Patents
Literature
2455results about "Slack adjusters" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
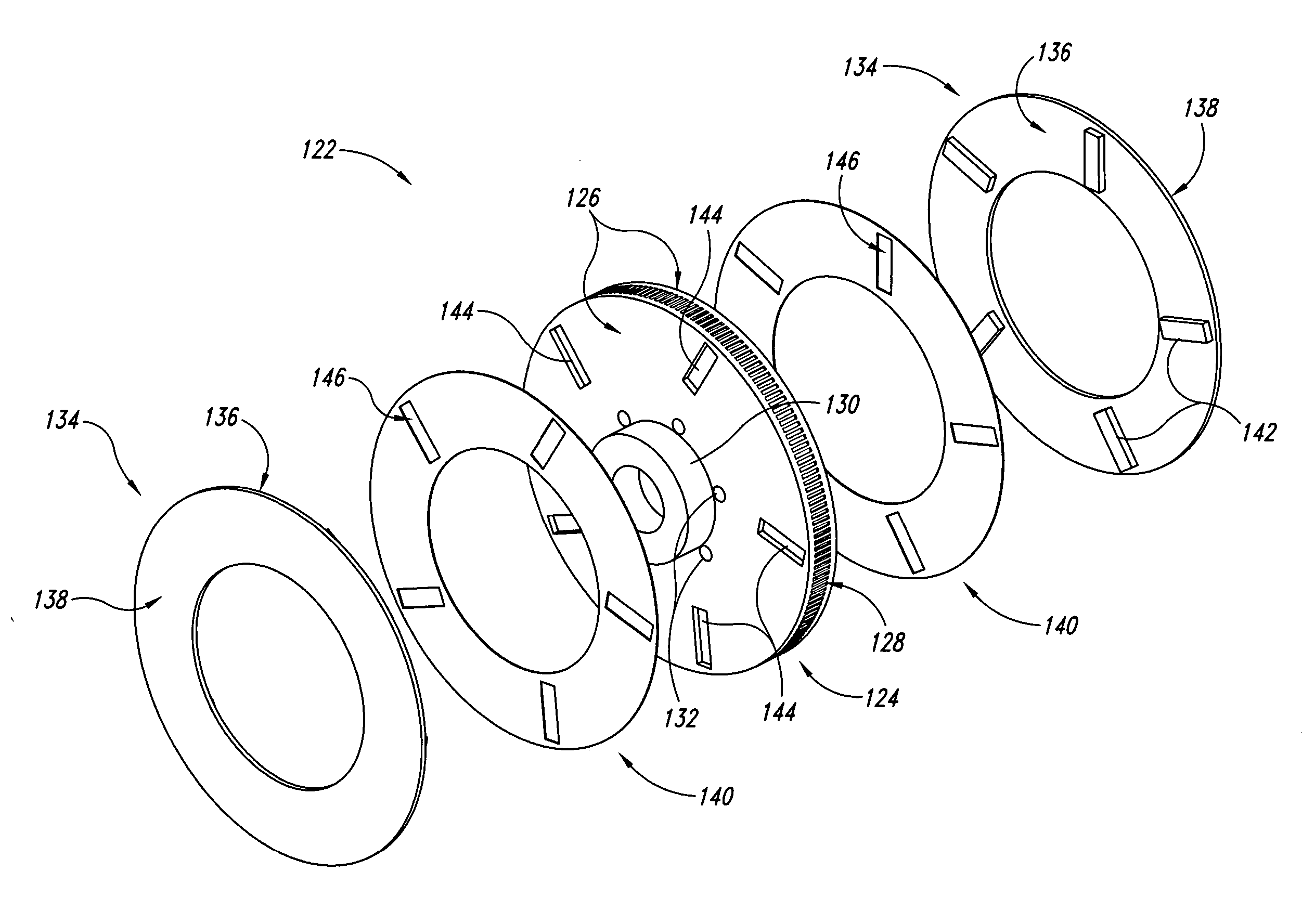
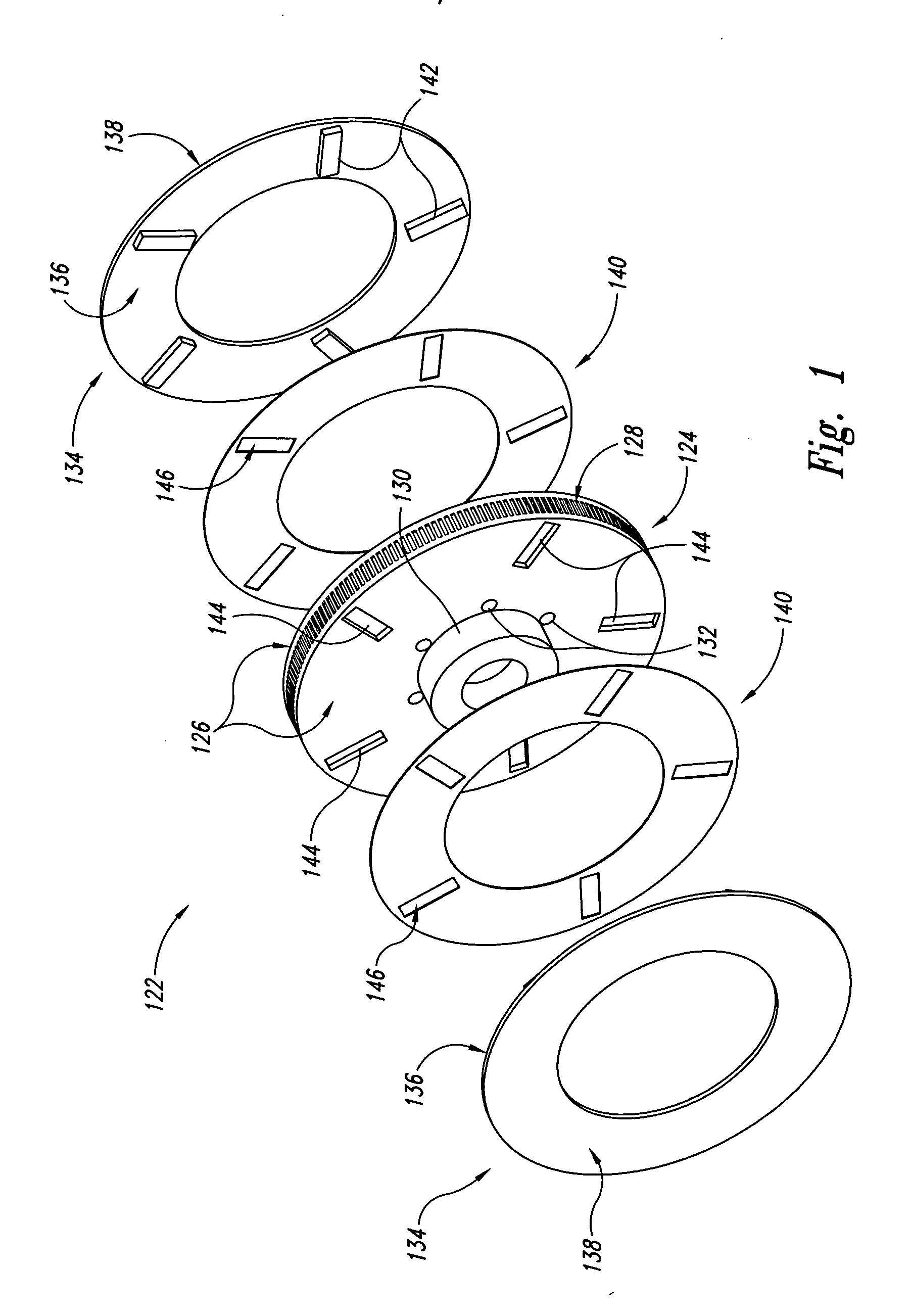
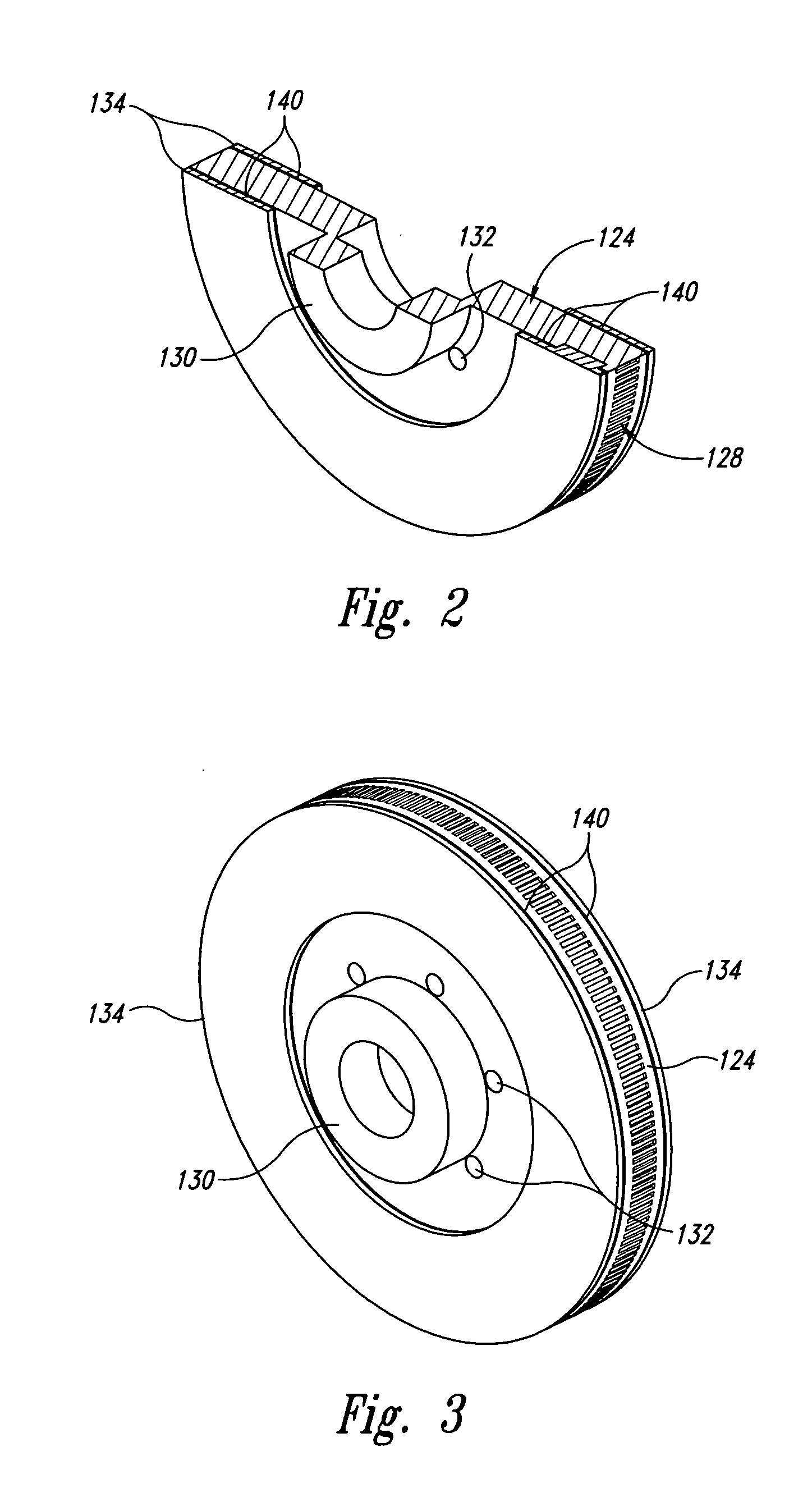
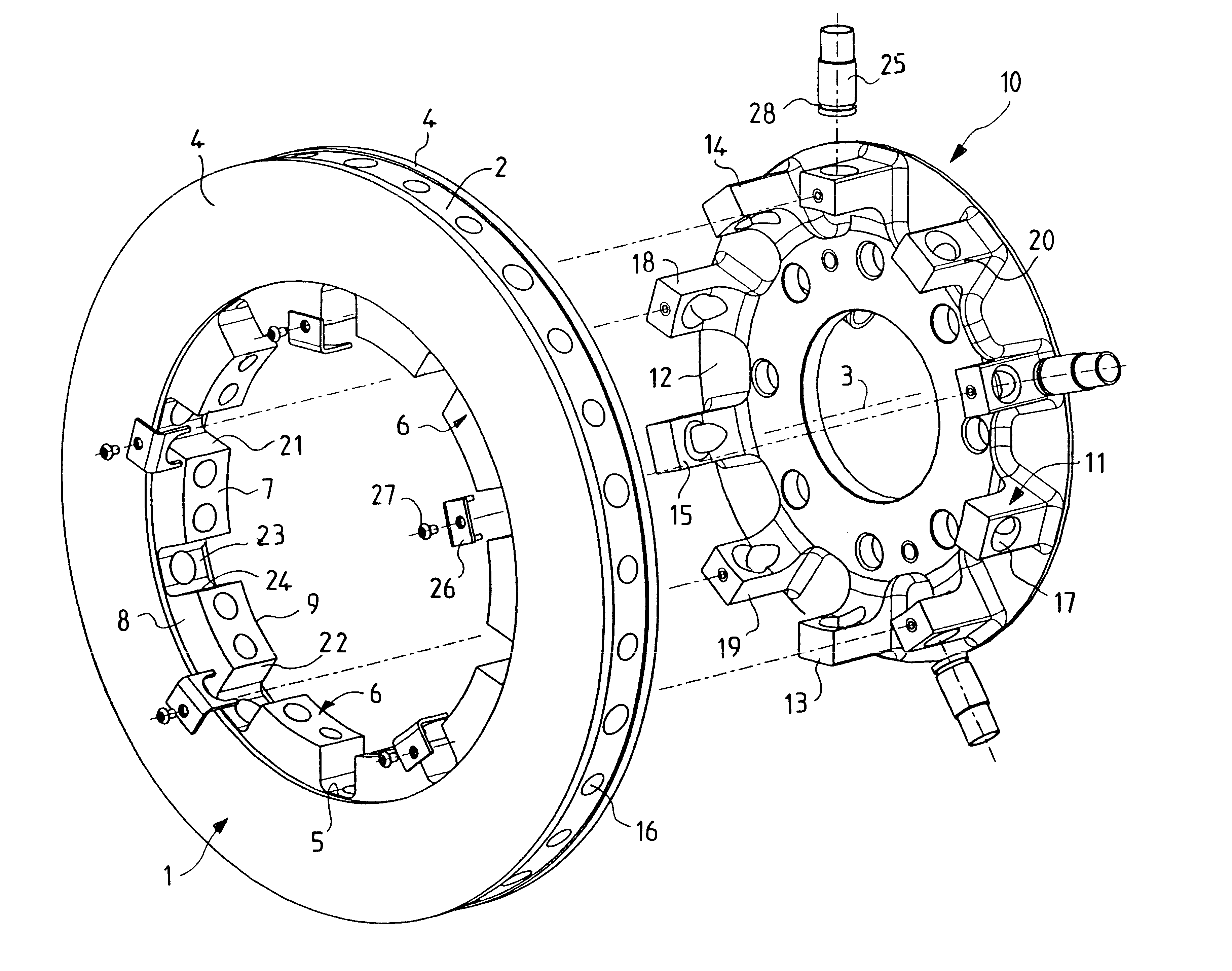
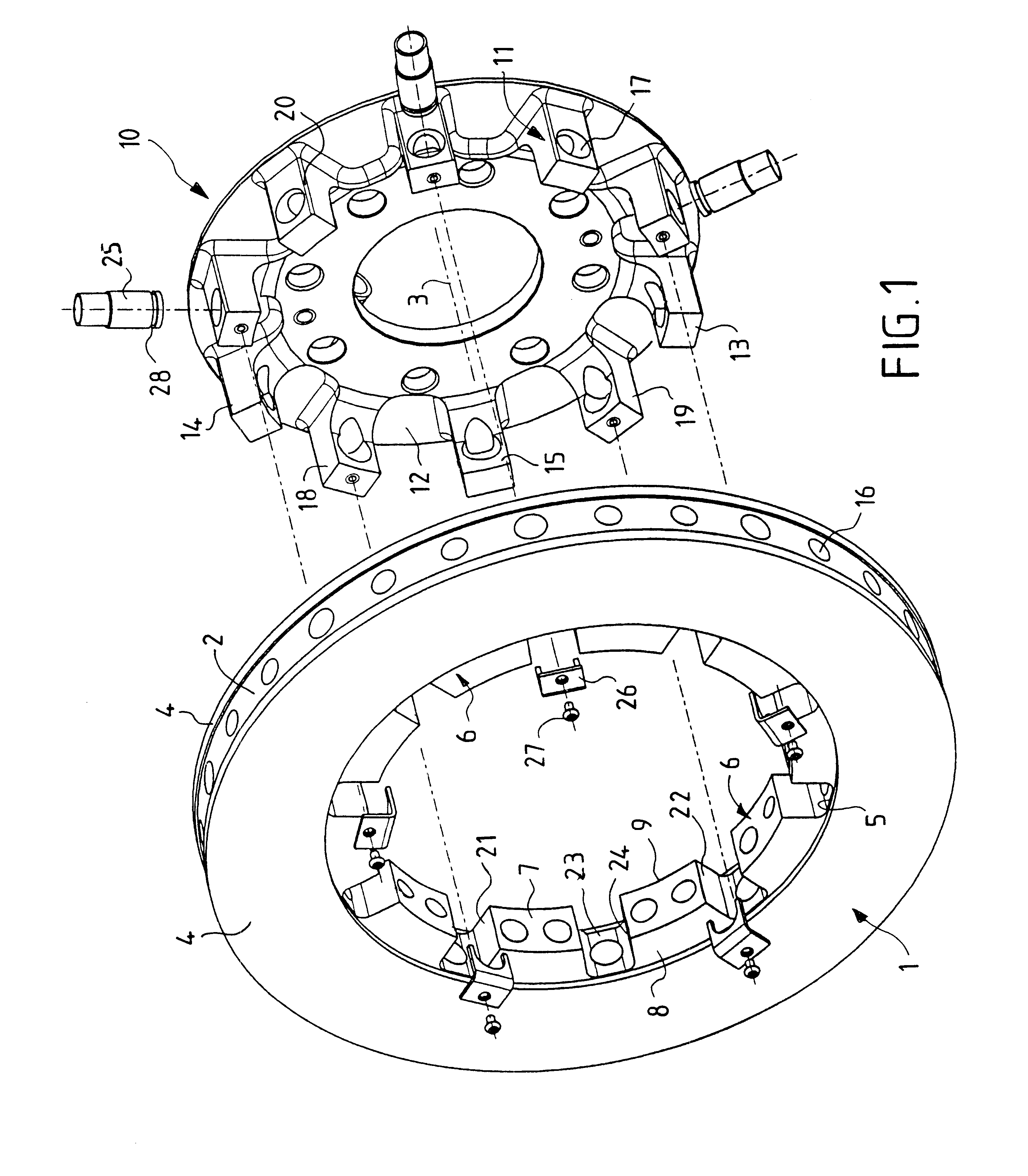
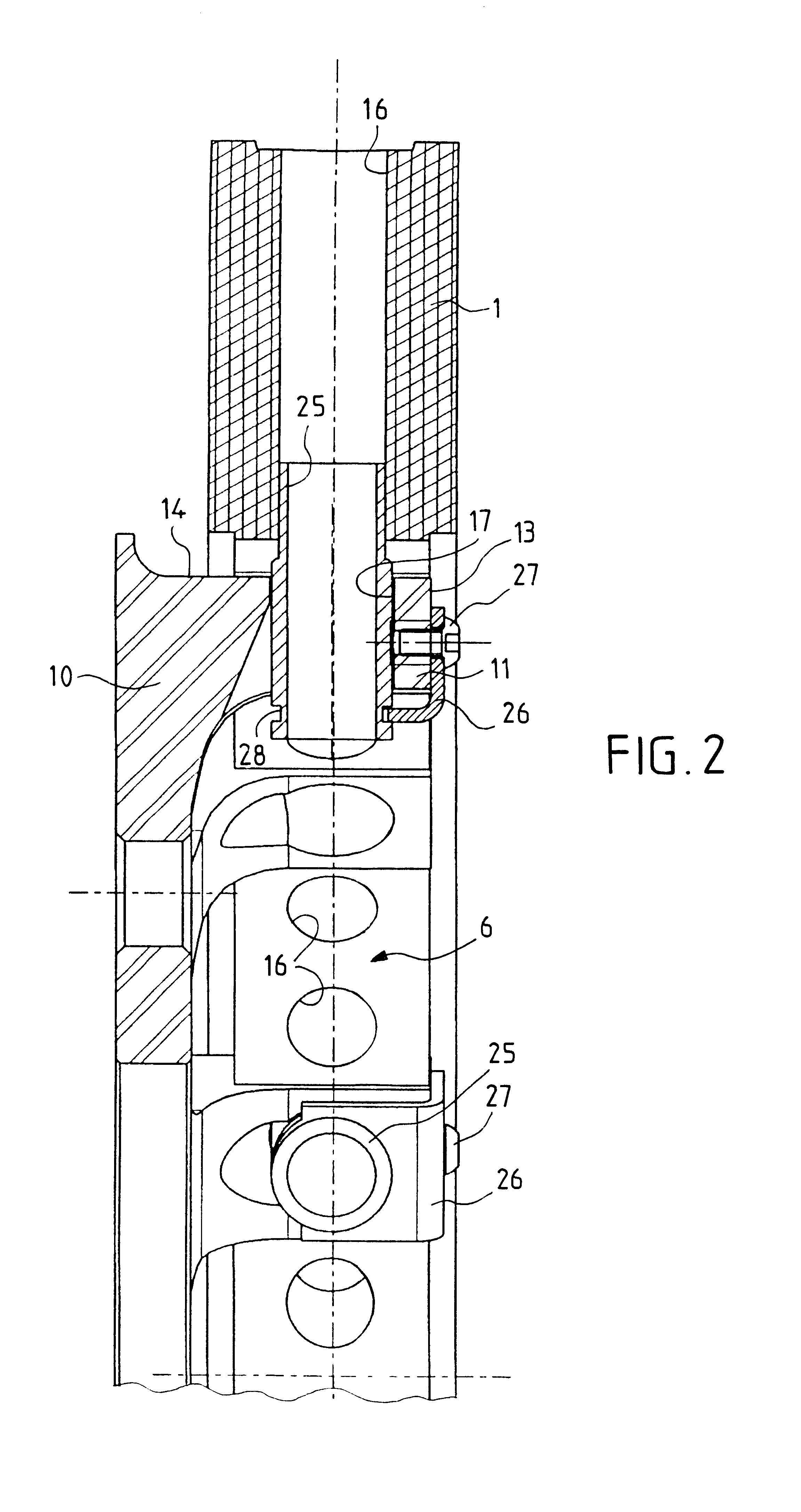
Disc brake rotor assembly and method for producing same
InactiveUS20050183909A1Improve thermal conductivityOptimize acoustic frequency transferBraking element arrangementsNoise/vibration controlAdhesiveMetal alloy
Novel composite disc brake rotor assemblies are provided, along with novel and efficient methods for manufacturing them. Preferably, the rotor assemblies comprise annular wear plates formed of particle reinforced aluminum-based metal matrix composite (MMC), ceramic matrix composite (CMC), or of ‘carbon graphite foam.’ The wear plates, made of a first material, are attached to annular surfaces of a central rotor, made of a second material, by fusing bonding layers between the wear plates and the rotor surfaces. The bonding layers are comprised of at least one of a metal alloy having a melting temperature lower than that of either the first or second materials, and a high-temperature adhesive. Preferably, the wear plates comprise projections that are positioned within adjacent receiving recesses in the center rotor. The bonding layers and projections enhance thermal and acoustical transference between the wear plates and the center rotor section. Carbon graphite foam provides for substantially enhanced heat transference. Use of the fusable binding layer, or adhesive provides for an efficient, low cost method of manufacturing for composite disc brake rotor assemblies.
