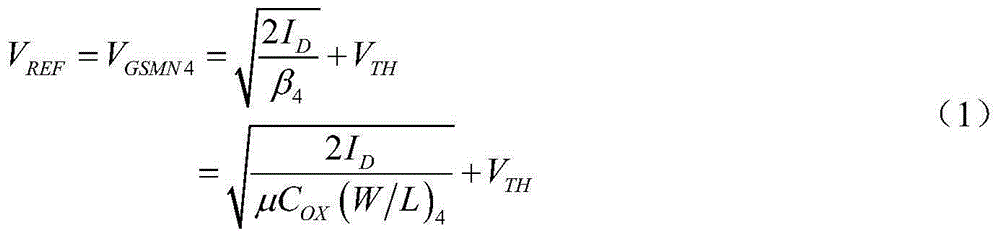Patents
Literature
154 results about "Substrate bias voltage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
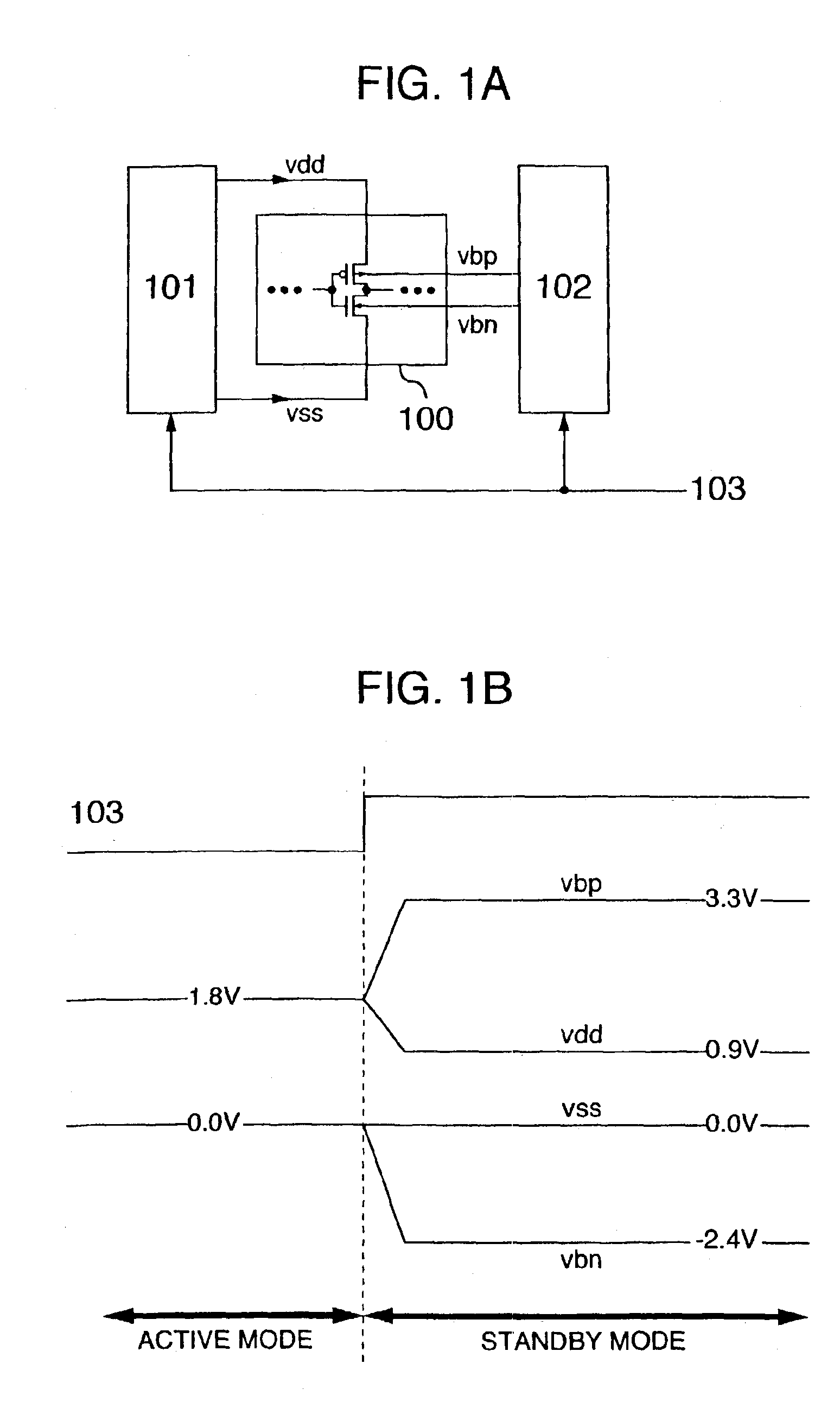
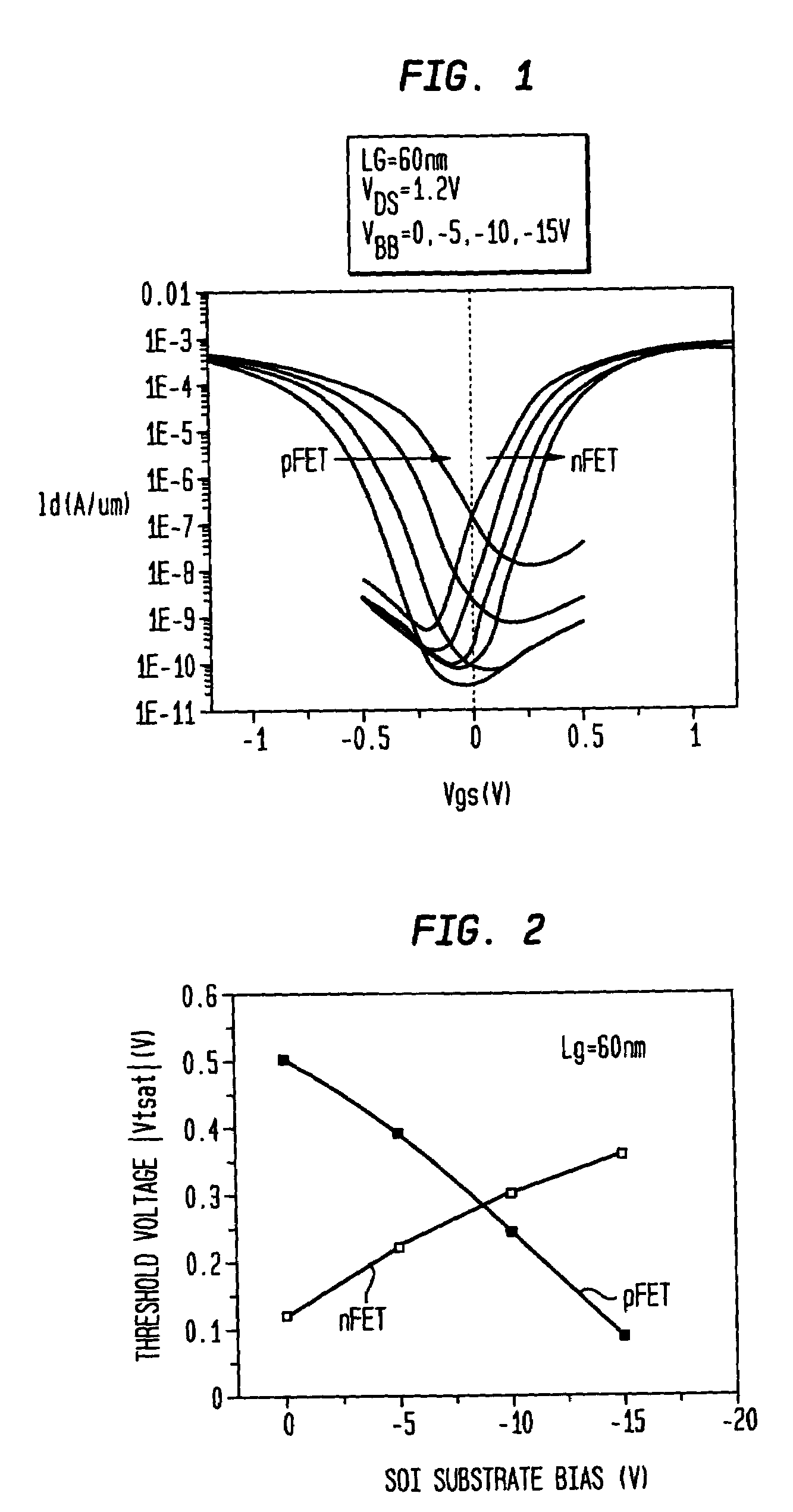
The substrate bias effect. The voltage applied to the back contact affects the threshold voltage of a MOSFET. The voltage difference between the source and the bulk, V BS changes the width of the depletion layer and therefore also the voltage across the oxide due to the change of the charge in the depletion region.
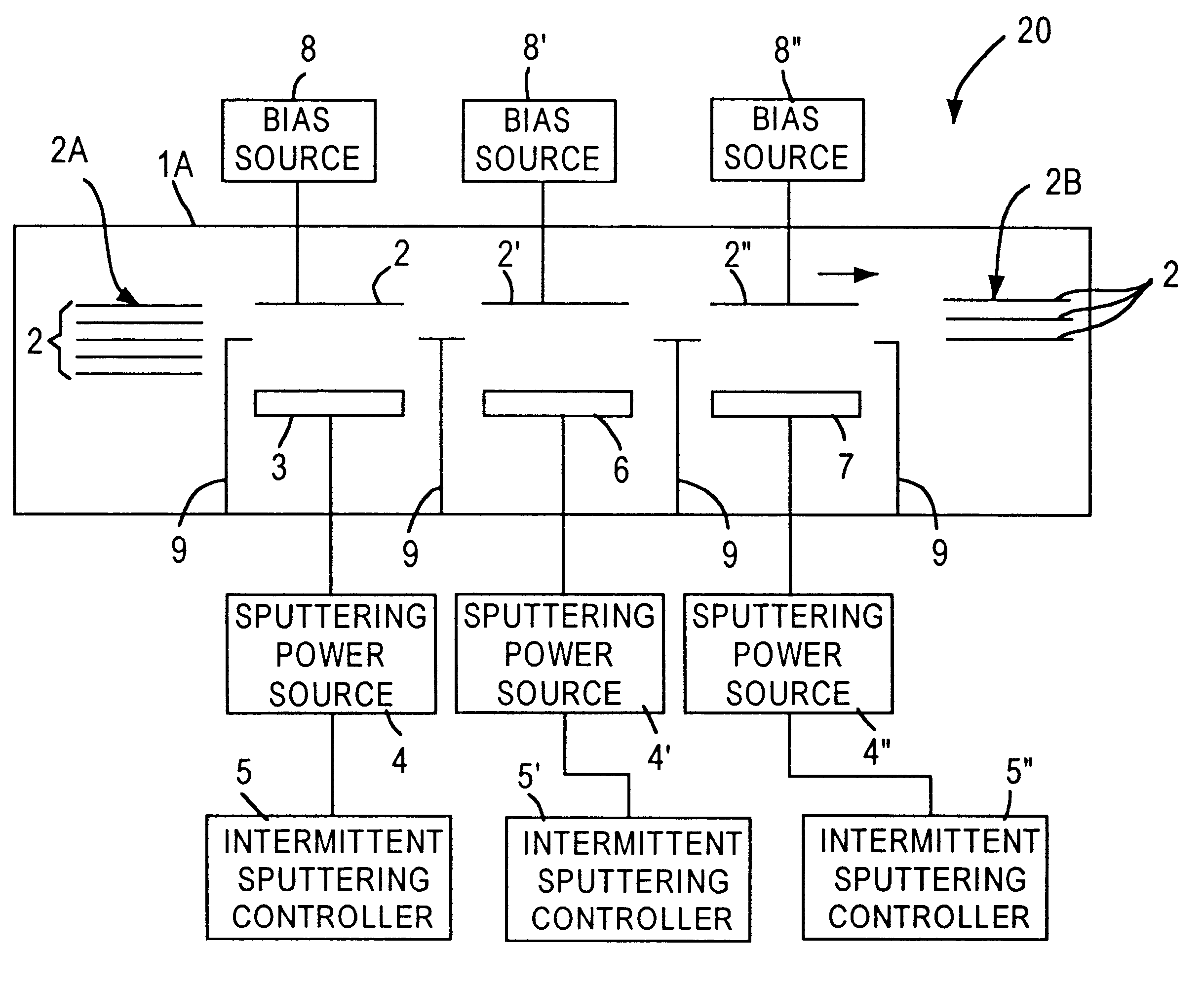
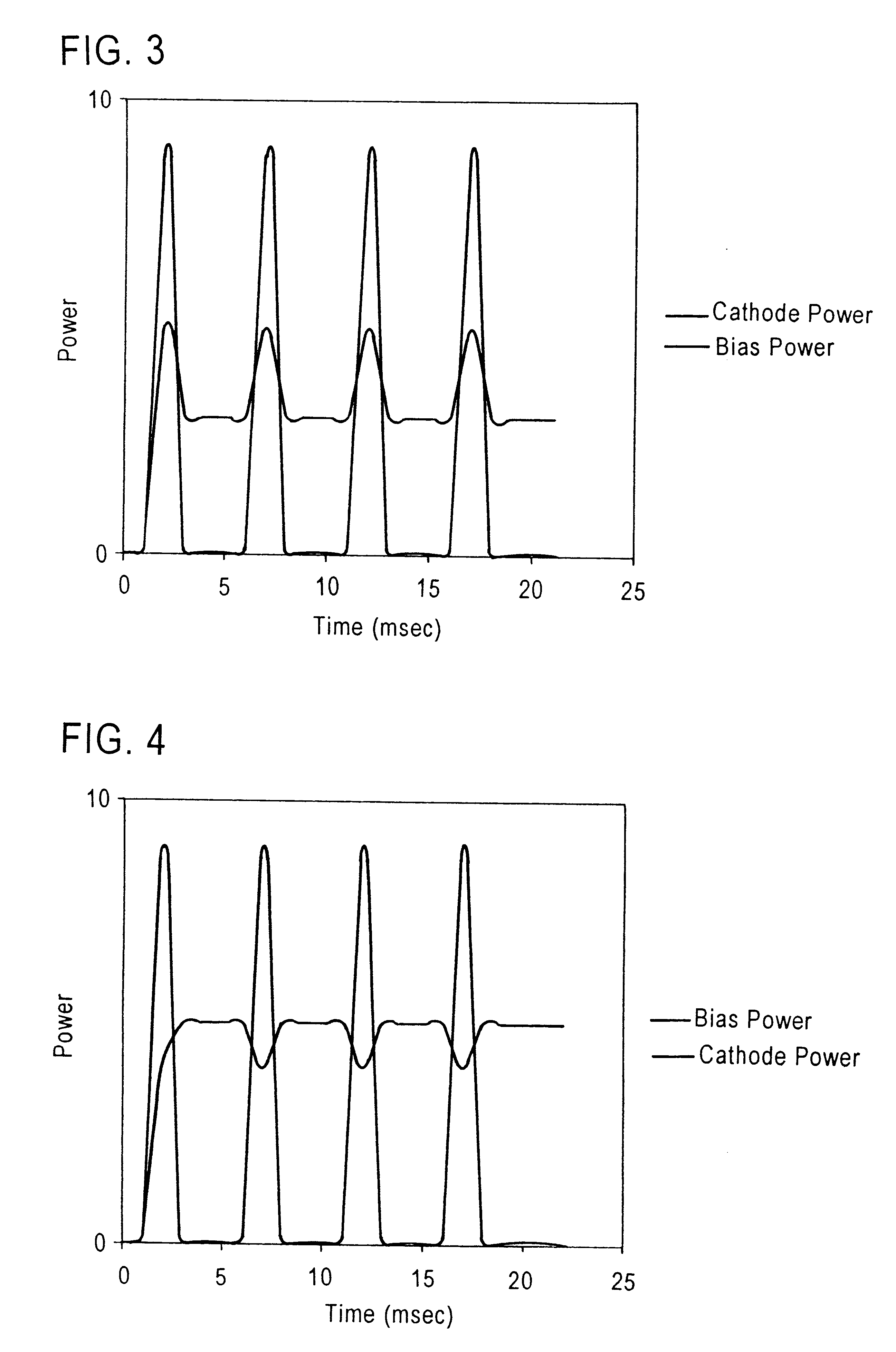
Sputter deposition utilizing pulsed cathode and substrate bias power
InactiveUS6290821B1Simple methodVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingOptoelectronicsSubstrate bias voltage
A method for depositing on a substrate surface a thin film layer comprising a target material comprises providing a cathode including a target having a sputtering surface comprised of the target material, with the target sputtering surface facing the substrate surface with a space therebetween, and sputtering the target material onto the substrate surface by applying a plurality of negative voltage pulses to the cathode while simultaneously applying a bias voltage to the substrate. Embodiments include depositing thin film layers onto static or moving substrates and application of constant or time-varying substrate bias voltage. The invention finds particular utility in the formation of high purity layers in the automated manufacture of magnetic data / information storage and retrieval media.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
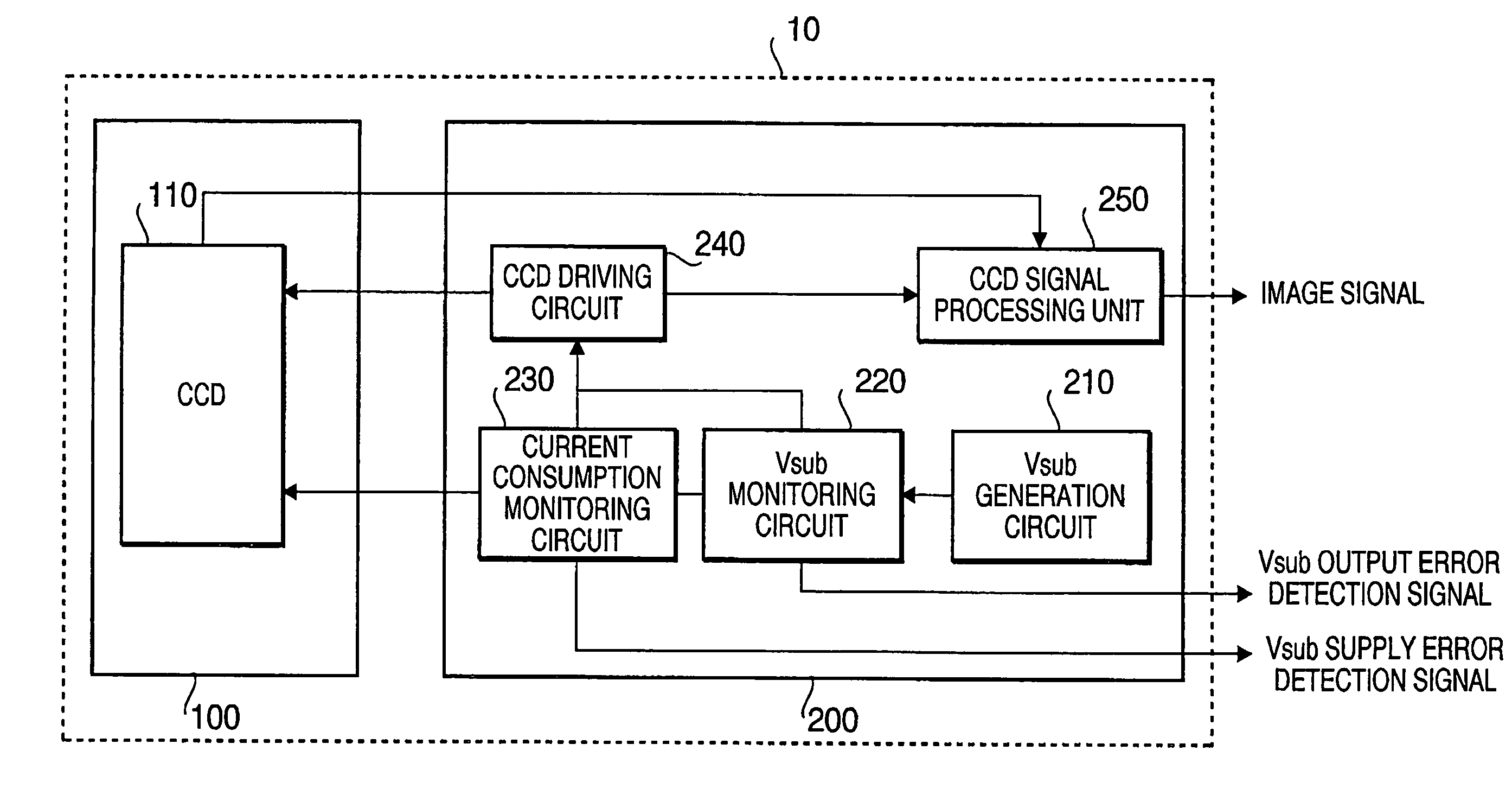
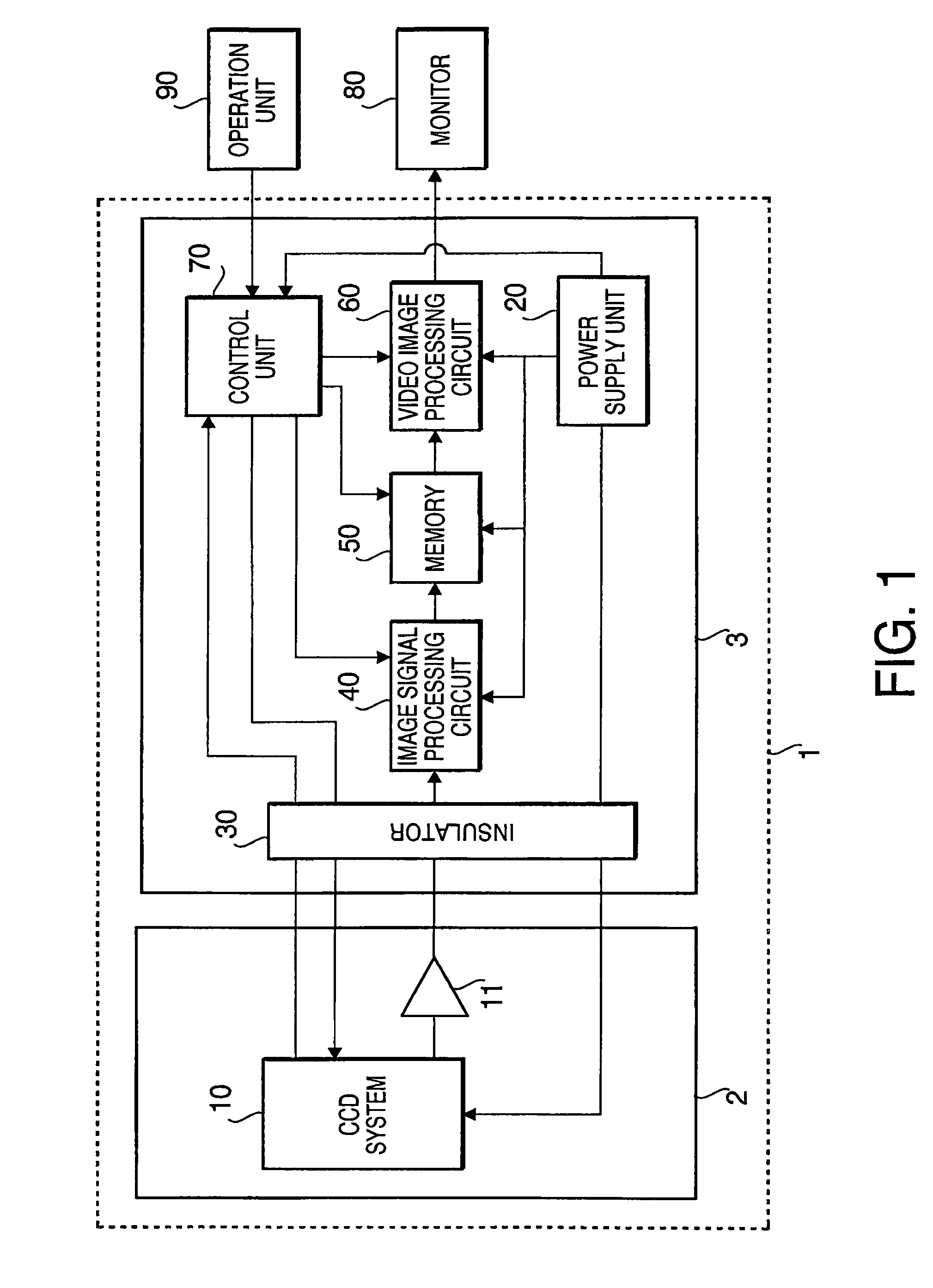
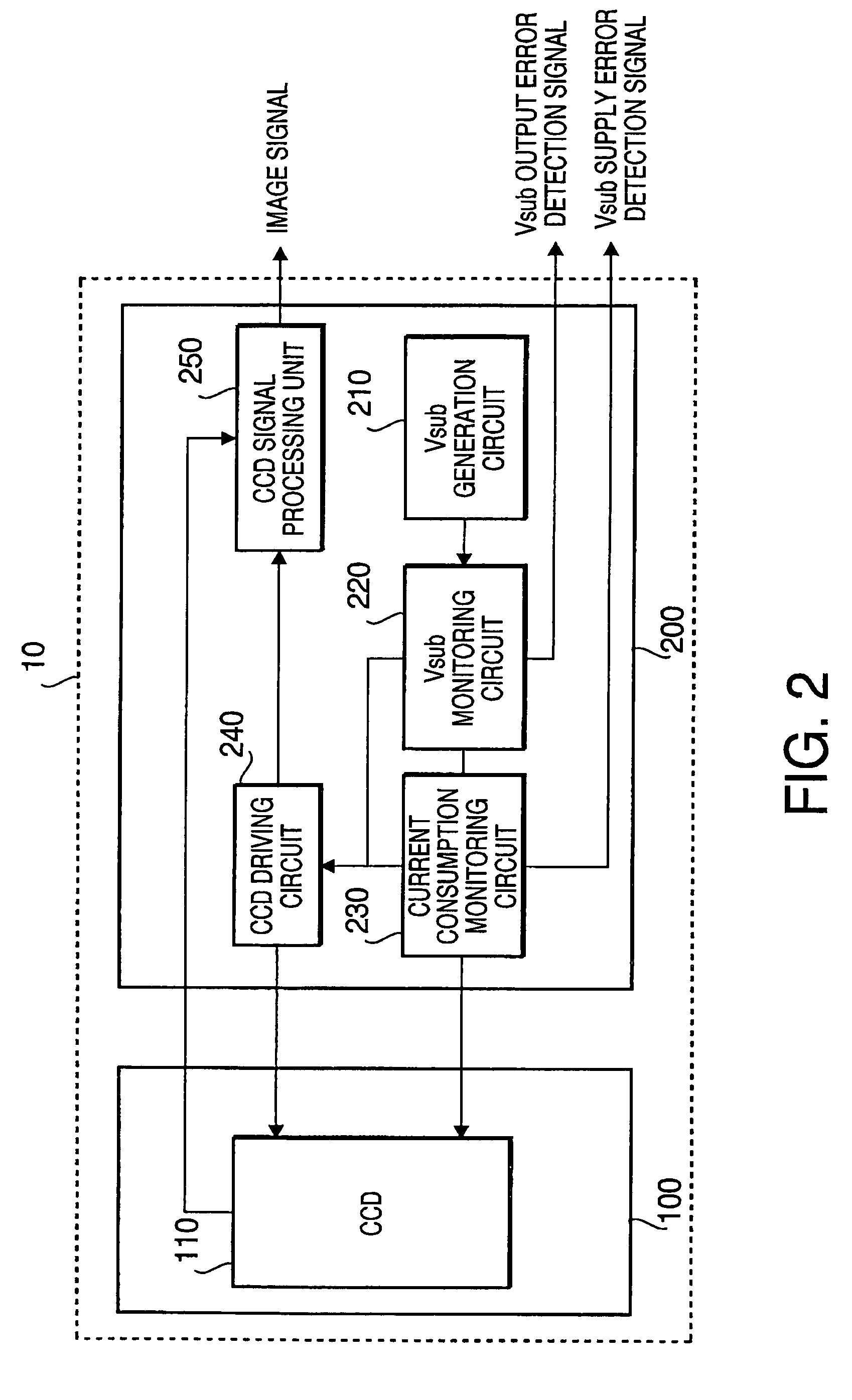
CCD breakage prevention system
InactiveUS7593051B2Avoid breakingTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsControl systemCurrent consumption
An electronic endoscope is provided with a CCD control system which can prevent CCD breakage caused by a latchup, etc. by detecting a Vsub output error and a Vsub supply error without placing any device near the CCD. The endoscope system has a scope including a CCD placed at the scope's distal end, a driving section that supplies a drive signal to a CCD and drives the CCD and a bias voltage generation that generates a substrate bias voltage, a processor, a voltage monitoring section that monitors the voltage value of the substrate bias voltage, a current consumption monitoring section that monitors the current consumption corresponding to the substrate bias voltage, a drive stopping section that stops supplying the drive signal to the CCD when the voltage monitoring section or the current consumption section determines an error occurs.
