Patents
Literature
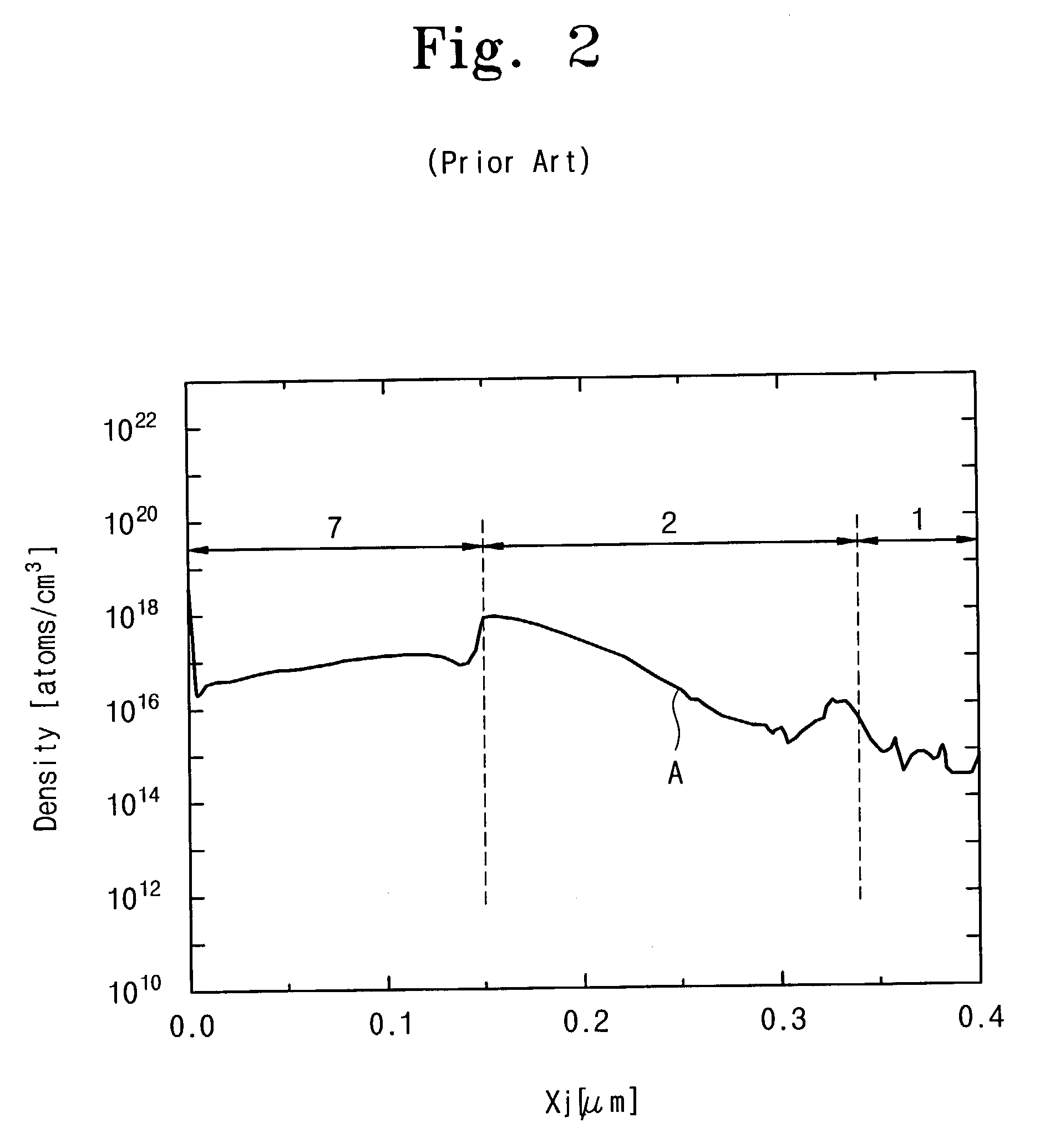
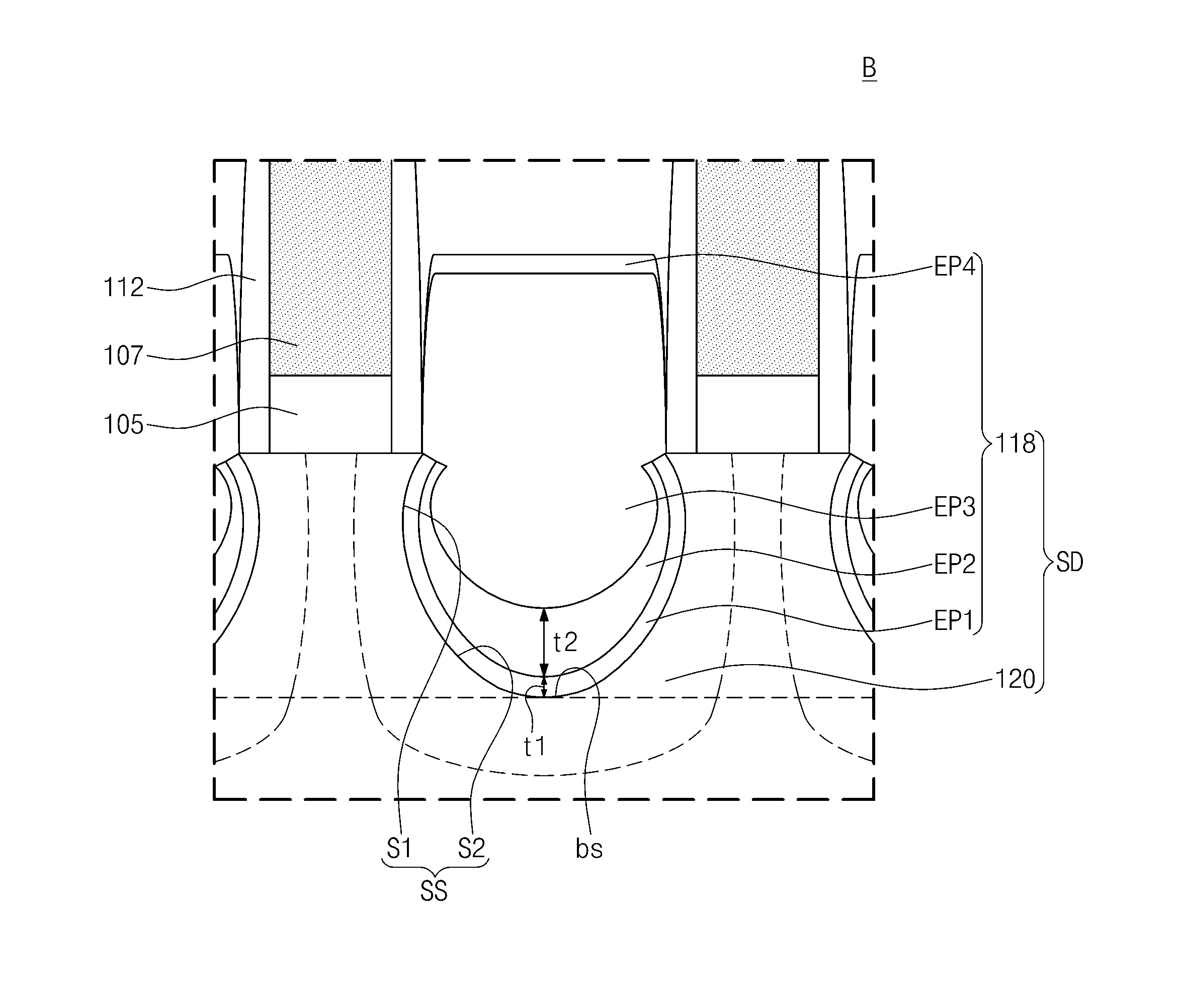
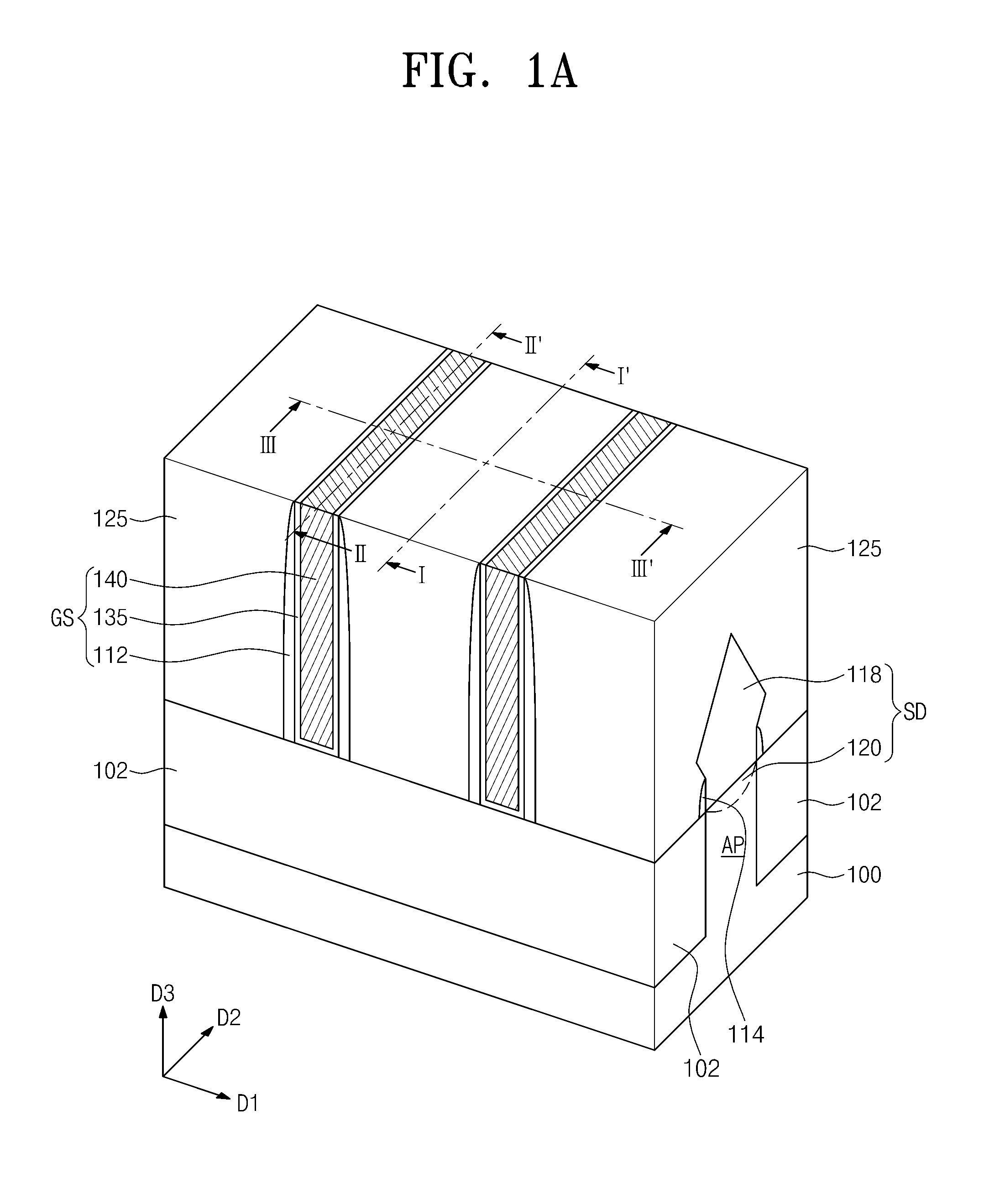
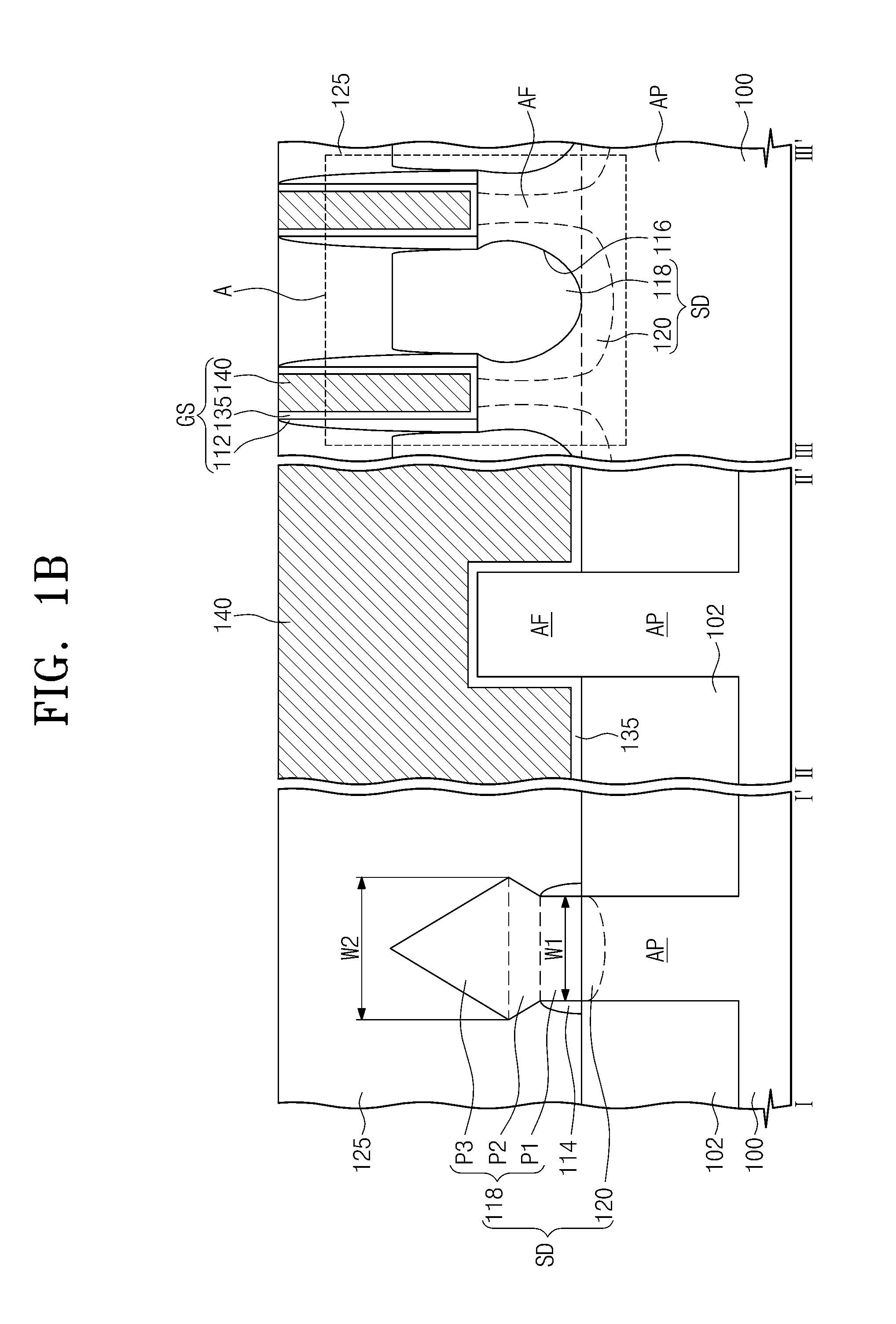
754 results about "Impurity diffusion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
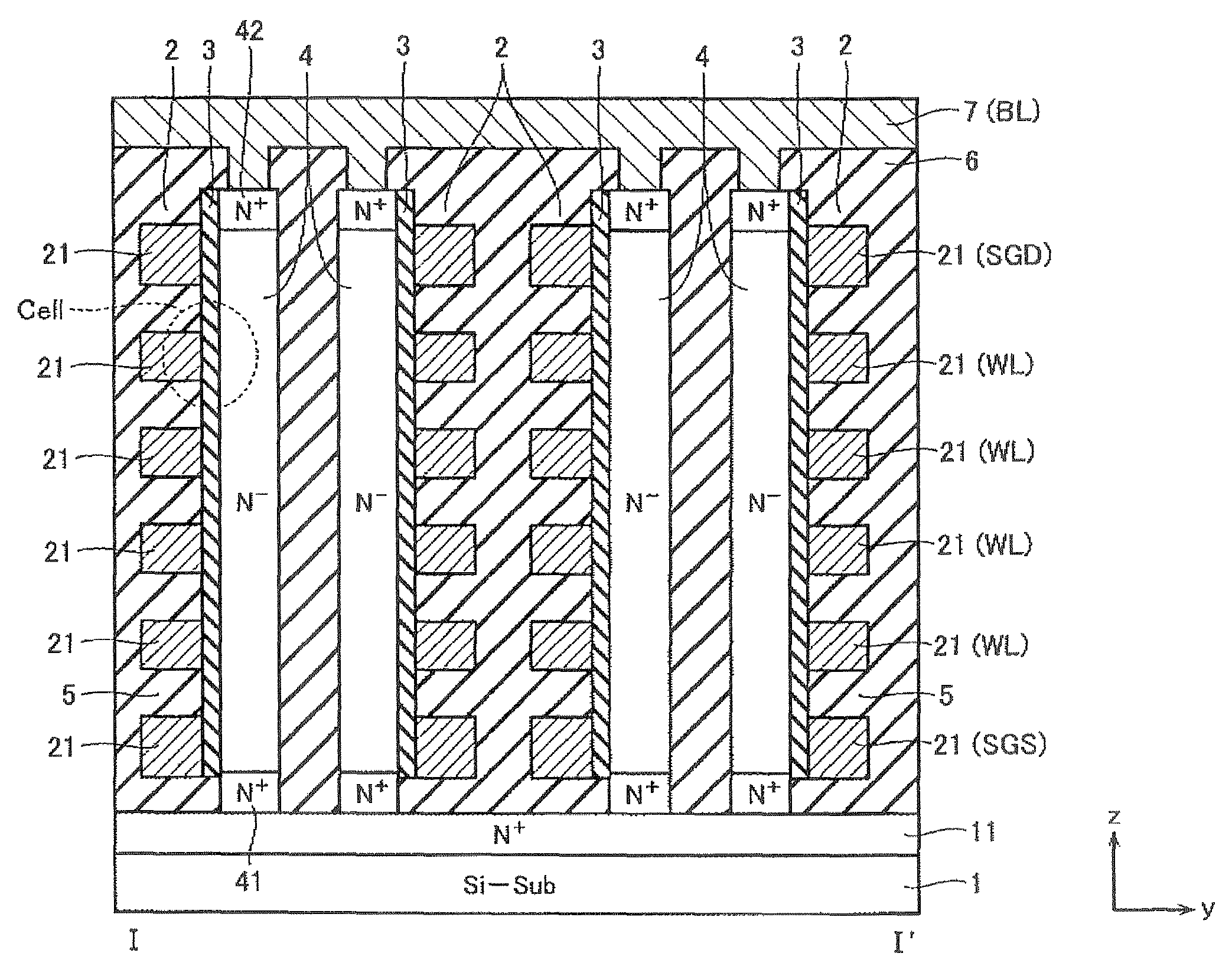
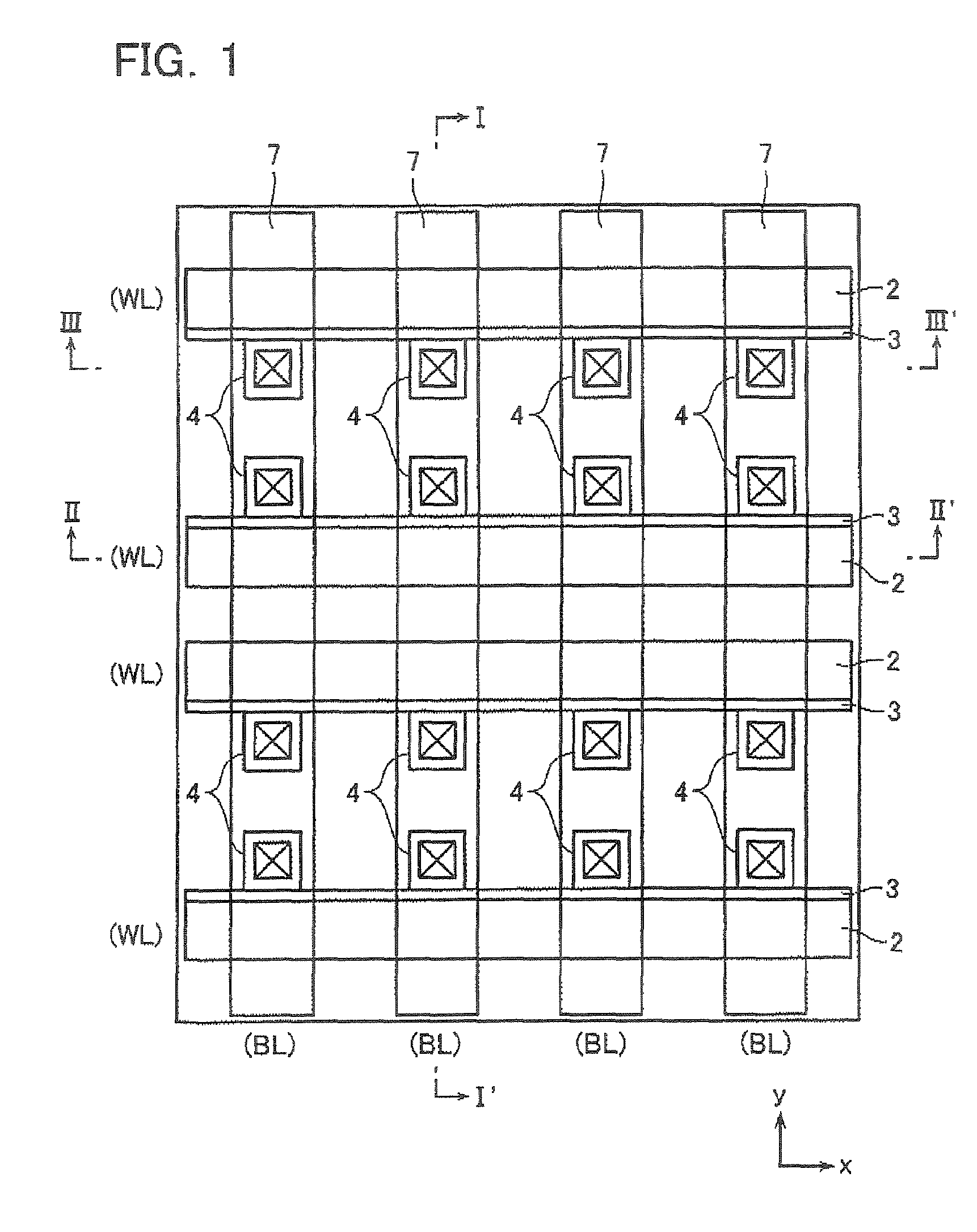
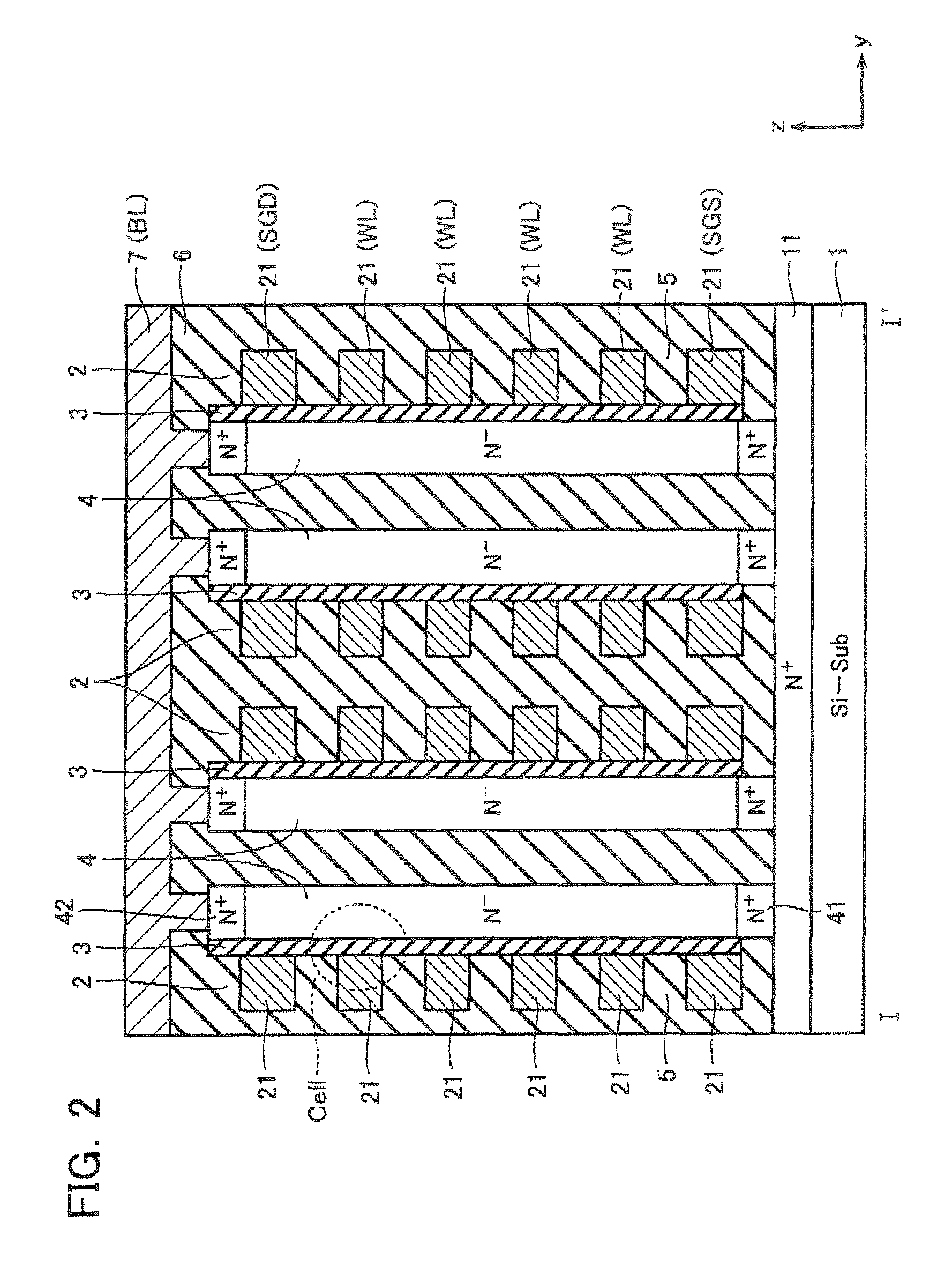
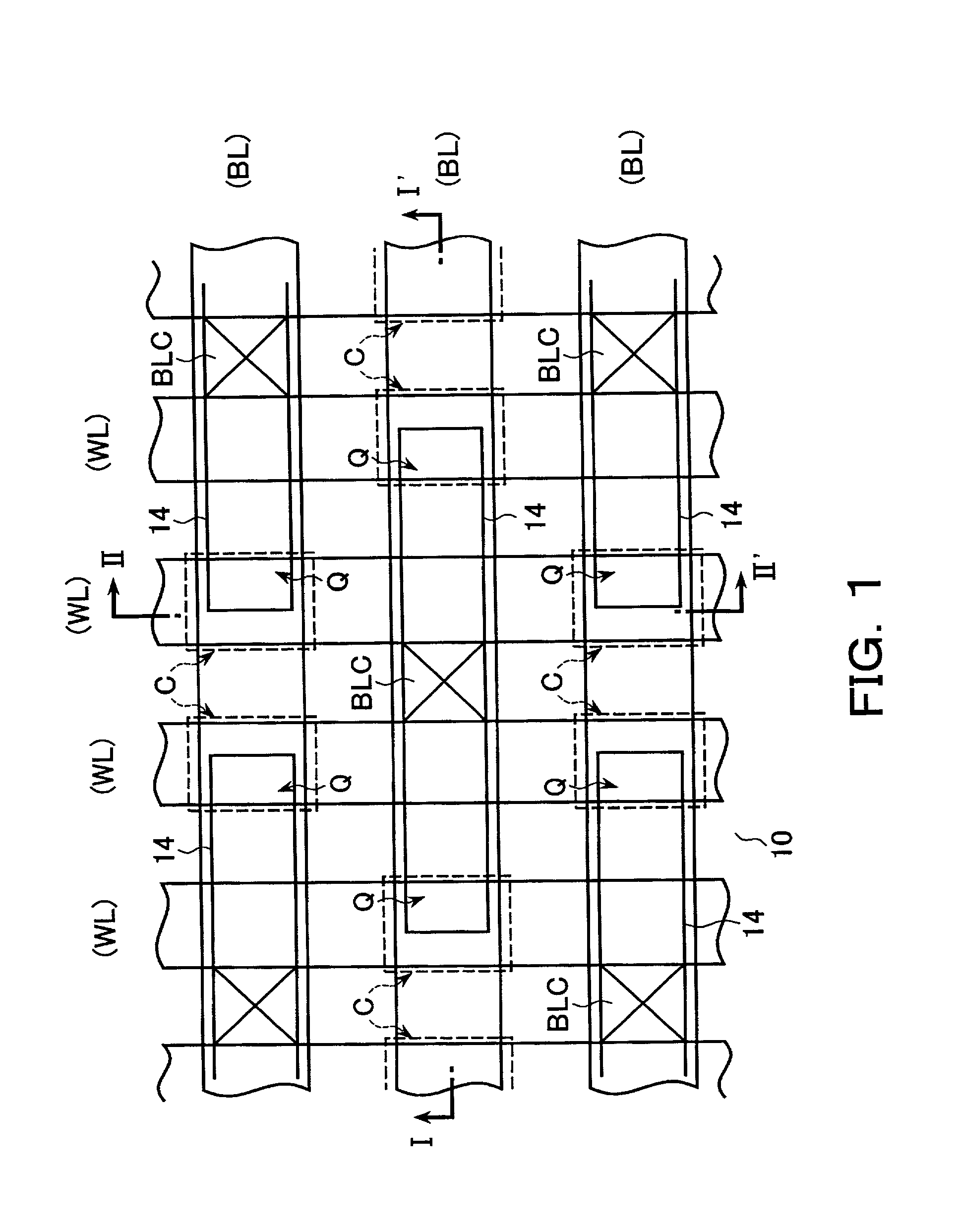
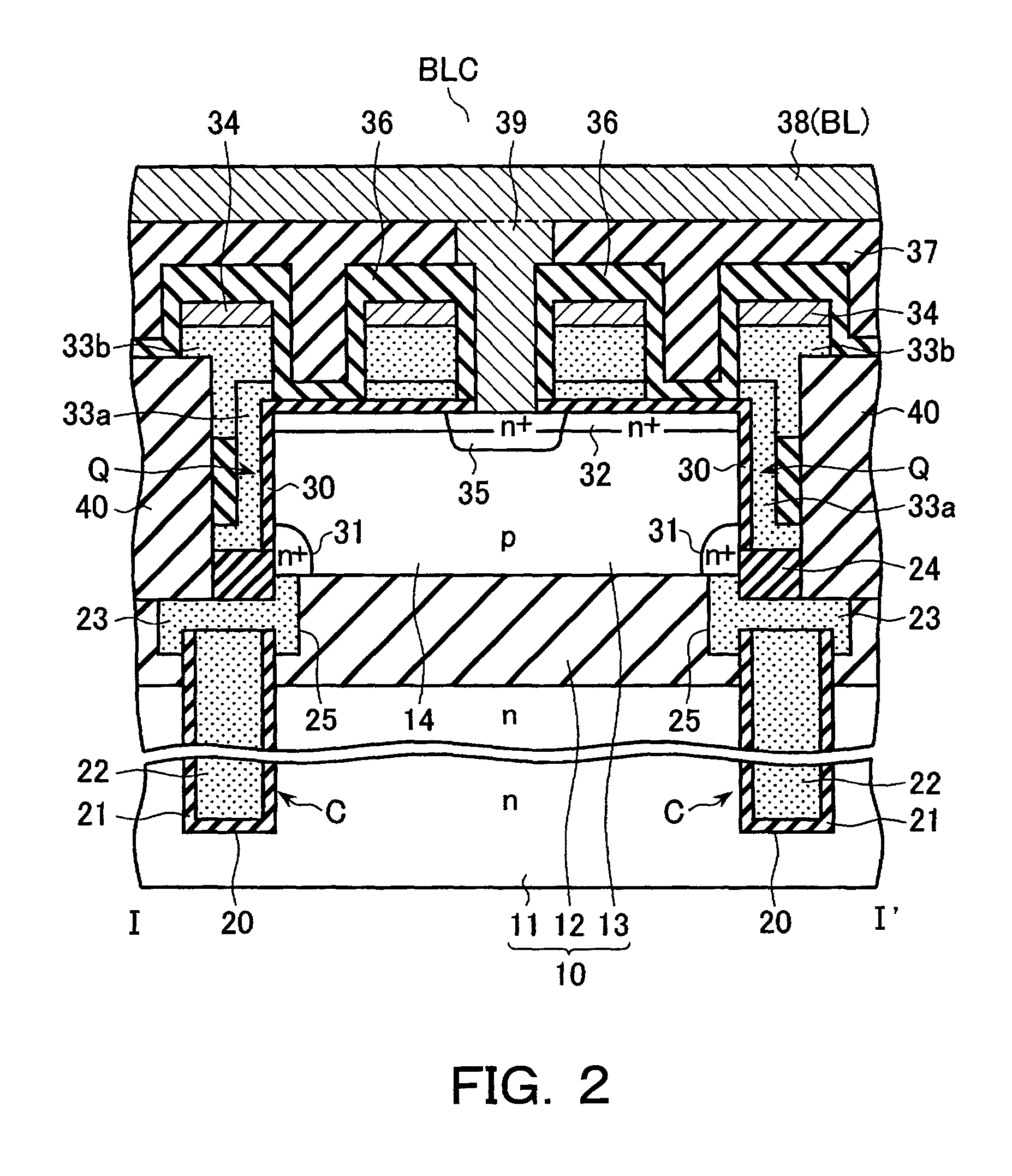
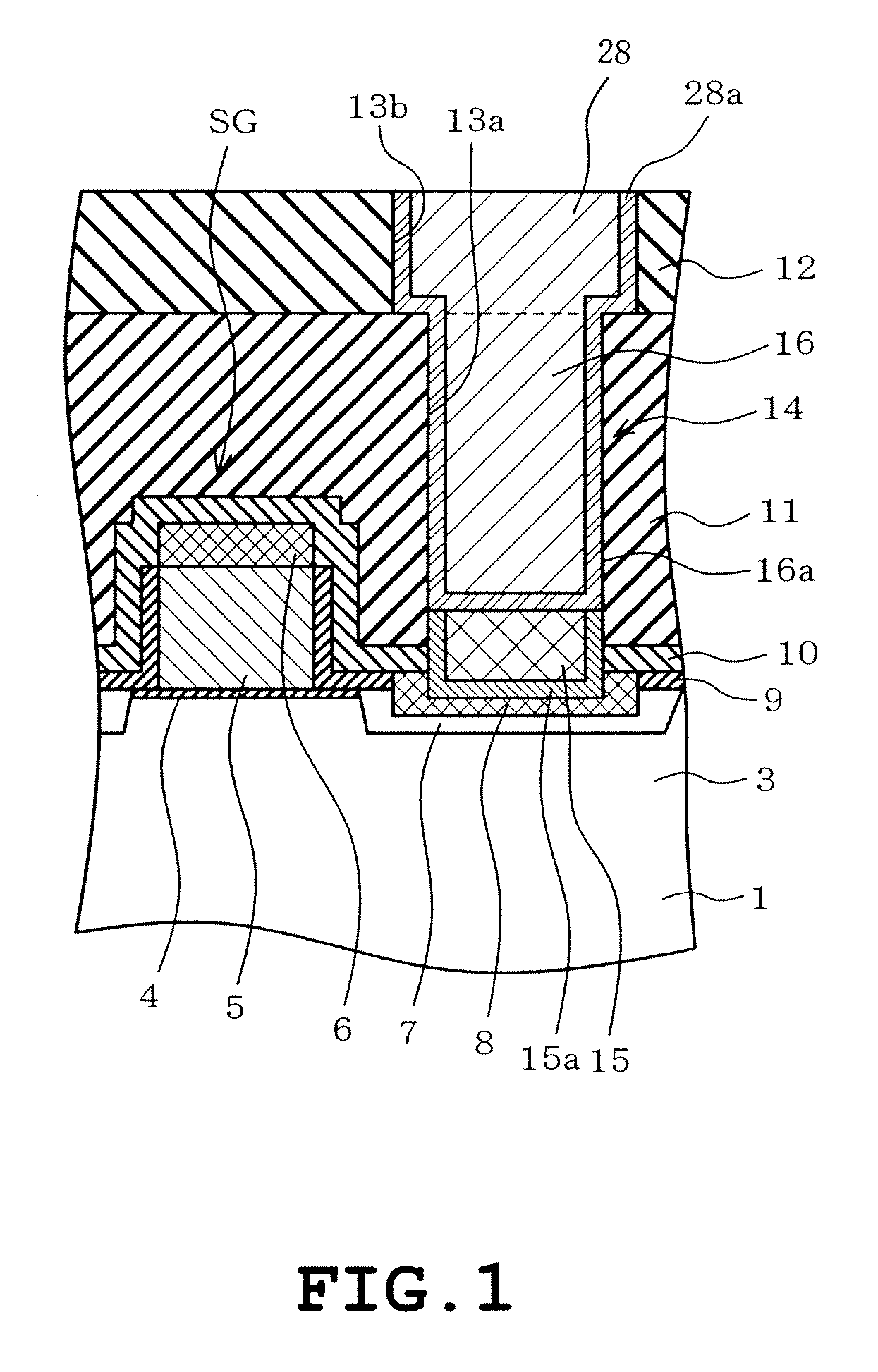
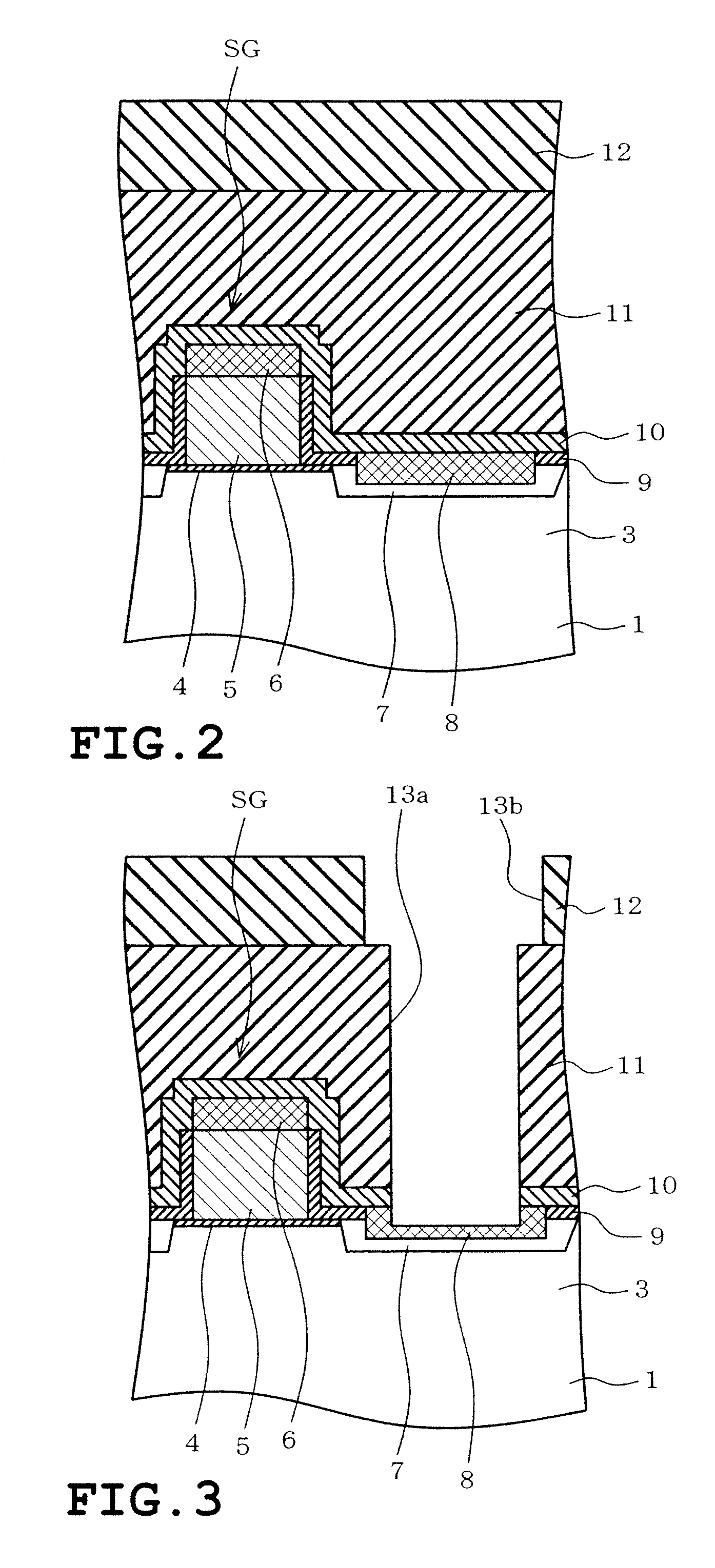
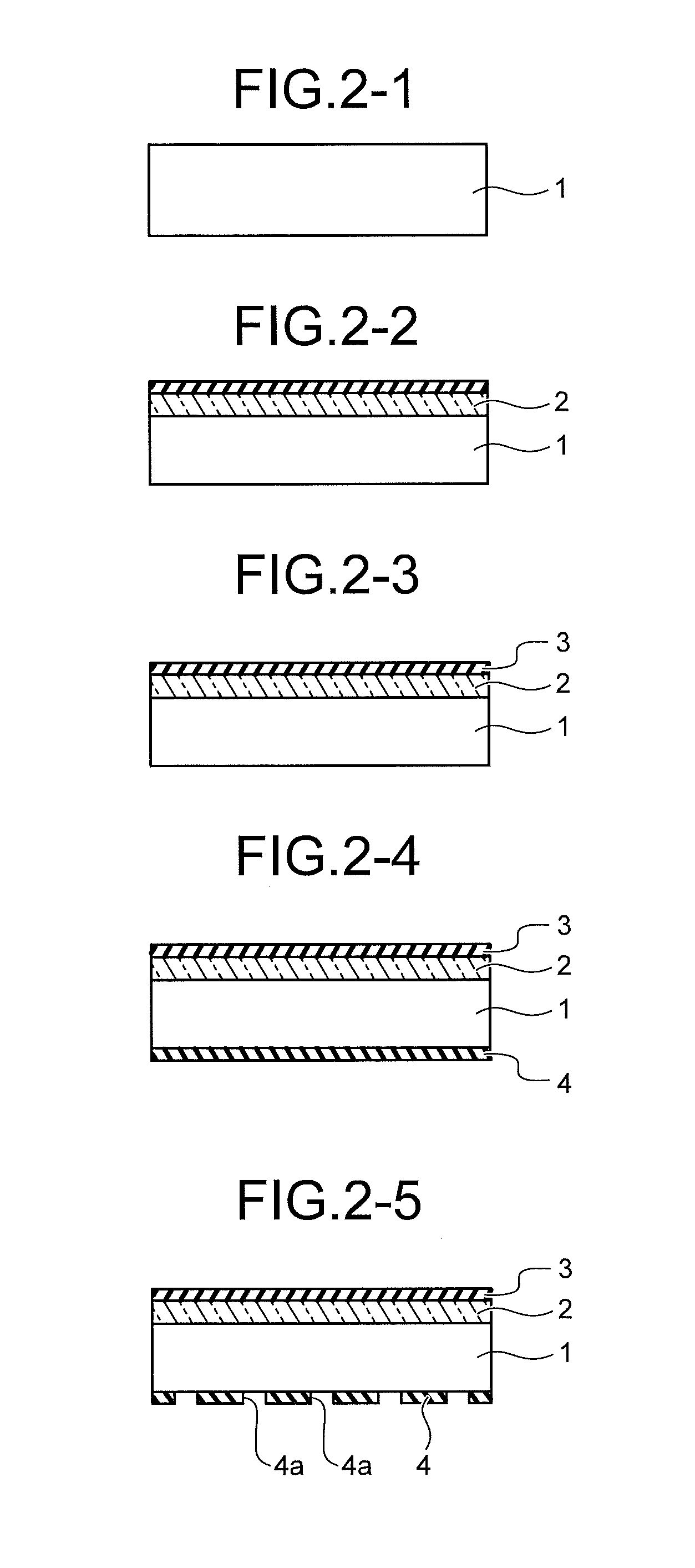
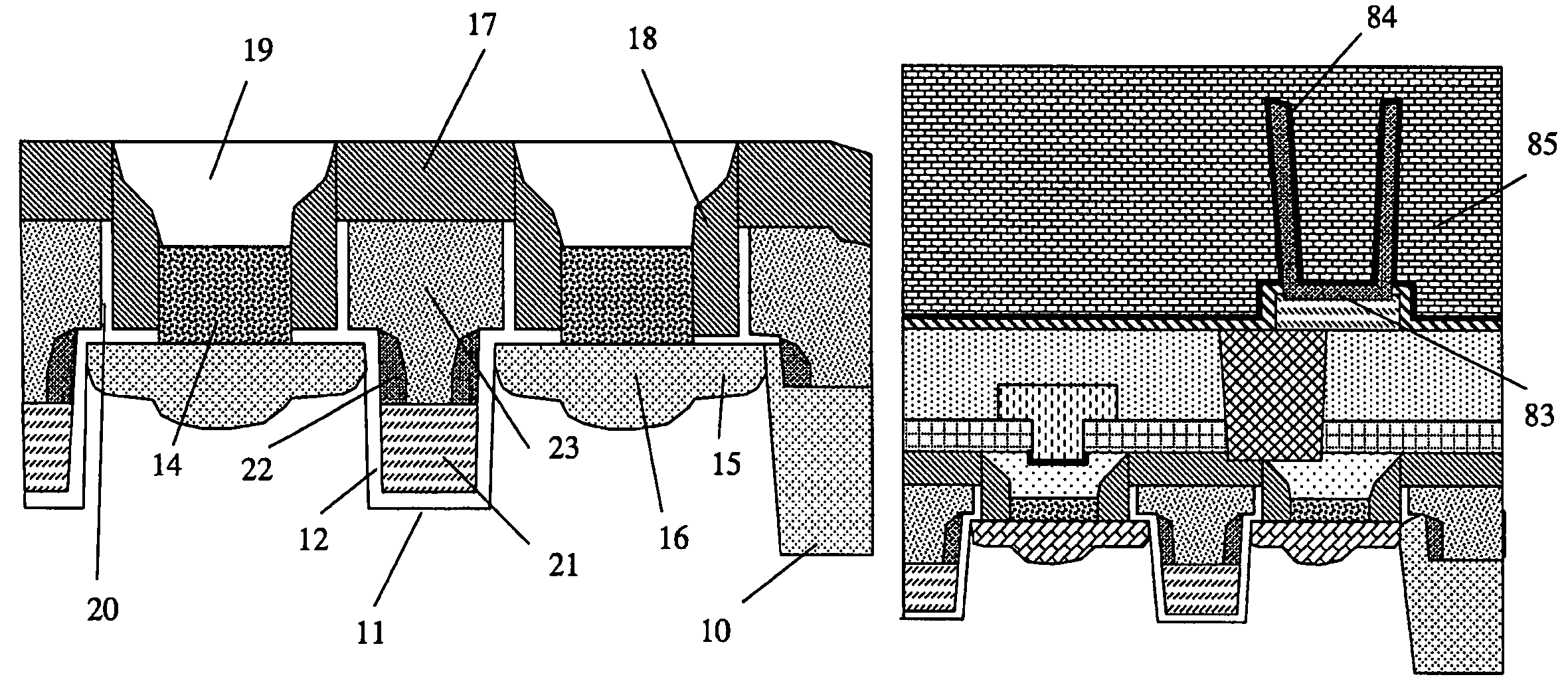
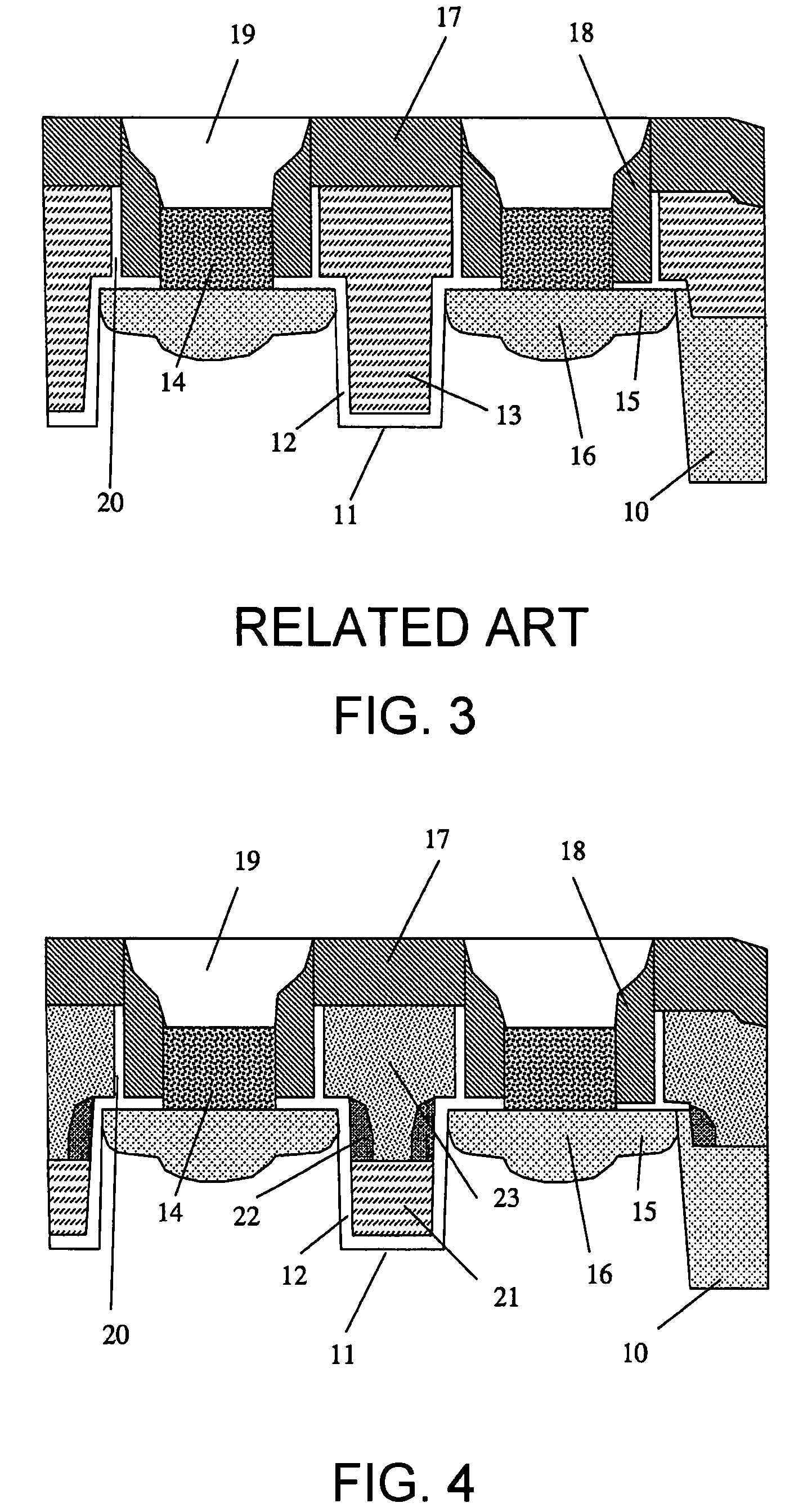
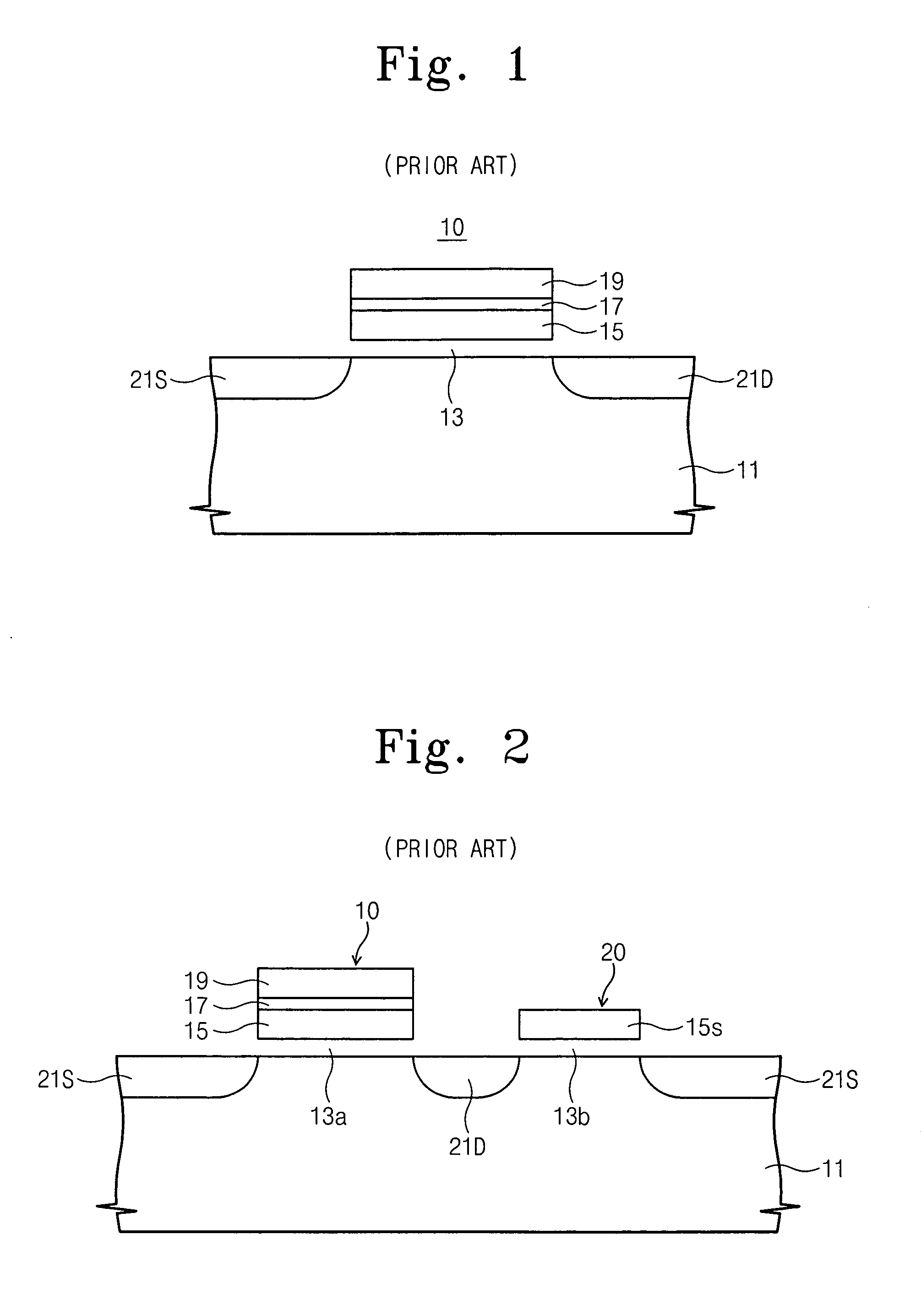
Semiconductor memory device including pillar-shaped semiconductor layers and a method of fabricating the same
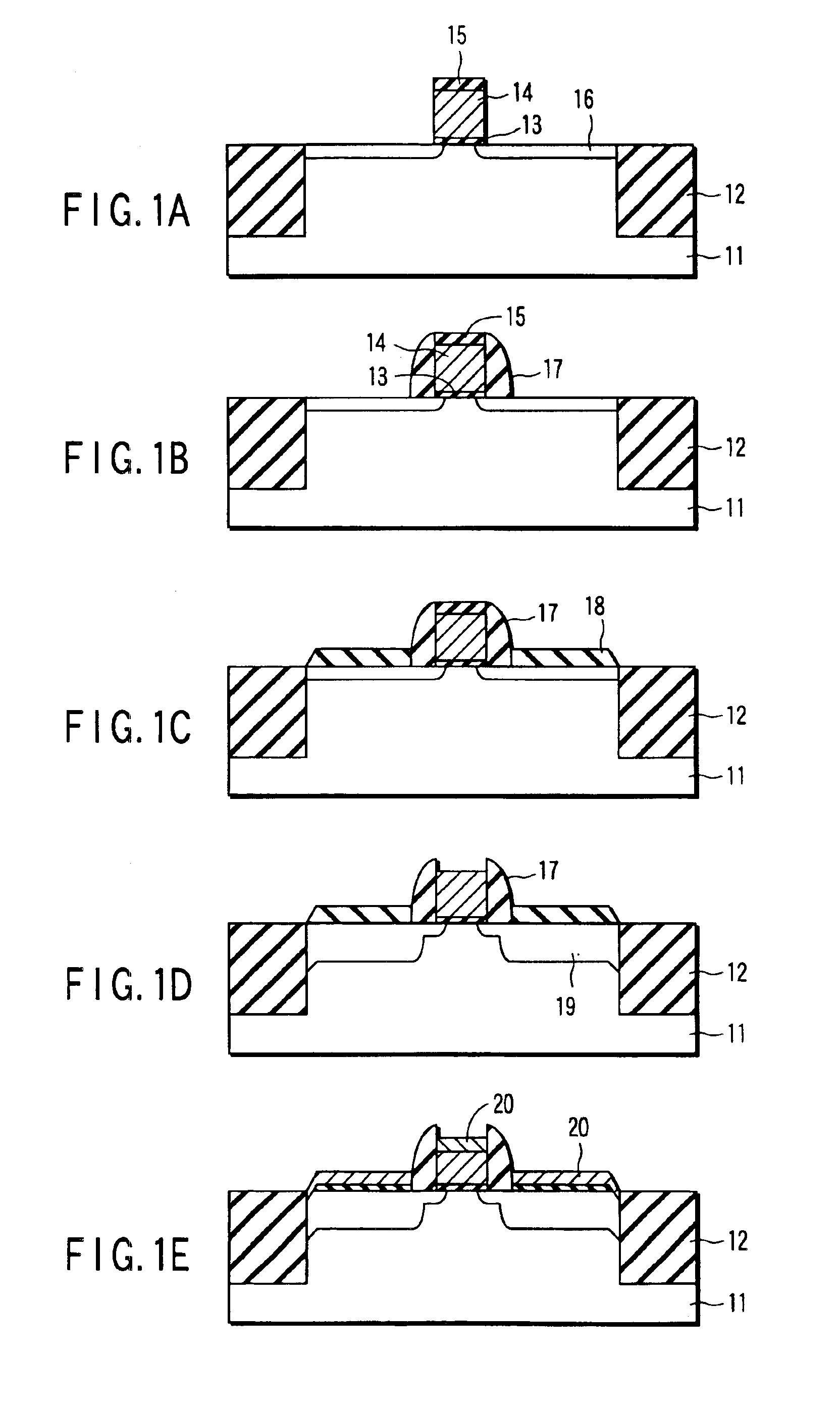
A semiconductor memory device includes: a semiconductor substrate, on which an impurity diffusion layer is formed in a cell array area; a gate wiring stack body formed on the cell array area, in which multiple gate wirings are stacked and separated from each other with insulating films; a gate insulating film formed on the side surface of the gate wiring stack body, in which an insulating charge storage layer is contained, pillar-shaped semiconductor layers arranged along the gate wiring stack body, one side surfaces of which are opposed to the gate wiring stack body via the gate insulating film, each pillar-shaped semiconductor layer having the same conductivity type as the impurity diffusion layer; and data lines formed to be in contact with the upper surfaces of the pillar-shaped semiconductor layers and intersect the gate wirings.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
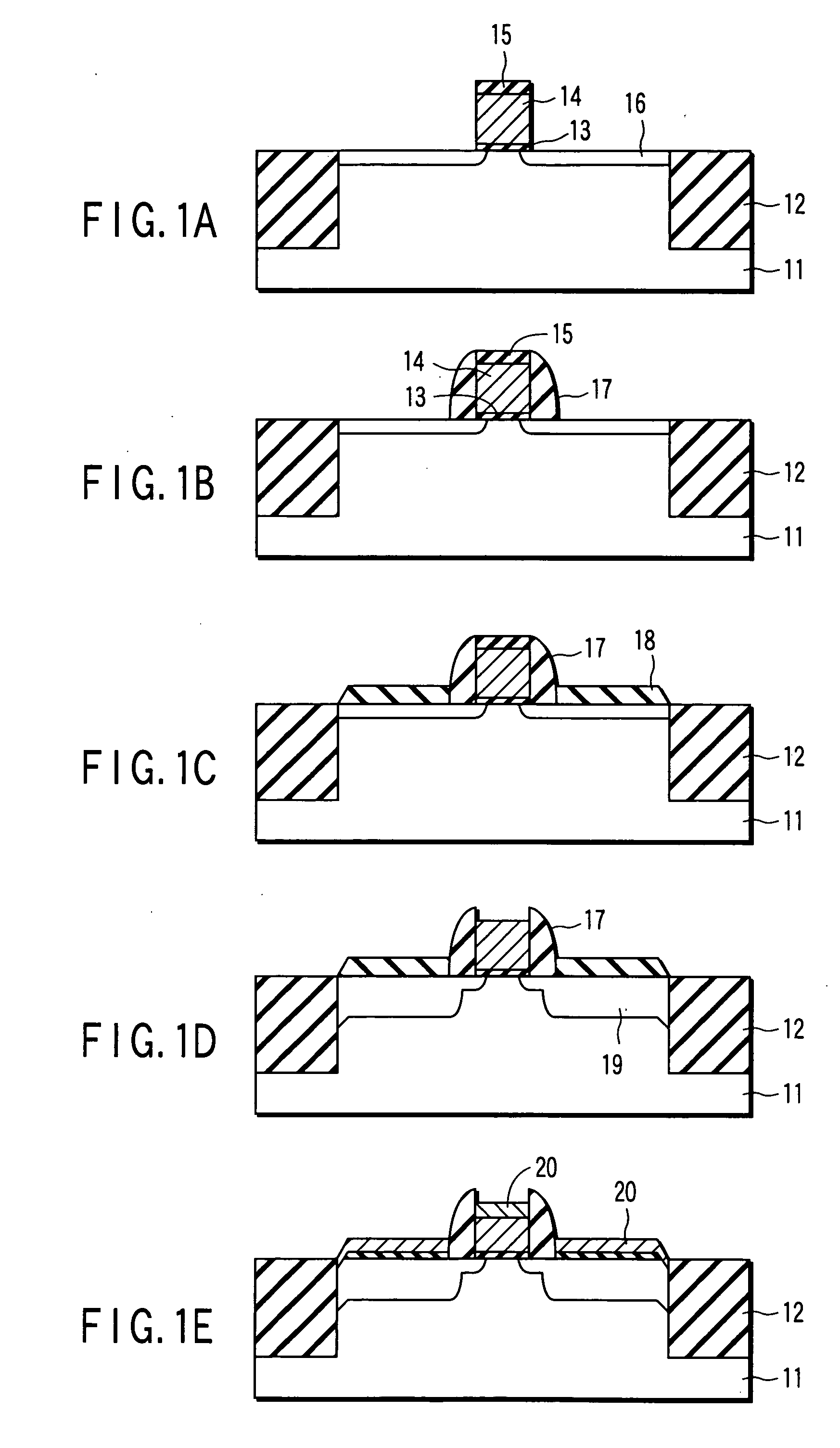
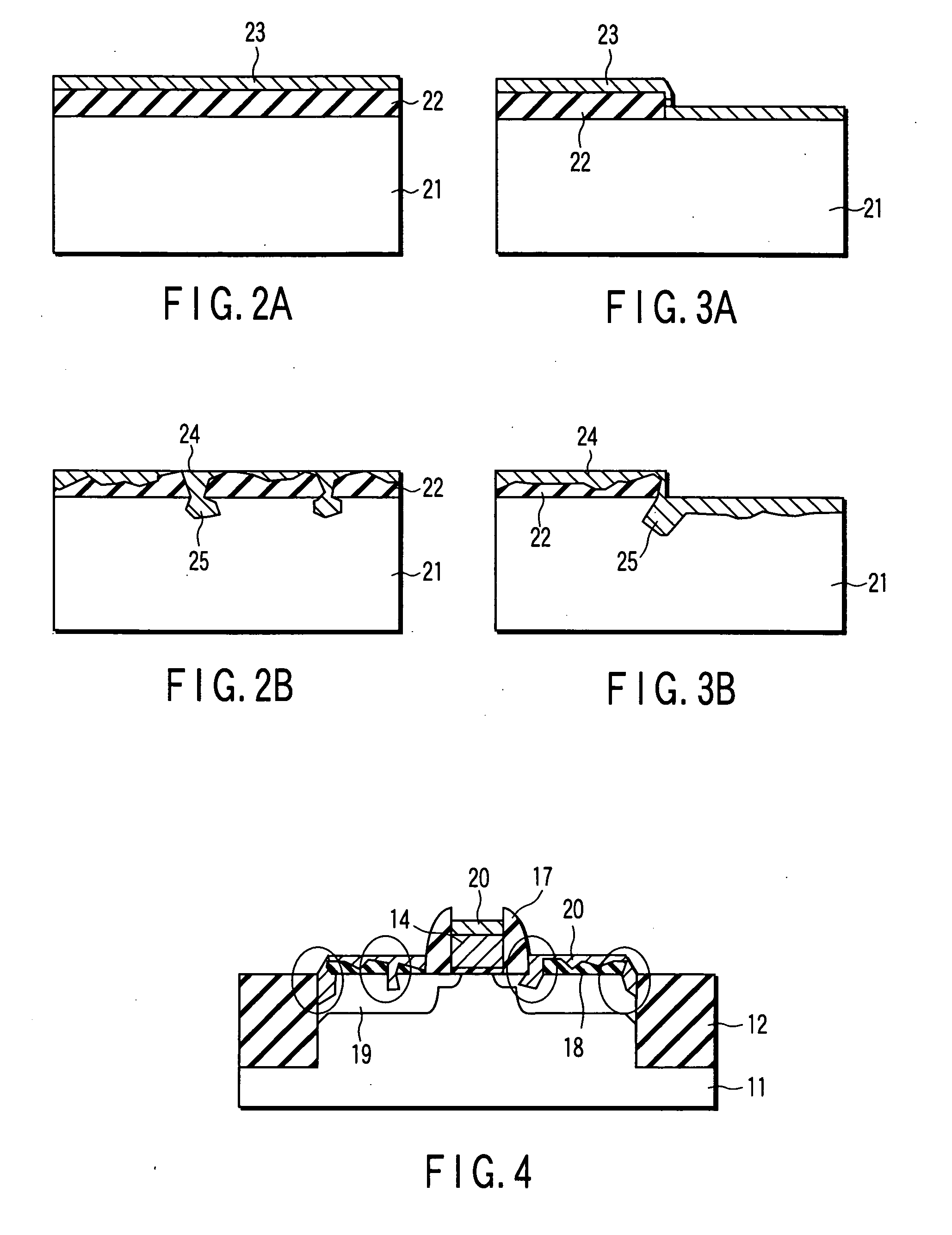
Semiconductor device and method of fabricating the same
