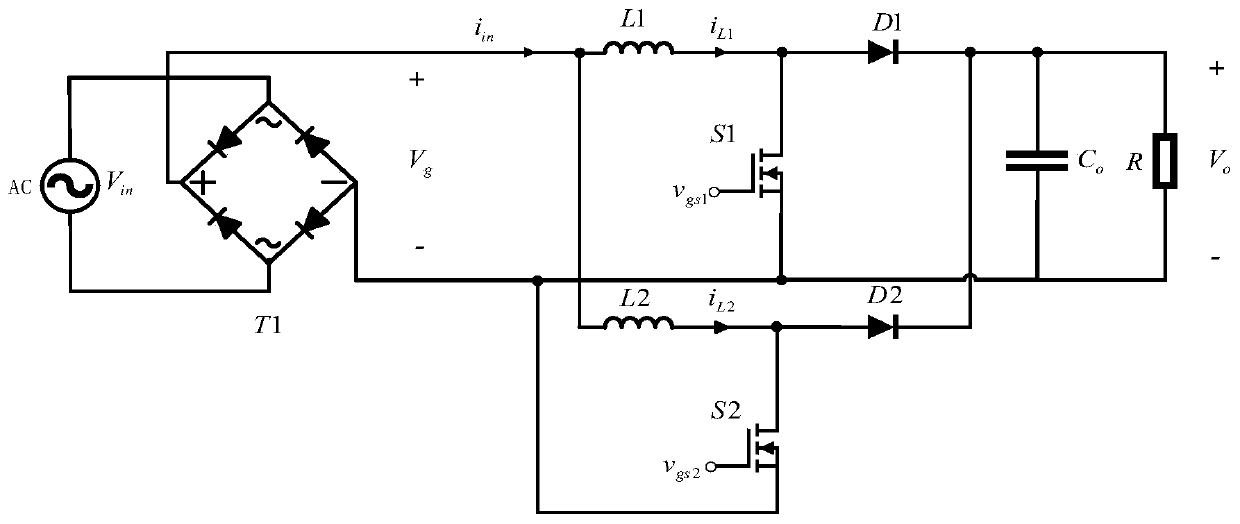
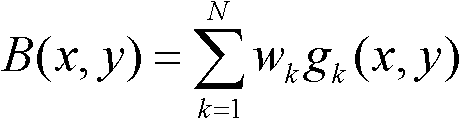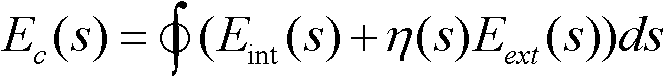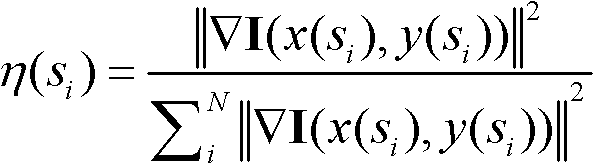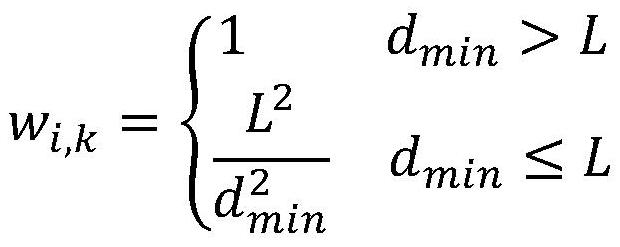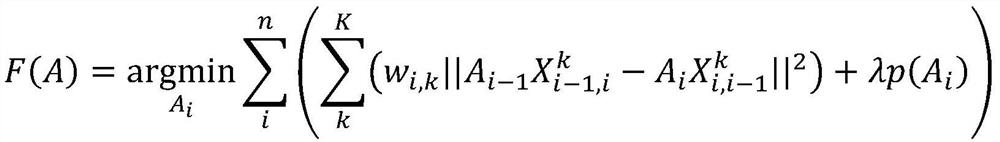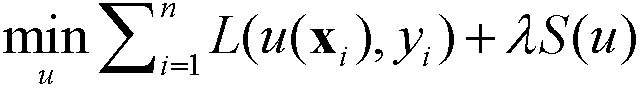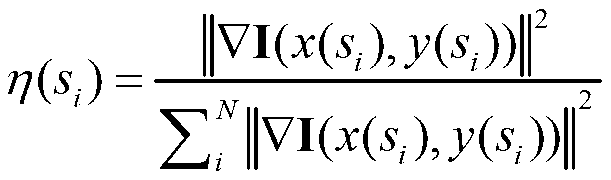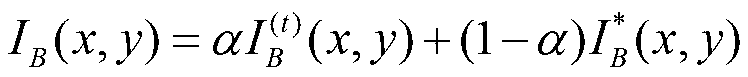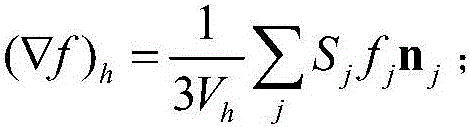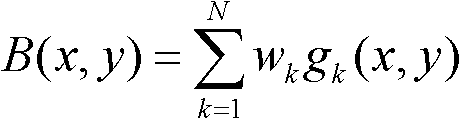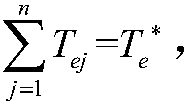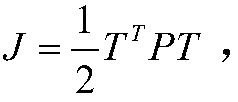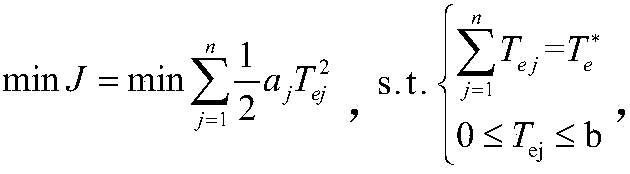Patents
Literature
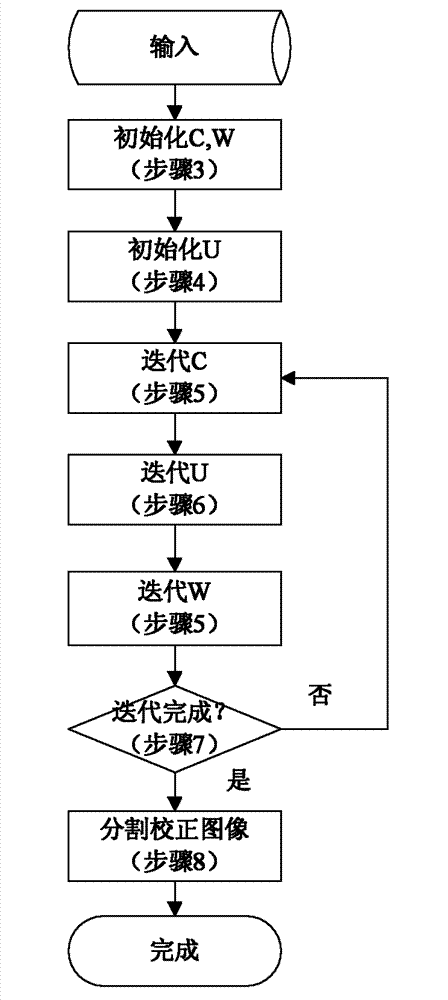
41 results about "Energy function minimization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
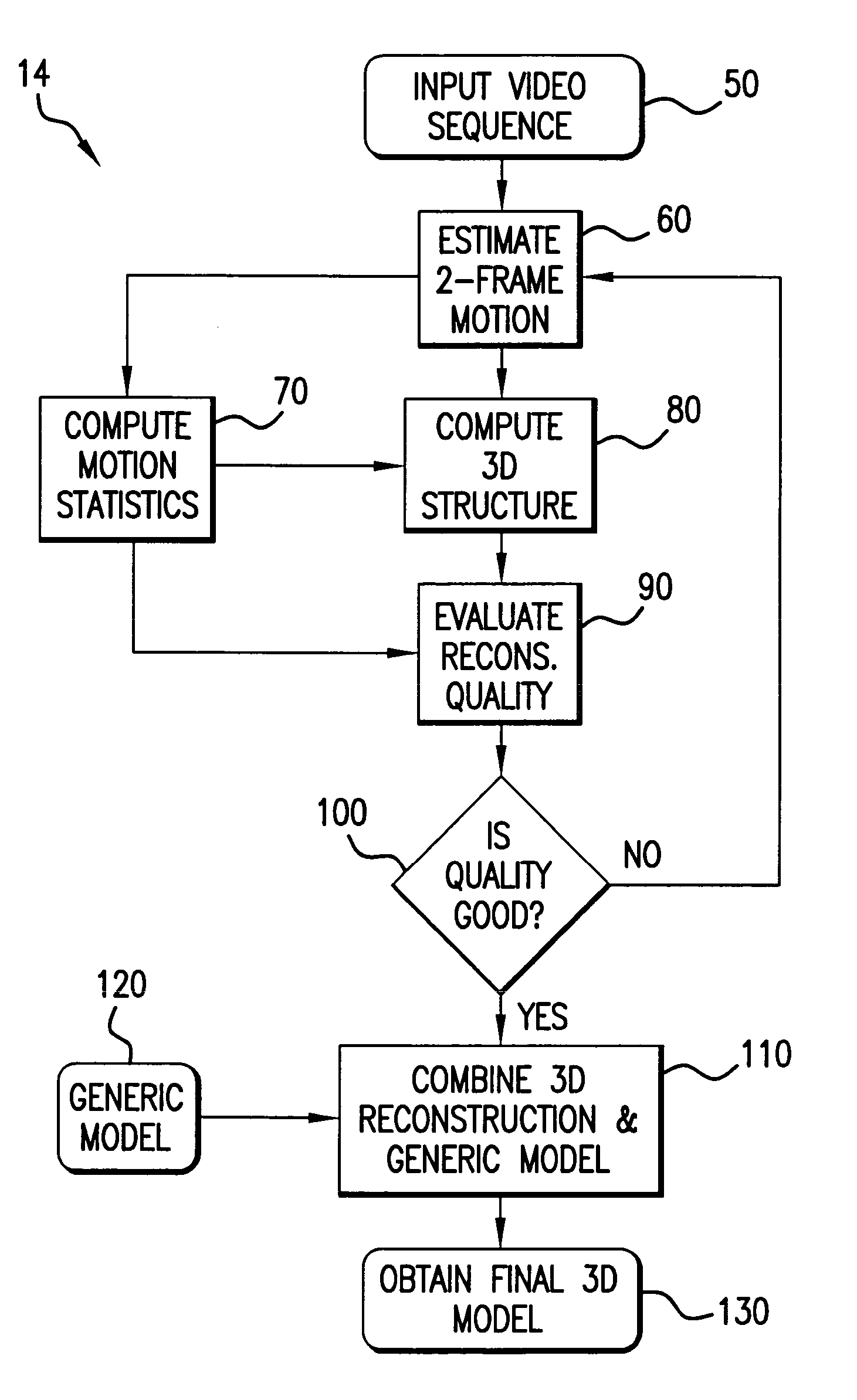
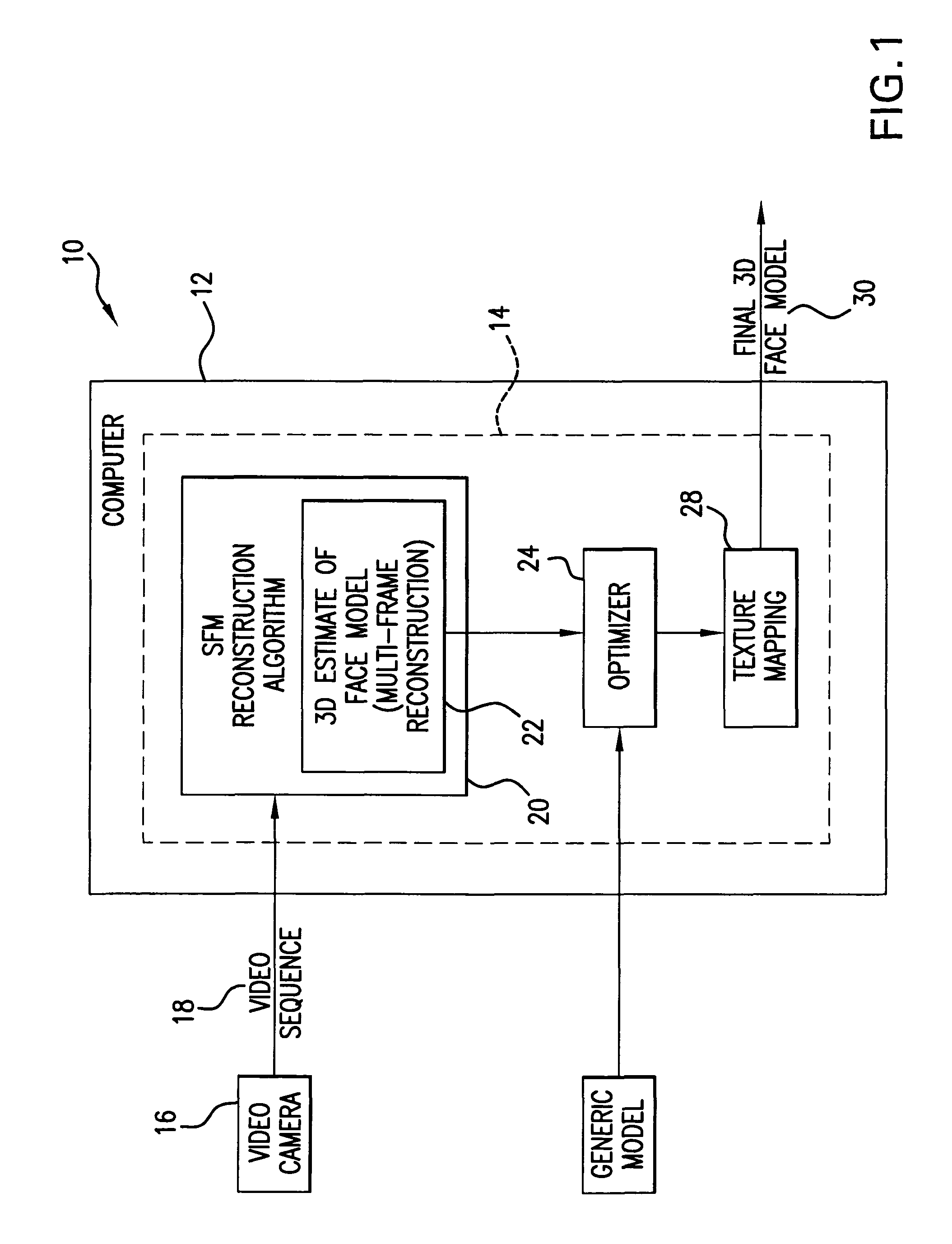
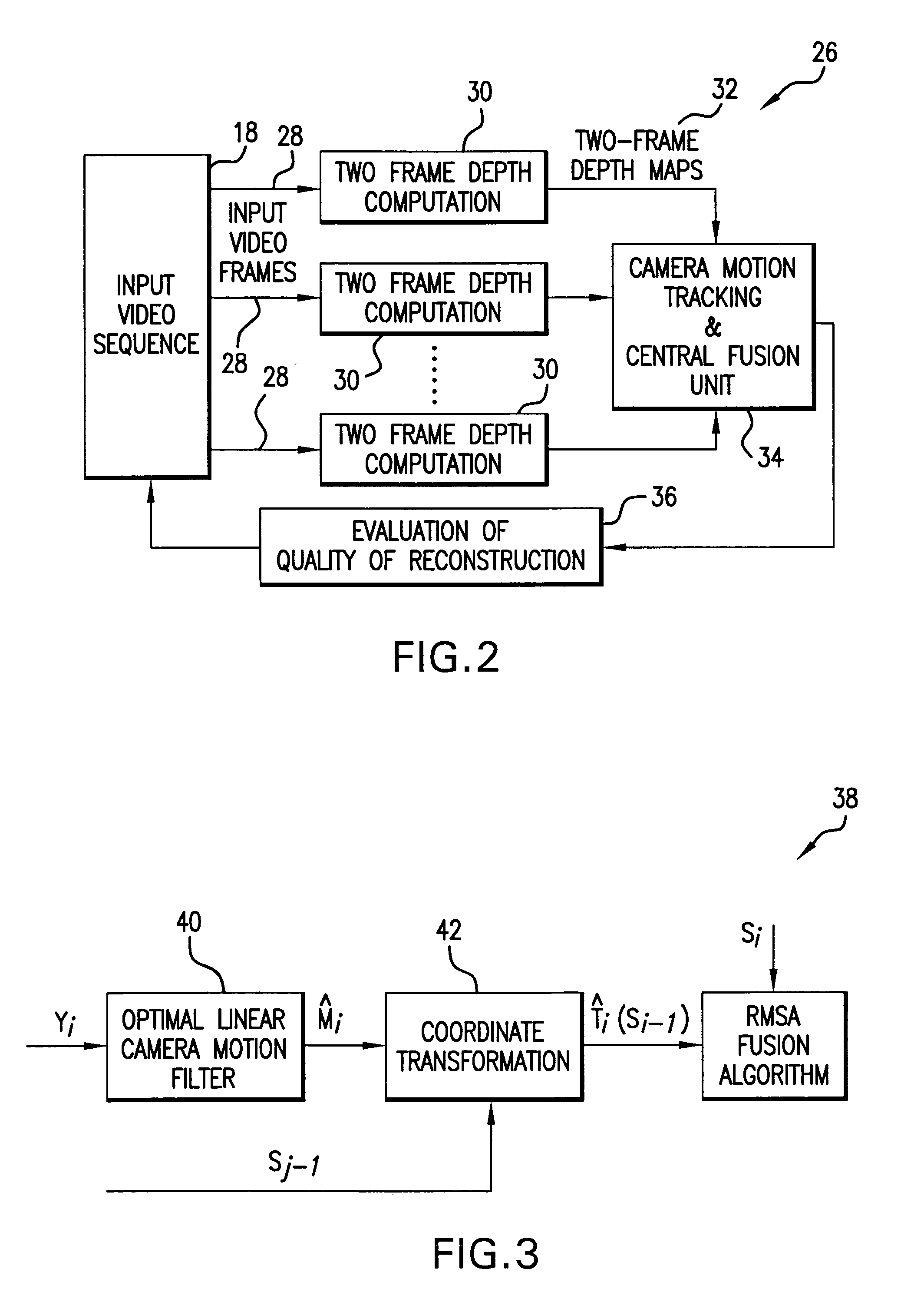
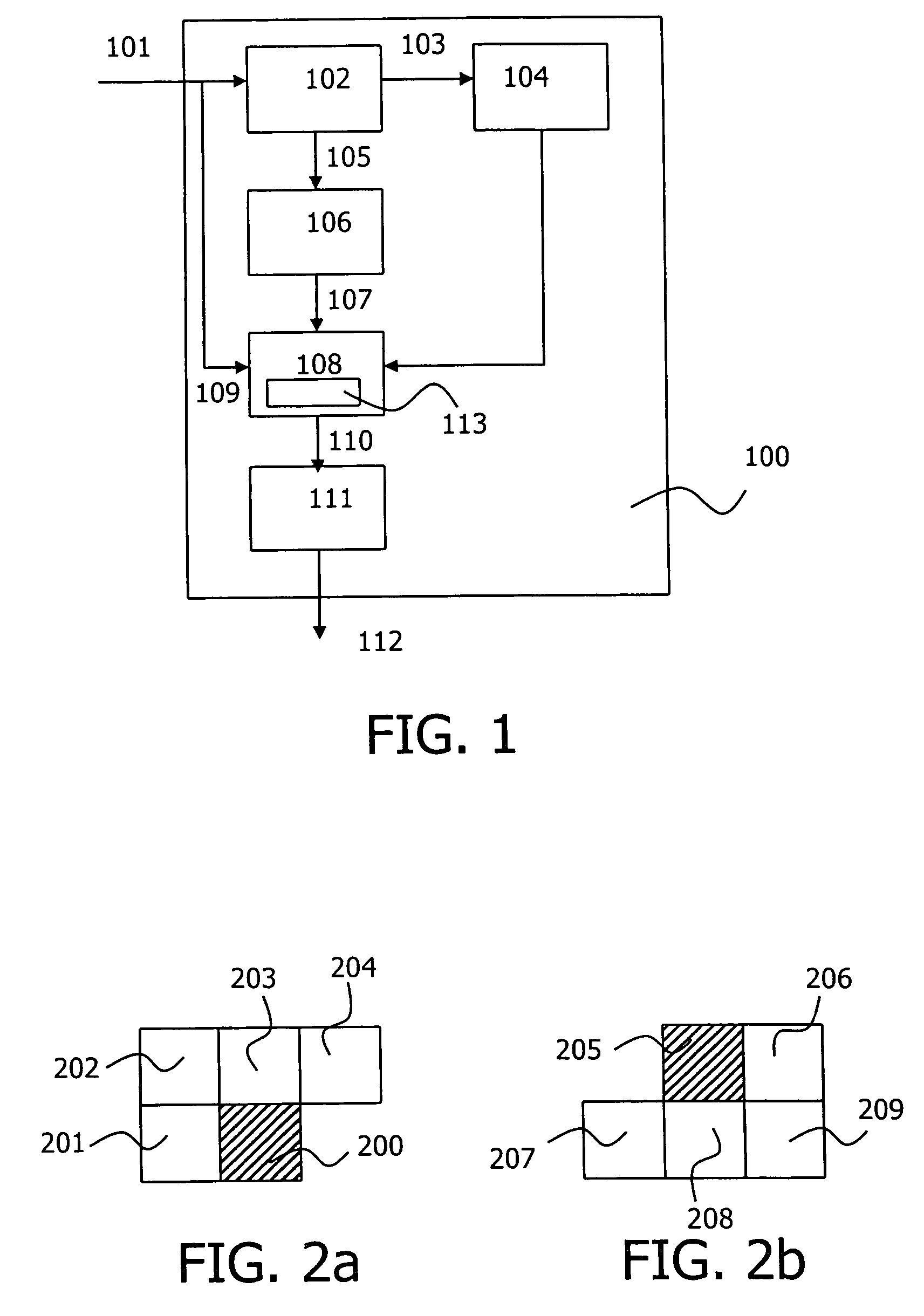
Method of three-dimensional object reconstruction from a video sequence using a generic model
InactiveUS7184071B2Inhibition effectInhibitionCharacter and pattern recognitionColor television detailsRate distortionEnergy function minimization
In a novel method of 3D modeling of an object from a video sequence using an SfM algorithm and a generic object model, the generic model is incorporated after the SfM algorithm generates a 3D estimate of the object model purely and directly from the input video sequence. An optimization framework provides for comparison of the local trends of the 3D estimate and the generic model so that the errors in the 3D estimate are corrected. The 3D estimate is obtained by fusing intermediate 3D reconstructions of pairs of frames of the video sequence after computing the uncertainty of the two frame solutions. The quality of the fusion algorithm is tracked using a rate-distortion function. In order to combine the generic model with the 3D estimate, an energy function minimization procedure is applied to the 3D estimate. The optimization is performed using a Metropolis-Hasting sampling strategy.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF
KNN (K-Nearest Neighbor) sorting algorithm based method for correcting and segmenting grayscale nonuniformity of MR (Magnetic Resonance) image
InactiveCN102135606AAccurate divisionVolume effect suppressionMagnetic measurementsSorting algorithmNear neighbor
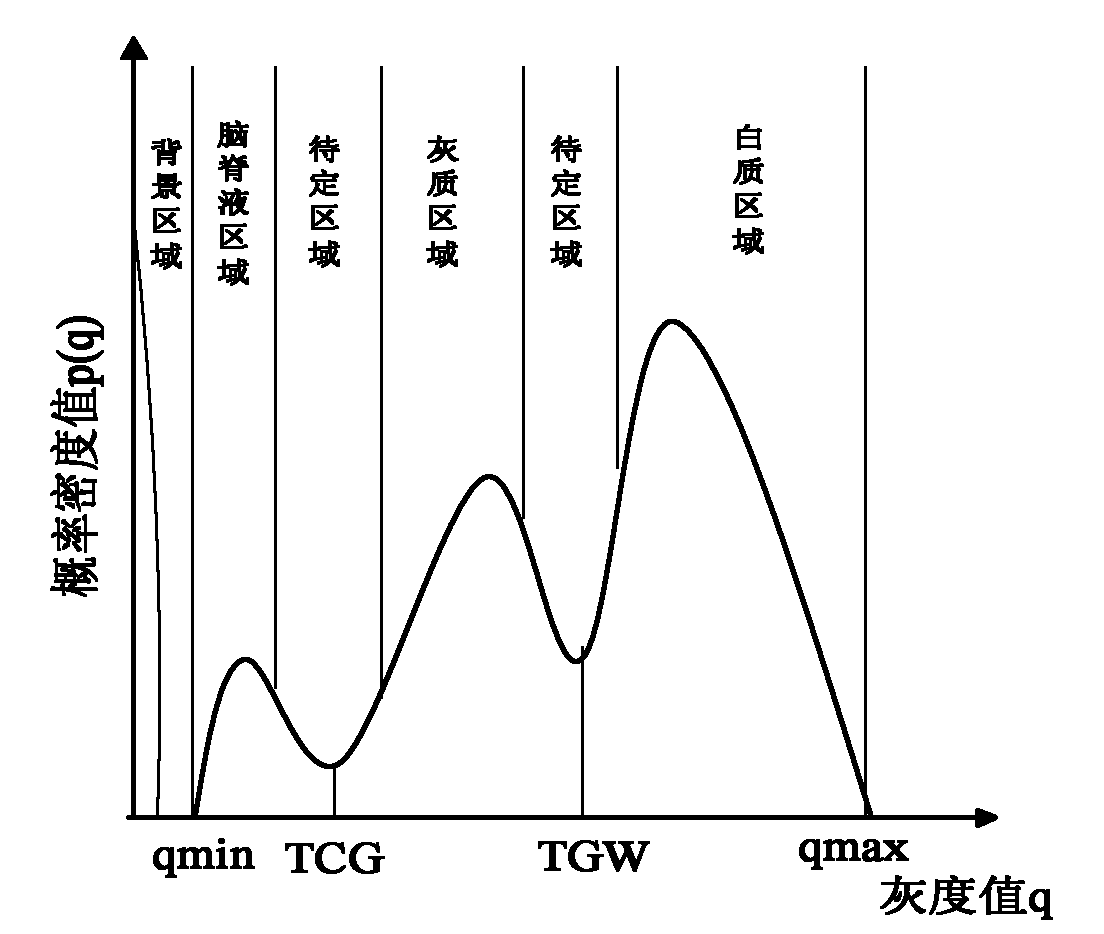
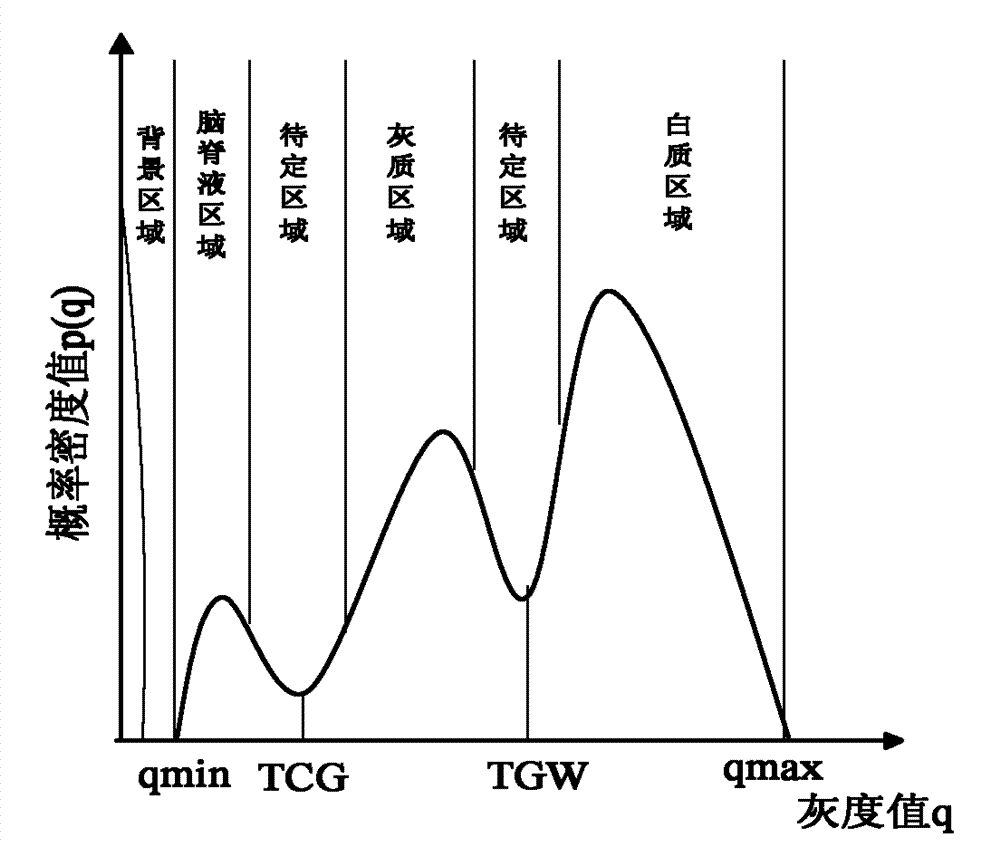
The invention relates to a KNN (K-Nearest Neighbor) sorting algorithm based method for correcting and segmenting the grayscale nonuniformity of an MR (Magnetic Resonance) image, belonging to the field of image processing. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly constructing a grayscale nonuniform field model by utilizing surface fitting knowledge and using a group of orthonormalization basis functions, and establishing energy functions; and then solving model parameters according to an energy function minimization principle to realize grayscale nonuniformity correction and image segmentation, wherein subordinate functions are solved by adopting an iterative algorithm and the KNN algorithm in the model parameter solving process, therefore a partial volume effect is greatly reduced while a grayscale nonuniform field is eliminated, and the influence of noises on the correction and the segmentation of the grayscale nonuniformity of the MR image is reduced. The subordinate functions are solved with KNN through the following steps of: firstly acquiring an accurate smooth normalization histogram by using a kernel estimation algorithm; then respectively solving a threshold value TCG between cerebrospinal fluids and gray matters and a threshold value TGW between the gray matters and white matters by using a maximum between-cluster variance method; carrying out rough sorting on the KNN sorting algorithm by utilizing the two threshold values; and finally accurately sorting points to be fixed by adopting the traditional KNN sorting algorithm.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Height measurement method based on video multi-target tracking
InactiveCN103735269AImprove accuracyReduce complexityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMulti target trackingMultiple frame
