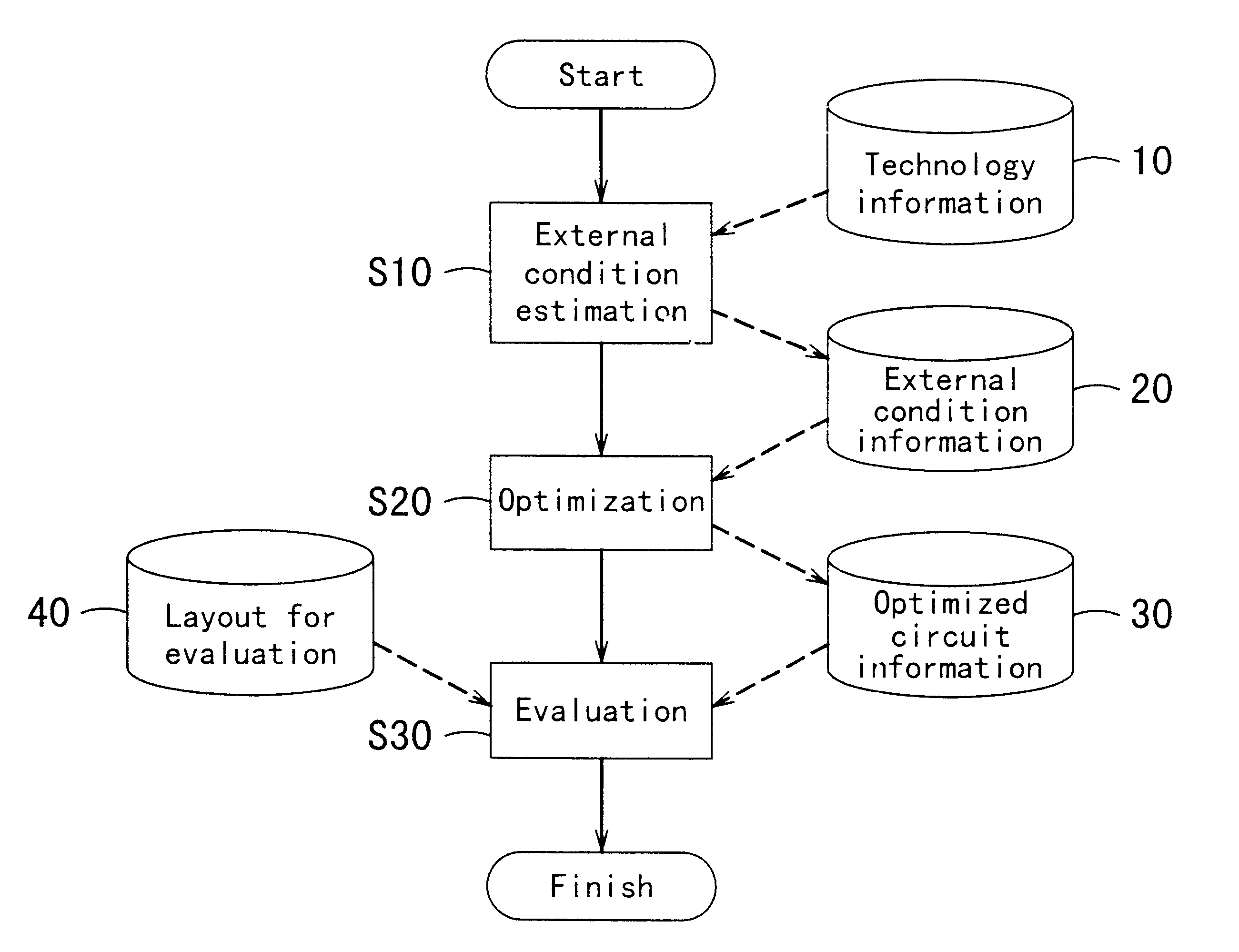
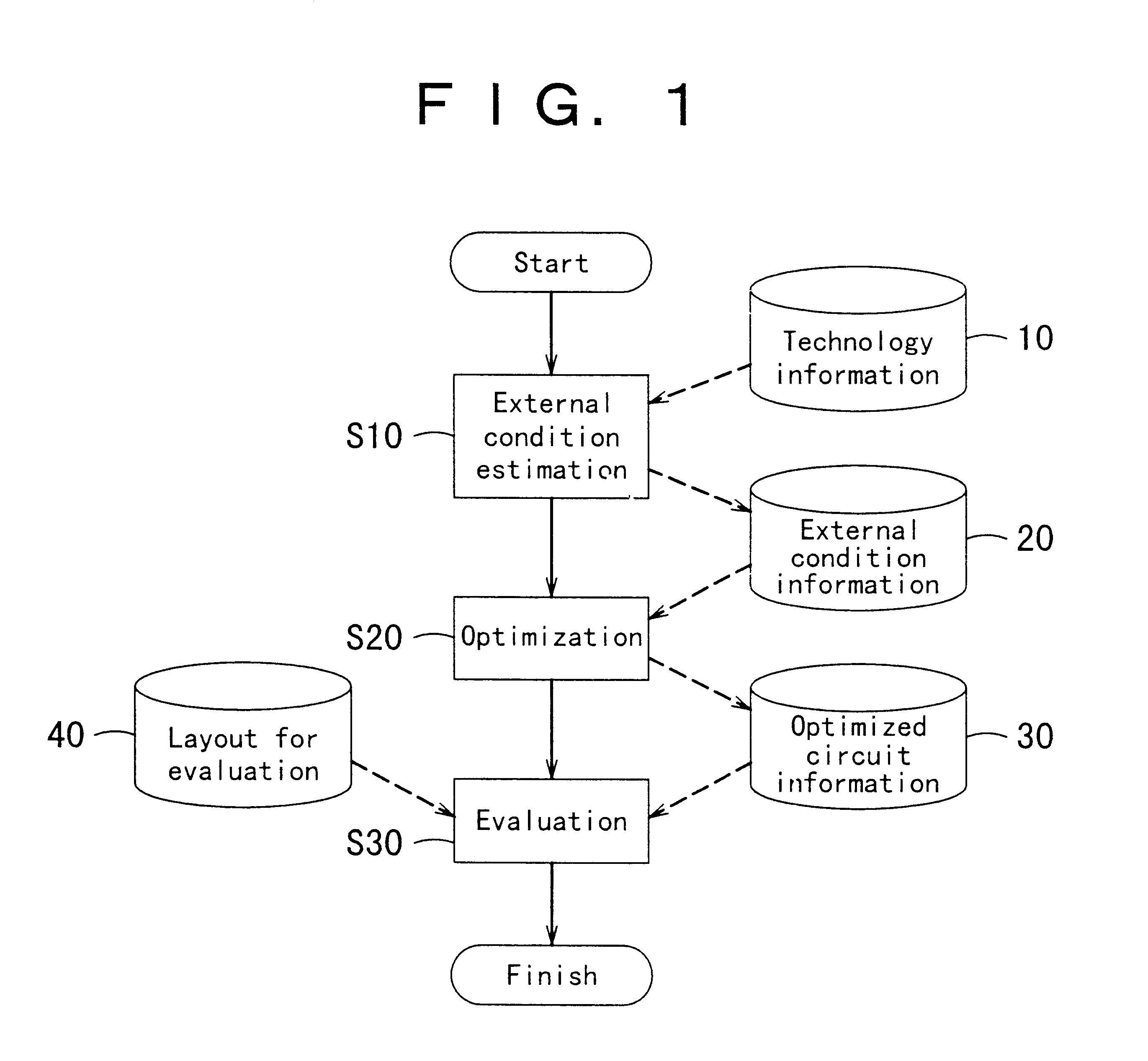
Patents
Literature
12877results about "CAD circuit design" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
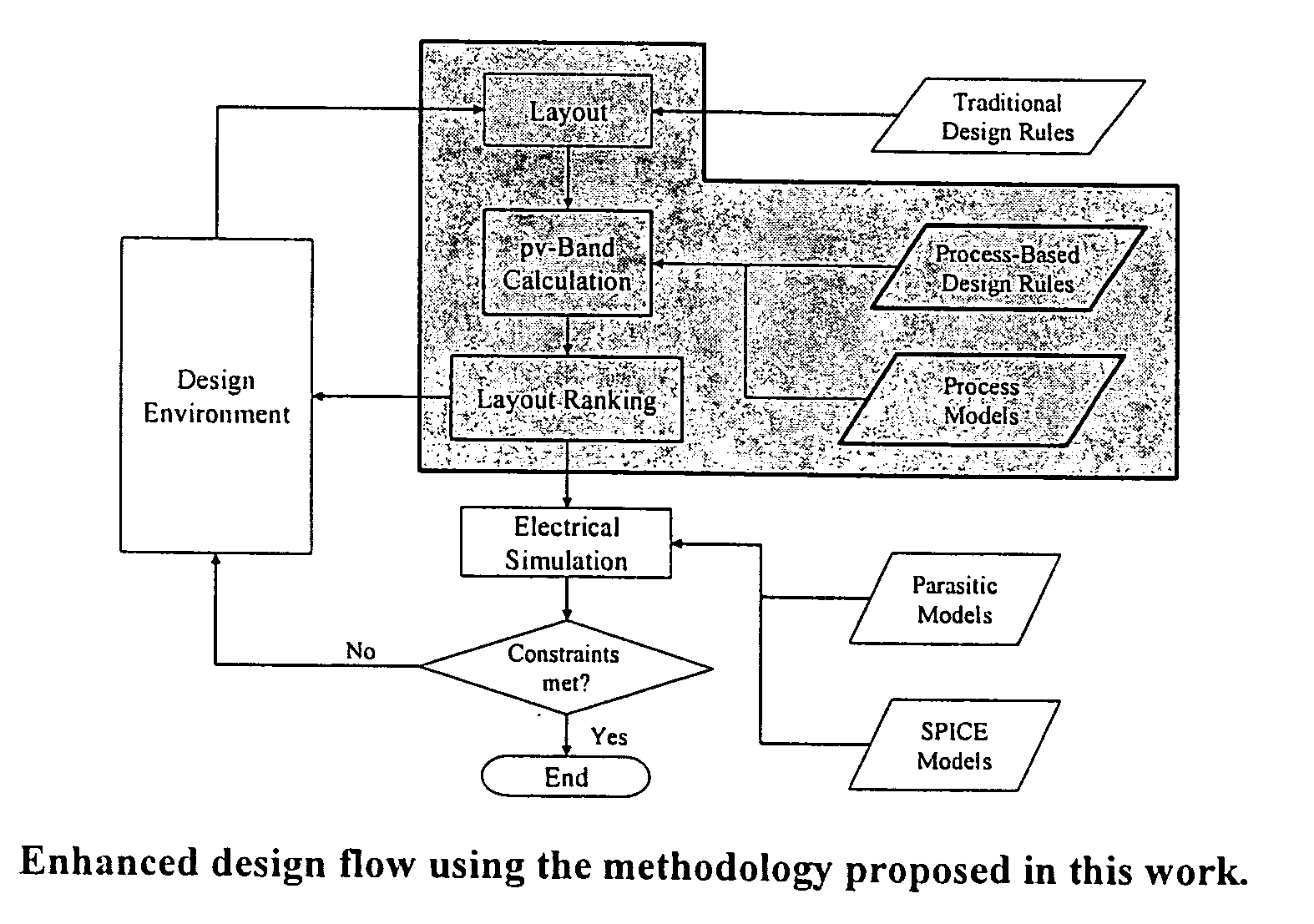
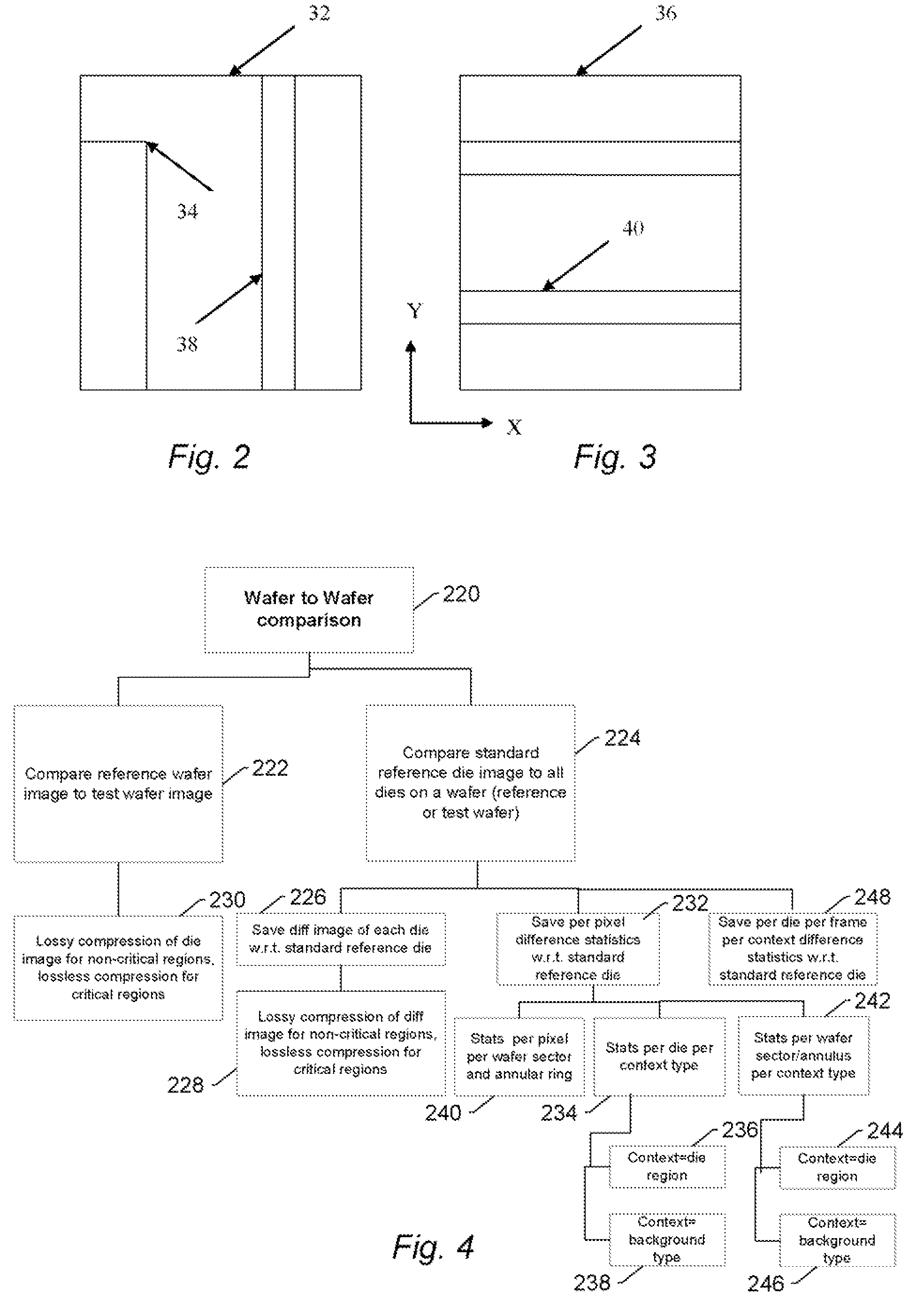
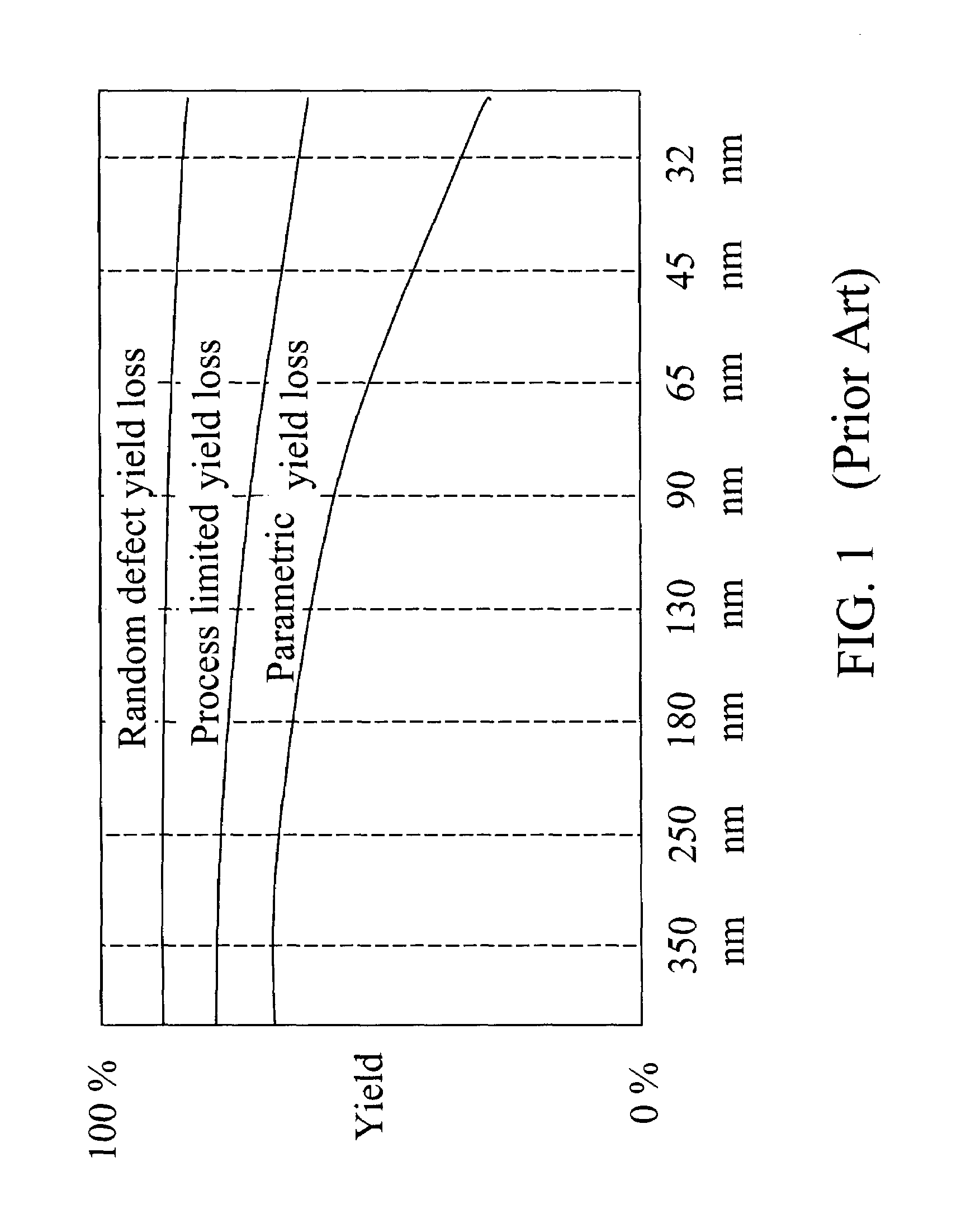
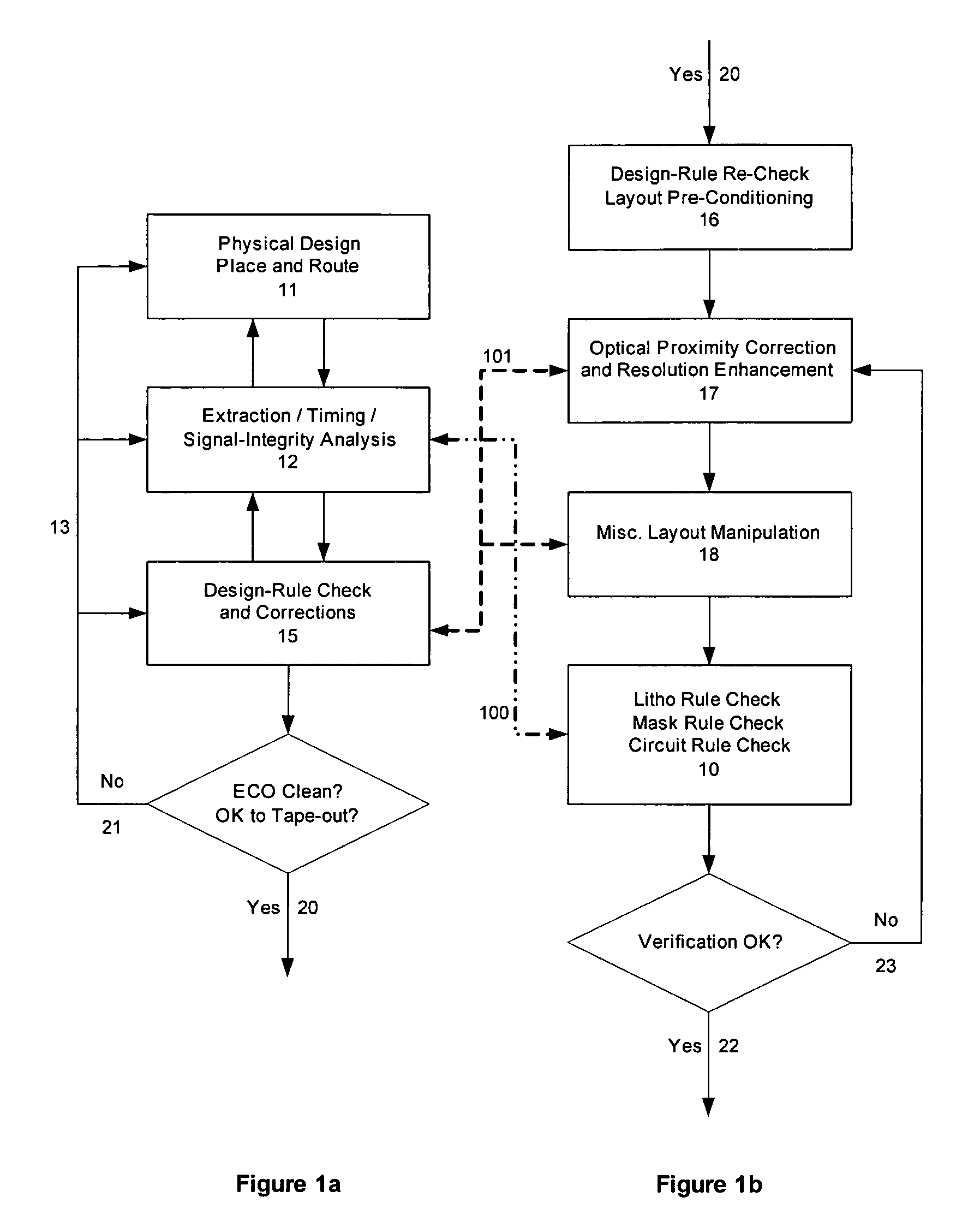
Integrated circuit layout design methodology with process variation bands
ActiveUS20050251771A1Constraint-based CADCAD circuit designSystems analysisIntegrated circuit layout
A system for analyzing IC layouts and designs by calculating variations of a number of objects to be created on a semiconductor wafer as a result of different process conditions. The variations are analyzed to determine individual feature failures or to rank layout designs by their susceptibility to process variations. In one embodiment, the variations are represented by PV-bands having an inner edge that defines the smallest area in which an object will always print and an outer edge that defines the largest area in which an object will print under some process conditions.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
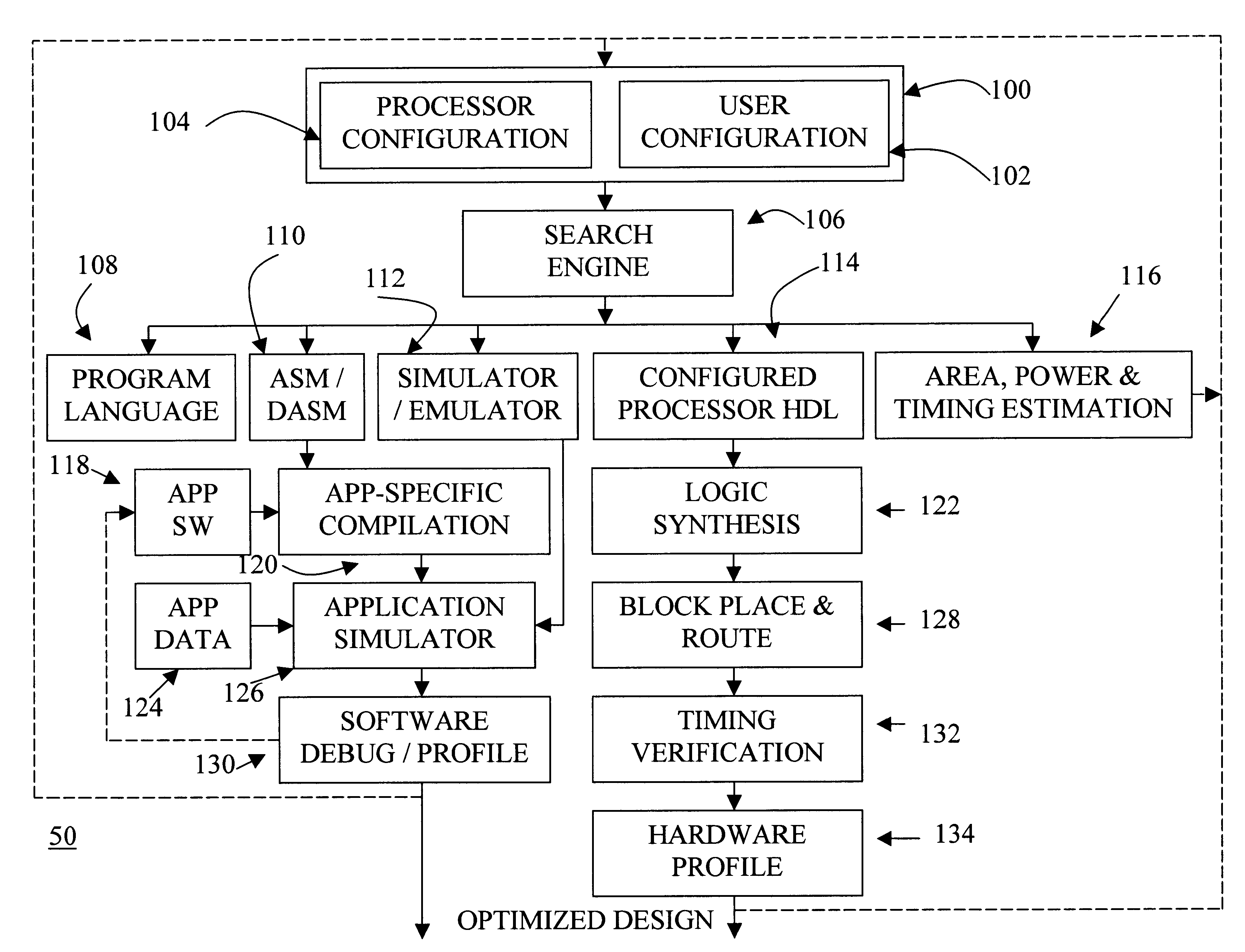
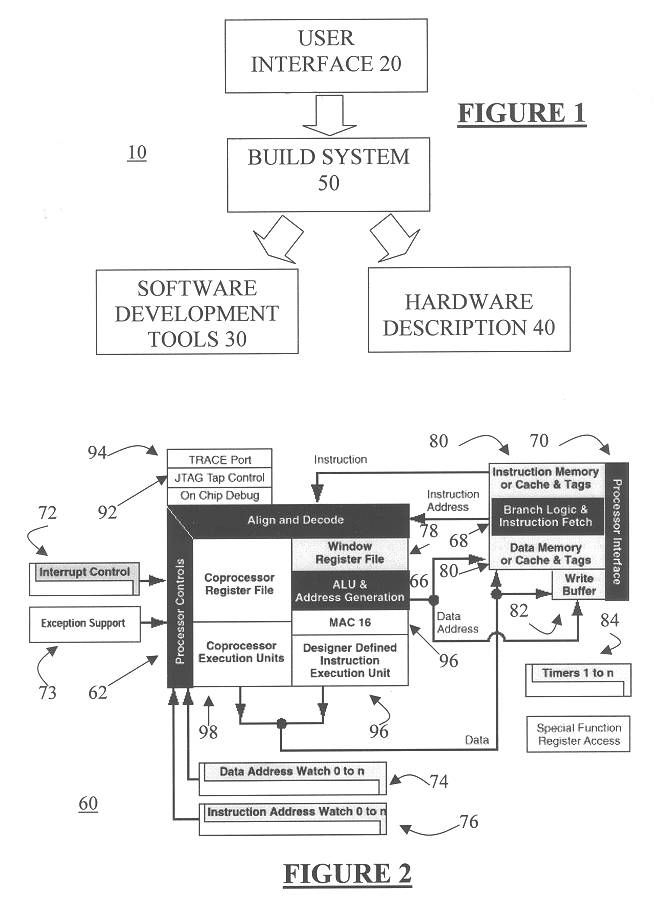
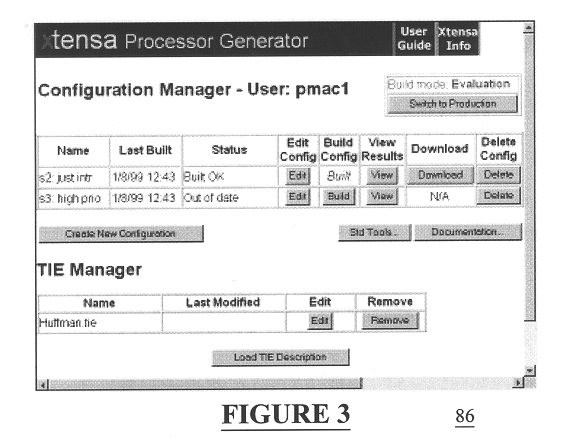
Automated processor generation system for designing a configurable processor and method for the same
InactiveUS6477683B1Decompilation/disassemblyCAD network environmentApplication softwareProcessor design
An automated processor design tool uses a description of customized processor instruction set extensions in a standardized language to develop a configurable definition of a target instruction set, a Hardware Description Language description of circuitry necessary to implement the instruction set, and development tools such as a compiler, assembler, debugger and simulator which can be used to develop applications for the processor and to verify it. Implementation of the processor circuitry can be optimized for various criteria such as area, power consumption, speed and the like. Once a processor configuration is developed, it can be tested and inputs to the system modified to iteratively optimize the processor implementation. By providing a constrained domain of extensions and optimizations, the process can be automated to a high degree, thereby facilitating fast and reliable development.
