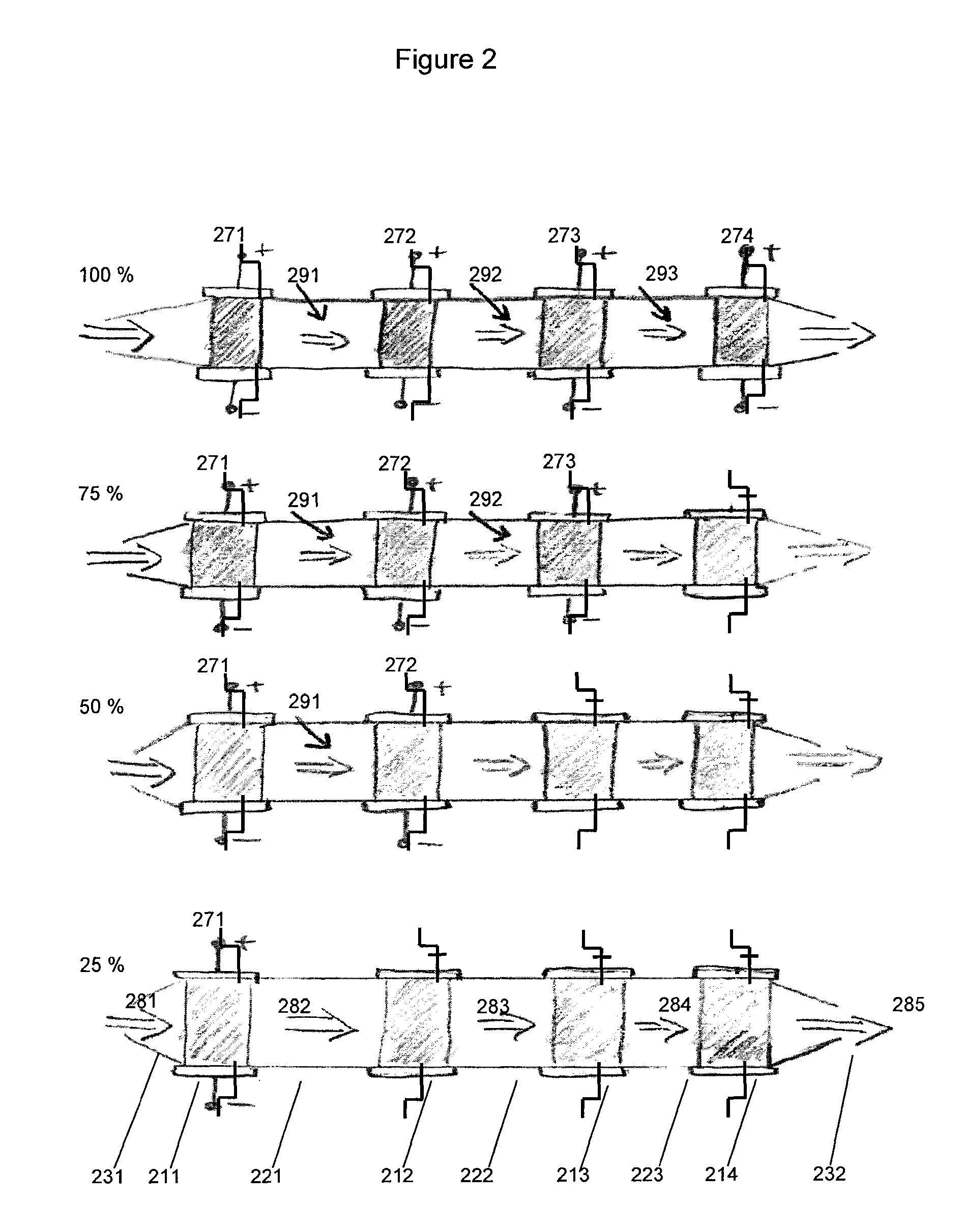
Patents
Literature
54 results about "Design for manufacturability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
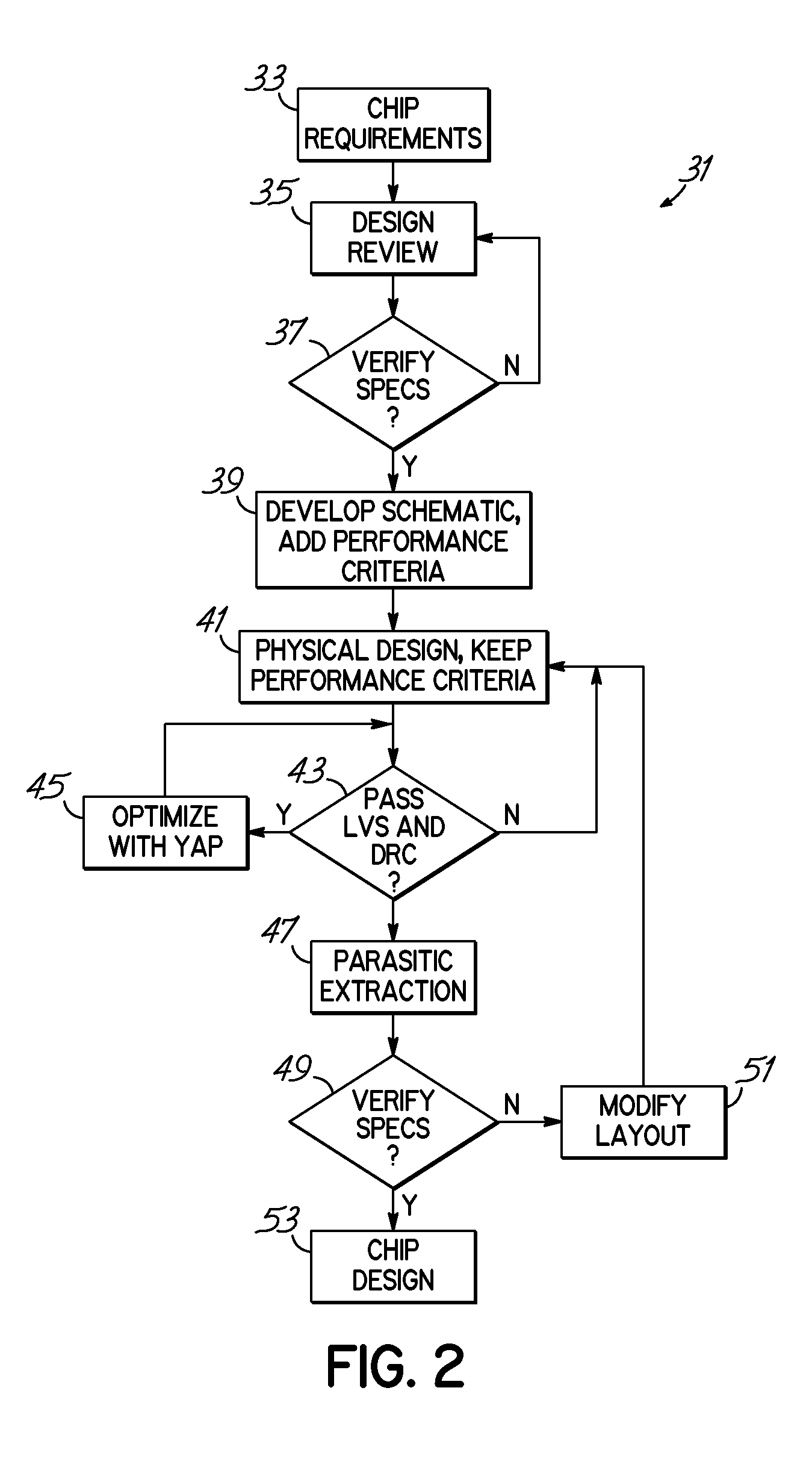
Design for manufacturability (also sometimes known as design for manufacturing or DFM) is the general engineering practice of designing products in such a way that they are easy to manufacture. The concept exists in almost all engineering disciplines, but the implementation differs widely depending on the manufacturing technology. DFM describes the process of designing or engineering a product in order to facilitate the manufacturing process in order to reduce its manufacturing costs. DFM will allow potential problems to be fixed in the design phase which is the least expensive place to address them. Other factors may affect the manufacturability such as the type of raw material, the form of the raw material, dimensional tolerances, and secondary processing such as finishing.
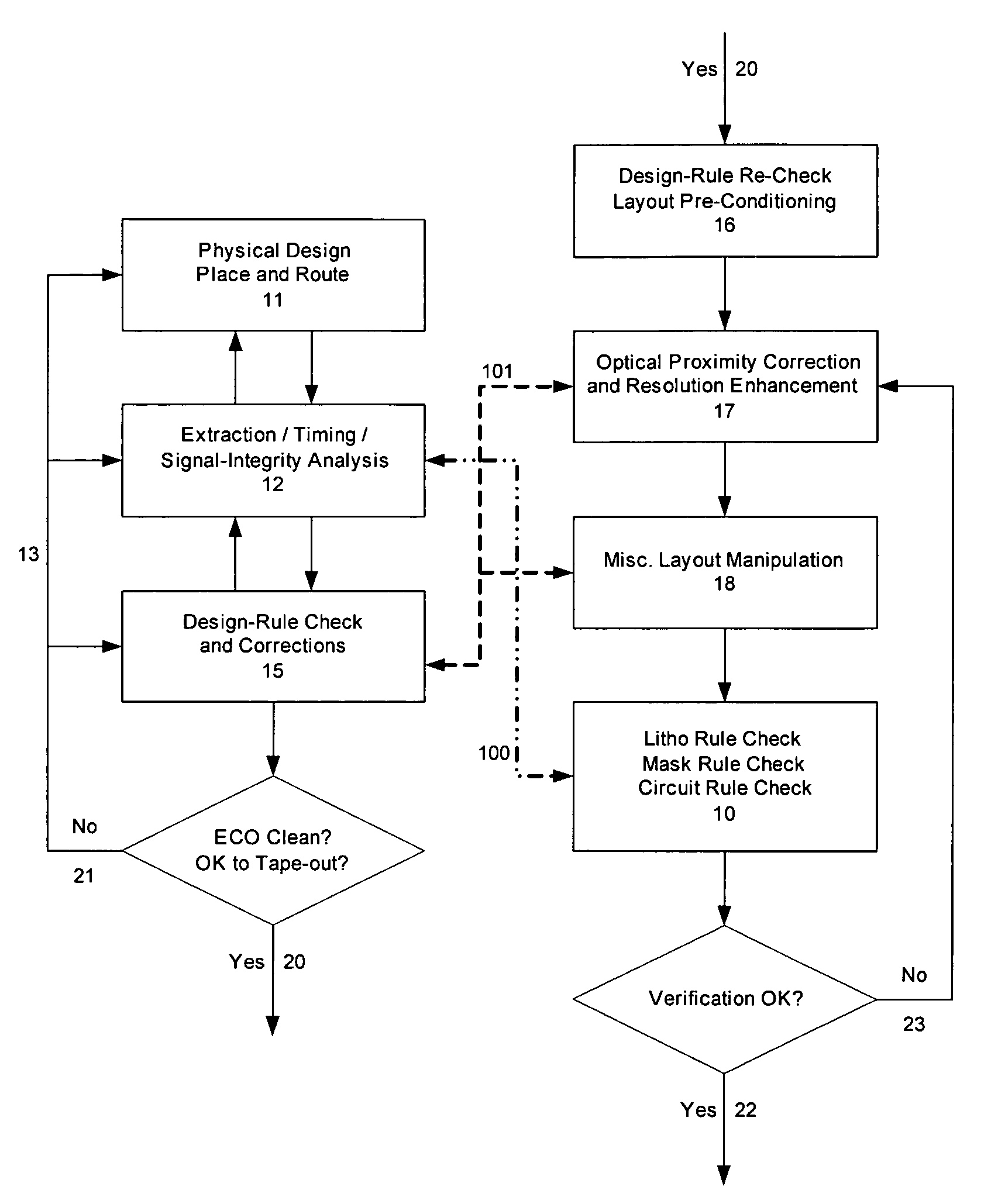
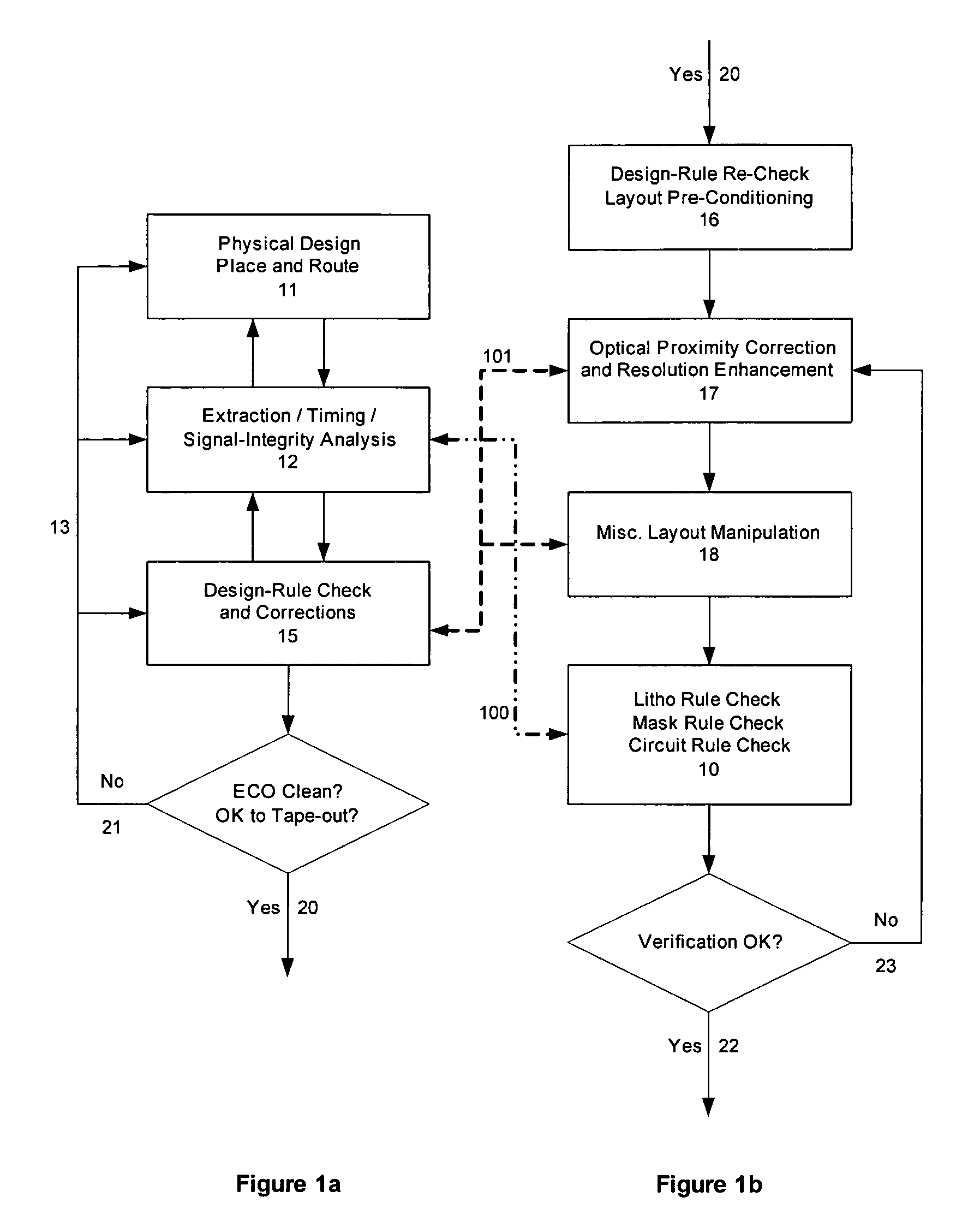
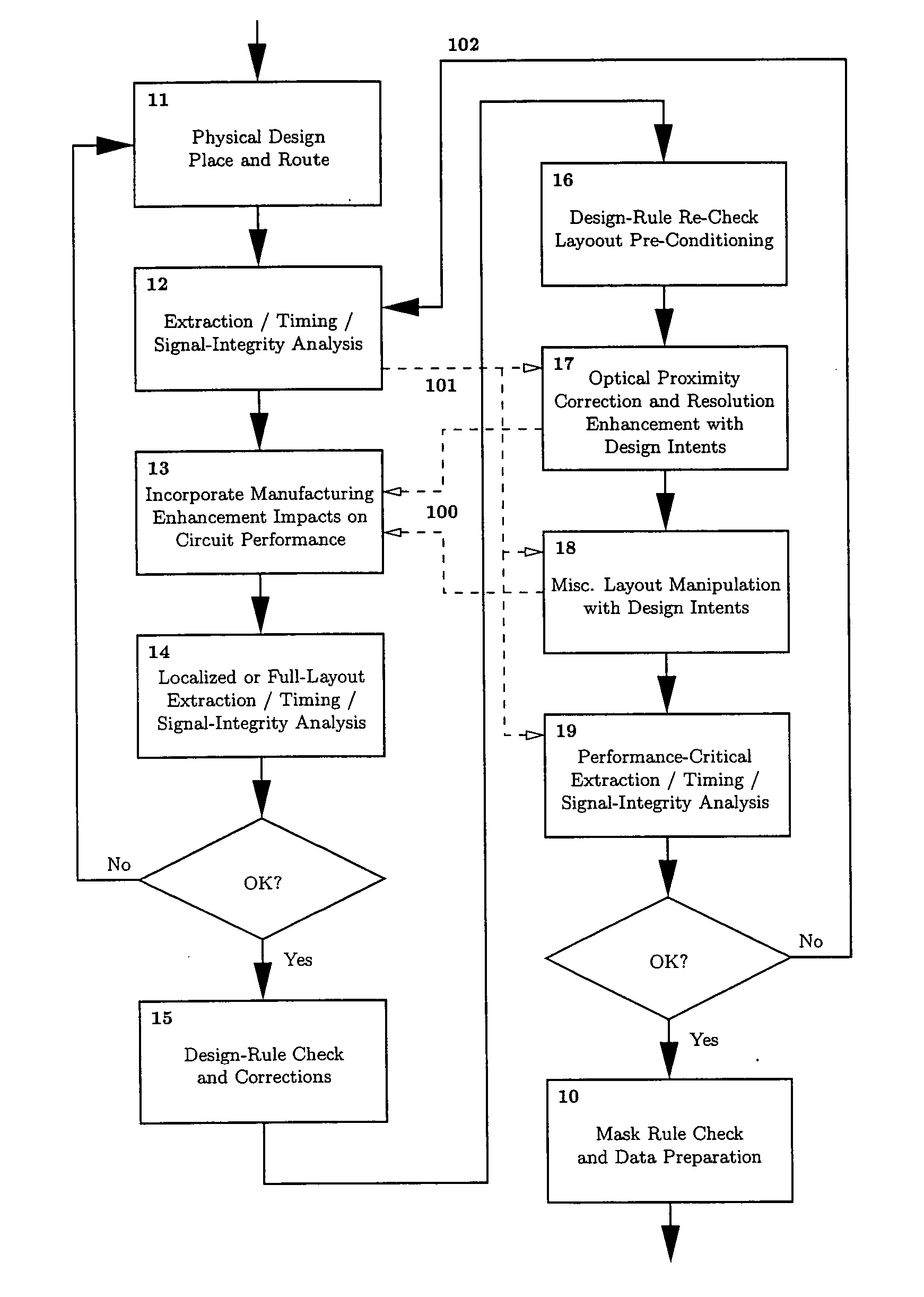
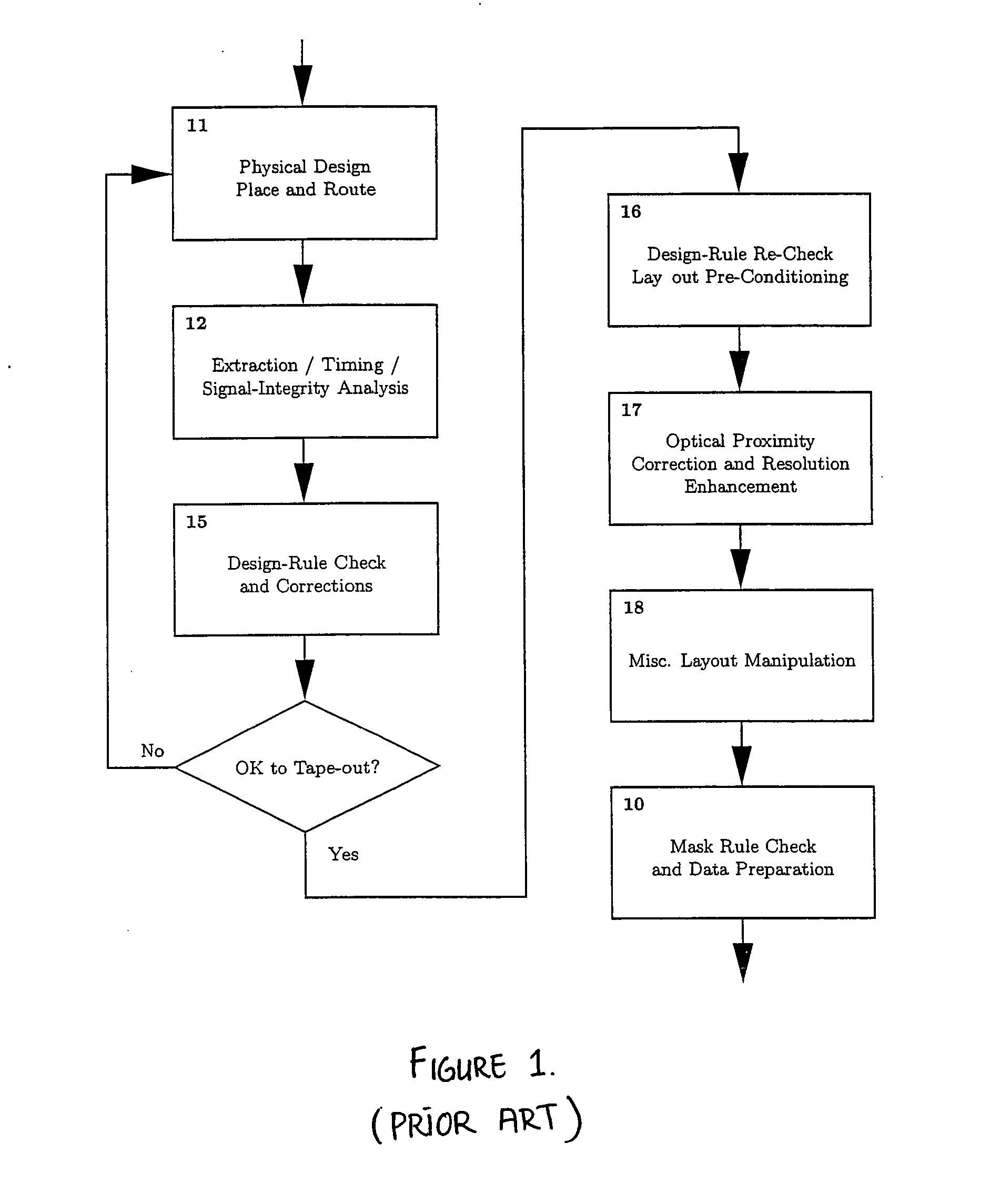
Method and apparatus for selective, incremental, reconfigurable and reusable semiconductor manufacturing resolution-enhancements
InactiveUS20050229130A1Improve manufacturabilityHigh yieldCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsImage resolutionPhysical verification
An automated design for manufacturability platform for integrated physical verification and manufacturing enhancement operations. Given original layouts and one or more associated resolution-enhanced layouts, intermediate resolution-enhancement state layouts are reconstructed, and selective localized resolution-enhancement reconfigurations, modifications, and / or perturbations are introduced on any existing enhancements in order to improve manufacturability and yield.