The invention discloses a height measurement method based on video multi-target tracking. The method includes the following steps that background modeling is conducted on video sequences collected by a camera, and foreground images are extracted through background subtraction; each frame image is mapped into an undirected network diagram G=<V, E>; an energy function is built; the built energy function is minimized, and label values of pixels of the current frame image are acquired, wherein the pixels belong to different targets and backgrounds,; different colors are given to the pixels which belong to the different targets, and a tracking frame of the multiple targets is determined; a vanishing point Vy where the camera is perpendicular to the horizontal plane and a vanishing line l of the horizontal plane are calculated; head feature points and foot feature points of the target to be detected in each frame image are extracted; the height of the targets to be detected in each frame image is calculated; the height measurement results of the multi-frame video sequences are merged, and the actual height of the targets to be detected is determined. According to the method, the camera does not need to be completely marked, only the vanishing point and the vanishing line of the horizontal plane need to be calculated, and therefore calculation complexity is reduced.
Owner:DALIAN NATIONALITIES UNIVERSITY
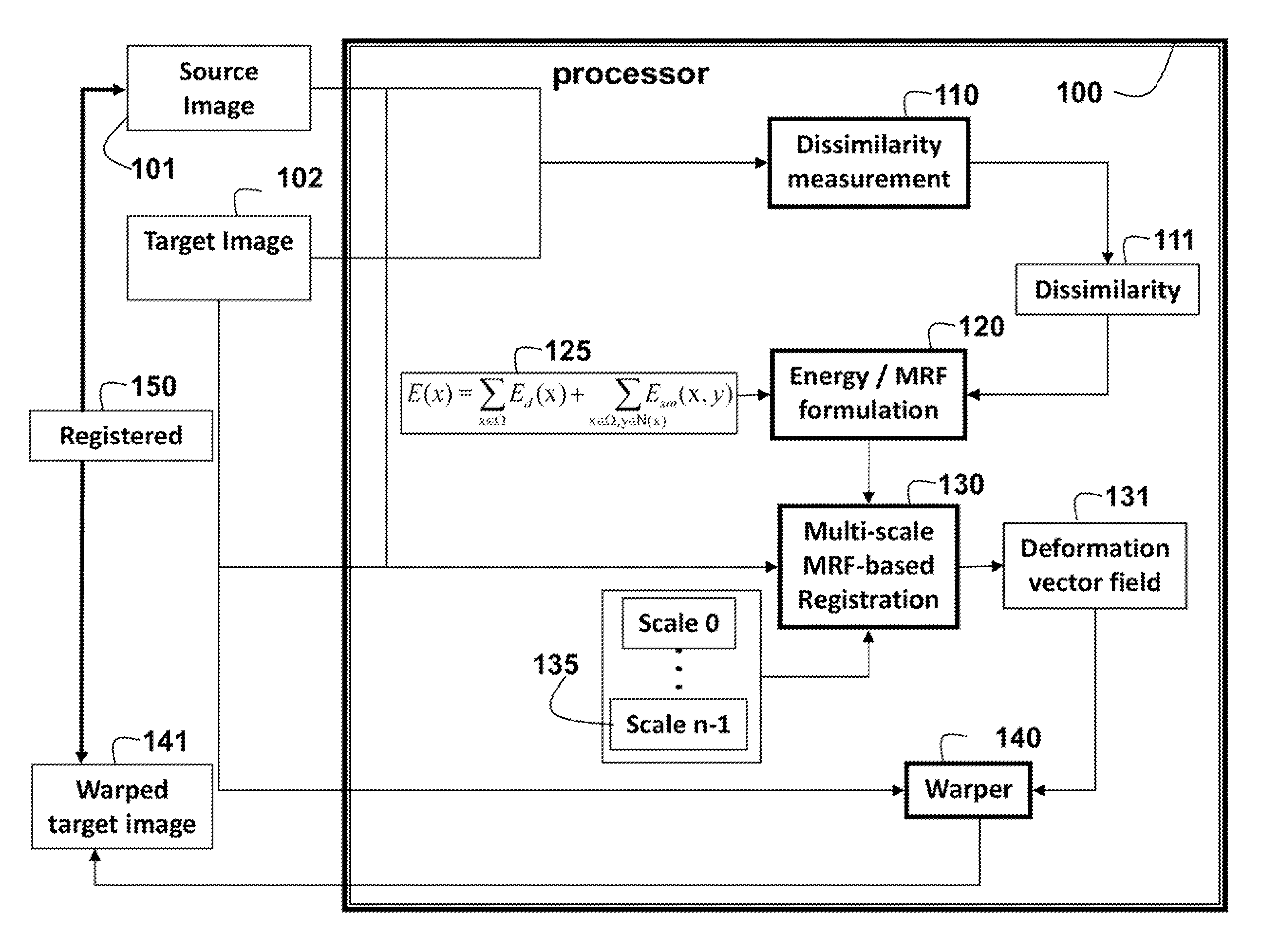
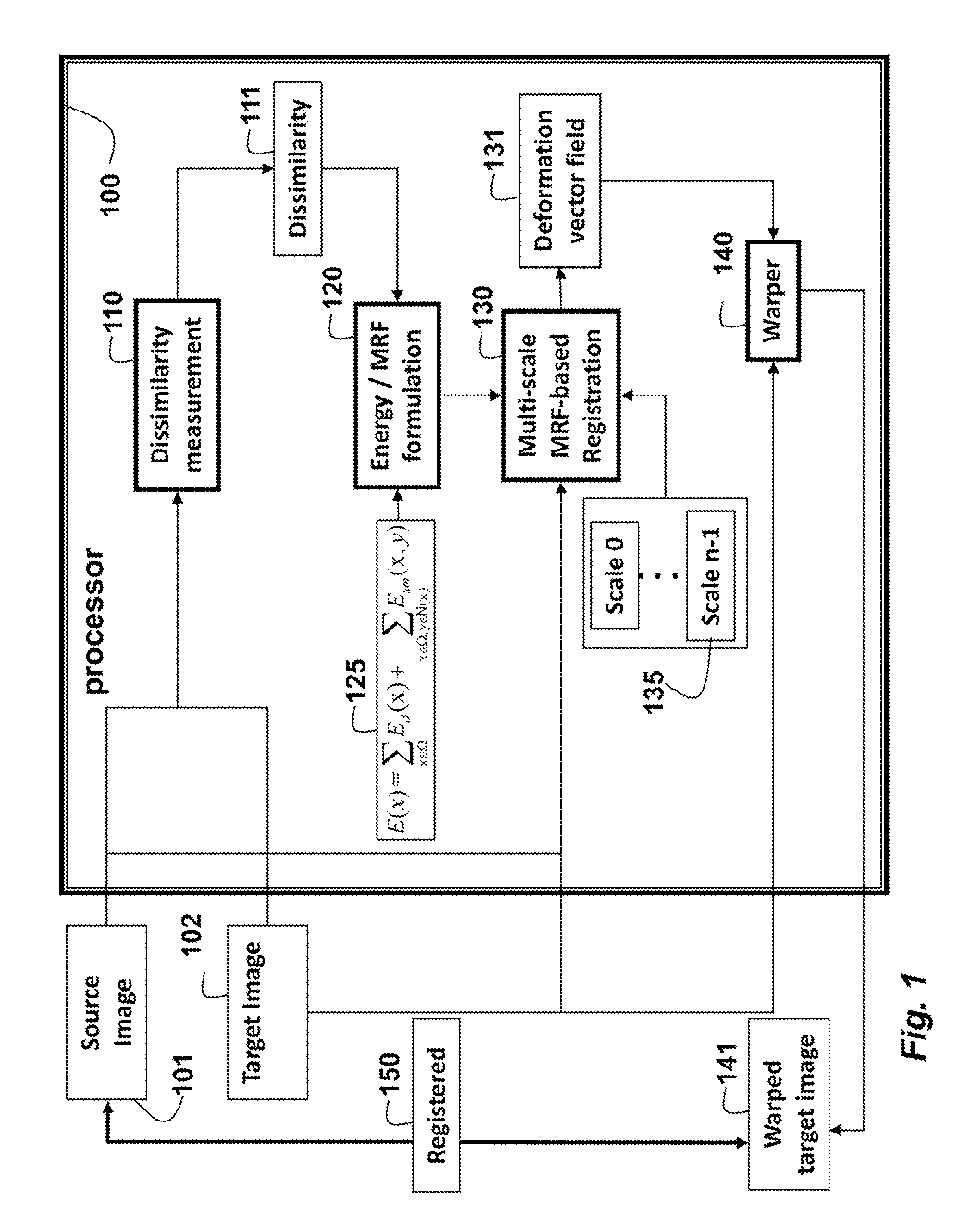
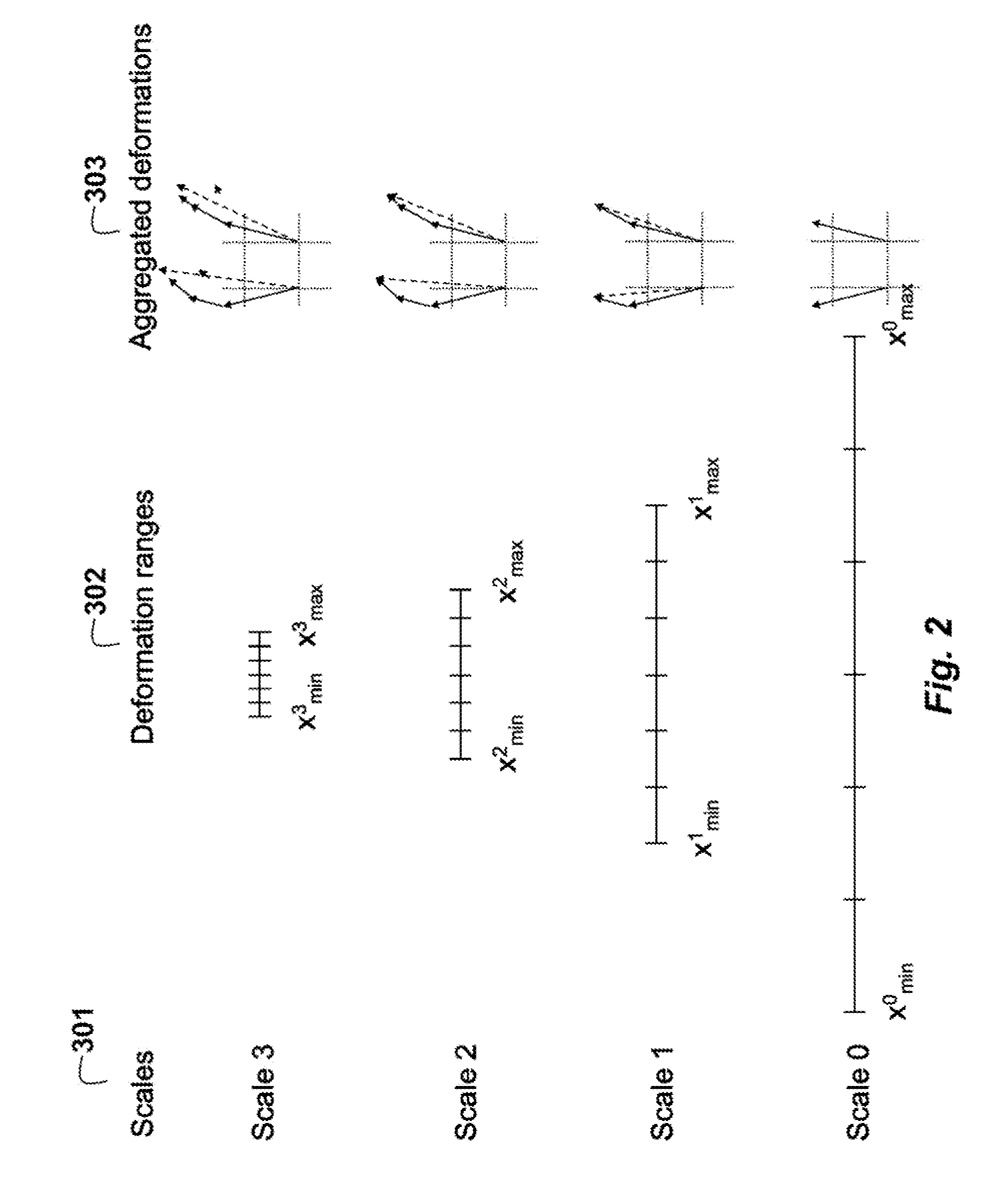
Method for Registering Deformable Images Using Random Markov Fields
ActiveUS20150317788A1Reduce in quantityConvenient and accurateImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionMarkov field
A method registers a source image with a target image, wherein the images are deformable, by first measuring dissimilarity between the source image and the target image. The dissimilarity minimized using a discrete energy function. At multiple scales, multi-scale Markov random field registration is applied to the source and target images to determine a deformation vector field. Then, the target image is warped according to the deformation field vector to obtain a warped target mage registered to the source image.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
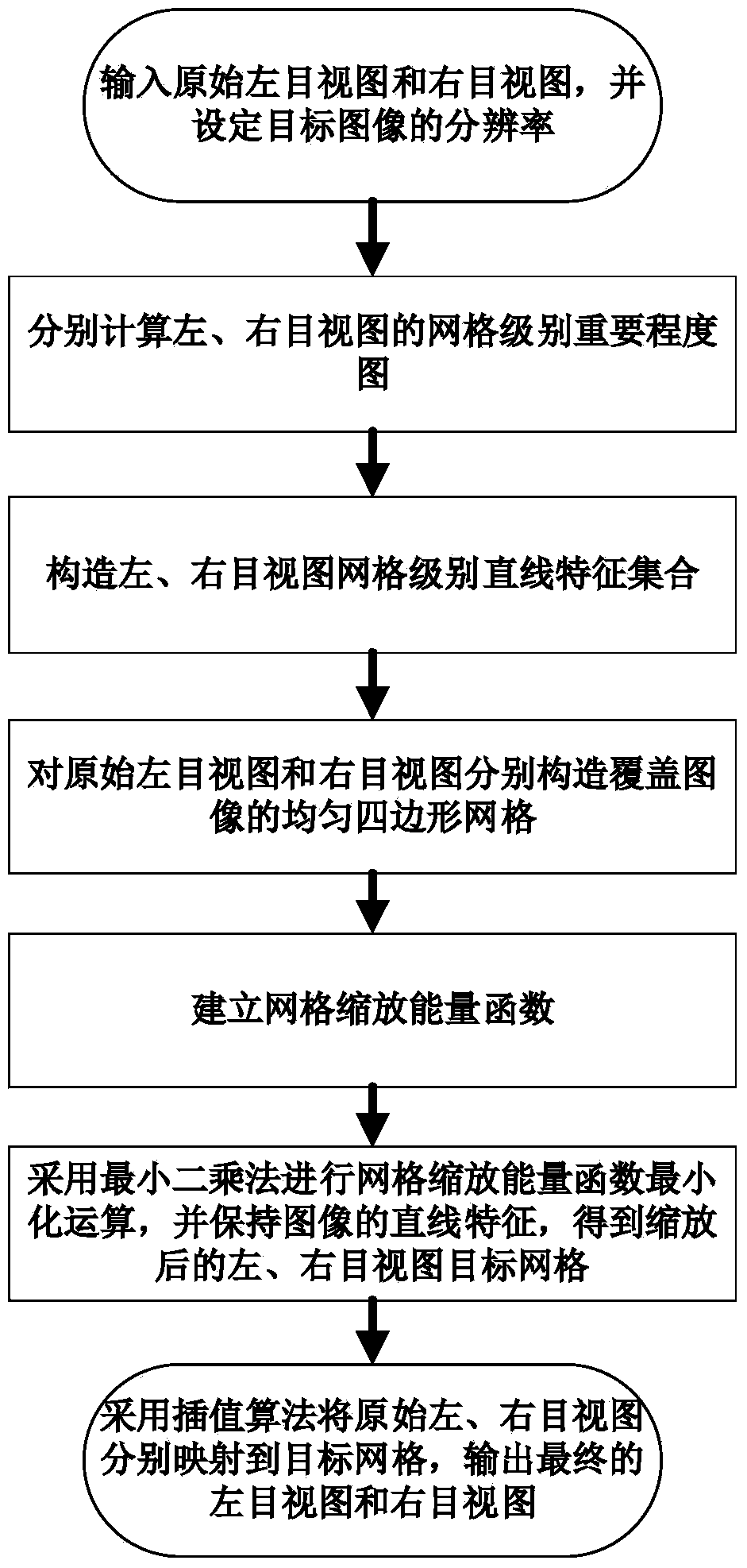
Content perception binocular image zooming method based on grid deformation
InactiveCN104166992AKeep Stereo InformationKeep Parallax ConsistencyImage analysisGeometric image transformationGrid deformationImage resolution
The invention discloses a content perception binocular image zooming method based on grid deformation. The method comprises the following steps: A, inputting an original left-eye view and an original right-eye view, and setting the resolution of an object image; B, respectively constructing uniform quadrilateral grids covering the image for the left-eye view and the right-eye view; C, respectively calculating grid-grade importance degree graphs of the left-eye view and the right-eye view; D, constructing a grid-grade linear characteristic set of the left-eye view and the right-eye view; E, according to the grid-grade importance degree graphs, establishing grid zooming energy functions; F, according to the grid-grade linear characteristic set, establishing linear characteristic constraints, and carrying out grid zooming energy function minimizing operation by use of least squares to obtain a left-eye view object grid and a right-eye view object grid after zooming; and G, mapping the original left-eye view and the original right-eye view respectively to an object grid by use of a mapping method, and outputting a final left-eye view and a final right-eye view. According to the invention, the linear characteristic of the zoomed image can reserved, important objects are prominent, and stereo information of a binocular image is maintained.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIVERSITY OF FOREIGN STUDIES +1
Piecewise planar reconstruction of three-dimensional scenes
ActiveCN102804231AImage enhancementImage analysisEnergy function minimizationComputer vision algorithms
Methods, systems, and computer-readable media for reconstruction a three-dimensional scene from a collection of two-dimensional images are provided. A computerized reconstruction system executes computer vision algorithms on the collection of two-dimensional images to identify candidate planes that are used to model visual characteristics of the environment depicted in the two-dimensional images. The computer vision algorithms may minimize an energy function that represents the relationships and similarities among features of the two-dimensional images to assign pixels of the two dimensional images to planes in the three dimensional scene. The three-dimensional scene is navigable and depicts viewpoint transitions between multiple two-dimensional images.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Two-dimensional-laser real-time detection method of workpiece surface profile
