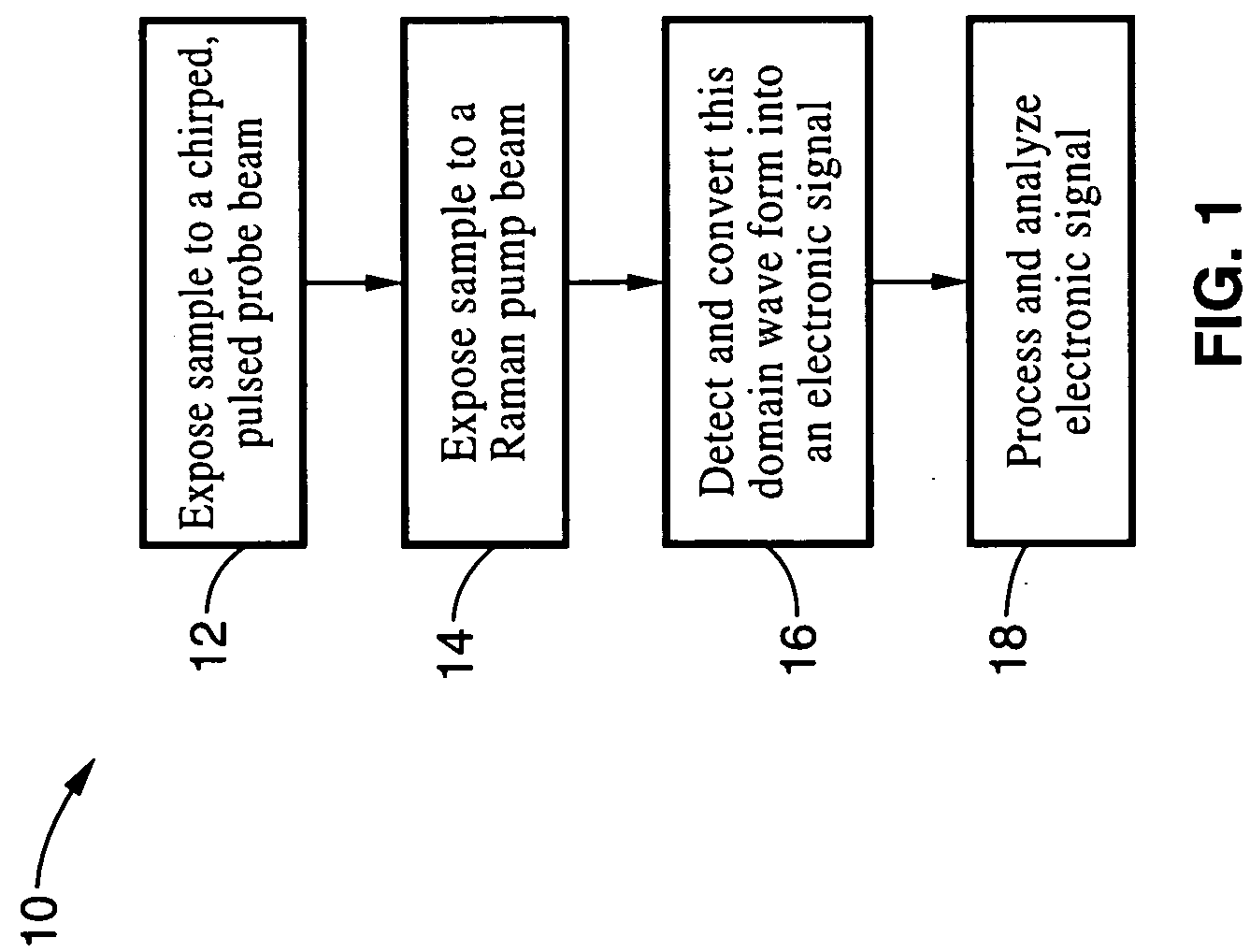
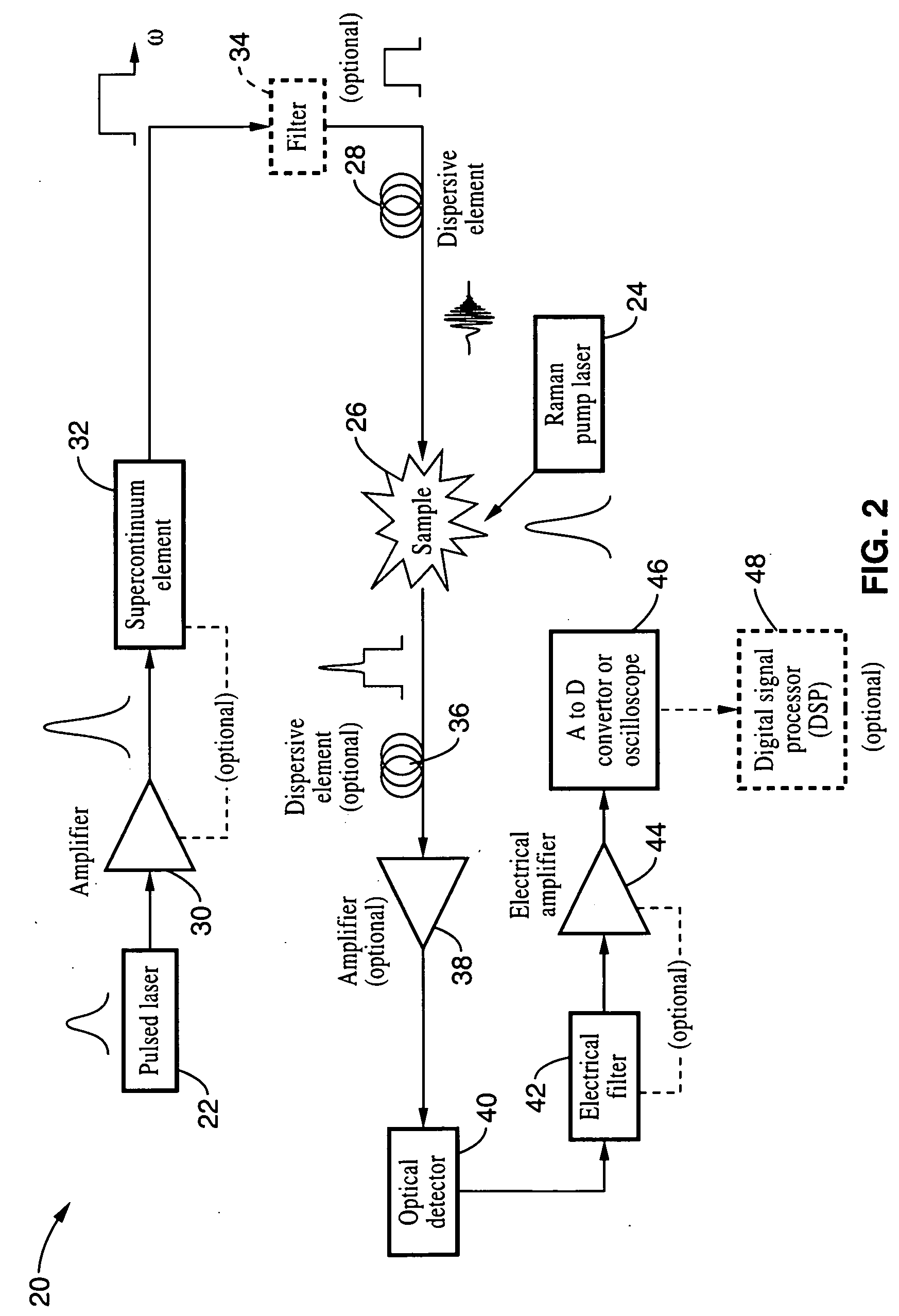
Apparatus and method for raman spectroscopy and microscopy with time domain spectral analysis
InactiveUS20090073432A1Eliminate needHigh speed moldingRaman/scattering spectroscopyRadiation pyrometrySpectroscopySpectrometer
An apparatus and method for measuring Raman-type spectra using optical dispersion to convert an optical spectrum into a waveform which can be detected directly in the time domain without the use of a conventional spectrometer. In the example of stimulated Raman spectroscopy, the apparatus and method exposes a sample to a chirped, pulsed probe beam and a Raman pump beam and the resulting Raman spectra is detected by an optical detector in the time domain, and analyzed. Alternatively, the Raman spectra from the probe and pump beams is chirped with a dispersive element prior to detection and analysis. Each probe pulse provides a snapshot of the Raman spectrum that is sampled in time so that neither repetitive waveforms nor static samples are required. Therefore, high speed acquisitions and high throughput assays can be conducted. To facilitate detection, these spectral signals can also be amplified using distributed Raman amplification directly in the dispersive element.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Solid state diamond Raman laser
InactiveUS20050163169A1High power applicationLaser using scattering effectsActive medium materialStimulate raman scatteringSingle crystal
A solid state Raman laser includes a laser pump for producing a first radiation at a high power and at a first wavelength along an optical path, a solid Raman active medium in the optical path of the first radiation, the medium including single crystal diamond having a first surface and a second surface, where the first radiation at a high power produces stimulated Raman scattering in the medium and the medium generates a second radiation at a second wavelength, a first optical element in the optical path of the first radiation, wherein the first optical element allows the first wavelength to be transmitted and allows the second wavelength to be reflected, and a second optical element in the optical path of the first radiation, wherein the second optical element allows the first wavelength to be transmitted and allows the second wavelength to be reflected.
Owner:SPECTRA SYST CORP
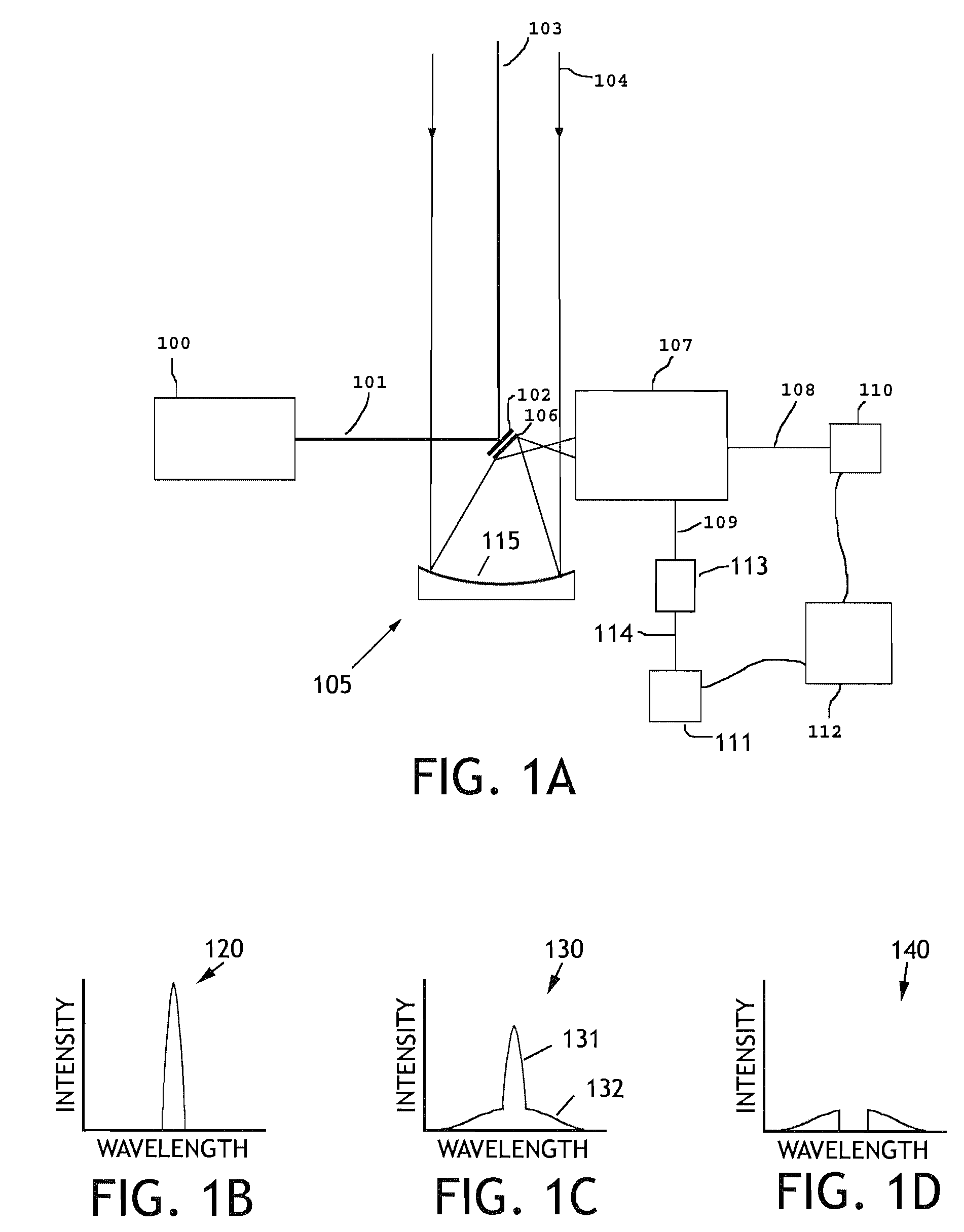
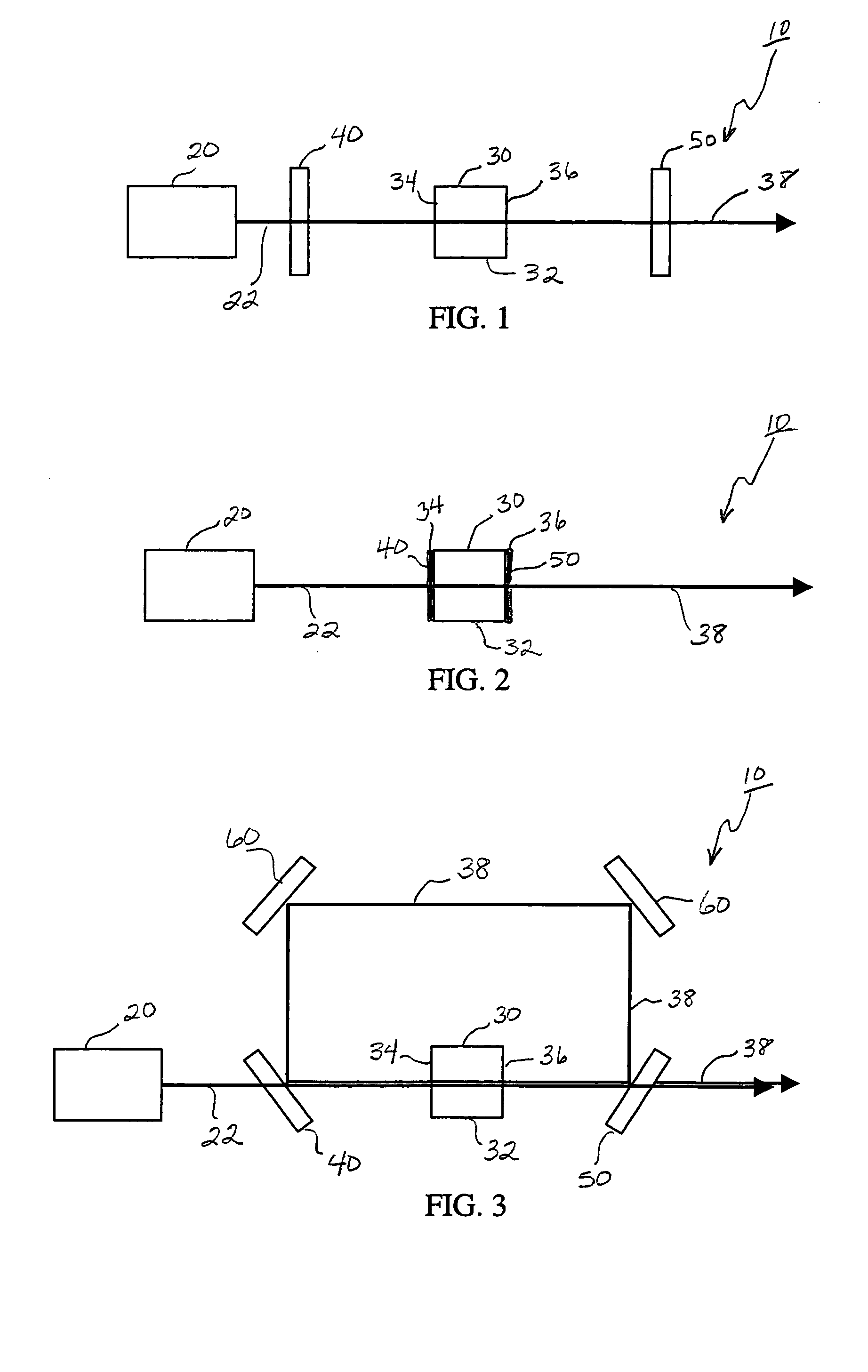
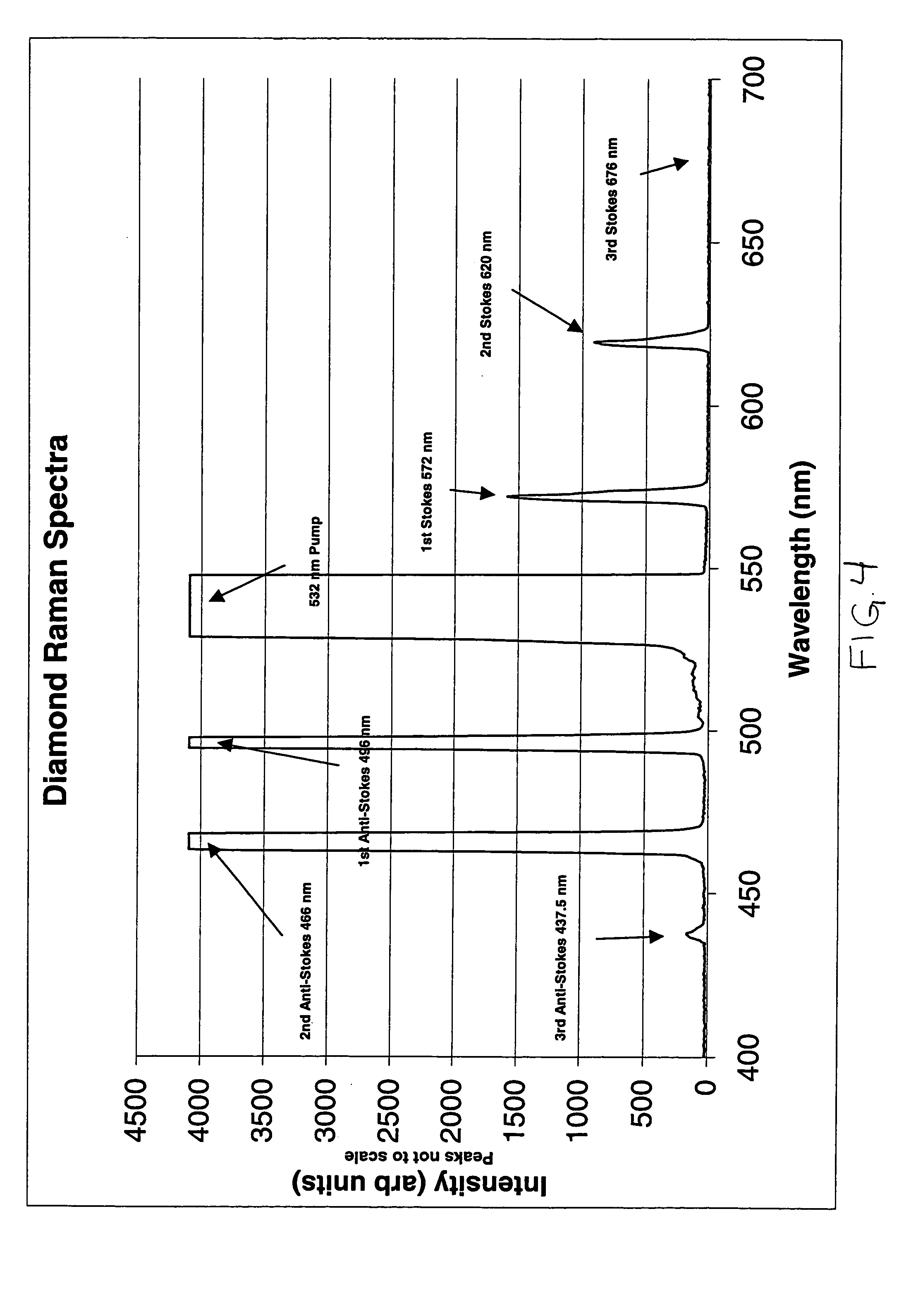
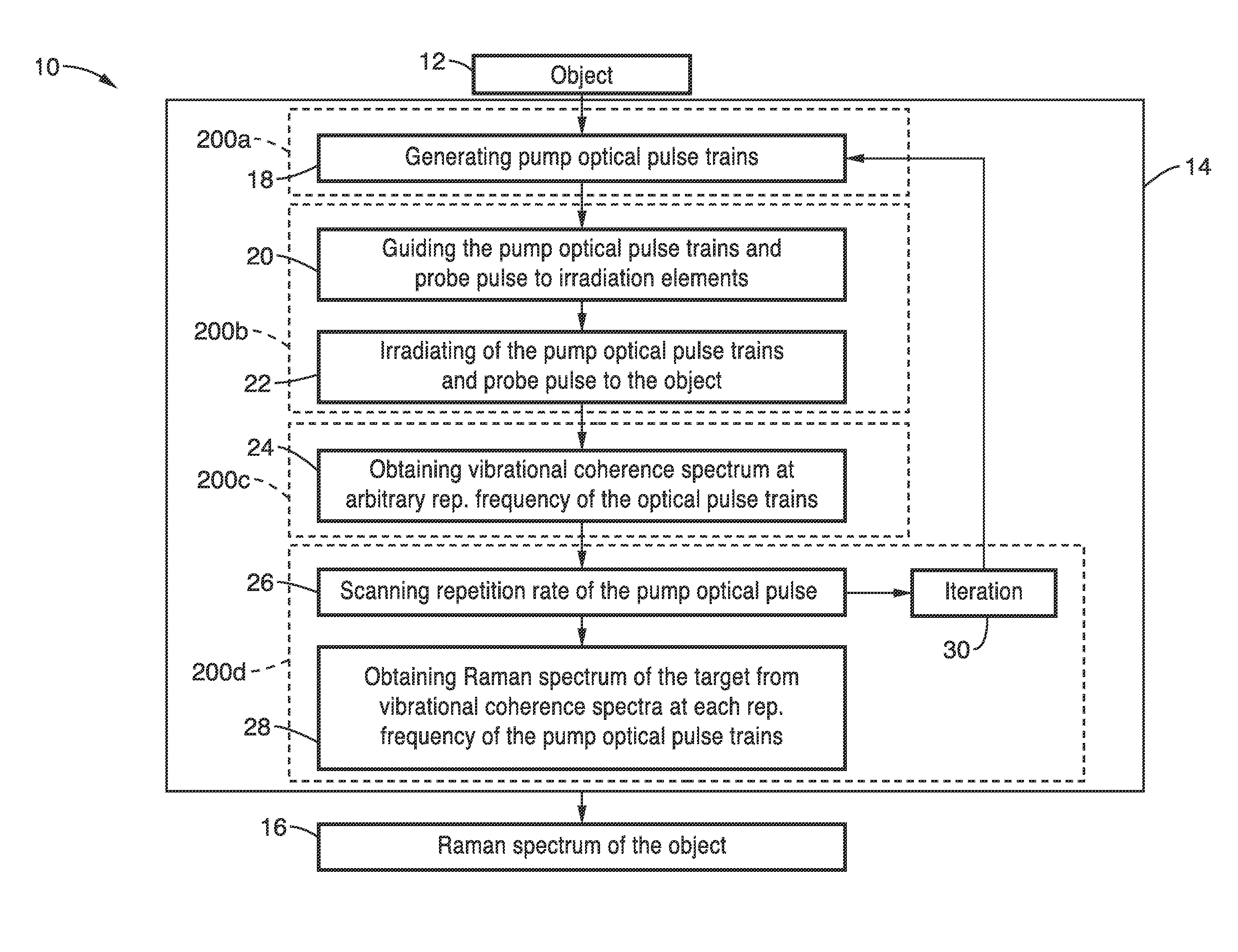
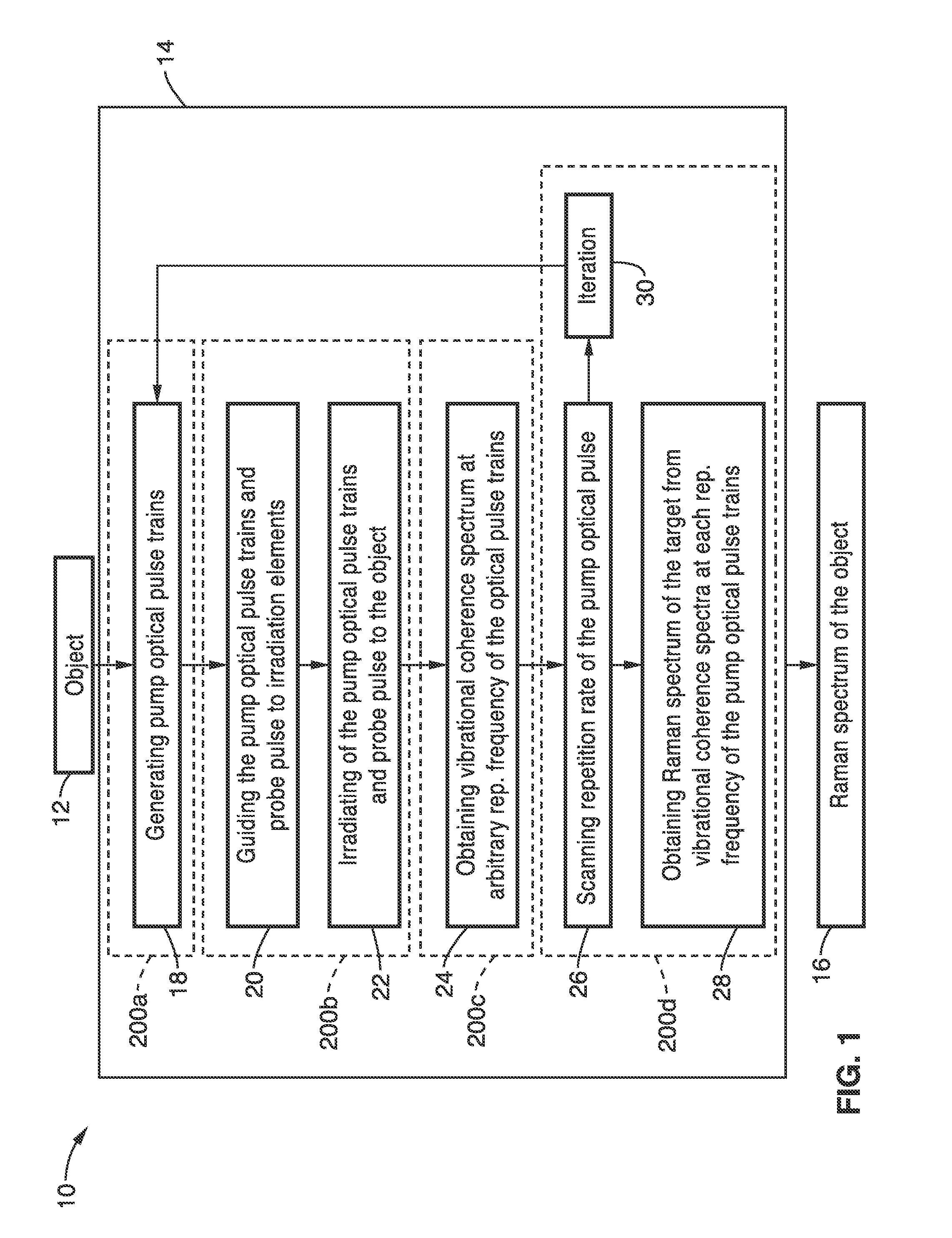
Apparatus and method for multiple-pulse impulsive stimulated raman spectroscopy
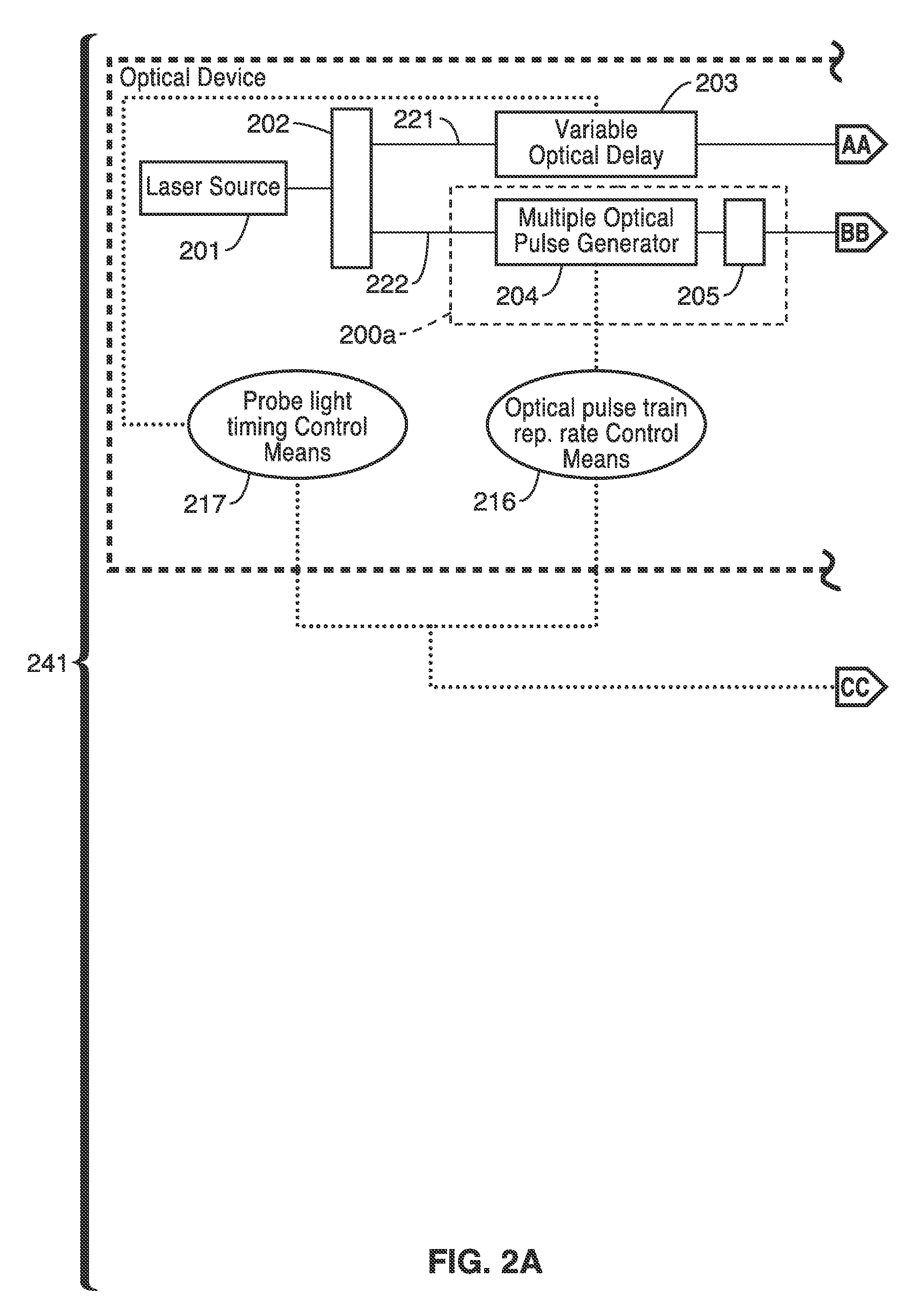
Spectroscopic measurements are described based on light-molecule interaction in response to a resonant rate optical pulse train so that a Raman spectrum is reflected containing at least two types of vibrational mode information (e.g., vibrational frequency, and vibrational phase relaxation) on the molecules comprising the object. A pump optical pulse train generation means is configured for generating an optical pulse train having an arbitrary repetition rate which is directed through irradiation means to the sample object. Light from the sample object is collected and vibrational coherence is detected for the sample object. The sample is tested across a plurality of different repetition frequencies. The detected information can be compared with data from other known samples from within a database when analyzing the information collected.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP +1
