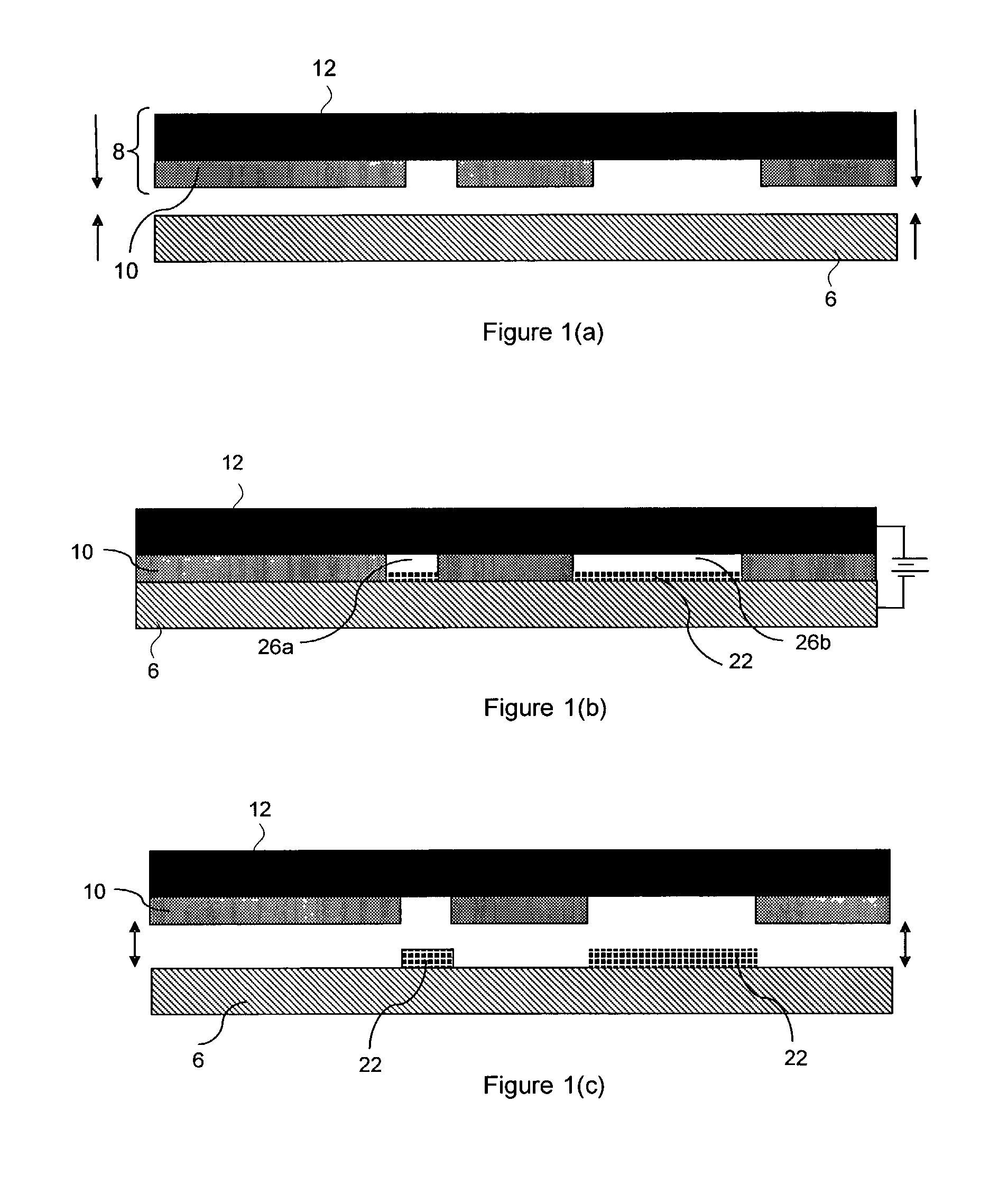
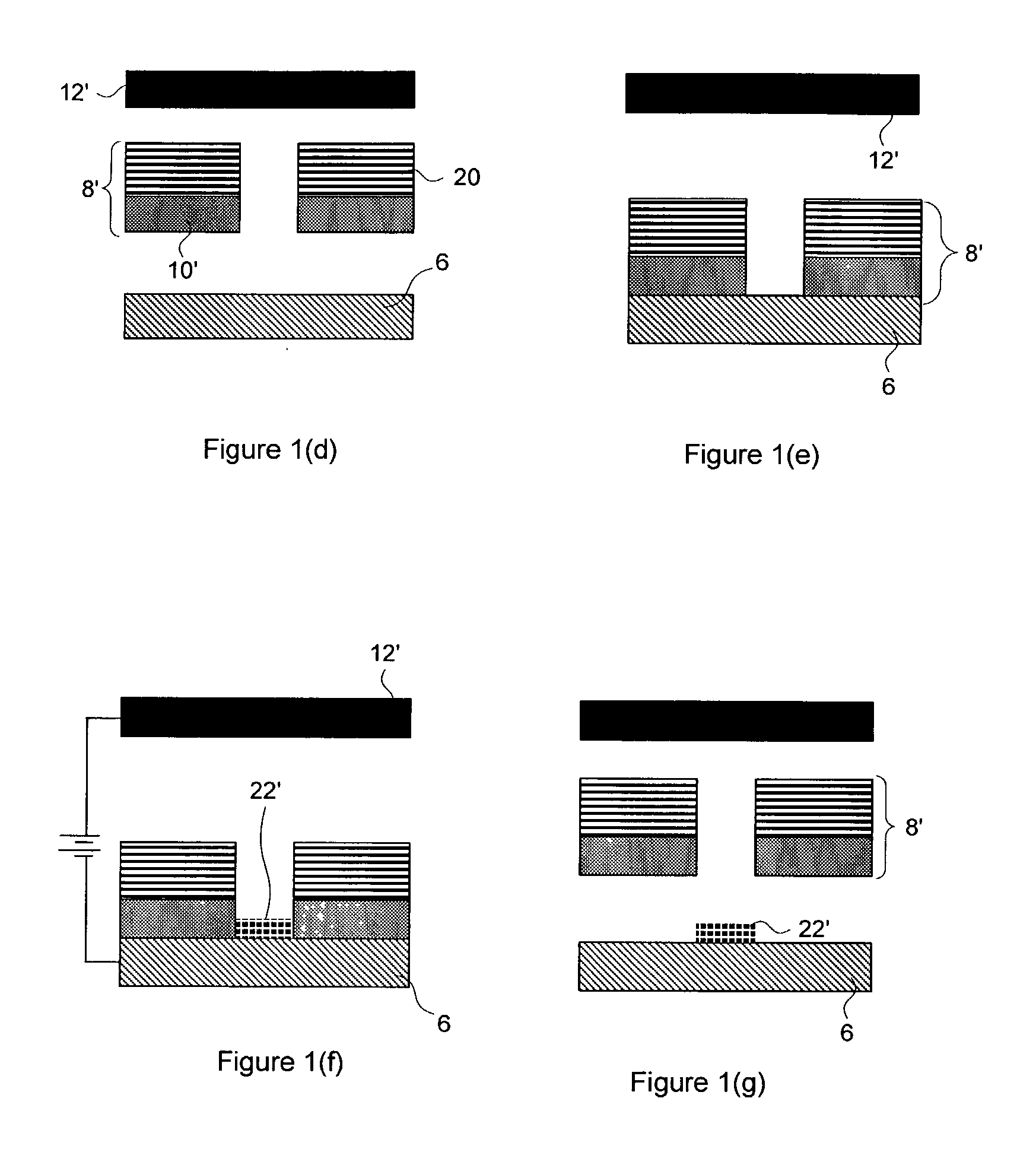
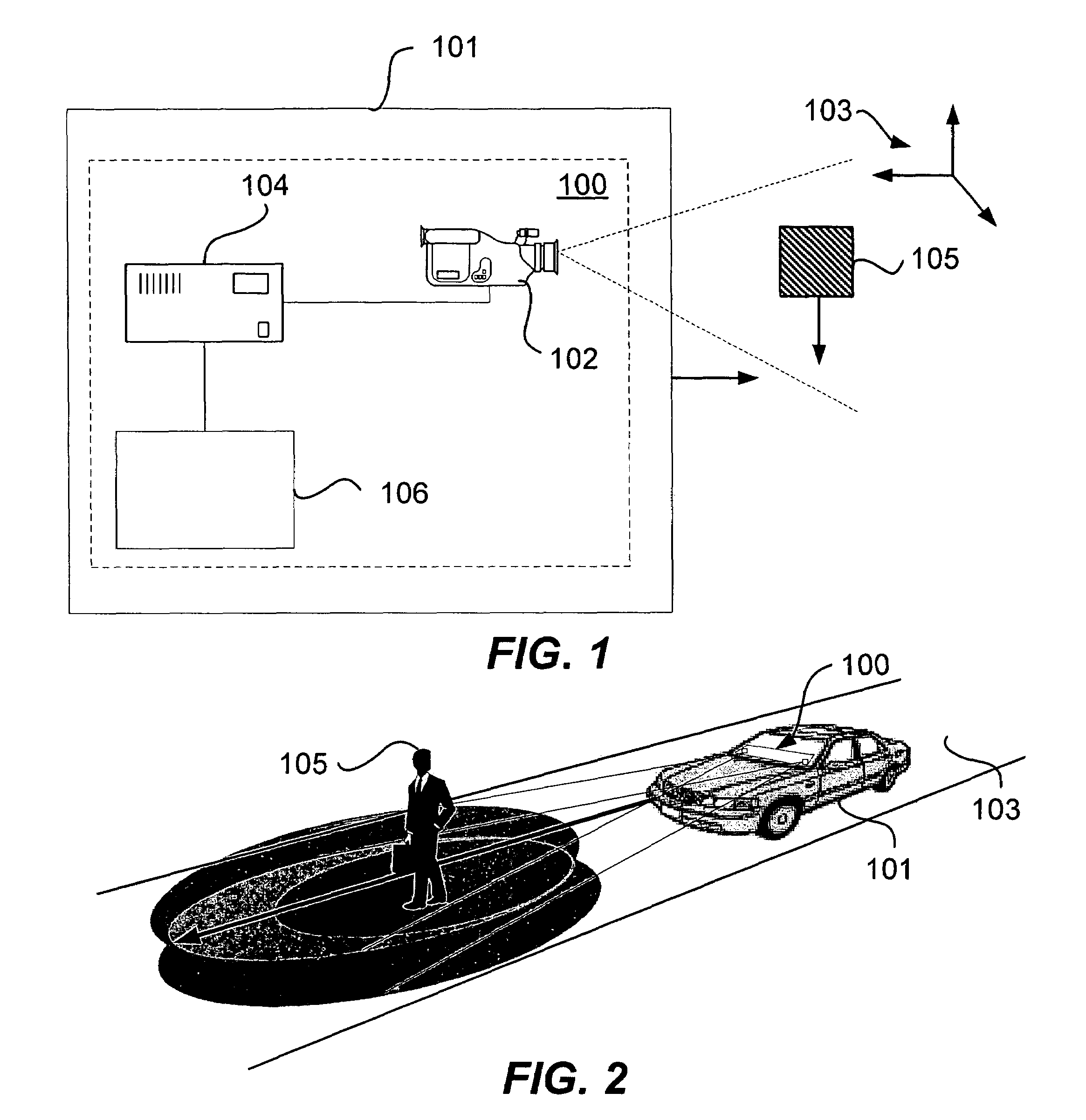
Patents
Literature
1253 results about "Translational motion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In aeronautics, translational motion means movement along a straight line, forwards or backward, left or right and up or down. When an airplane is circling an airport, it is continually changing its orientation and undergoing some degree of rotation.
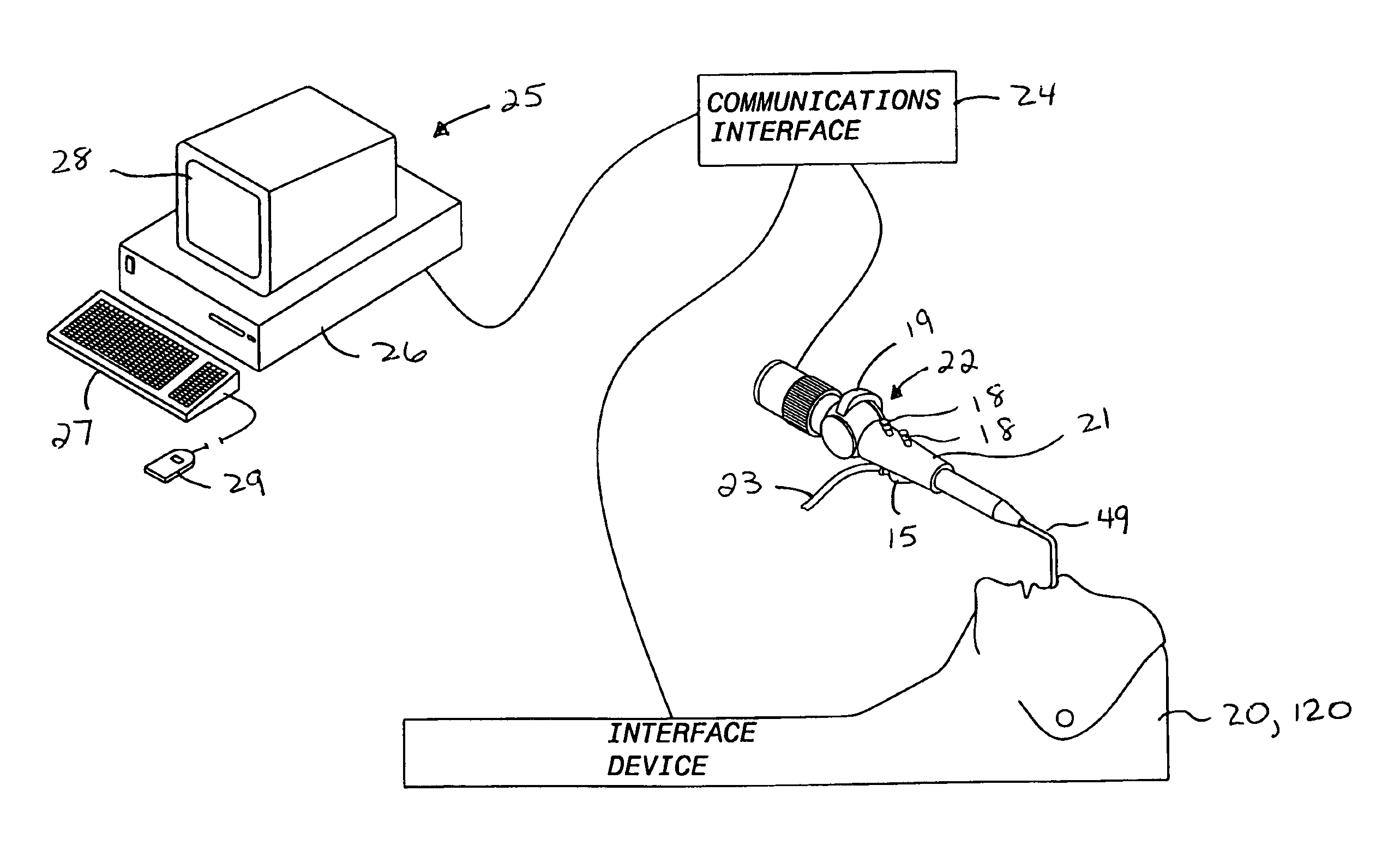
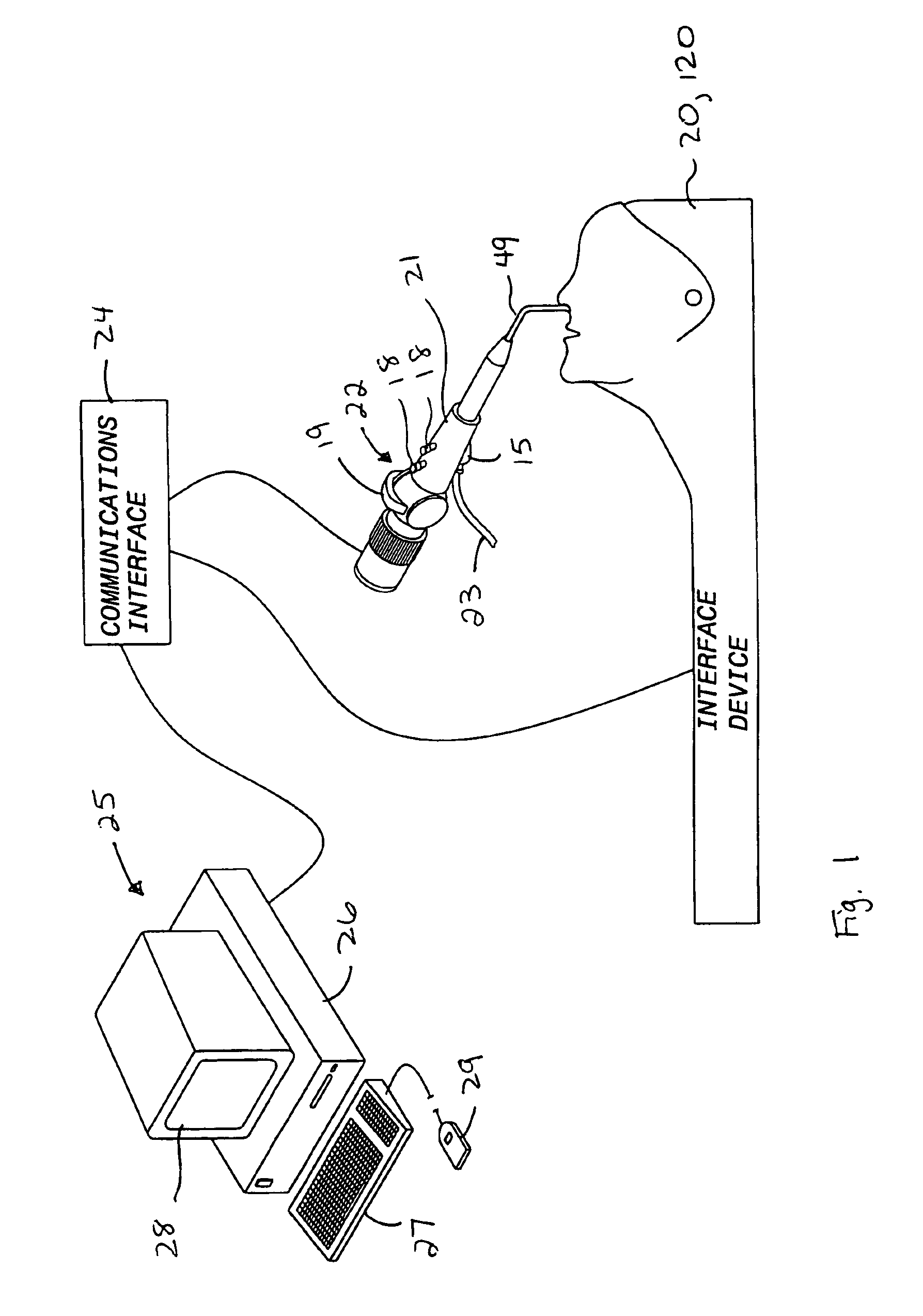
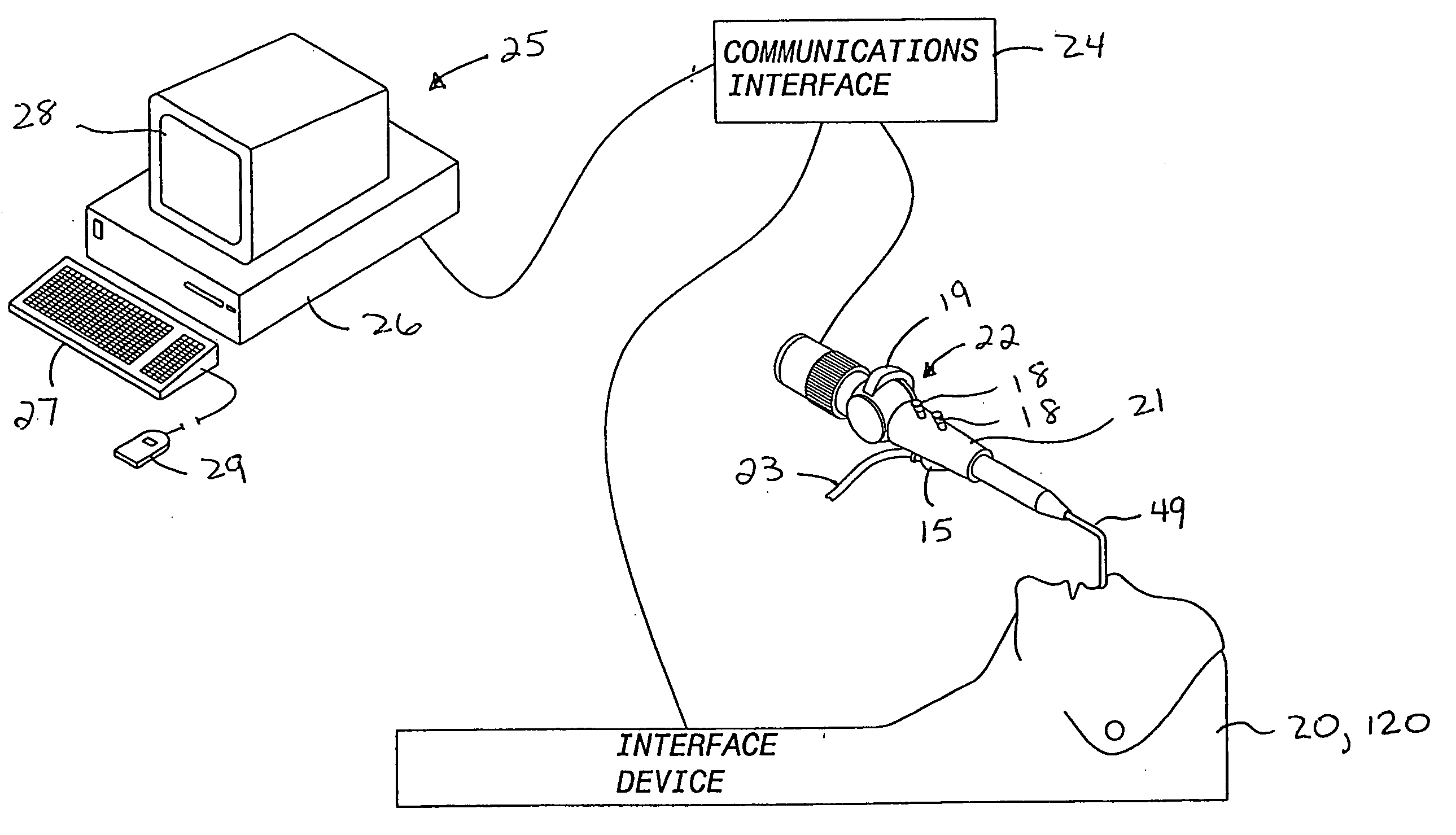
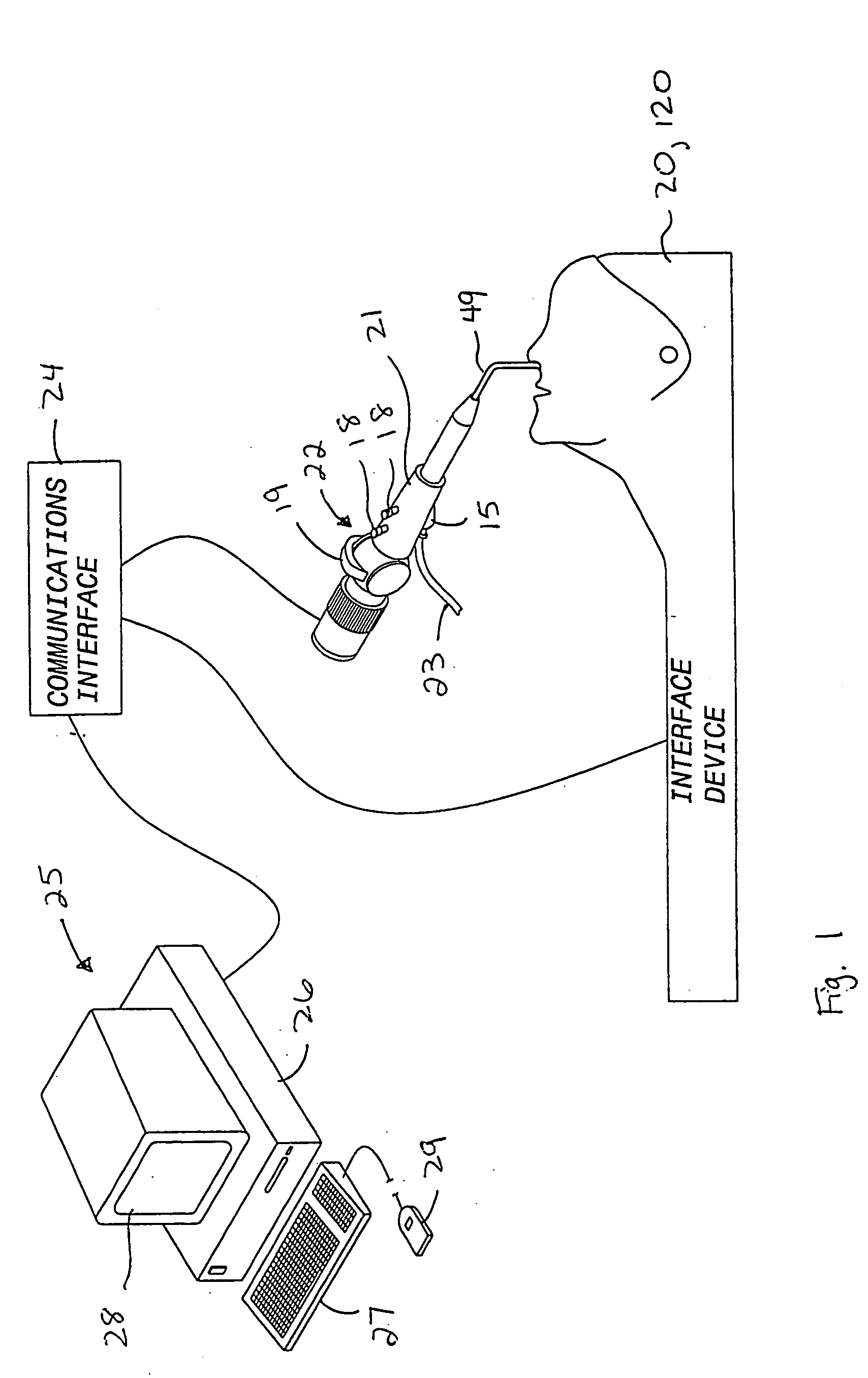
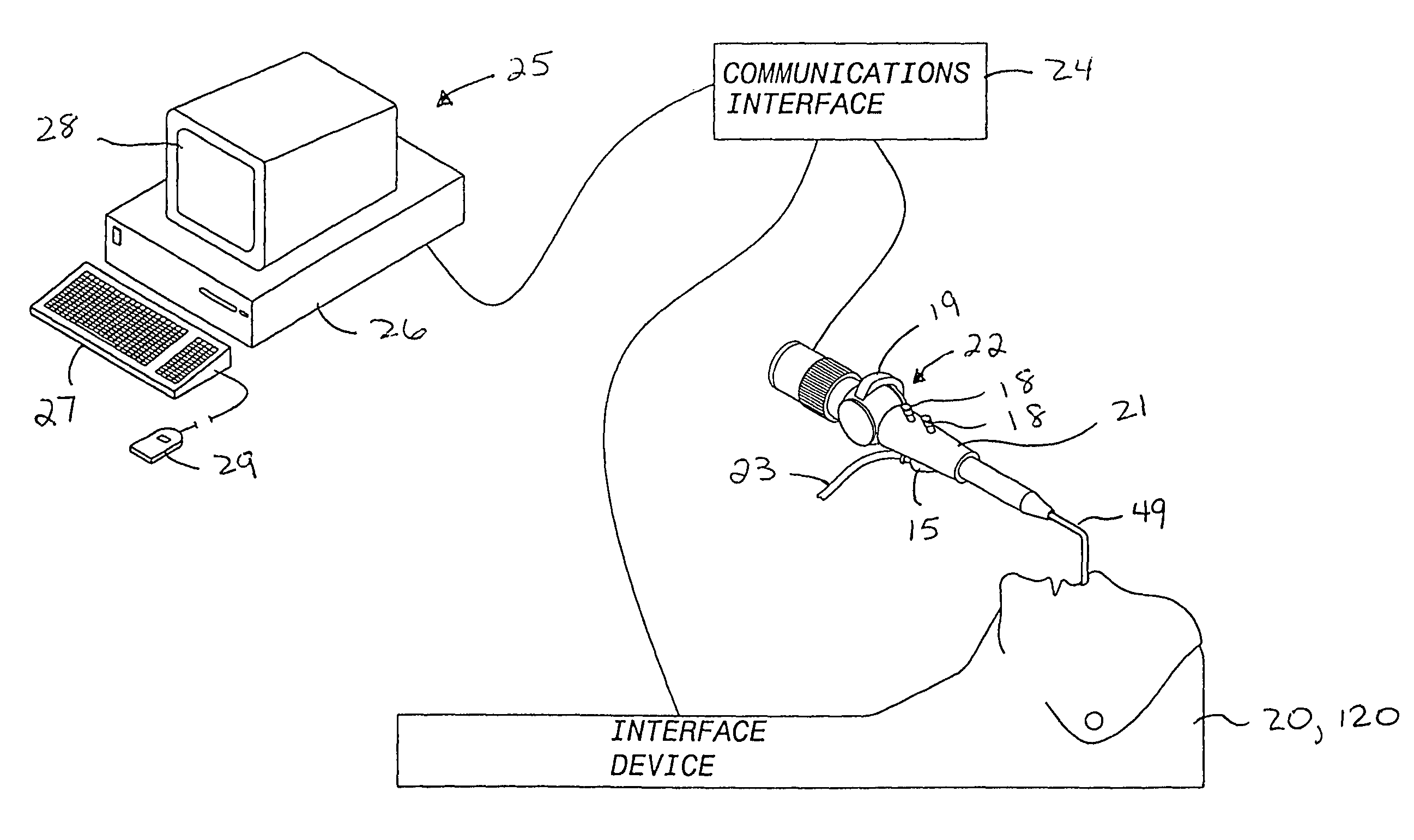
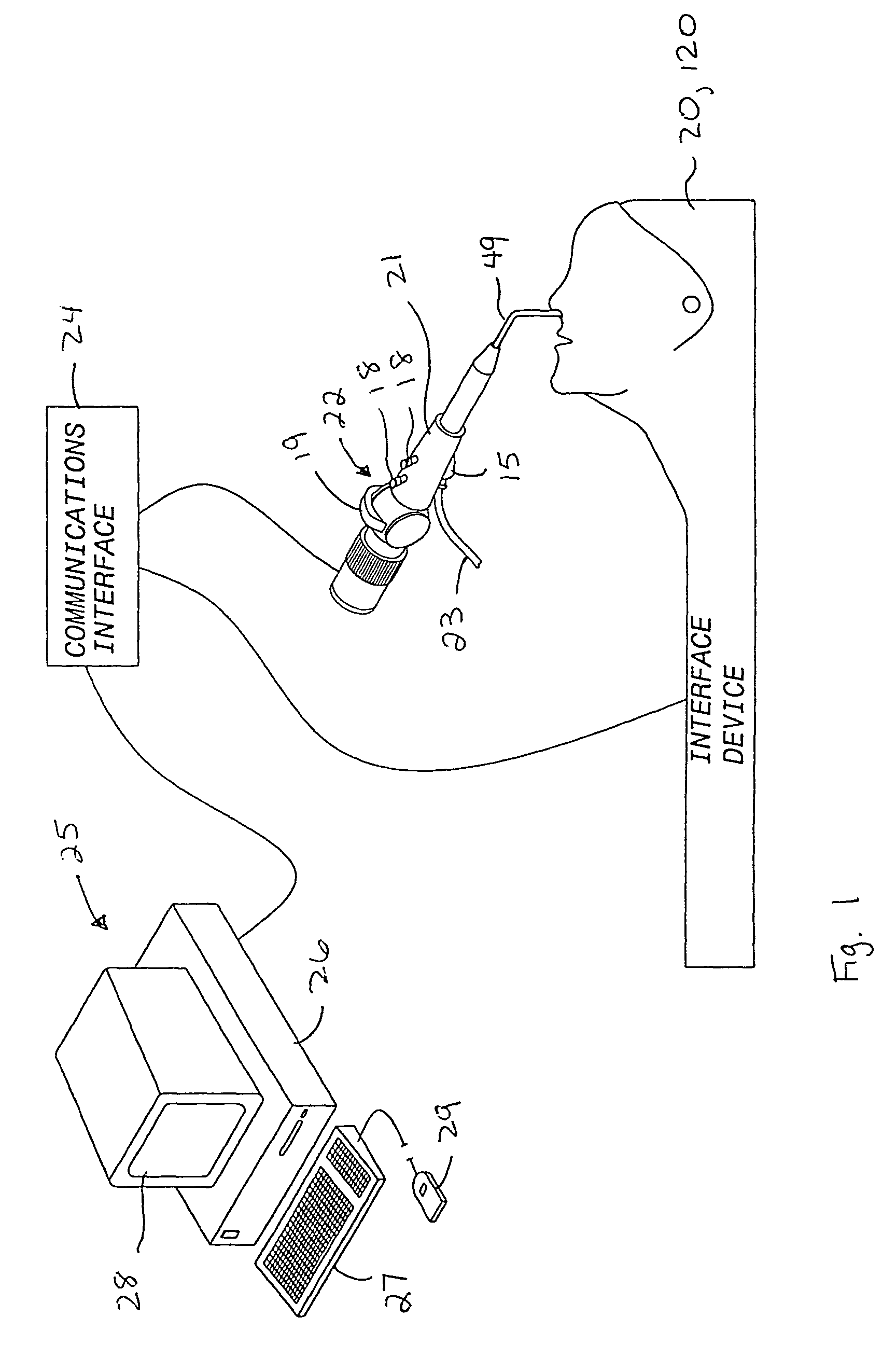
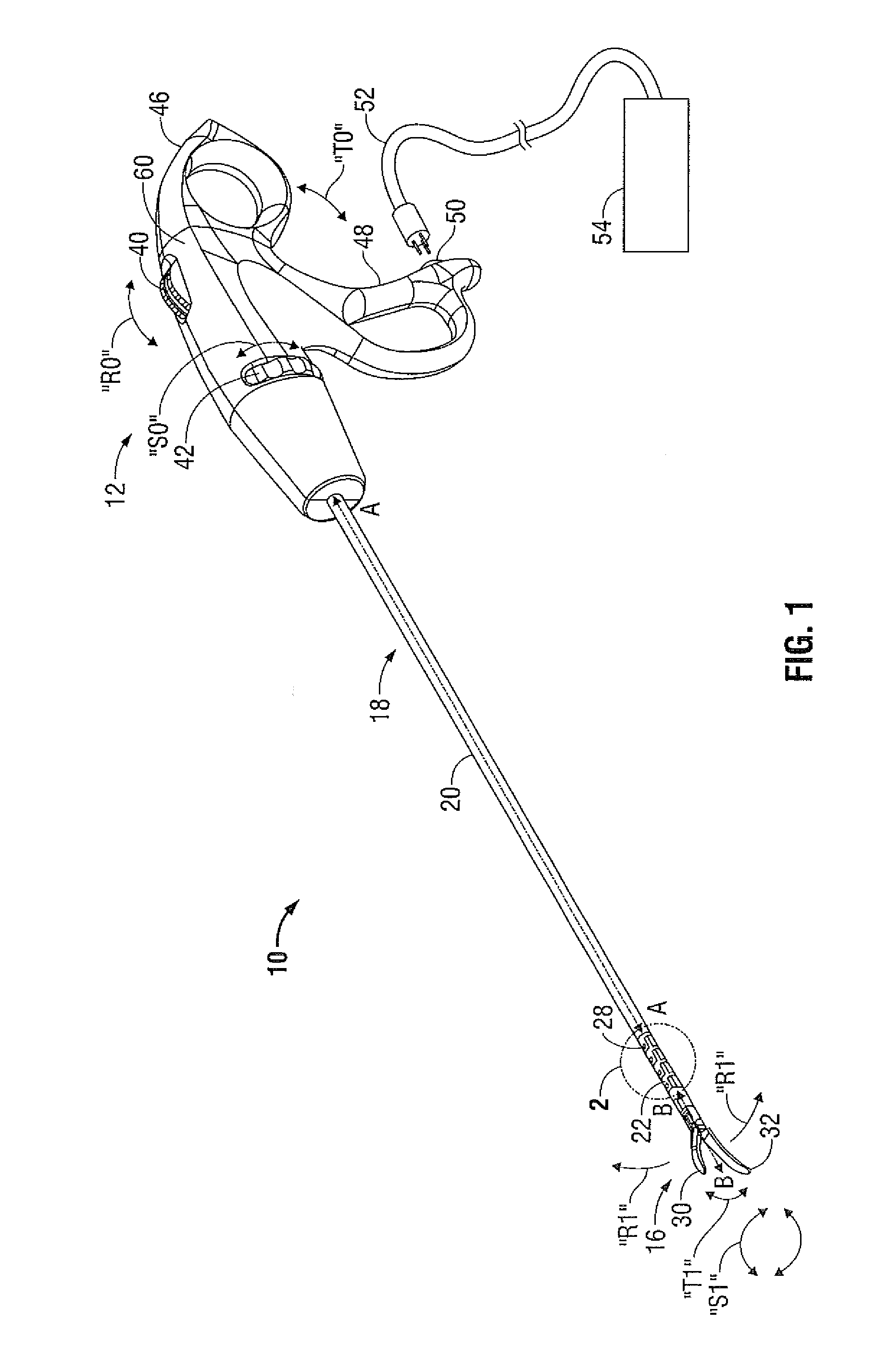
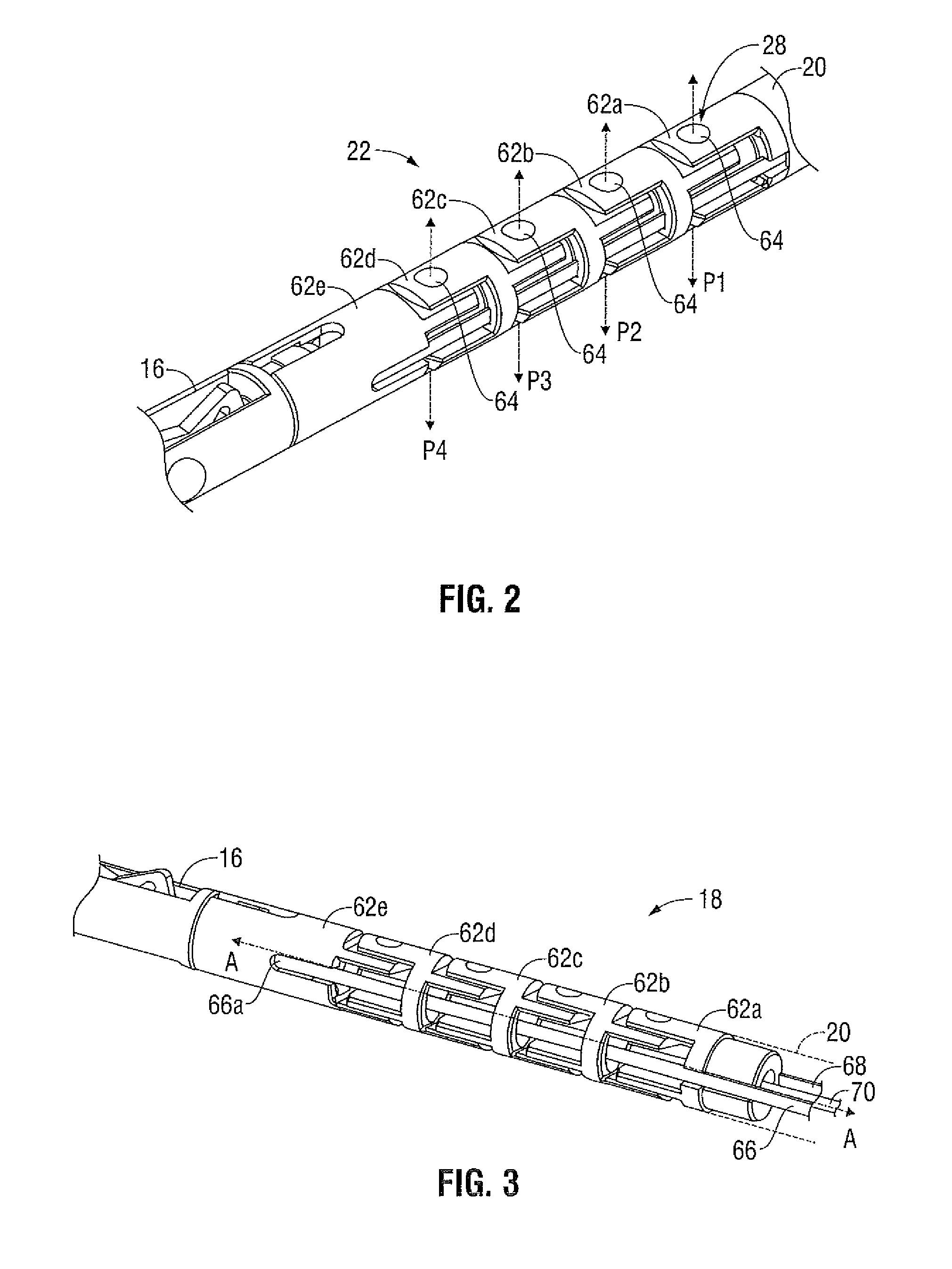
Interface device and method for interfacing instruments to medical procedure simulation systems
InactiveUS6929481B1Improve realismSimulate the realEducational modelsMeasuring instrumentDisplay device
An interface device and method for interfacing instruments to a medical procedure simulation system serve to interface peripherals in the form of mock medical instruments to the medical procedure simulation system computer to enable simulation of medical procedures. The interface device includes a housing having a mock bodily region of interest to facilitate insertion of a mock instrument, such as an endoscope tube, into the interface device. The mock bodily region of interest may be pivotable to simulate various patient orientations. The instrument is engaged by a capture mechanism in order to measure rotational and translational motion of the instrument. An actuator is disposed within the interface device to provide force feedback to the instrument. The measured motion is provided to the computer system to reflect instrument motion on the display during the simulation. Alternatively, the interface device may be configured to accommodate instrument assemblies having a plurality of nested instruments (e.g., sheath, catheter and wire), whereby the interface device individually grasps, measures manipulation of and provides force feedback to the nested instruments. In addition, the interface device may be configured to simultaneously accommodate a plurality of independently inserted instruments.
Owner:IMMERSION MEDICAL
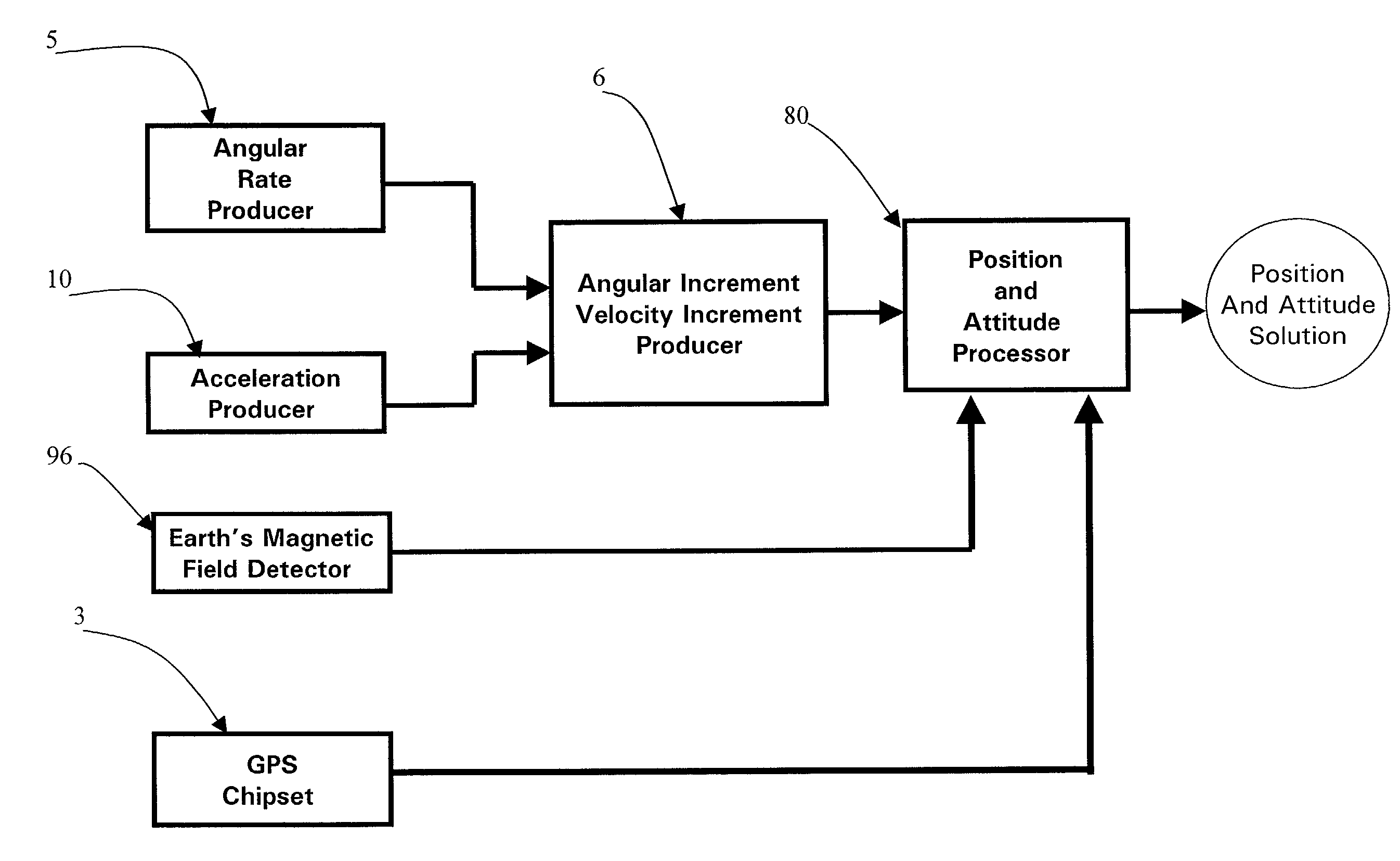
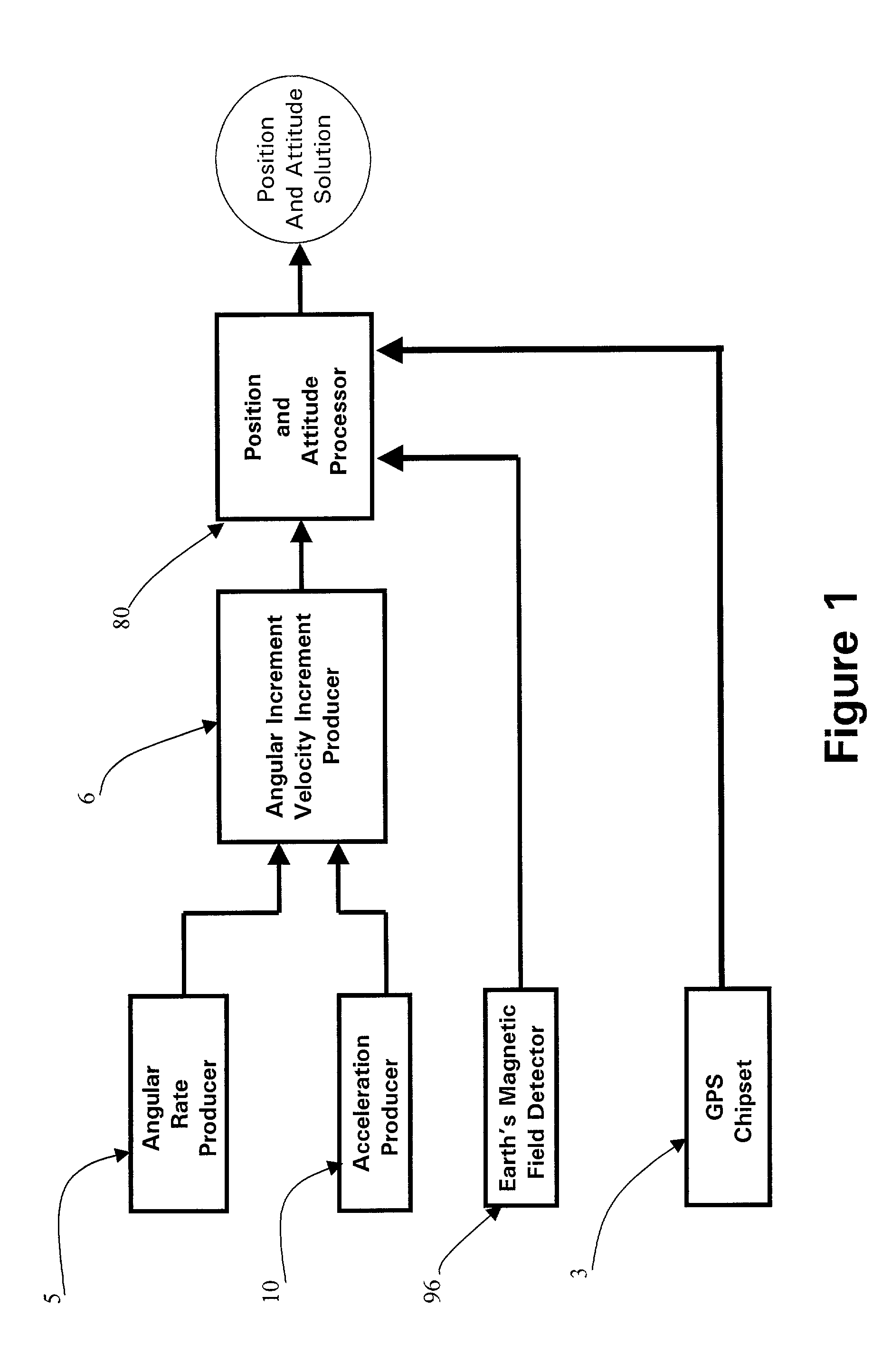
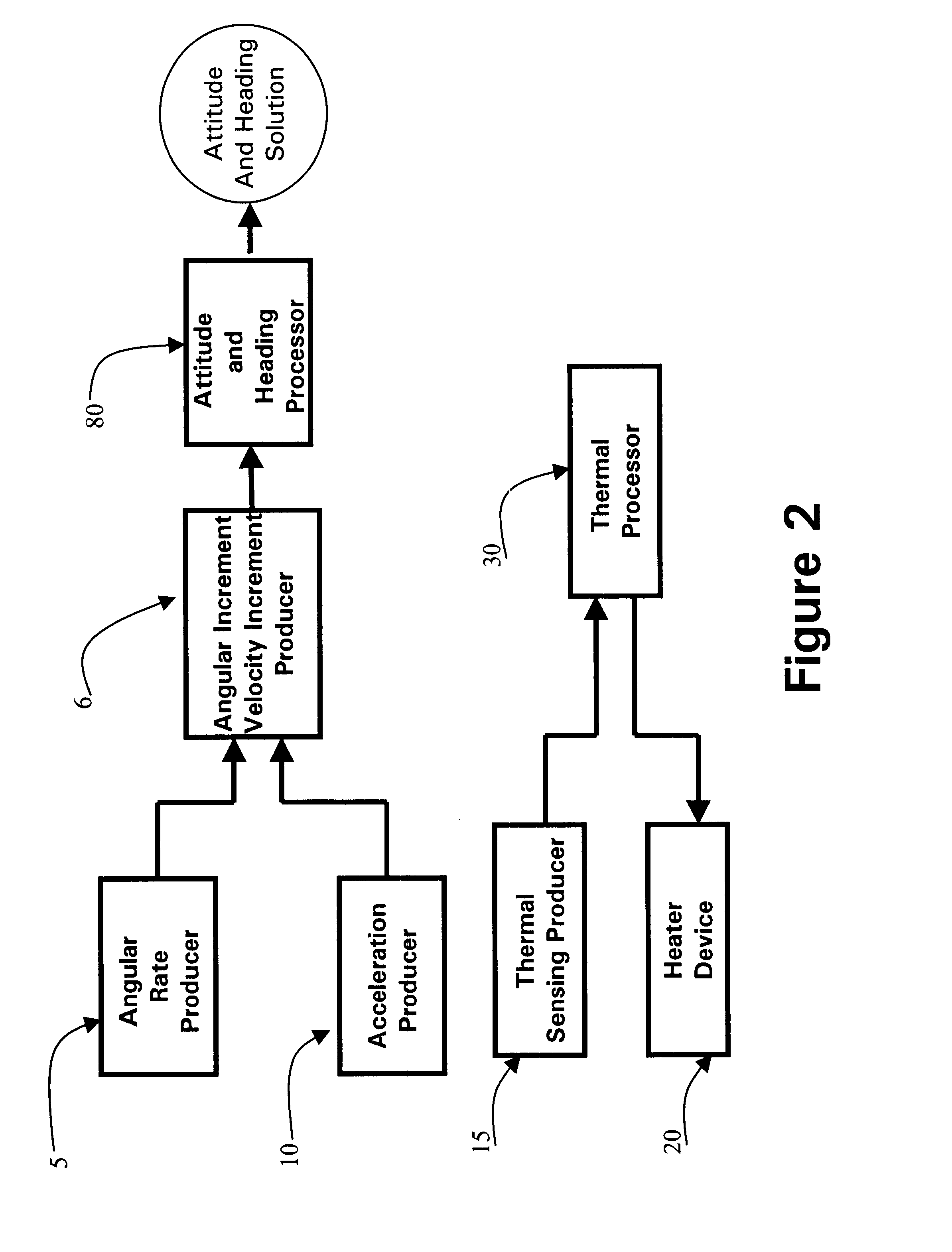