Owner:BENMAXX
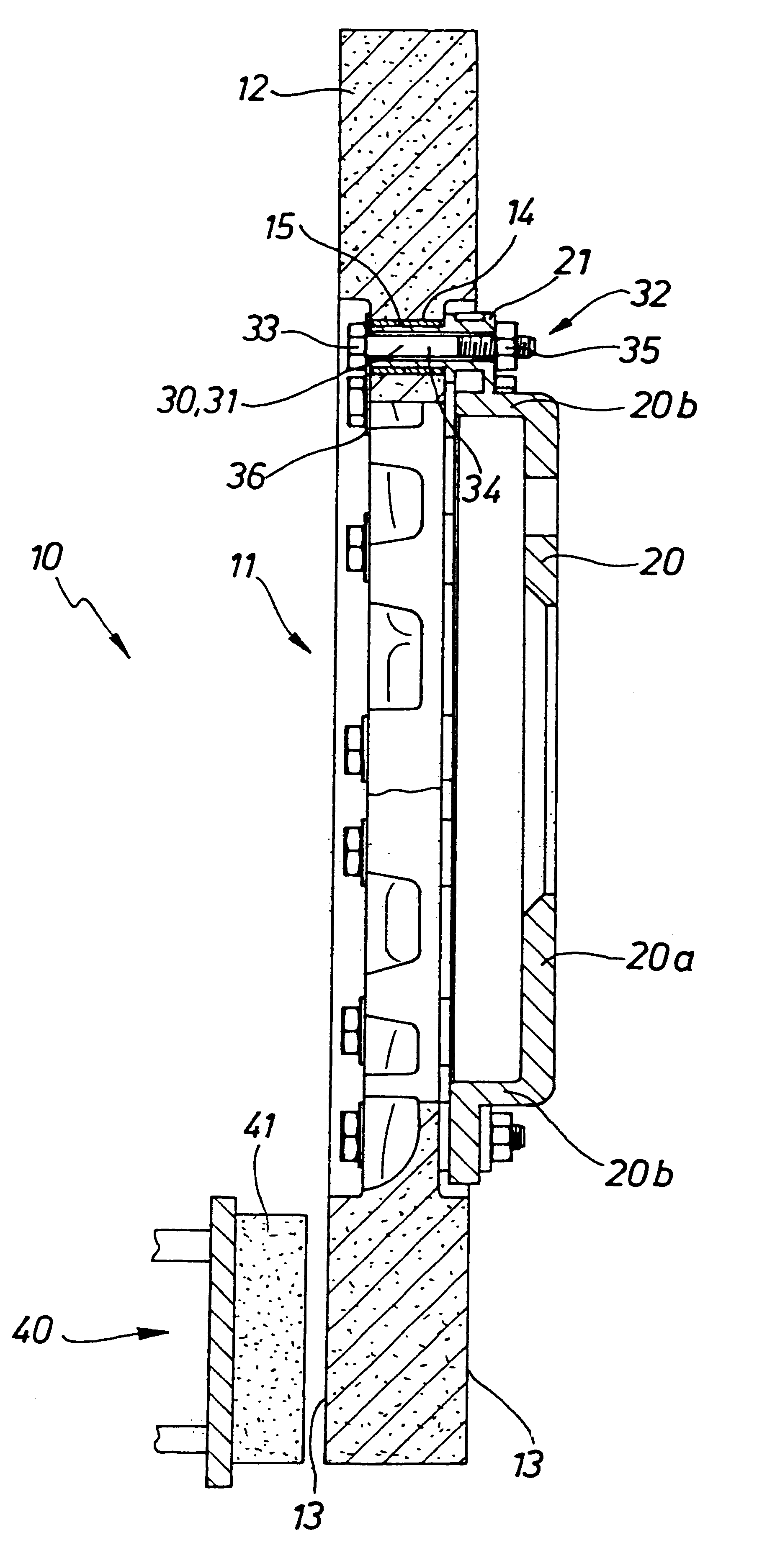
Brake unit
InactiveUS6302246B1Prolong lifeImprove flatnessBraking element arrangementsNoise/vibration controlEngineeringCeramic metal
A brake unit comprising at least one brake and at least one brake pad having at least one friction lining is described. The brake has a disk brake with a brake rotor made of a ceramic-metal composite (CMC) whose outer surface or surfaces at least partially form a friction surface for the at least one friction lining, and a disk brake cup that is mounted on the disk brake by way of one or more mounting elements. The friction surface of the disk brake has a hardness of approximately 1600 to 2500 HV, and the at least one friction lining has a coefficient of friction of approximately 0.3 to 0.5. The disk brake cup and / or the mounting elements form a corrosion-inhibiting attachment to the disk brake. The brake unit can be operated in corrosion-free fashion over a service life of at least approximately eight to 10 years or approximately 200,000 to 300,000 km.
Owner:FRENI BREMBO SPA
Pad retraction device
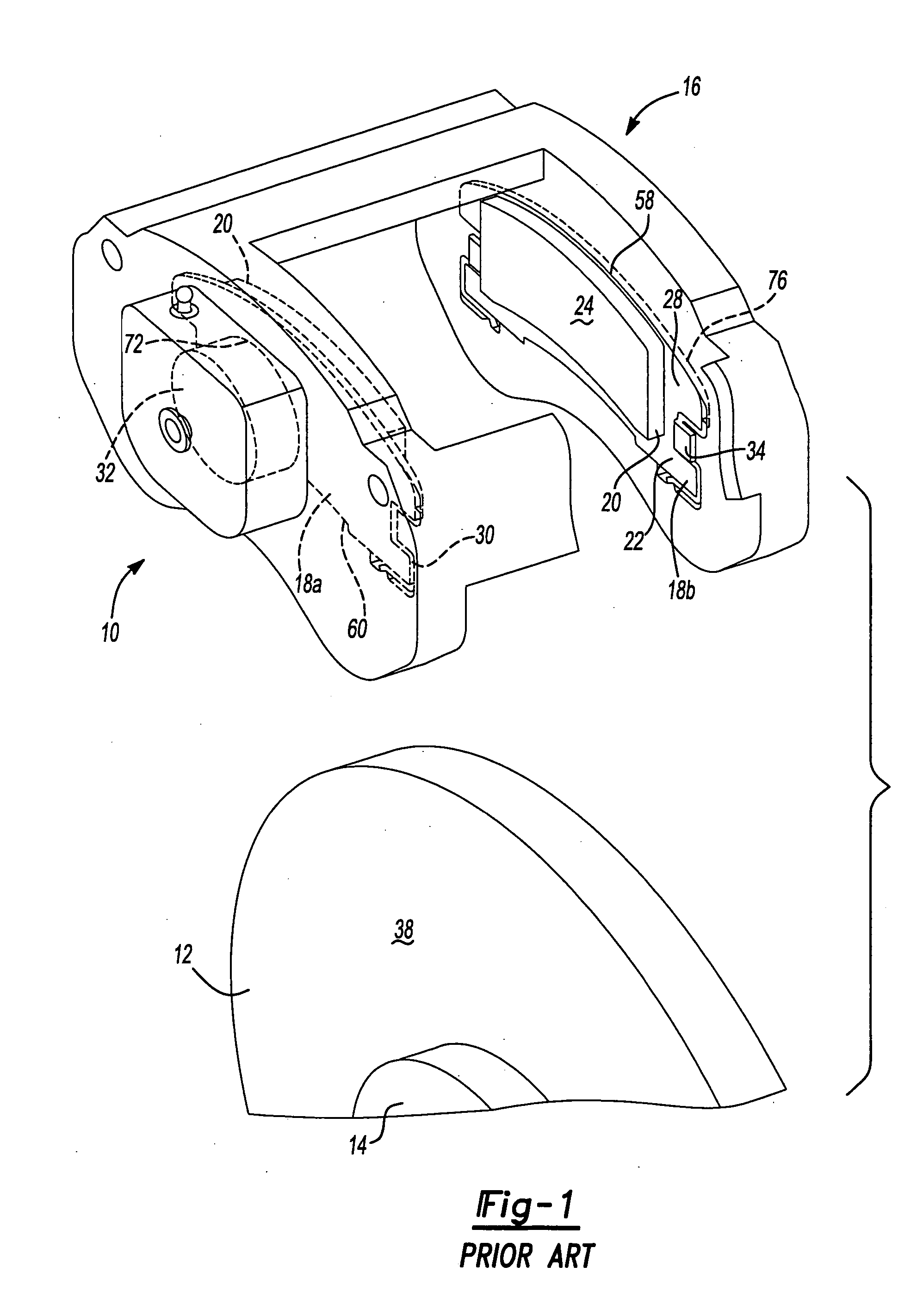
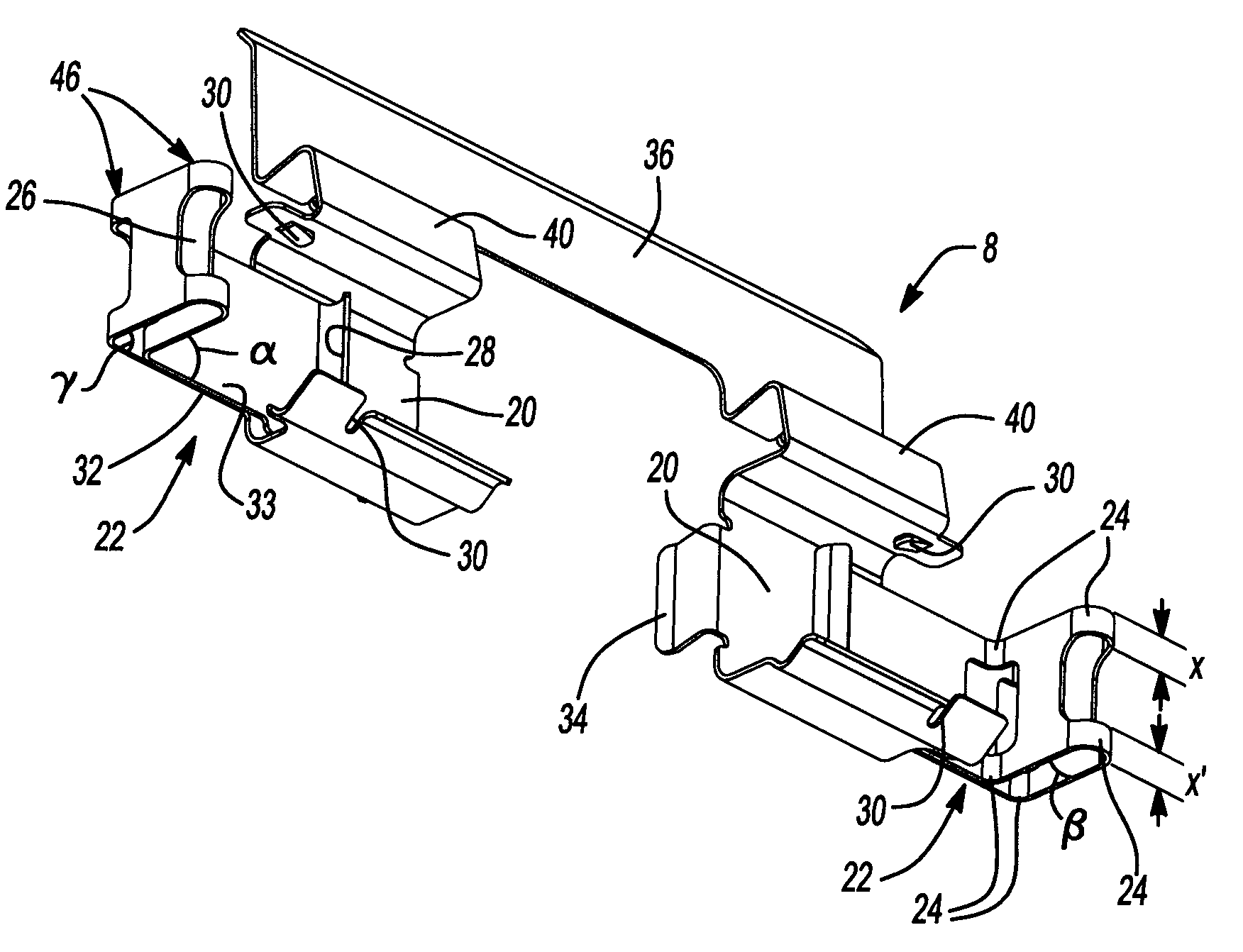
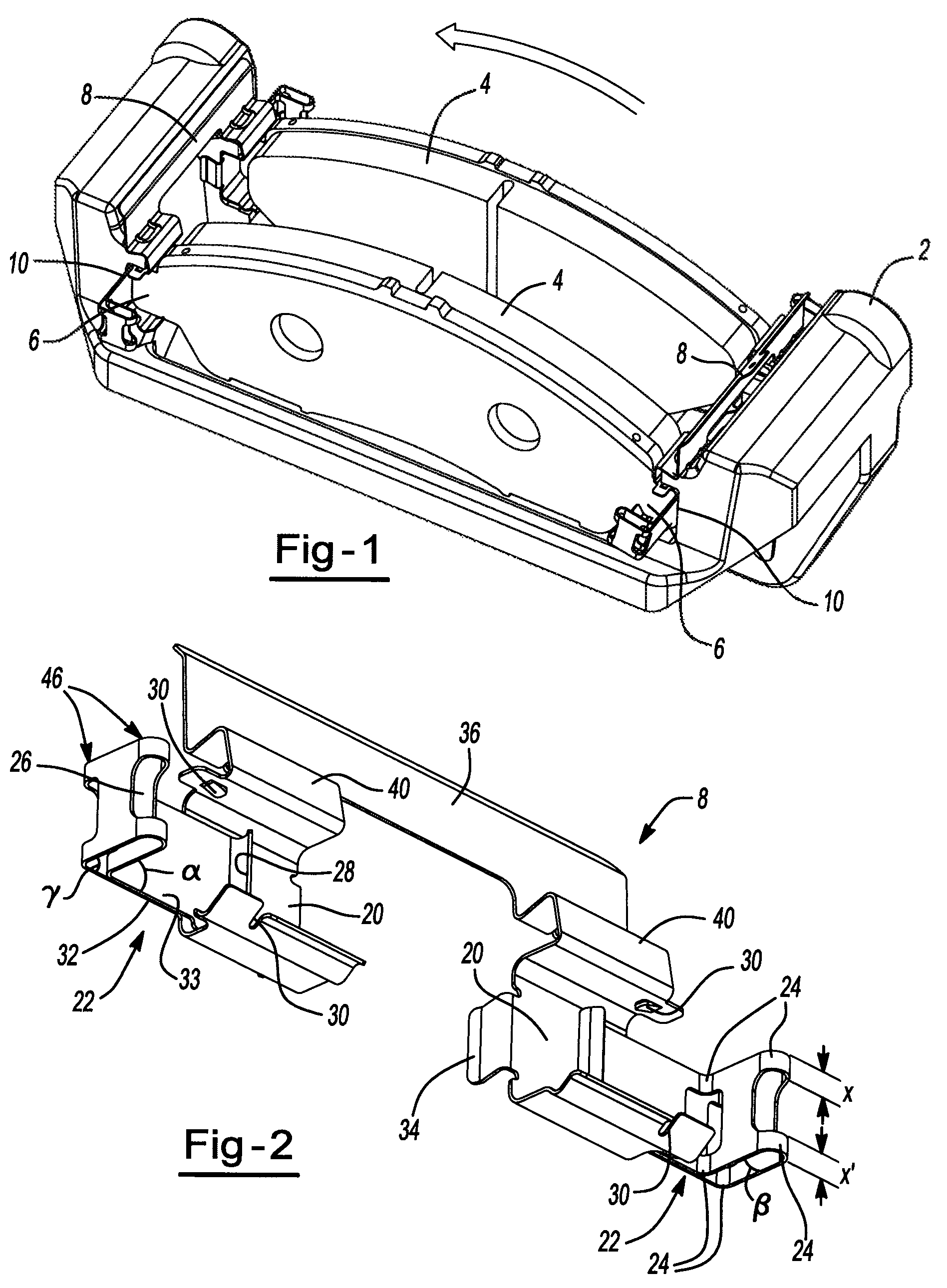
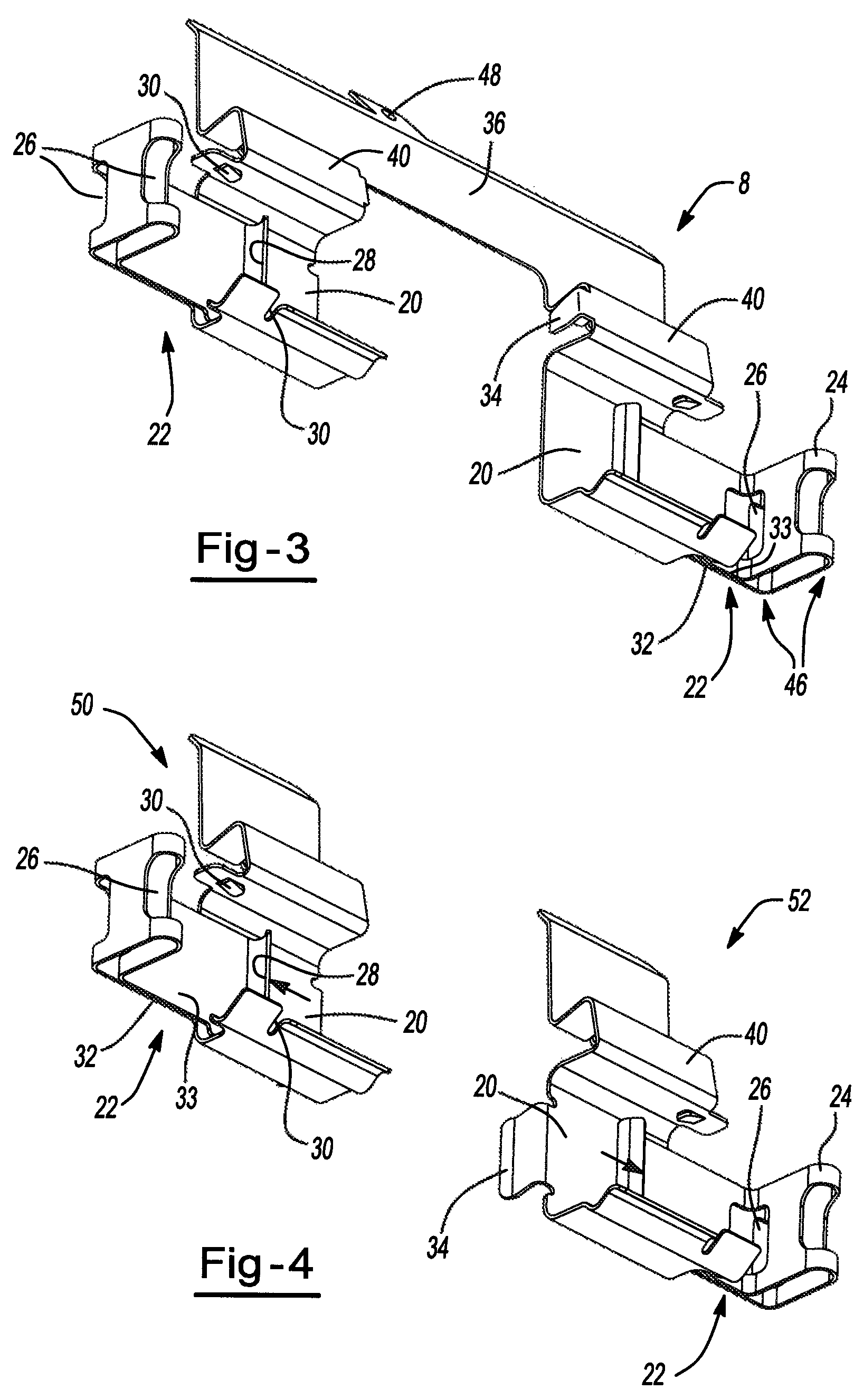
InactiveUS20110168503A1Constant forceRemove debrisSnap fastenersAxially engaging brakesBiomedical engineeringBody segment
A clip comprising: a body portion; one or more arms connected to the body portion and projecting away from the body portion; a deformable portion of the one or more arms that is distal from the body portion; and a lip on the one or more arms that is proximate to the body portion.