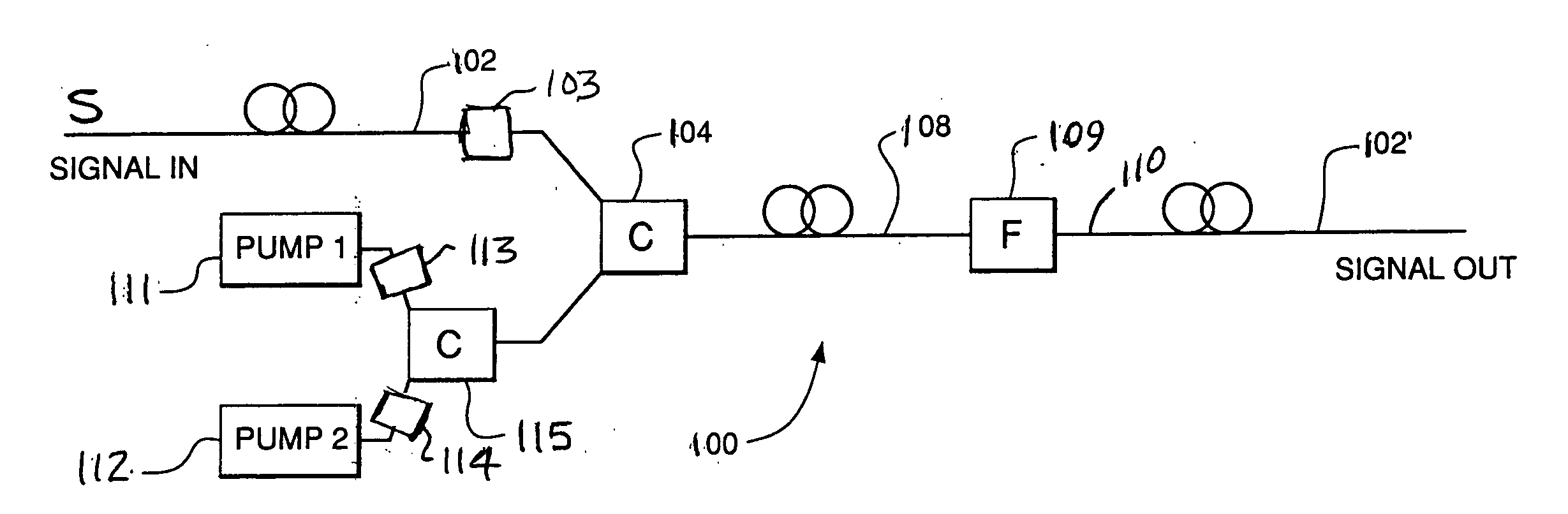
Light amplification element, light amplification apparatus and light amplification system
InactiveUS20050237602A1Efficient excitationEnhance stimulated Raman scatteringLaser using scattering effectsNon-linear opticsRough surfaceSurface plasmon
A small, low power consumption light amplifier using stimulated Raman scattering is provided. A Raman active section 18 and a rough surface metal part 21 are provided on one end face of an optical fiber 11, excitation light is irradiated onto the rough surface metal part 21, surface plasmon is generated and signal light 15 is amplified into amplified signal light 16 using stimulated Raman scattering in the interface between the rough surface metal part 21 irradiated with the signal light 15 which has propagated through the core 12 and the Raman active section 18.
Owner:NEC CORP
Multilevel pulse position modulation for efficient fiber optic communication
InactiveUS7149256B2Reduce transmit powerIncreasing aggregate data rateAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsTransmission monitoringTransmitted powerStimulate raman scattering
Decreasing the average transmitted power in an optical fiber communication channel using multilevel amplitude modulation in conjunction with Pulse Position Modulation (PPM). This multilevel PPM method does not entail any tradeoff between decreased power per channel and channel bandwidth, enabling a lower average transmitted power compared to On / Off Keying (OOK) with no reduction in aggregate data rate. Therefore, multilevel PPM can be used in high-speed Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexed (DWDM) systems where the maximum number of channels is traditionally limited by nonlinear effects such as self-phase modulation (SPM), cross-phase modulation (XPM), four-wave mixing (FWM), stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS), and stimulated Raman scattering (SRS). This modulation technique can enable an increased number of channels in DWDM systems, thereby increasing aggregate data rates within those systems.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Multiple Laser Projection System
InactiveUS20130162952A1Improve aspectProjectorsColor television detailsStimulate raman scatteringGreen laser
A method and apparatus for despeckling that includes a green laser diode, a DPSS laser, and stimulated Raman scattering light formed in an optical fiber. The laser diode light and stimulated Raman scattering light are combined to form a projected digital image. The output of the optical fiber may be split into two spectrums. The projected digital image may be stereoscopic with one image formed from the laser diode light and one spectrum, and the other image formed from the other spectrum.