Owner:HOYA CORP
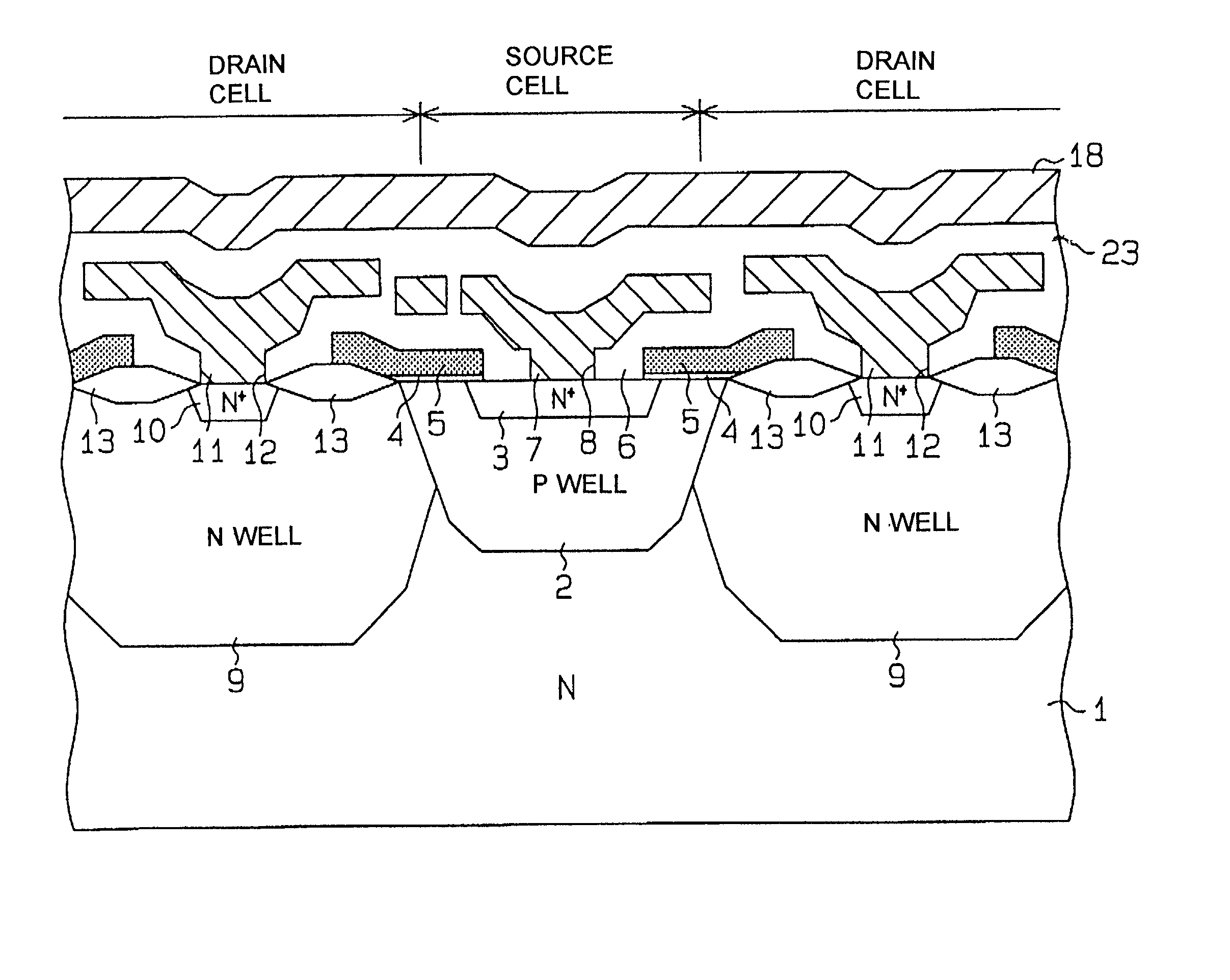
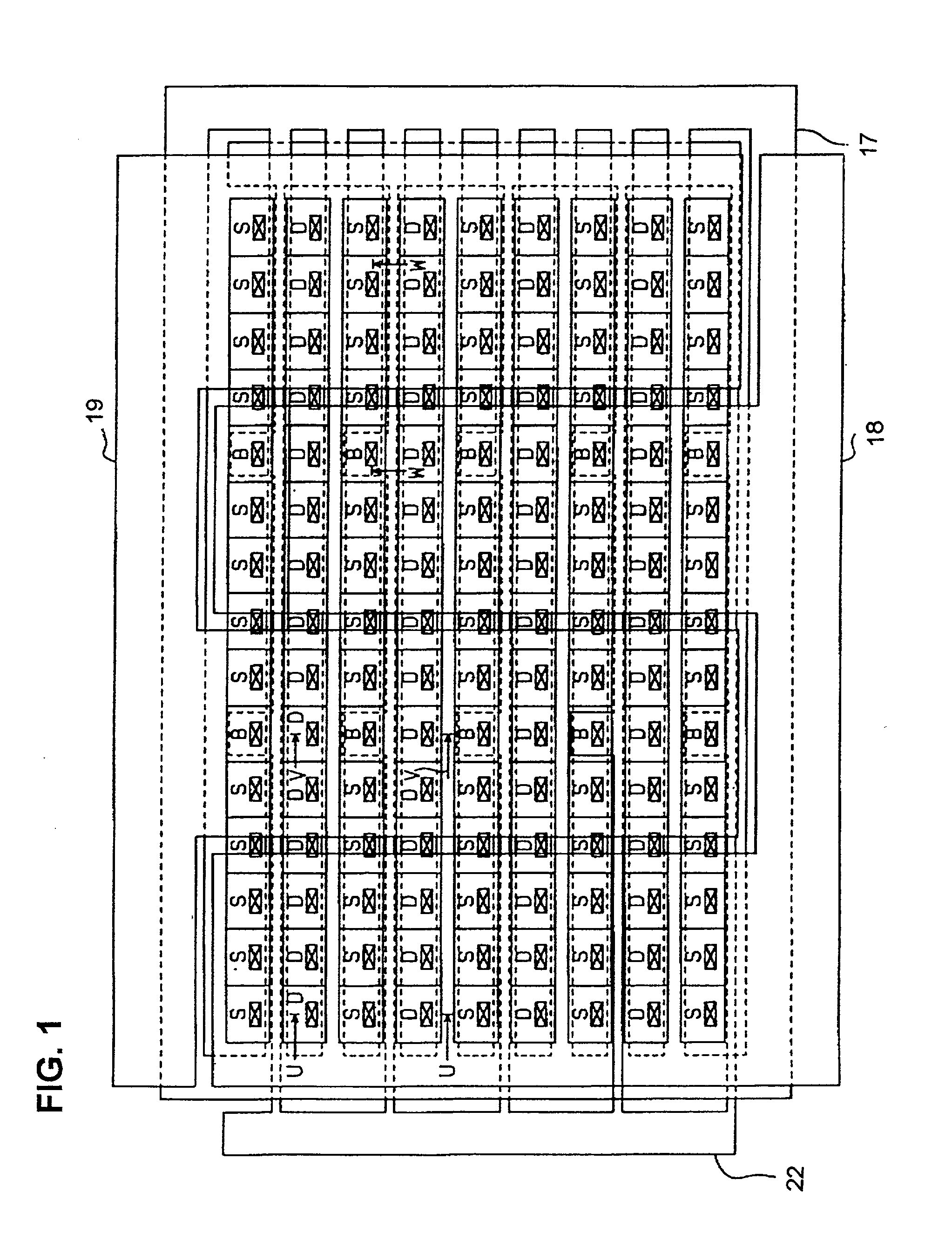
Power MOS transistor having capability for setting substrate potential independently of source potential
InactiveUS20020185681A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPotential differenceSubstrate bias voltage
A power MOS transistor formed of an array of source cells and drain cells on an IC chip substrate has a plurality of substrate contact cells, each formed external to the source cells, having respective substrate potential-setting electrodes to which an externally supplied substrate bias voltage can be applied, enabling the substrate potential to be set independently of the source potential of the transistor. It thereby becomes possible to modify the threshold voltage of the transistor or maintain a constant potential difference between the substrate potential and that of a gate input signal. Since the requirement for a substrate contact region within each source cell is eliminated, and the number of substrate contact cells can be fewer than that of the source cells, the chip area occupied by the transistor can be reduced by comparison with a prior art configuration providing such a substrate potential control capability.
Owner:DENSO CORP
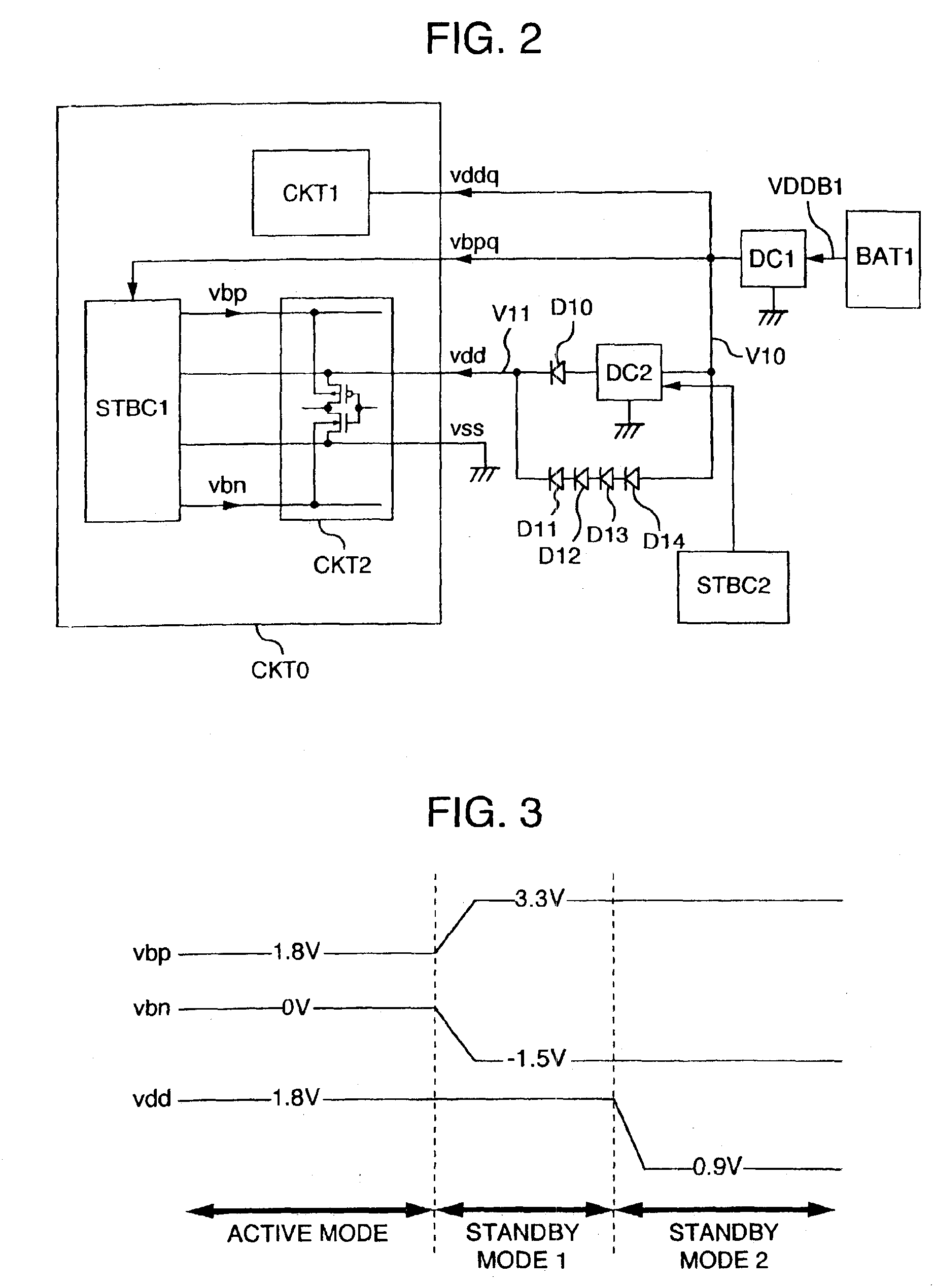
Semiconductor integrated circuit device including a substrate bias controller and a current limiting circuit
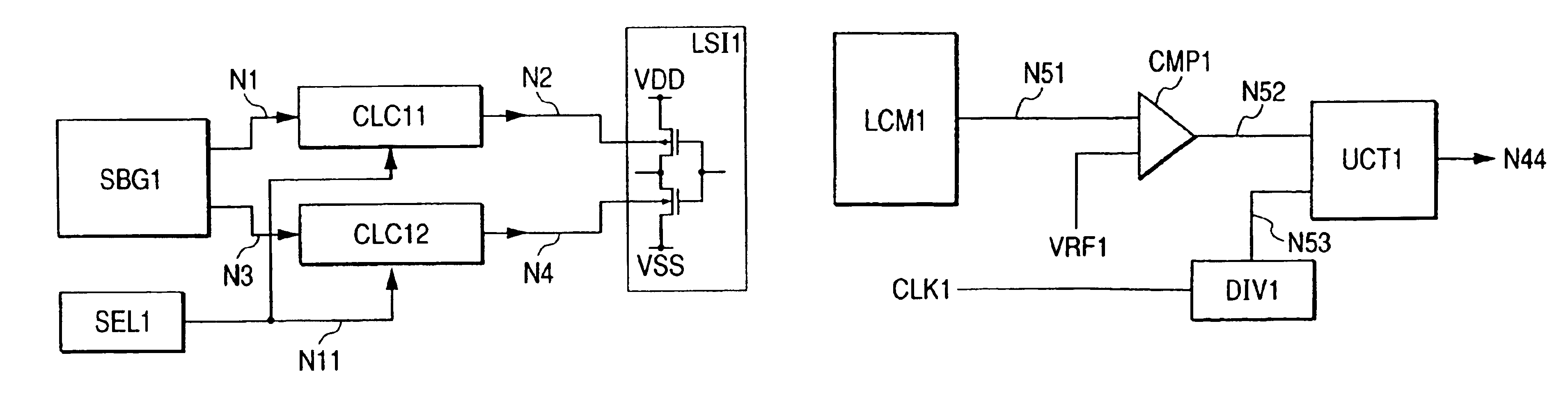
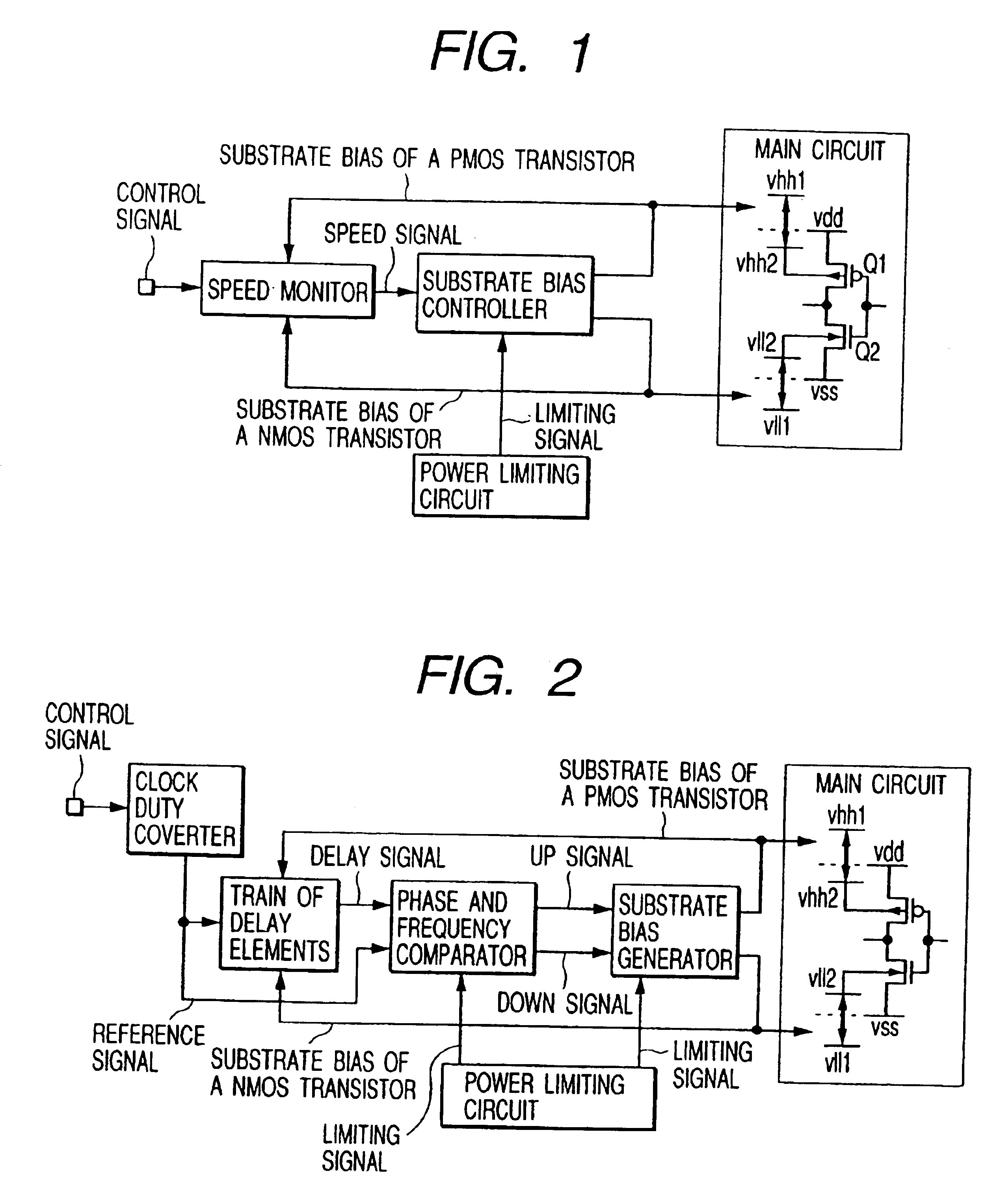
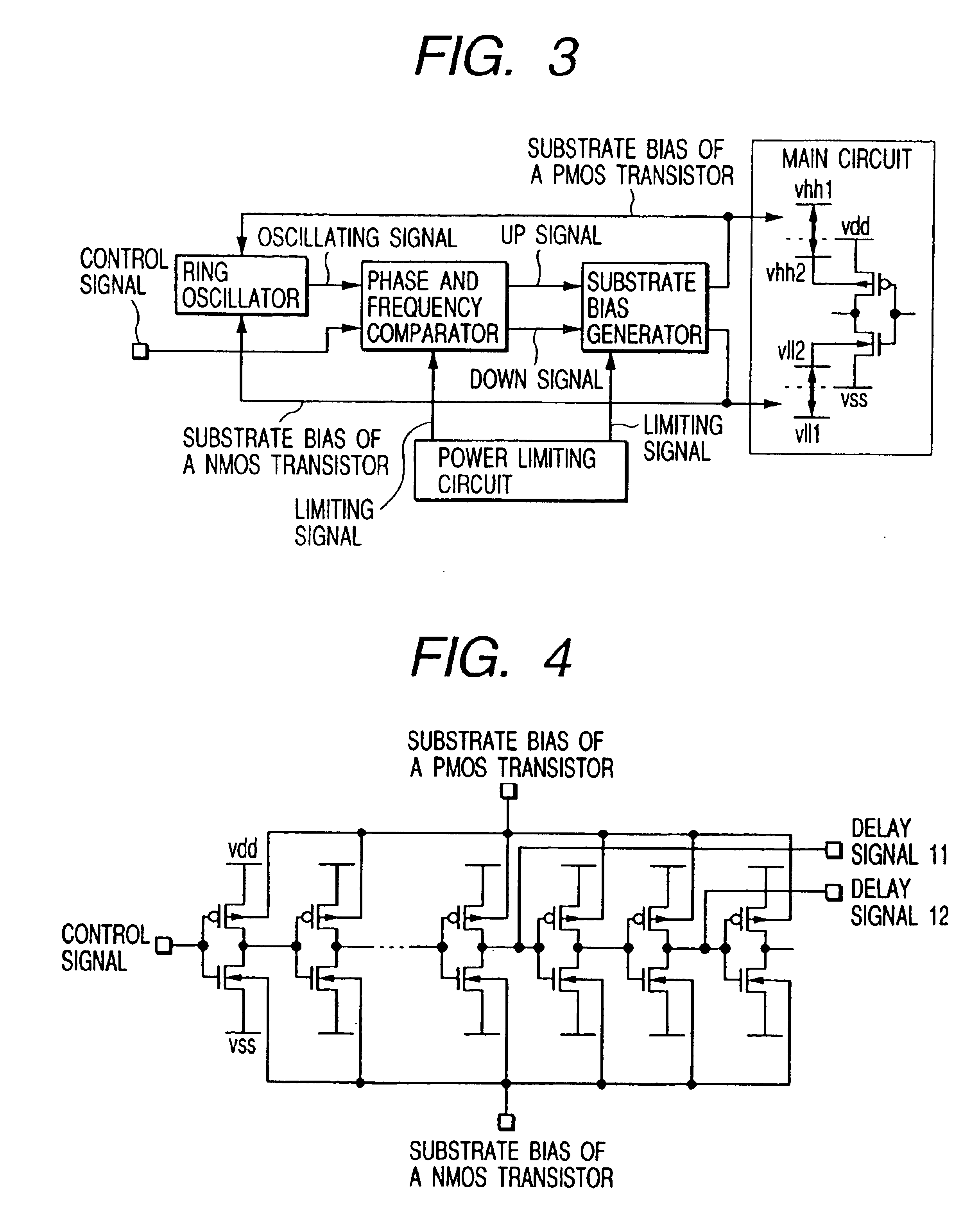
In a semiconductor integrated circuit device, for realizing high speed, as well as superior product yield rate and usability, while reducing circuit scale and improving on product yield rate and reliability thereof, a main circuit, constructed with CMOS elements, is coupled to a speed monitor circuit for forming a speed signal corresponding to an operating speed thereof and to a substrate bias controller for supplying corresponding substrate bias voltages to the main circuit in response to the speed monitor circuit. A current limiting circuit is also provided in conjunction with the substrate bias controller to prevent an overflow of current due to bias voltage.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
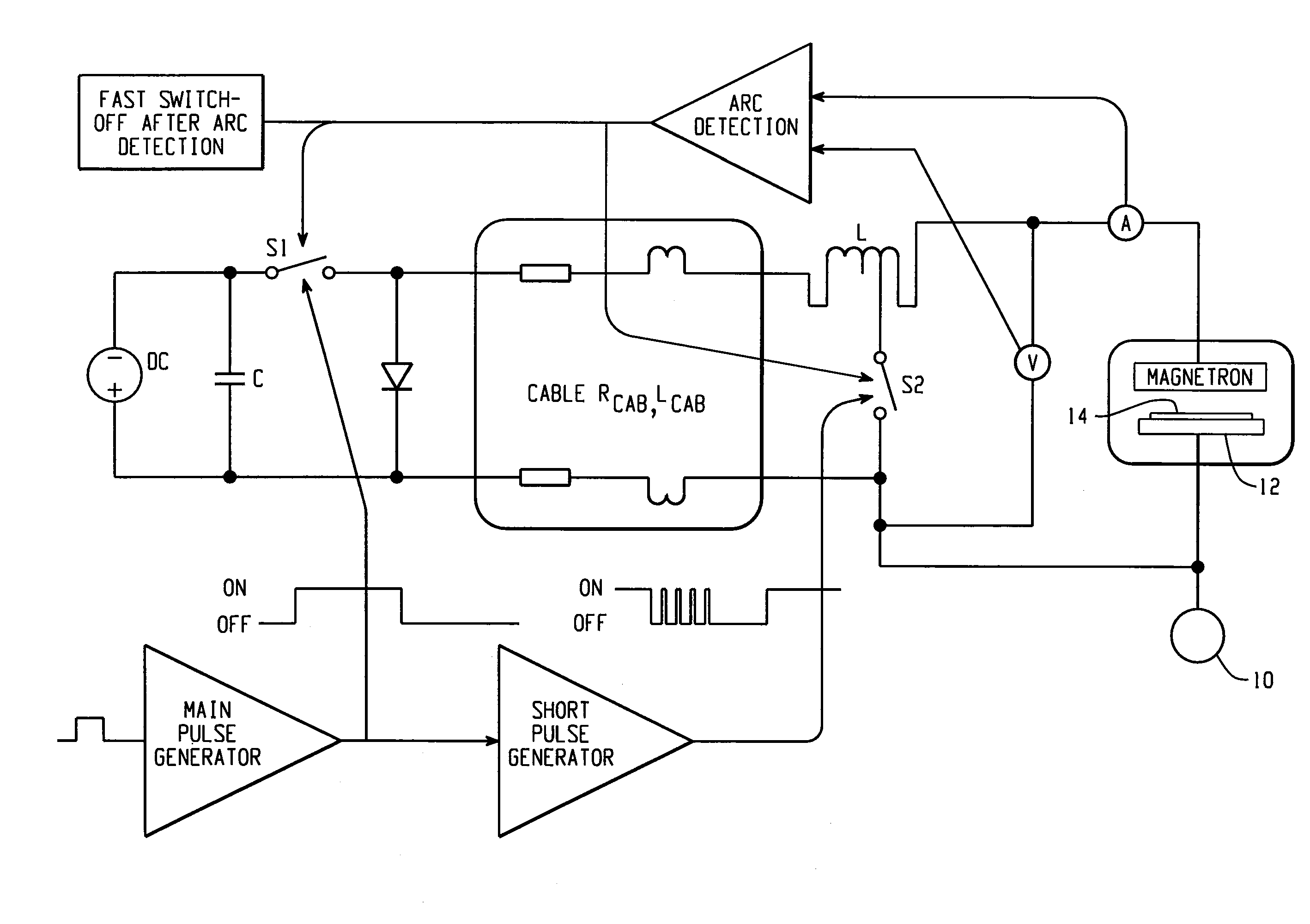
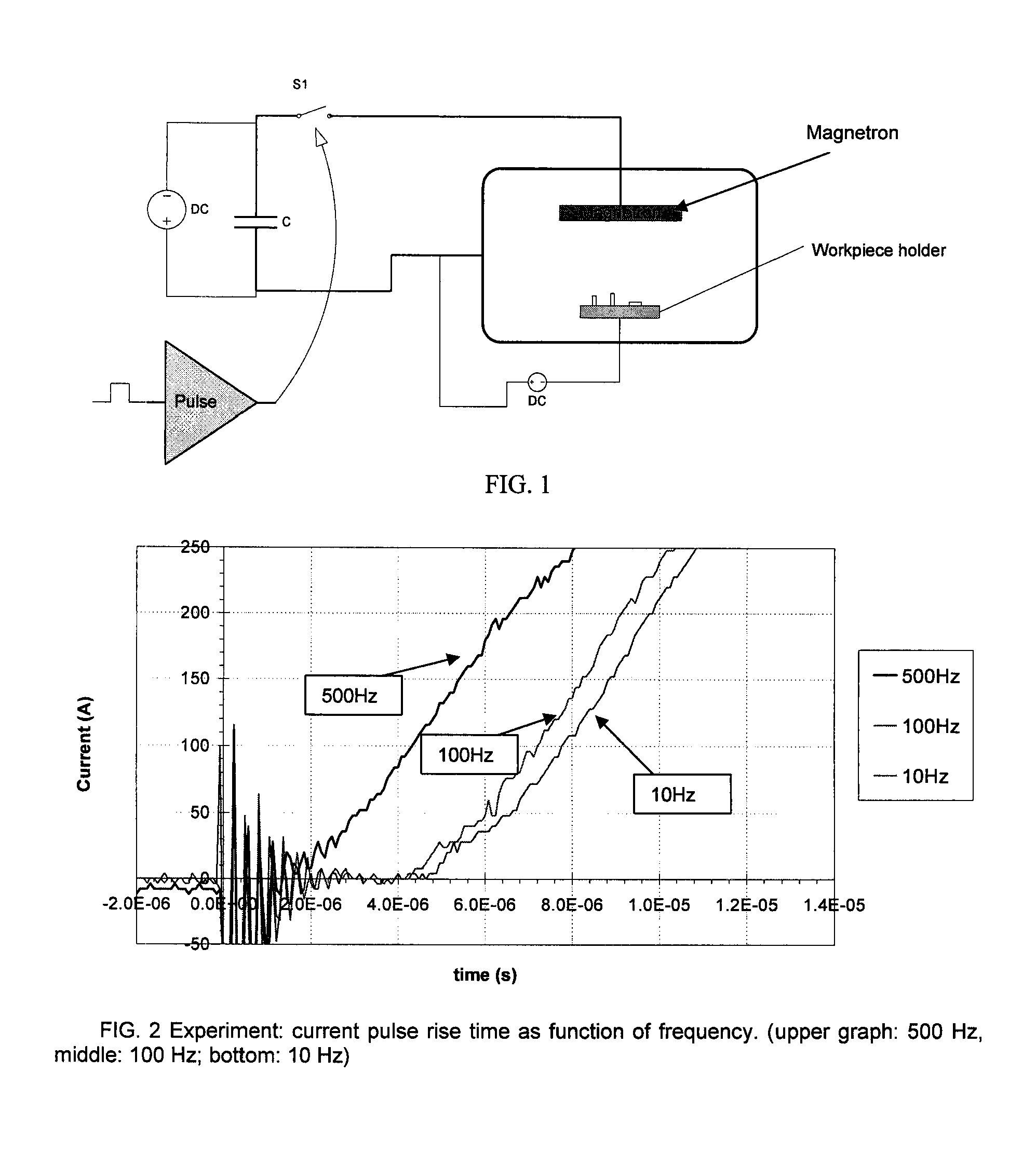
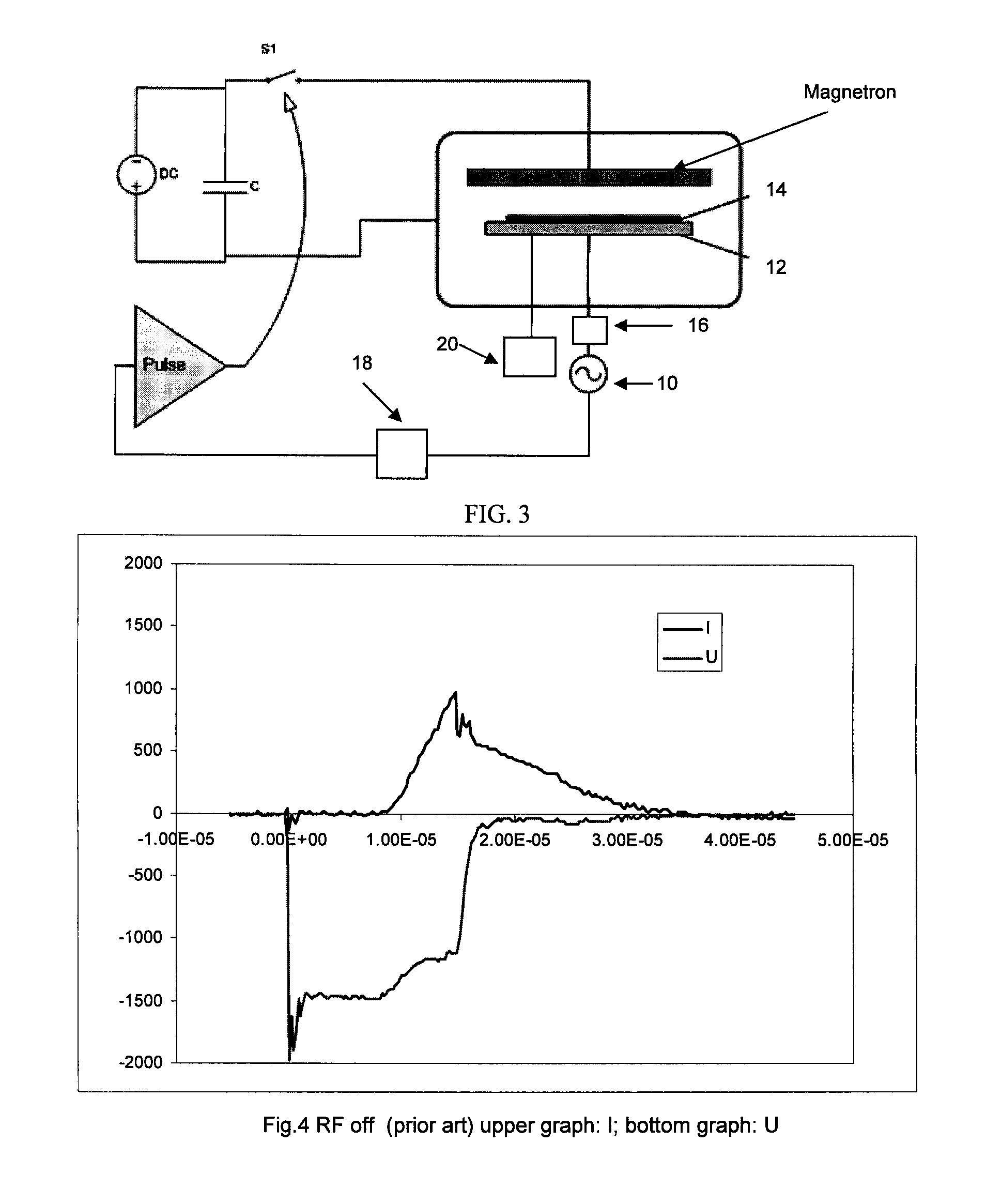
RF substrate bias with high power impulse magnetron sputtering (hipims)
An apparatus for generating sputtering of a target to produce a coating on a substrate with a current density on a cathode of a magnetron between 0.1 and 10 A / cm2 is provided. The apparatus comprises a power supply that is operably connected to the magnetron and at least one capacitor is operably connected to the power supply. A first switch is also provided. The first switch operably connects the power supply to the magnetron to charge the magnetron and the first switch is configured to charge the magnetron according to a first pulse. An electrical bias device is operably connected to the substrate and configured to apply a substrate bias.
Owner:OERLIKON ADVANCED TECH +1
Method for manufacturing surface antimicrobial, abrasion-proof metal/ceramic nano-multilayer film
ActiveCN101220454AHigh hardnessImprove wear resistanceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingWear resistantNitrogen gas
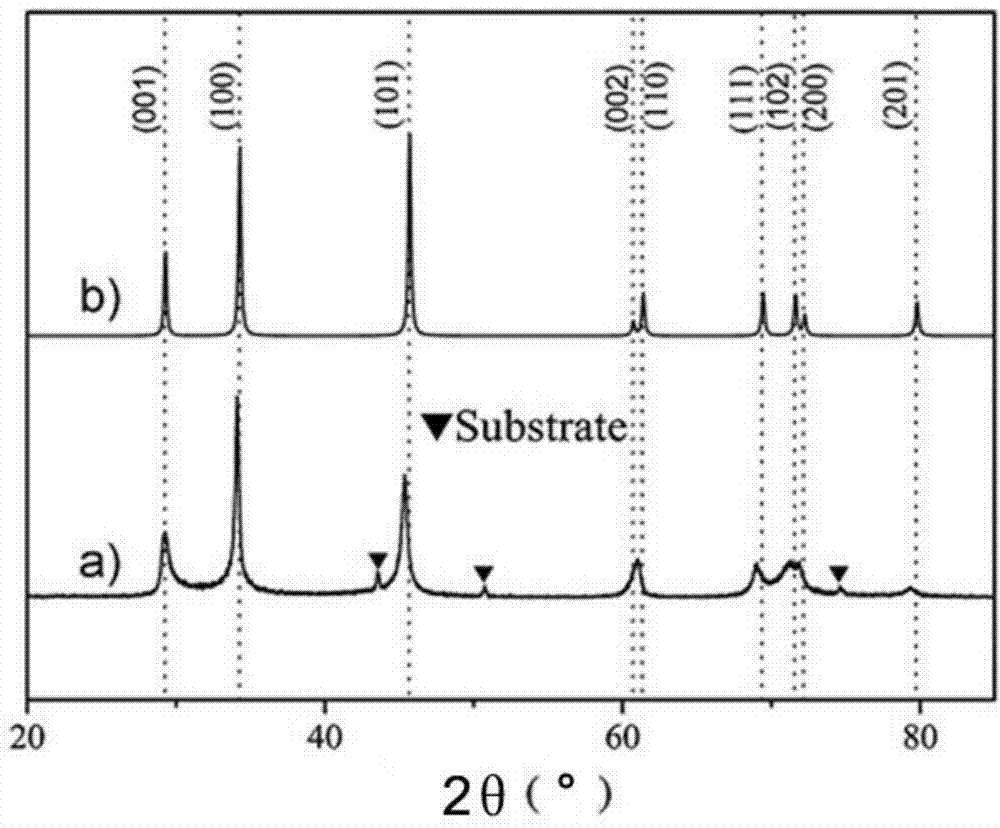
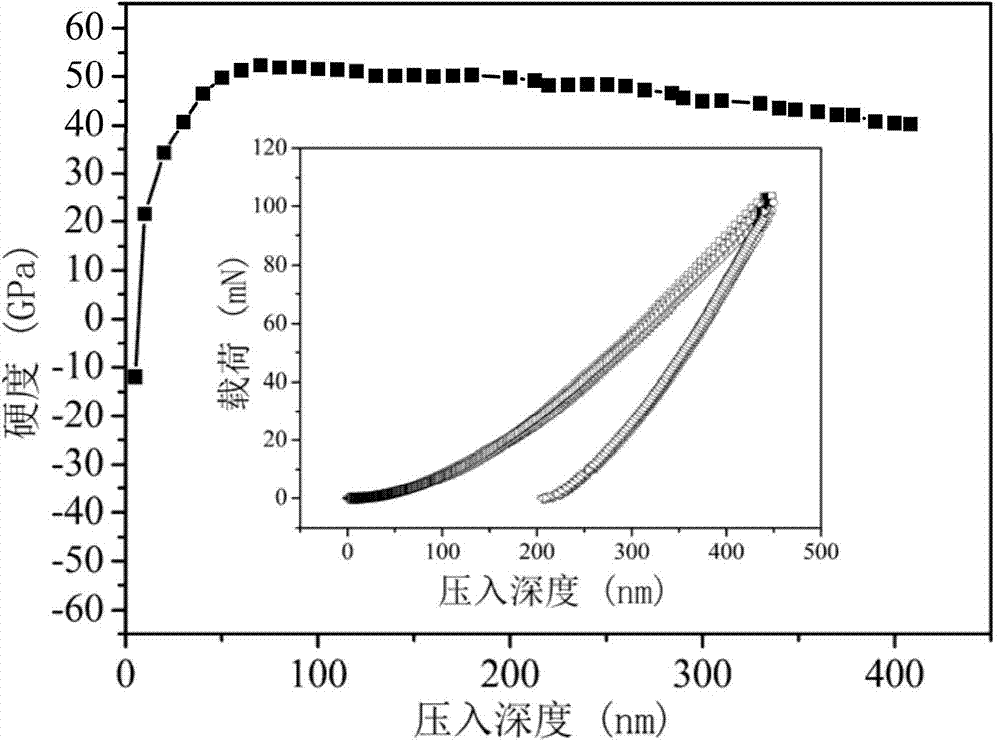