A semiconductor device has an element substrate including a semiconductor layer of a first conductivity type being formed over a semiconductor substrate with a dielectric film interposed therebetween. A groove is formed in the element substrate with a depth extending from a top surface of the semiconductor layer into the dielectric film, the groove having a width-increased groove portion in the dielectric film as to expose a bottom surface of the semiconductor layer. An impurity diffusion source is buried in the width-increased groove portion to be contacted with the bottom surface. A transistor is formed to have a first diffusion layer being formed through impurity diffusion from the impurity diffusion source to the bottom surface of the semiconductor layer, a second diffusion layer formed through impurity diffusion to the top surface of the semiconductor layer, and a gate electrode formed at a side face of the groove over the impurity diffusion source with a gate insulation film between the side face and the gate electrode.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method of forming silicon-on-insulator (SOI) semiconductor substrate and SOI semiconductor substrate formed thereby
InactiveUS7183172B2Inhibited DiffusionImpurity diffusion coefficientSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingImpurity diffusionDiffusion barrier
A method of forming an SOI semiconductor substrate and the SOI semiconductor substrate formed thereby, is provided. The method includes forming sequentially buried oxide, diffusion barrier and SOI layers on a semiconductor substrate. The diffusion barrier layer is formed by an insulating layer having a lower impurity diffusion coefficient as compared with the buried oxide layer. The diffusion barrier layer serves to prevent impurities implanted into the SOI layer from being diffused into the buried oxide layer or the semiconductor substrate.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor device and method of fabricating the same
ActiveUS20160087104A1Excellent electrical propertiesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesImpurity diffusionDevice material