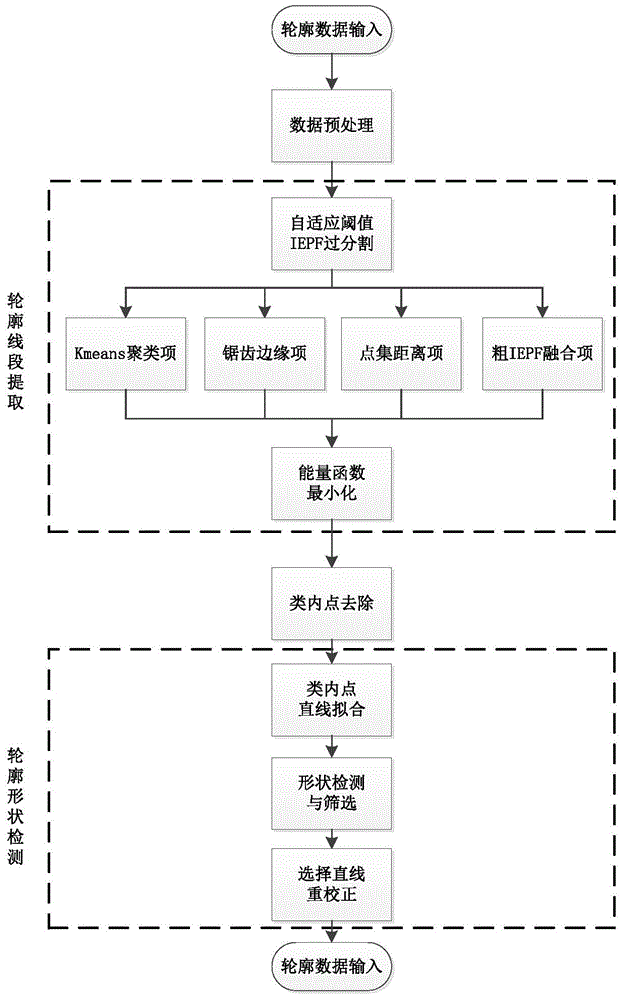
The invention provides a two-dimensional-laser real-time detection method of a workpiece surface profile. Aiming at profile point data of an environment or a target object, wherein the profile point data is acquired by a 2D laser sensor, firstly using an adaptive threshold IEPF algorithm to carry out over-segmentation on the profile point data; then, constructing an undirected graph, taking over-segmentation point set data as a undirected graph node, taking an over-segmentation point set fusion probability as a side of the undirected graph and calculating a fusion probability value; and then, constructing and segmenting an energy function of the undirected graph, providing an energy function minimization solution and acquiring a fusion result of the over-segmentation point set, wherein the fusion result of the over-segmentation point set is a line segment fitting result of point data; finally, using prior knowledge and a shape template to calculate a line segment fitting result so as to acquire a shape detection result. By using the method, disadvantages that a traditional algorithm is sensitive to a threshold and a data noise and robustness is not high are overcome; the method can be used for detection of a specific-shape workpiece of an industrial robot arm, autonomous motion robot scene understanding, unmanned vehicle environment cognition and other hot spot problems.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
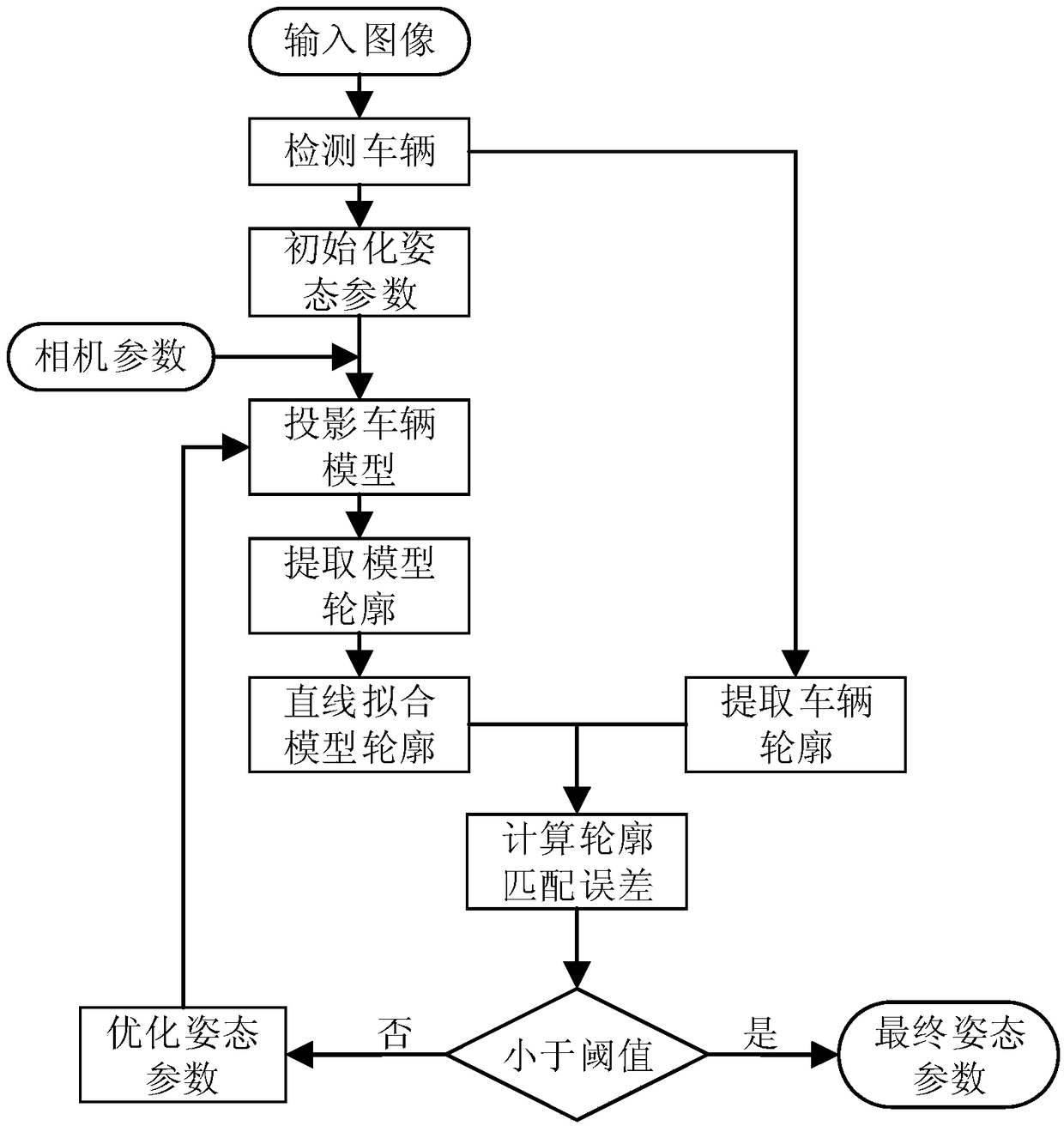
A 3D pose estimation method of image vehicle based on fine CAD model
InactiveCN109087323AImprove accuracyImprove robustnessImage enhancementImage analysisContour matchingEnergy function minimization
The invention discloses an image vehicle attitude estimation method based on a fine three-dimensional model. The method comprises steps: first, the position of the vehicle being detected from the image, and initializing the vehicle three-dimensional posture parameters, rendering the vehicle three-dimensional model to the image plane using the current posture parameters, extracting the contours ofthe image vehicle and the model vehicle respectively, using the matching error between the contours to construct the energy function, and adopting the Gauss-Newton algorithm to optimize the posture parameters, solving the energy function minimization problem, and obtaining the final result. In contour matching, the improved random sampling consistency (RANSAC) algorithm is used to fit the contourof the curve model with piecewise straight lines, and then the contour is matched with the real vehicle contour. The invention can accurately and robustly recover the three-dimensional posture parameters of the vehicle relative to the camera in the surveillance video in the complex surveillance scene, which is of great significance to the understanding and automatic processing of the surveillancevideo.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
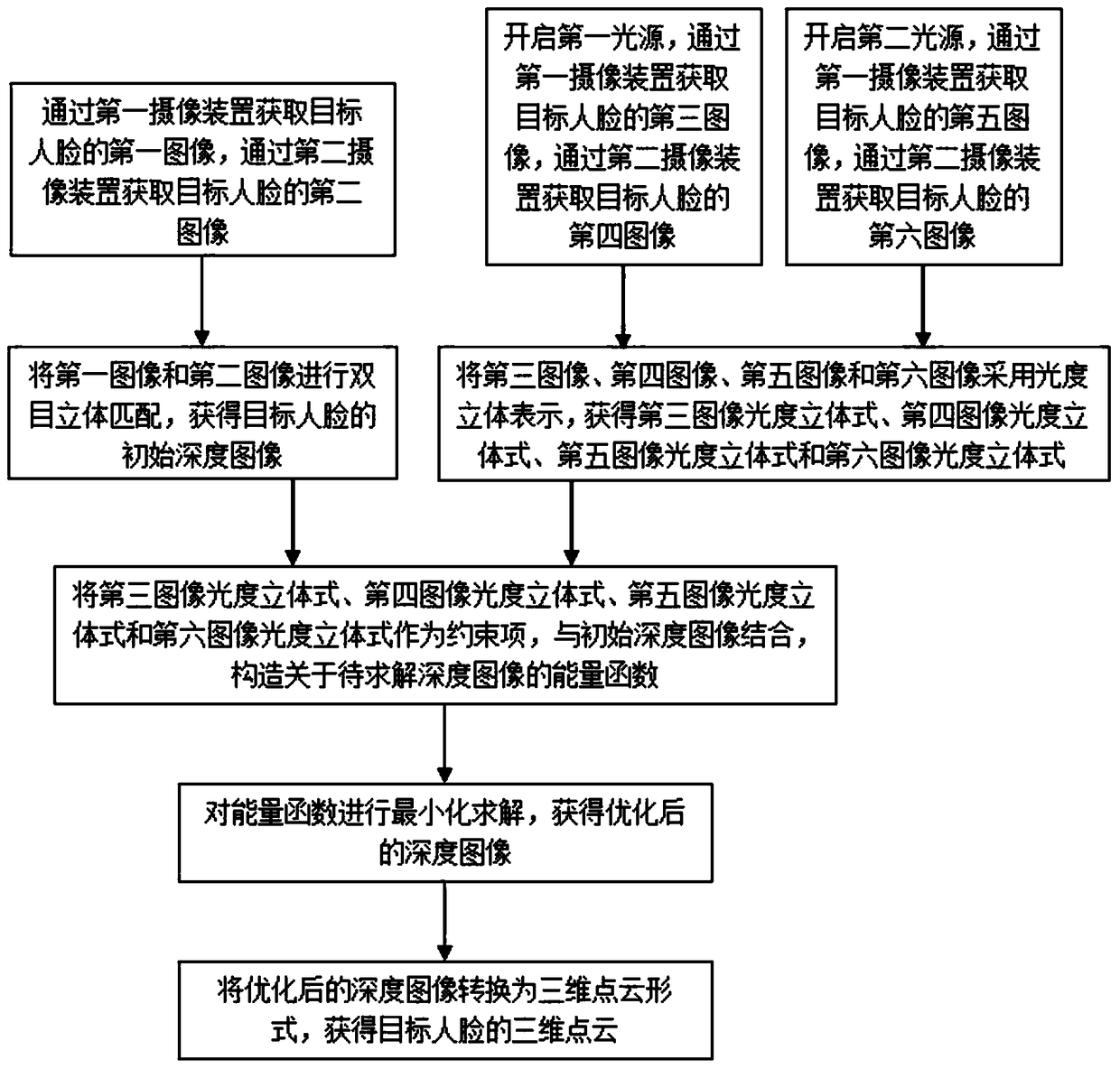
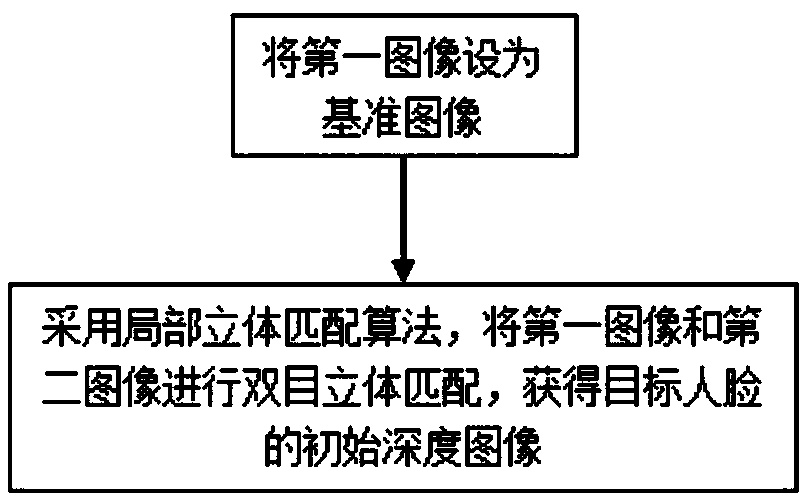
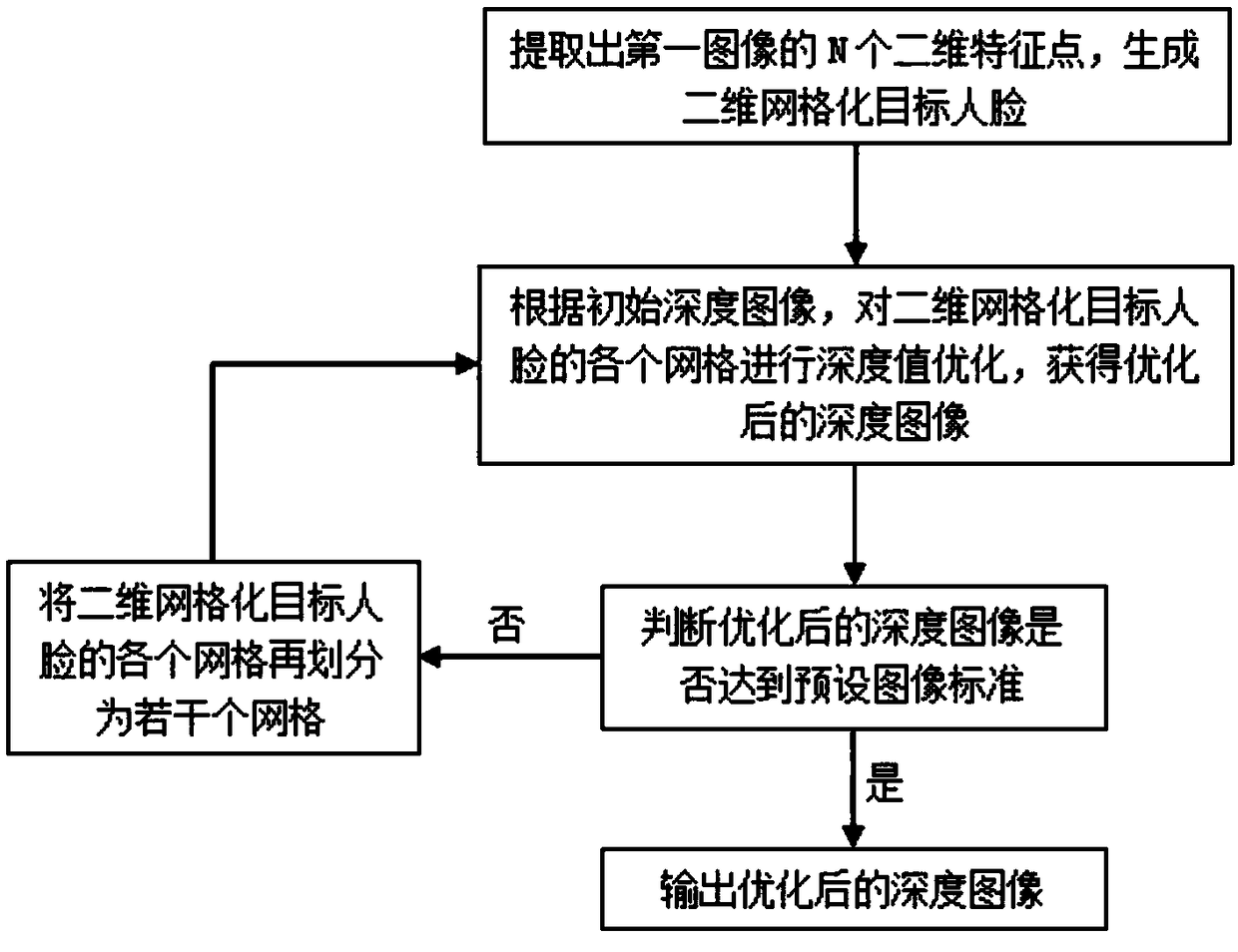
Method and system for three-dimensional face reconstruction based on binocular stereo and photometric stereo
The invention relates to the technical field of computer vision. The embodiment specifically discloses a method and a system for three-dimensional reconstruction of a human face based on binocular stereo and photometric stereo. The initial depth image of a target human face is obtained by binocular stereo matching. Four images of the target face collected by two light sources and two camera devices are represented by photometric stereo as constraint terms and combined with the initial depth image to construct the energy function of the depth image to be solved. The optimized depth image is obtained by minimizing the energy function, and the optimized depth image is transformed into a three-dimensional point cloud to obtain the three-dimensional point cloud of the target face. It solves theproblem that the existing photometric stereo vision needs at least three light sources for 3D reconstruction, and the scale-free feature has deformation, and realizes the accurate 3D reconstruction of human face without deformation.