Owner:PROJECTION VENTURES INC
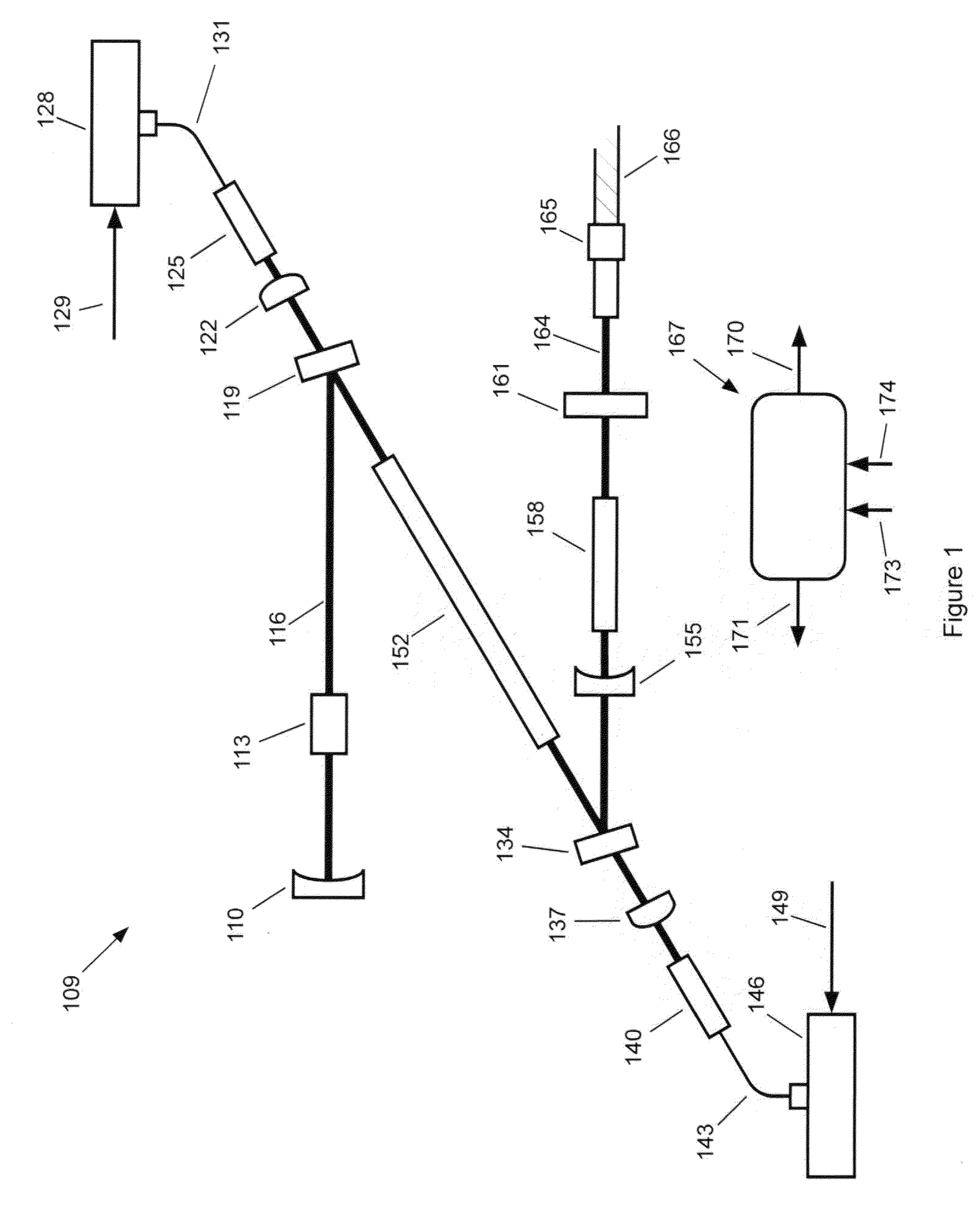
Method and apparatus for generation and transmission of high energy optical pulses for long range measurements
InactiveUS20060210269A1Increase distanceLower fibre scatter lossesRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansHigh energyImage resolution
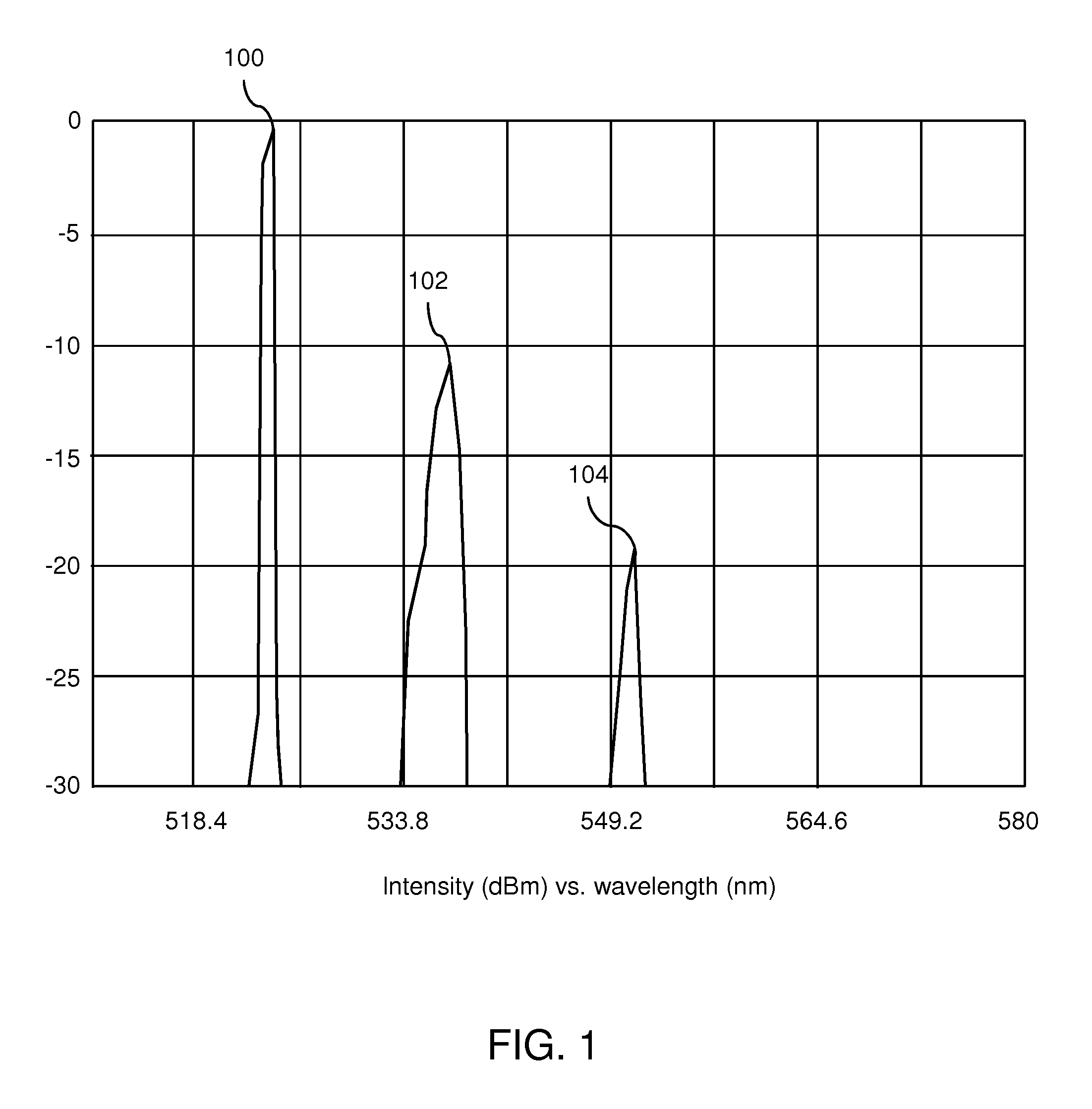
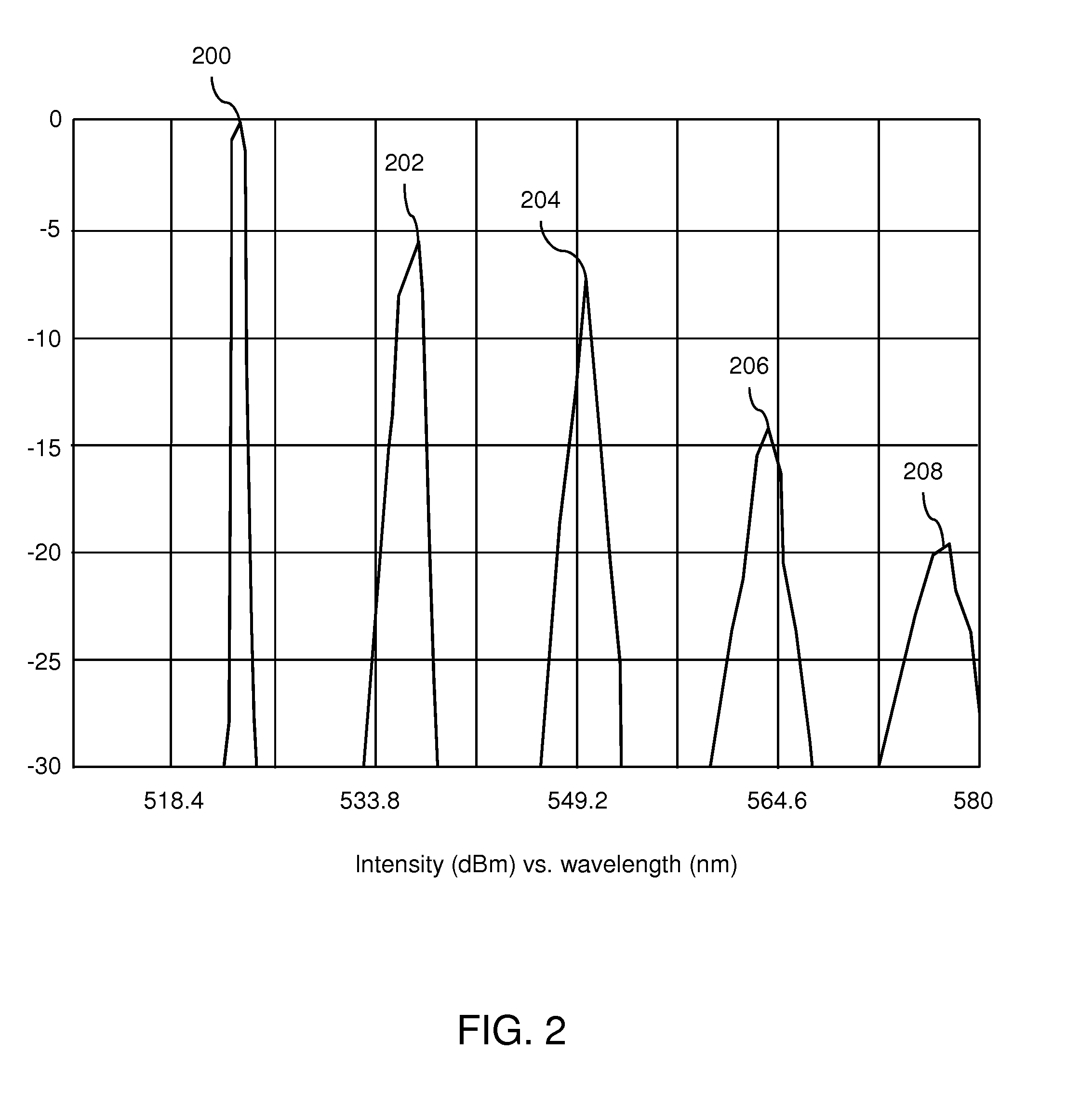
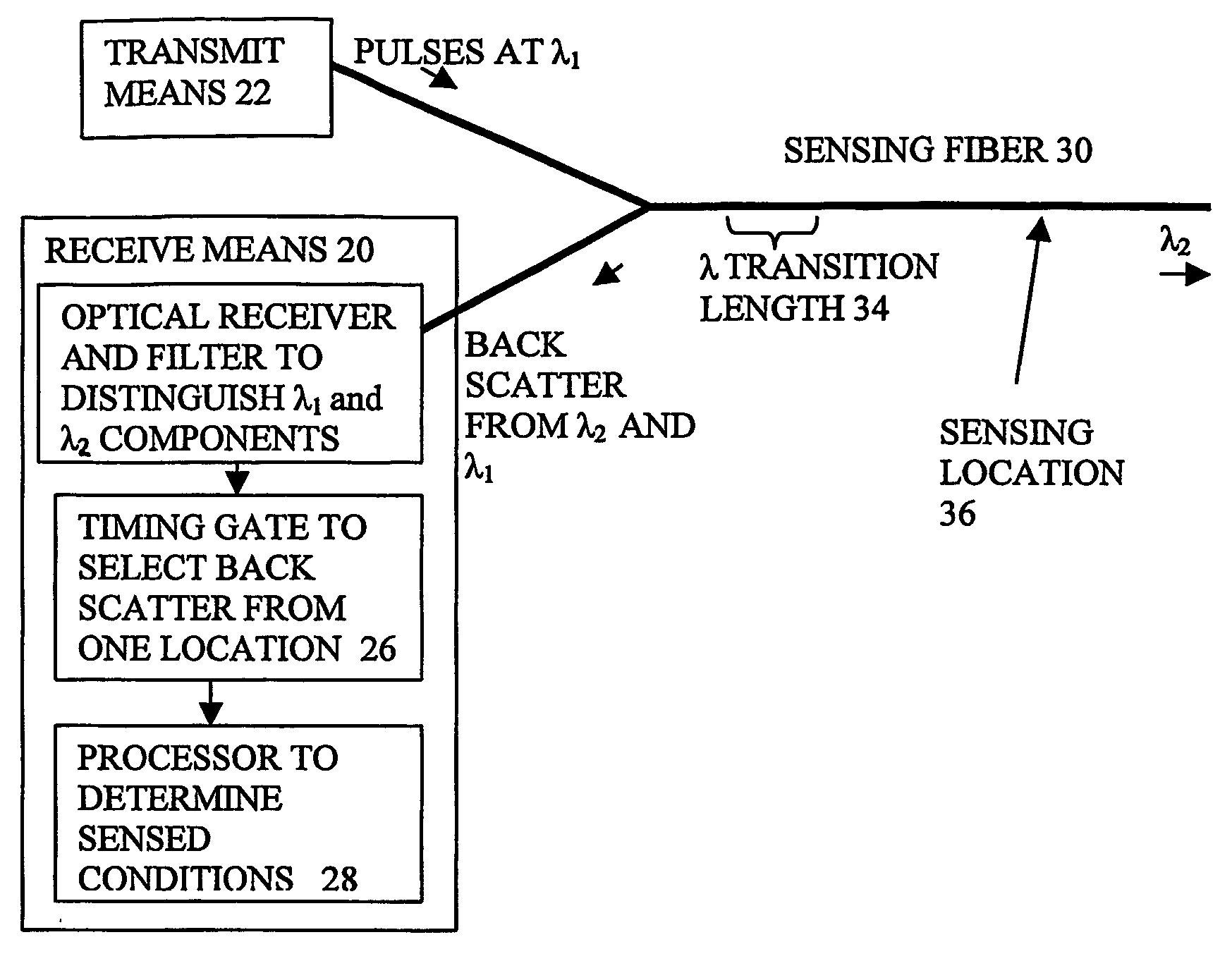
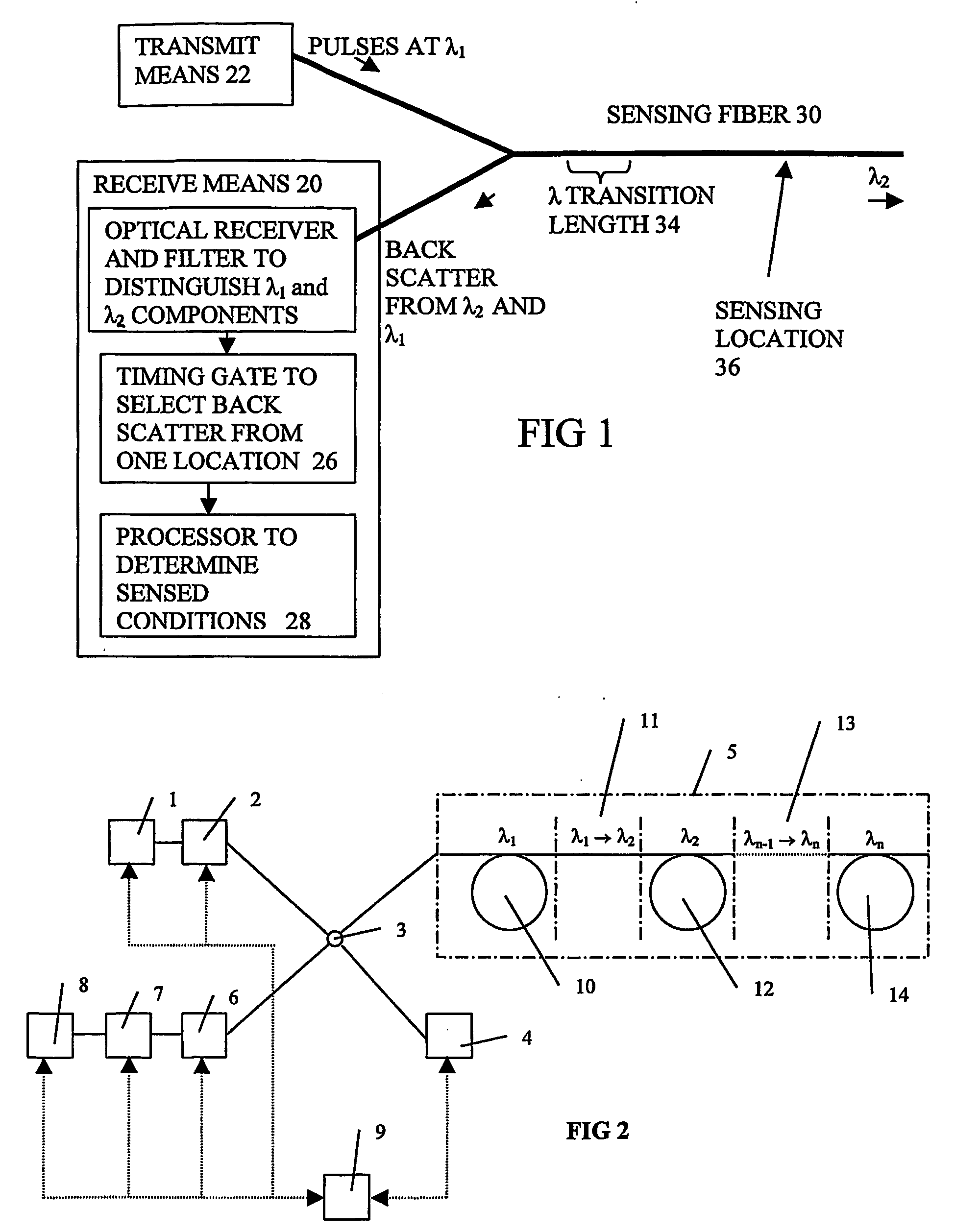
A method and apparatus for generating and transmitting high energy optical pulses are described. Distributed temperature sensors usually use Raman scattering in optical fibres as the means to determine the temperature. Here, light from a laser source is sent down a fibre and the small amount of light that is scattered back towards the source is analysed. As the fibre length increases, the resolutions of the temperature and loss measurements become poorer. This is because losses in an optical fibre attenuate the signal. An obvious solution to this problem is to launch more light into the fibre to compensate for the losses but stimulated Raman scattering limits how much light may be launched. The present invention solves this problem by using a pulse conversion method to maximise the resultant pulse energy while the power is kept below SRS threshold.
