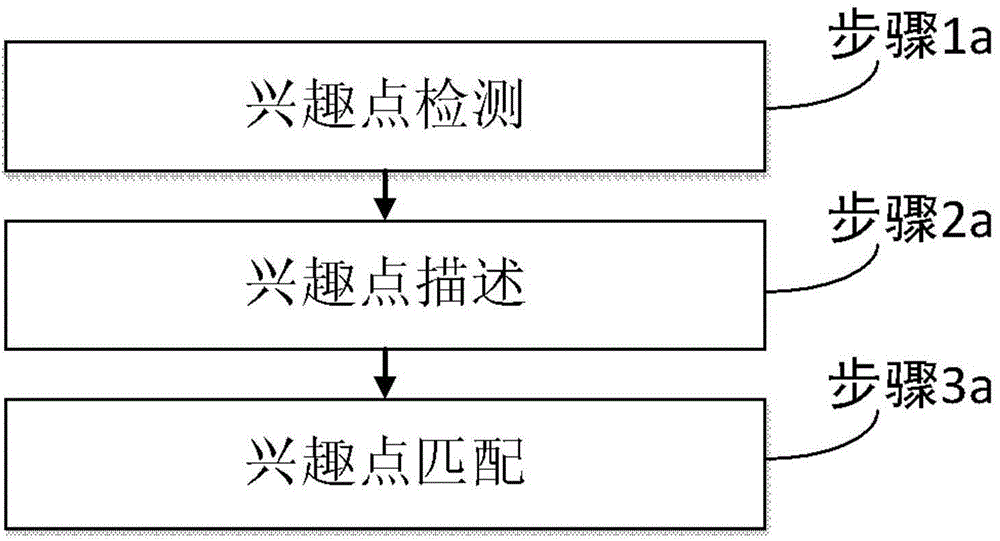
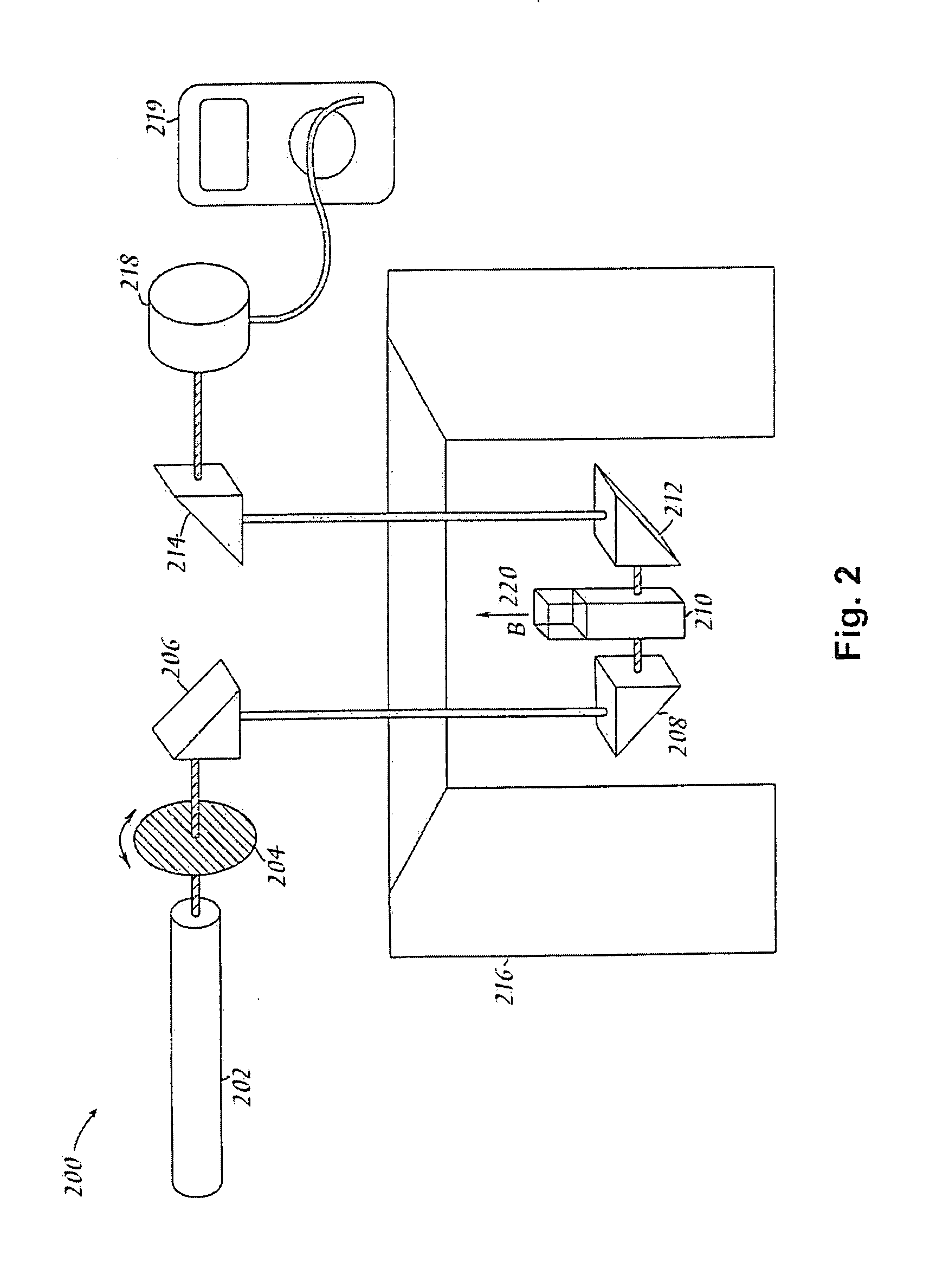
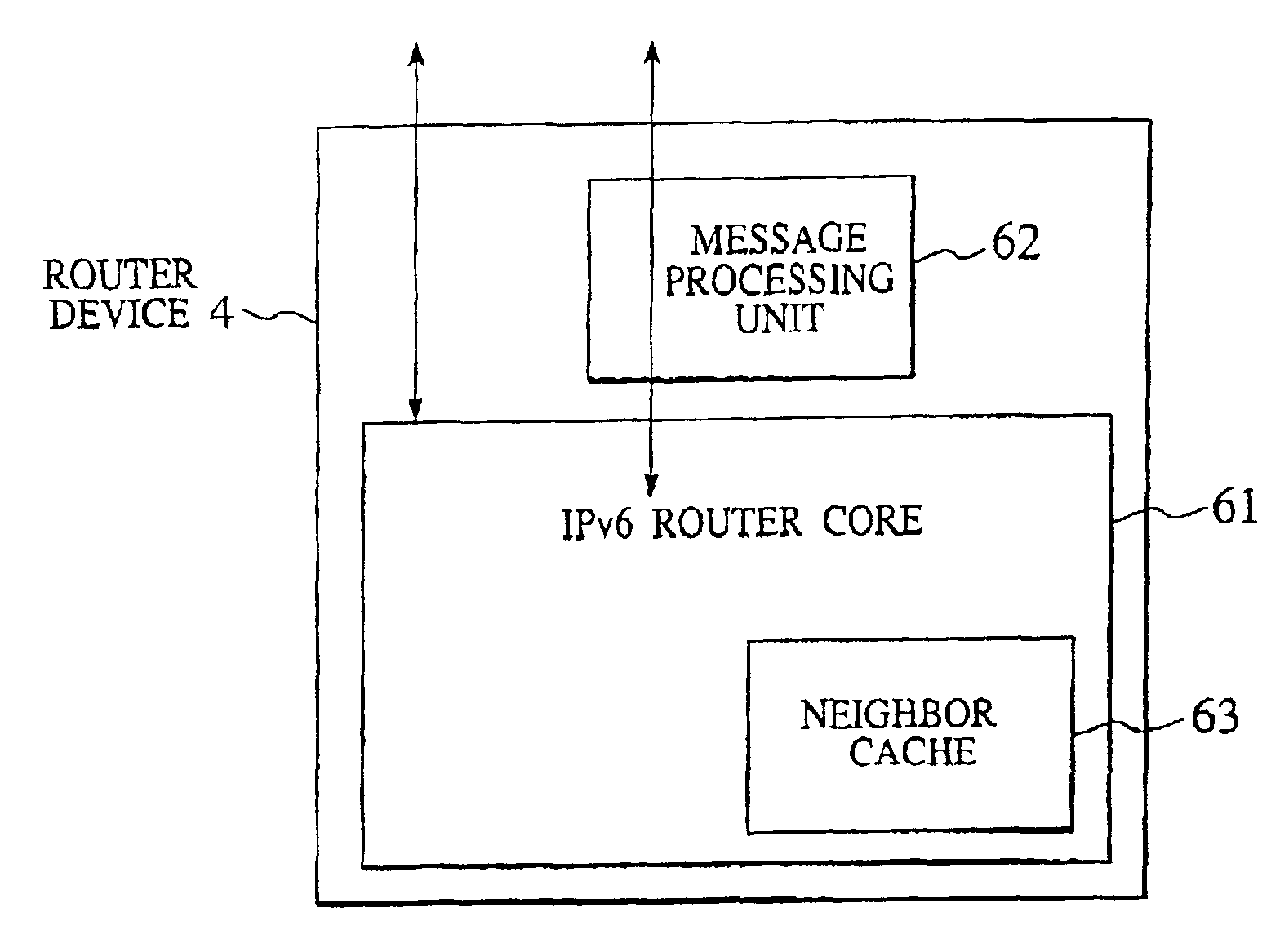
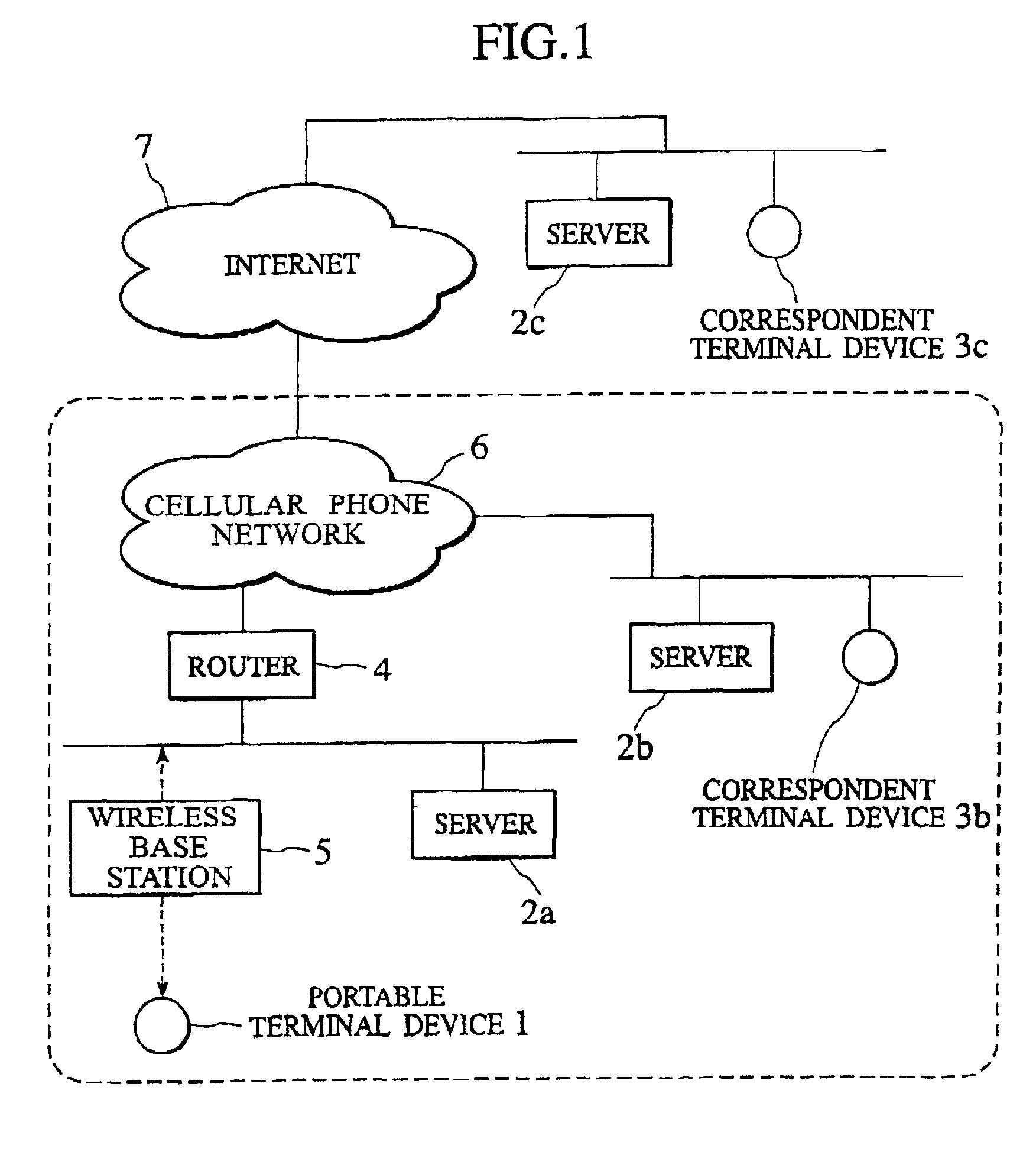
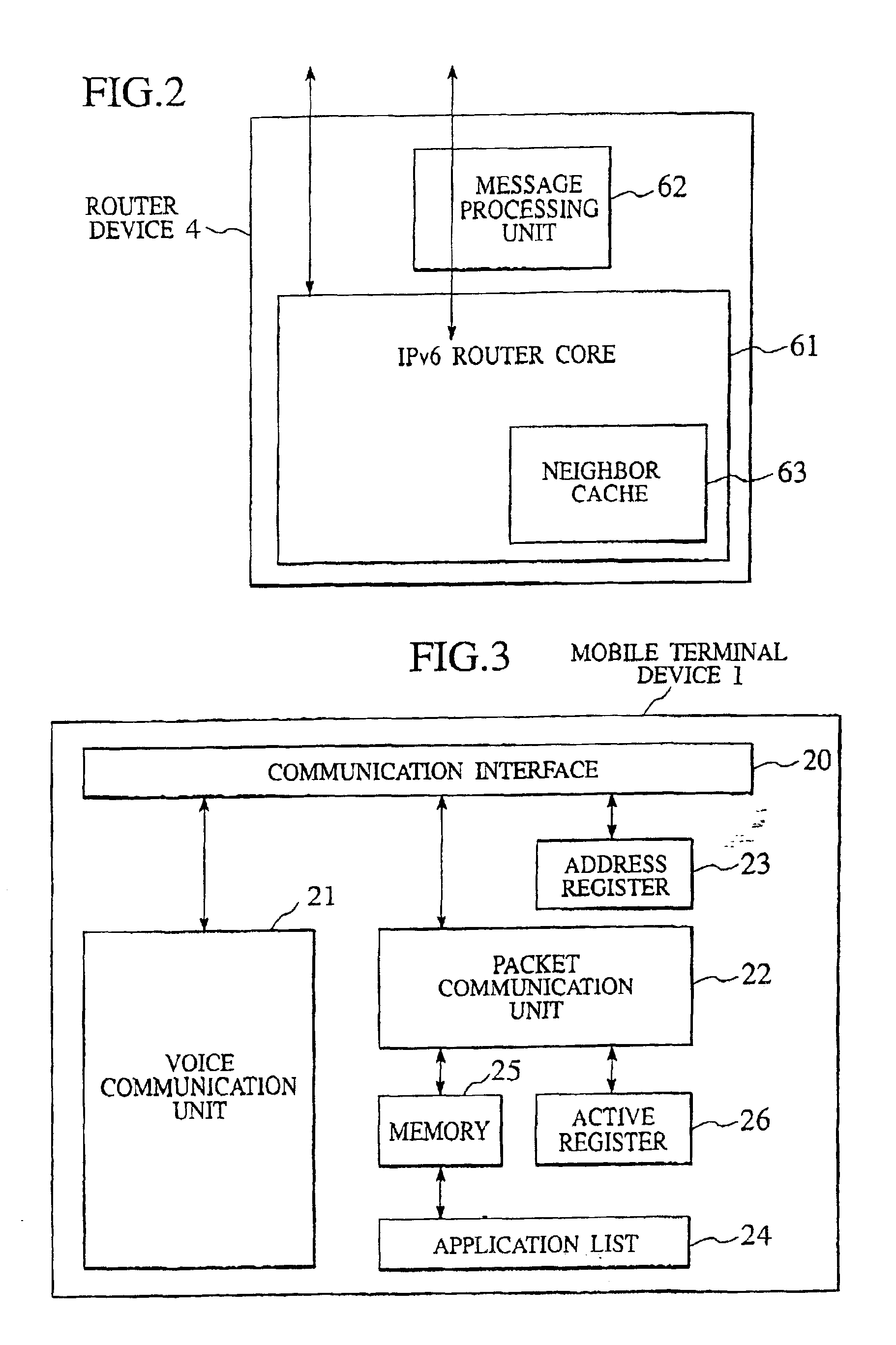
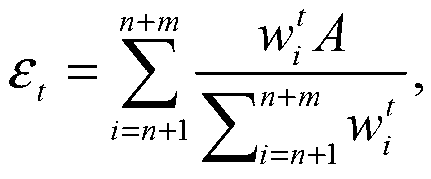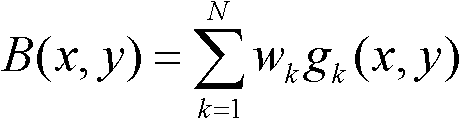Patents
Literature
107 results about "Nearest neighbour" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nearest Neighbour is housed in the Willem II Fabriek. If you would like to send us something, please be sure to include our studio number in the address line: studio 2.03. Thank you. Office: Boschveldweg 471F (studio 2.03)
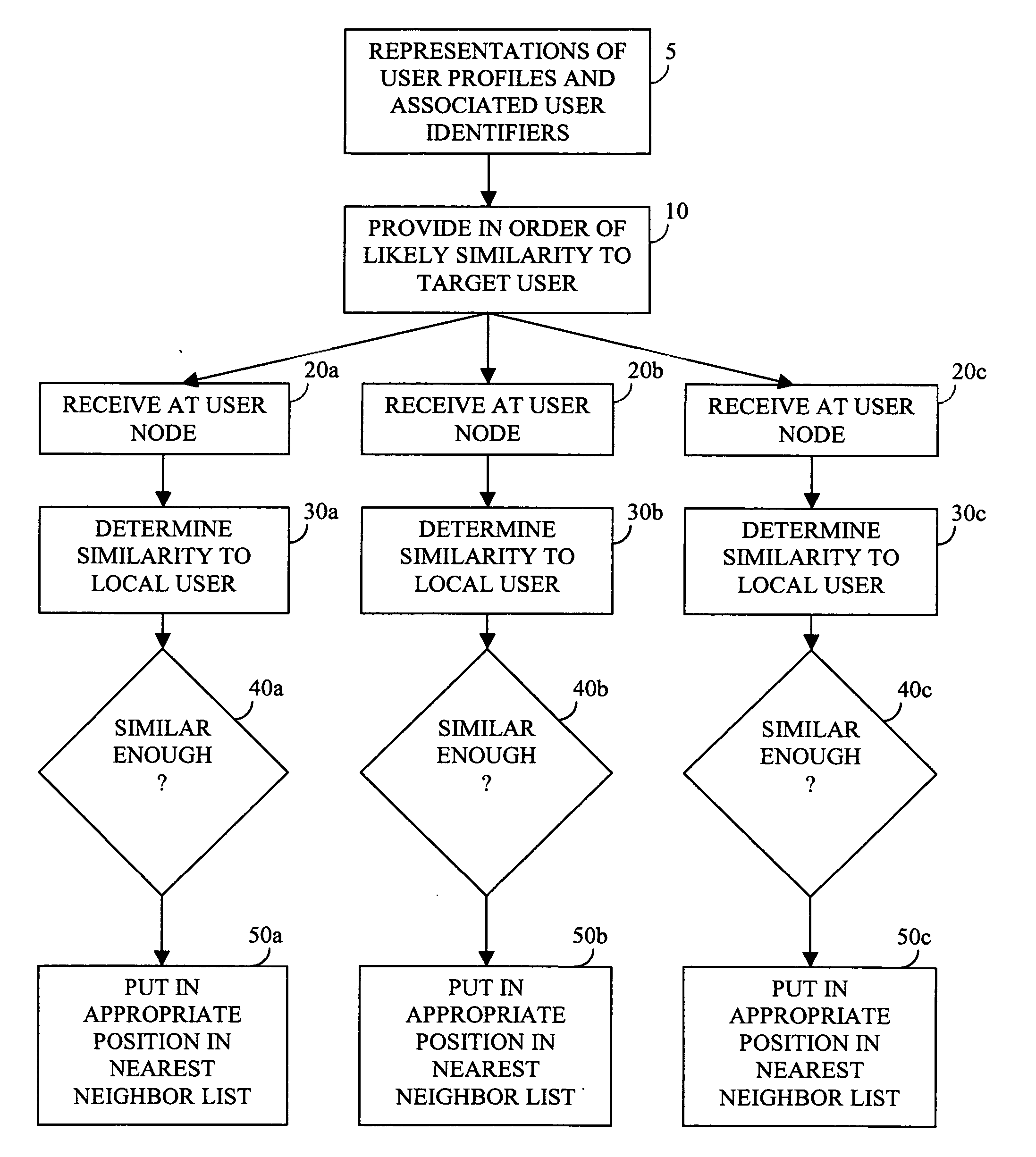
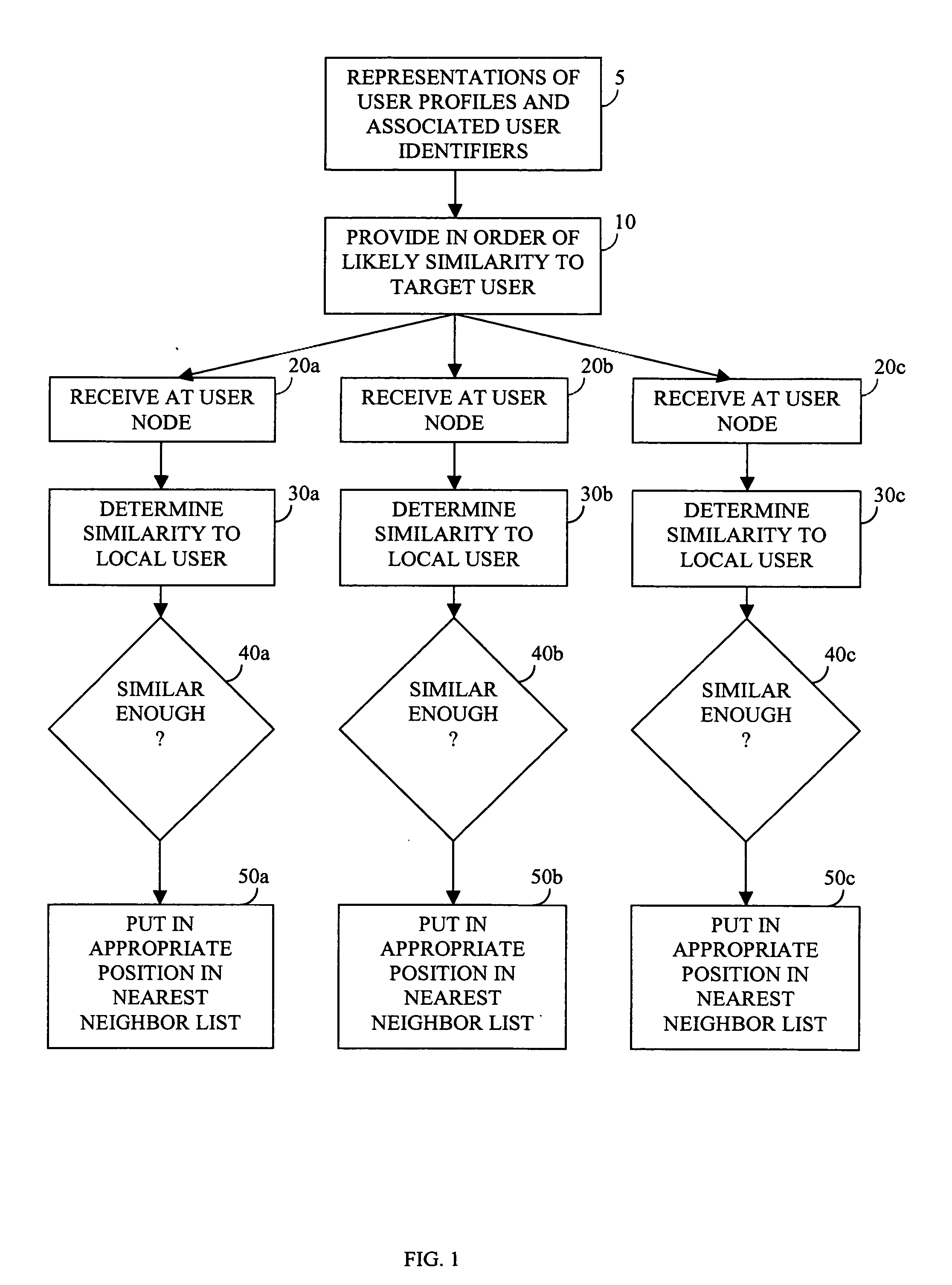
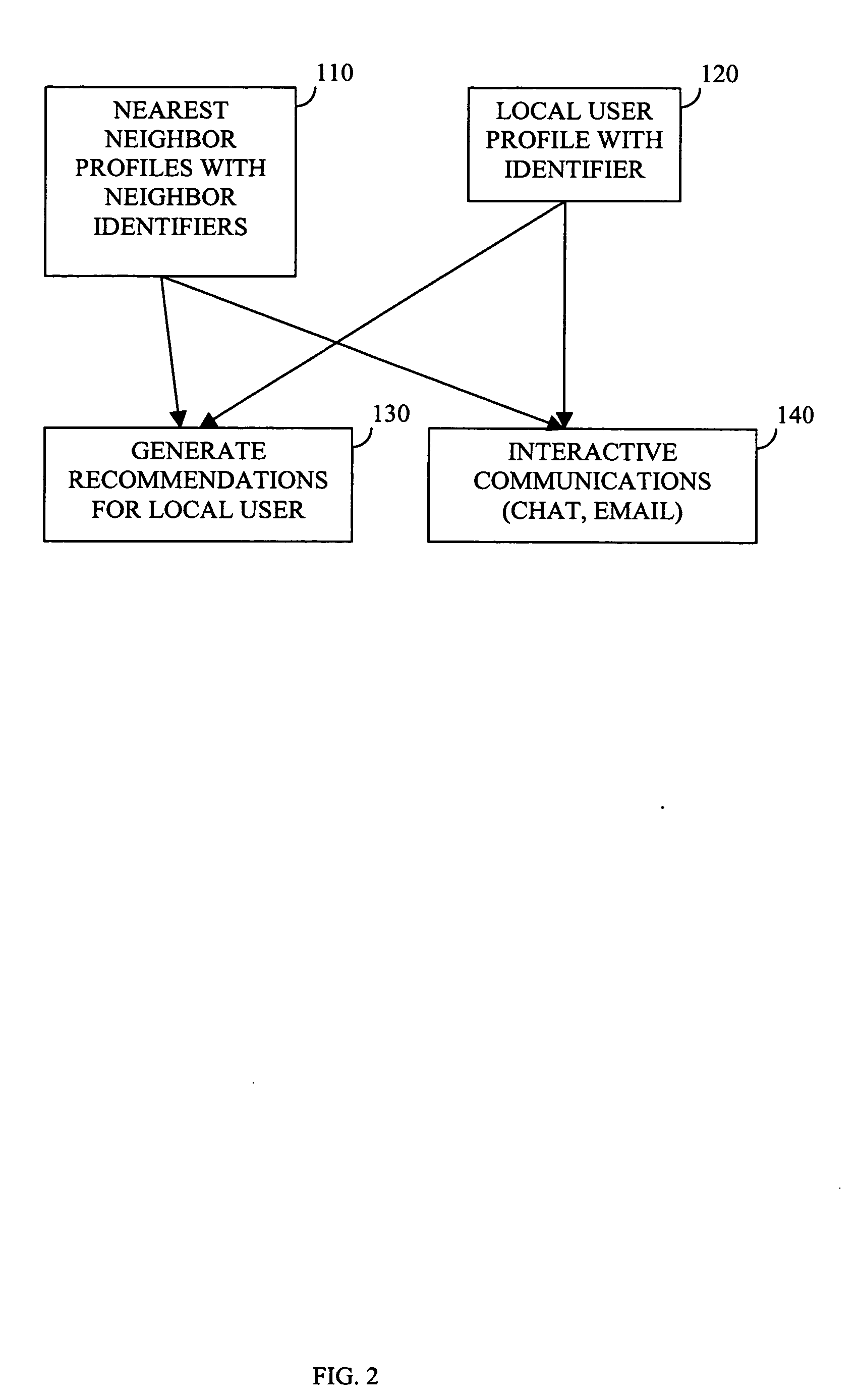
Enabling recommendations and community by massively-distributed nearest-neighbor searching
InactiveUS20060020662A1Reason to have confidenceGreat extremityMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksNear neighborEnd user
The computer associated with each of a potentially large number of end users is harnessed to provide a massively-distributed mechanism for finding the nearest neighbors of each user, according to tastes and / or interests. Once these nearest neighbors are determined, there taste or and / or interest profiles are leveraged for highly accurate recommendations, and their online addresses are leveraged for community purposes.