Owner:TENSILICA
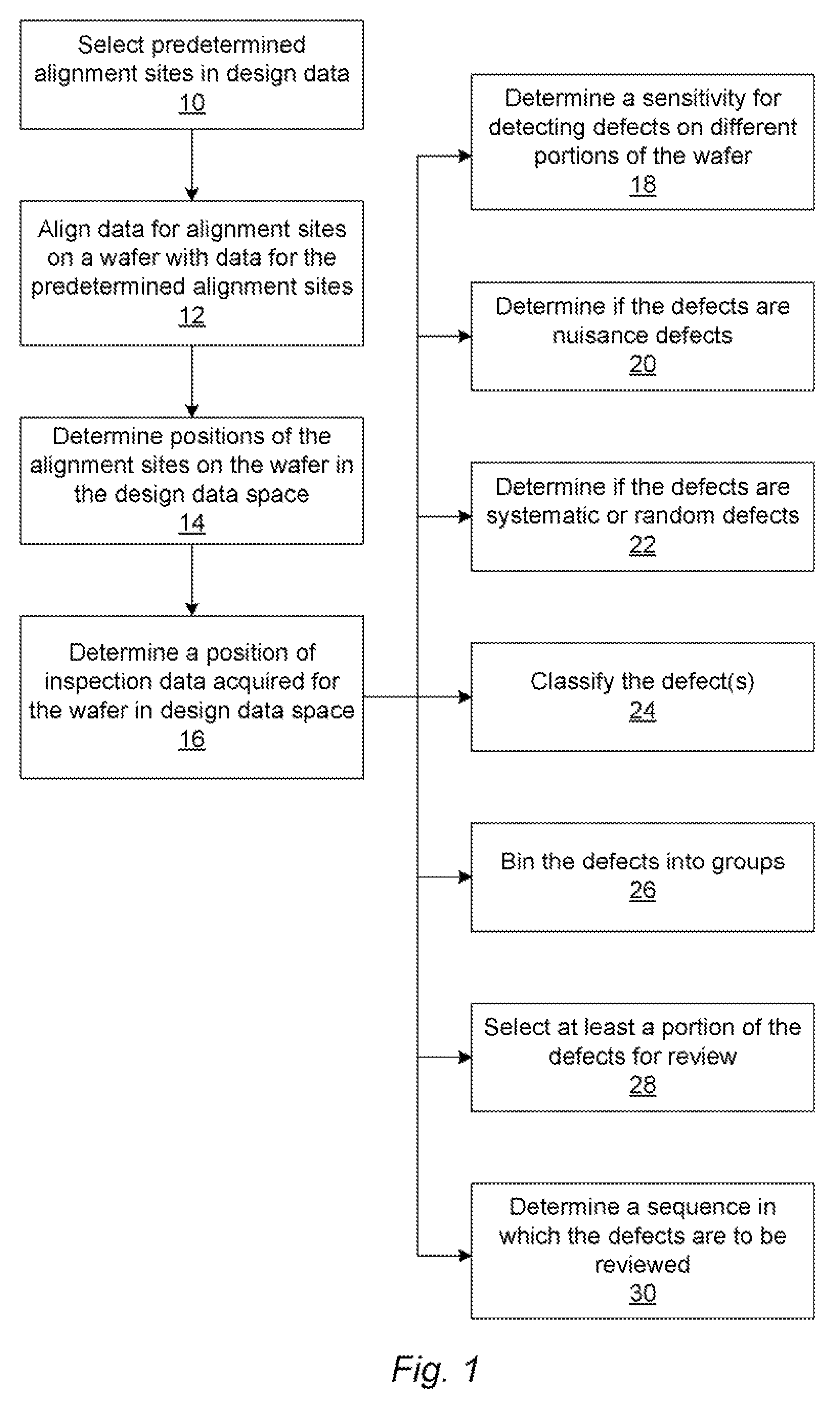
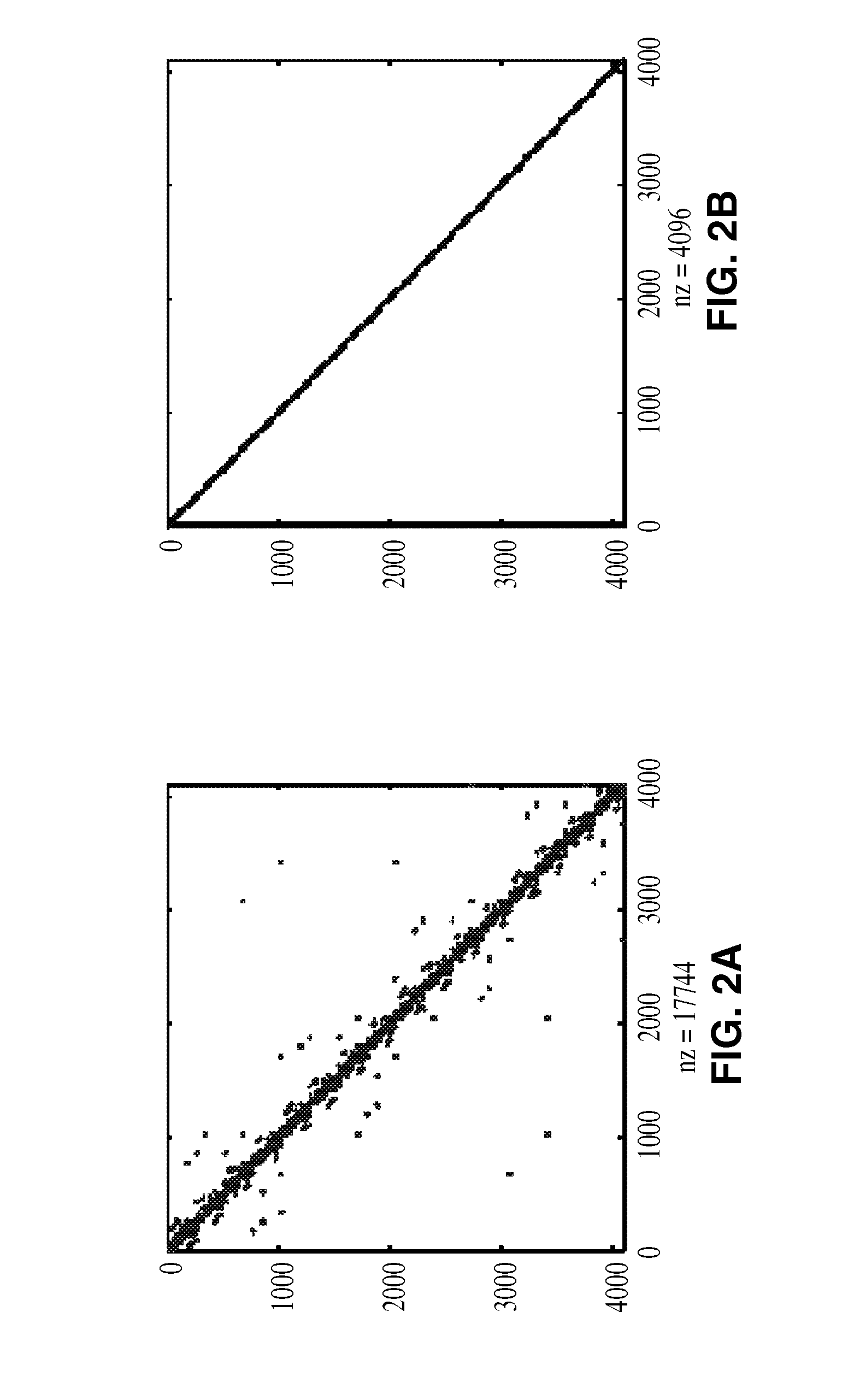
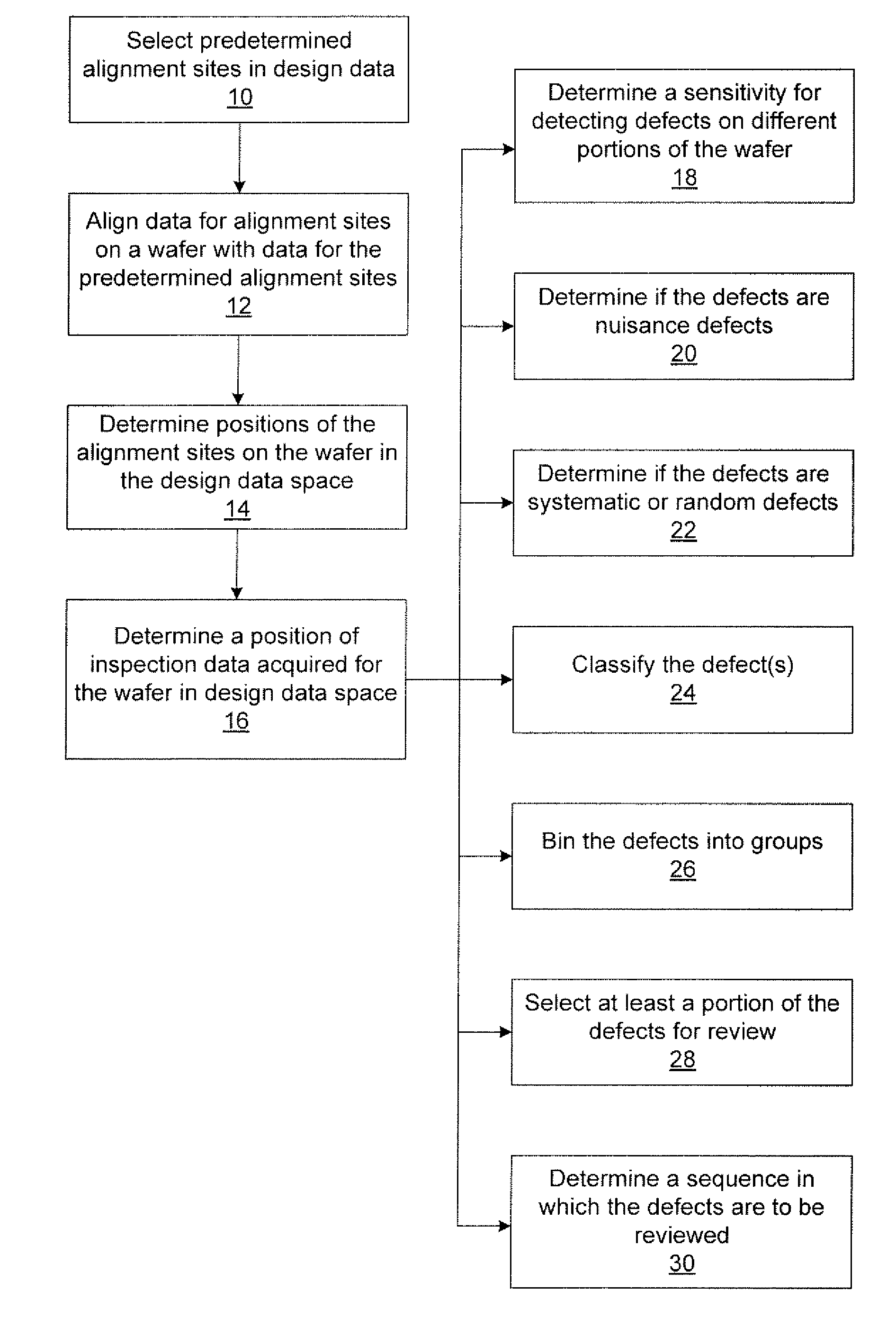
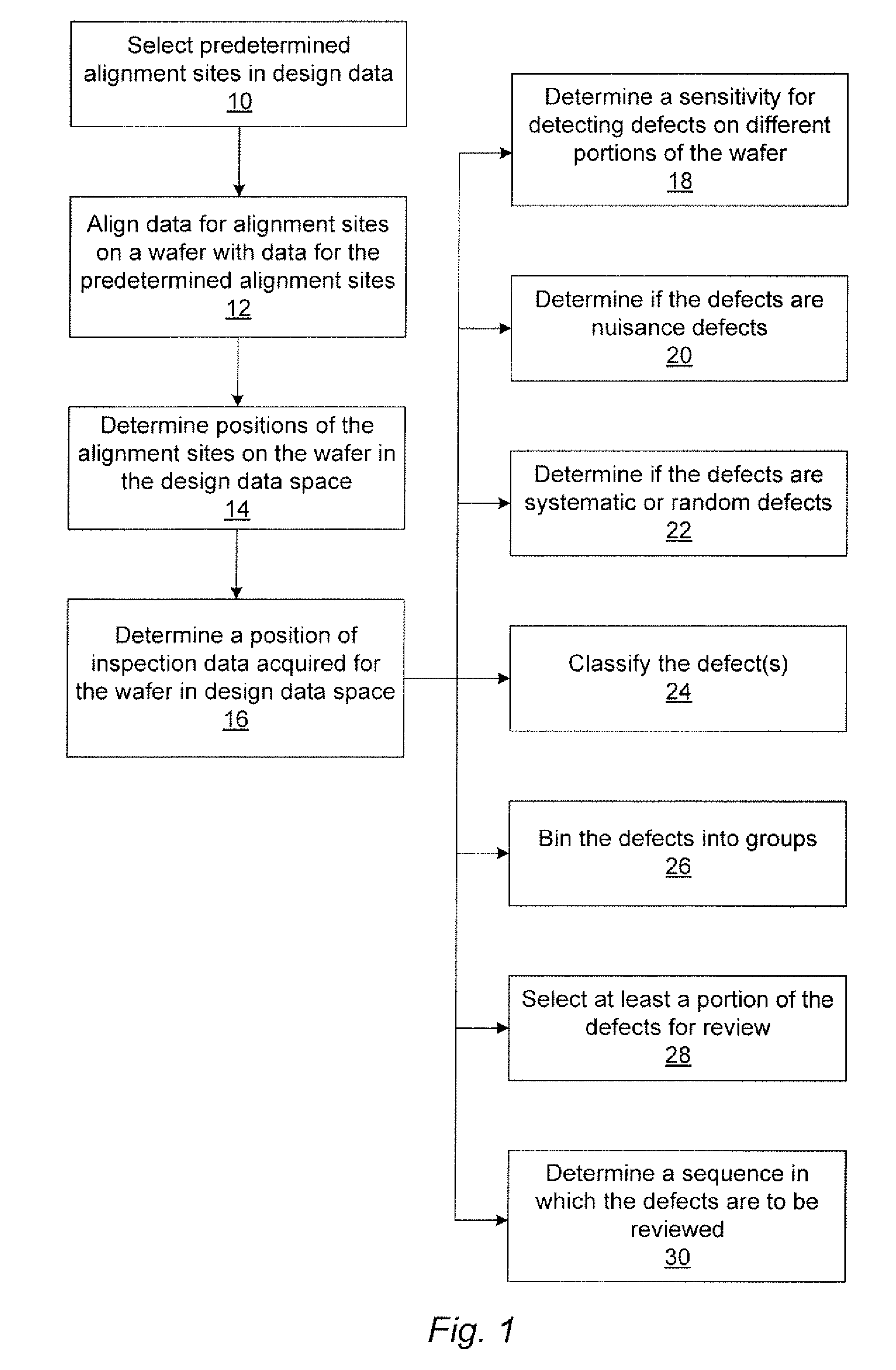
Methods and systems for utilizing design data in combination with inspection data
ActiveUS7676077B2Reduce errorsImprove defectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCharacter and pattern recognitionEngineeringDesign data
Various methods and systems for utilizing design data in combination with inspection data are provided. One computer-implemented method for determining a position of inspection data in design data space includes aligning data acquired by an inspection system for alignment sites on a wafer with data for predetermined alignment sites. The method also includes determining positions of the alignment sites on the wafer in design data space based on positions of the predetermined alignment sites in the design data space. In addition, the method includes determining a position of inspection data acquired for the wafer by the inspection system in the design data space based on the positions of the alignment sites on the wafer in the design data space. In one embodiment, the position of the inspection data is determined with sub-pixel accuracy.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
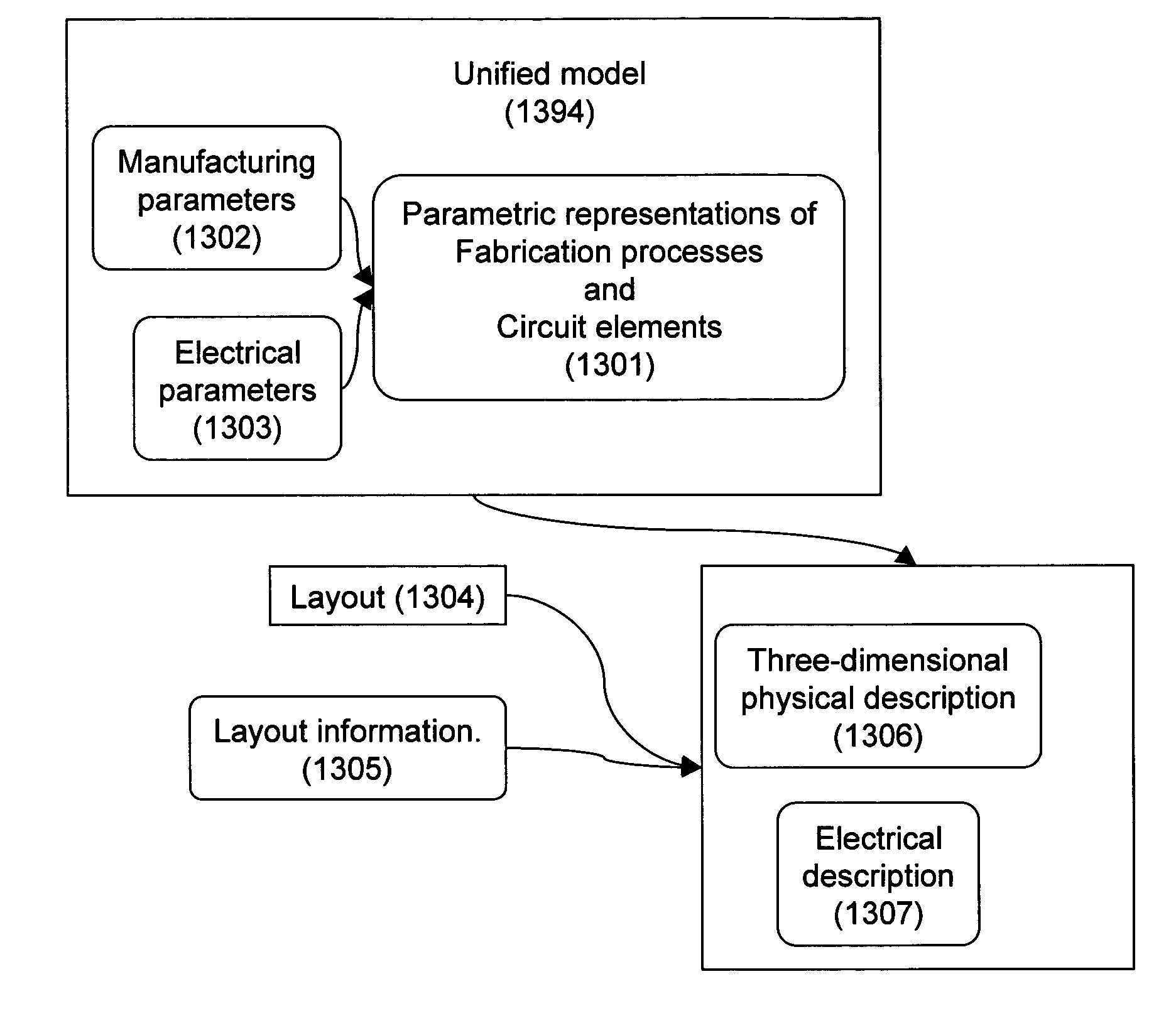
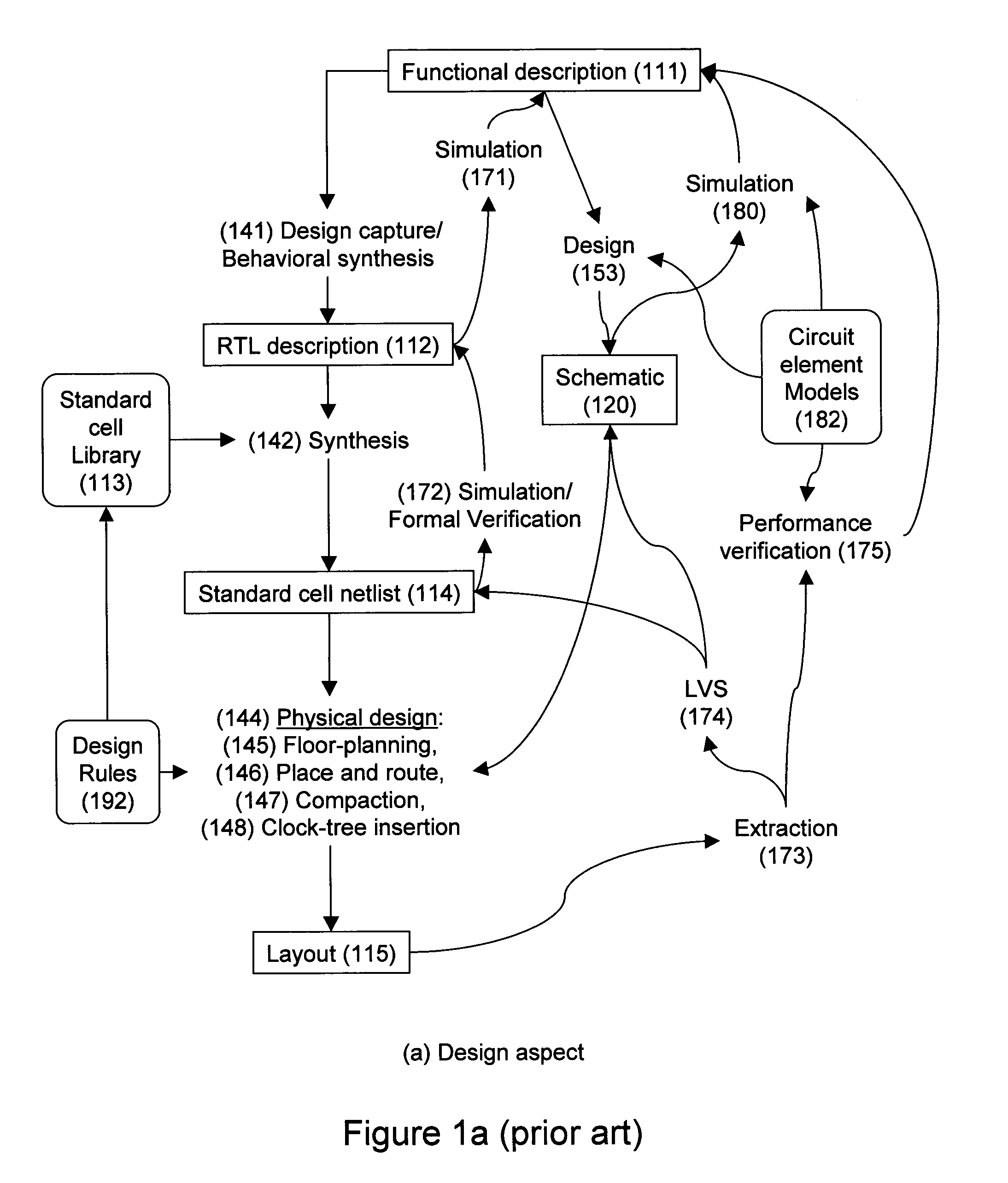
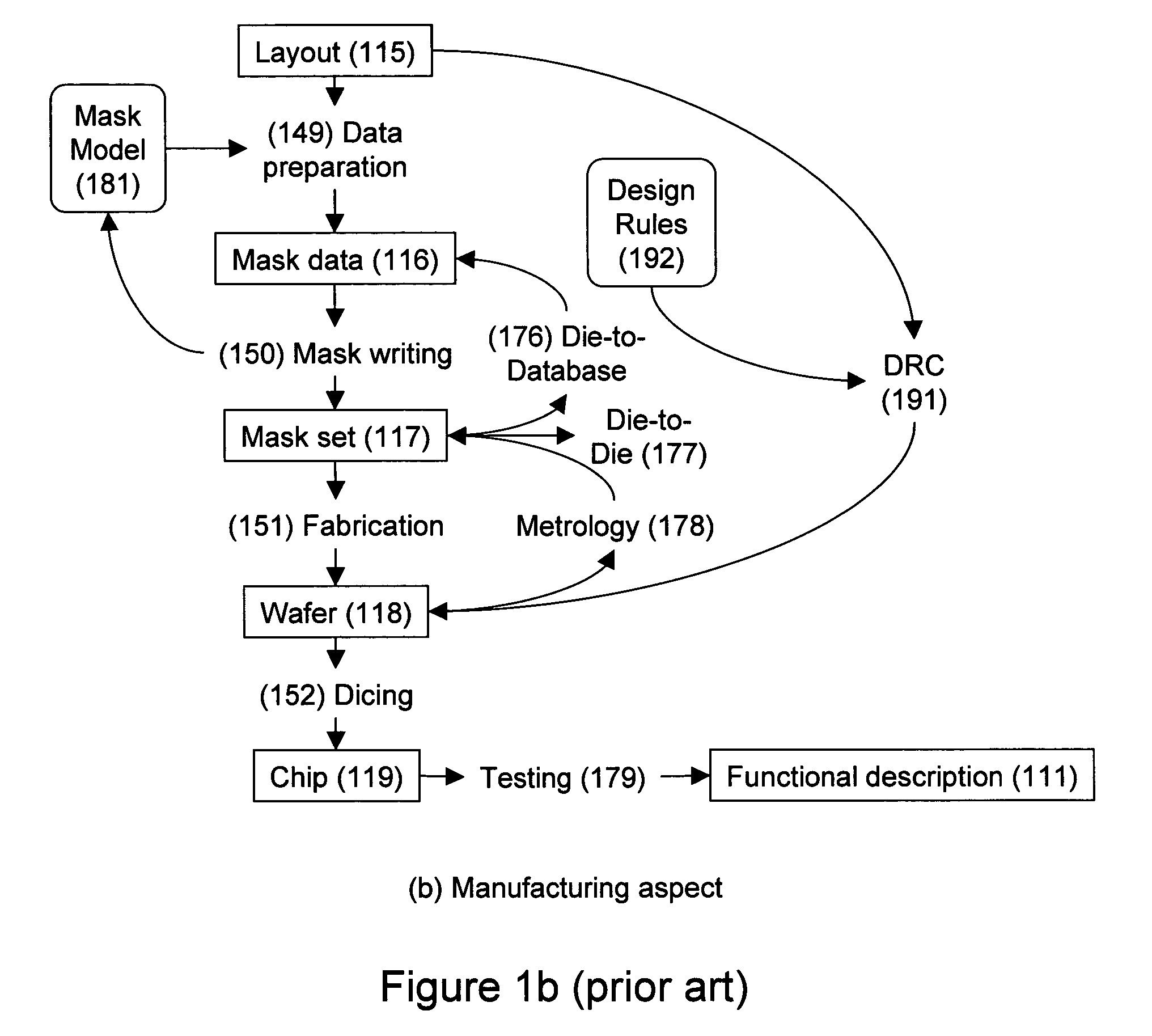
Design-manufacturing interface via a unified model
ActiveUS7155689B2Create additionalImprove accuracyCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsMiniaturizationEngineering
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Method for storing multiple levels of design data in a common database
InactiveUS6505328B1Increase flexibilityEasy to integrateSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCAD circuit designGraphicsLogic circuit design
Owner:MAGMA DESIGN AUTOMATION
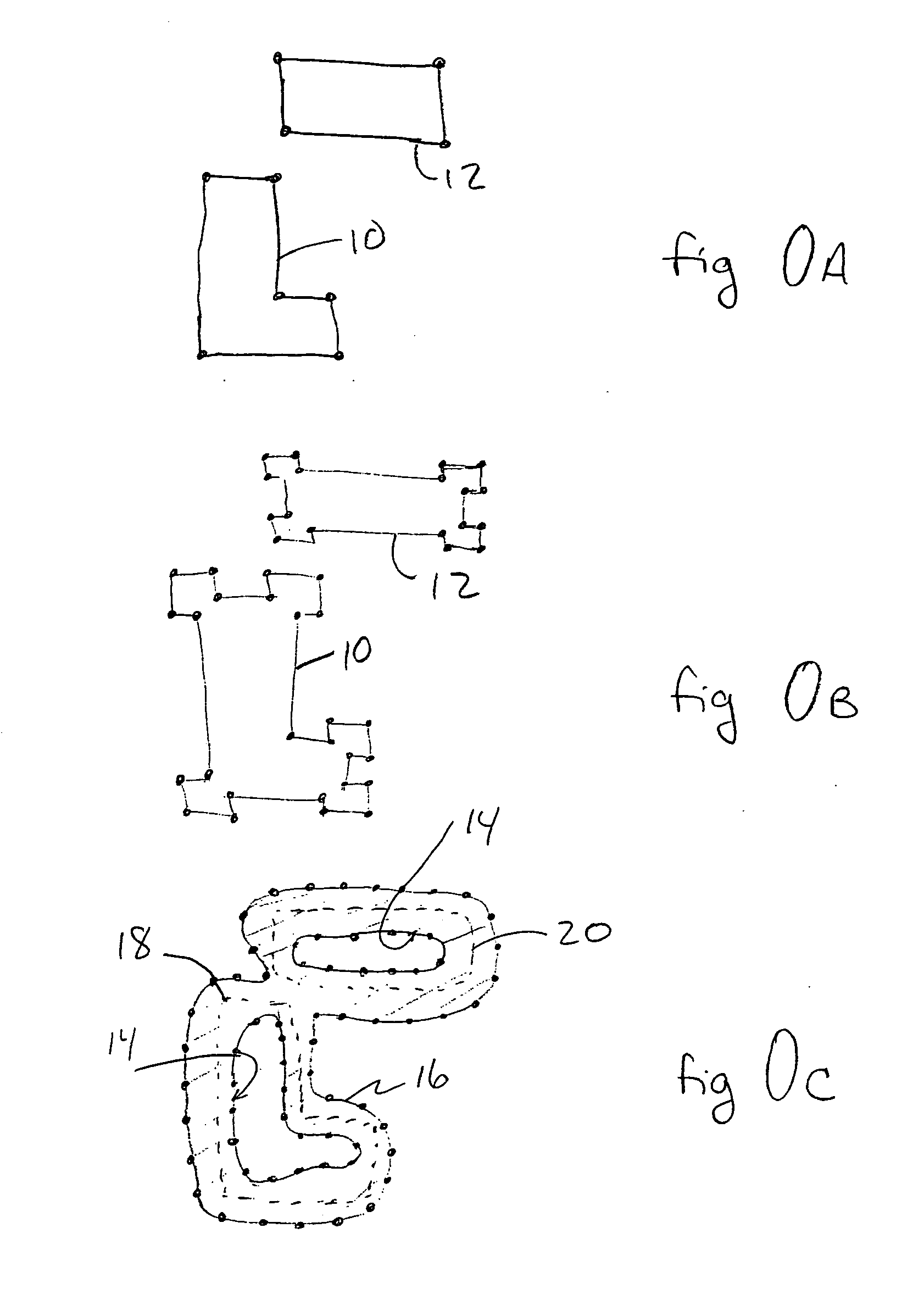
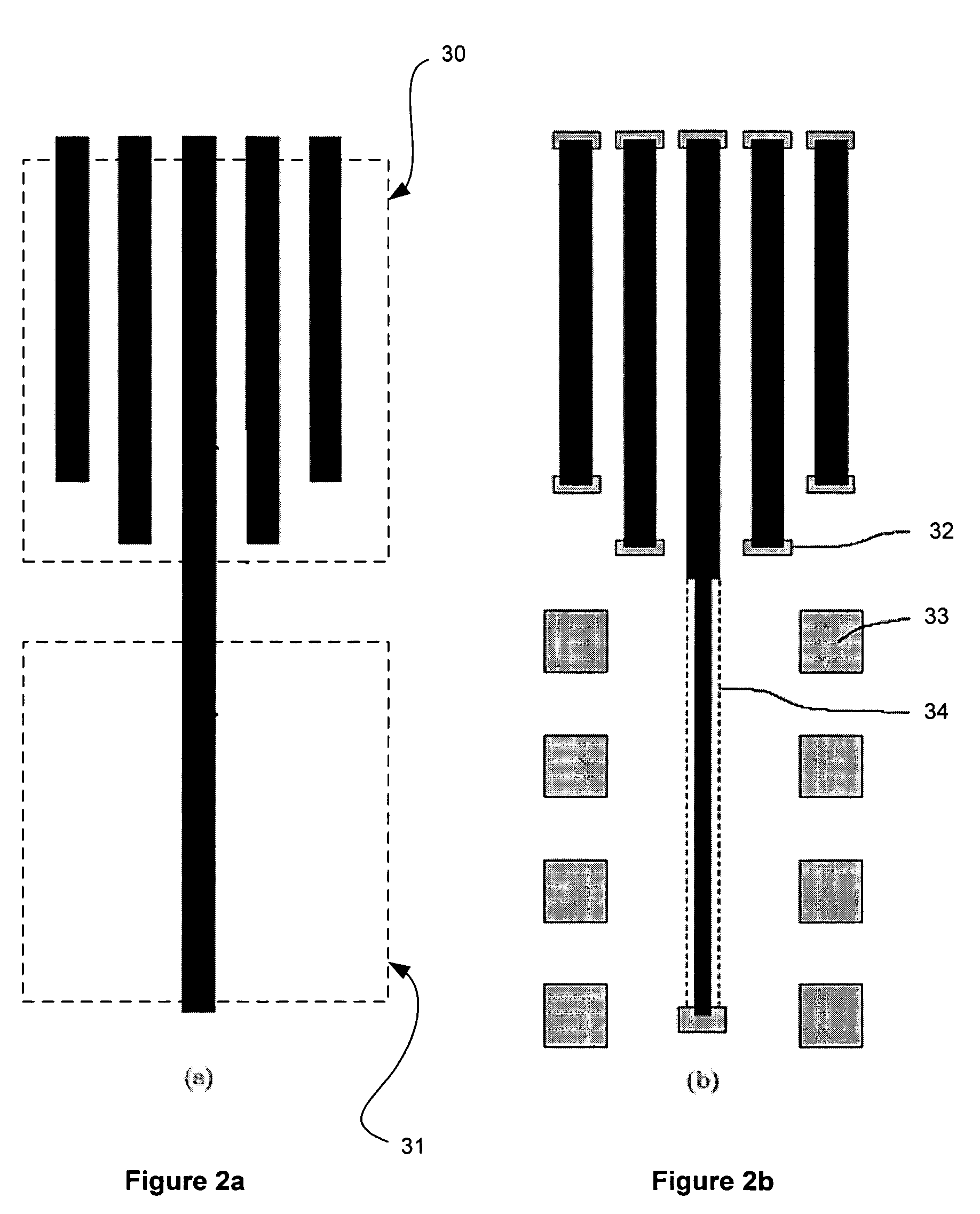
Layout method of semiconductor integrated circuit, layout structure thereof, and photomask for forming the layout structure
ActiveUS7137092B2Eliminate biasHigh dimensionalSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductorPhotomask
A plurality of standard cells 10 are arranged to form a channel-less standard cell array 1, which has vertical and horizontal sides. A plurality of first proximity dummy cells 20 are arranged along each of the vertical sides of the standard cell array to form a first proximity dummy bands 20 such that the upper and lower sides of the first proximity dummy cells are in contact with each other and such that the left or right side of each of the first proximity dummy cells is in contact with the vertical side of the standard cell array 1. Furthermore, a plurality of second proximity dummy bands are arranged along each of the horizontal sides of the standard cell array to form a second proximity dummy bands such that the upper or lower side of each of the second proximity dummy cells is in contact with the horizontal side of the standard cell 1.
Owner:KAWASAKI MICROELECTRONICS
Structured and parameterized model order reduction
InactiveUS20080072182A1Reduce redundancyNon-uniformity is constantDetecting faulty computer hardwareComputation using non-denominational number representationStructured modelOrder reduction
Model-order reduction techniques are described for RLC circuits modeling the VLSI layouts. A structured model order reduction is developed to preserve the block-level sparsity, hierarchy and latency. In addition, a structured and parameterized model order reduction is developed to generate macromodels for design optimizations of VLSI layouts. The applications are thermal via allocation under the dynamic thermal integrity and via stapling to simultaneously optimize thermal and power integrity.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods and systems for utilizing design data in combination with inspection data
