Patents
Literature
5979 results about "Kalman filter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In statistics and control theory, Kalman filtering, also known as linear quadratic estimation (LQE), is an algorithm that uses a series of measurements observed over time, containing statistical noise and other inaccuracies, and produces estimates of unknown variables that tend to be more accurate than those based on a single measurement alone, by estimating a joint probability distribution over the variables for each timeframe. The filter is named after Rudolf E. Kálmán, one of the primary developers of its theory.
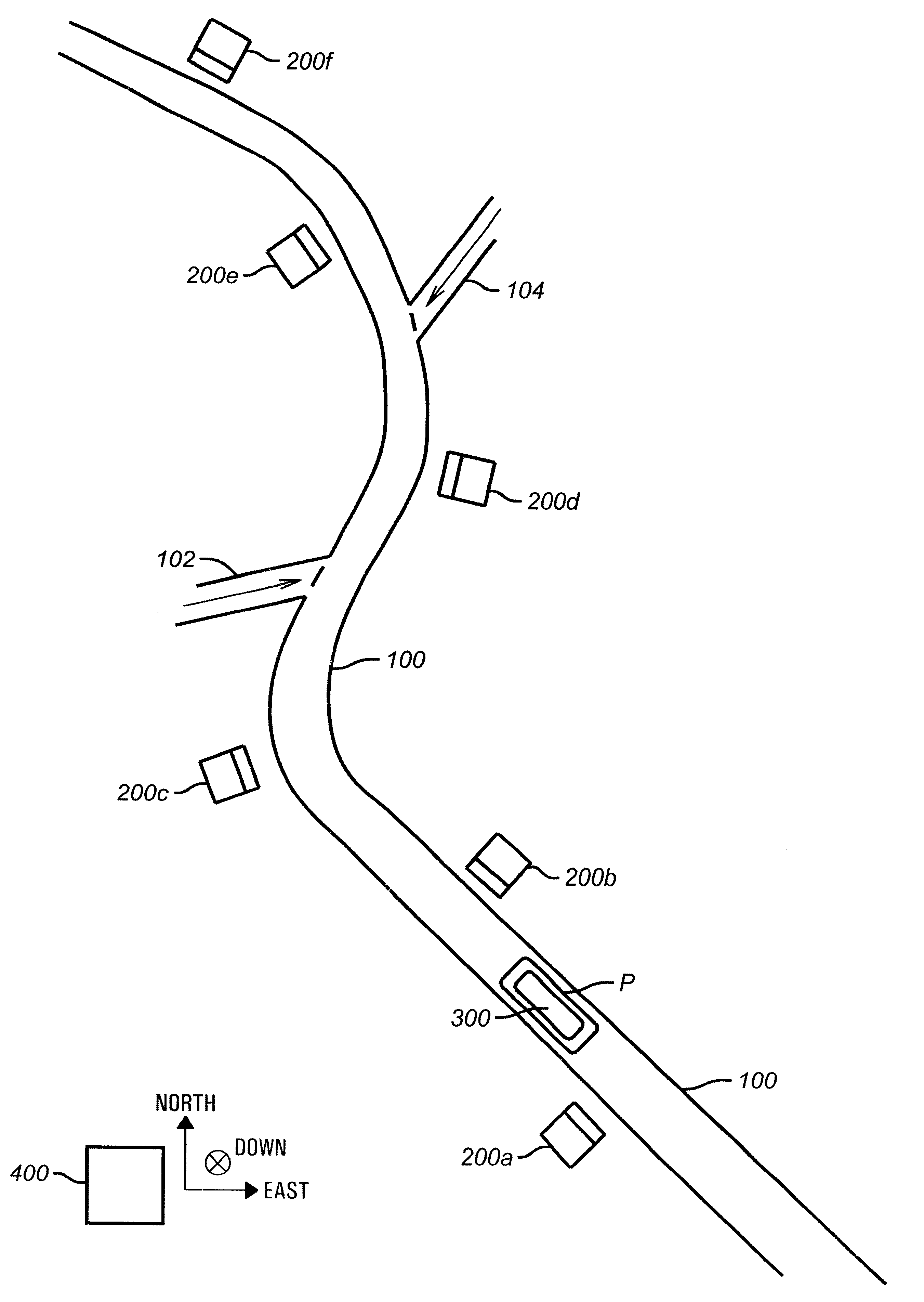
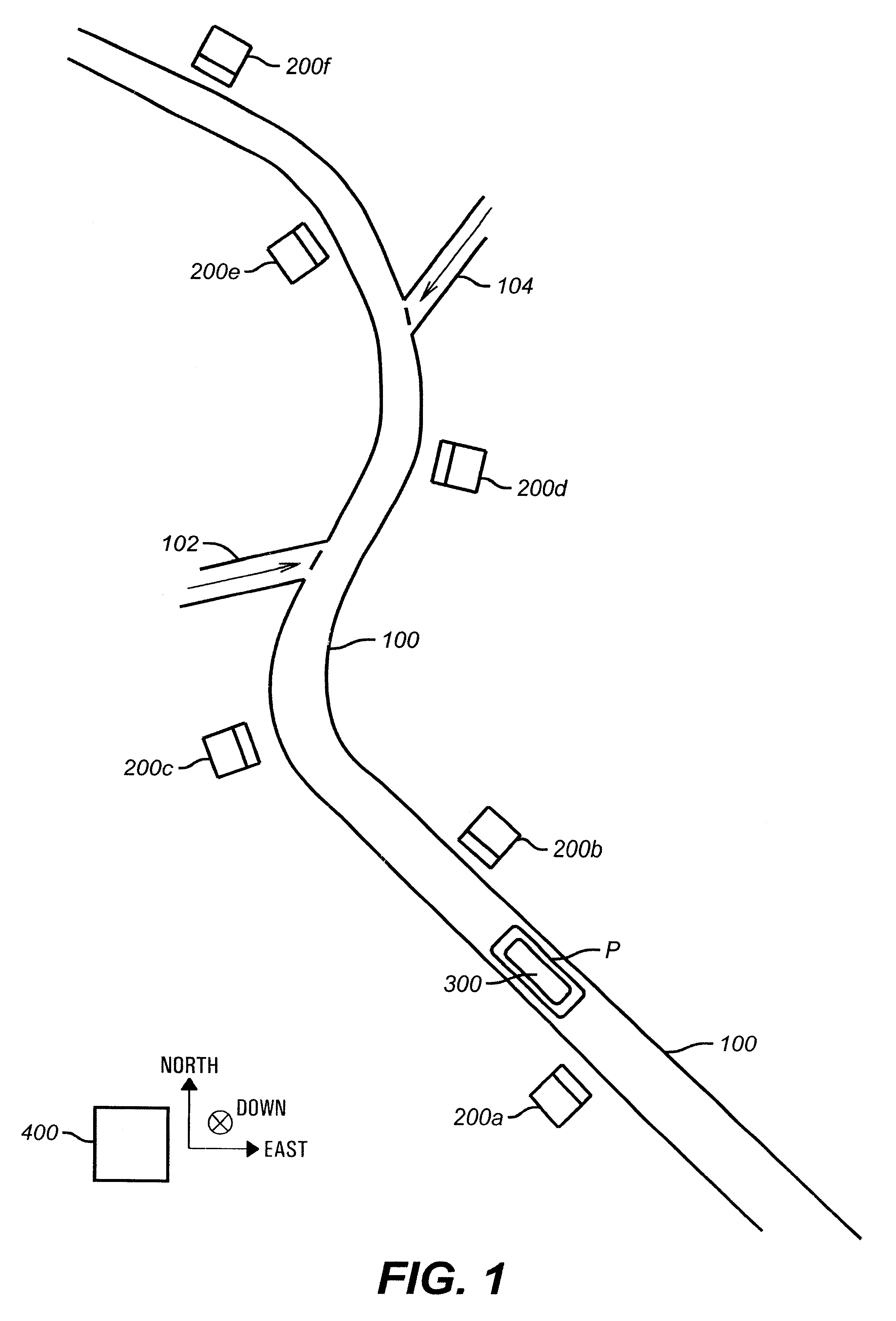
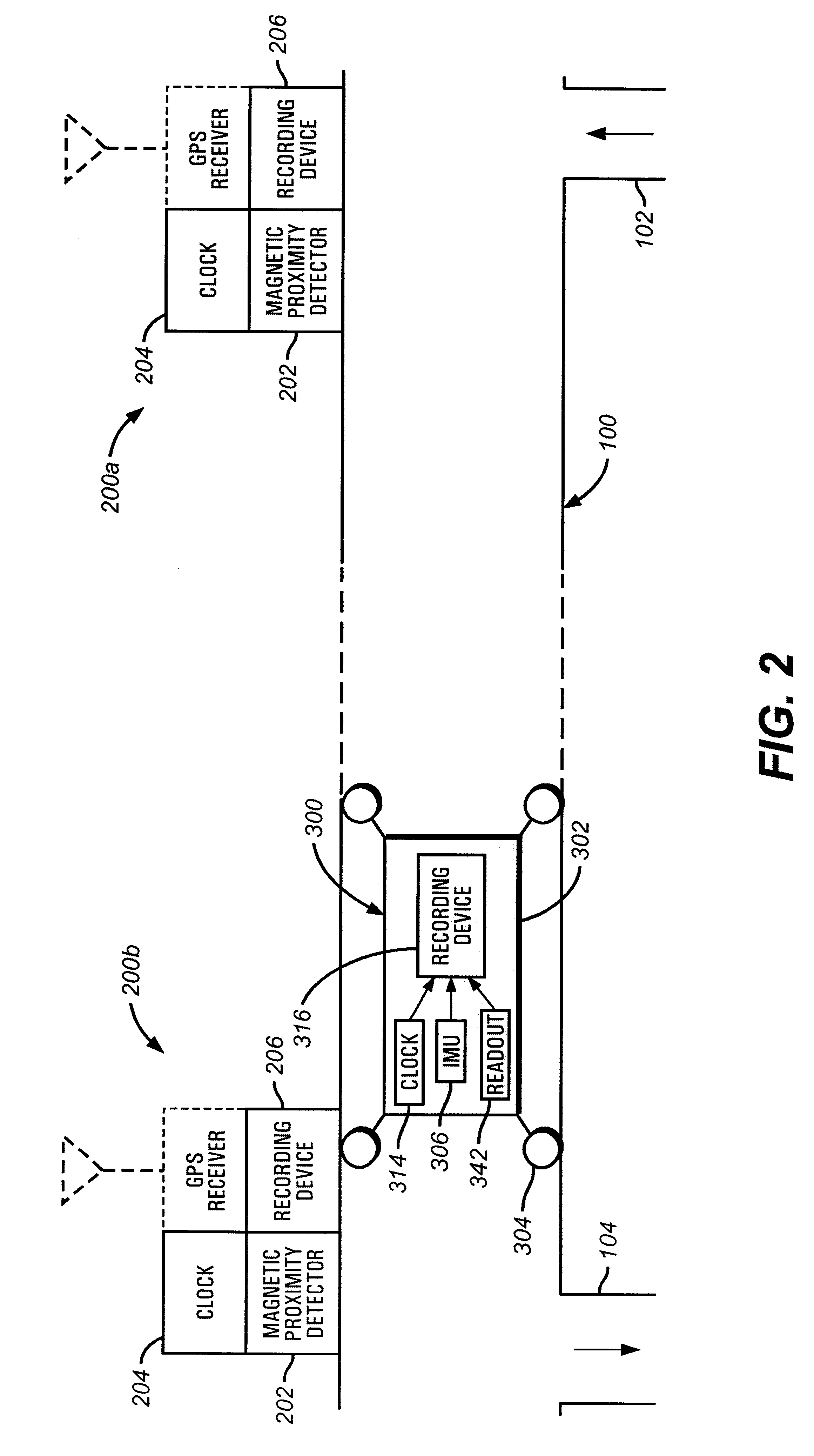
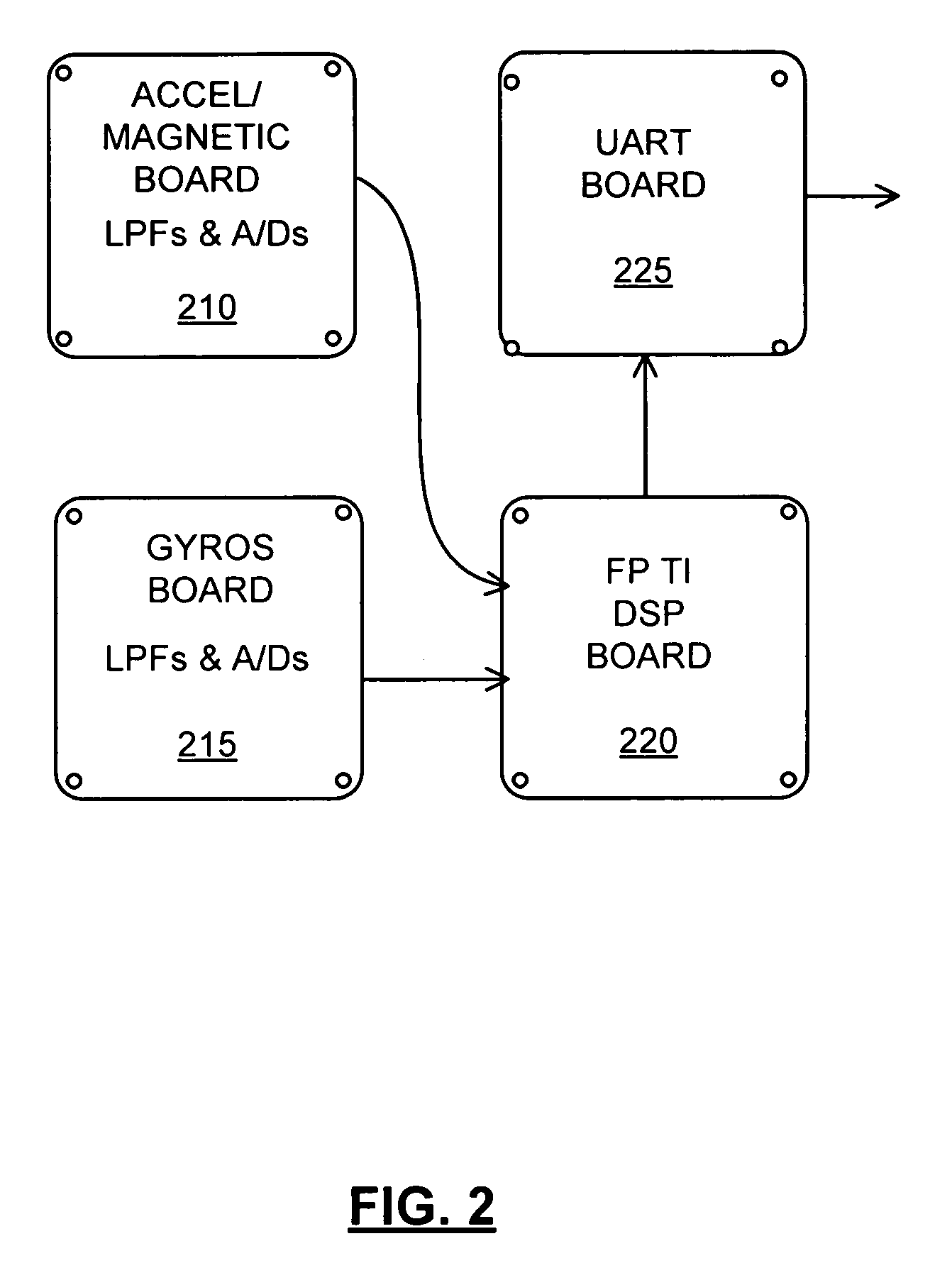
Method and apparatus for determining location of characteristics of a pipeline
InactiveUS6243657B1High degreeHigh precisionTime indicationSynchronous motors for clocksKaiman filterComputerized system
A pipeline inspection and defect mapping system includes a pig having an inertial measurement unit and a pipeline inspection unit for recording pig location and defect detection events, each record time-stamped by a highly precise onboard clock. The system also includes several magloggers at precisely known locations along the pipeline, each containing a fluxgate magnetometer for detecting the passage of the pig along the pipeline and further containing a highly precise clock synchronized with the clock in the pig. The locations of the various magloggers are known in a north / east / down coordinate system through a differential global positioning satellite process. Finally, a postprocessing off-line computer system receives downloaded maglogger, inertial measurement, and odometer data and through the use of several Kalman filters, derives the location of the detected defects in the north / east / down coordinate frame. Consequently, a task of identifying sites for repair activity is much simplified.
Owner:PIPELINE INTEGRITY INT INC FORMERLY BRITISH GAS INSPECTION SERVICES INC +1
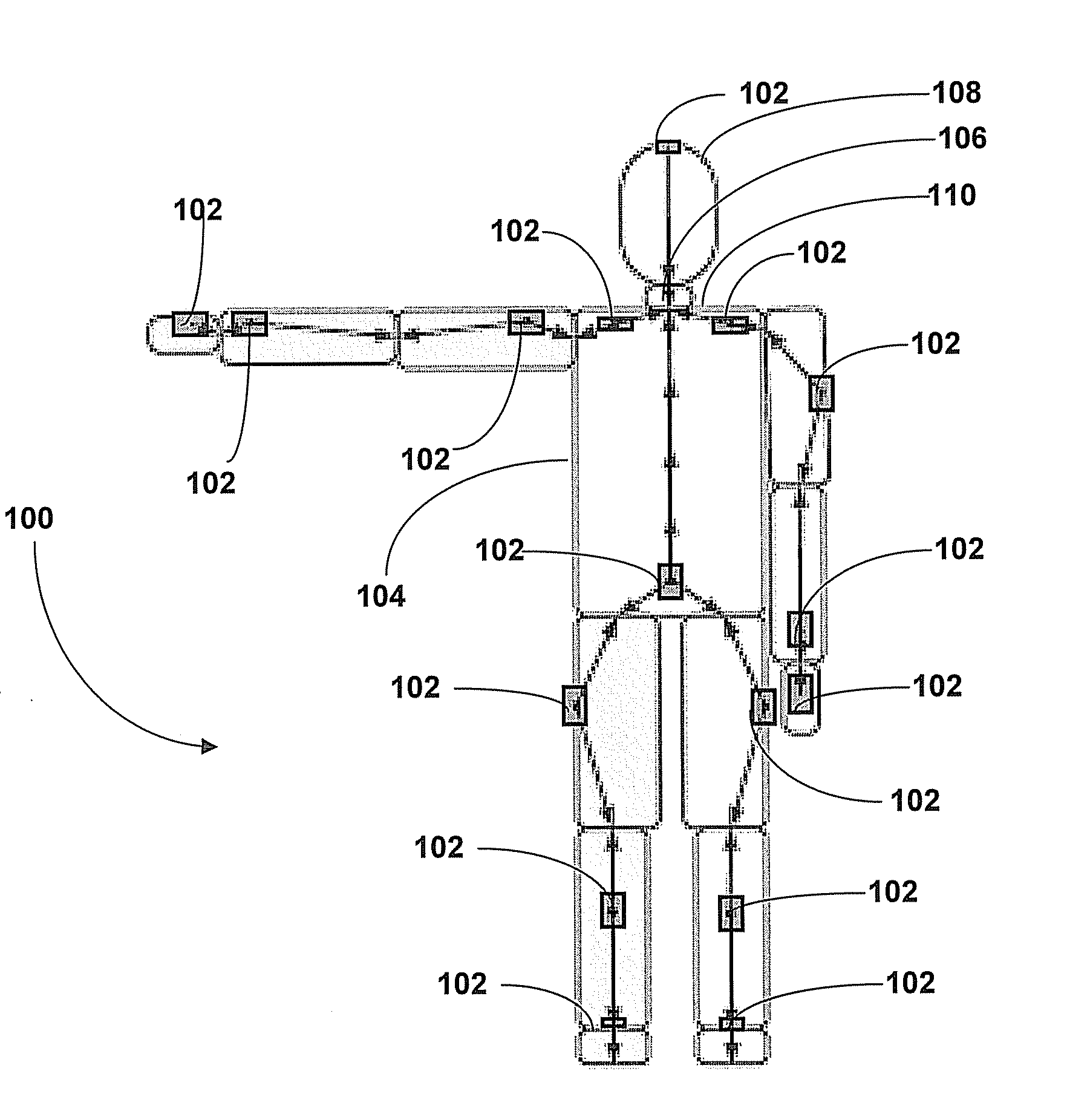
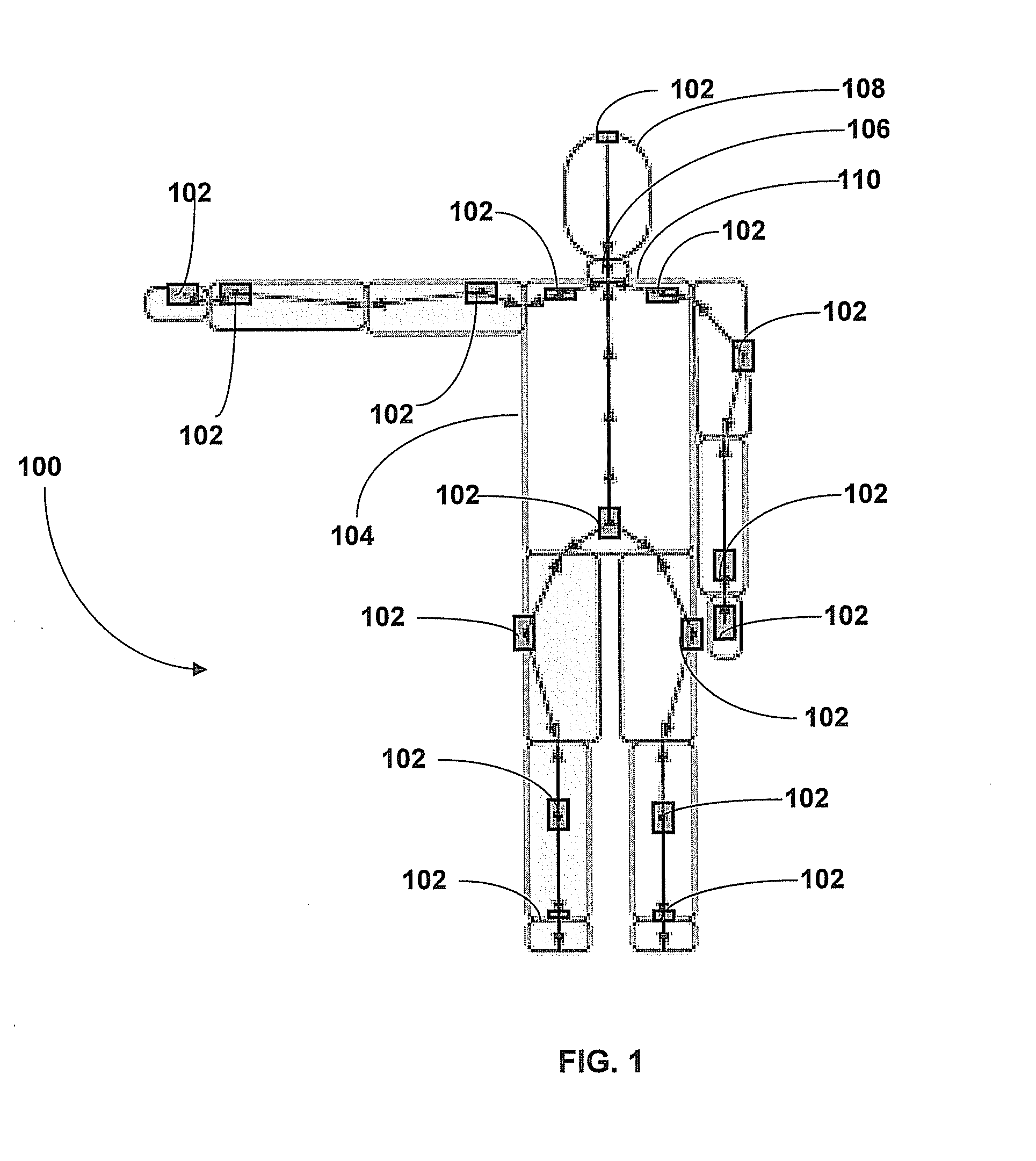
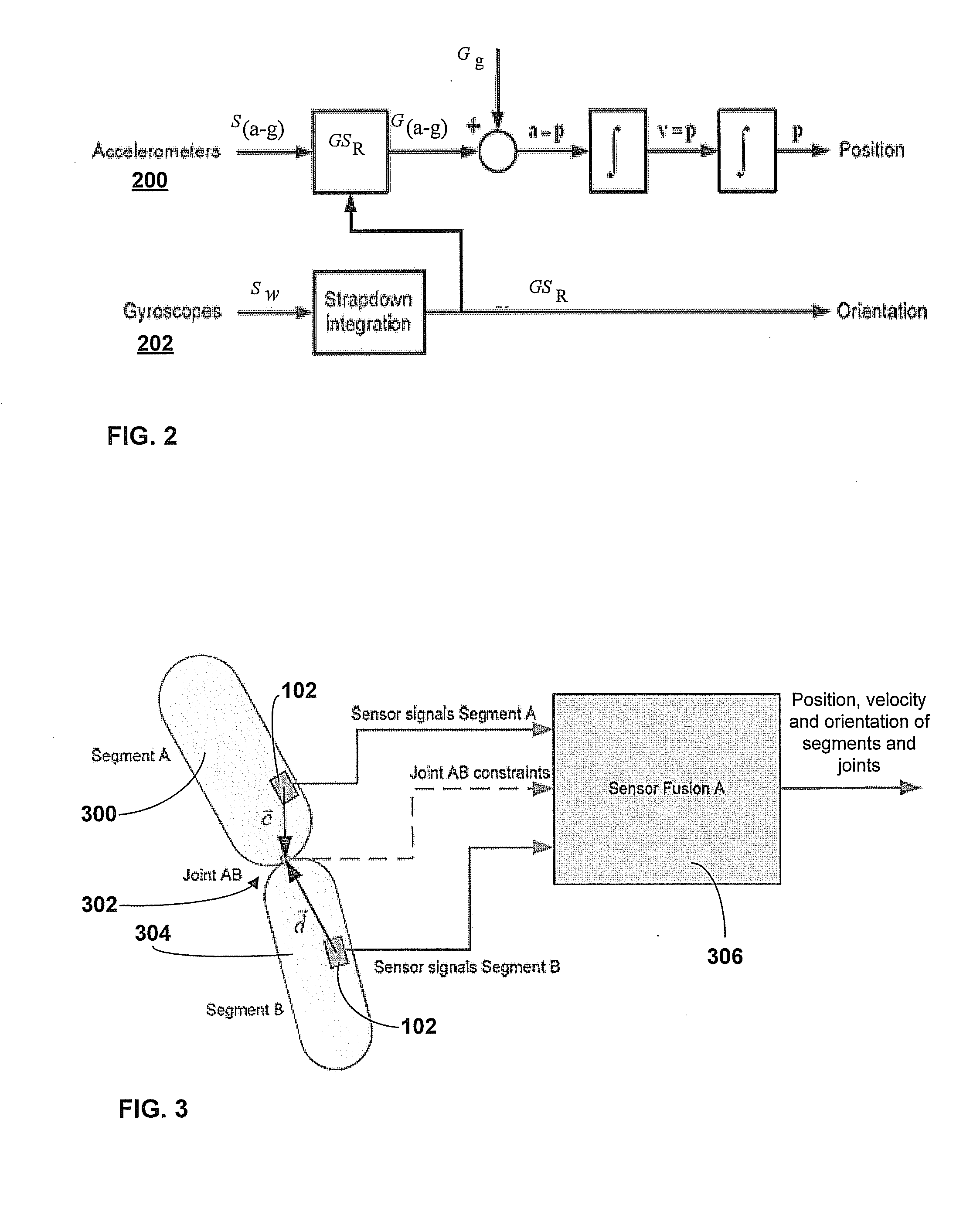
Motion Tracking System
ActiveUS20080285805A1High precisionAccurate recordProgramme-controlled manipulatorPerson identificationMovement trackingKalman filter
Owner:XSENS HLDG BV
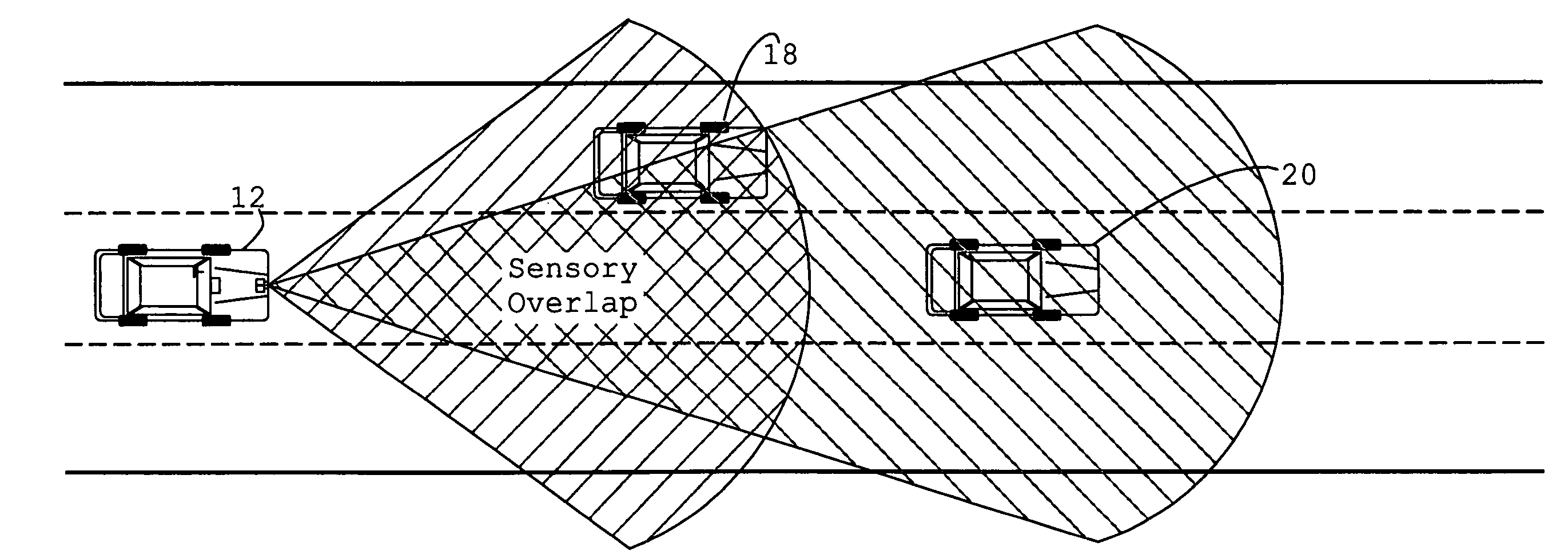
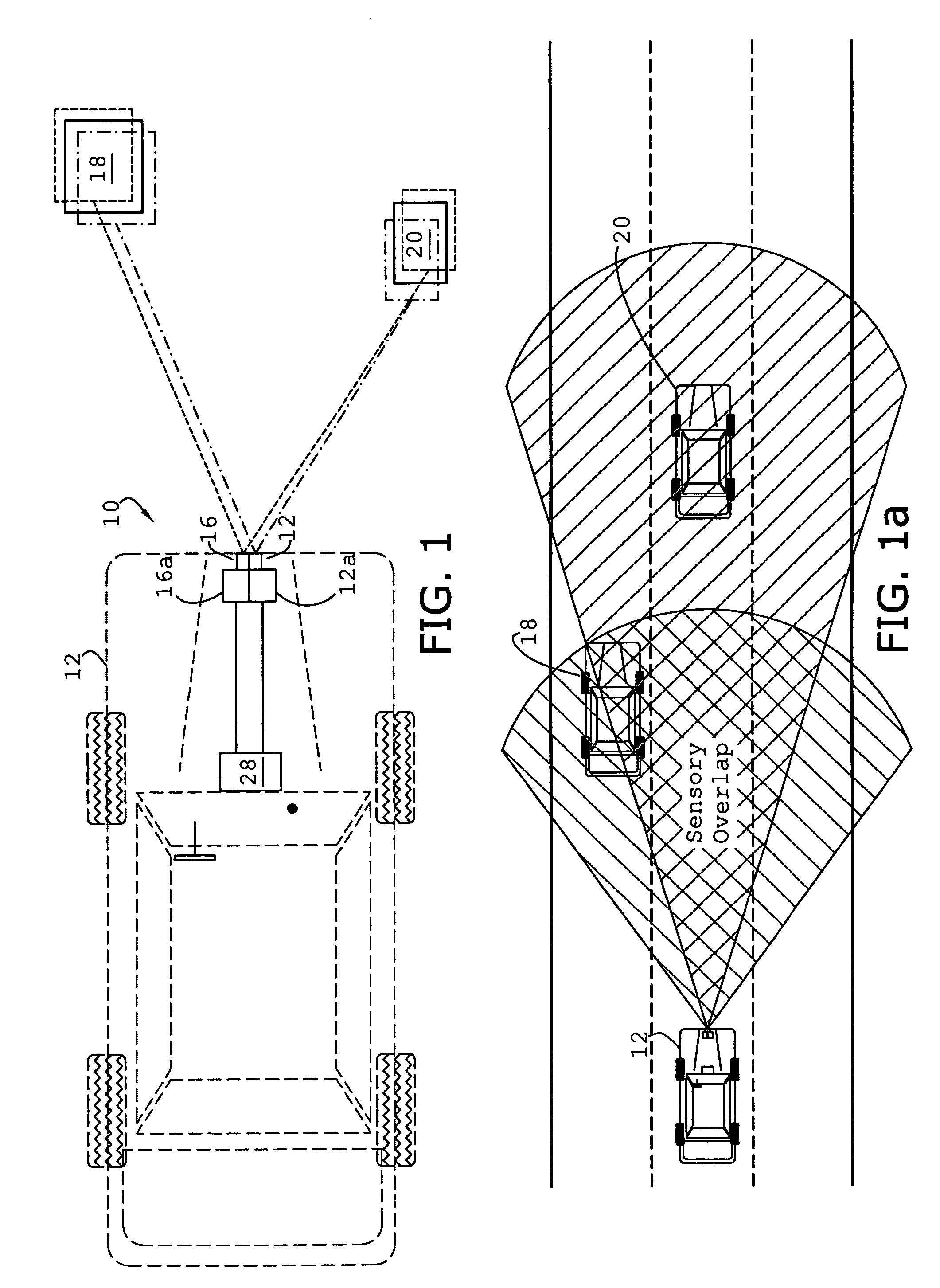
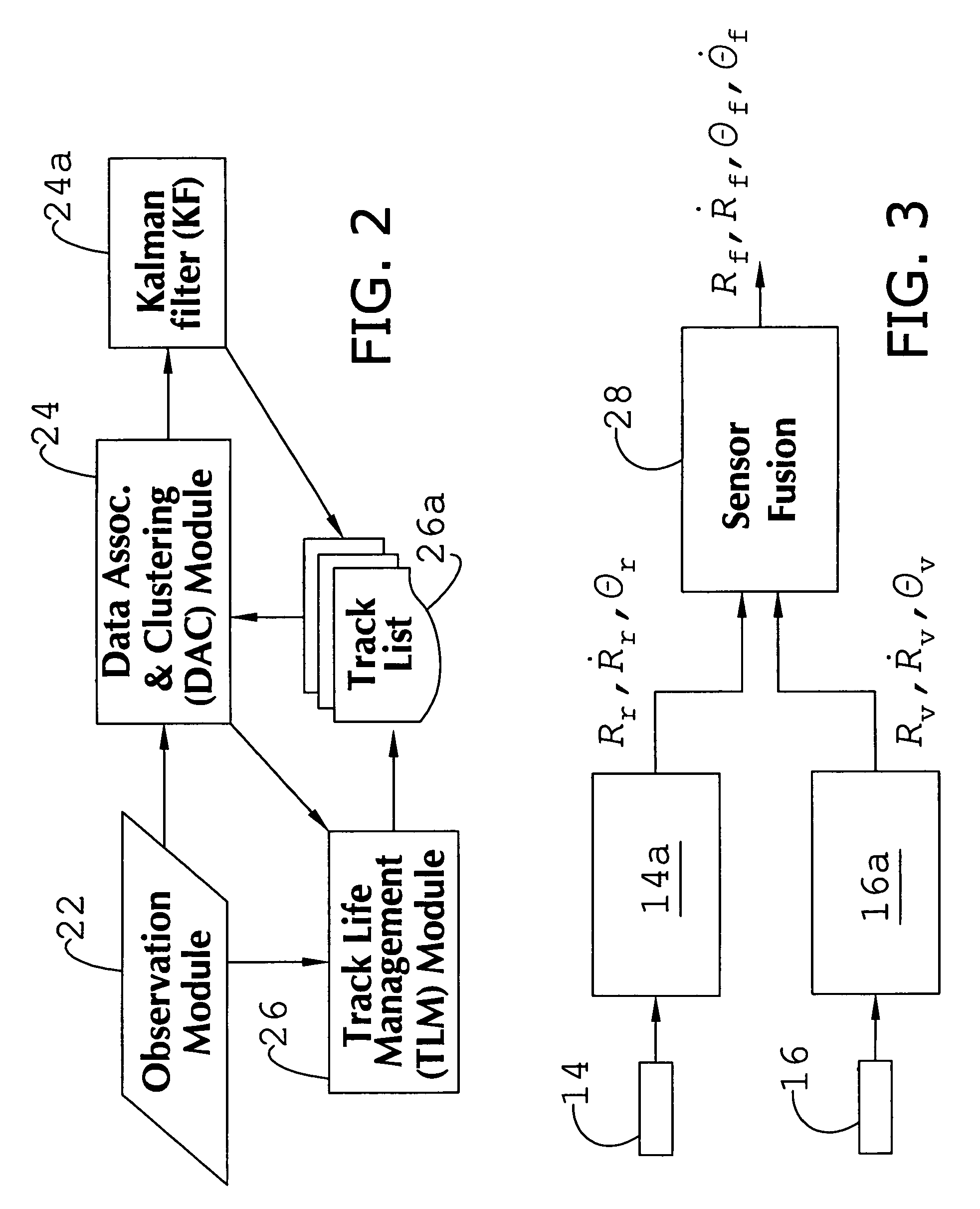
System and method of target tracking using sensor fusion
