Patents
Literature
2114 results about "State space" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
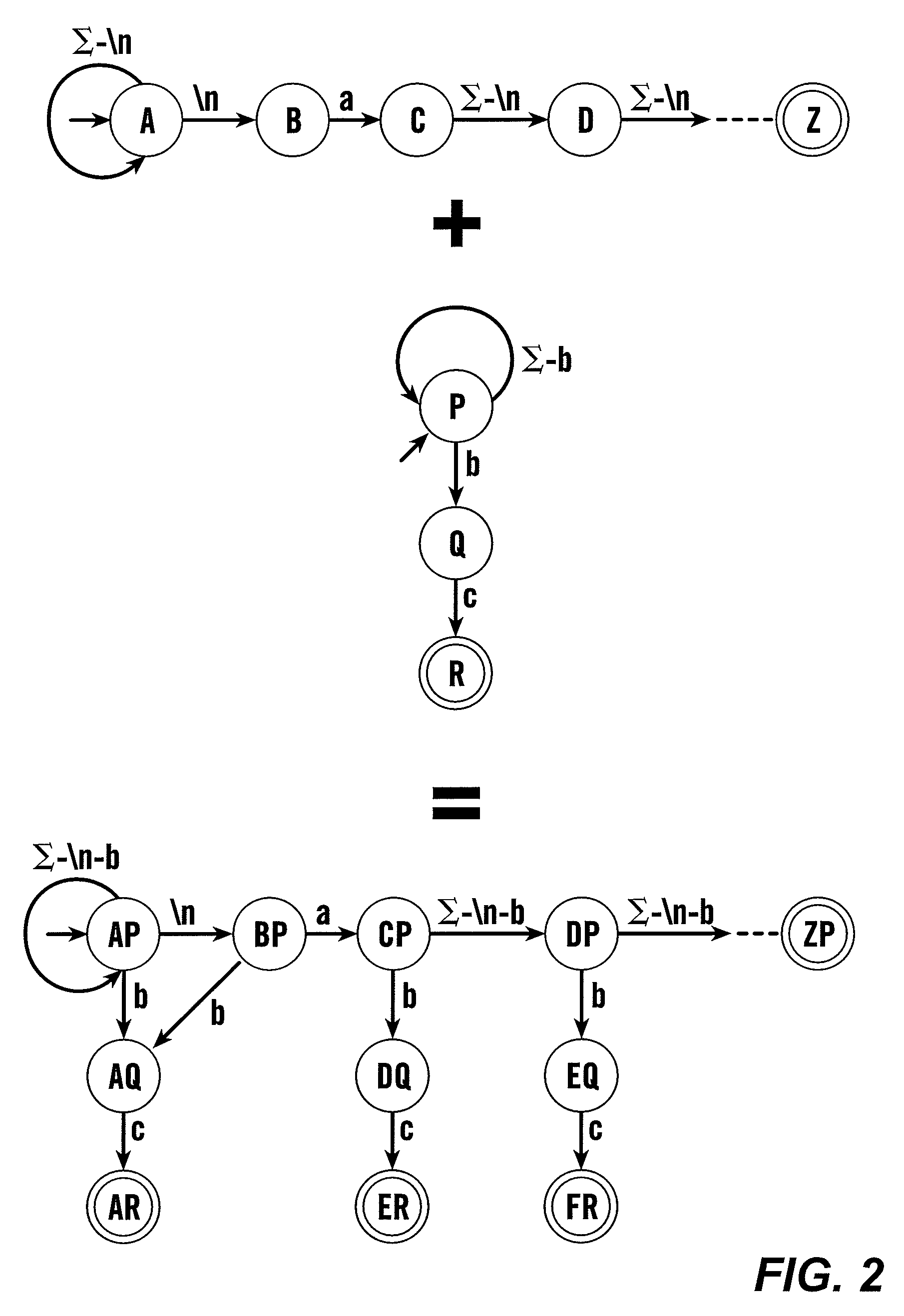
In the theory of discrete dynamical systems, a state space is the set of all possible configurations of a system. For example, a system in queueing theory defining the number of customers in a line would have state space {0, 1, 2, 3, ...}. State spaces can be either infinite or finite. An example of a finite state space is that of the toy problem Vacuum World, in which there are a limited set of configurations that the vacuum and dirt can be in.
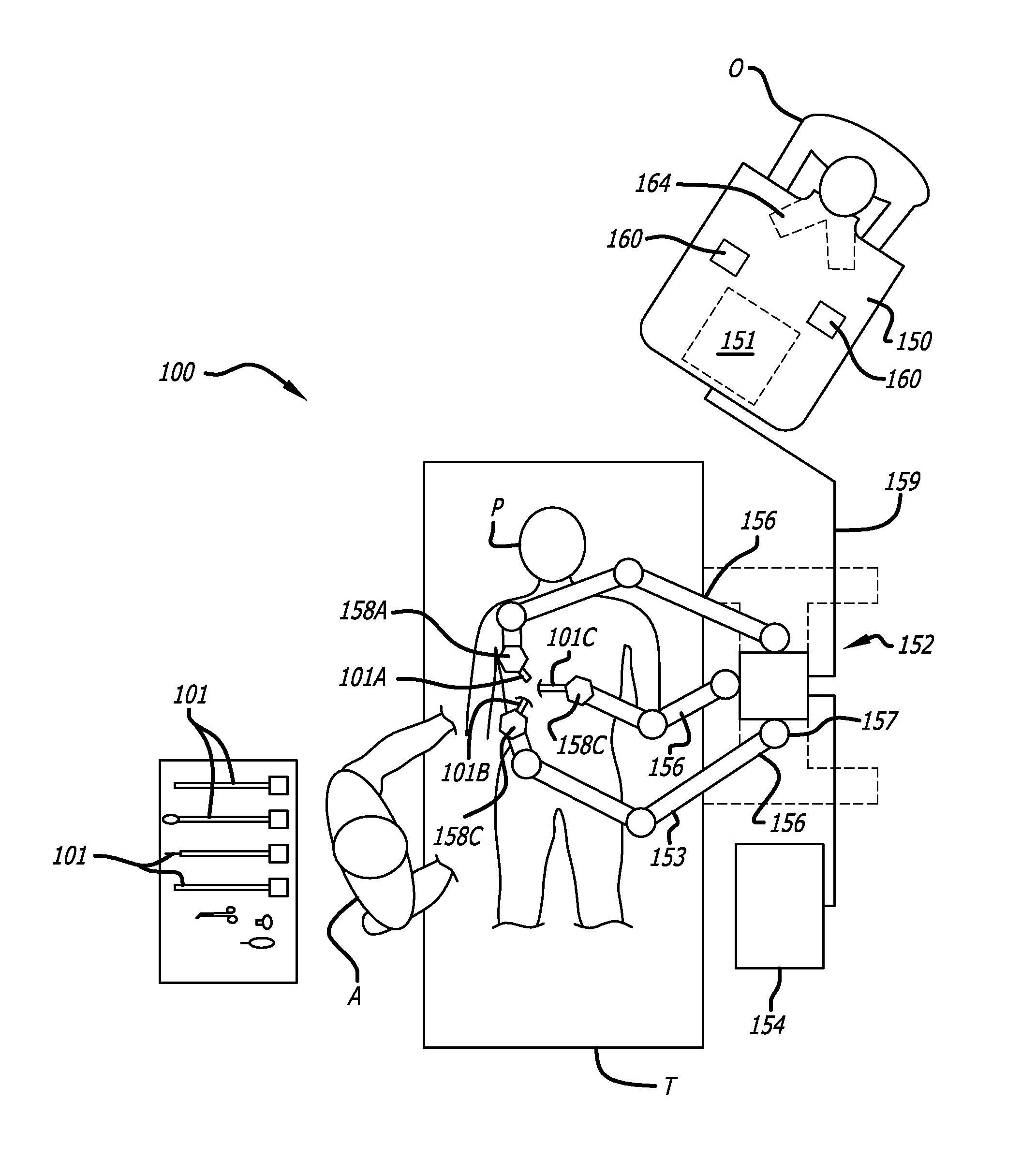
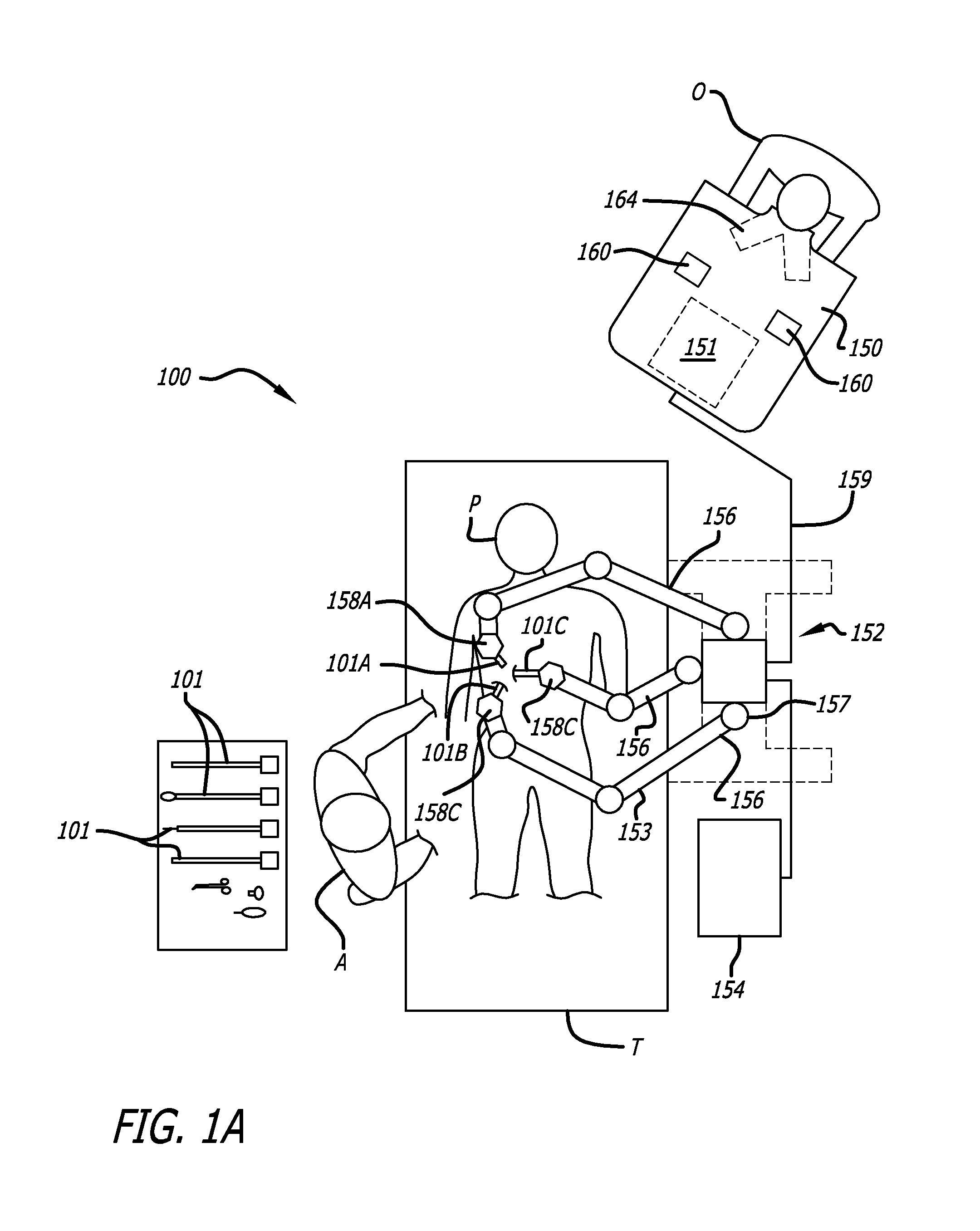
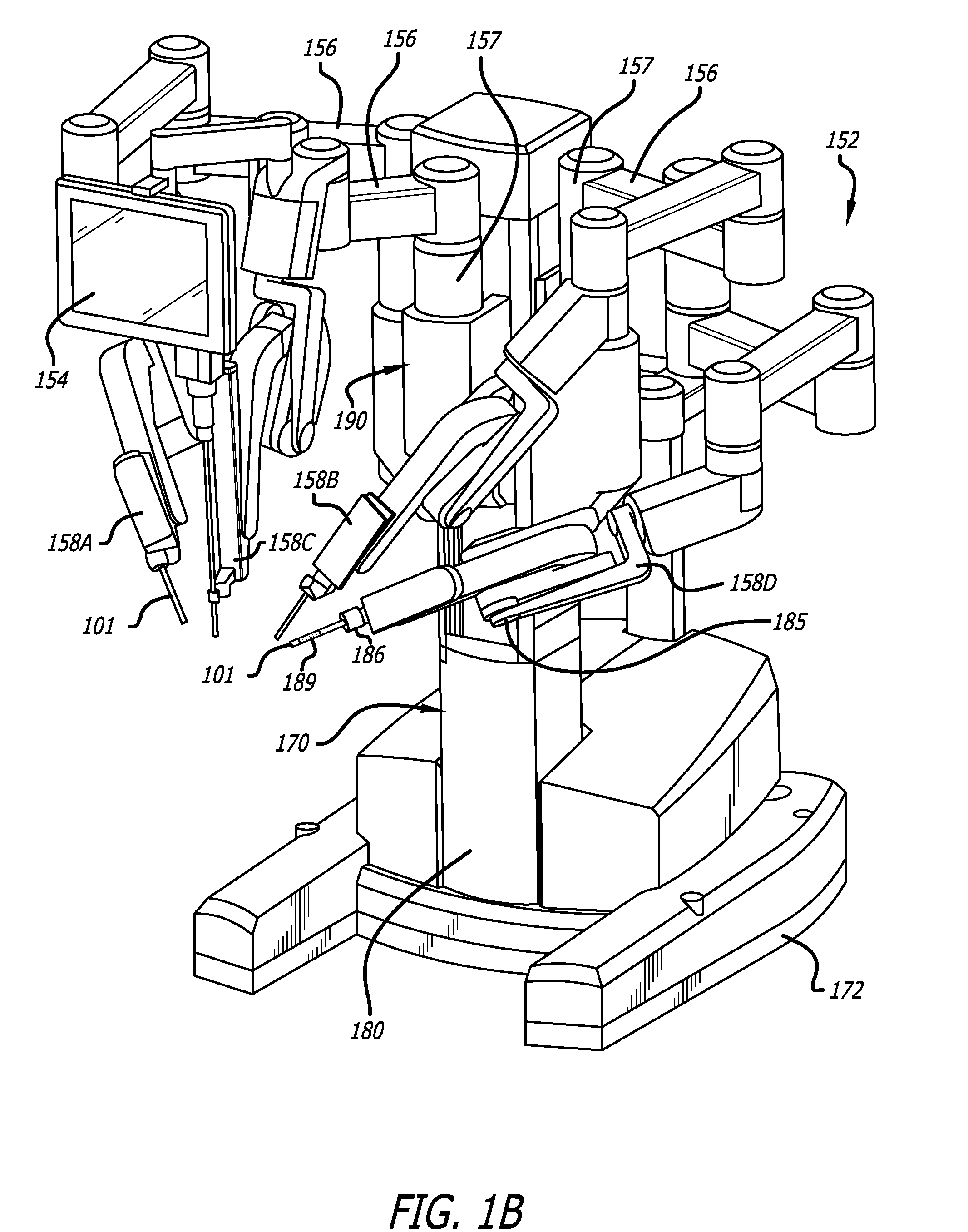
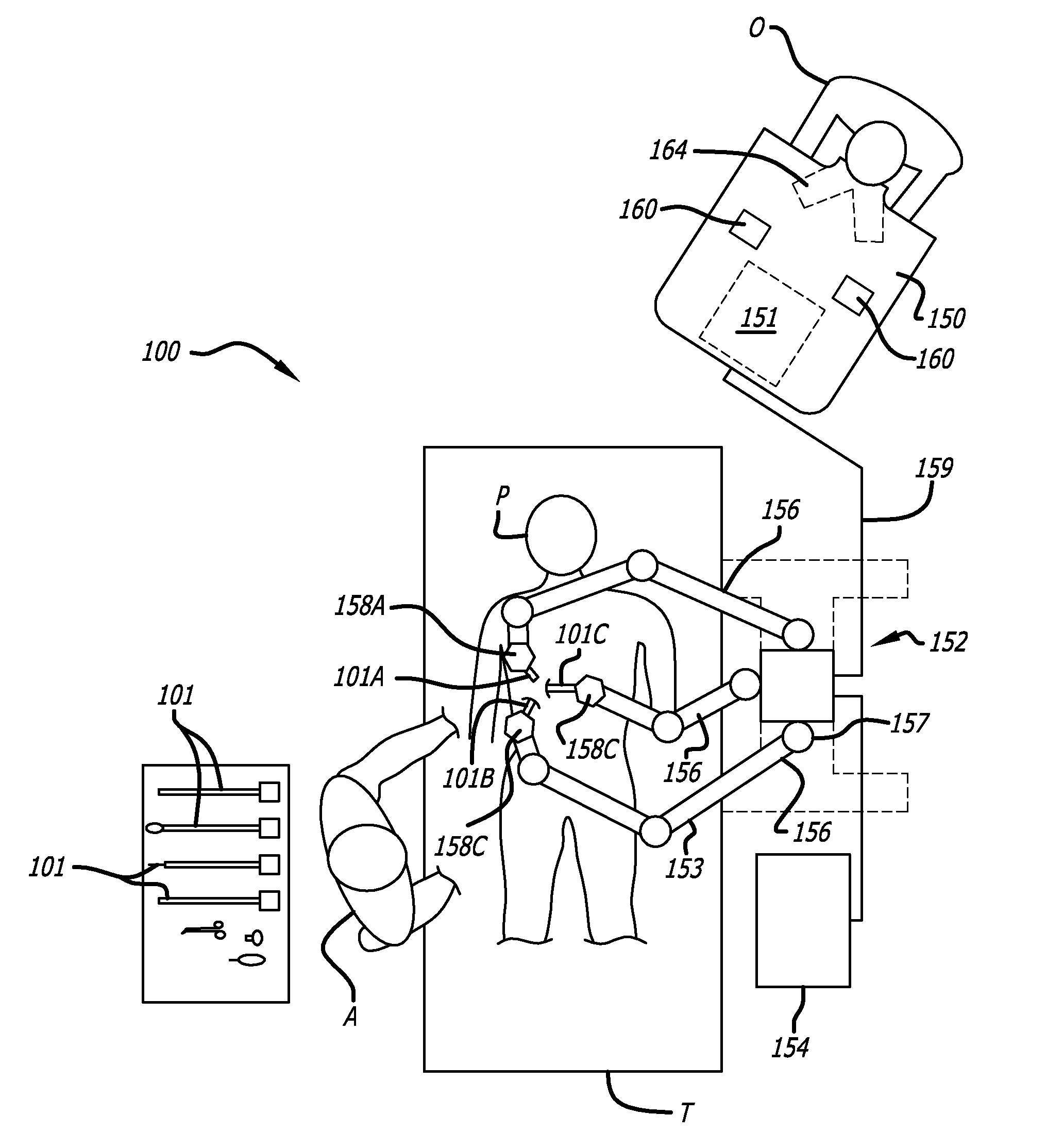
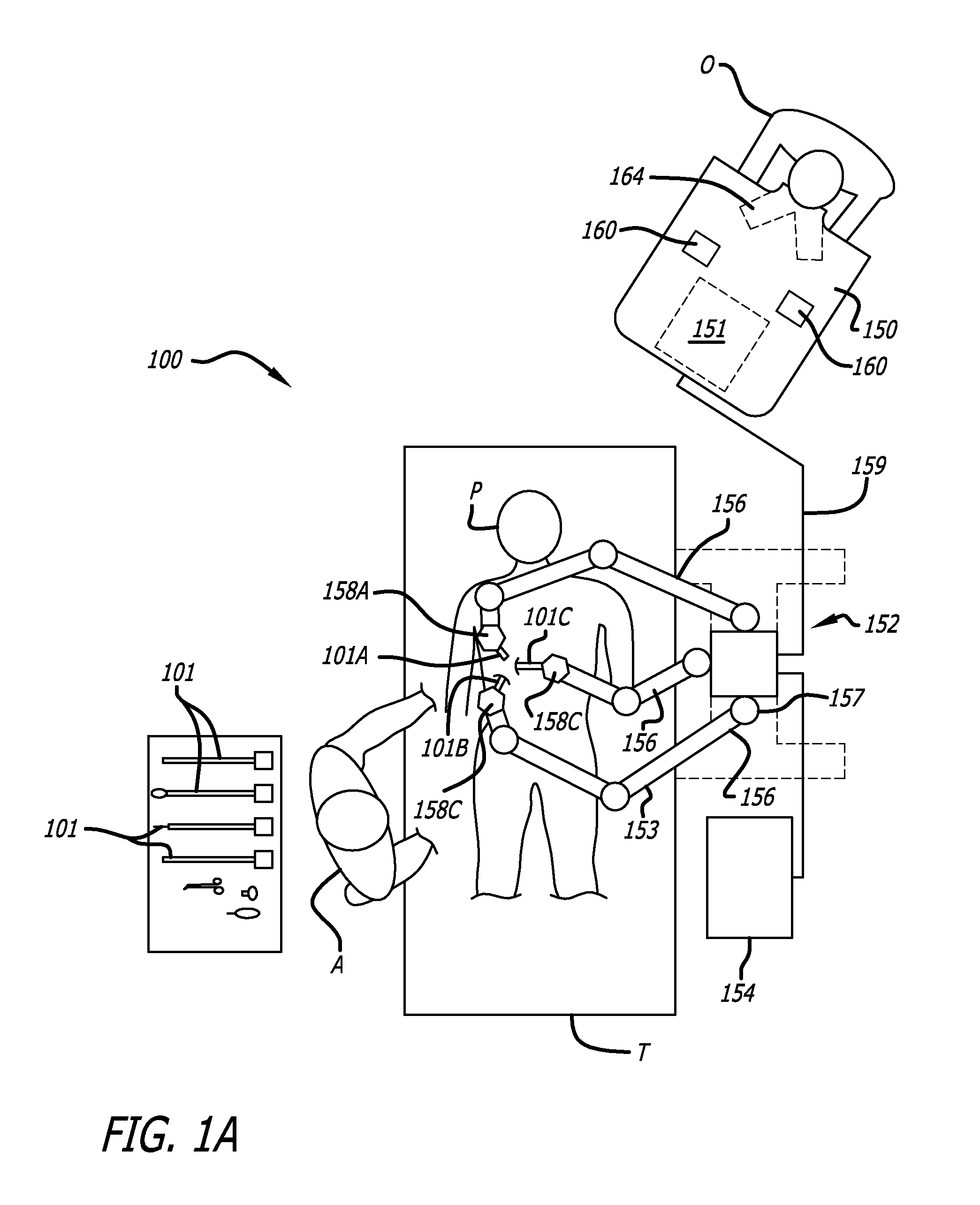
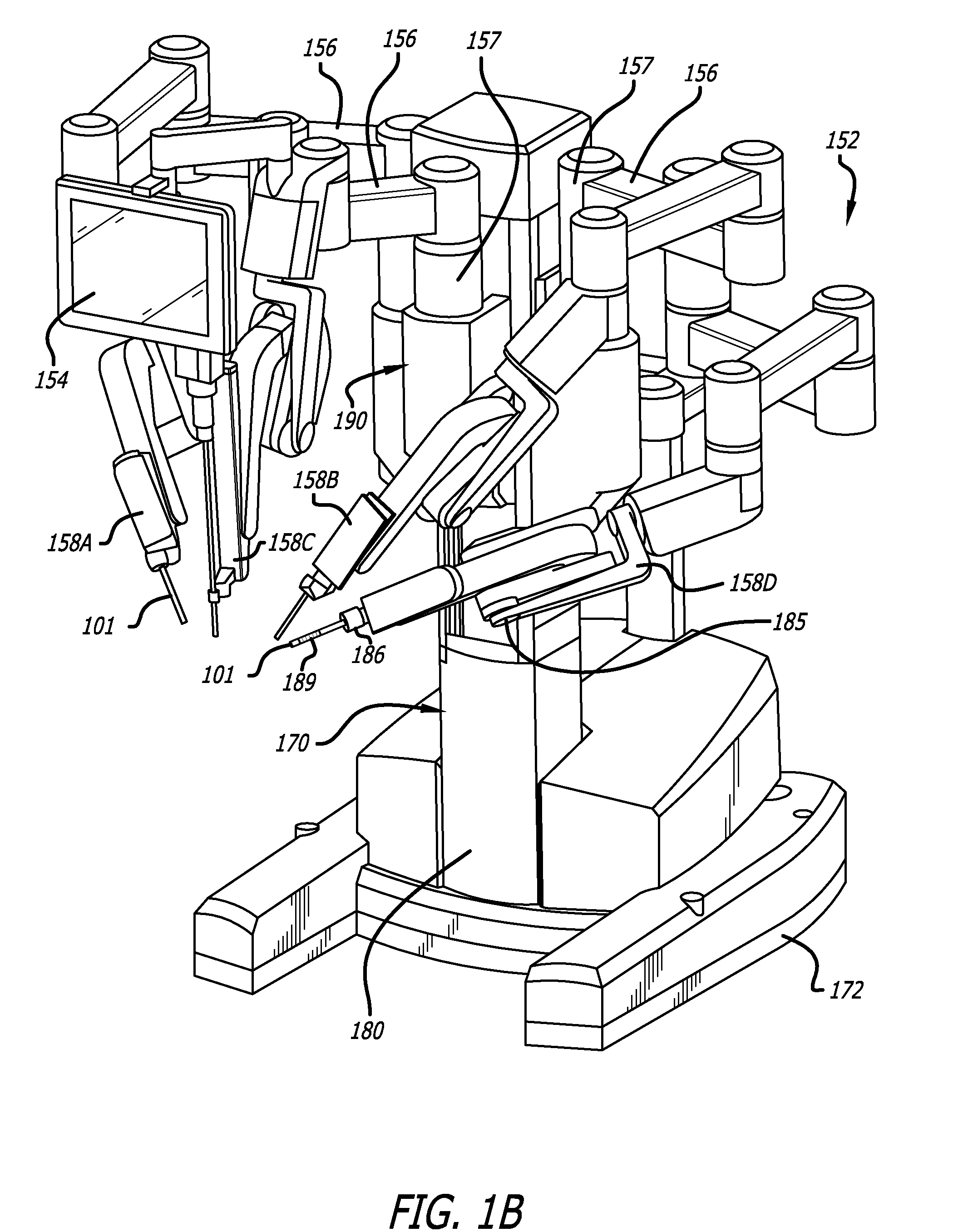
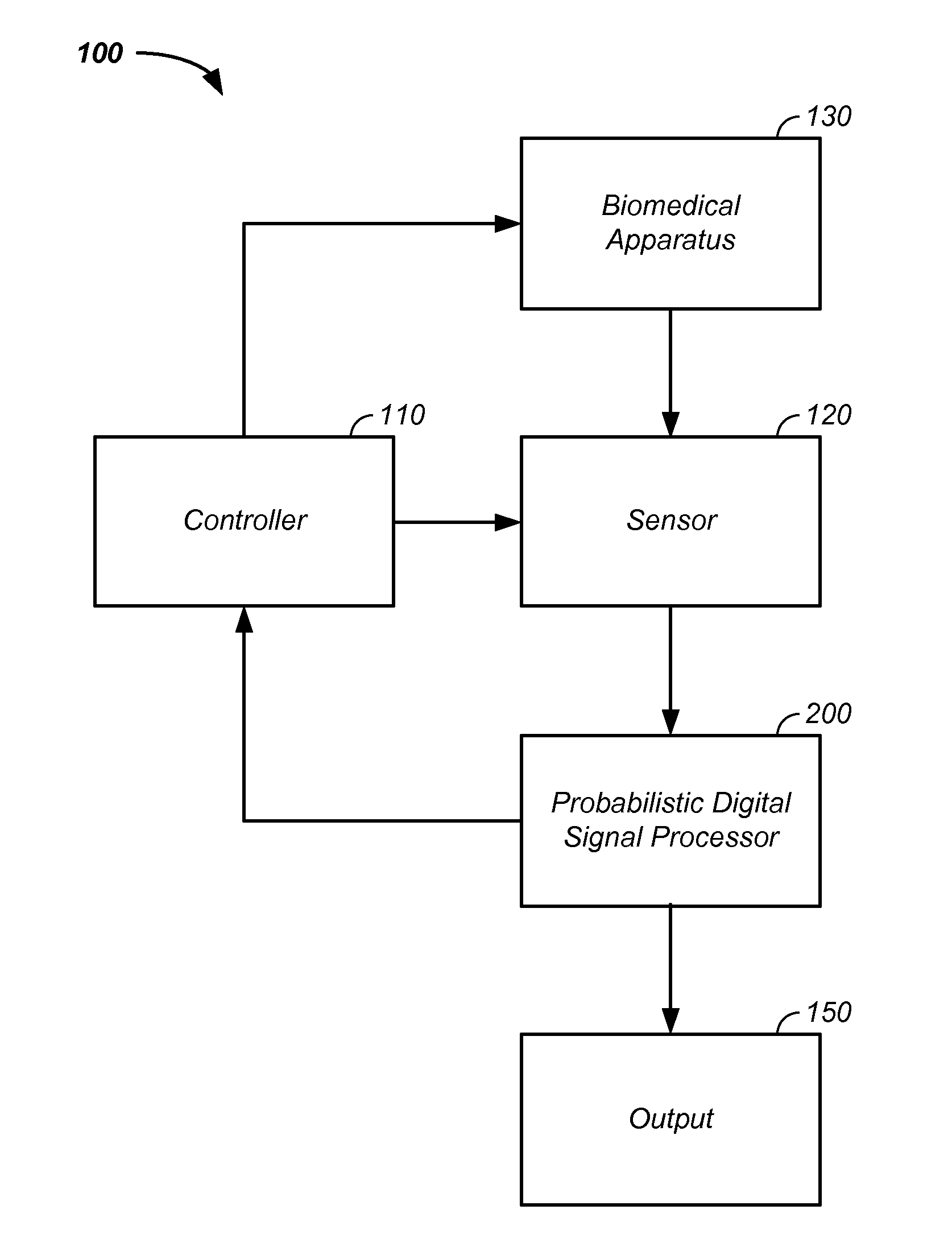
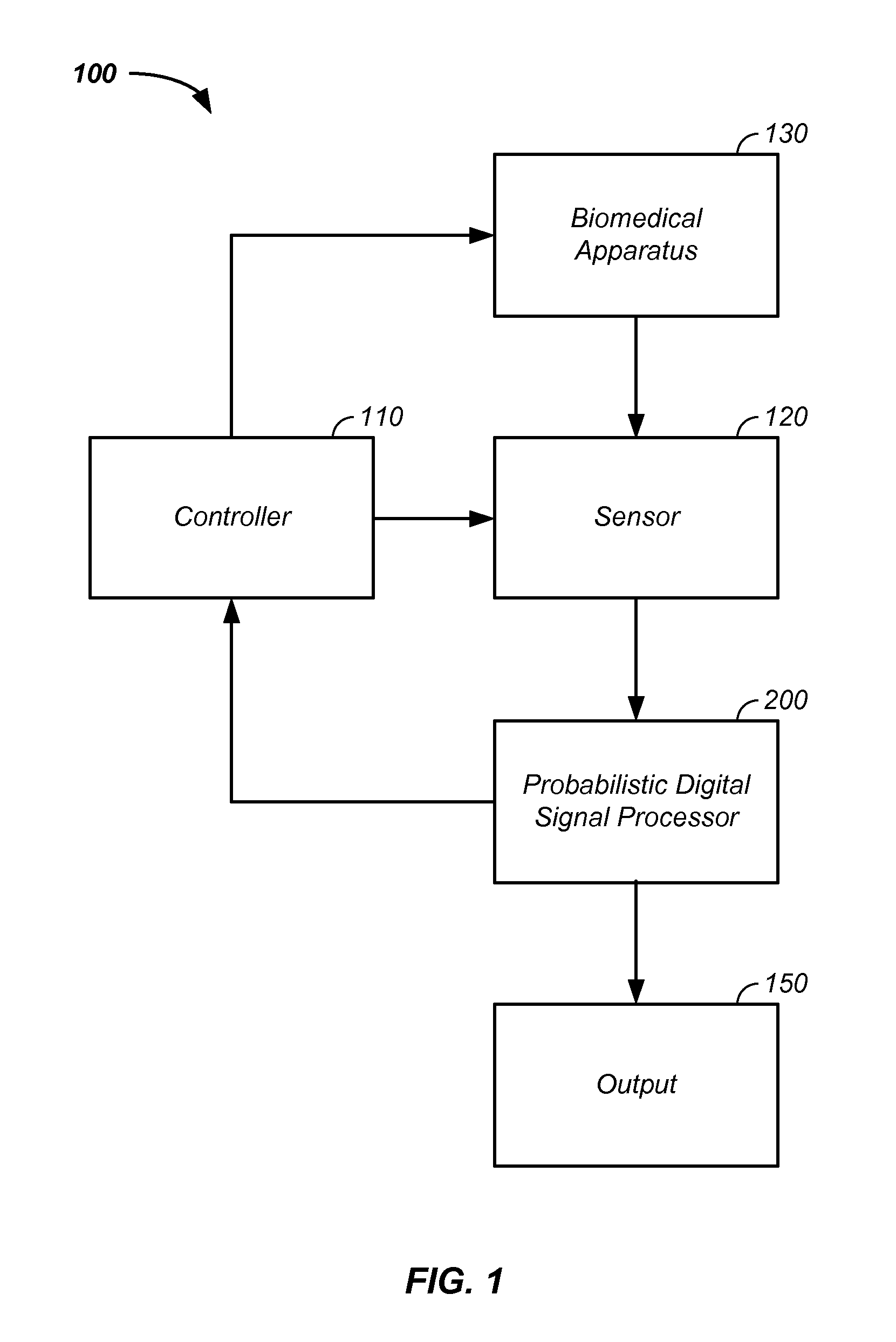
Tool tracking systems and methods for image guided surgery
ActiveUS20090088634A1Improve performanceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsProgramme-controlled manipulatorPostural orientationPerformed Imaging
In one embodiment of the invention, a tool tracking system is disclosed including a computer usable medium having computer readable program code to receive images of video frames from at least one camera and to perform image matching of a robotic instrument to determine video pose information of the robotic instrument within the images. The tool tracking system further includes computer readable program code to provide a state-space model of a sequence of states of corrected kinematics information for accurate pose information of the robotic instrument. The state-space model receives raw kinematics information of mechanical pose information and adaptively fuses the mechanical pose information and the video pose information together to generate the sequence of states of the corrected kinematics information for the robotic instrument. Additionally disclosed are methods for image guided surgery.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
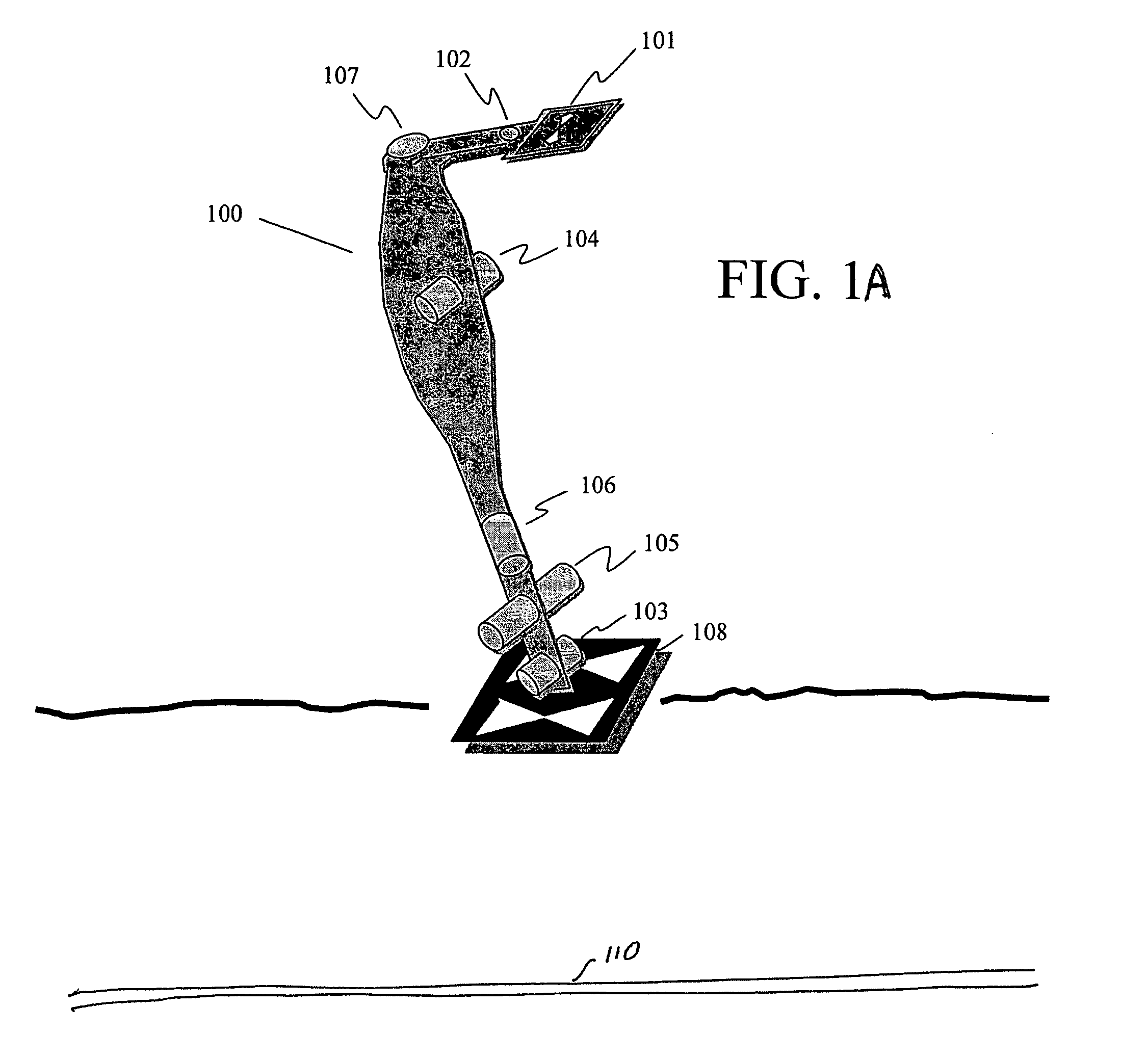
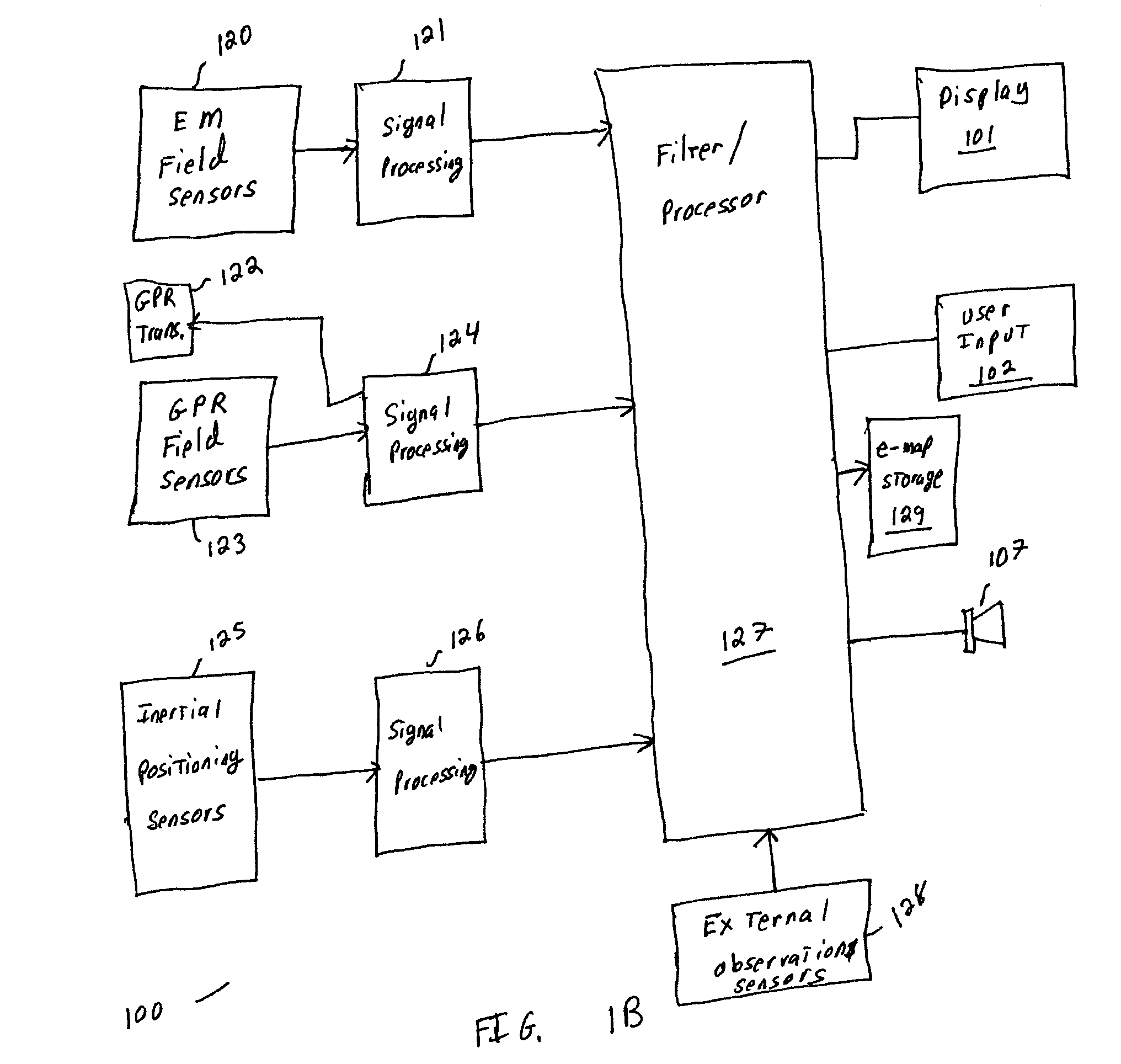
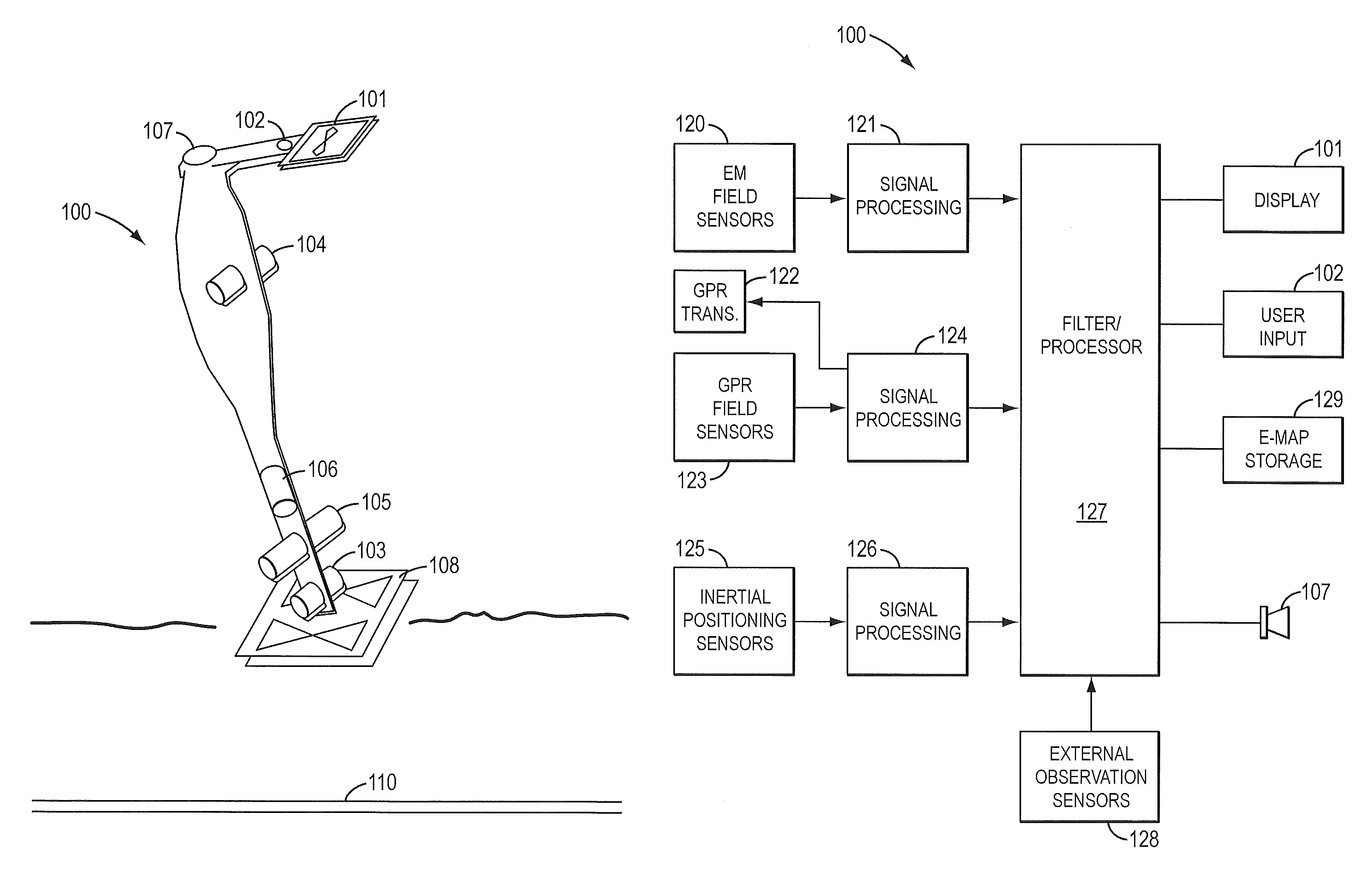
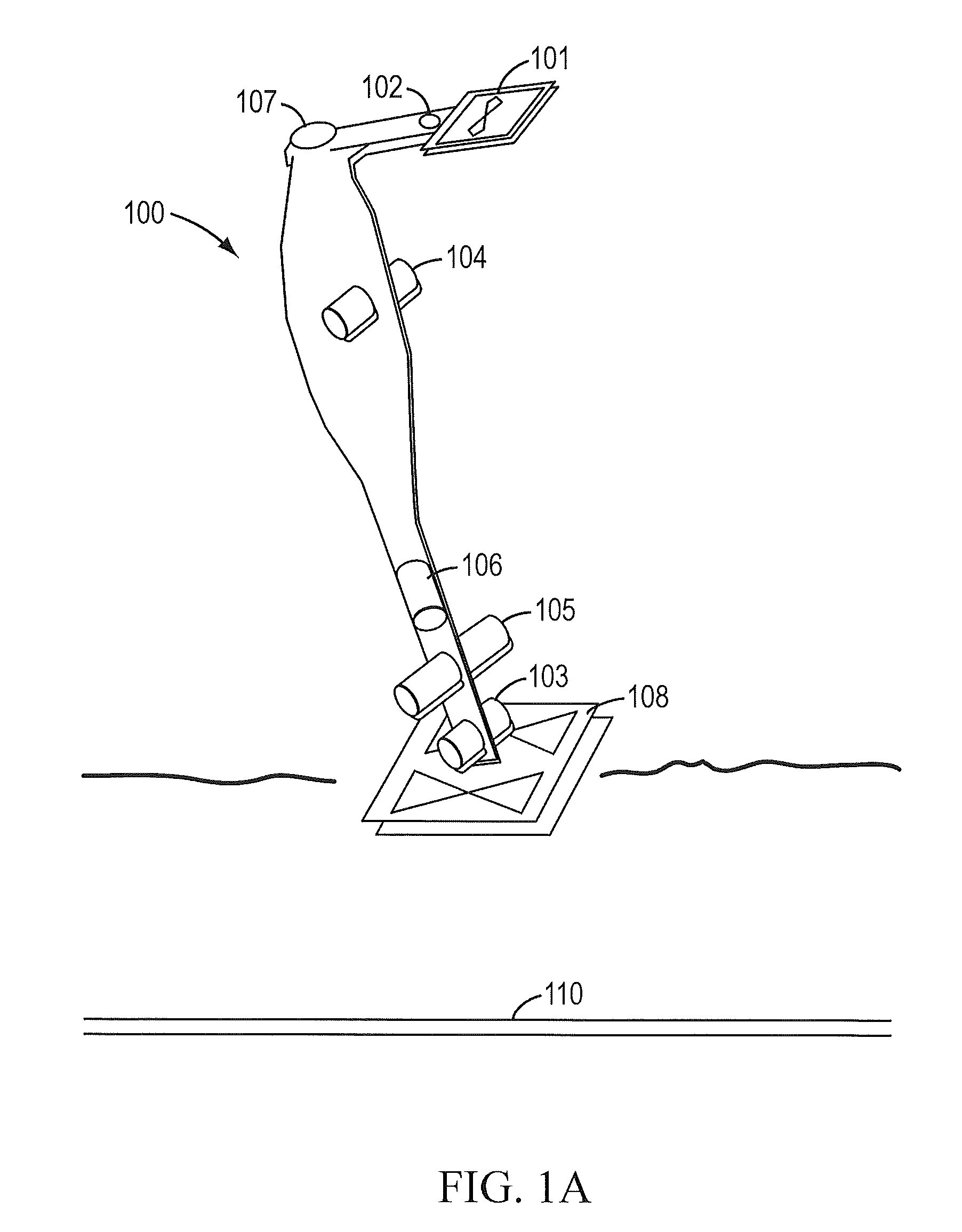
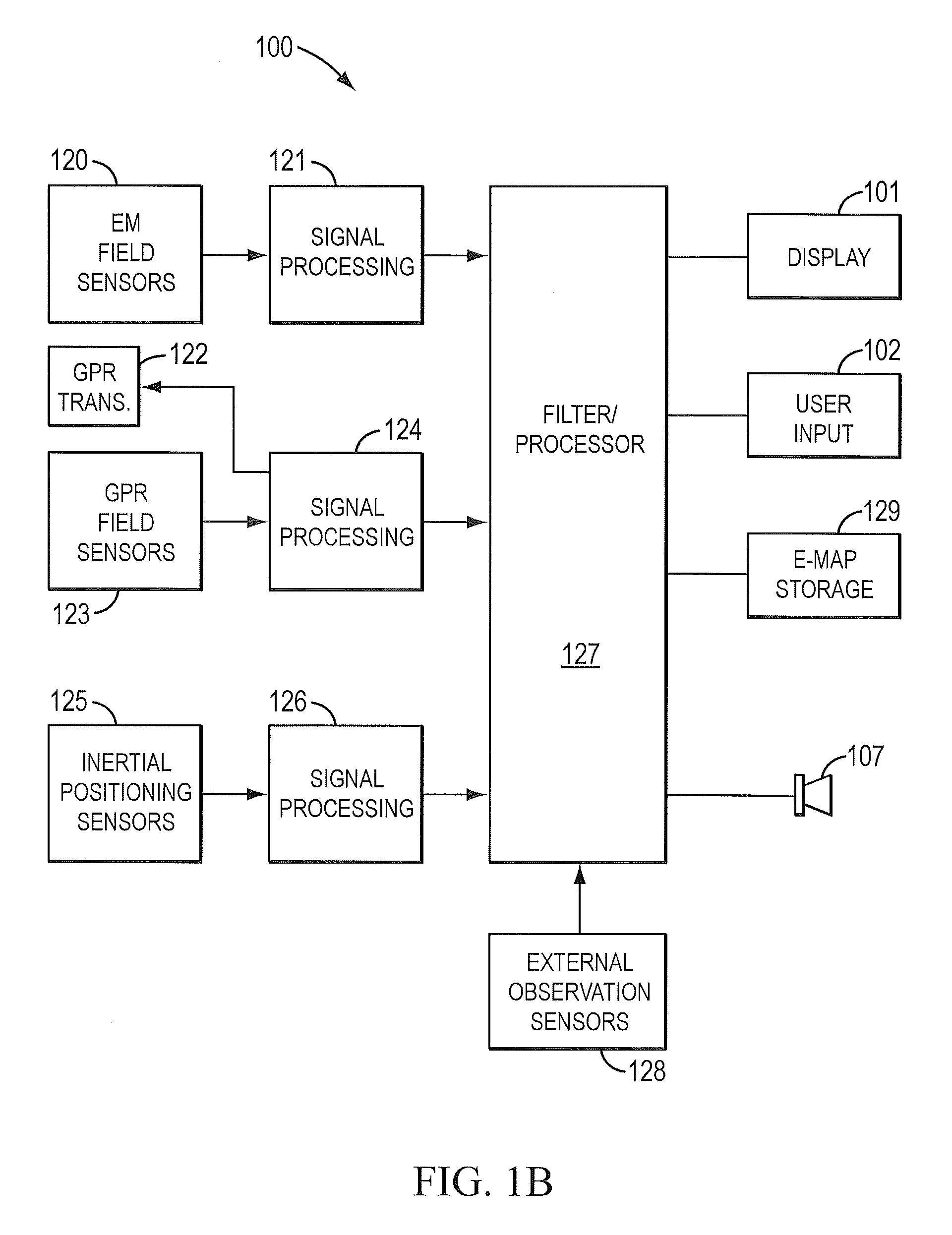
Sensor fusion for model-based detection in pipe and cable locator systems
ActiveUS20060055584A1Improve positionSatellite radio beaconingDetection using electromagnetic wavesAccelerometerGyroscope
Line locator systems that fuse traditional sensors used in a combined pipe and cable locator (electromagnetic coils, magnetometers, and ground penetrating radar antennas) with low cost inertial sensors (accelerometers, gyroscopes) in a model-based approach are presented. Such systems can utilize inexpensive MEMS sensors for inertial navigation. A pseudo-inertial frame is defined that uses the centerline of the tracked utility, or an aboveground fixed object as the navigational reference. An inertial sensor correction mechanism that limits the tracking errors over time when the model is implemented in state-space form using, for example, the Extended Kalman Filter (EKF) is disclosed.