Owner:EMERGENT MUSIC
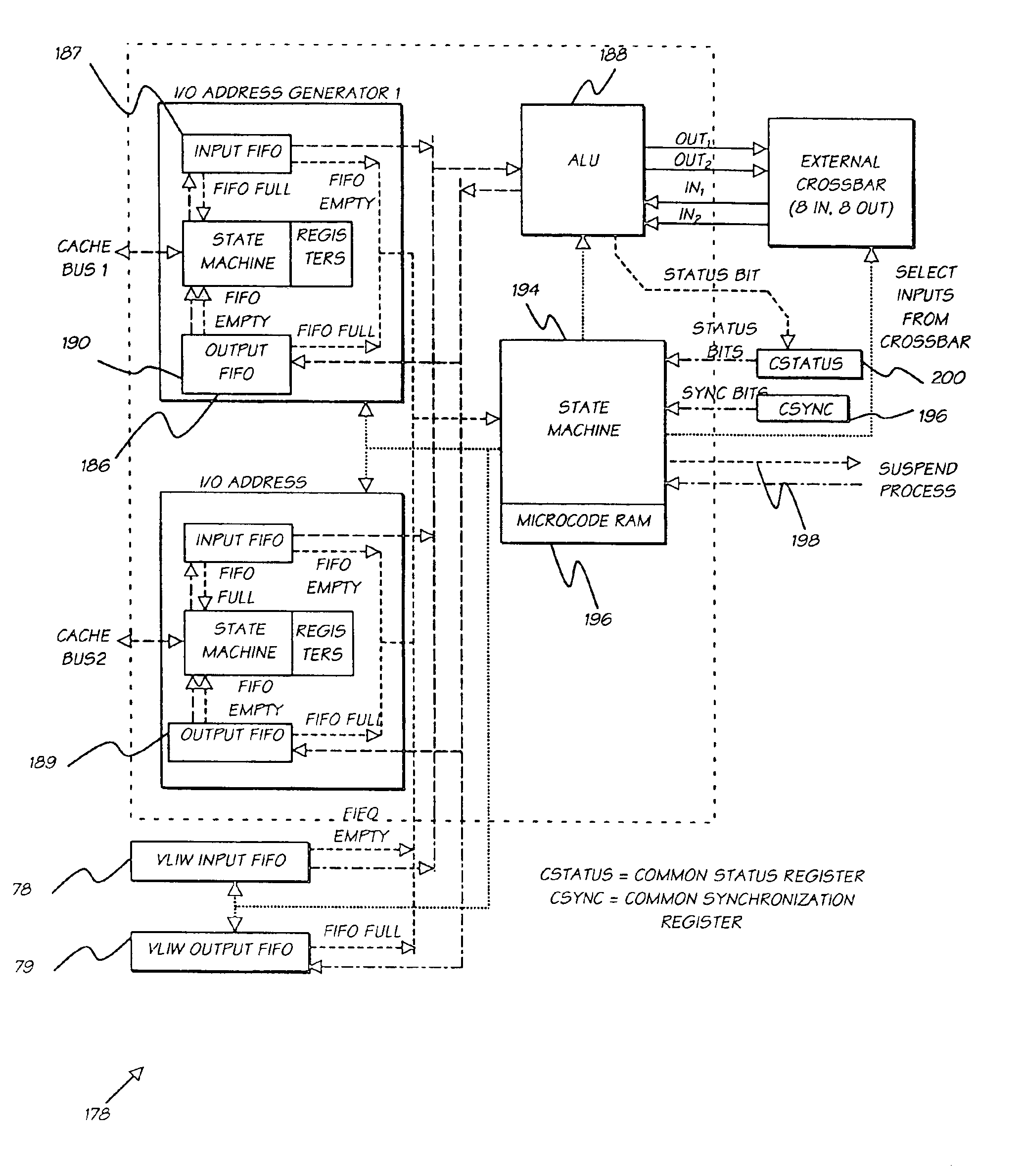
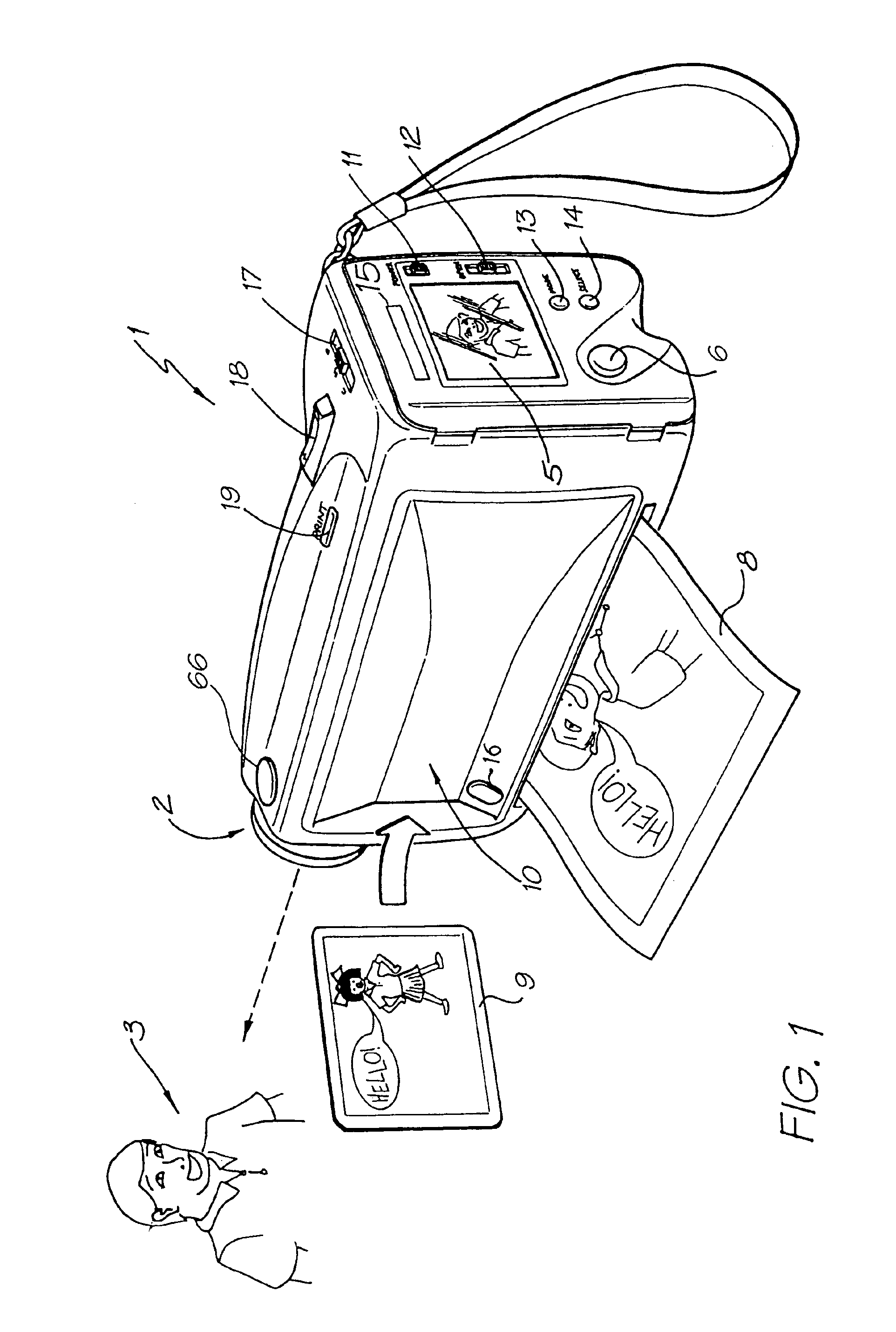
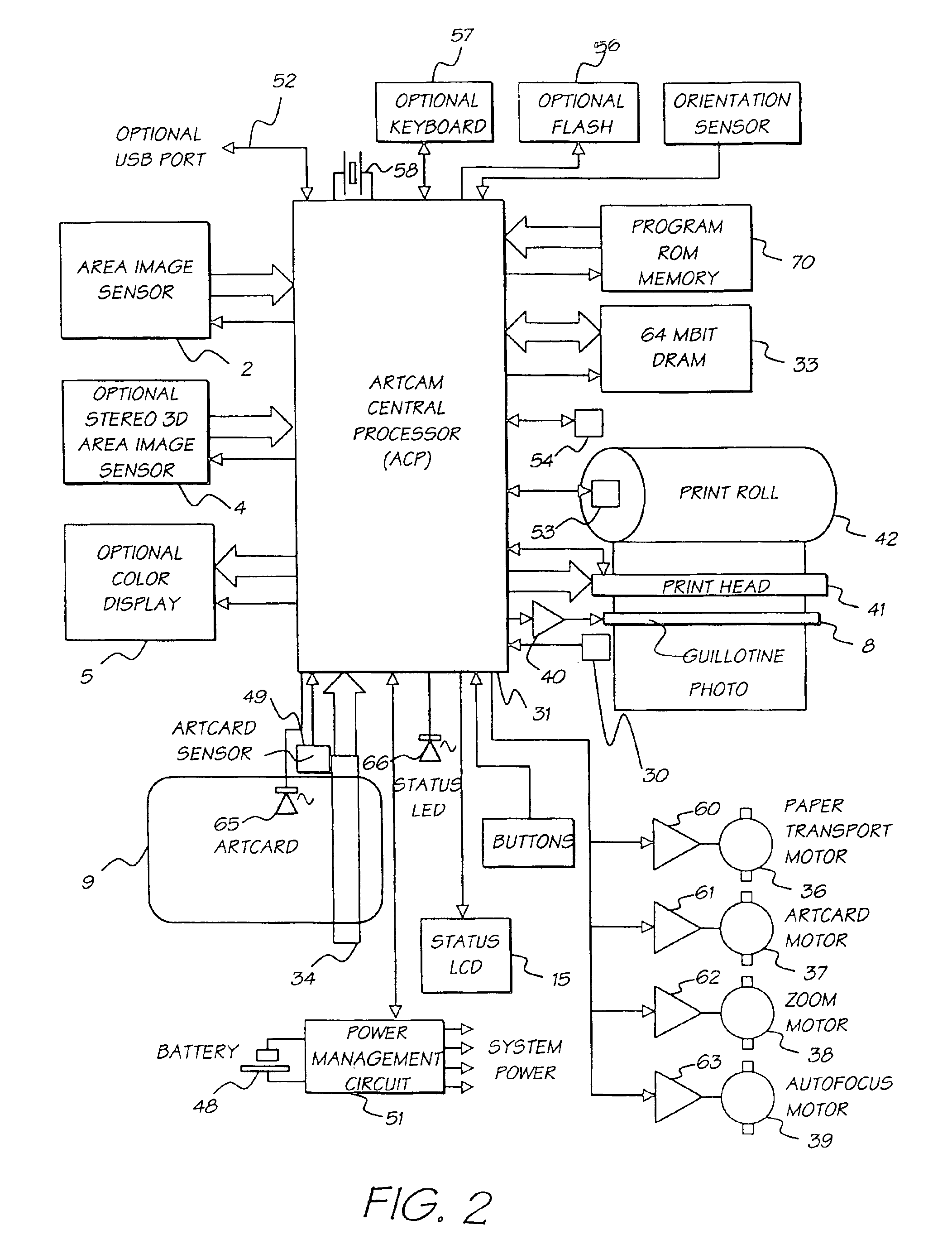
Digital camera system containing a VLIW vector processor
InactiveUS6879341B1Material nanotechnologyTelevision system detailsCrossbar switchArithmetic logic unit
A digital camera has a sensor for sensing an image, a processor for modifying the sensed image in accordance with instructions input into the camera and an output for outputting the modified image where the processor includes a series of processing elements arranged around a central crossbar switch. The processing elements include an Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) acting under the control of a writeable microcode store, an internal input and output FIFO for storing pixel data to be processed by the processing elements and the processor is interconnected to a read and write FIFO for reading and writing pixel data of images to the processor. Each of the processing elements can be arranged in a ring and each element is also separately connected to its nearest neighbors. The ALU receives a series of inputs interconnected via an internal crossbar switch to a series of core processing units within the ALU and includes a number of internal registers for the storage of temporary data. The core processing units can include at least one of a multiplier, an adder and a barrel shifter. The processing elements are further connected to a common data bus for the transfer of a pixel data to the processing elements and the data bus is interconnected to a data cache which acts as an intermediate cache between the processing elements and a memory store for storing the images.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
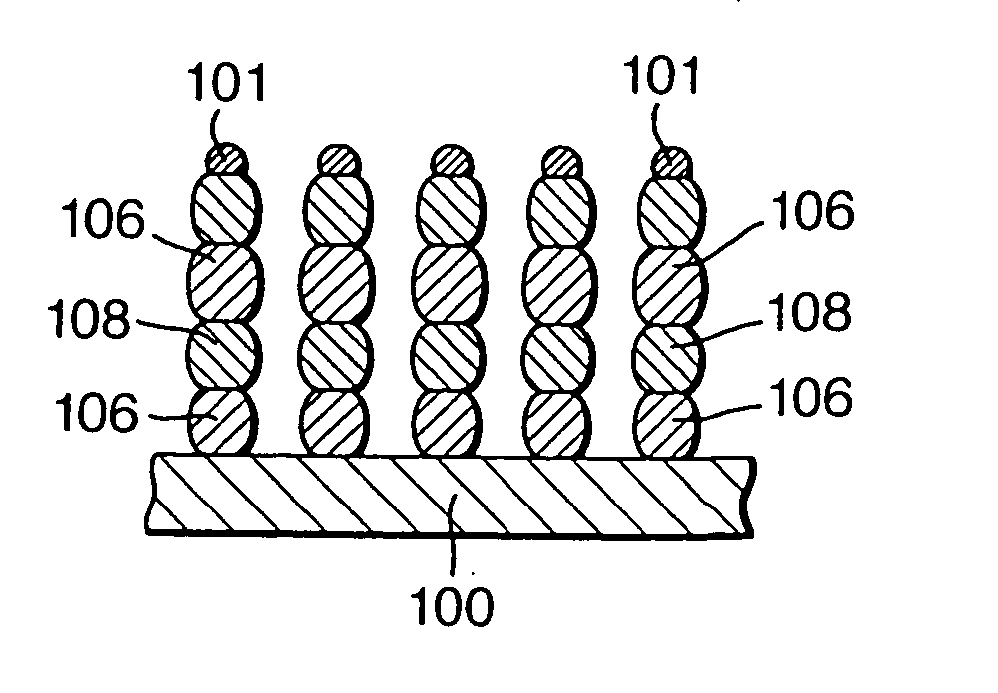
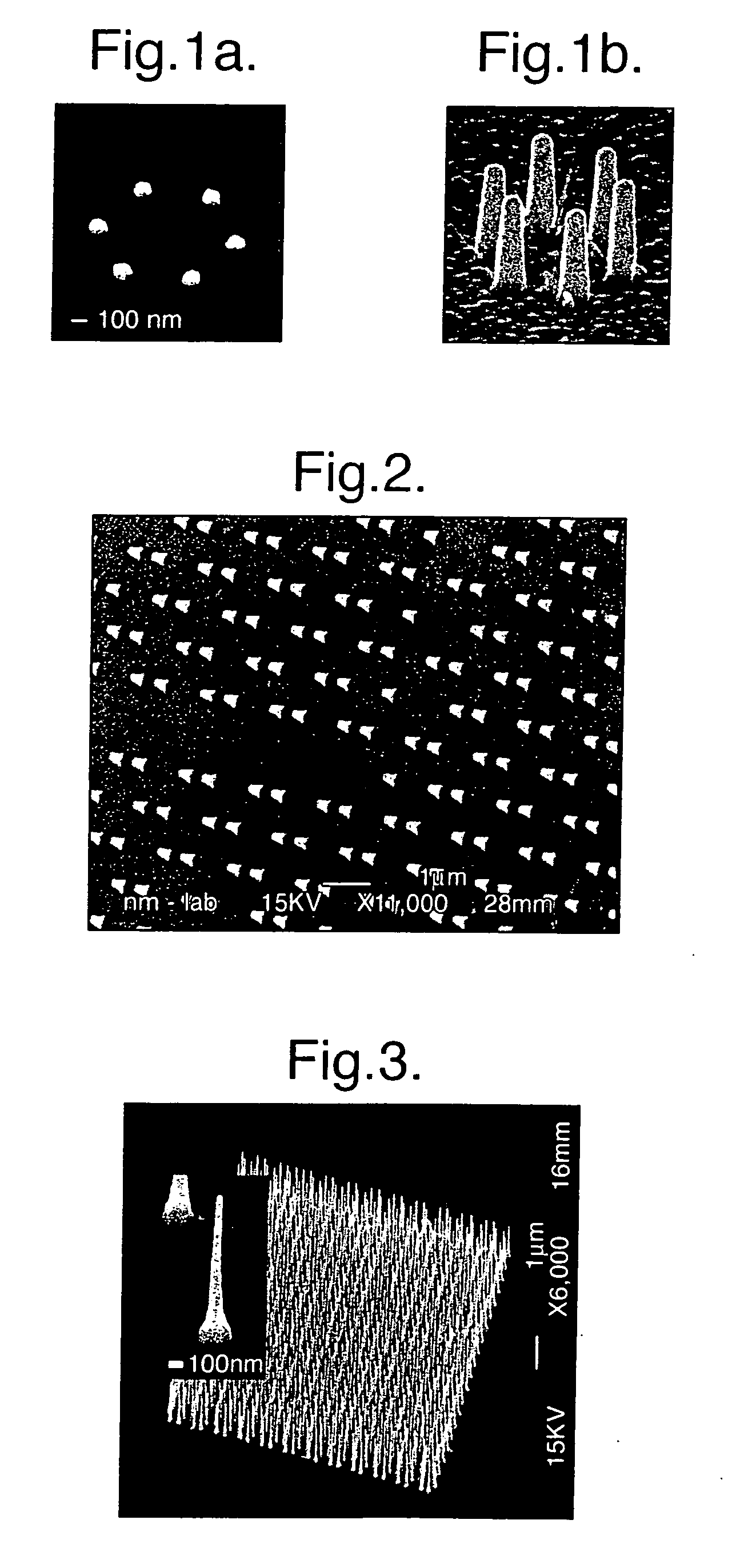
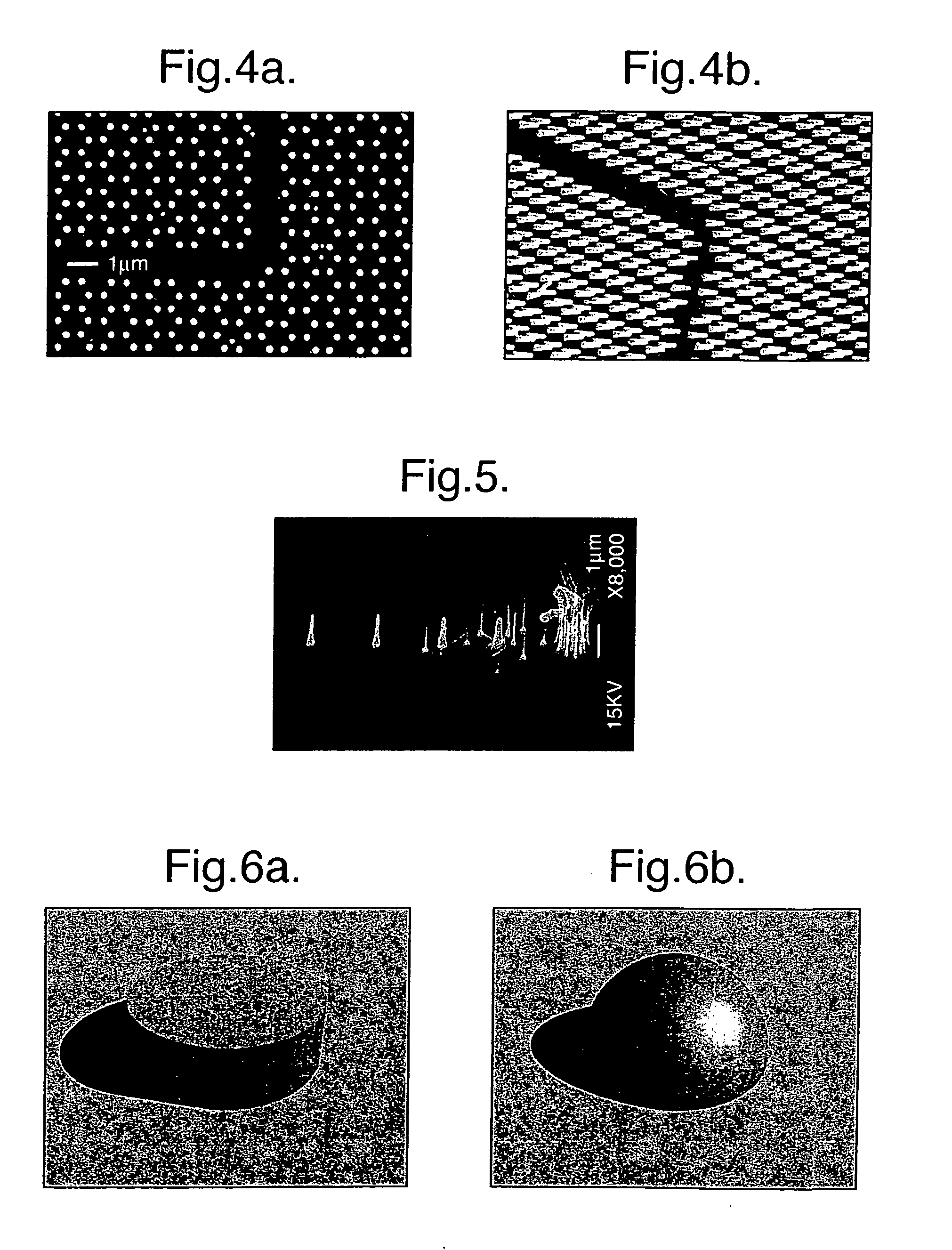
Precisely positioned nanowhiskers and nanowhisker arrays and method for preparing them
InactiveUS20050011431A1Increase forceImprove stabilityMaterial nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthPhotonic bandgapAdemetionine
A nanoengineered structure comprising an array of more than about 1000 nanowhiskers on a substrate in a predetermined spatial configuration, for use for example as a photonic band gap array, wherein each nanowhisker is sited within a distance from a predetermined site not greater than about 20% of its distance from its nearest neighbour. To produce the array, an array of masses of a catalytic material are positioned on the surface, heat is applied and materials in gaseous form are introduced such as to create a catalytic seed particle from each mass, and to grow, from the catalytic seed particle, epitaxially, a nanowhisker of a predetermined material, and wherein each mass upon melting, retains approximately the same interface with the substrate surface such that forces causing the mass to migrate across said surface are less than a holding force across a wetted interface on the substrate surface.
