Patents
Literature
746results about "Mechanically actuated brakes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
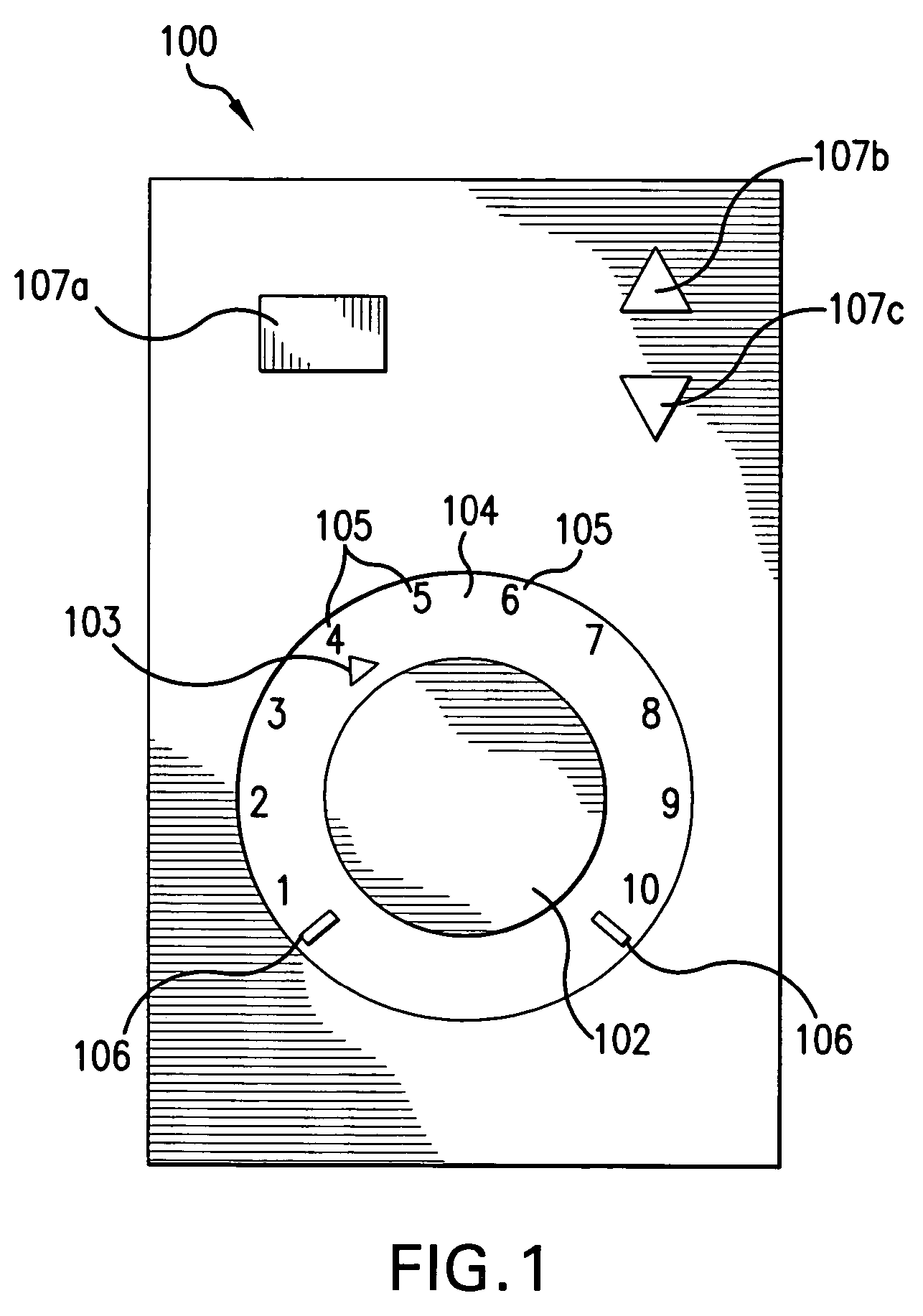
Miter saw with improved safety system
InactiveUS6945148B2Increase opportunitiesLimit and even prevent injuryOther plywood/veneer working apparatusMechanically actuated brakesEngineeringMechanical engineering
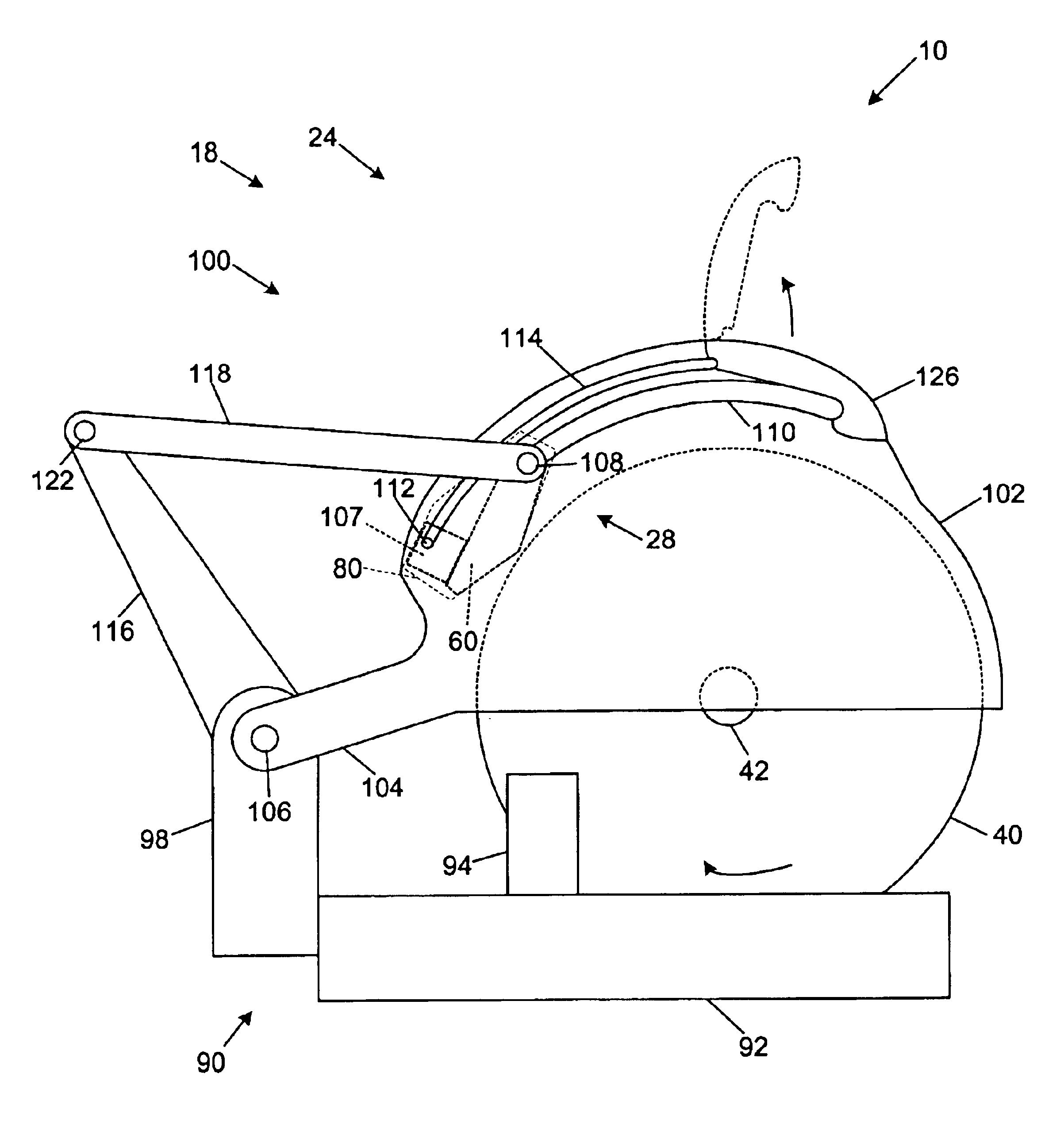
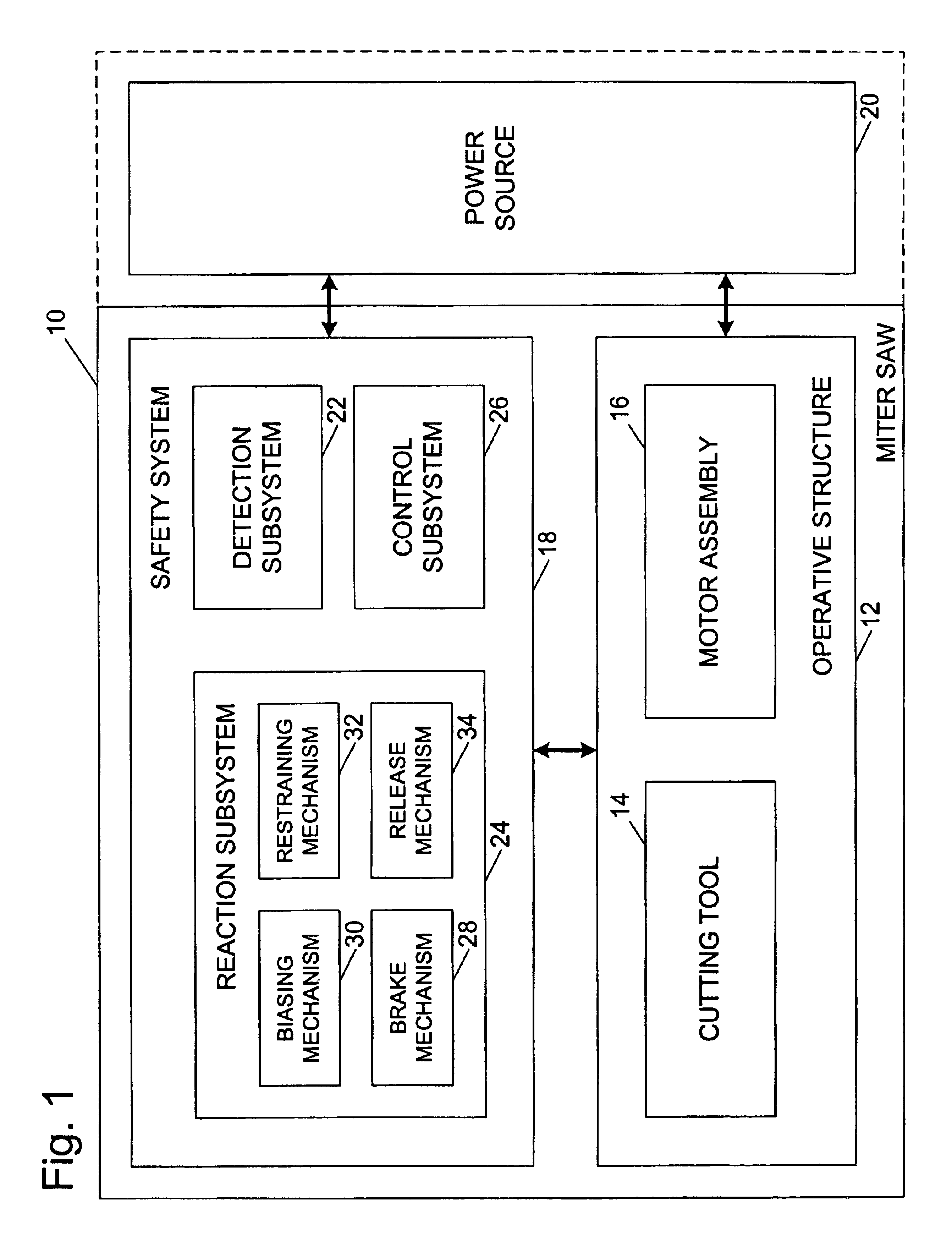
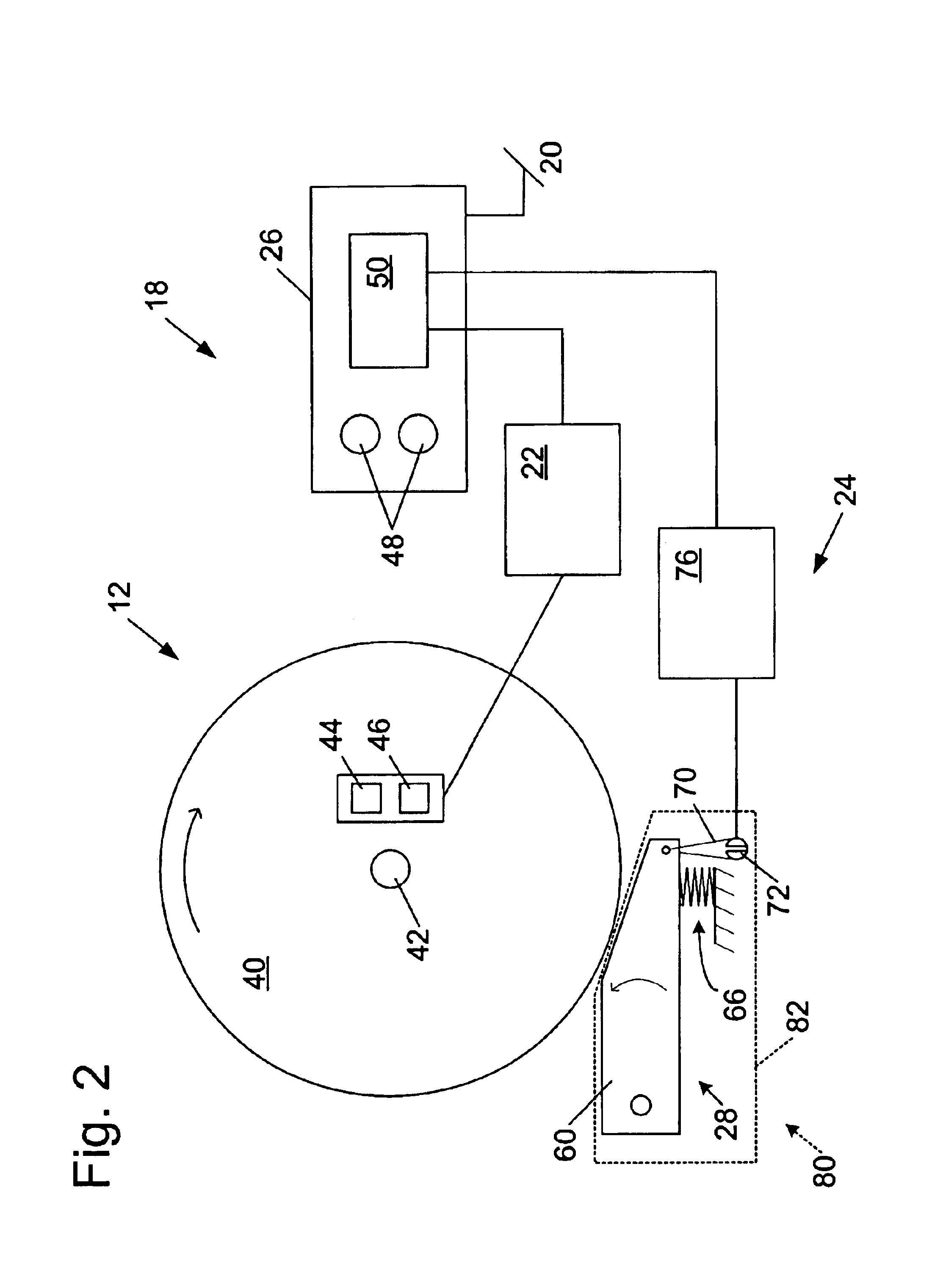
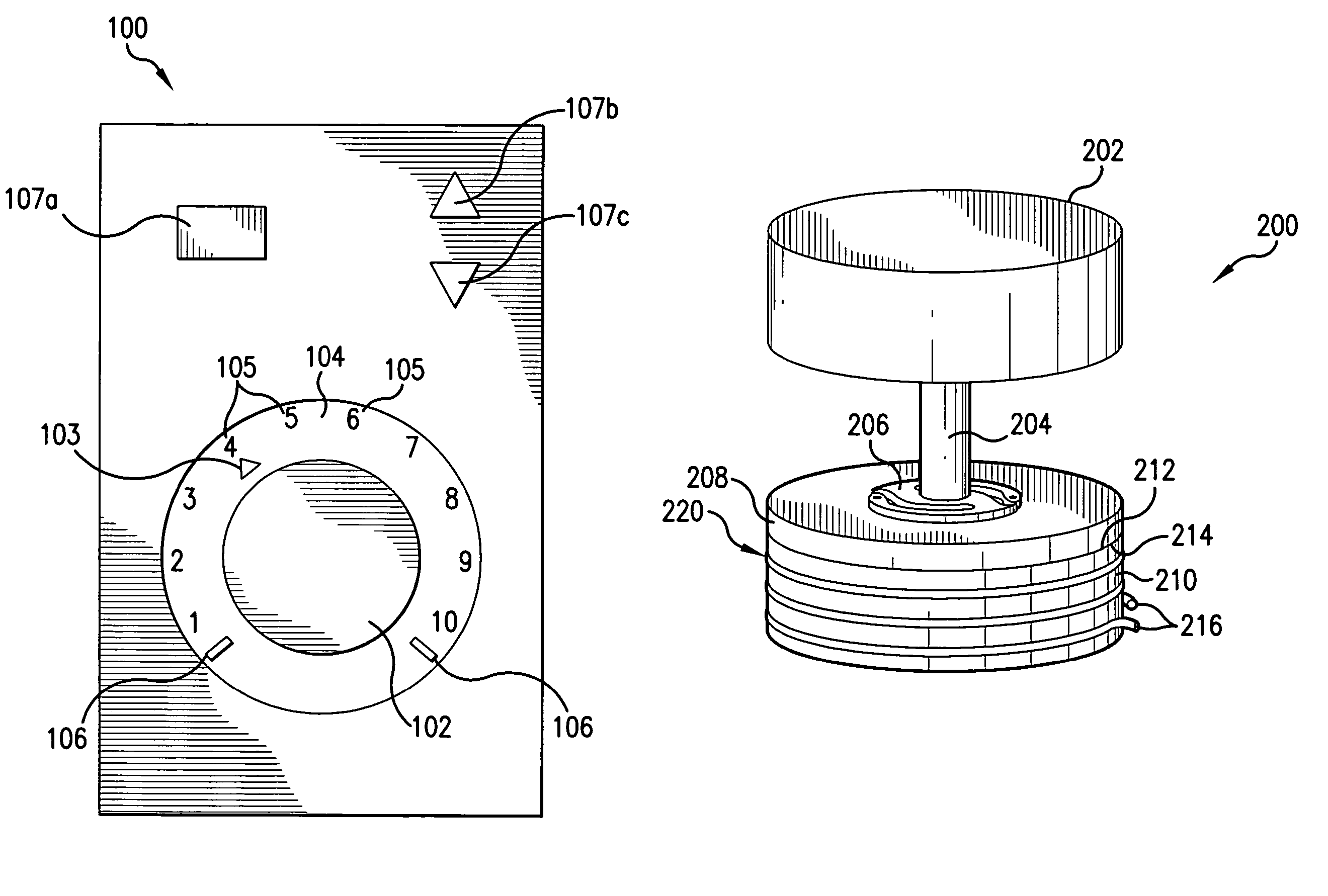
A miter saw is disclosed having a base, a blade supported by the base, a detection system adapted to detect a dangerous condition between a person and the blade, and a reaction system associated with the detection system to cause a predetermined action to take place upon detection of the dangerous condition. The blade is rotatable, and moves into a cutting zone to cut a workpiece. The predetermined action may be to stop the blade from rotating, to create an impulse against movement of the blade into the cutting zone, or to cause the blade to move away from the cutting zone.
Owner:SAWSTOP HLDG LLC
Systems and methods for providing a haptic device
ActiveUS8002089B2Degree of rotationControlling membersDynamo-electric brakes/clutchesEngineeringActuator
Systems and methods for providing a haptic device are described. In one described system, a first brake surface of a first element contacts a second brake surface of a second element. At least one actuator is configured to exert a force on at least one of the first and second elements. A flexure is coupled to at least one of the first element, the second element, a housing, a manipulandum, and a shaft coupled to the manipulandum. The flexure provides a degree of rotational flexibility to the manipulandum when the at least one actuator exerts the force. The described system may include a processor in communication with the at least one actuator for providing the haptic effects.