Owner:RPX CORP
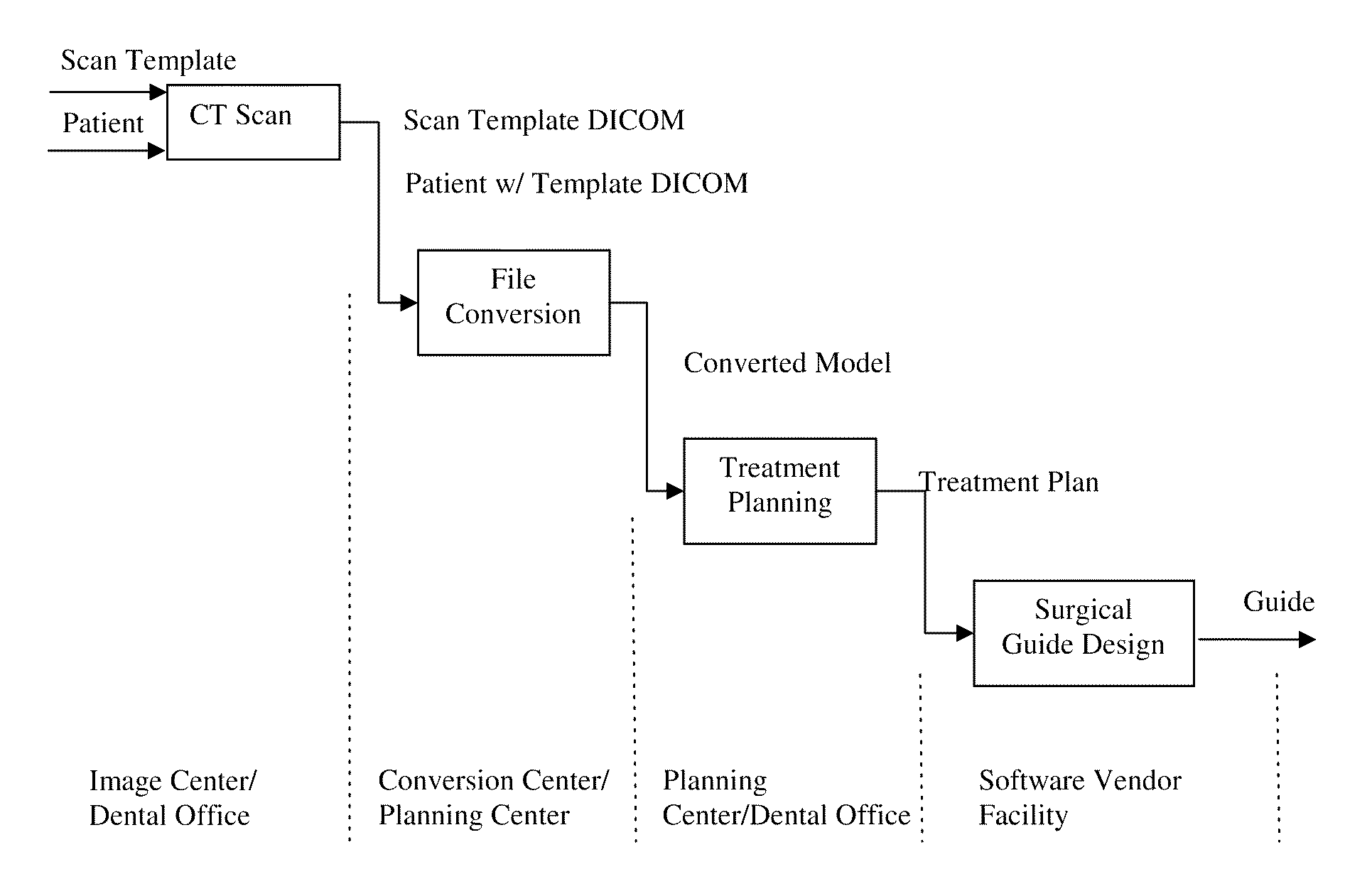
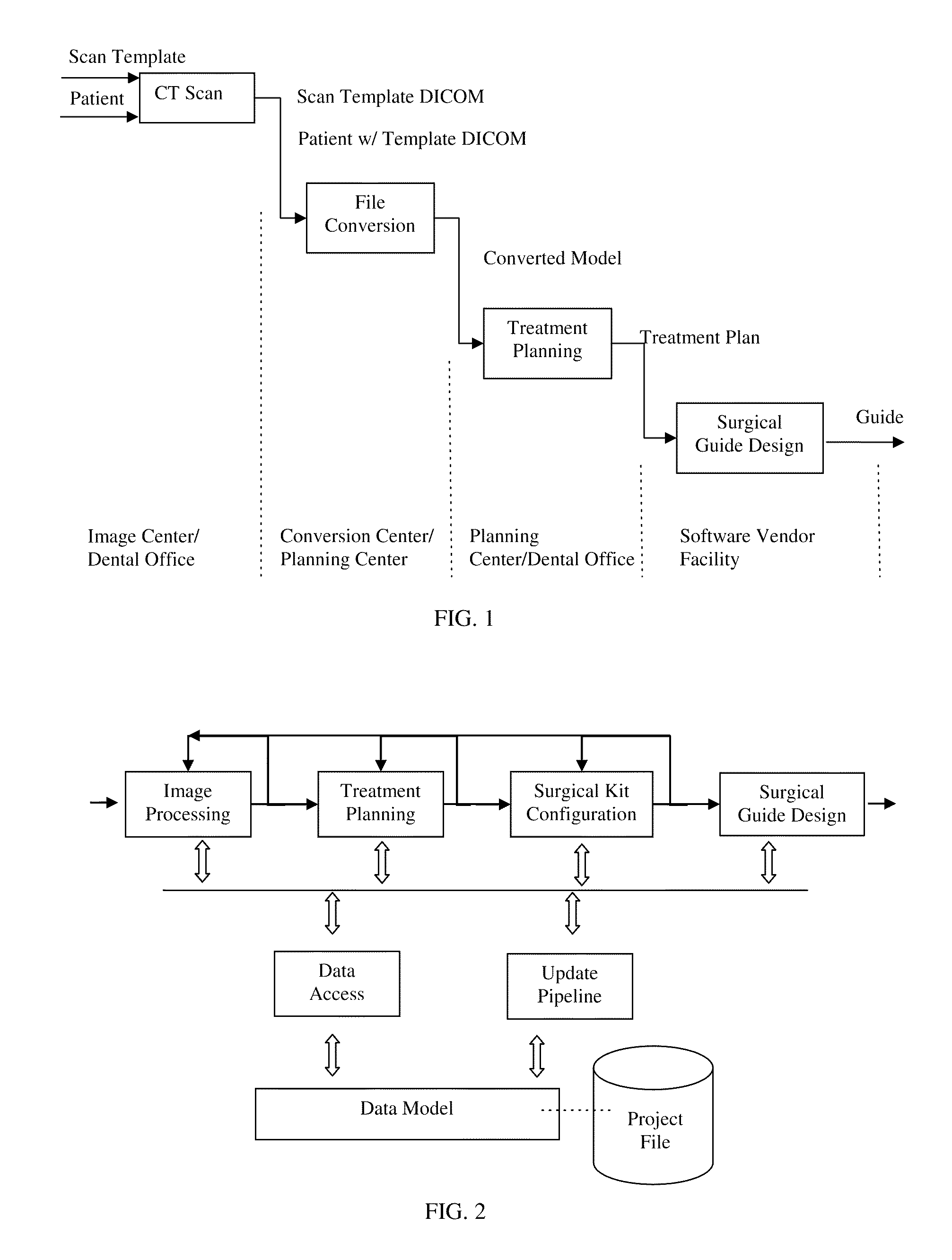
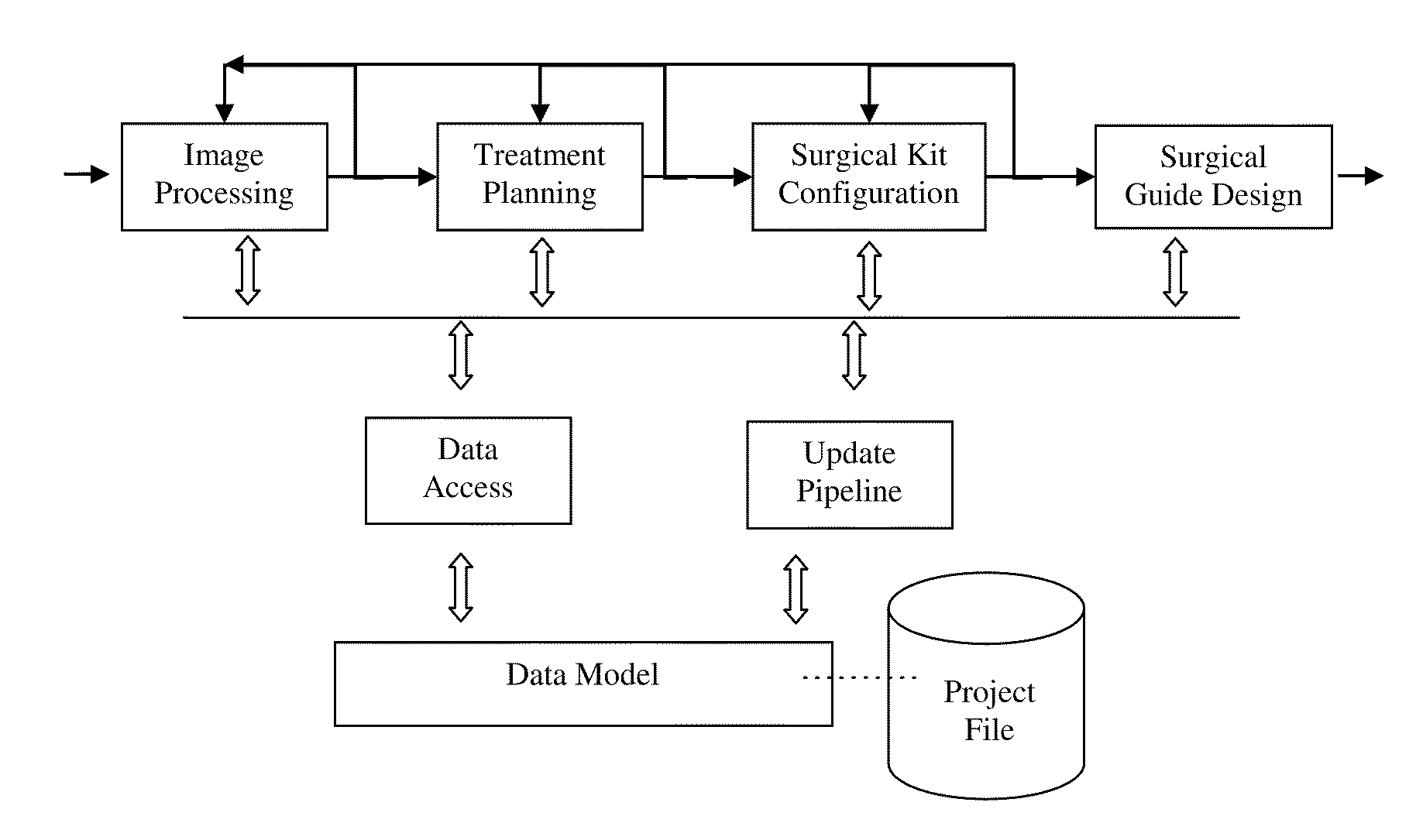
Method and software system for treatment planning and surgical guide CAD/CAM
ActiveUS8543234B2Process controlMedical simulationAdditive manufacturing apparatusImaging processingSoftware system
A method and interactive computer system for dental implant treatment planning, surgical guide design and manufacturing. In the heart of the method is a fully associative workflow integrating image processing, treatment planning, surgical kit configuration and surgical guide CAD / CAM in one single computer system. In this workflow, any changes of image processing parameters and implant information in the earlier stage are automatically propagated to the downstream. This characteristic is referred as associativity. The software aspect of the system is built upon this concept and its corresponding data model. This invention also includes an image processing and geometric modeling approach that is characterized as design for manufacturability and applicability. The integration of treatment planning and surgical guide CAD is further on integrated with manufacturing equipment to constitute a complete CAD / CAM solution, which is also fully associative.
Owner:GUIDEMIA TECH
Method and platform for integrated physical verifications and manufacturing enhancements
InactiveUS20050044514A1High storageHigh memoryDigital computer detailsComputer aided designPhysical verificationEngineering
An automated design for manufacturability platform which provides integrated physical verification and manufacturing enhancement operations. The platform uses an efficient data structure capable of handling and manipulating both layout circuit and geometry characteristics, which permits a wide range of operations such as timing analysis, design-rule checking and optical proximity corrections on a single platform. This feature eliminates the need to translate layout representations between various tools without the requirement of using a common database. Moreover, the platform's common user interface enables encapsulated information exchange between the design and the manufacturing teams, permiting early consideration of manufacturing distortion or enhancement impact on circuit performance.
