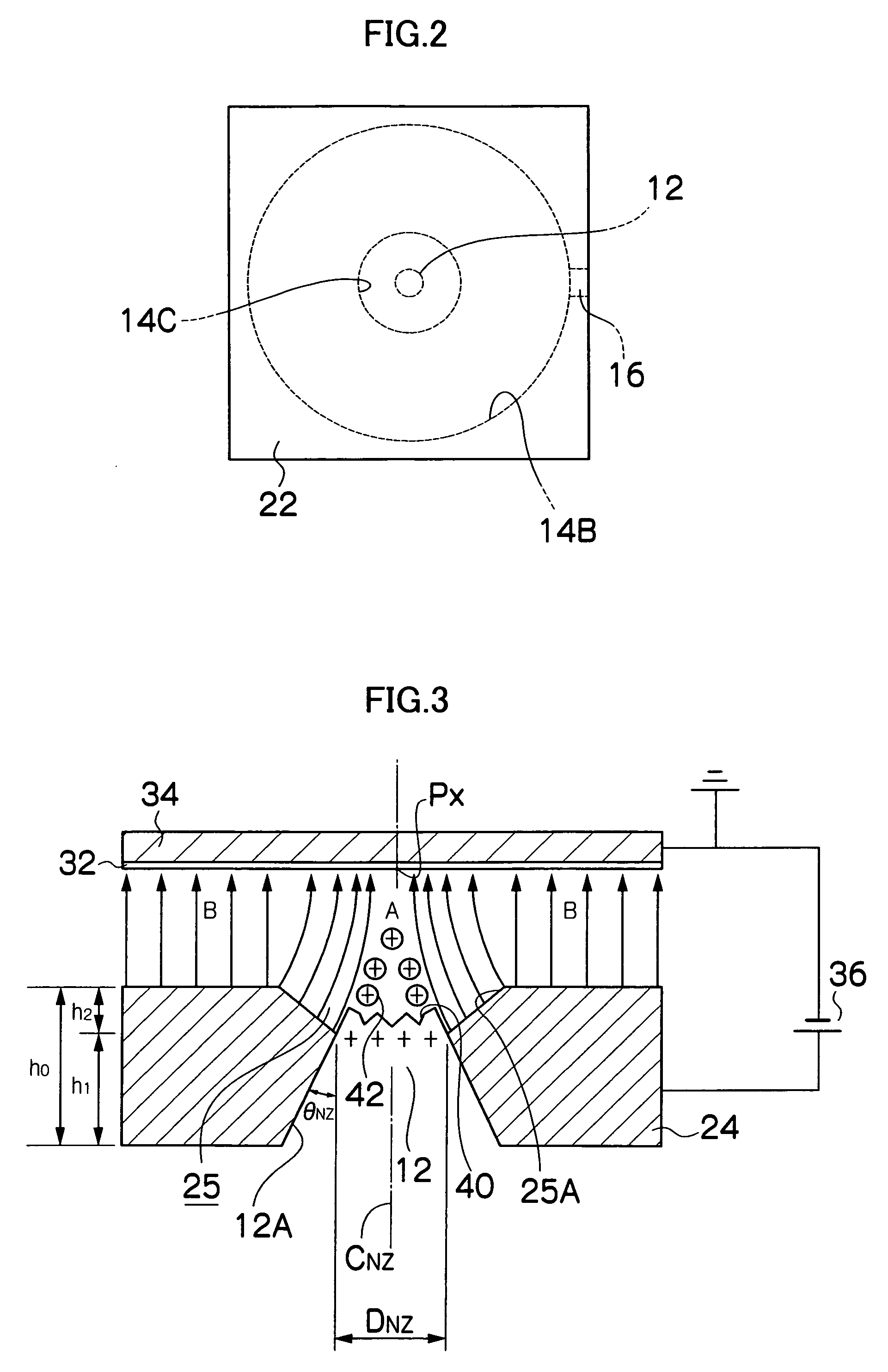
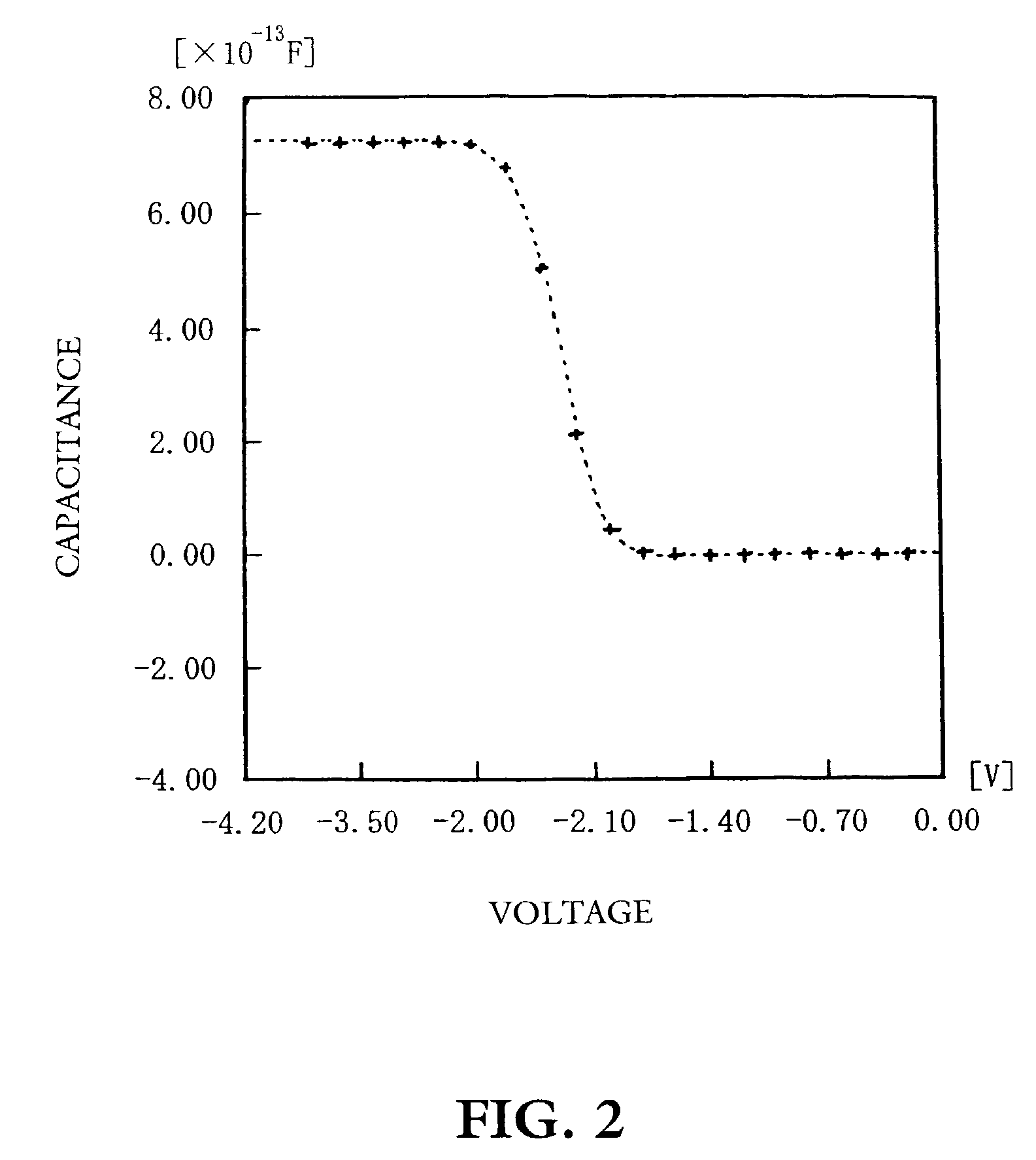
Patents
Literature
59results about How to "High speed molding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
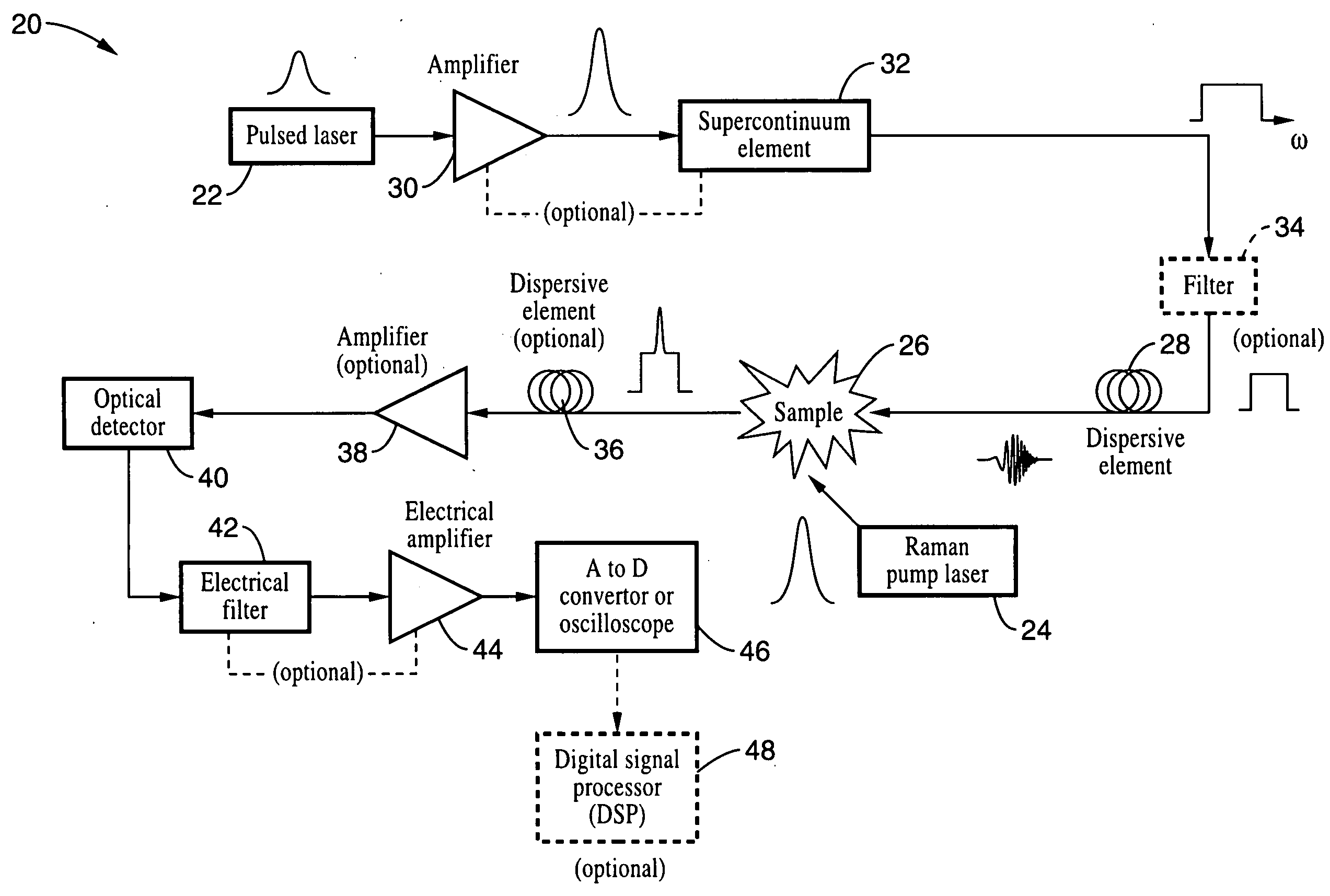
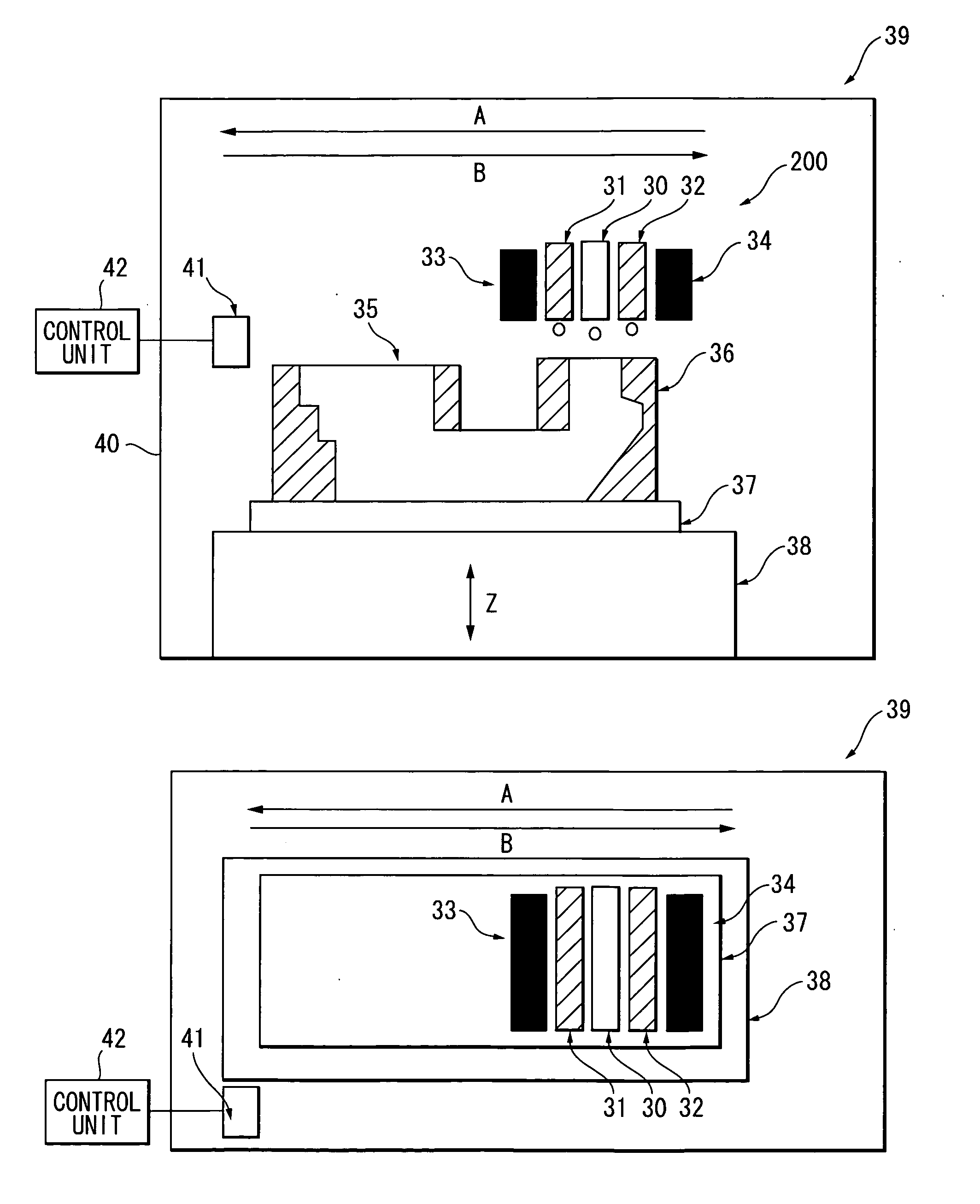
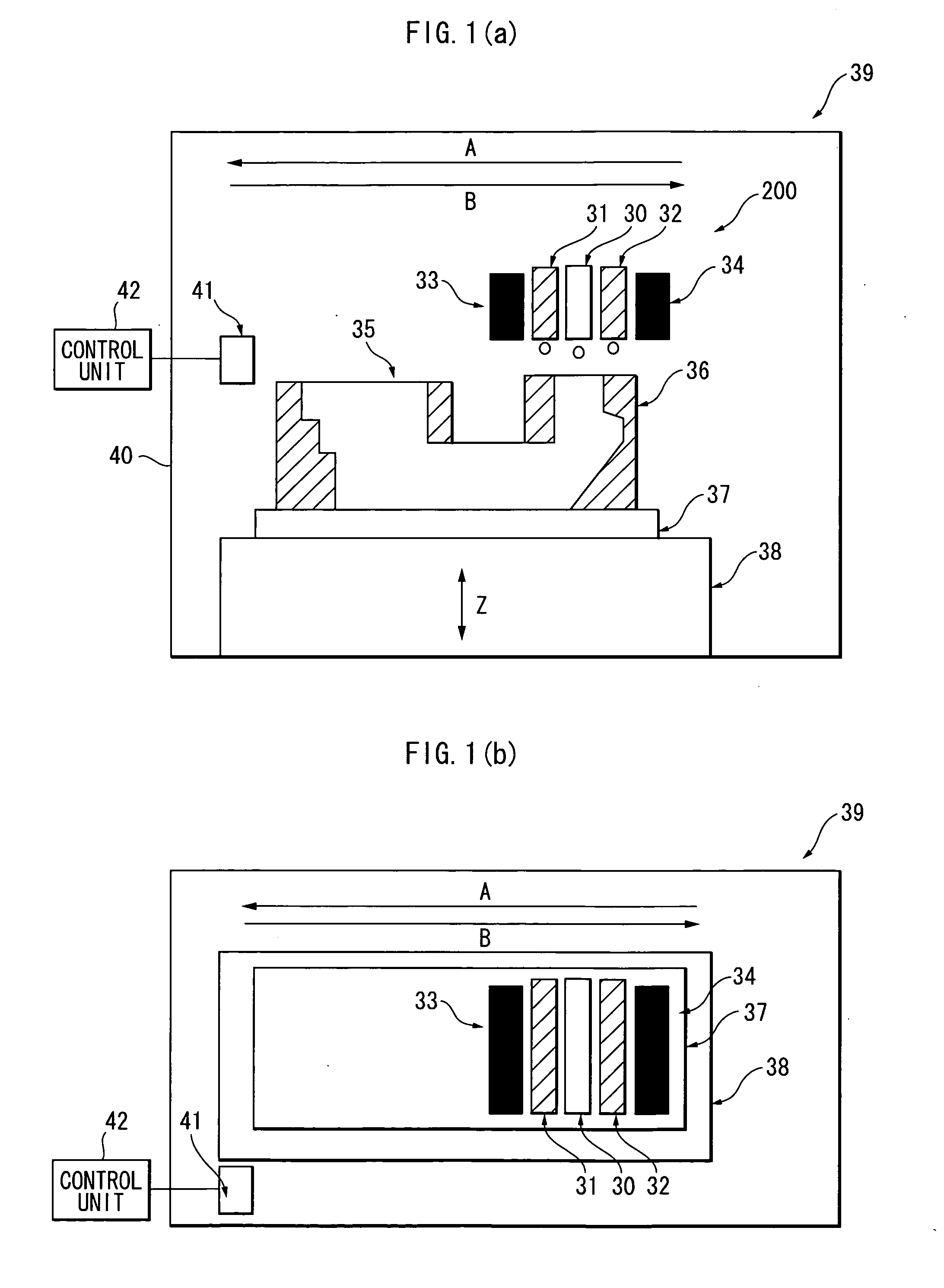
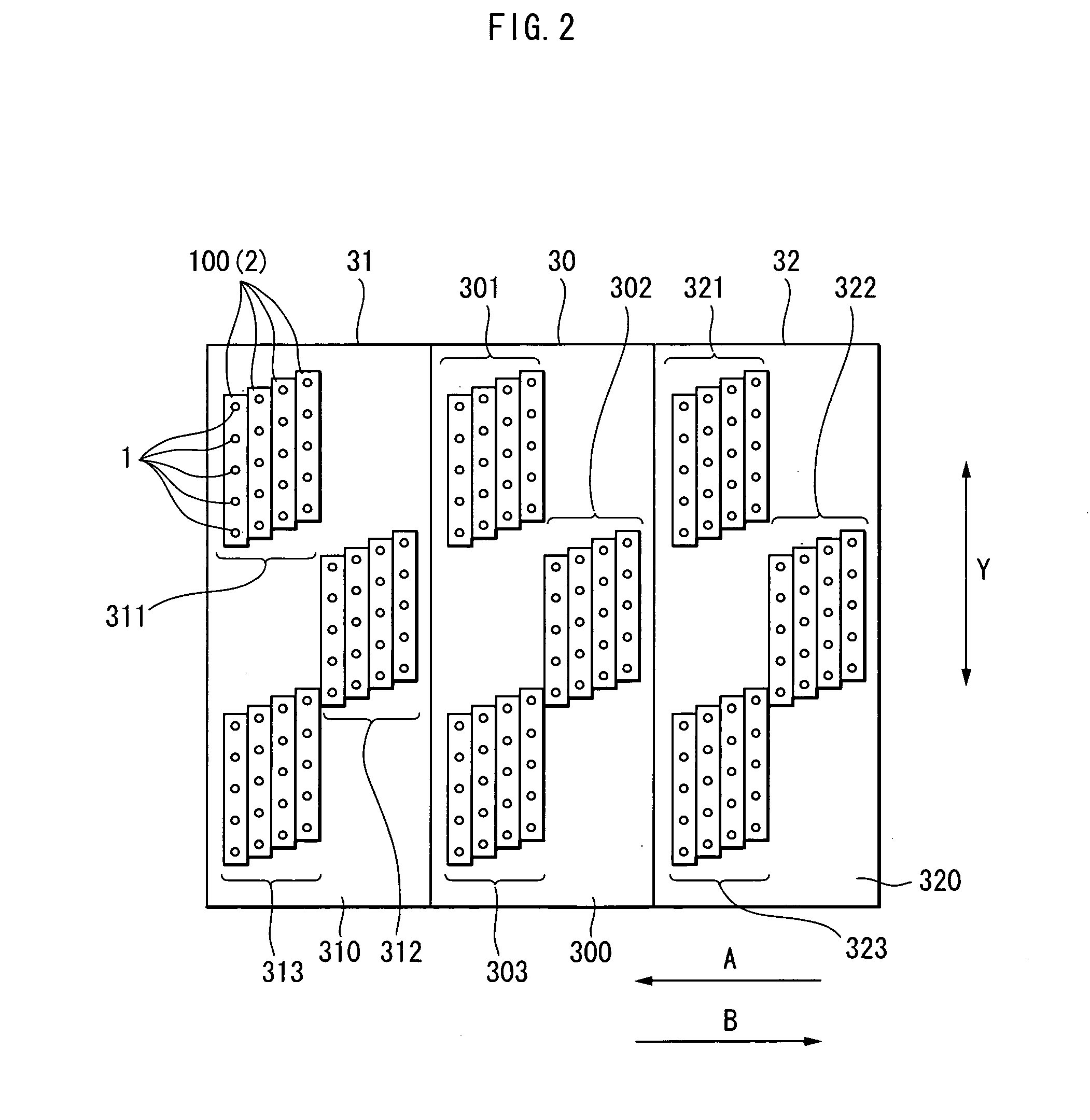
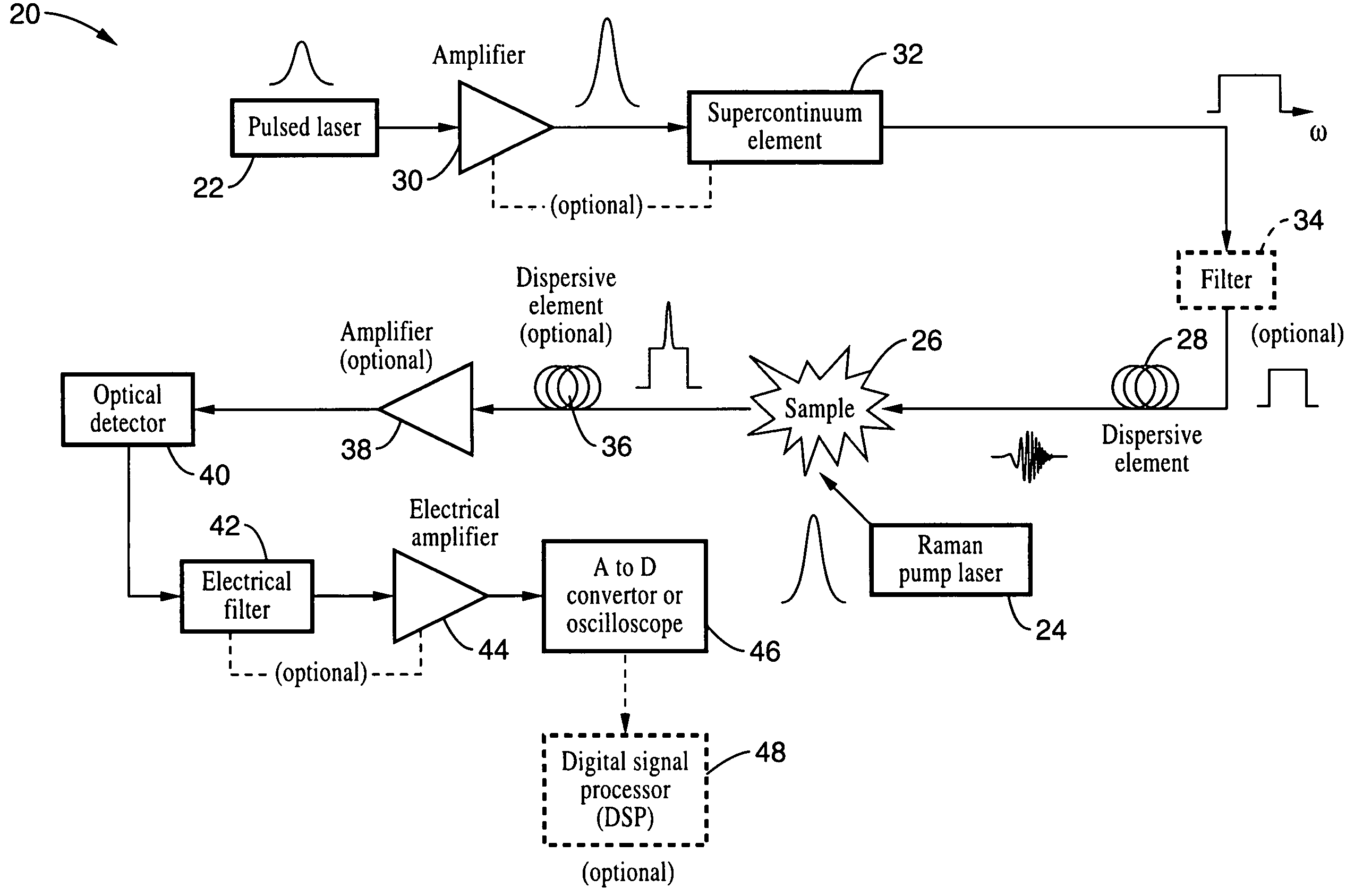
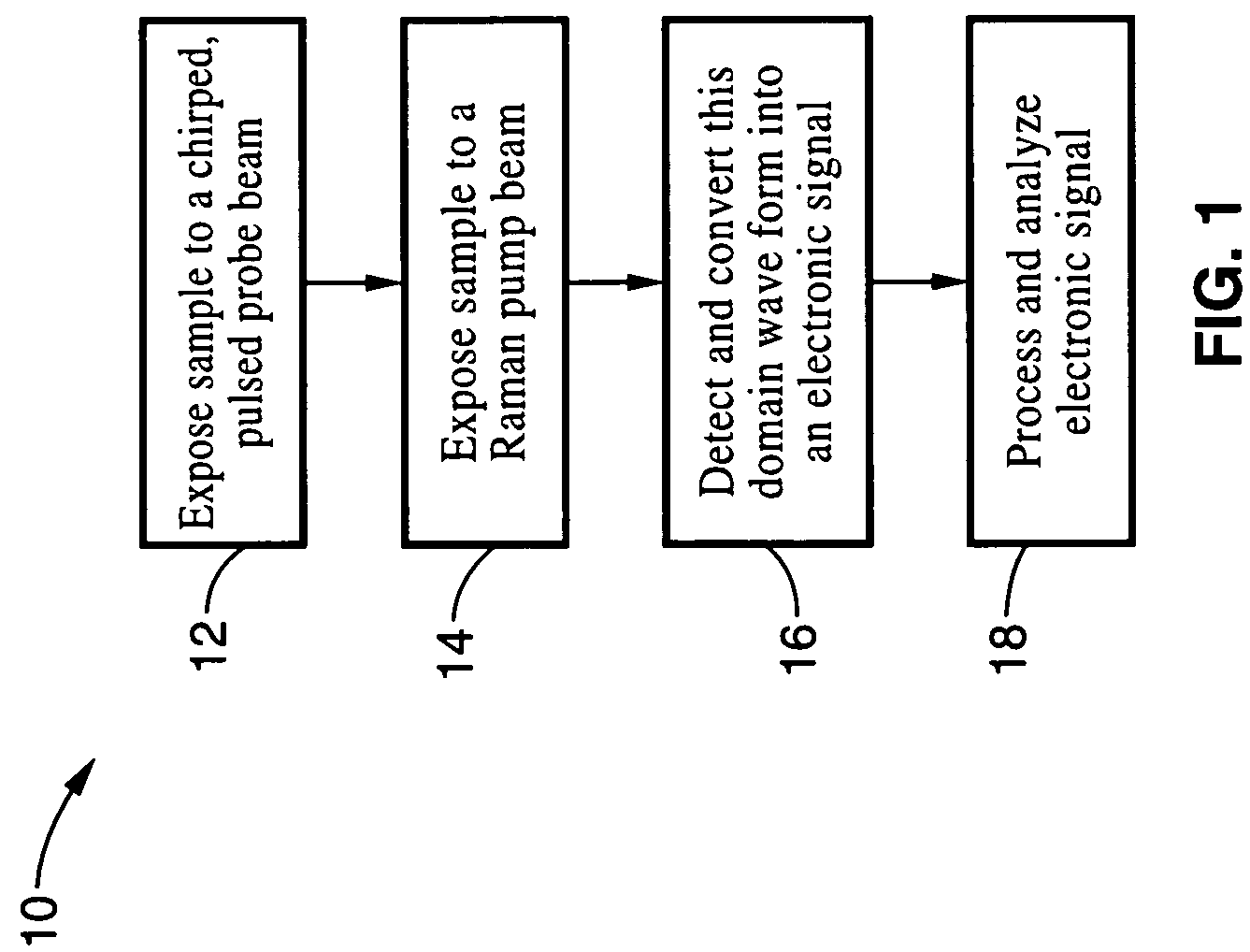
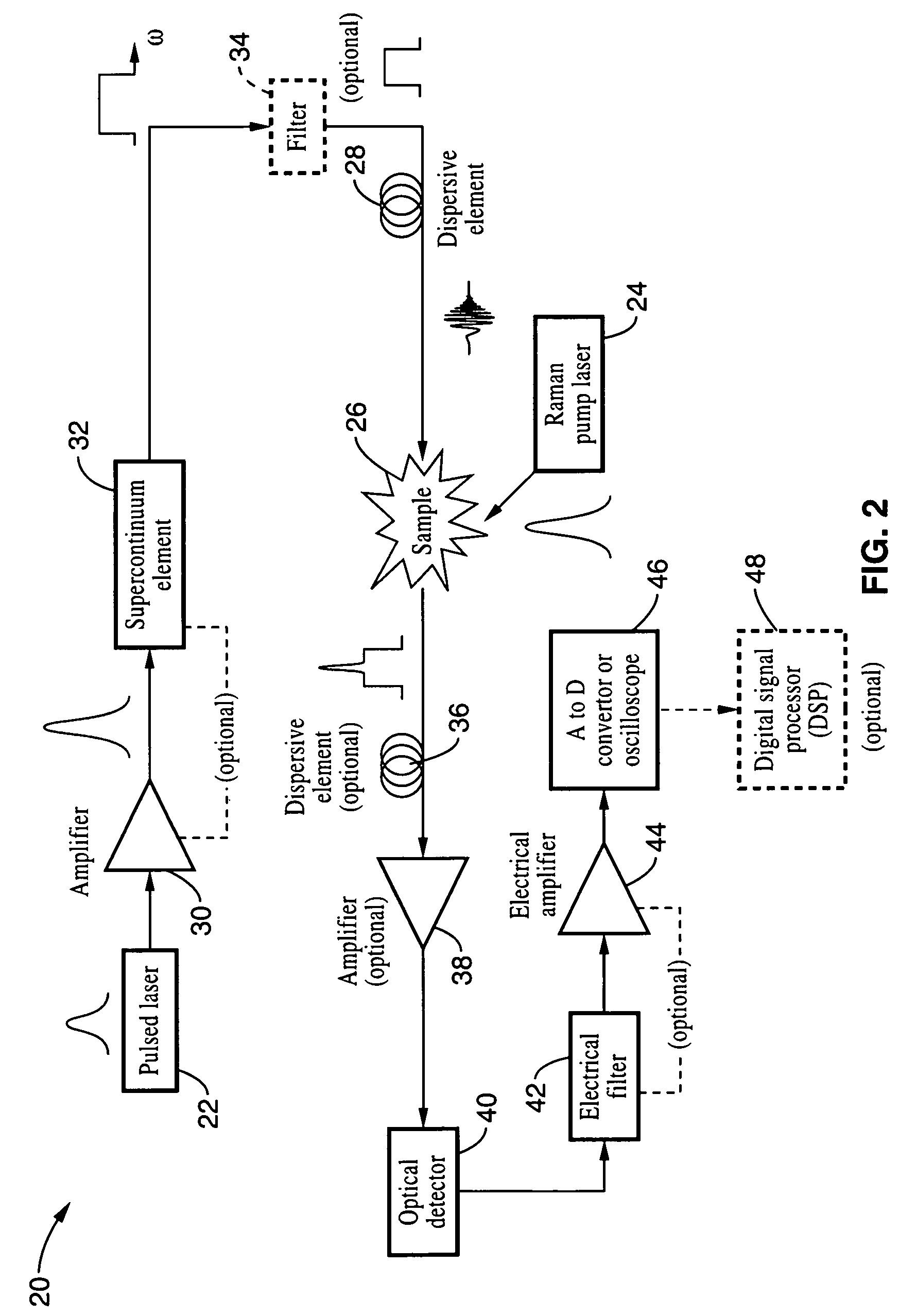
Apparatus and method for raman spectroscopy and microscopy with time domain spectral analysis
InactiveUS20090073432A1Eliminate needHigh speed moldingRaman/scattering spectroscopyRadiation pyrometrySpectroscopySpectrometer
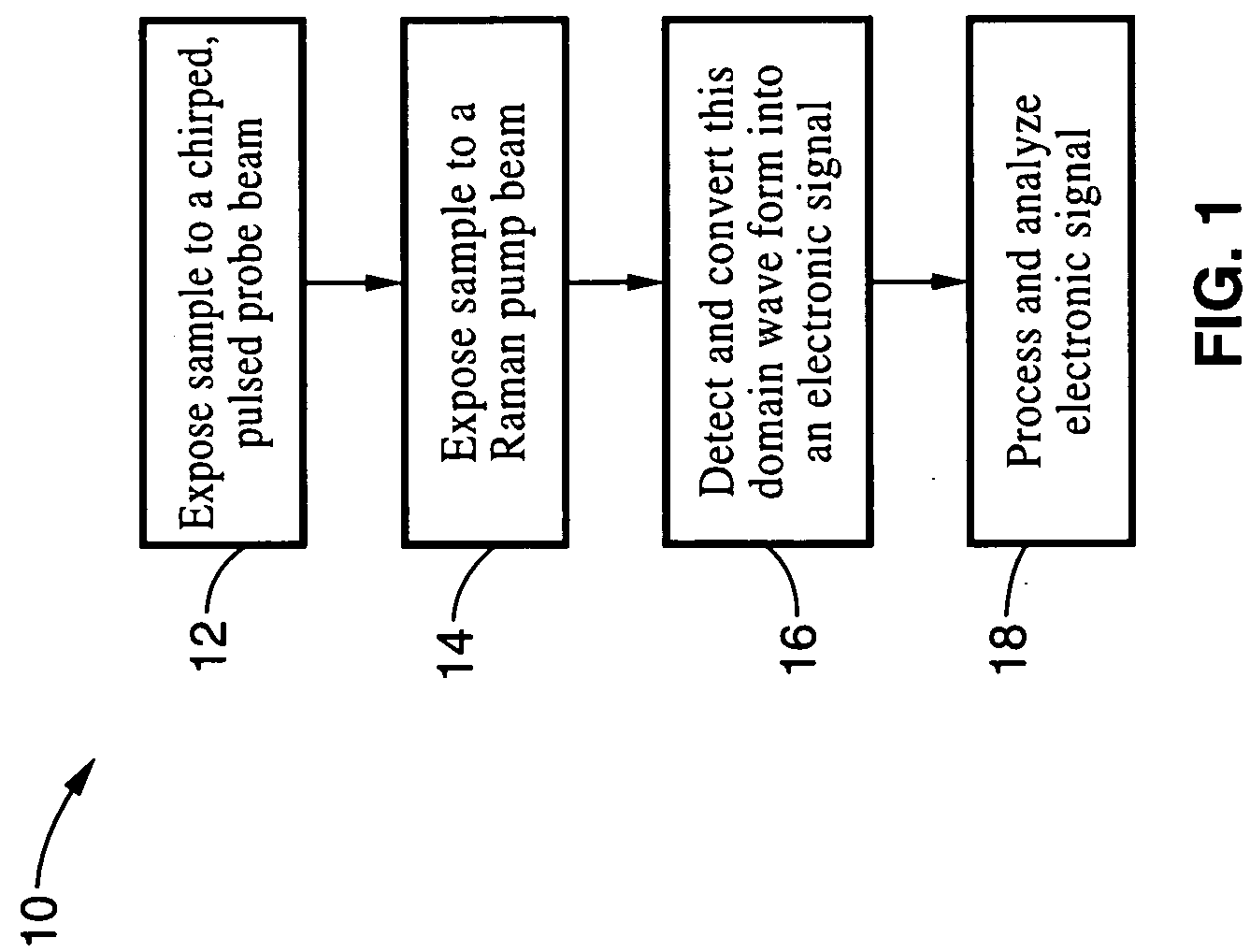
An apparatus and method for measuring Raman-type spectra using optical dispersion to convert an optical spectrum into a waveform which can be detected directly in the time domain without the use of a conventional spectrometer. In the example of stimulated Raman spectroscopy, the apparatus and method exposes a sample to a chirped, pulsed probe beam and a Raman pump beam and the resulting Raman spectra is detected by an optical detector in the time domain, and analyzed. Alternatively, the Raman spectra from the probe and pump beams is chirped with a dispersive element prior to detection and analysis. Each probe pulse provides a snapshot of the Raman spectrum that is sampled in time so that neither repetitive waveforms nor static samples are required. Therefore, high speed acquisitions and high throughput assays can be conducted. To facilitate detection, these spectral signals can also be amplified using distributed Raman amplification directly in the dispersive element.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