Owner:SENSORNET
Controlling optical signal transmission to reduce optical signal degradation
InactiveUS20080031621A1Transmission monitoringOptical multiplexStimulate raman scatteringRayleigh backscattering
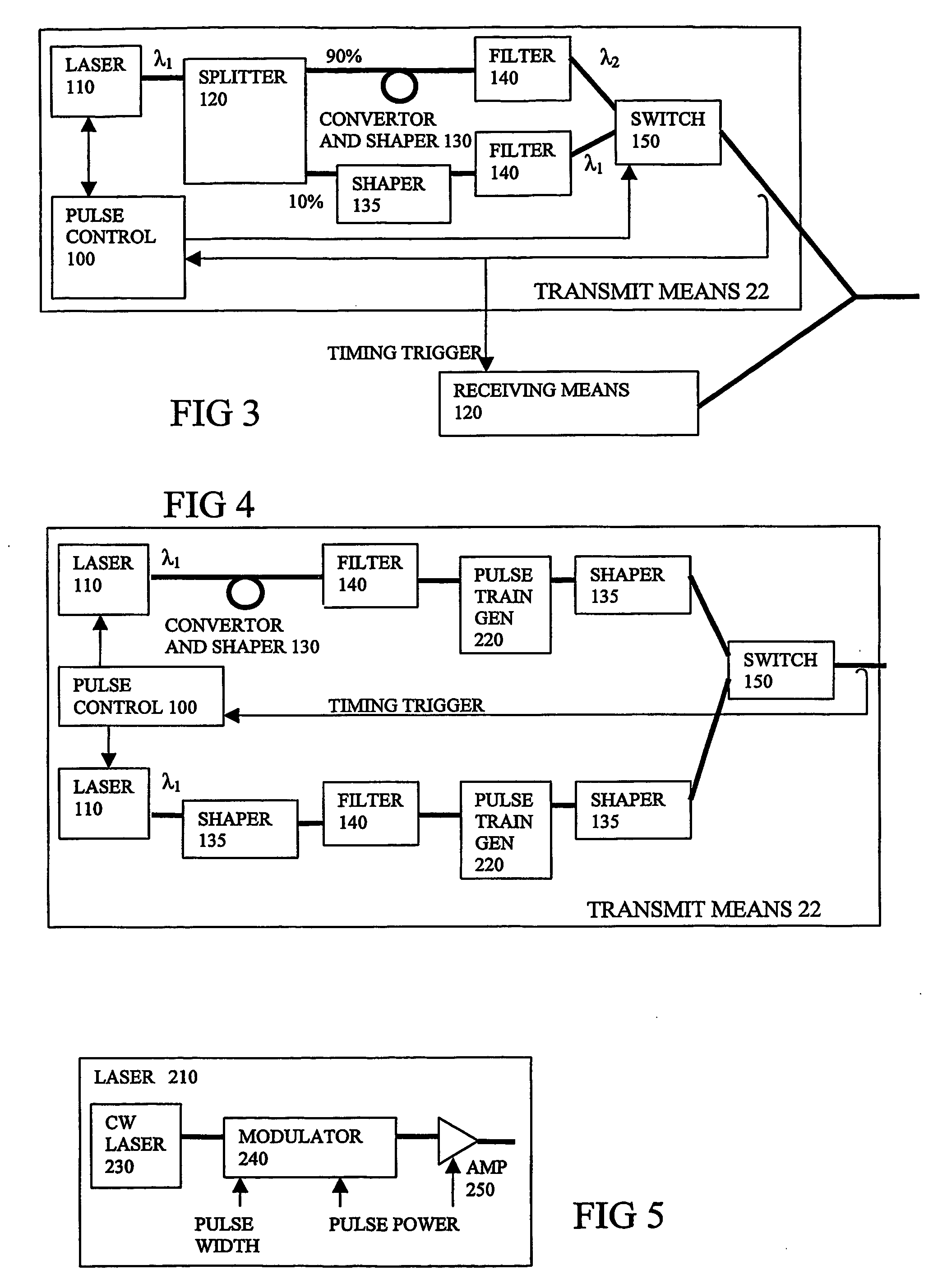
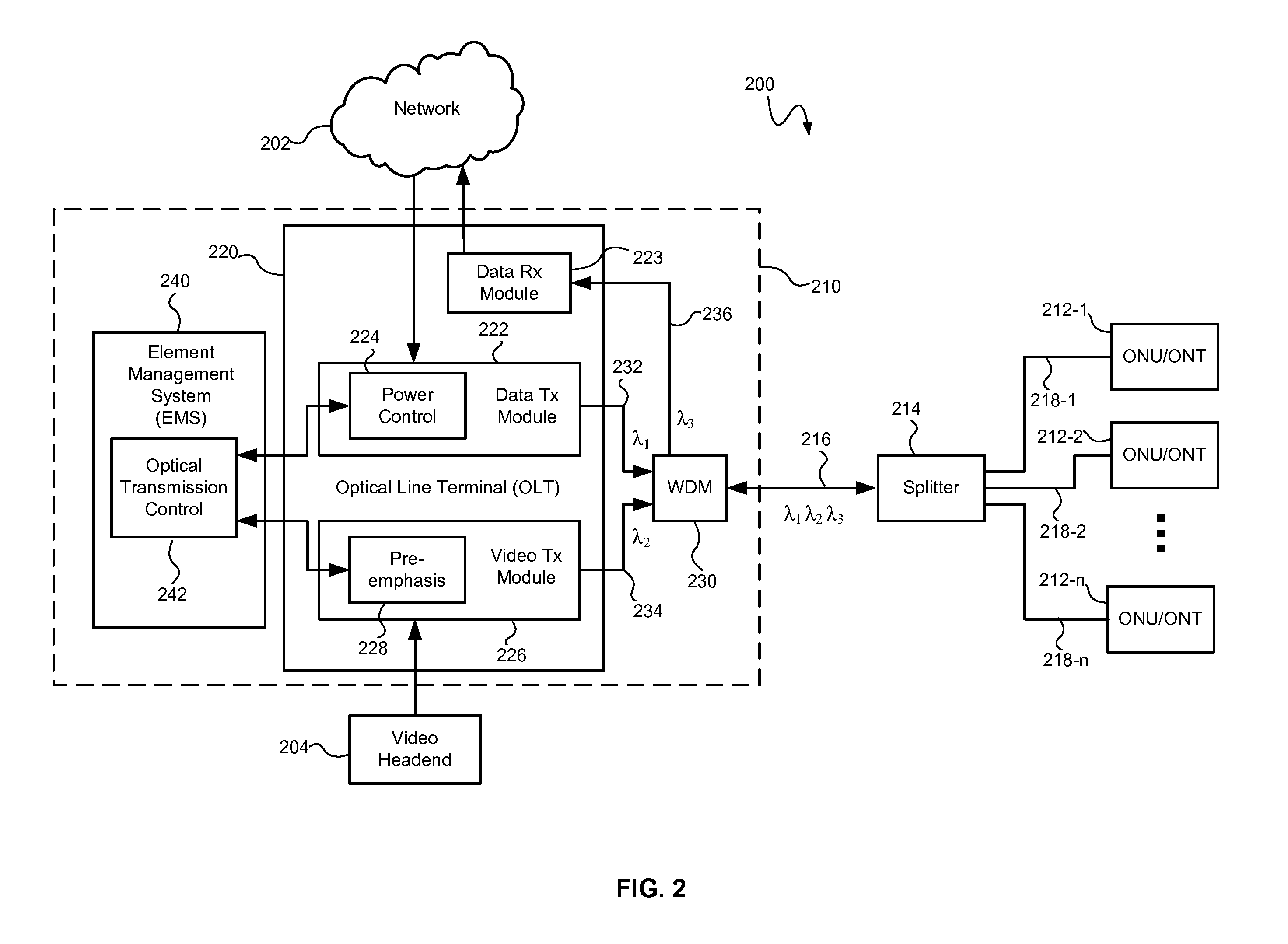
An optical transmission system and method may control optical signal transmission in an optical network, such as a passive optical network (PON), to reduce degradation of one or more optical signals traveling over the same optical waveguide. In particular, optical signal transmission may be controlled to reduce carrier to noise ratio (CNR) degradation of an optical signal (e.g., a multichannel video signal) resulting from the effects of stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) and / or double Rayleigh backscattering (DRBS). The CNR degradation may be reduced by controlling transmission of one or more of a plurality of optical signals in the optical network based on various parameters affecting the contribution to CNR degradation by SRS and / or DRBS and affecting the performance of the optical transmission system. The optical signal transmission may be controlled by adjusting a preemphasis and / or transmitted power of the optical signal(s).
Owner:APPLIED OPTOELECTRONICS
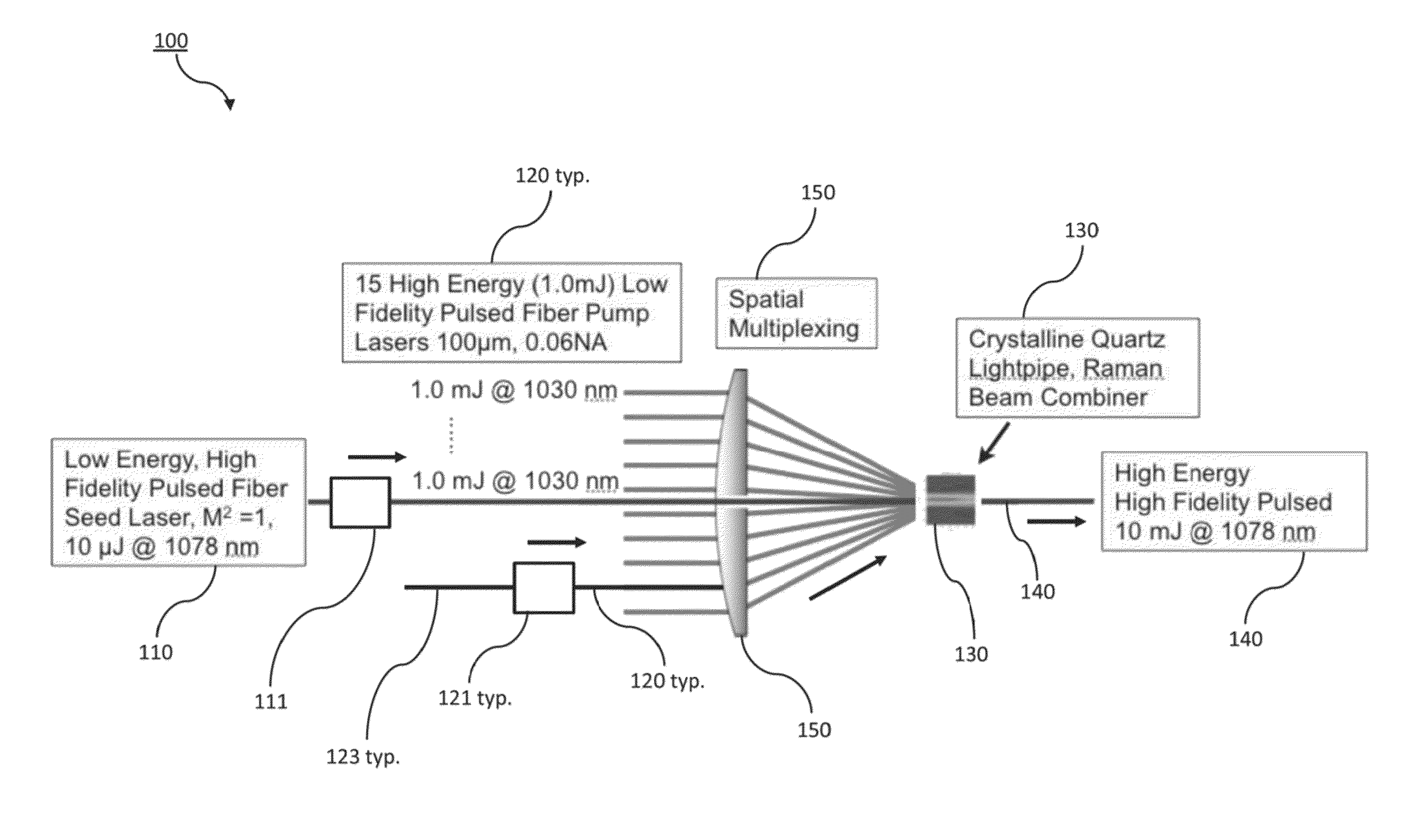
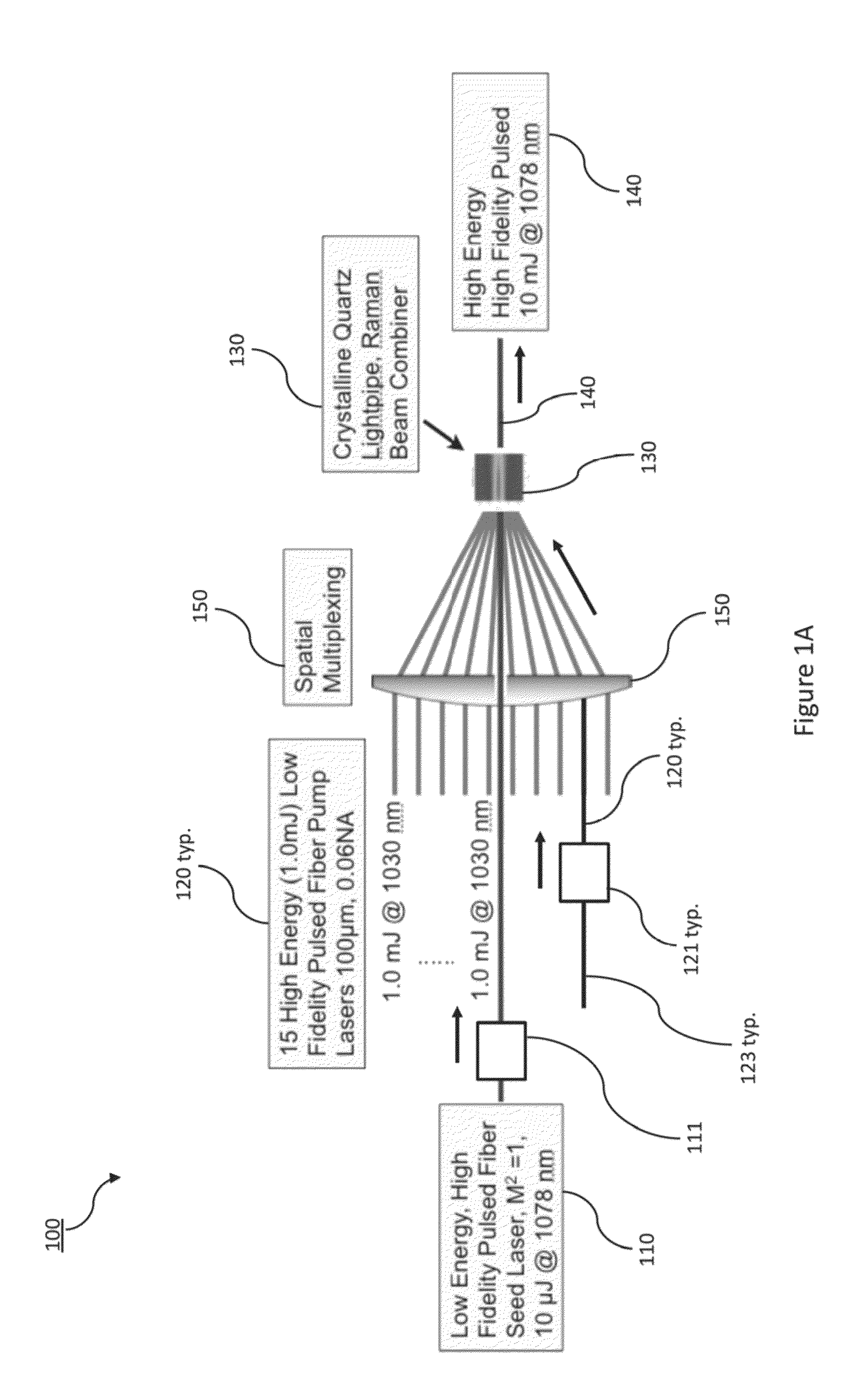
Raman beam combining for laser brightness enhancement
ActiveUS9172208B1Scale upLaser using scattering effectsOptical rangefindersStimulate raman scatteringOptoelectronics
An optical source capable of enhanced scaling of pulse energy and brightness utilizes an ensemble of single-aperture fiber lasers as pump sources, with each such fiber laser operating at acceptable pulse energy levels. Beam combining involves stimulated Raman scattering using a Stokes' shifted seed beam, the latter of which is optimized in terms of its temporal and spectral properties. Beams from fiber lasers can thus be combined to attain pulses with peak energies in excess of the fiber laser self-focusing limit of 4 MW while retaining the advantages of a fiber laser system of high average power with good beam quality.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Amplification with chalcogenide glass fiber
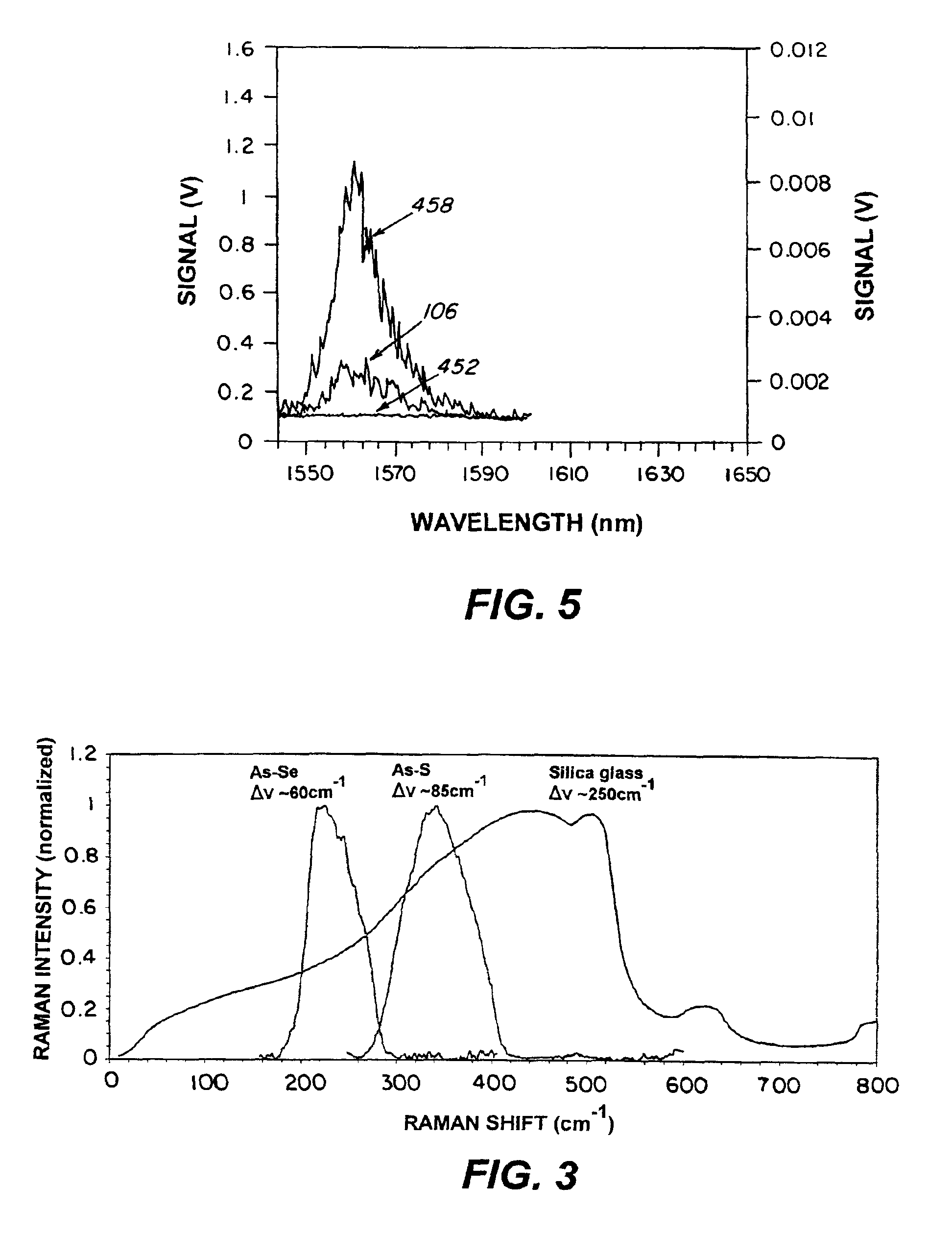
InactiveUS6928227B2High enough Raman gainLow enough lossLaser using scattering effectsActive medium materialGlass fiberFiber
This invention pertains to an optical device and method for using a chalcogenide glass waveguide to amplify a pump light beam by means of stimulated Raman scattering and obtaining a depleted pump light beam and an amplified beam at a wavelength higher than the wavelength of the depleted pump light beam.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Random-distribution feedback optical fiber laser
InactiveCN102354900AShorten the lengthIncrease output powerOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium shape and constructionRayleigh scatteringGrating
The invention relates to a random-distribution feedback optical fiber laser which can realize stable, space-irrelevant and continuous laser output, and belongs to the technical field of the optical fiber laser. The random-distribution feedback optical fiber laser comprises a pump laser, a wavelength division multiplexer, a fiber bragg grating, an Er-doped optical fiber, an optical fiber Raman laser and a long monomode optical fiber. The reflection effect of the fiber bragg grating is combined with the distributed Rayleigh scattering effect of the optical fiber to form a distributed random feedback optical resonant cavity; and the light is subjected to gain amplification by an Er-doped optical fiber and the stimulated Raman scattering effect. Compared with the random-distribution feedback optical fiber laser reported before, the threshold value of the pump laser and the length of the monomode optical fiber can be reduced, and the limitation on stimulated emission wavelength and the wavelength number by a Rayleigh gain peak is broken through, thereby realizing the purpose of tuning the laser wavelength. The random-distribution feedback optical fiber laser is suitable for fields, such as remote optical fiber sensing, remote communication and the like.