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
Hybrid electric linear actuator
InactiveUS6982502B1Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMechanical actuated clutchesElectric machinePermanent magnet synchronous motor
A hybrid linear actuator features a central load shaft on which a plurality of solid-state magnetostrictive thrusters are positioned in operative relation to electric motors of a permanent magnet synchronous type to impart linear thrust force to the load shaft through clutch units also positioned thereon and under control of force and stroke amplification of output force from motor shafts projecting from the motors.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
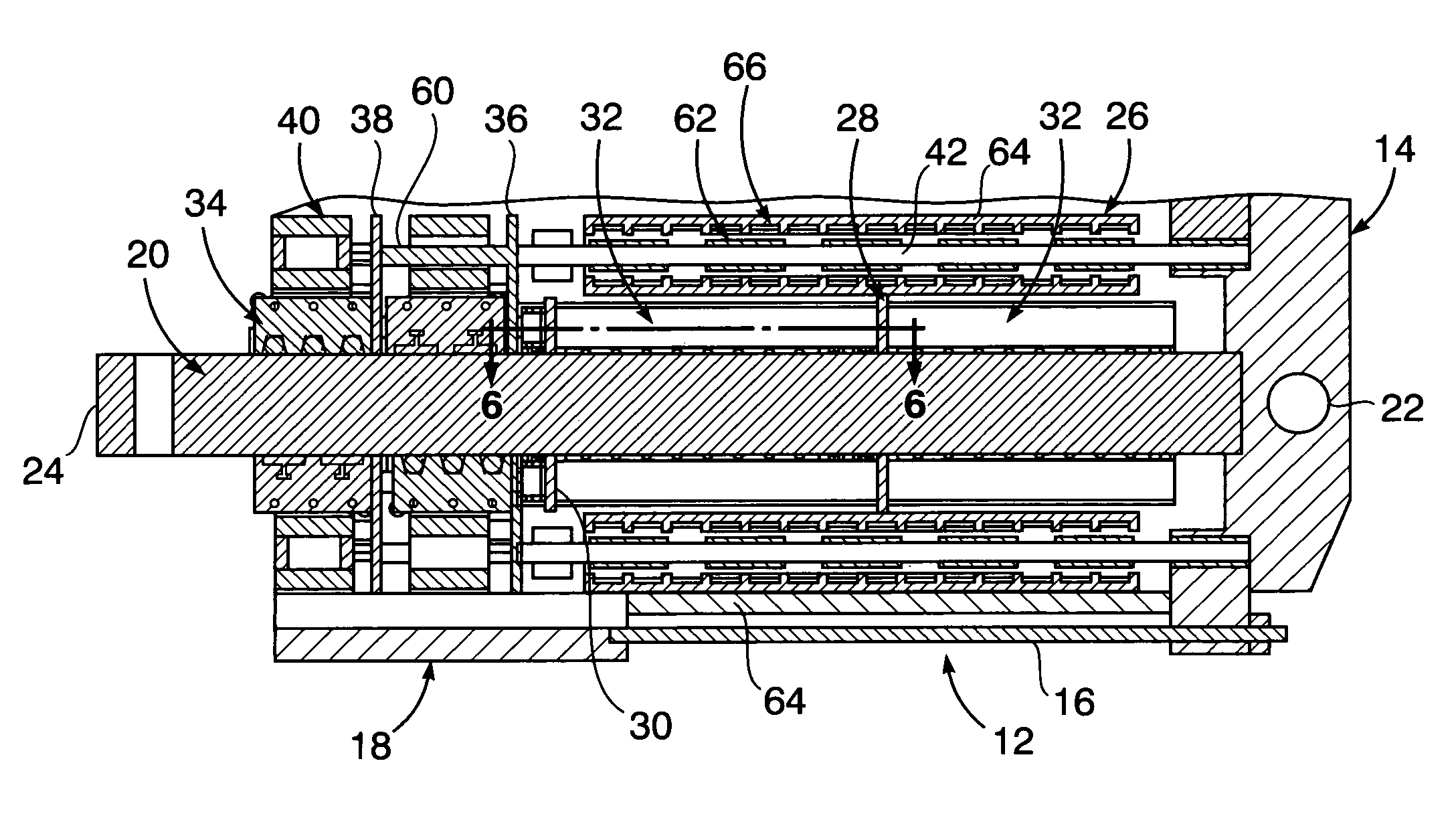
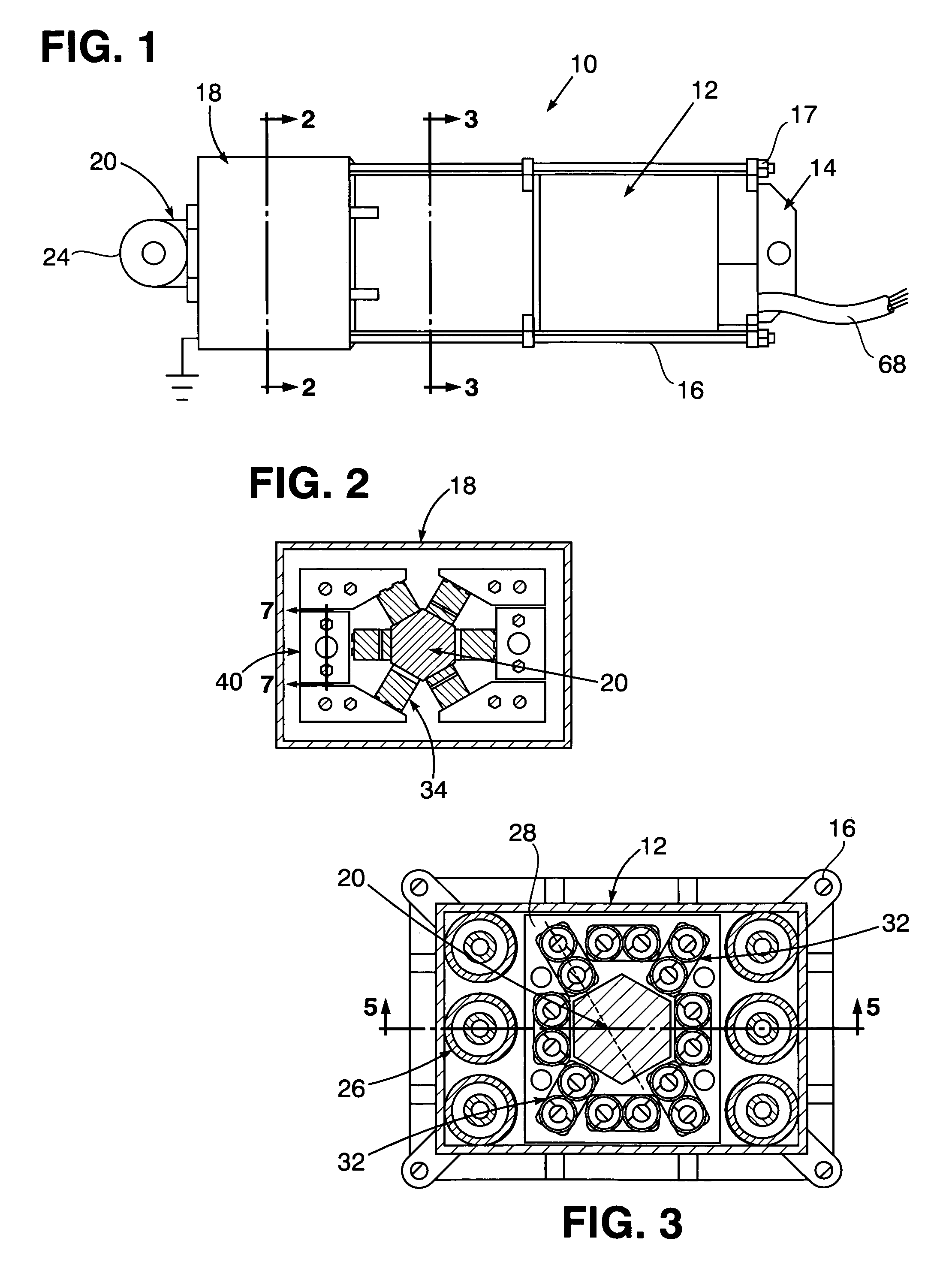
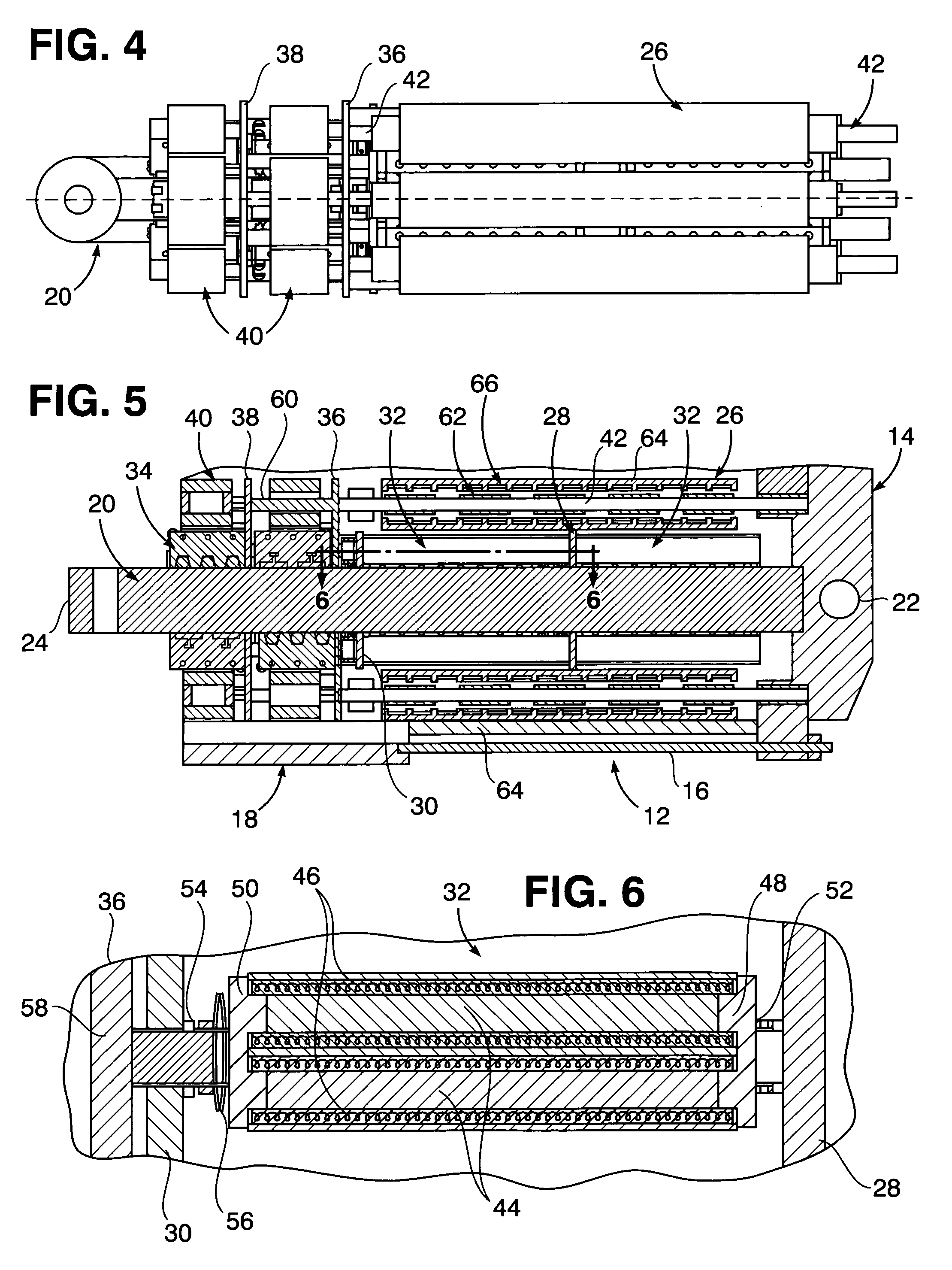
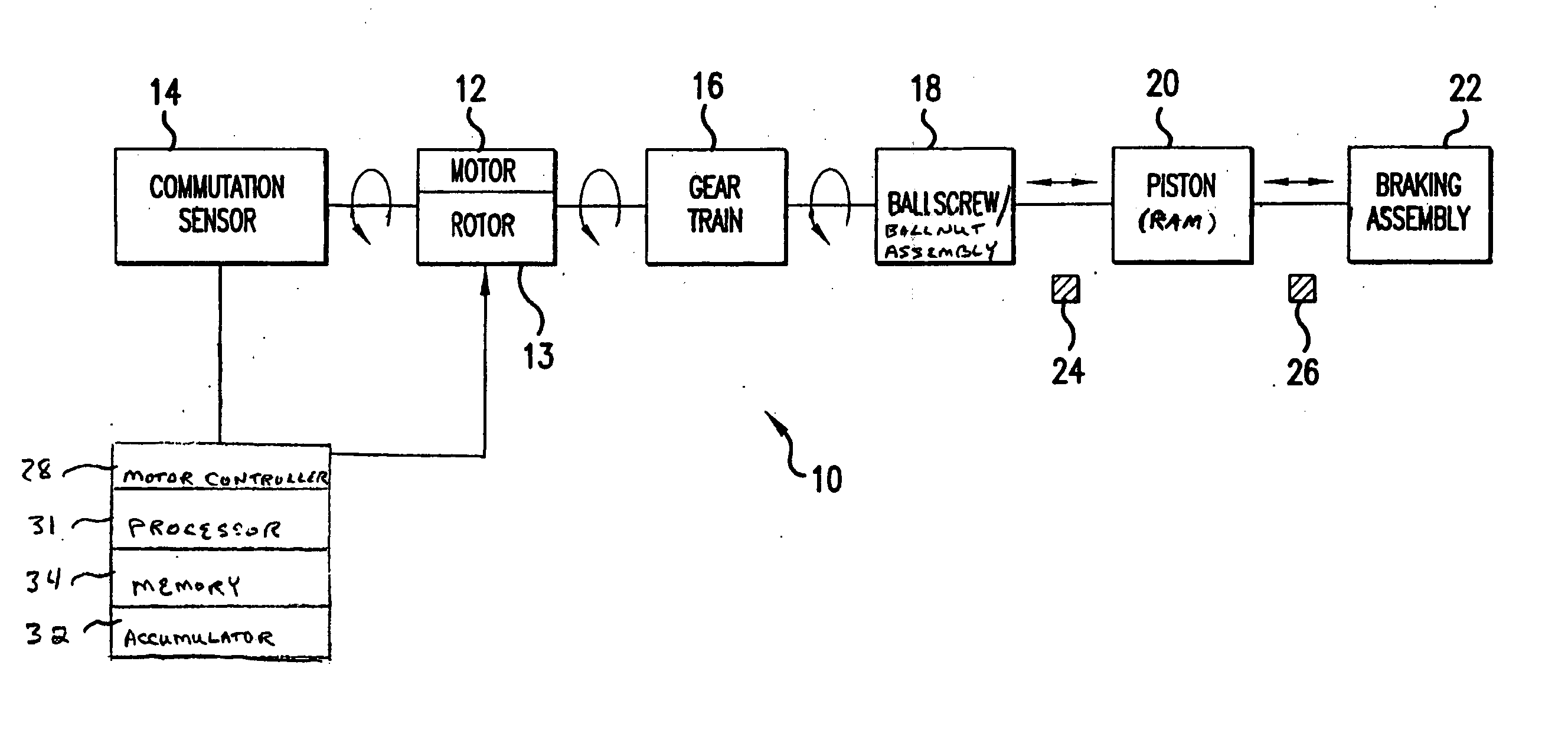
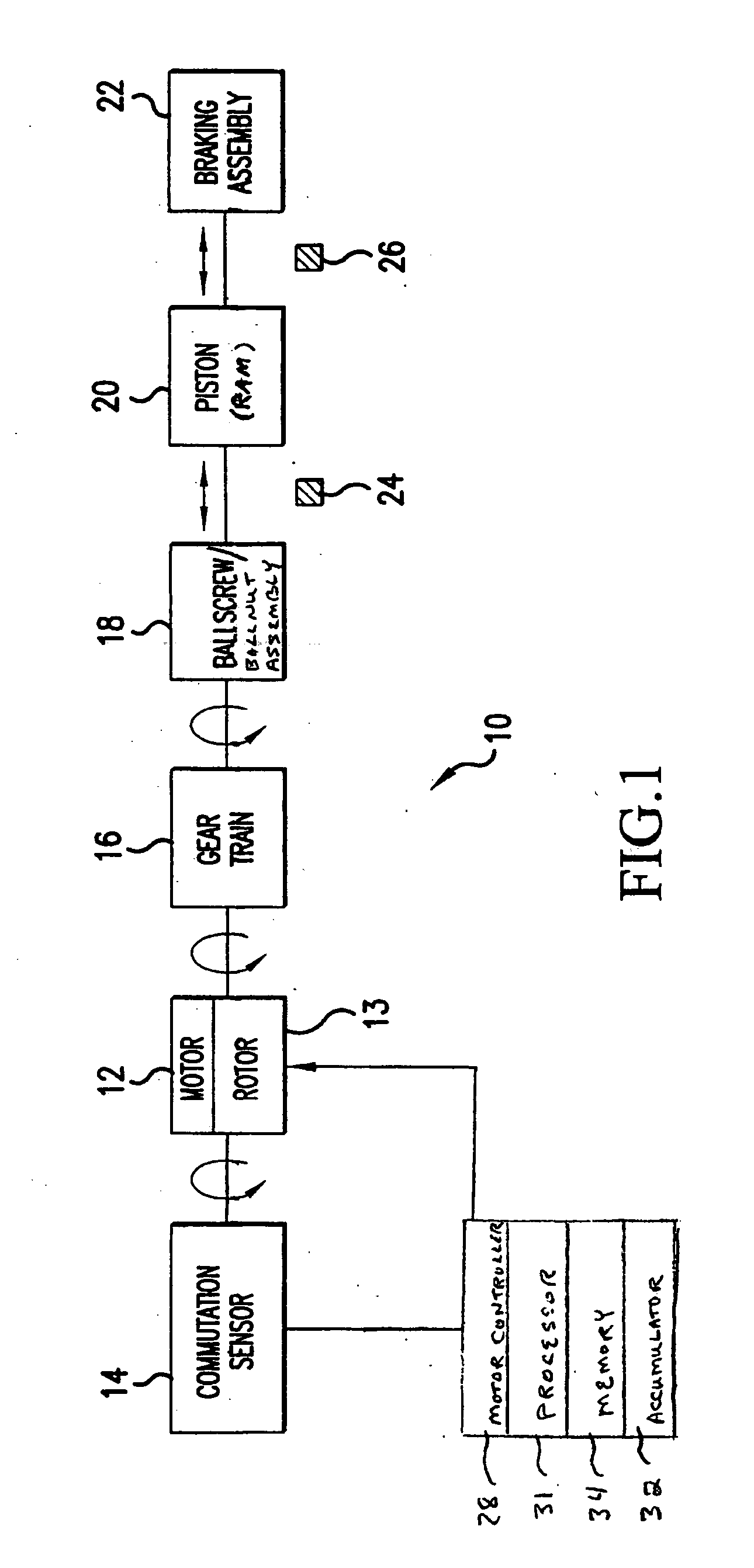
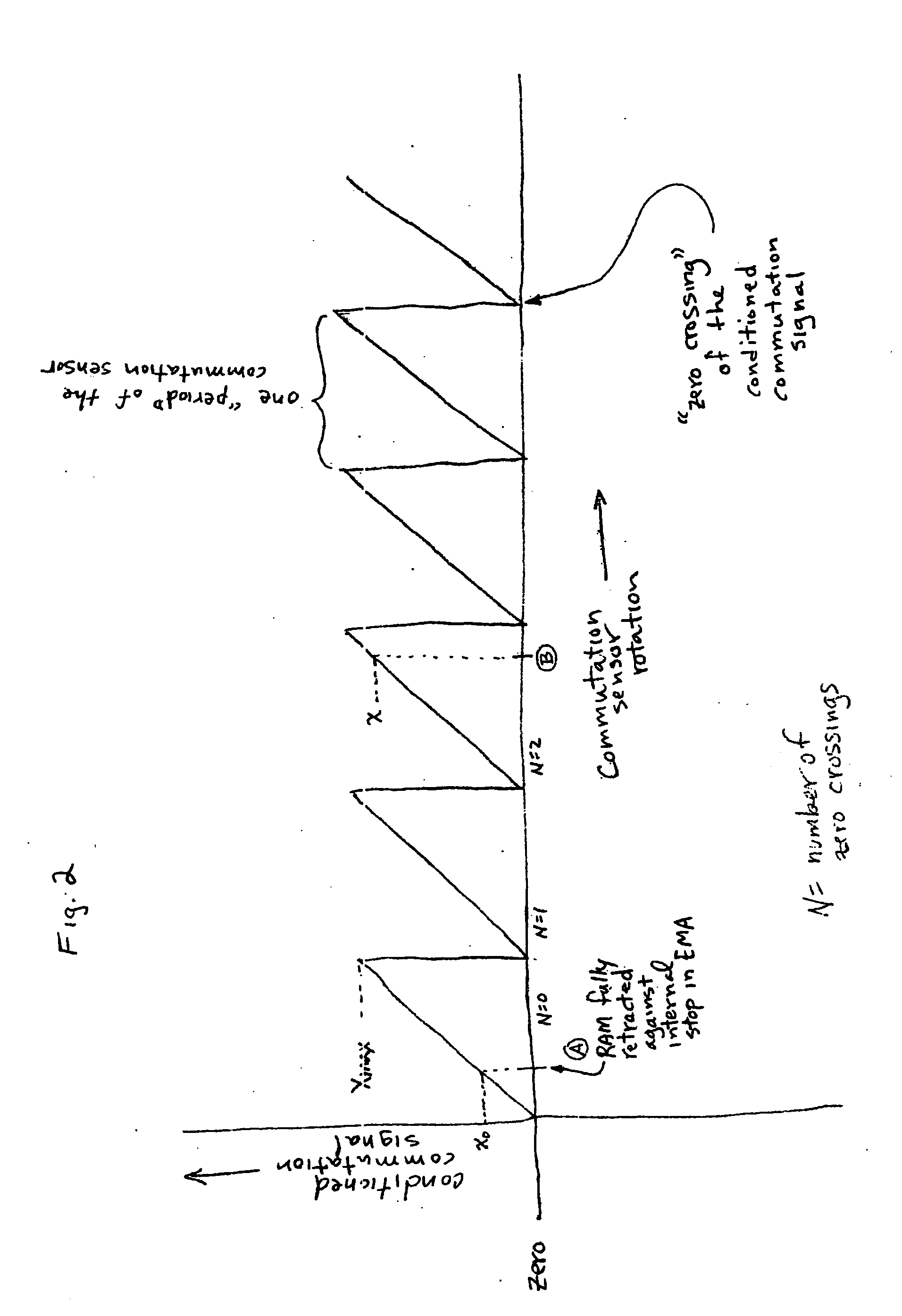
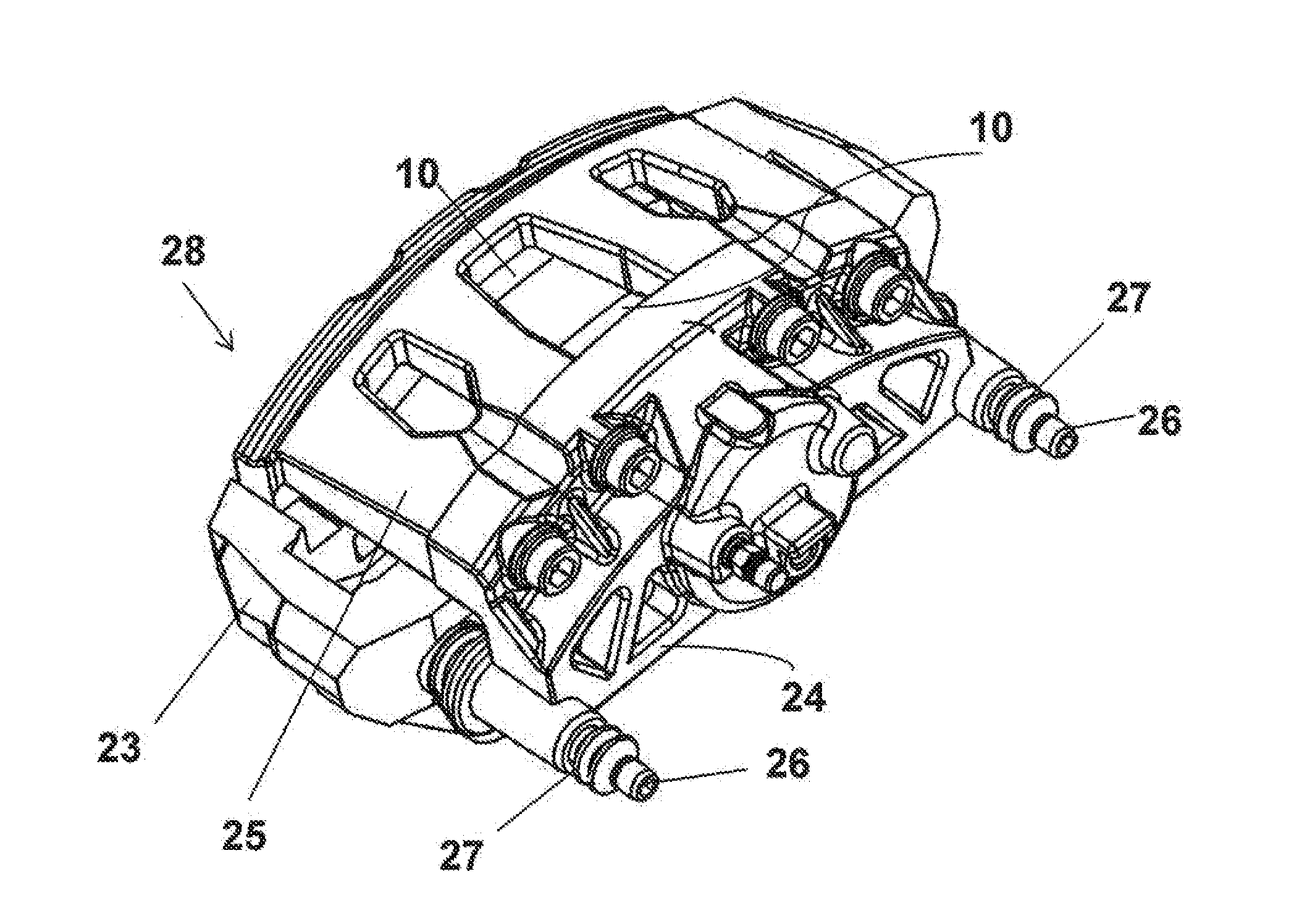
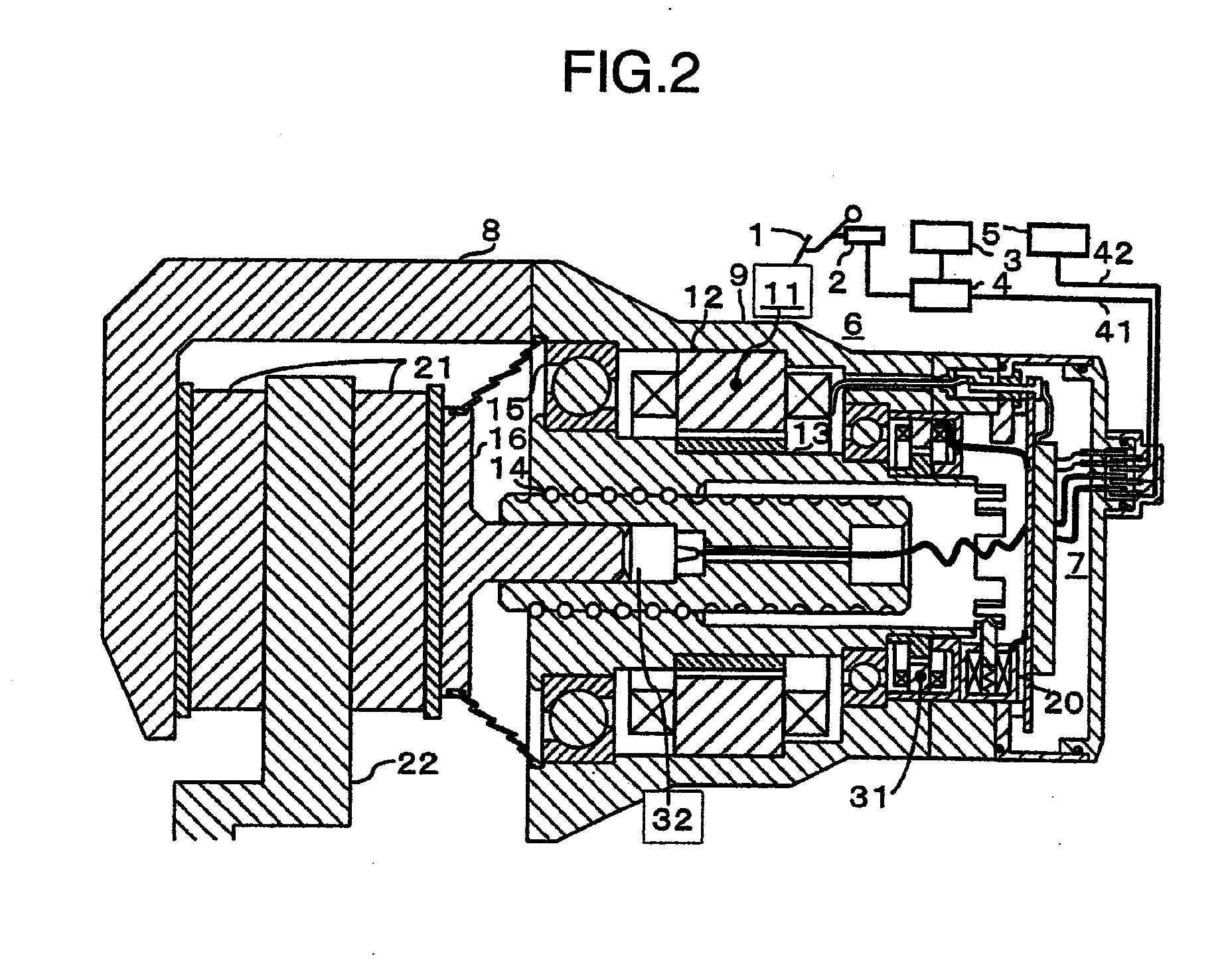
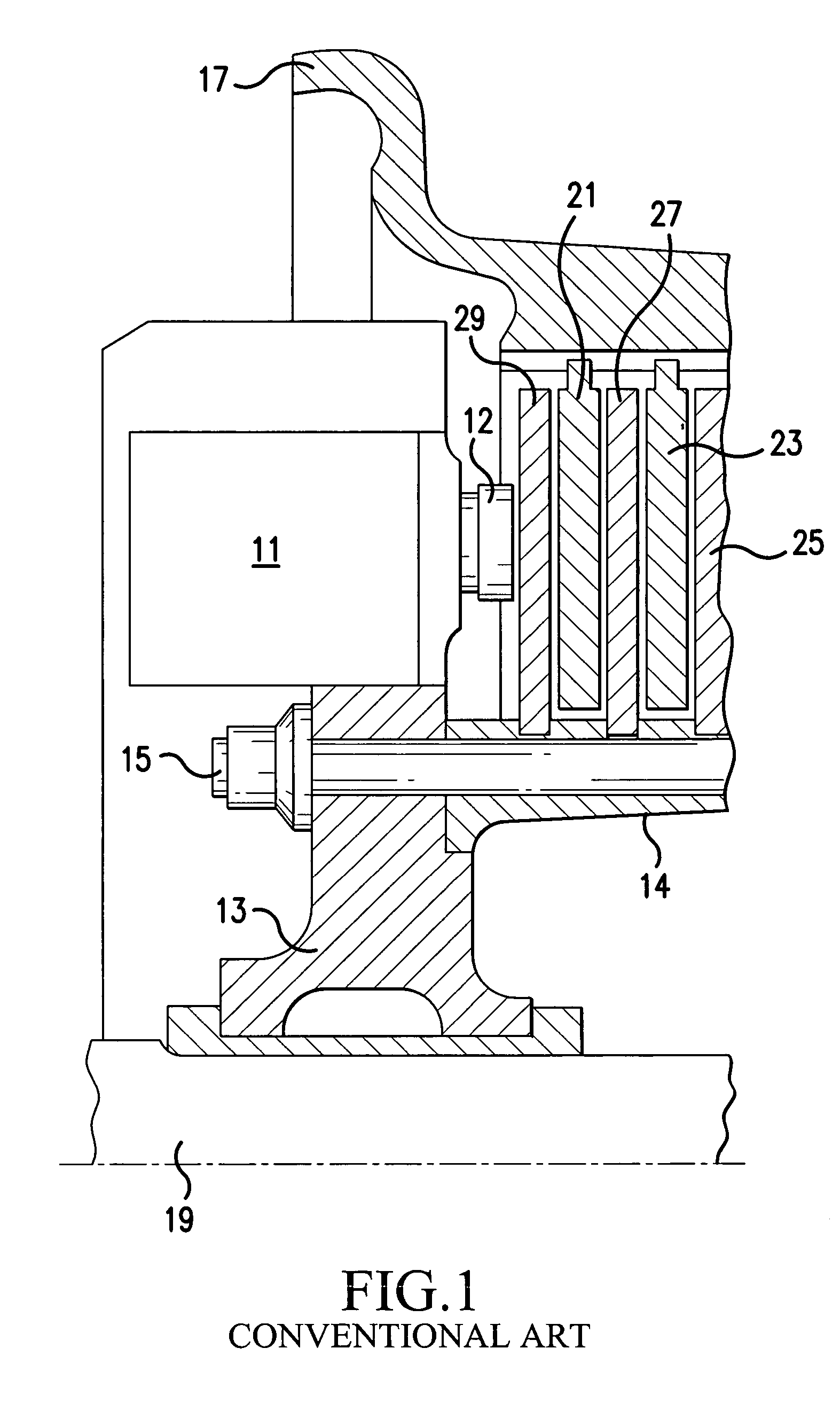
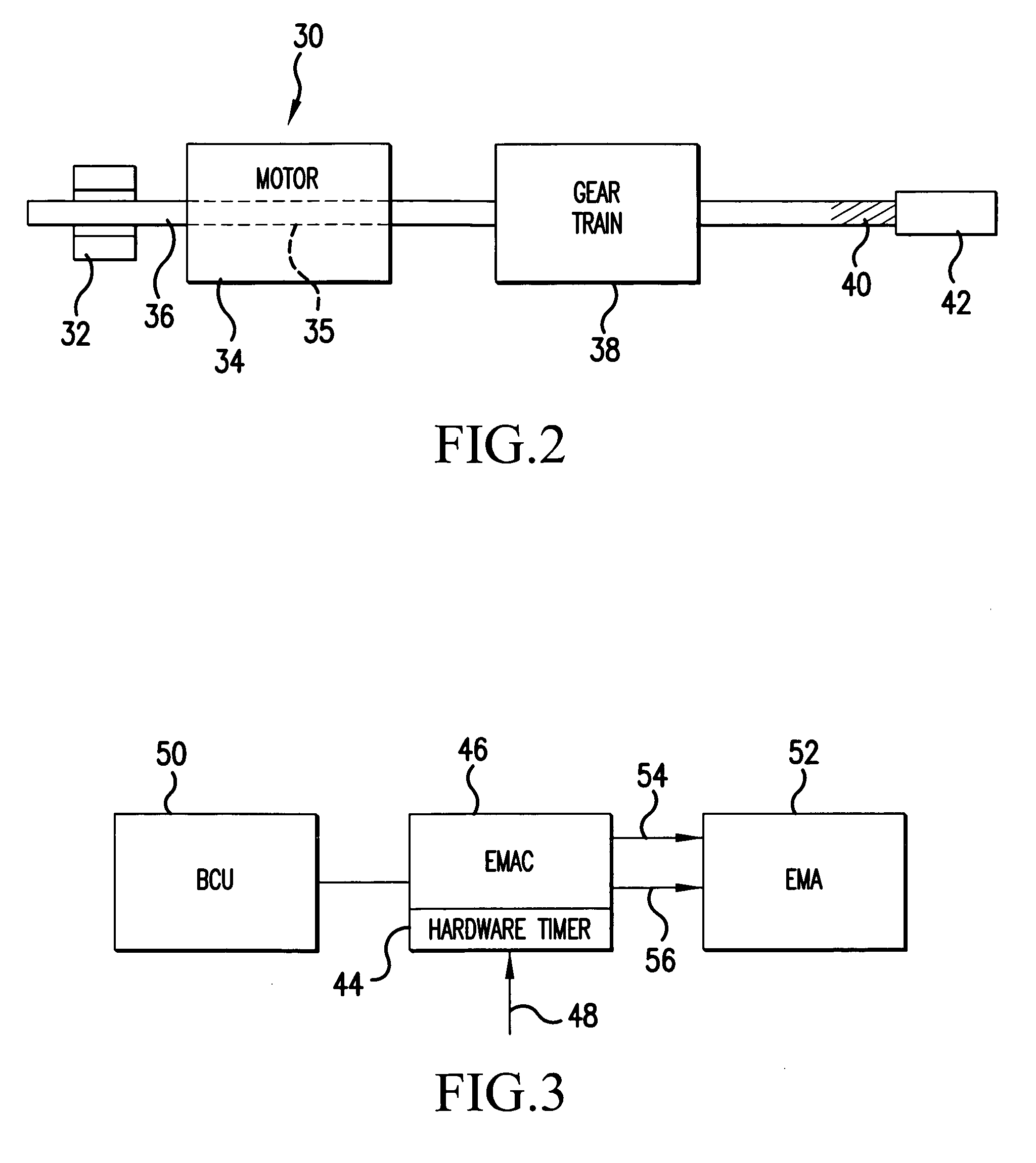
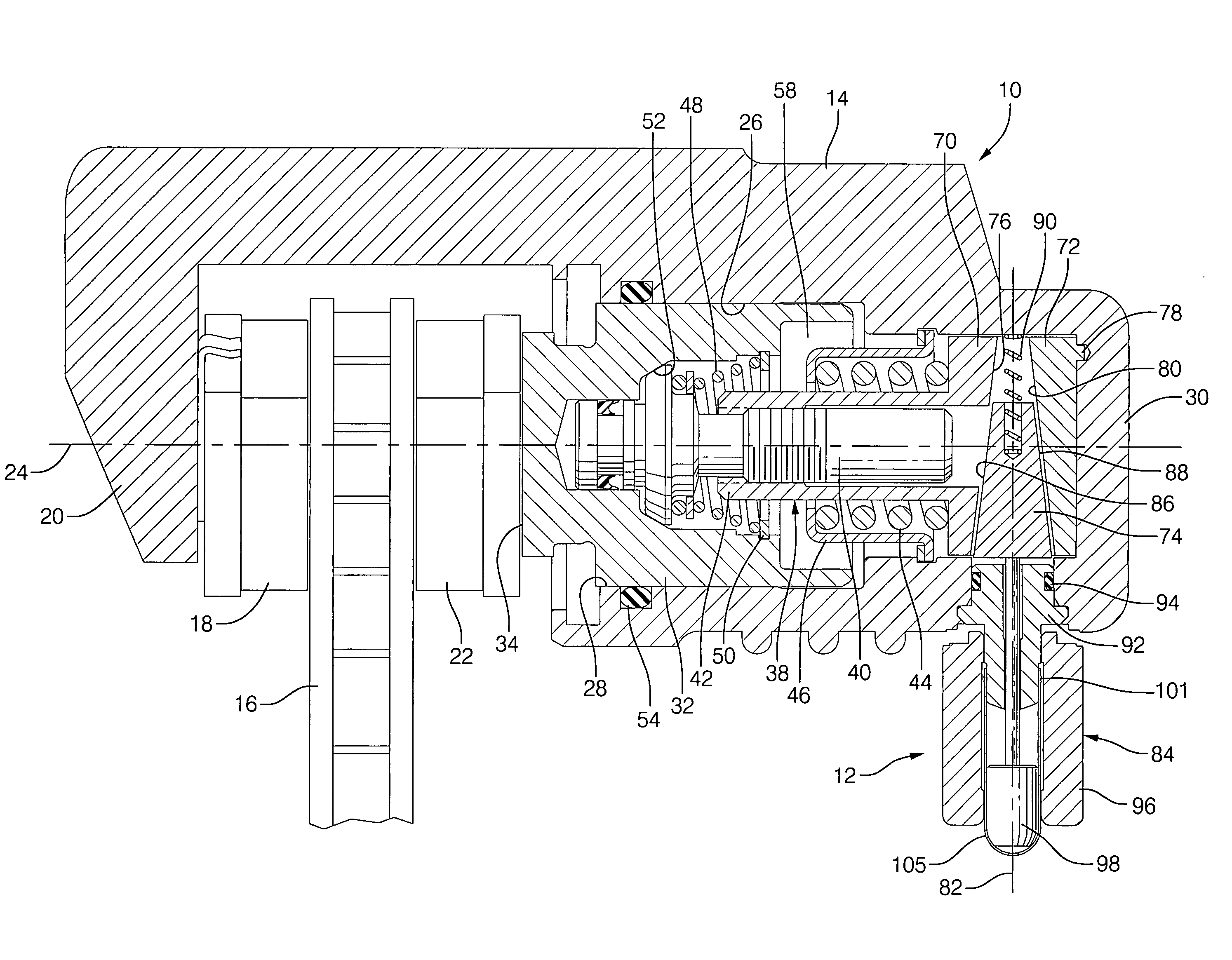
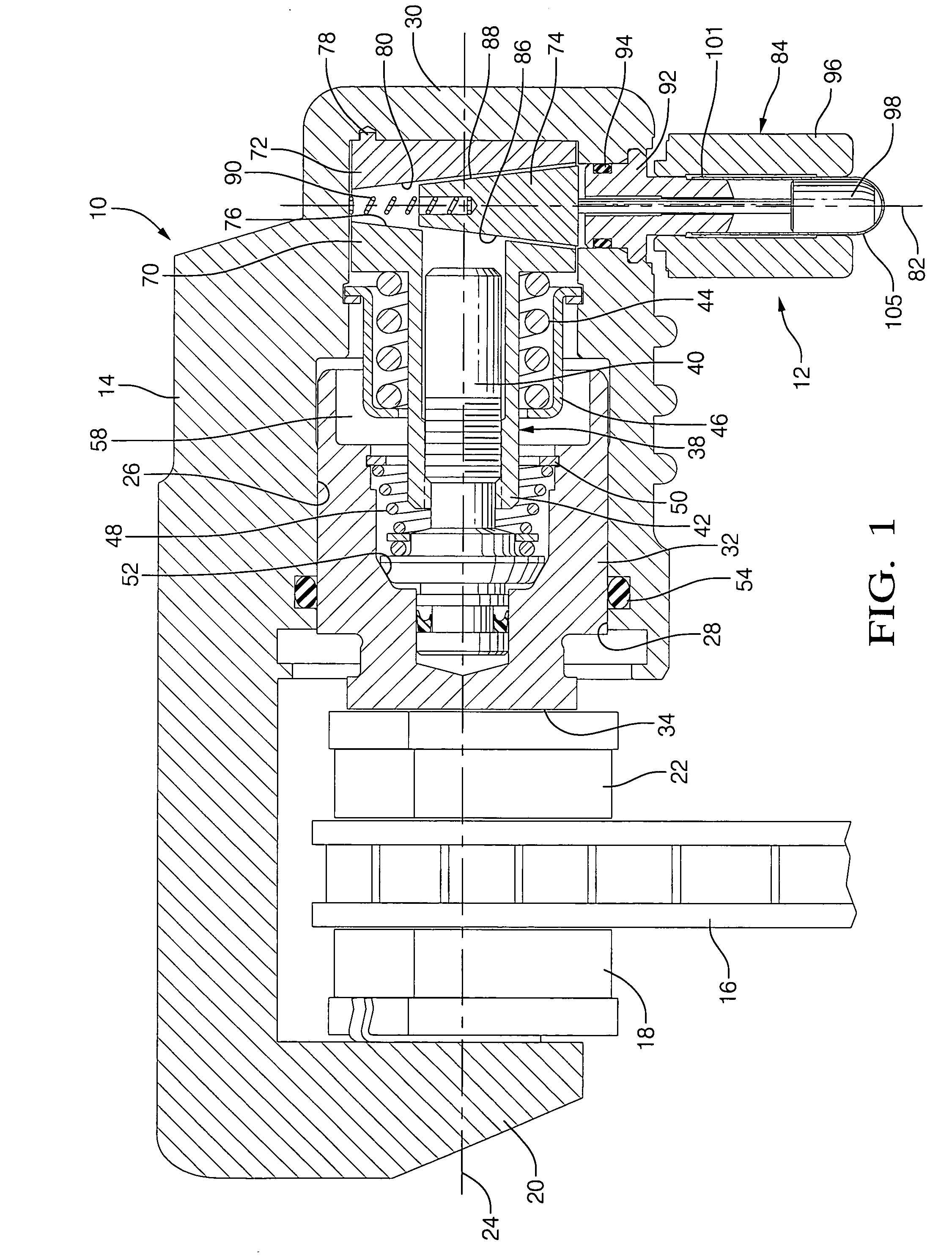
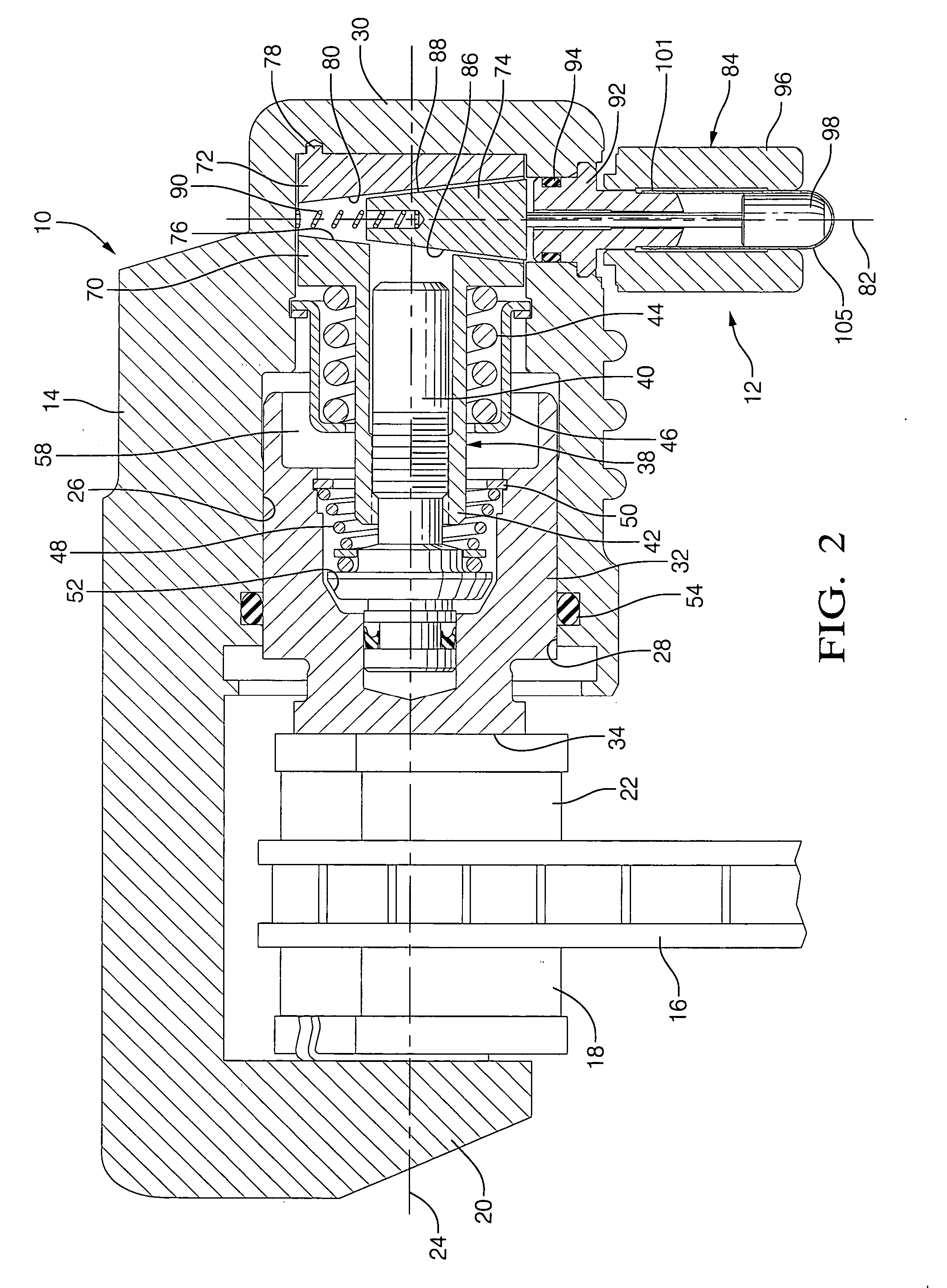
Electro-mechanical actuator braking apparatus and method using motor commutation sensor output to derive piston displacement