Owner:QUNANO
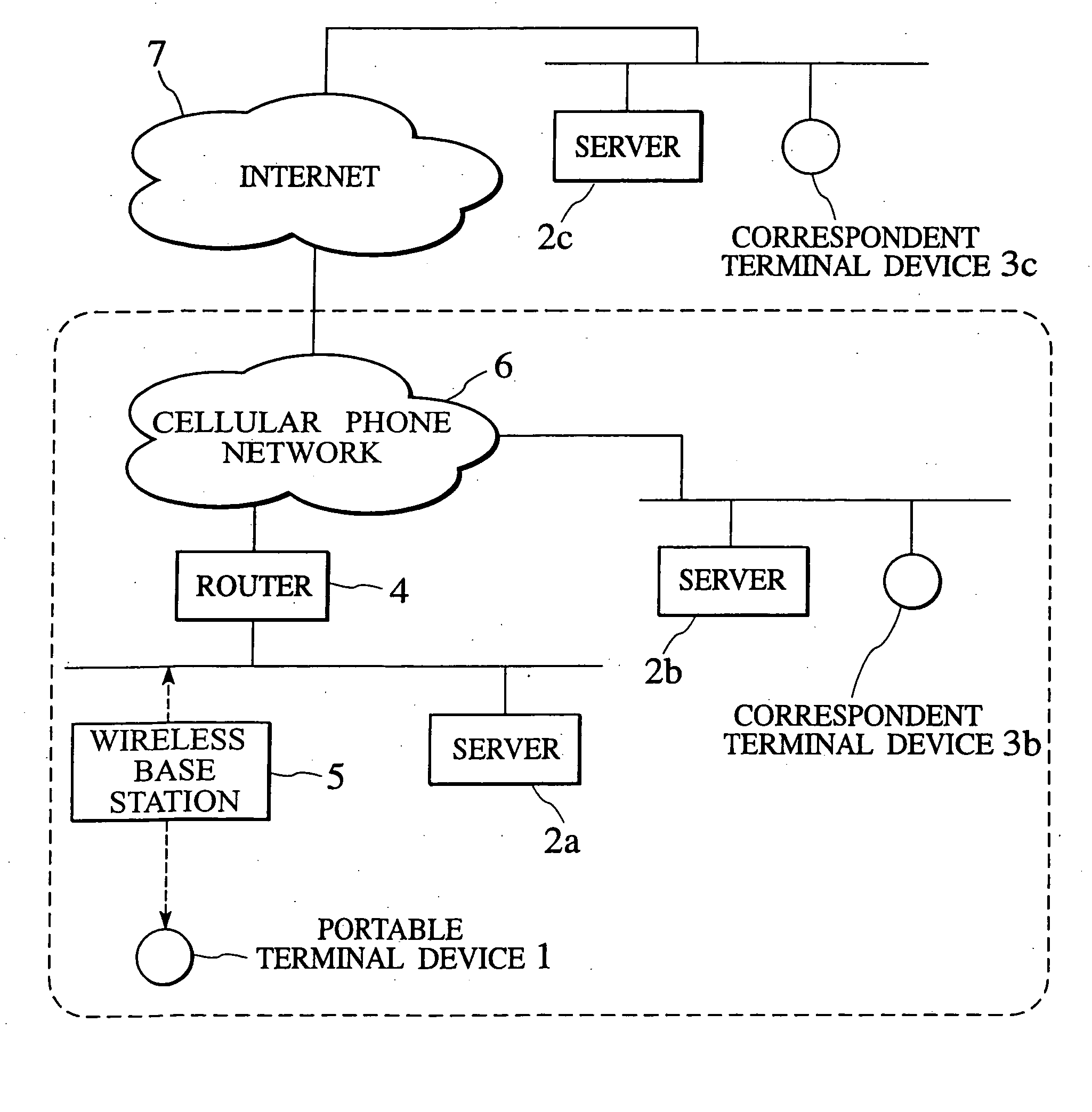
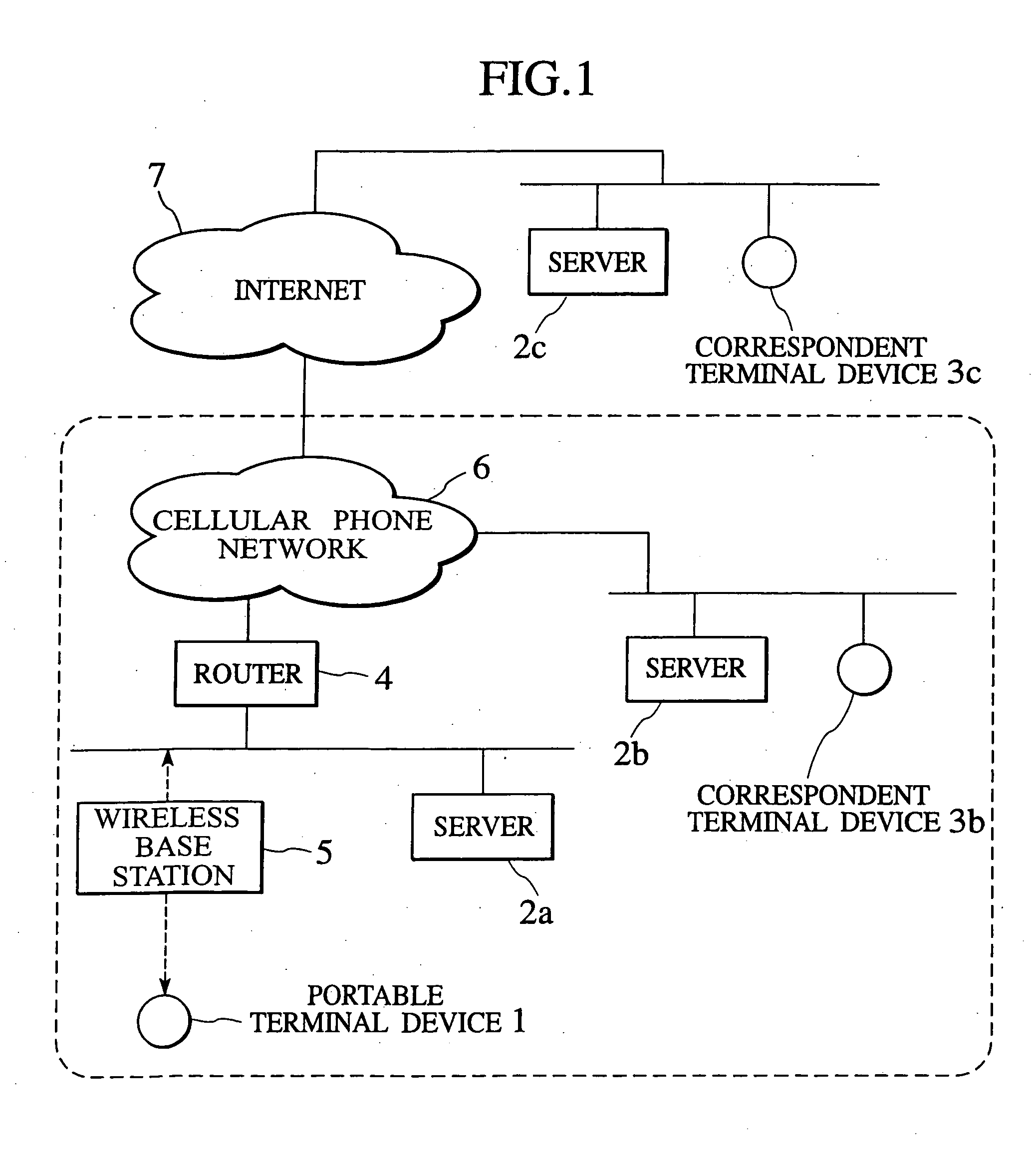
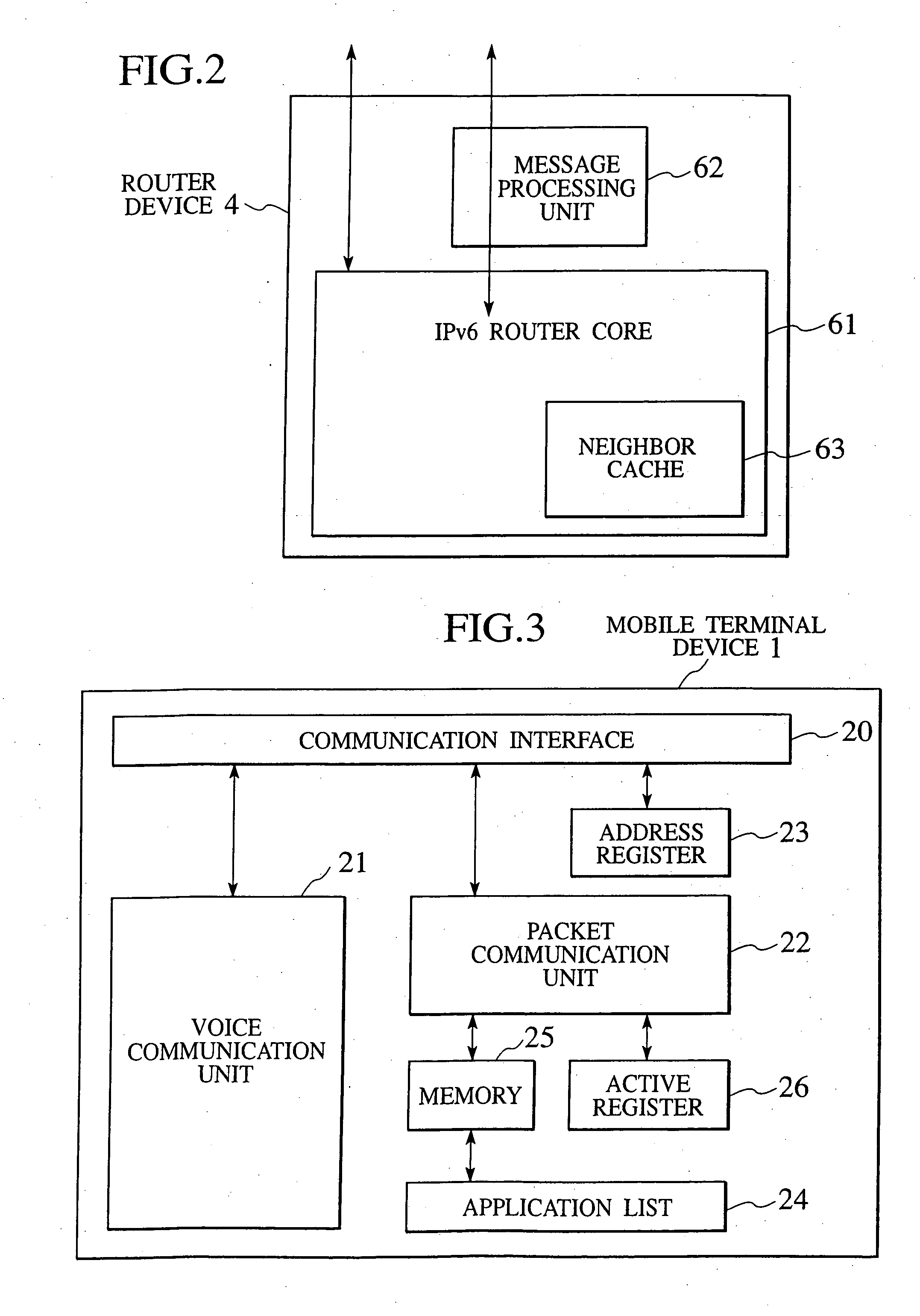
Packet transfer scheme using mobile terminal and router for preventing attacks using global address
In a mobile communication network providing an Internet service, the arrived packets are delivered from the nearest neighbor router device to the mobile terminal device according to the need such as when a prescribed application is activated or when a prescribed packet has arrived, by using message exchanges between the nearest neighbor router device and the mobile terminal device, so that it becomes possible to prevent the unnecessary packet attacks from the global Internet.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
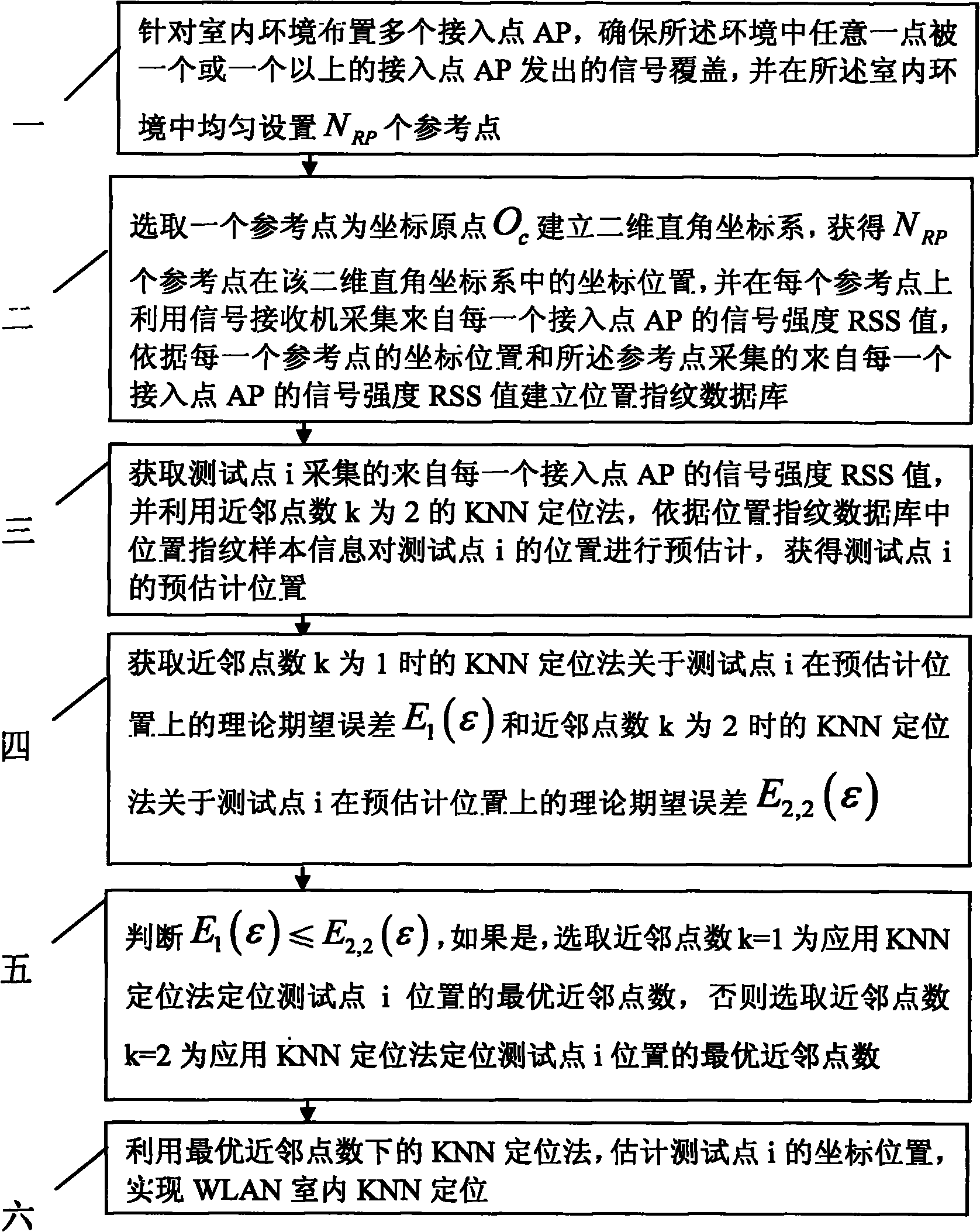
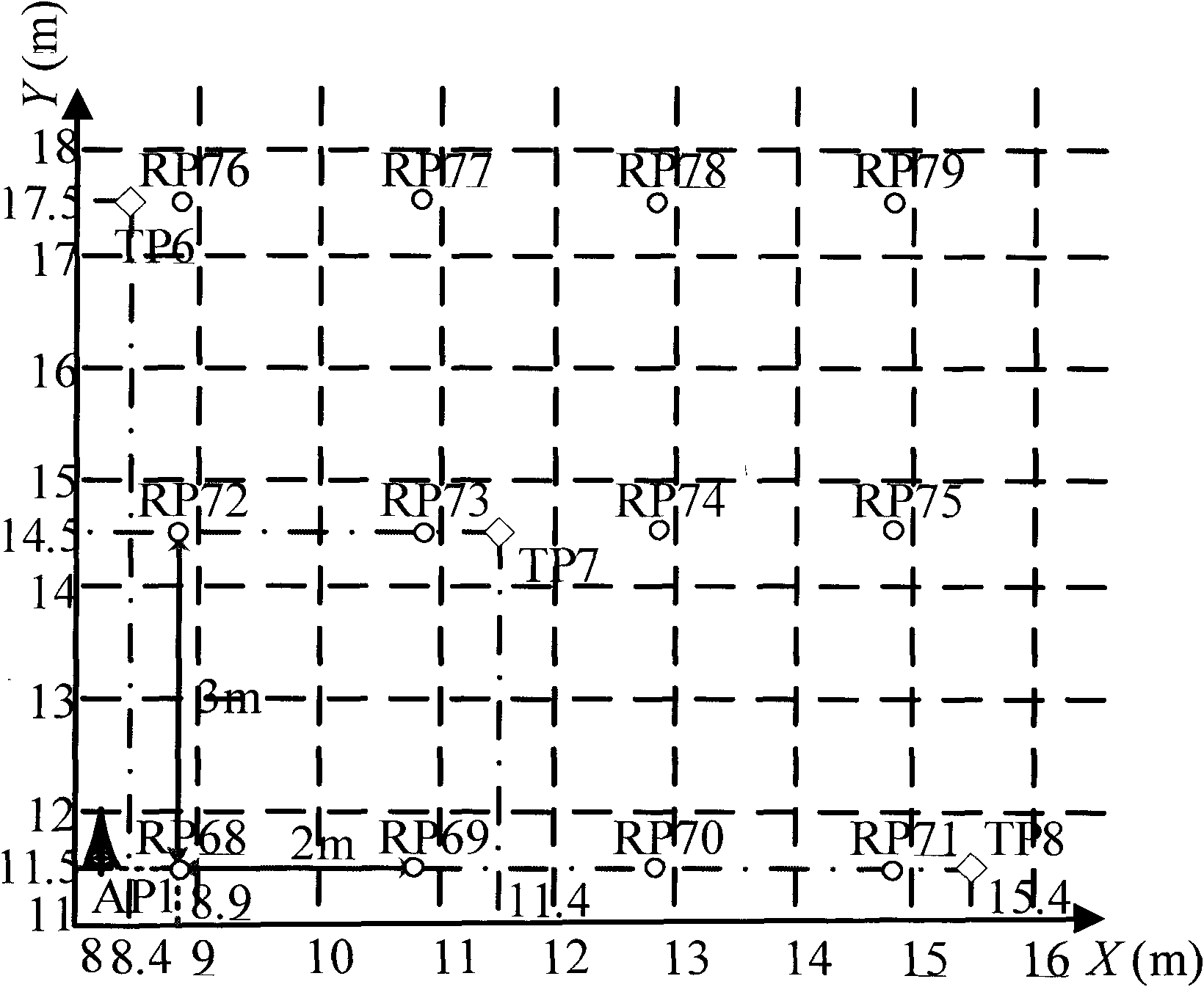
WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network) indoor KNN (K-Nearest Neighbor) positioning method based on near-neighbor point number optimization
InactiveCN101883424AEffective selectionImprove effectivenessNetwork topologiesAlgorithmNear neighbor
The invention relates to a WLAN indoor KNN positioning method based on near-neighbor point number optimization, which relates to the field of mode identification and solves the problem of reduced positioning precision caused by improper near-neighbor point number selection in the traditional WLAN indoor KNN positioning method. The WLAN indoor KNN positioning method comprises the following steps of: firstly establishing a complete WLAN positioning scene and a position fingerprint database; then, pre-estimating the position of a testing point according to the collected signal intensity at the testing point and the pre-stored position fingerprint data by utilizing a KNN positioning method with the near-neighbor number as 2; then obtaining the theoretical expected error of the testing point at a pre-estimated position by the KNN positioning method when the near-neighbor point numbers are 1 and 2, and selecting the near-neighbor point number corresponding to the KNN positioning method with higher theoretical precision as the optimum near-neighbor point number for estimating the position of the testing point; and finally realizing WLAN indoor KNN positioning by utilizing the KNN positioning method under the optimum near-neighbor point number. The invention is applicable to indoor positioning.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
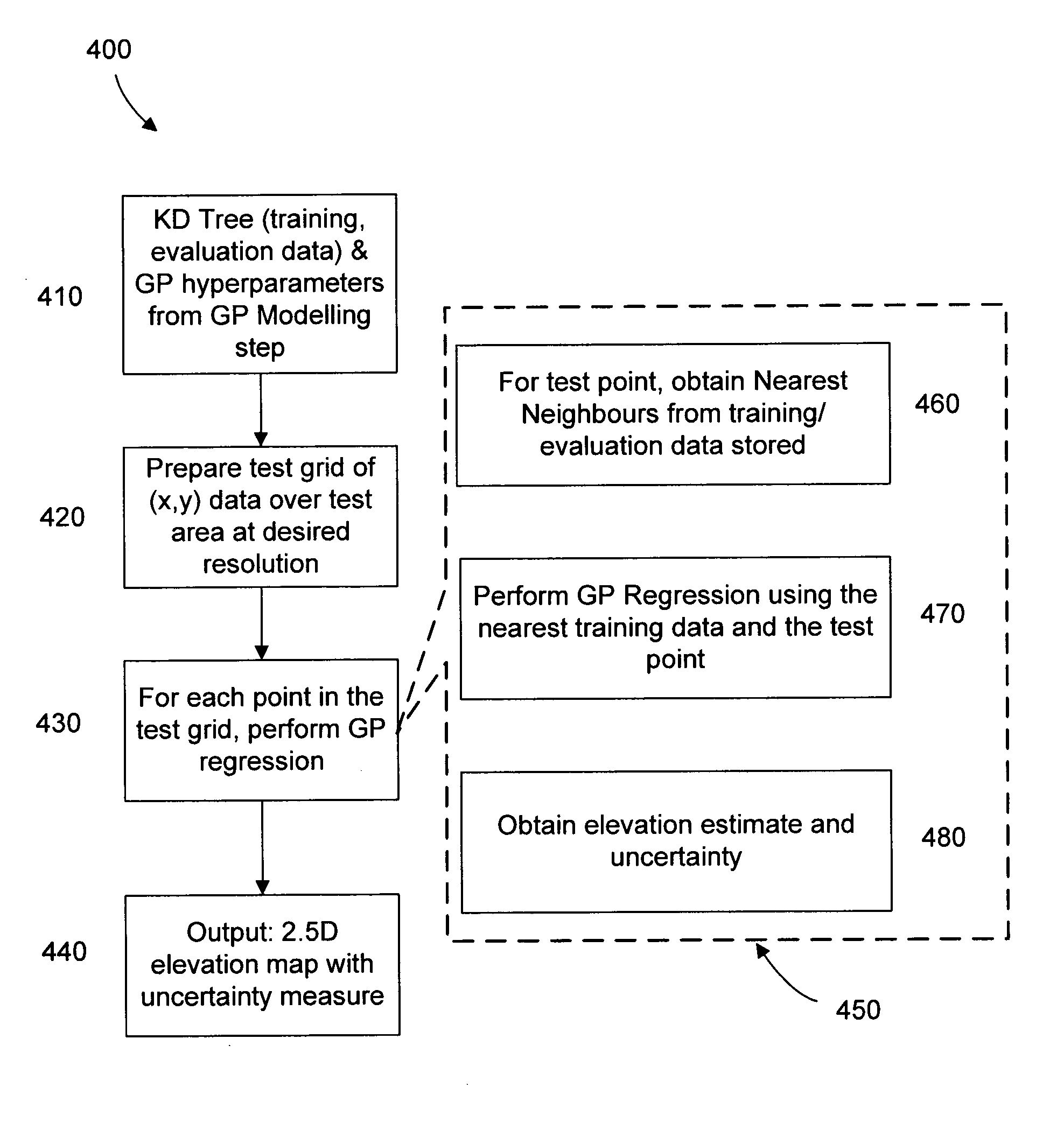
Method and system of data modelling
InactiveUS20110257949A1Kernel methodsComputation using non-denominational number representationData setTraining phase
A method for modelling a dataset includes a training phase, wherein the dataset is applied to a non-stationary Gaussian process kernel in order to optimize the values of a set of hyperparameters associated with the Gaussian process kernel, and an evaluation phase in which the dataset and Gaussian process kernel with optimized hyperparameters are used to generate model data. The evaluation phase includes a nearest neighbour selection step. The method may include generating a model at a selected resolution.