Owner:AKEBONO BRAKE
Device for fixing a ventilated brake disk axially on the hub of a motor vehicle wheel
InactiveUS6446765B1Easy to controlHigh speed usBraking element arrangementsAxially engaging brakesEngineeringMechanical engineering
An axial fixing device for axially fixing an annular brake disk on a wheel hub of a motor vehicle, the annular brake disk having the same axis of rotation as the hub and including radial ventilation ducts regularly distributed about its periphery. According to the invention, the hub has axial guide pieces in relief, or "lugs", for co-operating with fluting in an inner peripheral edge of the disk to center the disk, to lock it angularly, and to guide it axially relative to the hub, each lug of the hub having a radial through channel for co-operating with a corresponding ventilation duct of the disk, and the disk is held axially in the hub with play by axial holding means disposed between the disk and the hub.
Owner:MESSIER BUGATTI INC
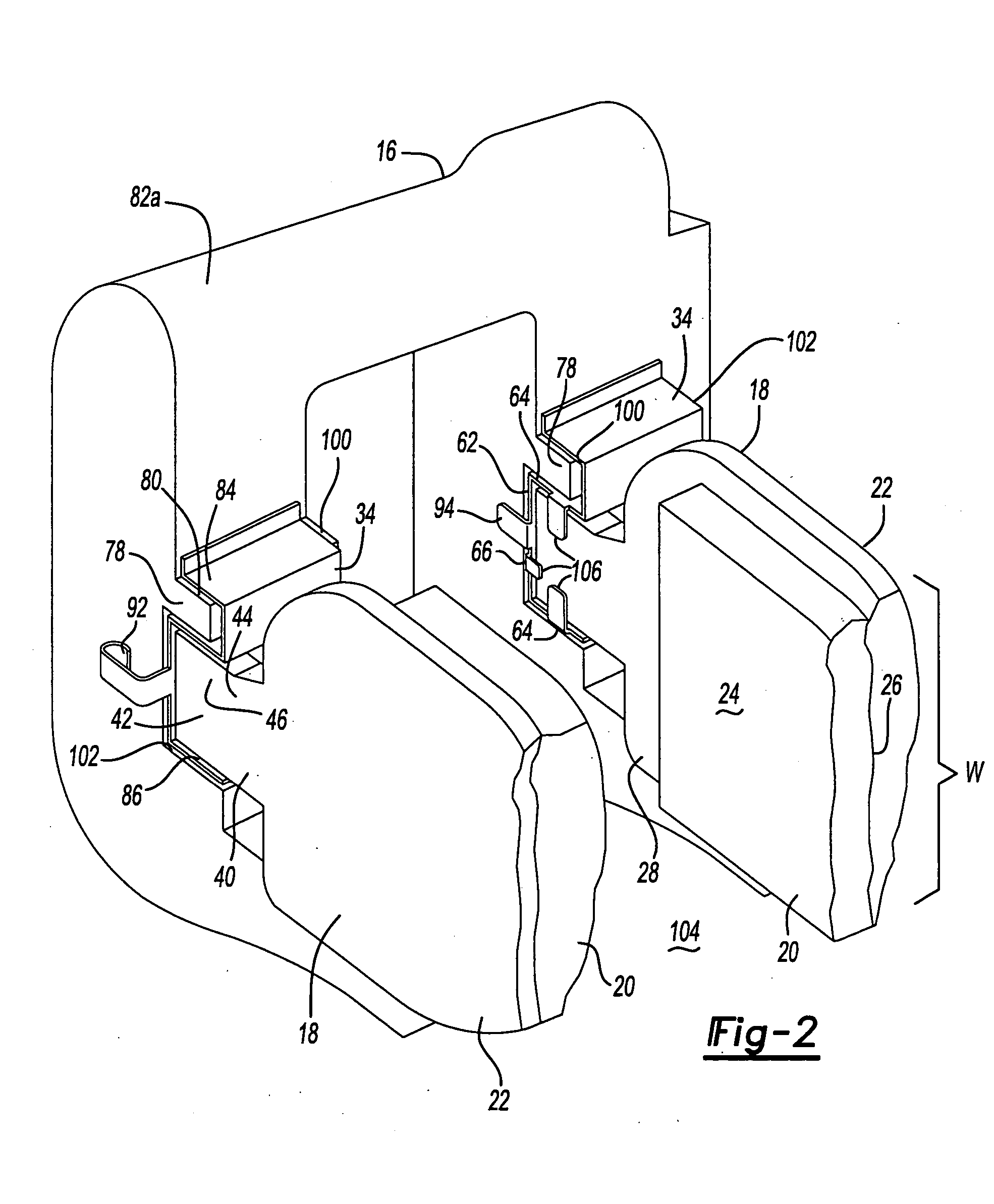
Pad retaining clips
A brake caliper mounting clip is disposed between a brake caliper having a brake pad channel and a brake pad having an edge member. The edge member moves in the brake pad channel between a rotor gap and a caliper housing. The clip further comprises a pad holding portion slidingly engaged with the edge member and having a plurality of pad retaining members. The pad retaining members are connected to the pad holding portion and disposed between the edge member and the rotor gap. The plurality of the pad retaining members is further configured to prevent the brake pad from falling into the rotor gap. Additionally the edge member of the brake pad and the plurality of pad retaining members are configured to prevent improper installation of the brake pads in the caliper.
Owner:AKEBONO BRAKE
Disk Brake And Production Method For A Disk Brake
ActiveUS20130008749A1Less componentsImprove stabilityBraking element arrangementsAxially engaging brakesSpring forceEngineering
A disk brake having a brake caliper and a brake actuation mechanism being supported in it, in which the brake actuation mechanism includes an amplification mechanism for introducing a clamping force, an adjustment device for compensation of lining wear with a torque clutch, a thrust element for transmitting the clamping force onto a brake disc and a reset device, which components are arranged around a rod, in which the torque clutch, for example, is formed as a roller-ramp-mechanism. A spring force can act onto the torque clutch by means of the reset device thereby forming a torque limit. Furthermore the invention relates to an assembly method for such a disc brake.
Owner:HALDEX BRAKE PROD AB
Vibration inhibiting structure for rotor
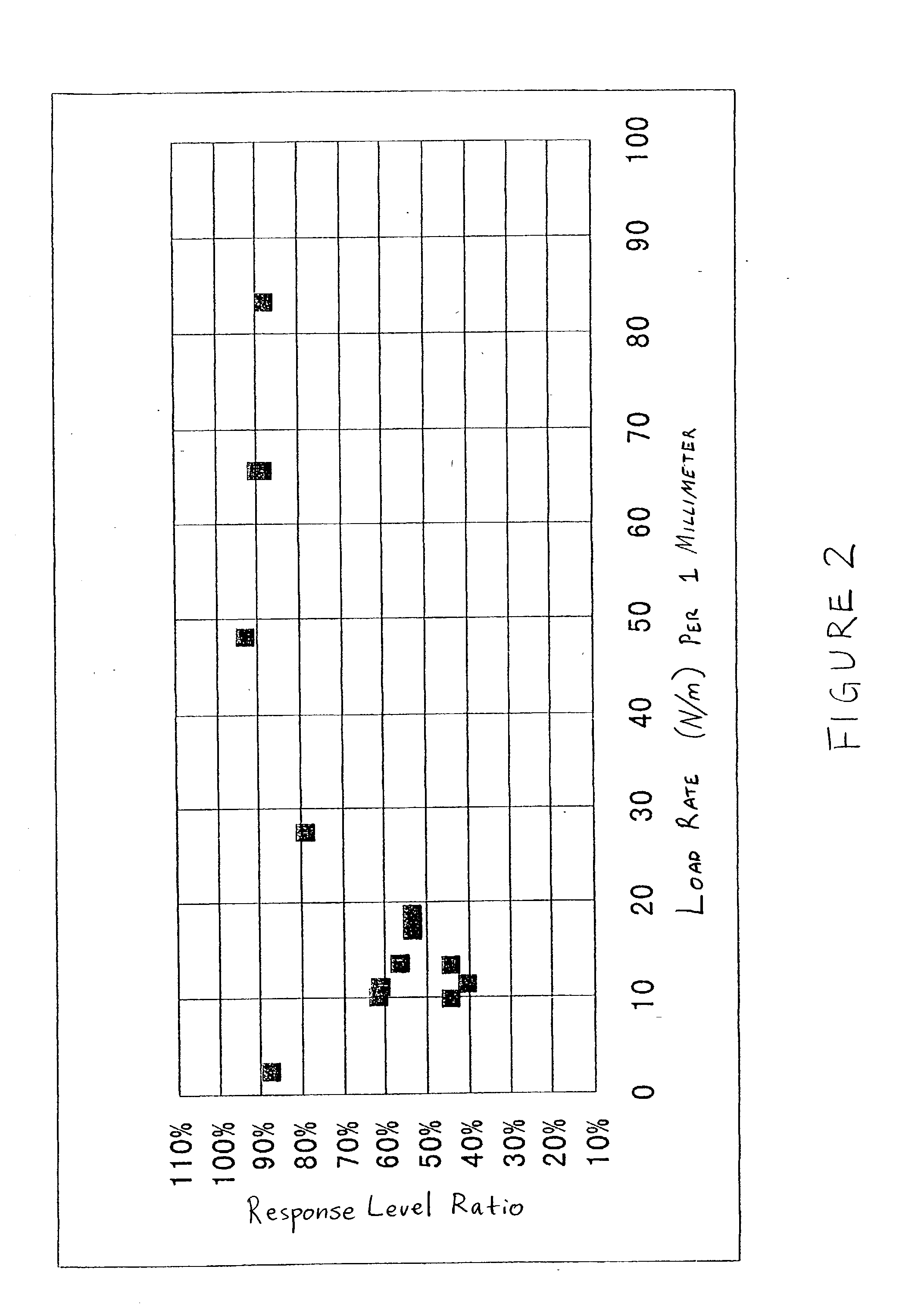
InactiveUS20030037999A1Improved vibration inhibiting structureSimple structureNoise/vibration controlBraking discsCoil springEngineering
A rotor such as a brake disk for a vehicle has a spring holder that circumferentially extends around an axis of the disk. A coil spring extends around the axis along the spring holder. The spring is loaded onto the spring holder by its own resilience. The spring has a load rate that generates a tension that allows the spring to move circumferentially relative to the spring holder.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
Pad retaining clips