A braking system is disclosed that includes a brake (22), a ram (20) shiftable in a linear direction relative to the brake (22) for actuating the brake (22), and a stop (24) for limiting movement of the ram (20). The system further includes a motor (12) for moving the ram (20) which motor (12) includes a stator and a rotor (13) and a commutation sensor (14) producing an output. A motor controller (28) receives a commutation signal based on the output and controls the motor (12) based on the commutation signal. A processor (31) also uses the commutation signal to generate a position signal indicative of the position of the ram (20) relative to the stop (24). Methods of using this system are also disclosed.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
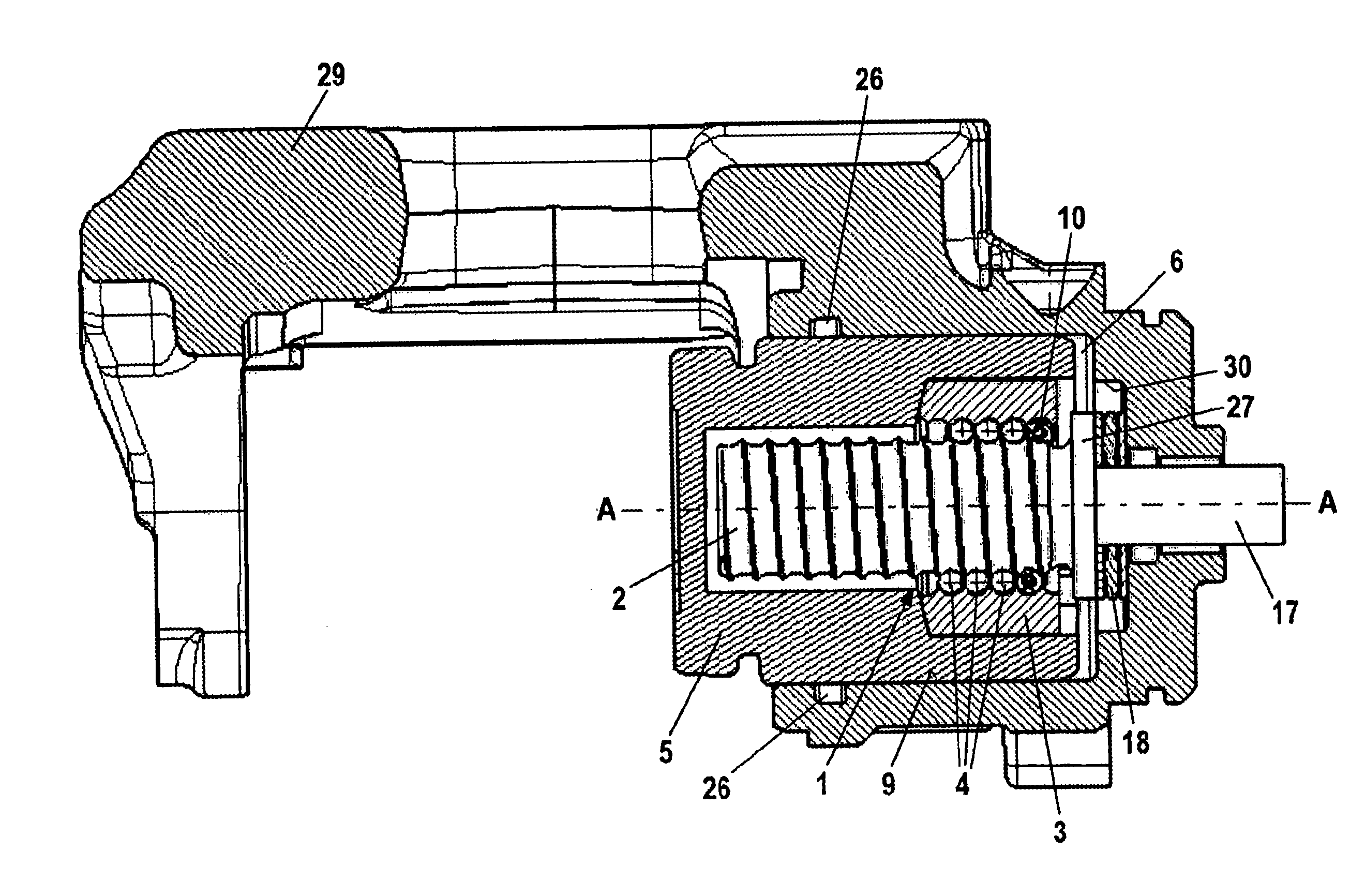
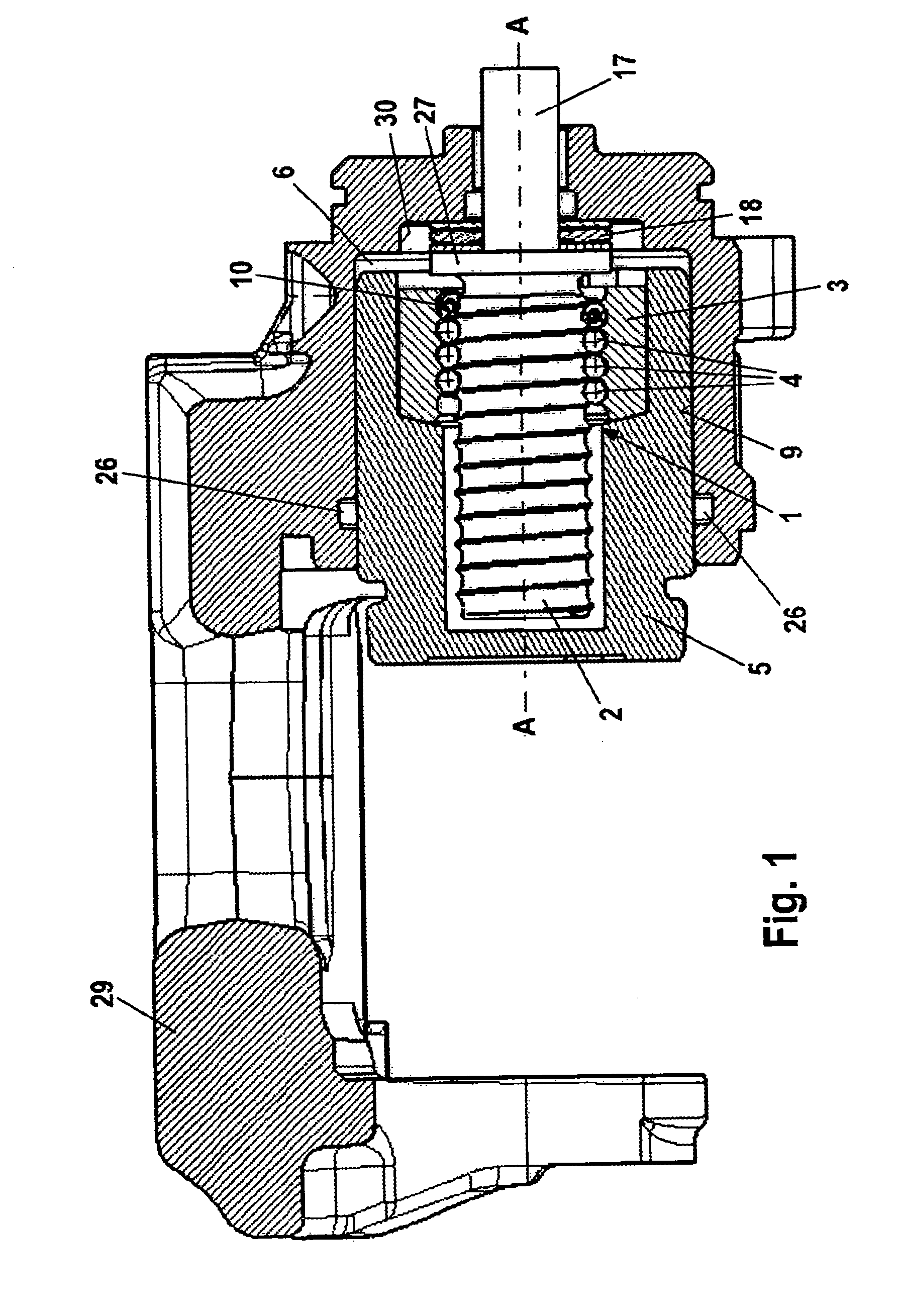
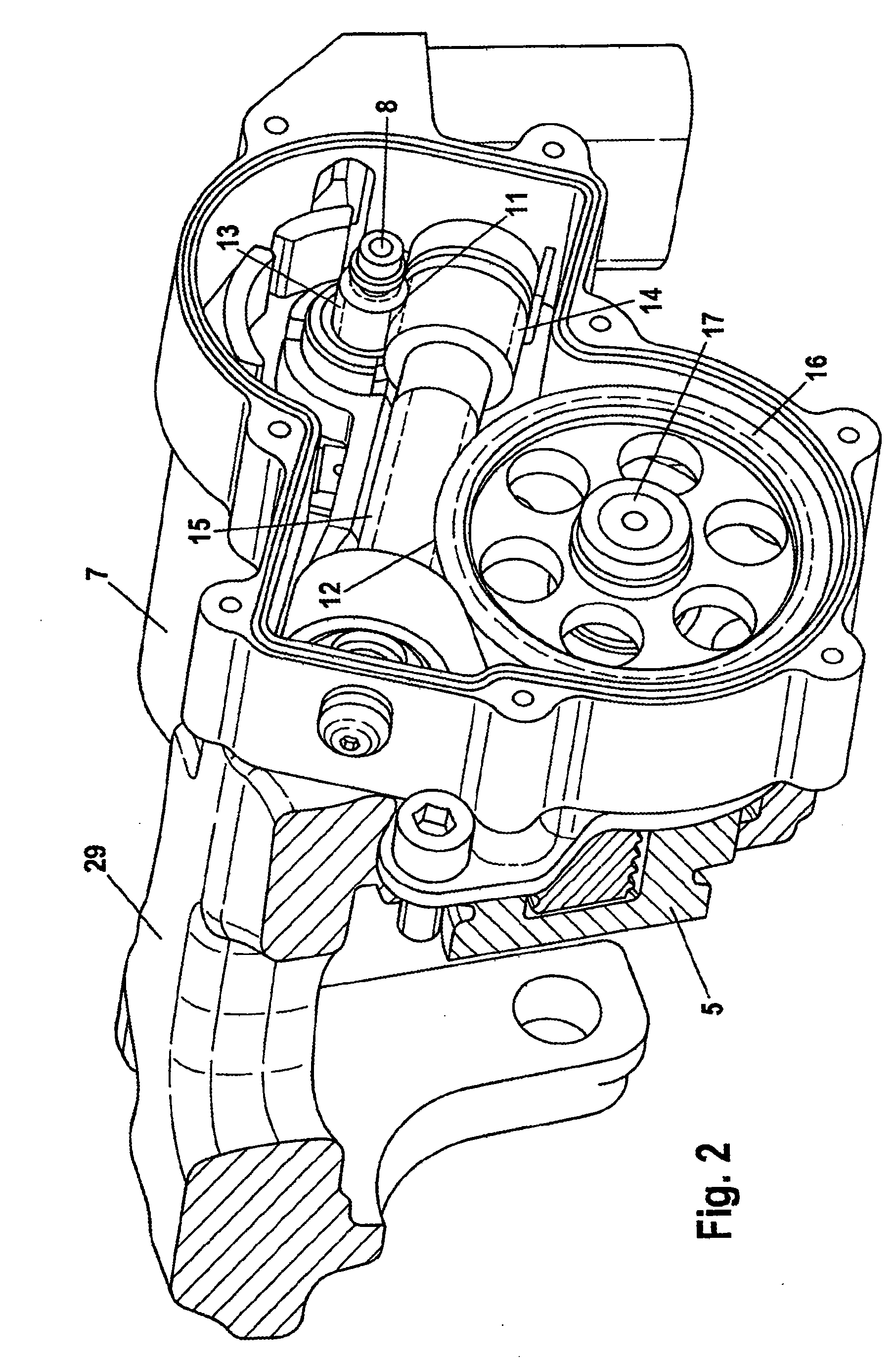
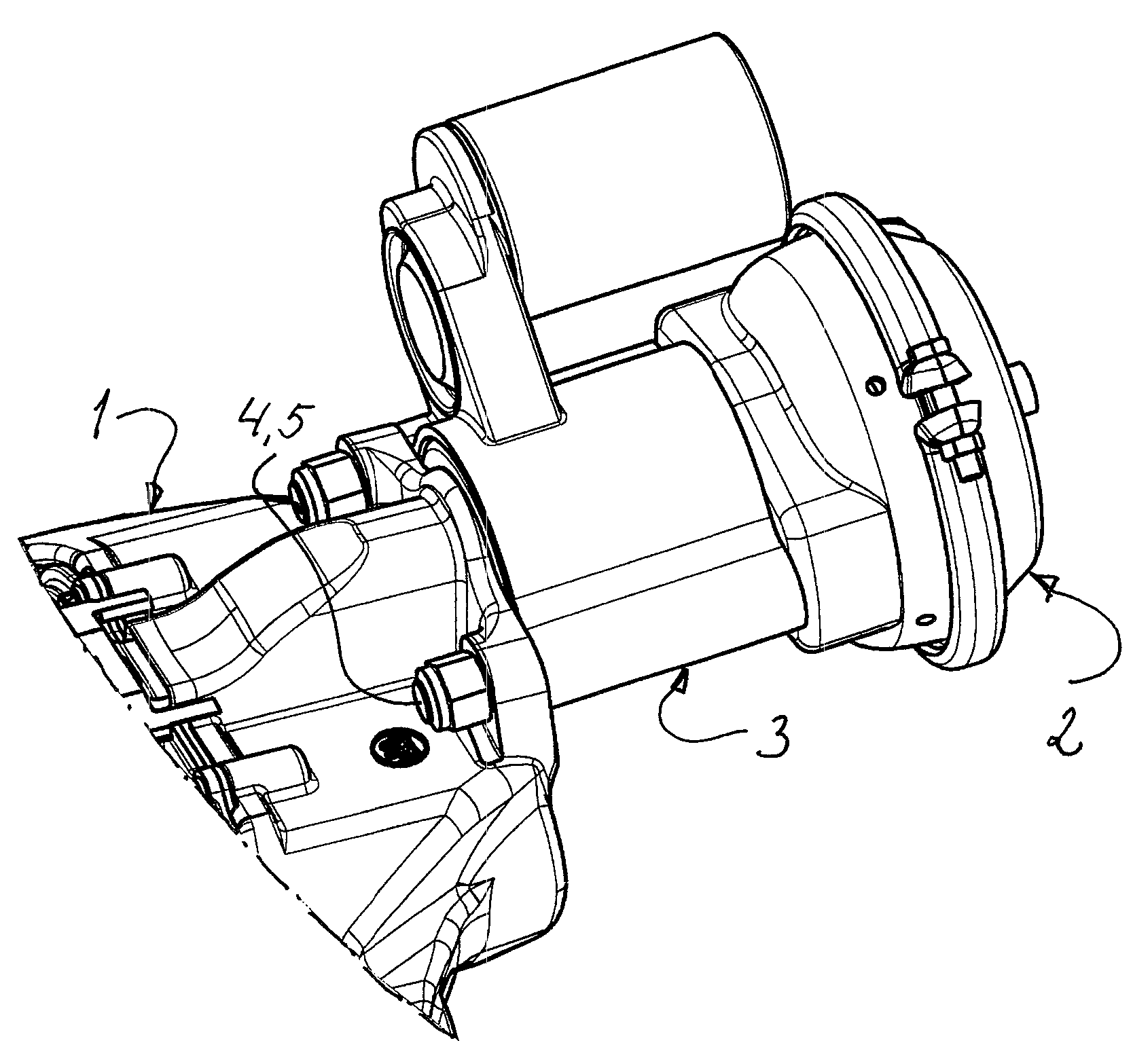
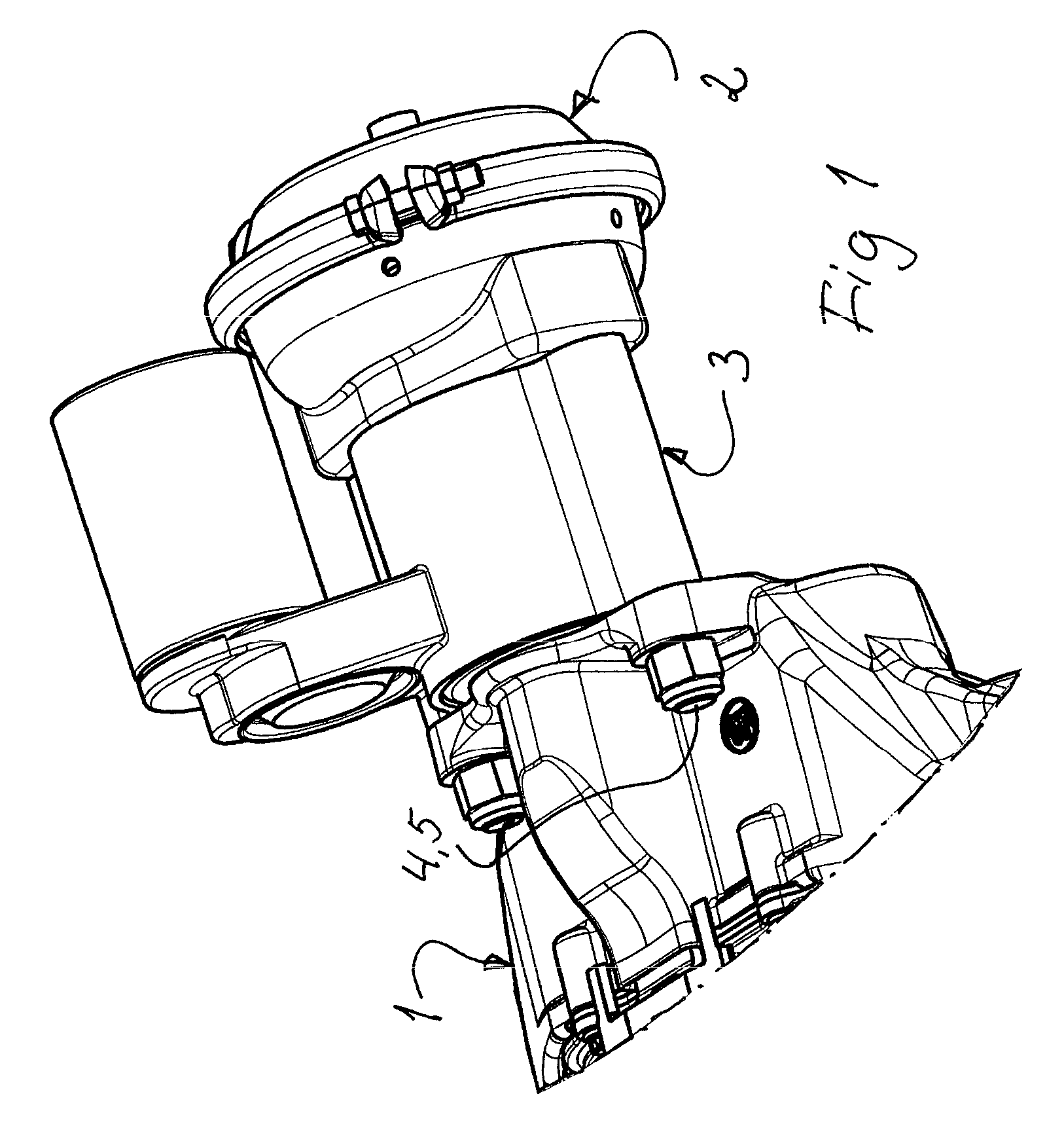
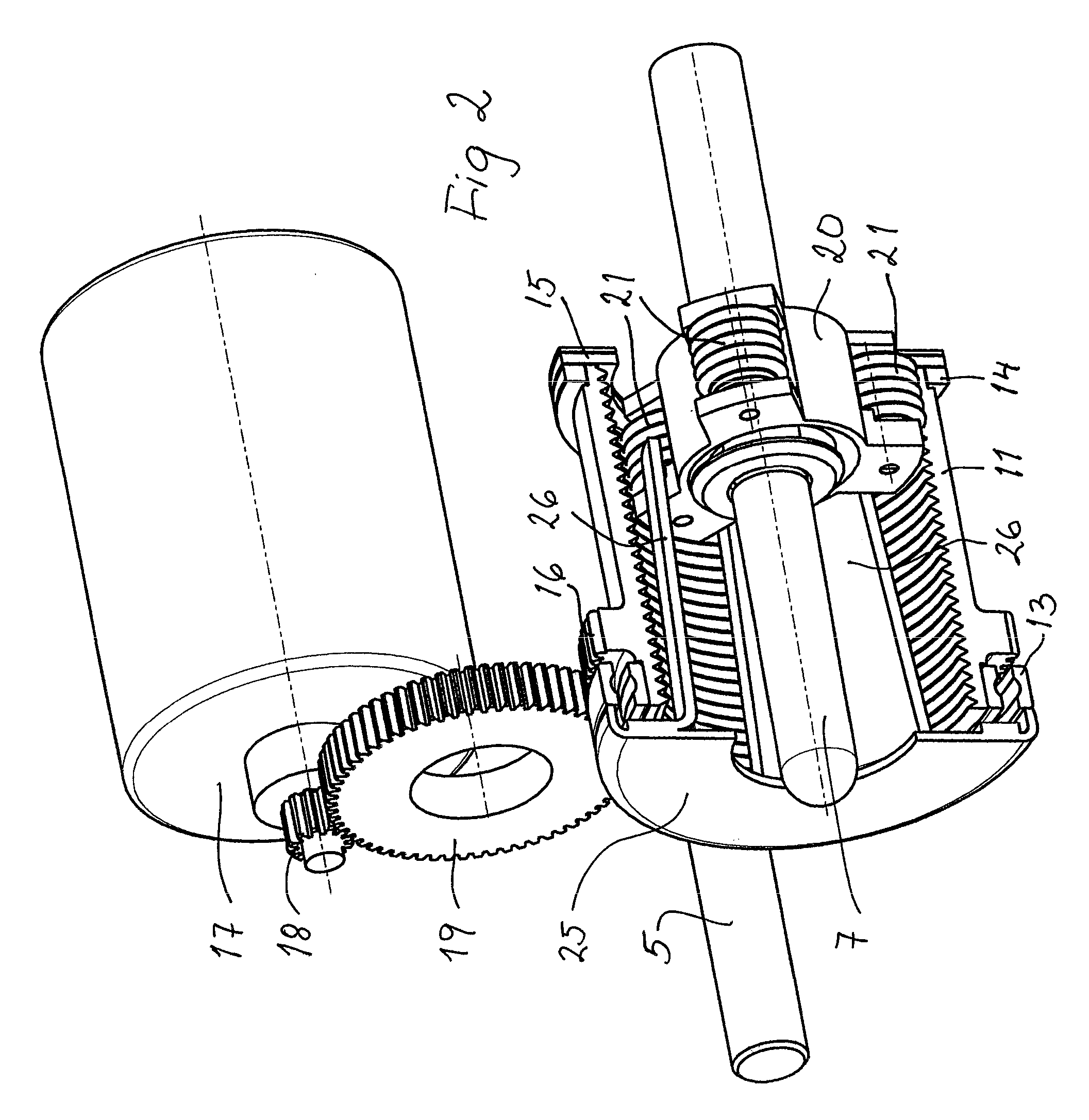
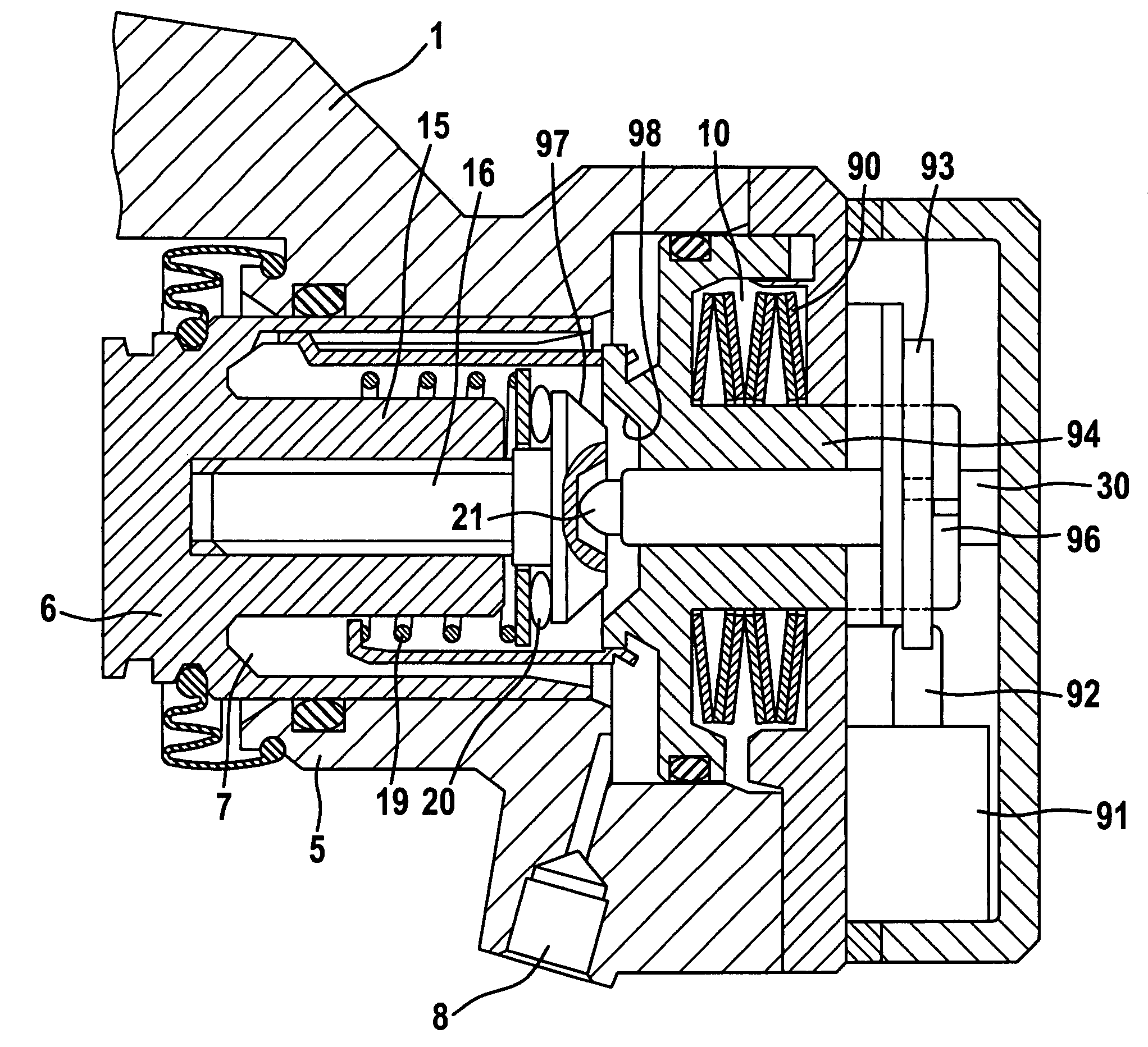
Combined Vehicle Brake With Electromechanically Operable Parking Brake and Gear For Converting A Rotary Movement Into A Translational Movement
ActiveUS20090283371A1Reduce power consumptionCost-effective manufacturingMechanically actuated brakesToothed gearingsParking brakePiston
A combined vehicle brake including a hydraulically actuated service brake and an electromechanically actuated parking brake device, a hydraulic operating pressure chamber in a brake housing being defined by a brake piston, which for performing service braking actions can be acted upon by hydraulic pressure fluid, so that the brake piston can be actuated along a piston longitudinal axis in order to produce a braking action, and the parking brake device acting on the brake piston by way of a transmission that translates the rotary motion of an electromechanical actuator into a translational motion and