Owner:THE UNIV OF SYDNEY
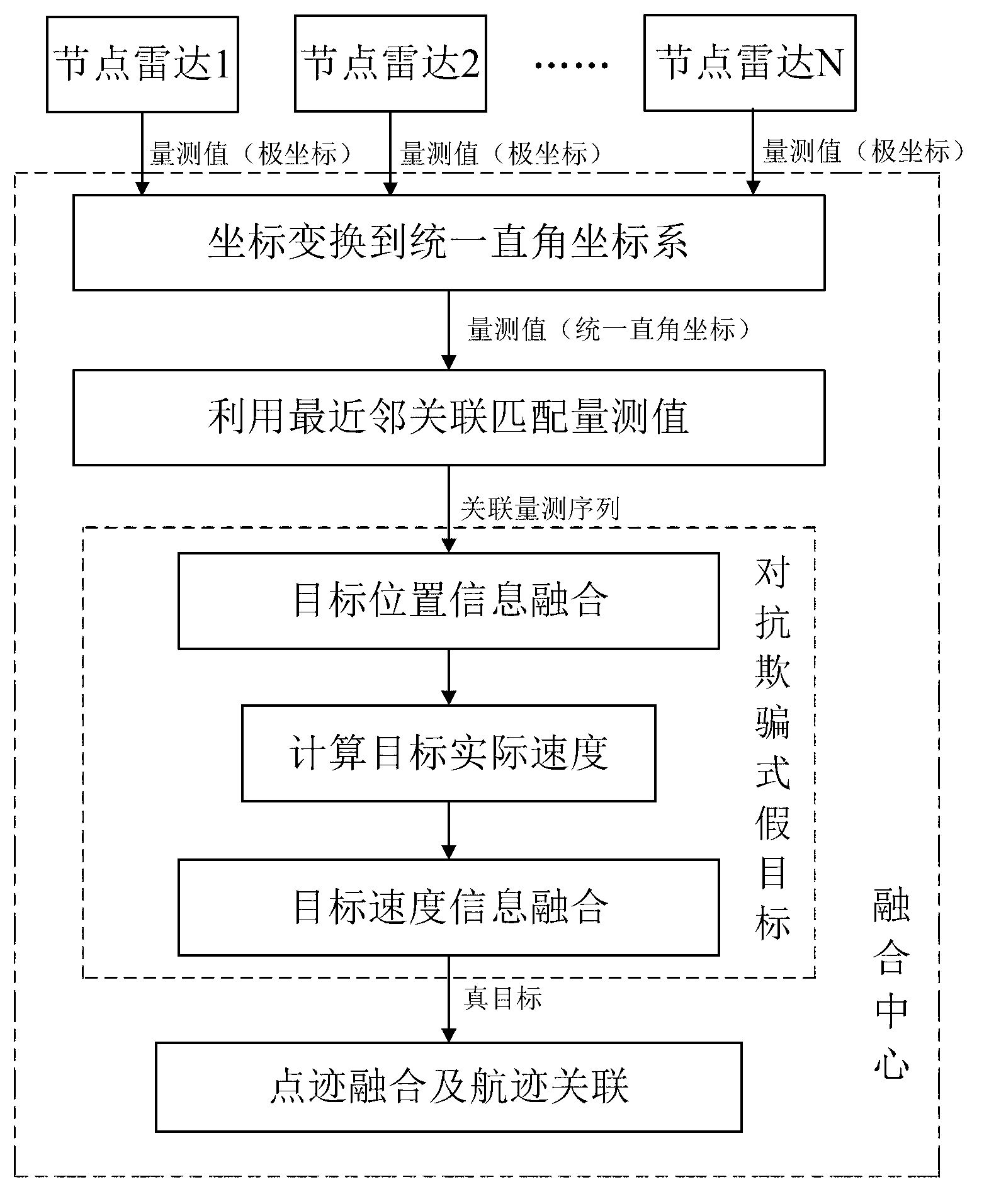
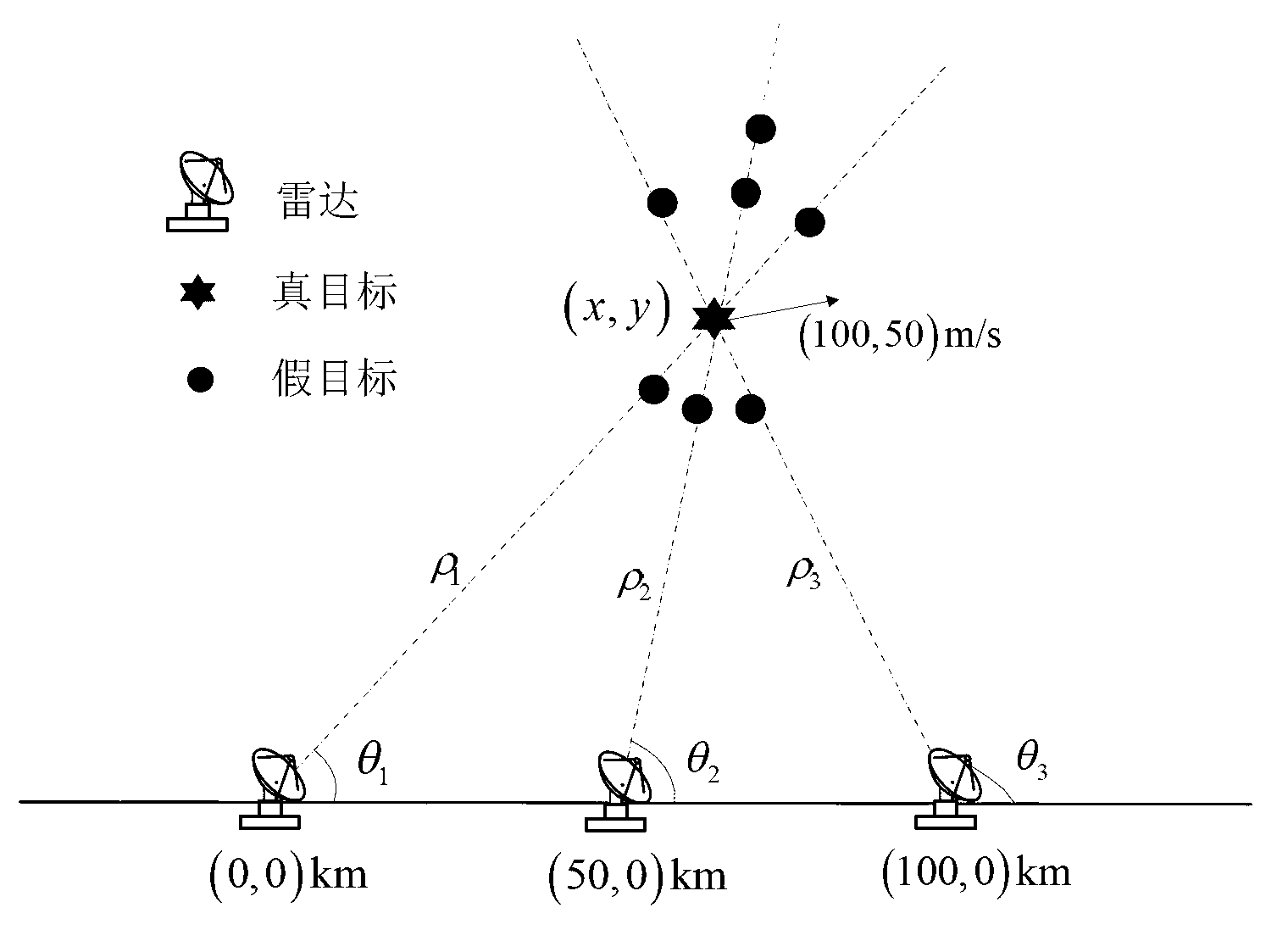
Method for countering deception false target by utilizing netted radar system
ActiveCN103018722AImprove recognition rateEfficient identificationWave based measurement systemsRadar systemsRectangular coordinates
The invention discloses a method for countering a deception false target by utilizing a netted radar system, which mainly solves the problem that deception probability is high in the event of countering the deception false target only by utilizing target position information fusion. The method comprises the following steps of: (1), carrying out coordinate transformation on measurements of node radars, namely, taking various node radars as a polar coordinate system of a reference original point, and transforming to a uniform rectangular coordinate system of the netted radar system; (2), matching measurements through a nearest neighbour association method so as to obtain an association measurement sequence; (3), identifying true and false targets by utilizing target position information, and reserving the association measurement sequence passing fusion testing; (4), obtaining a practical speed vector set corresponding to the reserved association measurement sequence; and (5), carrying out identification of true and false targets by utilizing target speed information, and further reducing the deception probability of netted radar. The method disclosed by the invention effectively reduces the deception probability of the netted radar and can be used for the netted radar to effectively resist deception interference.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Data distributing/obtaining method based on network information
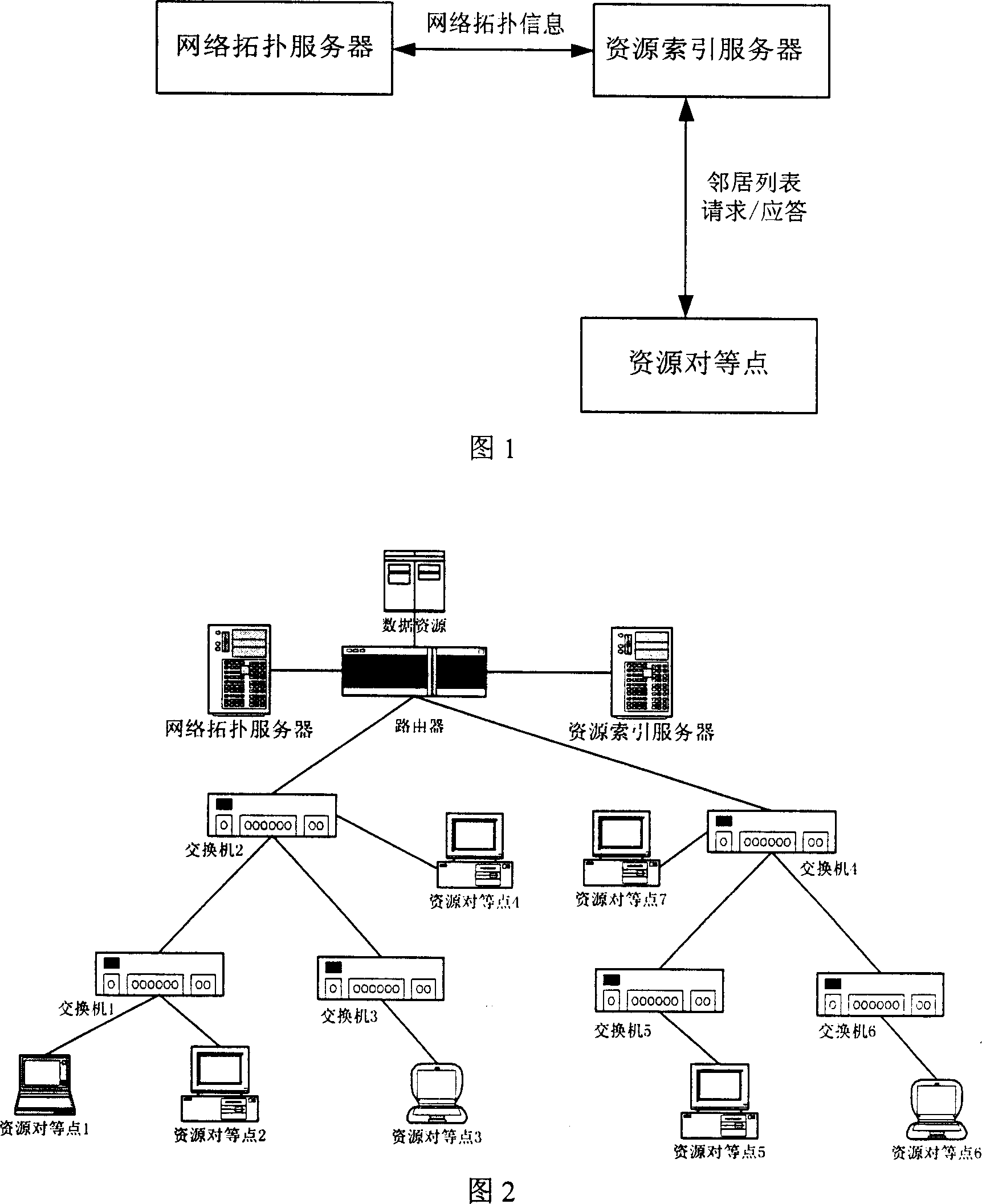
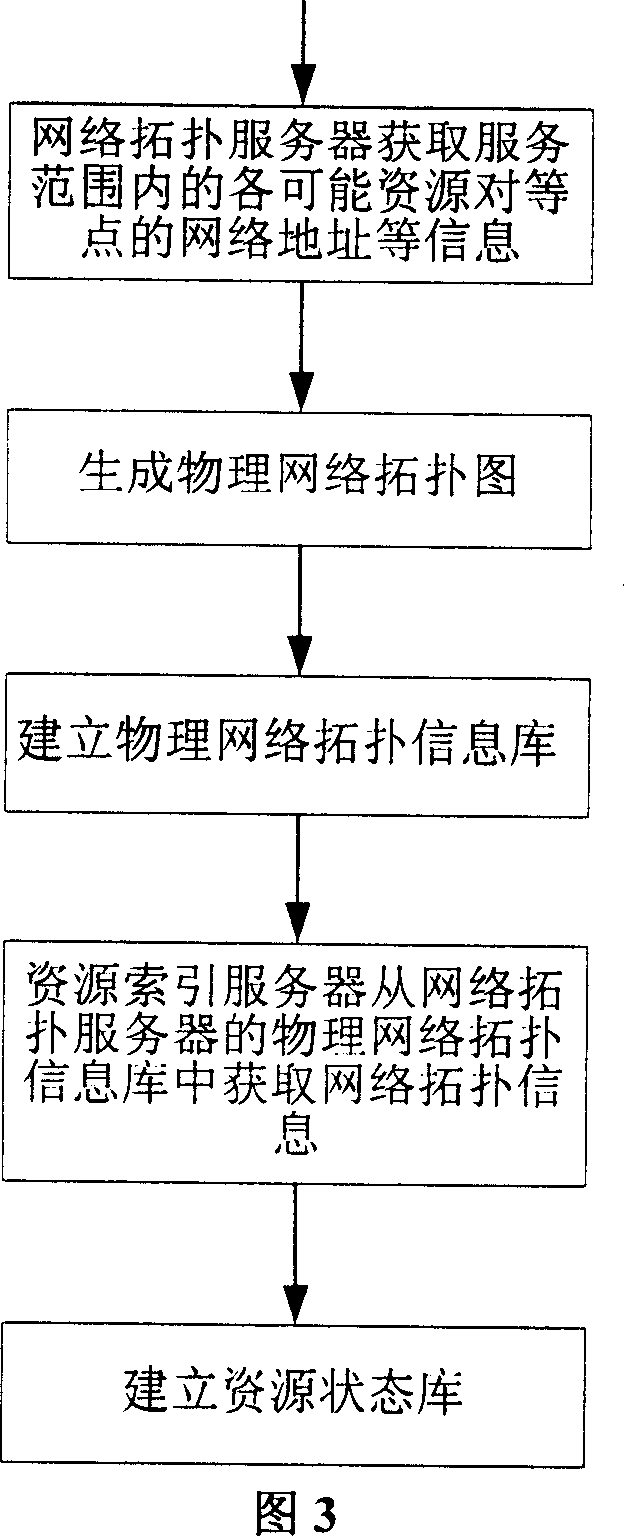
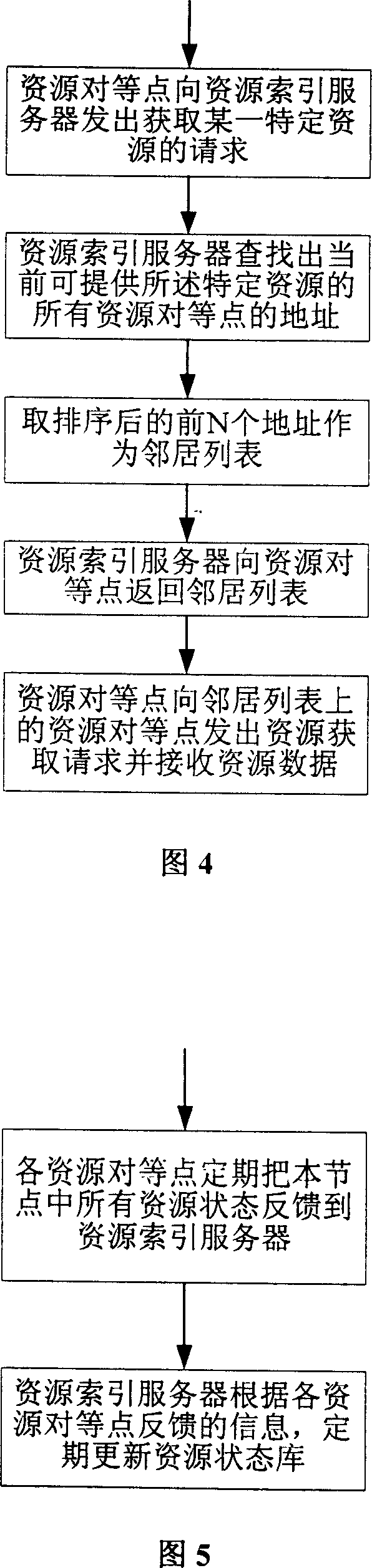
InactiveCN1988449AReduce the burden onMitigate multiple data pathsData switching by path configurationSpecial data processing applicationsDatapathData path
This invention relates to a data distribution and getting method based on network information, in which, said method includes: a resource getting node sends a request for getting resources to a resource index server, which searches for it in a resource state library to look for addresses of all resource peer points capable of providing said specific resources currently and feeds back a neighbor list to the resource getting node based on the neighbornhood principle, the getting node sends an obtaining request to the peer points on the list based on the addresses provided by the neighbor list and receives or uses resources, which fully utilizes a physical network topological information to get the lastest neighbor list and reduces multiple data paths resulted in using overlay network in the physical network.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
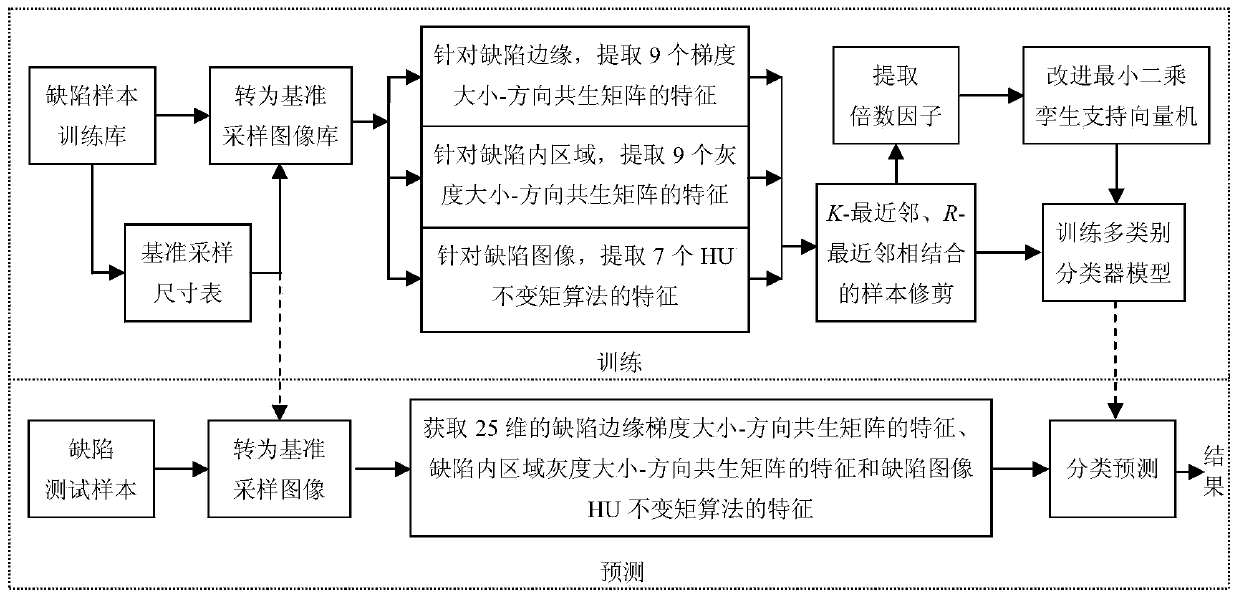
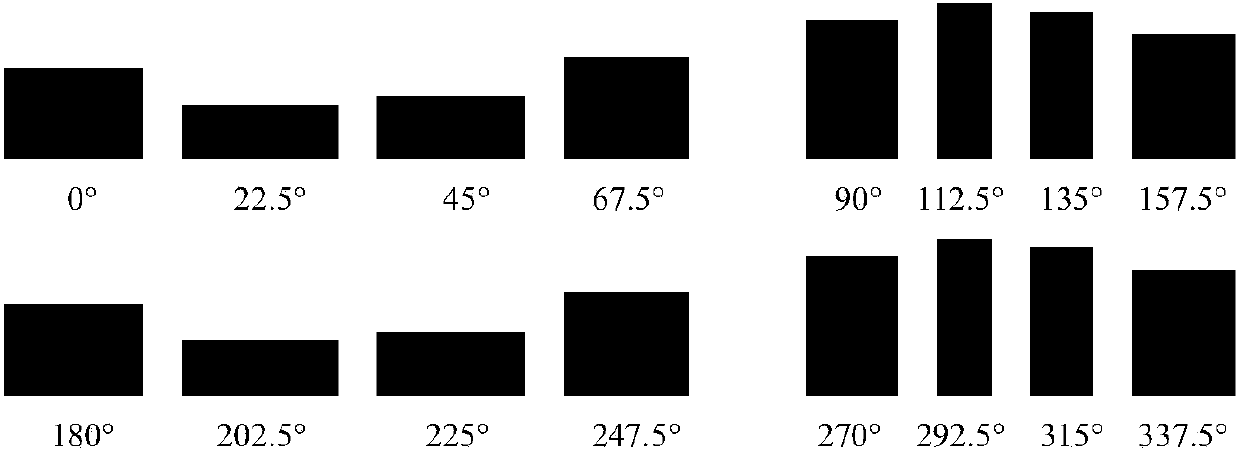
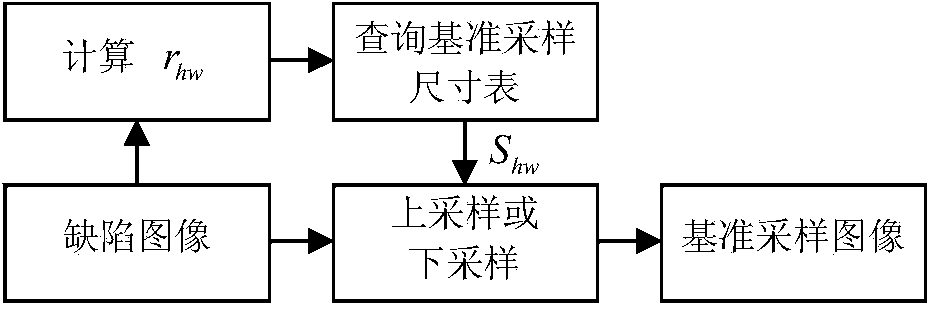
Band steel surface defect feature extraction and classification method
InactiveCN103745234AGuaranteed scale invarianceInhibit the influence of other unfavorable factorsCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorImaging processing
The invention discloses a band steel surface defect feature extraction and classification method, and belongs to the fields of mode recognition and image processing. The band steel surface defect feature extraction and classification method comprises the steps: extracting a reference sampling size chart of a band steel surface defect sample database; obtaining a reference sampling image, and constructing a gradient size and direction co-occurrence matrix; by aiming at a defect inner area of the reference sampling image, constructing a grayscale size and direction co-occurrence matrix; generating a feature vector sample training library; trimming a training sample set and extracting a multiplying factor by a method of combining K-nearest neighbour with R-nearest neighbour; improving a classifier by using a multiplying factor of the trimmed sample; obtaining a multi-class classifier model; according to the reference sampling size chart, converting the defect test sample into a reference sampling image, then extracting a 25-dimensional feature quantity, inputting the 25-dimensional feature quantity into the multi-class classifier model, and finishing the defect automatic recognition. According to the band steel surface defect feature extraction and classification method, the scale and rotation are not changed, the influence by other adverse factors is restrained, and recognition efficiency and accuracy are improved.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV LIAONING
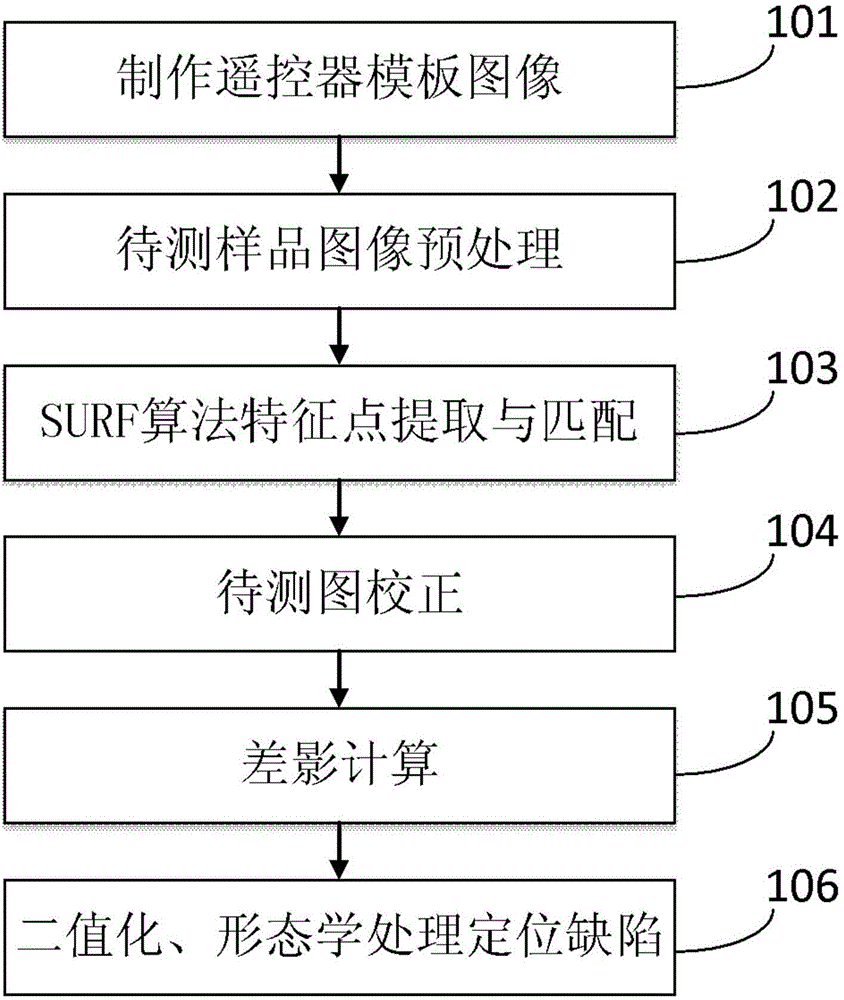
Method for automatically detecting printing defects of remote controller panel based on SURF (Speed-Up Robust Feature) algorithm
InactiveCN104568986AAccurate detectionAccurately detect and locate defectsMaterial analysis by optical meansSample imageMorphological processing
The invention discloses a method for automatically detecting the printing defects of a remote controller panel based on an SURF (Speed-Up Robust Feature) algorithm. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: carrying out histogram equalization on a to-be-detected sample image by making a remote controller template image, respectively acquiring feature points of the template image and the to-be-detected image through the SURF algorithm, matching the feature points by utilizing a partitioned and accelerated nearest neighbour matching method, acquiring a homography matrix according to a matching result, carrying out affine transformation on the to-be-detected image to obtain a correction image by utilizing the homography matrix, processing difference images of the template image and the correction image superposed with a mask, carrying out binaryzation and morphological processing on a difference image result, judging whether a to-be-detected sample is qualified, if the to-be-detected sample has a defect, locating the position of the defect; if the to-be-detected sample does not have a detect, judging that the to-be-detected sample is qualified, and completing detection. The method disclosed by the invention is capable of effectively detecting defects in the to-be-detected sample and accurately locating the positions of the defects.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
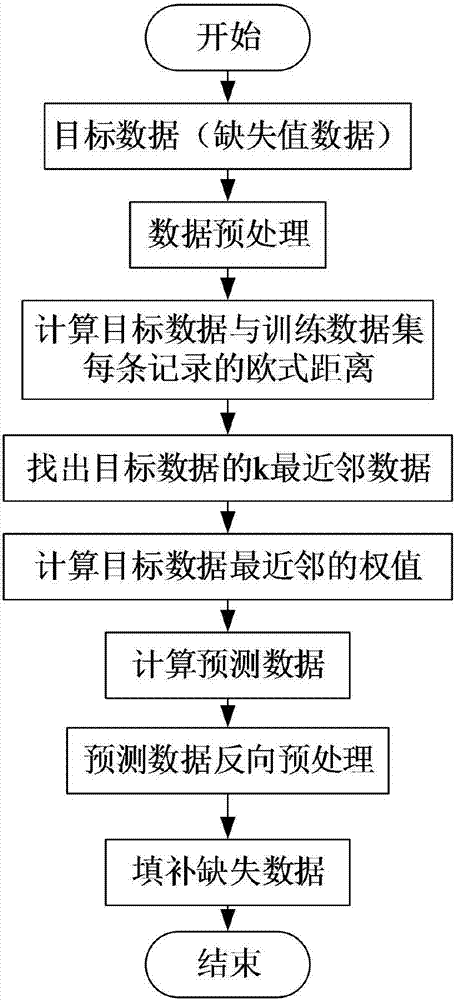
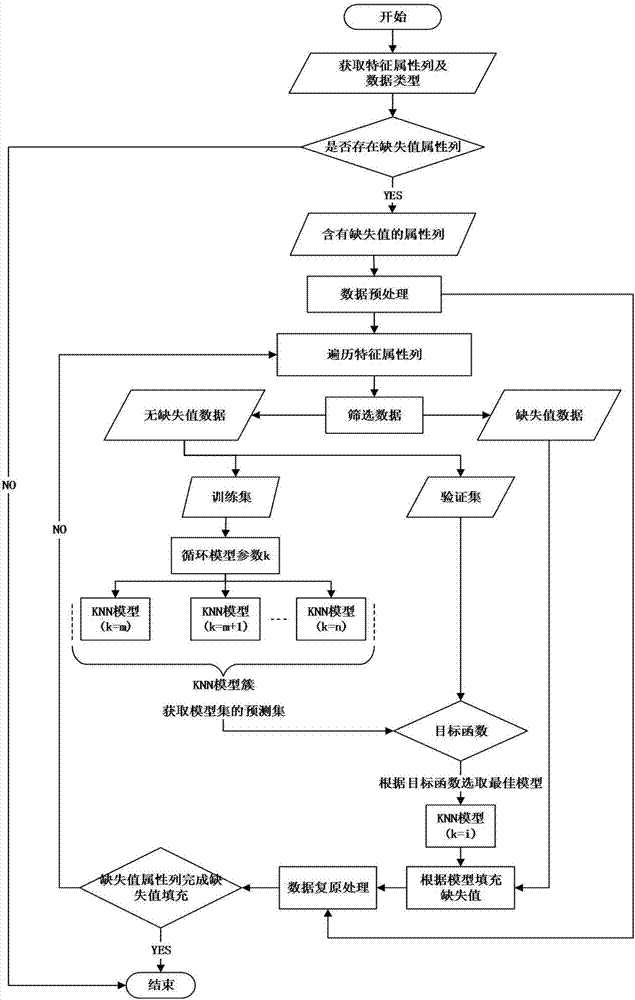
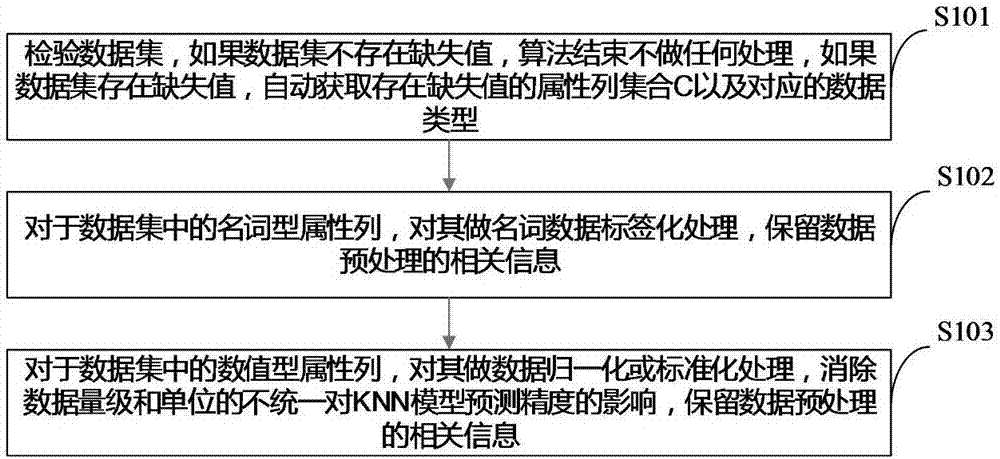
K-Nearest Neighbor (KNN) algorithm-based missing data filling method
The invention discloses a KNN algorithm-based missing data filling method. The method comprises the following steps of: automatically recognizing feature attributes with missing values in a data set; traversing the feature attributes with missing values and gradually filling the missing values by utilizing a KNN algorithm; in the process of filling the missing value of each feature attribute, iterating KNN algorithm parameters k to obtain a KNN model cluster configured by different parameters; and selecting an optimum model according to an optimal objective function, and carrying out missing value filling on missing data by utilizing the model. The algorithm parameters k have great influences on the KNN algorithm, and an optimization strategy is applied to the construction of missing value filling models, so that the model precision can be greatly improved, and correspondingly, the quality of the filled data is greatly improved.