The invention which discloses a preparation method for metal / ceramic nanometer multilayer films with antibacterial and wear resistant surfaces relates to a preparation method for nanometer multilayer films and solves the problem of high cost and great difficulty in preparing wholly antibacterial materials and low wear resistance of surfaced treated antibacterial materials. The method comprises the following steps: a magnetron sputtering method is adopted, the background vacuum degree is 10<- 4> to 10<- 2> Pa; sputtering against targets in the conditions of the gas flow ratio of 2 to 17:1 of argon to one gas of the three gases of nitrogen, acetylene or methane, total air pressure of 0.1 - 1.0Pa, magnetron sputtering currents of 0.2 - 50A, voltage of 300 - 600V, substrate bias voltage of minus 50 to minus 400V and deposition temperatures of 80 - 400 DEG C. The nanometer ceramic / metal multilayer films prepared by the invention have good wear resistance and the antibacterial rate of more than 95 percent; the invention has the advantages of no pollution, low cost, easy realization and good industrial application prospects.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
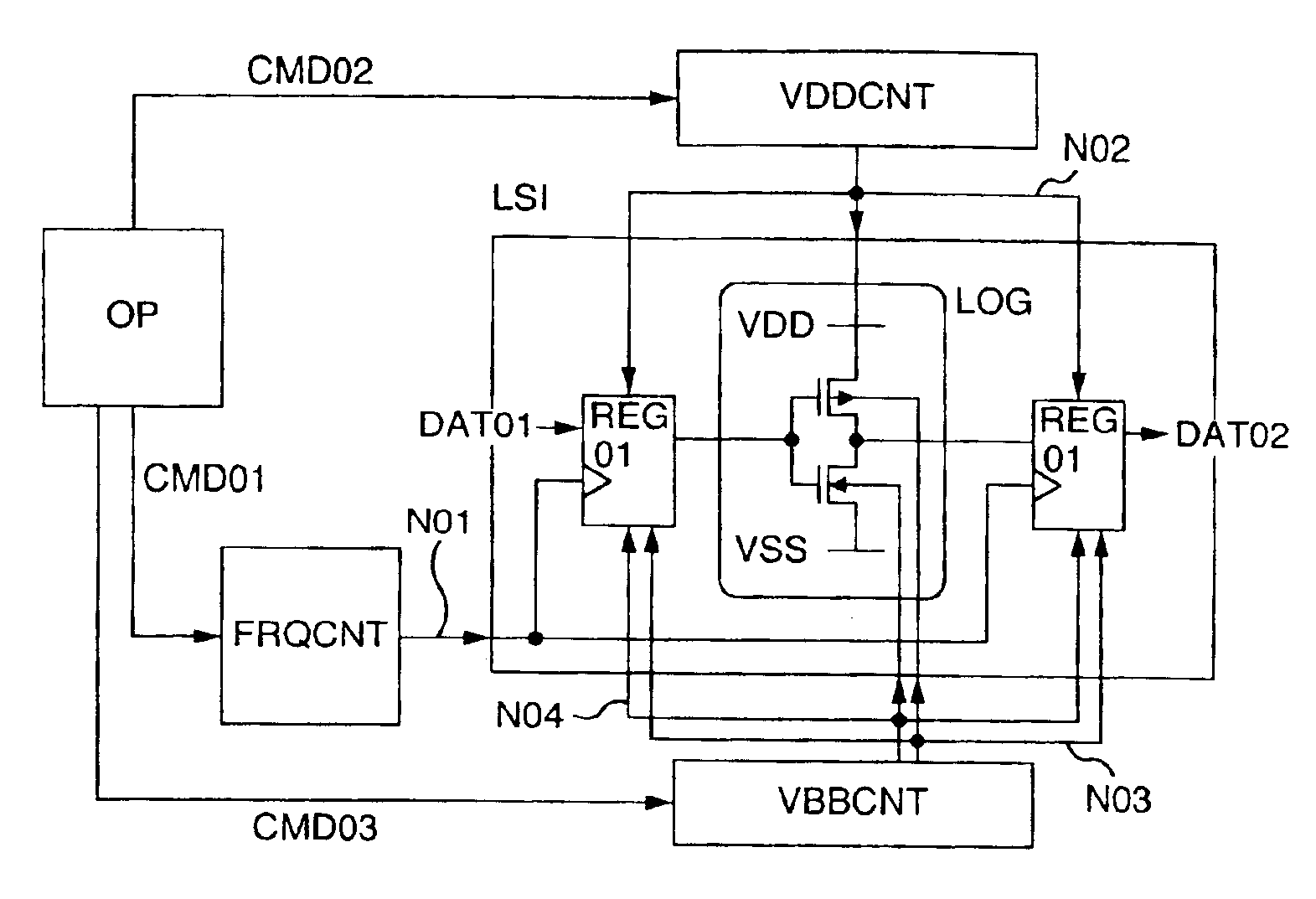
Semiconductor integrated circuit device in which operating frequency, supply voltage and substrate bias voltage are controllable to reduce power consumption
InactiveUS6943613B2Approximate performanceControl moreTransistorReliability increasing modificationsCMOSSubstrate bias voltage
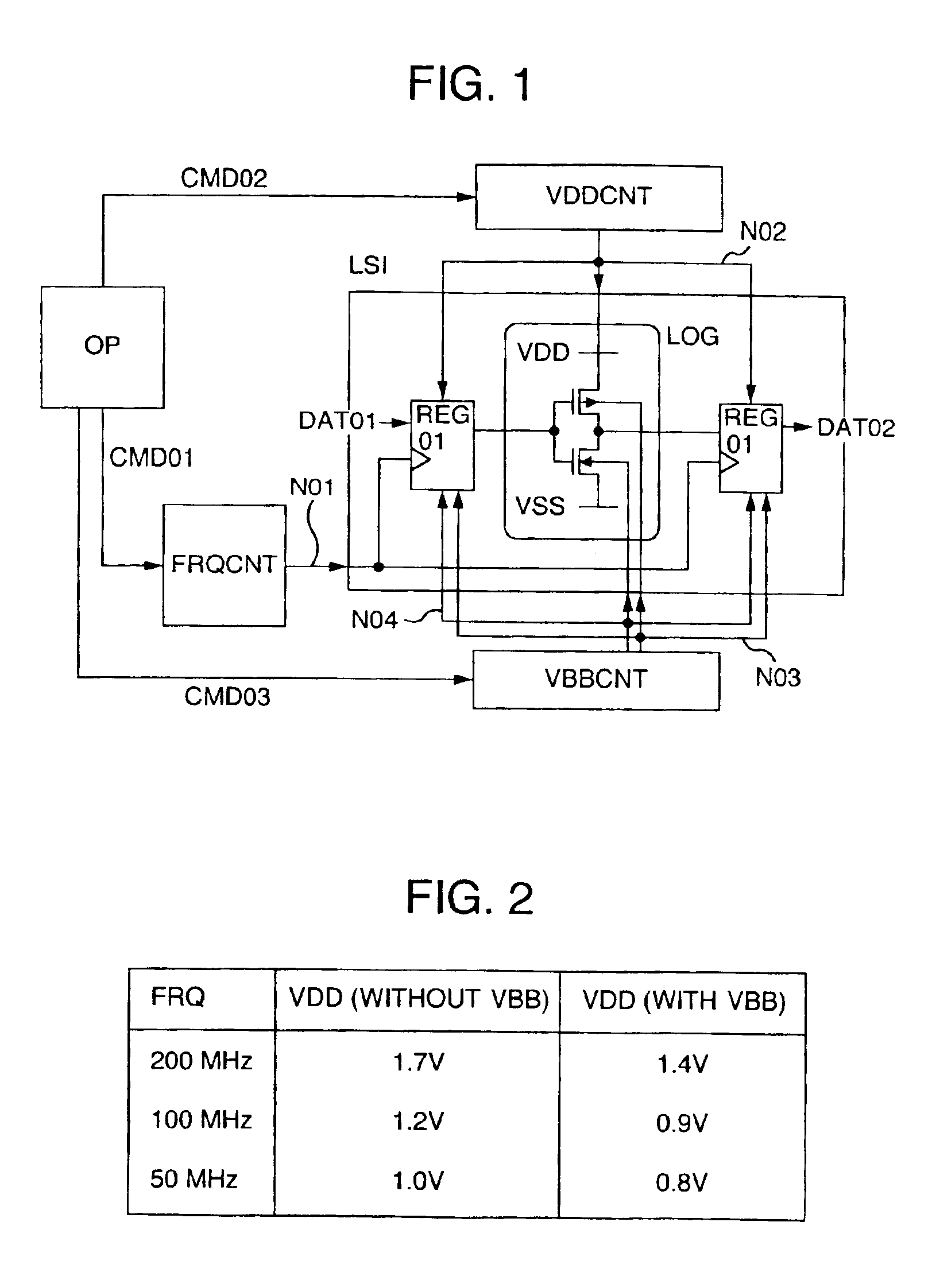
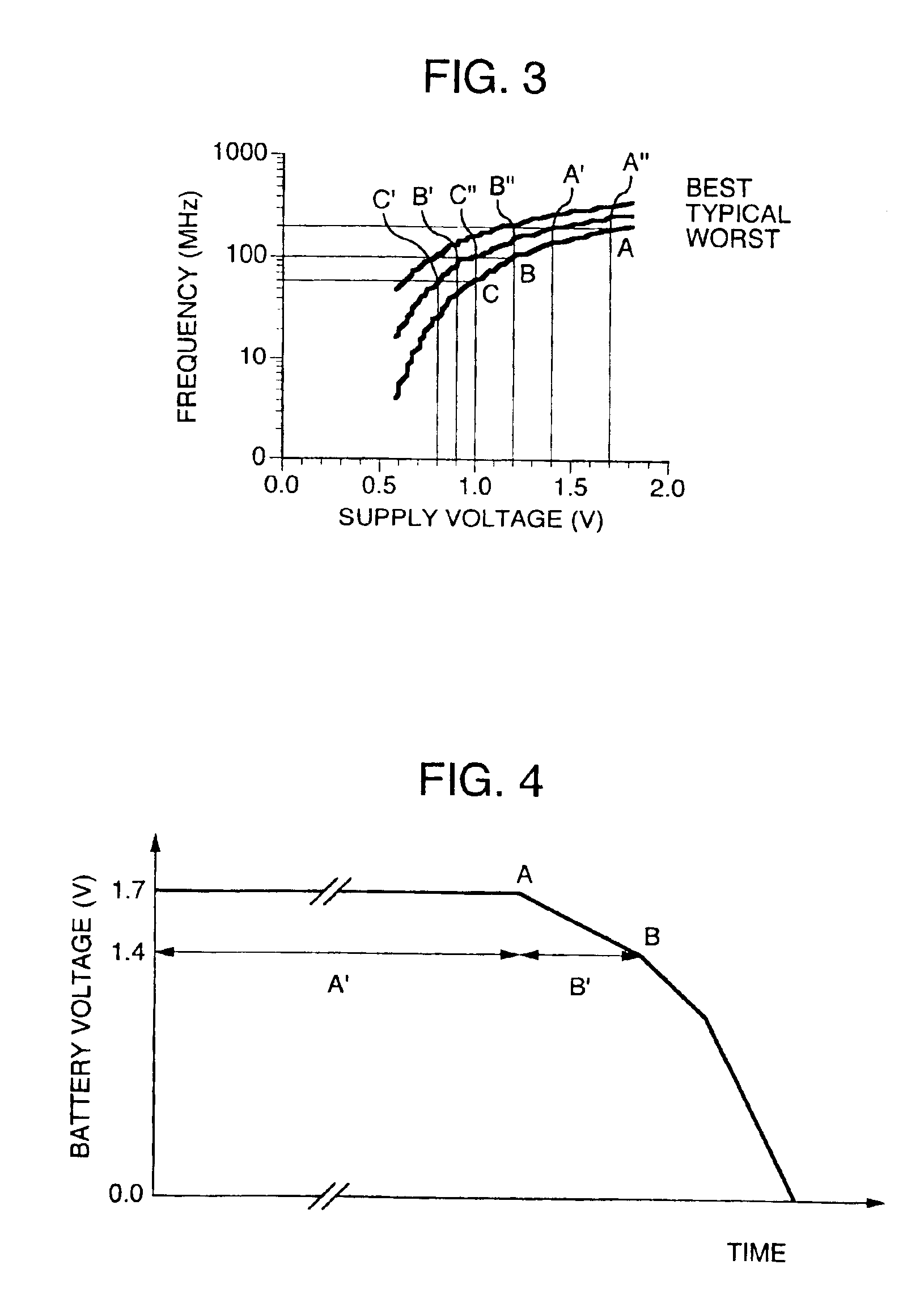
A semiconductor integrated circuit device includes control circuits FRQCNT, VDDCNT and VBBCNT that generate the optimum clock signal, supply voltage and substrate bias respectively and then supply them to a main circuit LSI. This operation makes it possible to suppress the variations of a CMOS circuit characteristic, thereby improving the circuit performance. Further, the low power consumption is realized without degrading the operating speed of the CMOS circuit or increasing the power consumption of the CMOS circuit.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
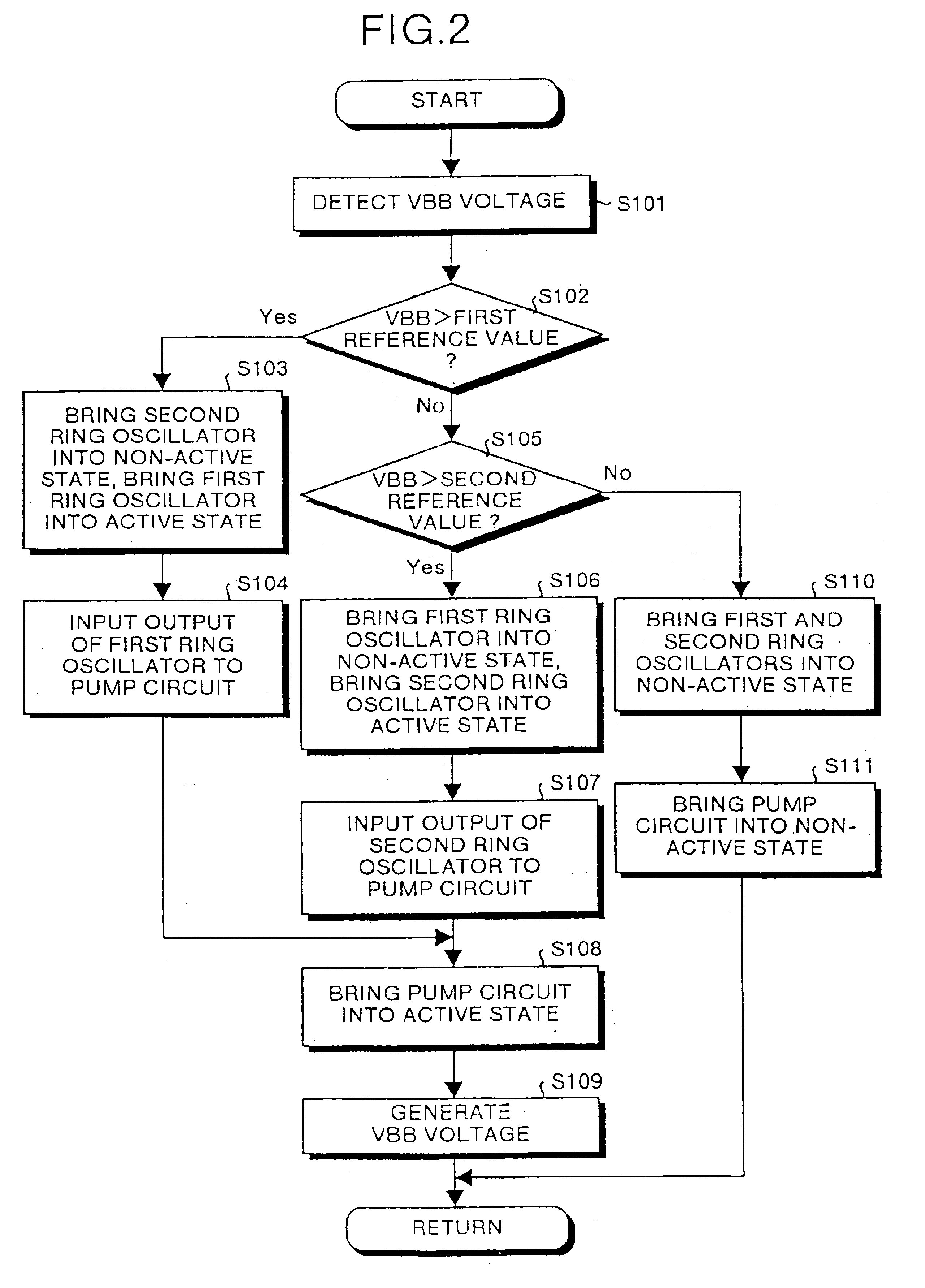
Substrate bias voltage generating circuit
InactiveUS6700434B2Simple designReduce power consumptionPulse generation by logic circuitsApparatus without intermediate ac conversionDetector circuitsSubstrate bias voltage
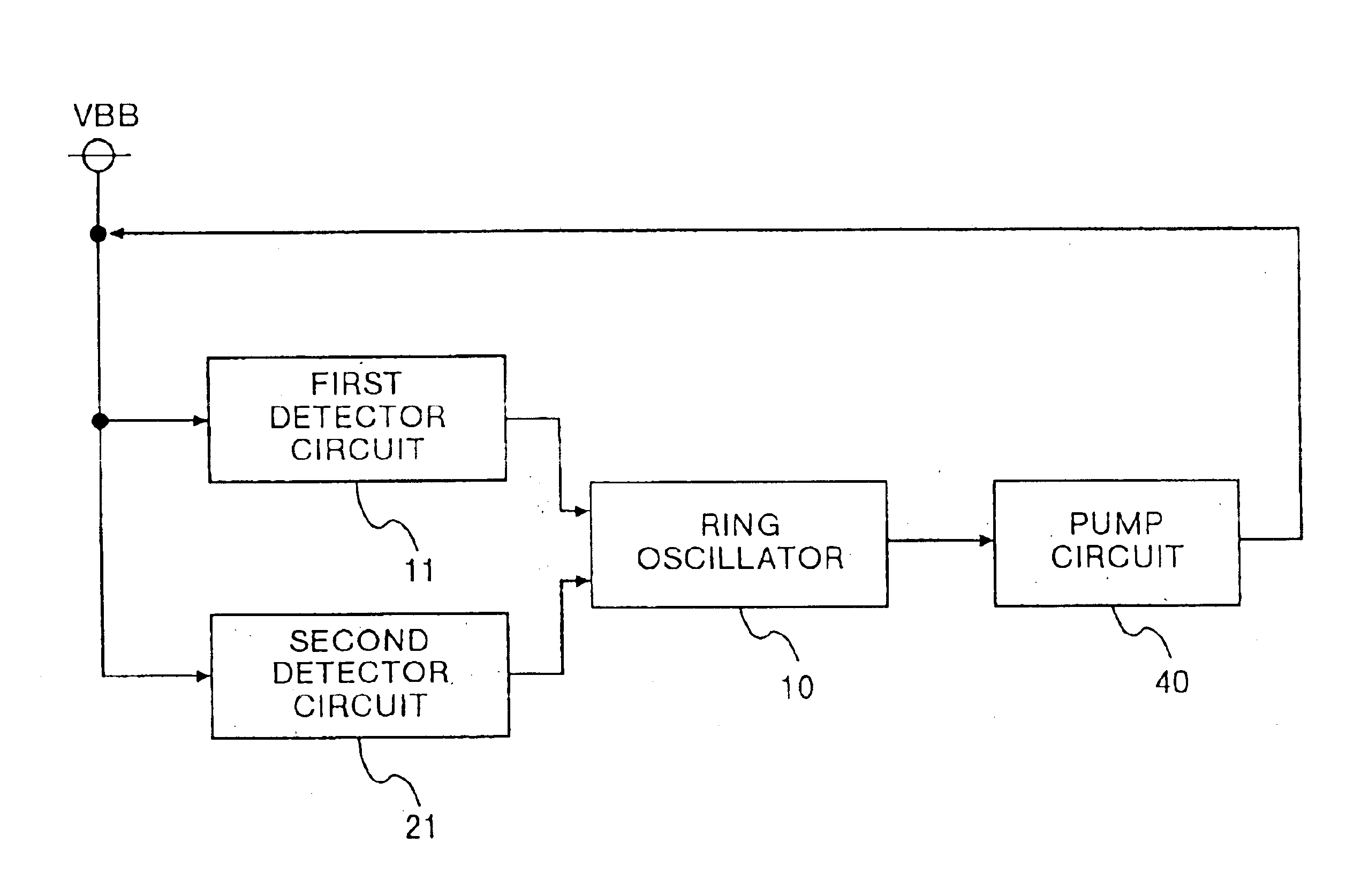
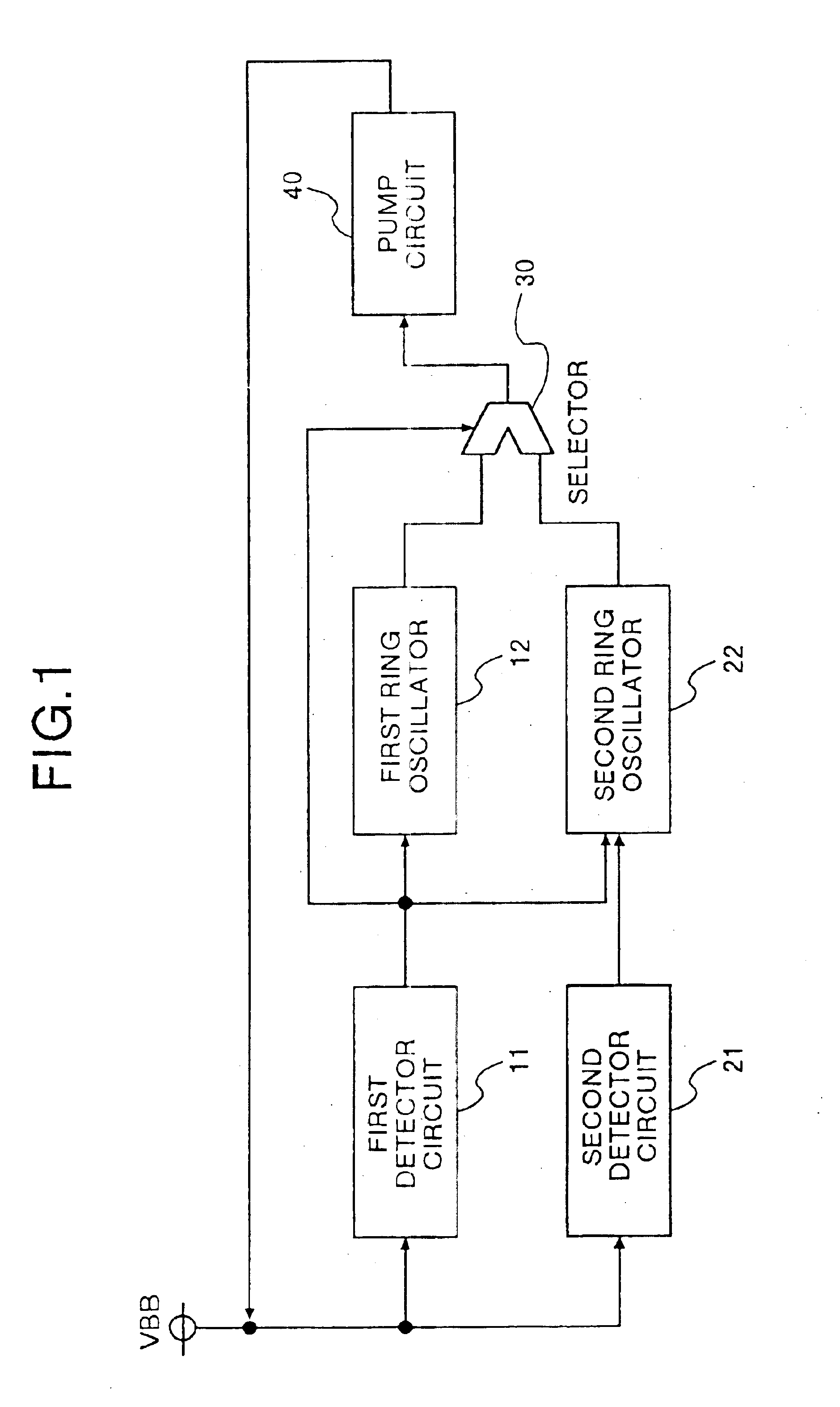
Oscillation outputs which are different for respective detector signals output from a first detector circuit and a second detector circuit, are obtained from a first ring oscillator and a second ring oscillator respectively corresponding to the detector circuits. A selector selects and outputs one of the oscillation outputs. Accordingly, it is sufficient to provide only one pump circuit in a circuit producing a substrate bias voltage.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Method of smoothing a trench sidewall after a deep trench silicon etch process
InactiveUS6846746B2Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTime segmentSubstrate bias voltage
Disclosed herein is a method of smoothing a trench sidewall after a deep trench silicon etch process which minimizes sidewall scalloping present after the silicon trench etch. The method comprises exposing the silicon trench sidewall to a plasma generated from a fluorine-containing gas, at a process chamber pressure within the range of about 1 mTorr to about 30 mTorr, for a time period within the range of about 10 seconds to about 600 seconds. A substrate bias voltage within the range of about −10 V to about −40 V is applied during the performance of the post-etch treatment method of the invention.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Damage-free sculptured coating deposition