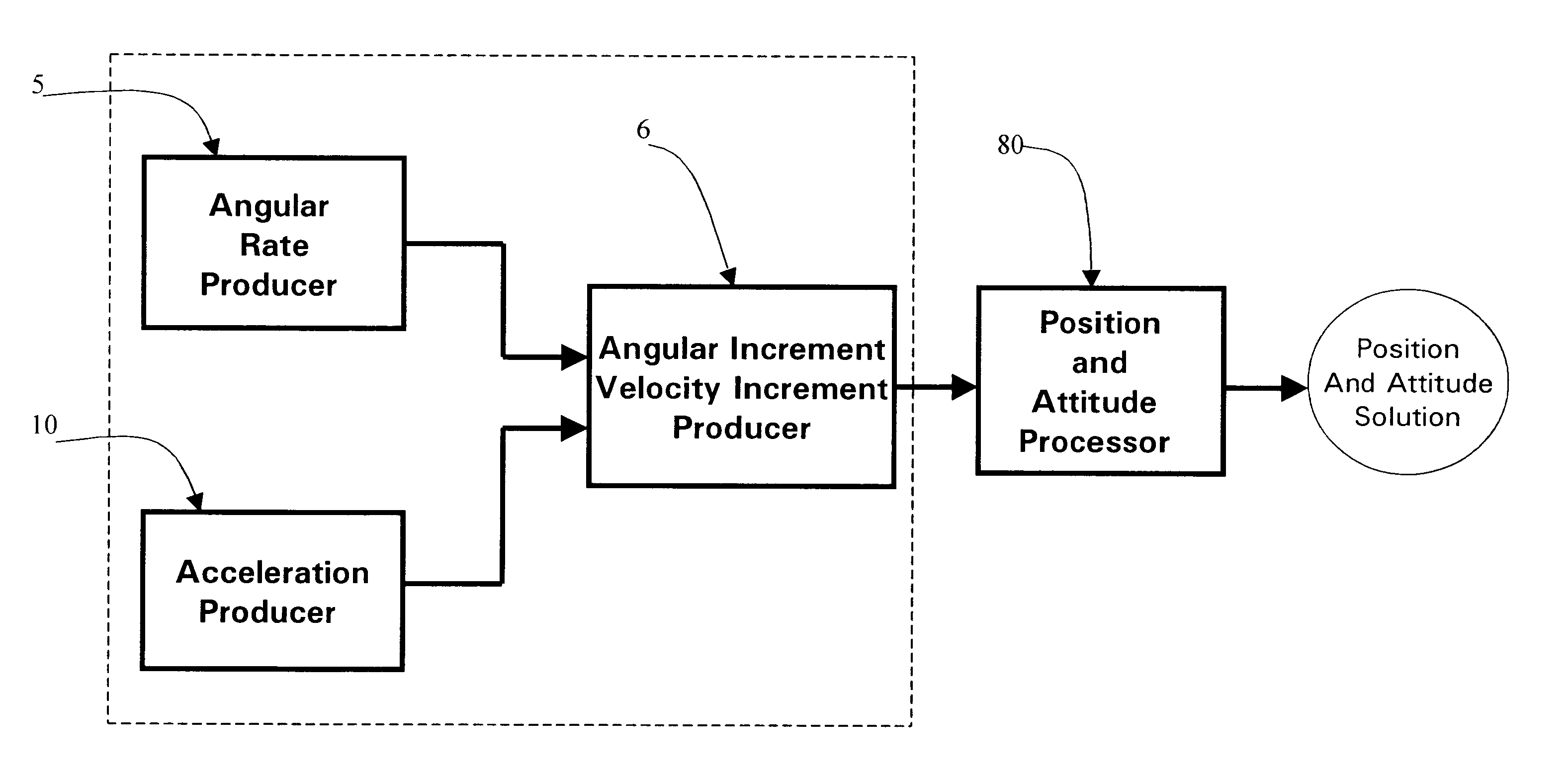
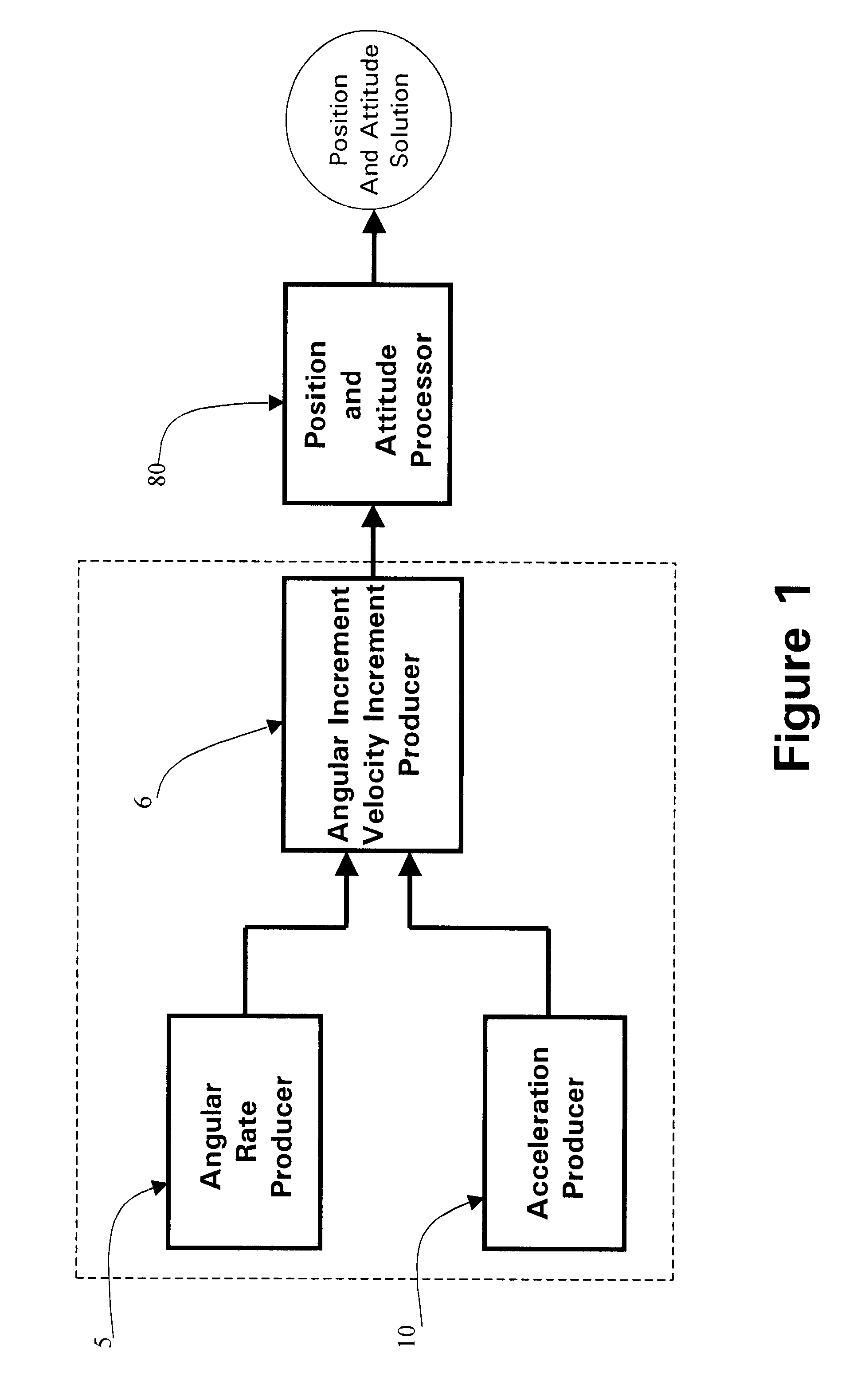
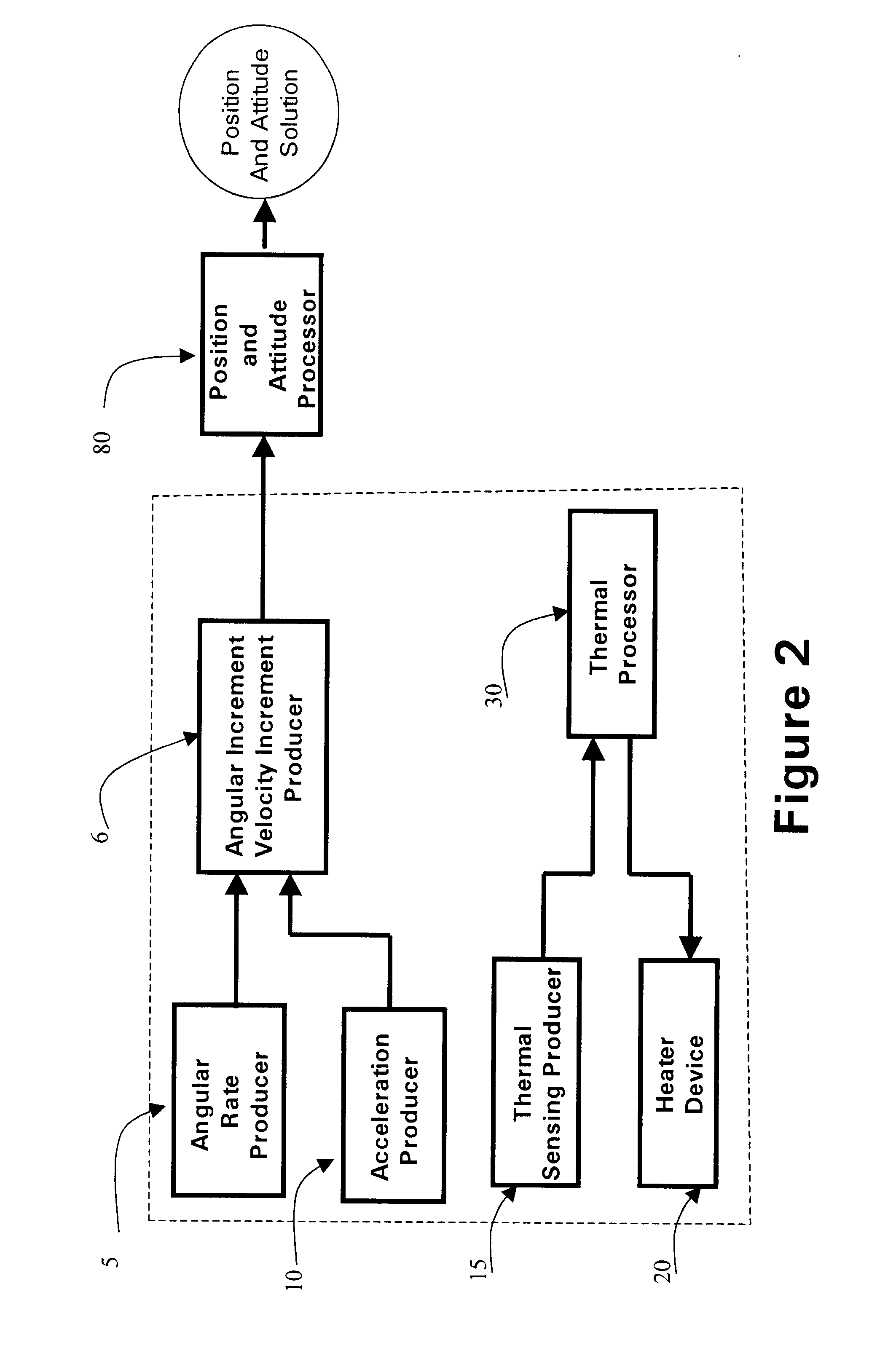
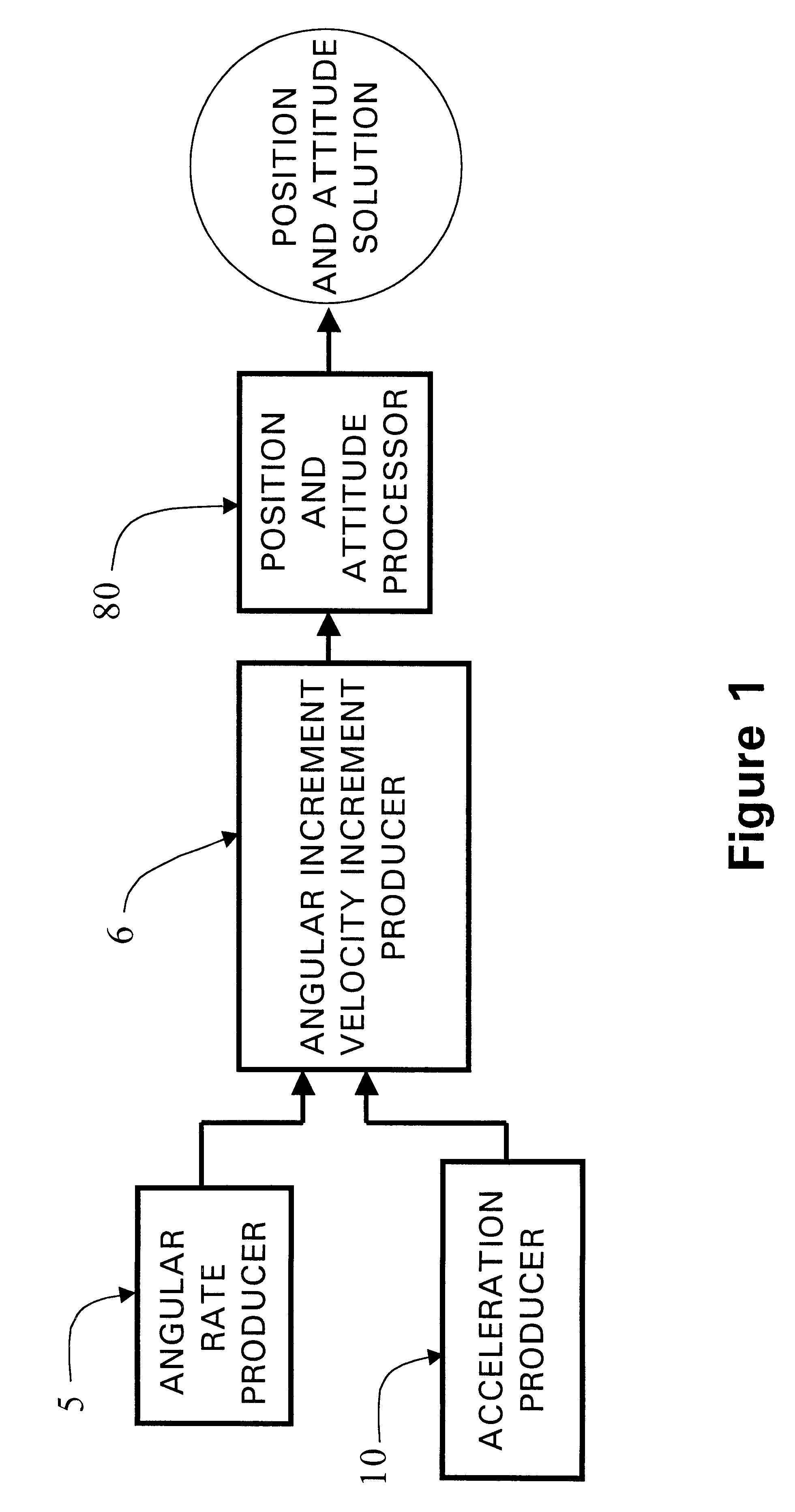
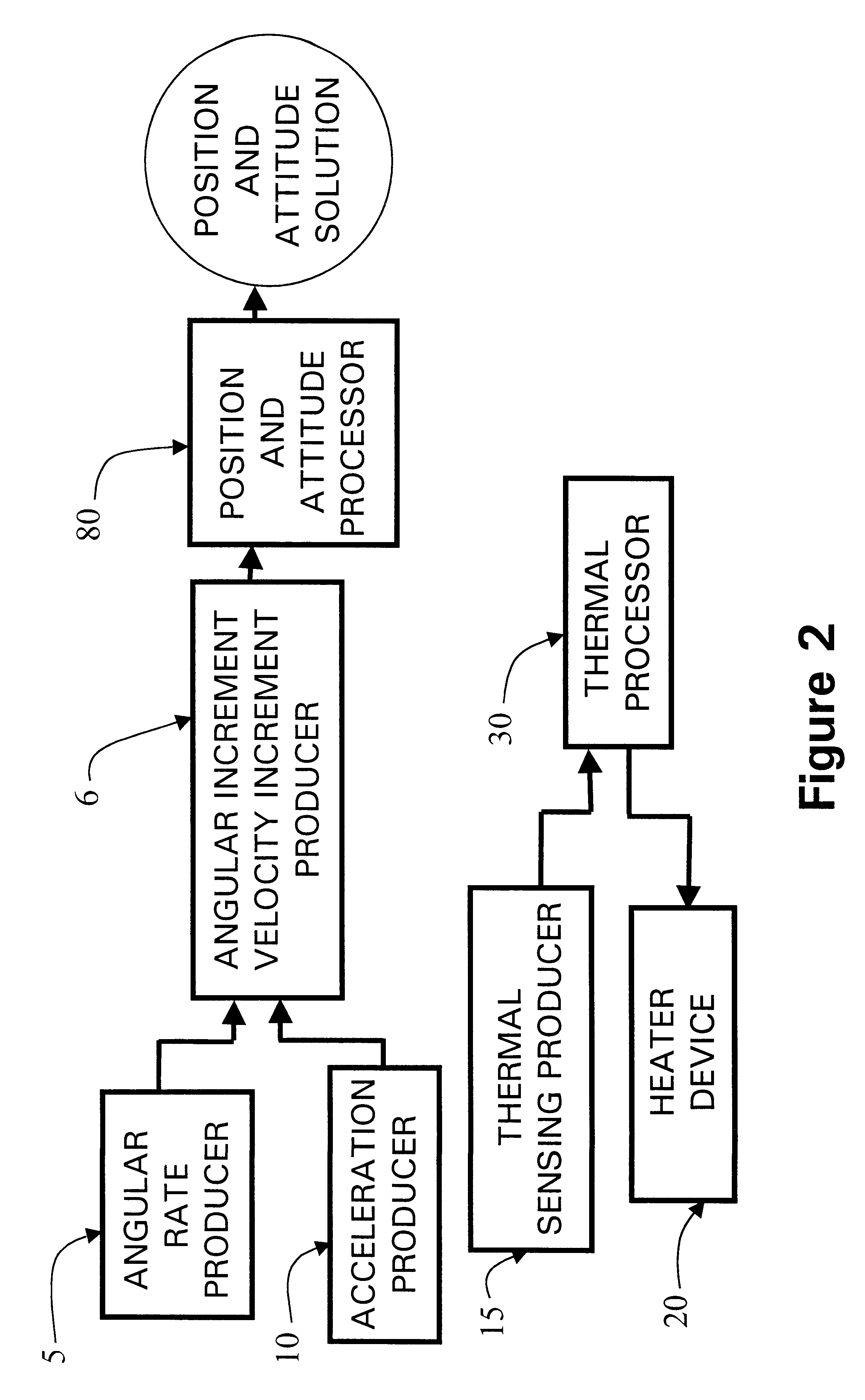
Micro integrated global positioning system/inertial measurement unit system
InactiveUS20020008661A1Precise positioningInstruments for road network navigationPosition fixationCarrier signalClosed loop
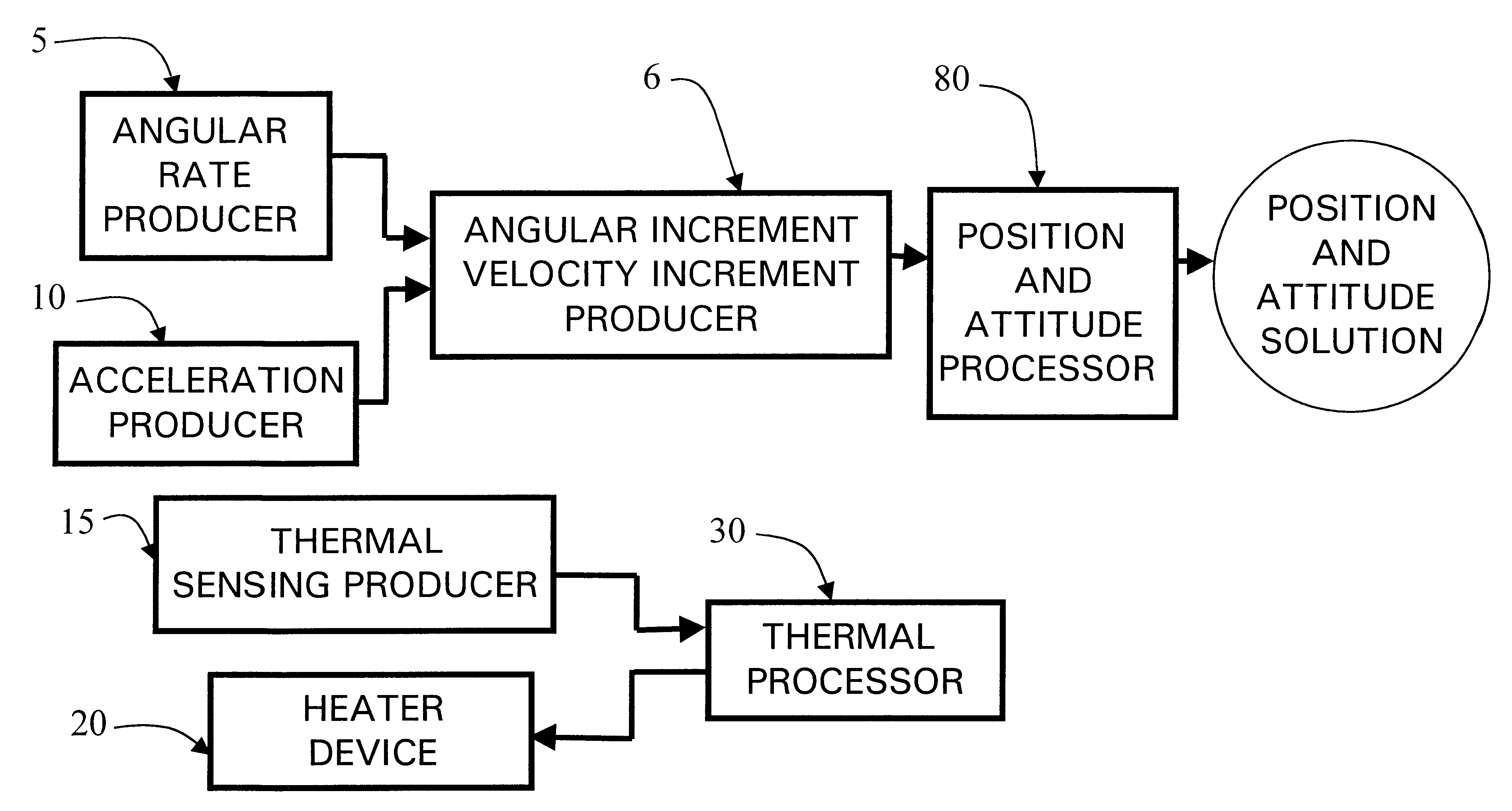
A micro integrated Global Positioning System (GPS) / Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) System, which is adapted to apply to output signals proportional to rotation and translational motion of a carrier and GPS measurements of the carrier, respectively from angular rate sensors, acceleration sensors, and GPS chipset, is employed with MEMS angular rate and acceleration sensors and GPS chipset. Compared with a conventional IMU / GPS system, the system of the present invention uses an integrated processing scheme by means of digital closed loop control of the dither driver signals for MEMS angular rate sensors, a feedforward open-loop signal processing scheme of the IMU, digital temperature control and compensation, the earth's magnetic field-based heading damping, robust error estimator, and compact sensor and circuit architecture and dramatically shrinks the size of mechanical and electronic hardware and power consumption, meanwhile, obtains highly accurate motion measurements.
Owner:AMERICAN GNC
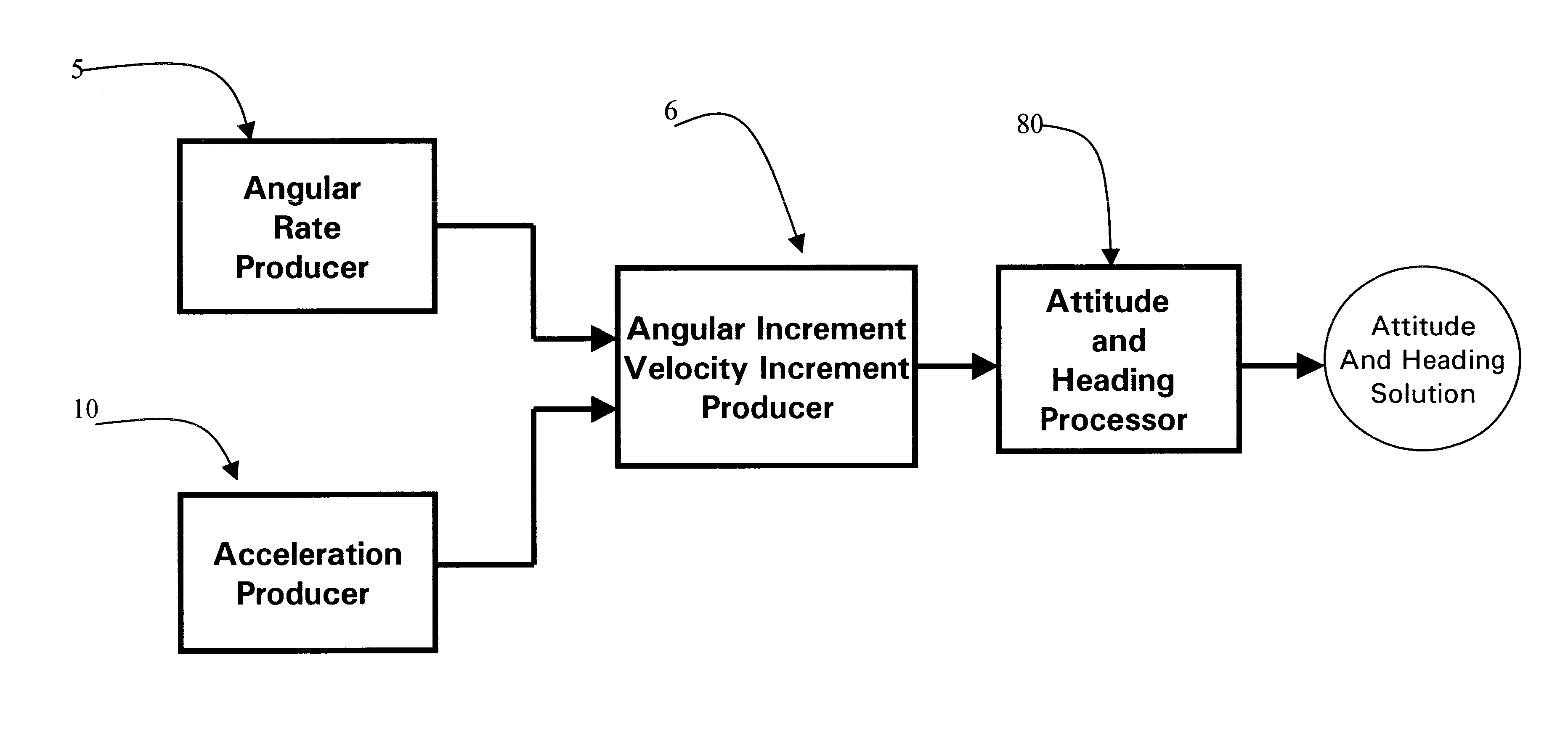
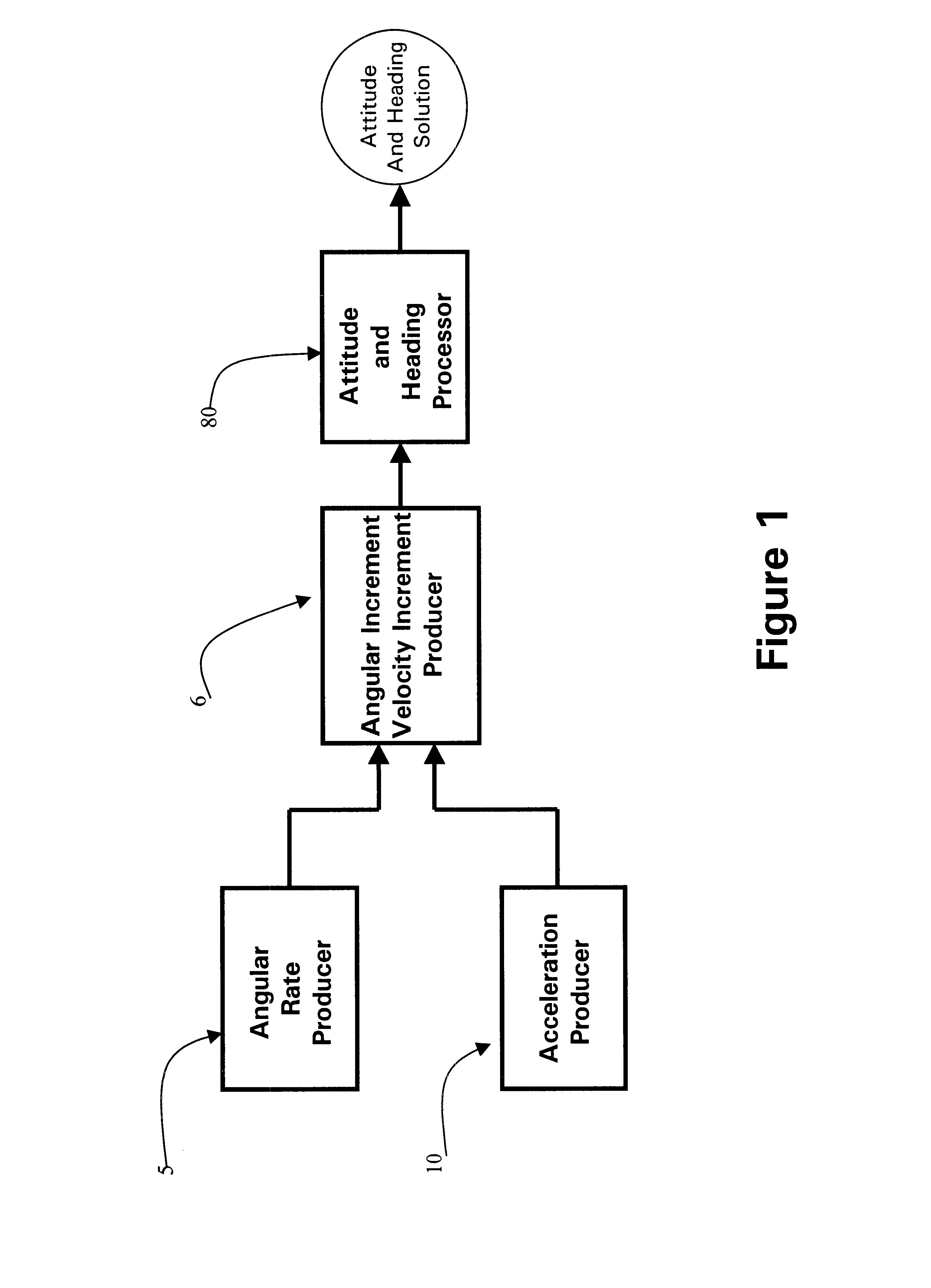
Processing method for motion measurement
InactiveUS6473713B1Small sizeAccurate measurementDigital data processing detailsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsTemperature controlEngineering
A processing method for motion measurement, which is adapted to apply to output signals proportional to rotation and translational motion of a carrier, respectively from rate sensors and acceleration sensors, is more suitable for emerging MEMS rate and acceleration sensors. Compared with a conventional IMU, the processing method utilizes a feedforward open-loop signal processing scheme to obtain highly accurate motion measurements by means of signal digitizing, temperature control and compensation, sensor error and misalignment calibrations, attitude updating, and damping control loops, and dramatically shrinks the size of mechanical and electronic hardware and power consumption, meanwhile, obtains highly accurate motion measurements.