Owner:BUSAN TRANSPORTATION CORPORATION
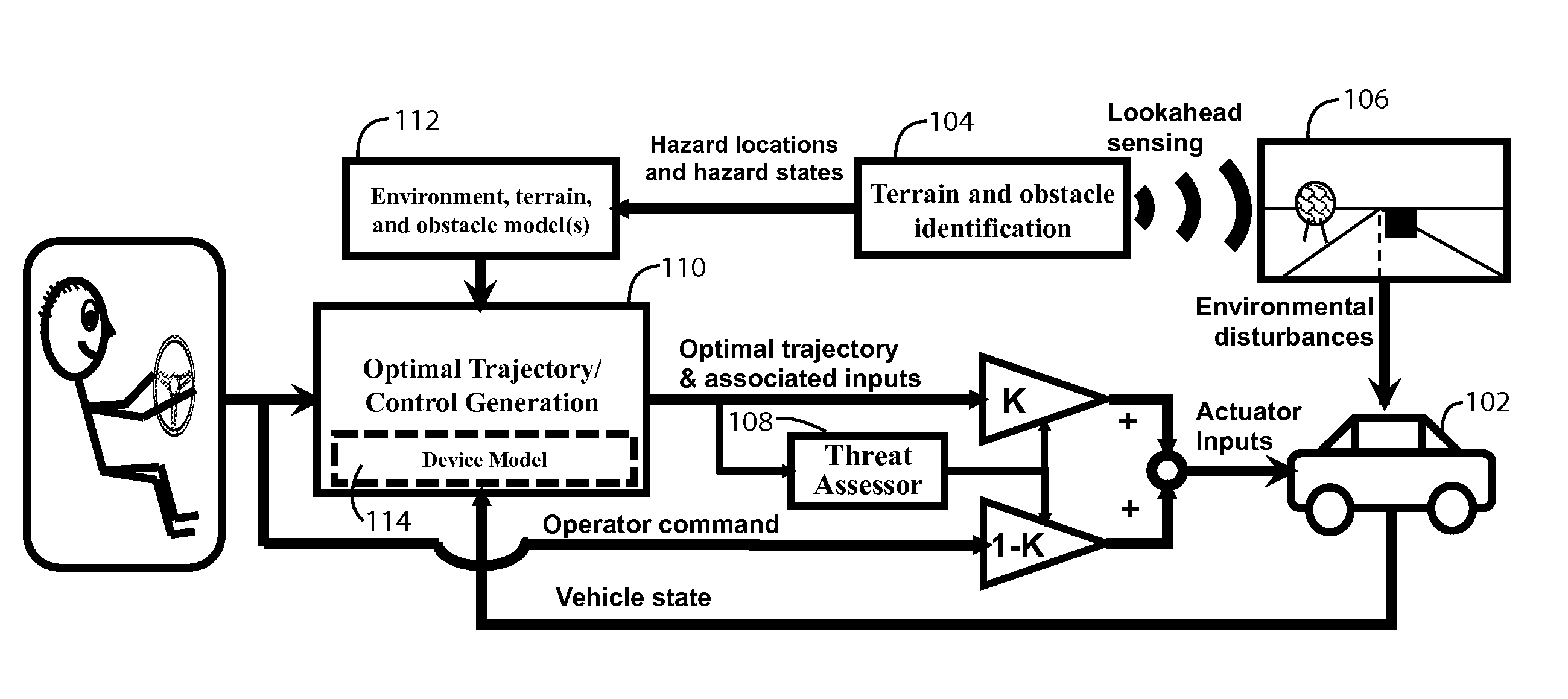
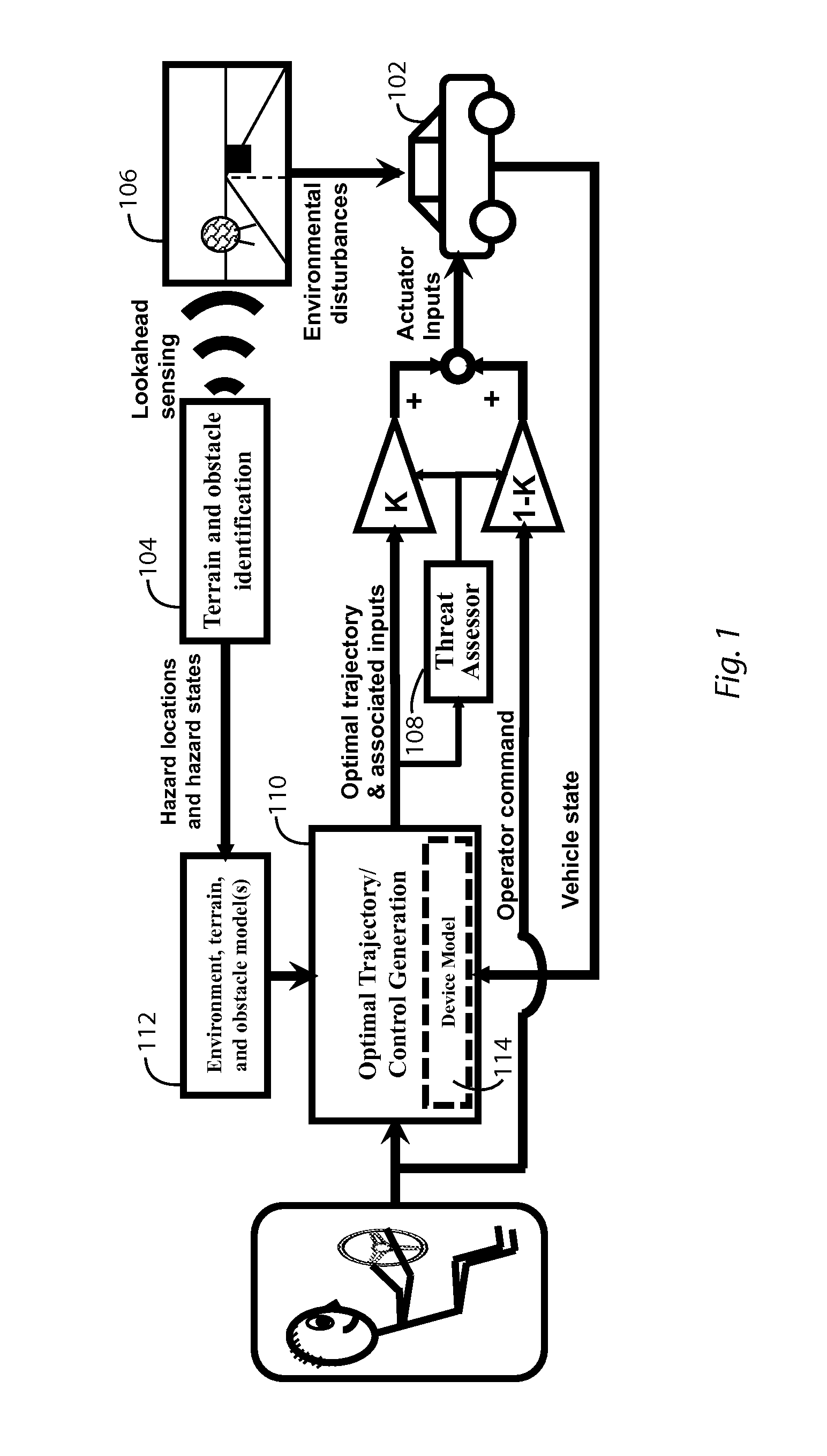
Integrated framework for vehicle operator assistance based on a trajectory and threat assessment
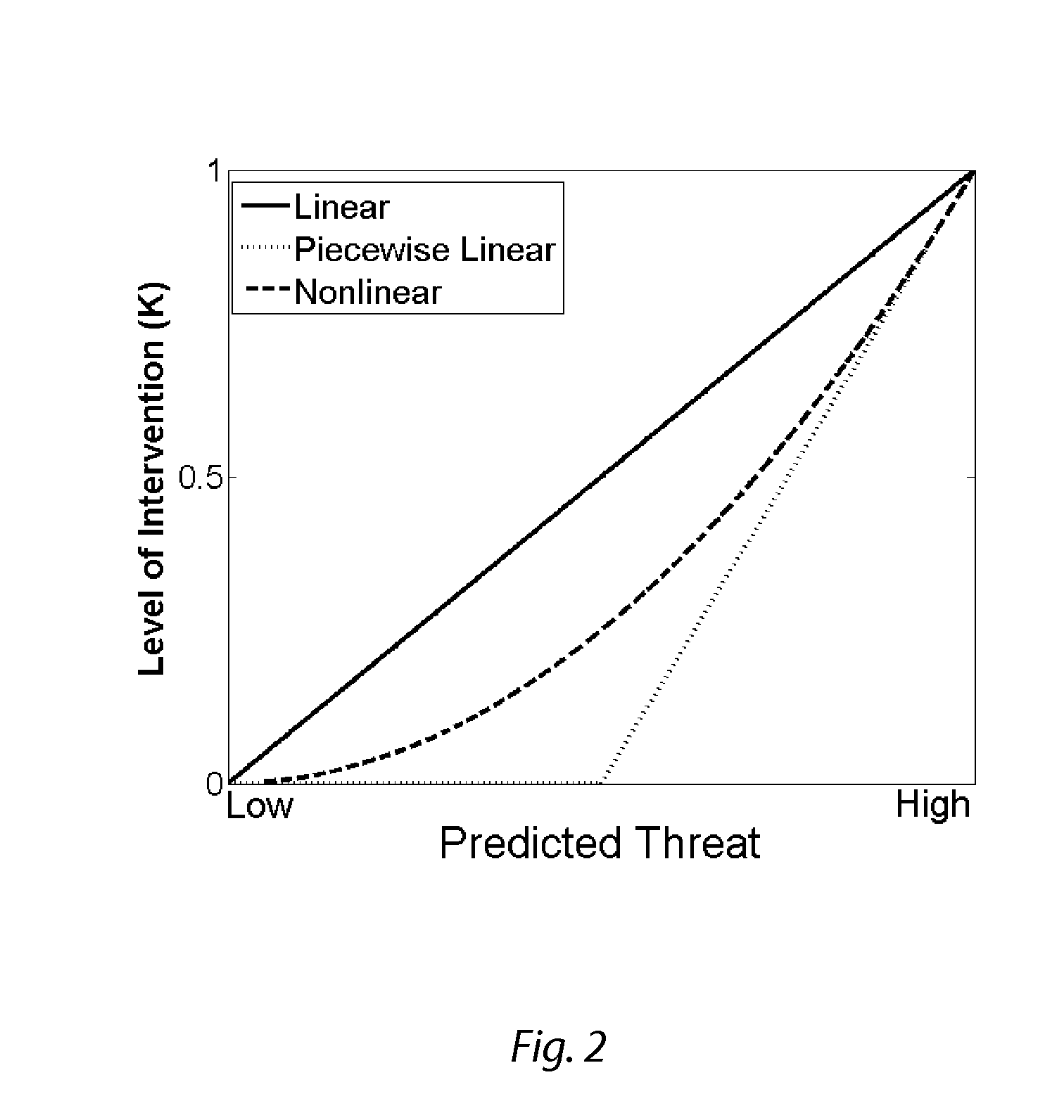
ActiveUS20120083947A1Autonomous decision making processDigital data processing detailsState spaceHazard avoidance
Various types and levels of operator assistance are performed within a unified, configurable framework. A model of the device with a model of the environment and the current state of the device and the environment are used to iteratively generate a sequence of optimal device control inputs that, when applied to a model of the device, generate an optimal device trajectory through a constraint-bounded corridor or region within the state space. This optimal trajectory and the sequence of device control inputs that generates it is used to generate a threat assessment metric. An appropriate type and level of operator assistance is generated based on this threat assessment. Operator assistance modes include warnings, decision support, operator feedback, vehicle stability control, and autonomous or semi-autonomous hazard avoidance. The responses generated by each assistance mode are mutually consistent because they are generated using the same optimal trajectory.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
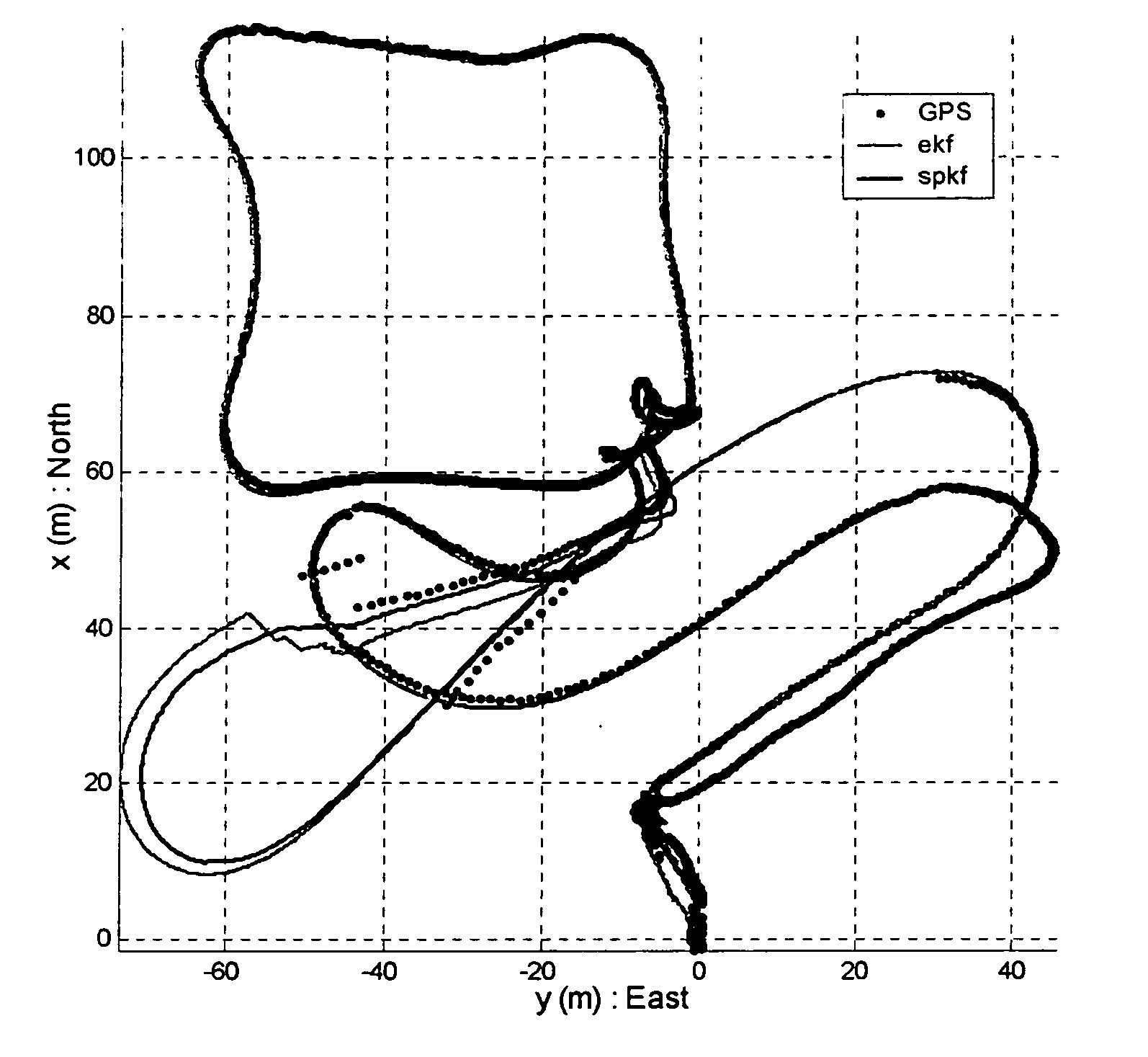
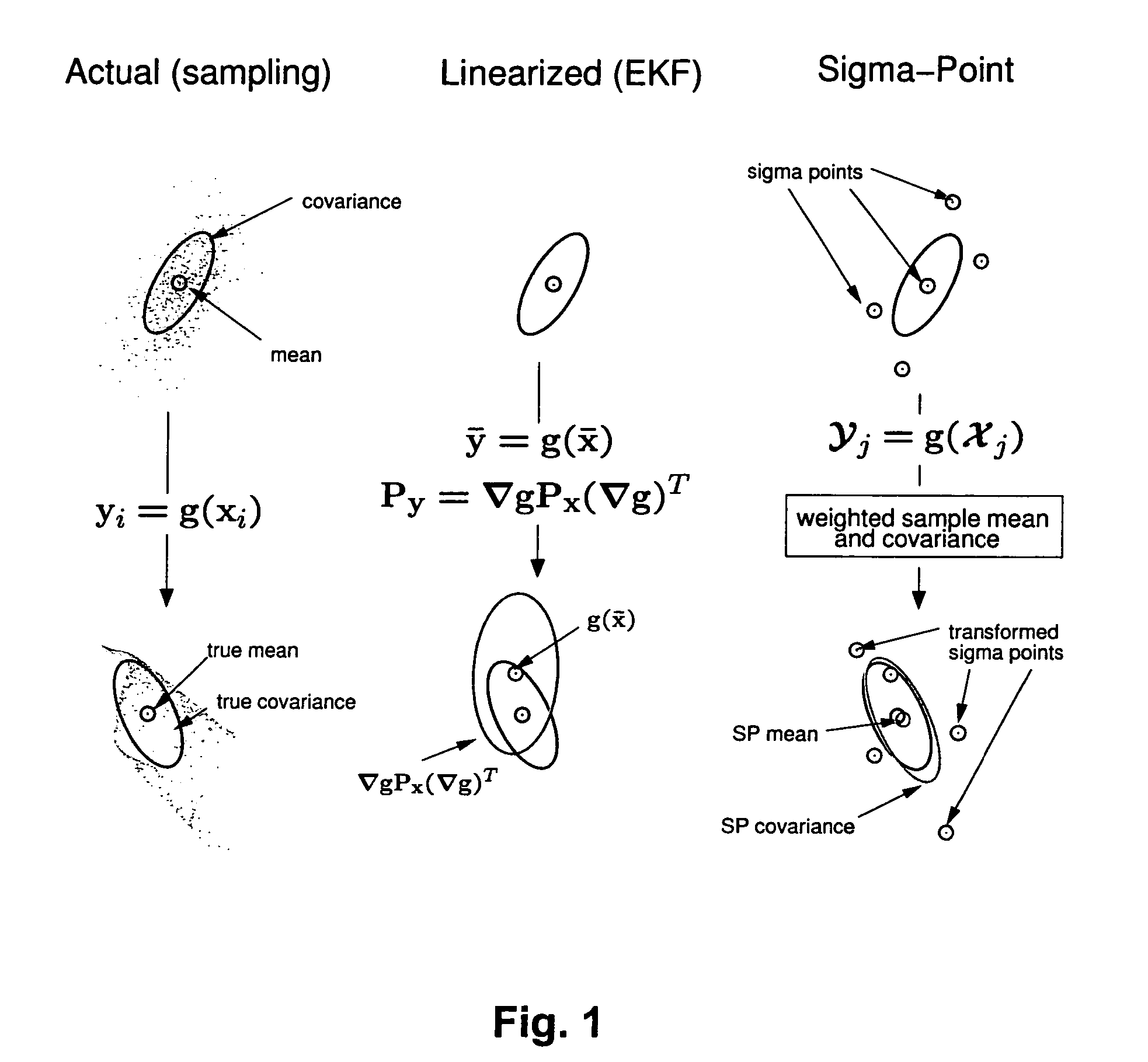
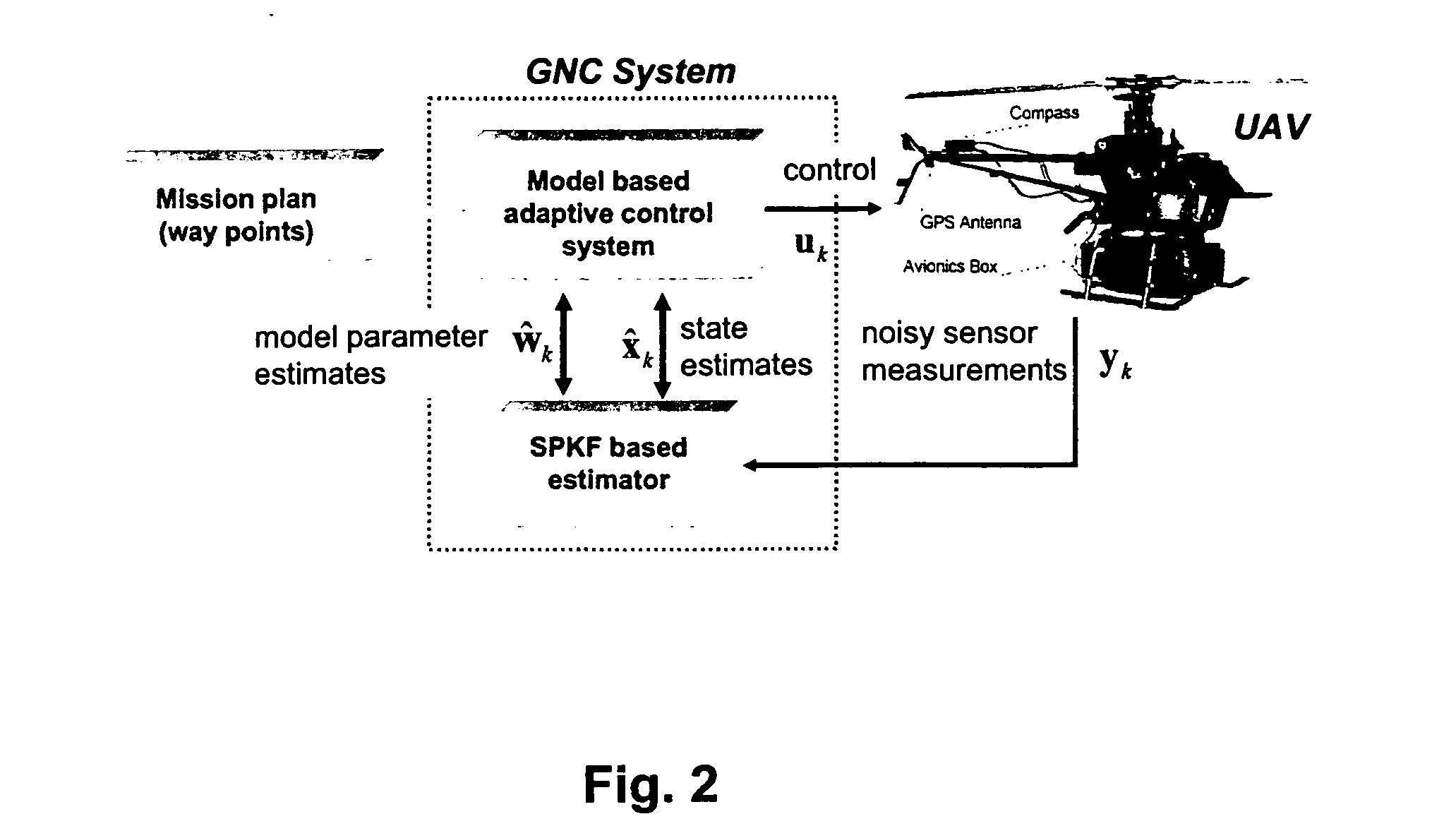
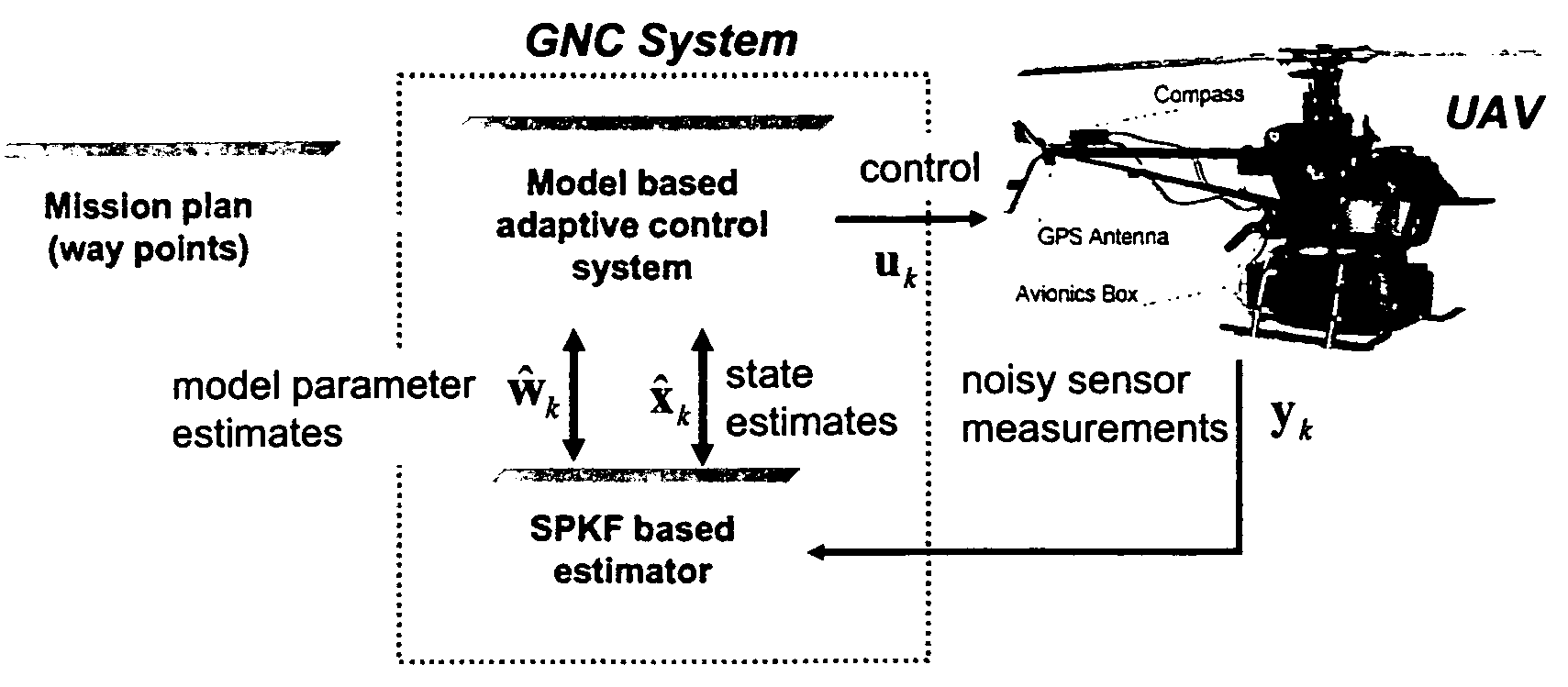
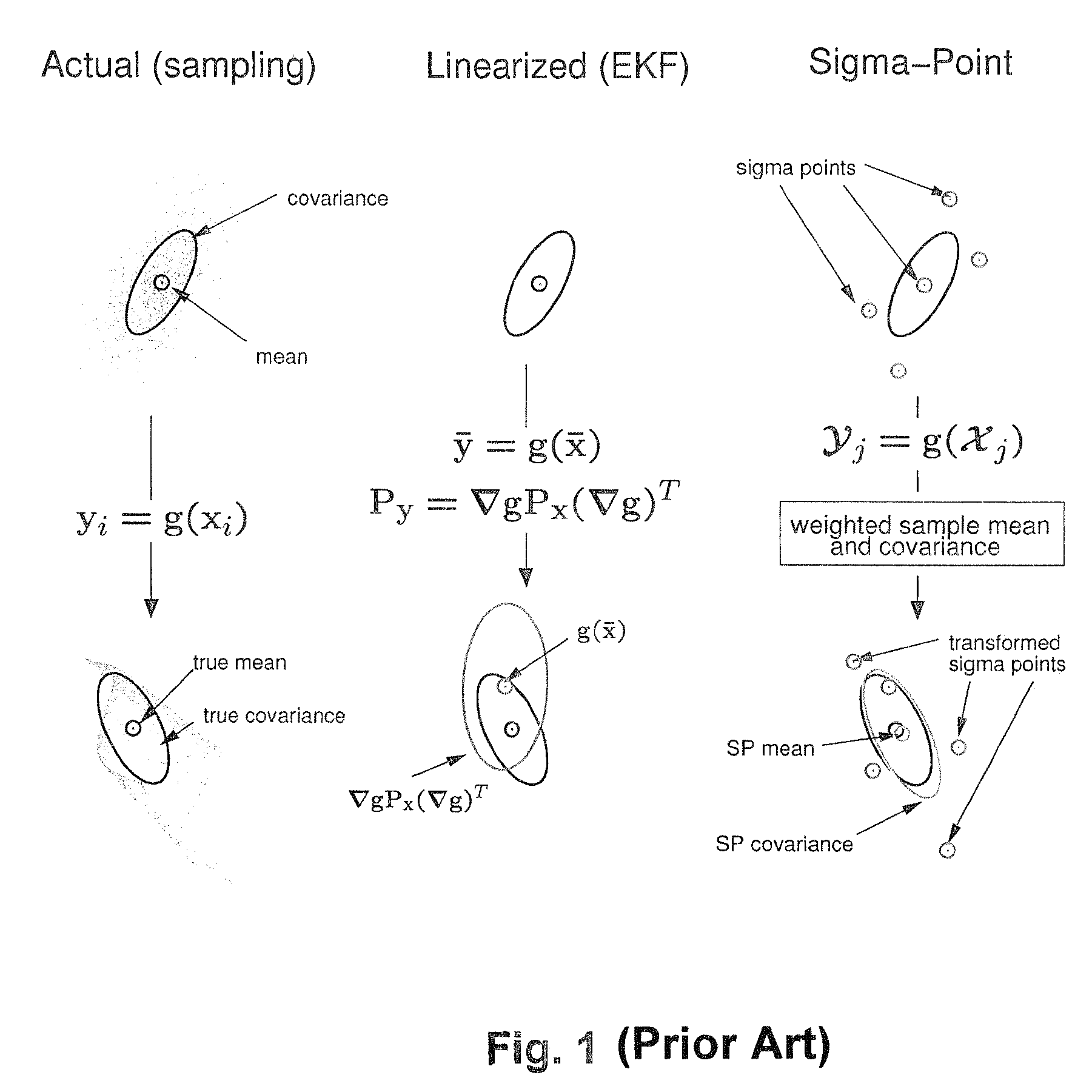
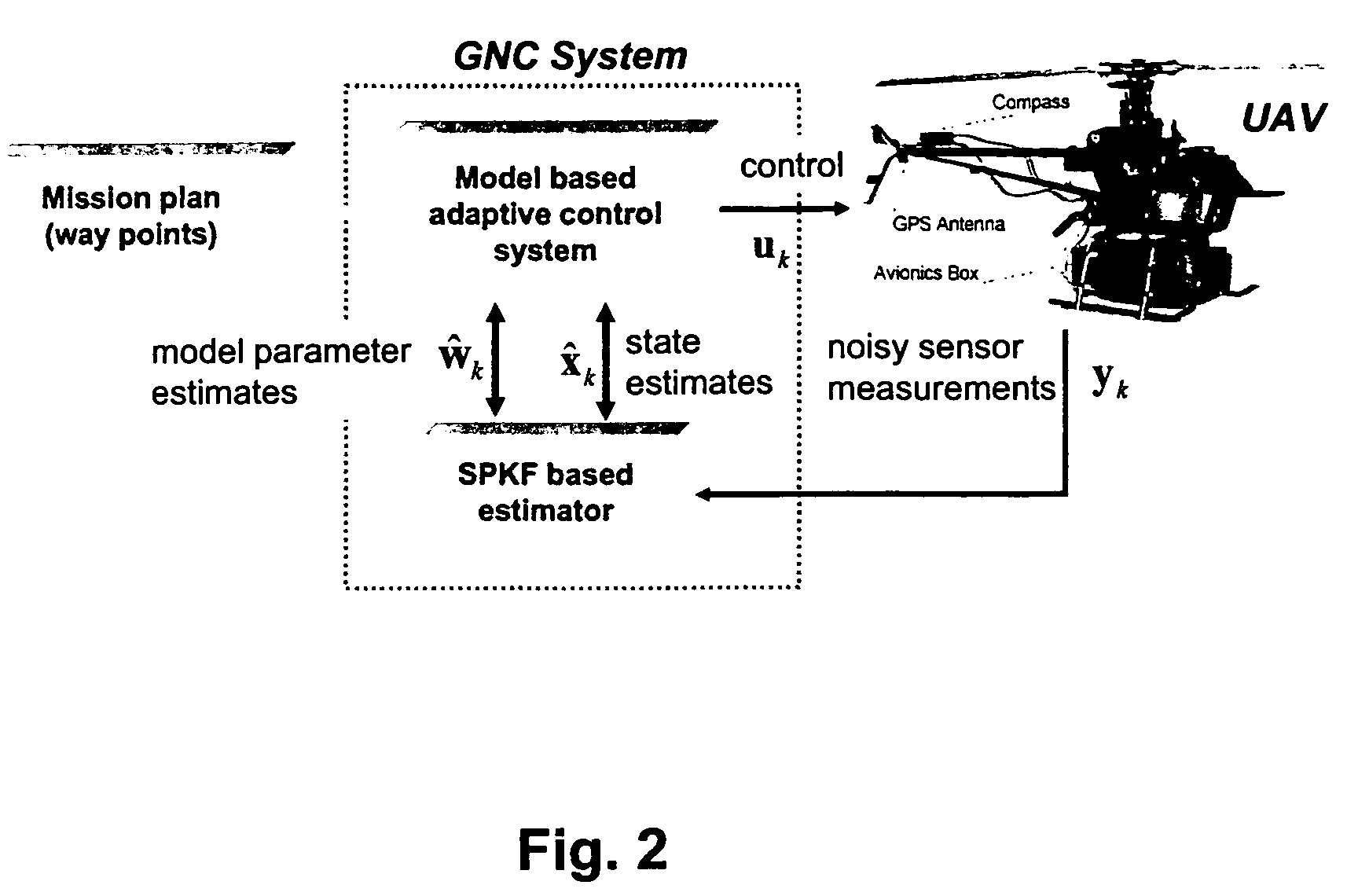
Navigation system applications of sigma-point Kalman filters for nonlinear estimation and sensor fusion
ActiveUS20050251328A1Improve estimation accuracyInstruments for road network navigationPosition fixationKaiman filterAlgorithm
A method of estimating the navigational state of a system entails acquiring observation data produced by noisy measurement sensors and providing a probabilistic inference system to combine the observation data with prediction values of the system state space model to estimate the navigational state of the system. The probabilistic inference system is implemented to include a realization of a Gaussian approximate random variable propagation technique performing deterministic sampling without analytic derivative calculations. This technique achieves for the navigational state of the system an estimation accuracy that is greater than that achievable with an extended Kalman filter-based probabilistic inference system.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV
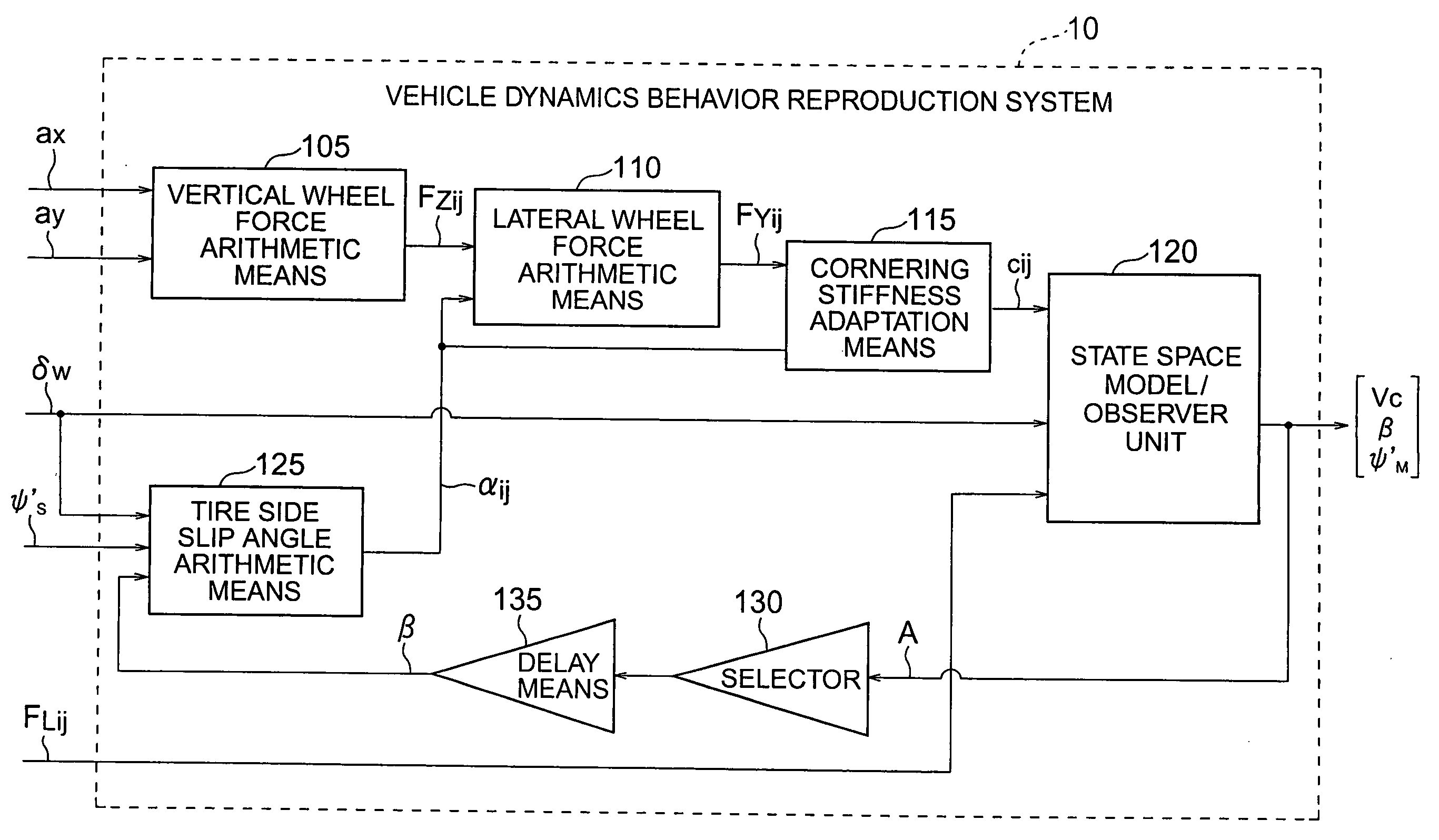
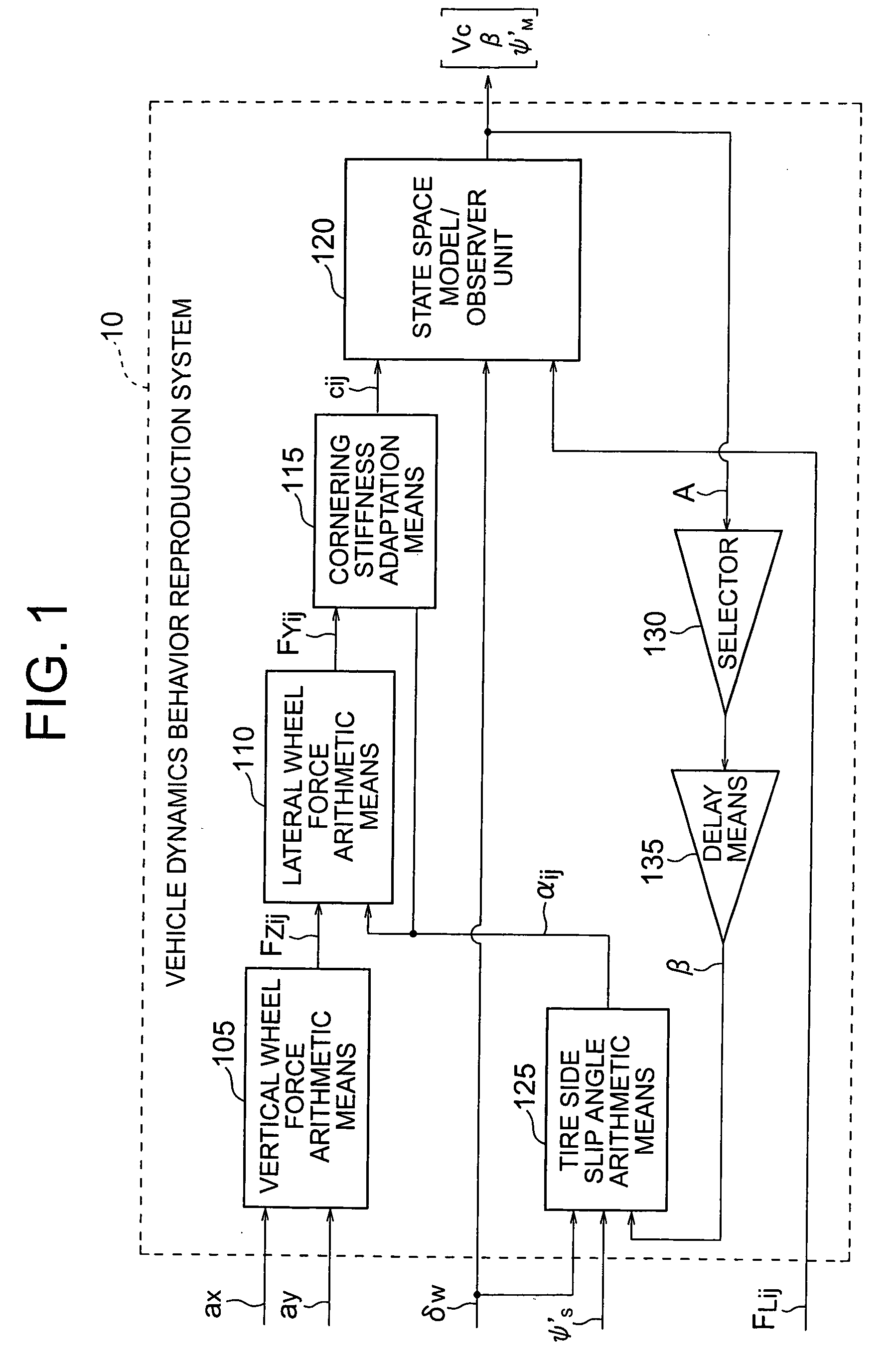
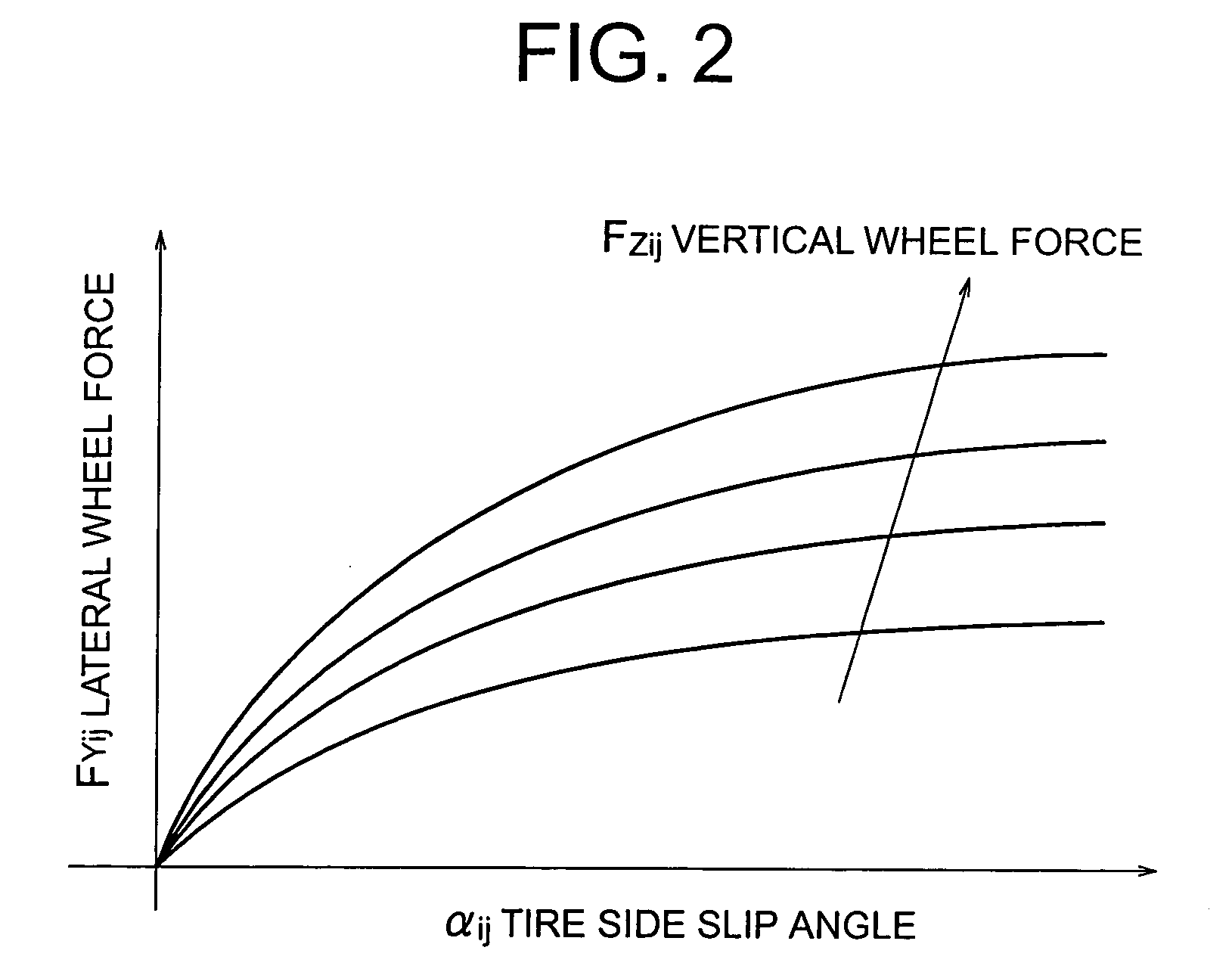
Vehicle dynamics behavior reproduction system