Owner:RPX CORP
Profit optimizer
InactiveUS20100161383A1Eliminate associated fixed overhead expenseHigh capacity valueForecastingResourcesCapacity valueProfit optimization
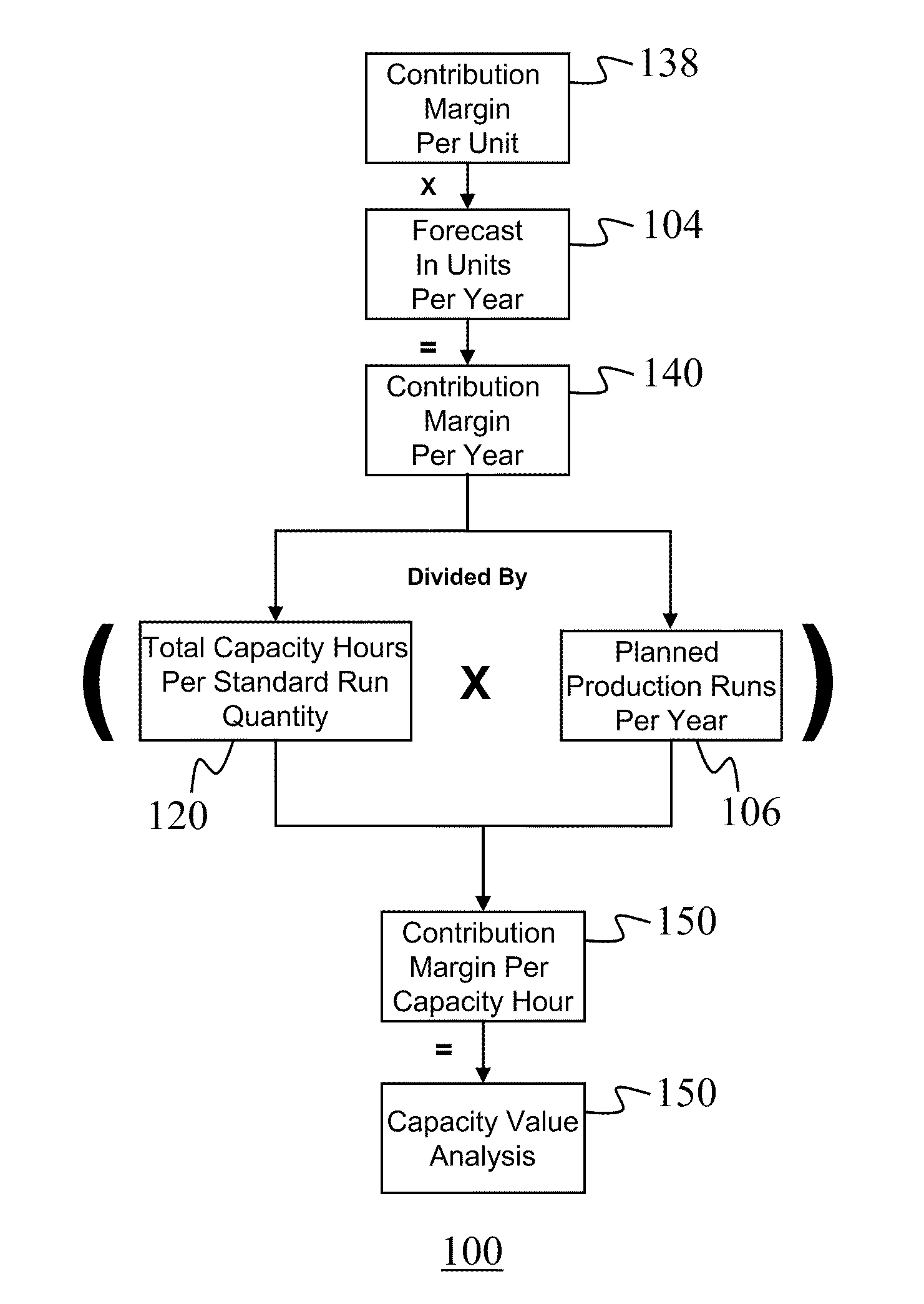
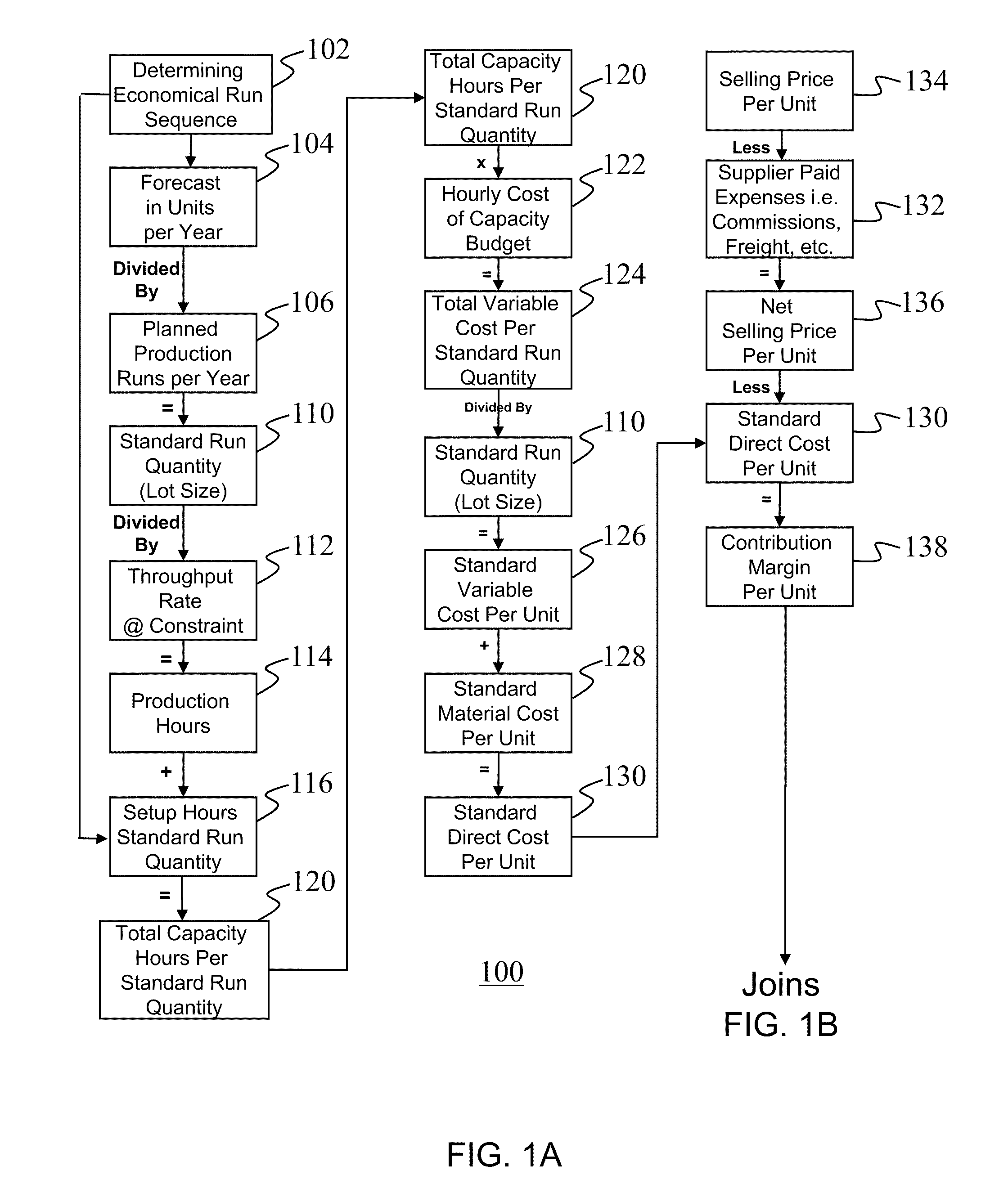
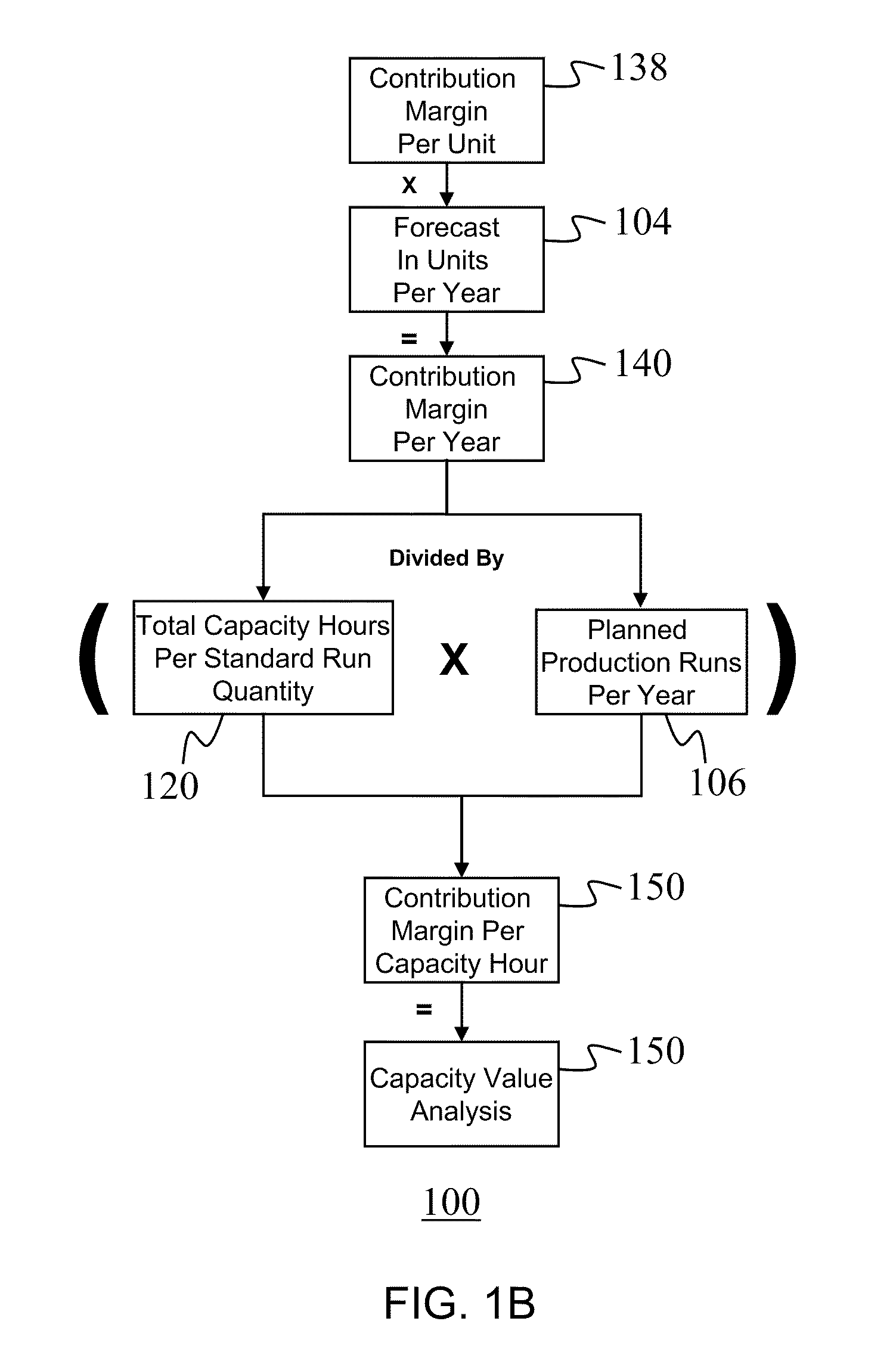
A system and method for analyzing the profitability of a company's products and services and then maximizing that profit is provided. A contribution margin per unit 138 is multiplied times the forecast in units per year 104. The product of this contribution margin per unit 138 times the forecast in units per year 104 is divided by the product of the total capacity hours per standard run 120 quantity and the planned production runs per year 106. The result is the contribution margin per capacity hour 150 which is also defined here as the capacity value analysis 150. The capacity value analysis 150 provides for determining product rationalization, and profitable growth determination, as well as a metric for profit optimization initiatives such as eliminating constraints, customer perceived value, design for manufacturability, reduced production frequency, and reduced setup time.
Owner:BUTLER GLEN ORES
Method and platform for integrated physical verifications and manufacturing enhancements
InactiveUS7100134B2Optimize circuit designDigital computer detailsComputer aided designPhysical verificationEngineering
An automated design for manufacturability platform which provides integrated physical verification and manufacturing enhancement operations. The platform uses an efficient data structure capable of handling and manipulating both layout circuit and geometry characteristics, which permits a wide range of operations such as timing analysis, design-rule checking and optical proximity corrections on a single platform. This feature eliminates the need to translate layout representations between various tools without the requirement of using a common database. Moreover, the platform's common user interface enables encapsulated information exchange between the design and the manufacturing teams, permiting early consideration of manufacturing distortion or enhancement impact on circuit performance.
Owner:RPX CORP
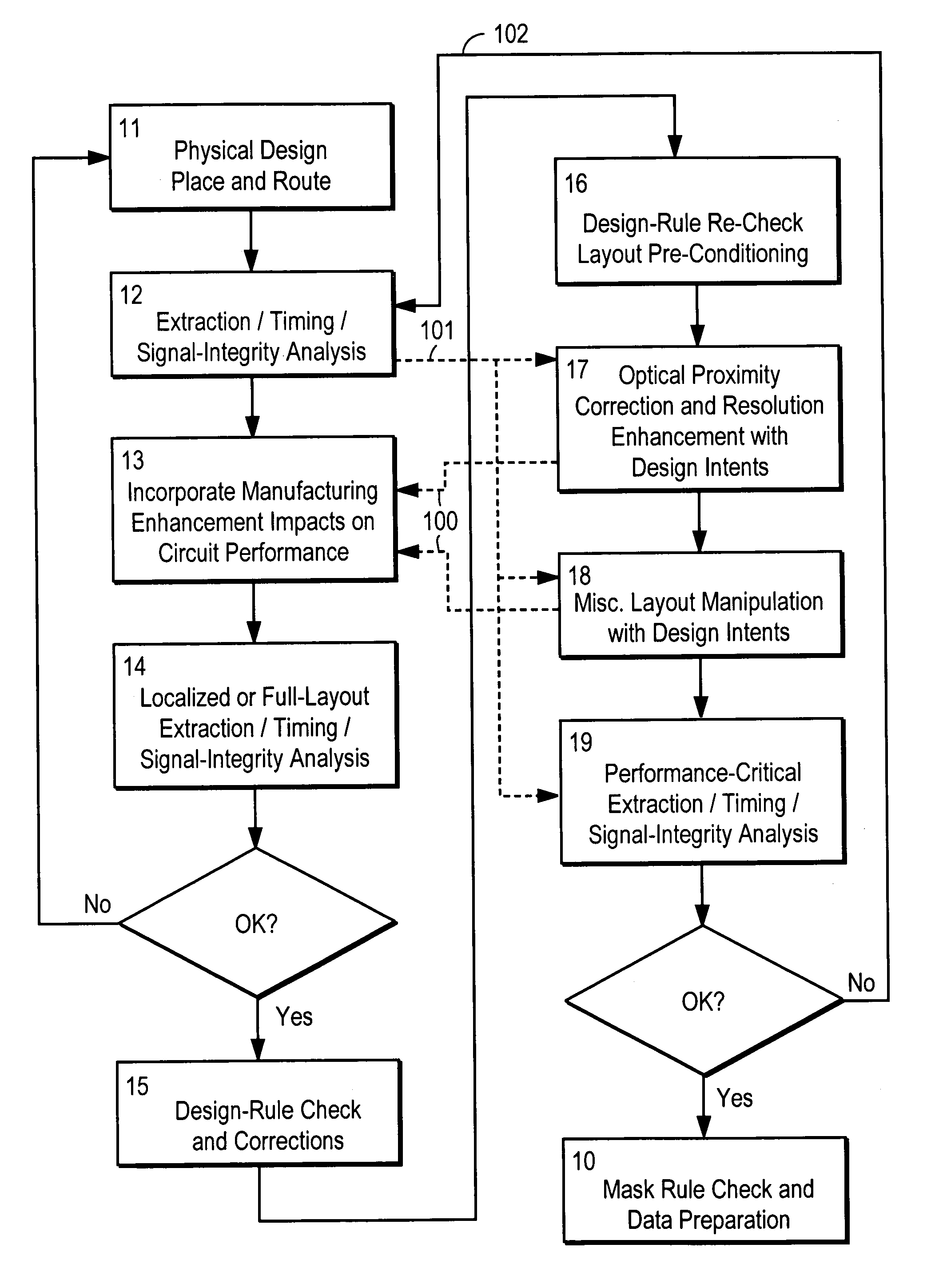
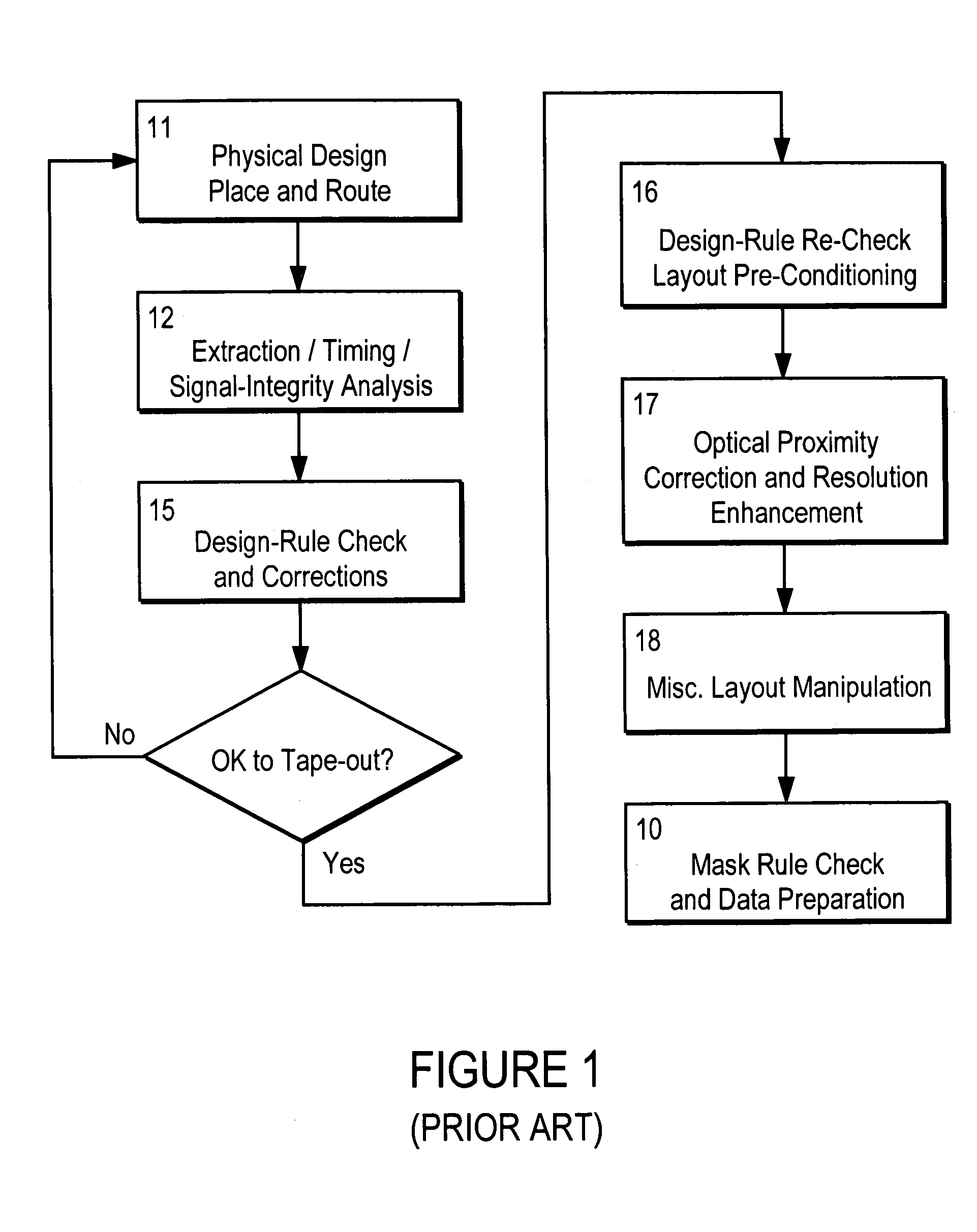
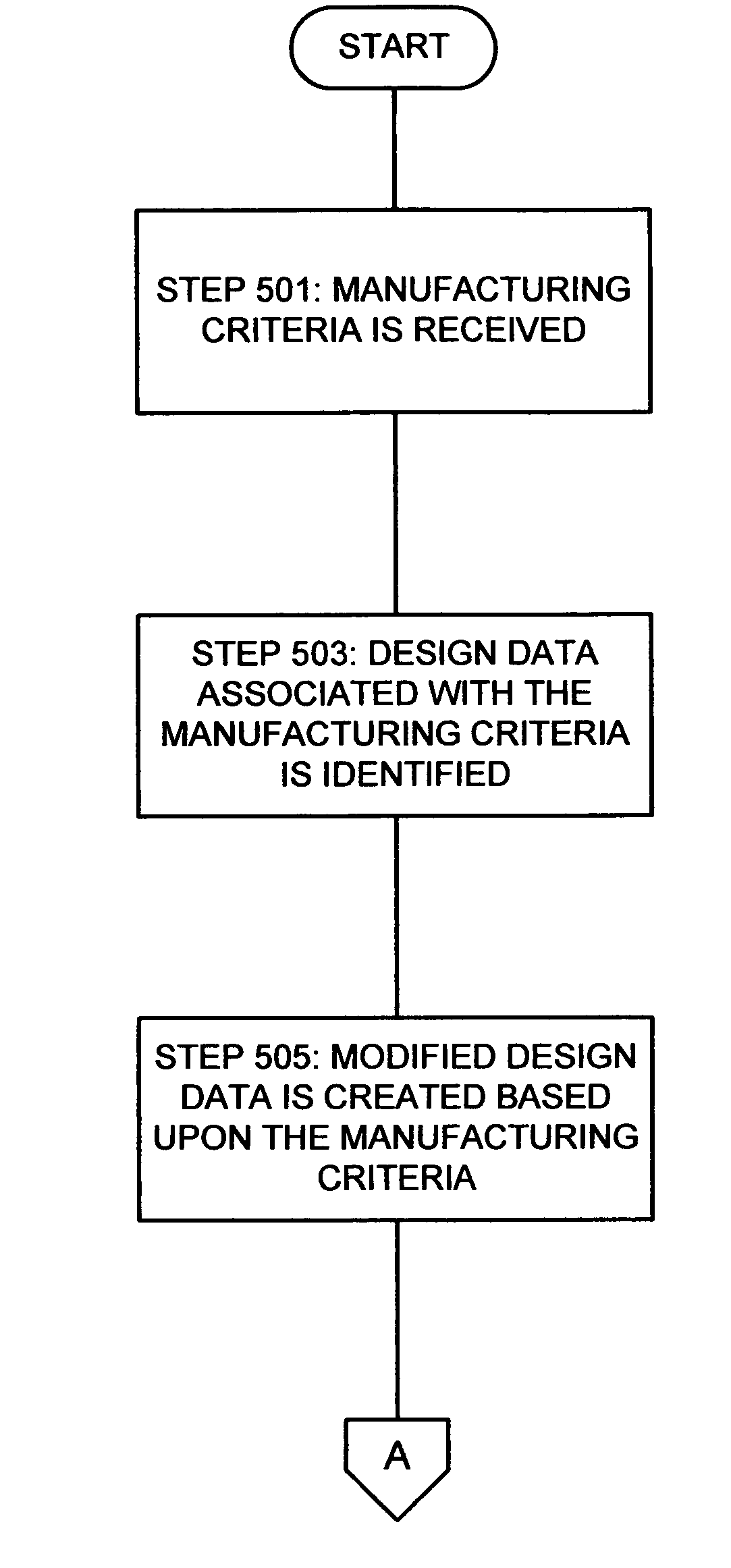
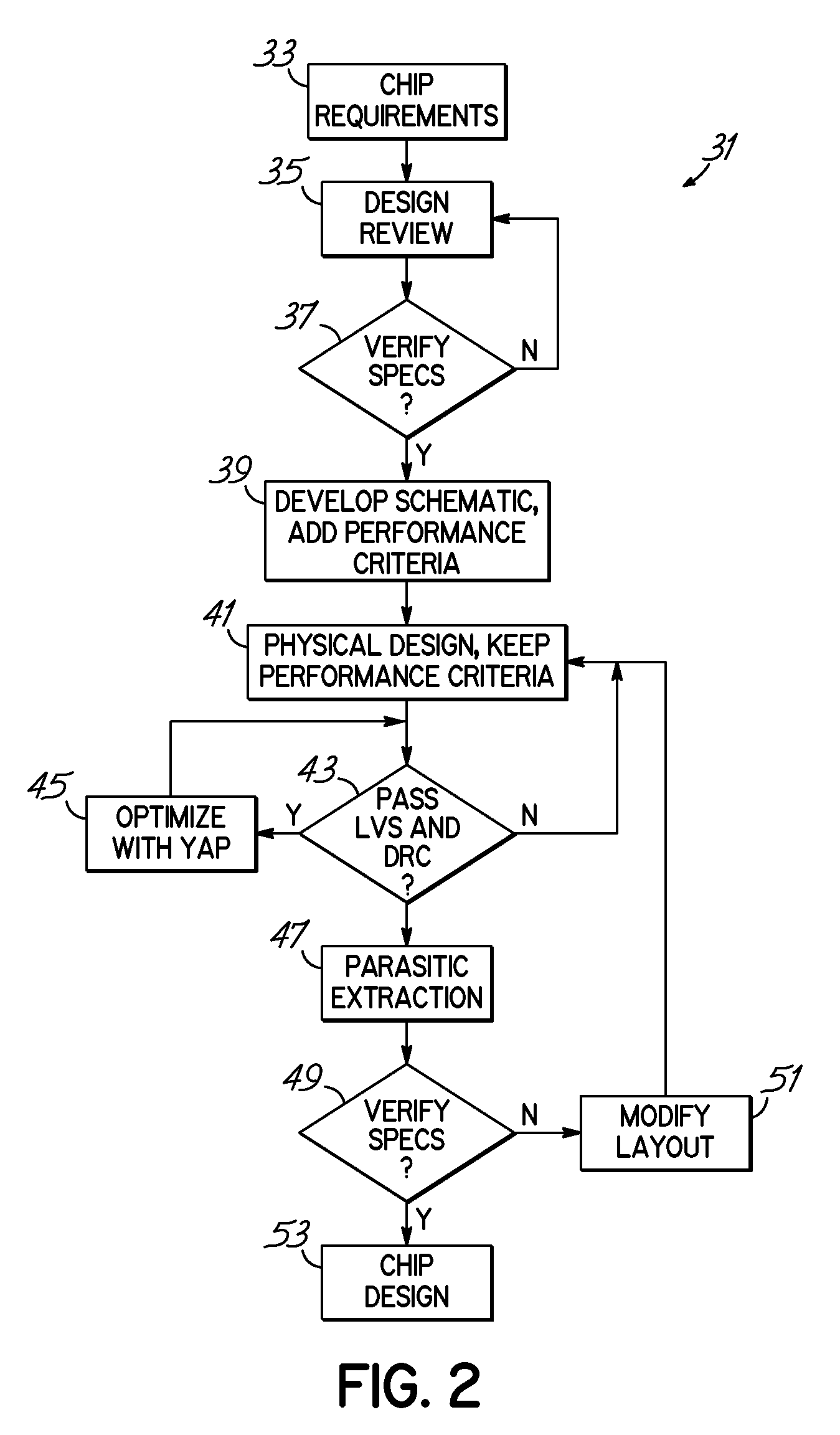
Design for manufacturability
InactiveUS20050015740A1Increase productionGuaranteed uptimeProgramme controlDigital computer detailsFoundryDesign for manufacturability
Techniques are disclosed for modifying an existing microdevice design to improve its manufacturability. With these techniques, a designer receives manufacturing criteria associated with data in a design. The associated design data then is identified and provided to the microdevice designer, who may choose to modify the design based upon the manufacturing criteria. In this manner, the designer can directly incorporate manufacturing criteria from the foundry in the original design of the microdevice.
