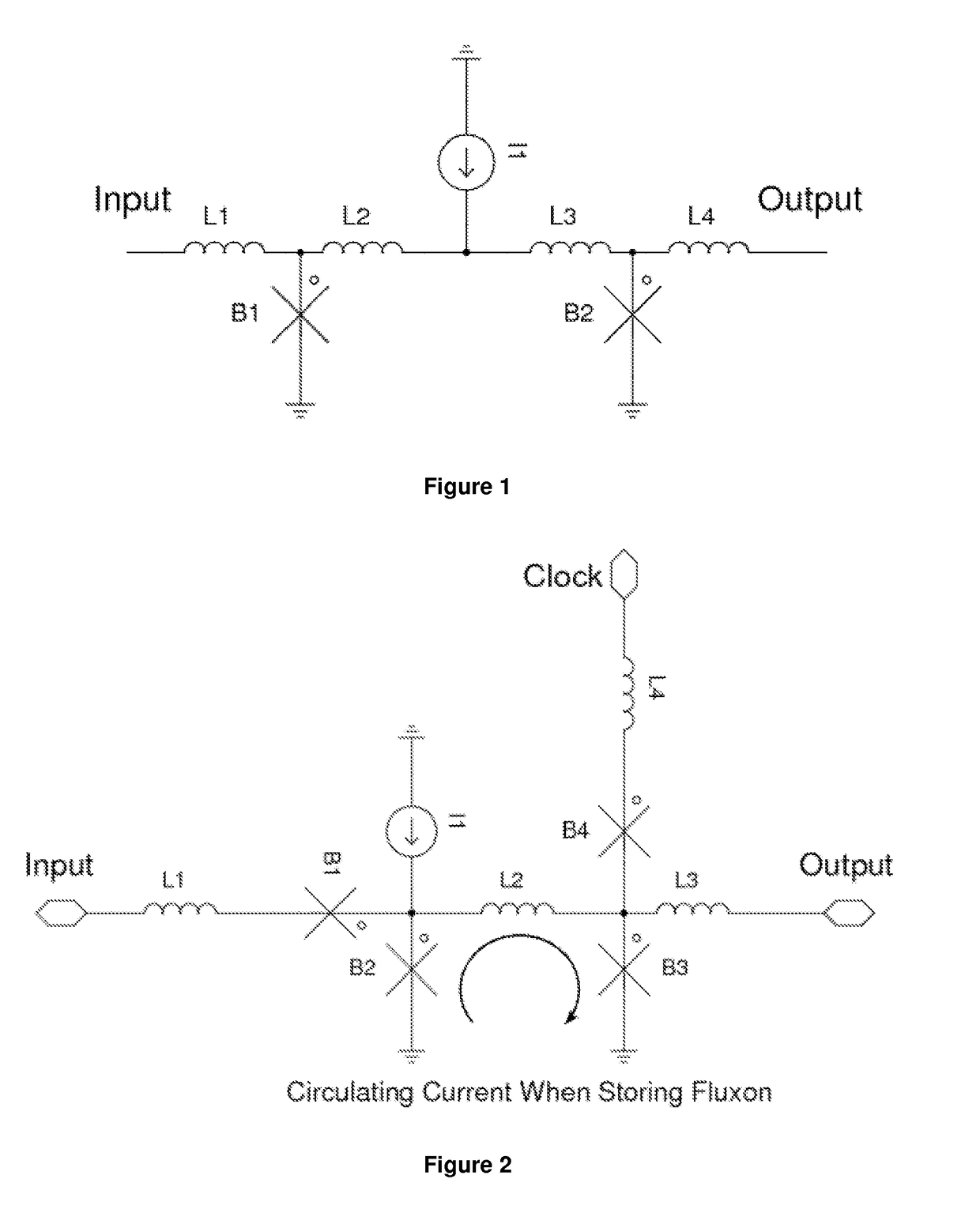
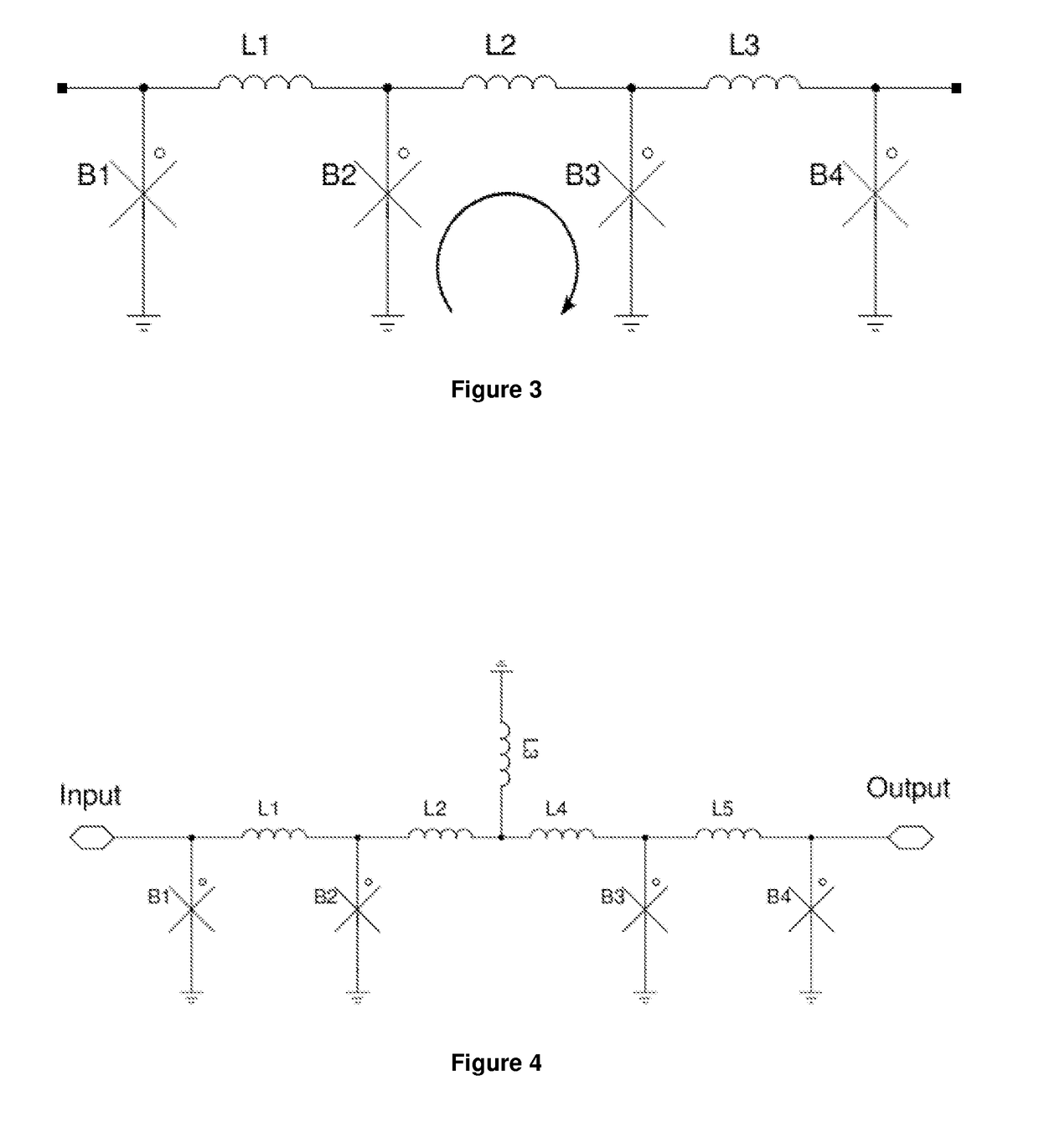
Patents
Literature
32 results about "Rapid single flux quantum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In electronics, rapid single flux quantum (RSFQ) is a digital electronic device that uses superconducting devices, namely Josephson junctions, to process digital signals. In RSFQ logic, information is stored in the form of magnetic flux quanta and transferred in the form of Single Flux Quantum (SFQ) voltage pulses. RSFQ is one family of superconducting or SFQ logic. Others include Reciprocal Quantum Logic (RQL), ERSFQ – energy-efficient RSFQ version that does not use bias resistors, etc. Josephson junctions are the active elements for RSFQ electronics, just as transistors are the active elements for semiconductor electronics. RSFQ is a classical digital, not quantum computing, technology.
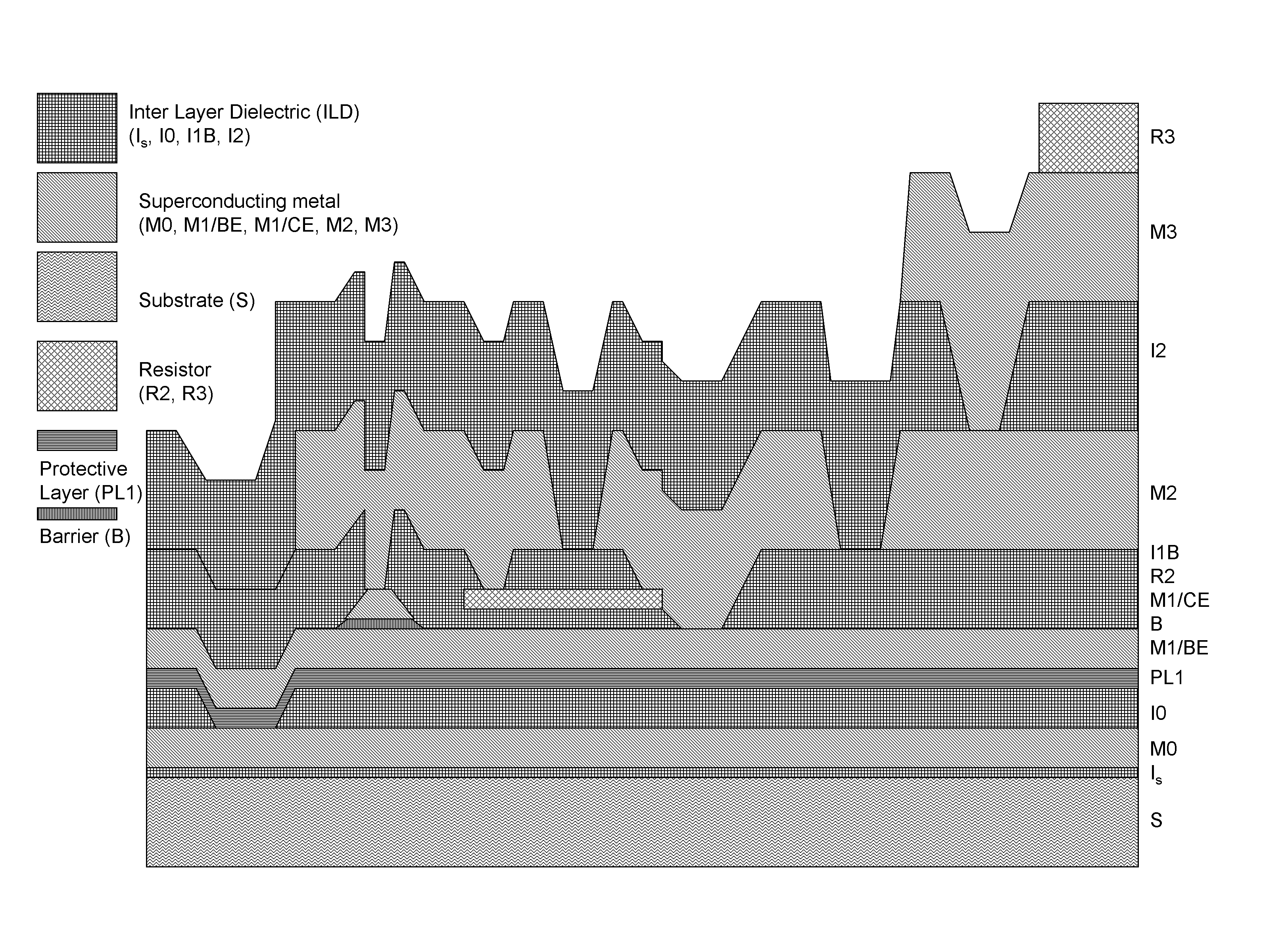
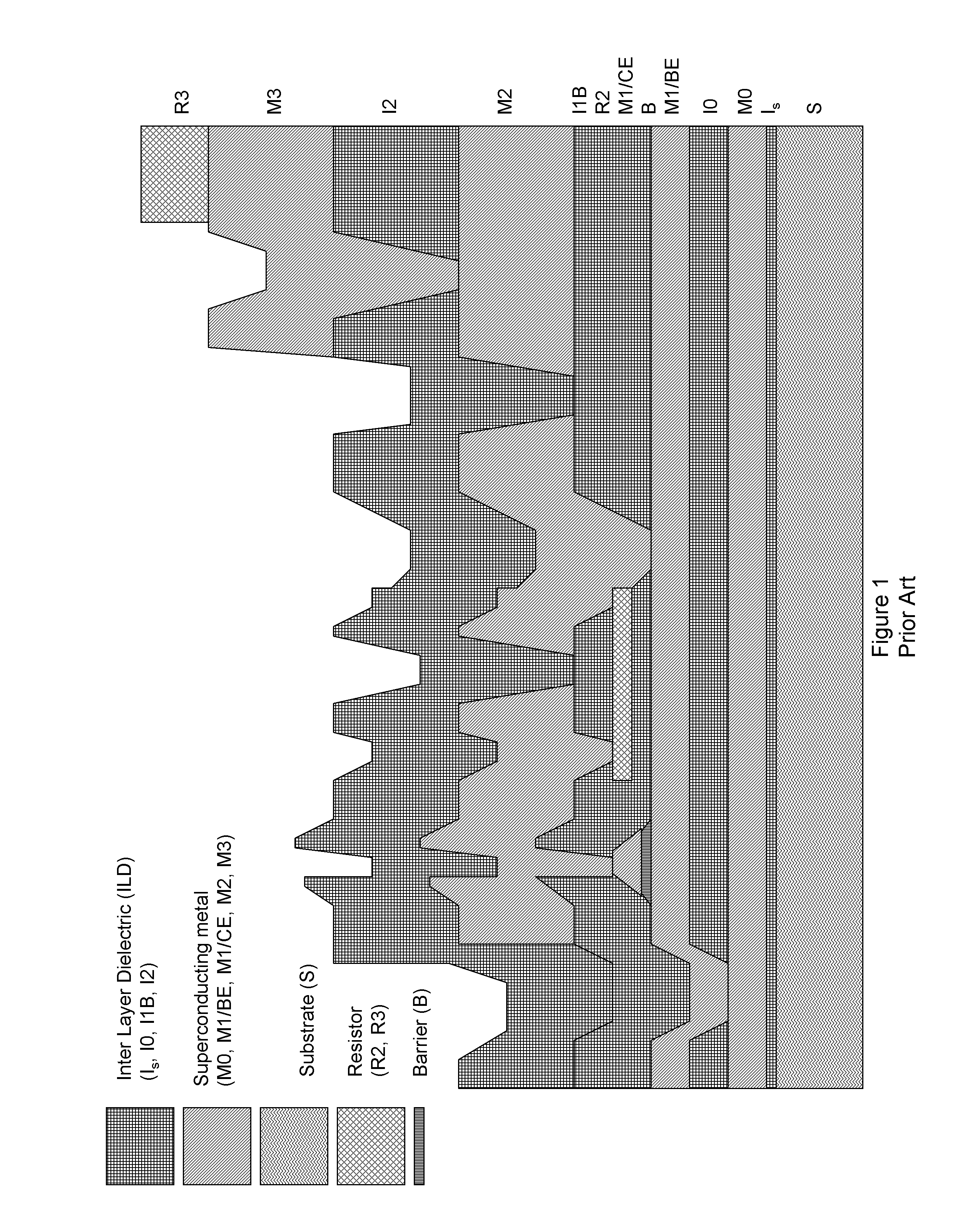
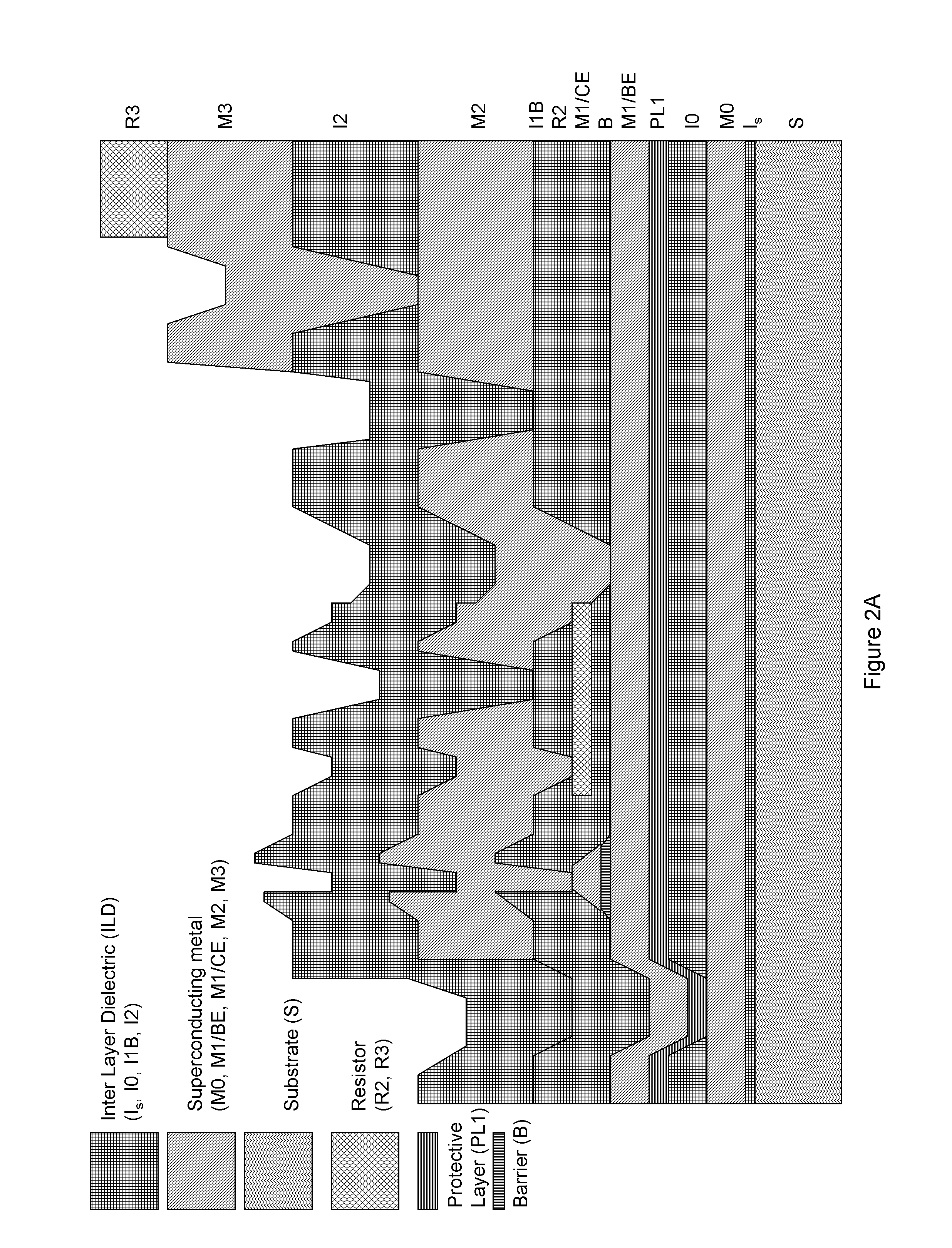
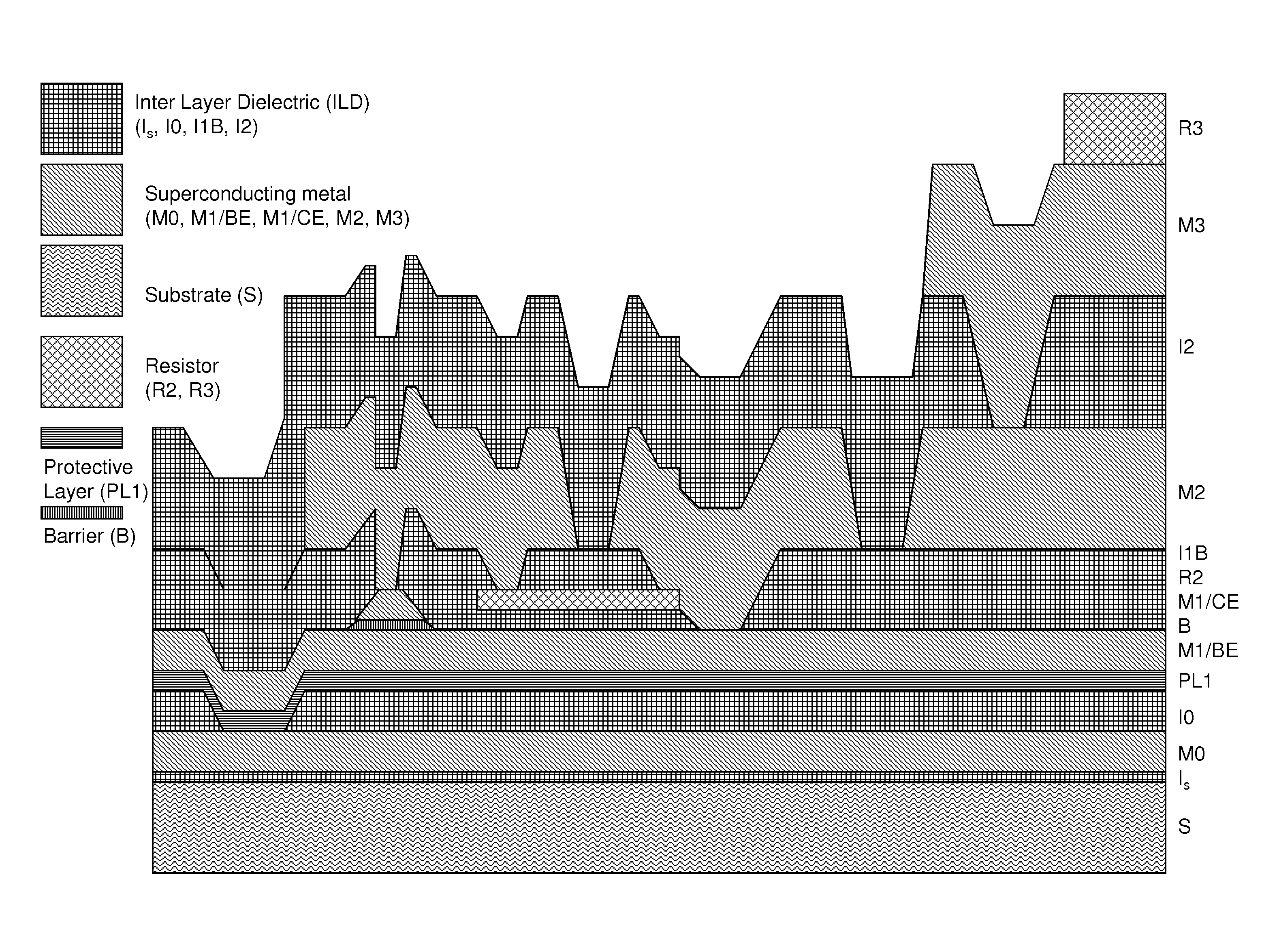
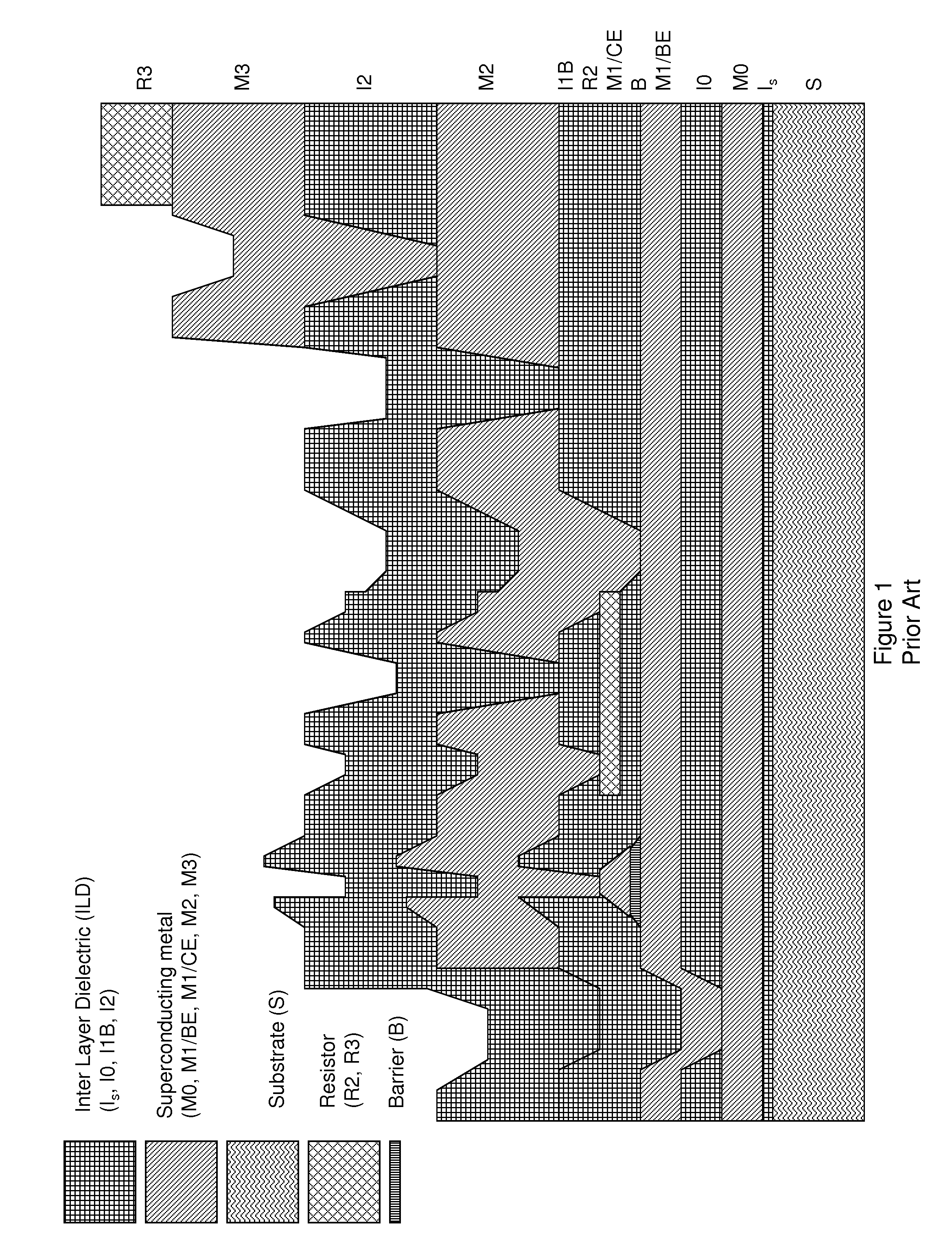
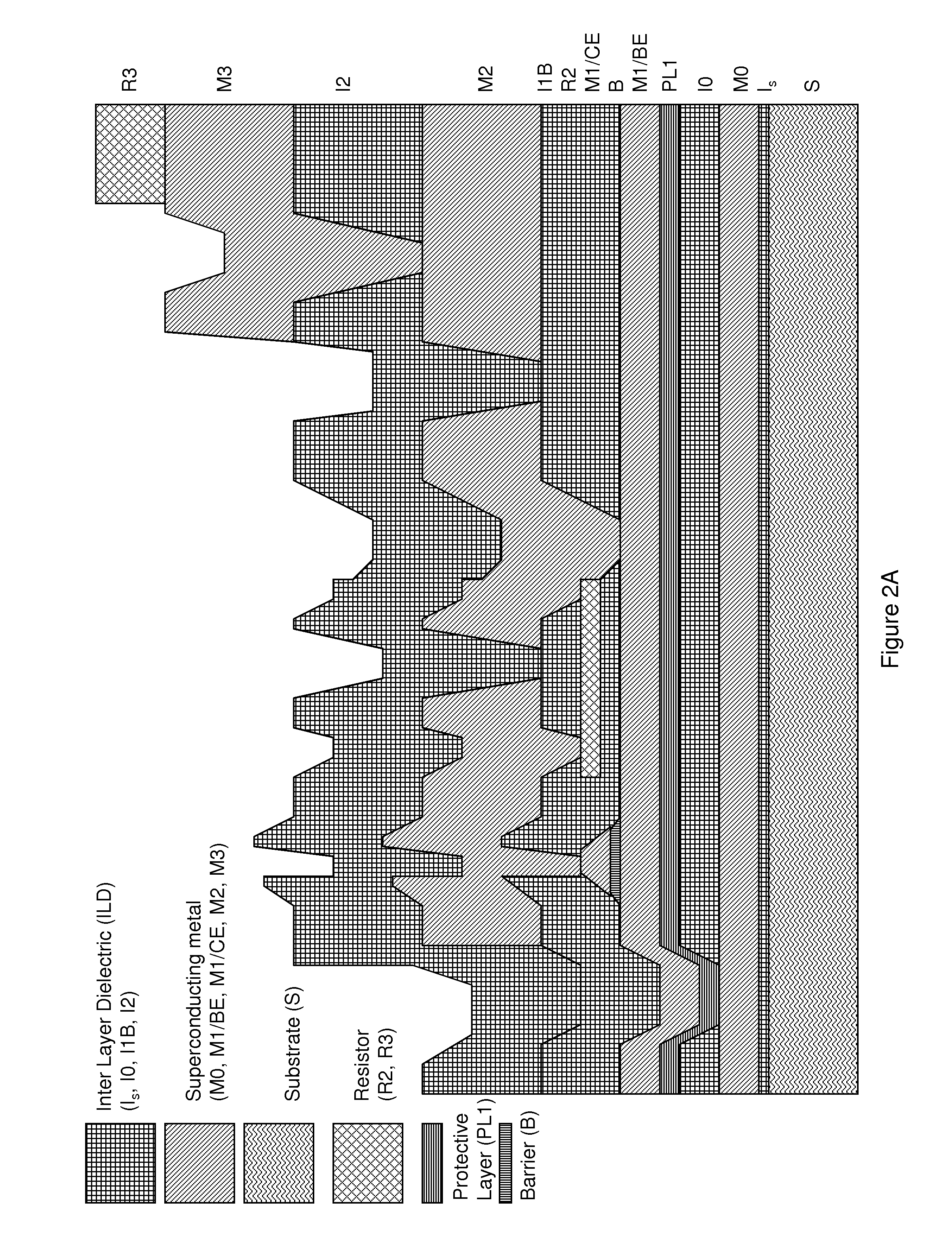
System and method for providing multi-conductive layer metallic interconnects for superconducting integrated circuits
ActiveUS8437818B1Reduce and prevent diffusion of impurityReduce non-uniformitySuperconductors/hyperconductorsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsImpurity diffusionRapid single flux quantum
Superconducting integrated circuits require several wiring layers to distribute bias and signals across the circuit, which must cross each other both with and without contacts. All wiring lines and contacts must be fully superconducting, and in the prior art each wiring layer comprises a single metallic thin film. An alternative wiring layer is disclosed that comprises sequential layers of two or more different metals. Such a multi-metallic wiring layer may offer improved resistance to impurity diffusion, better surface passivation, and / or reduction of stress, beyond that which is attainable with a single-metallic wiring layer. The resulting process leads to improved margin and yield in an integrated circuit comprising a plurality of Josephson junctions. Several preferred embodiments are disclosed, for both planarized and non-planarized processes. These preferred and other methods may be applied to digital circuits based on Rapid Single Flux Quantum logic, and to quantum computing using Josephson junction qubits.