Owner:CHENGDU TOPPLUSVISION TECH CO LTD
Binocular stereo matching method and apparatus based on oblique plane smoothing
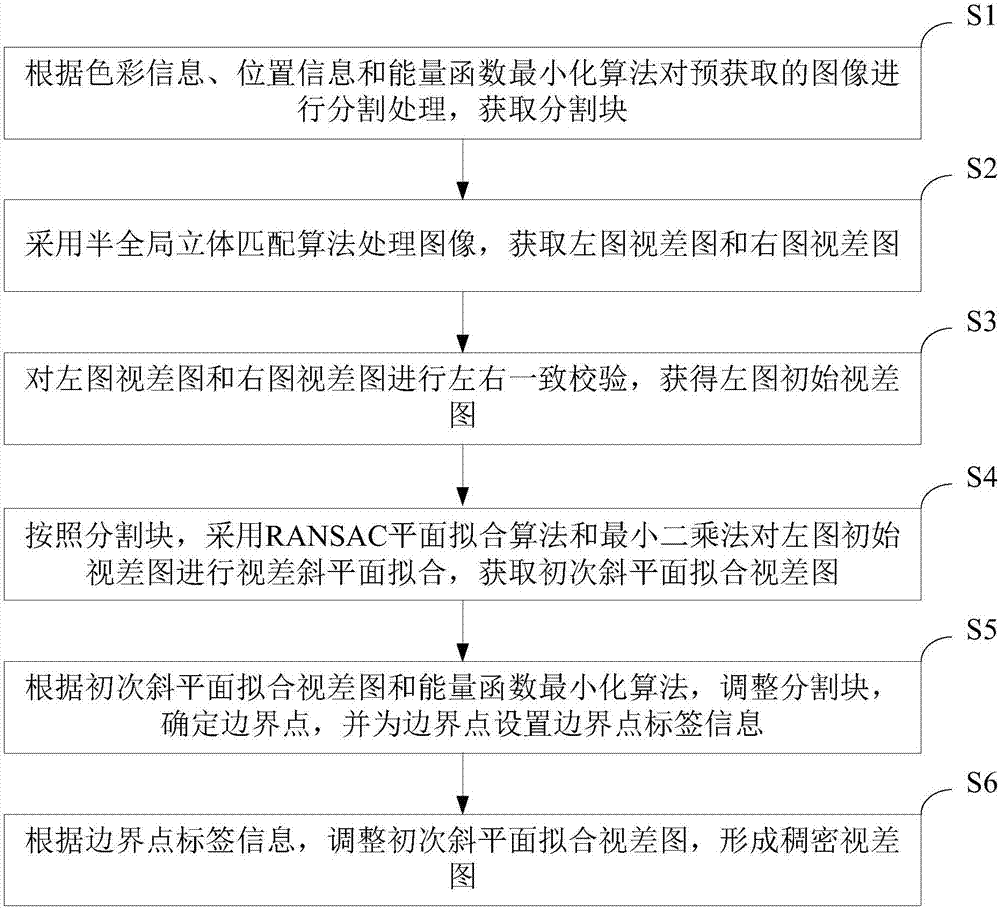
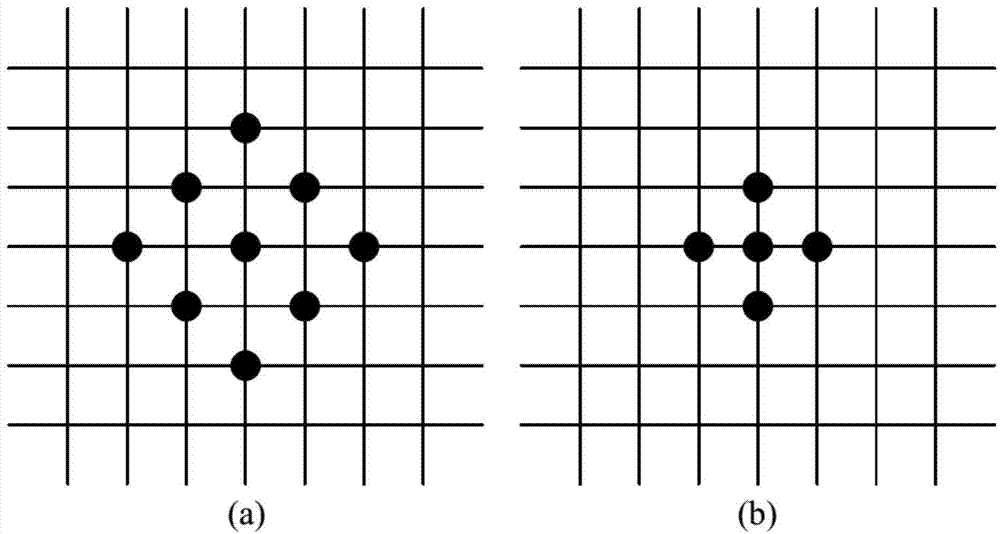
InactiveCN107016698ASolve the parallax break phenomenonImage Segmentation AccurateImage enhancementImage analysisParallaxStereo matching
The invention belongs to the technical field of image processing, and provides a binocular stereo matching method and apparatus based on oblique plane smoothing. The method includes: performing subsequent optimization on a semi-global stereo matching algorithm by employing an oblique plane smoothing algorithm; and segmenting an image by employing the thought of energy function minimization, classifying boundary points, and performing oblique plane smoothing on parallax fracture boundary points and shielding boundary points according to conditions. According to the binocular stereo matching method based on oblique plane smoothing, the phenomenon of parallax fracture can be solved, the final effect of a disparity map is smooth, and good smoothing effect can be achieved in shielding regions, low-texture regions, and depth discontinuous regions.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRANDCAR ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Robustness prospect detection method based on multi-view learning
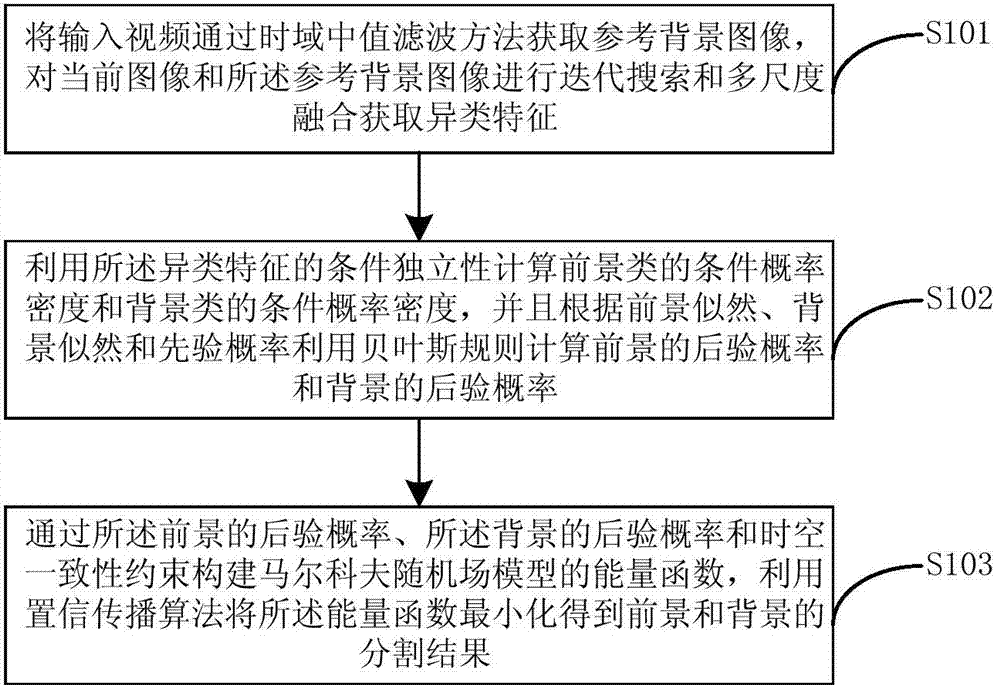
InactiveCN104766065AAchieve segmentationCharacter and pattern recognitionBayes' ruleEnergy functional
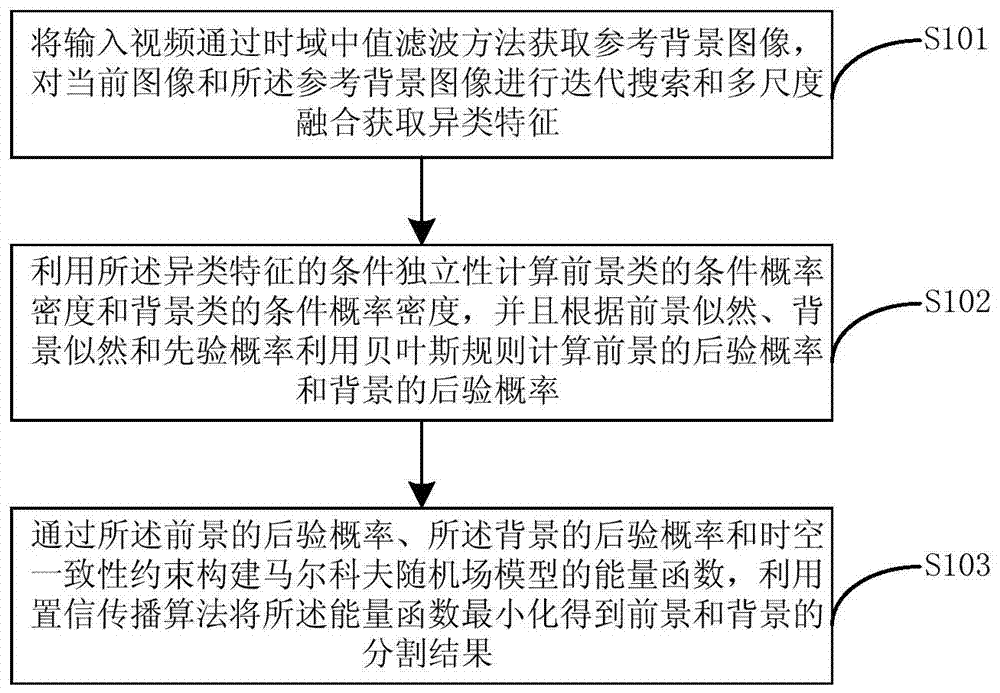
The invention provides a robustness prospect detection method based on multi-view learning. The method includes the steps that a reference background image is acquired by an input video through time domain median filtering method, and iterative search and multi-scale fusion are conducted on a current image and the reference background image to acquire heterogeneous characteristics; conditional probability density of prospects and conditional probability density of backgrounds are calculated by using condition independence of the heterogeneous characteristics, and a prospect posteriori probability and a background posteriori probability are calculated by using Bayes rules according to prospect likelihood, background likelihood and a prior probability; an energy function of a Markov random field model is established by means of the prospect posteriori probability, the background posteriori probability and space-time consistency constraint, the energy function is minimized by using a belief propagation algorithm, and segmented results of the prospect and the background are obtained. By means of the method, in a complex challenging environment, robustness prospect detection is achieved.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Human upper body detection and splitting method applied to low-contrast video
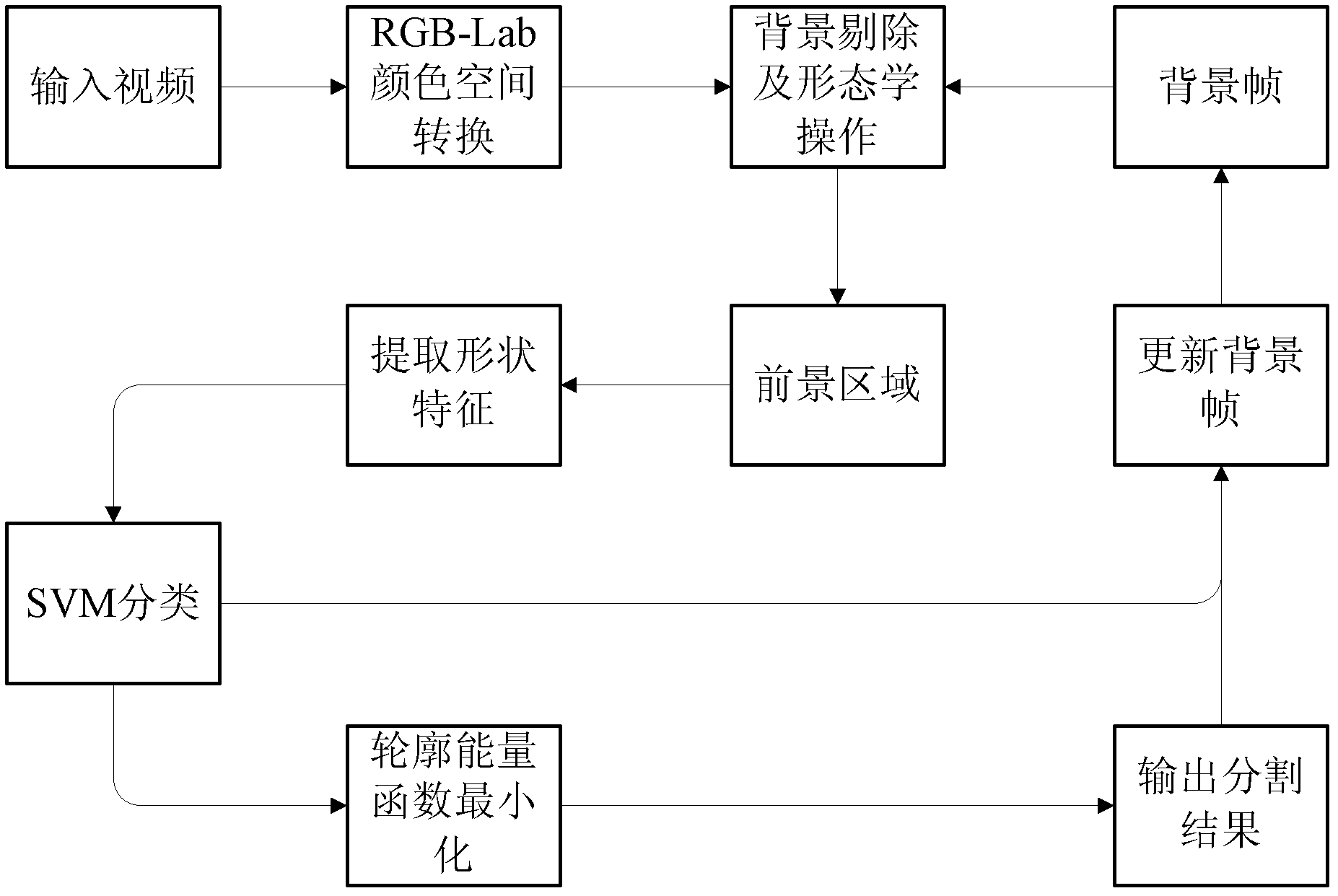
ActiveCN102521582AMeet application needsCharacter and pattern recognitionEnergy efficient computingSupport vector machineImage resolution
The invention relates to a human upper body detection and splitting method applied to a low-contrast video. The method mainly comprises two processes. In the first process, a communicated area representing a foreground object is extracted from a current frame by a background subtraction technology and a morphological method; and for each foreground area, the shape features of a polar-coordinate-based two-dimensional histogram corresponding to the foreground area are extracted as the input of a pre-trained support-vector-machine-based classifier, and a class tag corresponding to a human upper body class and a class tag corresponding to a non-human upper body class are output. In the second process, when an area which is identified as a human body area is misjudged as a non-human body area,the area is represented by an energy function, an inaccurate contour line is corrected by an energy function minimization process at the same time, and finally, a background frame is updated on the basis that an accurate foreground human body contour is obtained. By the method, a video with low contrast and resolution can be processed in real time, and both detection accuracy and a splitting result can meet the requirements of application.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Fan blade image segmentation and grid optimization splicing method
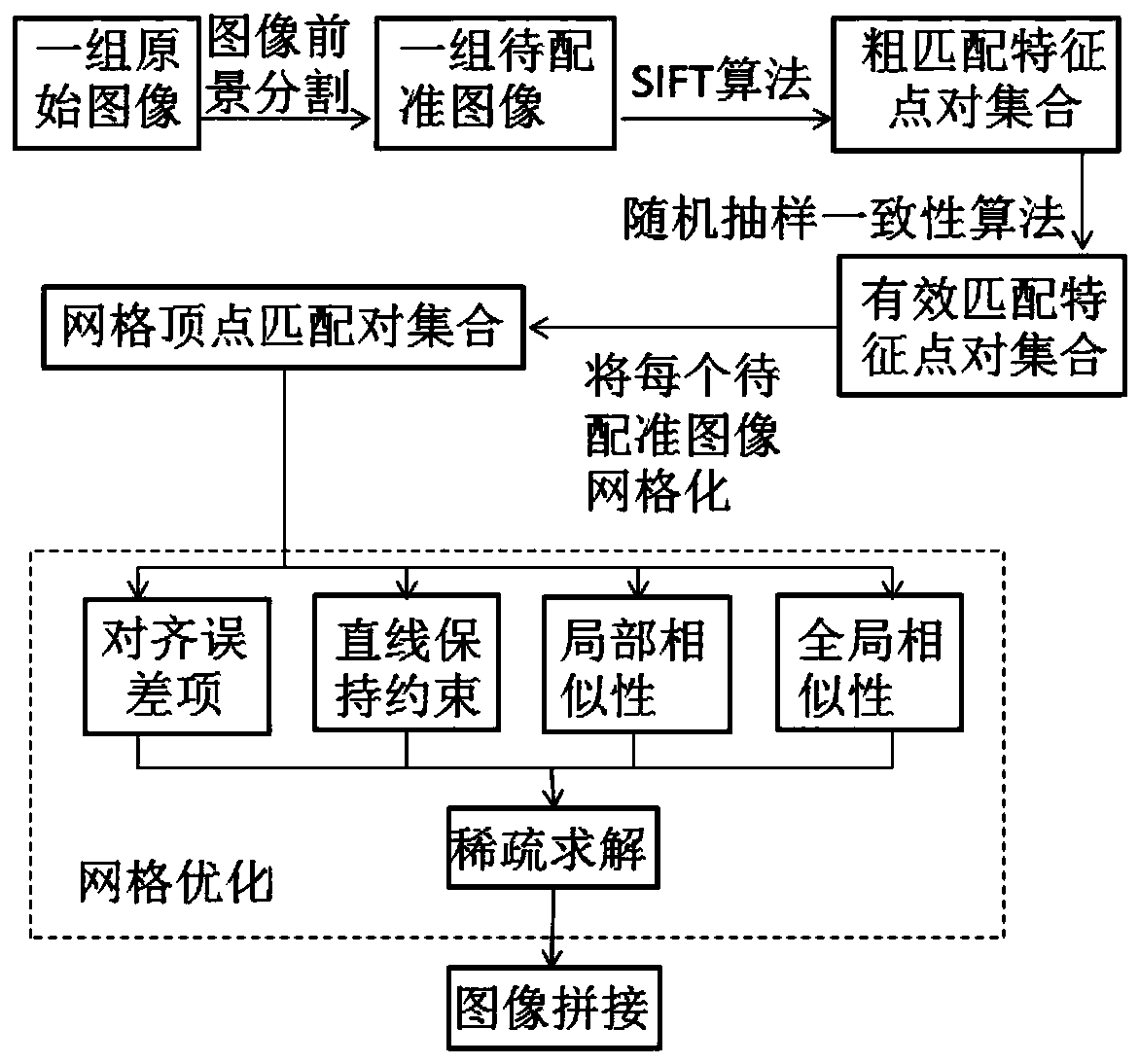
ActiveCN109961398ASolve the problem of target splicing failureSolve the problem of splicing failureImage enhancementImage analysisEnergy function minimizationImage segmentation
The invention discloses a fan blade image segmentation and grid optimization splicing method. The fan blade image segmentation and grid optimization splicing method comprises the following steps: S1,continuously collecting images of a single-sided fan blade to form a group of to-be-spliced original images; S2, using the U-net algorithm to carry out image foreground segmentation on each original image, and extracting a fan blade main body part to form a group of images to be registered; S3, gridding each image to be registered, establishing an index from 1 to m for a grid vertex of each to-be-registered image, then expressing x and y coordinates of the grid vertexes as a vector V of a 2m dimension, defining a global energy function about V, and minimizing the energy function to obtain a grid vertex optimal solution, and S4, completing image splicing according to the grid vertex optimal solution. The method has the advantages that the problem that target splicing fails due to the fact that the depth of field of the target and the background is too large is solved, natural splicing of multiple fan blades is achieved, and spliced images are small in visual effect distortion, continuous and real.