Provided are a semiconductor device and a method of fabricating the same. The device may include an active pattern protruding from a substrate, gate structures crossing the active pattern, and a source / drain region provided between adjacent ones of the gate structures. The source / drain region may include a source / drain epitaxial layer in a recessed region, which is formed in the active pattern between the adjacent ones of the gate structures. Further, an impurity diffusion region may be provided in the active pattern to enclose the source / drain epitaxial layer along inner surfaces of the recessed region.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
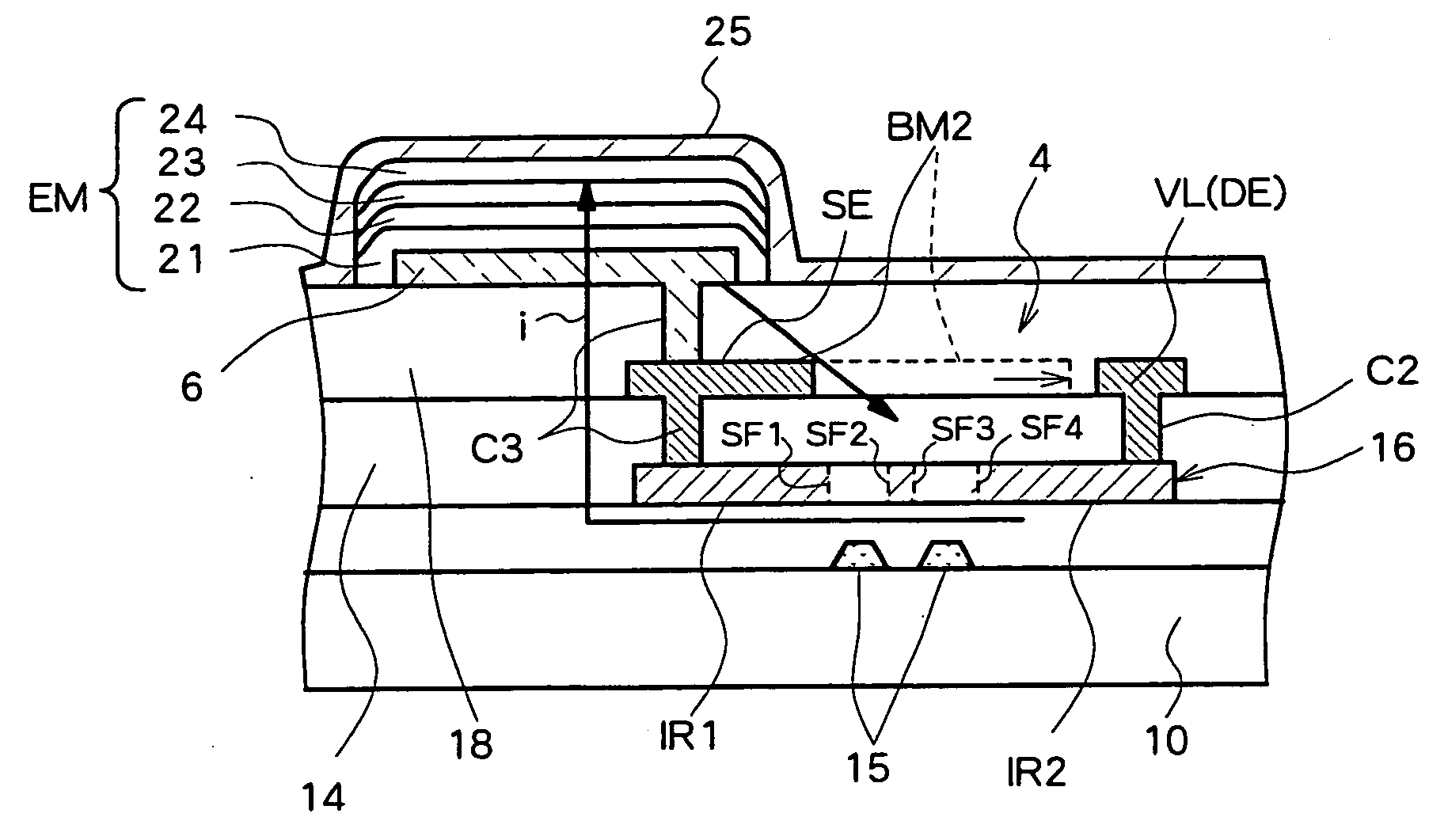
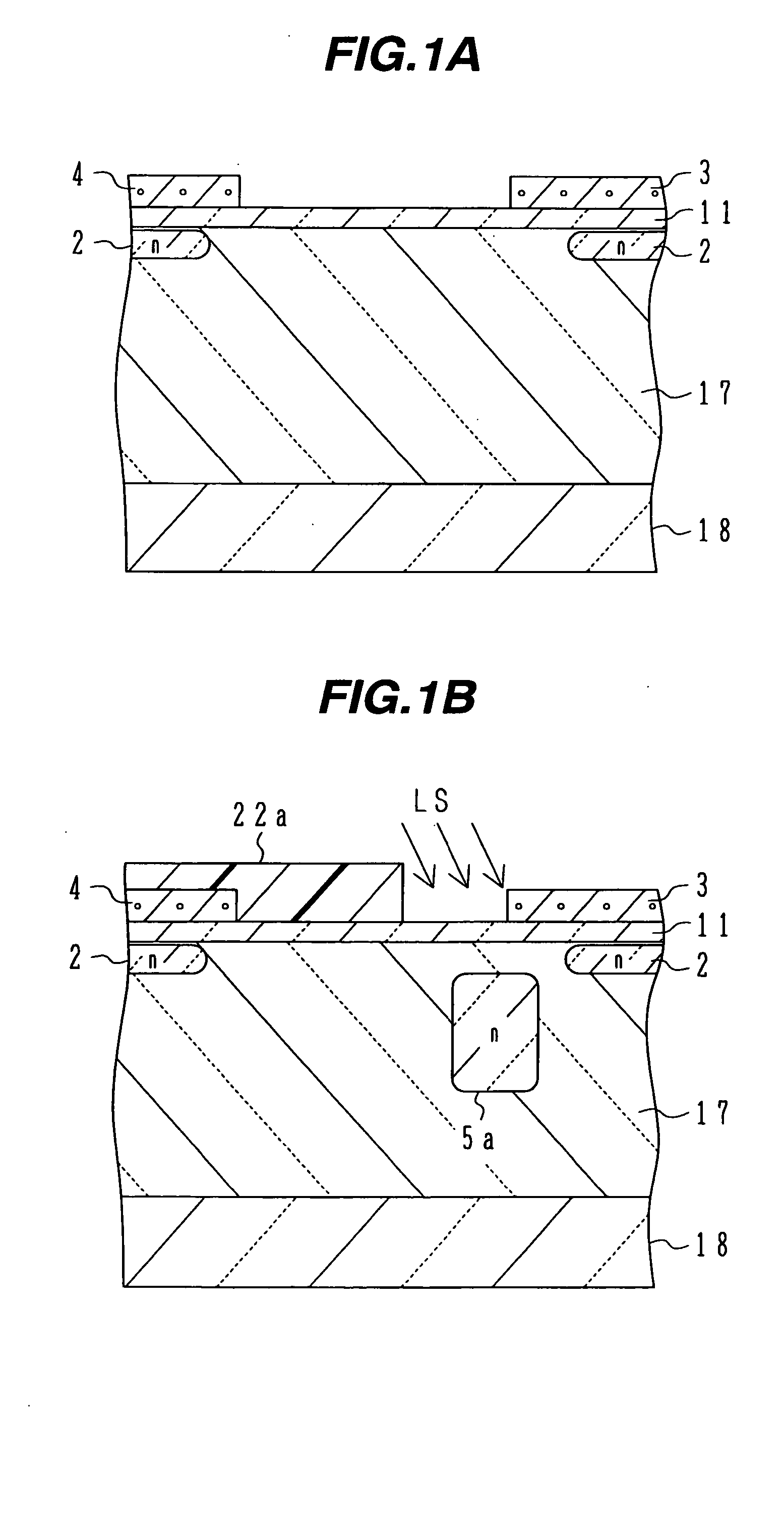
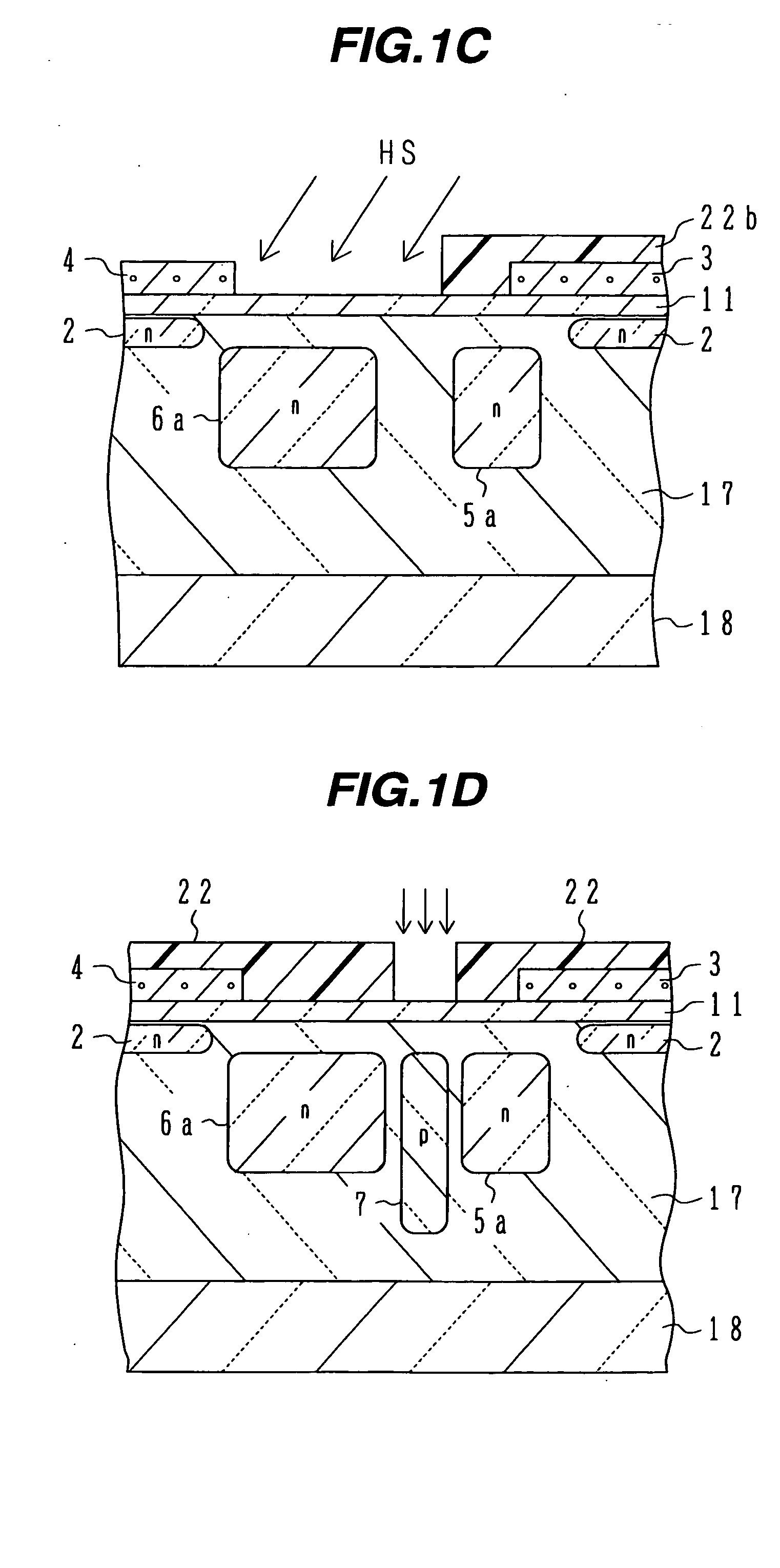
Image pickup device, method of producing image pickup device, and semiconductor substrate for image pickup device
InactiveUS20080297634A1Not be made thinImproved optical sensitivityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImpurity diffusionPhotoelectric conversion
An image pickup device including a semiconductor substrate that is irradiated with light from a first surface side thereof, and reading signal charges generated in the semiconductor substrate in accordance with the light from a second surface side thereof, wherein the semiconductor substrate includes: a photoelectric converting layer that includes a plurality of impurity diffusion layers on the second surface side of the semiconductor substrate, and that produces the signal charges by photoelectric conversion; and an embedded member that includes a light blocking material, and that is embedded in an impurity diffusion layer on a surface side of the photoelectric converting layer, the surface side facing the second surface side of the semiconductor substrate.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Electroluminescence display device
InactiveUS6958740B1Reduce resistanceAvoid it happening againTransistorDischarge tube luminescnet screensImpurity diffusionDisplay device
An EL element and an interface between a channel and an impurity diffusion area of a thin film transistor provided in the vicinity of the EL element are spaced apart. A light shielding film is provided between the EL element and the interface. By providing such a space and / or the light shielding film, generation of a leak current, which would otherwise be caused by light emitted from the self-emissive EL element entering the TFT, is reliably prevented, thereby ensuring that emitted light is not brighter than a predetermined luminance.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
