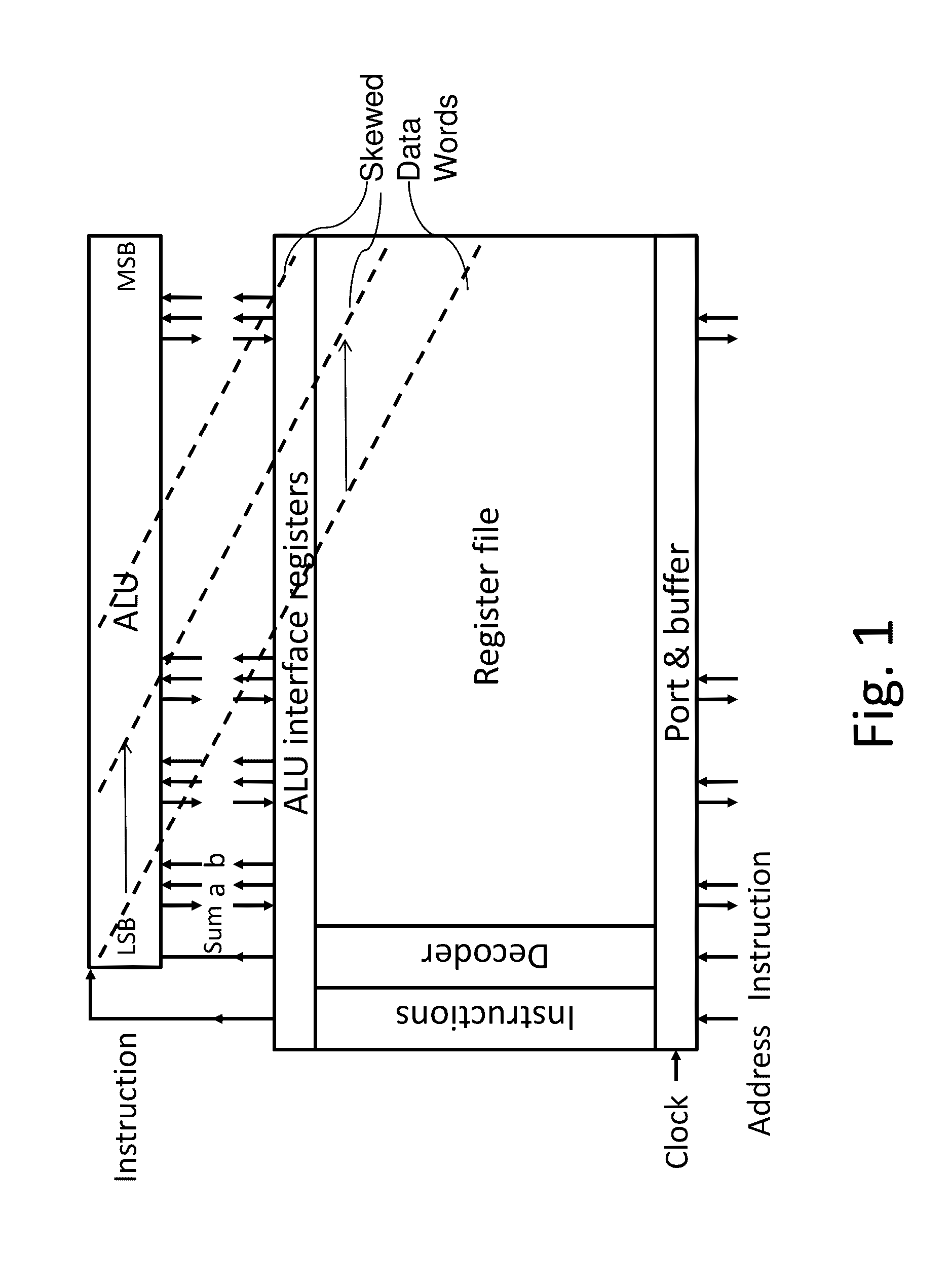
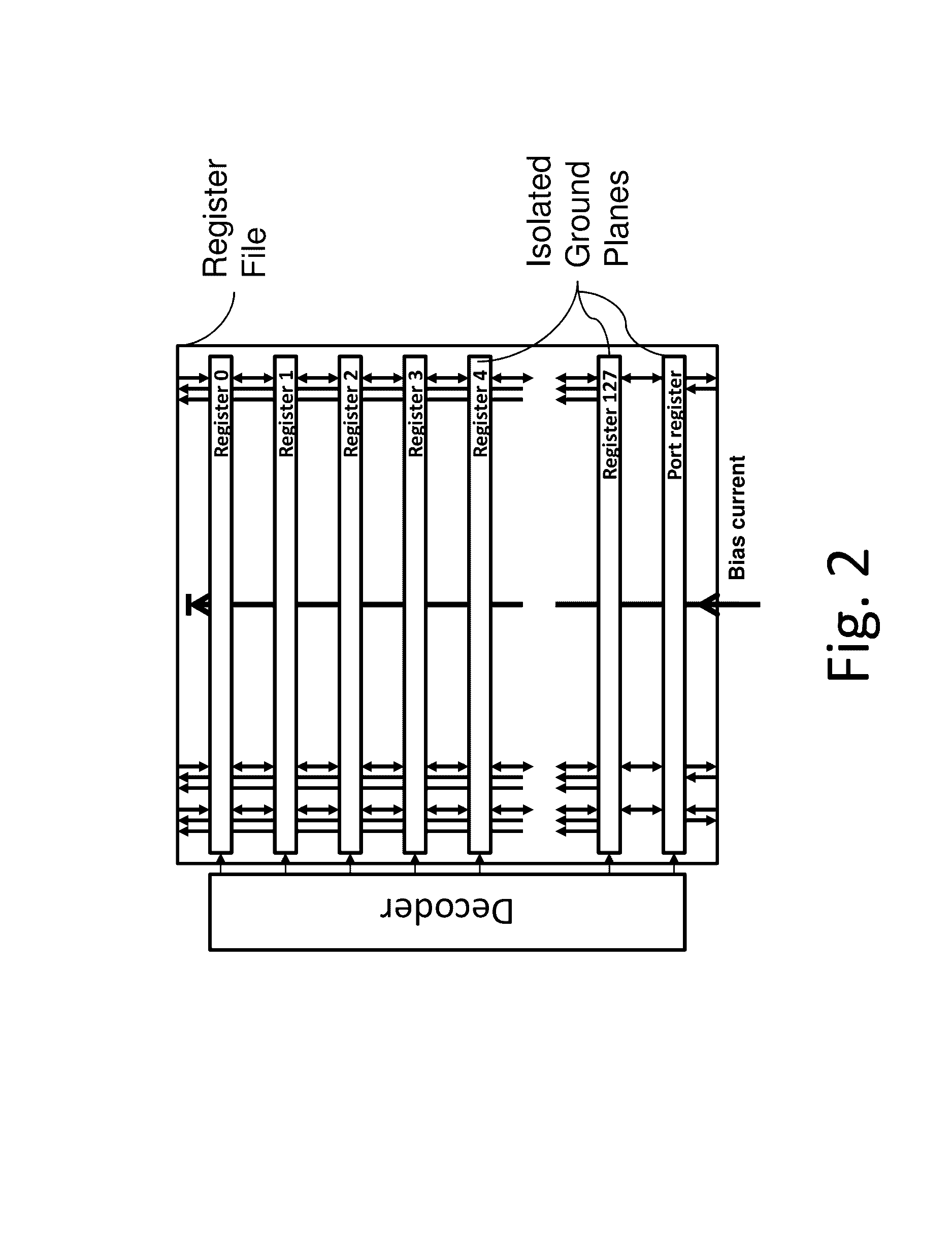
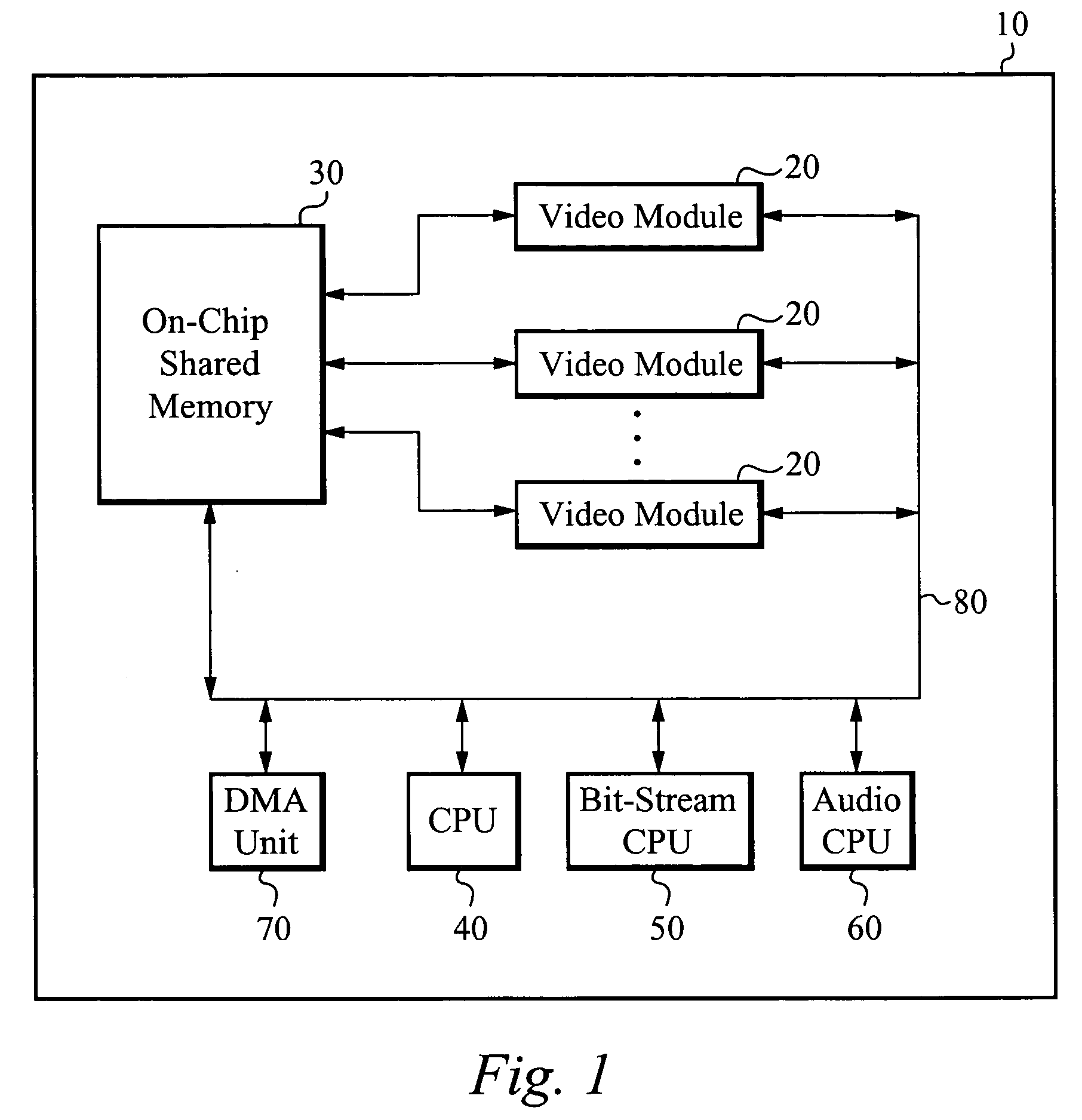
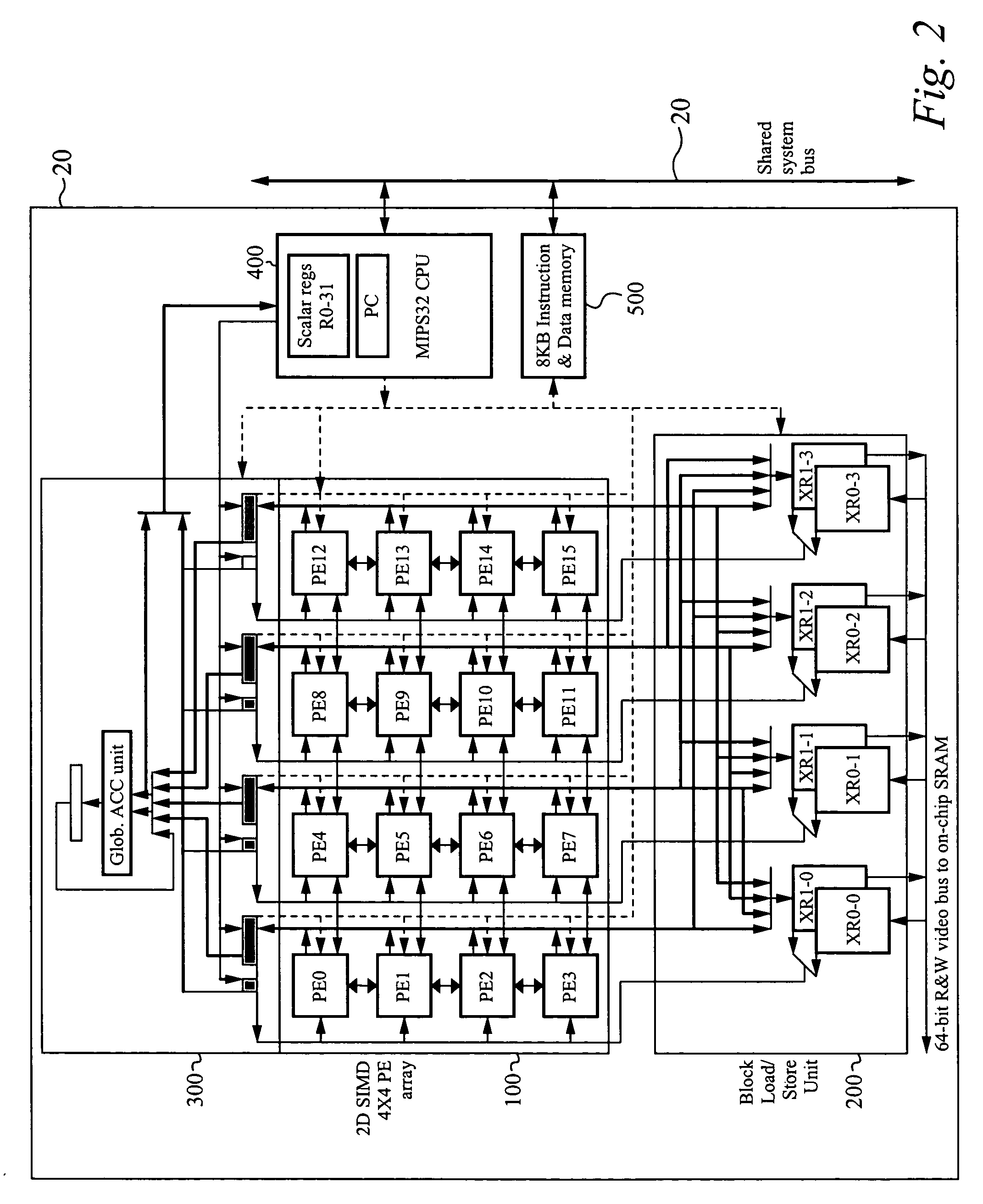
Patents
Literature
534 results about "Arithmetic logic unit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
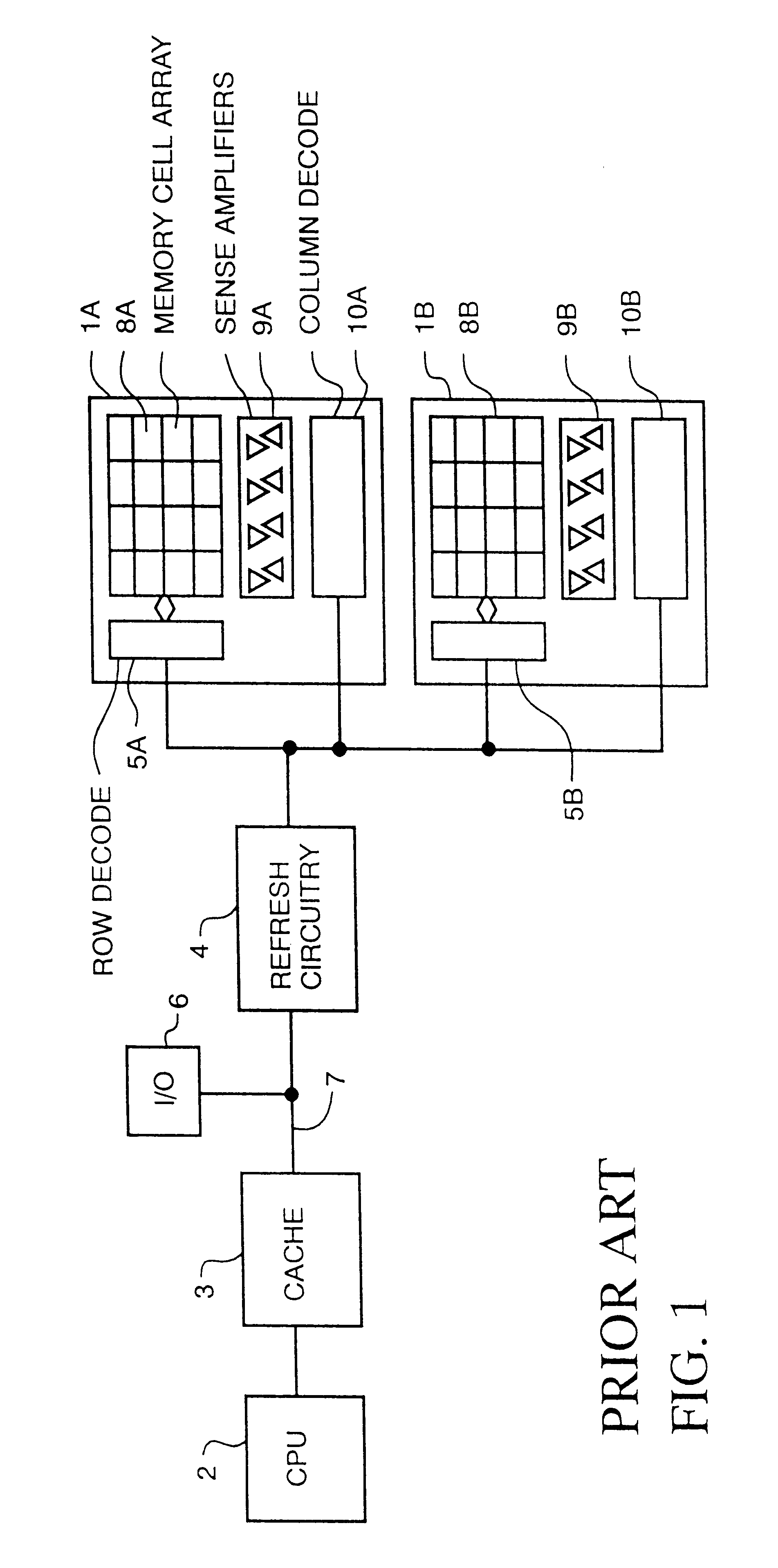
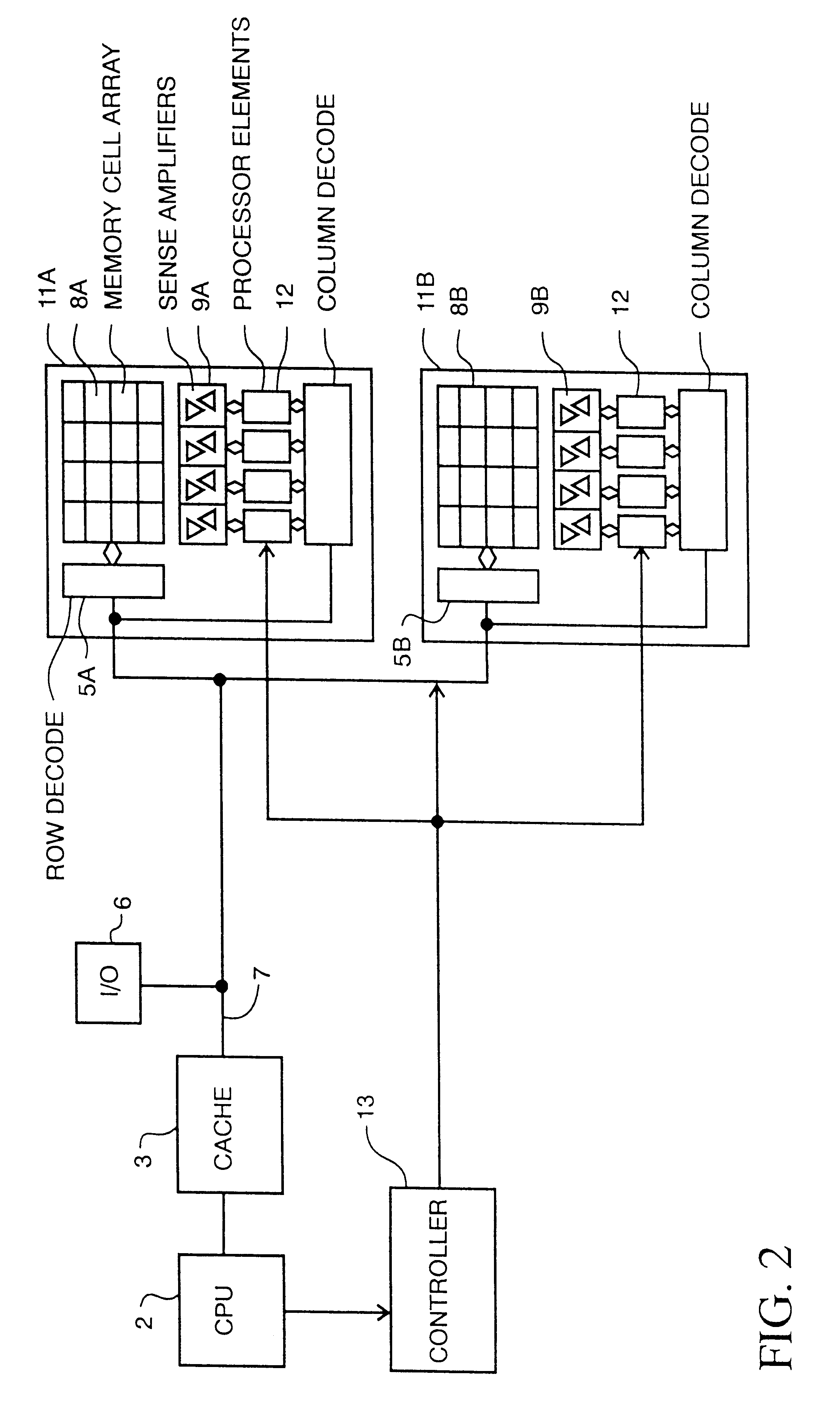
An arithmetic logic unit (ALU) is a combinational digital electronic circuit that performs arithmetic and bitwise operations on integer binary numbers. This is in contrast to a floating-point unit (FPU), which operates on floating point numbers. An ALU is a fundamental building block of many types of computing circuits, including the central processing unit (CPU) of computers, FPUs, and graphics processing units (GPUs). A single CPU, FPU or GPU may contain multiple ALUs.
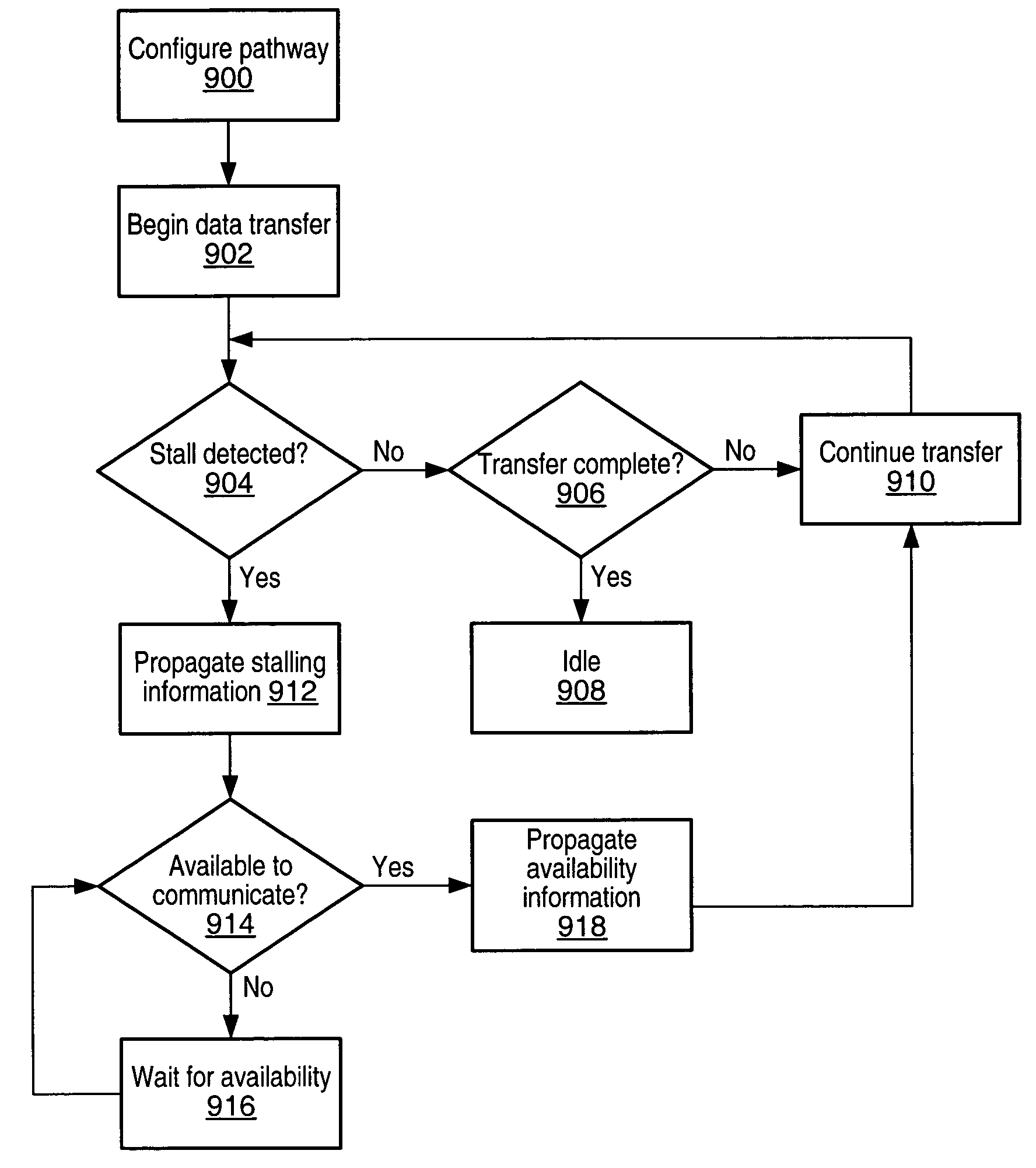
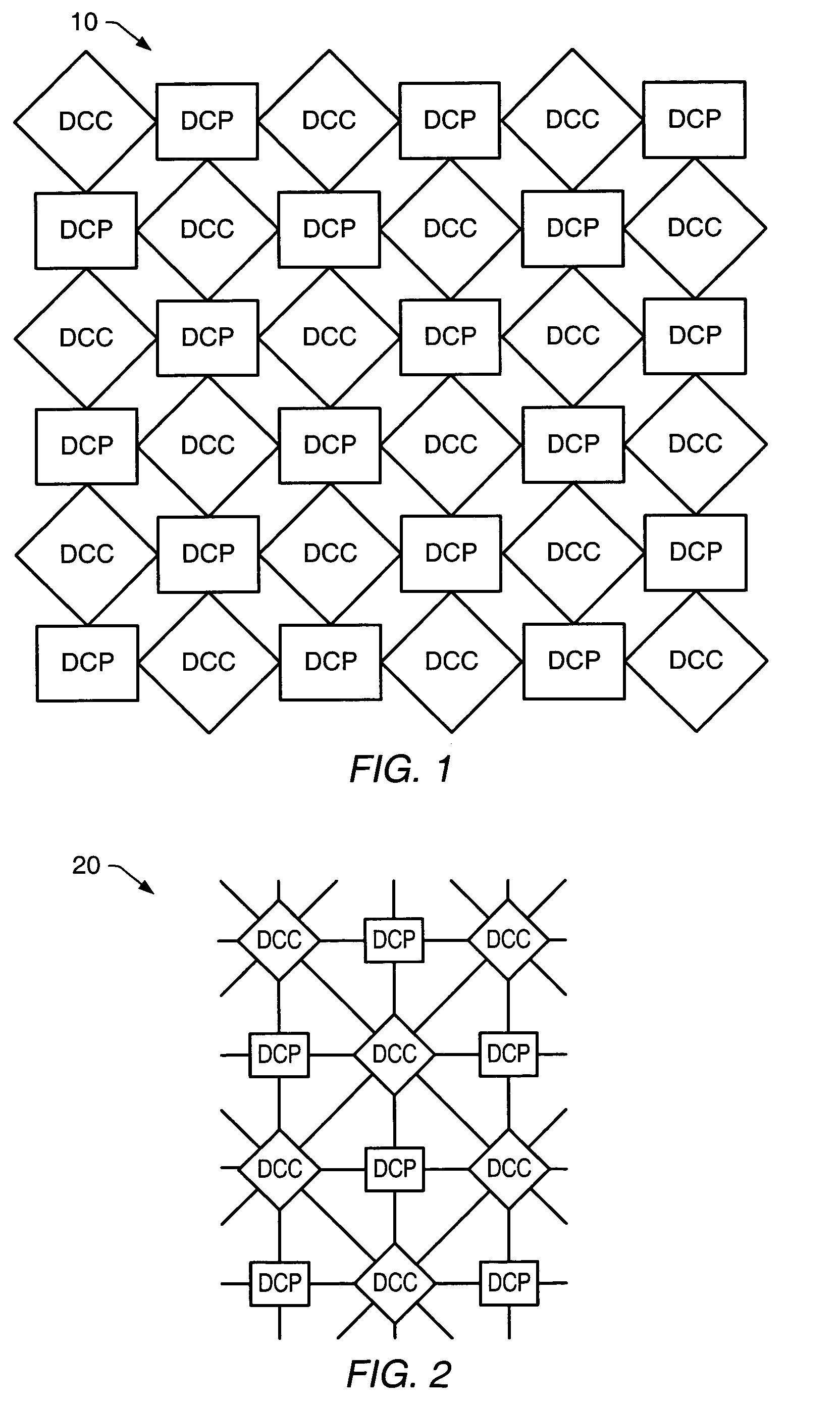
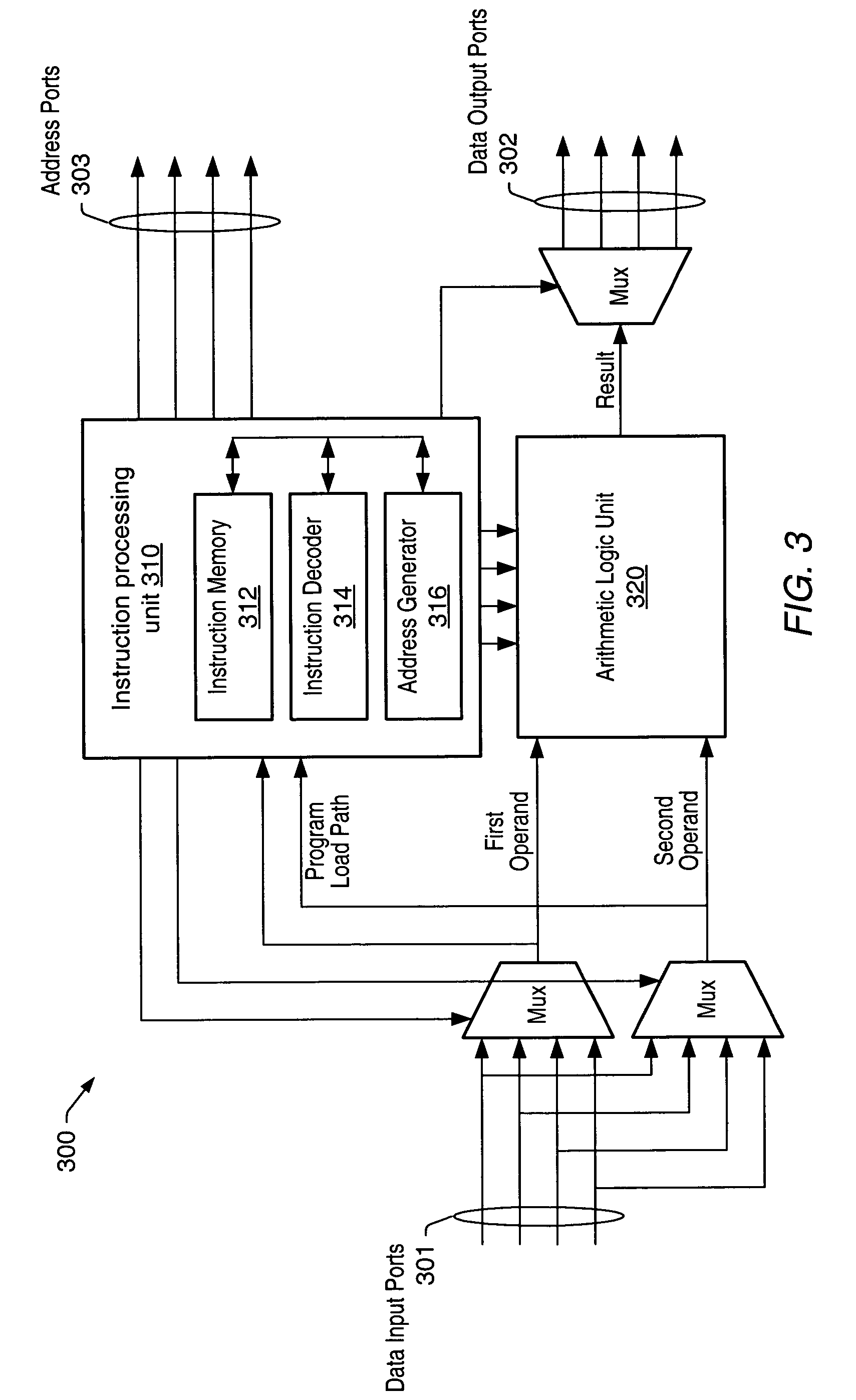
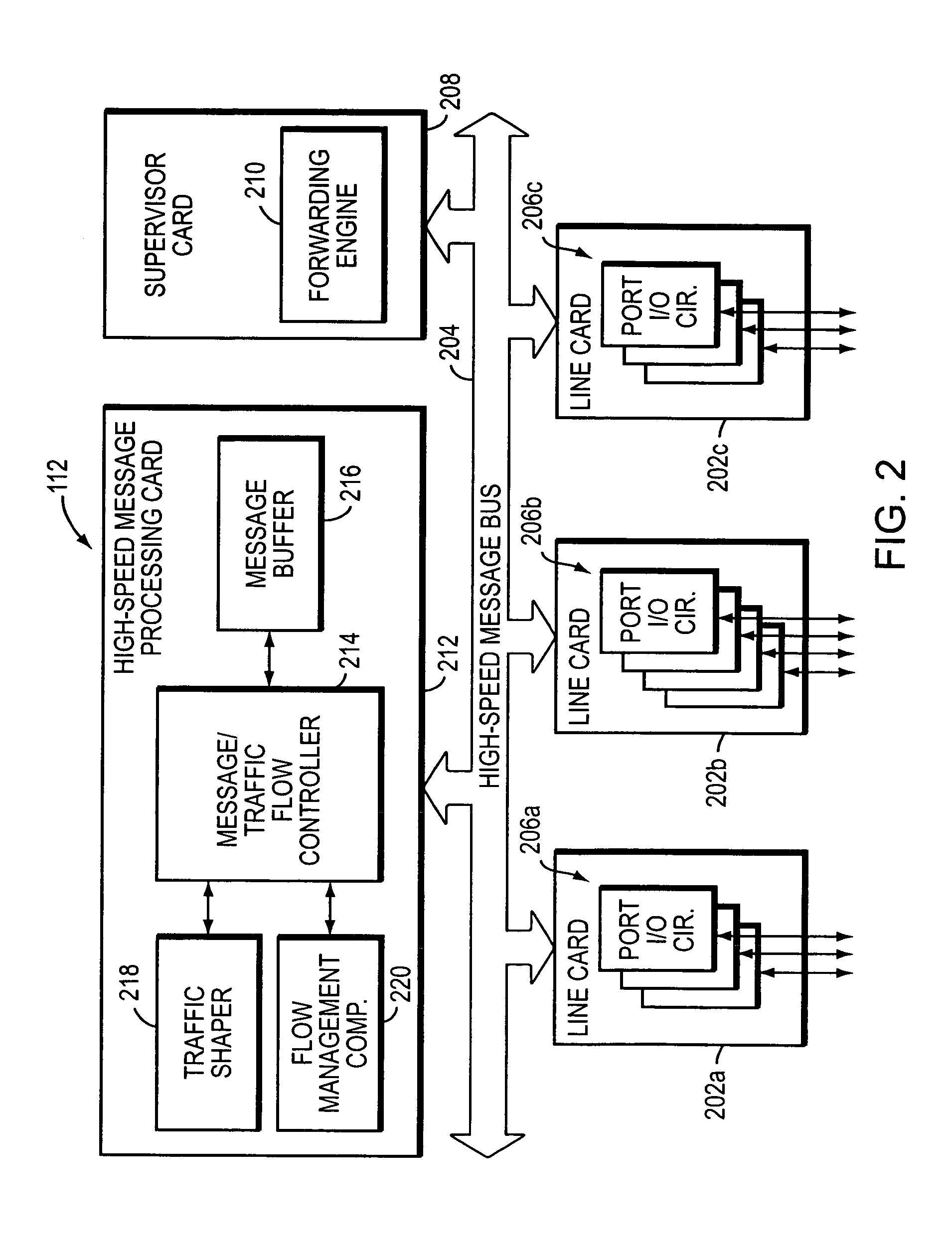
Processing system with interspersed stall propagating processors and communication elements
ActiveUS7415594B2Energy efficient ICTSingle instruction multiple data multiprocessorsArithmetic logic unitInstruction processing unit
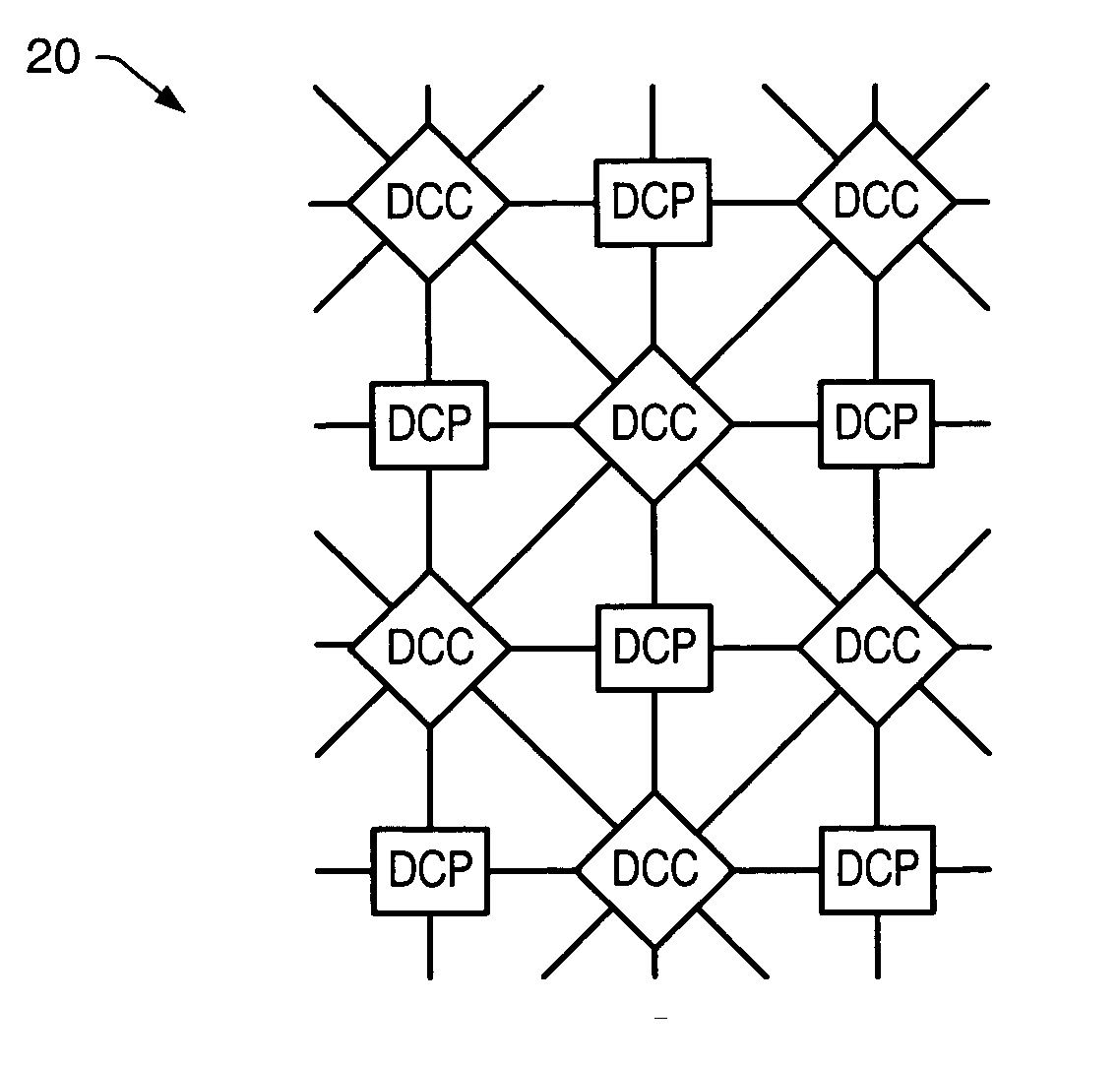
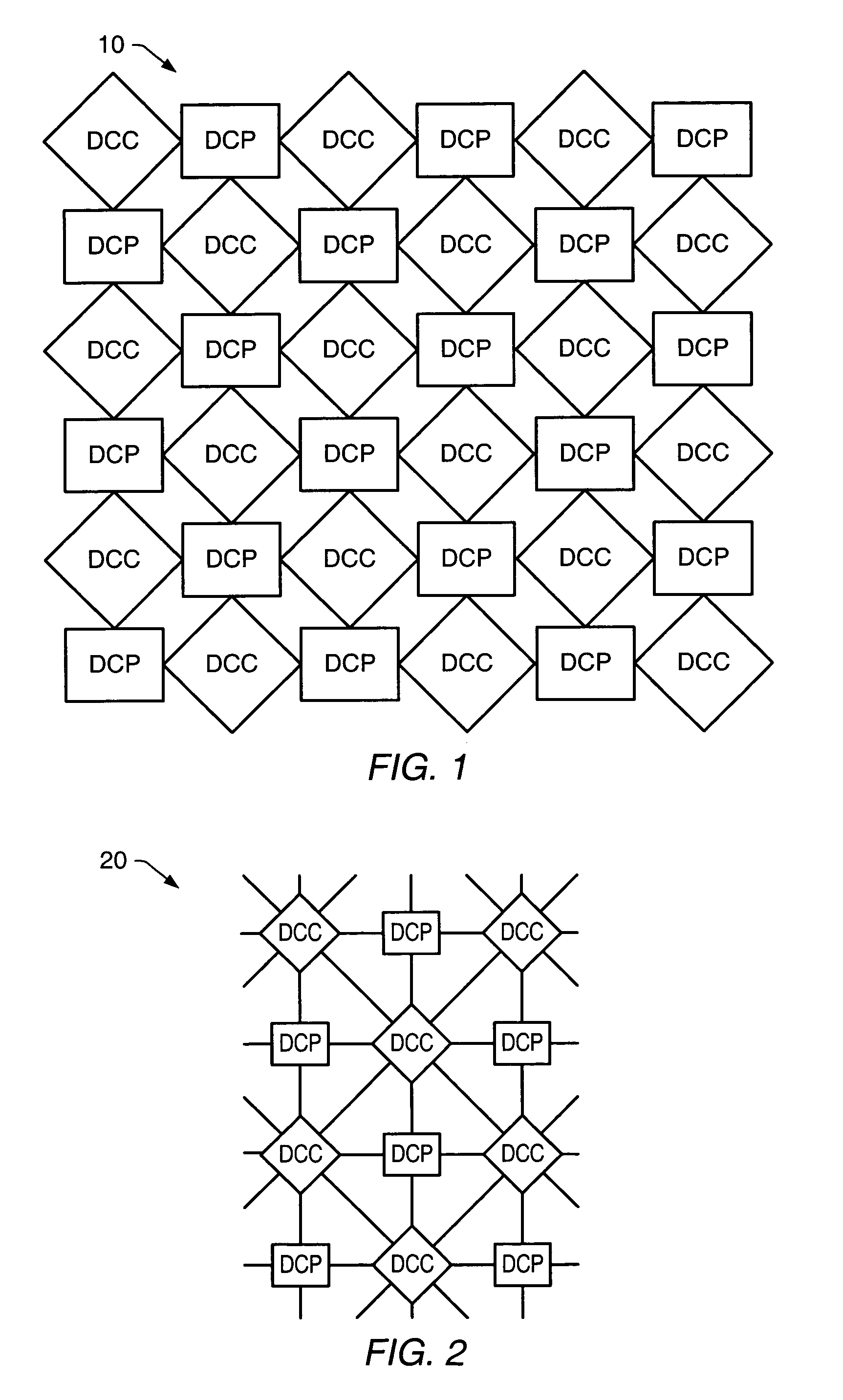
A processing system comprising processors and the dynamically configurable communication elements coupled together in an interspersed arrangement. The processors each comprise at least one arithmetic logic unit, an instruction processing unit, and a plurality of processor ports. The dynamically configurable communication elements each comprise a plurality of communication ports, a first memory, and a routing engine. For each of the processors, the plurality of processor ports is configured for coupling to a first subset of the plurality of dynamically configurable communication elements. For each of the dynamically configurable communication elements, the plurality of communication ports comprises a first subset of communication ports configured for coupling to a subset of the plurality of processors and a second subset of communication ports configured for coupling to a second subset of the plurality of dynamically configurable communication elements.
Owner:COHERENT LOGIX
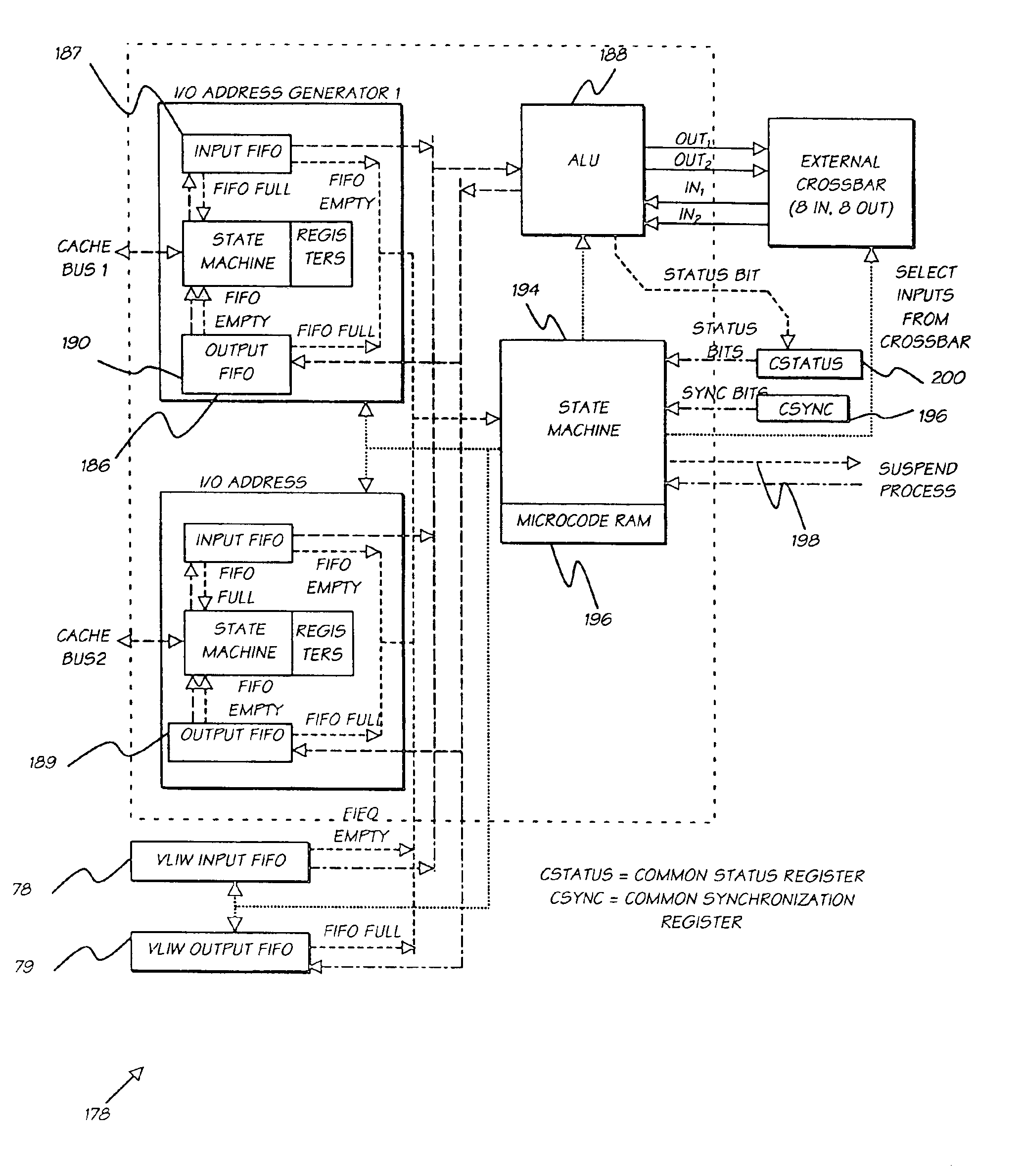
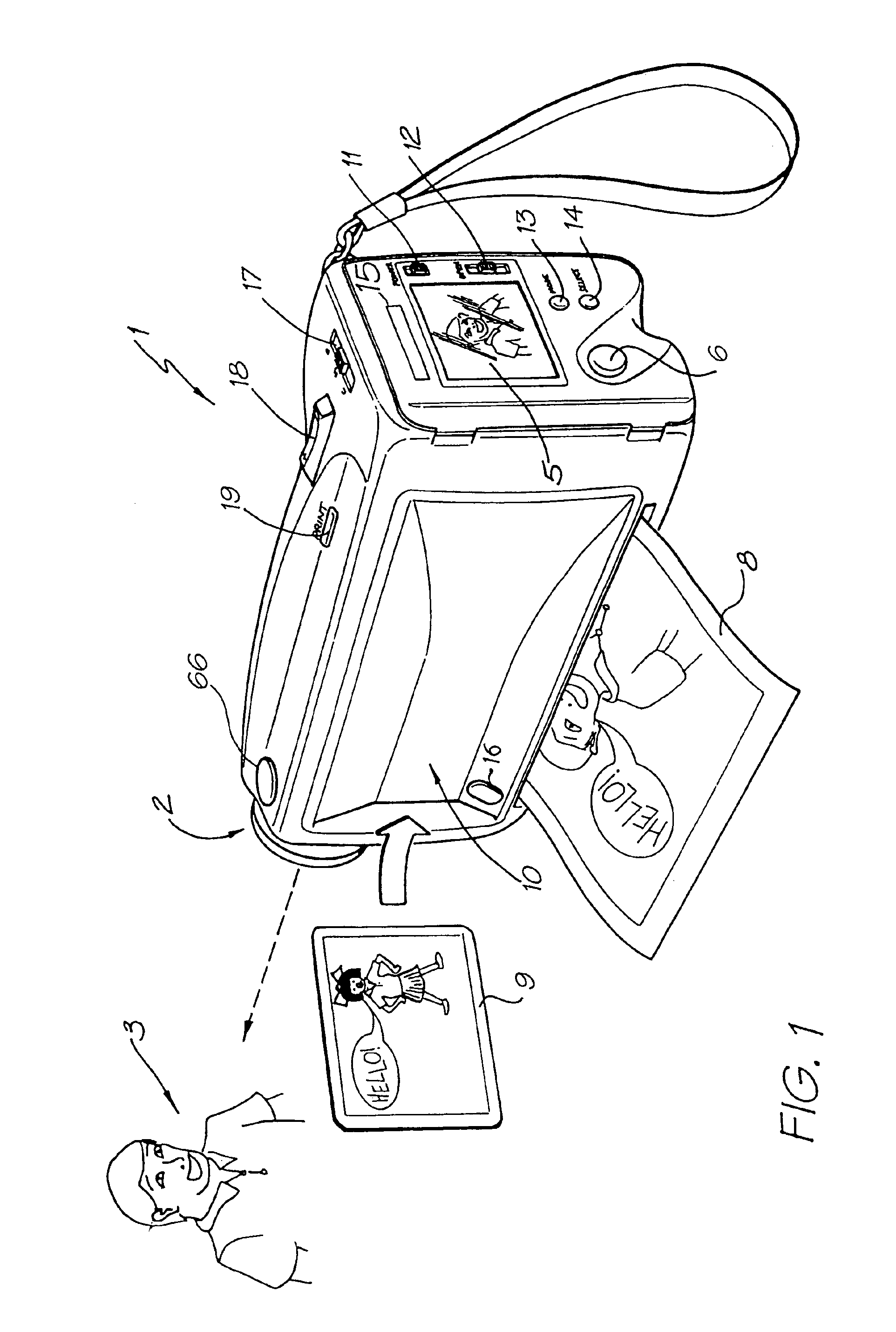
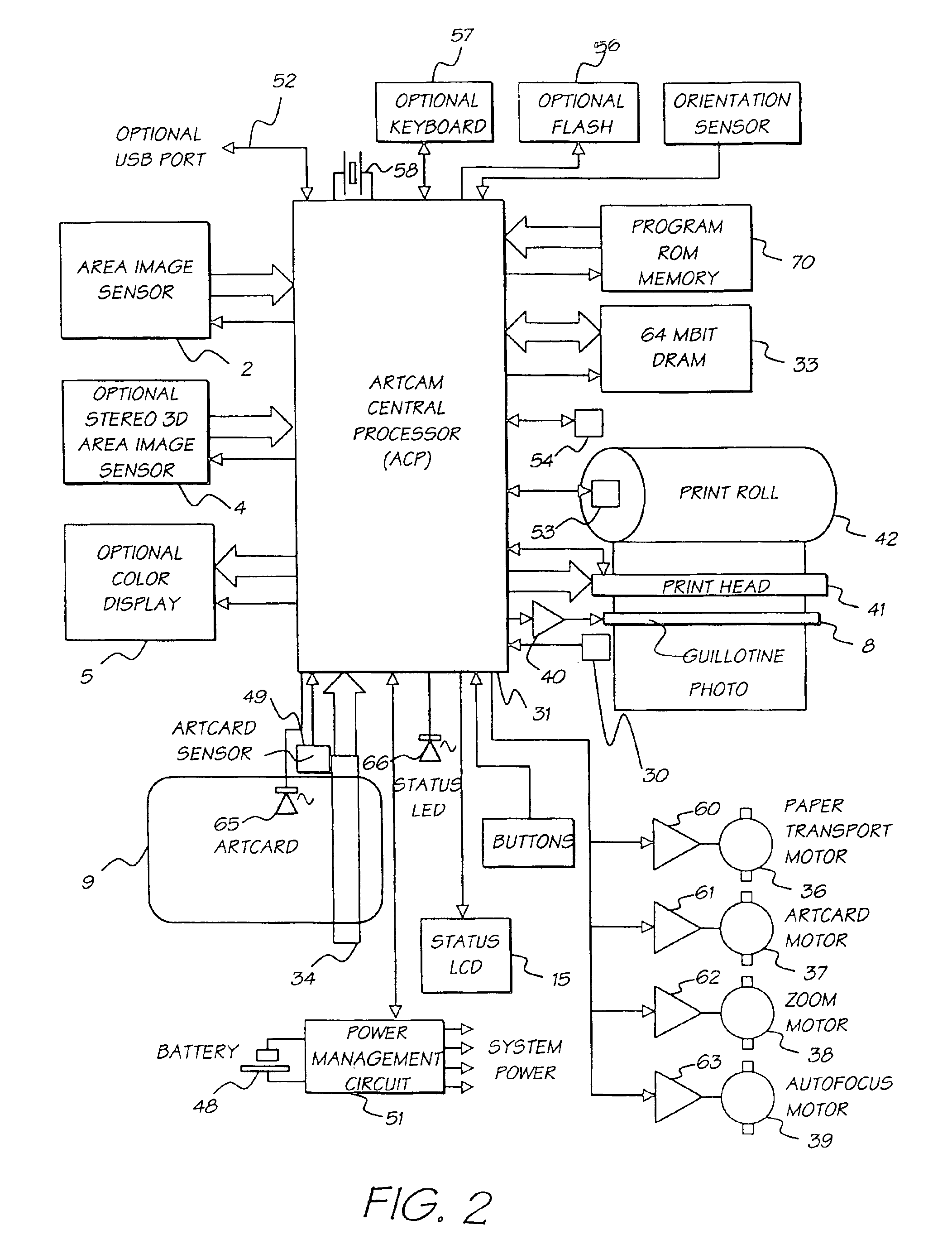
Digital camera system containing a VLIW vector processor
InactiveUS6879341B1Material nanotechnologyTelevision system detailsCrossbar switchArithmetic logic unit
A digital camera has a sensor for sensing an image, a processor for modifying the sensed image in accordance with instructions input into the camera and an output for outputting the modified image where the processor includes a series of processing elements arranged around a central crossbar switch. The processing elements include an Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) acting under the control of a writeable microcode store, an internal input and output FIFO for storing pixel data to be processed by the processing elements and the processor is interconnected to a read and write FIFO for reading and writing pixel data of images to the processor. Each of the processing elements can be arranged in a ring and each element is also separately connected to its nearest neighbors. The ALU receives a series of inputs interconnected via an internal crossbar switch to a series of core processing units within the ALU and includes a number of internal registers for the storage of temporary data. The core processing units can include at least one of a multiplier, an adder and a barrel shifter. The processing elements are further connected to a common data bus for the transfer of a pixel data to the processing elements and the data bus is interconnected to a data cache which acts as an intermediate cache between the processing elements and a memory store for storing the images.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Semiconductor device and semiconductor signal processing apparatus
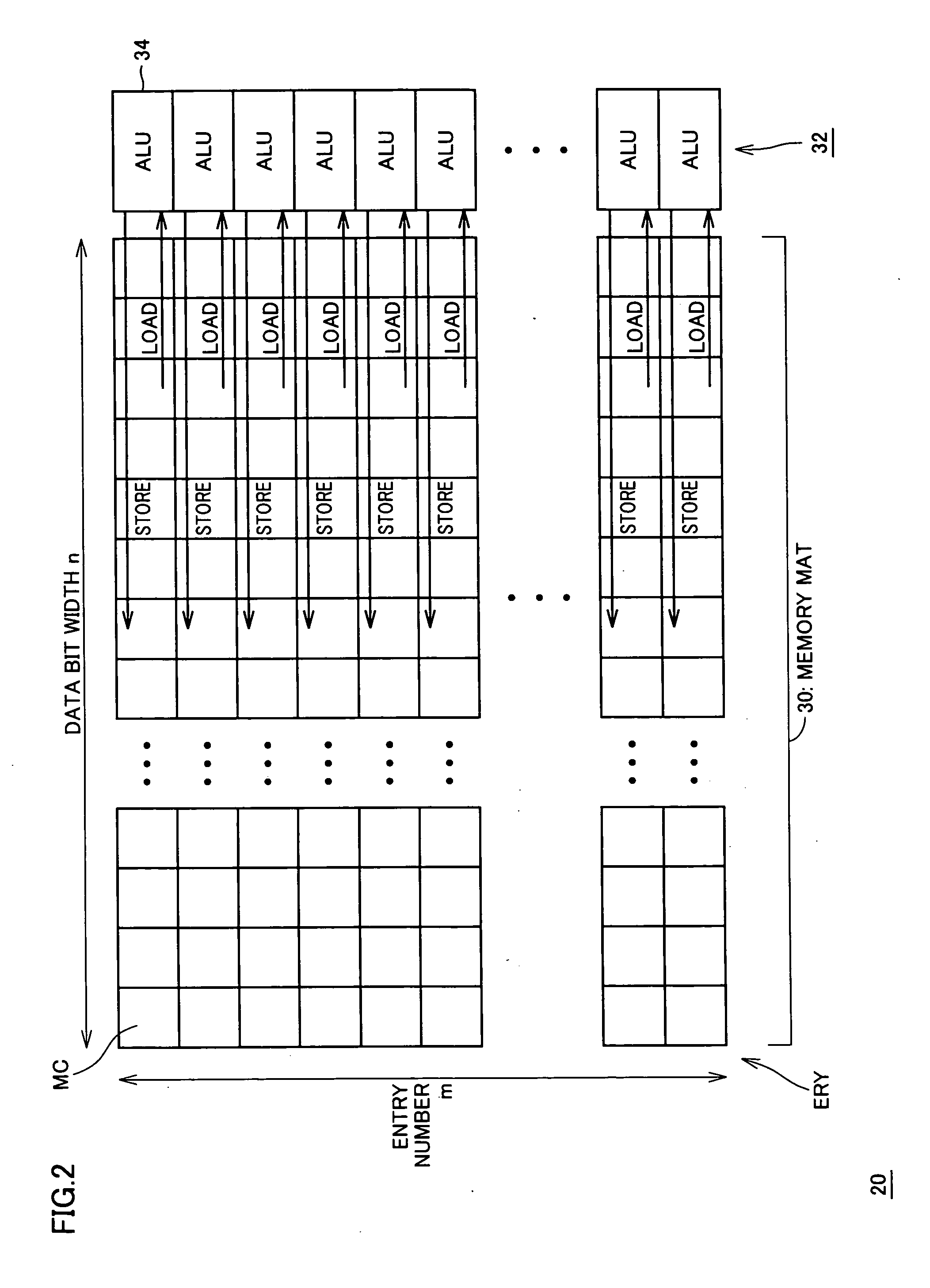
InactiveUS20050285862A1Operation control becomes easyEasy to processImage memory managementMultiple digital computer combinationsArithmetic logic unitDevice material