ActiveUS7460951B2Increasing precision and certaintyShorten the timeInstruments for road network navigationAnti-collision systemsSensor fusionEngineering
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
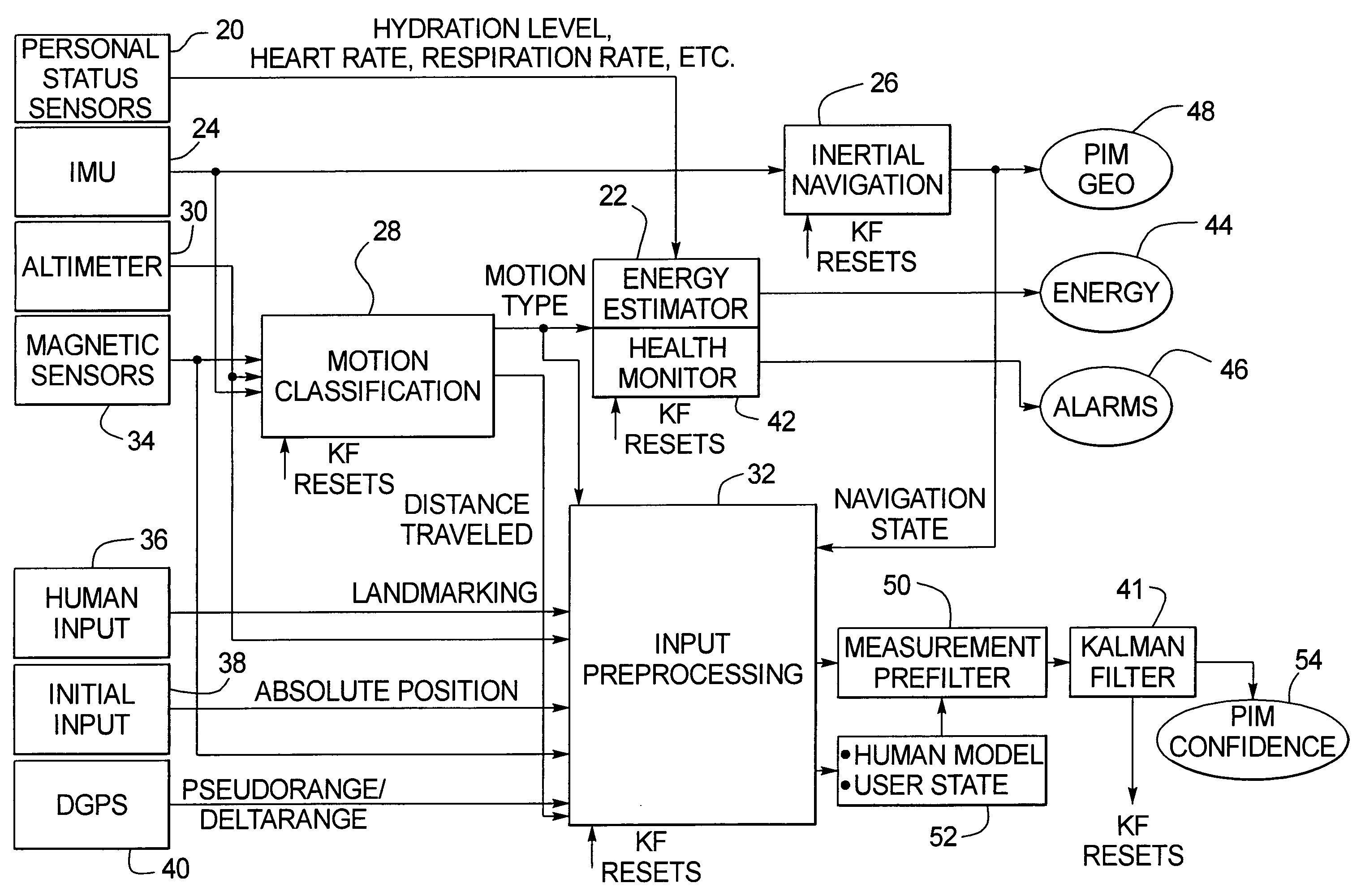
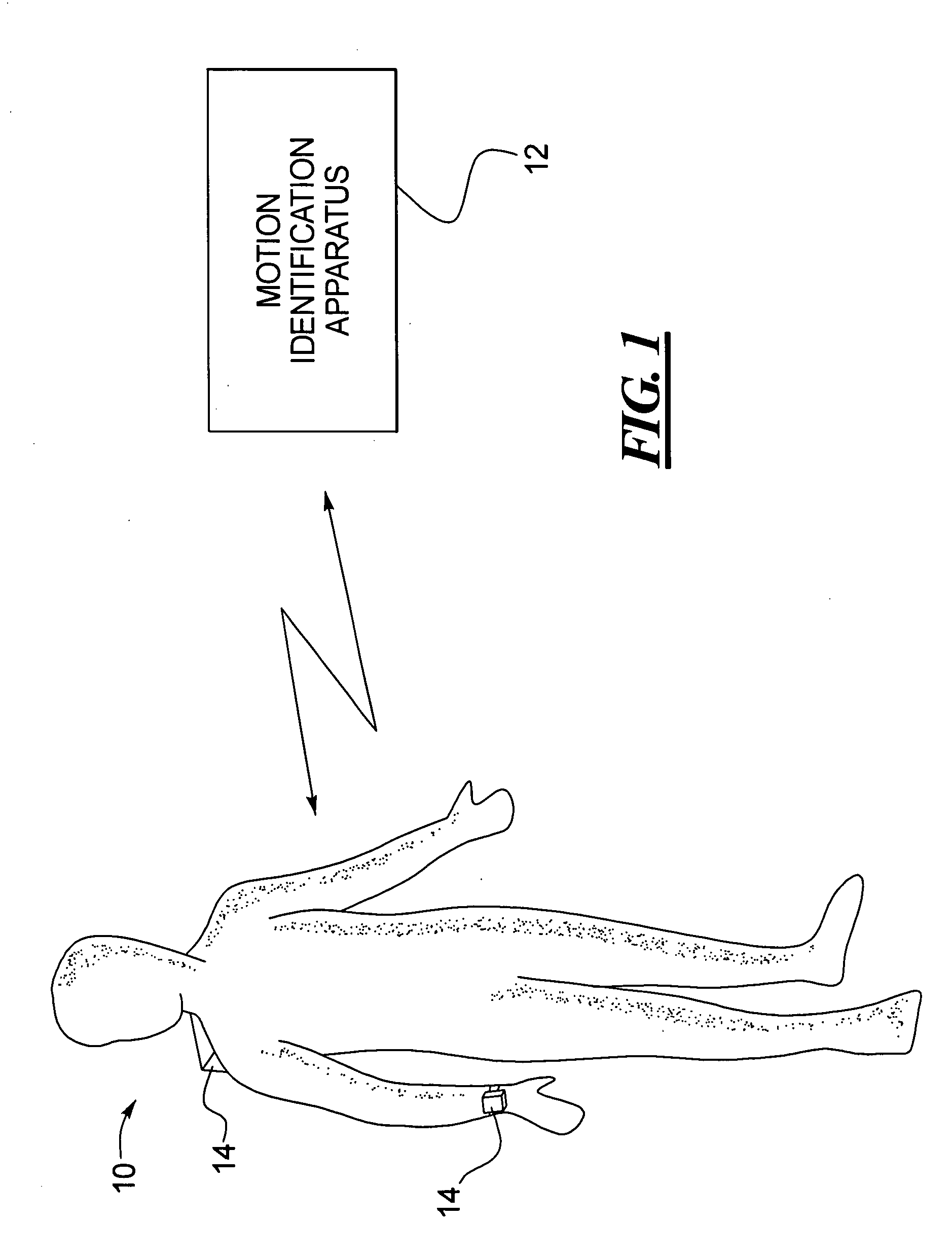
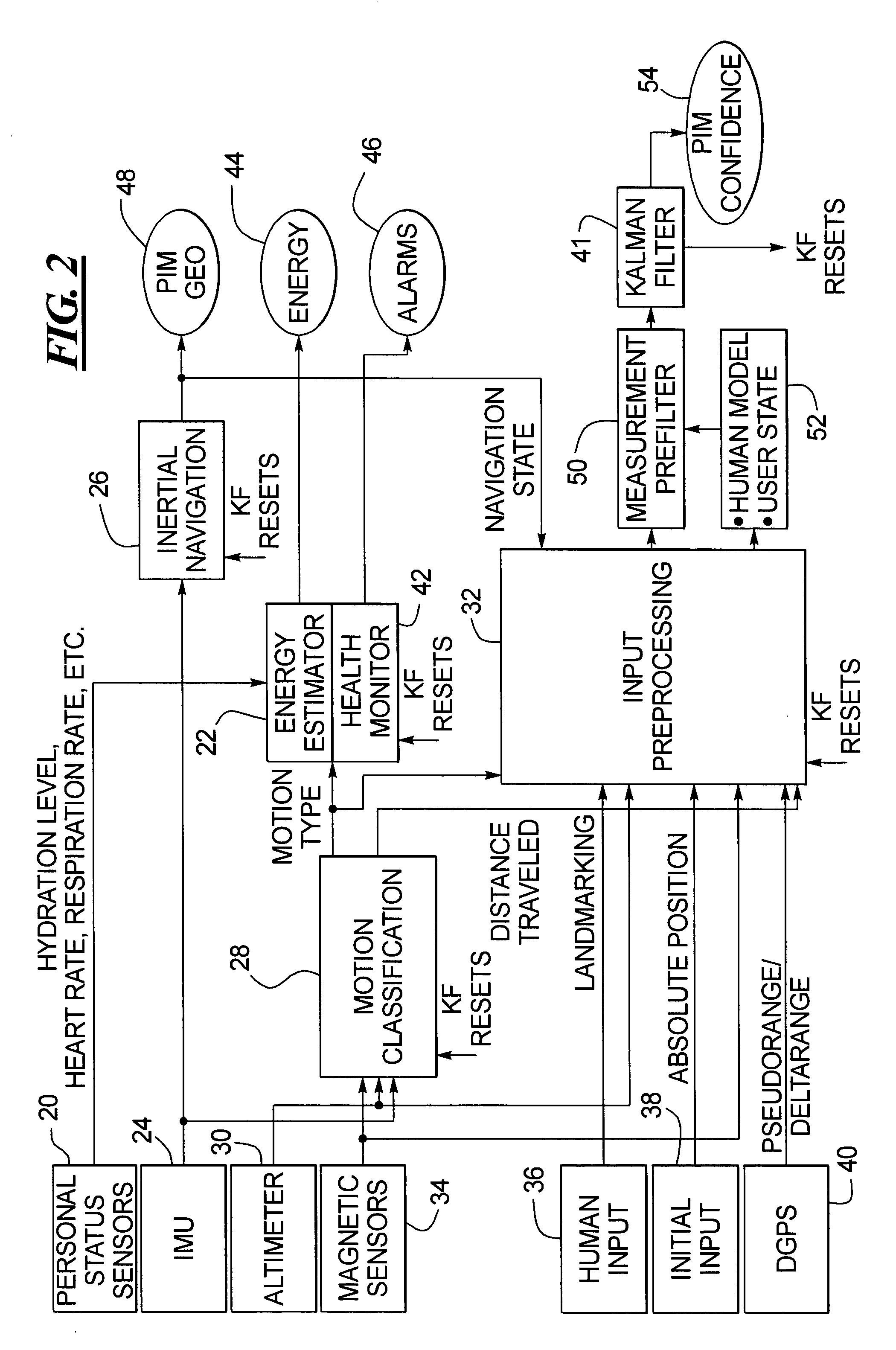
Human motion identification and measurement system and method
A system and method for classifying and measuring human motion senses the motion of the human and the metabolism of the human. A motion classification unit determines the motion type being carried out by the human and provides the motion classification information to an energy estimator and a health monitor. The energy estimator also receives the metabolism information and therefrom provides an estimate of energy expended by the human. The health monitor triggers an alarm if health related thresholds are traversed. The motion classification is also provided to a processing unit that in turn provides the data to a Kalman filter, which has an output that is provided as feedback to the motion classification unit, the energy estimator and health monitor. Altimeter, GPS and magnetic sensors may also be provided for monitoring the human motion, and initial input and landmark input data inputs are provided to the system.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
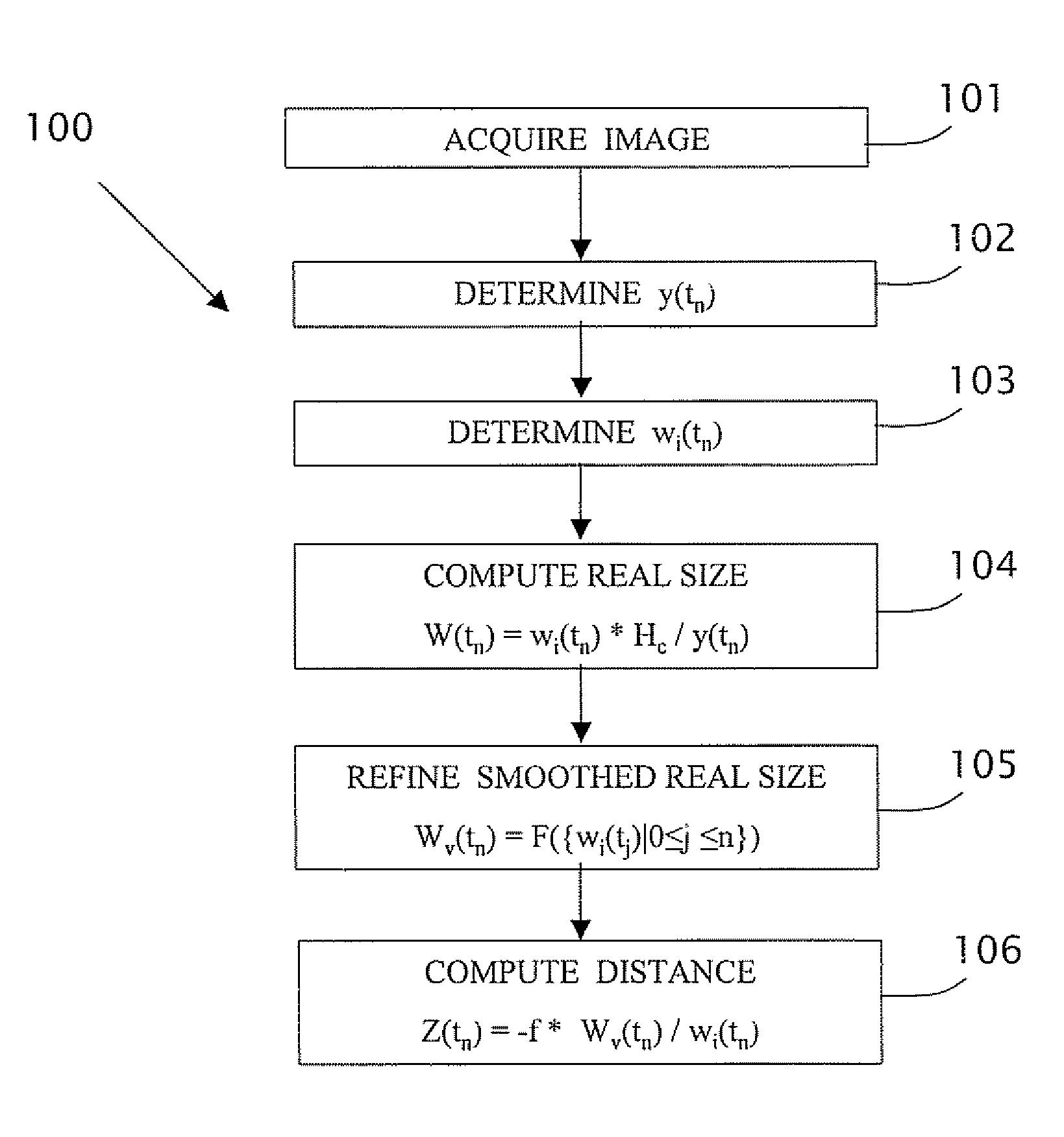
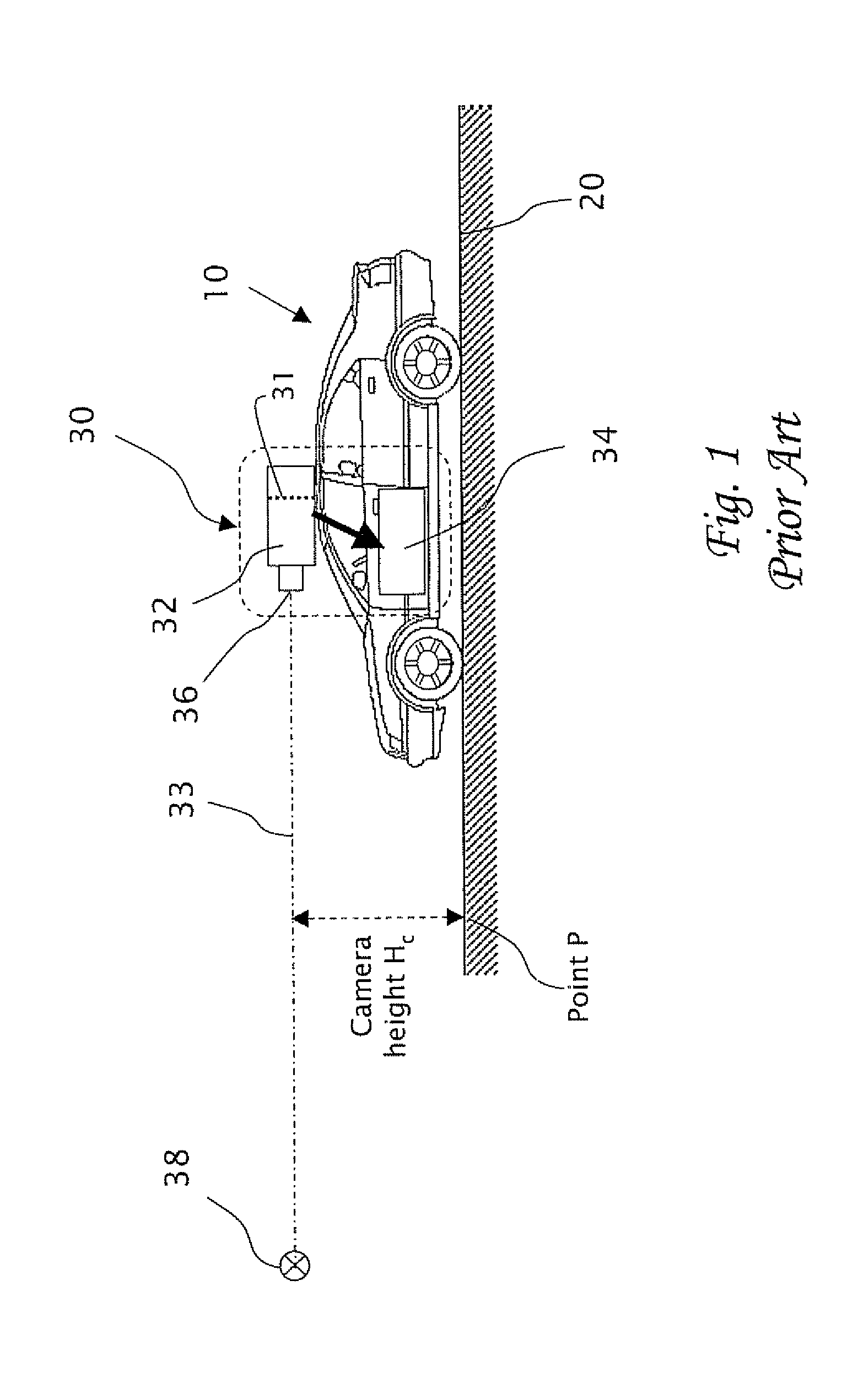
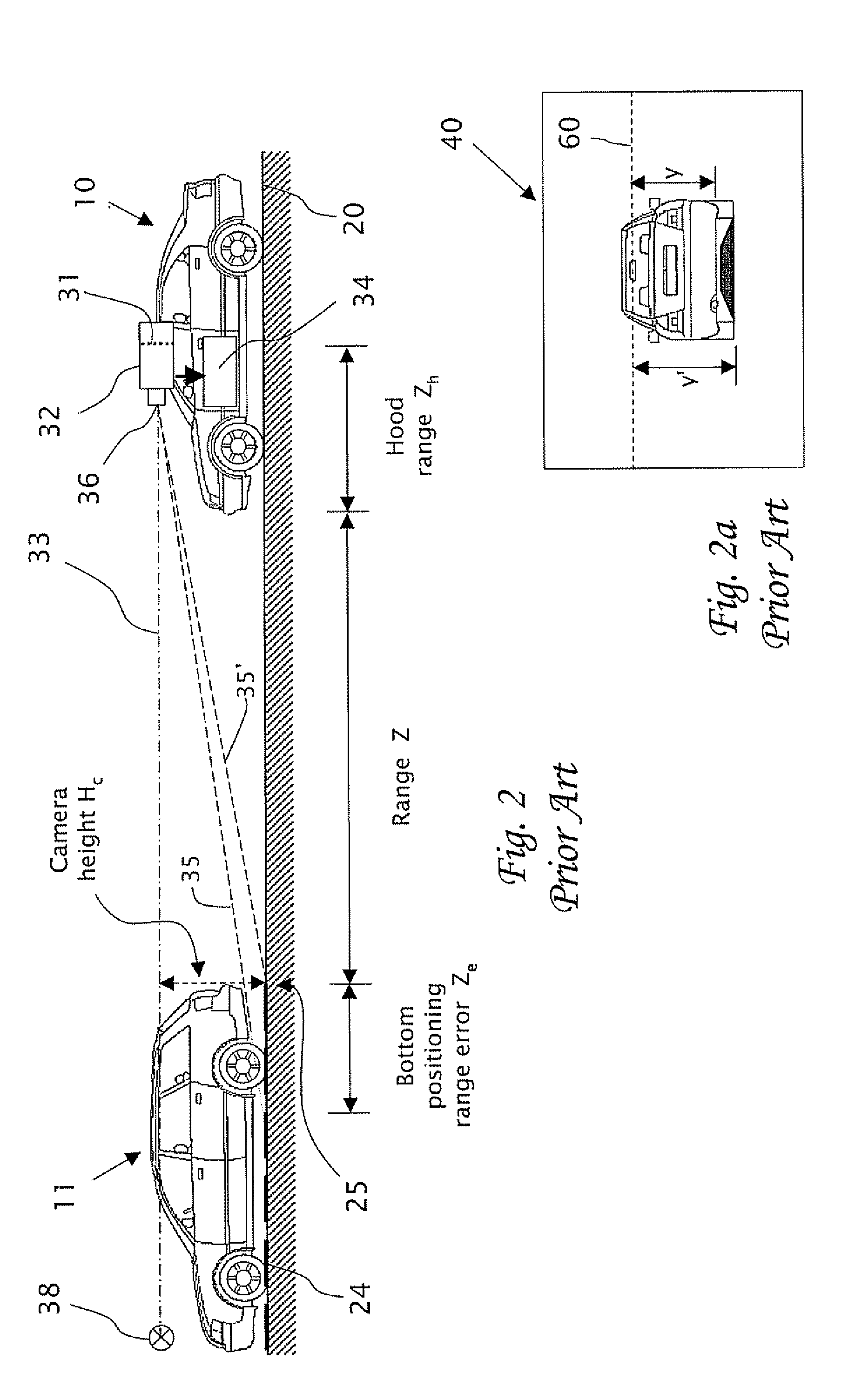
Estimating distance to an object using a sequence of images recorded by a monocular camera
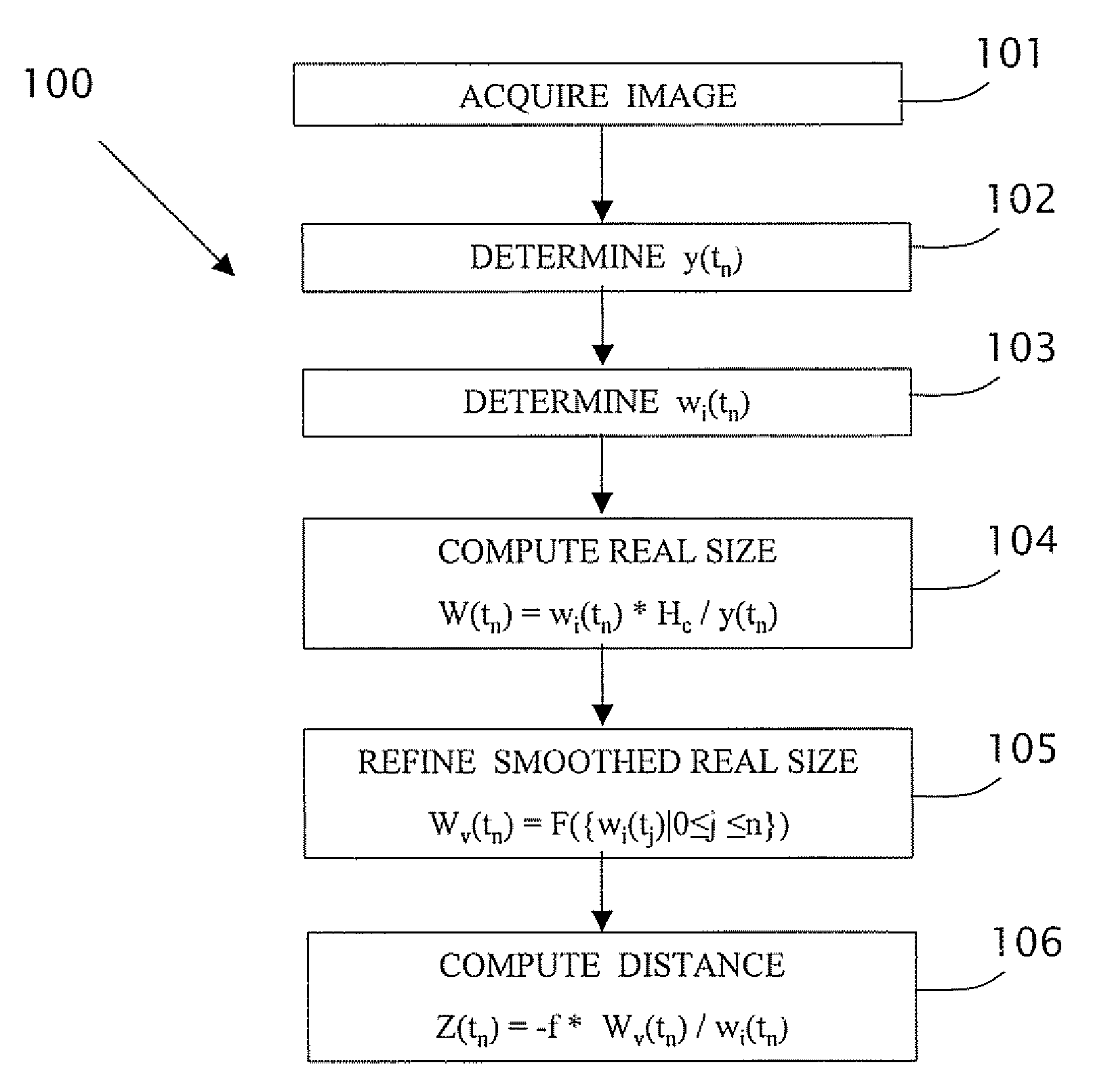
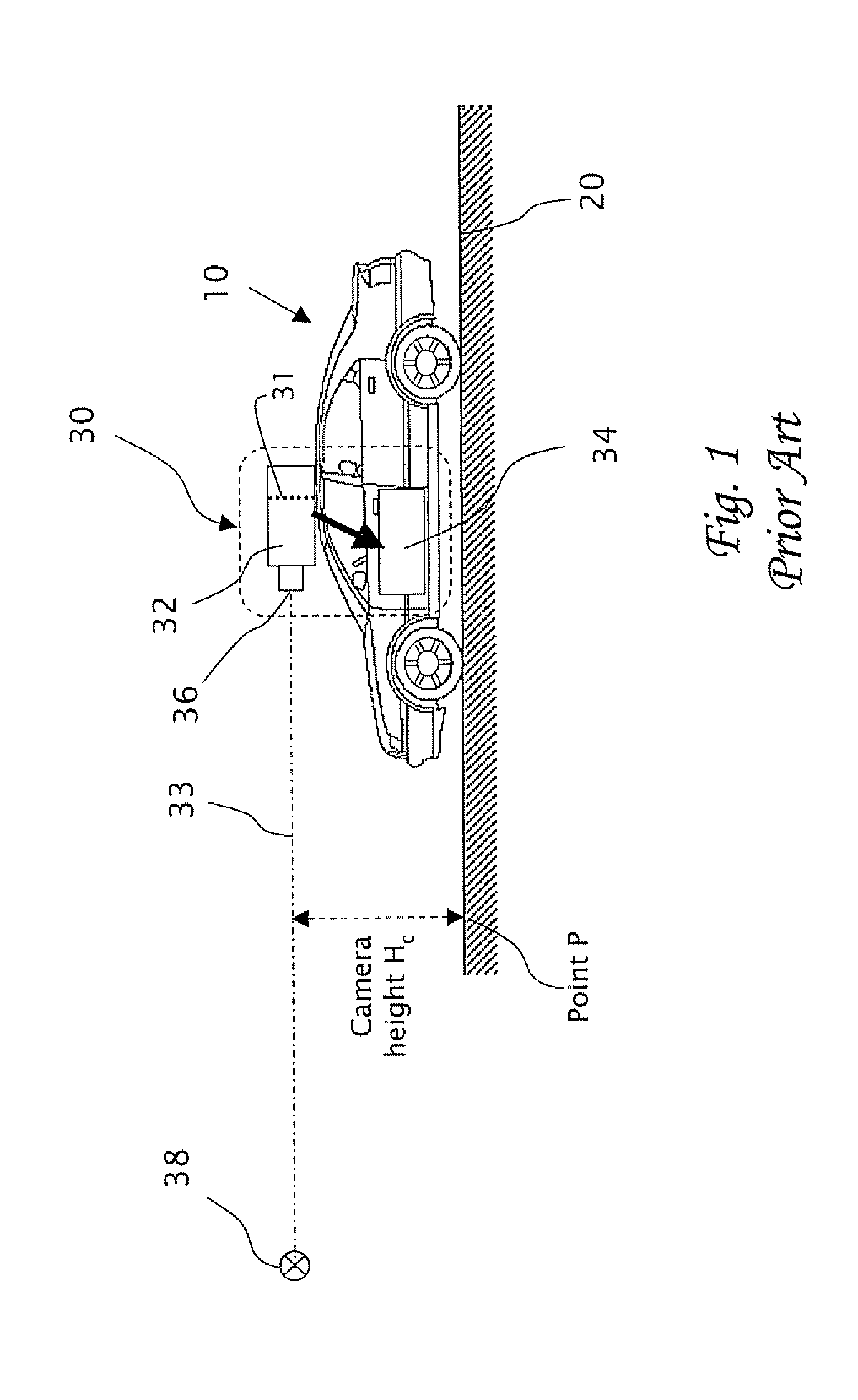
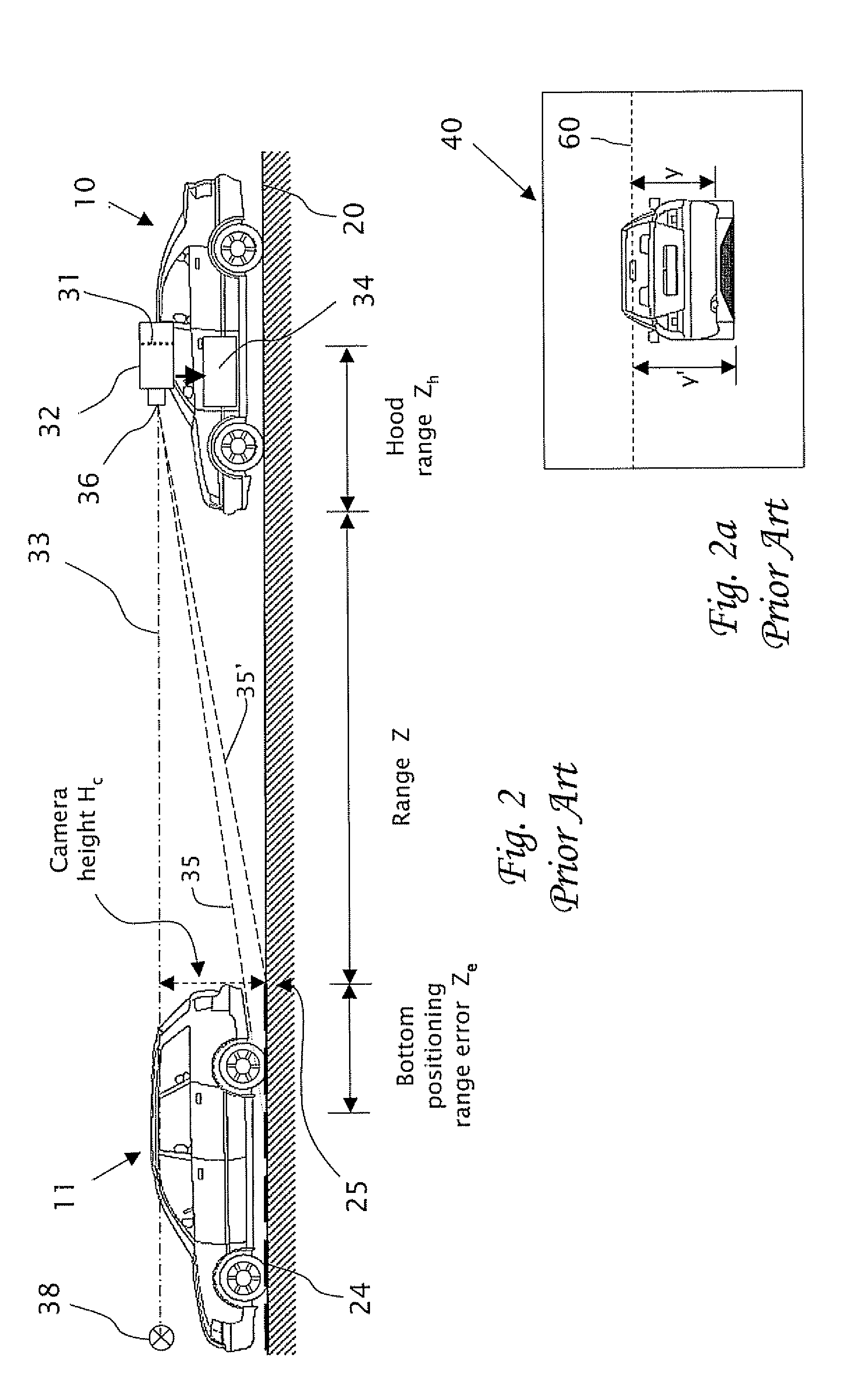
In a computerized system including a camera mounted in a moving vehicle. The camera acquires consecutively in real time image frames including images of an object within the field of view of the camera. Range to the object from the moving vehicle is determined in real time. A dimension, e.g. a width, is measured in the respective images of two or more image frames, thereby producing measurements of the dimension. The measurements are processed to produce a smoothed measurement of the dimension. The dimension is measured subsequently in one or more subsequent frames. The range from the vehicle to the object is calculated in real time based on the smoothed measurement and the subsequent measurements. The processing preferably includes calculating recursively the smoothed dimension using a Kalman filter.