Owner:SEEQC INC
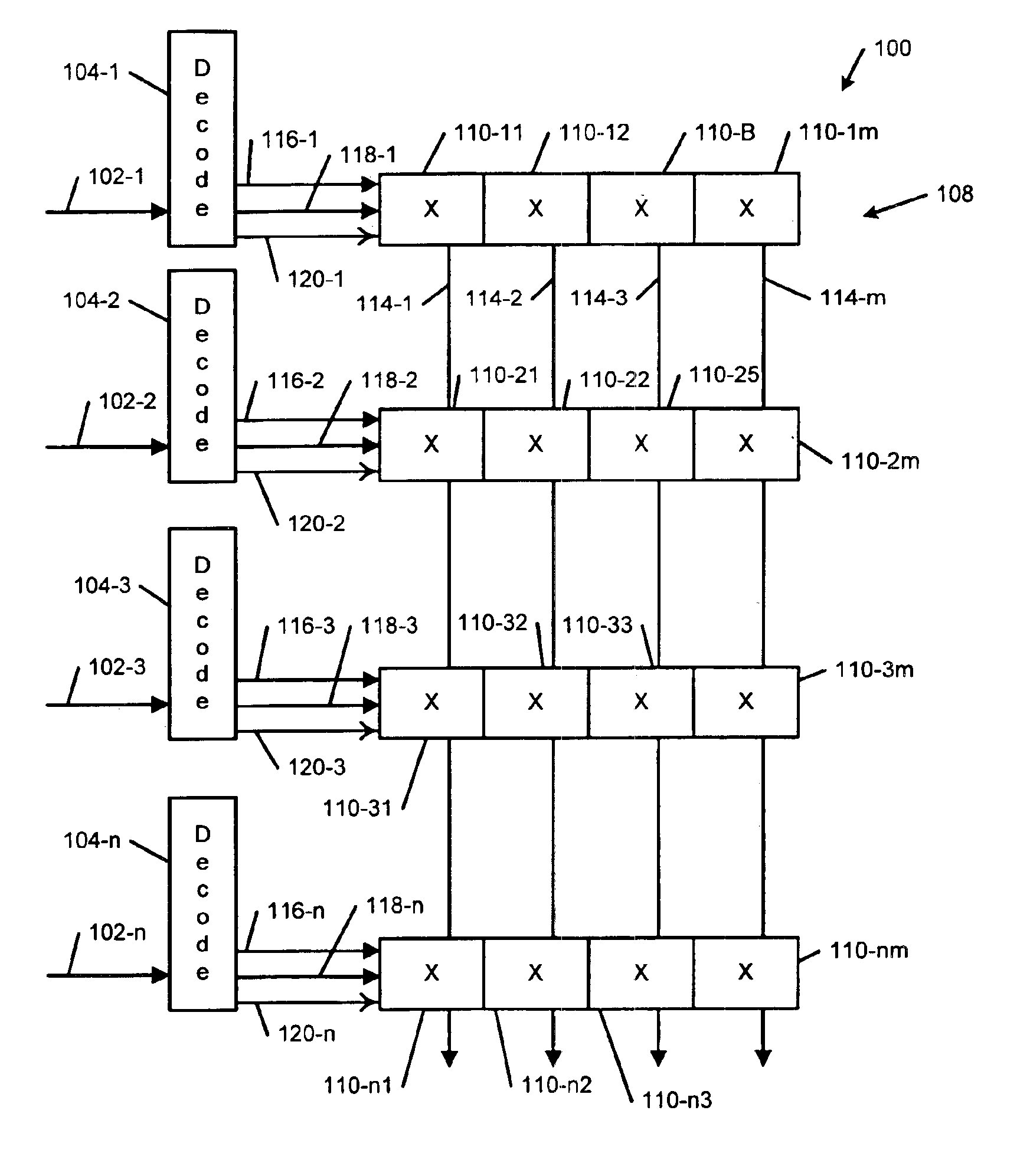
Scalable self-routing superconductor switch
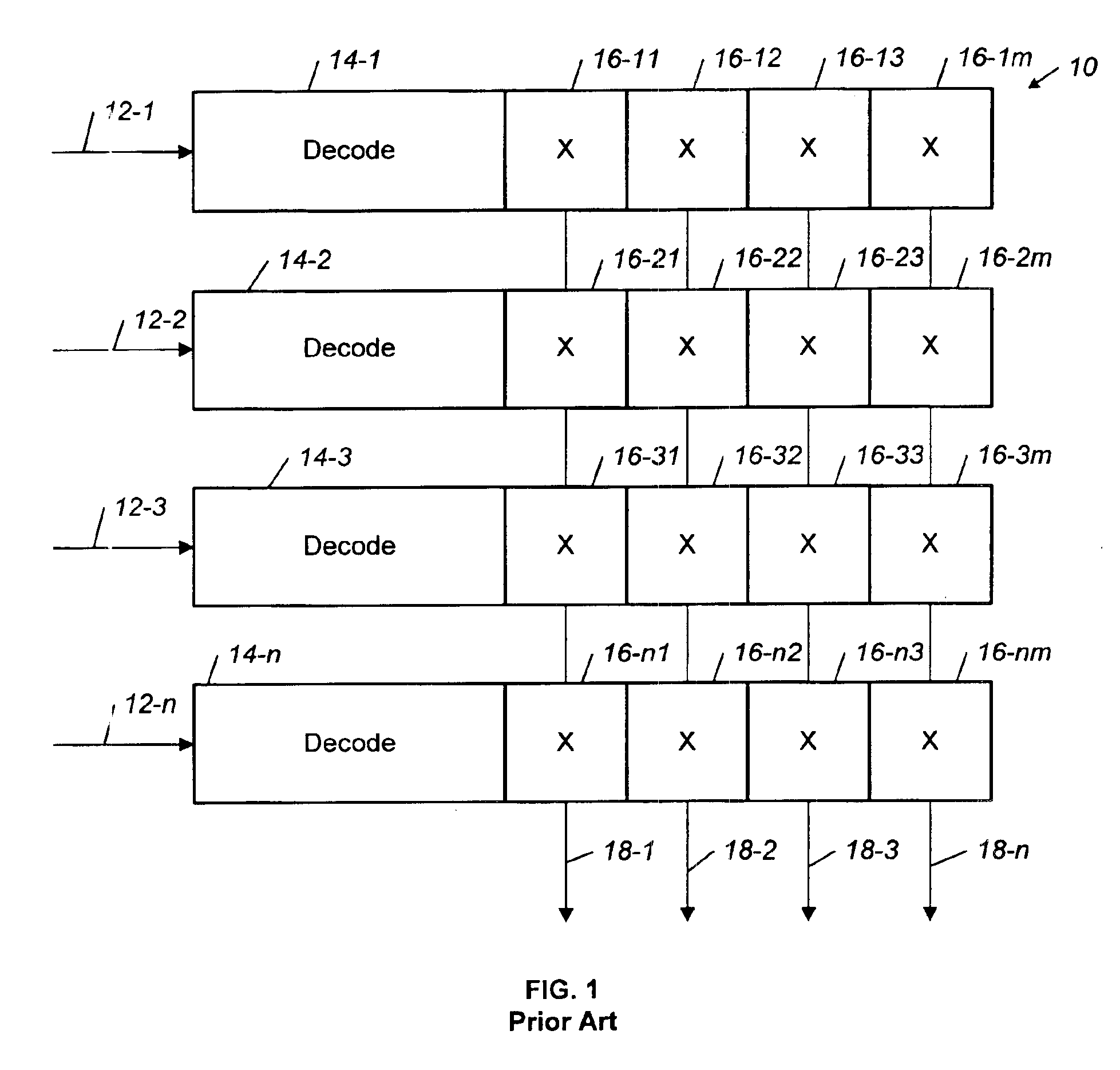
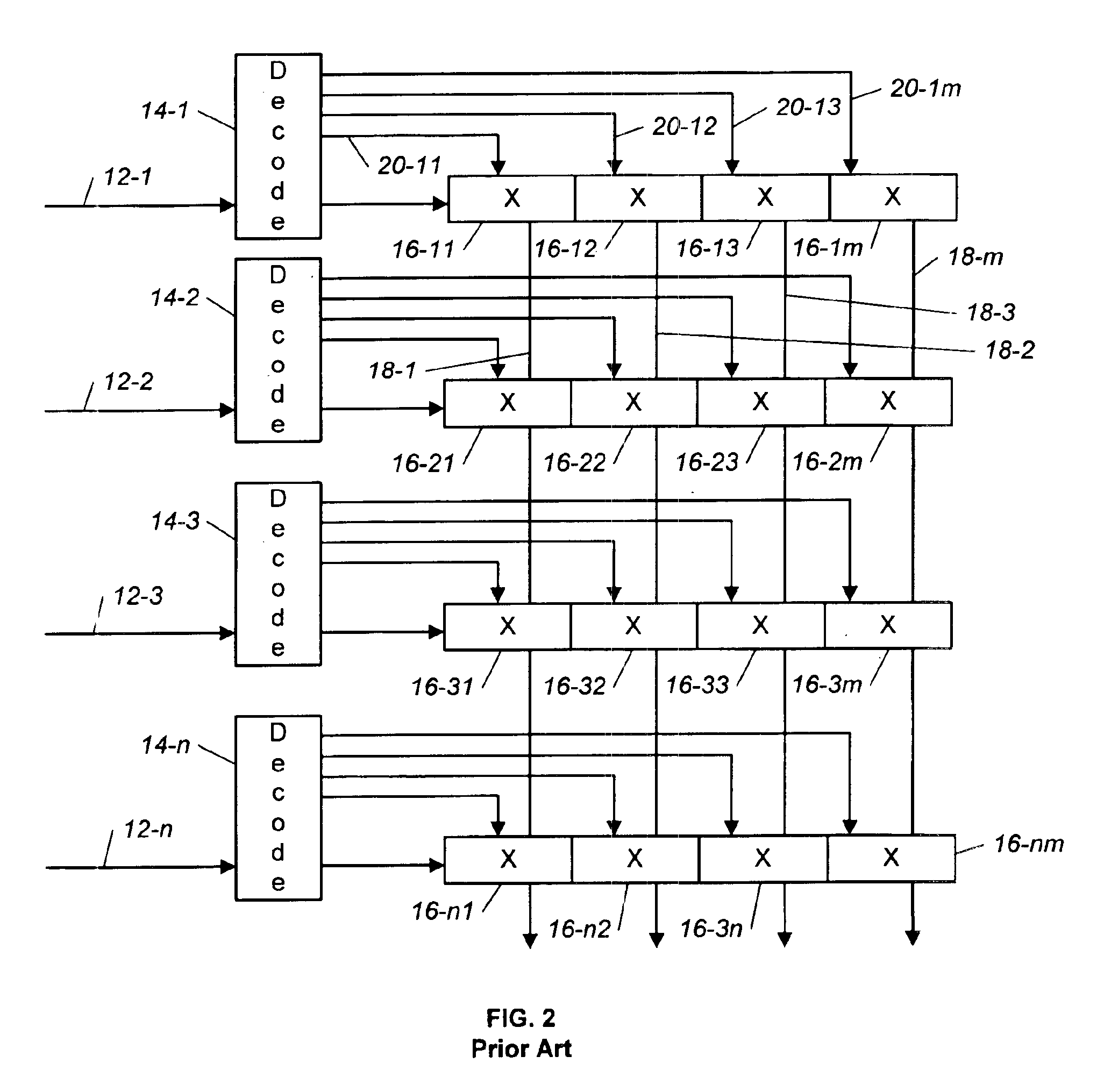
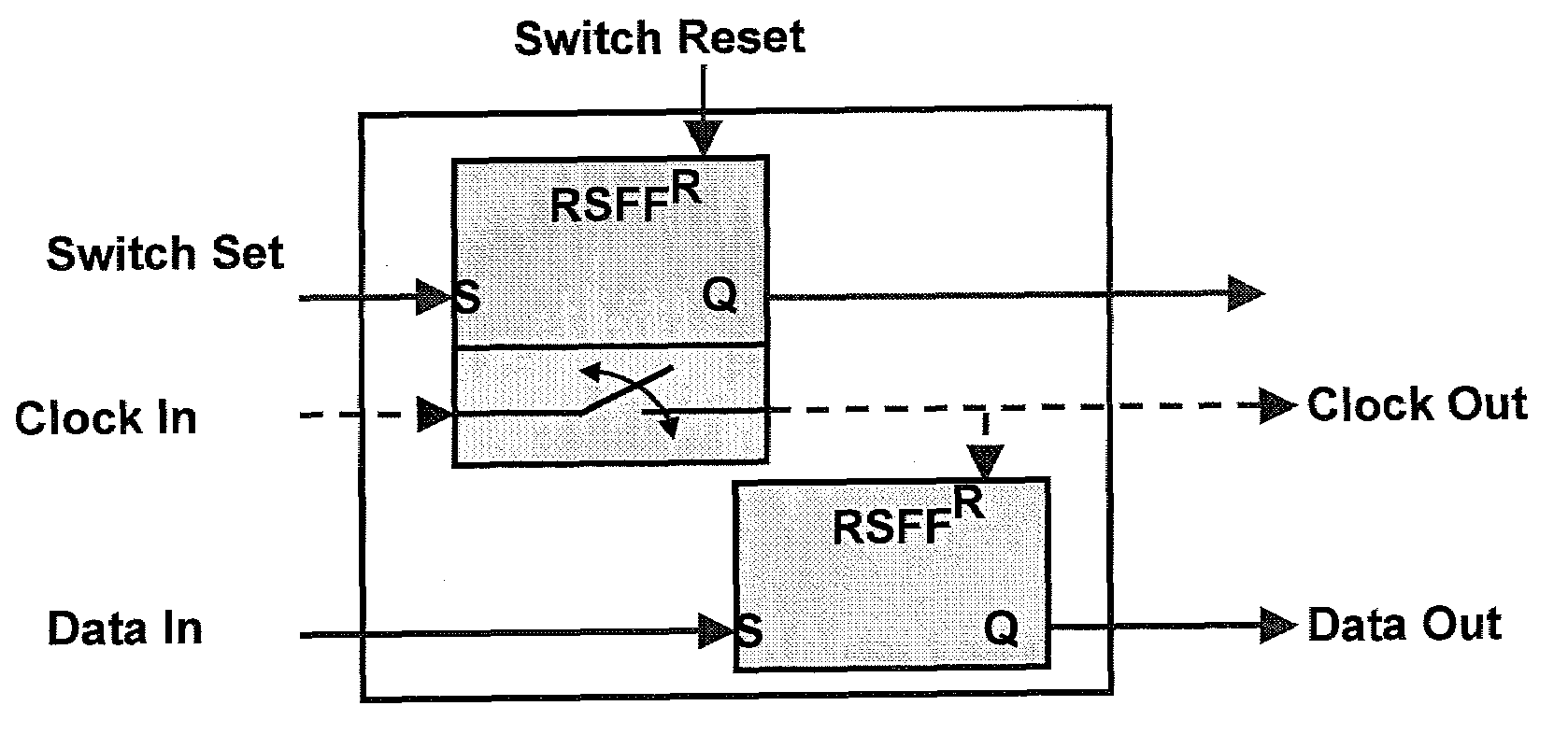
A crossbar switch includes a cross-point matrix with n input rows of cross-points and m output columns of cross-points. The crossbar switch further includes n decoders connected to the n input rows. Each of the n rows includes a single serial address input, a shift input and a data input. A serial address and data enter the address input and the data input in parallel. A shift sequence is transmitted on the single shift input. The data flows before the shift sequence on the shift input is complete. The data is shifted through the crossbar switch using a clock that is generated on-chip using a clock recovery circuit. The decoder converts a binary address input into a serial address and includes an N-bit counter with a plurality of toggle flip-flops. The crossbar switch is implemented using superconductor digital electronics such as rapid single flux quantum (RSFQ) logic.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMAN CORP
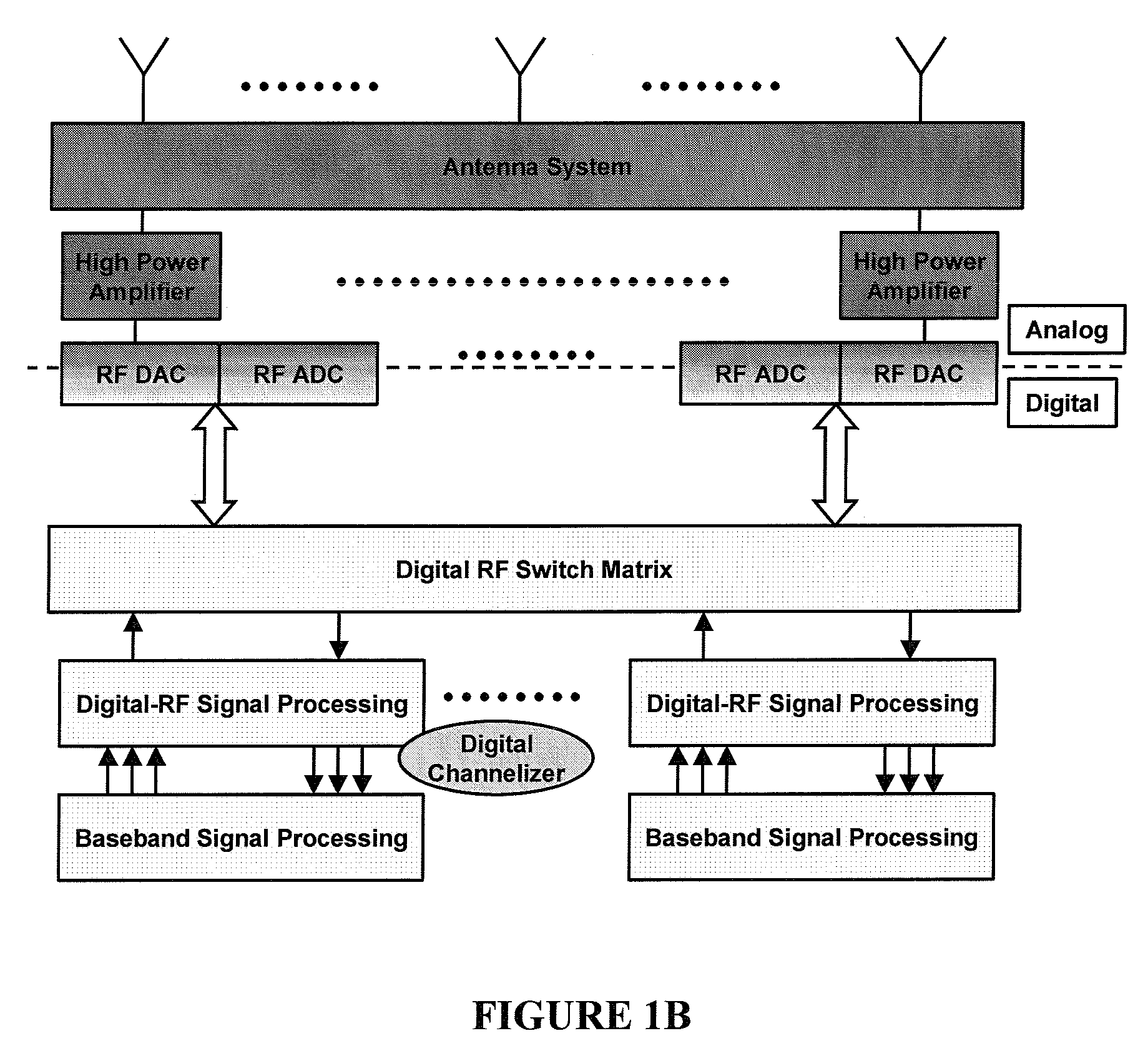
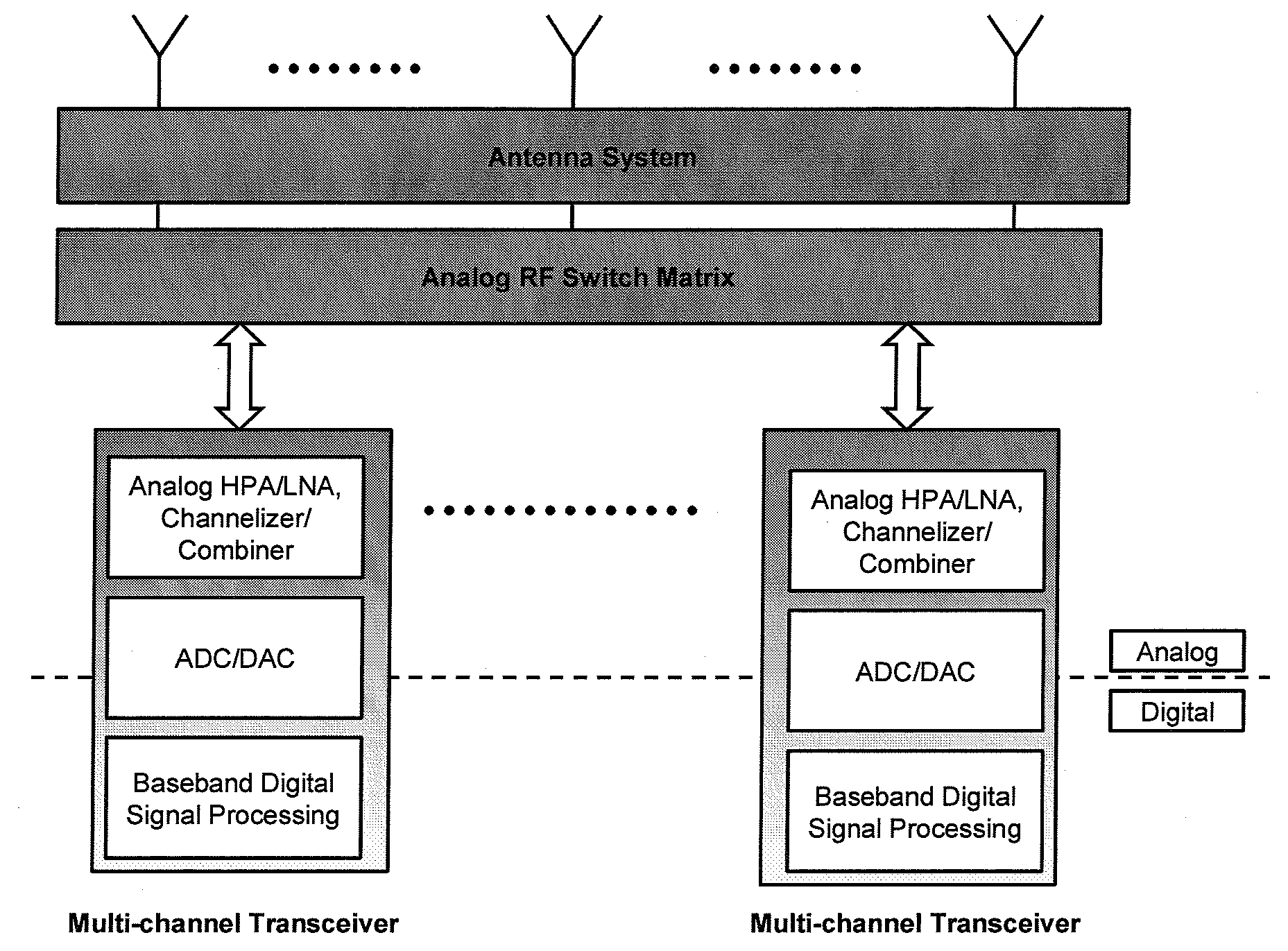
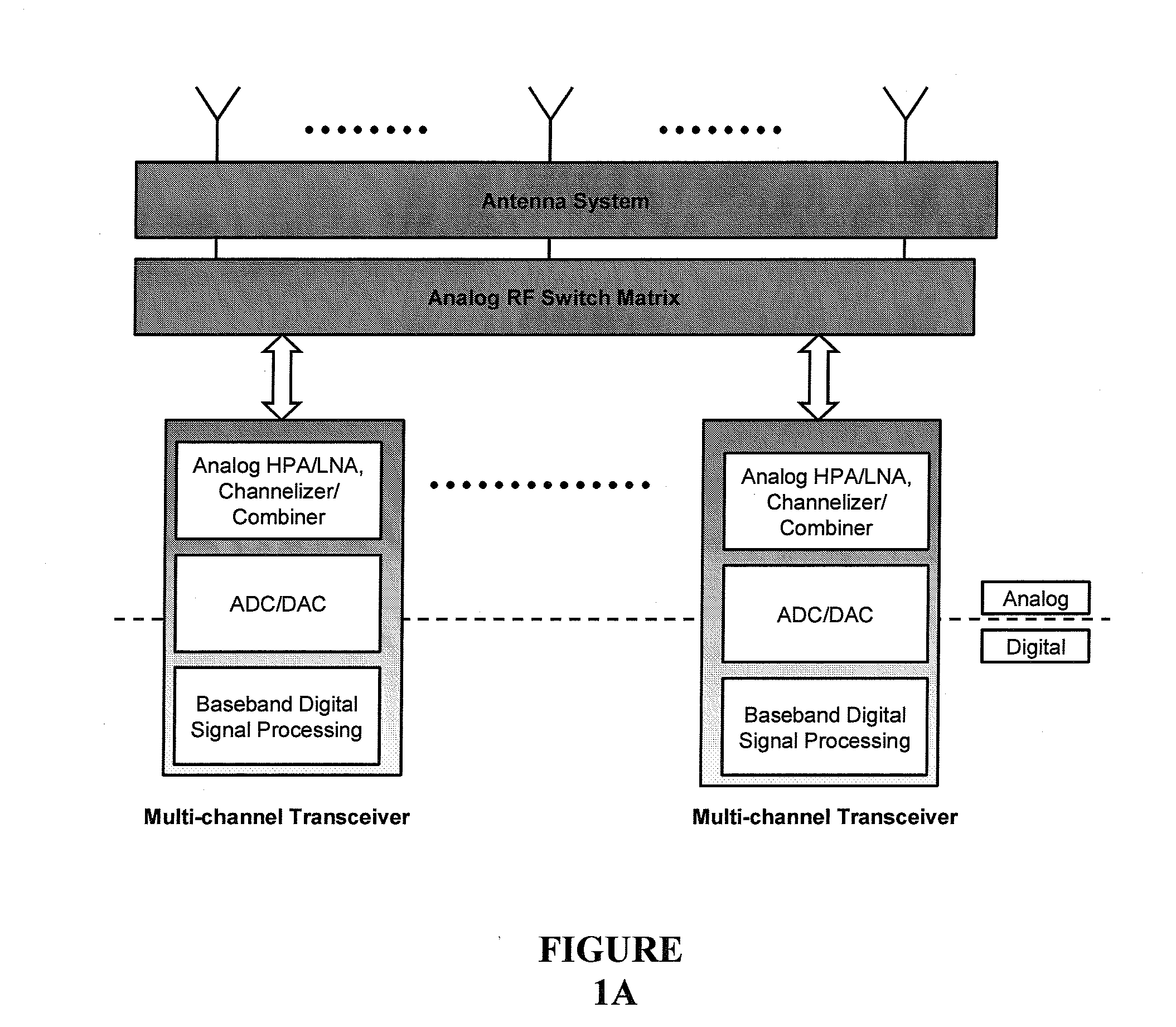
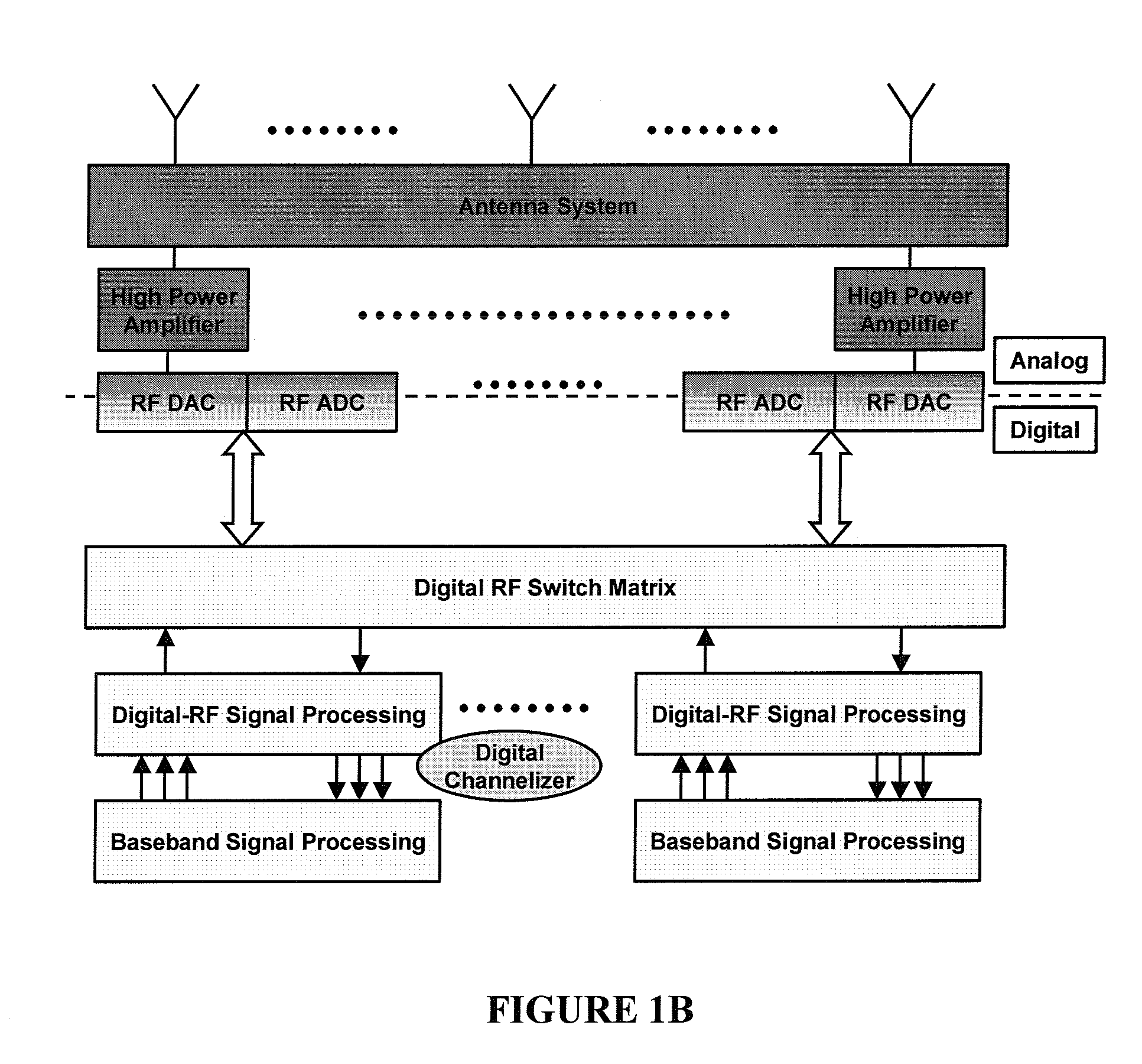
Digital routing switch matrix for digitized radio-frequency signals
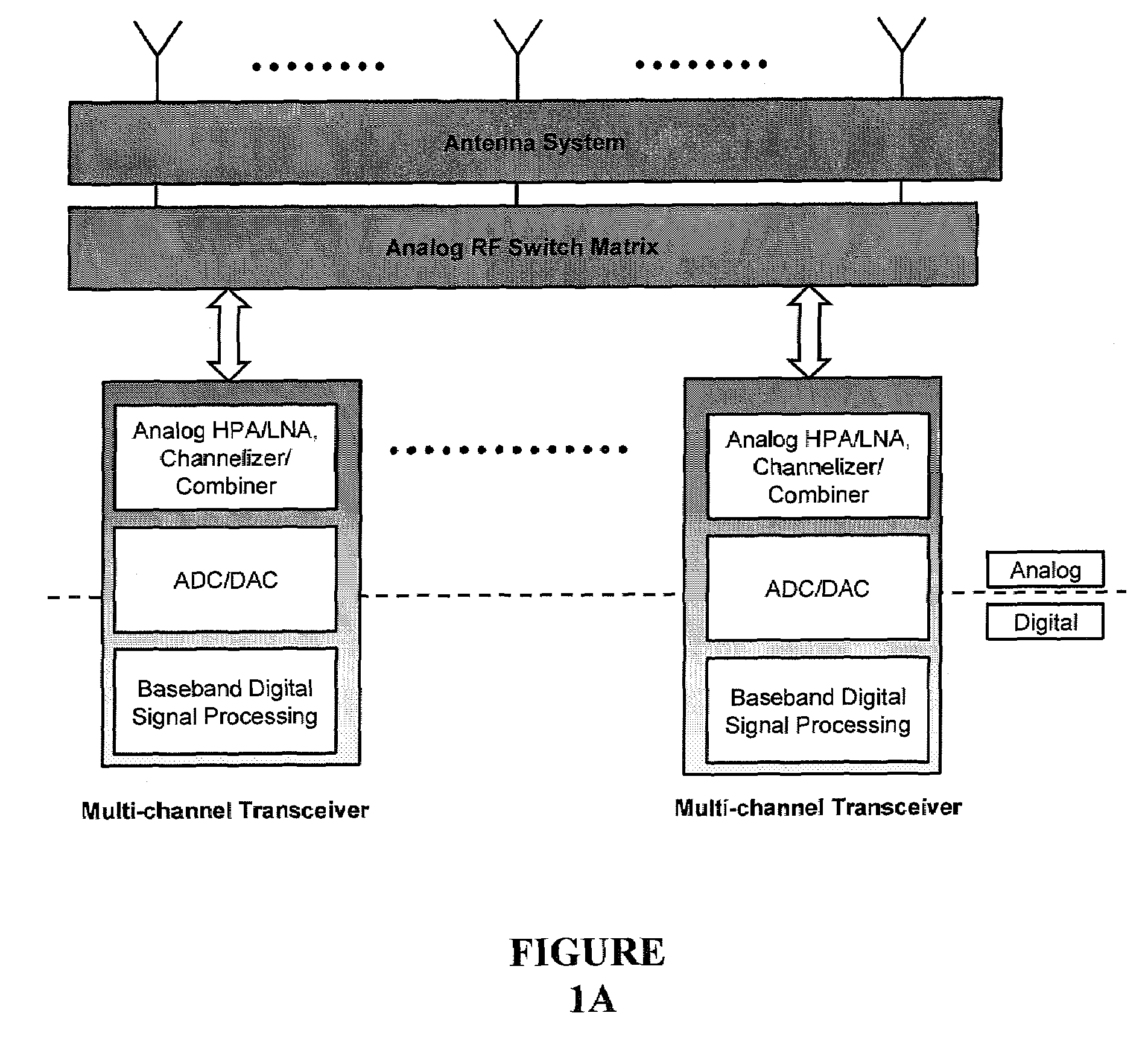
InactiveUS7362125B2Efficient executionPrecise processingElectronic switchingSubstation equipmentMulti bandTransceiver
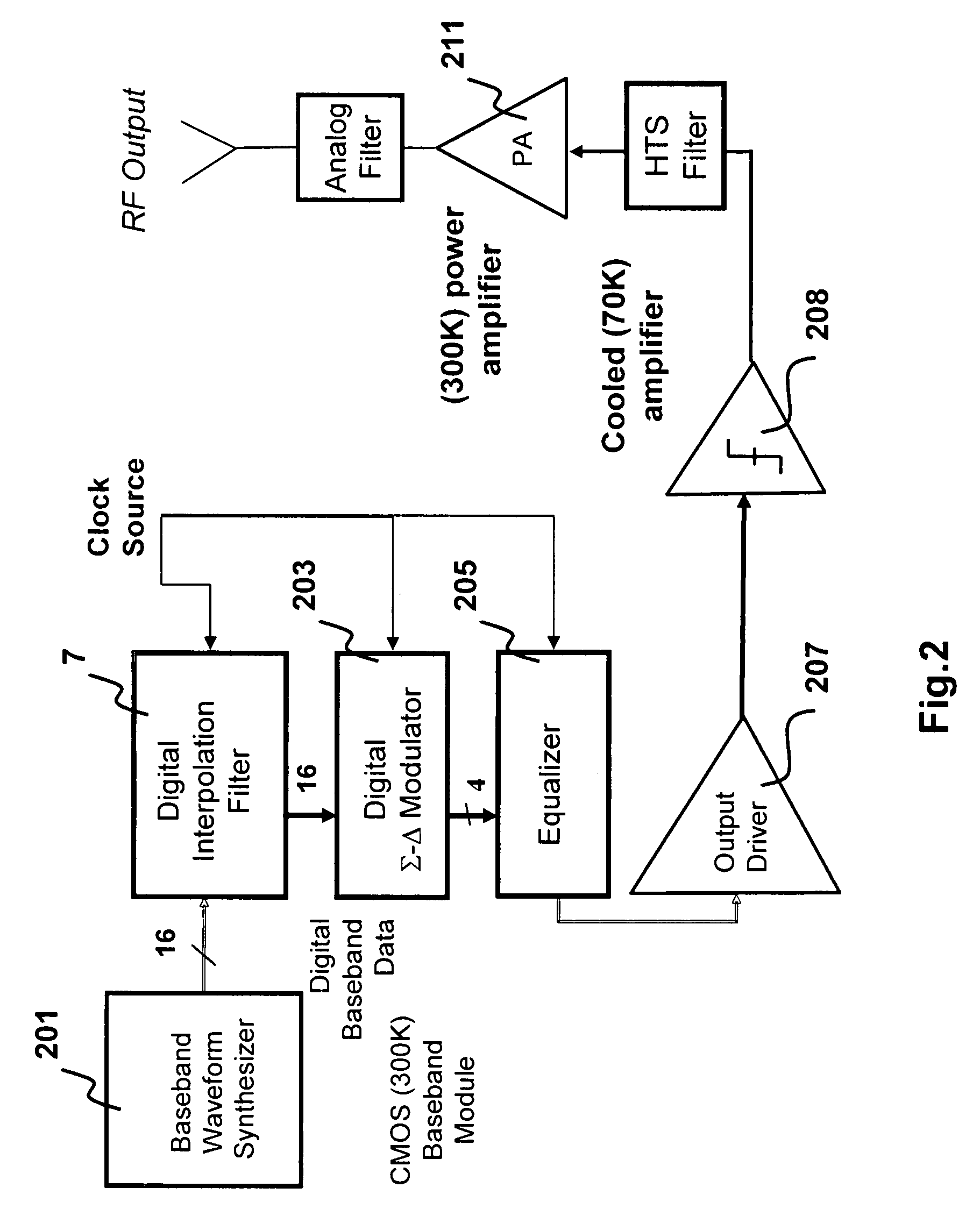
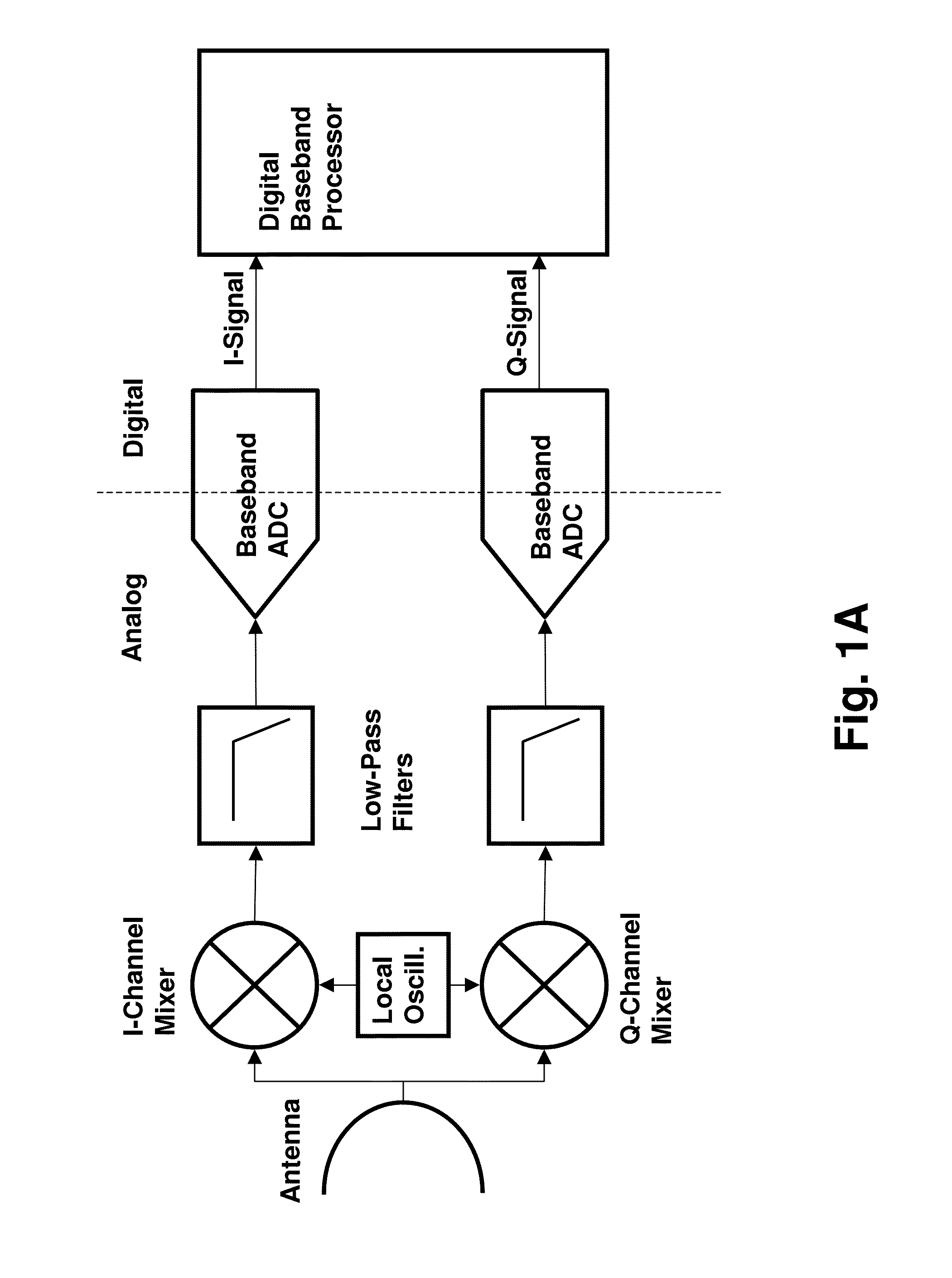
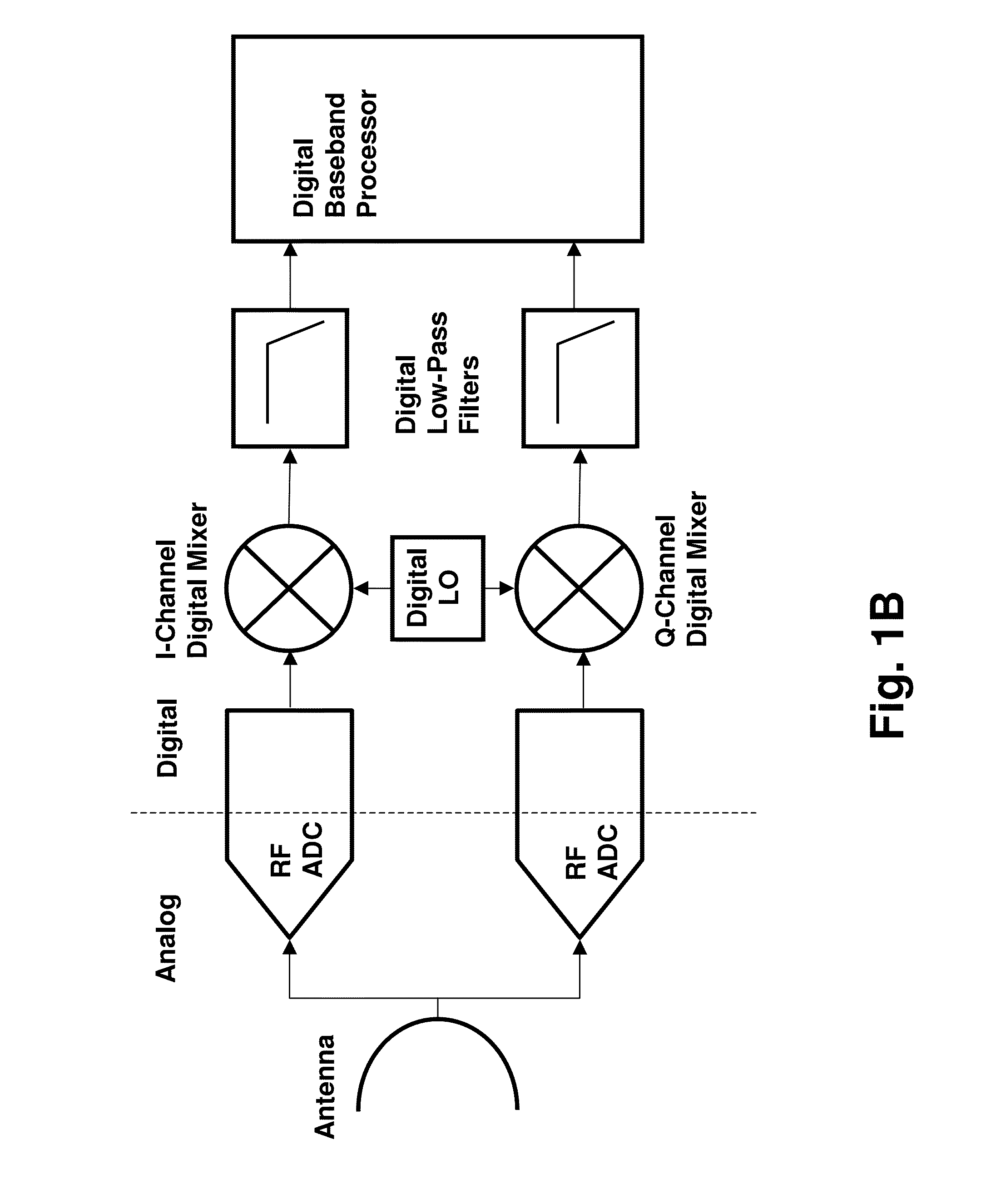
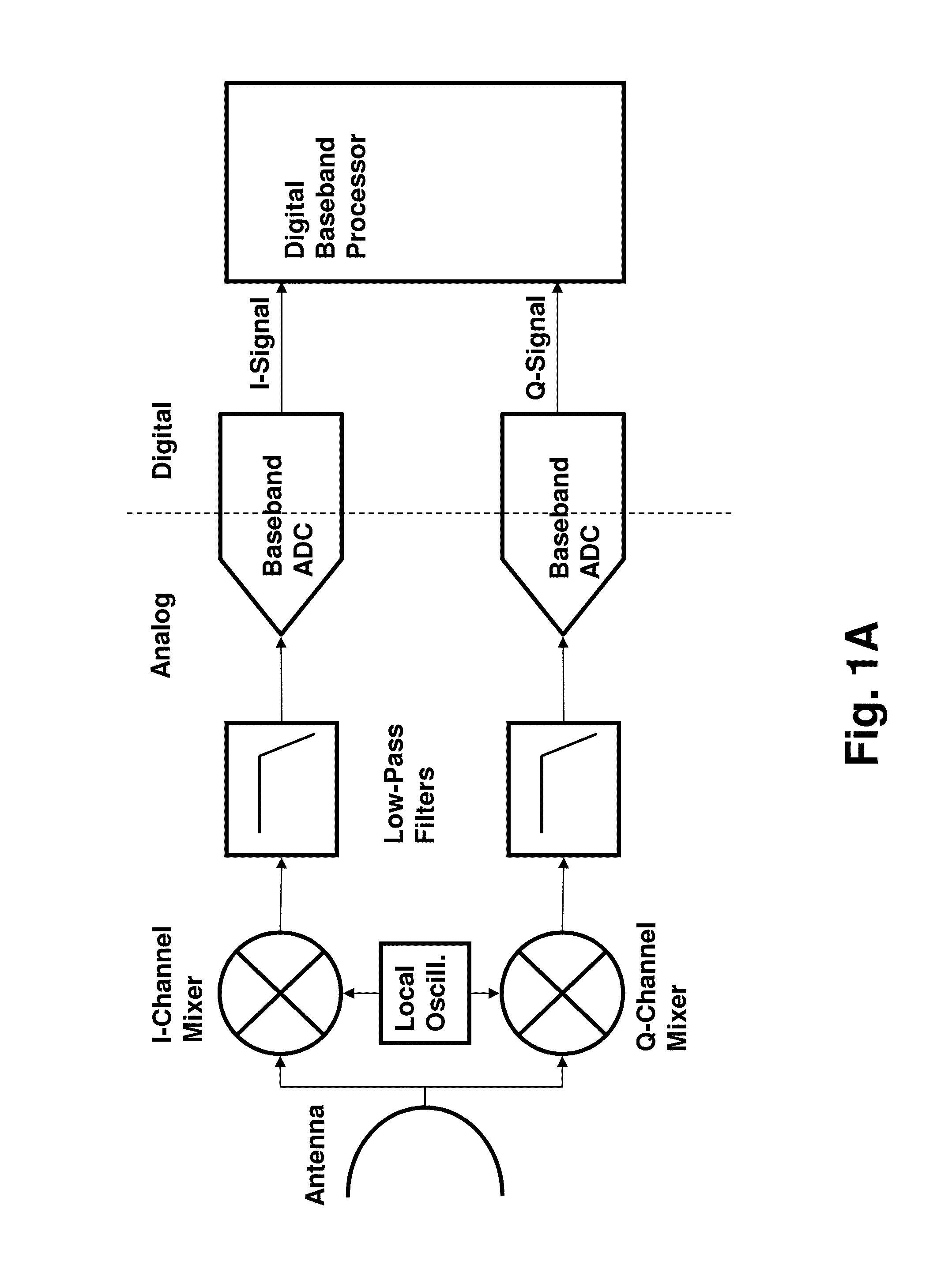
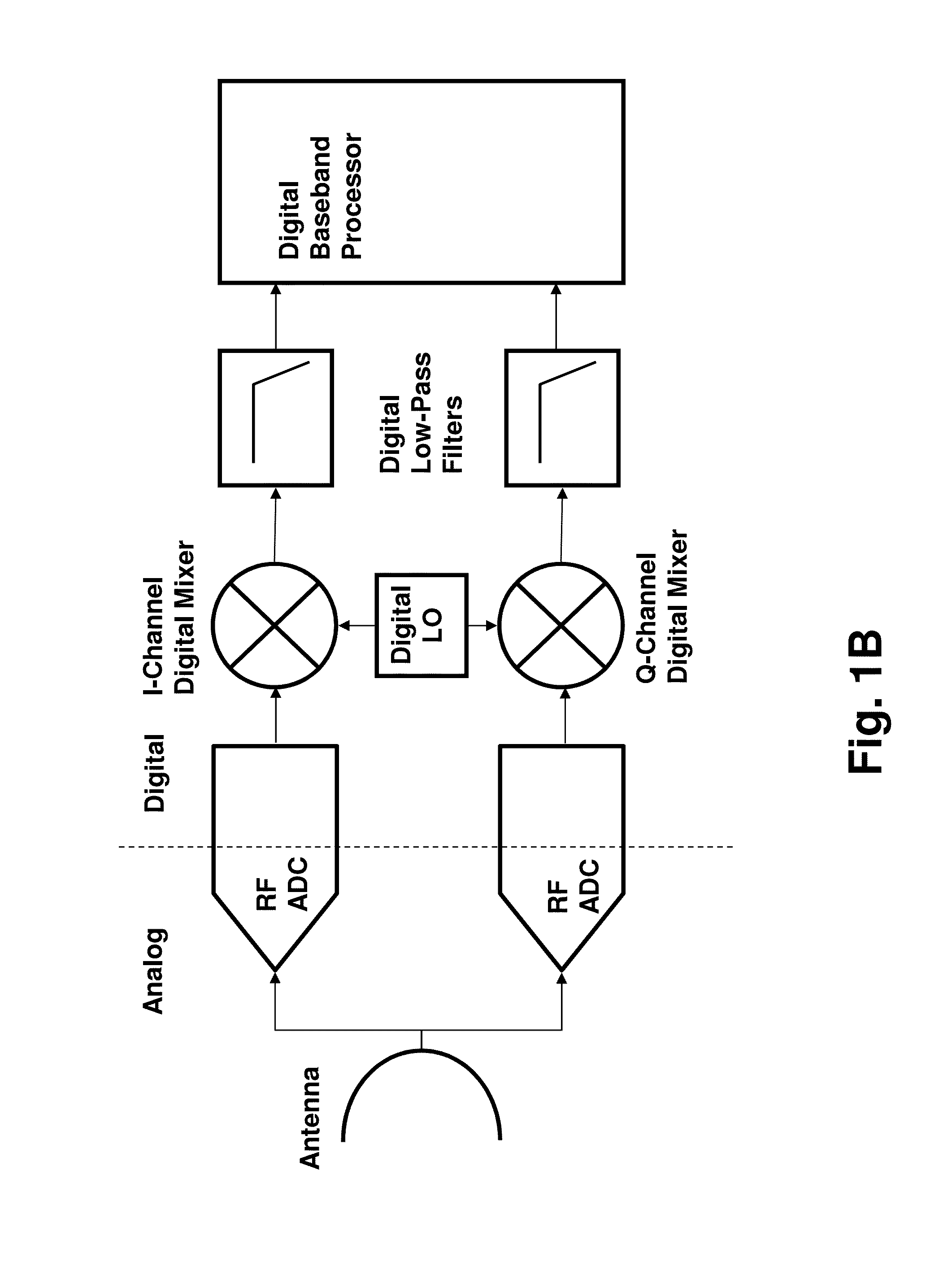
Routing and distribution of radio-frequency (RF) signals is commonly achieved in the analog domain. However, improved performance and simplified circuit architectures may be obtained by first digitizing the RF signal, and then carrying out all routing in the digital domain. A new generation of scalable digital switches has been developed, which routes both the data and clock signals together, this being necessary to maintain the integrity of the digitized RF signal. Given the extremely high switching speeds necessary for these applications (tens of GHz), this is implemented using Rapid-Single-Flux-Quantum (RSFQ) logic with superconducting integrated circuits. Such a digital switch matrix may be applied to either the receiver or transmitter components of an advanced multi-band, multi-channel digital transceiver system, and is compatible with routing of signals with different clock frequencies simultaneously within the same switch matrix.