Owner:MERIT DATA CO LTD
Semi-supervised learning-based multi-gesture facial expression recognition method
ActiveCN103186774AProven RobustnessCharacter and pattern recognitionLearning basedSupervised learning
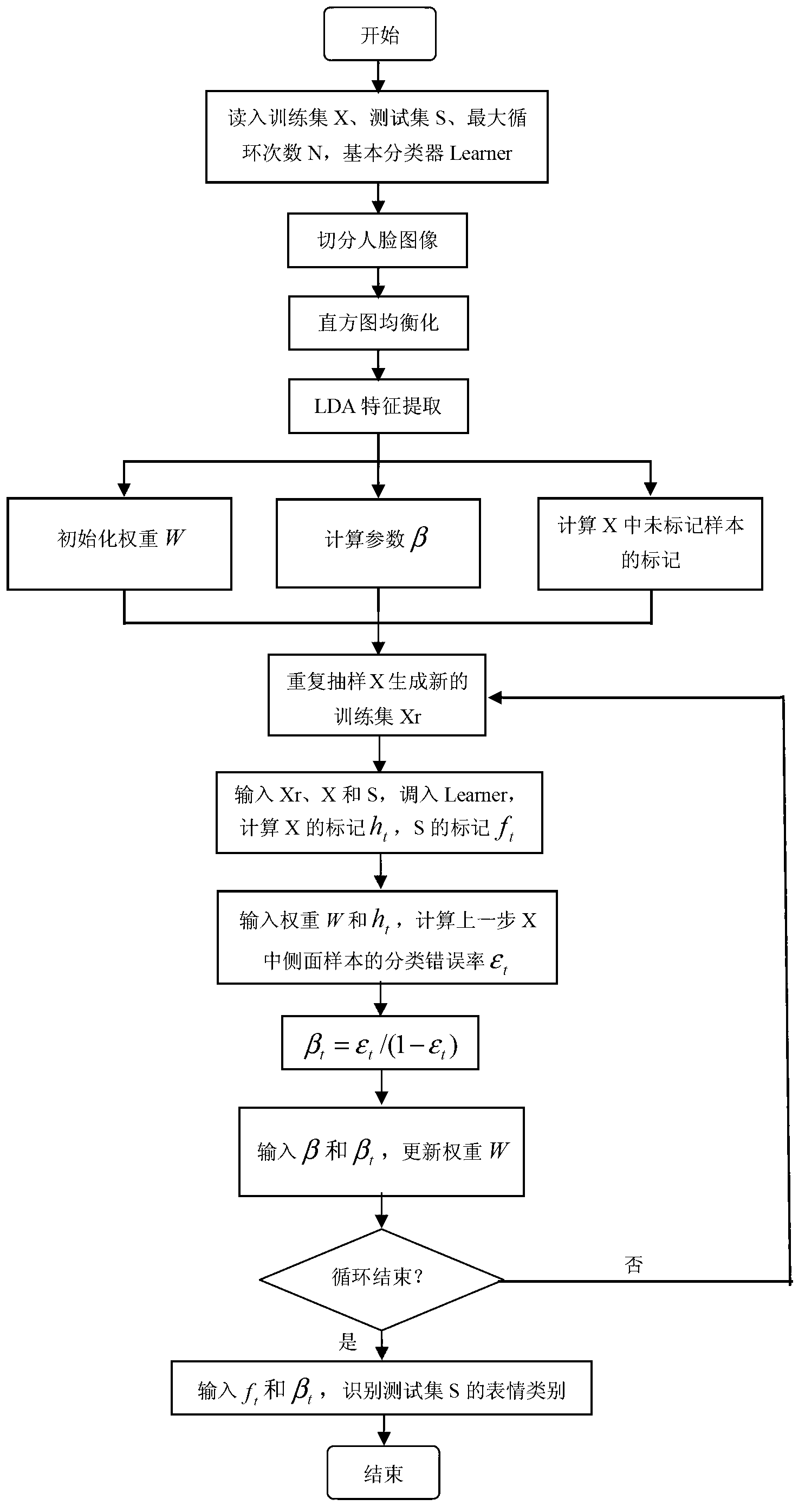
The invention relates to a semi-supervised learning-based multi-gesture facial expression recognition algorithm which comprises the steps of acquiring n front expression images and n side expression images of n persons to form a training set X and a testing set S, segmenting face regions of the front expression images and the side expression images, and carrying out illumination compensation on the face regions by using a histogram equalization method; then extracting expression characteristics of the images by adopting a linear discriminant analysis method, carrying out expression recognition on samples in the testing set S; marking each unmarked sample in the training set X by using marked samples in the training set X by adopting an Euclidean distance nearest neighbour method; re-sampling the training set X by adopting a round-robin mode to obtain a new training set Xr; scheduling a basic classifying device to calculate a mark ht of each sample in the training set X at the tth circle by using the new training set Xr, and calculating a mark ft of each sample in the testing set S at the tth circle by using the new training set Xr; and finally, calculating a classifying error rate epsilon t of the basic classifying device to side samples in the training set, and updating weights of all training samples in the training set X until reaching the circle ending condition.
Owner:北京格镭信息科技有限公司
Macroscopic ordered assembly of carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS20080210370A1Firmly assembledMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureNear neighborMicroscopic scale
The present invention is directed to the creation of macroscopic materials and objects comprising aligned nanotube segments. The invention entails aligning single-wall carbon nanotube (SWNT) segments that are suspended in a fluid medium and then removing the aligned segments from suspension in a way that macroscopic, ordered assemblies of SWNT are formed. The invention is further directed to controlling the natural proclivity or nanotube segments to self assemble into or ordered structures by modifying the environment of the nanotubes and the history of that environment prior to and during the process. The materials and objects are “macroscopic” in that they are large enough to be seen without the aid of a microscope or of the dimensions of such objects. These macroscopic ordered SWNT materials and objects have the remarkable physical, electrical, and chemical properties that SWNT exhibit on the microscopic scale because they are comprised of nanotubes, each of which is aligned in the same direction and in contact with its nearest neighbors. An ordered assembly of closest SWNT also serves as a template for growth of more and larger ordered assemblies. An ordered assembly further serves as a foundation for post processing treatments that modify the assembly internally to specifically enhance selected material properties such as shear strength, tensile strength, compressive strength, toughness, electrical conductivity, and thermal conductivity.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Packet transfer scheme using mobile terminal and router for preventing attacks using global address
InactiveUS6925087B2Avoid attackNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesTerminal equipmentNear neighbor
In a mobile communication network providing an Internet service, the arrived packets are delivered from the nearest neighbor router device to the mobile terminal device according to the need such as when a prescribed application is activated or when a prescribed packet has arrived, by using message exchanges between the nearest neighbor router device and the mobile terminal device, so that it becomes possible to prevent the unnecessary packet attacks from the global Internet.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
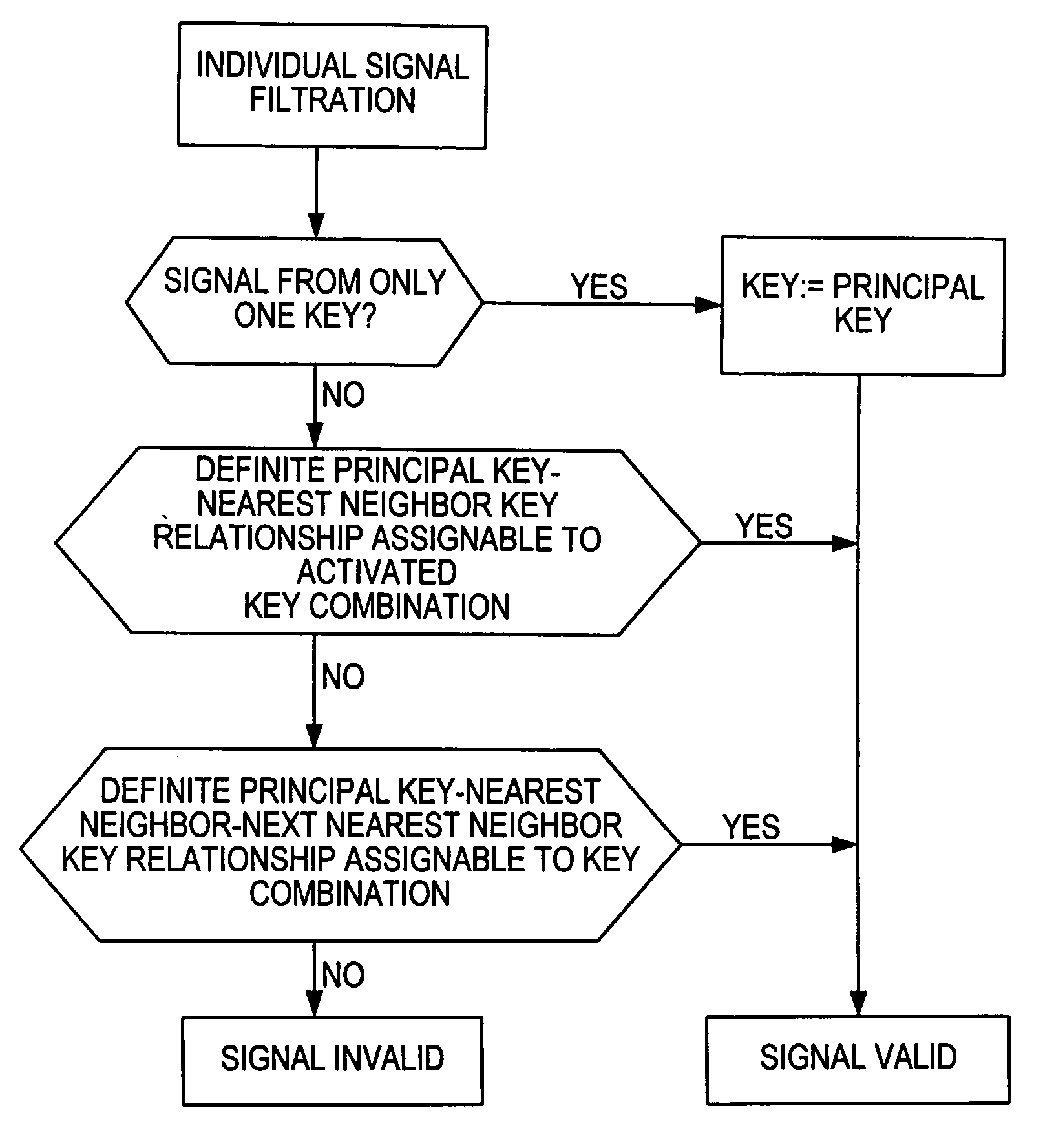
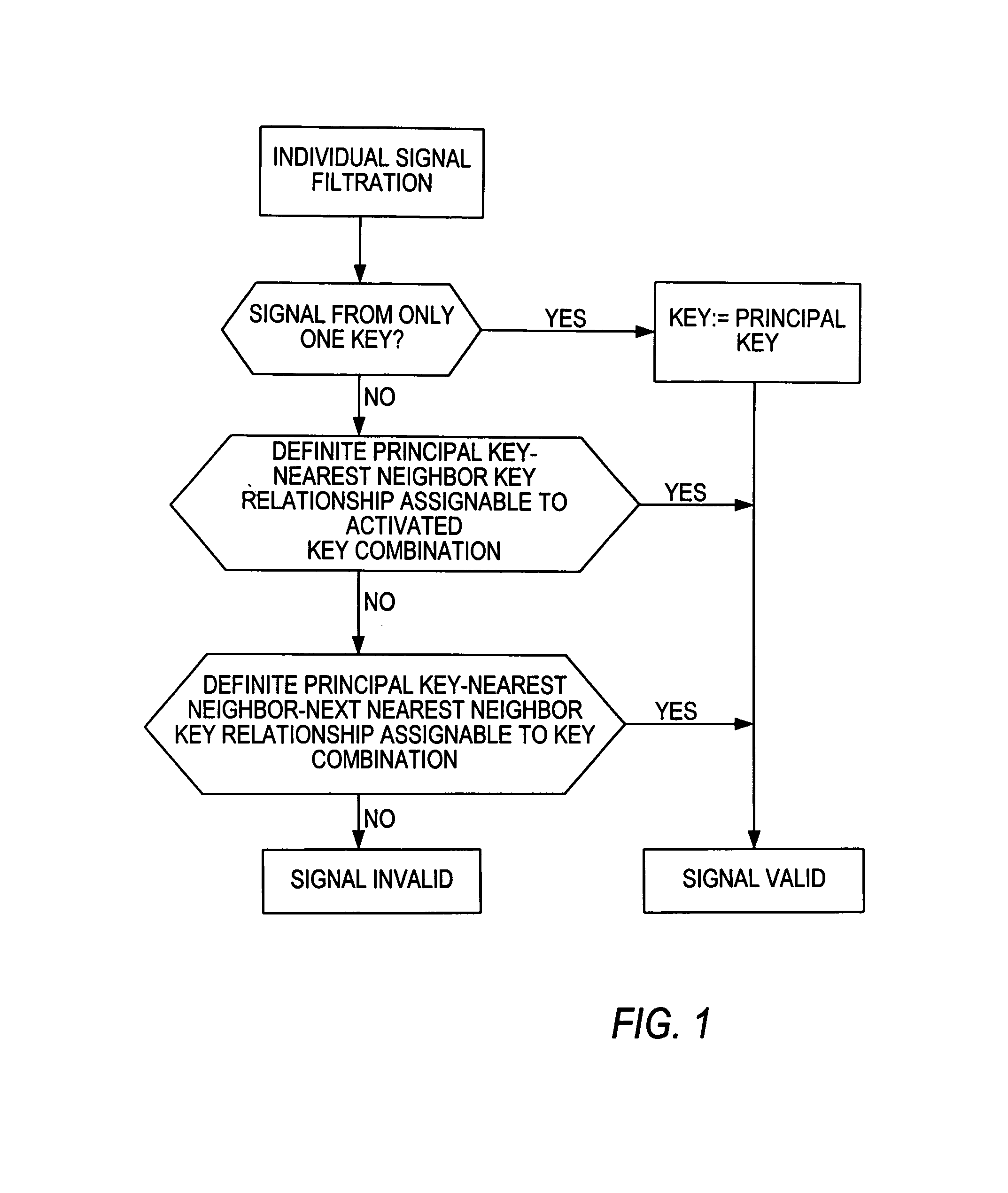
Method for automatic determination of validity or invalidity of input from a keyboard or a keypad
InactiveUS7135995B2Increase influenceEasy to operateInput/output for user-computer interactionElectronic switchingComputer hardwareNear neighbor
The method for automatic determination of validity or invalidity of input from miniaturized keypads or keyboards, in which more than one key is operated at the same time, includes designating a number of keys as principal keys and assigning each key neighboring each principal key as nearest neighbor or next nearest neighbor and then testing each signal produced by key operation. The signal is valid if it is produced by operation of only one single key. However testing continues if two or more keys produce the signal. Then the signal is valid when the two or more keys are correlated in an unambiguous principal key-nearest neighbor key relationship. If not, testing continues further and the signal is valid if the plural keys are correlated in an unambiguous principal key-nearest neighbor key-next nearest neighbor key relationship. Otherwise the signal is an invalid key input.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
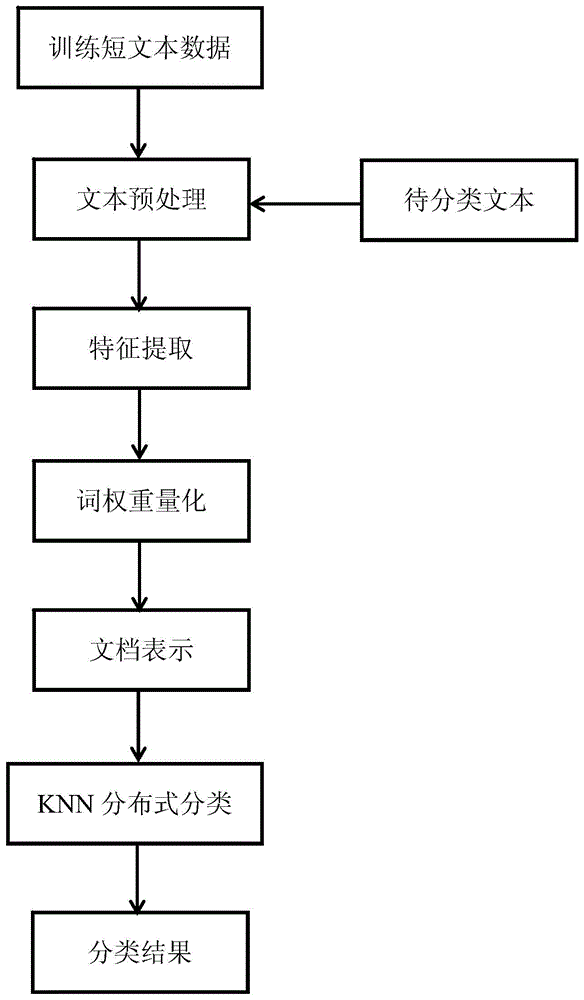
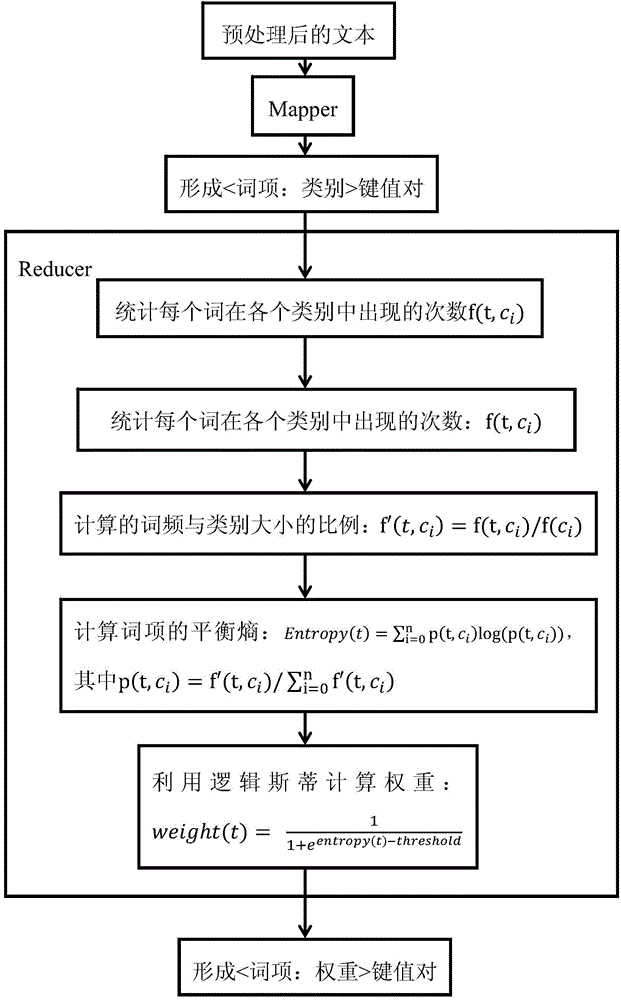
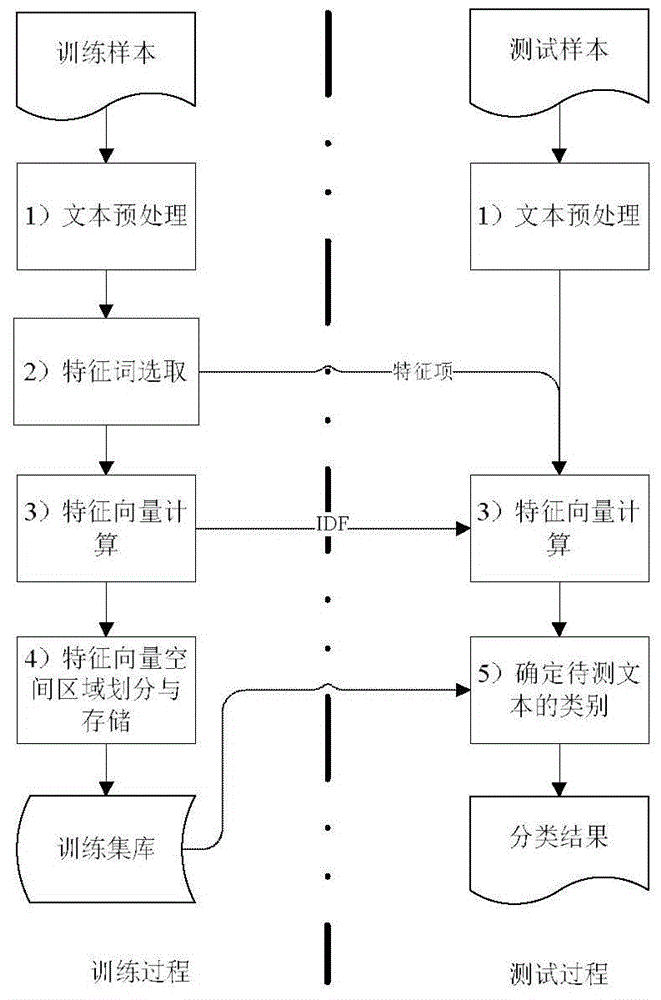