A memory cell mat is divided into a plurality of entries, and an arithmetic logic unit is arranged corresponding to each entry. Between the entries and the corresponding arithmetic logic units, arithmetic / logic operation is executed in bit-serial and entry-parallel manner. Where parallel operation is not very effective, data is transferred in entry-serial and bit-parallel manner to a group of processors provided at a lower portion of the memory mat. In this manner, a large amount of data can be processed at high speed regardless of the contents of operation or data bit width.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Sequential and video access for non-volatile memory arrays
An array of non-volatile memory cells arranged in logical columns and logical rows, and associated circuitry to enable reading or writing one or more memory cells on a row in parallel. In some embodiments, the array of memory cells may include a phase change material. In some embodiments, the circuitry may include a write driver, a read driver, a sense amplifier, and circuitry to isolate the memory cells from the sense amplifier with extended refresh. In some embodiments, the circuitry may further include shift registers and one or more arithmetic logic units to provide a video memory.
Owner:OVONYX MEMORY TECH LLC
Processing system with interspersed processors and communication elements
ActiveUS20040030859A1Energy efficient ICTSingle instruction multiple data multiprocessorsArithmetic logic unitInstruction processing unit
A processing system comprising processors and the dynamically configurable communication elements coupled together in an interspersed arrangement. The processors each comprise at least one arithmetic logic unit, an instruction processing unit, and a plurality of processor ports. The dynamically configurable communication elements each comprise a plurality of communication ports, a first memory, and a routing engine. For each of the processors, the plurality of processor ports is configured for coupling to a first subset of the plurality of dynamically configurable communication elements. For each of the dynamically configurable communication elements, the plurality of communication ports comprises a first subset of communication ports configured for coupling to a subset of the plurality of processors and a second subset of communication ports configured for coupling to a second subset of the plurality of dynamically configurable communication elements.
Owner:COHERENT LOGIX
Time-division-multiplexing general neural network processor
ActiveCN105184366AImprove general performanceSolve overheadPhysical realisationArithmetic logic unitTime-division multiplexing
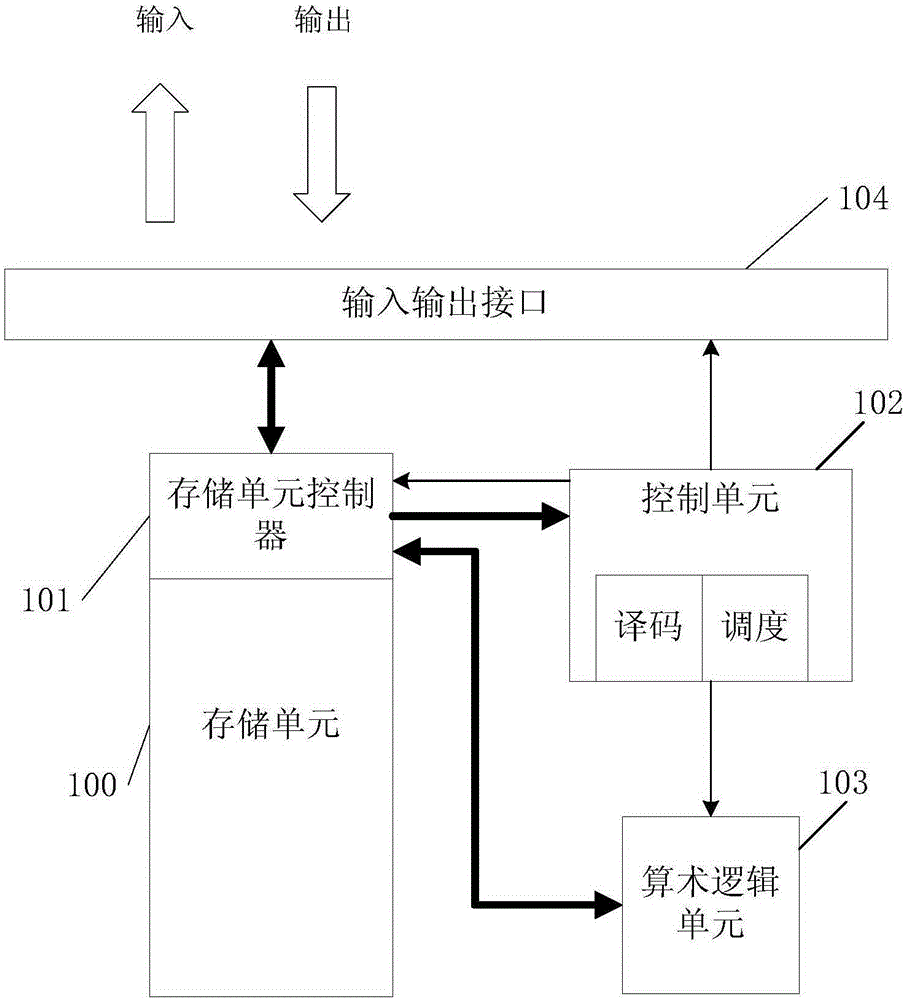
Provided in the invention is a time-division-multiplexing general neural network processor comprising at least one storage unit (100), at least one storage unit controller (101), at least one arithmetic logic unit (103), and a control unit (102). To be specific, the at least one storage unit (100) is used for storing an instruction and data. The at least one storage unit controller (101) corresponds to the at least one storage unit (100) and accesses the corresponding storage unit (100). The at least one arithmetic logic unit (103) is used for executing neural network computing. The control unit (102) connected with the at least one storage unit controller (101) and the at least one arithmetic logic unit (103) can obtain the instruction stored by the at least one storage unit (100) by the at least one storage unit controller (101) and parse the instruction to control the at least one arithmetic logic unit (103) to execute computation. The provided general neural network processor with high universality is suitable for computation of a large-scale neural network.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
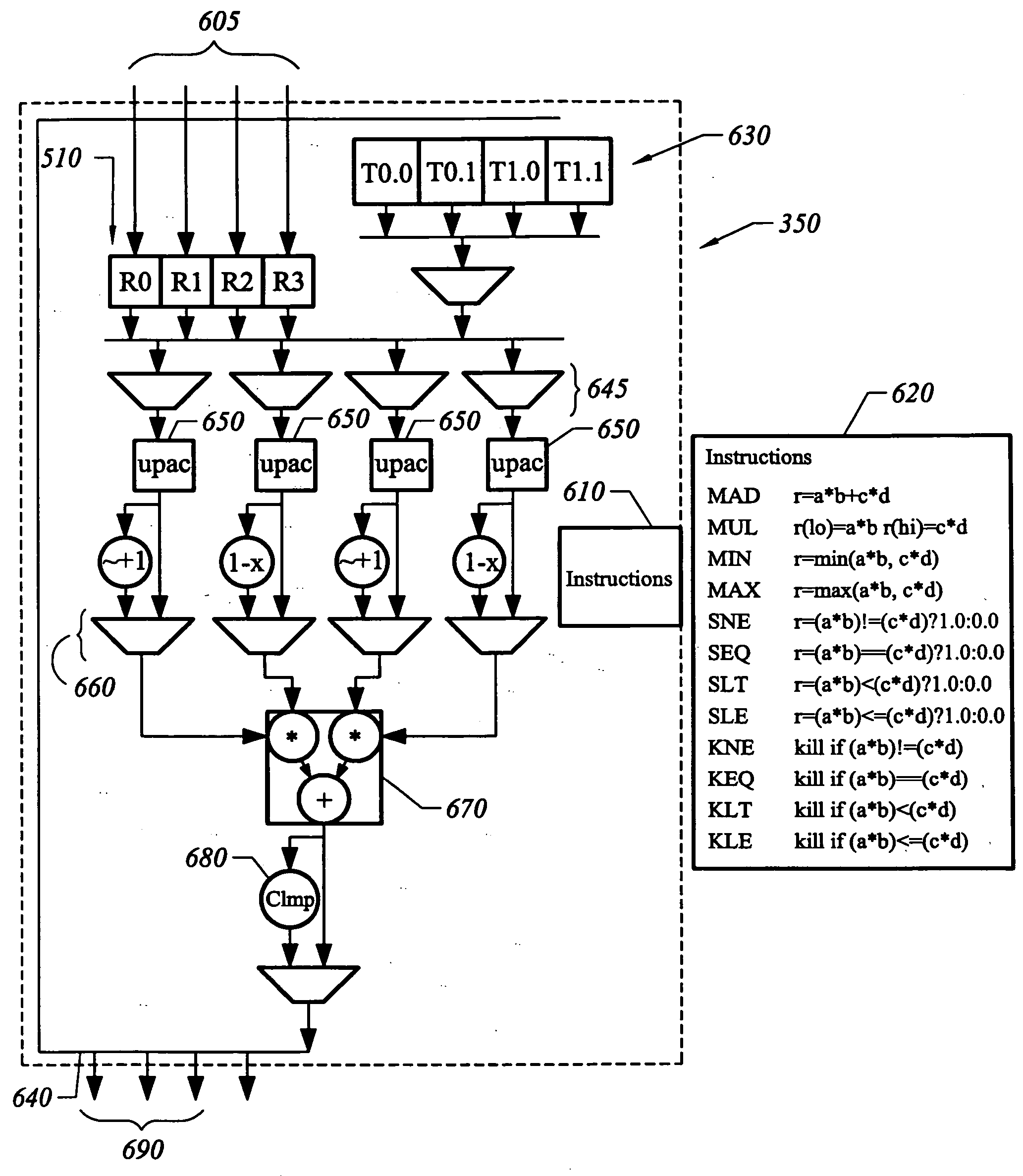
Graphics processing logic with variable arithmetic logic unit control and method therefor
Briefly, graphics data processing logic includes a plurality of parallel arithmetic logic units (ALUs), such as floating point processors or any other suitable logic, that operate as a vector processor on at least one of pixel data and vertex data (or both) and a programmable storage element that contains data representing which of the plurality of arithmetic logic units are not to receive data for processing. The graphics data processing logic also includes parallel ALU data packing logic that is operatively coupled to the plurality of arithmetic logic processing units and to the programmable storage element to pack data only for the plurality of arithmetic logic units identified by the data in the programmable storage element as being enabled.