We disclose a method of applying a sculptured layer of material on a semiconductor feature surface using ion deposition sputtering, wherein a surface onto which the sculptured layer is applied is protected to resist erosion and contamination by impacting ions of a depositing layer, said method comprising the steps of: a) applying a first portion of a sculptured layer with sufficiently low substrate bias that a surface onto which said sculptured layer is applied is not eroded away or contaminated in an amount which is harmful to said semiconductor device performance or longevity; and b) applying a subsequent portion of said sculptured layer with sufficiently high substrate bias to sculpture a shape from said the first portion, while depositing additional layer material. The method is particularly applicable to the sculpturing of barrier layers, wetting layers, and conductive layers upon semiconductor feature surfaces and is especially helpful when the conductive layer is copper. In the application of a barrier layer, a first portion of barrier layer material is deposited on the substrate surface using standard sputtering techniques or using an ion deposition plasma, but in combination with sufficiently low substrate bias voltage (including at no applied substrate voltage) that the surfaces impacted by ions are not sputtered in an amount which is harmful to device performance or longevity. Subsequently, a second portion of barrier material is applied using ion deposition sputtering at increased substrate bias voltage which causes resputtering (sculpturing) of the first portion of barrier layer material, while enabling a more anisotropic deposition of newly depositing material. A conductive material, and particularly a copper seed layer applied to the feature may be accomplished using the same sculpturing technique as that described above with reference to the barrier layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Semiconductor Integrated Circuit Device
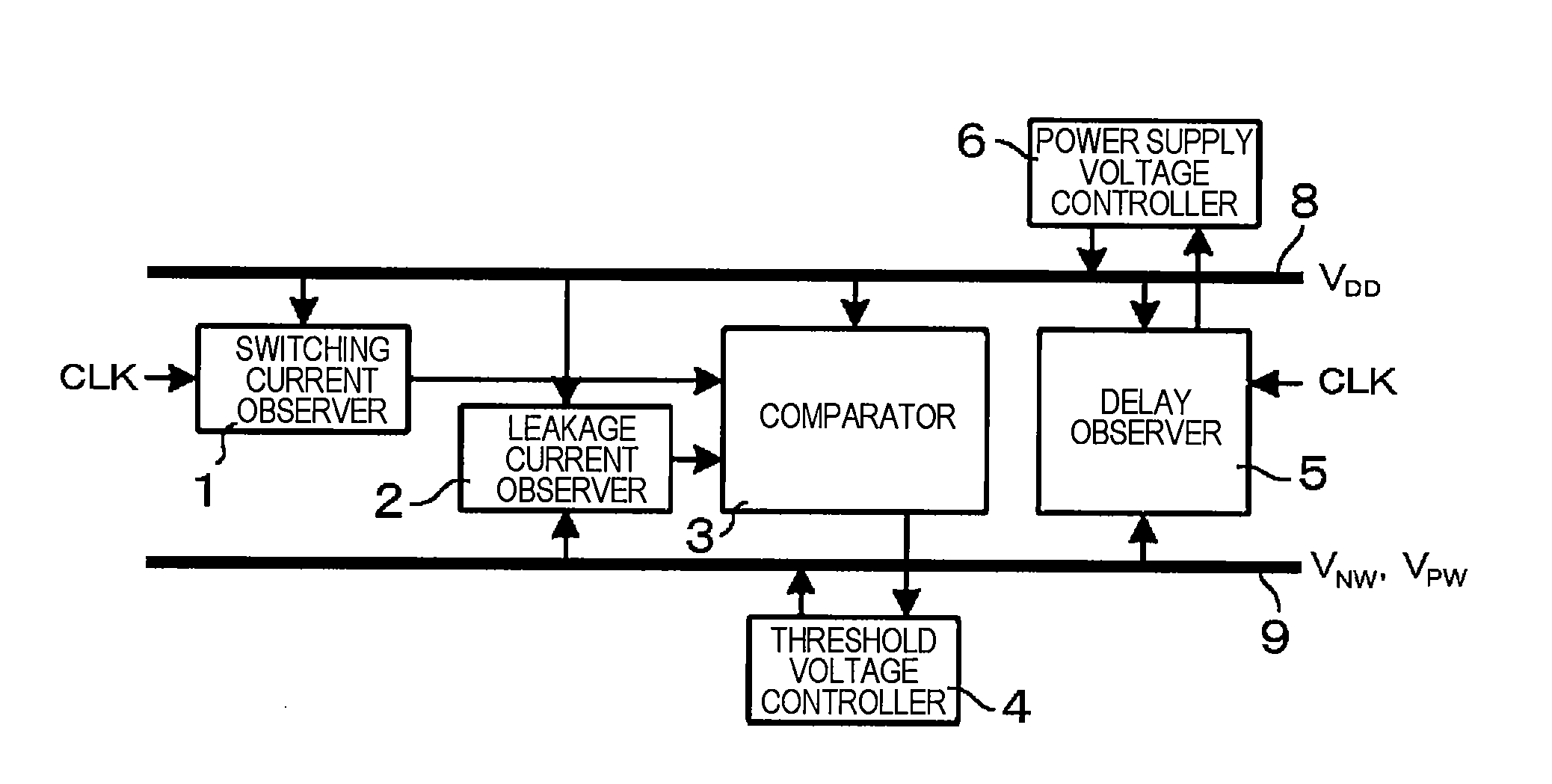
ActiveUS20080191791A1Minimizing operational powerReduce adverse effectsPower consumption reductionElectric pulse generator detailsSwitched currentDrain current
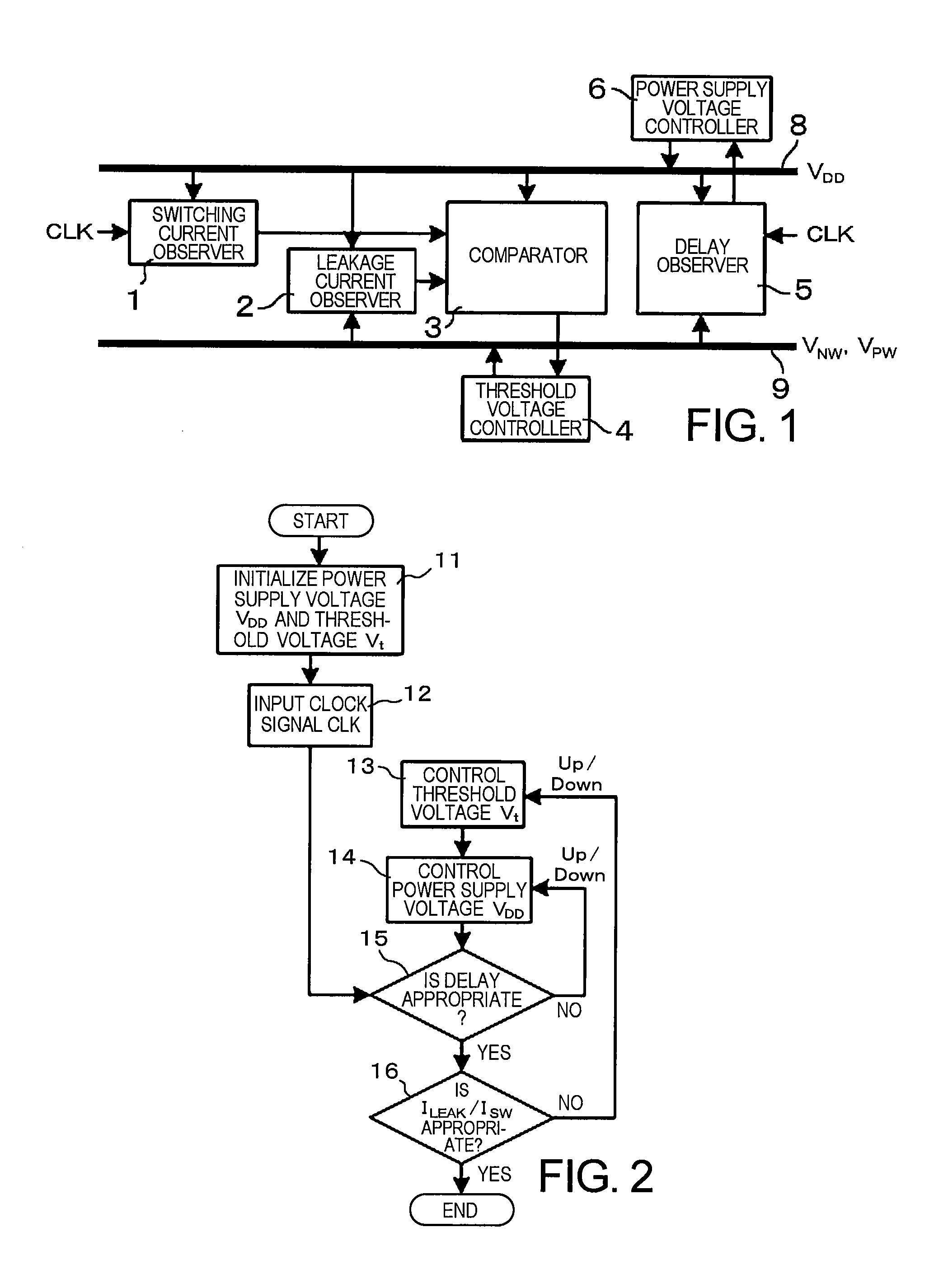
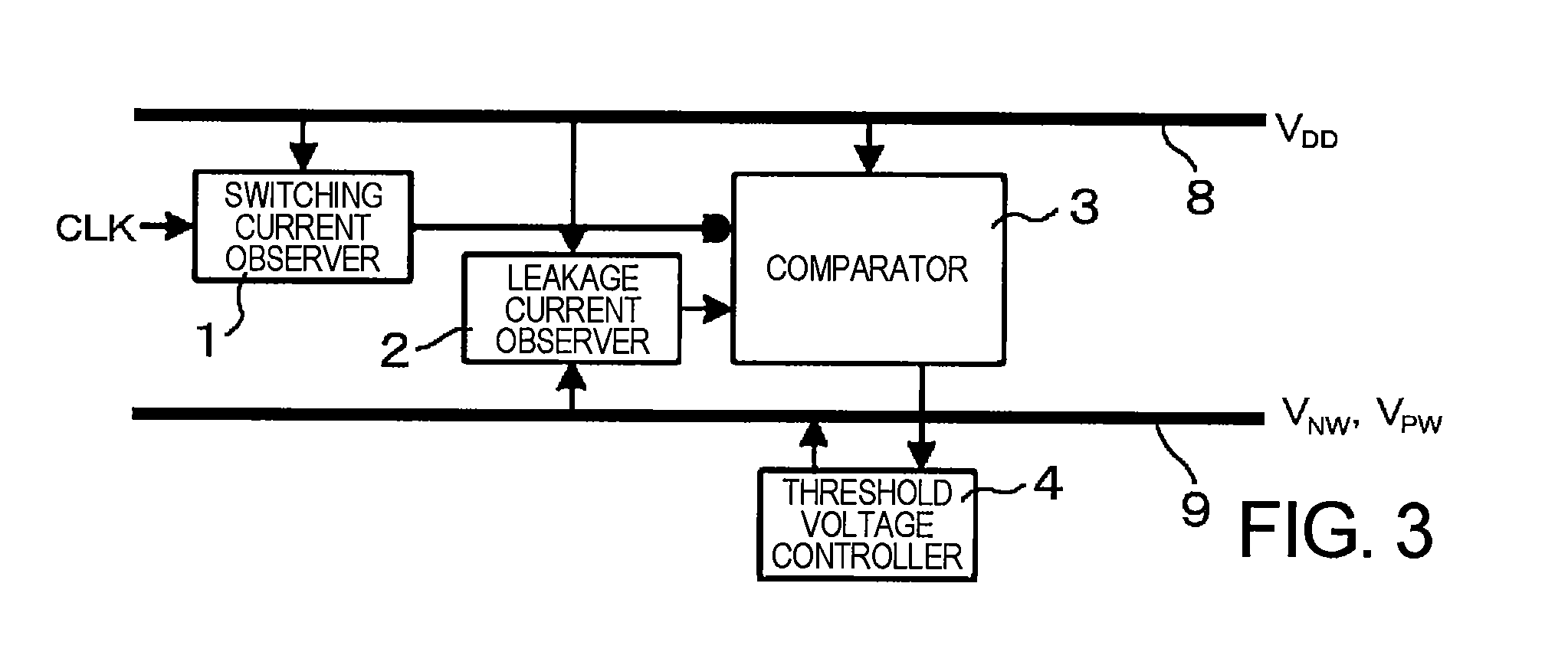
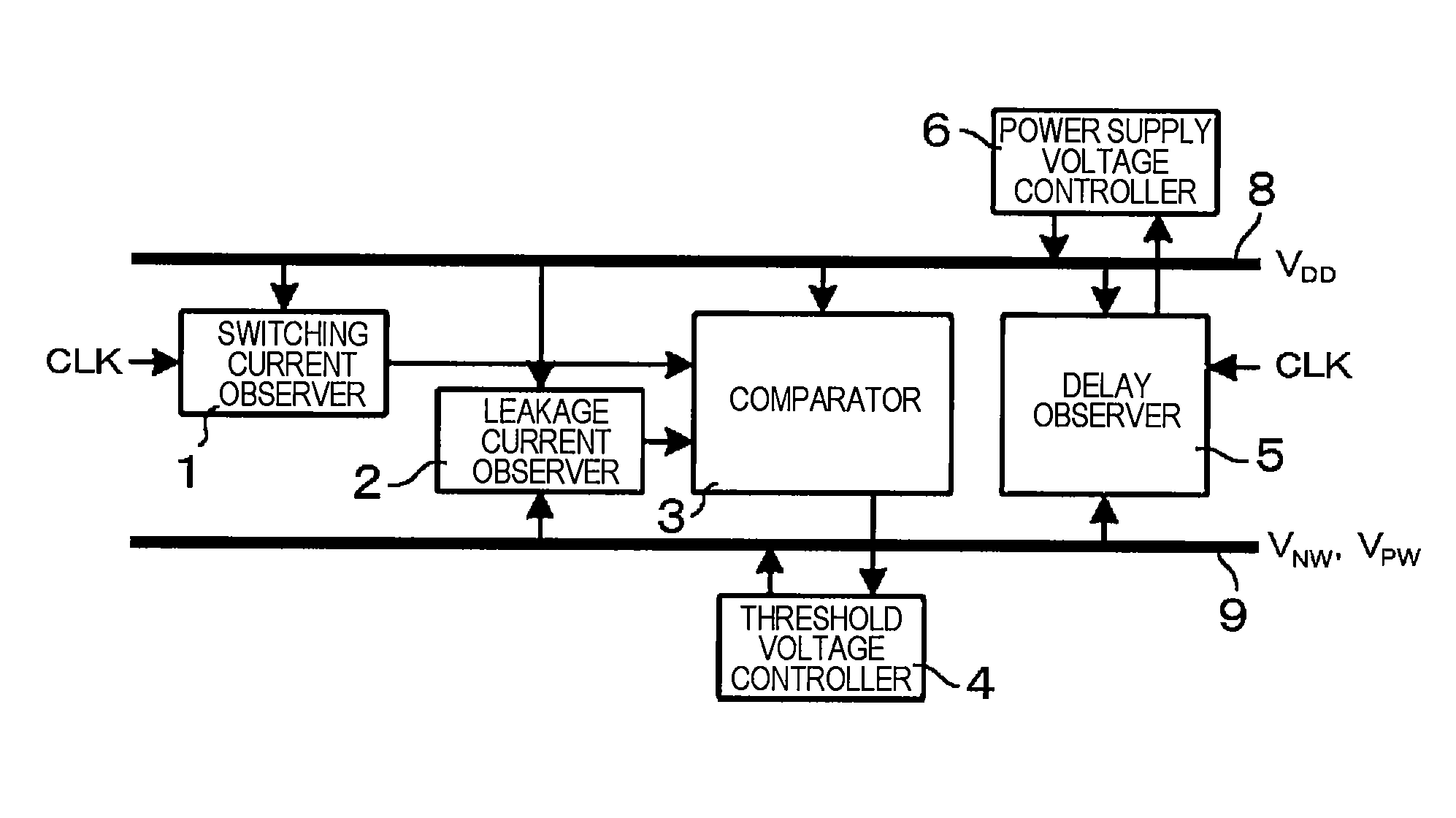
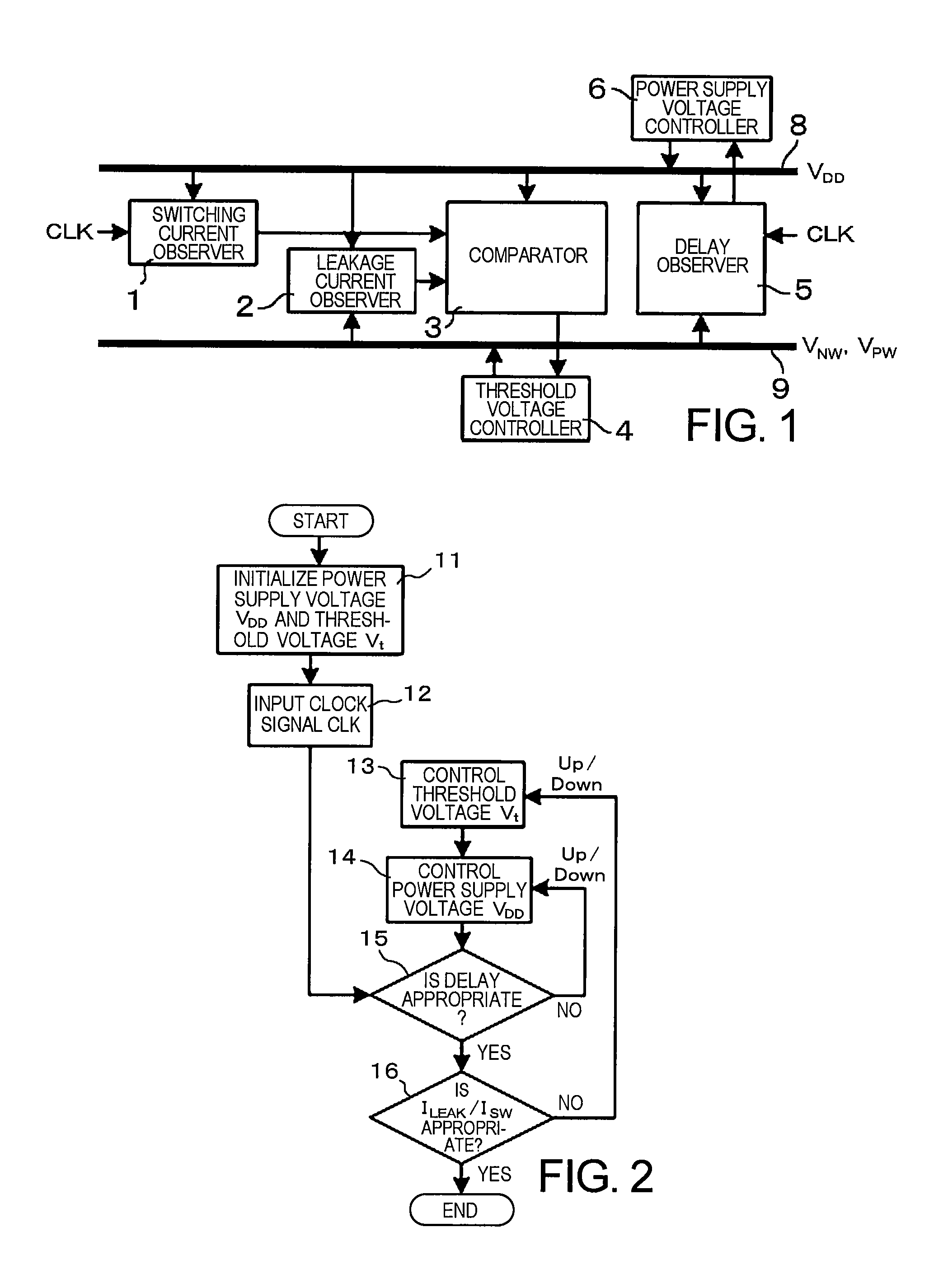
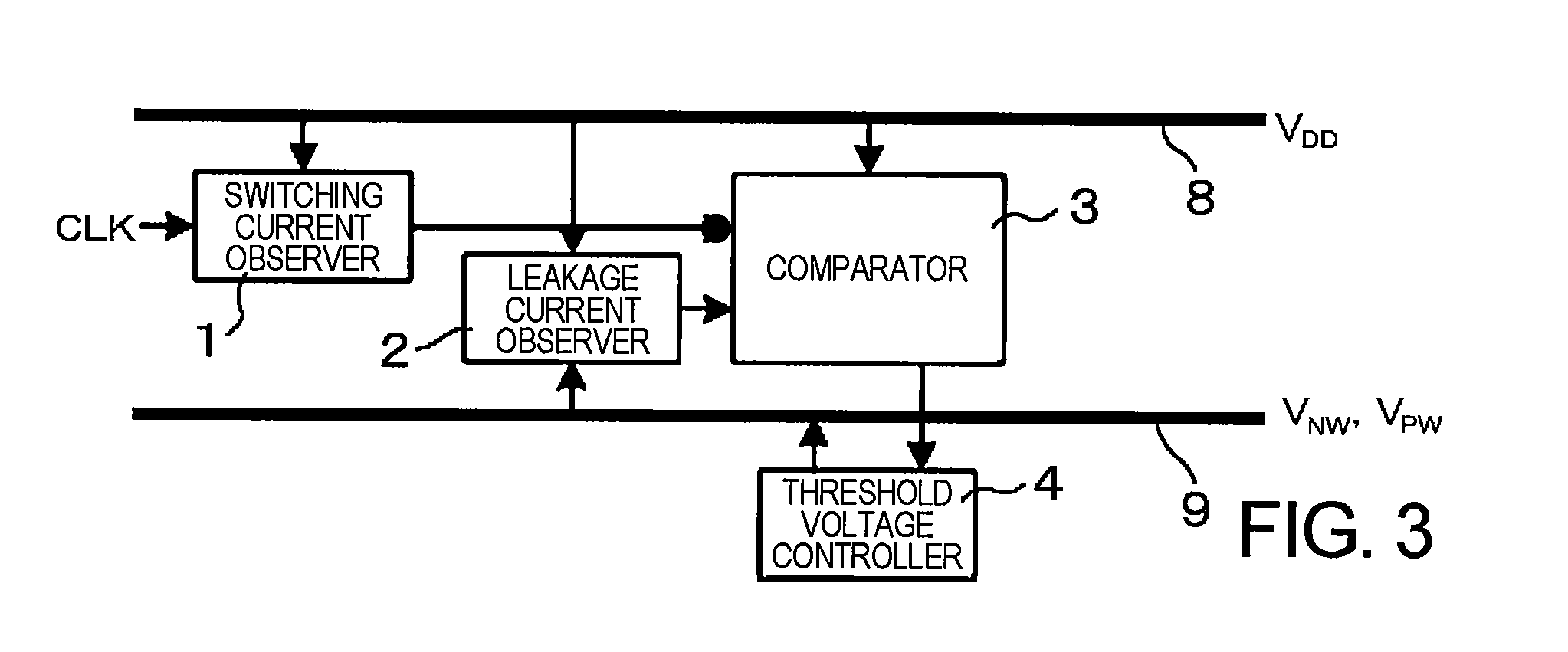
A semiconductor integrated circuit device includes: a switching current observer for observing a switching current; a leakage current observer for observing a leakage current; a comparator which compares the switching current and the leakage current with each other; a threshold voltage controller for controlling a substrate bias voltage in order to make a ratio of the switching current and the leakage current constant; a delay observer for observing a delay amount; and a power supply voltage controller for controlling a power supply voltage in order to keep the delay amount in a predetermined range. In the semiconductor integrated circuit device, a process which enables the minimization of an operation power is carried out by controlling the threshold voltage to make the ratio of the switching current and the leakage current constant at a given clock frequency and controlling the power supply voltage to guarantee the operating speed.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method of preventing diffusion of copper through a tantalum-comprising barrier layer