Owner:MENTOR GRAPHICS CORP
Design for manufacturability
InactiveUS20050234684A1Improve manufacturabilityIncrease productionProgramme controlCAD circuit designFoundryDesign for manufacturability
Techniques are disclosed for modifying an existing microdevice design to improve its manufacturability. With these techniques, a designer receives manufacturing criteria associated with data in a design. The associated design data then is identified and provided to the microdevice designer, who may choose to modify the design based upon the manufacturing criteria. In this manner, the designer can directly incorporate manufacturing criteria from the foundry in the original design of the microdevice.
Owner:MENTOR GRAPHICS CORP
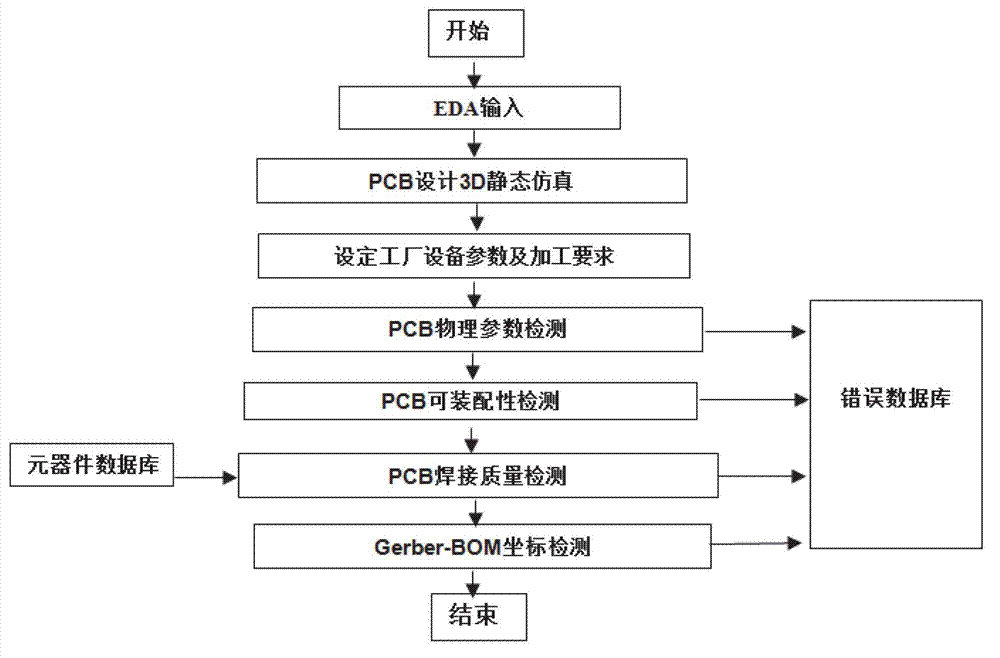
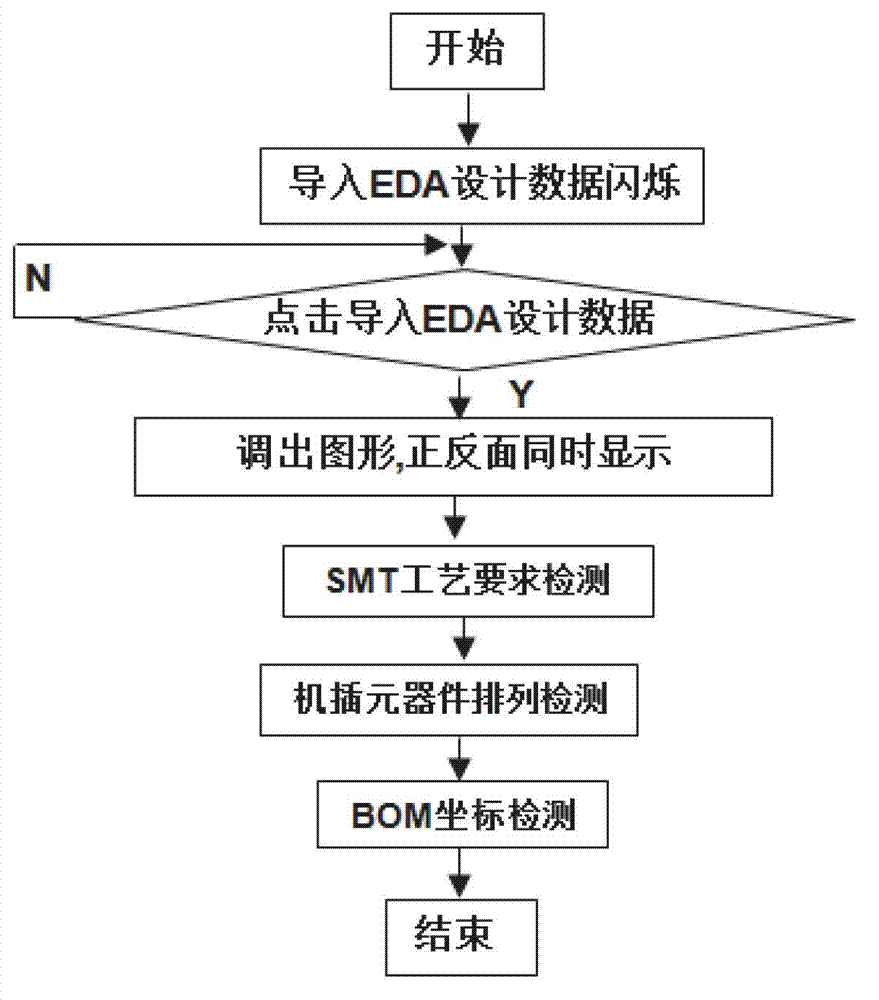
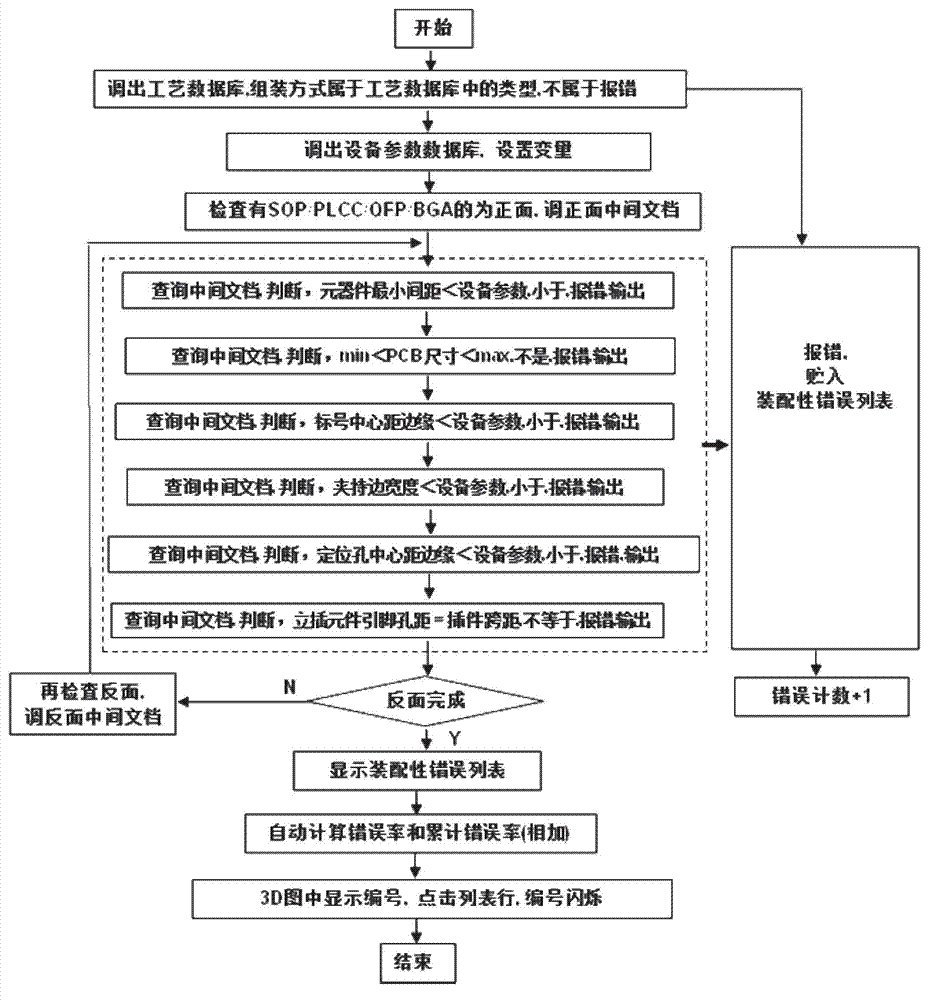
Visualization detection method of electronic product electronic design automation (EAD) design manufacturability
ActiveCN102930114AImprove efficiencyQuality improvementSpecial data processing applicationsInformation processingGraphics
The invention discloses a visualization detection method of electronic product electronic design automation (EDA) design manufacturability. Printed circuit board (PCB) three dimensional (3D) simulation of an EDA design document is conducted, PCBphysical parameter detection, PCB assembling ability, PCB welding quality detection and Gerber bill of material (BOM) coordinate detection are conducted in sequence, and specific error positions and types of former four steps of detection are displayed in visualization mode on a PCB 3D figure. On the basic of complete actual production experiences, the visualization detection method and a system of the EAD design manufacturability are developed according to international standard of information processing center (IPC), the PCB physical parameter detection, the PCB assembling ability, the PCB welding quality detection and the gerber BOM coordinate detection which are all designed by EDA are integrated, the various actual problems which are the contradictions of manufacture and design of PCB and are faced by enterprises are resolved, and efficiency and quality of electronic manufacture in particular to an original equipment manufacturer (OEM) are improved.
Owner:CHANGZHOU AUTOSMT INFORMATION TECH
Golf ball manufacturing method
ActiveUS20080217810A1High reboundImprove wear resistanceCeramic shaping apparatusGolf ballsThermoplastic elastomerThermoplastic polyurethane
The invention provides a method of manufacturing golf balls having a core and at least one cover layer which involves injecting a molten cover resin material around a core so as to form a cover layer. The cover resin material is a single resin composition made up of (A) a thermoplastic polyurethane, (B) a polyisocyanate compound and (C) a thermoplastic elastomer other than the thermoplastic polyurethane in a weight ratio (A):(B):(C)=100:{2-50}:{0-50}, and is injected with from 10 to 99% of the total number of isocyanate groups in component B remaining in an unreacted state within the cover resin material. The method of the invention provides a high manufacturability and a good amenability to mass production, and the manufactured golf balls thus obtained have a high rebound and excellent scuff resistance.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE SPORTS
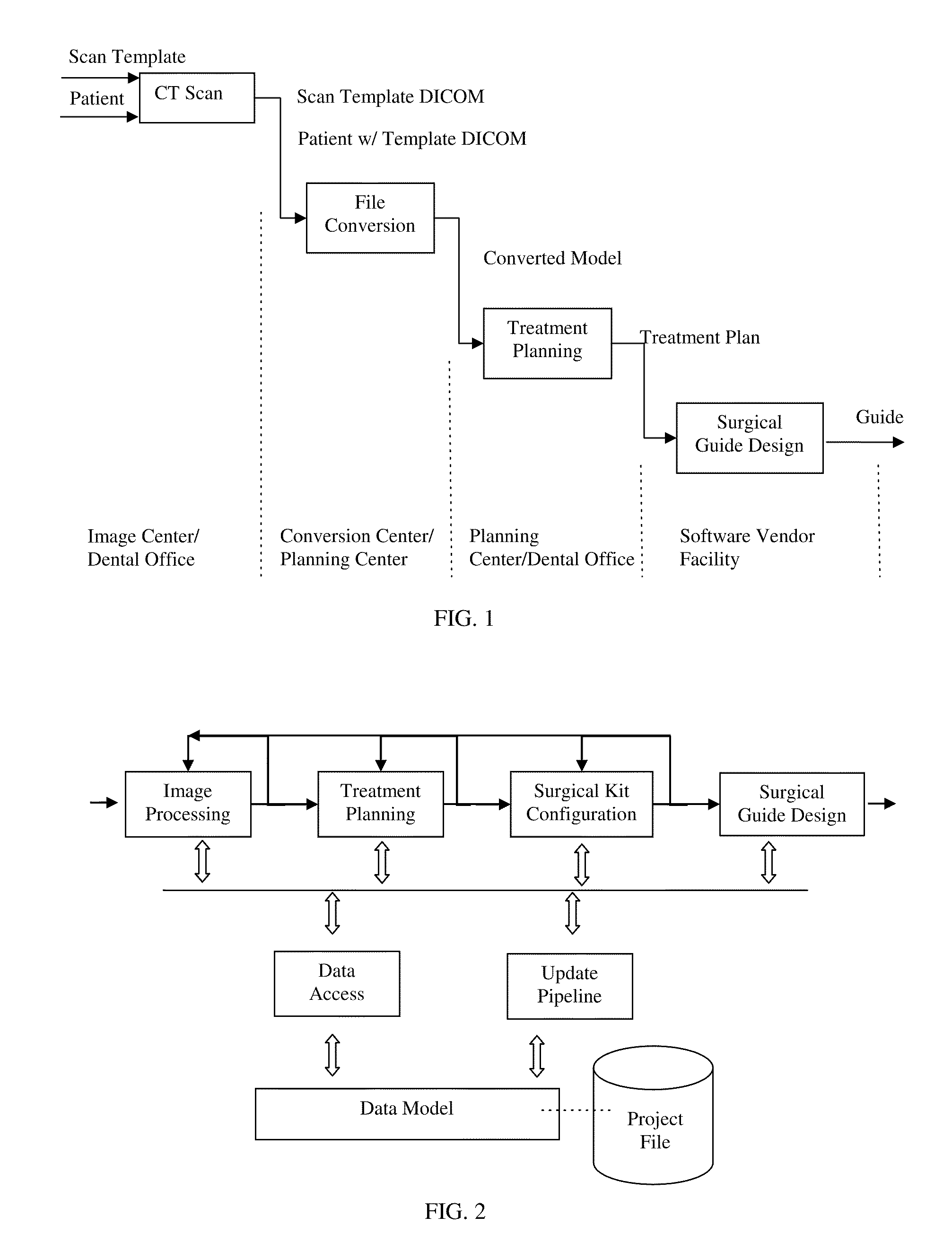
Method and software system for treatment planning and surgical guide cad/cam
ActiveUS20110301732A1Process controlMedical simulationAdditive manufacturing apparatusInteractive softwareAnatomical structures
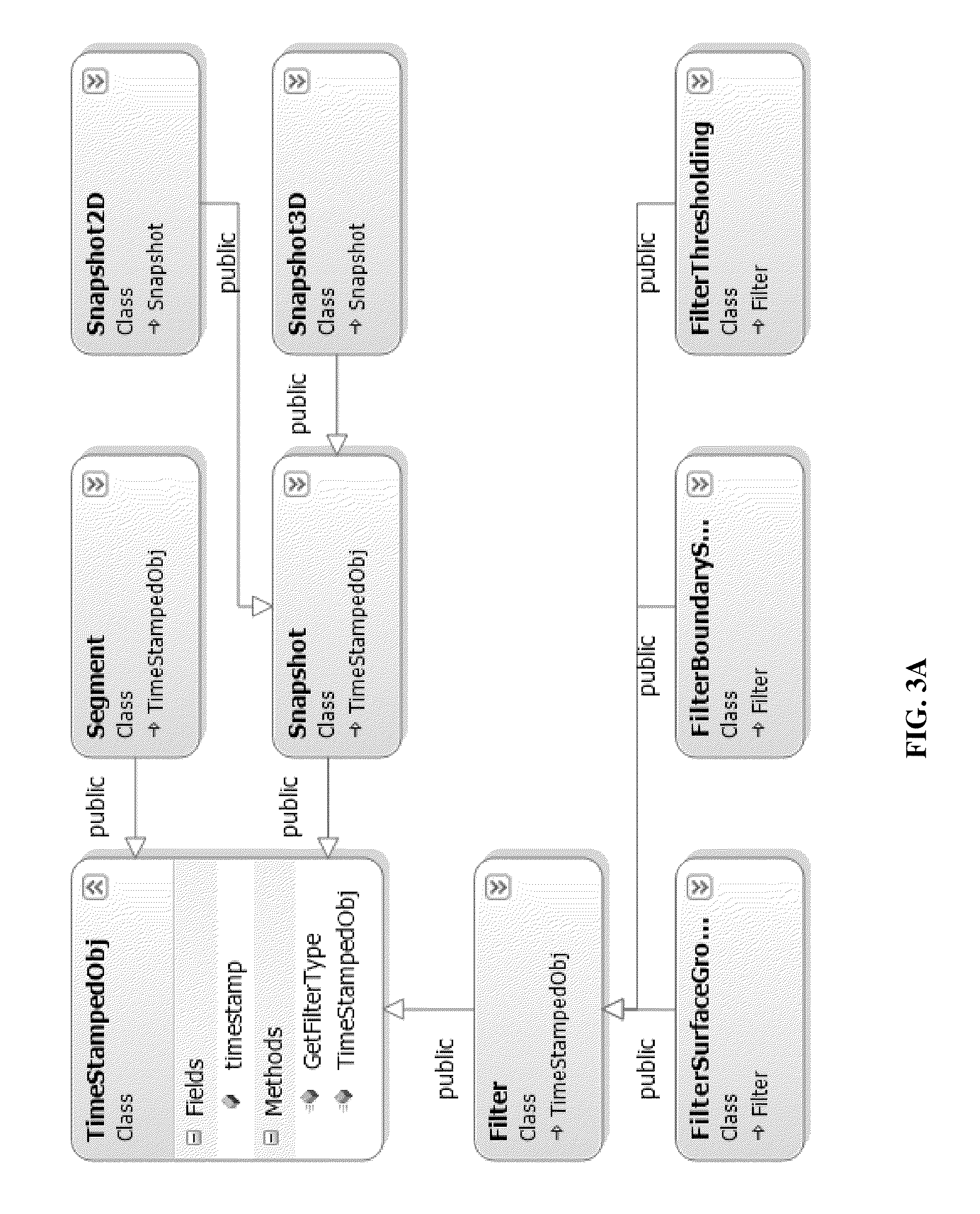
A method and interactive software system for treatment planning and surgical guide design. In the heart of the method is a fully associative workflow integrating image processing, treatment planning, surgical kit configuration and surgical guide CAD / CAM, wherein any changes in the earlier stage will be automatically propagated to the downstream. This characteristic is referred as associativity. The software system is built upon this concept and a corresponding data model. The status, as well as the display, of the workflow at certain time point is recorded as a snapshot, with which the system can always re-enter into the status of certain point of the saved operation history. Such a snapshot is called re-enterable snapshot. In this invention, the design of surgical guides is driven by a universal surgical kit configuration tool. This approach drives surgical guide design with kit parameters and enables the professionals to plan their cases according to the kit. It also serves as a tool for the users and suppliers to define their own surgical kits as well. It supports the concept of choosing surgical kits for individual implants in a single case. This invention also includes an image processing and geometric modeling approach that is characterized as design for manufacturability and applicability. It is integrated with the feature-based CAD module and rapid prototyping technology to constitute a complete CAD / CAM solution, which is also fully associative. The surgical guides resulted from this design can better fit the patients' anatomy and can be manufactured with other CAM technologies through standard format file exporting.