actuates the brake piston to perform parking brake actions and to keep it in the actuated position. Also disclosed is a transmission for translating a rotary motion into a translational motion by way of a screw spindle and a spindle nut, which are in contact with one another by way of multiple rolling elements.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
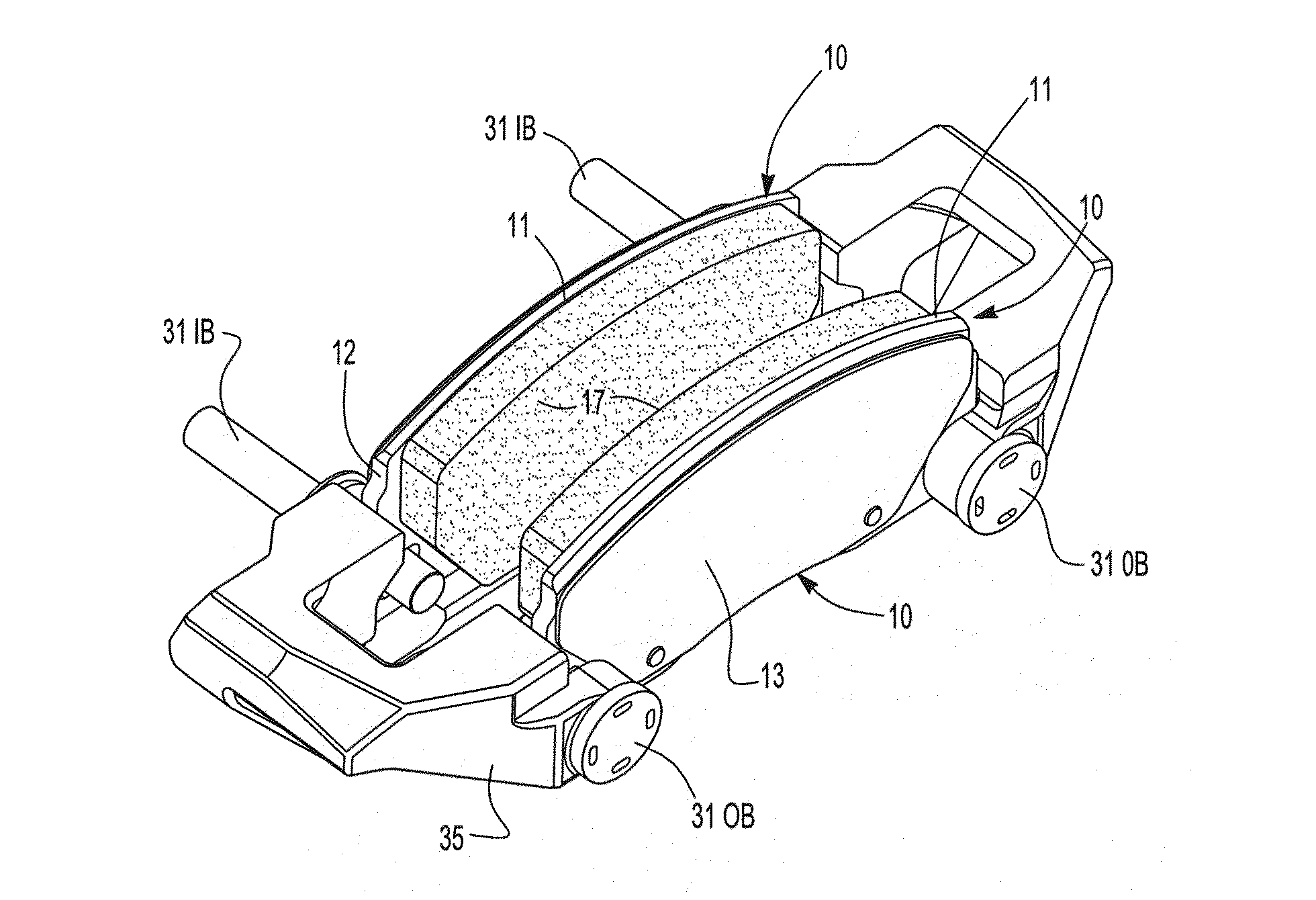
Brake systems, caliper assemblies and pads incorporating differential abutments
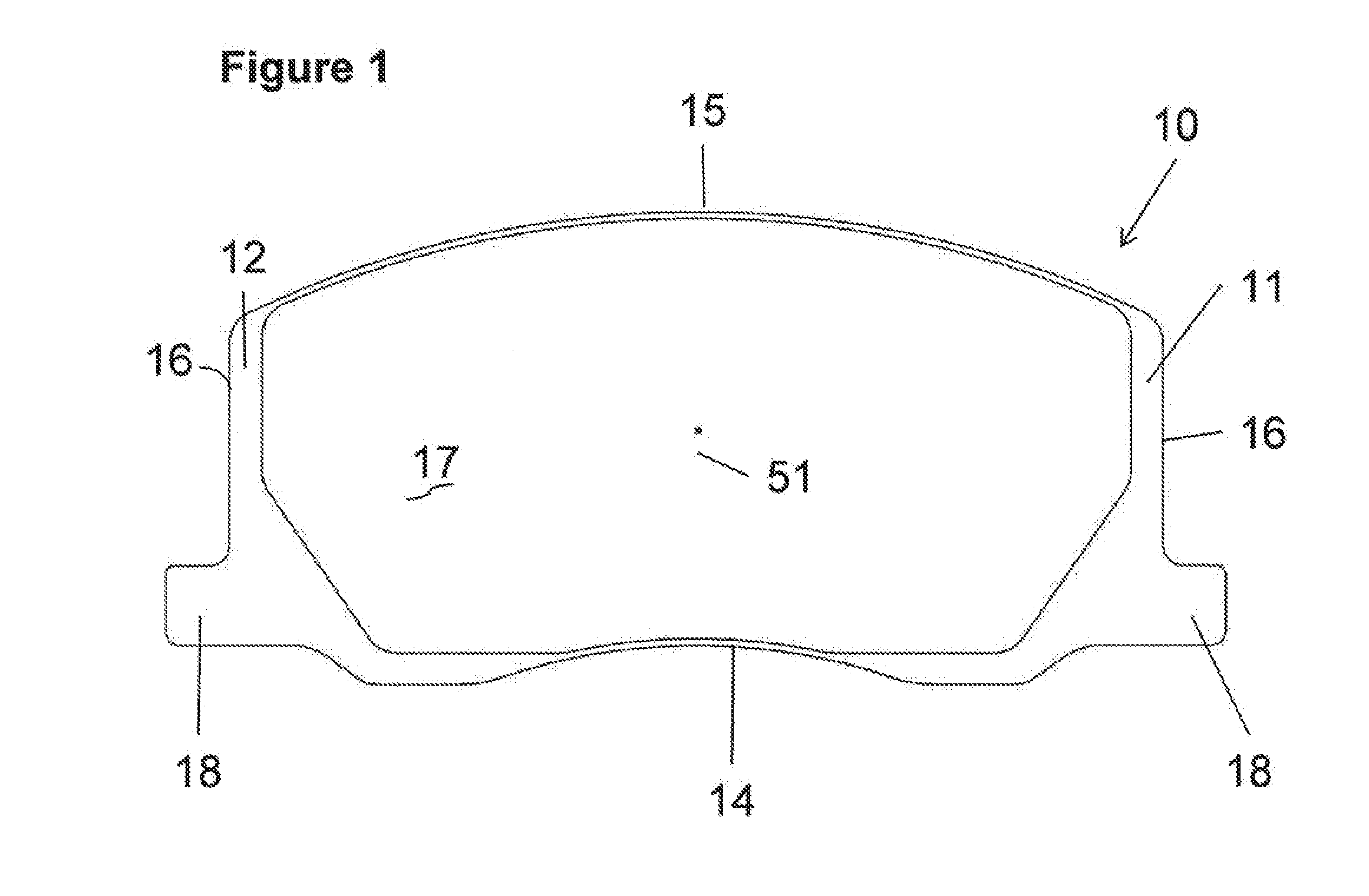
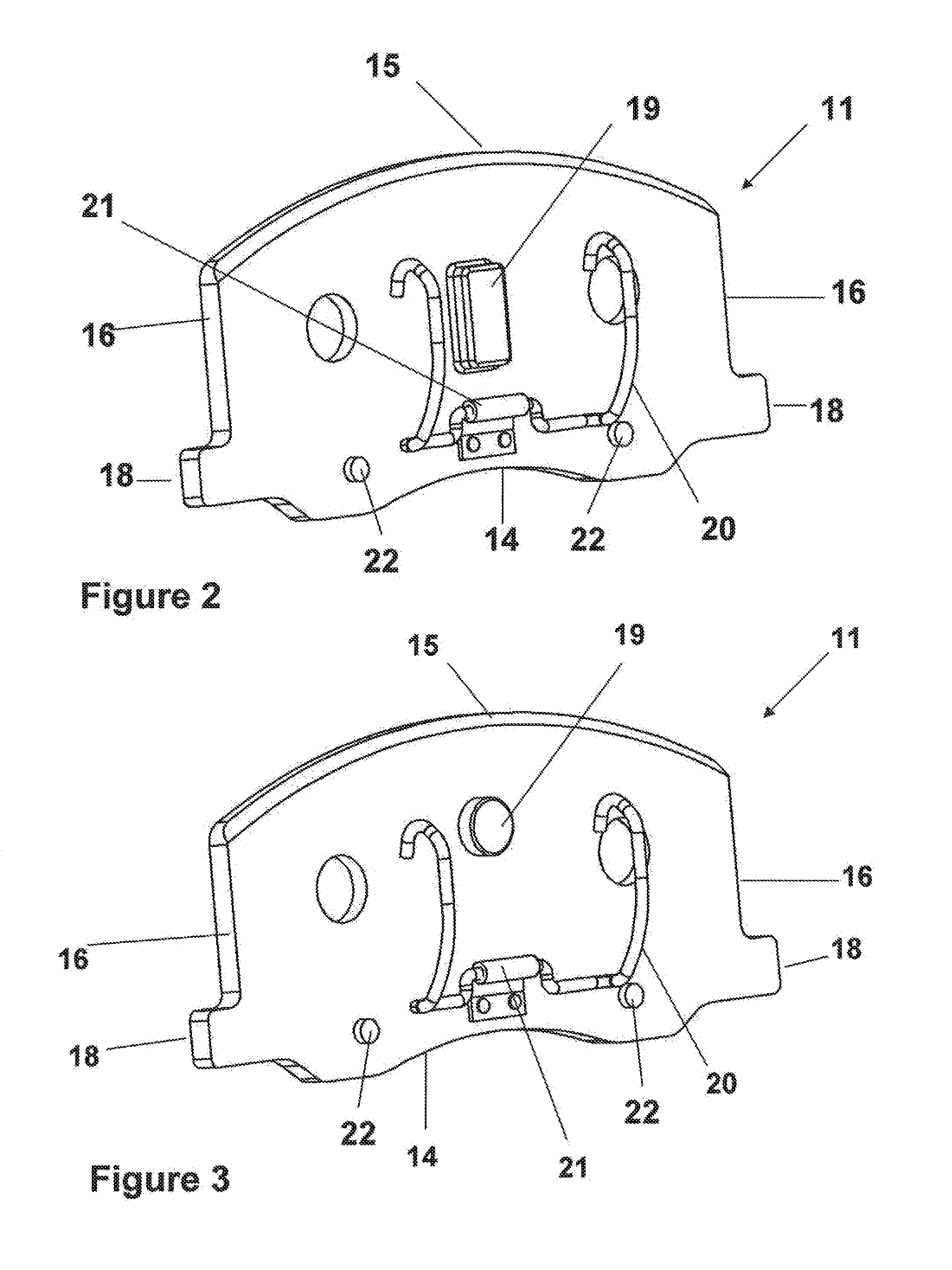
InactiveUS20120043168A1Transmission of forceImprove NVH performanceMechanically actuated brakesBraking membersPush pullEngineering
The present invention is directed to a unique solution for caliper assemblies, brake pads utilized in such caliper assemblies, support structures utilized in caliper assemblies and disc brake systems containing such caliper assemblies which utilize push pull or pull push abutment designs.
Owner:AKEBONO CORP (NORTH AMERICA)
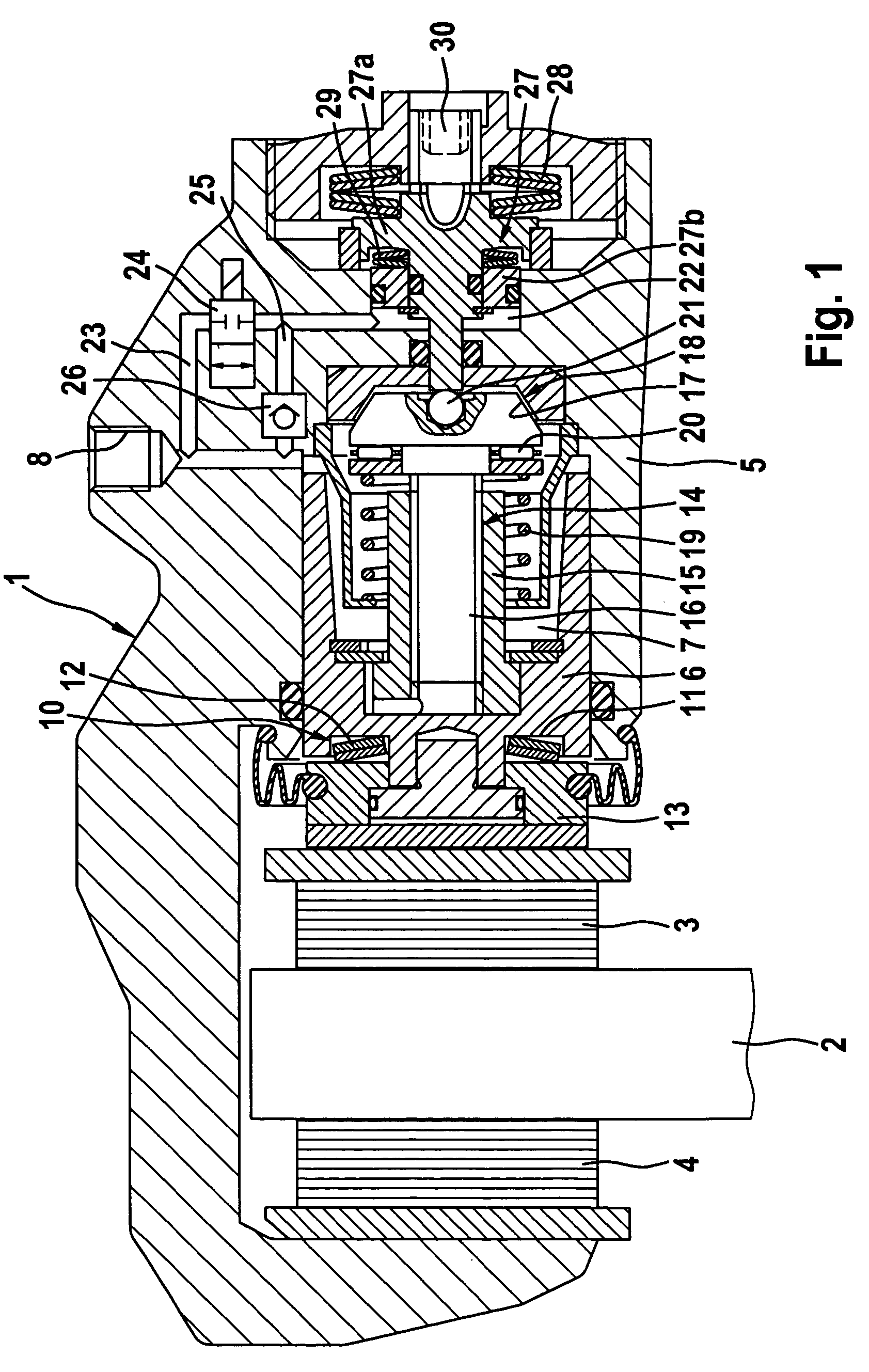
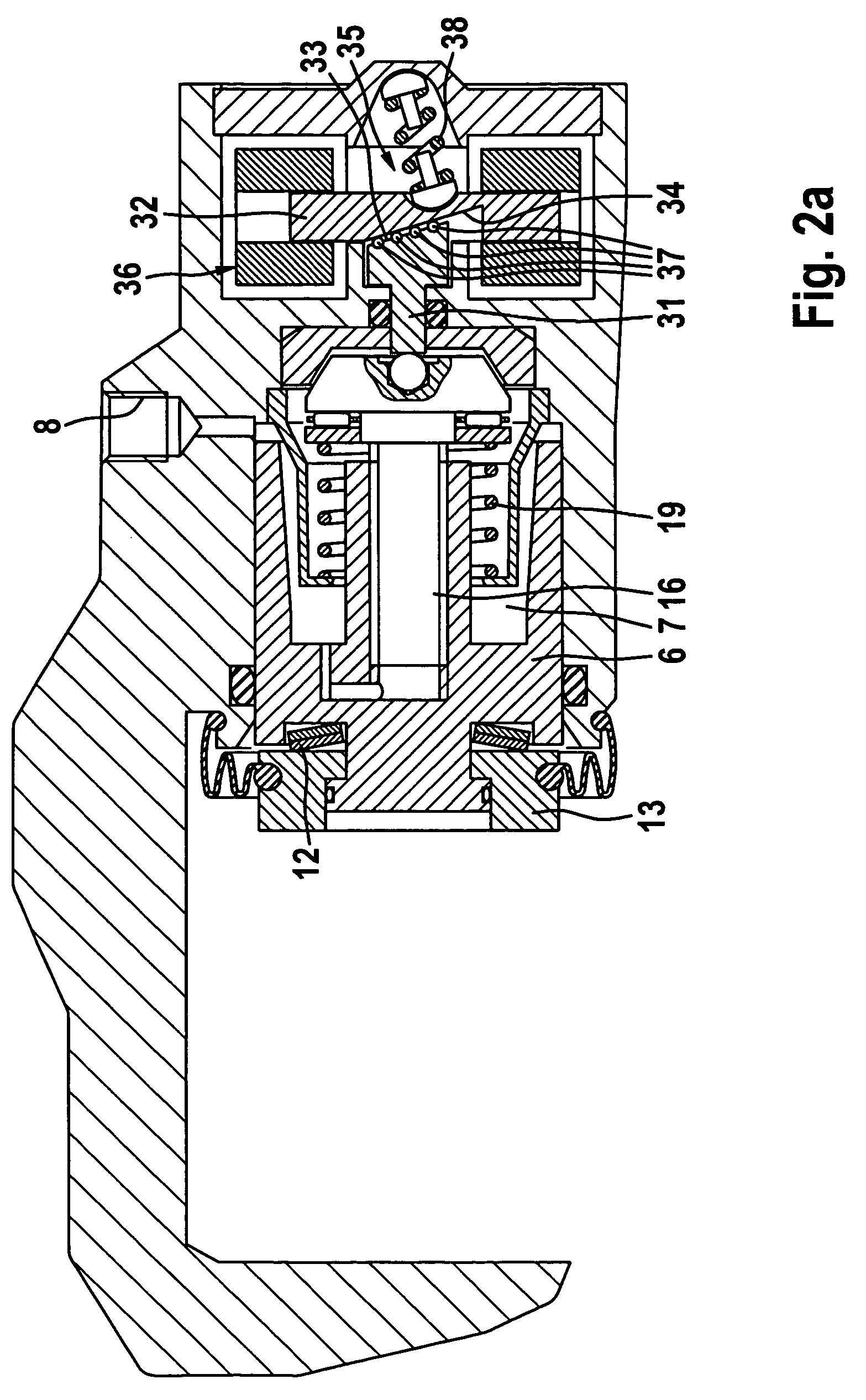
Fail-safe concept for an electromechanical brake
InactiveUS20050127749A1Security failsFatal consequenceBraking action transmissionMechanically actuated brakesControl systemExercise state
A control system for an electromechanical brake with self-reinforcement has: means for recognizing a brake failure means for detecting the actual state of motion of the device to be braked and means for opening and closing the brake upon recognition of a failure dependent upon the detected state of motion of the device to be braked. The means for recognizing the state of motion detection in particular the rotational velocity of a brake disk assigned to the brake.