ActiveUS20070156379A1Increase catch rateImprove signal-to-noise ratioSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCharacter and pattern recognitionEngineeringDesign data
Various methods and systems for utilizing design data in combination with inspection data are provided. One computer-implemented method for determining a position of inspection data in design data space includes aligning data acquired by an inspection system for alignment sites on a wafer with data for predetermined alignment sites. The method also includes determining positions of the alignment sites on the wafer in design data space based on positions of the predetermined alignment sites in the design data space. In addition, the method includes determining a position of inspection data acquired for the wafer by the inspection system in the design data space based on the positions of the alignment sites on the wafer in the design data space. In one embodiment, the position of the inspection data is determined with sub-pixel accuracy.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
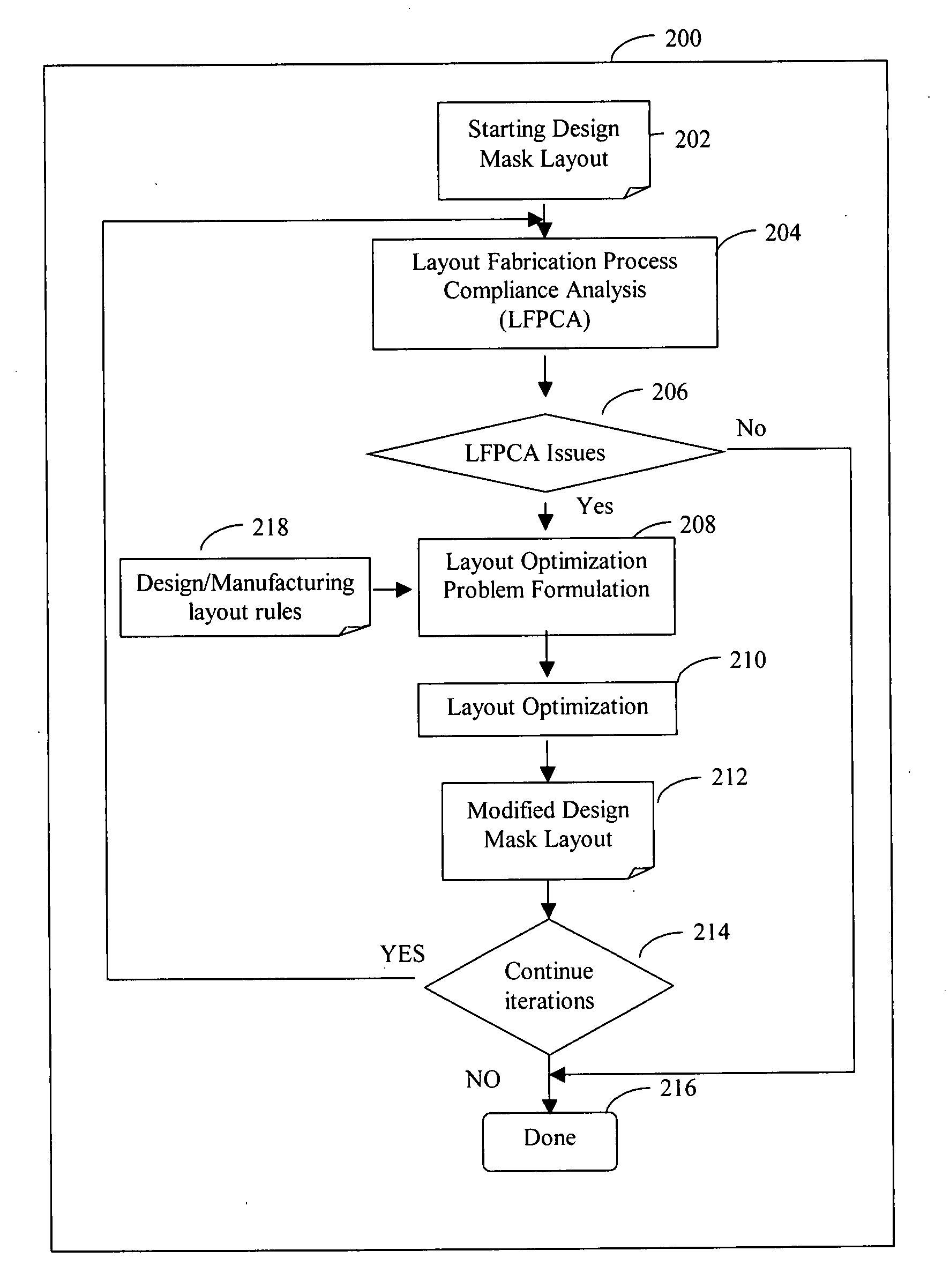
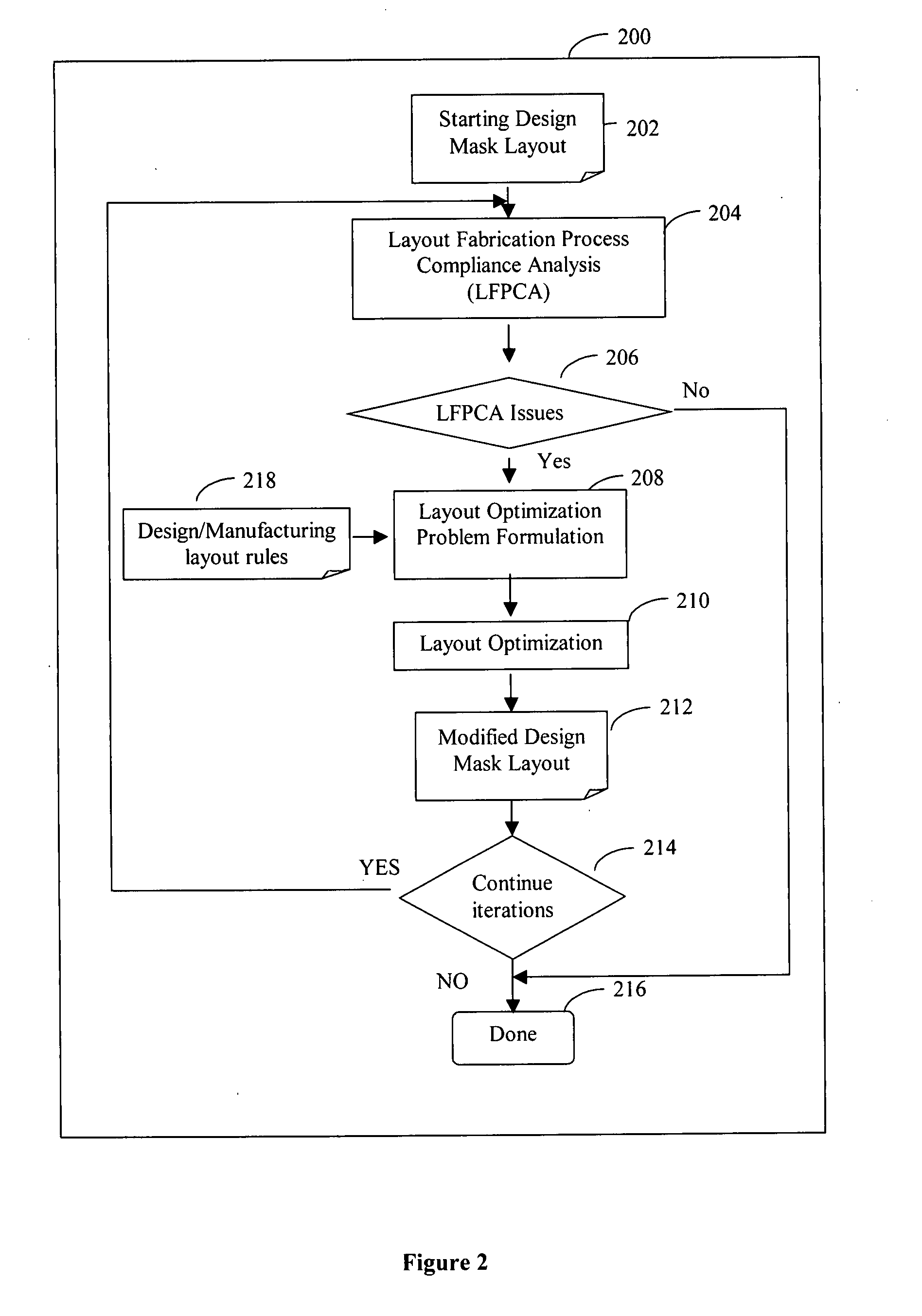
System and method of maximizing integrated circuit manufacturing yield with fabrication process simulation driven layout optimization
InactiveUS20080046846A1Maximizing manufacturing yieldYield maximizationCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationIntegrated circuit manufacturingEngineering
A system and a method of maximizing the manufacturing yield of integrated circuit (“IC”) design using IC fabrication process simulation driven layout optimization is described. An IC design layout is automatically modified through formulation of a layout optimization problem utilizing the results of layout fabrication process compliance analysis tools. The modification of layout is performed adaptively and iteratively to make an IC layout less susceptible to yield issues while maintaining design rule correctness and minimal circuit performance impact.
Owner:CHEW MARKO P +1
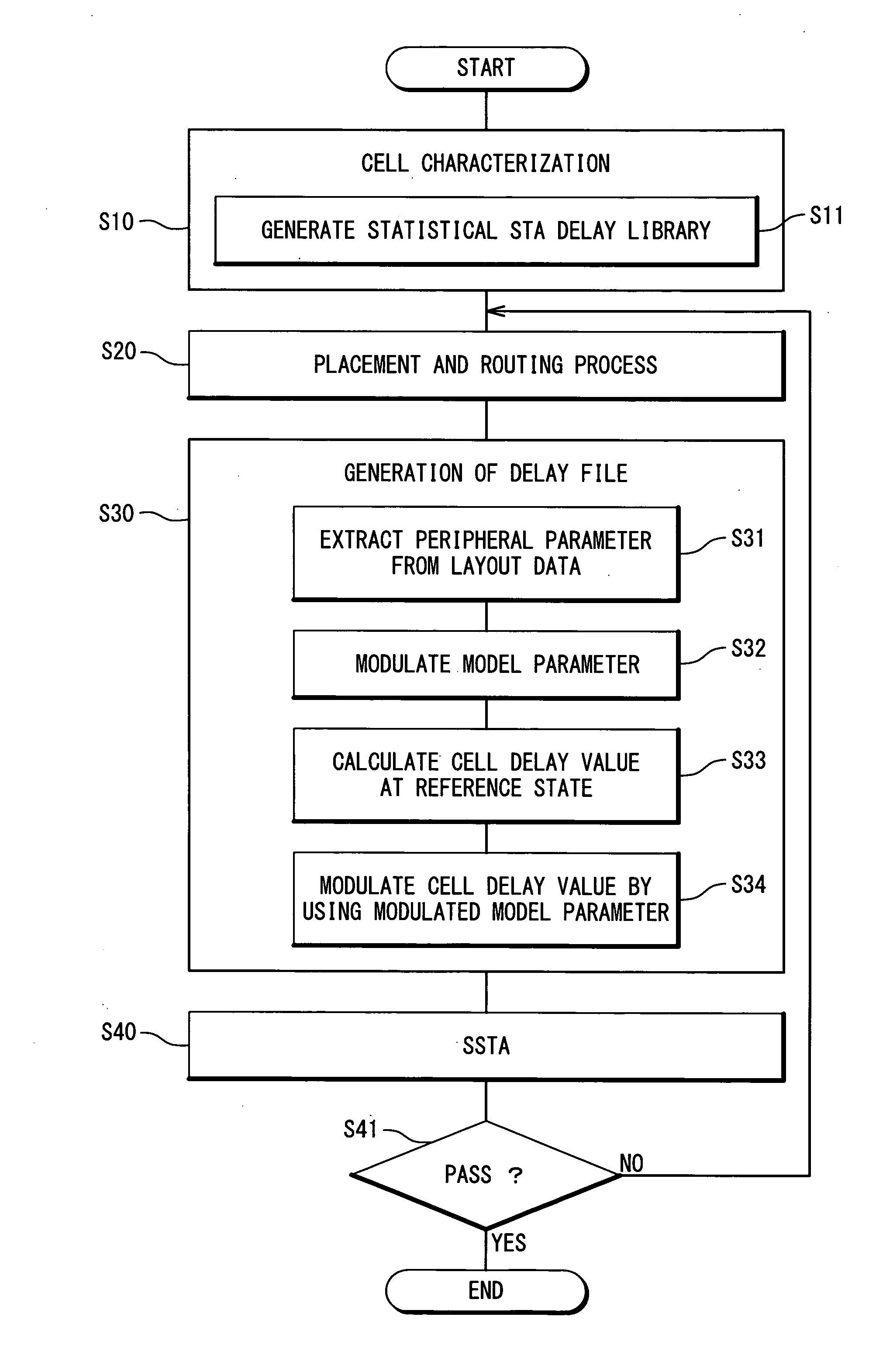
Method and program for designing semiconductor integrated circuit
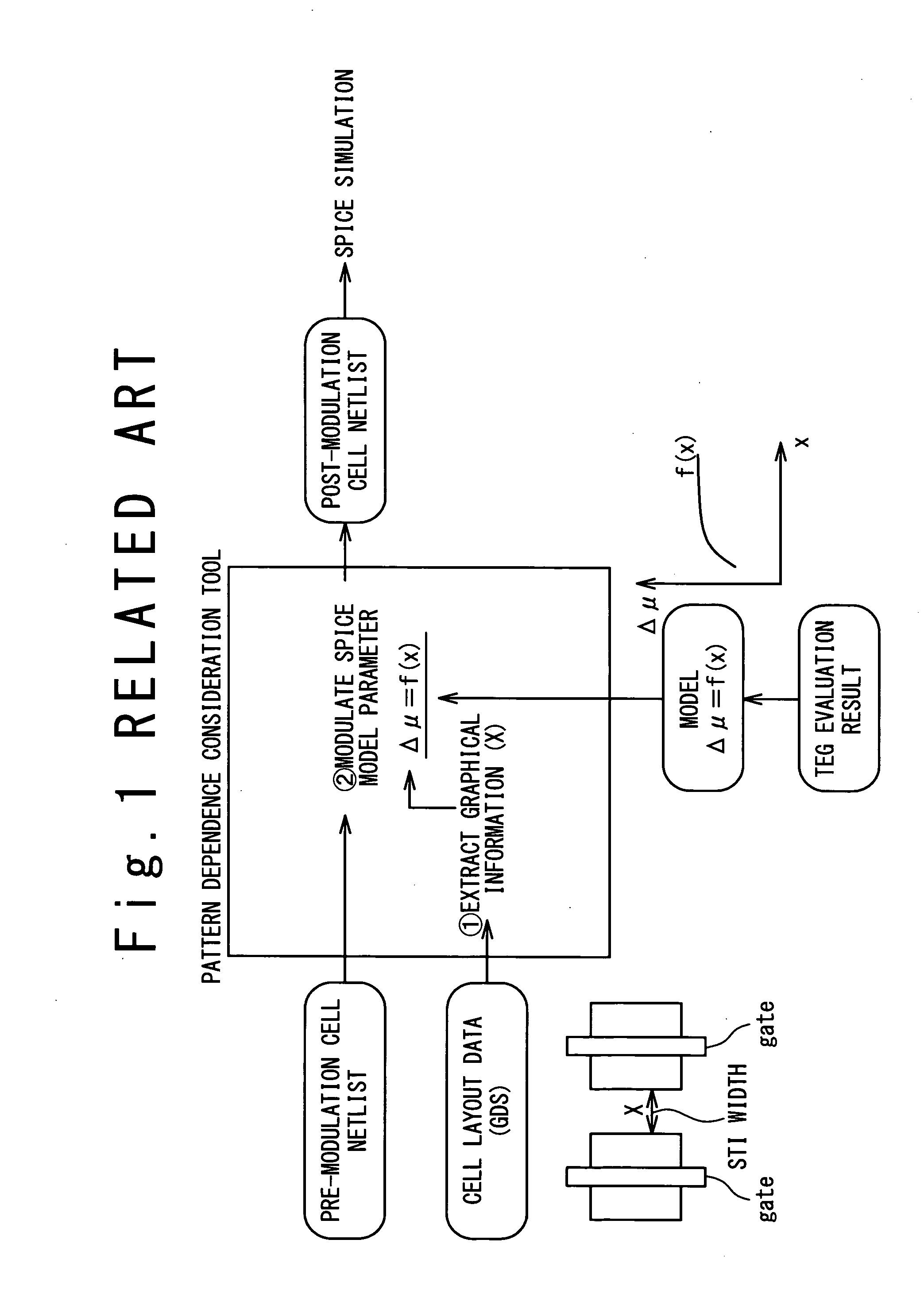
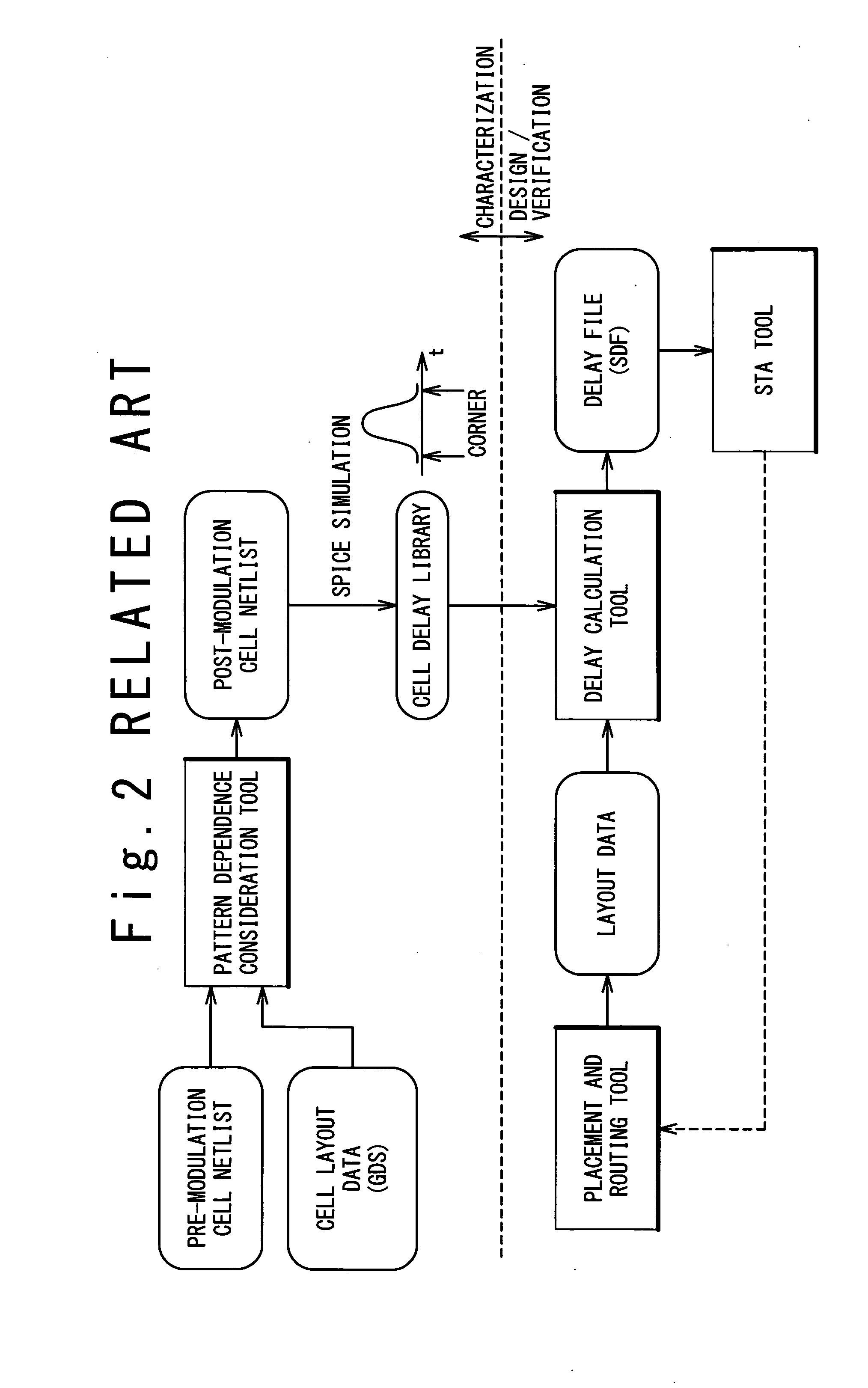
InactiveUS20090024974A1Increase in design/verification TAT can be preventedHigh delay accuracyCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationModel parametersCell based
A design method for an LSI includes: generating a delay library for use in a statistical STA, wherein the delay library provides a delay function that expresses a cell delay value as a function of model parameters of a transistor; generating a layout data; and calculating a delay value of a target cell based on the delay library and the layout data. The calculating includes: referring to the layout data to extract a parameter specifying a layout pattern around a target transistor; modulating model parameters of the target transistor such that the characteristics corresponding to the extracted parameter is obtained in a circuit simulation; calculating, by using the delay function, a reference delay value of the target cell; and calculating, by using the delay function and the modulation amount of the model parameter, a delay variation from the reference delay value depending on the modulation amount.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Memory using mixed valence conductive oxides
A memory using a mixed valence conductive oxides. The memory includes a mixed valence conductive oxide that is less conductive in its oxygen deficient state and a mixed electronic ionic conductor that is an electrolyte to oxygen and promotes an electric field effective to cause oxygen ionic motion.