Distributed mass short text KNN (K Nearest Neighbor) classification algorithm and distributed mass short text KNN classification system based on information entropy feature weight quantification
ActiveCN103955489AReasonable weight quantizationImprove classification performanceSpecial data processing applicationsText database clustering/classificationNear neighborK nearest neighbour
The invention discloses a distributed mass short text KNN (K Nearest Neighbor) classification algorithm and a distributed mass short text KNN classification system based on information entropy feature weight quantification. The algorithm mainly includes text preprocessing, weights for measuring features with information entropies, a document vector representation method and a KNN classification algorithm adopting indexing and caching techniques, and the whole algorithm is implemented on the basis of a MapReduce computing framework. By utilizing the information entropies of features in a training set, the invention effectively measures the effects of words in texts on classification, and moreover, based on the MapReduce computing framework, the algorithm can utilize mass clusters to efficiently classify mass short texts. The mass short text classification algorithm provided by the invention has the advantages of high accuracy, high operating efficiency and strong scalability.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
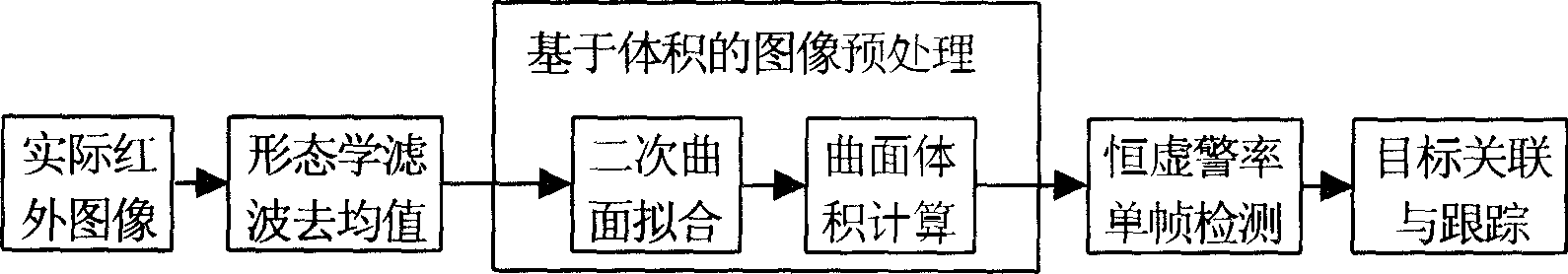
Infra red detecting and tracing method for weak target under complex background condition
InactiveCN1514408AStable memory tracking abilityImprove real-time performanceImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionSolidity
In the method, image background is obtained through morphology as demean value image containing target and noise can be obtained by deducting image background from original image, N / S ratio of processing result can be raised by applying pretreatment process based on elliptic paraboloid volume, sing frame detection result can be obtained by selecting detecting threshold with constant false alarm ratio standard, false target is further removed by utilizing solidity of target motion trail, target tracking applies most near neighbour coorelation method and target state is refreshed by applying kalman filtering based on uniform straight-line motion model and trail is utilized to predict possible position of target for carrying on stable tracking if target is lost.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Transformation-based method for indexing high-dimensional data for nearest neighbour queries
InactiveUS6834278B2Easy to deployQuick searchData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsData spaceHigh dimensional
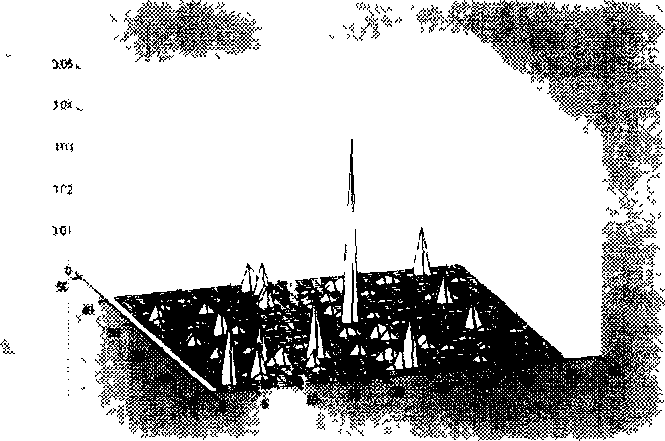
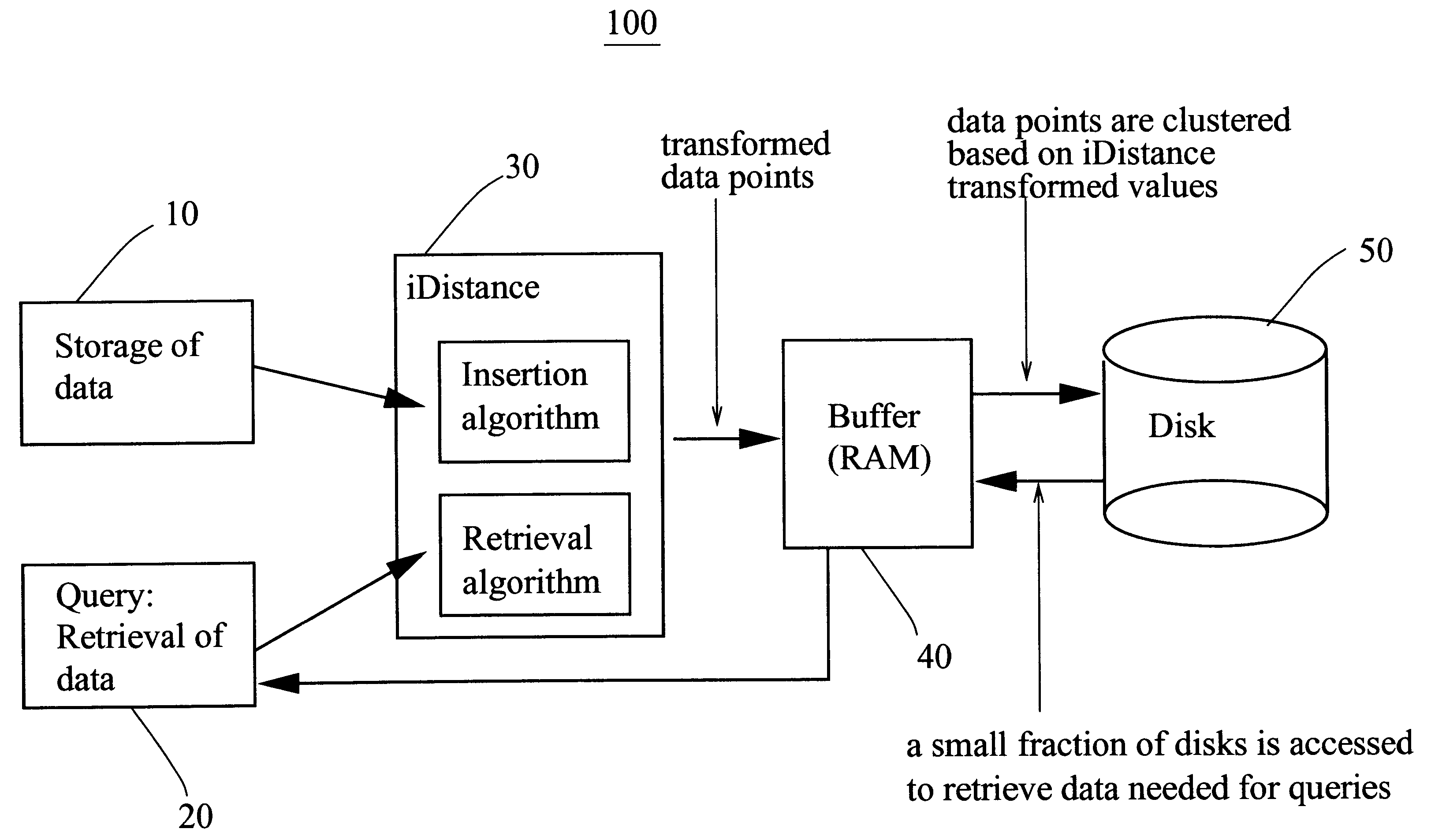
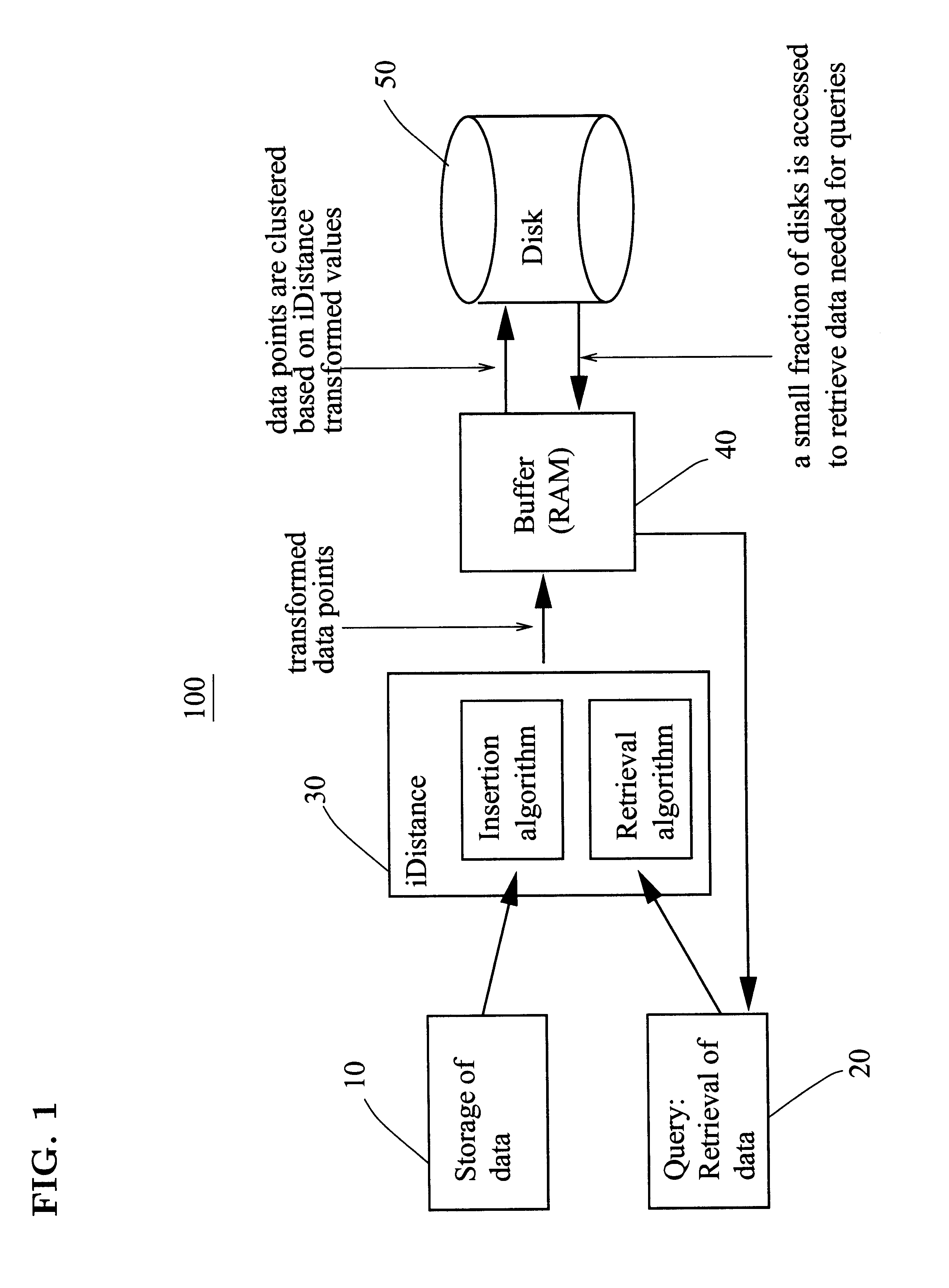
We disclose a transformation-based method for indexing high-dimensional data to support similarity search. The method, iDistance, partitions the data into clusters either based on some clustering strategies or simple data space partitioning strategies. The data in each cluster can be described based on their similarity with respect to a reference point, and hence they can be transformed into a single dimensional space based on such relative similarity. This allows us to index the data points using a B<+>-tree structure and perform similarity search using range search strategy. As such, the method is well suited for integration into existing DBMSs. We also study two data partitioning strategies, and several methods on selection of reference points. We conducted extensive experiments to evaluate iDistance, and our results demonstrate its effectiveness.
Owner:THOTHE TECH PRIVATE
Far distance identity identifying method based on walk
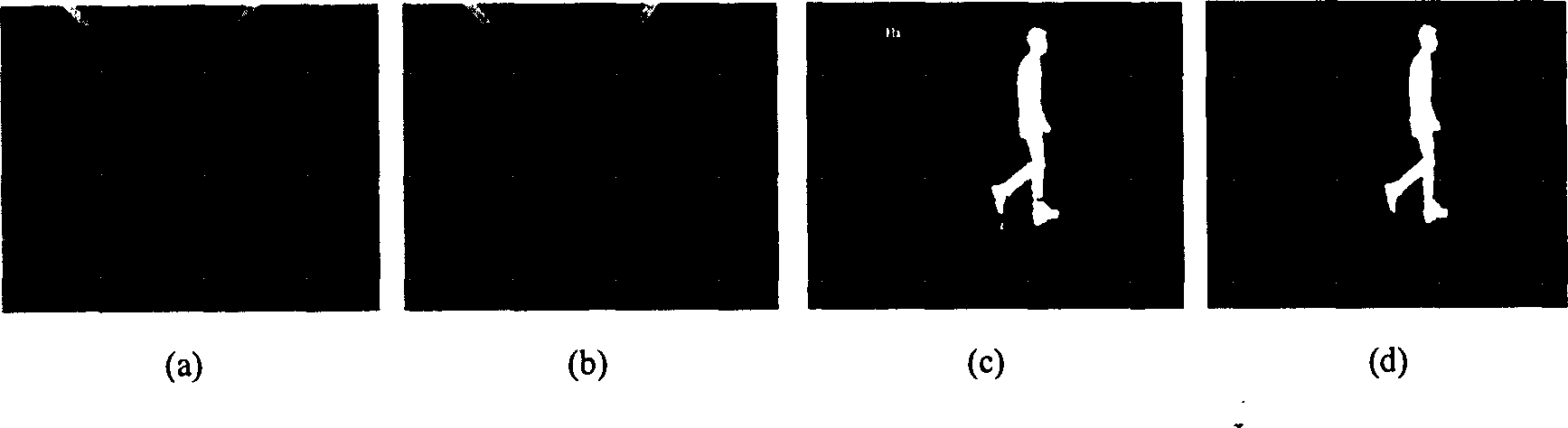
InactiveCN1426020ASolve the identification problemCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsPersonalizationFar distance
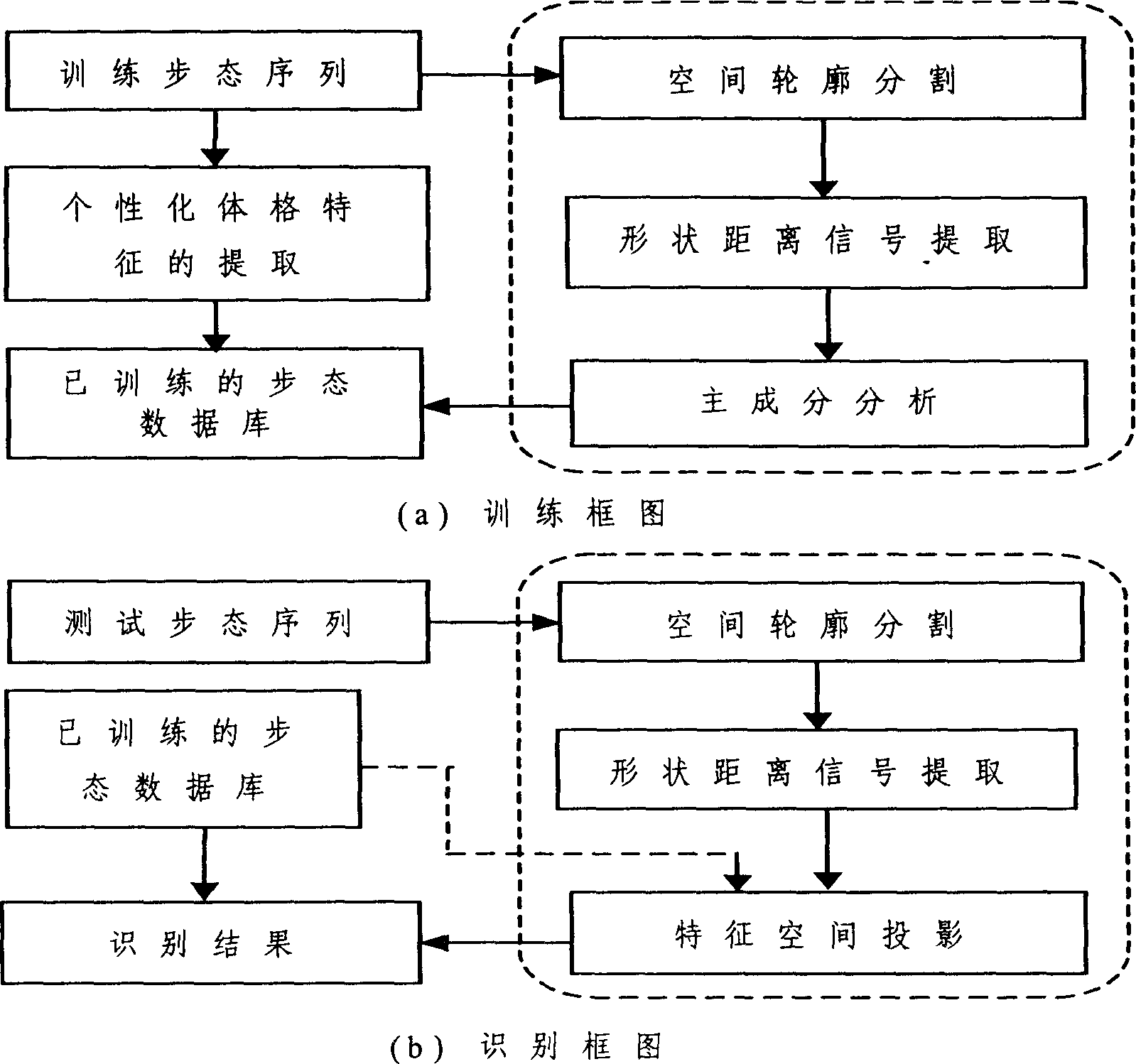
The far distance identity identifying method based on walk includes two processes of training and identifying. The training process includes the steps of obtaining training walk sequence, spatial contour cutting, shape and distance signal extraction, main component analysis, personalized physique characteristic extraction to extract visible personalized characteristic as additional characteristic for final vertification of walk classification, and obtaining trained walk data base. By means of statistic pivot element analysis method, far distance identify identifying system based on walk behavoir is realized. The present invention utilizes also improved background reduction method, characteristic space transformation of motion contour, and correlation identification or nearest neighbour rule in the characteristic extraction.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Desk chair mat
InactiveUS6946184B2Avoid skin abrasionPrevent penetrationLayered productsThin material handlingRegular patternNear neighbor
A desk chair mat has a substantially planar upper surface suitable for interaction with a chair support structure, a perimeter defining an outer edge of the mat, a lower surface parallel to the upper surface. An array of blunt projections extends downwardly from the lower surface for engagement with a carpet. Each blunt projection has a smooth end surface spaced below the lower surface by a distance sufficient to penetrate into the carpet pile. The array is generally a regular pattern of the blunt projections arranged at an angle with respect to each nearest neighbor to provide resistance to any lateral movement of the mat with respect to the carpet.