Owner:GUIDEMIA TECH
Method and system for designing design-for-manufacturability (DFM) simulator
ActiveCN105426648ASimple calculationMeet needsDesign optimisation/simulationCAD circuit designContact pressureEngineering
The invention discloses a method and system for designing a design-for-manufacturability (DFM) simulator. The method comprises the steps: receiving an integrated circuit design layout, and partitioning the integrated circuit design layout into simulation grids; computing the contact pressure of each simulation grid according to the integrated circuit design layout and chemical mechanical planarization (CMP) process data; simulating the morphology of each simulation grid, subjected to a simulation execution CMP process, according to the contact pressure of each simulation grid; optimizing the integrated circuit design layout according to the morphology of each simulation grid subjected to the execution CMP process. According to the method, the computing efficiency can be guaranteed while high-accuracy simulation is achieved, so that both the computing efficiency and accuracy can meet the practical needs of DFM simulator design.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Variable performance ranking and modification in design for manufacturability of circuits
InactiveUS7823106B2Improve performanceHigh yieldDetecting faulty computer hardwareComputer aided designRankingComputerized system
A method, computer system and program product introduce adding a variable performance ranking parameter to a diagram of a circuit to drive implementation of modifications that are yield improving, performance boosting, or performance-neutral. The information is paired to accomplish a more complete design for manufacturability modification in the design of circuits implemented on chips. In this matter, both yield and chip performance are improved.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
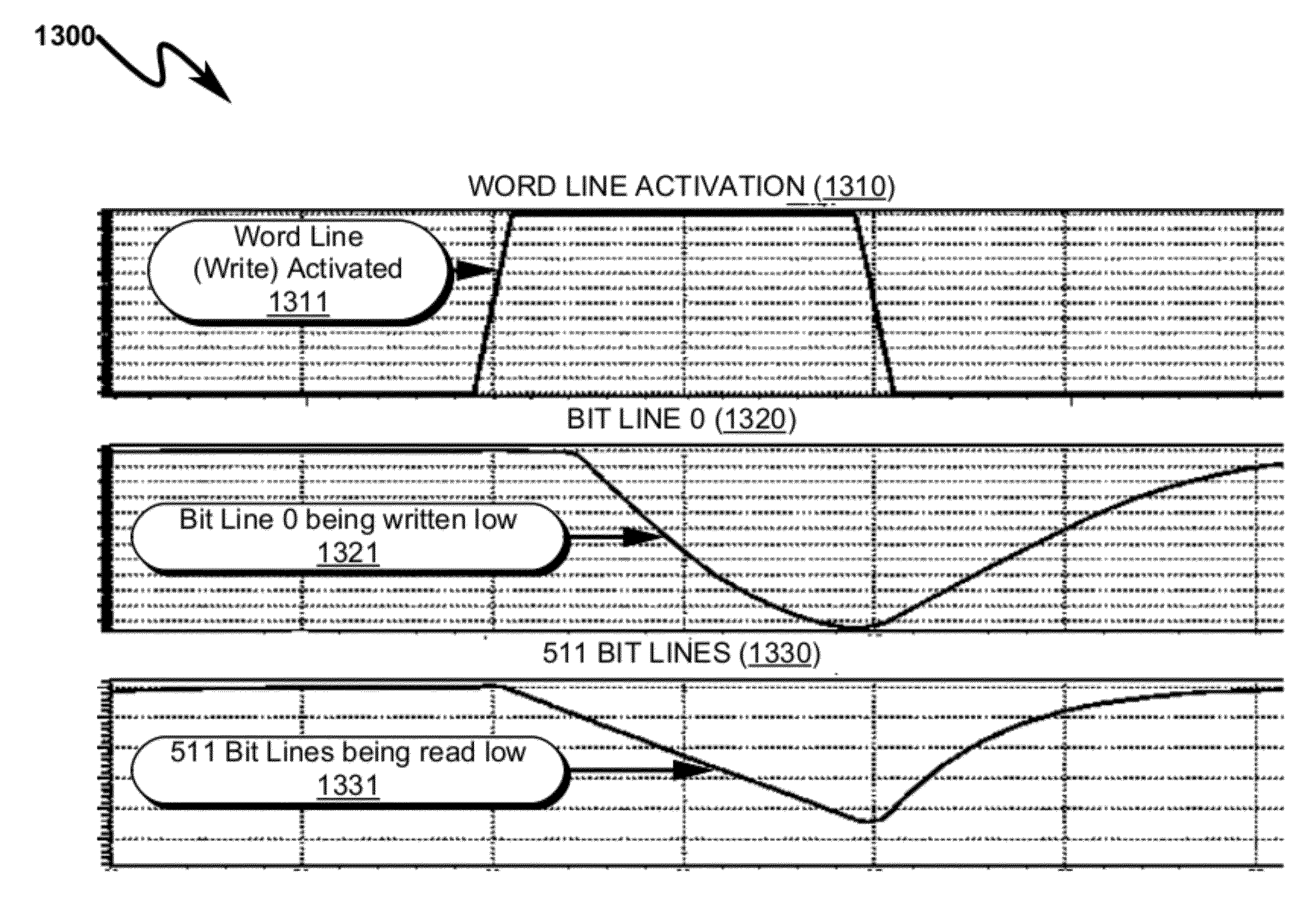
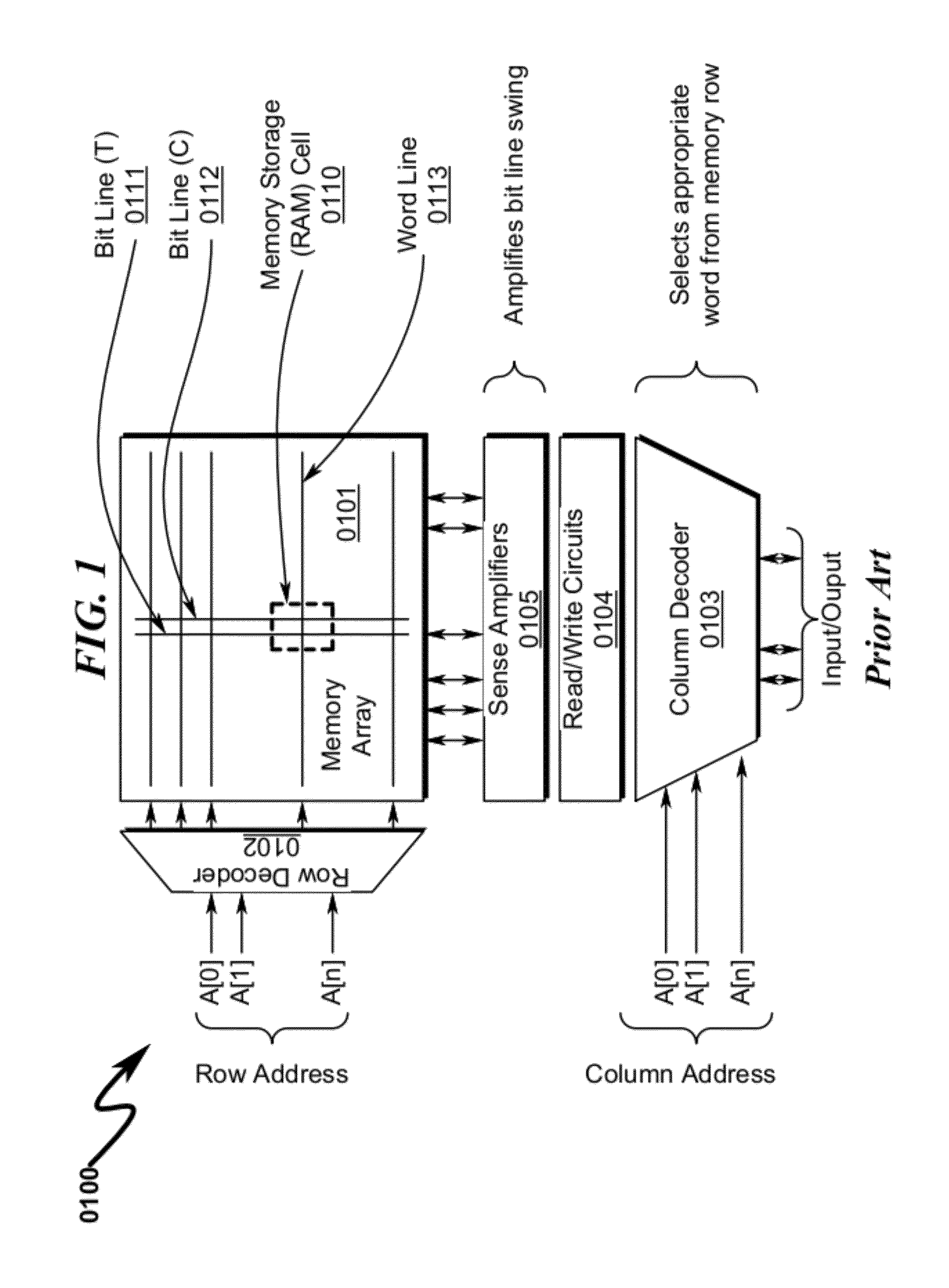
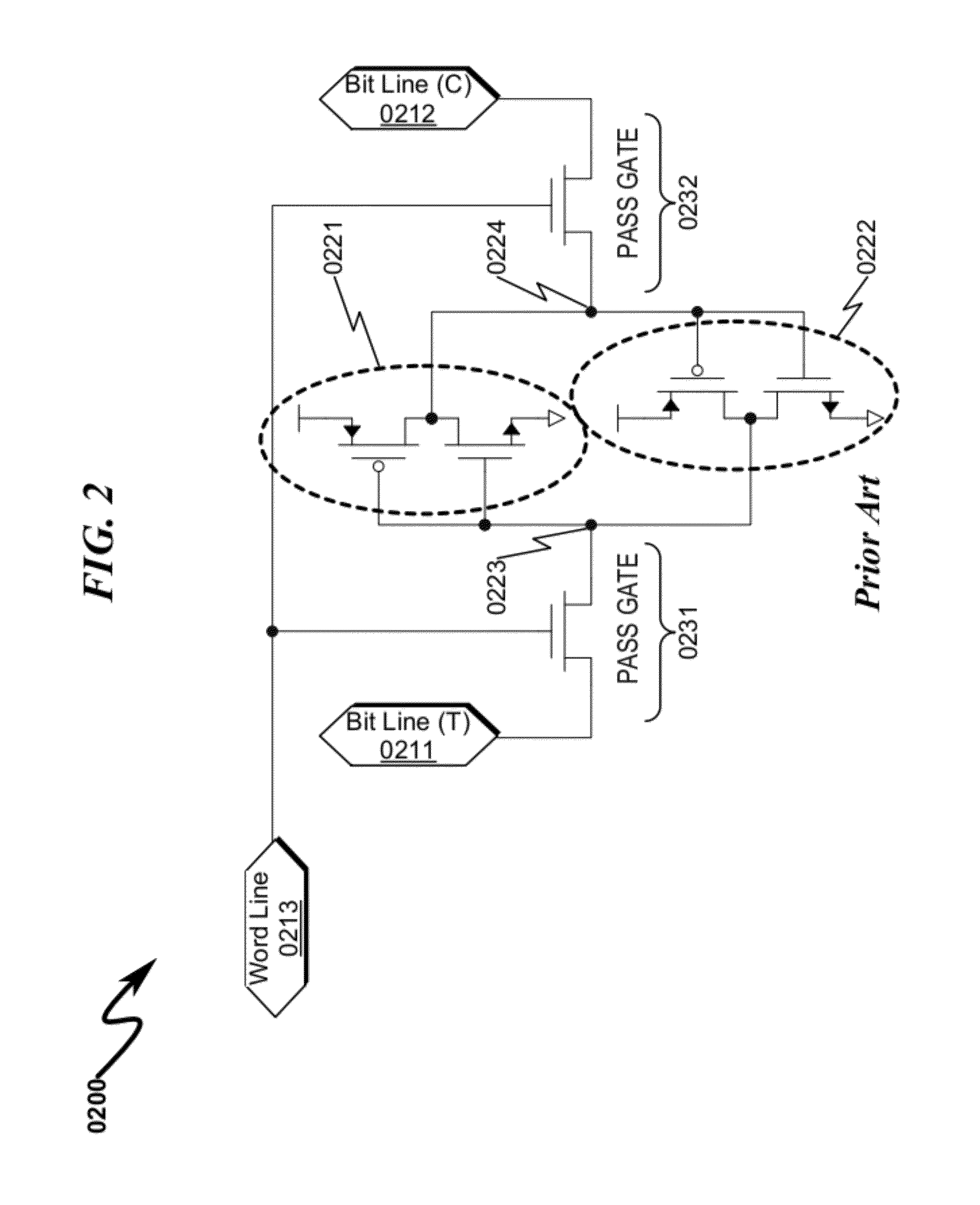
Memory Cell System and Method
InactiveUS20120230130A1Reduce dynamic power consumptionReduce in quantityDigital storageAudio power amplifierEngineering
A memory cell system / method incorporating reduced transistor counts and / or improved design-for-manufacturability (DFM) is disclosed. The system / method incorporates cross-coupled feedthru (3410) / feedback (3420) amplifiers to implement memory cell state memory, wherein the feedback amplifier incorporates a multi-state output drive capability (3423) allowing the memory cell to be read / written using only one access device (3430) connected to the output (3412) of the feedthru (3410) amplifier. The multi-state output drive capability (3423) modulates the feedback amplifier (3420) drive strength to enable reading / writing of the feedthru amplifier (3410) state with greatly reduced memory cell input fan-in requirements. The invention anticipates replacement of traditional DP / 8T / 6T / 4T memory cell structures with corresponding 6T / 6T / 5T / 3T memory cell configurations, resulting in a 16%-25% transistor reduction depending on memory array application context.
Owner:SHEPPARD DOUGLAS P
DFM (design for manufacturability) method for territory
ActiveCN103871949AEliminate the effects ofReduce difficultySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesGraphicsLocal pattern
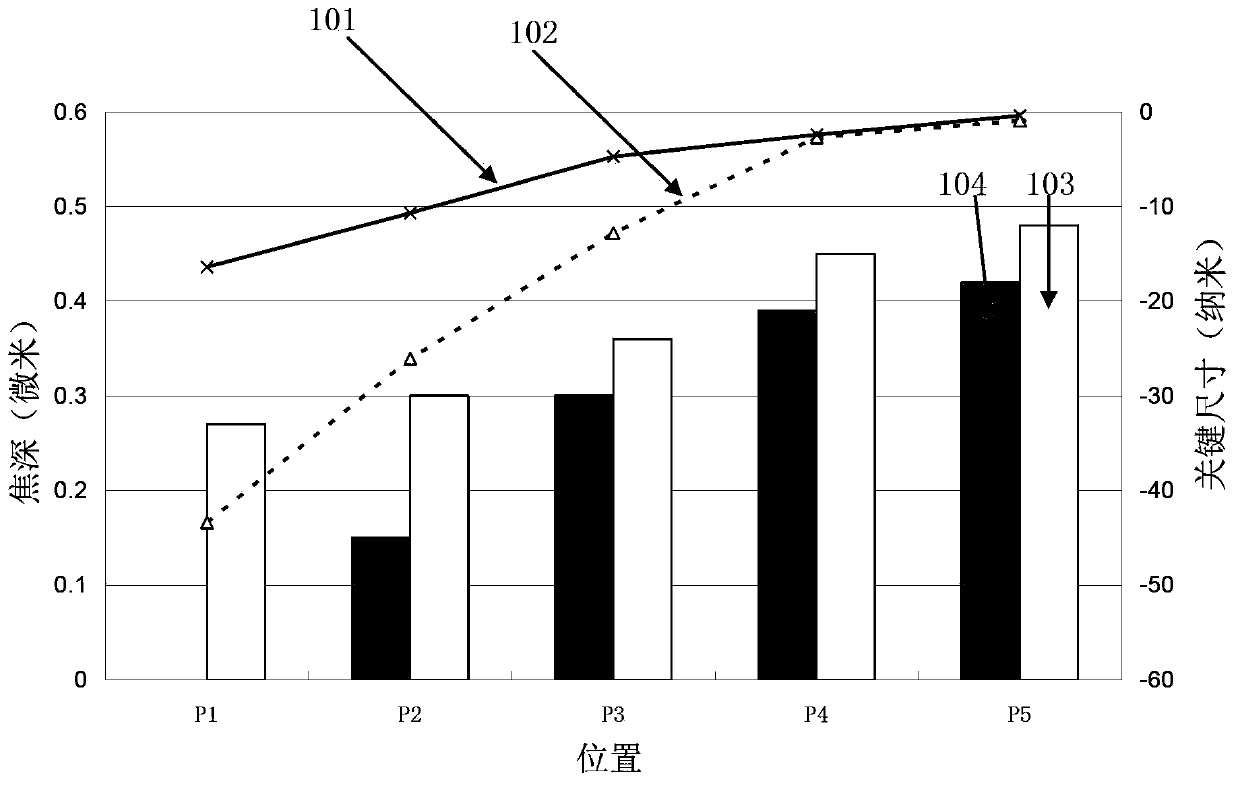
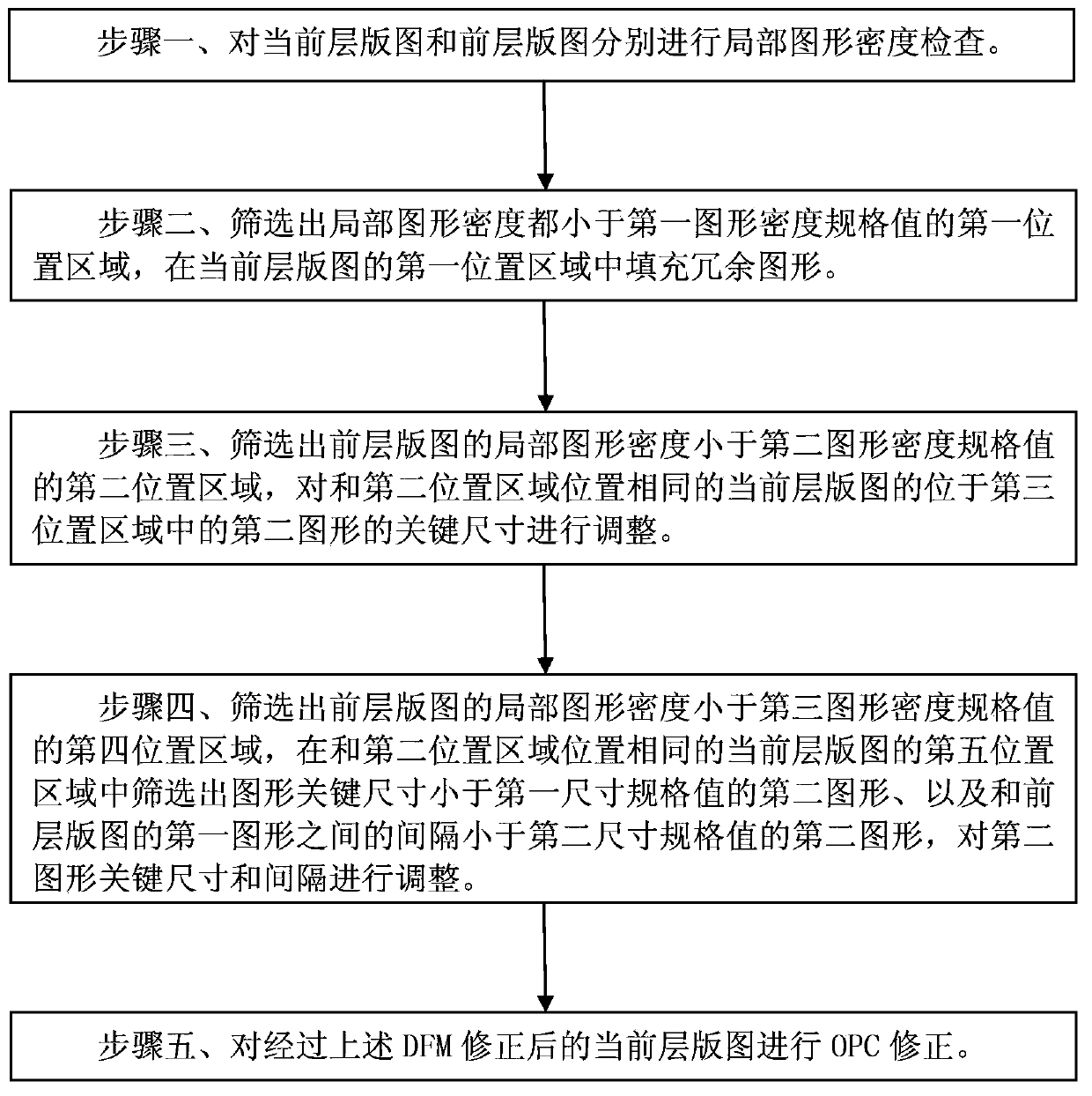
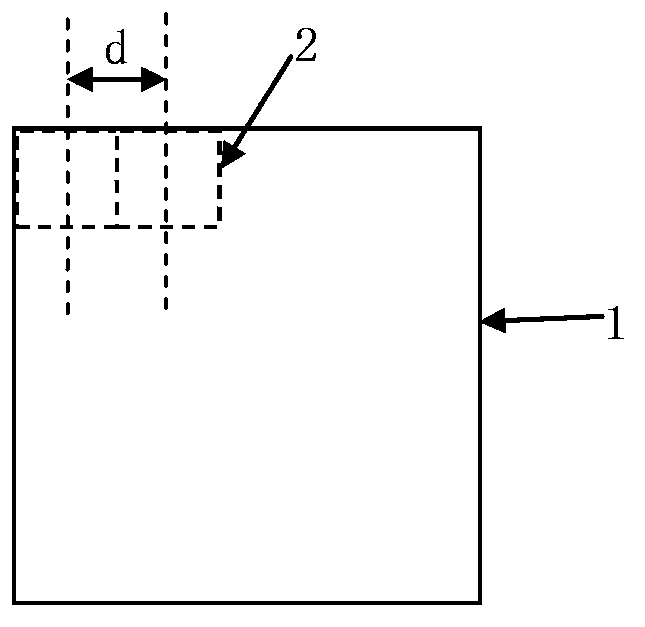
The invention discloses a DFM (design for manufacturability) method for a territory. The method comprises the following steps that a current layer territory and a former layer territory are respectively subjected to local pattern density inspection; each region with the local pattern density being smaller than a first image density specification value is screened out, and redundant patterns are filled in the regions; the region, with the local image density being smaller than a second image density specification value, of the former layer territory is screened out, and the CD (critical dimension) of the patterns in the same region of the current layer territory is regulated; the region, with the local pattern density being smaller than a third image density specification value, of the former layer territory is screened out, a second image with the pattern CD being smaller than a minimum specification value and the interval from the images of the former layer territory being smaller than a minimum distance specification value is screened out in the same region of the former layer territory, and the CD and the intervals are regulated; the corrected current layer territory is subjected to OPC (optical proximity correction). The DFM method has the advantages that the former layer image influence can be eliminated, and the photoetching process difficulty is reduced, so the design territory can be easily manufactured.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Serial connected fuel cell stack module assembly
InactiveUS20100297515A1Simple mechanical structureIncreased compact structureFuel cell heat exchangeFuel cells groupingHeat managementFuel cells
A large, scalable SOFC system based on modules, which may be connected in series on the cathode gas side. This offers compactness, simple stack / system interface and improved system performance. The modules are designed for manufacturability, well-balanced heat management and high fuel utilisation.