Owner:鲁能新能源(集团)有限公司
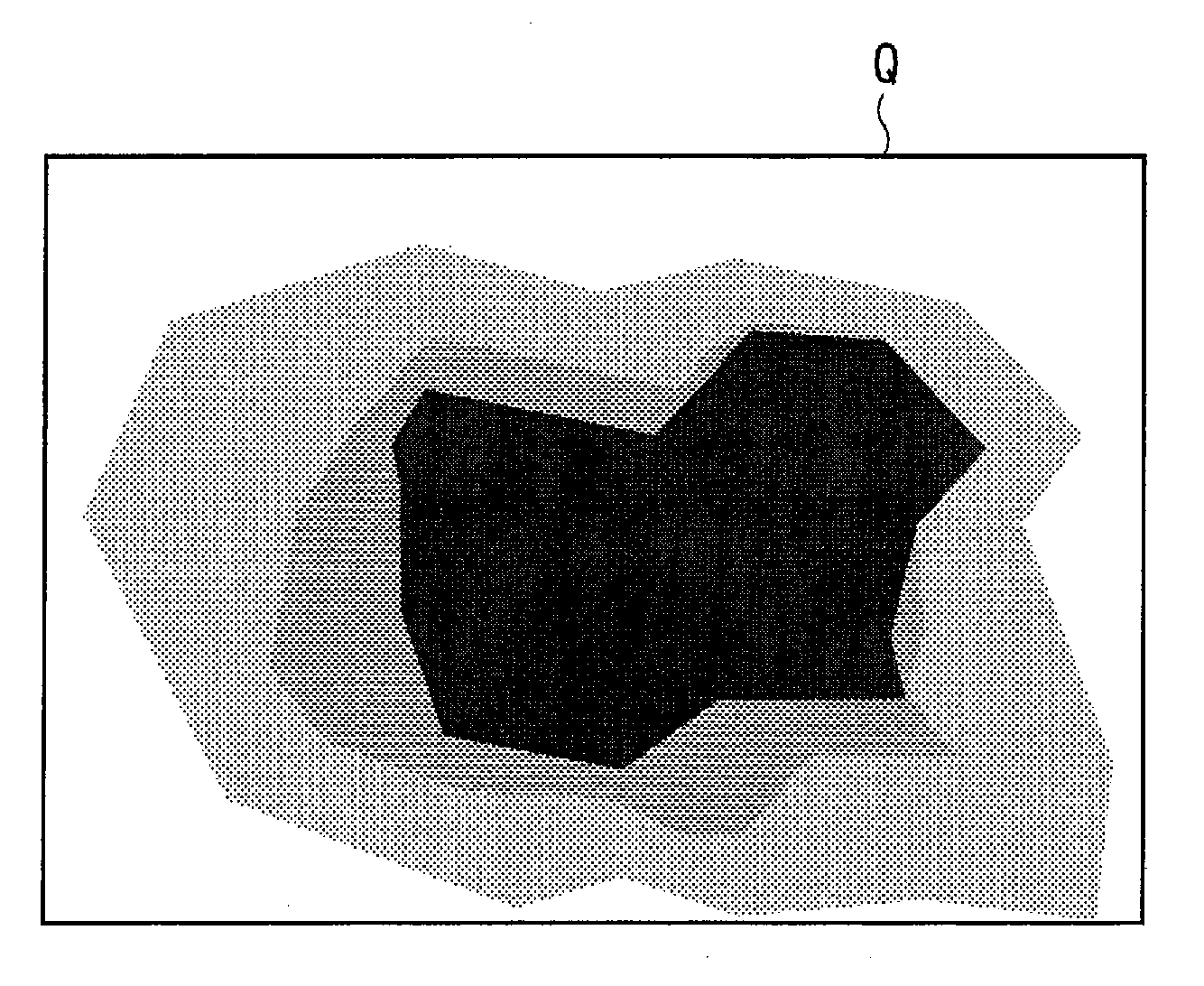
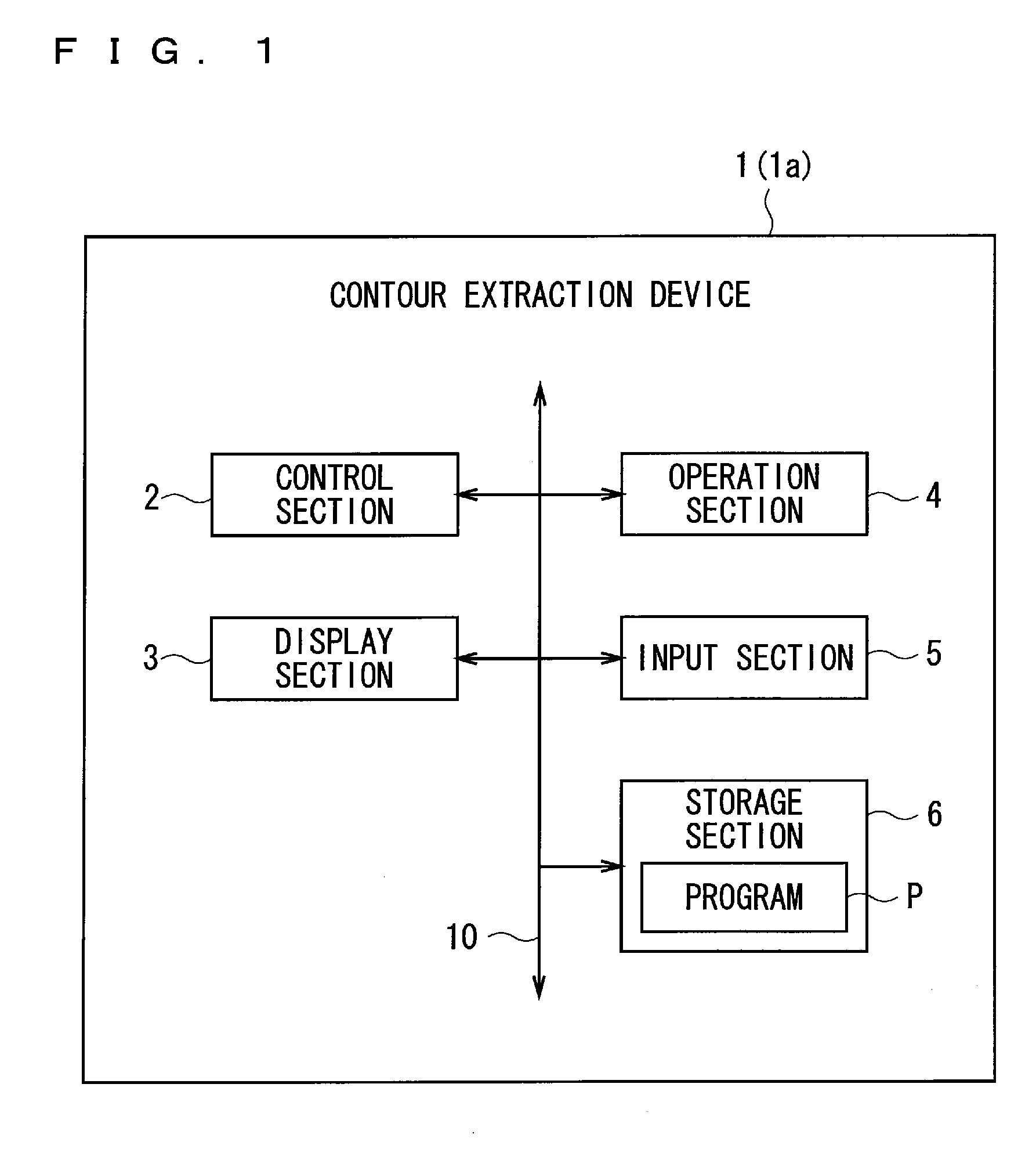
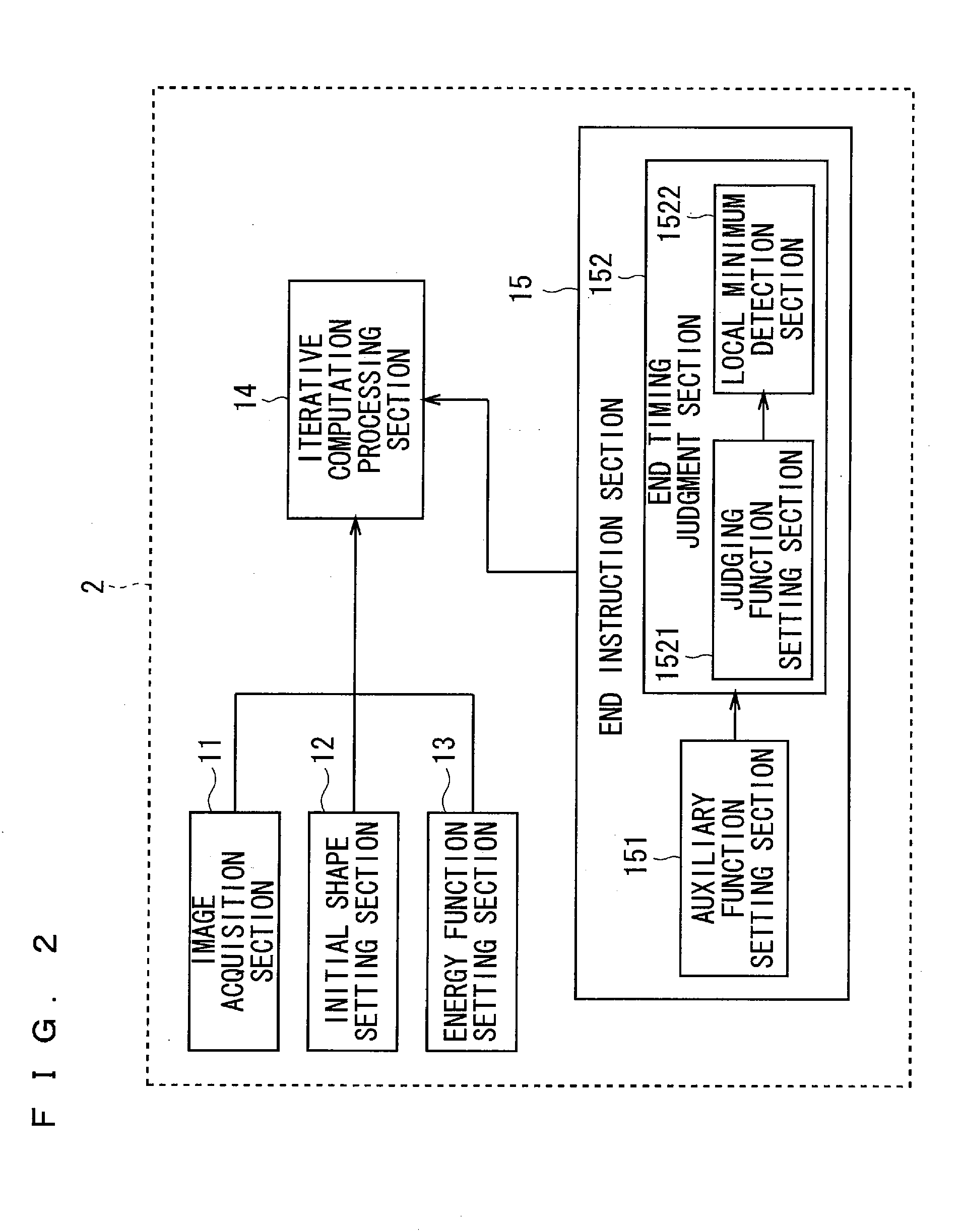
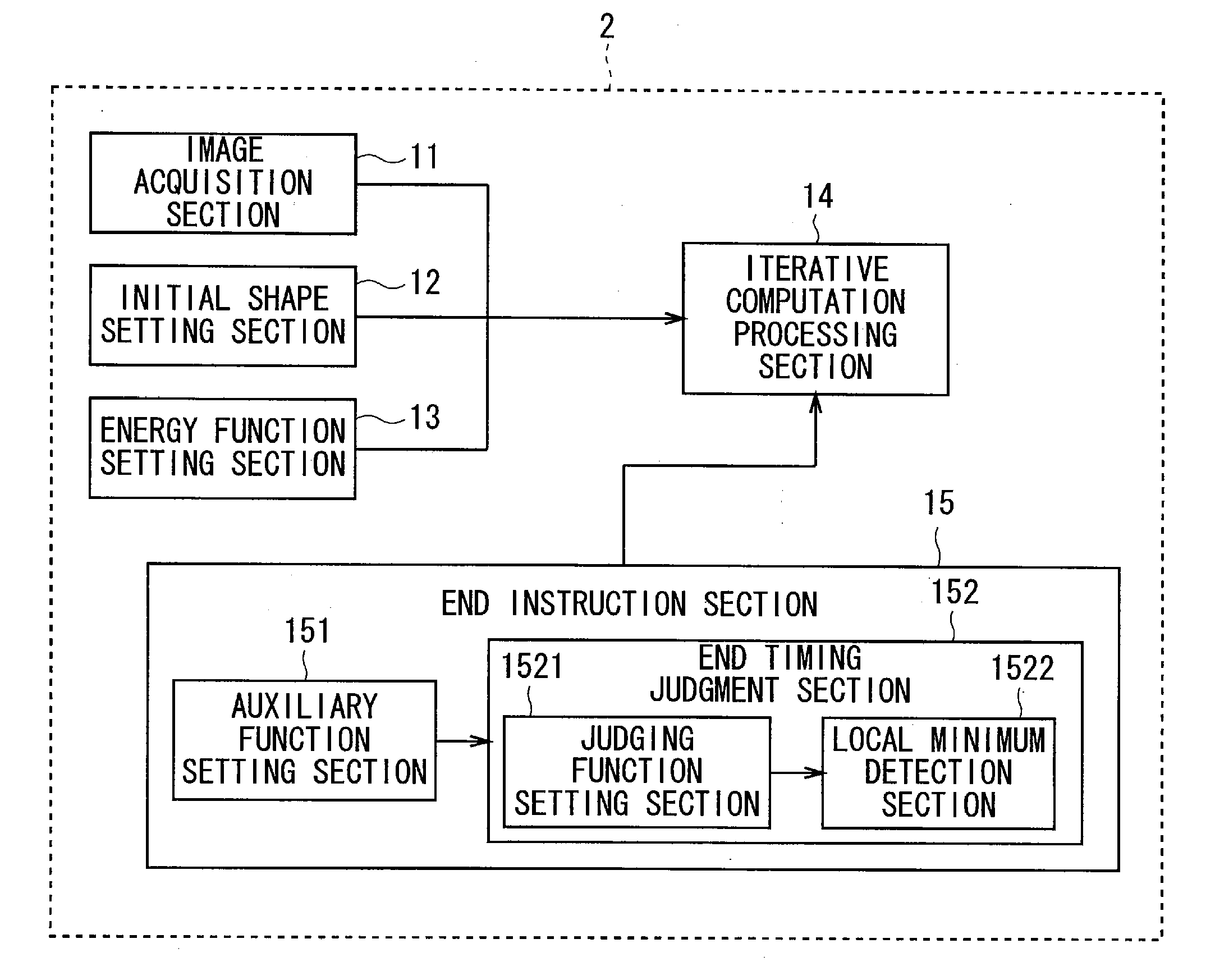
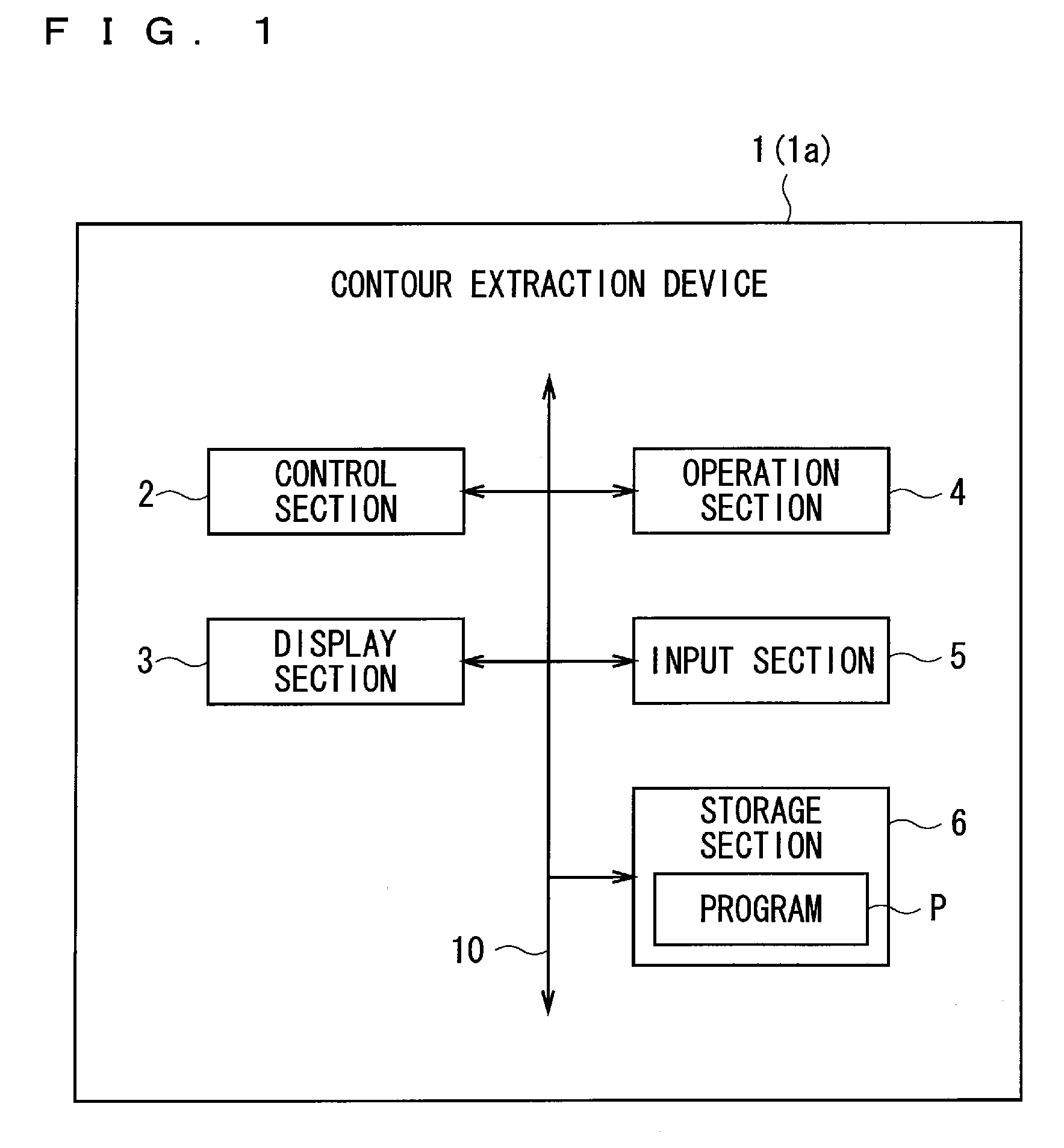
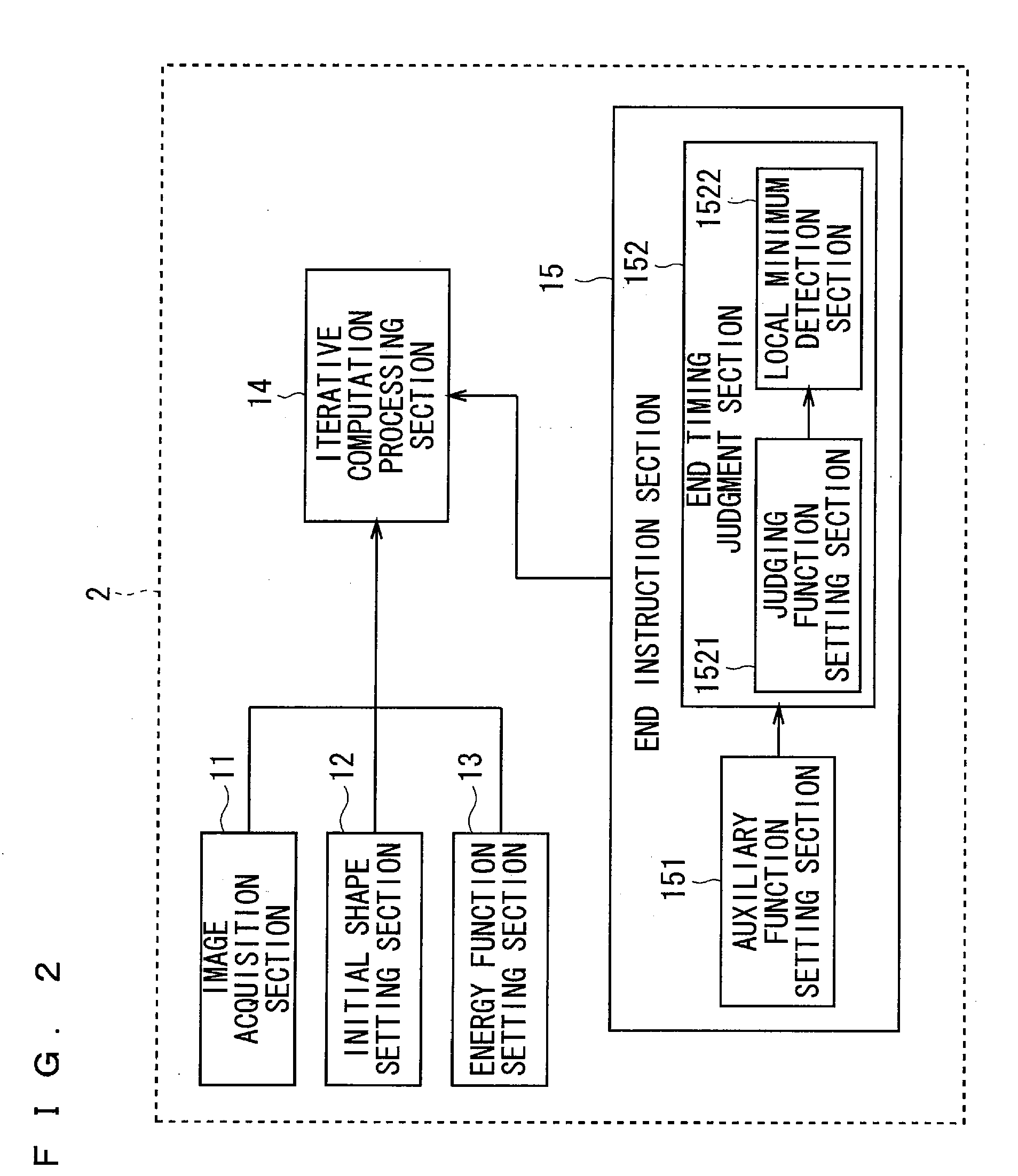
Contour extraction device and program
InactiveUS20120099799A1Rigorous processAppropriate balanceImage enhancementImage analysisEnergy function minimizationComputation process
An object of the present invention is to provide the technology capable of appropriately balancing the preciseness of contour extraction and calculation cost. In order to achieve this object, an energy function setting section sets an energy function that is expressed by a weighted linear sum of a plurality of kinds of energy terms defined correspondingly to a state of an active curve and is formulated so as to have a smaller value as approaching a shape of the contour to be extracted, and an iterative computation processing section minimizes the energy function by an iterative computation. An end instruction section sets an auxiliary function