Owner:ROBBINS III EDWARD S
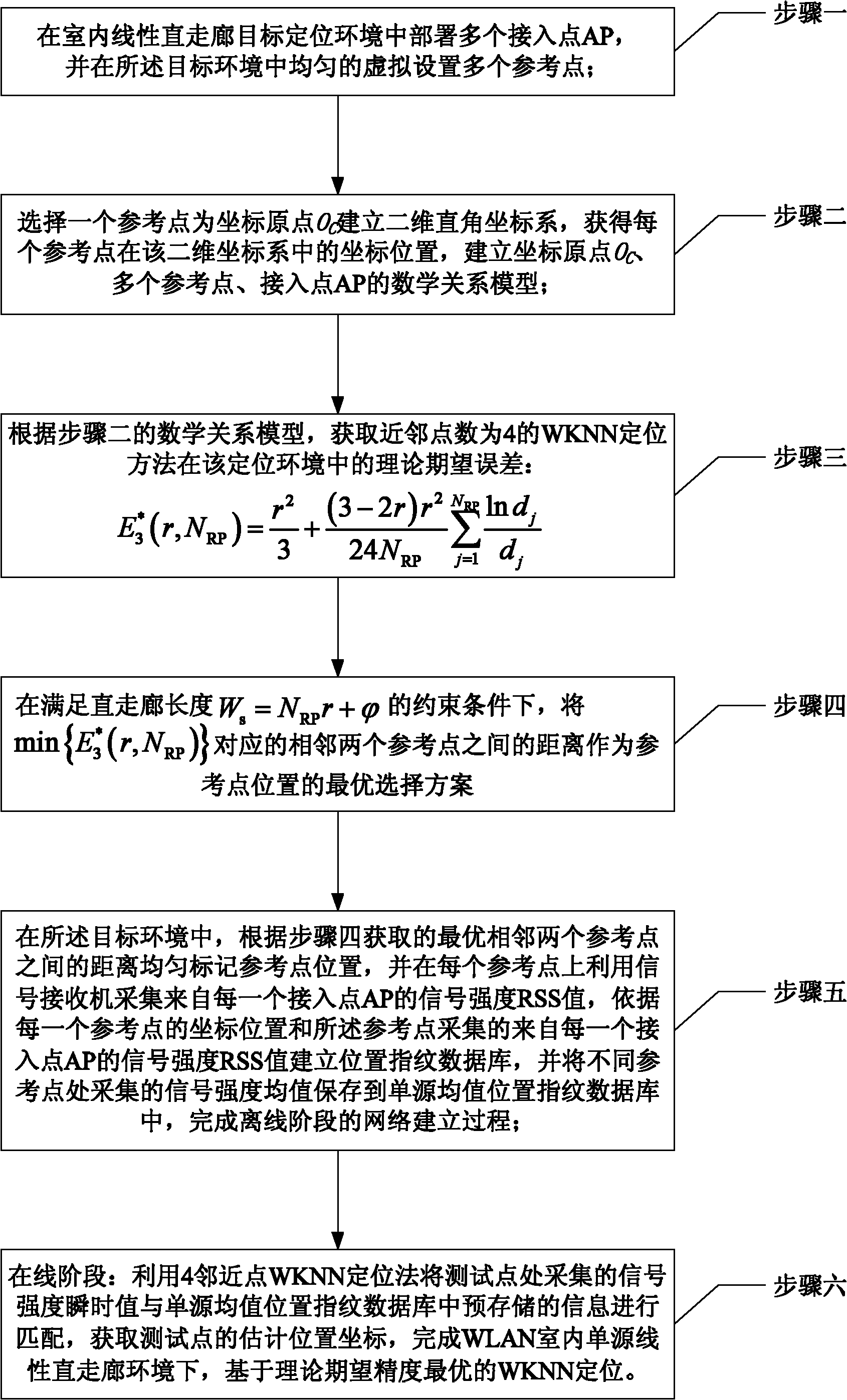
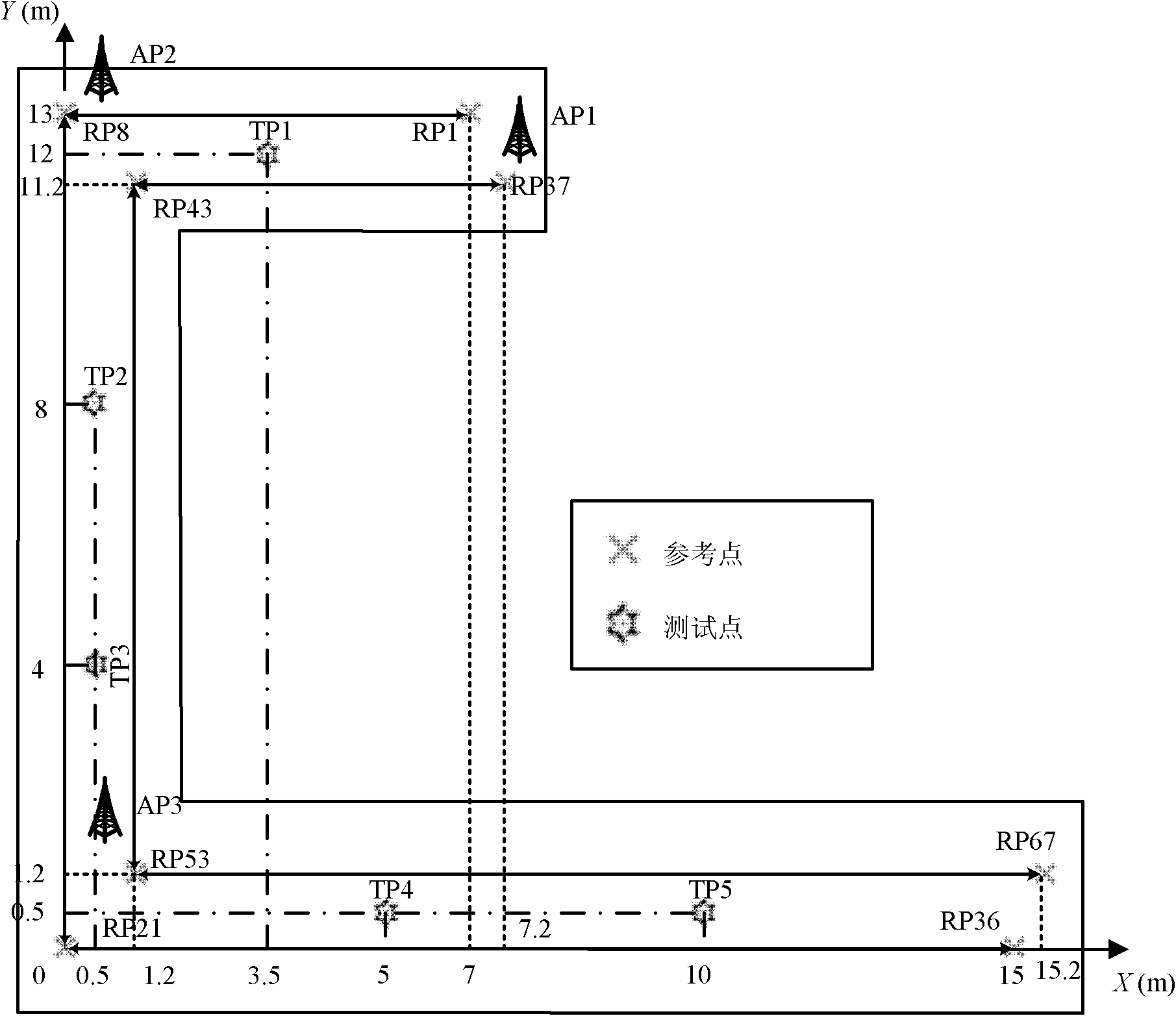
WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network) indoor single-source linear WKNN (Weighted K-Nearest Neighbor) locating method based on reference point position optimization
ActiveCN102325369ASolve the optimal number of reference pointsSolve the problem of selectivityNetwork topologiesNear neighborError criteria
The invention relates to a WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network) indoor single-source linear WKNN (Weighted K-Nearest Neighbor) locating method based on reference point position optimization, belonging to the field of mobile computing. The invention aims to solve the problem of selection of numbers and positions of optimal reference points in a WKNN locating algorithm under the existing WLAN indoor single-source linear environment. Aiming at the special single-source linear scene, firstly, a closed solution form of the WKNN locating algorithm with theoretic expected precision is computed at an offline state by aiming at the concrete practical single-source linear locating environment; then, reference points are subjected to optimal distribution by utilizing the relationship between an expected error and the position of the reference point as well as the relationship between the expected error and the size of a target region to meet the minimum expected error criterion, and a corresponding single-source average position fingerprint database is established; and finally, the position coordinates of a locating terminal are estimated by using a 4-neighbor-point WKNN locating method according to a signal intensity sample collected in real time at the present stage.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
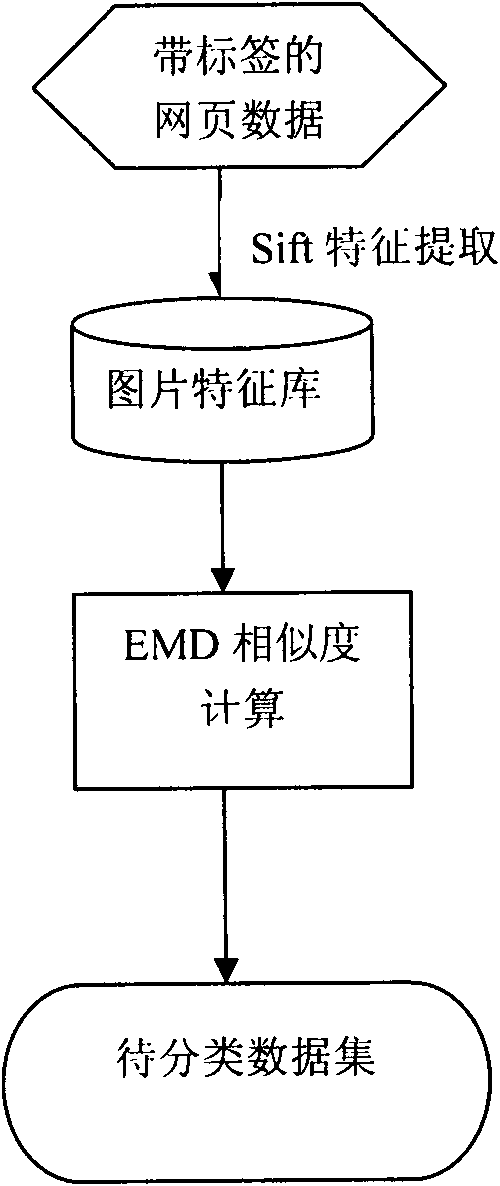
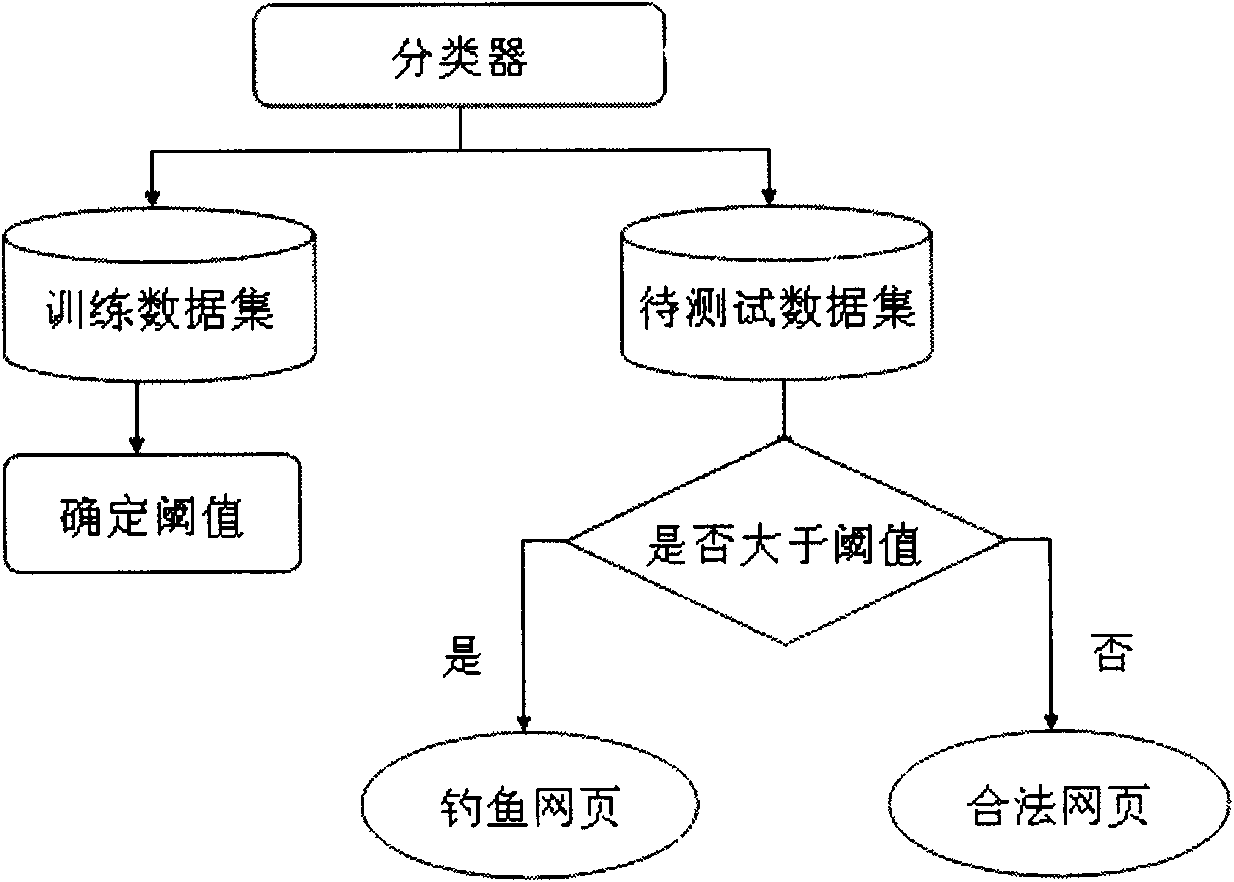
Method for detecting phishing webpage based on nearest neighbour and similarity measurement
InactiveCN102170447AHigh precisionImprove recallData switching networksSpecial data processing applicationsFeature extractionClassification methods
The invention relates to a method for detecting a phishing webpage based on nearest neighbour and similarity measurement, which comprises the following steps: a picture of a whole image of a webpage is taken as a start point, and the characteristic of unchanged dimension conversion is extracted; similar characteristics at phishing webpage detection stage are quickly queried, and are then submitted to a machine leaning and matching module to carry out identification; the machine leaning and matching module extracts characteristic data transmitted during a system training stage to carry out training, so that a parameter of webpage similarity threshold can be optimized; during the phishing webpage detection stage, the characteristic data transmitted by the characteristic extracting module is received, the similarity between webpages is calculated, and finally, the phishing webpage is judged according to the webpage similarity threshold; in addition, a sorting method-Bayesian addable regression tree is added to predict suspicious webpages; and the characteristics during the phishing webpage detection process are extracted to be used as an evidence of the phishing webpage detection, so that the high accuracy can be ensured, and simultaneously, the webpage detection time can be remarkably reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Improvement-based KNN (K Nearest Neighbor) text classification method
ActiveCN104408095AFast classificationTaking into account the accuracySpecial data processing applicationsText database clustering/classificationFeature vectorAlgorithm
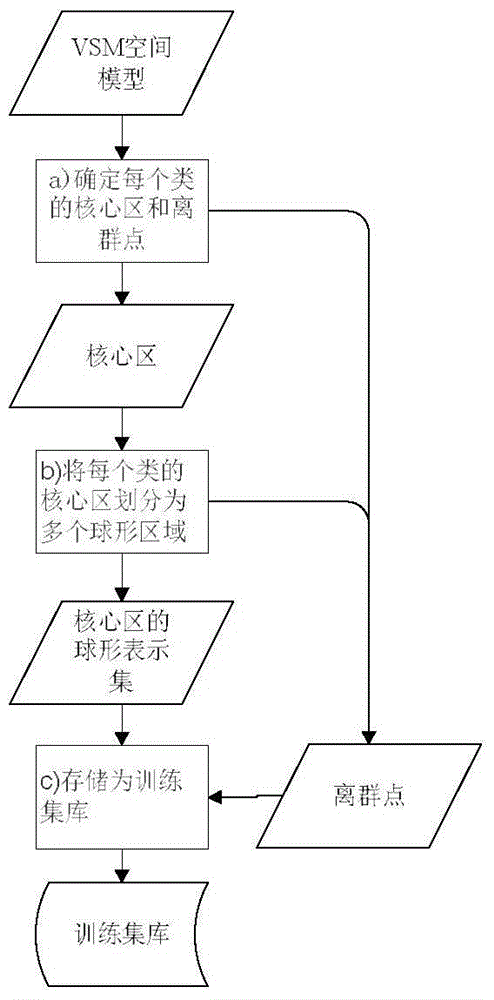
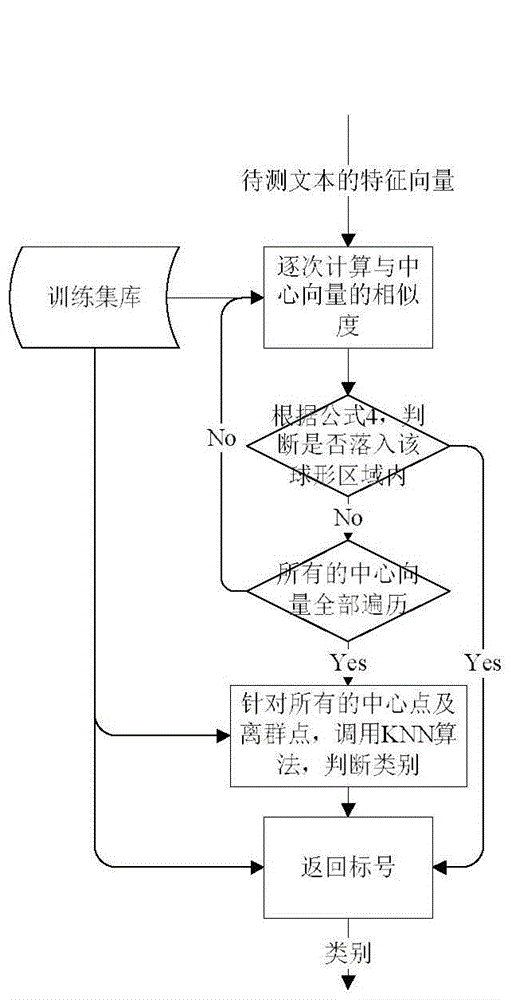
The invention provides an improvement-based KNN (K Nearest Neighbor) text classification method. The method comprises the following steps: preprocessing a training text, computing the feature vector of each training sample, and constructing a feature vector spatial model of a training set; defining a density and a distance, defining a density and a distance, defining a whole sample space into a plurality of spherical regions and outliers according to types, and storing as a training set library; during testing, judging whether a text to be tested falls into a certain spherical region, judging the type of the text to be tested according to a corresponding mark number, otherwise, using the outliers and the center point of each sphere as a training set library, calling a KNN algorithm, and judging the type of the text to be tested. By adopting the method provided by the invention, the classification speed, classification accuracy and data skew sensitivity are considered. The method can be well applied to the classification problem of non-spherical distribution, and is particularly suitable for a text classification problem having a high-dimension feature vector and a distribution irregularity feature.
Owner:CHINA TECHENERGY +1
Exercise recommendation method and device based on typical degree and difficulty
ActiveCN105138653AGood effectDescribe wellData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsFeature vectorPersonalization
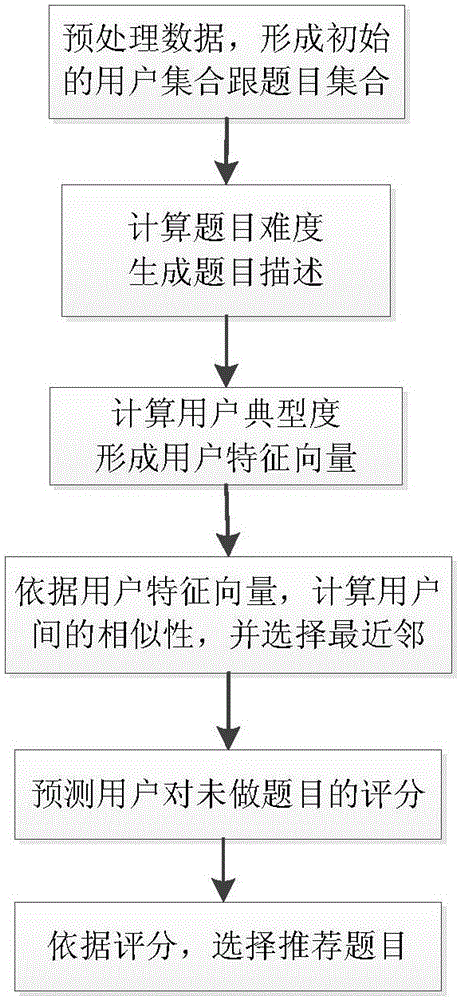
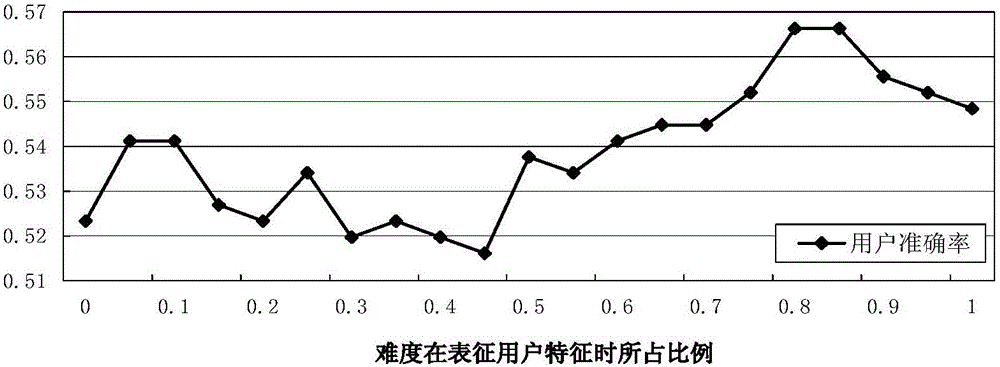
The invention discloses an exercise recommendation method based on the typical degree and difficulty. The method comprises the steps that exercise doing situations comprising the exercise number, difficulty and the passing rate of each target user on each type of exercises are calculated; according to feature vectors of the target users, the similarities between every two feature vectors of the target users are calculated, and many users with the highest similarity are selected for each target user as nearest neighbours; according to exercise doing situation of the nearest neighbour users, the scores of the target users for exercise not finished are predicted; a plurality of target exercises with the highest scores are selected as recommendation results of the target users. An exercise recommendation device comprises a calculating module, a first selecting module, a scoring module and a second selecting module. A traditional recommendation method is improved through the feature that exercises have the difficulty, and a good effect is obtained. The exercise recommendation method and device can be applied in a learning website in the future to help users to select learning content and formulate individualized learning schemes.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
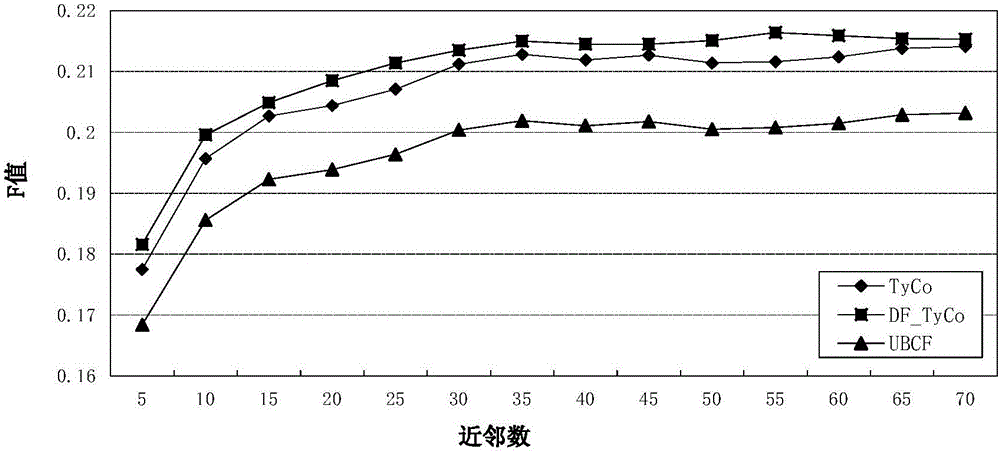
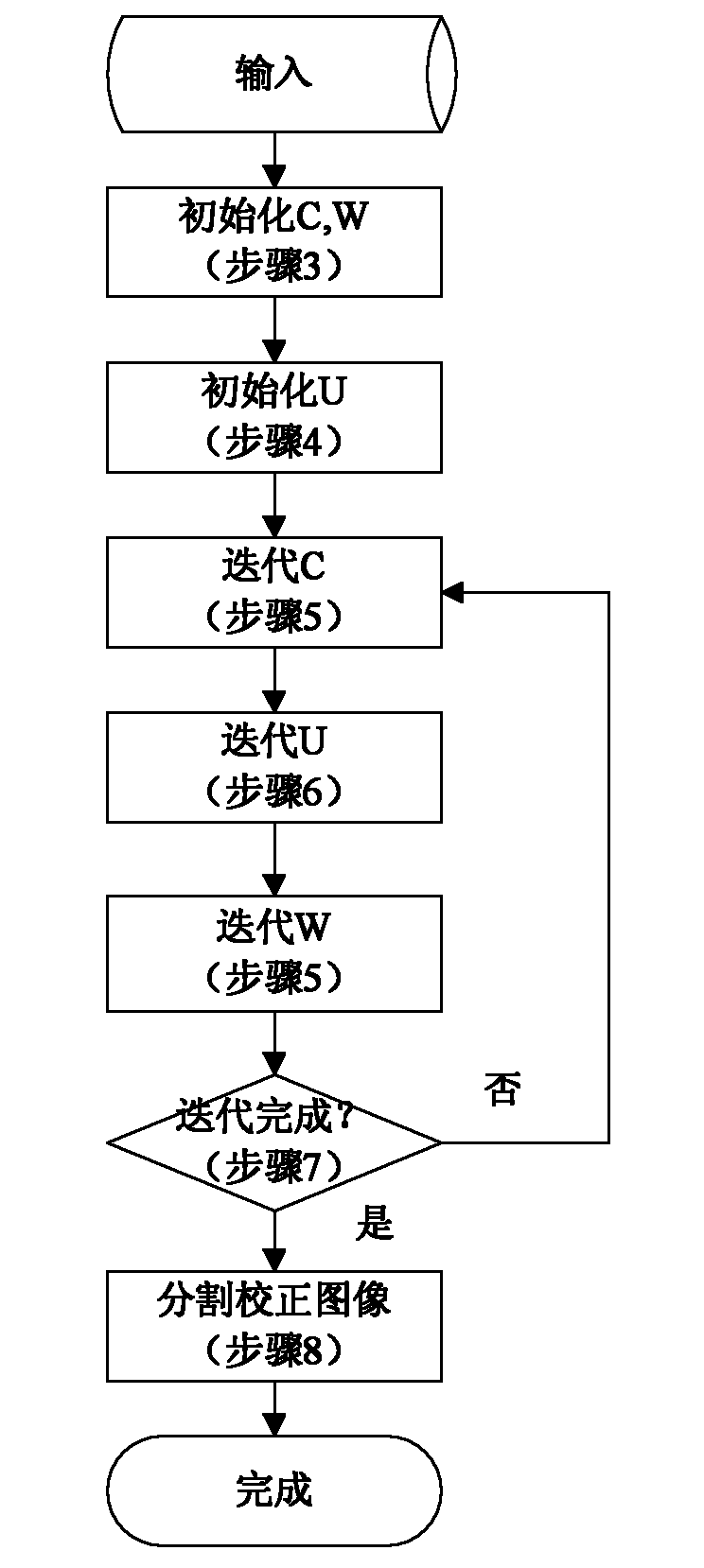
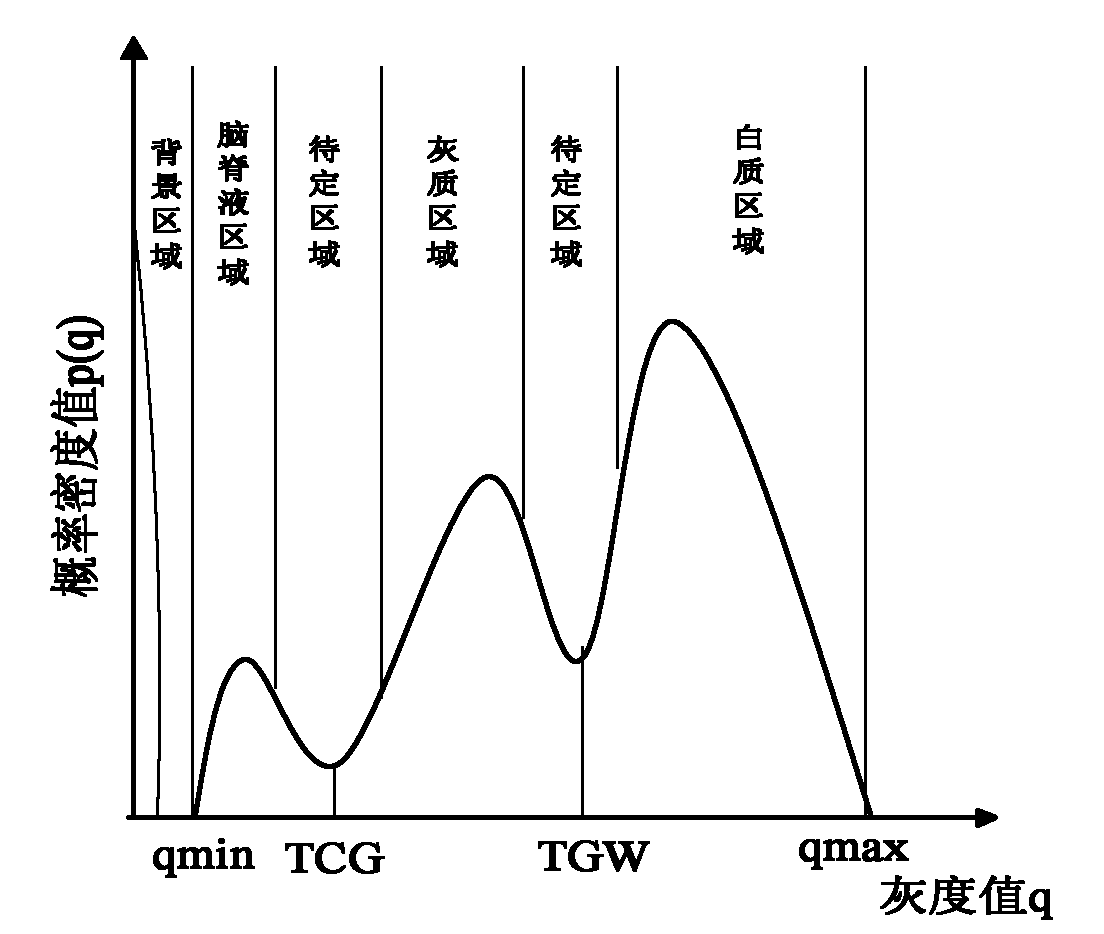
KNN (K-Nearest Neighbor) sorting algorithm based method for correcting and segmenting grayscale nonuniformity of MR (Magnetic Resonance) image
InactiveCN102135606AAccurate divisionVolume effect suppressionMagnetic measurementsSorting algorithmNear neighbor