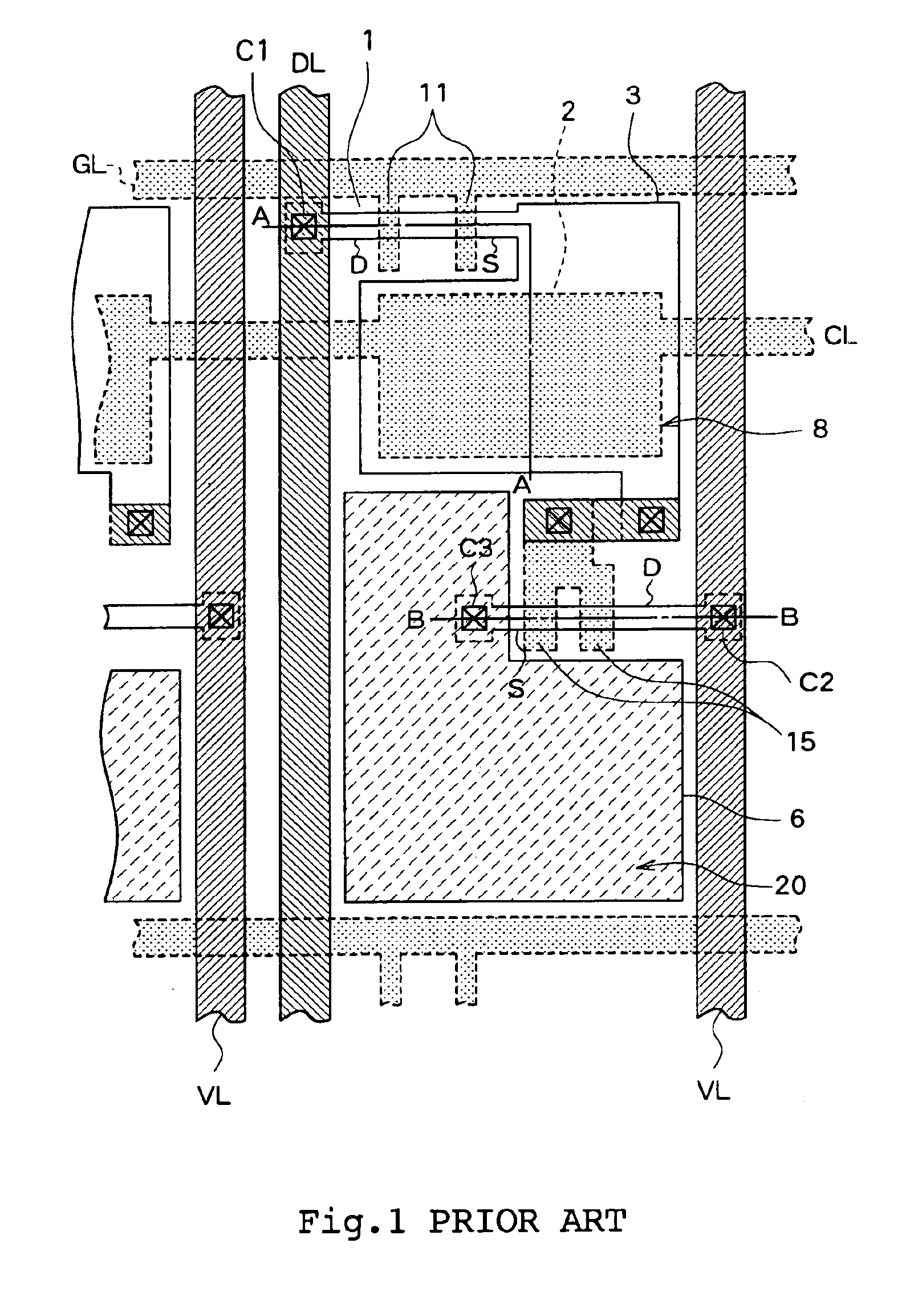
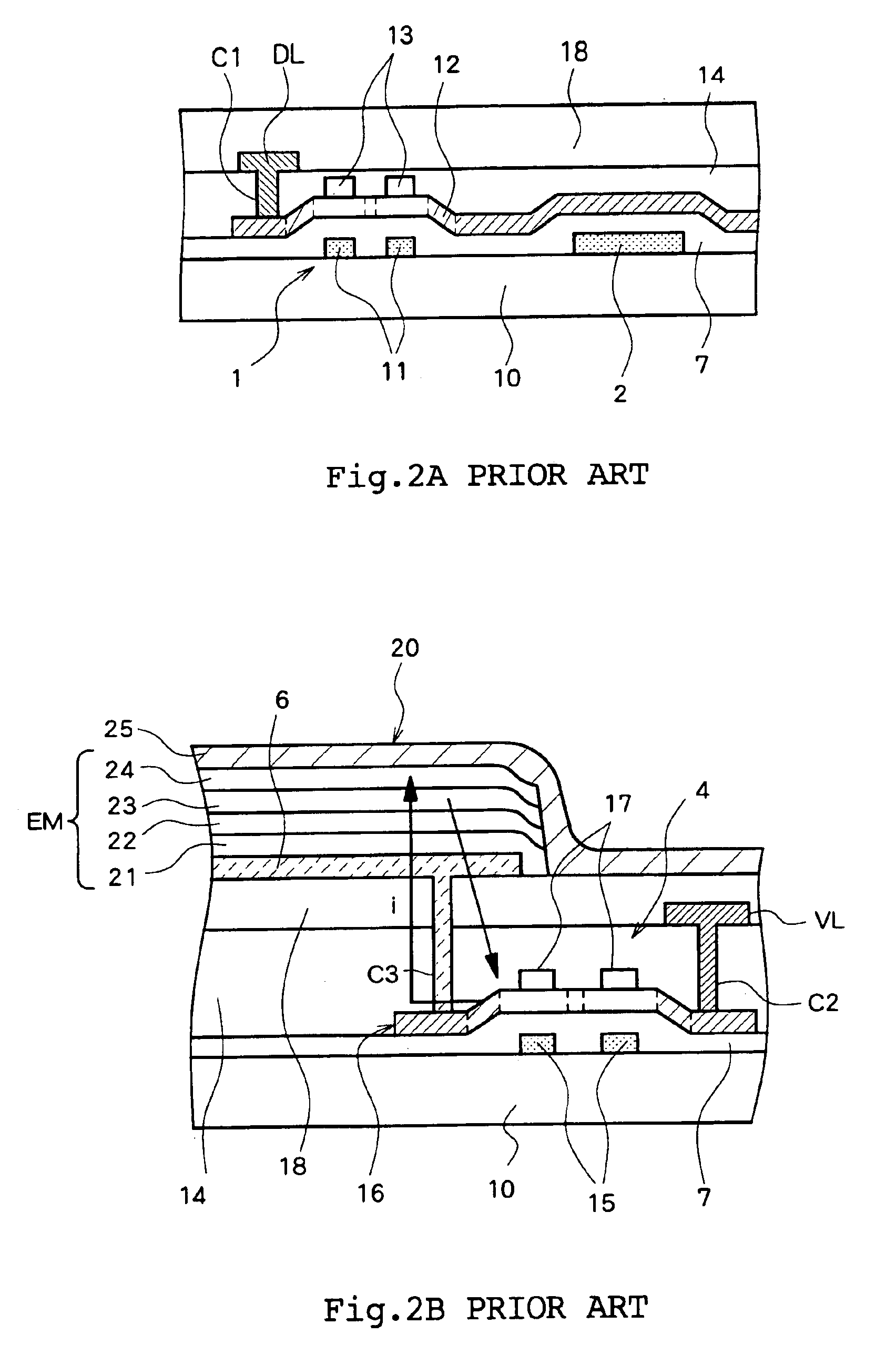
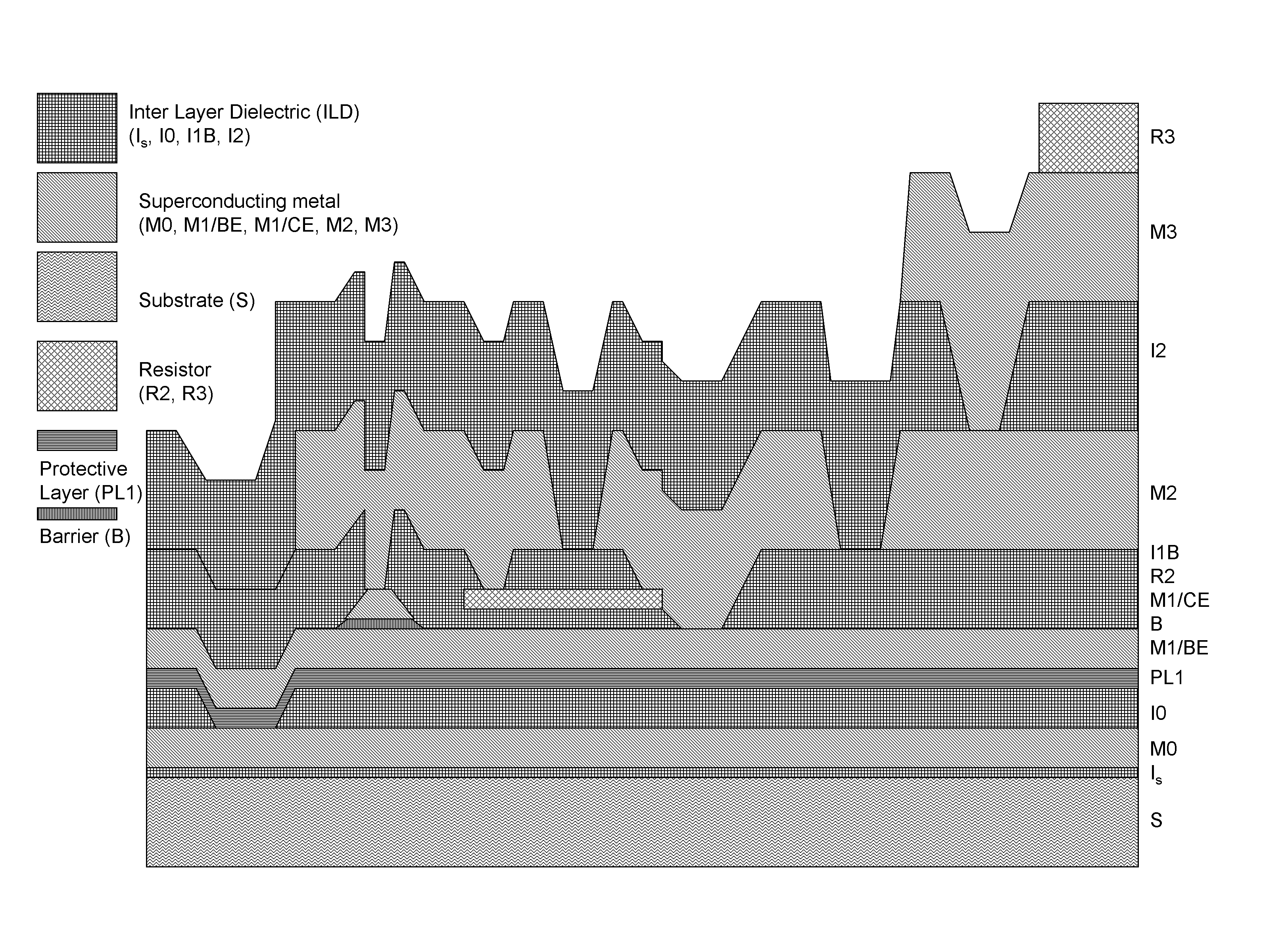
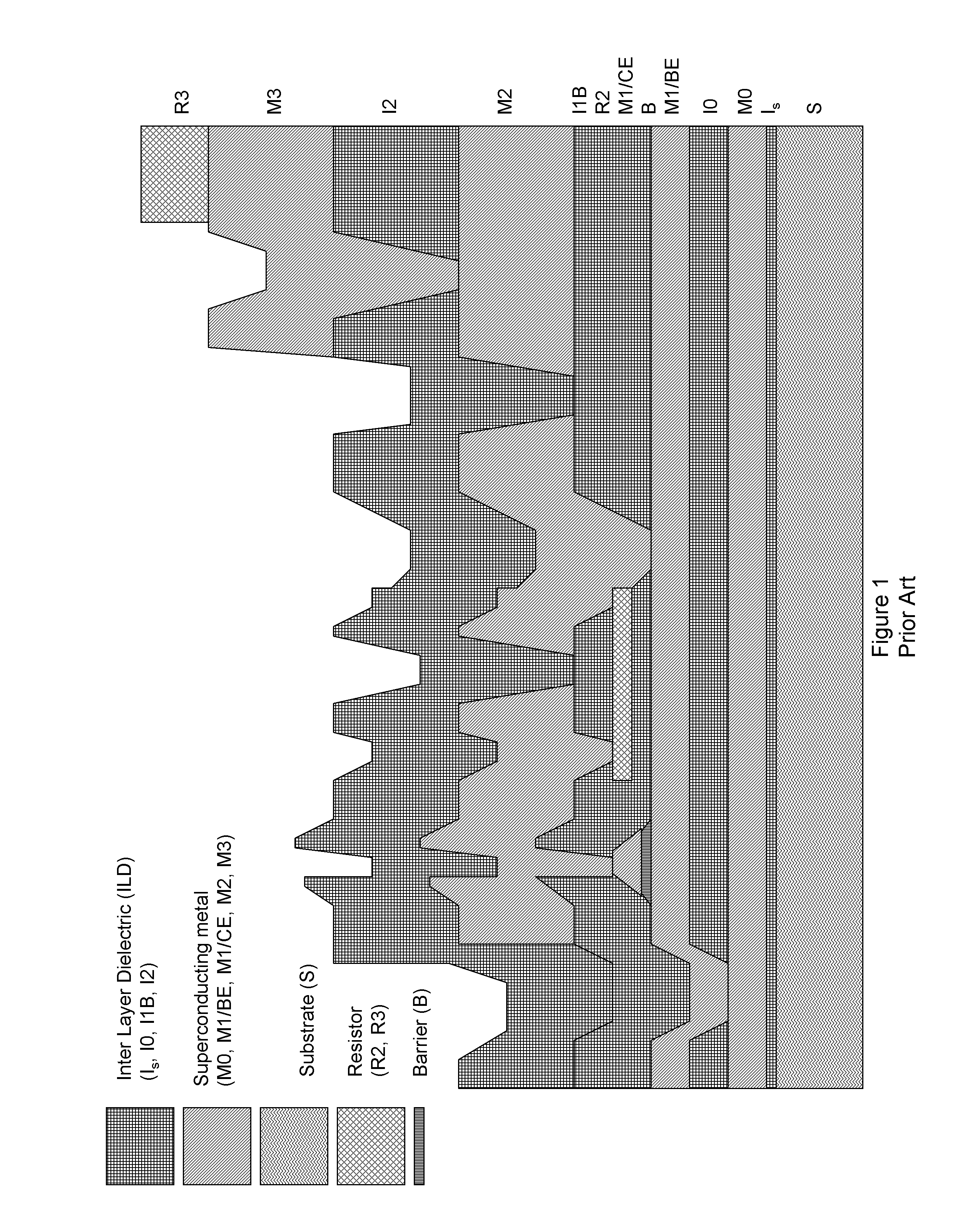
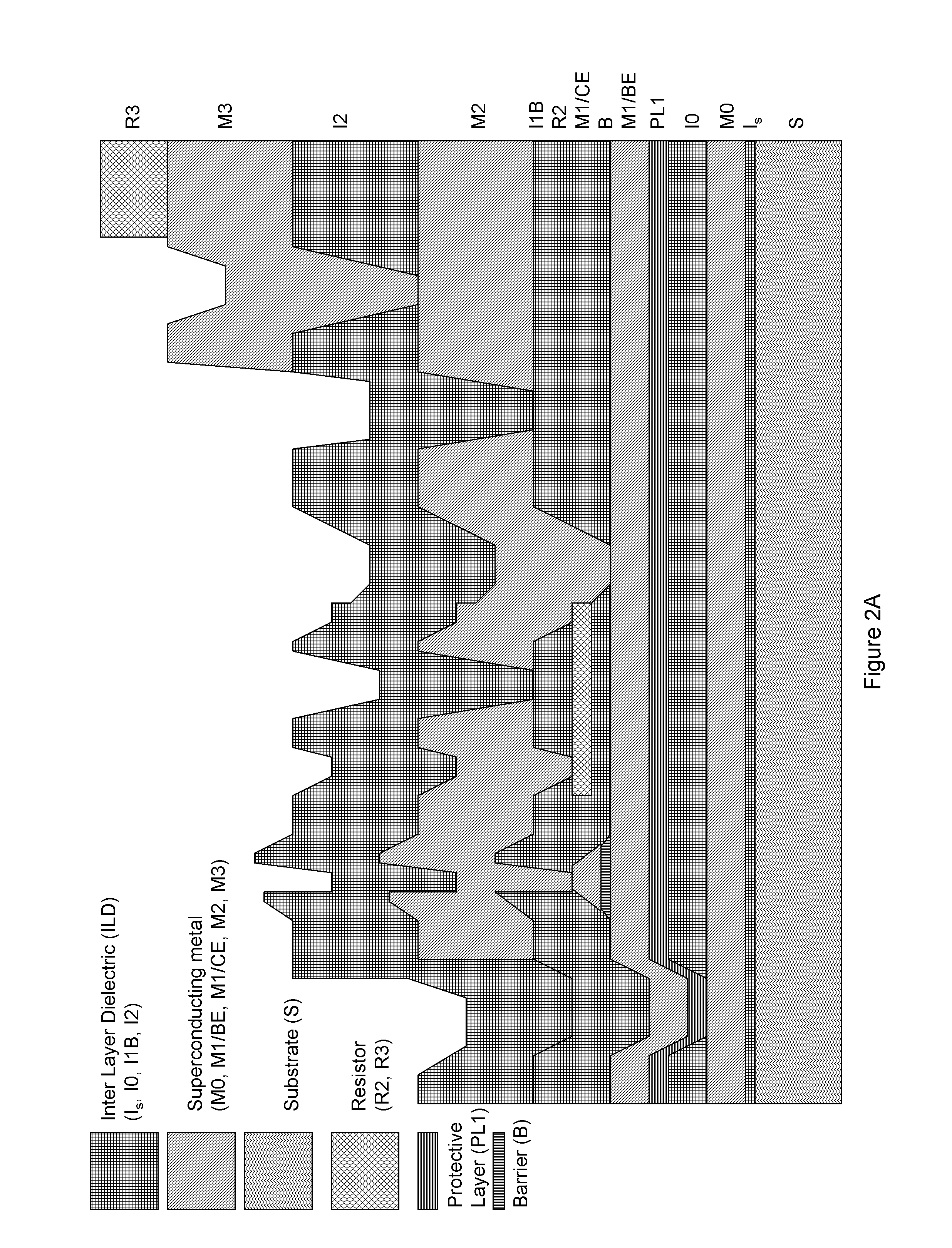
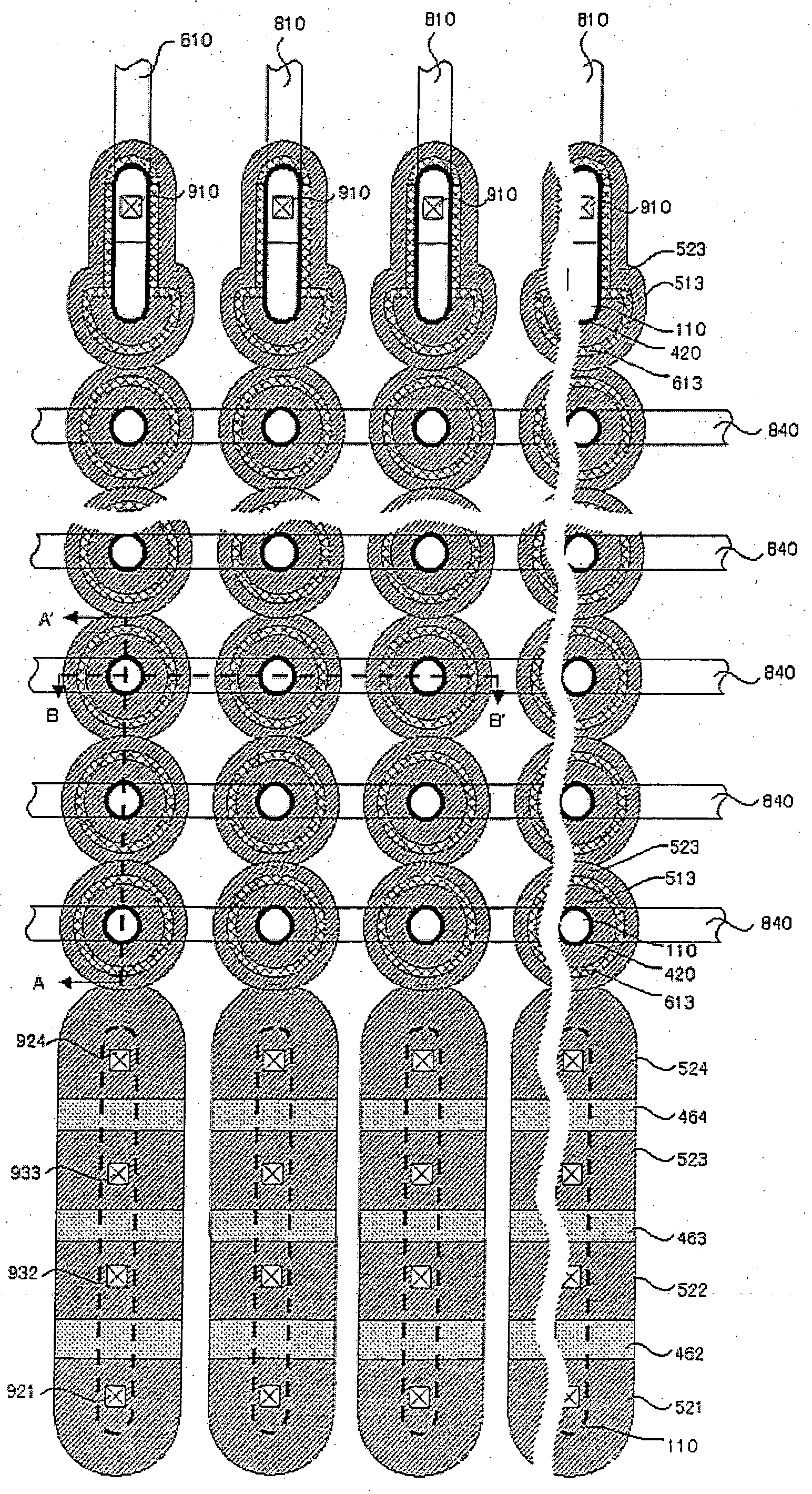
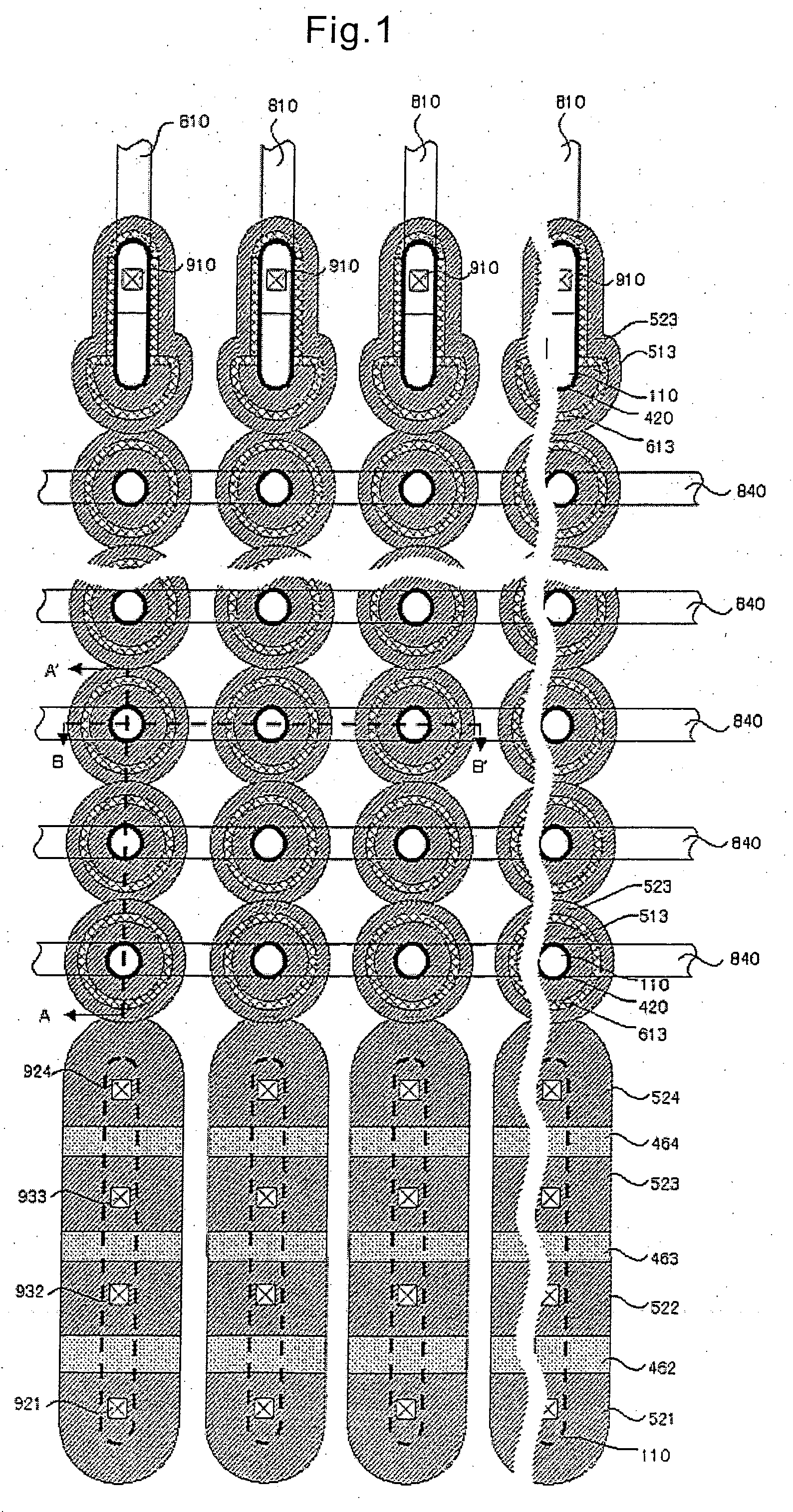
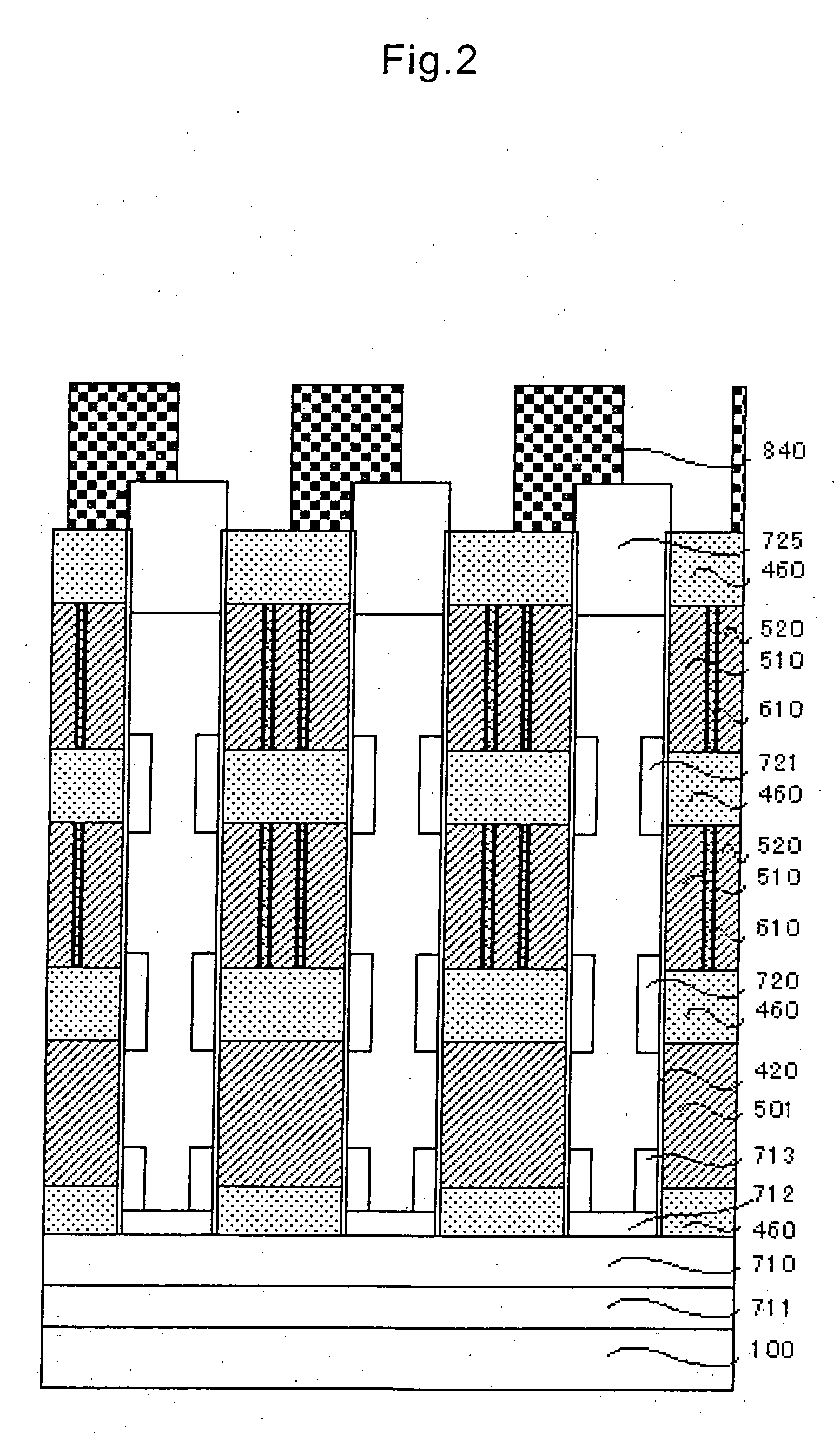
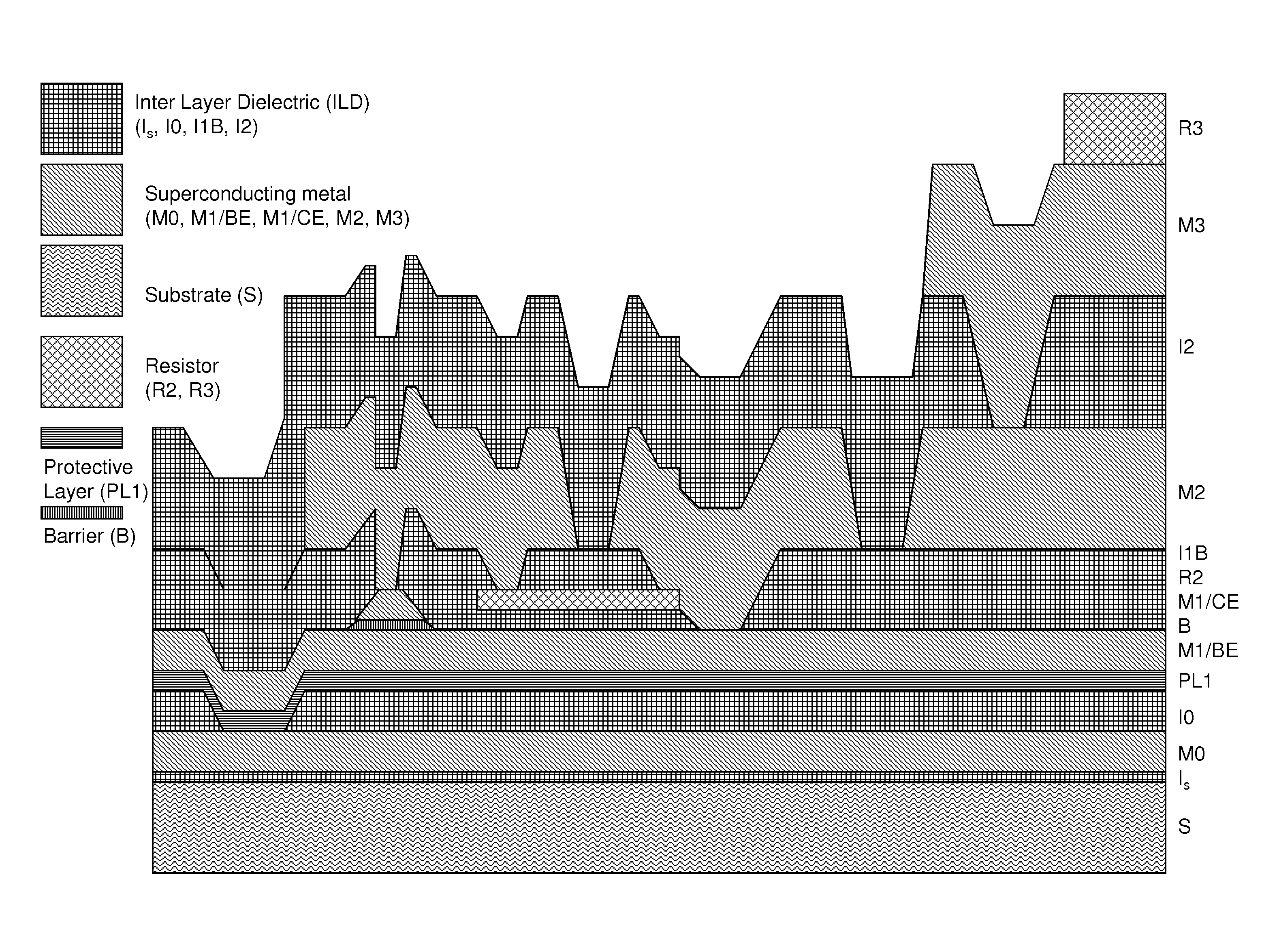
System and method for providing multi-conductive layer metallic interconnects for superconducting integrated circuits
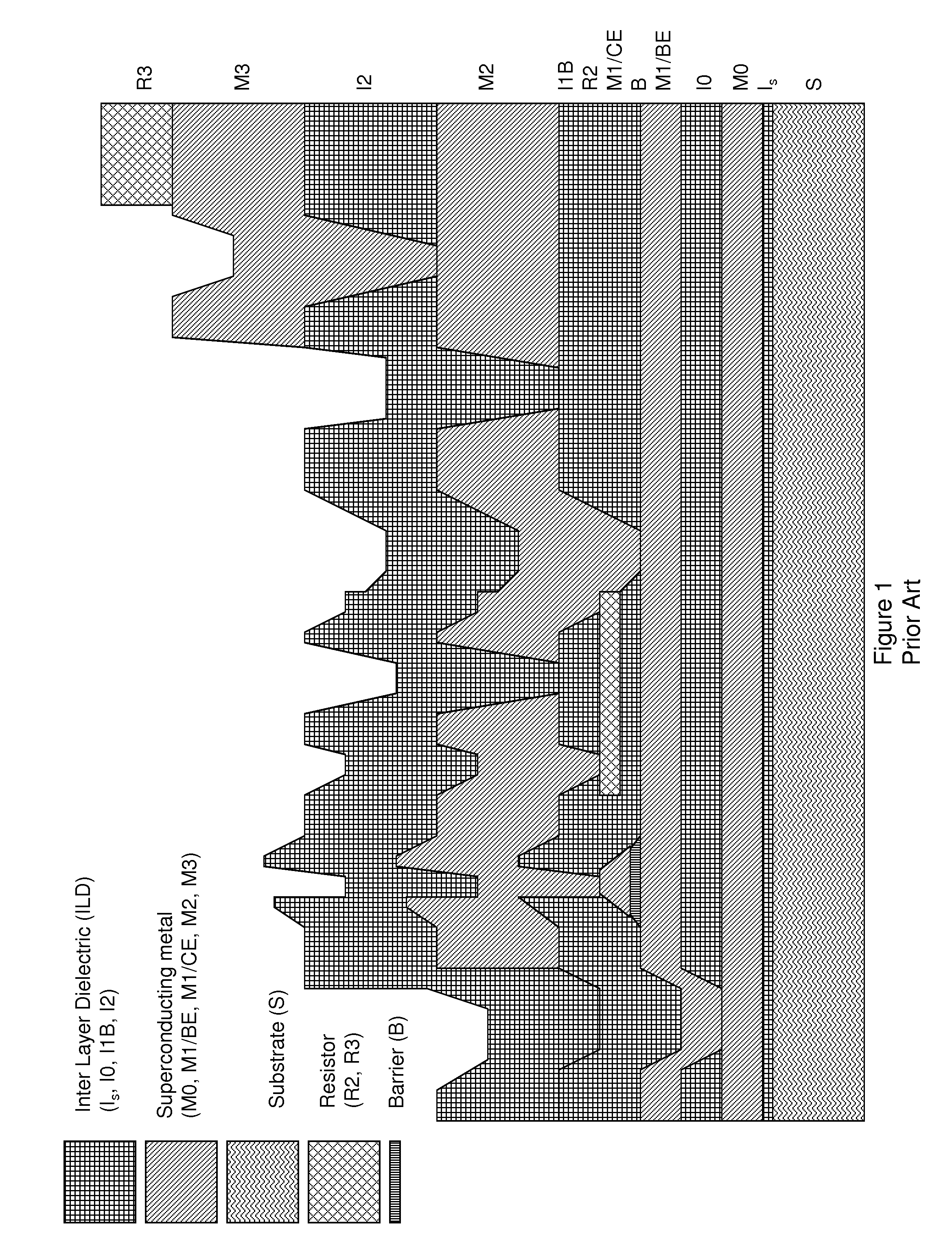
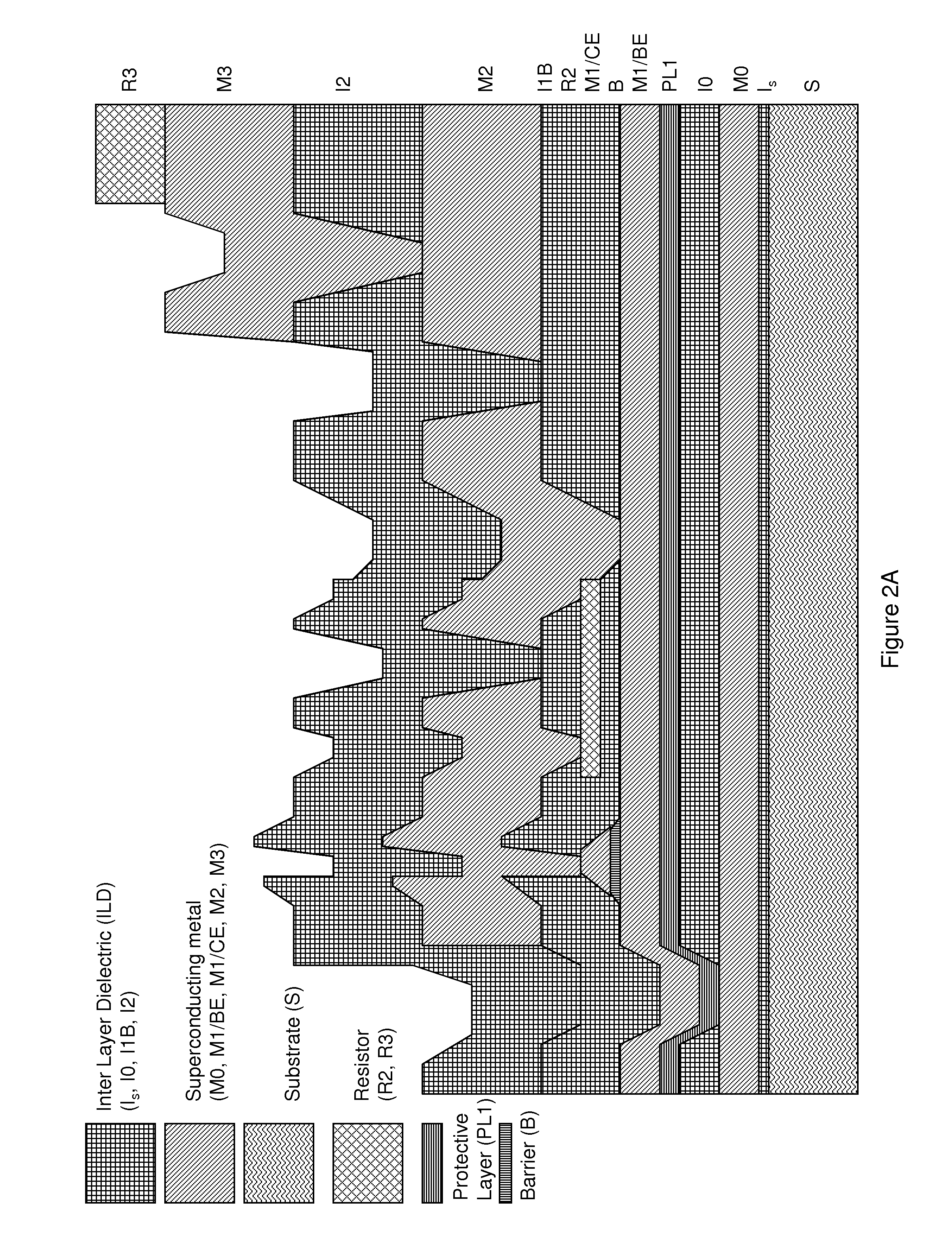
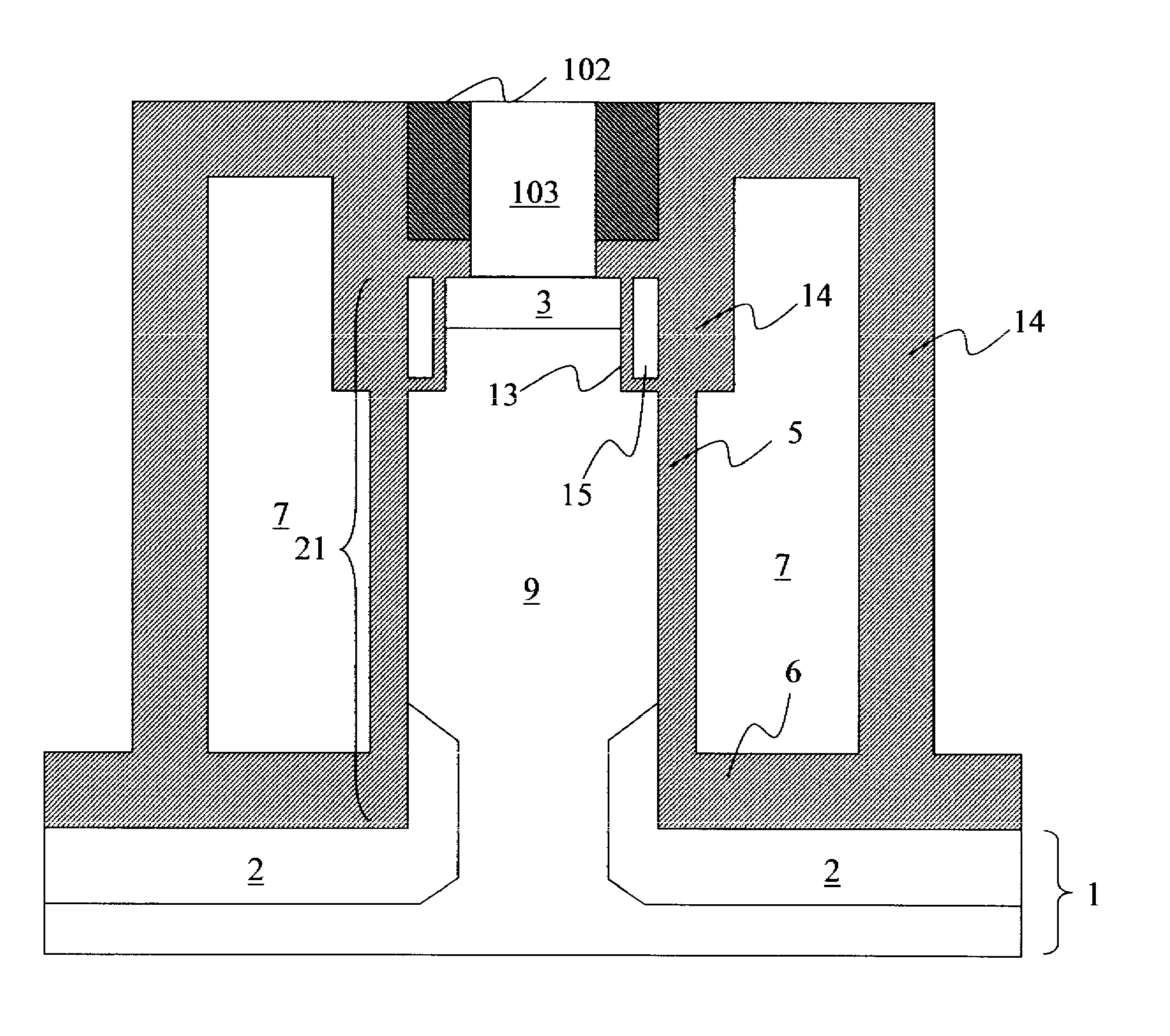
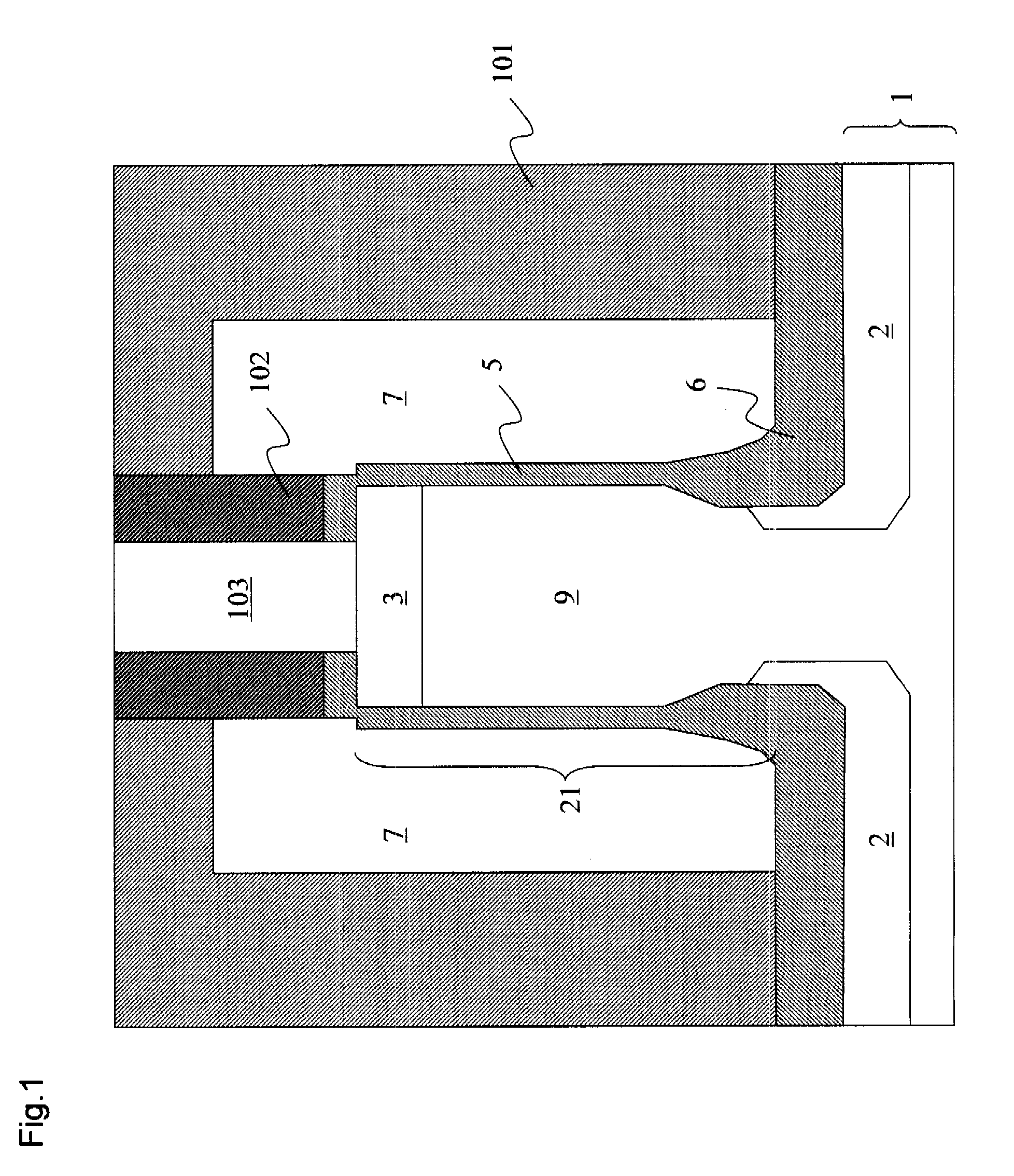
ActiveUS8437818B1Reduce and prevent diffusion of impurityReduce non-uniformitySuperconductors/hyperconductorsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsImpurity diffusionRapid single flux quantum
Superconducting integrated circuits require several wiring layers to distribute bias and signals across the circuit, which must cross each other both with and without contacts. All wiring lines and contacts must be fully superconducting, and in the prior art each wiring layer comprises a single metallic thin film. An alternative wiring layer is disclosed that comprises sequential layers of two or more different metals. Such a multi-metallic wiring layer may offer improved resistance to impurity diffusion, better surface passivation, and / or reduction of stress, beyond that which is attainable with a single-metallic wiring layer. The resulting process leads to improved margin and yield in an integrated circuit comprising a plurality of Josephson junctions. Several preferred embodiments are disclosed, for both planarized and non-planarized processes. These preferred and other methods may be applied to digital circuits based on Rapid Single Flux Quantum logic, and to quantum computing using Josephson junction qubits.