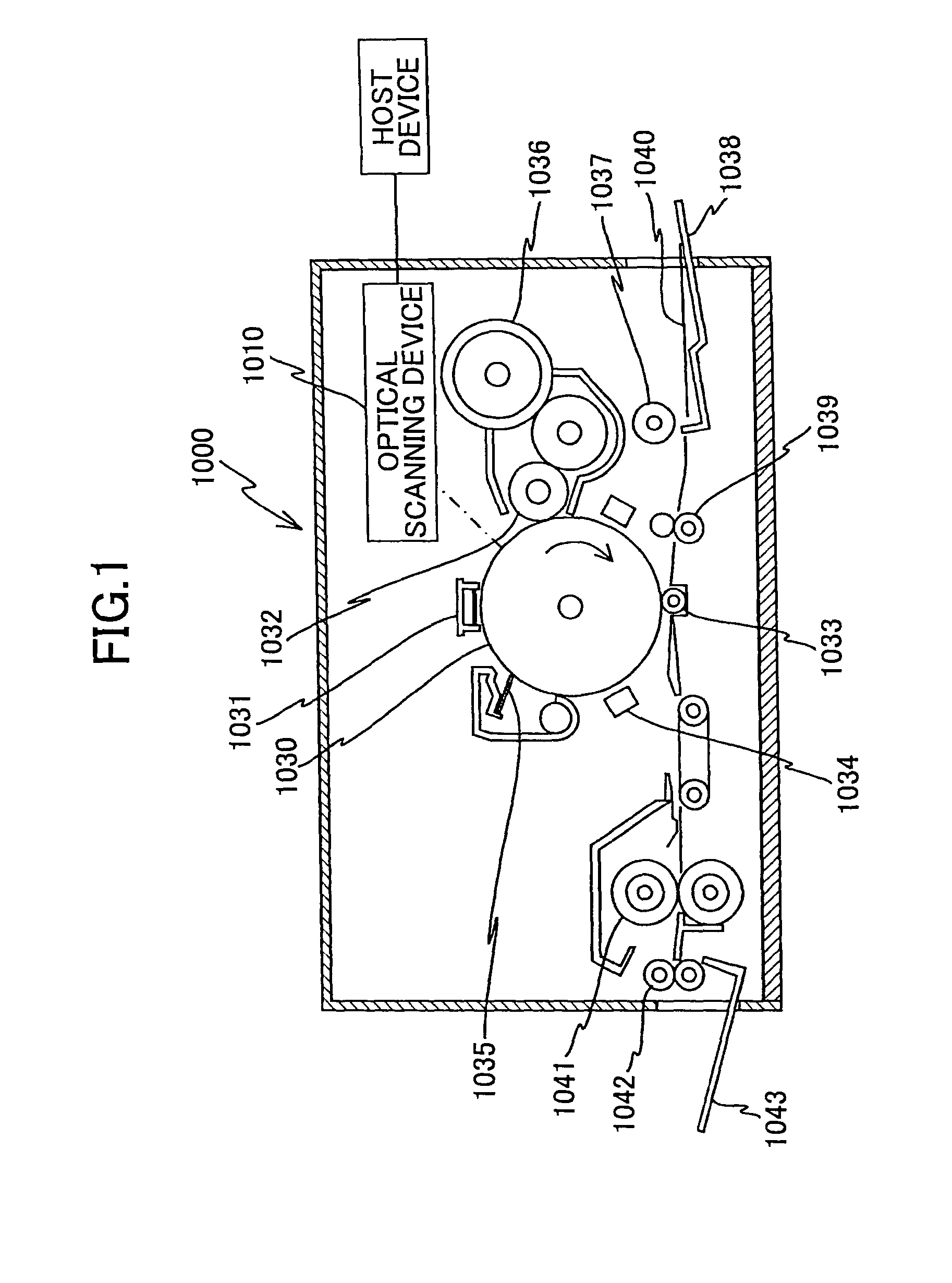
Surface emitting laser element, surface emitting laser array, optical scanning apparatus, image forming apparatus, and optical communication system
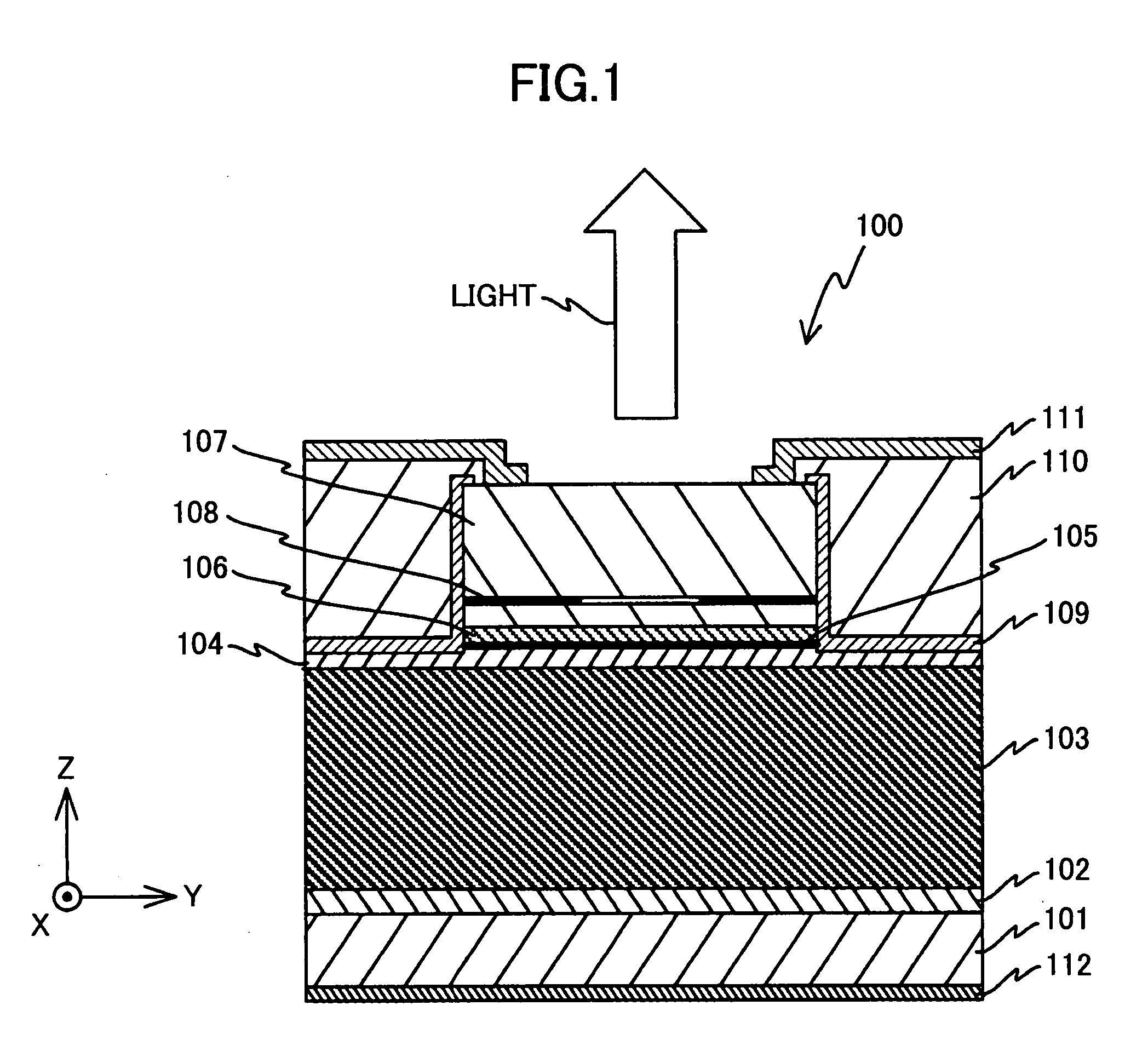
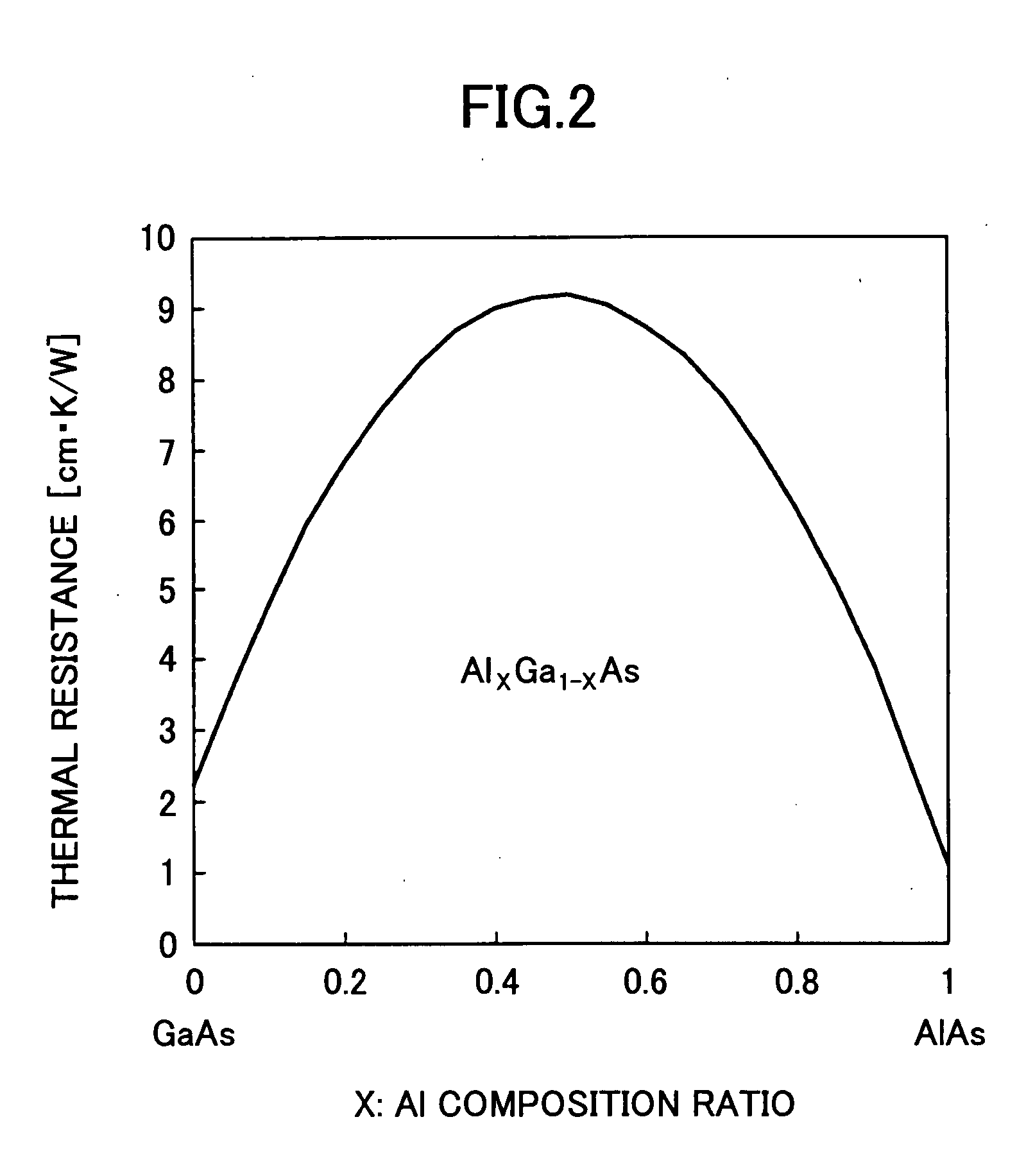
ActiveUS20080056321A1Improve heat dissipation propertyImprove cooling effectInking apparatusLaser optical resonator constructionVertical-external-cavity surface-emitting-laserVertical-cavity surface-emitting laser
A vertical cavity surface emitting laser element is disclosed that includes a substrate, a first semiconductor multilayer reflector including plural pairs of layers having differing refractive indexes and thermal resistances, a resonator region including an active layer, and a second semiconductor multilayer reflector including plural pairs of layers having differing refractive indexes and thermal resistances. At least one pair of layers of the first semiconductor multilayer reflector and / or the second semiconductor multilayer reflector includes a first layer with a lower thermal resistance that has an optical thickness greater than ¼ of the oscillation wavelength and a second layer with a higher thermal resistance that has an optical thickness less than ¼ of the oscillation wavelength. The sum of the optical thickness of the first layer and the optical thickness of the second layer is equal to m / 4 times the oscillation wavelength (m: even number≧2).