Owner:HYPRES
System and method for providing multi-conductive layer metallic interconnects for superconducting integrated circuits
ActiveUS8301214B1Reduce and prevent diffusion of impurityReduce non-uniformitySuperconductors/hyperconductorsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsImpurity diffusionRapid single flux quantum
Superconducting integrated circuits require several wiring layers to distribute bias and signals across the circuit, which must cross each other both with and without contacts. All wiring lines and contacts must be fully superconducting, and in the prior art each wiring layer comprises a single metallic thin film. An alternative wiring layer is disclosed that comprises sequential layers of two or more different metals. Such a multi-metallic wiring layer may offer improved resistance to impurity diffusion, better surface passivation, and / or reduction of stress, beyond that which is attainable with a single-metallic wiring layer. The resulting process leads to improved margin and yield in an integrated circuit comprising a plurality of Josephson junctions. Several preferred embodiments are disclosed, for both planarized and non-planarized processes. These preferred and other methods may be applied to digital circuits based on Rapid Single Flux Quantum logic, and to quantum computing using Josephson junction qubits.
Owner:SEEQC INC
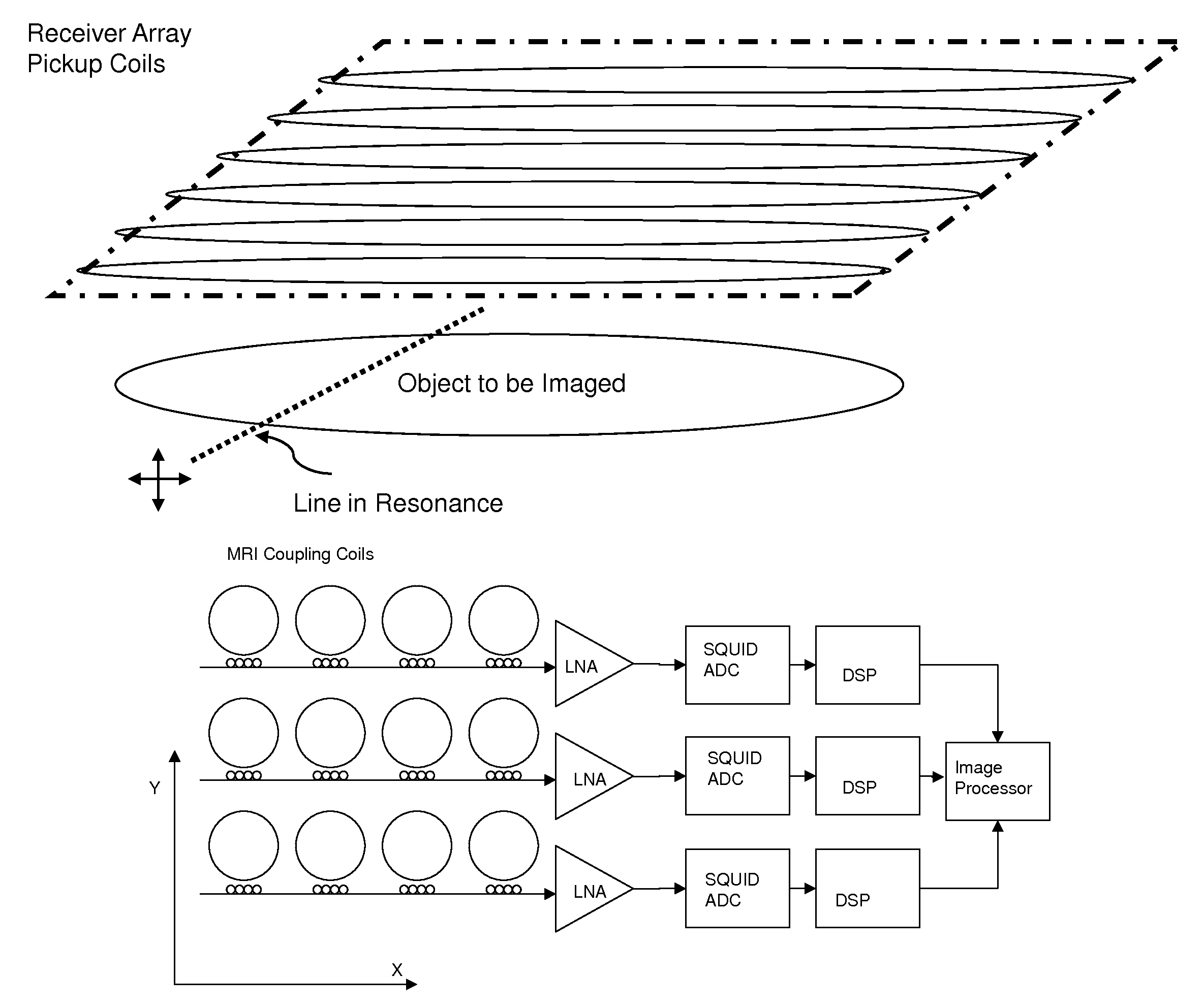
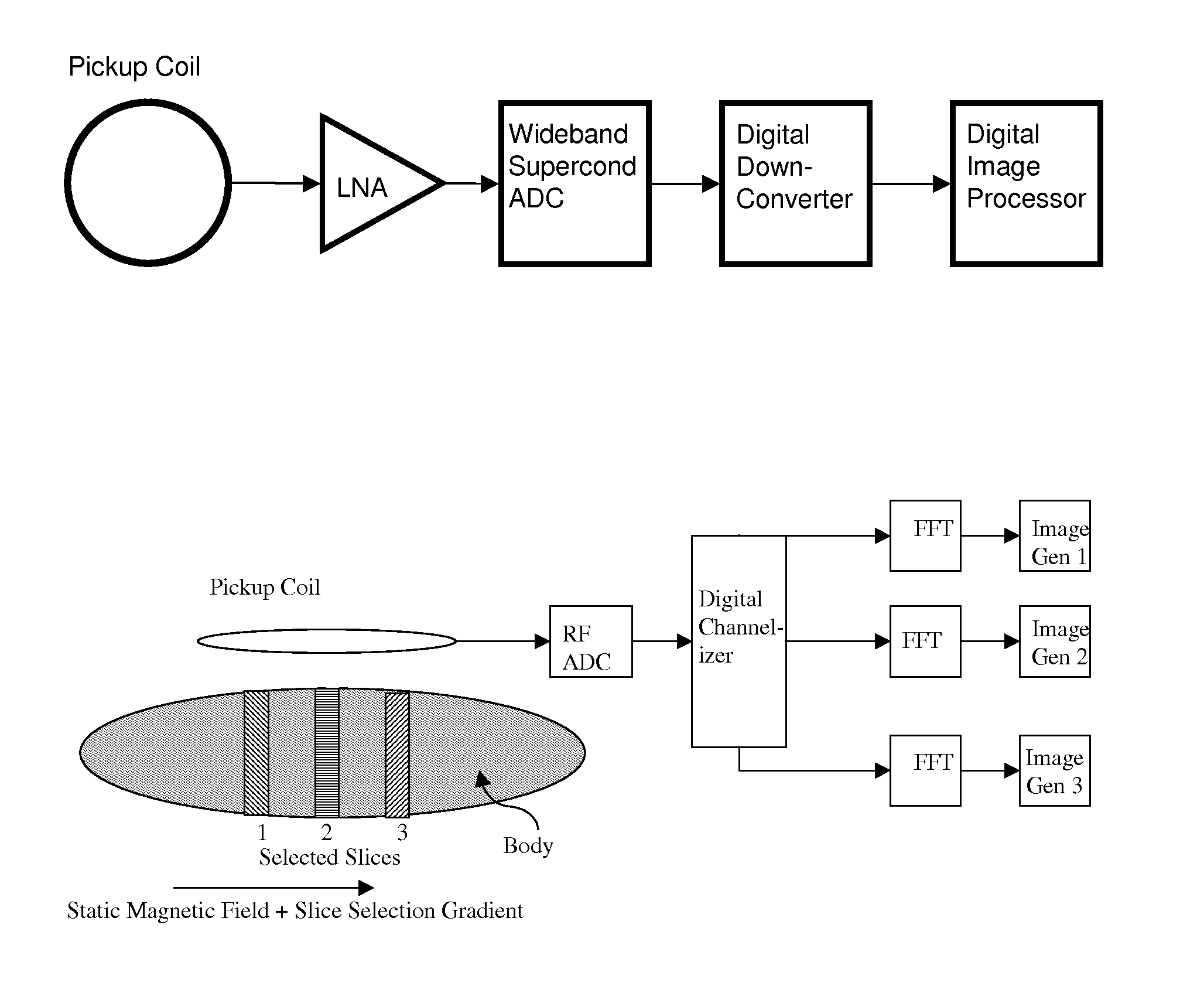
Magnetic resonance system and method employing a digital squid
ActiveUS8593141B1Fast imagingImprove spatial resolutionMagnetic property measurementsMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsVoxelData acquisition
A magnetic resonance system, comprising at least one SQUID, configured to receive a radio frequency electromagnetic signal, in a circuit configured to produce a pulsatile output having a minimum pulse frequency of at least 1 GHz which is analyzed in a processor with respect to a timebase, to generate a digital signal representing magnetic resonance information. The processor may comprise at least one rapid single flux quantum circuit. The magnetic resonance information may be image information. A plurality of SQUIDs may be provided, fed by a plurality of antennas in a spatial array, to provide parallel data acquisition. A broadband excitation may be provided to address a range of voxels per excitation cycle. The processor may digitally compensate for magnetic field inhomogeneities.
Owner:THE JOHNSON REVOCABLE TRUST DATED 6 25 2003
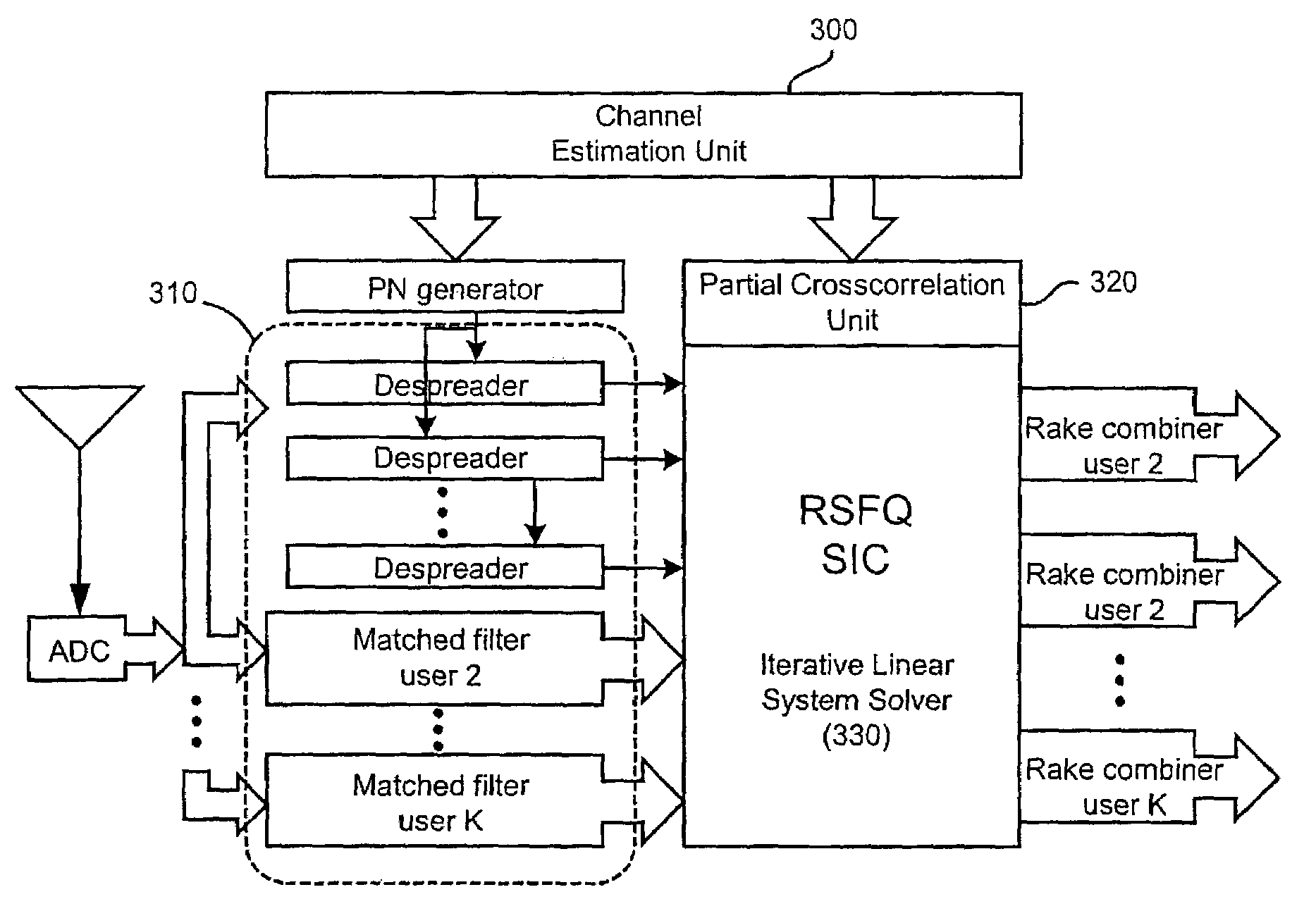
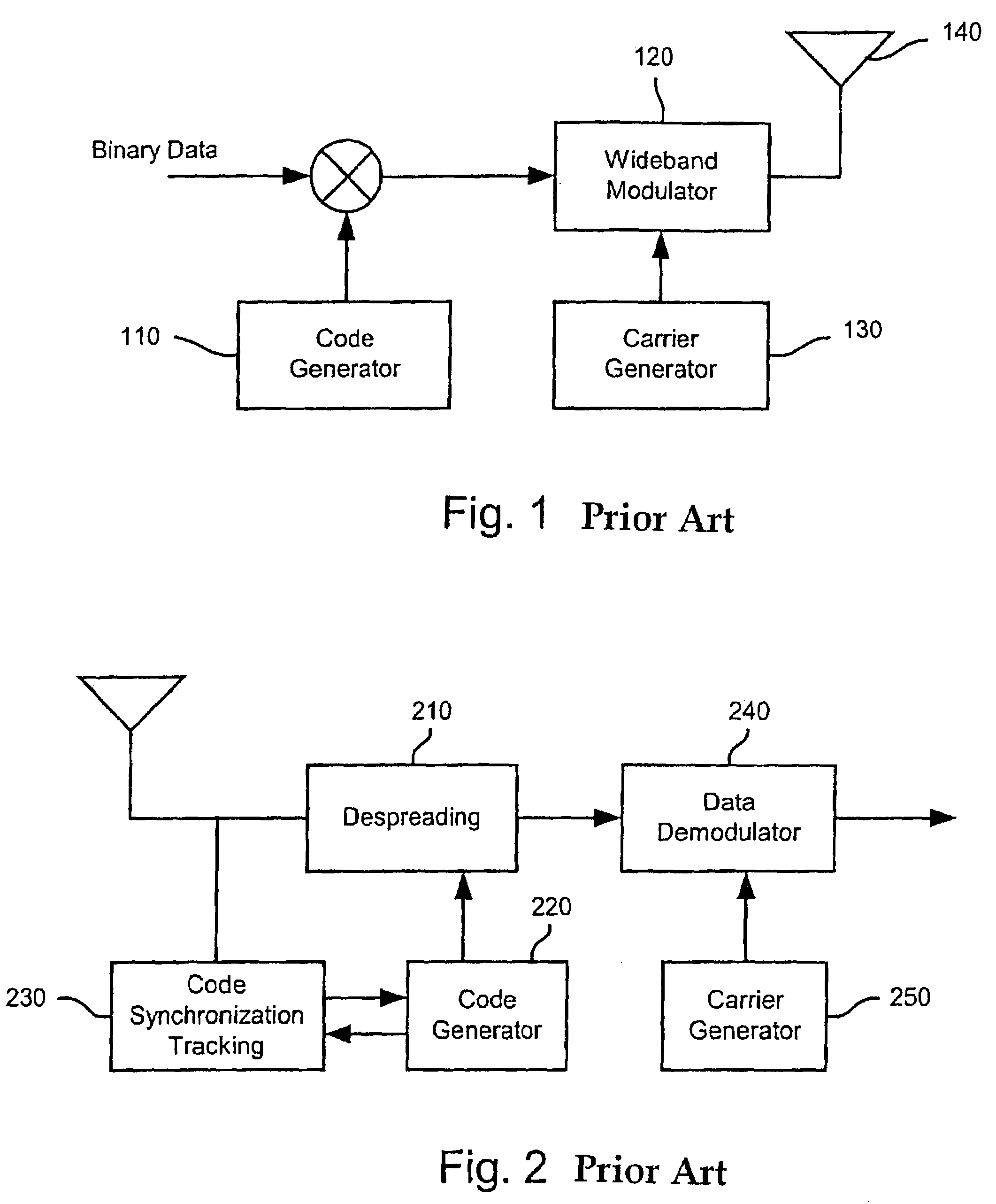
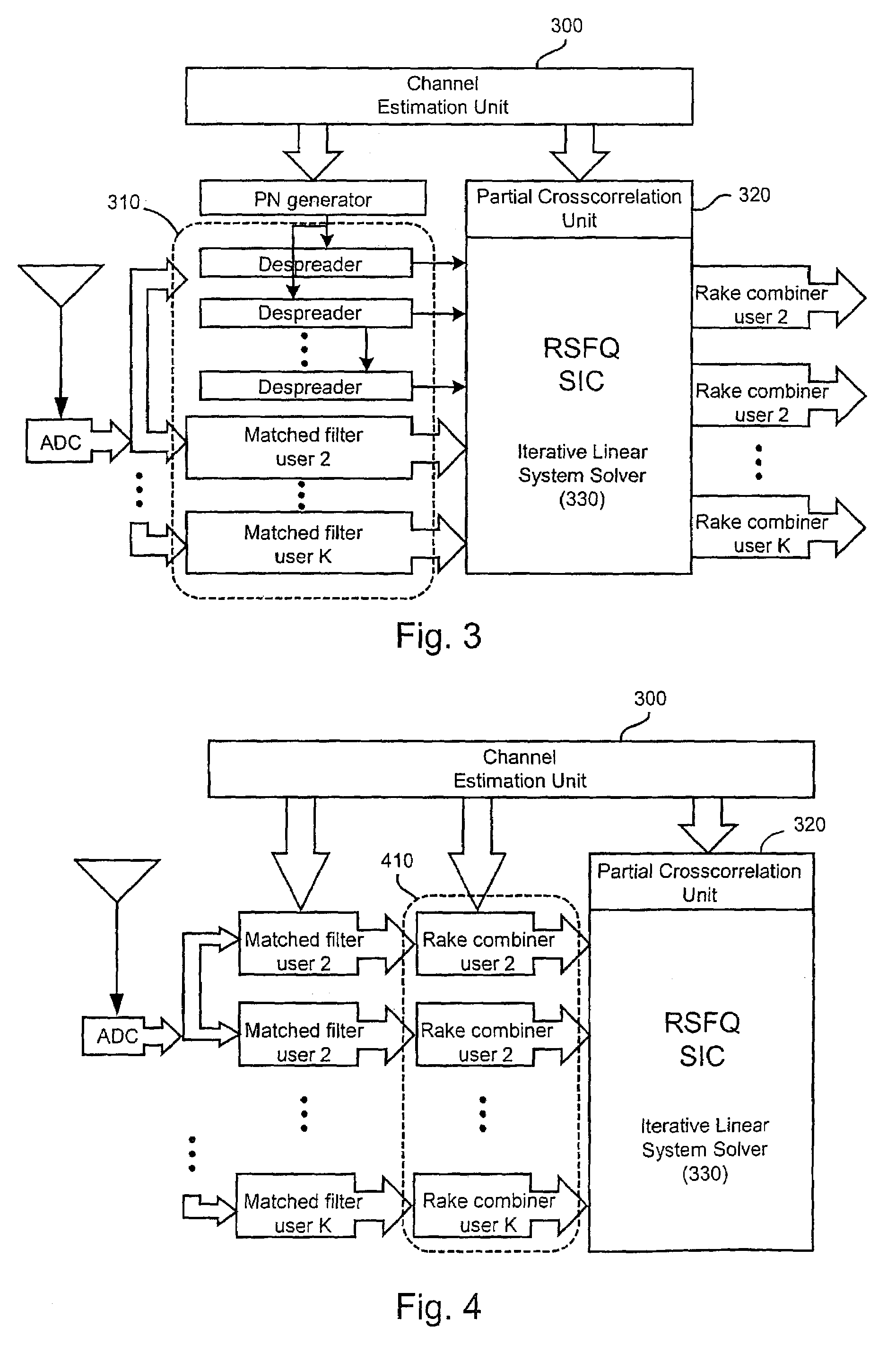
Method and apparatus for multi-user detection using RSFQ successive interference cancellation in CDMA wireless systems
InactiveUS7440490B2Reduce distractionsIncrease uplink capacityRadio transmissionInterference cancellerSystem capacity
A method and apparatus for using a multi-user detector for reducing multiple access interference (MAI) in a direct sequence CDMA wireless system such as W-CDMA. A superconducting rapid single flux quantum (RSFQ) RF digital receiver operating in combination with an RSFQ successive interference canceller (SIC) is located in the base stations of the wireless system. In the present invention, the RSFQ SIC is a vector machine capable of processing the cross-correlation matrices using an iterative method to decorrelate the user binary code sequences from the input signal in which the interference components are removed. According, the reduction in interference results in a significant increase in system capacity while improving cellular coverage area.