InactiveUS20040171250A1Vacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingDevice materialConductive materials
We disclose a method of applying a sculptured layer of material on a semiconductor feature surface using ion deposition sputtering, wherein a surface onto which the sculptured layer is applied is protected to resist erosion and contamination by impacting ions of a depositing layer, said method comprising the steps of: a) applying a first portion of a sculptured layer with sufficiently low substrate bias that a surface onto which said sculptured layer is applied is not eroded away or contaminated in an amount which is harmful to said semiconductor device performance or longevity; and b) applying a subsequent portion of said sculptured layer with sufficiently high substrate bias to sculpture a shape from said the first portion, while depositing additional layer material. The method is particularly applicable to the sculpturing of barrier layers, wetting layers, and conductive layers upon semiconductor feature surfaces and is especially helpful when the conductive layer is copper. In the application of a barrier layer, a first portion of barrier layer material is deposited on the substrate surface using standard sputtering techniques or using an ion deposition plasma, but in combination with sufficiently low substrate bias voltage (including at no applied substrate voltage) that the surfaces impacted by ions are not sputtered in an amount which is harmful to device performance or longevity. Subsequently, a second portion of barrier material is applied using ion deposition sputtering at increased substrate bias voltage which causes resputtering (sculpturing) of the first portion of barrier layer material, while enabling a more anisotropic deposition of newly depositing material. A conductive material, and particularly a copper seed layer applied to the feature may be accomplished using the same sculpturing technique as that described above with reference to the barrier layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Semiconductor integrated circuit device
ActiveUS7659772B2Reduce power consumptionManufacturing process is complexPower consumption reductionElectric pulse generator detailsSwitched currentEngineering
A semiconductor integrated circuit device includes: a switching current observer for observing a switching current; a leakage current observer for observing a leakage current; a comparator which compares the switching current and the leakage current with each other; a threshold voltage controller for controlling a substrate bias voltage in order to make a ratio of the switching current and the leakage current constant; a delay observer for observing a delay amount; and a power supply voltage controller for controlling a power supply voltage in order to keep the delay amount in a predetermined range. In the semiconductor integrated circuit device, a process which enables the minimization of an operation power is carried out by controlling the threshold voltage to make the ratio of the switching current and the leakage current constant at a given clock frequency and controlling the power supply voltage to guarantee the operating speed.