Owner:MOBILEYE VISION TECH LTD
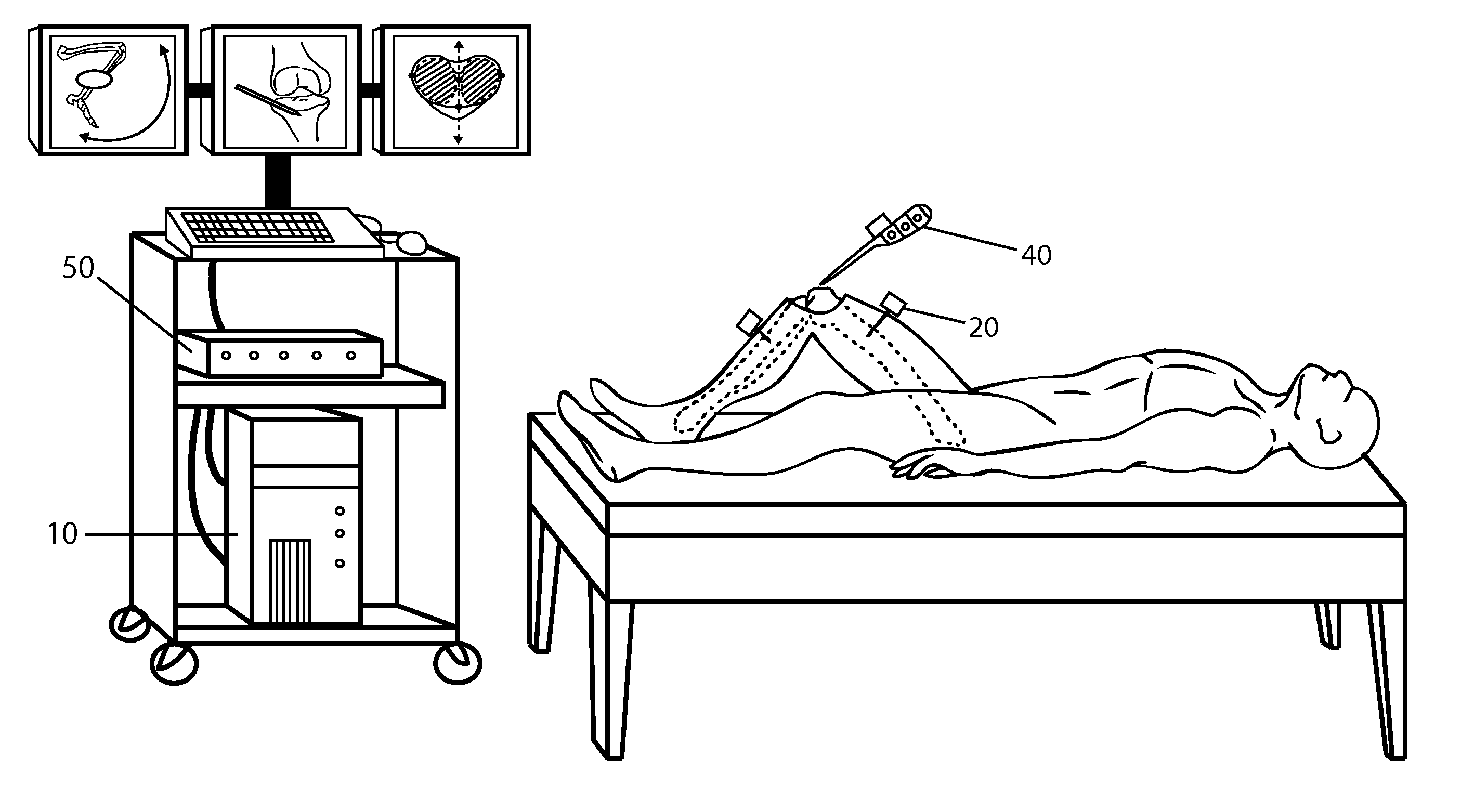
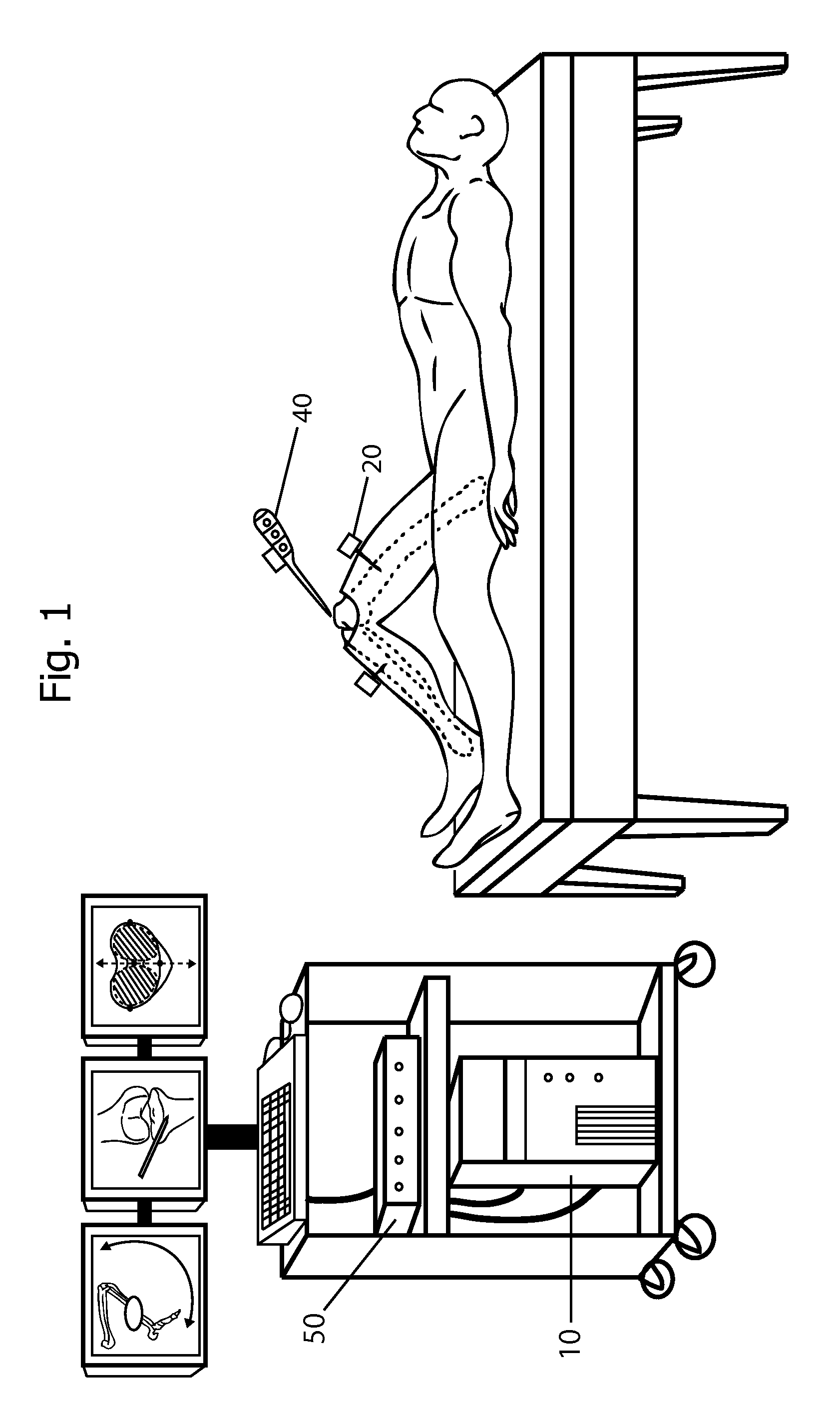
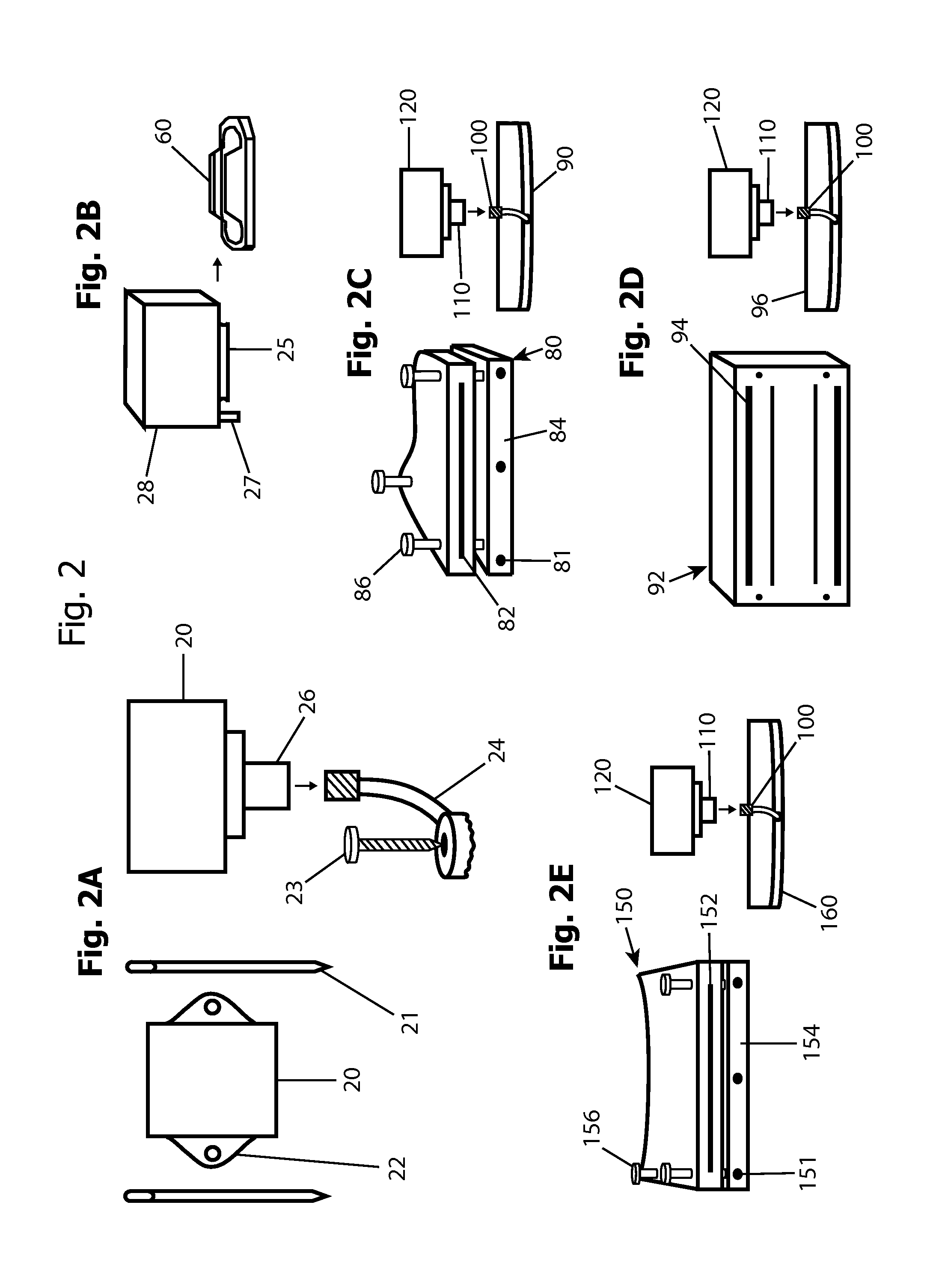
Inertial Sensor Based Surgical Navigation System for Knee Replacement Surgery
ActiveUS20110275957A1Improve accuracyGood precisionSurgical navigation systemsPerson identificationKnee JointNavigation system
An inertial sensor based surgical navigation system for knee replacement surgery is disclosed. Inertial sensors composed of six-degree-of-freedom inertial chips, whose measurements are processed through a series of integration, quaternion, and kalman filter algorithms, are used to track the position and orientation of bones and surgical instruments. The system registers anatomically significant geometry, calculates joint centers and the mechanical axis of the knee, develops a visualization of the lower extremity that moves in real time, assists in the intra-operative planning of surgical cuts, determines the optimal cutting planes for cut guides and the optimal prosthesis position and orientation, and finally navigates the cut guides and the prosthesis to their optimal positions and orientations using a graphical user interface.
Owner:BHANDARI SACHIN
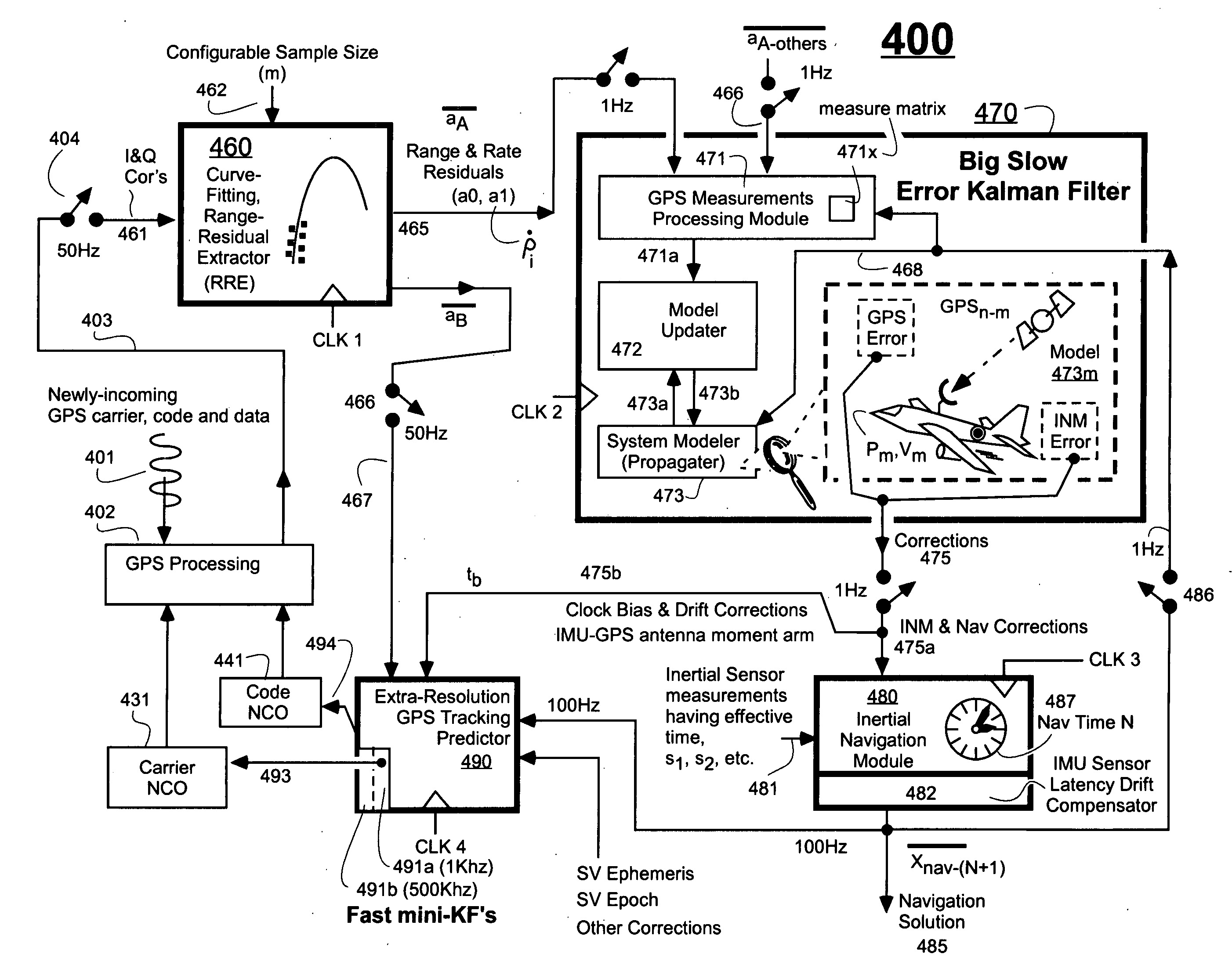
Ultra-tightly coupled GPS and inertial navigation system for agile platforms
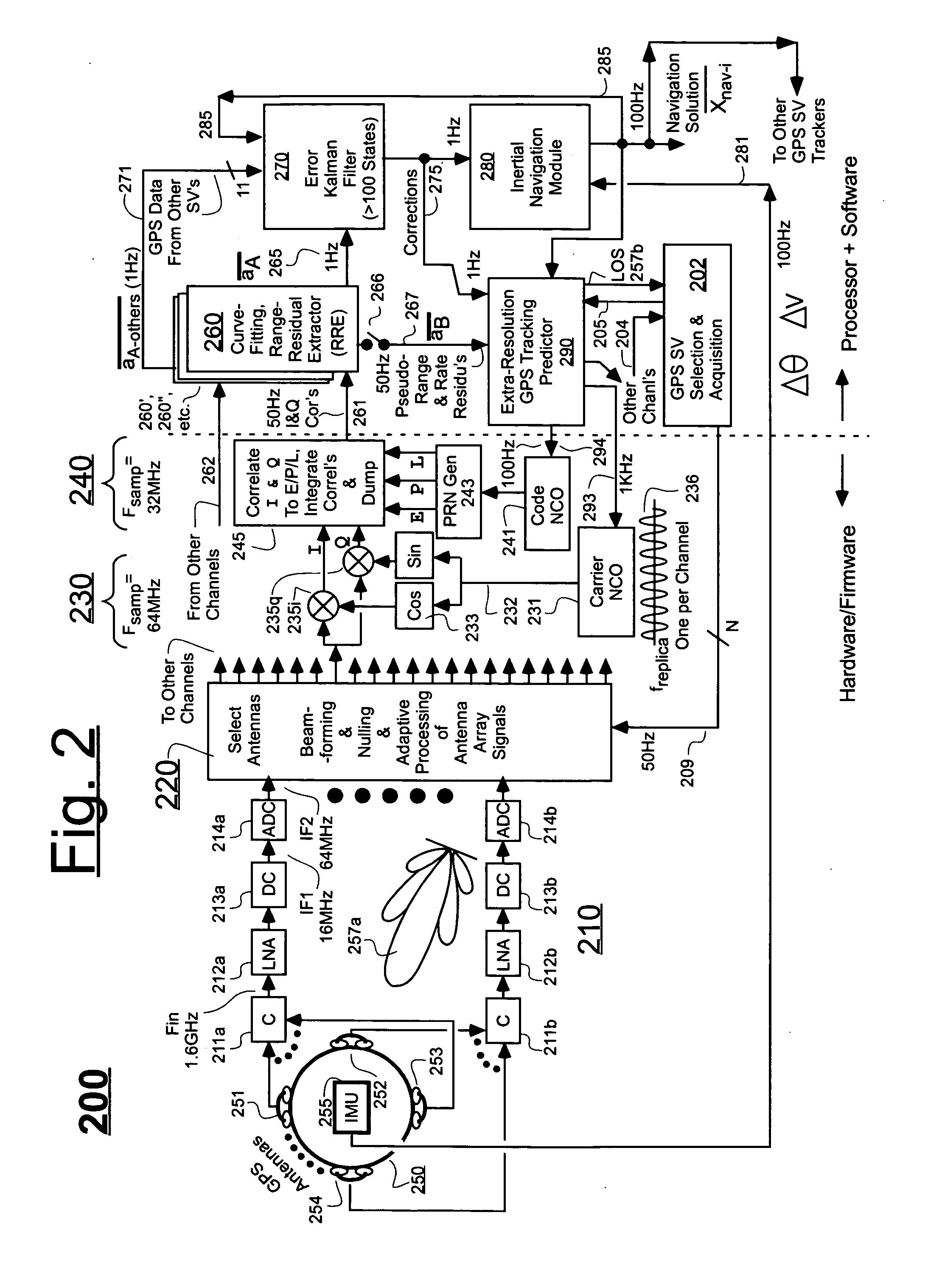
InactiveUS20070118286A1Cancel noiseReduce computing timeDigital data processing detailsNavigation instrumentsCurve fittingCarrier signal
An Ultra-Tightly Coupled GPS-inertial navigation system for use in a moving agile platform includes a range residual extractor that uses best curve fitting of a third order polynomial for estimating range residual. The curve-fitted residual is used to update an error Kalman filter. The error Kalman filter includes correction for navigation solution, and IMU and GPS parameters. The navigation solution together with GPS parameter corrections are used in a Tracking Predictor to generate high-sampling-rate carrier and code replicas. The curve-fitting error covariance indicates signal to noise ratio for the tracked GPS signal and may be used for early indication of interference or jamming.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
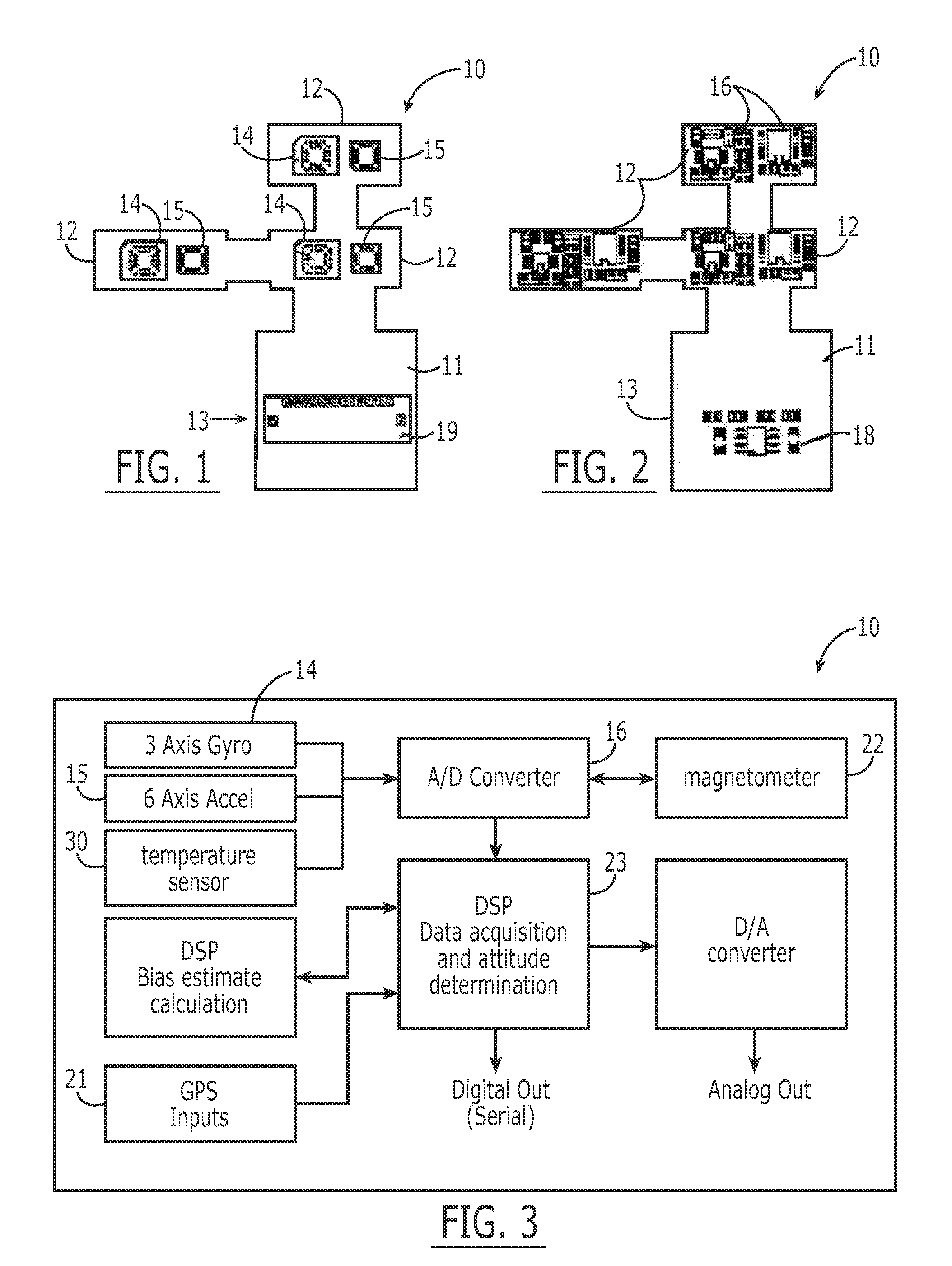
Miniaturized Inertial Measurement Unit and Associated Methods
InactiveUS20070032951A1Reduce noiseThe result is accurateNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsDigital computer detailsDigital signal processingAccelerometer
A self-contained, integrated micro-cube-sized inertial measurement unit is provided wherein accuracy is achieved through the use of specifically oriented sensors, the orientation serving to substantially cancel noise and other first-order effects, and the use of a noise-reducing algorithm such as wavelet cascade denoising and an error correcting algorithm such as a Kalman filter embedded in a digital signal processor device. In a particular embodiment, a pair of three sets of angle rate sensors are orientable triaxially in opposite directions, wherein each set is mounted on a different sector of a base orientable normal to the other two and comprising N gyroscopes oriented at 360 / N-degree increments, where N≧2. At least one accelerometer is included to provide triaxial data. Signals are output from the angle rate sensors and accelerometer for calculating a change in attitude, position, angular rate, acceleration, and / or velocity of the unit.
Owner:JAYMART SENSORS
Estimating Distance To An Object Using A Sequence Of Images Recorded By A Monocular Camera
In a computerized system including a camera mounted in a moving vehicle. The camera acquires consecutively in real time image frames including images of an object within the field of view of the camera. Range to the object from the moving vehicle is determined in real time. A dimension, e.g. a width, is measured in the respective images of two or more image frames, thereby producing measurements of the dimension. The measurements are processed to produce a smoothed measurement of the dimension. The dimension is measured subsequently in one or more subsequent frames. The range from the vehicle to the object is calculated in real time based on the smoothed measurement and the subsequent measurements. The processing preferably includes calculating recursively the smoothed dimension using a Kalman filter.
Owner:MOBILEYE VISION TECH LTD
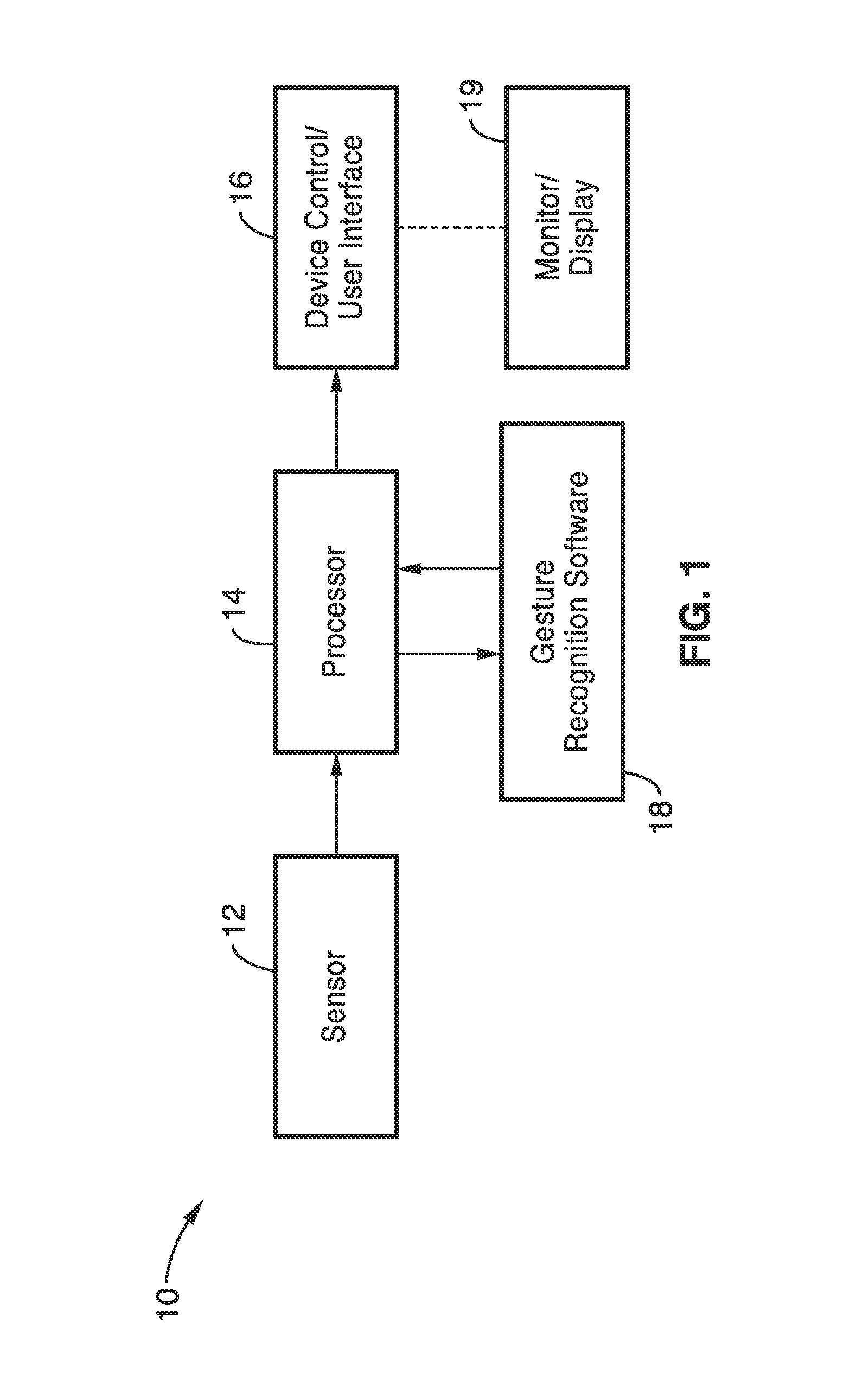
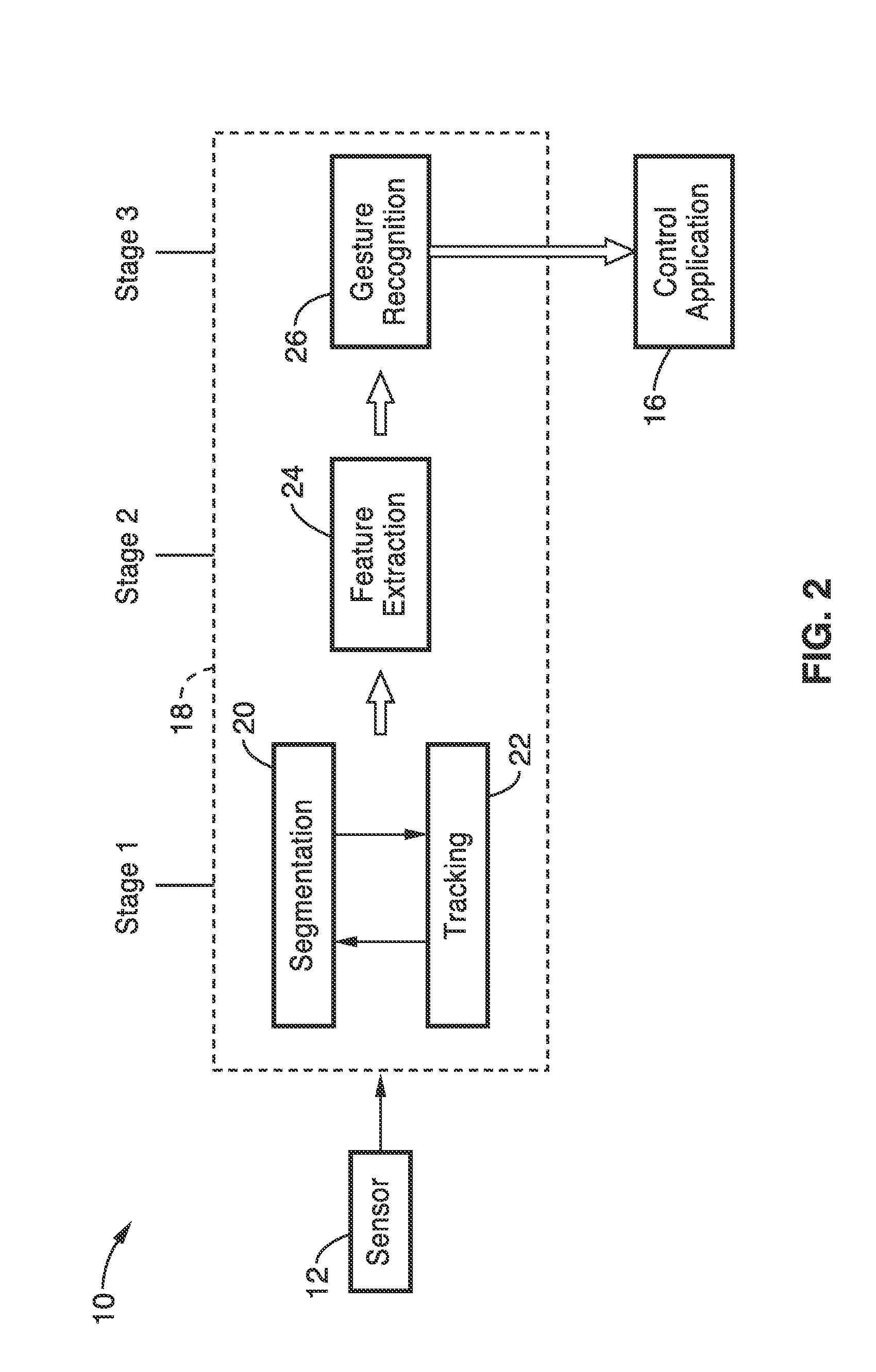
Gesture recognition system for TV control
ActiveUS20120069168A1Reduce computational complexityEasy to useImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionKaiman filter
A gesture recognition system using a skin-color based method combined with motion information to achieve real-time segmentation. A Kalman filter is used to track the centroid of the hand. The palm center, palm bottom, as well as the largest distance from the palm center to the contour from extracted hand mask are computed. The computed distance to a threshold is then compared to decide if the current posture is “open” or “closed.” In a preferred embodiment, the transition between the “open” and “closed” posture to decide if the current gesture is in “select” or “grab” state.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method and apparatus for adaptive filter based attitude updating
InactiveUS20050240347A1Improve abilitiesConveniently implementedNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsKaiman filterGyroscope
A six state Kalman filter is adapted based on a current acceleration mode of an INS device. Gyro measurements are used to determine the acceleration mode and the Kalman filter estimates bias and small angle error of the measurements based on the acceleration mode. The bias error corrects the gyro measurement and the small angle error is used along with the corrected gyro measurement to update an attitude sensed by the gyro.