InactiveUS20050154513A1Increase the scope of applicationEasy to solveDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesVehicle dynamicsNonlinear approximation
A vehicle dynamics behavior reproduction system capable of describing accurately behavior of a motor vehicle in a lateral direction even for nonlinear driving situation includes a vertical wheel force arithmetic means (105), a lateral wheel force arithmetic means (110), a cornering stiffness adaptation means (115), a state space model / observer unit (120), a selector (130), a delay means (135), and a tire side slip angle arithmetic means (125). Vertical wheel forces (FZij) and tire side slip angles (αij) are determined by using sensor information and estimated values while lateral wheel forces (FYij) are determined in accordance with a relatively simple nonlinear approximation equation. The lateral wheel force (FYij) and the tire side slip angle (αij) provide bases for adaptation of cornering stiffnesses at individual wheels. Vehicle motion is accurately described to a marginal stability by using adapted cornering stiffnesses (Cij) and other information.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
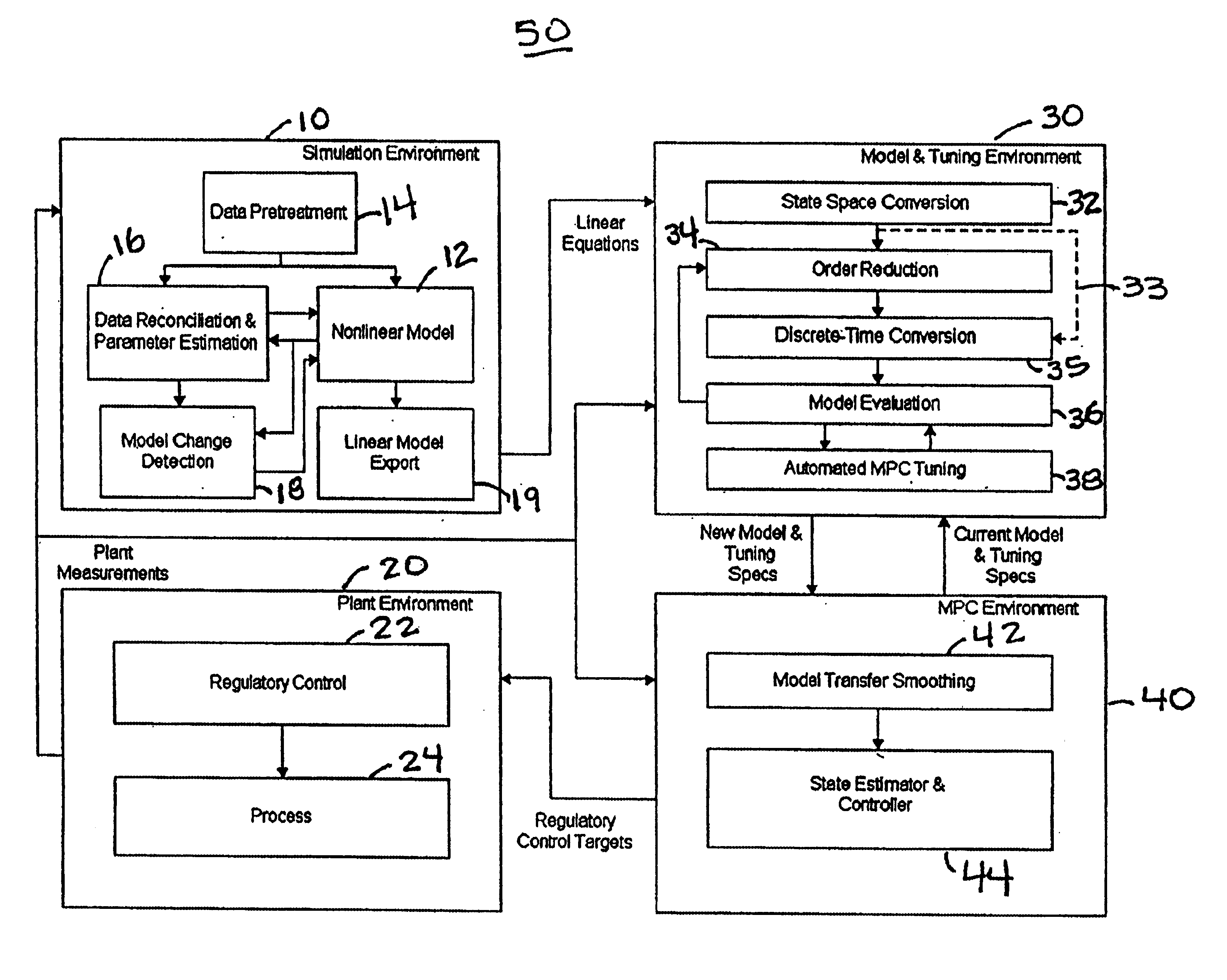
System and methodology and adaptive, linear model predictive control based on rigorous, nonlinear process model
InactiveUS6826521B1Analogue computers for chemical processesAdaptive controlSoftware systemPredictive controller
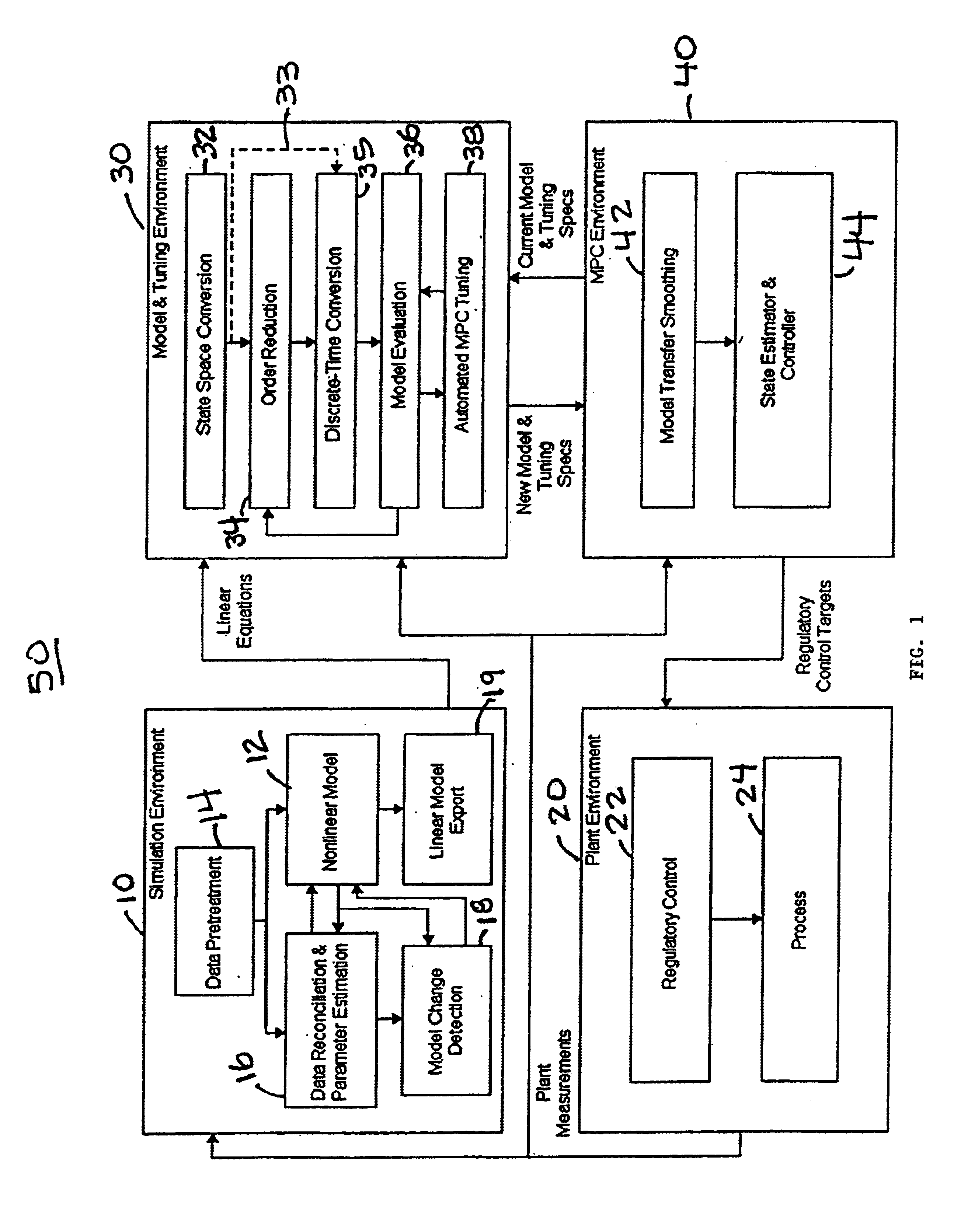
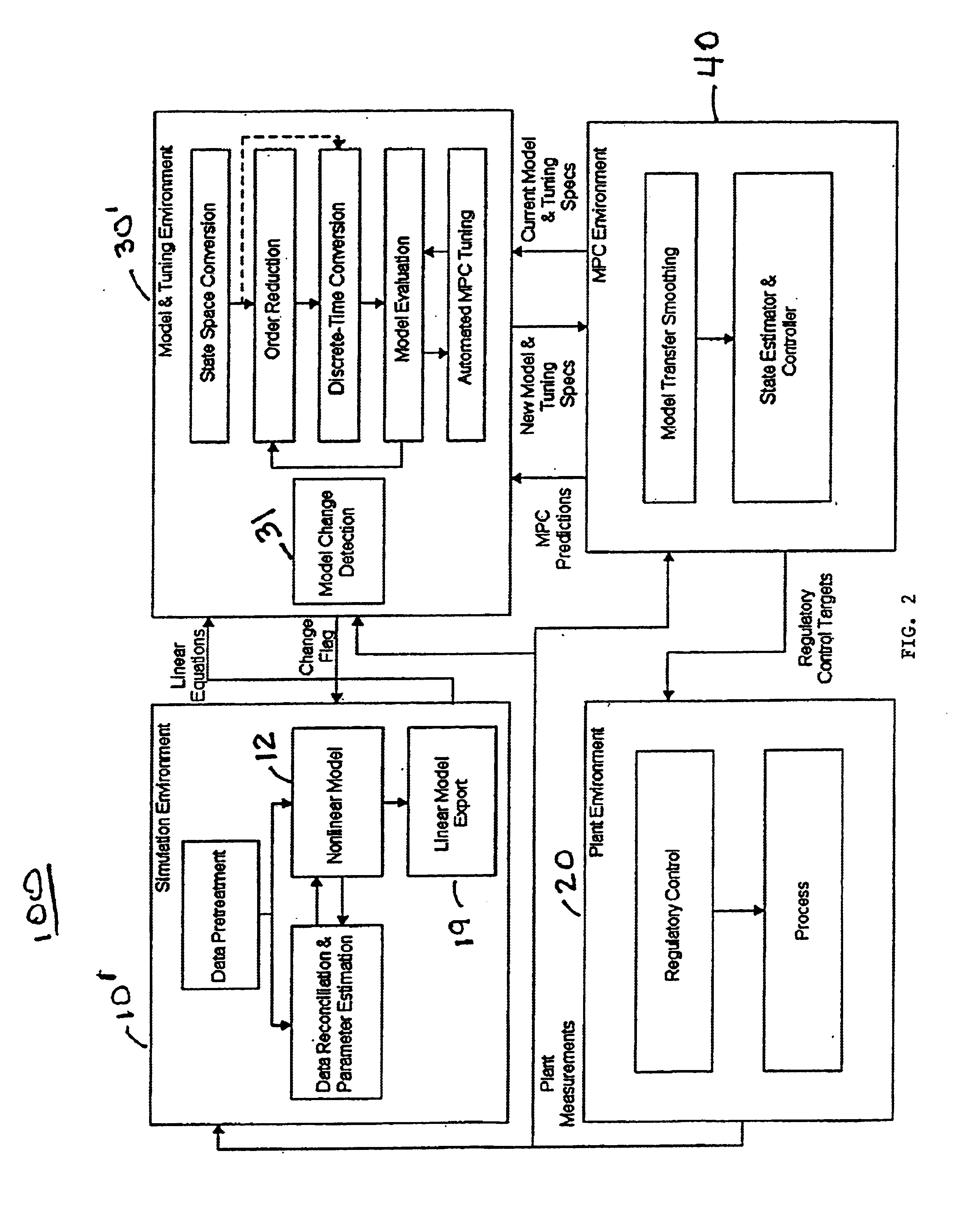
A methodology for process modeling and control and the software system implementation of this methodology, which includes a rigorous, nonlinear process simulation model, the generation of appropriate linear models derived from the rigorous model, and an adaptive, linear model predictive controller (MPC) that utilizes the derived linear models. A state space, multivariable, model predictive controller (MPC) is the preferred choice for the MPC since the nonlinear simulation model is analytically translated into a set of linear state equations and thus simplifies the translation of the linearized simulation equations to the modeling format required by the controller. Various other MPC modeling forms such as transfer functions, impulse response coefficients, and step response coefficients may also be used. The methodology is very general in that any model predictive controller using one of the above modeling forms can be used as the controller. The methodology also includes various modules that improve reliability and performance. For example, there is a data pretreatment module used to pre-process the plant measurements for gross error detection. A data reconciliation and parameter estimation module is then used to correct for instrumentation errors and to adjust model parameters based on current operating conditions. The full-order state space model can be reduced by the order reduction module to obtain fewer states for the controller model. Automated MPC tuning is also provided to improve control performance.