Owner:NEC CORP
Current detection circuit
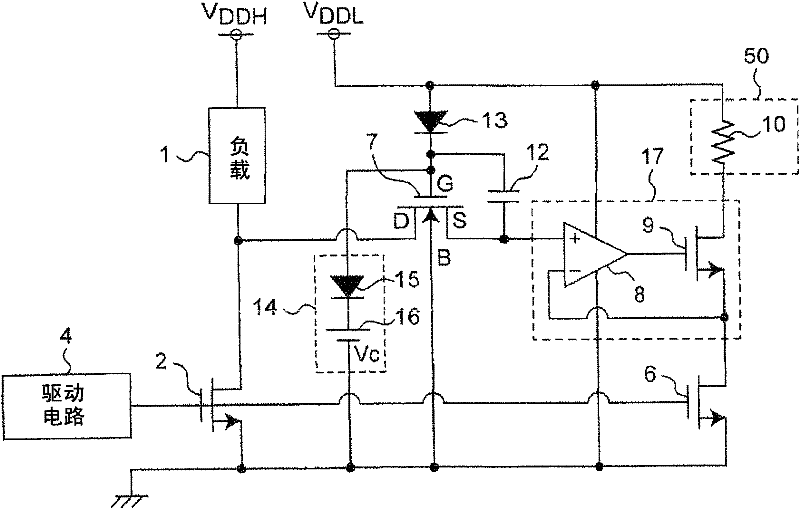
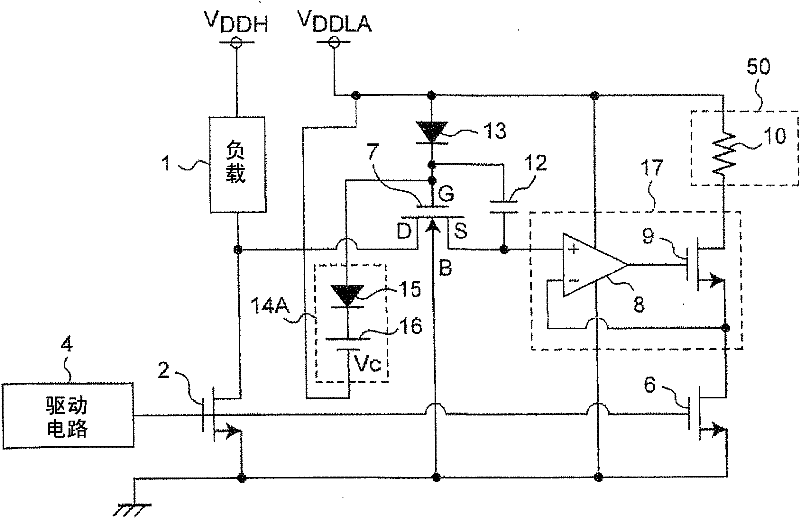
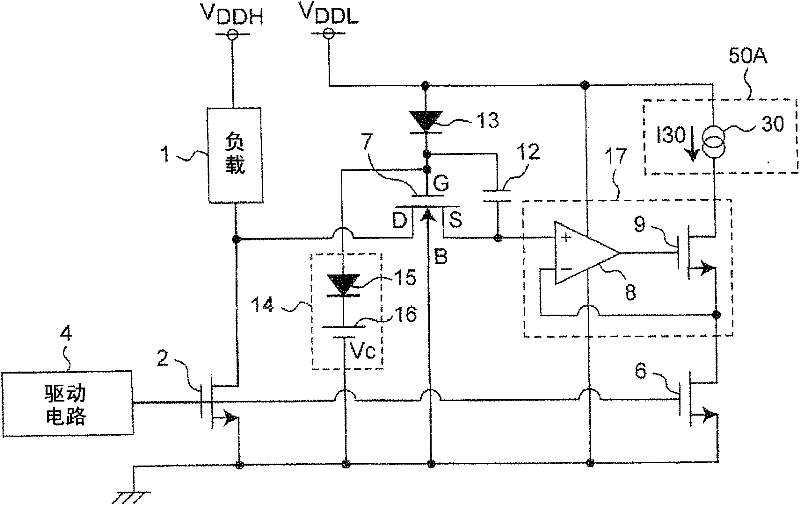
The present invention provides a current detection circuit. Using a electrostatic capacitor (12) and a diode (13), a gate voltage of a protecting MOSFET (7) is increased when a drain voltage of a power transistor (2) increases. A voltage clamp circuit (14) clamps the maximum voltage of the gate voltage of the protecting MOSFET (7)to a predetermined clamp voltage (Vc). A voltage control circuit (17) controls a drain voltage of a sense transistor (6) so as to substantially coincide with a source voltage of the protecting MOSFET (7). A detection circuit (40) detects the current of the drain of the sense transistor (6). Therefore, even if the substrate bias effect occurs in the protecting MOSFET of the current detection circuit of the power transistor, the current of a load is detected precisely by means of a high voltage negatively fed back by the operation amplifier on the basis of satisfying the resistant voltage between the source and gate of the protecting MOSFET.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Semiconductor memory device having the operating voltage of the memory cell controlled
An SRAM circuit which can be operated at a reduced operation margin, especially at a low operating voltage by increasing or optimizing the operation margin of the SRAM circuit. The threshold voltage of the produced transistor in the SRAM circuit is detected to compare the operating voltage of a memory cell with the operating voltage of a peripheral circuit in order to adjust it to the optimum value, and the substrate bias voltage is further controlled.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor integrated circuit
InactiveUS20080174359A1High yieldReduce power consumptionPower consumption reductionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceCMOS
A substrate bias technique is used in an active mode enabling a high yield, and an operating consumption power and the fluctuation of a signal delay in signal processing are reduced in the active mode. The additional PMOS and NMOS of the additional capacitance circuit are produced in the same production process as the PMOSs and the NMOSs of the CMOS circuits. The gate capacitance of the additional PMOS is coupled between the power supply wiring and the N well and the gate capacitance of the additional NMOS is coupled between the ground wiring and the P well. The noise on the power supply wiring is transmitted to the N well through the gate capacitance and the noise on the ground wiring is transmitted to the P well through the gate capacitance. The fluctuation of noise on the substrate bias voltage between the source and the well of PMOS and NMOS of the CMOS circuits is reduced.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Image pickup device capable of adjusting the overflow level of the sensor based on the read out mode
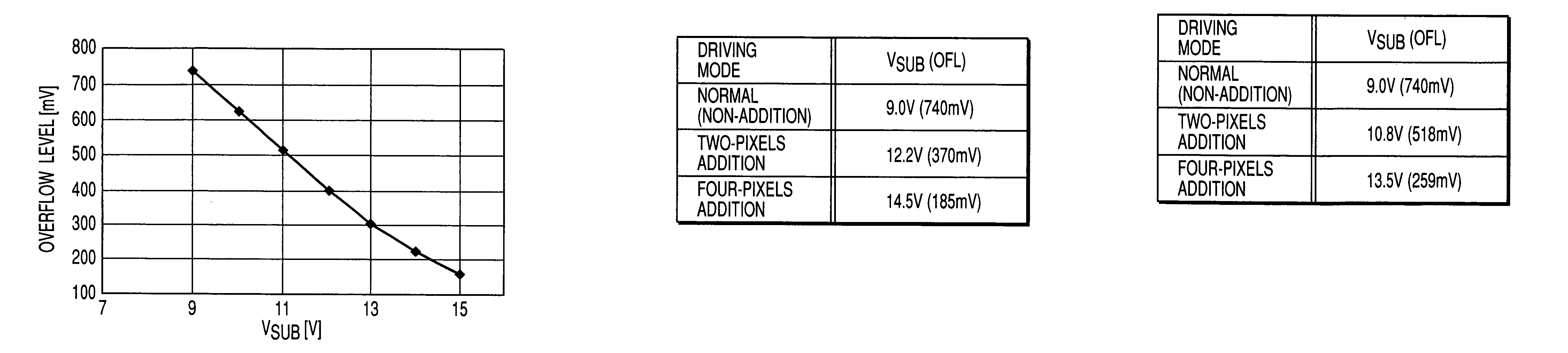
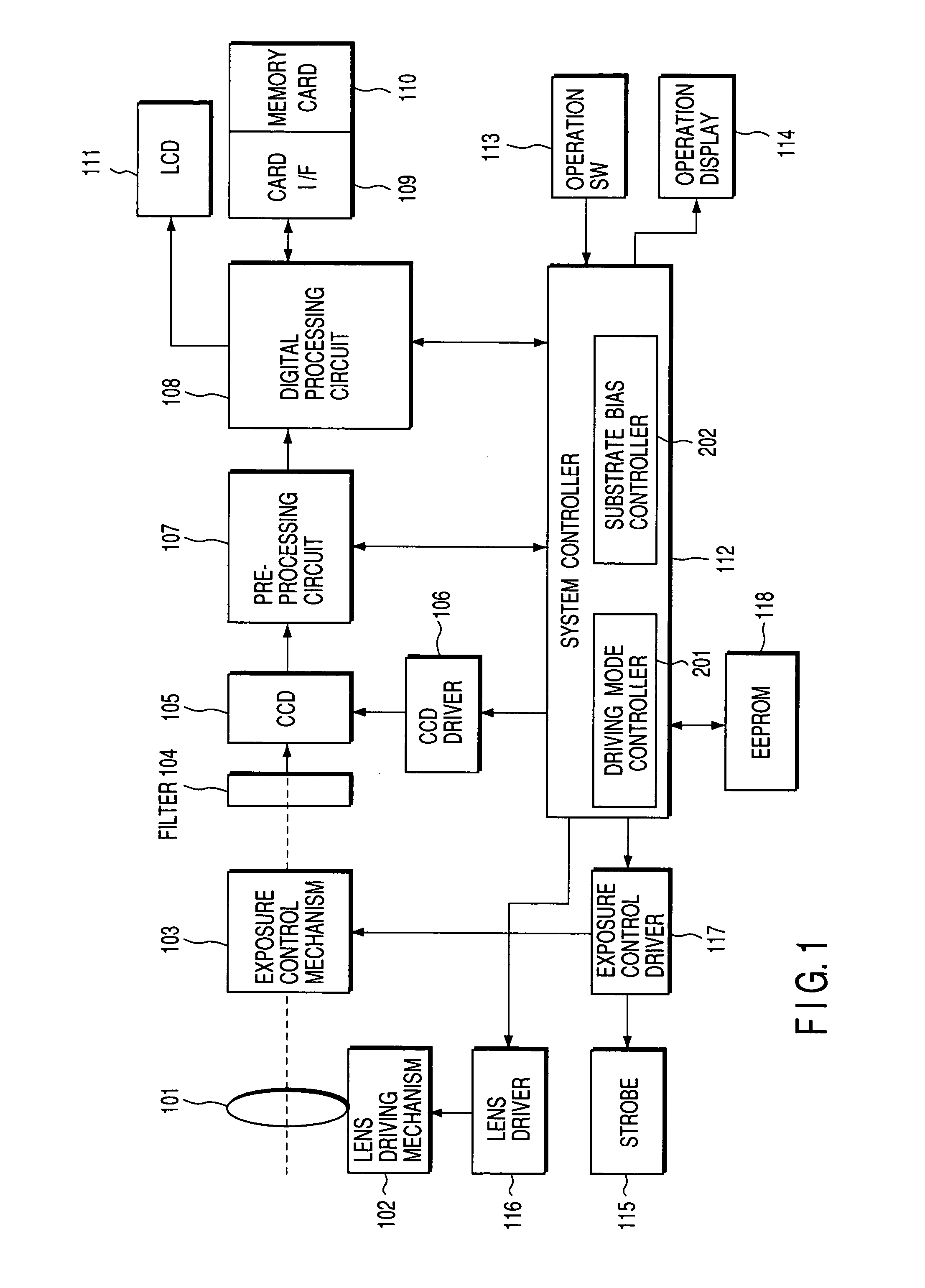
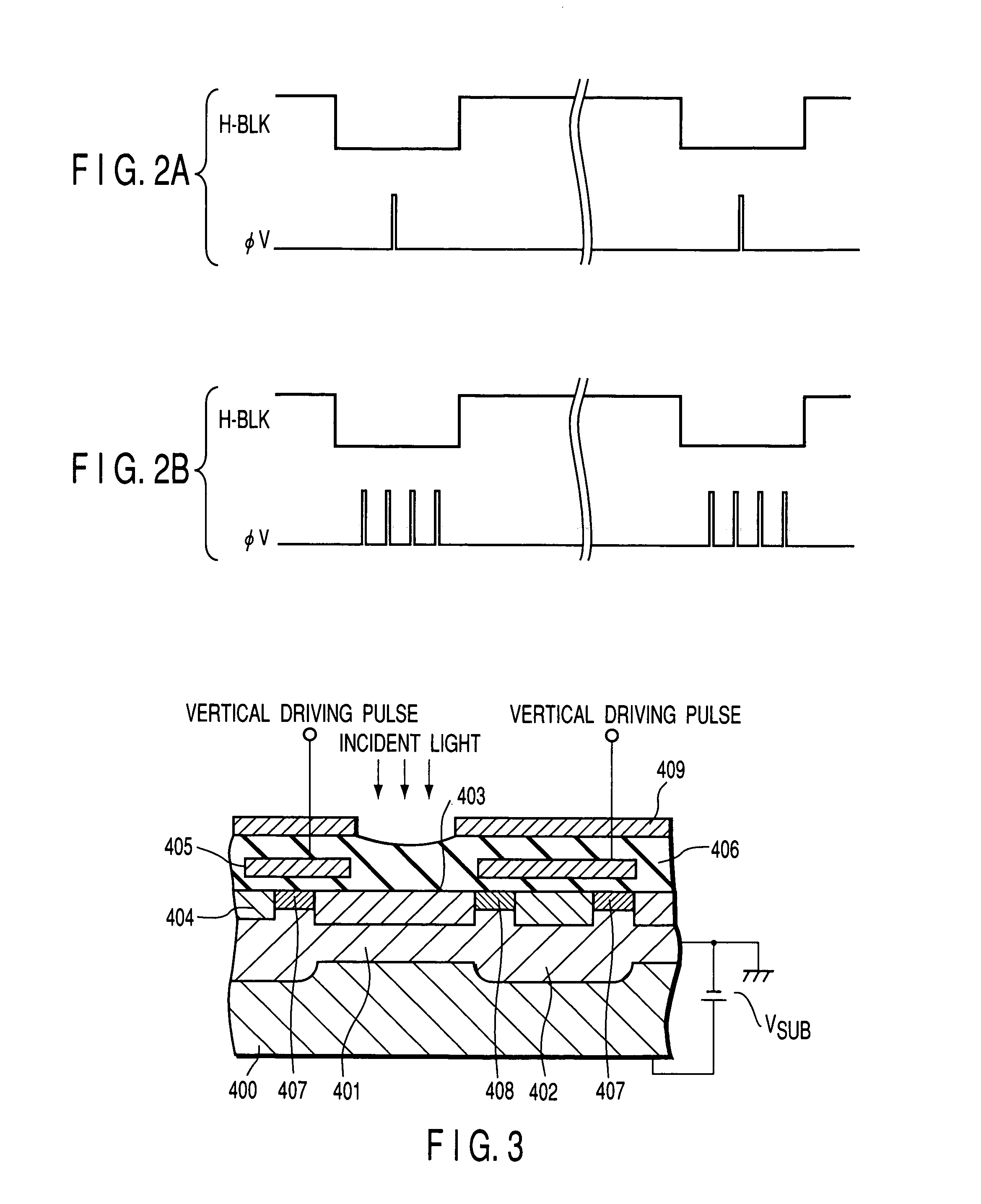
InactiveUS7102680B2Avoid noiseTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsEngineeringSubstrate bias voltage
The driving device of a solid-state imaging device comprises a driving unit for driving the solid-state imaging device in either an addition driving mode in which a plurality of pixels are added and read as a single pixel or a non-addition driving mode, and a substrate bias voltage supply for applying a bias voltage to the substrate of the solid-state imaging device according to the driving mode. The substrate bias voltage is set according to the number of pixels added in the addition driving mode so that the overflow level of the charge accumulating portion may be lower in the addition driving mode than in the normal driving mode. This suppresses the input of excess charges to the horizontal transfer path even in the addition driving mode, thereby preventing the generation of horizontal streak noise.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
AlB2 type WB2 hard coating and preparation technology thereof
InactiveCN104513954AImprove performanceBest friction and wear resistanceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingDeposition temperatureWear resistant
The invention discloses an AlB2 type WB2 hard coating and a preparation technology thereof, and belongs to the technical field of depositing a hard and wear-resistant coating on the surface of a metal material. Through regulating and controlling the coating composition, the deposition temperature, and substrate bias voltage, and adopting a direct current (DC) magnetron sputtering method, a WB2 (AlB2 type) hard and wear-resistant coating can be successfully formed on a high-speed steel or hard alloy substrate. The formed coating has the advantages of high microscopic hardness, low average friction coefficient, and low wear rate. The WB2 (AlB2 type) hard coating is successfully synthesized, thus the hardness and wear-resistant performance of the surfaces of cutters or tools are both prominently improved, and the coating also has an important meaning for theory research and practical application of superhard boride coatings.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Resistance-free reference voltage source
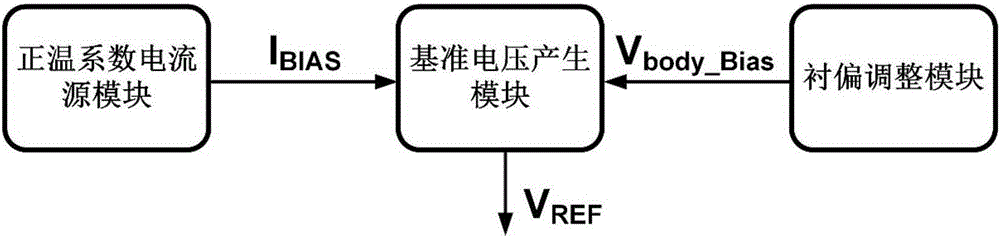
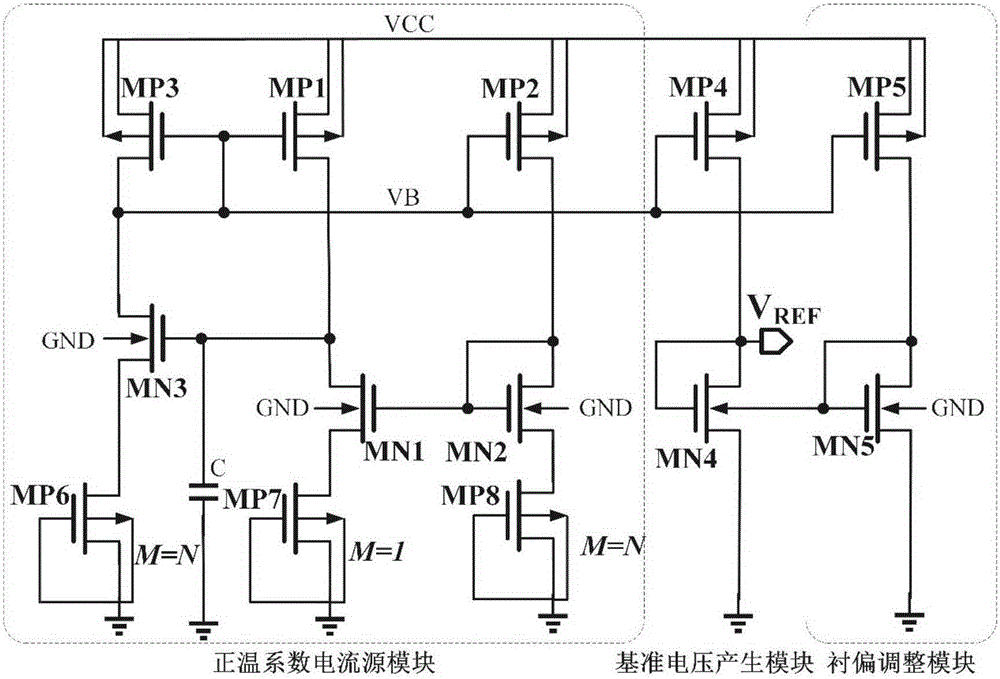
InactiveCN105242738AReduce power consumptionReduce layout areaElectric variable regulationComputational physicsSubstrate bias voltage
The invention belongs to the technical field of power supplies, and particularly relates to a resistance-free reference voltage source. The resistance-free reference voltage source comprises a positive temperature coefficient current source module, a reference voltage generating module and a substrate bias voltage regulation module; the positive temperature coefficient current source module and the substrate bias voltage regulation module are connected with the reference voltage generating module; the positive temperature coefficient current source module generates a positive temperature coefficient current to supply a bias current to an NMOS tube MN4 working in a saturation region; the substrate bias voltage regulation module regulates a substrate bias voltage for the NMOS tube MN4, and the effect of regulating the threshold value is achieved; a grid electrode and a drain electrode of NMOS are connected together to output the referent voltage, and influences of technical fluctuation on reference source output are overcome. The resistance-free reference voltage source has the advantages that the territory area is decreased by adopting a resistance-free technology, a low-reference voltage source is output simultaneously, and the precision of the reference voltage source can be effectively improved.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV OF INFORMATION TECH
