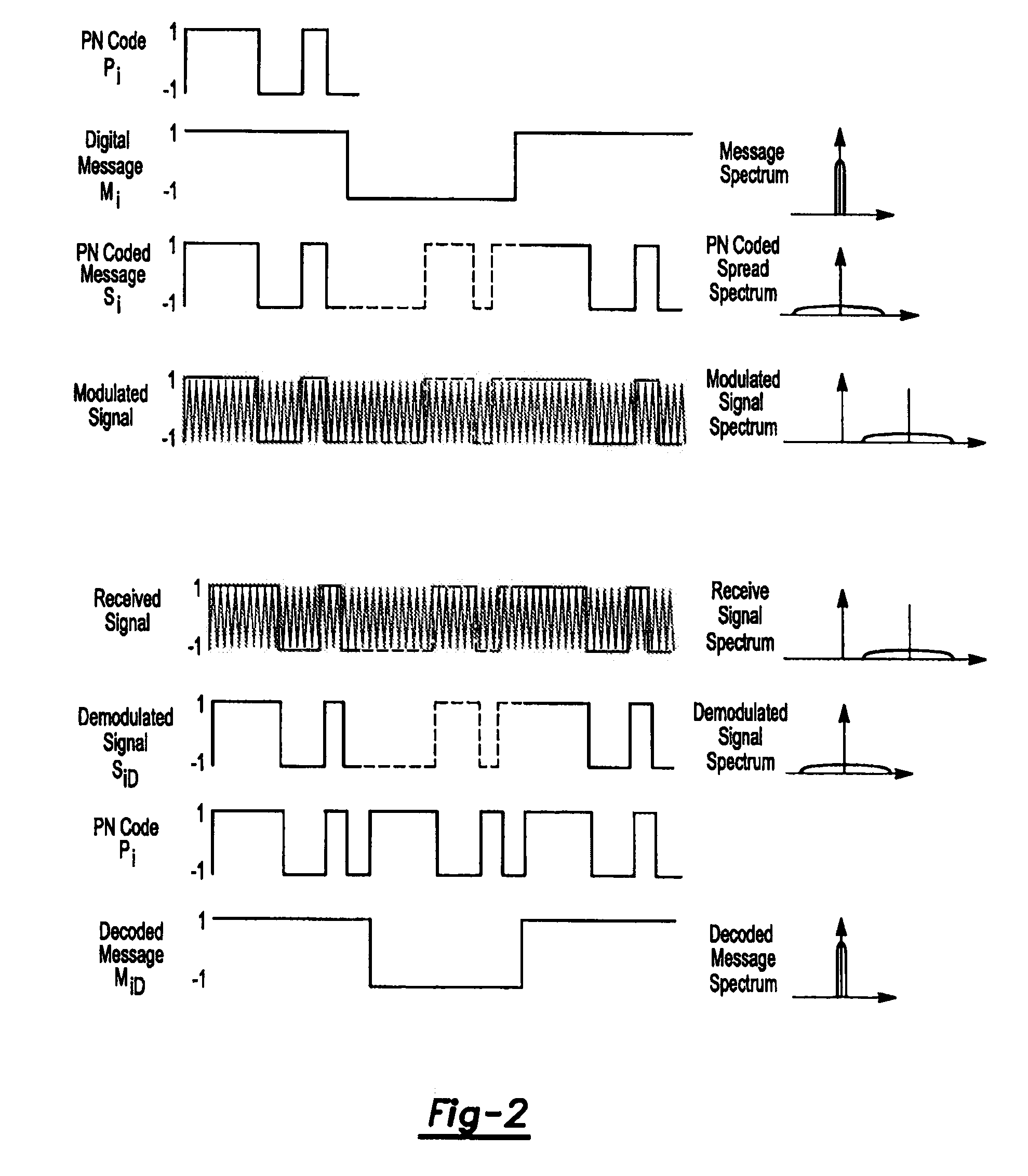
Patents
Literature
553 results about "Multilateration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
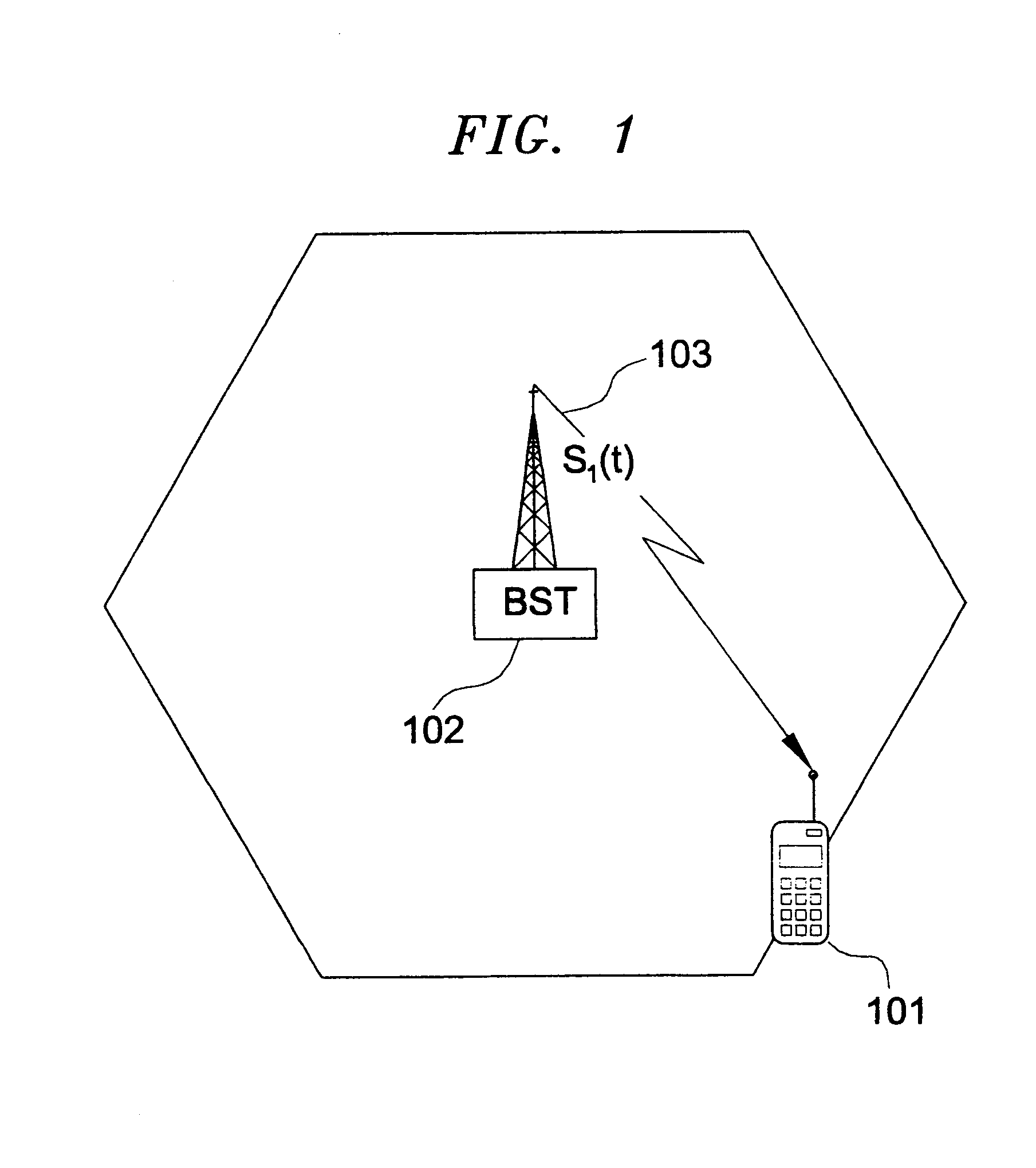
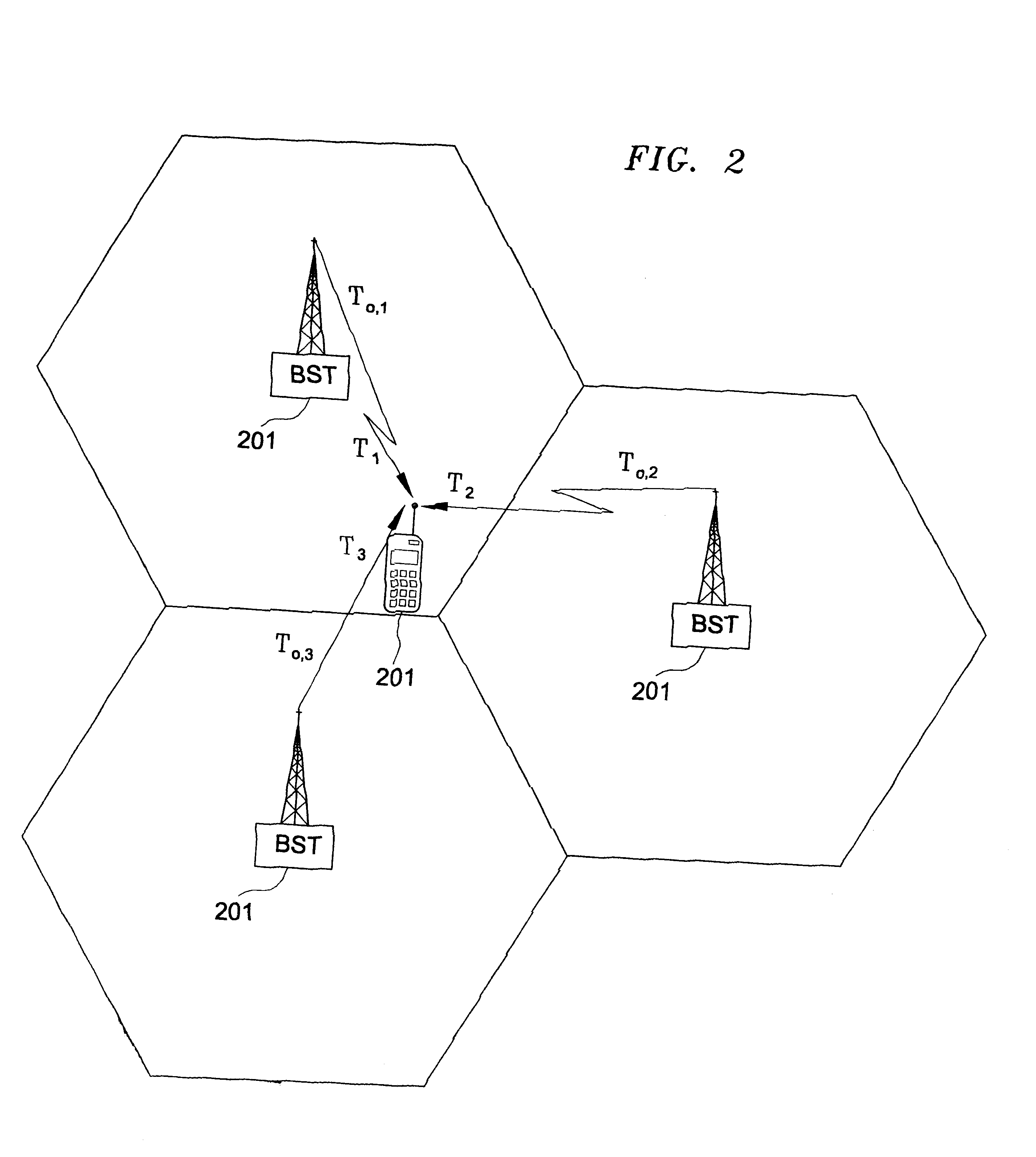
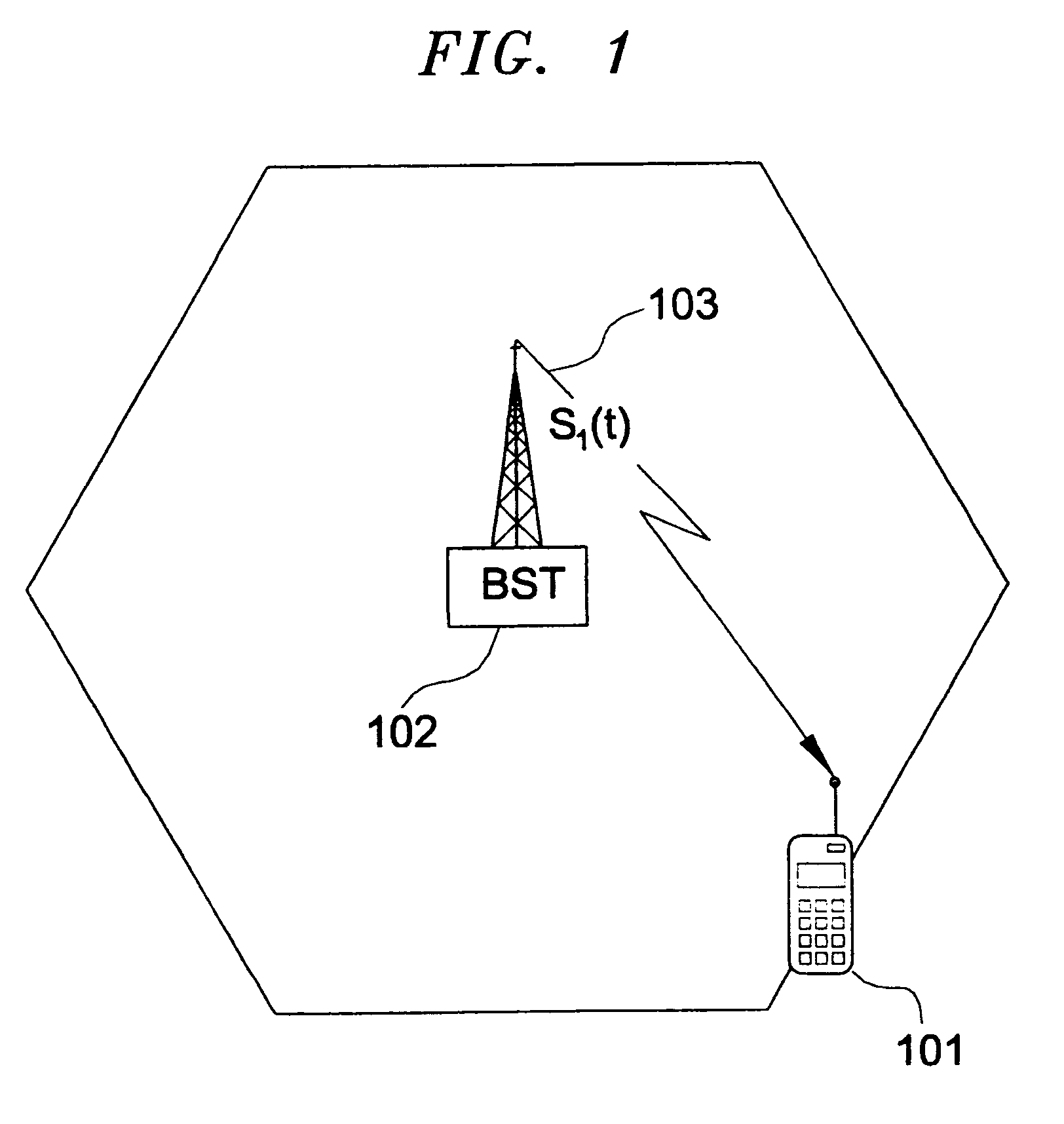
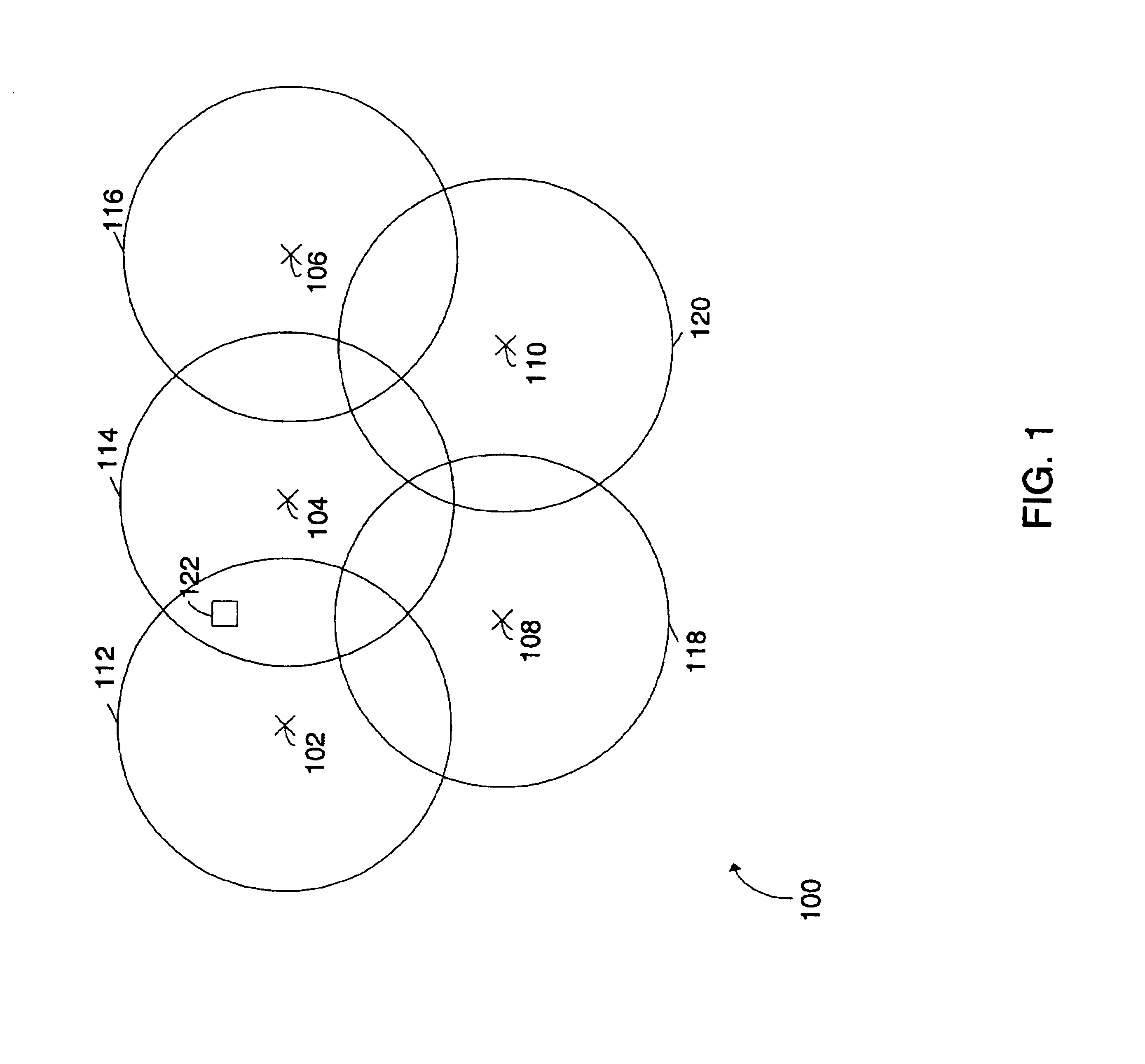
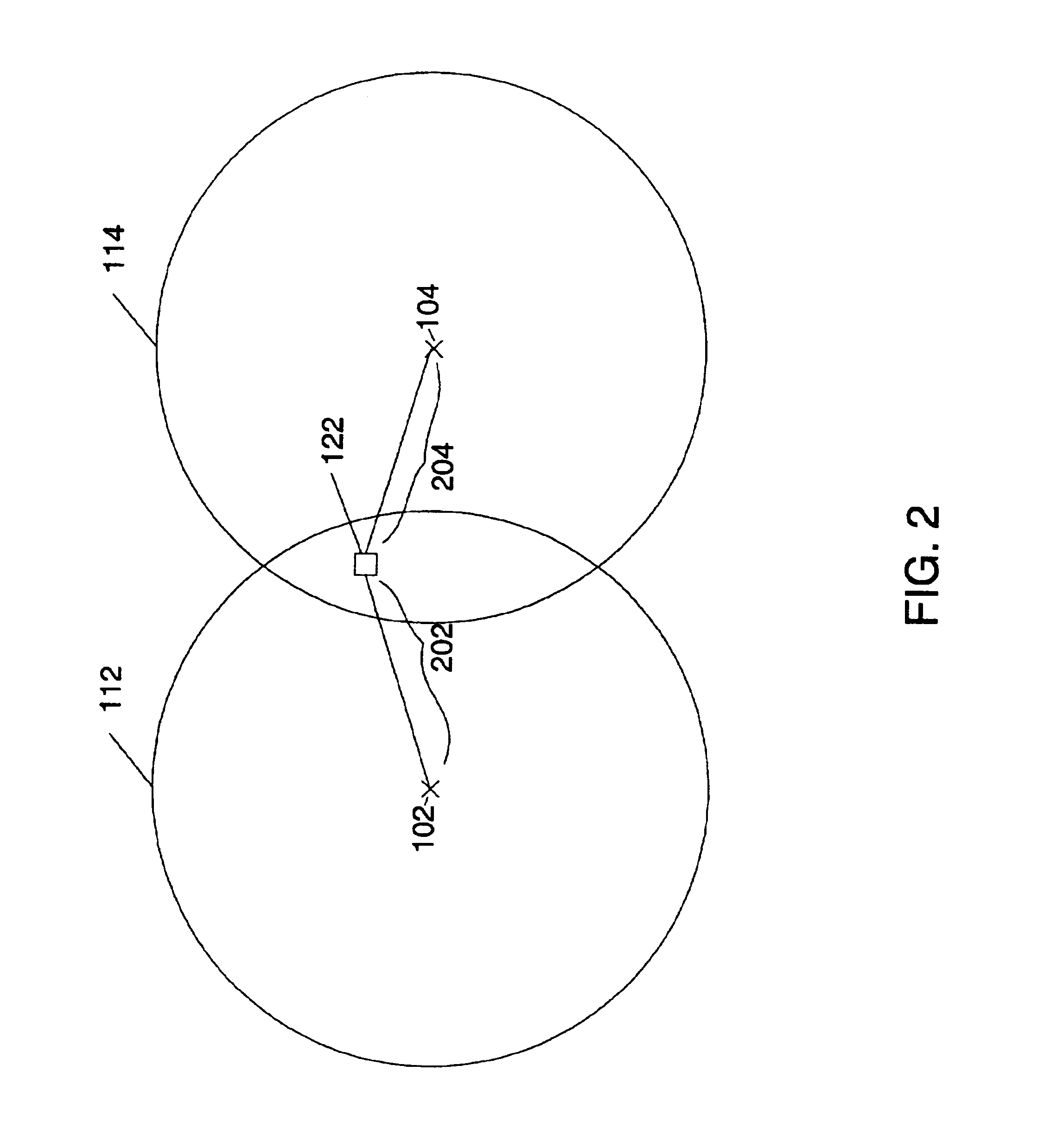
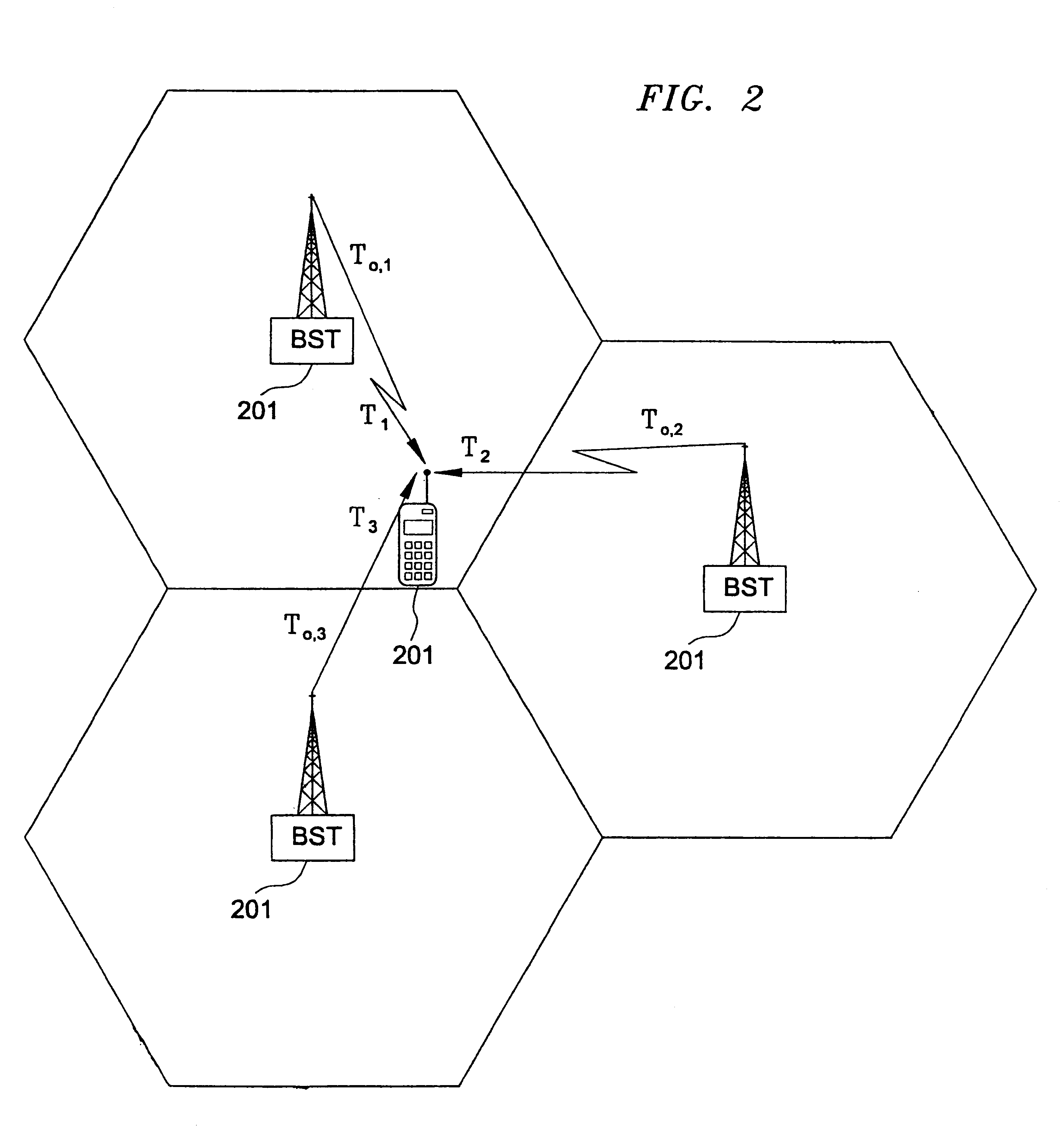
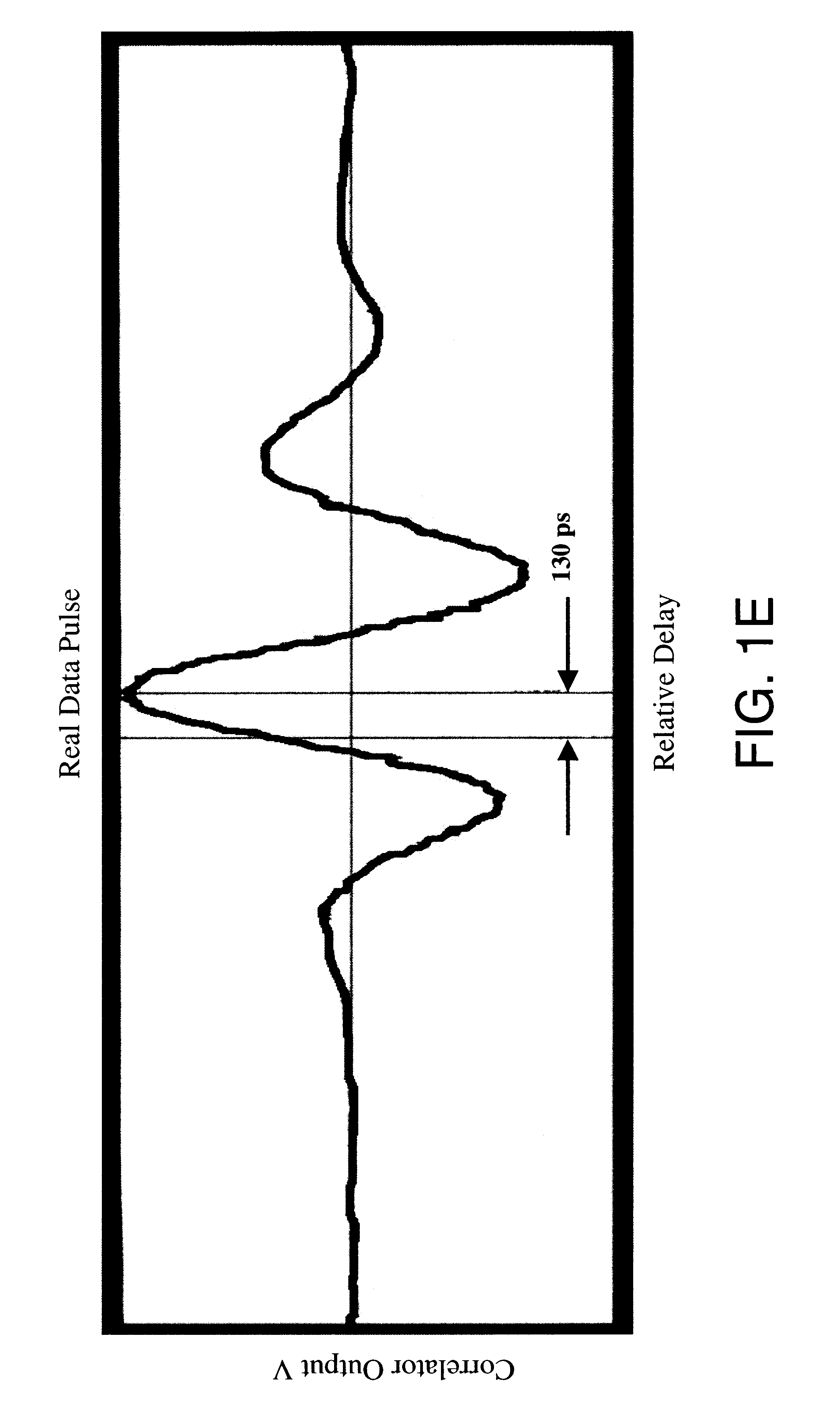
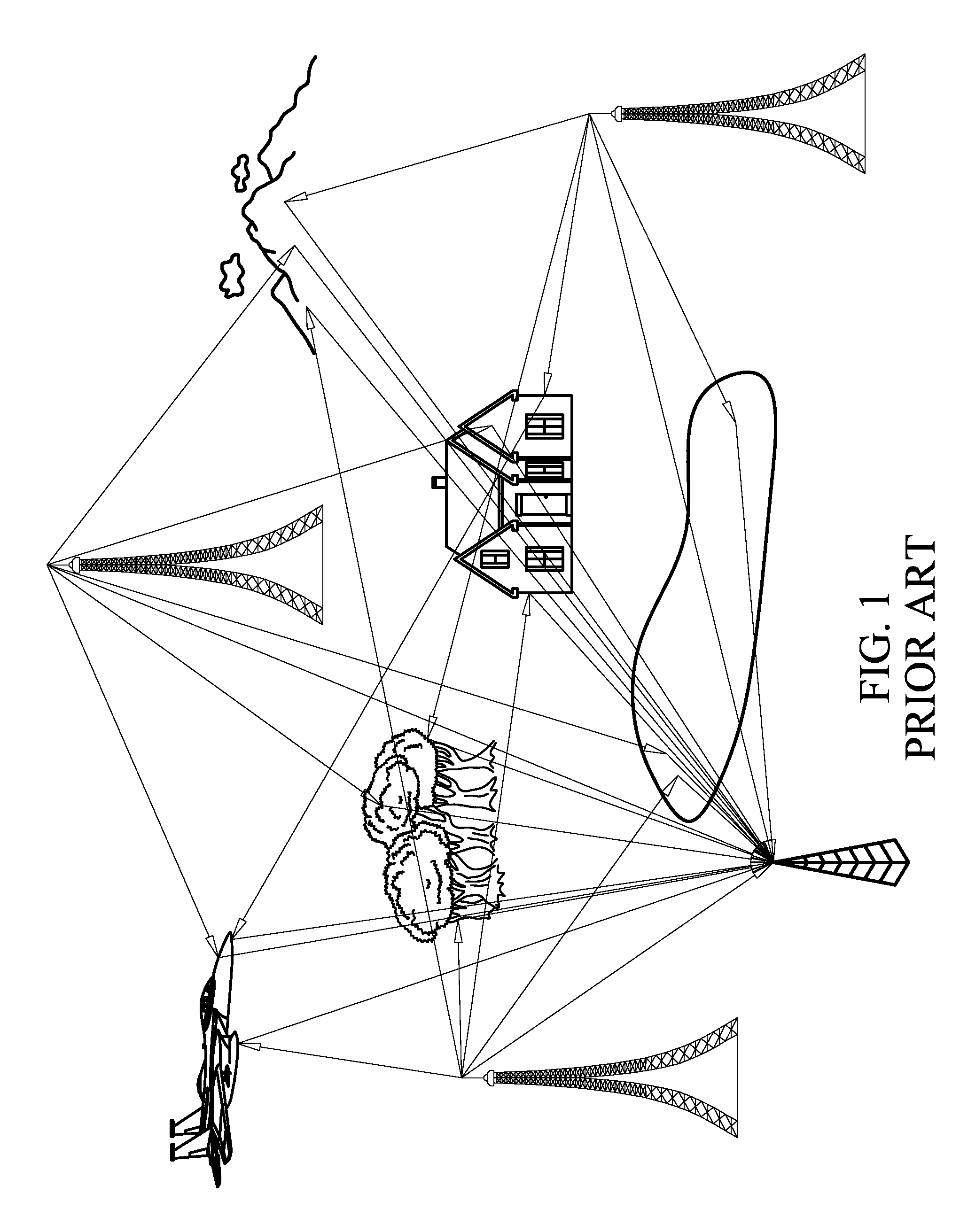
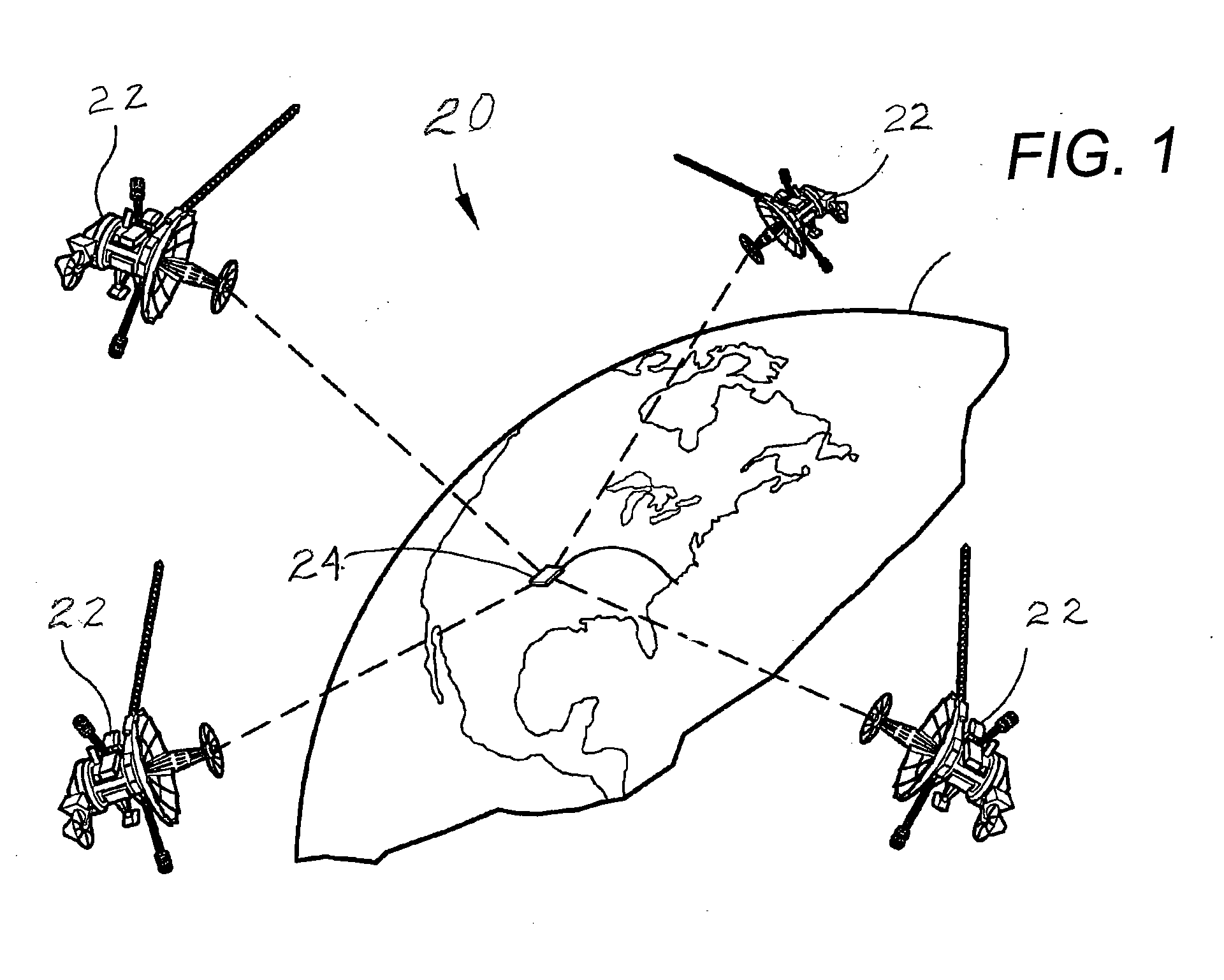
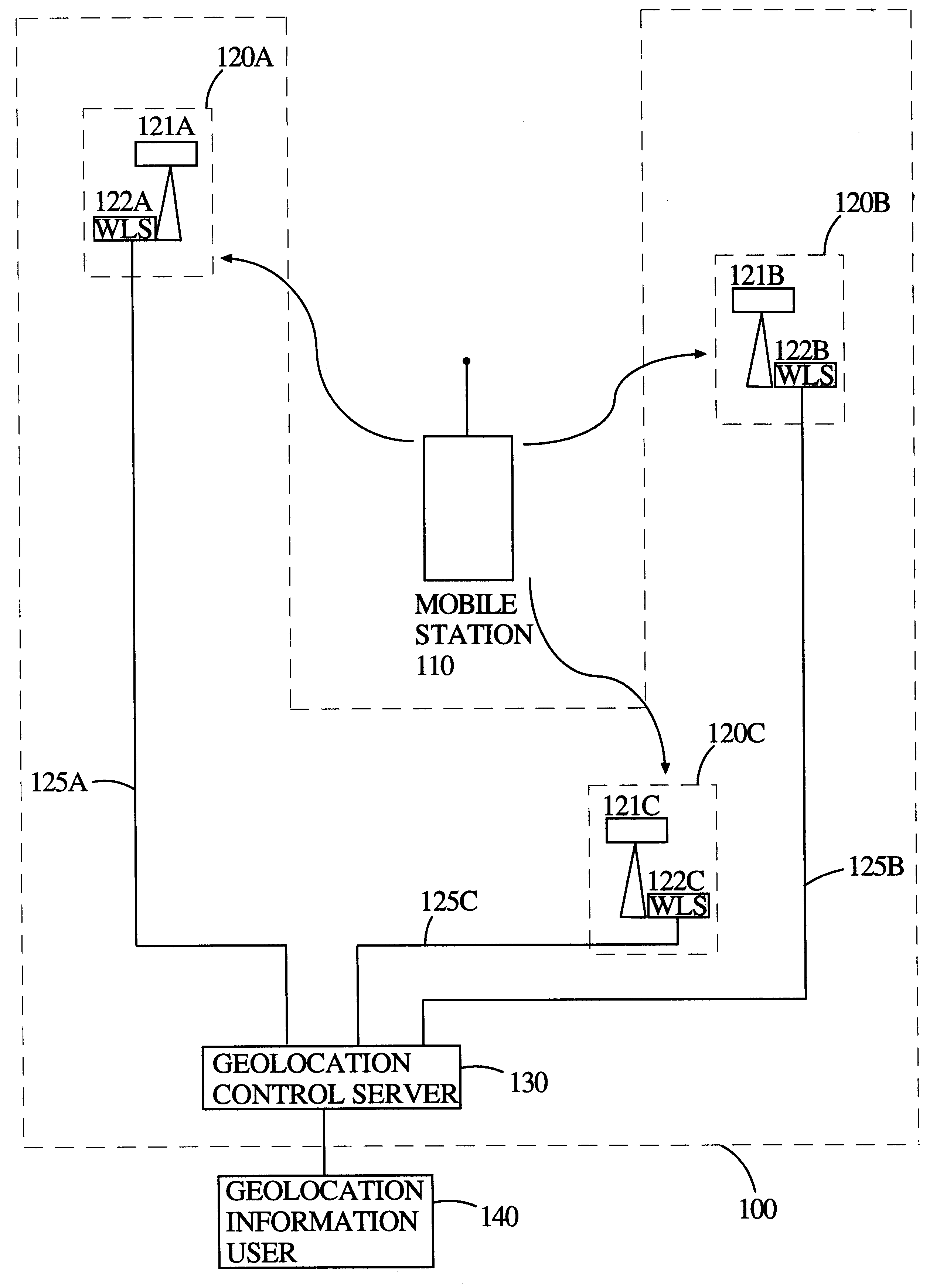
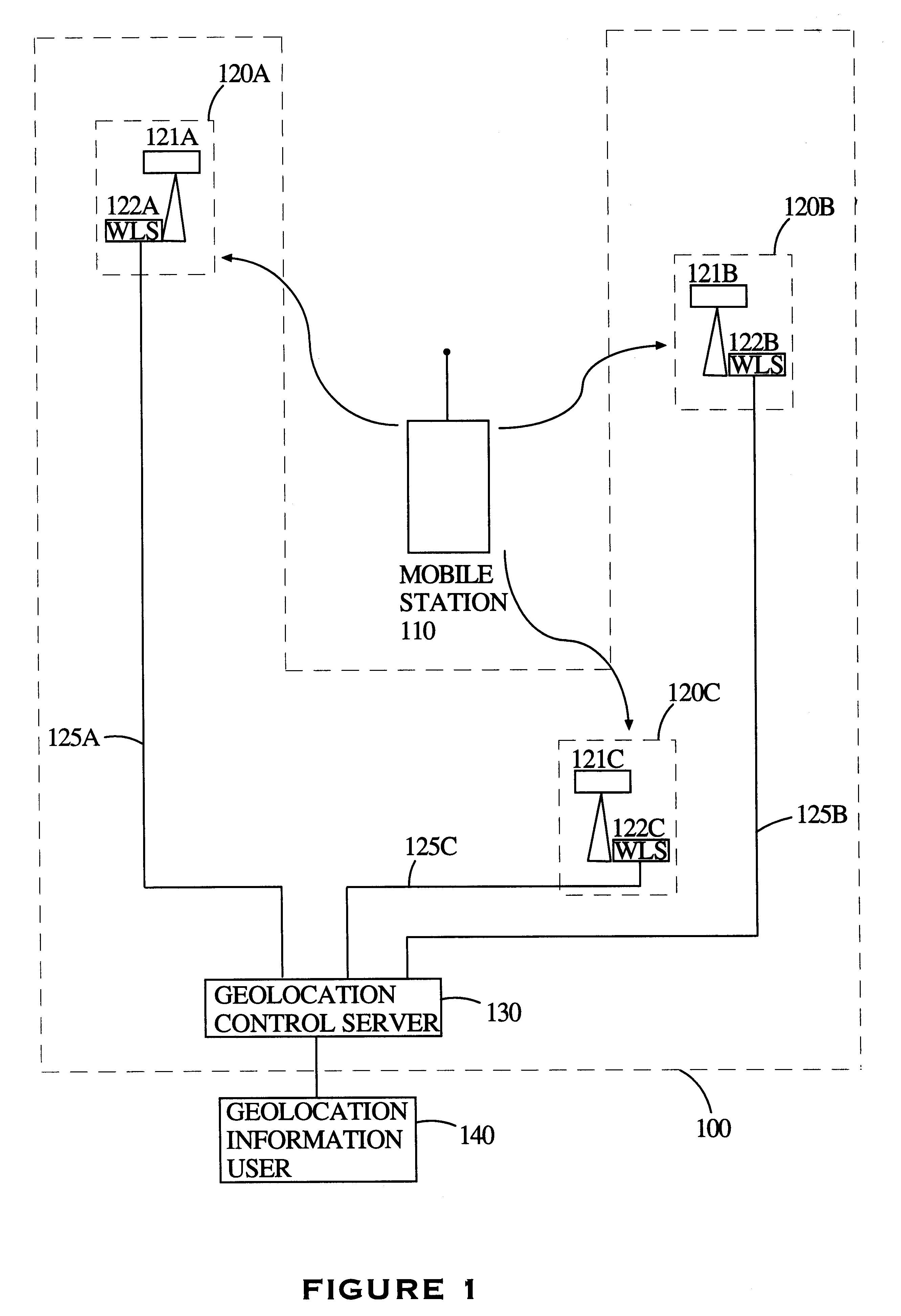
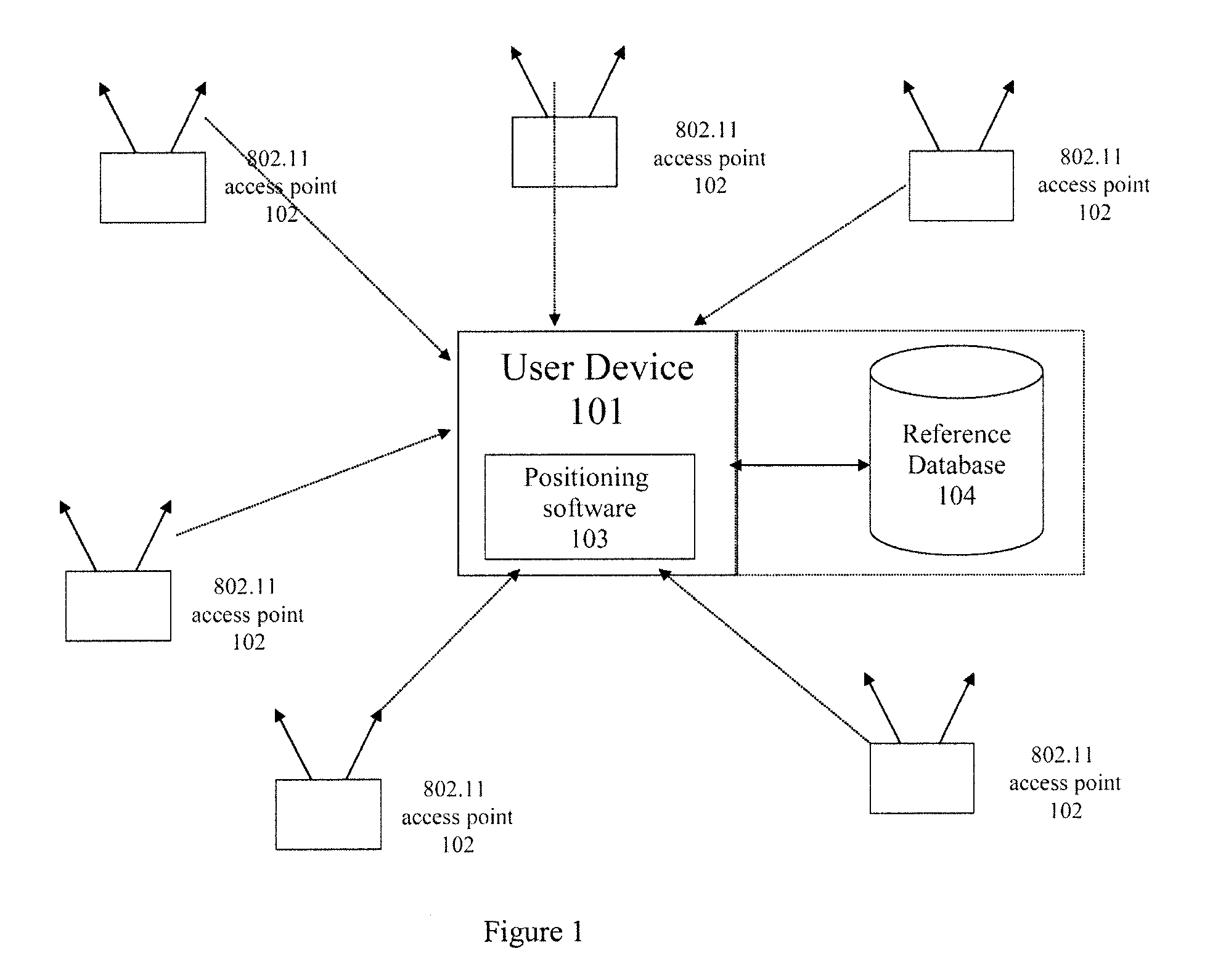
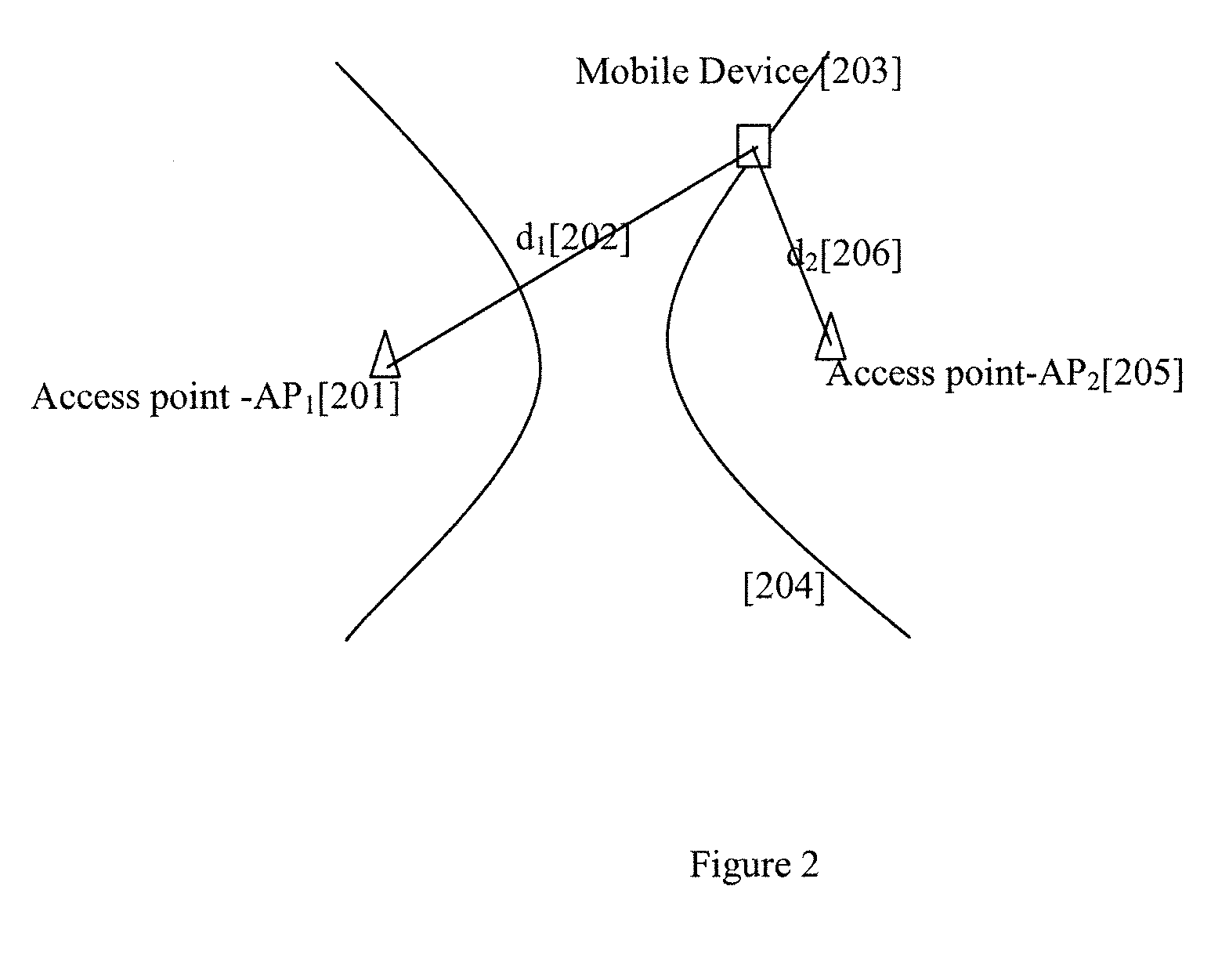
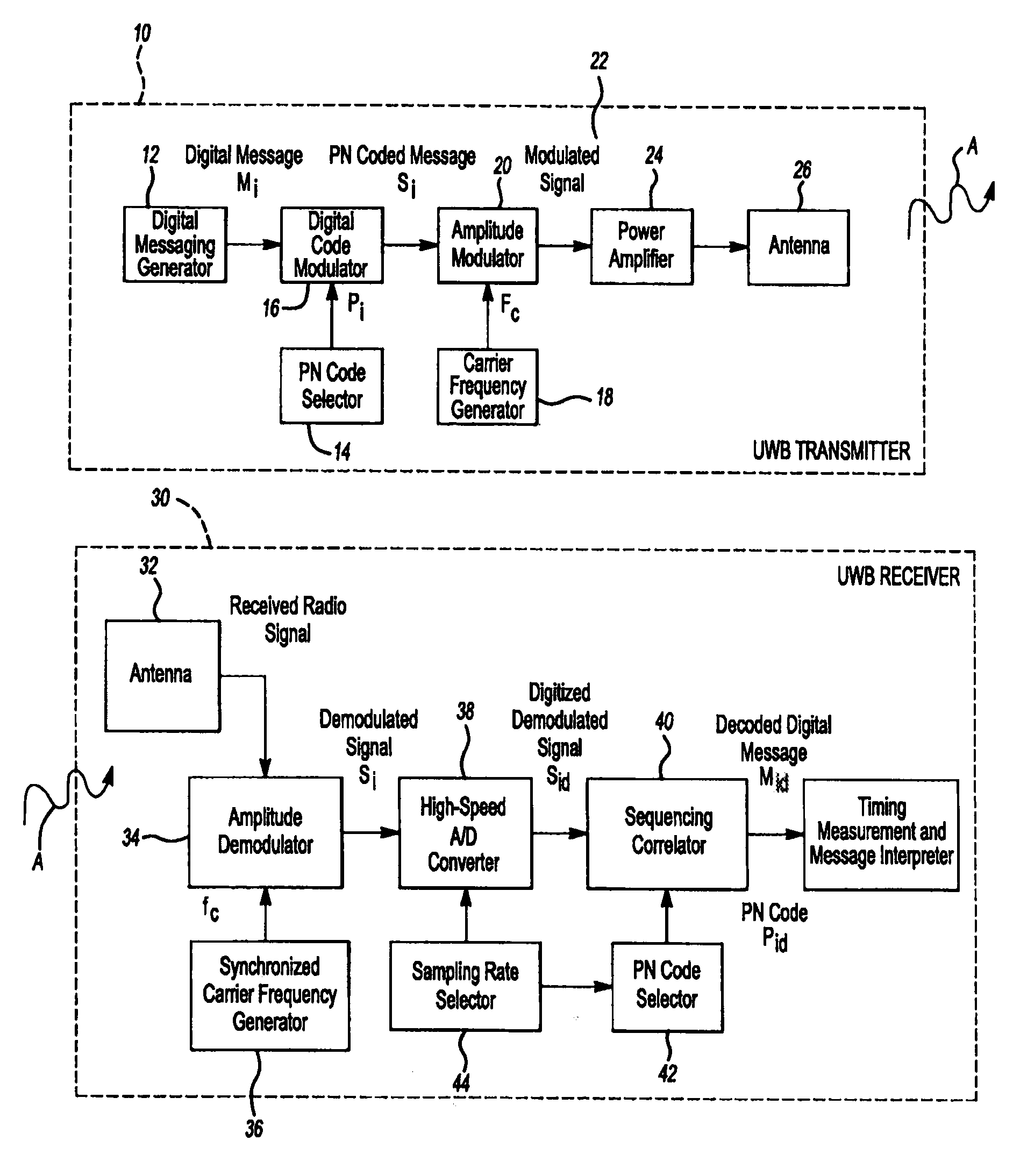
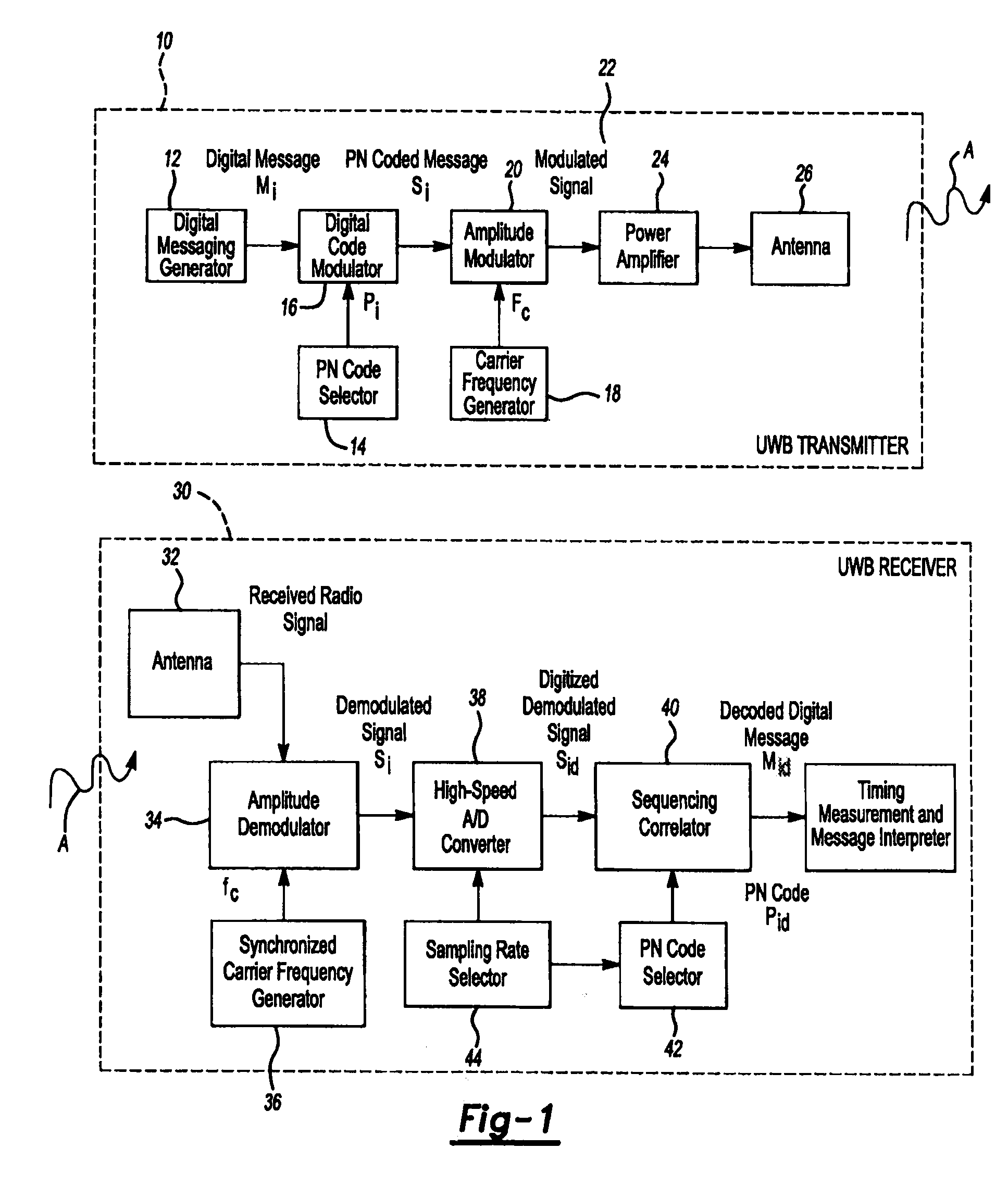
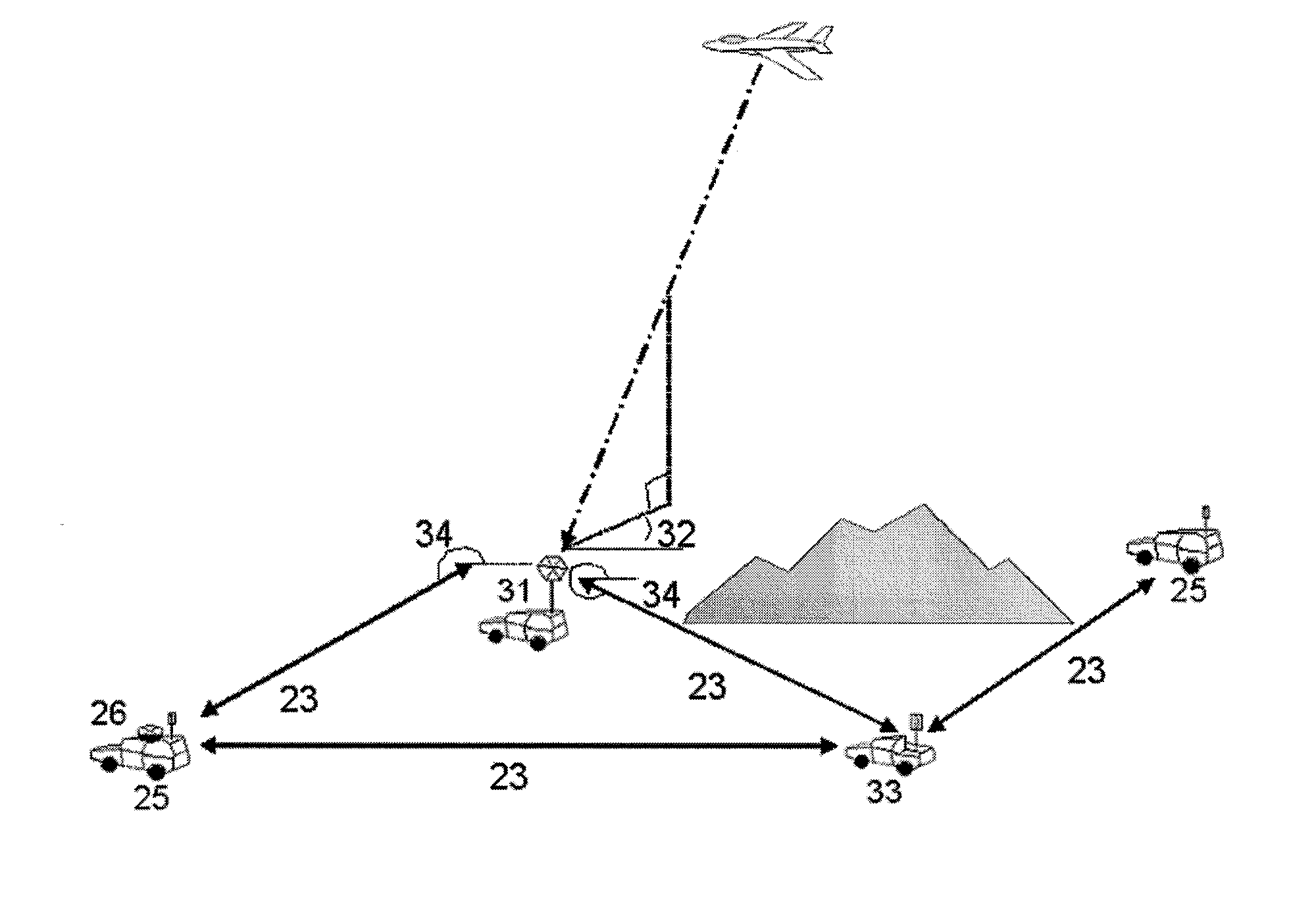
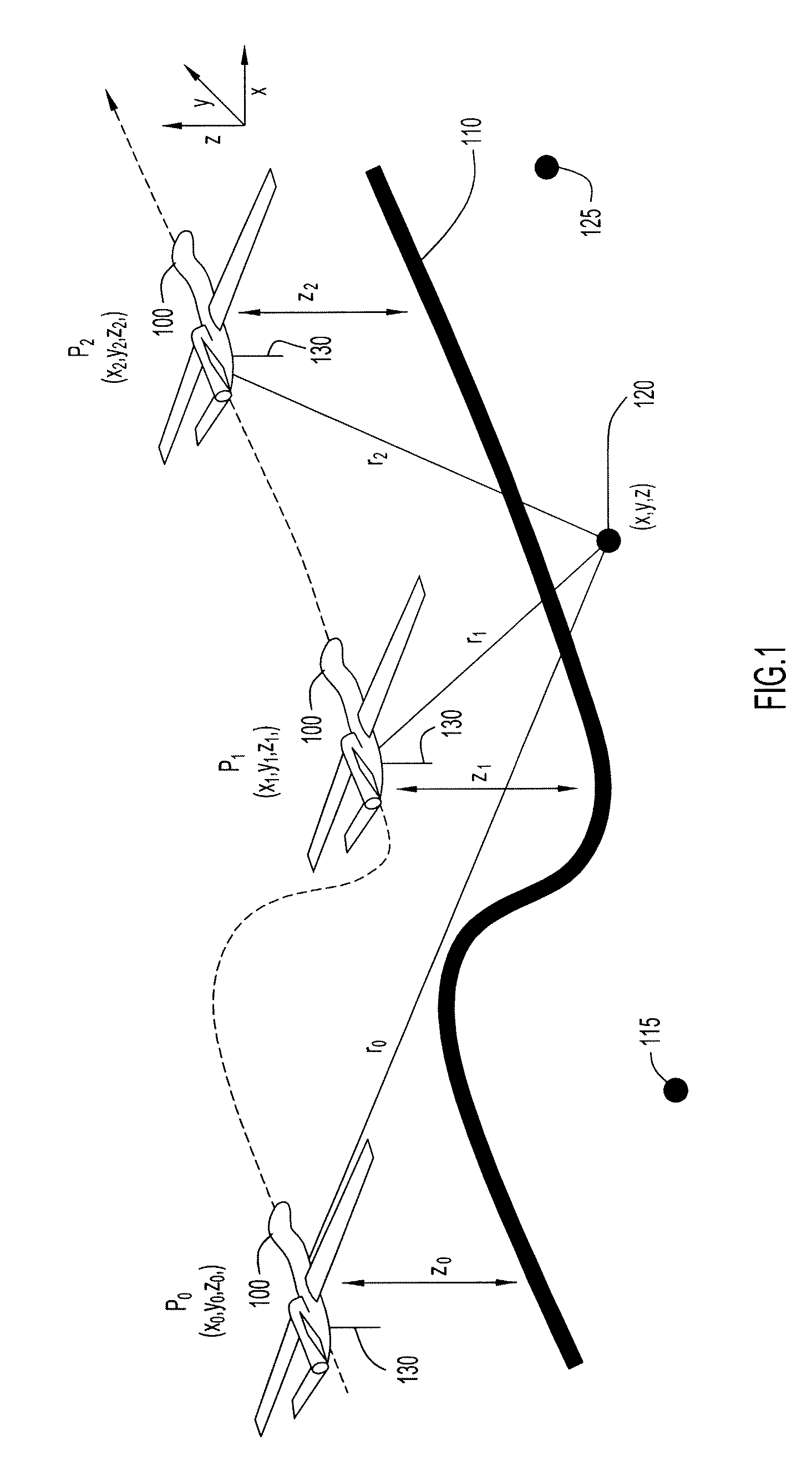
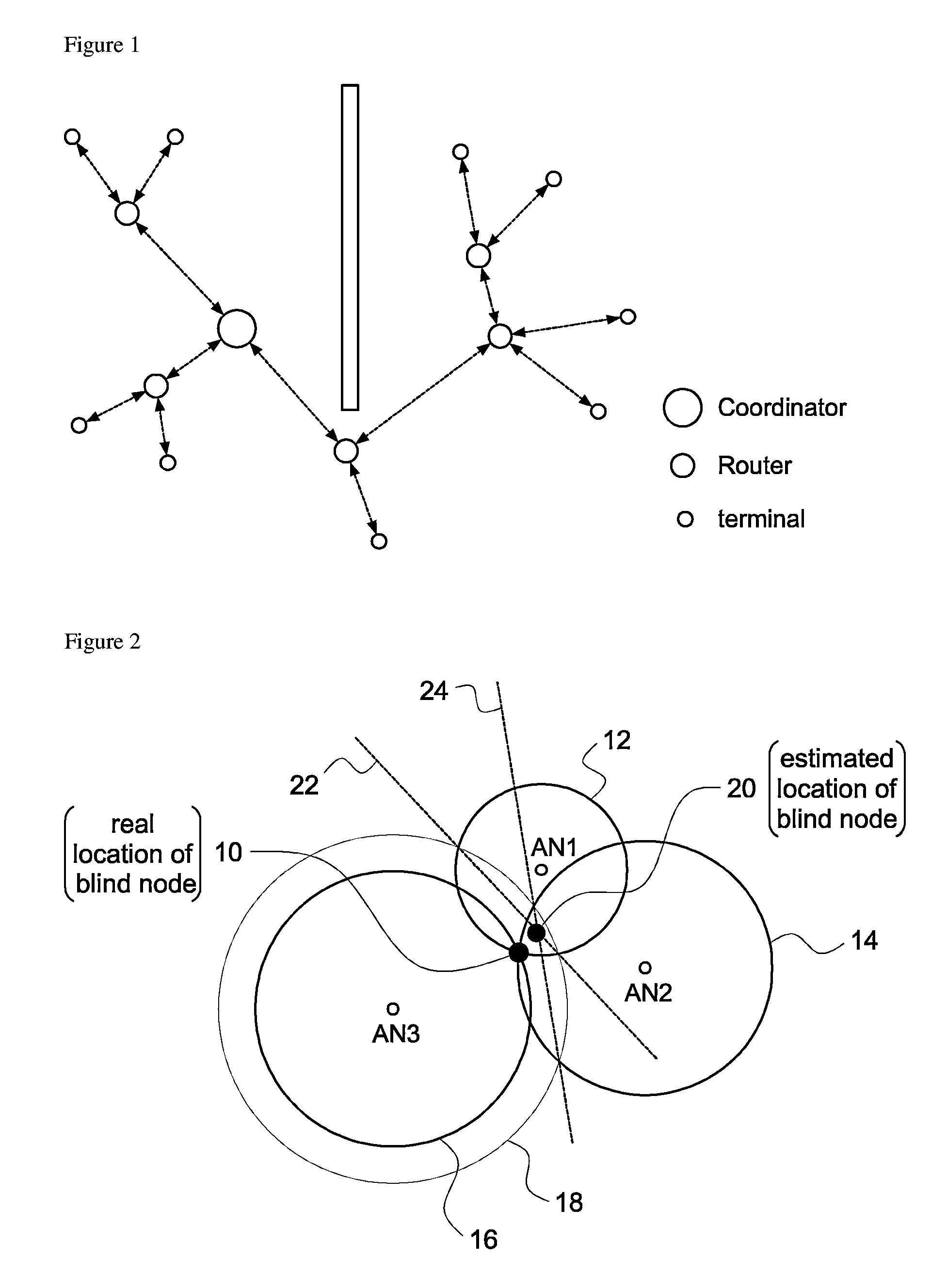
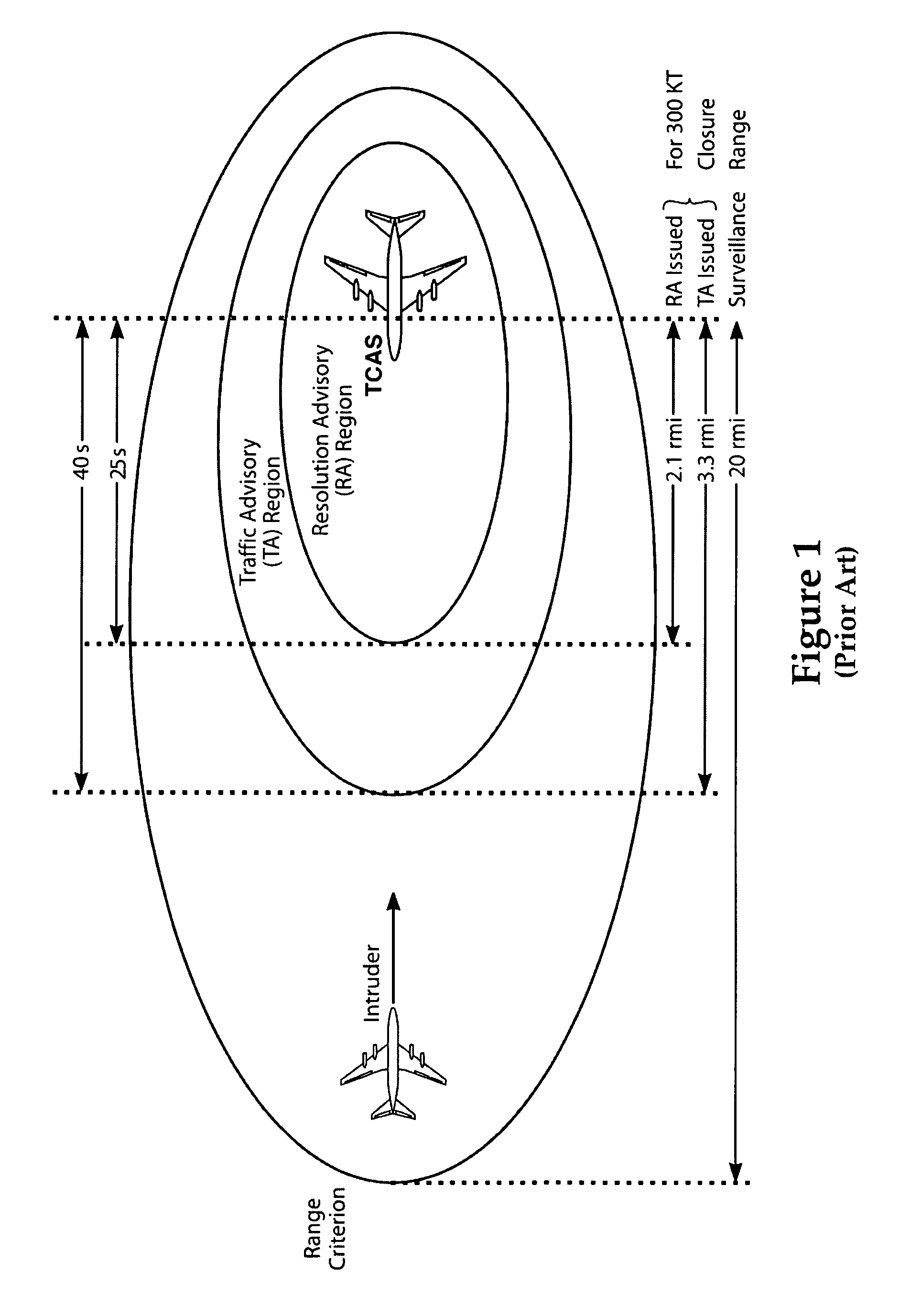
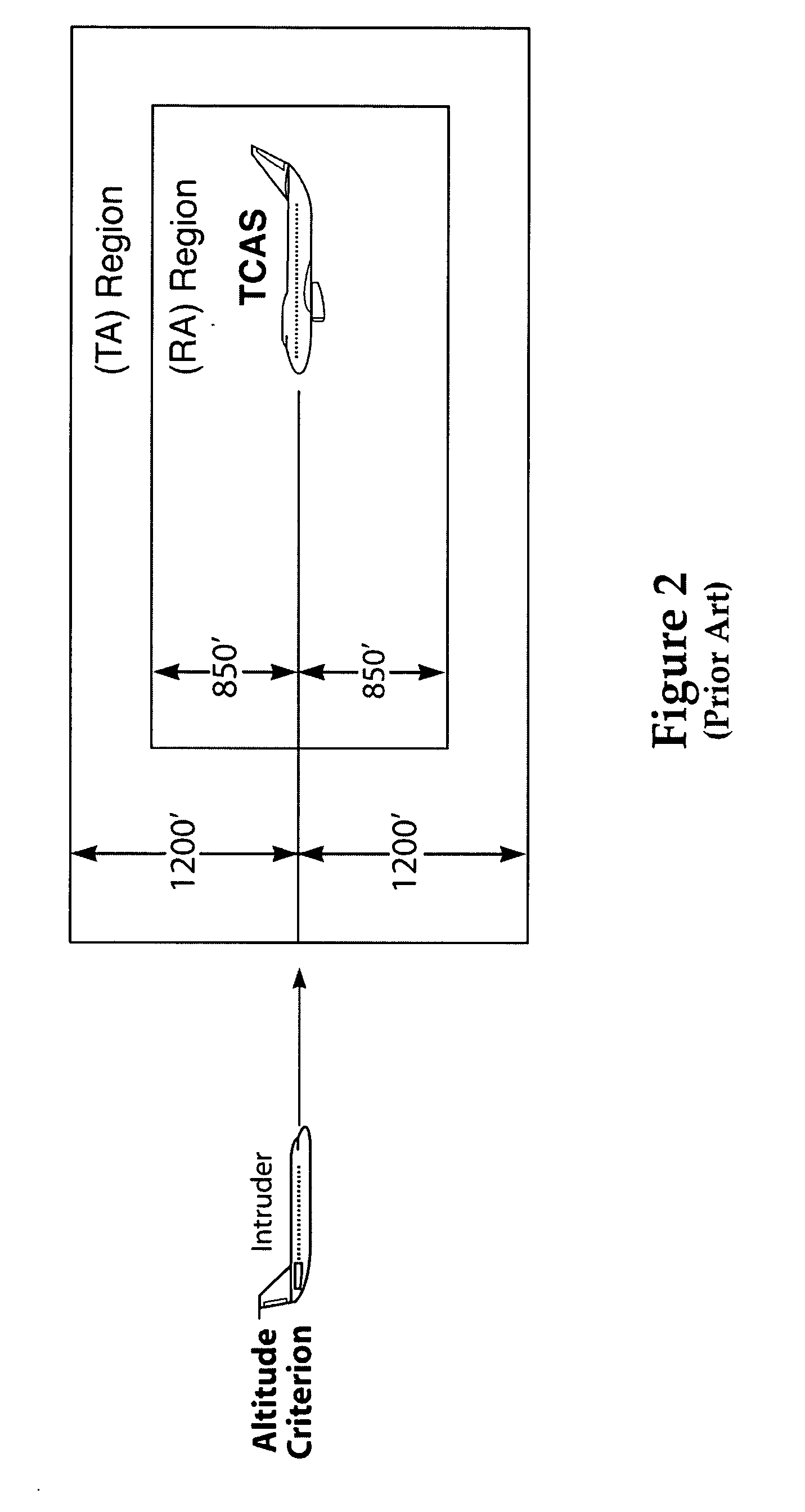
Multilateration is a navigation and surveillance technique based on the measurement of the times of arrival (TOAs) of energy waves (radio, acoustic, seismic, etc.) having a known propagation speed. The time origin for the TOAs is arbitrary. (By the reciprocity principle, any conceptual method that can be used for navigation can also be used for surveillance, and vice versa.) For surveillance, a subject of interest – in cooperative surveillance, often a vehicle – transmits to multiple receiving stations having synchronized 'clocks'. For navigation, multiple synchronized stations