Owner:UNITY SEMICON
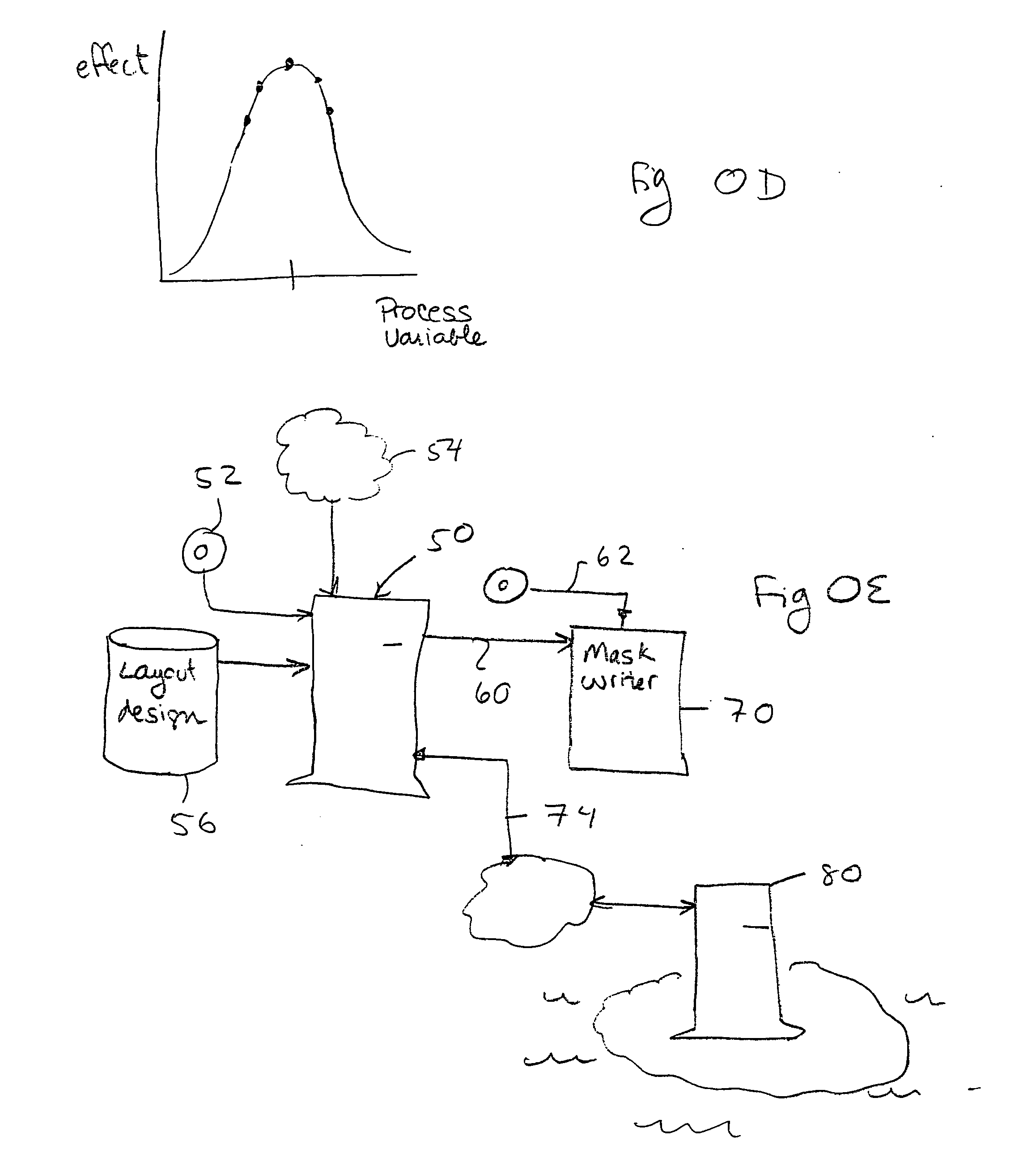
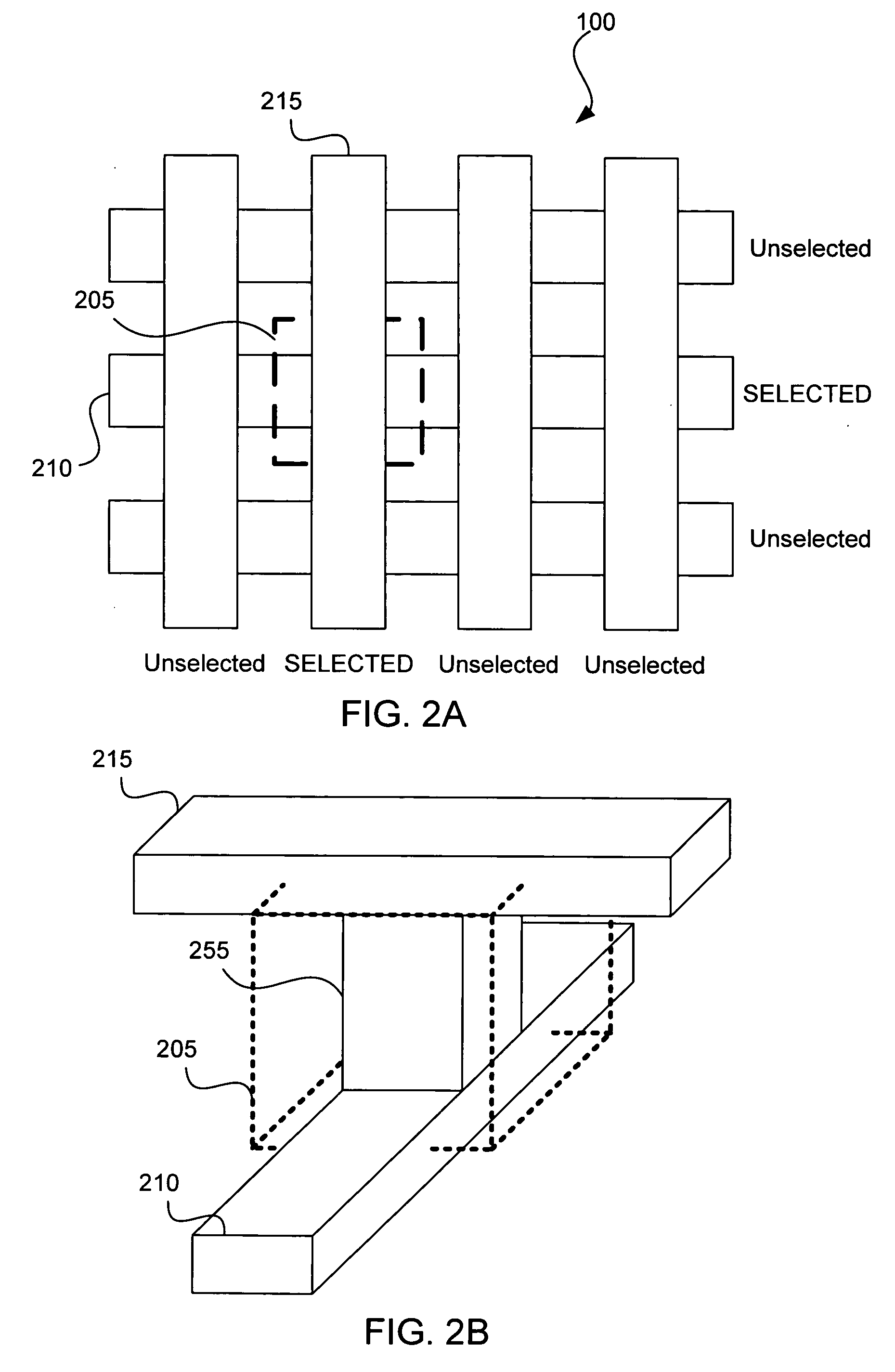
Method and apparatus for quickly determining the effect of placing an assist feature at a location in a layout
ActiveUS20070038973A1Quick effectOptimize locationPhotomechanical apparatusCAD circuit designEngineeringSystem usage
One embodiment of the present invention determines the effect of placing an assist feature at a location in a layout. During operation, the system receives a first value which was pre-computed by convolving a model with a layout at an evaluation point, wherein the model models semiconductor manufacturing processes. Next, the system determines a second value by convolving the model with an assist feature, which is assumed to be located at a first location which is in proximity to the evaluation point. The system then determines the effect of placing an assist feature using the first value and the second value. An embodiment of the present invention can be used to determine a substantially optimal location for placing an assist feature in a layout.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
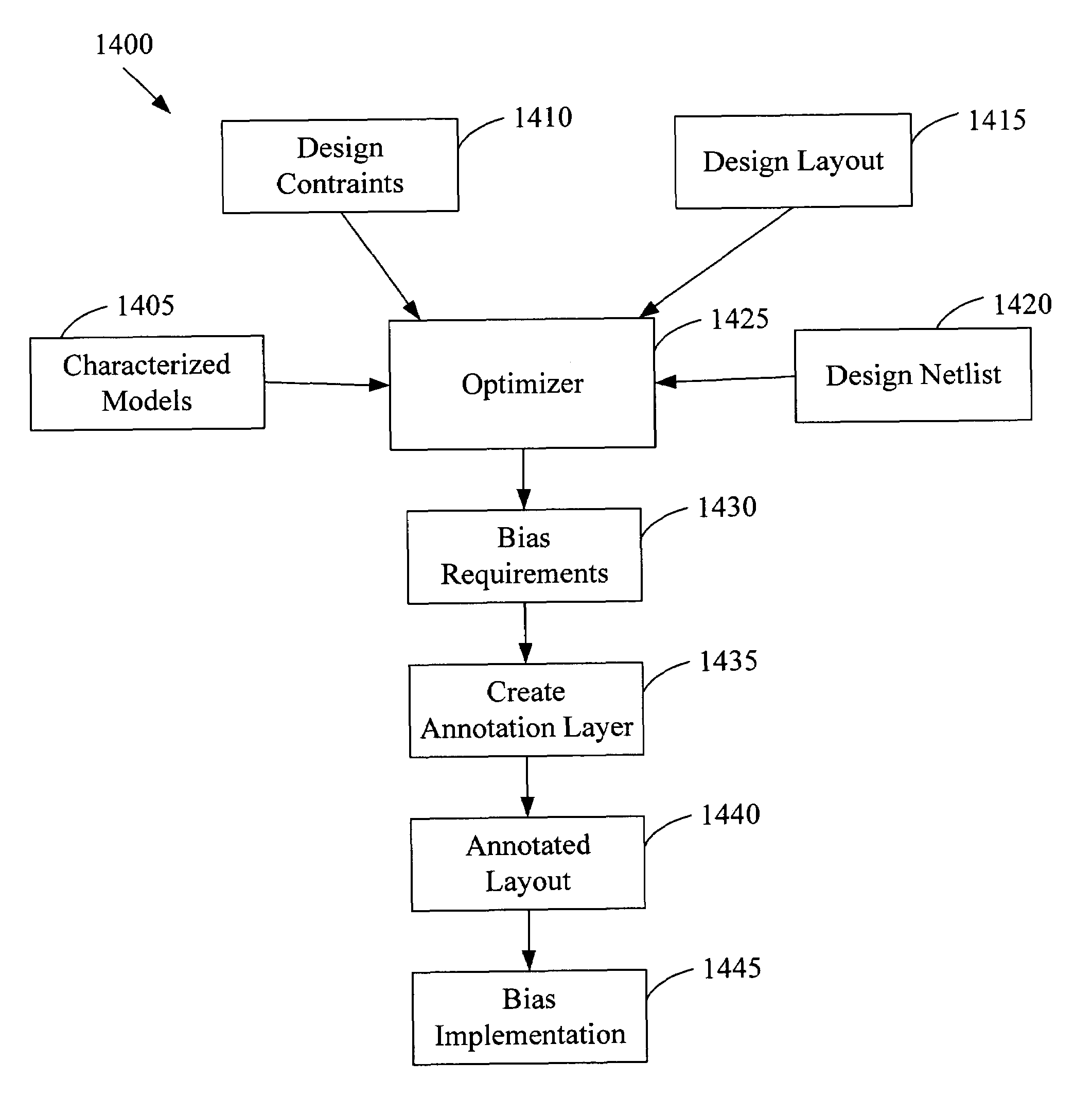
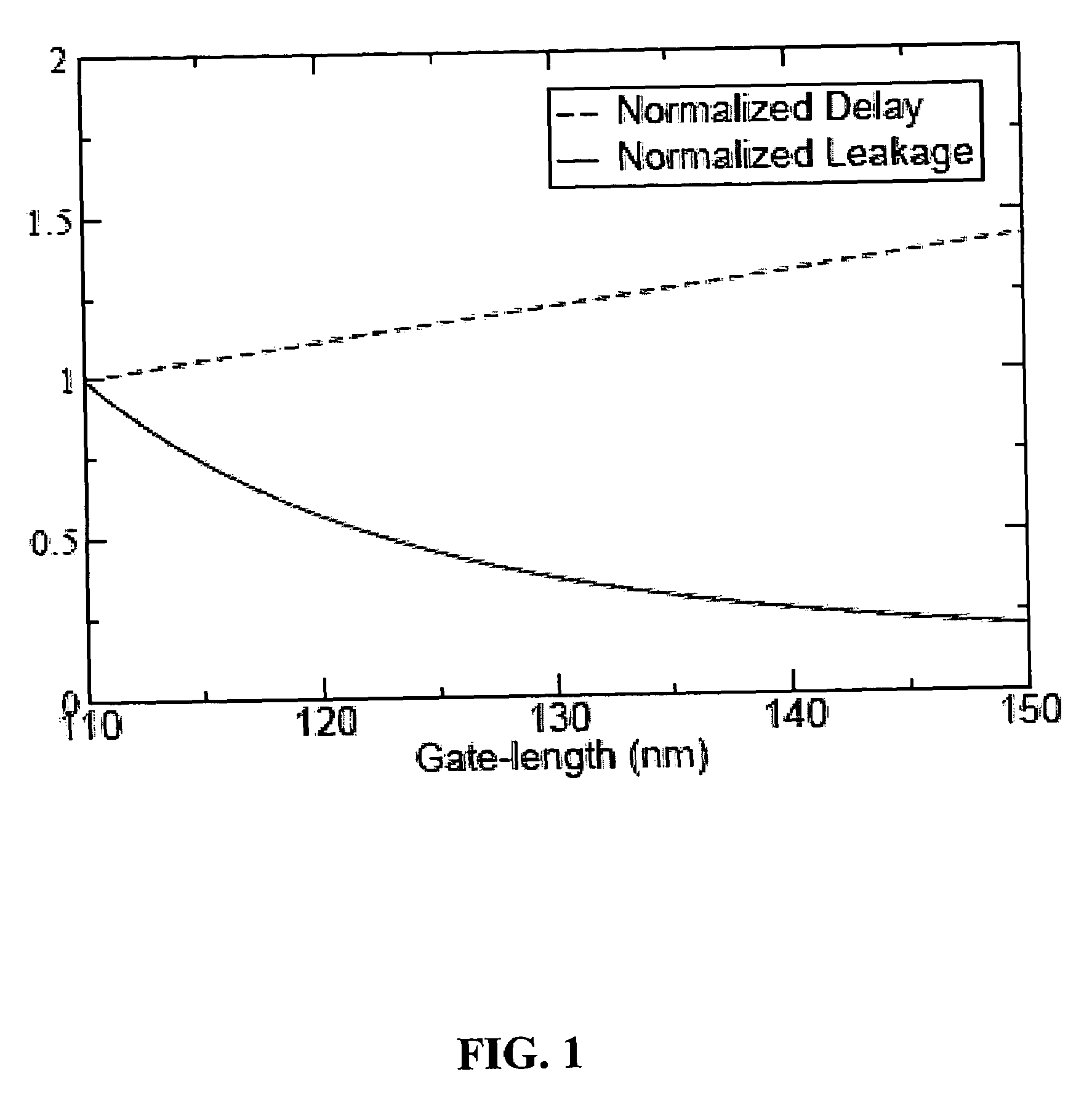
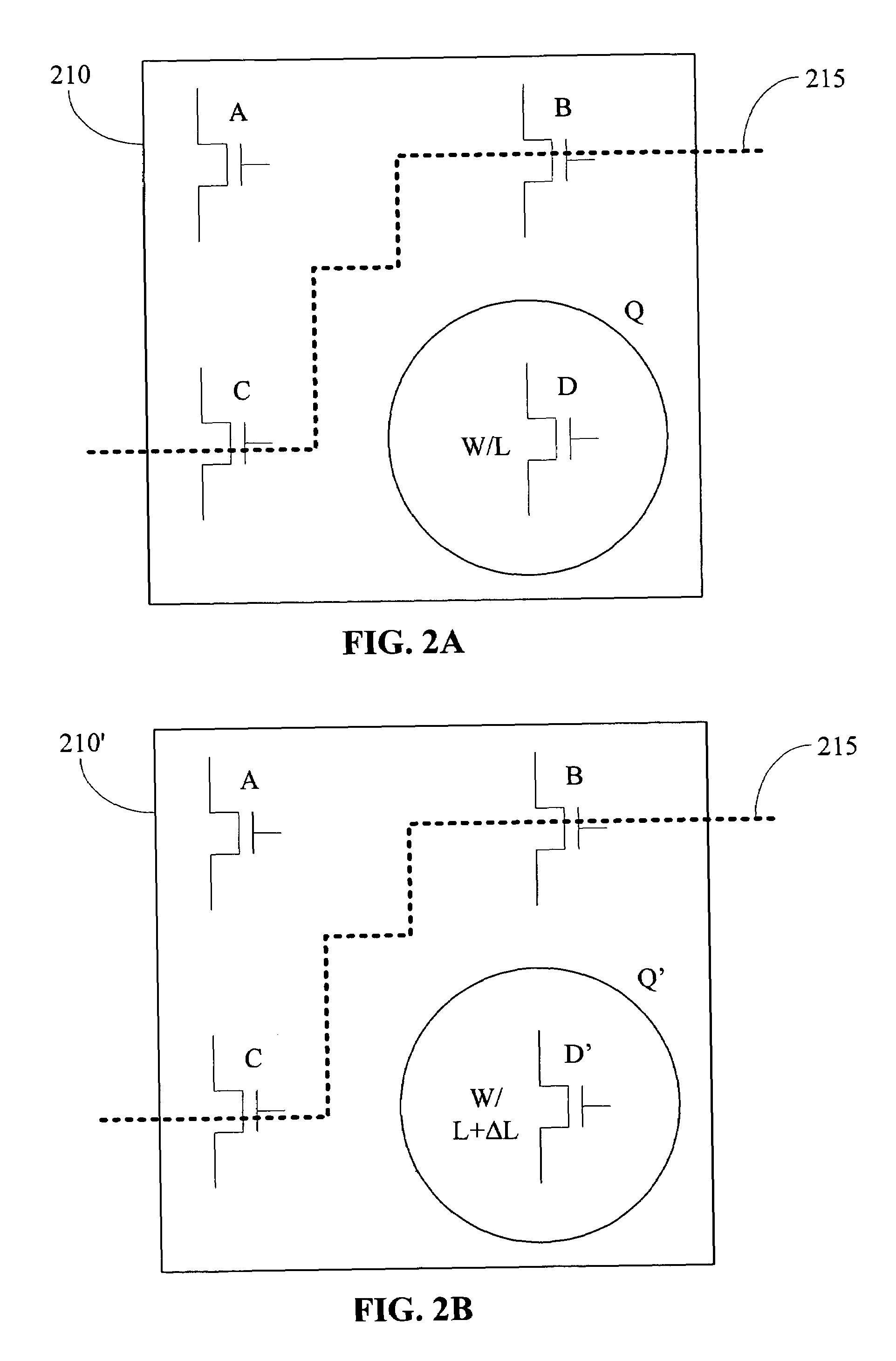
Gate-length biasing for digital circuit optimization
InactiveUS7441211B1Reduce impactImpairing time delay performance only linearlySolid-state devicesCAD circuit designEngineeringDigital electronics
Methods and apparatus for a gate-length biasing methodology for optimizing integrated digital circuits are described. The gate-length biasing methodology replaces a nominal gate-length of a transistor with a biased gate-length, where the biased gate-length includes a bias length that is small compared to the nominal gate-length. In an exemplary embodiment, the bias length is less than 10% of the nominal gate-length.