Owner:AMERICAN GNC
Remote centre of motion positioner
An apparatus having a member that revolves about a remote center of motion (RCM) and a base link coupled to a mounting fixture. A first and second link are pivotably coupled to the member at respective distances from the RCM and are translatable relative to the base link along a first direction, at a fixed ratio of displacement. The ratio of respective distances equals a fixed ratio of displacement. The apparatus has a translational motion generator for a first and second element along parallel opposing directions. The translational motion generator is disposed on the first link and enables motion parallel to the first direction. The base link is fixed in position, the first element is fixed to the base link and the second element is fixed to the second link, such that the first and second link may translate relative to the base link with fixed ratio of displacement.
Owner:KATHOLIEKE UNIV LEUVEN
Interface device and method for interfacing instruments to medical procedure simulation systems
InactiveUS20060046235A1Improve realismSimulate the realEducational modelsMeasuring instrumentDisplay device
An interface device and method for interfacing instruments to a medical procedure simulation system serve to interface peripherals in the form of mock medical instruments to the medical procedure simulation system computer to enable simulation of medical procedures. The interface device includes a housing having a mock bodily region of interest to facilitate insertion of a mock instrument, such as an endoscope tube, into the interface device. The mock bodily region of interest may be pivotable to simulate various patient orientations. The instrument is engaged by a capture mechanism in order to measure rotational and translational motion of the instrument. An actuator is disposed within the interface device to provide force feedback to the instrument. The measured motion is provided to the computer system to reflect instrument motion on the display during the simulation. Alternatively, the interface device may be configured to accommodate instrument assemblies having a plurality of nested instruments (e.g., sheath, catheter and wire), whereby the interface device individually grasps, measures manipulation of and provides force feedback to the nested instruments. In addition, the interface device may be configured to simultaneously accommodate a plurality of independently inserted instruments.