Owner:STOP
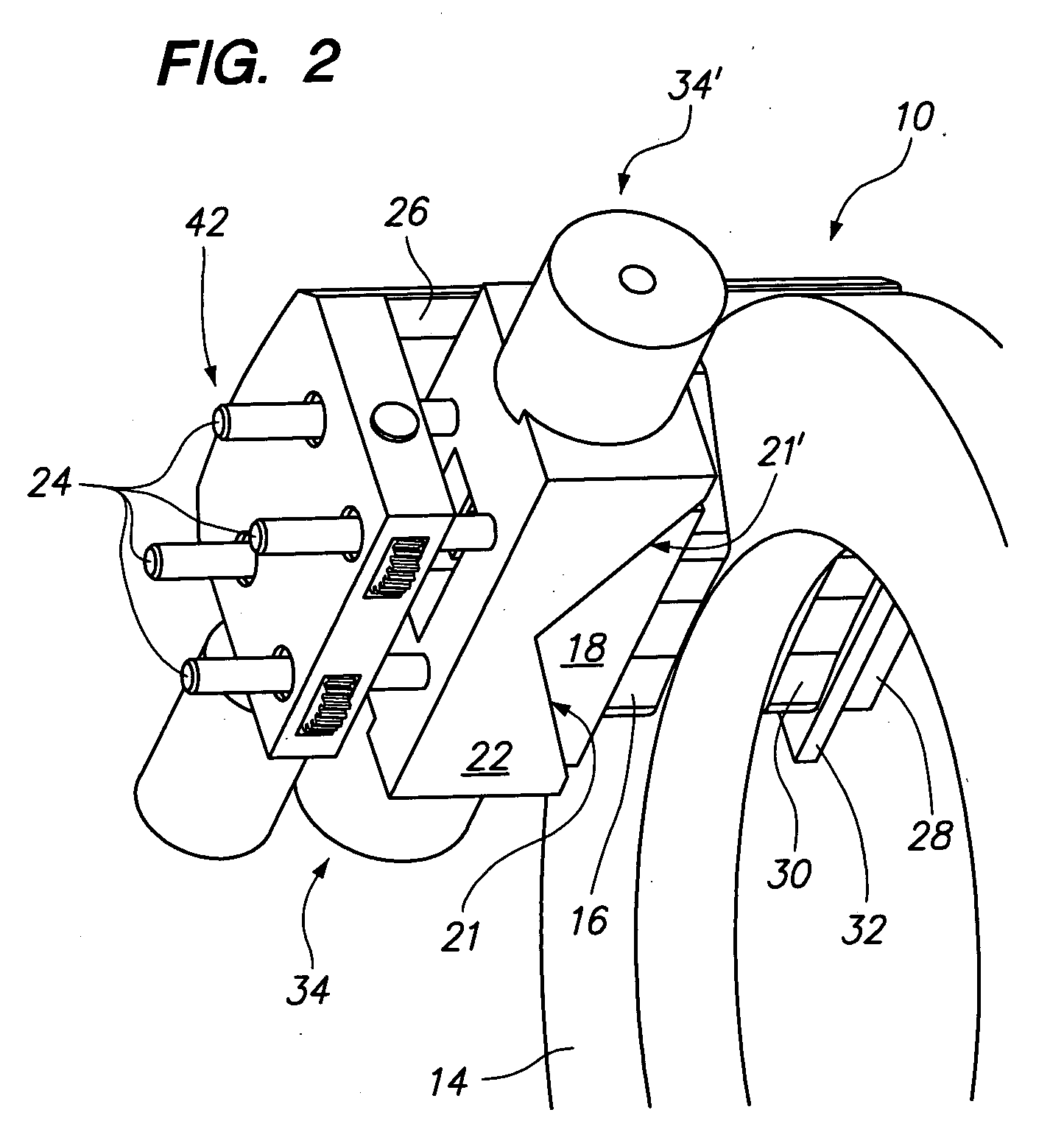
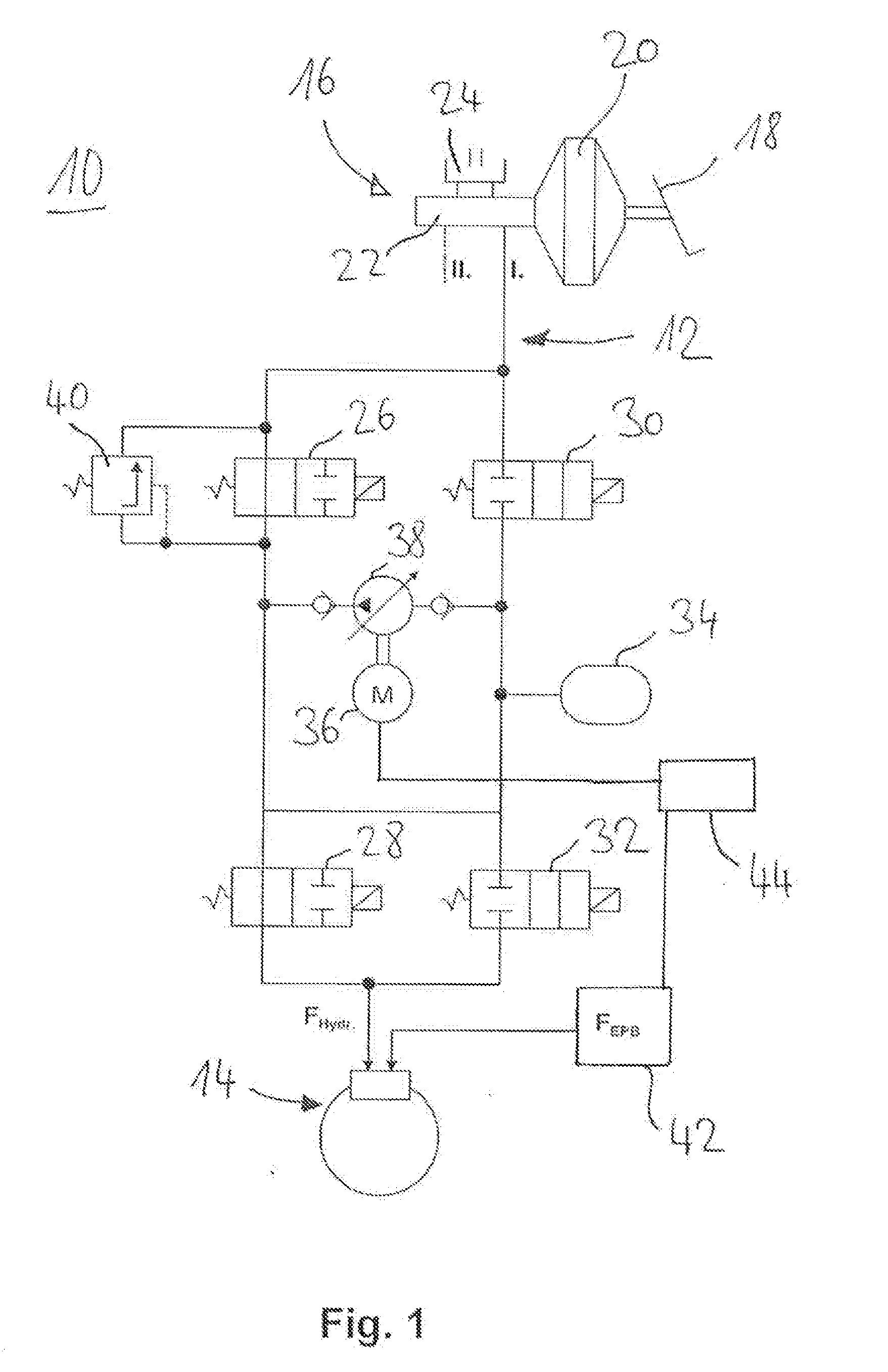
Procedure for Actuating a Hydraulic Parking Brake
ActiveUS20110042171A1Increase the amount of fluidReduce background noiseAnalogue computers for trafficMechanically actuated brakesEngineeringActuator
A procedure for actuating a parking brake is described, the parking brake comprising a brake piston which is received in a hydraulic chamber and is displaceable within the hydraulic chamber by means of a hydraulic actuator on the one hand and a mechanical actuator on the other. During operation of the parking brake the mechanical actuator is activated in a first step in order to displace the brake piston in the hydraulic chamber in such a way that a volume of a hydraulic fluid contained in the hydraulic chamber is increased. At a subsequent time the hydraulic actuator is activated in order to build up or increase a clamping force of the parking brake. The hydraulically generated or increased clamping force is then maintained by means of the mechanical actuator.
Owner:LUCAS AUTOMOTIVE GMBH
Caliper assembly for disc brake system
InactiveUS20120085597A1Improve NVH performanceImprove component performanceMechanically actuated brakesSlack adjustersEngineeringCalipers
A caliper assembly comprising: a brake pad comprising a carrier plate having two opposing faces and a top edge a bottom edge and two opposing side edges, wherein on one face is friction material and on the opposing face is a projection adapted to seat in a matched hole or recess in a caliper body, the two opposing side edges each having an ear which is adapted to seat in pad locator indentations in a support structure; a support structure comprising a recess for housing at least one brake pad and at least two pad locator indentations adapted for receiving the ears located on the two opposing sides of the brake pad and at least two caliper body locator indentations for seating two ears defined by the caliper body; and a caliper body having a hole or recess adapted for seating the projection on the opposing face of the brake pad and having two ears on each opposing side which are adapted to seat in the caliper body locator indentations of the support structure; wherein the ears of the brake pad are seated in the pad locator indentations of the support structure, the projection on the opposing face of the brake pad is seated in the hole or recess located in the caliper body, and a clip which engages the opposing face of the brake pad and the caliper body and holds the brake pad in position with respect to the caliper body and the ears of the caliper body are seated in the caliper body locator indentations in the support structure.
Owner:AKEBONO BRAKE
Disc brake with parking function
InactiveUS20070062769A1Easy to operateShorten speedMechanically actuated brakesElectrodynamic brake systemsEngineeringCalipers
A disc brake enables a parking apparatus to be operated via actuation of an electric motor, thereby permitting easy operation of the parking apparatus. The disc brake comprises a piston to compress a friction pad used for braking of a disc, a caliper housing to receive the piston such that the piston moves linearly therein, and having a cylinder section to which a hydraulic pressure for braking is applied, an actuation shaft rotatably installed within the cylinder section, and having a male screw formed thereon, a compression sleeve installed within the piston to compress or release the piston while linearly moving therein by rotation of the actuation shaft, and having a female screw formed thereon to engage with the male screw of the actuation shaft, an electric motor to rotate the actuation shaft, a multi-stage reduction gear train to transmit rotational force of the electric motor to the actuation shaft. The multi-stage reduction gear train has a central axis deviated from that of the electric motor, and a shaft connected with a shaft of the electric motor via a power transmission unit
Owner:HL MANDO CORP
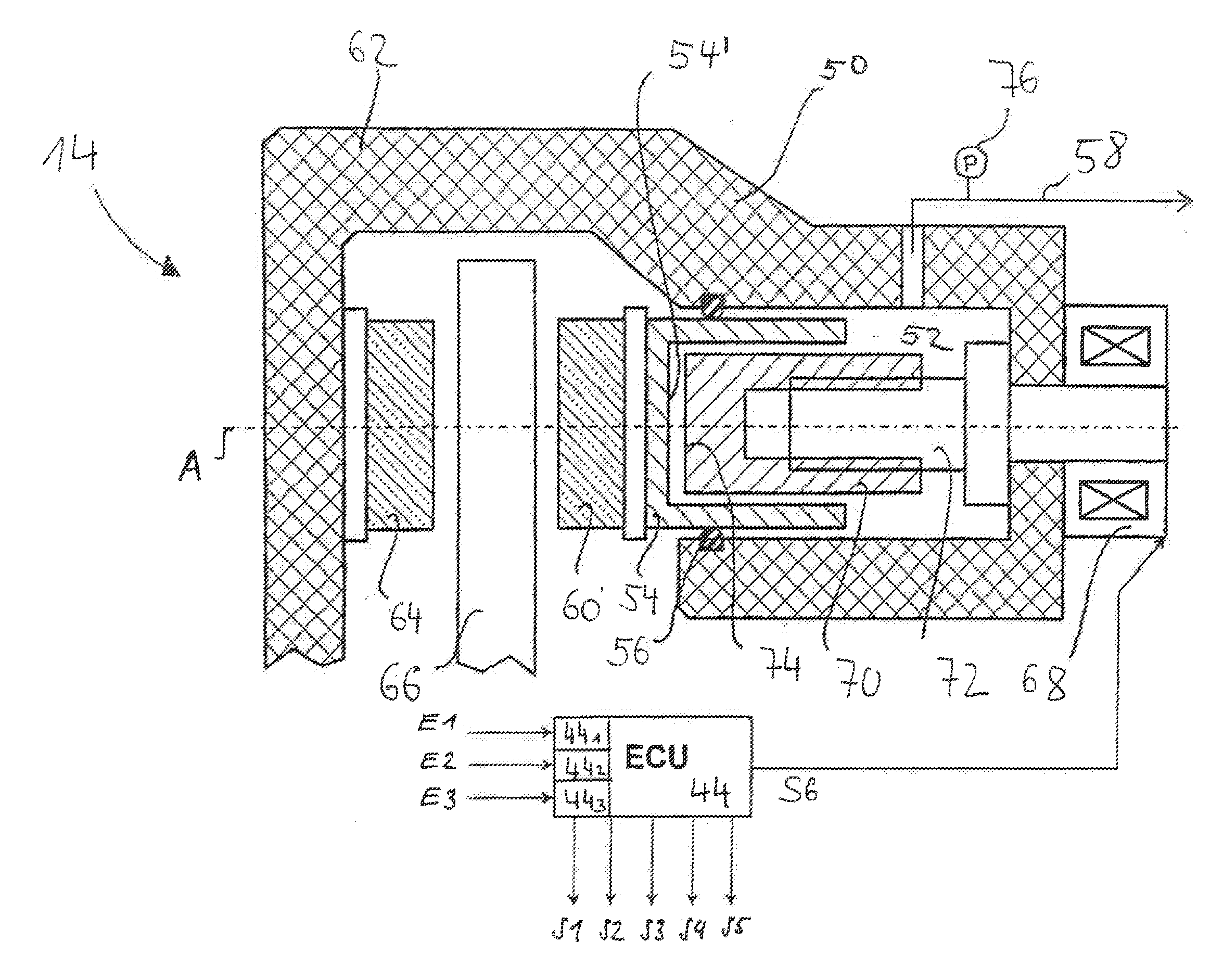
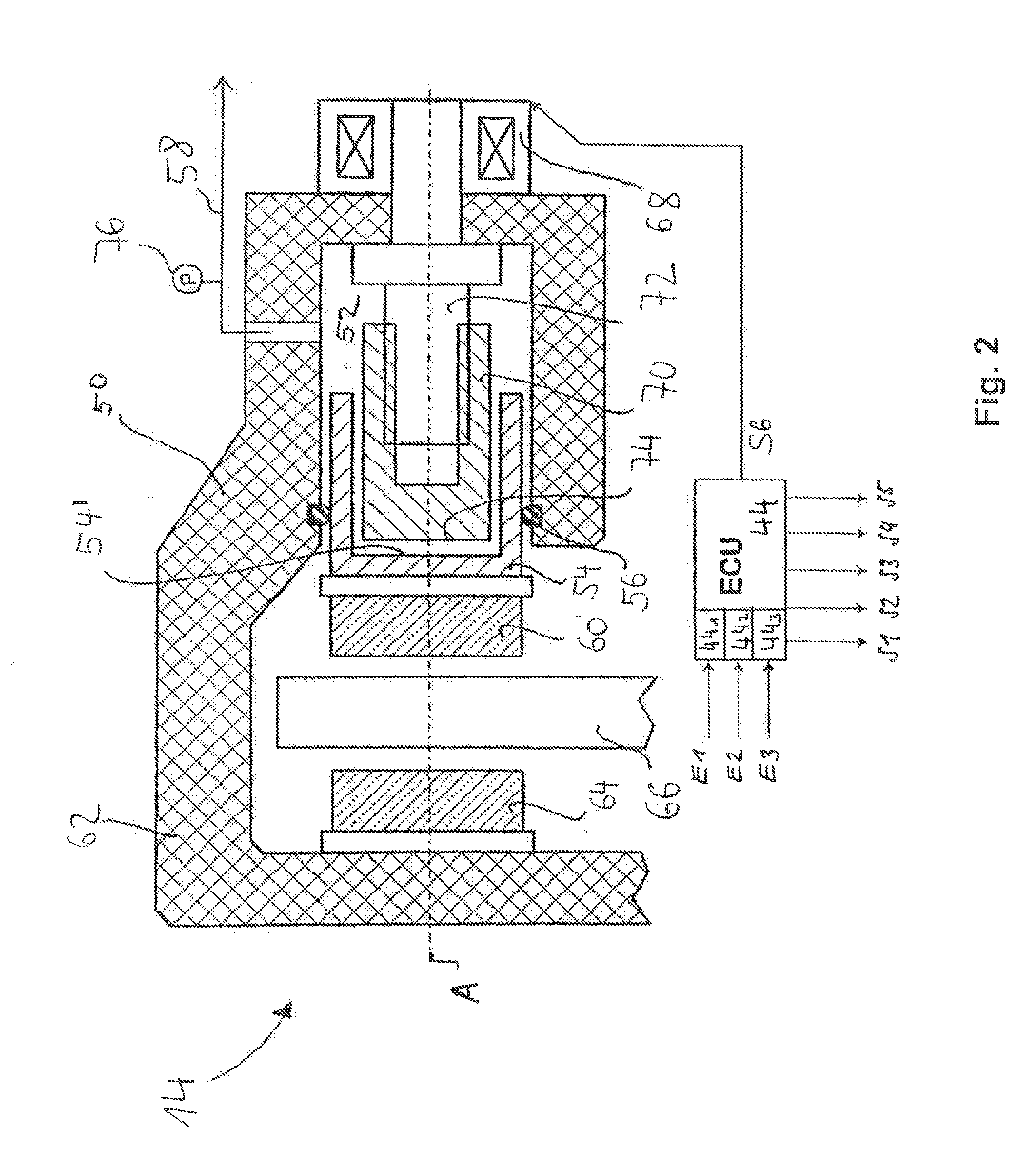
Electric Brake
ActiveUS20090218179A1Secure sufficient braking forceSecure responsivenessAnalogue computers for trafficBraking action transmissionActuatorControl theory
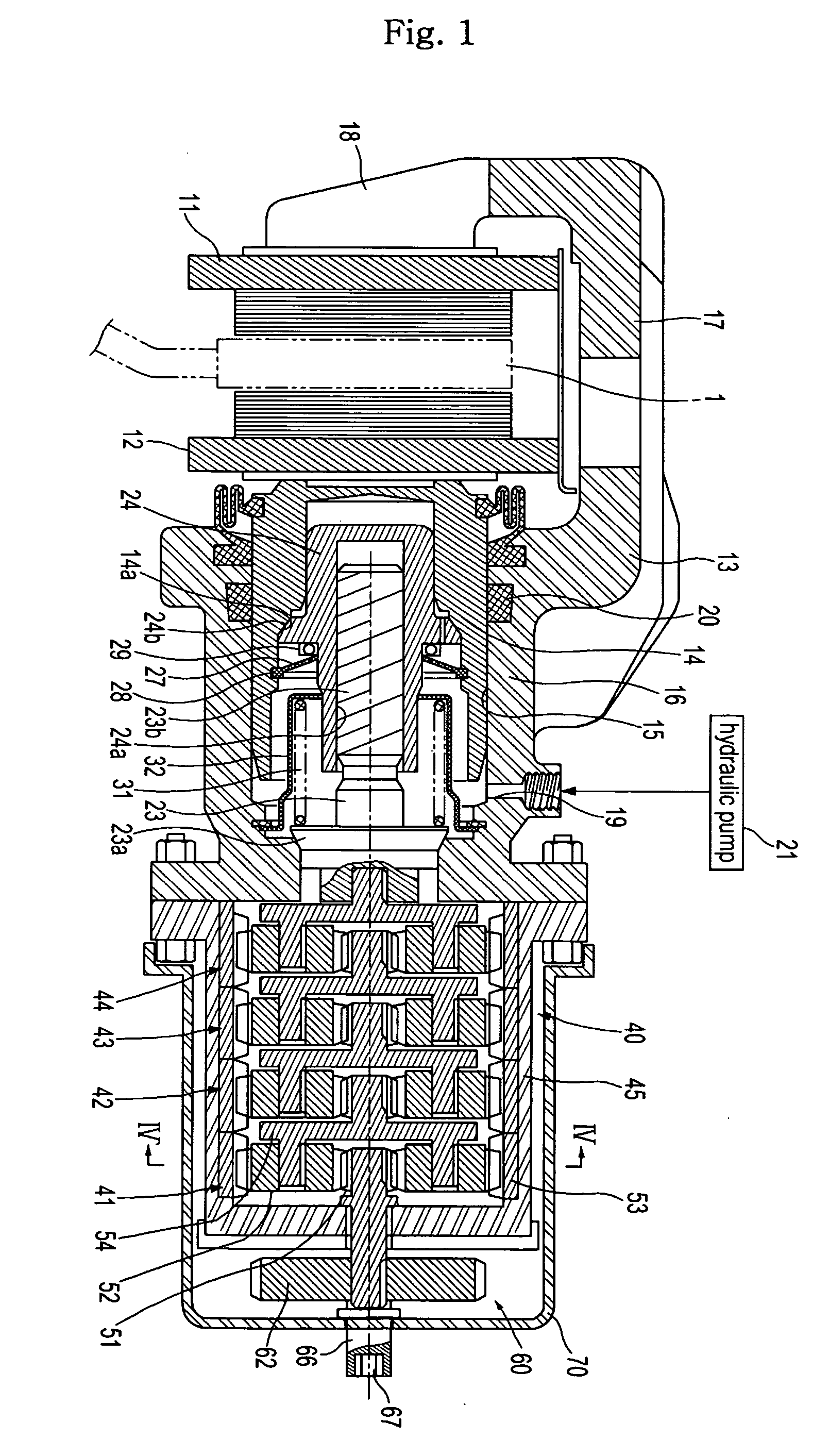
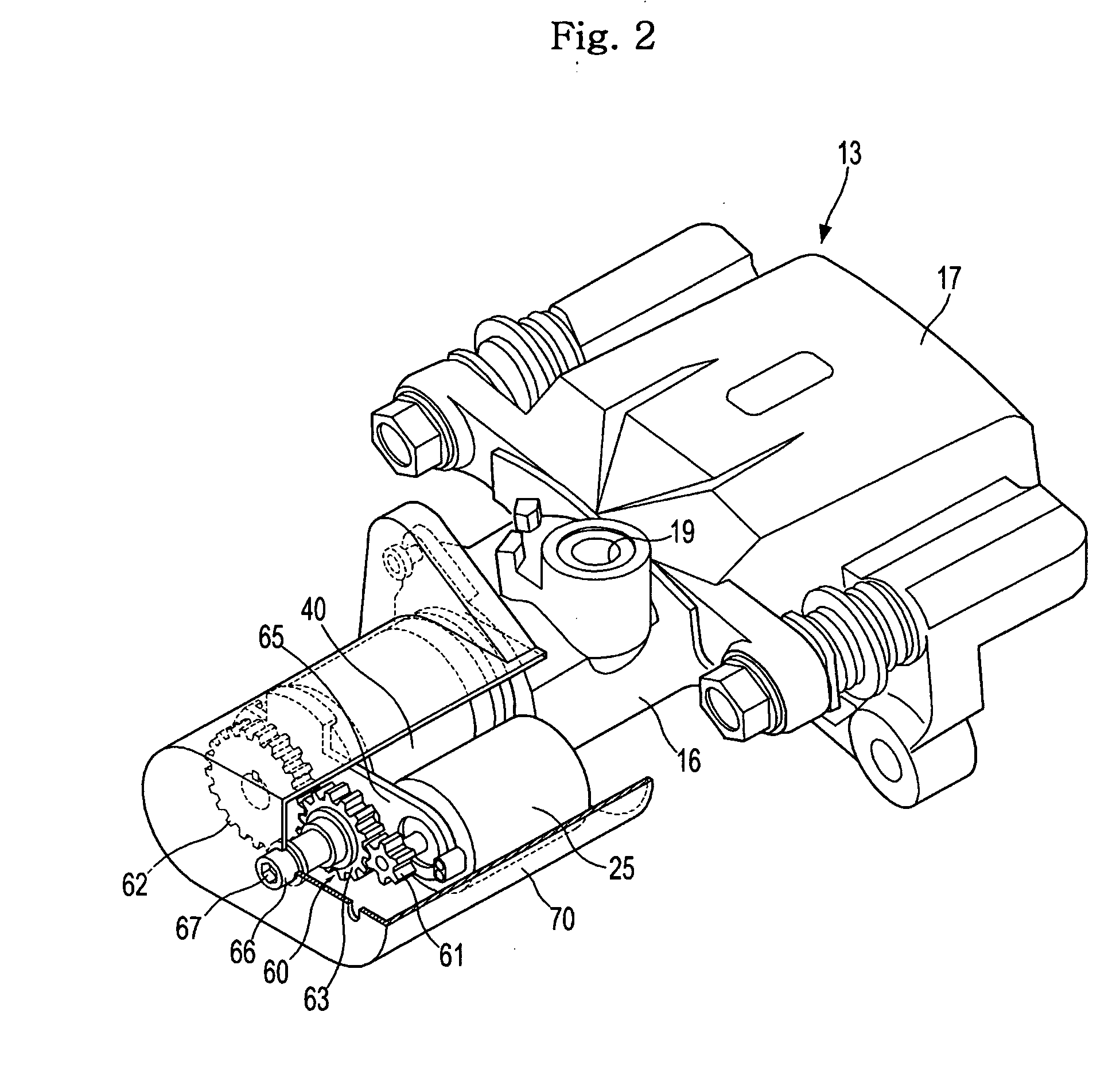
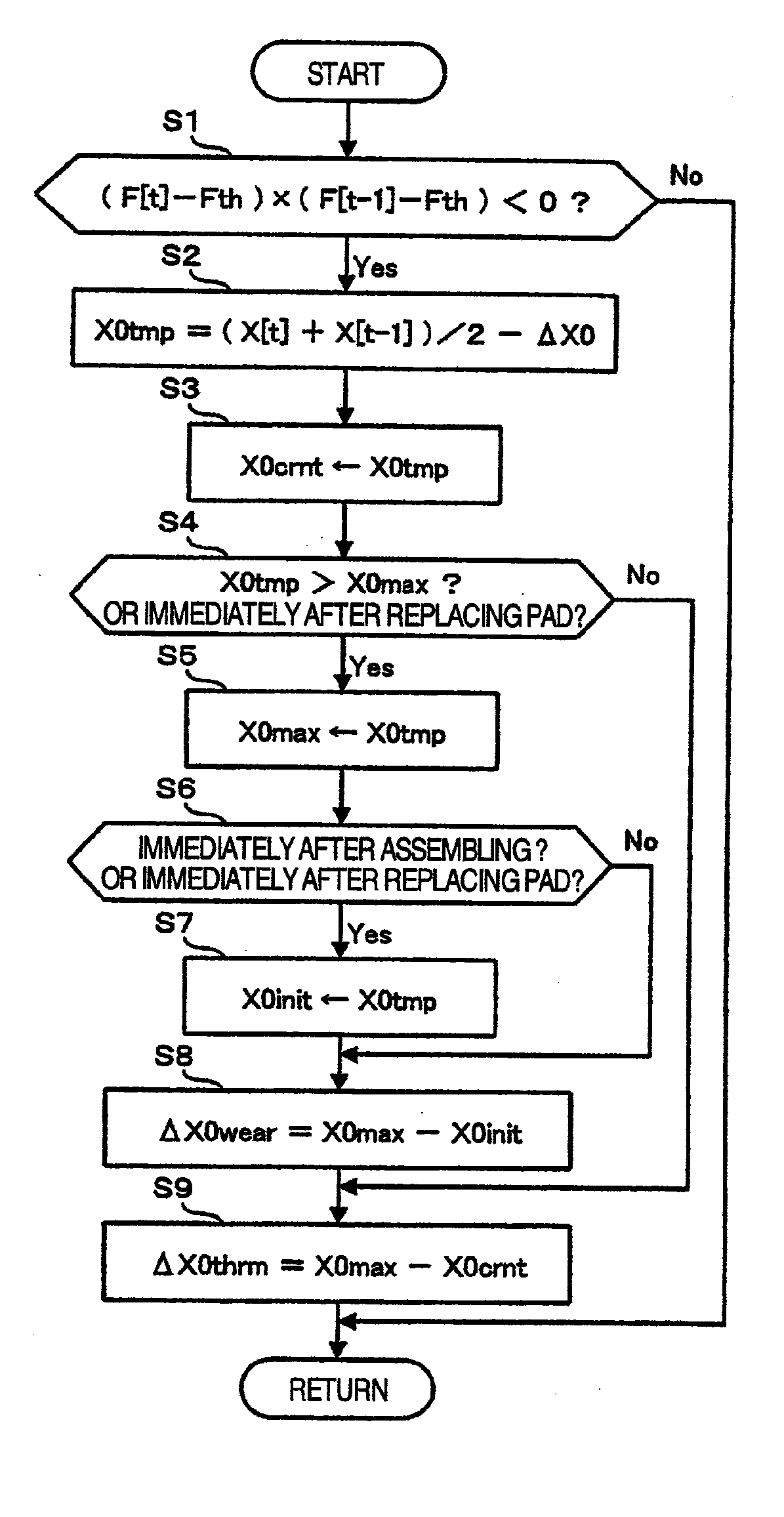
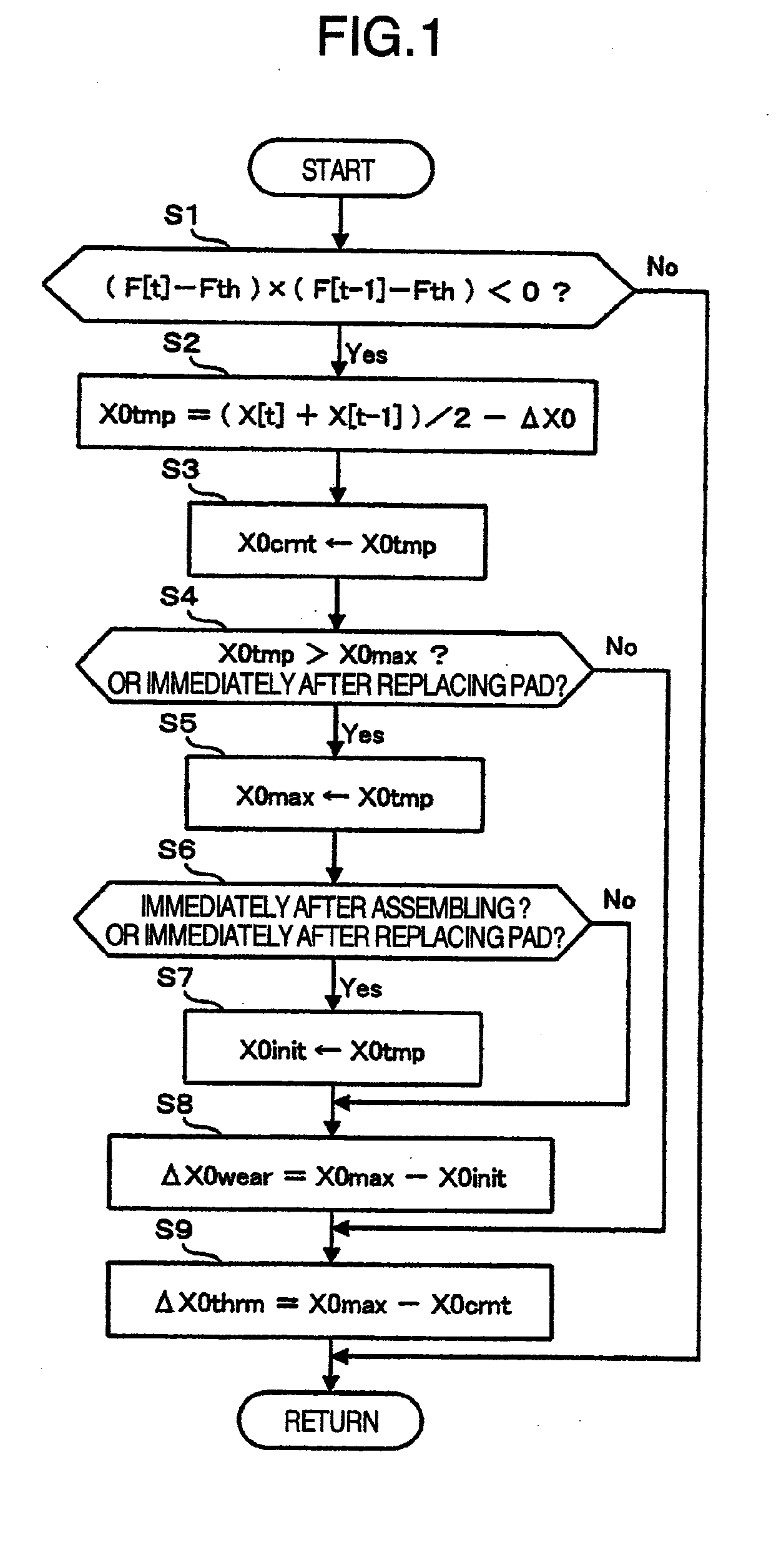
Provided is an electric brake capable of accurately estimating the brake pad temperature and securing a sufficient braking force and response. An electric brake has a disc rotor rotating with a wheel, an actuator for rectilinearly actuating a piston in the axial direction of the disc rotor by using an electric motor, a drive controller for controlling the drive of the actuator, a brake pad pressed by the piston to give a frictional resistance to the disc rotor in the direction of rotation, and a braking start position detector for detecting a braking start position of the piston where the disc rotor is brought into contact with the brake pad. The drive controller stores the braking start position detected by the braking start position detector as the maximum braking start position. When the braking start position shifts in the pressing force-increasing direction, the drive controller updates the value stored as the maximum braking-start position.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Disc Brake and an Additional Brake Actuator Therefore
InactiveUS20080217117A1Easy to combineMinimal modificationMechanically actuated brakesBrake actuating mechanismsEngineeringCalipers
A disc brake comprises a disc brake caliper, which includes a brake application mechanism with an input element, and a service brake actuator providing a brake application force to the input element via a push rod. An electromechanical brake actuator is arranged between the caliper and the service brake actuator and applies its force at will on the push rod.