Owner:ABB AUTOMATION INC
Tool tracking systems, methods and computer products for image guided surgery
ActiveUS8073528B2Programme-controlled manipulatorImage enhancementPostural orientationPerformed Imaging
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
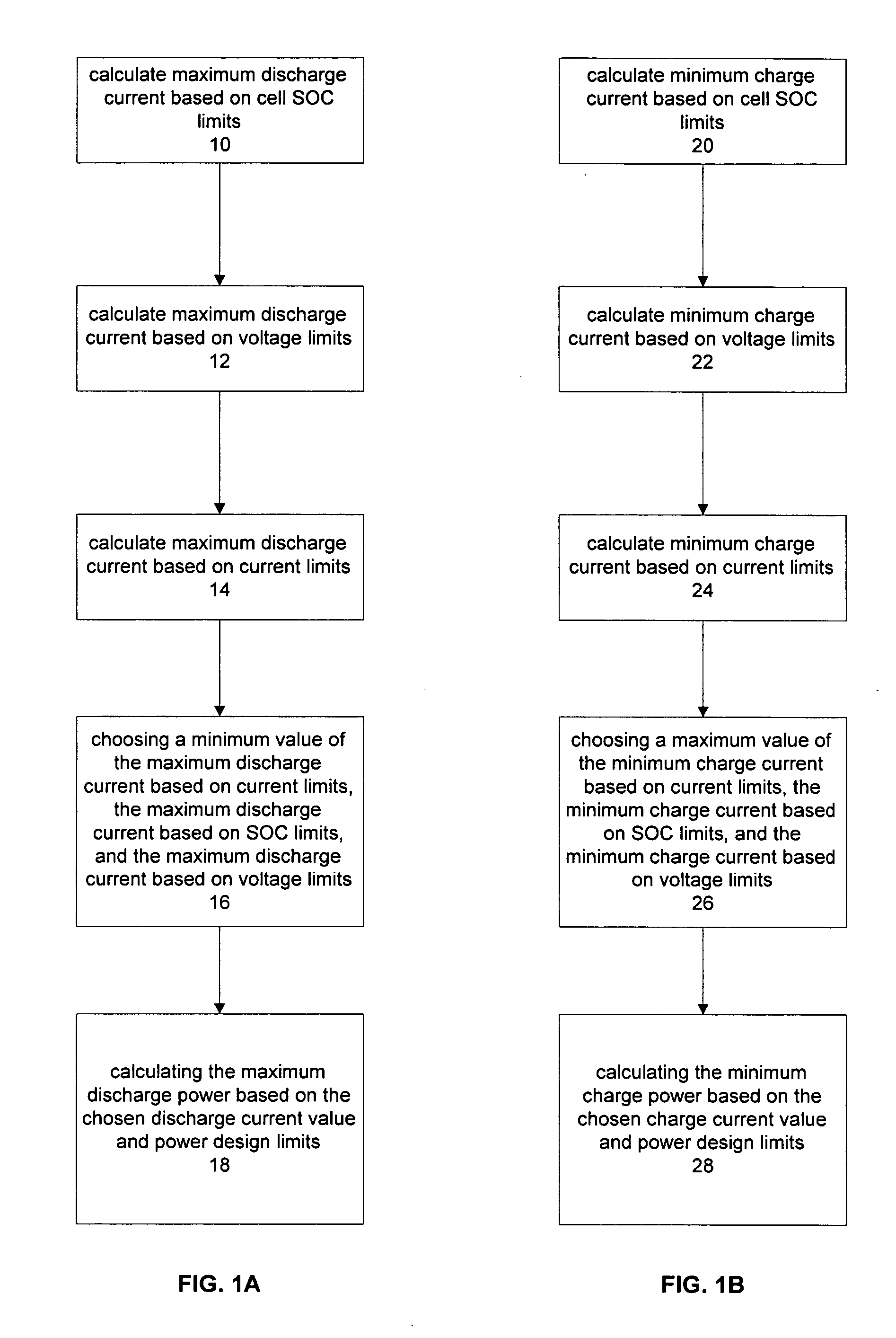
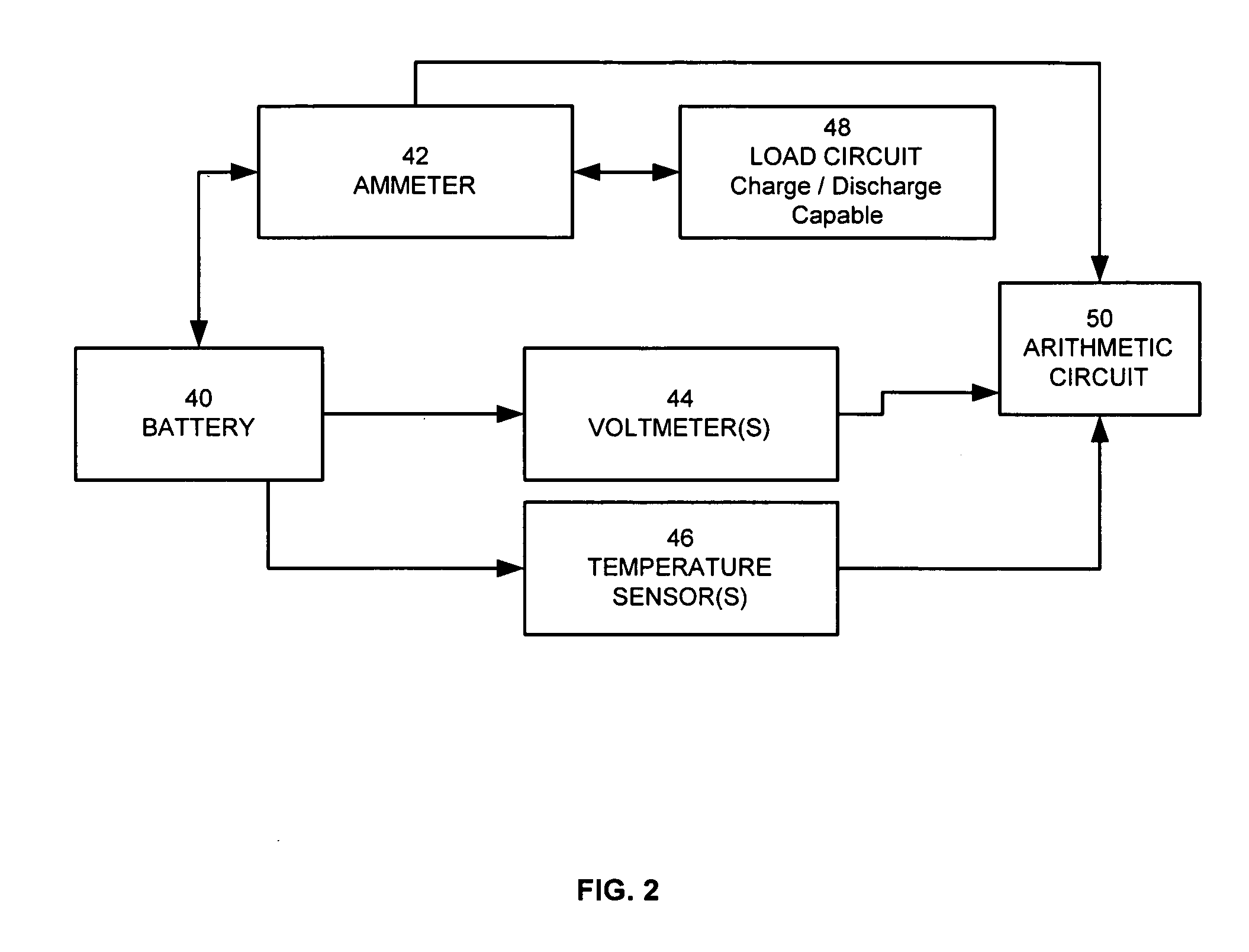
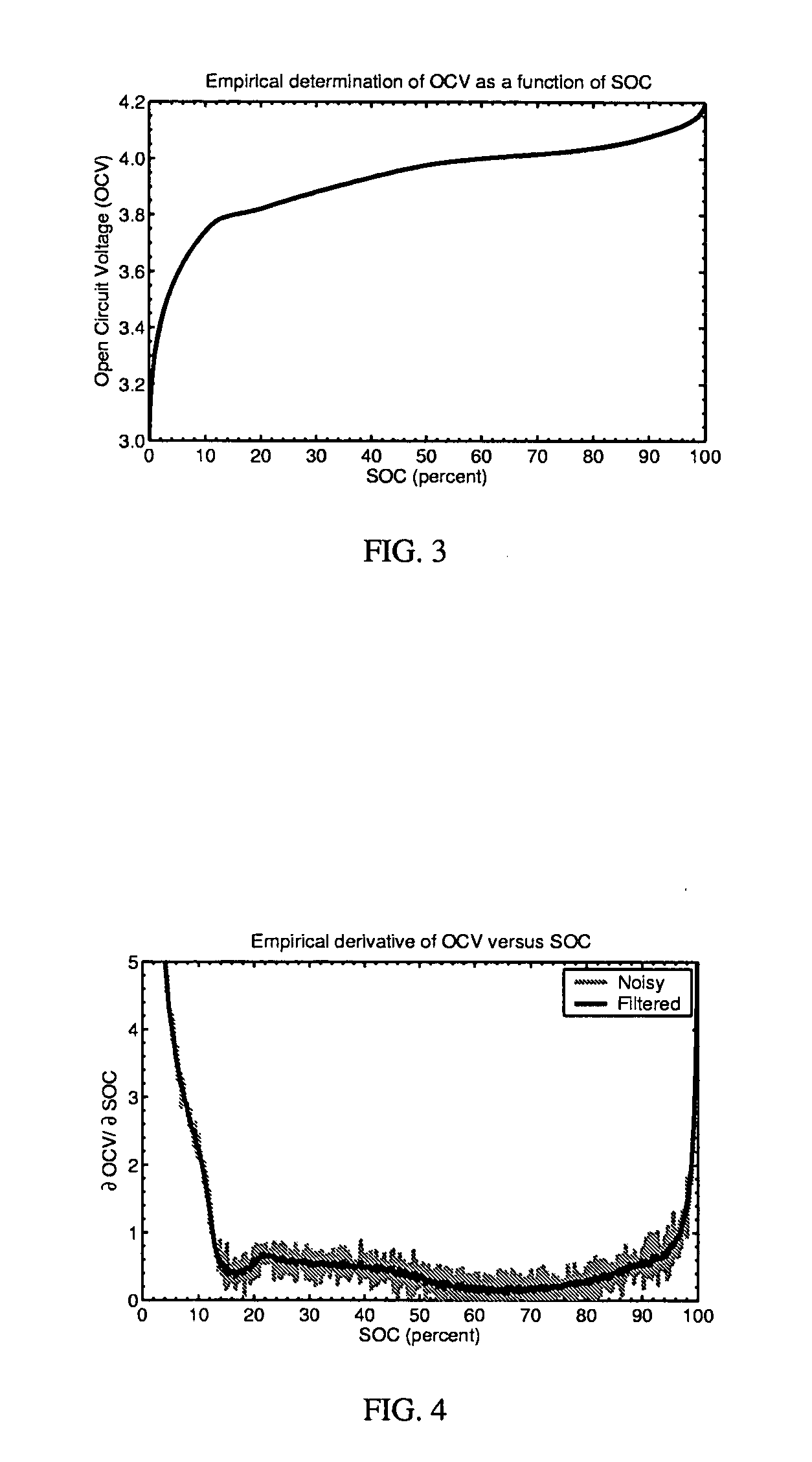
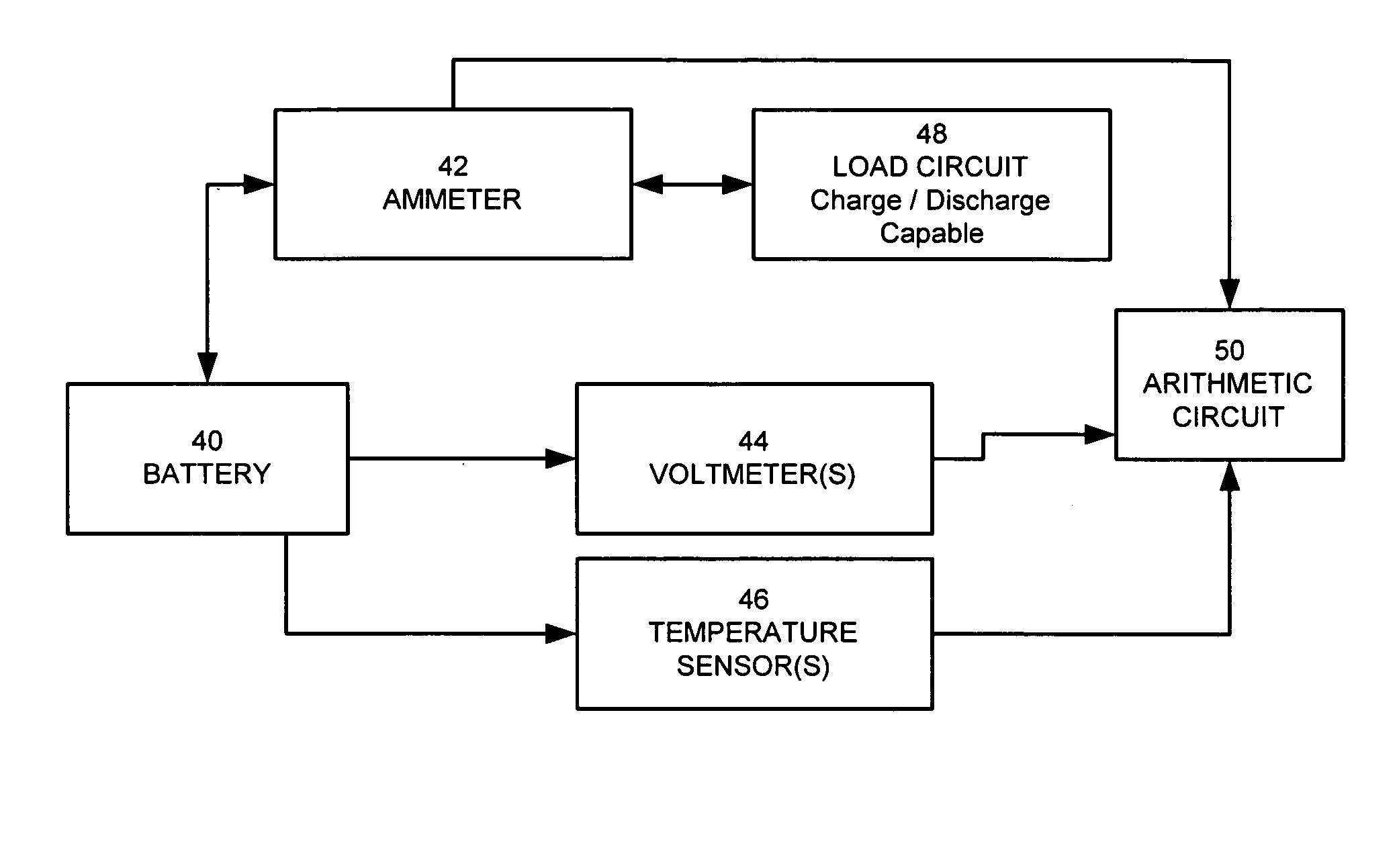
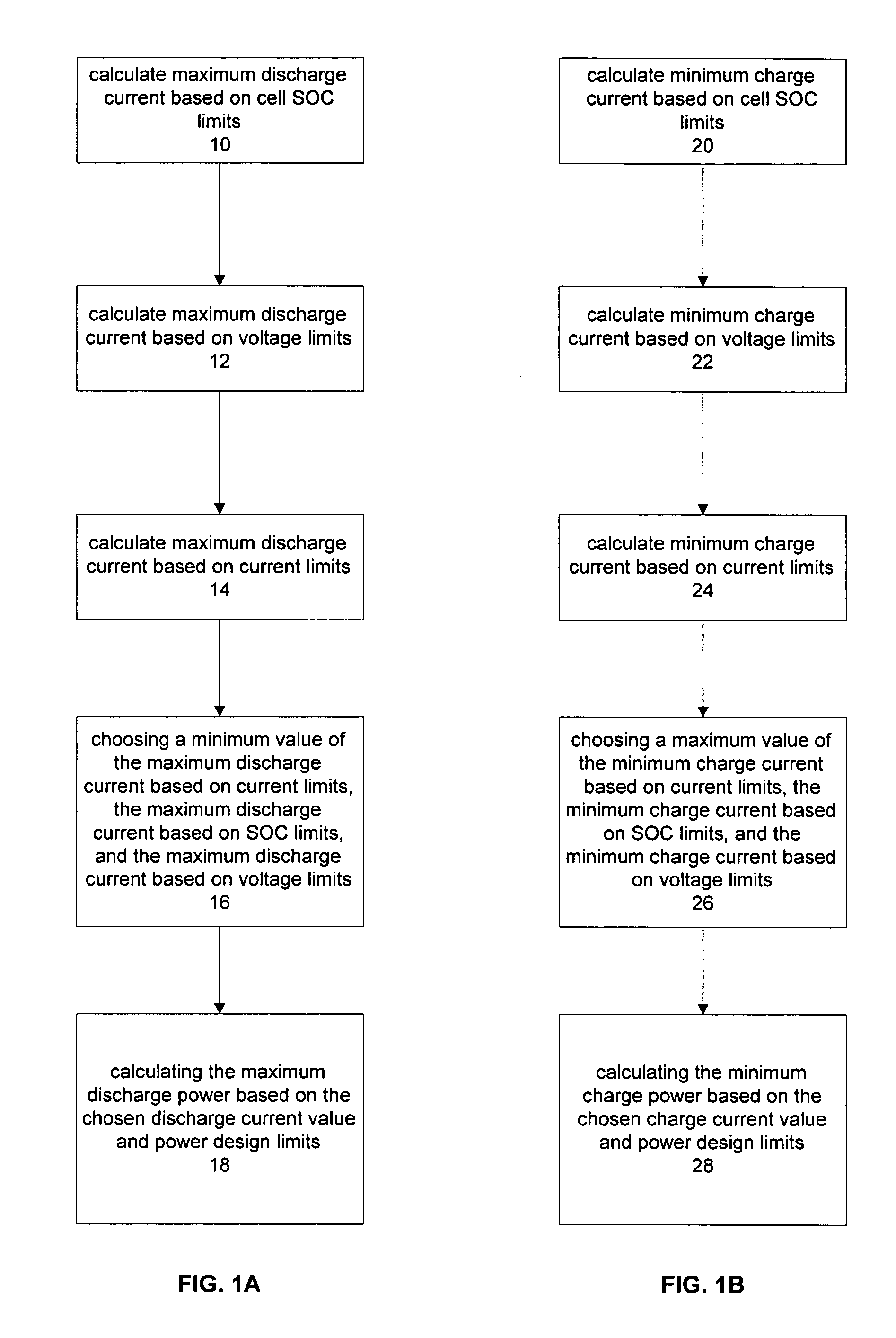
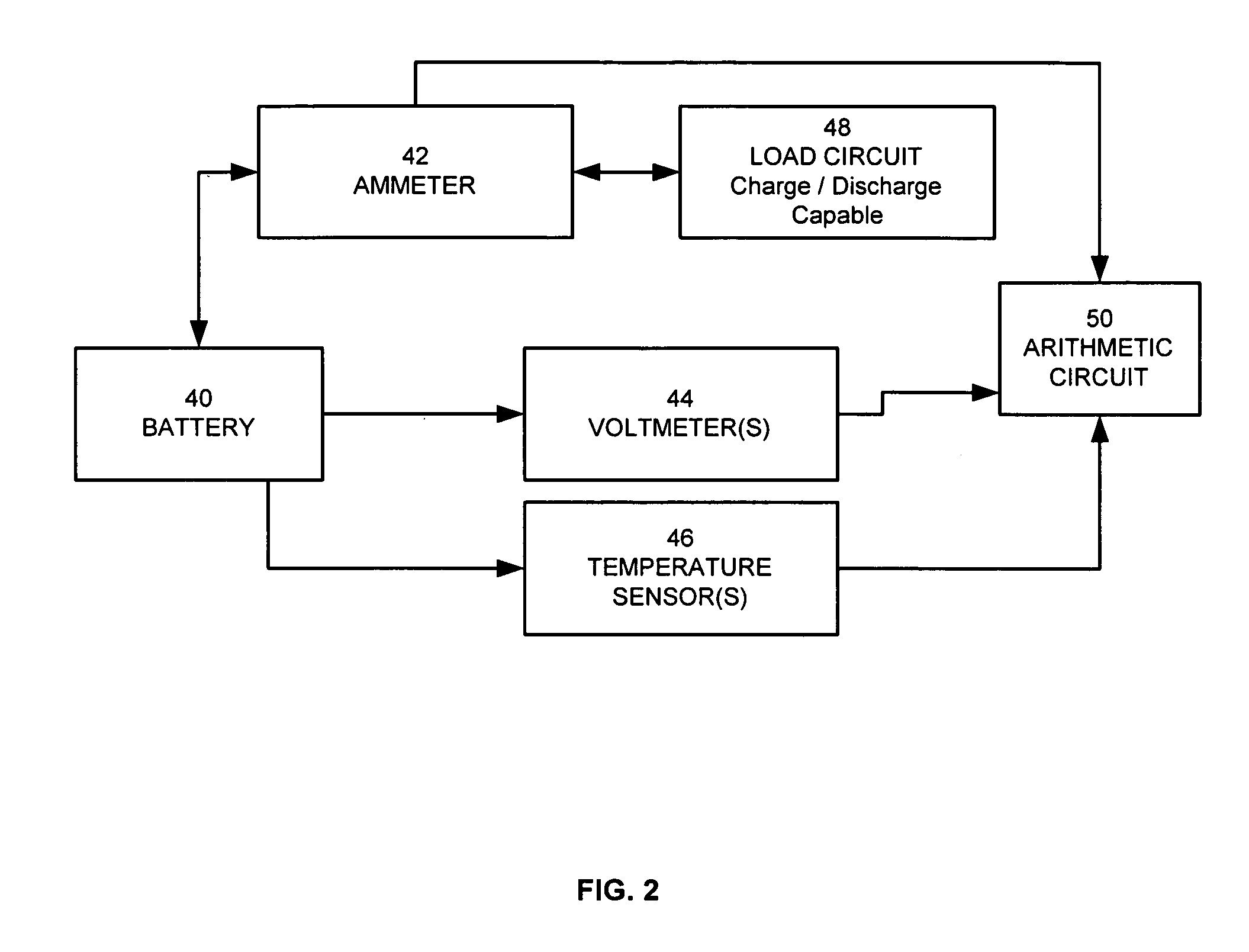
Method for calculating power capability of battery packs using advanced cell model predictive techniques
ActiveUS20050110498A1Batteries circuit arrangementsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPower capabilityElectrical battery
The present invention relates to a method and an apparatus for estimating discharge and charge power of battery applications, including battery packs used in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEV) and Electric Vehicles (EV). One charge / discharge power estimating method incorporates voltage, state-of-charge (SOC), power, and current design constraints and works for a user-specified prediction time horizon Δt. At least two cell models are used in calculating maximum charge / discharge power based on voltage limits. The first is a simple cell model that uses a Taylor-series expansion to linearize the equation involved. The second is a more complex and accurate model that models cell dynamics in discrete-time state-space form. The cell model can incorporate a inputs such as temperature, resistance, capacity, etc. One advantage of using model-based approach is that the same model may be used in both Kalman-filtering to produce the SOC and the estimation of maximum charge / discharge current based on voltage limits.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
Temporal anomaly detection on automotive networks
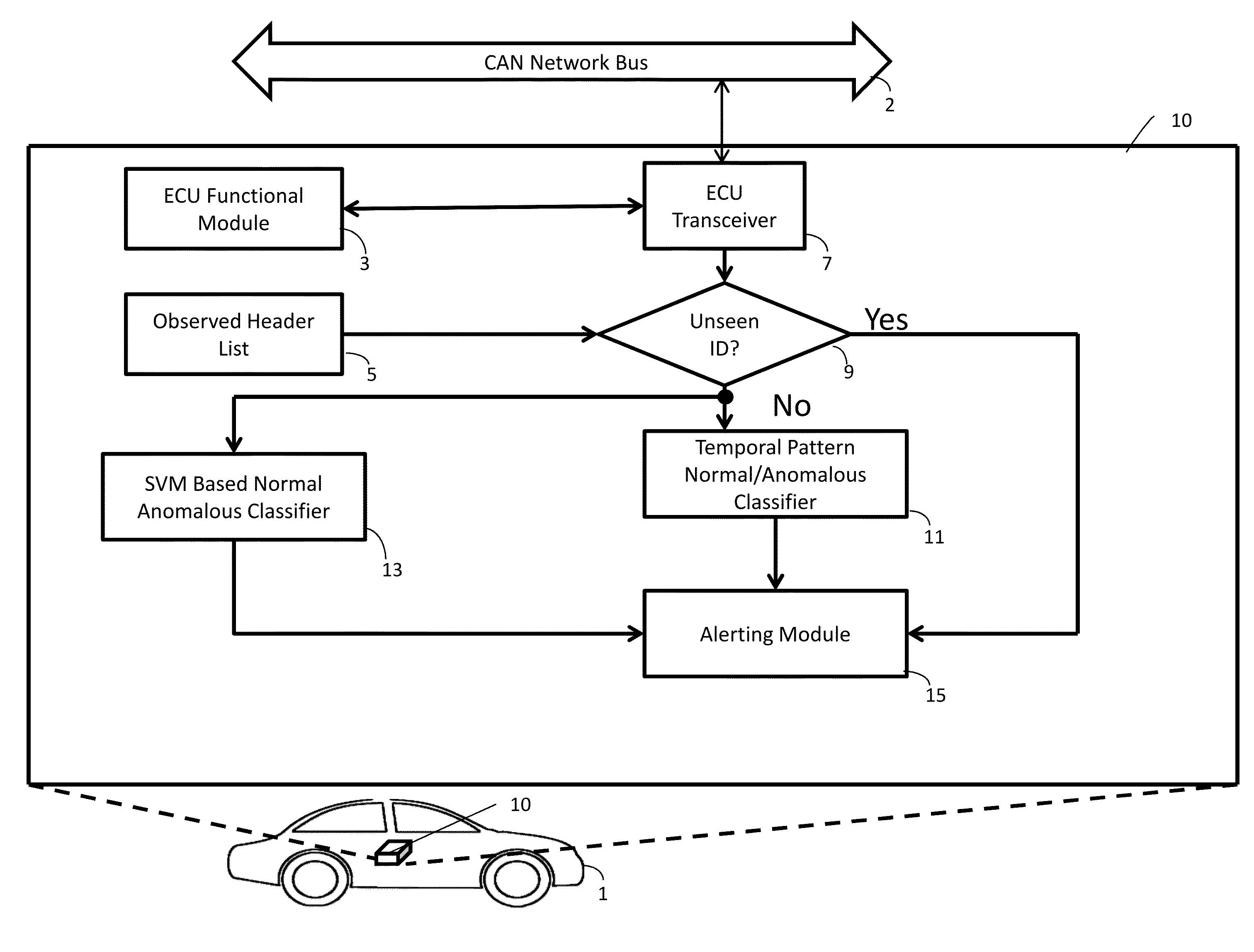
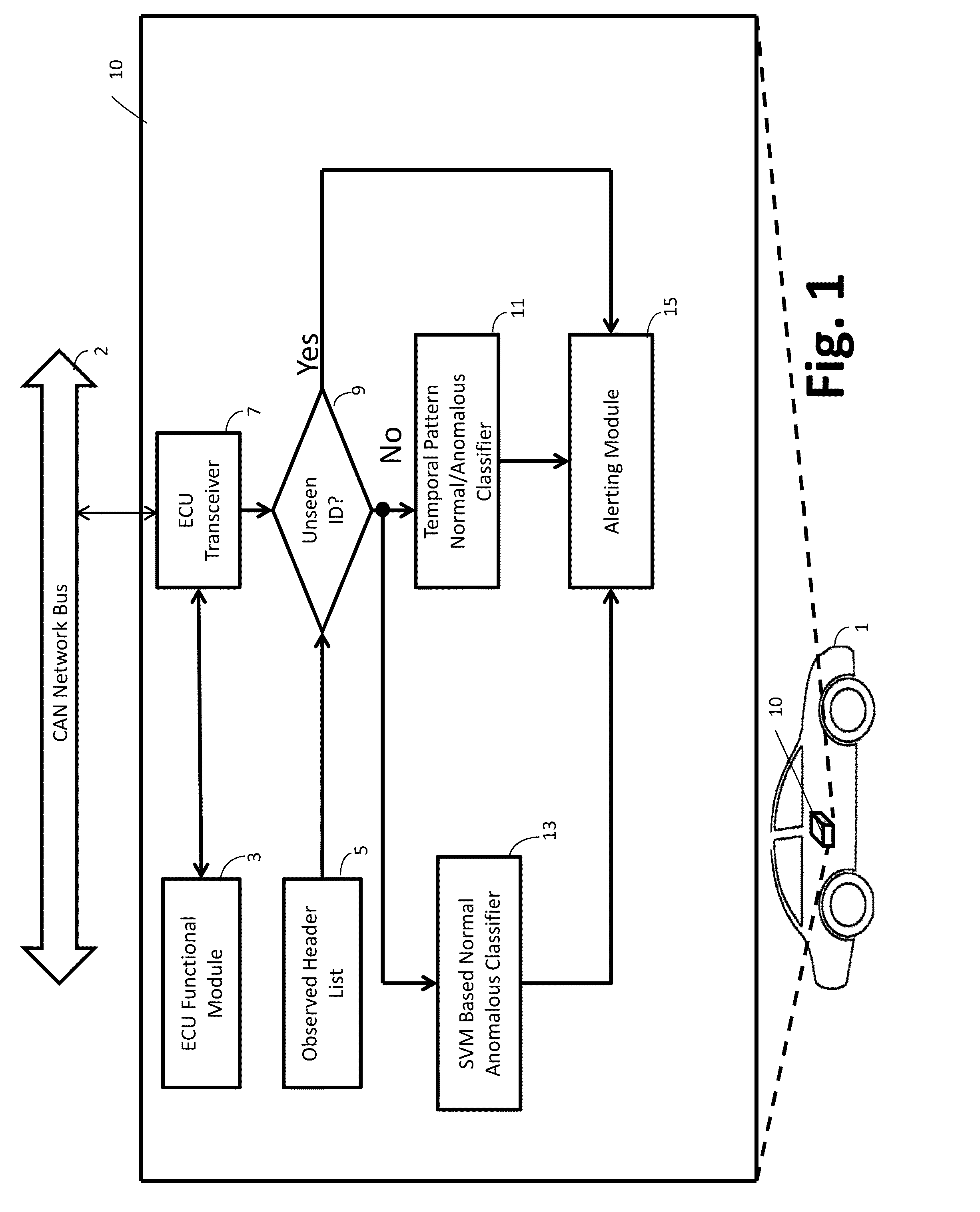
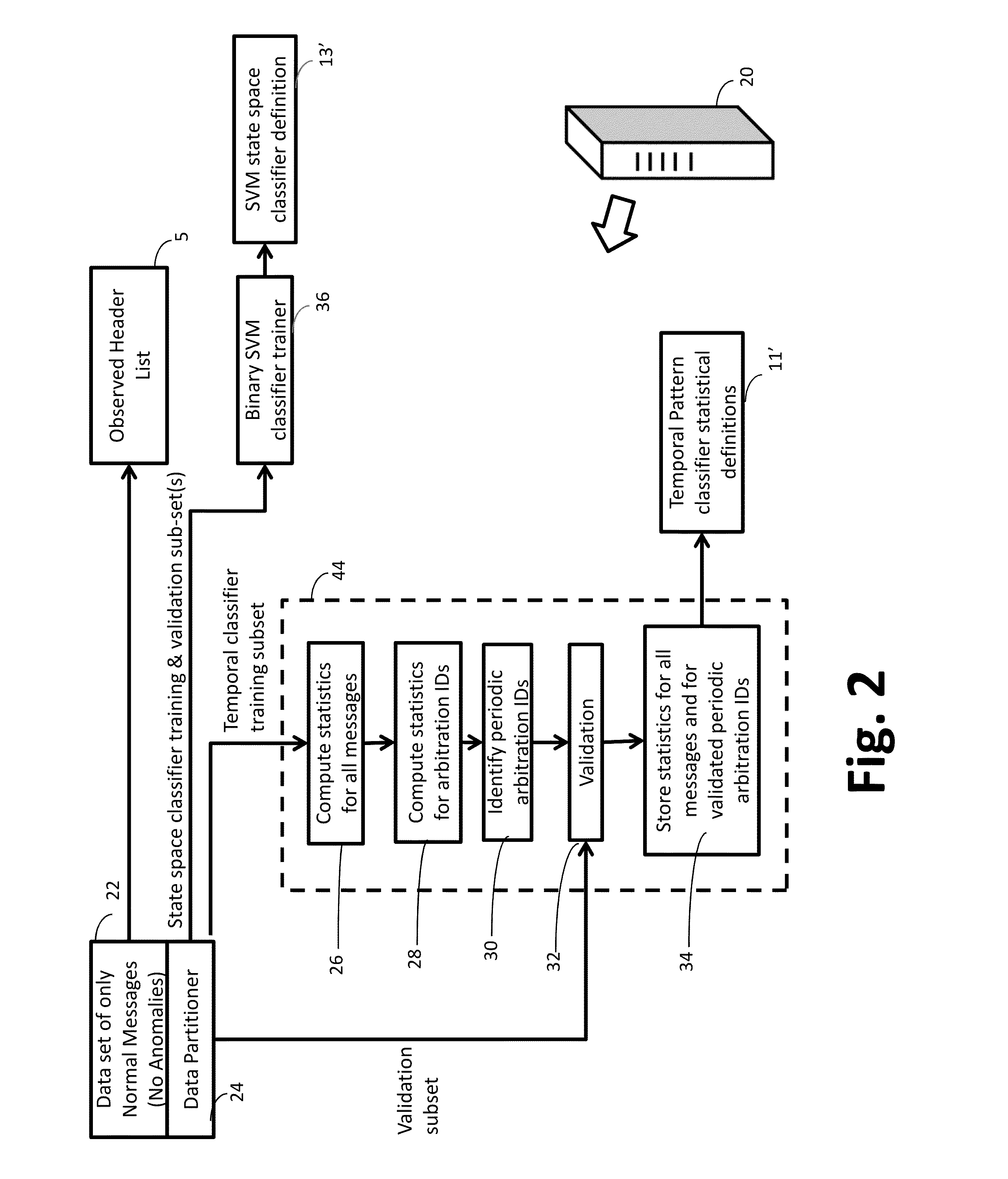
An anomaly detector for a Controller Area Network (CAN) bus performs state space classification on a per-message basis of messages on the CAN bus to label messages as normal or anomalous, and performs temporal pattern analysis as a function of time to label unexpected temporal patterns as anomalous. The anomaly detector issues an alert if an alert criterion is met that is based on the outputs of the state space classification and the temporal pattern analysis. The temporal pattern analysis may compare statistics of messages having analyzed arbitration IDs with statistics for messages having those analyzed arbitration IDs in a training dataset of CAN bus messages, and a temporal pattern is anomalous if there is a statistically significant deviation from the training dataset. The anomaly detector may be implemented on a vehicle Electronic Control Unit (ECU) communicating via a vehicle CAN bus. The anomaly detector does not rely on an database of messages and their periodicity from manufacturers (dbc files) and in that sense is truly a zero knowledge detector.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Sensor fusion for model-based detection in pipe and cable locator systems
ActiveUS7834801B2Improve positionSatellite radio beaconingElectric/magnetic detectionGyroscopeAccelerometer
Line locator systems that fuse traditional sensors used in a combined pipe and cable locator (electromagnetic coils, magnetometers, and ground penetrating radar antennas) with low cost inertial sensors (accelerometers, gyroscopes) in a model-based approach are presented. Such systems can utilize inexpensive MEMS sensors for inertial navigation. A pseudo-inertial frame is defined that uses the centerline of the tracked utility, or an aboveground fixed object as the navigational reference. An inertial sensor correction mechanism that limits the tracking errors over time when the model is implemented in state-space form using, for example, the Extended Kalman Filter (EKF) is disclosed.