Owner:IMMERSION MEDICAL
Method and apparatus for matching portions of input images
InactiveUS20070185946A1Overcome difficultiesLinear complexityImage enhancementTelevision system detailsAmbiguityImage segmentation
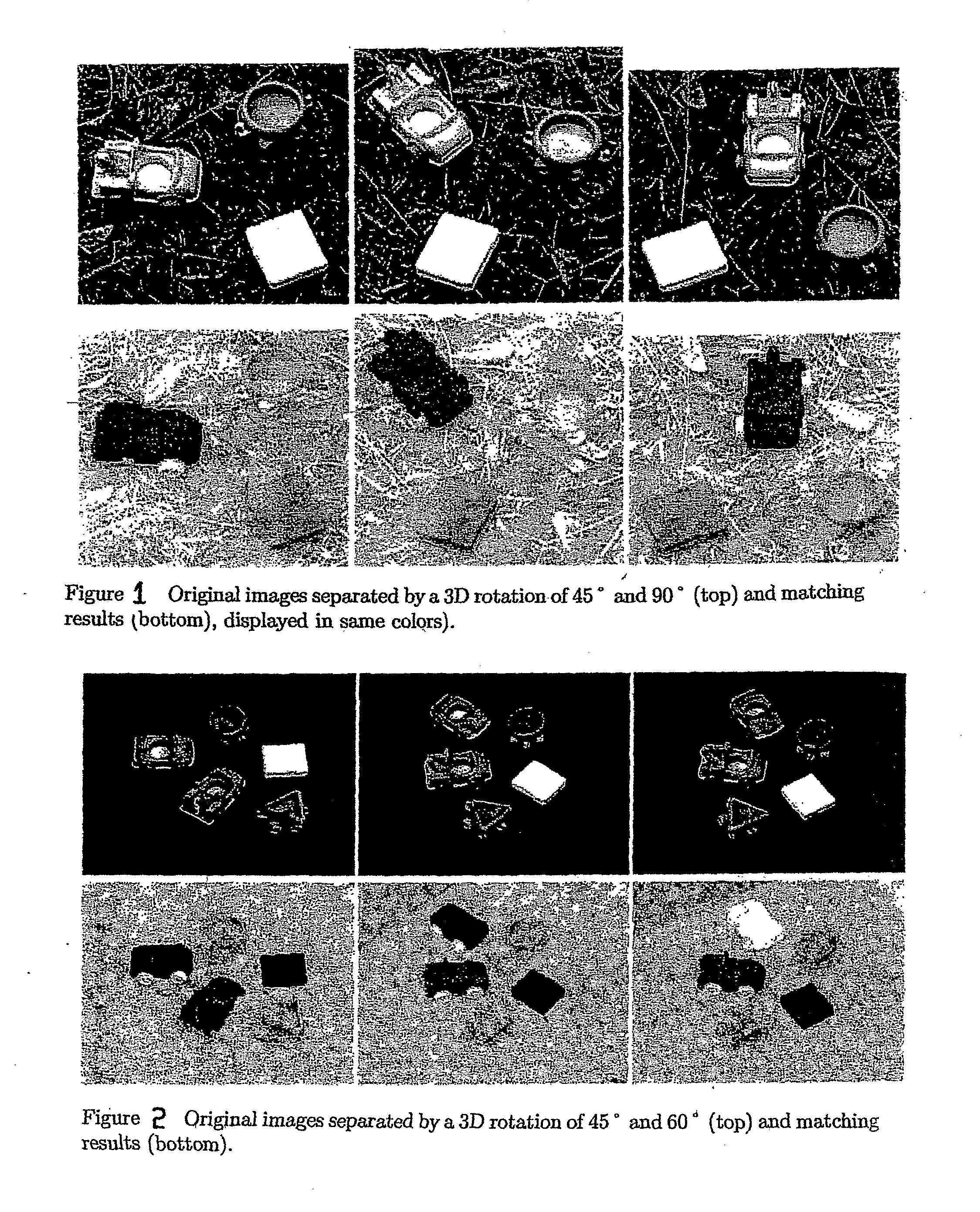
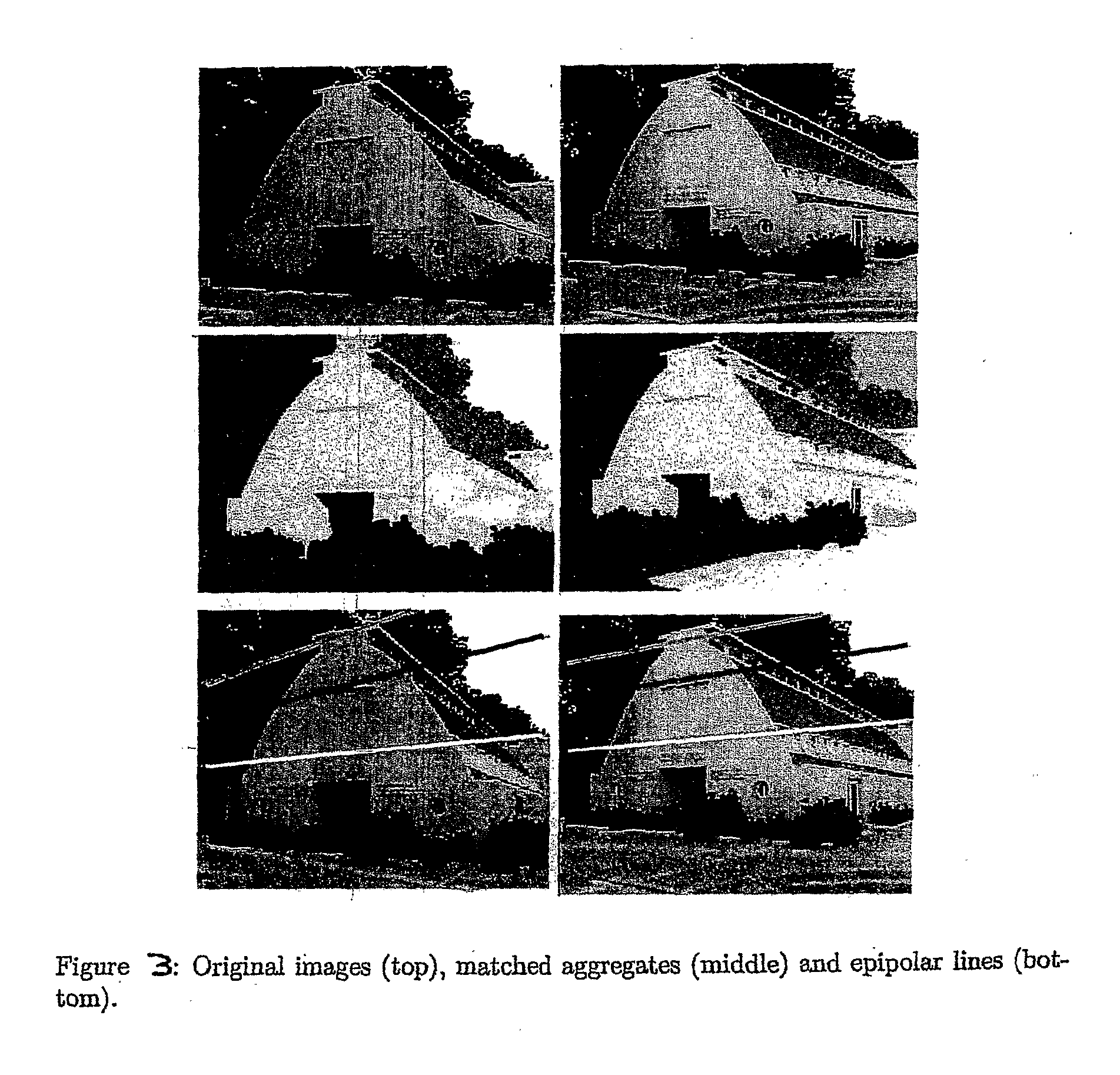
A method and apparatus for finding correspondence between portions of two images that first subjects the two images to segmentation by weighted aggregation (10), then constructs directed acylic graphs (16,18) from the output of the segmentation by weighted aggregation to obtain hierarchical graphs of aggregates (20,22), and finally applies a maximally weighted subgraph isomorphism to the hierarchical graphs of aggregates to find matches between them (24). Two algorithms are described; one seeks a one-to-one matching between regions, and the other computes a soft matching, in which is an aggregate may have more than one corresponding aggregate. A method and apparatus for image segmentation based on motion cues. Motion provides a strong cue for segmentation. The method begins with local, ambiguous optical flow measurements. It uses a process of aggregation to resolve the ambiguities and reach reliable estimates of the motion. In addition, as the process of aggregation proceeds and larger aggregates are identified, it employs a progressively more complex model to describe the motion. In particular, the method proceeds by recovering translational motion at fine levels, through affine transformation at intermediate levels, to 3D motion (described by a fundamental matrix) at the coarsest levels. Finally, the method is integrated with a segmentation method that uses intensity cues. The utility of the method is demonstrated on both random dot and real motion sequences.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Image prediction method and relevant device
ActiveCN104539966AReduce computational complexityAvoid passingDigital video signal modificationComputation complexityMotion vector
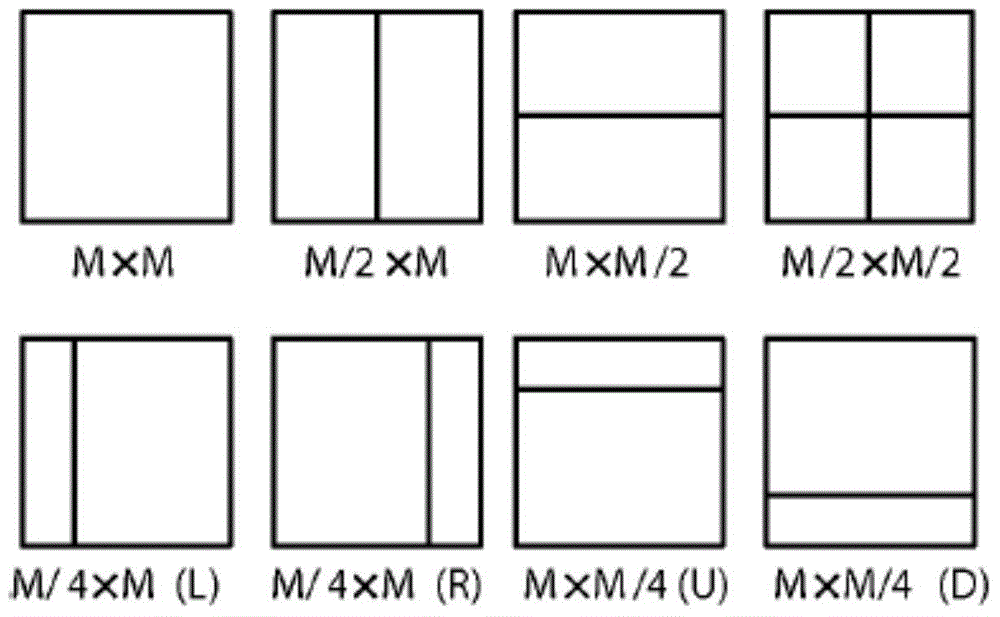
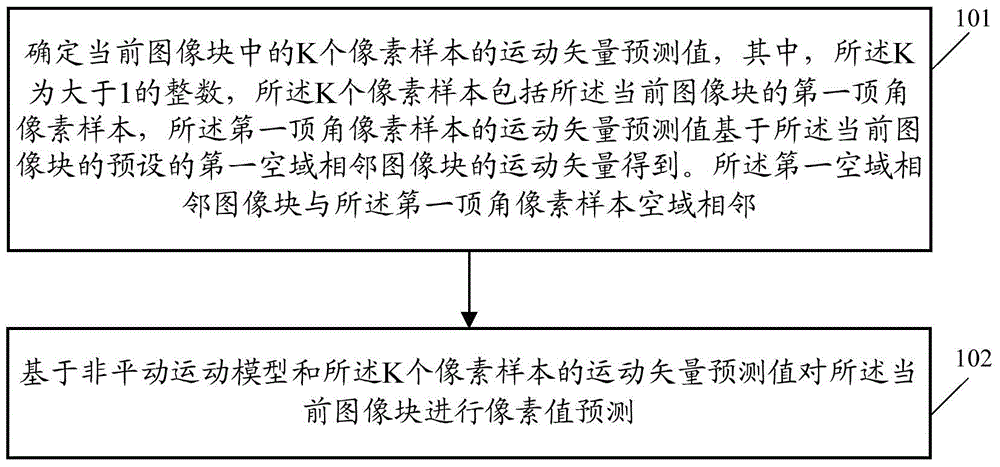
The embodiment of the invention discloses an image prediction method and a relevant device. The image prediction method comprises the following steps: determining the motion vector predictors of K pixel samples in a current image block, wherein K is an integer greater than 1, the K pixel samples comprise a first vertex angle pixel sample of the current image block, the motion vector predictor of the first vertex angle pixel sample is obtained on the basis of the motion vector of a preset first spatial domain adjacent image block of the current image block, and the first spatial domain adjacent image block is adjacent to a first vertex angle pixel sample spatial domain; and predicting the pixel value of the current image block on the basis of a non-translational motion model and the motion vector predictors of the K pixel samples. According to the scheme in the embodiment of the invention, the computation complexity of image prediction based on the non-translational motion model is lowered.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD +1
Interface device and method for interfacing instruments to vascular access simulation systems
InactiveUS7308831B2Improve realismSimulate the realCosmonautic condition simulationsData processing applicationsControl signalSkin traction
An interface device and method for interfacing instruments to a vascular access simulation system serve to interface peripherals in the form of mock or actual medical instruments to the simulation system to enable simulation of medical procedures. The interface device includes a catheter unit assembly for receiving a catheter needle assembly, and a skin traction mechanism to simulate placing skin in traction or manipulating other anatomical sites for performing a medical procedure. The catheter needle assembly and skin traction mechanism are manipulated by a user during a medical procedure. The catheter unit assembly includes a base, a housing, a bearing assembly and a shaft that receives the catheter needle assembly. The bearing assembly enables translation of the catheter needle assembly, and includes bearings that enable the shaft to translate in accordance with manipulation of the catheter needle assembly. The shaft typically includes an encoder to measure translational motion of a needle of the catheter needle assembly, while the interface device further includes encoders to measure manipulation of the catheter needle assembly in various degrees of freedom (e.g., translation, pitch and yaw) and the skin traction mechanism. Alternatively, the shaft may include an additional encoder to measure translational motion of an instrument inserted through the catheter needle assembly. The simulation system receives measurements from the interface device encoders and updates the simulation and display, while providing control signals to the force feedback device to enable application of force feedback to the catheter needle assembly.
Owner:IMMERSION MEDICAL
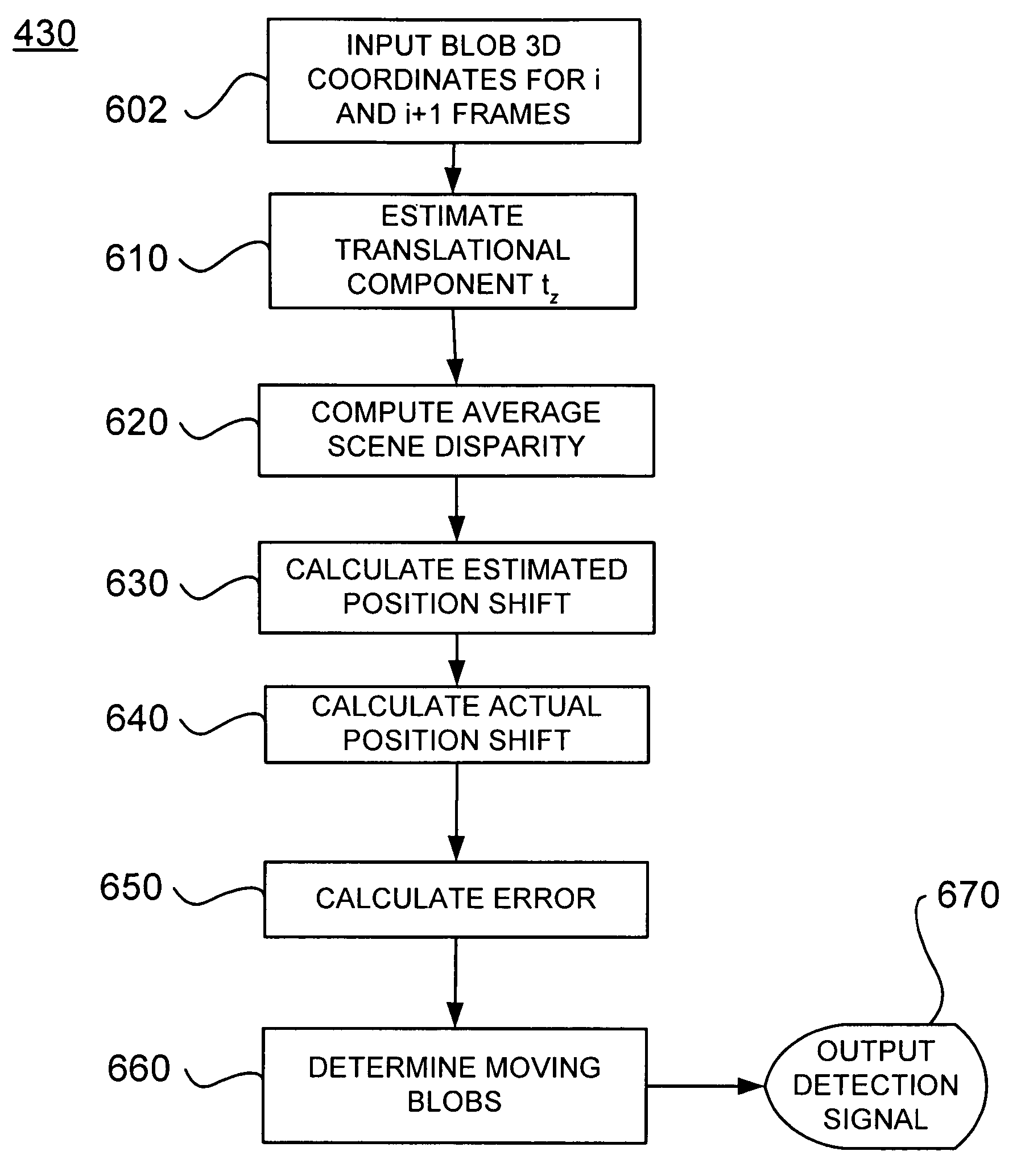
Moving object detection using low illumination depth capable computer vision
Moving object detection is based on low illumination image data that includes distance or depth information. The vision system operates on a platform with a dominant translational motion and with a small amount of rotational motion. Detection of moving objects whose motions are not consistent with the movement of the background is complementary to shape-based approaches. For low illumination computer-based vision assistance a two-stage technique is used for simultaneous and subsequent frame blob correspondence. Using average scene disparity, motion is detected without explicit ego-motion calculation. These techniques make use of characteristics of infrared sensitive video data, in which heat emitting objects appear as hotspots.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Medical device with one-way rotary drive mechanism
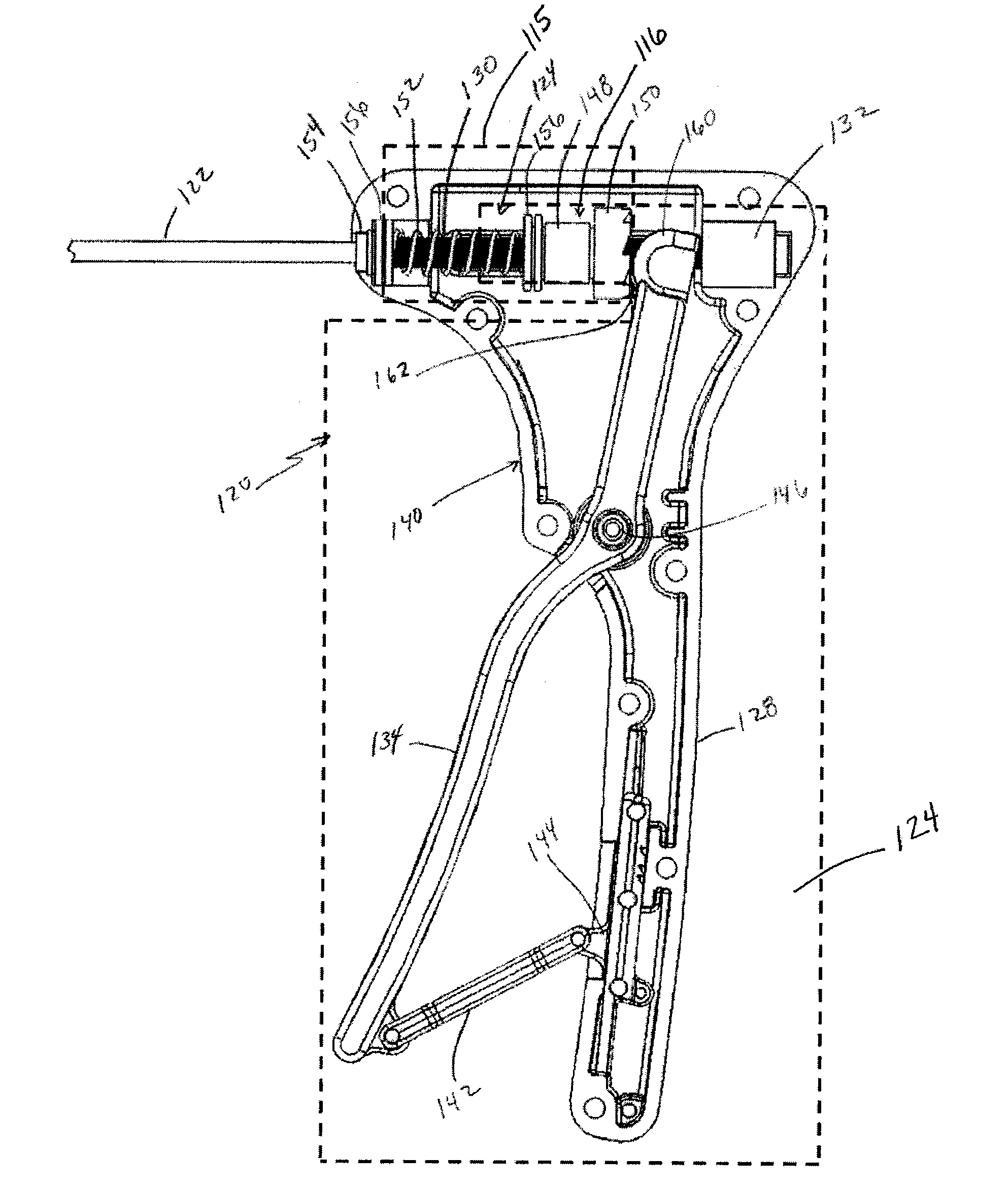
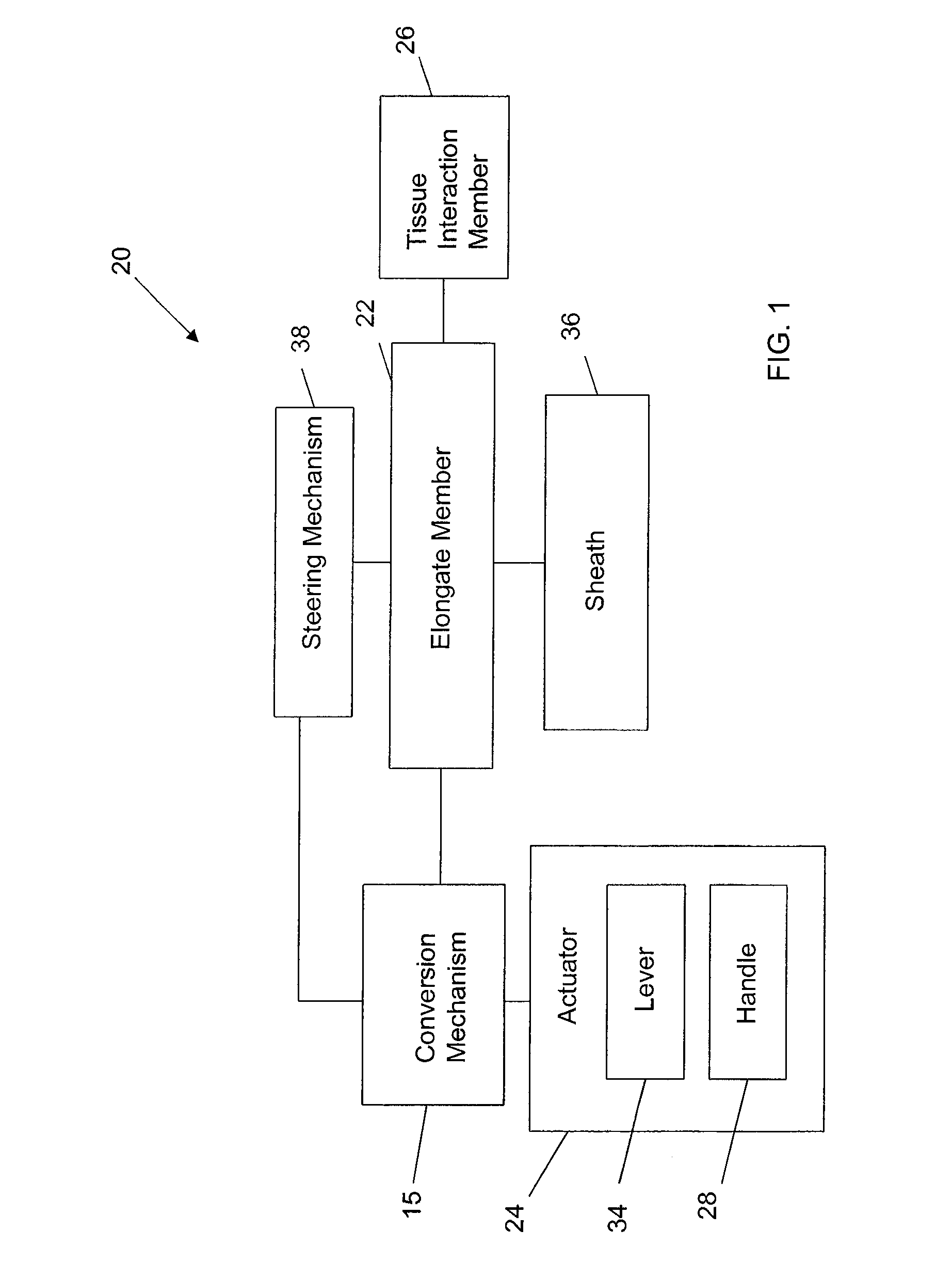
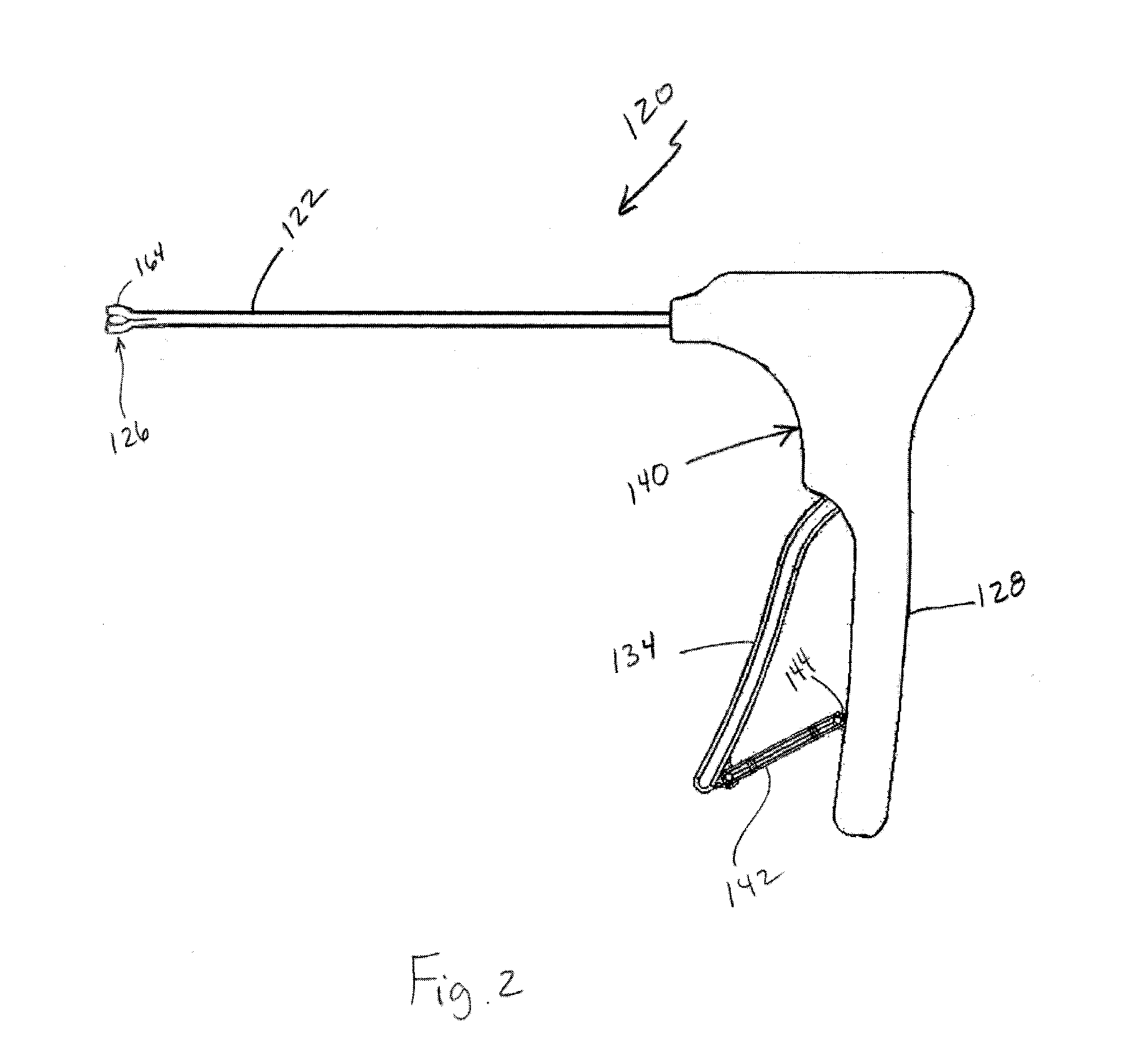
Apparatuses and methods for accessing and disrupting a tissue are disclosed herein. In one embodiment, a method includes inserting a distal end portion of an elongate member into a biological body. After inserting the elongate member, an actuator is manually actuated to produce translational motion of a drive element. The translational motion is converted into rotational movement of the distal end portion of the elongate member. In one embodiment, an apparatus includes an elongate member having a tissue interaction member at a distal end portion that is configured to be inserted within a biological body. A conversion mechanism is coupled to the elongate member and includes a drive element. An actuator is coupled to the conversion mechanism and is configured to cause translational motion of the drive element. The conversion mechanism is configured to convert the translational motion of the drive element into rotational motion of the elongate member.