Owner:HALDEX BRAKE PROD AB
Electric brake
In an electric brake of the present invention, a plunger of an actuator is connected through a pin to a pivot arm to which an engaging pawl engageable with a tooth portion of a ratchet is pivotably attached. A lower surface (a force-receiving portion) of the pin is adapted to receive an upward force which is applied by a tool inserted through a bolt hole threadably engaged with a watertight bolt. When the parking brake is operated (the engaging pawl is engaged with the tooth portion of the ratchet), if supply of current to the coil becomes impossible, the pin is moved upward by means of the tool, to thereby separate the engaging pawl from the tooth portion. Therefore, an emergency action to release the parking brake can be manually conducted.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
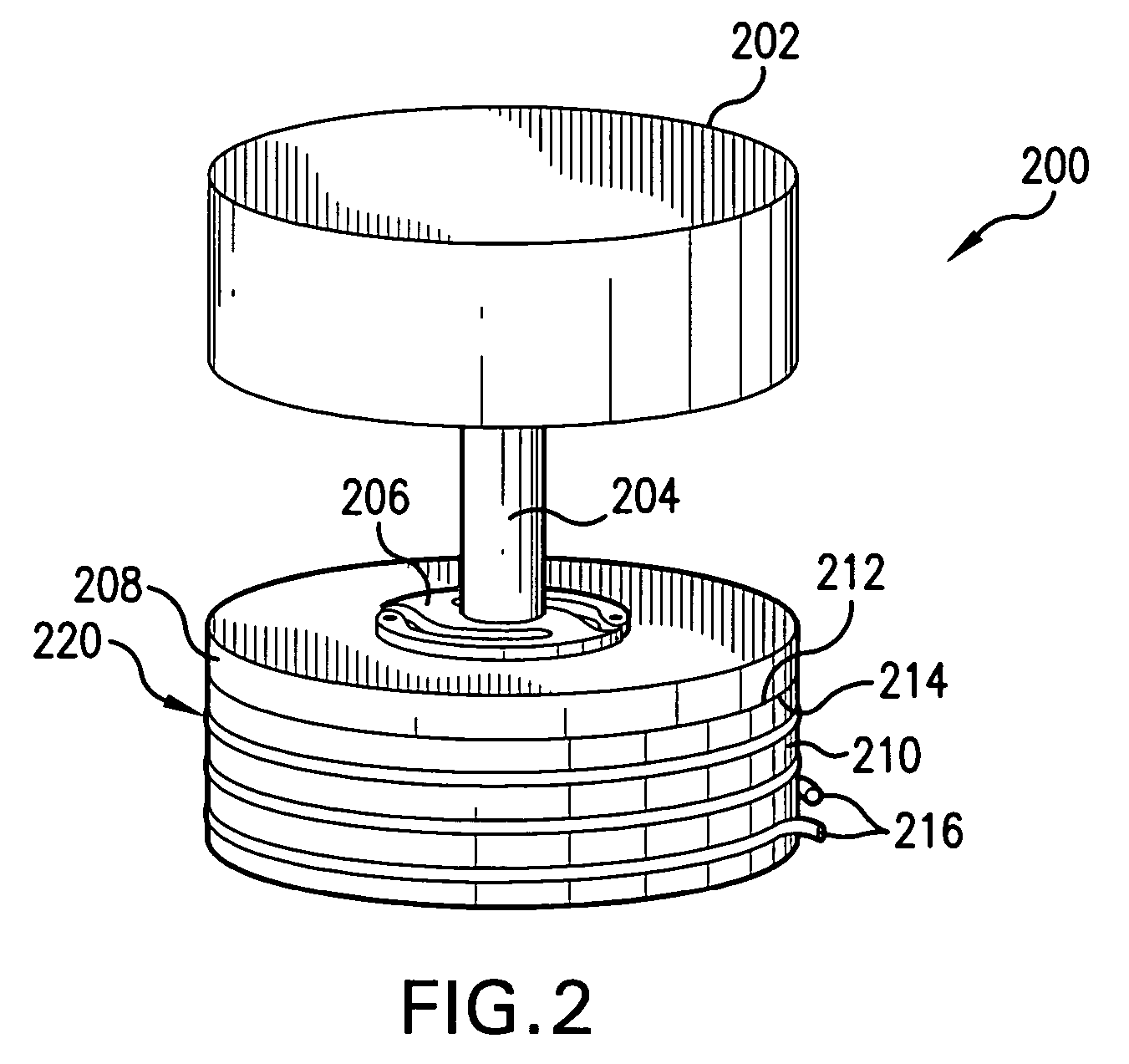
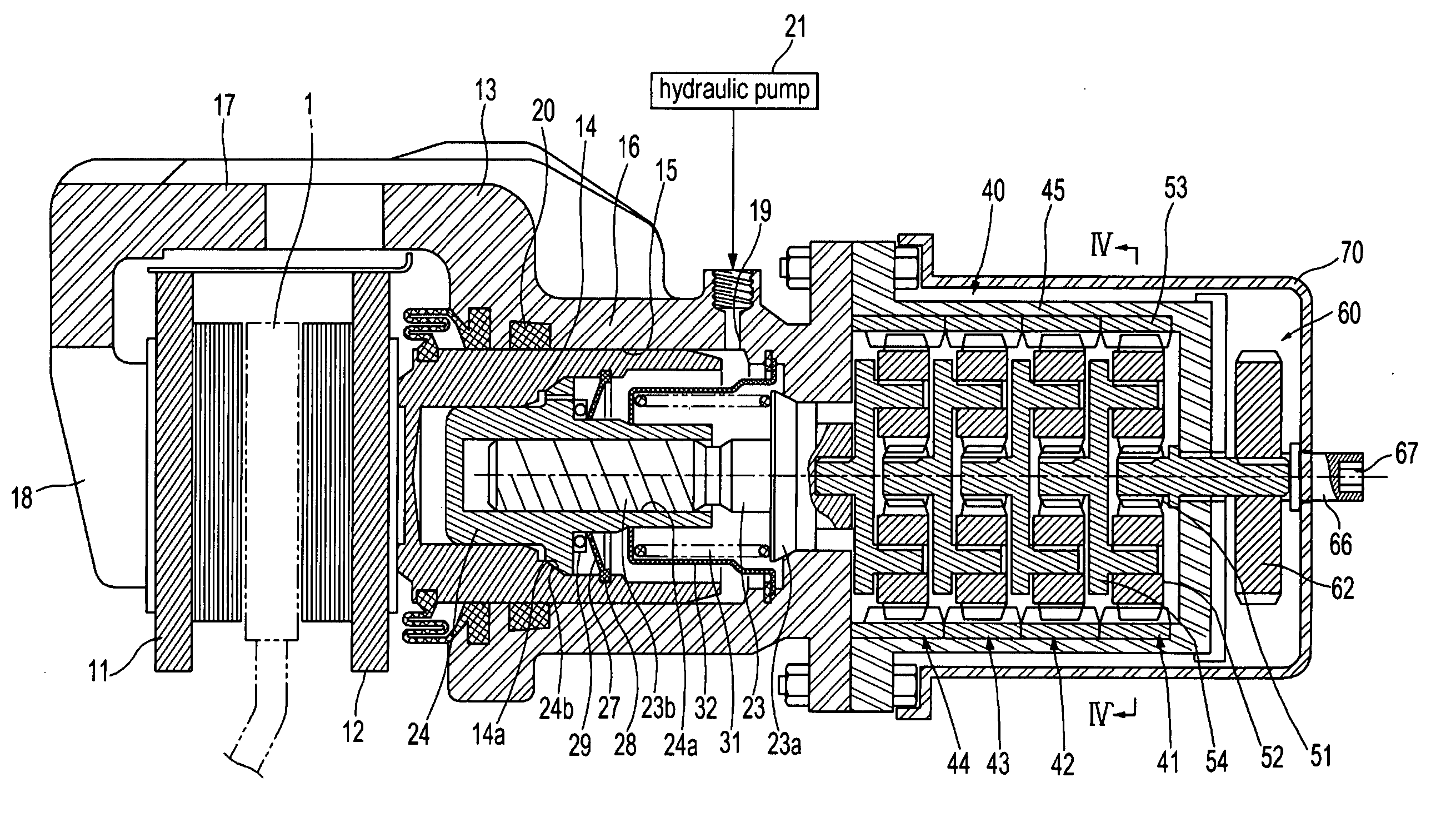
Electric park brake mechanism and method of operating an electric brake to perform a park brake function
ActiveUS20050109568A1Prevent movementBraking action transmissionMechanically actuated brakesEngineeringParking brake
An electromechanical braking system is disclosed that includes a brake rotor, a brake stator, an EMA (52) having a rotor shaft (36), a ram (42) operably connected to the EMA (52) having a first end movable between a first position urging the brake stator against the brake rotor and a second position, a clamp device (32) shiftable between a first clamping position in clamping engagement with the rotor shaft (36) and a second clamping position and a clamp controller (46) for shifting the clamping device (32) between the first and second clamping positions. A method of using the braking system as a parking brake is also disclosed.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Electric linear motion actuator and electric brake assembly
InactiveUS20100320043A1Smooth transmissionFluid actuated brakesMechanically actuated brakesLinear motionActuator
Owner:NTN CORP
Disk brake with a parking brake function
InactiveUS20070158148A1Large piston thrustRestrict movementMechanically actuated brakesElectrodynamic brake systemsCalipersParking brake
A disk brake with a parking brake mechanism capable of exerting a large piston thrust required for operating a parking brake, without adversely affecting operation of a service brake. A parking brake mechanism 32, which is driven by an electric motor provided outside a housing 30, is incorporated in a caliper 14 in which a piston 26 is slidably disposed in a cylinder 24. The parking brake mechanism 32 is slidably fitted via a seal member 36 into the piston 26 and provided with a nut member 37 that is prevented from rotating relative to the piston 26 by engagement of a pin 48 and a pin hole 49; and a shaft 35 that is screwed into the nut member 37. During a service brake operation, the piston 26 alone is moved by a hydraulic pressure under a small piston thrust. During a parking brake operation, the piston 26 and the nut member 37 are moved together by applying a hydraulic pressure and operating the electric motor at the same time, to exert a large piston thrust, by using a large pressure receiving area of the piston 26 and the nut member 37 combined.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
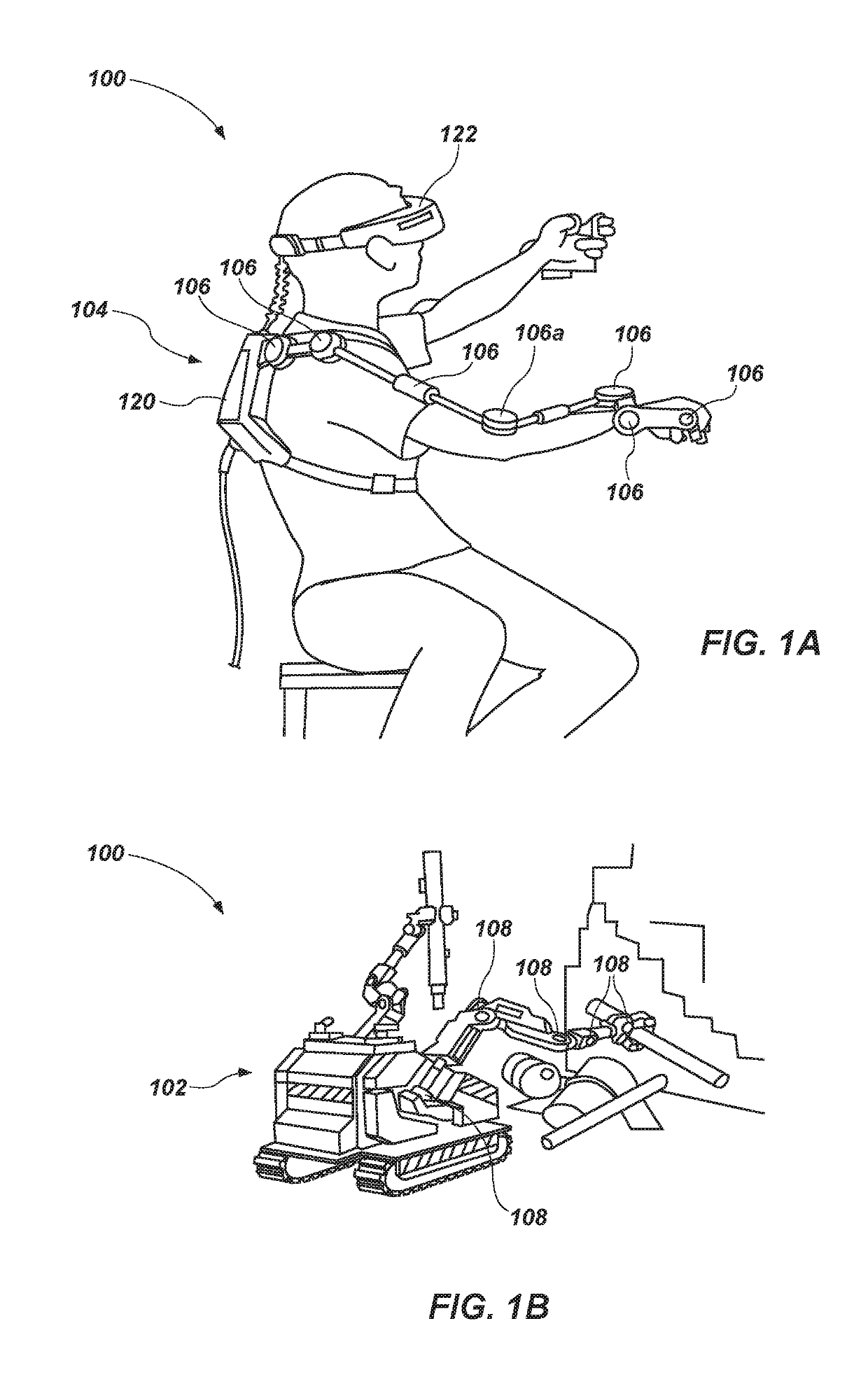
Resistance-Based Joint Constraint for a Master Robotic System
A master robotic system for translating a force at a slave robotic system to the master robotic system comprises a plurality of master brake joints rotatably coupling a plurality of robotic links. Each master brake joint corresponds to a respective slave joint of a slave robotic system. Each master brake joint comprises a first braking component (e.g., sheet disk(s)) coupled to a first robotic link and a second braking component (e.g., sheet disk(s)) coupled to a second robotic link, and an actuator operable to act upon the first braking component and the second braking component, to generate a braking force between the first braking component and the second braking component, in response to a control signal corresponding to a sensed force sensed by the slave robotic system. The actuator can comprise a bi-directional actuator, or a cam, piezoelectric, dielectric, or hydraulic actuator, each having minimal power requirements to maximize the braking force of the master brake joint.
Owner:SARCOS CORP
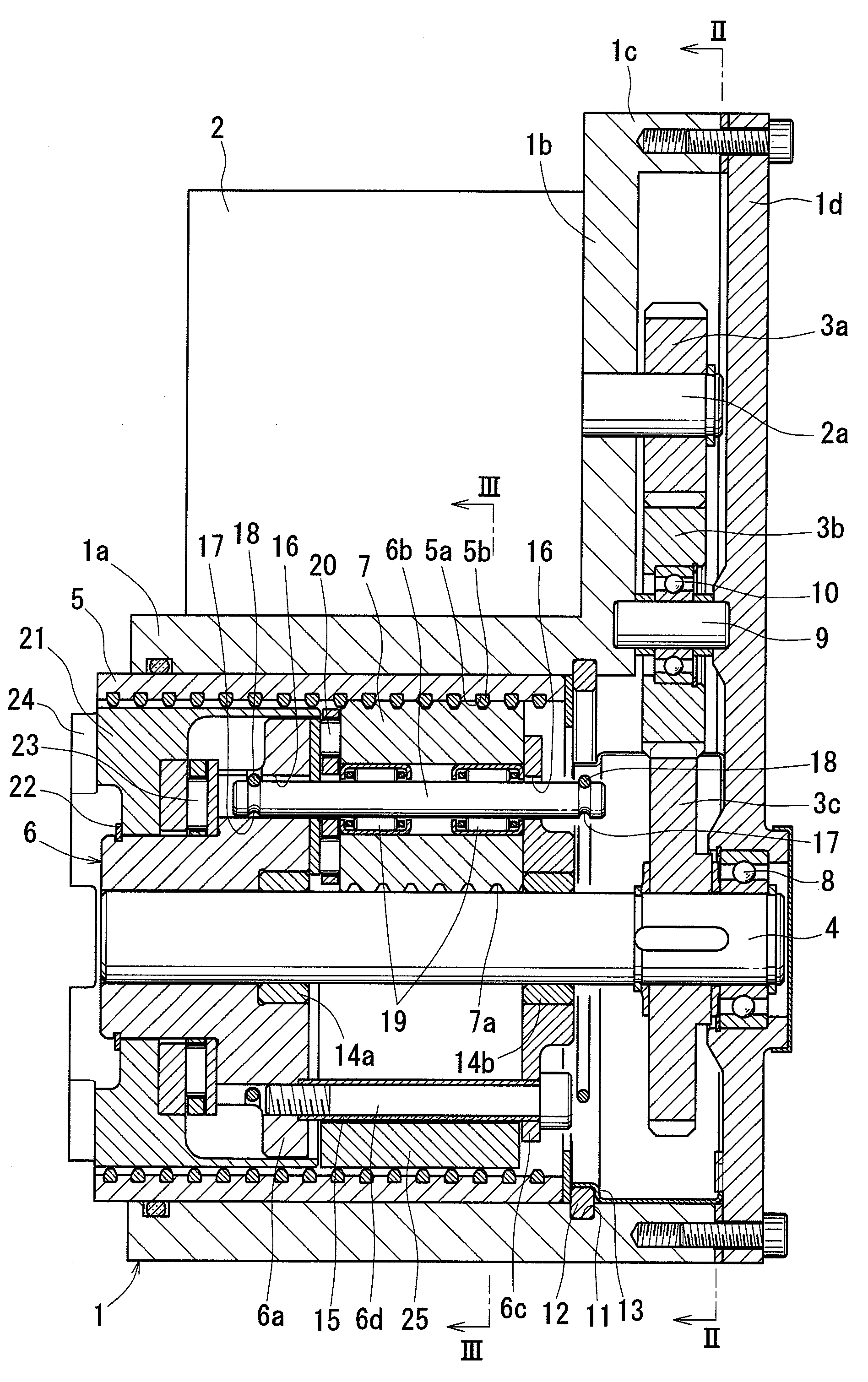
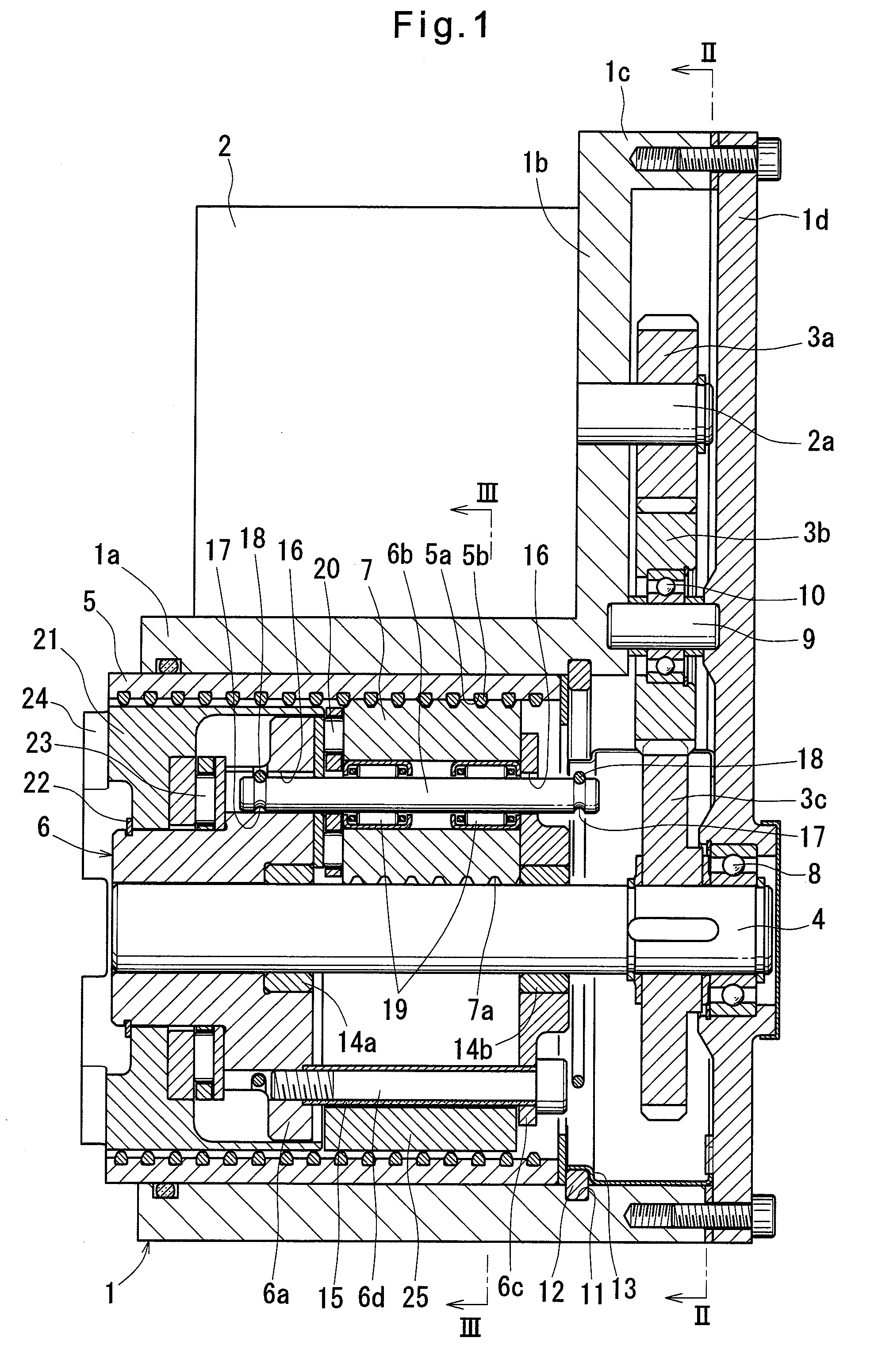
Disk brake
InactiveUS20100163351A1Poor responsivenessImprove responseMechanically actuated brakesBrake actuating mechanismsDriver/operatorEngineering
An object of the present invention is to provide a disk brake having excellent responsiveness. A rotation preventing mechanism 34A prevents a rotation of a carrier 41 (one output member) in a direction causing a piston 12 to return. An internal gear 46 (the other output member) rotates by a predetermined degree to act on the rotation preventing mechanism 34A. When the motor 38 causes a sun gear (input member) to rotate such that the piston 12 moves in a return direction, a rotation of the internal gear 46 according to the rotation of the sun gear 44 releases rotation prevention of the rotation preventing mechanism 34A to the carrier 41. It is possible to release the parking brake without use of a worm gear which is used in the conventional arts for holding a thrust force (self-holding). As a result, it is possible to quickly release the parking brake, and therefore a driver can start to run without delay after parking brake release, whereby the responsiveness is improved.
Owner:HITACHI AUTOMOTIVE SYST LTD
Electric Direct-Acting Actuator and Electric Brake Device
InactiveUS20080110704A1Low costWell formedMechanically actuated brakesElectrodynamic brake systemsLinear motionReducer
An electric direct-acting actuator is proposed which can maintain a large power increasing function without mounting a separate speed reducer.A plurality of planetary rollers 7 are disposed between the radially outer surface of a rotor shaft 5 of an electric motor and the radially inner surface of an outer ring member 1 fixed in position around the rotor shaft 5 so as to be rotatable about the rotor shaft 5 and about their own axes when the rotor shaft 5 rotates. A helical rib is defined by a rib member 9 engaged in a helical groove 8 formed in the radially inner surface of the outer ring member 1. The helical rib is engaged in circumferential grooves 10 formed in the radially outer surface of each planetary roller 7 at the same pitch as the turns of the helical rib. Thus, the rotary motion of the rotor shaft 5 is converted to a linear motion of the planetary rollers 7, so that it is possible to ensure a large power increasing function without mounting a separate speed reducer.