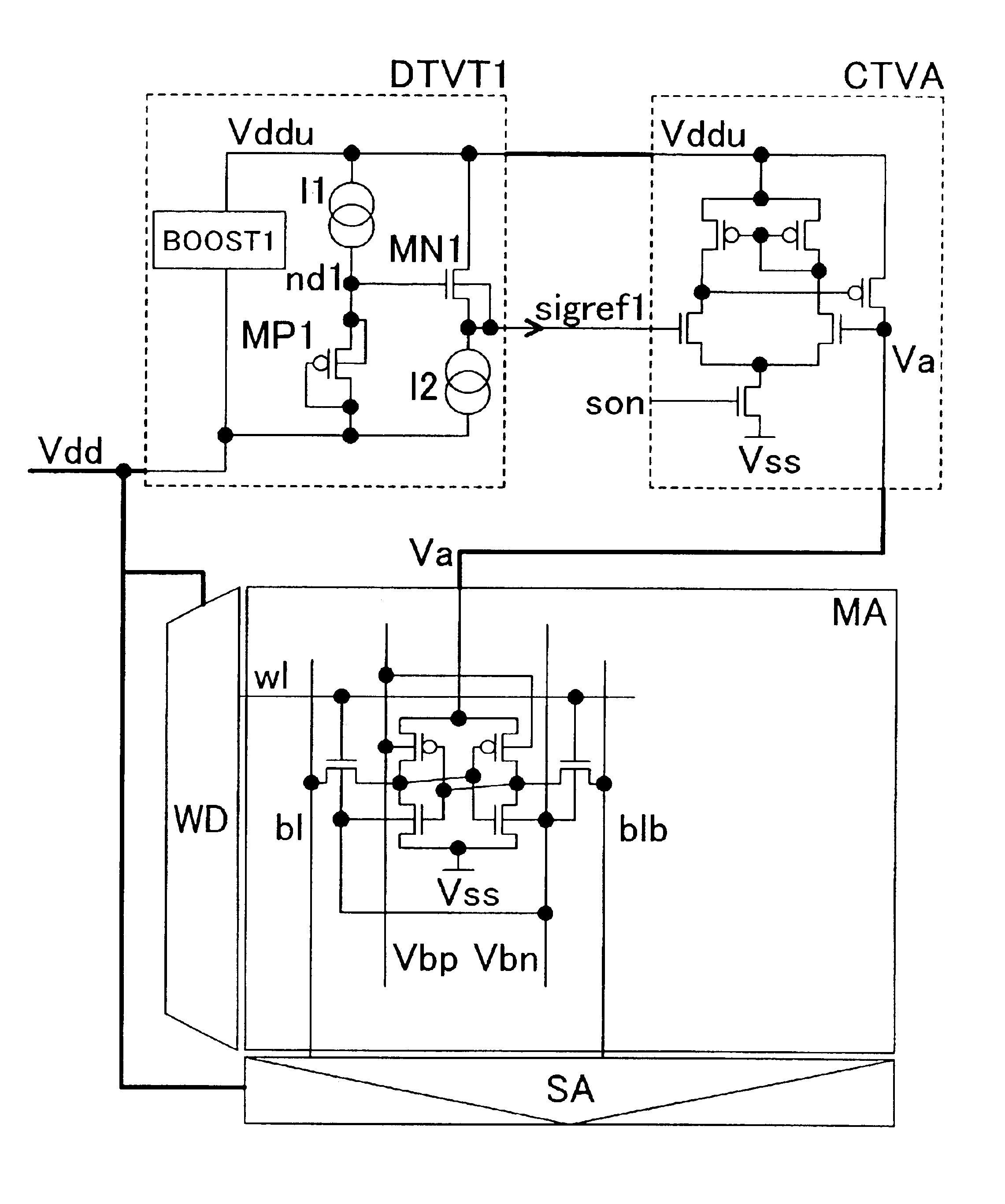
Substrate bias voltage generator and method of generating substrate bias voltage
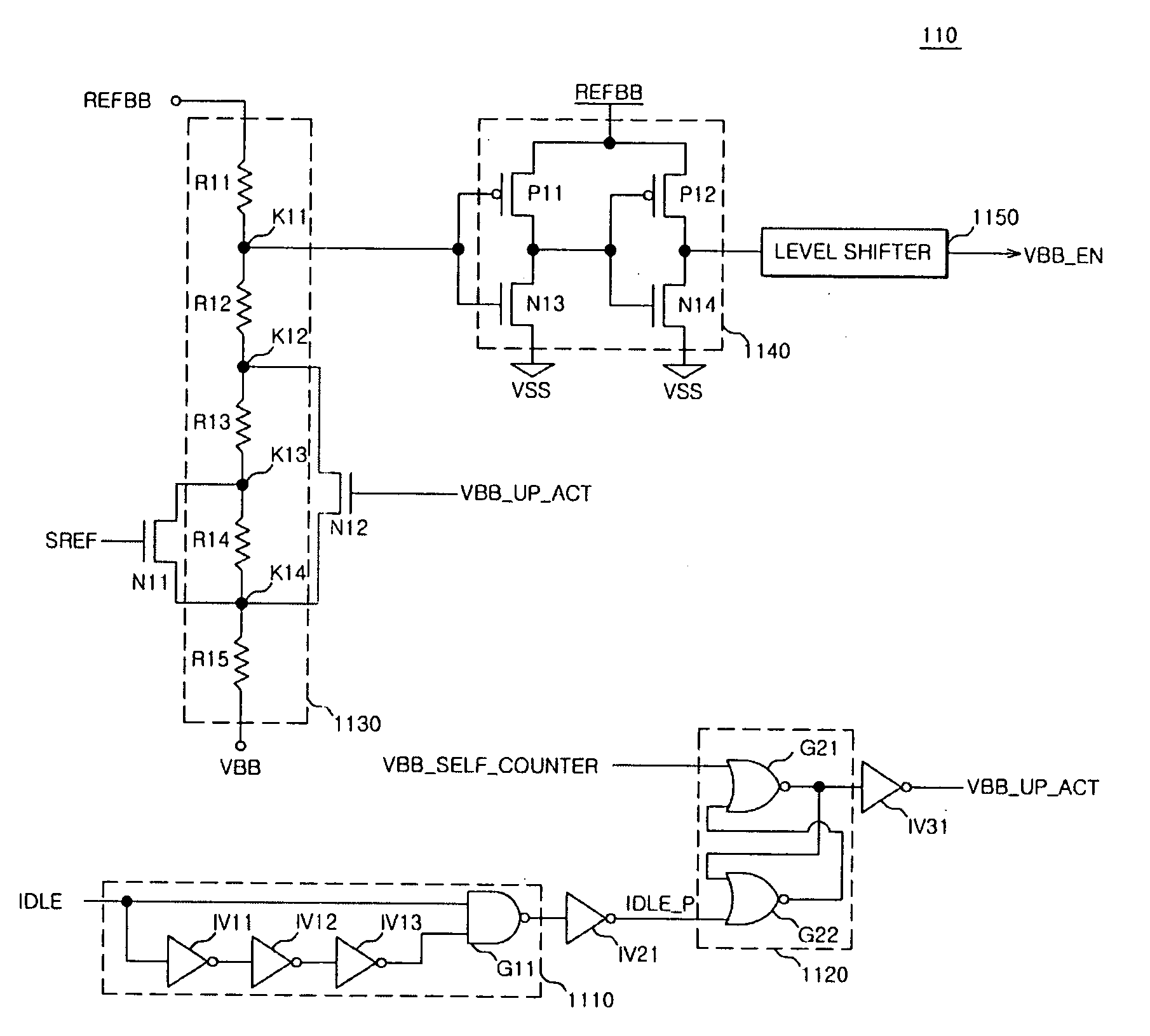
InactiveUS20070153611A1Improve refresh characteristicImprove data storage capabilityDigital storageElectric pulse generator detailsVoltage generatorNormal mode
A substrate bias voltage detection unit compares a level of a substrate bias voltage with a reference voltage in response to a self-refresh signal, an idle signal, and a refresh count signal so as to output an oscillating driving signal, enables the oscillating driving signal when the substrate bias voltage is equal to or higher than a first level in a normal mode, disables the oscillating driving signal when the substrate bias voltage is at a second level in a self-refresh mode, and disables the oscillating driving signal when the substrate bias voltage is at a third level in the self-refresh mode. An oscillation unit outputs an oscillating signal according to the oscillating driving signal. A voltage pumping unit controls pumping of the substrate bias voltage according to an output signal of the oscillation unit and then outputs a pumped substrate bias voltage.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Semiconductor apparatus and complimentary MIS logic circuit
InactiveUS20060186472A1Reduce power consumptionRun at high speedTransistorSolid-state devicesCapacitanceImpurity diffusion
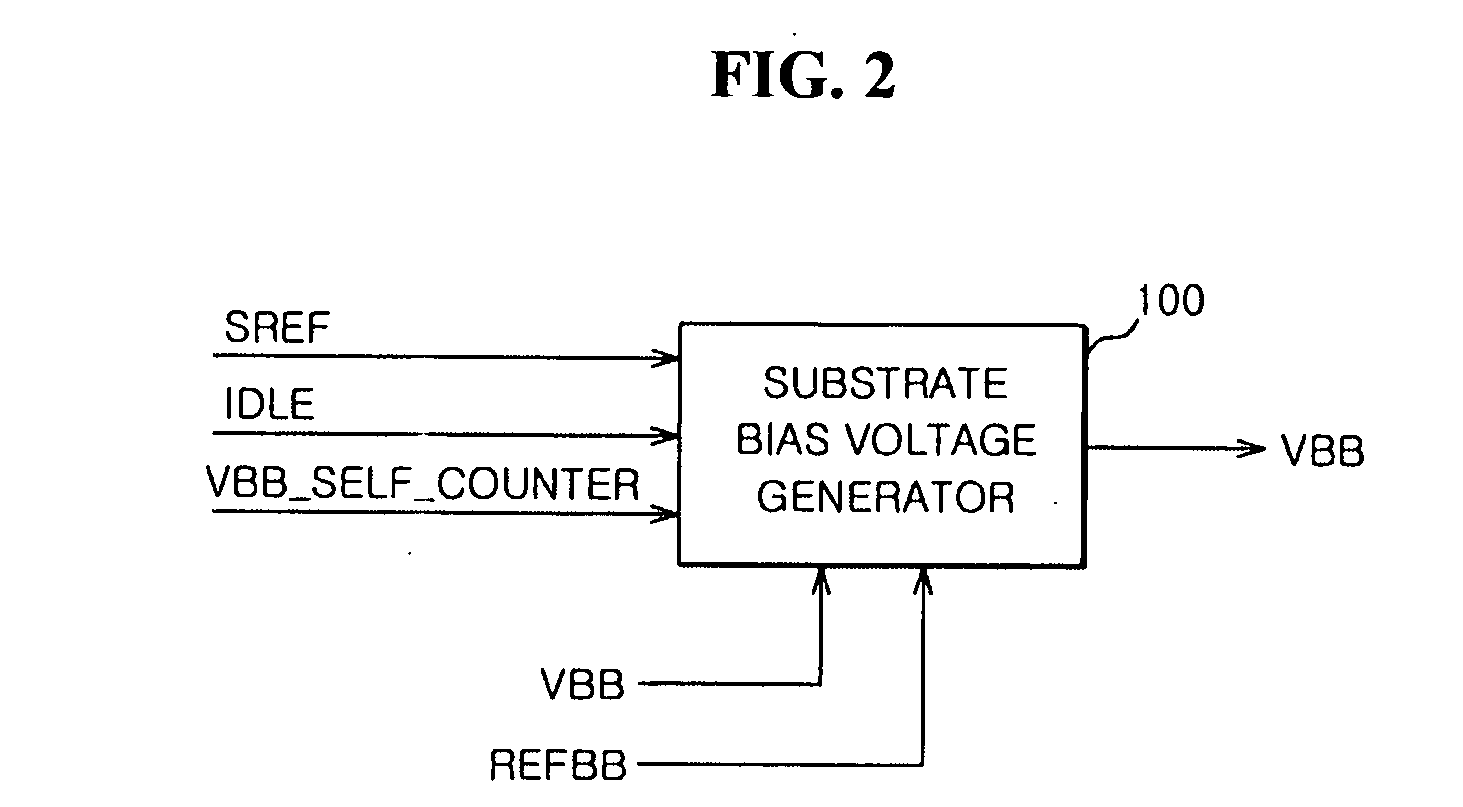
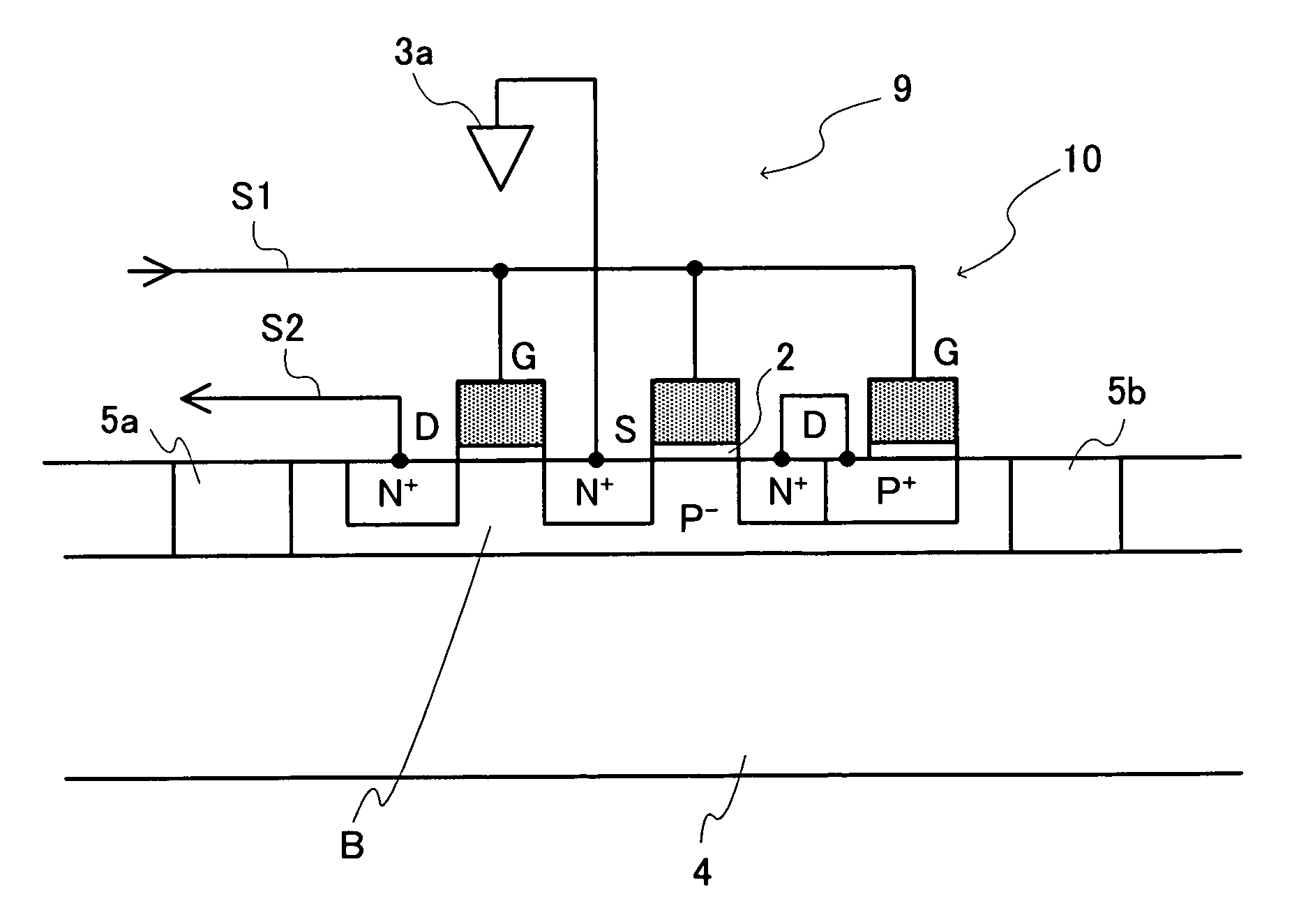
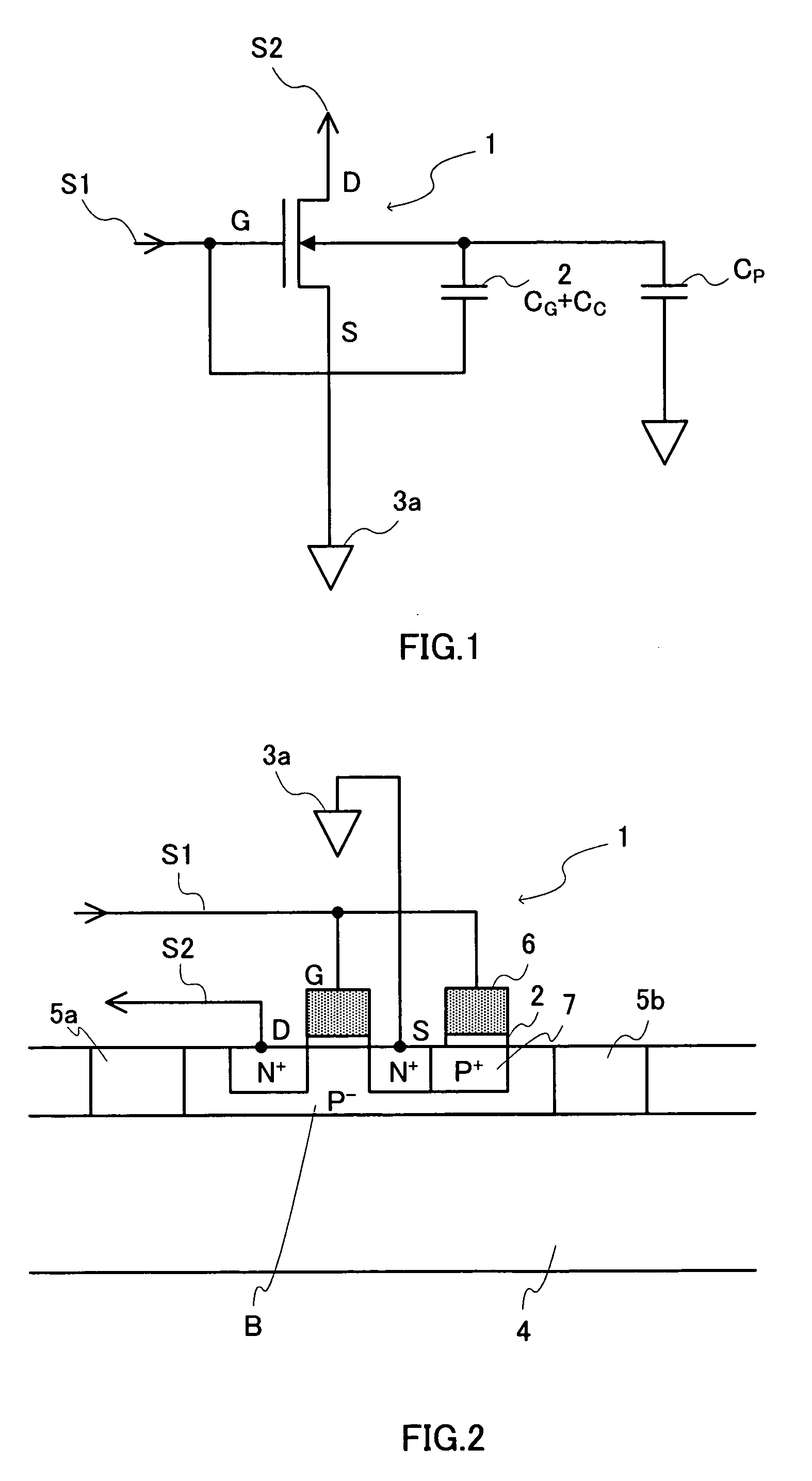
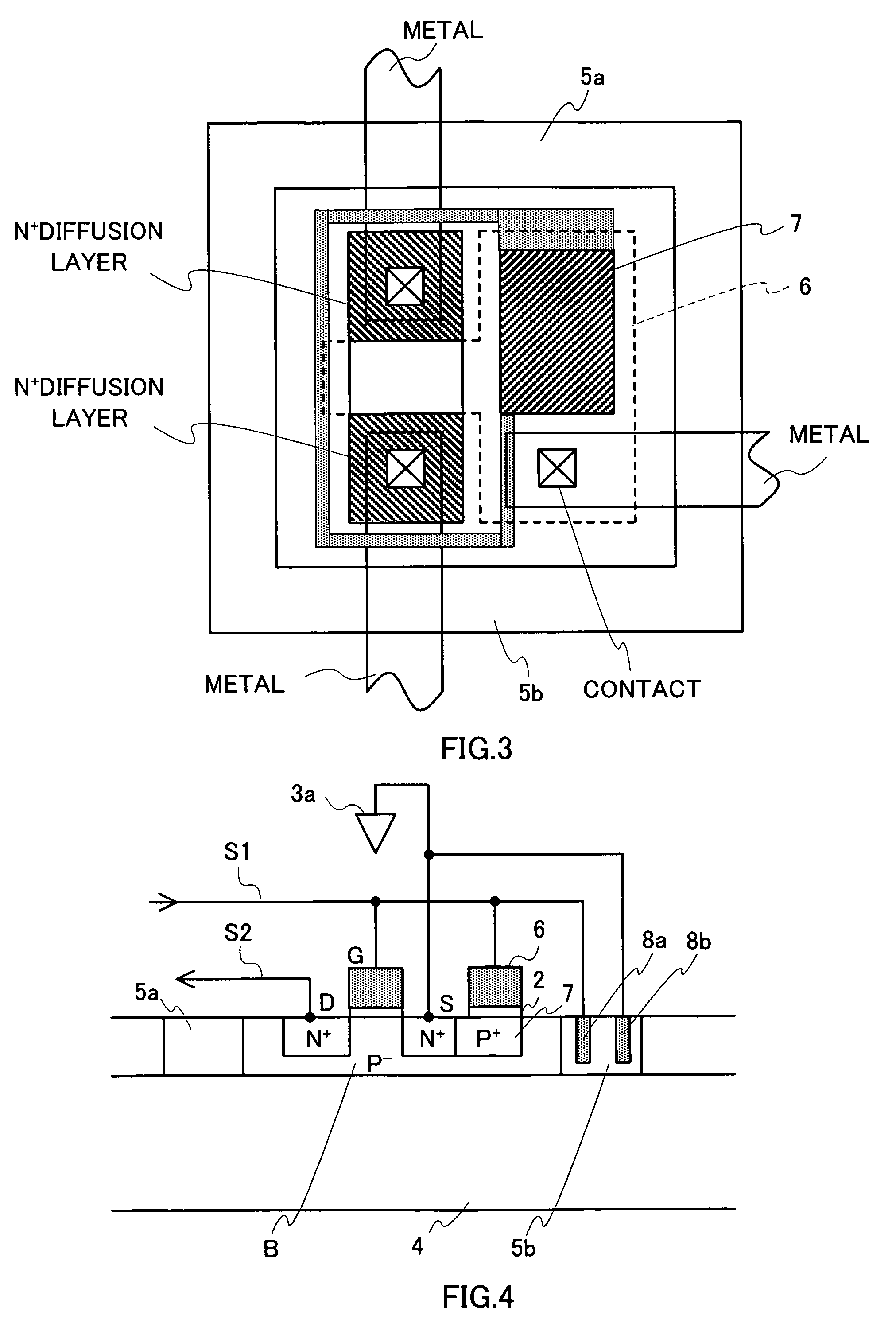
A configuration is adopted comprising an NchMOS transistor 1 equipped with an insulating isolation layer 4 providing insulation and isolation using an SOI structure, and a capacitor formed using an insulating film, with a silicon substrate B being made thin and substrate capacitance being reduced. The NchMOS transistor 1 is equipped with insulating isolation regions 5a, 5b that are perfectly depleted or partially depleted in a manner close to being perfectly depleted. An electrode 6 connected to a gate electrode G of the NchMOS transistor 1 and an impurity diffusion layer 7 are connected via a capacitor 2. A source electrode S is connected to a power supply terminal 3a, a gate electrode G is connected to an internal signal line S1, and a drain electrode D is connected to an internal signal line S2. Substrate bias voltage is then controlled using capacitor coupling when the NchMOS transistor 1 is turned on / off.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
Reduction of leakage current and program disturbs in flash memory devices
InactiveUS20070247907A1Reduce diffusion of electronReduce in quantityRead-only memoriesDigital storageBit lineEngineering
A flash memory system configured in accordance with an example embodiment of the invention employs a virtual ground array architecture. During programming operations, target memory cells are biased with a negative substrate bias voltage to reduce or eliminate leakage current that might otherwise conduct through the target memory cells. The negative substrate bias voltage also reduces the occurrence of program disturbs in cells adjacent to target cells by extending the depletion region deeper below the bit line that corresponds to the drain of the target device. The negative substrate bias voltage may also be applied to target memory cells during verification operations (program verify, soft program verify, erase verify) to reduce or eliminate leakage current that might otherwise introduce error in the verification operations.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
Semiconductor integrated circuit apparatus
InactiveUS6946865B2Raise the threshold voltageDecreasing drain voltagePower reduction by control/clock signalElectronic circuit testingSubstrate bias voltageControl circuit
A semiconductor integrated circuit apparatus includes a first controlled circuit halving at least one MOS transistor and a substrate bias control unit for generating a substrate bias voltage of the MOS transistor, wherein when the substrate bias control unit is set in a first mode, a comparatively large current is allowed to flow between the source and drain of the MOS transistor, while when the substrate bias control unit is set in a second mode, the comparatively large current allowed to flow between the source and drain of the MOS transistor is controlled to a current of smaller value. The value of the substrate bias applied to the first controlled circuit is larger in the second mode than in the first mode for the substrate bias of the PMOS transistor, and smaller in the second mode than in the first mode for the substrate bias of the NMOS transistor. The power supply voltage applied to the first controlled circuit is controlled to a smaller value in the second mode than in the first mode.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
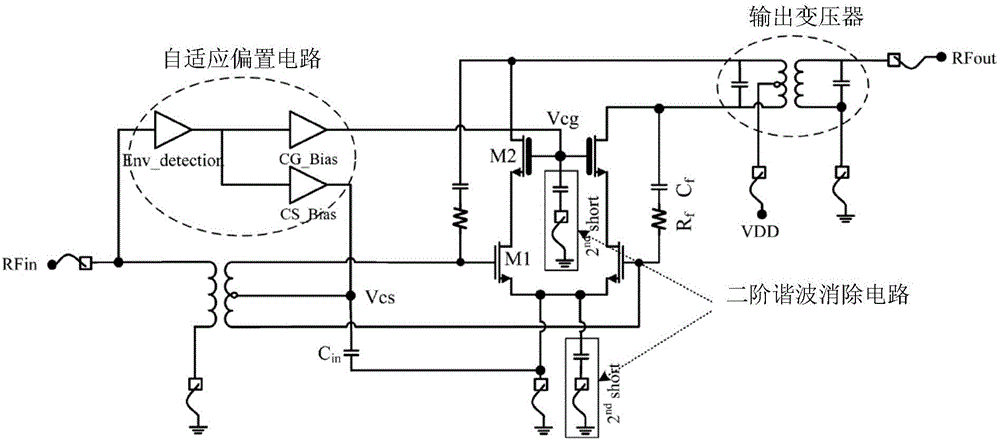
CMOS power amplifier with high linearity
ActiveCN106712729AImprove linearityImprove efficiencyAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionPower amplifiersAudio power amplifierSubstrate bias voltage
The invention discloses a CMOS power amplifier with high linearity. The CMOS power amplifier comprises an amplifier unit and an envelope detection unit. The amplifier unit comprises one or more power transistors used for performing power amplification on input signals to obtain output signals. The envelope detection unit detects the input signals of the power transistors and generates envelope signals to serve as substrate bias voltages of the corresponding power transistors. According to the CMOS power amplifier disclosed by the invention, as the substrate voltages of the power transistors are adjusted by the envelope signals of the input signals of the power transistors, the linearity of the power amplifier can be effectively improved, and compared with the prior art of adjusting the grid voltages or supply voltages of the power transistors by adopting the envelope signals, the linearity is improved more effectively. The CMOS power amplifier further has a certain effect of improving the efficiency of the power amplifier.