Owner:BUSAN TRANSPORTATION CORPORATION
Navigation system applications of sigma-point Kalman filters for nonlinear estimation and sensor fusion
ActiveUS7289906B2Instruments for road network navigationNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsKaiman filterAlgorithm
A method of estimating the navigational state of a system entails acquiring observation data produced by noisy measurement sensors and providing a probabilistic inference system to combine the observation data with prediction values of the system state space model to estimate the navigational state of the system. The probabilistic inference system is implemented to include a realization of a Gaussian approximate random variable propagation technique performing deterministic sampling without analytic derivative calculations. This technique achieves for the navigational state of the system an estimation accuracy that is greater than that achievable with an extended Kalman filter-based probabilistic inference system.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV
Diversified doppler for single platform geolocation
InactiveUS9007262B1Robust and accurate solutionOvercomes drawbackPosition fixationGeolocationParticle filtering algorithm
The described invention allows for rapid geolocation of one or more RF emitters using a single moving collection platform. Inaccuracies of conventional frequency of arrival (FOA) geolocation methods are overcome by solving simultaneously for emitter location and a potential emitter drift associated with an observed emitter frequency. Certain embodiments may utilize particle filtering algorithms to recursively update multimodal state densities that are typical of solutions involving both unknown emitter location and nonstationary emitter carrier drift. Moreover, certain properties of particle filters may be exploited to provide a geolocation solution given a complex multimodal state space composed of emitter location and a non-stationary emitter frequency required for FOA.
Owner:LEIDOS
Method for calculating power capability of battery packs using advanced cell model predictive techniques
ActiveUS7321220B2Batteries circuit arrangementsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPower capabilityEngineering
The present invention relates to a method and an apparatus for estimating discharge and charge power of battery applications, including battery packs used in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEV) and Electric Vehicles (EV). One charge / discharge power estimating method incorporates voltage, state-of-charge (SOC), power, and current design constraints and works for a user-specified prediction time horizon Δt. At least two cell models are used in calculating maximum charge / discharge power based on voltage limits. The first is a simple cell model that uses a Taylor-series expansion to linearize the equation involved. The second is a more complex and accurate model that models cell dynamics in discrete-time state-space form. The cell model can incorporate a inputs such as temperature, resistance, capacity, etc. One advantage of using model-based approach is that the same model may be used in both Kalman-filtering to produce the SOC and the estimation of maximum charge / discharge current based on voltage limits.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
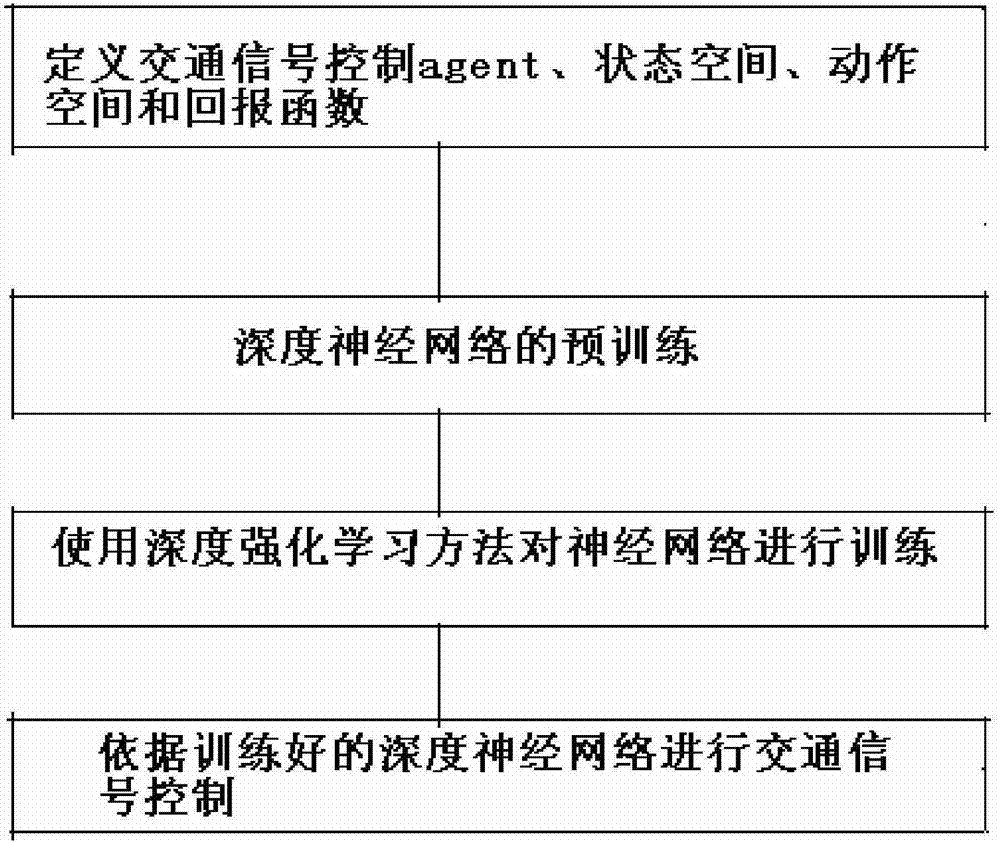
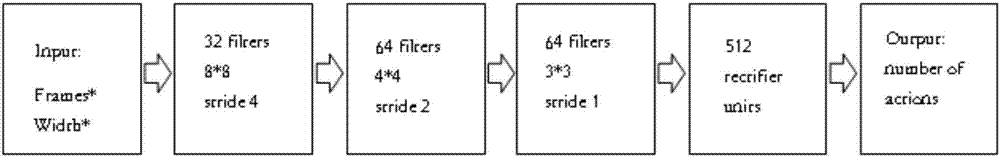
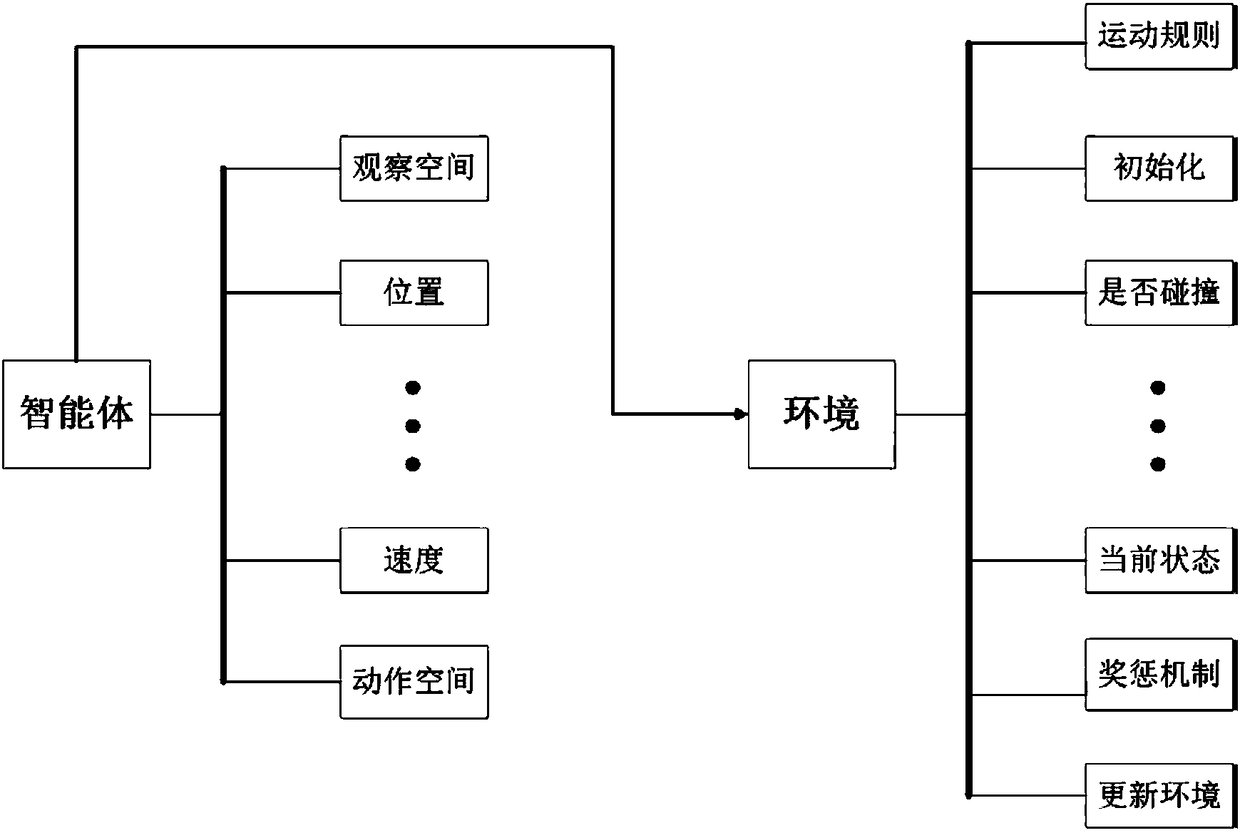
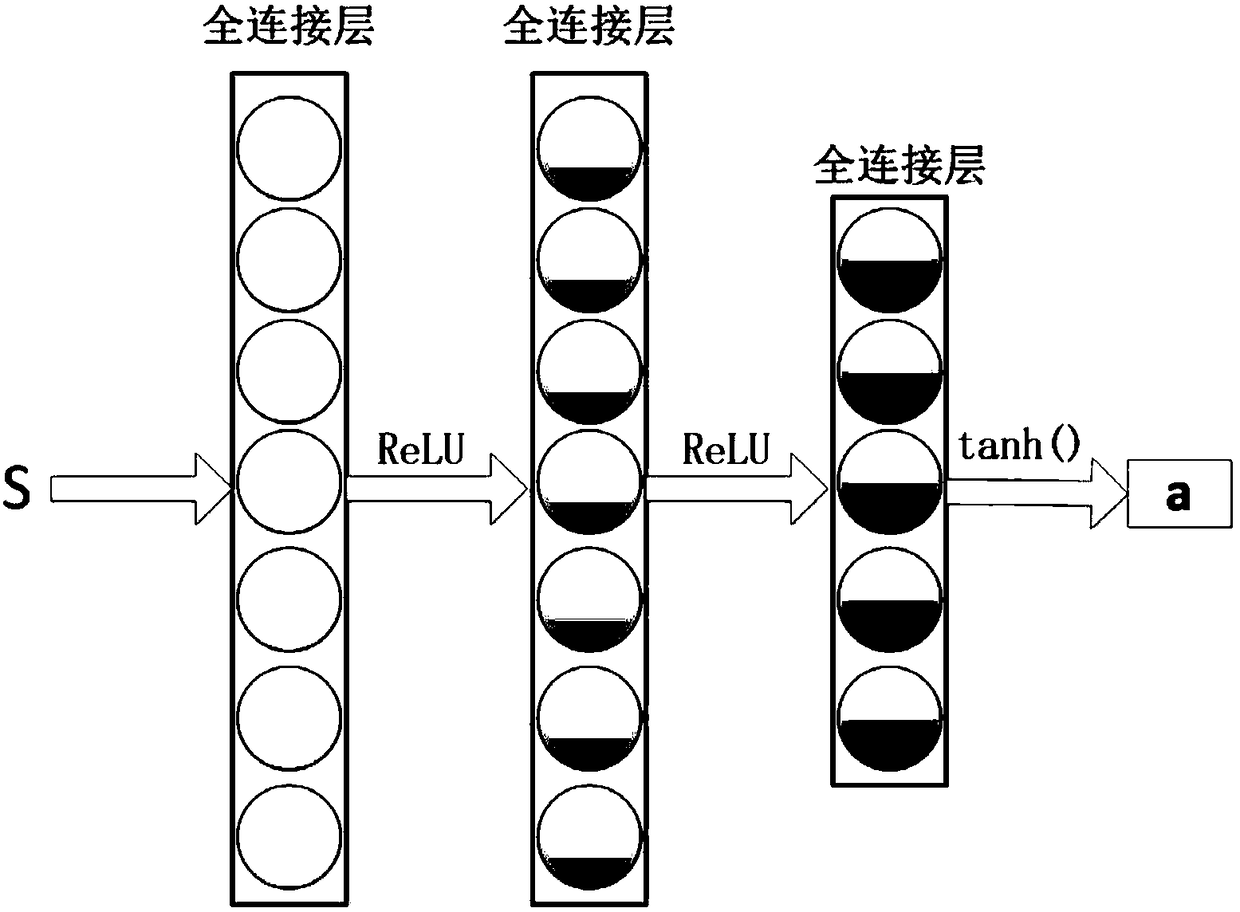
Traffic signal self-adaptive control method based on deep reinforcement learning
InactiveCN106910351ARealize precise perceptionSolve the problem of inaccurate perception of traffic statusControlling traffic signalsNeural architecturesTraffic signalReturn function
The invention relates to the technical field of traffic control and artificial intelligence and provides a traffic signal self-adaptive control method based on deep reinforcement learning. The method includes the following steps that 1, a traffic signal control agent, a state space S, a motion space A and a return function r are defined; 2, a deep neutral network is pre-trained; 3, the neutral network is trained through a deep reinforcement learning method; 4, traffic signal control is carried out according to the trained deep neutral network. By preprocessing traffic data acquired by magnetic induction, video, an RFID, vehicle internet and the like, low-layer expression of the traffic state containing vehicle position information is obtained; then the traffic state is perceived through a multilayer perceptron of deep learning, and high-layer abstract features of the current traffic state are obtained; on the basis, a proper timing plan is selected according to the high-layer abstract features of the current traffic state through the decision making capacity of reinforcement learning, self-adaptive control of traffic signals is achieved, the vehicle travel time is shortened accordingly, and safe, smooth, orderly and efficient operation of traffic is guaranteed.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
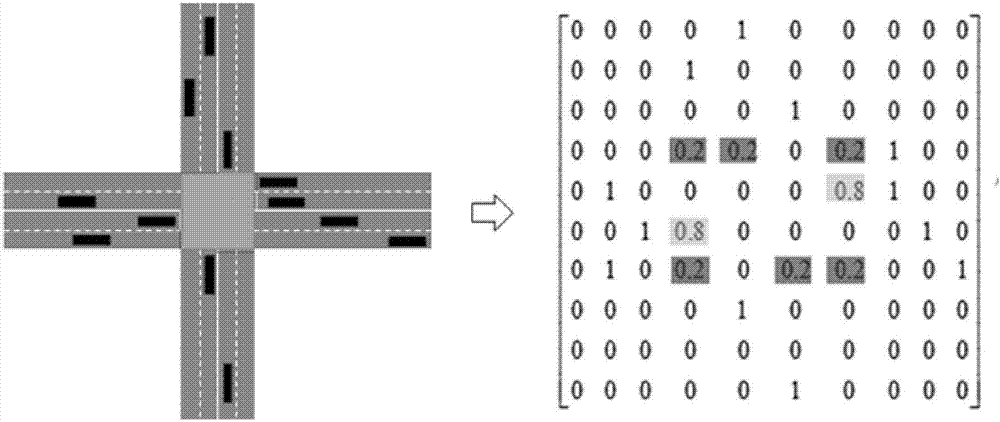
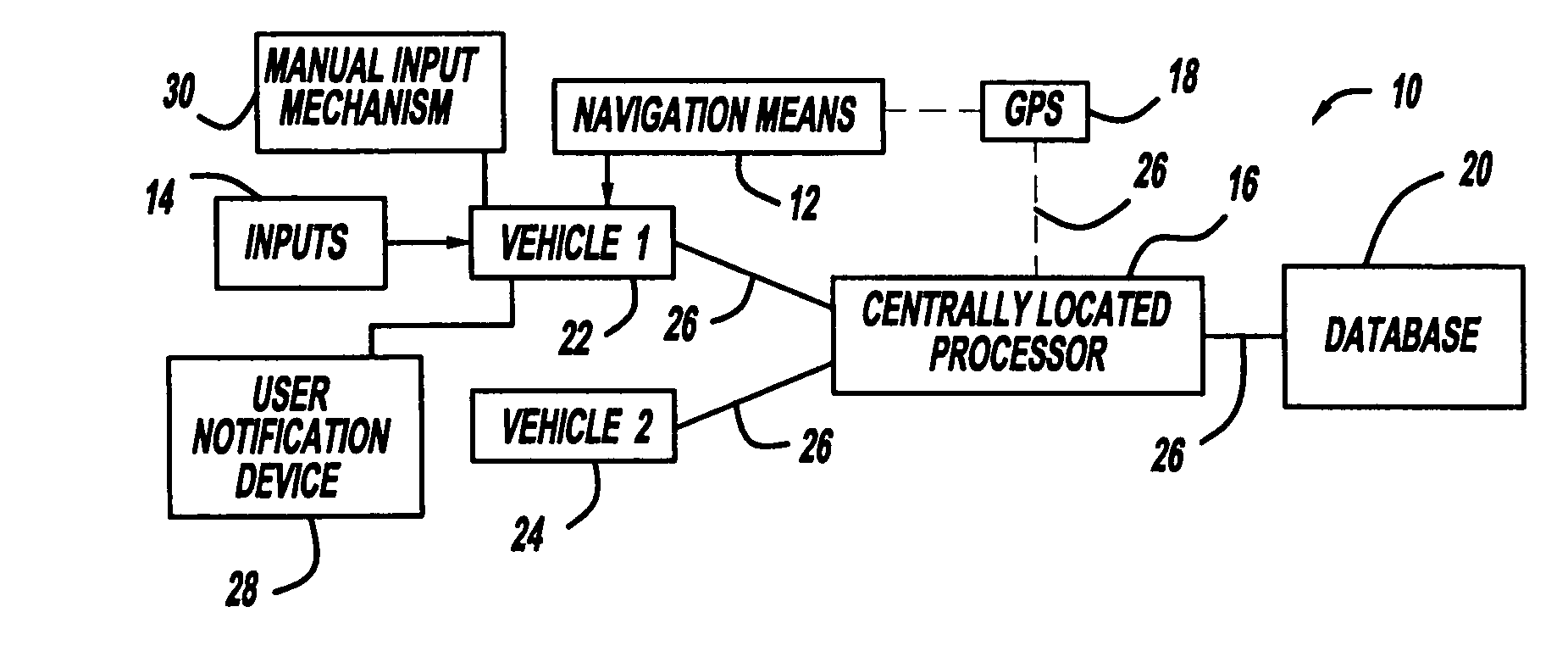
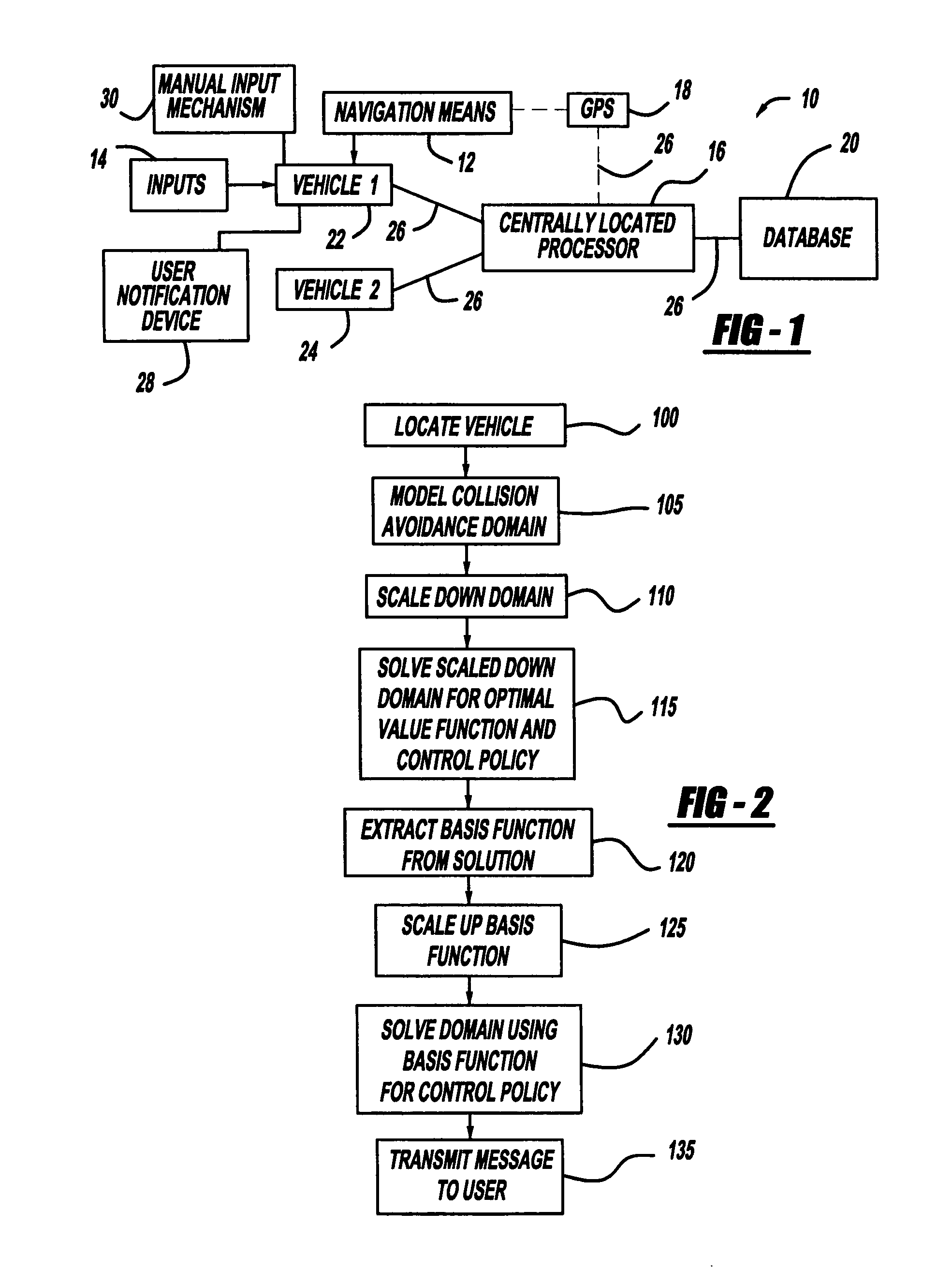
System and method of collision avoidance using intelligent navigation
ActiveUS7167799B1Implemented cost-effectivelyPotential collisionAnti-collision systemsPosition fixationGeolocationState space
A system and method of intelligent navigation with collision avoidance for a vehicle is provided. The system includes a global positioning system and a vehicle navigation means in communication with the global positioning system. The system also includes a centrally located processor in communication with the navigation means, and an information database associated with the controller, for identifying a location of a first vehicle and a second vehicle. The system further includes an alert means for transmitting an alert message to the vehicle operator regarding a collision with a second vehicle. The method includes the steps of determining a geographic location of a first vehicle and a second vehicle within an environment using the global positioning system on the first vehicle and the global positioning system on the second vehicle, and modeling a collision avoidance domain of the environment of the first vehicle as a discrete state space Markov Decision Process. The methodology scales down the model of the collision avoidance domain, and determines an optimal value function and control policy that solves the scaled down collision avoidance domain. The methodology extracts a basis function from the optimal value function, scales up the extracted basis function to represent the unscaled domain, and determines an approximate solution to the control policy by solving the rescaled domain using the scaled up basis function. The methodology further uses the solution to determine if the second vehicle may collide with the first vehicle and transmits a message to the user notification device.