formulated so as to monotonously increase in accordance with the number of iteration times of iterative computation and sets a judging function expressed by a linear sum of the auxiliary function and the energy function. Then, a point of time when a local minimum appears in the judging function in the course of the iterative computation is judged as the end timing of iterative computing.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA MEDICAL & GRAPHICS INC
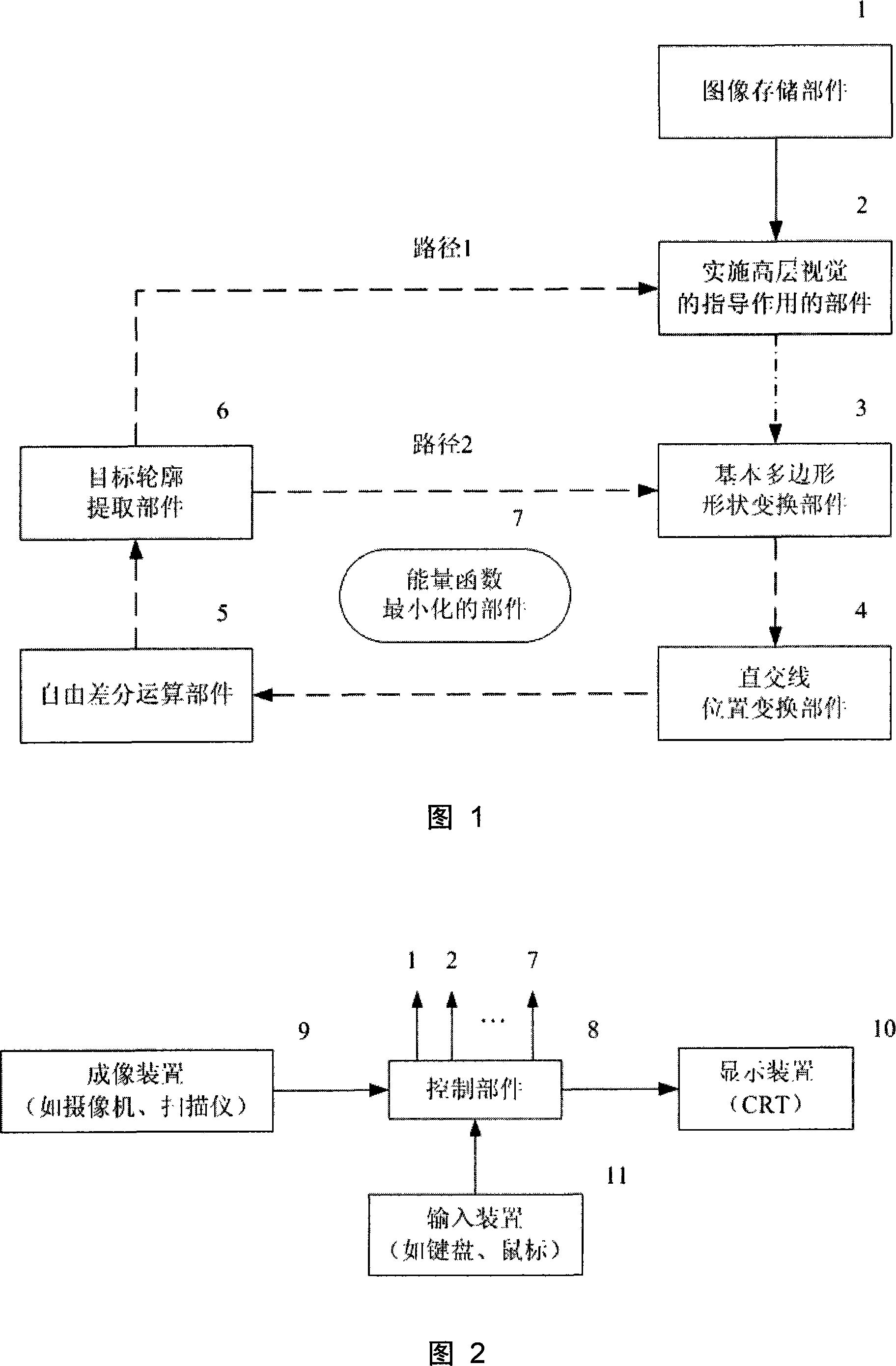
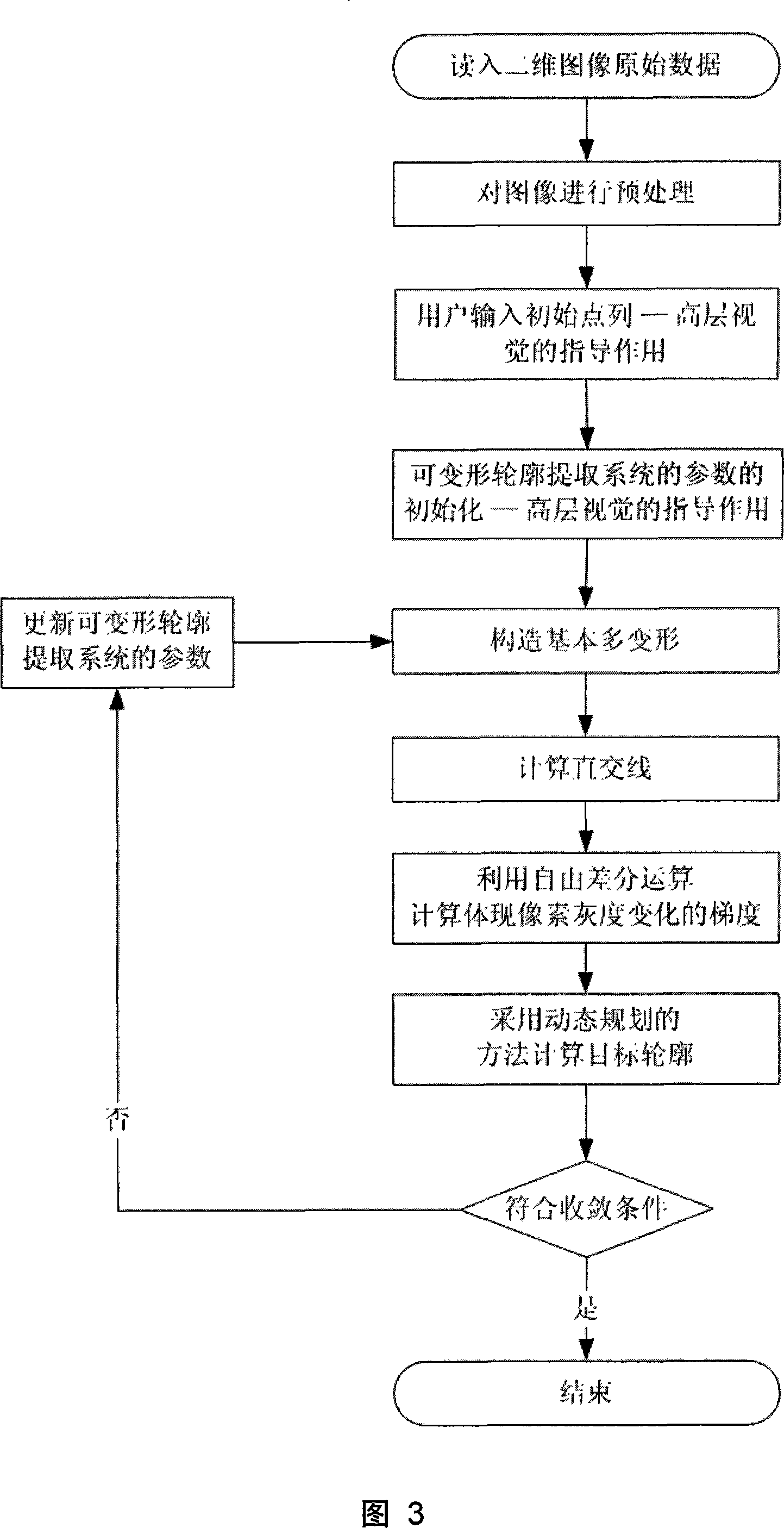
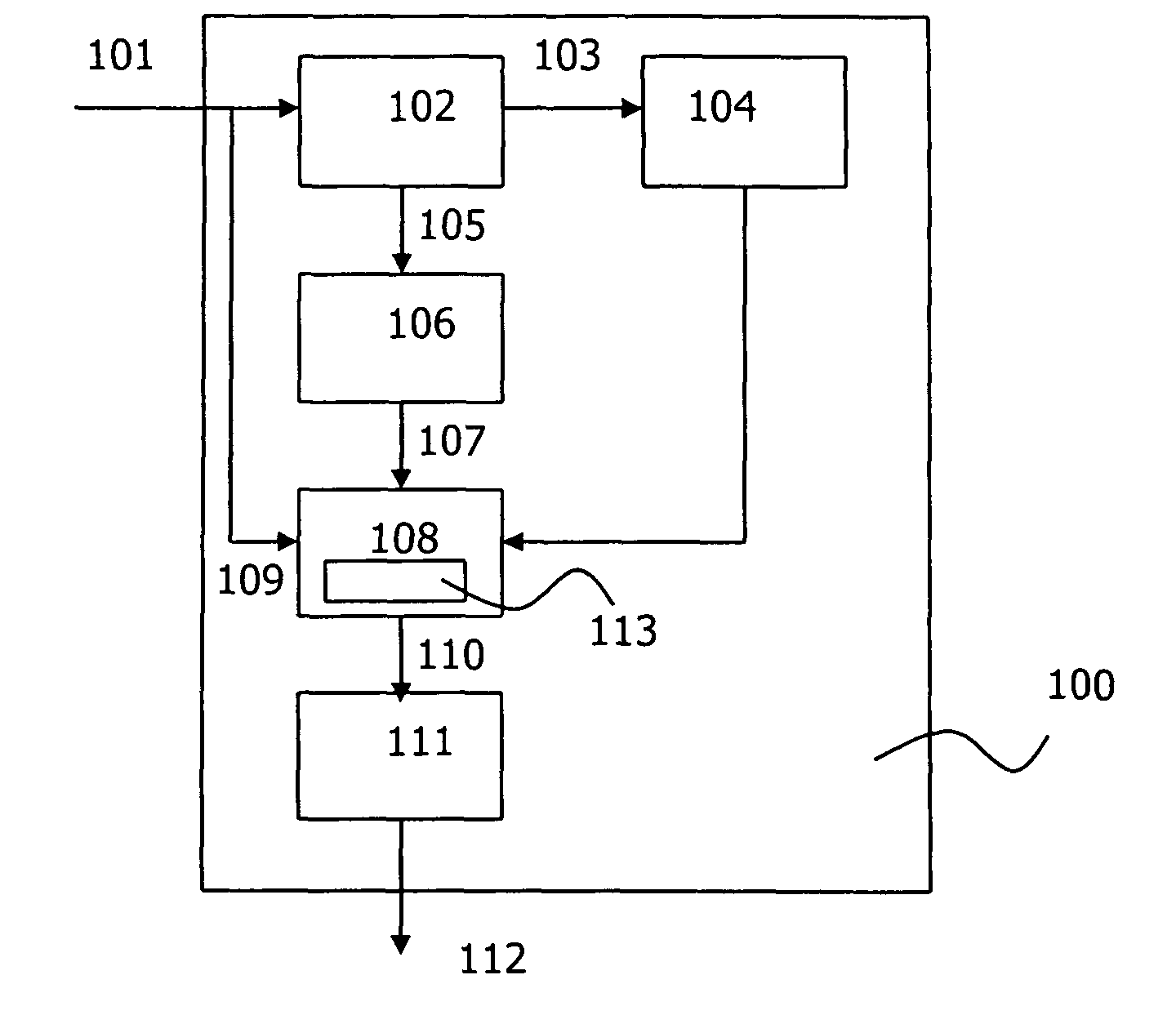
Freely differences calculus and deformable contour outline extracting system
InactiveCN101136105AHigh speedQuality improvementImage enhancementEnergy function minimizationComputer graphics (images)
The invention comprises: a image memory 1, a component for executing the high level vision 2, a basic polygon transform component 3, an orthogonal location transform component 4, a free difference operation component 5, a target outline extracting component 6, and an energy function minimizing component 7.