Owner:RICOH KK
Surface-emitting laser array, optical scanning device, and image forming device
ActiveUS20100214633A1Reduce the impact of heatSmall sizeLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionLaser arrayOptoelectronics
A surface-emitting laser array includes a plurality of light emitting parts arranged in a two-dimensional formation having two orthogonal directions. When the plurality of light emitting parts are orthogonally projected on a virtual line parallel to one of the two orthogonal directions, a spacing between two of the plurality of light emitting parts along the virtual line is equal to an integral multiple of a predetermined value. The plurality of light emitting parts include a first light emitting part, a second light emitting part adjacent to the first light emitting part, and a third light emitting part adjacent to the second light emitting part, and a spacing between the first and second light emitting parts differs from a spacing between the second and third light emitting parts.
Owner:RICOH KK
ZnO film, method for manufacturing the same, and luminescent element including the same
InactiveUS6733895B2Increase speedLow costPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSputteringOptoelectronics
A p-type ZnO film is formed on a sapphire substrate by RF magnetron sputtering in an atmosphere of a mixture of Ar and N2 gases, using a Zn metal target doped with Y2O3. The p-type ZnO film can be easily formed even on a large-sized substrate.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Three-dimensional laminating molding device
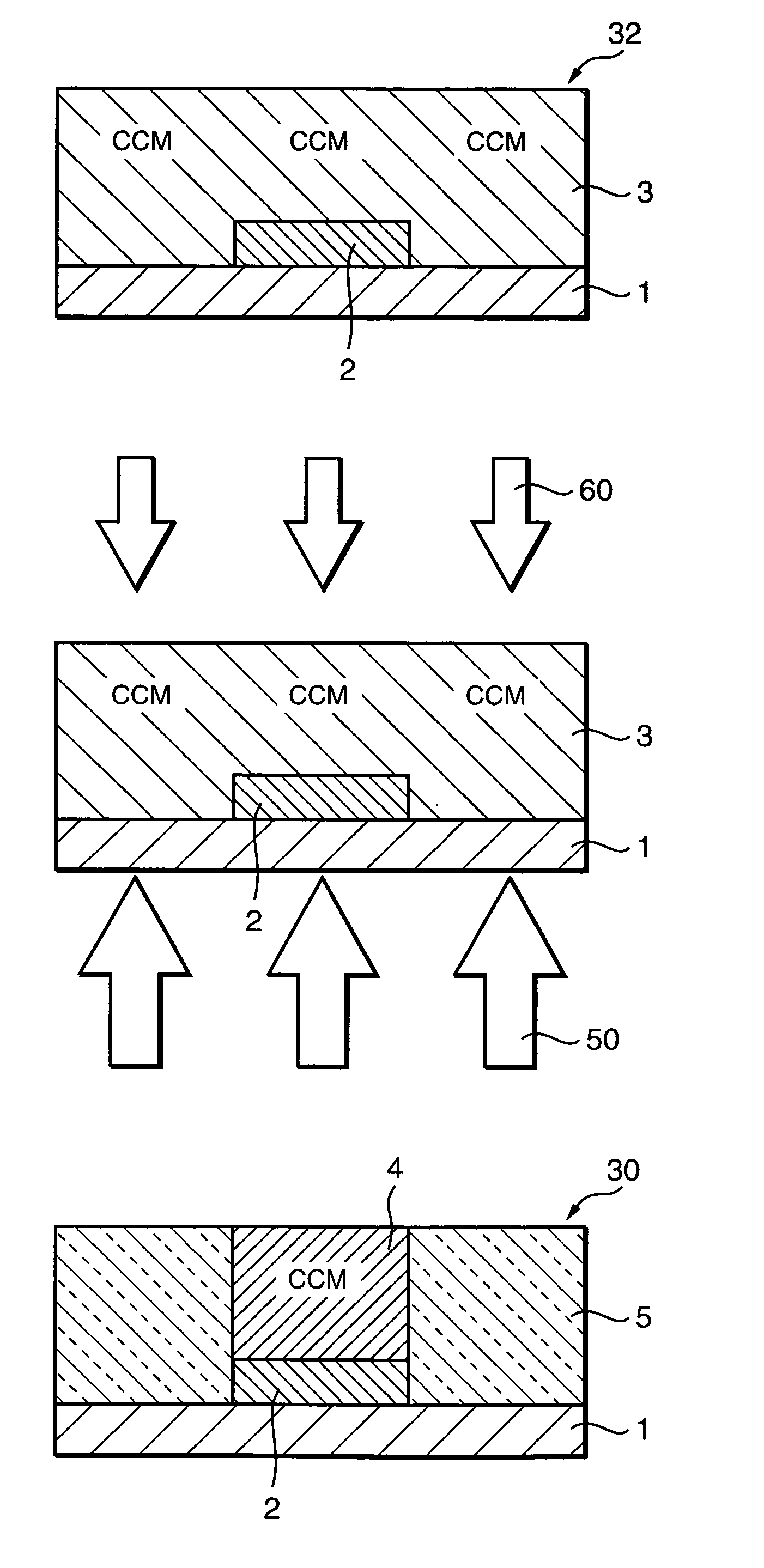
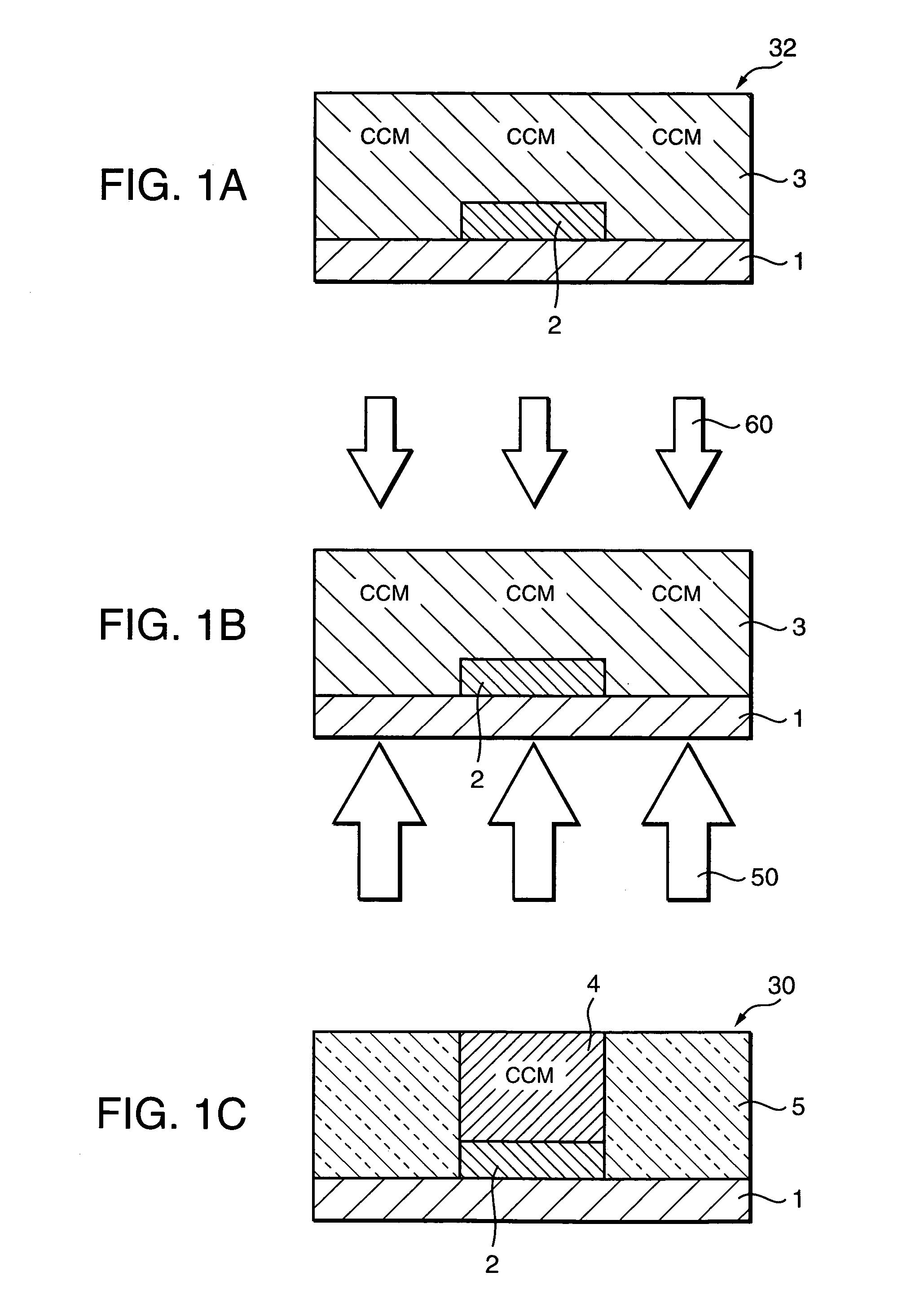
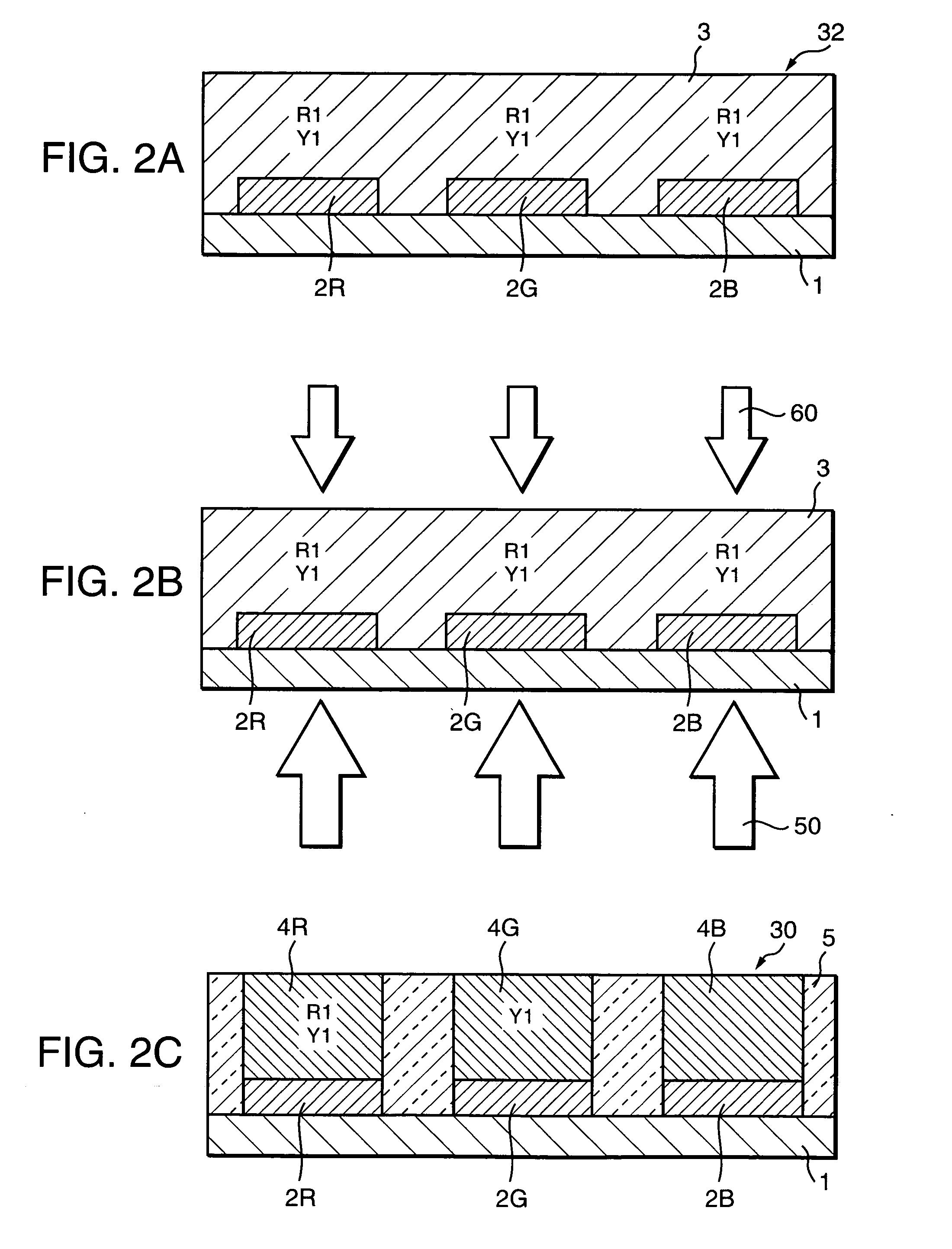
InactiveUS7104773B2Increase speedHigh speed moldingConfectionerySweetmeatsRoom temperatureInternal temperature
Owner:RICOH PRINTING SYST
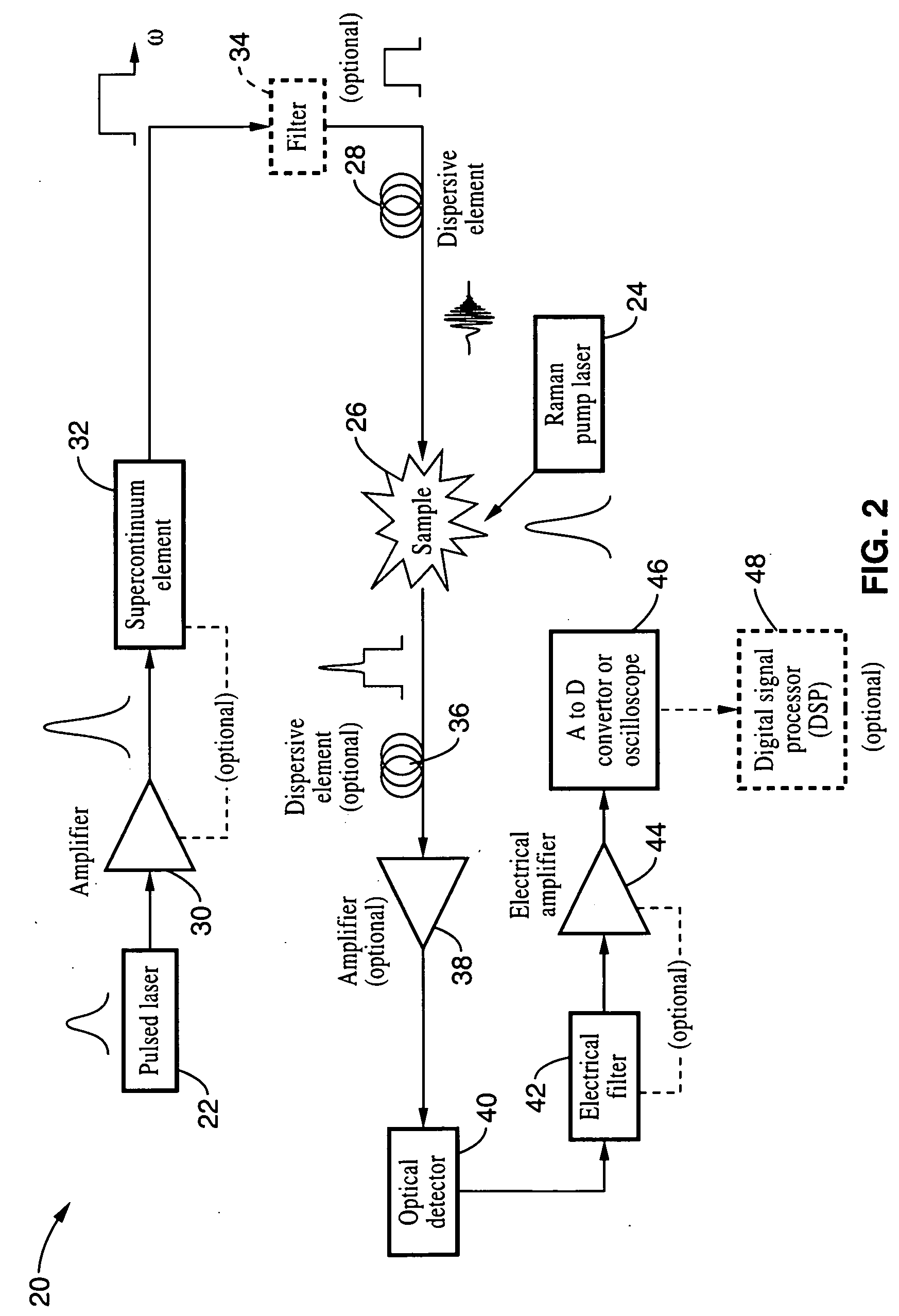
Apparatus and method for Raman spectroscopy and microscopy with time domain spectral analysis
InactiveUS7821633B2Eliminate needHigh speed moldingRadiation pyrometryRaman/scattering spectroscopySpectroscopySpectrometer
An apparatus and method for measuring Raman-type spectra using optical dispersion to convert an optical spectrum into a waveform which can be detected directly in the time domain without the use of a conventional spectrometer. In the example of stimulated Raman spectroscopy, the apparatus and method exposes a sample to a chirped, pulsed probe beam and a Raman pump beam and the resulting Raman spectra is detected by an optical detector in the time domain, and analyzed. Alternatively, the Raman spectra from the probe and pump beams is chirped with a dispersive element prior to detection and analysis. Each probe pulse provides a snapshot of the Raman spectrum that is sampled in time so that neither repetitive waveforms nor static samples are required. Therefore, high speed acquisitions and high throughput assays can be conducted. To facilitate detection, these spectral signals can also be amplified using distributed Raman amplification directly in the dispersive element.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
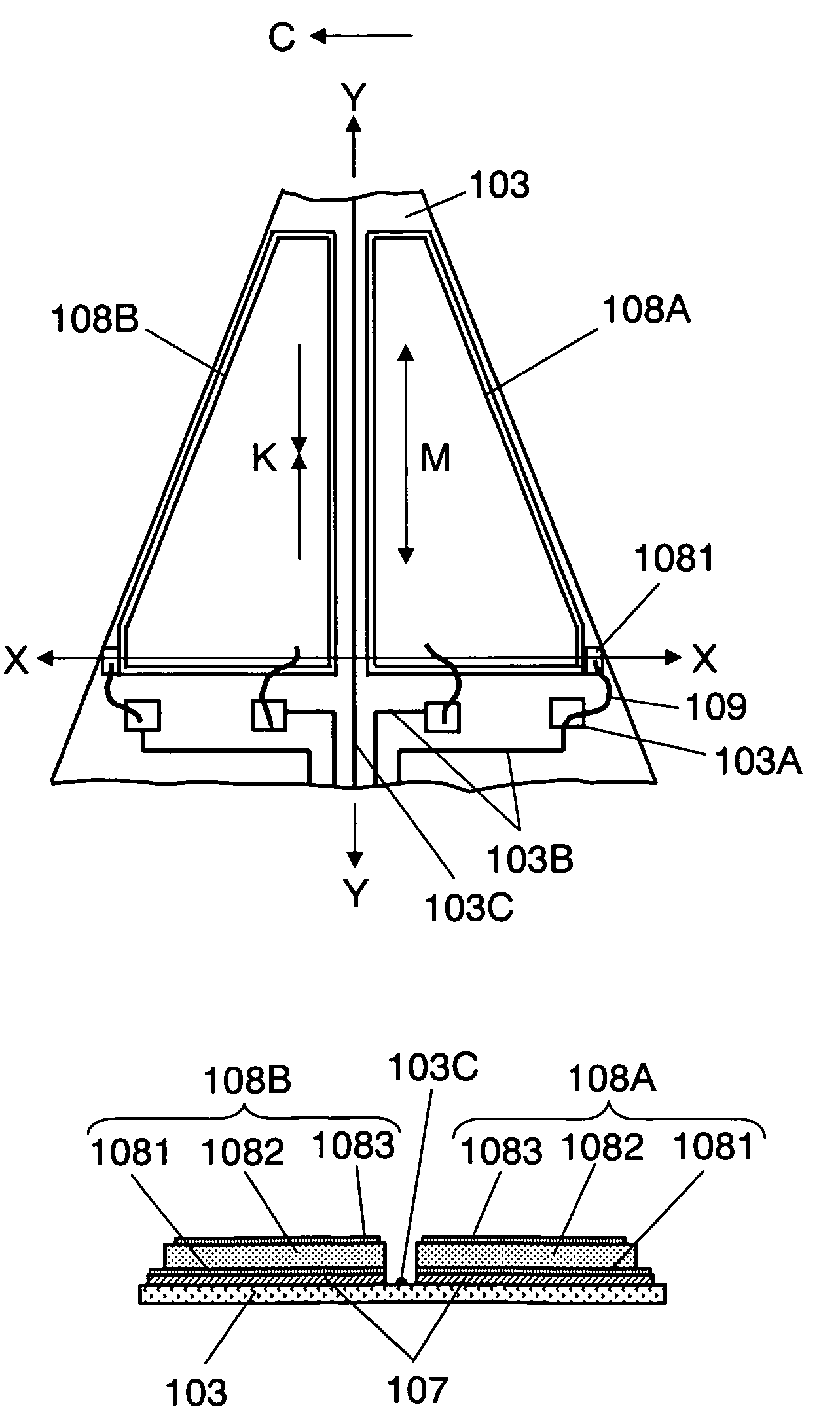
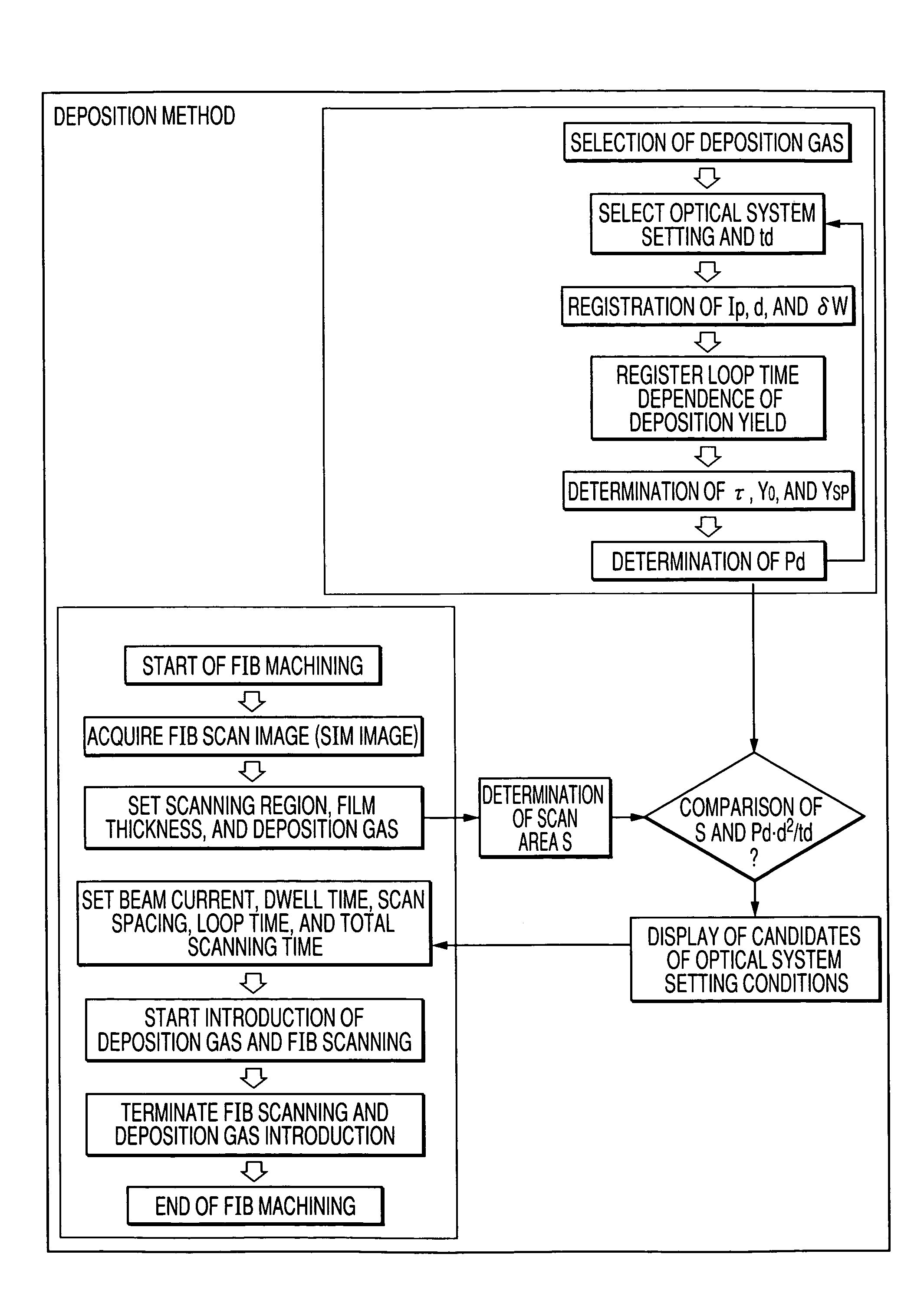
Method for depositing a film using a charged particle beam, method for performing selective etching using the same, and charged particle beam equipment therefor
InactiveUS20050066899A1High speed moldingEfficiently formedElectric discharge tubesVacuum evaporation coatingDisplay deviceIrradiation
Certain film deposition and selective etching technology may involve scanning of a charged particle beam along with a deposition gas and etching gas, respectively. In conventional methods, unfortunately, the deposition rate or the selective ratio is oftentimes decreased depending on optical system setting, scan spacing, dwell time, loop time, substrate, etc. Accordingly, an apparatus is provided for finding an optical system setting, a dwell time, and a scan spacing. These parameters are found to realize the optimal scanning method of the charged particle beam from the loop time dependence of the deposition rate or etching rate. This deposition rate or etching rate are measurements stored in advance for a desired irradiation region where film deposition or selective etching should be performed. The apparatus displays a result of its judgment on a display device.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Ink jet recording head, ink jet cartridge with ink jet recording head, and ink jet recording apparatus