A brake caliper mounting clip is disposed between a brake caliper having a brake pad channel and a brake pad having an edge member. The edge member moves in the brake pad channel between a rotor gap and a caliper housing. The clip further comprises a pad holding portion slidingly engaged with the edge member and having a plurality of pad retaining members. The pad retaining members are connected to the pad holding portion and disposed between the edge member and the rotor gap. The plurality of the pad retaining members is further configured to prevent the brake pad from falling into the rotor gap. Additionally the edge member of the brake pad and the plurality of pad retaining members are configured to prevent improper installation of the brake pads in the caliper.
Owner:AKEBONO BRAKE
Disc brake with parking function
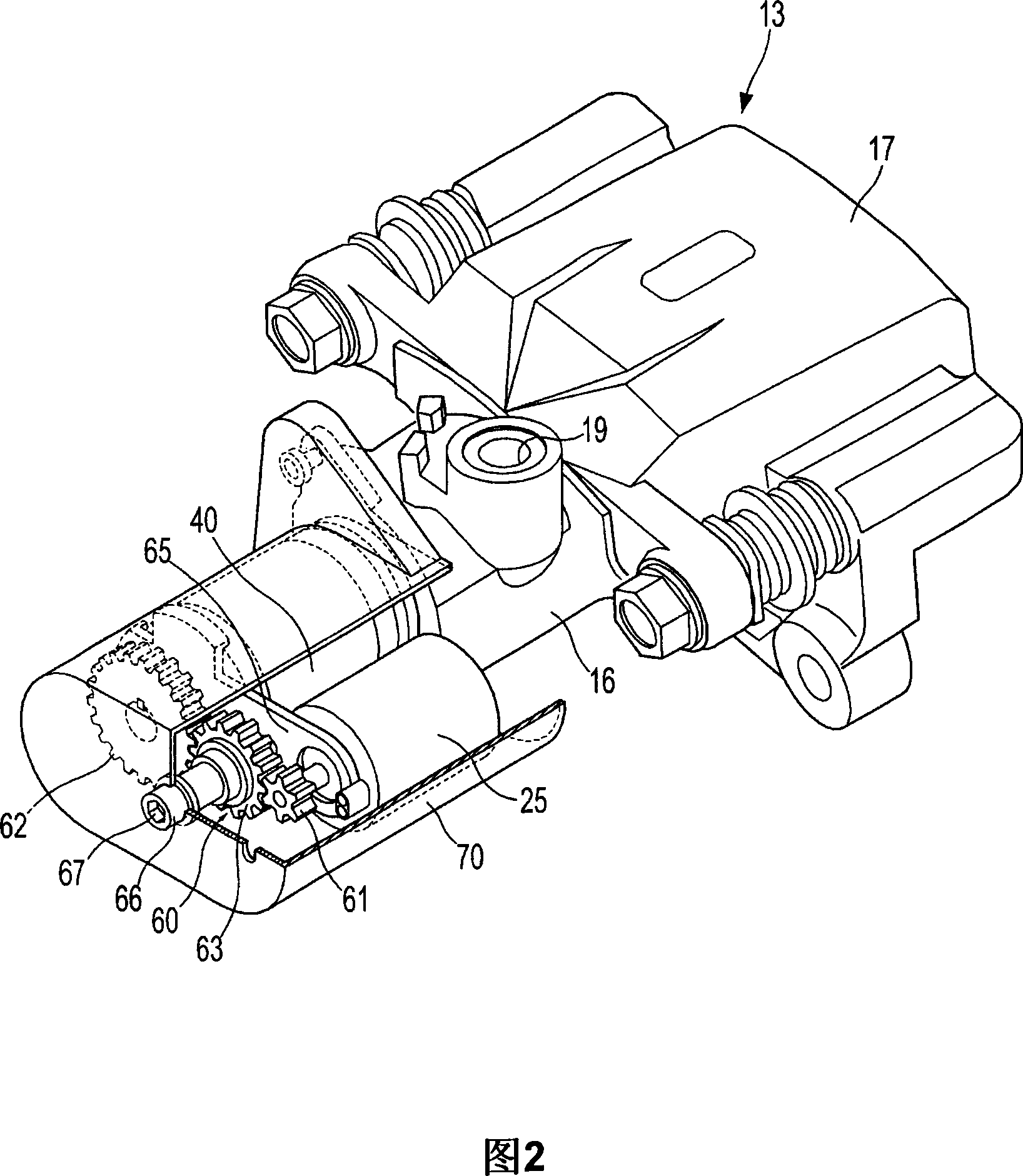
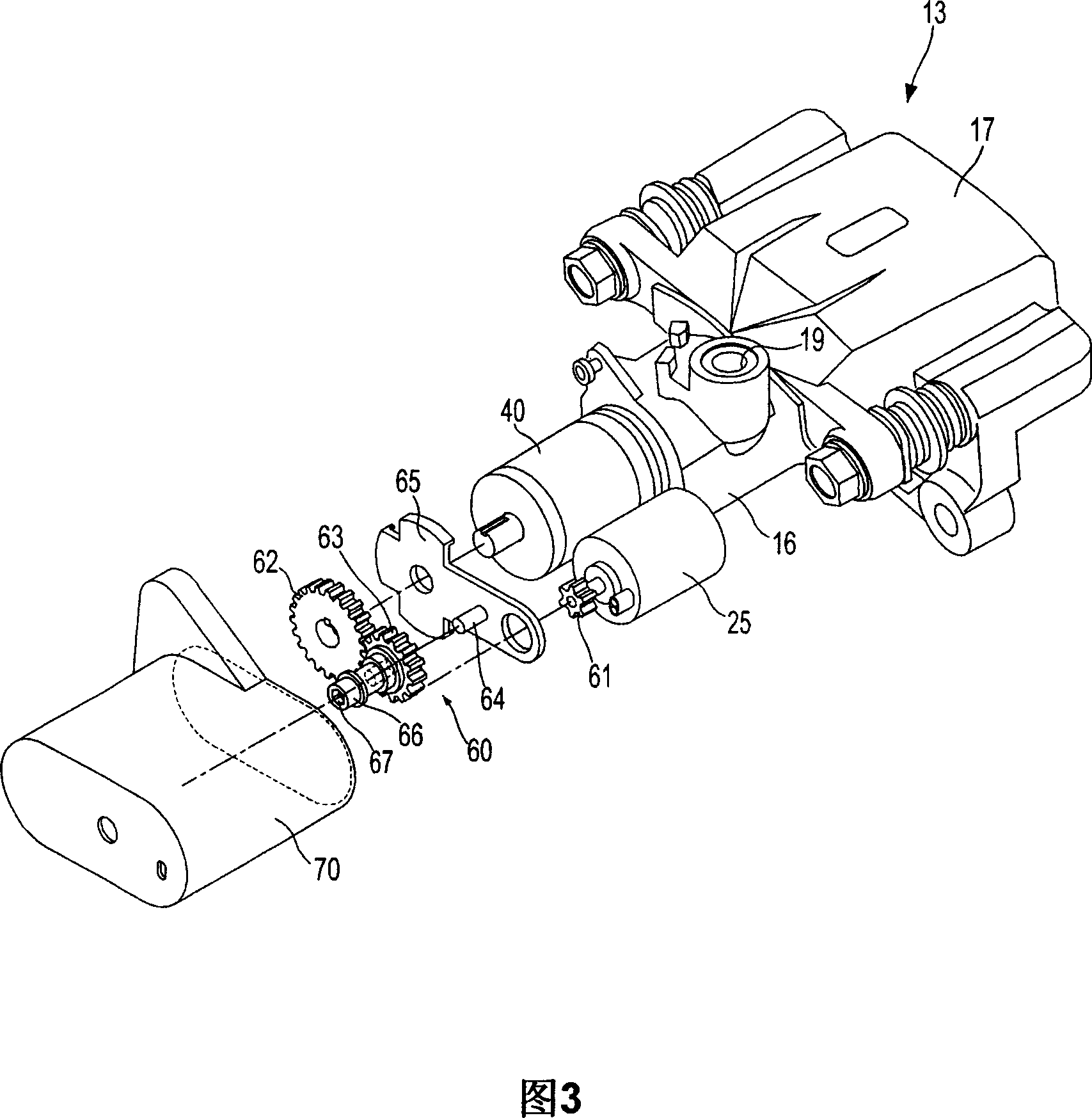
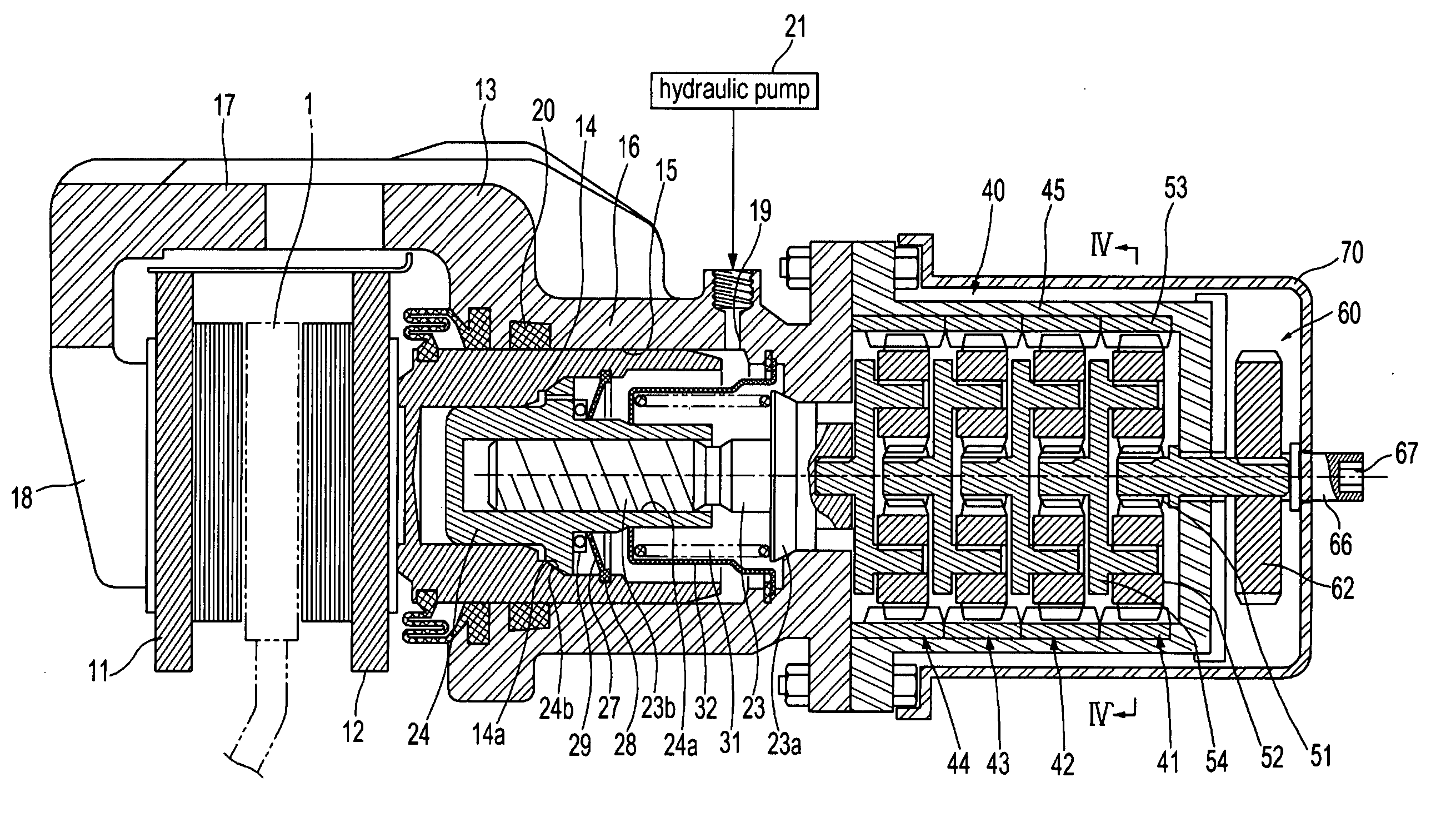
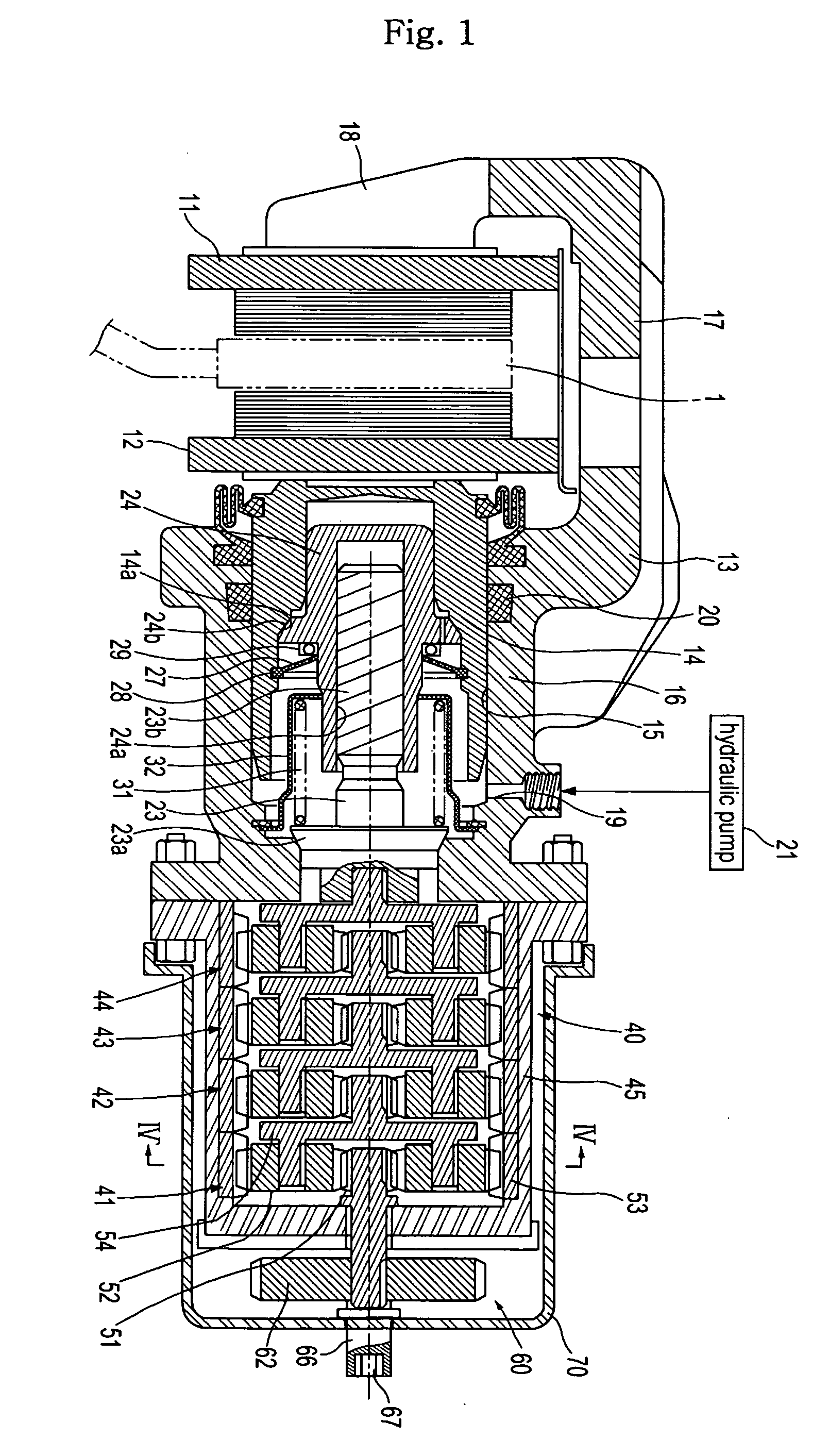
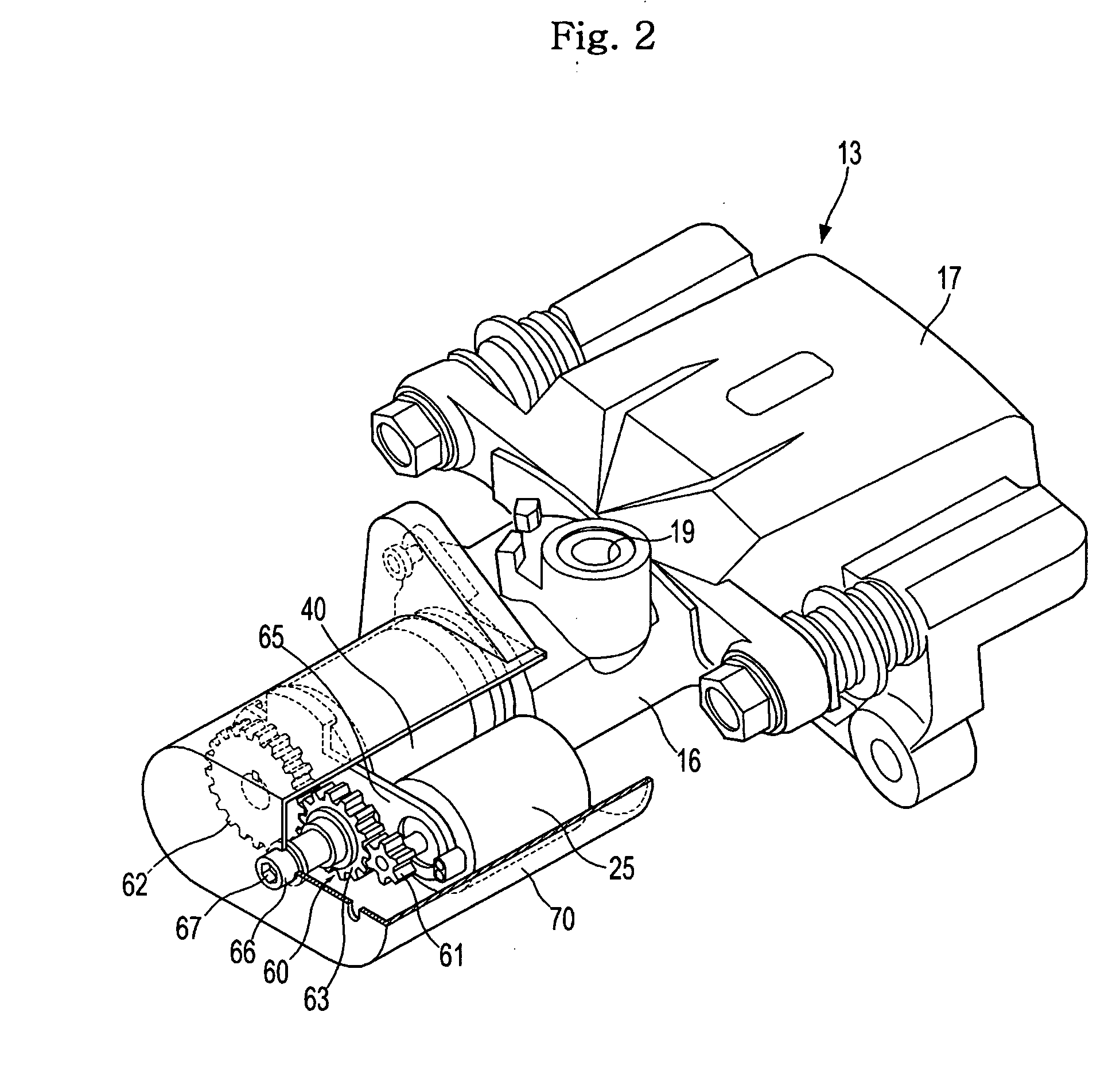
A disc brake enables a parking apparatus to be operated via actuation of an electric motor, thereby permitting easy operation of the parking apparatus. The disc brake comprises a piston to compress a friction pad used for braking of a disc, a caliper housing to receive the piston such that the piston moves linearly therein, and having a cylinder section to which a hydraulic pressure for braking is applied, an actuation shaft rotatably installed within the cylinder section, and having a male screw formed thereon, a compression sleeve installed within the piston to compress or release the piston while linearly moving therein by rotation of the actuation shaft, and having a female screw formed thereon to engage with the male screw of the actuation shaft, an electric motor to rotate the actuation shaft, a multi-stage reduction gear train to transmit rotational force of the electric motor to the actuation shaft. The multi-stage reduction gear train has a central axis deviated from that of the electric motor, and a shaft connected with a shaft of the electric motor via a power transmission unit.
Owner:HL MANDO CORP
Disk brake
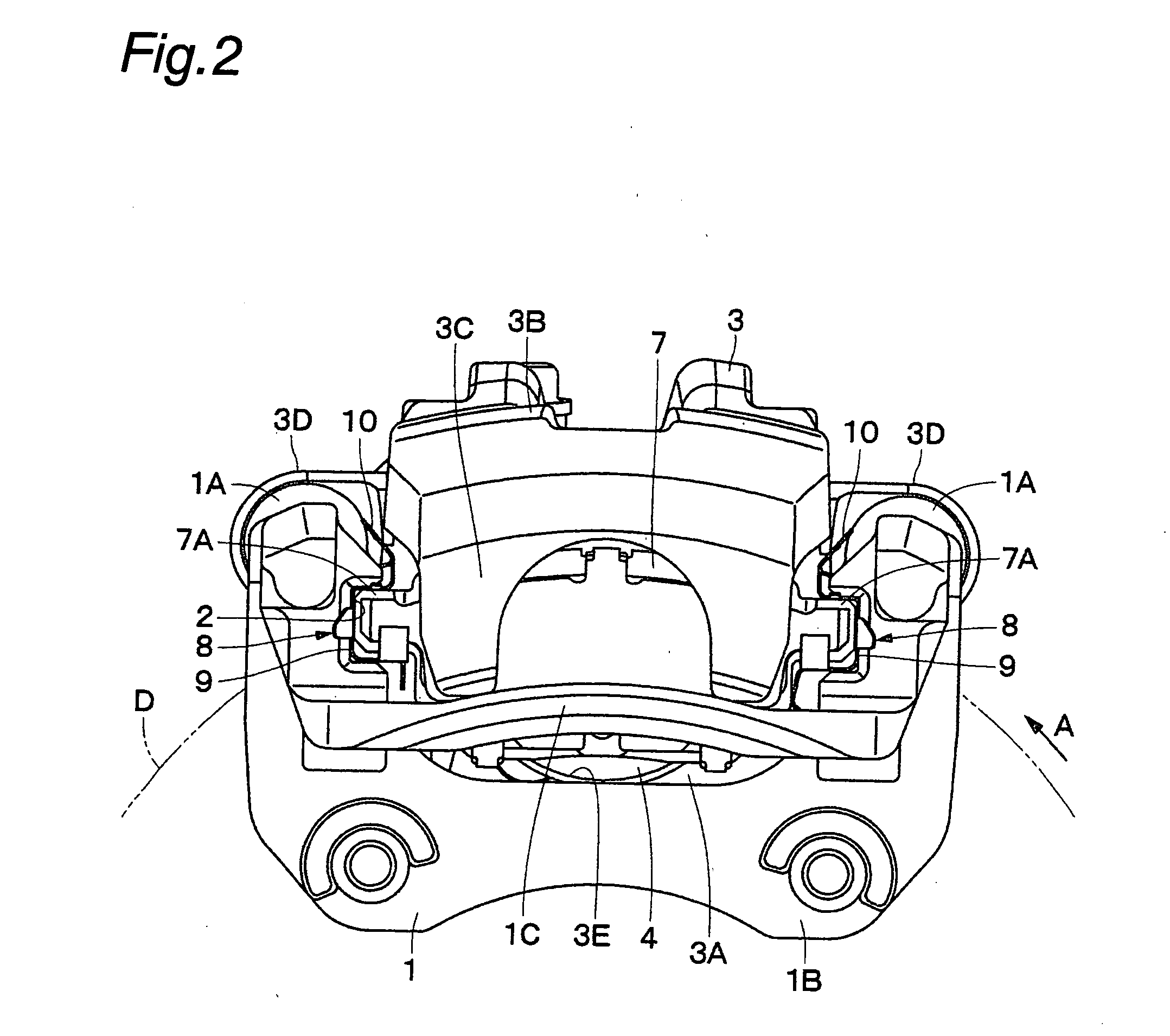
ActiveUS20070251772A1High strengthAvoid deformationAxially engaging brakesSlack adjustersMechanical engineeringDisc brake
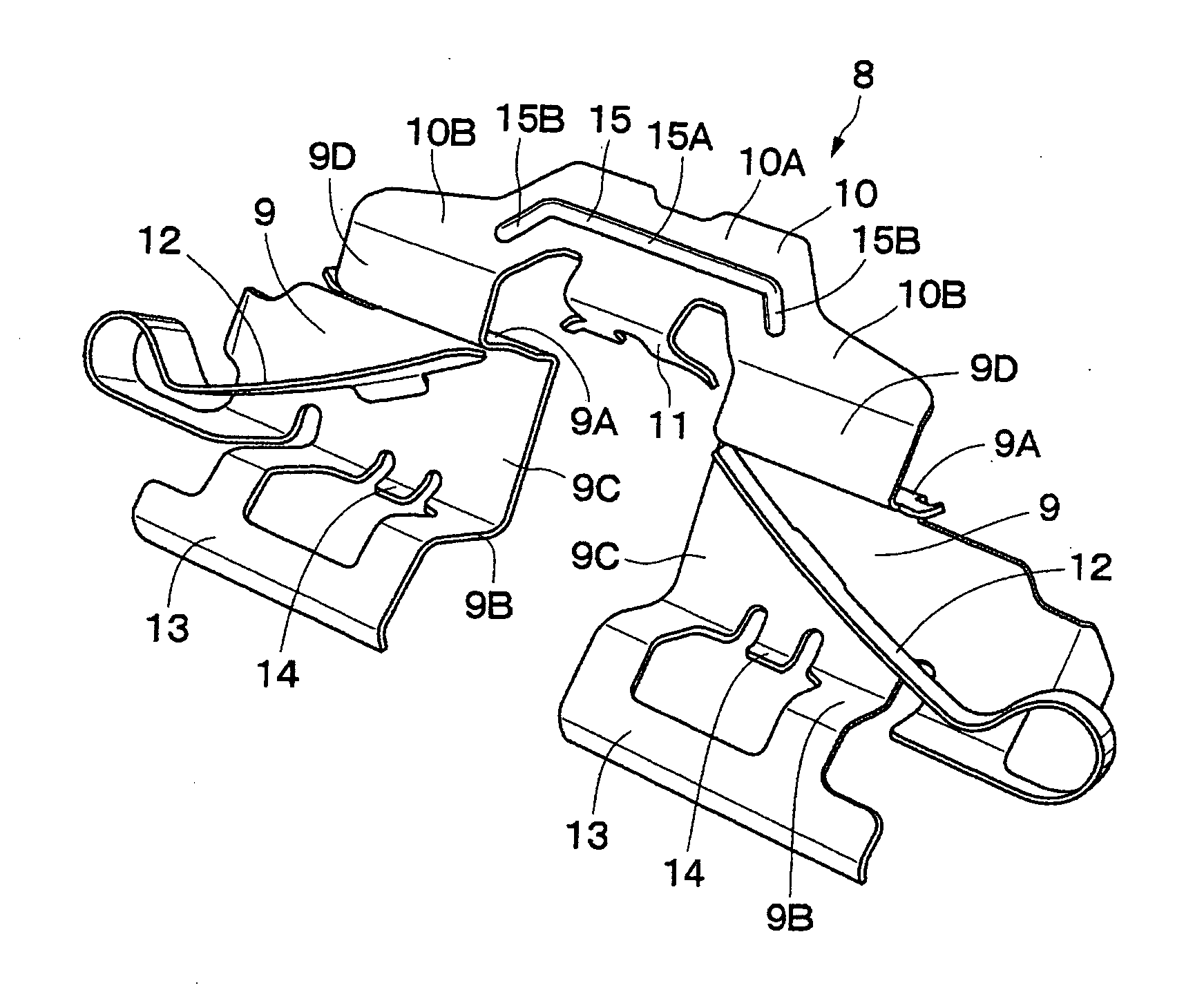
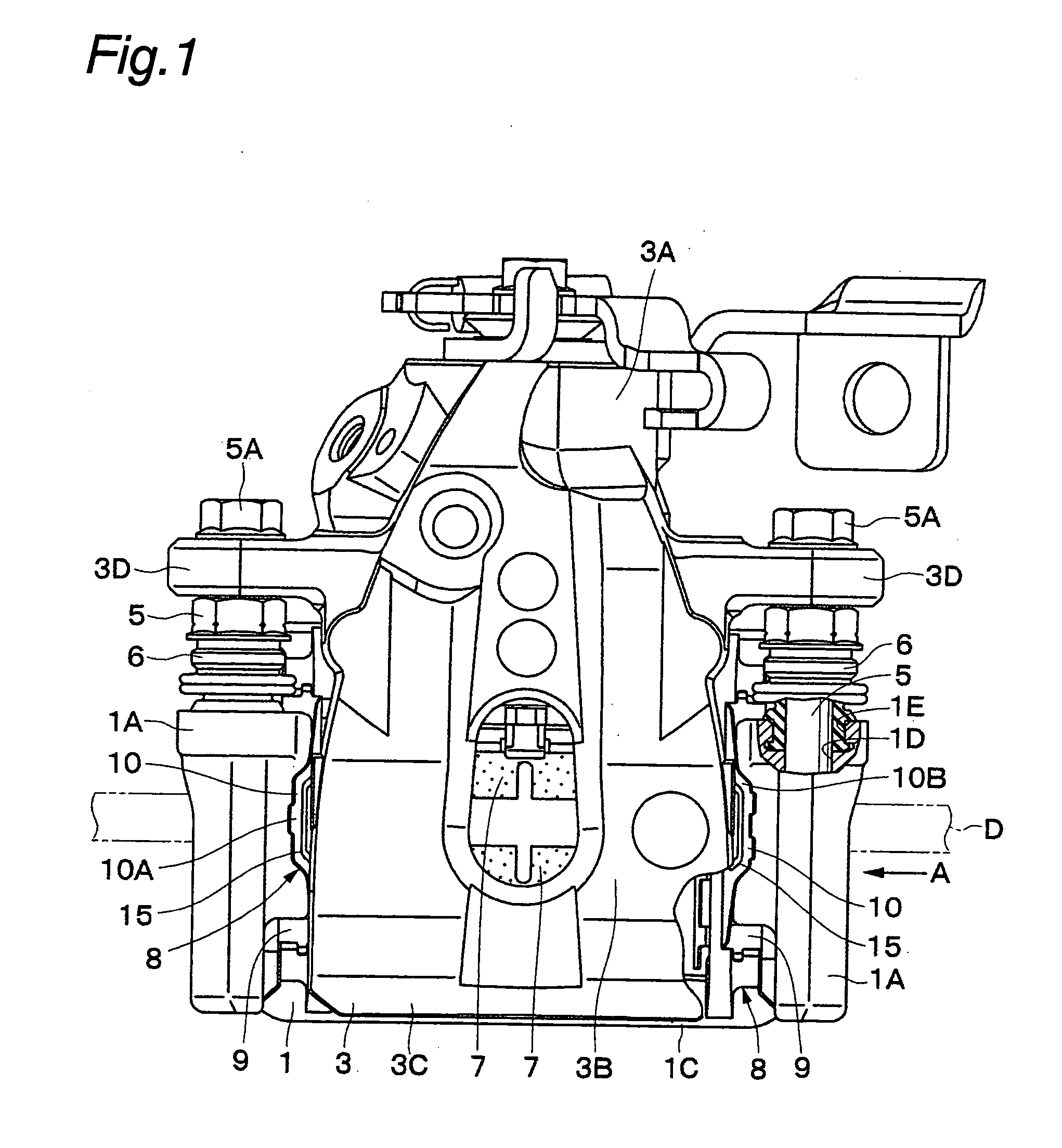
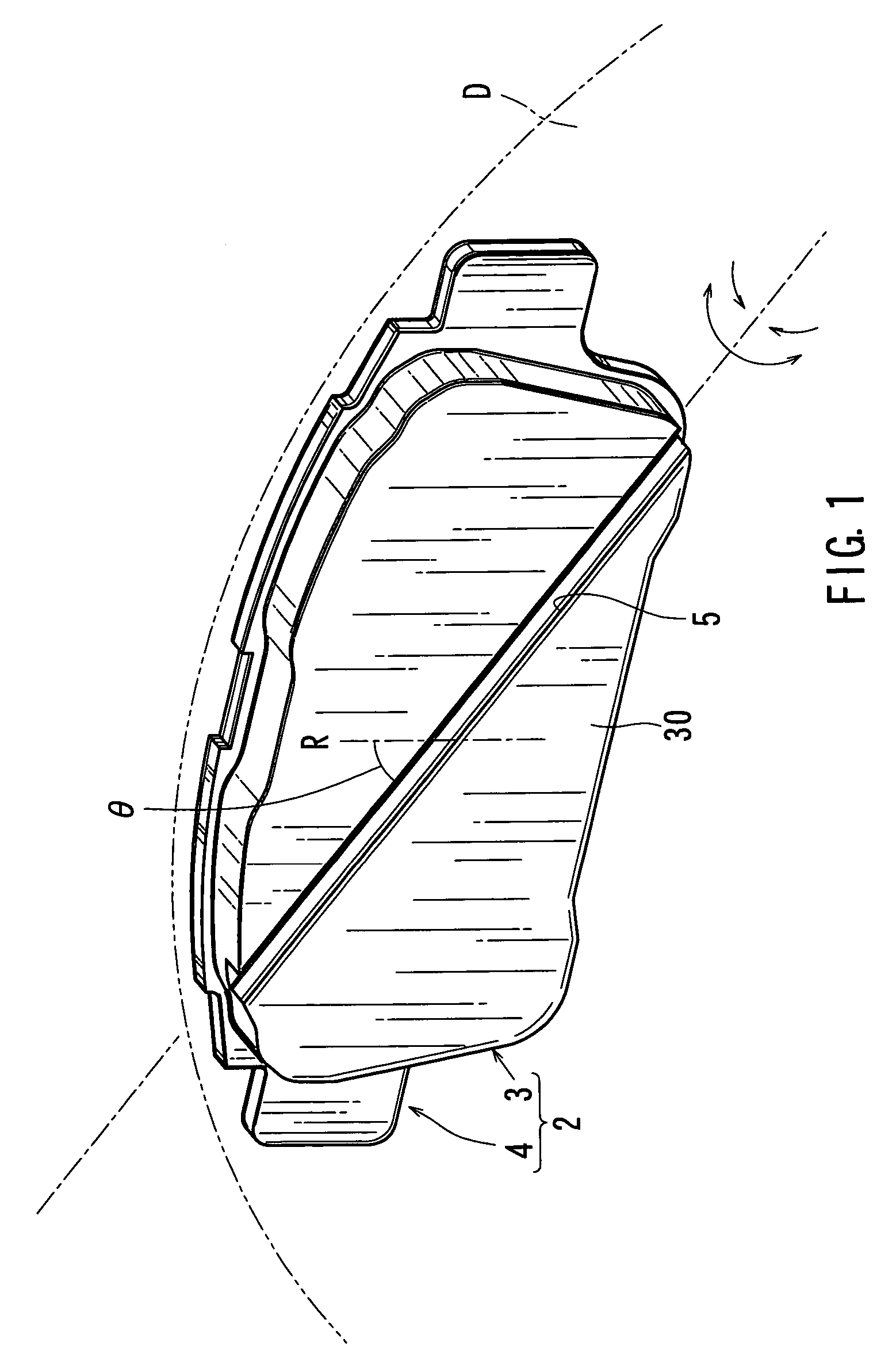
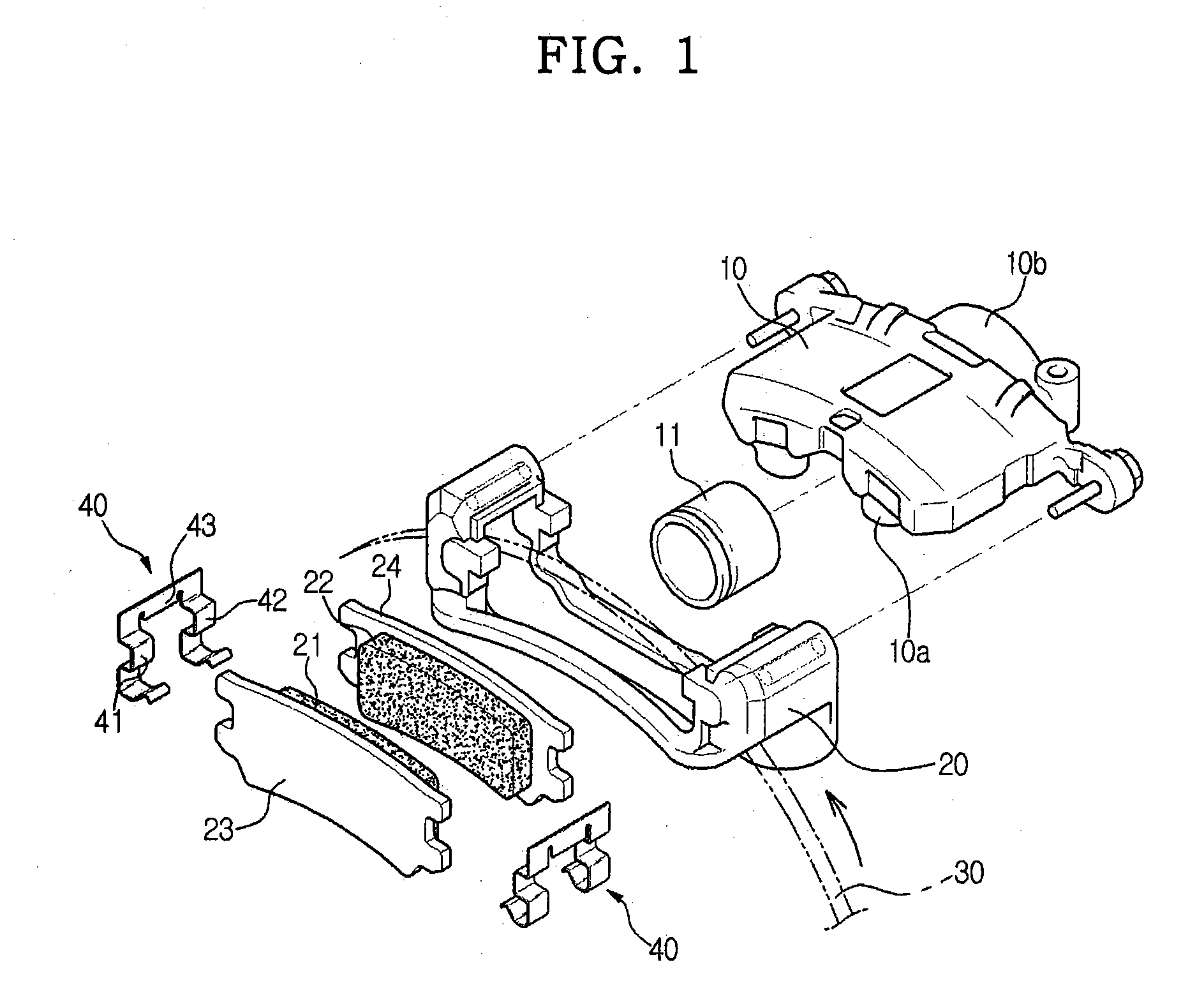
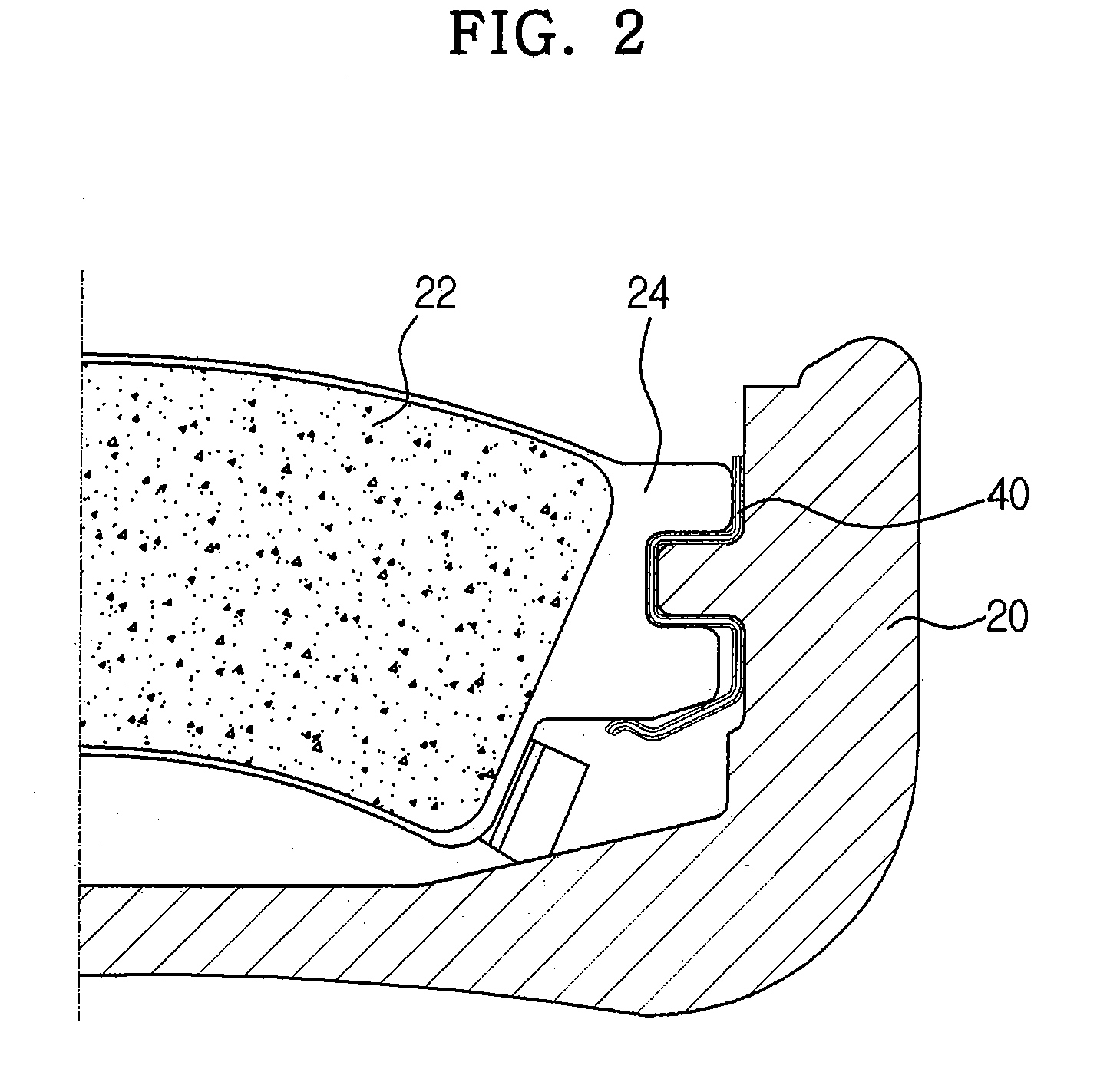
The strength and rigidity of pad springs are increased with a simple structure to prevent deformation and so forth of the pad springs caused by external force. A mounting member 1 is provided with pad springs 8 for resiliently supporting friction pads 7. Each pad spring 8 has guide plates 9, a connecting plate 10, an engagement plate 11, radially urging portions 12, circumferentially urging portions 13, reinforcement 15, etc. The reinforcement 15 includes a rectilinear reinforcement 15A formed on a flat plate portion 10A of the connecting plate 10 by embossing, for example, and oblique reinforcements 15B formed on joint portions 10B of the connecting plate 10. Thus, the joint portions 10B and so forth of the pad springs 8 can be prevented from being deformed by external force when the brake is activated or during assembling operation, for example, and hence it is possible to prevent positional displacement of the guide plates 9, etc. that would otherwise be caused by the deformation of the joint portions 10B.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Disc brake assembly