Owner:LIAONING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Microscopic sequence image automatic splicing method, system and device based on affine transformation
ActiveCN112381718ASolve the problem of limited imaging field of viewImprove stitching accuracyGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionMicroscopic image
The invention belongs to the technical field of computer vision and image processing, particularly relates to a microscopic sequence image automatic splicing method, system and device based on affinetransformation, and aims to solve the problems that in the prior art, the influence of image deformation on splicing in the microscopic image shooting process cannot be effectively solved, splicing errors can be accumulated and spread, therefore, the expected splicing effect cannot be achieved. The method comprises the following steps: extracting features of an overlapping region of a microscopicsequence image and carrying out feature matching; endowing each pair of feature points with different weights according to the position information of the features on the image; fitting changes between adjacent images through an affine transformation model, and setting a globally optimized energy function; minimizing the energy function to obtain an affine transformation relationship of each adjacent image; and performing splicing according to the affine transformation relationship to obtain a microscopic spliced image. Through the global splicing method, the influence of error accumulation and image edge distortion on the result in the splicing process is avoided, and the image with higher splicing precision can be obtained.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
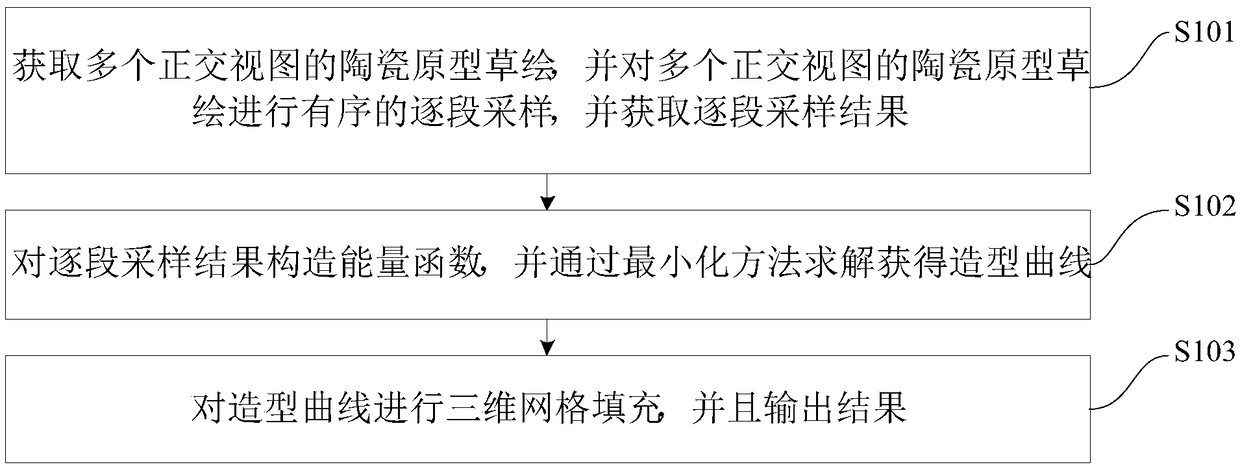
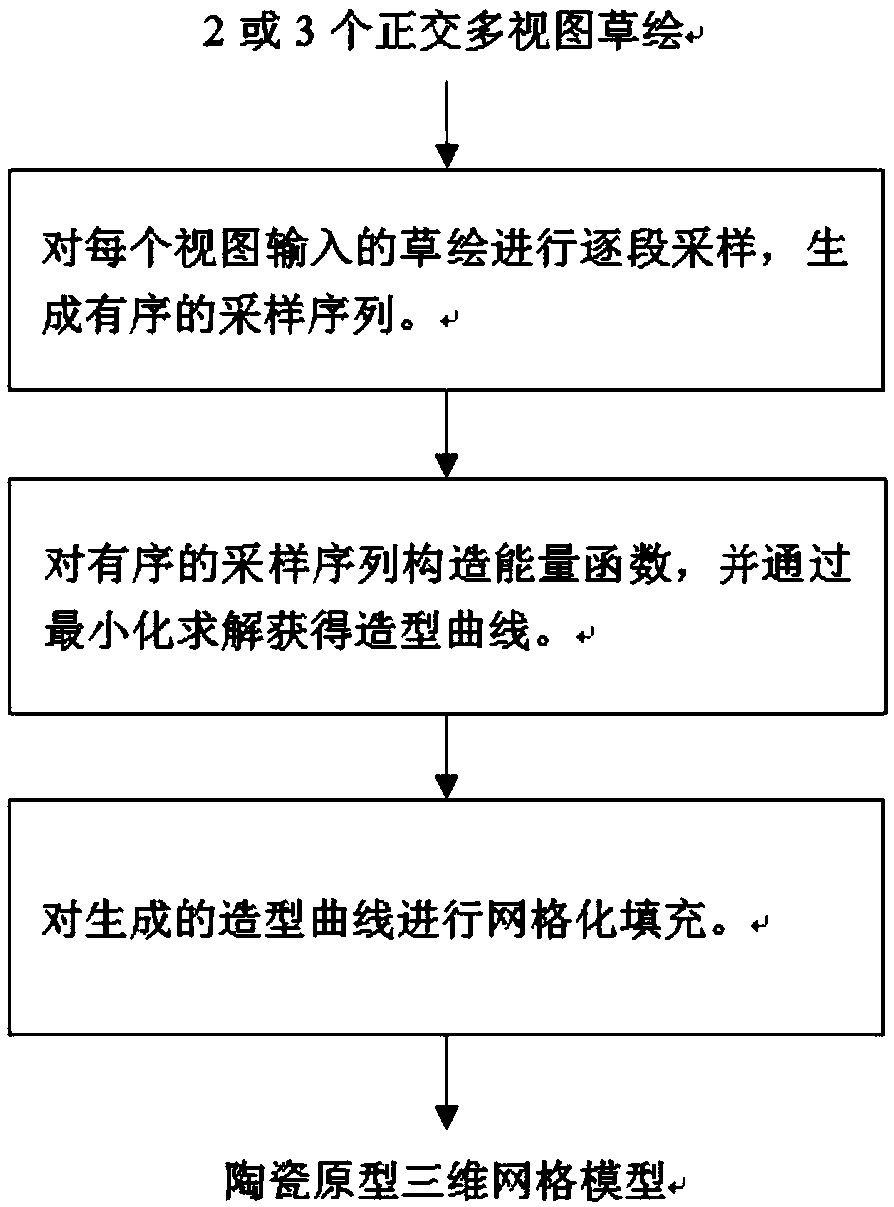
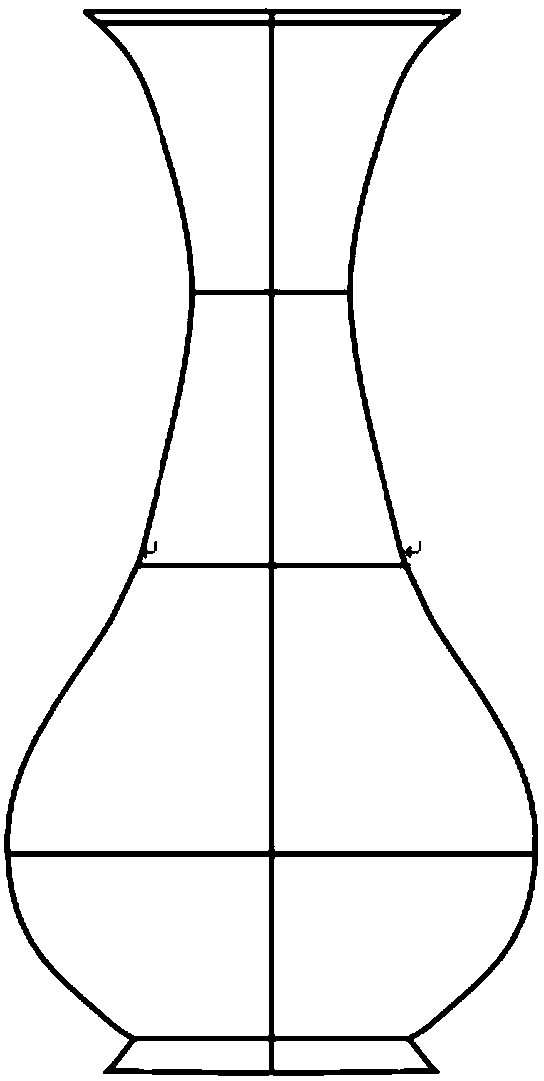
Ceramic prototype three-dimensional mesh model generation method and device based on multi-view sketching
ActiveCN109166174AImprove efficiency3D modellingComputer graphics (images)Energy function minimization
The invention discloses a ceramic prototype three-dimensional mesh model generation method and device based on multi-view sketching, wherein the method comprises the following steps: acquiring ceramicprototype sketches of a plurality of orthogonal views, sequentially sampling the ceramic prototype sketches of the plurality of orthogonal views one by one, and acquiring the segment-by-segment sampling results; constructing an energy function according to the segment-by-segment sampling results, and obtaining the modeling curve by a minimization method; conducting three-dimensional mesh fillingon the modeling curve, and outputting the result. This method takes advantage of the characteristics of ceramic prototype design, takes the sketch of multiple views as input, and constructs the three-dimensional mesh model by correlation sampling and energy function minimization. The method improves the efficiency of ceramic prototype construction and is simple and easy to implement.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Contour extraction device and program
InactiveUS8532392B2Rigorous processAppropriate balanceImage enhancementImage analysisEnergy function minimizationComputation process
An object of the present invention is to provide the technology capable of appropriately balancing the preciseness of contour extraction and calculation cost. In order to achieve this object, an energy function setting section sets an energy function that is expressed by a weighted linear sum of a plurality of kinds of energy terms defined correspondingly to a state of an active curve and is formulated so as to have a smaller value as approaching a shape of the contour to be extracted, and an iterative computation processing section minimizes the energy function by an iterative computation. An end instruction section sets an auxiliary function formulated so as to monotonously increase in accordance with the number of iteration times of iterative computation and sets a judging function expressed by a linear sum of the auxiliary function and the energy function. Then, a point of time when a local minimum appears in the judging function in the course of the iterative computation is judged as the end timing of iterative computing.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA MEDICAL & GRAPHICS INC
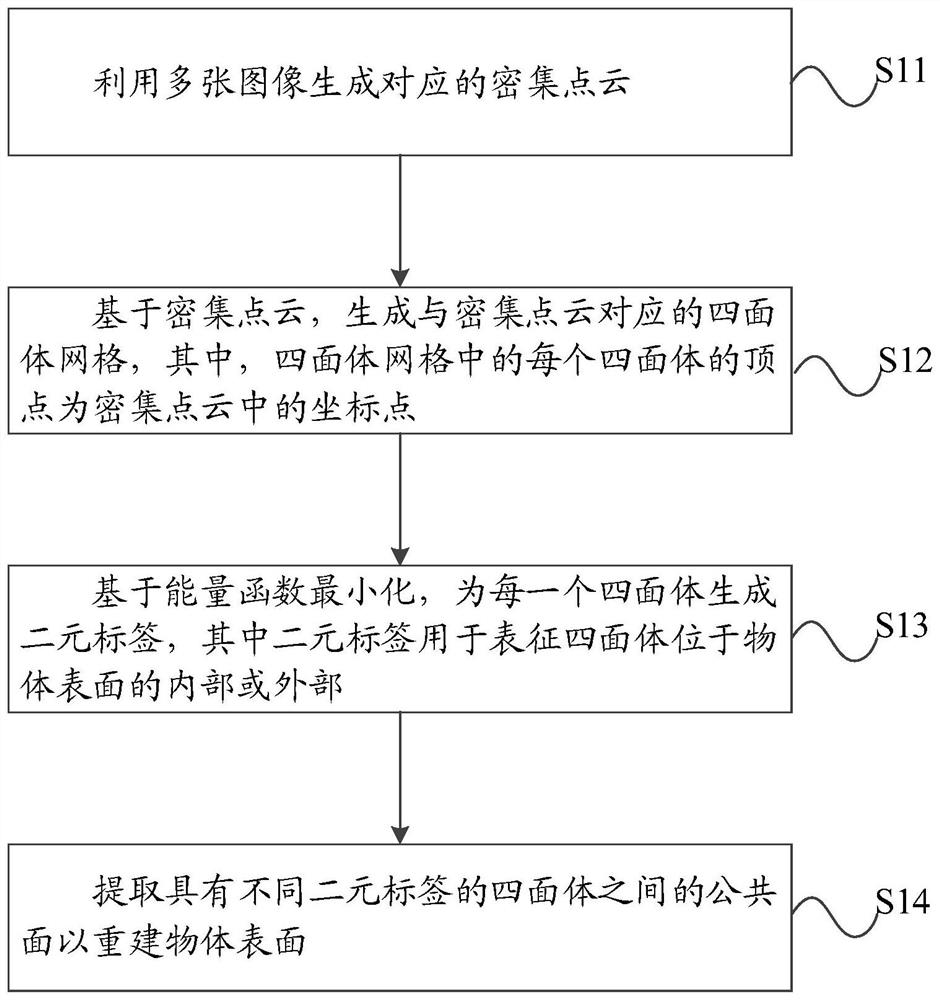
Method for reconstructing object surface and device thereof and computer storage medium
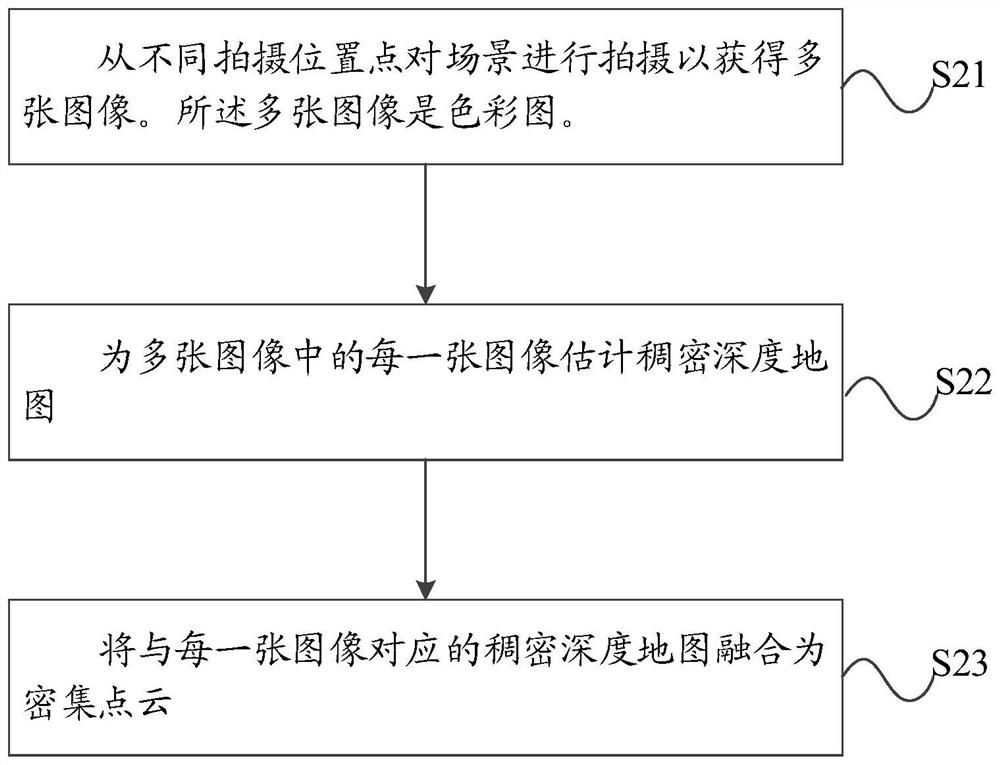
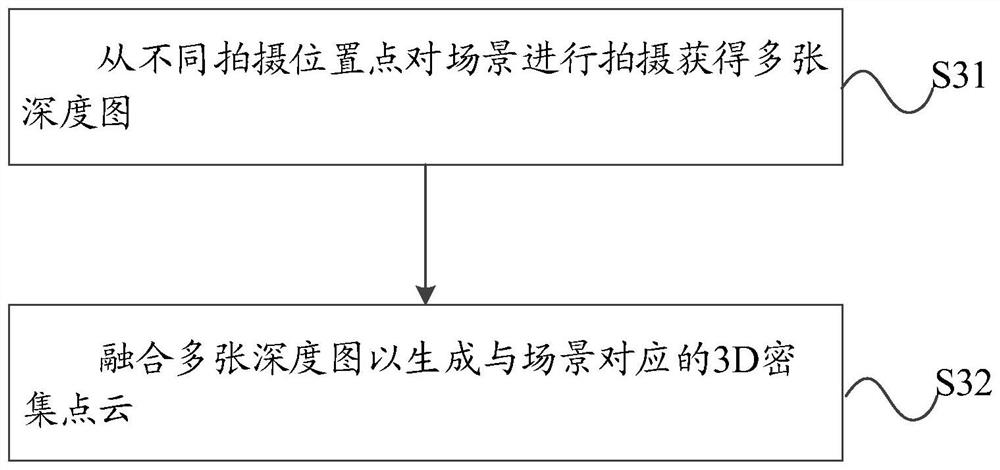
PendingCN114049466AReduce negative impactImprove reconstruction accuracyDetails involving processing steps3D modellingGrid densityPoint cloud
The invention discloses a method for reconstructing an object surface and a device thereof and a computer storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: generating a corresponding dense point cloud through a plurality of images, and the plurality of images can be obtained through photographing a scene from different photographing position points; based on the dense point cloud, generating a tetrahedral mesh corresponding to the dense point cloud, the vertex of each tetrahedron in the tetrahedral mesh being a coordinate point in the dense point cloud; generating a binary label for each tetrahedron based on energy function minimization, the binary labels being used for representing that the tetrahedrons are located inside or outside the surface of the object; and extracting a common surface between the tetrahedrons with different binary labels to reconstruct the surface of the object. The energy function comprises the sum of first penalty terms corresponding to the tetrahedron and the sum of second penalty terms corresponding to the common surface, and the second penalty terms comprise grid density weights. Through the above mode, the negative influence of the noise points on the surface details of the reconstructed object is reduced, and the reconstruction precision is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SENSETIME TECH DEV CO LTD
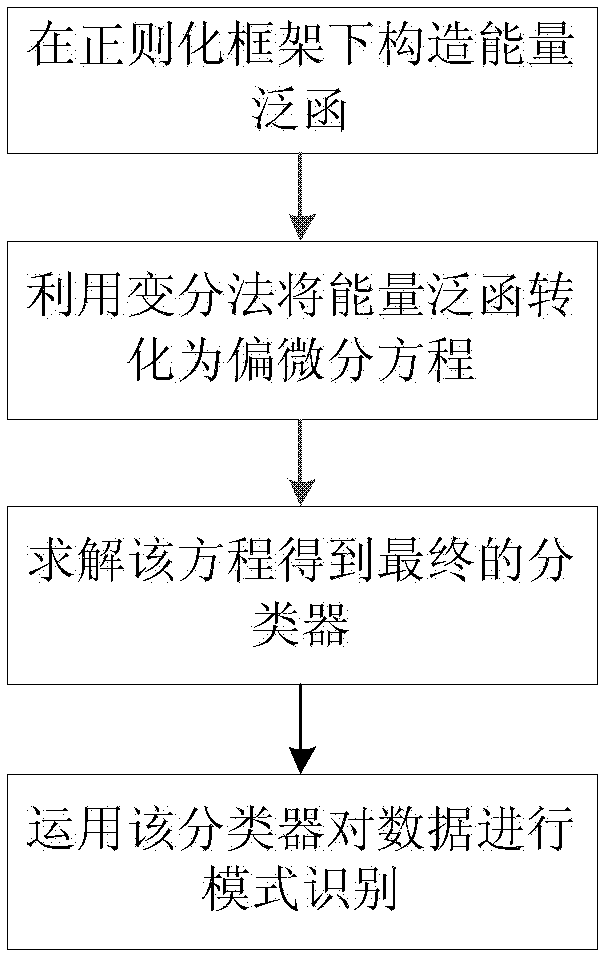
Total variation and euler elastic rod-based supervised mode identification method
Disclosed in the invention is a total variation and euler elastic rod-based supervised mode identification method, comprising: constructing a total variation and Euler elastic rod-based energy function under the framework of least square regularization; utilizing a variational method to convert solution of energy function minimization into solution of a corresponding Euler-Lagrange differential equation; solving the differential equation to further obtain a final classifier; and carrying out mode identification on data by utilizing the classifier. According to the invention, a novel method is provided for solution of a supervised mode identification problem and in general, can be applied to solution of a classification problem like handwriting digit identification; and the provided method enables an effect that is comparable with one caused by an existing popular method to be realized for most of data sets.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Method and device for choosing a mode of coding
ActiveUS8059722B2Cost optimizationLow costPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningEnergy function minimizationComputer science
The present invention relates to a method and a device for choosing a mode of coding from among a plurality of modes of coding for a subset of blocks included in a set of blocks. An energy function over the set of blocks for each of the modes of coding is calculated and calculation elements of the energy function are stored for at least the subset of blocks. A first mode of coding, minimizing the energy function over the set of blocks is chosen. The energy function over the subset of blocks for each of the modes of coding is thereafter calculated by using the calculation elements stored for the subset of blocks and by said subset, of a cost of coding for the modes of coding distinct from the first mode of coding. The choice of a mode of coding minimizing the energy function over the subset is then effected.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