Owner:KYPHON
Method and apparatus for micro electro-mechanical systems and their manufacture
InactiveUS20020127760A1Less driving voltageSemiconductor electrostatic transducersSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOut of plane motionActuator
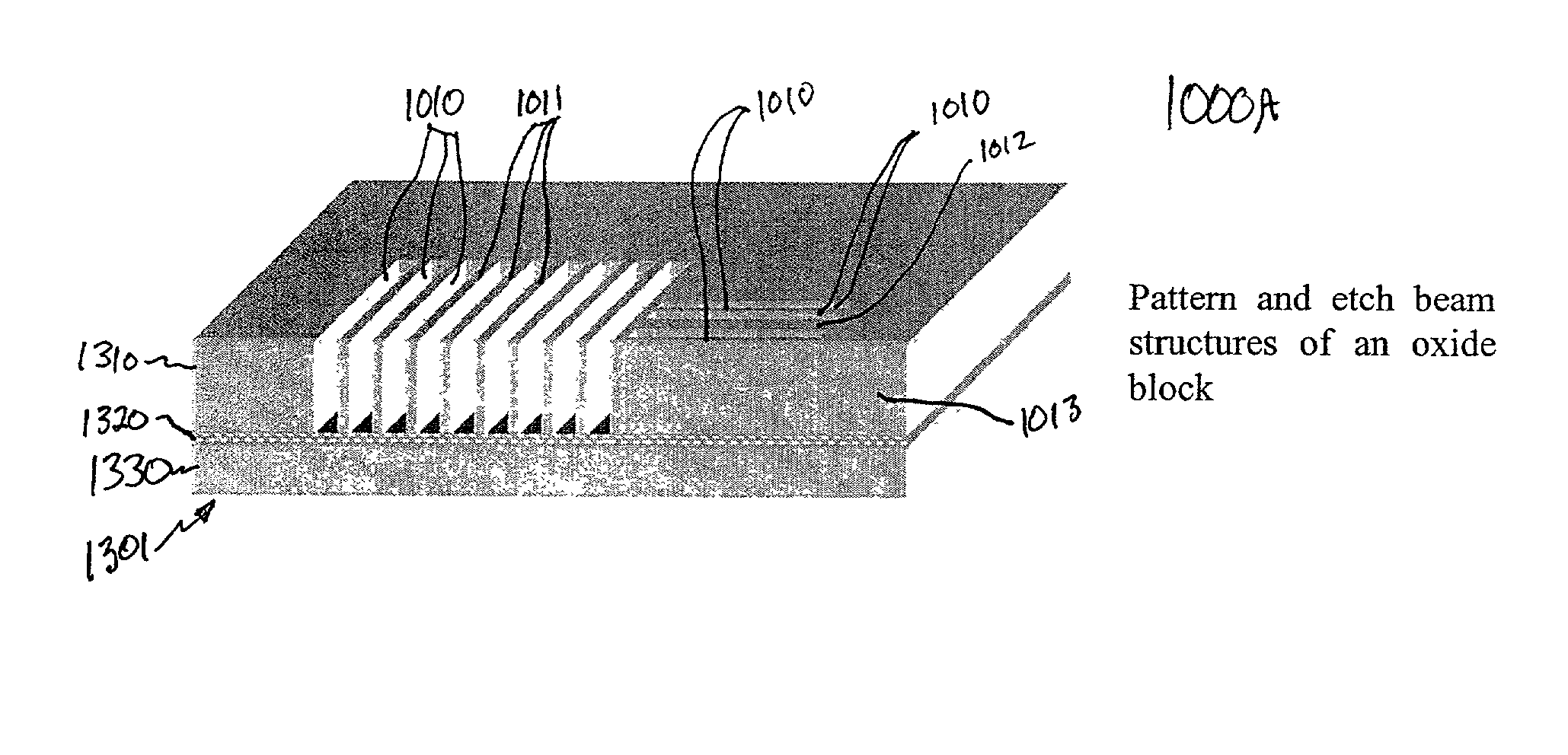
The present invention provides a fabrication process that integrates high-aspect-ratio silicon structures with polysilicon surface micromachined structures. In some embodiments the process includes forming an oxide block by etching a plurality of trenches to leave a plurality of vertical-walled silicon structures standing on the substrate, thermally and substantially completely oxidizing the vertical-walled silicon structures, and substantially filling spaces between the oxidized vertical-walled silicon structures with an oxide of silicon to form the oxide block. The process retains not only the high-aspect-ratio silicon structures possible with deep reactive ion etching (DRIE) but also the design flexibility of polysilicon surface micromachining. Using this process, polysilicon platforms have been fabricated, which are actuated by high-aspect-ratio combdrives for many applications such as x-y-z stages and scanning devices. The actuators include an asymmetric combdrive that actuates in torsional / out-of-plane motions, and a high-aspect-ratio combdrive that drives in translational motion.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Circuit card captivation and ejection mechanism including a lever to facilitate removal of the mechanism from a housing
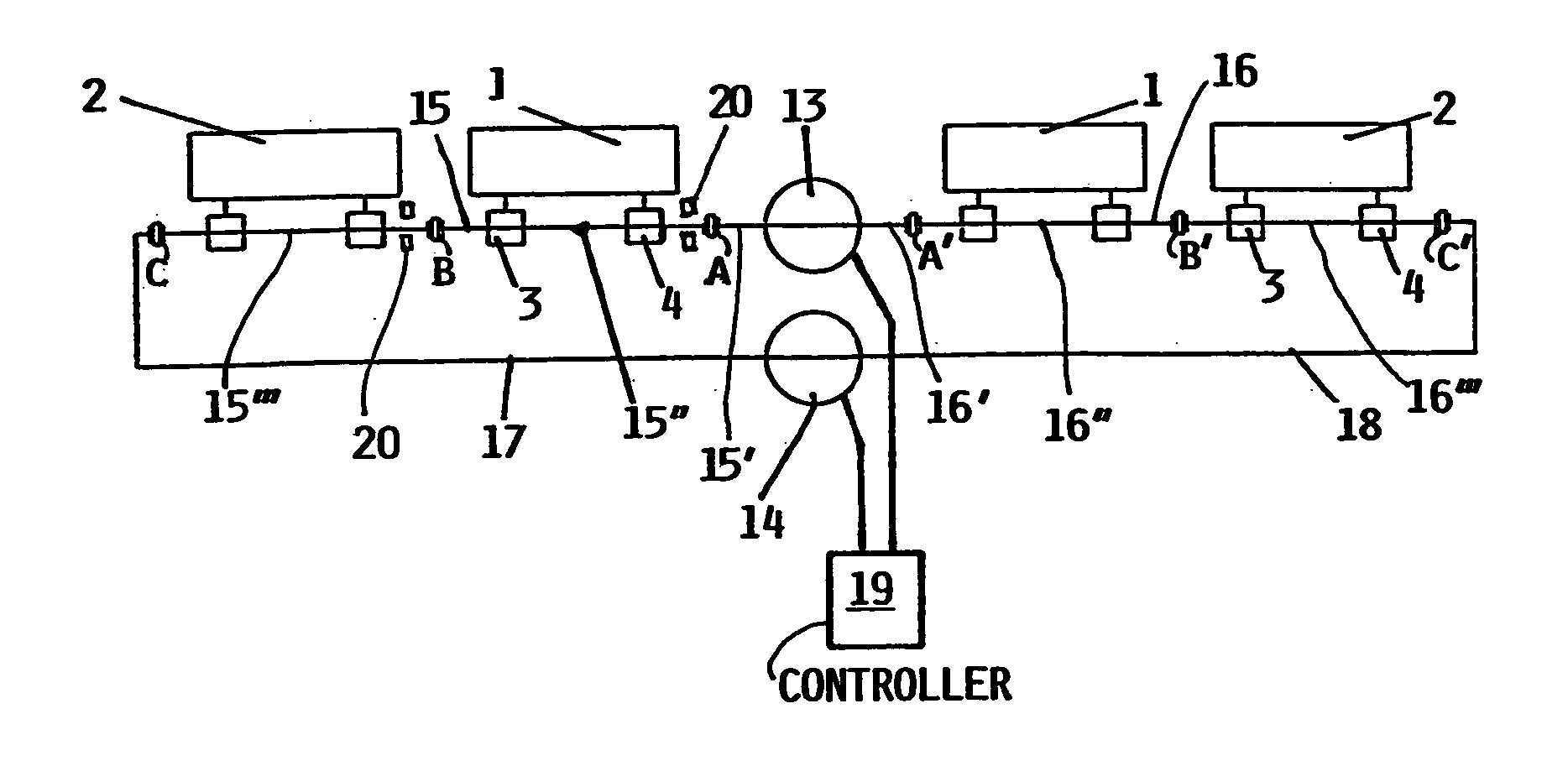
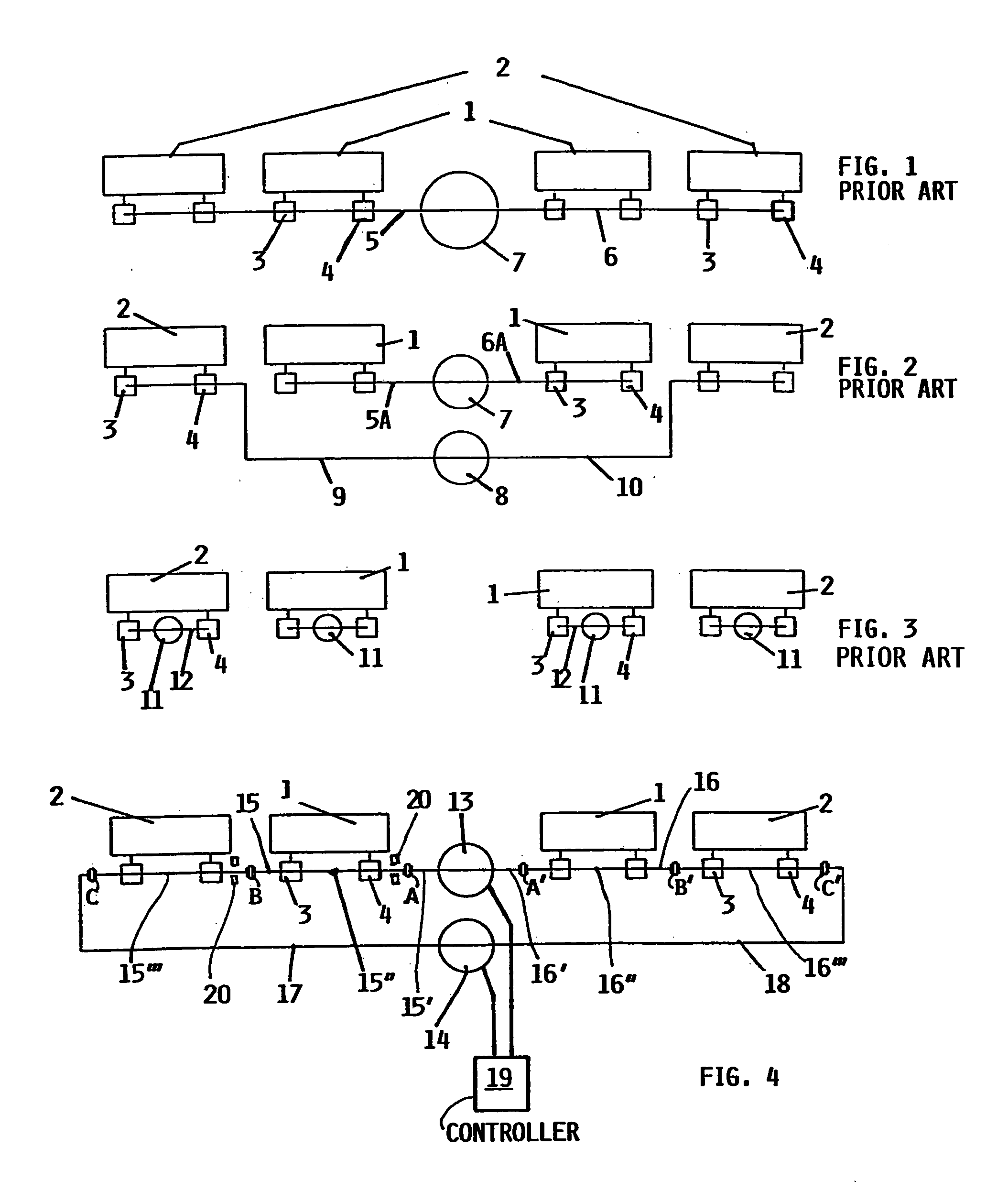
A removable apparatus for carrying a circuit board includes a carrying plate having a notch to receive a stationary pin of an enclosure and a faceplate connected to one end of the carrying plate. A rotating cam connects to the carrying plate and acts on the pin to move the apparatus relative to the pin during insertion into and removal from the enclosure. The cam includes two different surfaces, each of which acts to move the apparatus either into or out of the enclosure. A linkage is connected to the cam and extends through the faceplate, connecting to a lever on the exterior of the faceplate. The lever is used to rotate the cam, which in conjunction with the pin provides translational motion either to mate a connector on the circuit board with a corresponding connector in the enclosure or to separate the mated connectors, depending on the direction of rotation.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
Aircraft flap or slat drive system with redundant drives and shaft drive lines
ActiveUS20050029407A1No loss of functionalityEasy constructionAircraft stabilisationActuated personallyActuatorControl theory
An aircraft flap (or slat) drive apparatus includes first and second centralized drive units that respectively rotationally drive first and second drive lines in both wings. The first drive line includes shaft segments connected end-to-end by selectively engageable separating devices. The outboard ends of the first and second drive lines are coupled through one of the separating devices, in each wing. At least one actuator mechanism connects each flap to a respective shaft segment of the first drive line, and converts the drive line rotational motion to a flap translational motion. If a component breaks, jams, or otherwise fails, it is isolated by disengaging the two adjacent separating devices with the faulty component therebetween, so that the rest of the apparatus remains functional. Each one or both of the drive units can drive one or more or all of the flaps through the interconnected first and second drive lines.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