Owner:ATI TECH INC
Method for operating low power programmable processor
ActiveUS20060152519A1General purpose stored program computerCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputational scienceGraphics
A graphics processor is disclosed having a programmable Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) stage for processing pixel packets. Scalar arithmetic operations are performed in the ALUs to implement a graphics function.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
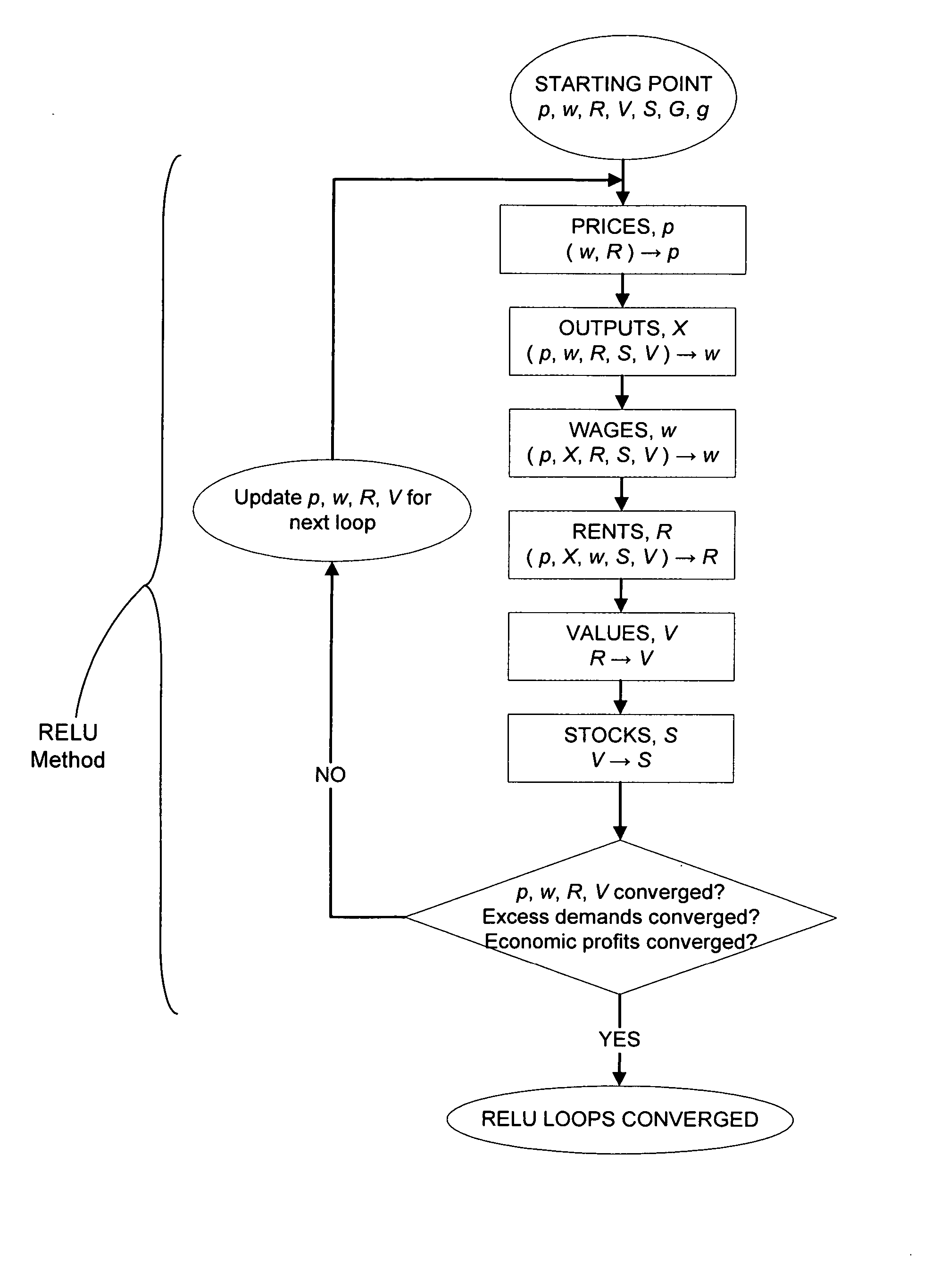
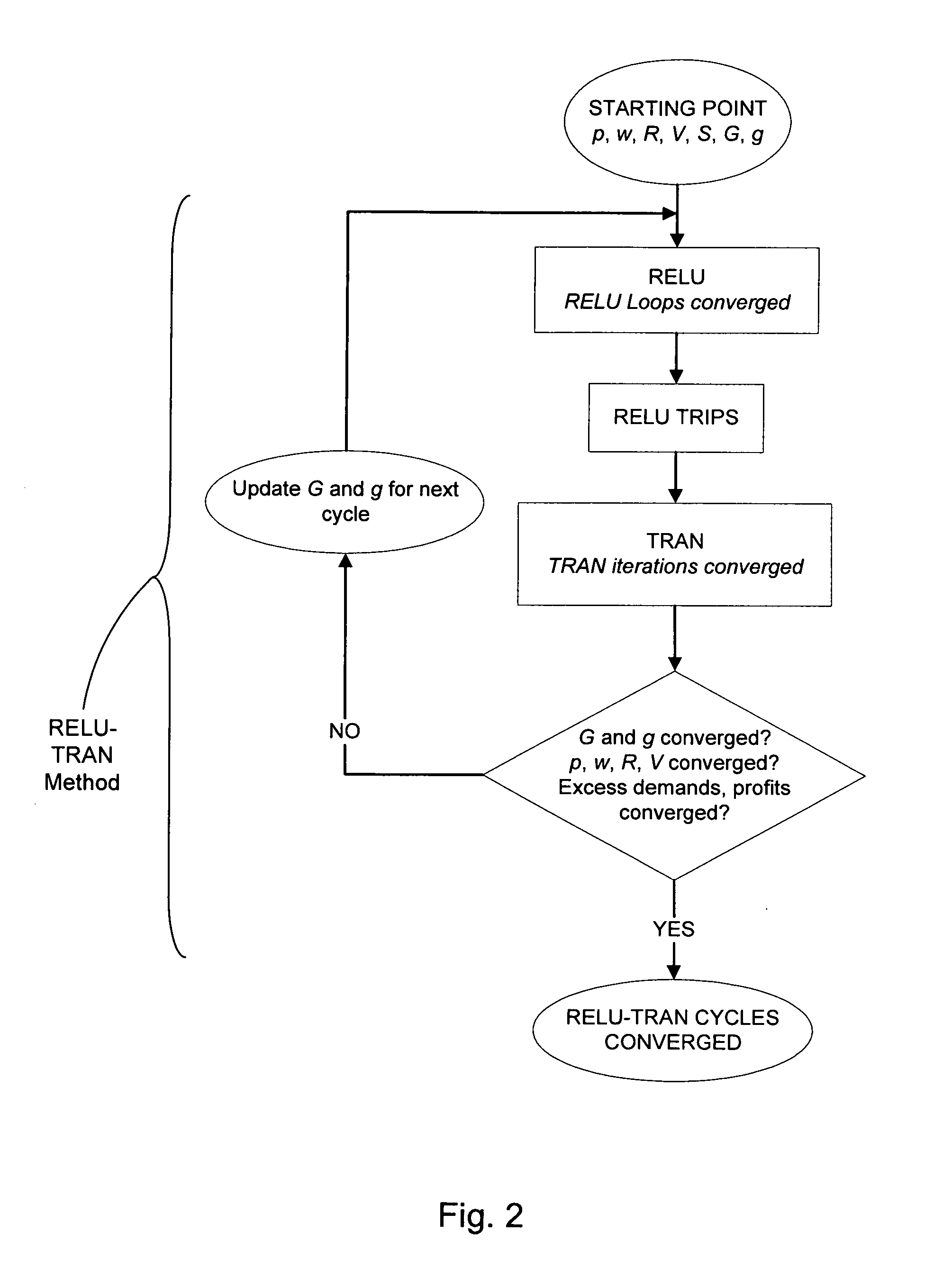
Computer based system to generate data for implementing regional and metropolitan economic, land use and transportation planning
The present invention comprises a method for forecasting future economic conditions, land utilization and transportation network utilization and performance of a metropolitan area having a plurality of economic zones, the method includes the steps of: a) receiving a set of calibration values from a first input device; b) calculating a set of calibration constants with a first arithmetic logic unit; c) receiving a set of initial values for a set of desired outputs from a second input device, wherein the set of desired outputs includes regional economic, land use and transportation outputs; d) calculating the regional economic and land use outputs with a second arithmetic logic unit, wherein the regional economic and land use outputs include a first group of variable travel demands; e) calculating an origin to destination matrix with a third arithmetic logic unit, wherein the origin to destination matrix includes two-way daily person trips between an origin economic zone and a destination economic zone; f) calculating the transportation outputs with a fourth arithmetic logic unit, wherein the transportation outputs include a second group of variable travel demands; h) repeating steps d) through f) until the first group of variable travel demands is substantially the same as the second group of variable travel demands; and, g) providing the set of desired outputs to an output device.
Owner:ANAS ALEX
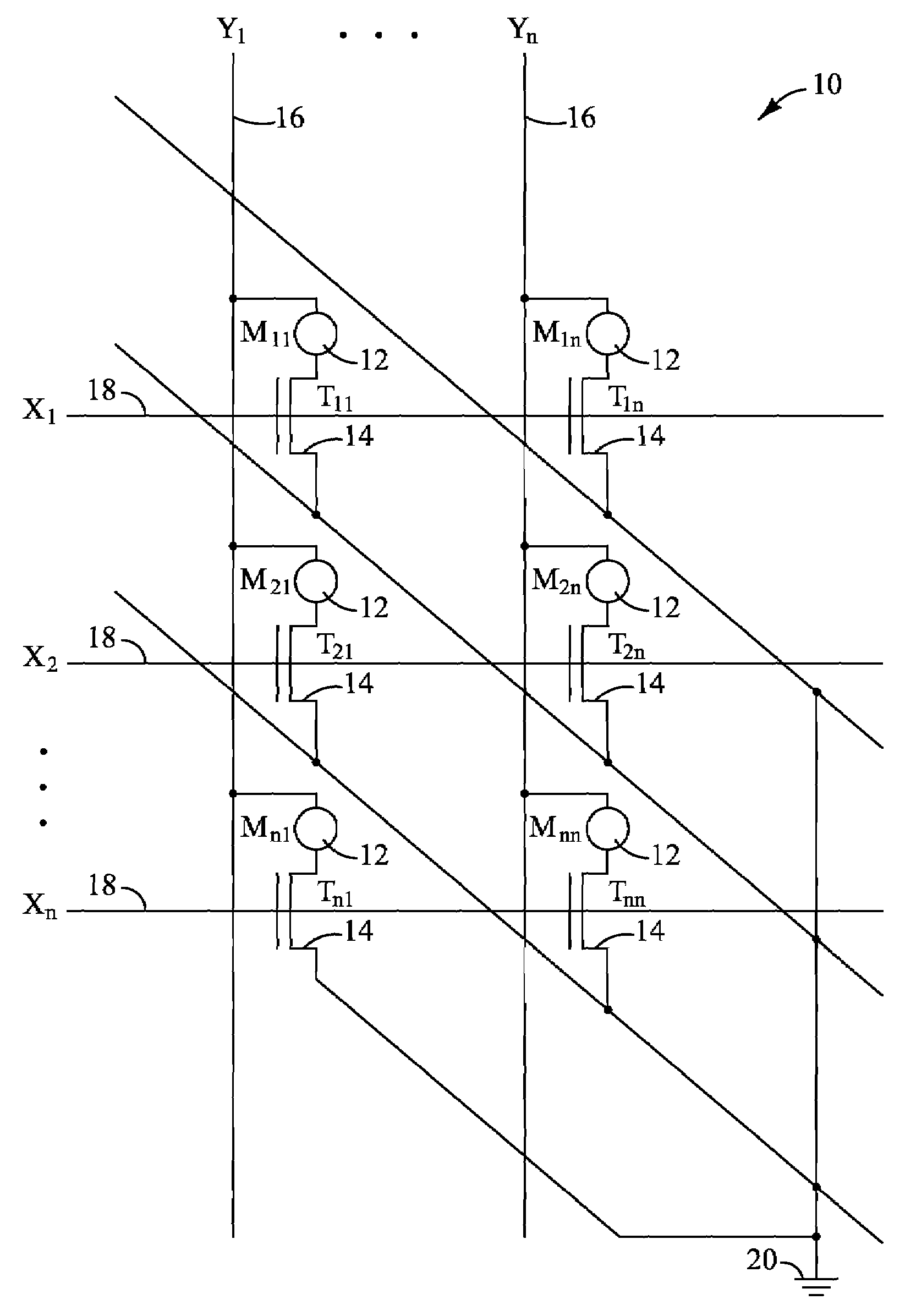
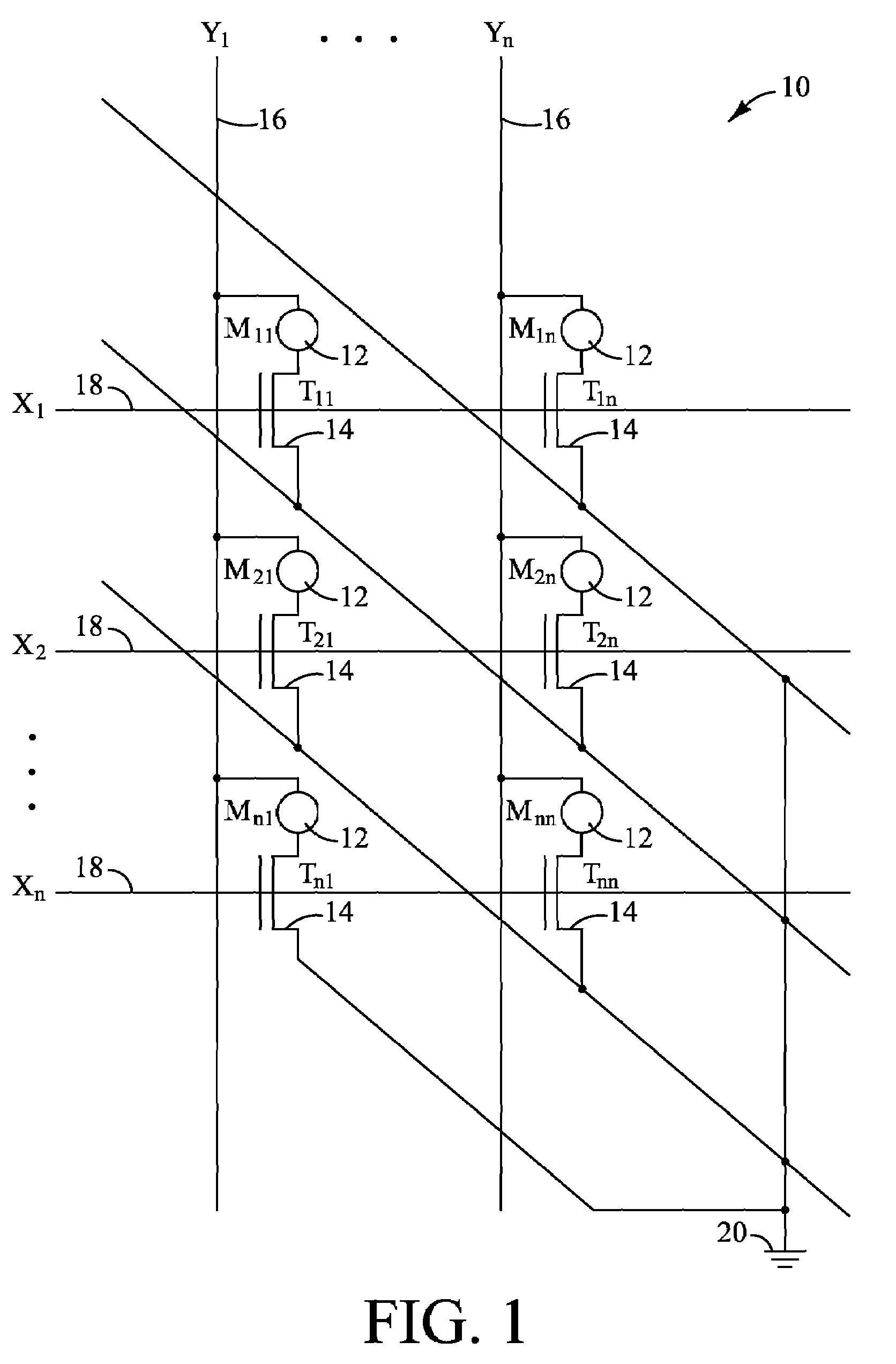
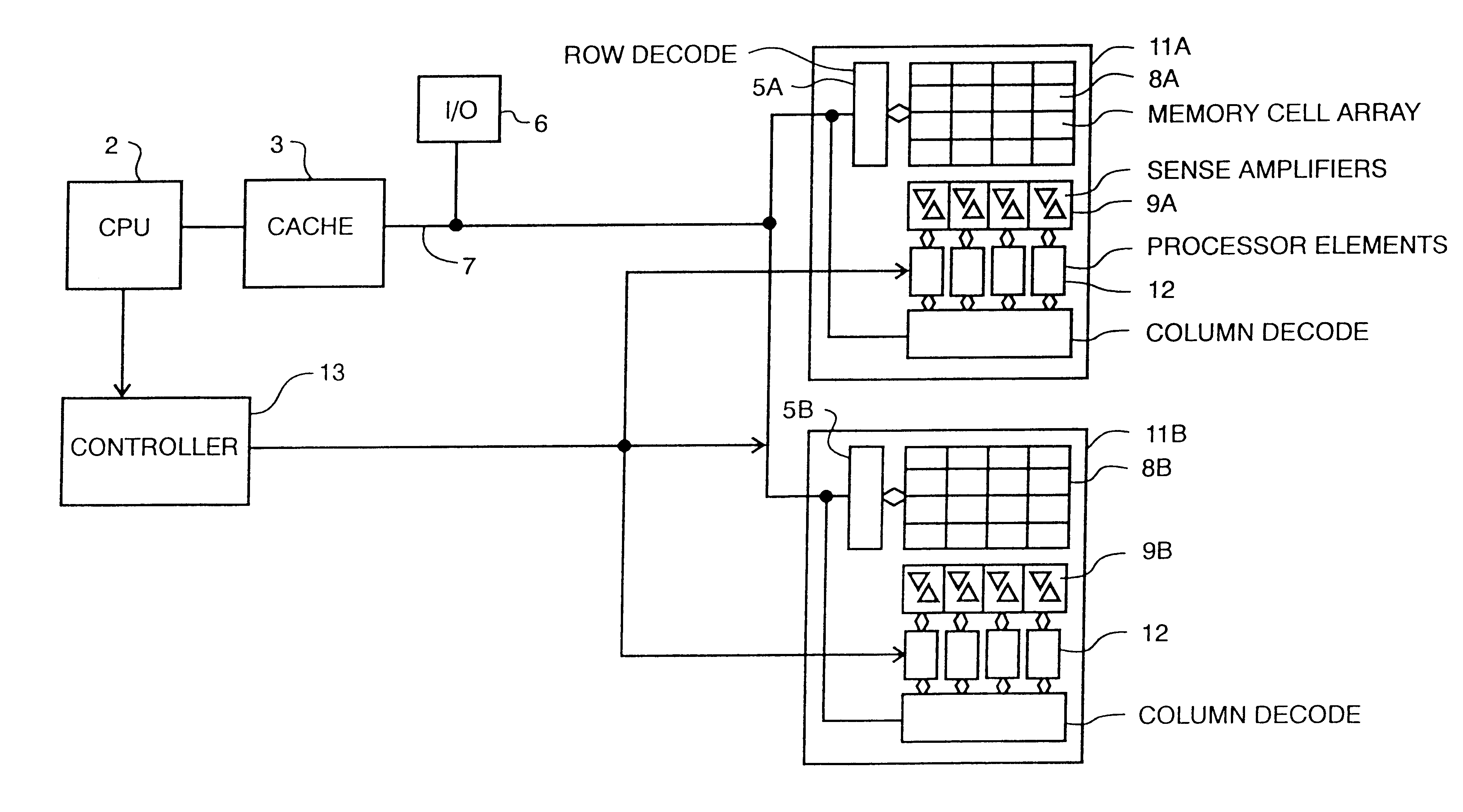
Memory device with multiple processors having parallel access to the same memory area
InactiveUS6279088B1Energy efficient ICTOperational speed enhancementArithmetic logic unitRead-modify-write
A digital computer performs read-modify-write (RMW) processing on each bit of a row of memory in parallel, in one operation cycle, comprising: (a) addressing a memory, (b) reading each bit of a row of data from the memory in parallel, (c) performing the same computational operation on each bit of the data in parallel, using an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) in a dedicated processing element, and (d) writing the result of the operation back into the original memory location for each bit in the row.
Owner:SATECH GRP A B LLC
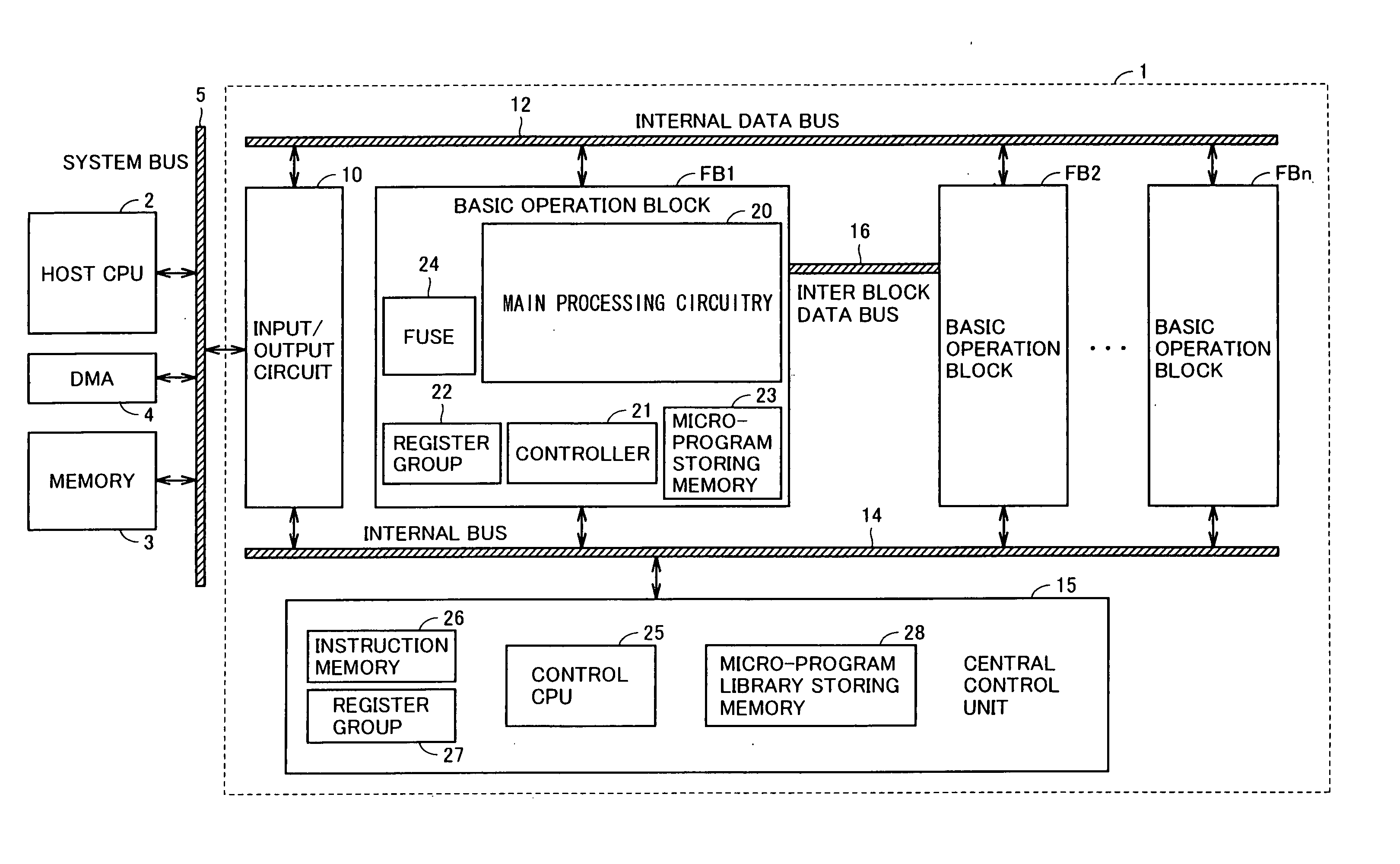
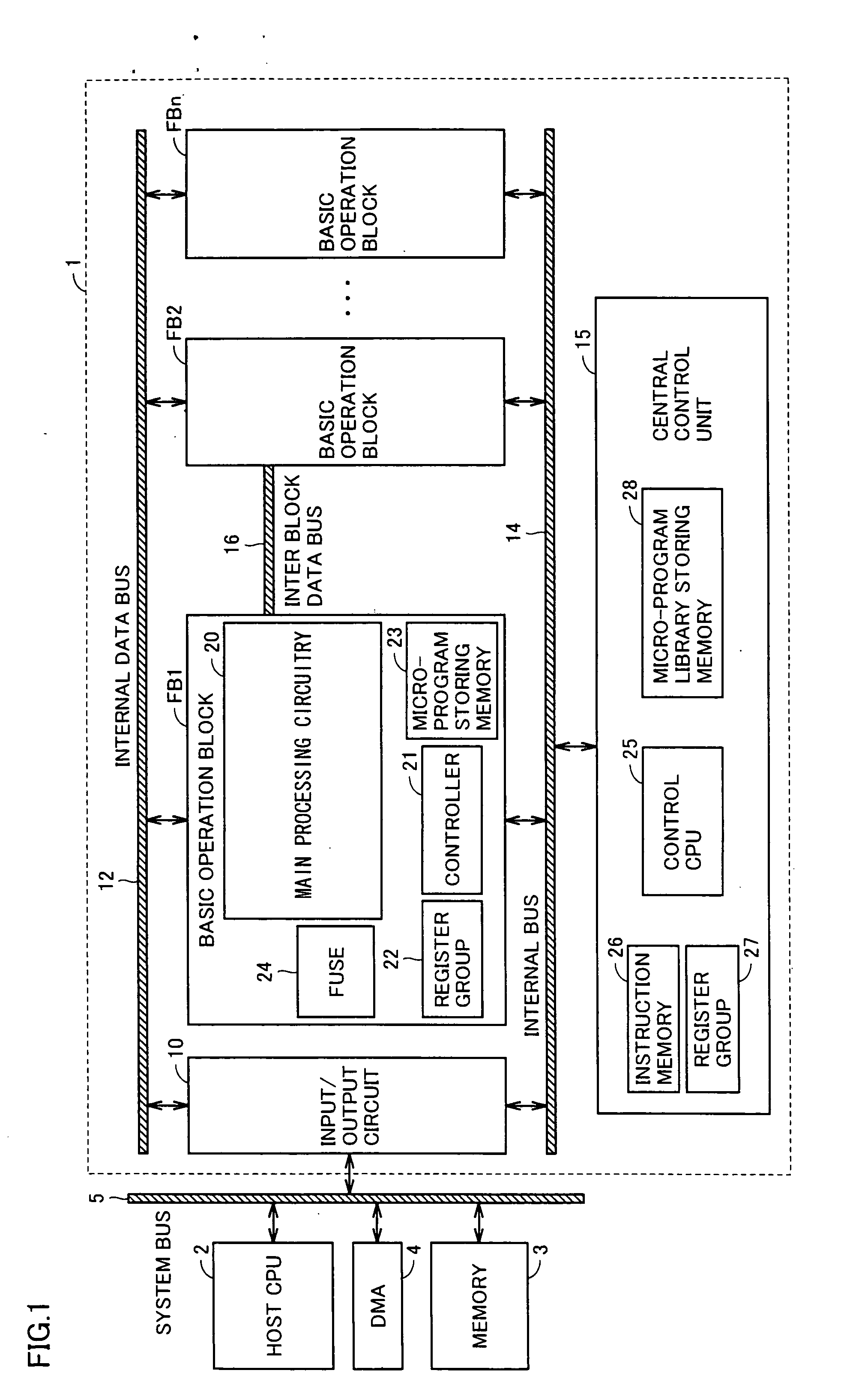
Long Instruction Word Controlling Plural Independent Processor Operations
InactiveUS20080077771A1Instruction analysisComputation using non-contact making devicesIntegrated circuitStatus register
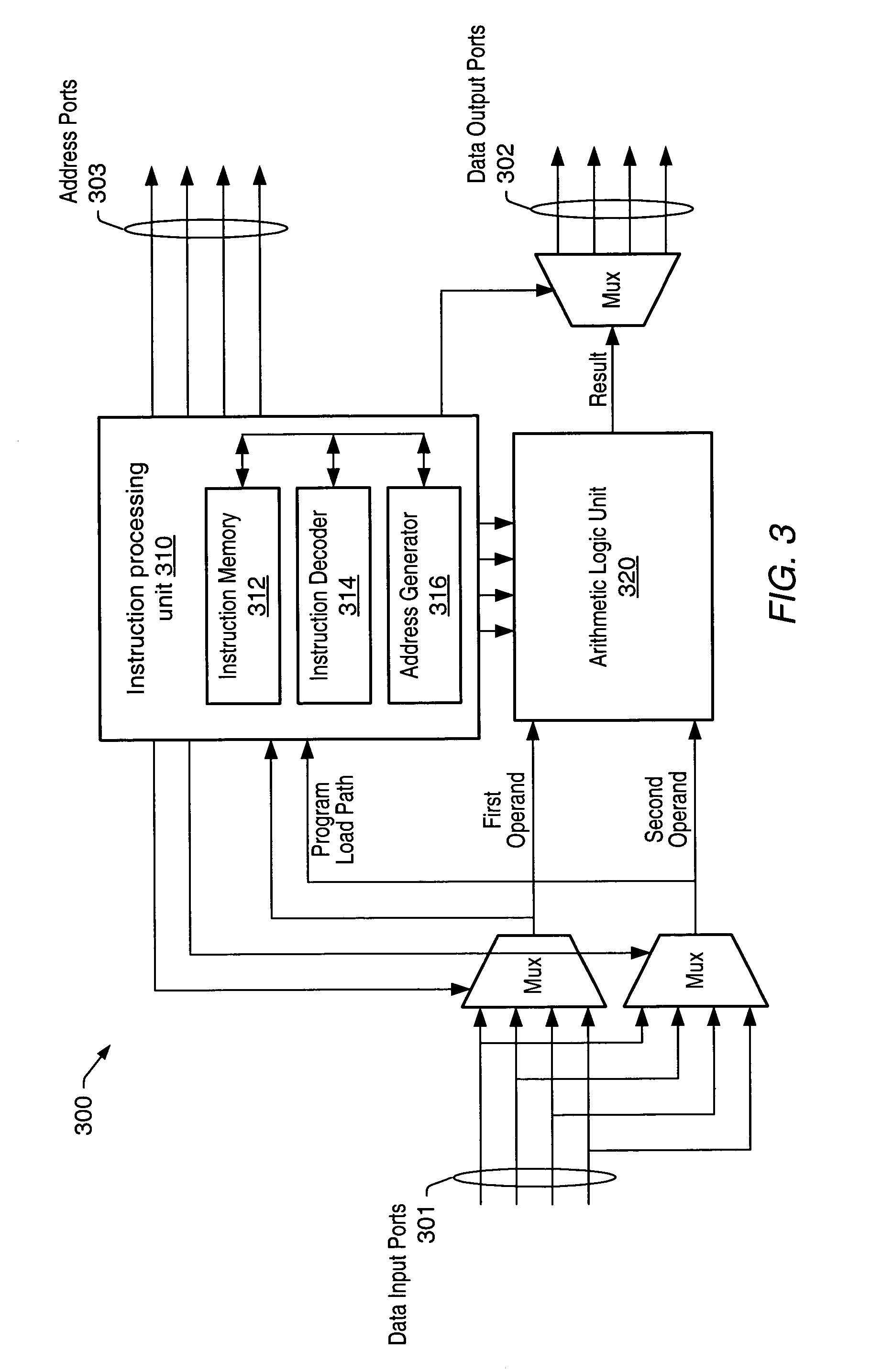