Owner:TOYOTA MOTOR CO LTD
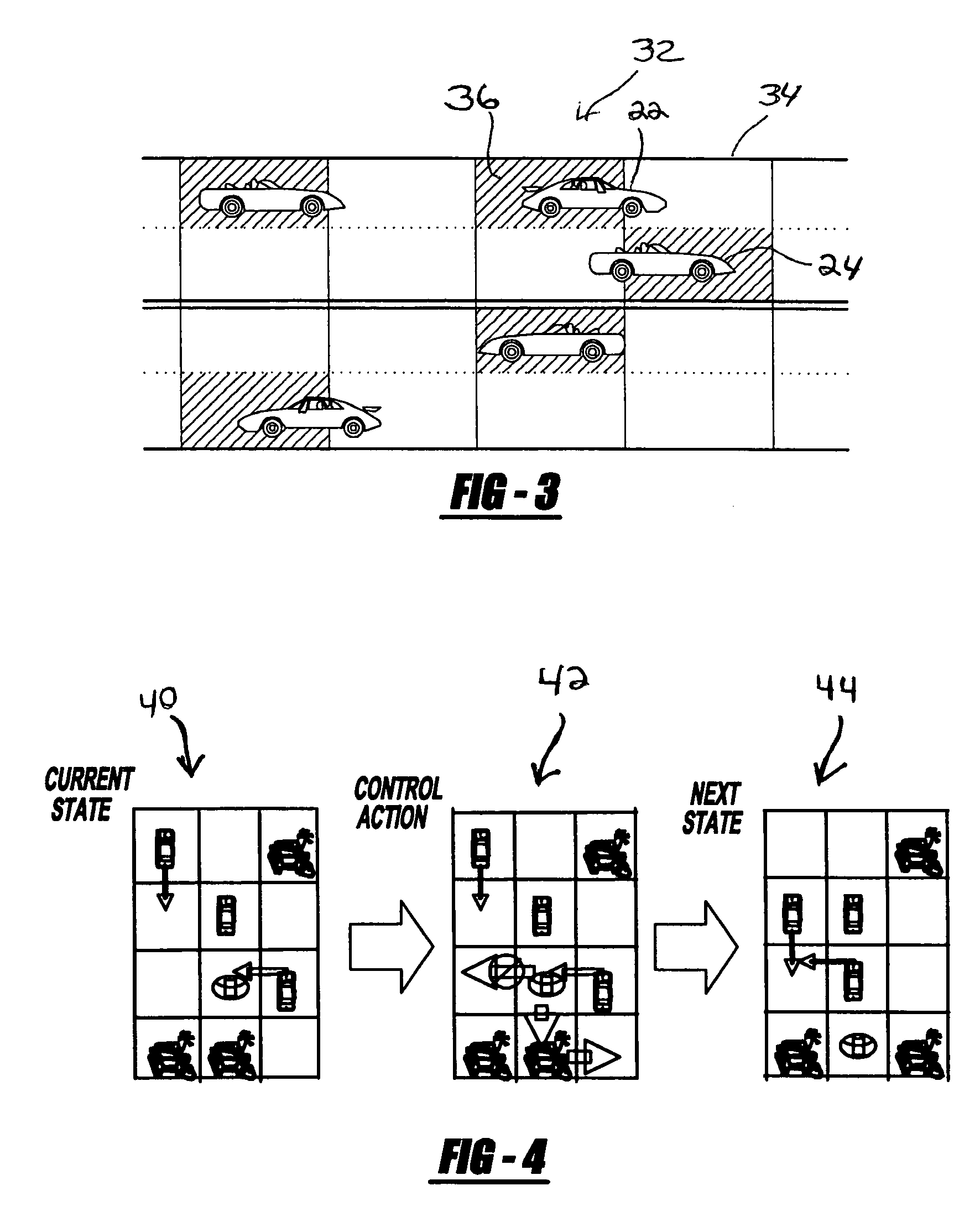
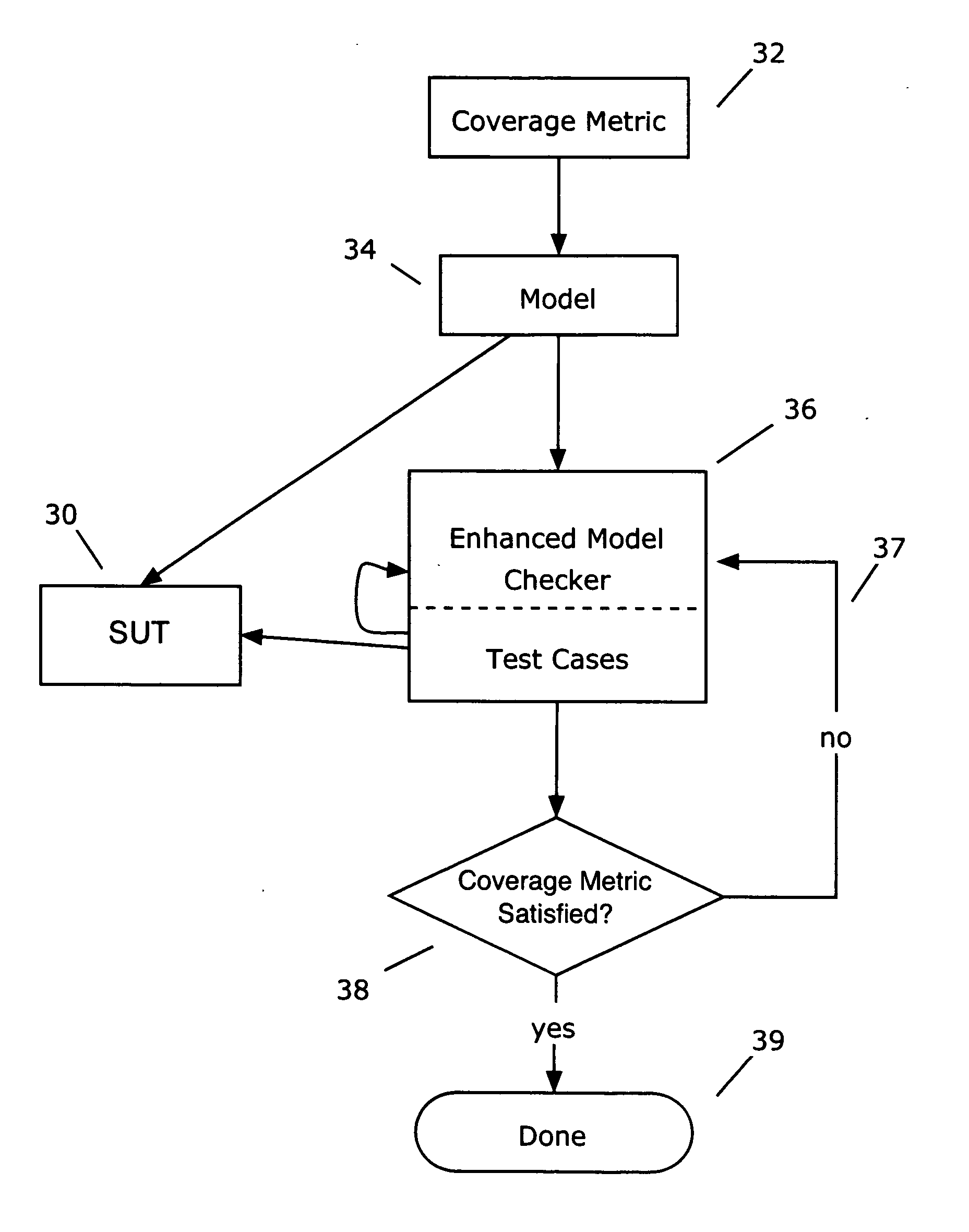
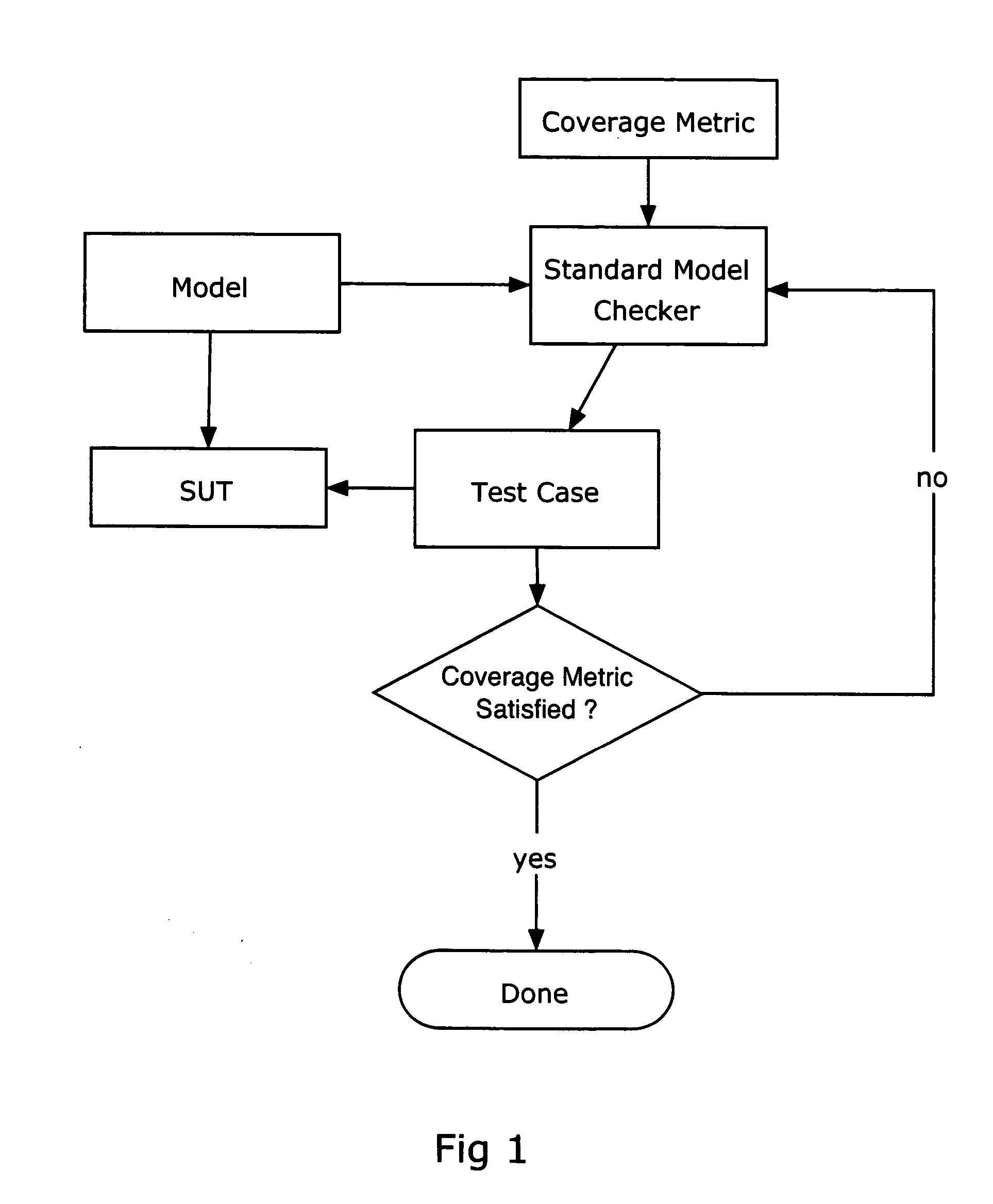
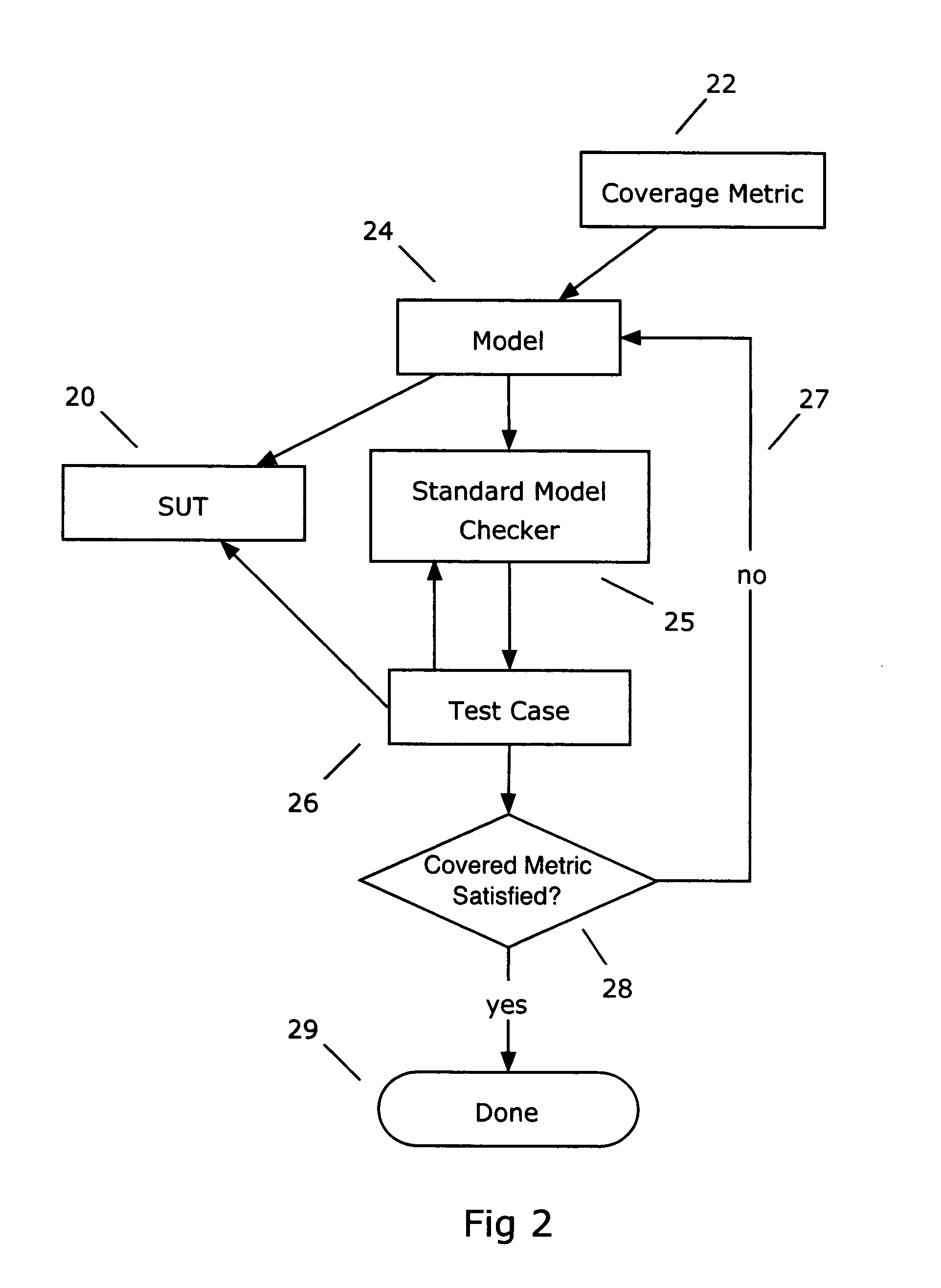
Formal methods for test case generation
ActiveUS20060010428A1Reduce development costsQuick testError detection/correctionComputation using non-denominational number representationSoftware systemFormal methods
The invention relates to the use of model checkers to generate efficient test sets for hardware and software systems. The method provides for extending existing tests to reach new coverage targets; searching *to* some or all of the uncovered targets in parallel; searching in parallel *from* some or all of the states reached in previous tests; and slicing the model relative to the current set of coverage targets. The invention provides efficient test case generation and test set formation. Deep regions of the state space can be reached within allotted time and memory. The approach has been applied to use of the model checkers of SRI's SAL system and to model-based designs developed in Stateflow. Stateflow models achieving complete state and transition coverage in a single test case are reported.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
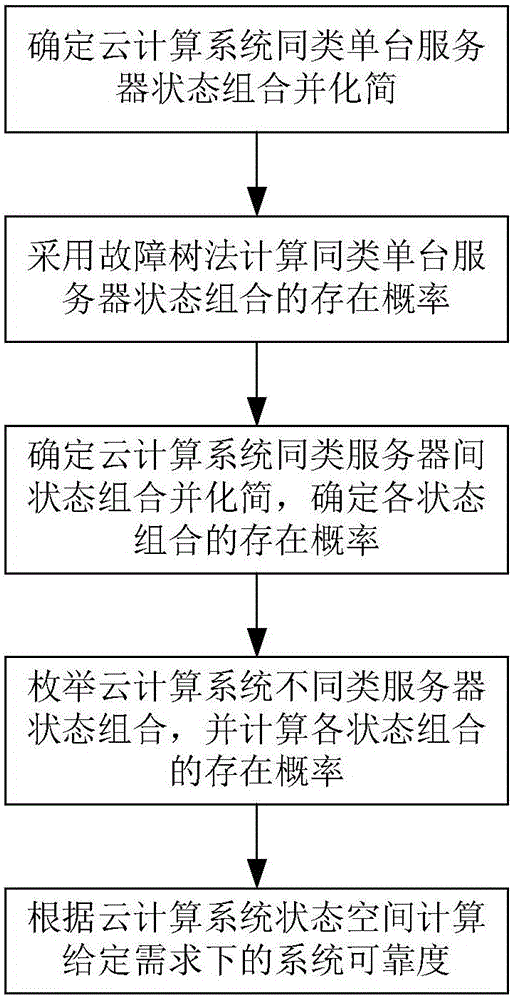
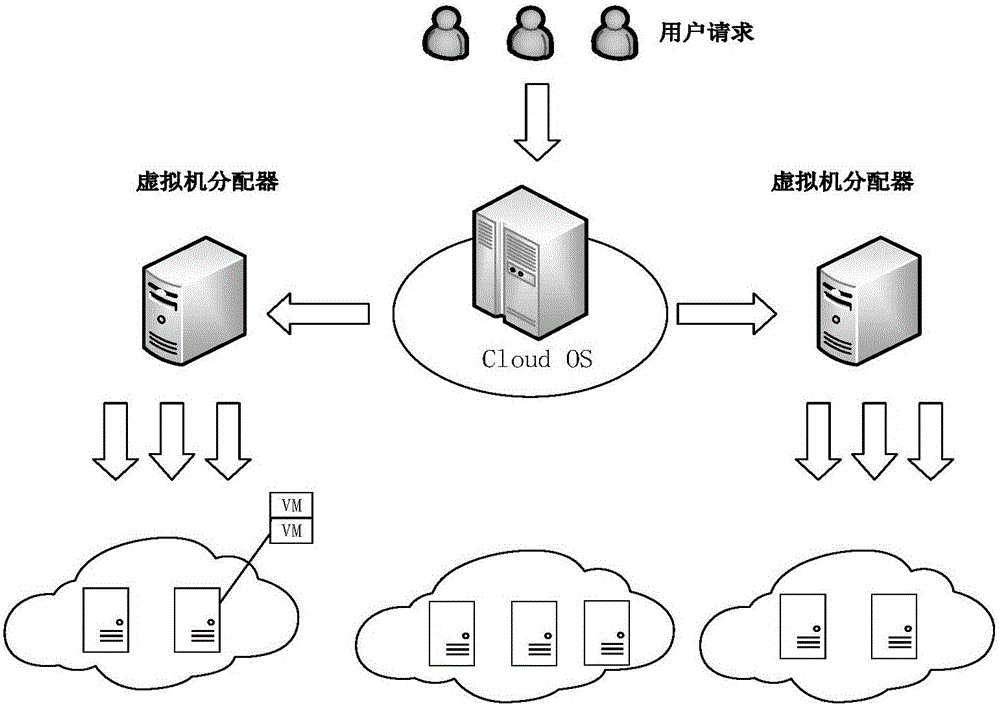
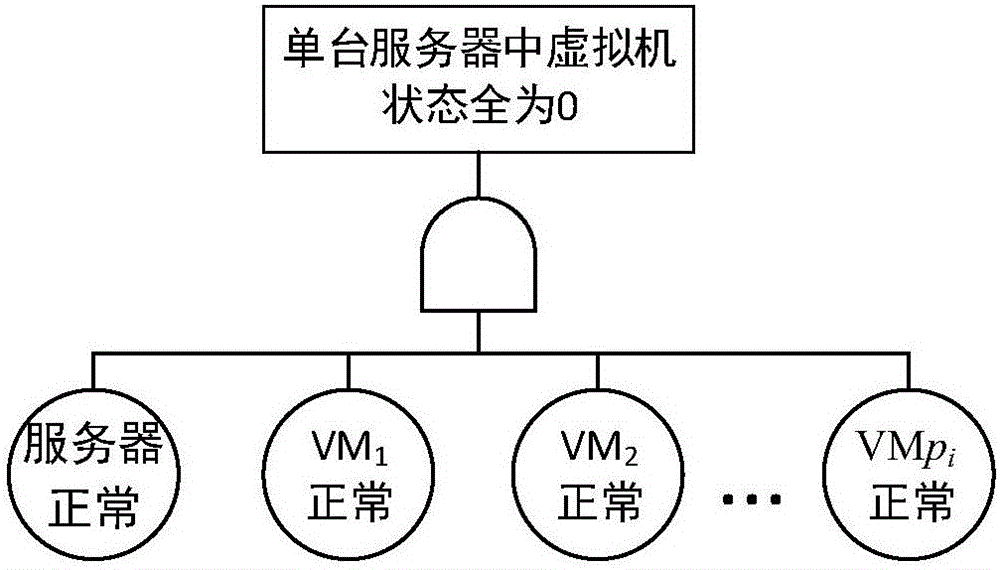
Cloud computing system reliability modeling method considering common cause fault
ActiveCN105740084ASolve ill-considered common cause failuresImprove modeling efficiencyReliability/availability analysisSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationState spaceSpatial computing
The invention discloses a cloud computing system reliability modeling method considering a common cause fault, and belongs to the technical field of network reliability. The method comprises the steps of determining a state combination of a similar single server of a cloud computing system and performing simplification; calculating an existence probability of the simplified state combination of the similar single server by adopting a fault tree method; determining state combinations of similar servers of the cloud computing system, performing simplification, and calculating an existence probability of each state combination; enumerating state combinations of different servers of the cloud computing system, and calculating an existence probability of each state combination; and according to the state space of the cloud computing system, calculating the system reliability according to a given demand. According to the method, a common cause fault of all virtual machines running in the servers, caused by server faults, is considered, the state space modeling is adopted, and the state space is simplified, so that the problem of state space explosion during system scale increment is solved and the modeling efficiency is improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
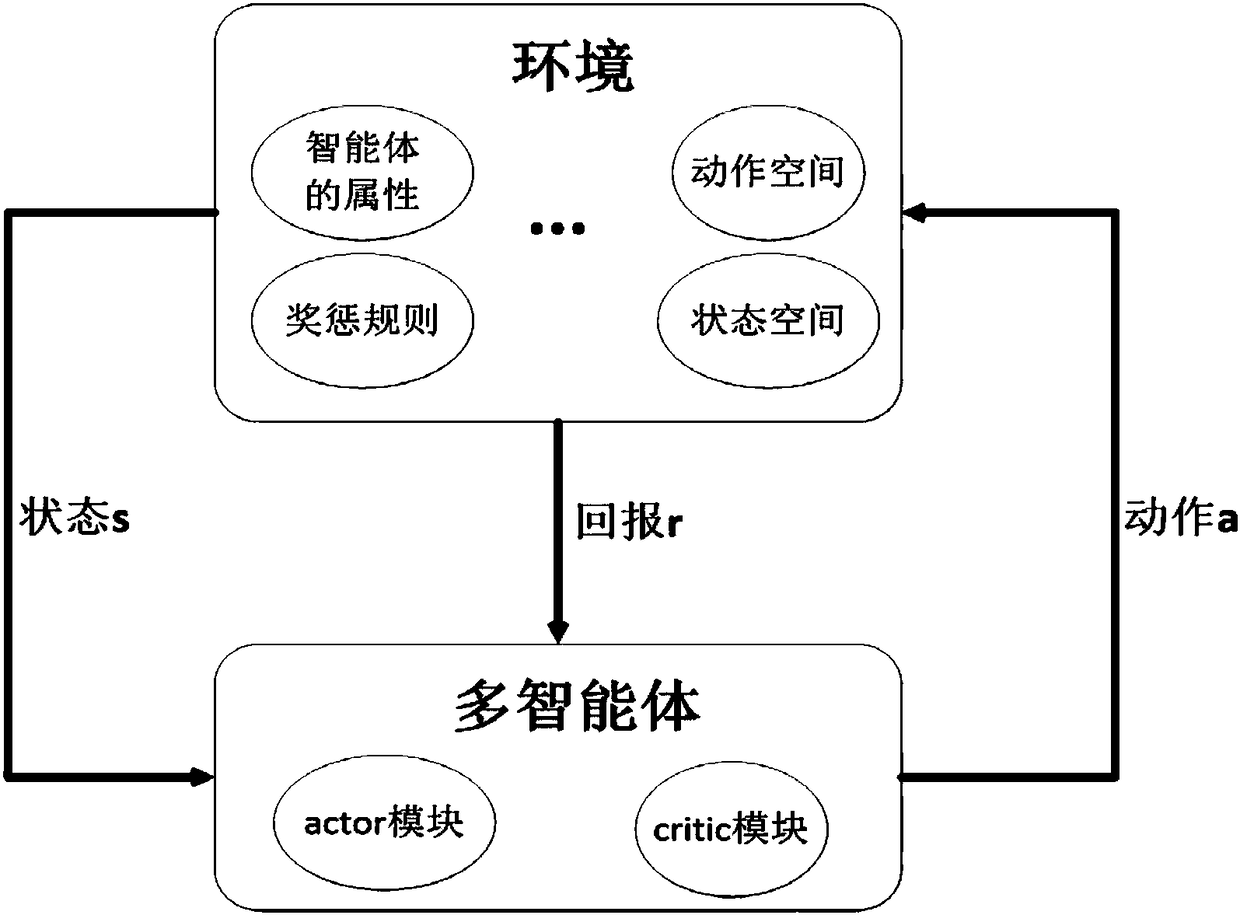
Heterogeneous multi-agent collaborative decision-making method based on depth deterministic policy gradient
InactiveCN108600379AAchieve collaborative decision-makingData switching networksState spaceComputer science
The invention relates to a heterogeneous multi-agent collaborative decision-making method based on a depth deterministic policy gradient, belonging to the collaborative decision-making field of a heterogeneous intelligent unmanned system, comprising the following steps of: firstly, defining heterogeneous multi-agent characteristic attributes and reward and punishment rules, defining multi-agent state space and action space, and constructing multi-agent motion environment for collaboratively making decision; then, establishing an actor module for decision-making action and a critic module for evaluating feedback based on the depth-deterministic strategy gradient algorithm, and training the parameters of the learning model; using the trained model to obtain the multi-agent state sequence; and evaluating the situation of the multi-agent motion state sequence according to the reward and punishment rules set in the environment. The invention may construct reasonable sports environment according to actual needs, achieve the purpose of intelligent sensing and strategy optimization through the synergy between multiple agents in the system, and has a positive effect on the development of the unmanned system field in China.
Owner:INST OF SOFTWARE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Extended finite state automata and systems and methods for recognizing patterns using extended finite state automata
Deterministic finite automata (DFAs) are popular solutions to deep packet inspection because they are fast and DFAs corresponding to multiple signatures are combinable into a single DFA. Combining such DFAs causes an explosive increase in memory usage. Extended finite automata (XFAs) are an alternative to DFAs that avoids state-space explosion problems. XFAs extend DFAs with a few bytes of “scratch memory” used to store bits and other data structures that record progress. Simple programs associated with automaton states and / or transitions manipulate this scratch memory. XFAs are deterministic in their operation, are equivalent to DFAs in expressiveness, and require no custom hardware support. Fully functional prototype XFA implementations show that, for most signature sets, XFAs are at least 10,000 times smaller than the DFA matching all signatures. XFAs are 10 times smaller and 5 times faster or 5 times smaller and 20 times faster than systems using multiple DFAs.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Method for estimating charge state of power cell
InactiveCN102608542AIn line with the actual useReduce estimation errorElectrical testingDiscretizationData system
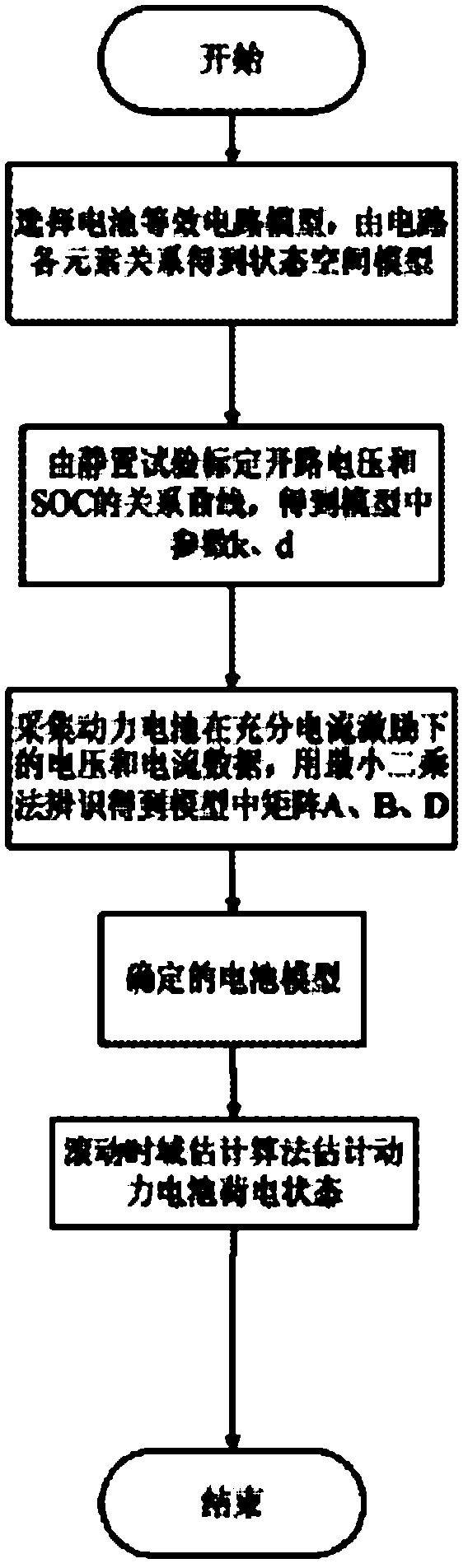
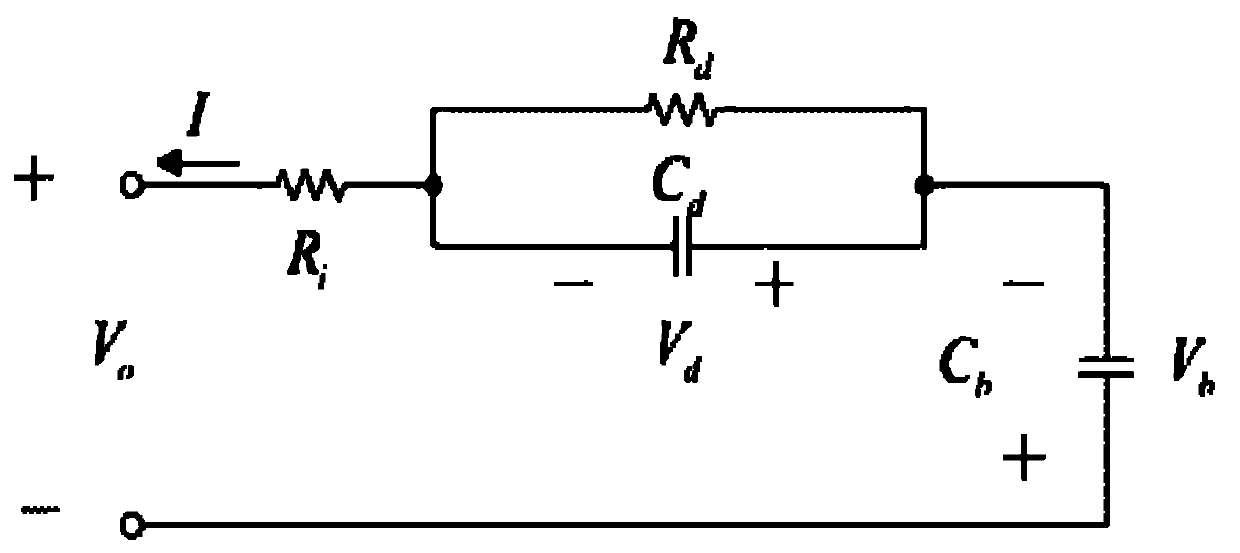
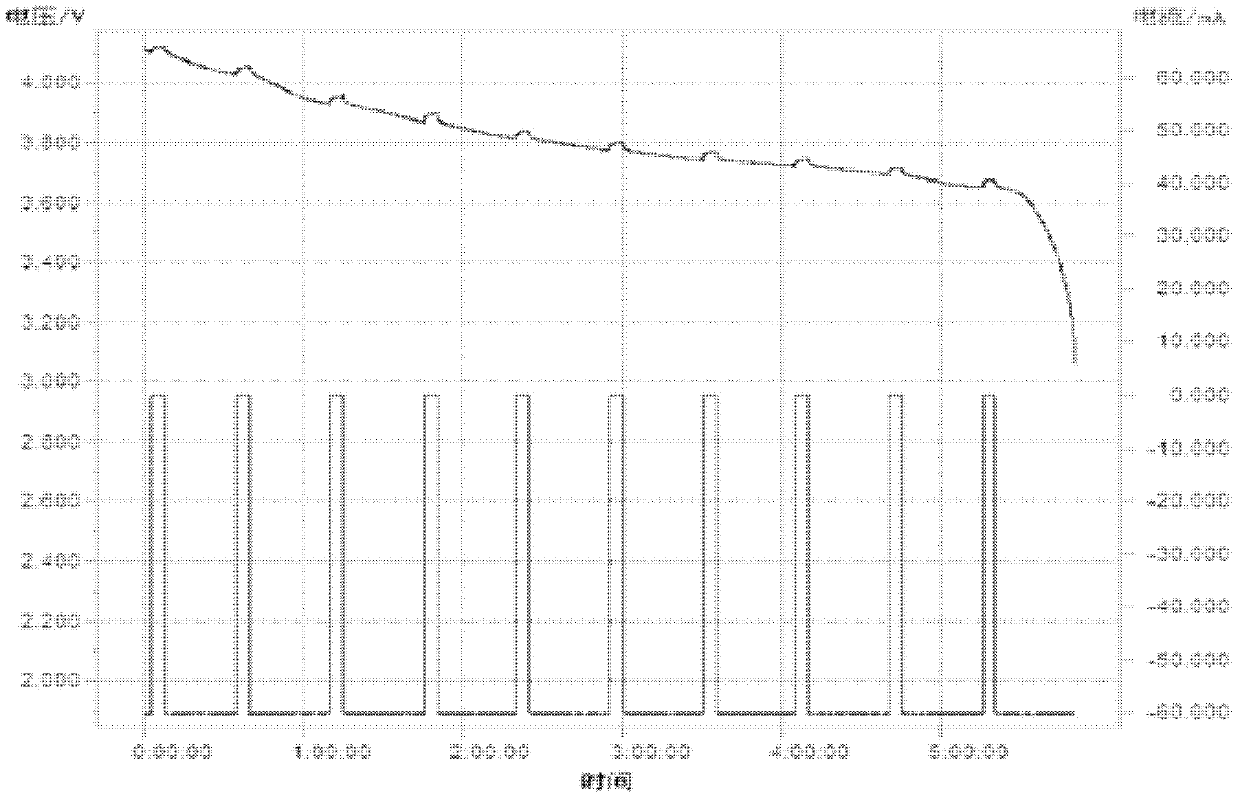
The invention discloses a method for estimating the charge state of a power cell, which comprises the following steps that: 1. a continuous state space model capable of expressing the relationship of each element in an expression circuit is obtained by an equivalent circuit model of a power cell; the relationship between the open-circuit voltage and the cell charge state is obtained through the standing experiment of the power cell, and the cell charge state is introduced into the continuous state space model of the power cell as a state variable; the power battery model under the noise environment is obtained by combining the noise information; and finally the continuous state space model is subjected to linearization and discretization so as to obtain a linear discrete state space model; 2. a relationship curve of the open-circuit voltage and the cell charge state is obtained through the standing experiment of the power cell, and a parameter k and a parameter d in the power cell model are obtained approximately; 3. parameters of the power cell model are obtained through the identification of current and voltage data collected by a data collecting system; and 4. the power cell charge state is estimated by utilizing a moving horizon estimation method based on the determined power cell model.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
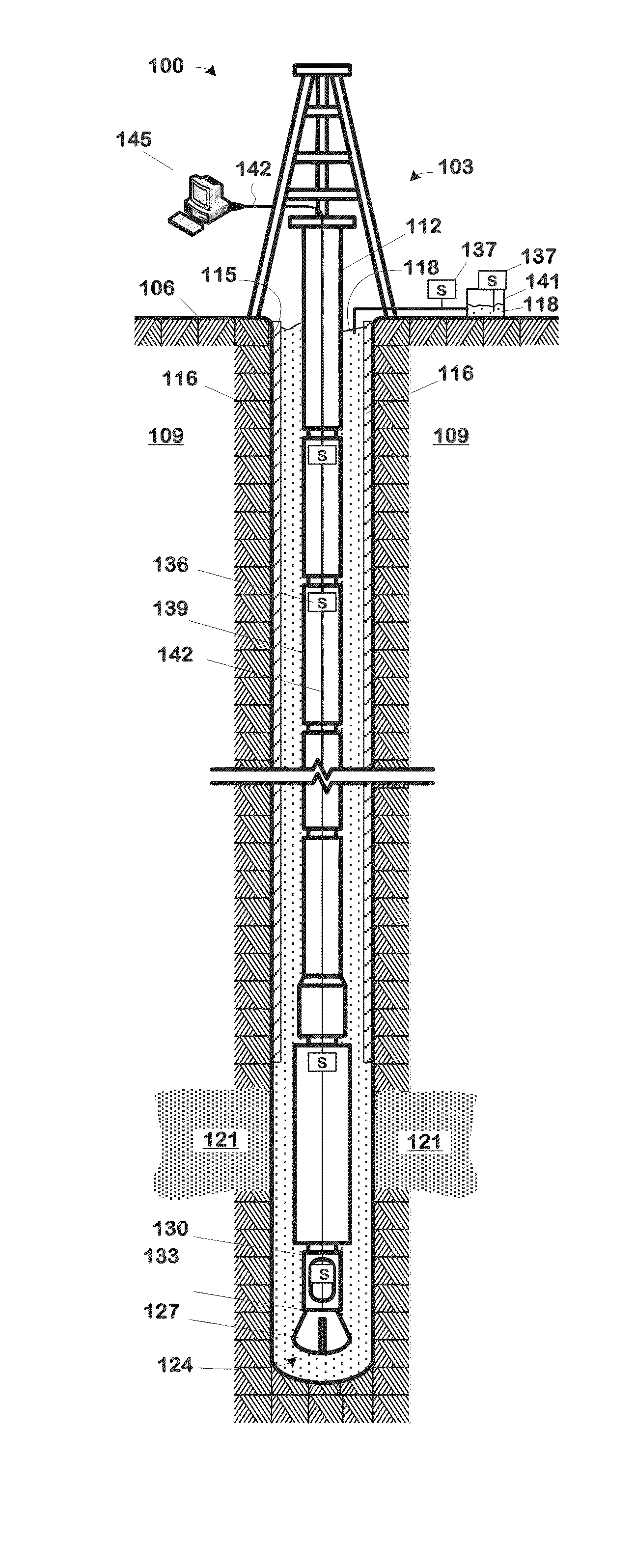
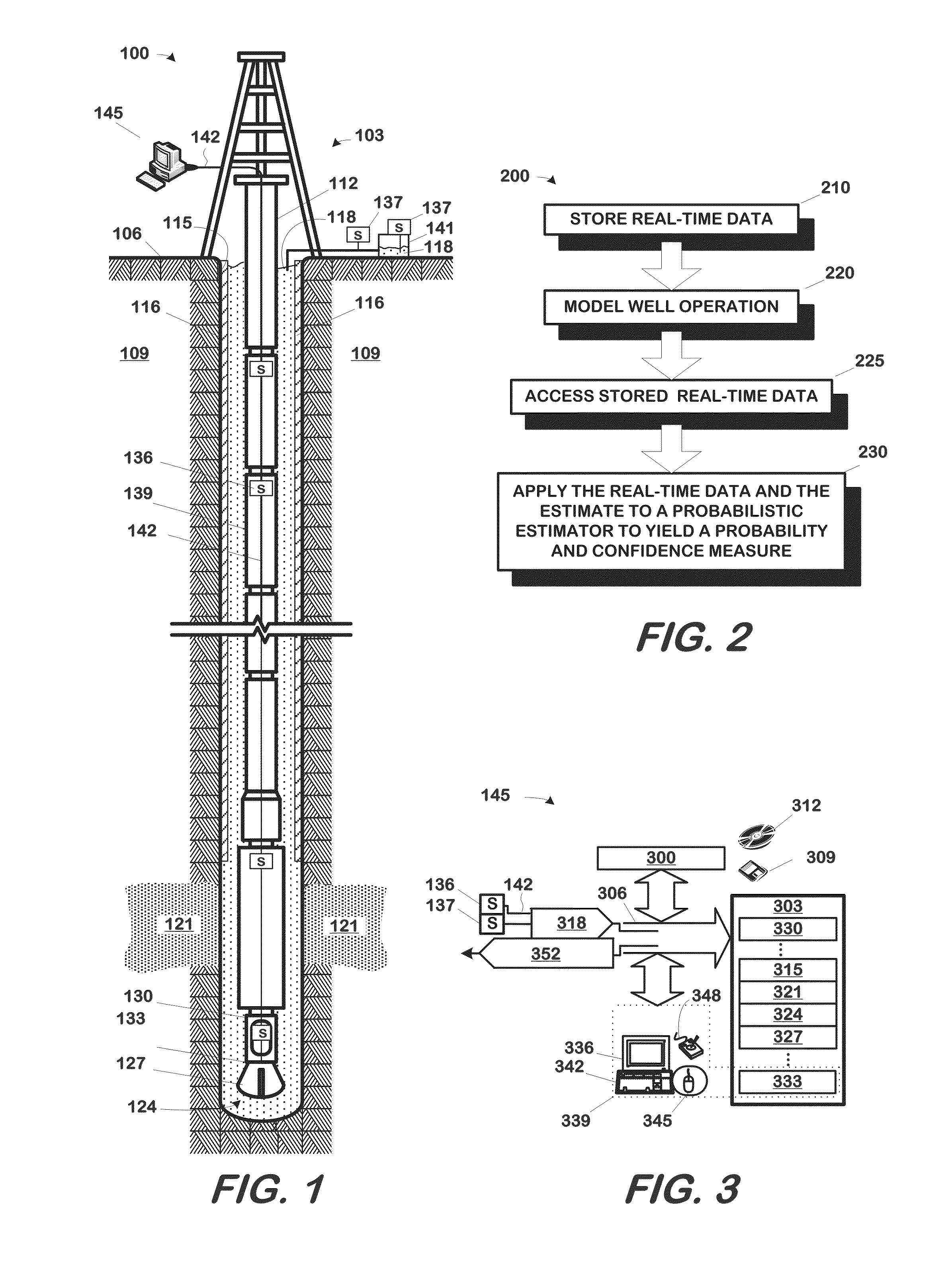
Method and apparatus for early detection of kicks
A well monitoring system particularly useful in detecting kicks in the well includes a well, a well system, and a computing apparatus. The well defines a wellbore and the well system includes at least one sensor measuring at least one well condition. The computing apparatus hosts a well monitoring software component that performs a method to detect a kick in a well. The method includes: storing a set of real-time data from a measurement of a well condition by the sensor, the measurements being correlative to an unplanned fluid influx into the well; modeling the operation of the well with a physics-based, state space model of the well system to obtain an estimate of the well condition; and applying the real-time data set and the estimate to a probabilistic estimator to yield a probability of an occurrence of a kick and a confidence measure for the probability.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
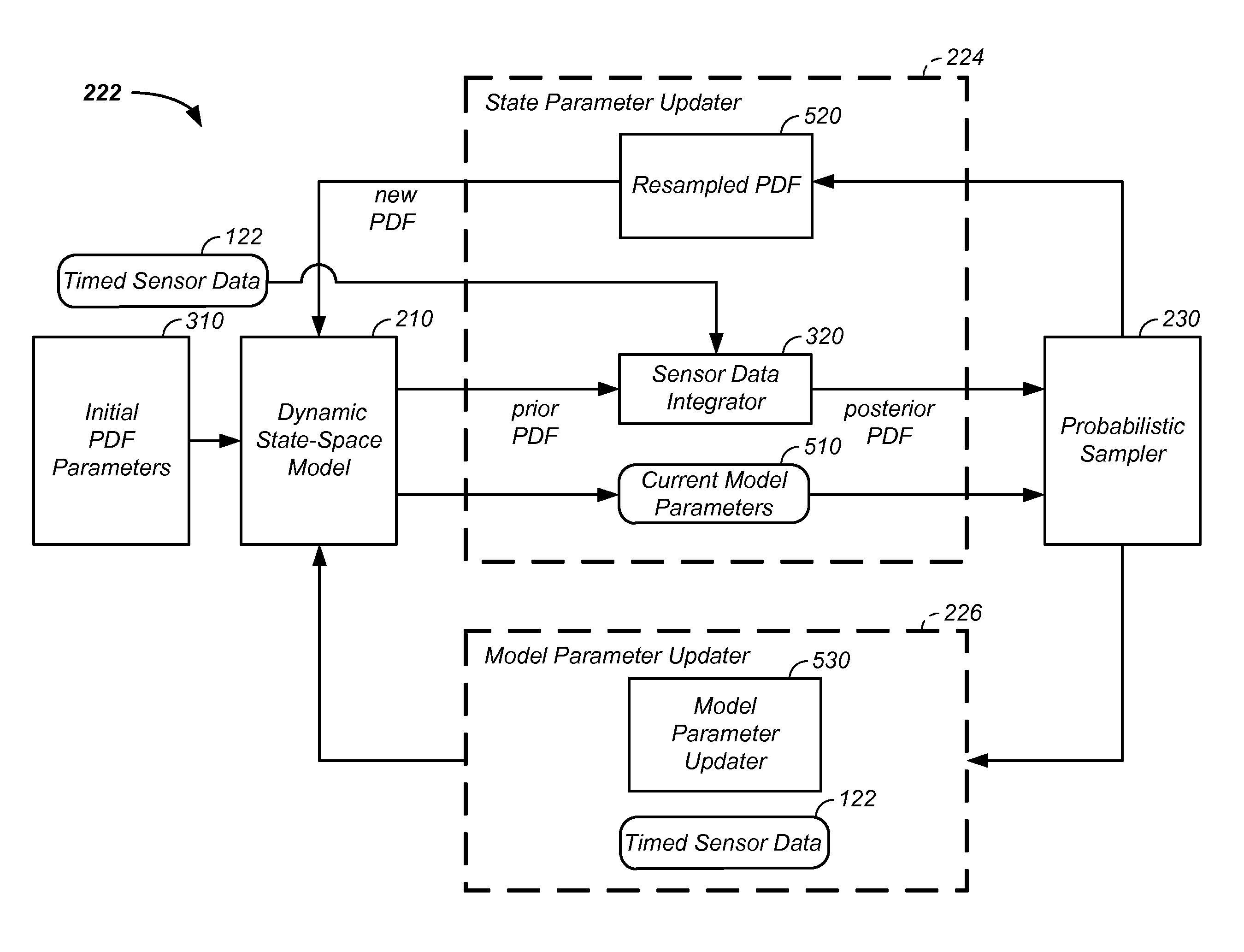
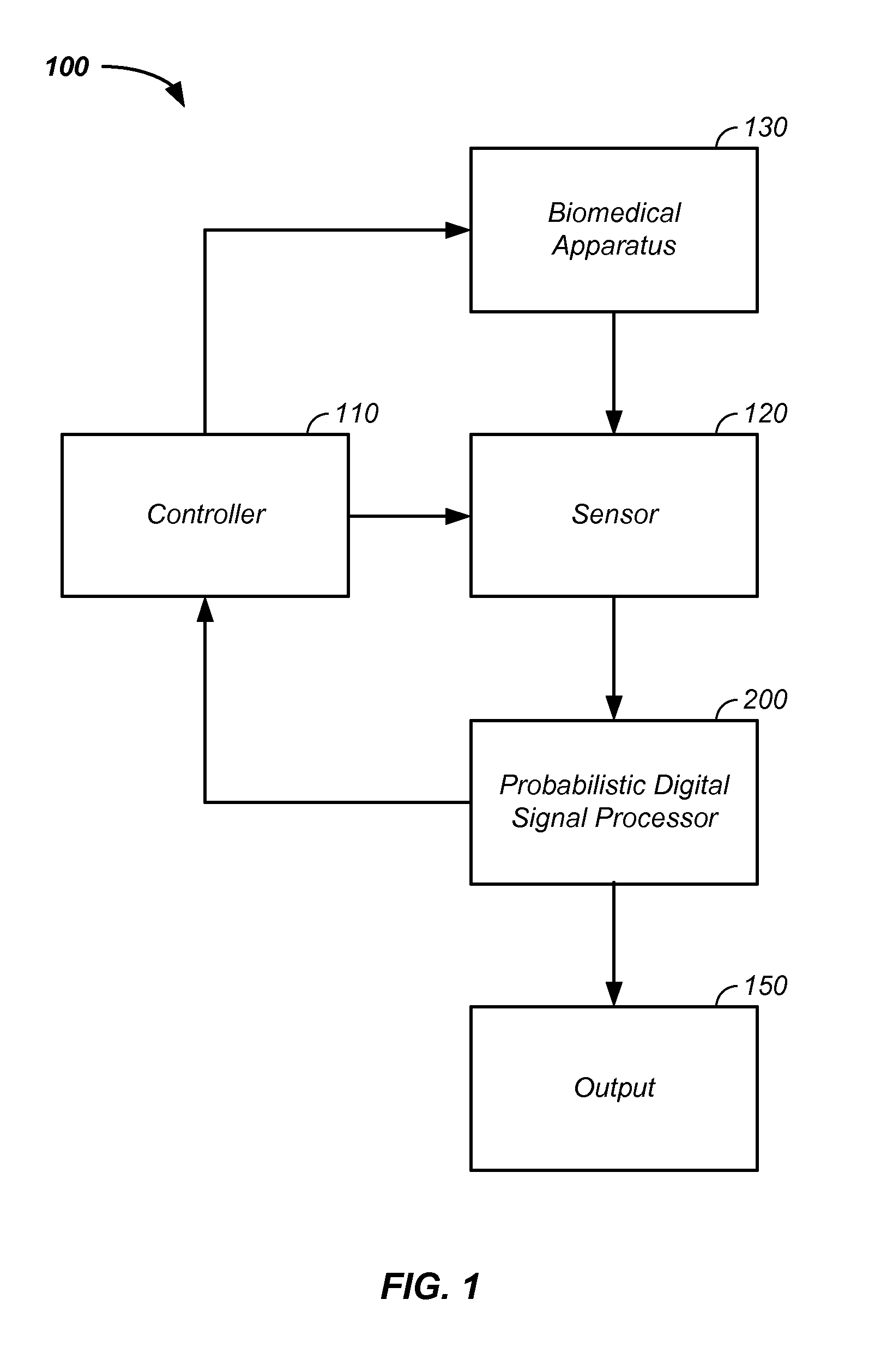
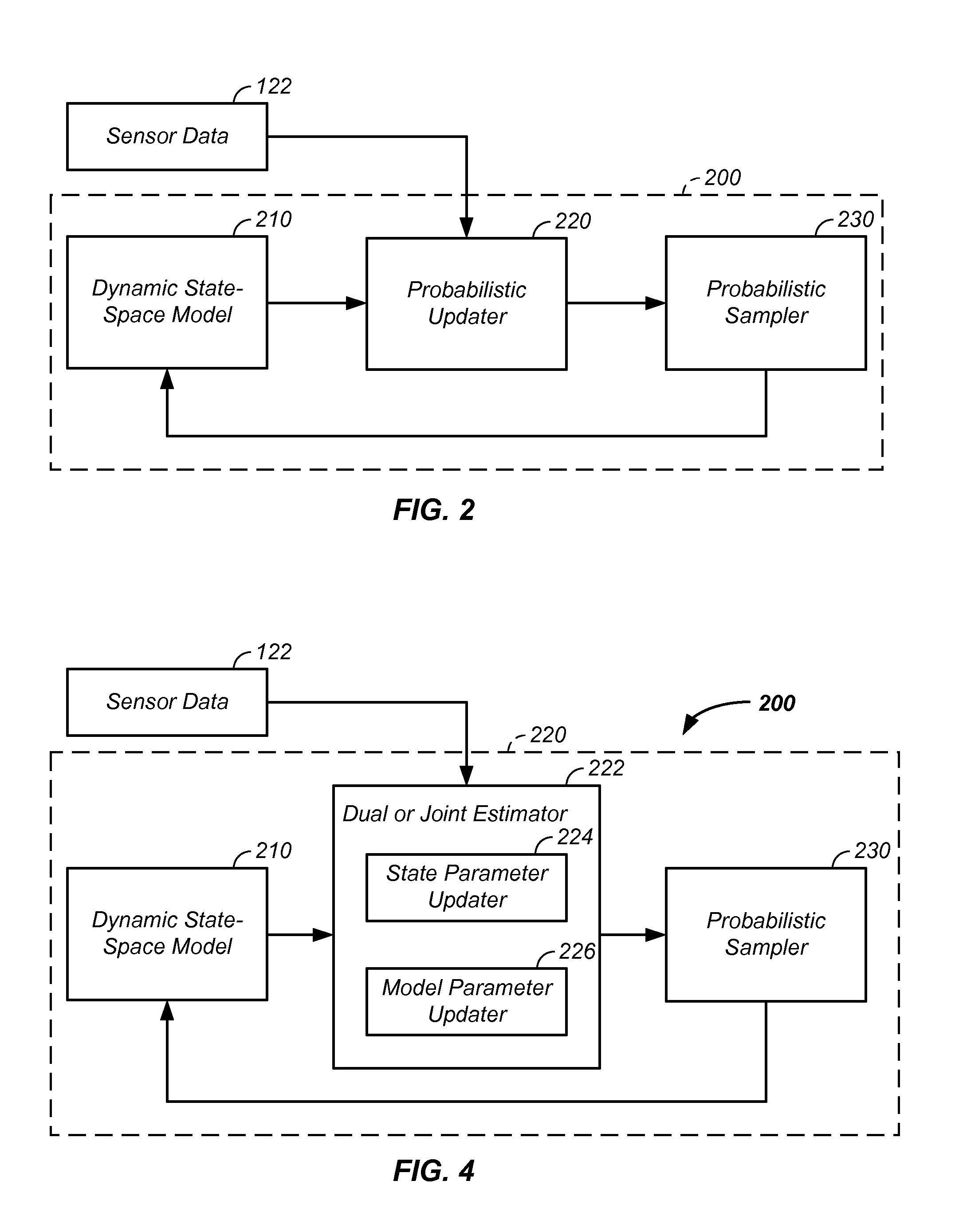
Probabilistic parameter estimation using fused data apparatus and method of use thereof
A probabilistic digital signal processor using data from multiple instruments is described. In one example, an analyzer is configured to: receive discrete first and second input data, related to a first and second sub-system of the system, from a first and second instrument, respectively. A system processor is used to fuse the first and second input data into fused data. The system processor optionally includes: (1) a probabilistic processor configured to convert the fused data into at least two probability distribution functions and (2) a dynamic state-space model, the dynamic state-space model including at least one probabilistic model configured to operate on the at least two probability distribution functions. The system processor iteratively circulates the at least two probability distribution functions in the dynamic state-space model in synchronization with receipt of updated input data, processes the probability distribution functions, and generates an output related to the state of the system.