transmit to a user receiver. To find the coordinates of a user in n dimensions (typically, n = 2 or n = 3), at least n + 1 TOAs must be measured. Multilateration systems are also called hyperbolic systems, for reasons discussed below.
Wireless tracking system and method utilizing multiple location algorithms
The present invention provides a solution to mistaken location calculations based on multipath effects. The present invention determines a real-time location of an object in a facility using a combination of location algorithms, with a signal characteristic for a wireless signal from a communication device attached to the object received at a sensor of a mesh network. The location algorithms preferably include at least two of a proximity algorithm, a radial basis function algorithm, a maximum likelihood algorithm, a genetic algorithm, a minimum mean squared error algorithm, a radiofrequency fingerprinting algorithm, a multilateration algorithm, a time difference of arrival algorithm, a signal strength algorithm, a time of arrival algorithm, an angle of arrival algorithm, a spatial diversity algorithm, and a nearest neighbor algorithm.
Owner:CENTRAK INC
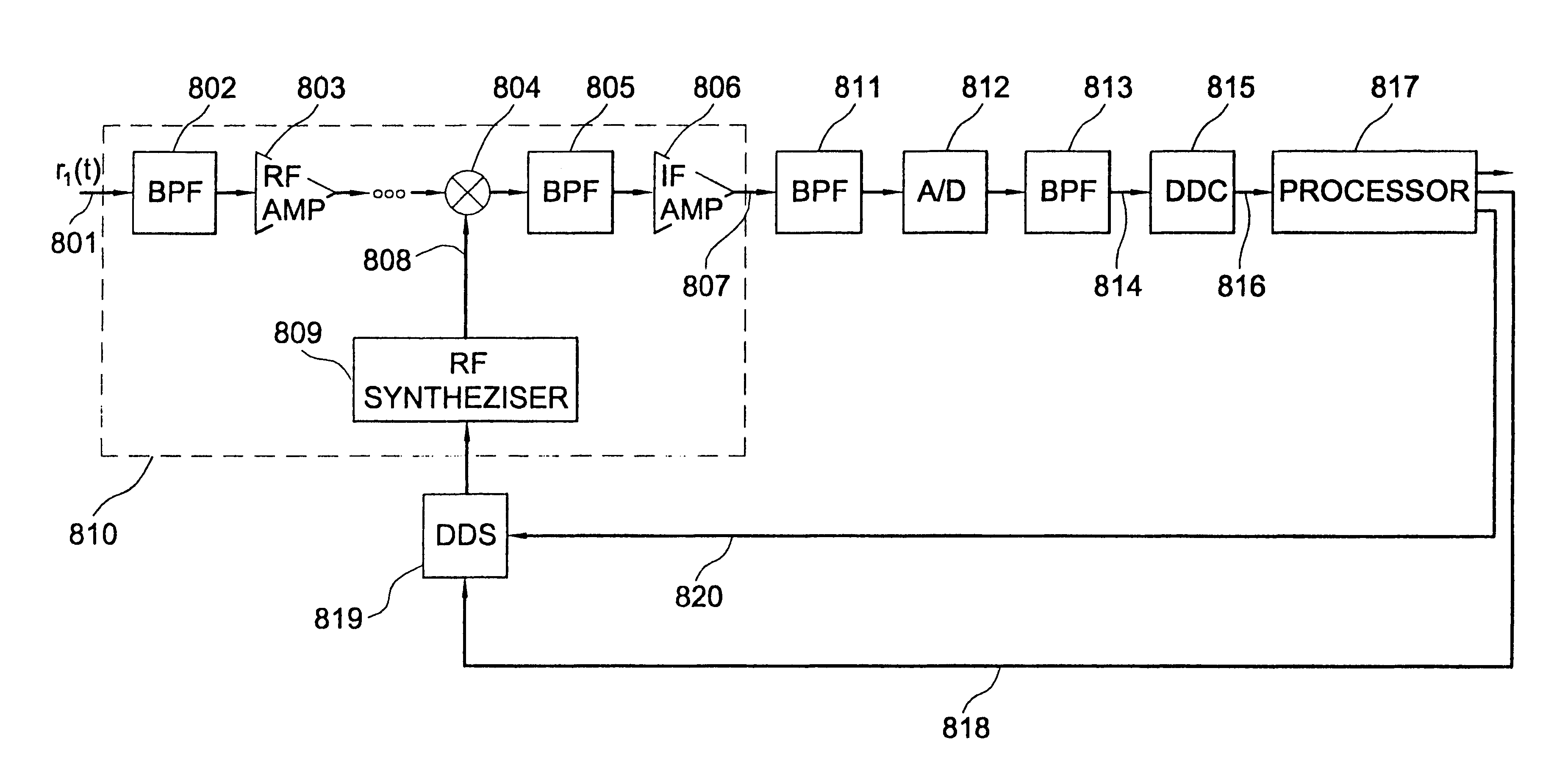
Methods and apparatus to position a mobile receiver using downlink signals part IV
The invention consists of methods and apparatus to estimate the position and velocity of a Mobile Receiver (MR) using either the Time Of Arrival (TOA) of signals received by the MR, their Phase Of Arrival (POA), their Strength Of Arrival (SOA), their