Owner:YANG YUN CHUN
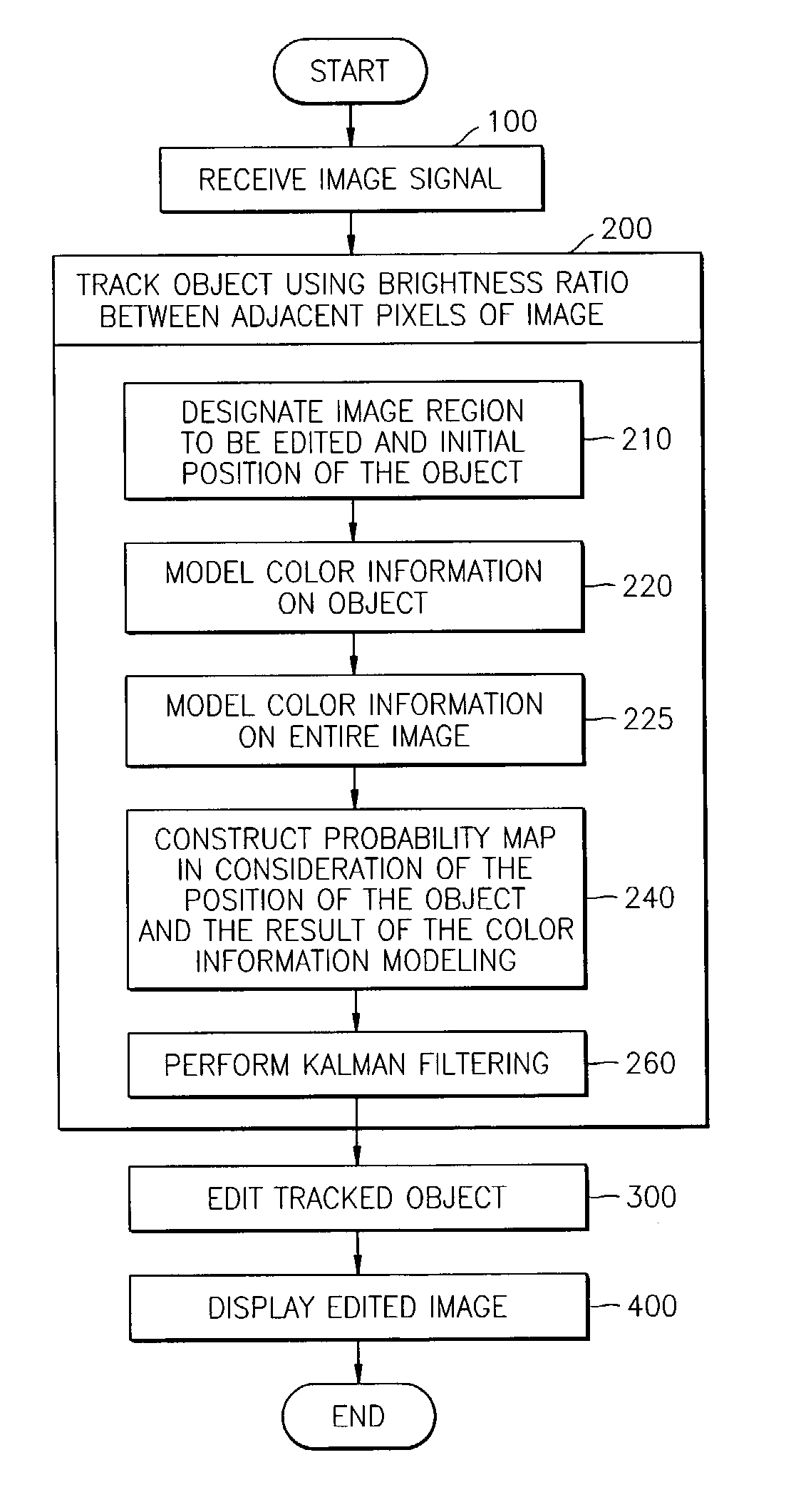
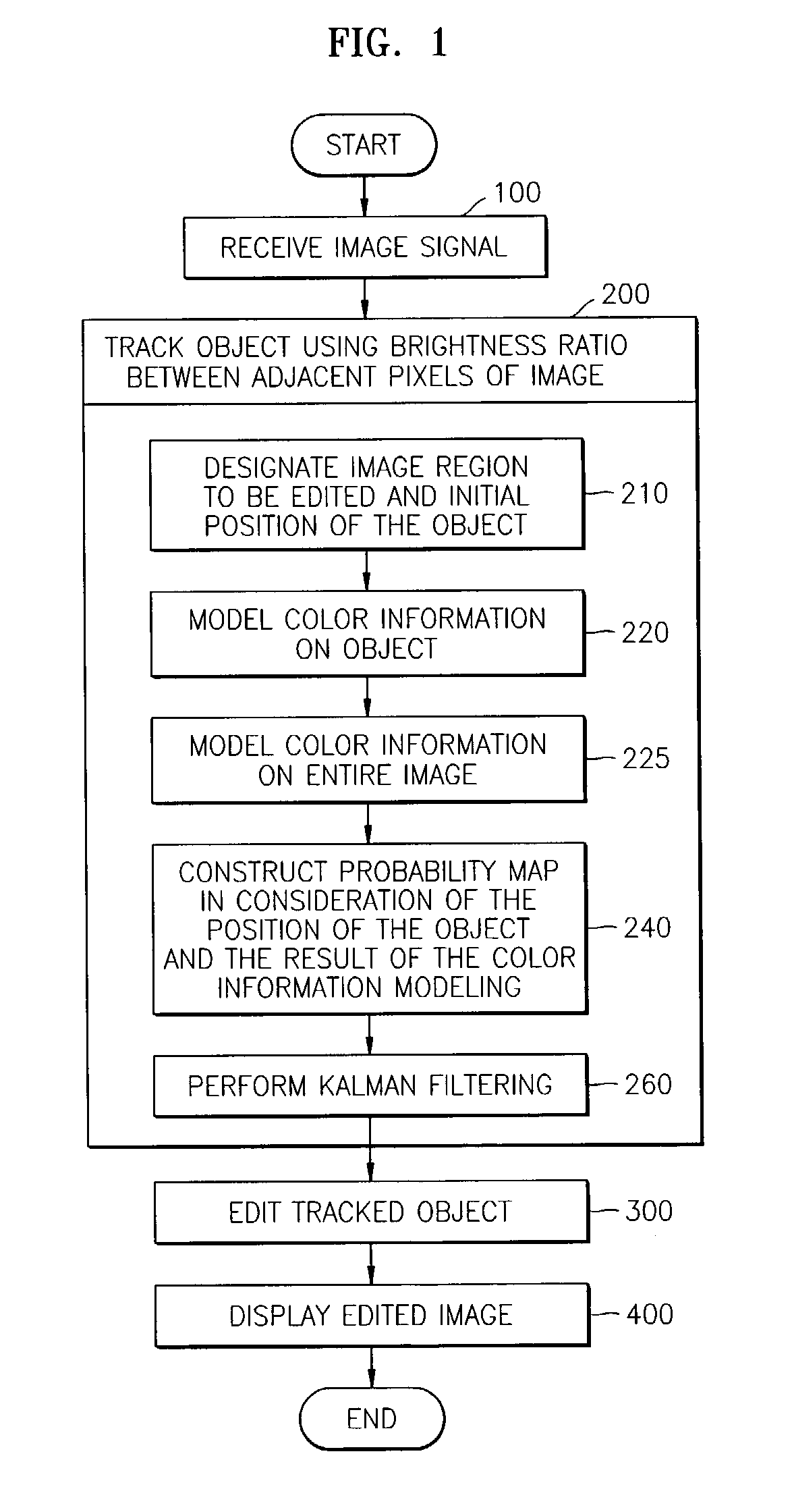
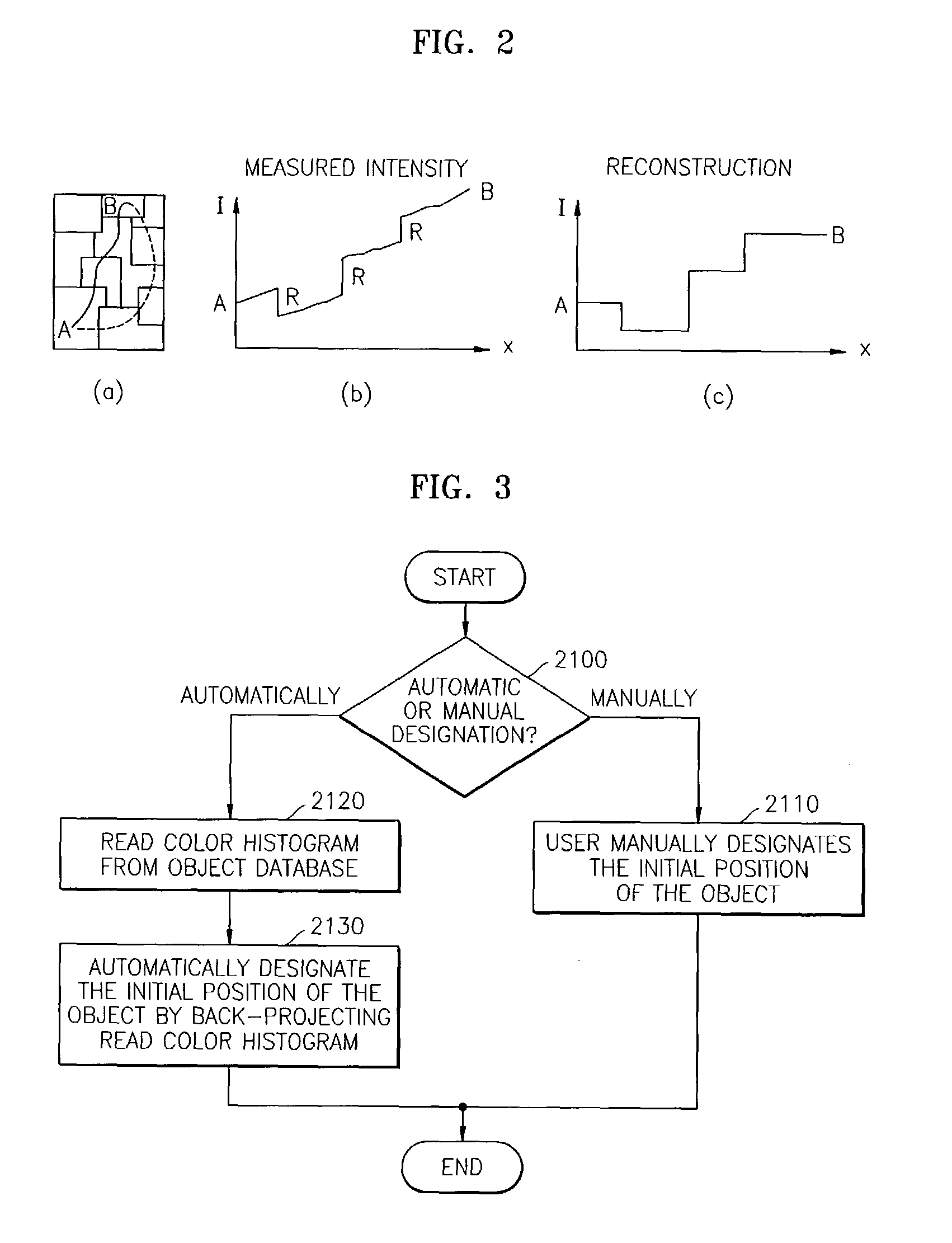
Illumination-invariant object tracking method and image editing system using the same
ActiveUS7171023B2Reliably region of imageImage analysisColor signal processing circuitsIlluminanceComputer science
An illumination-invariant object tracking method and an image editing system using the same are provided. The illumination-invariant object tracking method involves: designating an initial position of an object of interest to be tracked in an image; constructing a probability map for object tracking in consideration of a color ratio of adjacent pixels in the image; and performing Kalman filtering based on the initial position of the object and the probability map. The image editing system based on the illumination-invariant object tracking method includes: a data input unit which receives an image to be edited; an object tracking unit which tracks a target object in consideration of a color ratio of adjacent pixels in the image; an image editing unit which edits and outputs an edited image in a predetermined region of the image, in response to information on the position, size, and boundary of the tracked target object.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Machine vision and inertial navigation fusion-based mobile robot motion attitude estimation method
InactiveCN102538781AReduce cumulative errorHigh positioning accuracyNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsVisual perceptionInertial navigation system
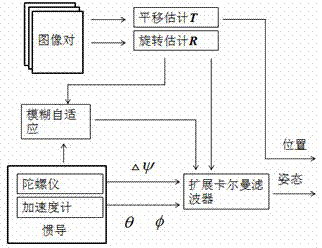
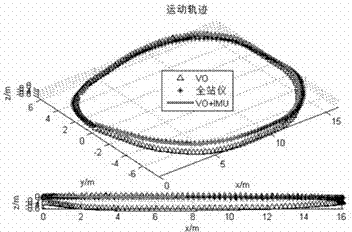
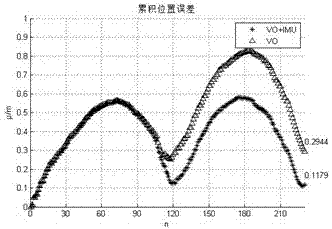
The invention discloses a machine vision and inertial navigation fusion-based mobile robot motion attitude estimation method which comprises the following steps of: synchronously acquiring a mobile robot binocular camera image and triaxial inertial navigation data; distilling front / back frame image characteristics and matching estimation motion attitude; computing a pitch angle and a roll angle by inertial navigation; building a kalman filter model to estimate to fuse vision and inertial navigation attitude; adaptively adjusting a filter parameter according to estimation variance; and carrying out accumulated dead reckoning of attitude correction. According to the method, a real-time expanding kalman filter attitude estimation model is provided, the combination of inertial navigation and gravity acceleration direction is taken as supplement, three-direction attitude estimation of a visual speedometer is decoupled, and the accumulated error of the attitude estimation is corrected; and the filter parameter is adjusted by fuzzy logic according to motion state, the self-adaptive filtering estimation is realized, the influence of acceleration noise is reduced, and the positioning precision and robustness of the visual speedometer is effectively improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
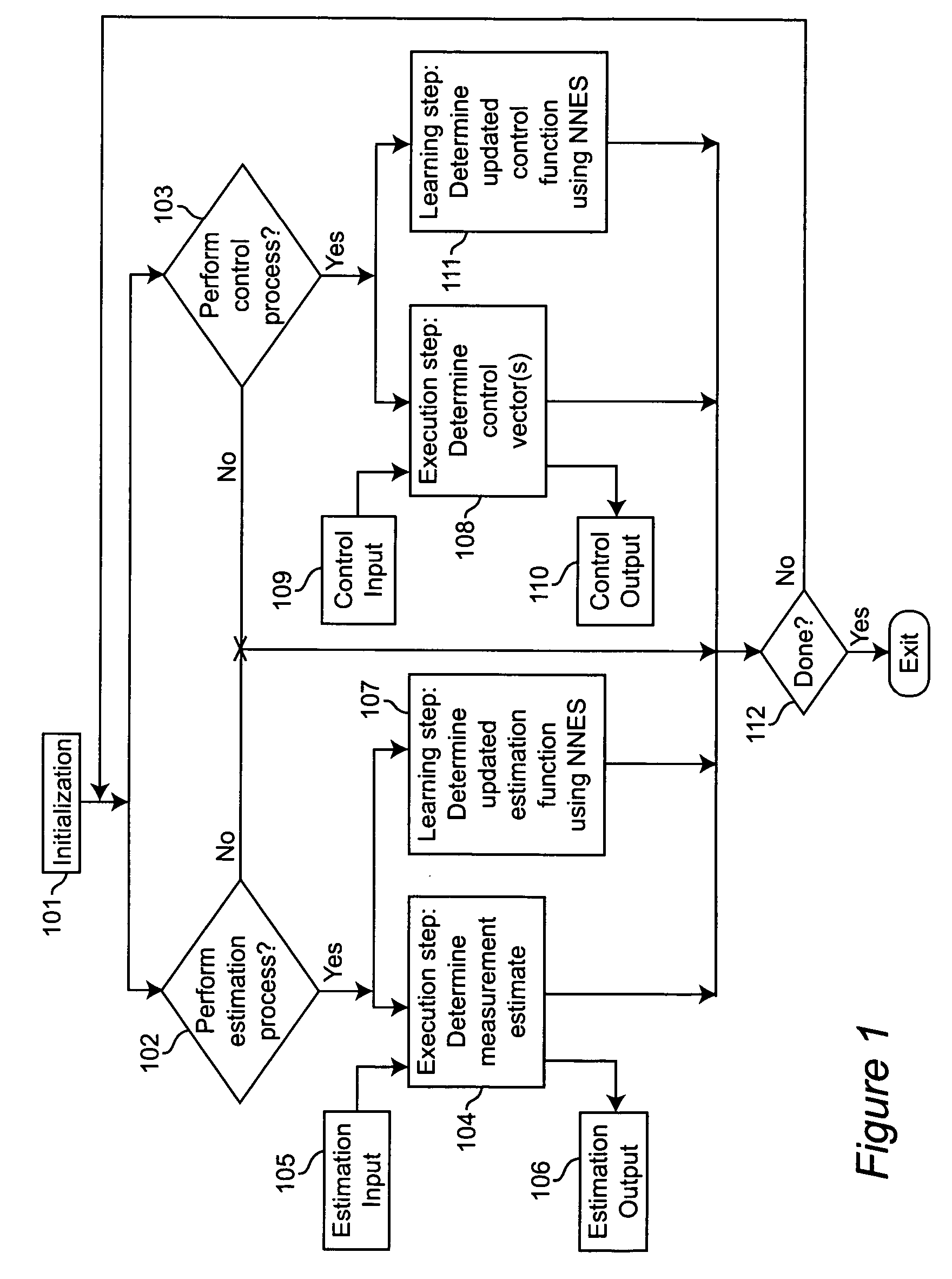
Neural networks for prediction and control
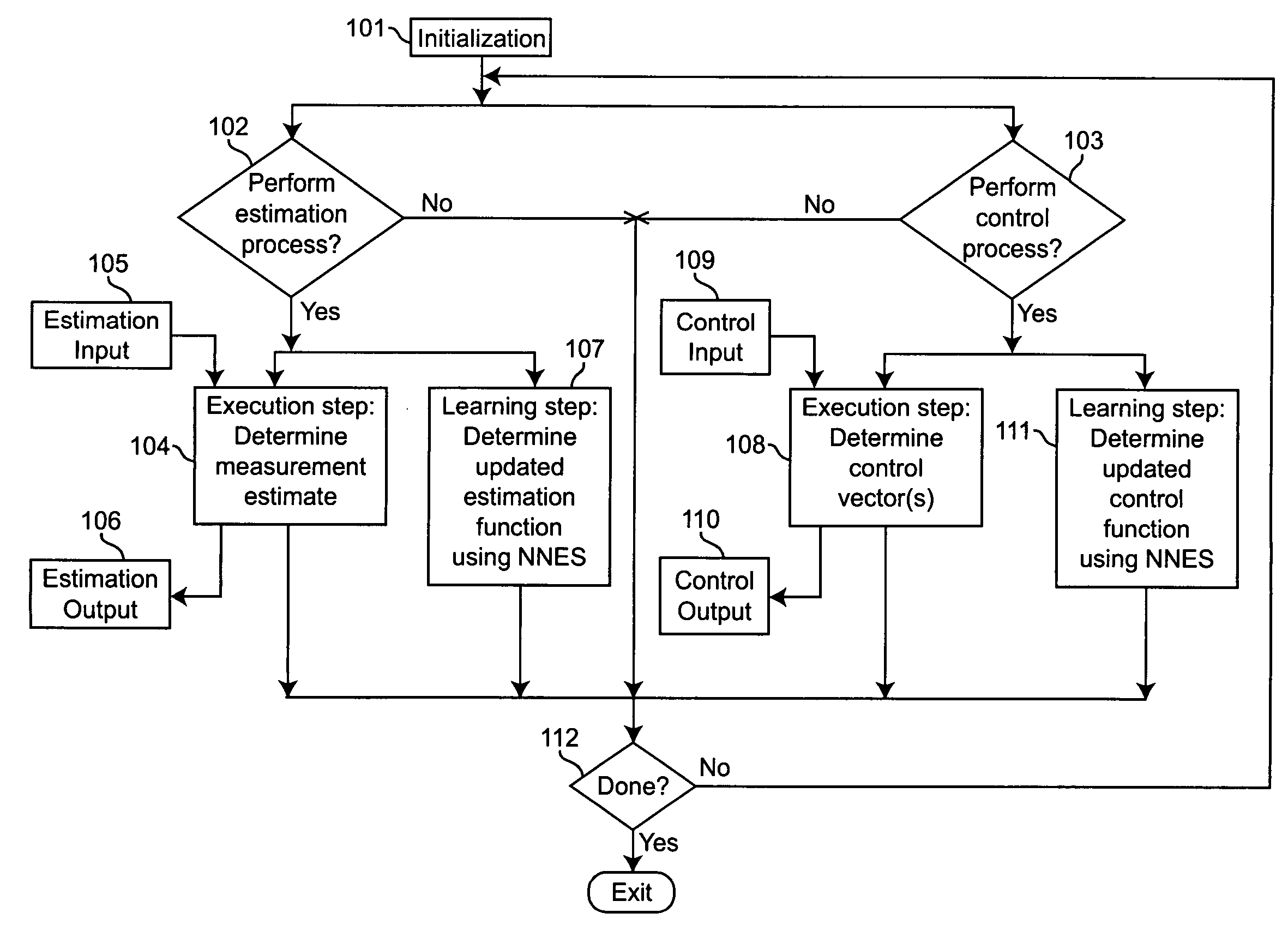
Neural networks for optimal estimation (including prediction) and / or control involve an execution step and a learning step, and are characterized by the learning step being performed by neural computations. The set of learning rules cause the circuit's connection strengths to learn to approximate the optimal estimation and / or control function that minimizes estimation error and / or a measure of control cost. The classical Kalman filter and the classical Kalman optimal controller are important examples of such an optimal estimation and / or control function. The circuit uses only a stream of noisy measurements to infer relevant properties of the external dynamical system, learn the optimal estimation and / or control function, and apply its learning of this optimal function to input data streams in an online manner. In this way, the circuit simultaneously learns and generates estimates and / or control output signals that are optimal, given the network's current state of learning.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
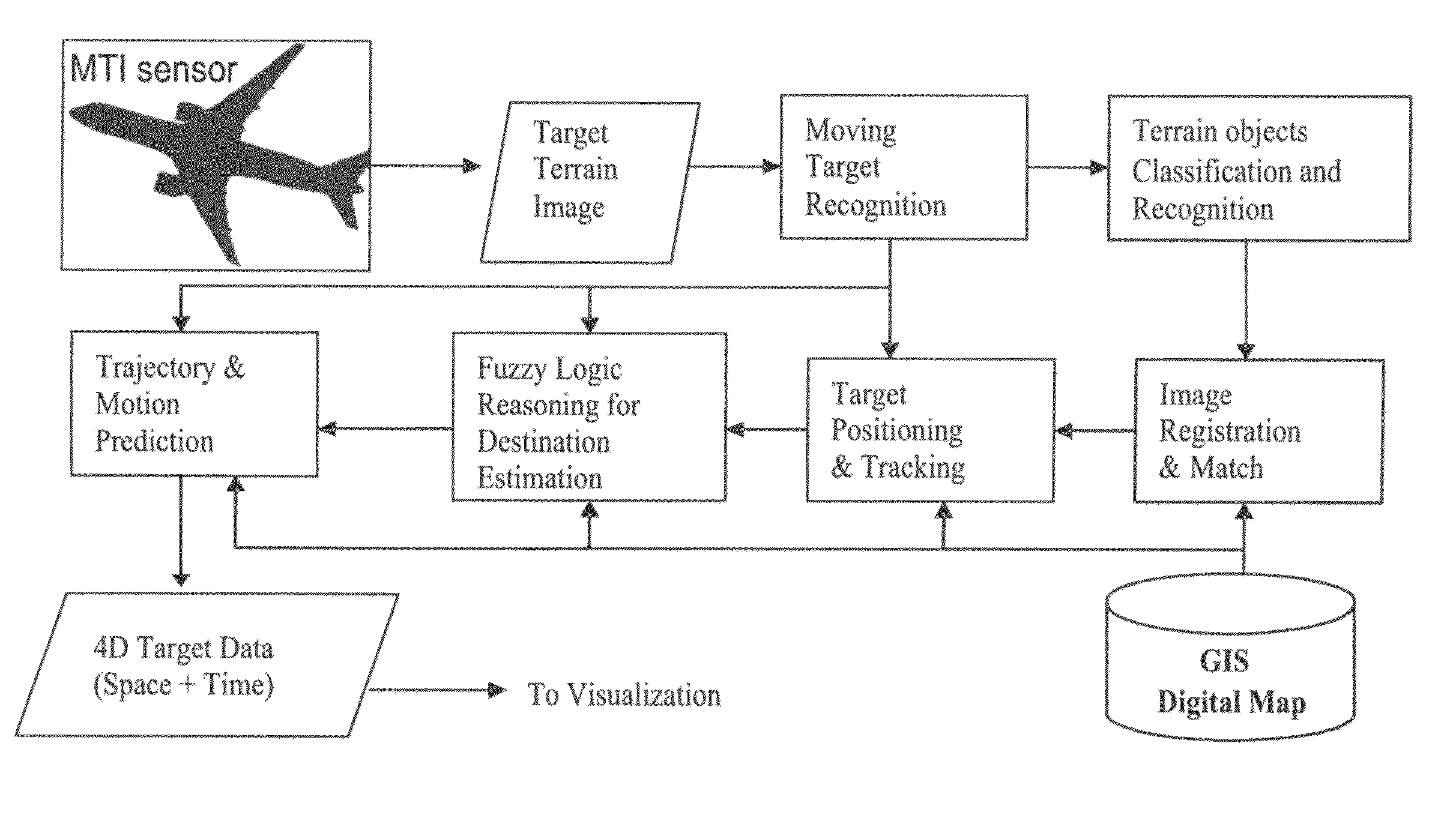
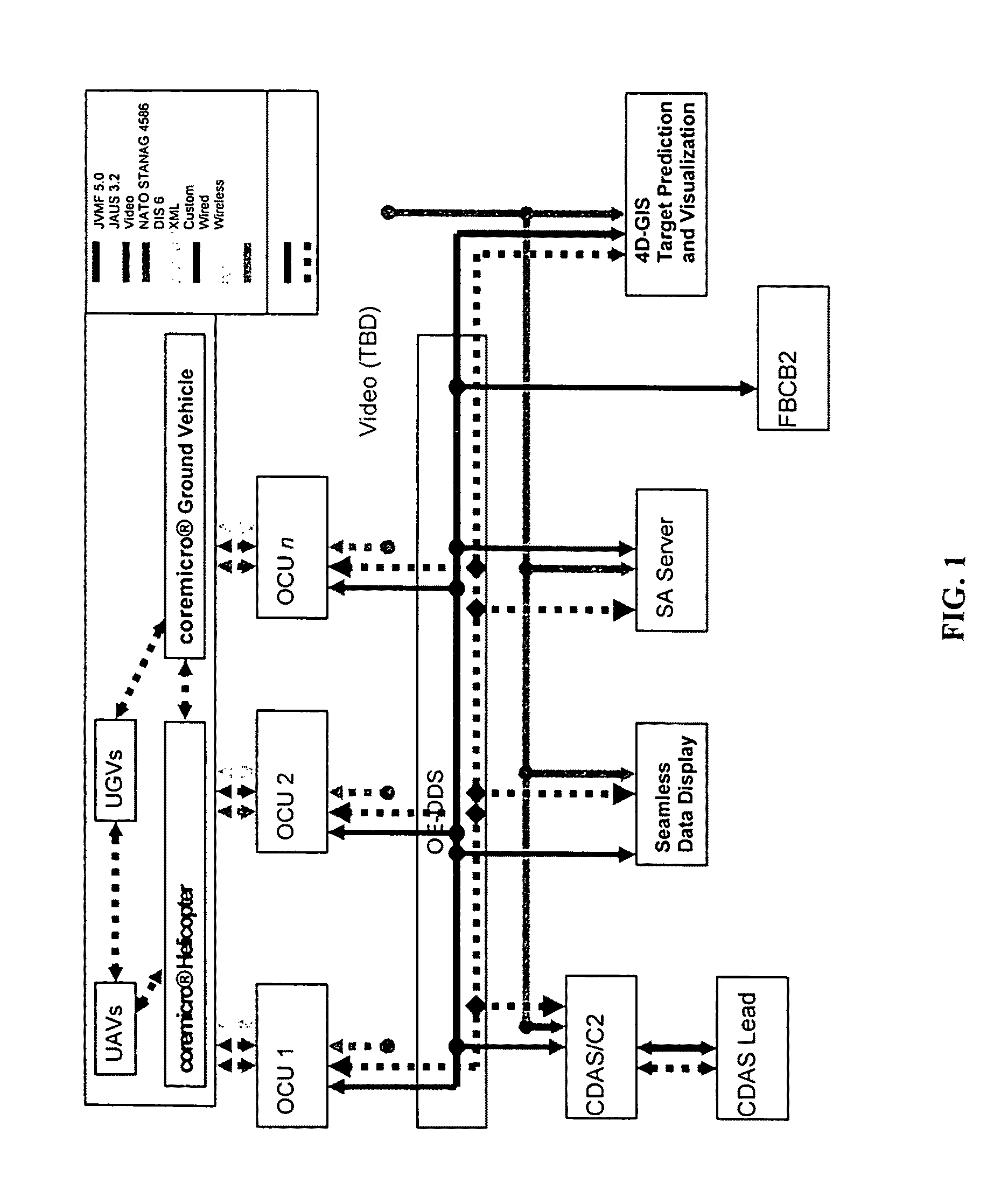
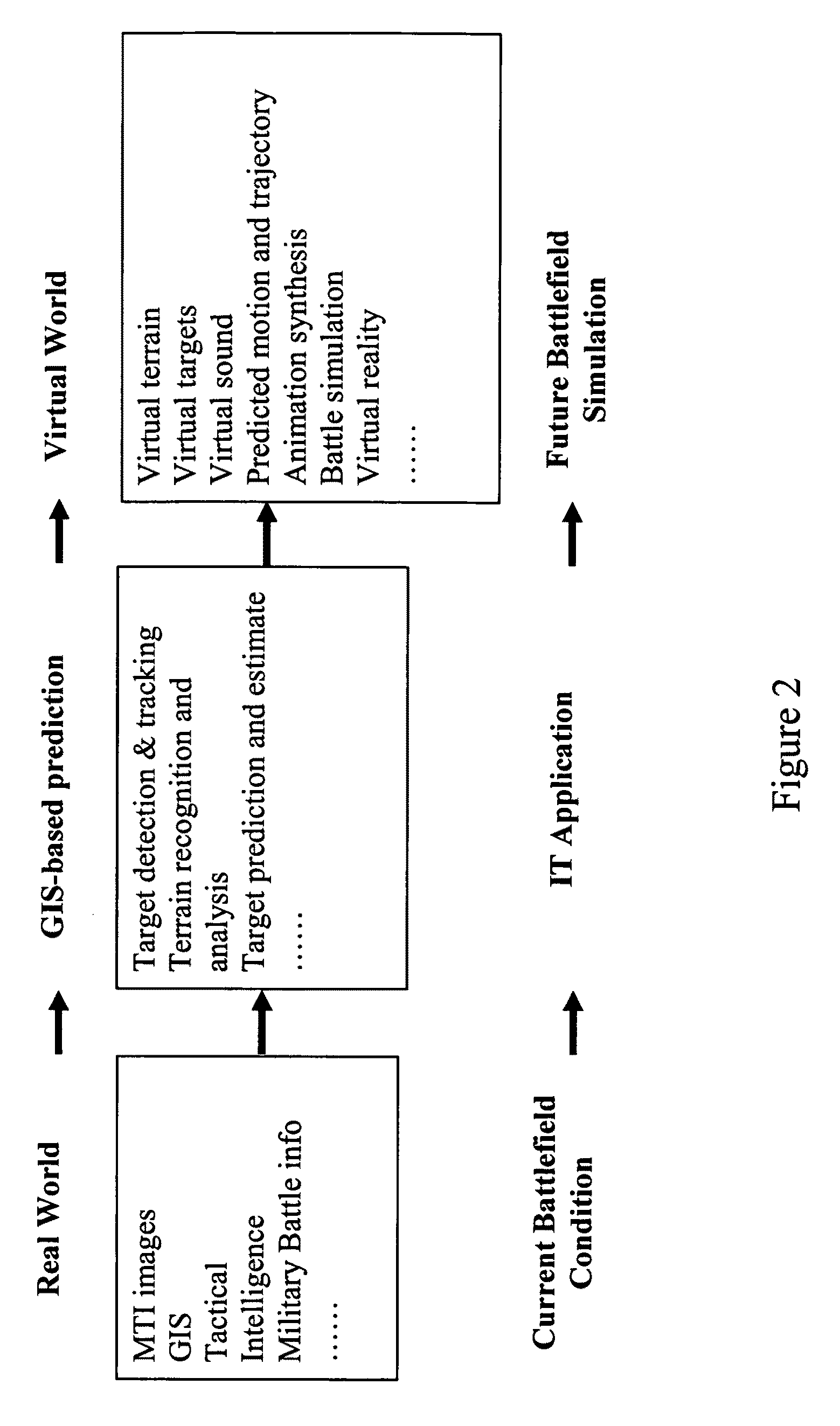
4D GIS based virtual reality for moving target prediction
ActiveUS8229163B2Precise processConfidenceImage enhancementImage analysisFuzzy logic inferenceLandform
The technology of the 4D-GIS system deploys a GIS-based algorithm used to determine the location of a moving target through registering the terrain image obtained from a Moving Target Indication (MTI) sensor or small Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) camera with the digital map from GIS. For motion prediction the target state is estimated using an Extended Kalman Filter (EKF). In order to enhance the prediction of the moving target's trajectory a fuzzy logic reasoning algorithm is used to estimate the destination of a moving target through synthesizing data from GIS, target statistics, tactics and other past experience derived information, such as, likely moving direction of targets in correlation with the nature of the terrain and surmised mission.
Owner:AMERICAN GNC
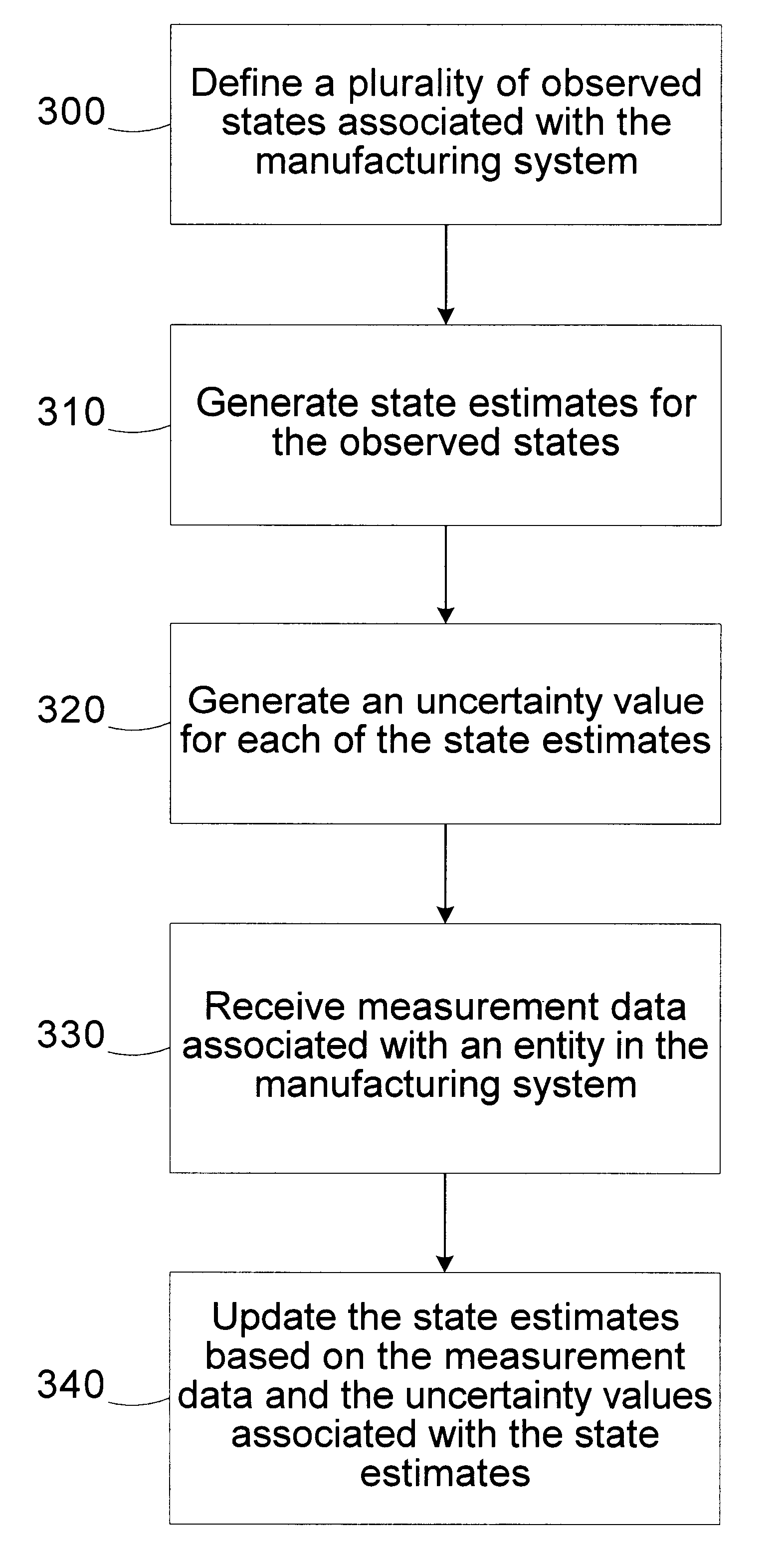
Kalman filter state estimation for a manufacturing system
InactiveUS6757579B1Error detection/correctionDigital computer detailsKaiman filterManufacturing systems
A method for monitoring a manufacturing system includes defining a plurality of observed states associated with the manufacturing system. State estimates are generated for the observed states. An uncertainty value is generated for each of the state estimates. Measurement data associated with an entity in the manufacturing system is received. The state estimates are updated based on the measurement data and the uncertainty values associated with the state estimates. A system for monitoring a manufacturing system includes a controller configured to define a plurality of observed states associated with the manufacturing system, generate state estimates for the observed states, generate an uncertainty value for each of the state estimates, receive measurement data associated with an entity in the manufacturing system, and update the state estimates based on the measurement data and the uncertainty values associated with the state estimates.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
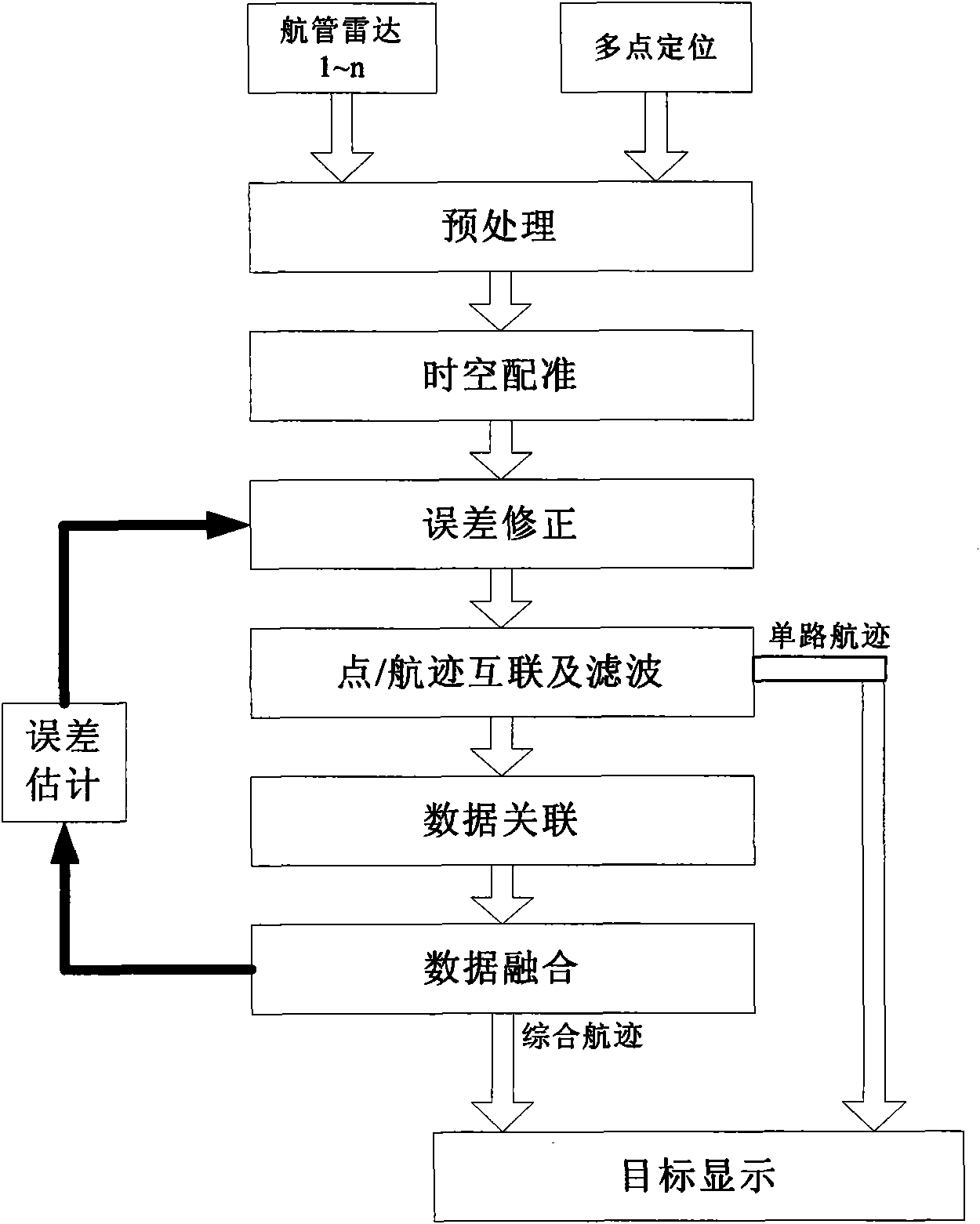
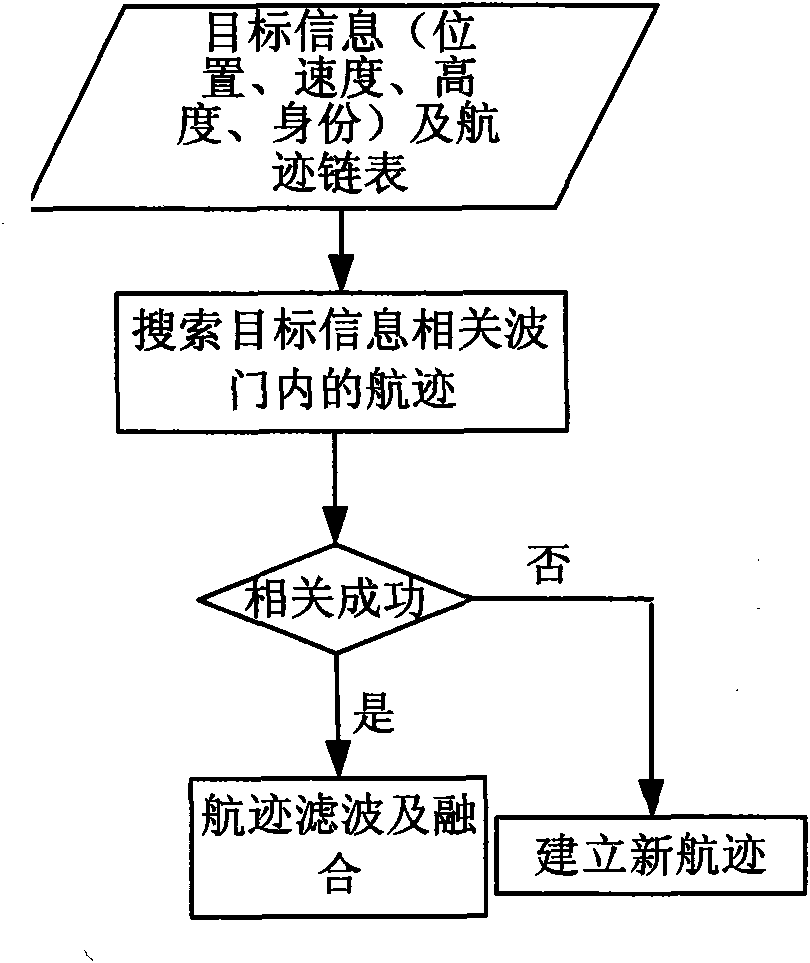
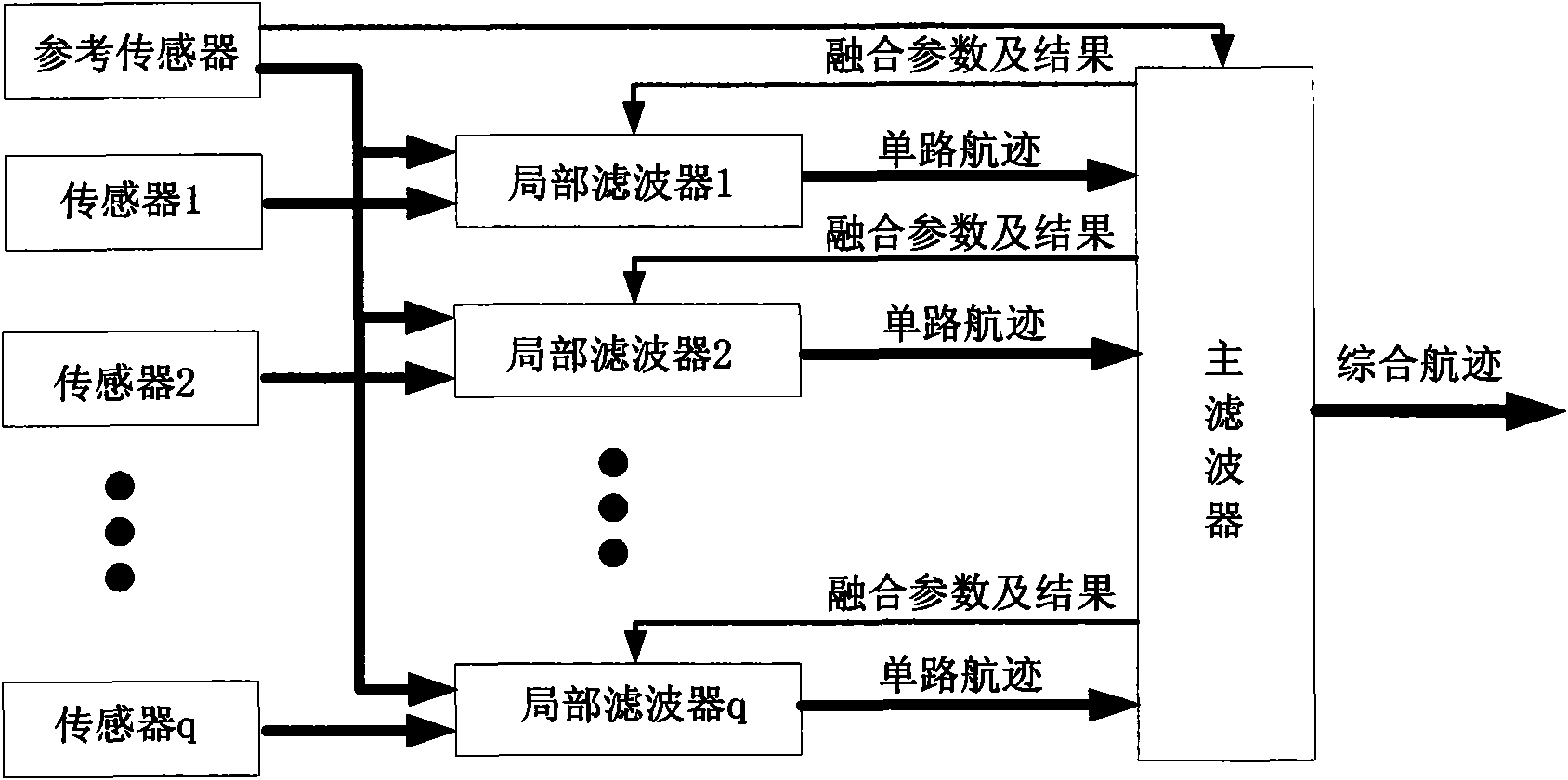
Federated Kalman filtering-based method for fusing multilateration data and radar data
InactiveCN101655561AReduce performanceCorrection errorRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadarFiltration
The invention relates to a Federated Kalman filtering-based method for fusing multilateration data and radar data, comprising seven processes: pretreatment, time and space registration, error correction, single-sensor line tracking or airborne trace interconnection and filtration, data association, data fusion as well as error estimation. On the basis of multiclass monitoring information, the technical scheme of the invention establishes data association mapping relations among all classes of targets, constructs a process method fusing the multilateration system data and the radar data, realizes deep fusion of all classes of information and comprehensive utilization on effective information, ensures high updating rate of a multilateration system and the whole precision of system monitoringwhen period is less than or equal to 1sec, reduces impact of radar measuring error on system monitoring precision, and significantly improves the tracking precision of the system.