Owner:KIDIYAROVA SHEVCHENKO ANNA +2
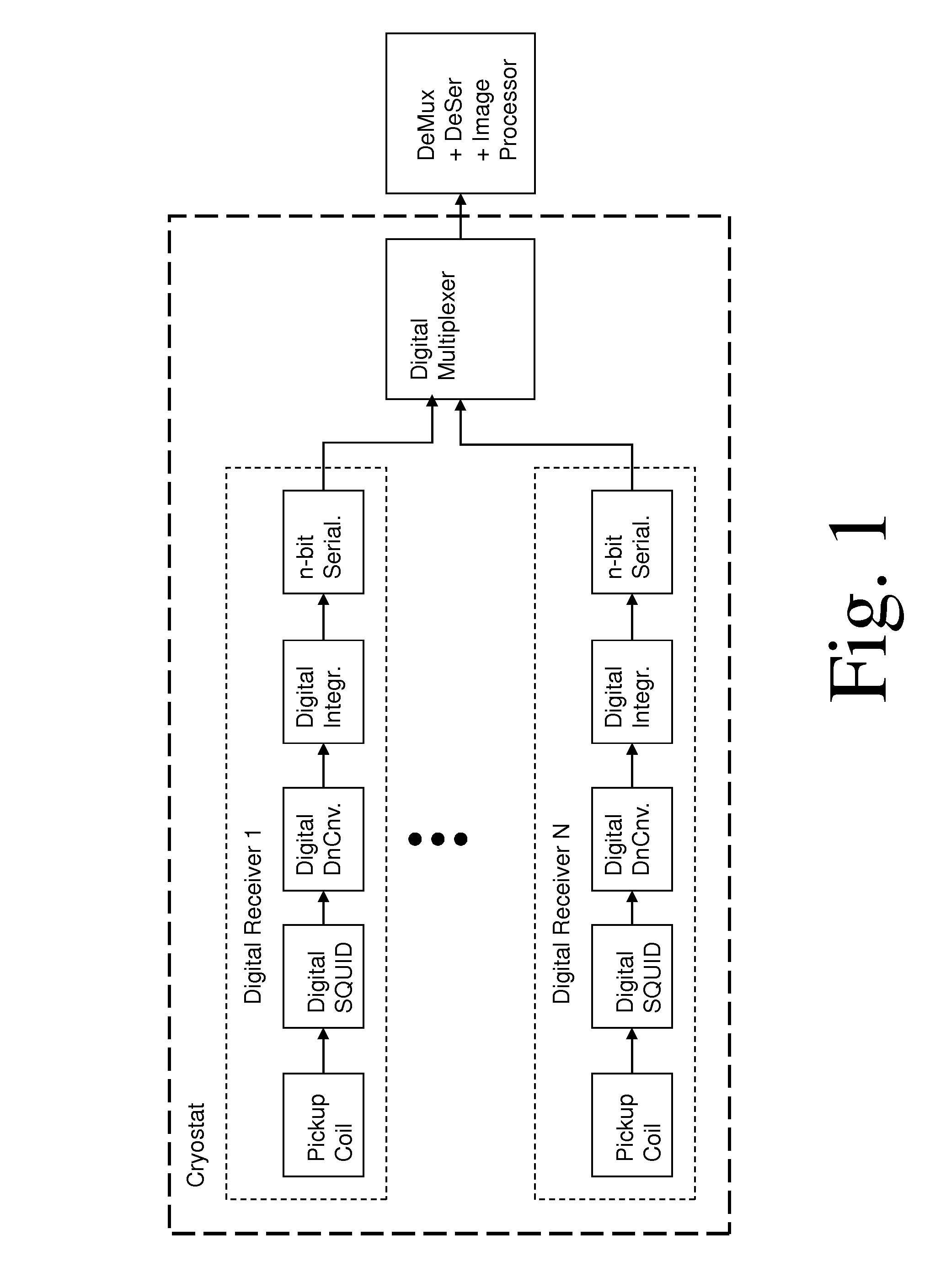
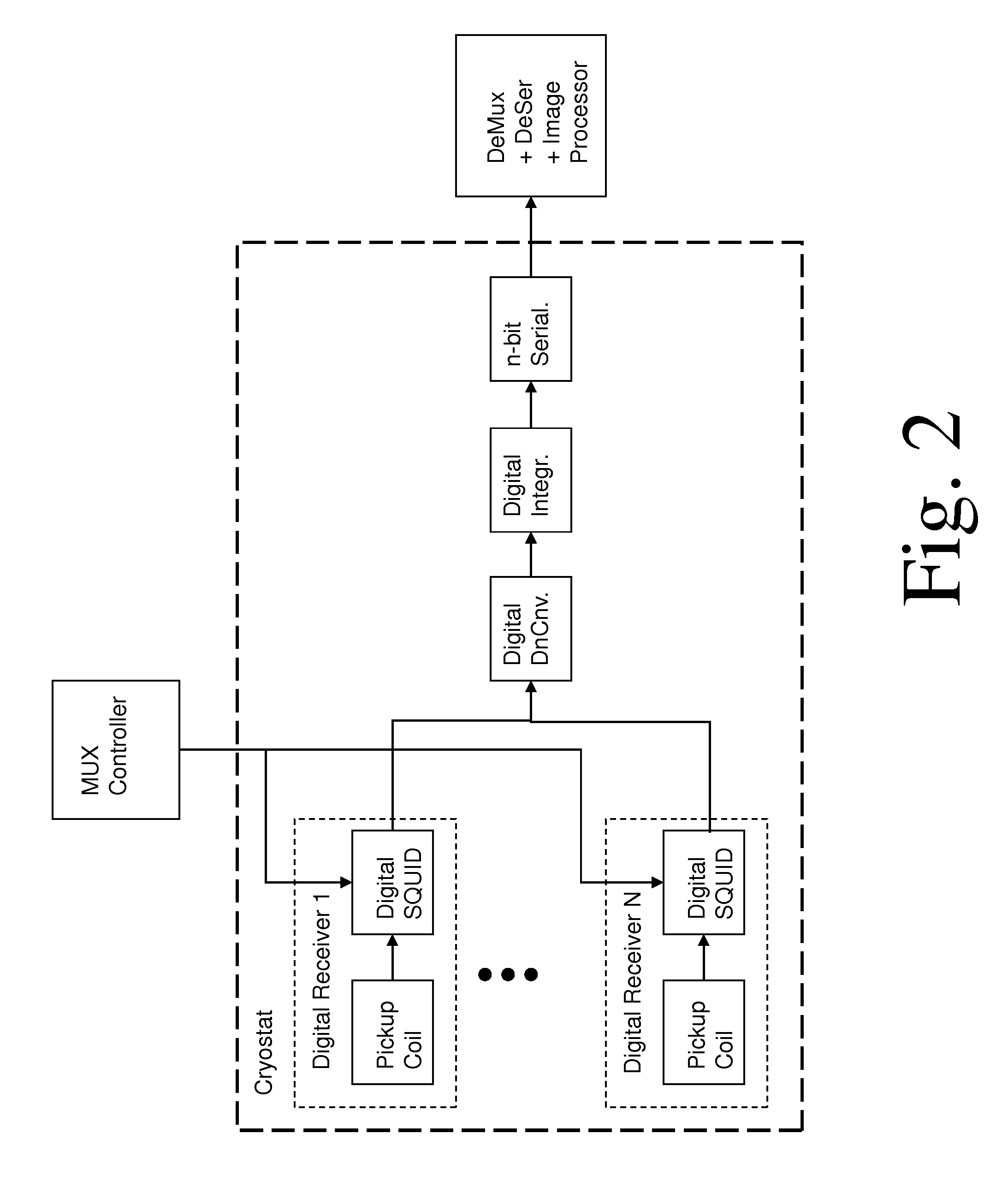
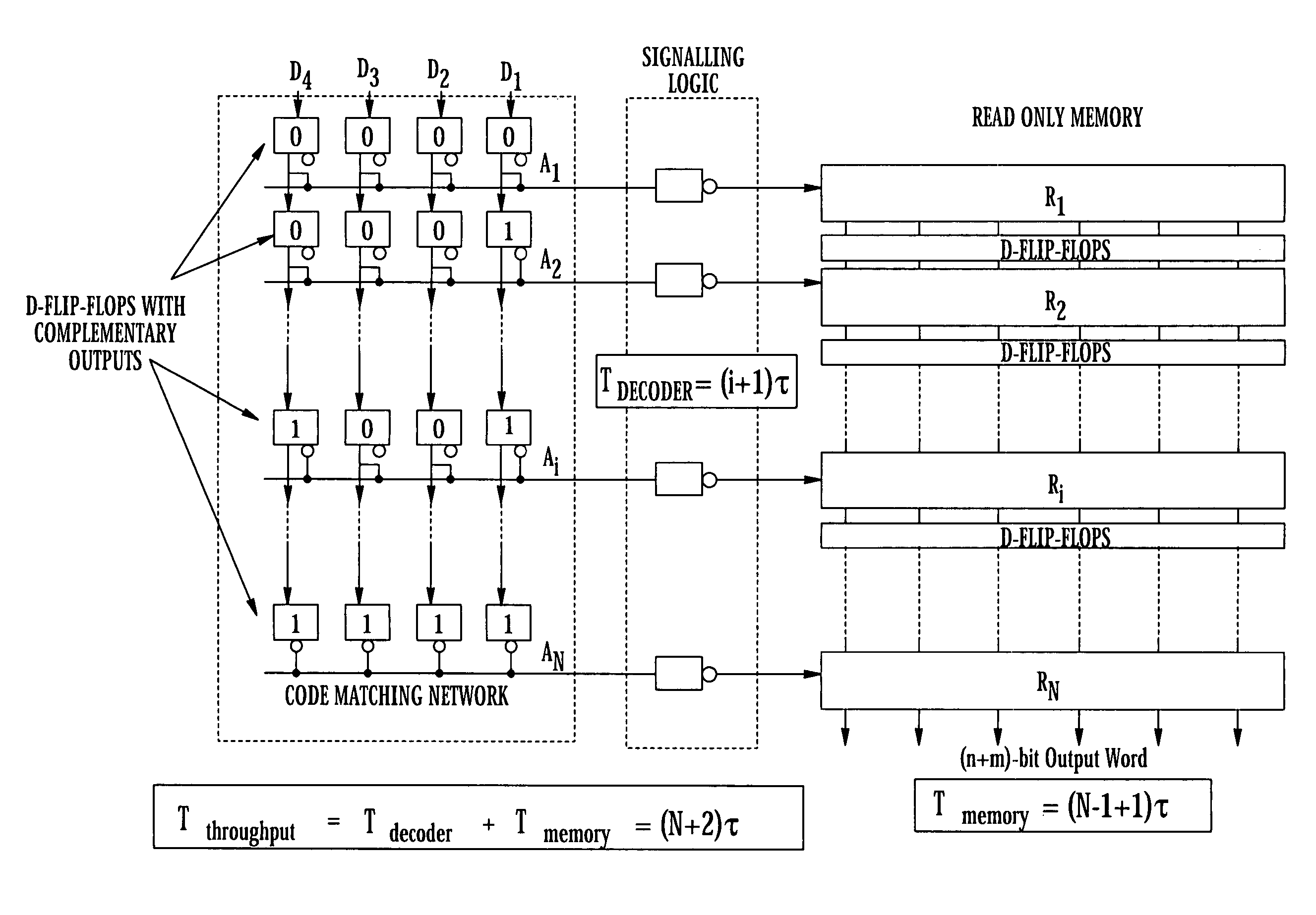
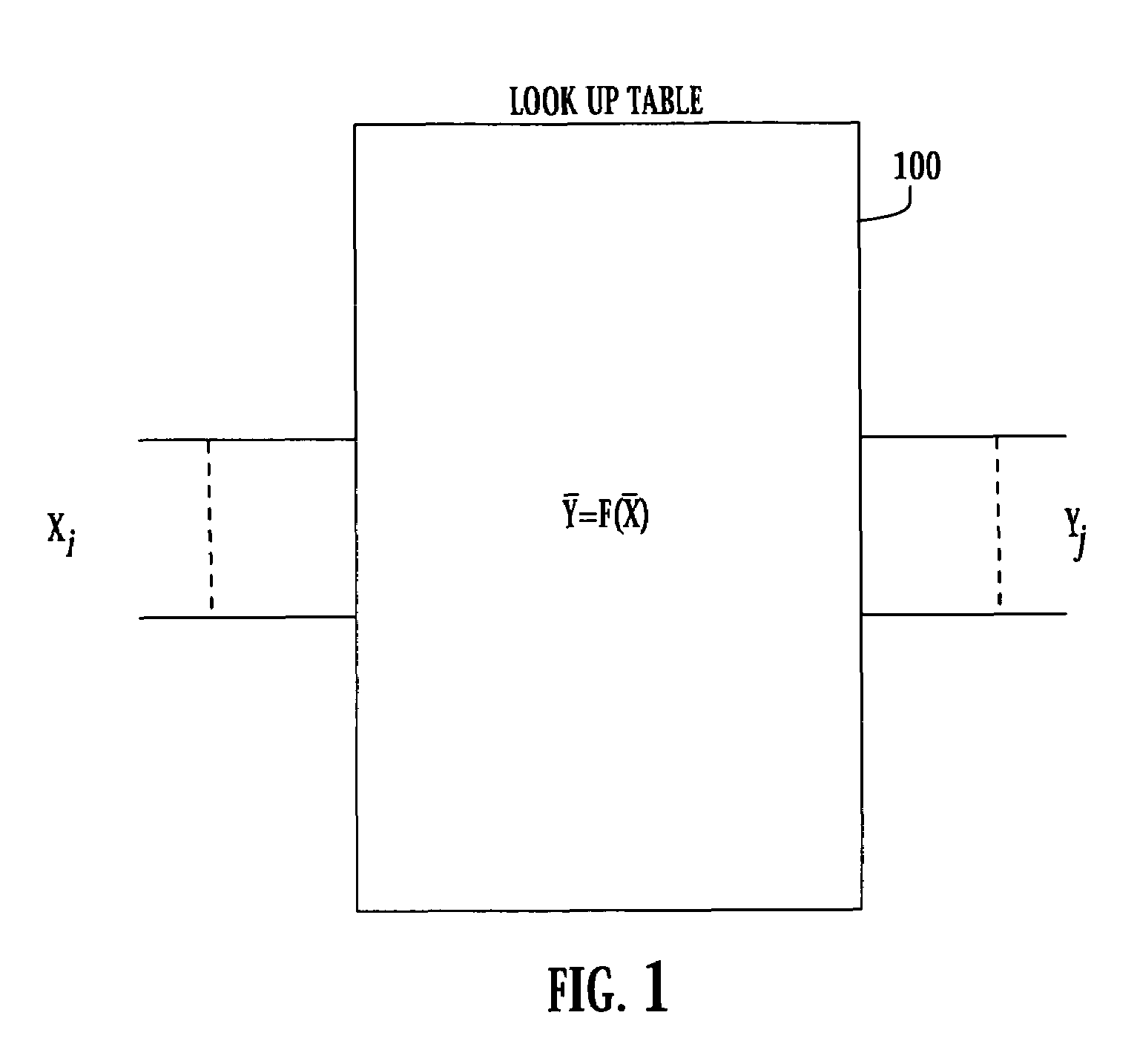
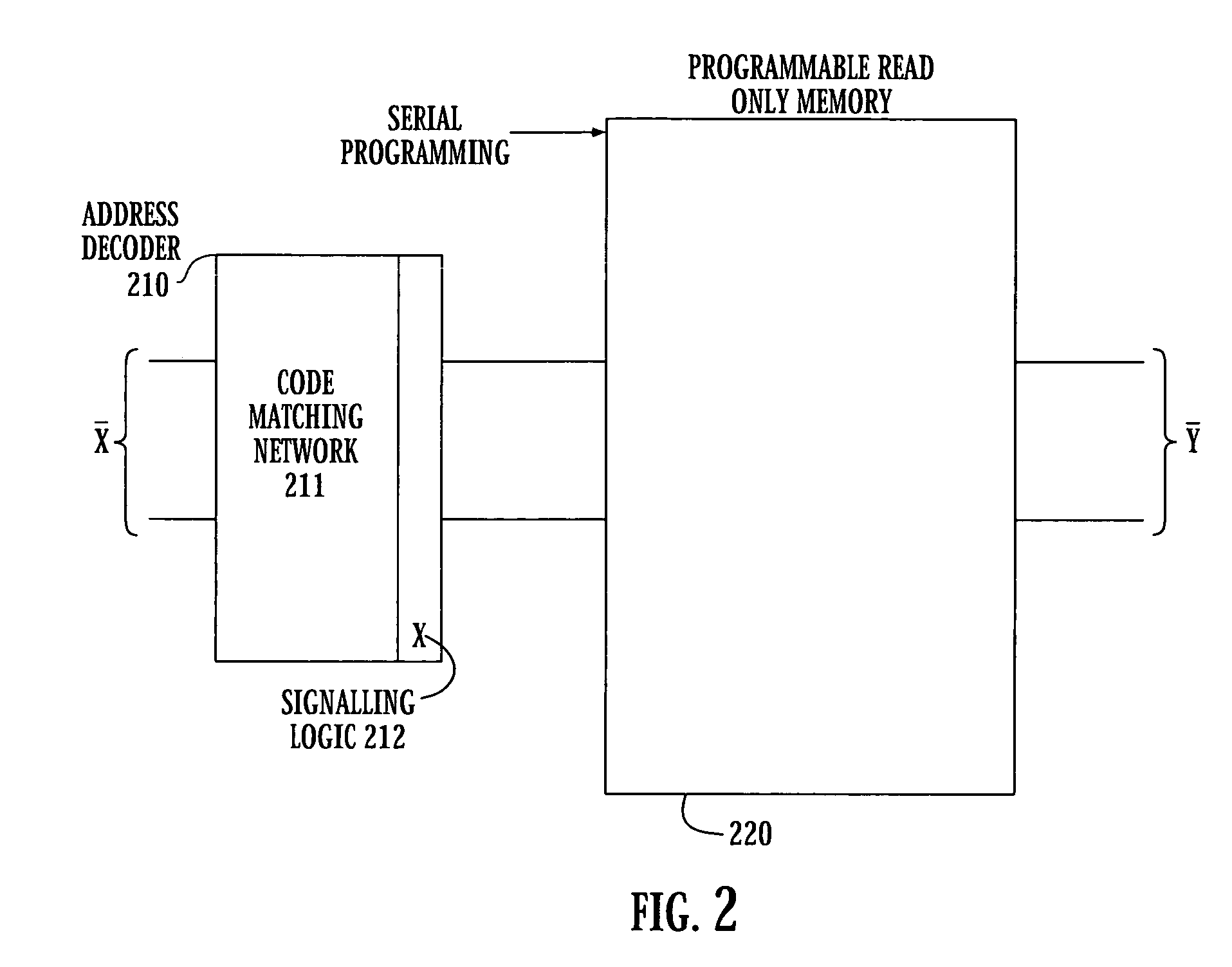
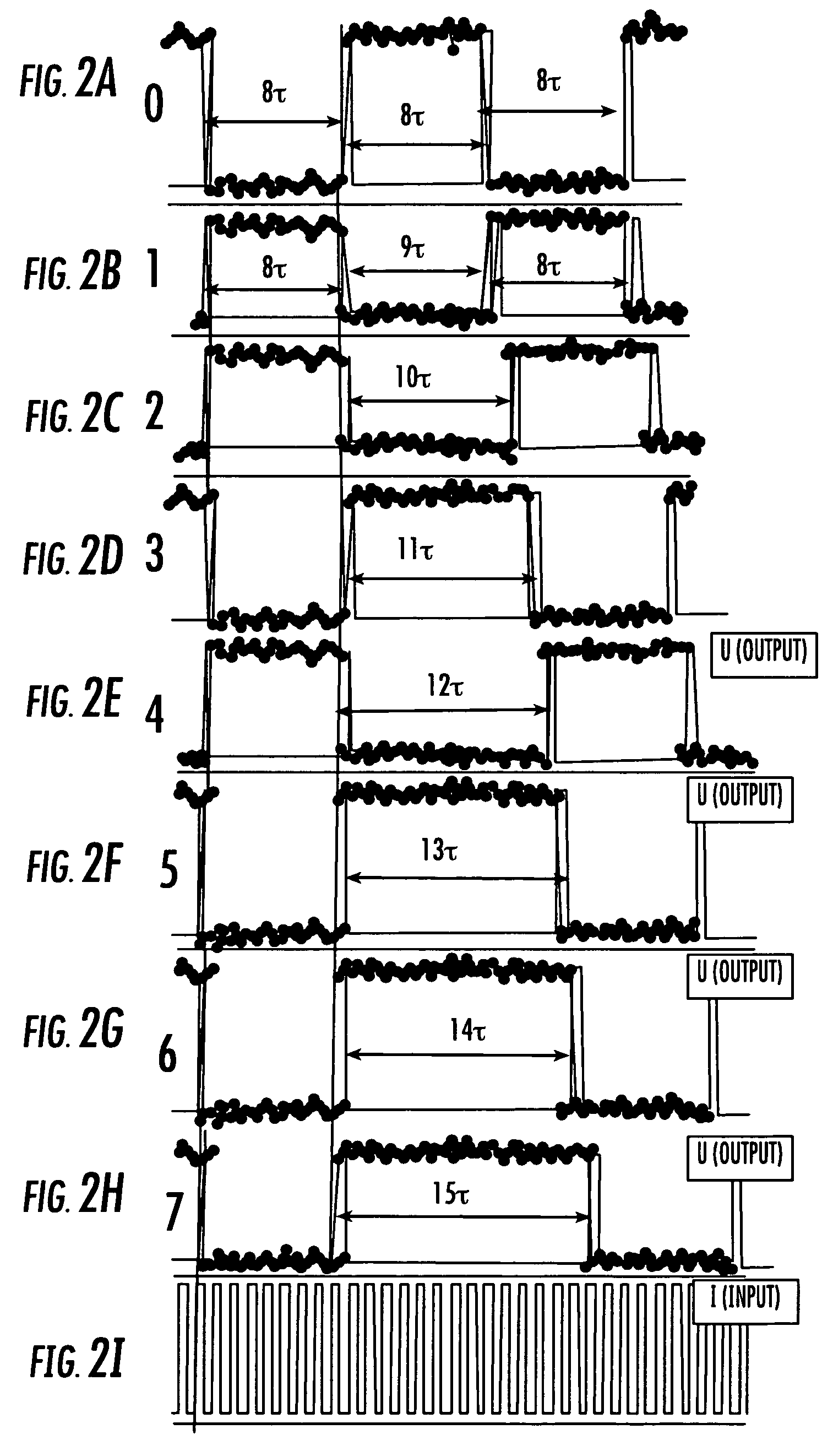
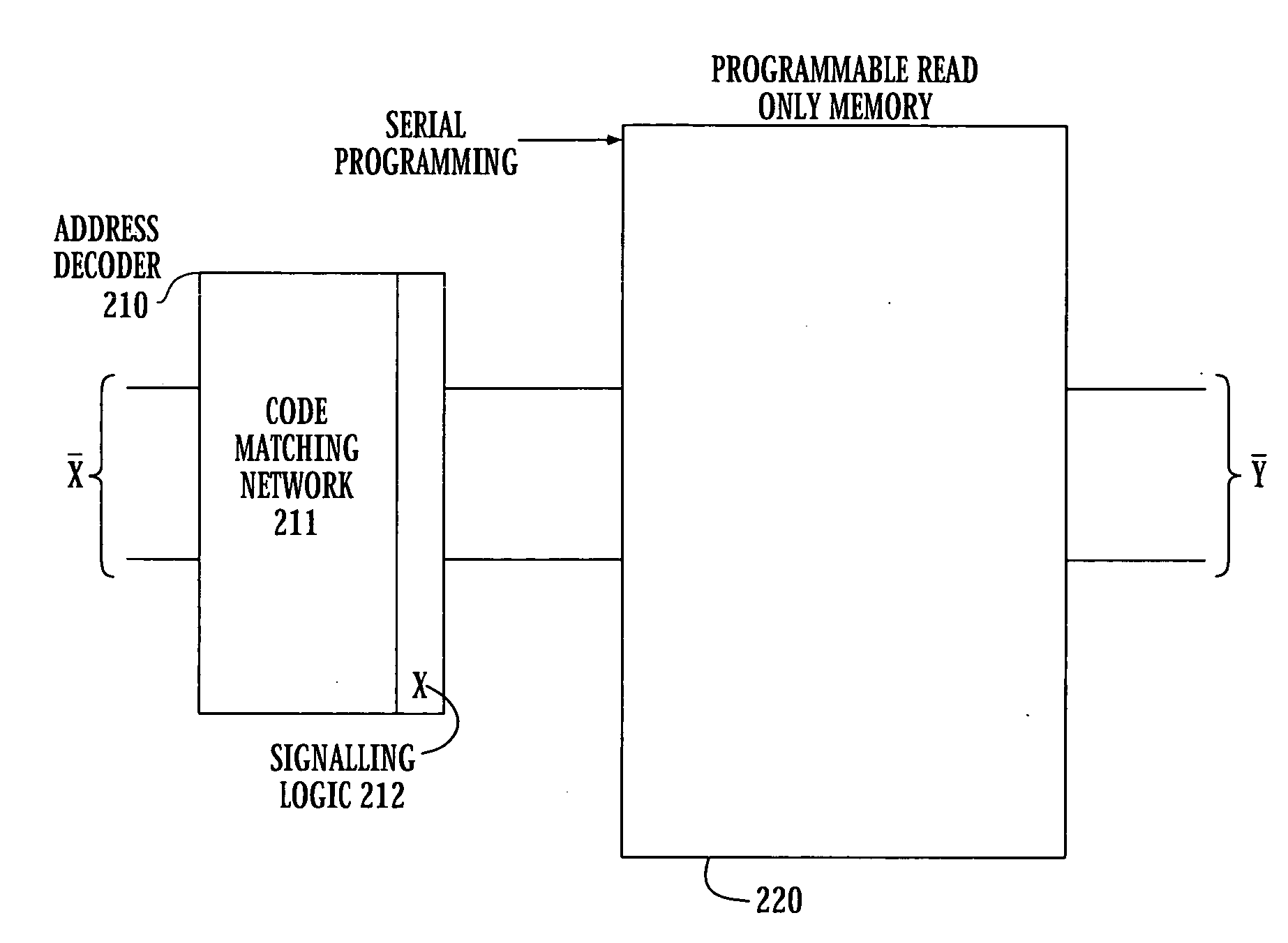
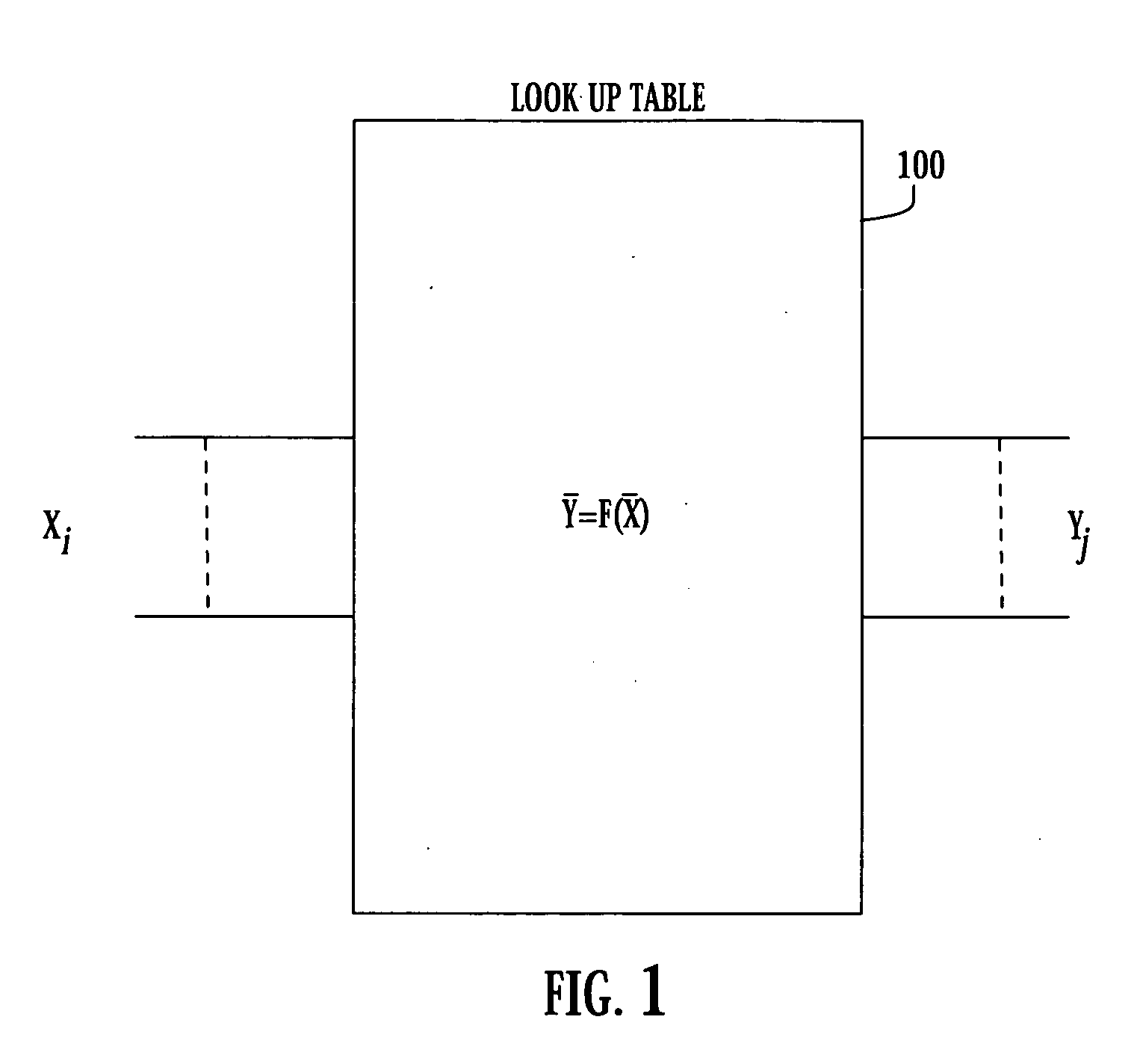
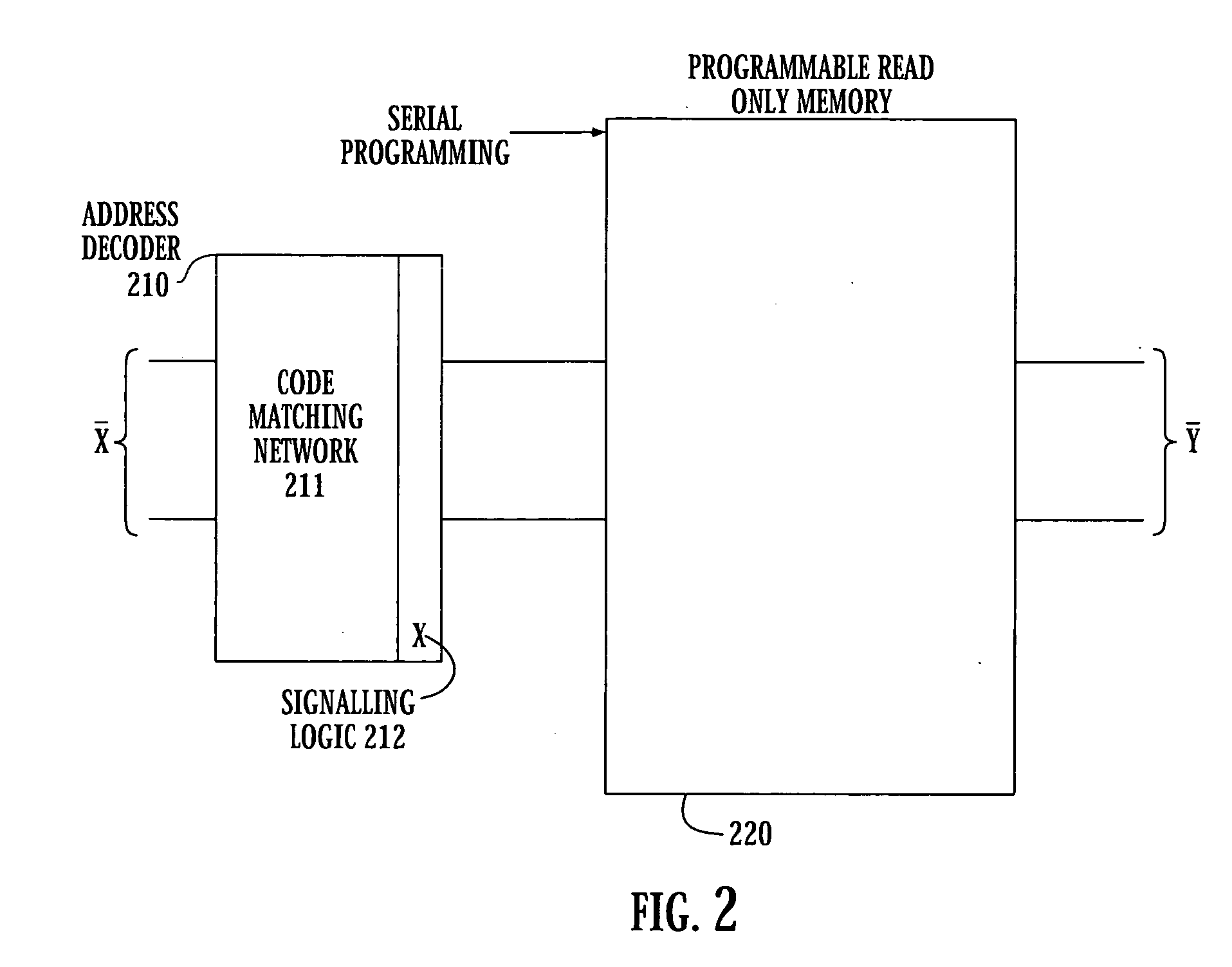
Superconducting circuit for high-speed lookup table
ActiveUS7443719B2Superconductors/hyperconductorsRead-only memoriesProgrammable read-only memoryReprogramming
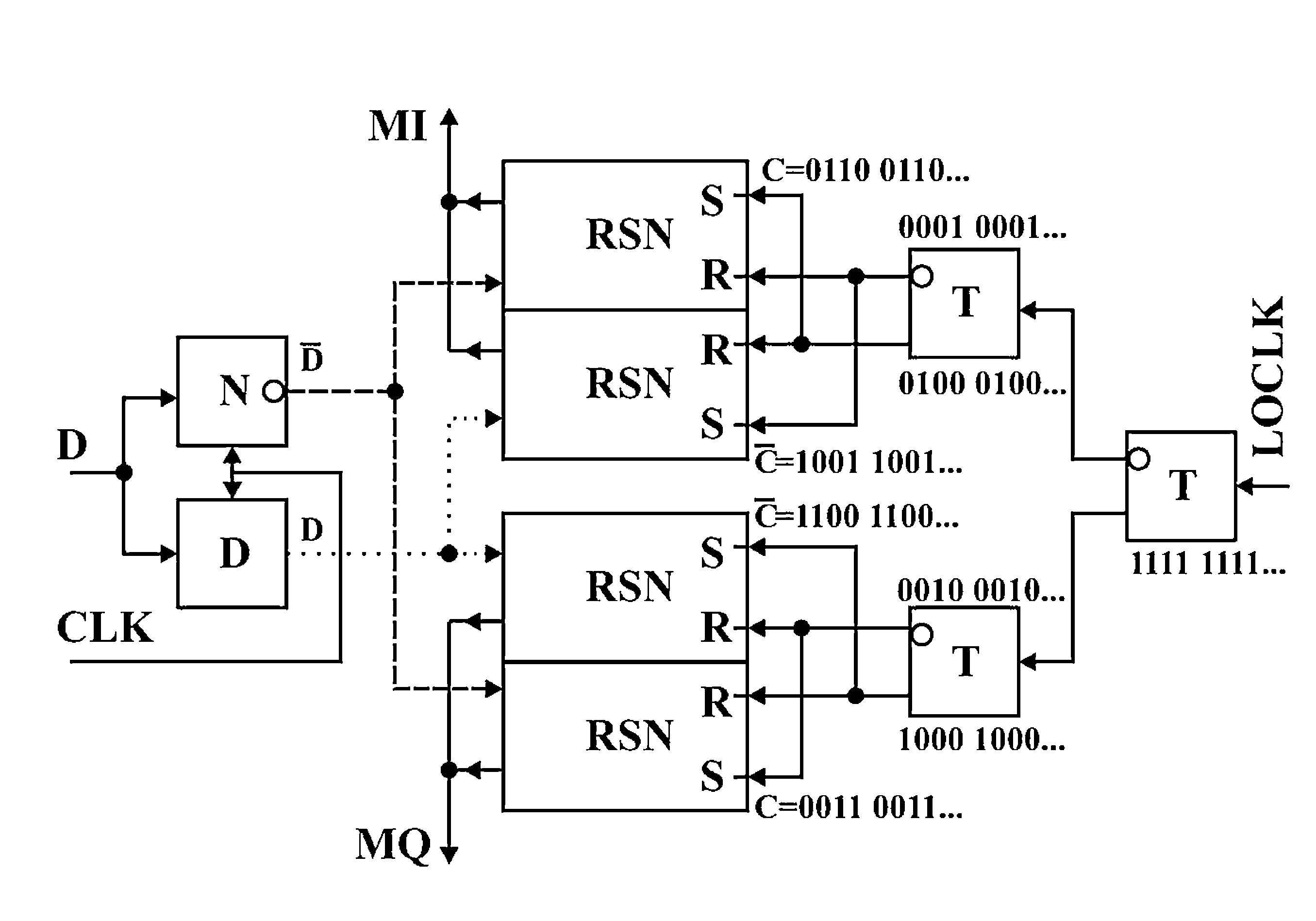
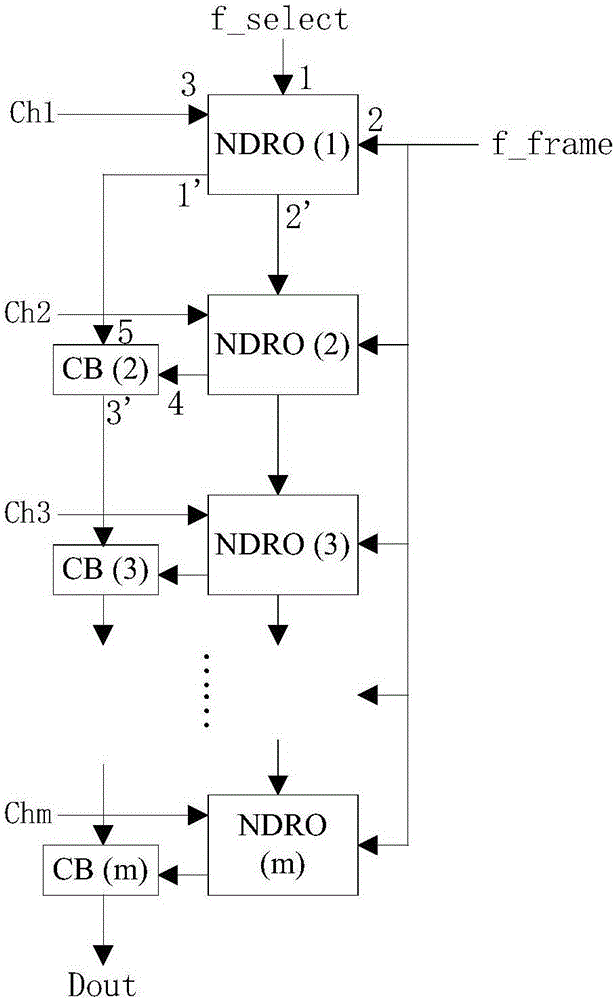
A high-speed lookup table is designed using Rapid Single Flux Quantum (RSFQ) logic elements and fabricated using superconducting integrated circuits. The lookup table is composed of an address decoder and a programmable read-only memory array (PROM). The memory array has rapid parallel pipelined readout and slower serial reprogramming of memory contents. The memory cells are constructed using standard non-destructive reset-set flip-flops (RSN cells) and data flip-flops (DFF cells). An n-bit address decoder is implemented in the same technology and closely integrated with the memory array to achieve high-speed operation as a lookup table. The circuit architecture is scalable to large two-dimensional data arrays.
Owner:SEEQC INC
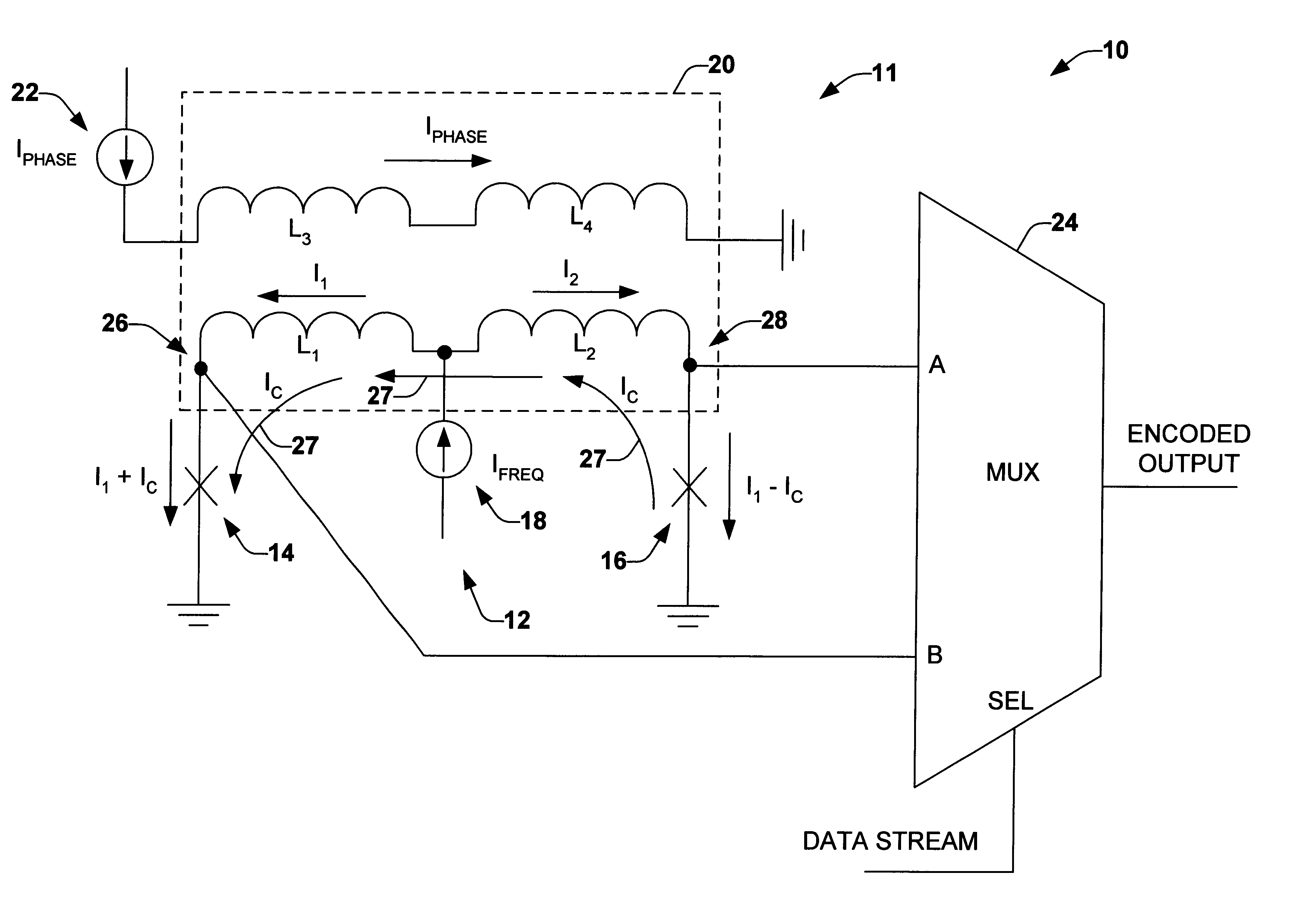
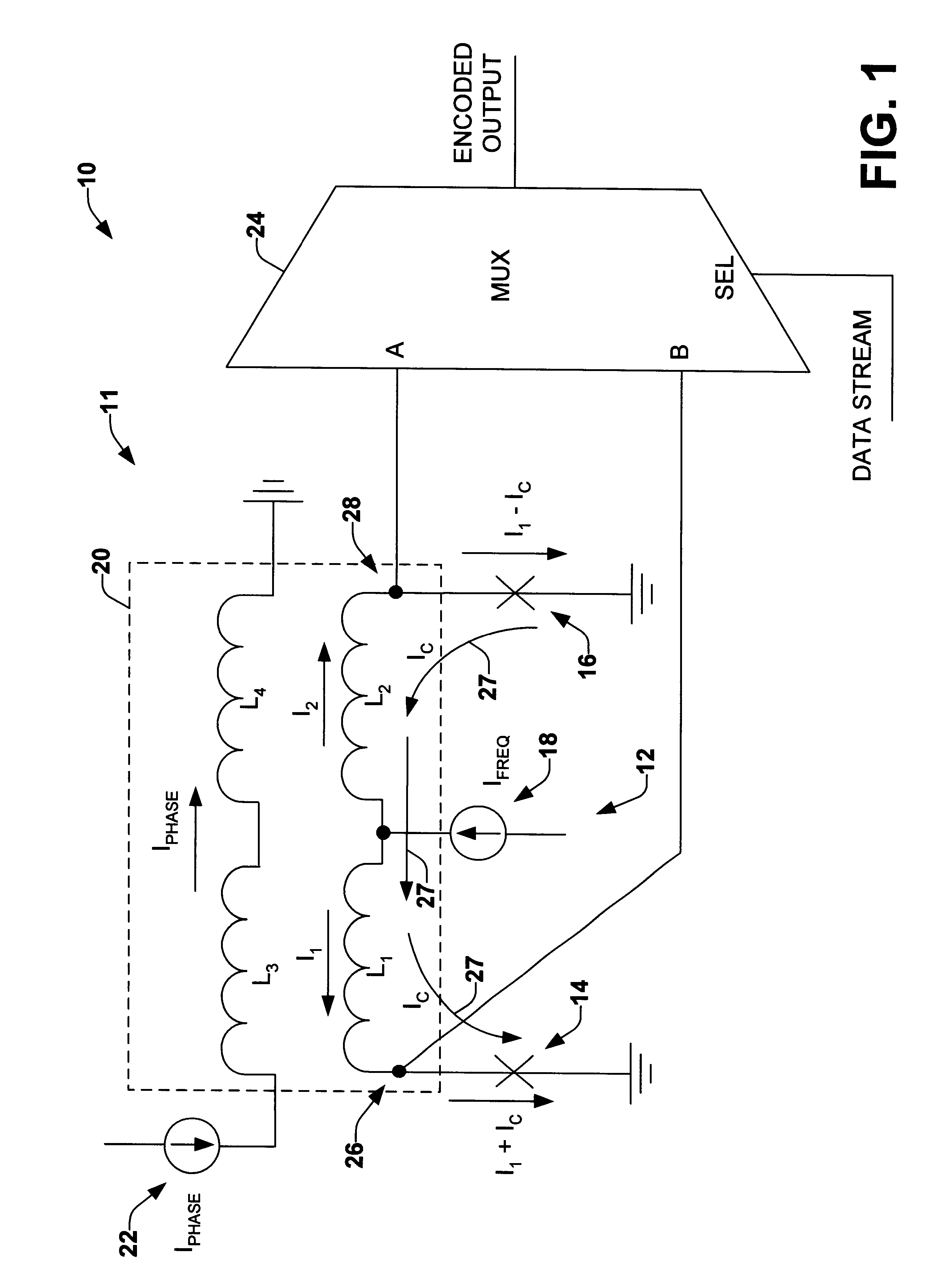
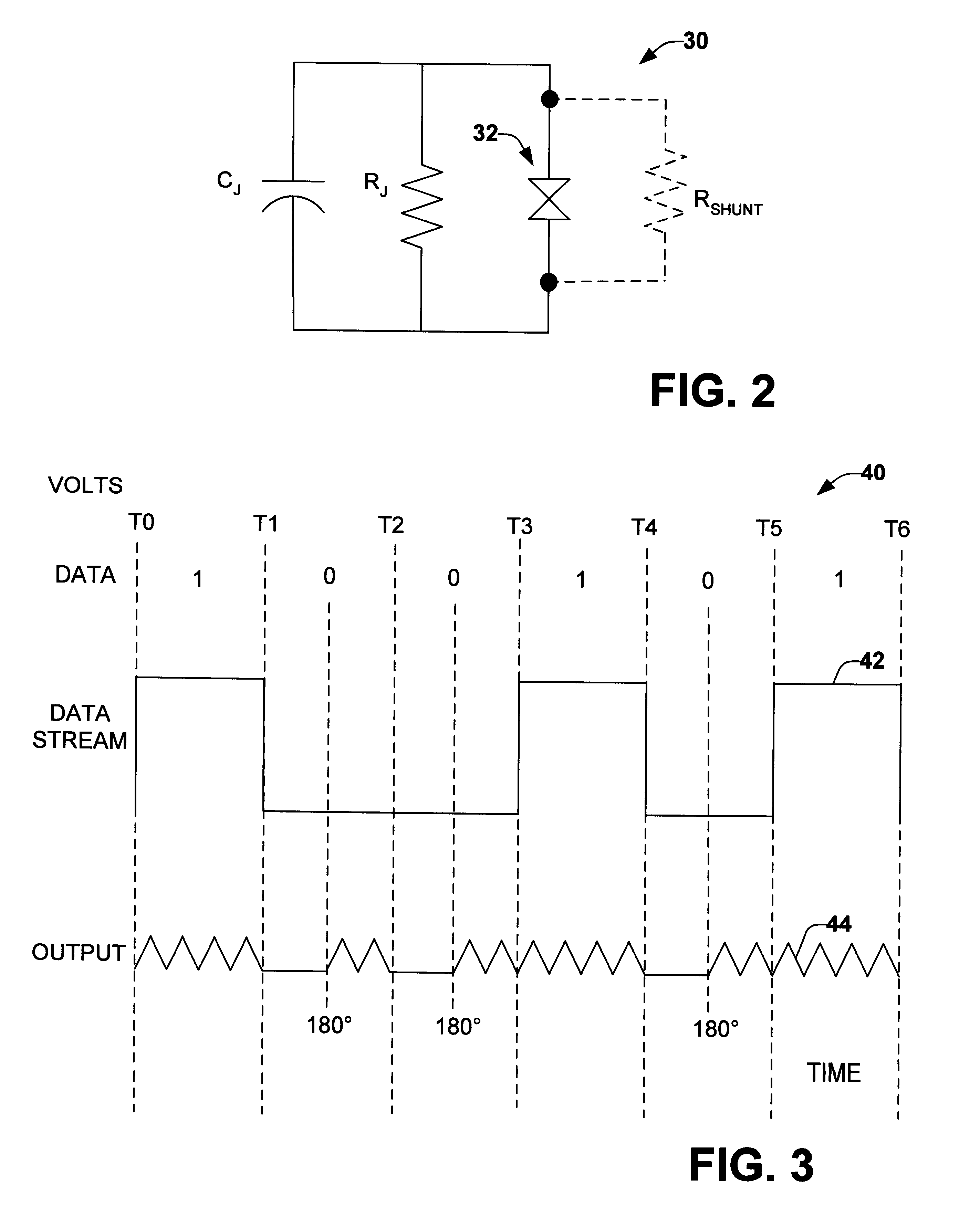
PSK RSFQ output interface
InactiveUS6756925B1Well formedElectric signal transmission systemsPulse automatic controlVoltage pulseData stream
A Rapid Single-Flux-Quantum ("RSFQ") encoder output interface device is provided. The RSFQ output interface device includes a variable phase multi-junction voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) that provides multiple clock signals having similar frequencies based on a DC bias current setting. The multiple clock signals are phase shifted from one other based on a flux bias current setting. The clock signals are then mixed together according to logic states of a data stream to provide an encoded output data stream. The encoded output data stream can be in a phase shifted keying (PSK) format. The PSK format can be provided in binary, quadrature or other PSK formats. The Single-Flux-Quantum (SFQ) voltage pulses of the encoded output data stream are converted to a voltage level appropriate for transmitting over a wire.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP +1
Magnetic resonance system and method employing a digital SQUID
ActiveUS8618799B1Fast imagingImprove spatial resolutionMagnetic property measurementsMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsVoxelData acquisition
A magnetic resonance system, comprising at least one SQUID, configured to receive a radio frequency electromagnetic signal, in a circuit configured to produce a pulsatile output having a minimum pulse frequency of at least 1 GHz which is analyzed in a processor with respect to a timebase, to generate a digital signal representing magnetic resonance information. The processor may comprise at least one rapid single flux quantum circuit. The magnetic resonance information may be image information. A plurality of SQUIDs may be provided, fed by a plurality of antennas in a spatial array, to provide parallel data acquisition. A broadband excitation may be provided to address a range of voxels per excitation cycle. The processor may digitally compensate for magnetic field inhomogeneities.