Owner:HALDOR TOPSOE AS
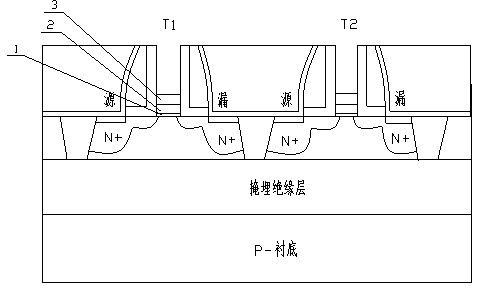
Manufacturing method of twin-transistor and zero-capacitance dynamic RAM (Random Access Memory)
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of a twin-transistor and zero-capacitance dynamic RAM (Random Access Memory), aiming at providing the manufacturing method of the twin-transistor and zero-capacitance dynamic RAM which is manufactured by adopting a silicon of insulator-based gate-last process and has a design for manufacturability. In the process, the characteristics different from the characteristics of greater Overlap between a T1 source / drain electrode and a gate and greater distance Underlap between a T2 source / drain electrode and the gate in a conventional CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Transistor) process are effectively achieved by self aligning; the manufacturing method is suitable for manufacturing of an integrated circuit in the gate-last process of a high-dielectric-constant oxidation layer metal gate of below 45nm; and by adjusting work functions of the gates of the T1 and the T2, which are close to the source electrode and the drain electrode, or doping types of channel regions at the lower parts of the gates, which are close to the source electrode and the drain electrode through ion implantation, the channel regions in the channel regions of the T1, which are close to the source electrode and the drain electrode, are inverted to be the same types with the source region and the drain region under the condition of no increase of the pressure of the gates and diffusion regions below the gates of the source electrode and the drain electrode of the T2 are inverted into the opposite types of the source region and the drain region under the condition of no increase of the pressure of the gates.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUALI MICROELECTRONICS CORP
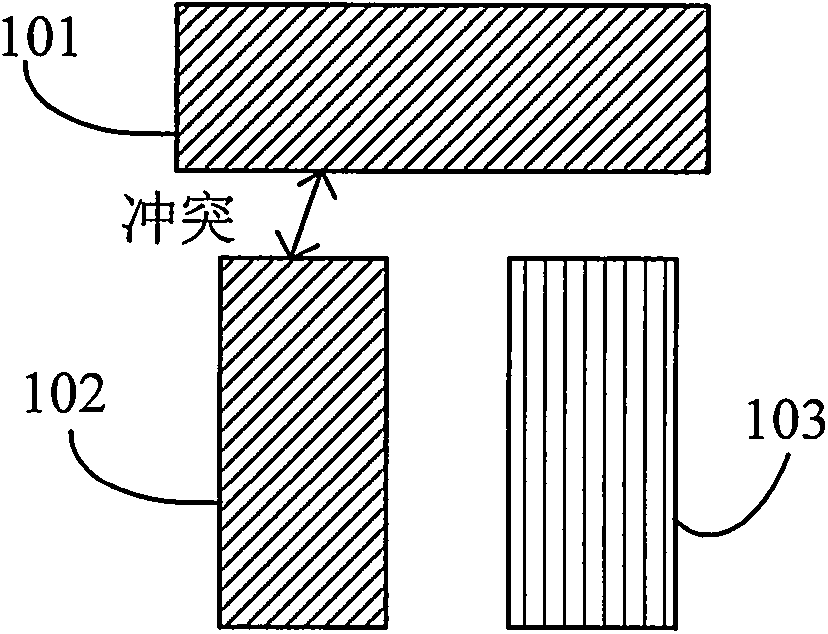
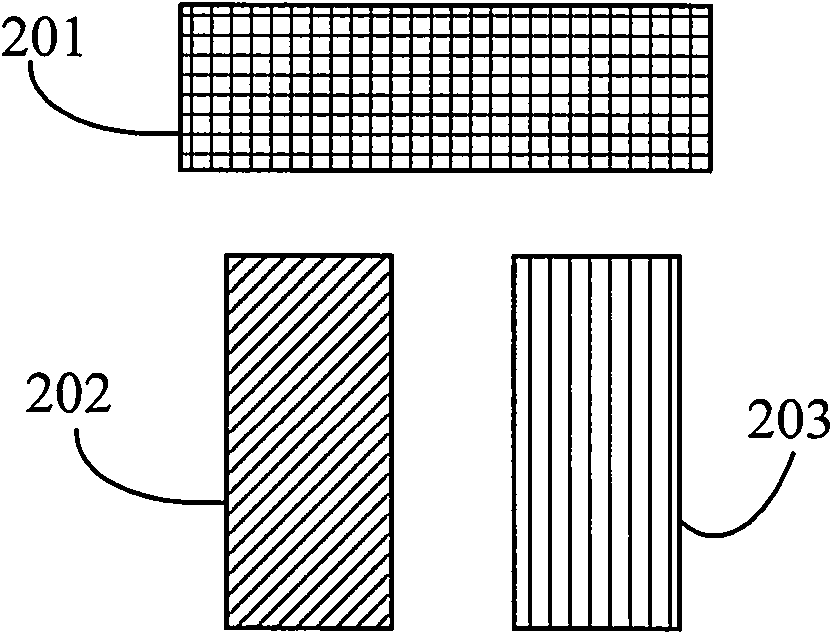
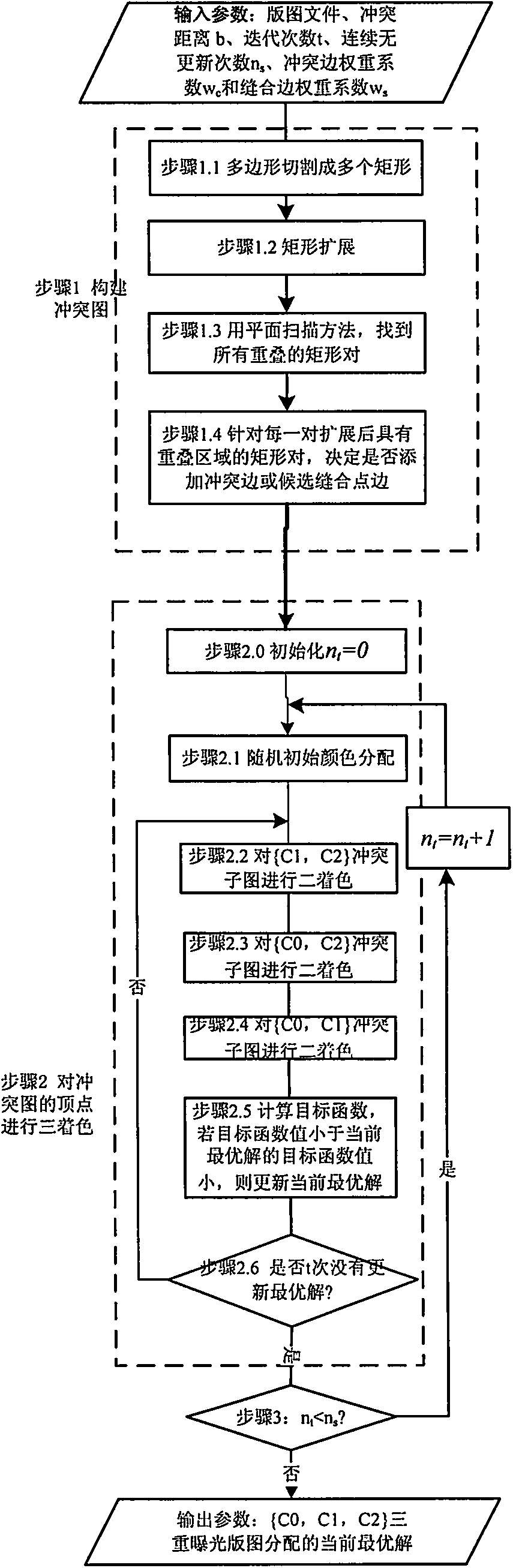
Graph pattern decomposition method adopting triple patterning photoetching technology
ActiveCN104346490AEasy programmingReduce correlationSpecific program execution arrangementsSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmGraph patterns
The invention belongs to the field of design for manufacturability of semiconductor photoetching technologies, and particularly relates to a graph pattern decomposition method adopting a triple patterning photoetching technology. The method comprises steps of firstly, establishing a conflict graph through a rectangle expansion method, then randomly producing a three-colored initial solution, fixing one color in each turn of optimization, performing two-colored optimization on a conflict sub-graph of the rest two colors through a double patterning pattern distribution method, repeating the iterative optimization process until the current optimum solution is not undated for multiple times, and finally, repeatedly calling the above steps and selecting an optimal three-colored result as an output result. According to method, the existing double patterning pattern distribution method is adopted, an optimal strategy obtained through multiple computation is adopted, and a globally optimal solution is searched, so that the purpose of distributing a graph pattern through the triple patterning photoetching technology is realized.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Stiffeners for cast light-metal door headers
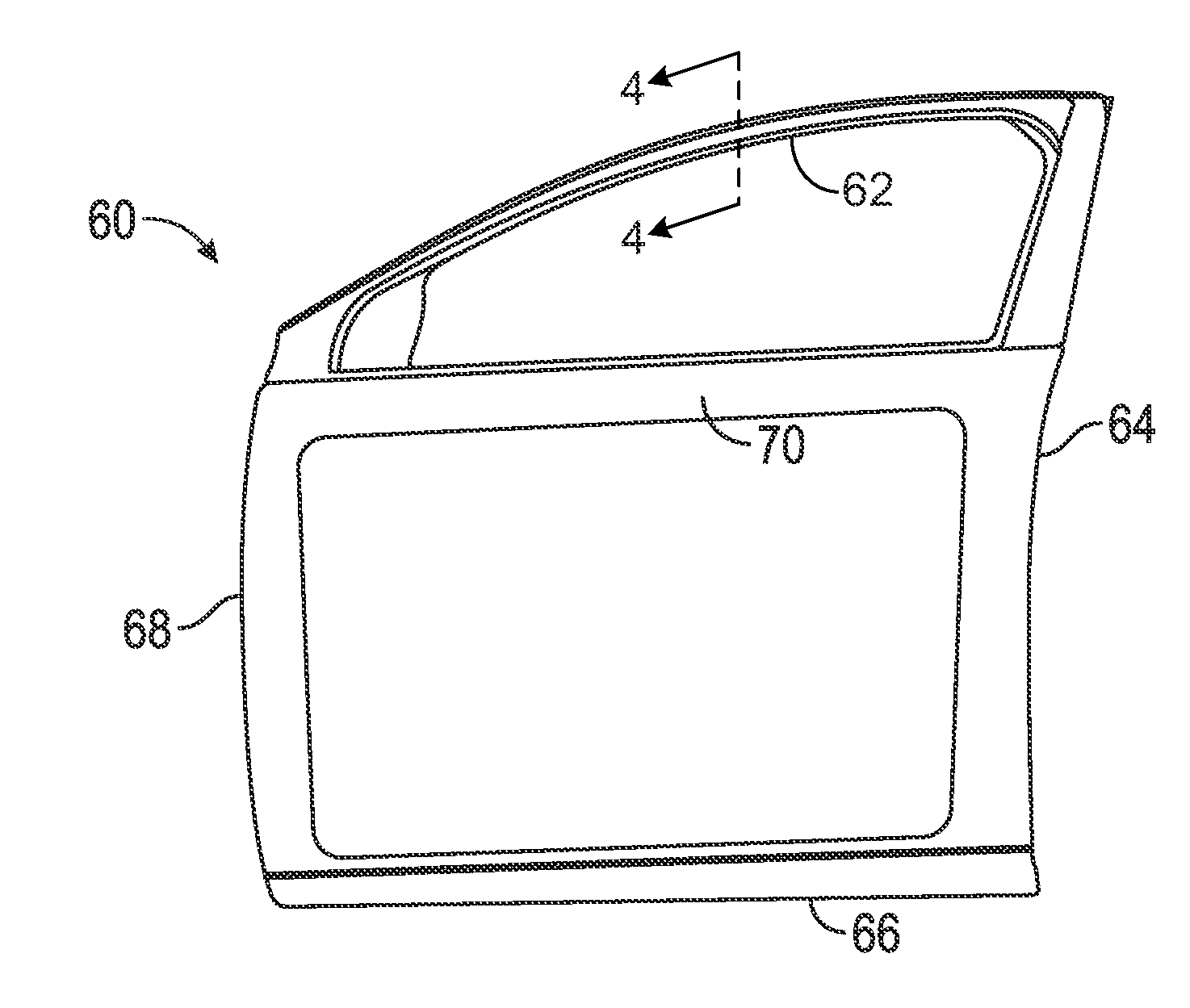
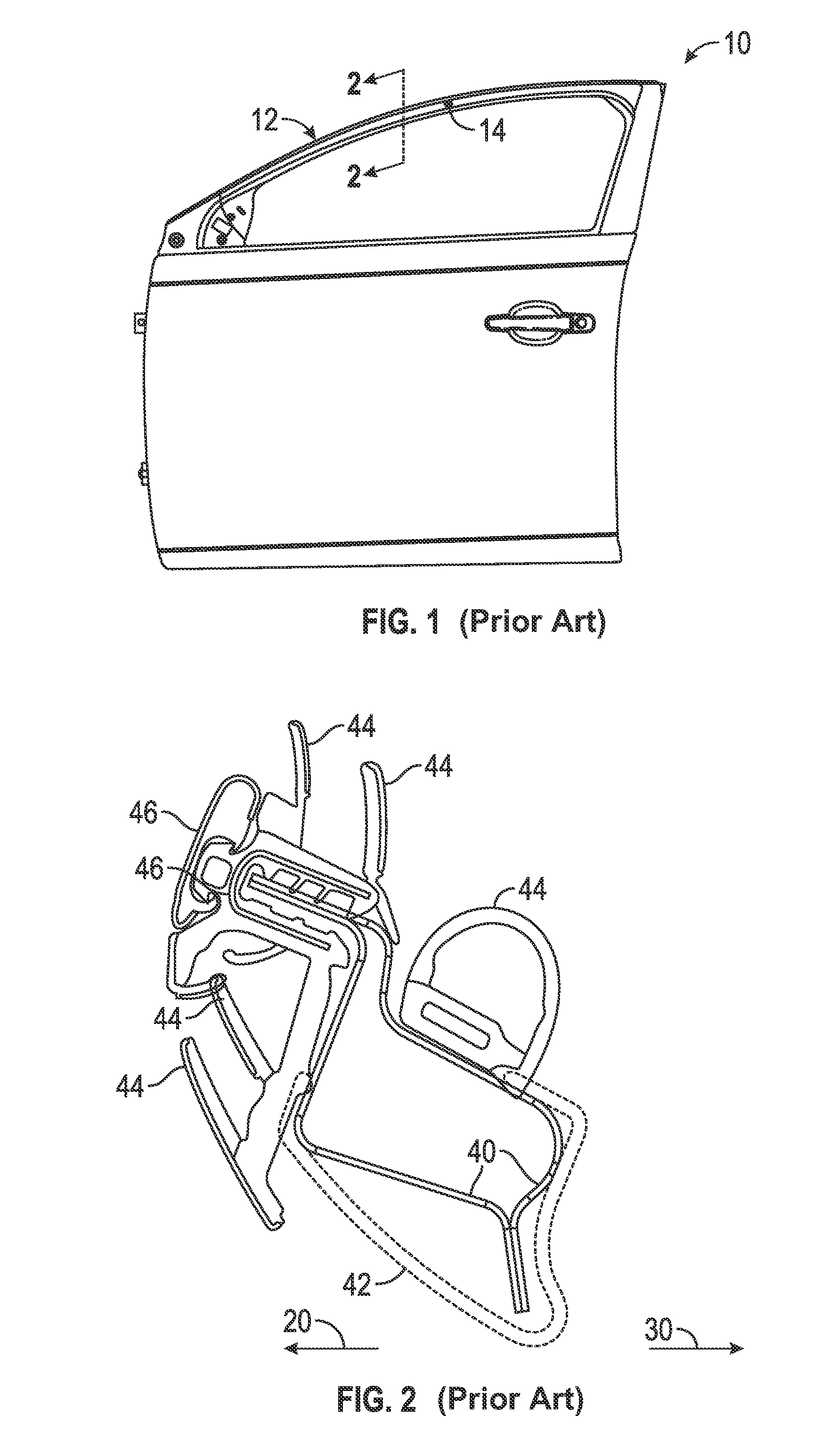
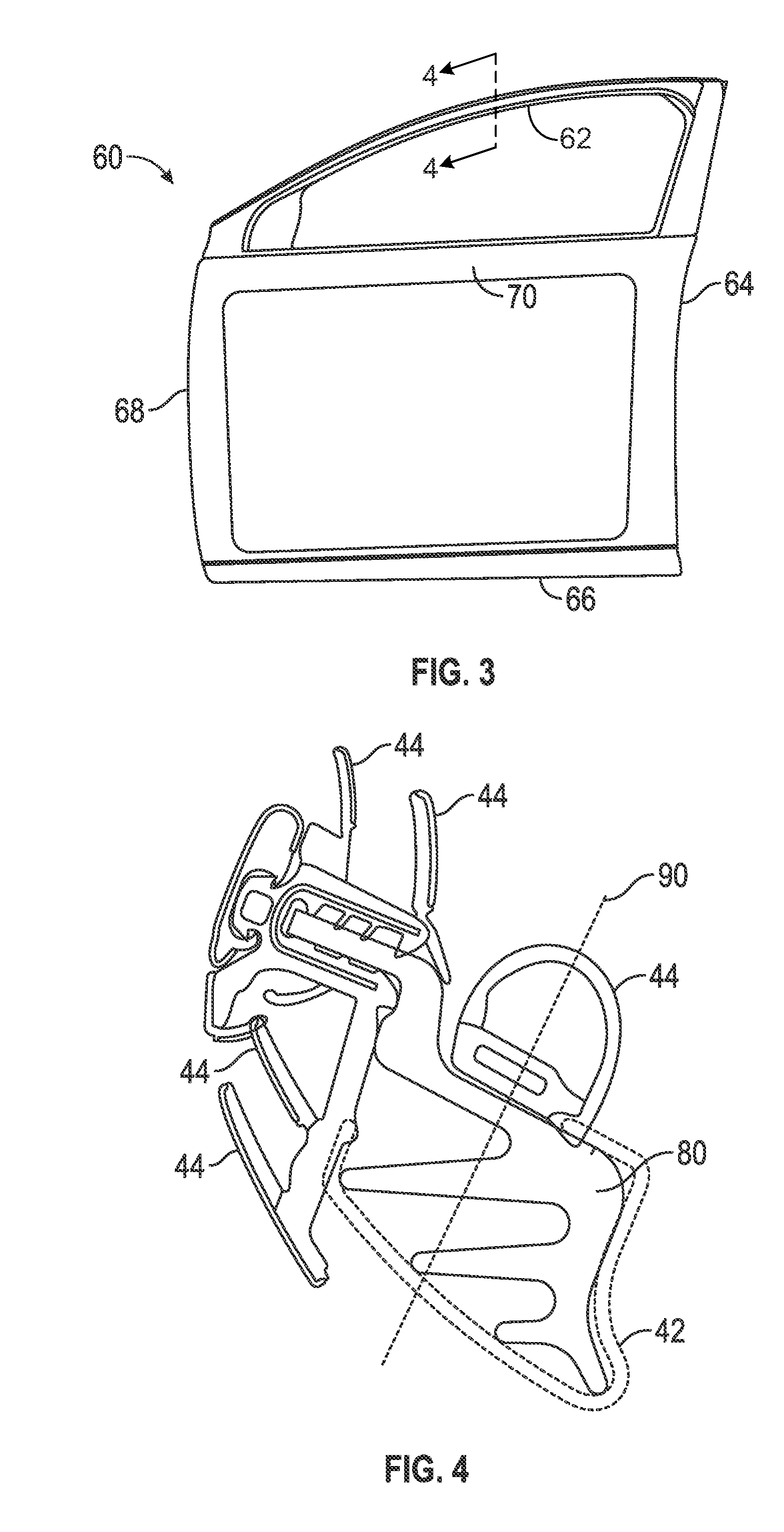
InactiveUS20160096418A1Maximum incremental bending stiffnessEasy to useEngine sealsWindow/door framesLateral stiffnessRoll forming
Stiffeners are disclosed which can be added to the header section of cast light-metal door panels. The header section casting can be designed for manufacturability, and to meet nominal lateral stiffness specifications while making effective use of material. The stiffeners can be cast in place in the header or attached to the header section after casting via snap-fit features, adhesive or both. The stiffeners can themselves be made of a light-weight metal such as aluminum, and can be produced by roll forming, stamping or extrusion. By effectively yielding a closed-section door header shape, the stiffeners provide maximum incremental bending stiffness in the header while adding a minimum amount of incremental material and mass.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
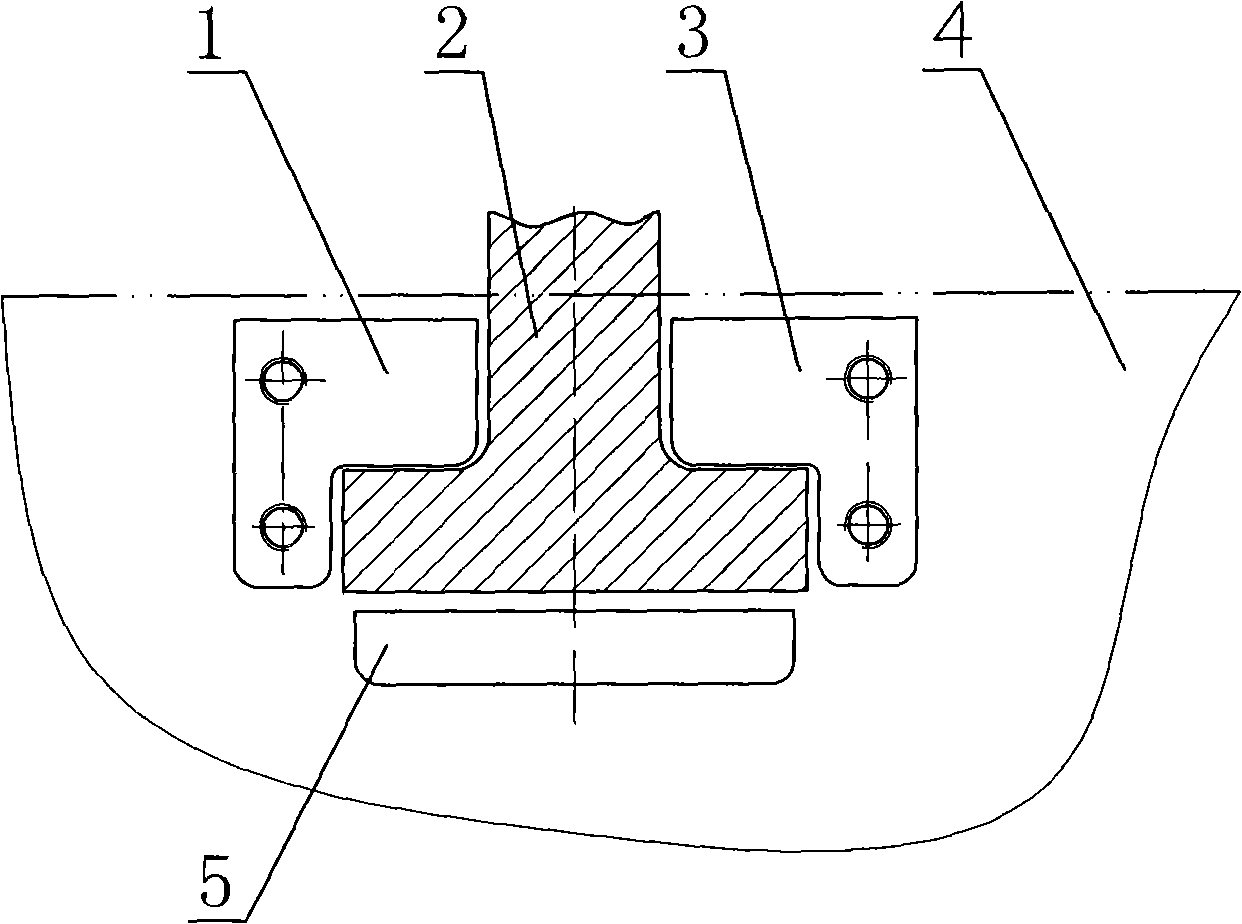
Lifting appliance