Owner:NANJING LES INFORMATION TECH
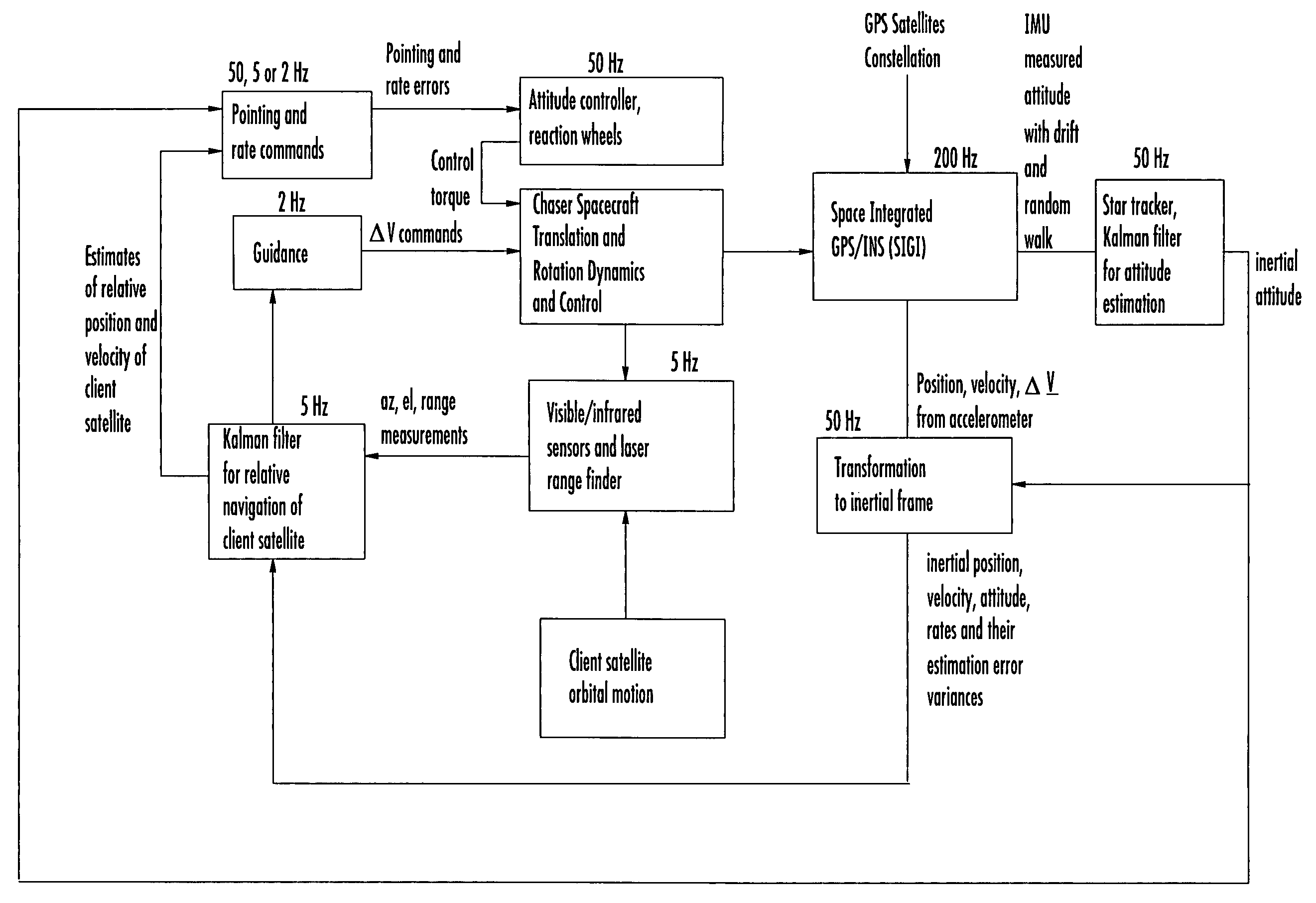
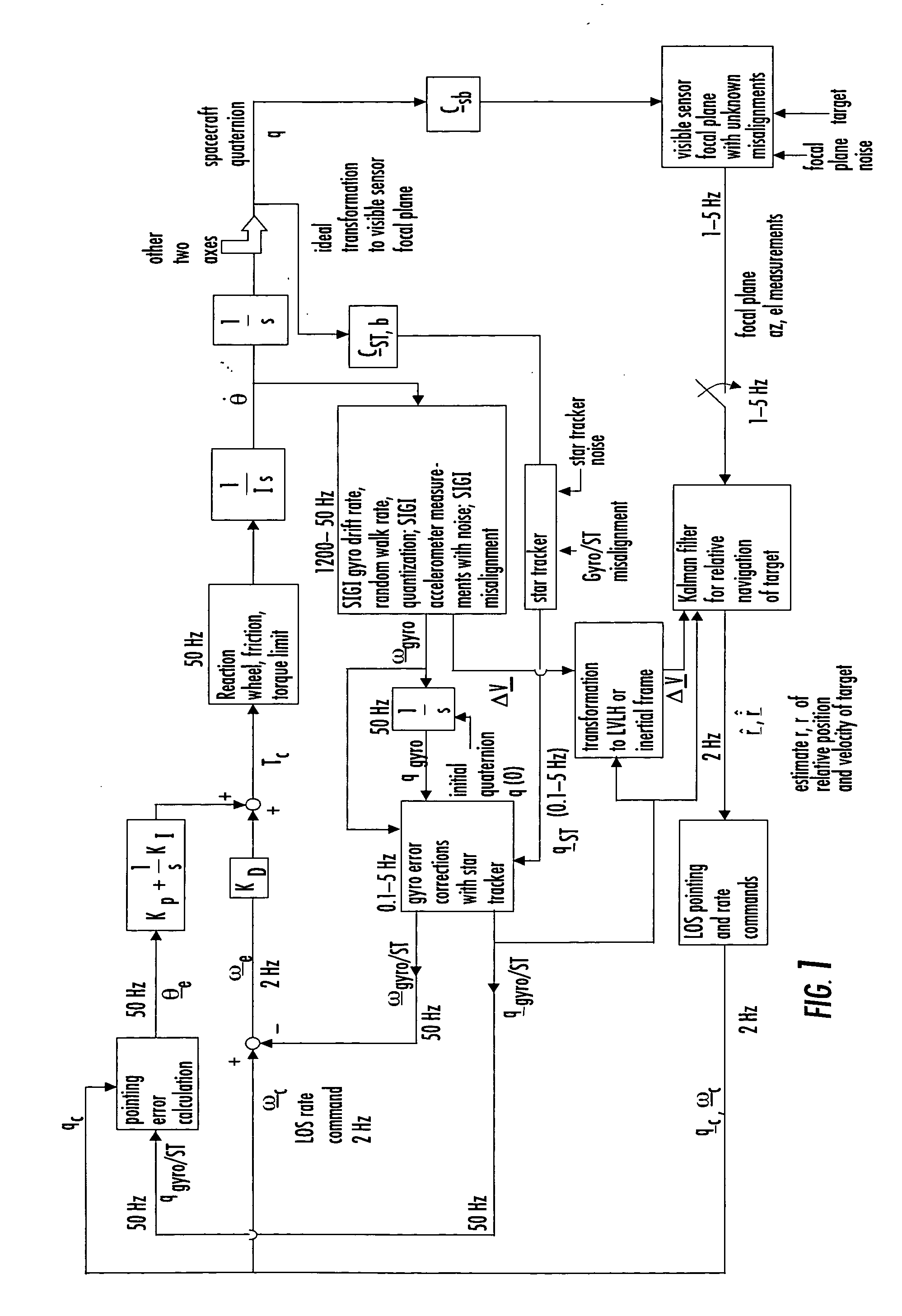
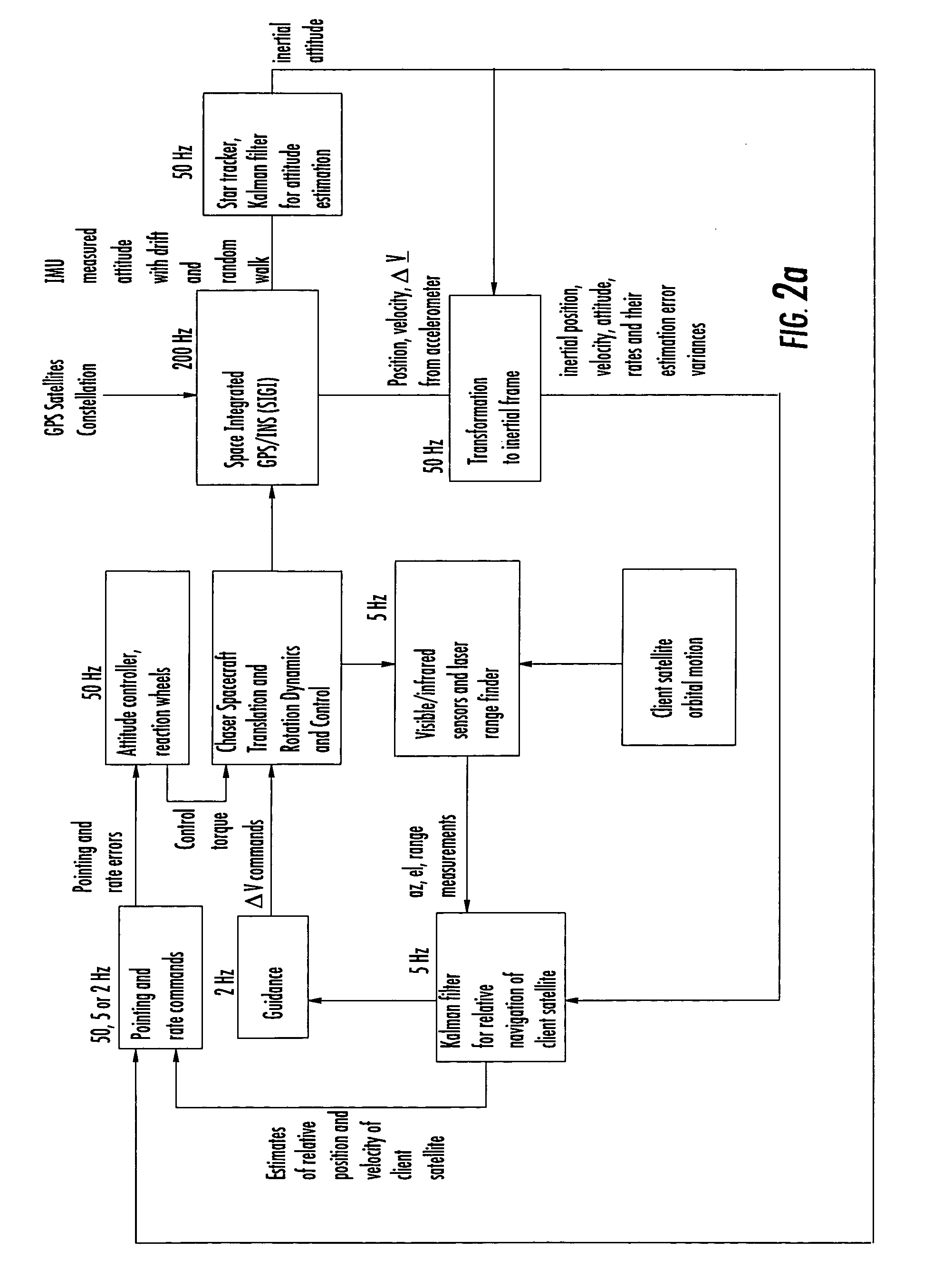
Laser range finder closed-loop pointing technology of relative navigation, attitude determination, pointing and tracking for spacecraft rendezvous
InactiveUS20050060092A1Improved functionality and precisionImprove ObservabilityInstruments for road network navigationCosmonautic vehiclesGyroscopeClosed loop
A closed-loop LRF pointing technology to measure the range of a target satellite from a chaser satellite for rendezvous is provided that includes several component technologies: LOS angle measurements of the target satellite on a visible sensor focal plane and the angles' relationships with the relative position of the target in inertial or LVLH frame, a relative navigation Kalman filter, attitude determination of the visible sensor with gyros, star trackers and a Kalman filter, pointing and rate commands for tracking the target, and an attitude controller. An analytical, steady-state, three-axis, six-state Kalman filter is provided for attitude determination. The system and its component technologies provide improved functionality and precision for relative navigation, attitude determination, pointing, and tracking for rendezvous. Kalman filters are designed specifically for the architecture of the closed-loop system to allow for pointing the laser rangefinder to a target even if a visible sensor, a laser rangefinder, gyros and a star tracker are misaligned and the LOS angle measurements from the visible sensor are interrupted.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
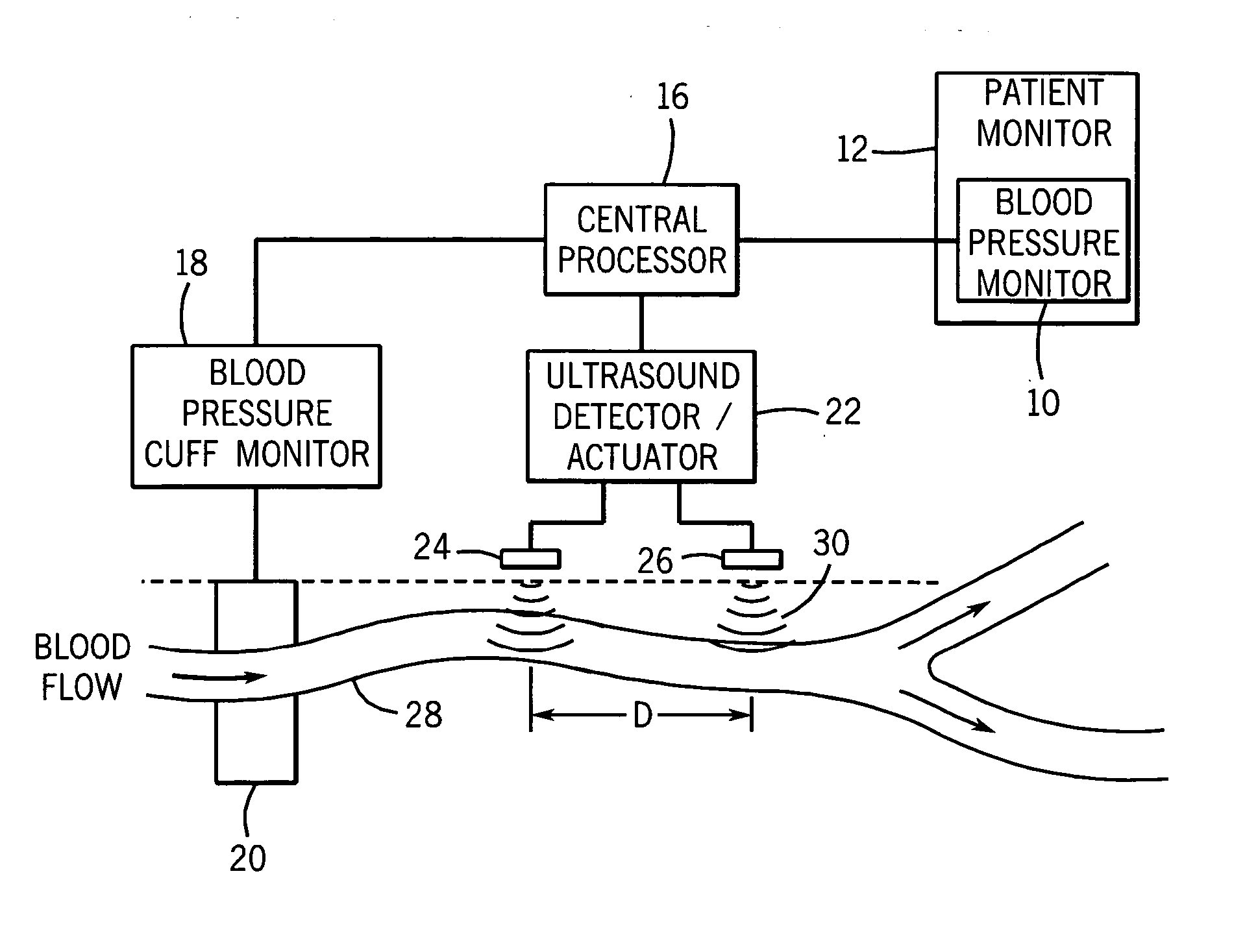
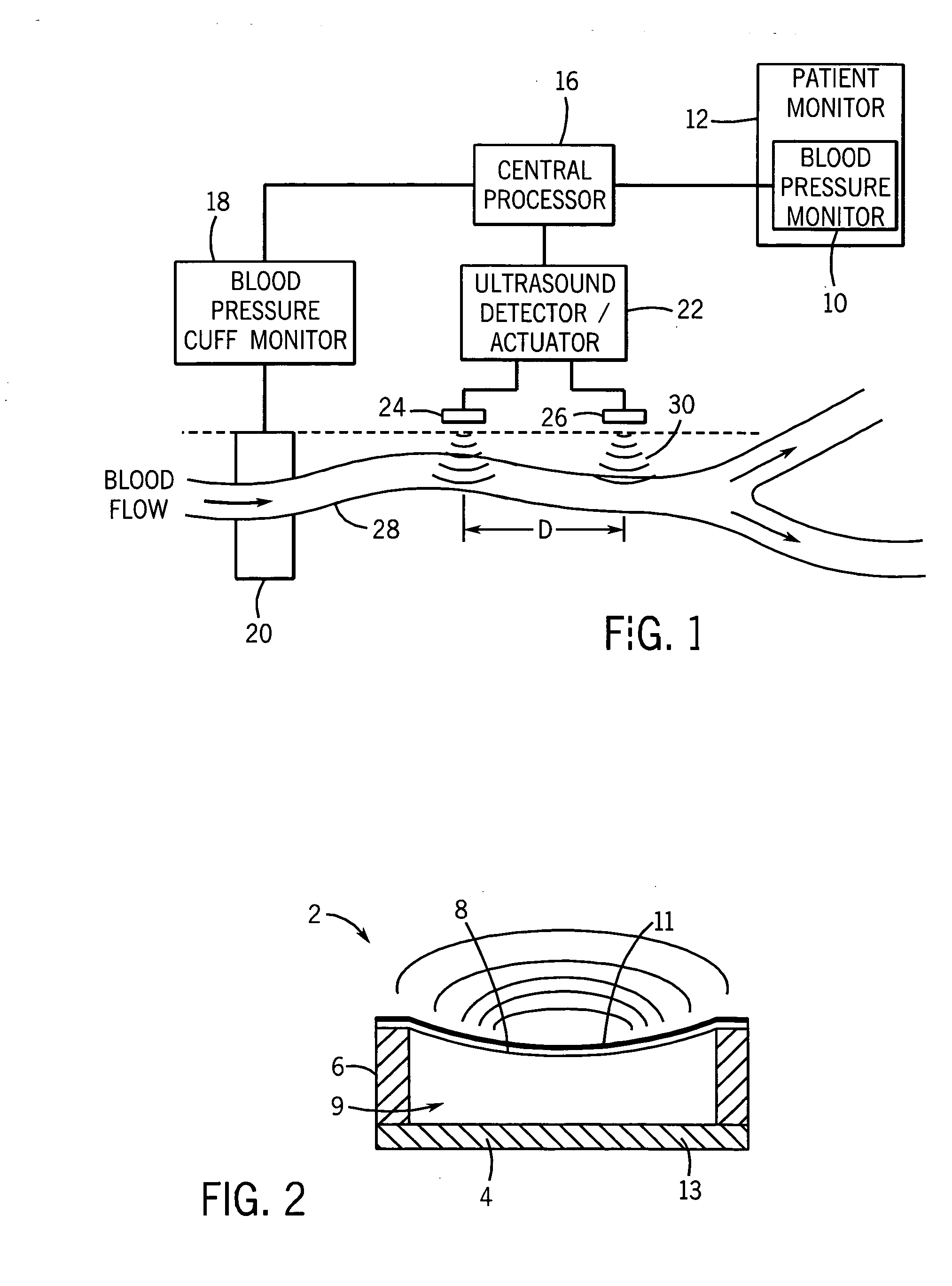
Continuous, non-invasive technique for determining blood pressure using a transmission line model and transcutaneous ultrasound measurements
ActiveUS20060211942A1Good estimateImprove accuracyBlood flow measurement devicesPerson identificationState variableBlood pressure
A method and technique for the continuous, non-invasive measurement of blood pressure. The blood pressure measurement technique of the present invention utilizes ultrasound measurements to determine the diameter of the blood vessel in which the blood pressure is being measured as well as the flow rate of blood at both an input point and an output point along the blood vessel. The system utilizes a transmission line model to relate various blood vessel measurements with electrical components. The transmission line model, in combination with data management techniques including state variable representations and Kalman filtering, is used to develop a blood pressure measurement in real time.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST INFORMATION TECH
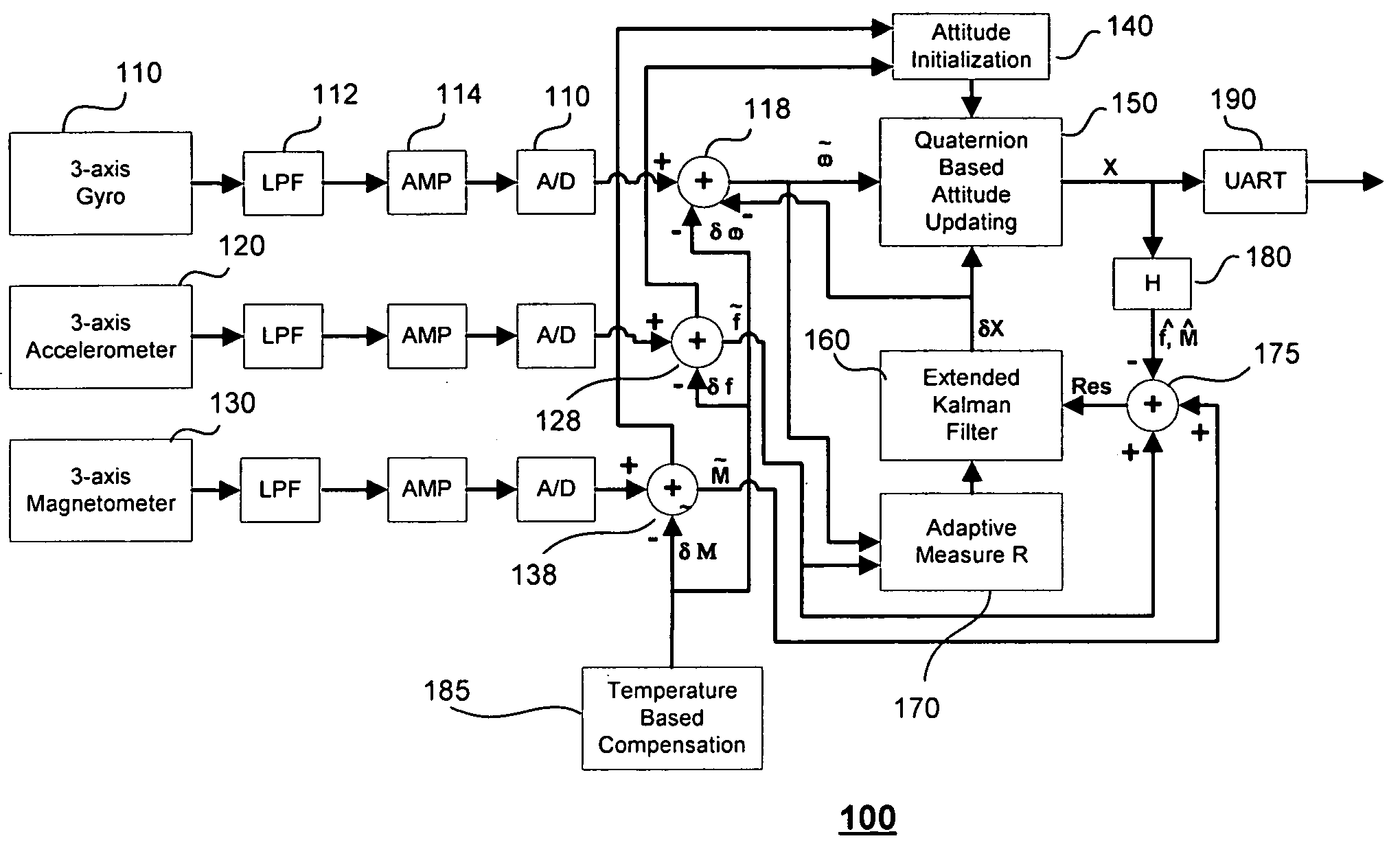
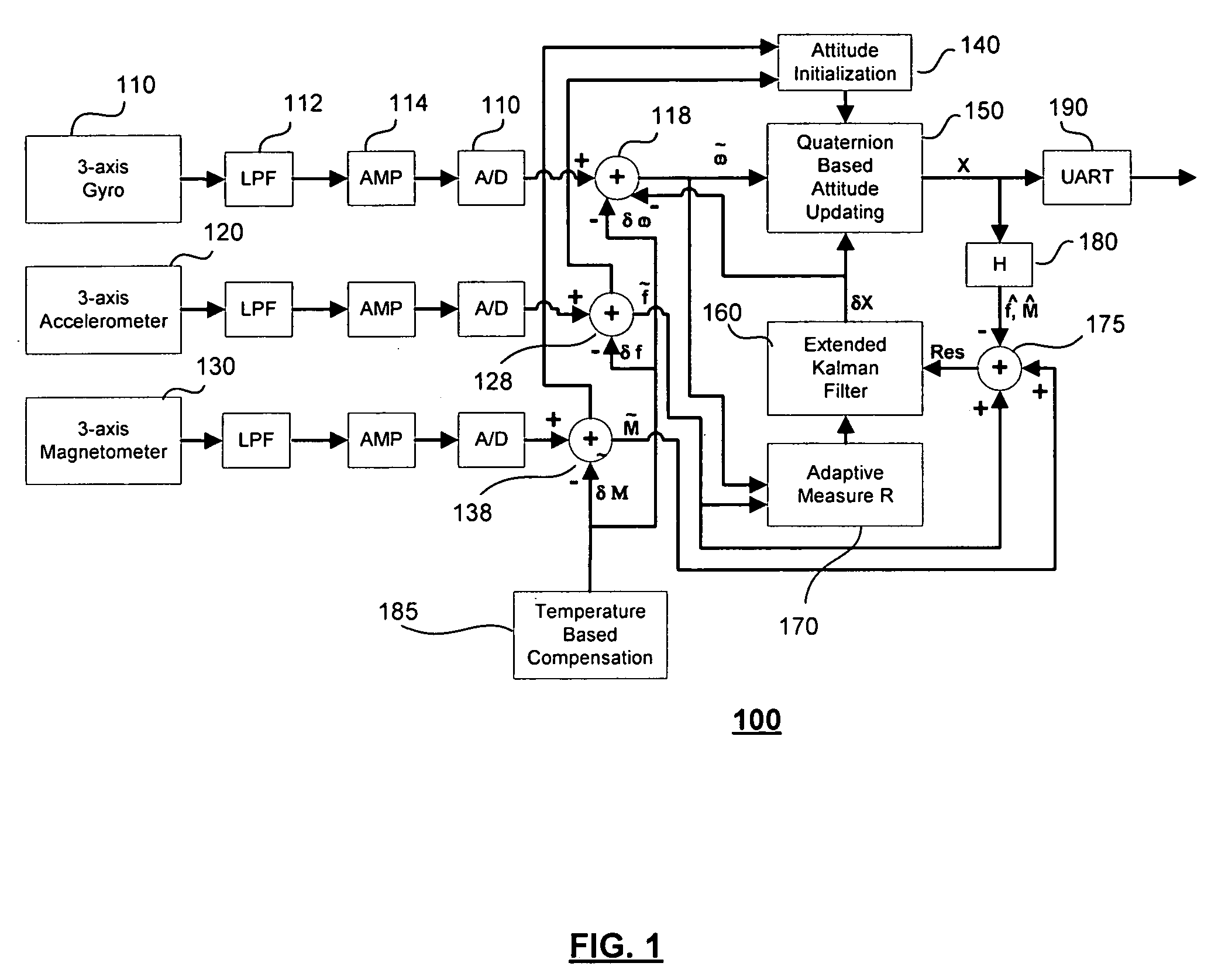
Dynamic attitude measurement method and apparatus
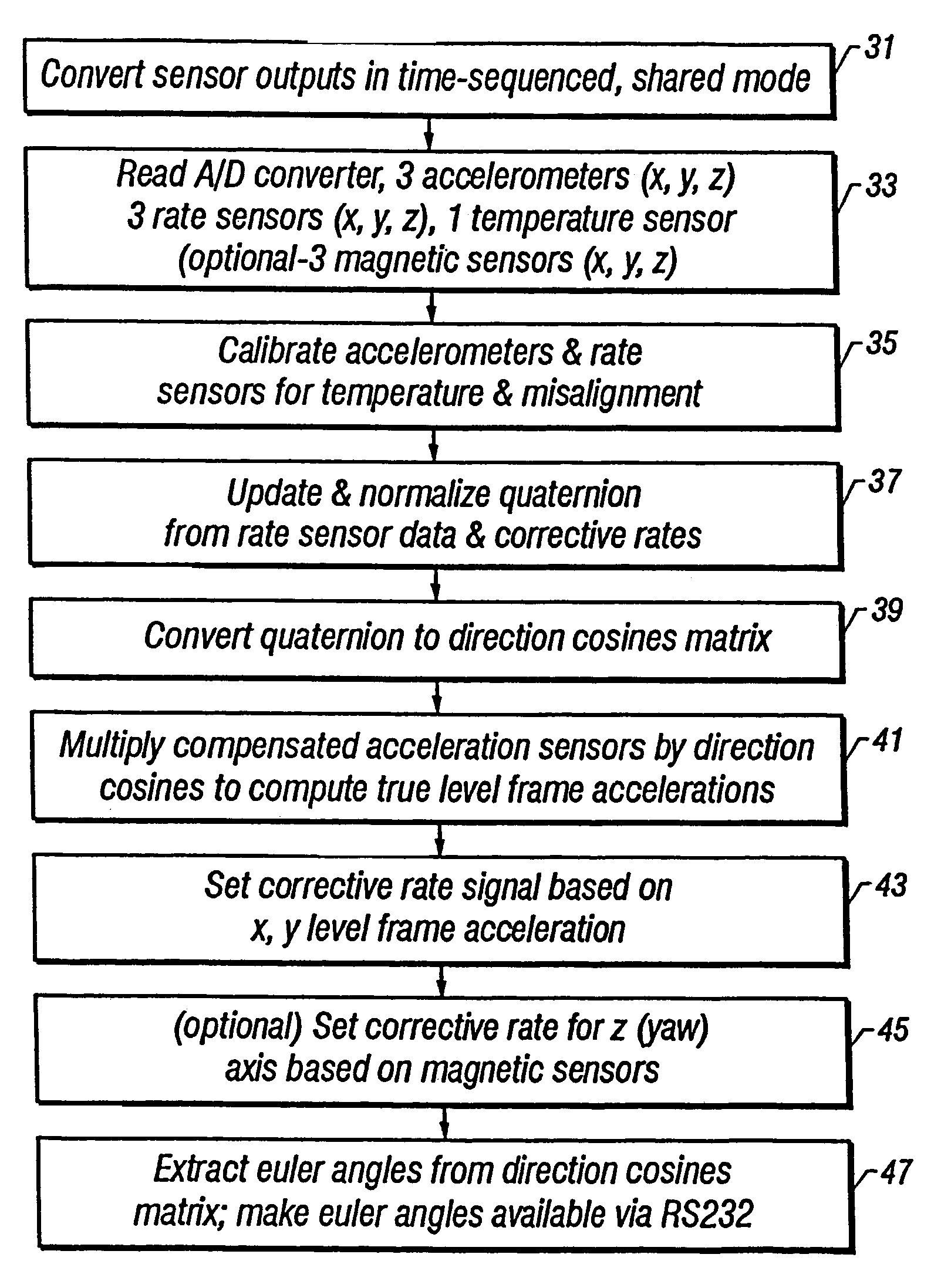
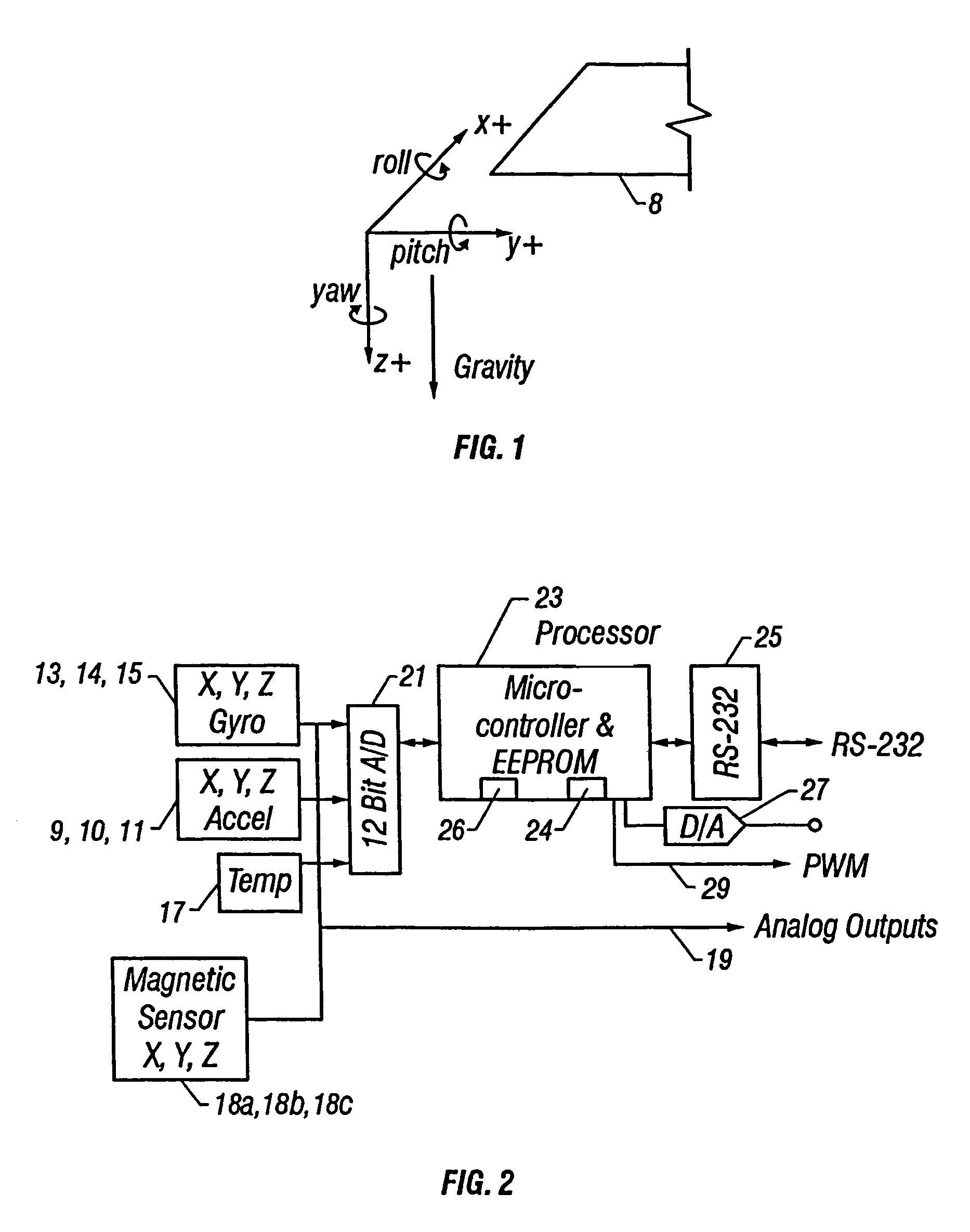
InactiveUS7216055B1Accurate representationHighly accurate output dataNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsDigital computer detailsAngular rate sensorKalman filter
A method and system senses the attitude of an accelerating object by measuring acceleration with accelerometers in three orthogonal axes and measuring angular rate with angular rate sensors disposed about each such axis to compute attitude of the object accurately relative to a vertical axis. A processor updates a quaternion representation of attitude based upon the angular rate of the object, and a corrective rate signal is determined from level frame acceleration as a reference for a Kalman filter in calculating the attitude of the object. When velocity or airspeed is available from an external source, an aiding algorithm is employed to provide accurate attitude representations throughout all flight regimes.