Owner:VITAL METRIX INC
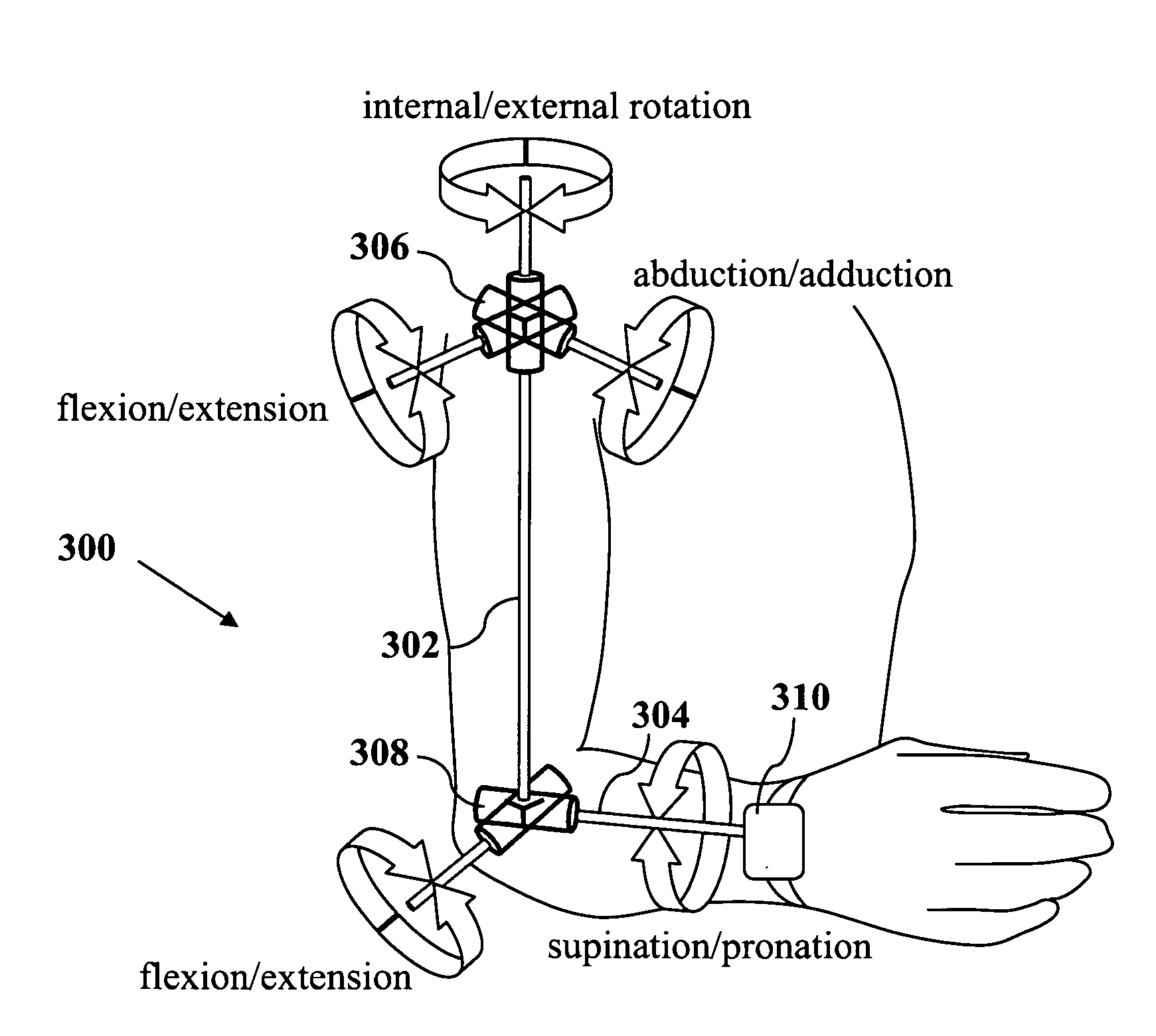
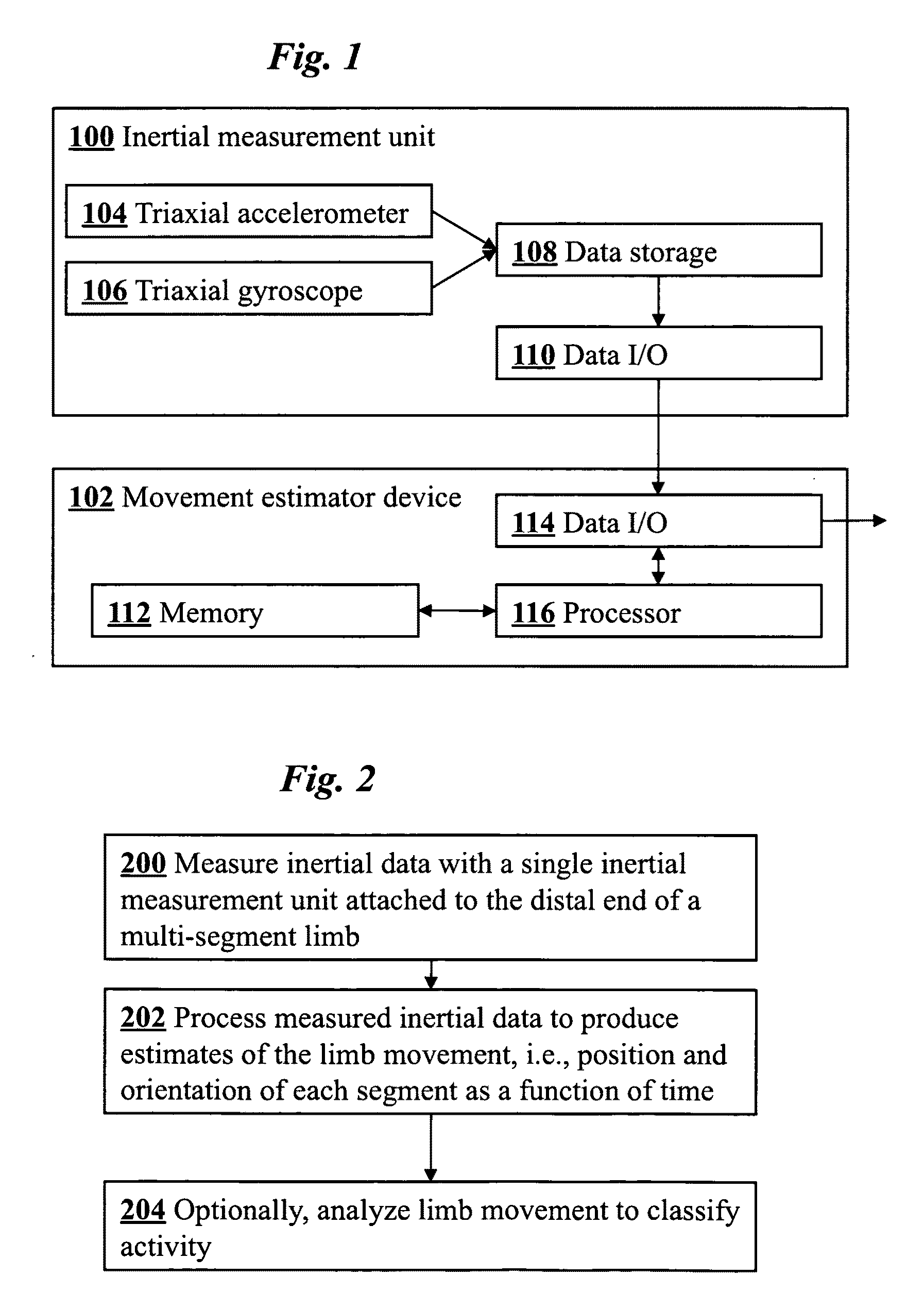
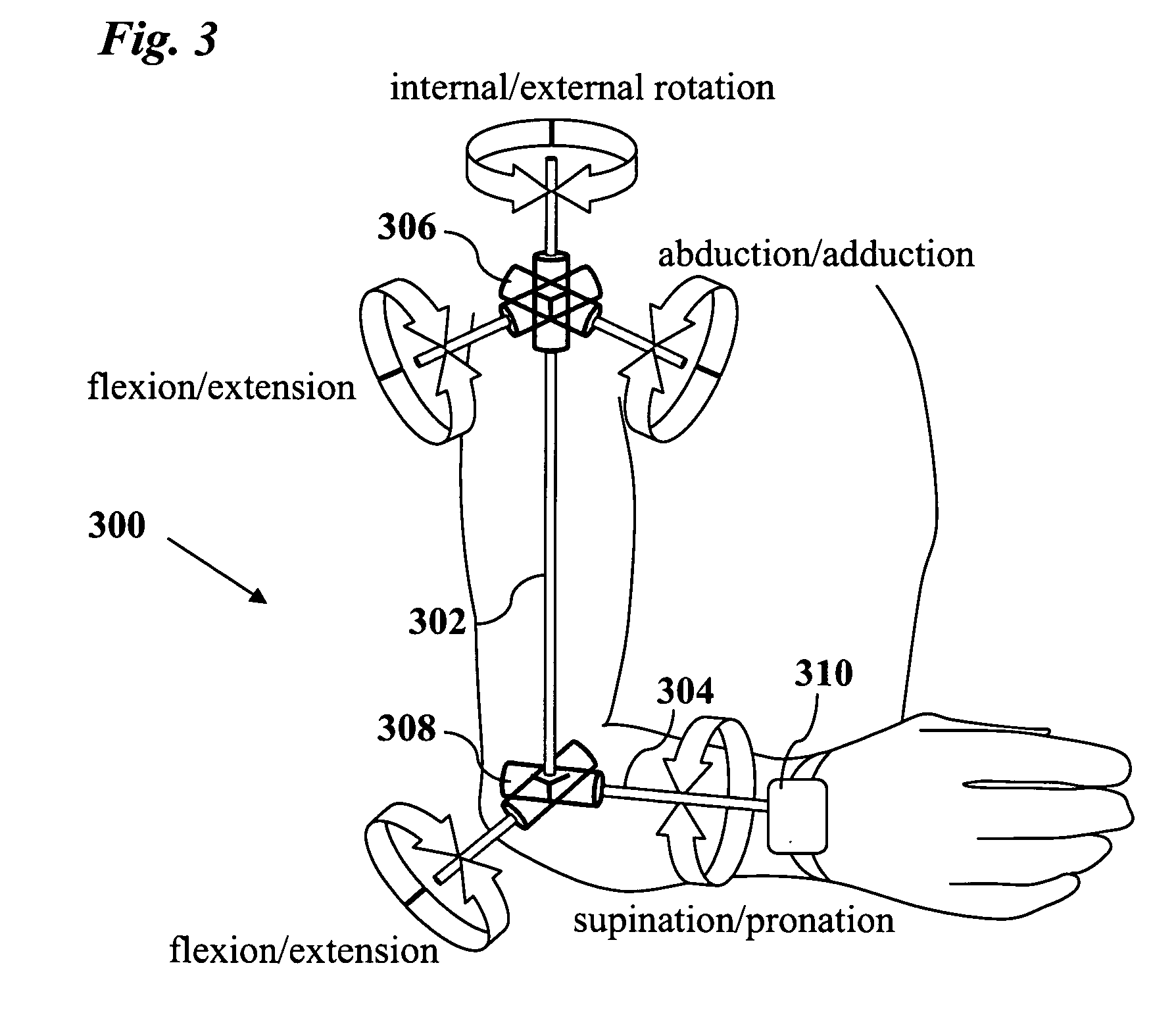
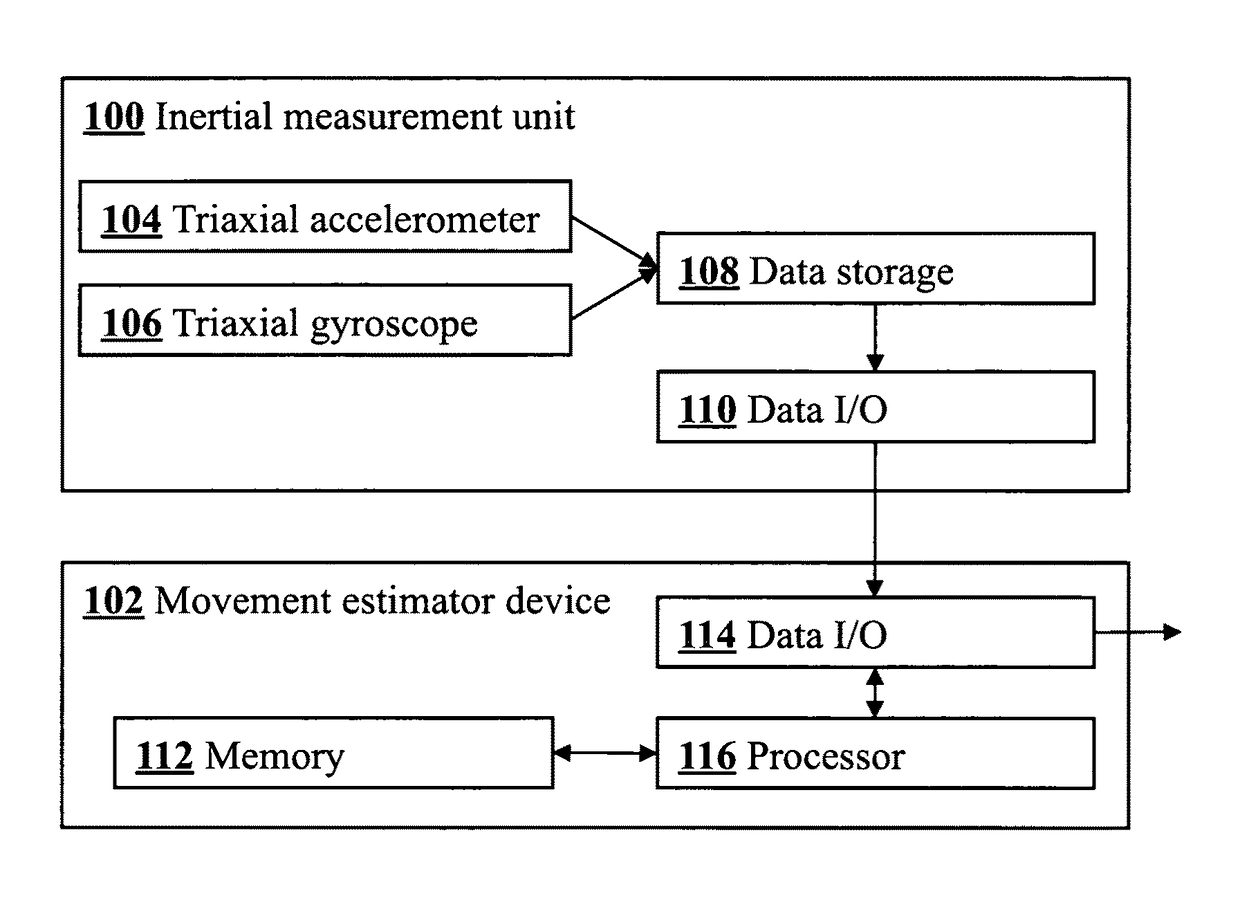
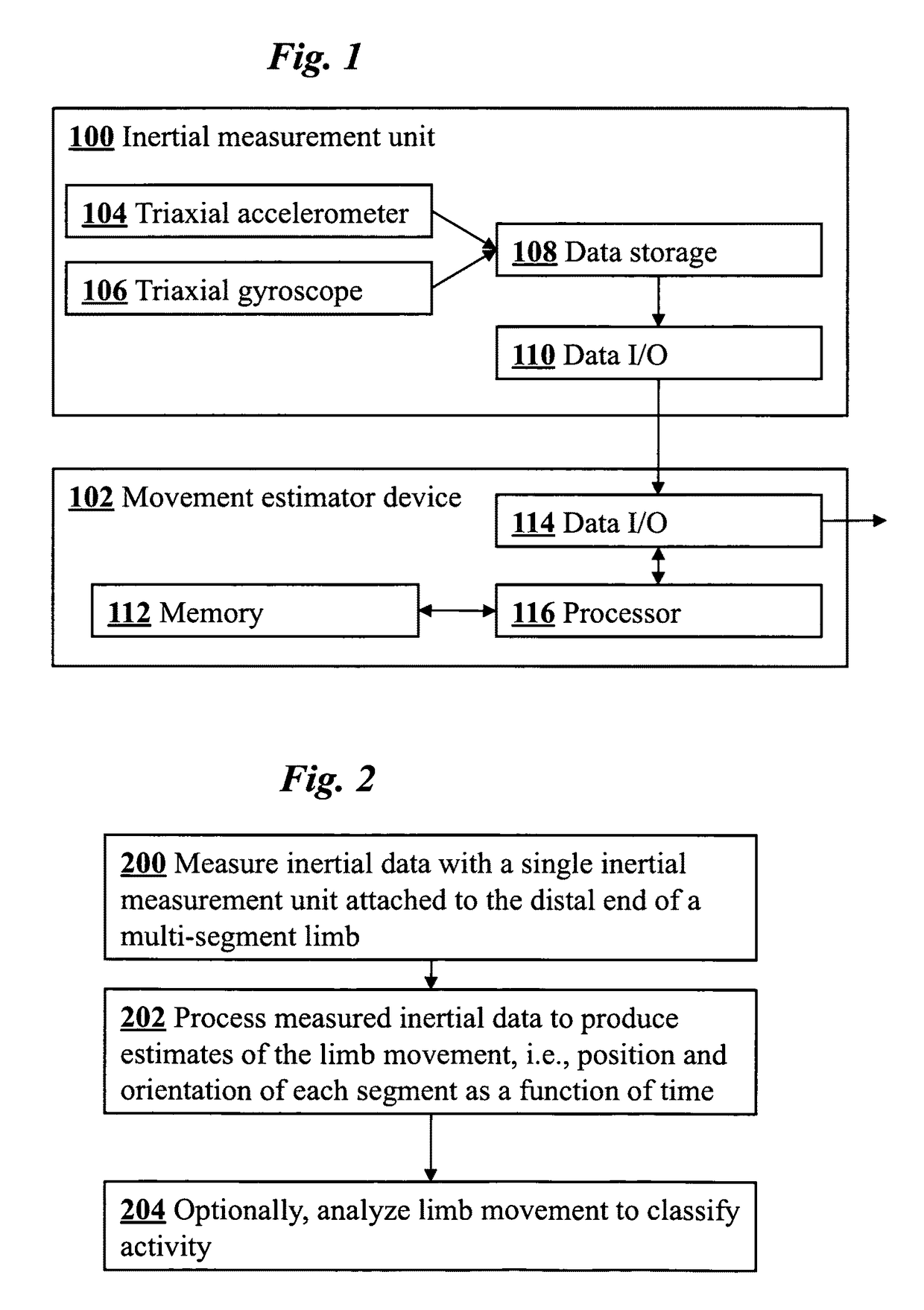
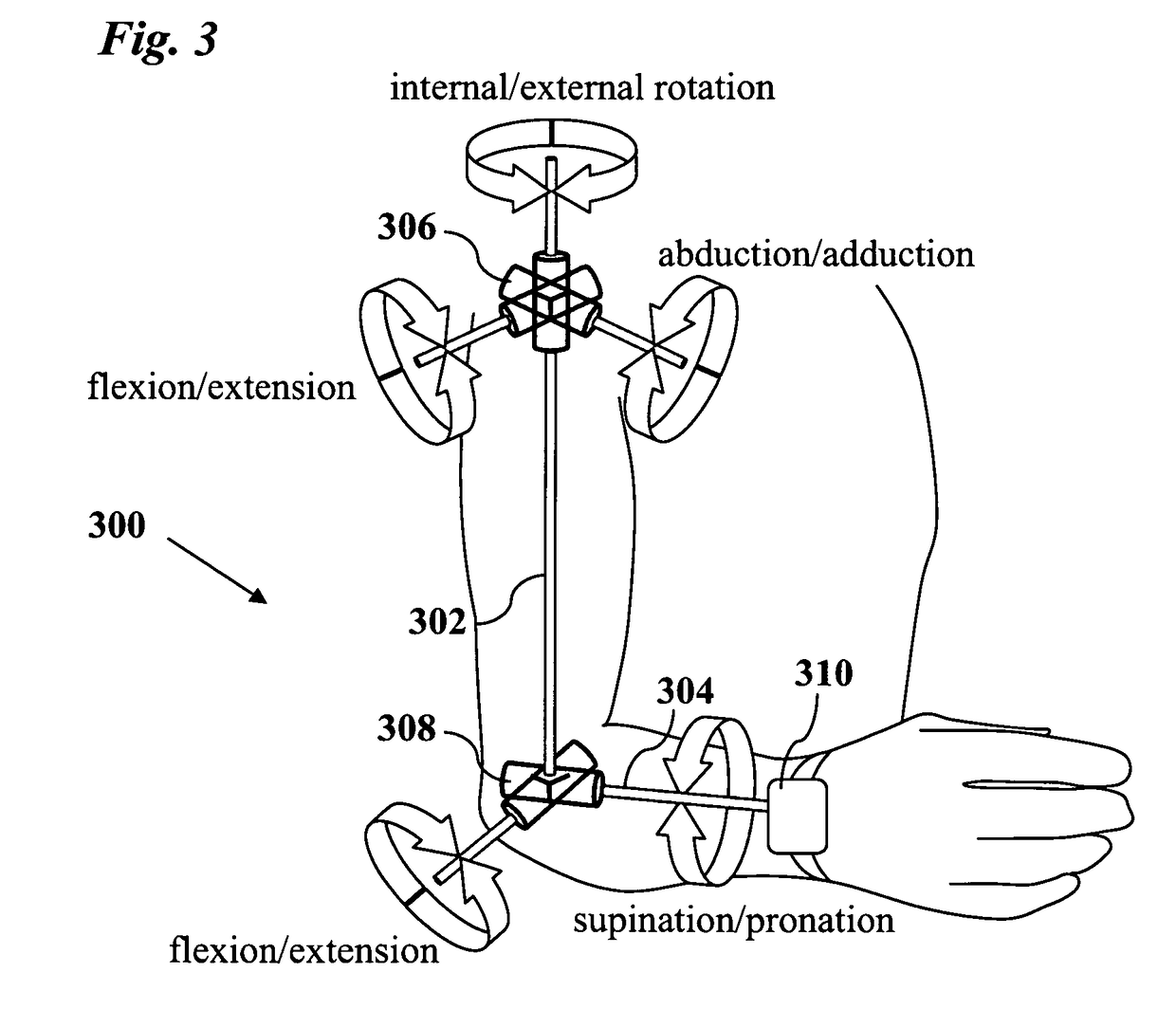
Joint angle tracking with inertial sensors
ActiveUS20090204031A1Accurate estimateAccurate trackingPerson identificationInertial sensorsEngineeringMulti segment
A method for estimating joint angles of a multi-segment limb from inertial sensor data accurately estimates and tracks the orientations of multiple segments of the limb as a function of time using data from a single inertial measurement unit worn at the distal end of the limb. Estimated joint angles are computed from measured inertial data as a function of time in a single step using a nonlinear state space estimator. The estimator preferably includes a tracking filter such as an unscented Kalman filter or particle filter. The nonlinear state space estimator incorporates state space evolution equations based on a kinematic model of the multi-segment limb.
Owner:OREGON ACTING BY & THROUGH THE STATE BOARD OF HIGHER EDUCATION ON BEHALF OF THE PORTLAND STATE UNIV THE STATE OF
Joint angle tracking with inertial sensors
ActiveUS9597015B2Accurately estimate and trackImprove usabilityPerson identificationInertial sensorsKaiman filterState space
A method for estimating joint angles of a multi-segment limb from inertial sensor data accurately estimates and tracks the orientations of multiple segments of the limb as a function of time using data from a single inertial measurement unit worn at the distal end of the limb. Estimated joint angles are computed from measured inertial data as a function of time in a single step using a nonlinear state space estimator. The estimator preferably includes a tracking filter such as an unscented Kalman filter or particle filter. The nonlinear state space estimator incorporates state space evolution equations based on a kinematic model of the multi-segment limb.