A disc brake assembly includes a rotor, a caliper, brake pads and an optional filter. The optional filter can be disposed within a shroud which covers at least about 70% of the distal side periphery on at least one of the two sides of the rotor. The disc brake also includes an impeller or other means for providing air flow to the disc brake assembly. The impeller can be provided by the rotor itself or it can be provided by a separate component which is powered either directly or indirectly by the rotor.
Owner:GELB JOSEPH
Fail-safe concept for an electromechanical brake
InactiveUS20050127749A1Security failsFatal consequenceBraking action transmissionMechanically actuated brakesControl systemExercise state
A control system for an electromechanical brake with self-reinforcement has: means for recognizing a brake failure means for detecting the actual state of motion of the device to be braked and means for opening and closing the brake upon recognition of a failure dependent upon the detected state of motion of the device to be braked. The means for recognizing the state of motion detection in particular the rotational velocity of a brake disk assigned to the brake.
Owner:STOP
Orientated carbon nanotube composite, process for producing orientated carbon nanotube, and, produced using orientated carbon nanotube composite, pneumatic tire, wheel for vehicle, tire wheel assembly and disk brake
InactiveUS20060061011A1Improve efficiencyImprove conductivityMaterial nanotechnologyBraking discsRubber materialCarbon nanotube
A carbon nanotube orientated composite formed by orientating carbon nanotubes in a given direction in a matrix having a heat conductivity lower than that of carbon nanotube, in which at least a part of carbon nanotubes are contacted with each other to be continuous from one end to the other end between both ends in the orientated direction, is provided as a material having a heat conductivity considerably higher than that of copper, aluminum or the like or a material to be disposed in rubber material having a low heat releasing characteristic to considerably improve the heat conduction, and also there are provided a method of producing the same as well as a pneumatic tire, a wheel for a vehicle, a tire-wheel assembly and a disc brake using this material.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Disk brake devices
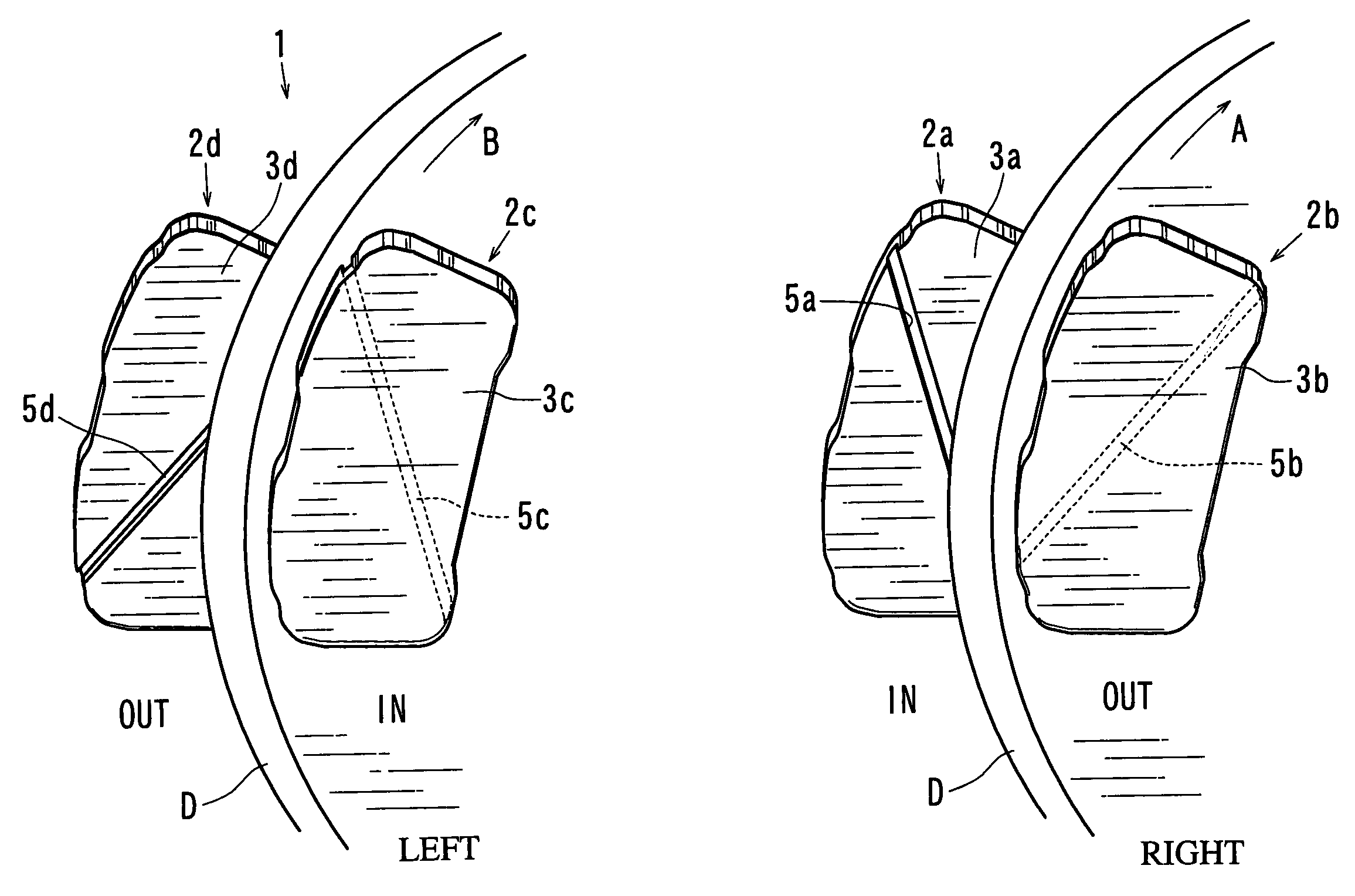
ActiveUS7111709B2Effectively reduce the squealing soundsImprove distortionNoise/vibration controlBraking membersEngineeringMechanical engineering
A disk brake device includes a pair of brake disks and right and left pairs of pads. Each pad includes a twisting compliant section that extends along a line inclined by an angle relative to a radial direction of the corresponding brake disk. The twisting compliant section facilitates the twisting of the pad about the compliant section. The twisting compliant sections of the right inner pad and the left inner pad are inclined in opposite directions relative to the twisting compliant sections of the right outer pad and the right inner pad. The twisting compliant sections of the right inner pad and the left inner pad are inclined in substantially the same direction with one another.