Owner:ACEINNA TRANSDUCER SYST CO LTD
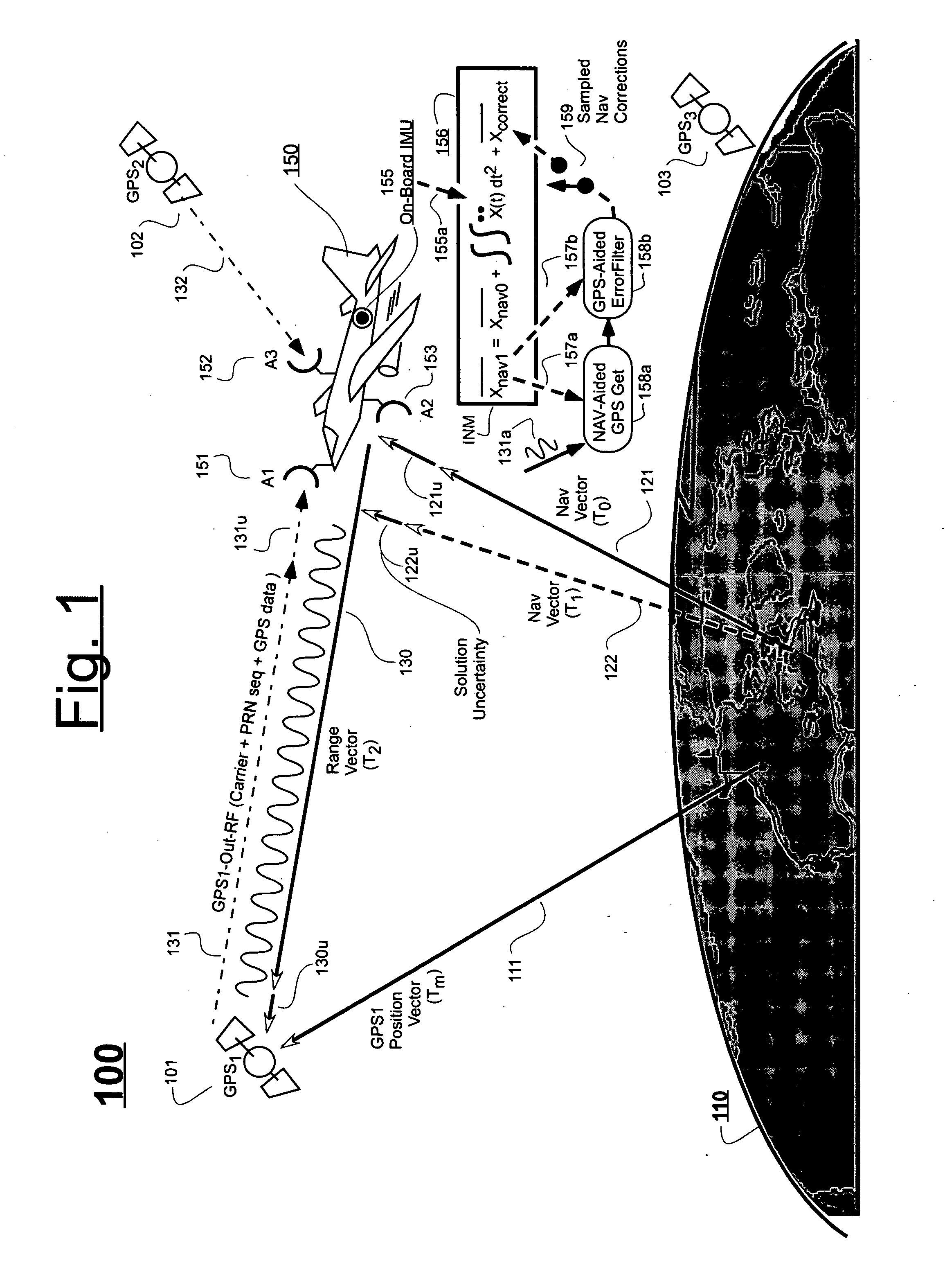
Inertial GPS navigation system with modified kalman filter
ActiveUS7193559B2Eliminate the effects ofShorten the timeAcceleration measurement using interia forcesNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsPhase differenceDirect observation
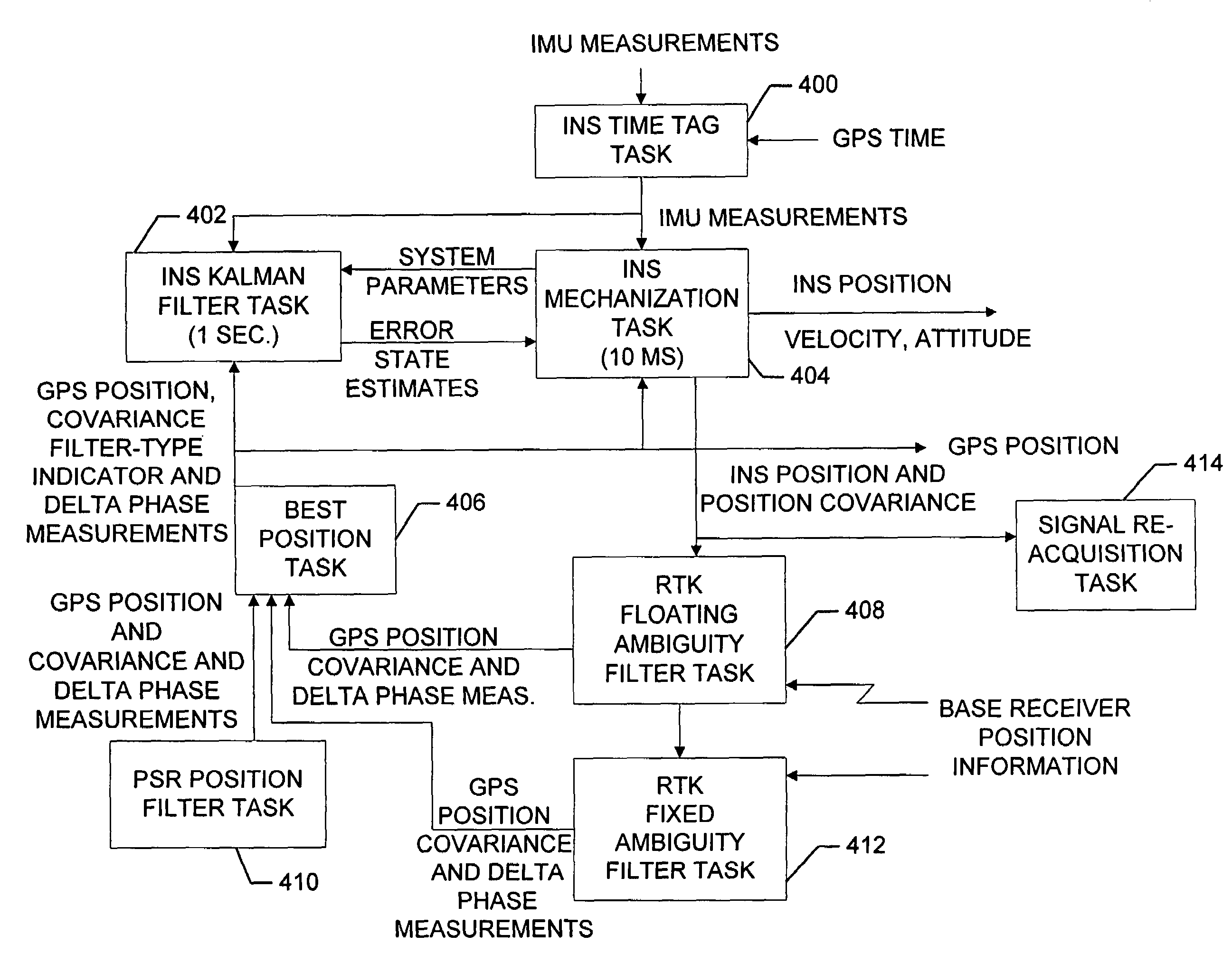
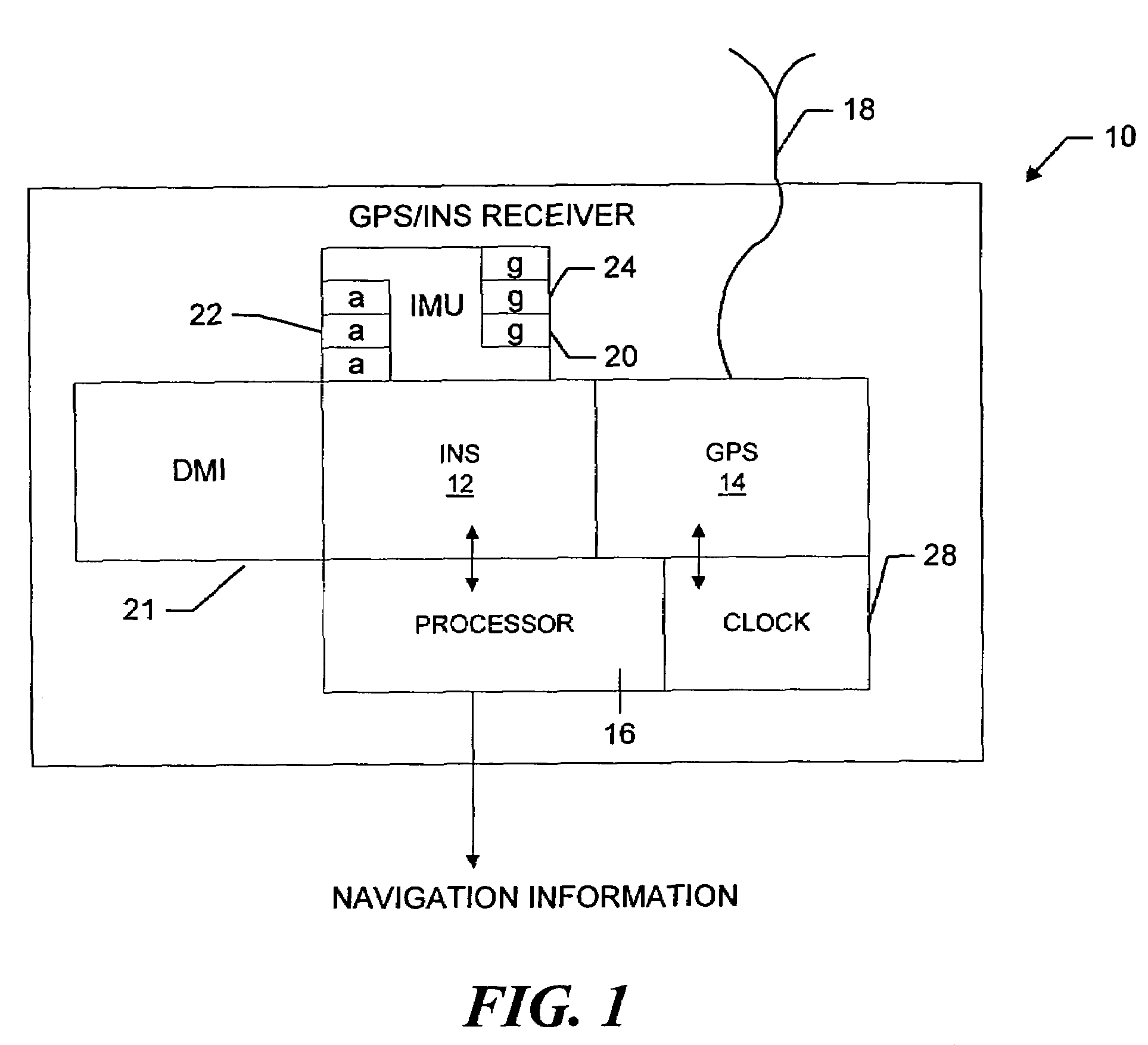
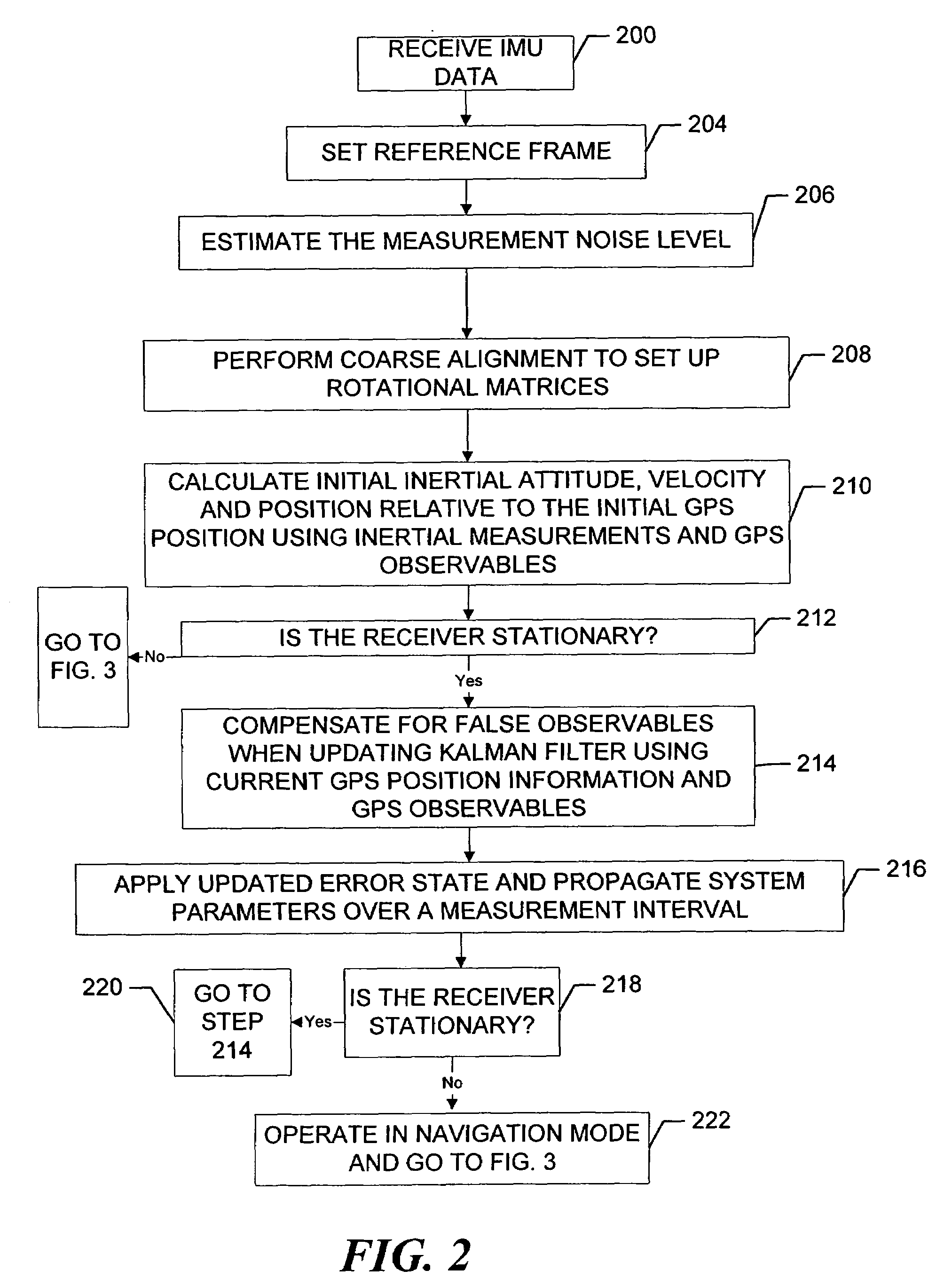
An inertial (“INS”) / GPS receiver includes an INS sub-system which incorporates, into a modified Kalman filter, GPS observables and / or other observables that span previous and current times. The INS filter utilizes the observables to update position information relating to both the current and the previous times, and to propagate the current position, velocity and attitude related information. The GPS observable may be delta phase measurements, and the other observables may be, for example, wheel pick-offs (or counts of wheel revolutions) that are used to calculate along track differences, and so forth. The inclusion of the measurements in the filter together with the current and the previous position related information essentially eliminates the effect of system dynamics from the system model. A position difference can thus be formed that is directly observable by the phase difference or along track difference measured between the previous and current time epochs. Further, the delta phase measurements can be incorporated in the INS filter without having to maintain GPS carrier ambiguity states. The INS sub-system and the GPS sub-system share GPS and INS position and covariance information. The receiver time tags the INS and any other non-GPS measurement data with GPS time, and then uses the INS and GPS filters to produce INS and GPS position information that is synchronized in time. The GPS / INS receiver utilizes GPS position and associated covariance information and the GPS and / or other observables in the updating of the INS filter. The INS filter, in turn, provides updated system error information that is used to propagate inertial current position, velocity and attitude information. Further, the receiver utilizes the inertial position, velocity and covariance information in the GPS filters to speed up GPS satellite signal re-acquisition and associated ambiguity resolution operations
Owner:NOVATEL INC
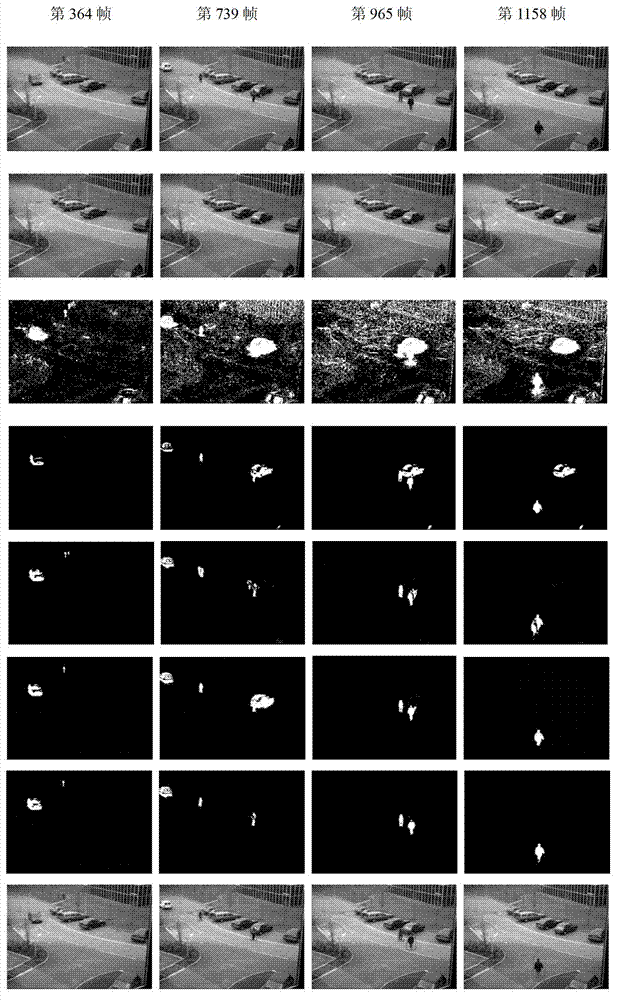
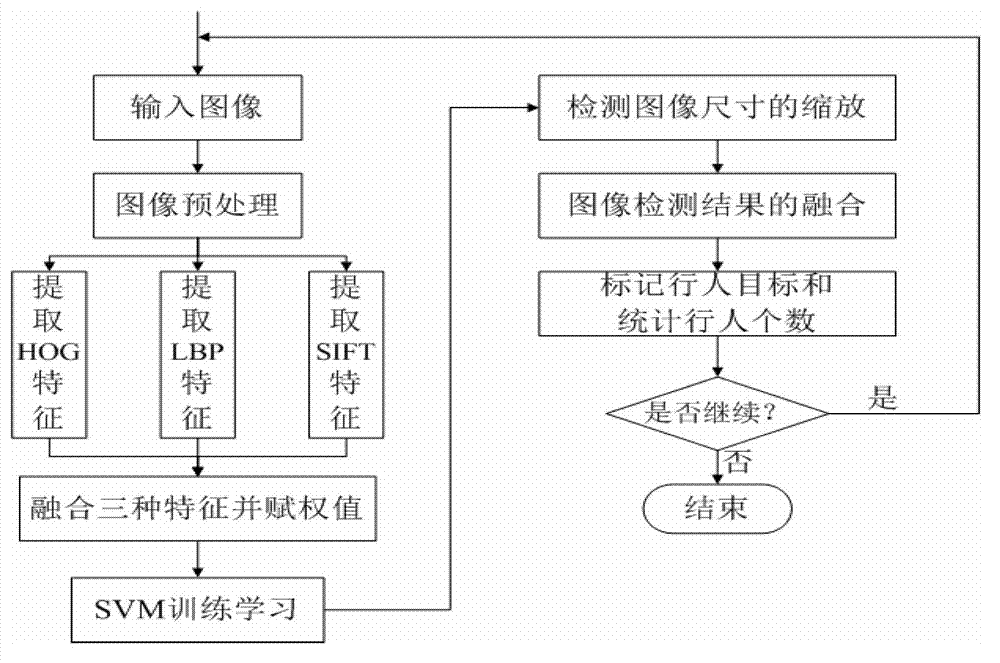
Improved weighting region matching high-altitude video pedestrian recognizing method
InactiveCN103049751ARealize precise identificationSmall targetCharacter and pattern recognitionContext sensingSubway station
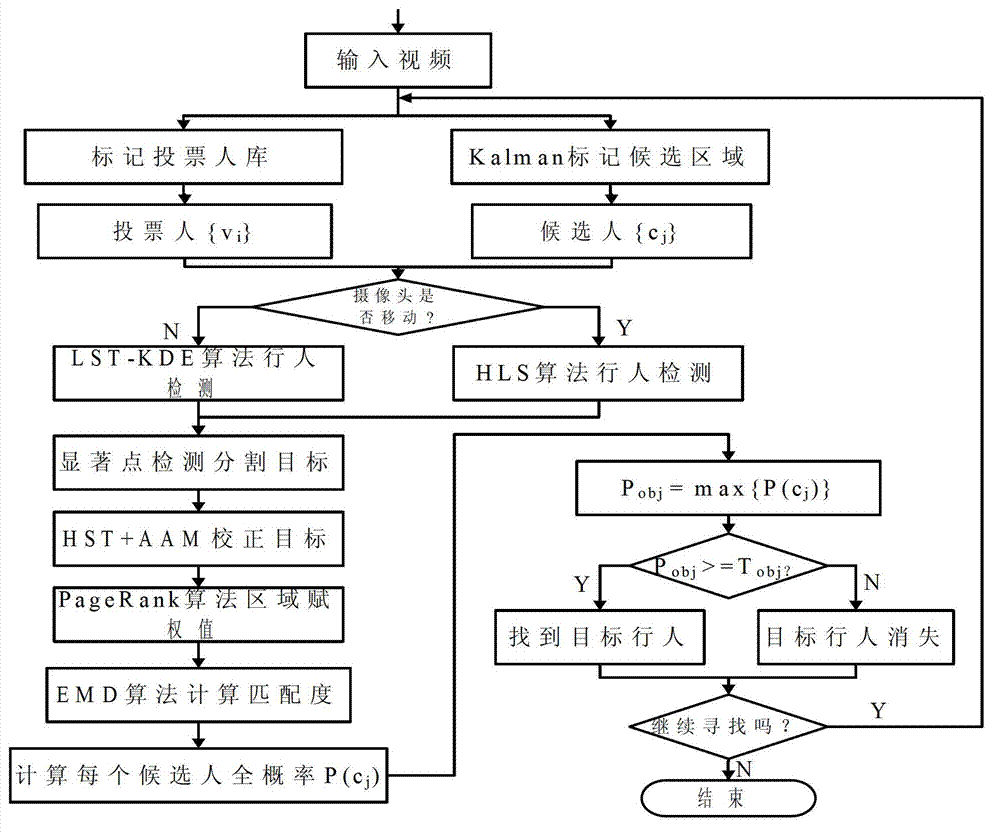
The invention discloses an improved weighting region matching high-altitude video pedestrian recognizing method (KS-WRM (KS-weighting matching region)). The improvement is reflected as follows: 1) confirming a candidate region by utilizing Kalman filtering; 2) fixing a camera or not by adopting different pedestrian detecting strategies; 3) proposing a pedestrian detecting method of an HLS (hue, lightness and saturation) model with multi-characteristic fusion; and 4) dividing pedestrians based on CA obvious region detection of context sensing. According to the invention, pedestrians can be recognized accurately under complex occasions of blur details, complex backgrounds, noise influences and the like. And the improved weighting region matching high-altitude video pedestrian recognizing method (KS-WRM) provided by the invention can be used for pedestrian detection and recognition at places with high visitor flow rate, such as remote sensing satellite images, malls, subway stations, railway stations, airports, as well as intelligent traffic control, intelligent vehicle auxiliary driving, pedestrian flow rate statistics and analysis places.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
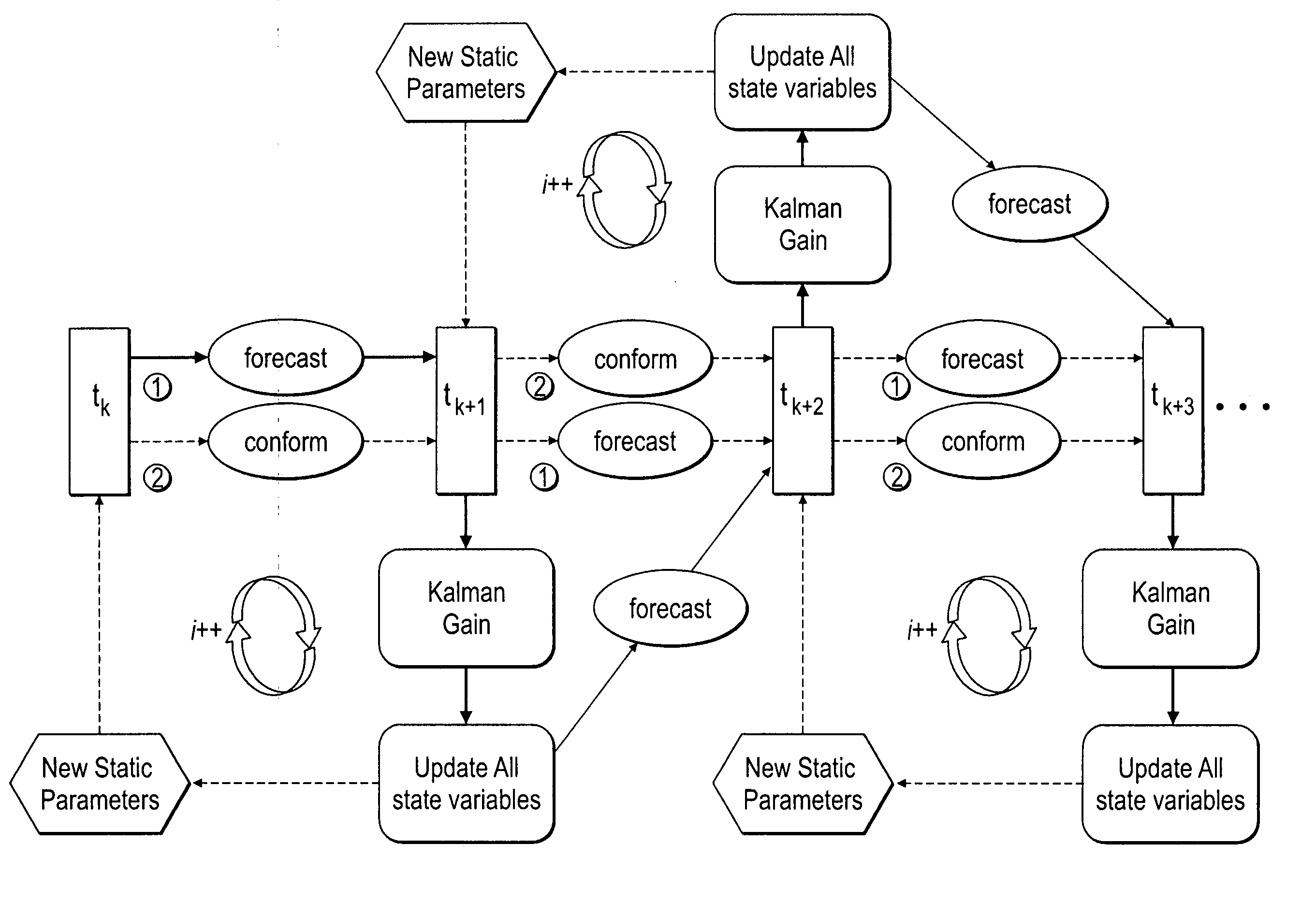
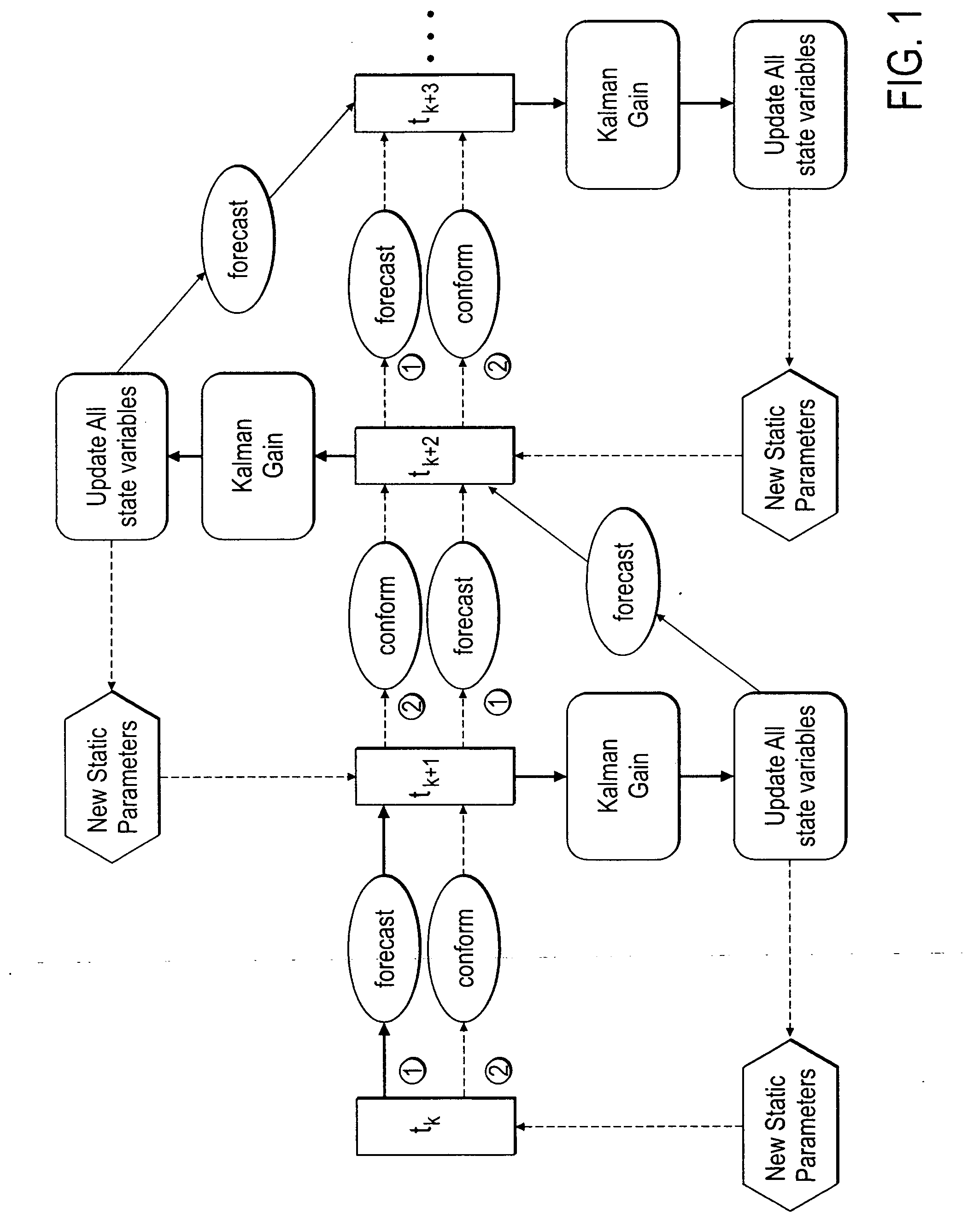
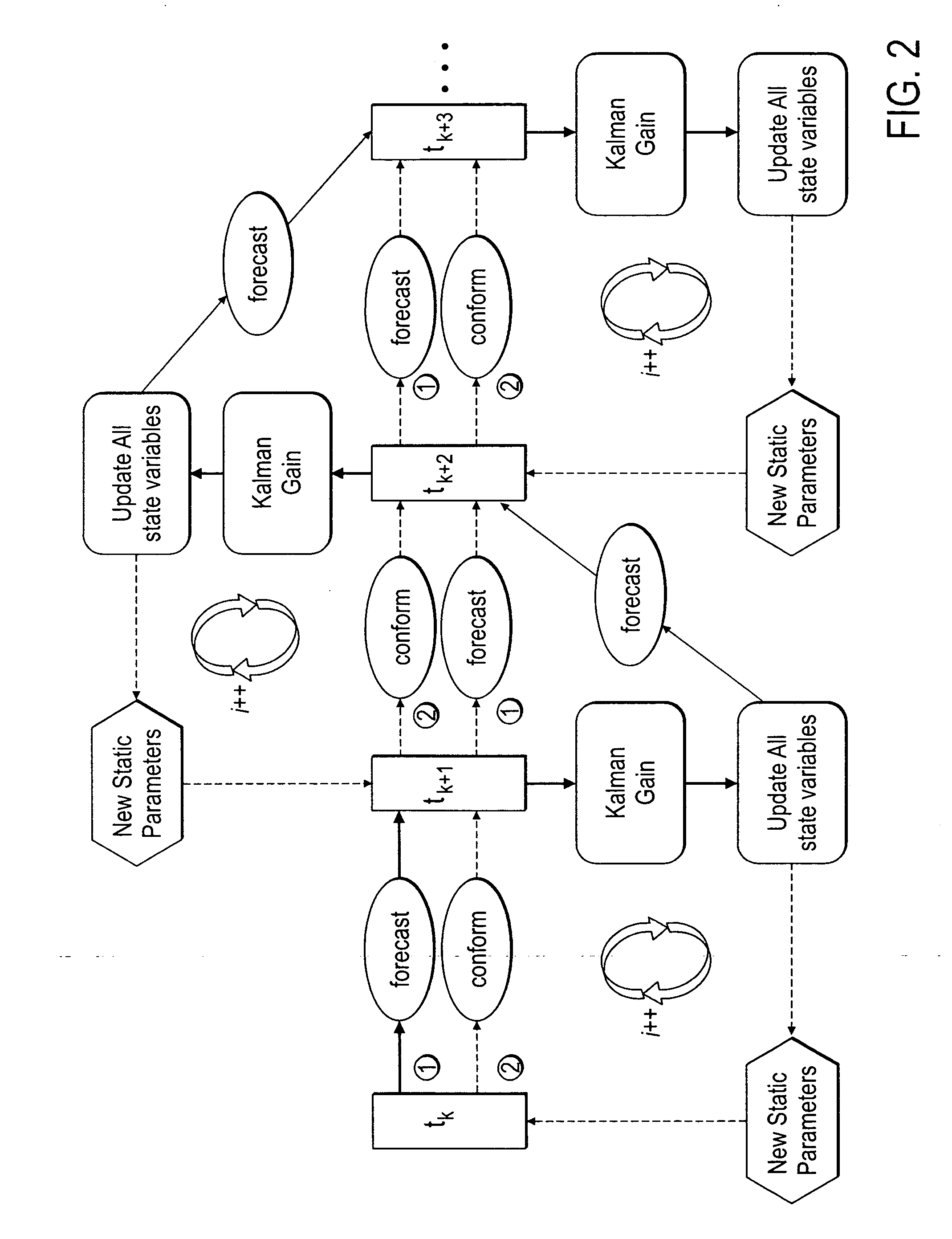
Method, system and apparatus for real-time reservoir model updating using ensemble Kalman filter
ActiveUS20070118346A1Reduce in quantityEnsure correct executionFluid removalComputation using non-denominational number representationKaiman filterState variable
A method, system and apparatus for real-time reservoir model updating using ensemble Kalman filters is described. The method includes a conforming step for bring bringing static and dynamic state variables into conformance with one another during a time step of the updating. Also, an iterative damping method is used in conjunction with the conformance step to account for nonGaussian and nonlinear features in a system. Also, a re-sampling method is described which reduces the ensemble size of reservoir models which are to be updated.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Unscented Kalman filter-based method for tracking inertial pose according to acceleration compensation
InactiveCN101726295AAvoid errorsThe estimate is accurateNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsAccelerometerGyroscope
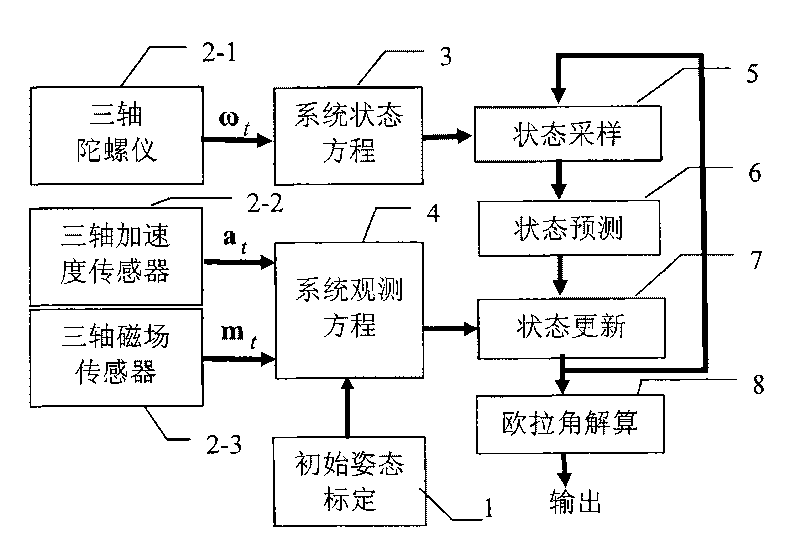
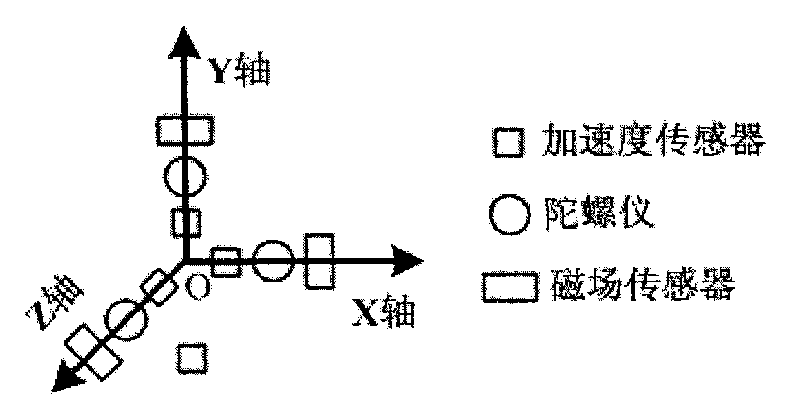