Owner:RPX CORP
Methods and systems for determining a position of inspection data in design data space
Various methods and systems for determining a position of inspection data in design data space are provided. One computer-implemented method includes determining a centroid of an alignment target formed on a wafer using an image of the alignment target acquired by imaging the wafer. The method also includes aligning the centroid to a centroid of a geometrical shape describing the alignment target. In addition, the method includes assigning a design data space position of the centroid of the alignment target as a position of the centroid of the geometrical shape in the design data space. The method further includes determining a position of inspection data acquired for the wafer in the design data space based on the design data space position of the centroid of the alignment target.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
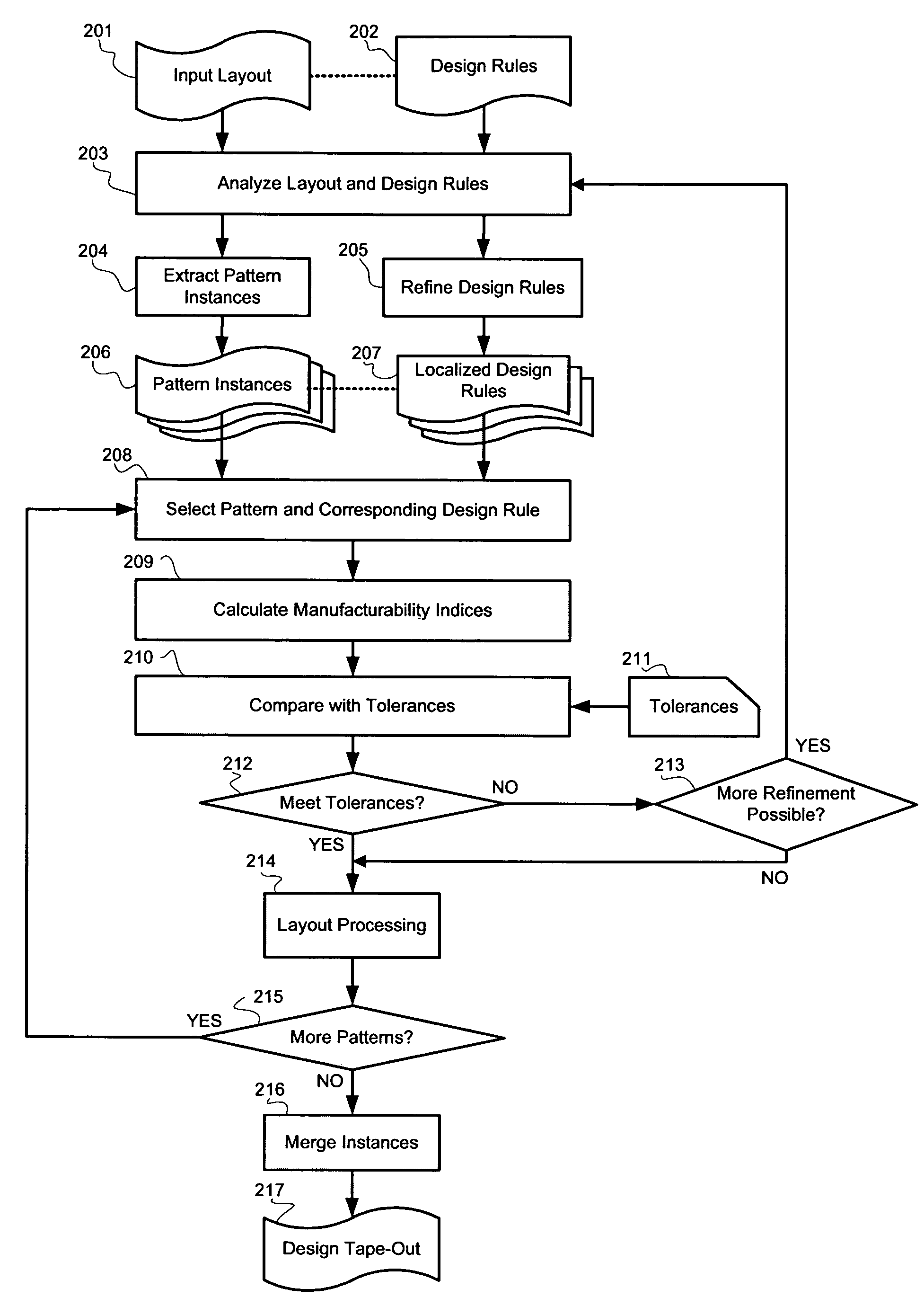
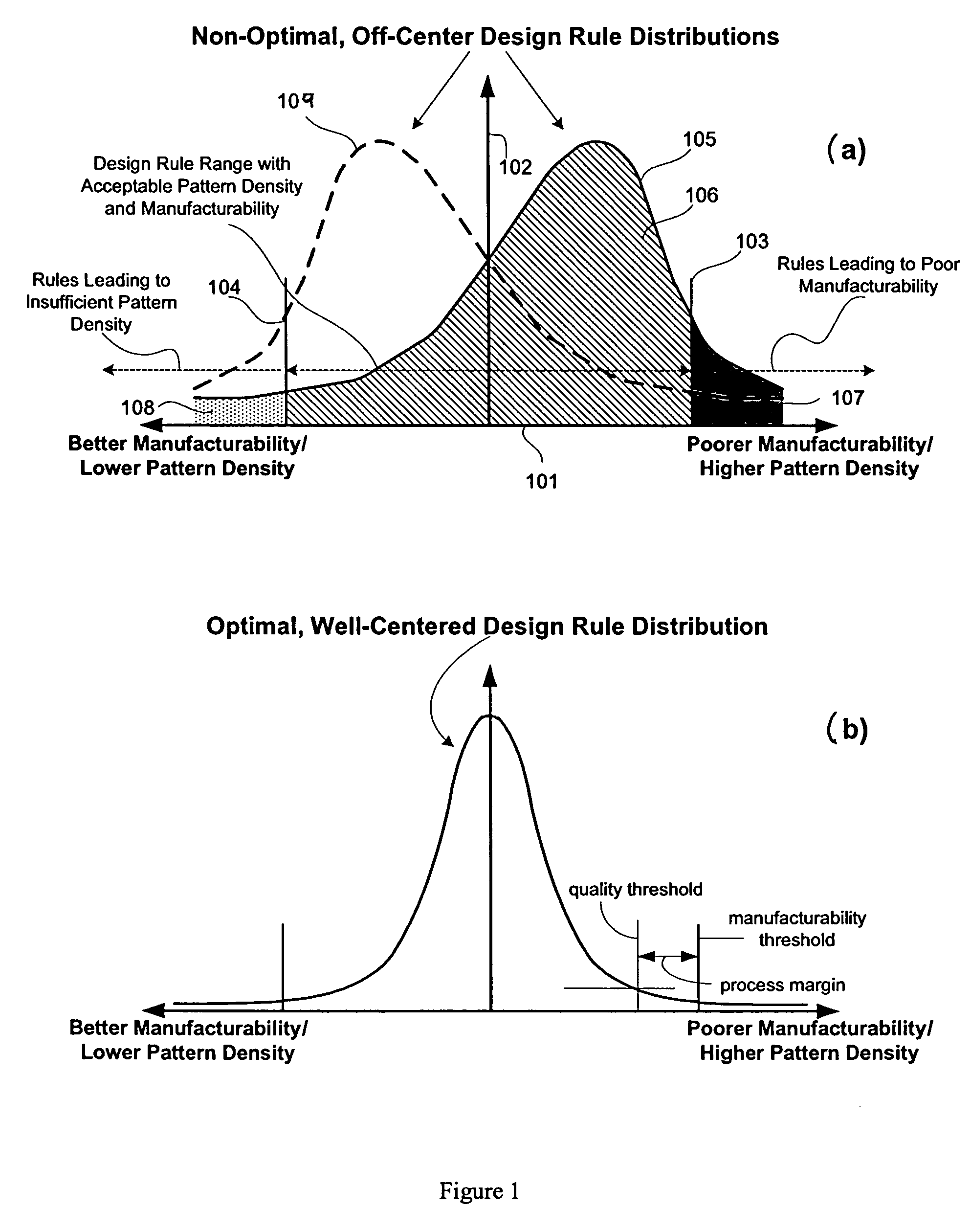
System for designing integrated circuits with enhanced manufacturability
ActiveUS7523429B2Improve manufacturabilityLittle interferencePressersMattress sewingGranularityEngineering
A system and method for integrated circuit design are disclosed to enhance manufacturability of circuit layouts through generation of hierarchical design rules which capture localized layout requirements. In contrast to conventional techniques which apply global design rules, the disclosed IC design system and method partition the original design layout into a desired level of granularity based on specified layout and integrated circuit properties. At that localized level, the design rules are adjusted appropriately to capture the critical aspects from a manufacturability standpoint. These adjusted design rules are then used to perform localized layout manipulation and mask data conversion.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
FPGA with register-intensive architecture
ActiveUS7028281B1Minimize resourceReduce consumptionSolid-state devicesCAD circuit designProcessor registerMultiplexer
Field programmable gate arrays (FPGA's) may be structured in accordance with the disclosure to have a register-intensive architecture that provides, for each of plural function-spawning LookUp Tables (e.g. a 4-input, base LUT's) within a logic block, a plurality of in-block accessible registers. A register-feeding multiplexer means may be provided for allowing each of the plural registers to equivalently capture and store a result signal output by the corresponding, base LUT of the plural registers. Registerable, primary and secondary feedthroughs may be provided for each base LUT so that locally-acquired input signals of the LUT may be fed-through to the corresponding, in-block registers for register-recovery purposes without fully consuming (wasting) the lookup resources of the associated, base LUT. A multi-stage, input switch matrix (ISM) may be further provided for acquiring and routing input signals from adjacent, block-interconnect lines (AIL's) and / or block-intra-connect lines (e.g., FB's) to the base LUT's and / or their respective, registerable feedthroughs. Techniques are disclosed for utilizing the many in-block registers and / or the registerable feedthroughs and / or the multi-stage ISM's for efficiently implementing various circuit designs by appropriately configuring such register-intensive FPGA's.
Owner:LATTICE SEMICON CORP
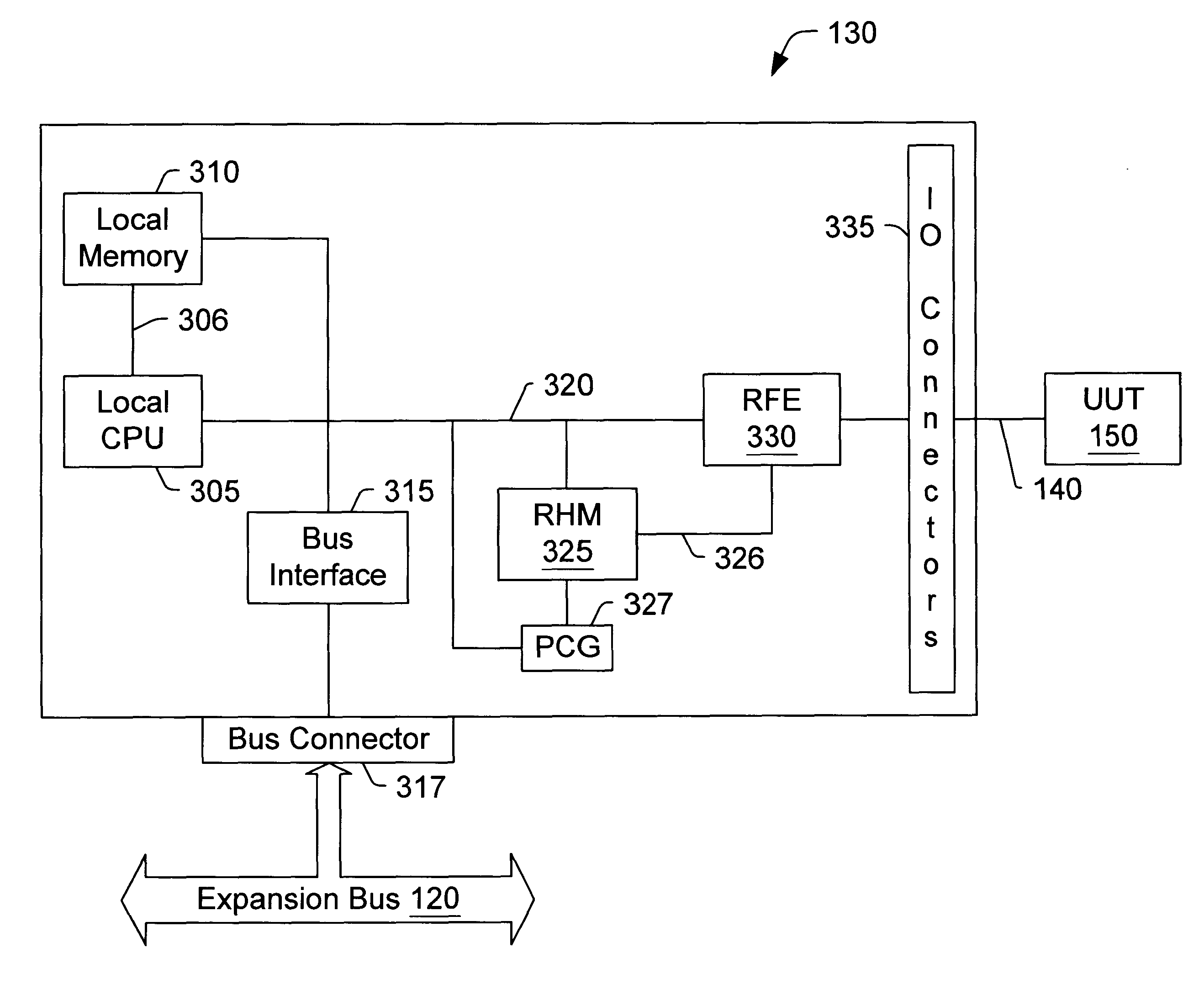
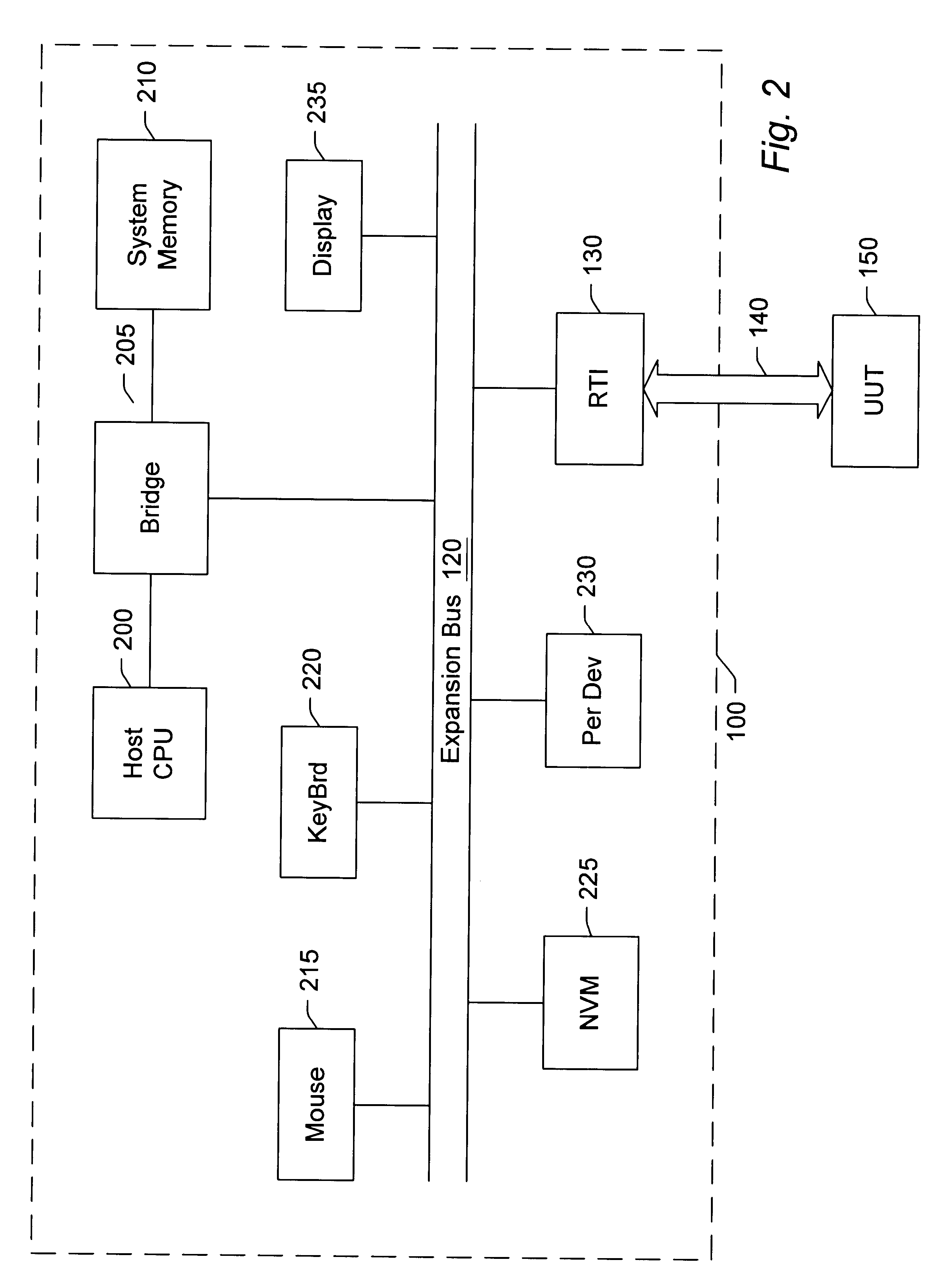
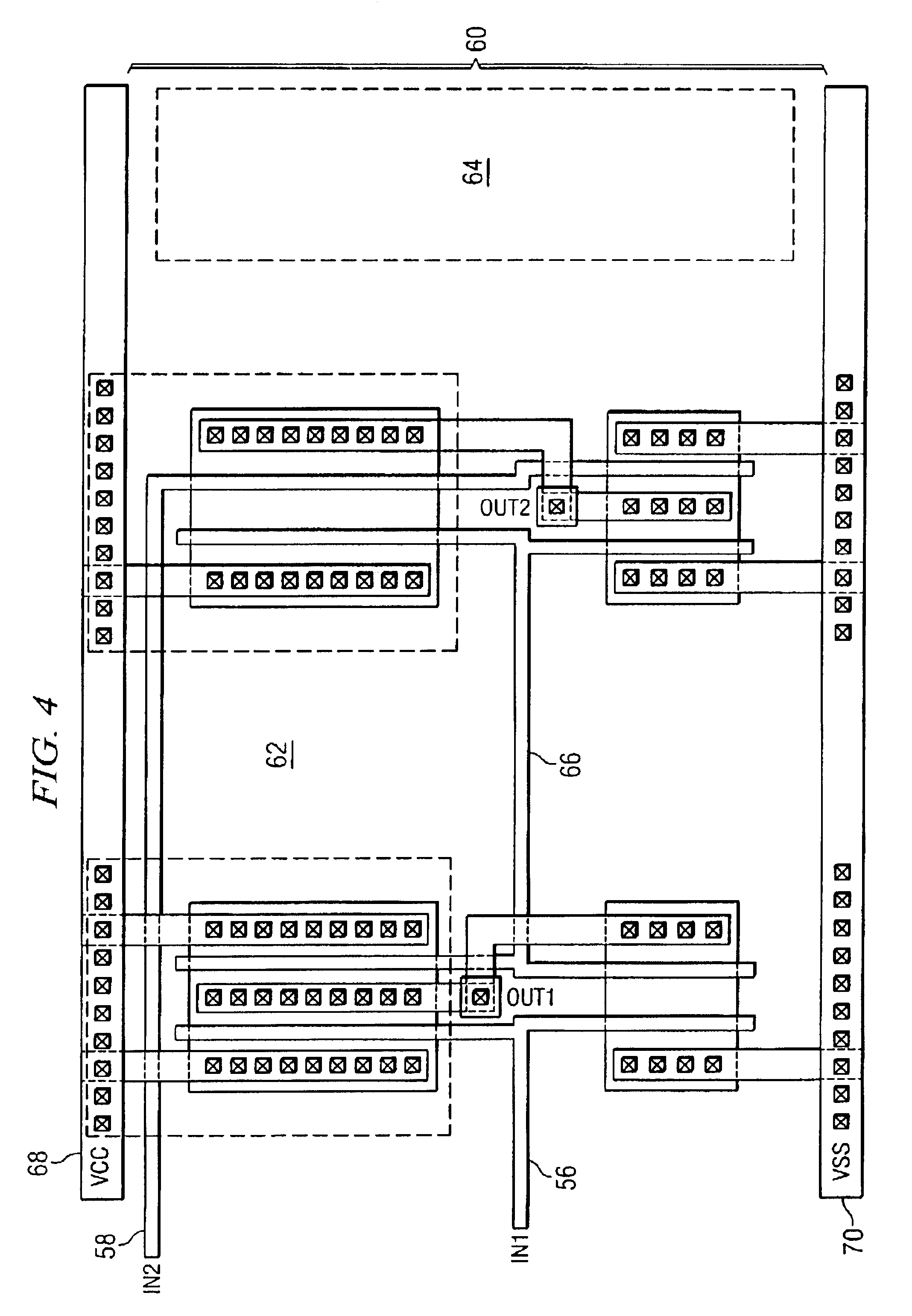
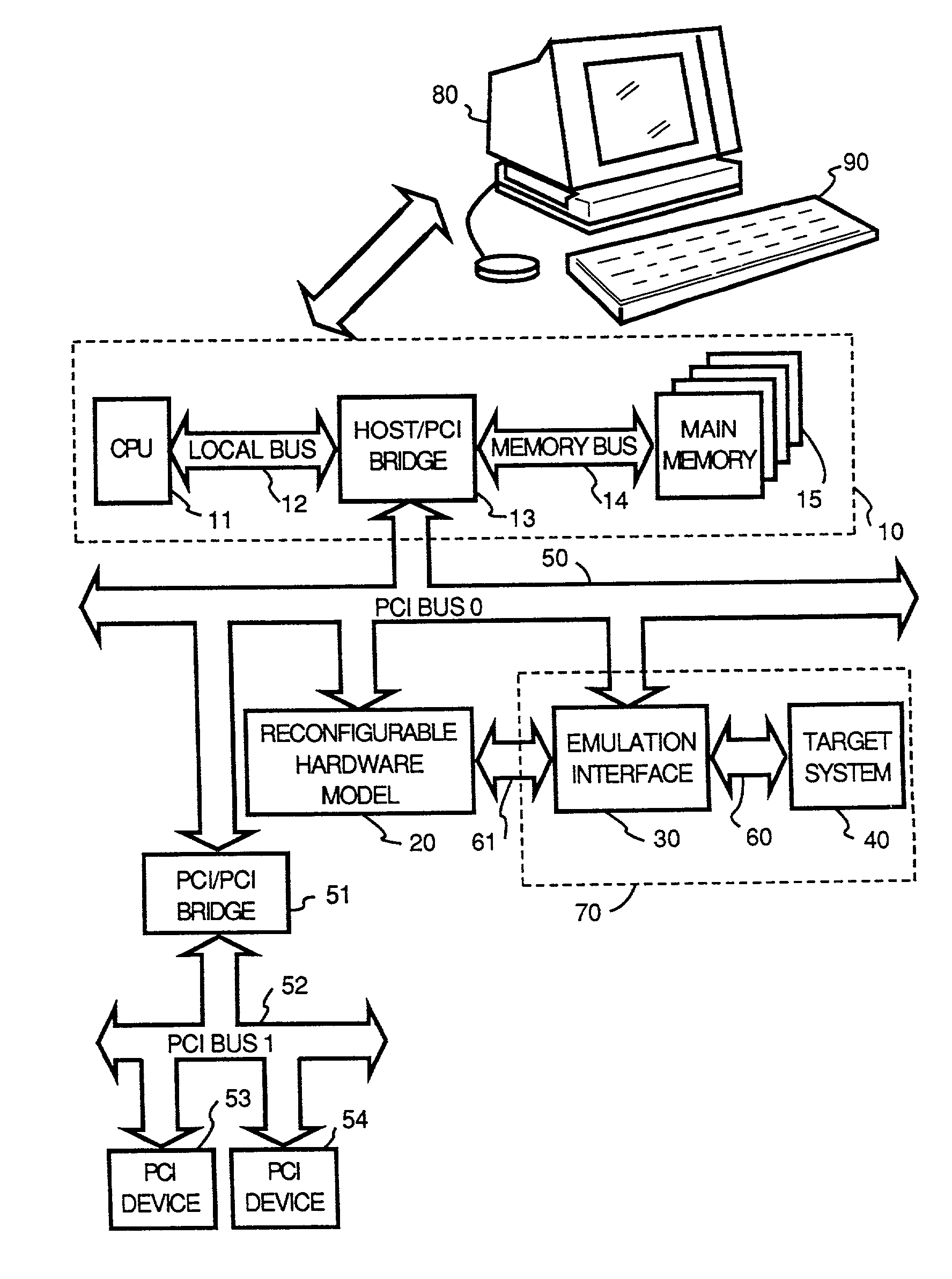
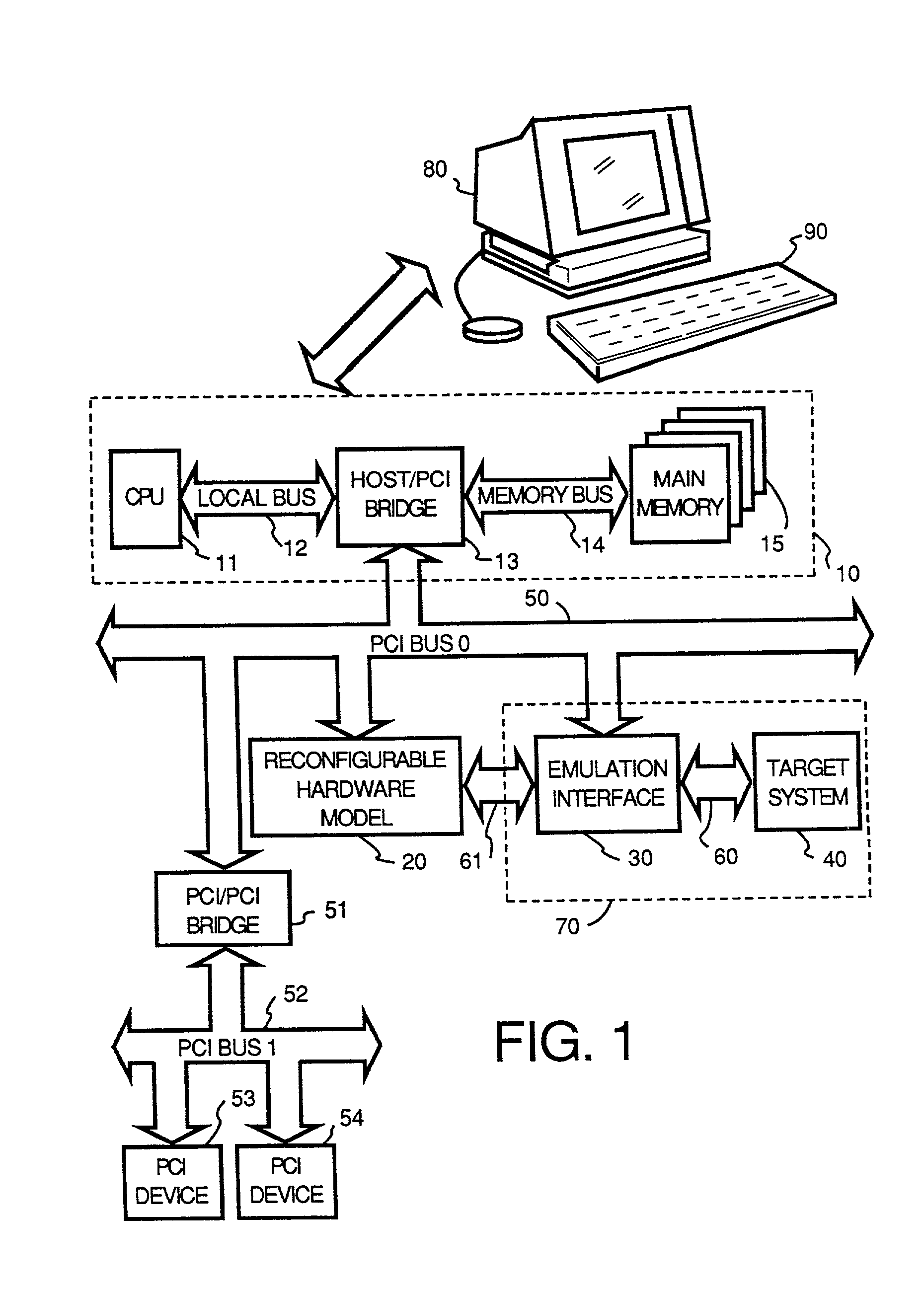
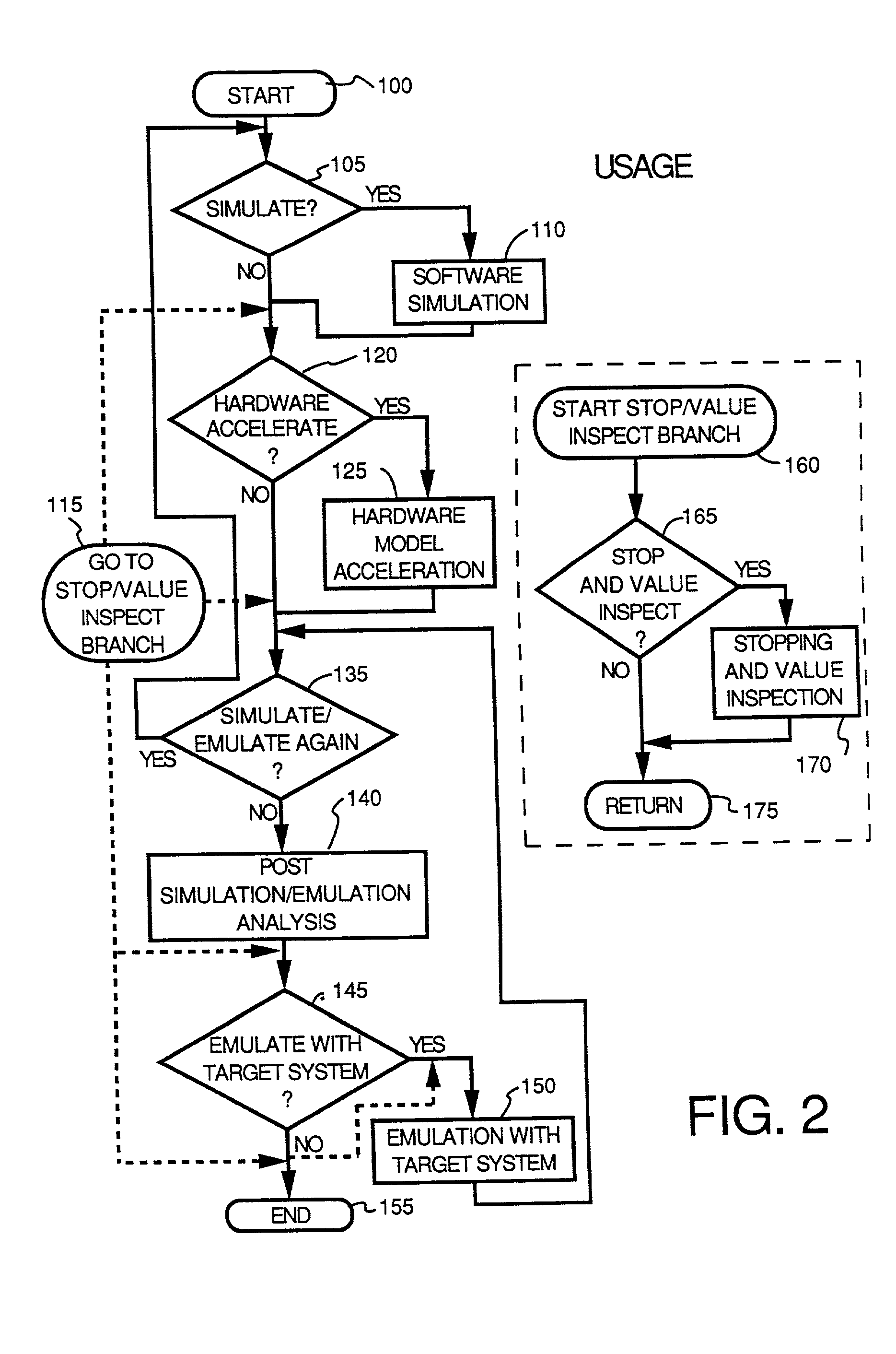
Reconfigurable test system
A reconfigurable test system including a host computer coupled to a reconfigurable test instrument. The reconfigurable test instrument includes reconfigurable hardware-i.e. a reconfigurable hardware module with one or more programmable elements such as Field Programmable Gate Arrays for realizing an arbitrary hardware architecture and a reconfigurable front end with programmable transceivers for interfacing with any desired physical medium-and optionally, an embedded processor. A user specifies system features with a software configuration utility which directs a component selector to select a set of software modules and hardware configuration files from a series of libraries. The modules are embedded in a host software driver or downloaded for execution on the embedded CPU. The configuration files are downloaded to the reconfigurable hardware. The entire selection process is performed in real-time and can be changed whenever the user deems necessary. Alternatively, the user may create a graphical program in a graphical programming environment and compile the program into various software modules and configuration files for host execution, embedded processor execution, or programming the reconfigurable hardware.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
Methods and system for analysis and management of parametric yield
InactiveUS20090106714A1Improve accuracyCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationDesign phaseThermionic emission
Impact on parametric performance of physical design choices for transistors is scored for on-current and off-current of the transistors. The impact of the design parameters are incorporated into parameters that measure predicted shift in mean on-current and mean off-current and parameters that measure predicted increase in deviations in the distribution of on-current and the off-current. Statistics may be taken at a cell level, a block level, or a chip level to optimize a chip design in a design phase, or to predict changes in parametric yield during manufacturing or after a depressed parametric yield is observed. Further, parametric yield and current level may be predicted region by region and compared with observed thermal emission to pinpoint any anomaly region in a chip to facilitate detection and correction in any mistakes in chip design.