Owner:ADVICS CO LTD
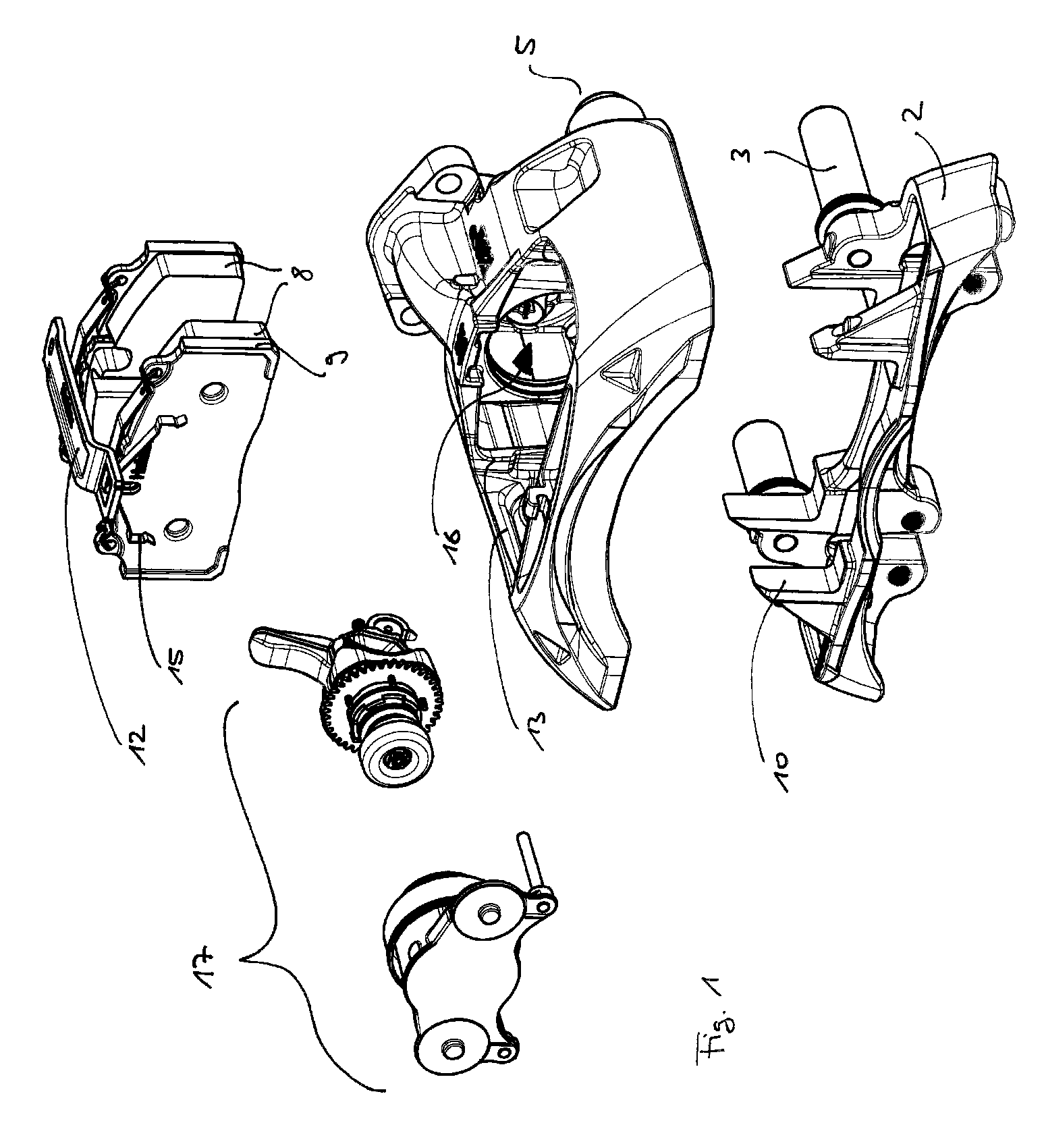
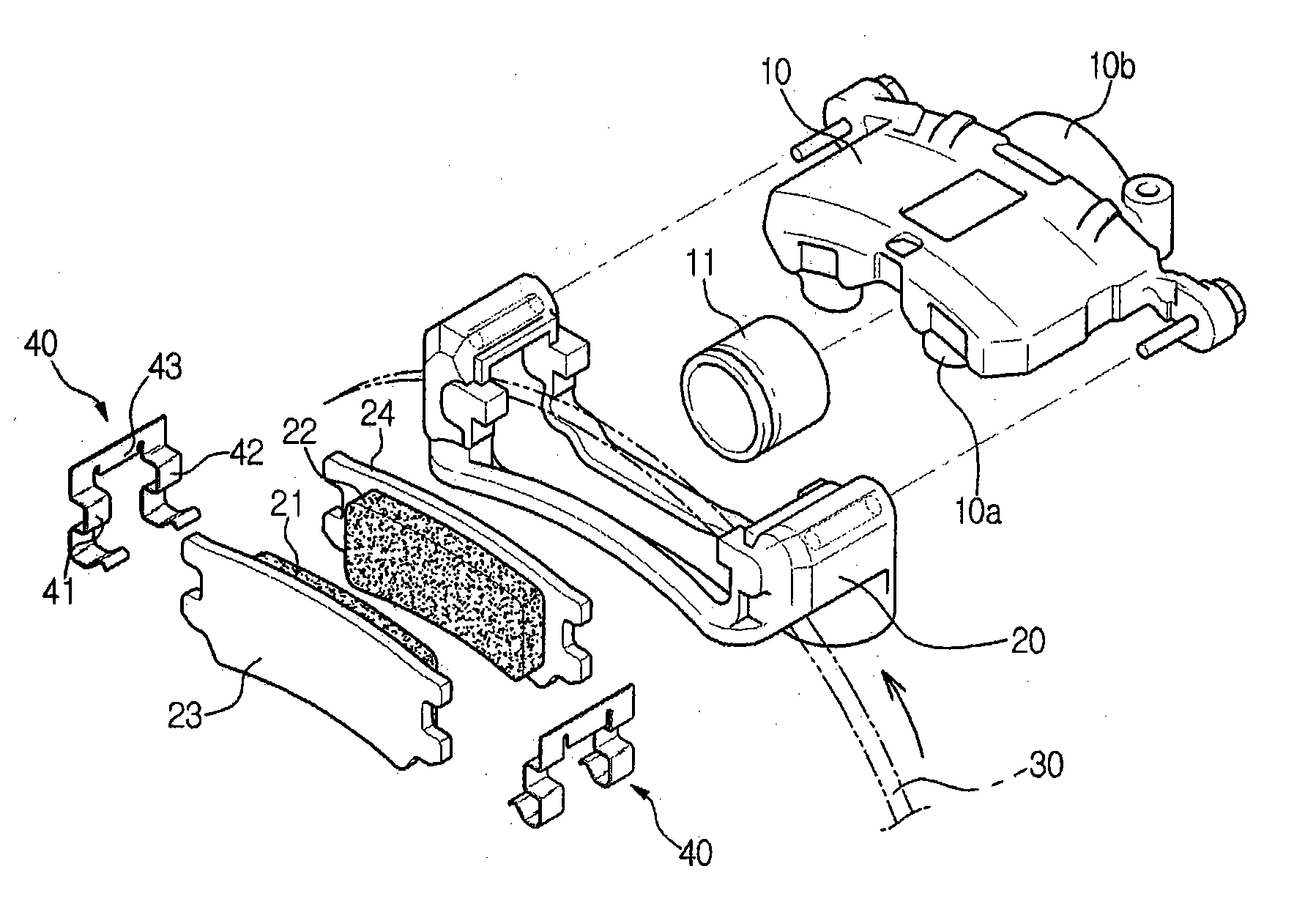
Caliper assembly for disc brake system
InactiveUS20120085597A1Improve NVH performanceImprove component performanceMechanically actuated brakesSlack adjustersEngineeringCalipers
A caliper assembly comprising: a brake pad comprising a carrier plate having two opposing faces and a top edge a bottom edge and two opposing side edges, wherein on one face is friction material and on the opposing face is a projection adapted to seat in a matched hole or recess in a caliper body, the two opposing side edges each having an ear which is adapted to seat in pad locator indentations in a support structure; a support structure comprising a recess for housing at least one brake pad and at least two pad locator indentations adapted for receiving the ears located on the two opposing sides of the brake pad and at least two caliper body locator indentations for seating two ears defined by the caliper body; and a caliper body having a hole or recess adapted for seating the projection on the opposing face of the brake pad and having two ears on each opposing side which are adapted to seat in the caliper body locator indentations of the support structure; wherein the ears of the brake pad are seated in the pad locator indentations of the support structure, the projection on the opposing face of the brake pad is seated in the hole or recess located in the caliper body, and a clip which engages the opposing face of the brake pad and the caliper body and holds the brake pad in position with respect to the caliper body and the ears of the caliper body are seated in the caliper body locator indentations in the support structure.
Owner:AKEBONO BRAKE
Disc brake with parking function
InactiveUS20070062769A1Easy to operateShorten speedMechanically actuated brakesElectrodynamic brake systemsEngineeringCalipers
A disc brake enables a parking apparatus to be operated via actuation of an electric motor, thereby permitting easy operation of the parking apparatus. The disc brake comprises a piston to compress a friction pad used for braking of a disc, a caliper housing to receive the piston such that the piston moves linearly therein, and having a cylinder section to which a hydraulic pressure for braking is applied, an actuation shaft rotatably installed within the cylinder section, and having a male screw formed thereon, a compression sleeve installed within the piston to compress or release the piston while linearly moving therein by rotation of the actuation shaft, and having a female screw formed thereon to engage with the male screw of the actuation shaft, an electric motor to rotate the actuation shaft, a multi-stage reduction gear train to transmit rotational force of the electric motor to the actuation shaft. The multi-stage reduction gear train has a central axis deviated from that of the electric motor, and a shaft connected with a shaft of the electric motor via a power transmission unit
Owner:HL MANDO CORP
Road vehicle brake disc made of carborundum foamed ceramics/aluminum alloy composite materials and production method of road vehicle brake disc
ActiveCN104235237AReduce weightImprove feeding capacityBraking membersSlack adjustersNanoceramicAlloy composite
The invention discloses a road vehicle brake disc made of carborundum foamed ceramics / aluminum alloy composite materials and a production method of the road vehicle brake disc. The body of the reinforced-aluminum-alloy brake disc with a carborundum foamed ceramics framework is made of reinforced aluminum alloy materials such as aluminum alloy or nano ceramics particles or carbon nano-tubes. The carborundum foamed ceramics framework is integrally casted on two symmetrical friction surfaces of the brake disc, and heat dissipation grooves or air holes can be casted or do not need to be casted on the friction surfaces. A plurality of heat dissipation ribs are casted in the peripheral direction of non-friction surfaces. Mounting holes are formed in the disc body. The production method includes the steps of production of the carborundum foamed ceramics framework, preprocessing of the framework, design and production of a casting mold of the brake disc, lower-pressure casting of the brake disc, heat treatment of the brake disc, precision processing of the brake disc and storage of a finished product. The brake disc is simple in production technology, light in weight, high and stable in friction factor, high in heat conductivity, long in service life and applicable to existing road vehicles.
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG DONGDA HUITONG NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
Coulomb friction damped disc brake caliper bracket
A Coulomb friction damped disc brake caliper bracket, wherein damping is provided by Coulomb friction, most preferably at the outboard tie-bar thereof. In one form, at least one clamping member applies compressive force externally to the caliper bracket, and in a second form, at least one interfacial boundary is internally disposed in the caliper bracket. Provided thereby is a mechanically distinguishable surface boundary between two surfaces which are in mutual contact such that a state of Coulomb friction exists therebetween.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
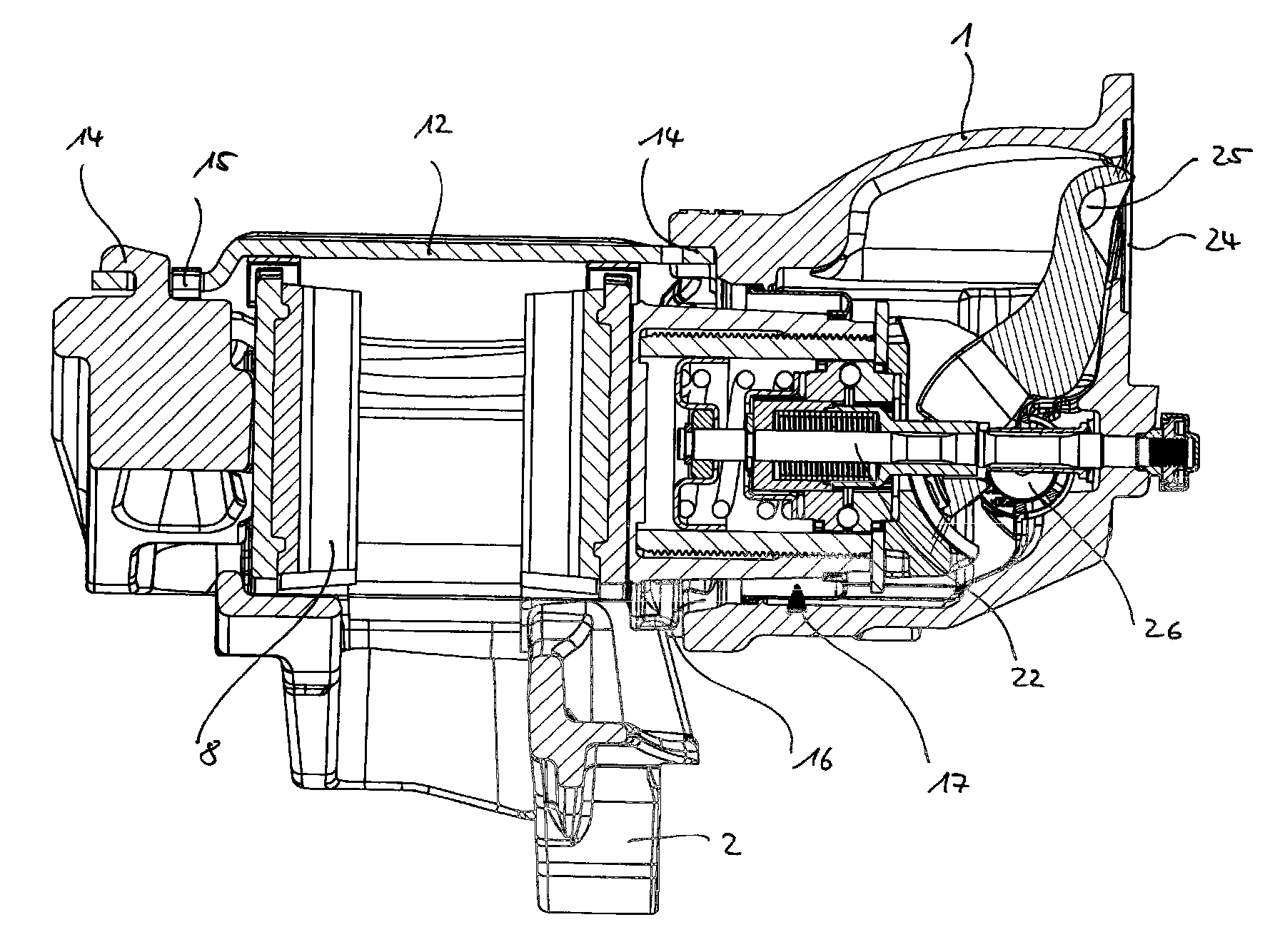
Electric-motor brake apparatus
InactiveUS6173820B1Generation of braking forceConstant actuation travel of the brake apparatus are assuredAxially engaging brakesElectrodynamic brake systemsParking brakeAutomotive engineering
The invention relates to a brake apparatus with an electric service motor, which serves to actuate the brake via an actuating device. To enable setting an air clearance, the apparatus includes a readjuster for setting the air clearance, the brake is actuated with the readjuster and then reversed by a defined length. To realize a parking braking function, the apparatus includes a parking brake that can be repositioned from a released position to a braking position and that acts on the actuating device.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Automobile brake controlled by wire
ActiveCN102853000ASave installation spaceIt has the function of deceleration and torque increaseAxially engaging brakesBrake actuating mechanismsAuto regulationLinear motion
The invention discloses an automobile brake controlled by a wire, which comprises a brake disc, wherein a friction plate is arranged on each of the two sides of the brake disc; the friction plates are fixedly connected with a piston which can axially move along a brake caliper body and is connected with a trapezoid nut; the trapezoid nut can axially move along an inner hole of the piston and is in fit connection with a trapezoid threaded end of a screw rod; a driving nut is movably arranged on a ball screw section of the screw rod and is fixedly connected with a worm gear; the worm gear is engaged with a worm which is fixedly connected with an output end of a driving motor of the brake to covert the rotation motion of the driving motor of the brake into linear motion; and the driving motor of the brake is perpendicular to a brake caliper of the brake. The automobile brake controlled by the wire has automatic regulation and parking braking functions, can improve reinforcement effect, is high in braking performance, simple in structure, convenient to mount, easy to maintain and less in energy consumption, and can ensure the constancy of brake response speed of a vehicle so as to further ensure the braking performance.
Owner:RES INST OF ZHEJIANG UNIV TAIZHOU
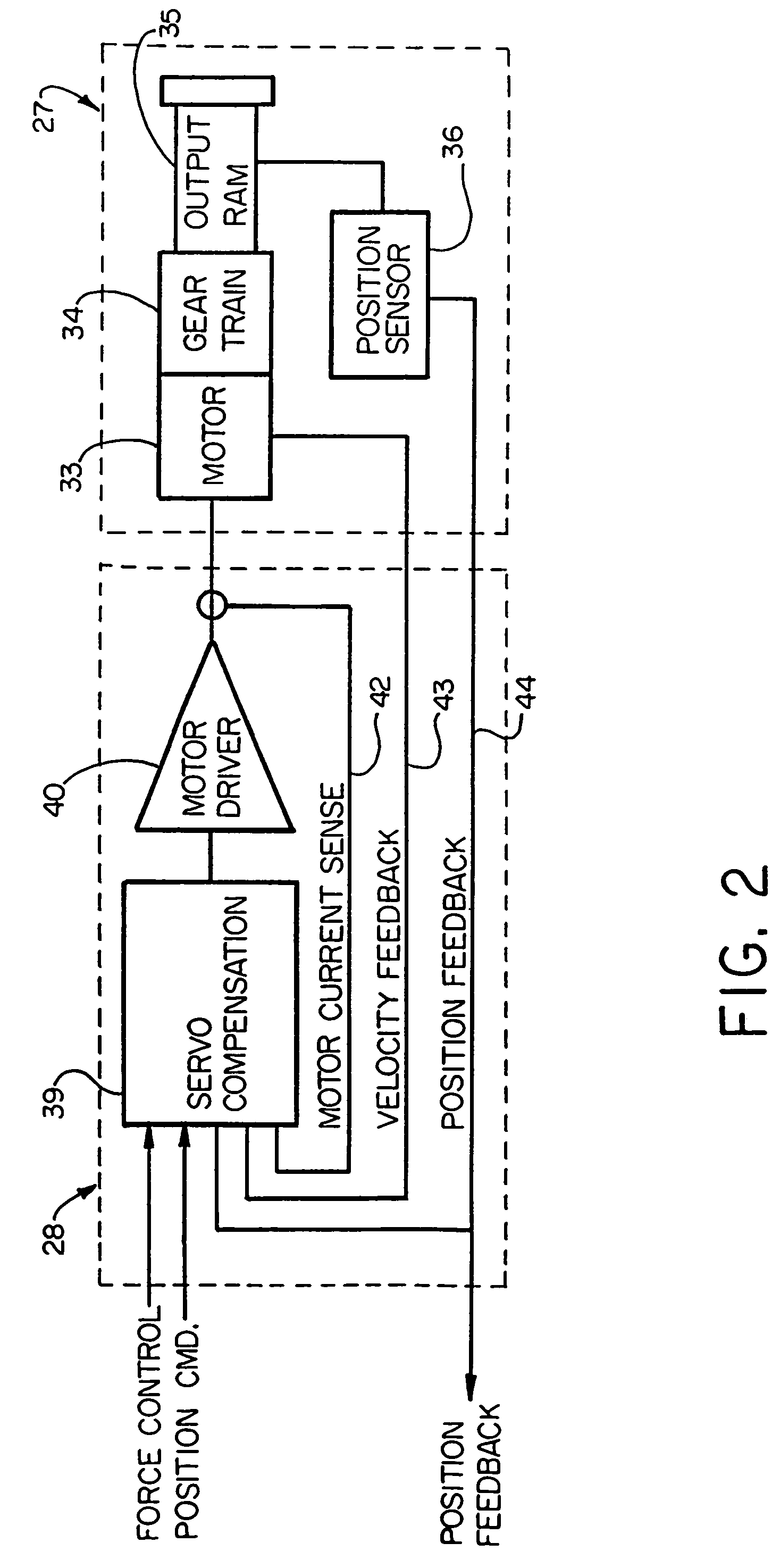
Electronic aircraft braking system with brake wear measurement, running clearance adjustment and plural electric motor-actuator ram assemblies
InactiveUS7108107B2Easy maintenanceIncrease weightAxially engaging brakesBraking action transmissionElectric aircraftActuator
An electrically actuated aircraft brake system and method which provides for brake wear measurement, brake running clearance adjustment, ram position-based control and improved construction and operation. Brake wear and running clearance measurement are obtained by analyzing the output of position sensing circuitry. The position sensing circuitry, preferably including a LVDT position sensor, is also used to determine braking load, a brake controller including circuitry for effecting displacement of one or more reciprocating rams to load a brake disk stack by a predetermined amount based on a present displacement value of the position signal obtained from the position sensor. The position sensor preferably includes a LVDT transducer connected between the reciprocating ram and a brake housing, and the motive device preferably includes a servo motor. Also provided is an actuator housing including a guideway for each ram, the guideway and ram having the same polygonal cross-section, whereby the ram nut is guided and restrained from rotation by the guideway as it is translated by a ball screw in threaded engagement with the ram nut for selective movement into and out of forceful engagement with the brake disk stack for applying and releasing braking force on a rotatable wheel. An electric motor is drivingly connected to each ball screw by a first gear integral with the ball screw, a second gear in mesh with the first gear, and a pinion on a rotating drive shaft of the electric motor.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
Disc brake for vehicle
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Control of brake noise by tuned mass dampers
InactiveUS20060266599A1Noise is producedImprove efficiencyNoise/vibration controlSlack adjustersTuned mass damperBrake pad
This invention relates to the braking system of a vehicle and a method to attenuate noise-producing vibrations of components of the braking system by the use of tuned mass dampers of various designs mounted with respect to the brake pads and / or damper plate of a disc brake system. In another embodiment, the tuned mass dampers are attached to the brake shoes and / or drum brake backplate of a drum brake system.