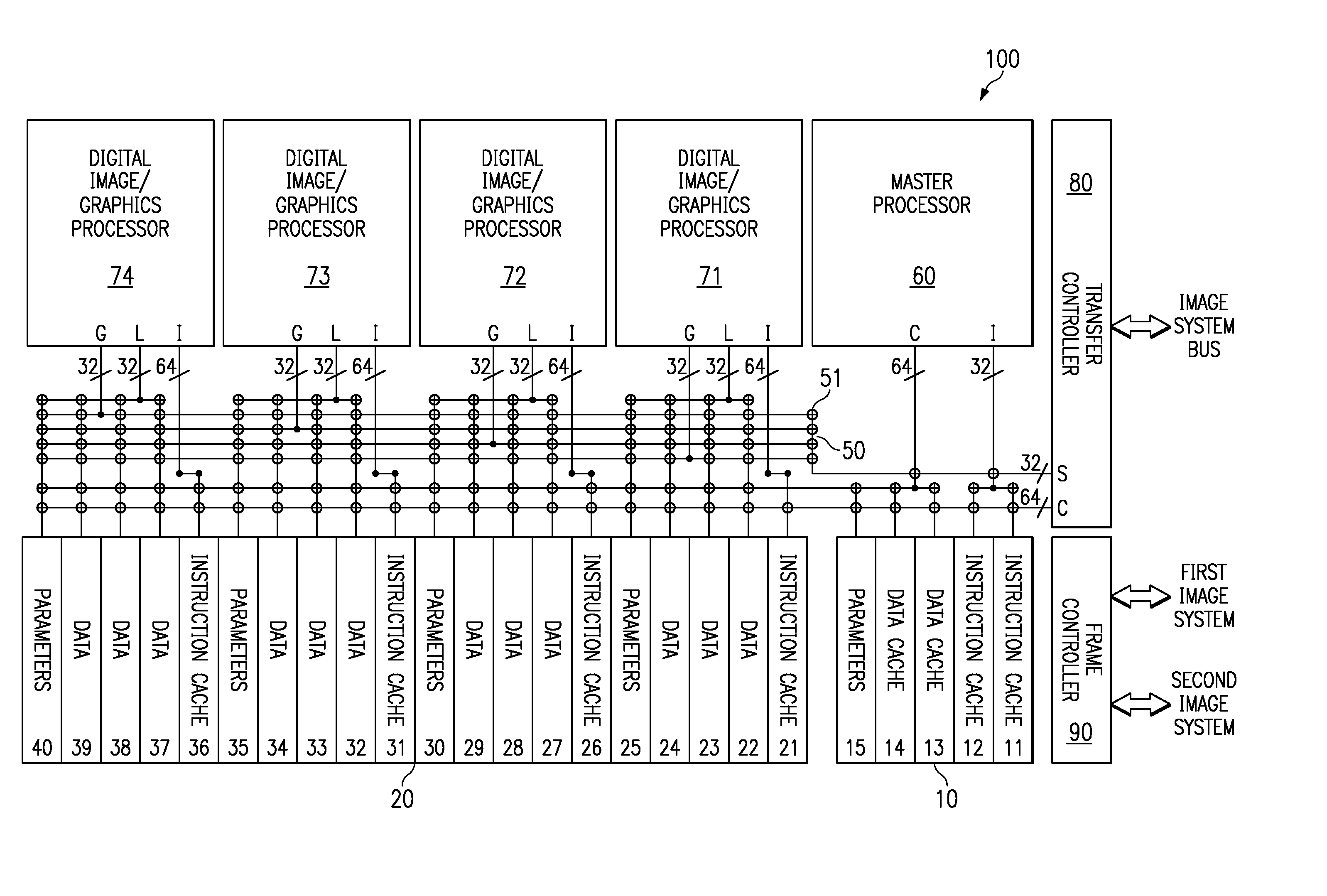
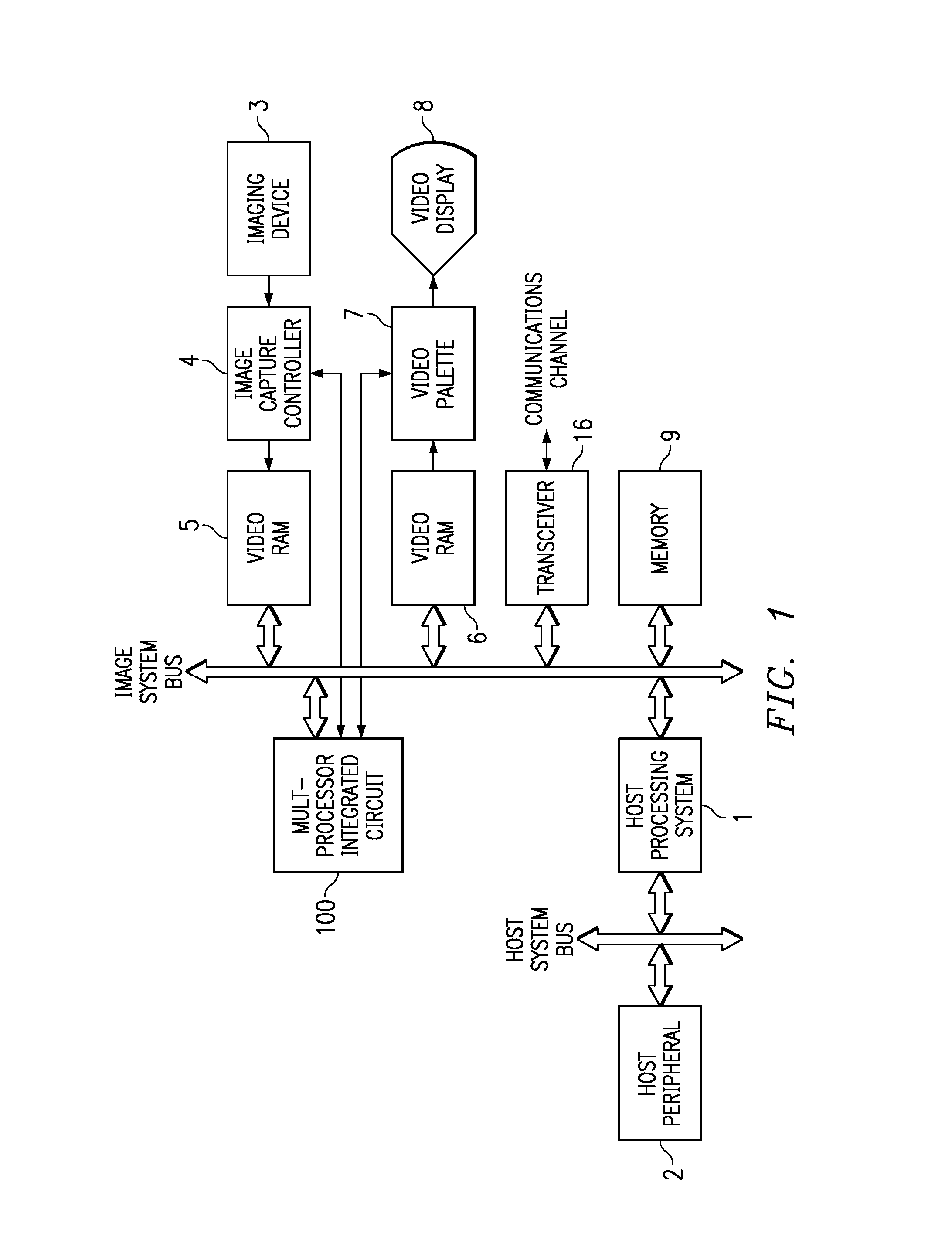
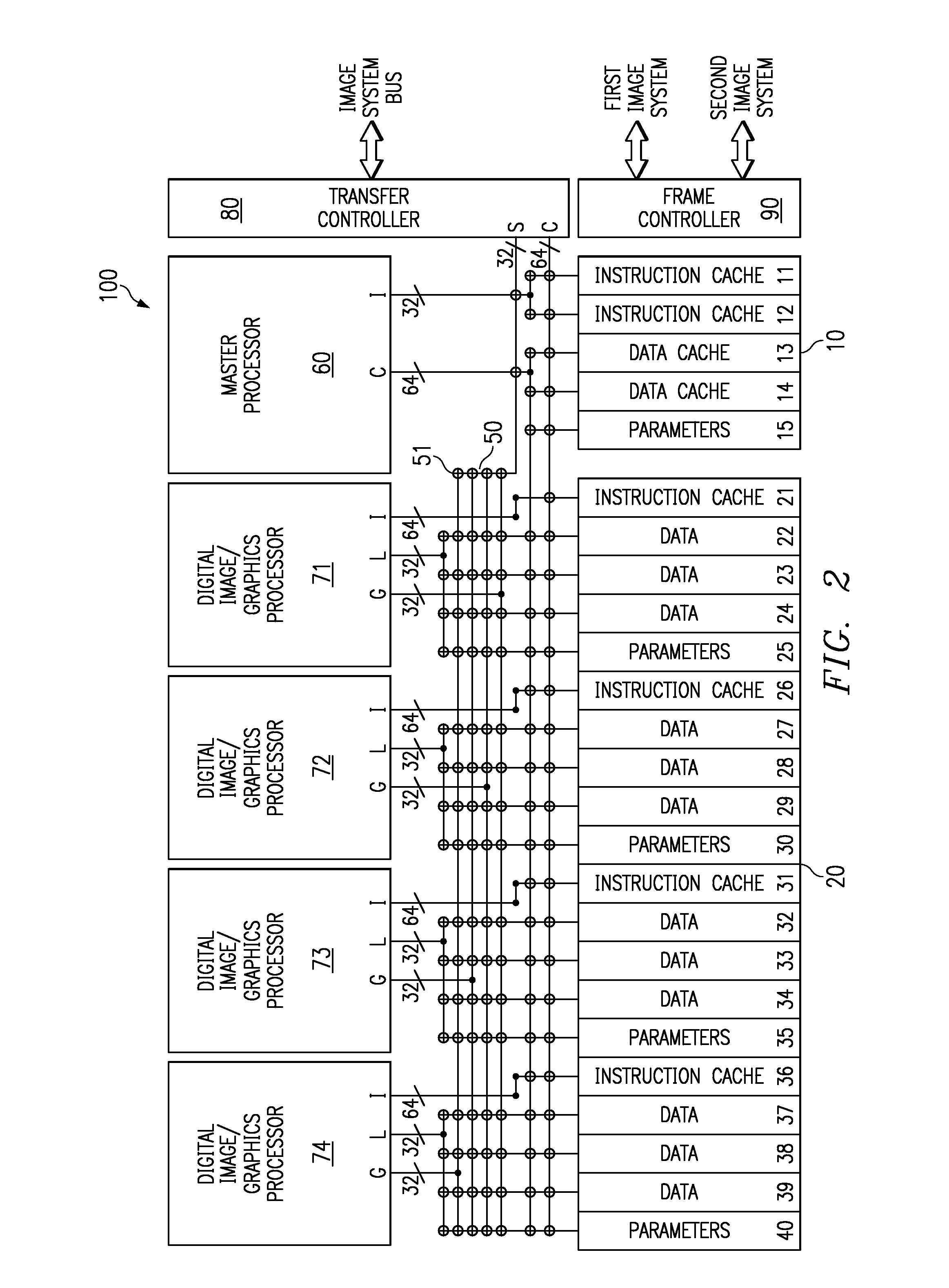
This invention is a data processing apparatus which operates on instruction controlling plural processor actions. Each instruction includes a data unit section and a data transfer section. These instruction sections are independent and may include differing options. In the preferred embodiment, each instruction is 64 bits. The data unit section includes a data operation field that indicates the type of arithmetic logic unit operation and six operand fields. The six operand fields include four source data register fields and two destination register fields. The data unit (110) includes a multiplication unit (220) and an arithmetic logic unit (230). The data unit (110) may include a barrel rotator (235) for one input of the arithmetic logic unit (230). The rotated data may be stored in the first destination register instead of the multiply result. The address unit (120) operations according to the data transfer operation field. This could be a load, a store or a register to register move. Operations may be conditional based upon conditions stored in a status register (210). The status register (210) is set by a prior output of the arithmetic logic unit (230) and the instruction may specify some of the status bits protect from change. The address unit (120) preferably includes a plurality of base address registers (611), a full adder (615) and a left shifter (614). The full adder (615) may add an index as scaled by the left shifter to the base address or subtract the scaled index from the base address. The full adder (615) output may update the base address register (611), either before supply of the address or following supply of the address. The index may be recalled from an index register (612) or an immediate value. In the preferred embodiment of this invention, the data unit (110) including the data registers (200), the multiplication unit (220) and the arithmetic logic unit (230), the address unit (120) and the instruction decode logic (250, 660) are embodied in at least one digital image / graphics processor (71, 72, 73, 74) as a part of a multiprocessor (100) formed in a single integrated circuit used in image processing.
Owner:GUTTAG KARLM +2
Method for implementing advanced encryption standards using a very long instruction word architecture processor
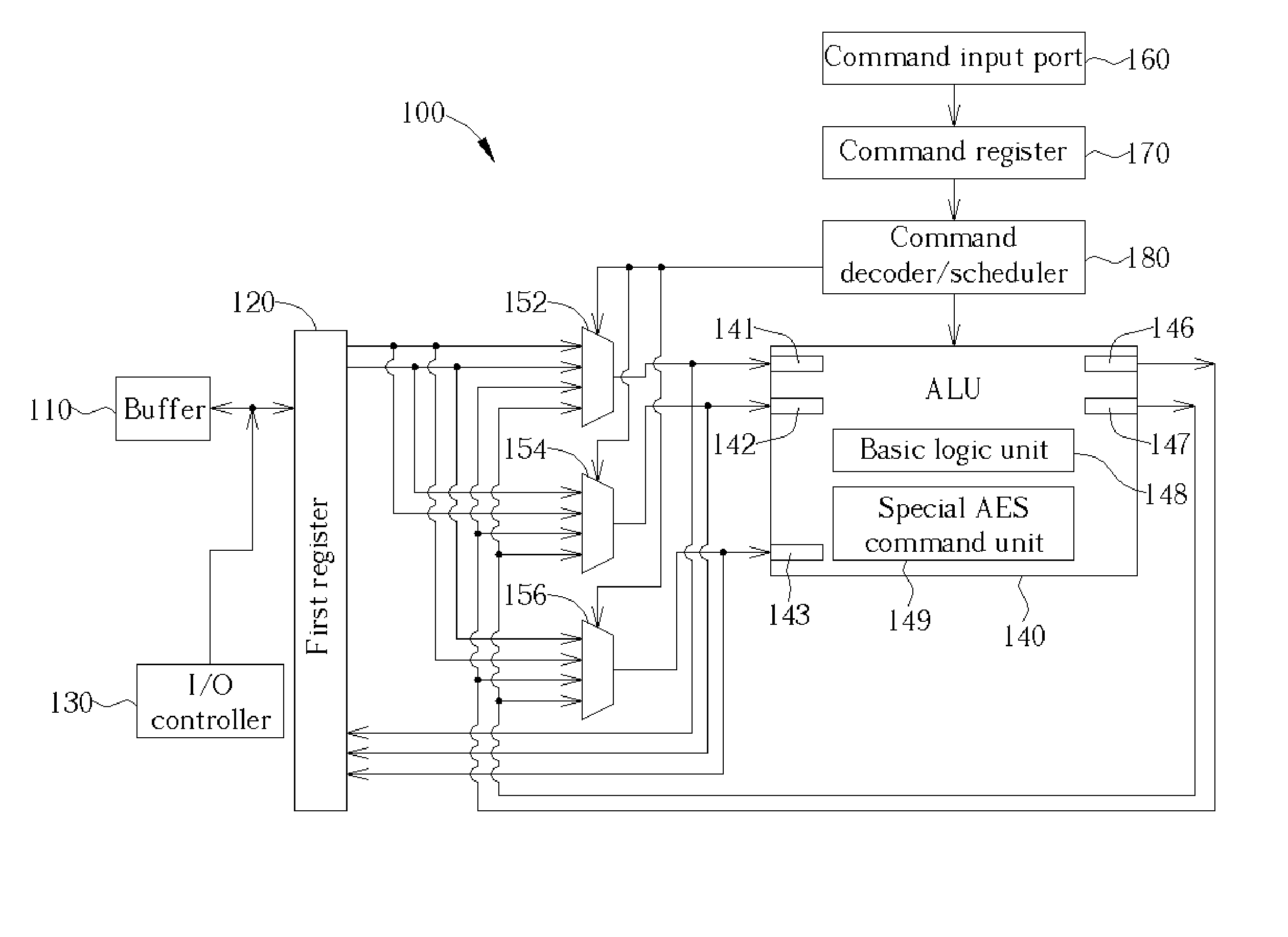
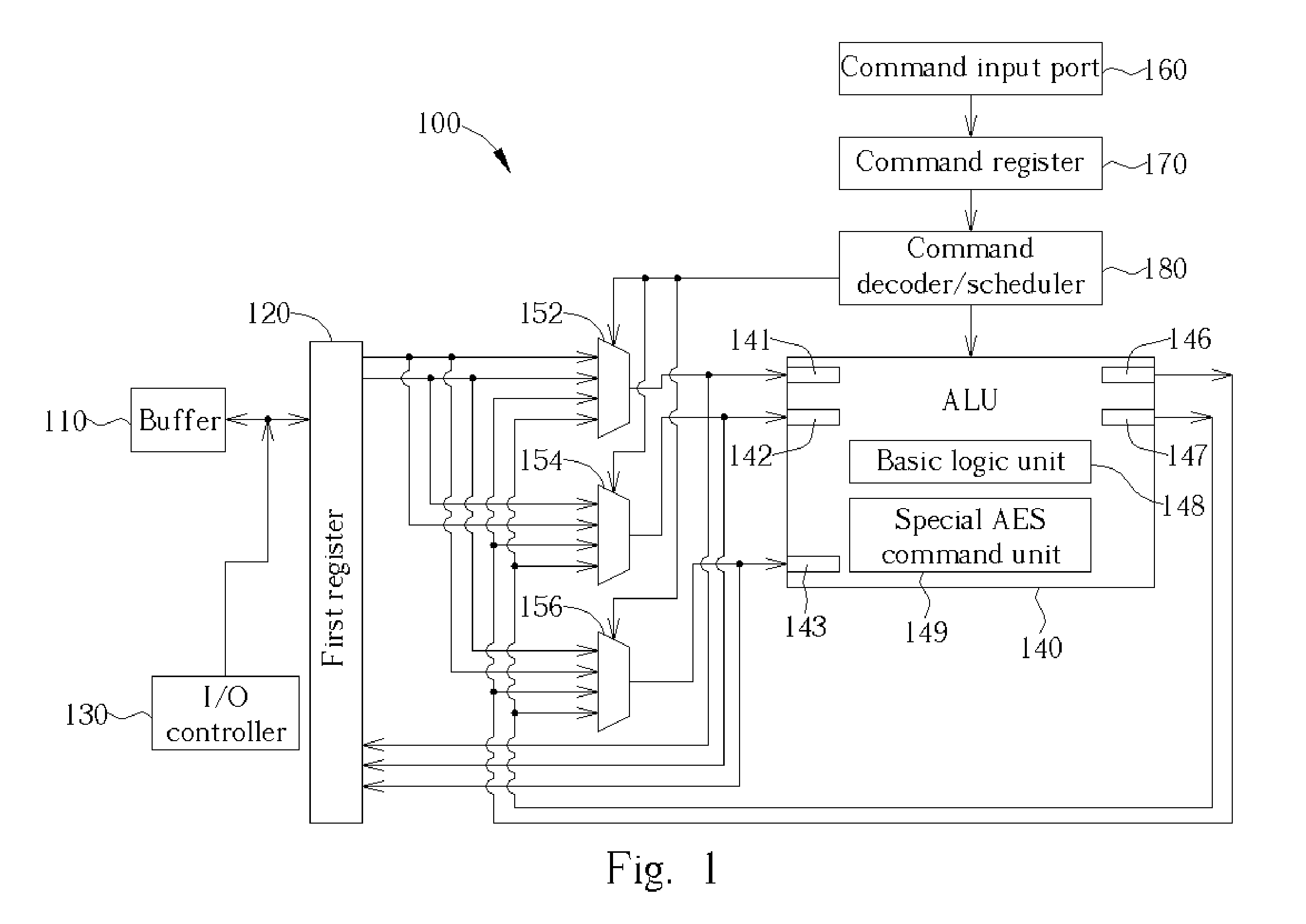
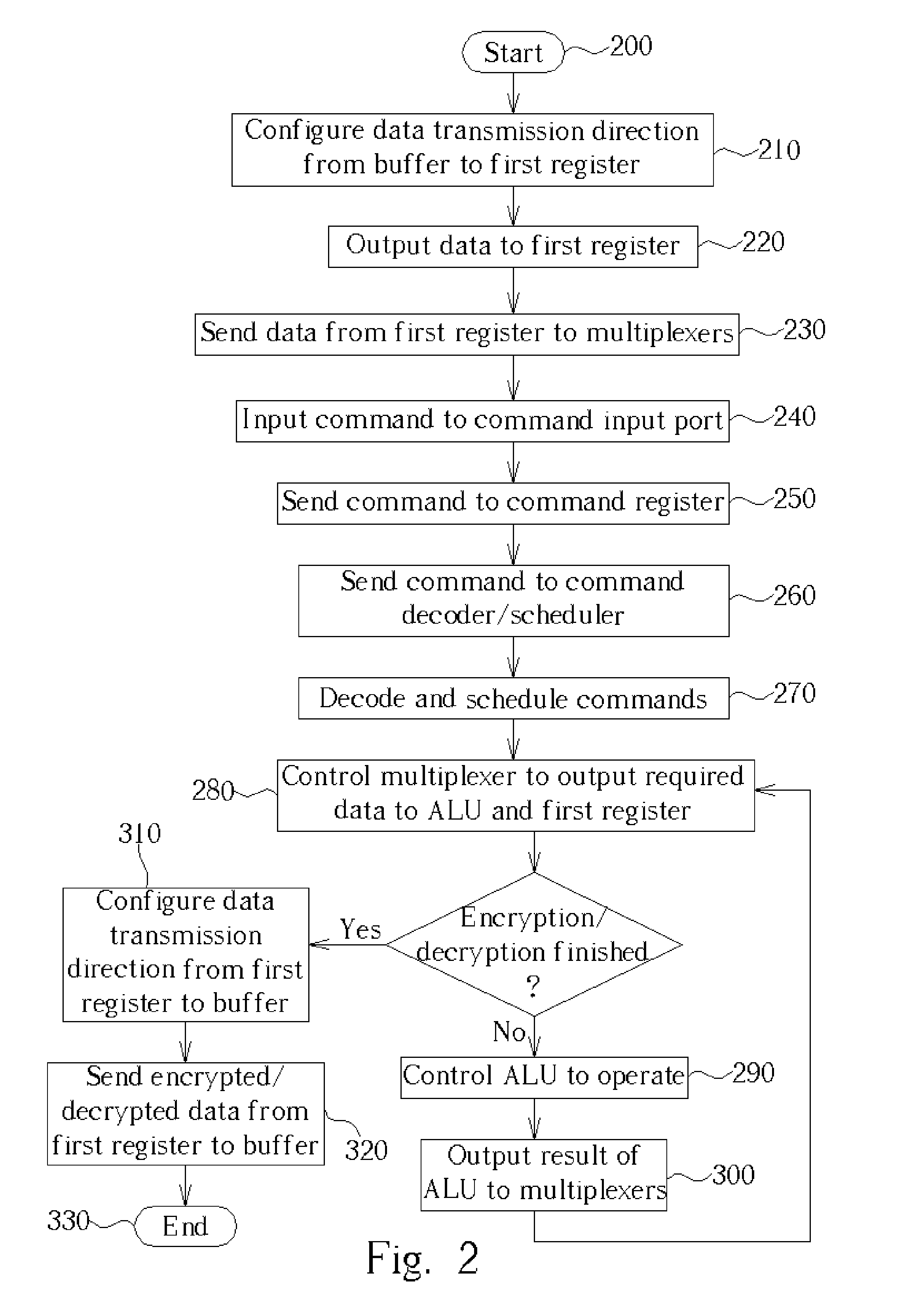
InactiveUS20050147239A1Encryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesInternal/peripheral component protectionArithmetic logic unitProcessor register
A method for implementing Advanced Encryption Standards (AES) by a very long instruction word (VLIW) architecture processor. The method includes inputting the instructions for AES into the processor, decoding and scheduling the input instructions, controlling at least one of a plurality of multiplexers to output data from a first register of the processor and / or an arithmetic logic unit to the first register and / or the arithmetic logic unit according to the decoded and scheduled instructions, controlling the arithmetic logic unit to perform operations, and outputting results of the operations to the plurality of the multiplexers.