An ink jet recording head includes at least three nozzle array groups; each of the nozzle array group including, a first nozzle array including a plurality of ejection outlets for ejecting ink, and a second nozzle array including a plurality of ejection outlets for ejecting the ink, the second nozzle array being disposed adjacent to the first nozzle array with an ink supply port for supplying the ink interposed therebetween, wherein an opening area of the ejection outlets of second nozzle array is smaller than an opening area of the ejection outlets of first nozzle array, wherein the nozzle array groups eject three different kinds of inks, respectively, when the ink jet recording head moves relative to a recording material, wherein the nozzle arrays of adjacent ones of the nozzle array group are arranged in the order of the first nozzle array of one of the adjacent nozzle array groups, the second nozzle array of the one of the adjacent nozzle array groups, the second nozzle array of the other one of the adjacent nozzle array groups, and the first nozzle array of the other one of the adjacent nozzle array groups; and the recording head further including a third nozzle array provided in each of the adjacent ones of the nozzle array groups, the third nozzle array including a plurality of ejection outlets for ejecting the ink, wherein an opening area of the ejection outlets of third nozzle array is smaller than an opening area of the ejection outlets of second nozzle array, wherein the third nozzle array being disposed in the same side as the second nozzle array with respect to the ink supply port, and wherein the nozzle array group which does not constitute the adjacent nozzle array groups is supplied with the ink having a highest lightness among the three kinds of inks.
Owner:CANON KK
Method and apparatus for manufacturing a color conversion filter
ActiveUS20050084775A1Simple manufacturing processHigh-resolution patterningElectroluminescent light sourcesOptical filtersDecompositionUltraviolet lights
A method and apparatus for manufacturing a color conversion filter. The method includes forming a color filter layer on a transparent substrate. A coloring matter layer containing color conversion coloring matter and an optical radical generating agent are formed on the substrate and the filter layer. The coloring matter layer is exposed to coloring matter decomposition light applied through the substrate and the filter layer. The coloring matter layer also is exposed to auxiliary ultraviolet light applied from the side of the coloring matter layer. This forms a color conversion layer at a position corresponding to the filter layer. The optical radical generating agent is heat vaporized. The color conversion coloring matter is decomposed by light whose wavelength is outside a range that the color filter layer transmits. The coloring matter decomposition light includes a wavelength component that decomposes the color conversion coloring matter. The color conversion layer emits, through wavelength profile conversion, light that the color filter layer transmits.
Owner:SHARP KK
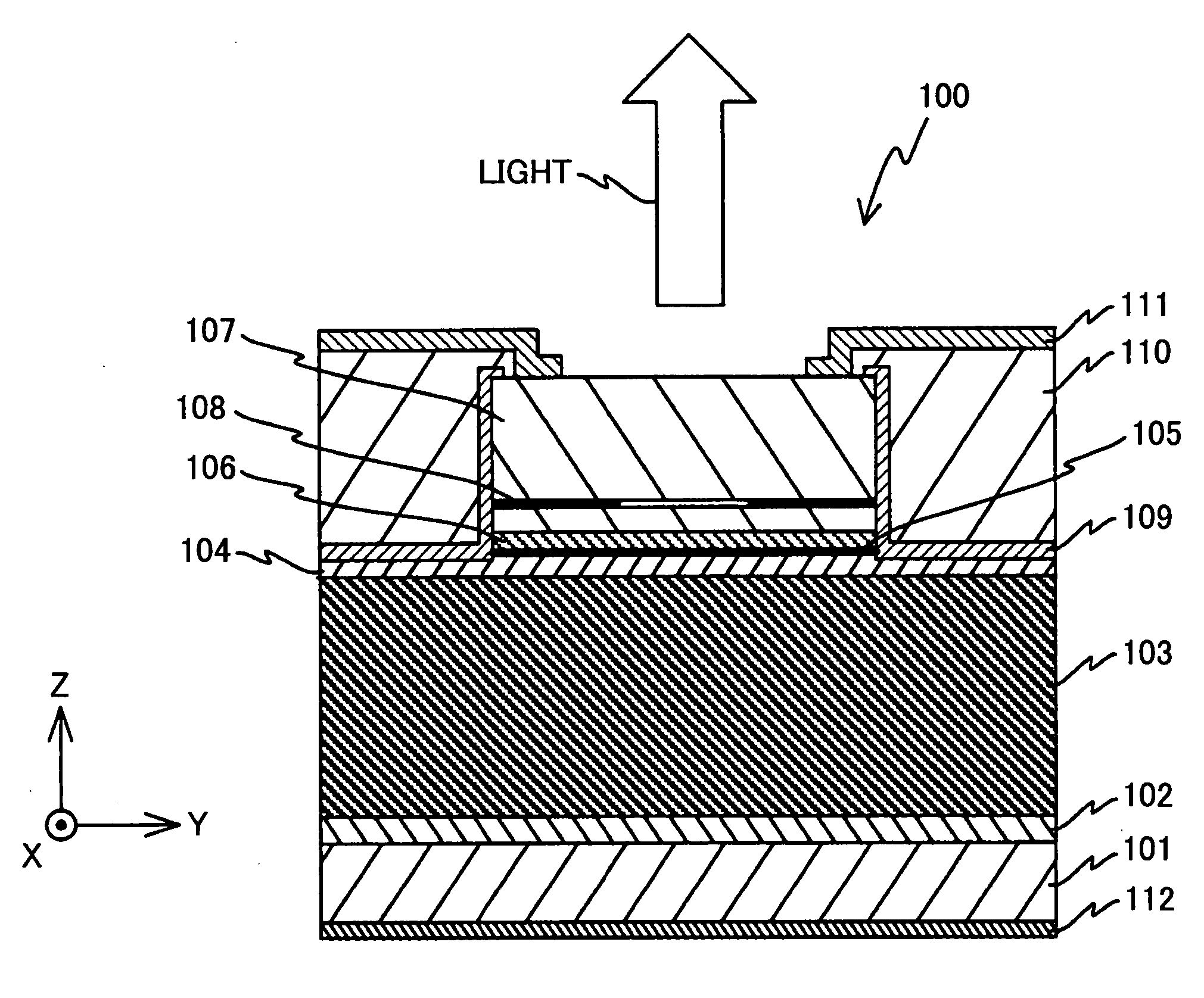
Apparatus and method for manufacturing photoelectric conversion elements, and photoelectric conversion element
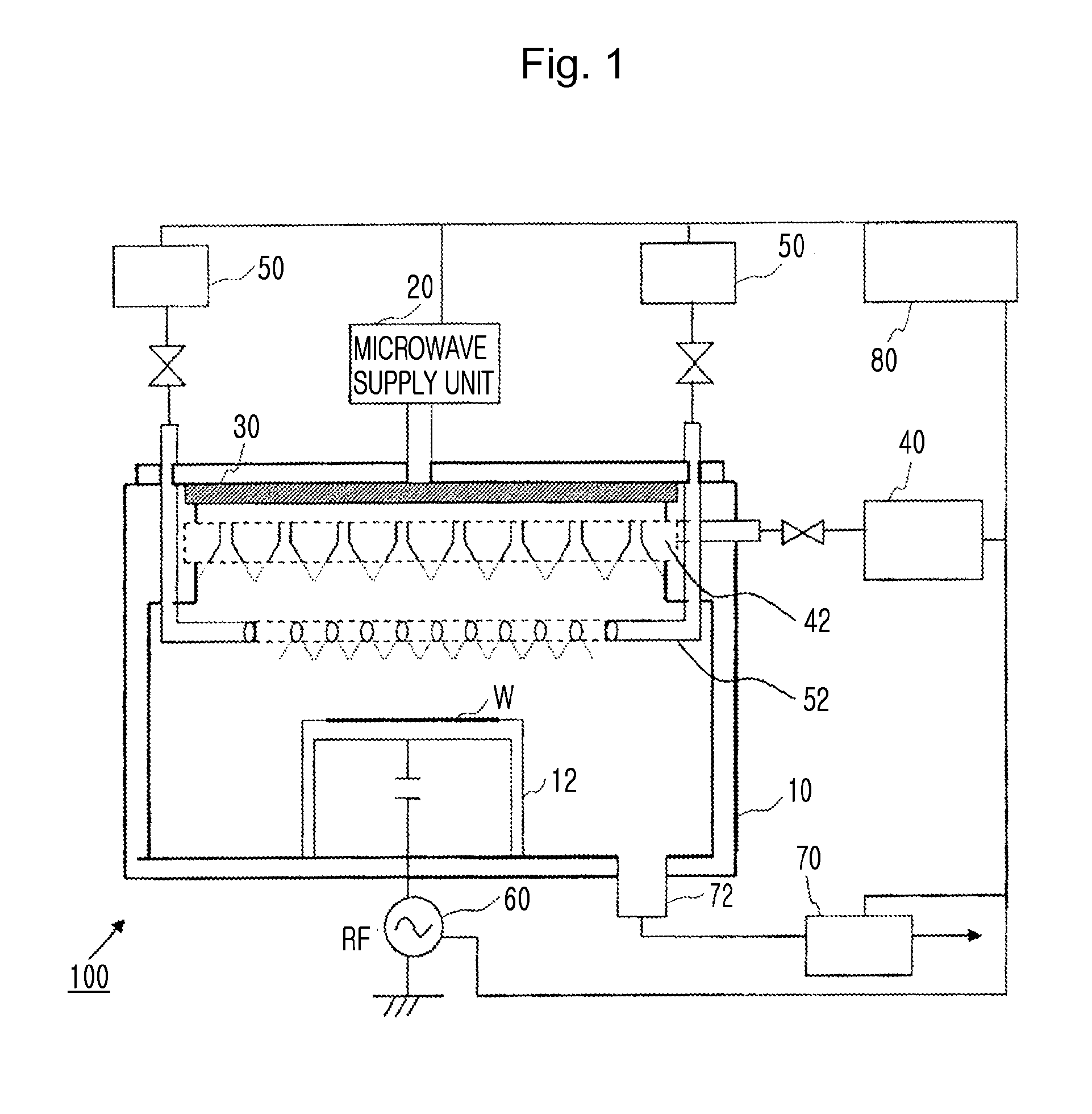
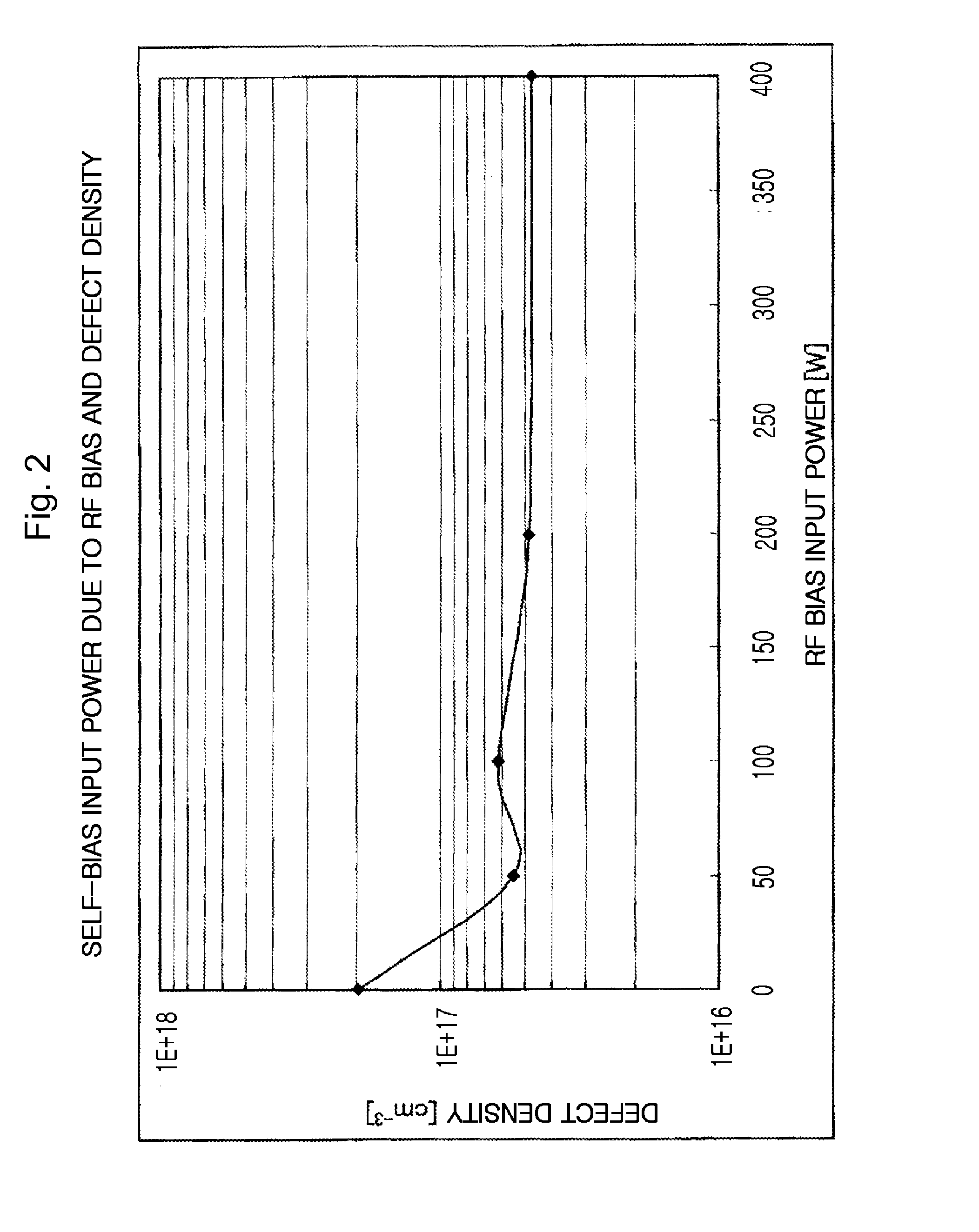
InactiveUS20100275981A1Reduce defect densityHigh speedFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicrowave applicationsVoltage
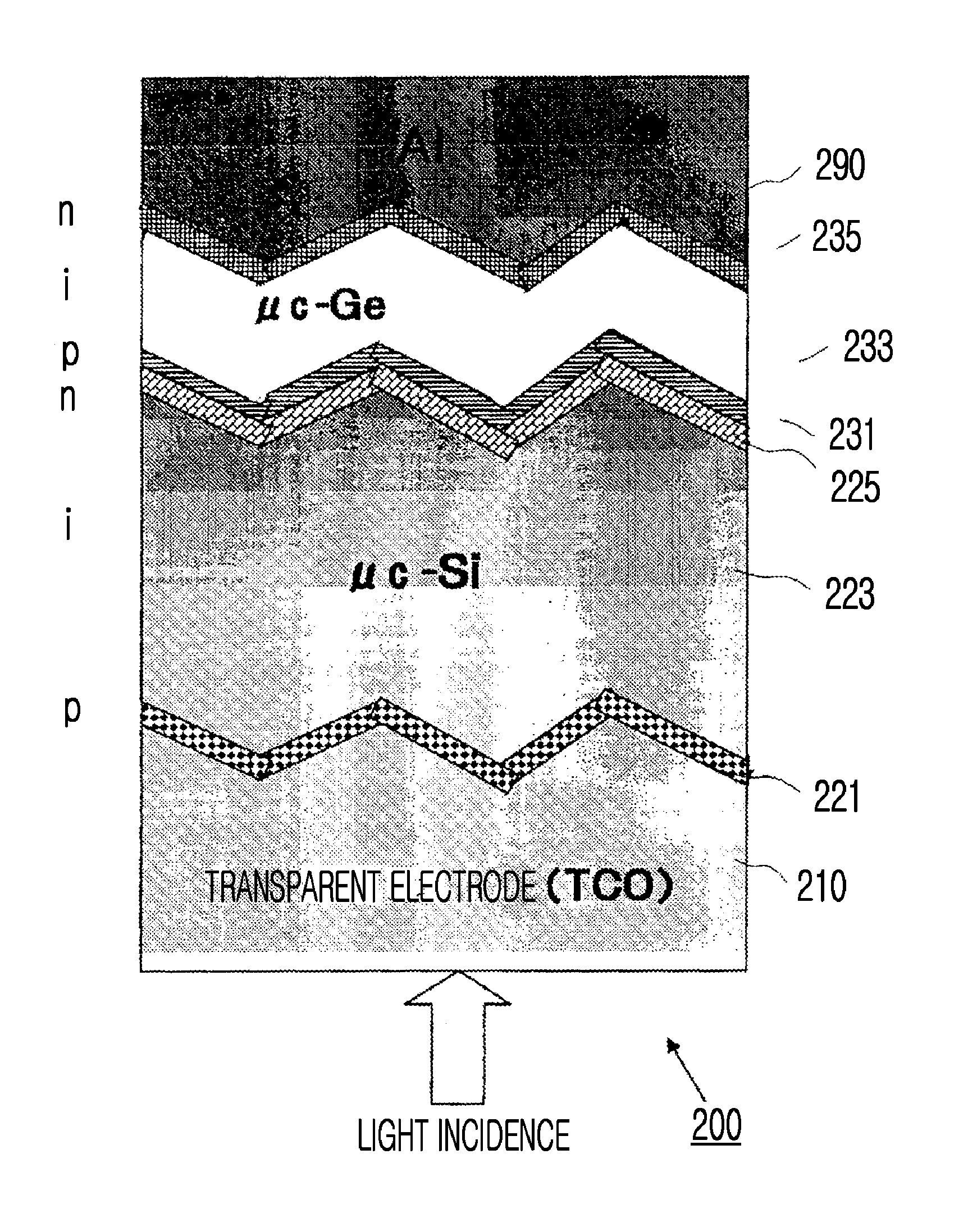
An apparatus and method for manufacturing photoelectric conversion elements, and a photoelectric conversion element, the apparatus and method being capable of highly efficiently forming a film at a high speed with microwave plasma, preventing oxygen from mixing, and reducing the number of defects. The invention provides a photoelectric conversion element manufacturing apparatus 100 that forms a semiconductor stack film on a substrate by using microwave plasma CVD. The apparatus includes a chamber 10 which is a enclosed space containing a base, on which the a subject substrate for thin-film formation is mounted, a first gas supply unit 40 which supplies plasma excitation gas to a plasma excitation region in the chamber 10, a pressure regulation unit 70 which regulates pressure in the chamber 10, a second gas supply unit 50 which supplies raw gas to a plasma diffusion region in the chamber 10, a microwave application unit 20 which applies microwaves into the chamber 10, and a bias voltage application unit 60 which selects and applies a substrate bias voltage to the substrate W according to the type of gas.