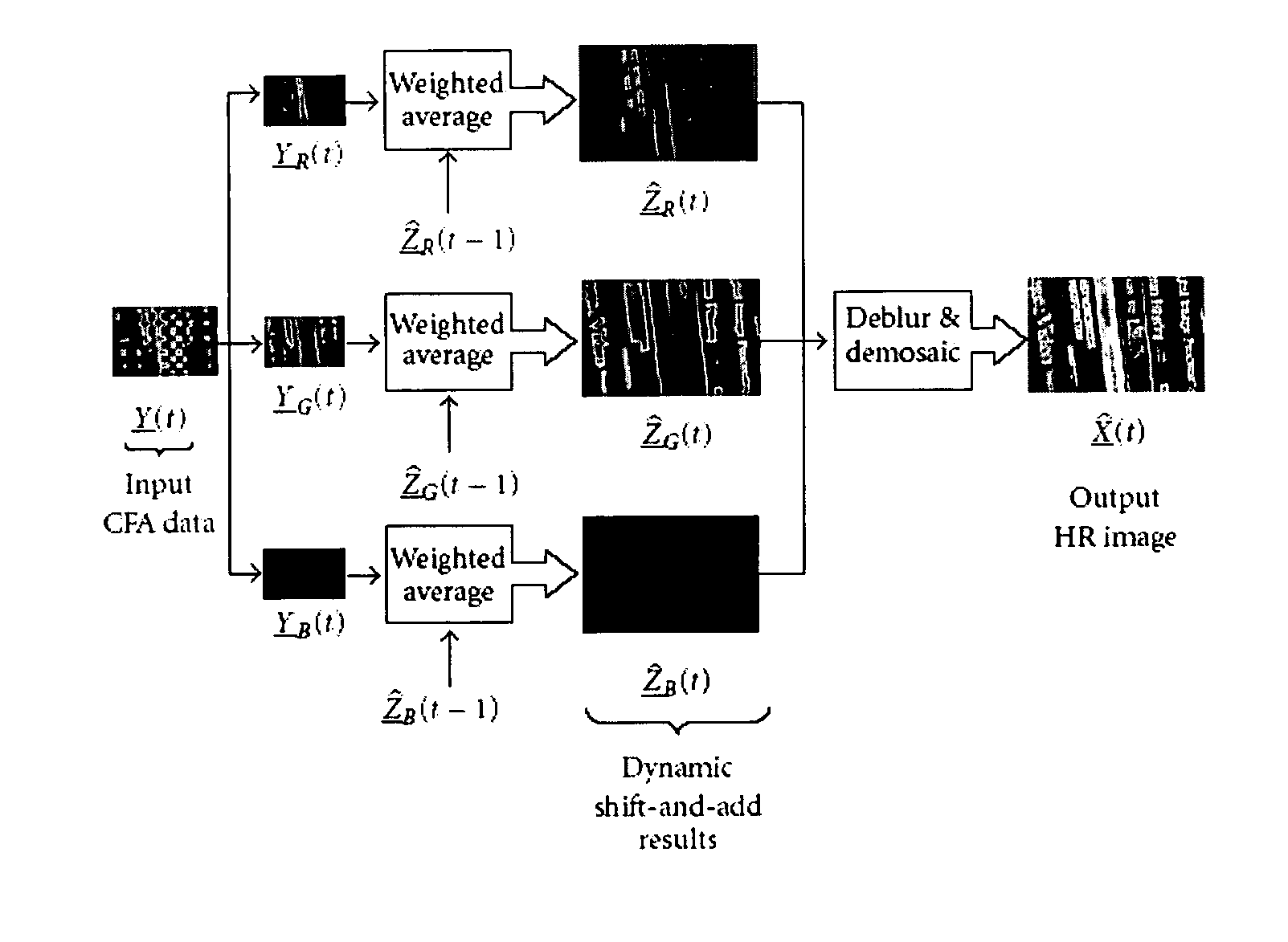
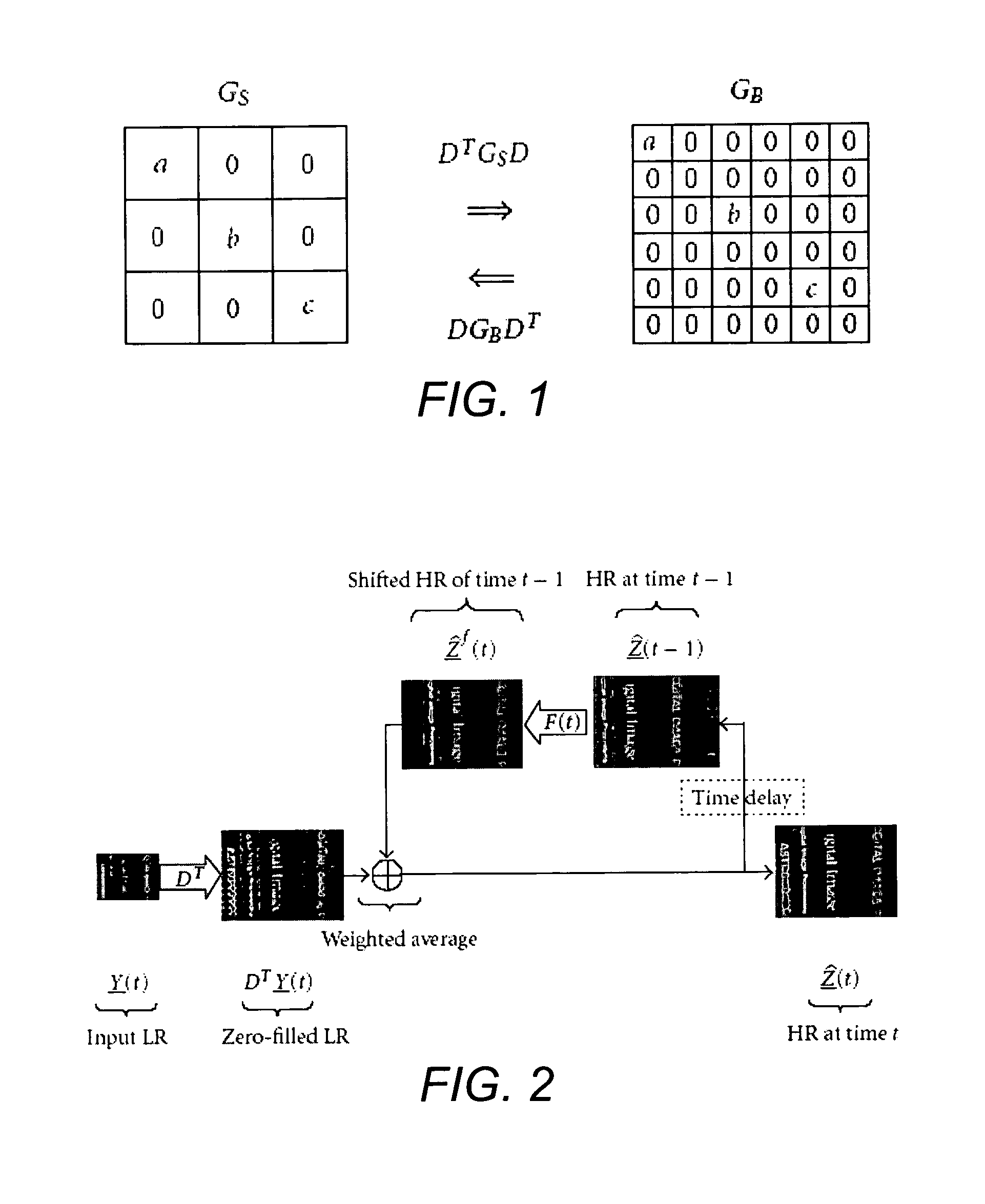
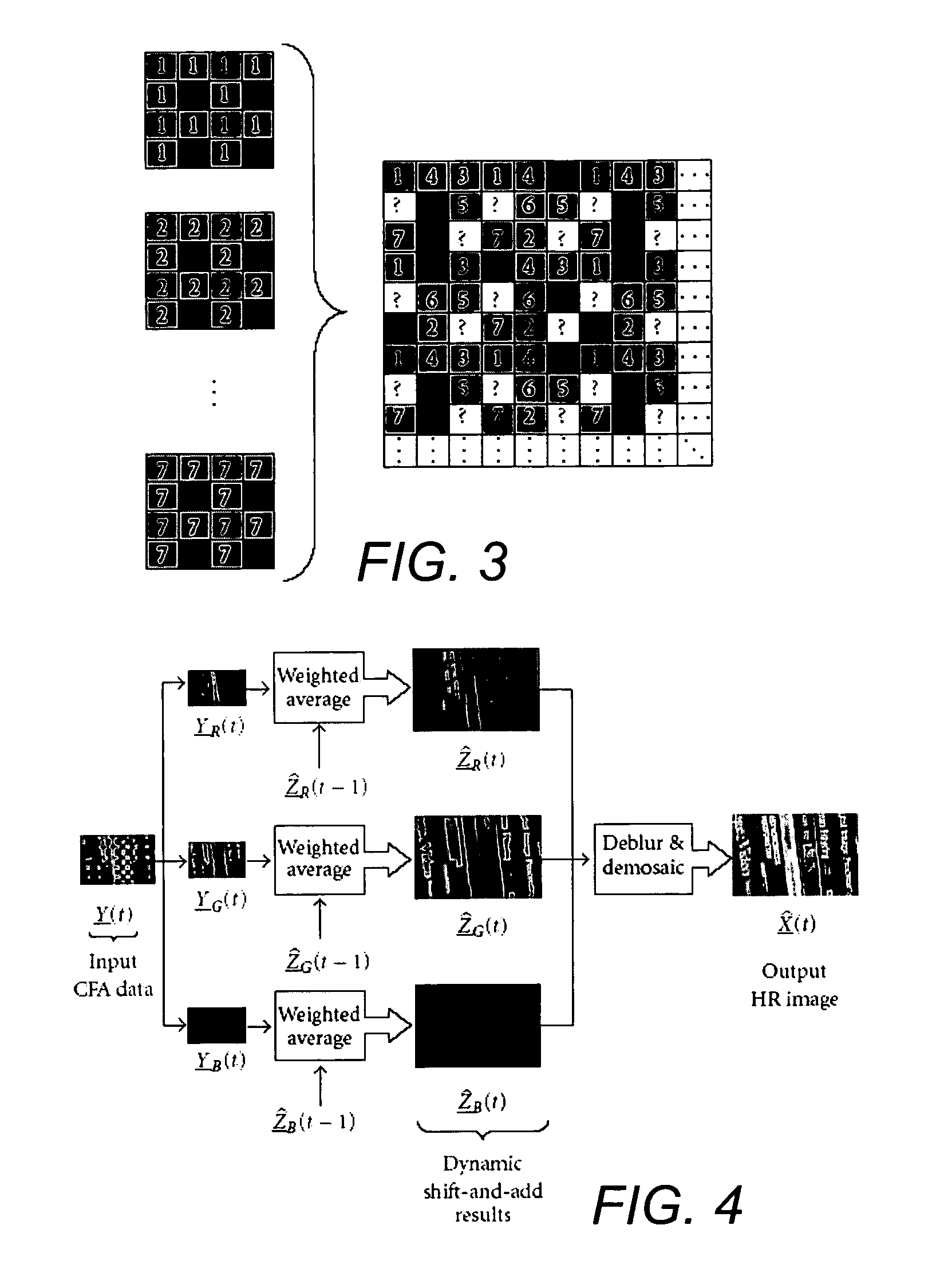
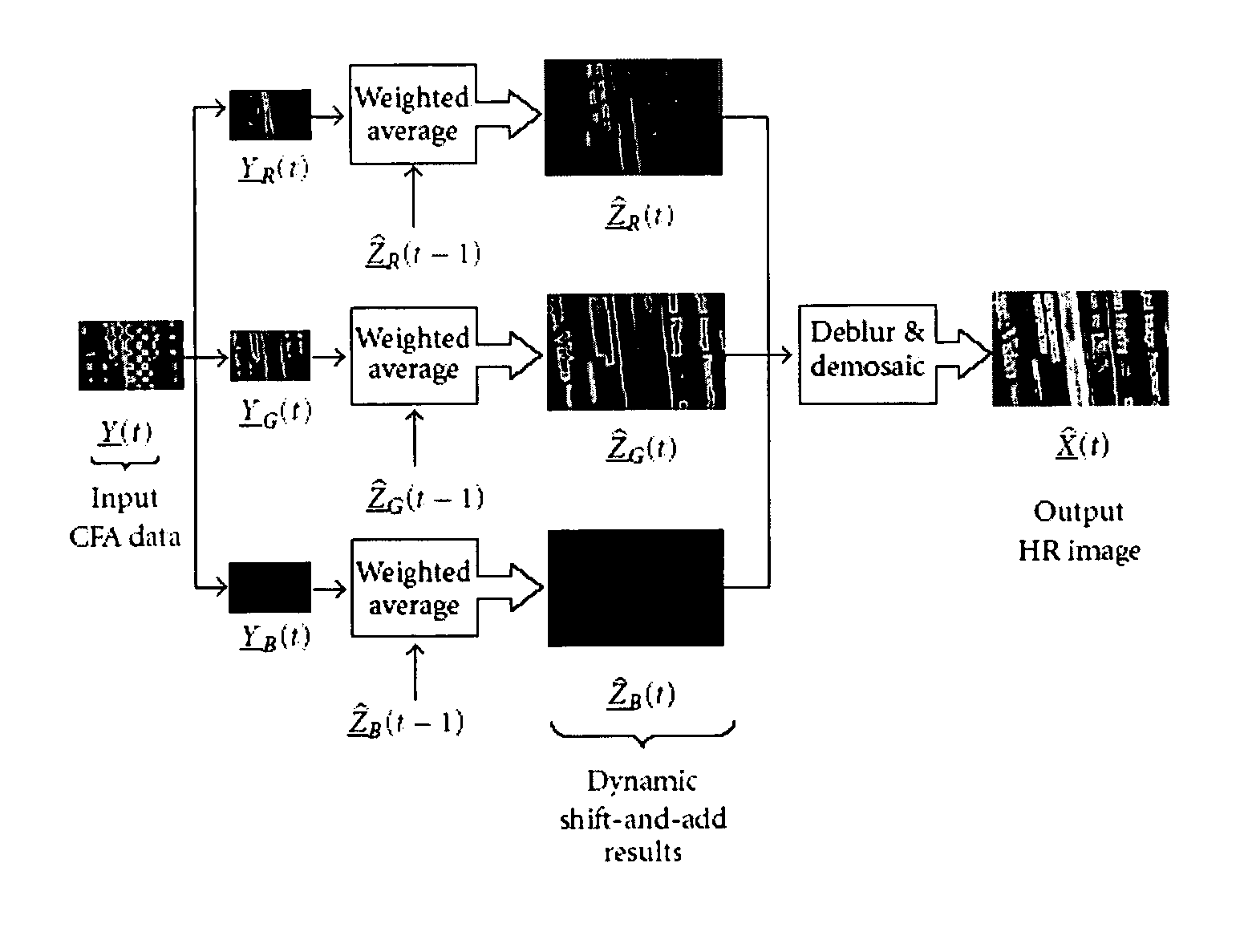
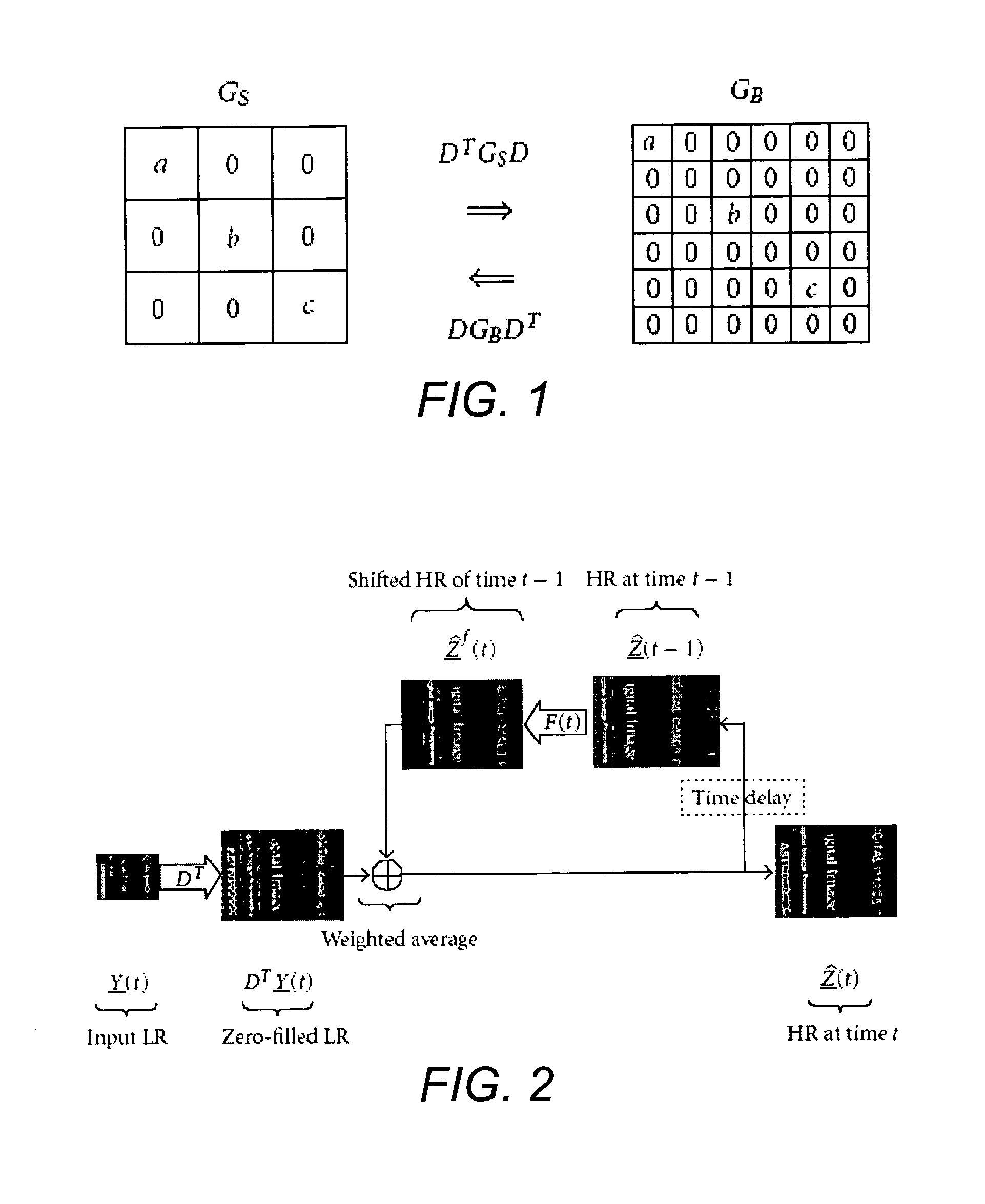
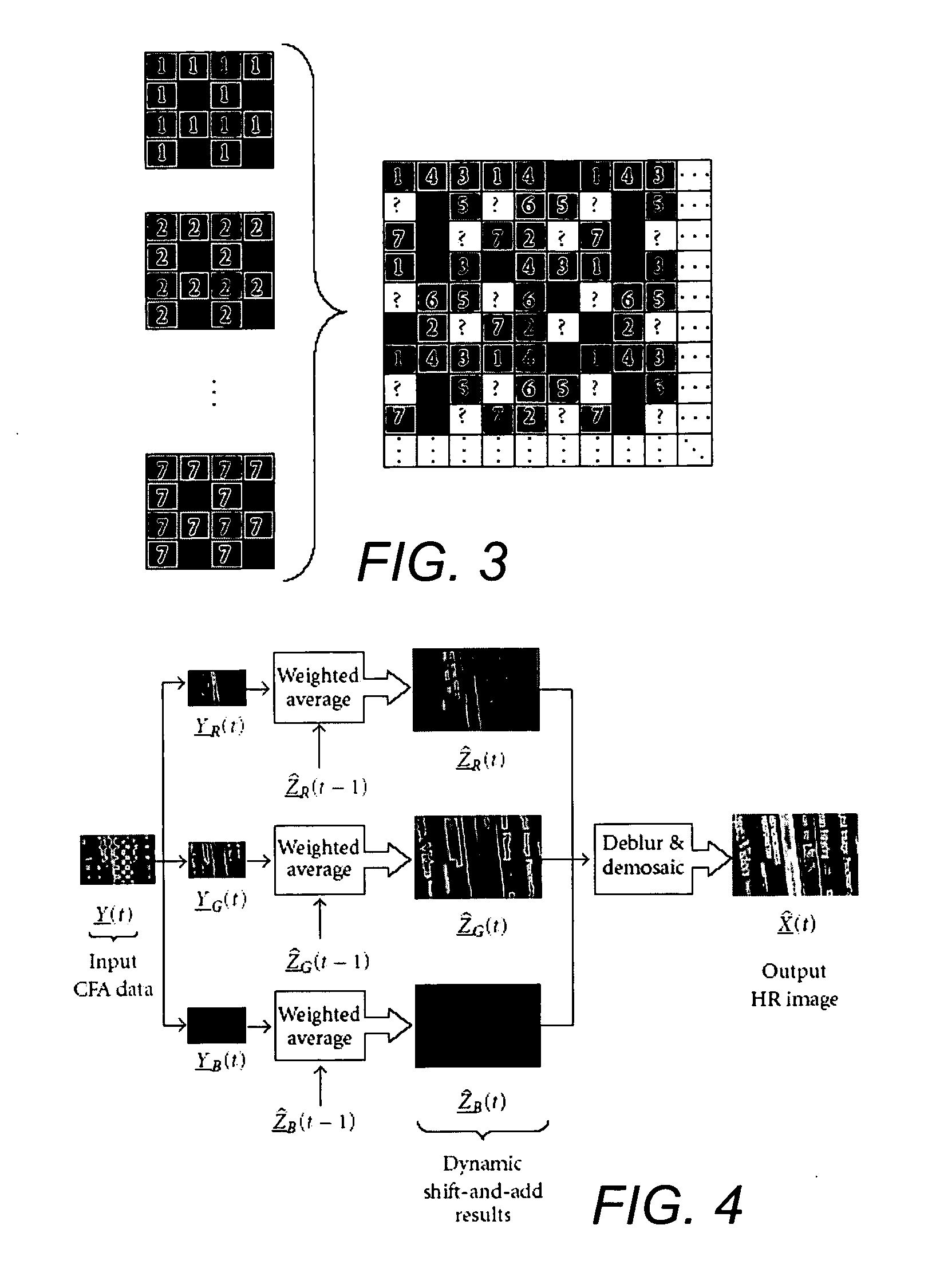
Dynamic reconstruction of high-resolution video from color-filtered low-resolution video-to-video super-resolution
ActiveUS7379612B2Quality improvementReduce memory requirementsGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionKaiman filterImage resolution
A method is provided of solving the dynamic super-resolution (SR) problem of reconstructing a high-quality set of monochromatic or color superresolved images from low-quality monochromatic, color, or mosaiced frames. The invention includes a joint method for simultaneous SR, deblurring, and demosaicing, this way taking into account practical color measurements encountered in video sequences. For the case of translational motion and common space-invariant blur, the proposed invention is based on a very fast and memory efficient approximation of the Kalman filter (KF). Experimental results on both simulated and real data are supplied, demonstrating the invention algorithms, and their strength.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
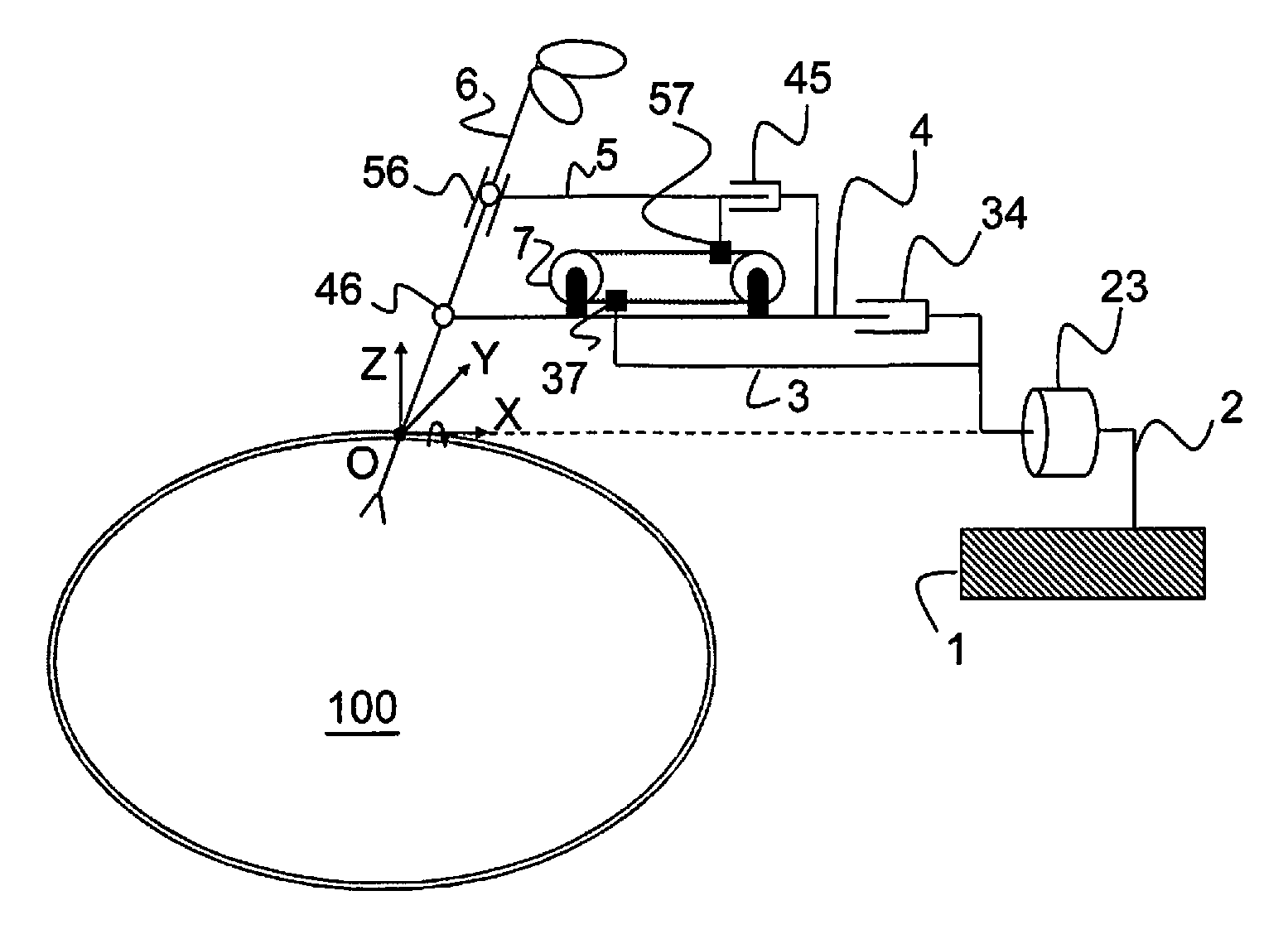
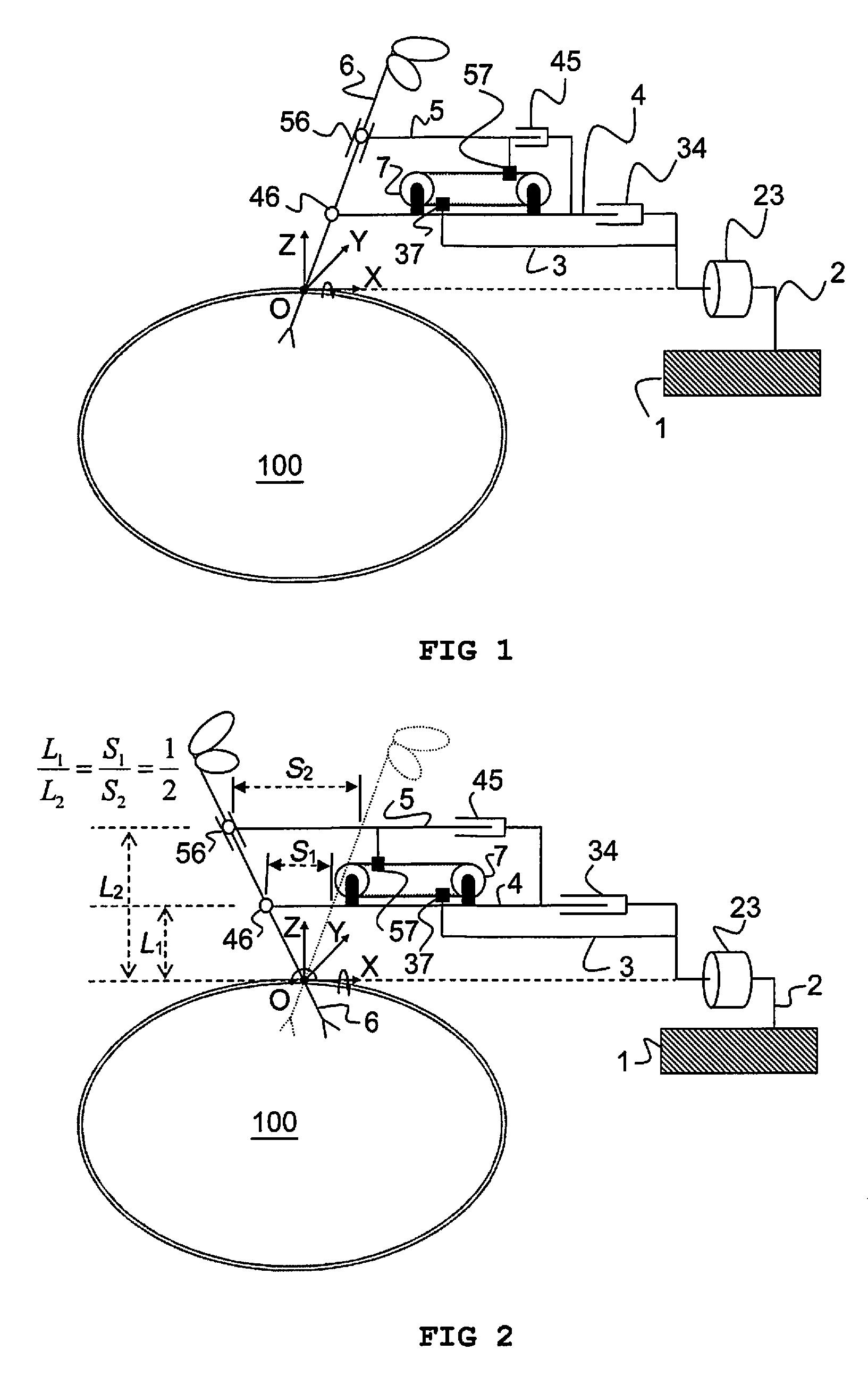
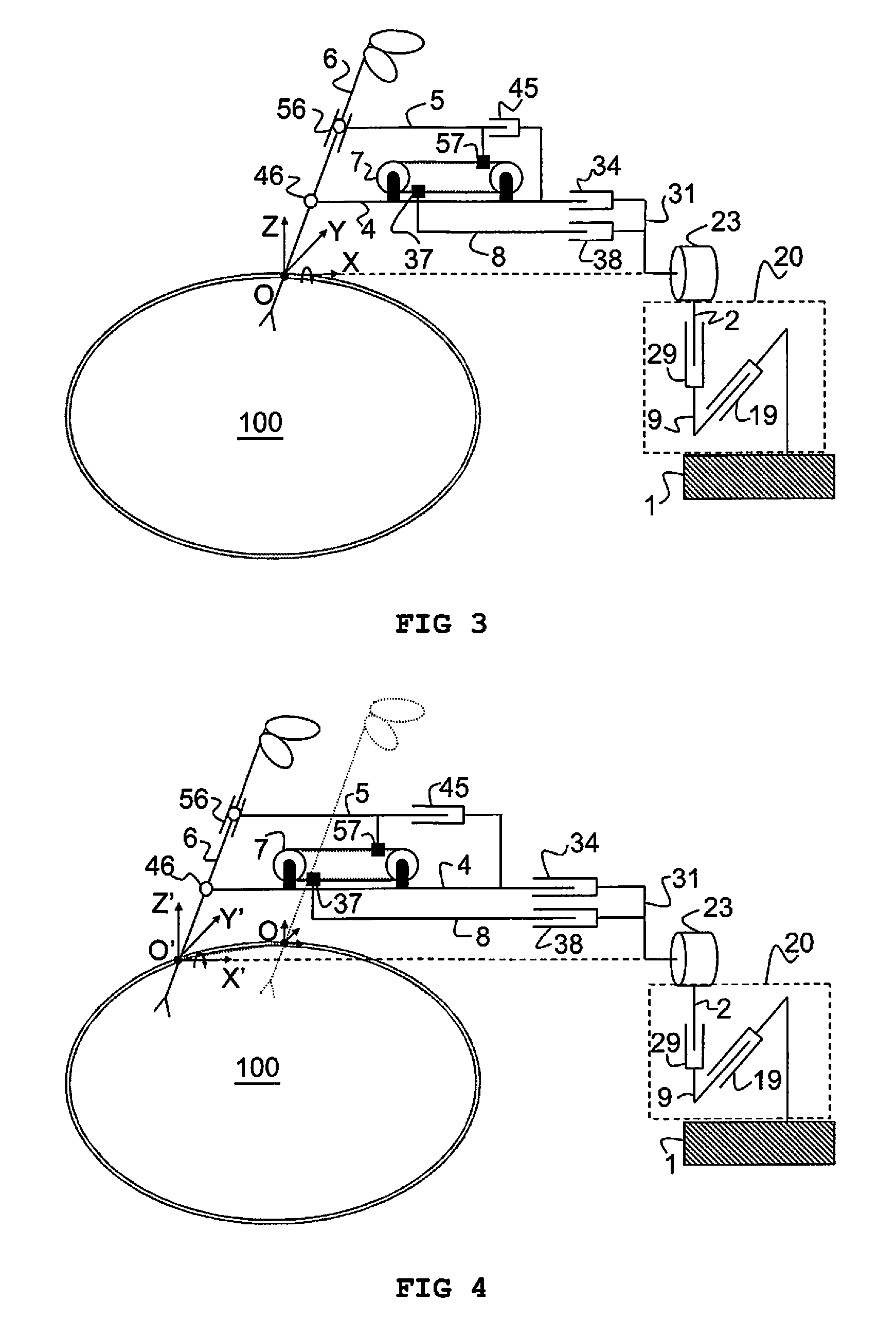
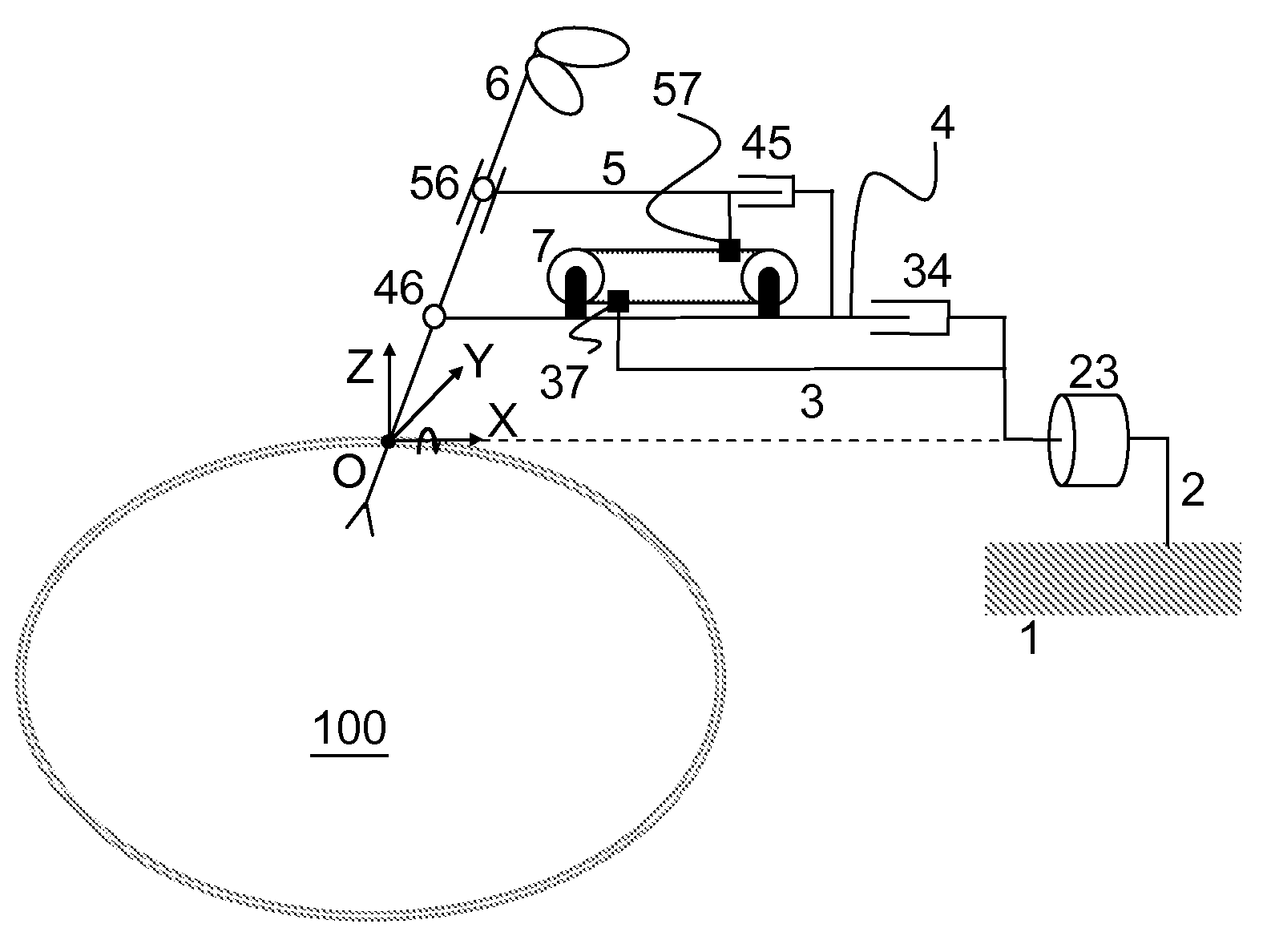
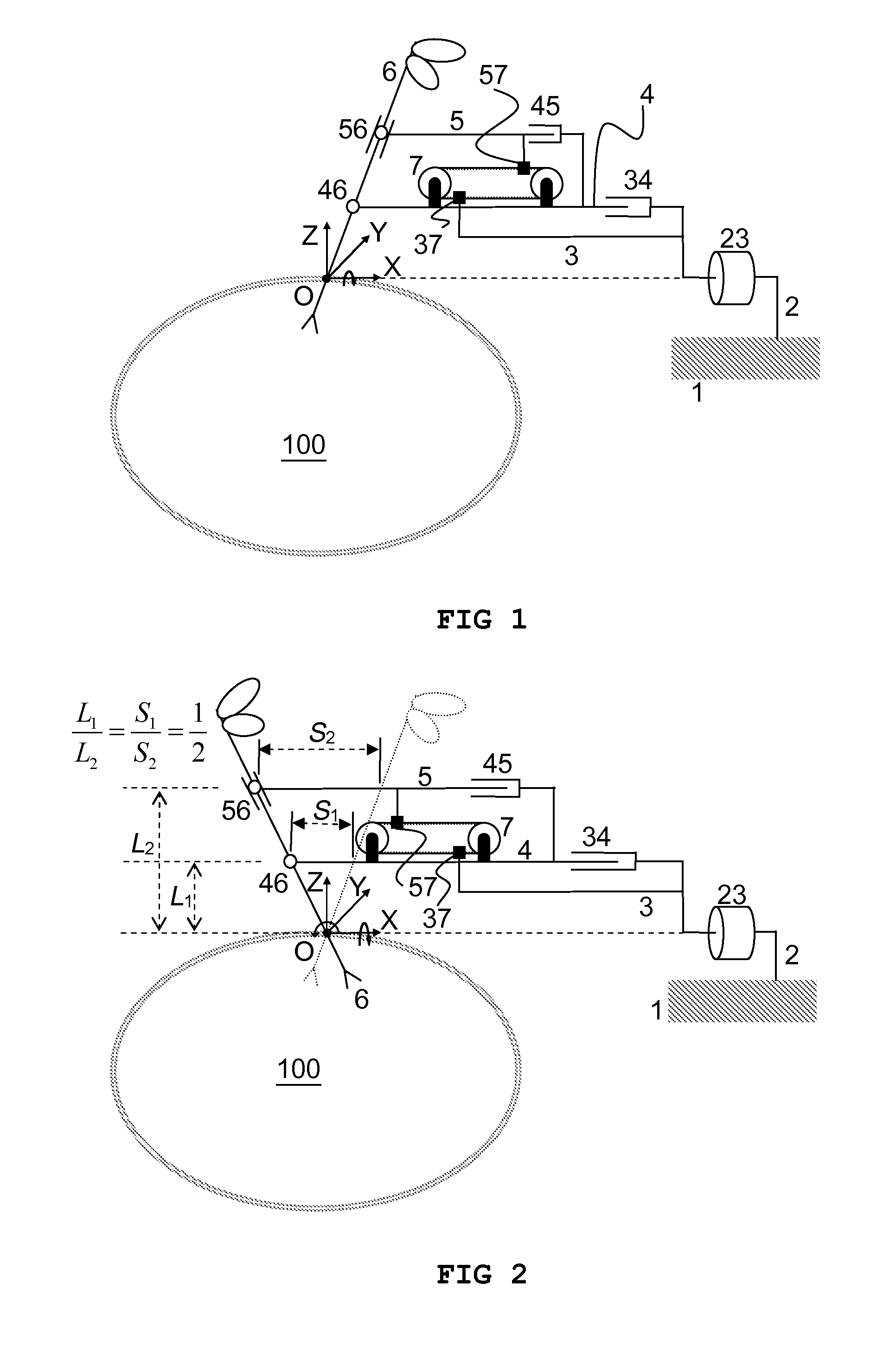
Remote centre of motion positioner
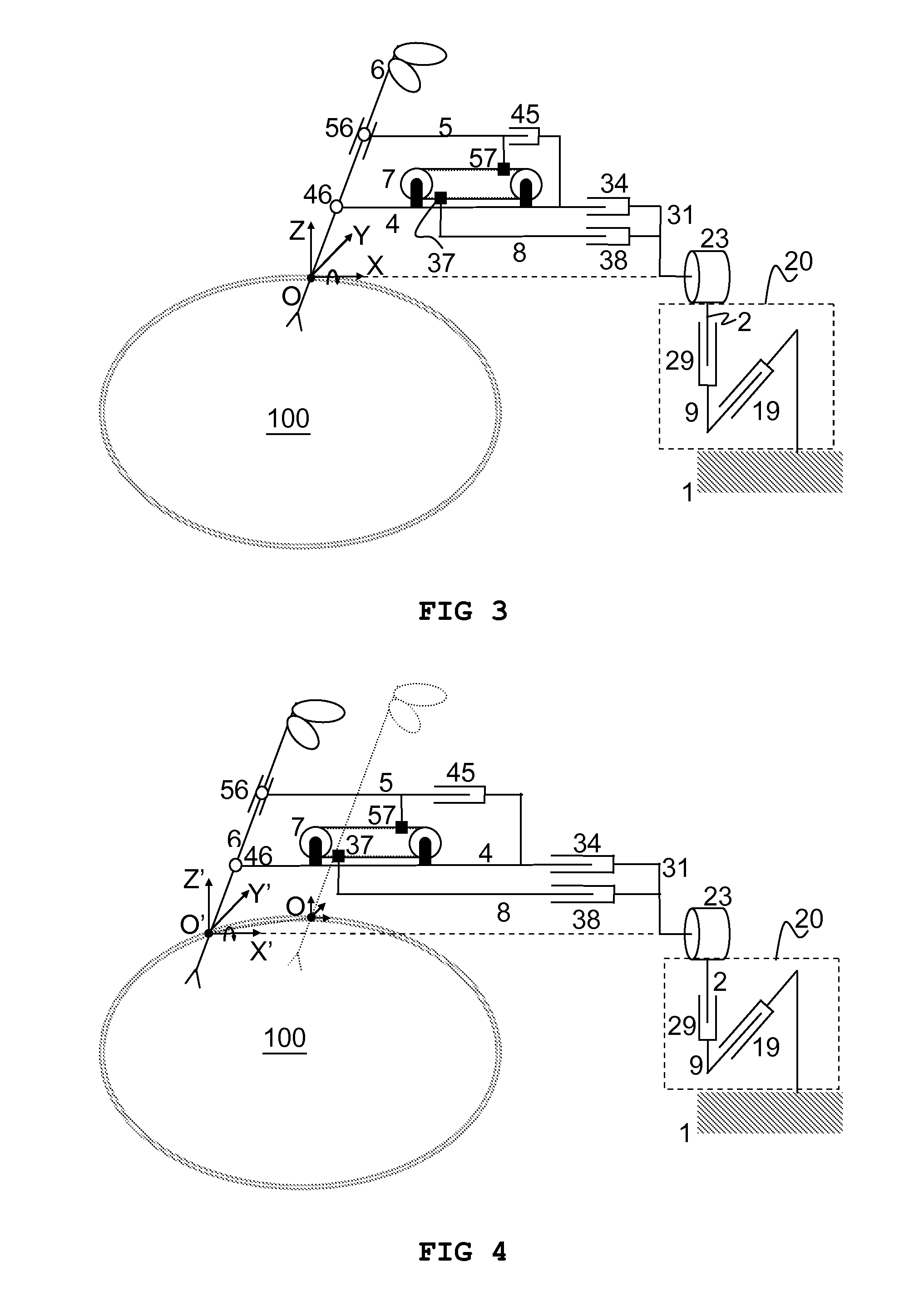
InactiveUS20120132018A1Increase stiffnessSolve the real problemDiagnosticsSurgical manipulatorsFixed ratioEngineering
Apparatus comprising a member (6) arranged to revolve about a remote centre of motion (O) and a base link (3) coupled to a mounting fixture (1). A first link (4) and a second link (5) are pivotably coupled to the member at respective distances (L1, L2) from the remote centre of motion (O) and are translatable relative to the base link (3) along a first direction and at a fixed ratio of displacement. The ratio of said respective distances equals said fixed ratio of displacement, enabling the member (6) to revolve about the remote centre of motion. The apparatus is characterised in that it comprises means (7) for generating translational motion of a first element (37) and of a second element (57) along parallel but opposite directions. The means for generating translational motion is provided on the first link (4) and is arranged to provide motion parallel to the first direction. The base link is fixed in a position, the first element (37) is fixed to the base link (3) and the second element (57) is fixed to the second link (5), such that generation of said translational motion of the first element (37) and of the second element (57) enables the first link (4) and the second link (5) to translate relative to the base link (3) with said fixed ratio of displacement.