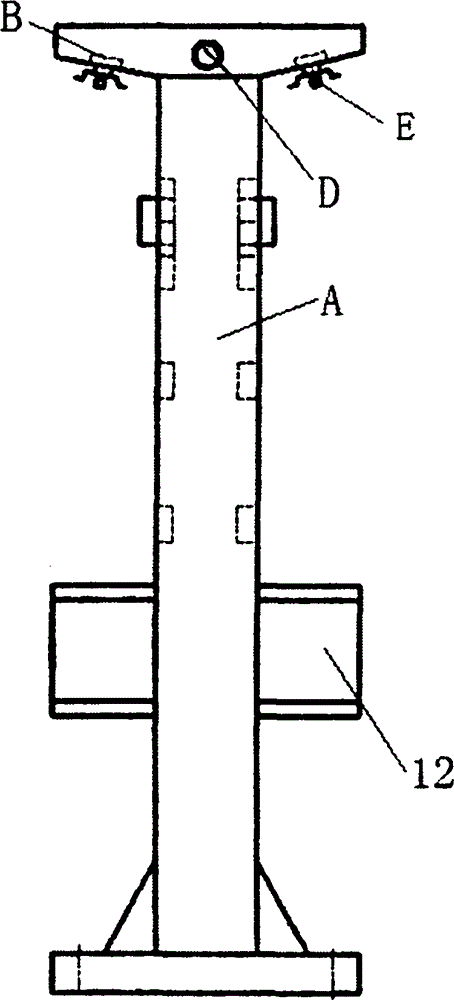
InactiveCN101269779ASuitable for liftingCompact structureLoad-engaging elementsTransformerEngineering
The invention discloses a lifting device which comprises a ventral shield fastening part, a T-shaped hanger and a cover plate, the ventral shield fastening part is fixed on the ventral shield of an object to be lifted, the T-shaped hanger and the cover plate can be detachably connected and fixed with the ventral shield fastening part, the T-shaped hanger is inverted in an inverted T-shaped space formed by the cover plate and the ventral shield fastening part, and the upper end of the inverted T-shaped hanger exposes. The lifting device has the advantages of compact structure, small occupied space, good intensity, scientific and reasonable design as well as good manufacturability and commonality. The lifting device is especially suitable for the lifting of a high capacity transformer body with a five-column type iron core structure.
Owner:XD JINAN TRANSFORMER
Automotive tie-rod end sealing structure
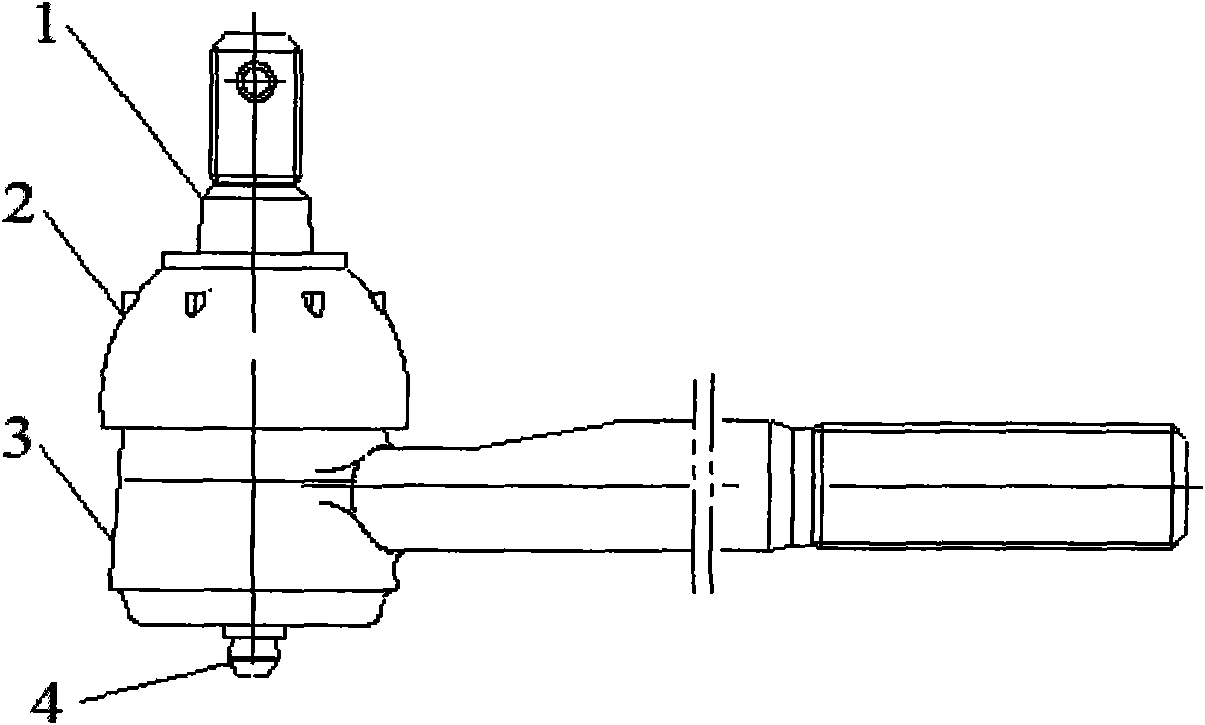
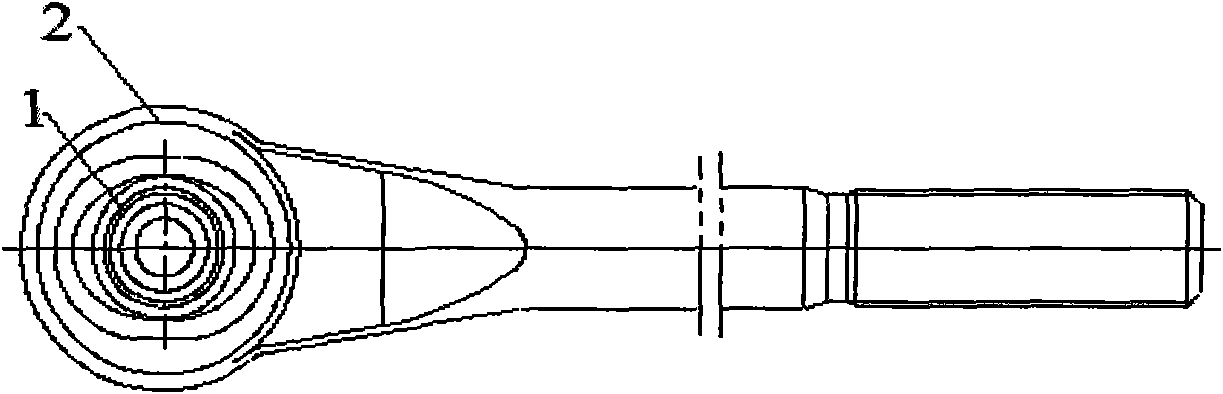
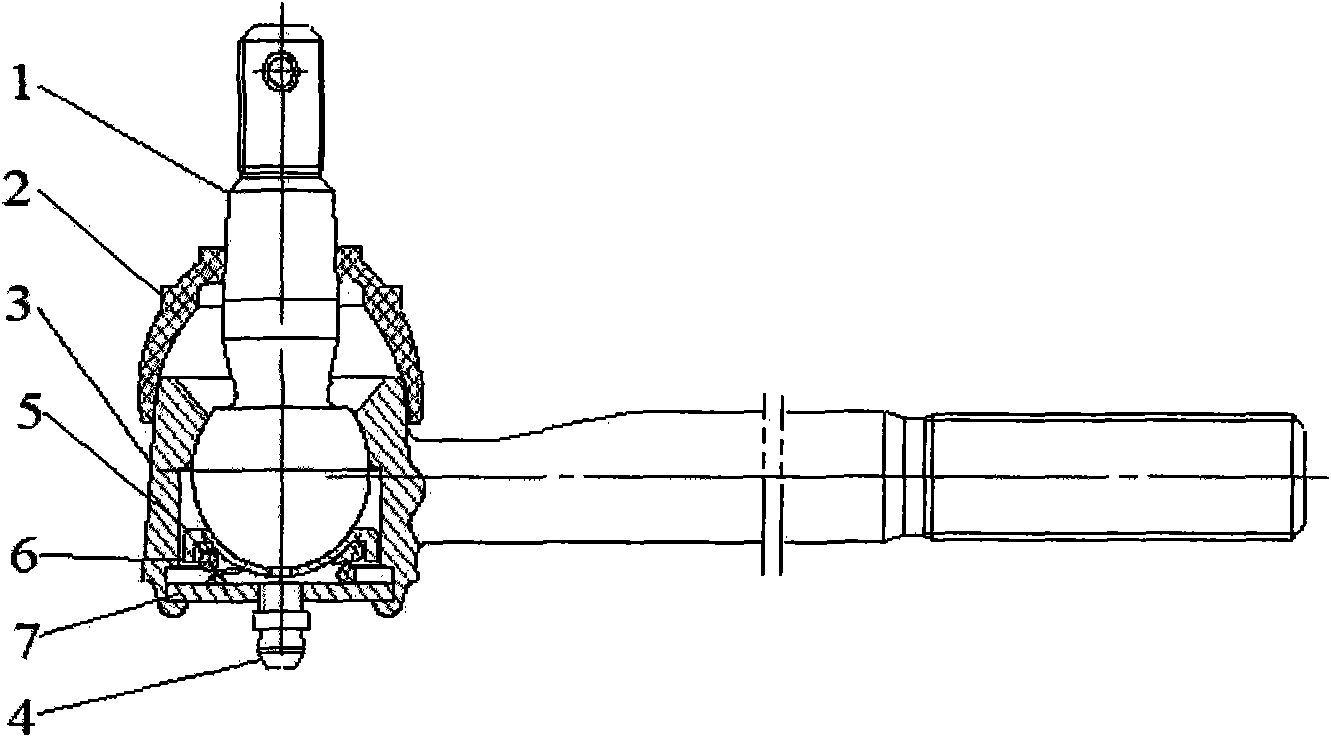
InactiveCN101603563AReduce coefficient of frictionReasonable structureSteering linkagesPivotal connectionsEngineeringDesign for manufacturability
The invention discloses an automotive tie-rod end sealing structure. A dust cover (2) is made of flexible material, one end of which is sleeved on a ball shell (3), the other end is sleeved on the rod body of a ball pin (1); an annular groove is arranged on an outer circle on the end of the dust cover (2) sleeved on the ball shell (3), wherein a large collar (8) is arranged in the groove for clamping and securing the dust cover (2) on the ball shell (3); an annular groove is arranged on the other end of the dust cover (2) sleeved on the rod body of the ball pin (1), wherein a small collar (9) is arranged in the groove for clamping and securing the dust cover (2) on the rod body of the ball pin (1). Employing the technical scheme, the invention has reasonable structure, good manufacturability, prevention of abrasion on the pivot angle of the products, reduction of friction coefficient between the friction surfaces, good sealing performance, and improvement of the comprehensive performance of the products.
Owner:WUHU NANDA AUTO IND
Throttle body
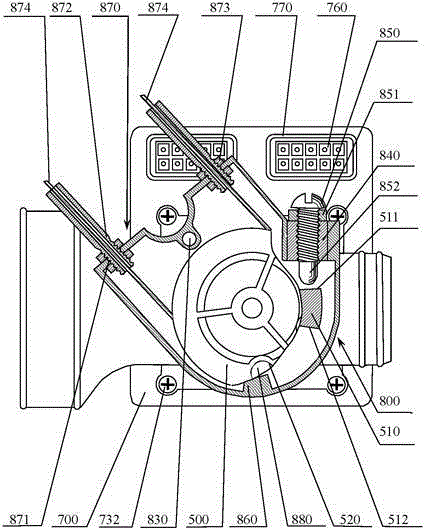
InactiveCN104912671AResolve shrinkageSolve the creepEngine controllersMachines/enginesInlet channelMaintainability
The invention aims to disclose a throttle body. The throttle body comprises a throttle main body provided with an air inlet channel inside, a throttle shaft perpendicular to the air inlet channel, a throttle piece embedded and fixed on the throttle shaft, a wire pull wheel fixed at one end of the throttle shaft, and a return spring acting on the throttle shaft, wherein an electric control unit is arranged on the side surface of the throttle main body; a permanent magnet is arranged at one end, near the electric control unit, of the throttle shaft, and is concentric with the throttle shaft; and a hall chip for inducing a magnetic field rotating angle of the permanent magnet is welded on a circuit board near the permanent magnet. Compared with the prior art, the throttle body has the characteristics of light and firm structure, no deformation in use, compact structure, good maintainability, good manufacturability, suitability for separate manufacturing of mechanical and electronic parts, good debugging and reliability and long service life, and realizes the purpose.
Owner:浙江朗杰电子有限公司
Serial connected fuel cell stack module assembly
InactiveUS8841042B2Reduce necessityMechanically compactFuel cell heat exchangeFuel cells groupingCold airFuel cells
A large, scalable SOFC system based on modules, which may be connected in series on the cathode gas side. The fuel cell stacks are aligned side by side and assembled into a stack module with cathode inlets on one face of the module and the cathode outlets on the other face of the module. The stack modules are serially connected in a simple manner by placing the stack modules one after the other, so that the outlet face of the first module faces the inlet face of the second module and so on. In the chamber between two stack modules, the air is cooled for example by addition of cold quench air or by a heat exchanger. This offers compactness, simple stack / system interface and improved system performance. The modules are designed for manufacturability, well-balanced heat management and high fuel utilization.