Owner:ADMTEK INCORPORATED
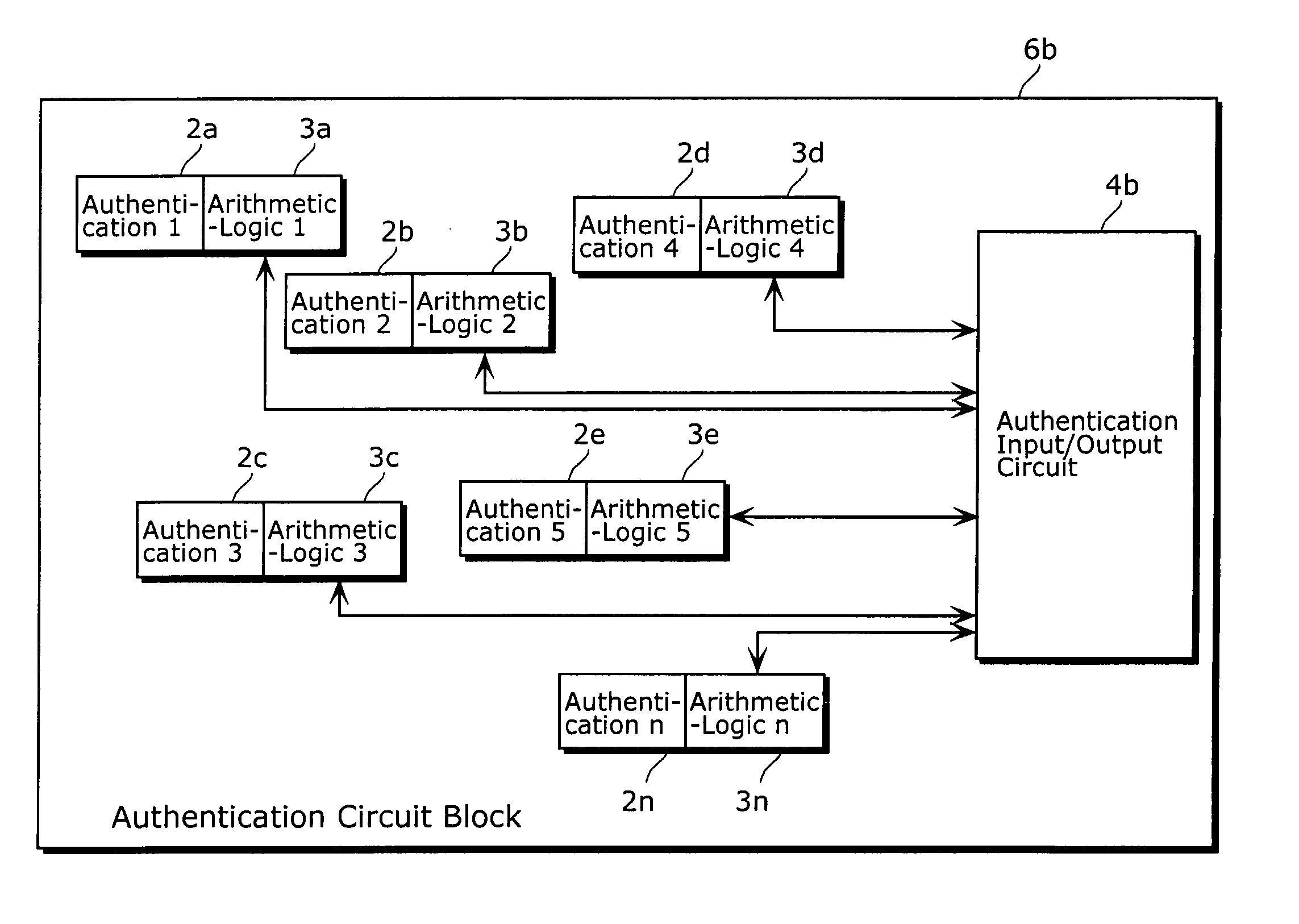
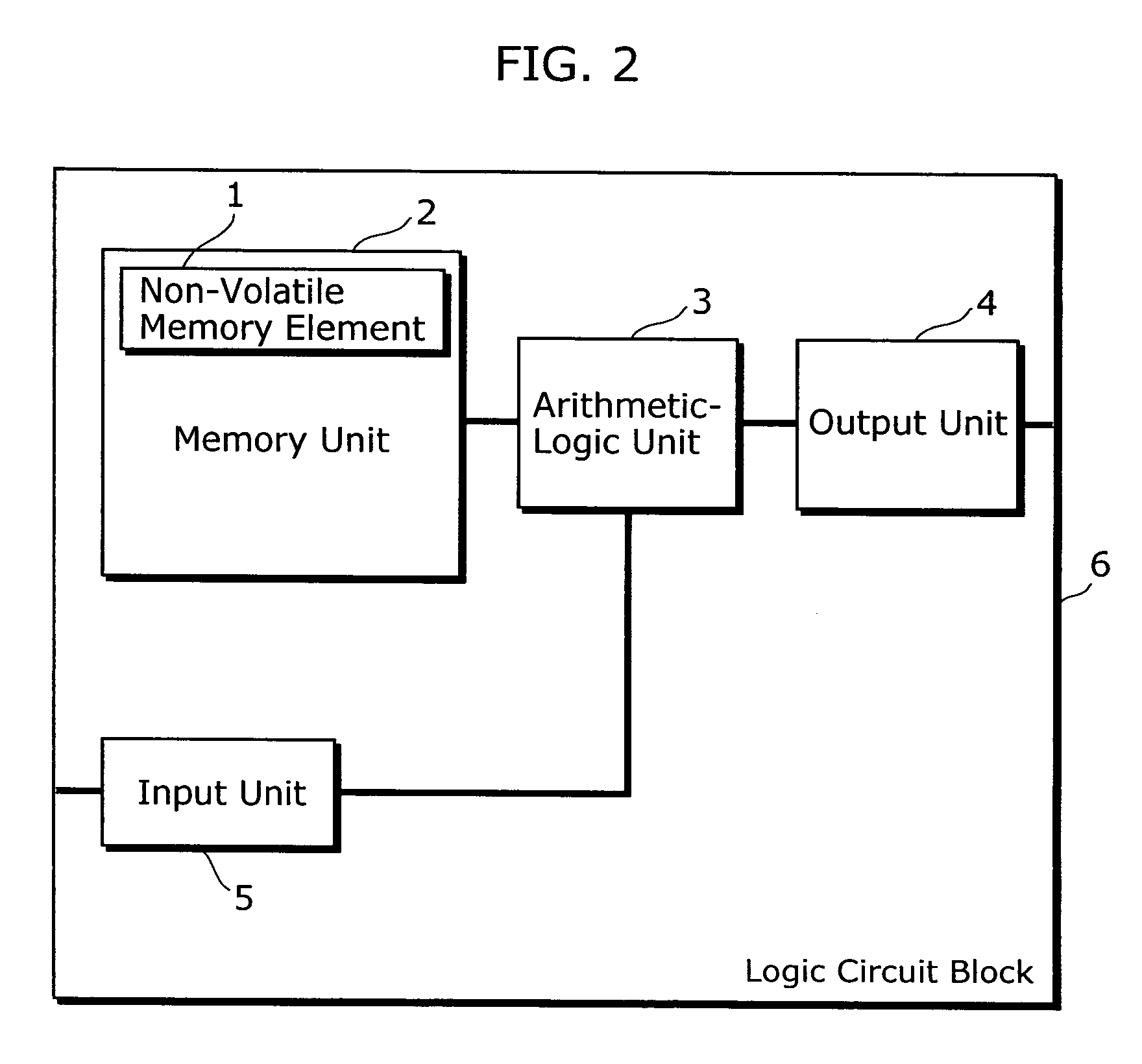
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20060095975A1Reduce riskIncrease speedDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationArithmetic logic unitDevice material
A semiconductor device of the present invention includes: at least one of non-volatile memory unit operable to store data; at least one of an arithmetic-logic unit operable to perform an arithmetic-logic operation using data which is stored in the memory unit and data that is inputted from outside; and an output unit operable to output a result of arithmetic-logic operation performed by the arithmetic-logic unit; wherein the memory unit, the arithmetic-logic unit, and the output unit are included in a functional block, and an output line of each of the memory unit is connected only to one of at least one of the arithmetic-logic unit.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
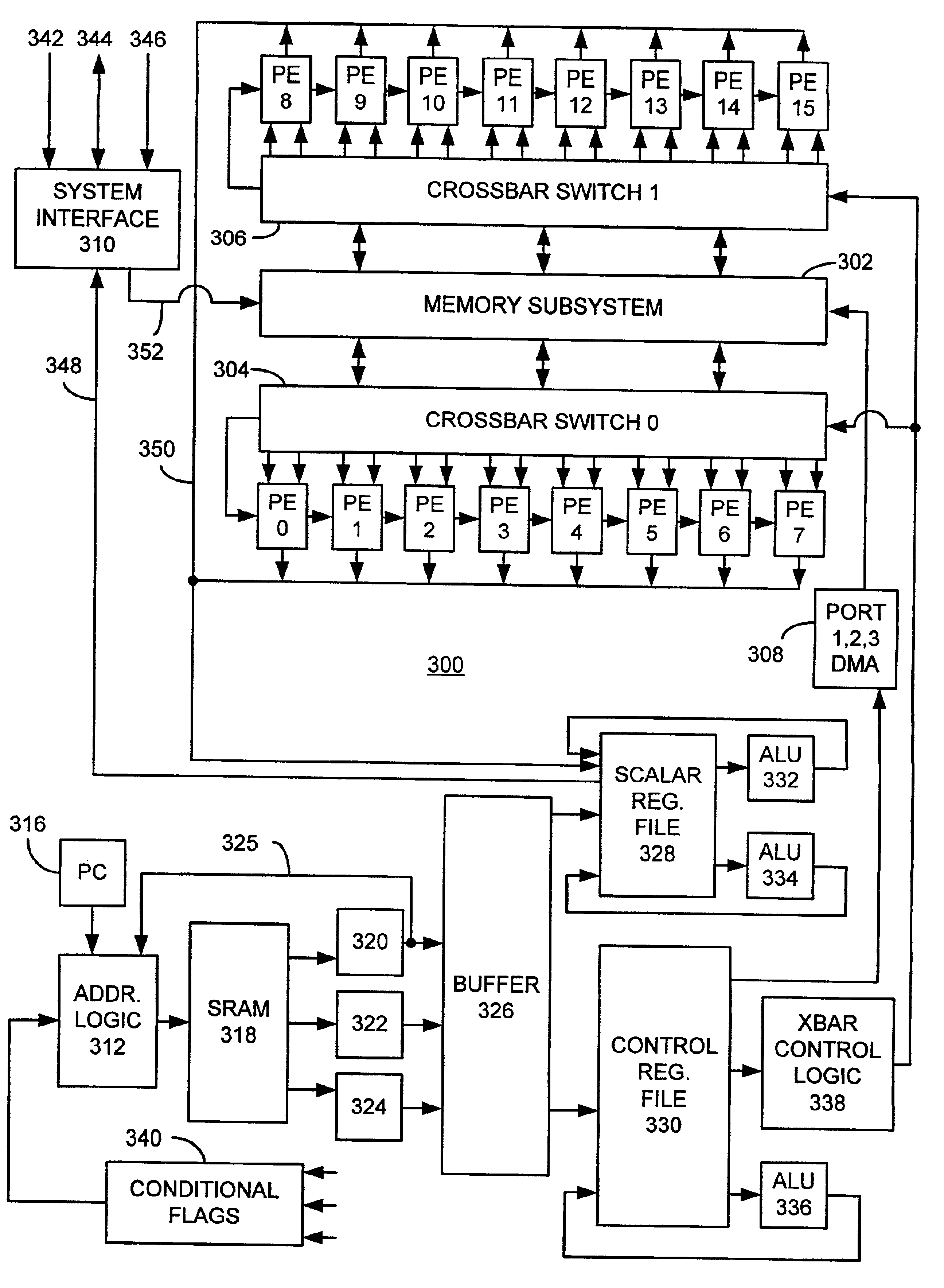
Programmable motion estimation module with vector array unit
InactiveUS6868123B2Reduce power consumptionTelevision system detailsImage enhancementDigital videoMicrocontroller
A programmable motion estimation module for processing pixel values from a sequence of digital video images. The module includes a programmable microcontroller, scalar and control register files, arithmetic logic units, a direct memory access unit and a vector array processor. The vector array processor includes a series of processing elements, a memory subsystem for storing pixel values and a crossbar switch for distributing pixel values from the memory subsystem to the processing elements. The module provides a flexible platform that can be programmed to implement a variety of different Motion Estimation (ME) algorithms using an associated Instruction Set Architecture without the need to modify the hardware.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
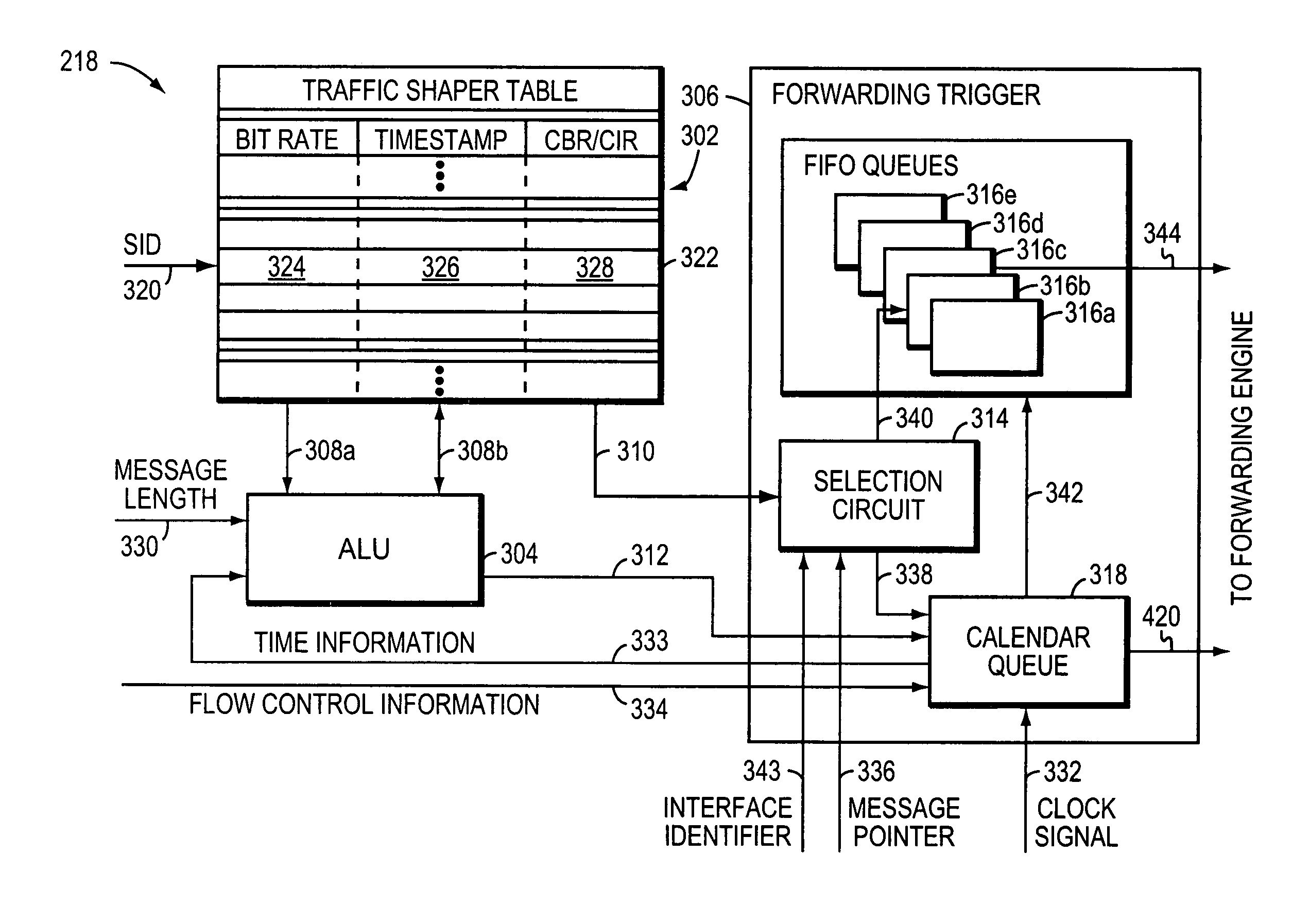
Method and apparatus for performing high-speed traffic shaping
A network traffic shaper for shapping transmission of network messages includes a system time generator for generating a system time, an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) for computing a transmission start time for each network message in response to the system time, and a retrieve time generator adapted to increment a retrieve time at a rate faster than the system time. As network messages are received, they are stored in a queue along with an associated transmission start time for each message. A forwarding trigger transmits a store network messages when its associated transmission start time matches the retrieve time. Alternately, a second transmission start time representing an excess bandwidth transmission start time may be computed for each network message. If excess bandwidth is detected, a message may be transmitted when its second transmission start time matches the retrieve time.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
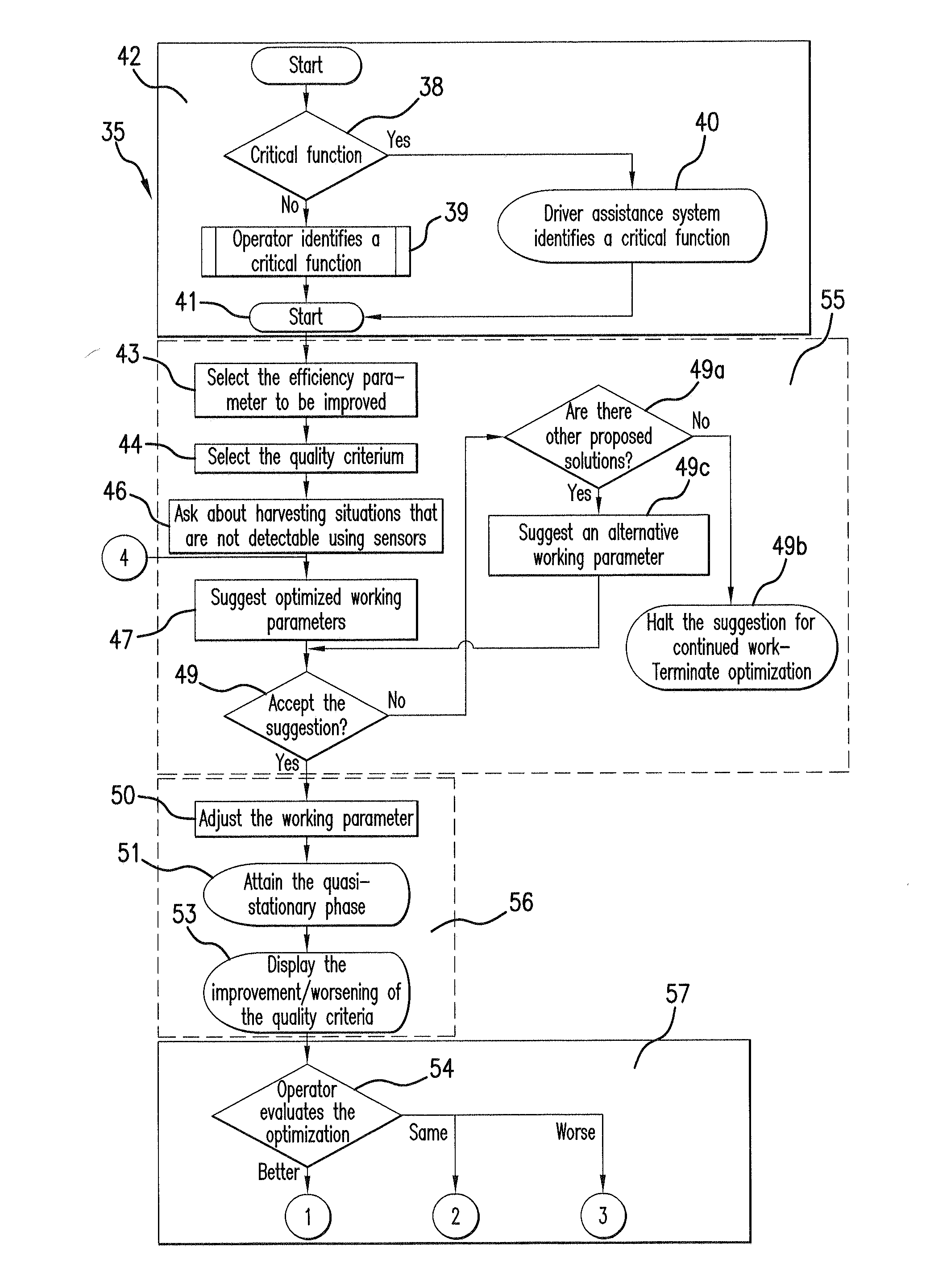
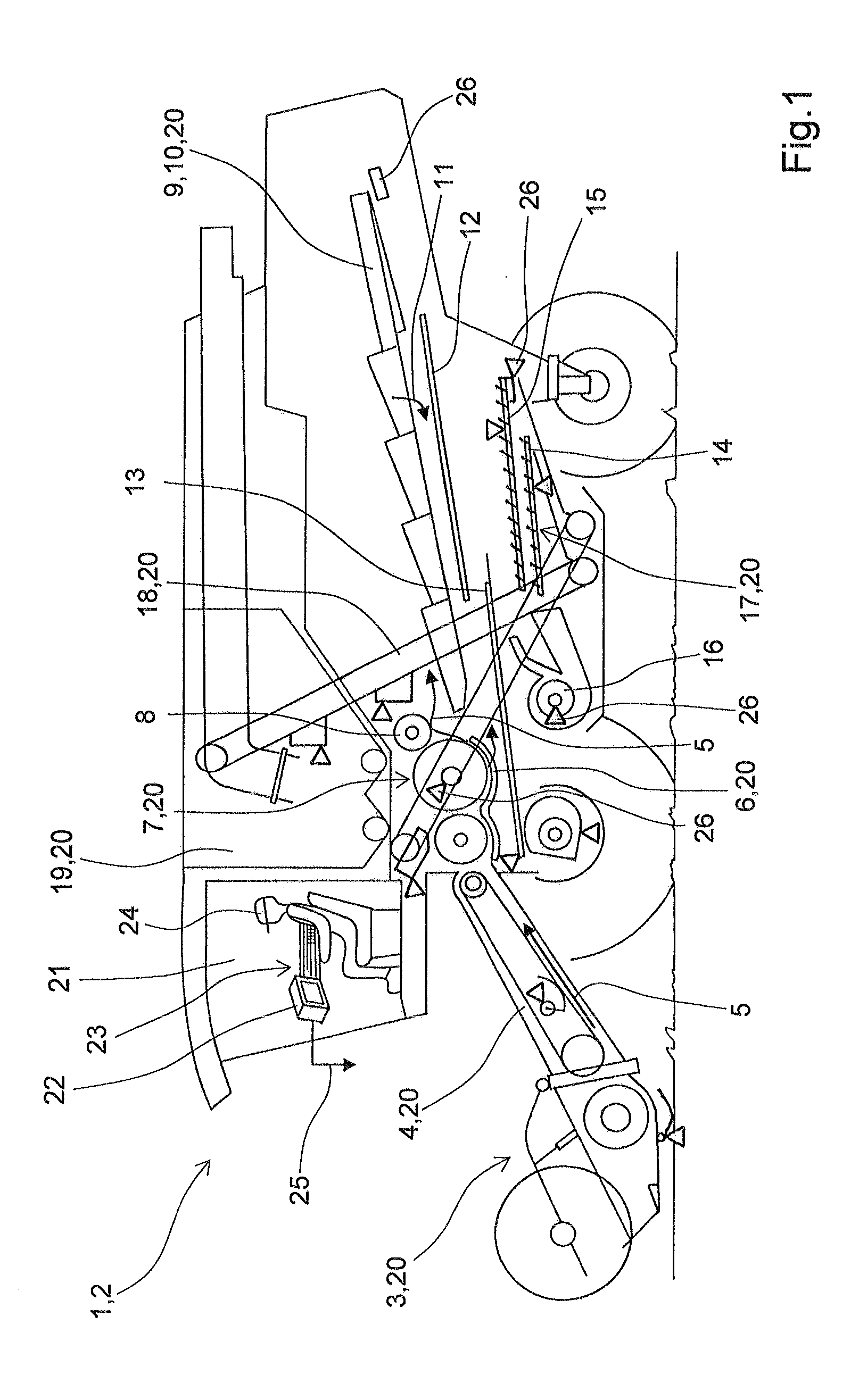
Driver assistance system for agricultural working machines
ActiveUS20100217474A1Improve efficiencyVehicle testingAnalogue computers for trafficArithmetic logic unitDriver/operator
A driver assistance system for an agricultural working machine, in particular a combine harvester has a large number of working mechanisms, an arithmetic logic unit, and at least one display unit, in which the arithmetic logic unit may process information generated by machine-internal sensor systems, external information, and information that is storable in the arithmetic logic unit, and in which the driver assistance system overcomes—with consideration for at least a selection of the available information—critical functions of the agricultural working machine in that efficiency parameters of the agricultural working machine are optimized via interactive, natural-language communication between the operator of the agricultural working machine and the driver assistance system.
Owner:CLAAS SELBSTFAHRENDE ERNTEMASCHINEN GMBH
Field-programmable gate array based accelerator system
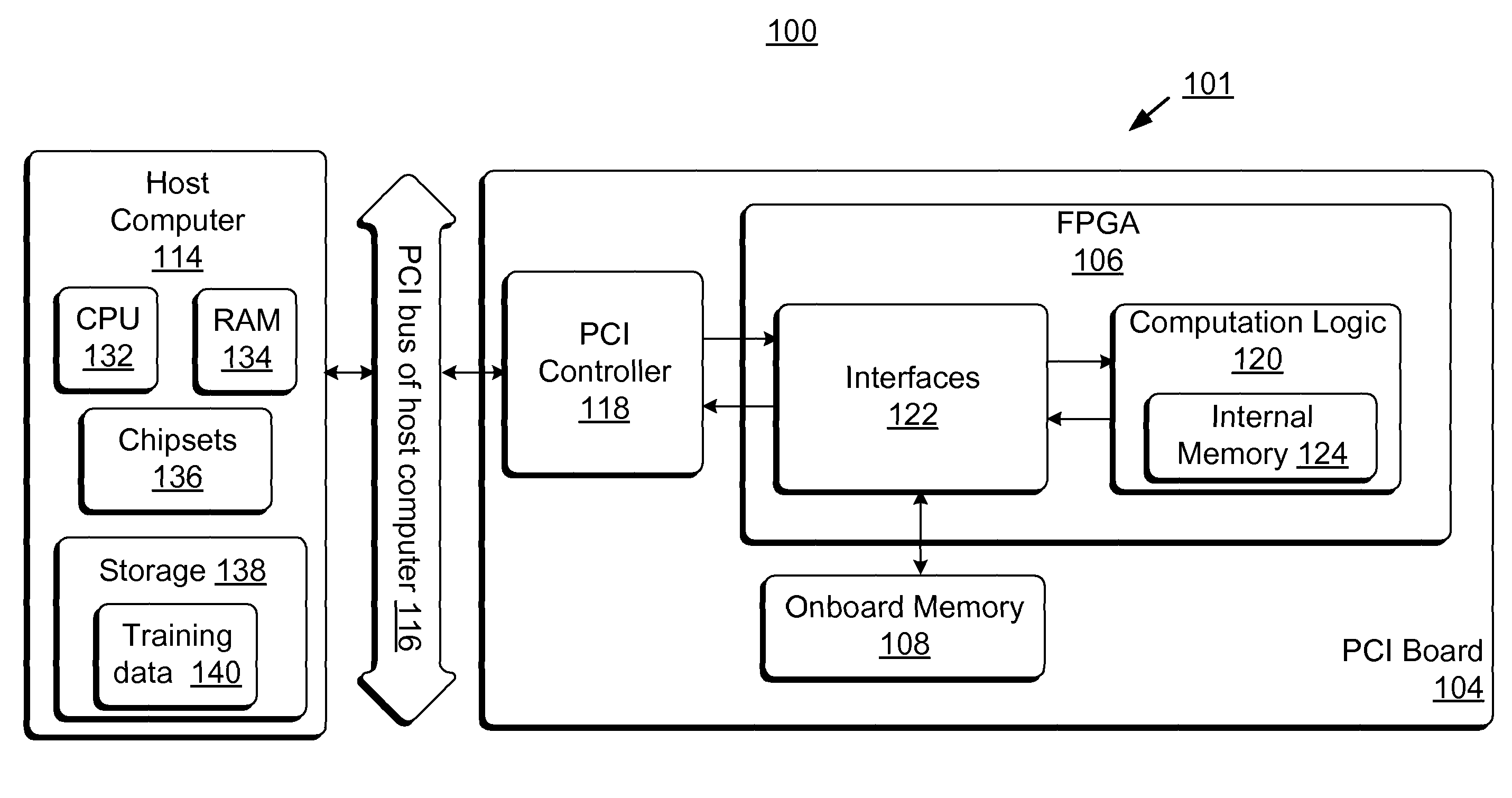
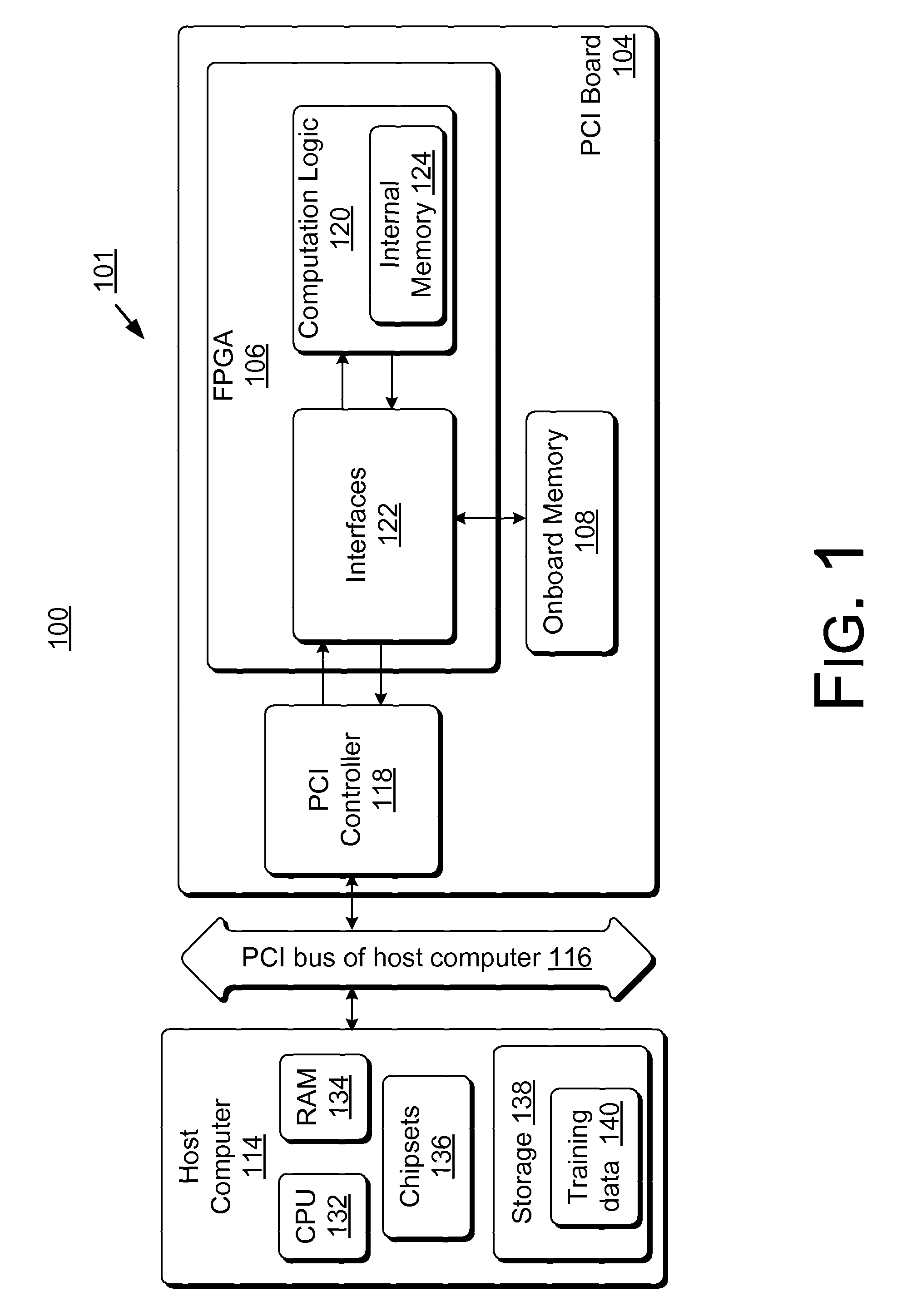
ActiveUS8131659B2Less timeLess costDigital computer detailsDigital dataHidden layerArithmetic logic unit
Accelerator systems and methods are disclosed that utilize FPGA technology to achieve better parallelism and processing speed. A Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) is configured to have a hardware logic performing computations associated with a neural network training algorithm, especially a Web relevance ranking algorithm such as LambaRank. The training data is first processed and organized by a host computing device, and then streamed to the FPGA for direct access by the FPGA to perform high-bandwidth computation with increased training speed. Thus, large data sets such as that related to Web relevance ranking can be processed. The FPGA may include a processing element performing computations of a hidden layer of the neural network training algorithm. Parallel computing may be realized using a single instruction multiple data streams (SIMD) architecture with multiple arithmetic logic units in the FPGA.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and method for cryogenic hybrid technology computing and memory
ActiveUS9520180B1Easy to combineTransmission lineCosmetic preparationsQuantum computersLow inductanceDatapath
A system and method for high-speed, low-power cryogenic computing are presented, comprising ultrafast energy-efficient RSFQ superconducting computing circuits, and hybrid magnetic / superconducting memory arrays and interface circuits, operating together in the same cryogenic environment. An arithmetic logic unit and register file with an ultrafast asynchronous wave-pipelined datapath is also provided. The superconducting circuits may comprise inductive elements fabricated using both a high-inductance layer and a low-inductance layer. The memory cells may comprise superconducting tunnel junctions that incorporate magnetic layers. Alternatively, the memory cells may comprise superconducting spin transfer magnetic devices (such as orthogonal spin transfer and spin-Hall effect devices). Together, these technologies may enable the production of an advanced superconducting computer that operates at clock speeds up to 100 GHz.