Owner:NTN CORP
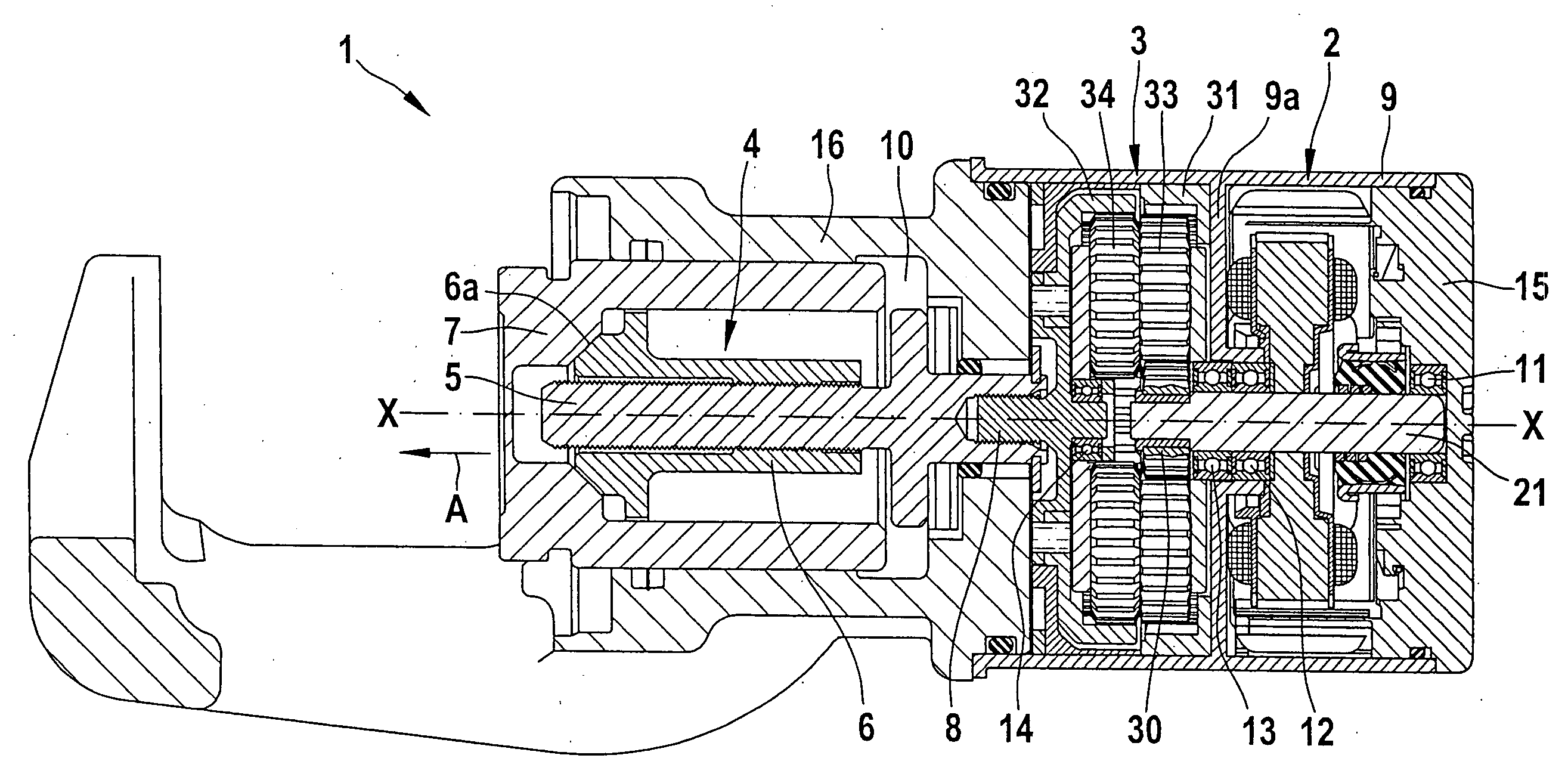
Screw actuator, and brake caliper comprising such actuator
InactiveUS6814190B1Improve compactnessBraking action transmissionMechanically actuated brakesLinear motionEngineering
A screw actuator which has a housing, a motor, an actuating member and a screw mechanism which provides a linear movement of the actuating member with respect to the housing in response to a rotational movement of the motor. The screw mechanism has a screw and a nut engaging each other by rolling elements, one of the screw or the nut is rotatbly supported with respect to the housing, and a reduction gear means. The nut is fixed with repect to the housing, and the screw is rotatably supported with respect to the housing by mean of rolling elements.
Owner:SKF ENG & RES CENT
Hydraulic brake actuator comprising electrically actuable lock for park brake
ActiveUS20050173206A1Reliable park brakeLow costMechanically actuated brakesBrake actuating mechanismsActuatorControl theory
In an automotive vehicle braking system, a hydraulic brake actuator includes a wedge for locking a hydraulic piston in a brake position for purposes of applying a park brake. To apply the park brake, hydraulic pressure is increased to advance the piston to urge the brake pads against the rotor. With the piston in the brake position, an electrical solenoid is energized to advance the wedge to engage the piston. The wedge includes an inclined surface that contacts an inclined surface connected to the piston or the housing, with sufficient frictional force to maintain the wedge in the advanced position without requiring hydraulic pressure or electrical power. Thus, the park brake remains applied even when the vehicle is turned off.
Owner:CHANGZHOU BWI AUTOMOTIVE ELECTRONIC TECH CO LTD +1
Combined service and parking brake apparatus and method for executing an emergency braking action
ActiveUS20070068746A1Simple and compact designImprove sealingMechanically actuated brakesElectrodynamic brake systemsElectricityElectric drive
A combined service and parking brake apparatus, having a brake unit equipped with a brake disc and at least one brake pad in which a fluid pressure actuatable brake piston is able to place the brake pad against the brake disc and having a parking brake unit which includes an electric drive unit, a transmission, and a spindle unit equipped with a nut and spindle in order to mechanically lock the brake unit in a parking brake position, and in which the electric drive unit, the transmission, and the spindle unit are situated in series on a common axis.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Electric linear motion actuator and electric brake system
ActiveUS20130048443A1Precision productionGenerate accuratelyMechanically actuated brakesToothed gearingsElectricityLinear motion
An electric brake system is proposed which includes an electric linear motion actuator and can generate the required braking force with high accuracy. A load sensor (30) is provided in a motion converting mechanism of the actuator which converts the rotary motion of a rotary shaft (4) to which the rotation of an electric motor (2) is transmitted to linear motion of an outer ring member (5) as an output member. The load sensor (30) detects the pushing force with which the outer ring member (5) linearly drives a driven member. With this arrangement, if the driven member is a braking member of an electric brake system, it is possible to directly detect the braking force applied by the driven member and thus to accurately generate the required braking force.
Owner:NTN CORP
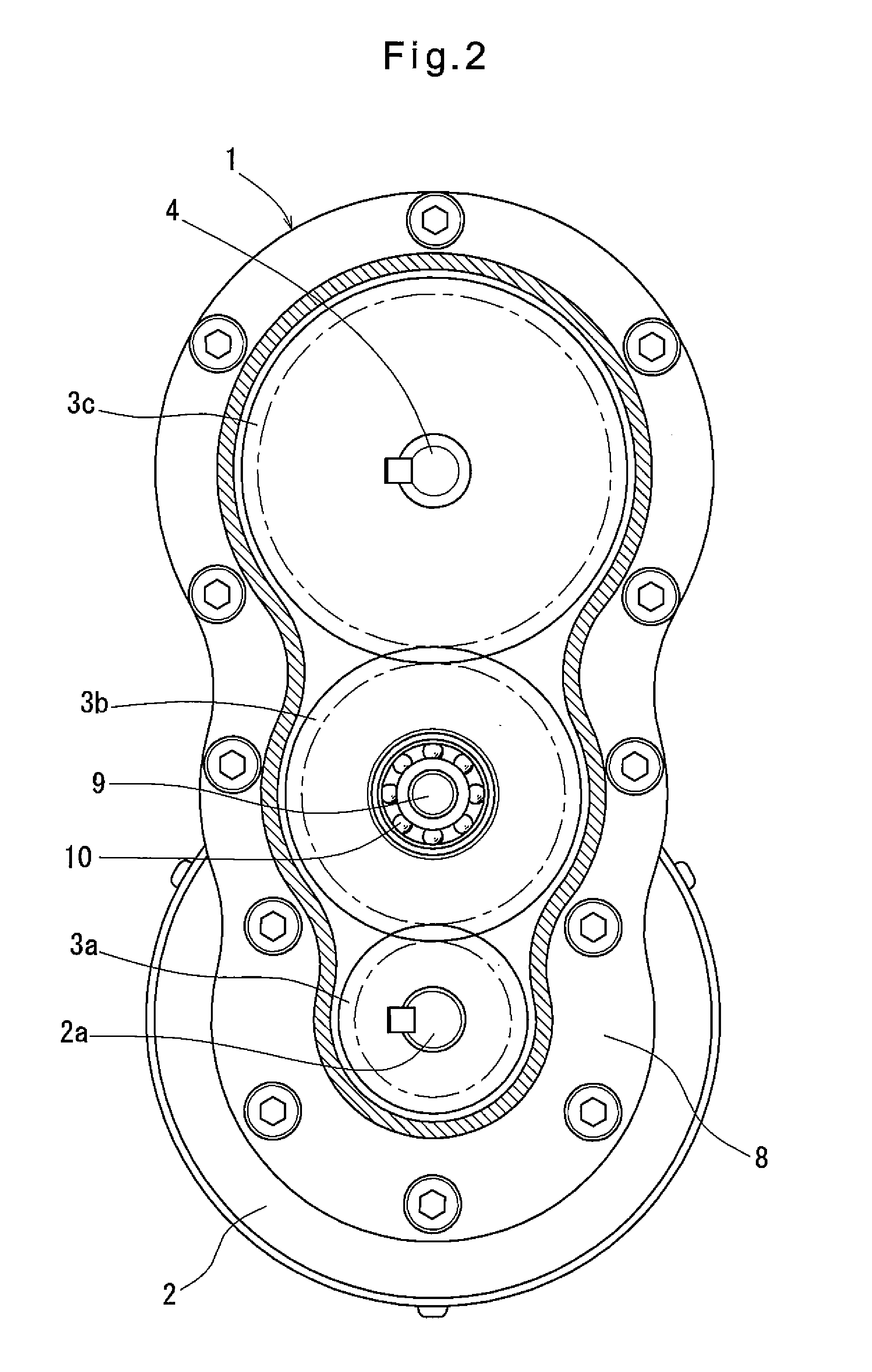
Planetary gearbox with integral service brake
ActiveUS20130161148A1Protect environmentLow costBraking element arrangementsMechanically actuated brakesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A brake mechanism includes a fixed housing in which the brake mechanism substantially resides. A plate closes the fixed housing and includes a cylindrical portion extending partially within the fixed housing. A parking piston and a service piston are employed to act against a brake stack which includes a plurality of stators and rotors interleaved together. A wear adjuster is press-tit onto the cylindrical portion of the plate and engages the service piston daring actuation of the service piston and compensates for wear of friction material from the rotors or stators such that the distance between the service piston and the brake stack is substantially the same during the life of the brake mechanism. If neither the service piston nor the parking piston engage the brake stack prohibiting rotation of the input drive, the planetary gear set drives the rotating output drive with respect to the fixed housing.
Owner:FAIRFIELD MFG CO INC
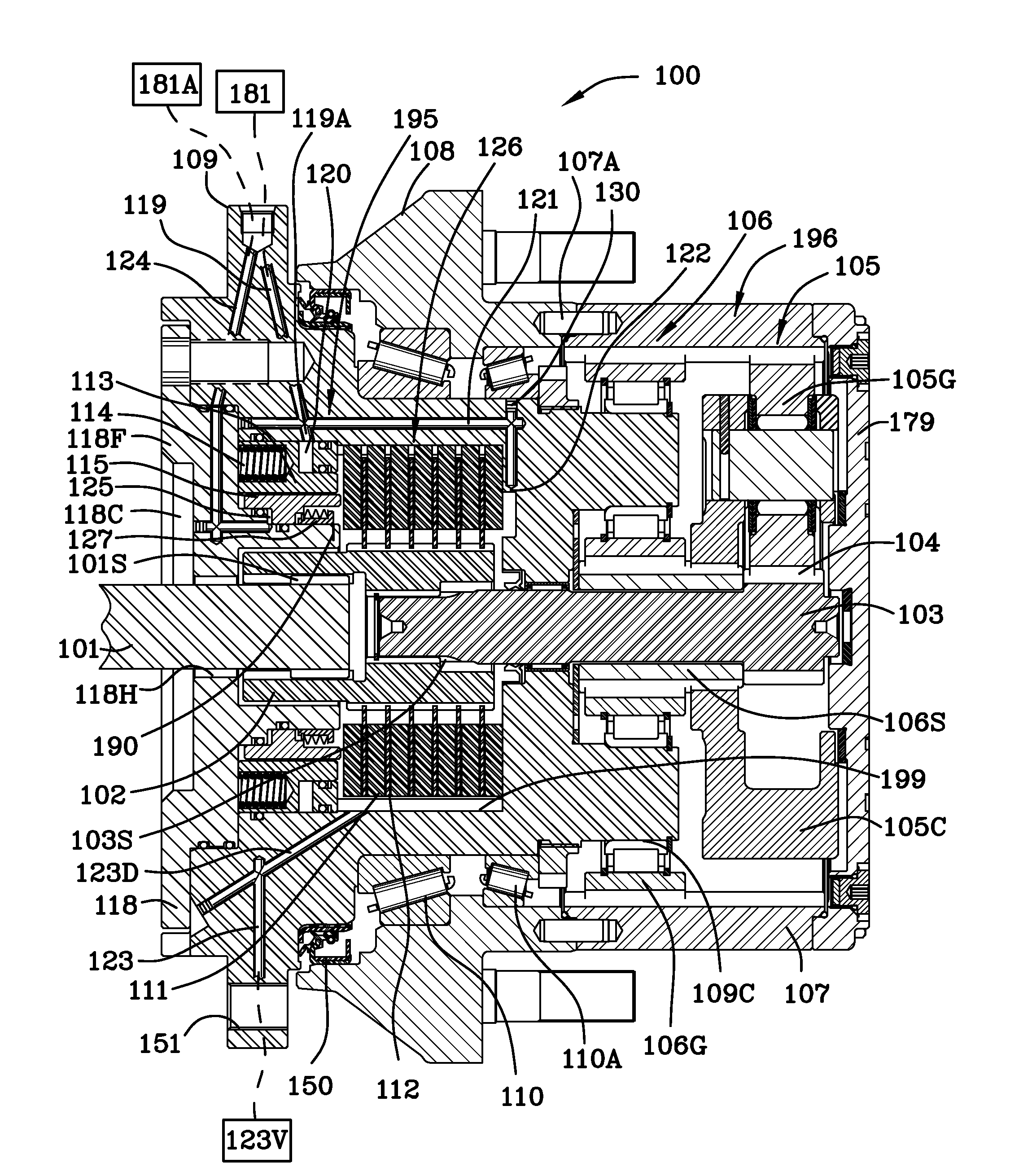
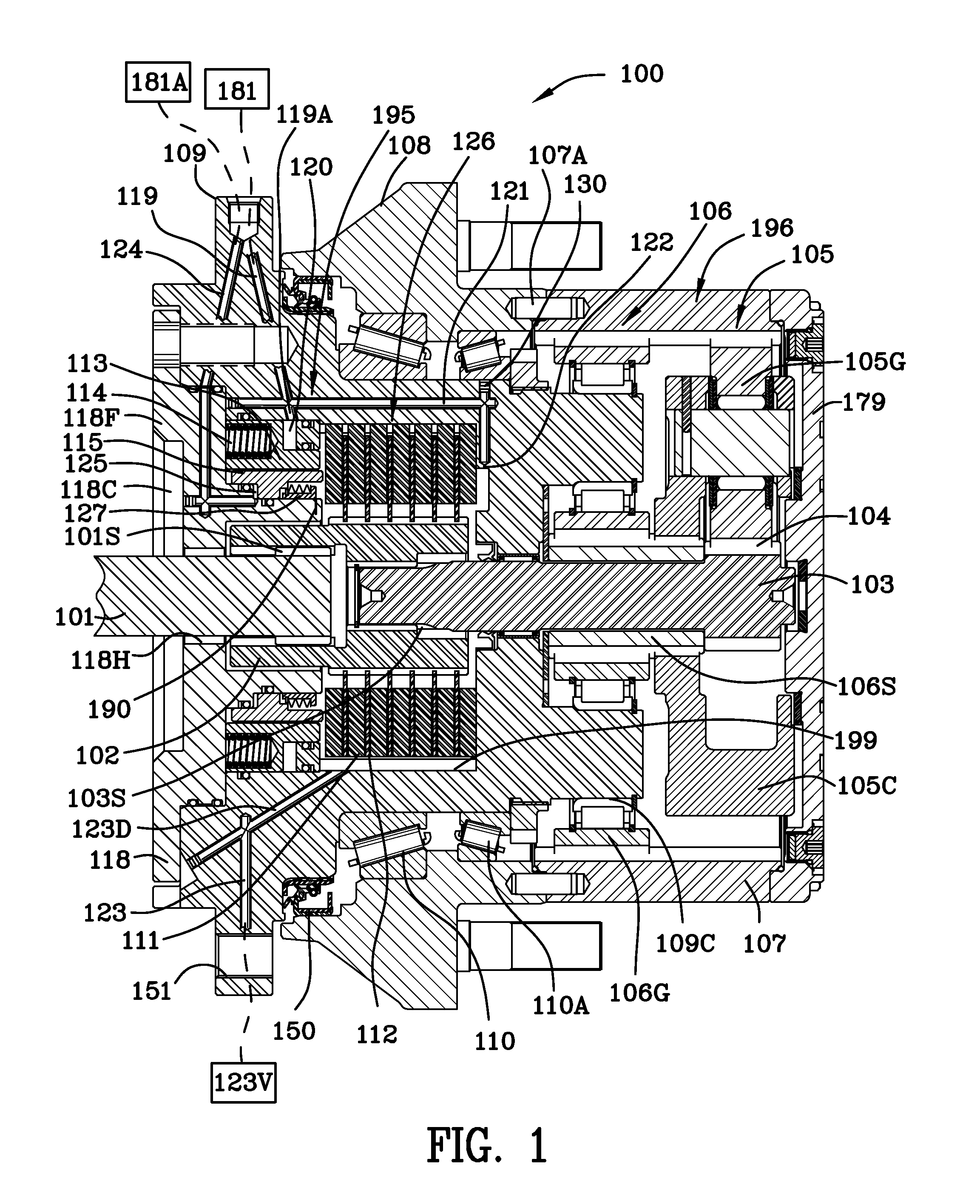
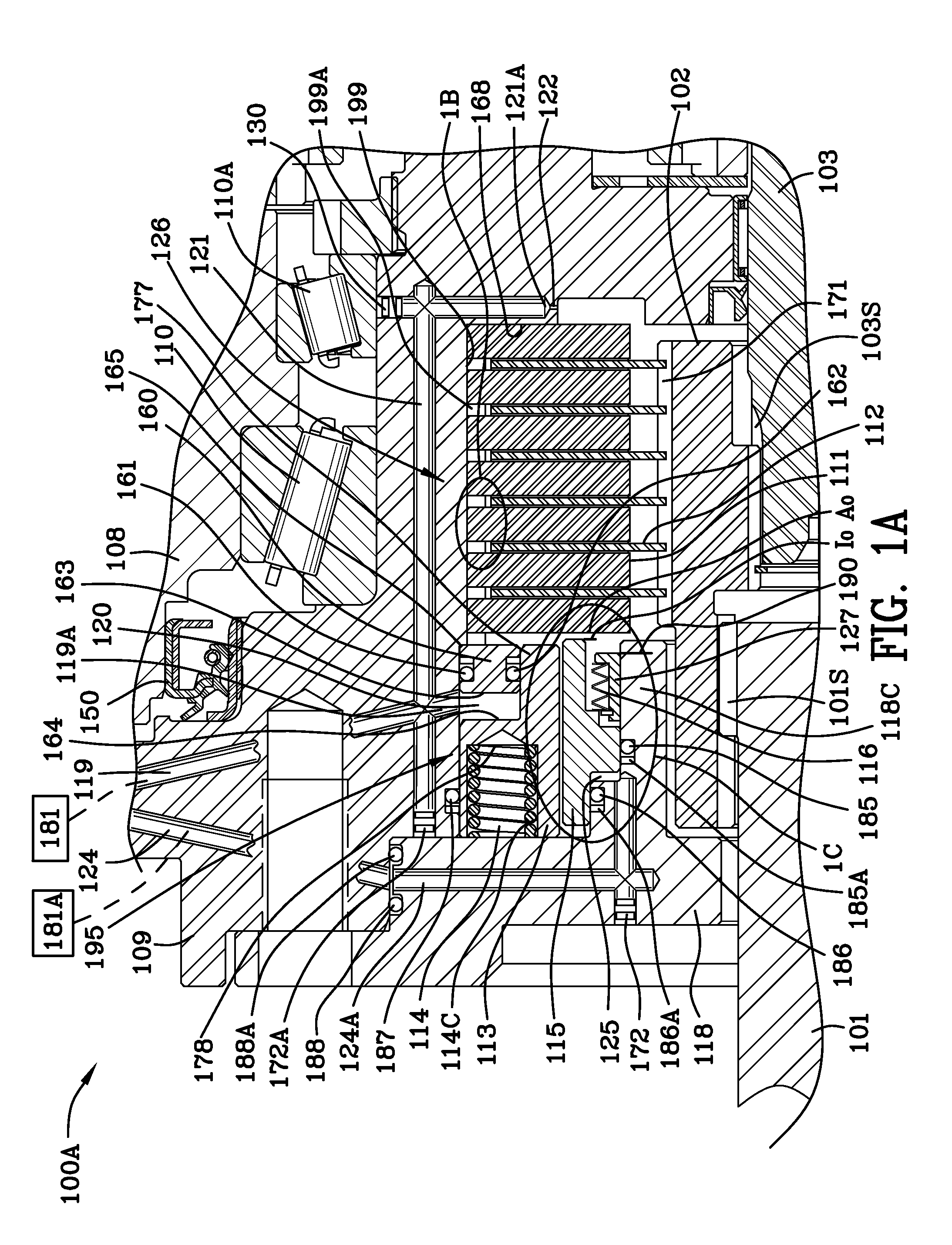
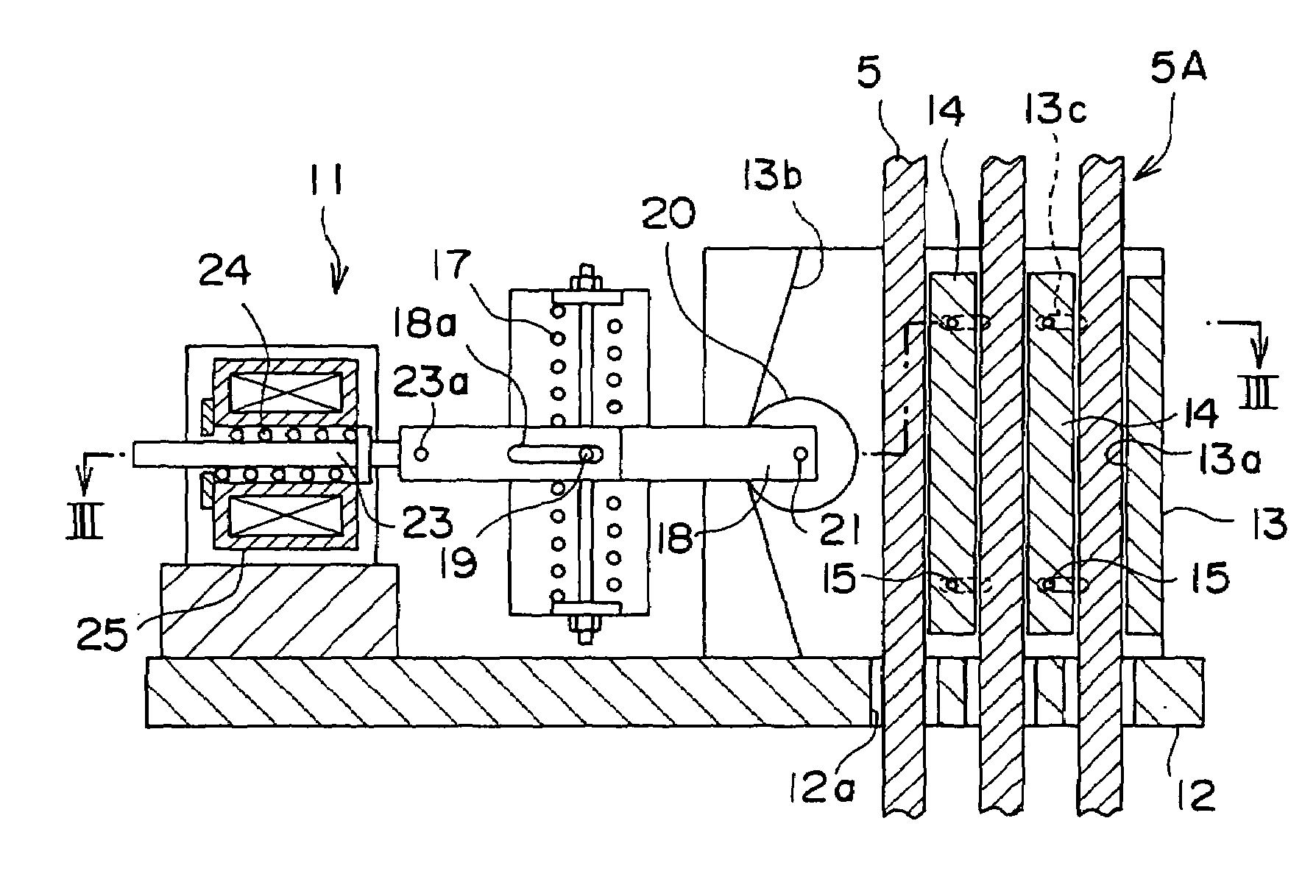
Motion control apparatus
ActiveUS20050183907A1Inhibit transferMechanically actuated brakesRail brake actuationEngineeringMotor control
A brake (10) having application for a linear or rotational motion device includes a housing (120) in which a first piston (140), a wedge (142) and a second piston (144) cooperate to engage a friction facing (136) through a plurality of rollers (152, 154, 156, 158). The three part piston assembly (148) allows a braking action and prevents torsional forces that are non-axial to the axis of the first piston (140) and second piston (144). The pistons (140, 144) are biased by compression springs (176) and may be actuated by a fluid.