Owner:THE JOHNSON REVOCABLE TRUST DATED 6 25 2003
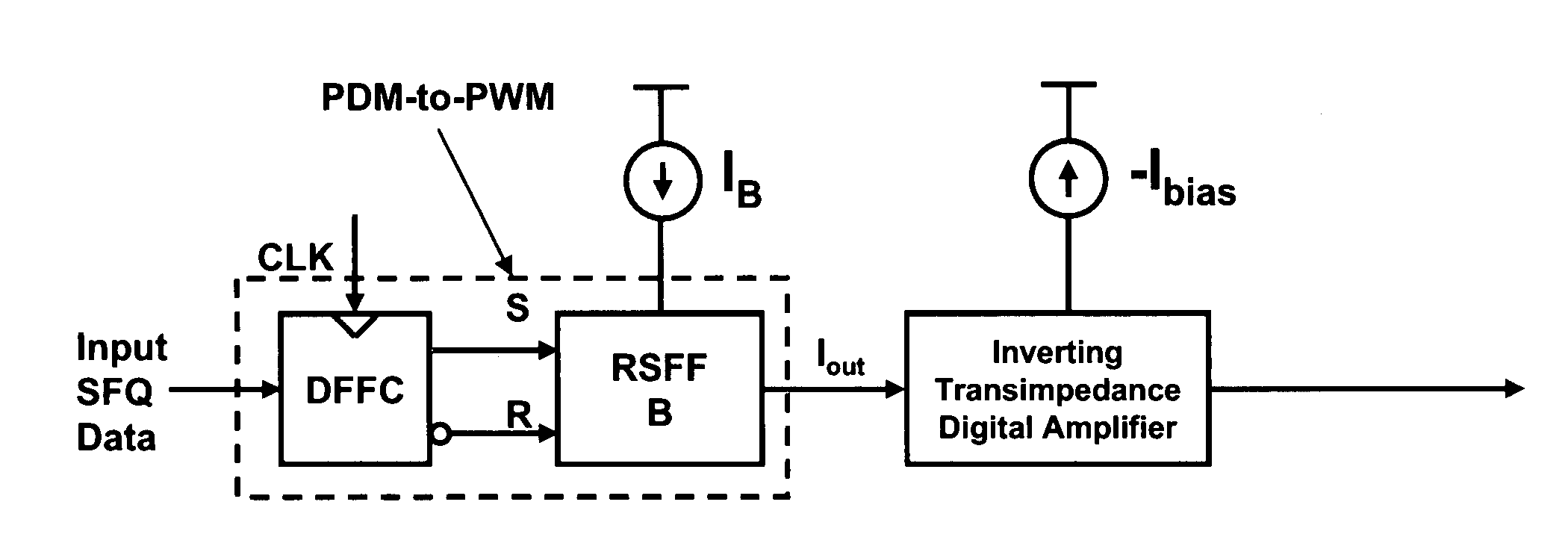
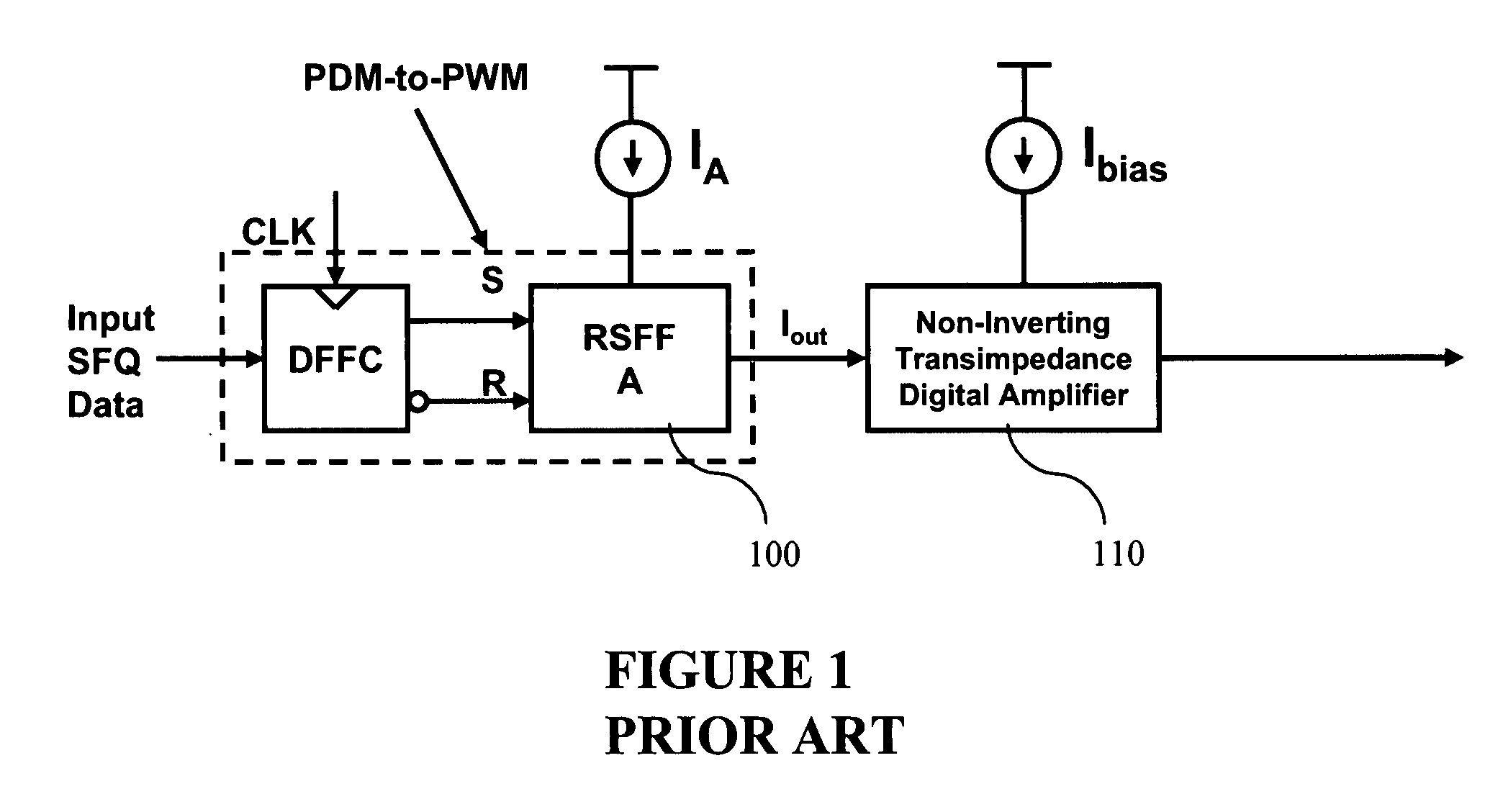
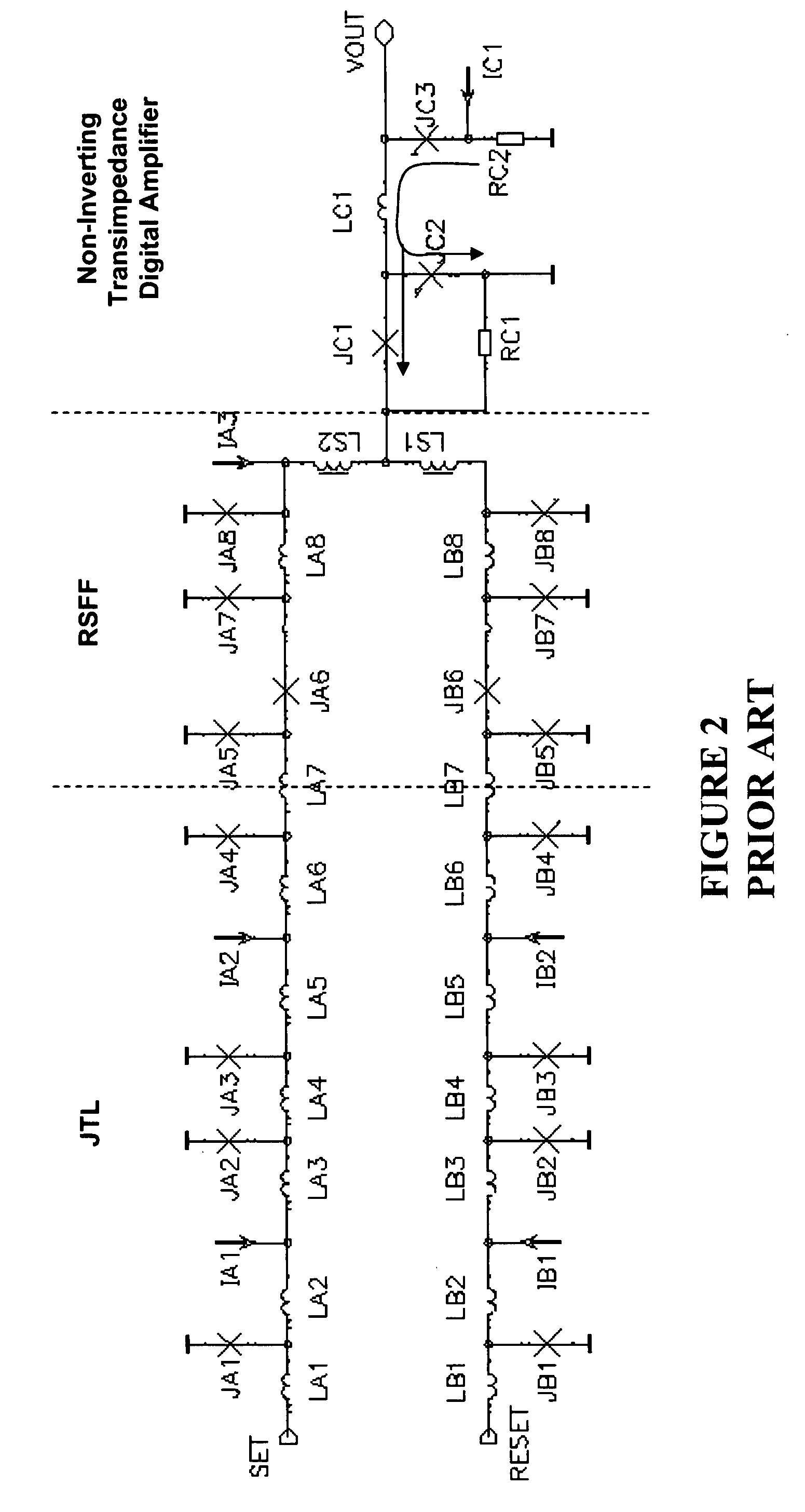
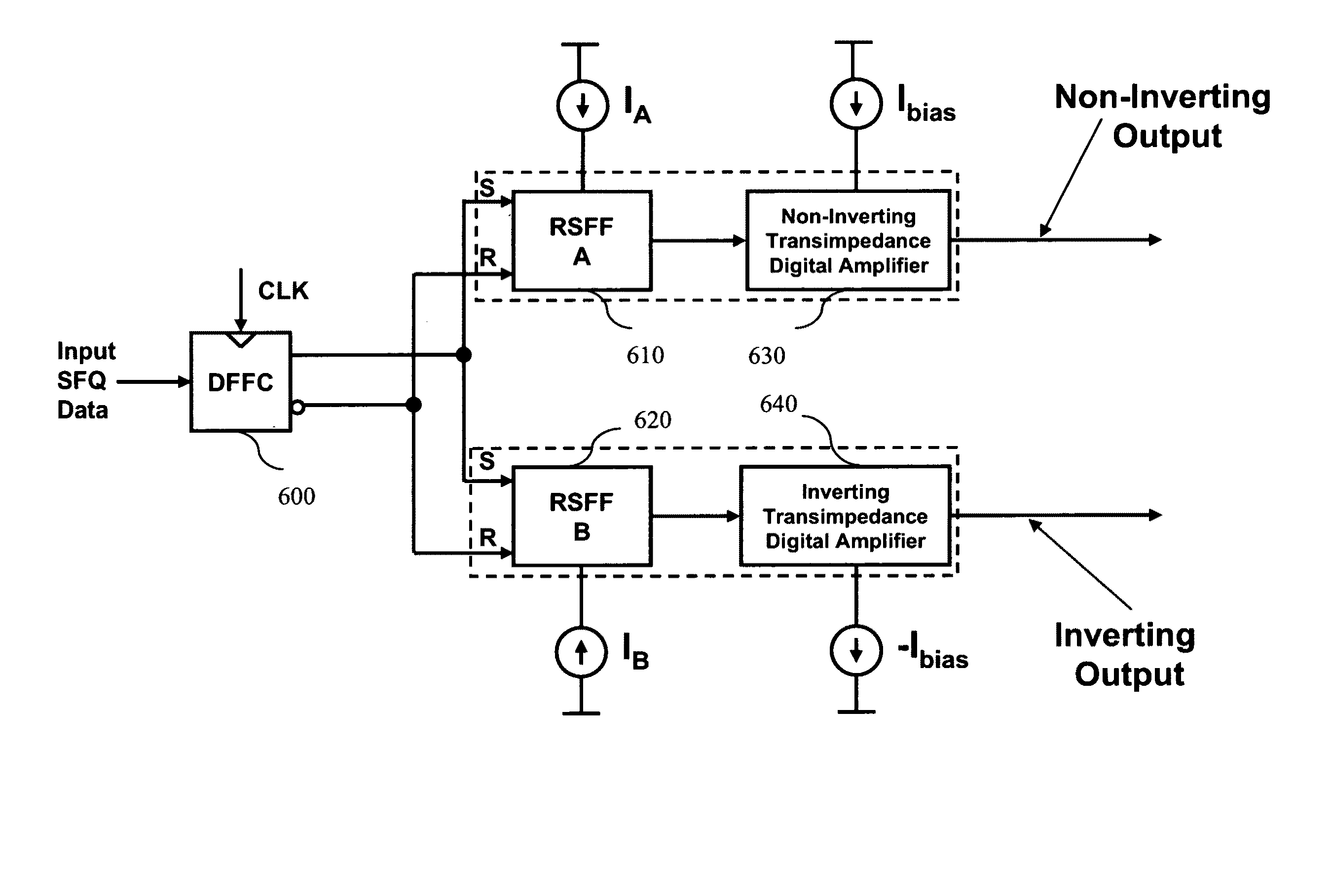
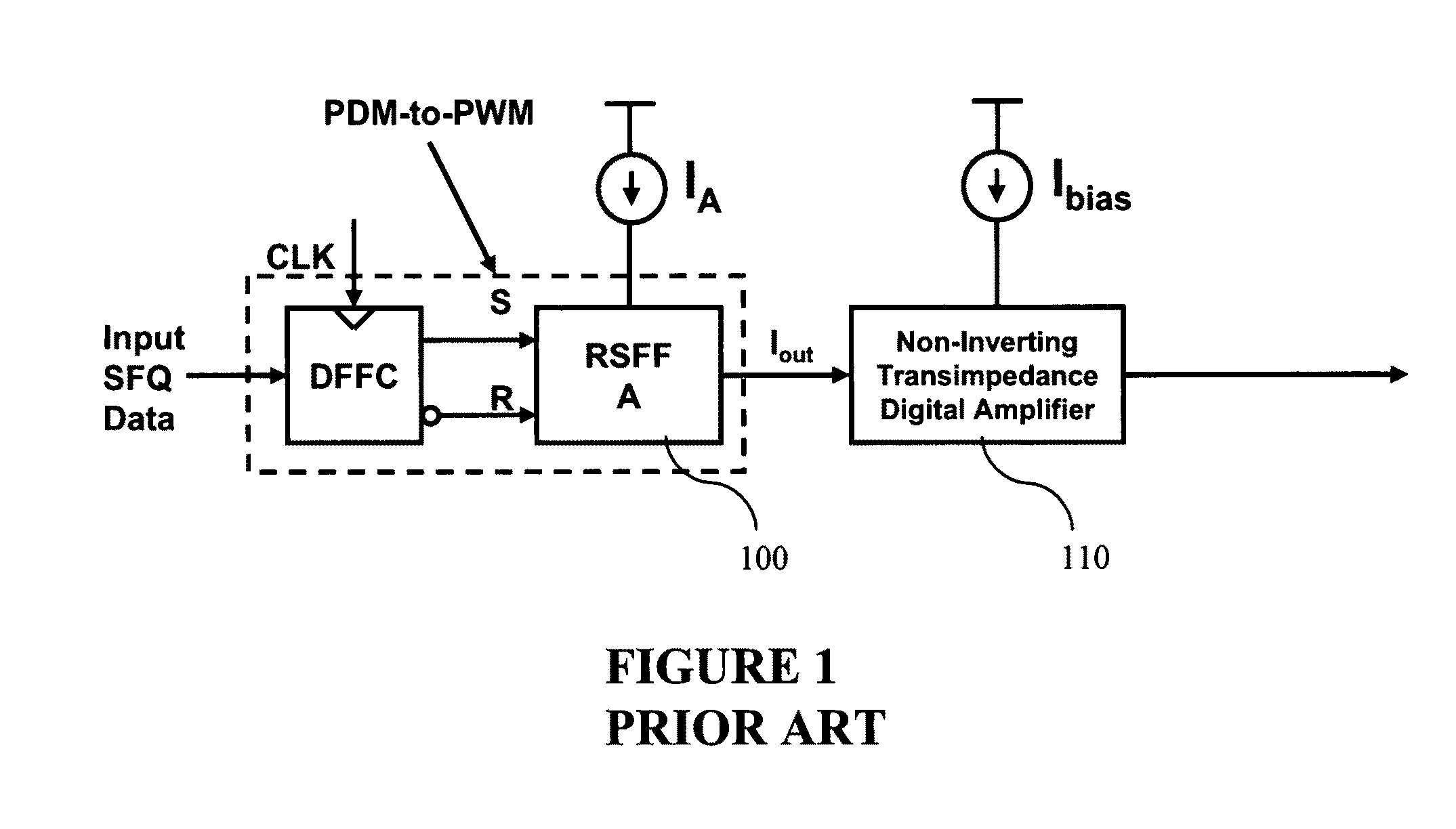
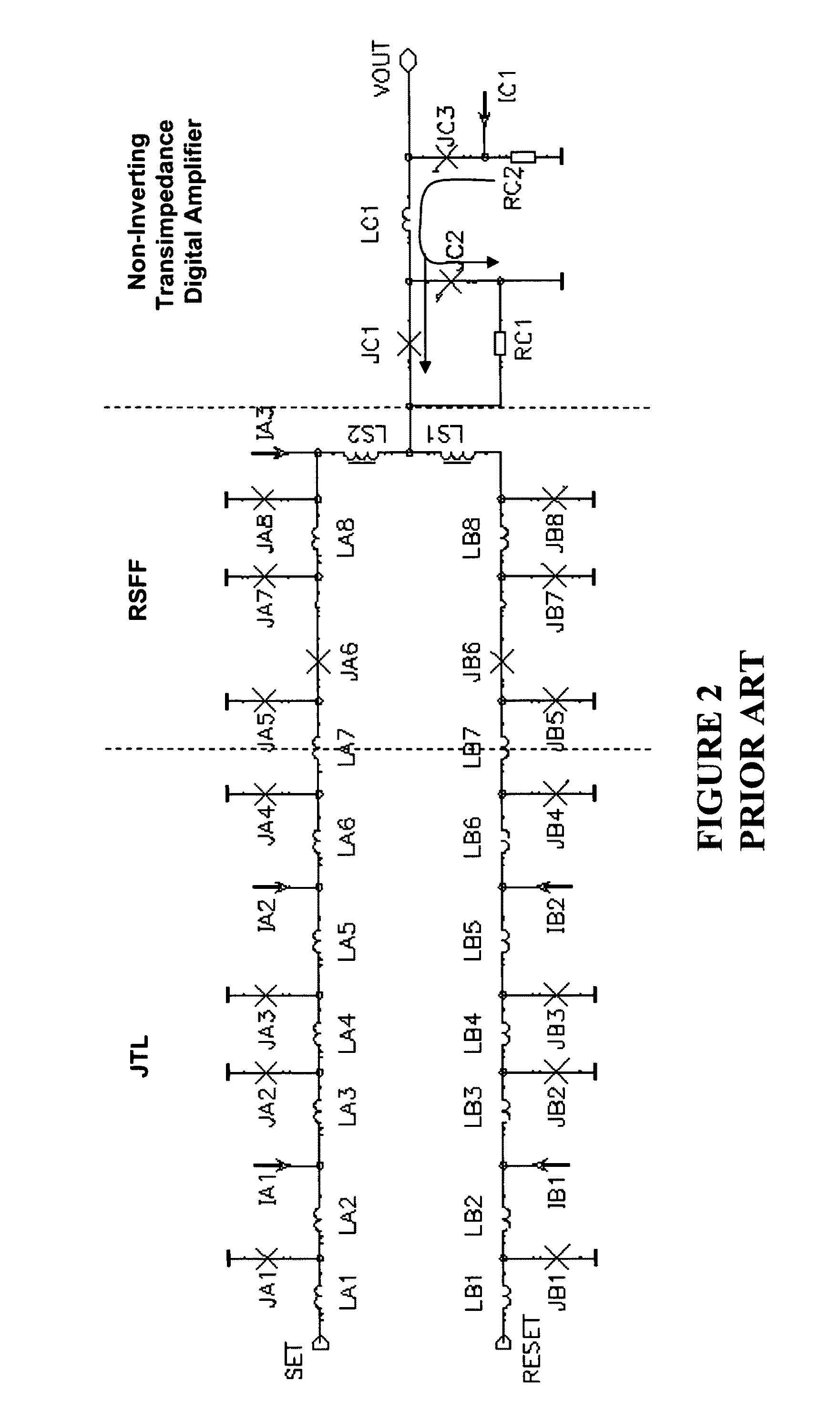
Ultra fast differential transimpedance digital amplifier for superconducting circuits
InactiveUS20090002014A1Less powerImprove yieldPulse transformerElectronic switchingRapid single flux quantumUltra fast
Supercooled electronics often use Rapid Single Flux Quantum (RSFQ) digital circuits. The output voltages from RSFQ devices are too low to be directly interfaced with semiconductor electronics, even if the semiconductor electronics are cooled. Techniques for directly interfacing RSFQ digital circuits with semiconductor electronics are disclosed using a novel inverting transimpedance digital amplifier in conjunction with a non-inverting transimpedance digital amplifier to create a differential transimpedance digital amplifier that permits direct interfacing between RSFQ and semiconductor electronics.
Owner:HYPRES
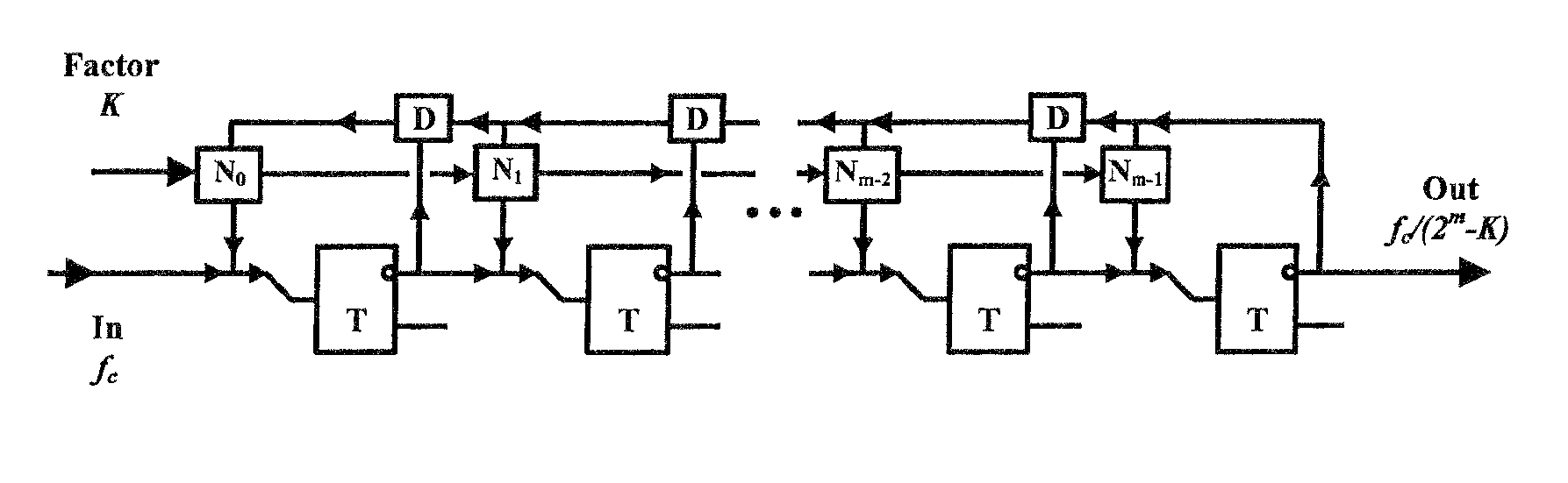
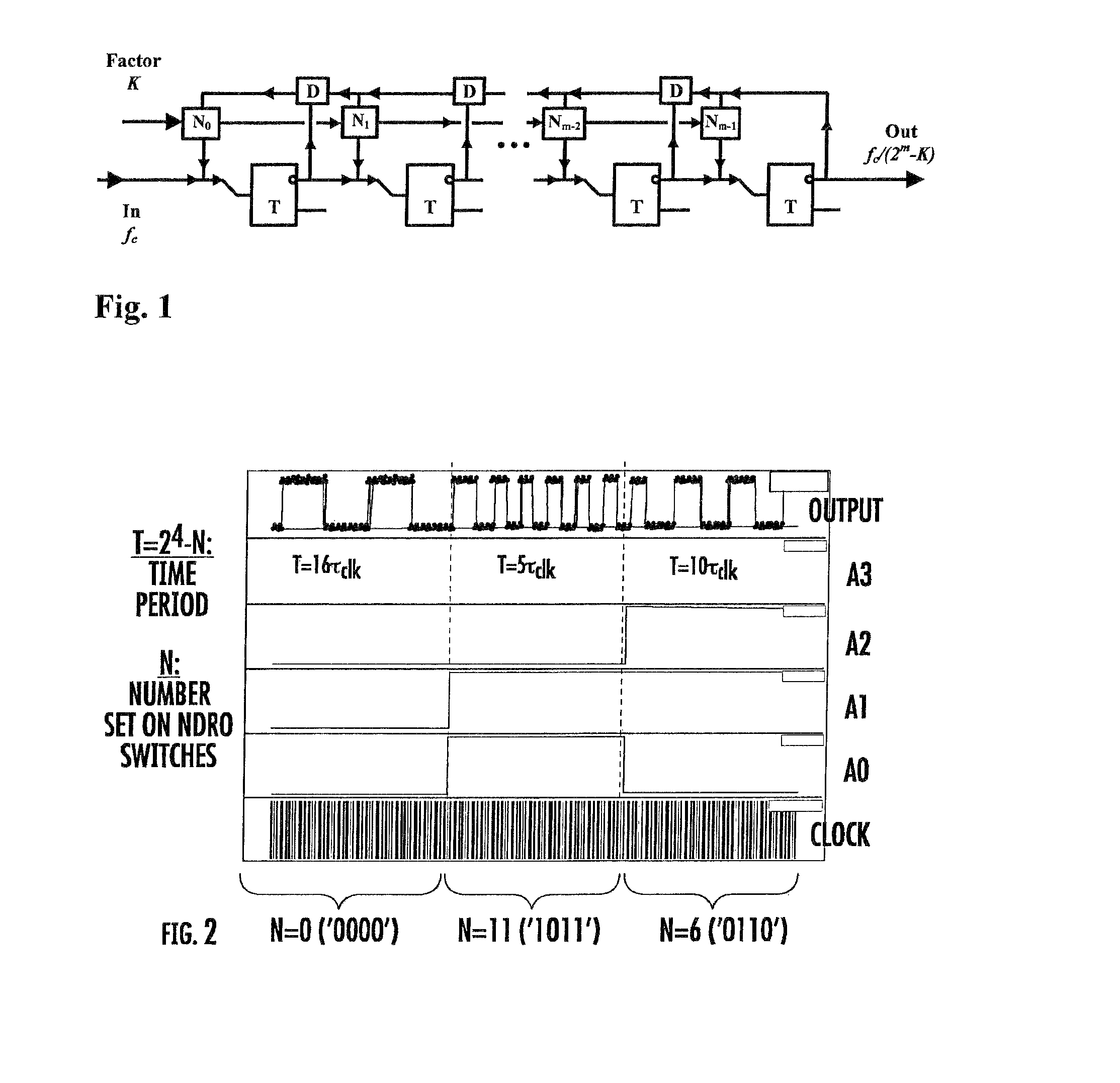
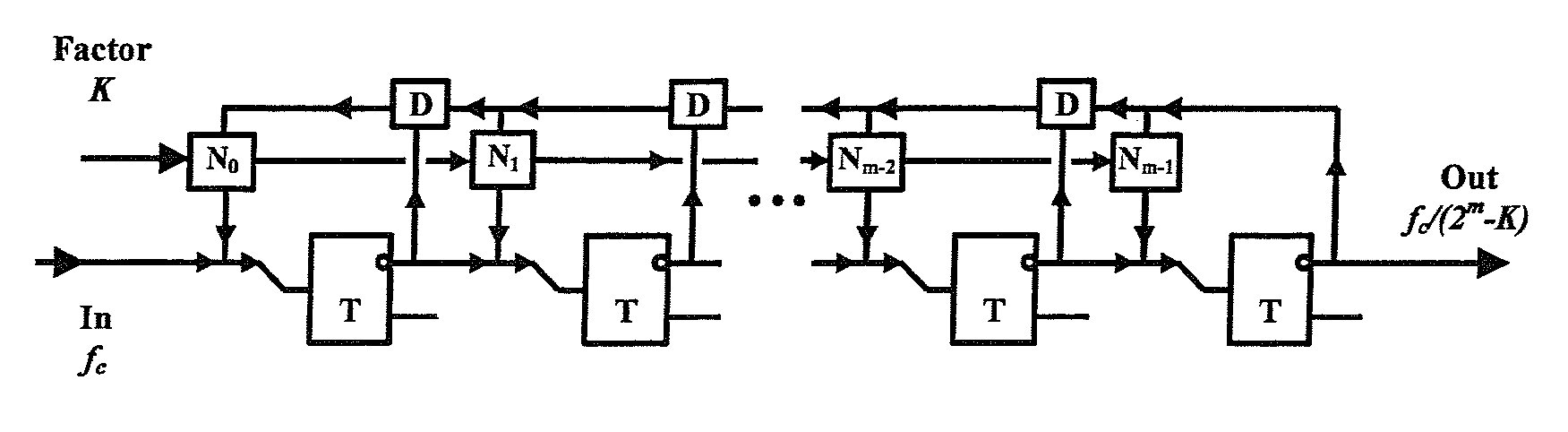
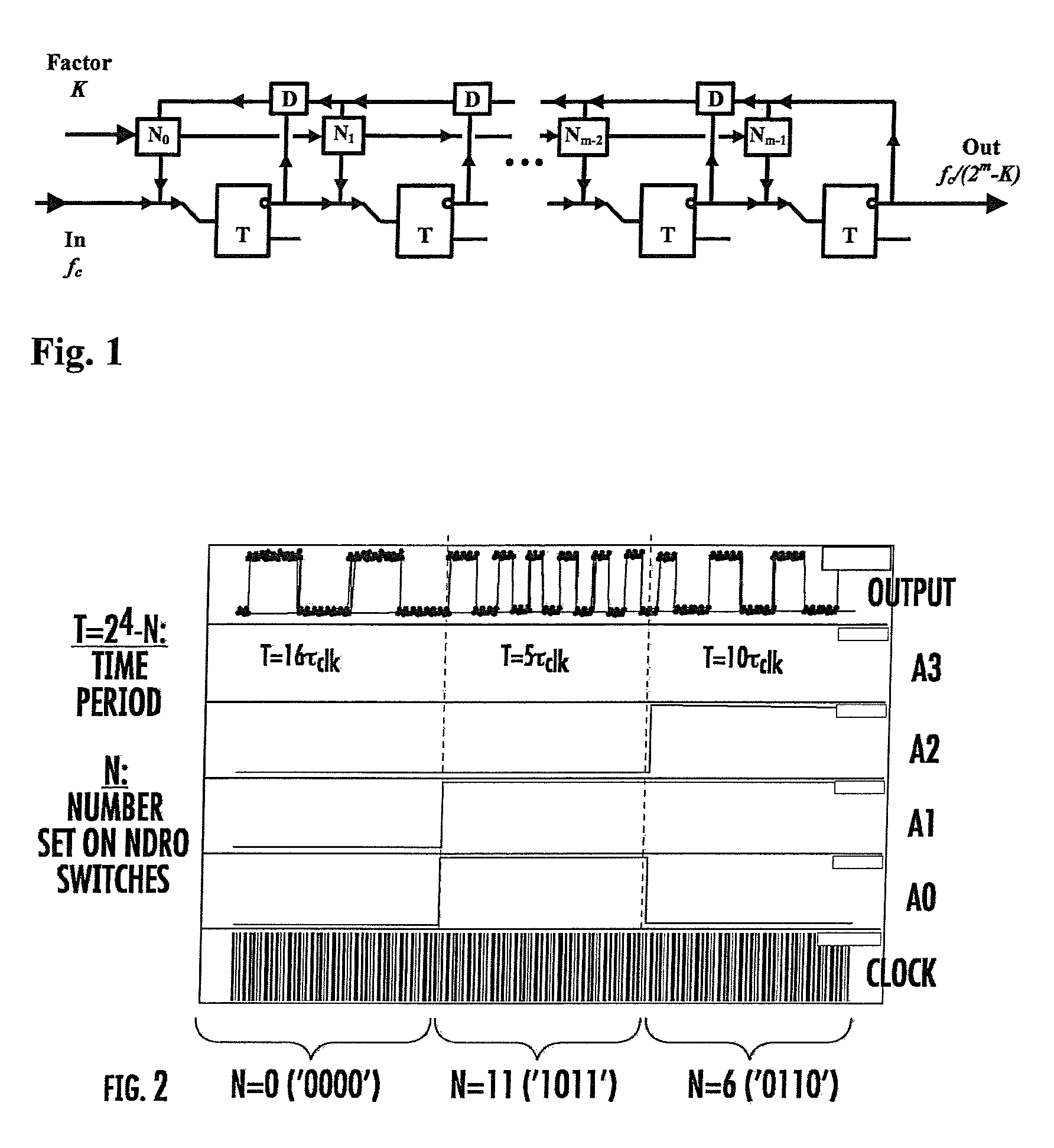
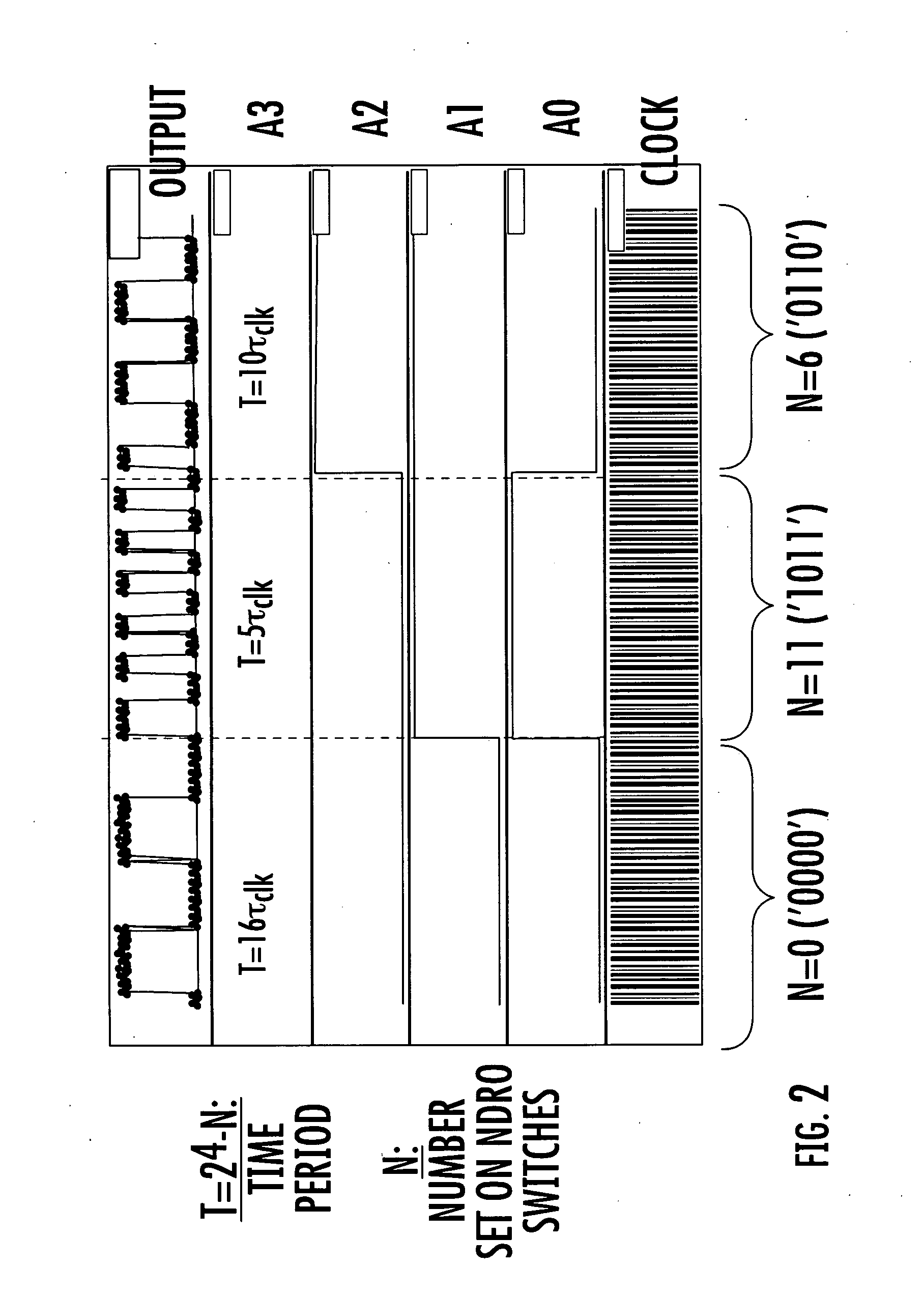
Digital programmable frequency divider
ActiveUS7944253B1Counting chain pulse countersOscillations generatorsNon destructiveRapid single flux quantum
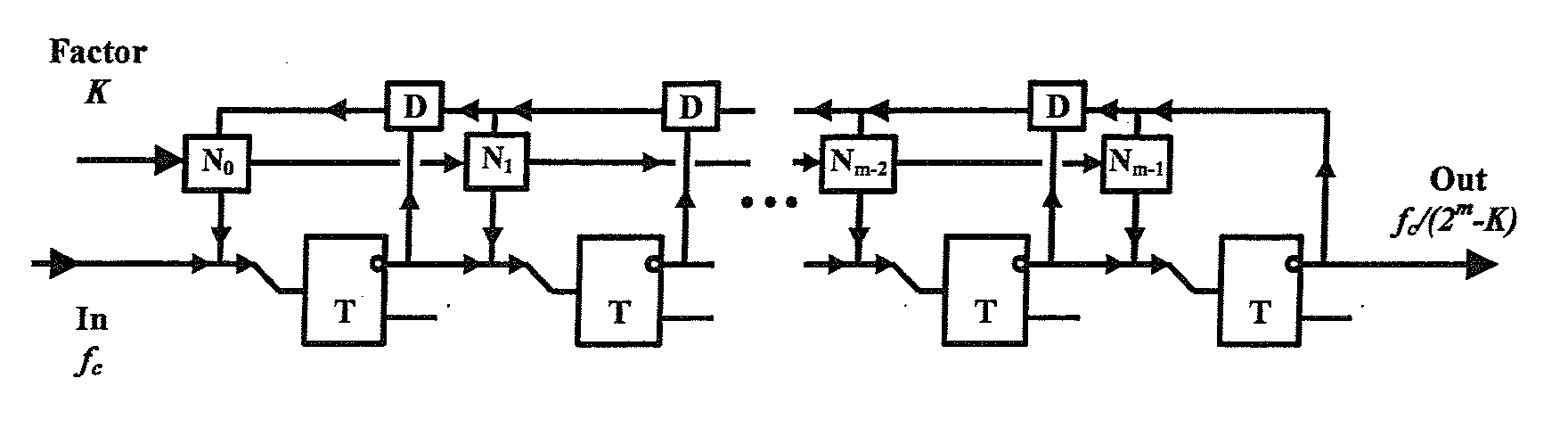
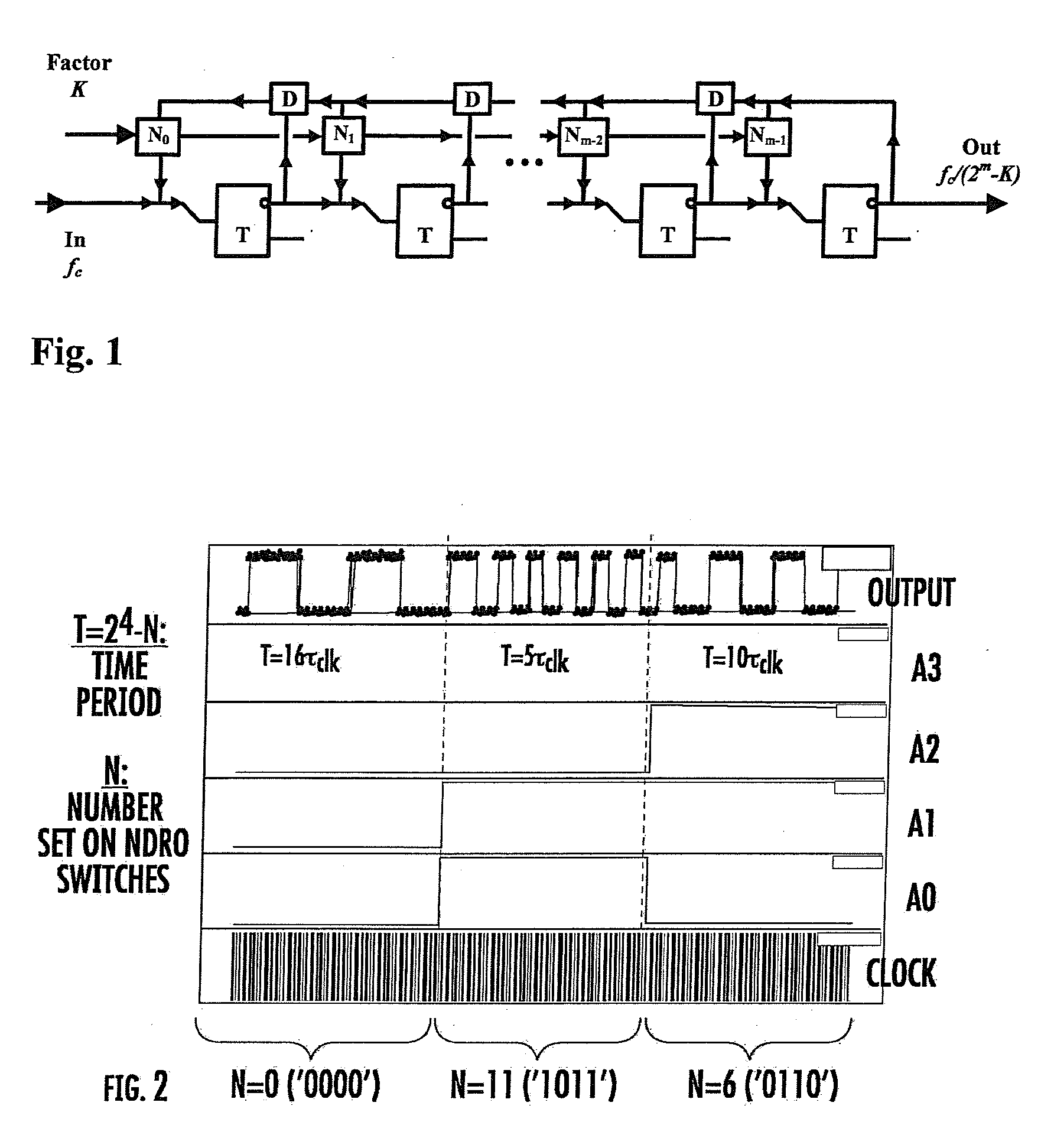
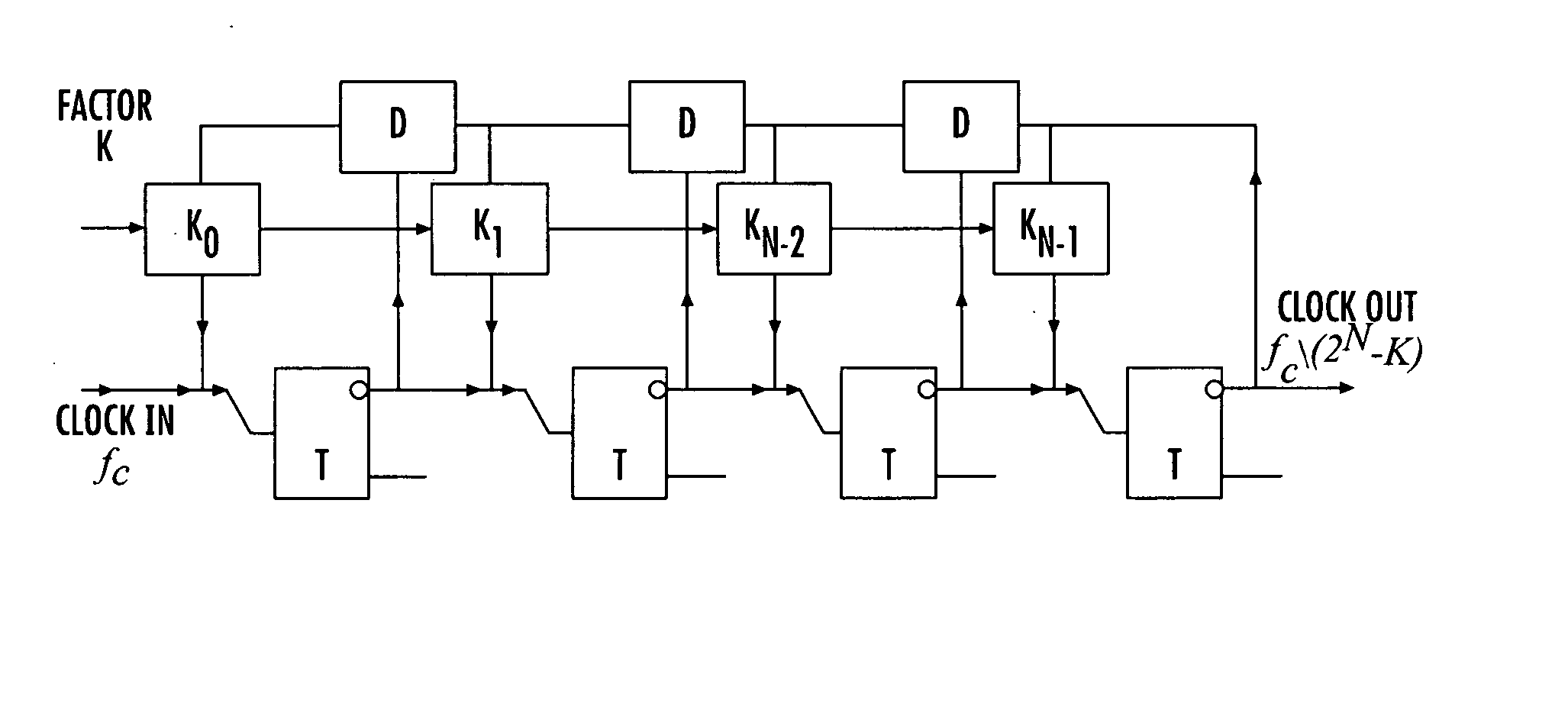
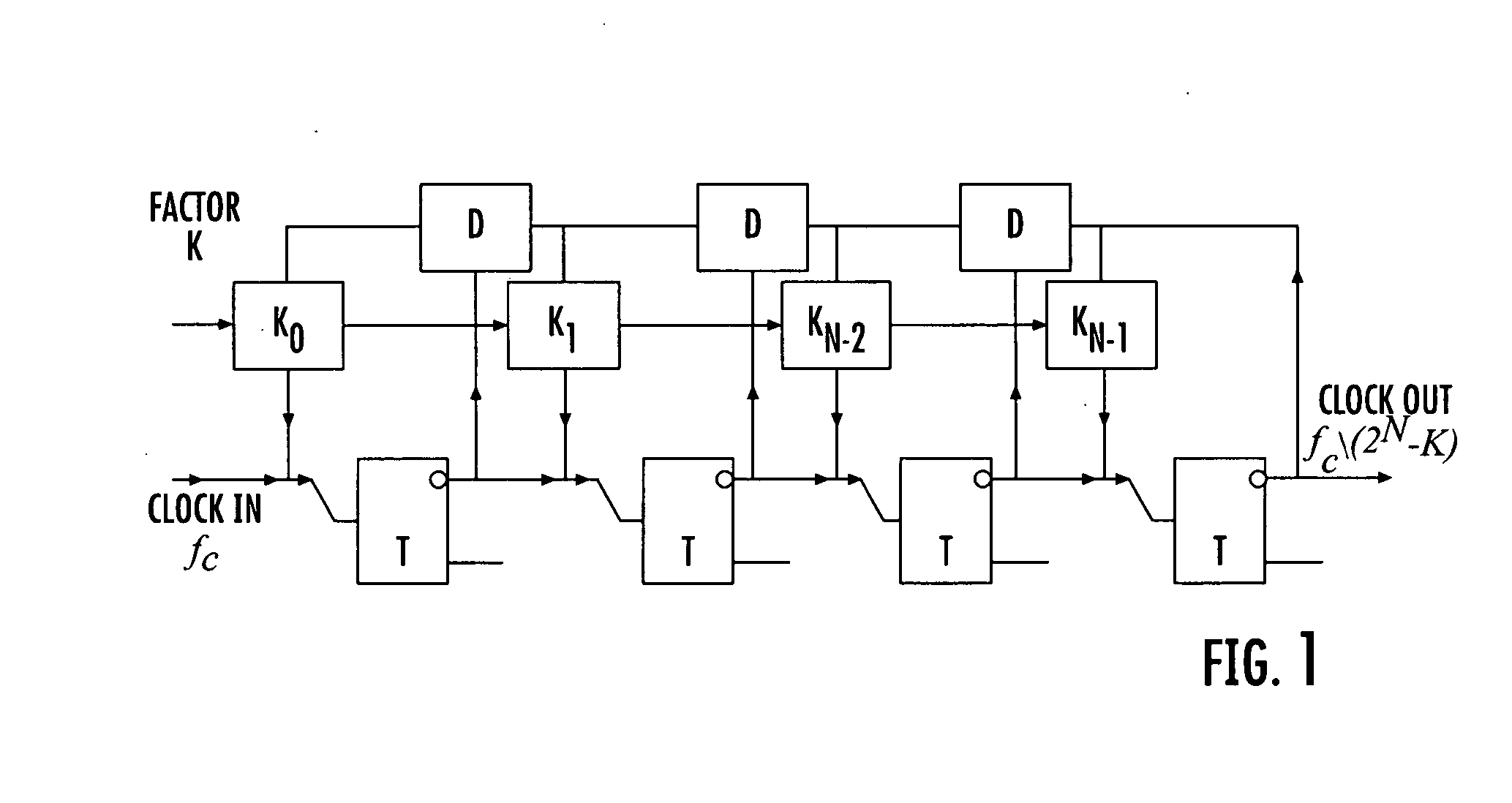
A digital programmable frequency divider is constructed of Rapid Single Flux Quantum (RSFQ) logic elements. The logic elements may include an RSFQ non-destructive readout cell (NDRO), RSFQ D flip-flop and an RSFQ T flip-flop. A digital word comprising N bits is used to control the amount of frequency division and the frequency divider selectively imparts a respective frequency division for any of 2n states that can be represented by the digital word. The RSFQ logic elements utilize Josephson junctions which operate in superconducting temperature domains.