Frequency Of Arrival (FOA), or a combination thereof, with respect to a reference produced by a Reference Receiver (RR) of known location. In order to solve for the coordinates of the MR, the invention uses either hyperbolic multilateration based on Time Difference Of Arrival (TDOA), or linear multiangulation based on Phase Difference Of Arrival (PDOA), or both. In order to solve for the velocity of the MR, the patent uses FOA based on Frequency Difference Of Arrival (FDOA).
Owner:CELL LOC LOCATION TECH
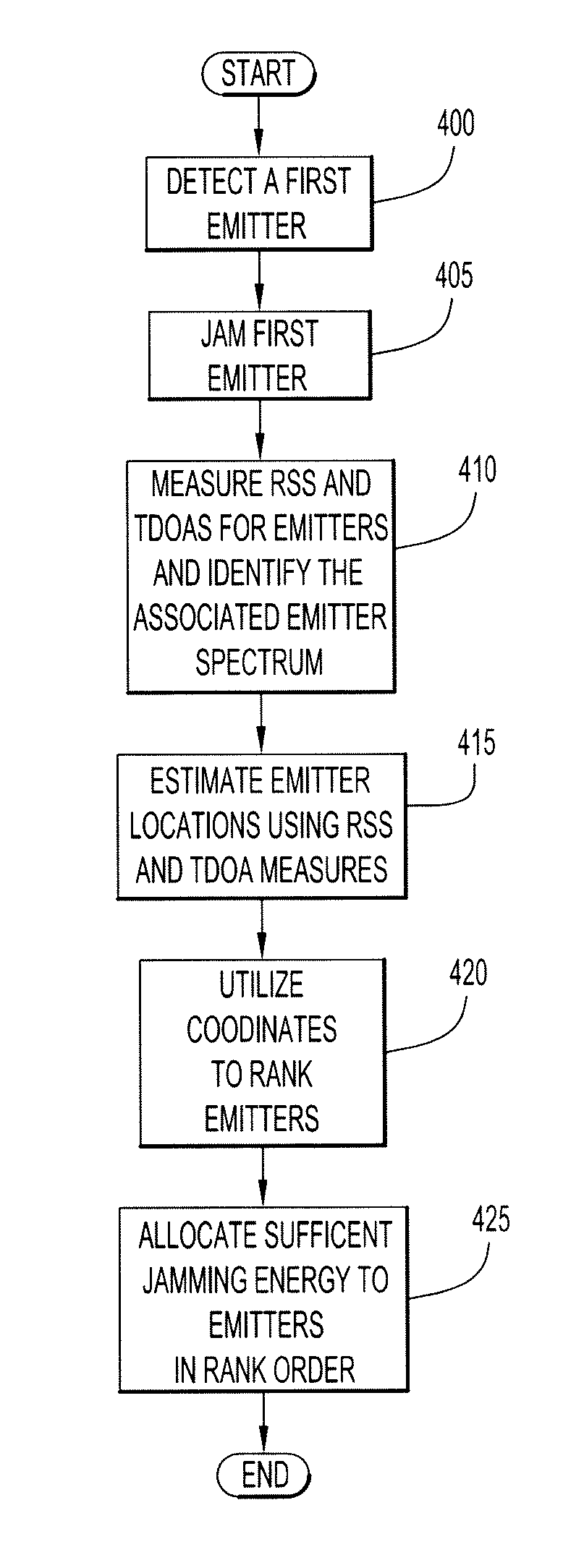
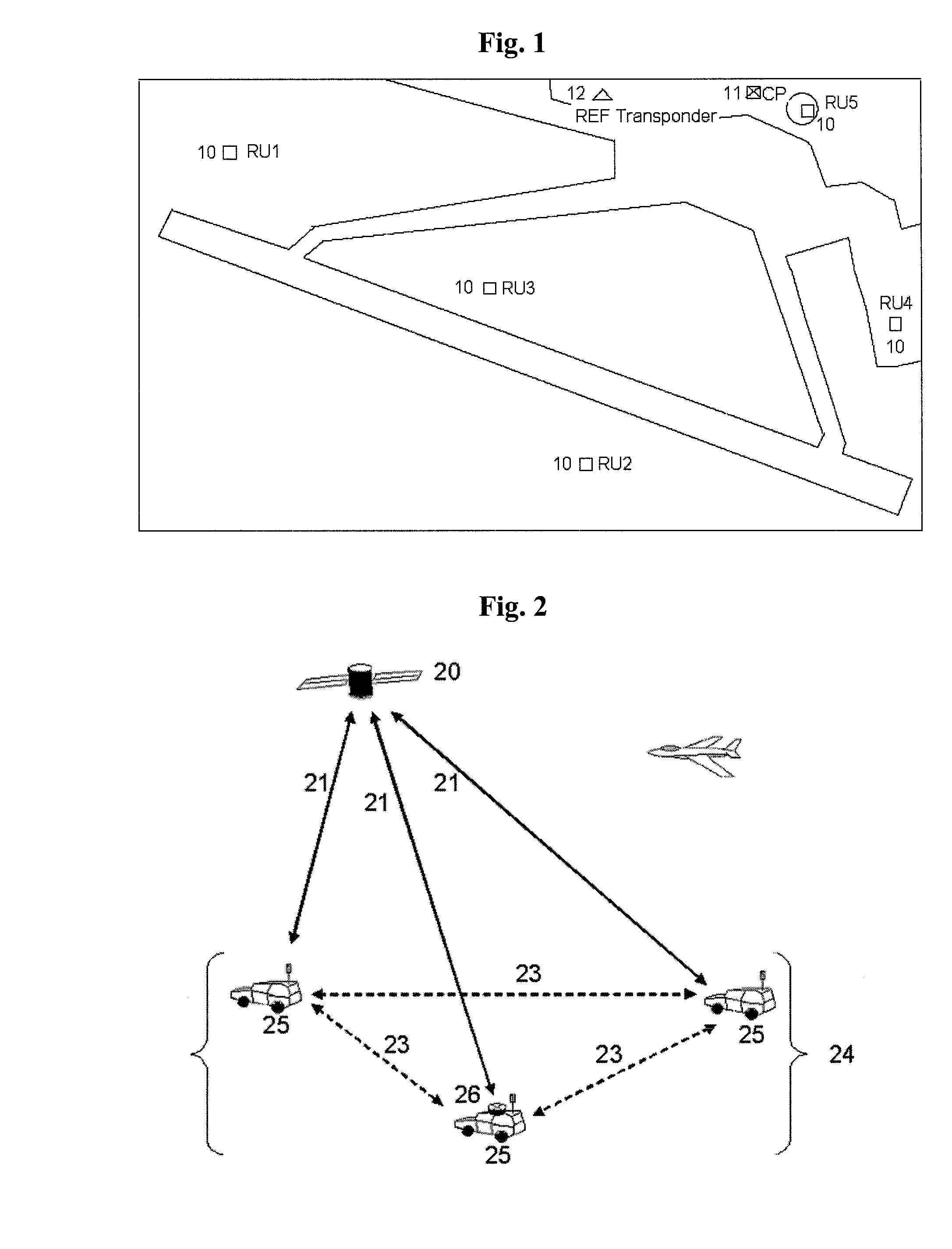
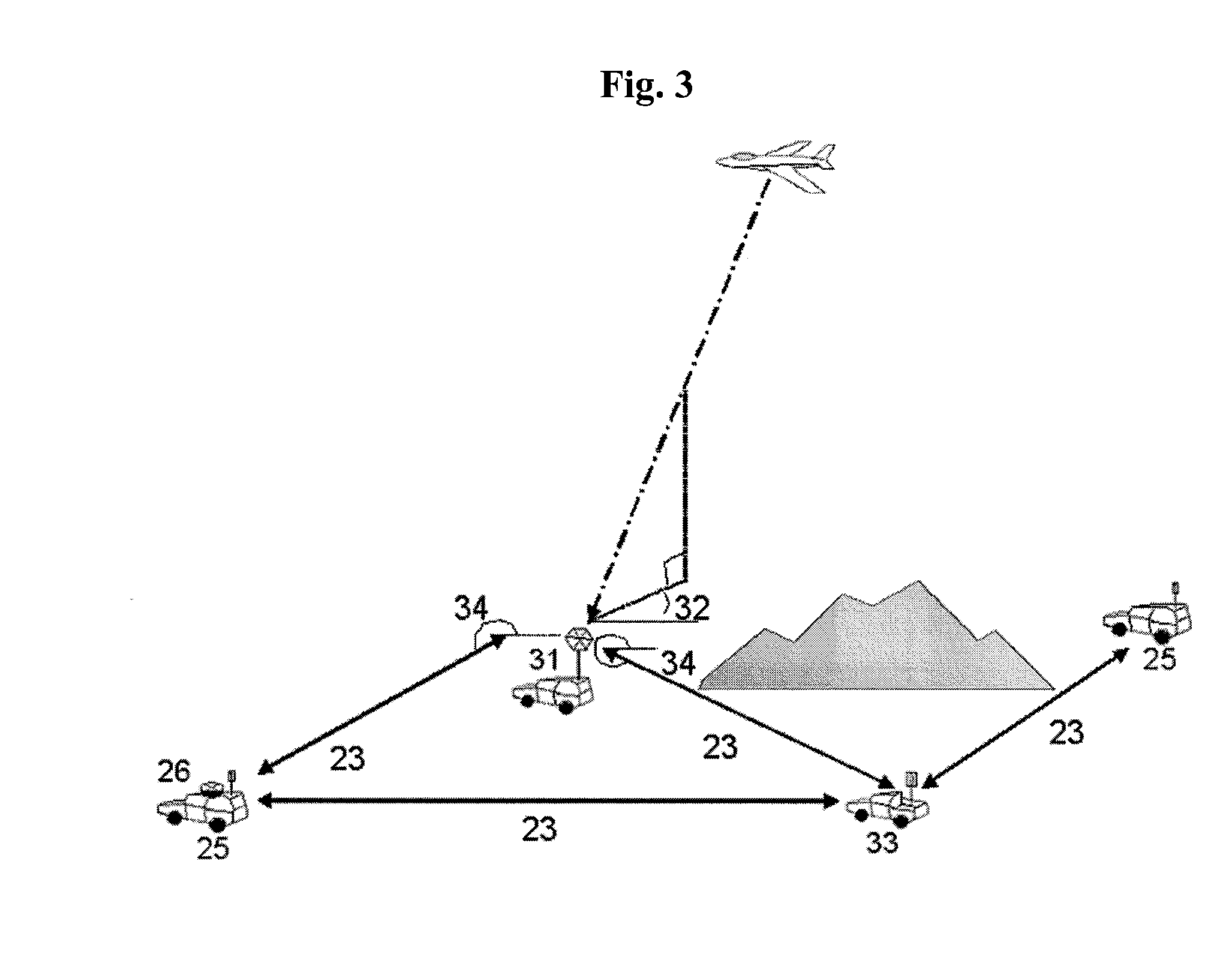
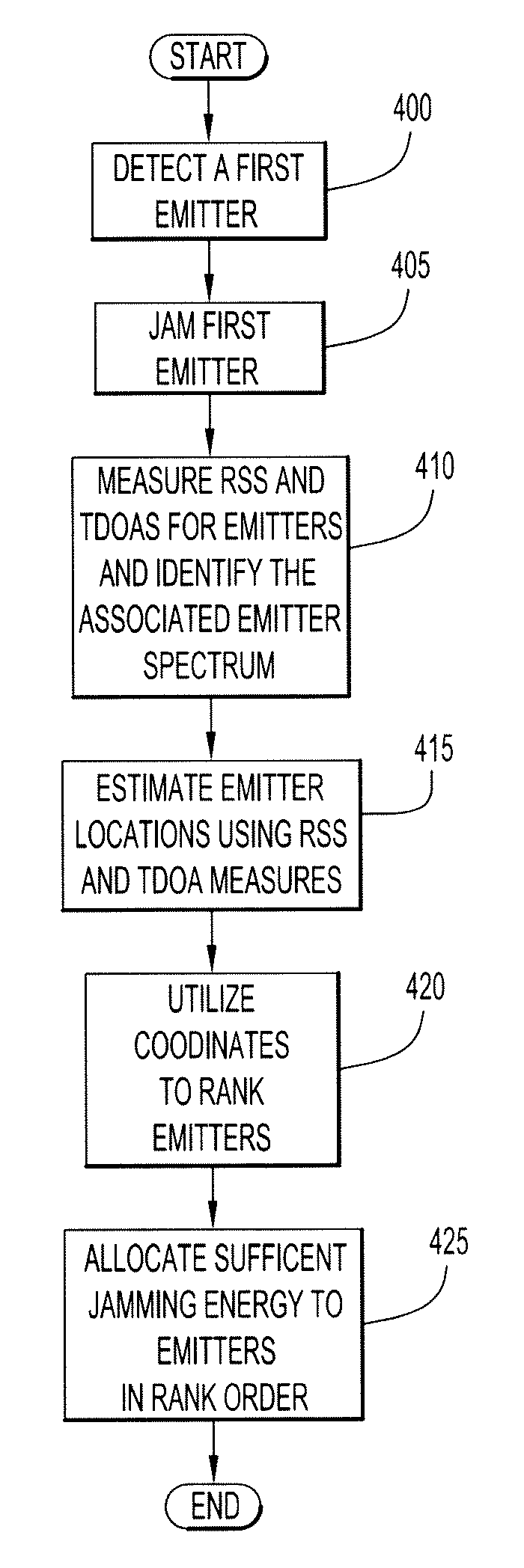
System and method for allocating jamming energy based on three-dimensional geolocation of emitters
ActiveUS8615190B2Cost-effectiveSmallWave based measurement systemsTelephonic communicationGeolocationEnergy based
According to an embodiment of the present invention jamming energy is allocated to a plurality of emitters based on a three-dimensional (3-D) emitter geolocation technique that determines the geolocation of radio frequency (RF) emitters based on energy or received signal strength (RSS) and / or time differences of arrival (TDOAs) of transmitted signals. The three-dimensional (3-D) emitter geolocations are used to rank emitters of interest according to distance and available radio frequency (RF) jamming energy is allocated to the emitters in rank order. The techniques may be employed with small unmanned air vehicles (UAV), and obtains efficient use of jamming energy when applied to radio frequency (RF) emitters of interest.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Methods and apparatus to position a mobile receiver using downlink signals, part I
InactiveUS6208297B1Reduce the impactReduce impactDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationPhase differenceImage resolution
The invention comprises of methods and apparatus to estimate the position and velocity of a Mobile Receiver (MR) using either the Time Of Arrival (TOA) of signals received by the MR, their Phase Of Arrival (POA), their Strength Of Arrival (SOA), their Frequency Of Arrival (FOA), or a combination thereof, with respect to a reference produced by a Reference Receiver (RR) of known location. In order to solve for the coordinates of the MR, the invention uses either hyperbolic multilateration based on Time Difference Of Arrival (TDOA), or linear multiangulation based on Phase Difference Of Arrival (PDOA), or both. In order to solve for the velocity of the MR, the patent uses FOA based on Frequency Difference Of Arrival (FDOA). An important contribution of this invention is the way the MR receives, processes and combines available signals for location purposes. Another important contribution of this invention is the way the RR receives, processes and combines available signals for reference purposes. Yet another important contribution of the invention is the application of Super-Resolution (SR) techniques at both the MR and the RR to increase the resolution of the estimated TOAs, POAs, SOAs, or FOAs.