Owner:NEXEN GROUP INC
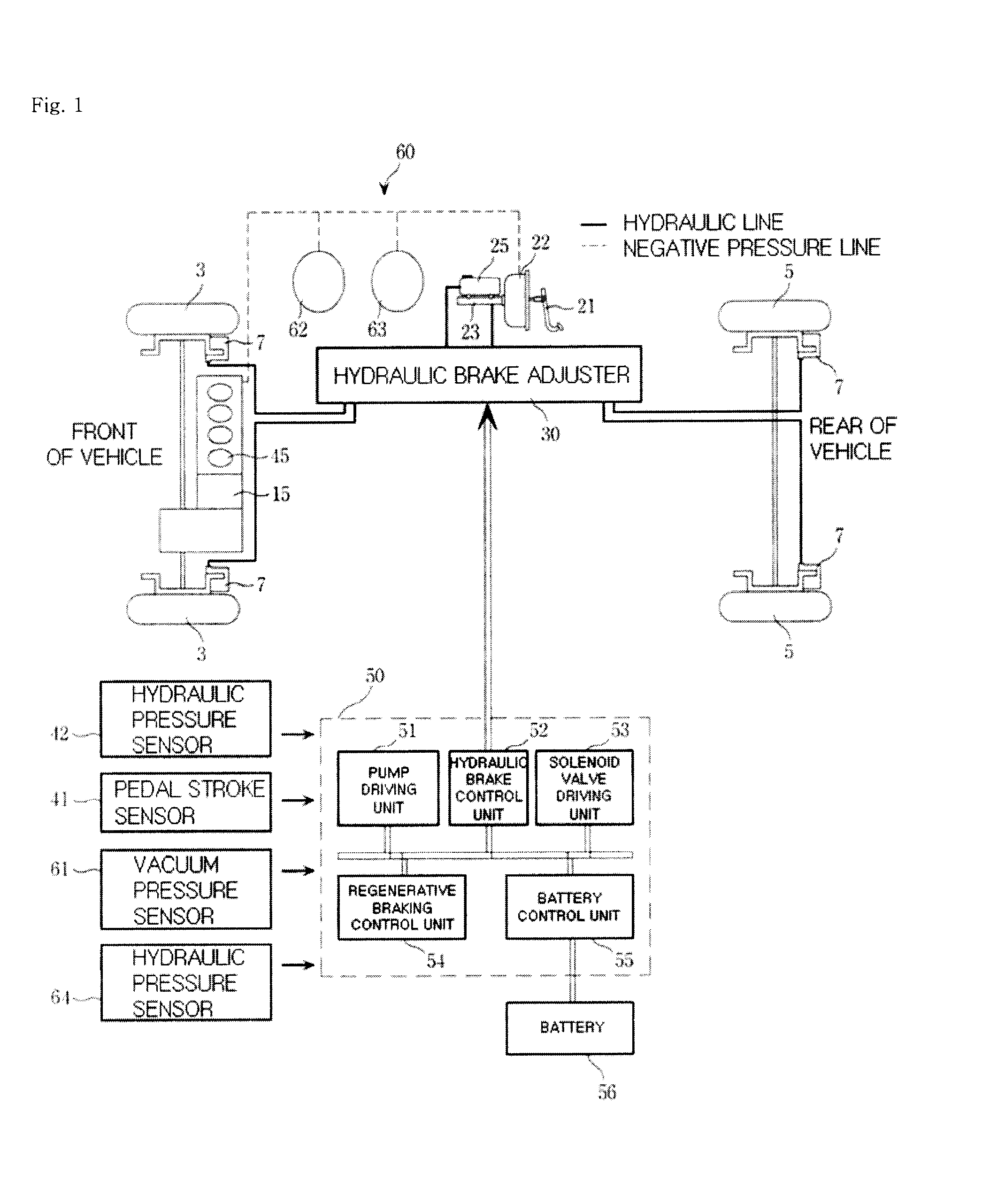
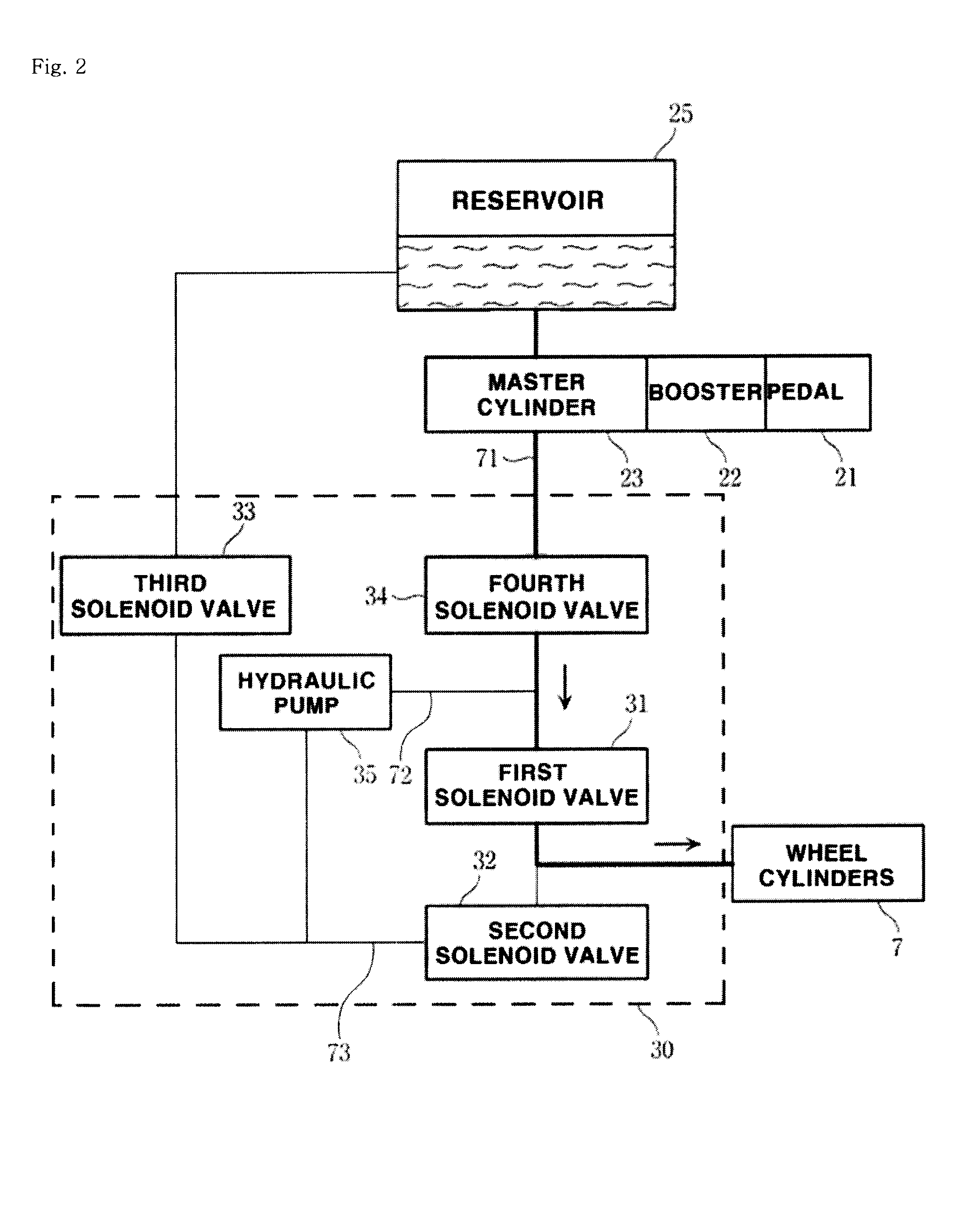
Brake system for hybrid electric vehicle and control method thereof
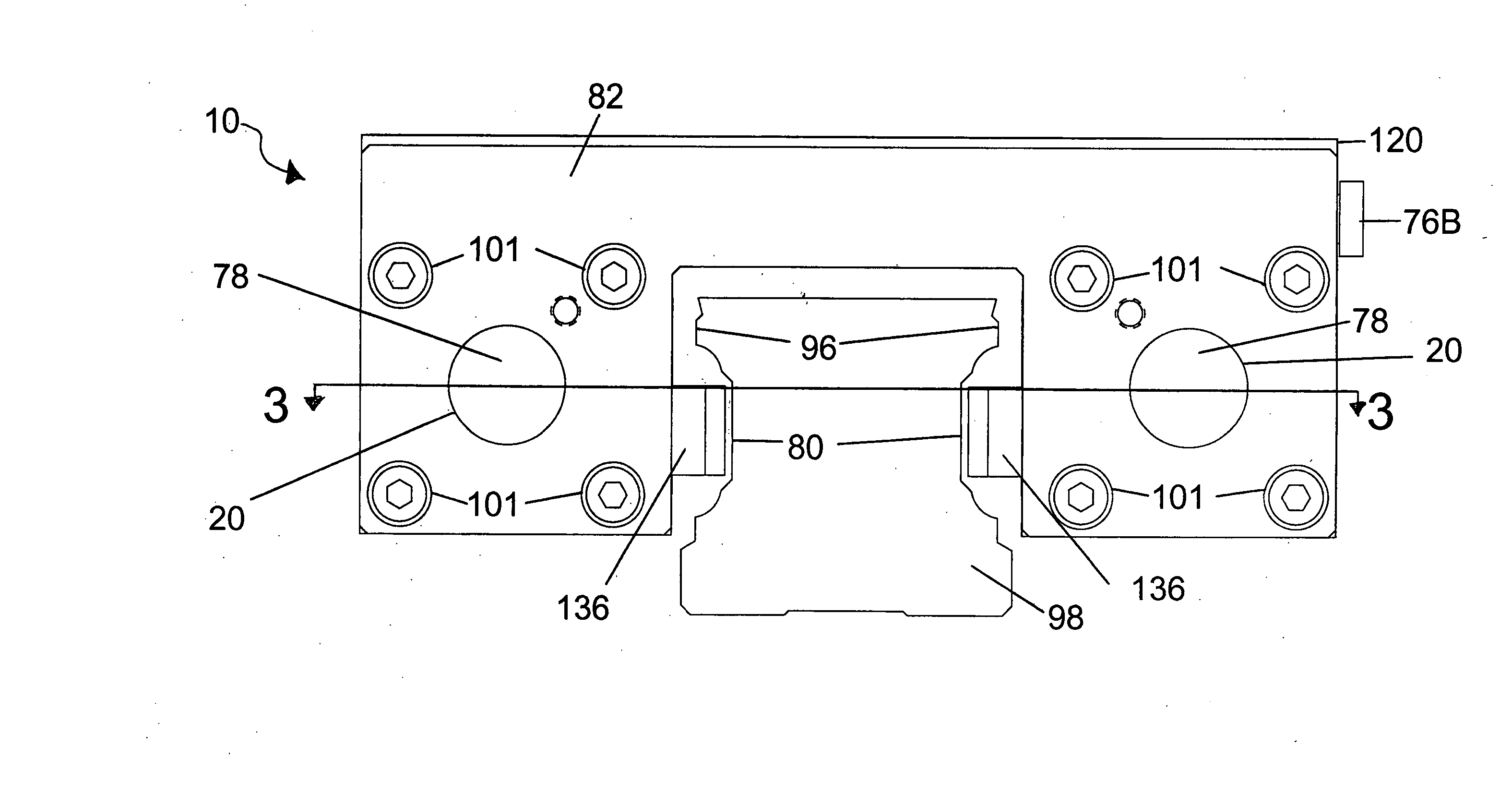
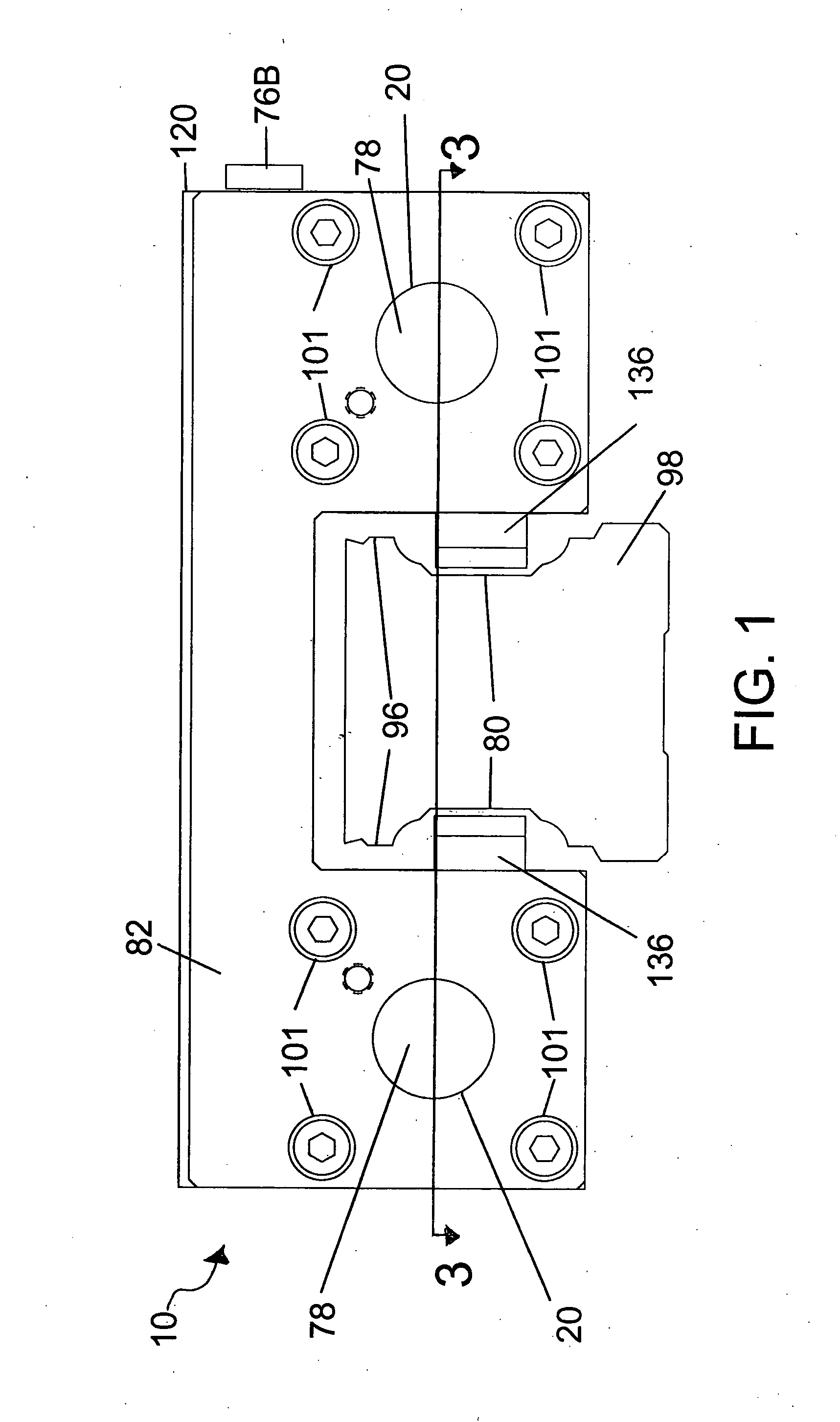
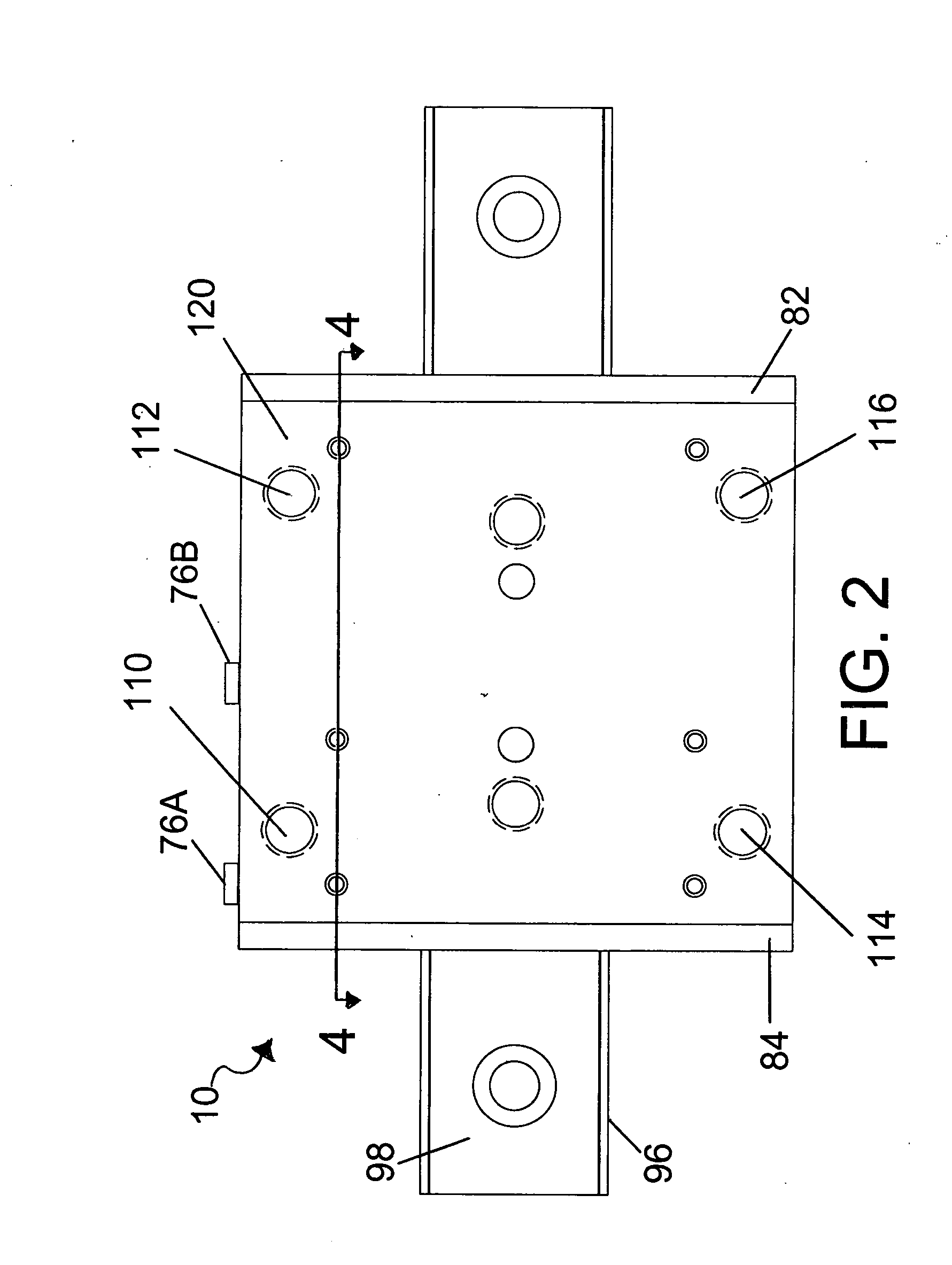
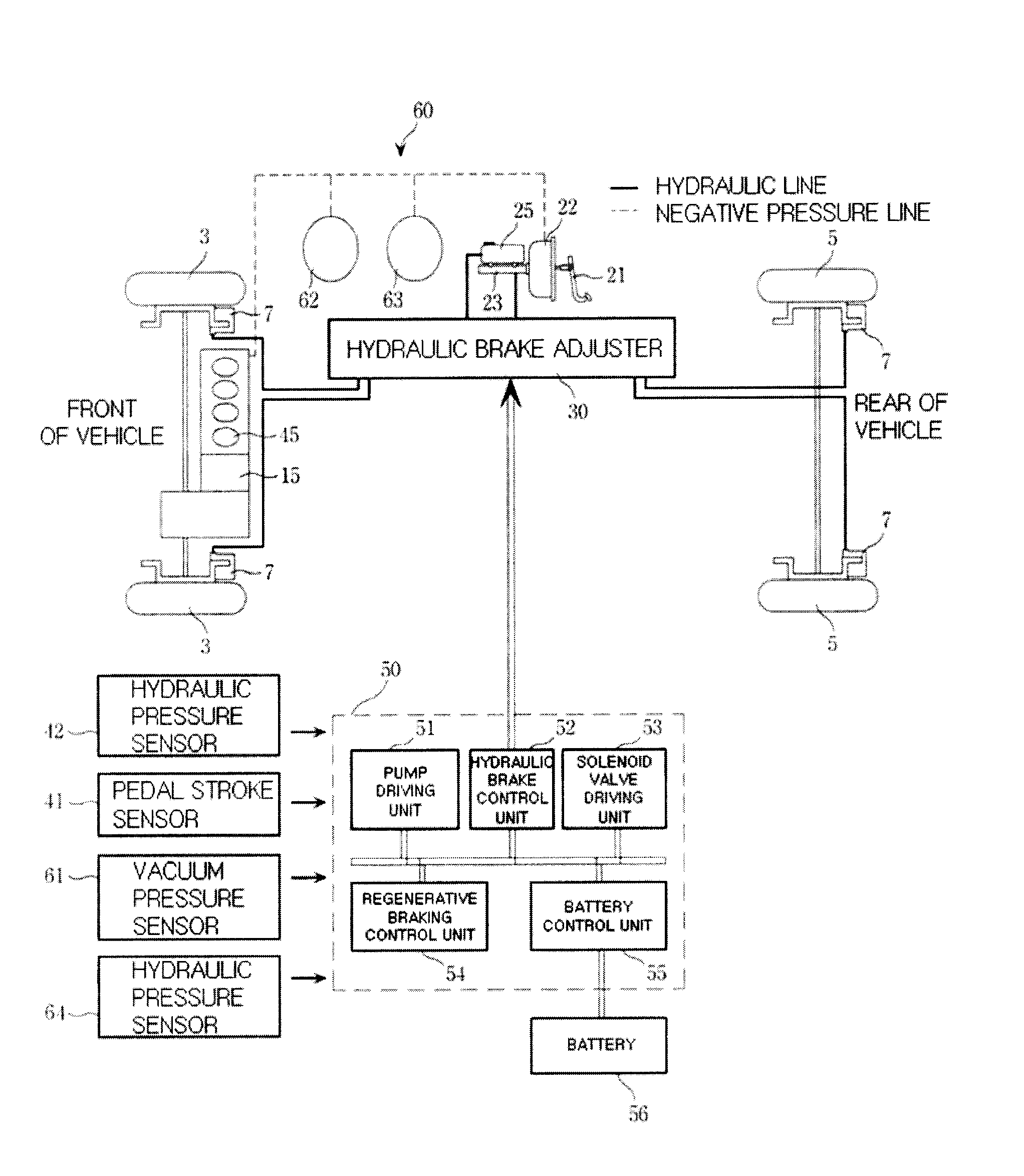
InactiveUS20080210497A1Reduce hydraulic pressureHybrid vehiclesMechanically actuated brakesDrive motorEngineering
The present invention provides a brake system and its control method for a hybrid electric vehicle, comprising a driving motor generating a regenerative braking torque; a hydraulic pressure supplying unit including a brake pedal, a booster and a master cylinder, a first hydraulic line, and a reservoir; a hydraulic brake adjuster for controlling a hydraulic braking pressure; a target braking force detection unit, including a pedal stroke sensor and a hydraulic pressure sensor, for detecting a target braking torque of a driver; and a control unit controlling the driving motor by calculating a maximum regenerative braking torque based on a rotational speed of the driving motor, etc. and controlling the hydraulic brake adjuster to change a hydraulic braking torque to meet the target braking torque in accordance with the thus calculated maximum regenerative braking torque by compensating an braking torque with the hydraulic braking torque.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Electric Braking Apparatus and Vehicle Having Thereof
ActiveUS20080059023A1Braking element arrangementsMechanically actuated brakesEngineeringContact position
An electric braking apparatus which first moves a piston in a detaching direction or passes a current to move the piston in the detaching direction in order to detect a pad contacting position. Furthermore, while the piston moves in the detaching direction, pad non-contact judgment is performed. After a pad non-contact state is confirmed, the piston is moved in a pressing direction to detect the pad contacting position. When the piston does not move in the detaching direction, it is judged that a parking brake has an ON-state, and it is waited until a host system instructs parking brake release.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Parking brake assembly for railway vehicle brake system
ActiveUS20080179144A1Simple and safe operationRule out the possibilityMechanically actuated brakesRail brake actuationIn vehicleActuator
A parking brake assembly for a railway car includes a ratchet mounted for rotation on a threaded piston rod of a brake actuator and a holding pawl engageable with the ratchet for maintaining a push rod of the parking brake assembly to apply braking force when the air pressure is lost in the brake pipe and releasing the push rod to accordingly release the braking force when the supply of air pressure in the brake pipe is restored. An operating lever and a cylinder connected thereto are provided for selectively rotating the holding pawl. Valve is provided for supplying air pressure to and evacuating it from the cylinder. Release mechanism is provided for manually releasing the braking force. The parking brake assembly is employed with either truck-mounted or carbody-mounted braking system.
Owner:WABTEC HLDG CORP
Hydraulic vehicle brake
InactiveUS7434669B2Simple and low-costFluid actuated brakesBraking action transmissionMobile vehicleMotorized vehicle
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
Emergency brake apparatus of elevator
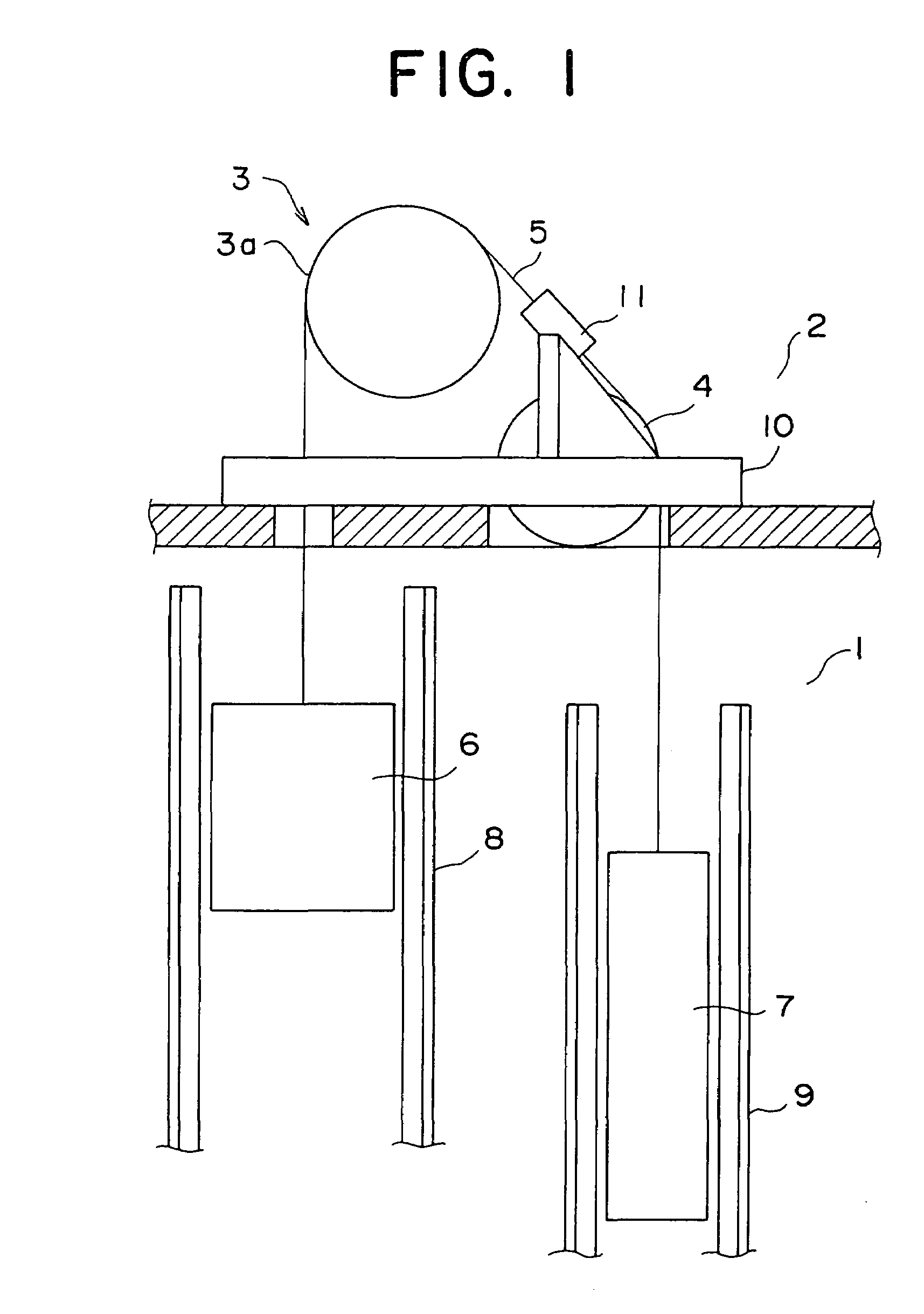
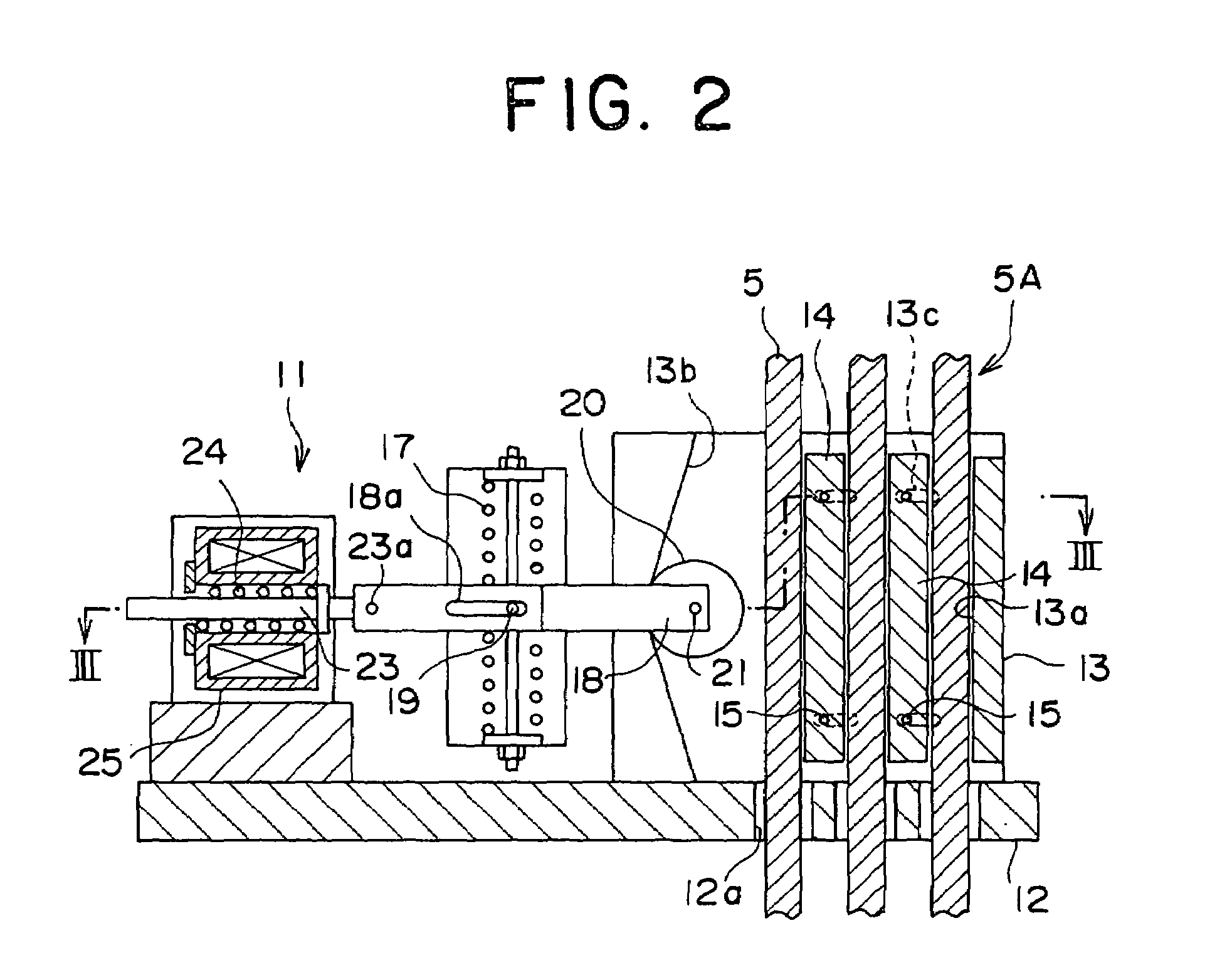
InactiveUS7080717B2Small sizeMechanically actuated brakesFilament handlingEngineeringEmergency situations
In an elevator emergency braking apparatus, a braking device main body has a main body braking surface facing a main rope and positioned at a first side of a main rope array, and a tapered surface facing the main body braking surface on an opposite side of the main rope array. An intermediate braking piece is disposed between mutually-adjacent main ropes inside the braking device main body. The intermediate braking piece is displaceable in a direction to be placed separably in contact with the main body braking surface. A wedge member is disposed between the tapered surface and the main rope array. The wedge member is separated from the main ropes during normal operation, and wedged between the tapered surface and the main ropes during braking.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com