Owner:SEEQC INC
Parallel vector processing
InactiveUS7196708B2Color signal processing circuitsRegister arrangementsArithmetic logic unitProcessor register
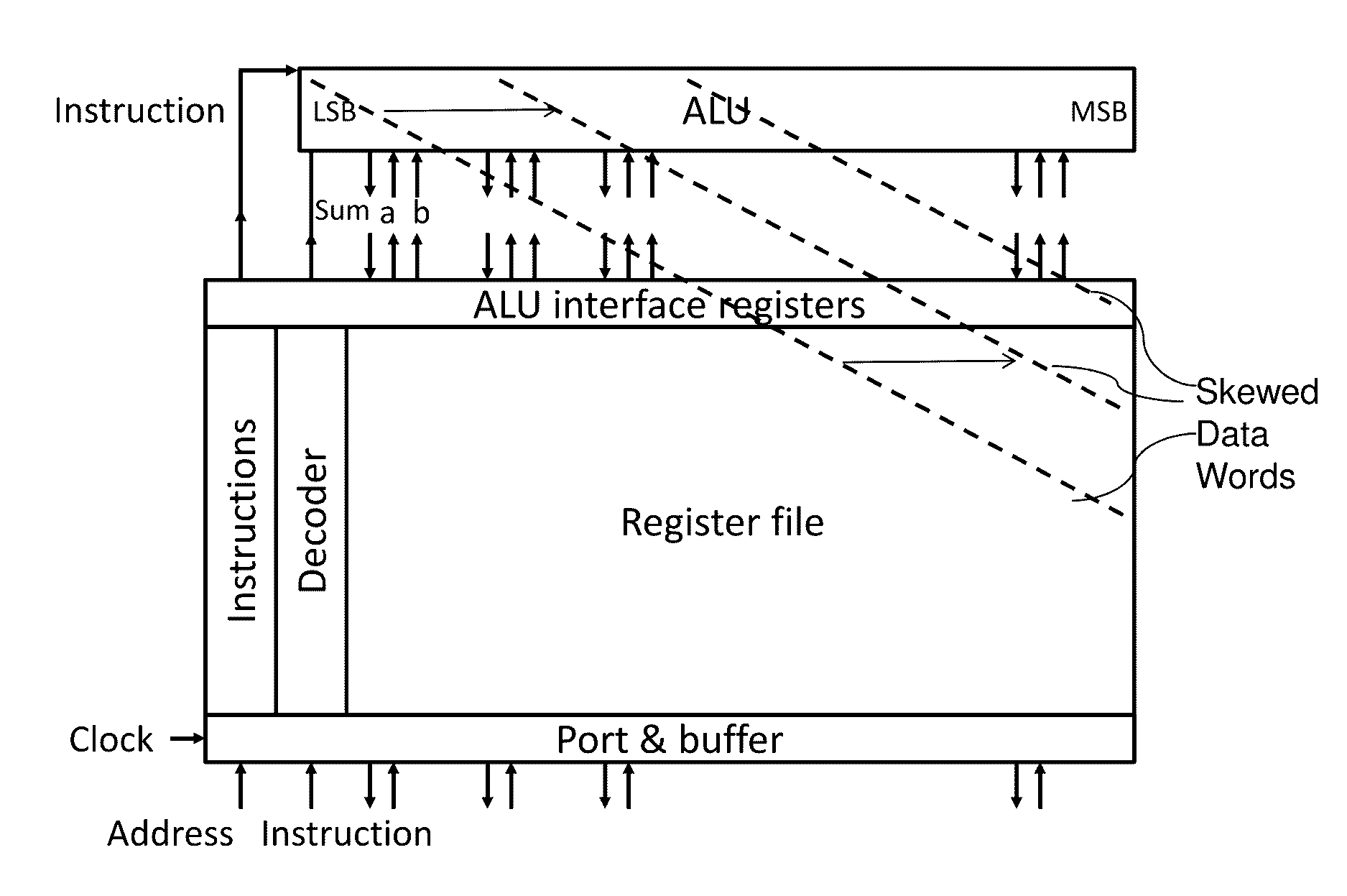
A video platform architecture provides video processing using parallel vector processing. The video platform architecture includes a plurality of video processing modules, each module including a plurality of processing elements (PEs). Each PE provides parallel vector processing. Specifically, means are provided to read all elements of one or two source vector registers in each PE simultaneously, process the read elements by a set of arithmetic-logical units (ALUs), and write back all results to one of the vector registers, all of which occurs in one PE cycle. To provide such parallel vector processing capabilities, the datapath of each PE is built as a set of identical PE processing slices, each of which includes an integer arithmetic-logical unit (ALU), a vector register bank, and a block register bank. A block / vector register bank holds all I elements of row J in a two-dimensional I×J data blocks for all block / vector registers provided by the architecture.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
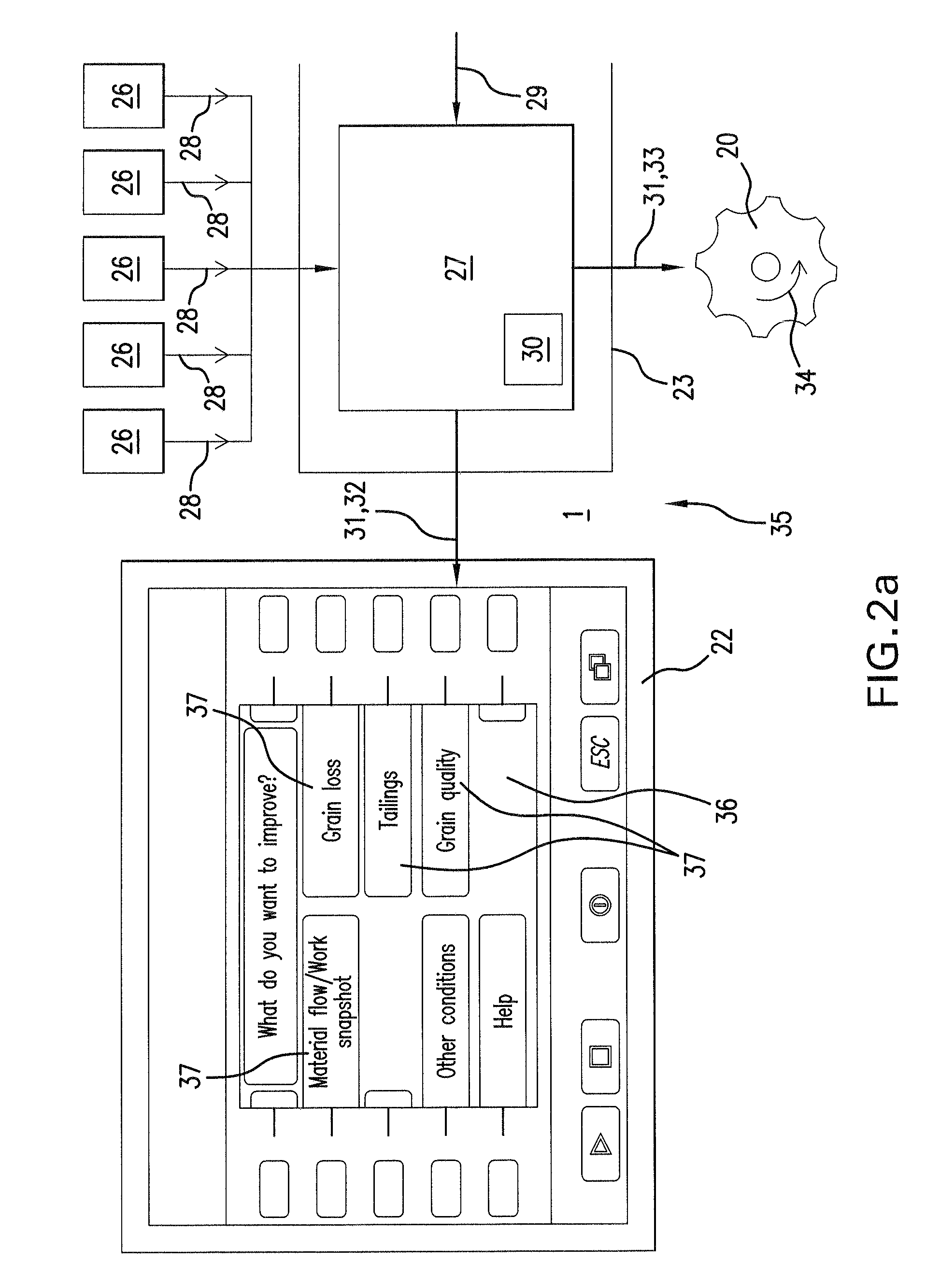
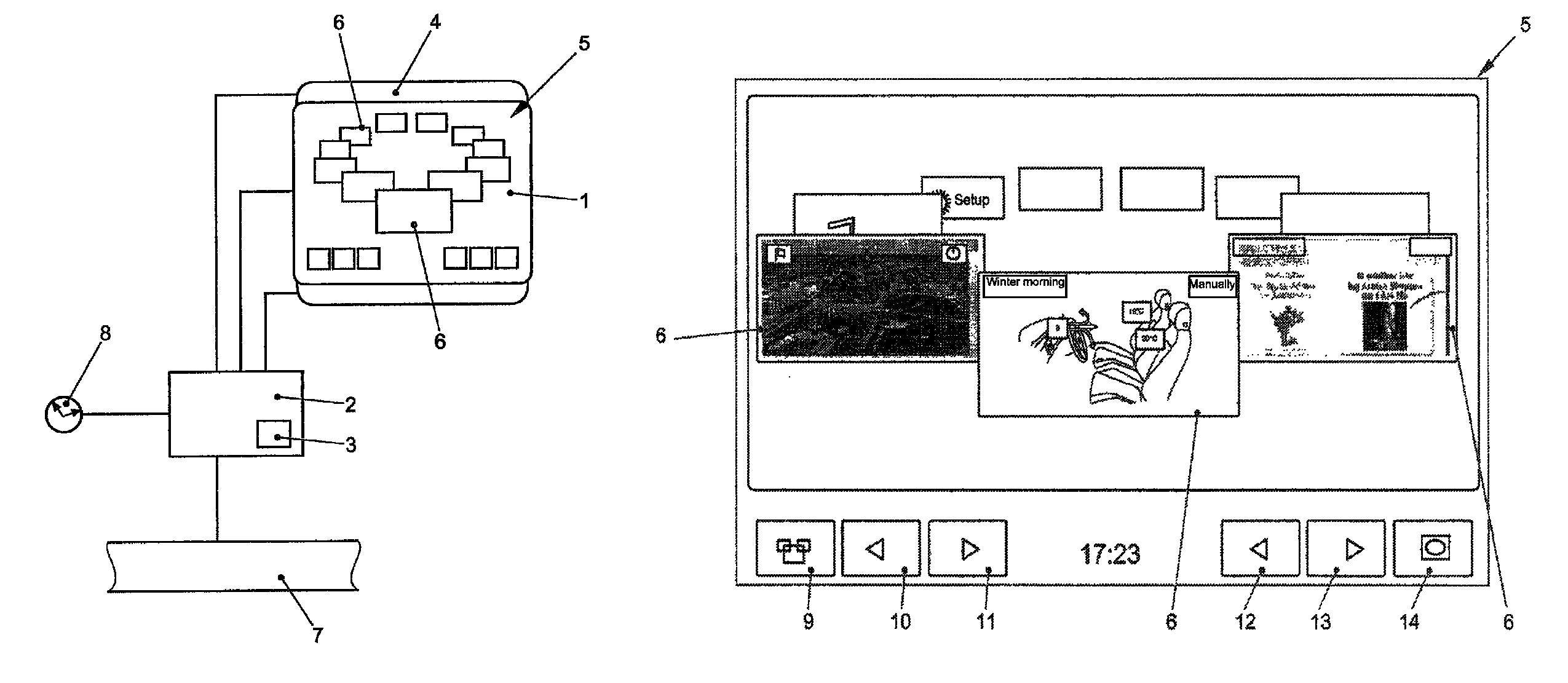
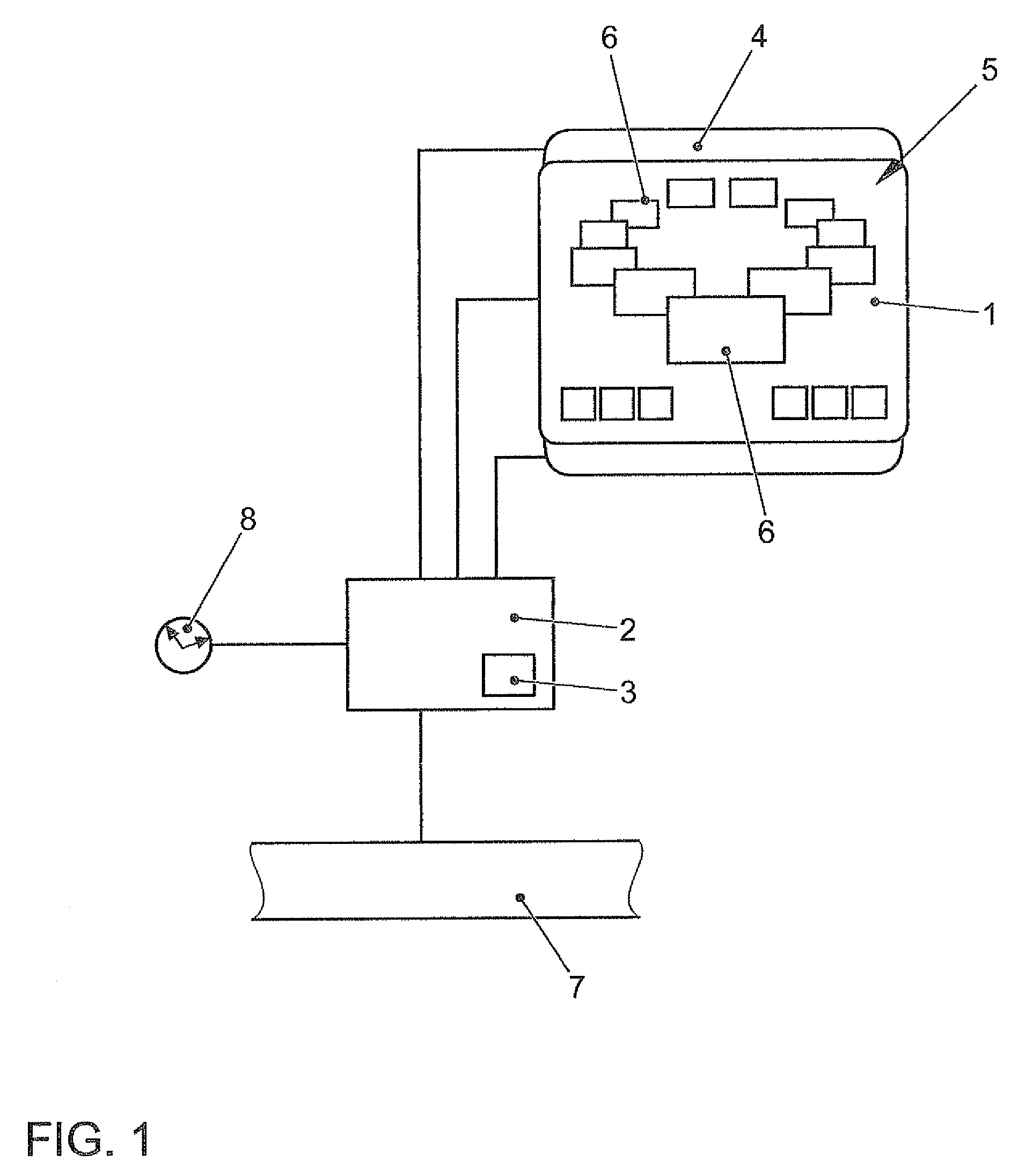
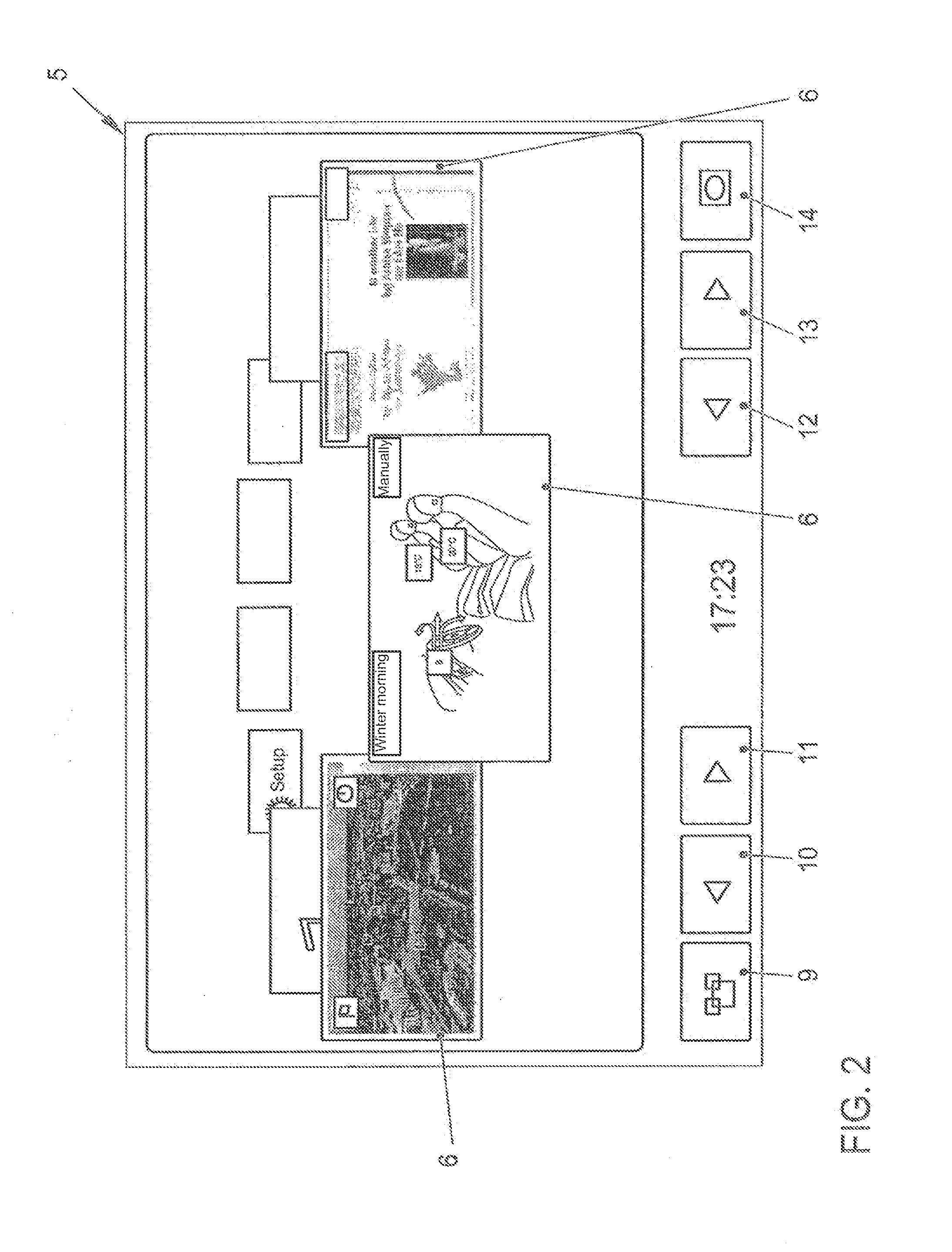
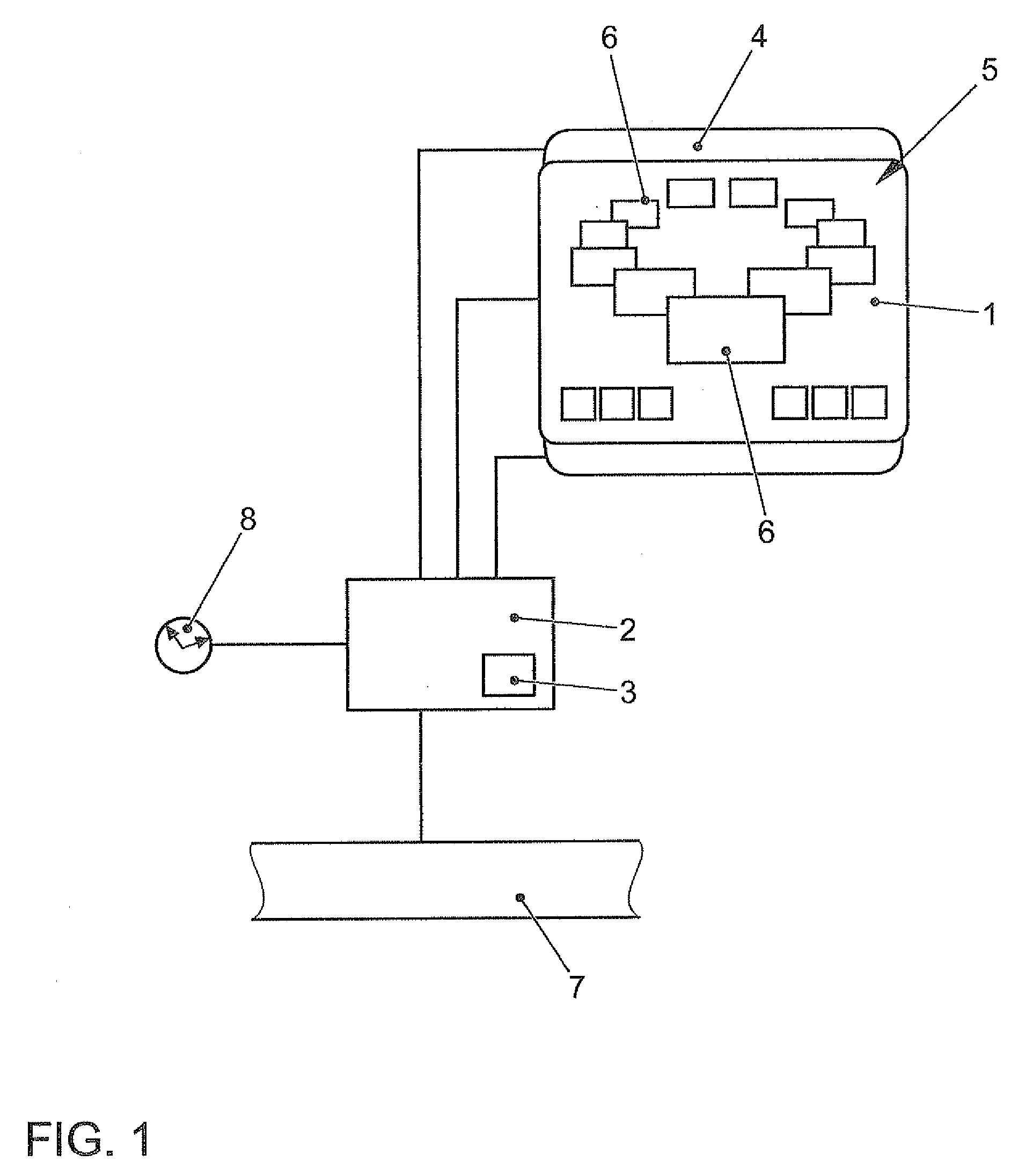
Method for displaying information in a vehicle and display device for a vehicle
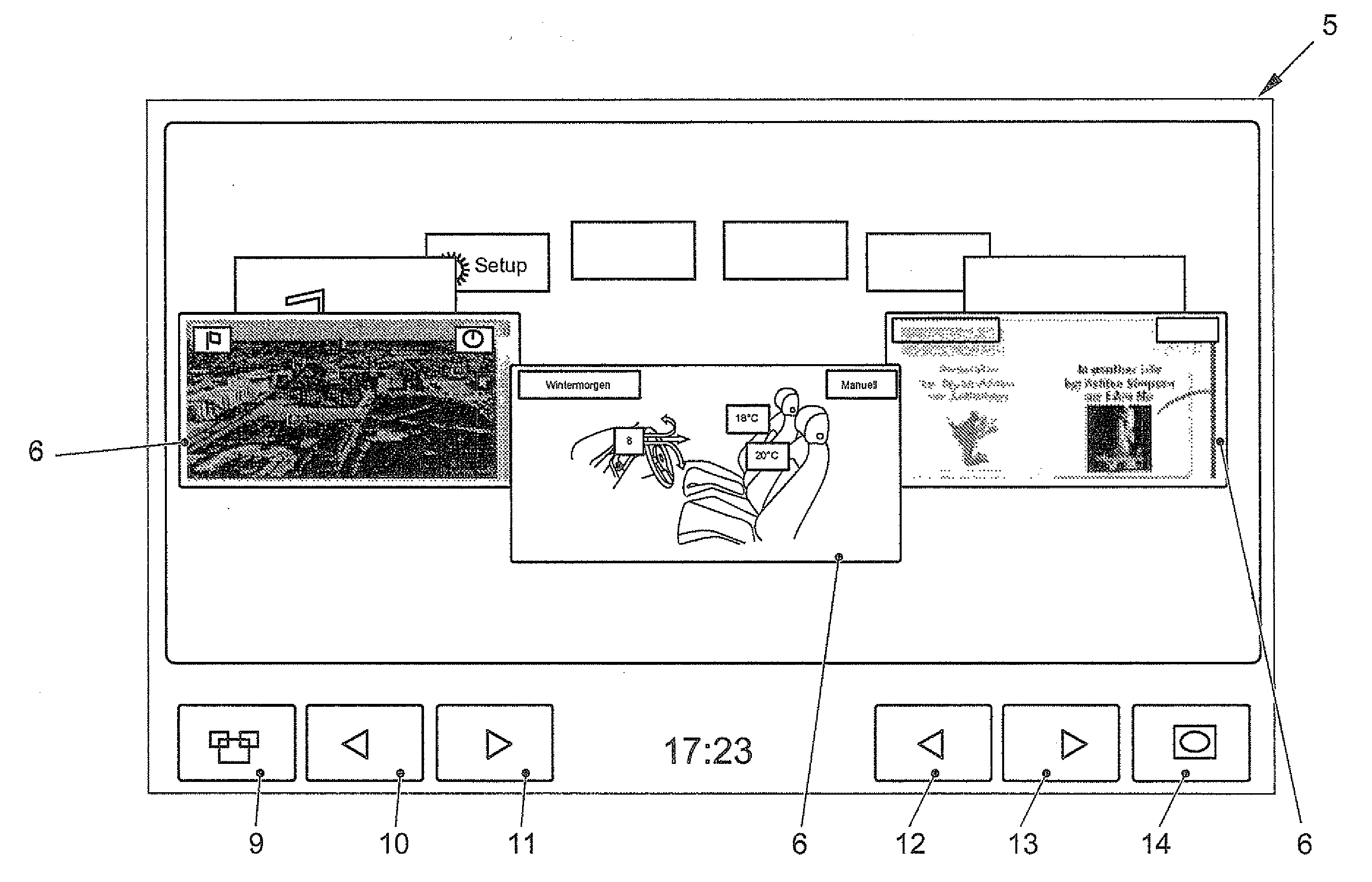
ActiveUS8477108B2Rapid and intuitive and simple operator controlSafety is not impairedInstrument arrangements/adaptationsCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsArithmetic logic unit
In a method for displaying information in a motor vehicle, a plurality of objects are represented graphically with the aid of a display mounted in a motor vehicle. A user-interface device generates graphics data which control the display such that the graphical objects are shown disposed on a virtual, perspectively displayed ring, and that in response to an input with the aid of an input device, an arithmetic logic unit of the user-interface device alters the graphics data such that the graphical objects on the virtual ring rotate like a carousel. A corresponding display device is provided.
Owner:VOLKSWAGEN AG
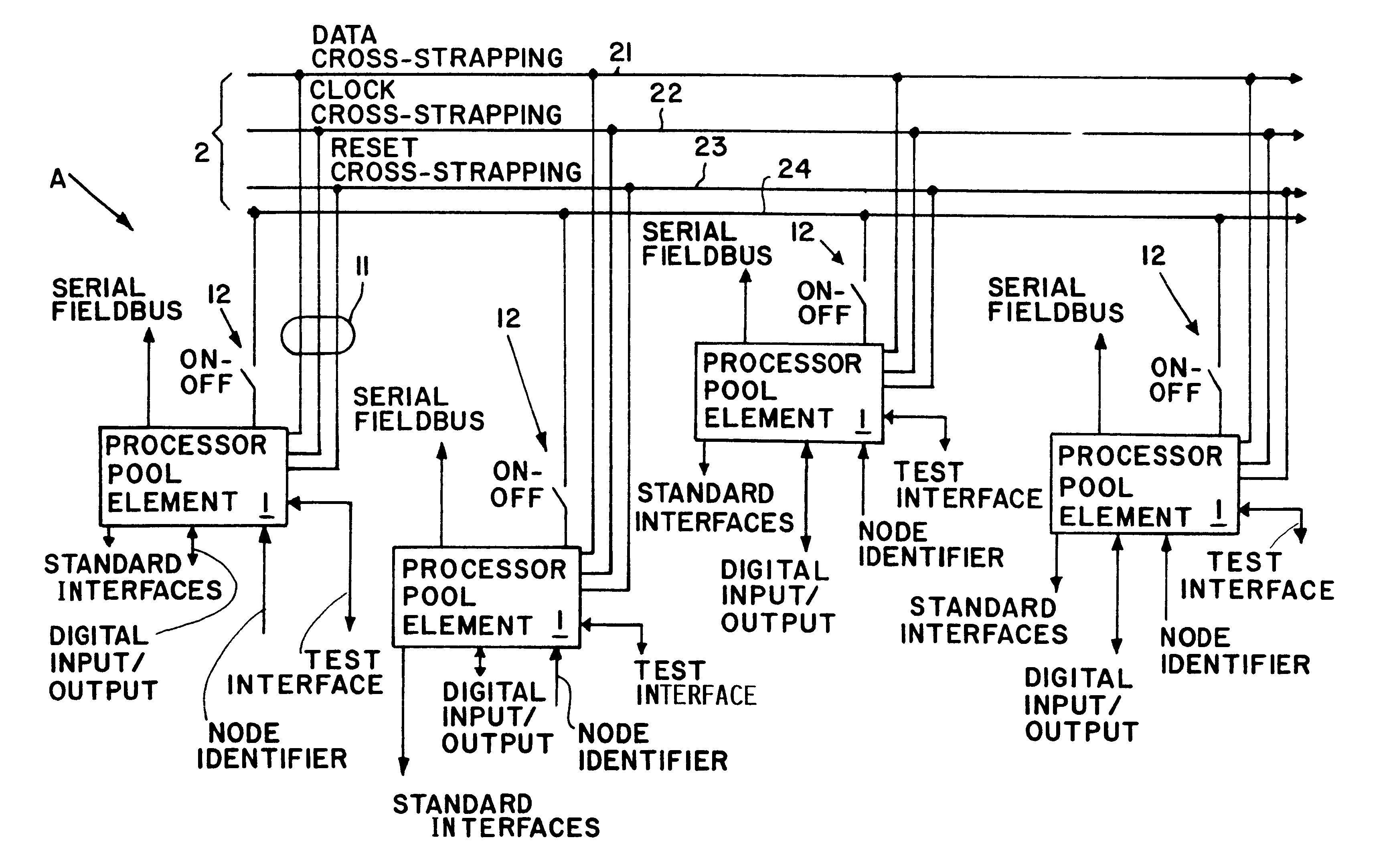
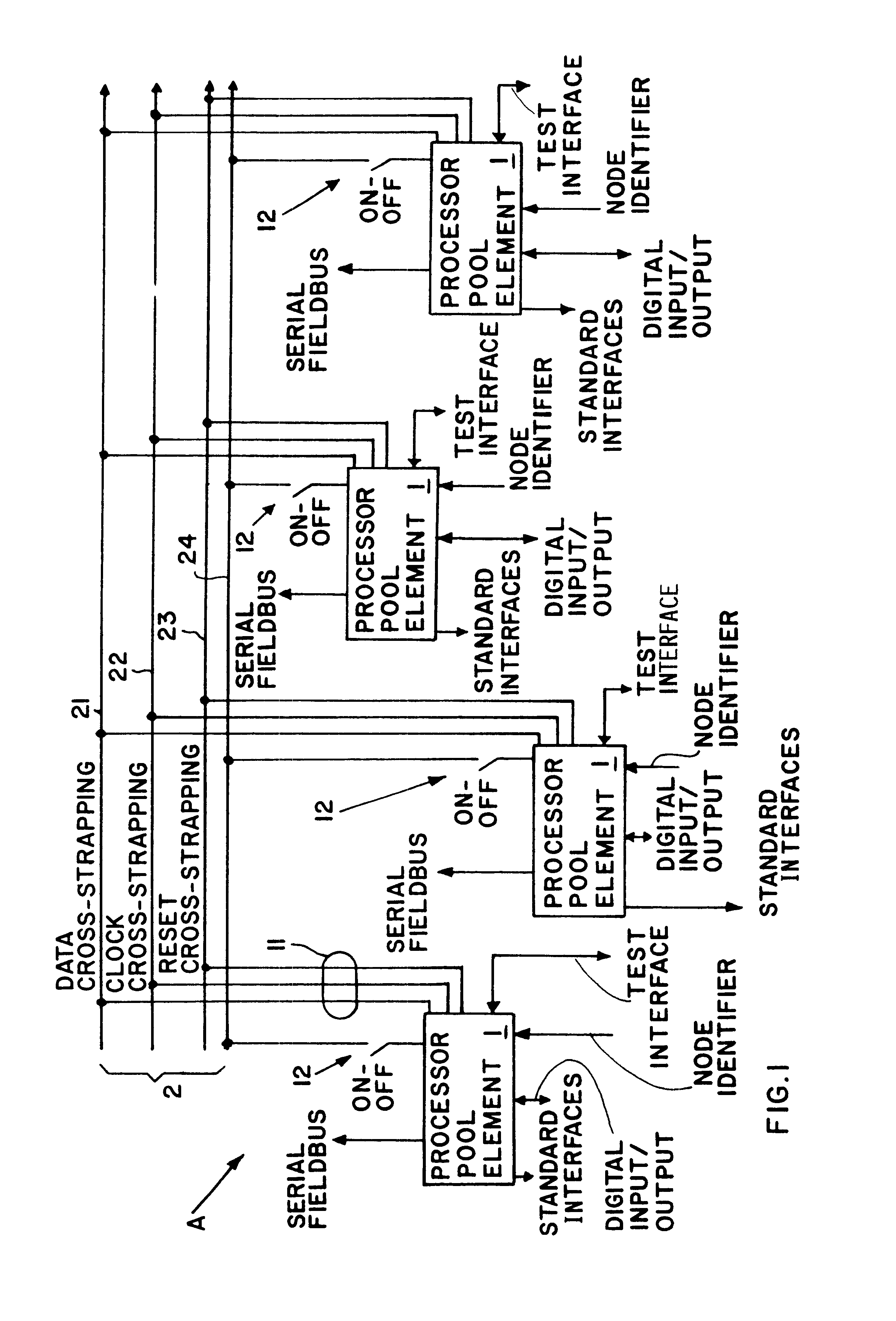
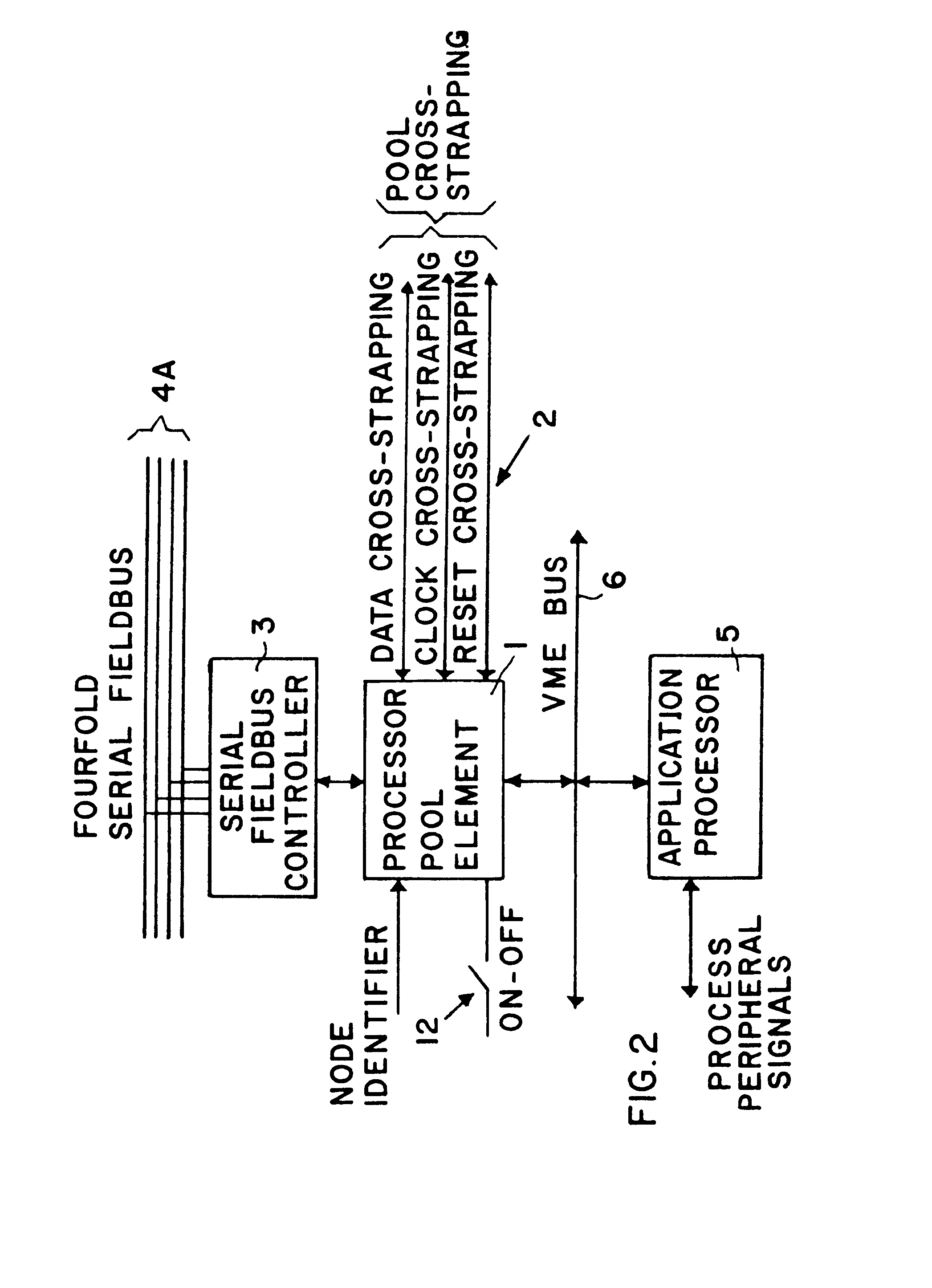
Method and apparatus for fault tolerant execution of computer programs
InactiveUS6434712B1Maximum countEconomically manufacturedRedundant hardware error correctionArithmetic logic unitProcessor element
A circuit arrangement for the fault tolerant execution of digital computer programs includes a plurality of arithmetic logic units embodied as processor pool elements connected together so that they can each execute the program in parallel. The processor elements are connected to each other through respective data, clock and reset cross-strapping interconnect lines, and are each connected to one or more serial field buses. Each processor element includes at least one microprocessor controller for controlling the functions of the processor element in such a manner that any selected number of the processor elements can be automatically actuated at any time to simultaneously execute the program in parallel and thereby achieve a prescribed degree of redundancy in the circuit arrangement. The data cross-strapping line transmits data among the several processor elements, the clock signal cross-strapping line achieves a compelled synchronization of all of the processor elements, and the reset cross-strapping line carries out the deactivation of any processor element that is recognized as carrying out a faulty execution of the program or that is not necessary for achieving the required degree of redundancy. A deactivated processor element may later be reactivated to again participate in the parallel execution of the program.
Owner:DAMELERKLESLER AVIATION
Reducing memory accesses for enhanced in-memory parallel operations
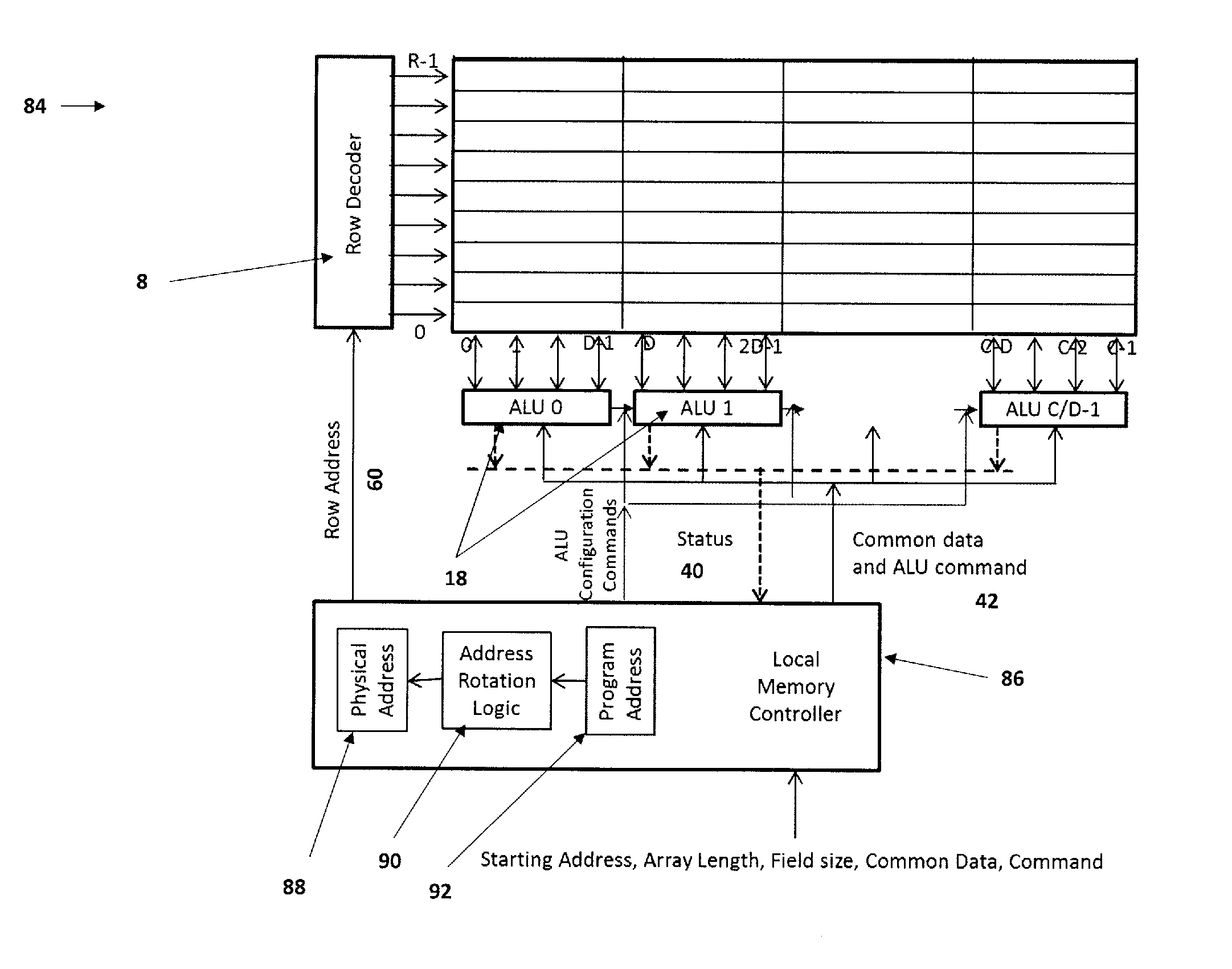
ActiveUS20150089166A1Reduce program execution timeWeaken energyMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMemory addressArithmetic logic unit
A memory storage system is that includes a memory element having a memory address for a physical memory. A memory controller receives a command for accessing the memory element using a program-generated address and dynamically transforms the program-generated address into the memory address for the physical memory using a rotation module and configuration information. A data word accessed by the physical address is then provided to a set of arithmetic logic units (ALUs) where multiple computations are performed simultaneously so as top reduce program execution time and energy. The configuration information provided to the rotation unit configures the set of ALUs.