Owner:SEEQC INC
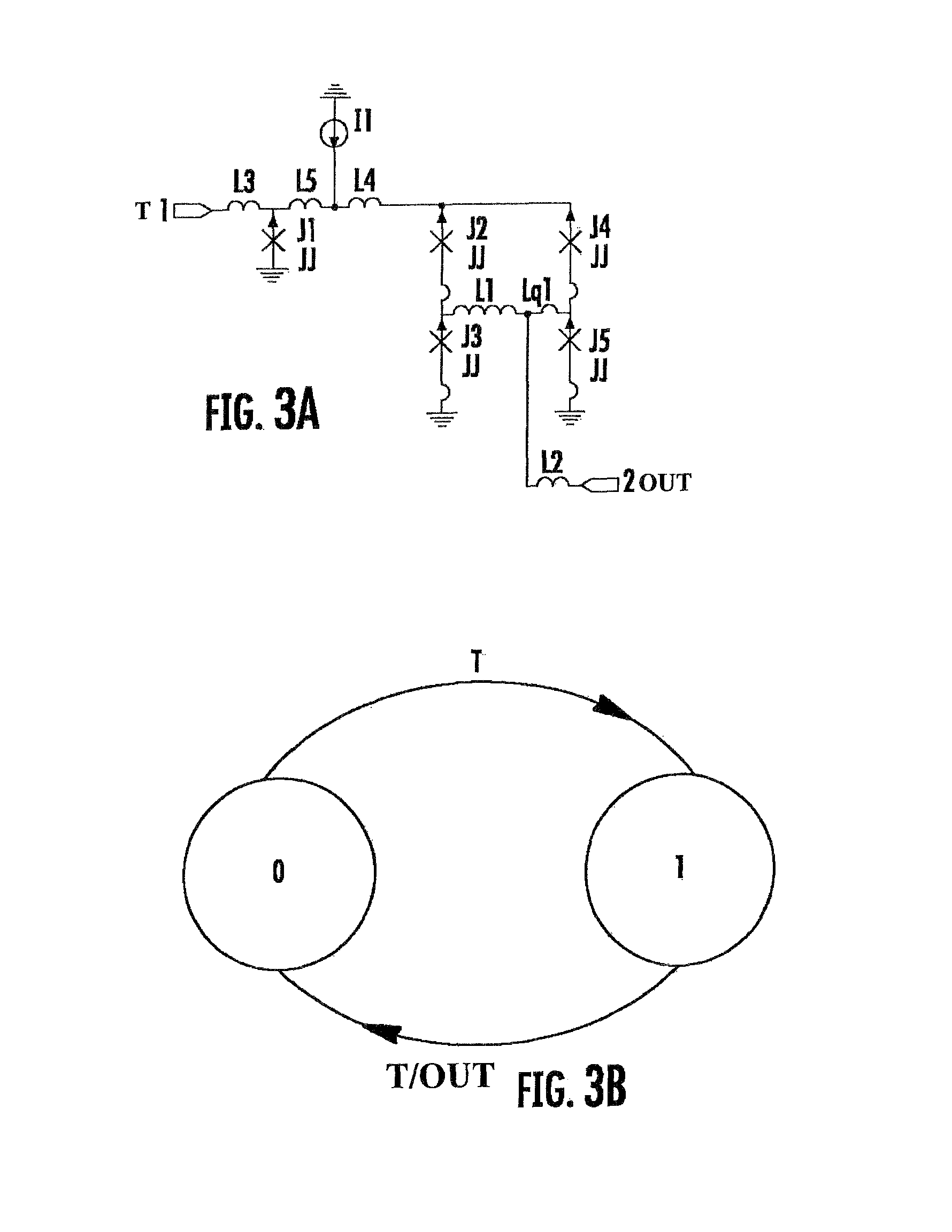
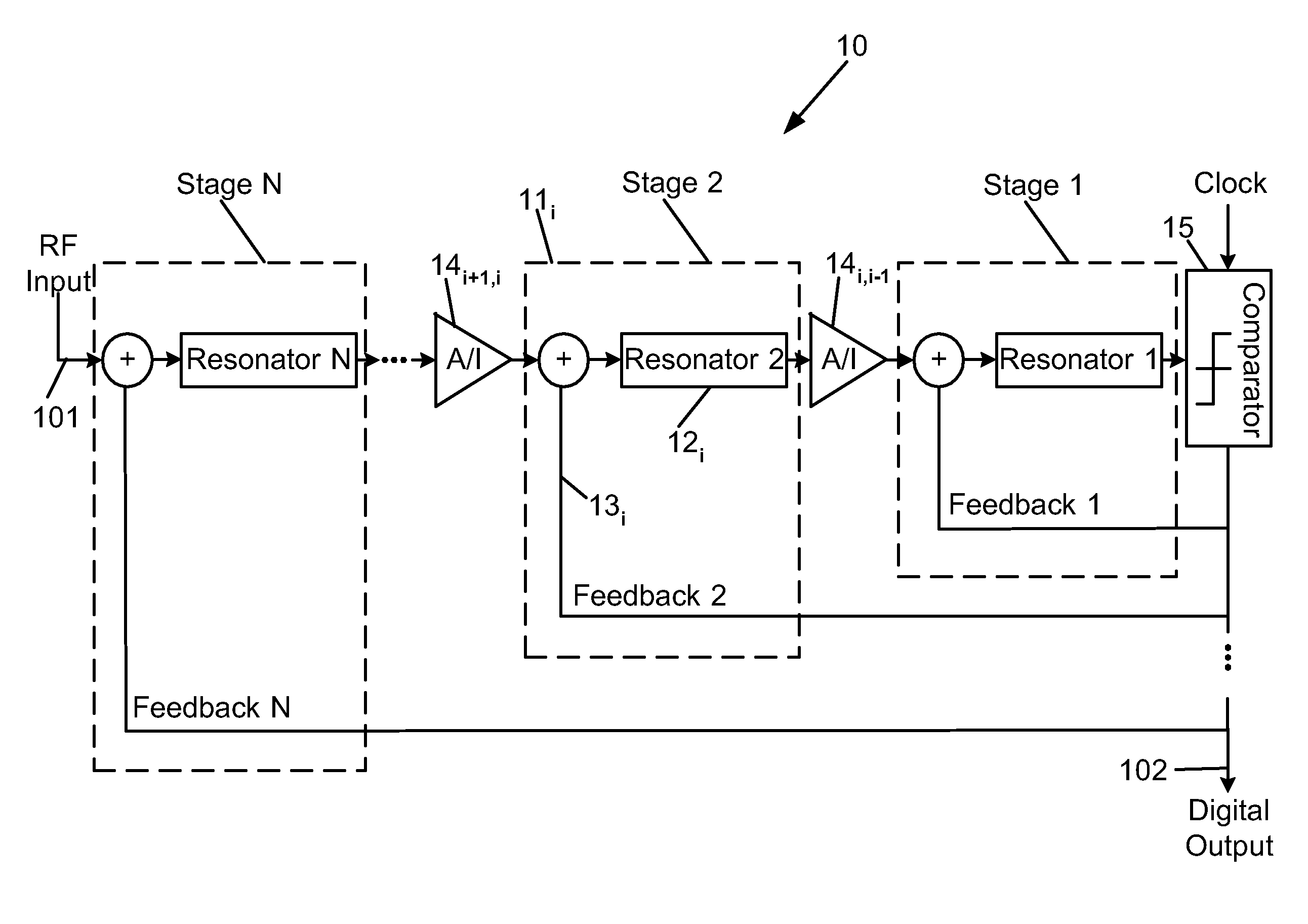
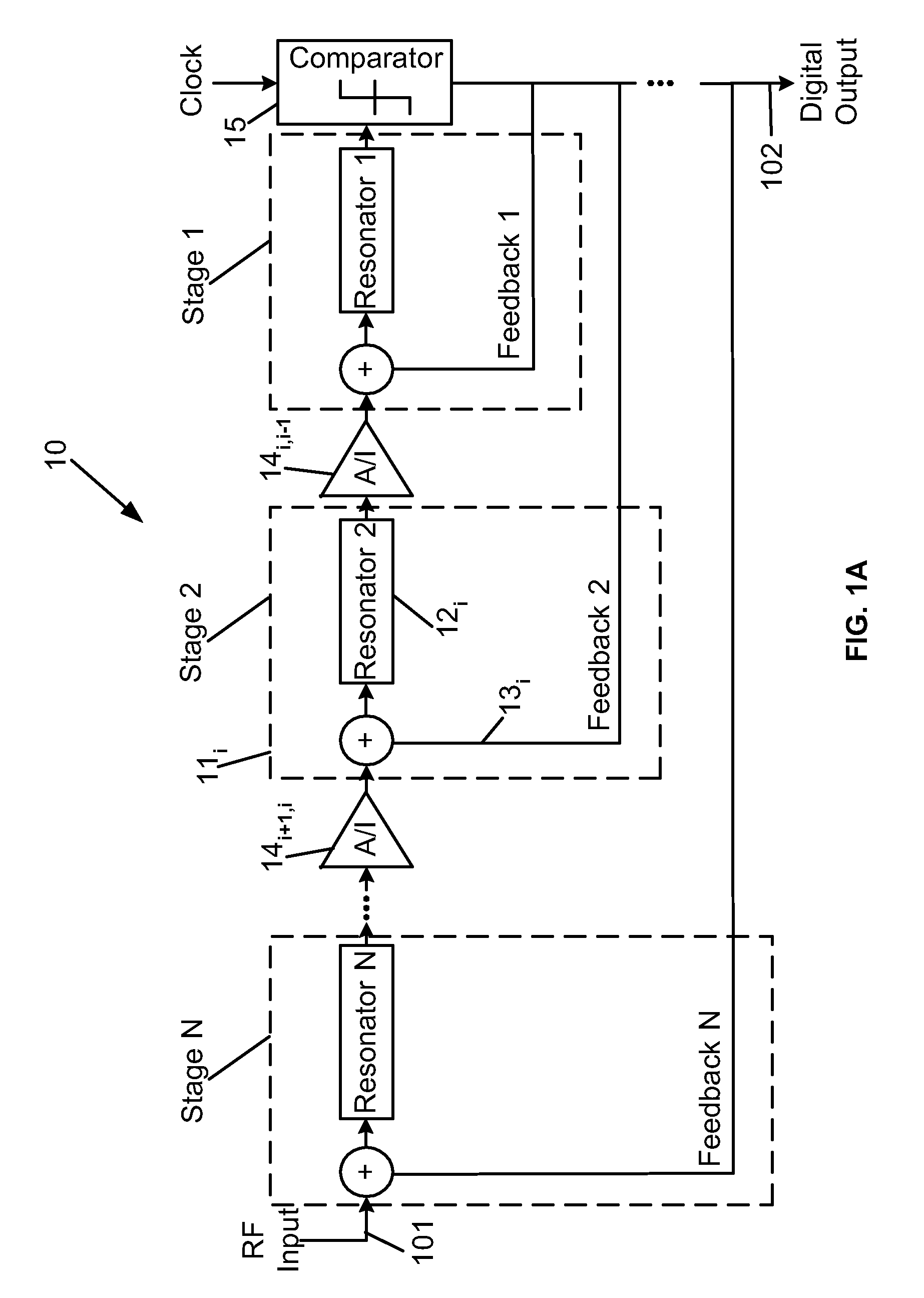
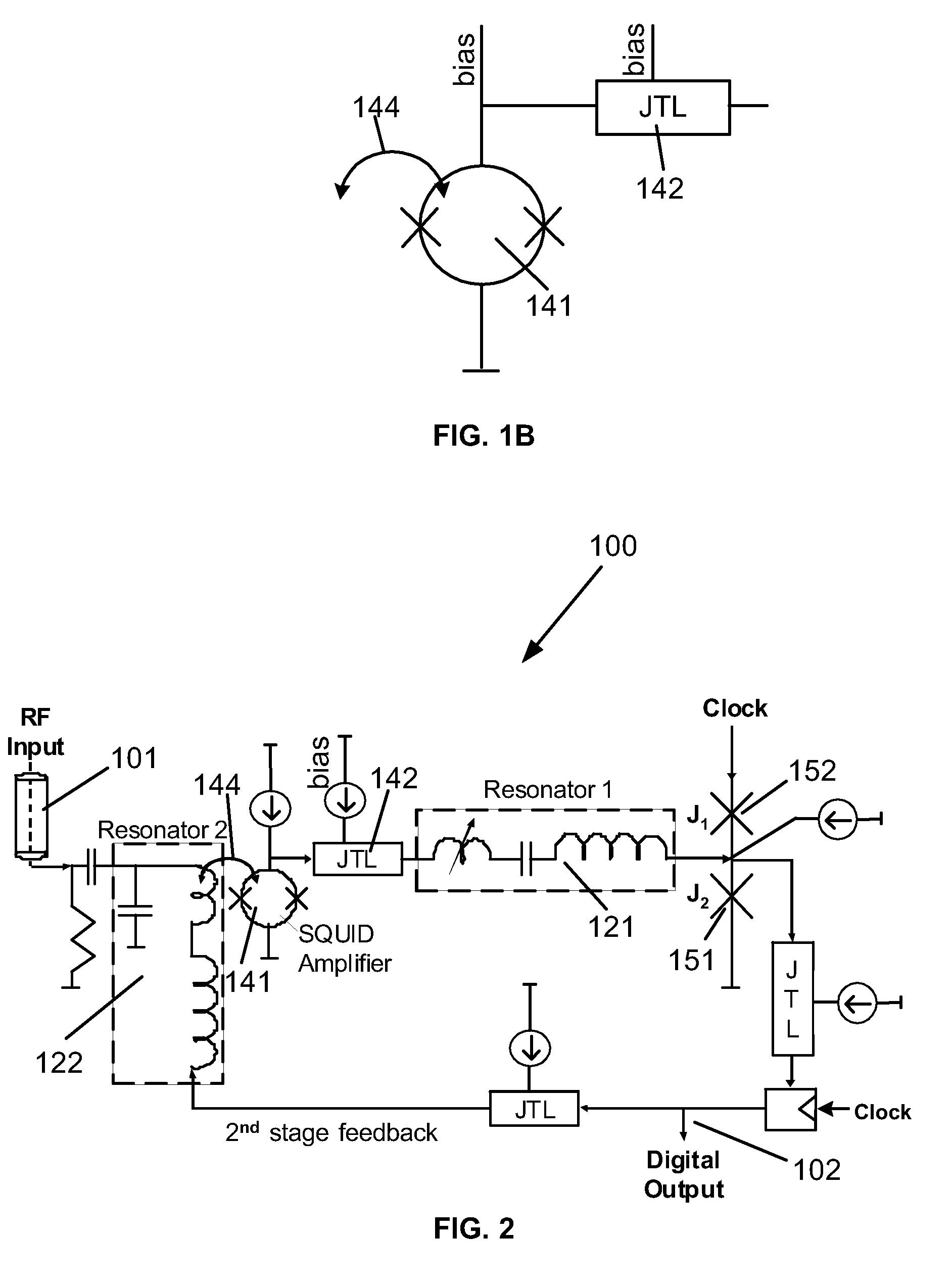
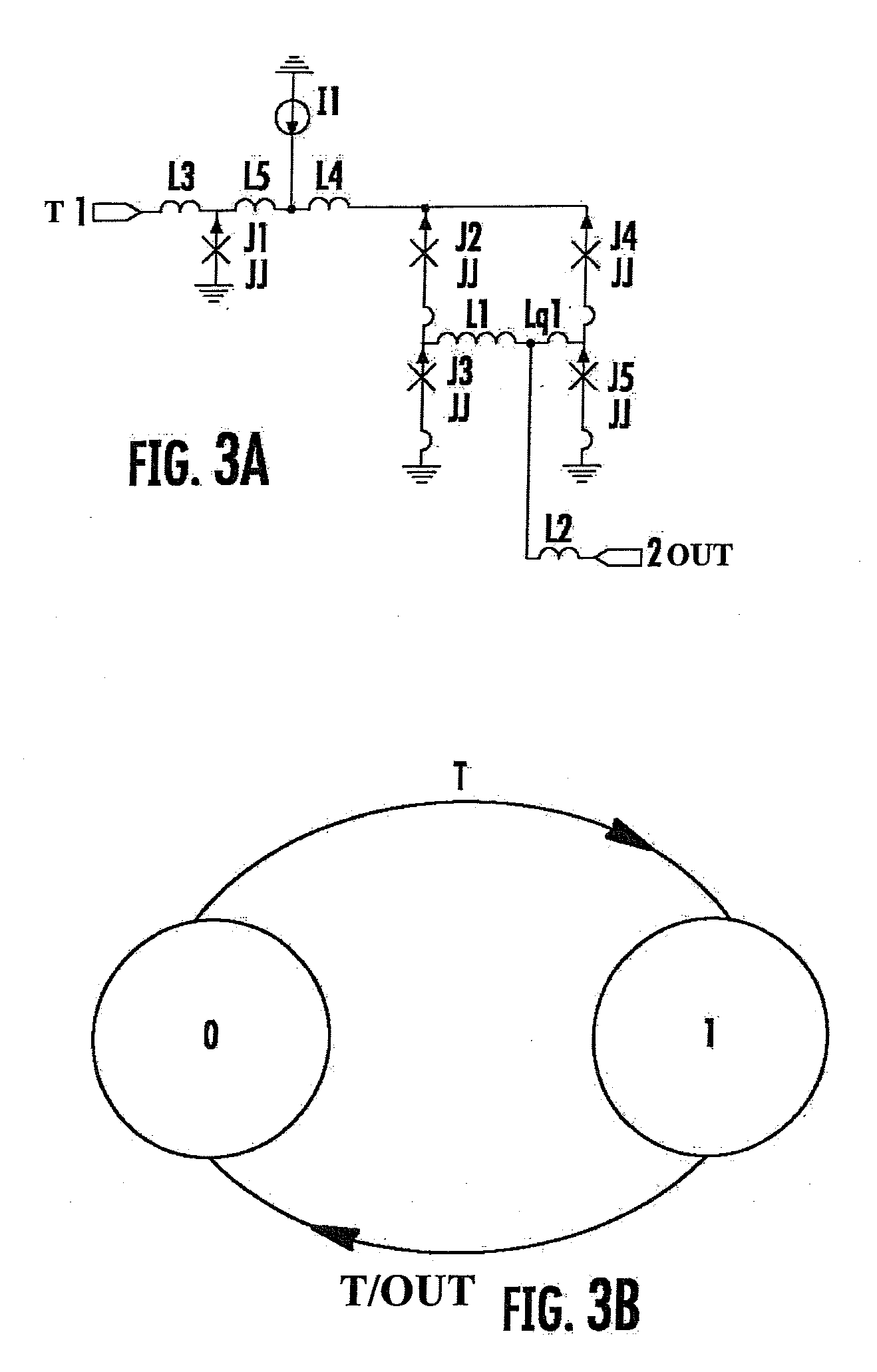
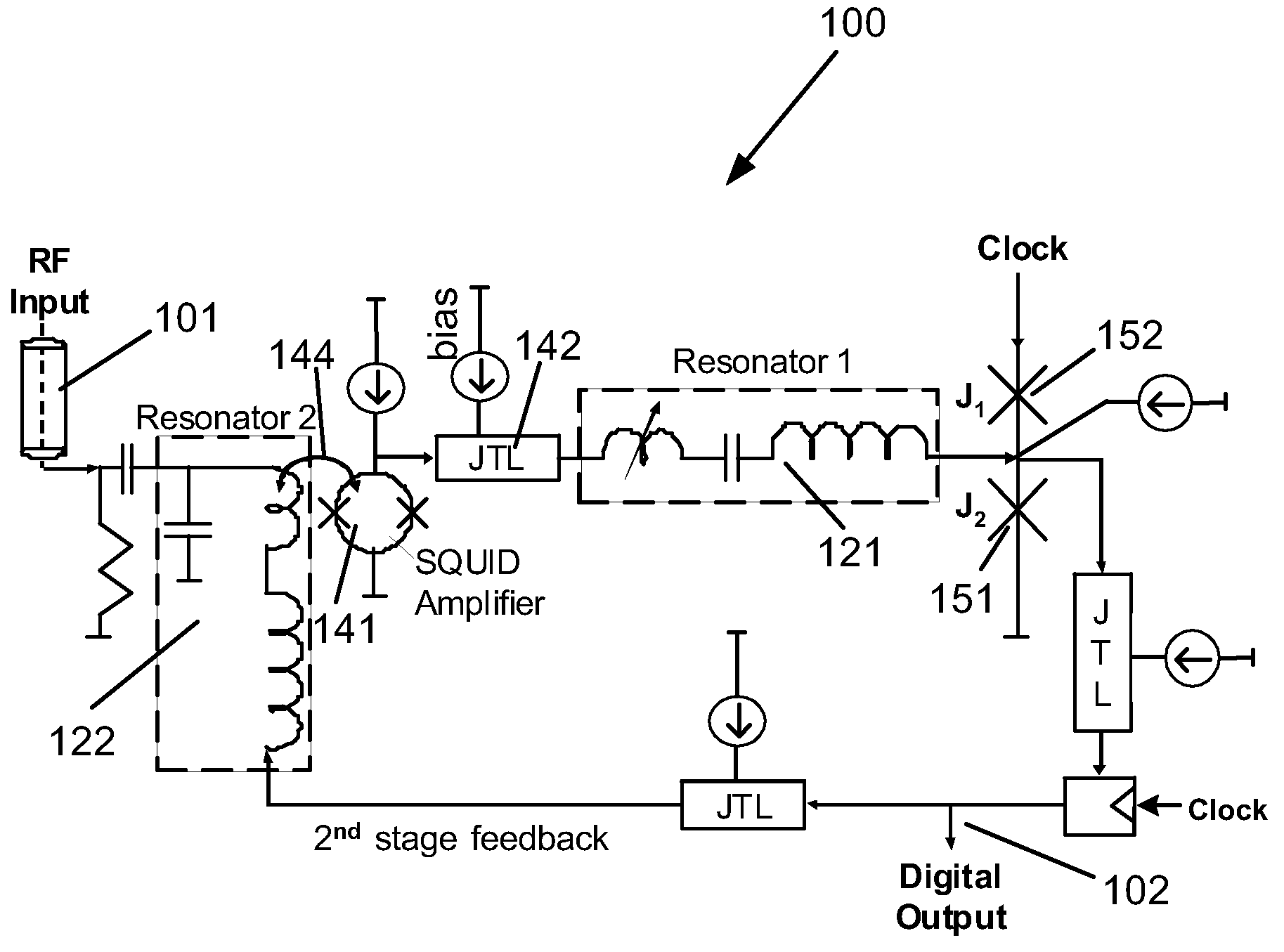
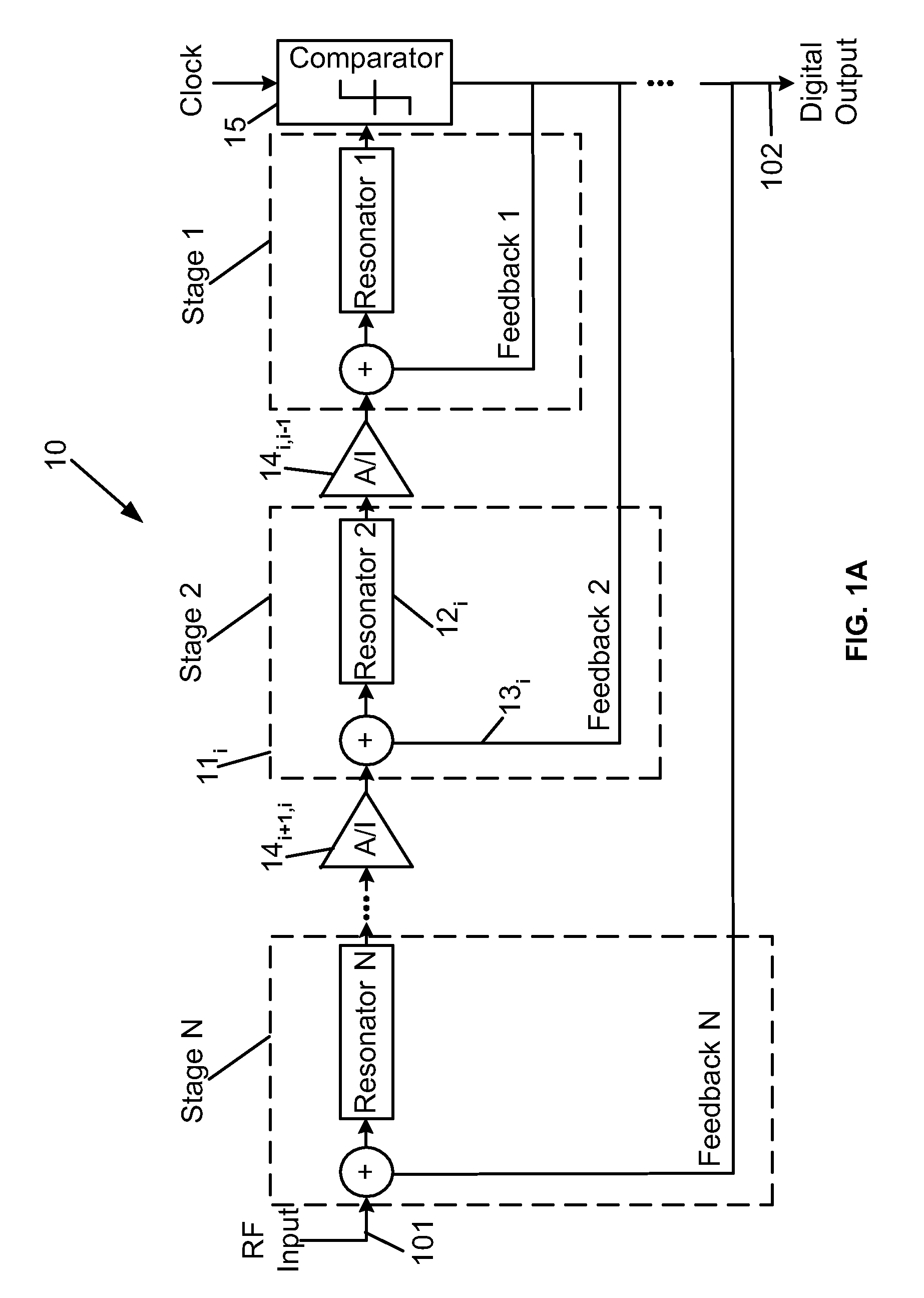
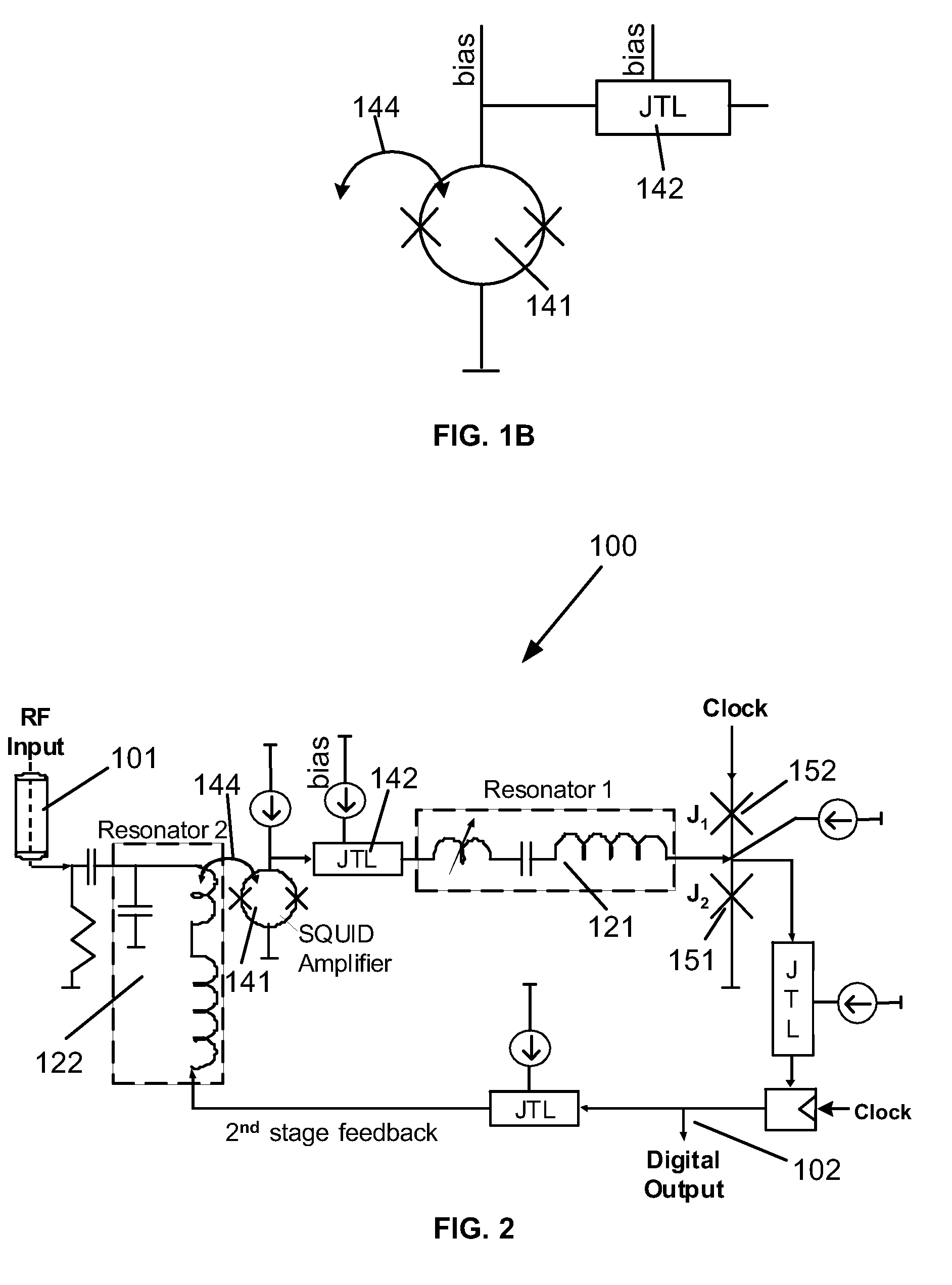
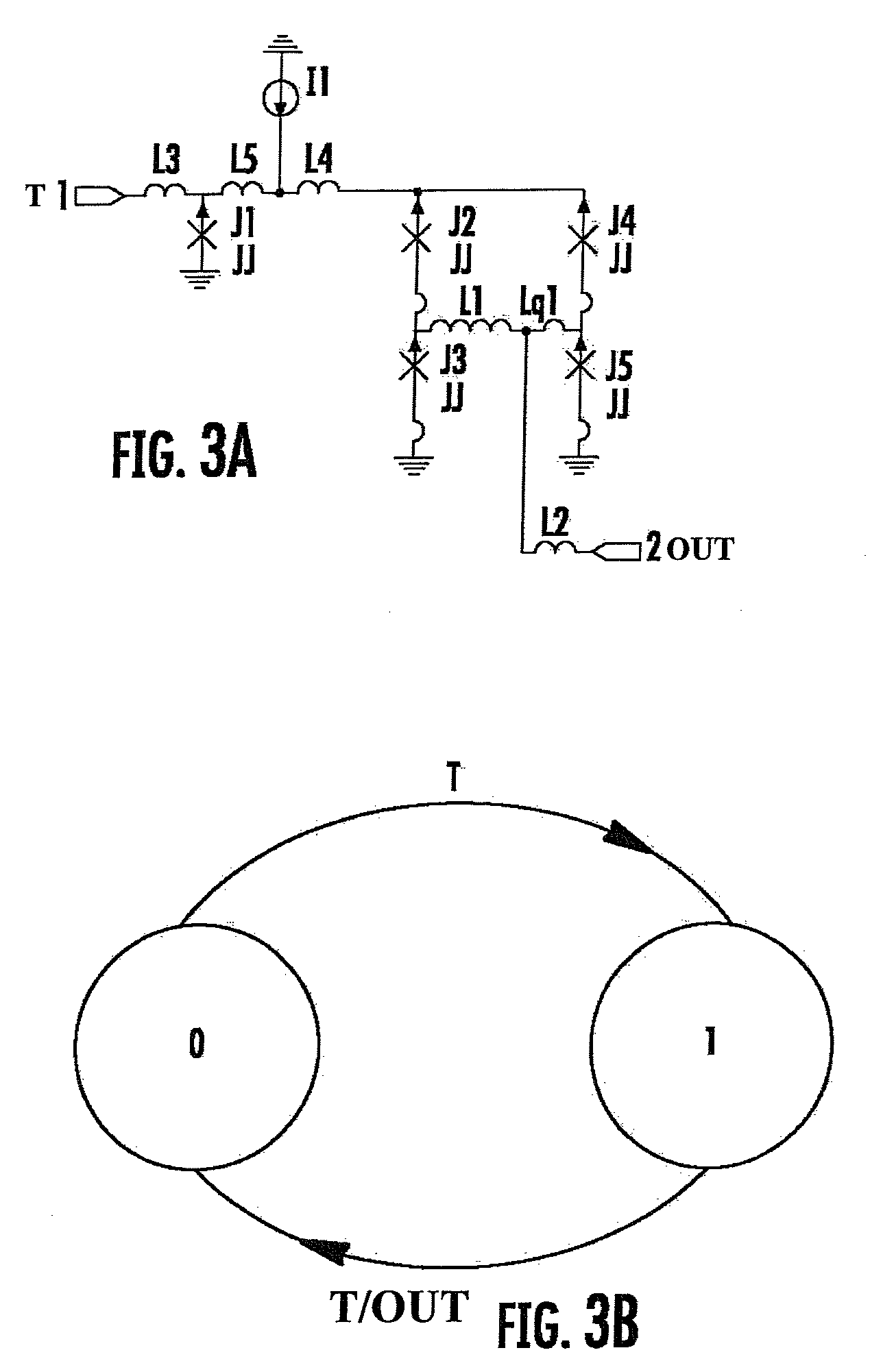
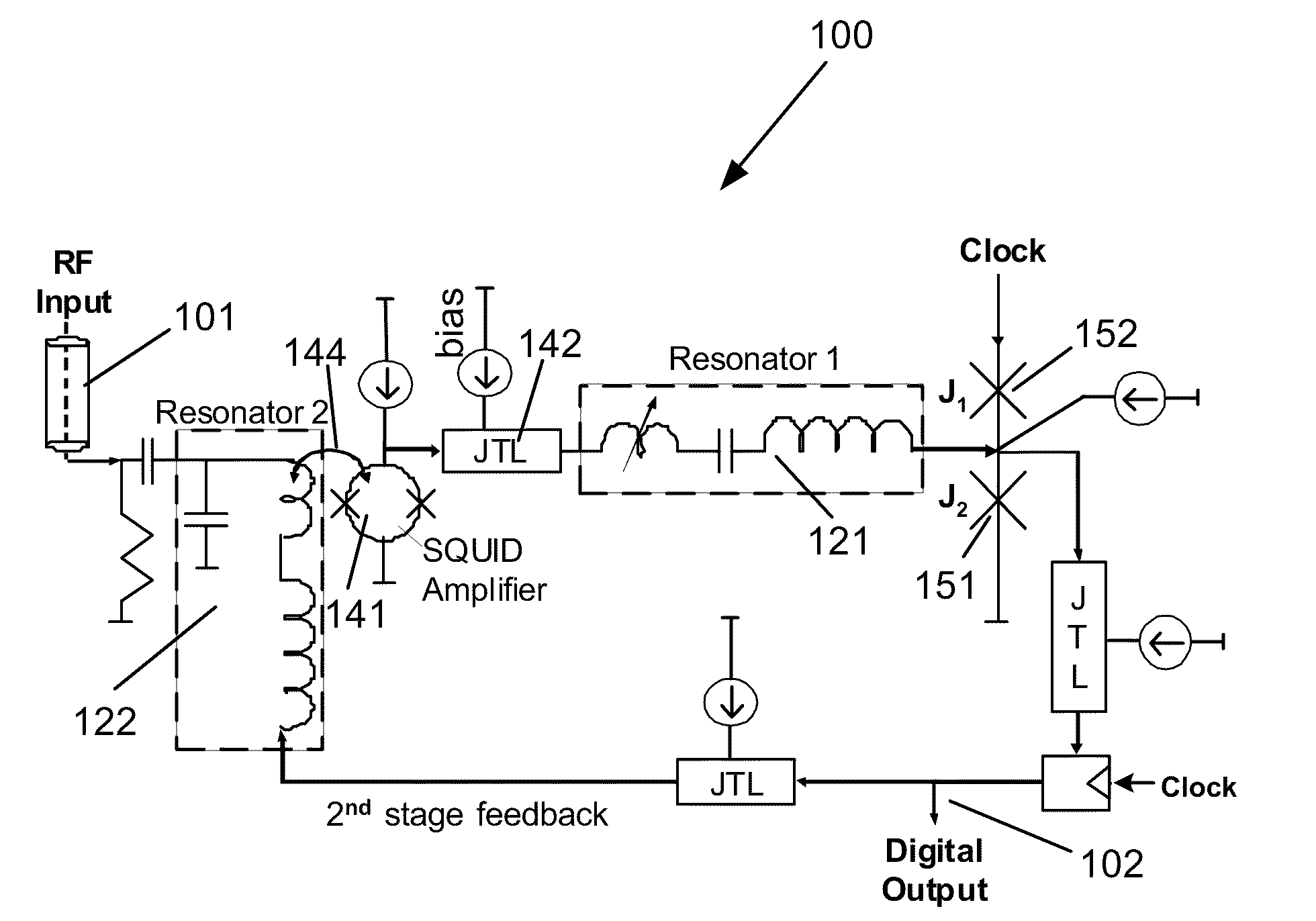
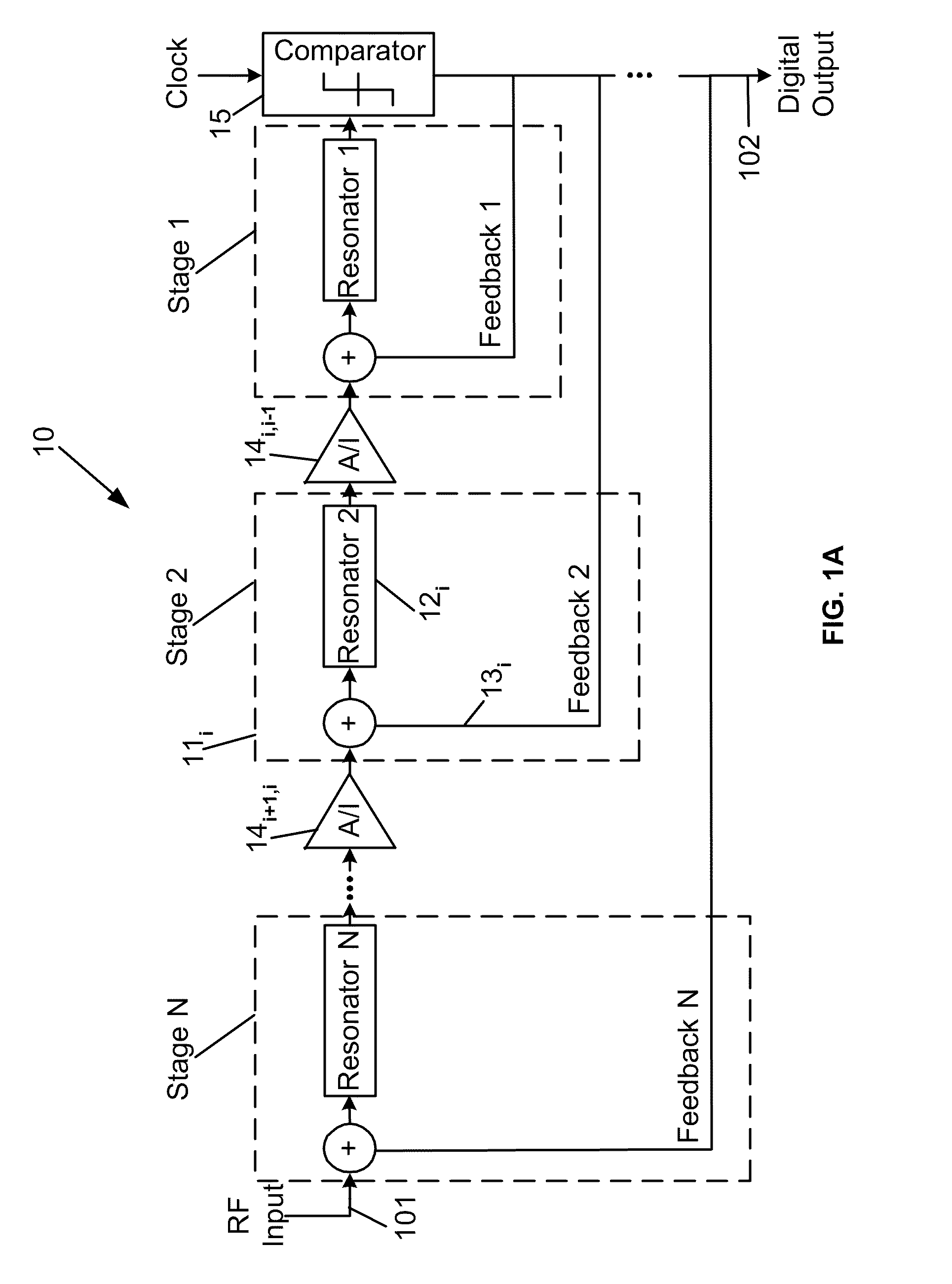
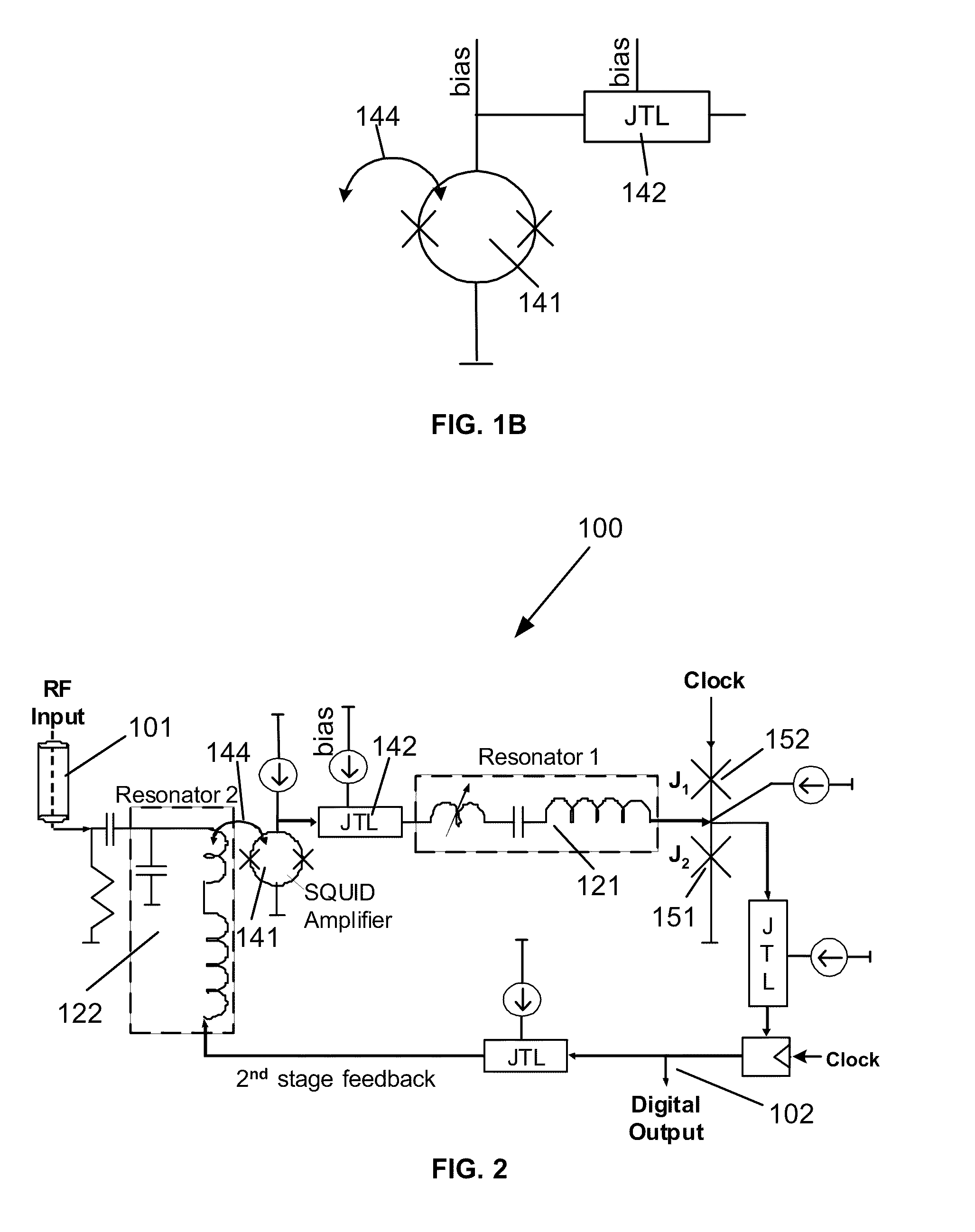
Superconductor analog-to-digital converter
ActiveUS7598897B2Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionRapid single flux quantumEngineering
A superconducting Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) employing rapid-single-flux-quantum (RSFQ) logic is disclosed. The ADC has only superconductor active components, and is characterized as being an Nth-order bandpass sigma-delta ADC, with the order “N” being at least 2. The ADC includes a sequence of stages, which stages include feedback loops and resonators. The ADC further includes active superconducting components which directionally couple resonator pairs of adjacent stages. The active superconducting components electrically shield the higher order resonator from the lower order resonator. These active superconductor components include a superconducting quantum interference device (SQUID) amplifier, which is inductively coupled to the higher order resonator, and may include a Josephson transmission line (JTL), which is configured to electrically connect the SQUID amplifier to the lower order resonator. The first stage of ADC may employ an implicit feedback loop.
Owner:HYPRES
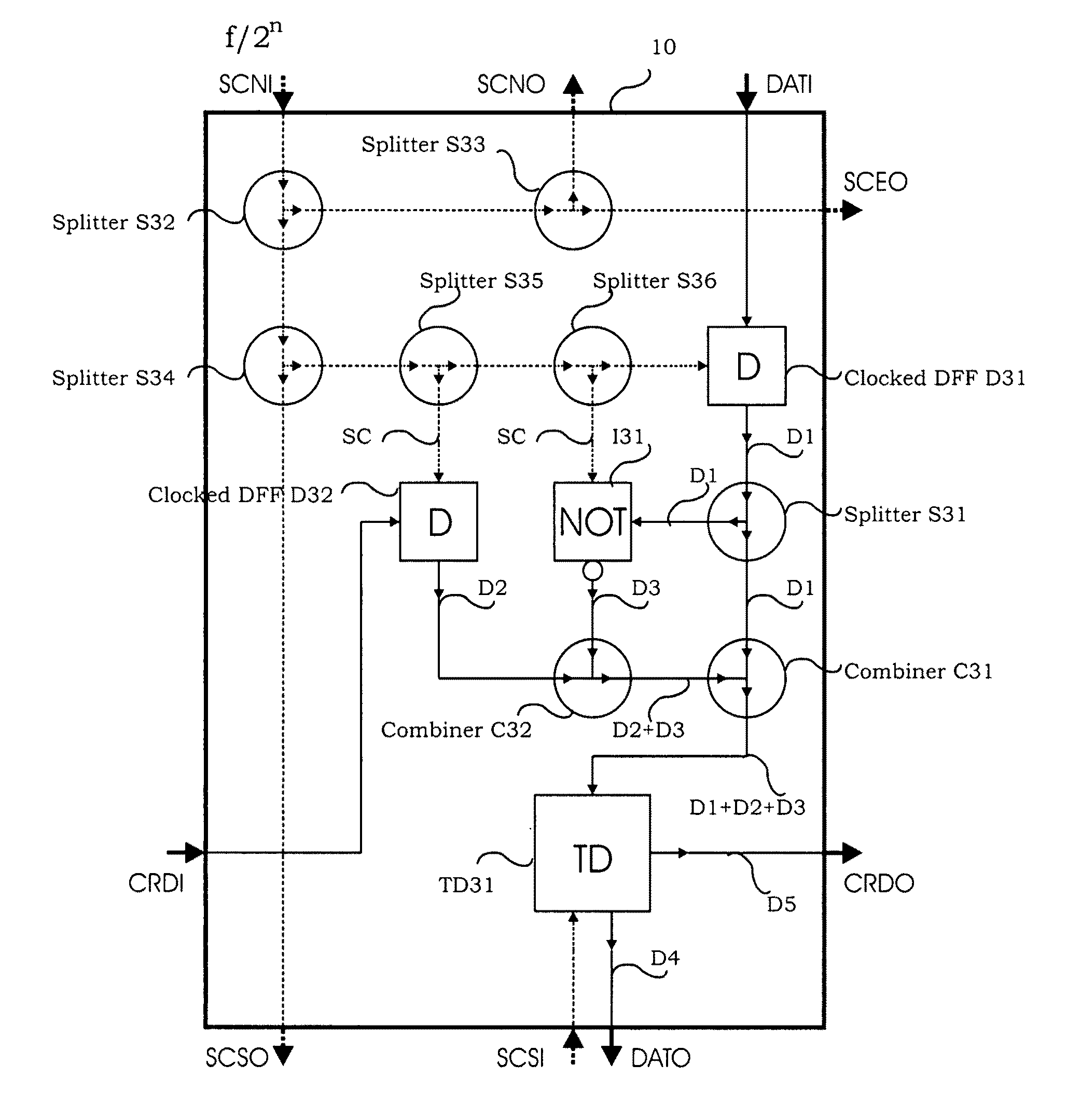
Ultra fast circuitry for digital filtering
ActiveUS20080231353A1Accurate timingEasy to operateComputation using non-contact making devicesSolid-state devicesUltra high speedNon destructive
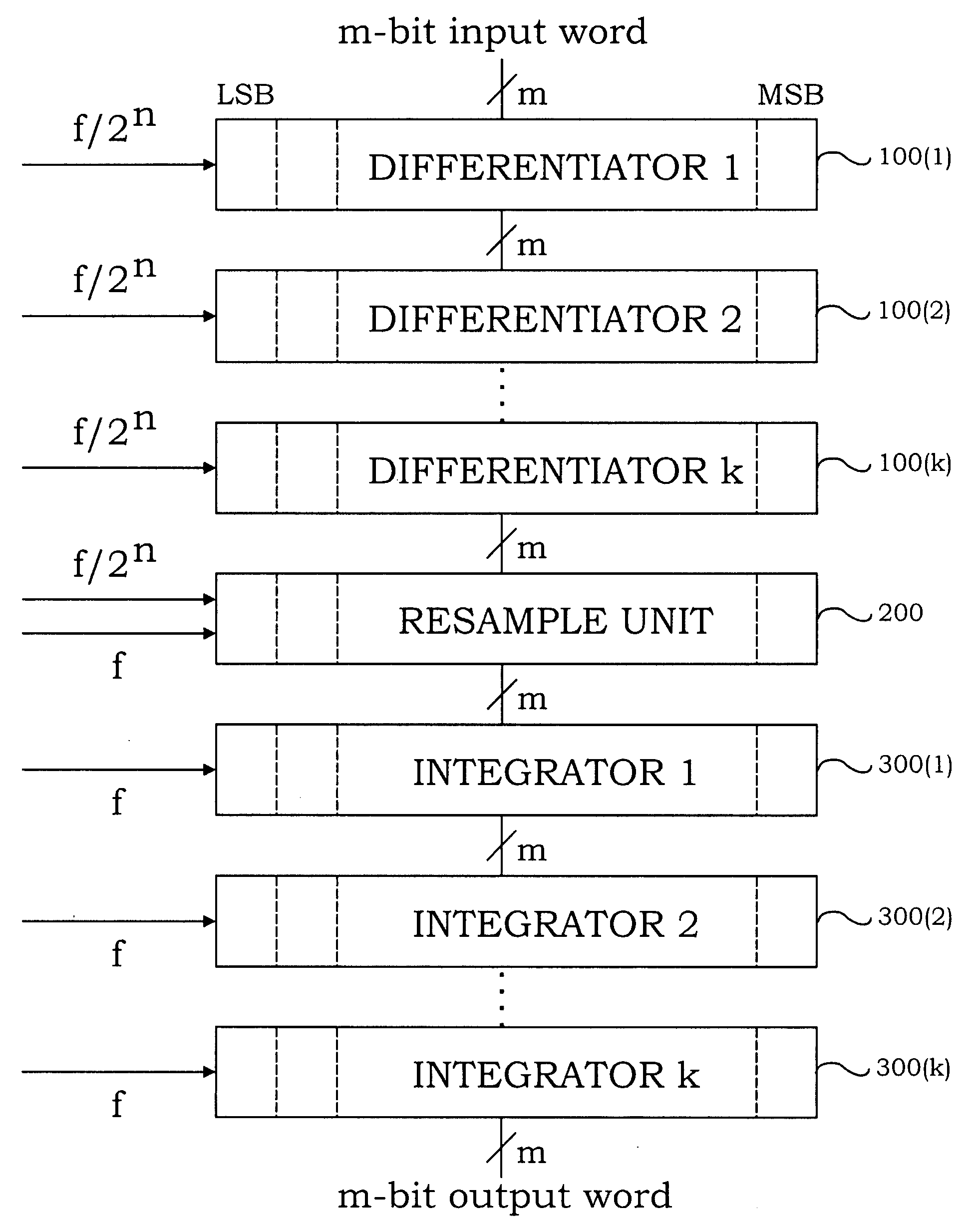
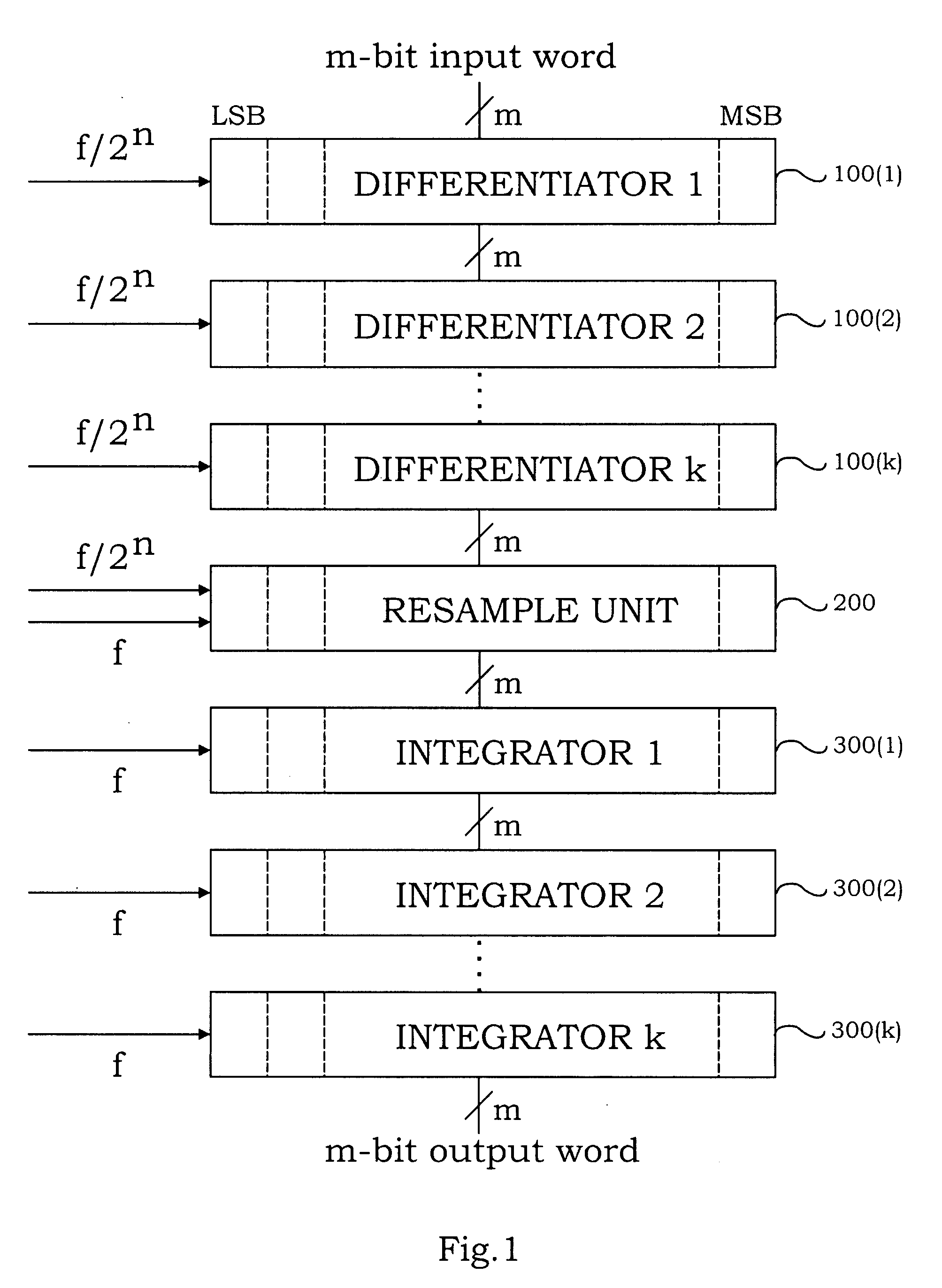
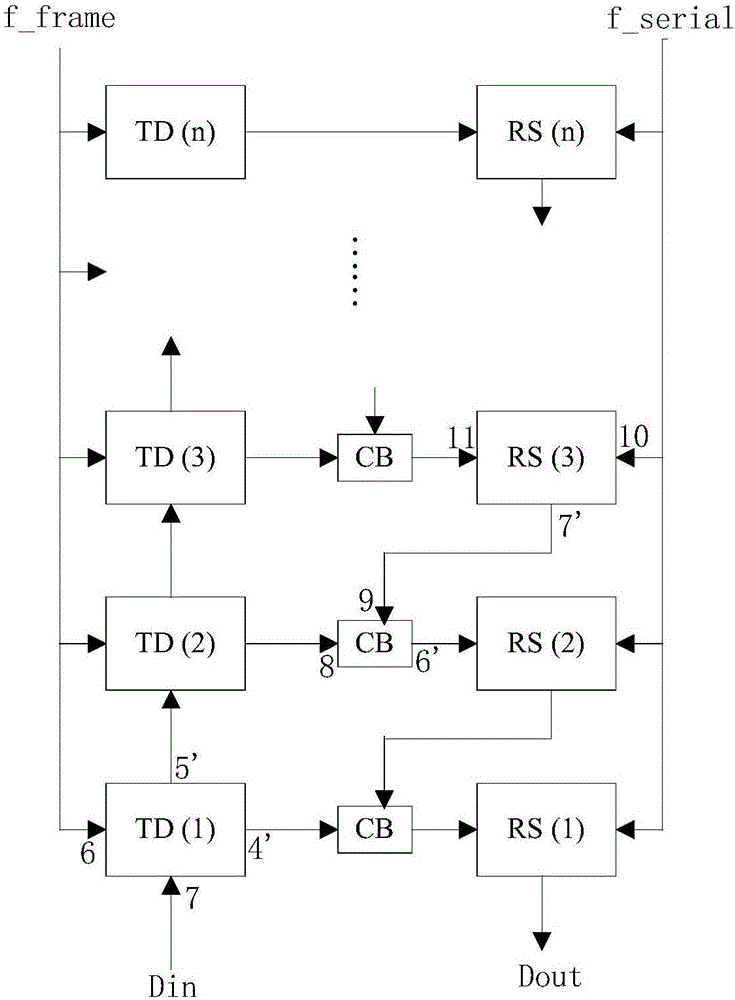
The invention includes a novel differentiator cell, a novel resample unit cell, and precision synchronization circuitry to ensure proper timing of the circuits and systems at the anticipated ultra-high speed of operation. The novel differentiator cell includes circuitry for combining a carry input signal, a data bit signal and the output signal of a NOT cell and applying the signals as distinct and separate pulses to the input of a toggle flip-flop (TFF) for producing an asynchronous carry output and a clocked data output. The novel differentiator cells can be interconnected to form a multi-bit differentiator circuit using appropriate delay and synchronization circuitry to compensate for delays in producing the carry output of each cell which is applied to a succeeding cell. The novel resample cell includes a non-destructive reset-set flip-flop (RSN) designed to receive a data bit, at its set input, at a slow clock rate, which data is repeatedly read out of the RSN at a fast clock rate, until the RSN is reset. The novel differentiator and resampler cells can be interconnected, for example, to form the differentiator and up-sampling sections of a digital interpolation filter (DIF). Also, the relative clocking of bit slices (columns) in such a DIF may be achieved by using the fast clock signal to synchronize the slow clock which controls data entry. The circuits of the invention can be advantageously implemented with Josephson Junctions in rapid-single-flux-quantum (RSFQ) logic.
Owner:SEEQC INC
Superconducting multi-bit digital mixer
ActiveUS8401600B1Accurate timingSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsShift registerLocal oscillator signal
A superconducting multi-bit digital mixer, designed using rapid single flux quantum (RSFQ) logic, for multiplying two independent digital streams, at least one of these comprising a plurality of parallel bit lines, wherein the output is also a similar plurality of bit lines. In a preferred embodiment, one of the digital streams represents a local oscillator signal, and the other digital stream digital radio frequency input from an analog-to-digital converter. The multi-bit mixer comprises an array of bit-slices, with the local oscillator signal generated using shift registers. This multi-bit mixer is suitable for an integrated circuit with application to a broadband digital radio frequency receiver, a digital correlation receiver, or a digital radio frequency transmitter. A synchronous pulse distribution network is used to ensure proper operation at data rates of 20 GHz or above.
Owner:HYPRES
Digital Programmable Frequency Divider
ActiveUS20080186064A1Counting chain pulse countersOscillations generatorsNon destructiveRapid single flux quantum
A digital programmable frequency divider is constructed of Rapid Single Flux Quantum (RSFQ) logic elements. The logic elements may include an RSFQ non-destructive readout cell (NDRO), and RSFQ D flip-flop and an RSFQ T flip-flop. A digital word comprising N bits is used to control the amount of frequency division and the frequency divider selectively imparts a respective frequency division for any of 2N states that can be represented by the digital word. The RSFQ logic elements utilize Josephson junctions which operate in superconducting temperature domains.