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV +1
Image forming apparatus and method
InactiveUS20070146433A1Interfere with depositionHigh quality printingOther printing apparatusImage resolutionImage formation
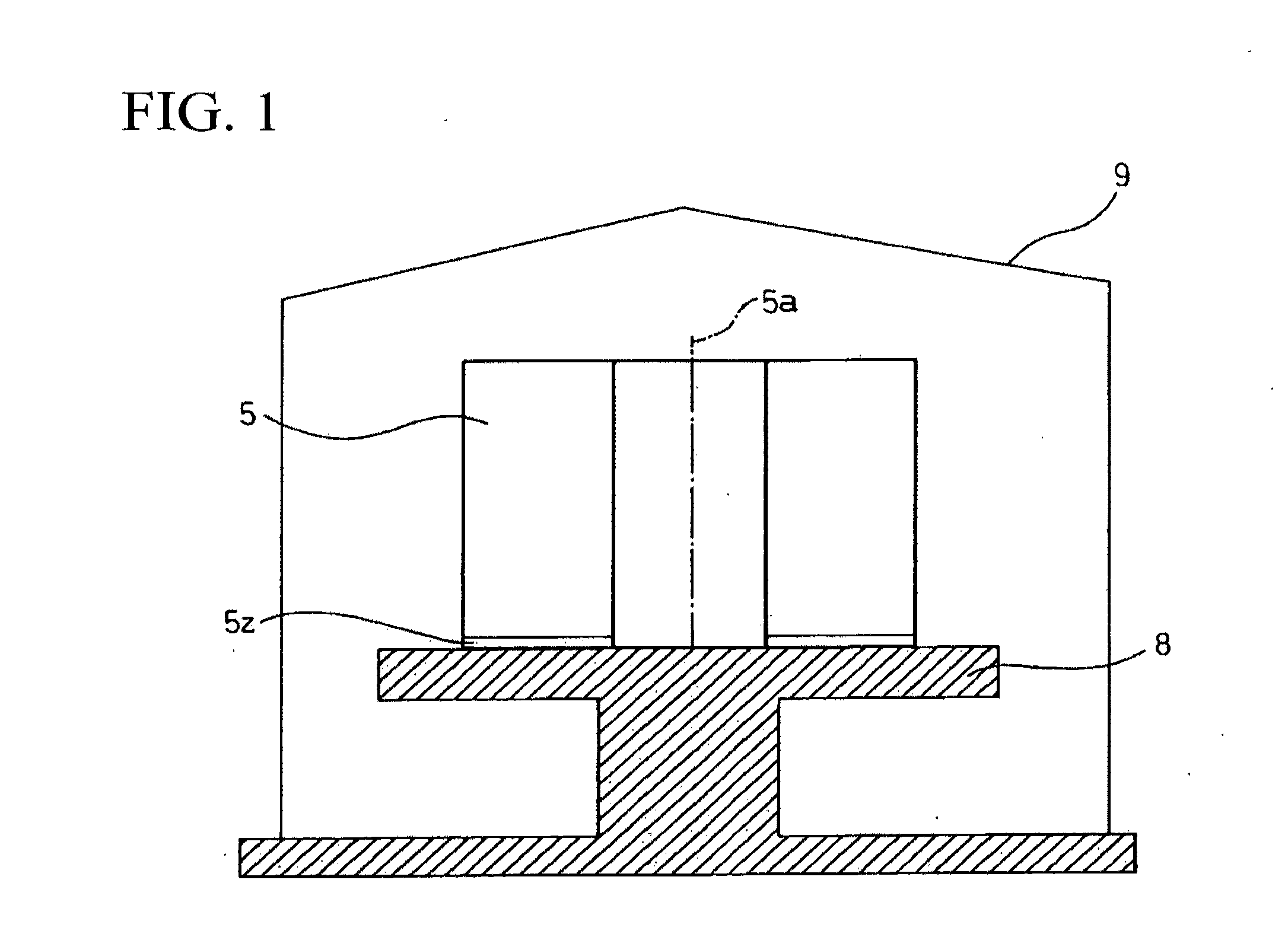
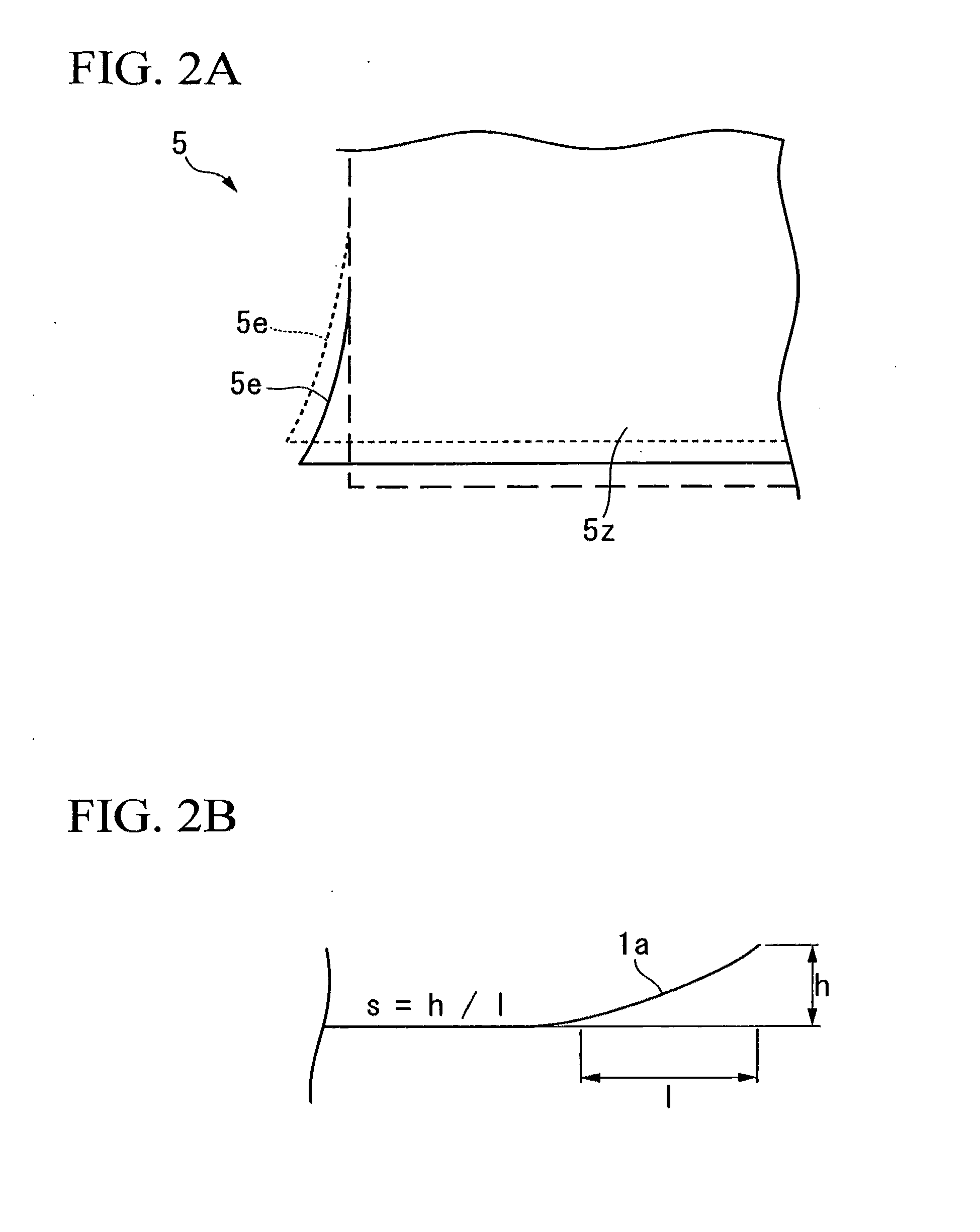
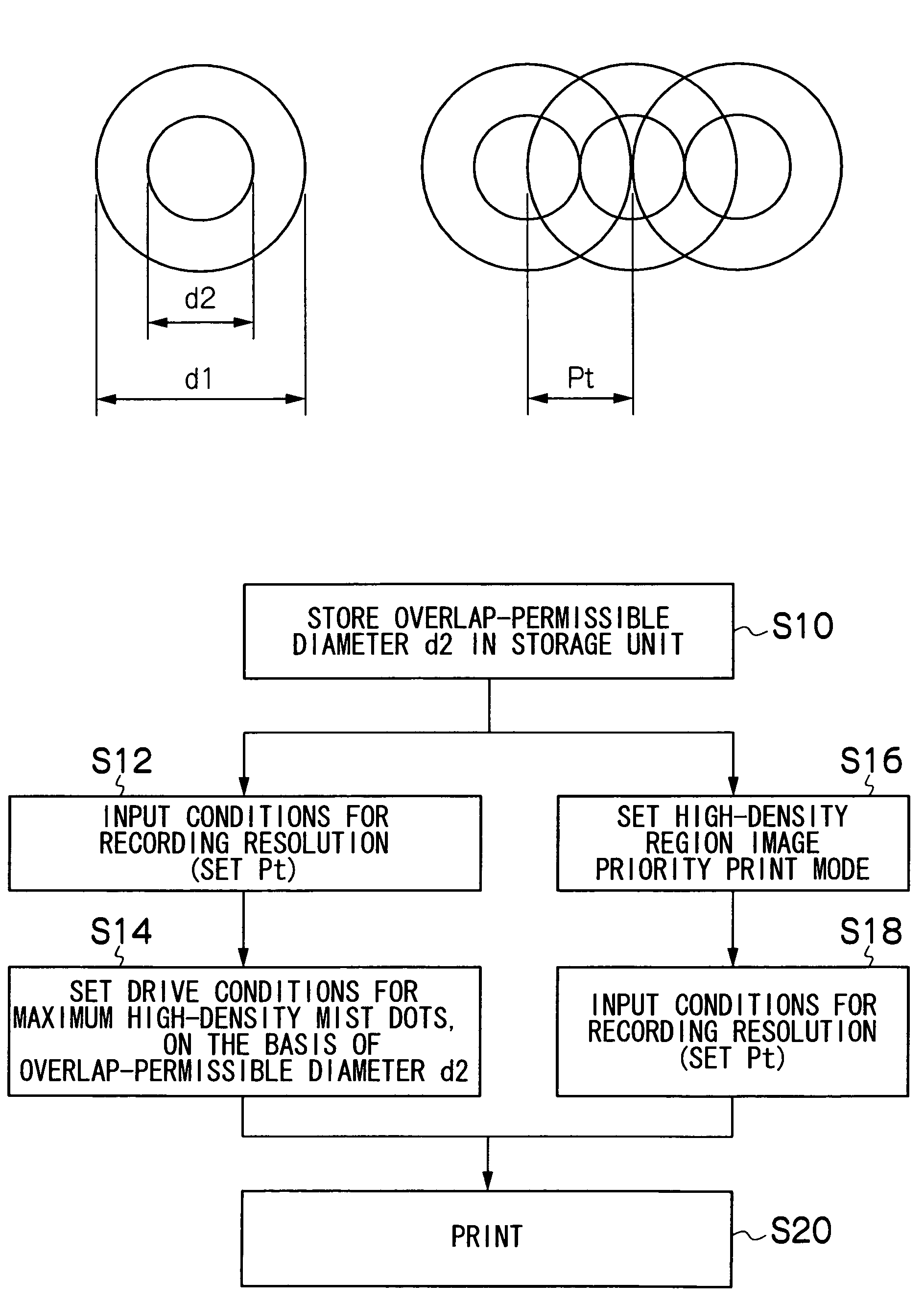
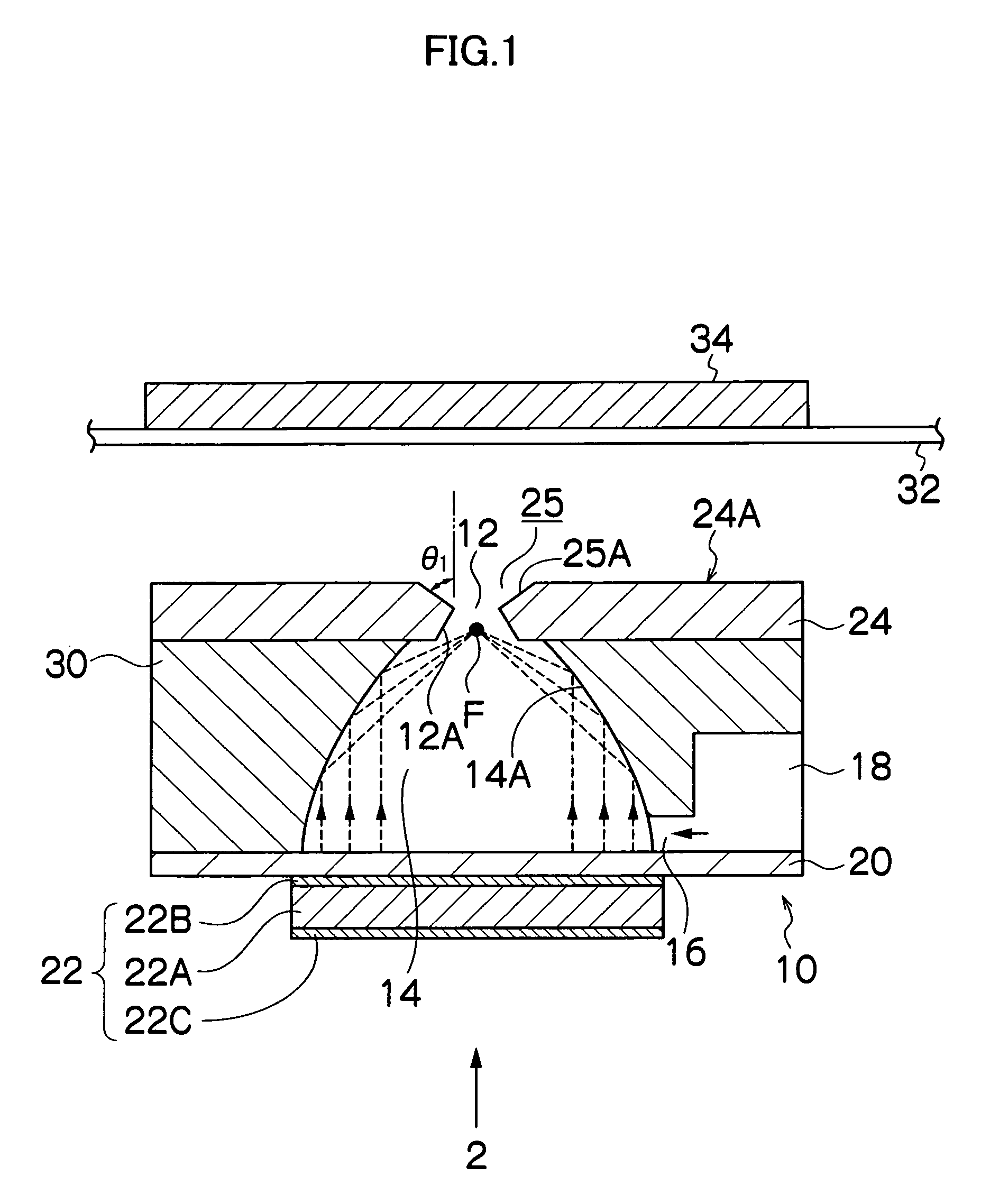
The image forming apparatus includes: a liquid chamber into which ink is filled; an ejection port through which the ink is ejected from the liquid chamber; a mist generation device which generates a mist from a surface of the ink inside the ejection port by applying vibration energy to the ink in the liquid chamber; an electric field generation device which generates an electric field causing the mist ejected from the ejection port to move to a recording medium; and a setting device which sets at least one of drive conditions of the mist generation device and a recording resolution in such a manner that a relationship Pt≧d2 is satisfied, where d2 is an overlap-permissible diameter which is a minimum distance between centers of two mist dots formed by the mist on the recording medium that allows shapes of the two mist dots to be fixed as a prescribed shape when the two mist dots are deposited on the recording medium substantially simultaneously under substantially same ejection conditions so as to overlap partially with each other, and Pt is a pitch between the centers of the two mist dots defined by the recording resolution.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Preparation of a synthetic quartz glass grain
ActiveUS20180362385A1Easy to prepareIncrease speedMaterial analysis by optical meansGlass shaping apparatusSilica particleVitreous Bodies
One aspect relates to a process for the preparation of a quartz glass grain, including providing a silicon dioxide granulate from a pyrogenically produced silicon dioxide powder, making a glass melt out of silicon dioxide granulate, making a quartz glass body out of at least part of the glass melt and reducing the size of the quartz glass body to obtain the quartz glass grain. One aspect further relates to a quartz glass grain which is obtainable by this process. One aspect further relates to opaque quartz glass bodies, which are obtainable by further processing of the quartz glass grain.