Owner:CAPITOL ENERGY RESOURCES INC +1
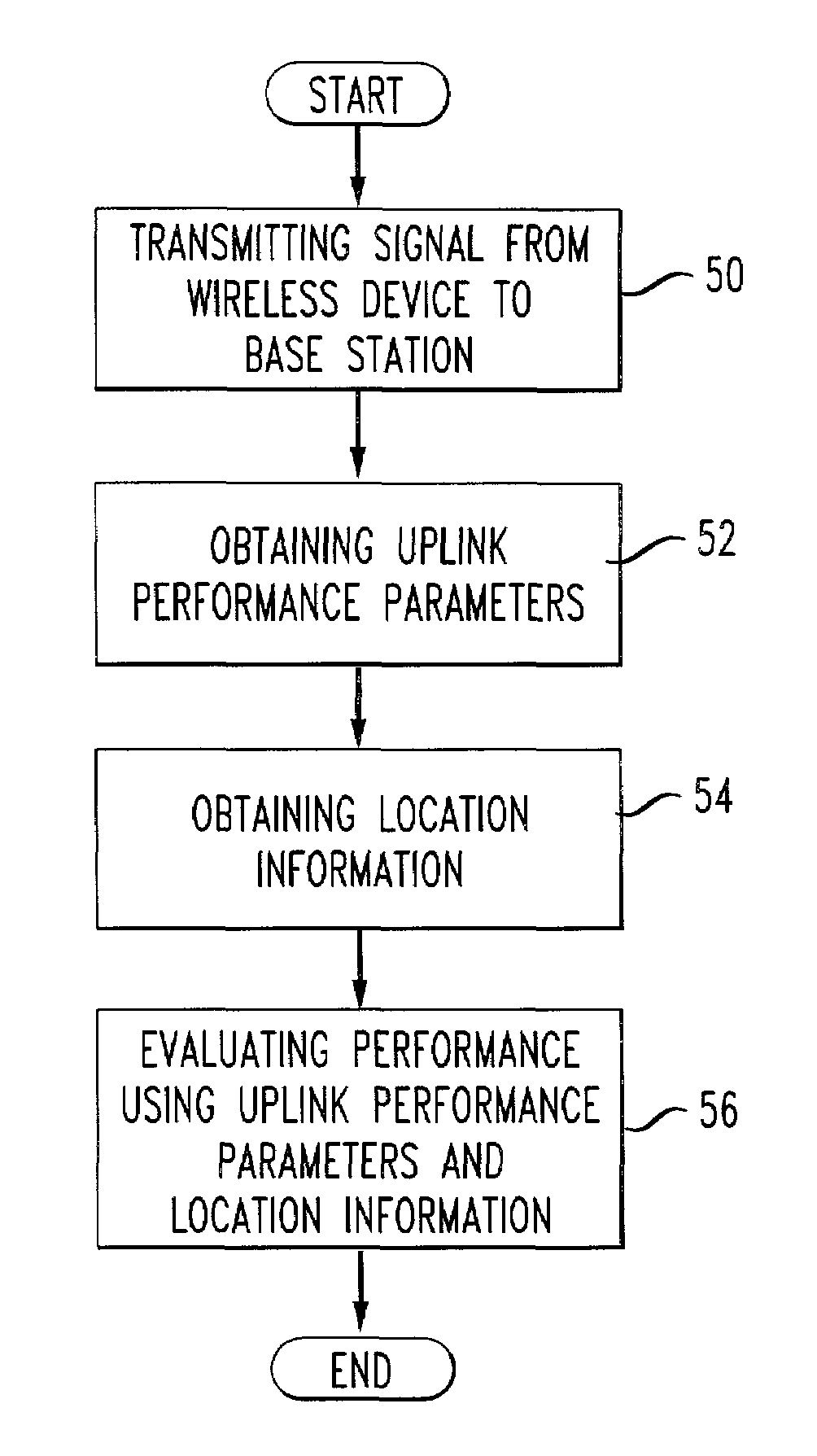
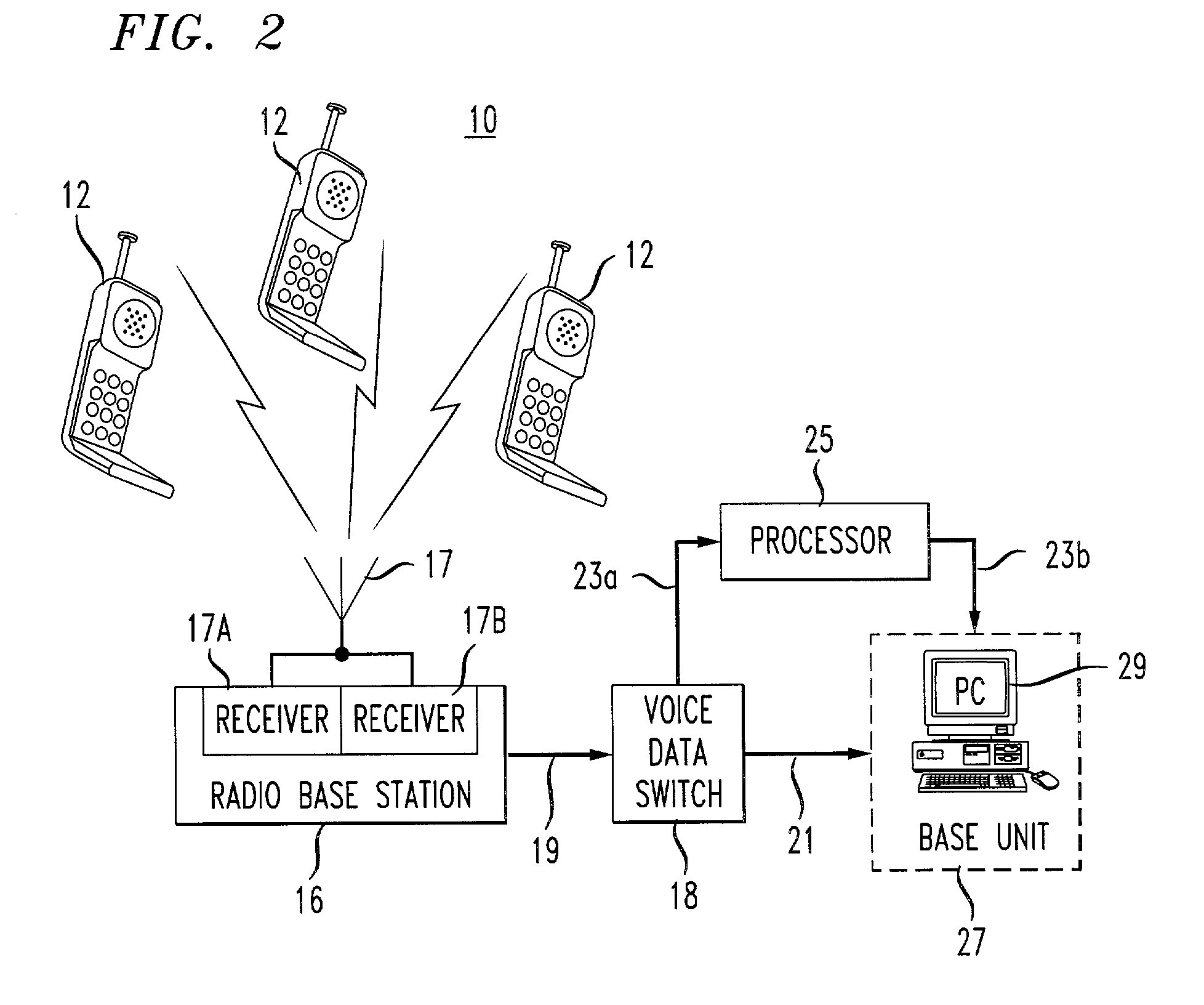
Monitoring network performance using individual cell phone location and performance information
A system and method of collecting call data from a Mobile Telephone Switching Office and combining this data with location information of a wireless device (or devices) to generate information reports concerning the electromagnetic coverage of a cell site. The collection of call data from a switch permits consideration of uplink information in the analysis of system performance. This information combined with location information obtained using a time difference of arrival (TDOA) technique allows the cell site to be evaluated and to remove transient effects associated with, for example, local terrain and other physical impairments.
Owner:AT&T WIRELESS SERVICES
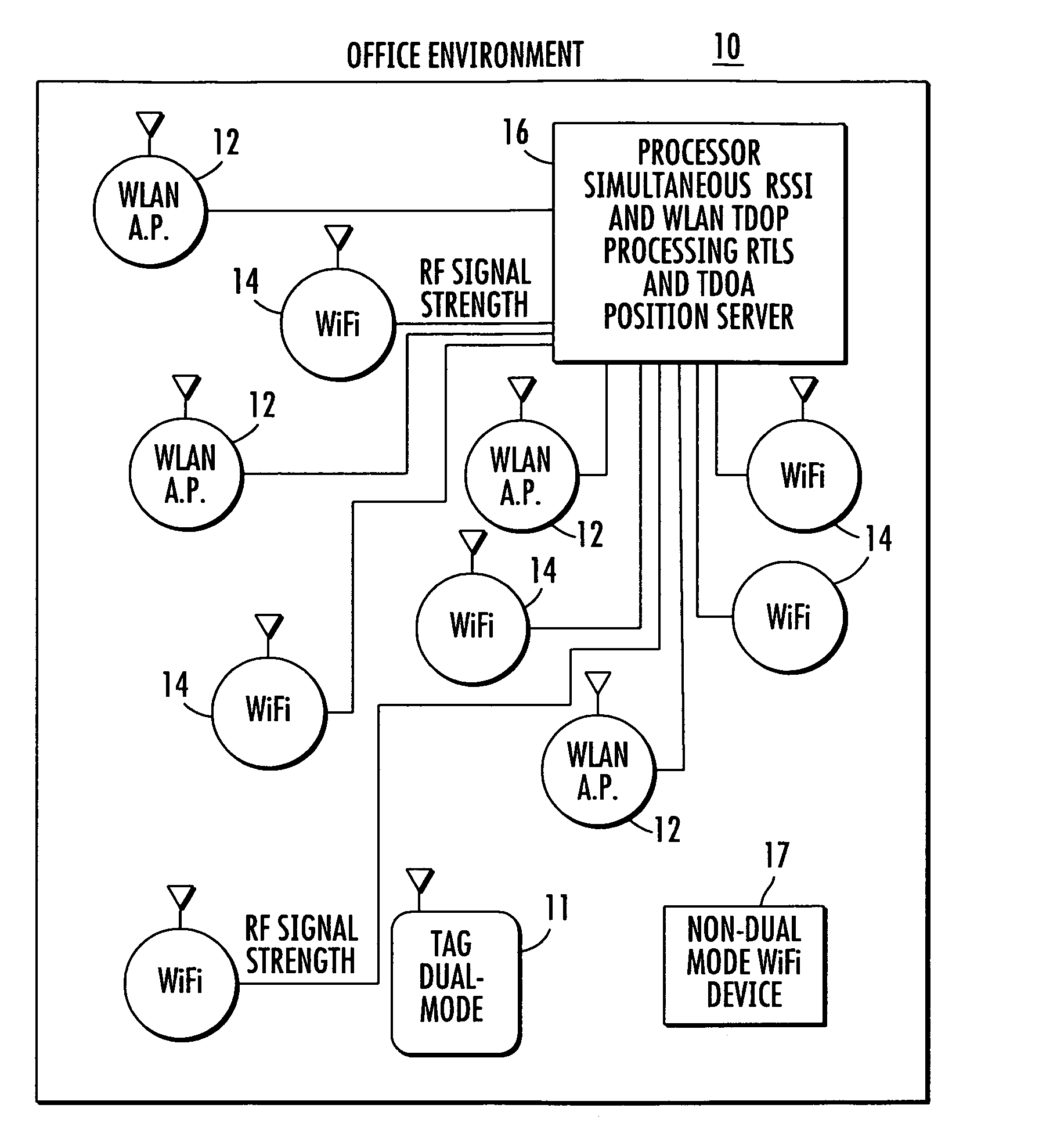
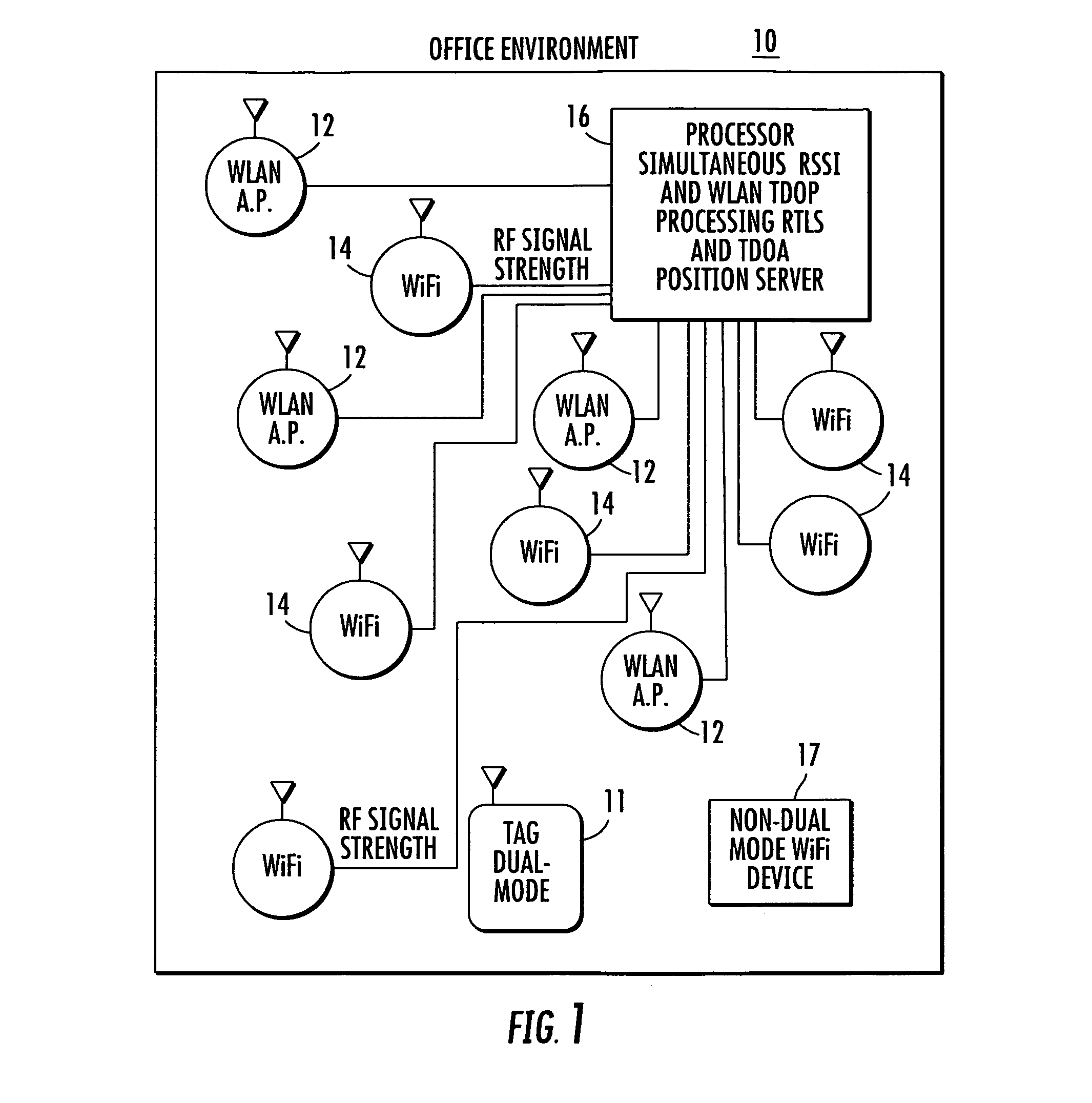
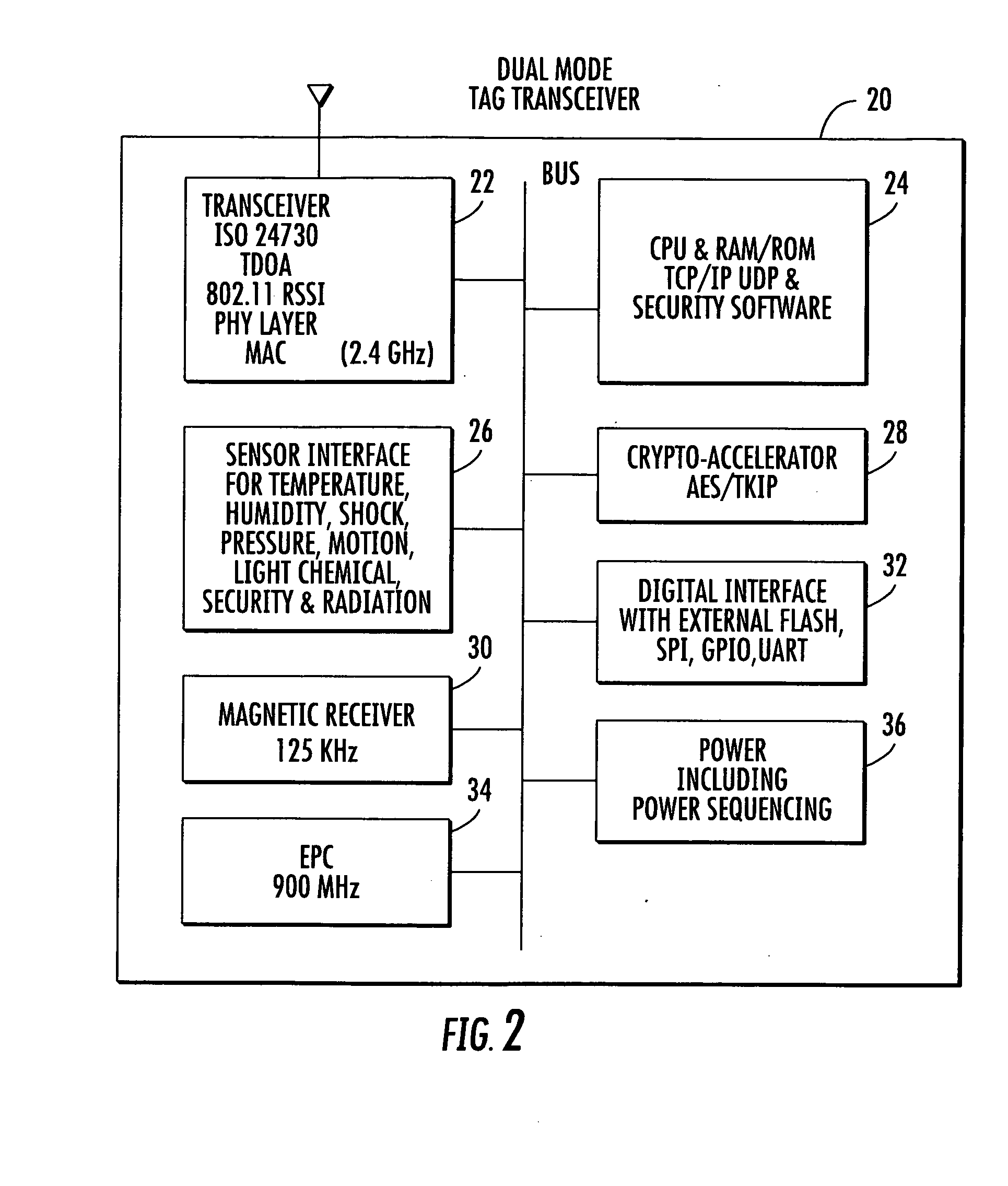
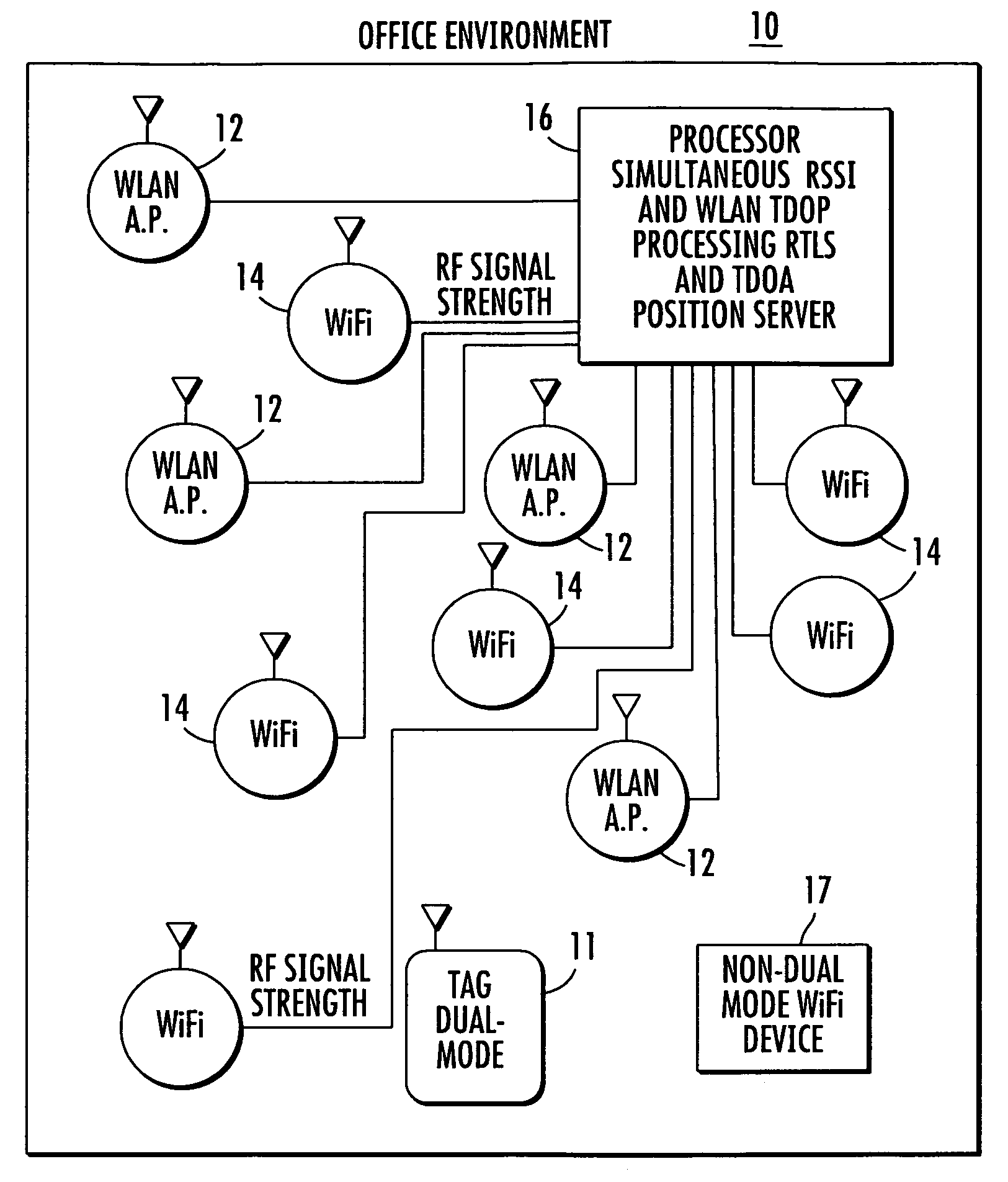
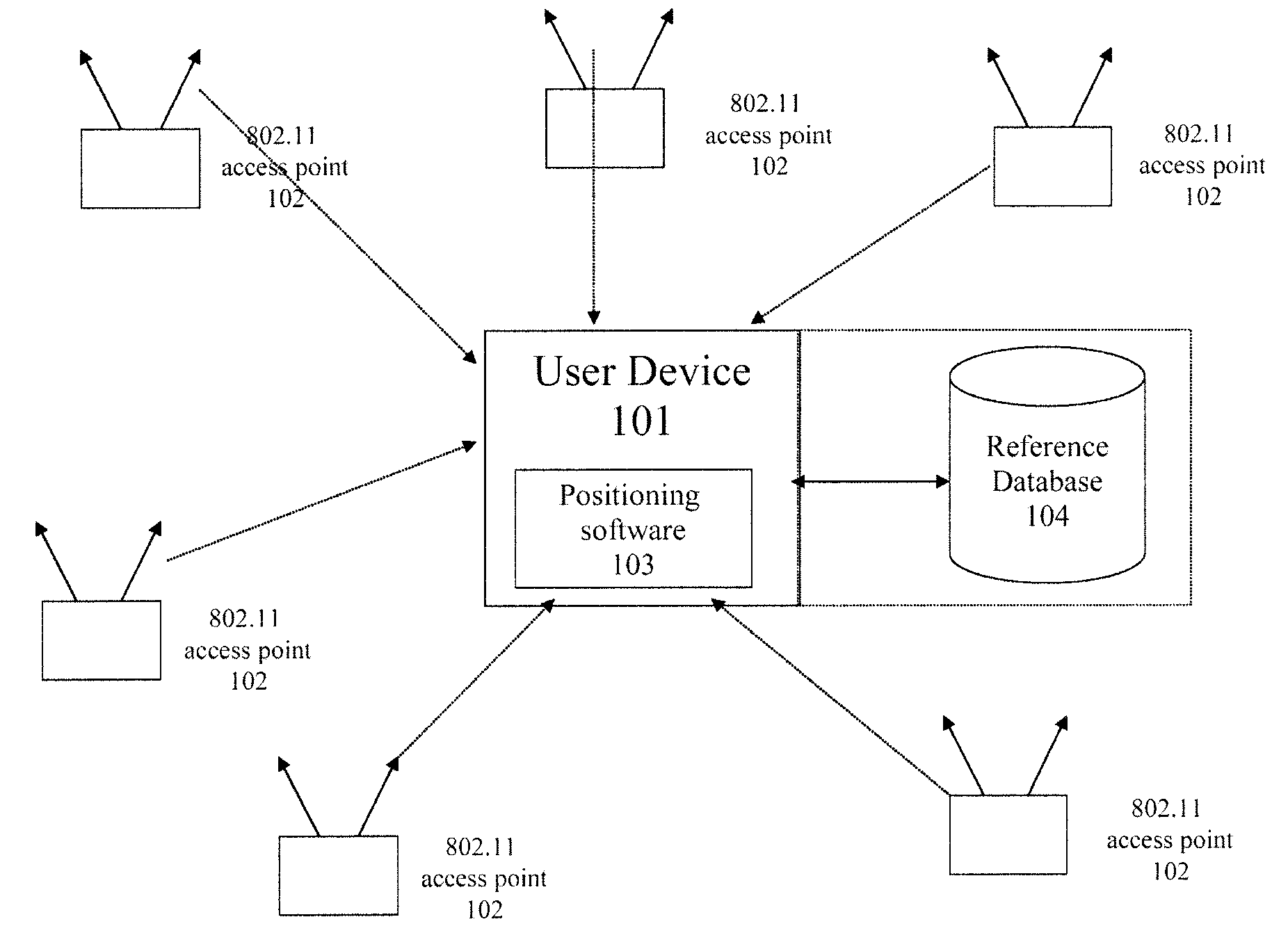
Location system for wireless local area network (WLAN) using RSSI and time difference of arrival (TDOA) processing
ActiveUS20080130604A1Direction finders using radio wavesNetwork topologiesDual modeReceived signal strength indication
A wireless local area network includes a plurality of access point stations that receive and transmit communications signals within the wireless local area network. A first set of access point stations are WiFi compliant and measure signal strength and determine the received signal strength indication (RSSI). A second set of access point stations are operable in accordance with the time of arrival (TOA) real time location standard (RTLS). A dual mode mobile station is operative for multimode communication with both the WiFi and RTLS compliant access point stations. A location processor is operatively connected with each of the access point stations and processes the RSSI and creates a RSSI locate map and processes communication signals from the second set of access point stations and determines which signals are first-to-arrive signals to locate the mobile station and update the RSSI locate map and locate any non-dual mode WiFi devices.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
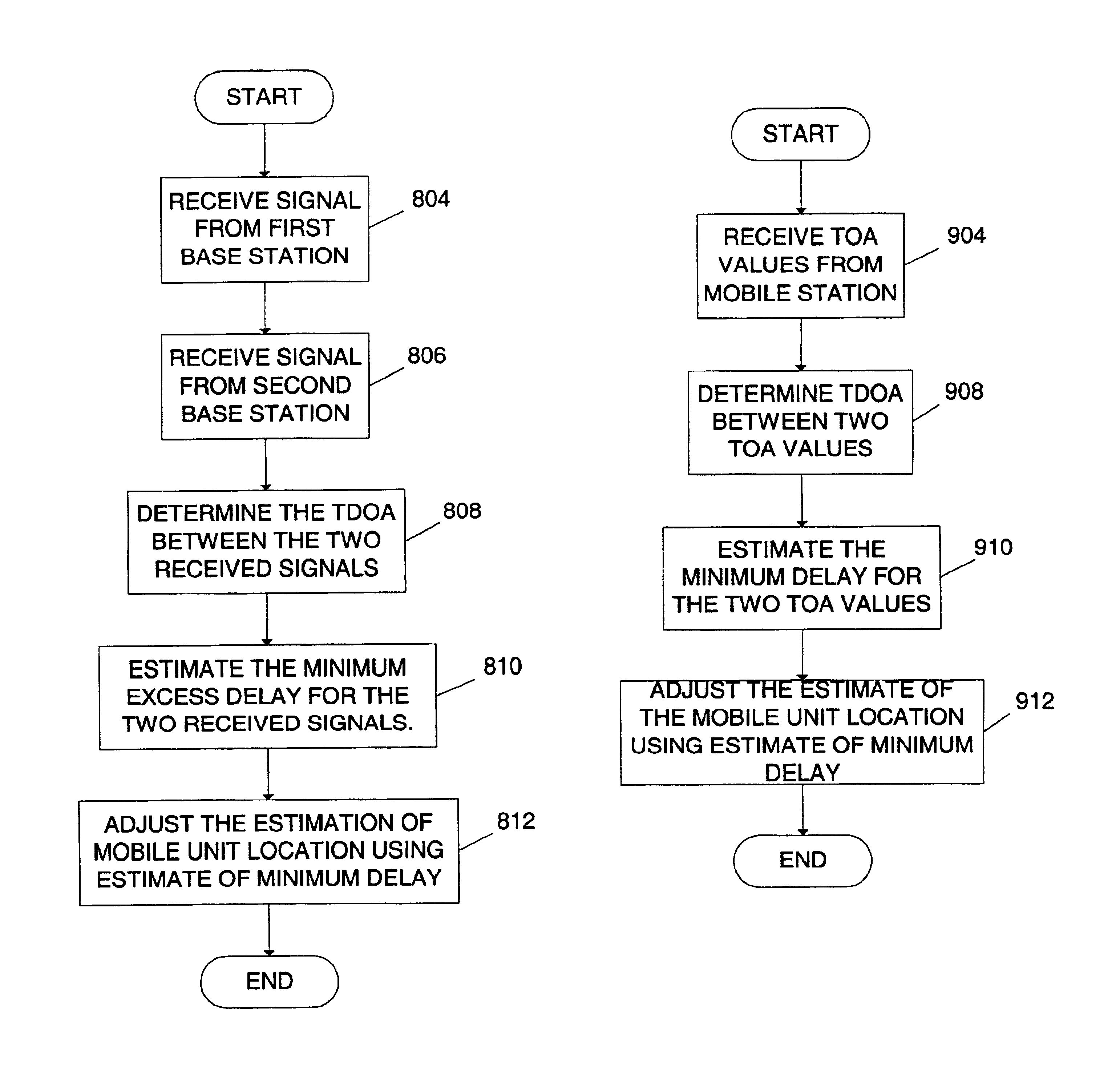
Method and apparatus for detecting excess delay in a communication signal
InactiveUS6941144B2Improve reliabilityConstrain measurementPosition fixationTelephonic communicationEngineeringMultilateration
A method and apparatus of determining a lower bound of an excess delay in a time of arrival measurement of a received signal. Determining the lower bound of an excess delay in a time of arrival measurements includes receiving signals from at least two base stations and determining the time difference of arrival between the received signals from their respective base stations. Then estimating a lower bound of excess delay introduced into the signals received from the base stations based on the time of arrival of the signals from the respective base stations and a known distance between the base stations. The lower bound of excess delay may be used to adjust the estimate of a mobile unit's location based on the time of arrival measurements of the received signals.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Methods and apparatus to position a mobile receiver using downlink signals, part II