Owner:MATERIAL SCIENCES CORPORATION
Stereoscopic video magnification and navigation system
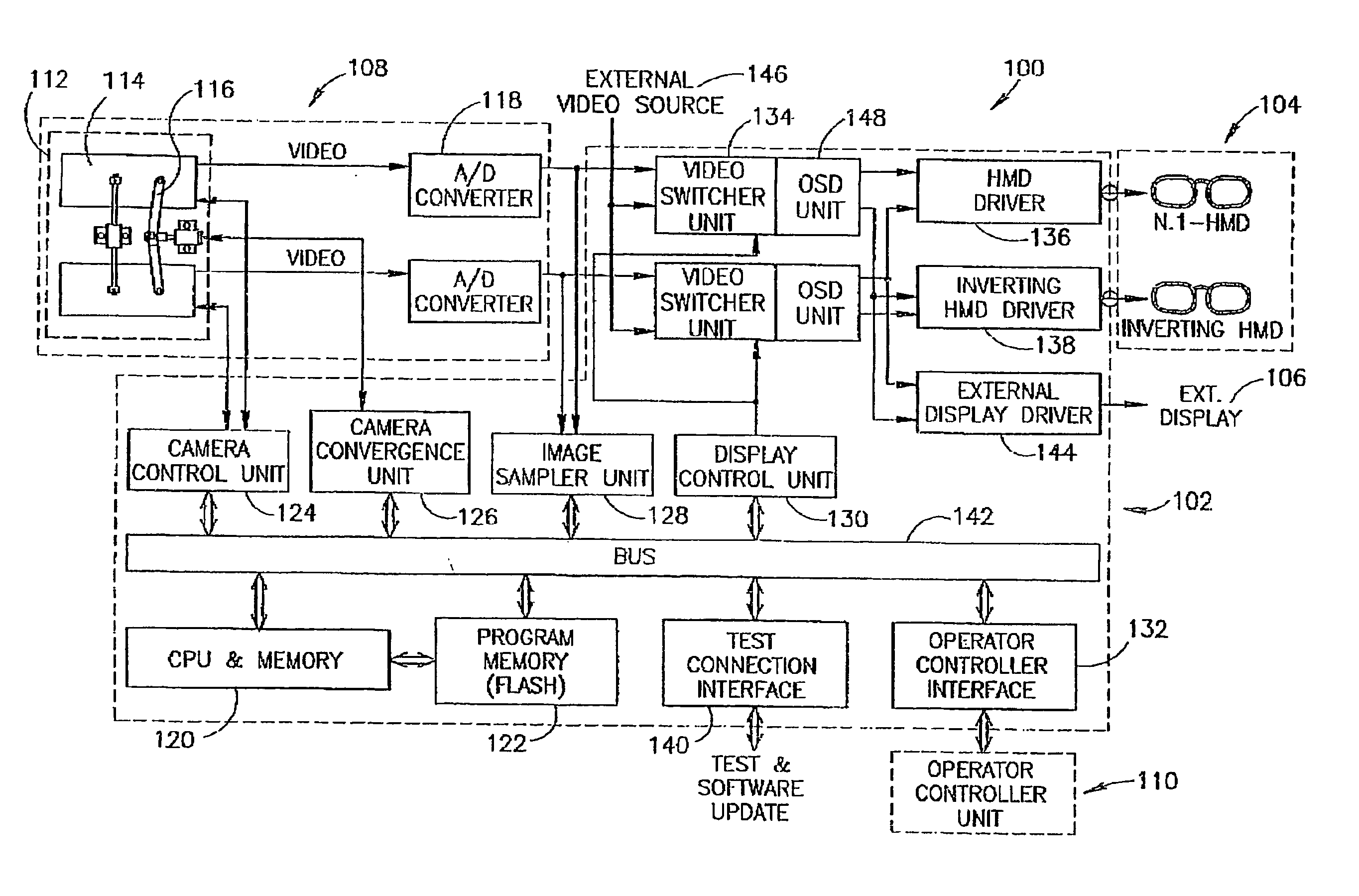
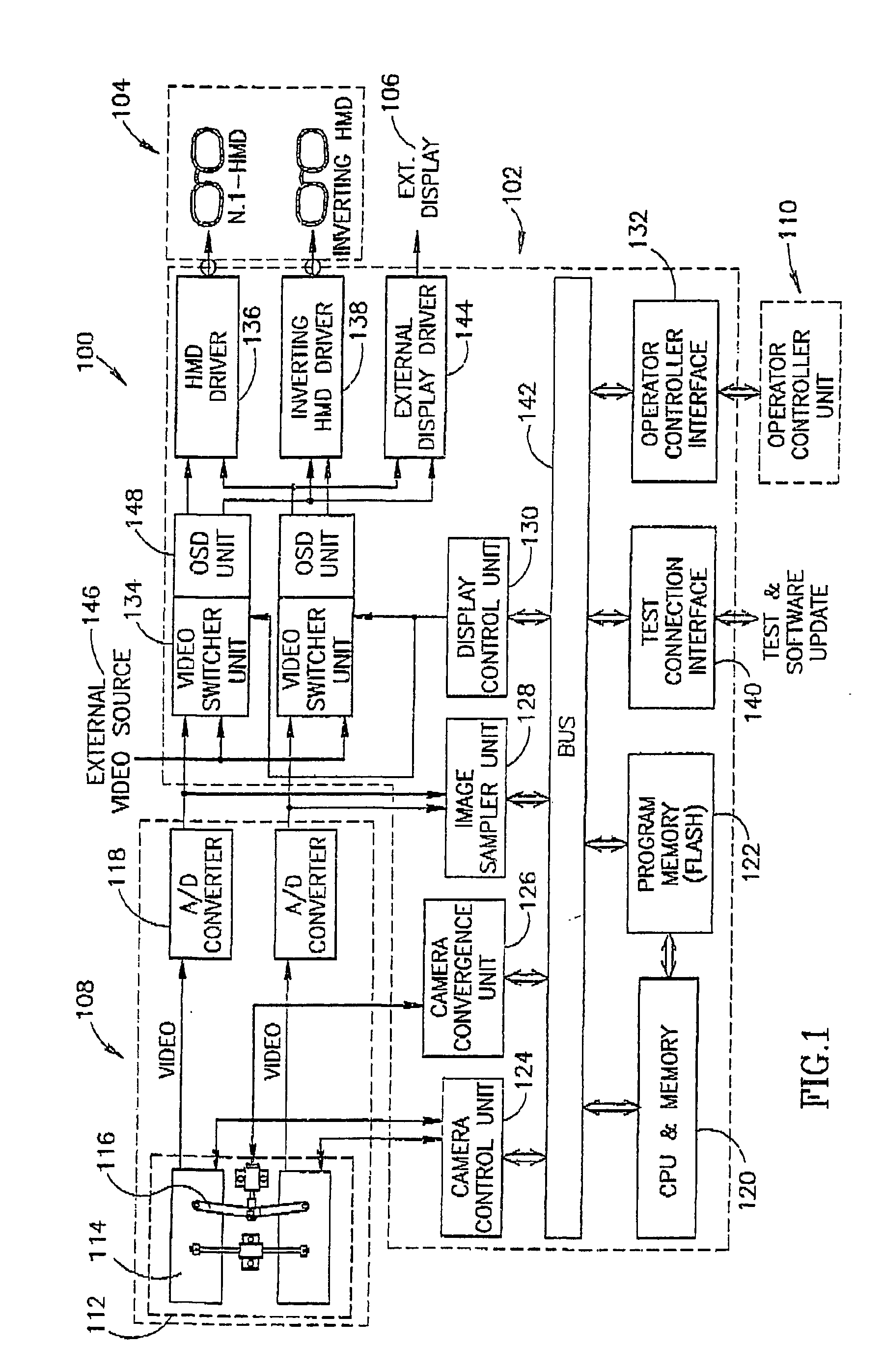
InactiveUS20050090730A1Accurate informationImprove ergonomicsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsStereoscopic videoDisplay device
An apparatus and method for providing stereoscopic magnified observation enabling an operator to perform surgical procedures without having to remove his eyes from the operating field comprising a head mounted display for provding the operator with stereoscopic magnified images in an operating field, a camera module for providing stereoscopic magnified images, an operator controller unit for enabling an operator to control the operation of the apparatus; and an interface processing unit for processing and dynamically presenting the stereoscopic magnified images in an operating field.
Owner:FRENI BREMBO SPA
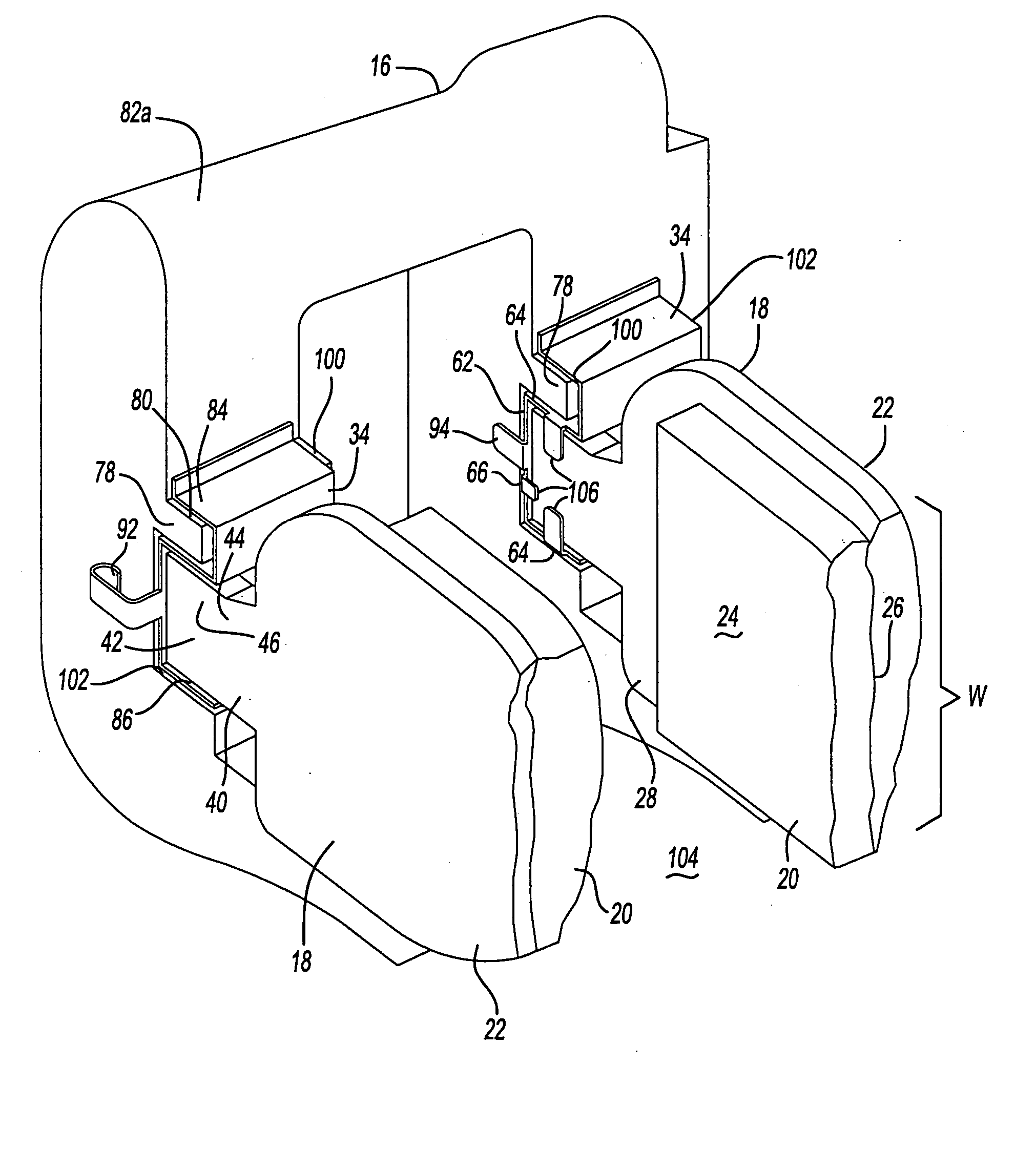
Multi-disk friction device selective lubrication on demand
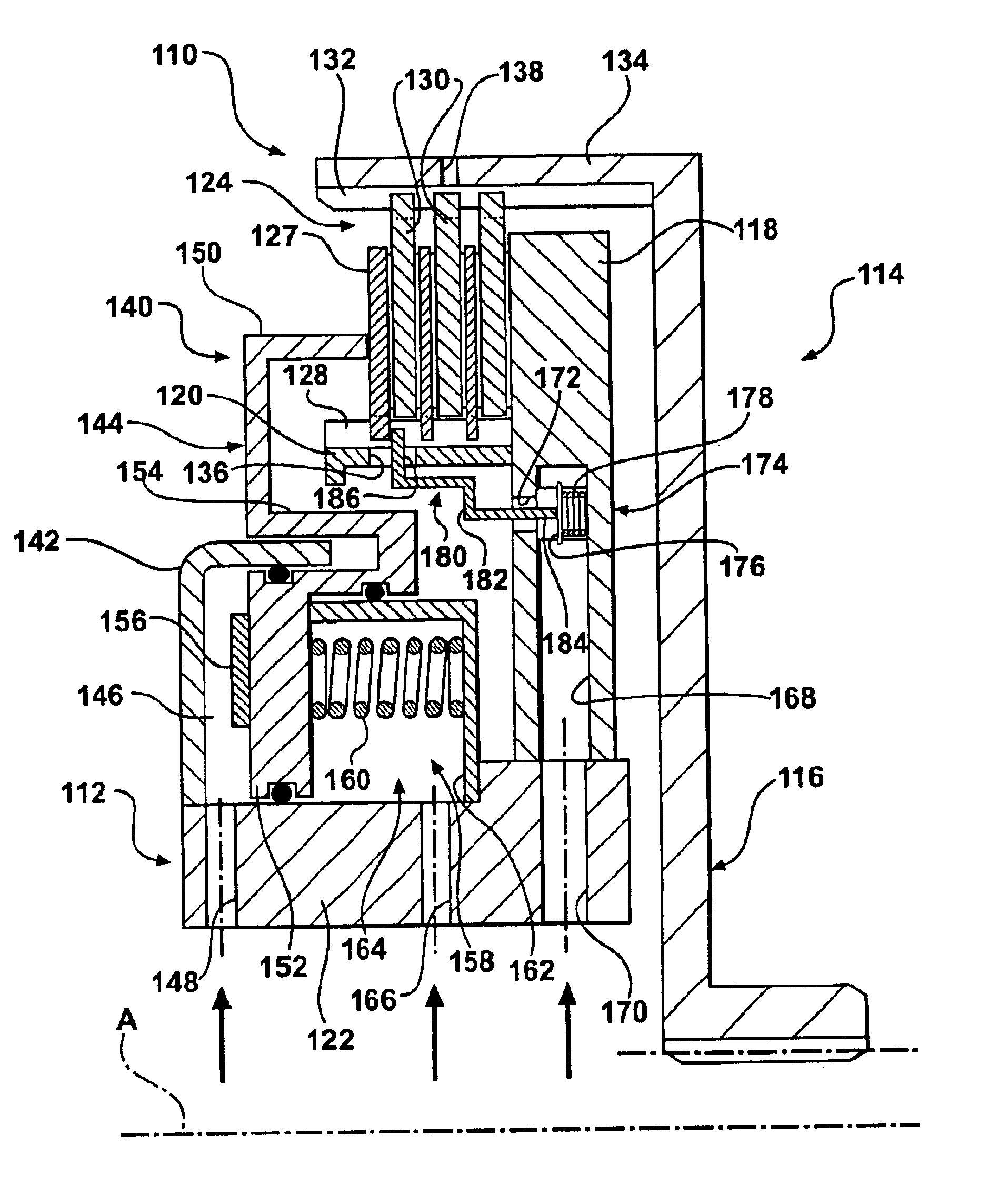
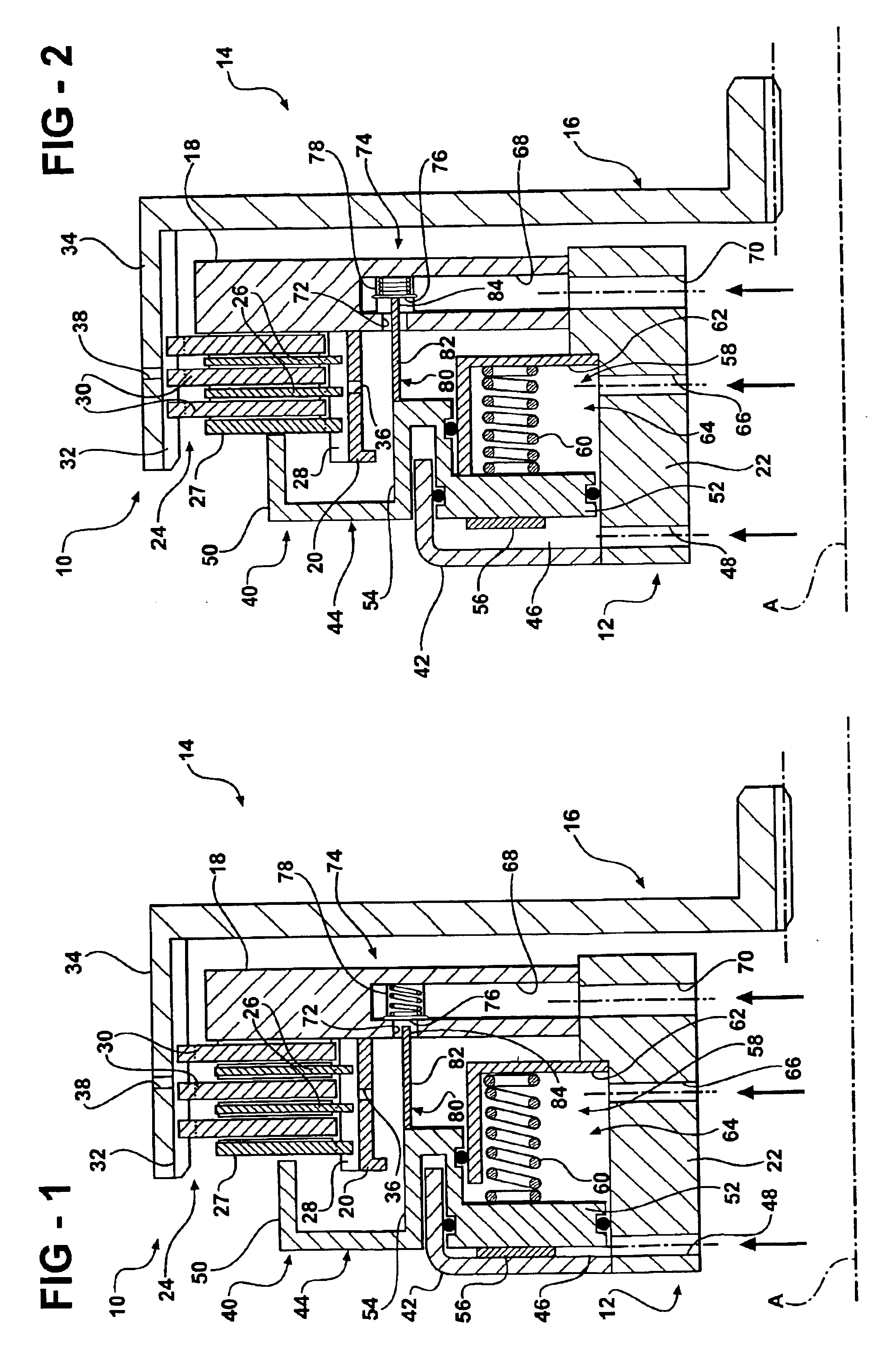
A friction device (10, 110) having a drive member (12, 112) and a driven member (14, 114) which define a clutch housing (16, 116) therebetween. A clutch pack (24, 124) is interposed between the drive and driven members and is operable to connect and disconnect the drive and driven members for transferring and interrupting torque therebetween. A control valve (74, 174) is supported in the clutch housing (16, 116) and is moveable between open and closed positions. The control valve (74, 174) is operable to control the flow of cooling fluid from the source to the clutch pack (24, 124). The friction device also includes an actuator (80, 180) that is operatively connected to either a piston assembly (40) or the clutch pack (124) and is adapted to engage the control valve (74, 174) such that movement of the piston assembly (40) from its disengaged position to its engaged position moves the control valve (74, 174) from its closed position to its open position to selectively allow flow of pressurized cooling fluid past the control valve (74, 174) and into contact with the clutch pack (24, 124) when the drive and driven members are connected.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
Brake assembly with tuned mass damper
InactiveUS7032723B2Effective dampingEasily damagedNoise/vibration controlBraking membersSnubberTuned mass damper
A tuned mass damper for sound-dampening brake squeal noise is located within a hole formed in a brake component such as a backplate supporting a brake pad. The location of the hole and the weight and geometry of the tuned mass damper are tailored to provide effective damping for the particular frequencies that are to be eliminated in the brake system. Locating the tuned mass damper inside of a hole in the component has packaging and manufacturing advantages, and results in a tuned mass damper that is less susceptible to damage when in use. The hole may be blind, the bottom of the hole being thin enough to serve as a spring member to which a vibration damping mass is attached. In one embodiment, the tuned mass damper is a module adapted for insertion into the hole in the brake backplate. Contact between the module and inner surfaces of the hole transfers mechanical vibration of the backplate to the tuned mass damper.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Pad retraction device
InactiveUS8397880B2Constant forceRemove debrisSnap fastenersAxially engaging brakesBiomedical engineeringBody segment
A clip comprising: a body portion; one or more arms connected to the body portion and projecting away from the body portion; a deformable portion of the one or more arms that is distal from the body portion; and a lip on the one or more arms that is proximate to the body portion.