Owner:HERAEUS QUARZGLAS
Injection molding control method
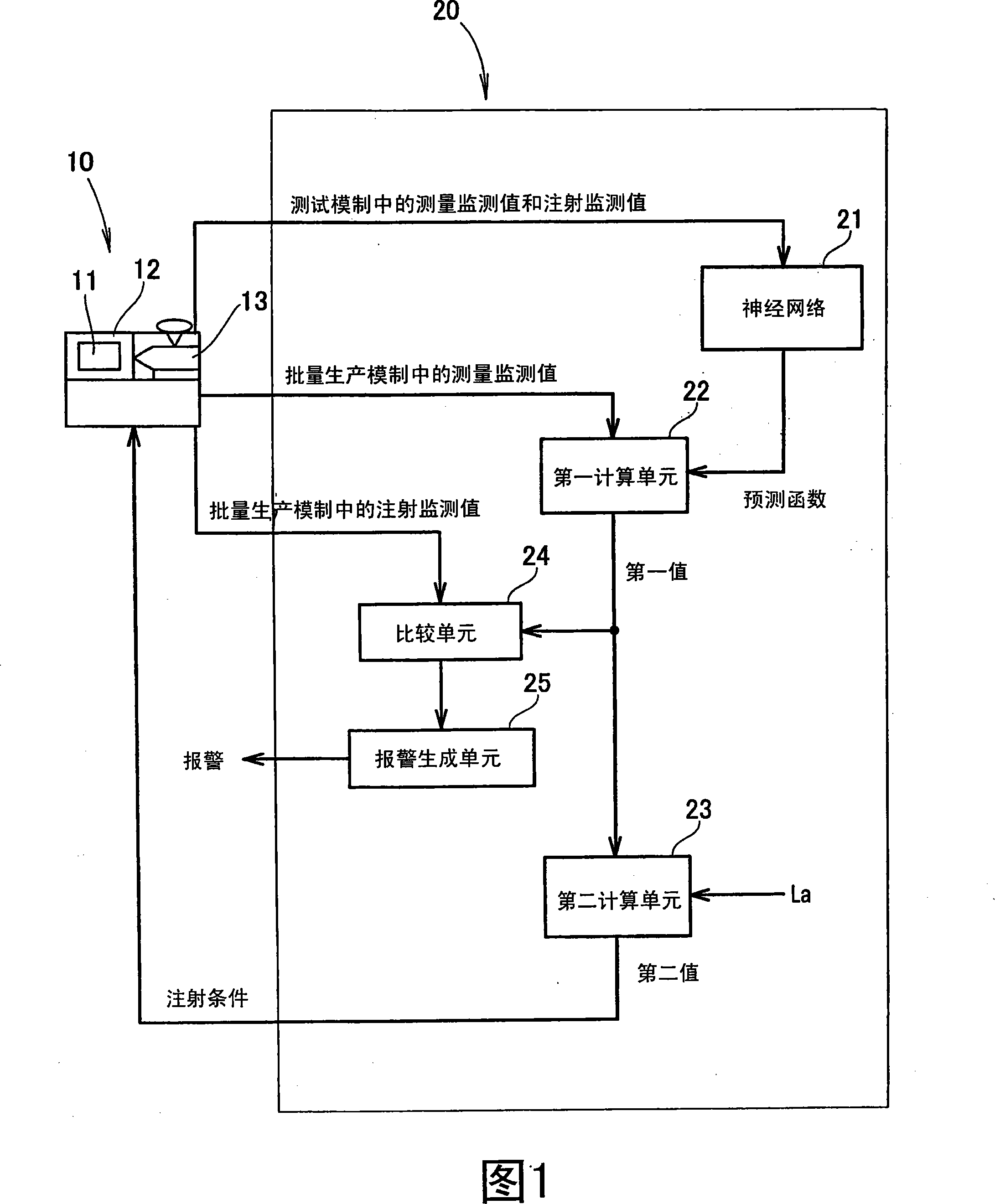
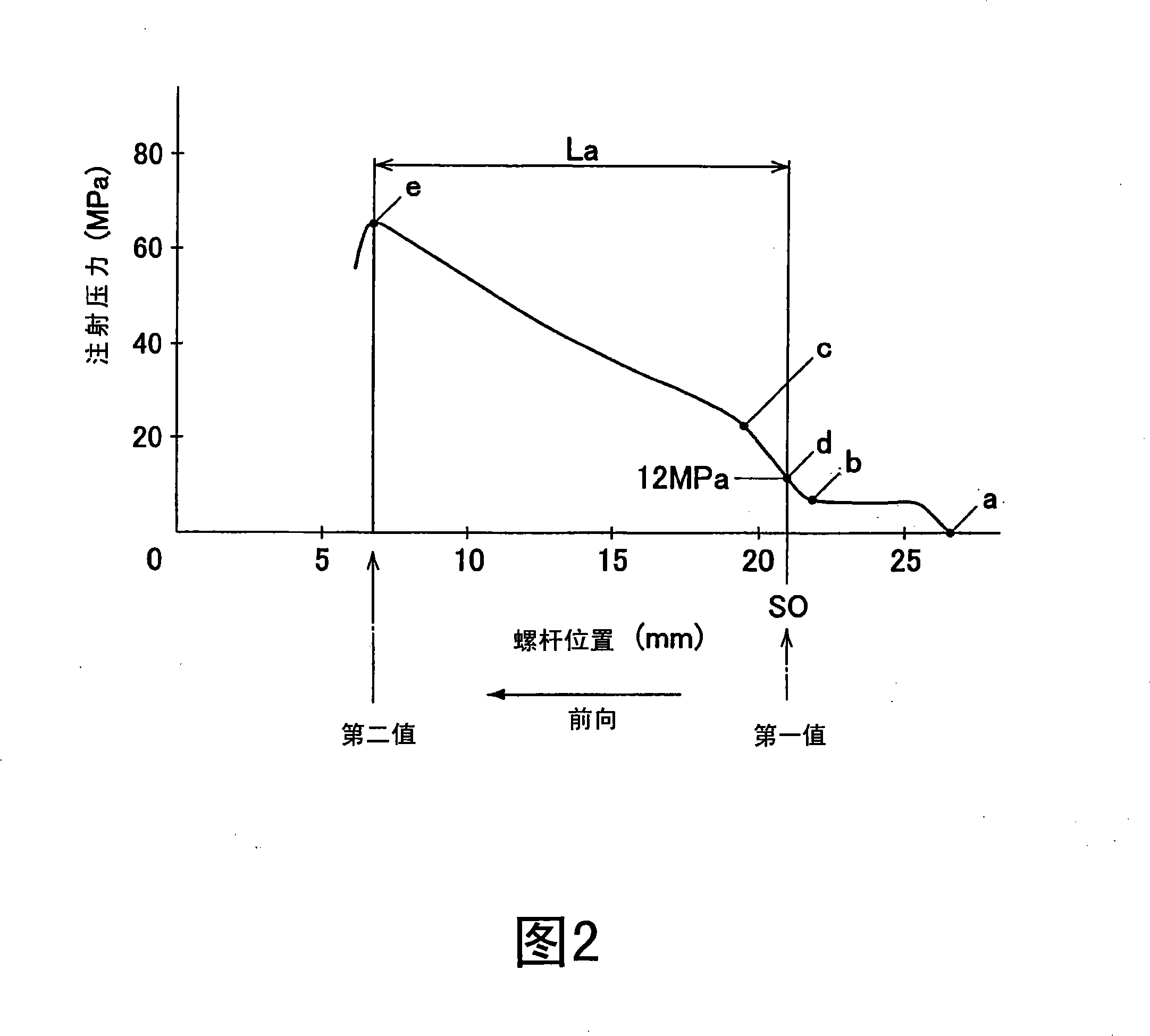
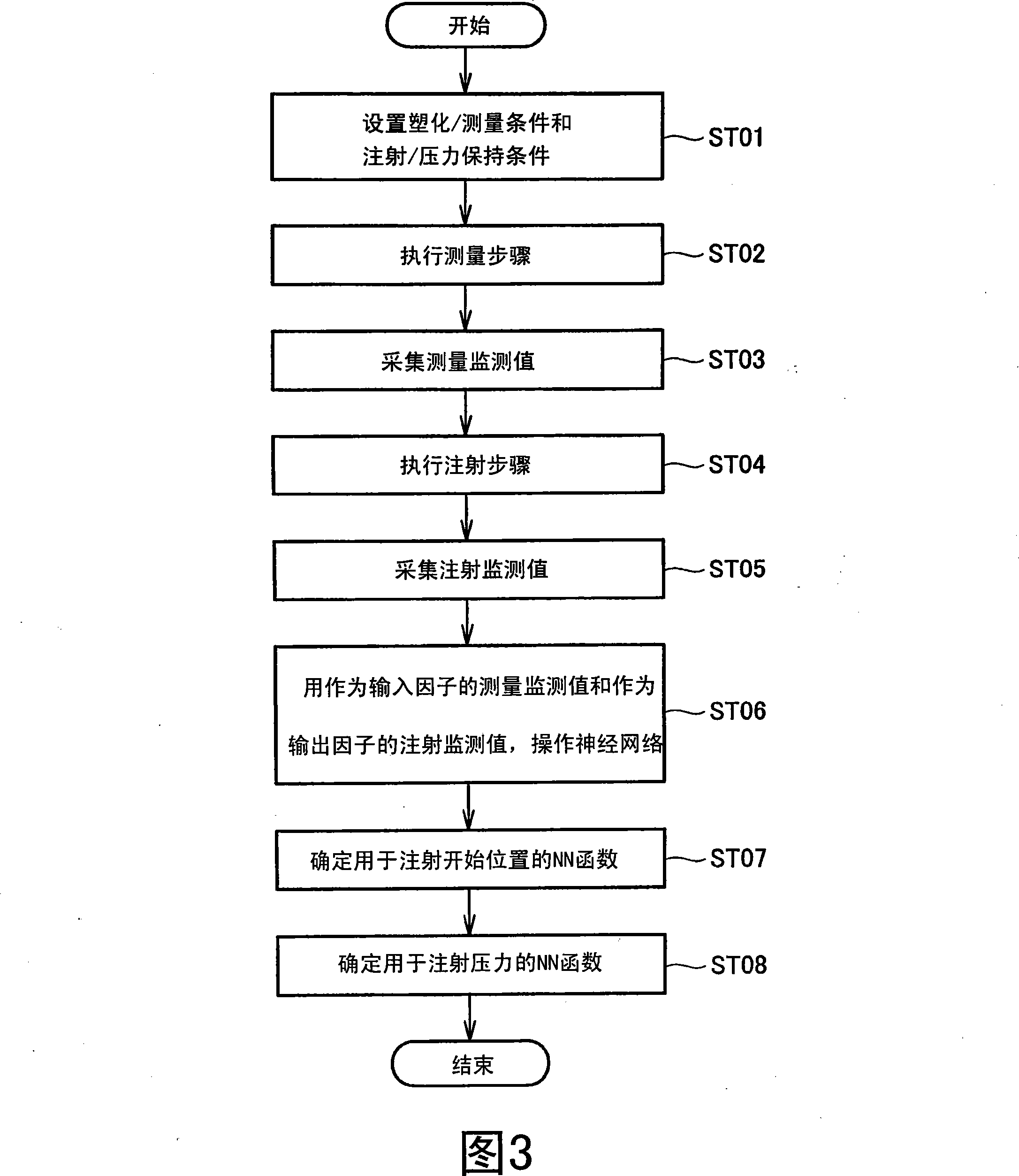
InactiveCN101168283AHigh speed moldingPlastic recyclingProgramme control in sequence/logic controllersTiming marginEngineering
An injection molding control method that uses a neural network is disclosed. The control method determines an injection condition according to a prediction function, a first value, and a second value. The prediction function is implemented in test molding, and the first value and second value are implemented in a measurement step that has a time margin. The injection condition predicted for mass-production molding is determined prior to the injection step, and the need for computation during the injection step is thereby eliminated.
Owner:NISSEI PLASTIC IND CO LTD
Grain-oriented electrical steel sheet and producing method therefor
InactiveUS20120028069A1Reduce widthIncrease productionInorganic material magnetismFurnace typesElectrical steelSteel plates
A producing method of a grain-oriented electrical steel sheet includes forming a preferentially-deformable portion at an end region of a steel sheet so as to be parallel with the rolling direction of the steel sheet; coiling the steel sheet; and performing a final annealing to the steel sheet after disposing the steel sheet in a manner such that the end region becomes the lower side of the steel sheet.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL & SUMITOMO METAL CORP
Image forming apparatus and method
InactiveUS7314269B2High quality printingIncrease speedOther printing apparatusImage resolutionImage formation
The image forming apparatus includes: a liquid chamber into which ink is filled; an ejection port through which the ink is ejected from the liquid chamber; a mist generation device which generates a mist from a surface of the ink inside the ejection port by applying vibration energy to the ink in the liquid chamber; an electric field generation device which generates an electric field causing the mist ejected from the ejection port to move to a recording medium; and a setting device which sets at least one of drive conditions of the mist generation device and a recording resolution in such a manner that a relationship Pt≧d2 is satisfied, where d2 is an overlap-permissible diameter which is a minimum distance between centers of two mist dots formed by the mist on the recording medium that allows shapes of the two mist dots to be fixed as a prescribed shape when the two mist dots are deposited on the recording medium substantially simultaneously under substantially same ejection conditions so as to overlap partially with each other, and Pt is a pitch between the centers of the two mist dots defined by the recording resolution.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
ZnO film, method for manufacturing the same, and luminescent element including the same
InactiveUS20030064541A1Increase speedLow costPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSputteringOptoelectronics
A p-type ZnO film is formed on a sapphire substrate by RF magnetron sputtering in an atmosphere of a mixture of Ar and N2 gases, using a Zn metal target doped with Y2O3. The p-type ZnO film can be easily formed even on a large-sized substrate.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Piezoelectric device and its manufacturing method
InactiveUS7102274B2Excellent piezoelectric propertiesEase of mass productionPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesThin membranePiezoelectric thin films
A piezoelectric device includes a first electrode film, a second electrode film, and a piezoelectric thin film enclosed by the first electrode film and second electrode film, in which the piezoelectric thin film is an oxide piezoelectric thin film having an oxygen deficiency amount of more than 0% and not more than 10% of the stoichiometric composition. The piezoelectric device composed of the piezoelectric thin film having such oxygen deficiency has a greater piezoelectric performance as compared with the oxide piezoelectric thin film in an oxidized state of stoichiometric composition, and by manufacturing under such a condition, the film forming speed is increased, so that the mass producibility can be improved.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method for depositing a film using a charged particle beam, method for performing selective etching using the same, and charged particle beam equipment therefor
InactiveUS7242013B2Film can be formedHigh speed moldingElectric discharge tubesVacuum evaporation coatingDisplay deviceProduct gas
Certain film deposition and selective etching technology may involve scanning of a charged particle beam along with a deposition gas and etching gas, respectively. In conventional methods, unfortunately, the deposition rate or the selective ratio is oftentimes decreased depending on optical system setting, scan spacing, dwell time, loop time, substrate, etc. Accordingly, an apparatus is provided for finding an optical system setting, a dwell time, and a scan spacing. These parameters are found to realize the optimal scanning method of the charged particle beam from the loop time dependence of the deposition rate or etching rate. This deposition rate or etching rate are measurements stored in advance for a desired irradiation region where film deposition or selective etching should be performed. The apparatus displays a result of its judgment on a display device.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Vacuum deposition apparatus and control method thereof
InactiveUS20090238951A1Precise internal electrodes of chip componentsHigh speed moldingLiquid surface applicatorsFixed capacitor electrodesHigh rateEngineering
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Ink jet recording head, ink jet cartridge with ink jet recording head, and ink jet recording apparatus
An ink jet recording head includes at least three nozzle array groups, each including at least two nozzle arrays with an ink supply port interposed therebetween and each ejecting a different ink. Opening areas of the ejection outlets of the nozzle arrays in each array group are of different sizes. Two adjacent nozzle array groups each include three nozzle arrays. The nozzle array group not identified as one of the two adjacent nozzle array groups is supplied with ink having a highest lightness among the three kinds of inks.
Owner:CANON KK
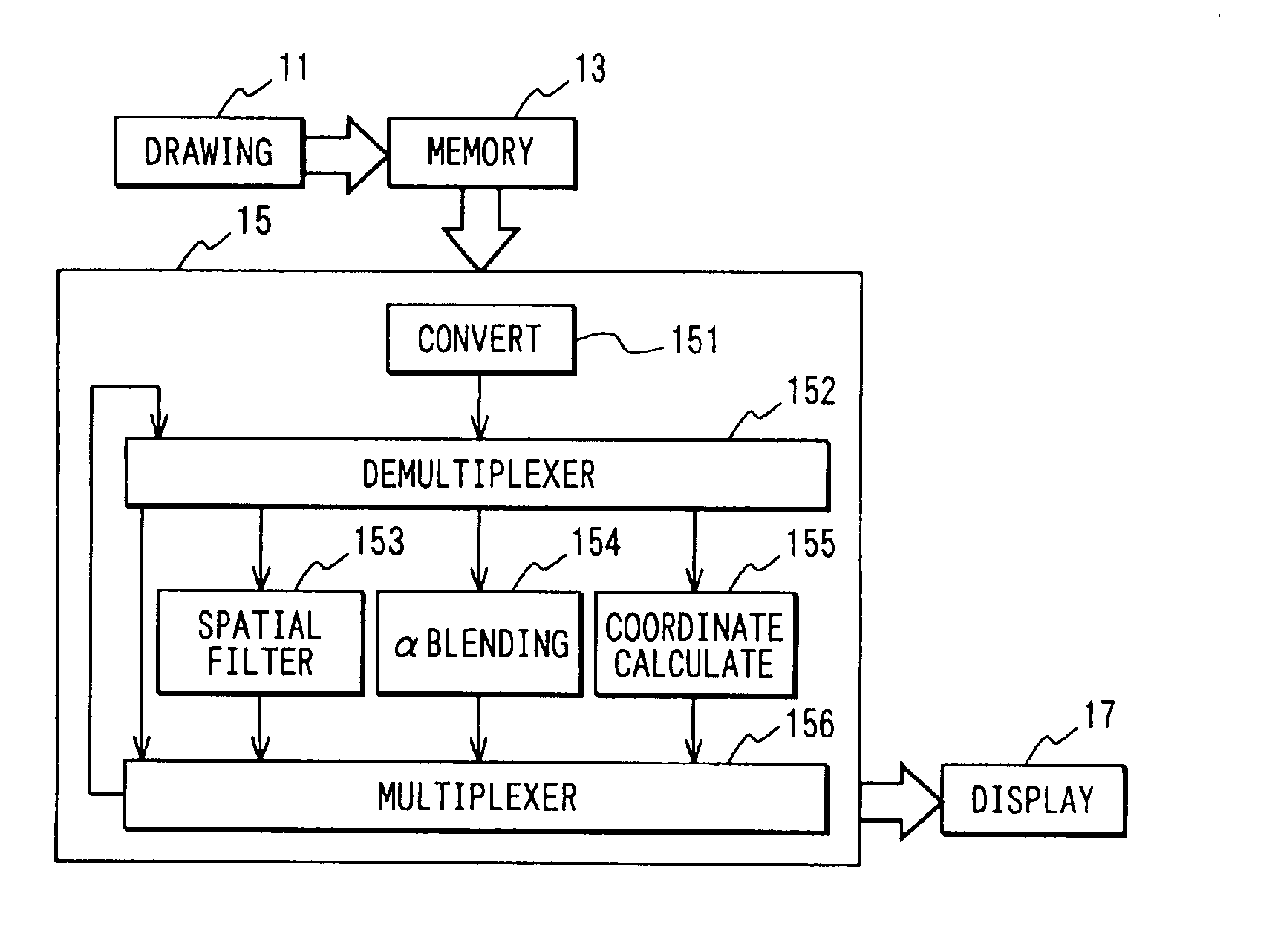
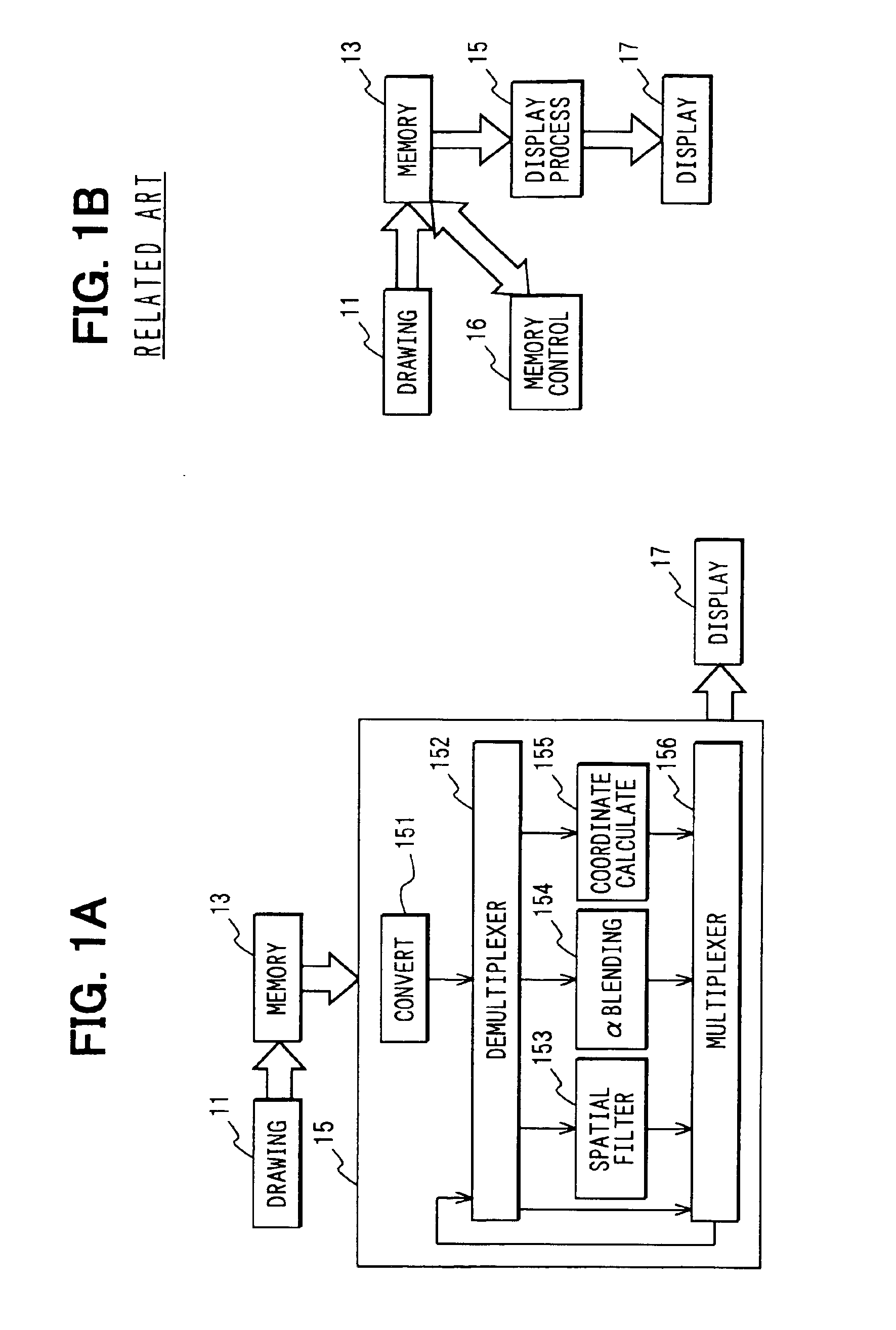
Image processing apparatus having processing operation by coordinate calculation
InactiveUS6879329B2Increase speedHigh speed moldingTelevision system detailsImage analysisImaging processingGrating
An image processing apparatus draws an image, stores the drawn image in a memory, reads image data from the memory along a raster direction, and executes a processing operation required for a display with respect to the read image data to output the processed image data to a display device. A display processing unit executes a processing operation including a coordinate calculation with respect to the image data read out along the raster direction. As a result, the image can be formed at high speed even under transition state of displayed images.
Owner:DENSO CORP
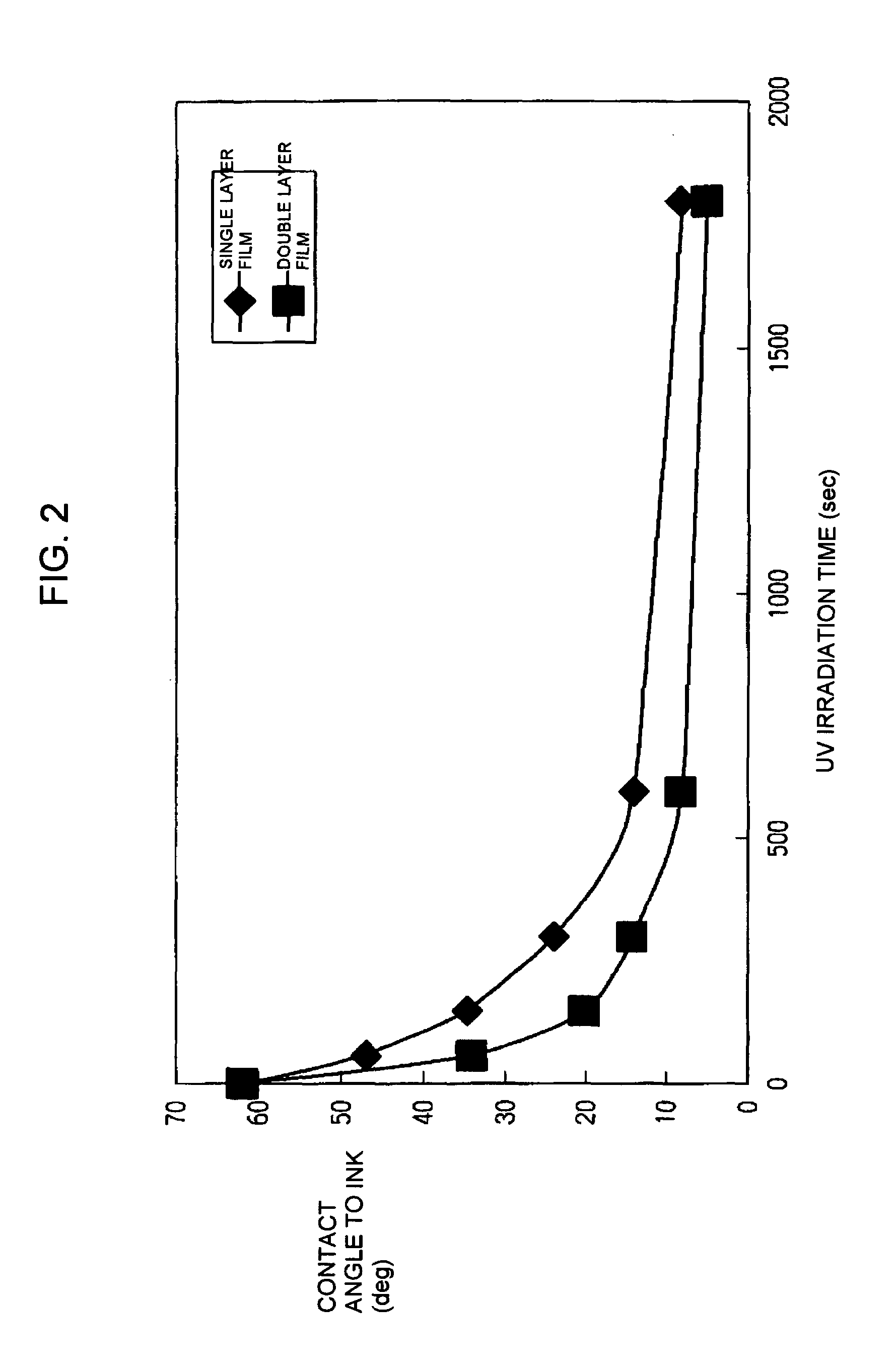
Optical laminate and optical element
InactiveUS20060072197A1Efficient productionStable formationSynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsOptical propertyEngineering
There is provided an optical element that, even when a transparent base material is formed of triacetylcellulose, is in a boat bottom form in section and has streaks, can realize the formation of an anti-dazzling layer in a stable and efficient manner and can realize the control of optical characteristics with higher accuracy. There is also provided an optical laminate comprising: a transparent base material; and an anti-dazzling layer provided on a surface of the transparent base material through a smoothing transparent resin layer for smoothing the surface of the transparent base material, characterized in that the transparent base material consists essentially of triacetylcellulose, the thickness of the smoothing transparent resin layer is regulated to fall within a range of 0.5 to 2.0 μm, and the smoothing transparent resin layer is provided directly on the transparent base material without through any other layer. The optical element comprises the optical laminate.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Molding material for 3D printing based on crushed amorphous glass having irregular shape, molding method for 3D printing, and molded body
ActiveUS20180194662A1Improve liquidityImprove sinterabilityMaterial nanotechnologyAdditive manufacturing apparatusShell moldingGlobular shaped
The present invention relates to a forming material for three-dimensional (3D) printing, a forming method for 3D printing, and a formed object, wherein, while being based on an amorphous glass powder shaped irregularly, the forming material for 3D printing ensures excellent flowability and sinterability such that it enables the formation of high-quality products at high speed. The forming material for 3D printing consists of a parent glass powder in the form of an unmelted powder irregularly shaped by crushing amorphous glass; and a spherical nanopowder that has an average particle diameter equal to or less than 1 / 50th of the average particle diameter of the parent glass powder and is mixed in such a way that it can be disposed on a surface of the parent glass powder to enhance the flowability of the irregularly shaped parent glass powder during the formation of an object by 3D printing.