Owner:唐山市神州科贸有限公司
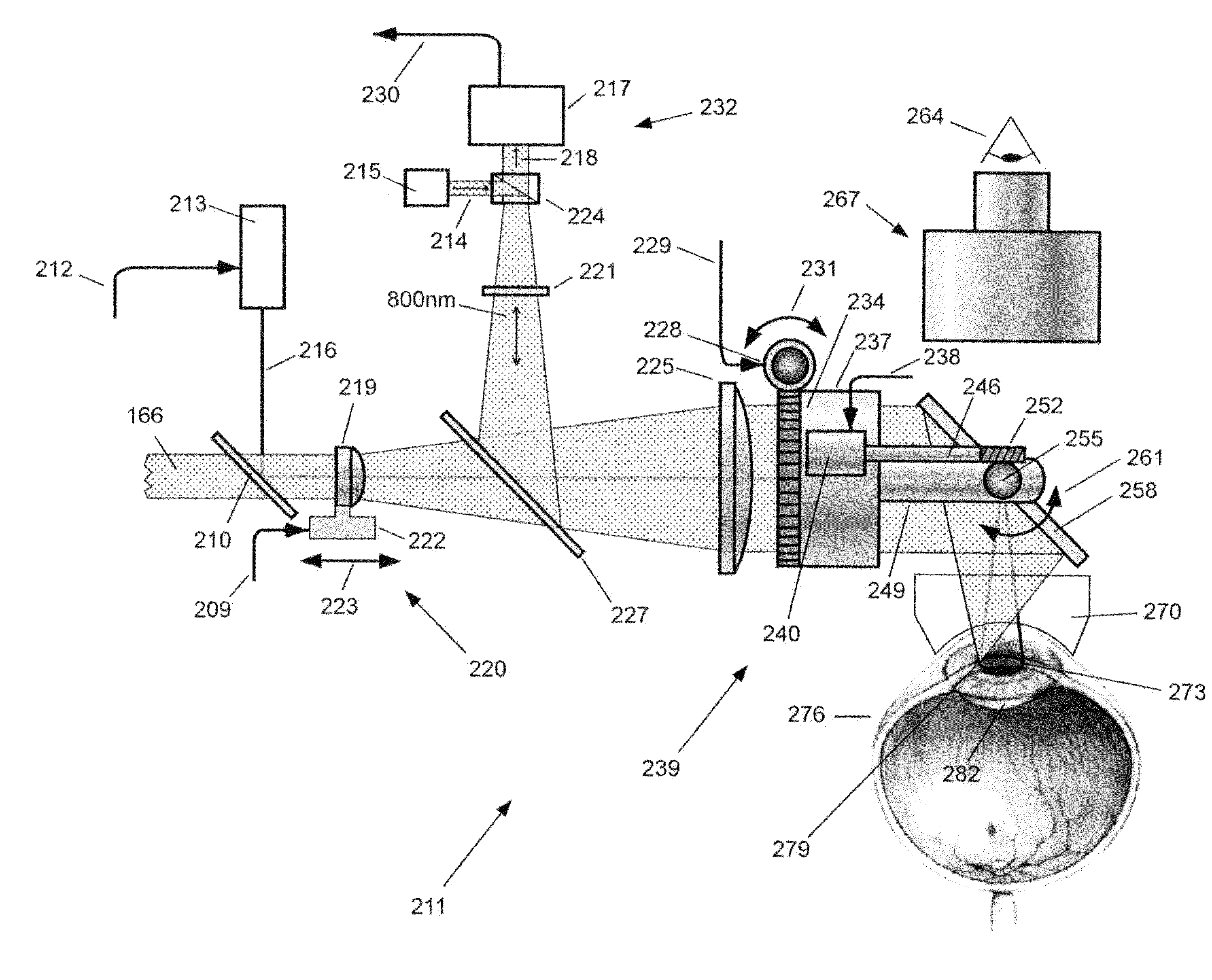
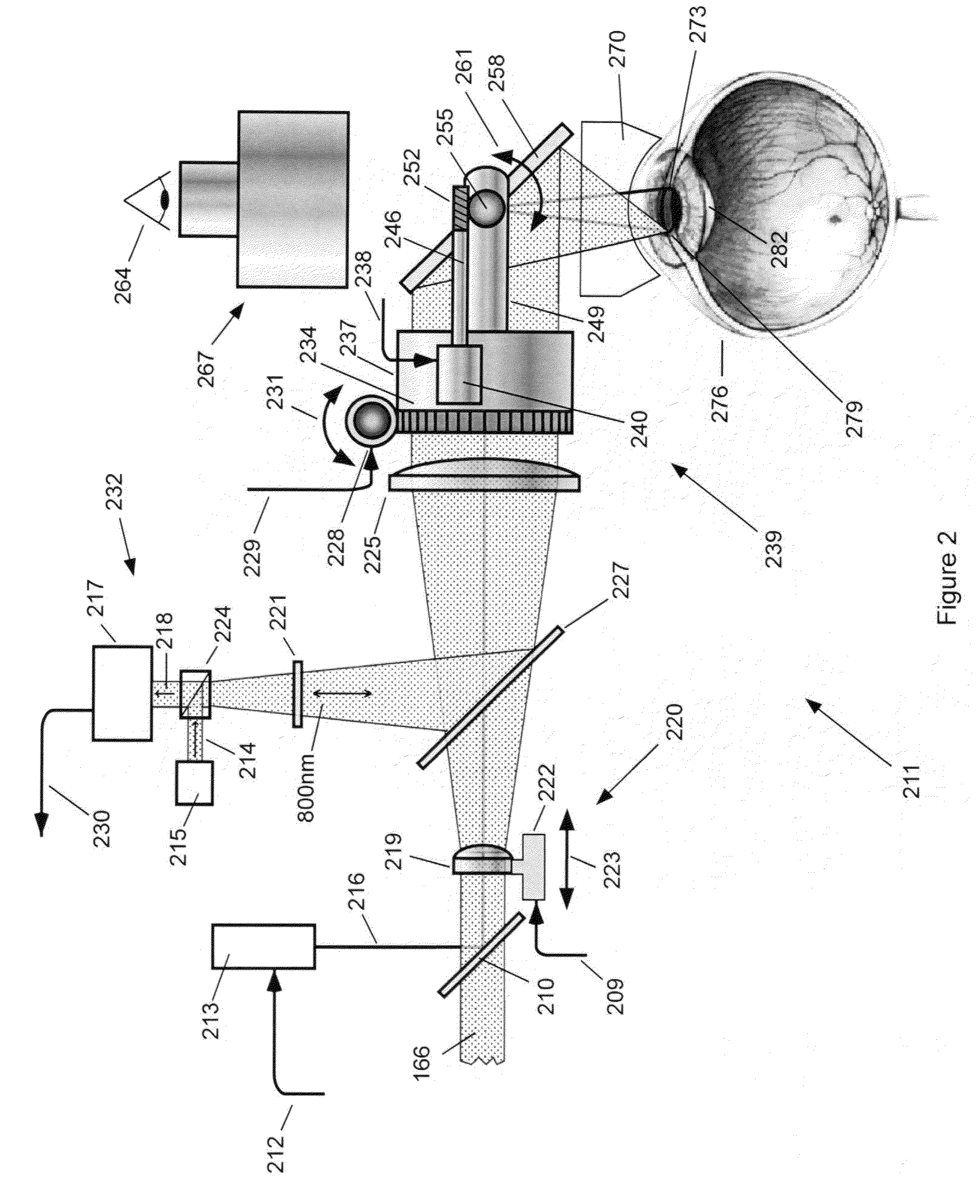
Automated Non-Invasive Capsulectomy and Anterior Segment Surgical Apparatus and Method
InactiveUS20110245814A1Reduce required pulse energyImprove eyesightLaser surgeryDiagnosticsNd:YAG laserNon invasive
An economical computer-controlled non-invasive laser apparatus and method to perform anterior segment surgery in an eye are disclosed. The laser source may include a pumping laser, a Nd:YAG laser cavity gain media, a stimulated Raman converter crystal, intracavity beam diameter-reducing optics, and an intracavity Q-switching crystal. The laser pulses have a selected wavelength for anterior segment surgery. A laser pulse delivery and treatment control mechanism and method for the practicing surgeon are also provided. The laser pulses and delivery system may be used in anterior segment surgery for cataracts, where the laser pulses may be used to form the capsulotomy, to form the corneal incision or to disintegrate contents of the capsule before removal. The laser and delivery system may also the used to treat a capsule and lens for correcting or preventing presbyopia and to treat a cornea to correct visual deficiencies in an eye.
Owner:LUMEDICA +1
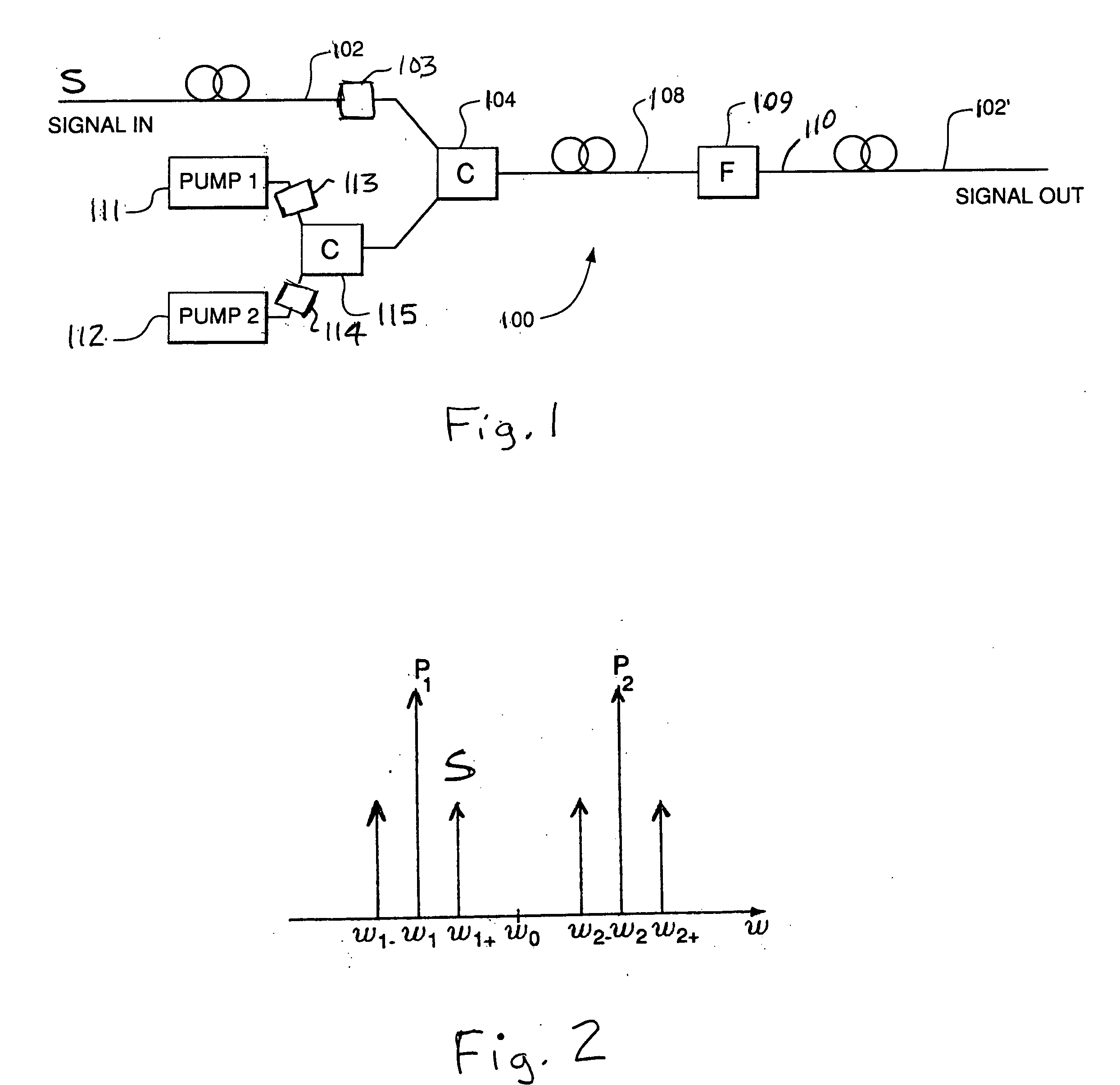
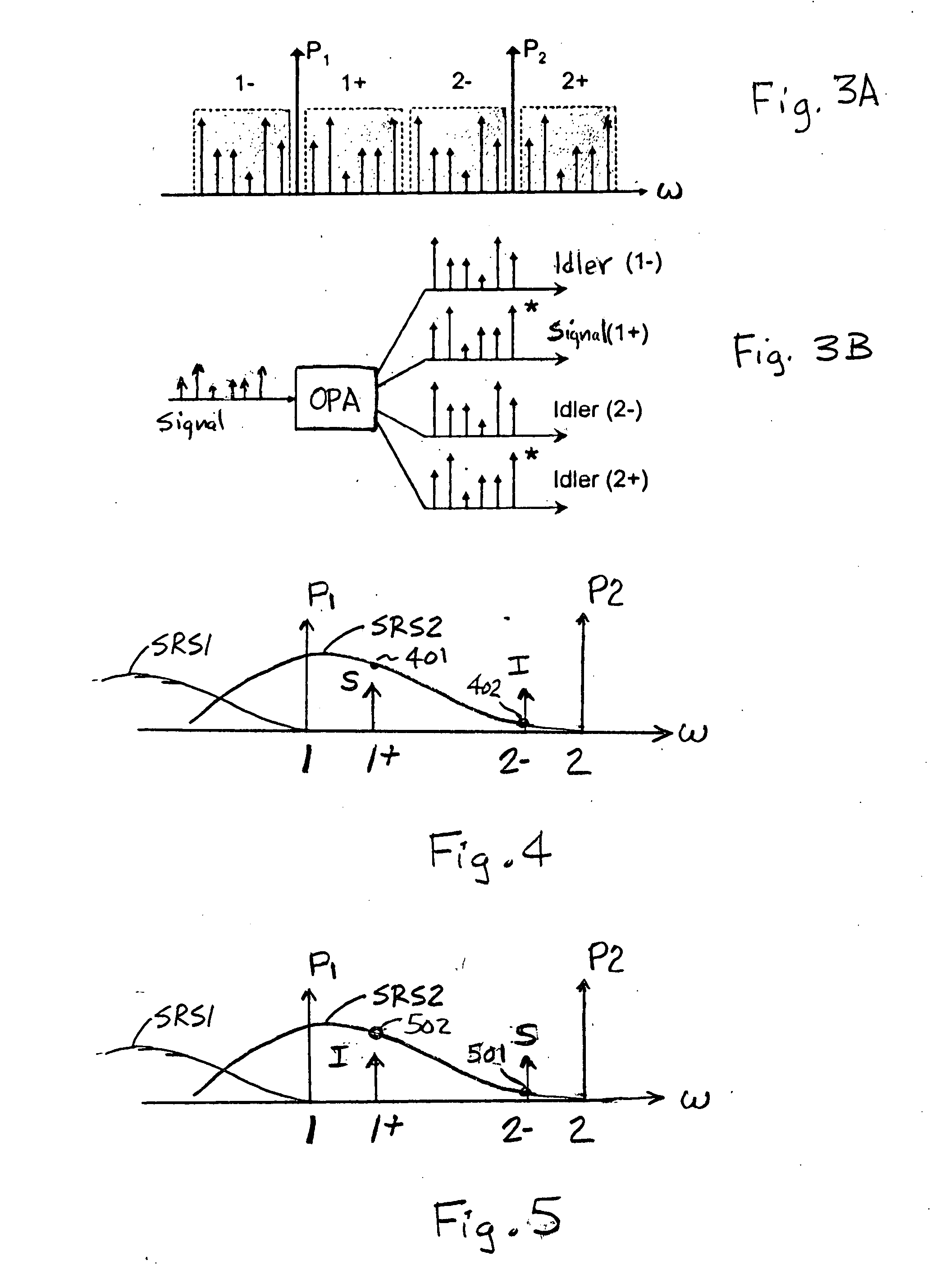
Two-pump optical parametric devices having reduced stimulated raman scattering noise levels
InactiveUS20080130097A1Reduce noise levelNoise levelParametric amplifiersElectromagnetic transmissionParallel polarizationOptical parametric amplifier
Two-pump optical parametric devices (OPDs), and methods of operating the same, generate desired output signals and idlers having reduced stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) noise levels. When the two-pump OPD is used as a two-pump optical parametric amplifier (OPA), the pumps are polarized perpendicular to each other, and the lower-frequency sideband (signal or idler) is polarized parallel to the lower-frequency pump (perpendicular to the higher-frequency pump). The desired output may be an amplified signal or a generated idler. When the two-pump OPD is used as a two-pump optical frequency converter (OFC), the pumps can be polarized parallel to one another, in which case the signal and idler are both perpendicular to the pumps, or perpendicular to one another, in which case the lower-frequency sideband (signal or idler) is polarized parallel to the lower-frequency pump (perpendicular to the higher-frequency pump).