Owner:RDA MICROELECTRONICS SHANGHAICO LTD
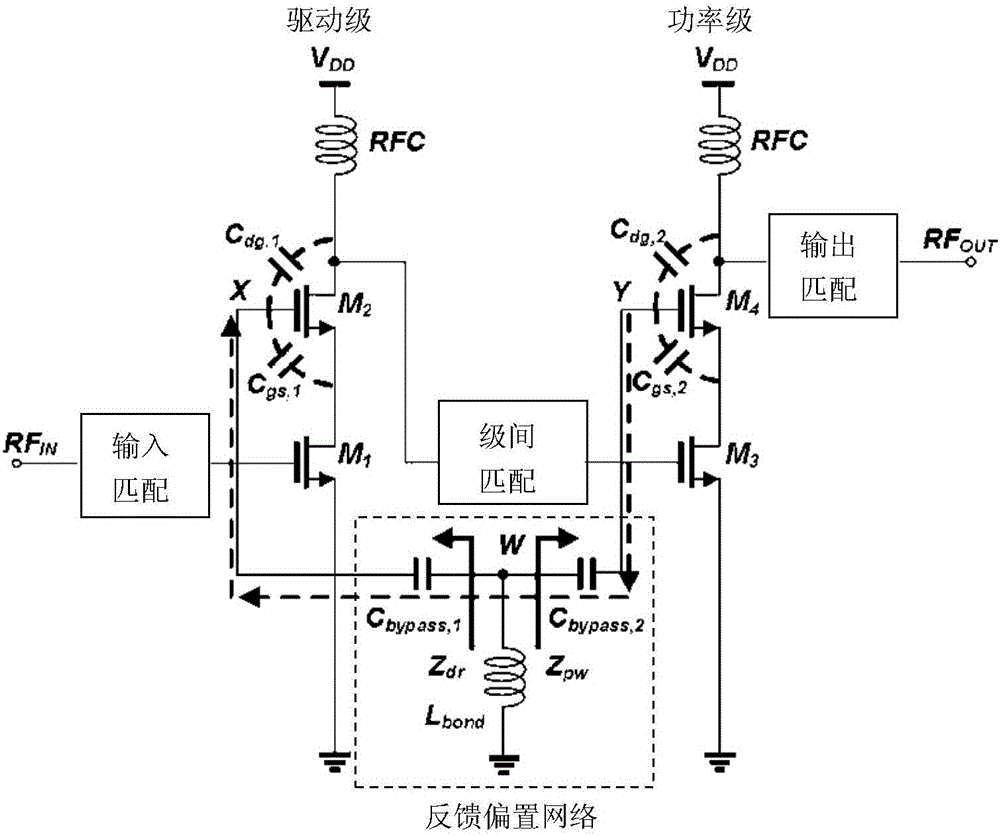
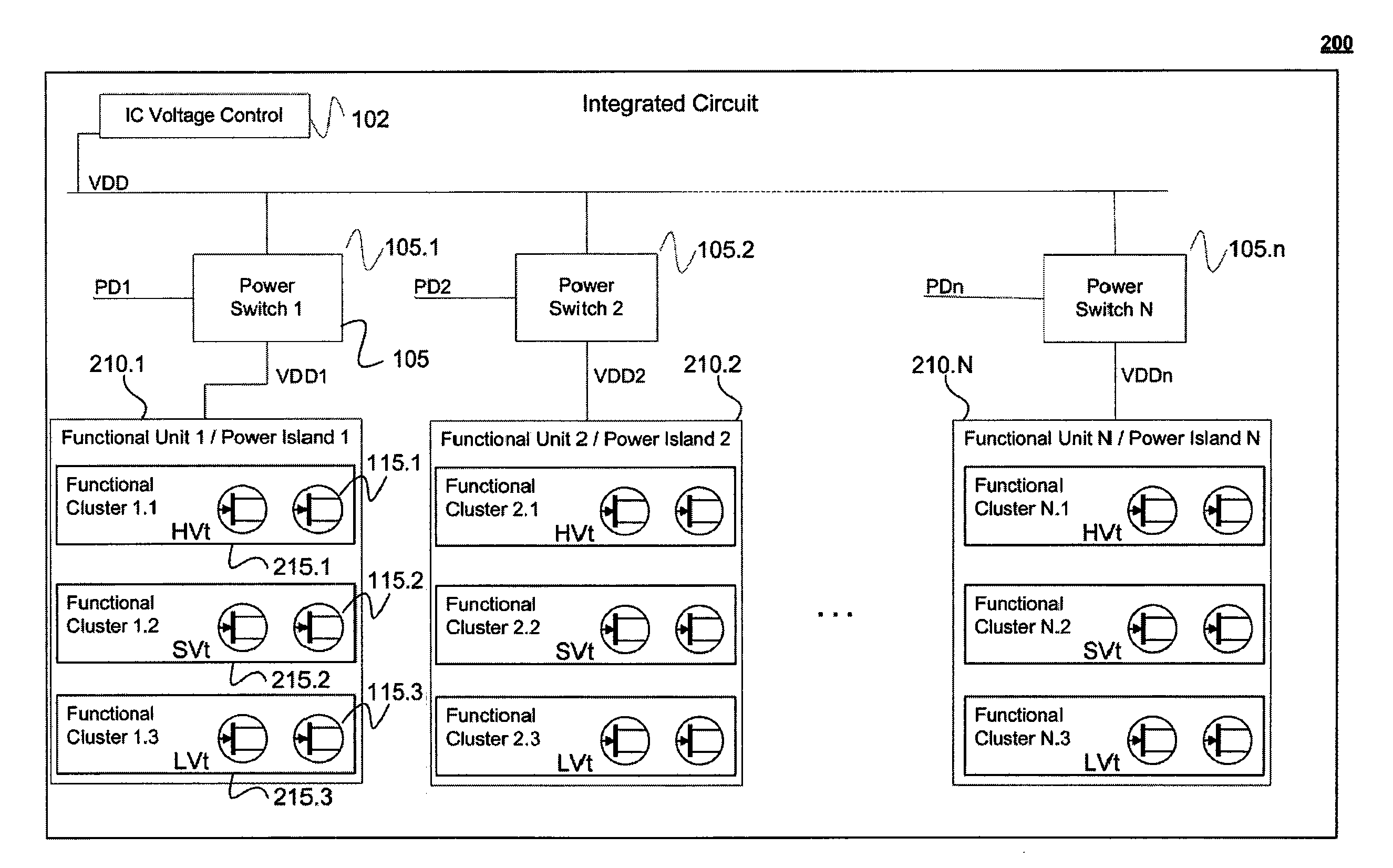
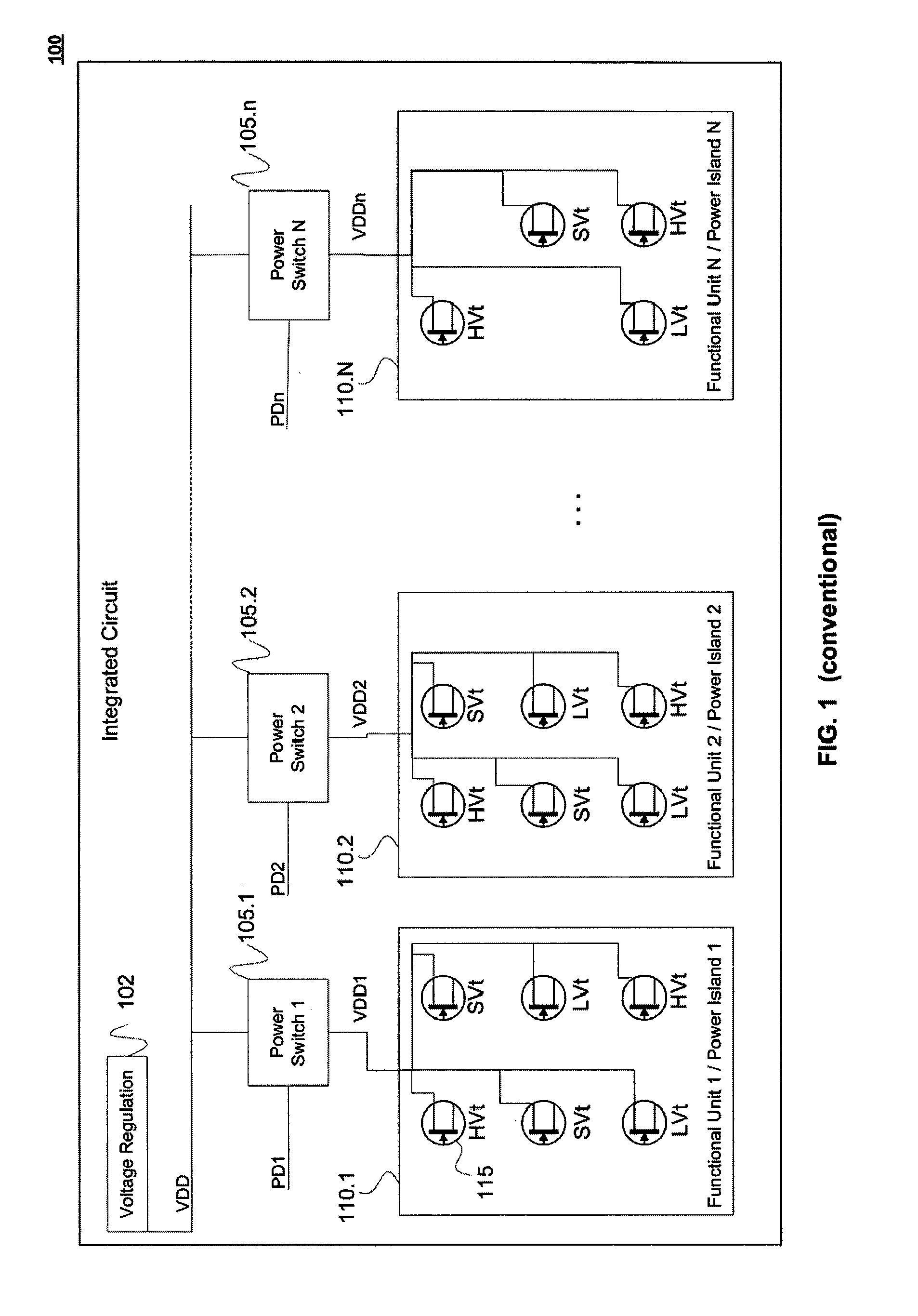
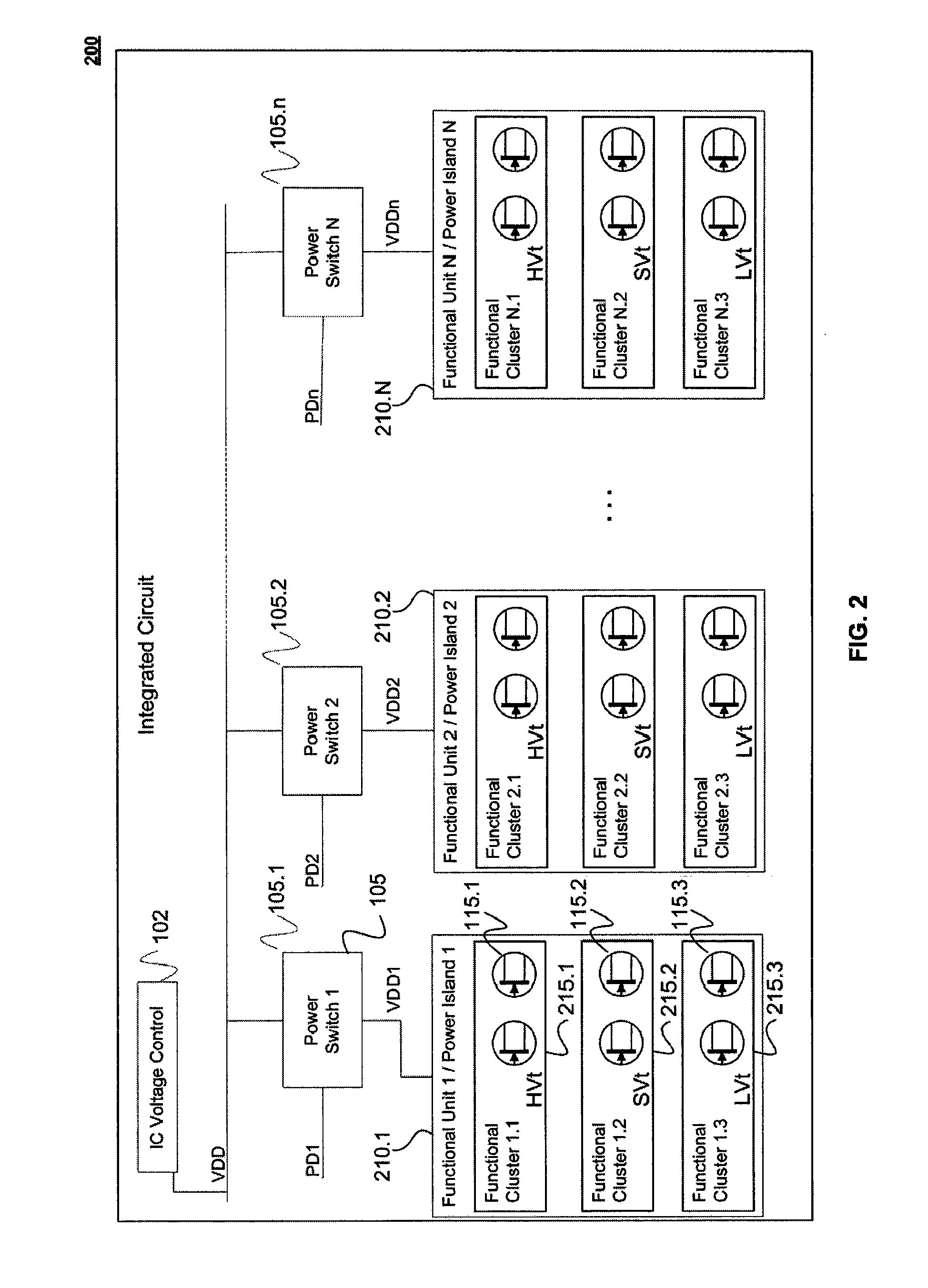
Integrated Circuit with Modular Dynamic Power Optimization Architecture
ActiveUS20100005328A1Reduce power supply voltageReduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementComputer moduleModularity
A system and method for regulating power consumption within an integrated circuit (IC) with a modular design. The IC is designed so that any one distinct functional module within the IC utilizes only transistors with a substantially same or similar critical voltage level, which may for example be the threshold voltage of the transistors. Consequently, the supply voltage delivered to each functional modules can be lowered to the minimum voltage necessary to enable the transistors within the module to operate. Similarly, modules within the IC may be designed with transistors which share a common value for a substrate bias voltage or a clock speed, or with a combination of common values for several electrical factors. In this way, it is possible to reduce power consumption by fine-tuning the voltages supplied to (or clock speeds driving) specific modules, in a way which is custom-tuned to each module.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Semiconductor memory device having the operating voltage of the memory cell controlled
An SRAM circuit operates at a reduced operation margin, especially at a low operating voltage by increasing or optimizing the operation margin of the SRAM circuit. The threshold voltage of the produced transistor in the SRAM circuit is detected to compare the operating voltage of a memory cell with the operating voltage of a peripheral circuit in order to adjust it to the optimum value, and the substrate bias voltage is further controlled.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Methods of applying substrate bias to SOI CMOS circuits
InactiveUS7479418B2Reduce the differenceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSSoi cmos
The present invention relates to methods for reducing the threshold voltage difference between an n-type field effect transistor (n-FET) and a p-type field effect transistor (p-FET) in a complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) circuit located on a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) substrate. Specifically, a substrate bias voltage is applied to the CMOS circuit for differentially adjusting the threshold voltages of the n-FET and the p-FET. For example, a positive substrate bias voltage can be used to reduce the threshold voltage of the n-FET but increase that of the p-FET, while a negative substrate bias voltage can be used to increase the threshold voltage of the n-FET but reduce that of the p-FET. Further, two or more substrate bias voltages of different magnitudes and / or directions can be used for differentially adjusting the n-FET and p-FET threshold voltages in two or more different CMOS circuits or groups of CMOS circuits.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Semiconductor integrated circuit device and wearable device
ActiveUS20160180923A1Efficient processIncrease the number of mountsTransistorSolid-state devicesSubstrate bias voltageSystem controller
To provide a semiconductor device which can be stably operated while achieving a reduction of the power consumption.A semiconductor device includes a CPU, a system controller which designates an operation speed of the CPU, P-type SOTB transistors, and N-type SOTB transistors. The semiconductor device is provided with an SRAM which is connected to the CPU, and a substrate bias circuit which is connected to the system controller and is capable of supplying substrate bias voltages to the P-type SOTB transistors and the N-type SOTB transistors. Here, when the system controller designates a low speed mode to operate the CPU at a low speed, the substrate bias circuit supplies the substrate bias voltages to the P-type SOTB transistors and the N-type SOTB transistors.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Current multiplexing low noise amplifier
ActiveCN104539242AThird-order transconductance reduction or eliminationImprove linearityAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceEngineeringLinearity
The invention discloses a current multiplexing low noise amplifier. The current multiplexing low noise amplifier comprises three amplifying circuits in cascaded connection, corresponding biasing circuits and an output circuit, wherein a first-stage amplifying circuit is taken as an input stage and consists of a source degeneration inductance common-source amplifier; a third-stage amplifying circuit is taken as an output stage and comprises a linear compensating circuit; a second NMOS (N-channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor) tube is taken as a main amplifier; a third NMOS tube is a linear compensating tube; the gates and the drains of the two NMOS tubes are connected in parallel together respectively; the gate-source voltages of the two NMOS tubes are the same and a substrate electrode of the third NMOS tube is connected with a substrate bias voltage, so that the second NMOS tube works in a saturation region while the third NMOS tube works in a sub-threshold region and a third-order trans-conductance coefficient of the output-stage amplifying circuit is decreased or eliminated through the mutual cancelling of a positive third-order trans-conductance coefficient in the sub-threshold region and a negative third-order trans-conductance coefficient in the saturation region. Through adoption of the current multiplexing low noise amplifier, the gain can be increased; the power consumption is lowered; a high noise coefficient is achieved; and the linearity can be enhanced.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Copper nanowire / copper film composite structure and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102345096AAvoid destructionAvoid pollutionVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSurface plasmonSubstrate bias voltage
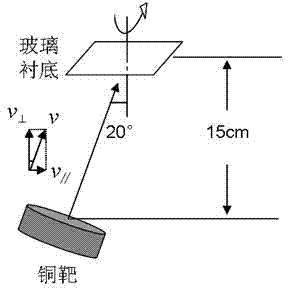
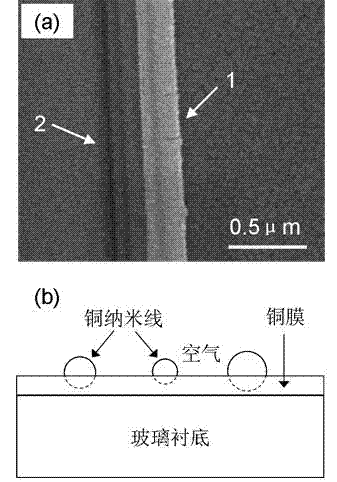
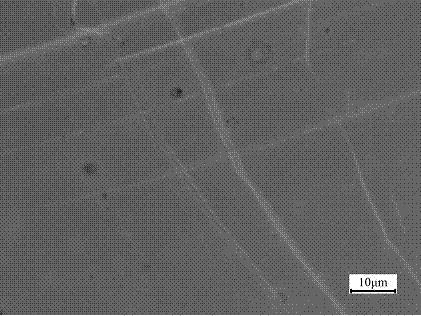
The invention provides a copper nanowire / copper film composite structure and a preparation method thereof, and aims to provide a copper nanowire / copper film composite structure and a magnetron sputtering preparation method thereof. The invention employs a small deposition angle direct current magnetron sputtering deposition technology and prepares a copper nanowire / copper film composite structure on a glass substrate by proper adjusting of film thickness, substrate temperature and substrate bias voltage. The copper nanowire / copper film composite structure provided by the invention has smooth copper nanowire surface, uniform radial thickness, a length of 0.1-5mm, a diameter of 100-500nm and a copper film thickness of 50-100nm. The copper nanowire is parallel to the copper film surface and embedded in the copper film with a thickness less than that of the copper nanowire. According to the invention, metal copper film surface is embedded with sub-wavelength copper nanowire, which has potential application prospect infields related to surface plasma.
Owner:溧阳常大技术转移中心有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com