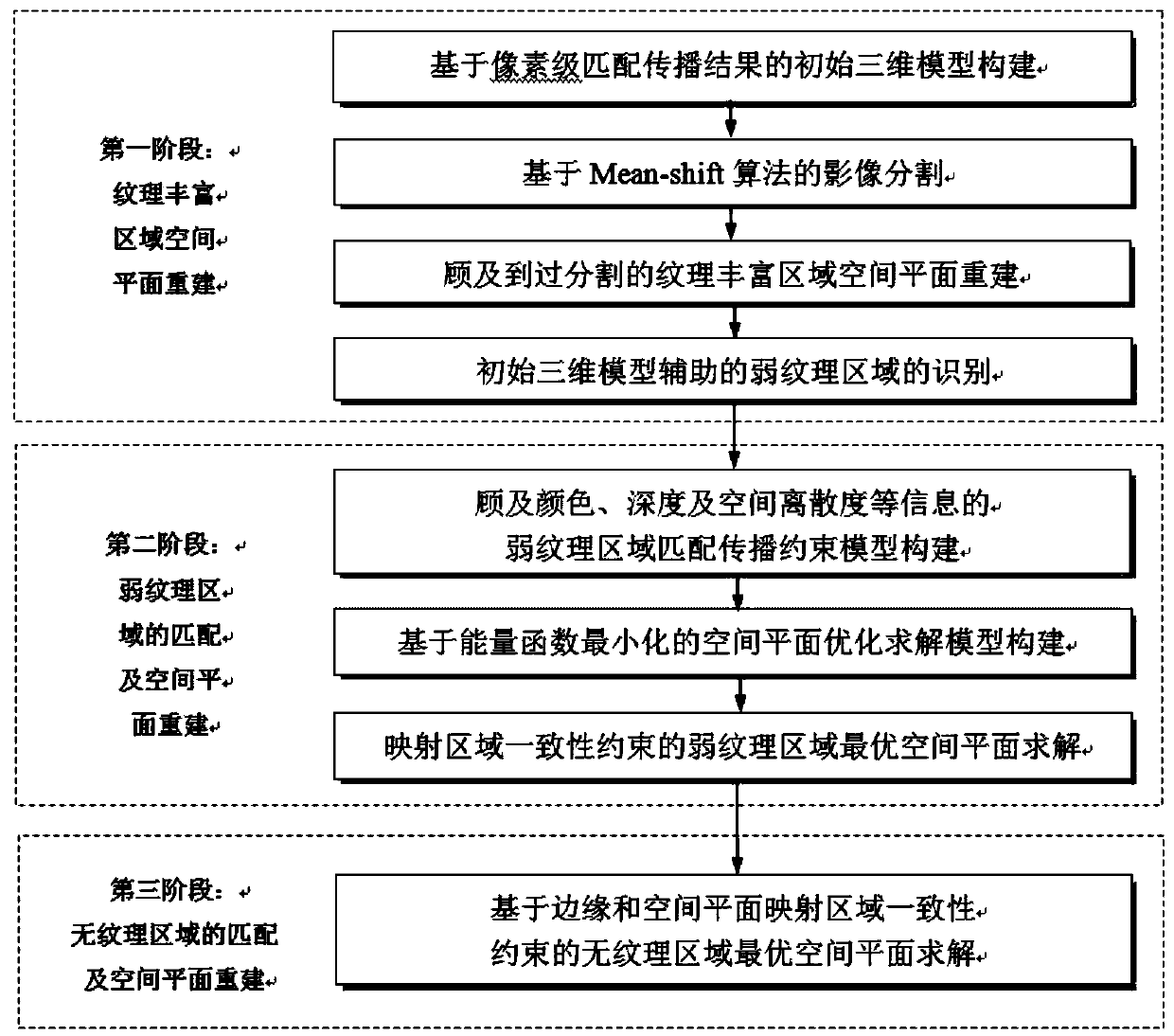
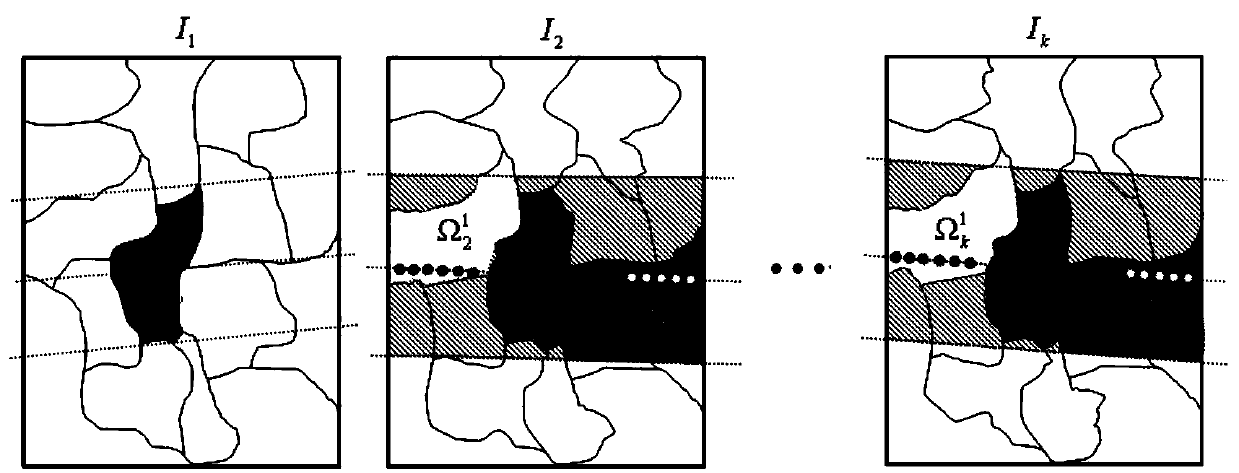
Three-dimensional reconstruction method considering multi-stage matching propagation of weak texture area
InactiveCN111197976AGuarantee authenticityGuaranteed accuracyPicture interpretationEnergy function minimizationImage segmentation
A three-dimensional reconstruction method considering multi-stage matching propagation of a weak texture area comprises the following steps of completing pixel-level matching transmission through an existing algorithm, while creating an initial three-dimensional model to complete spatial plane reconstruction of an area rich in texture; based on image segmentation and the three-dimensional model constraint constructed in a first stage, completing matching of a weak texture region and spatial plane reconstruction under an energy function minimization framework; under an energy function minimization framework, adopting a multi-constraint optimization method and the like to solve matching and reliable three-dimensional reconstruction of a texture-free area. According to the method, the problemthat in the prior art, the image matching and reconstruction effect is generally not ideal for areas with weak textures, areas without textures and areas with repeated textures is solved, and the phenomena of 'jolt 'of the water surface, 'cavities' of the wall body and the like in a three-dimensional reconstruction result are avoided. The influence of factors such as illumination change, perspective distortion, weak texture and repeated texture areas in a scene is overcome, and a guarantee is provided for a real effect and surveying and mapping level precision.
Owner:SHANDONG TANGKOU COAL +1
A Altitude Measurement Method Based on Video Multi-Target Tracking
InactiveCN103735269BImprove accuracyReduce complexityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMulti target trackingVideo sequence
Owner:DALIAN NATIONALITIES UNIVERSITY
Human upper body detection and splitting method applied to low-contrast video
ActiveCN102521582BMeet application needsCharacter and pattern recognitionEnergy efficient computingSupport vector machineImage resolution
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for obtaining geometric mass center of object
ActiveCN106530350AComputationally efficientReduce computational costImage analysisEnergy function minimizationGradient function
The invention relates to a method for obtaining a geometric mass center of an object, and the method is used for the object formed by a 3D manifold. The method comprises that the internal distance of the 3D manifold is calculated; an energy function model aimed at the 3D manifold is constructed, an energy function is minimized by using a gradient descent method, and a gradient function corresponding to the 3D manifold is obtained; according to the obtained gradient function of the energy function of the 3D manifold, a shortest path between two points in the 3D manifold is obtained; and N different initial values are selected randomly from points in the 3D manifold, the energy function is optimized, an optimal energy function value is obtained, and a point corresponding to the optimal energy function value serves as the geometric mass center of the object. The method can ensure that the mass center is positioned inside the 3D manifold and is not influenced by the appearance of the object, and adverse influence of noise and deformation can be avoided.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
KNN (K-Nearest Neighbor) sorting algorithm based method for correcting and segmenting grayscale nonuniformity of MR (Magnetic Resonance) image
InactiveCN102135606BAccurate divisionVolume effect suppressionImage enhancementMagnetic measurementsSorting algorithmNear neighbor
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Robust foreground detection method based on multi-view learning
InactiveCN104766065BAchieve segmentationCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionTemporal consistency
The robust foreground detection method based on multi-view learning provided by the present invention includes: obtaining a reference background image through the time-domain median filtering method of the input video, performing iterative search and multi-scale fusion acquisition on the current image and the reference background image Heterogeneous features; use the conditional independence of the heterogeneous features to calculate the conditional probability density of the foreground class and the conditional probability density of the background class, and use Bayes' rule to calculate the posterior of the foreground according to the foreground likelihood, background likelihood and prior probability The posterior probability of probability and background; construct the energy function of Markov random field model through the posterior probability of described foreground, the posterior probability of described background and space-time consistency constraint, utilize belief propagation algorithm to minimize described energy function Segmentation results of foreground and background are obtained. The invention can realize robust foreground detection in complex and challenging environments.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A Temporal Consistent Depth Video Estimation Method Based on Adaptive Weights
ActiveCN105187813BTime Domain Continuity ImprovementQuality improvementSteroscopic systemsTime domainViewpoints
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Multiple-motor coordinated control method based on power traction uniformity
ActiveCN109484419AAmount of consistent outputImprove anti-interference abilityElectric locomotivesTraction systemEnergy function minimization
The invention provides a multiple-motor coordinated control method based on electric locomotive traction total quantity uniformity. The method includes that a multiple-motor coordinated control framework uniform in total quantity is built, a multiple-traction system distribution strategy based on energy function minimization is provided, and multiple motors are enabled to complete output torque adjustment by means of optimal dynamic adjusting. A sliding mode variable structure controller is established aiming at each independent traction subsystem, and actual output torque of each motor is tracked and fed back. The control method is high in interference ability, good in tracking performance and capable of still maintaining output total equantity and uniformity in total quantity needed fortotal quantity, and basically constant traction total amount in the process of electric locomotive running is ensured.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF TECH
Non-linear control method for on-board charger PFC converter based on discrete energy function control
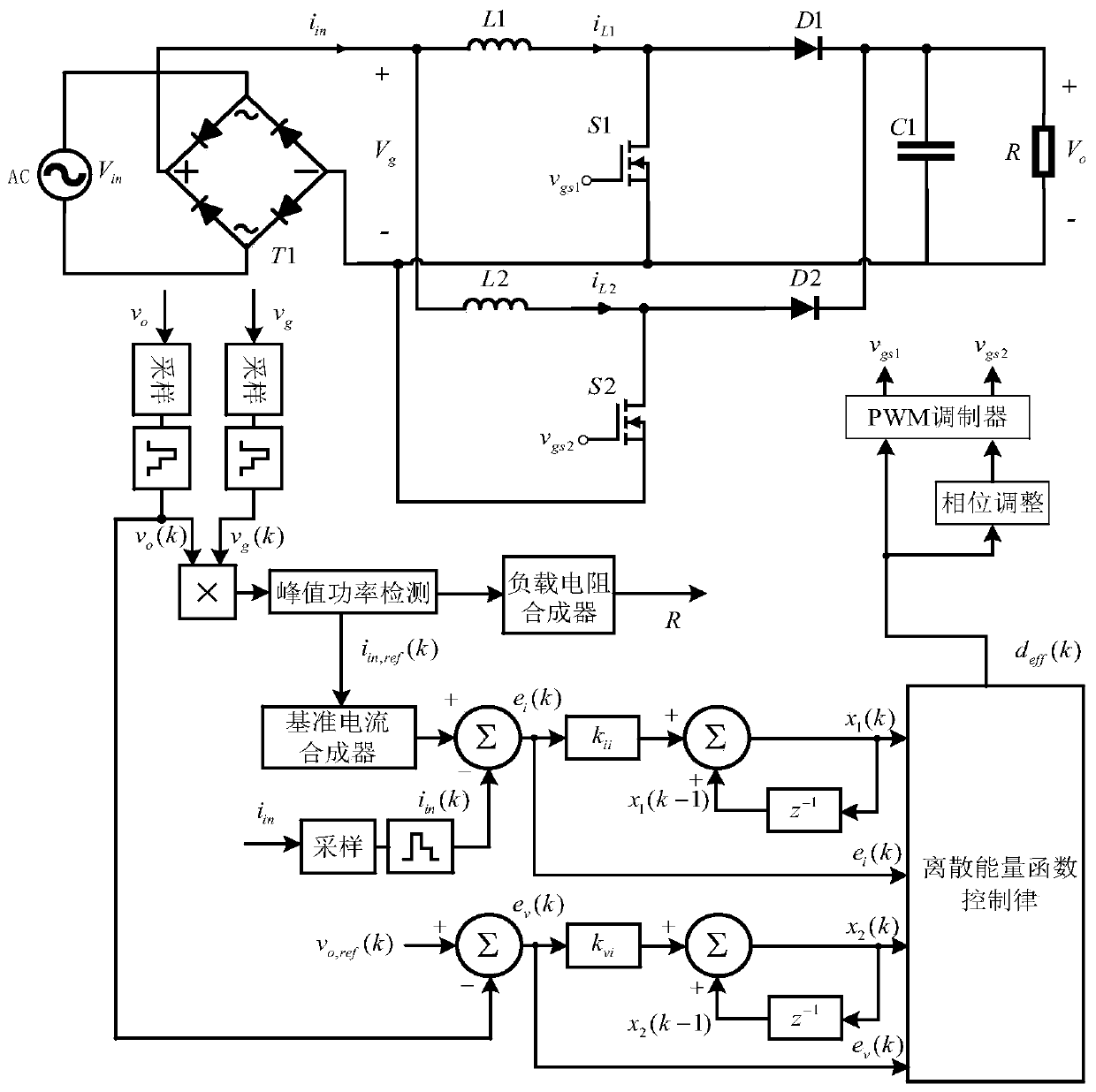
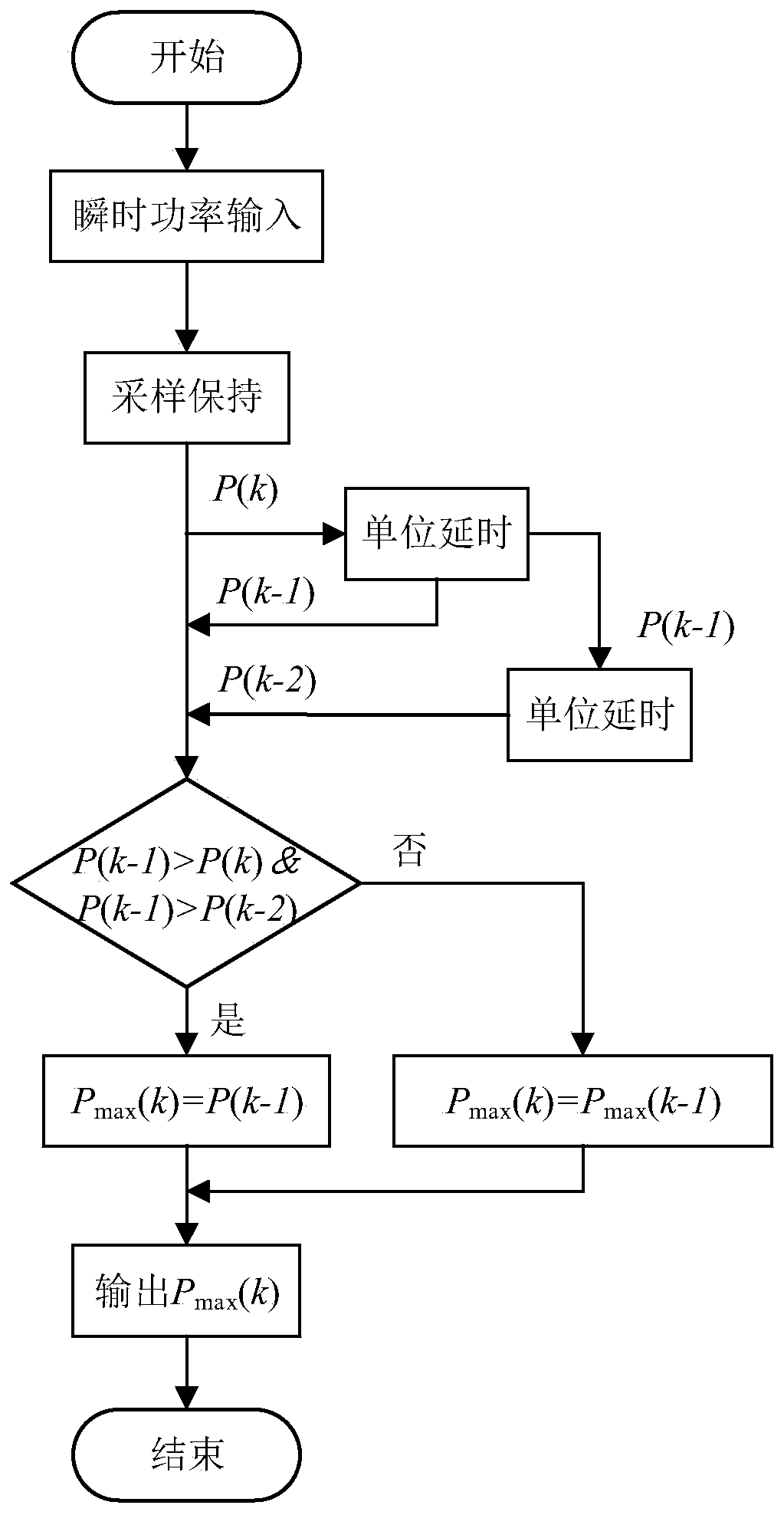
InactiveCN110277929AIncrease lossSolve the problem of slow dynamic responseAc-dc conversion without reversalDc-dc conversionLinear controlOn board
The invention discloses a non-linear control method for an on-board charger PFC converter based on discrete energy function control, which includes the steps of sampling input voltage and current, detecting peak input power, and synthesizing a load reference value and an input power reference value according to the peak input power; building a discrete state space model of an interleaved parallel PFC Boost converter according to the Euler discretization method; and designing a discrete energy function controller of the interleaved parallel PFC Boost converter system according to the discrete energy function minimization control method. The invention proposes an algorithm based on the discrete energy function control, which effectively solves the problem of slow dynamic response of PFC under the original control algorithm. In addition, the non-linear control method simplifies the design of the converter, improves the control effect of the system and has good flexibility and steady-state output characteristics.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com