Owner:MENTOR GRAPHICS CORP
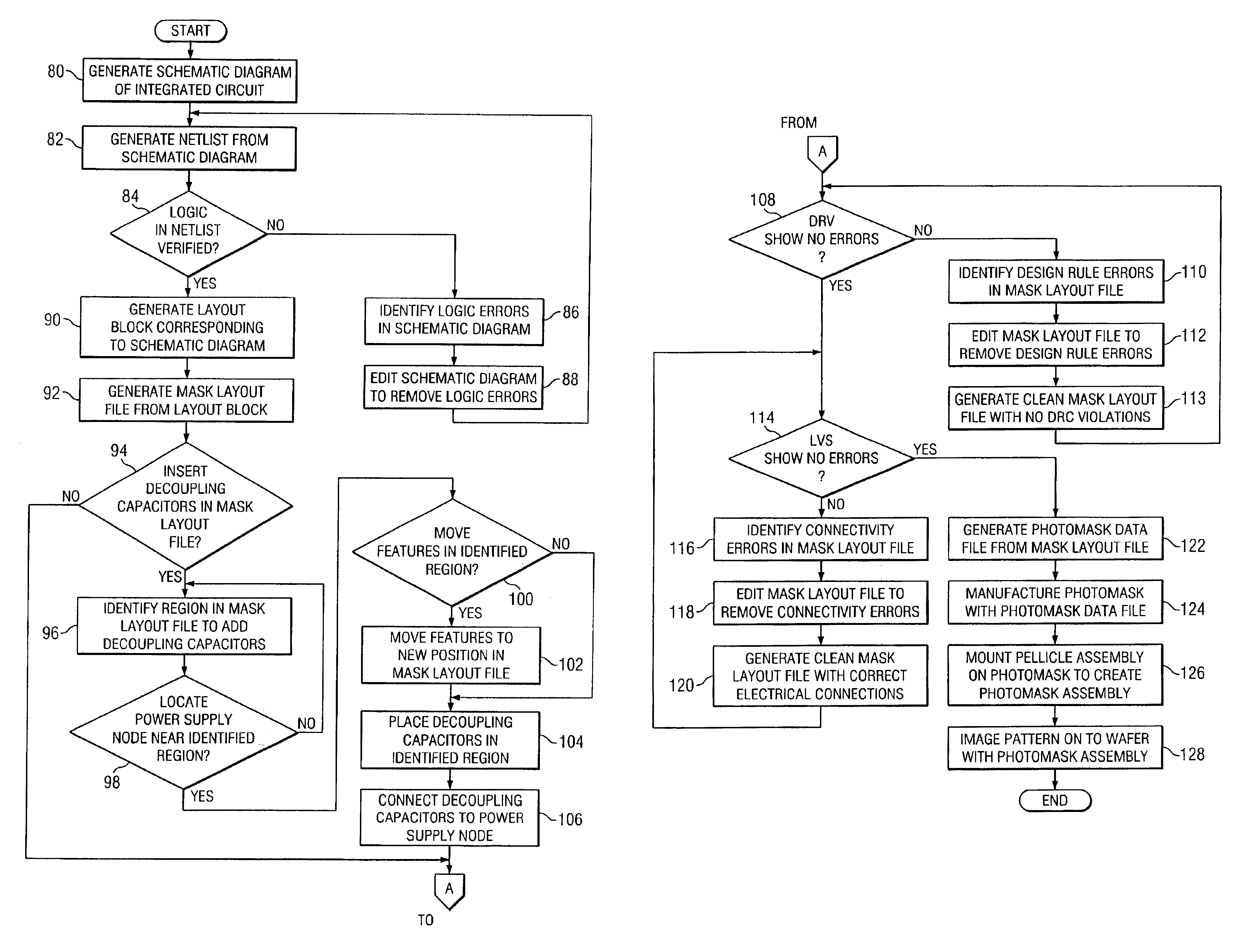
System and method for generating a mask layout file to reduce power supply voltage fluctuations in an integrated circuit
InactiveUS6877144B1Reduce voltage fluctuationsReduce power supply voltage fluctuationCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsEmbedded systemDecoupling capacitor
A system and method for generating a mask layout file to reduce power supply voltage fluctuations in an integrated circuit are disclosed. The method includes analyzing a pattern in a mask layout file to identify a region in the pattern to add one or more decoupling capacitors. Once the region is identified, a feature located in the identified region is moved based on a design rule from a first position to a second position in the mask layout file to create a space in the identified region. The decoupling capacitors are automatically placed in the space in the identified region.
Owner:CELERICS TECH
Behavior processor system and method
InactiveUS20060117274A1Decrease in performanceCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationCoded elementWorkstation
The debug system described in this patent specification provides a system that generates hardware elements from normally non-synthesizable code elements for placement on an FPGA device. This particular FPGA device is called a Behavior Processor. This Behavior Processor executes in hardware those code constructs that were previously executed in software. When some condition is satisfied (e.g., If . . . then . . . else loop) which requires some intervention by the workstation or the software model, the Behavior Processor works with an Xtrigger device to send a callback signal to the workstation for immediate response.
Owner:VERISITY DESIGN
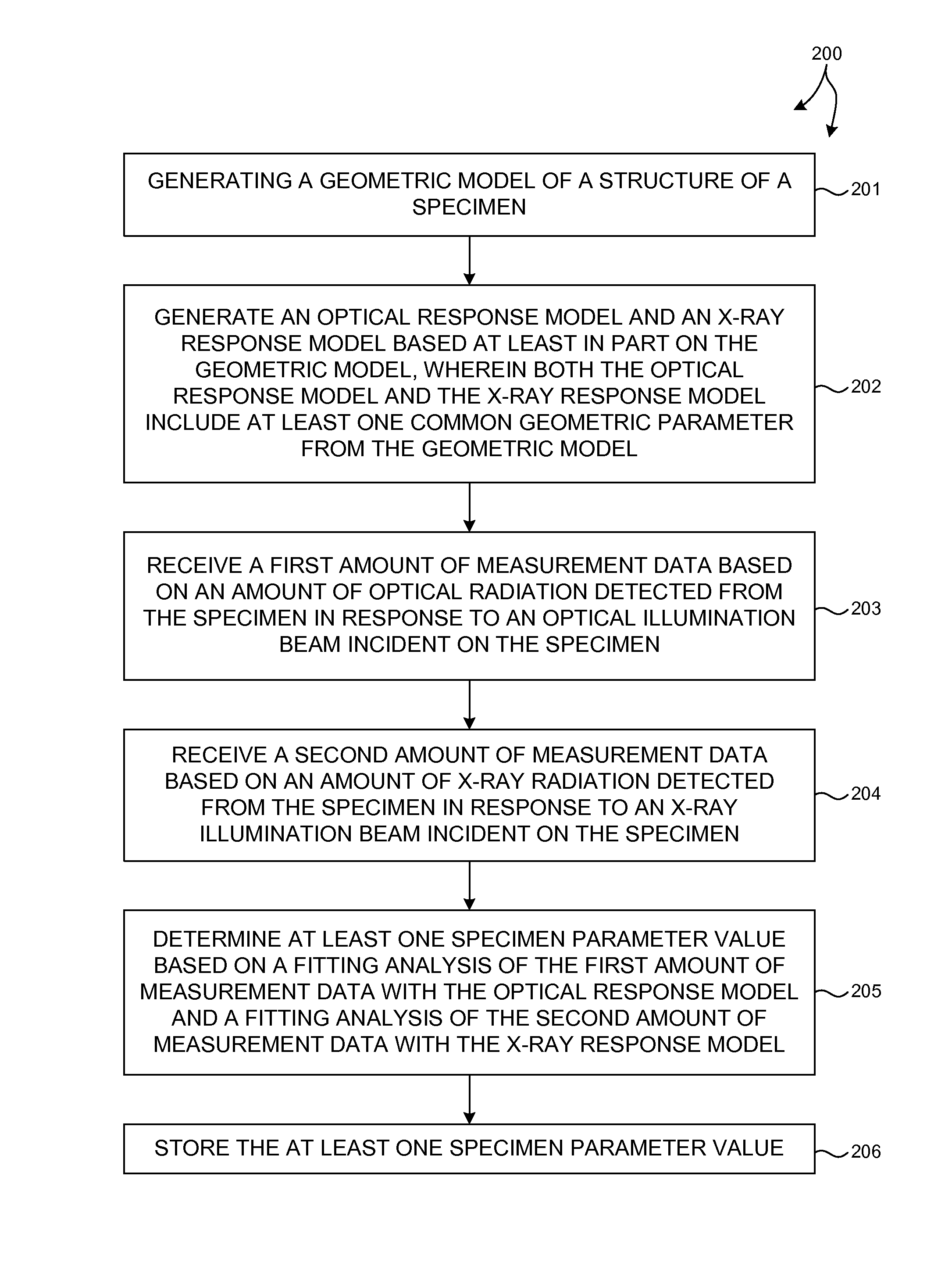
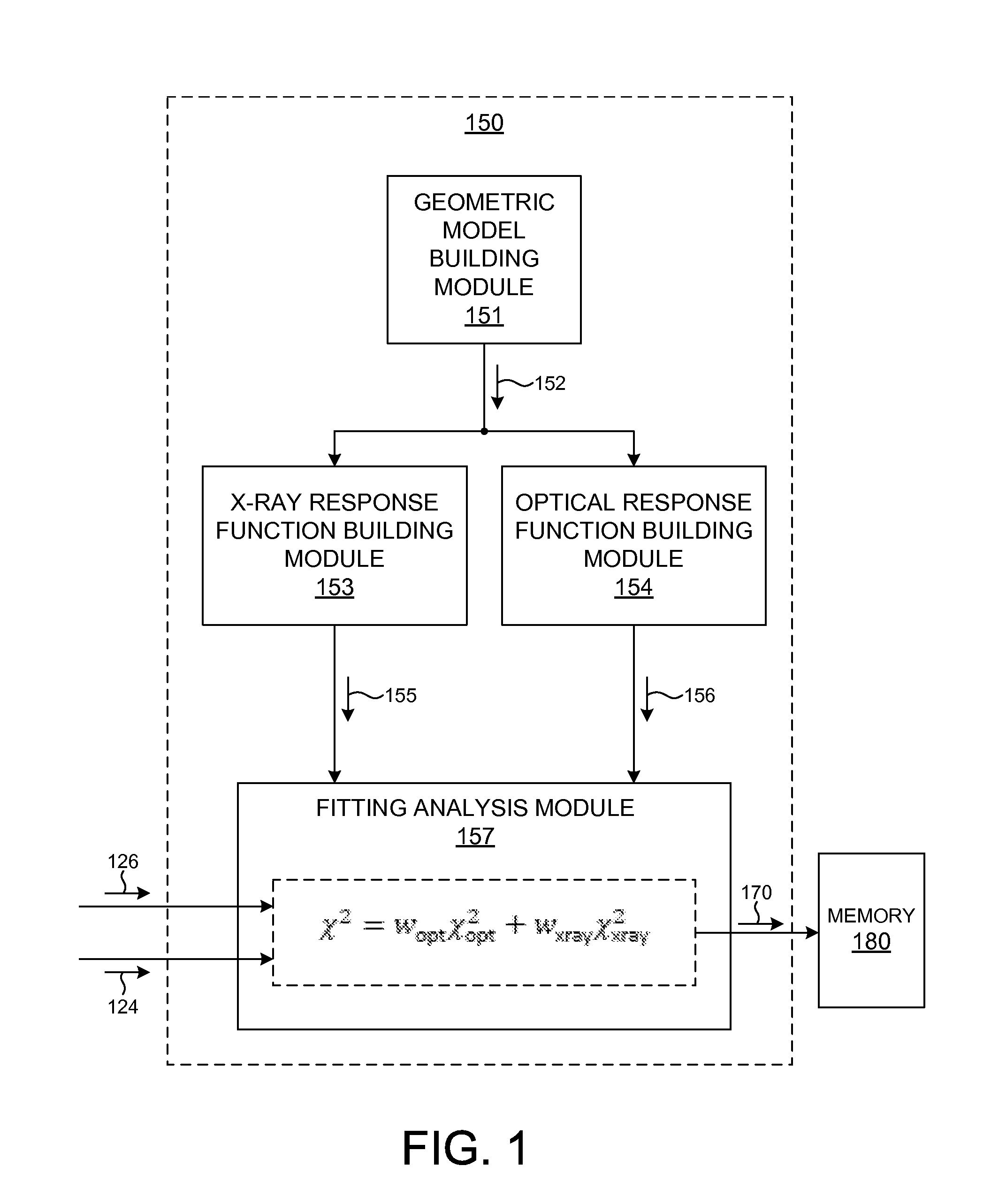
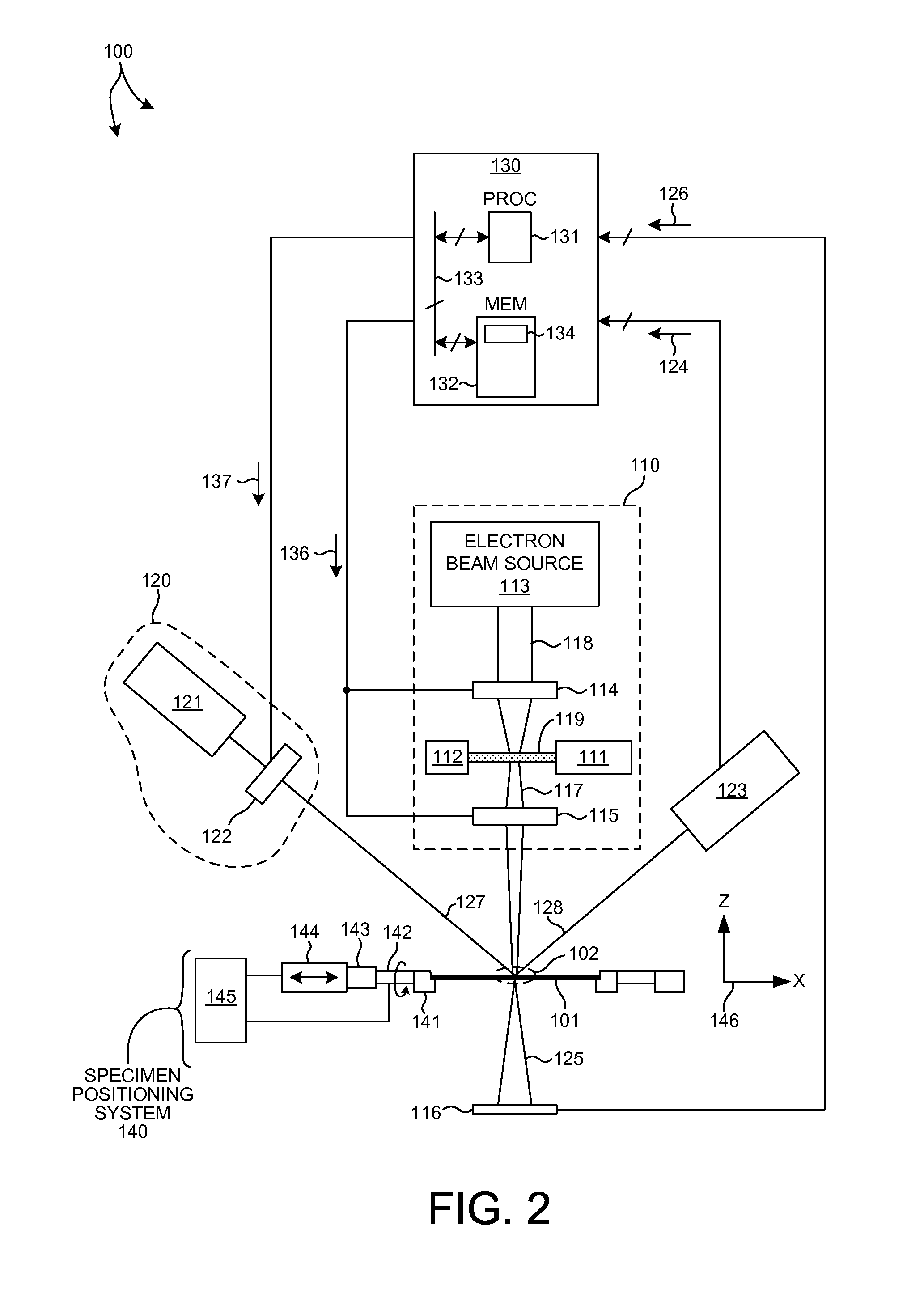
Model building and analysis engine for combined x-ray and optical metrology
ActiveUS20140019097A1Reduce in quantityReduce correlationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPhotomechanical apparatusX-rayGeometric modeling
Structural parameters of a specimen are determined by fitting models of the response of the specimen to measurements collected by different measurement techniques in a combined analysis. Models of the response of the specimen to at least two different measurement technologies share at least one common geometric parameter. In some embodiments, a model building and analysis engine performs x-ray and optical analyses wherein at least one common parameter is coupled during the analysis. The fitting of the response models to measured data can be done sequentially, in parallel, or by a combination of sequential and parallel analyses. In a further aspect, the structure of the response models is altered based on the quality of the fit between the models and the corresponding measurement data. For example, a geometric model of the specimen is restructured based on the fit between the response models and corresponding measurement data.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
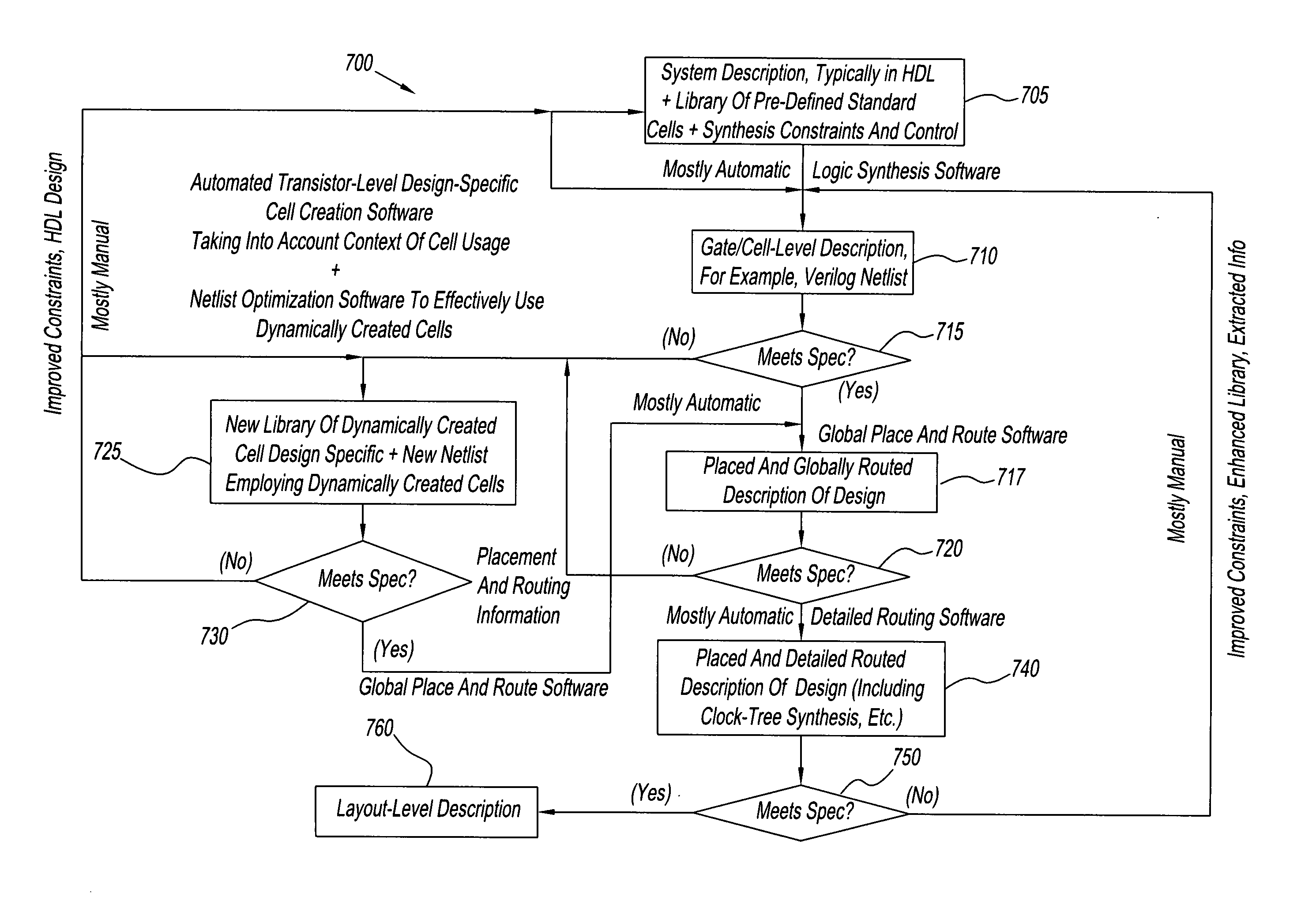
Method for automated design of integrated circuits with targeted quality objectives using dynamically generated building blocks
InactiveUS7225423B2Improve propertiesMinimize the numberCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationTarget analysisComputer architecture
A system and method for designing ICs, including the steps of: analyzing and optimizing a target IC design based on design-specific objectives; partitioning the optimized target IC design into pre-defined standard-cells from one or more libraries and creating design-specific cells specifically having unique functionality and characteristics not found amongst the standard-cells; identifying and determining a minimal subset of the standard-cells and design-specific cells, the interconnection of which represents the target IC design; generating the necessary views, including layout and characterizing of the design-specific cells included in a unique, minimal subset, wherein the IC design is subject to objectives and constraints of the target IC.