InactiveUS6204812B1Use minimizedLow costDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationPhase differenceMultilateration
The invention consists of methods and apparatus to estimate the position and velocity of a Mobile Receiver (MR) using either the Time Of Arrival (TOA) of signals received by the MR, their Phase Of Arrival (POA), their Strength Of Arrival (SOA), their Frequency Of Arrival (FOA), or a combination thereof, with respect to a reference produced by a Reference Receiver (RR) of known location. In order to solve for the coordinates of the MR, the invention uses either hyperbolic multilateration based on Time Difference Of Arrival (TDOA), or linear multiangulation based on Phase Difference Of Arrival (PDOA), or both. In order to solve for the velocity of the MR, the patent uses FOA based on Frequency Difference Of Arrival (FDOA). An important contribution of this invention is the way the MR receives, processes and combines available signals for location purposes. Another important contribution of this invention is the way the RR receives, processes and combines available signals for reference purposes.
Owner:CELL LOC LOCATION TECH
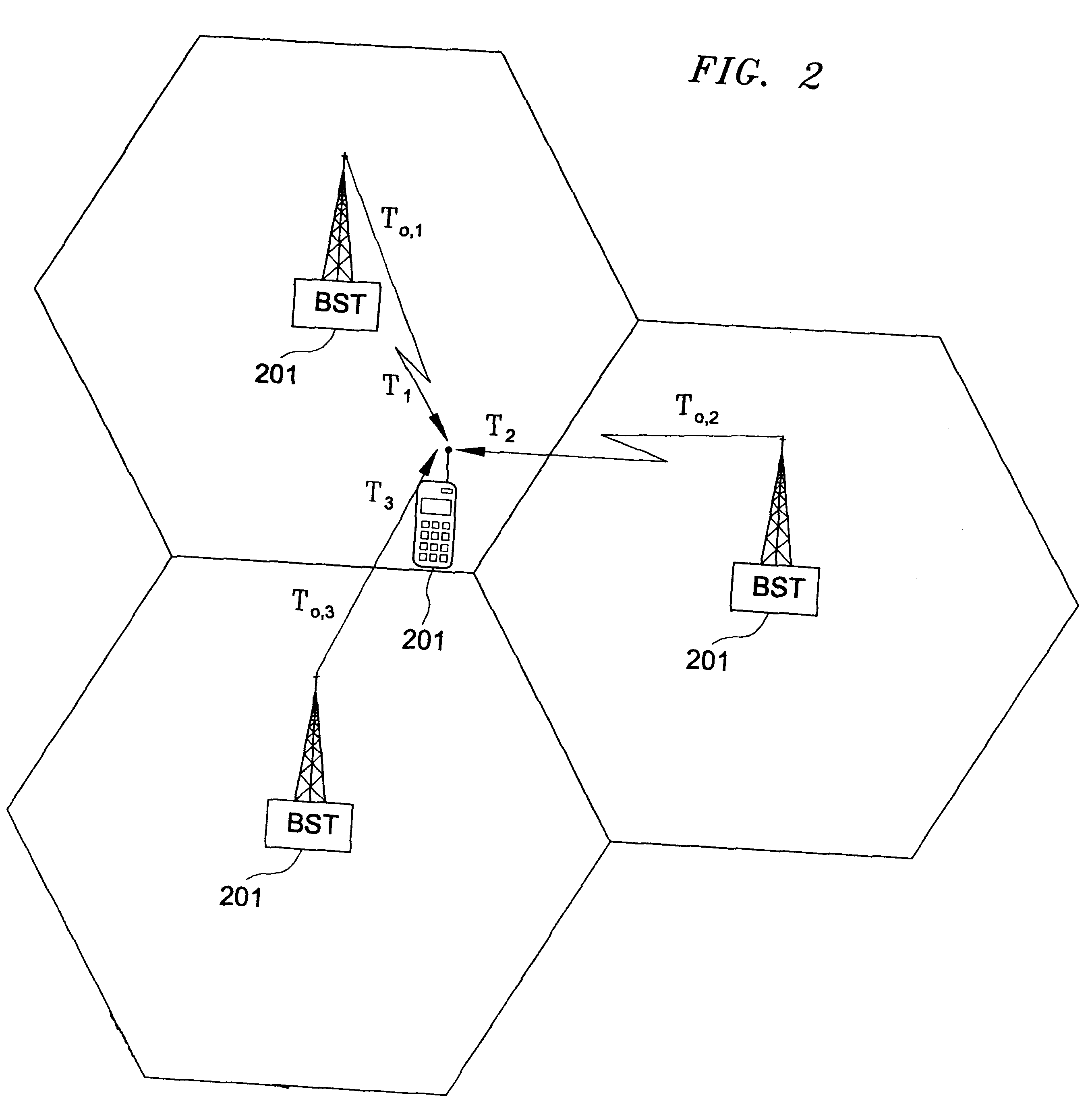
Method and system for mobile station positioning in cellular communication networks
InactiveUS6901264B2Improve accuracy of manyExpand coverageDirection finders using radio wavesNavigation instrumentsMultilaterationMobile station
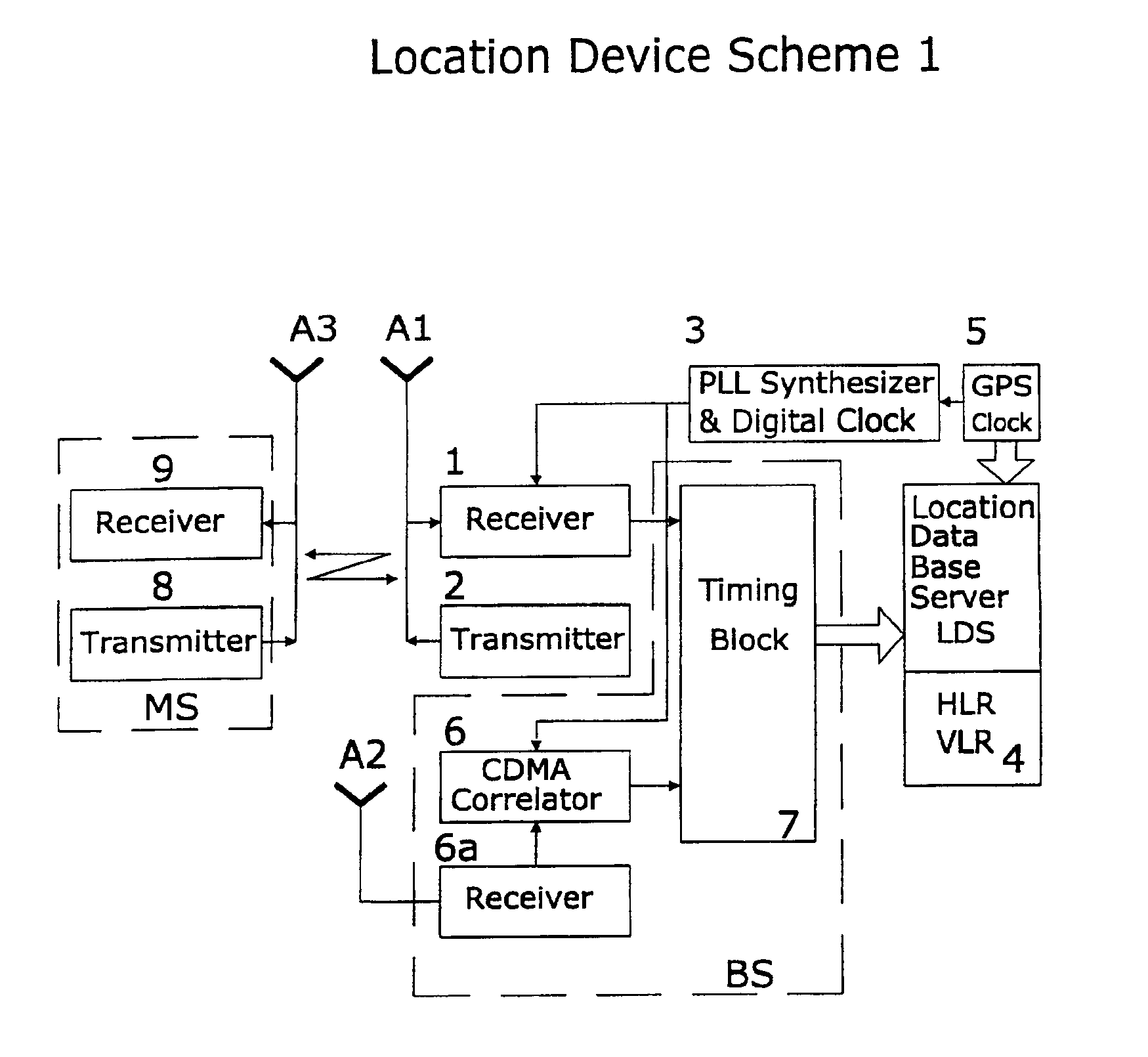
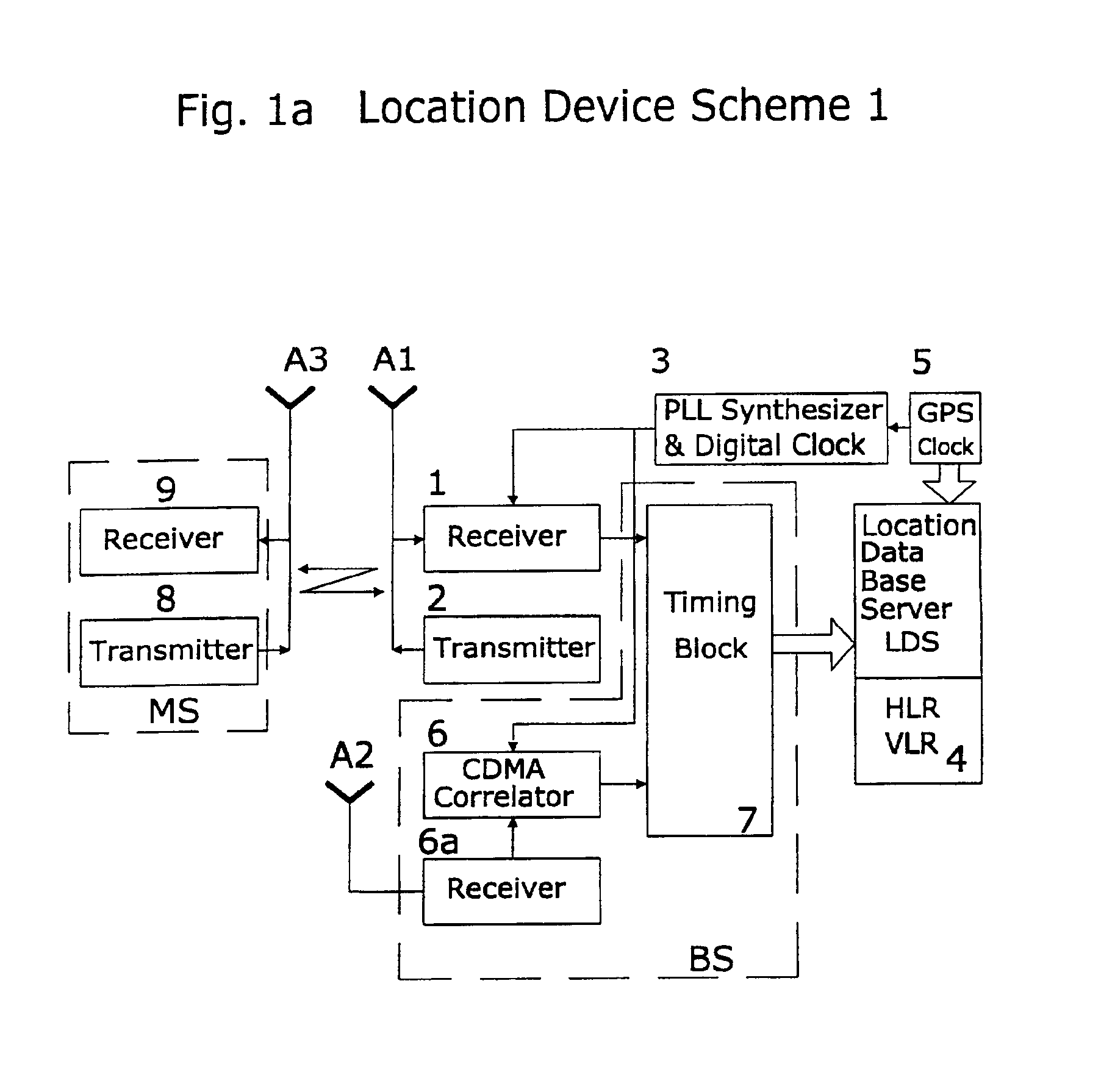
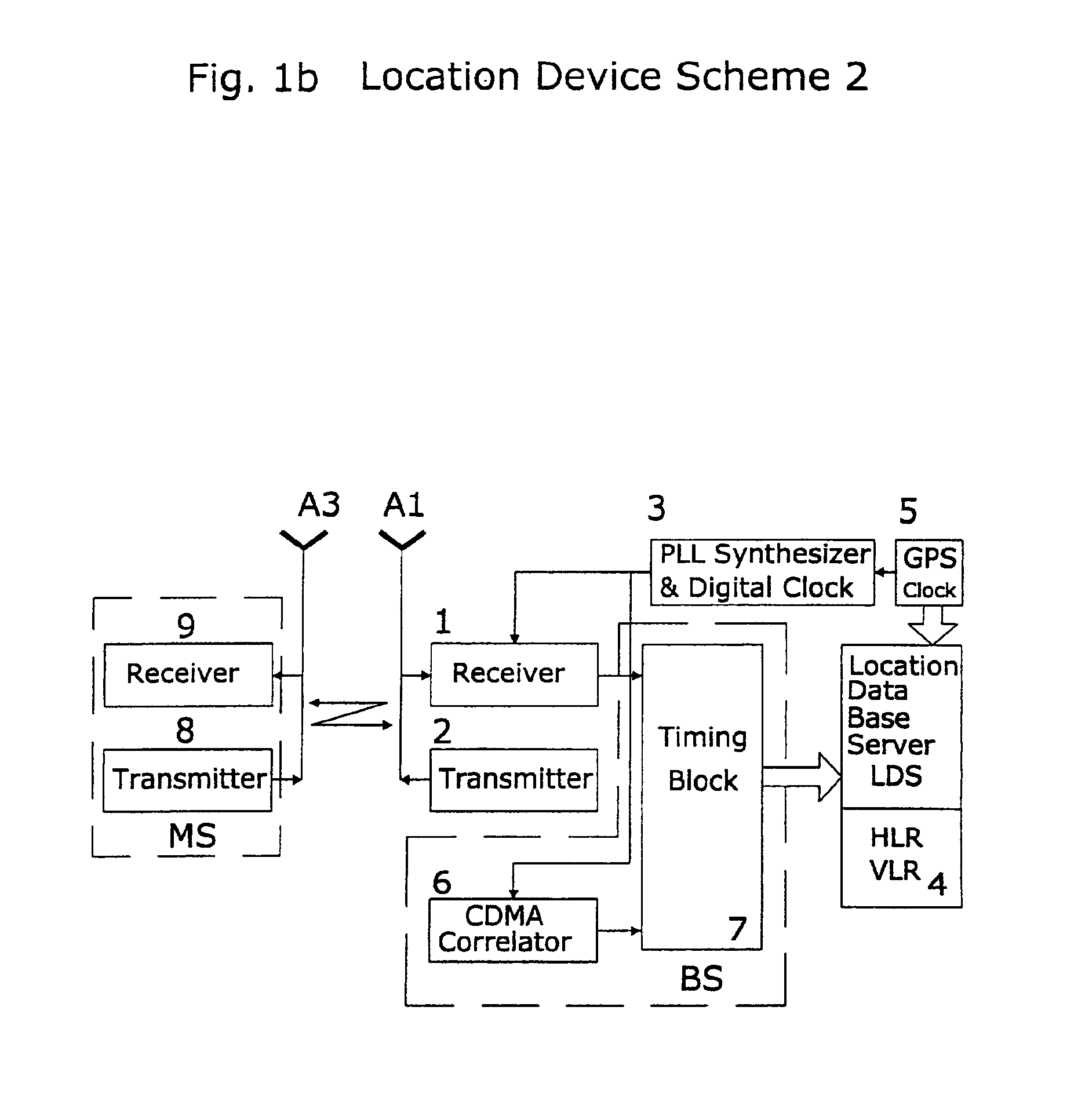
A system of cell phone positioning in real time is provided with specialized location device installations on multiplicity of base stations BSs in CDMA and TDMA cellular communication networks. The purpose of the positioning system is to enable tracking and locating large quantities of anonymous mobile cell phones MS in any number of network cells to be used for real time traffic-forecasting systems, emergency services E911, and other client-initiated position requests. Location data thus obtained can be continuously updated from vehicular-based cellular phones, collected, processed and used as a basis for input to intelligent transportation systems, such as real time urban traffic guidance for vehicular congestion and intelligent traffic control systems. The system is capable of covering large urban geographical areas and number of independent cell structures serving thousands of mobile cell phone clients. It is an independent plug-in solution with specialized synchronized location device installations in each cell BS. Centrally located specialized location software based on Time of Arrival (TOA) and Time Difference of Arrival (TDOA) methods for high speed location processing in central Location Database Server (LDS). The inventive system consists of number of component functions: Operator-initiated functions, location device functions and software enabled positioning functions.