Owner:SEEQC INC
Methods for making a dielectric stack in an integrated circuit
InactiveUS7038284B2Simple materialIncrease deposition rateTransistorNanotechDielectricGate dielectric
An ultrathin aluminum oxide and lanthanide layers, particularly formed by an atomic layer deposition (ALD) type process, serve as interface layers between two or more materials. The interface layers can prevent oxidation of a substrate and can prevent diffusion of molecules between the materials. In the illustrated embodiments, a high-k dielectric material is sandwiched between two layers of aluminum oxide or lanthanide oxide in the formation of a transistor gate dielectric or a memory cell dielectric. Aluminum oxides can serve as a nucleation layer with less than a full monolayer of aluminum oxide. One monolayer or greater can also serve as a diffusion barrier, protecting the substrate from oxidation and the high-k dielectric from impurity diffusion. Nanolaminates can be formed with multiple alternating interface layers and high-k layers, where intermediate interface layers can break up the crystal structure of the high-k materials and lower leakage levels.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
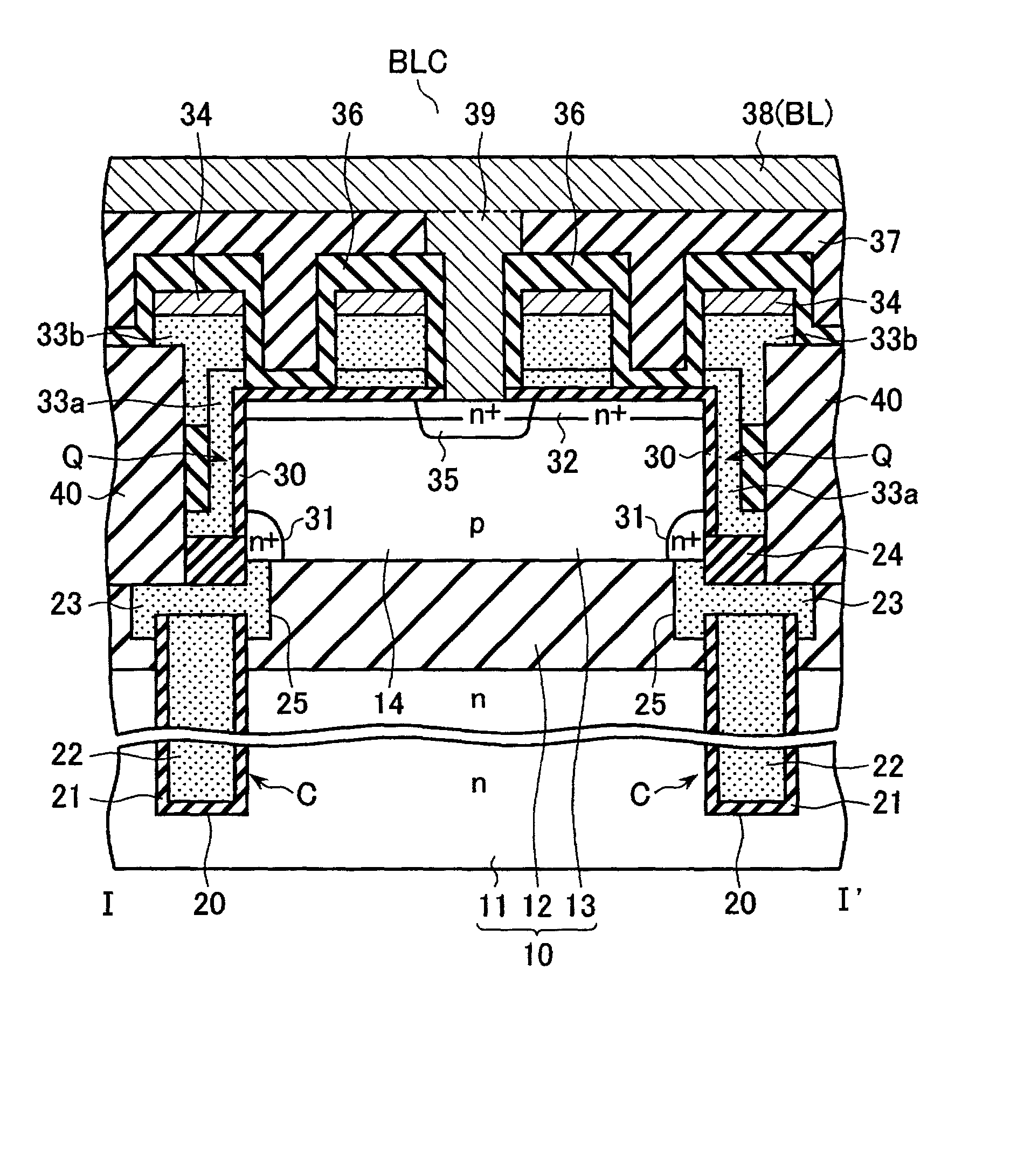
Memory cell unit, nonvolatile semiconductor storage device including memory cell unit, and memory cell array driving method
ActiveUS20050063237A1Field intensity is preventedImprove reliabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesImpurity diffusionSemiconductor storage devices
A memory cell unit including: a semiconductor substrate having a source diffusion layer in at least a part of a surface thereof; a column-shaped semiconductor layer provided on the semiconductor substrate, and having a drain diffusion layer provided in an uppermost portion thereof and a first low concentration impurity diffusion layer provided in an entire bottom portion thereof; a memory cell arrangement which includes a plurality of memory cells provided in a peripheral wall of the column-shaped semiconductor layer and connected in series perpendicularly to the substrate, the memory cells each having a charge storage layer and a control gate; a second impurity diffusion layer provided at a lower end of the memory cell arrangement; and a selection transistor having a gate electrode provided around the peripheral wall of the column-shaped semiconductor layer and connecting the second impurity diffusion layer and the first impurity diffusion layer; wherein the first impurity diffusion layer extends into a part of a channel region provided in the peripheral wall of the column-shaped semiconductor layer in opposed relation to the gate electrode of the selection transistor.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System and method for providing multi-conductive layer metallic interconnects for superconducting integrated circuits
ActiveUS8301214B1Reduce and prevent diffusion of impurityReduce non-uniformitySuperconductors/hyperconductorsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsImpurity diffusionRapid single flux quantum
Superconducting integrated circuits require several wiring layers to distribute bias and signals across the circuit, which must cross each other both with and without contacts. All wiring lines and contacts must be fully superconducting, and in the prior art each wiring layer comprises a single metallic thin film. An alternative wiring layer is disclosed that comprises sequential layers of two or more different metals. Such a multi-metallic wiring layer may offer improved resistance to impurity diffusion, better surface passivation, and / or reduction of stress, beyond that which is attainable with a single-metallic wiring layer. The resulting process leads to improved margin and yield in an integrated circuit comprising a plurality of Josephson junctions. Several preferred embodiments are disclosed, for both planarized and non-planarized processes. These preferred and other methods may be applied to digital circuits based on Rapid Single Flux Quantum logic, and to quantum computing using Josephson junction qubits.
Owner:SEEQC INC
Method for manufacturing vertical mos transistor
InactiveUS20090042347A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesImpurity diffusionSilicon oxide
A method for manufacturing a vertical MOS transistor comprising forming a protrusion-like region, forming a silicon oxide film on an exposed surface of the protrusion-like region and a surface of the silicon semiconductor substrate, increasing a film thickness of at least the silicon oxide film on the silicon semiconductor substrate by thermal oxidation to form a first insulating film, forming a lower impurity diffusion region, removing the silicon oxide film to expose a silicon side of the protrusion-like region, thermally oxidizing the silicon side to form a second insulating film having a thinner film thickness than a film thickness of the first insulating film, forming a gate electrode over a side of the protrusion-like region, and forming an upper impurity diffusion region.
Owner:LONGITUDE SEMICON S A R L
Semiconductor device and production method therefor
InactiveUS20050017319A1Improve responseVoltageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesImpurity diffusionDevice material
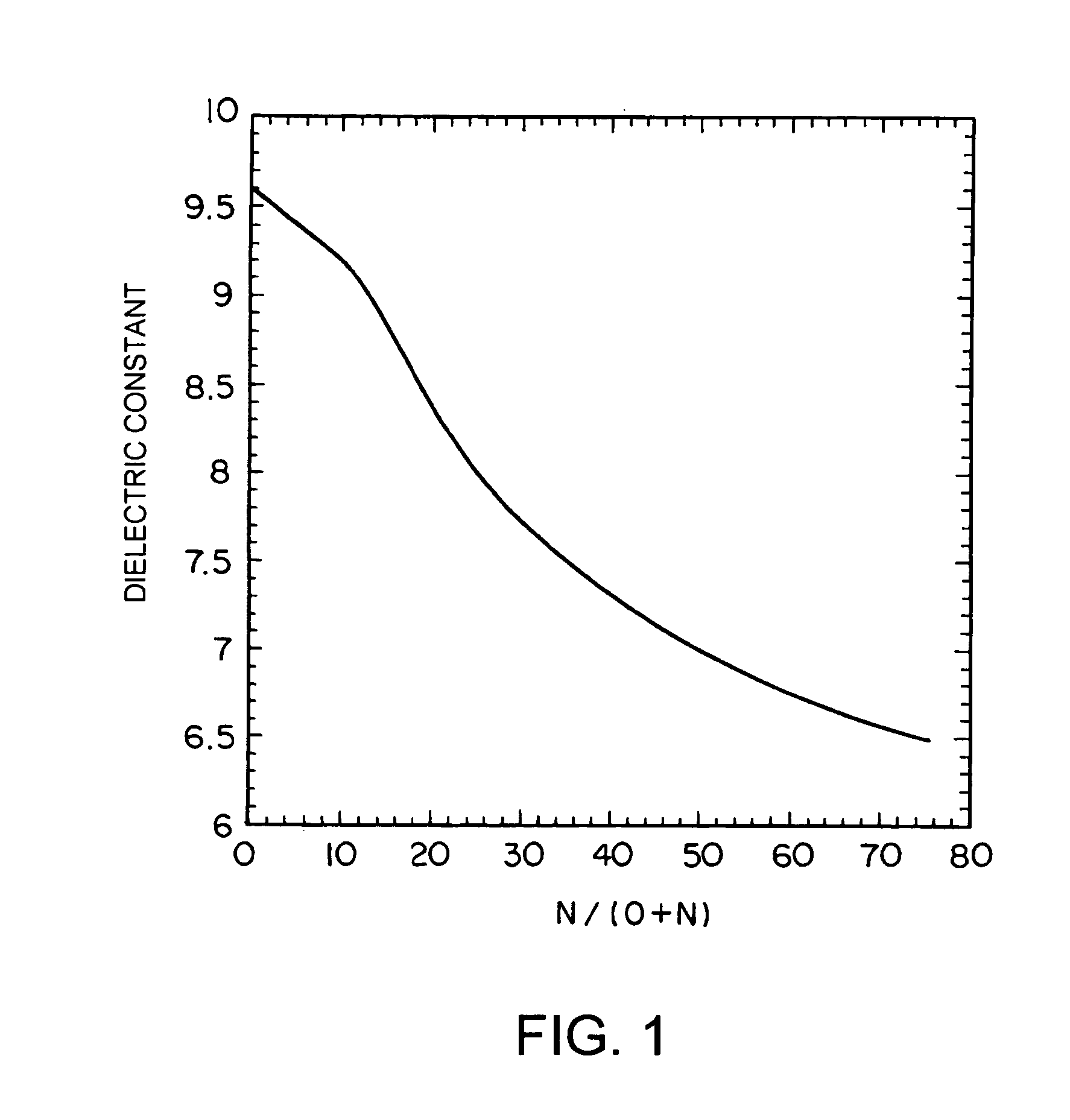
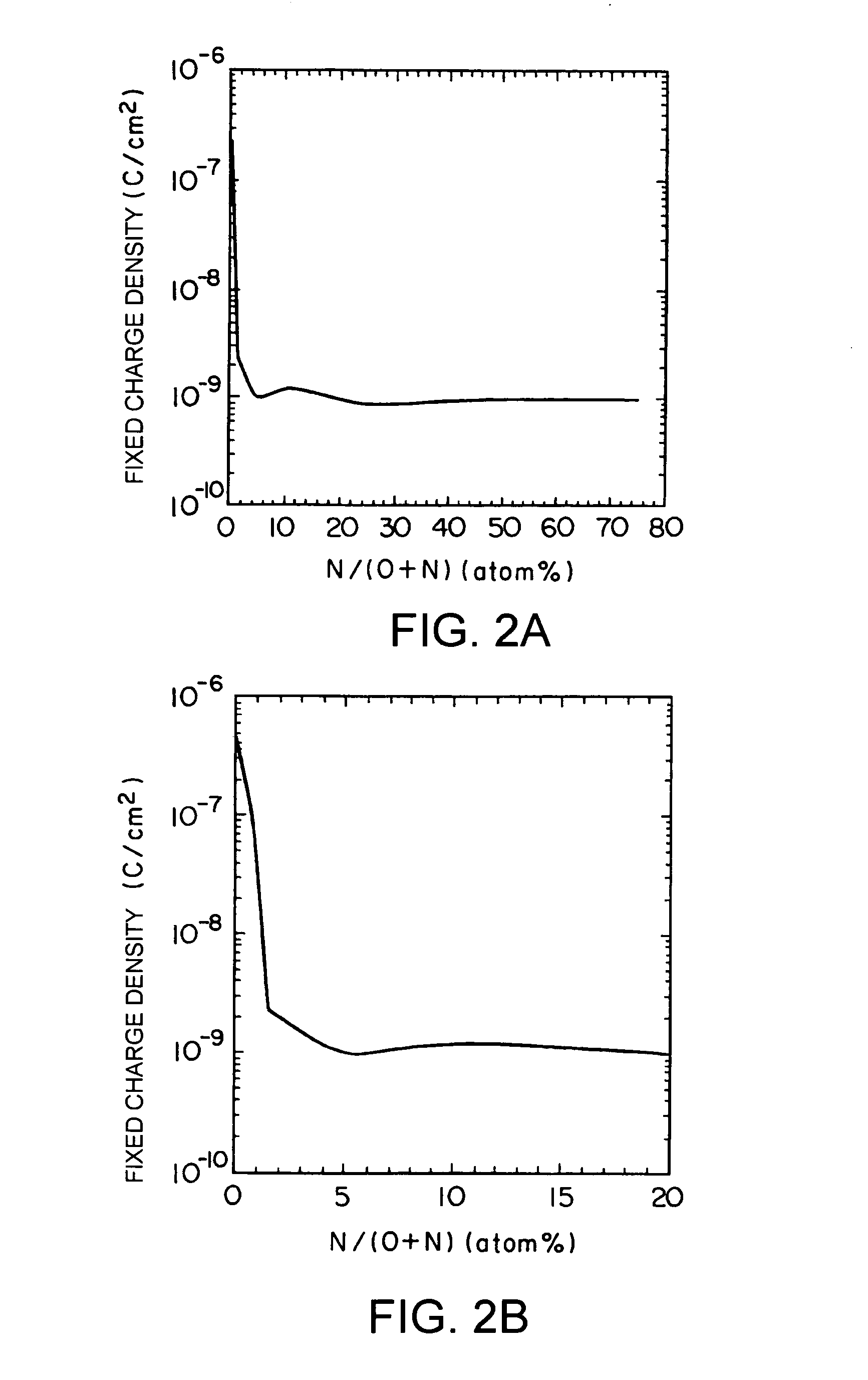
A semiconductor device has an MIS (metal-insulating film-semiconductor) structure, and a film mainly containing Al, O, and N atoms is used on a semiconductor. Alternatively, a semiconductor device has an MIS structure, and a film mainly containing Al, O, and N atoms is provided as a gate insulating film on a channel region between a source and a drain. Characteristics required of a gate insulating film of a 0.05 μm-gate-length-generation semiconductor transistor are satisfied. In particular, no fixed charge is included in the film, and impurity diffusion is reduced.