Owner:OPEN-SILICON
Method for correcting a mask design layout
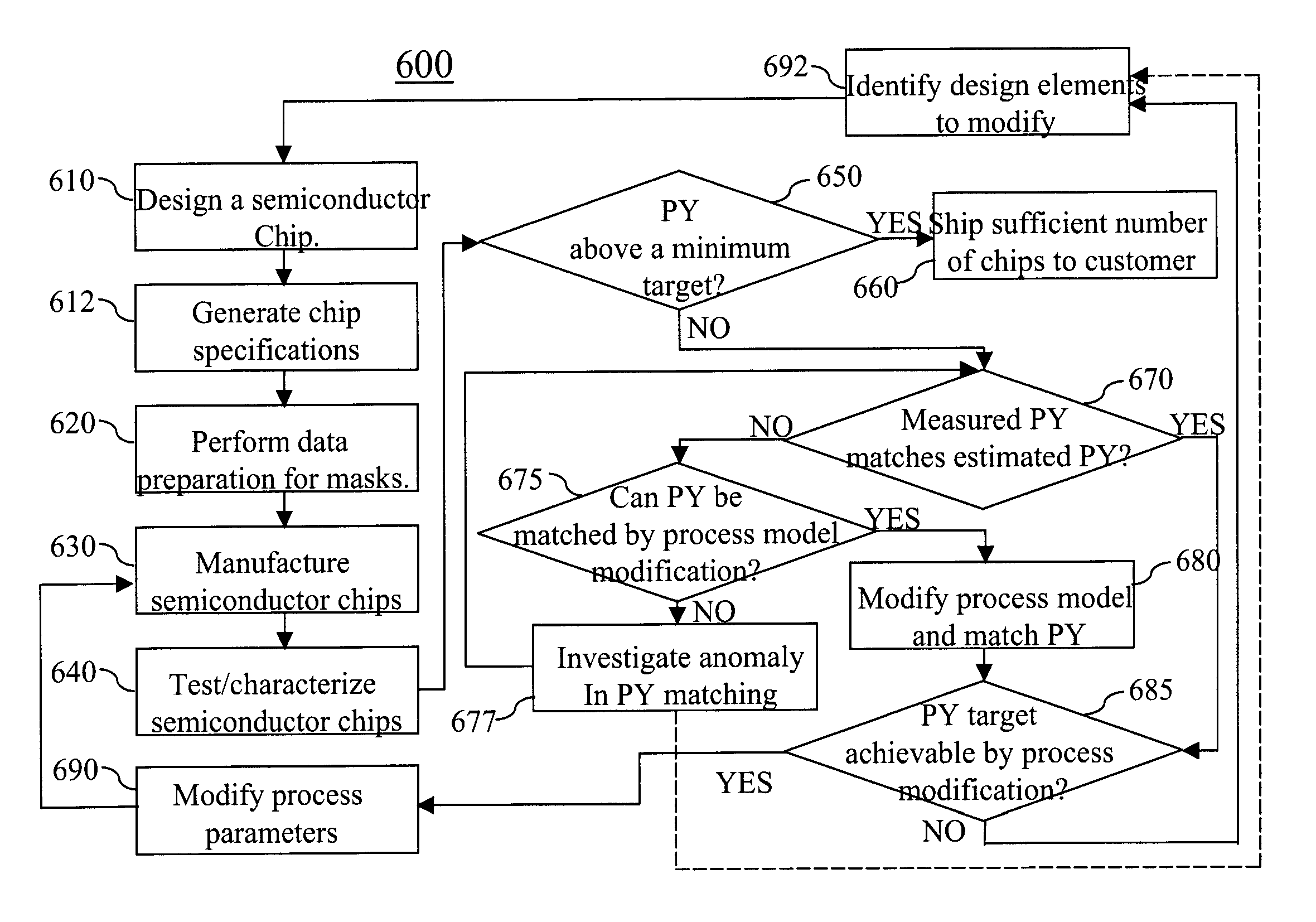
InactiveUS7149999B2Low costMinimal costCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsCorrection algorithmImage resolution
A method for performing a mask design layout resolution enhancement includes determining a level of correction for a mask design layout for a predetermined parametric yield with a minimum total correction cost. The mask design layout is corrected at a determined level of correction based on a correction algorithm if the correction is required. In this manner, only those printed features on the mask design layout that are critical for obtaining a desired performance yield are corrected, thereby reducing total cost of correction of the mask design layout.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN +1
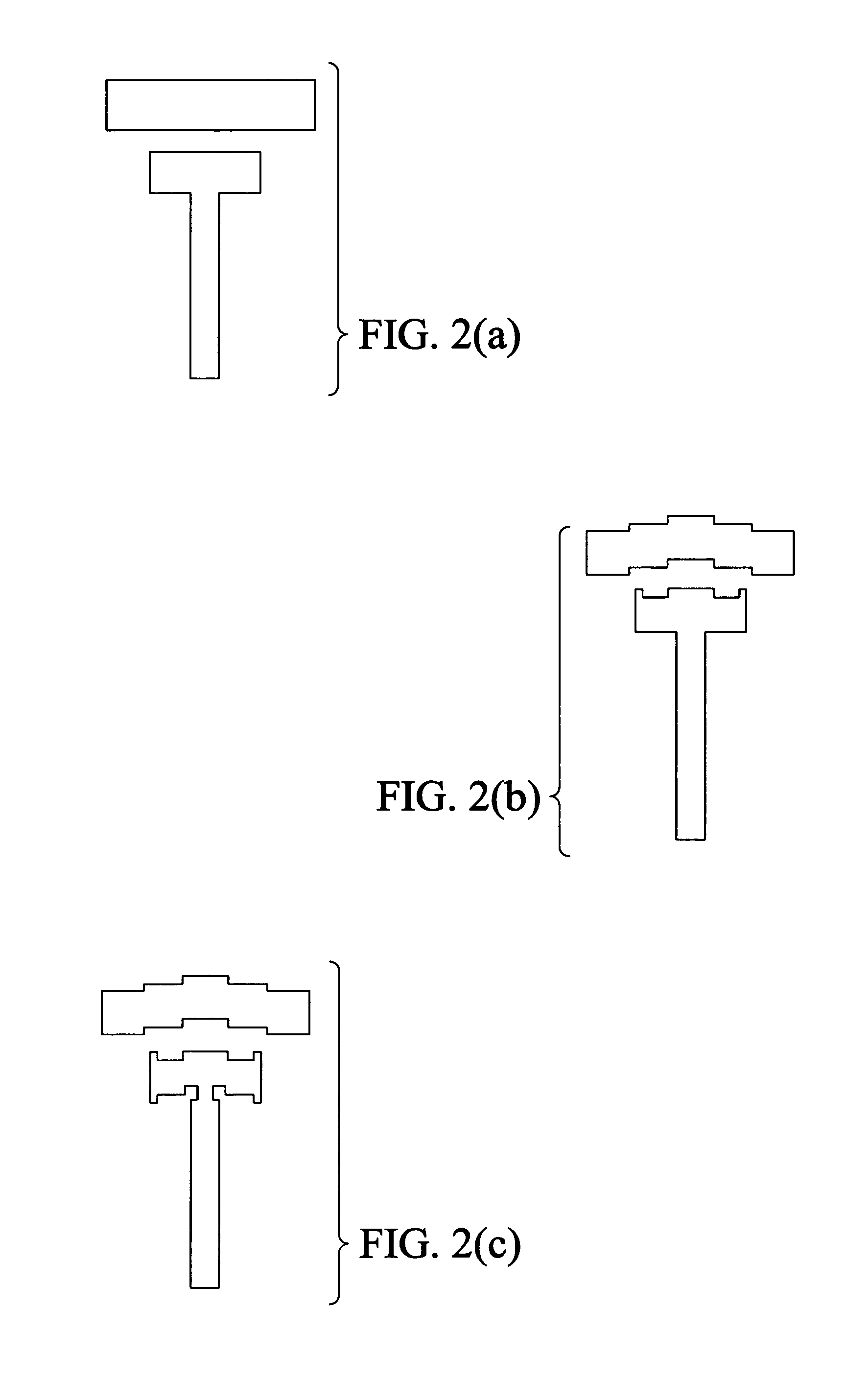
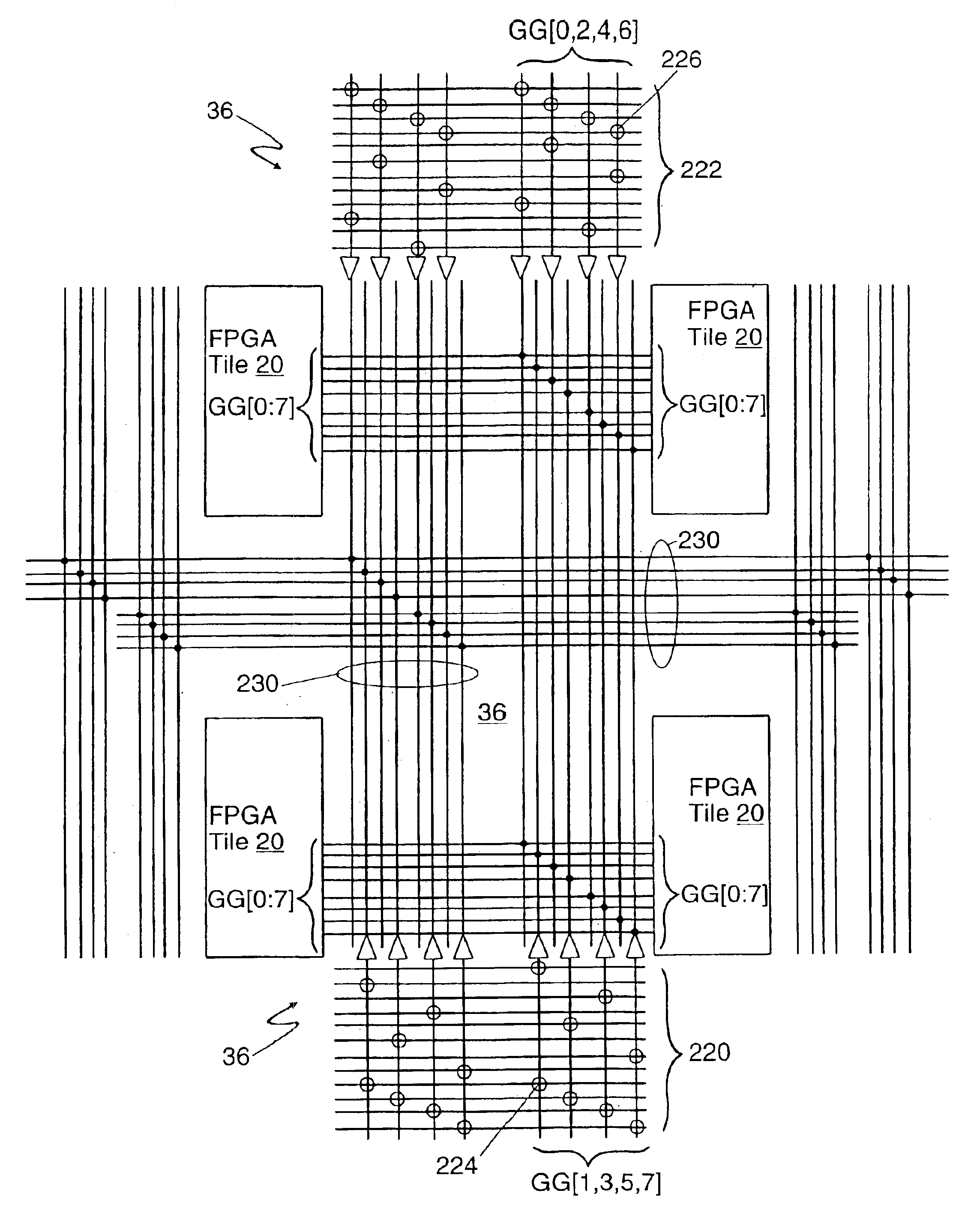
Tileable field-programmable gate array architecture
InactiveUS6888375B2Solid-state devicesCAD circuit designElectrical conductorField-programmable gate array
An apparatus includes a field-programmable gate array (FPGA). The FPGA includes a first FPGA tile, and the first FPGA tile includes a plurality of functional groups (FGs), a third set of routing conductors, in addition to a first set of routing conductors and a second set of routing conductors and a plurality of interface groups (IGs). The plurality of FGs are arranged in rows and columns with each of the FGs being configured to receive tertiary input signals as well as regular input signals, perform a logic operation, and generate regular output signals. The third set of routing conductors is coupled to the first set of output ports of the FGs and configured to receive signals, route signals within the first FPGA tile, and provide input signals to the third set of input ports of the FGs. The plurality of IGs surround the plurality of FGs such that one IG is positioned at each end of each row and column. Each of the IGs is coupled to the third set of routing conductors and configured to transfer signals from the third set of routing conductors to outside of the first FPGA tile.
Owner:MICROSEMI SOC
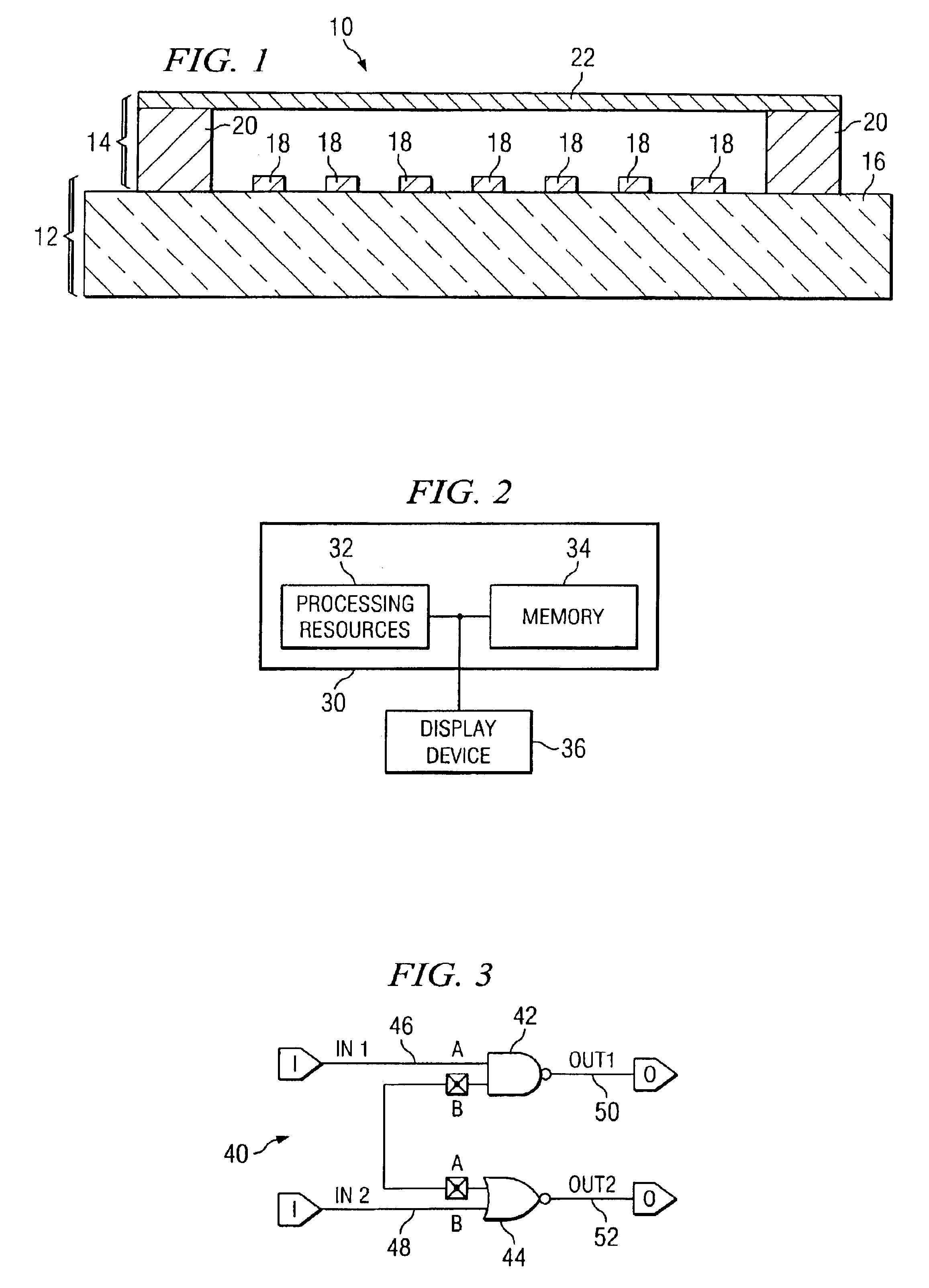
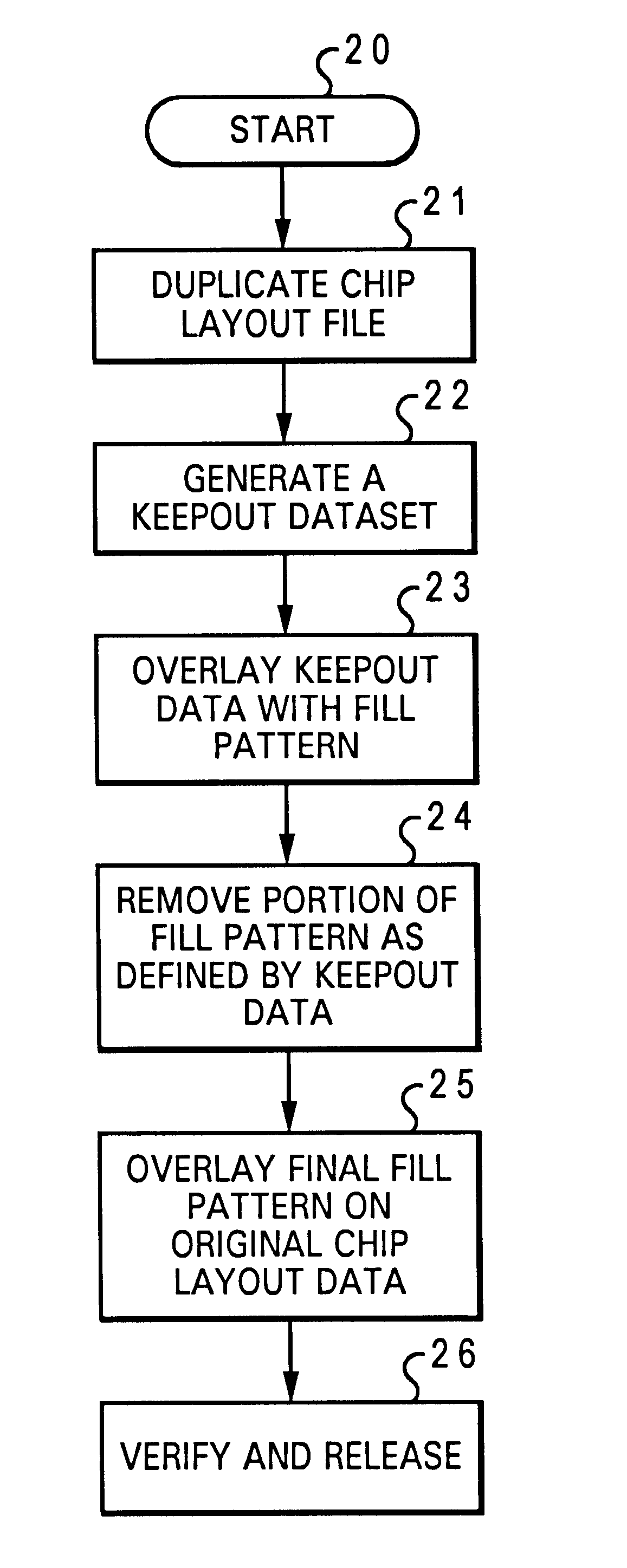
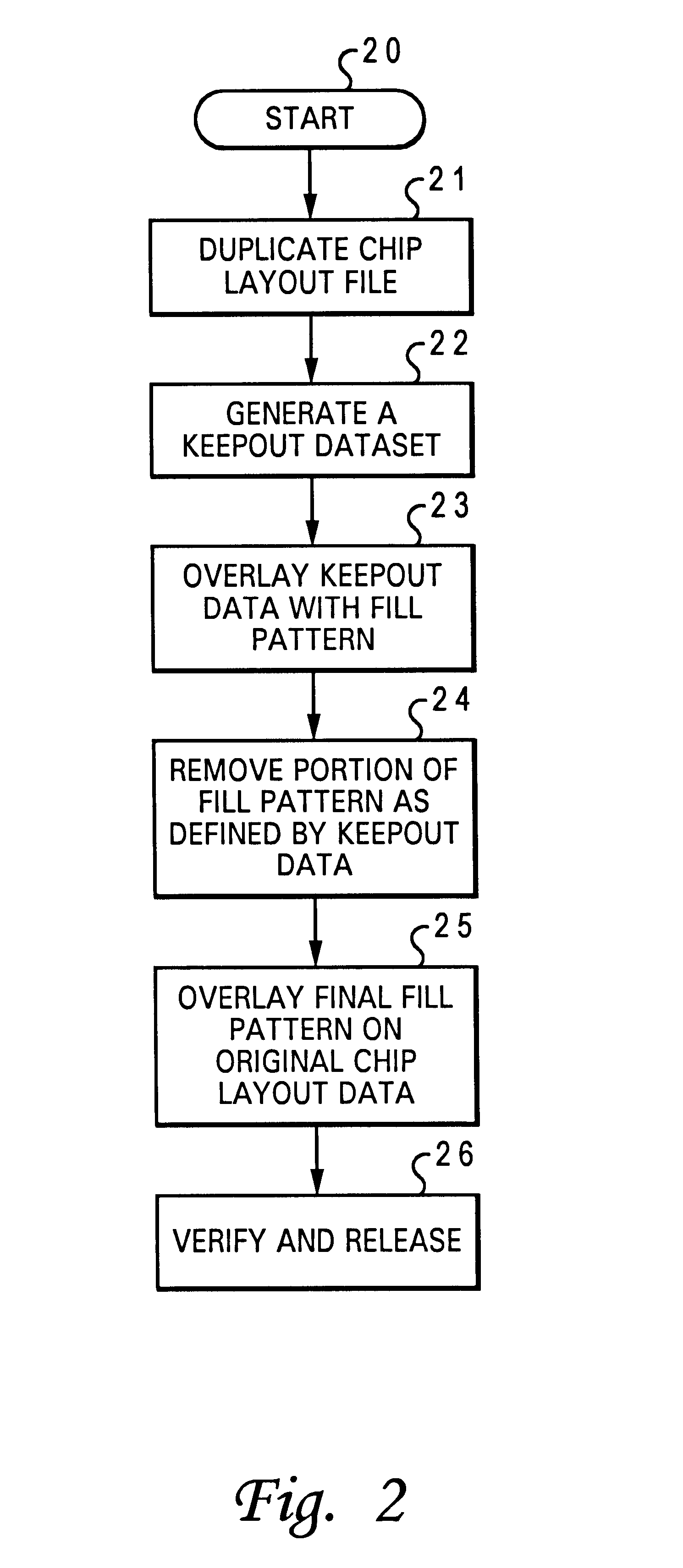
Method for providing a fill pattern for an integrated circuit design
InactiveUS6609235B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingComputer architectureIntegrated circuit design
A method for providing a fill pattern for integrated circuit designs is disclosed. A keepout file having keepout data is generated from a chip design layout file having chip design layout data. The keepout file includes a map of areas of an integrated circuit design where fill patterns cannot be placed. The map of areas from the keepout file is then overlaid with a fill pattern to yield a fill-pattern file. Fill patterns from the fill-pattern file is removed from locations that coincide with locations as defined by the keepout data to yield a final-fill file with crucial fill pattern data. The crucial fill pattern data from the final-fill file is overlaid on the design layout data in the chip design layout file to yield a complete design layout file. Finally, the design rule integrity and logical to physical correspondence of the complete design layout file is verified.
Owner:MIND FUSION LLC
Method and apparatus for selective, incremental, reconfigurable and reusable semiconductor manufacturing resolution-enhancements
InactiveUS20050229130A1Improve manufacturabilityHigh yieldCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsImage resolutionPhysical verification
An automated design for manufacturability platform for integrated physical verification and manufacturing enhancement operations. Given original layouts and one or more associated resolution-enhanced layouts, intermediate resolution-enhancement state layouts are reconstructed, and selective localized resolution-enhancement reconfigurations, modifications, and / or perturbations are introduced on any existing enhancements in order to improve manufacturability and yield.