Owner:MAKOR ISSUES & RIGHTS
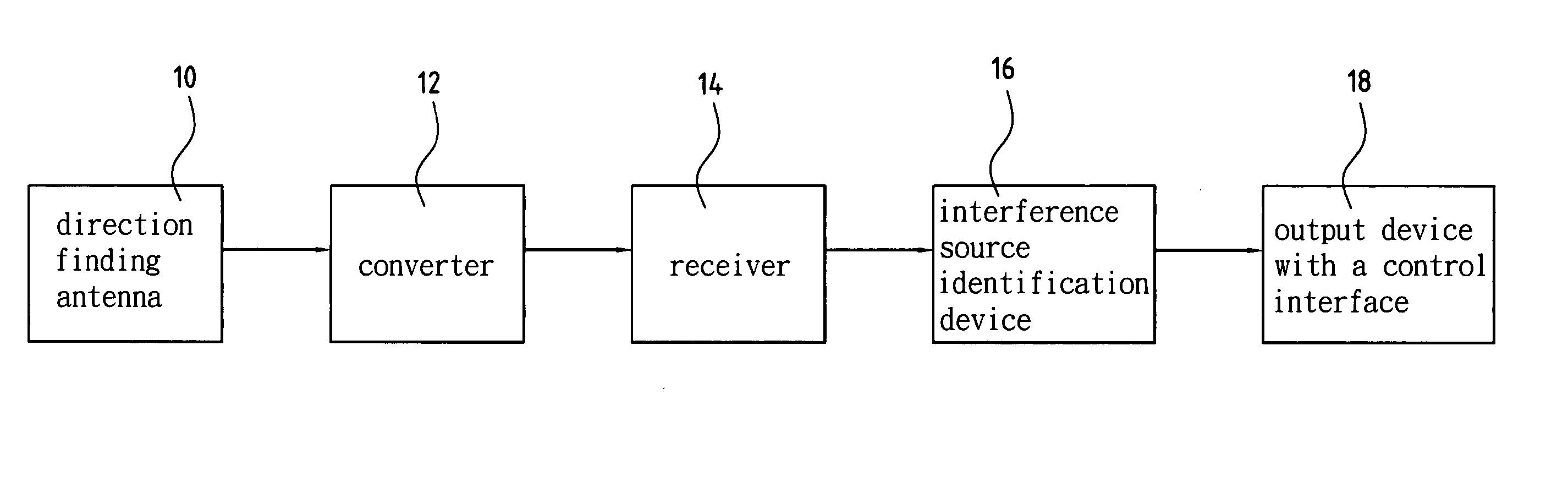
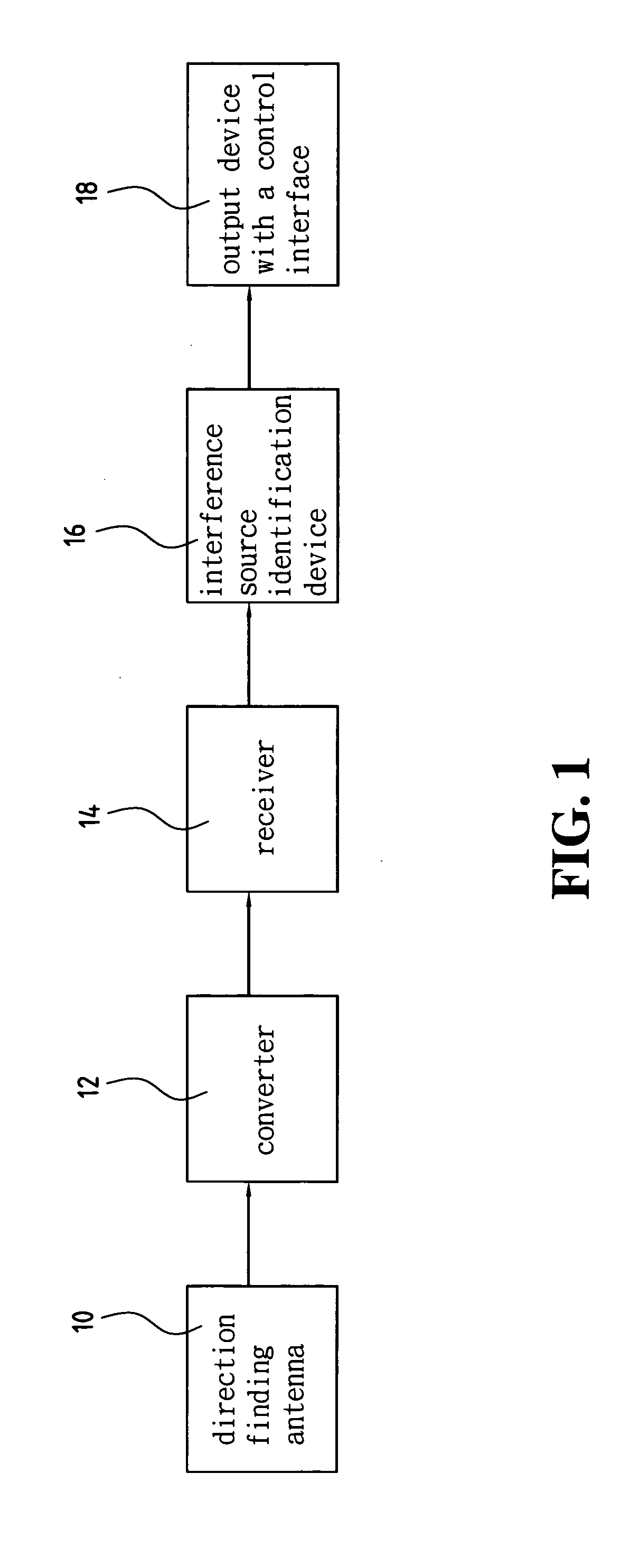
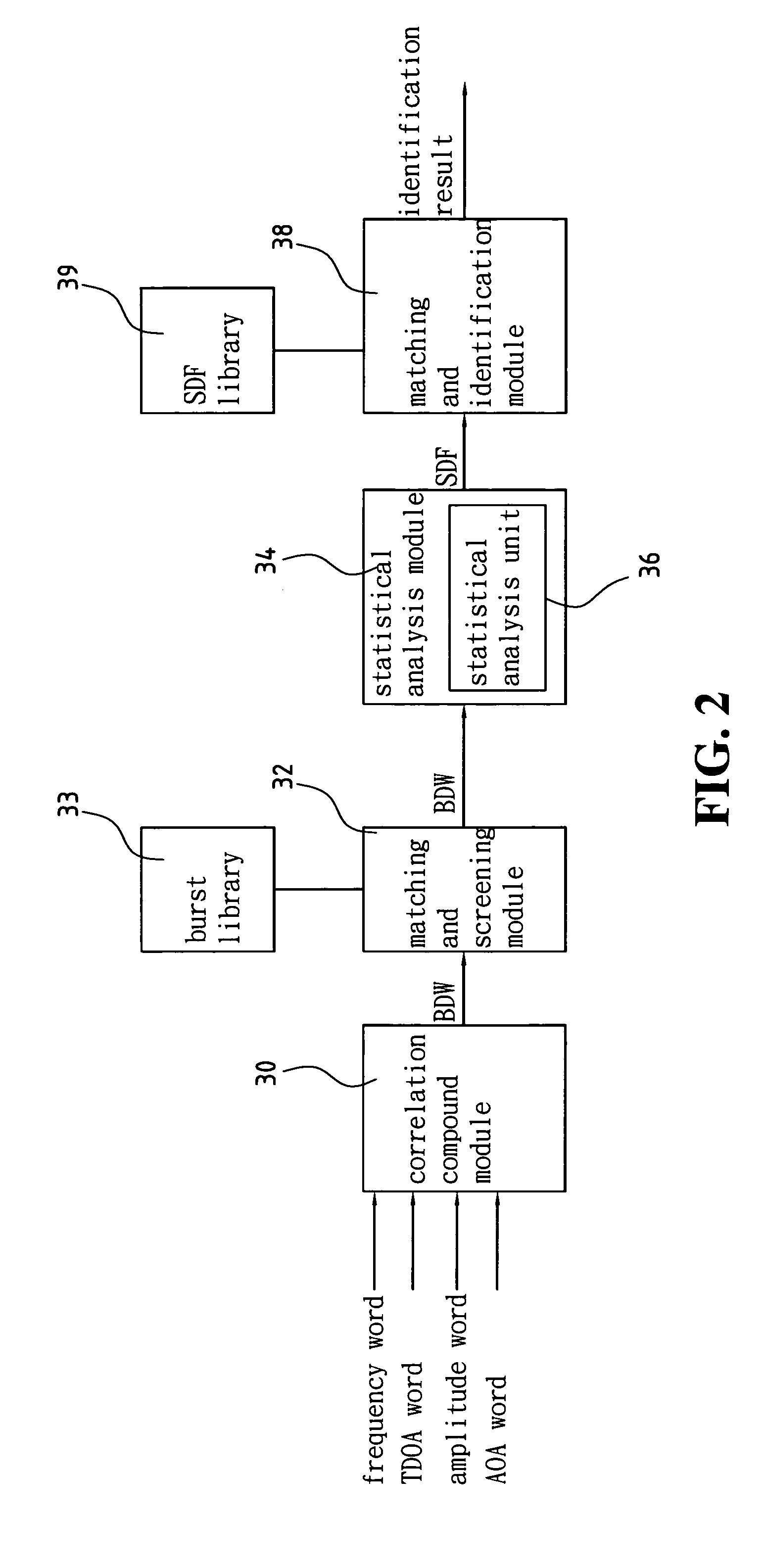
Device and method for identifying interference source in wireless communications
InactiveUS20050117676A1Improve transmission performanceError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorLine-faulsts/interference reductionDiscriminatorMultilateration
A device for identifying interference source in wireless communications is provided, including a correlation compound module, a matching and screening module, a statistical analysis module, and a match identification module. The correlation compound module uses the time of arrival (TOA) of the burst as the synchronization basis to compound the correlated frequency word, time difference of arrival (TDOA) word, amplitude word and angle of arrival (AOA) word to form a burst descriptor word (BDW). The matching and screening module uses the BWD to match the burst library to screen out the non-interference sources. The statistic analysis module uses the screened outcome for statistical analysis, and obtains a source discriminator file (SDF). The matching and identification module uses the SDF to search the interference source library for matching and obtains an identification result.
Owner:ACCTON TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION
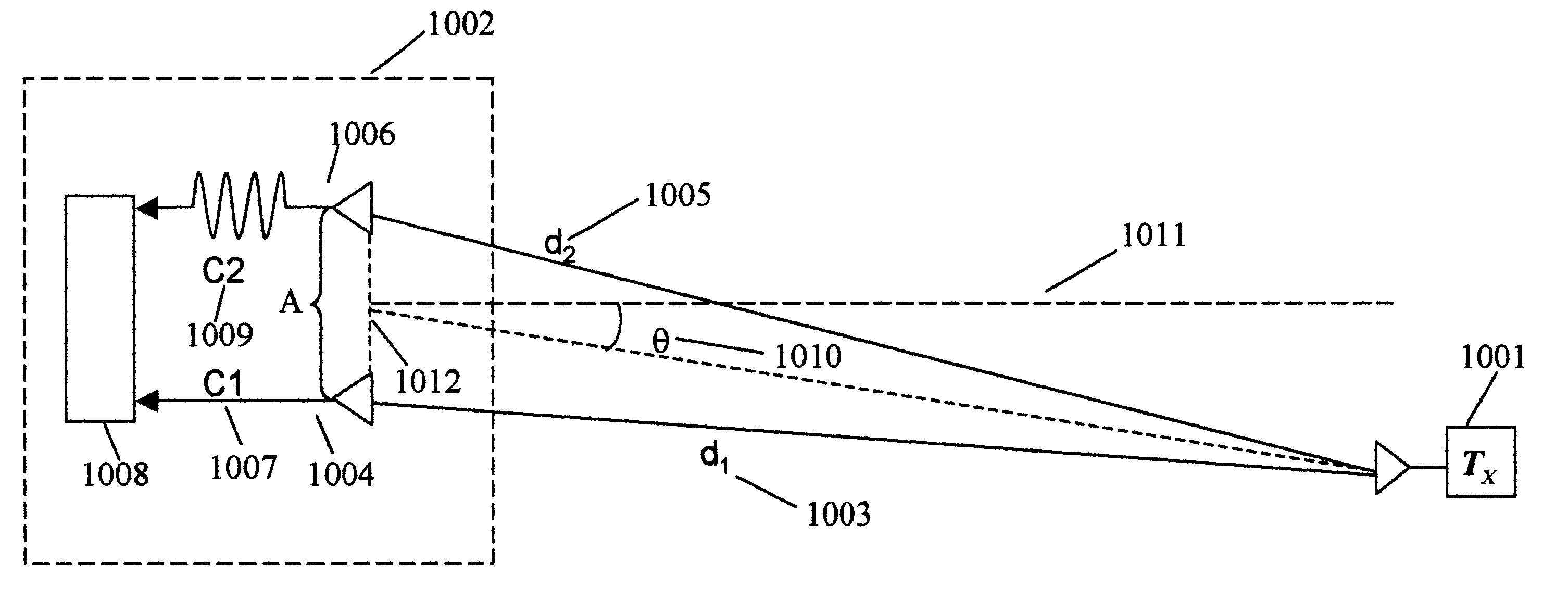
Impulse radio receiver and method for finding angular offset of an impulse radio transmitter
InactiveUS6760387B2Radio wave direction/deviation determination systemsAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsLeading edgeRadio reception
A system and method for determining angular offset of an impulse radio transmitter using an impulse radio receiver coupled to two antennae. The antennae are separated by some known distance, and, in one embodiment, one antennae is coupled to the radio with cable delay. Impulse signals from the antennae are measured to determine the time difference of arrival of one such signal received by one antenna compared to that of the other antenna. Time differential is measured by autocorrelation of the entire impulse radio scan period, by detecting the leading edges of both incoming signals or various combinations of these methods. Using a tracking receiver, the pulses may be continuously tracked thus providing real time position information.