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20100044781A1Suppression of short channel effectsHigh currentSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesDriving currentImpurity diffusion
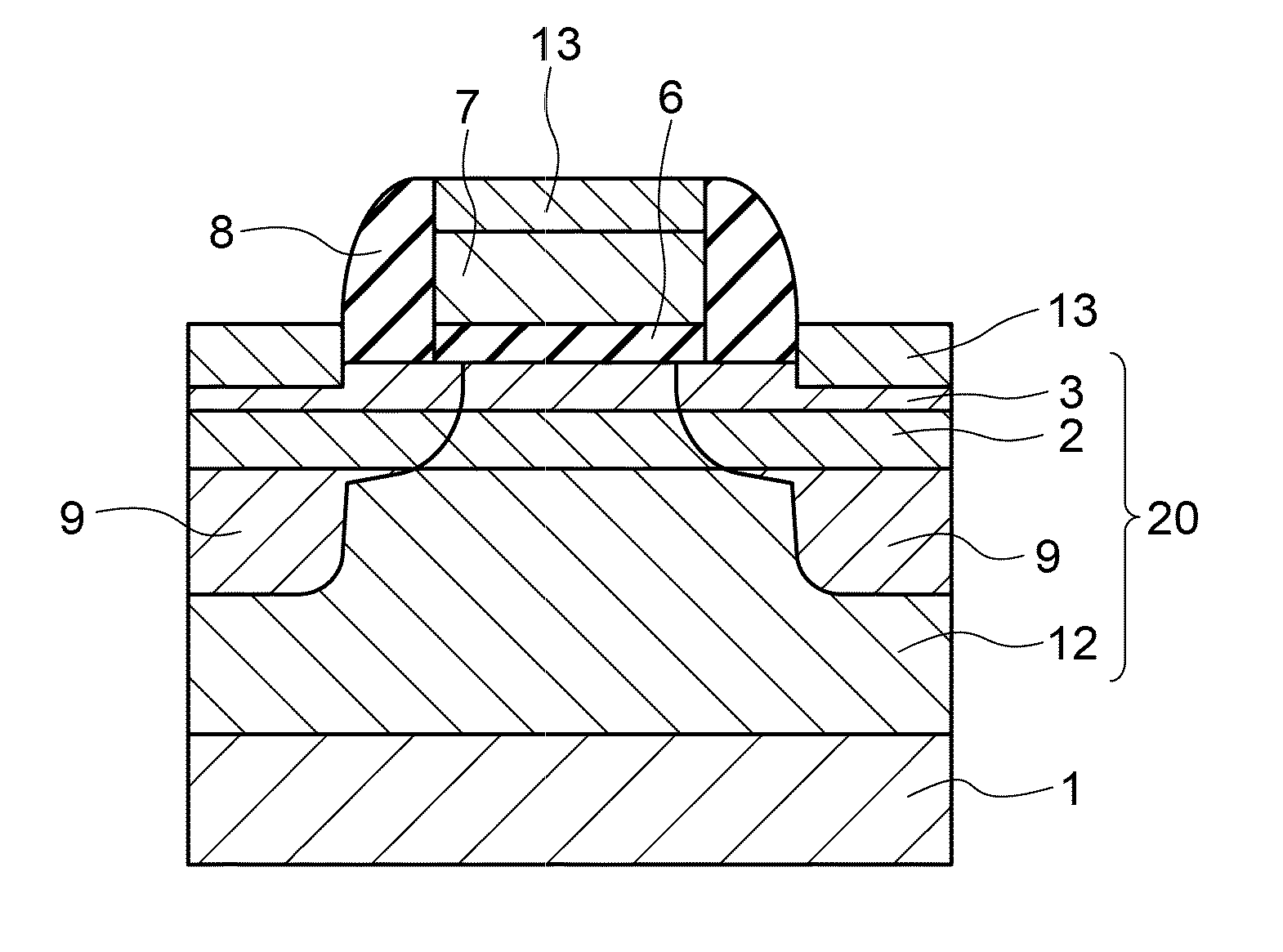
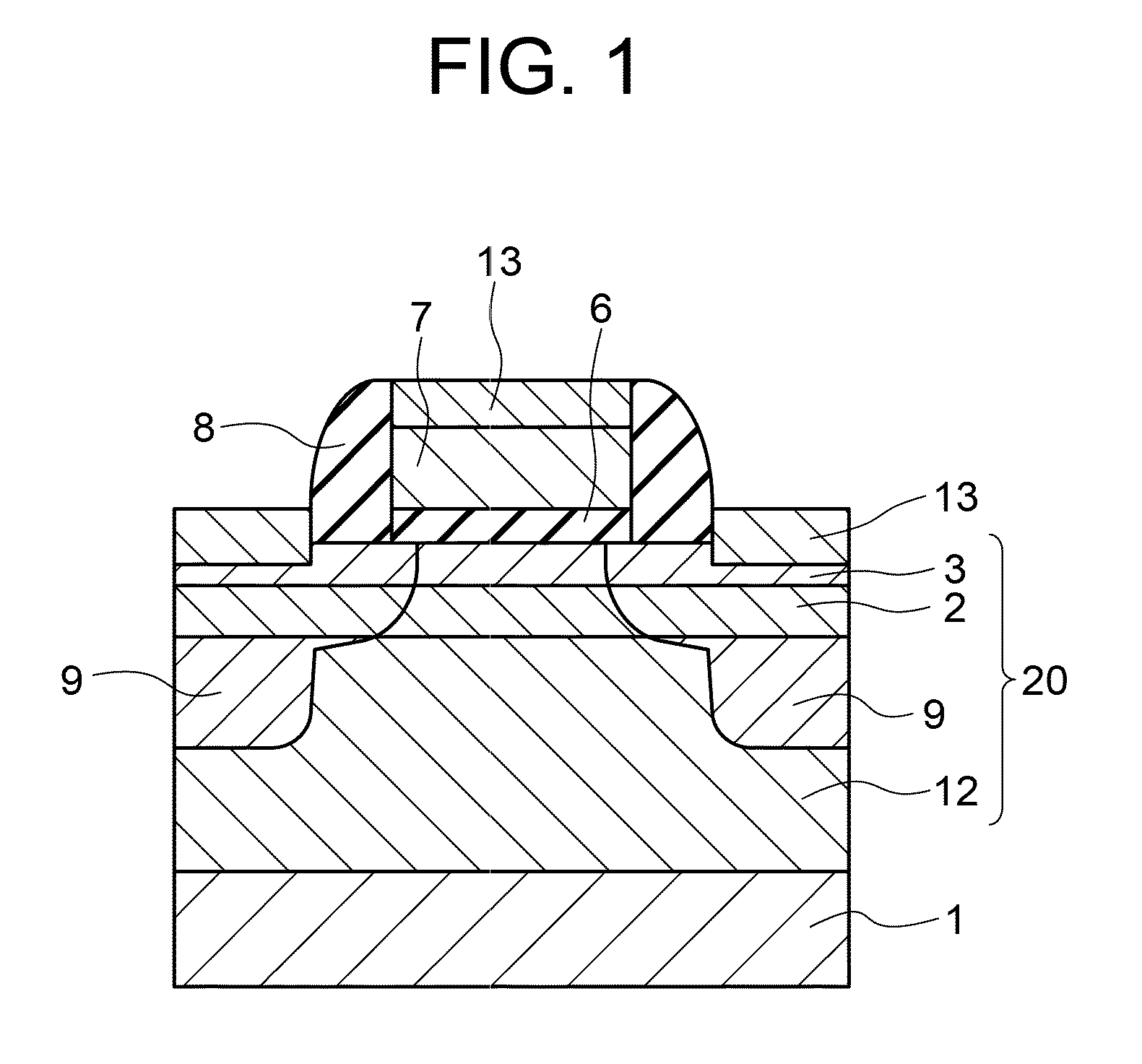
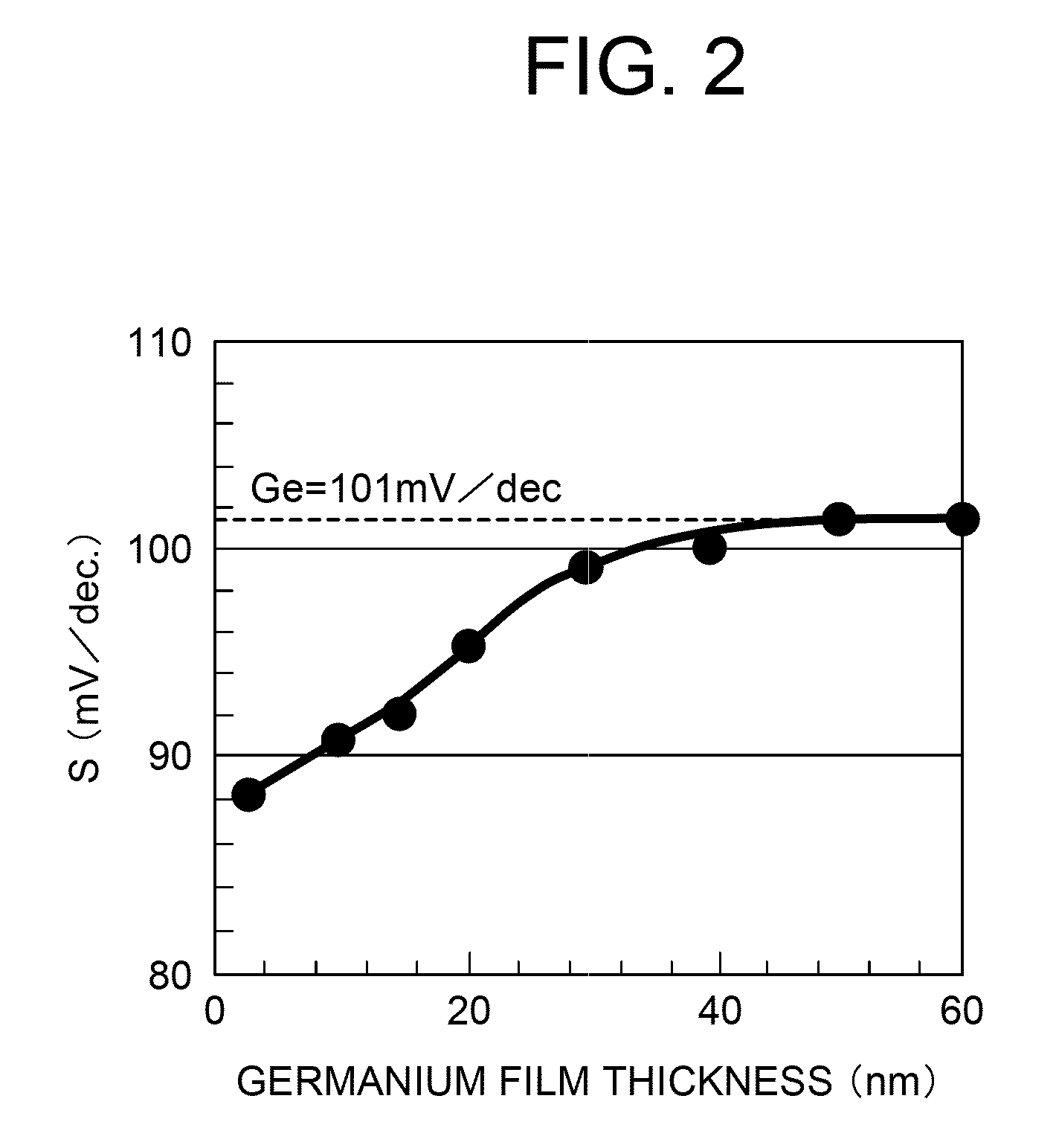
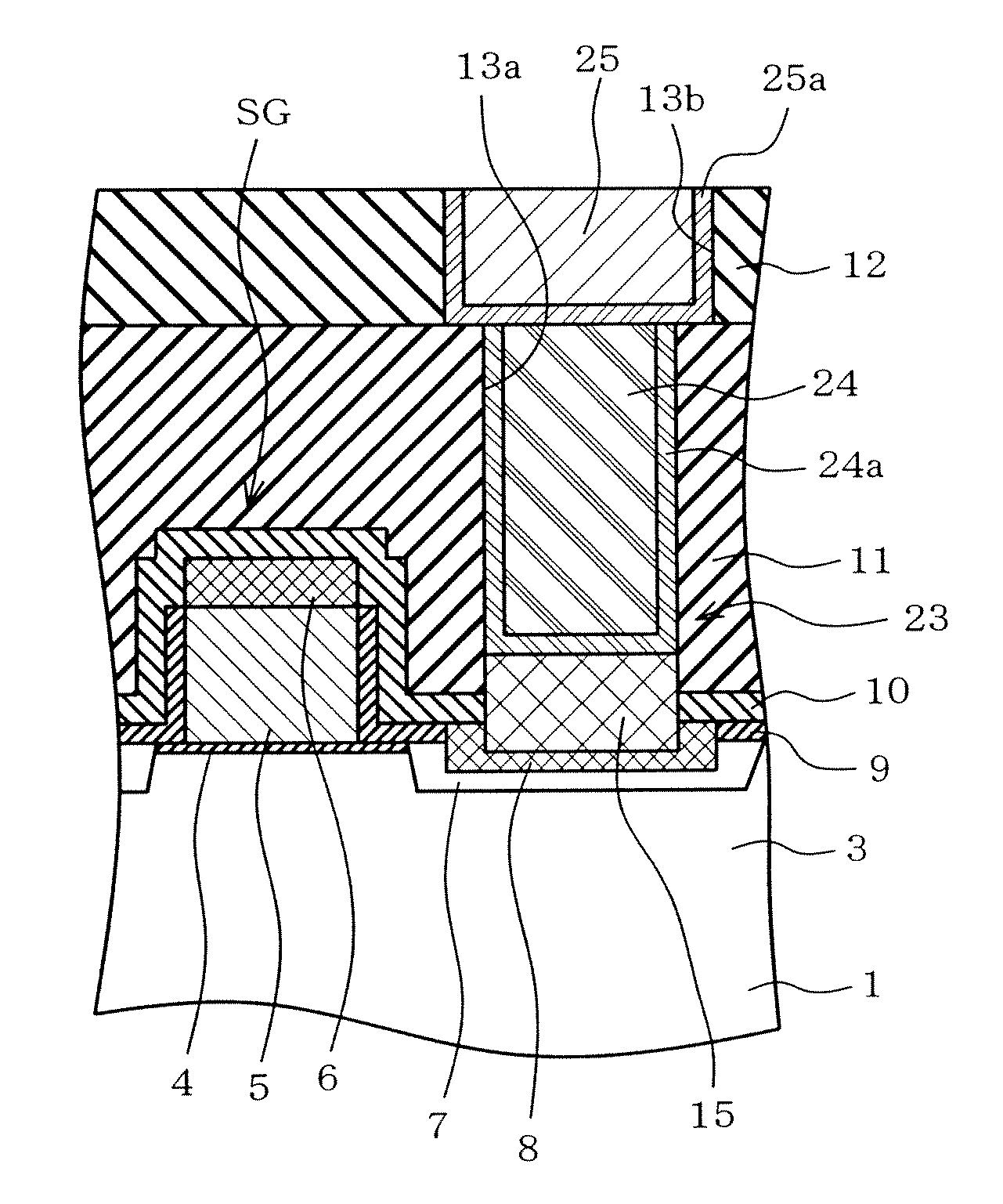
To suppress short channel effects and obtain a high driving current by means of a semiconductor device having an MISFET wherein a material having high mobility and high dielectric constant, such as germanium, is used for a channel. A p-type well is formed on a surface of a p-type silicon substrate. A silicon germanium layer having a dielectric constant higher than that of the p-type silicon substrate is formed to have a thickness of 30 nm or less on the p-type well. Then, on the silicon germanium layer, a germanium layer having a dielectric constant higher than that of the silicon germanium layer is formed to have a thickness of 3-40 nm by epitaxial growing. The germanium layer is permitted to be a channel region; and a gate insulating film, a gate electrode, a side wall insulating film, an n-type impurity diffusion region and a silicide layer are formed.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor device and method of fabricating the same
InactiveUS20080099921A1Suppress DiffuseLower resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorImpurity diffusion
A semiconductor device includes a semiconductor substrate including an impurity diffusion region within an upper surface thereof, an insulating film formed on an upper surface of the impurity diffusion region, and a contact plug formed in the insulating film so that the contact plug contacts the impurity diffusion region. The contact plug includes a first conductor layer contacting the upper surface of the impurity diffusion region and a second conductor layer formed on the first conductor layer including copper (Cu) or copper alloy layers, and the first conductor layer including a material which suppresses diffusion of the copper of the second conductor layer to the semiconductor substrate.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS6849900B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSurface layerImpurity diffusion
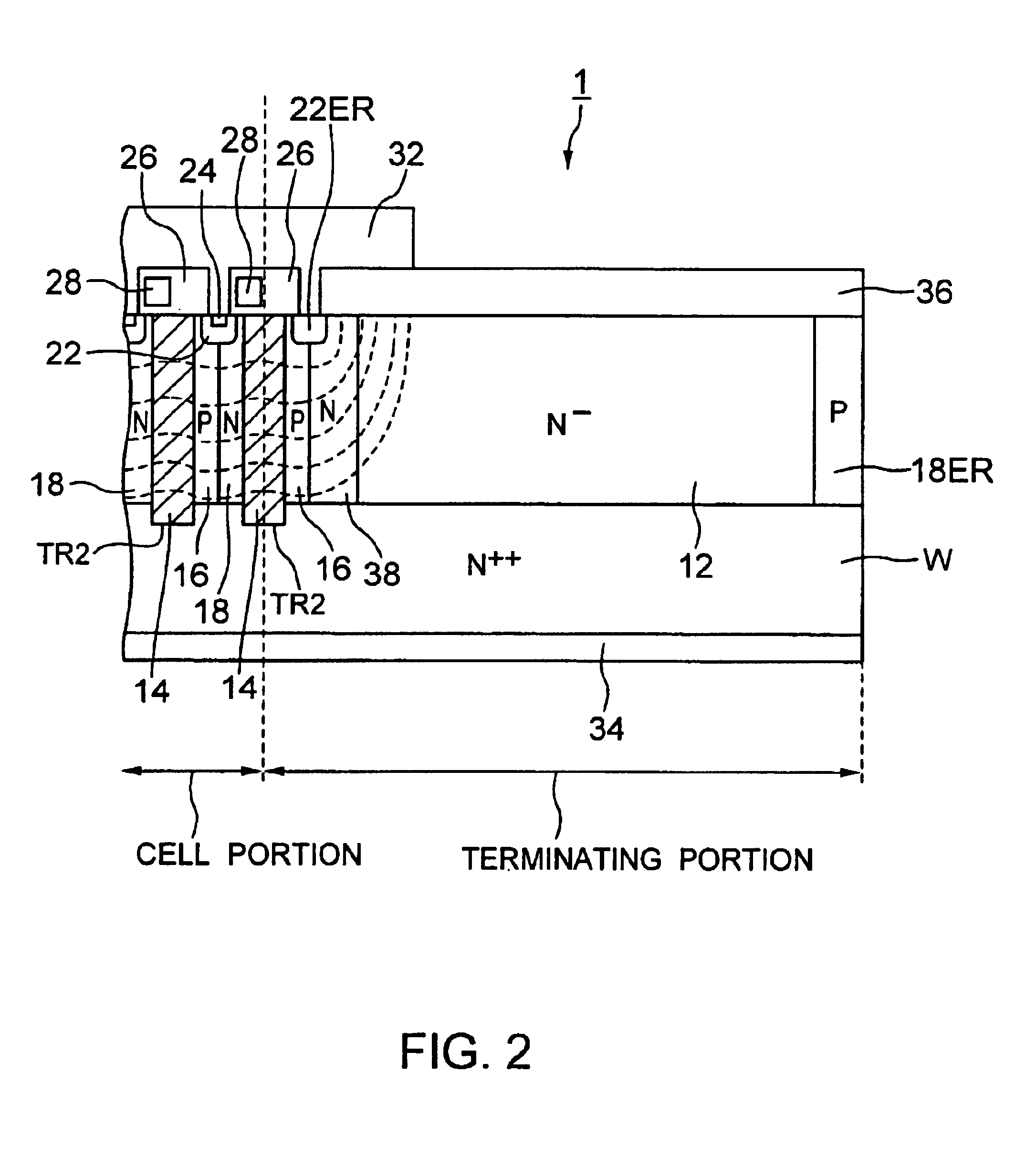
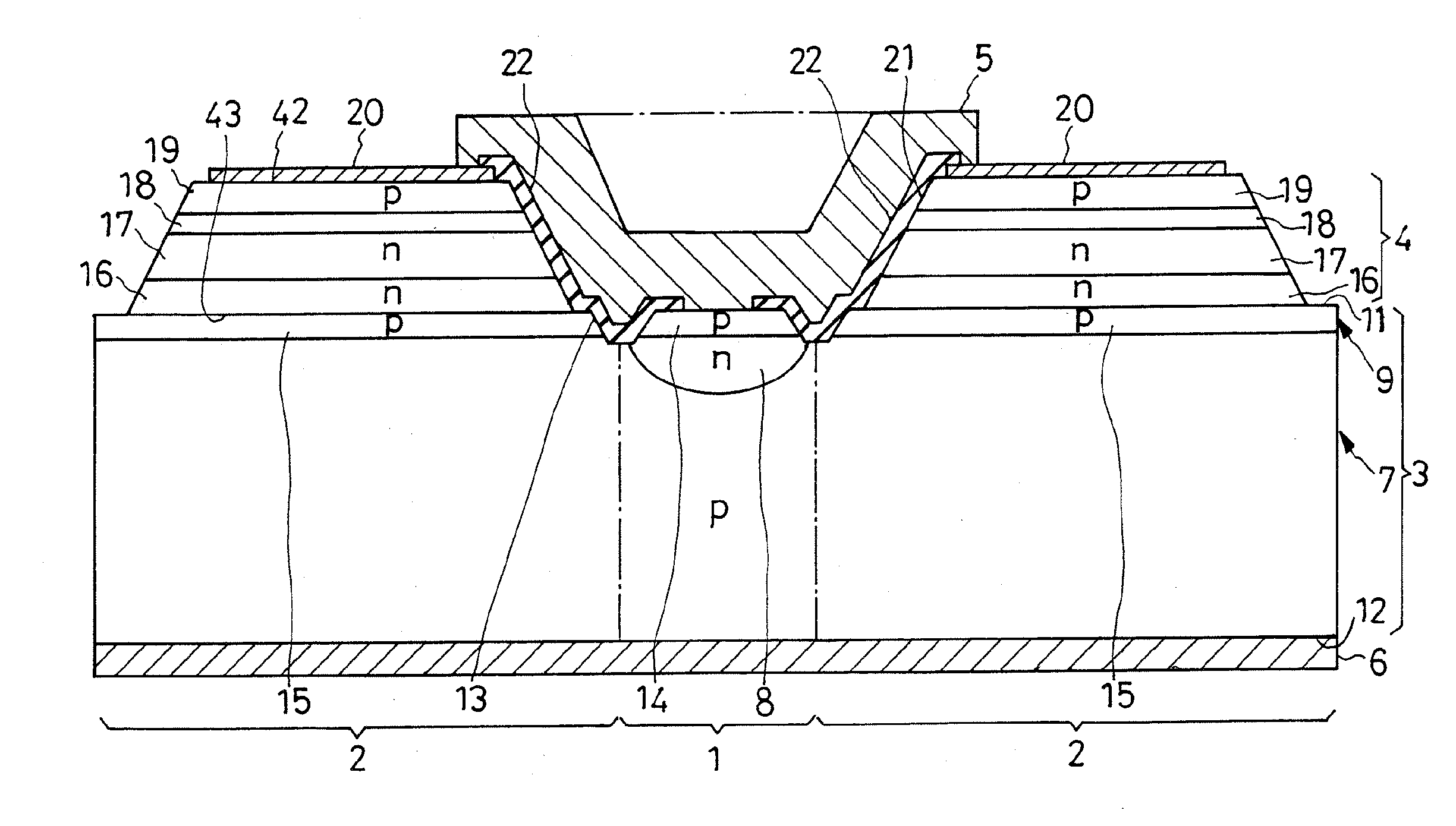
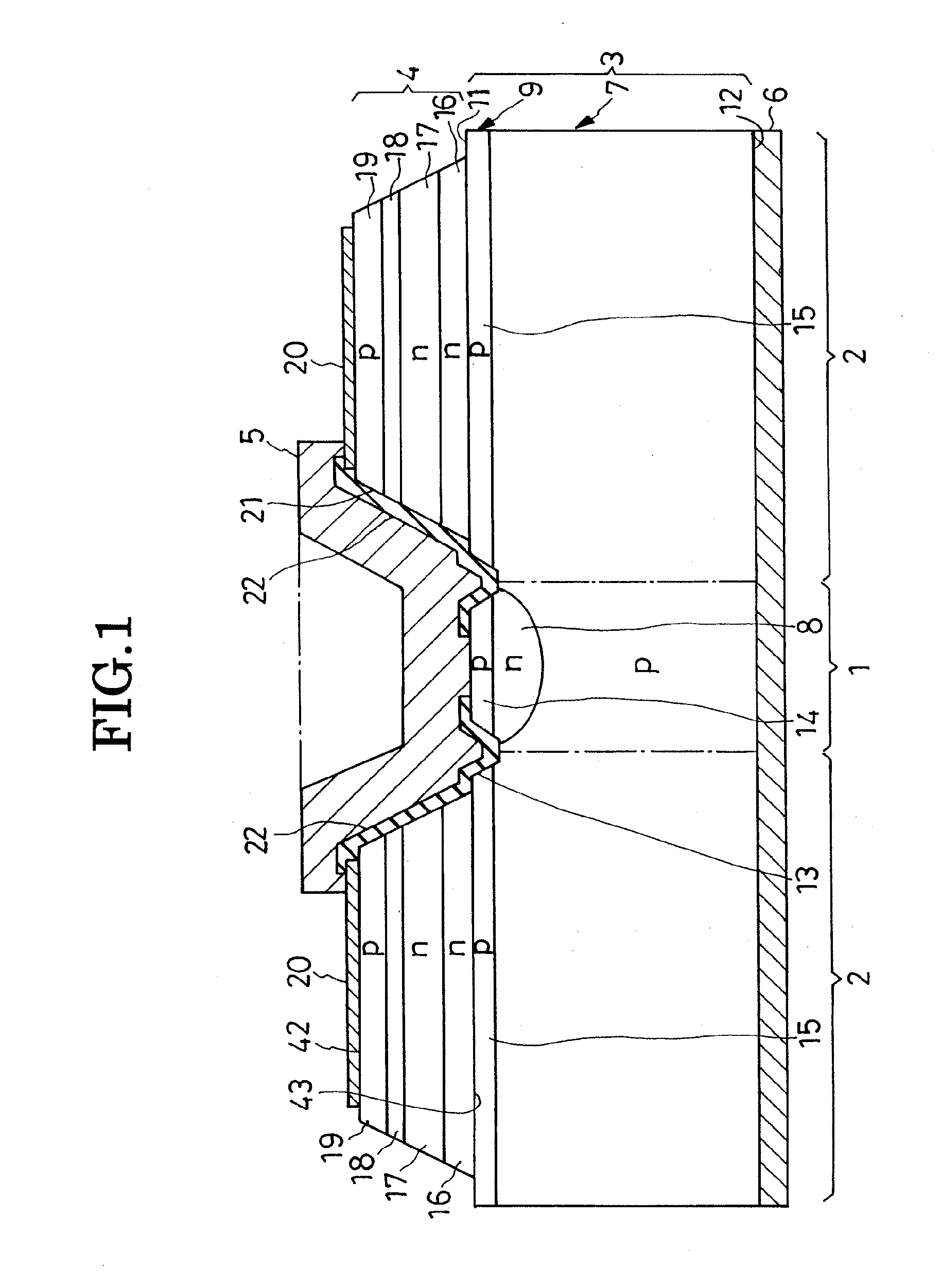
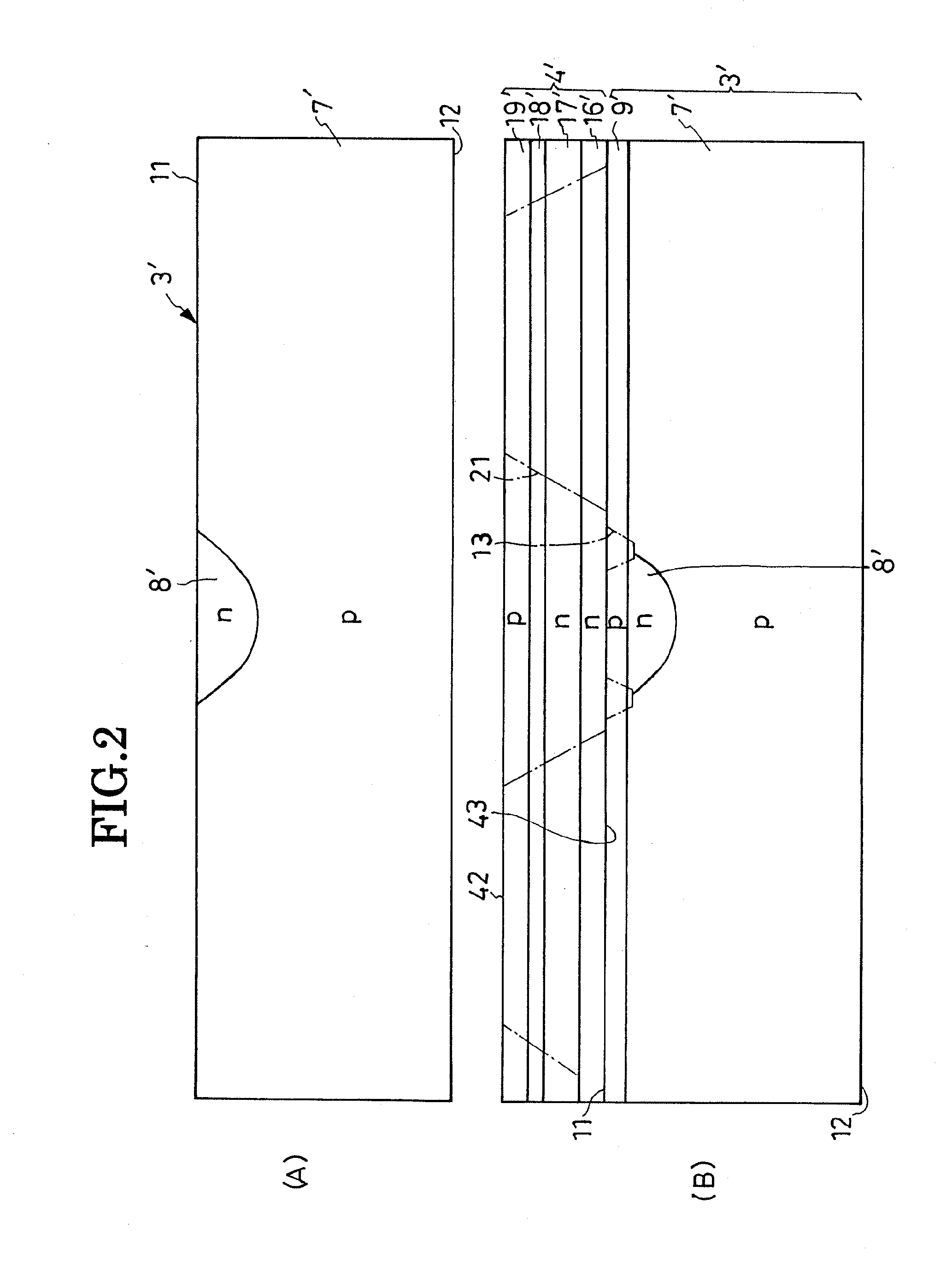
A semiconductor device includes: a semiconductor substrate of a first conductivity type; a semiconductor layer of a first conductivity type formed on a first main surface of the semiconductor substrate, the semiconductor layer including a first region for a cell portion and a second region for a terminating portion, the second region being positioned in an outer periphery of the first region, the terminating portion maintaining breakdown voltage by extending a depletion layer to relieve an electric field; junction pairs of semiconductor layers periodically arranged so as to form a line from the first region to the second region in a first direction parallel to the first main surface in the semiconductor layer and having mutually opposite conductivity types of impurities, each of the junction pair being composed of a first impurity diffusion layer