Owner:LUCATA CORP
Residue number arithmetic logic unit
ActiveUS20130311532A1Improve performanceConservingProgram controlComputation using denominational number representationArithmetic logic unitNumbering system
Methods and systems for residue number system based ALUs, processors, and other hardware provide the full range of arithmetic operations while taking advantage of the benefits of the residue numbers in certain operations. In one or more embodiments, an RNS ALU or processor comprises a plurality of digit slices configured to perform modular arithmetic functions. Operation of the digit slices may be controlled by a controller. Residue numbers may be converted to and from fixed or mixed radix number systems for internal use and for use in various computing systems.
Owner:OLSEN IP RESERVE
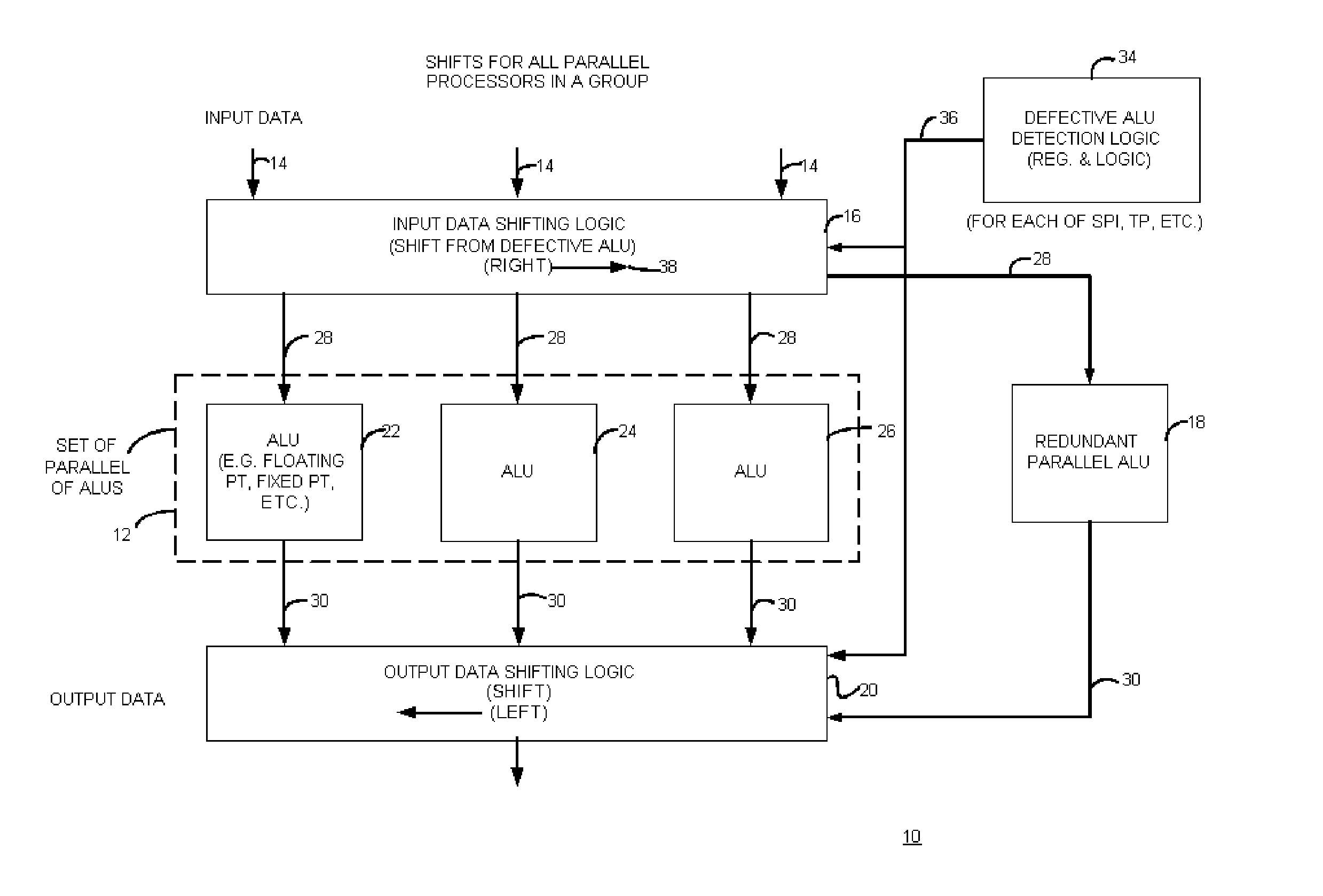
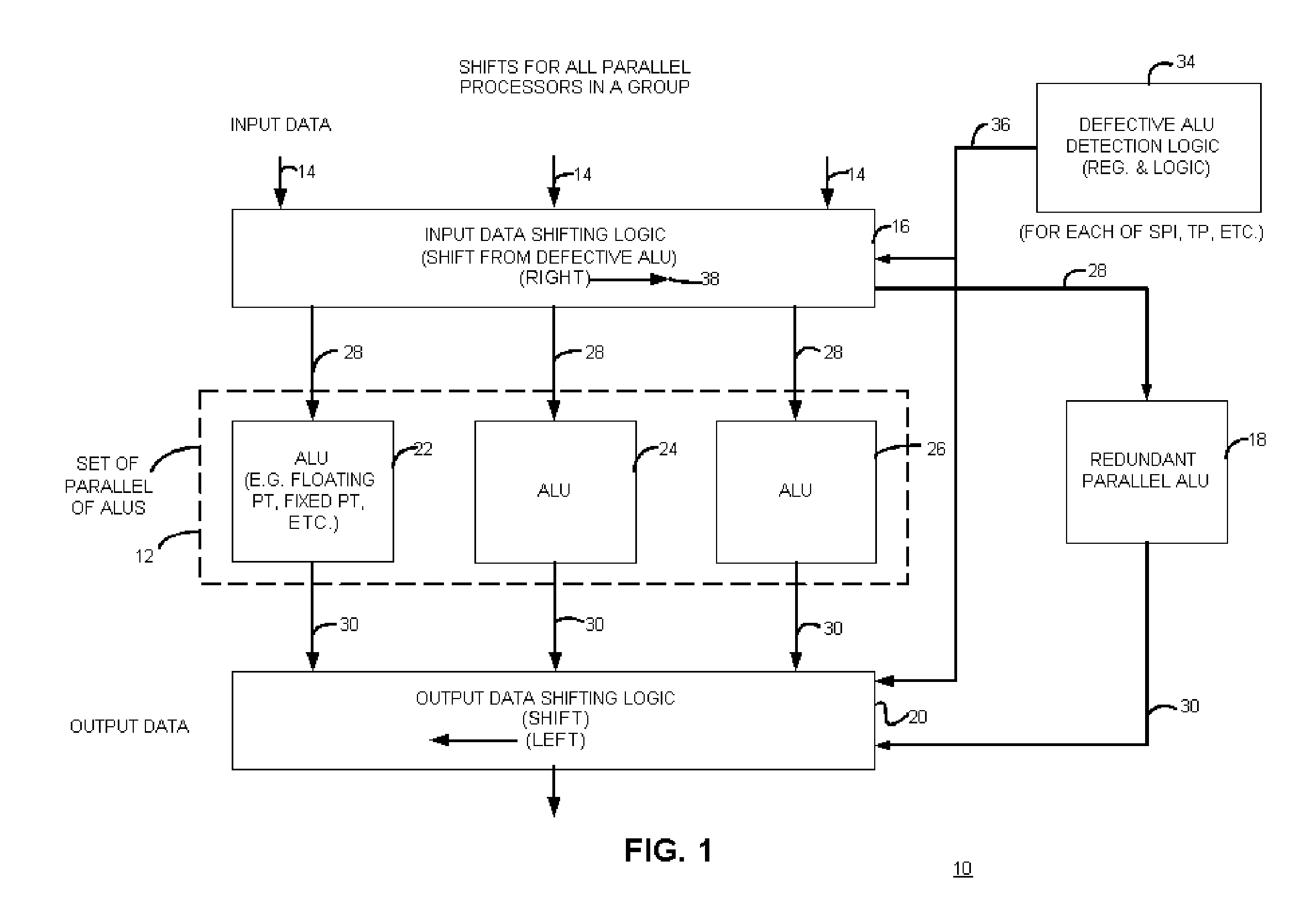
Apparatus with redundant circuitry and method therefor
ActiveUS20060053188A1Error detection/correctionComputation using denominational number representationArithmetic logic unitComputer science
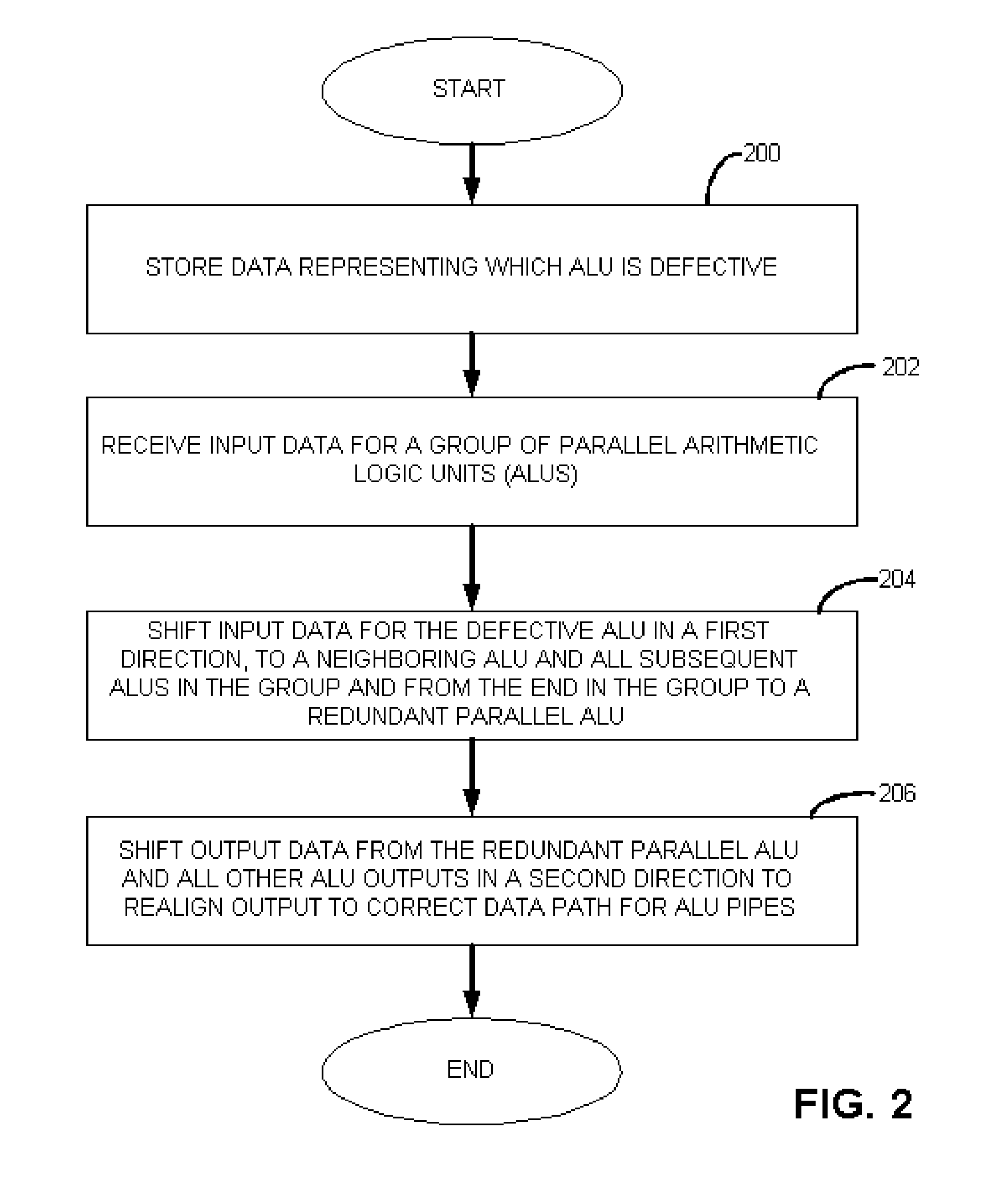
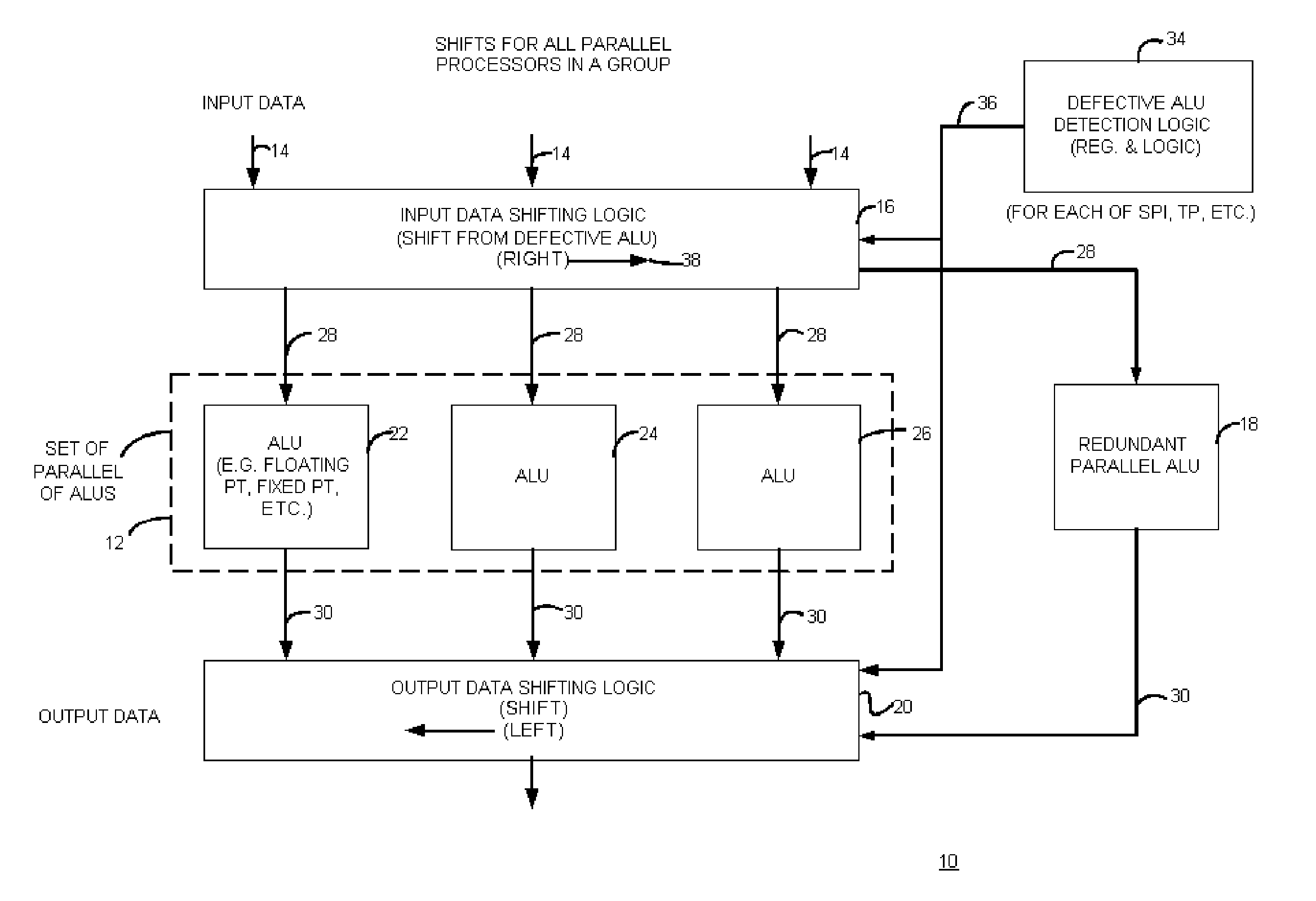
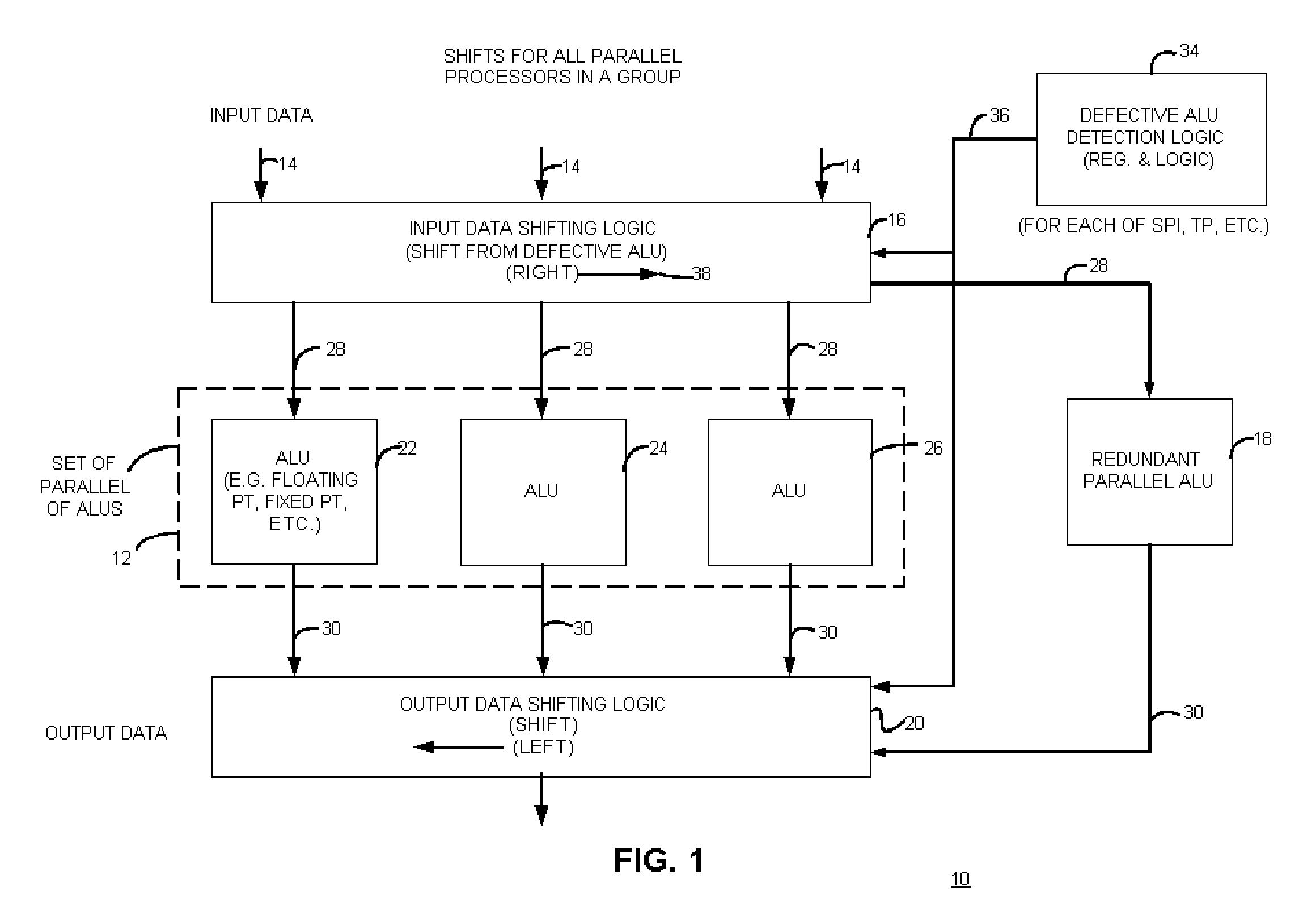
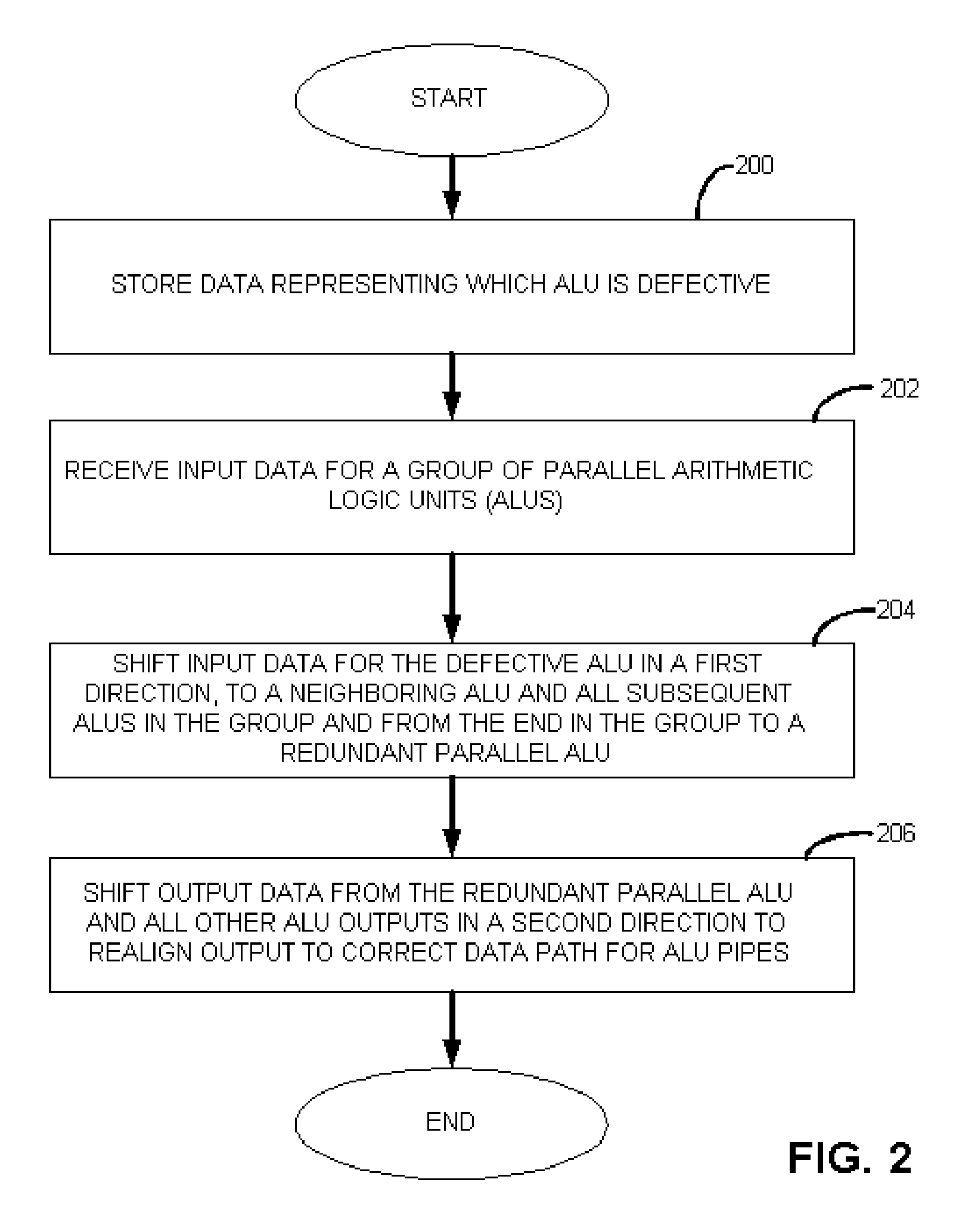
An apparatus with circuit redundancy includes a set of parallel arithmetic logic units (ALUs), a redundant parallel ALU, input data shifting logic that is coupled to the set of parallel ALUs and that is operatively coupled to the redundant parallel ALU. The input data shifting logic shifts input data for a defective ALU, in a first direction, to a neighboring ALU in the set. When the neighboring ALU is the last or end ALU in the set, the shifting logic continues to shift the input data for the end ALU that is not defective, to the redundant parallel ALU. The redundant parallel ALU then operates for the defective ALU. Output data shifting logic is coupled to an output of the parallel redundant ALU and all other ALU outputs to shift the output data in a second and opposite direction than the input shifting logic, to realign output of data for continued processing, including for storage or for further processing by other circuitry.
Owner:ATI TECH INC
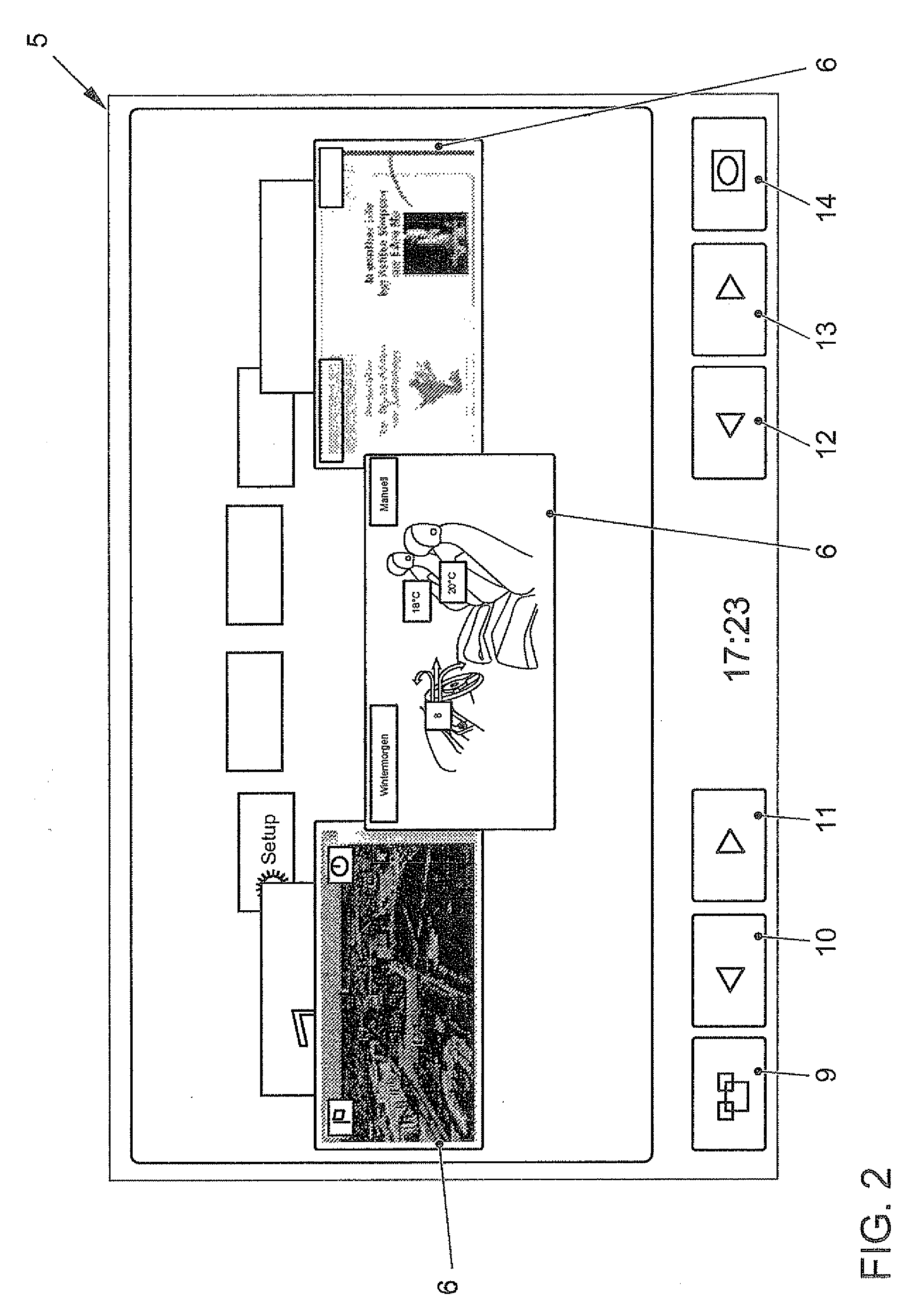
Method for displaying information in a vehicle and display device for a vehicle
ActiveUS20110205162A1Rapid and intuitive and simple operator controlSafety is not impairedInstrument arrangements/adaptationsCathode-ray tube indicatorsMobile vehicleArithmetic logic unit
In a method for displaying information in a motor vehicle, a plurality of objects are represented graphically with the aid of a display mounted in a motor vehicle. A user-interface device generates graphics data which control the display such that the graphical objects are shown disposed on a virtual, perspectively displayed ring, and that in response to an input with the aid of an input device, an arithmetic logic unit of the user-interface device alters the graphics data such that the graphical objects on the virtual ring rotate like a carousel. A corresponding display device is provided.
Owner:VOLKSWAGEN AG
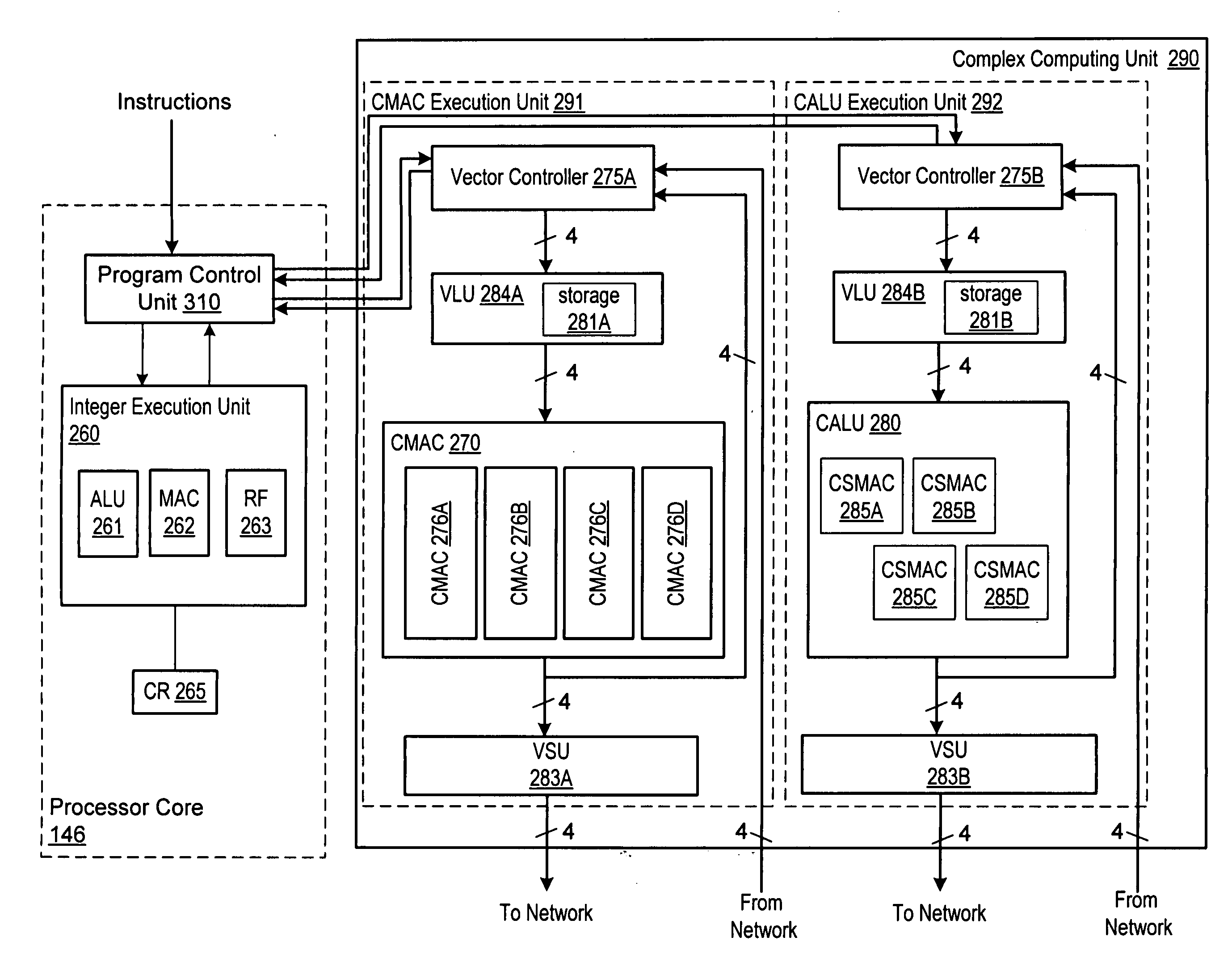
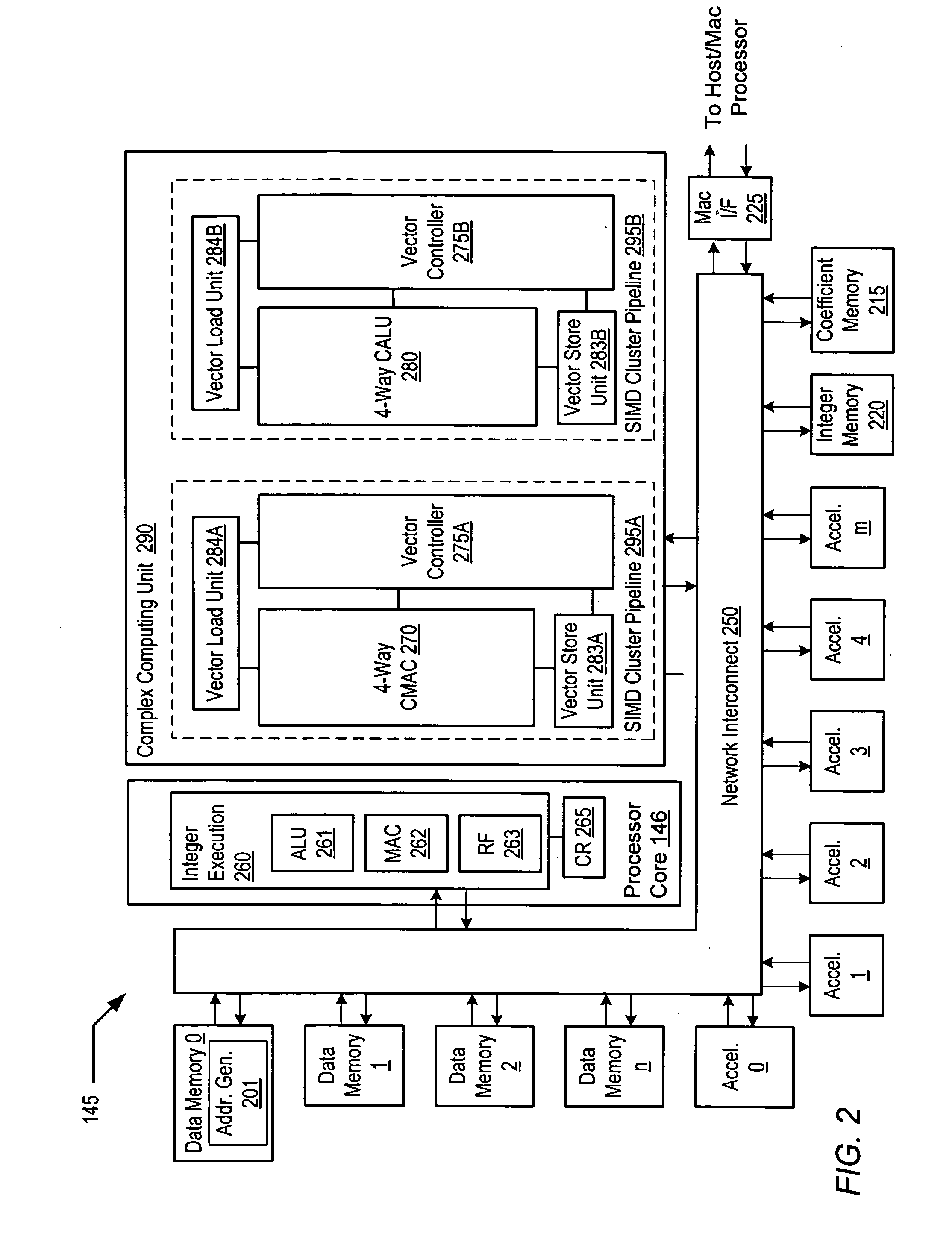
Programmable digital signal processor including a clustered SIMD microarchitecture configured to execute complex vector instructions
ActiveUS20060271764A1General purpose stored program computerSpecific program execution arrangementsArithmetic logic unitLine tubing
A programmable digital signal processor including a clustered SIMD microarchitecture includes a plurality of accelerator units, a processor core and a complex computing unit. Each of the accelerator units may be configured to perform one or more dedicated functions. The processor core includes an integer execution unit that may be configured to execute integer instructions. The complex computing unit may be configured to execute complex vector instructions. The complex computing unit may include a first and a second clustered execution pipeline. The first clustered execution pipeline may include one or more complex arithmetic logic unit datapaths configured to execute first complex vector instructions. The second clustered execution pipeline may include one or more complex multiplier accumulator datapaths configured to execute second complex vector instructions.