Owner:KATHOLIEKE UNIV LEUVEN
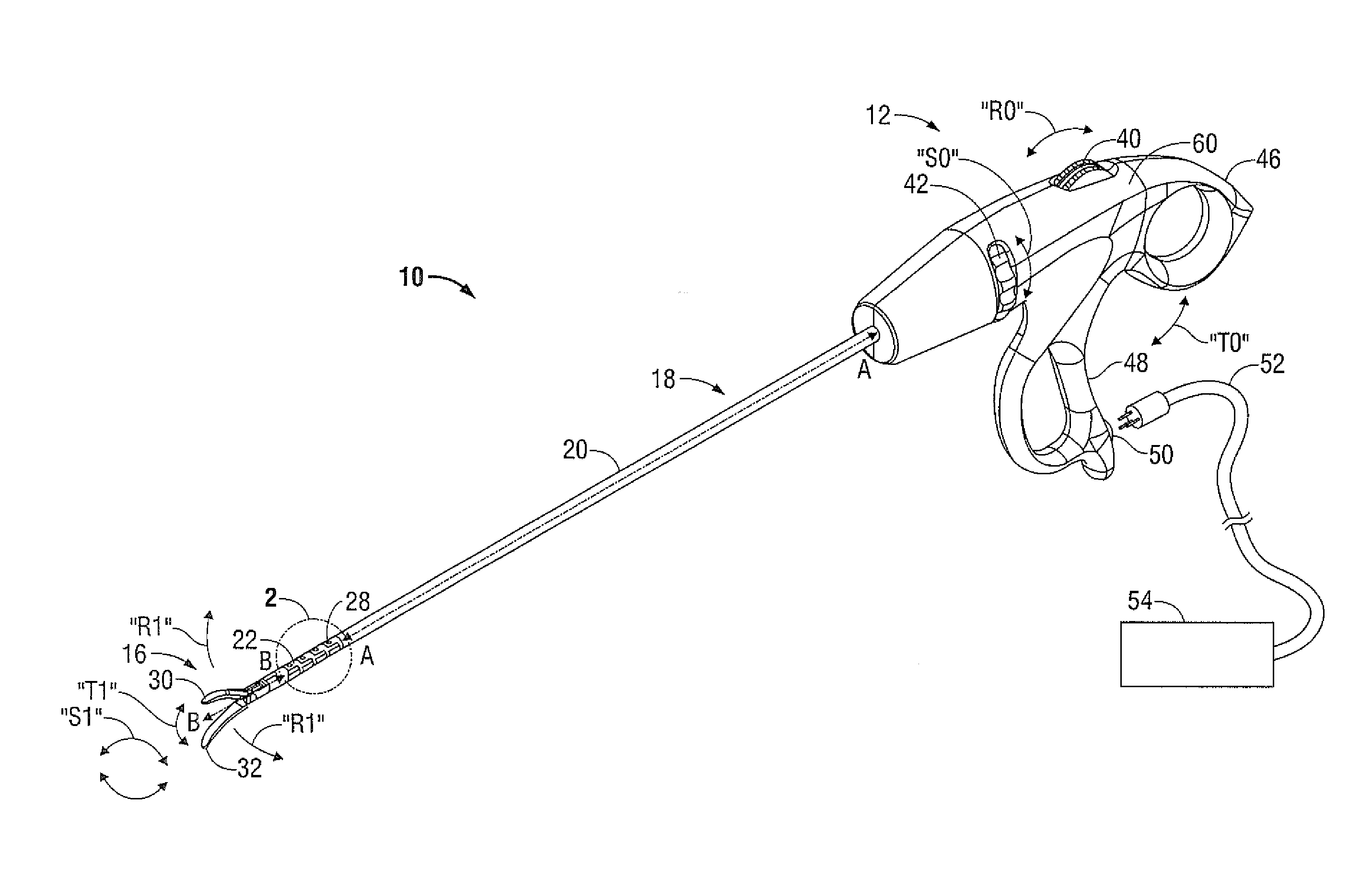
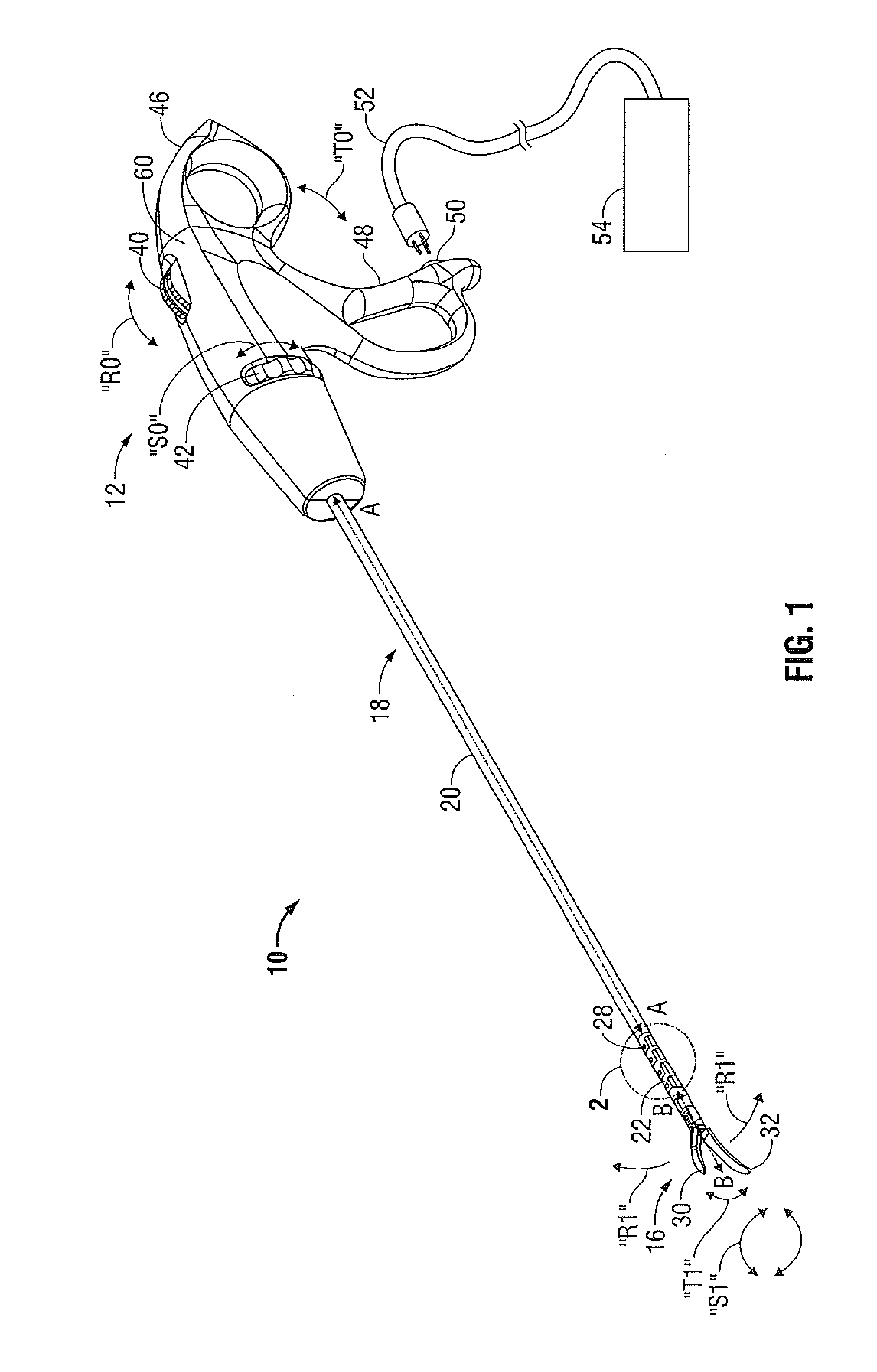
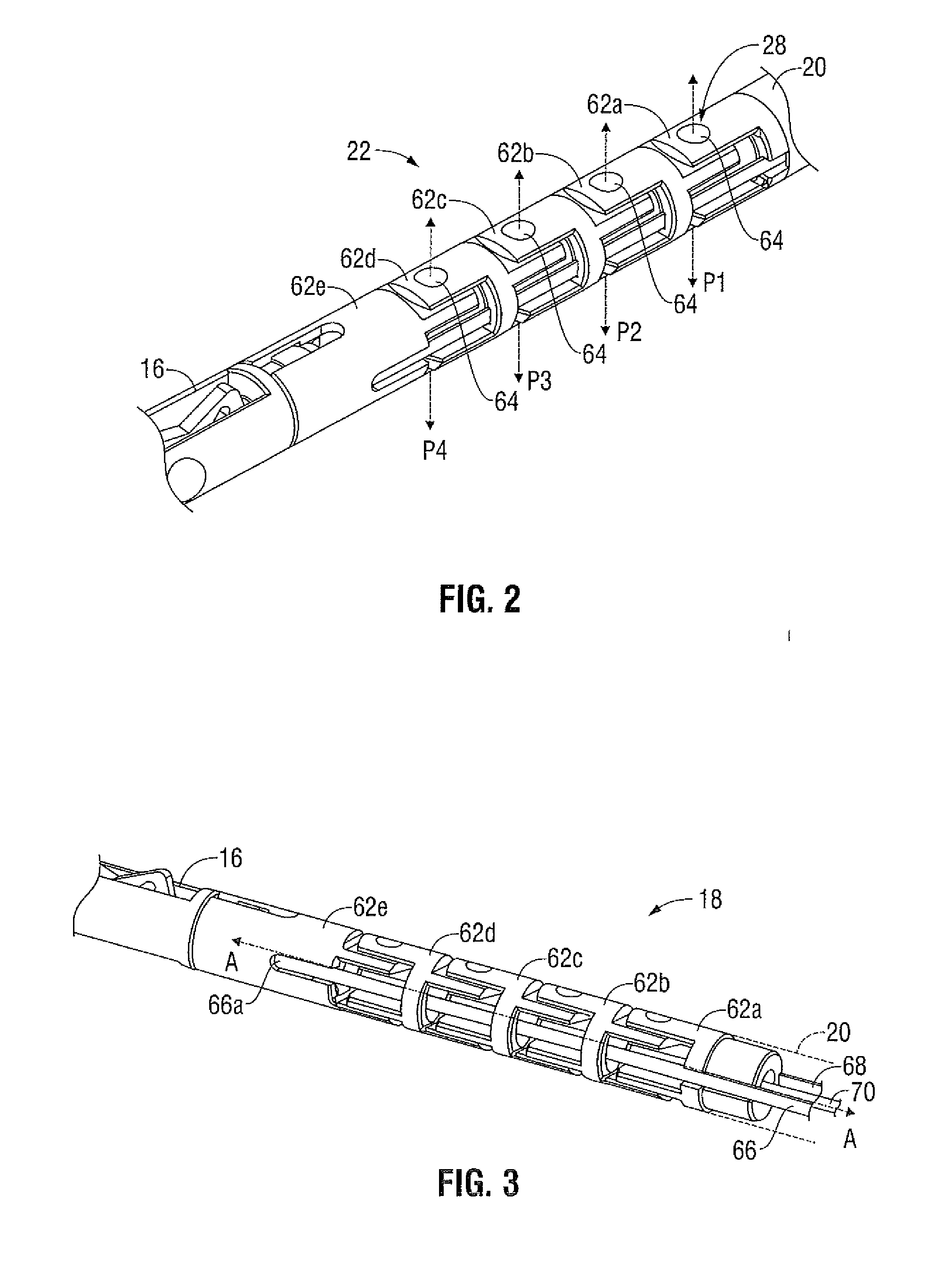
Drive Mechanism for Articulation of a Surgical Instrument
A surgical instrument includes a housing, an end effector and an elongated shaft extending therebetween. The elongated shaft includes a distal portion that is movable between aligned and articulated configurations. A pair of drive cables extends through the elongated shaft and is coupled to the distal portion such that reciprocal longitudinal motion of the drive cables induces movement of the distal portion between the aligned and articulated configurations. An articulation drive mechanism is operable to induce reciprocal longitudinal motion of the drive cables. The drive mechanism includes an actuator and a pair of torsion members that are rotatable about two distinct axes in response to movement of the actuator. A respective follower is operatively coupled to each torsion member to translate in a respective longitudinal direction in response to rotation of the torsion members, and each follower is coupled to a respective drive cable to impart translational motion thereto.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Interface device and method for interfacing instruments to medical procedure simulation systems
An interface device and method for interfacing instruments to a medical procedure simulation system serve to interface peripherals in the form of mock medical instruments to the medical procedure simulation system computer to enable simulation of medical procedures. The interface device includes a housing having a mock bodily region of interest to facilitate insertion of a mock instrument, such as an endoscope tube, into the interface device. The mock bodily region of interest may be pivotable to simulate various patient orientations. The instrument is engaged by a capture mechanism in order to measure rotational and translational motion of the instrument. An actuator is disposed within the interface device to provide force feedback to the instrument. The measured motion is provided to the computer system to reflect instrument motion on the display during the simulation. Alternatively, the interface device may be configured to accommodate instrument assemblies having a plurality of nested instruments (e.g., sheath, catheter and wire), whereby the interface device individually grasps, measures manipulation of and provides force feedback to the nested instruments. In addition, the interface device may be configured to simultaneously accommodate a plurality of independently inserted instruments.
Owner:IMMERSION MEDICAL
Methods of and apparatus for making high aspect ratio microelectromechanical structures
Various embodiments of the invention present techniques for forming structures (e.g. HARMS-type structures) via an electrochemical extrusion (ELEX(TM)) process. Preferred embodiments perform the extrusion processes via depositions through anodeless conformable contact masks that are initially pressed against substrates that are then progressively pulled away or separated as the depositions thicken. A pattern of deposition may vary over the course of deposition by including more complex relative motion between the mask and the substrate elements. Such complex motion may include rotational components or translational motions having components that are not parallel to an axis of separation. More complex structures may be formed by combining the ELEX(TM) process with the selective deposition, blanket deposition, planarization, etching, and multi-layer operations of EFAB(TM).
Owner:MEMGEN
Moving object detection using low illumination depth capable computer vision
Moving object detection is based on low illumination image data that includes distance or depth information. The vision system operates on a platform with a dominant translational motion and with a small amount of rotational motion. Detection of moving objects whose motions are not consistent with the movement of the background is complementary to shape-based approaches. For low illumination computer-based vision assistance a two-stage technique is used for simultaneous and subsequent frame blob correspondence. Using average scene disparity, motion is detected without explicit ego-motion calculation. These techniques make use of characteristics of infrared sensitive video data, in which heat emitting objects appear as hotspots.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Devices and methods for ablating and removing a tissue mass
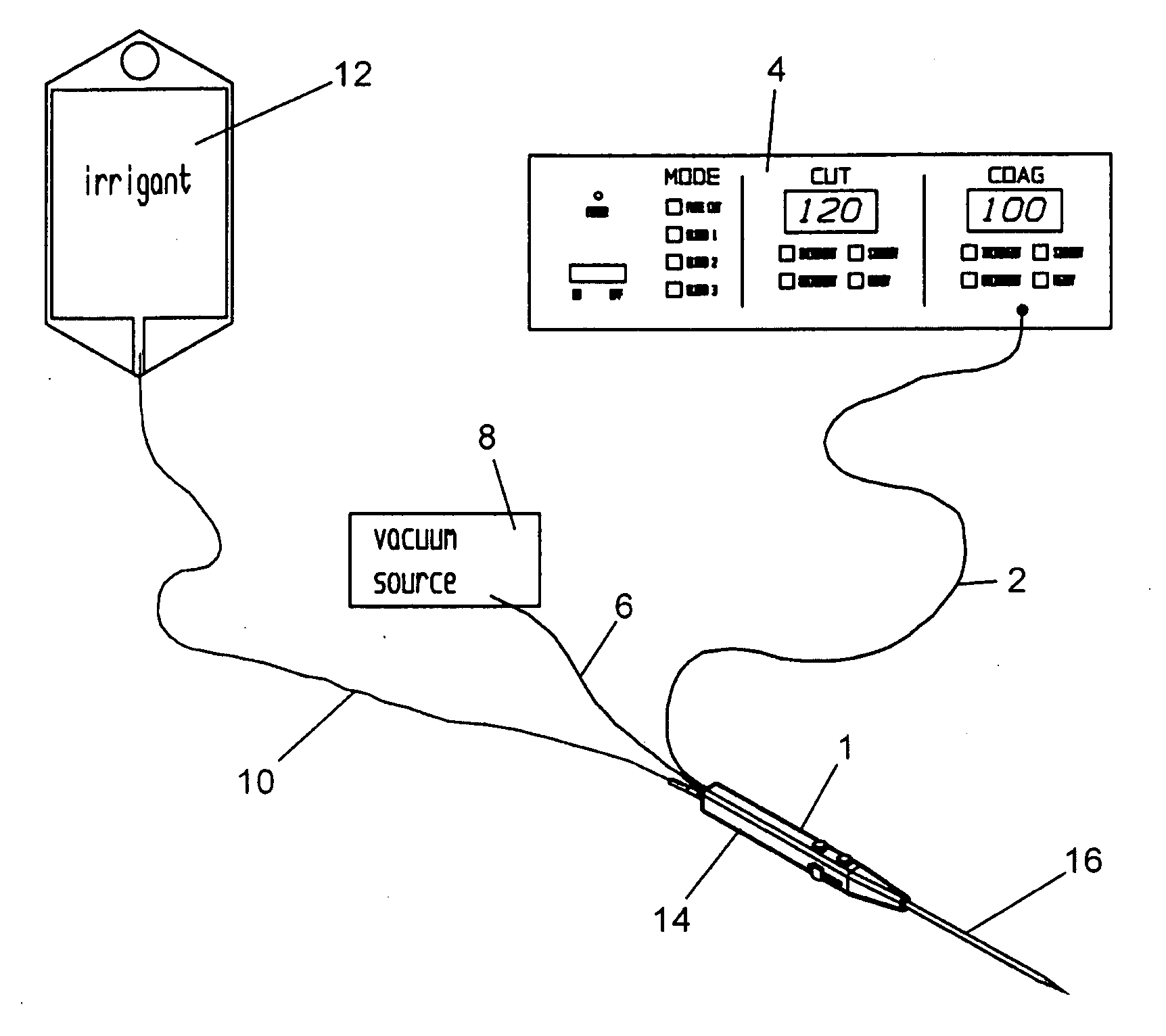
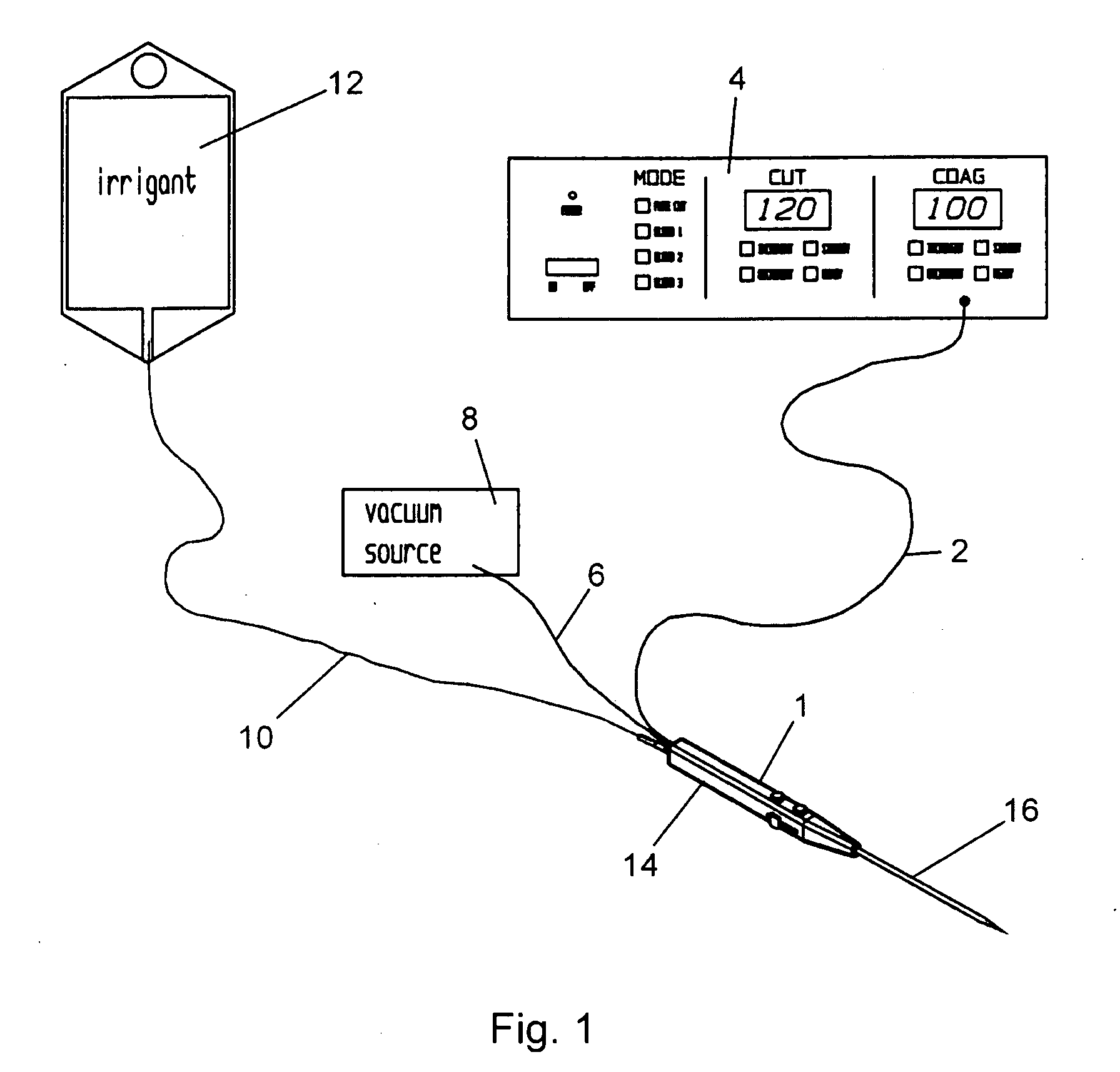
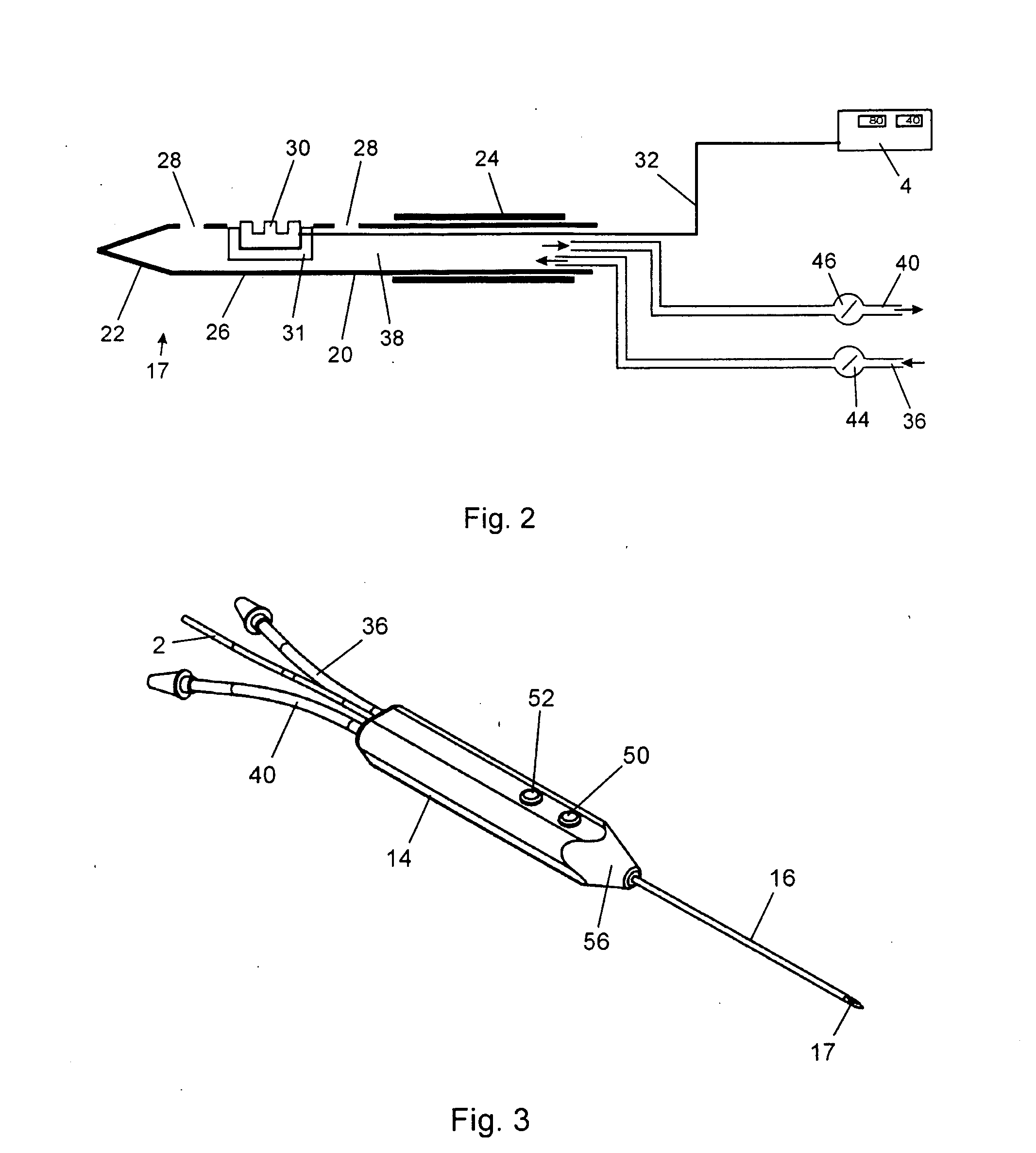
Disclosed herein are high efficiency surgical devices and methods of using same using radio frequency (RF) electrical power to destroy, vaporize and remove soft tissues, such as tumors, both malignant and benign, from within a target surgical site. In one particularly preferred embodiment, the electrosurgical device employs a combination of rotary and translational motion to incrementally vaporize a calculated volume of tissue. According to the principles of this invention, the electrosurgical devices can be used with externally supplied conductive or non-conductive irrigants, whether liquid, gas, or a combination thereof, as well as without externally supplied liquids, a mode of operation often referred to as “dry field” environment. The electrosurgical devices may further optionally include aspiration components to permit removal of vaporization by-products.
Owner:ELECTROMEDICAL ASSOCS
Movable-arm-type powder bed powder spreading device
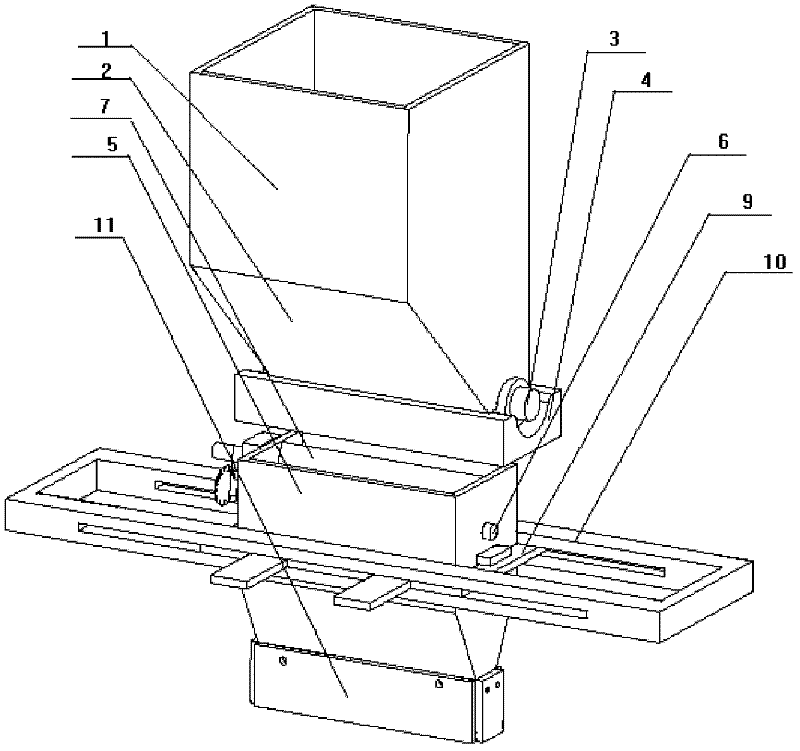
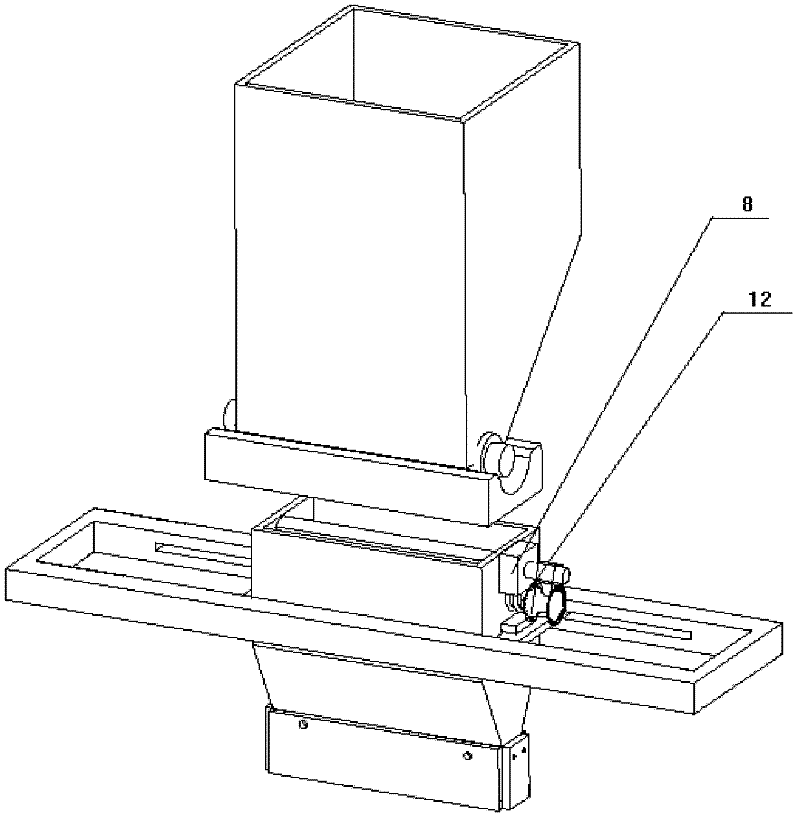
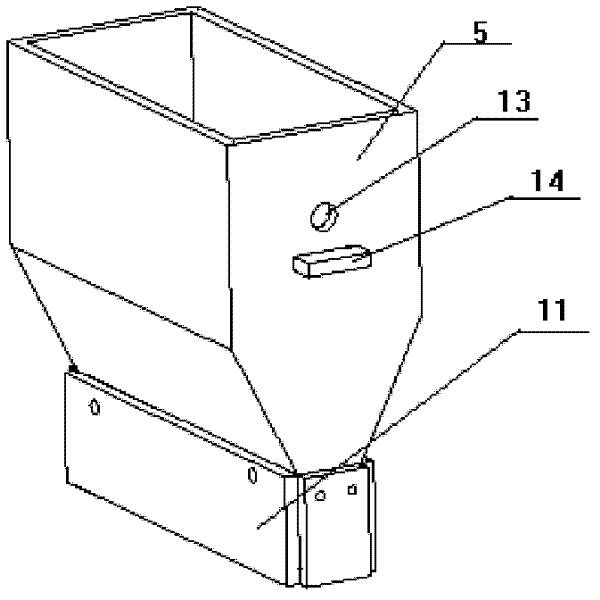
The invention discloses a powder spreading device for rapid forming equipment. The device mainly comprises a quantitative powder conveying device, a movable silo, a movable arm, a movable frame and the like. The quantitative powder conveying device is used for supplying powder to the movable silo. Whether the powder falls down or not is controlled through a rotating sheet. According to the section of parts, the movable silo does regular translational motion within a working plane under the drive of the movable arm and the movable frame, and a scraper on the silo can realize dynamic powder spreading. By combining the movable arm and the movable silo with the movable frame, defining the powder within the area of the parts and adjusting the magnitude and the position of spread powder according to the change of the section of the parts, not only can the amount of the used powder is greatly saved, but also the powder spreading speed is high; and the structural design of the powder spreading device is simple, the powder spreading device is convenient to disassemble and assemble, the realization is easy, the cost is lower and the powder spreading device has an important application value to the improvement of the overall technical level of a powder bed quick forming technology.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
System and method for tracking eyeball motion
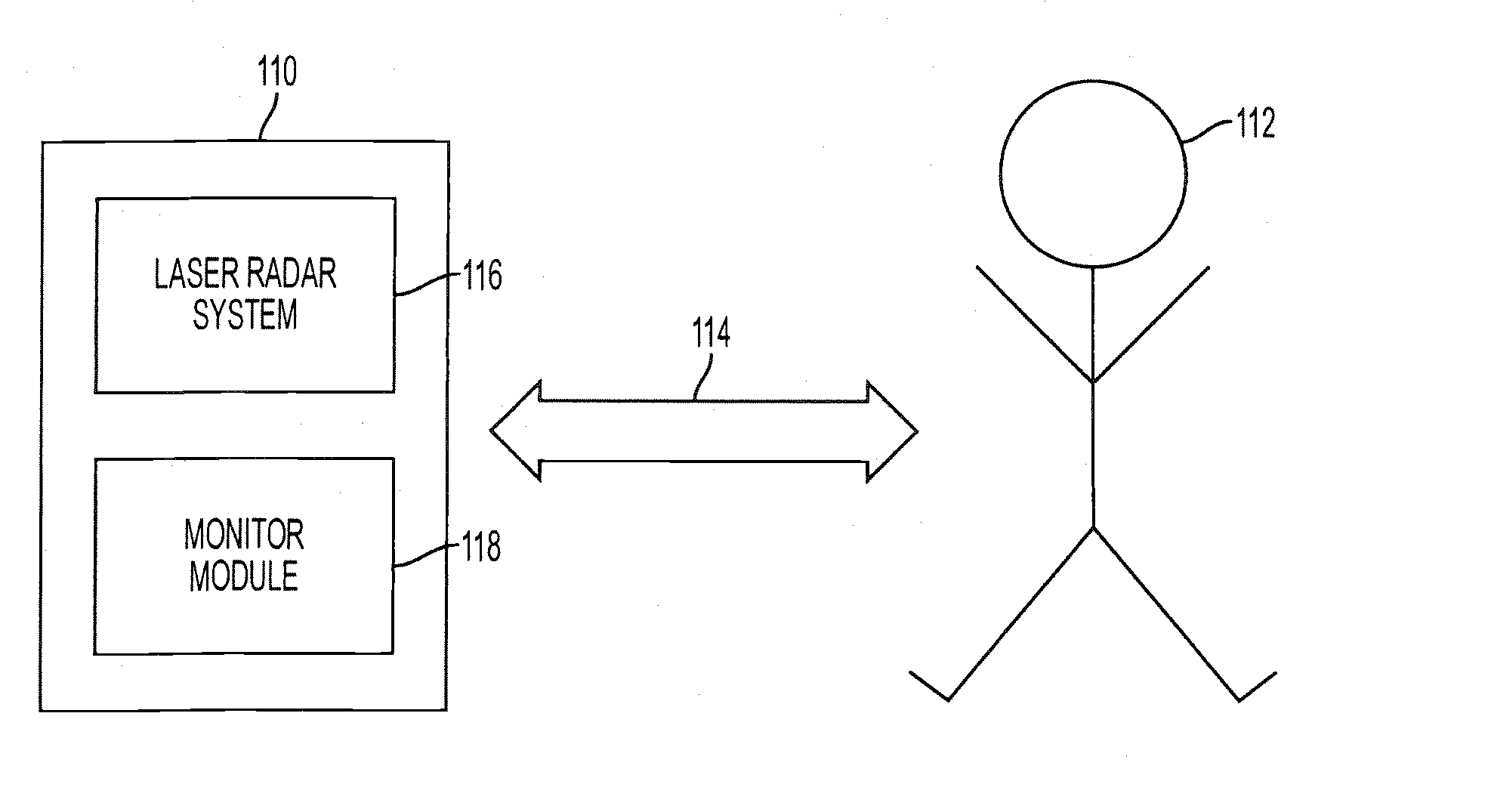
ActiveUS20070171367A1Increase speedReduce intrusionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsRadarRotation velocity
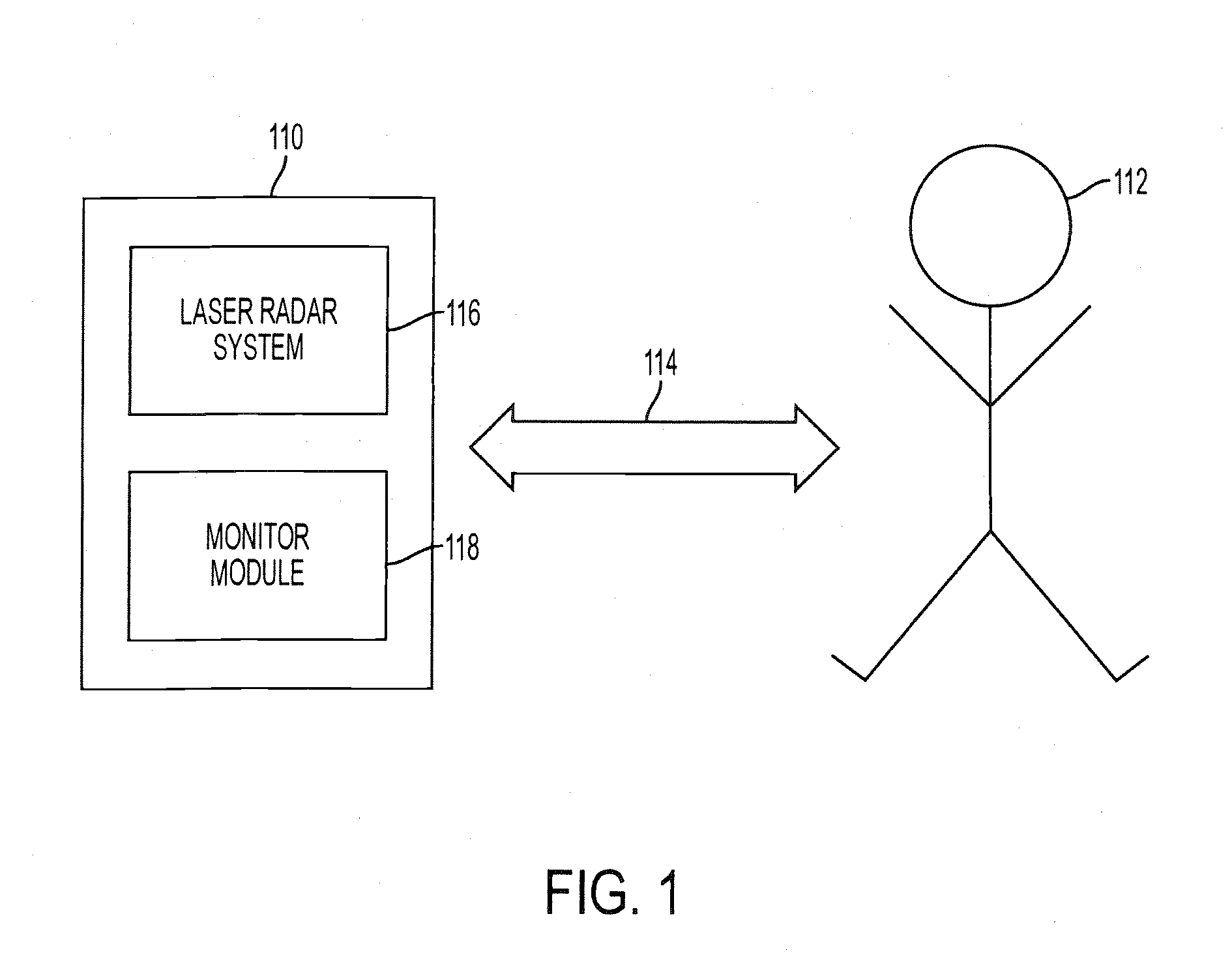
Detecting position information related to a face, and more particularly to an eyeball in a face, using a detection and ranging system, such as a Radio Detection And Ranging (“RADAR”) system, or a Light Detection And Ranging (“LIDAR”) system. The position information may include a location of the eyeball, translational motion information related to the eyeball (e.g., displacement, velocity, acceleration, jerk, etc.), rotational motion information related to the eyeball (e.g., rotational displacement, rotational velocity, rotational acceleration, etc.) as the eyeball rotates within its socket.