Owner:RPX CORP
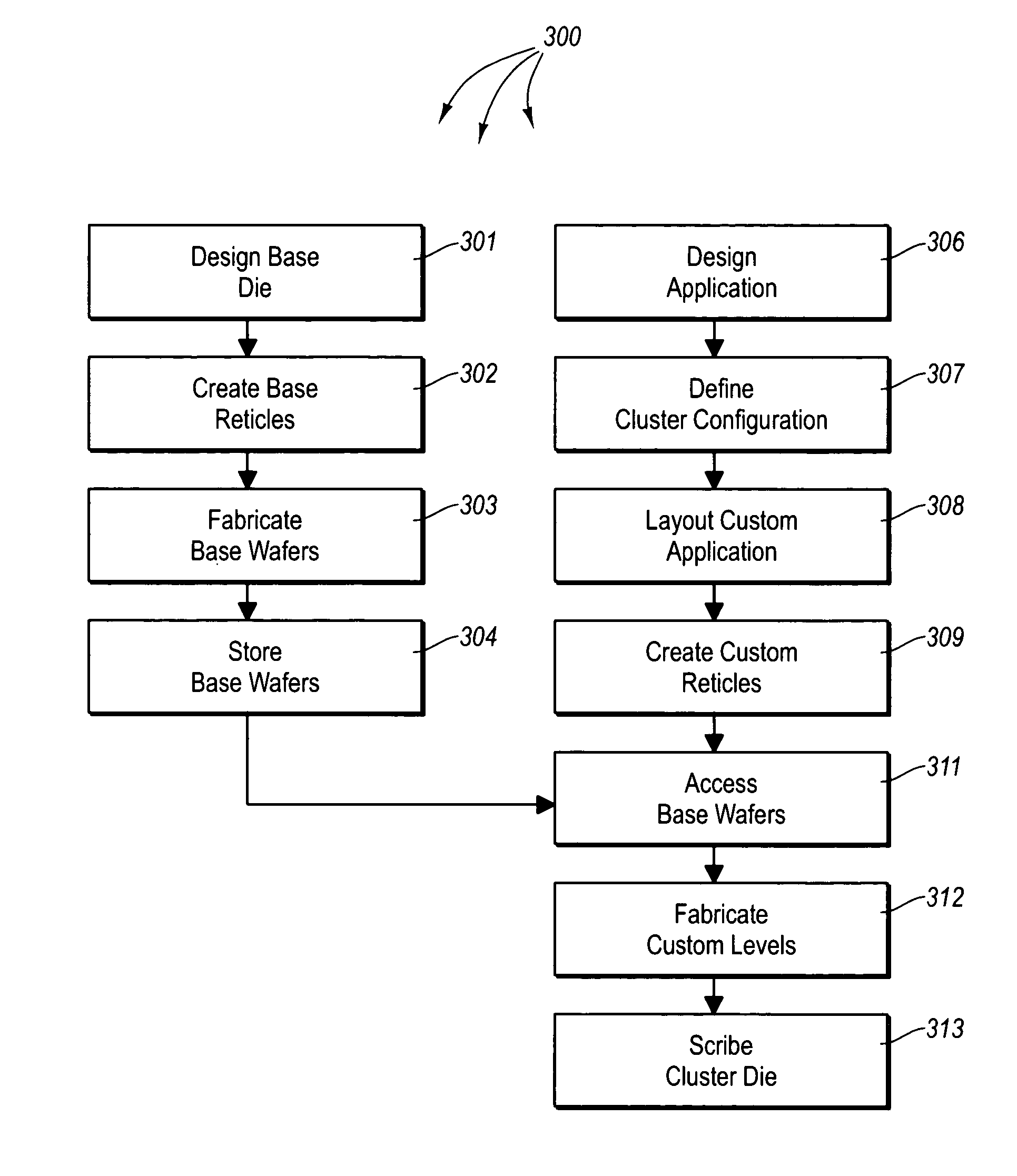
Structured ASIC device with configurable die size and selectable embedded functions
ActiveUS7337425B2Reduce the numberReduce tooling costsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesGeneral purposeChip size
One embodiment of the present invention provides for a master or universal base and base tooling which addresses the general purpose Structured ASIC requirements. Another embodiment of the present invention provides for a common set of base tooling from which the master / universal base is created as well as additional custom bases with customized selection and quantity of embedded Platform ASIC functions. Embodiments can utilize conventional Structured ASIC architecture and processing and are compatible with traditional probing and packaging.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Method for design of partial circuit
InactiveUS6553544B2Easily and precisely estimateAvoid difficult choicesCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationEngineeringDesign objective
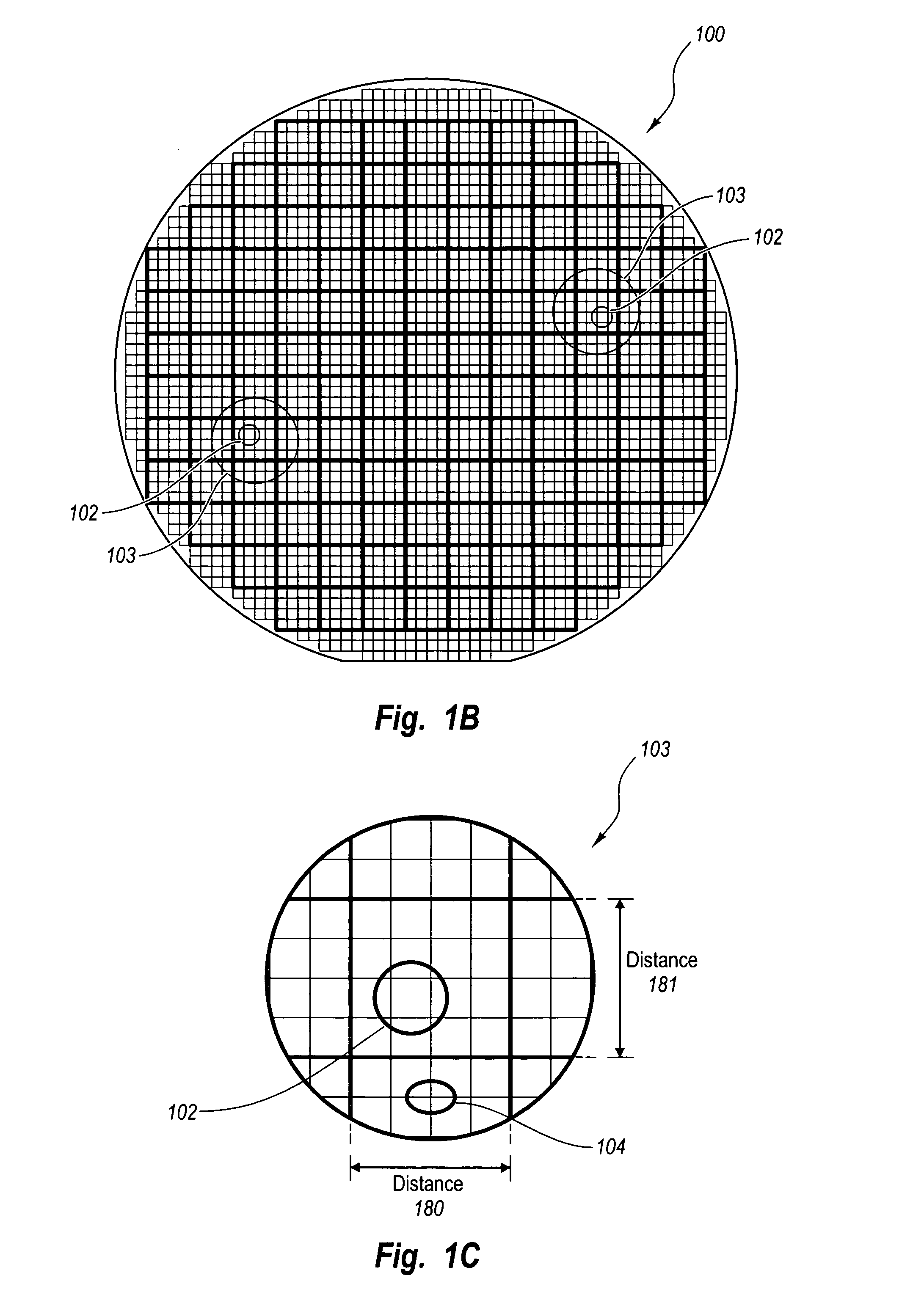
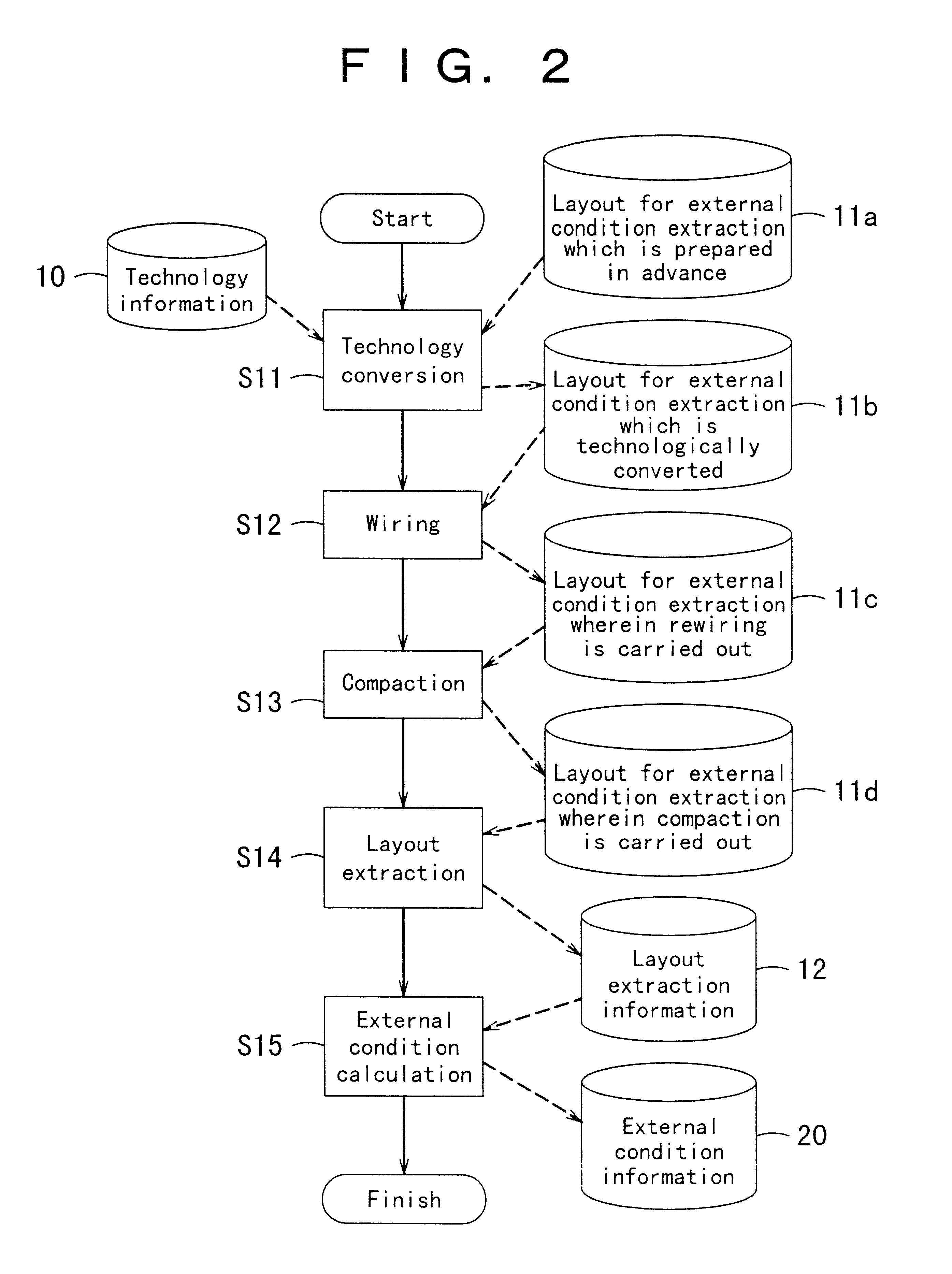
There is no conventional method for precisely estimating under what external conditions each partial circuit, such as a library cell, is utilized in an actual integrated circuit at the time of designing the partial circuit. Therefore, by estimating the external conditions of a partial circuit when used in an integrated circuit so that the partial circuit is designed in accordance with the external conditions, the partial circuit having optimal performance for the external conditions can be designed. The step of external condition estimation can be formed so as to include the technology conversion step which technologically converts the layout for external condition extraction, that is prepared in advance, based on the technology information of an integrated circuit, which is the design objective; the layout extraction step of extracting layout extraction information which is external information influencing the operation of the partial circuit from the layout for external condition extraction that has been technologically converted; and the external condition calculation step of calculating external conditions of the partial circuit from the layout extraction information. In addition, by simply replacing the designed partial circuit with a partial circuit of a circuit for evaluation, the evaluation of the designed partial circuit can be easily carried out.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
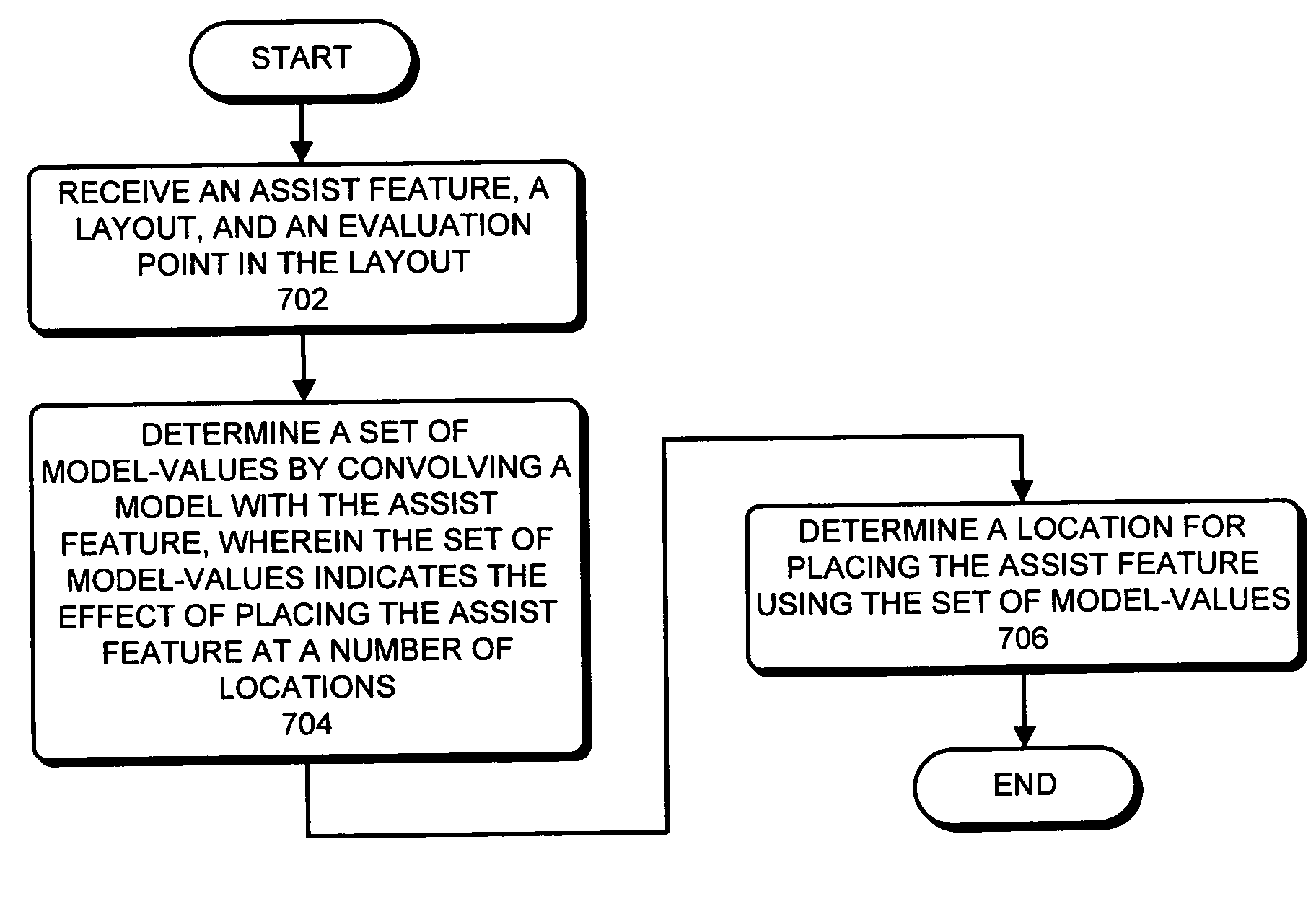
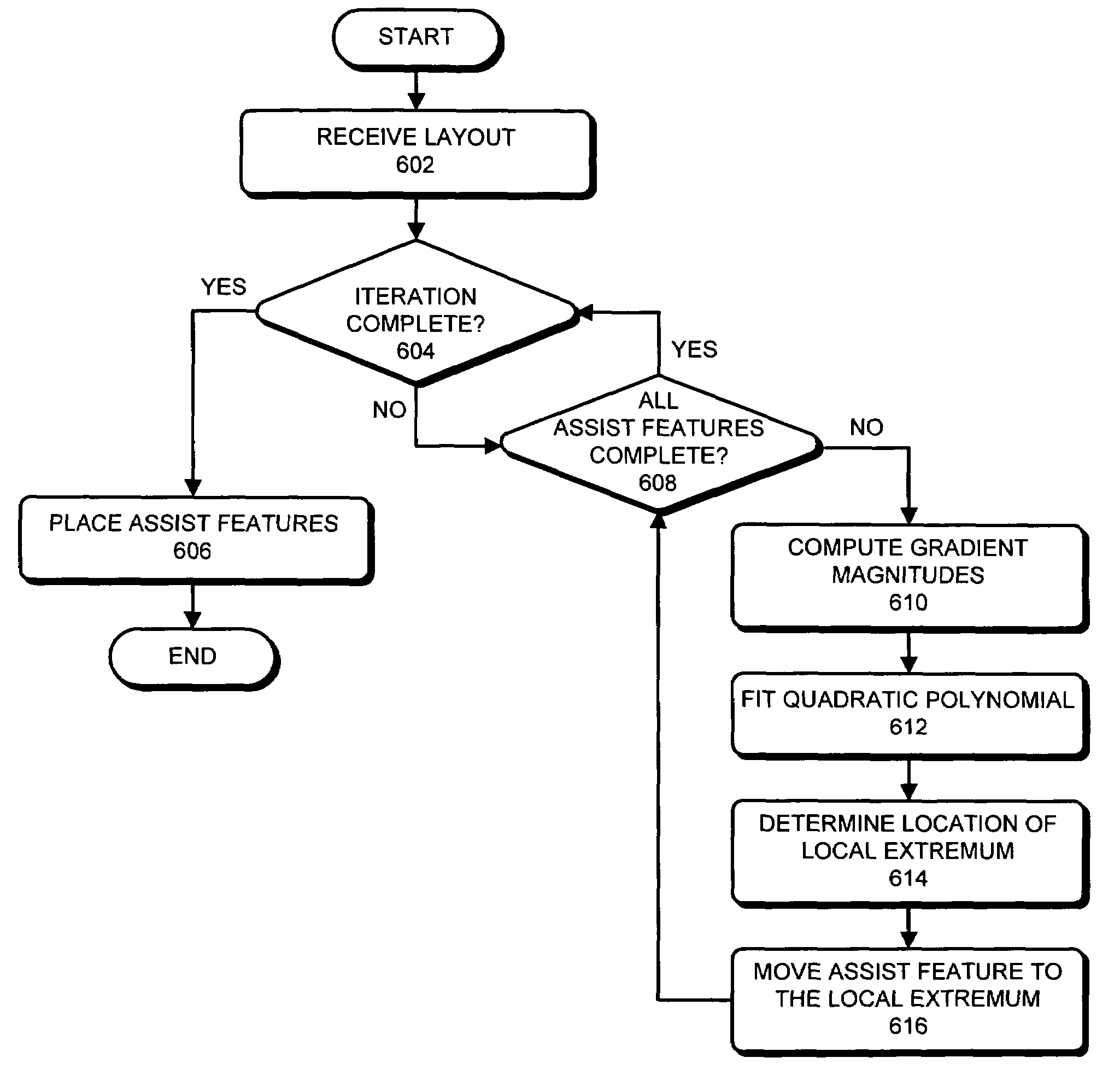
Method and apparatus for placing assist features by identifying locations of constructive and destructive interference
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that determines a location in a layout to place an assist feature. During operation, the system receives a layout of an integrated circuit. Next, the system selects an evaluation point in the layout. The system then chooses a candidate location in the layout for placing an assist feature. Next, the system determines the final location in the layout to place an assist feature by, iteratively, (a) selecting perturbation locations for placing representative assist features in the proximity of the candidate location, (b) computing aerial-images using an image intensity model, the layout, and by placing representative assist features at the candidate location and the perturbation locations, (c) calculating image-gradient magnitudes at the evaluation point based on the aerial-images, and (d) updating the candidate location for the assist feature based on the image-gradient magnitudes.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Methods and systems for placement and routing
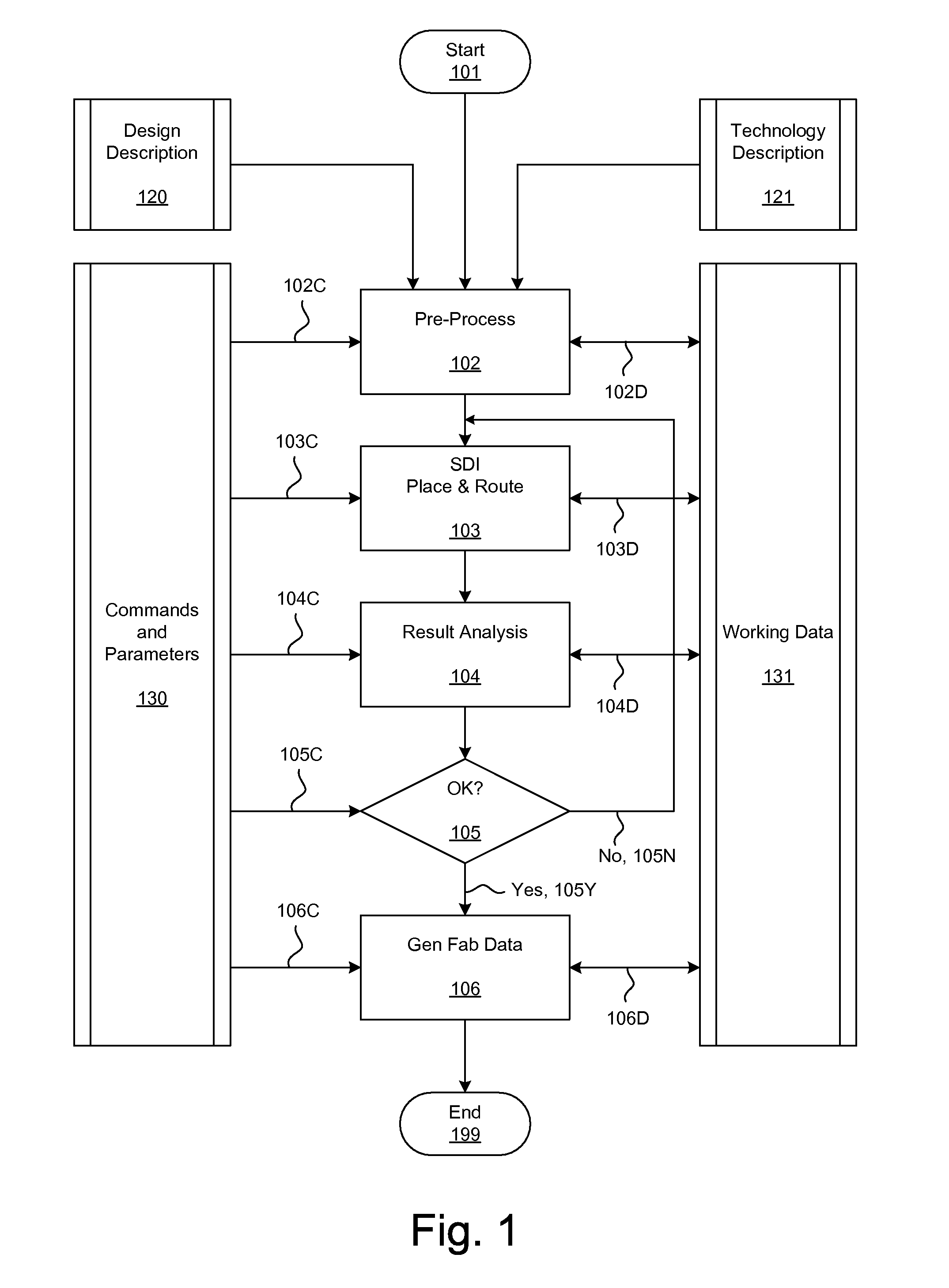
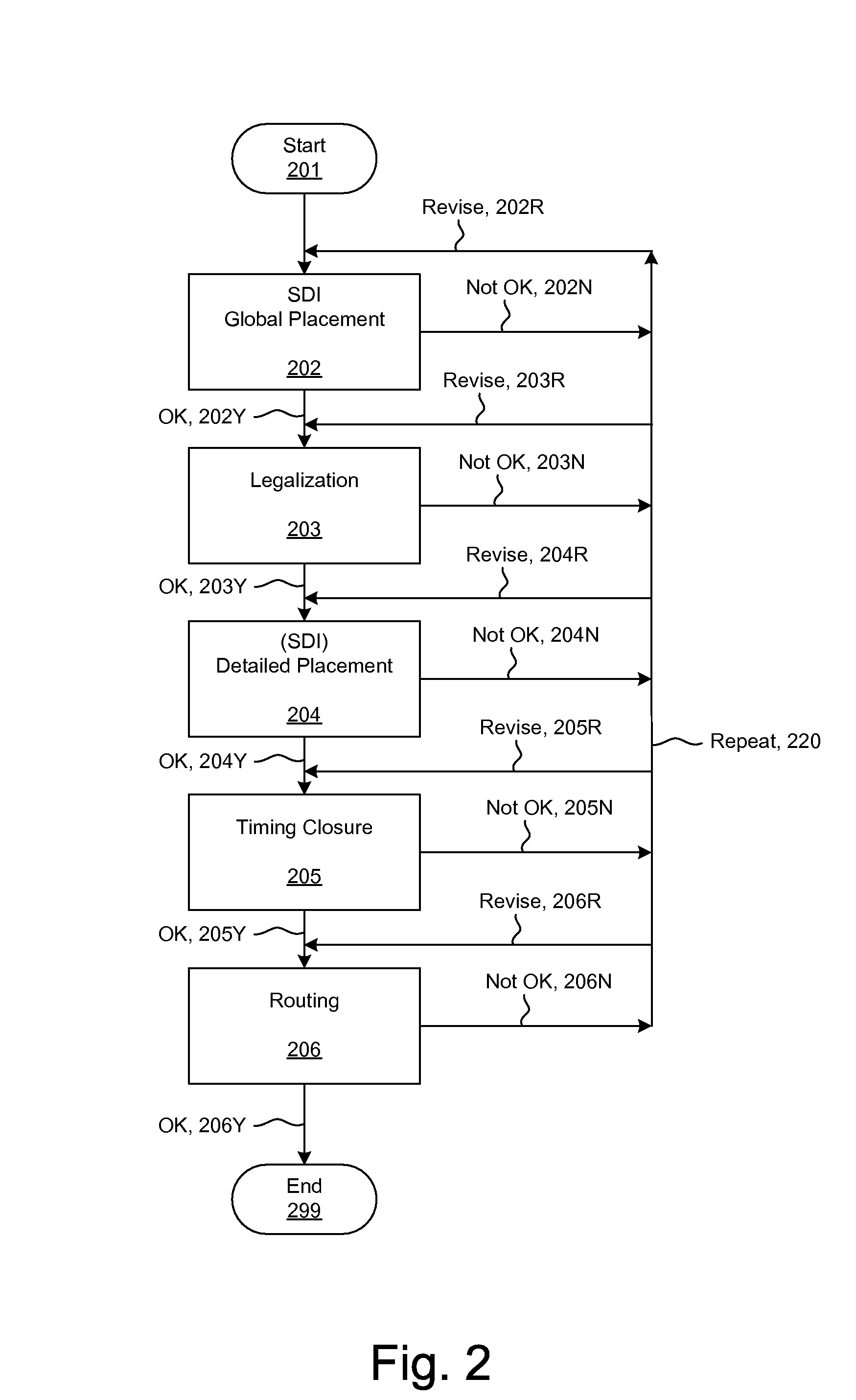
ActiveUS20090254874A1Influence optimizeImprove performanceCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationElectrical resistance and conductanceCapacitance
Techniques for placement of integrated circuit elements include global placement, detailed placement, timing closure, and routing. The integrated circuit is described by a netlist specifying interconnections of morphable devices. The detailed placement uses, for example, Simultaneous Dynamical Integration, wherein the morphable-devices correspond to nodes influenced by forces, including timing forces. The timing forces are derived, for example, from a timing graph; path delay; slack; and drive resistance of the elements. The timing closure uses timing-driven buffering and timing-driven resizing to reduce maximum delay and / or transition time, and / or to fix hold time. Nets having high capacitance and / or fanout, and timing critical nets are preferentially processed. Timing-driven buffering applies buffering solutions to segments of route trees, combines solutions of adjoining segments, and prunes sets of solutions. Timing-driven resizing morphably replaces selected elements with upsized versions thereof.
Owner:CALLAHAN CELLULAR L L C
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com