Owner:OREGON ACTING BY & THROUGH THE STATE BOARD OF HIGHER EDUCATION ON BEHALF OF THE PORTLAND STATE UNIV THE STATE OF
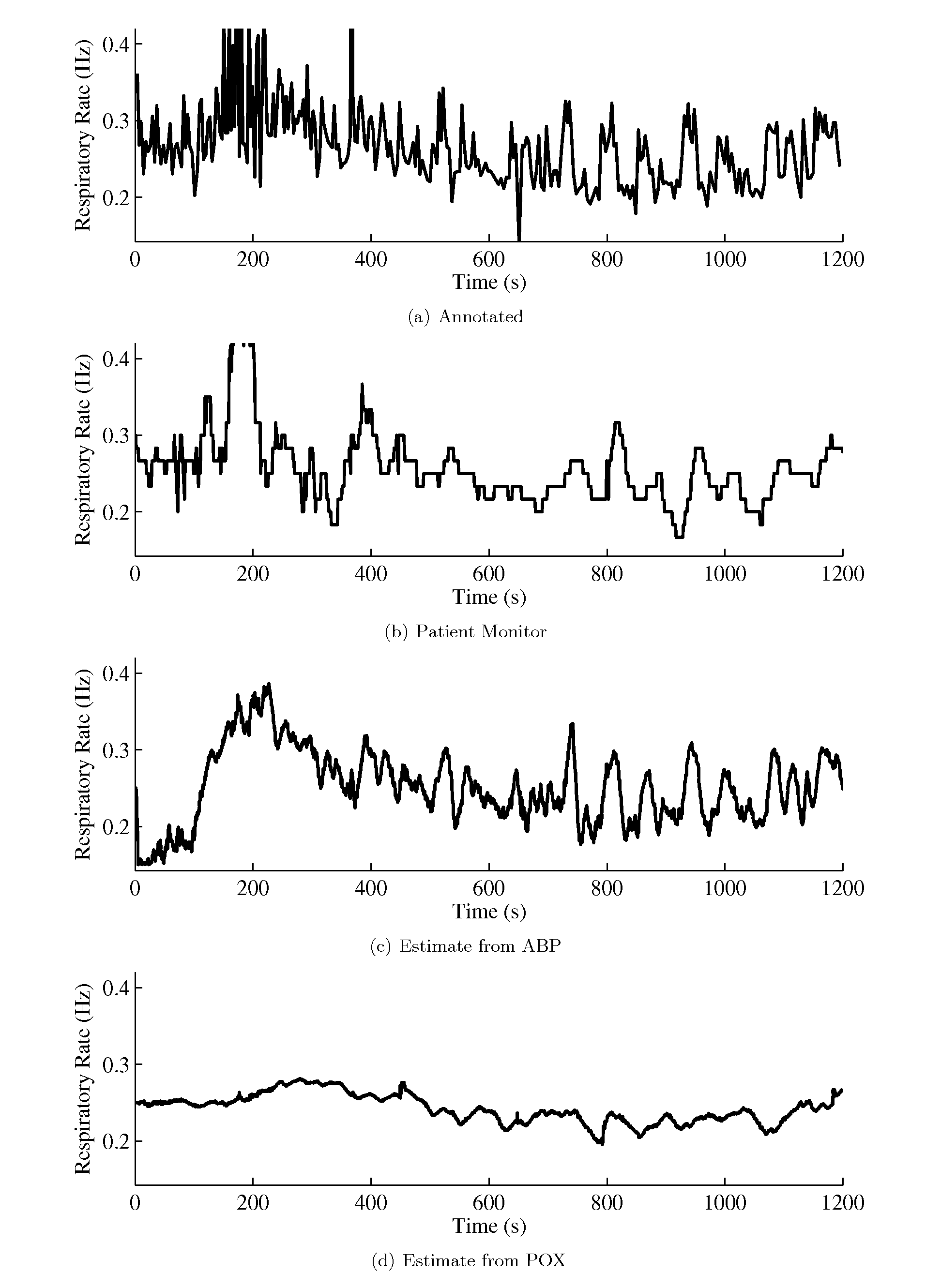
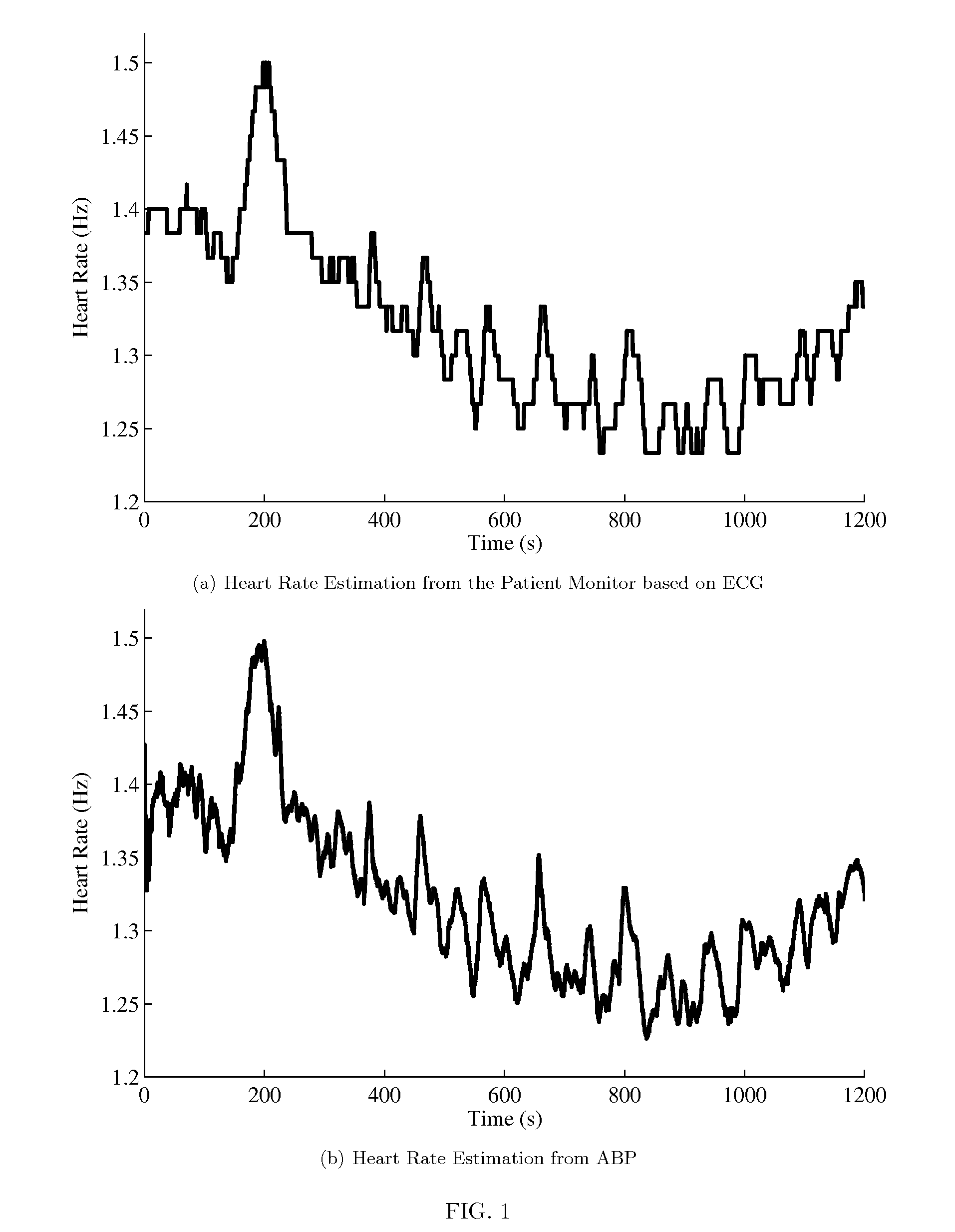
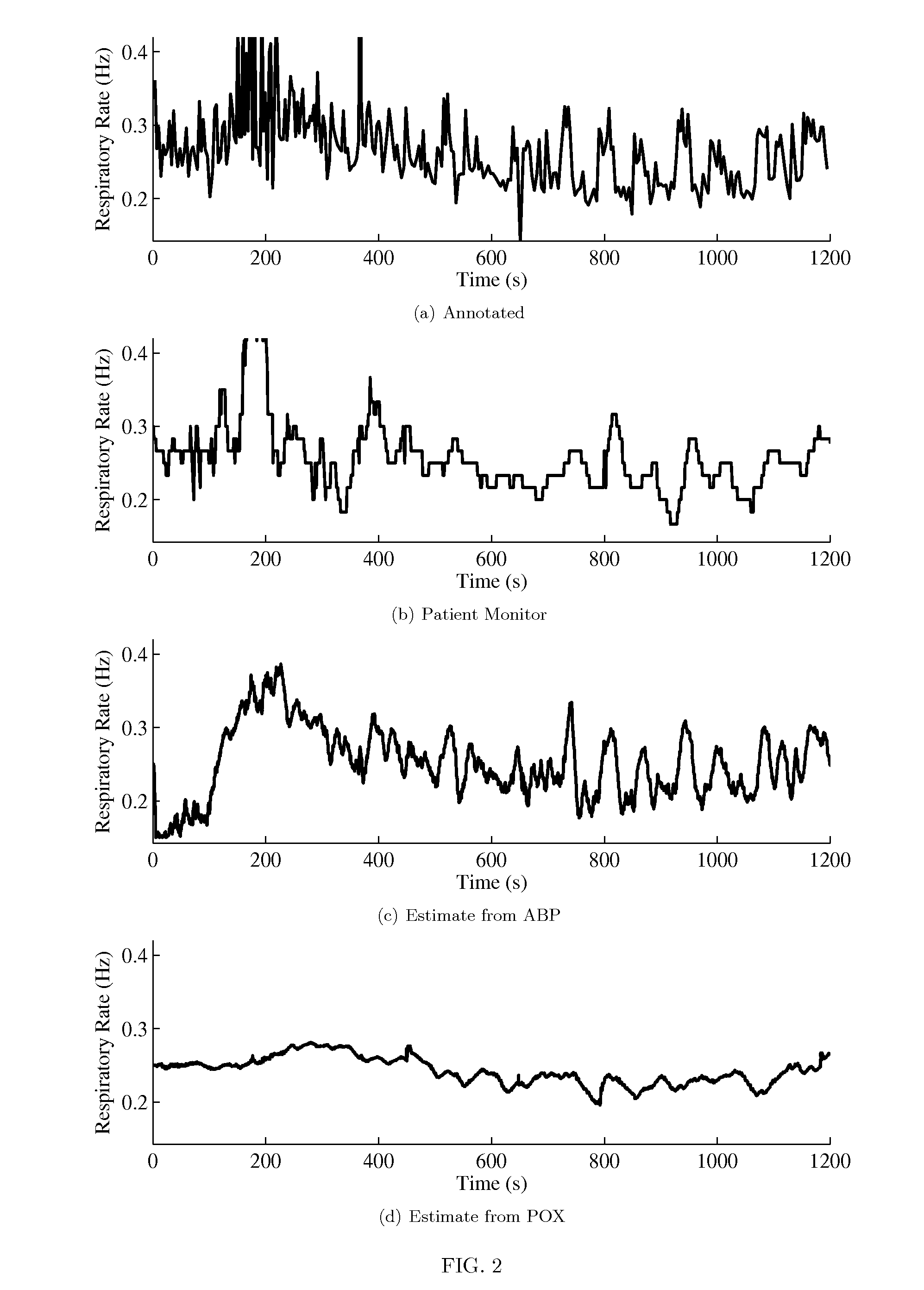
Method, system, and apparatus for cardiovascular signal analysis, modeling, and monitoring
The present invention provides a method, system, and apparatus to monitor cardiovascular signals such as arterial blood pressure (ABP), pulse oximetry (POX), and intracranial pressure (ICP). The system can be used to calculate and monitor useful clinical information such as heart rate, respiratory rate, pulse pressure variation (PPV), harmonic phases, pulse morphology, and for artifact removal. The method uses a statistical state-space model of cardiovascular signals and a generalized Kalman filter (EKF) to simultaneously estimate and track the cardiovascular parameters of interest such as the cardiac fundamental frequency and higher harmonics, respiratory fundamental frequency and higher harmonics, cardiac component harmonic amplitudes and phases, respiratory component harmonic amplitudes and phases, and PPV.
Owner:PORTLAND STATE UNIV +1
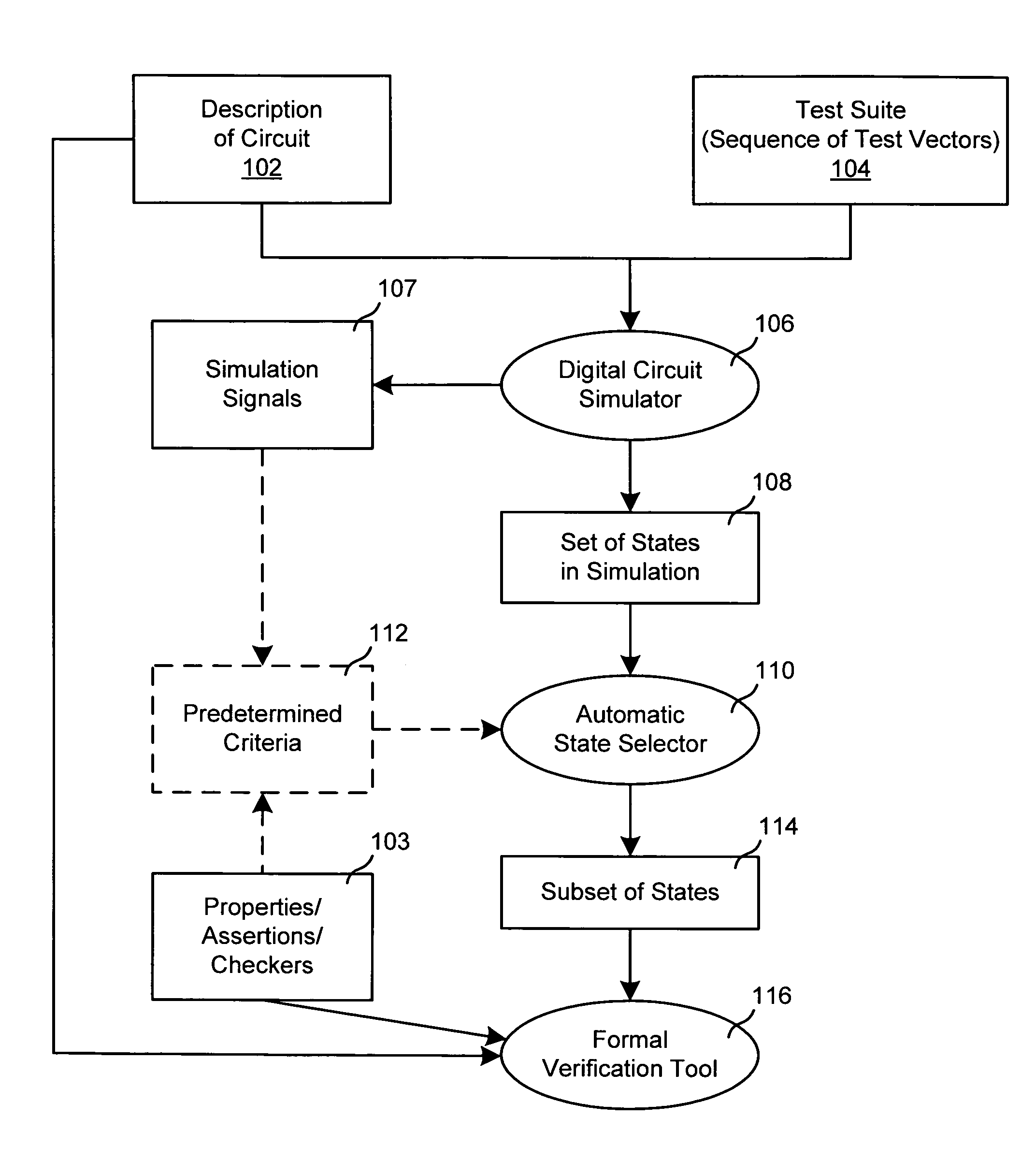
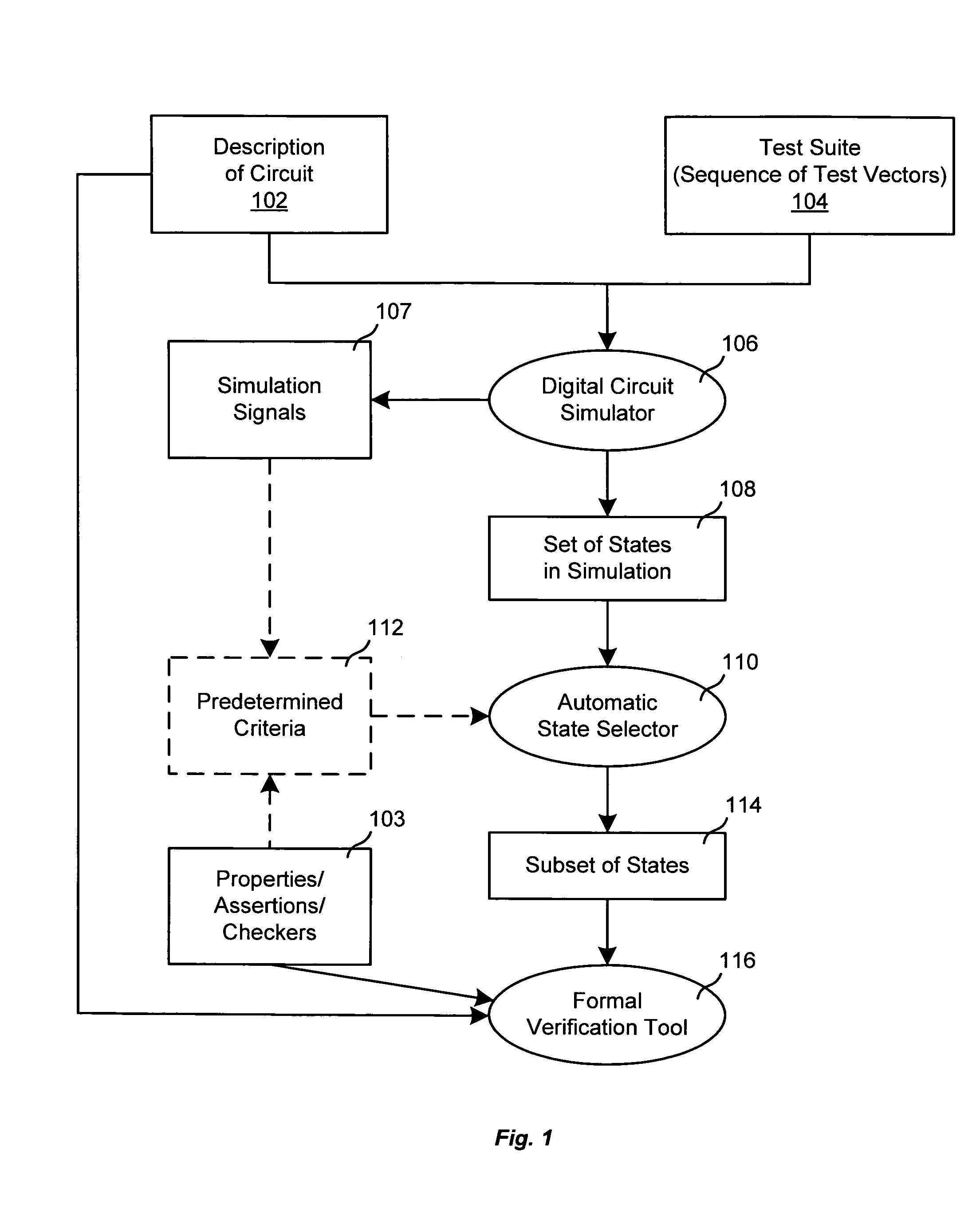
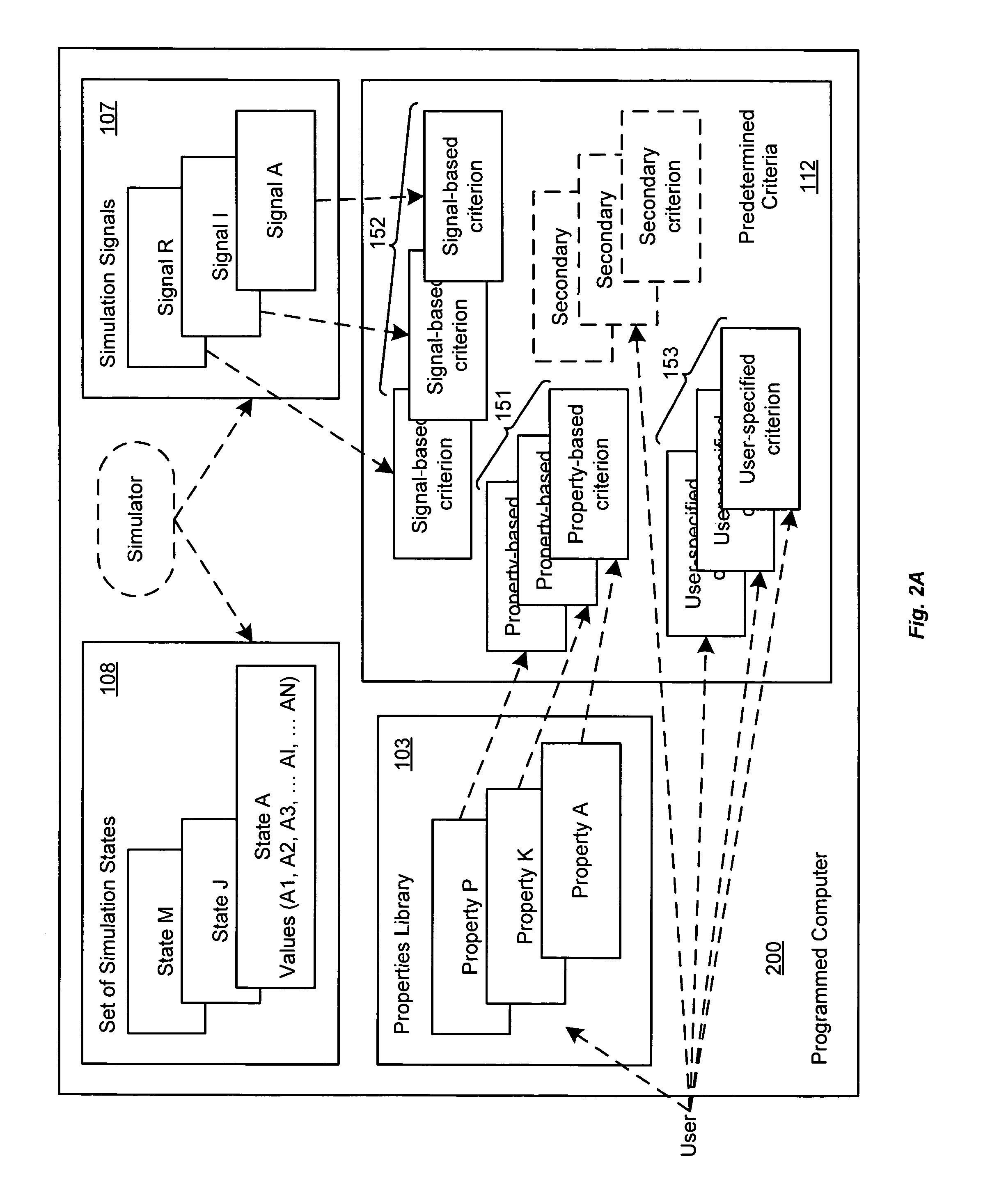
Selection of initial states for formal verification
ActiveUS7454324B1Raise the possibilityCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationState spaceFormal verification
A computer is programmed to automatically select a state or a set of states of a digital circuit that are visited during simulation, for use as one or more initial states by a formal verification tool. Such automatic selection of one or more simulation states reduces the set of all simulation states to a small subset, thereby to address the state space explosion problem. Depending on the embodiment, the programmed computer uses one or more criteria provided by a library and / or by the user, in making its selection of states. Such criteria may be based on a property (assertion / checker) of the digital circuit and / or a signal generated during simulation. Furthermore, after such criteria (also called “primary criteria”) are applied, the selected states may be pruned by application of additional criteria (also called “secondary criteria”) prior to formal analysis.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Heterogeneous cloud wireless access network resource allocation method based on deep reinforcement learning
ActiveCN110493826AMaximize total throughputMeet stability requirementsNetwork traffic/resource managementNonlinear approximationSmall sample
The invention relates to a heterogeneous cloud wireless access network resource allocation method based on deep reinforcement learning, and belongs to the technical field of mobile communication. Themethod comprises the following steps: 1) taking queue stability as a constraint, combining congestion control, user association, subcarrier allocation and power allocation, and establishing a random optimization model for maximizing the total throughput of the network; 2) considering the complexity of the scheduling problem, the state space and the action space of the system are high-dimensional,and the DRL algorithm uses a neural network as a nonlinear approximation function to efficiently solve the problem of dimensionality disasters; and 3) aiming at the complexity and the dynamic variability of the wireless network environment, introducing a transfer learning algorithm, and utilizing the small sample learning characteristics of transfer learning to enable the DRL algorithm to obtain an optimal resource allocation strategy under the condition of a small number of samples. According to the method, the total throughput of the whole network can be maximized, and meanwhile, the requirement of service queue stability is met. And the method has a very high application value in a mobile communication system.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
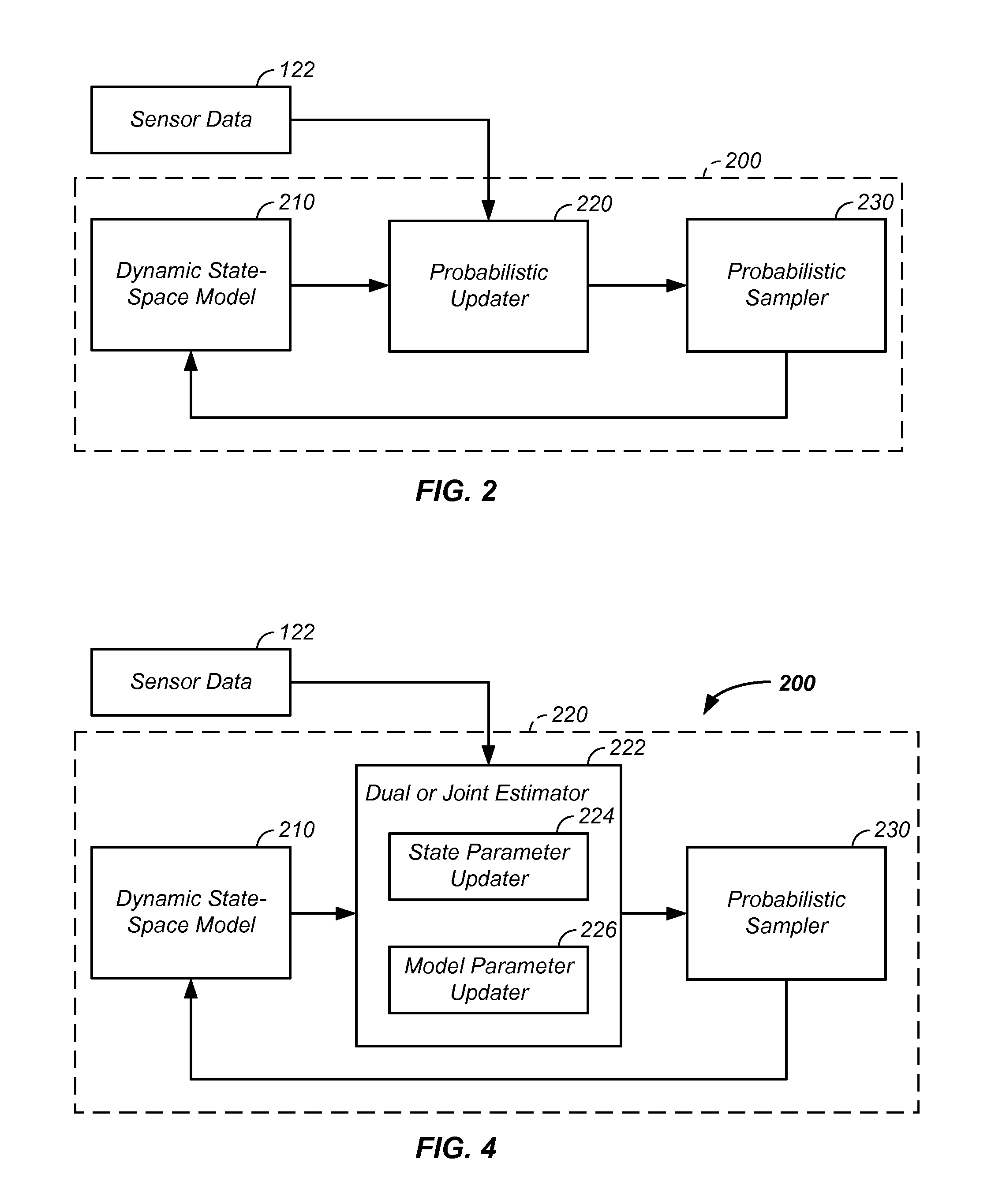
Sensor fusion and probabilistic parameter estimation method and apparatus
A probabilistic digital signal processor using data from multiple instruments is described. Initial probability distribution functions are input to a dynamic state-space model, which operates on state and / or model probability distribution functions to generate a prior probability distribution function, which is input to a probabilistic updater. The probabilistic updater integrates sensor data from multiple instruments with the prior to generate a posterior probability distribution function passed (1) to a probabilistic sampler, which estimates one or more parameters using the posterior, which is output or re-sampled in an iterative algorithm or (2) iteratively to the dynamic state-space model. For example, the probabilistic processor operates on fused data using a physical model, where the data originates from a mechanical system or a medical meter or instrument, such as an electrocardiogram or pulse oximeter to generate new parameter information and / or enhanced parameter information.
Owner:VITAL METRIX INC
Automatic driving test case generation method based on scenes and tasks
ActiveCN110597711AReduce complexityComprehensive descriptionSoftware testing/debuggingSimulationState space
The invention provides an automobile automatic driving test case generation method based on scenes and tasks, and the method comprises the following steps: 1), selecting typical traffic behaviors in acomplex and multi-element road traffic scene, and constructing a test task library; 2) defining terms of a traffic scene and related elements thereof, describing concepts, attributes and hierarchicalrelationships of scene elements, and constructing an ontology model of the road traffic scene; 3) generating a traffic scene based on the traffic scene model and the traffic behavior task library, the traffic scene being generally composed of a plurality of traffic participants, a specific time-space road environment and a traffic scene, and generally including a plurality of driving tasks; and 4) further describing a traffic scene in detail by defining a parameter range and correlation of variables in the state space, and selecting representative discrete values for combination by applying boundary value analysis, equivalence class division and other methods in software testing to generate a plurality of test cases.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
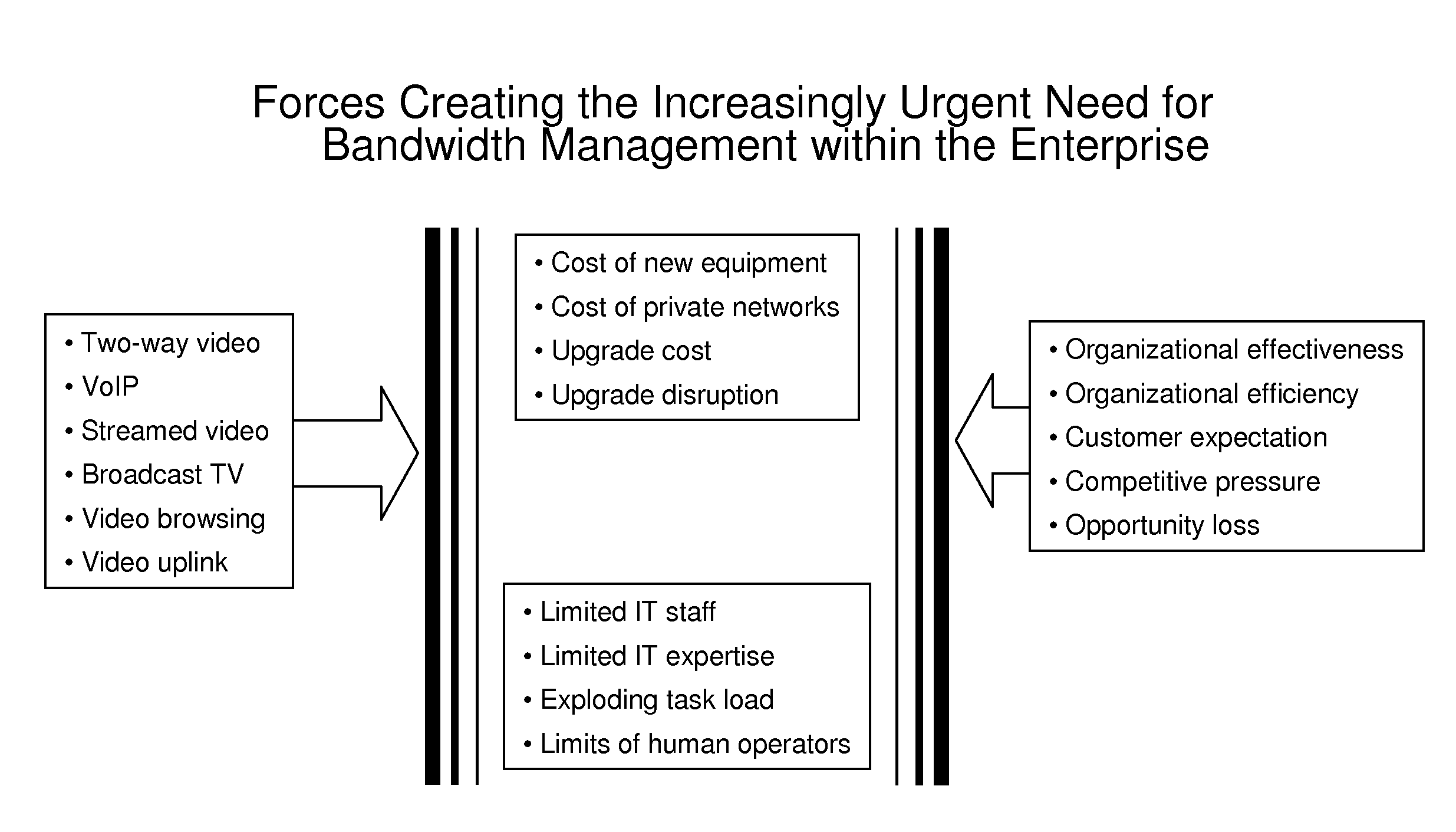
NEXT-GENERATION BANDWIDTH MANAGEMENT CONTROL SYSTEMS FOR MULTIPLE-SERVICE CALLS, SESSIONS, PACKET-LEVEL PROCESSES, AND QoS PARAMETERS - PART 1: STRUCTURAL AND FUNCTIONAL ARCHITECTURES
InactiveUS20130003543A1Easy to adaptError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsClosed loopStructure of Management Information
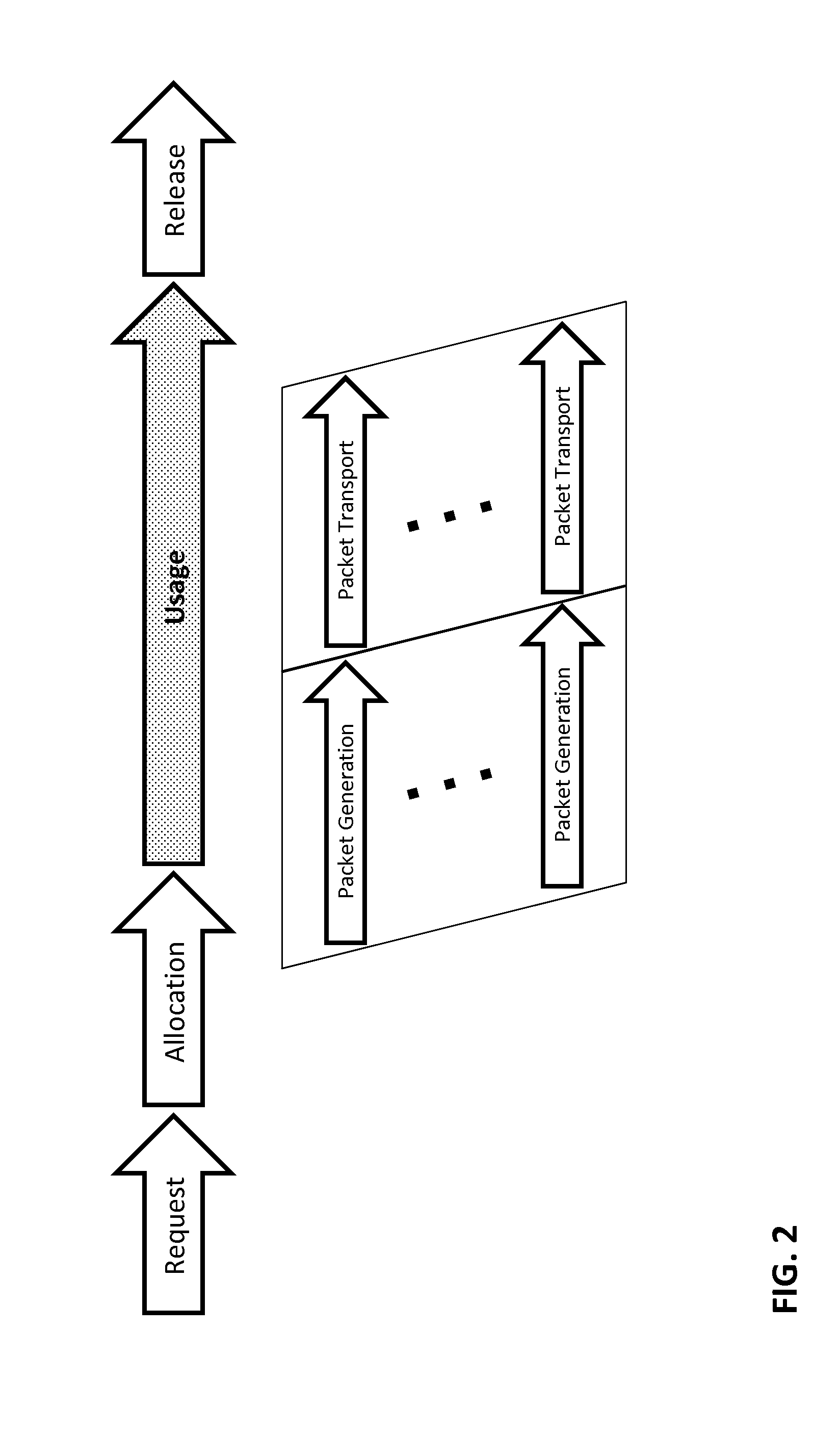
System and method for addressing immense, long-standing problem of bandwidth management, for example, in enterprise networks, VPNs, real-time and stored video services, mobile applications, wireless networks, and cloud computing applications. Described features include an automatic closed-loop control system infrastructure encompassing multiple time-scales and performing control actions optimized to the extent possible with respect to administrator-provided performance metrics. One aspect utilizes available or innovatively accessible means of session and QoS control (settings in configuration files, gateway APIs, QoS parameters, application bit-rate settings, etc.) within the context of practical multiple-vendor products in evolving multiple-service networks. Another aspect utilizes available or innovatively accessible means of session and QoS observations (values in reporting log files, gateway APIs, network monitoring, etc.) within the context of practical multiple-vendor products in evolving multiple-service networks. Traffic-measurement controlled adaptive reservations for distributed myopic single-service gatekeepers effectively shapes the permitted state-space boundary over a range of arbitrary curvatures.
Owner:AVISTAR COMM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com