Owner:SEEQC INC
Superconductor Analog-to-Digital Converter
ActiveUS20090153381A1Electric signal transmission systemsDelta modulationRapid single flux quantumEngineering
A superconducting Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) employing rapid-single-flux-quantum (RSFQ) logic is disclosed. The ADC has only superconductor active components, and is characterized as being an Nth-order bandpass sigma-delta ADC, with the order “N” being at least 2. The ADC includes a sequence of stages, which stages include feedback loops and resonators. The ADC further includes active superconducting components which directionally couple resonator pairs of adjacent stages. The active superconducting components electrically shield the higher order resonator from the lower order resonator. These active superconductor components include a superconducting quantum interference device (SQUID) amplifier, which is inductively coupled to the higher order resonator, and may include a Josephson transmission line (JTL), which is configured to electrically connect the SQUID amplifier to the lower order resonator. The first stage of ADC may employ an implicit feedback loop.
Owner:HYPRES
Digital programmable frequency divider
ActiveUS7554369B2Counting chain pulse countersOscillations generatorsSoftware engineeringRapid single flux quantum
A digital programmable frequency divider is constructed of Rapid Single Flux Quantum (RSFQ) logic elements. The logic elements may include an RSFQ non-destructive readout cell (NDRO), RSFQ D flip-flop and an RSFQ T flip-flop. A digital word comprising N bits is used to control the amount of frequency division and the frequency divider selectively imparts a respective frequency division for any of 2N states that can be represented by the digital word. The RSFQ logic elements utilize Josephson junctions which operate in superconducting temperature domains.
Owner:SEEQC INC
Superconductor Analog-to-Digital Converter
InactiveUS20100026537A1Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionRapid single flux quantumEngineering
A superconducting Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) employing rapid-single-flux-quantum (RSFQ) logic is disclosed. The ADC has only superconductor active components, and is characterized as being an Nth-order bandpass sigma-delta ADC, with the order “N” being at least 2. The ADC includes a sequence of stages, which stages include feedback loops and resonators. The ADC further includes active superconducting components which directionally couple resonator pairs of adjacent stages. The active superconducting components electrically shield the higher order resonator from the lower order resonator. These active superconductor components include a superconducting quantum interference device (SQUID) amplifier, which is inductively coupled to the higher order resonator, and may include a Josephson transmission line (JTL), which is configured to electrically connect the SQUID amplifier to the lower order resonator. The first stage of ADC may employ an implicit feedback loop.
Owner:HYPRES
Ultra fast differential transimpedance digital amplifier for superconducting circuits
InactiveUS7570075B2Improved gain-bandwidth productsIncrease speedPulse transformerElectronic switchingAudio power amplifierUltra fast
Supercooled electronics often use Rapid Single Flux Quantum (RSFQ) digital circuits. The output voltages from RSFQ devices are too low to be directly interfaced with semiconductor electronics, even if the semiconductor electronics are cooled. Techniques for directly interfacing RSFQ digital circuits with semiconductor electronics are disclosed using a novel inverting transimpedance digital amplifier in conjunction with a non-inverting transimpedance digital amplifier to create a differential transimpedance digital amplifier that permits direct interfacing between RSFQ and semiconductor electronics.
Owner:HYPRES
Ultra fast circuitry for digital filtering
InactiveUS7991814B2Easy to operateComputation using non-contact making devicesSolid-state devicesUltra high speedNon destructive
Owner:SEEQC INC
Digital Routing Switch Matrix for Digitized Radio-Frequency Signals
InactiveUS20070293160A1Efficient executionPrecise processingElectronic switchingSubstation equipmentMulti bandTransceiver
Routing and distribution of radio-frequency (RF) signals is commonly achieved in the analog domain. However, improved performance and simplified circuit architectures may be obtained by first digitizing the RF signal, and then carrying out all routing in the digital domain. A new generation of scalable digital switches has been developed, which routes both the data and clock signals together, this being necessary to maintain the integrity of the digitized RF signal. Given the extremely high switching speeds necessary for these applications (tens of GHz), this is implemented using Rapid-Single-Flux-Quantum (RSFQ) logic with superconducting integrated circuits. Such a digital switch matrix may be applied to either the receiver or transmitter components of an advanced multi-band, multi-channel digital transceiver system, and is compatible with routing of signals with different clock frequencies simultaneously within the same switch matrix.