Owner:INHA UNIV RES & BUSINESS FOUNDATION
Fluorinated copolymer composition
To provide a fluorinated copolymer composition from which a molded product excellent in the heat resistance and the stress crack resistance can be produced with good productivity.A fluorinated copolymer composition comprising ETFE and copper oxide, wherein the ETFE has repeating units (A) based on ethylene, repeating units (B) based on tetrafluoroethylene and repeating units (C) based on another monomer, in a molar ratio of the repeating units (A) to the repeating units (B) of from 38 / 62 to 44 / 56, and contains the repeating units (C) in an amount of from 0.1 to 2.6 mol % in all the repeating units of the ETFE; the content of the copper oxide is from 0.2 to 10 ppm based on the ETFE; and the volume flow rate of the fluorinated copolymer composition at 297° C. is from 15 to 150 g / 10 min.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for manufacturing a zinc oxide thin film at low temperatures
ActiveUS20070042216A1Easy to controlLower electrical resistivityVacuum evaporation coatingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptoelectronicsCrystallographic defect
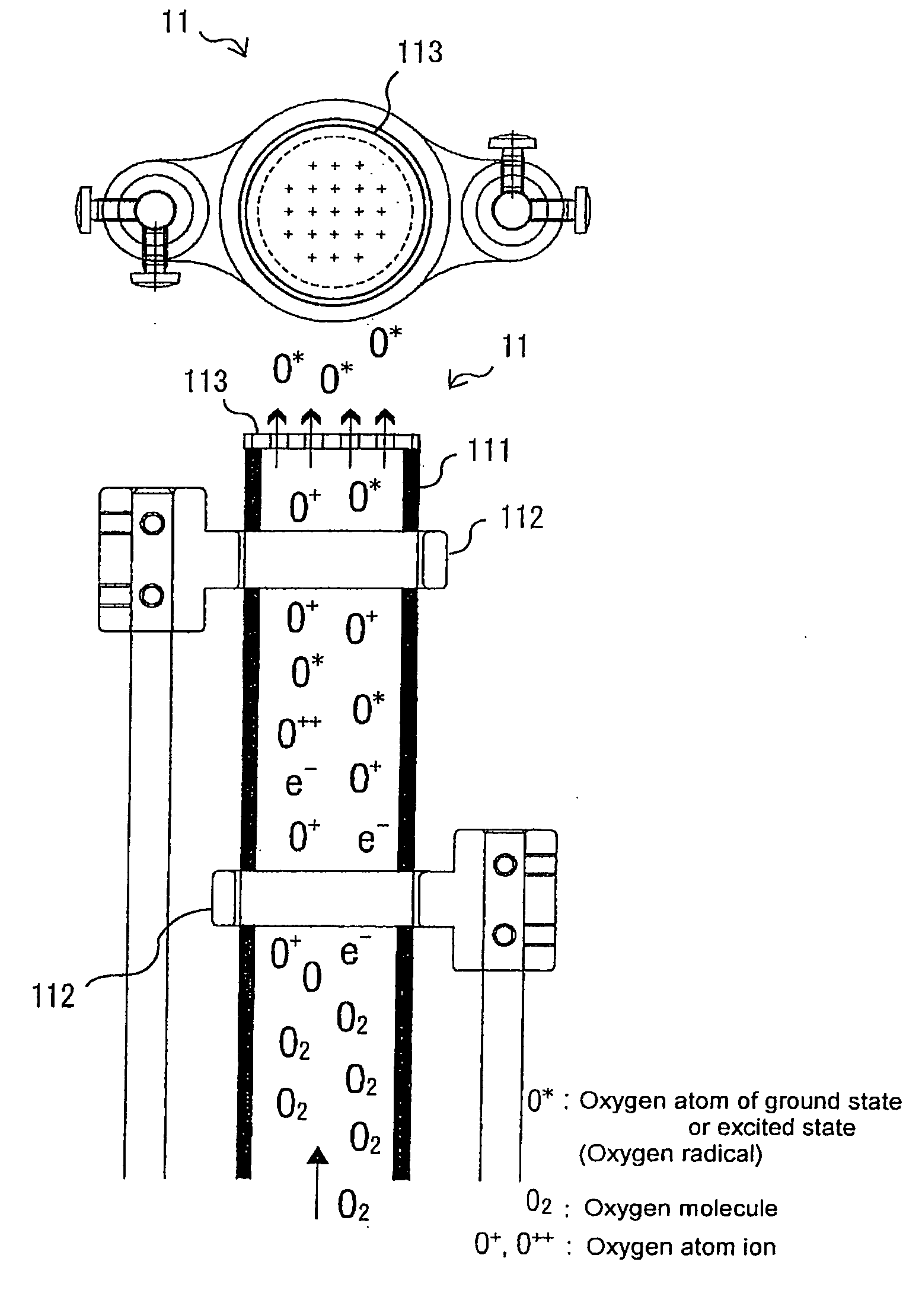
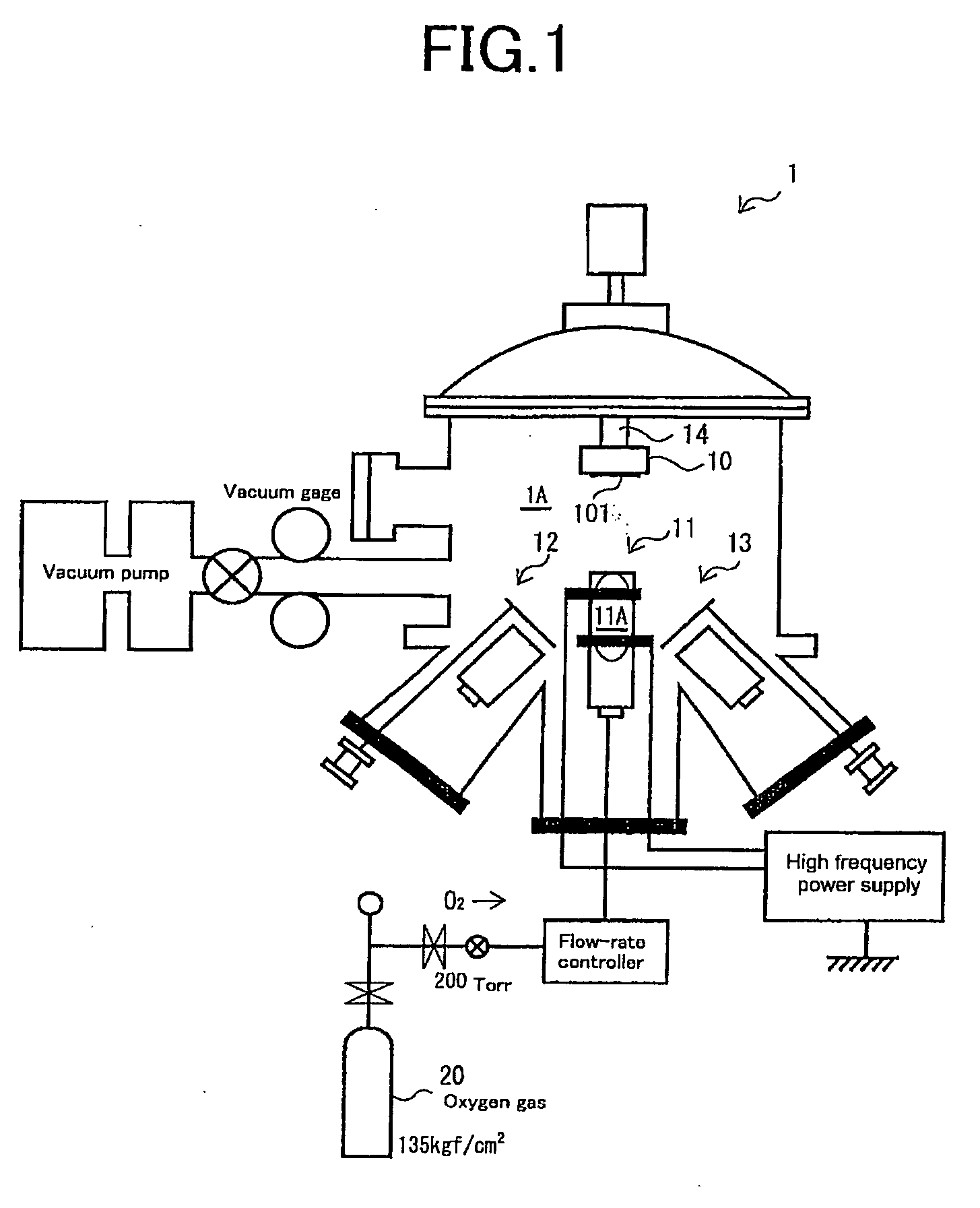
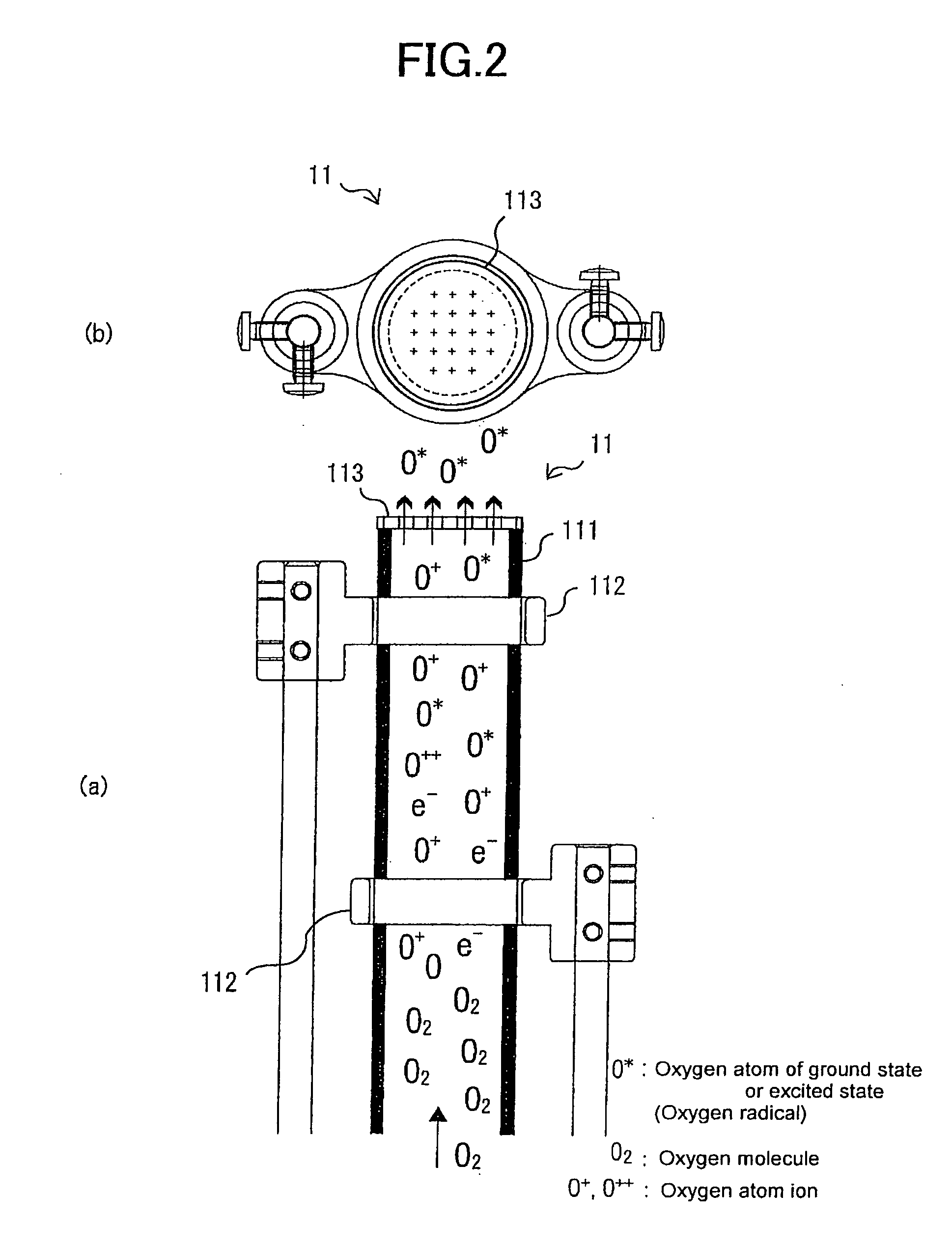
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for forming a zinc oxide thin film with high transparency and high conductivity on a surface of a flexible substrate such as plastic without the indispensable requirement of doping impurities. In the method of forming a zinc oxide thin film by reacting oxygen radicals and zinc atoms on a surface of a substrate placed in a film-forming chamber evacuated to a vacuum, the density of crystal defects that are defects of the atomic arrangement of the zinc oxide thin film is controlled by the temperature of the substrate, and the zinc oxide thin film is thereby formed. It is suitable to form the film while maintaining the temperature of the substrate at 400° C. or less to intentionally disturb the regularity of the atomic arrangement of the zinc oxide thin film.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF YAMANASHI +2
Stamping machine
ActiveUS20070000299A1Increase speedHigh speed moldingShaping toolsForging hammersEngineeringMechanical engineering
The present invention is related to a stamping machine for stamping an item at a high speed. The stamping machine comprises a case having an opening, at least one guide shaft formed in an interior of the case and extending in a first direction, a pedestal movable along the at least one guide shaft in the first direction for holding the worked item, and a stamping part for pressing the working tool against the worked item held on the pedestal. The stamping part comprises at least one guide shaft formed in an interior of the stamping part and extending in a second direction, a head driver formed in the interior of the stamping part and extending in the second direction, and a stamping head movable along the at least one guide shaft and the head driver in the second direction, wherein the stamping head is proximal to the pedestal.
Owner:ROLAND DG CORP
Manufacturing method of fine structure, optical element, integrated circuit, and electronic instrument
InactiveUS7070701B2Easily decomposed and eliminatedIncrease speedDecorative surface effectsOptical filtersFine structureElectronic instrument
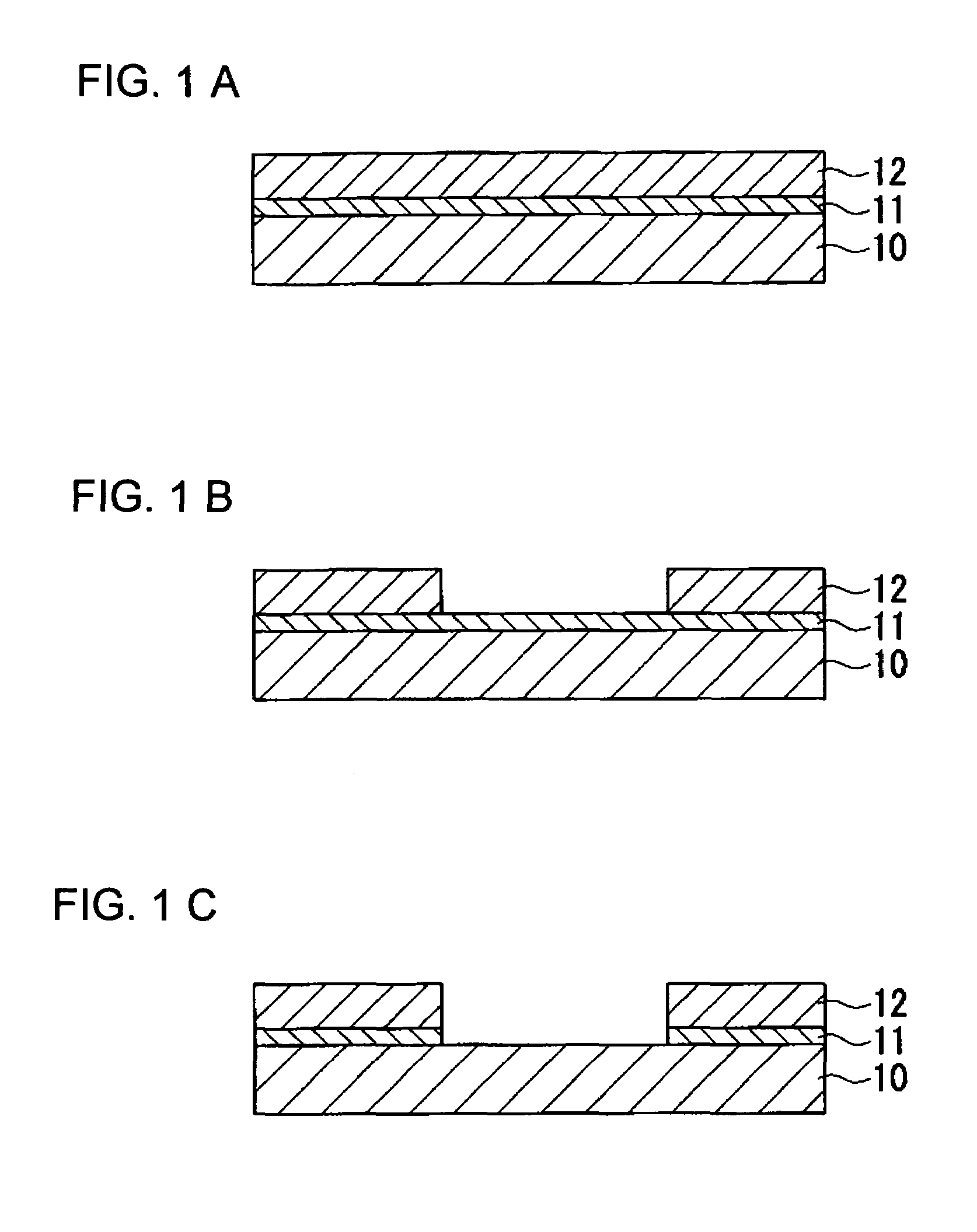
A fine structure manufacturing method is provided. The method comprises providing a lyophilic film on a treated surface of a substrate on which a pattern having a desired form is to be formed, providing a liquid-repellent film on an upper surface of the lyophilic film, the liquid-repellent film having liquid repellency relative to a liquid material used for forming the pattern, and eliminating a part of the liquid-repellent film located on an area where the pattern is to be formed.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Surface-emitting laser array, optical scanning device, and image forming device
ActiveUS8179414B2Reduce the impact of heatSmall sizeLaser detailsElectrographic process apparatusLaser arrayOptoelectronics
A surface-emitting laser array includes a plurality of light emitting parts arranged in a two-dimensional formation having two orthogonal directions. When the plurality of light emitting parts are orthogonally projected on a virtual line parallel to one of the two orthogonal directions, a spacing between two of the plurality of light emitting parts along the virtual line is equal to an integral multiple of a predetermined value. The plurality of light emitting parts include a first light emitting part, a second light emitting part adjacent to the first light emitting part, and a third light emitting part adjacent to the second light emitting part, and a spacing between the first and second light emitting parts differs from a spacing between the second and third light emitting parts.