Owner:RPX CORP +1
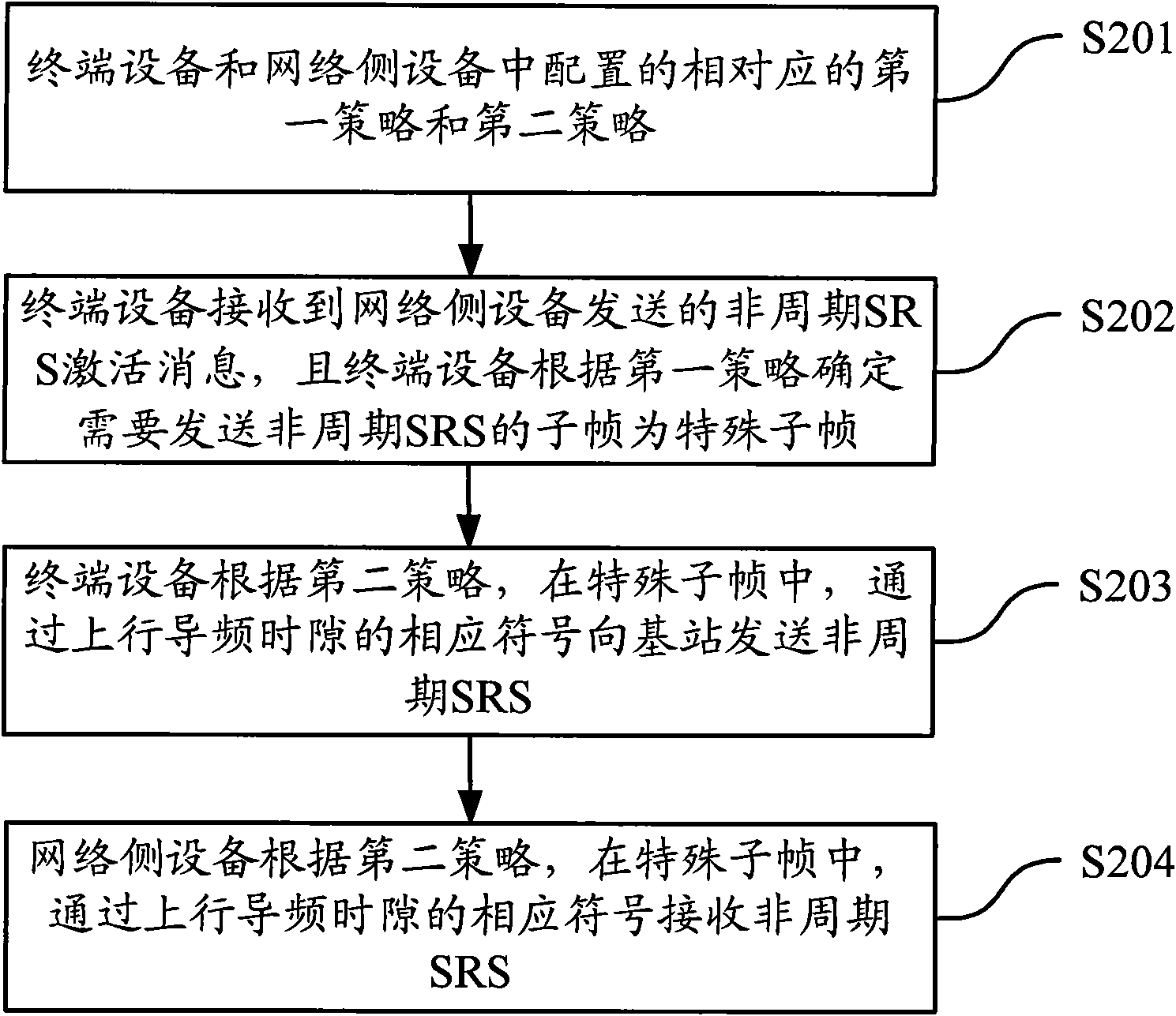
Transmission method and equipment of non-periodic SRS (Stimulated Raman scattering) in TDD (Time Division Duplexing) system
ActiveCN102404074AResolve transmissionMinor changesError prevention/detection by using return channelTime-division multiplexTime-division multiplexingReference structure
The embodiment of the invention discloses a transmission method and equipment of non-periodic SRS (signal reference structure) in a TDD (Time Division Duplexing) system. By adopting the technical scheme of the embodiment of the invention and defining the sign of non-periodic SRS transmission in a special sub-frame of the TDD system, the condition that the transmission position cannot be determined when a plurality of signs which can be used for non-periodic SRS transmission exist in an uplink pilot frequency timeslot is avoided, the non-periodic SRS transmission problem in the special sub-frame of the TDD system is solved, and the modification on corresponding indication information is little, and no excessive system resource is occupied.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
High-power high-efficiency supercontinuum source
InactiveCN103022867AIncrease output powerLow costCladded optical fibreActive medium shape and constructionManufacturing technologyPicosecond
The invention provides a high-power high-efficiency supercontinuum source. By reasonably designing characteristics of photonic crystal fibers, long-pulse pump laser (picosecond, nanosecond laser) acts on a normal dispersion area for the photonic crystal fibers, the central wavelengths of stimulated front stages of Raman-Stokes peaks are positioned in an abnormal dispersion area close to a zero dispersion point of the photonic crystal fibers, and the stimulated Raman-Stokes laser peaks serve as a new pump source for stimulating supercontinuum and meet the requirement of an abnormal dispersion pump mechanism. The supercontinuum source simultaneously has the advantages of a normal dispersion pump mechanism and the abnormal dispersion pump mechanism, and high average output power and continuum output with high optical conversion efficiency and a wider supercontinuum range can be realized. By the aid of mature high-power fiber laser technology, photonic crystal fiber manufacturing technology and photonic crystal fiber post-treatment technology, system cost is reduced, and industrial production and application are facilitated.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
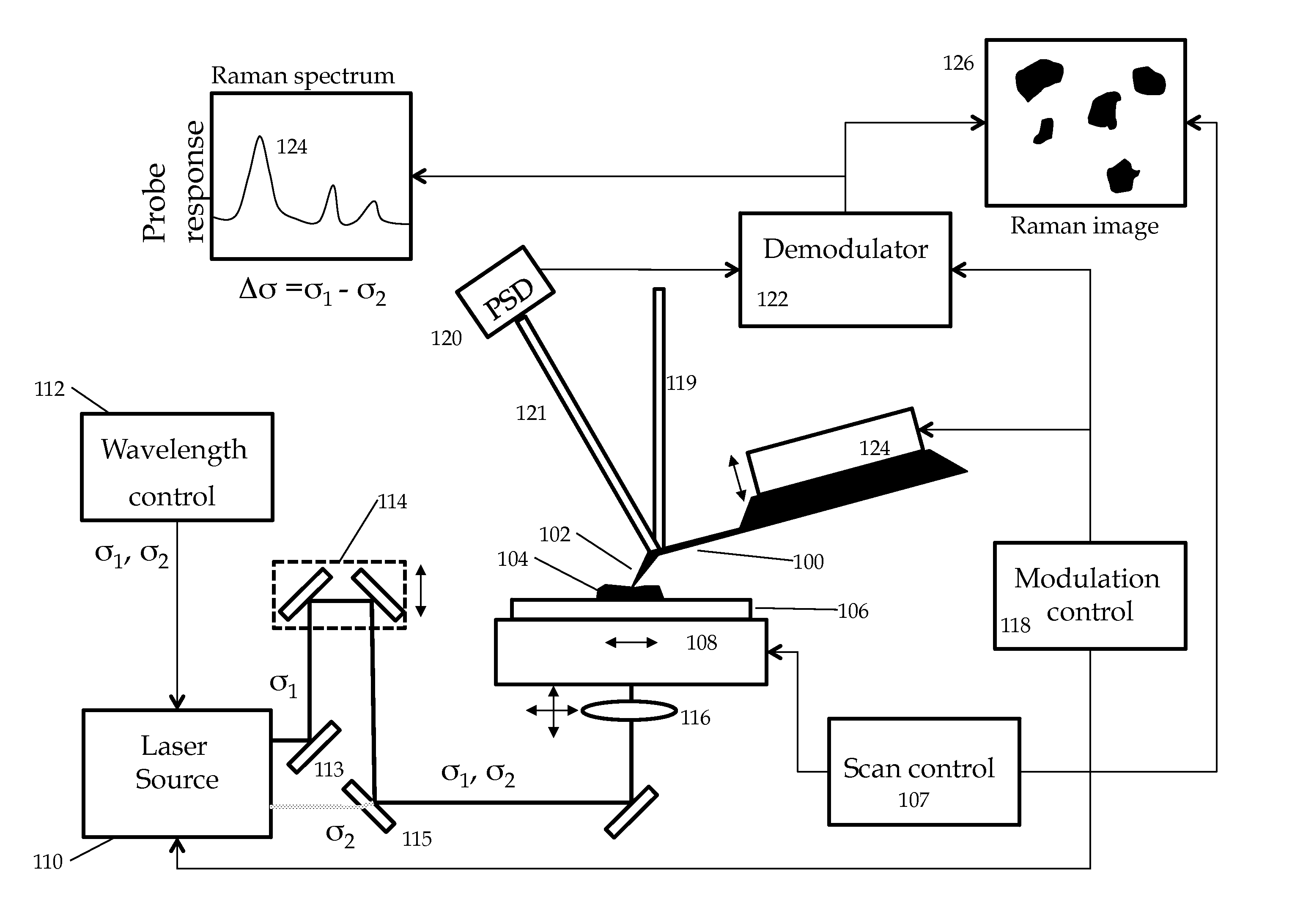
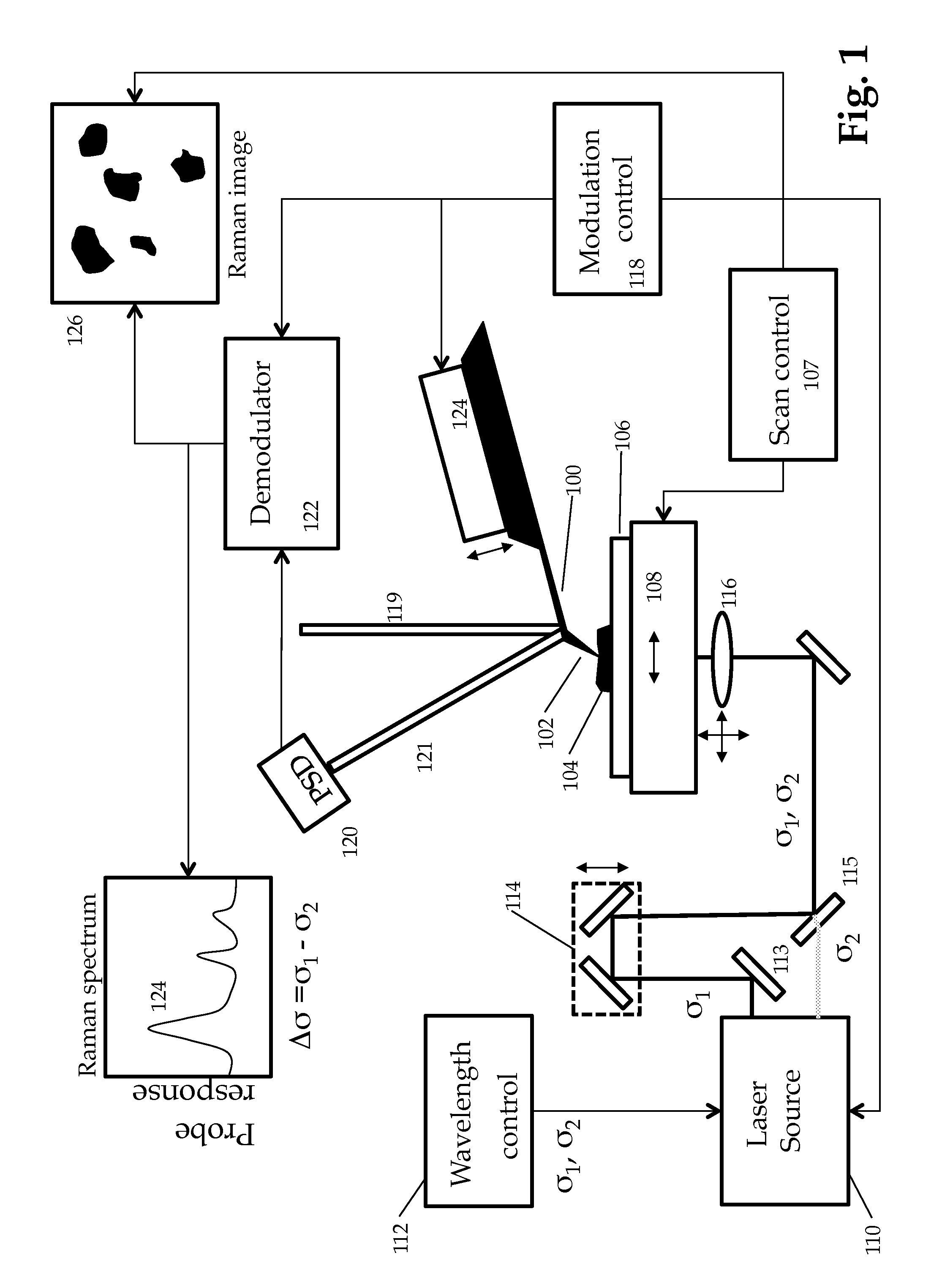
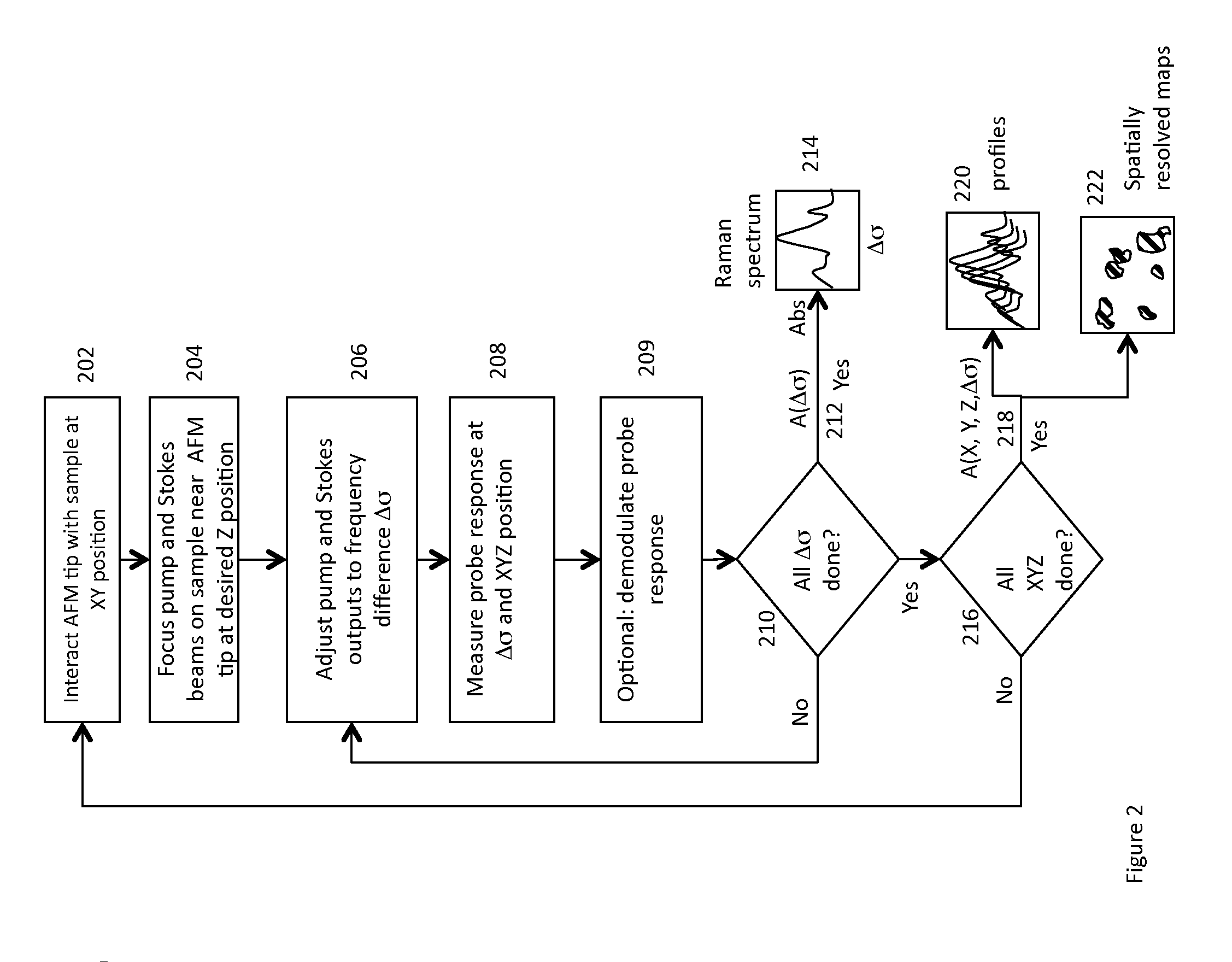
Stimulated raman nanospectroscopy
ActiveUS9046492B1High resolutionHigh sensitivityRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringHigh spatial resolutionImage resolution