Owner:AEVA INC
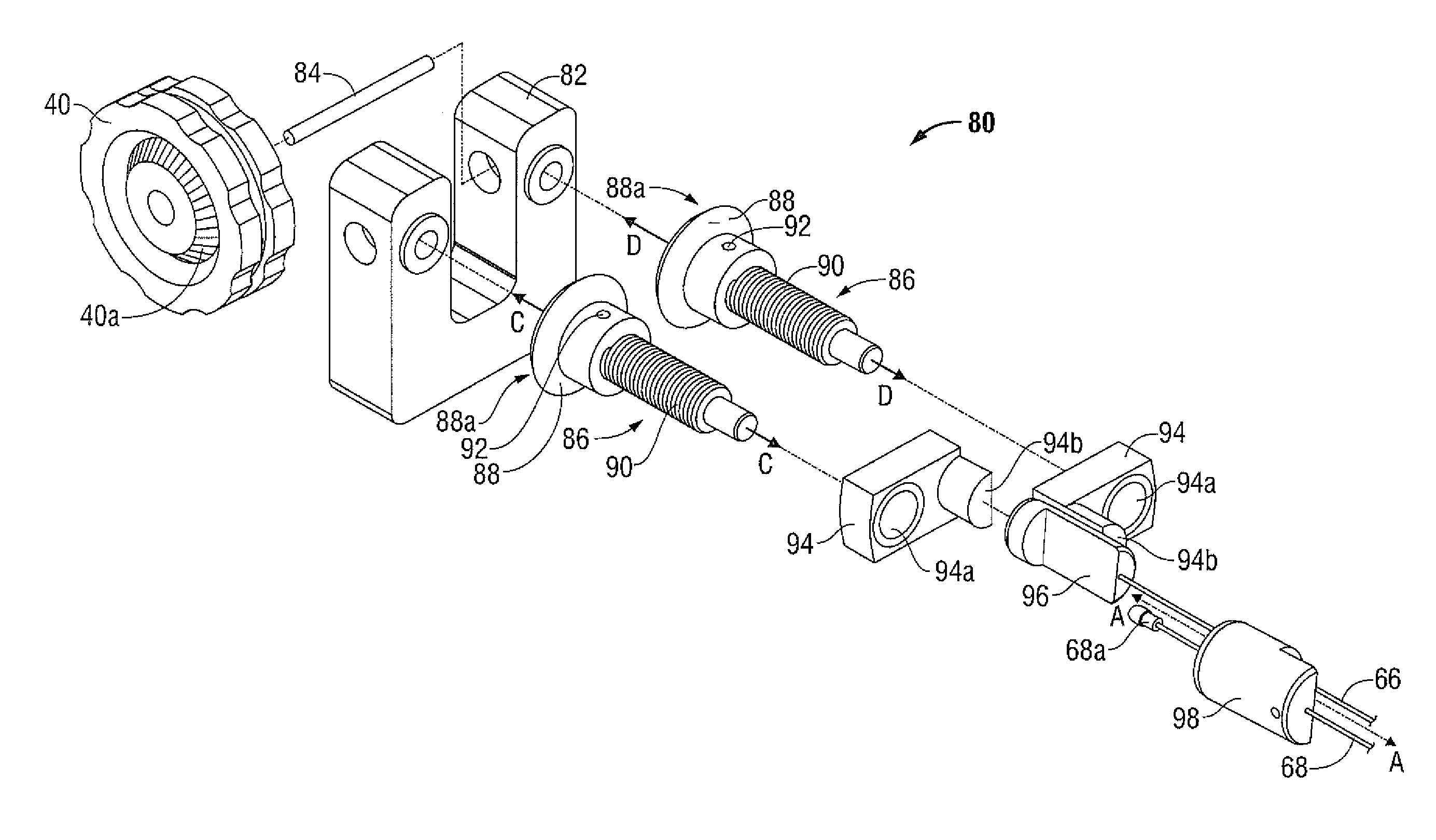
Combined Vehicle Brake With Electromechanically Operable Parking Brake and Gear For Converting A Rotary Movement Into A Translational Movement
ActiveUS20090283371A1Reduce power consumptionCost-effective manufacturingMechanically actuated brakesToothed gearingsParking brakePiston
A combined vehicle brake including a hydraulically actuated service brake and an electromechanically actuated parking brake device, a hydraulic operating pressure chamber in a brake housing being defined by a brake piston, which for performing service braking actions can be acted upon by hydraulic pressure fluid, so that the brake piston can be actuated along a piston longitudinal axis in order to produce a braking action, and the parking brake device acting on the brake piston by way of a transmission that translates the rotary motion of an electromechanical actuator into a translational motion and actuates the brake piston to perform parking brake actions and to keep it in the actuated position. Also disclosed is a transmission for translating a rotary motion into a translational motion by way of a screw spindle and a spindle nut, which are in contact with one another by way of multiple rolling elements.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
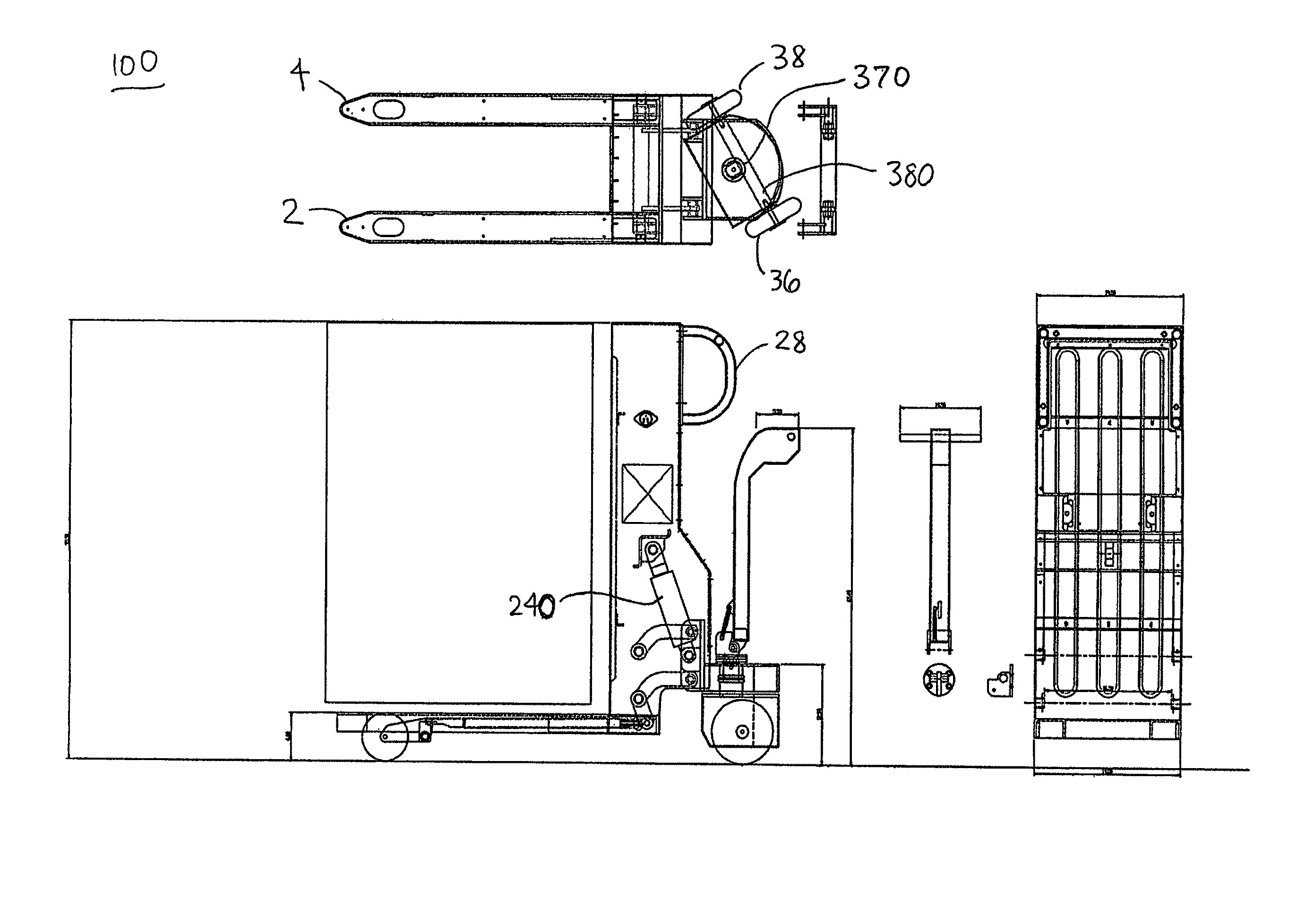
Pallet jack system and method for the transportation of stackable packaged goods pallets
A pallet jack is disclosed that comprises a left tine and a right tine. The pallet jack includes a lifting mechanism that may include an electrically powered hydraulic pump to effectuate the lifting motion. The pallet jack may also include power-driven wheels that are connected by an axle, thereby facilitating translational motion of the pallet jack. The wheels may be maximally spaced by using a maximum-length axle that is slightly longer than the width of the pallet jack body, thereby optimizing load stability.
Owner:COCA-COLA BOTTLING CO UNITED INC
Dynamic reconstruction of high-resolution video from color-filtered low-resolution video-to-video super-resolution
ActiveUS20070071362A1Quality improvementReduce memory requirementsGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionKaiman filterImage resolution
A method is provided of solving the dynamic super-resolution (SR) problem of reconstructing a high-quality set of monochromatic or color superresolved images from low-quality monochromatic, color, or mosaiced frames. The invention includes a joint method for simultaneous SR, deblurring, and demosaicing, this way taking into account practical color measurements encountered in video sequences. For the case of translational motion and common space-invariant blur, the proposed invention is based on a very fast and memory efficient approximation of the Kalman filter (KF). Experimental results on both simulated and real data are supplied, demonstrating the invention algorithms, and their strength.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Drive mechanism for articulation of a surgical instrument
A surgical instrument includes a housing, an end effector and an elongated shaft extending therebetween. The elongated shaft includes a distal portion that is movable between aligned and articulated configurations. A pair of drive cables extends through the elongated shaft and is coupled to the distal portion such that reciprocal longitudinal motion of the drive cables induces movement of the distal portion between the aligned and articulated configurations. An articulation drive mechanism is operable to induce reciprocal longitudinal motion of the drive cables. The drive mechanism includes an actuator and a pair of torsion members that are rotatable about two distinct axes in response to movement of the actuator. A respective follower is operatively coupled to each torsion member to translate in a respective longitudinal direction in response to rotation of the torsion members, and each follower is coupled to a respective drive cable to impart translational motion thereto.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Micro inertial measurement unit
InactiveUS6671648B2Precise positioningSmall sizeDigital computer detailsSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsTemperature controlAngular rate sensor
A micro inertial measurement unit, which is adapted to apply to output signals proportional to rotation and translational motion of a carrier, respectively from angular rate sensors and acceleration sensors, is employed with MEMS rate and acceleration sensors. Compared with a conventional IMU, the processing method utilizes a feedforward open-loop signal processing scheme to obtain highly accurate motion measurements by means of signal digitizing, temperature control and compensation, sensor error and misalignment calibrations, attitude updating, and damping control loops, and dramatically shrinks the size of mechanical and electronic hardware and power consumption, meanwhile, obtains highly accurate motion measurements.
Owner:AMERICAN GNC
Imprinting apparatus with independently actuating separable modules
ActiveUS20050178280A1Reduce in quantityNanoinformaticsPhotomechanical apparatusActuatorHorizontal and vertical
Owner:KOREA INST OF MASCH & MATERIALS
Pot utensils ' movement device and cooking device adopting said pot utensils ' movement
InactiveCN101138467ALower performance requirementsRealize straight-line shaking pan movementCooking vesselsReciprocating motionSemi automatic
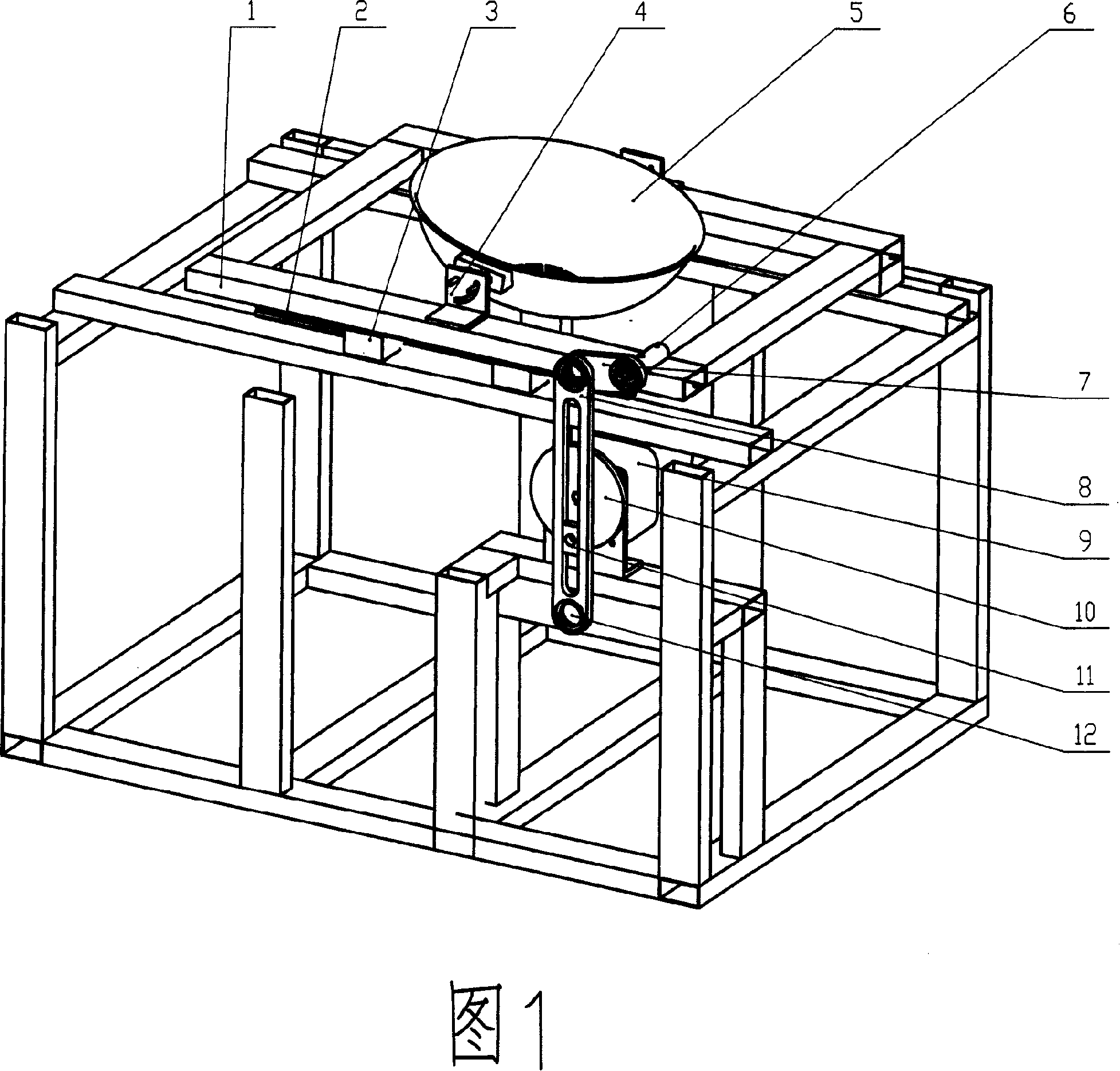
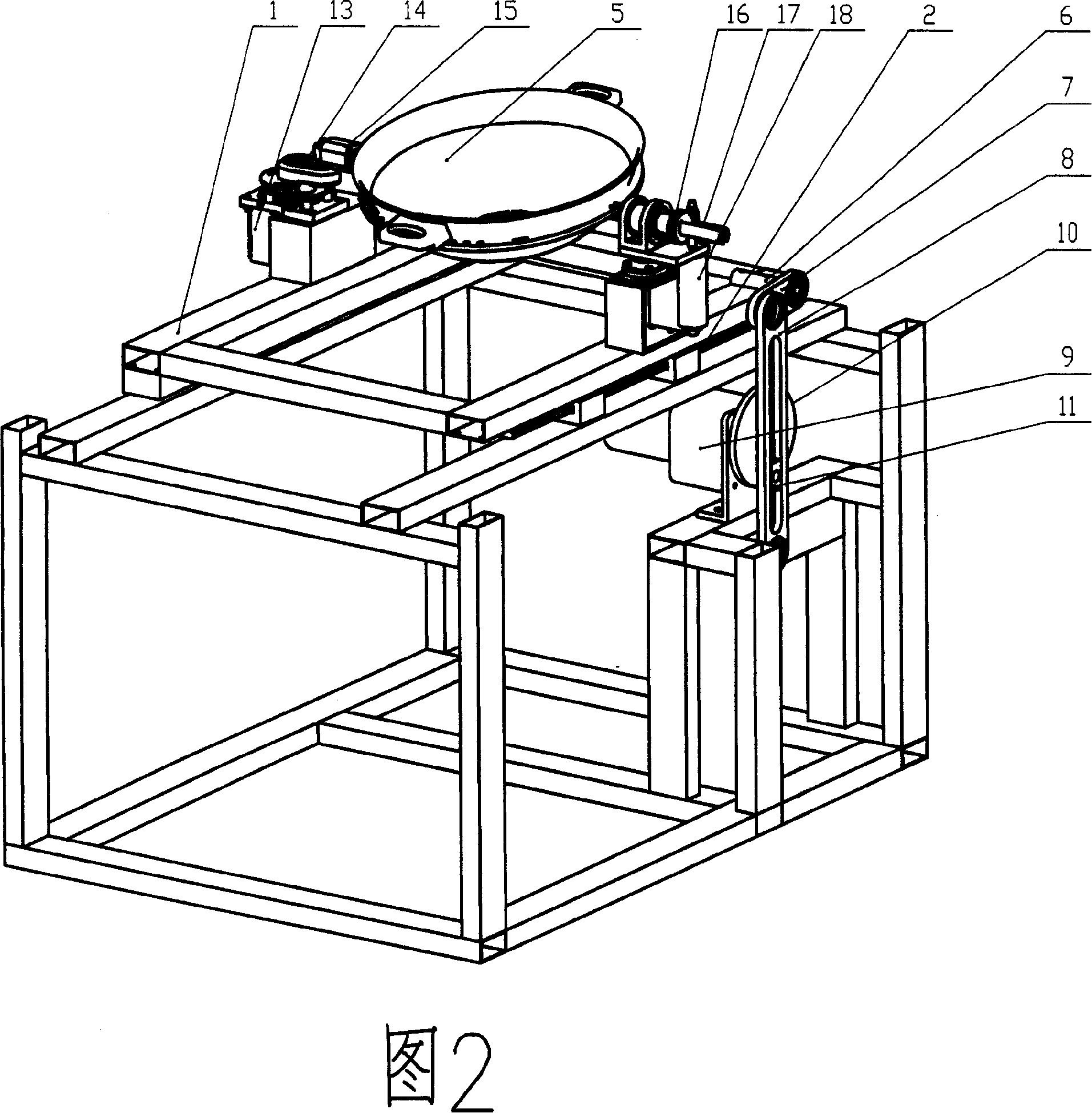
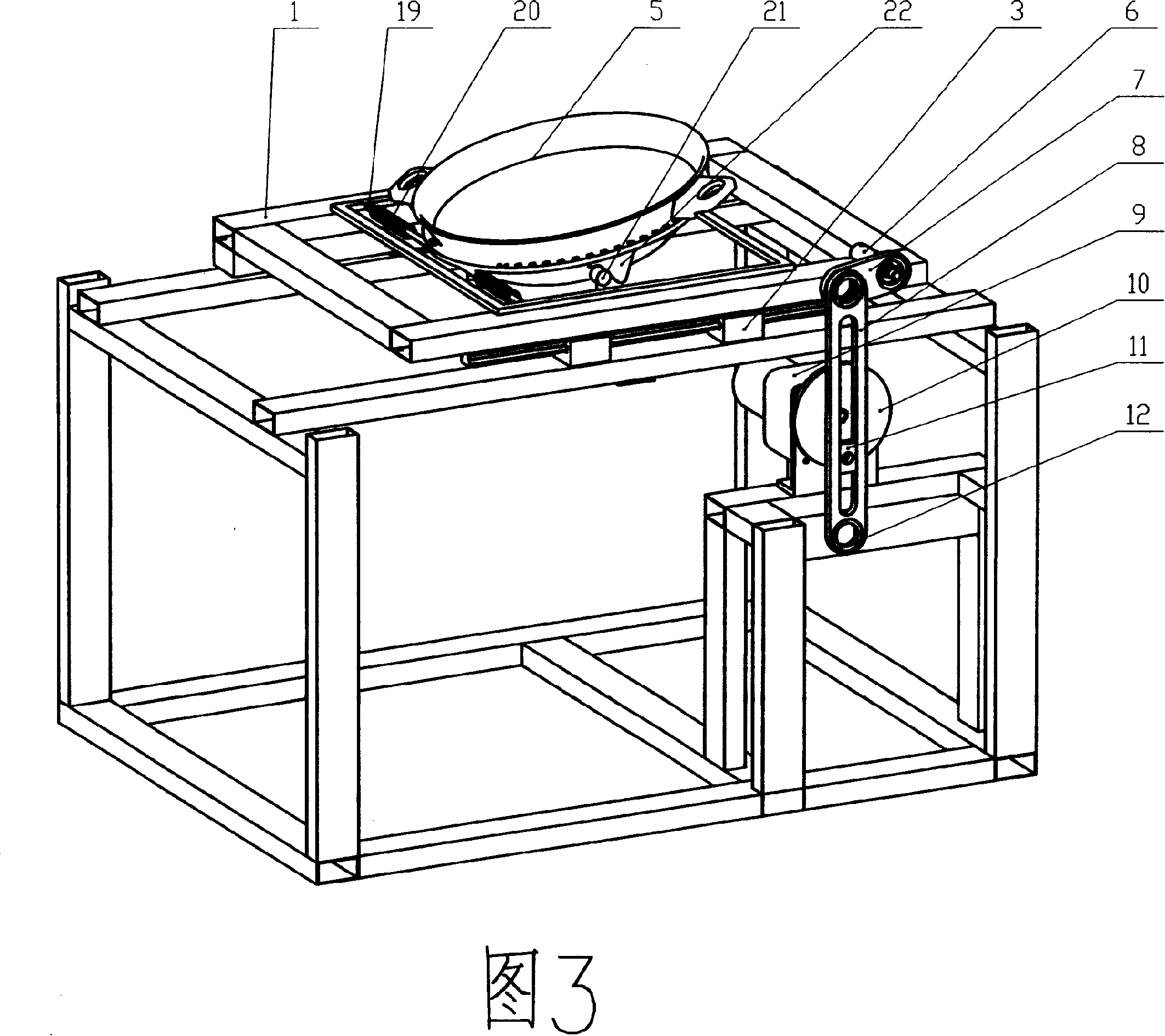
The present invention discloses a pot motion device used in automatic or semi-automatic cooking equipment and the cooking equipment adopting the pot motion device. The pot motion device of the present invention comprises (1) a pot; (2) a translational motion mechanism which is connected with the pot and reciprocally moves between two endpoints; (3) a frame which accommodates the translation motion mechanism to move reciprocally; (4) a first driving device. The pot motion device of the present invention also can further include an angle regulation mechanism which keeps an inclined angle between the pot and a motion direction during the reciprocating motion and / or a speed switch mechanism which drives the translational motion mechanism to move and makes an acceleration generated from the translational motion mechanism. When the acceleration is small, the pot motion device of the present invention can shake the pot. And when the acceleration is bigger, the device can turnover the pot.
Owner:AIC ROBOTICS TECH
Core inertial measurement unit
InactiveUS6522992B1Precise positioningSmall sizeDigital data processing detailsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsTemperature controlAngular rate sensor
A core inertial measurement unit, which is adapted to apply to output signals proportional to rotation and translational motion of a carrier, respectively from angular rate sensors and acceleration sensors, is employed with MEMS rate and acceleration sensors. Compared with a conventional IMU, the processing method utilizes a feedforward open-loop signal processing scheme to obtain highly accurate motion measurements by means of signal digitizing, temperature control and compensation, sensor error and misalignment calibrations, attitude updating, and damping control loops, and dramatically shrinks the size of mechanical and electronic hardware and power consumption, meanwhile, obtains highly accurate motion measurements.
Owner:AMERICAN GNC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com