Owner:HYPRES
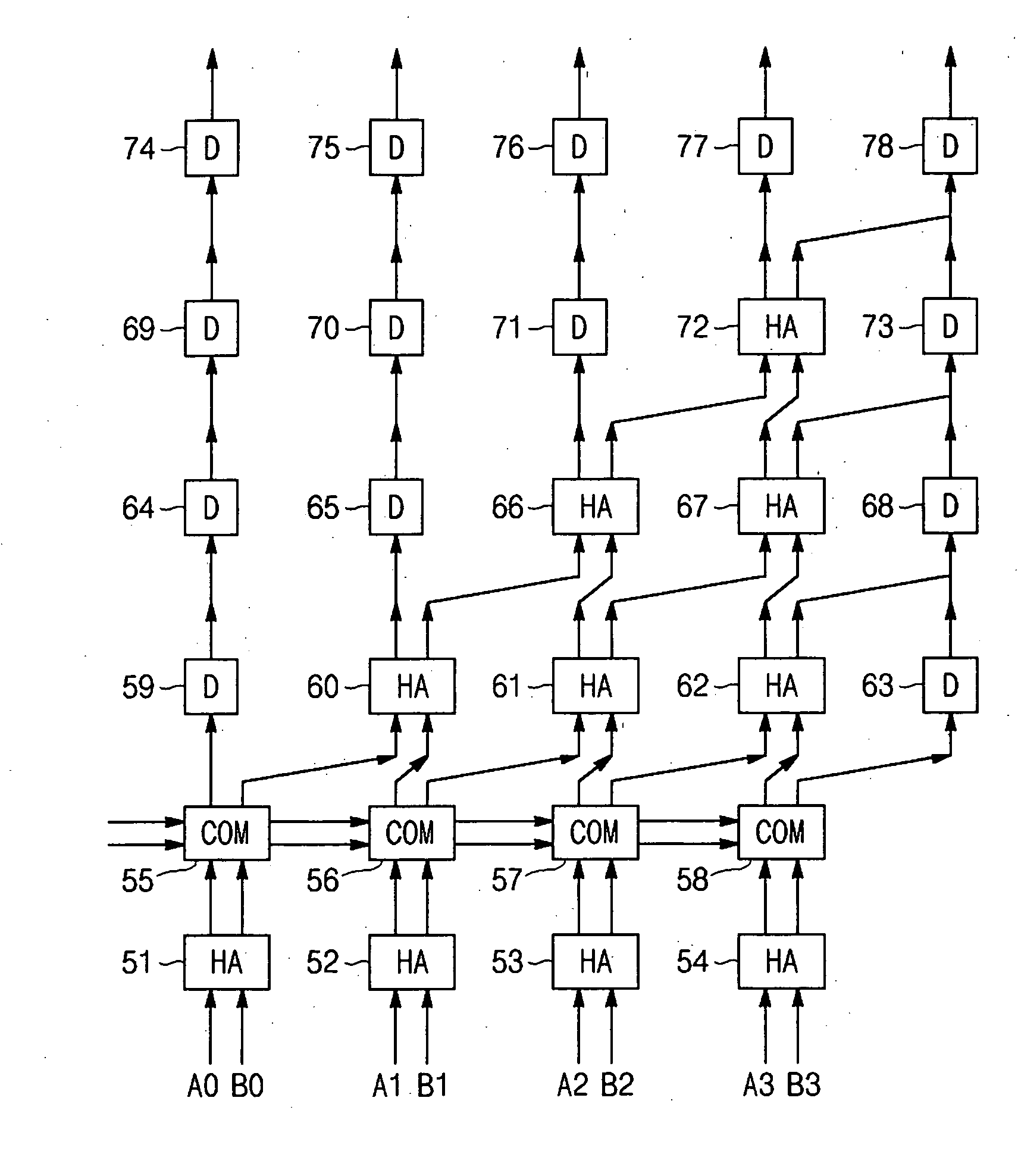
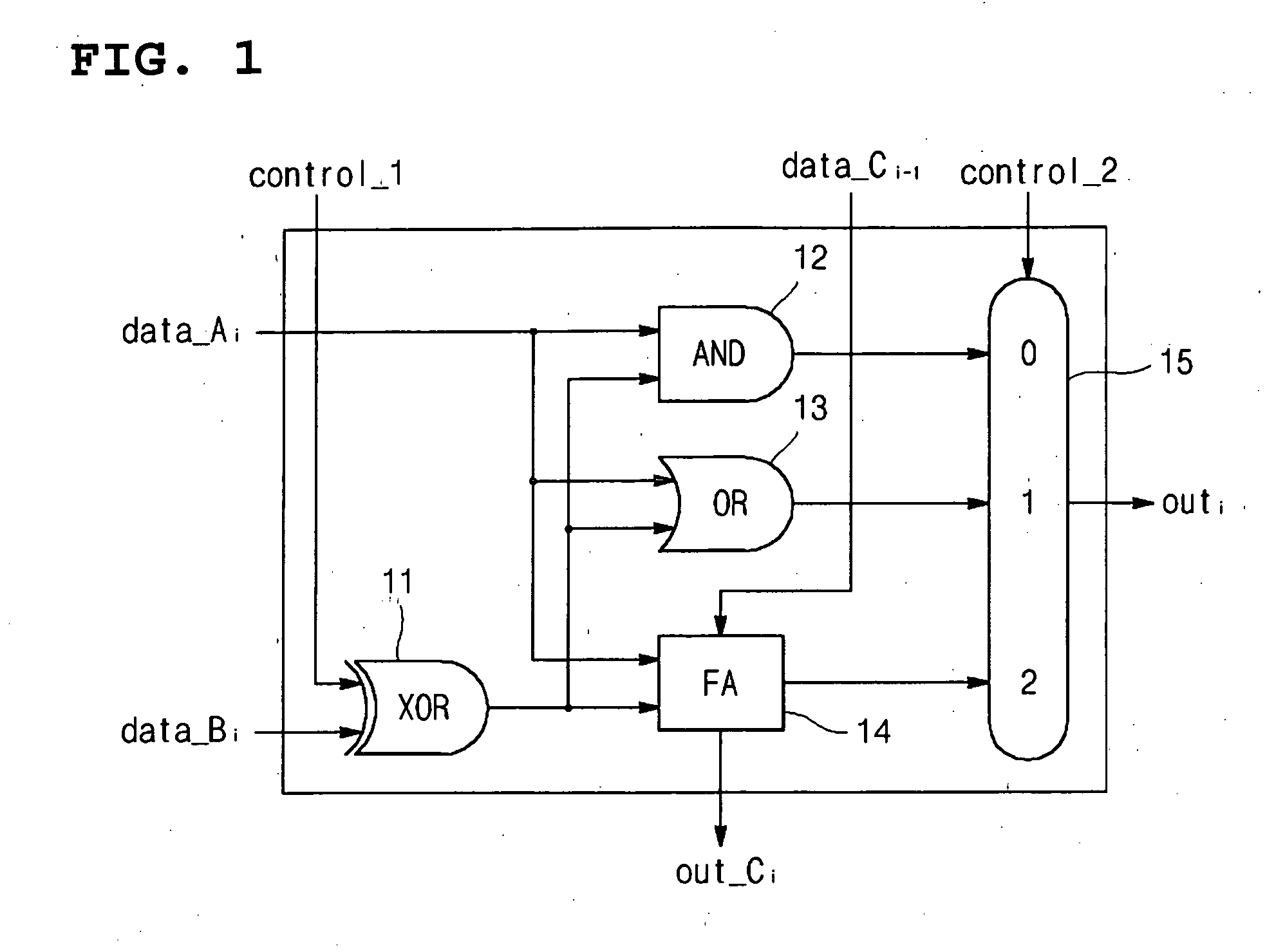
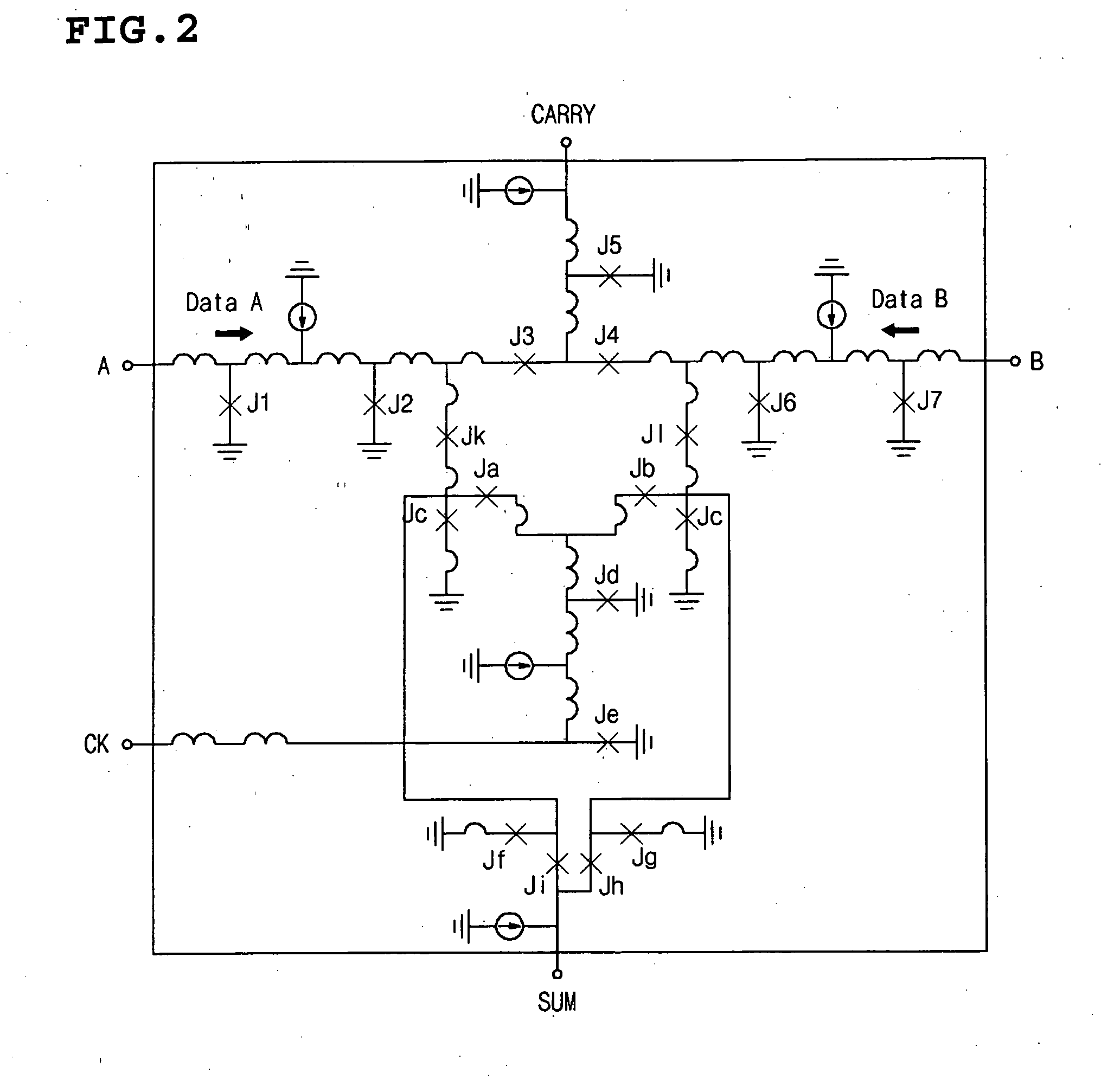
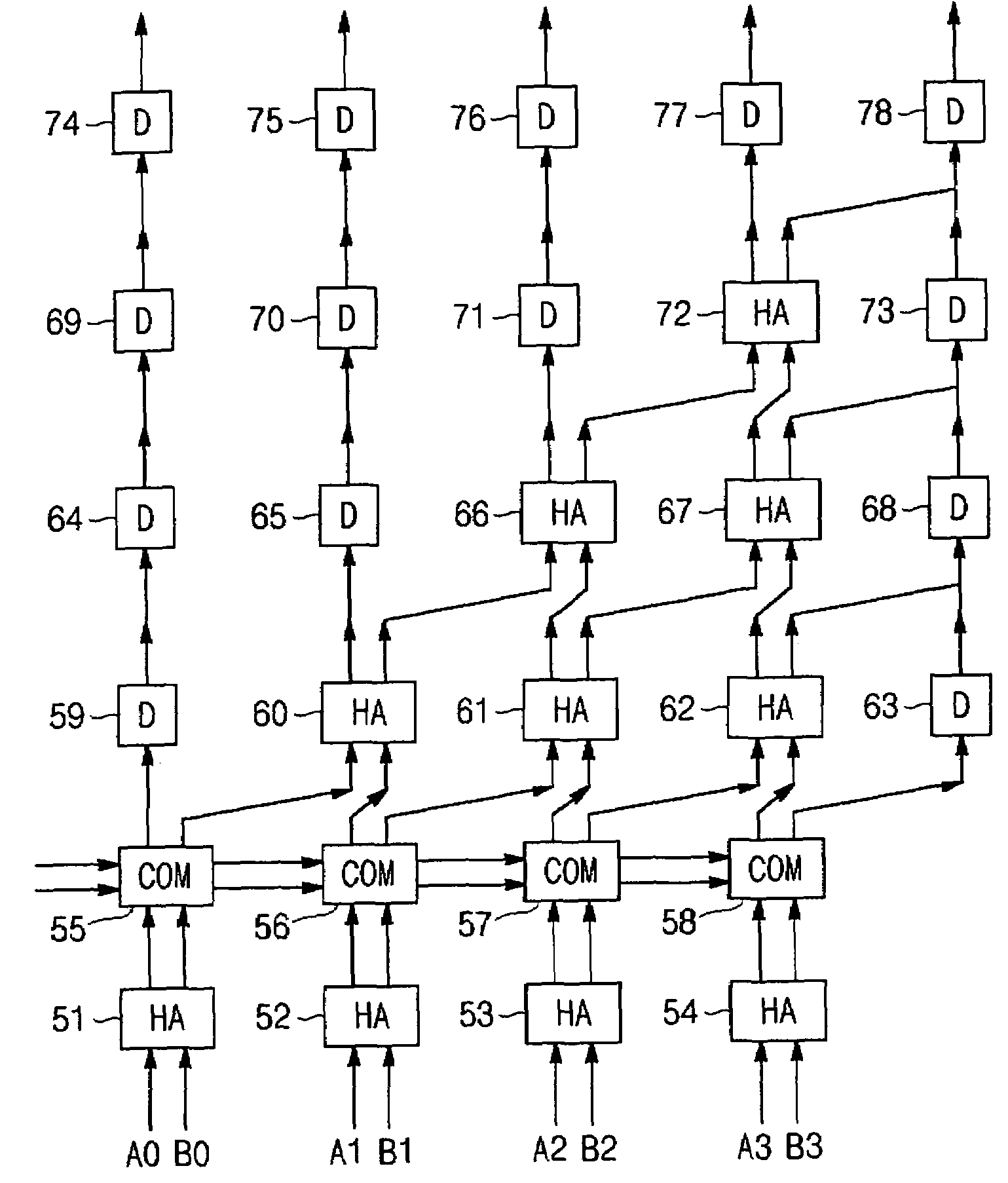
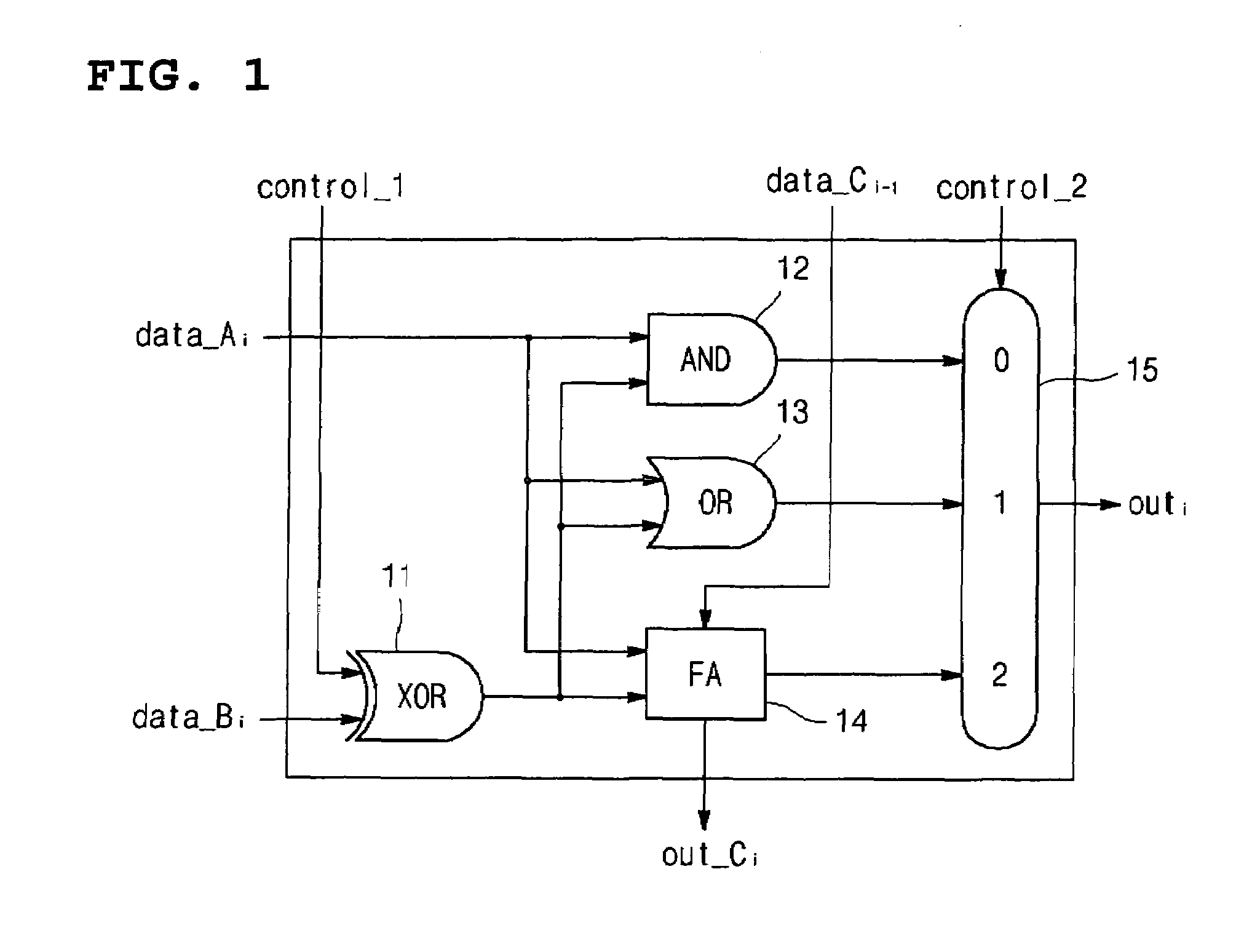
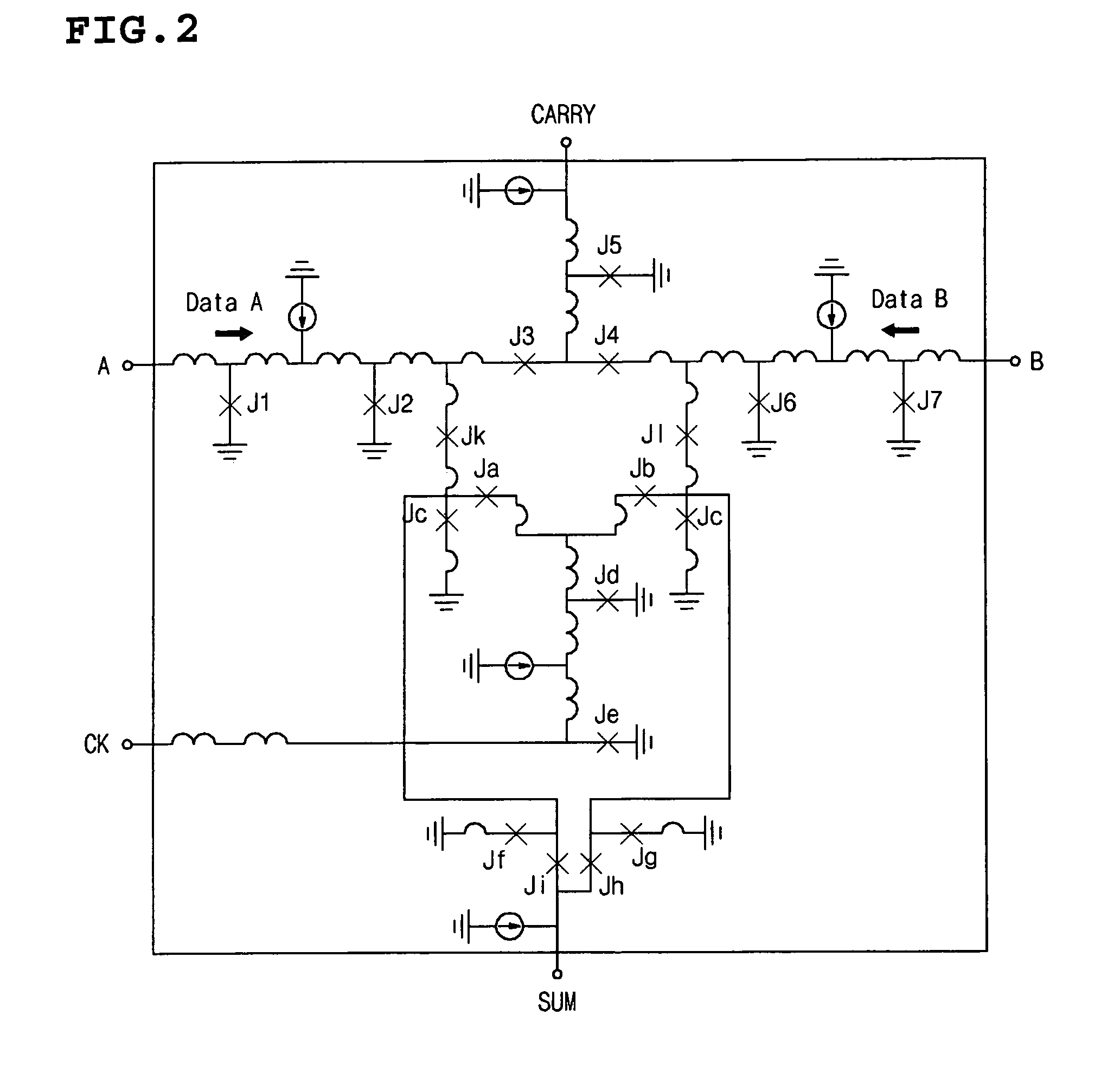
Arithmetic and logic unit using half adder
InactiveUS20050235027A1Computation using non-contact making devicesGear teeth manufacturing toolsAnd logic unitLogic cell
The present invention discloss an ALU that can be operated as an OR gate, an AND gate, an adder gate and an exclusive OR gate using a half adder that uses a superconductor rapid single flux quantum logic device. The ALU using a half adder includes a half adder using a superconductor rapid single flux quantum logic device as a logic circuit, and a switching unit that has input ports respectively connected to a sum output port and a carry output port of the half adder and is operated as an OR gate, an AND gate, an adder gate and an exclusive OR gate using output signals of the half adder. The switching unit includes a first switch having an input port connected to the sum output port of the half adder, a second switch having an input port connected to the carry output port of the half adder and an output port connected to an output port of the first switch, and a third switch having an input port connected to the carry output port of the half adder.
Owner:HYPRES +1
Digital programmable phase generator
ActiveUS7508230B2Analogue/digital conversionPulse generation by super conductive devicesPhase shiftedRapid single flux quantum
A programmable phase shifter is constructed of Rapid Single Flux Quantum (RSFQ) logic elements. The logic elements may include an RSFQ inverter and an RSFQ T flip-flop. A digital word comprising N bits is used to control the amount of phase shift and the phase shifter selectively imparts a respective phase shift for any of 2N states that can be represented by the digital word. The RSFQ logic elements utilize Josephson junctions which operate in the superconducting temperature domain.
Owner:SEEQC INC
Superconducting circuit for high-speed lookup table
ActiveUS20070194958A1Rapid parallel pipelined readoutSlow serial reprogramming of memory contentSuperconductors/hyperconductorsRead-only memoriesProgrammable read-only memoryRapid single flux quantum
A high-speed lookup table is designed using Rapid Single Flux Quantum (RSFQ) logic elements and fabricated using superconducting integrated circuits. The lookup table is composed of an address decoder and a programmable read-only memory array (PROM). The memory array has rapid parallel pipelined readout and slower serial reprogramming of memory contents. The memory cells are constructed using standard non-destructive reset-set flip-flops (RSN cells) and data flip-flops (DFF cells). An n-bit address decoder is implemented in the same technology and closely integrated with the memory array to achieve high-speed operation as a lookup table. The circuit architecture is scalable to large two-dimensional data arrays.
Owner:SEEQC INC
Arithmetic and logic unit using half adder
InactiveUS7376691B2Computation using non-contact making devicesGear teeth manufacturing toolsArithmetic logic unitAnd logic unit
The present invention discloses an ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit) that can be operated as an OR gate, an AND gate, an adder gate and an exclusive OR gate using a half adder that uses a superconductor rapid single flux quantum logic device. The ALU using a half adder includes a half adder using a superconductor rapid single flux quantum logic device as a logic circuit, and a switching unit that has input ports respectively connected to a sum output port and a carry output port of the half adder and is operated as an OR gate, an AND gate, an adder gate and an exclusive OR gate using output signals of the half adder. The switching unit includes a first switch having an input port connected to the sum output port of the half adder, a second switch having an input port connected to the carry output port of the half adder and an output port connected to an output port of the first switch, and a third switch having an input port connected to the carry output port of the half adder.
Owner:HYPRES +1
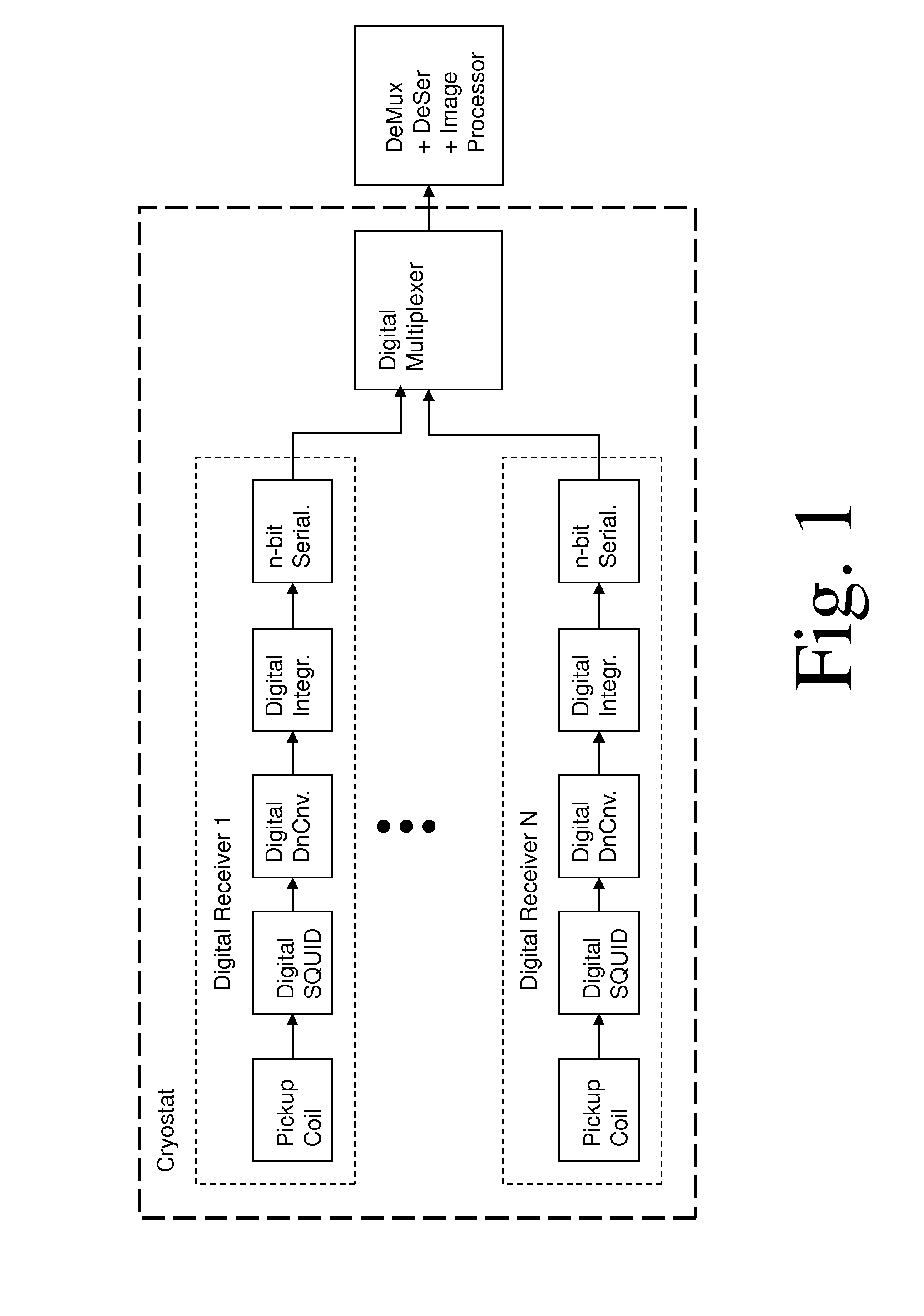
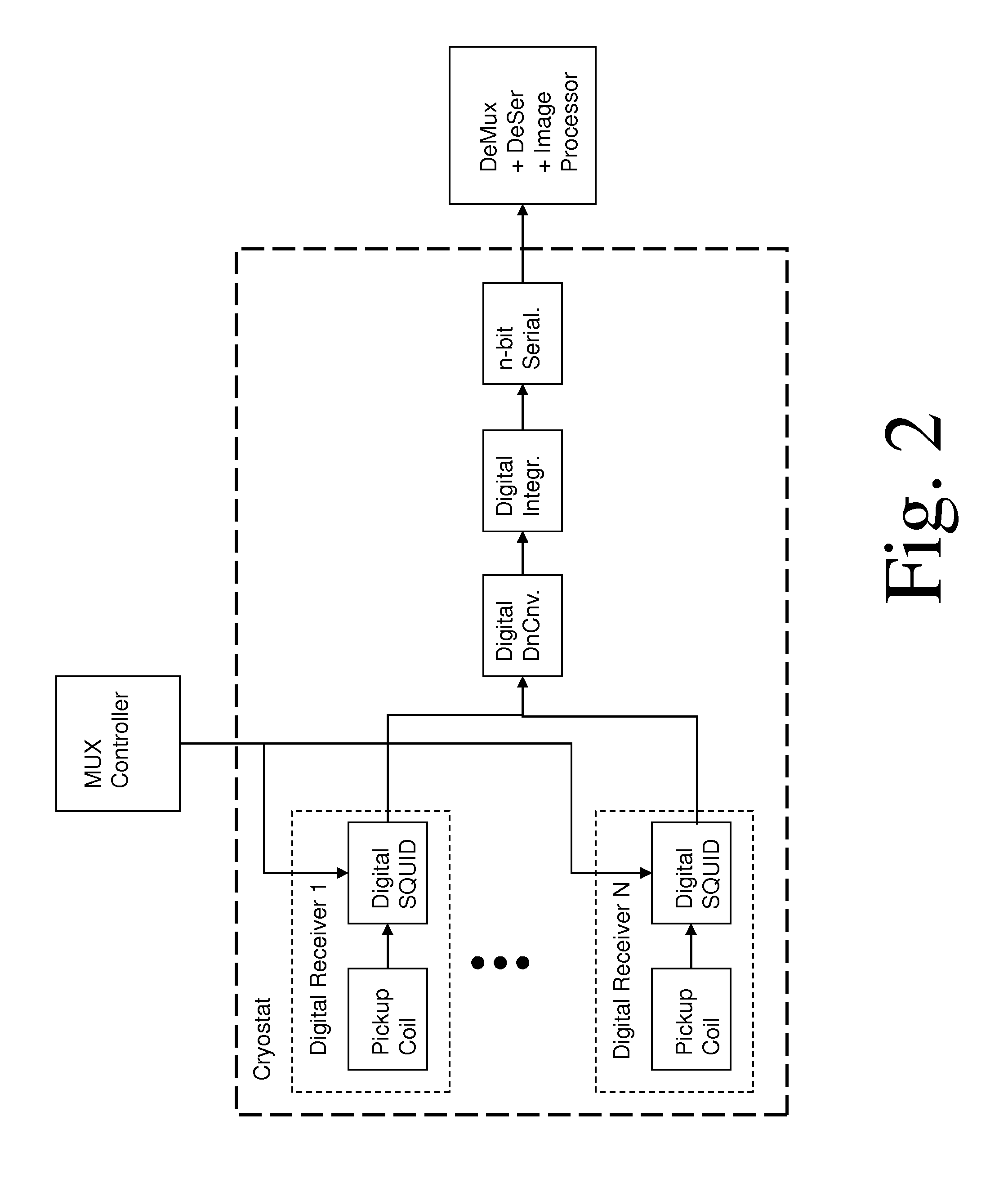
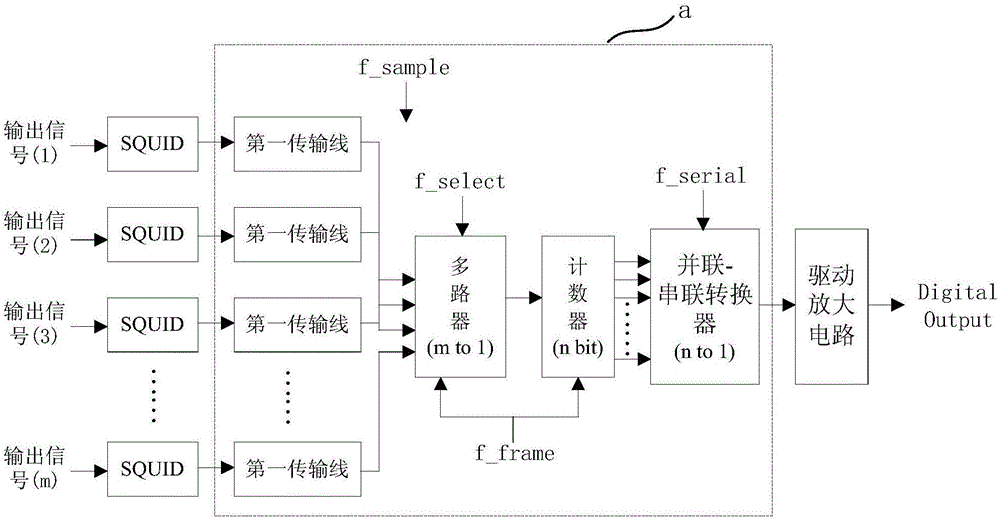
Low-temperature superconductive reading circuit based on ERSFQ and reading system
ActiveCN106767944AImprove noise immunityReduce the number of transmission linesConverting sensor output electrically/magneticallySensor arrayRapid single flux quantum
The present invention provides a low-temperature superconductive reading circuit based on the ERSFQ (Energy-efficient Rapid Single Flux Quantum) and a reading system. The circuit comprises: m superconduction quantum interference devices connected with a low-temperature superconductive sensor array and configured to convert the multi-output signals of the low-temperature superconductive sensor array to multiple SFQ pulse signals; an ERSFQ circuit connected with the m superconduction quantum interference devices and configured to convert the multiple SFQ pulse signals into the binary system one-way pulse signals for outputting; and a driving amplification circuit connected with the ERSFQ circuit and configured to perform amplification output of the binary system one-way pulse signals, wherein m is an integer of larger than 1. The low-temperature superconductive reading circuit based on ERSFQ and the reading system solve the problems that the reading amplification circuit is large in heat load and the circuit system anti-noise interference capability is bad in the prior art.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Digital programmable frequency divider
InactiveUS20070075752A1Counting chain pulse countersPulse counters with static storageNon destructiveRapid single flux quantum
A digital programmable frequency divider is constructed of Rapid Single Flux Quantum (RSFQ) logic elements. The logic elements may include an RSFQ non-destructive readout cell (NDRO), and RSFQ D flip-flop and an RSFQ T flip-flop. A digital word comprising N bits is used to control the amount of frequency division and the frequency divider selectively imparts a respective frequency division for any of 2N states that can be represented by the digital word. The RSFQ logic elements utilize Josephson junctions which operate in superconducting temperature domains.
Owner:HYPRES
Digital programmable phase generator
ActiveUS20070075729A1Analogue/digital conversionPulse generation by super conductive devicesPhase shiftedRapid single flux quantum
A programmable phase shifter is constructed of Rapid Single Flux Quantum (RSFQ) logic elements. The logic elements may include an RSFQ inverter and an RSFQ T flip-flop. A digital word comprising N bits is used to control the amount of phase shift and the phase shifter selectively imparts a respective phase shift for any of 2N states that can be represented by the digital word. The RSFQ logic elements utilize Josephson junctions which operate in the superconducting temperature domain.
Owner:SEEQC INC
Superconducting multi-bit digital mixer
ActiveUS8744541B1Accurate timingSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsShift registerLocal oscillator signal
A superconducting multi-bit digital mixer, designed using rapid single flux quantum (RSFQ) logic, for multiplying two independent digital streams, at least one of these comprising a plurality of parallel bit lines, wherein the output is also a similar plurality of bit lines. In a preferred embodiment, one of the digital streams represents a local oscillator signal, and the other digital stream digital radio frequency input from an analog-to-digital converter. The multi-bit mixer comprises an array of bit-slices, with the local oscillator signal generated using shift registers. This multi-bit mixer is suitable for an integrated circuit with application to a broadband digital radio frequency receiver, a digital correlation receiver, or a digital radio frequency transmitter. A synchronous pulse distribution network is used to ensure proper operation at data rates of 20 GHz or above.
Owner:HYPRES
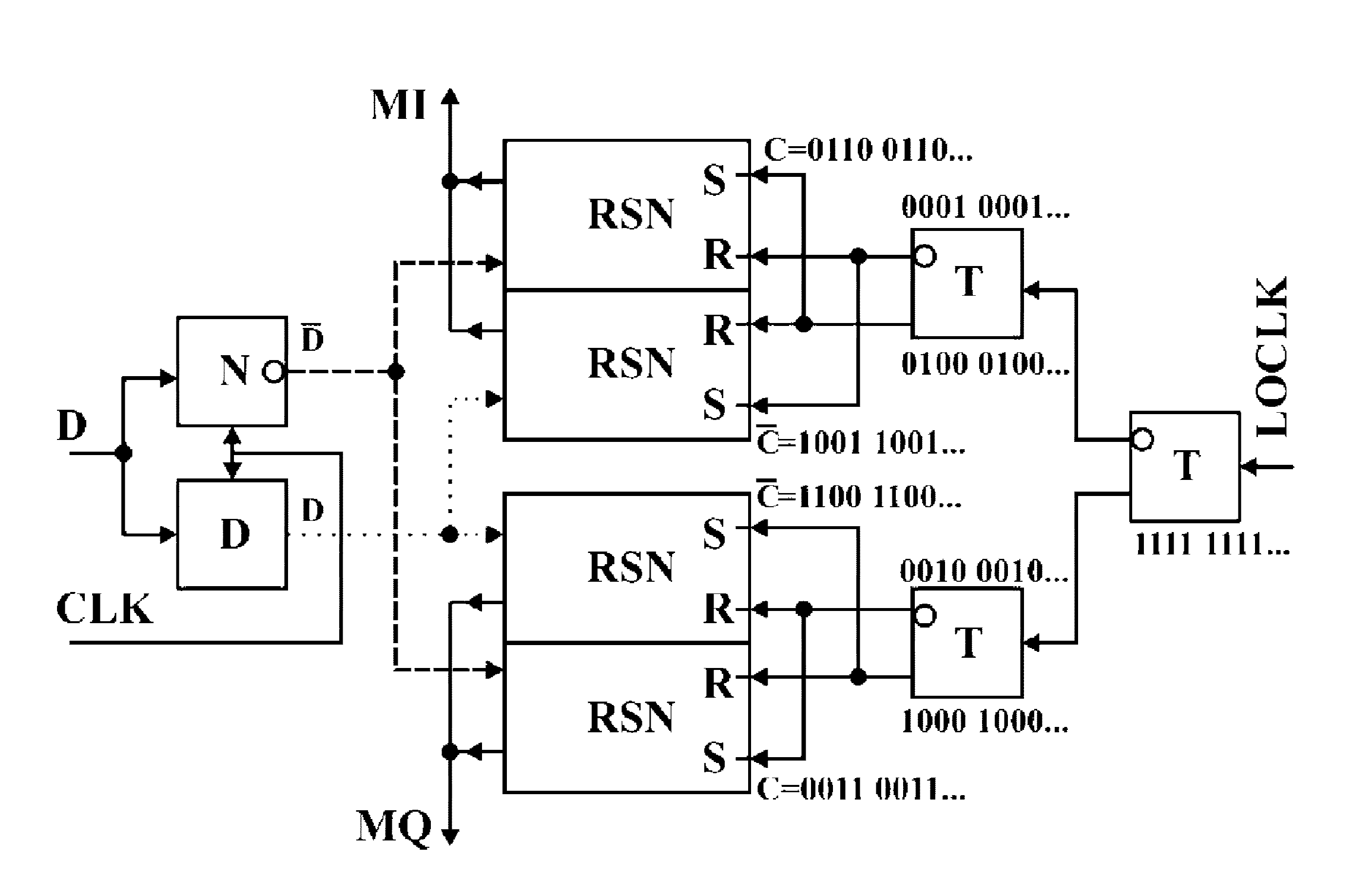
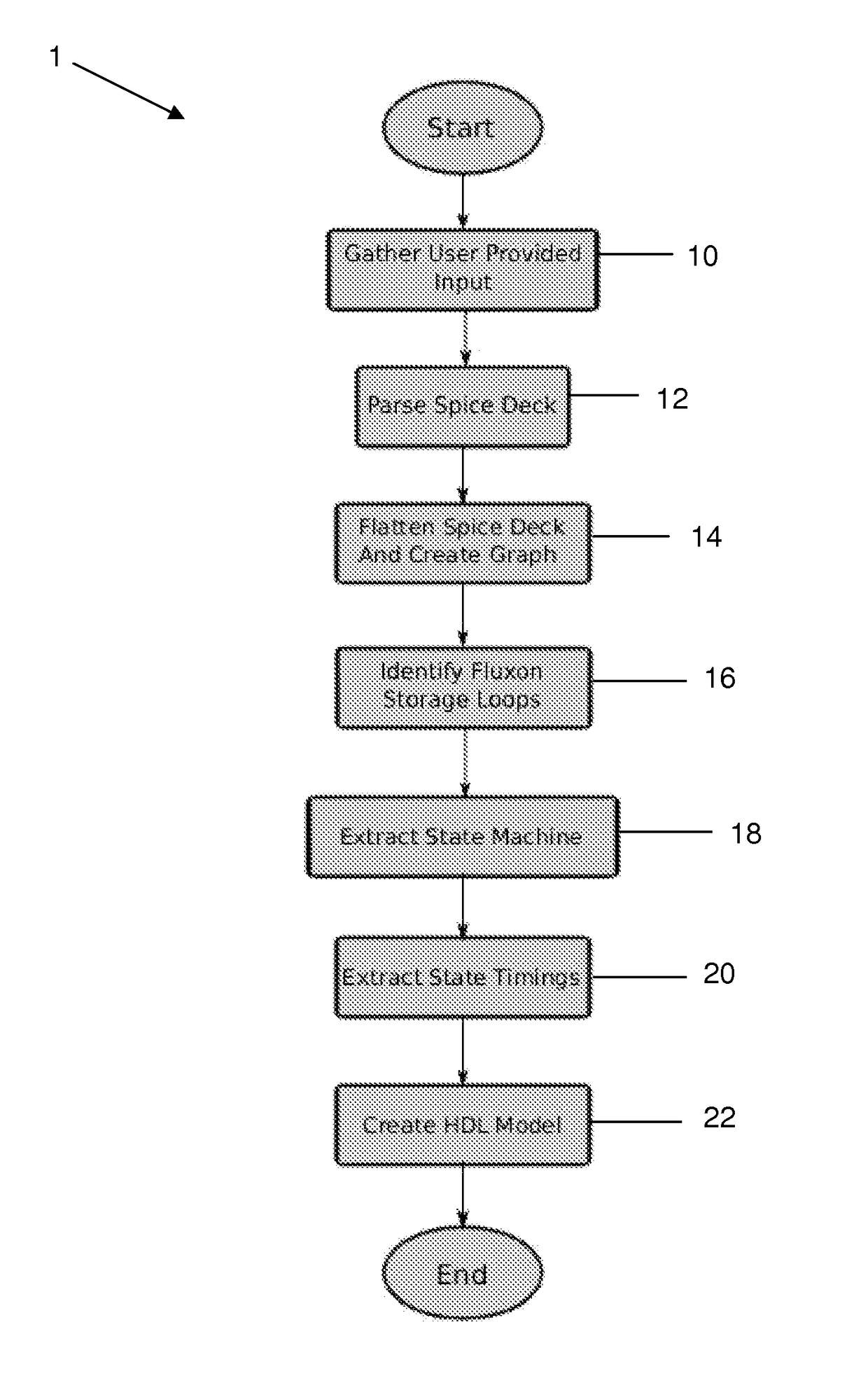
Automated state machine extraction for rapid-single flux-quantum circuits
InactiveUS9710586B2CAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsInterconnectivityTheoretical computer science
Owner:STELLENBOSCH UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com