of a second conductivity type formed from a surface of the semiconductor layer toward the semiconductor substrate and a second impurity diffusion layer of a first conductivity type formed from the surface of the semiconductor layer toward the semiconductor substrate and adjacently to the first impurity diffusion layer; a base layer of a second conductivity type selectively formed on each surface layer of the junction pairs which are formed in the first region, so as to connect with the first impurity diffusion layer and the second impurity diffusion layer in the same manner; a source layer of a first conductivity type selectively formed on each surface layer of the base layers of the second conductive type; a control electrode formed above each surface of the base layers and above each surface of the source layers via an insulating film; a first main electrode formed so as to cover the control electrode and to contact the source layers and the base layers in the same manner; and a second main electrode formed on a second main surface opposite to the first main surface of the semiconductor substrate.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
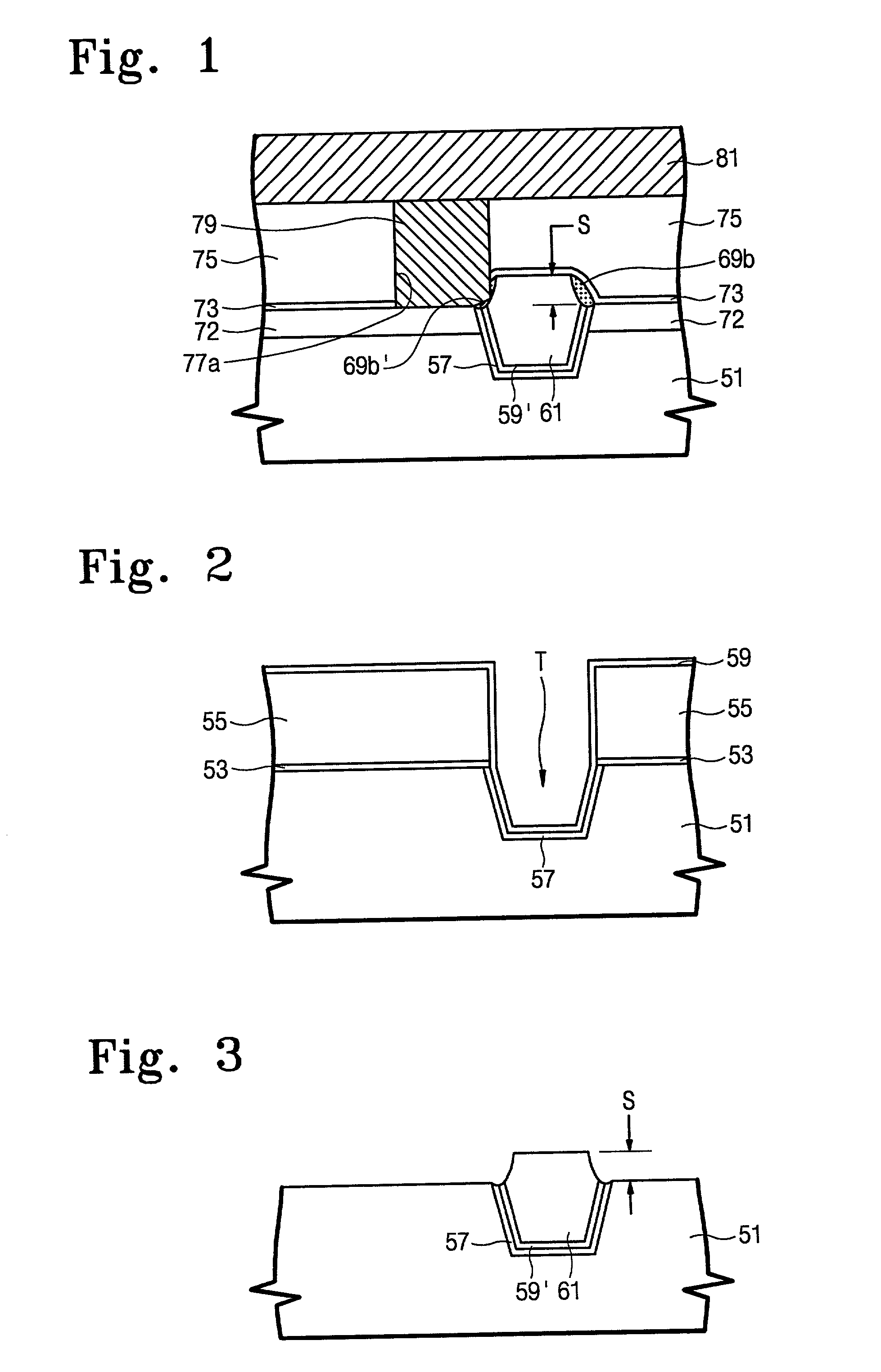
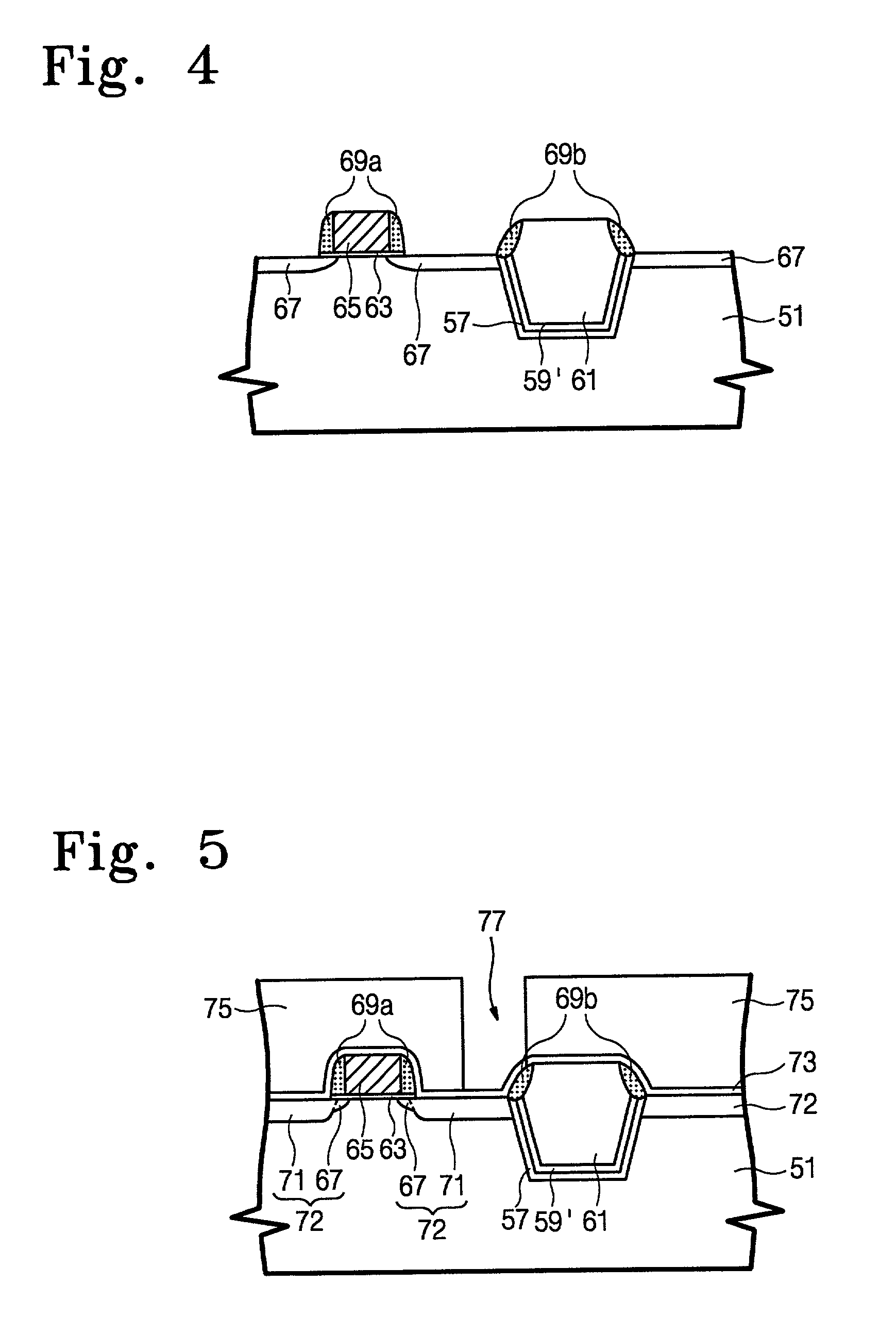
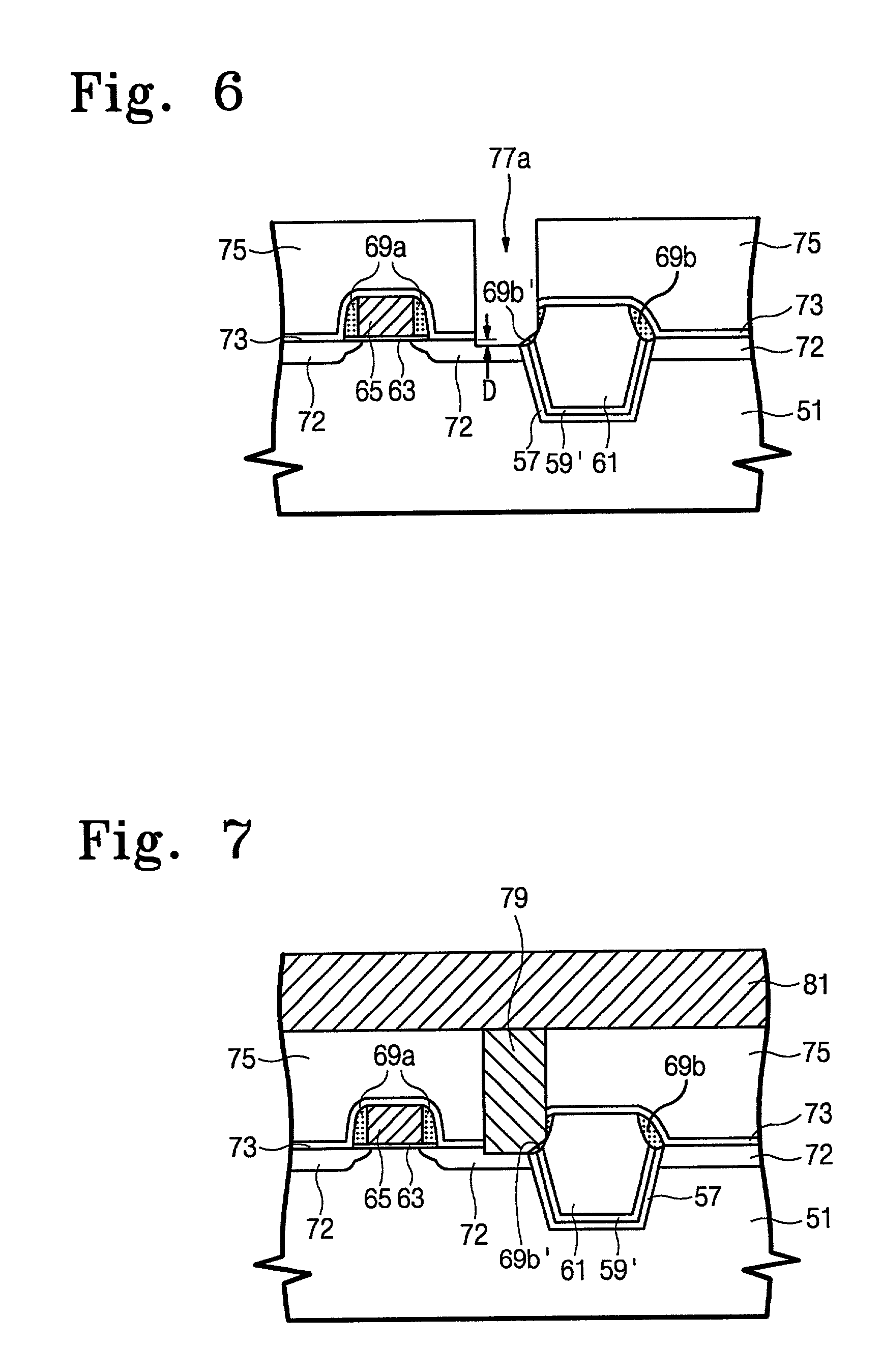
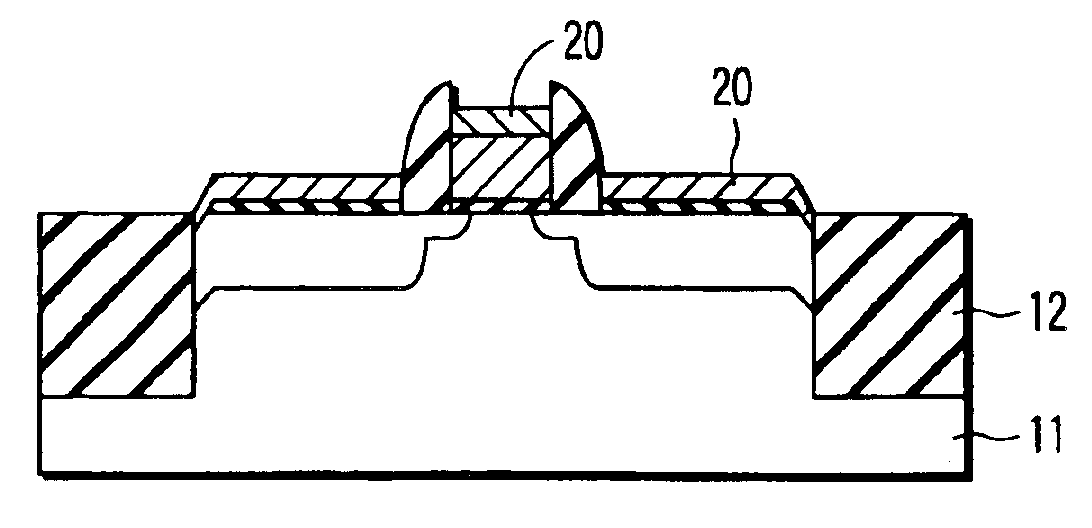
Method of forming an isolation layer and method of manufacturing an image device using the same
InactiveUS20080102557A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingImpurity diffusionIsolation layer
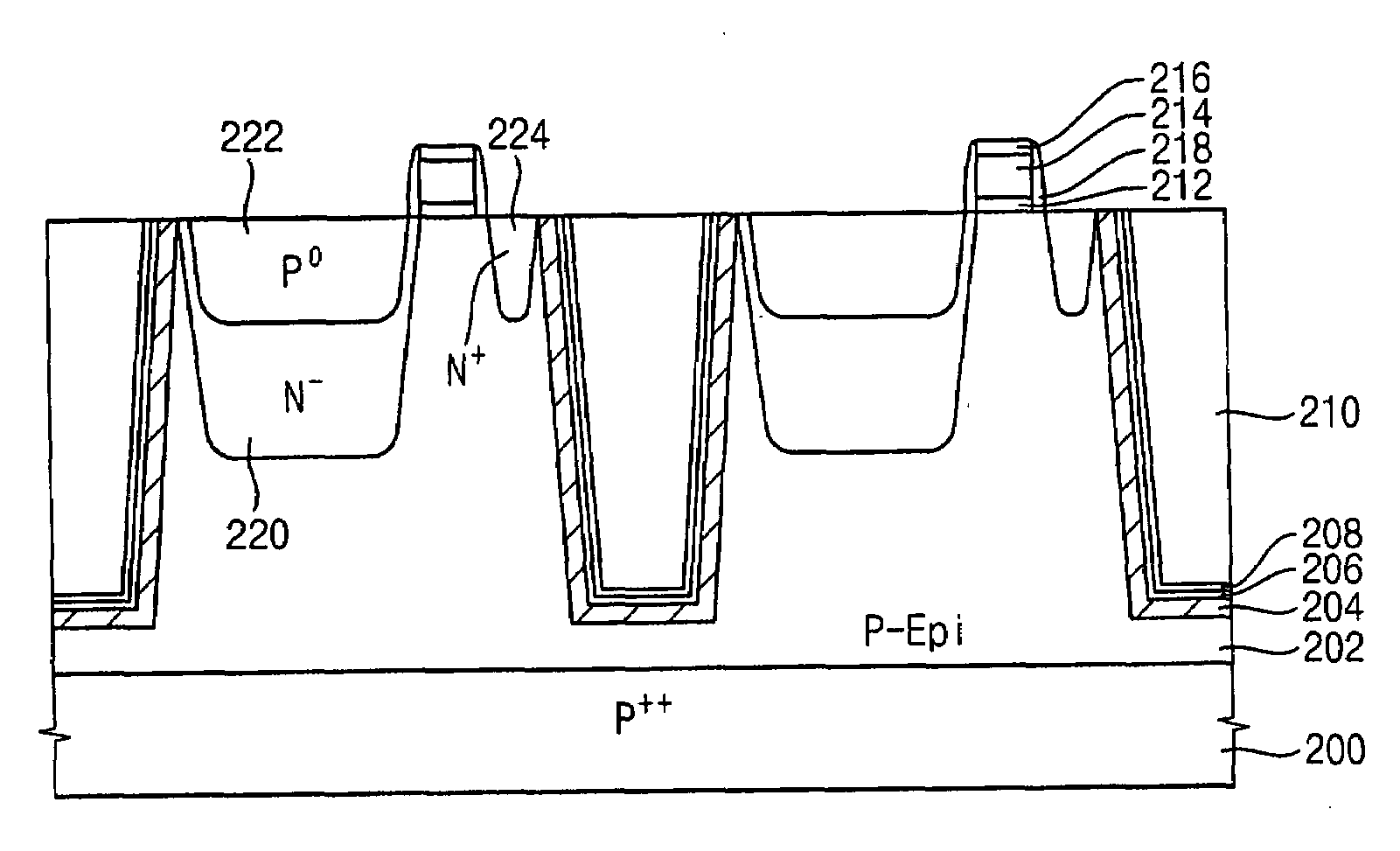
A method of forming an isolation layer includes forming mask pattern structure on a substrate to partially expose the substrate, etching the substrate using the mask pattern as an etching mask to form a trench, forming an impurity diffusion region at an inner face of the trench, and filling the trench with the isolation layer. A method of manufacturing an image device includes the method of forming an isolation layer, and at least additionally forming unit pixels including a photo diode and transistors on an active region defined by the isolation layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Solid-state imaging device, method of driving the same, and electronic system including the device
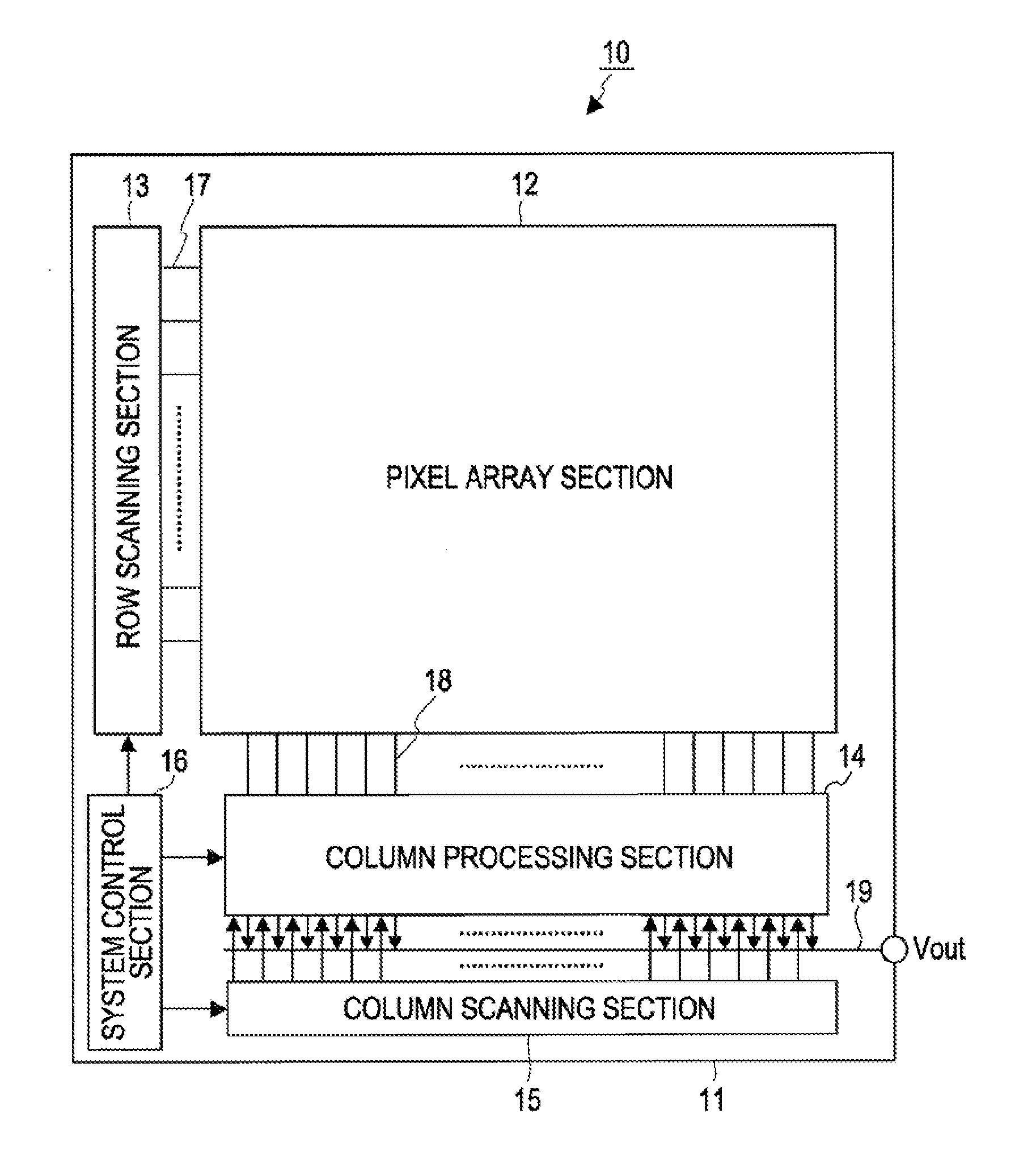
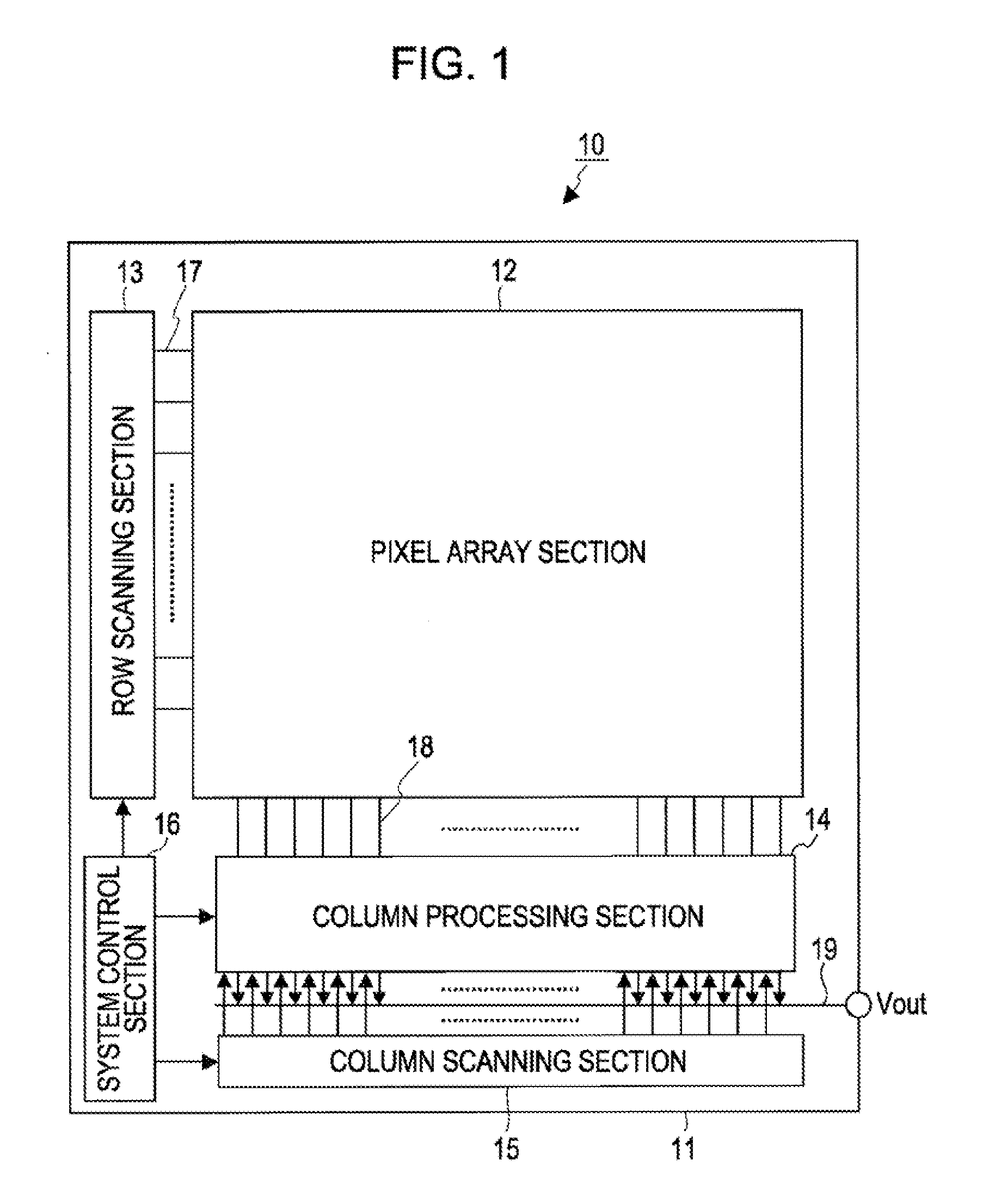
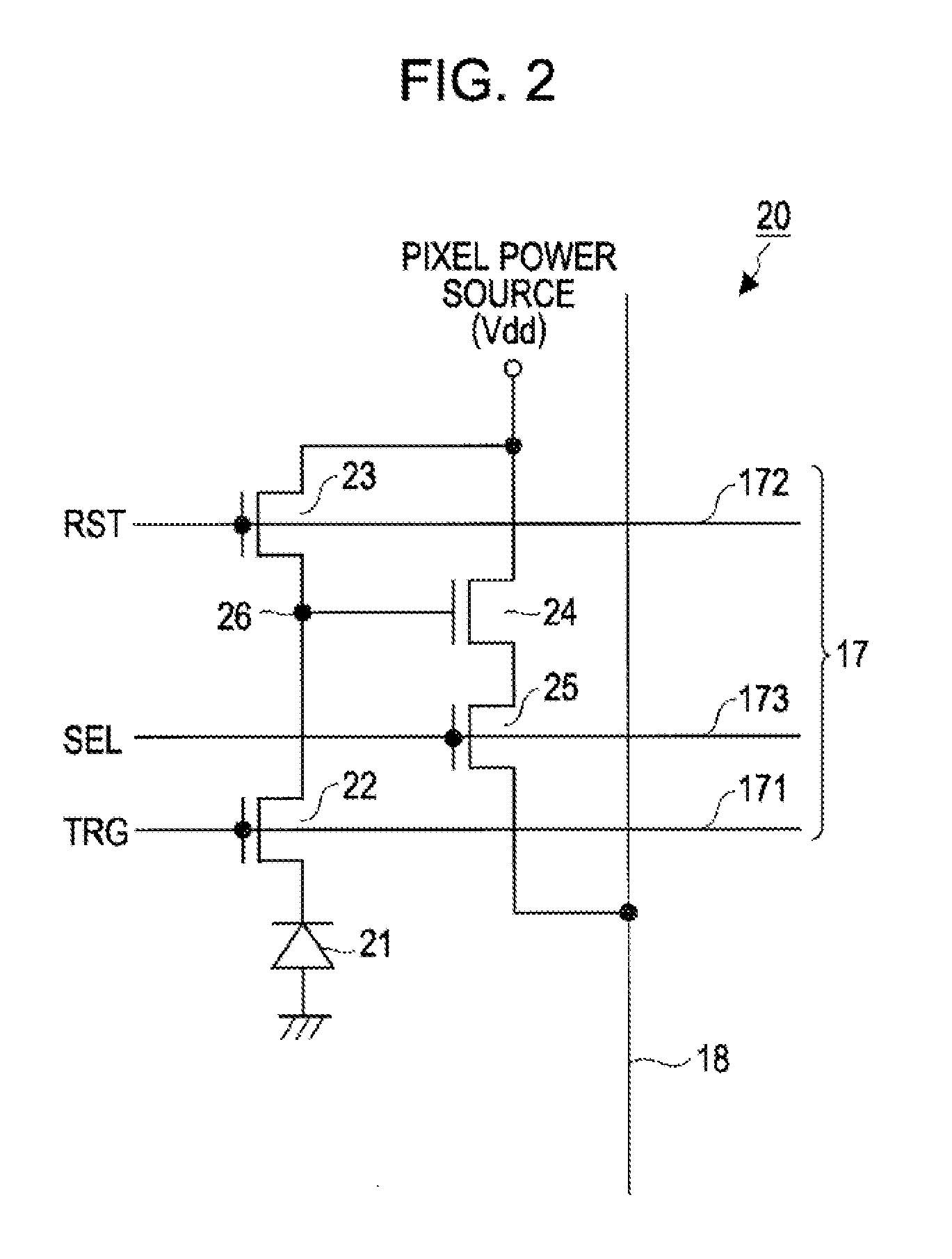
InactiveUS20100309357A1Cancel noiseEliminate fluctuationsTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsElectronic systemsImpurity diffusion
A solid-state imaging device includes: a unit pixel including a photoelectric conversion section, an impurity-diffusion region capable of temporarily accumulating or holding electric charges generated by the photoelectric conversion section, and a reset transistor resetting the impurity-diffusion region by a voltage of a voltage-supply line, and having an impurity concentration such that at least the reset transistor side of the impurity-diffusion region becomes a depletion state; and a drive circuit changing the voltage of the voltage-supply line from a first voltage lower than a depletion potential of the reset transistor side of the impurity-diffusion region to a second voltage higher than the depletion potential while the reset transistor is on.