Owner:RICOH KK
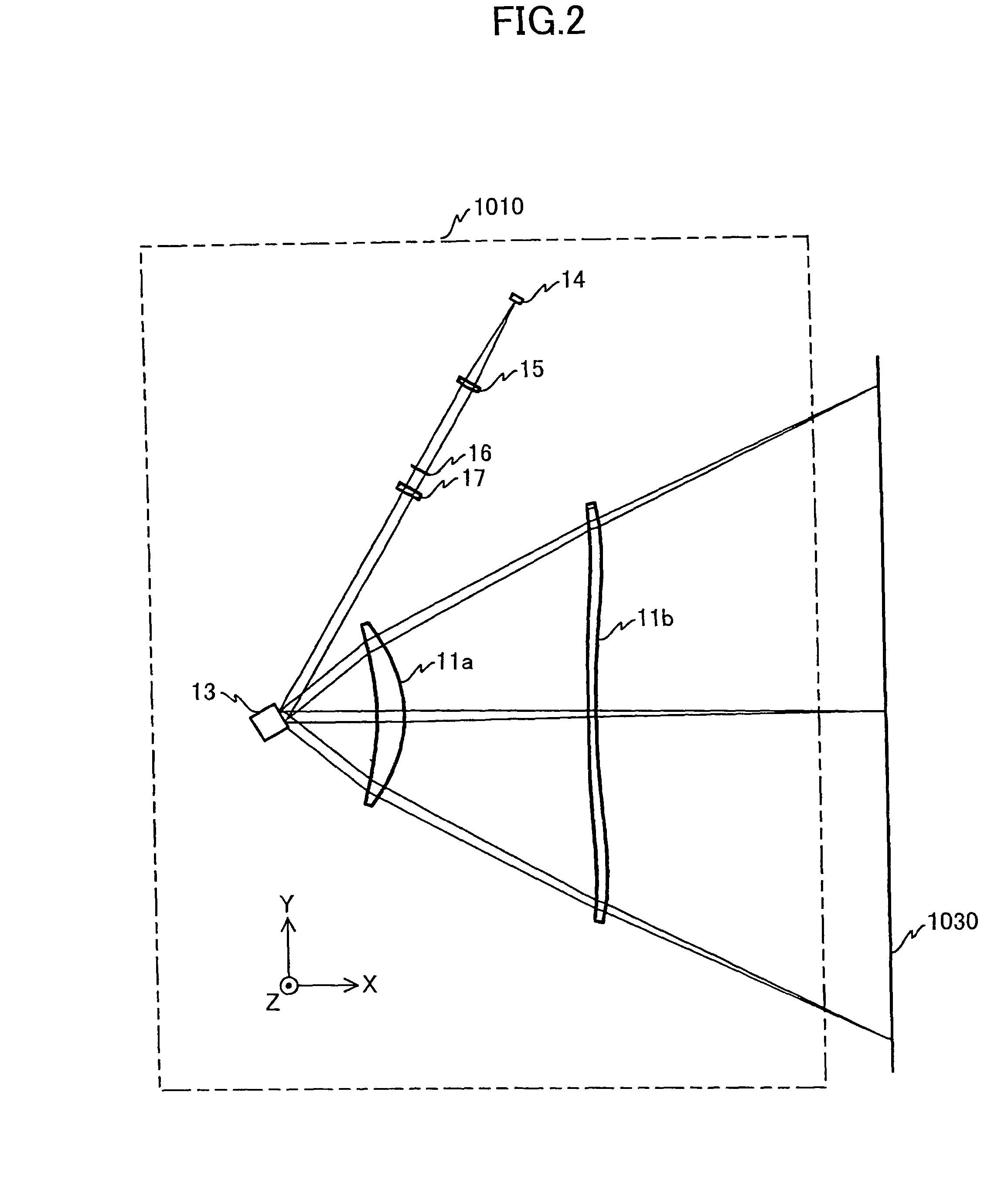
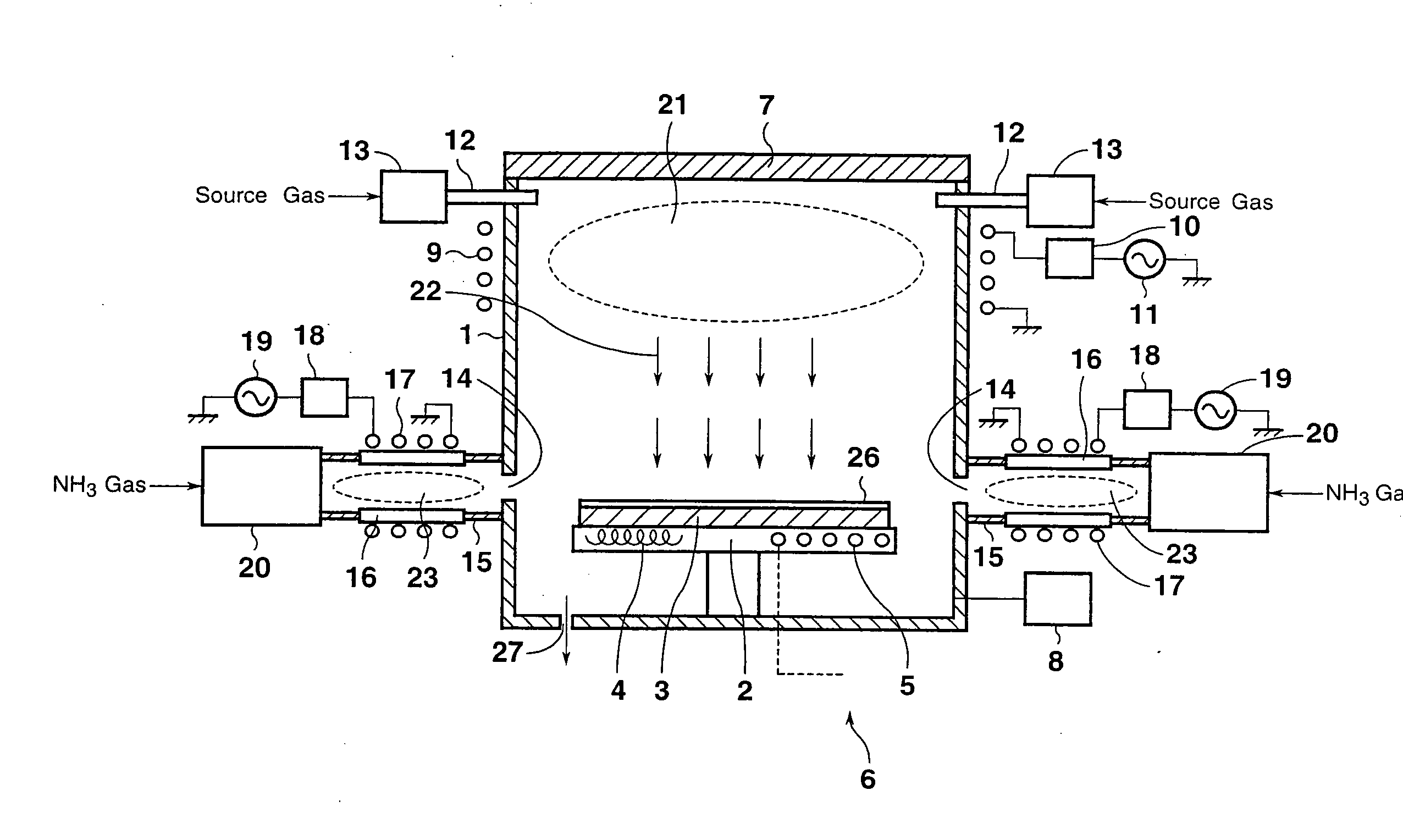
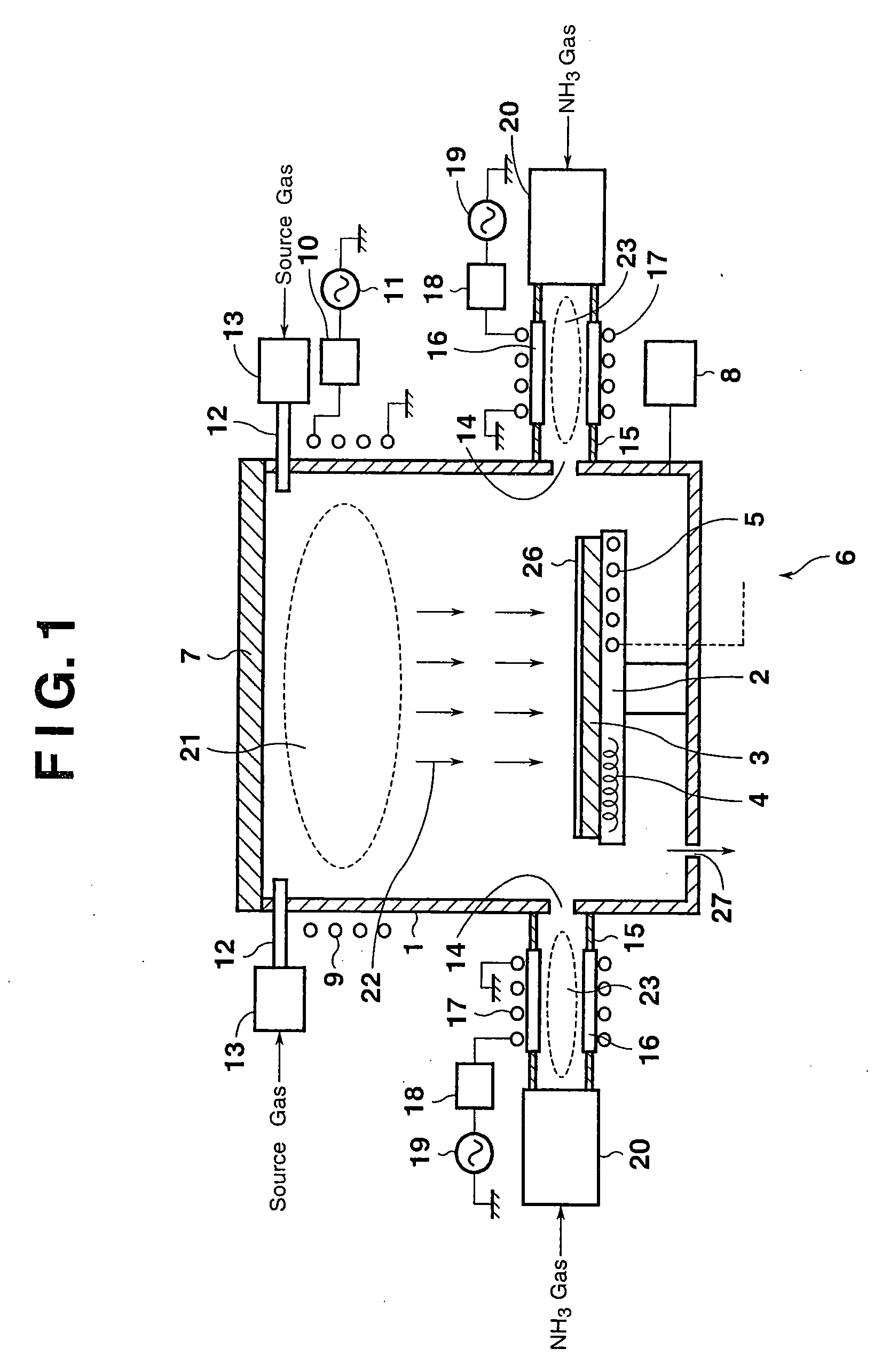
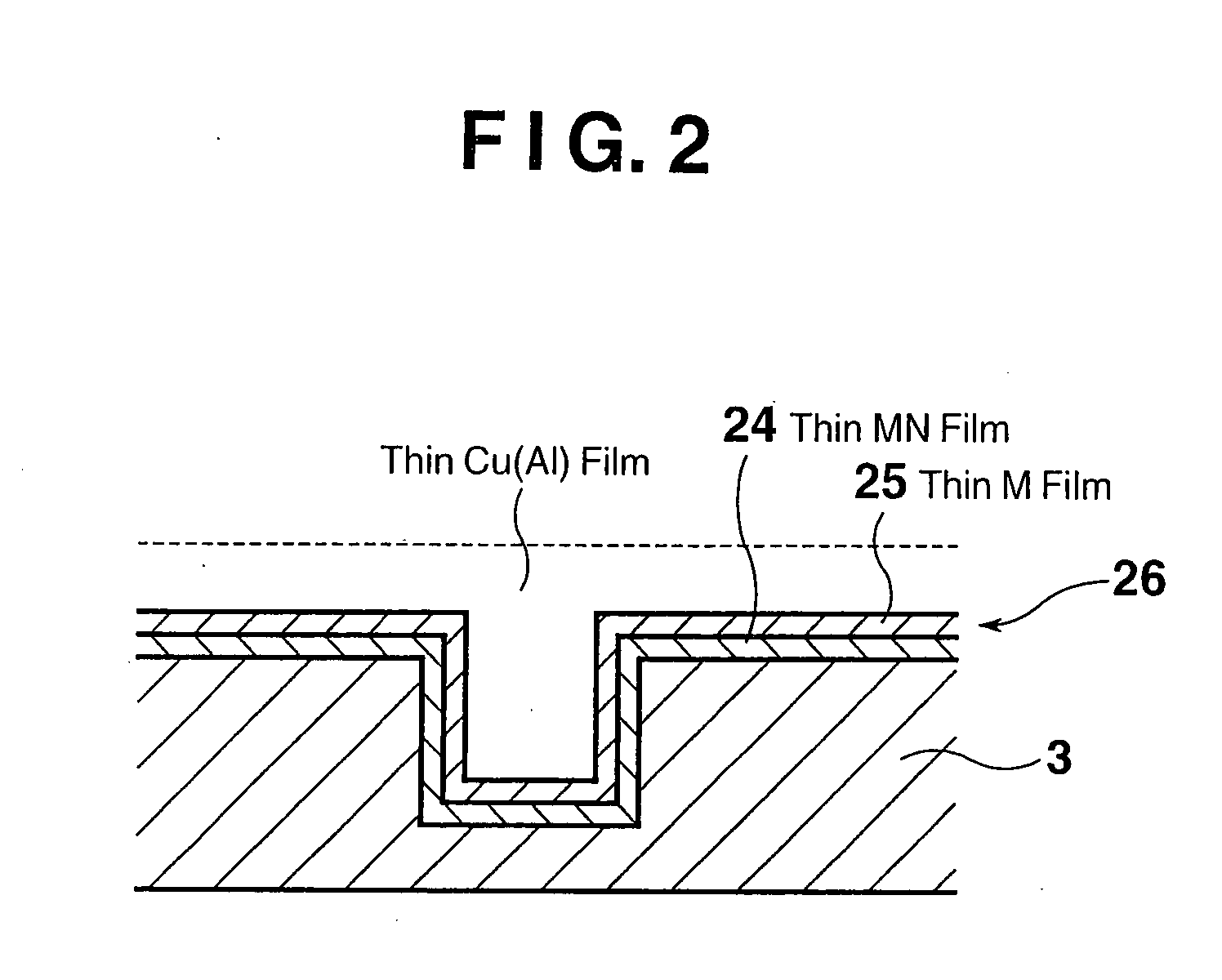
Barrier metal film production method
InactiveUS20070272655A1Low costExcellent burial propertyDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitrogenNitrogen gas
A Cl2 gas plasma is generated at a site within a chamber between a substrate and a metal member. The metal member is etched with the Cl2 gas plasma to form a precursor. A nitrogen gas is excited in a manner isolated from the chamber accommodating the substrate. A metal nitride is formed upon reaction between excited nitrogen and the precursor, and formed as a film on the substrate. After film formation of the metal nitride, a metal component of the precursor is formed as a film on the metal nitride on the substrate. In this manner, a barrier metal film with excellent burial properties and a very small thickness is produced at a high speed, with diffusion of metal being suppressed and adhesion to the metal being improved.
Owner:CANON ANELVA CORP
Manufacturing method and manufacturing device for electronic component
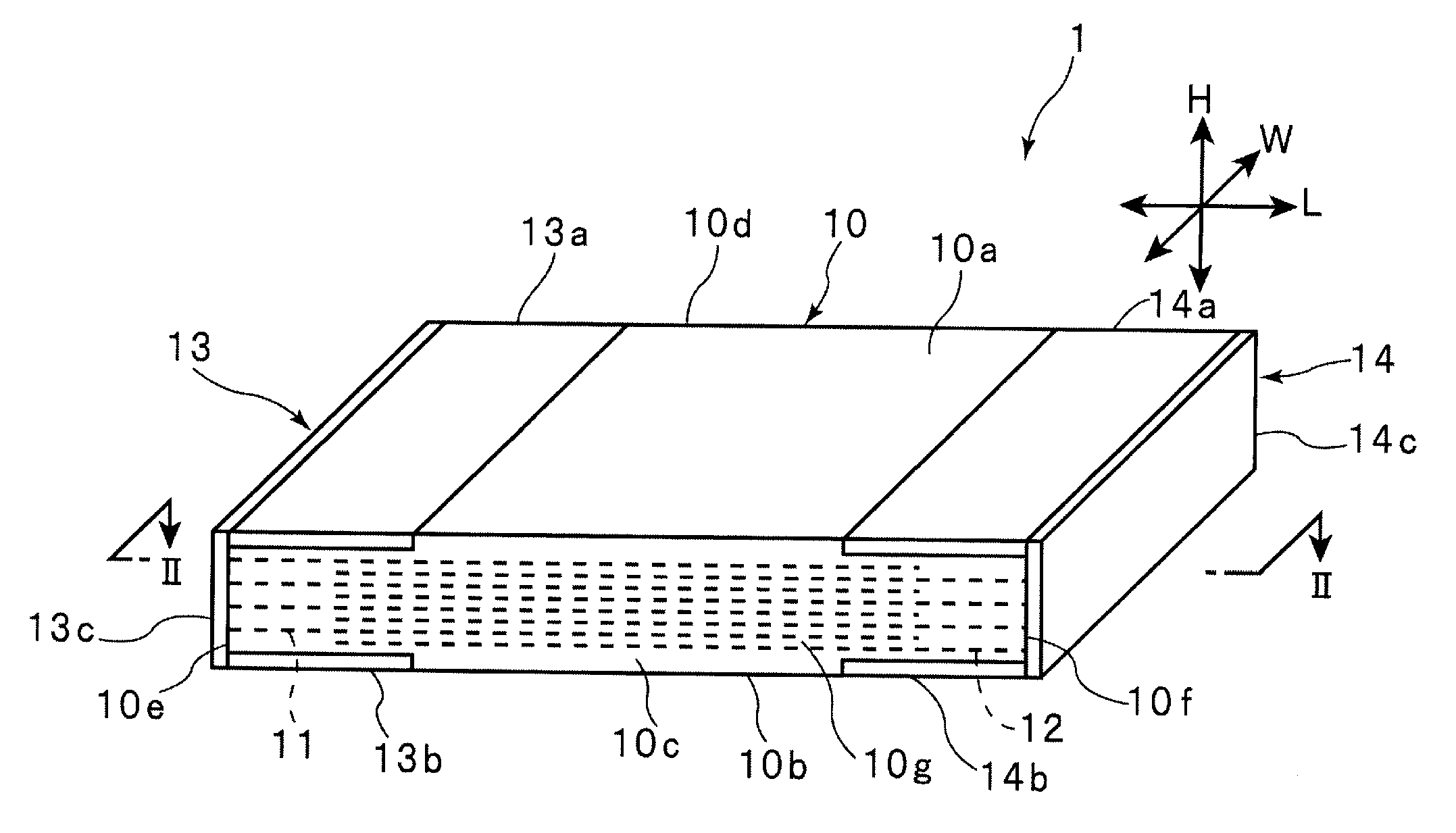
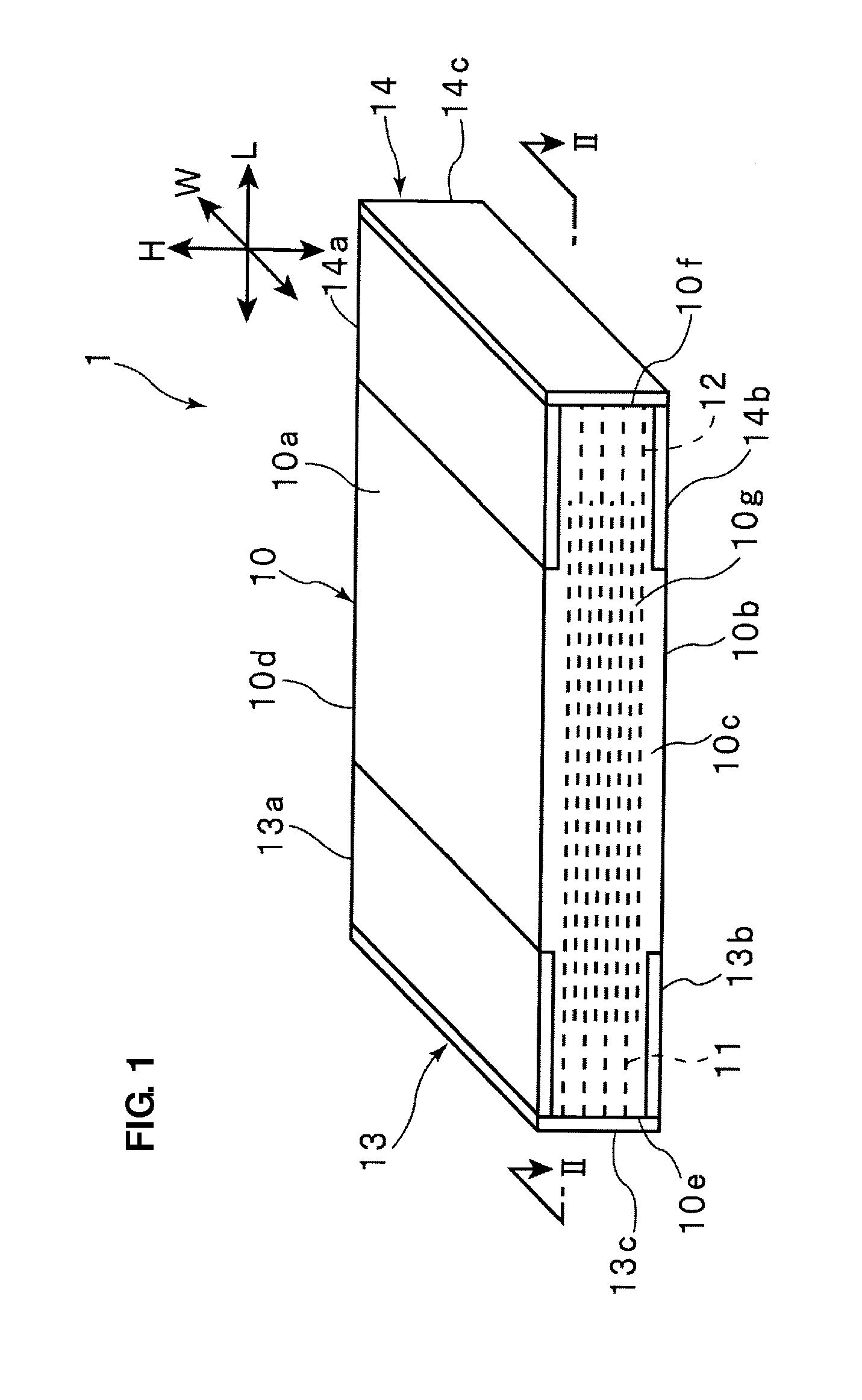
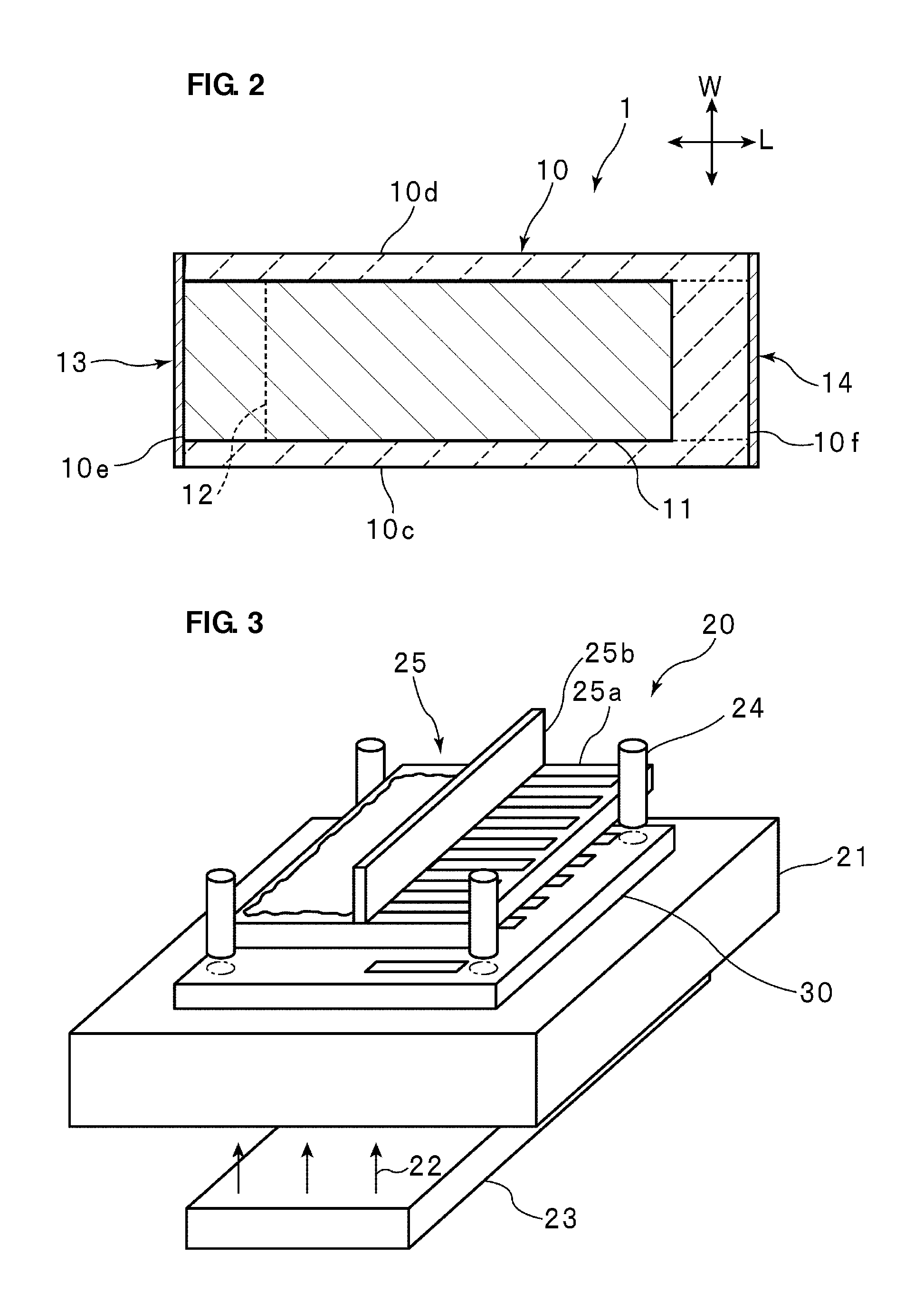
ActiveUS20120073100A1High precisionForming accuratelyFixed capacitor dielectricStacked capacitorsEngineeringElectronic component
A manufacturing method for an electronic component forms with a high degree of accuracy a portion of an outer electrode on a main surface of a dielectric block. Light irradiated from a second main surface side is detected by a detector disposed on a first main surface side, thereby detecting the positions of first and second inner electrodes, and a conductive layer is formed in a portion on a first main surface, determined based on the detection result by the detector, thereby forming first portions of individual first and second outer electrodes.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com