Owner:HALDOR TOPSOE AS
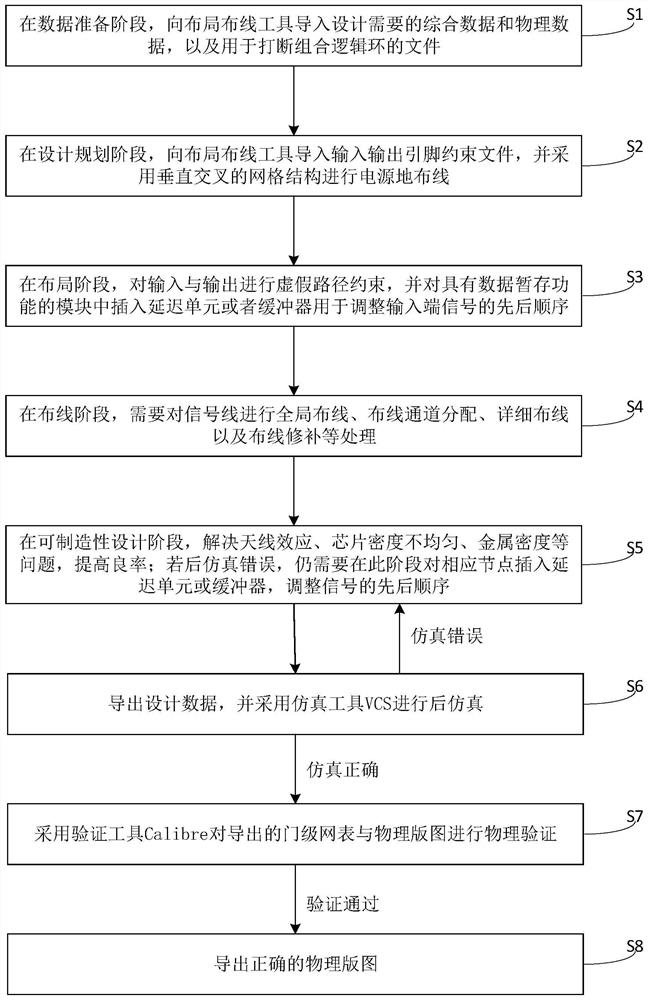
Asynchronous circuit physical implementation method and system
ActiveCN112651207ACompatible Design FlowRealize the physical designComputer aided designEnergy efficient computingAntenna effectPathPing
The invention discloses an asynchronous circuit physical implementation method and system, and the method comprises the steps: performing a data preparation stage: importing comprehensive data, physical data and a file for interrupting a combinational logic ring; in the design planning stage, inputting an IO pin constraint file; in the layout stage, carrying out false path constraint on IO; in the wiring stage, carrying out global wiring, wiring channel distribution, detailed wiring and wiring repair on the signal lines; in the manufacturability design stage, the antenna effect problem, the chip density non-uniformity problem and the metal density problem are solved; exporting design data, performing post-simulation, and returning to the manufacturability design stage for processing if errors occur in simulation; and performing physical verification on the exported gate-level netlist and the physical layout. The invention provides a novel asynchronous circuit physical implementation scheme, which can realize the physical design of a large-scale asynchronous integrated circuit based on a synchronous design tool, is compatible with the current synchronous circuit design process, and can be widely applied to the technical field of integrated circuits.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Differential alternating phase shift mask optimization
InactiveUS20060166105A1Improve balanceImproved OPC performanceOriginals for photomechanical treatmentSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringIntegrated circuit layout
A method of designing a mask for projecting an image of an integrated circuit design in lithographic processing, wherein the integrated circuit layout has a plurality of segments of critical width. The method comprises creating a first mask design by aligning mask features used to assist in projecting critical width segments with the critical width segments of the integrated circuit design, such that the first mask design meets predetermined manufacturability design rules, and creating a second mask design by aligning mask features with the critical width segments of the integrated circuit design, such that the second mask design meets predetermined lithographic design rules in regions local to the critical width segments. The method then includes identifying design features of the second mask design that violate the predetermined manufacturability design rules, and then creating a third mask design derived from the second mask design wherein the mask features of the second mask design that violate the predetermined manufacturability rules are selectively replaced by mask features from the first mask design so that the third mask design meets the predetermined manufacturability design rules. By way of example, the mask features used to assist in projecting critical width segments may comprise alternating phase shifting regions or sub-resolution assist features.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Stiffeners for casting light-metal door headers
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Variable Performance Ranking and Modification in Design for Manufacturability of Circuits
InactiveUS20090235214A1Improve device performanceGood yield performanceDetecting faulty computer hardwareComputer aided designRankingComputerized system
A method, computer system and program product introduce adding a variable performance ranking parameter to a diagram of a circuit to drive implementation of modifications that are yield improving, performance boosting, or performance-neutral. The information is paired to accomplish a more complete design for manufacturability modification in the design of circuits implemented on chips. In this matter, both yield and chip performance are improved.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
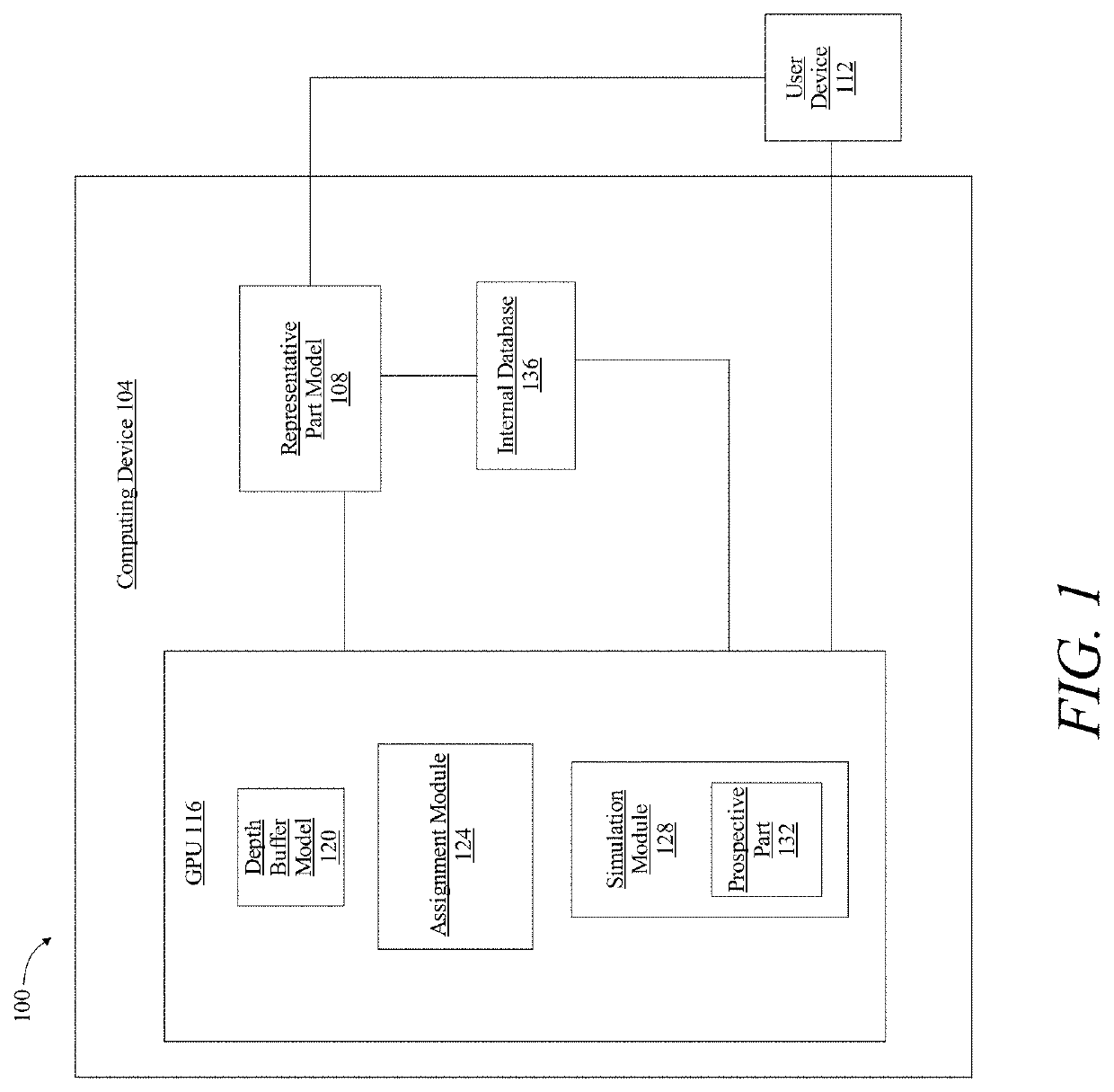
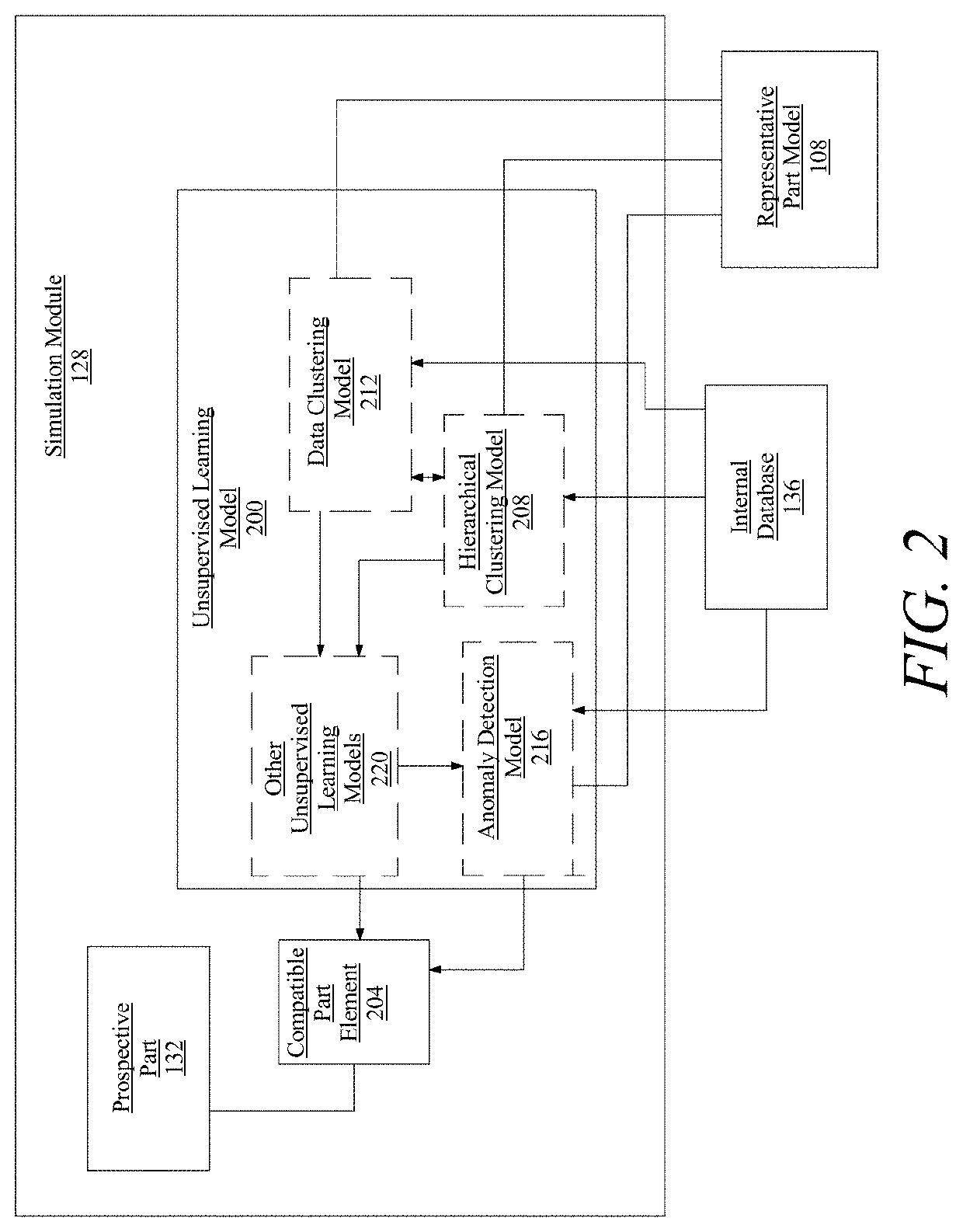
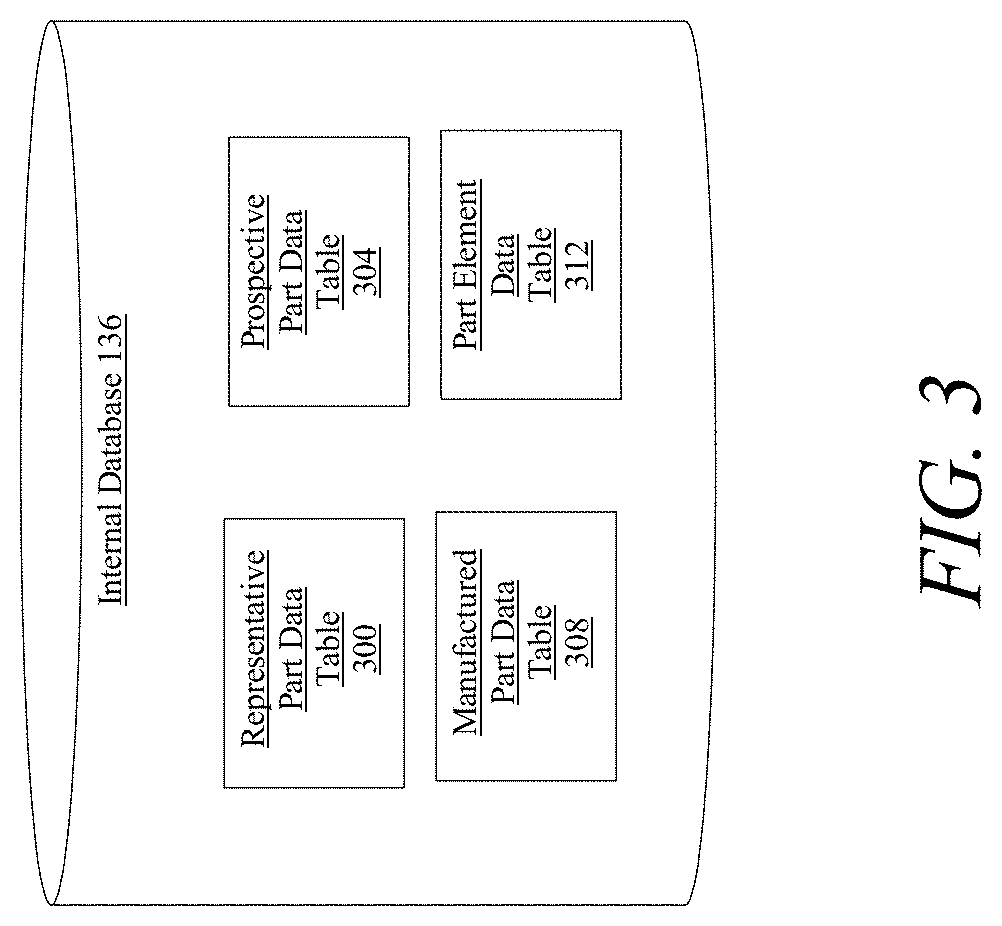
Methods and systems for generating an instant design for manufacturability of a part at a computing device
A system for generating an instant design for manufacturability of a part includes a computing device configured to receive a representative part model, wherein the representative part model comprises a plurality of sides, to generate, at a graphics processing unit, a depth buffer model of the representative part model, to determine, at an assignment module operating on the graphics processing unit, each orientation of the plurality of orientations of the representative part model as a function of each depth buffer of the plurality of depth buffers, and to generate, at a simulation module operating on the graphics processing unit, a prospective part, wherein generating a prospective part further comprises generating a simulated casing of the representative part model. The system is further designed and configured to display the prospective part to a user device.
Owner:PROTOLABS INC
Indoor illumination installation simulation device
The invention discloses an indoor illumination installation simulation device and relates to the technical field of teaching or demonstration tools. The indoor illumination installation simulation device comprises a device body, an upper eave installation plate and an openable installation plate with a door shaft, wherein round power cable installation holes are formed in the two ends of the top of the device body, rubber protection rings are nested in the round power cable installation holes, the upper eave installation plate is arranged above the two sides of the device body and the openable installation plate with the door shaft is arranged below the upper eave installation plate; a fluorescent lamp is arranged on the upper eave installation plate. The indoor illumination installation simulation device can simulate a concealed wiring process of indoor illumination installation in actual engineering. The indoor illumination installation simulation device has the advantages of strong simulation ability, good manufacturability, high disassembling and assembling flexibility, convenience in operation, capability of repetitive training and the like.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Closed-down manual brake
InactiveCN101230884AReliable parking brakeReliable parking brake performanceSlack adjustersDrive shaftEngineering
The invention discloses a shut-down manual brake, which relates to a brake device, and the invention aims at providing a manual brake with reliable performance of shut-down and braking and good manufacturability. The invention has the technical proposal that the shut-down manual brake comprises a drive shaft and a transmission mechanism among conjunctions combined with the drive shaft, and spiral ramp convex bodies are uniformly distributed on the end face of the drive shaft along a circle; spiral ramp convex bodies which are meshed with the spiral ramp convex bodies on the end face of the drive shaft are uniformly distributed on the end face of the conjunction along the circle, and the end face of the conjunction is opposite to the end face the drive shaft. The invention is used for engineering machinery.
Owner:SICHUAN CHENGDU CHENGGONG CONSTR MACHINERY +1
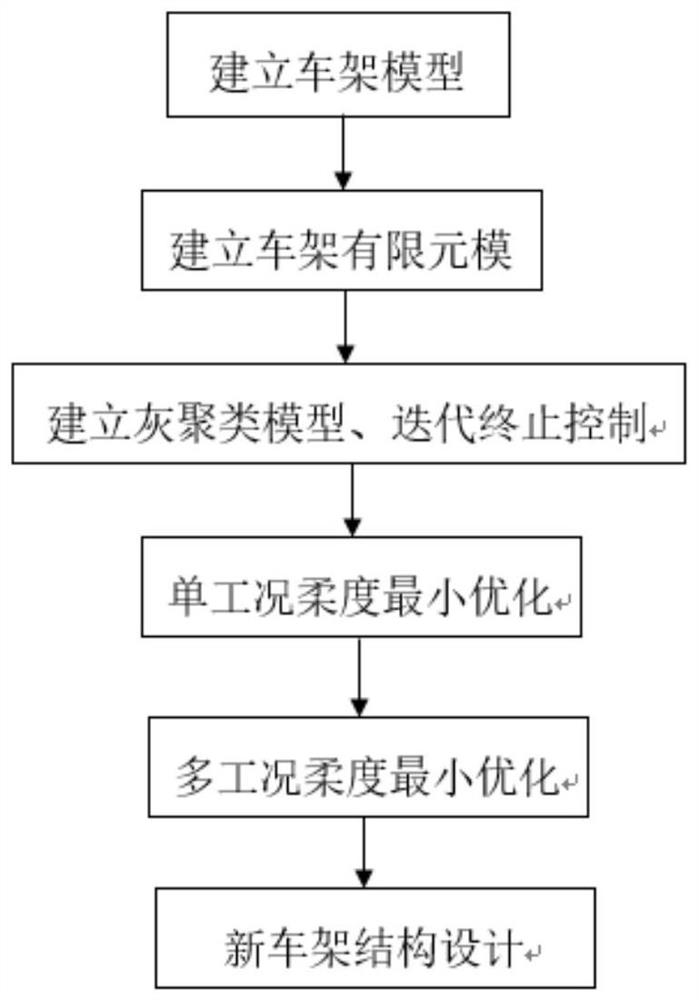
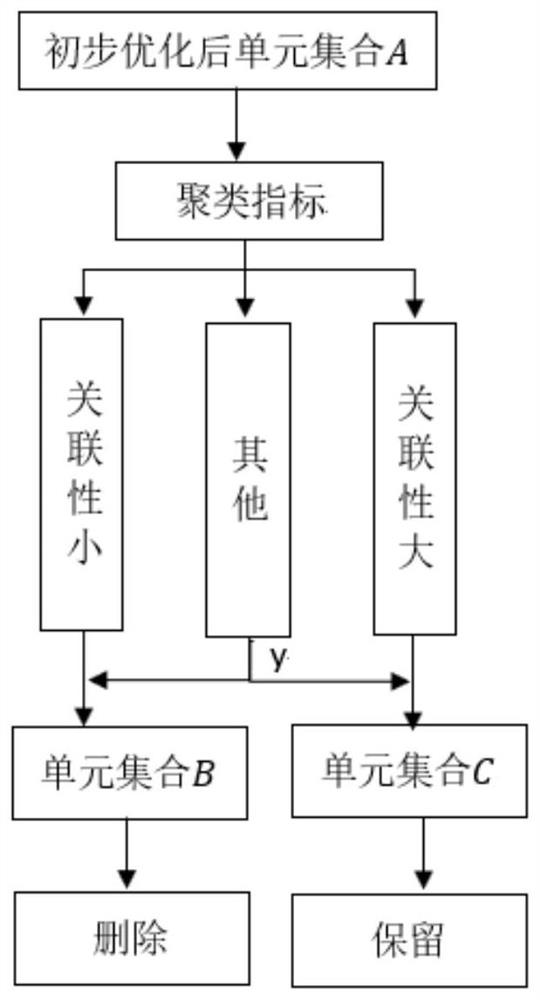
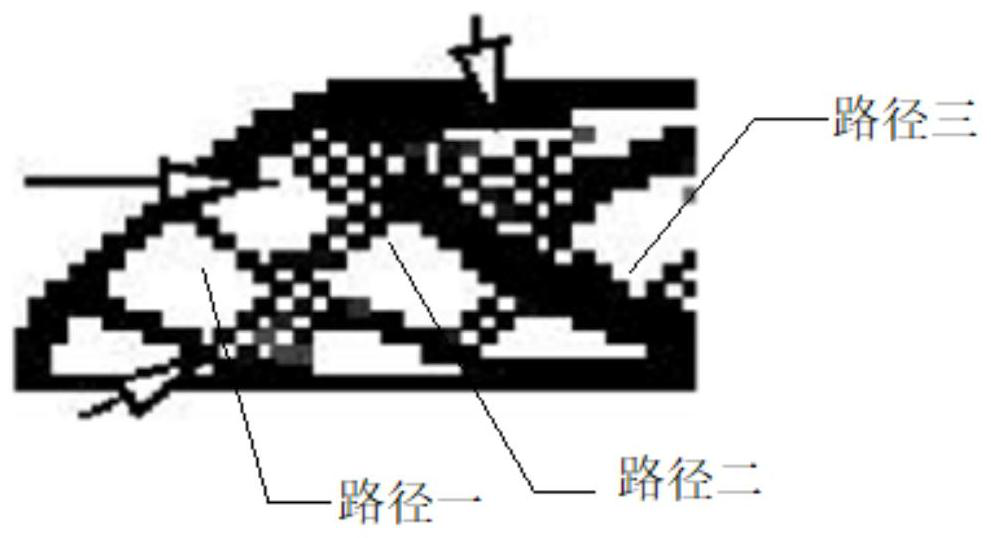
Multi-working-condition frame topological optimization method based on grey clustering algorithm model
PendingCN113239457AInhibition phenomenonImprove manufacturabilityGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationCluster algorithmAlgorithm
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com