Owner:AKEBONO BRAKE
Pad spring of disc brake and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20090277729A1Relieve stressReduce vibrationMetal rolling stand detailsCoatingsVehicle frameEngineering
Disclosed are a pad spring of a disc brake, which guides the sliding motion of pad plates and reduces vibration transmitted from the pad plates to a carrier concurrently, and continuously maintains these functions for a long time, and a method for manufacturing the same. In a pad spring of a disc brake, in which a pair of pad plates sliding towards a disc is accommodated in a carrier fixed to a vehicle frame such that friction pads are respectively attached to the facing inner surfaces of the pad plates so as to press both surfaces of the disc rotated together with the rotation of a wheel and thus fix the disc, and pad springs for guiding the sliding motion of the pad plates and preventing vibration applied to the pad plates from being transmitted to the carrier are interposed among the pad plates and the carrier, one surface of the pad spring contacting the pad plates is coated with a low frictional material and the other surface of the pad spring contacting the carrier is coated with an elastic material.
Owner:KIM DOE HEE
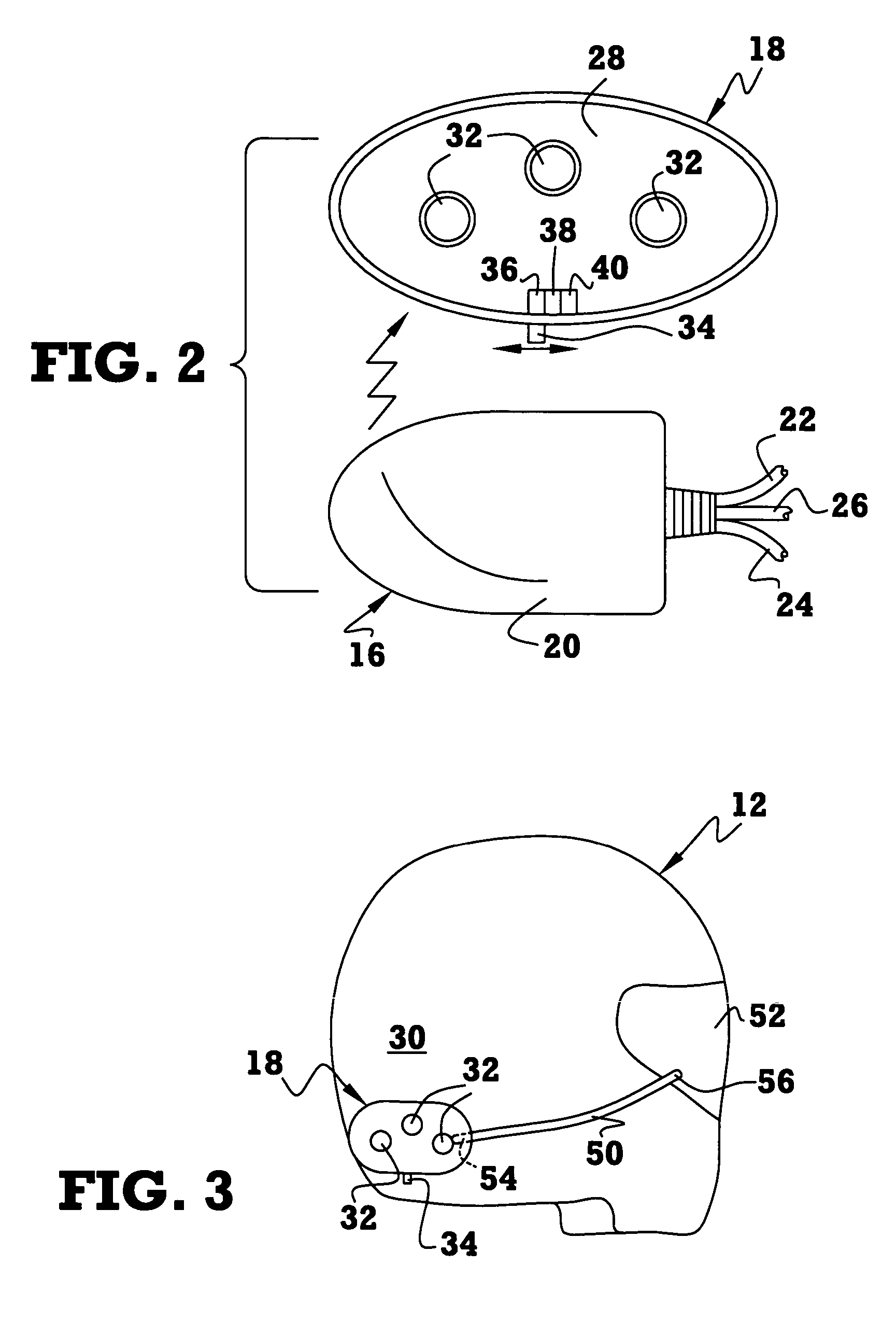
Brake light warning system for safety helmets and method of operation
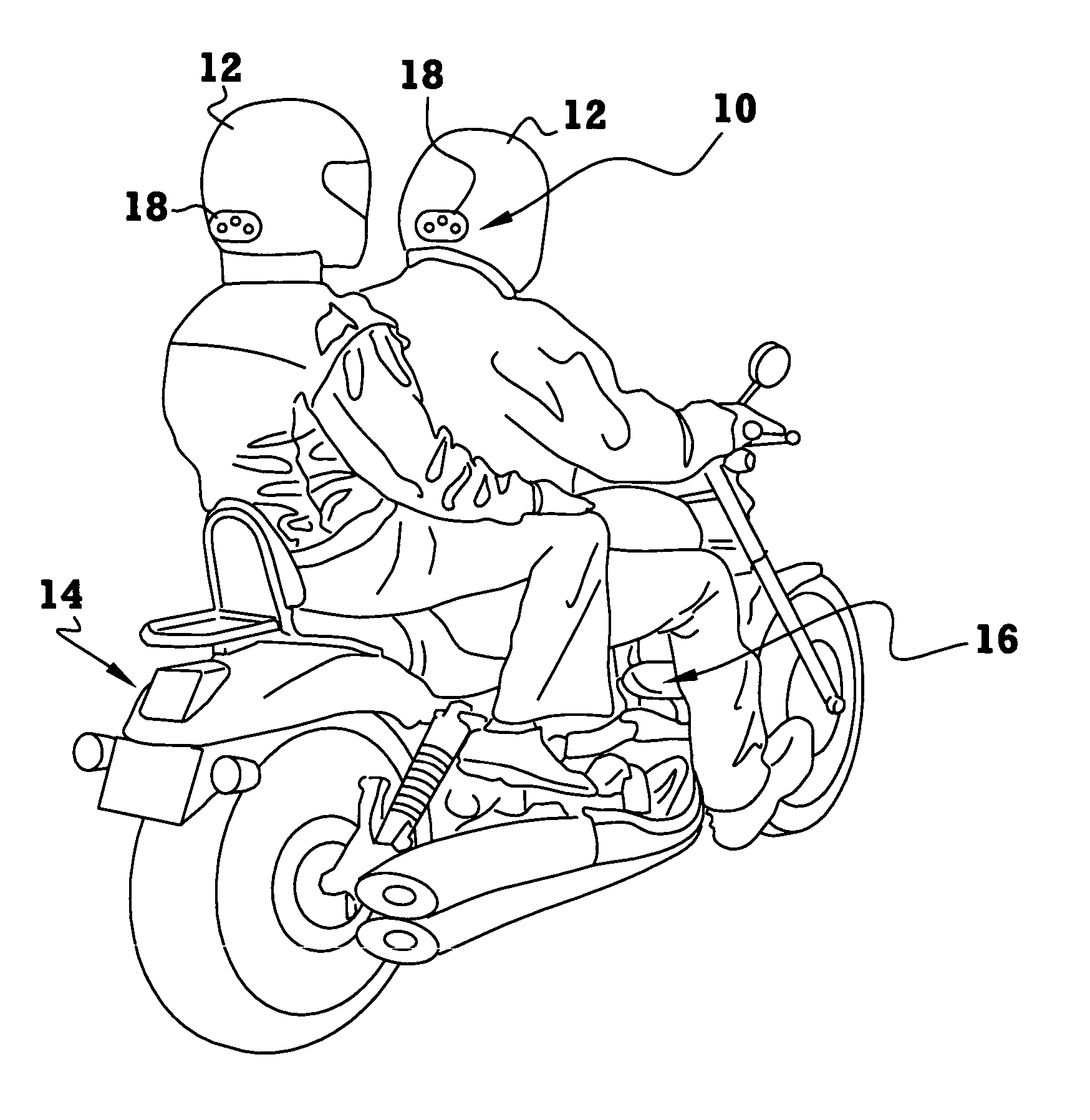
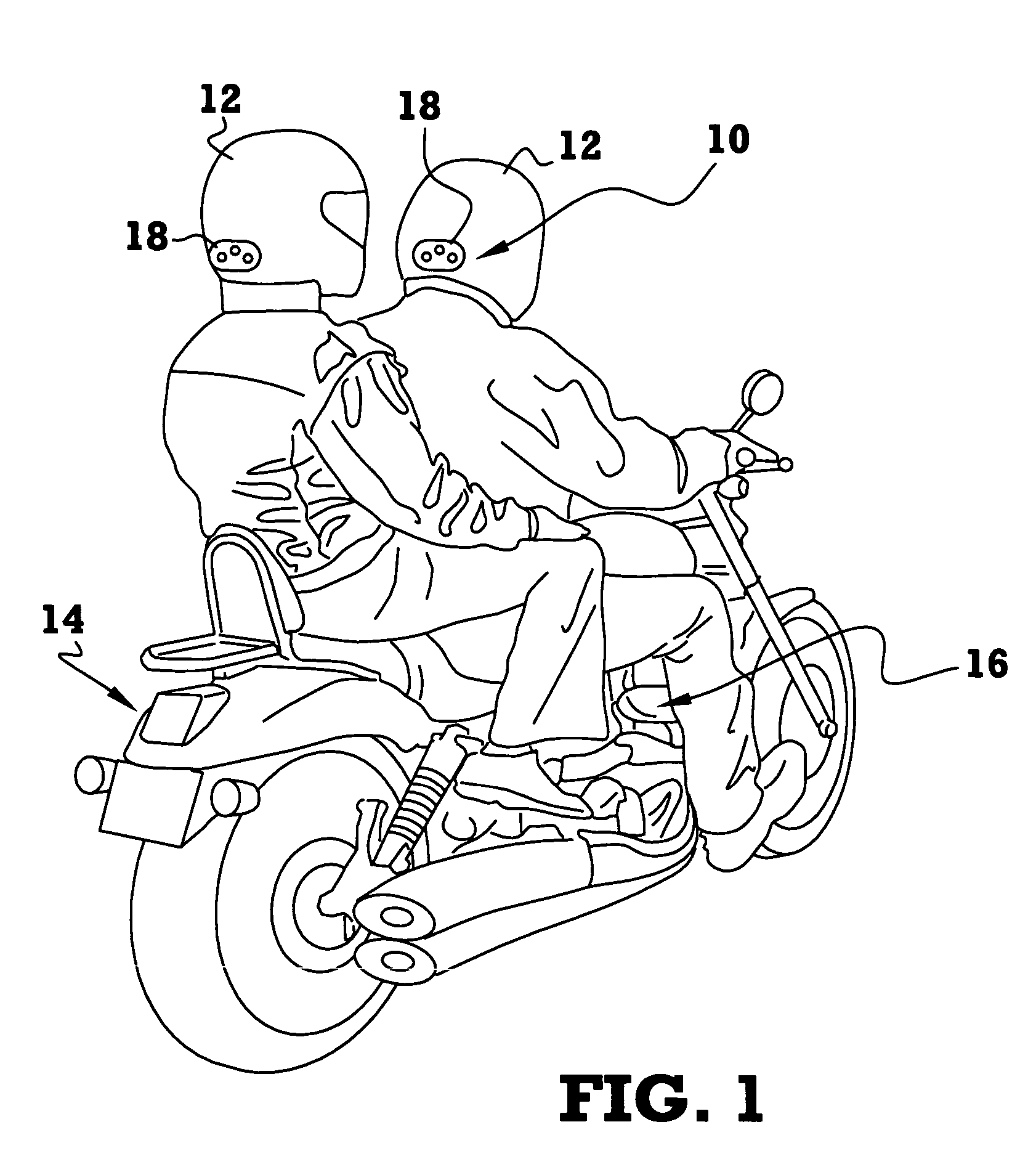
A brake light warning system for safety helmets includes a transmitter module adapted for mounting to a vehicle, such as a motorcycle, and a receiver module adapted for mounting to a safety helmet. The transmitter module is configured to continuously transmit a transmission signal when a brake of the vehicle is disengaged and discontinue transmission of the transmission signal when a brake of the vehicle is engaged. The receiver module is configured to detect a presence or absence of the transmission signal from the transmitter module. The receiver module has at least one light generating element that illuminates or increases in brightness upon detection of the absence of the transmission signal to indicate that the vehicle brake is engaged.
Owner:COMPONENT CONCEPTS LLC
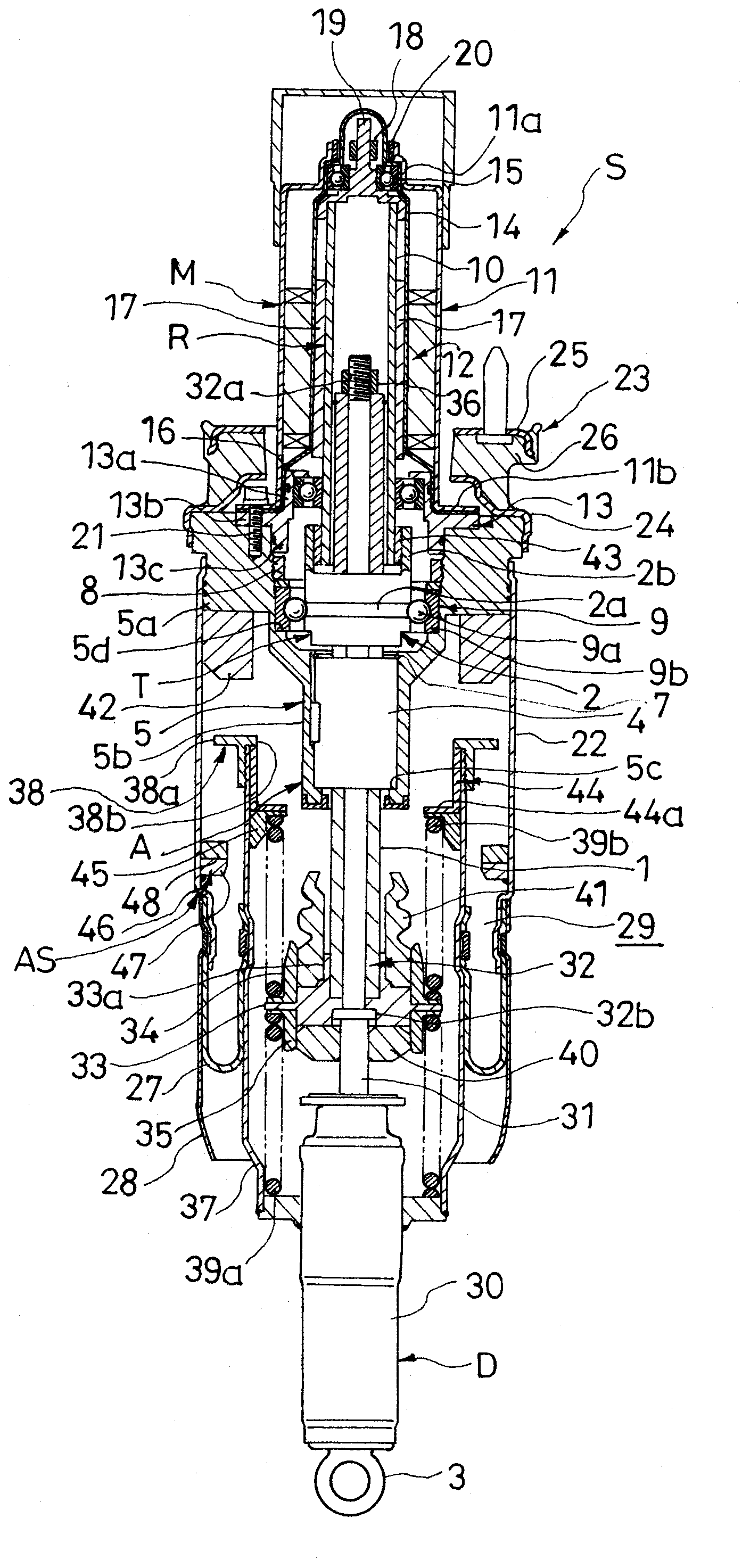
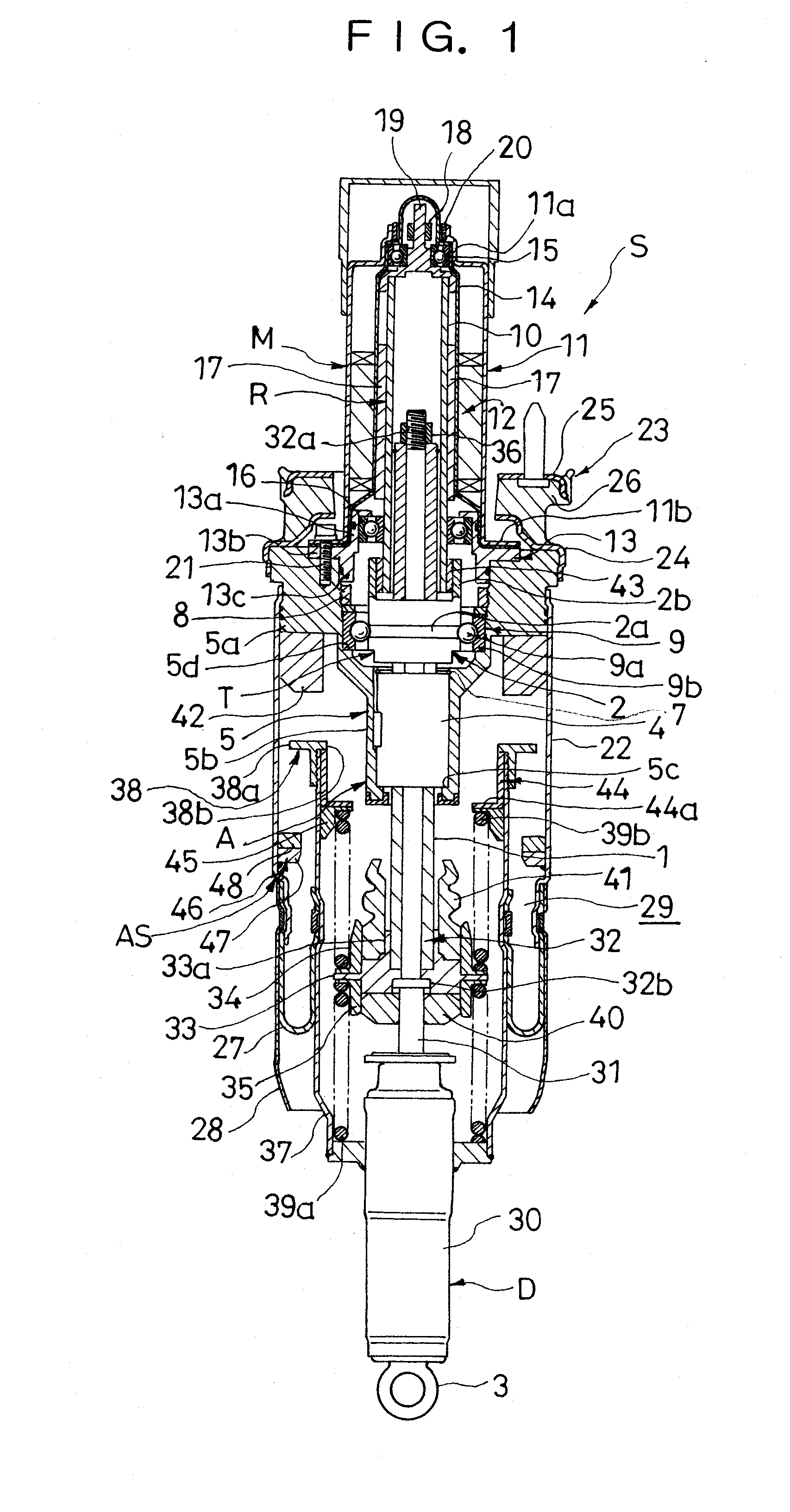
Suspension device
ActiveUS20090321201A1Weight moreReduce overall outer diameterLiquid resistance brakesSpringsLinear motionAir spring
According to problem solving means of the present invention, in a suspension device (S) comprising a motion transforming mechanism (T) for transforming a linear motion of a linear motion member (1) into a rotational motion of a rotating member (2) and a motor (M) connected to the rotating member (2) in the motion transforming mechanism (T), an air spring (AS) is provided, the air spring (AS) including a tubular air chamber (22) connected to the motor (M), an air piston (37) connected to the linear motion member (1) and being tubular and smaller in diameter than the air chamber (22), and a diaphragm (27) interposed between the air chamber (22) and the air piston (37), a stopper (38a) is provided on an outer periphery of the air piston (37), and a stopper seat (46) is provided on an inner periphery of the air chamber (22) so as to be put in abutment against the stopper (38a) upon maximum extension of the suspension device involving relative separation of the air chamber (22) and the air piston (37) with respect to each other.
Owner:KYB CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com