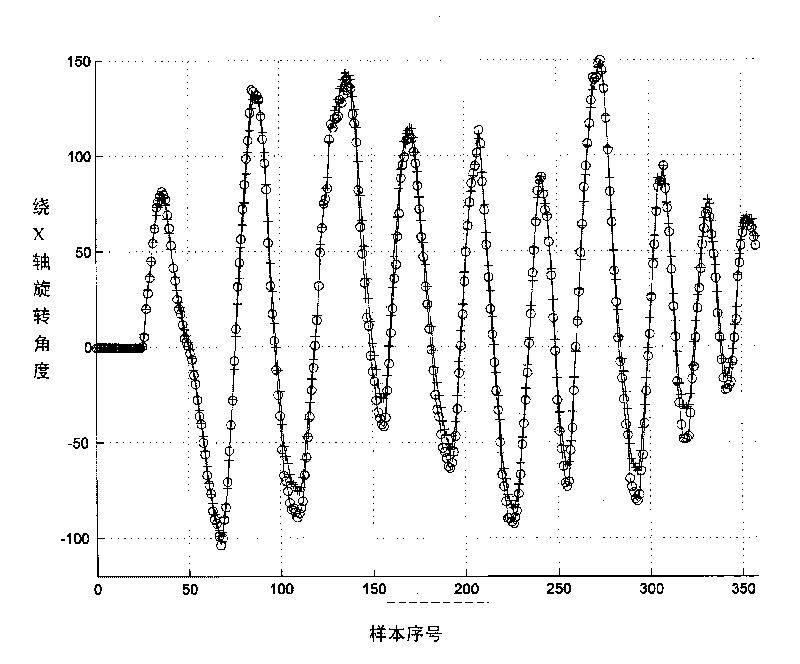
The invention provides an unscented Kalman filter-based method for tracking an inertial pose according to acceleration compensation, which is used for an inertial measurement unit integrating a three-axis micro-gyroscope, a three-axis micro-accelerometer and a three-axis magnetoresistive sensor, and realizes pose tracking estimation on a device carrier by using rotary angular velocity vectors, acceleration vectors and magnetic field sensor vectors which are detected by the device by means of filter technology. The method comprises the following steps: 1) treating the acceleration vectors as combination of the acceleration vectors and gravity acceleration vectors of the device carrier self, and constructing observation equations respectively for amplitude and normalized direction vectors of the acceleration vectors and the gravity acceleration vectors; 2) describing quaternion, accumulated error vectors of the gyroscope and the acceleration vectors of the device carrier self by using the pose to construct a system state vector; and 3) realizing a filter estimating process of the system by using the unscented Kalman filter technology because of nonlinearity of the observation equations. Compared with the conventional method ignoring the acceleration of the carrier self, the method not only can provide a more accurate estimation result, but also widens the application range of the system.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Position-tracking system
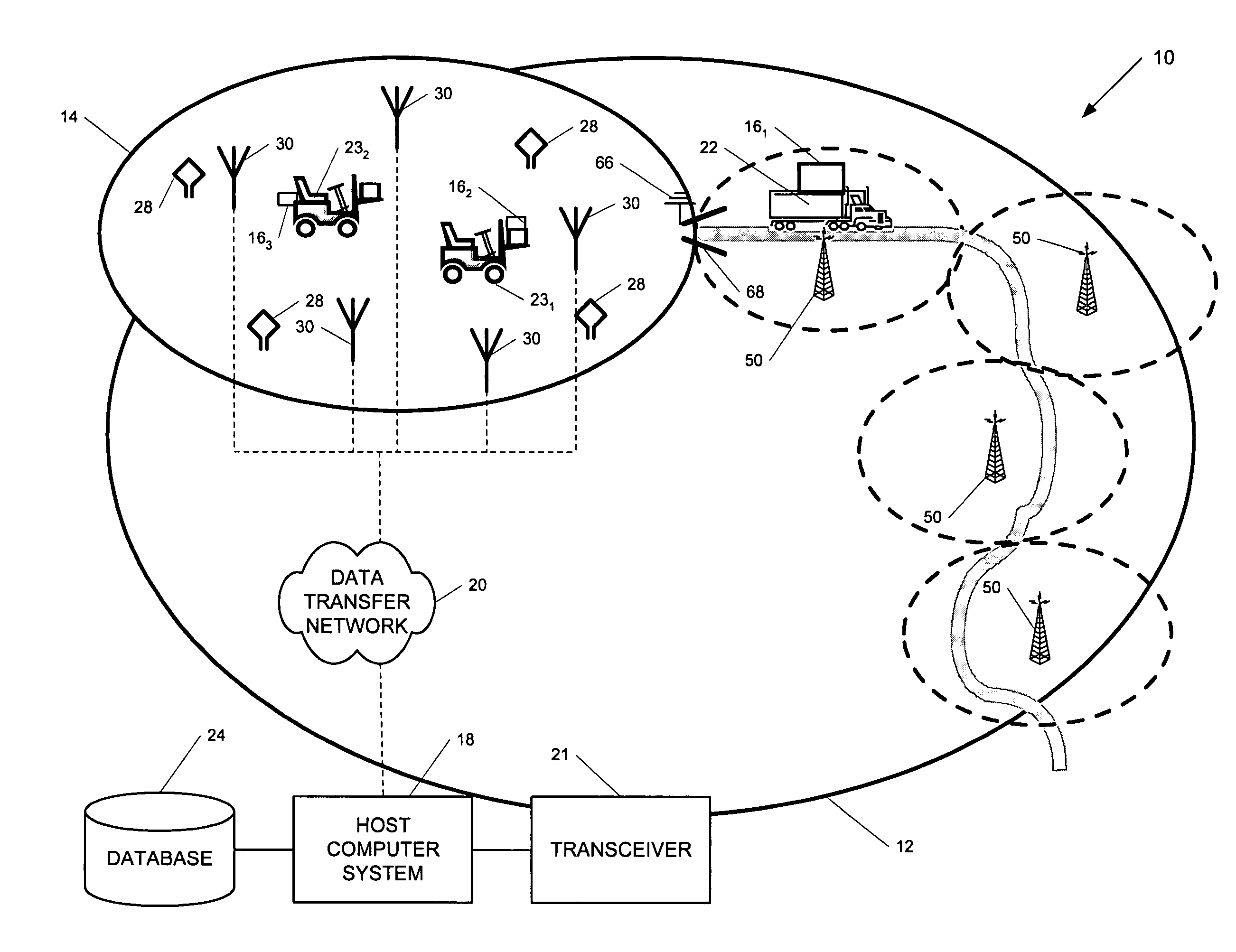
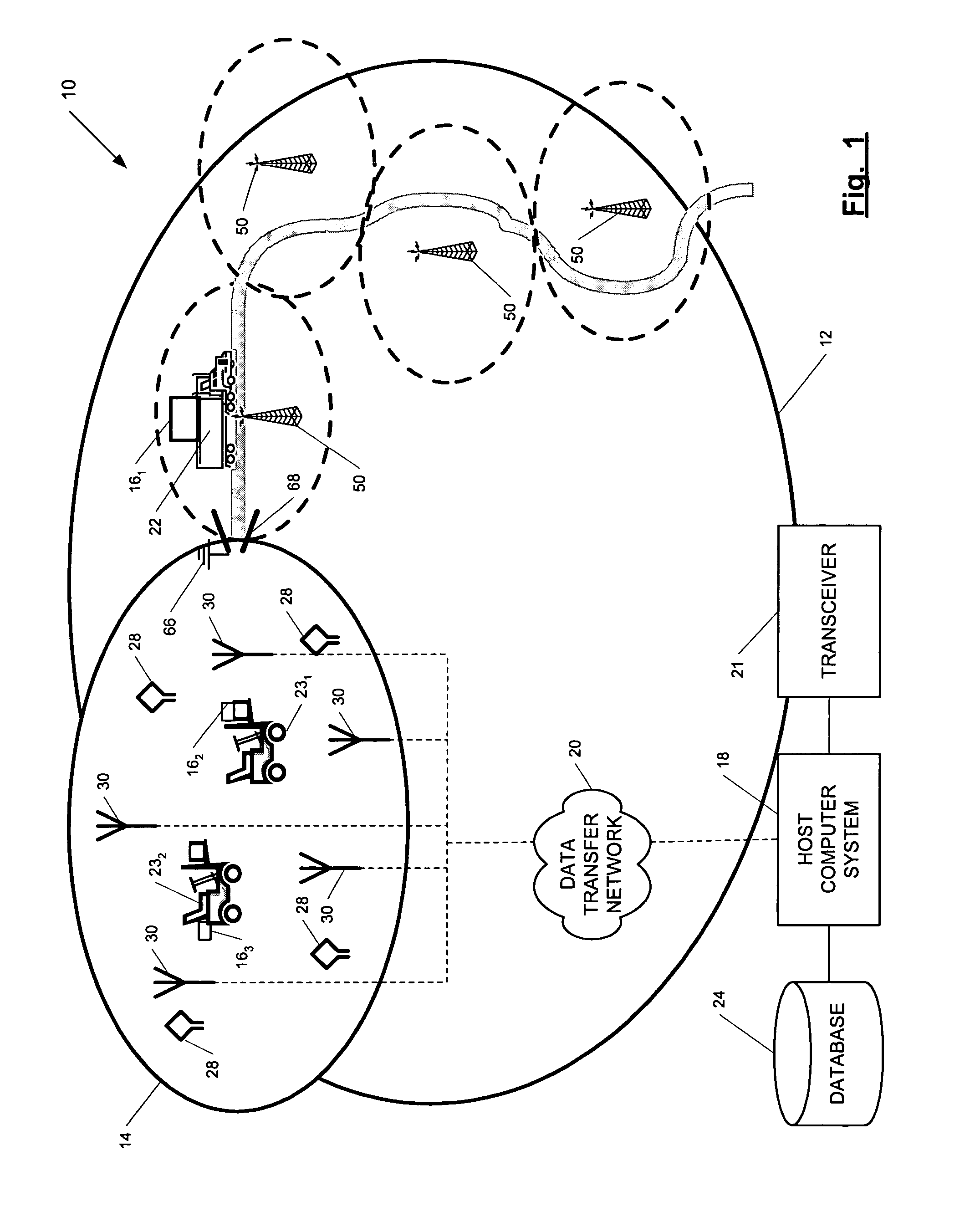
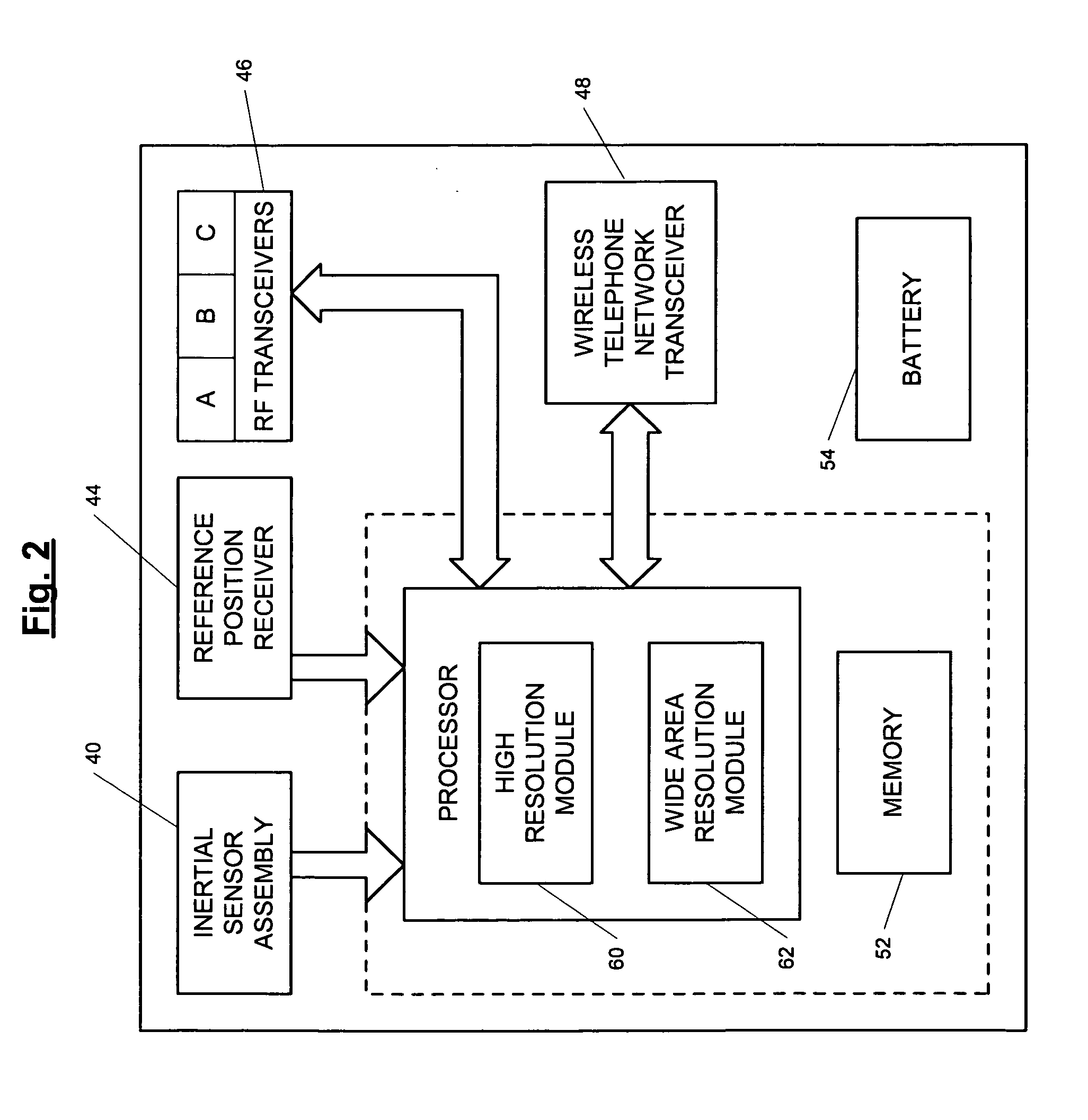
ActiveUS7236091B2High position resolutionImprove accuracyRoad vehicles traffic controlElectric/electromagnetic visible signallingObject basedTransceiver
A position-tracking system for tracking the position of an object is disclosed. According to various embodiments, the tracking system includes a tracking device that is connected to or otherwise affixed to the object to be tracked. The tracking device may include, among other things, an inertial sensor assembly, radio transceivers and a processor. The position tracking system may also include a host processing system that is in communication with the tracking device. The position tracking system may provide variable-resolution position information based on the environment in which the object is moving. In a “wide resolution” area, the system may compute a general position for the object based on a wireless telephone network Cell-ID / map correlation architecture. In a high-resolution area, greater position resolution may be realized from the combination of a wireless aiding system and inputs from the inertial sensors. In the high-resolution mode, the system may exploit distinct patterns of motion that can be identified as motion “signatures” that are characteristic of certain types of motion. Kinematic (or object movement) models may be constructed based on these motion signatures and the position tracking system may estimate the state of the object based on the kinematic model for the current mode of the object. Adaptive and cascaded Kalman filtering may be employed in the analysis to more accurately estimate the position and velocity of the object based on the motion pattern identified.
Owner:PINC SOLUTIONS
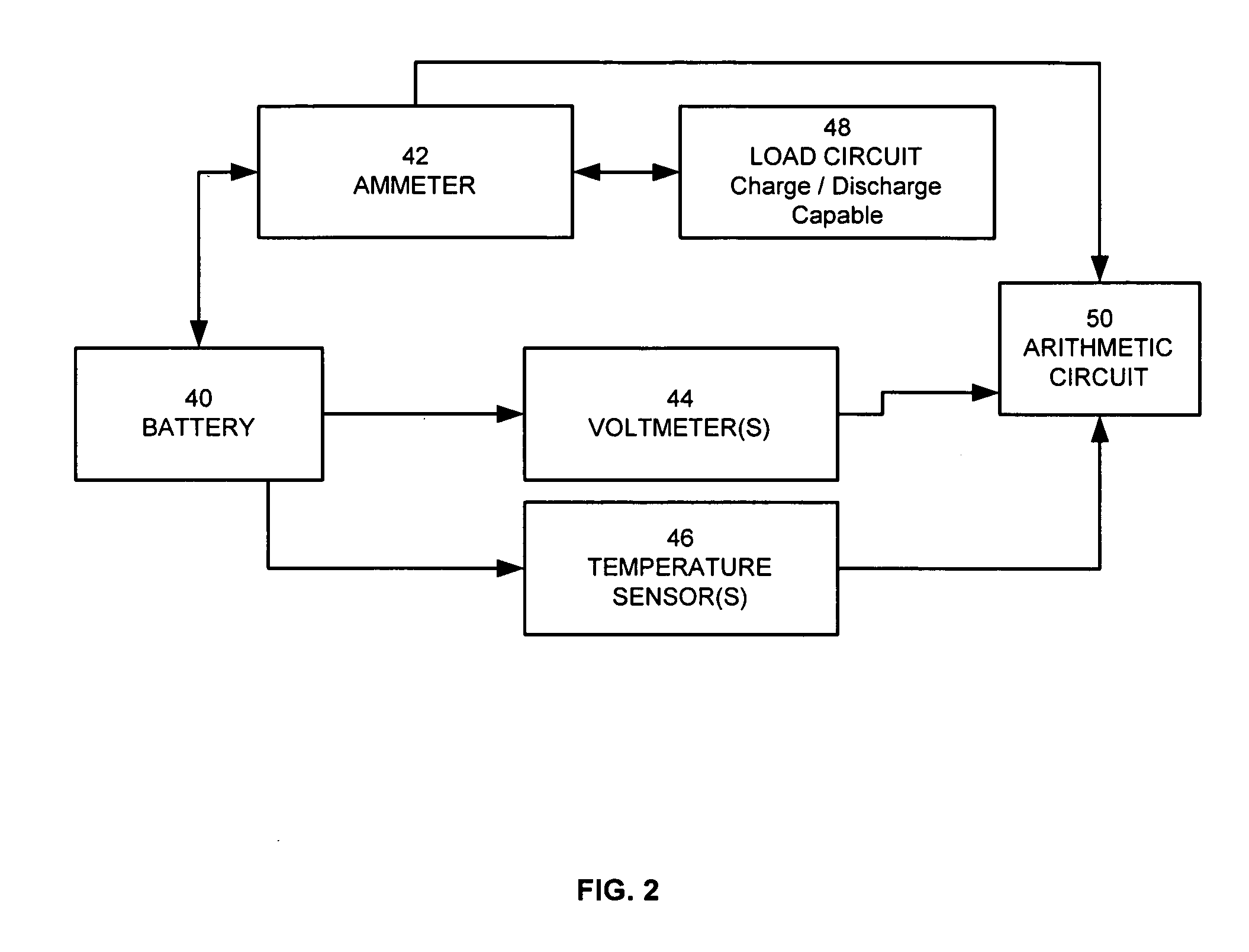
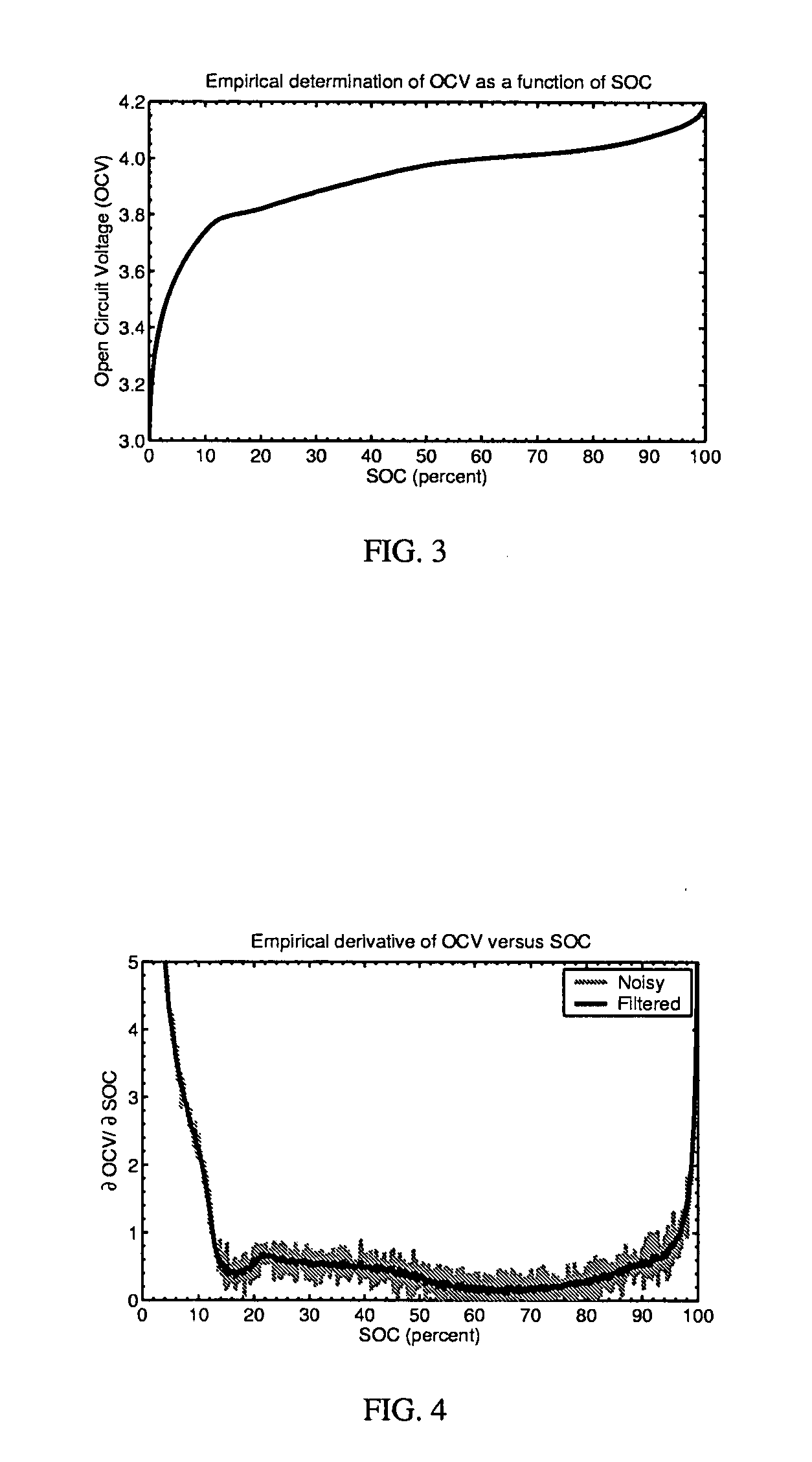
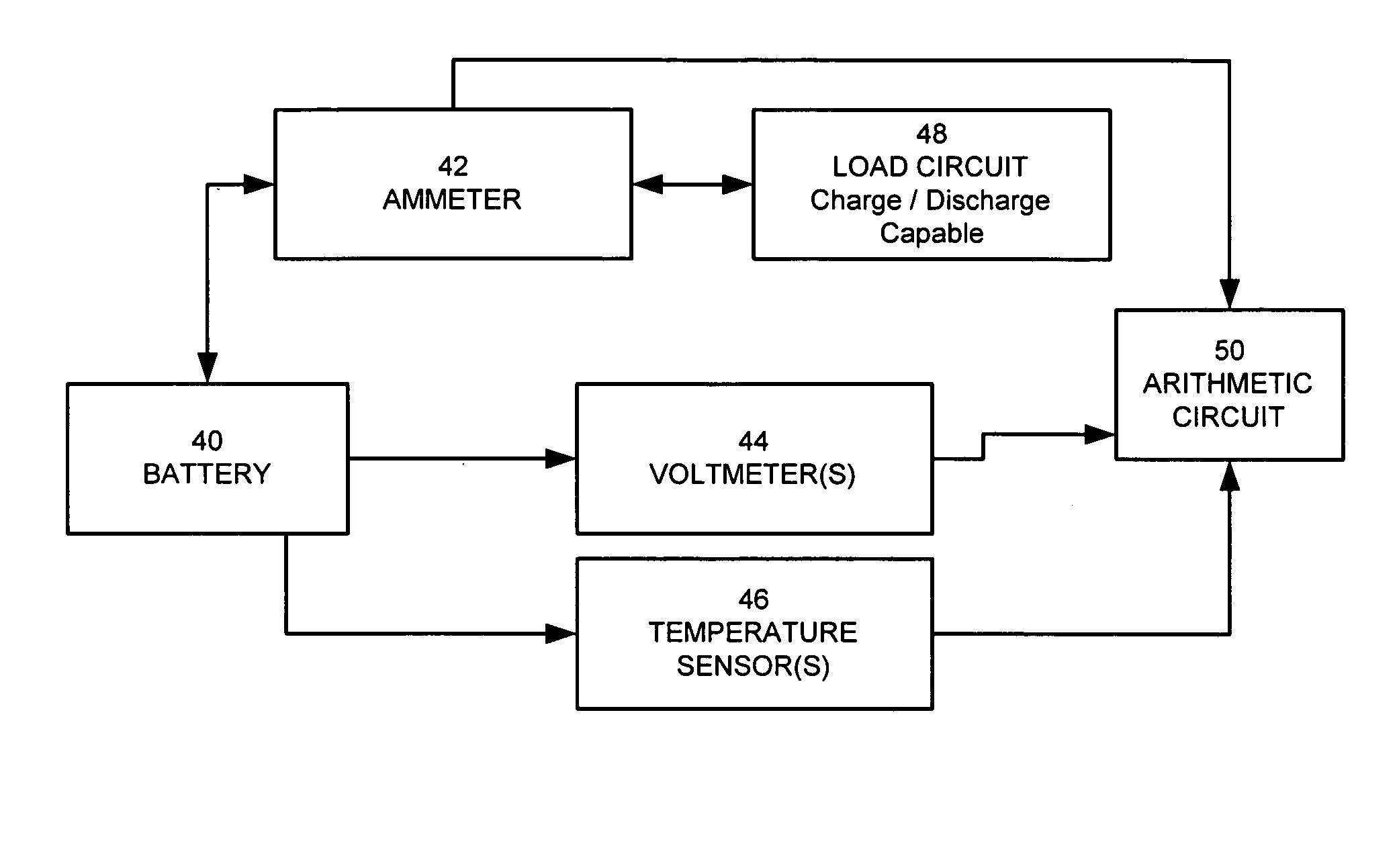
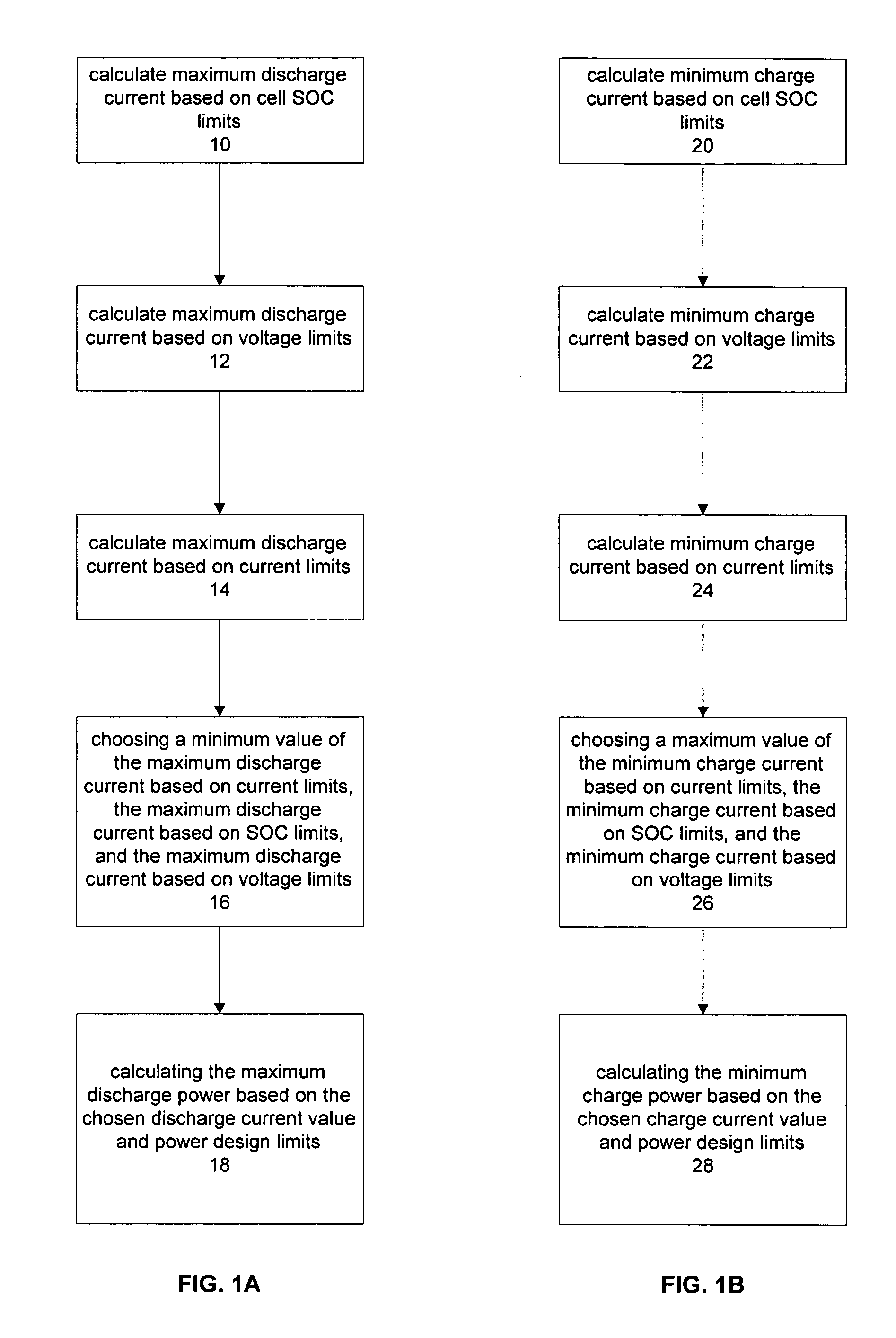
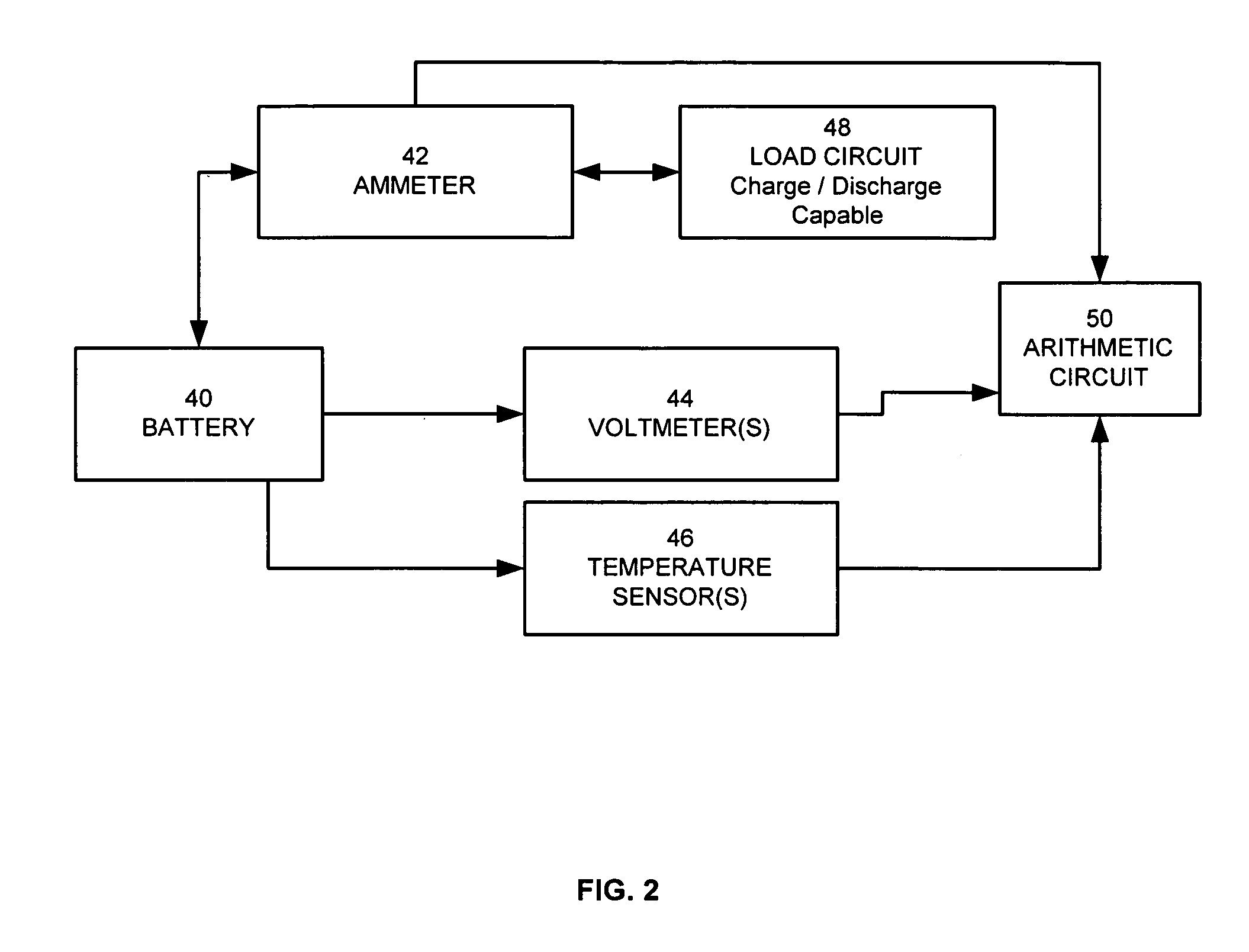
Method for calculating power capability of battery packs using advanced cell model predictive techniques
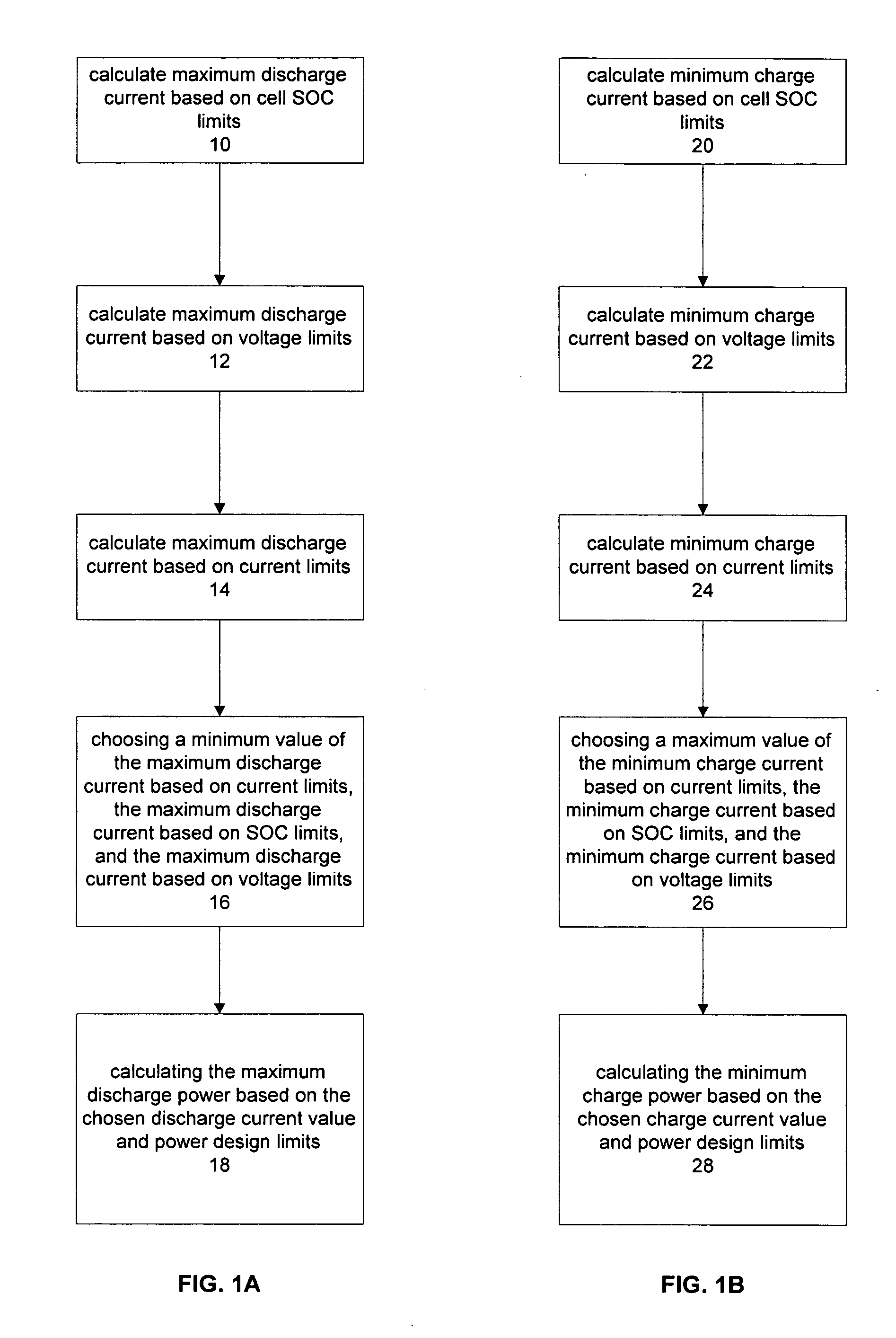
ActiveUS20050110498A1Batteries circuit arrangementsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPower capabilityElectrical battery
The present invention relates to a method and an apparatus for estimating discharge and charge power of battery applications, including battery packs used in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEV) and Electric Vehicles (EV). One charge / discharge power estimating method incorporates voltage, state-of-charge (SOC), power, and current design constraints and works for a user-specified prediction time horizon Δt. At least two cell models are used in calculating maximum charge / discharge power based on voltage limits. The first is a simple cell model that uses a Taylor-series expansion to linearize the equation involved. The second is a more complex and accurate model that models cell dynamics in discrete-time state-space form. The cell model can incorporate a inputs such as temperature, resistance, capacity, etc. One advantage of using model-based approach is that the same model may be used in both Kalman-filtering to produce the SOC and the estimation of maximum charge / discharge current based on voltage limits.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
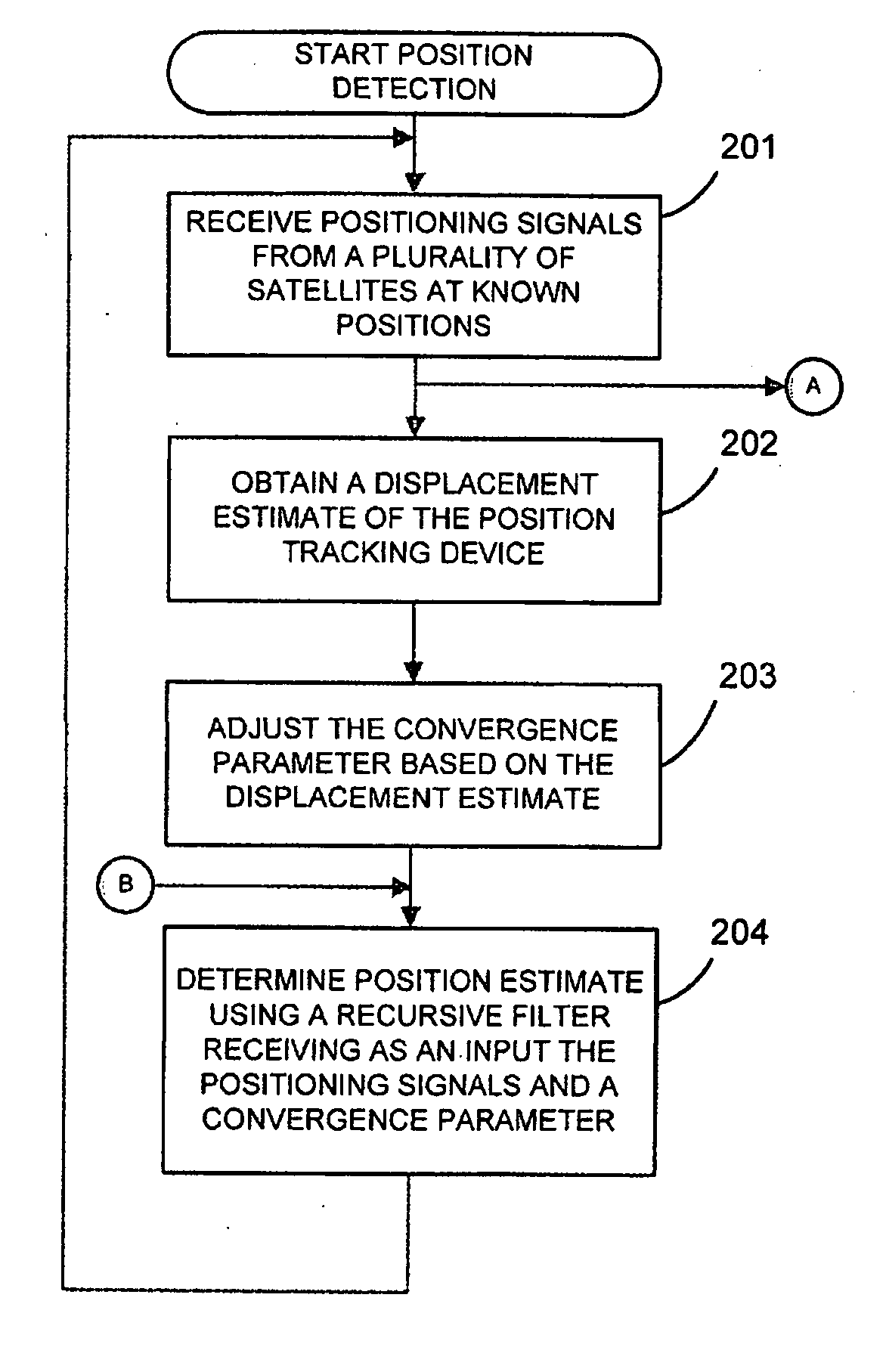
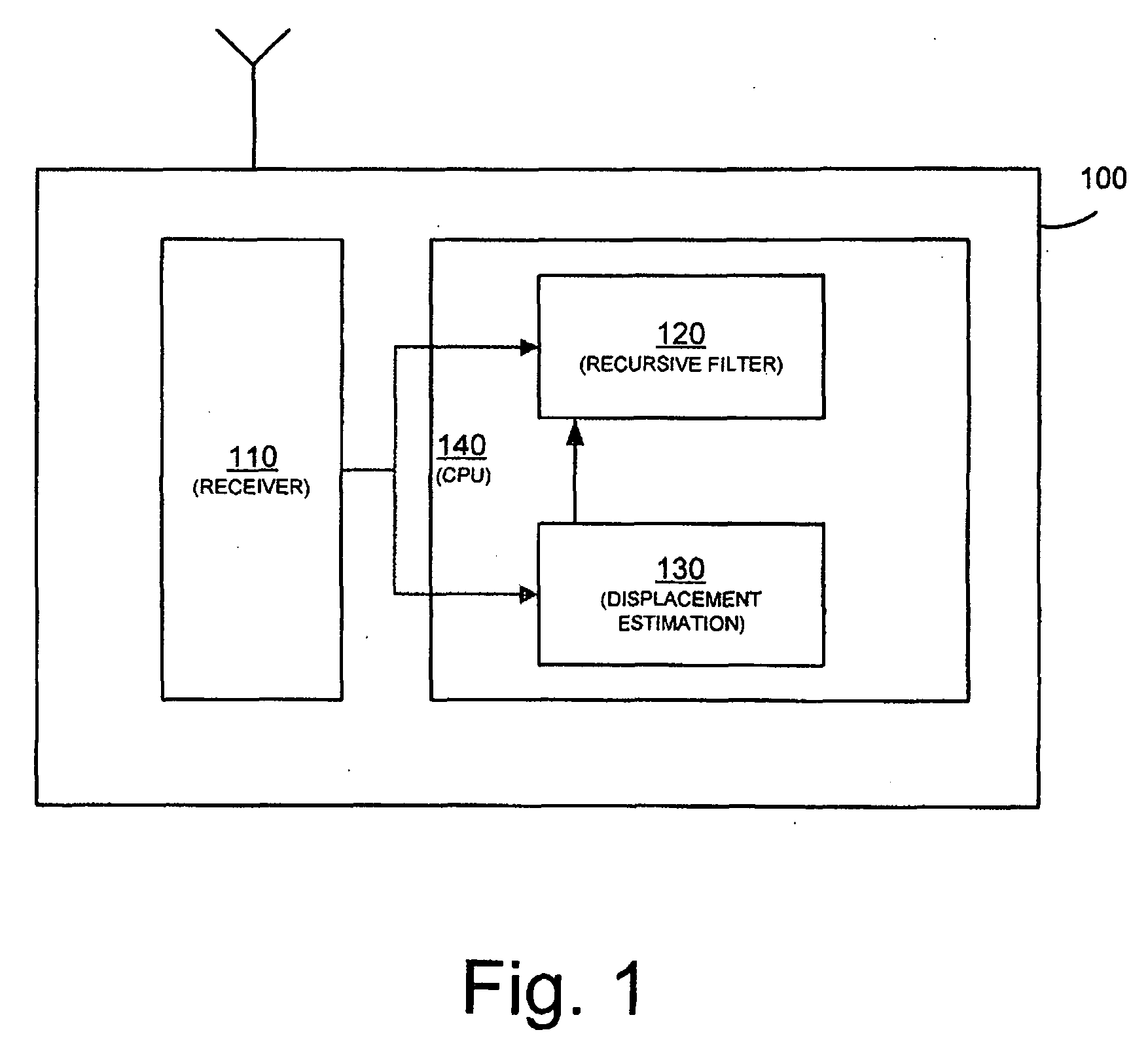
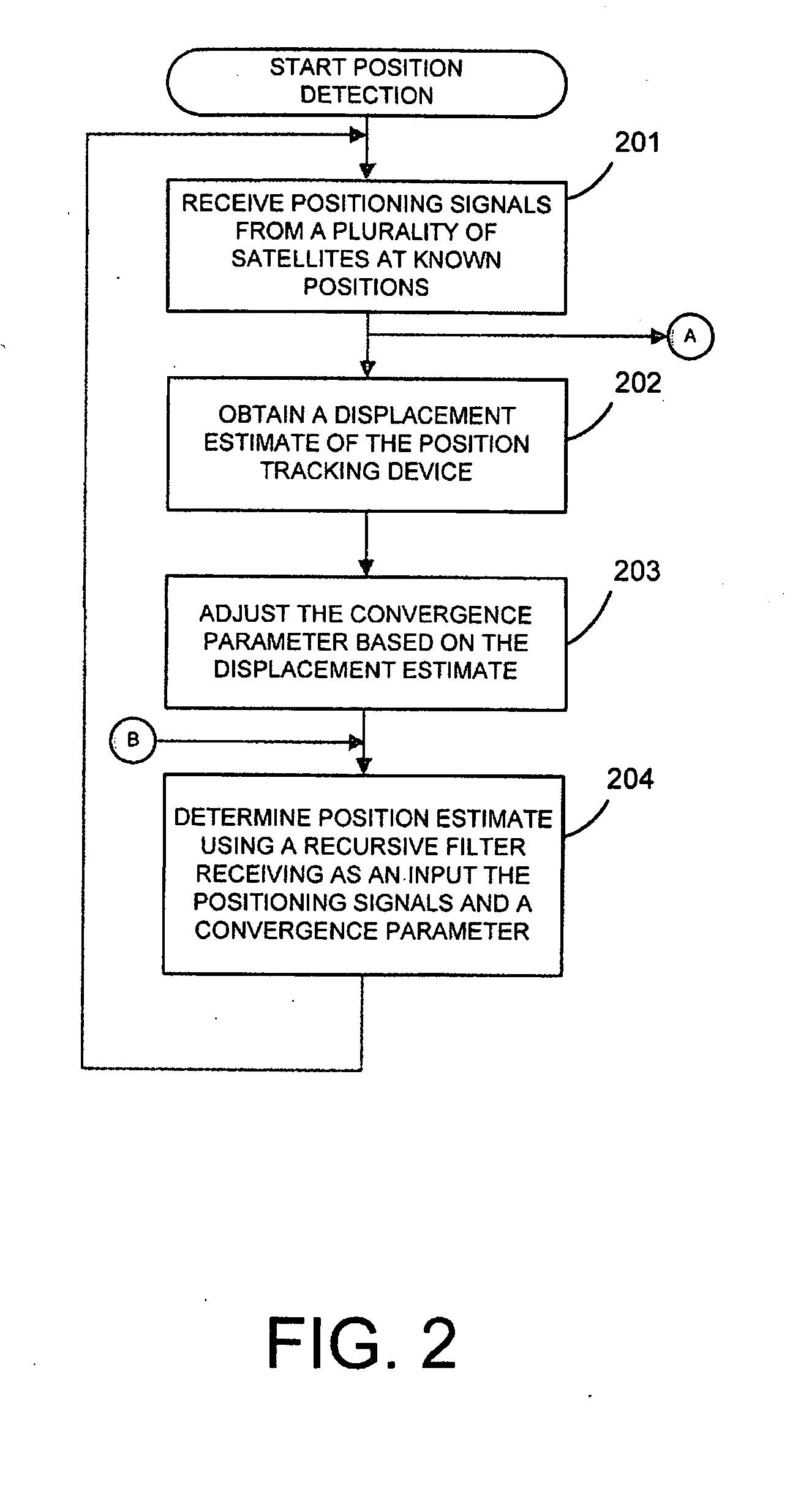
Position tracking device and method
ActiveUS20100141515A1Improve accuracyPosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingKaiman filterLocation tracking