A method for achieving measurable sample heating in the vicinity of a probe microscope tip using Stimulated Raman Spectroscopy. Two laser sources, preferably in the UV visible or near IR illuminate the sample, preferably in overlapping diffraction limited spots. At least one of the sources is swept through a frequency range such that the difference frequency corresponds to IR spectral regions of interest. Selective Absorption by differing sample materials at the difference frequency causes measurable sample heating detectable by the probe tip related to IR spectral absorption bands. Thus very high spatial resolution IR spectroscopy may be achieved.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
Graphite Raman locked mode laser
ActiveCN102104231AImprove applicabilityCompact structureLaser using scattering effectsActive medium materialStimulate raman scatteringGraphite
The invention relates to a graphite Raman locked mode laser characterized in that laser gain is provided by a stimulated Raman scattering effect with a flexible wavelength and combined with a graphite Raman locked mode device with a wide saturated absorption band to realize locked mode laser output. The whole device of the graphite Raman locked mode laser is formed by a mechanism of combining a stimulated Raman gain medium with the graphite Raman locked mode device, is compact in structure and convenient to integrate and can be applied to a plurality of fields.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
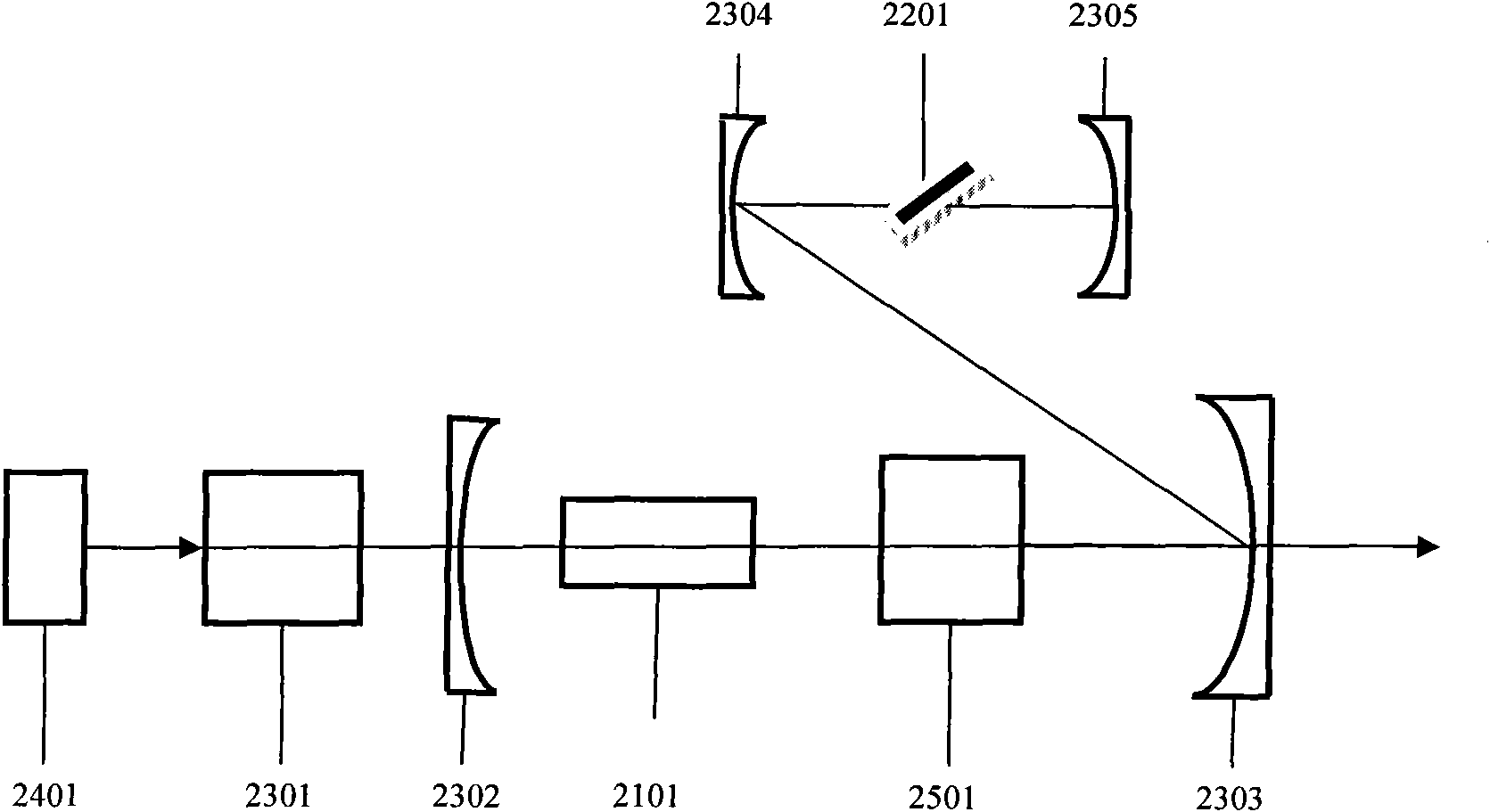
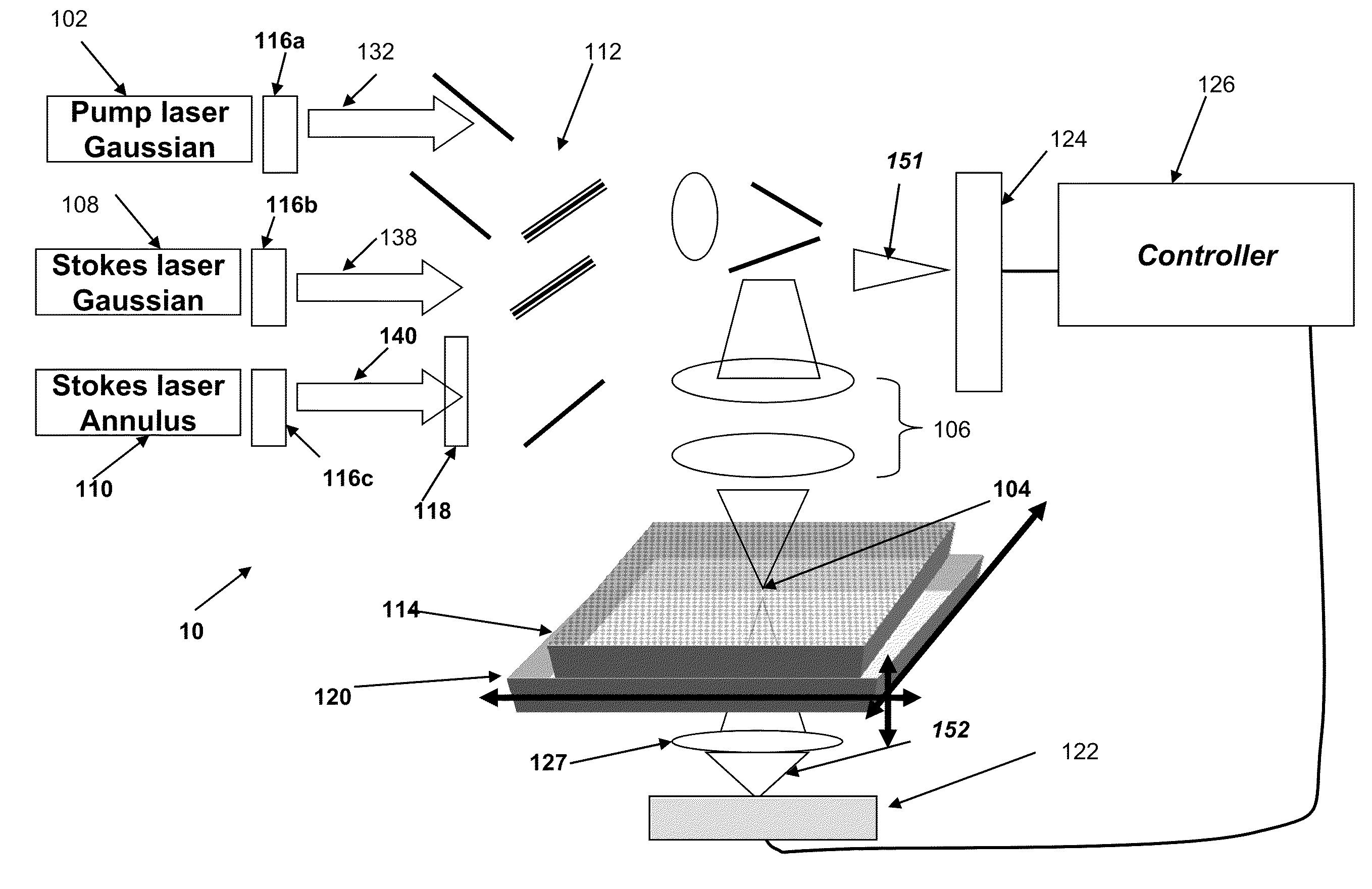
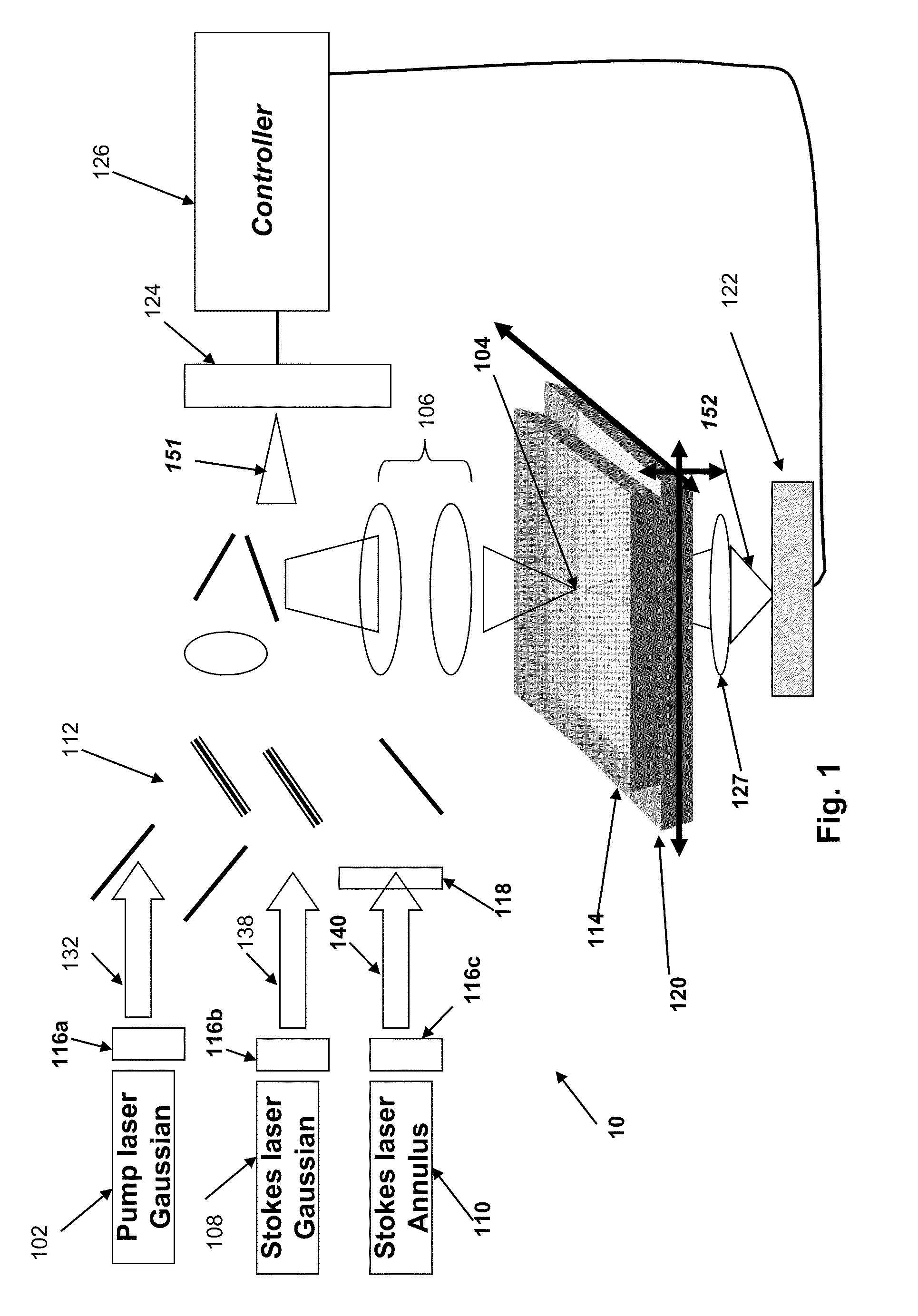
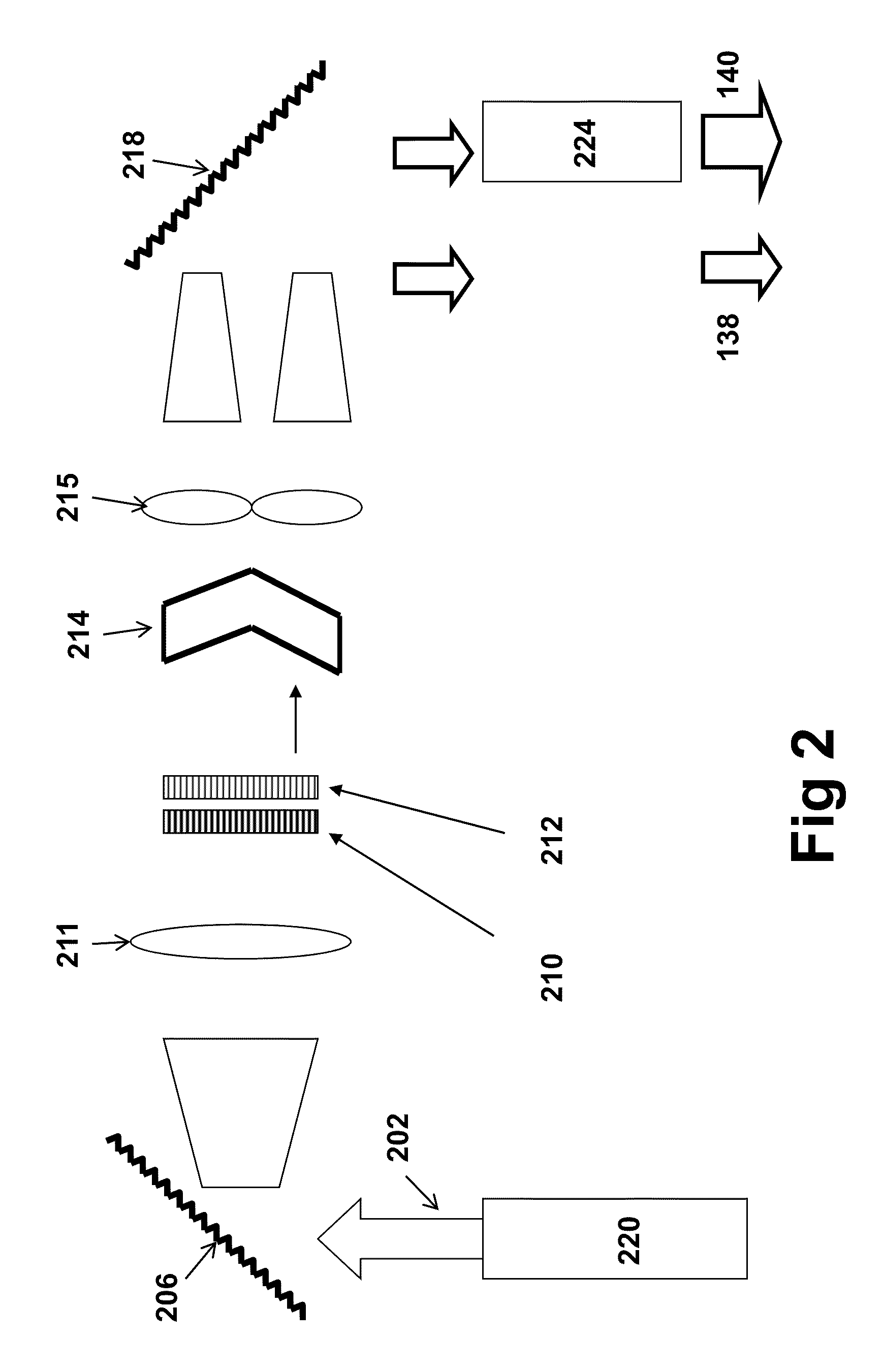
Method and system for stimulated Raman microscopy beyond the diffraction limit
Systems and methods for probing a Raman signature of a sample with a resolution exceeding the diffraction limit are described. These systems, called GASSE (Gain Saturated Stimulated Emission) and iGASSE (interferometric GASSE), are detecting a Raman signal produced in a sample located at the focal spot of a Gaussian pump pulse. Two additional pulsed laser beams (Stokes beams), a central Stokes beam having a Gaussian beam profile and another Stokes beam having an annular beam profile, are also focused to the focal spot. The spatial and temporal phases of the laser pulses are adjusted to produce destructive interference over most of the temporal width of Stokes pulses, which causes emission from the central Stokes beam to narrow well below the diffraction limit. A two-dimensional image of the sample is produced by scanning the combined beams across the sample. The system may find applications in biomedical and semiconductor technology.