The invention relates to a KNN (K-Nearest Neighbor) sorting algorithm based method for correcting and segmenting the grayscale nonuniformity of an MR (Magnetic Resonance) image, belonging to the field of image processing. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly constructing a grayscale nonuniform field model by utilizing surface fitting knowledge and using a group of orthonormalization basis functions, and establishing energy functions; and then solving model parameters according to an energy function minimization principle to realize grayscale nonuniformity correction and image segmentation, wherein subordinate functions are solved by adopting an iterative algorithm and the KNN algorithm in the model parameter solving process, therefore a partial volume effect is greatly reduced while a grayscale nonuniform field is eliminated, and the influence of noises on the correction and the segmentation of the grayscale nonuniformity of the MR image is reduced. The subordinate functions are solved with KNN through the following steps of: firstly acquiring an accurate smooth normalization histogram by using a kernel estimation algorithm; then respectively solving a threshold value TCG between cerebrospinal fluids and gray matters and a threshold value TGW between the gray matters and white matters by using a maximum between-cluster variance method; carrying out rough sorting on the KNN sorting algorithm by utilizing the two threshold values; and finally accurately sorting points to be fixed by adopting the traditional KNN sorting algorithm.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
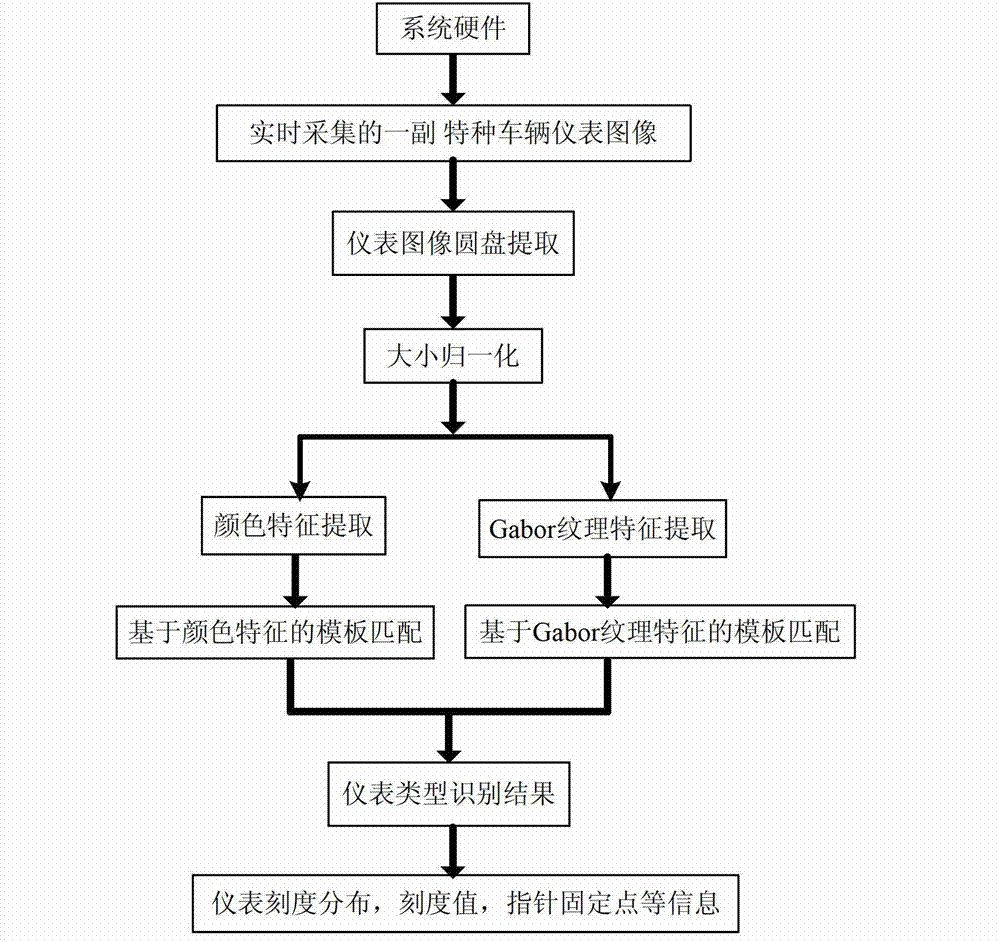
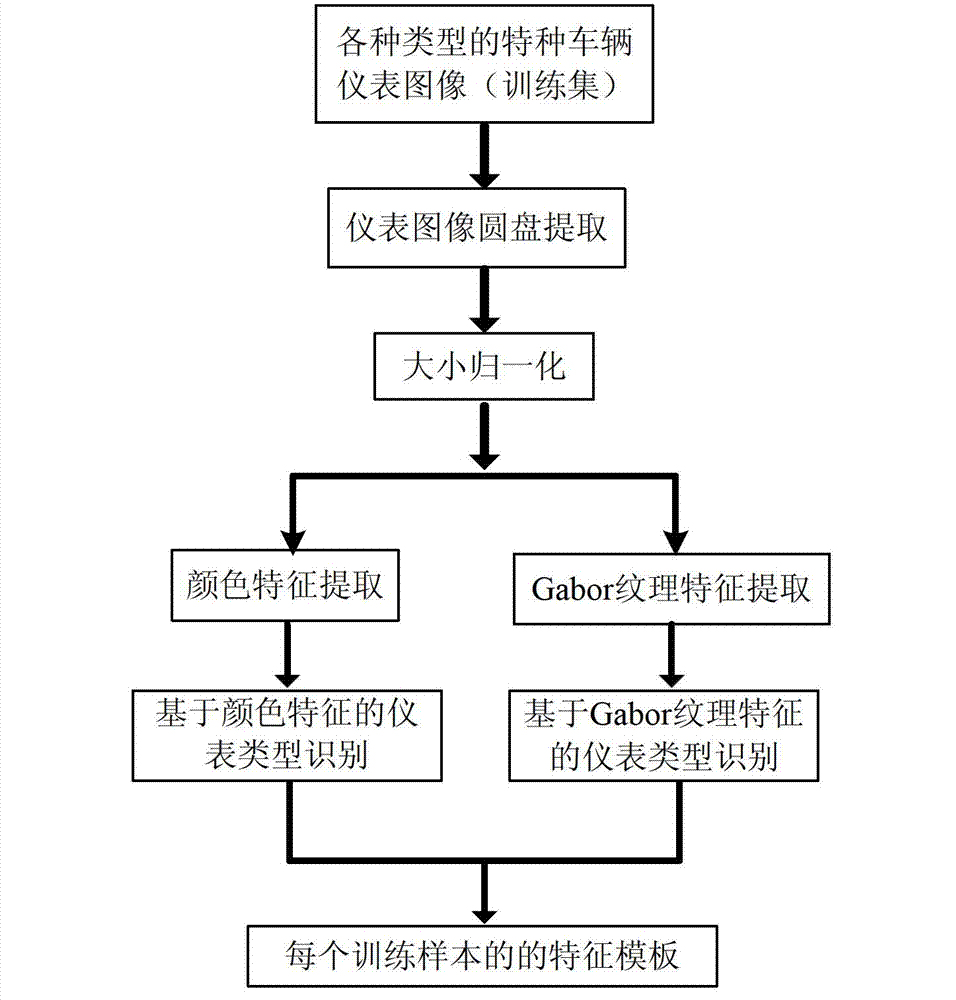
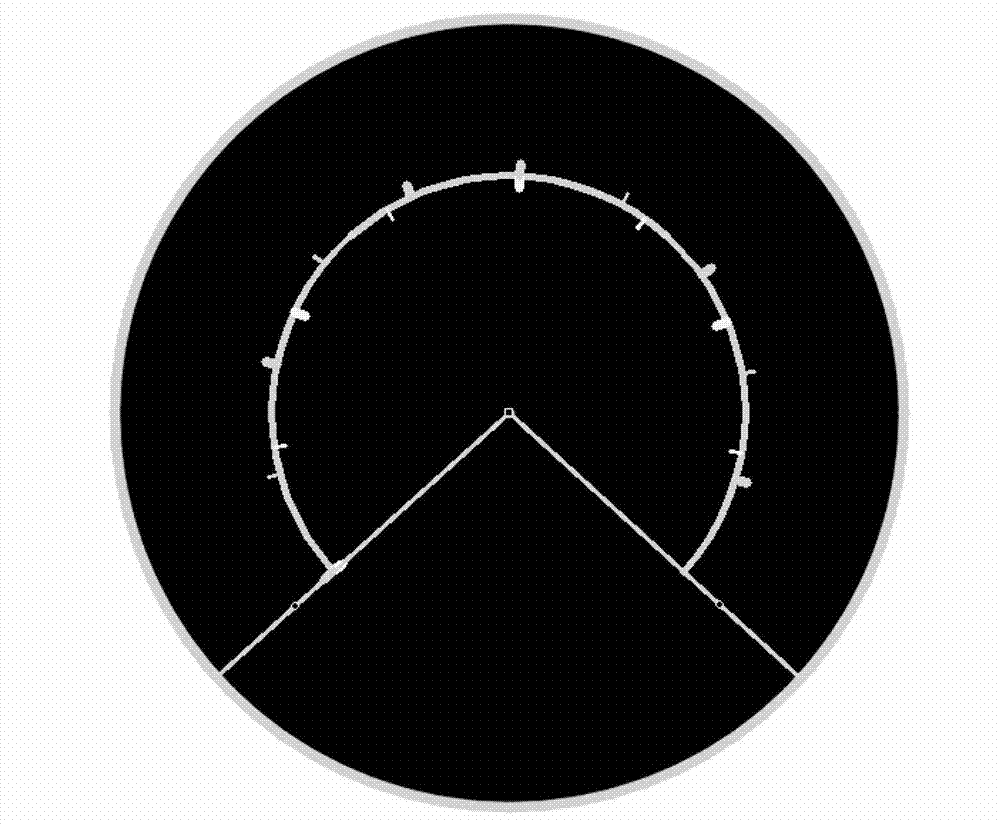
Special vehicle instrument type identification and calibration method based on image characteristics
The invention provides a special vehicle instrument type identification and calibration method based on image characteristics, and belongs to the field of image processing and mode identification. The method includes the steps of firstly collecting several special vehicle instrument images according to each type of several special vehicle instruments, and reserving representative images as training samples through manual judgment, secondly carrying out normalization to quality of the images through an image preprocessing method according to each training sample, then extracting a disk of the instrument images and carrying out the size normalization to the instrument images according to radius of the disk, thirdly respectively extracting color features and Gabor texture features of the special vehicle instrument images after the normalization, and finally aiming at all training samples, and building models for each type of instruments through respectively using of the color features and the Gabor texture features as vector quantities. After the feature models of the training samples of each type of instruments are built, with regards to the collected real-time images, the method can also be used to carry out image preprocessing and image quality normalization, respectively carries out mode match aiming at the feature templates of each type of instrument training samples with the two features, and obtains instrument classifying results through a nearest neighbour rule.
Owner:63963 TROOP OF THE PLA +1
Dynamic nearest neighbour inquiry method on basis of regional coverage
InactiveCN102073689ATroubleshoot queriesCutting costsSpecial data processing applicationsGrid densityData mining
The invention relates to a dynamic nearest neighbour inquiry method on the basis of regional coverage and belongs to the technical field of mobile data index. The method comprises the following steps of: inputting position information of personnel; dividing a battle space into grids; indexing soldiers; recognizing the grids by using a Voronoi graph structure for regions with sparse soldiers in a battlefield; setting a value between 0 and 1 as a threshold value; when the density of the grids is more than the threshold value, determining the position of a nearest neighbour teammate by adopting a best-first nearest neighbour inquiry method (BNFF); and when the density of the grids is less than the threshold value, determining the position of the nearest neighbour teammate by adopting a Voronoi graph nearest neighbour method. By the dynamic nearest neighbour inquiry method on the basis of regional coverage, the cost of updating indexes is reduced. Meanwhile, compared with the existing method, the inquiry efficiency of the dynamic nearest neighbour inquiry method on the basis of regional coverage is obviously improved. The method can play a great role on the battlefield and provide a furthest rapid and accurate result for each requester.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Method for finding optimal path in road network based on graph embedding
InactiveCN102156756ANarrow down the search spaceSpecial data processing applicationsLower limitAlgorithm
The invention belongs to the technical field of a spatial database, specifically relates to a method for finding an optimal path in a road network based on graph embedding. The method comprises the following steps of: defining point sets M1, M2, ..., and Mn of n attributions in a road network; and defining a starting point s and an ending point t; providing upper and lower limits according to a graph embedding frame by taking s as the starting point; finding out a greedy path Rg by finding the nearest neighbour with iteration; then traversing the point sets M1, M2, ..., and Mn of the n attributions according to a sequence; pruning the existing path by combining with the upper and lower limits and taking the length of the greedy path as the upper limit; and finally counting the residual candidate paths precisely to find the optimal path. The finding method based on graph embedding provided by the invention has the advantages that the searching space is greatly reduced, and the finding efficiency is high.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
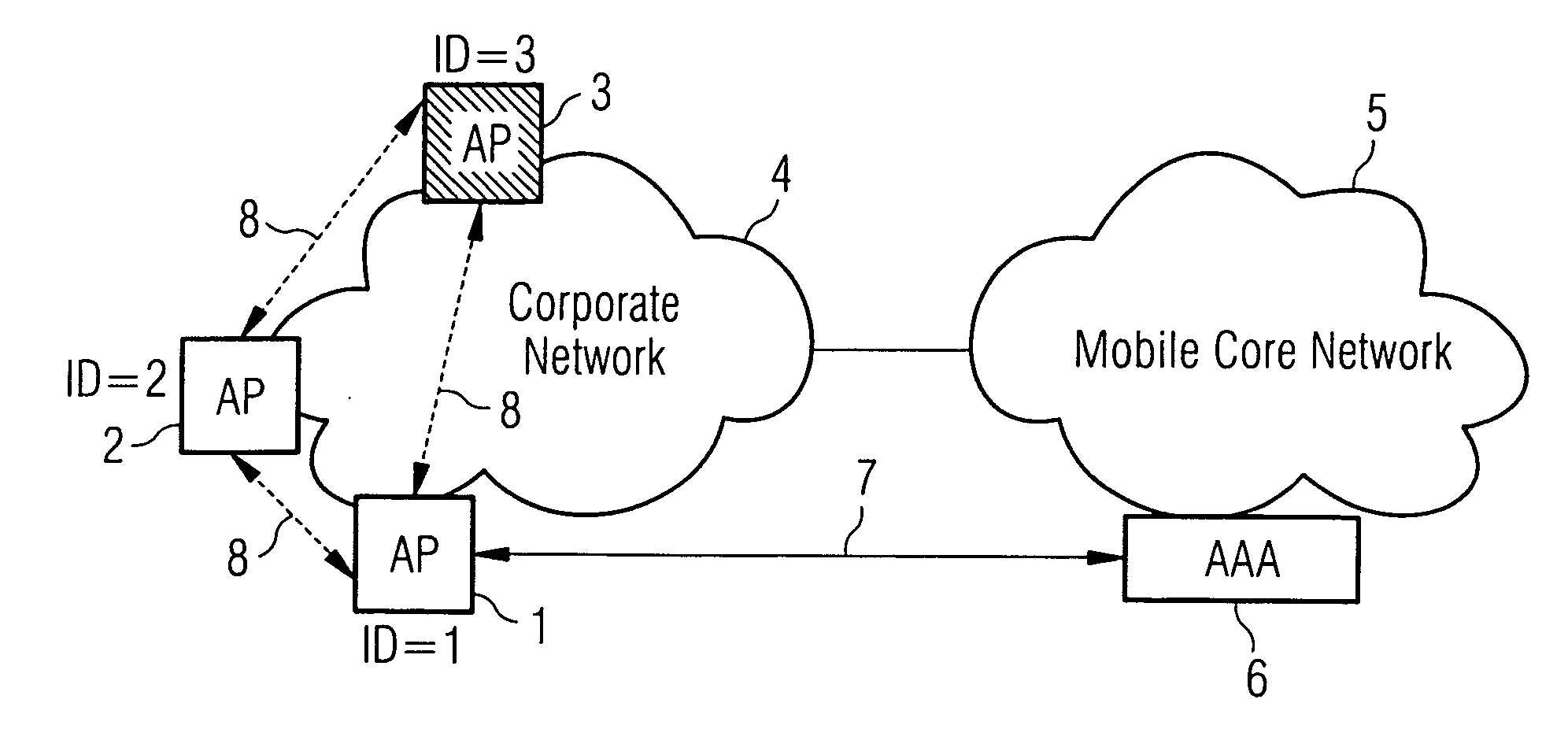
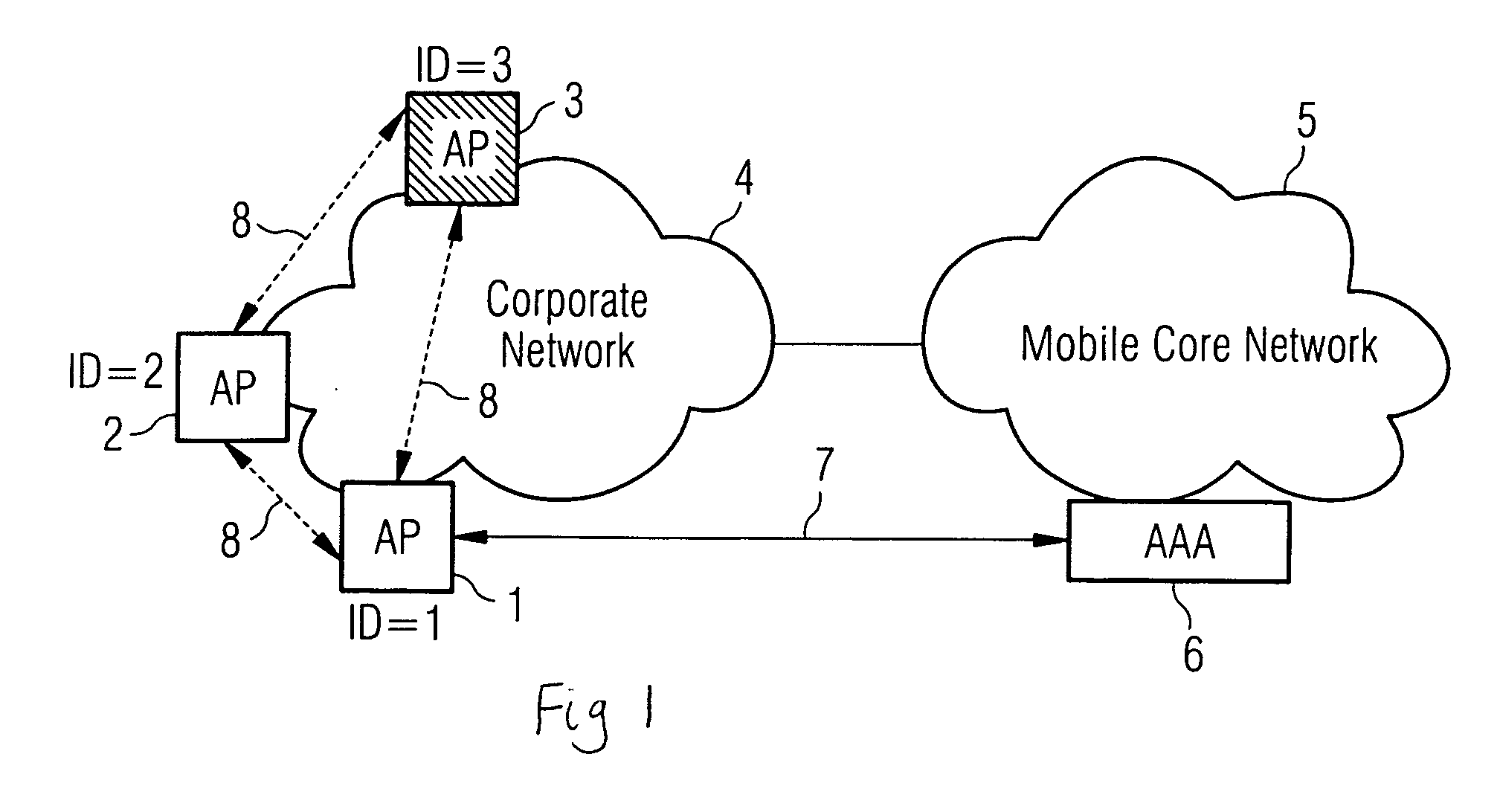
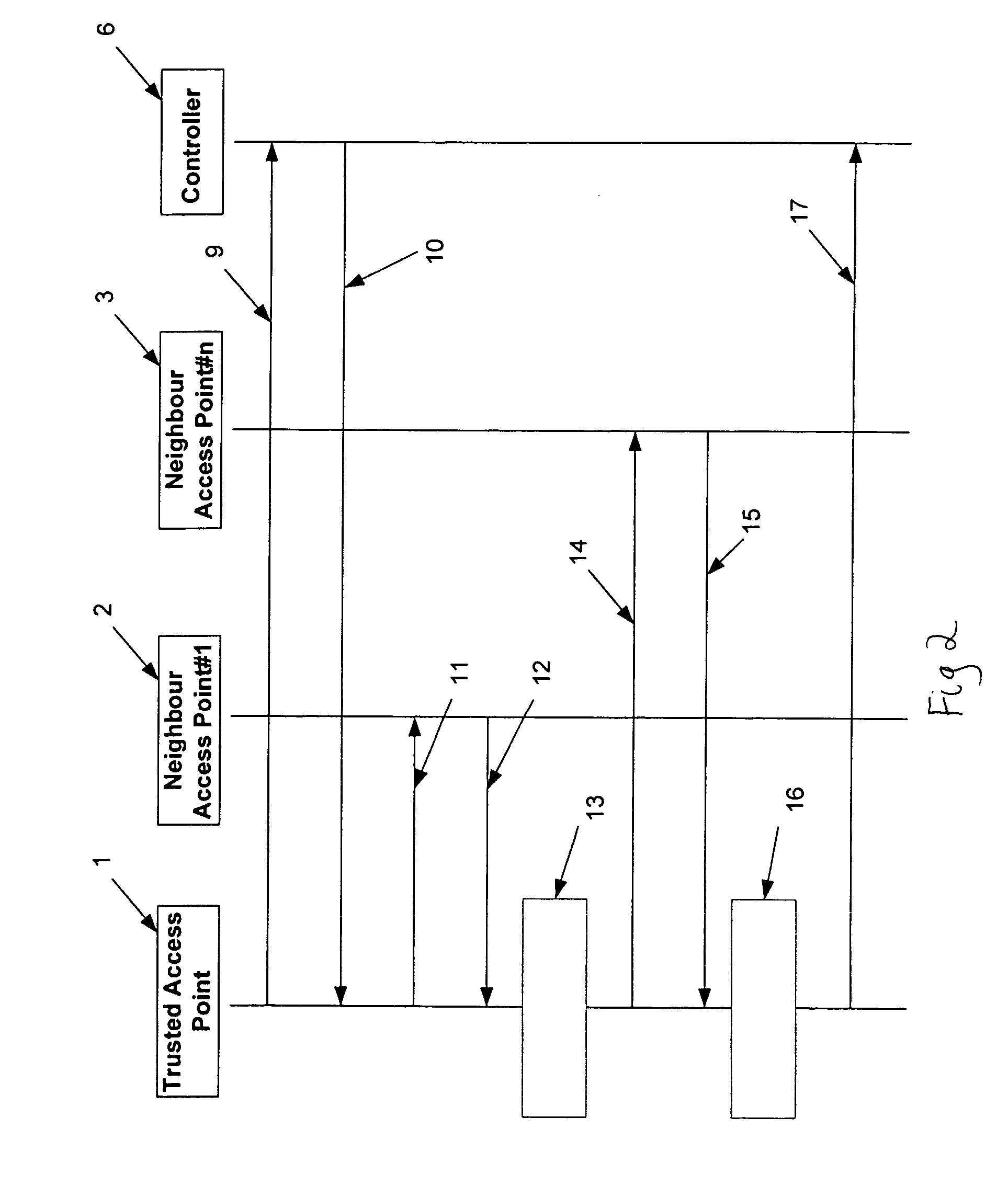
Method of authenticating access points on a wireless network
InactiveUS20070058601A1Avoid mistakesRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesWireless networkReal-time computing
A method of authenticating access points (1, 2, 3) on a wireless network (4) comprises sending a list of nearest neighbours (2, 3) from a trusted access point (1) to a controller (6). At the trusted access point (1), test data related to each of the listed nearest neighbours is received from the controller. Each neighbour (2, 3) is interrogated using its respective test data and the response compared with an expected response. A reliability indication is returned to the controller (6).
Owner:ROKE MANOR RES LTD
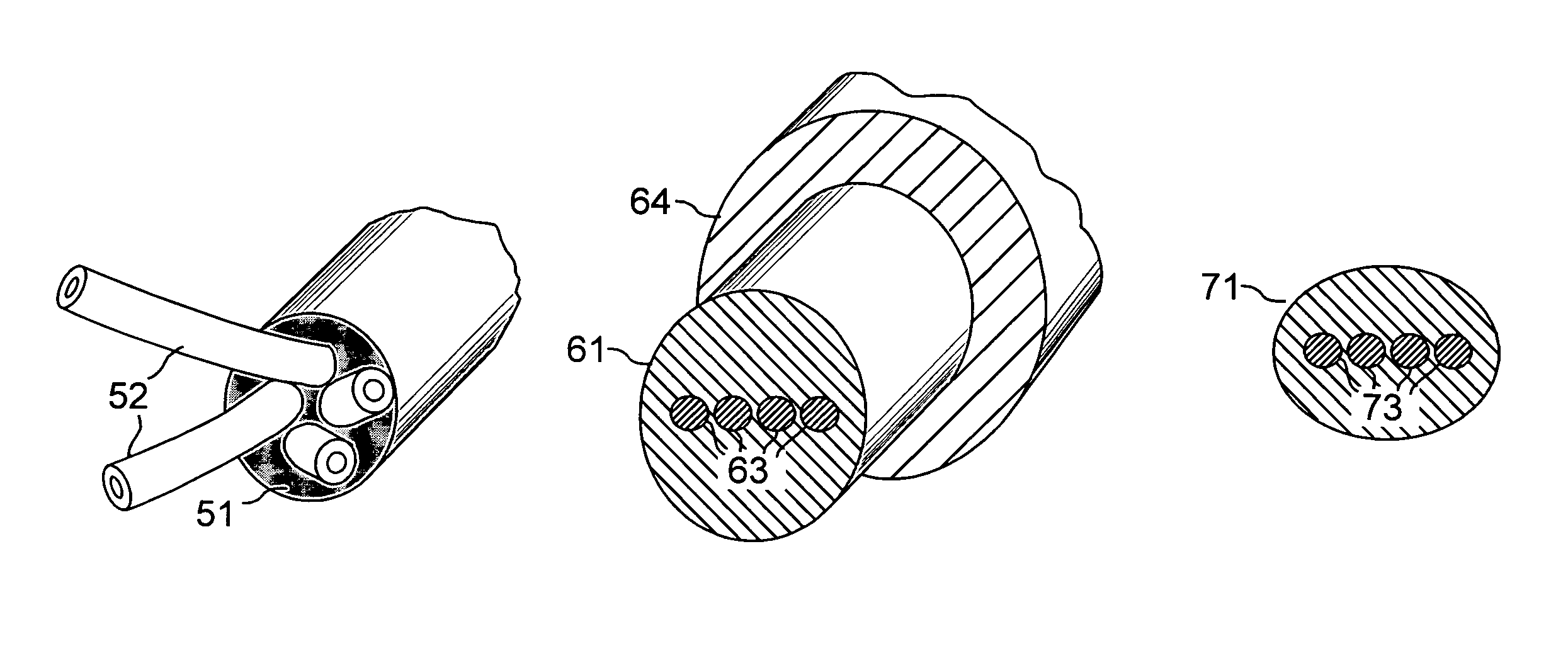
Optical fiber cables
The specification describes an improved optical fiber cable wherein the cable cross section is round and contains a plurality of bundled optical fibers. The bundle may comprise randomly spaced fibers or fibers aligned in a ribbon configuration. The bundle is encased in a polymer encasement that couples mechanically to each optical fiber. Preferably, the fibers are spaced from the nearest neighbor to improve coupling. In some embodiments the encasement is relatively hard, and is deliberately made to adhere to the optical fiber bundle. Consequently the encasement medium functions as an effective stress translating medium that deliberately translates stresses on the cable to the optical fibers. The cable construction of the invention is essentially void free, and provides a dry cable with water blocking capability.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com