The present application relates to tracking a position of a device, e.g. for detecting slow and rapid earth deformation, by making use of a recursive filter having the filter characteristic adapted to a detected type of motion. If the motion of the position tracking device is rapid, the filter characteristic is set such that the rapid motion can be tracked with the necessary speed. On the other hand, if the motion is slow, e.g. during times of a normal tectonic drift, the filter characteristic is set such that the motion is slowly tracked with the advantage of efficient noise reduction, i.e. noise in the input signal is effectively barred and does not pass through the filter to the output signal. Thus, in times of rapid motion the convergence speed of the filter output signal to the input signal is set high for fast convergence and in times of slow motion the convergence speed of the filter output signal to the input signal is set low for a slow convergence. The filter may be a Kalman filter.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
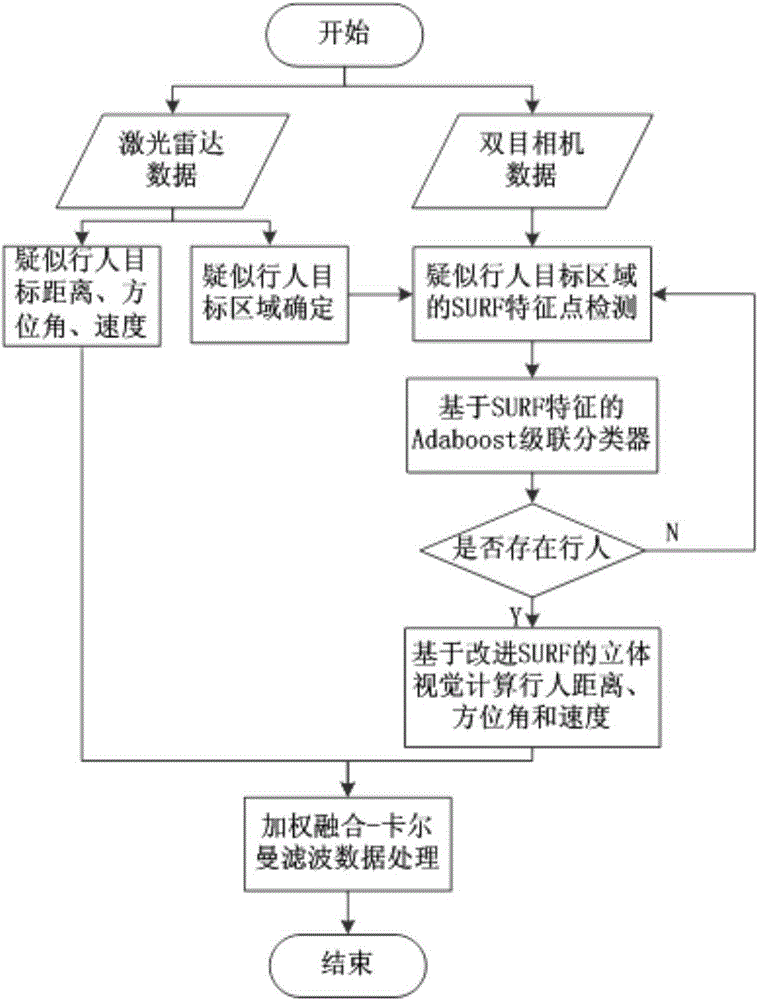
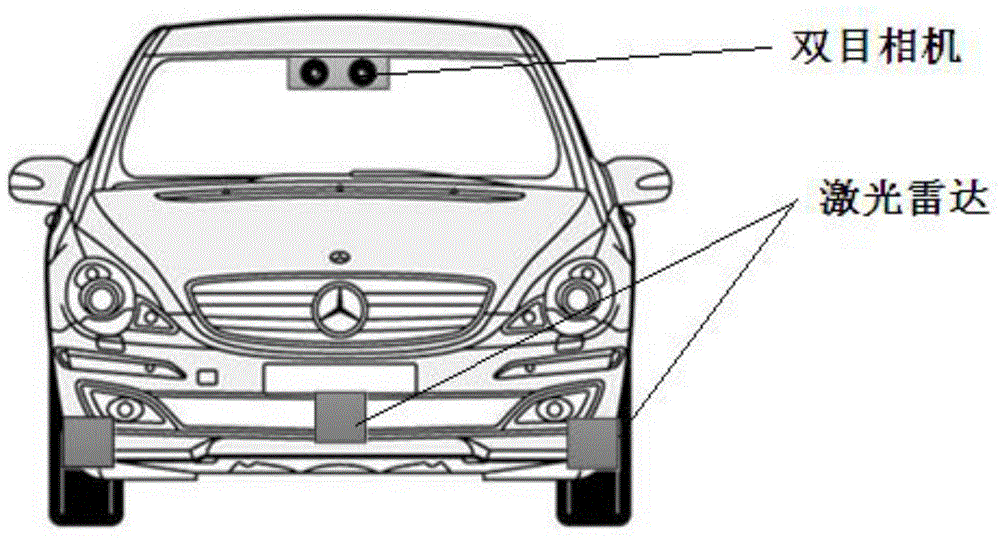
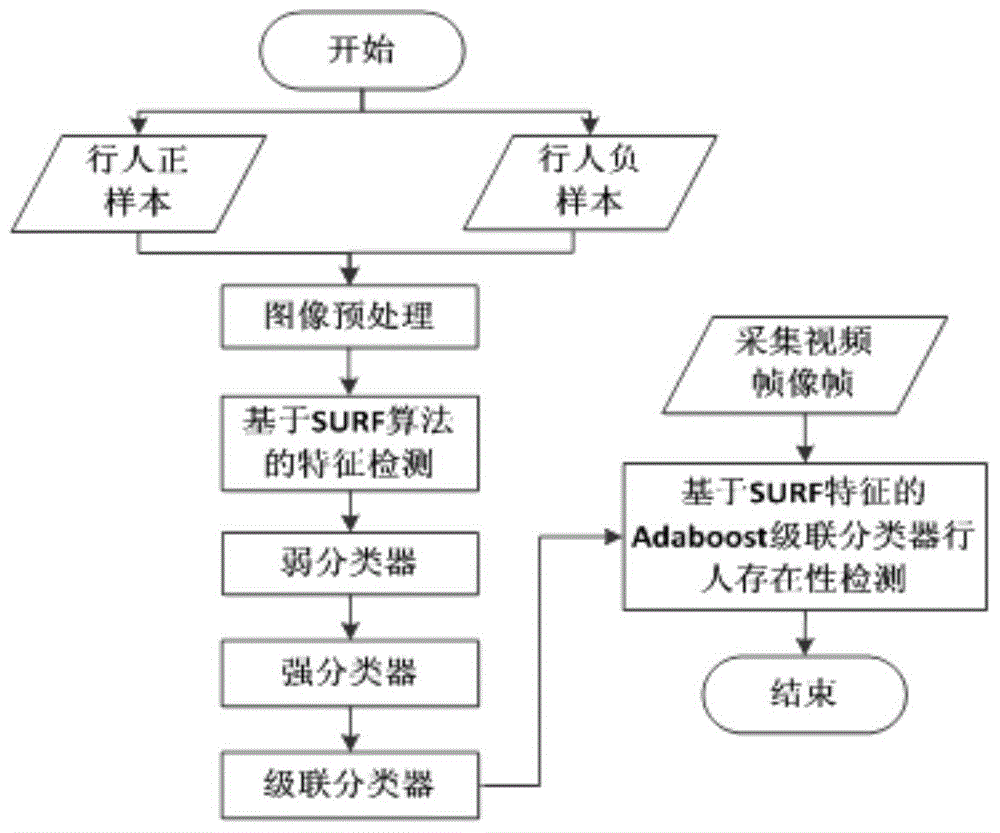
Detection method and system, based on laser radar and binocular camera, for pedestrian in front of vehicle
ActiveCN104573646AHigh measurement accuracyThe data is accurate and completeCharacter and pattern recognitionActive safetyVisual perception
The invention belongs to the field vehicle active safety, and particularly discloses a detection method and system, based on laser radar and binocular camera, for a pedestrian in front of vehicle. The method comprises the following steps: collection data of the front of the vehicle through the laser radar and the binocular camera; respectively processing the data collected by the laser radar and the binocular camera, so as to obtain the distance, azimuth angle and speed value of the pedestrian relative to the vehicle; correcting the information of the pedestrian through a Kalman filter. The method comprehensively utilizes a stereoscopic vision technology and a remote sensing technology, integrates laser radar and binocular camera information, is high in measurement accuracy and pedestrian detection accuracy, and can effectively reduce the occurrence rate of traffic accidents.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
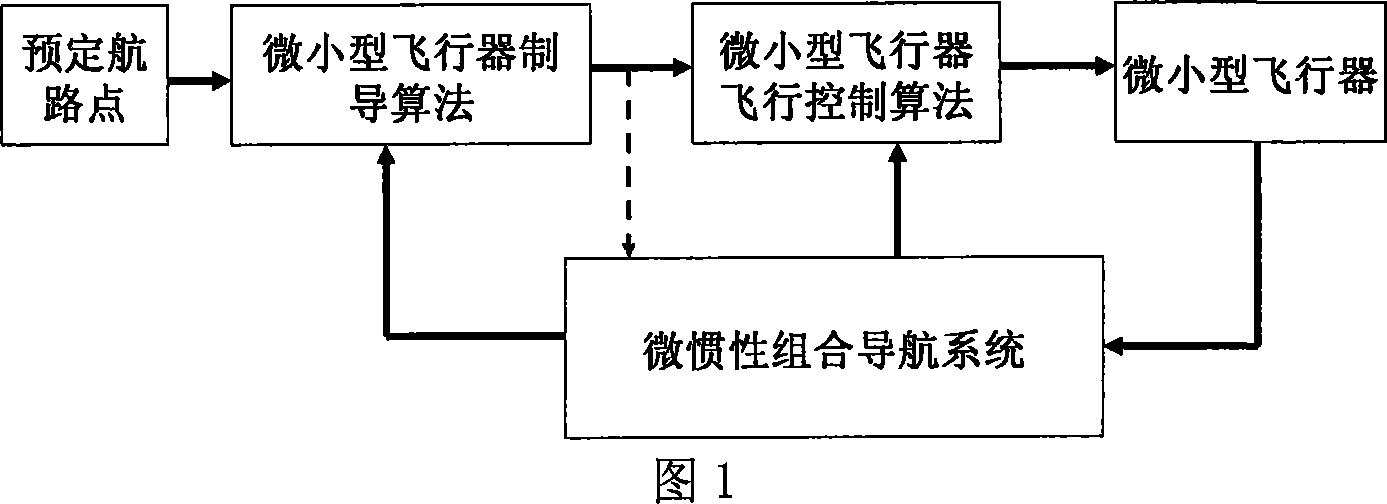
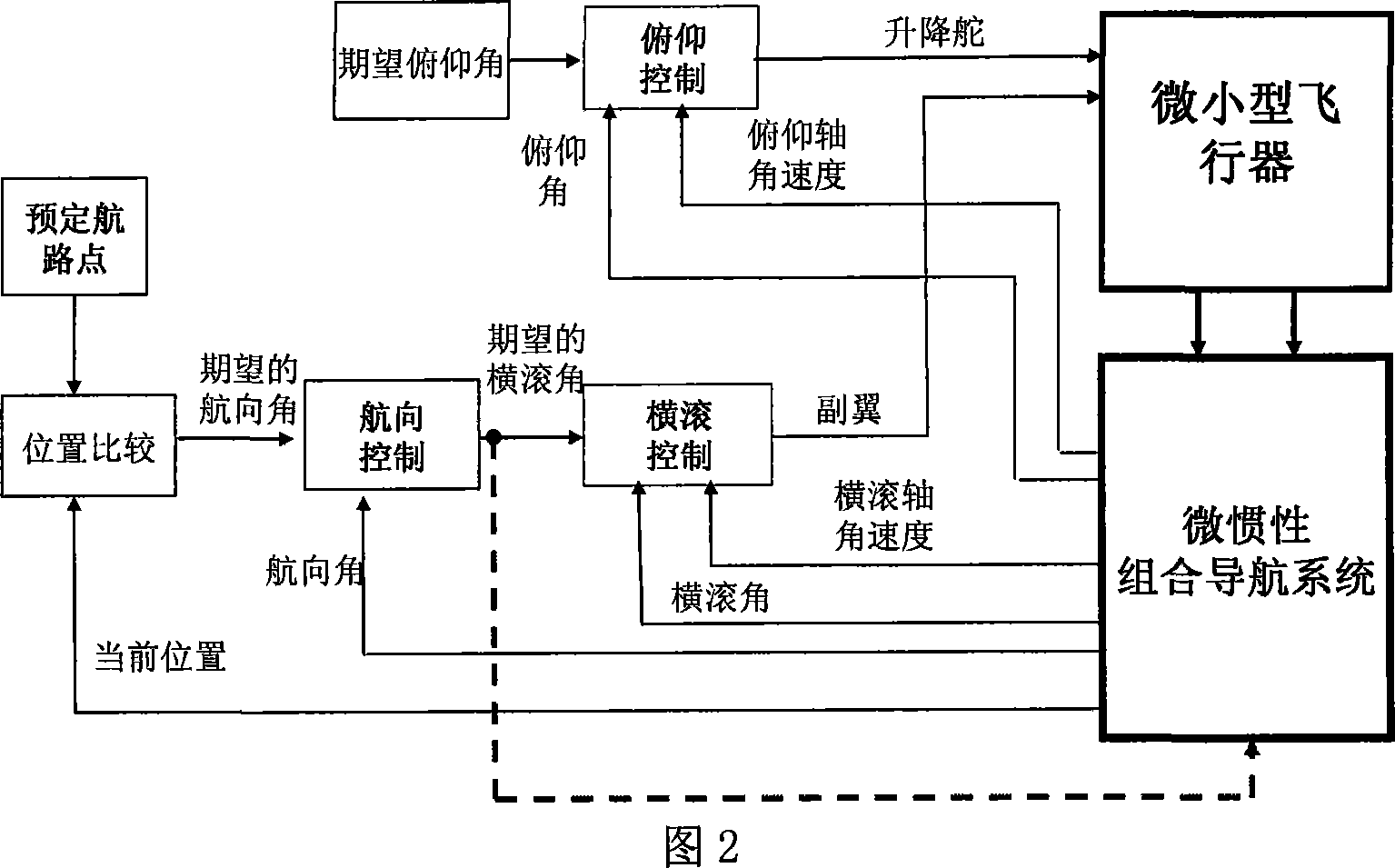
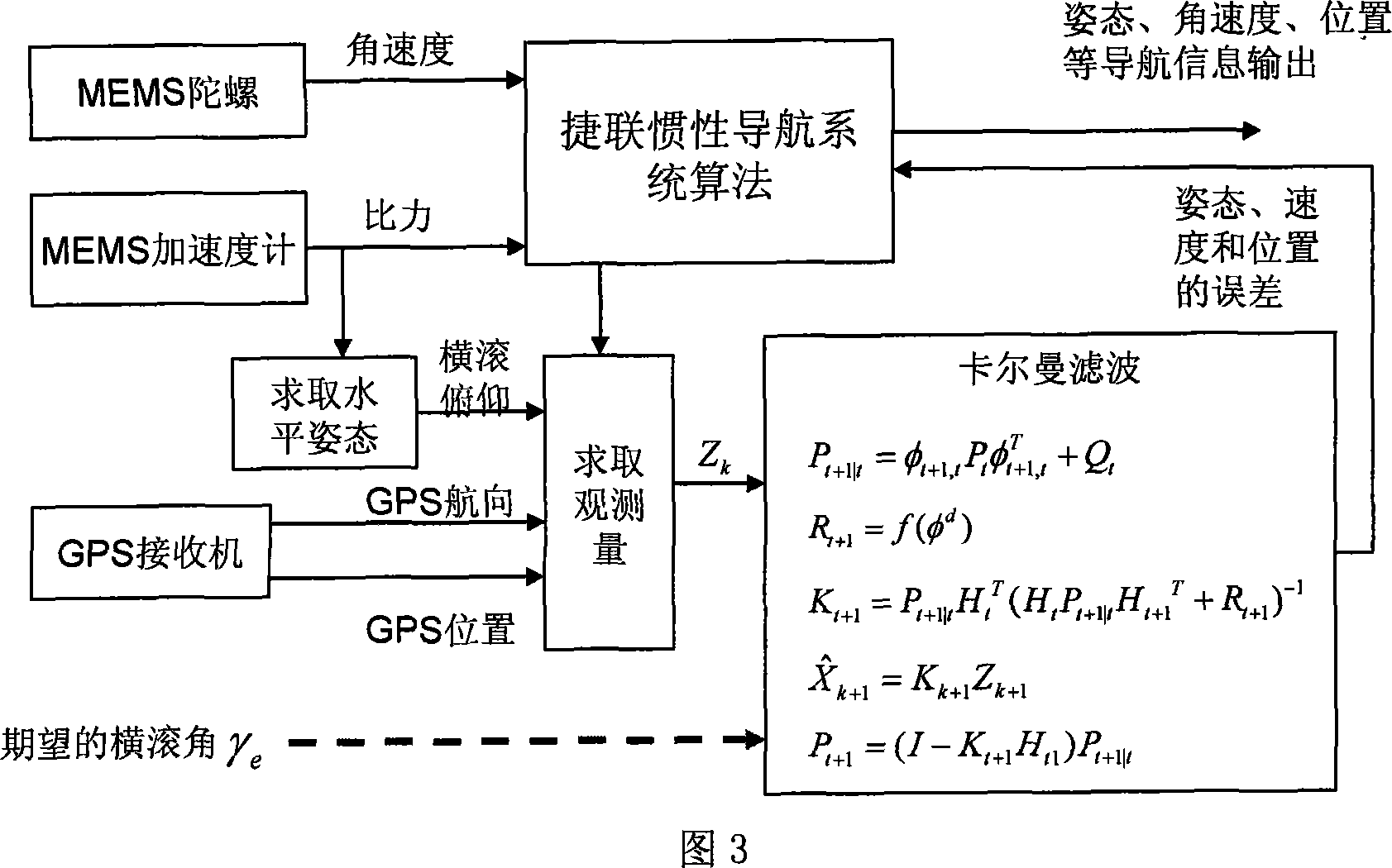
Attitude determination method of mini-aircraft inertial integrated navigation system
InactiveCN101033973AImprove flight qualityHigh precisionNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsGuidance systemAccelerometer
This invention relates to a kind of attitude definition method of micro inertia mixed navigation system of microminiature aero craft, belongs to microminiature vehicle attitude definition method. The method utilize guidance information, control Kalman filter noise matrices, to realize self-adapting adjust according to flight status; through parameter adjust to realize attitude definition of micro inertia mixed navigation system on dynamic airborne conditions; the specific process: through GNC closed loop circuit guidance algorithm, to gain aero craft barrel angle; through sensor picking, obtain vehicle rate and specific force; by strap inertial navigation algorithm to resolve out vehicle attitude, velocity and position information; by accelerometer and GPS data to count pose and position measurement information of aero craft; real-time compute horizontal attitude variance of Kalman filter observation noise matrices, through Kalman filter to estimate error of strap inertial guidance system; Amend above acquired pose, velocity and position information, and took as feedback information to import in control system.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Method for calculating power capability of battery packs using advanced cell model predictive techniques
ActiveUS7321220B2Batteries circuit arrangementsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPower capabilityEngineering
The present invention relates to a method and an apparatus for estimating discharge and charge power of battery applications, including battery packs used in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEV) and Electric Vehicles (EV). One charge / discharge power estimating method incorporates voltage, state-of-charge (SOC), power, and current design constraints and works for a user-specified prediction time horizon Δt. At least two cell models are used in calculating maximum charge / discharge power based on voltage limits. The first is a simple cell model that uses a Taylor-series expansion to linearize the equation involved. The second is a more complex and accurate model that models cell dynamics in discrete-time state-space form. The cell model can incorporate a inputs such as temperature, resistance, capacity, etc. One advantage of using model-based approach is that the same model may be used in both Kalman-filtering to produce the SOC and the estimation of maximum charge / discharge current based on voltage limits.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com