Owner:FREL ROBERT D
Pulsed cascaded Raman laser
A pulsed cascaded Raman laser (10) includes a pulsed light source (102) for generating a pulsed light (104) having an optical spectrum centered at a source wavelength. A non-linear Raman conversion fiber (106) is coupled to the pulsed light source (102). The pulsed light (104) traverses the nonlinear Raman conversion fiber (106) and the source power at the source wavelength is converted to a power output of an output signal (108) having an output wavelength longer than the source wavelength by a cascaded Stimulated Raman Scattering process, such that most of the source power is converted to the power of the last Stokes order in a single pass through the non-linear Raman conversion fiber (106).
Owner:CORNING INC
Single light source automatic calibration in distributed temperature sensing
InactiveUS20100312512A1Accurate temperature profileRadiation pyrometryThermometers using physical/chemical changesFiberOptoelectronics
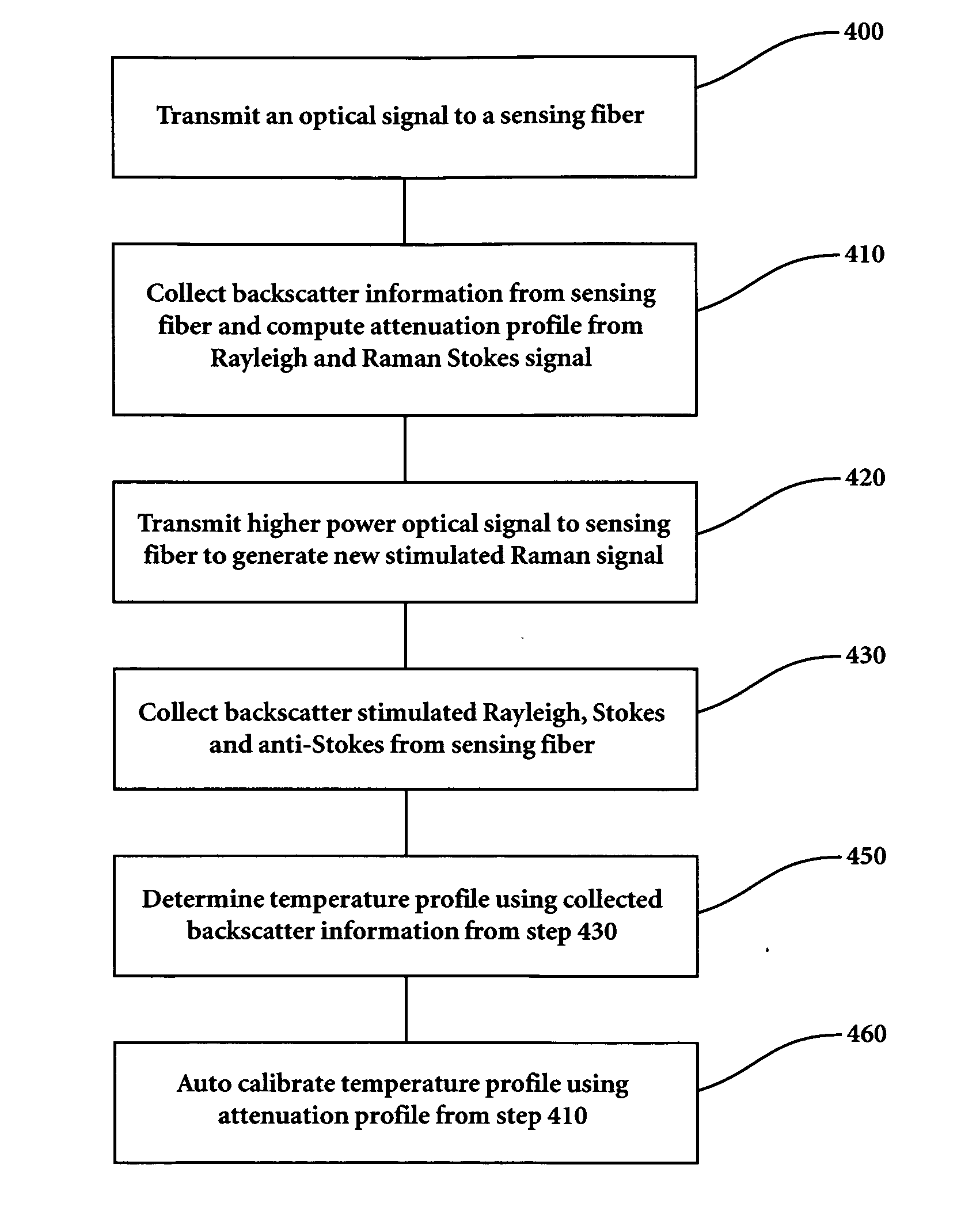
System and method for auto correcting temperature measurement in a system using a fiber optic distributed sensor and a single light source by making use of both spontaneous and stimulated Raman backscattering.
Owner:AJGAONKAR MAHESH U
Ultra-remote distributed fiber raman photons temperature sensor integrated with raman amplifier
InactiveCN101162175AImprove transmission distanceAvoid lossThermometers using physical/chemical changesCoupling light guidesFiberStimulate raman scattering
The present invention discloses an ultra-long-range distributed fiber Raman photon temperature sensor of an integrated Raman amplifier, and comprises a distributed fiber Raman photon temperature sensor, a distributed fiber Raman amplifier and a fiber grating narrowband reflecting filter. The distributed fiber Raman amplifier is adopted to be embedded into the distributed fiber Raman photon temperature sensor; the gain of the amplifier is used to overcome fiber loss, strengthen the intensity of spontaneous Raman scattering light in the fiber, improve signal-to-noise ratio of the distributed fiber Raman photon temperature sensor system, augment the transmission distance of the distributed fiber Raman photon temperature sensor and improve temperature-measuring precision. With the fiber stimulated Raman scattering effect, the fiber spontaneous Raman scattering effect and the optical time domain reflection principle, the invention skillfully merges the technologies of the distributed fiber Raman amplifier and the distributed fiber Raman photon temperature sensor and achieves the ultra-long-range distributed fiber Raman temperature sensor.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
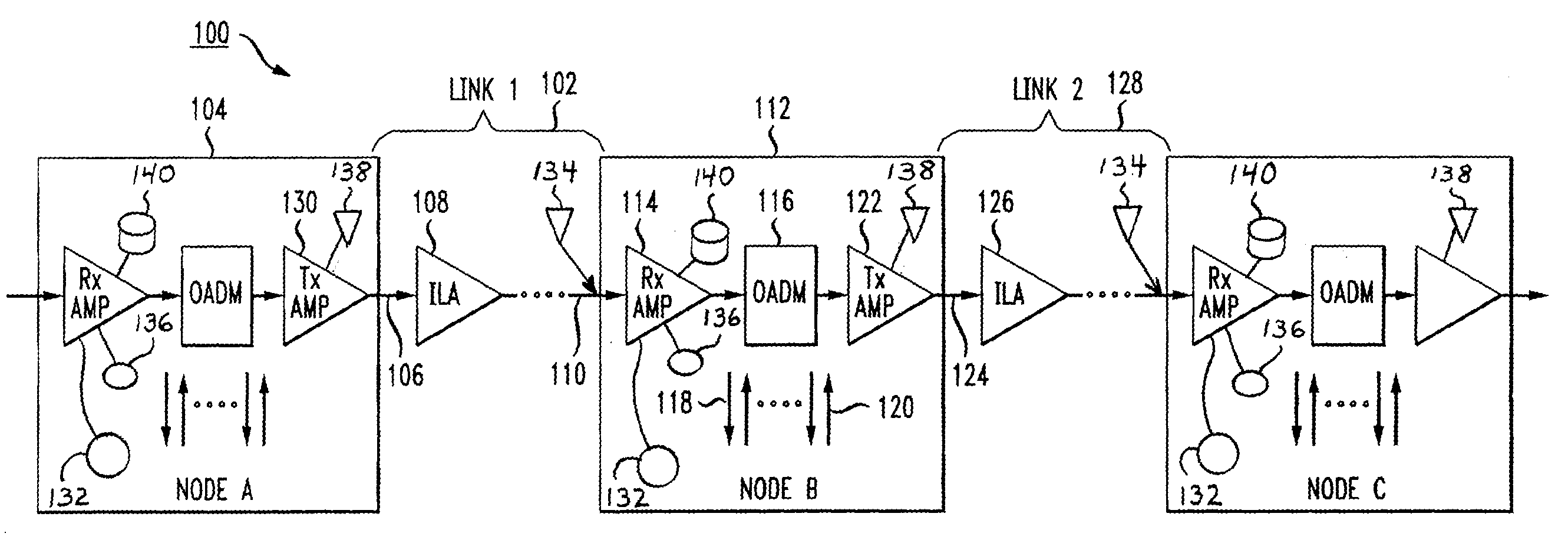
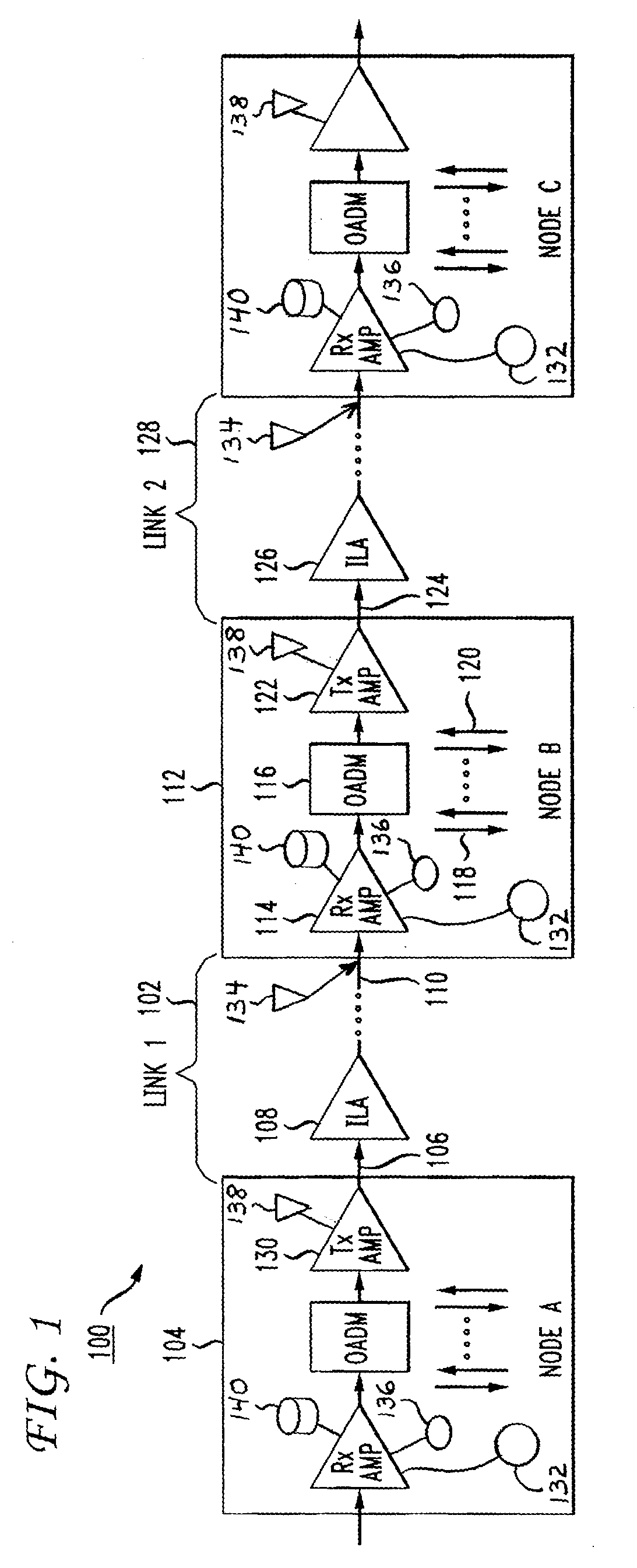
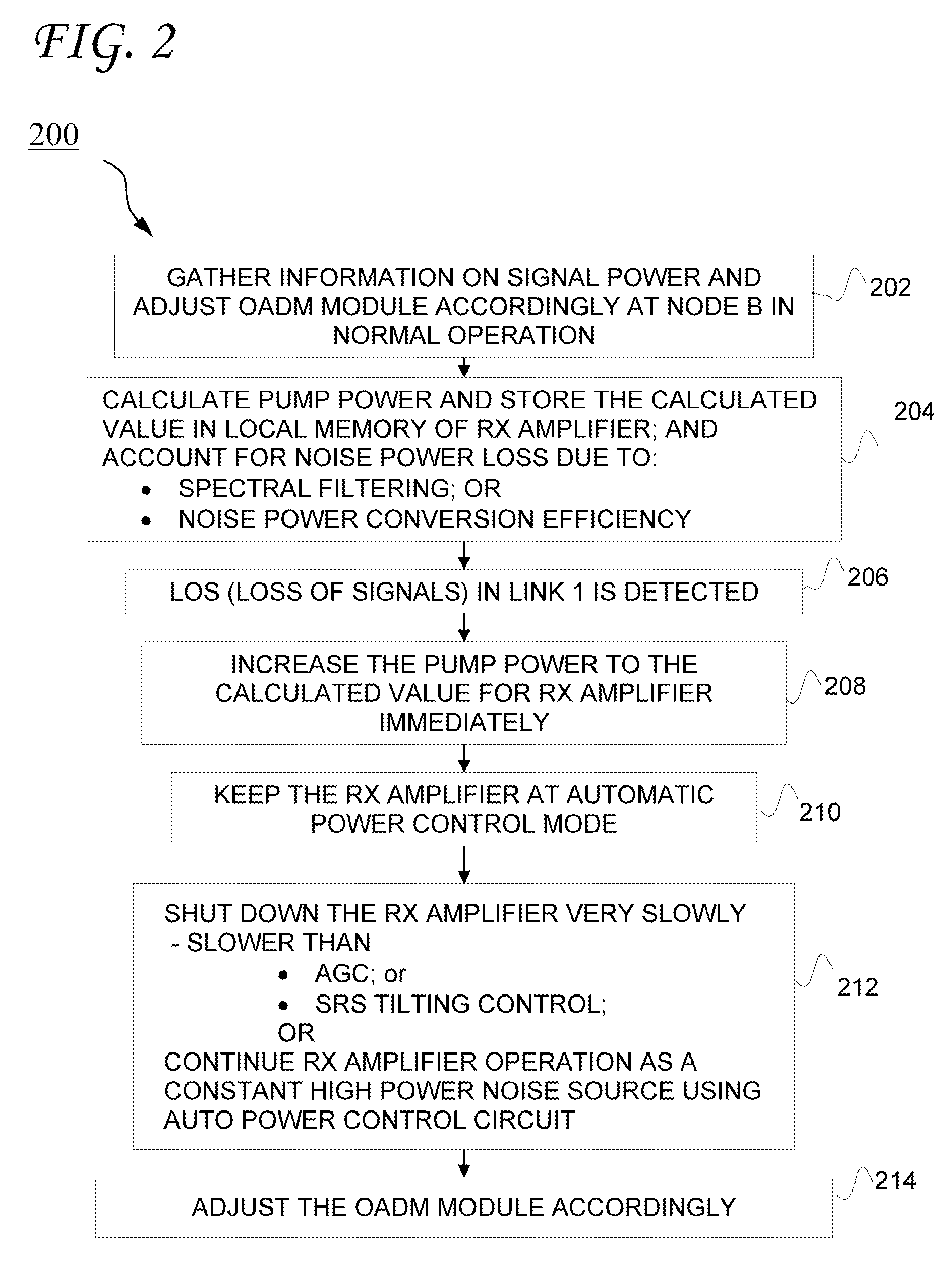
Transient control solution for optical networks
InactiveUS20090116842A1Eliminate the effects ofLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsFiberMultiplexing
An optically amplified wavelength division multiplexing network has the functionality to add / drop channels at the optical add / drop multiplexing (OADM) nodes. The OADM node includes a receiver amplifier, an OADM module, and a transmitter amplifier. Once the OADM node detects a loss of signal (LOS) due to a fiber cut or network element failure upstream, the receiver amplifier is kept in operation as a noise source. The output of the receiver amplifier is immediately raised by increasing pump power to compensate for the LOS. The noise power received at the transmitter amplifier from the receiver amplifier is substantially equal to the signal power expected before LOS. The transient effect of downstream optical amplifiers is therefore completely suppressed and the inter-channel stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) induced spectrum tilt does not change. After the noise power is raised, the receiver amplifier may be shut down at a speed much slower than the speed of downstream amplifier control circuitry.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP II L P
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com