Owner:SONY CORP
Electroluminescence display device
InactiveUS20050082540A1High color reproductionSharp displayTransistorStatic indicating devicesImpurity diffusionDisplay device
An EL element and an interface between a channel and an impurity diffusion area of a thin film transistor provided in the vicinity of the EL element are spaced apart. A light shielding film is provided between the EL element and the interface. By providing such a space and / or the light shielding film, generation of a leak current, which would otherwise be caused by light emitted from the self-emissive EL element entering the TFT, is reliably prevented, thereby ensuring that emitted light is not brighter than a predetermined luminance.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Semiconductor device
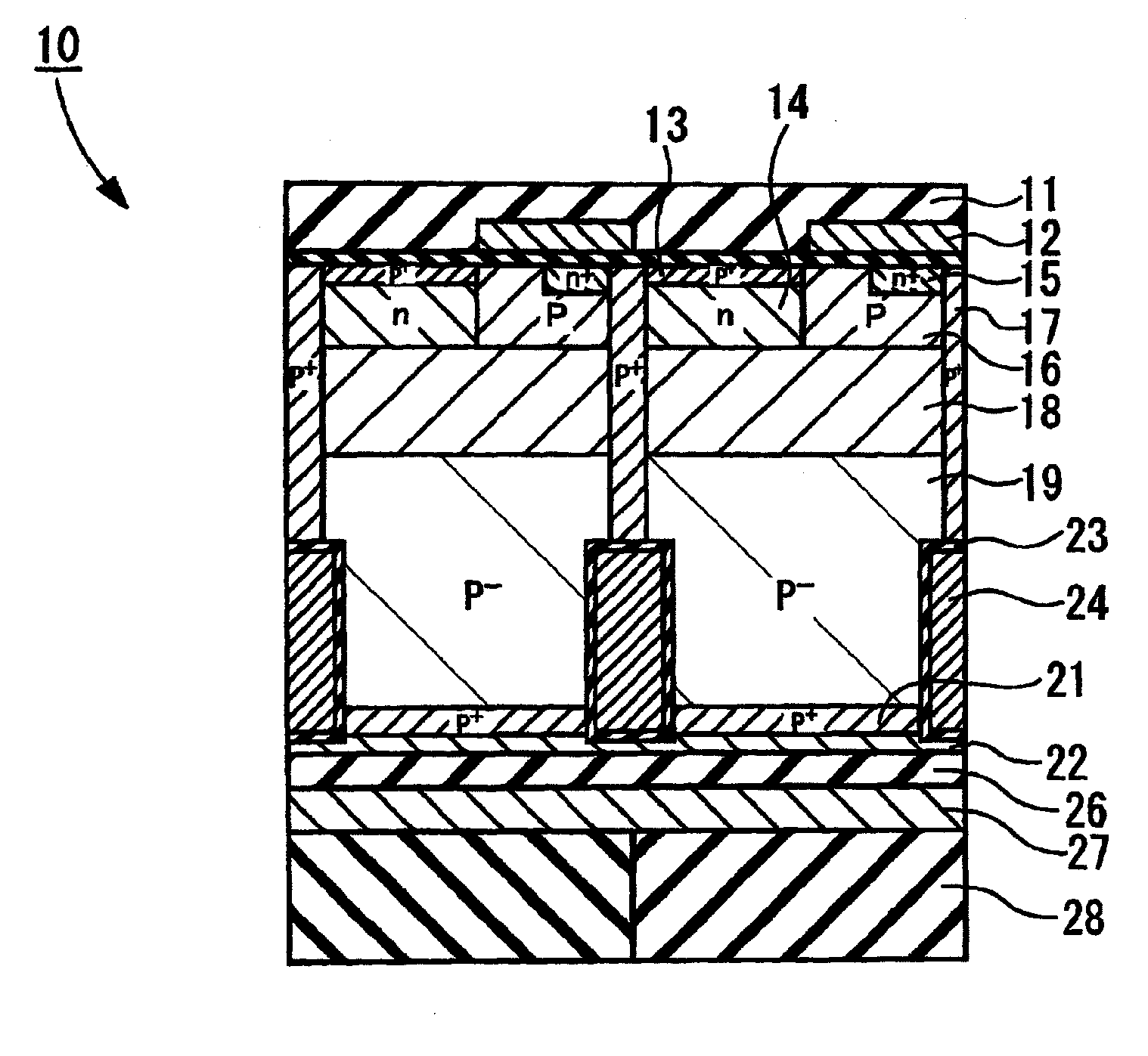
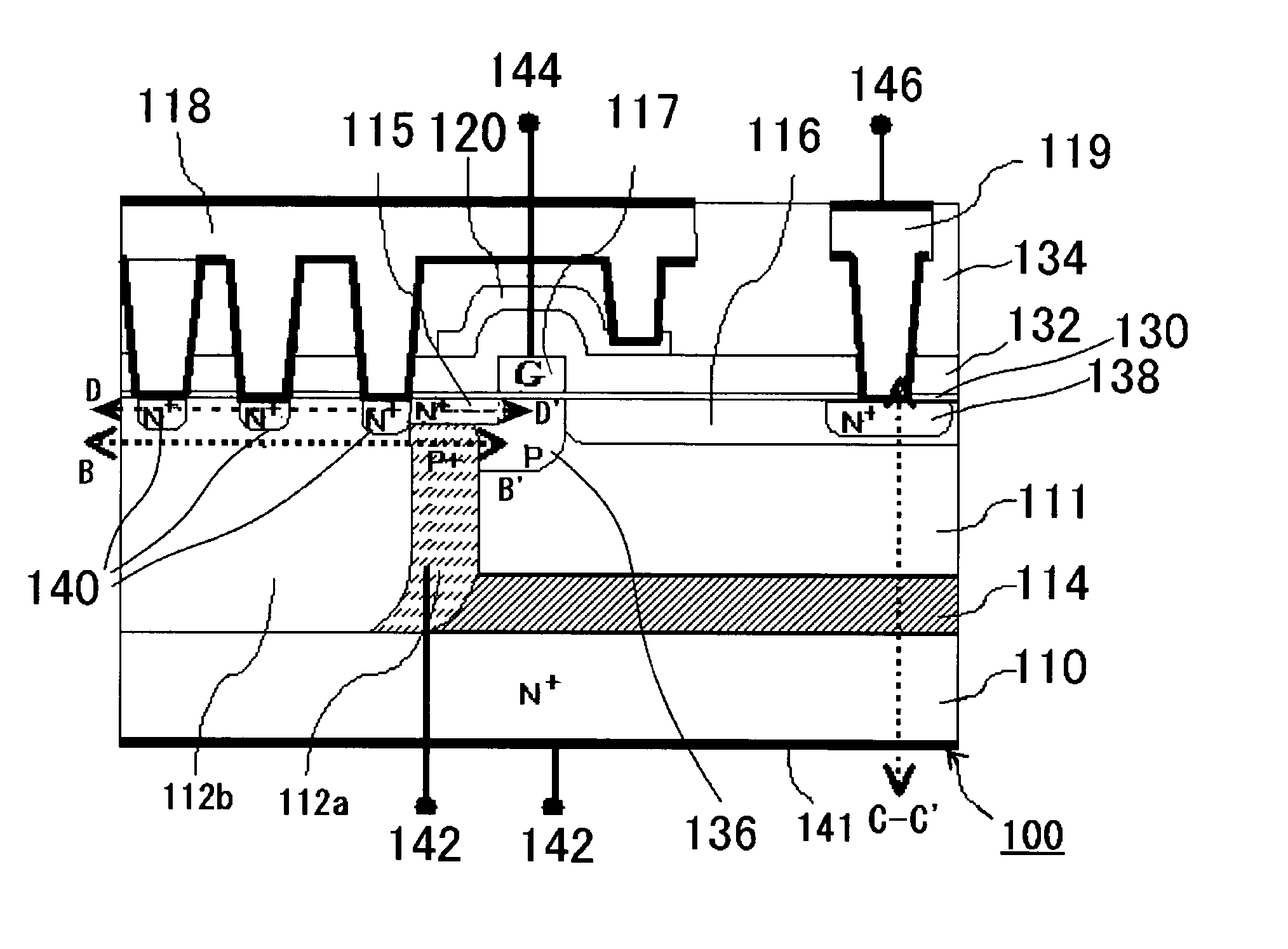
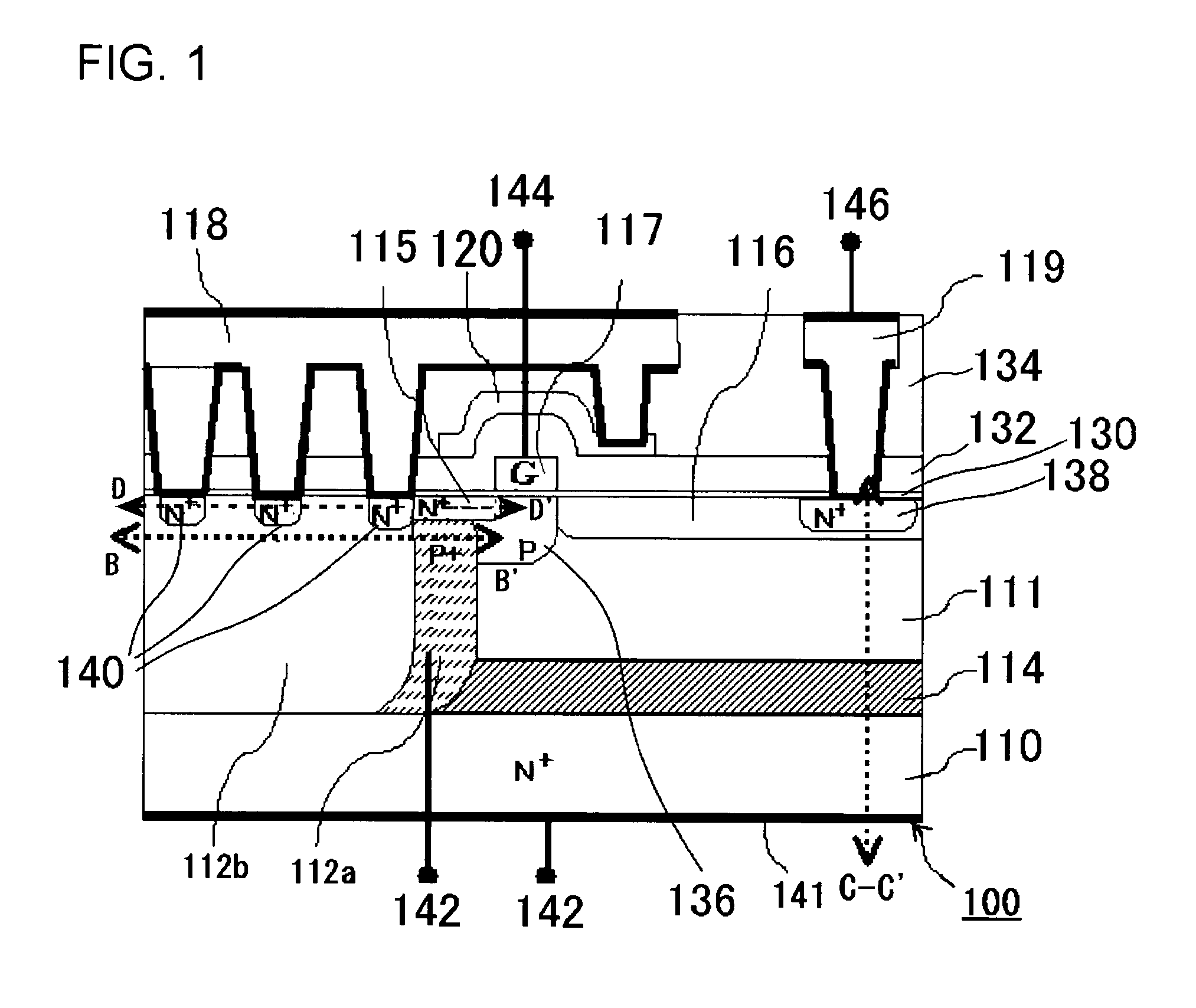
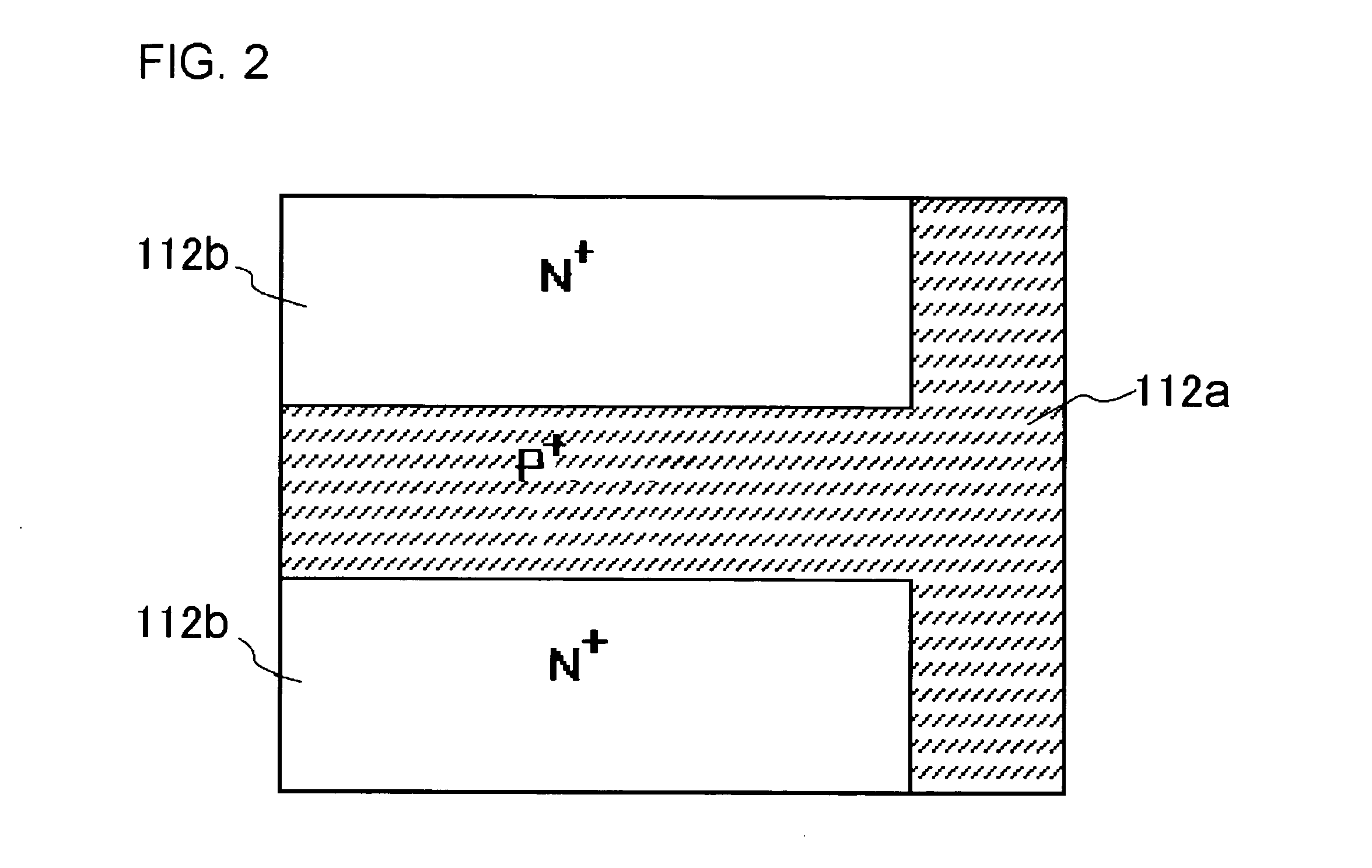
InactiveUS20050269601A1Extending of the semiconductor substrate can be preventedHigh film thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMOSFETHigh concentration
The semiconductor device comprises: a semiconductor substrate (N+ substrate 110) containing a first conductivity type impurity implanted therein; a second conductivity type impurity-implanted layer (P+ implanted layer 114) at relatively high concentration, formed on the semiconductor substrate (N+ substrate 110); a second conductivity type impurity epitaxial layer (P− epitaxial layer 111) at relatively low concentration, formed on the second conductivity type impurity-implanted layer (P+ implanted layer 114); and a field effect transistor 100 (N-channel type lateral MOSFET 100)composed of a pair of impurity diffusion regions (N+ source diffusion layer 115 and N− drain layer 116) provided in the second conductivity type impurity epitaxial layer (P− epitaxial layer 111) and a gate electrode 117 provided over a region sandwiched with the pair of impurity diffusion regions (N+ source diffusion layer 115 and N− drain layer 116).
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Overvoltage-protected light-emitting semiconductor device, and method of fabrication
InactiveUS20080308823A1More compact constructionEasy and economical to manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesOvervoltageDevice material
A light-generating semiconductor region is grown by epitaxy on a silicon substrate. The light-generating semiconductor region is a lamination of layers of semiconducting nitrides containing a Group III element or elements. The silicon substrate has a p-type impurity-diffused layer formed therein by thermal diffusion of the Group III element or elements from the light-generating semiconductor region as a secondary product of the epitaxial growth of this region on the substrate. The p-type impurity-diffused layer is utilized as a part of overvoltage protector diodes which are serially interconnected with each other and in parallel with the LED section of the device between a pair of electrodes.
Owner:SANKEN ELECTRIC CO LTD
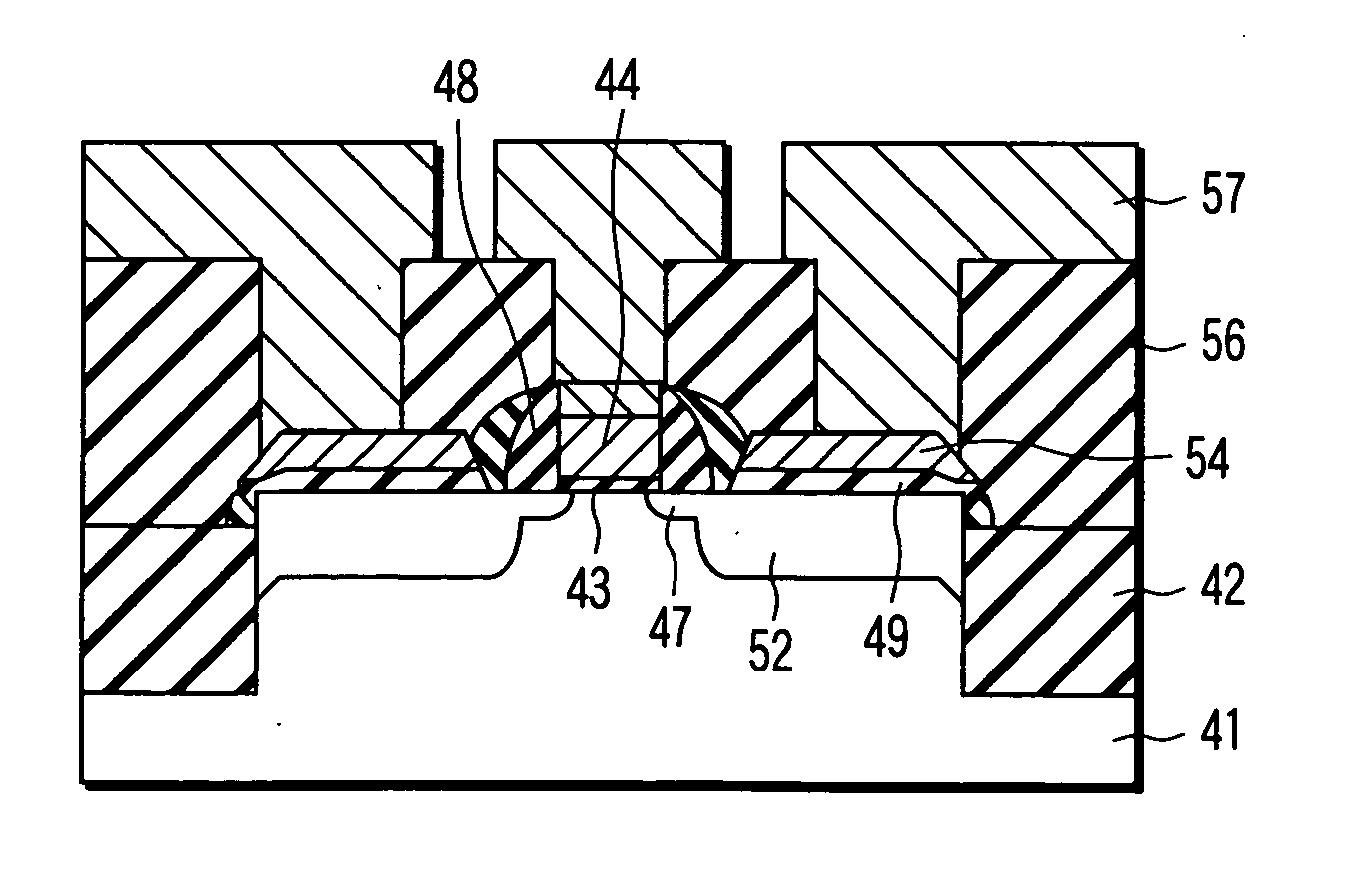
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing semiconductor device
ActiveUS20070290329A1Reduced space required for installationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesImpurity diffusionZener diode
In a semiconductor device 100, a light emitting element 120 has been mounted on an upper plane of a semiconductor substrate 102. In an impurity diffusion region of the semiconductor substrate 102, a P conducting type of a layer 104, and an N layer 106 have been formed, while an N conducting type impurity is implanted to the P layer 104, and then the implanted impurity is diffused to constitute the N layer 106. A zener diode 108 made of a semiconductor device has been formed by the P layer 104 and the N layer 106.
Owner:SHINKO ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
Manufacture of solid state imager having plurality of photosensors per each pixel
A second conductivity type well is formed in a first conductivity type semiconductor substrate. Vertical CCD channels of the first conductivity type are formed in the second conductivity type well. Vertical transfer electrodes are formed above the vertical CCD channels to form vertical CCDs along with the vertical CCD channels. A first impurity diffusion layer is formed in the well by implanting first conductivity type impurities along a first direction crossing the normal direction of the semiconductor substrate. A second impurity diffusion layer is formed in the well by implanting first conductivity type impurities along a second direction crossing the normal direction of the semiconductor substrate. A third impurity diffusion layer of the second conductivity type is formed between the first and second impurity diffusion layer. A fourth impurity diffusion layer of the second conductivity type is formed in the well above the first to third impurity diffusion layers.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Solar Cell and Manufacturing Method Thereof
InactiveUS20110143486A1Simple manufacturing processReduce the amount of powerPV power plantsFinal product manufactureHigh concentrationImpurity diffusion
Forming an impurity diffusion layer of the second conductivity type and an antireflective film on one surface side of a semiconductor substrate of the first conductivity type; applying the first electrode material onto the antireflective film; forming a passivation film on the other surface side of the semiconductor substrate; forming openings in the passivation film to reach the other surface side; applying a second electrode material containing impurity elements of the first conductive type to fill the openings and not to be in contact with the second electrode material of adjacent openings; applying a third electrode material onto the passivation film to be in contact with the entire second electrode material; forming at a time, by heating the semiconductor substrate at a predetermined temperature after applying the first electrode material and the third electrode material, the first electrodes, a high-concentration region, and the second electrodes and third electrode.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
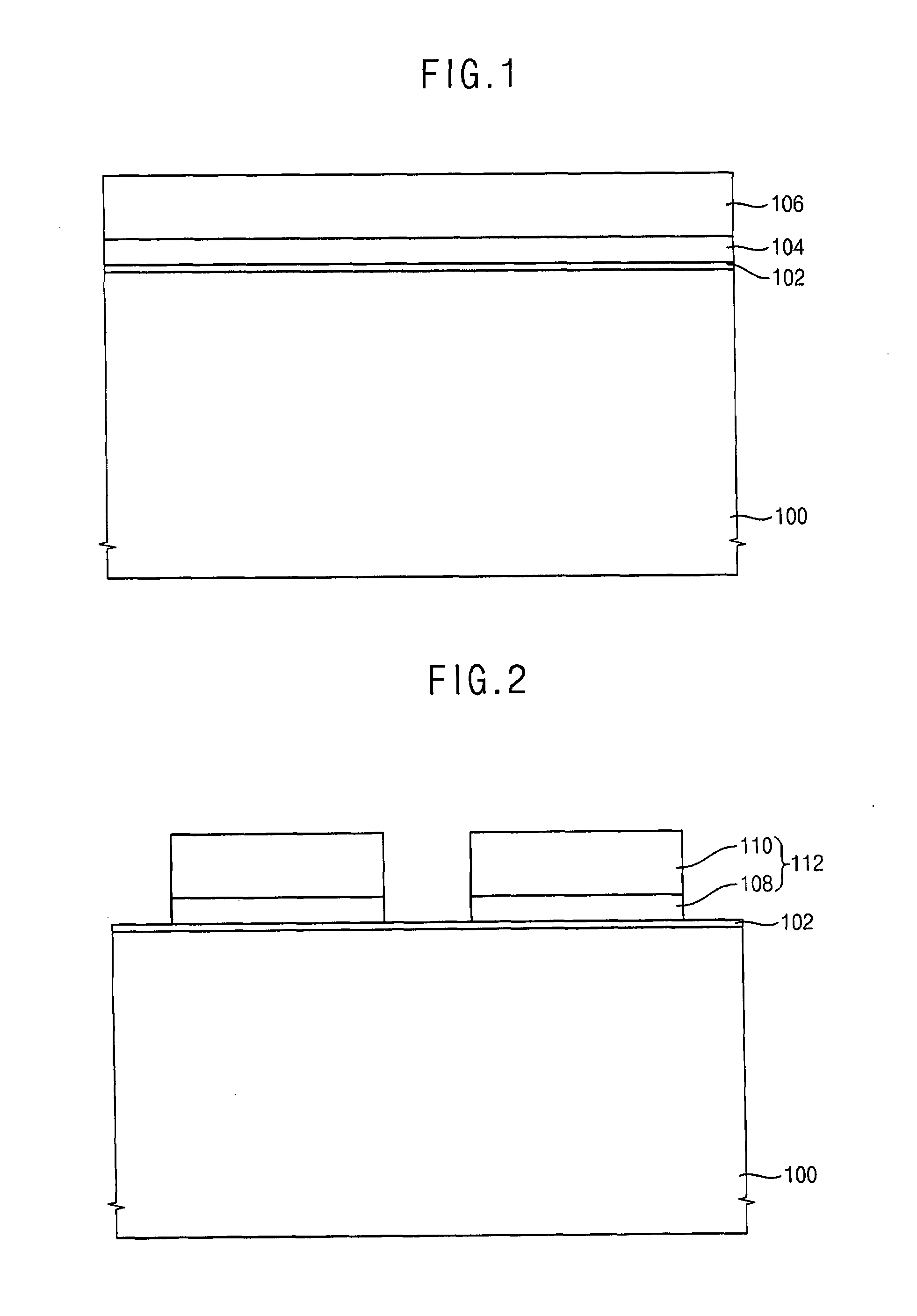
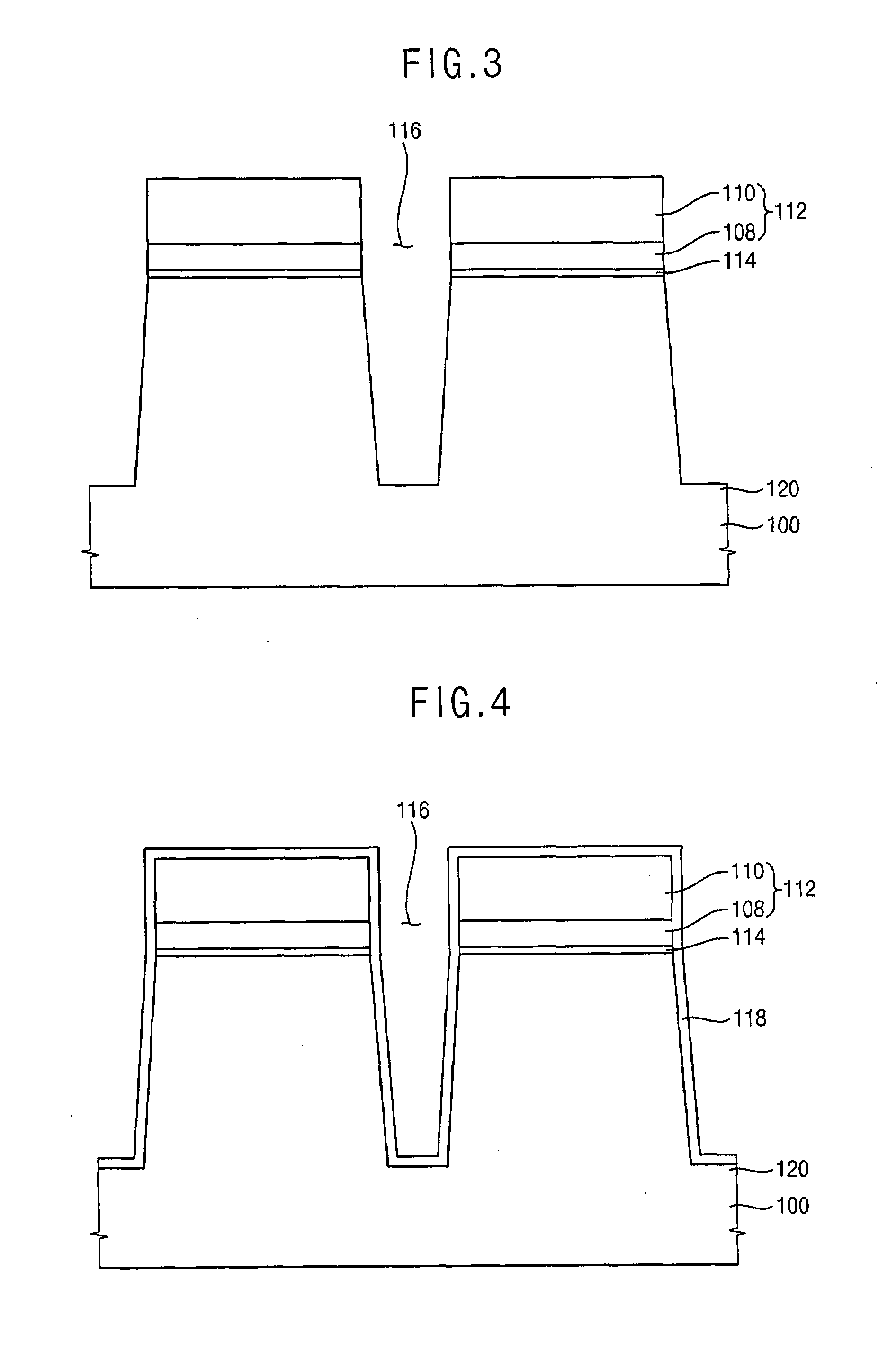
ActiveUS20050006637A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesImpurity diffusionDevice material
There is disclosed is a semiconductor device which comprises a semiconductor substrate, isolation regions formed within the semiconductor substrate to define the active region, a pair of impurity diffusion regions formed within the element region in a manner to have surfaces elevated from the isolation region, a SiGe film formed on an upper surface of the impurity diffusion region so as to cover partly the side surface of the impurity diffusion region, a Ge concentration in the SiGe film being higher at a lower surface of the SiGe film than at an upper surface of the SiGe film, a metal silicide layer formed on the SiGe film, and a gate electrode formed in the active region of the semiconductor substrate with a gate insulating film interposed therebetween and having a sidewall insulating film formed on the side surface.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Borderless contact structure and method of forming the same
InactiveUS20010009805A1Improves contact leakage current characteristicIncrease currentSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesImpurity diffusionDevice material
A borderless contact structure and method of forming thereof are provided. A device isolation region having a protrusion is formed at a predetermined region of a semiconductor substrate. The top surface of the protrusion is higher in level than that of the semiconductor substrate. An impurity diffusion region is formed in an active region surrounded by the device isolation region. An etch stop spacer is formed on a sidewall of the protrusion. An etch stop layer and an interlayer insulating layer are sequentially formed on the resultant structure including the impurity diffusion region, the device isolation region and the etch stop spacer. A contact hole opening the interlayer insulating layer and the etch stop layer is formed to expose at least a portion of the impurity diffusion region. Accordingly, during the etching process for forming the borderless contact hole exposing both the impurity diffusion region and the device isolation region adjacent to the impurity diffusion region, the device isolation region adjacent to the impurity diffusion region is not recessed, thereby improving leakage current characteristics of the semiconductor device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS6924518B2TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingImpurity diffusionMetal silicide
There is disclosed is a semiconductor device which comprises a semiconductor substrate, isolation regions formed within the semiconductor substrate to define the active region, a pair of impurity diffusion regions formed within the element region in a manner to have surfaces elevated from the isolation region, a SiGe film formed on an upper surface of the impurity diffusion region so as to cover partly the side surface of the impurity diffusion region, a Ge concentration in the SiGe film being higher at a lower surface of the SiGe film than at an upper surface of the SiGe film, a metal silicide layer formed on the SiGe film, and a gate electrode formed in the active region of the semiconductor substrate with a gate insulating film interposed therebetween and having a sidewall insulating film formed on the side surface.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Display device and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS20150009105A1Small sizeStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesImpurity diffusionData lines
Provided is an active matrix display device using an organic EL panel including: a plurality of pixel circuits each including an organic light emitting diode arranged in a pixel region of the organic EL panel and a plurality of transistors configured to drive the organic light emitting diode; a plurality of scanning lines arranged along a first direction in the organic EL panel; and a plurality of data lines arranged along a second direction that is orthogonal to the first direction. In at least one set of pixel circuits that are adjacent in the first direction, gate electrodes and impurity diffusion regions of the plurality of transistors have an axisymmetric layout. Gate electrodes of at least one set of transistors that are symmetrically arranged in the at least one set of pixel circuits are integrated.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20090315092A1Lower threshold voltageFacilitate threshold voltage controlTransistorSolid-state devicesImpurity diffusionEngineering
A semiconductor device provided with a field-effect transistor, the field-effect transistor including: a active region defined by element isolating region 3 formed on semiconductor substrate 1; gate electrode 5 provided so as to intersect the active region and having at least a part thereof embedded in a gate trench formed on semiconductor substrate 1; and SOI structure channel layer 4 formed in the active region so that one lateral face thereof is opposite to a part of gate electrode 5 embedded in the gate trench and the other lateral face thereof is in contact with a lateral face of element isolating region 3, wherein impurity diffusion layer 5 that functions as a source / drain region is disposed above channel layer 4, and impurity diffusion layer 9 and channel layer 4 are formed spaced apart from each other.
Owner:ELPIDA MEMORY INC
Semiconductor device and manufacture method thereof
The present invention provides a trench gate Tr having a first gate electrode and a second gate electrode in the inside of a groove. The first gate electrode is provided in a groove lower part defining a channel of the Tr with a gate oxide film interposed between the first gate electrode and the substrate. The second gate electrode is provided in a groove upper part facing a Tr impurity diffusion layer, with a gate oxide film and a groove side wall film interposed between the second gate electrode and the groove upper part. The provision of the composite film consisting of the gate oxide film and the groove side wall between gate electrode and the substrate in the groove upper part enables reduction of the parasitic capacitance of the gate electrode.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Nonvolatile memory devices and methods of forming the same
InactiveUS20060071265A1Small sizeInhibition effectTransistorSolid-state devicesImpurity diffusionDevice material
A nonvolatile memory device includes first and second impurity diffusion regions formed in a semiconductor substrate, and a memory cell formed on a channel region of a semiconductor substrate between the first and second impurity diffusion regions. The memory cell includes a stacked gate structure formed on the channel region, and first and second select gates formed on the channel regions and opposite sidewalls of the stacked gate structure. Since the first and second select gates are spacer-shaped to be self-aligned on opposite sidewalls of the stacked gate structure, a size of a memory cell is reduced to enhance an integration density of a semiconductor device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com