Owner:CORESONIC AB
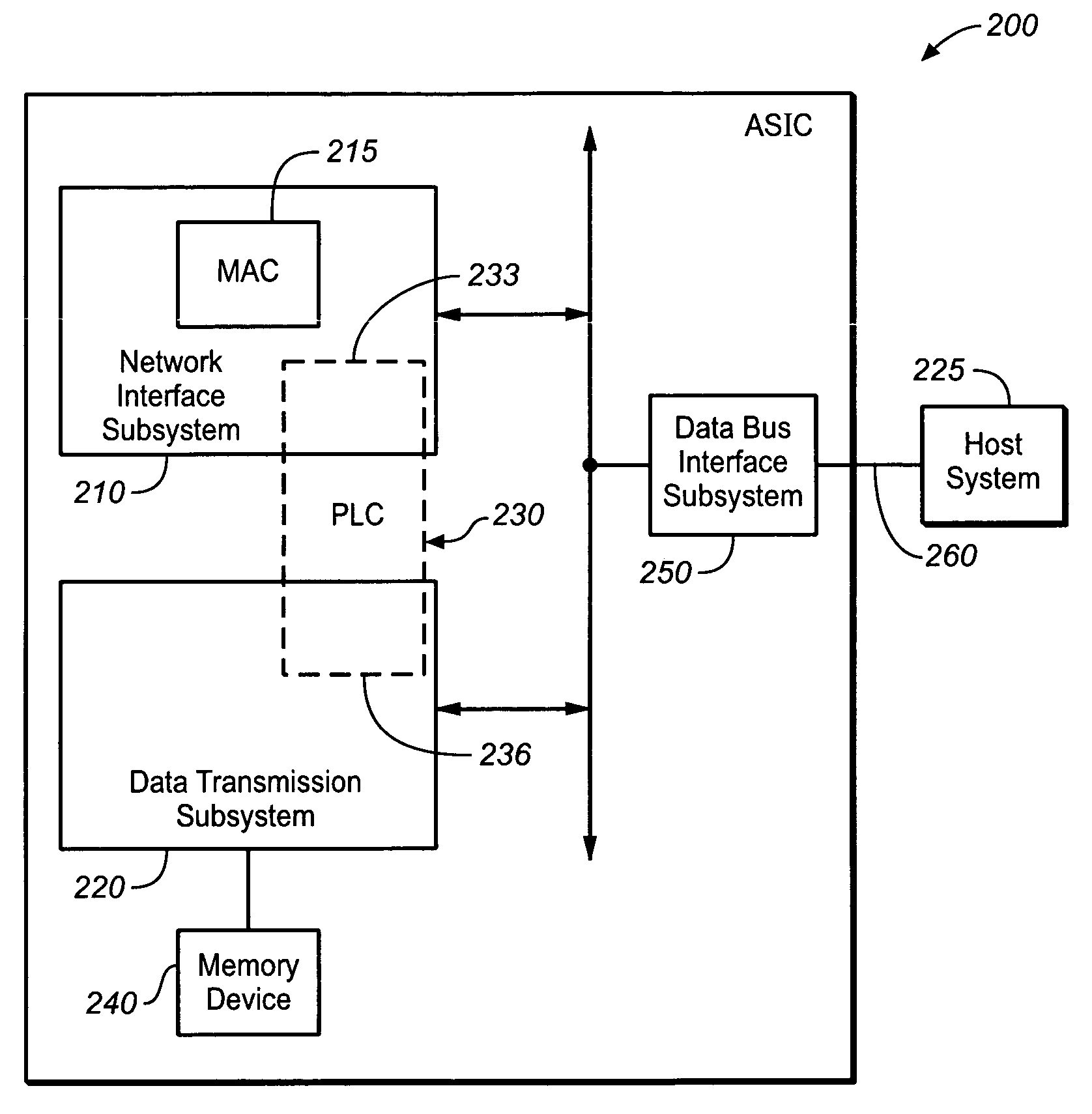
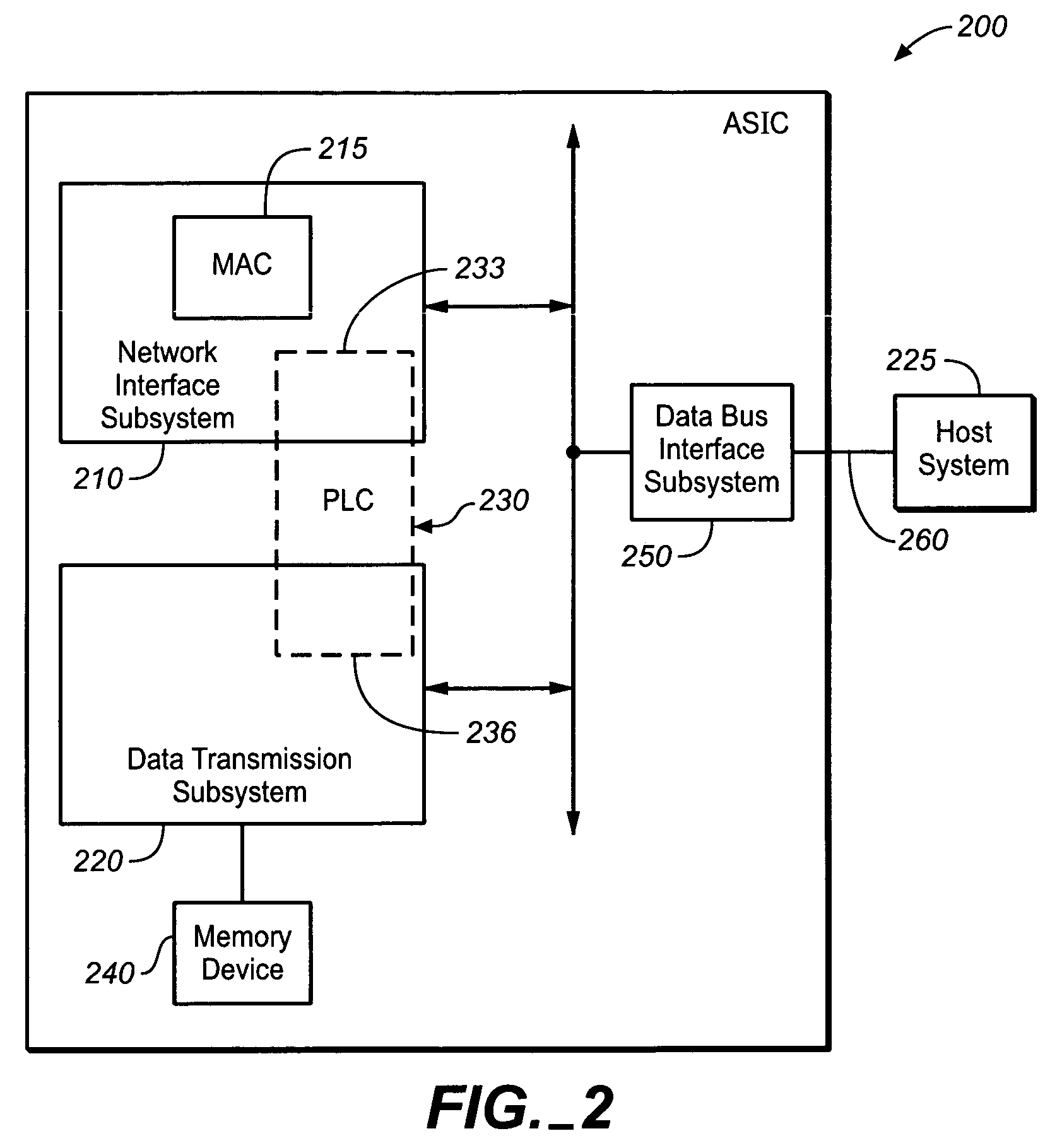
Application specific integrated circuit having a programmable logic core and a method of operation thereof
ActiveUS7042899B1Store-and-forward switching systemsNetwork connectionsArithmetic logic unitProgrammable logic controller
The present invention provides an application specific integrated circuit and a method of operation thereof. In one advantageous embodiment, the application specific integrated circuit includes a programmable logic core having an array of dynamically configurable arithmetic logic units. This particular embodiment further includes a network interface subsystem that includes a media access controller. The network interface is configured to employ a first portion of the programmable logic core that interfaces with the media access controller and that is configurable to process control data. This embodiment further includes a data transmission subsystem associated with a memory device, and configured to employ a second portion of the programmable logic core that stores received data from the network interface subsystem to the memory device and sends transmission data from the memory device to the network interface subsystem in response to an instruction from a host system.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Multi-Directional Motion Estimation Using Parallel Processors and Pre-Computed Search-Strategy Offset Tables
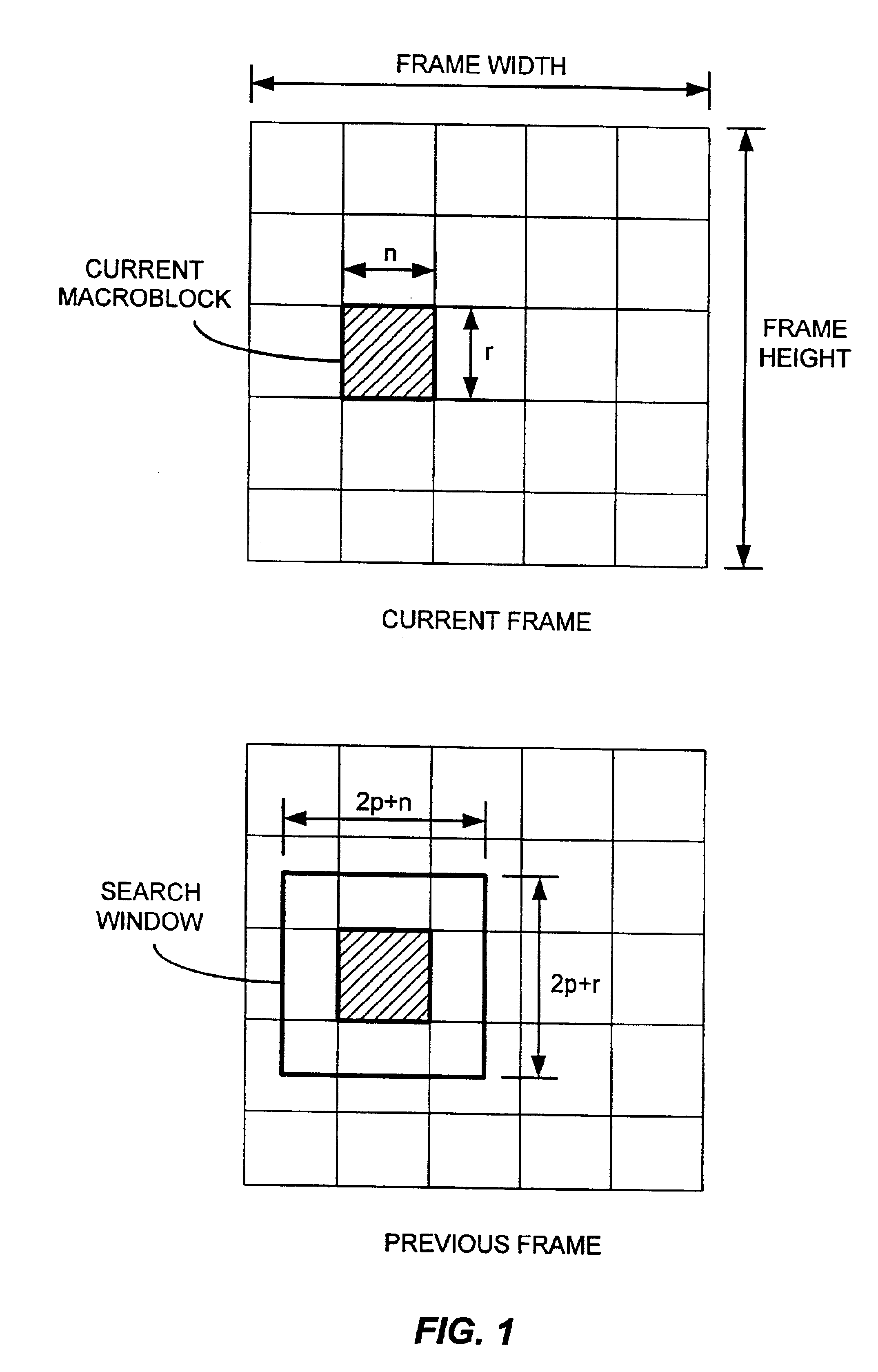
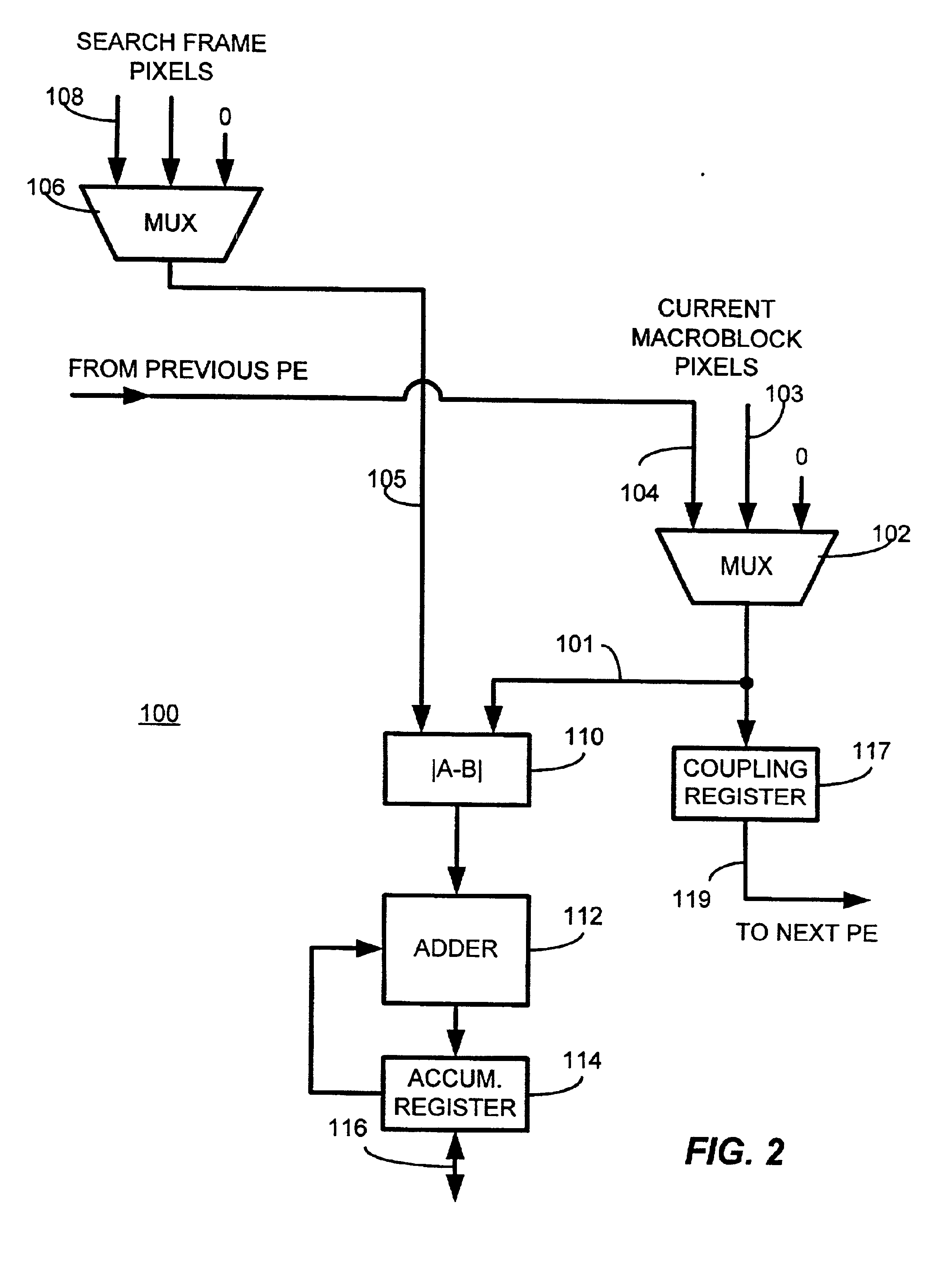
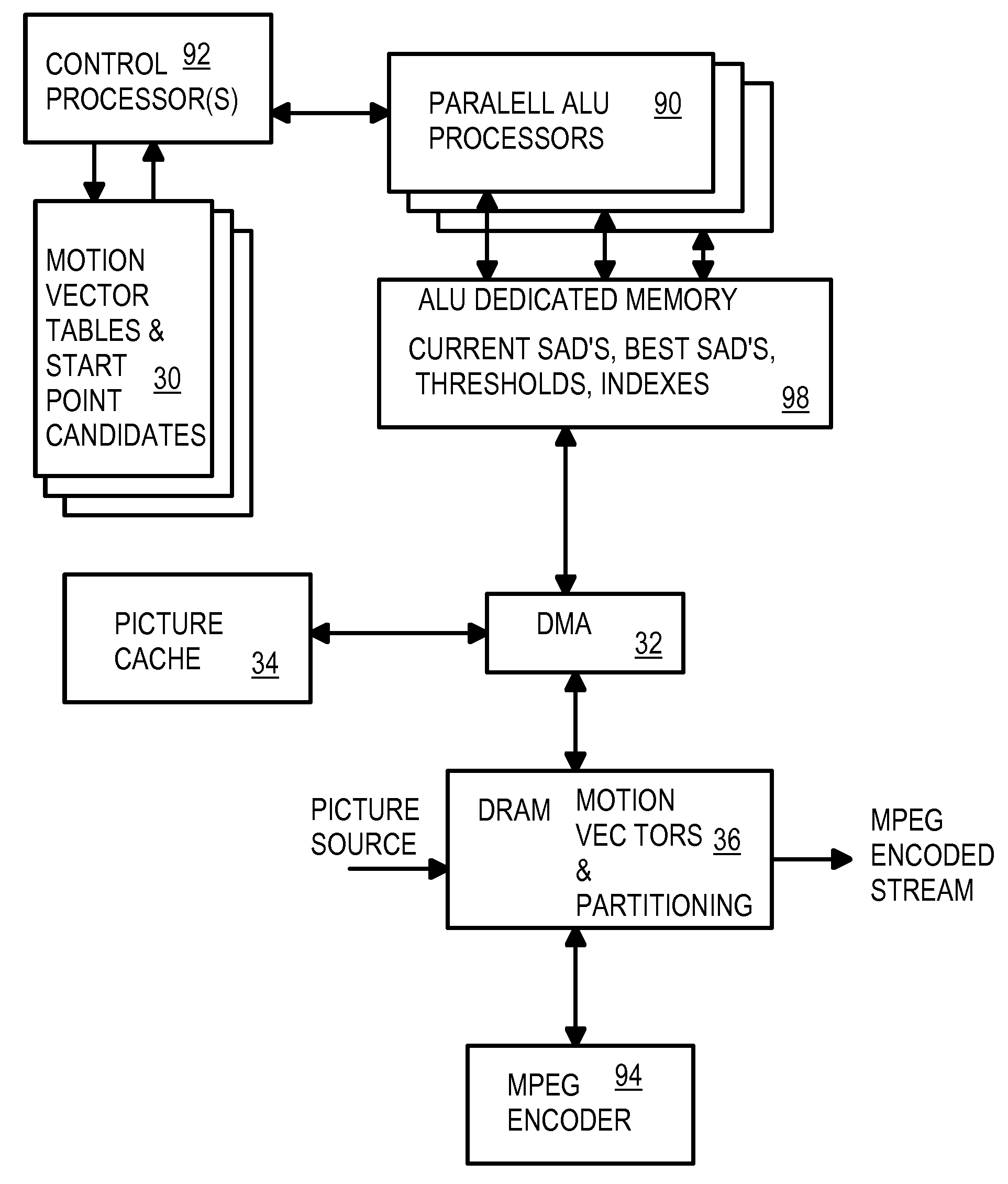
A motion estimator uses many parallel Arithmetic-Logic-Unit (ALU) processors to simultaneously perform searches in many directions from a starting point. Each processor follows a different path outward from the starting point, generating sum-of-absolute differences (SADs) for each point in the path. A best SAD for the path is kept, along with an index into motion vector tables containing X,Y points for all paths. Current and best SAD's, thresholds, and indexes are stored in an ALU dedicated memory. When the number of best SAD's meeting thresholds exceeds a target, the current search-level ends. The index of the overall best SAD locates a new starting point, and a next-denser search-level is performed in the same manner, but over a smaller search area. Each processor calculates SAD's for one 16×16 macroblock, four 8×8 blocks, and 16 4×4 blocks and the net best SAD of these 3 types determines partitioning.
Owner:NEOMAGIC
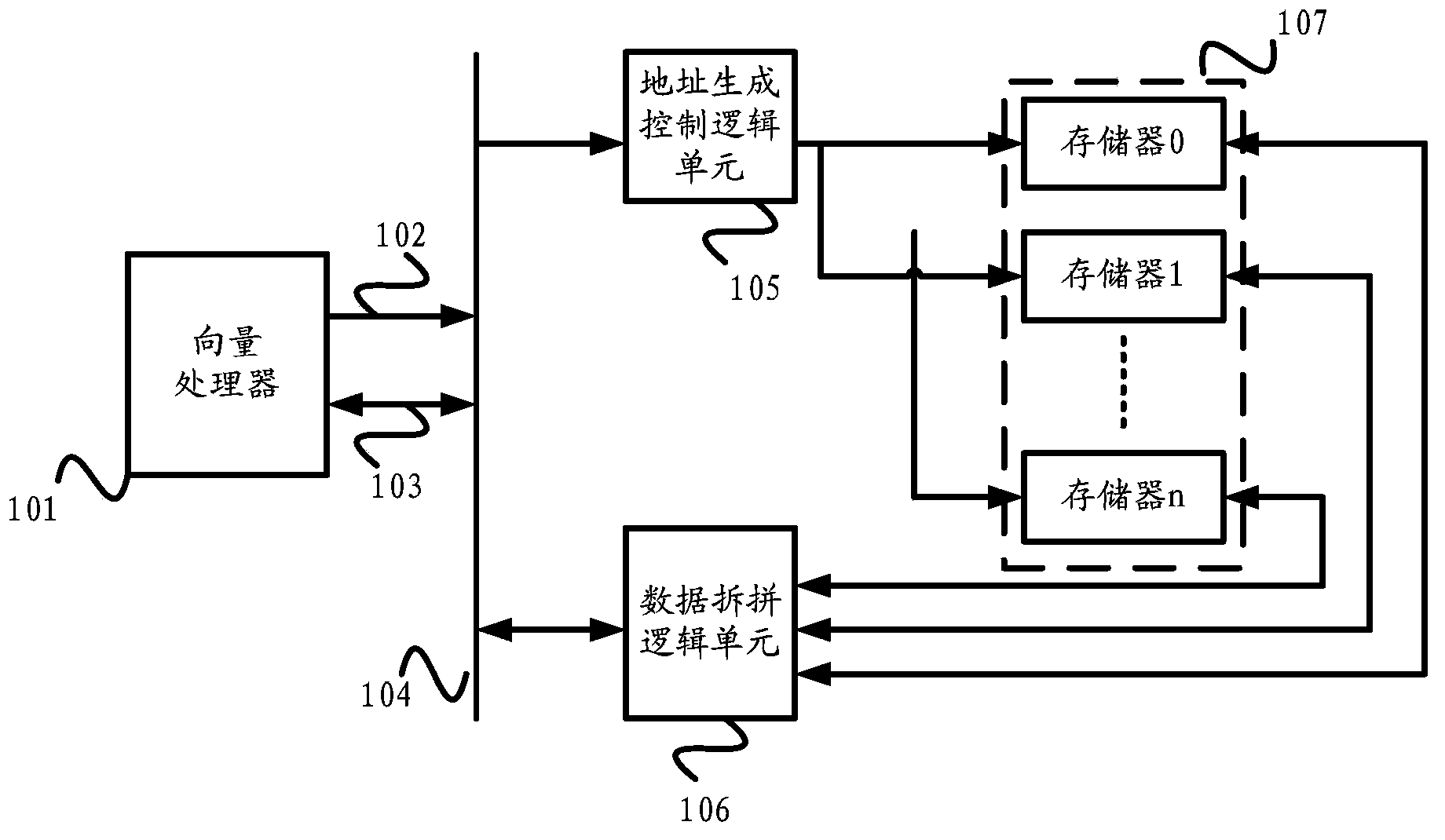
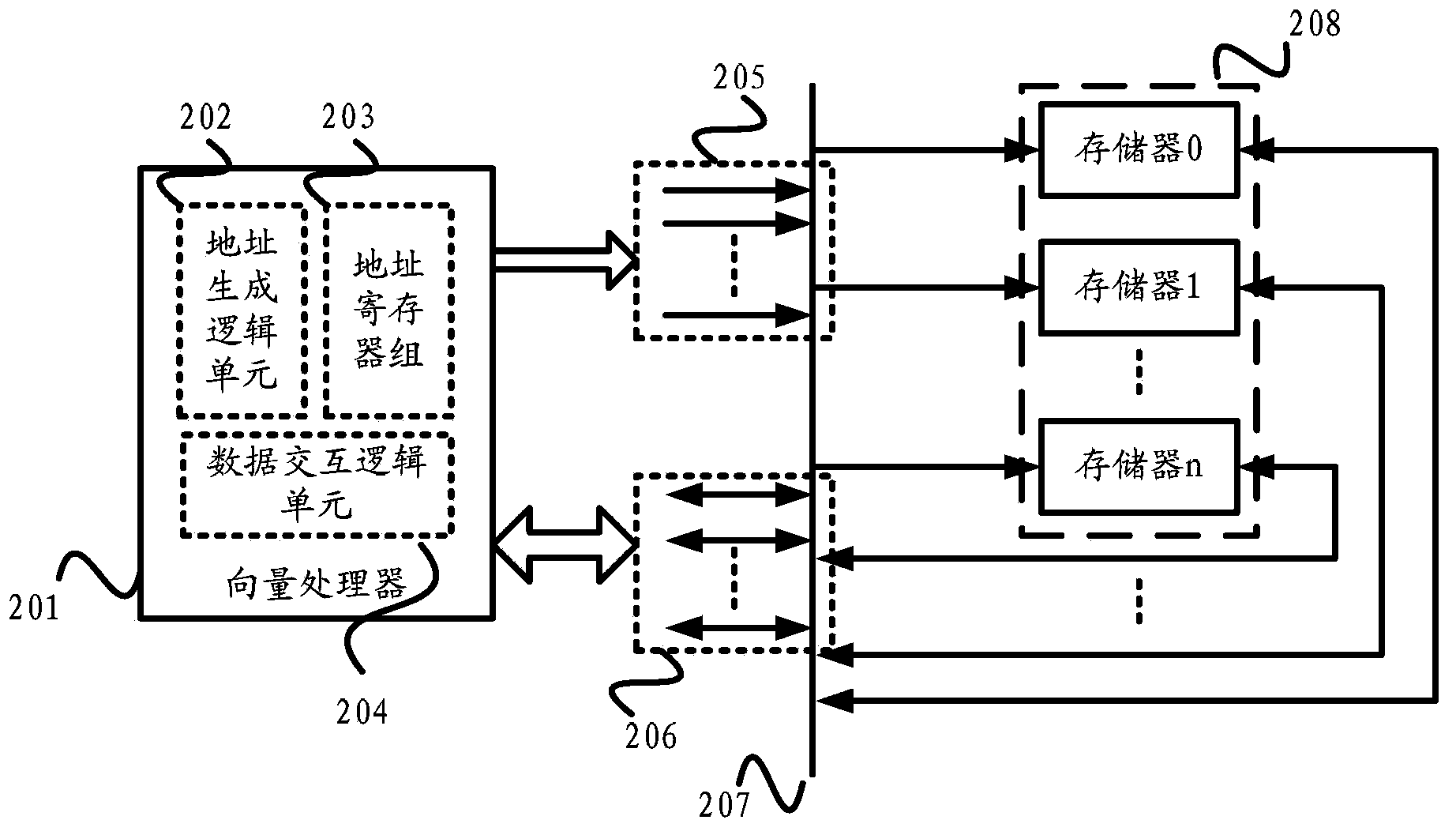
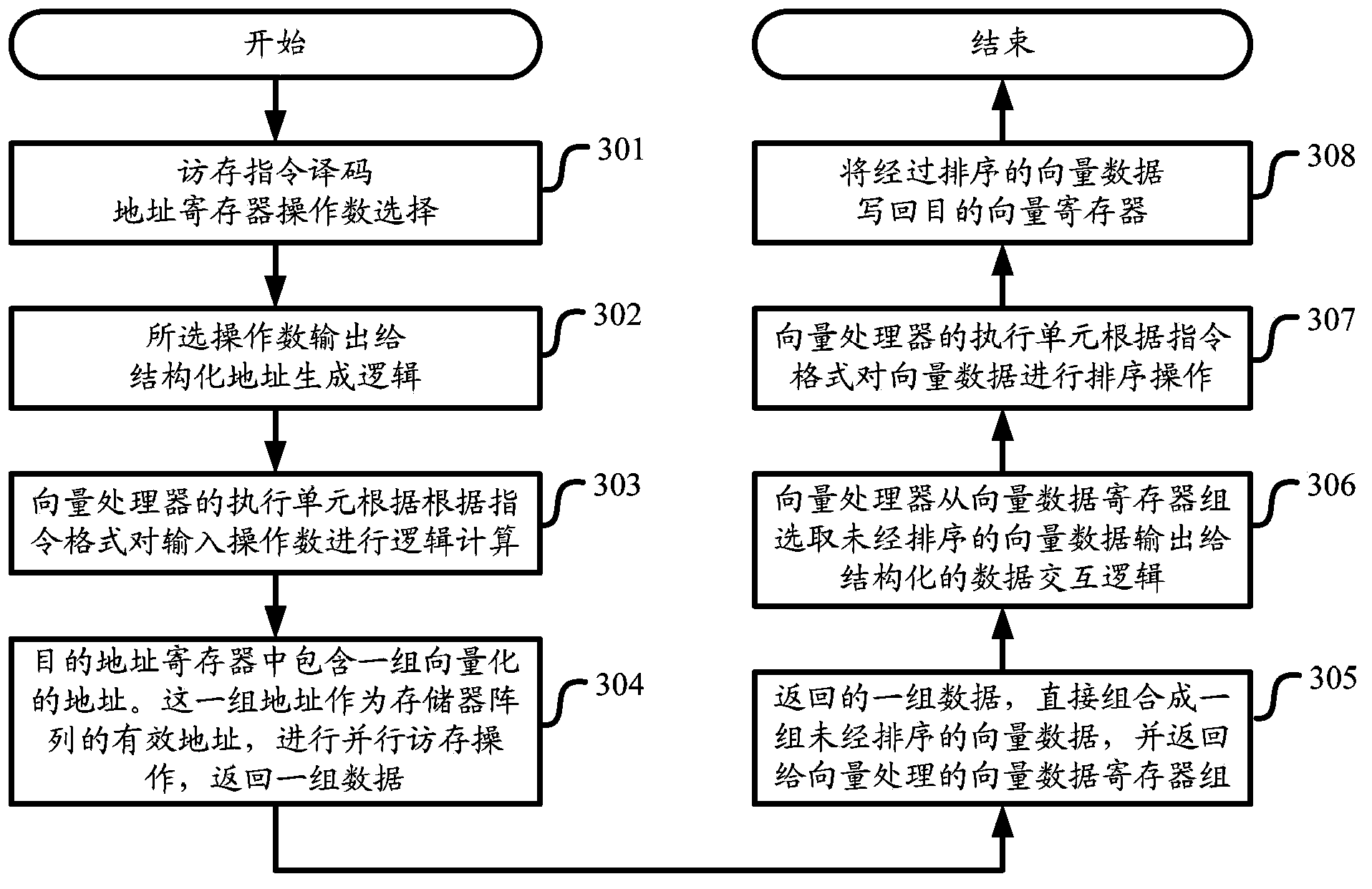
Vector processor and vector data access and interaction method thereof
ActiveCN103699360AImprove efficiencyProcessing speedMachine execution arrangementsArithmetic logic unitLogic cell
The invention discloses a vector processor and a vector data access and interaction method thereof. The vector processor comprises an address register set, an address generation logic unit and a data interaction logic unit, wherein the address register set is used for storing an operand and vectorized address data and transmitting the vectorized address data to a memory set through an address bus interface, and the vectorized address data are used for accessing the memory set; the address generation logic unit is used for calculating the vectorized address data according to the operand through an arithmetic logic unit and storing the vectorized address data in the address register set; the data interaction logic unit is used for carrying out splitting / splicing operation on vector data, which are accessed from the memory set through the address bus interface, through the arithmetic logic unit. According to the vector processor and the vector data access and interaction method thereof, the efficient arithmetic logic unit of the vector processor can be utilized sufficiently, so that the data processing speed is high and the efficiency is high.
Owner:北京中科晶上科技股份有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com