Owner:HUMATICS CORP
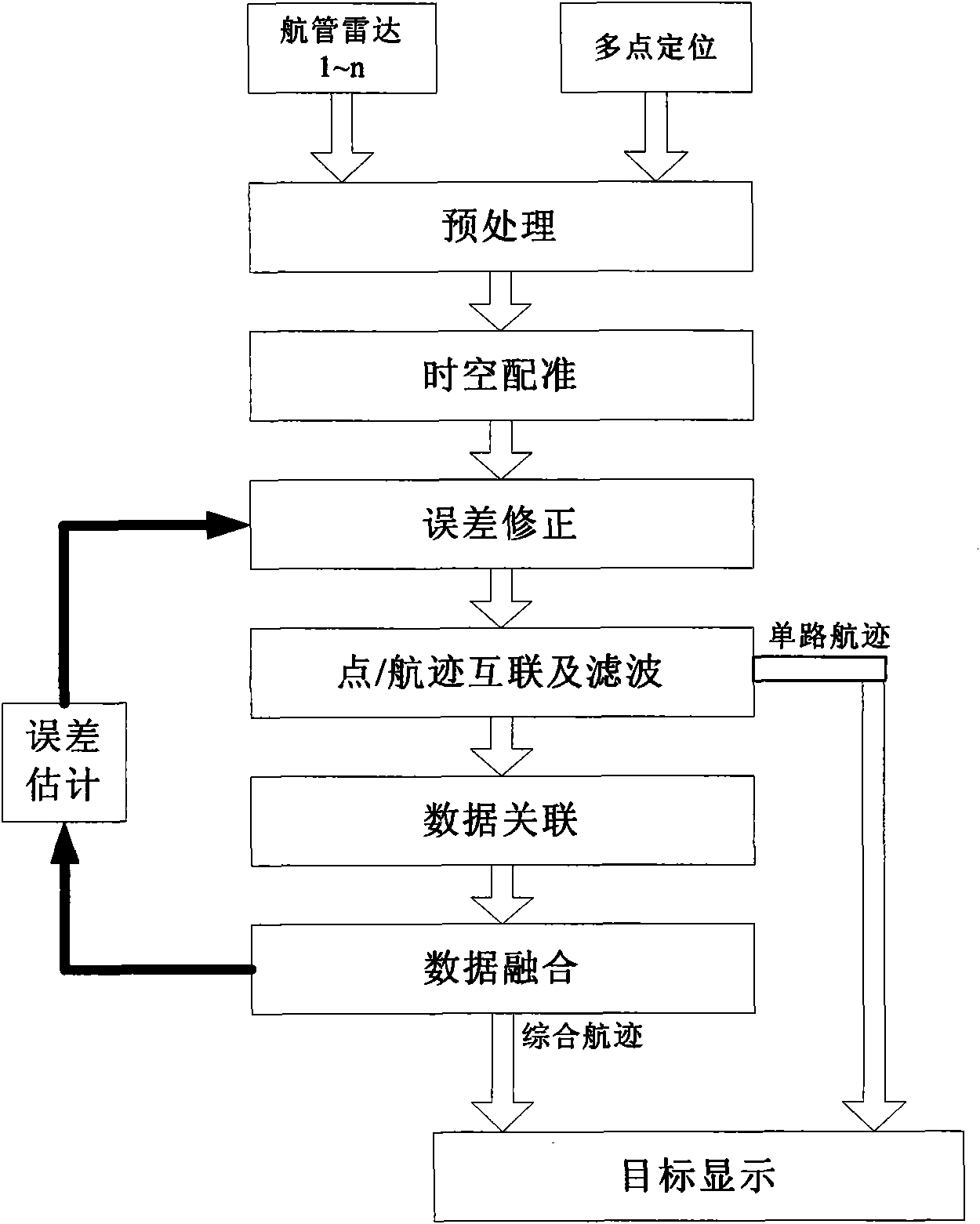
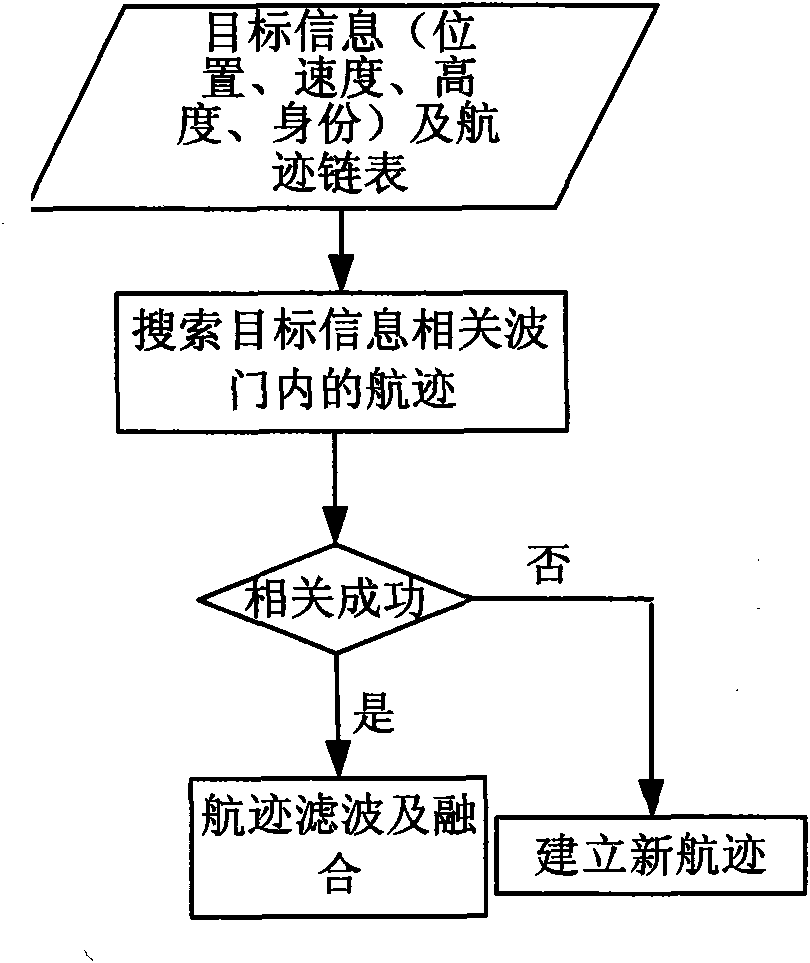
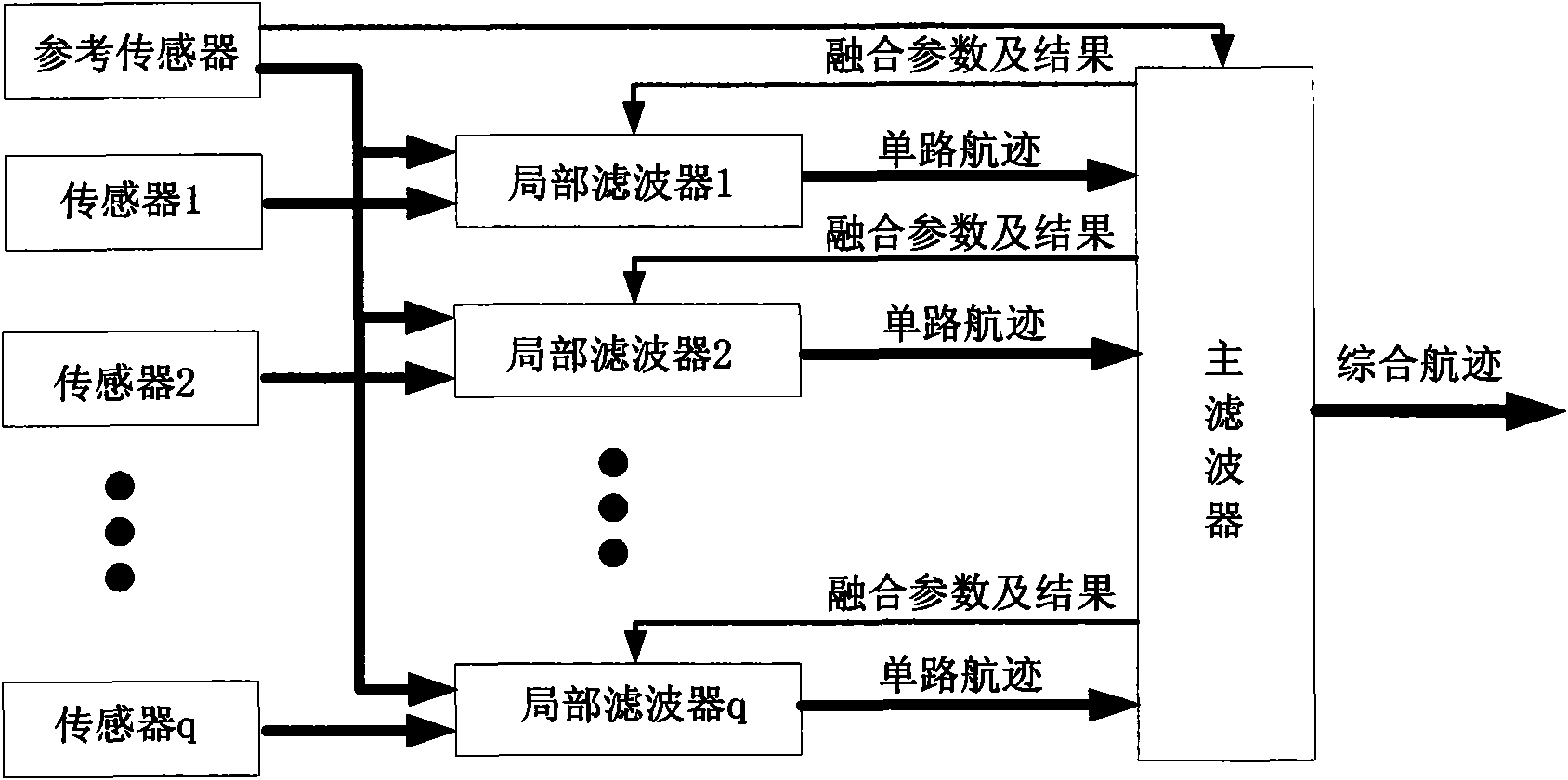
Federated Kalman filtering-based method for fusing multilateration data and radar data
InactiveCN101655561AReduce performanceCorrection errorRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadarFiltration
The invention relates to a Federated Kalman filtering-based method for fusing multilateration data and radar data, comprising seven processes: pretreatment, time and space registration, error correction, single-sensor line tracking or airborne trace interconnection and filtration, data association, data fusion as well as error estimation. On the basis of multiclass monitoring information, the technical scheme of the invention establishes data association mapping relations among all classes of targets, constructs a process method fusing the multilateration system data and the radar data, realizes deep fusion of all classes of information and comprehensive utilization on effective information, ensures high updating rate of a multilateration system and the whole precision of system monitoringwhen period is less than or equal to 1sec, reduces impact of radar measuring error on system monitoring precision, and significantly improves the tracking precision of the system.
Owner:NANJING LES INFORMATION TECH
Location system for wireless local area network (WLAN) using RSSI and time difference of arrival (TDOA) processing
A wireless local area network includes a plurality of access point stations that receive and transmit communications signals within the wireless local area network. A first set of access point stations are WiFi compliant and measure signal strength and determine the received signal strength indication (RSSI). A second set of access point stations are operable in accordance with the time of arrival (TOA) real time location standard (RTLS). A dual mode mobile station is operative for multimode communication with both the WiFi and RTLS compliant access point stations. A location processor is operatively connected with each of the access point stations and processes the RSSI and creates a RSSI locate map and processes communication signals from the second set of access point stations and determines which signals are first-to-arrive signals to locate the mobile station and update the RSSI locate map and locate any non-dual mode WiFi devices.
Owner:ZEBRA TECH CORP
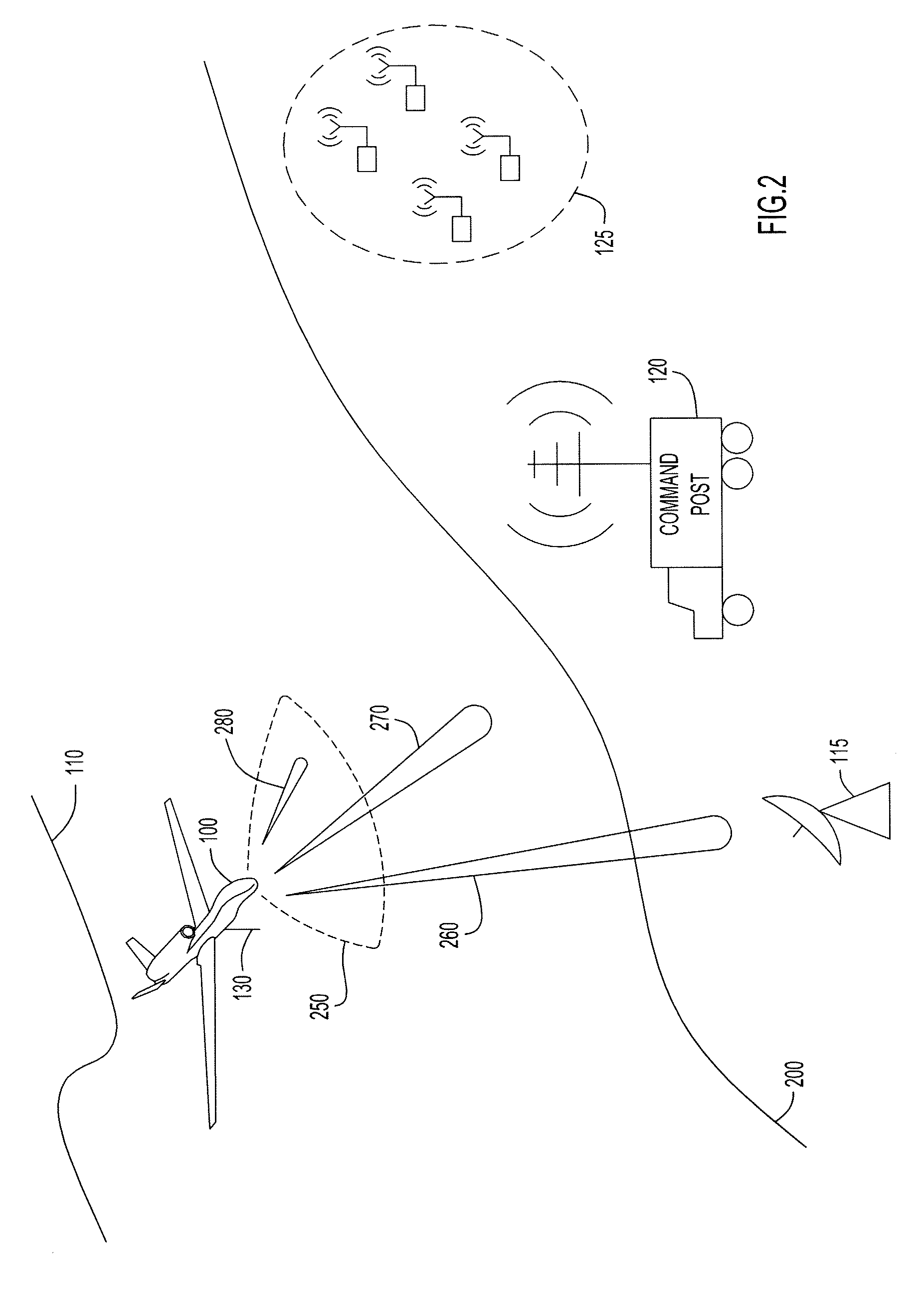
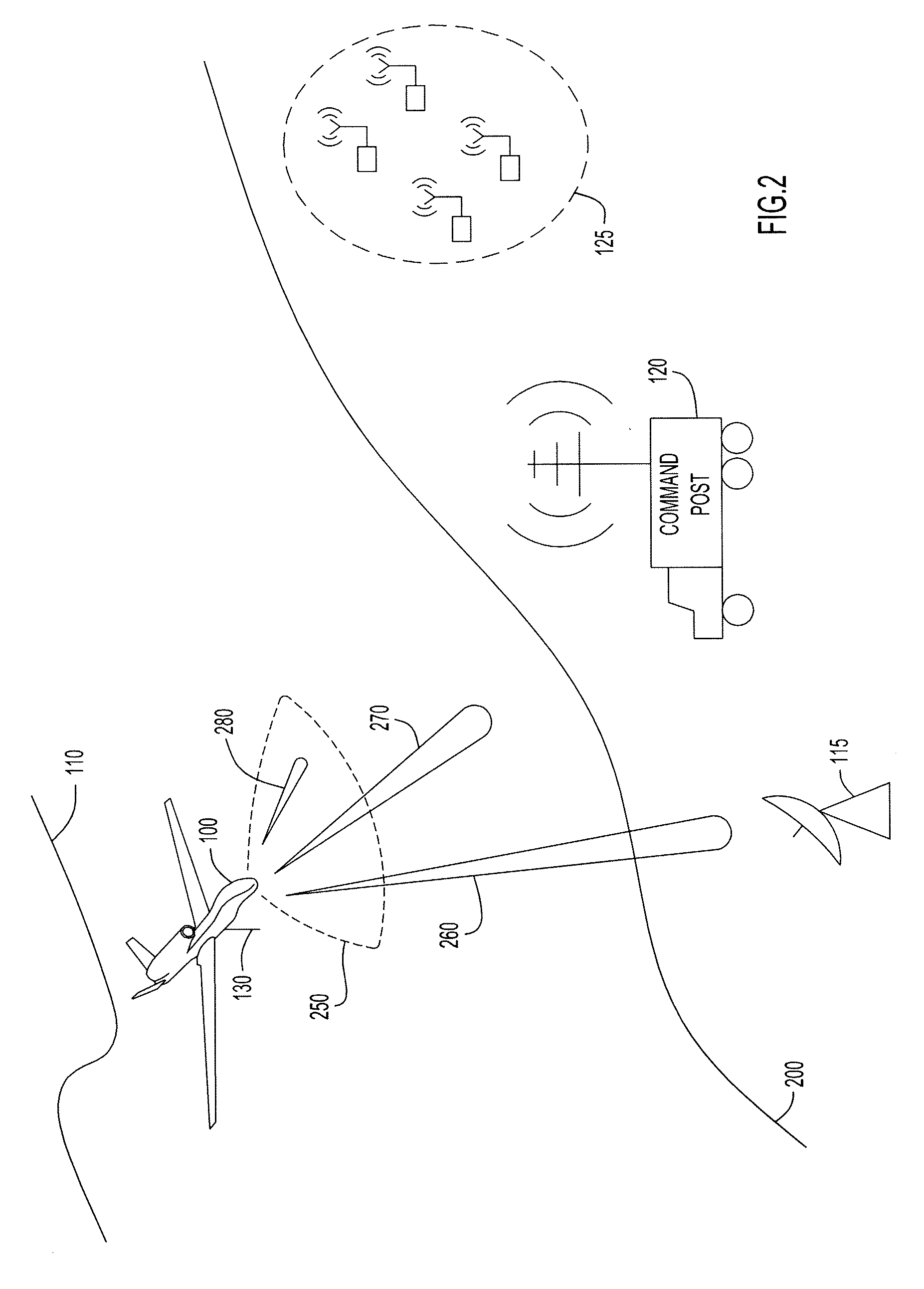
Enhanced Passive Coherent Location Techniques to Track and Identify UAVs, UCAVs, MAVs, and Other Objects
InactiveUS20080088508A1ConfidenceDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationMicro air vehicleRadar
A system and technique is described which has the capability to track and identify, in real time, various aircraft and objects including Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), Unmanned Combat Aerial Vehicles (UCAVs), and Micro Aerial Vehicles (MAVs). The system uses a combination of techniques including conventional automatic dependent surveillance broadcast (ADS-B), transponder multilateration, broadband emitter multilateration, primary and secondary radar, and passive coherent location. A series of enhancement to conventional passive coherent location are described.
Owner:ERA AS
Method and System for User Equipment Location Determination on a Wireless Transmission System
ActiveUS20110286349A1Improve audibilityReduce signal to noise ratioError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsFrequency reuseResource block
Neighbor cell hearability can be improved by including an additional reference signal that can be detected at a low sensitivity and a low signal-to-noise ratio, by introducing non-unity frequency reuse for the signals used for a time difference of arrival (TDOA) measurement, e.g., orthogonality of signals transmitted from the serving cell sites and the various neighbor cell sites. The new reference signal, called the TDOA-RS, is proposed to improve the hearability of neighbor cells in a cellular network that deploys 3GPP EU-TRAN (LTE) system, and the TDOA-RS can be transmitted in any resource blocks (RB) for POSCH and / or MBSFN subframe, regardless of whether the latter is on a carrier supporting both PMCH and POSCH or not. Besides the additional TDOA-RS reference signal, an additional synchronization signal (TDOA-sync) may also be included to improve the hearability of neighbor cells.
Owner:APPLE INC
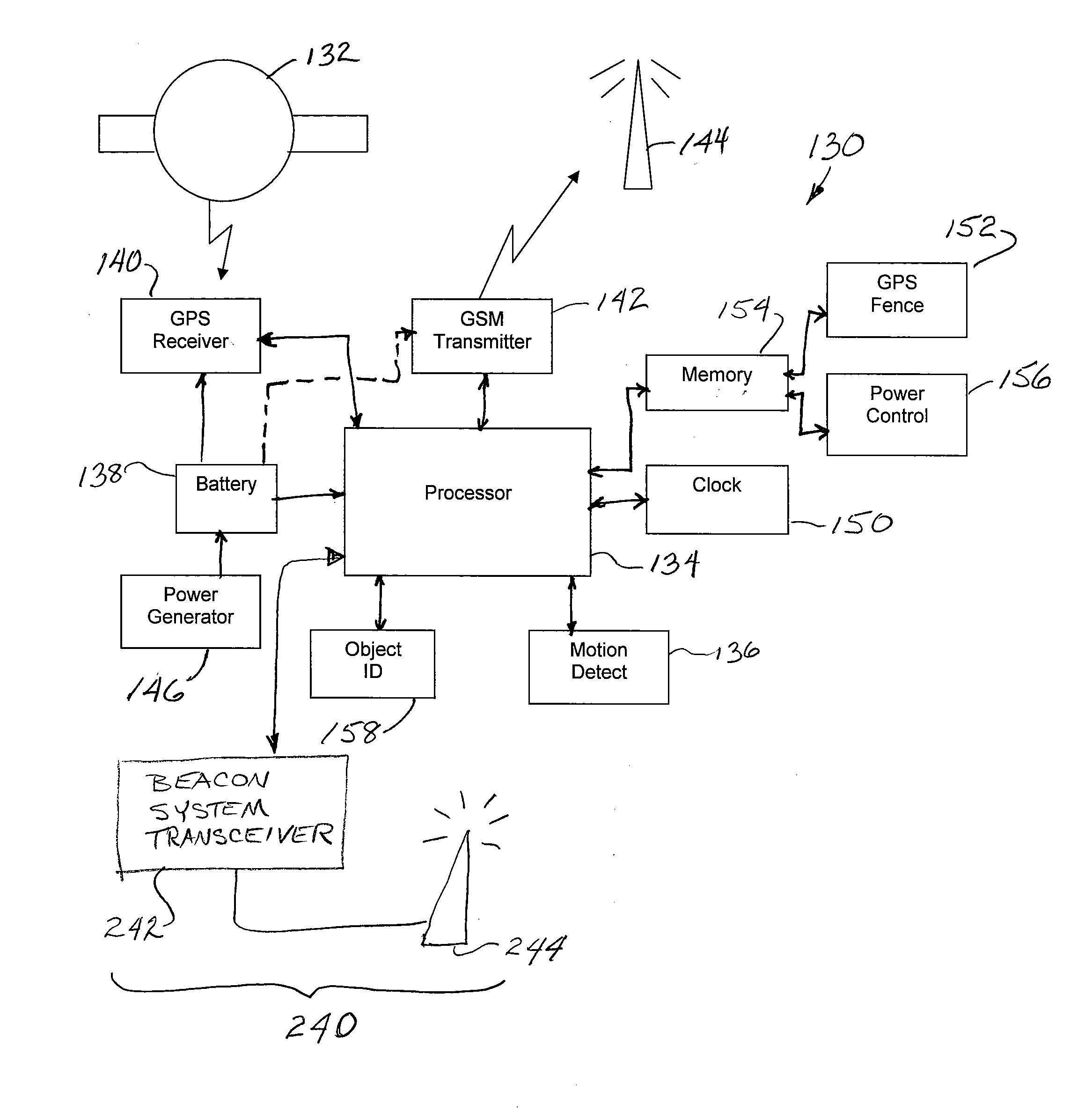
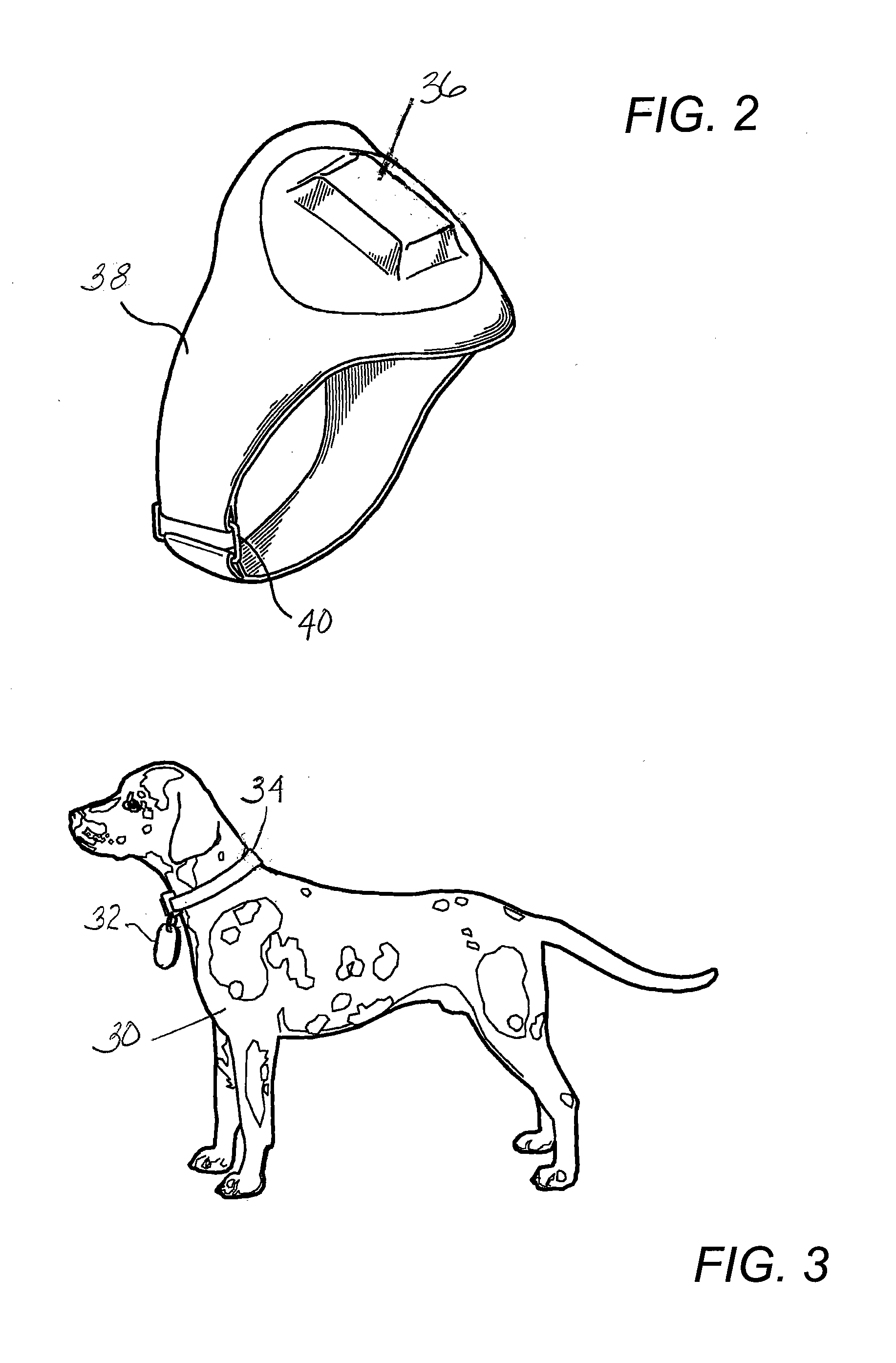
Self-charging power controlled system for locating animals by GPS
InactiveUS20120206296A1Reduce weightReduce energy consumptionSatellite radio beaconingAlarmsMotion detectorPower control system
A portable tracking unit attached to a movable object, such as an animal's collar, includes a GPS receiver to receive GPS signals from multiple satellites for use in multilateration calculations in determining the current position of the tracking unit. A processor in the tracking unit processes the GPS data signals to determine the tracking unit's position, and a GSM mobile wireless transmitter is used to transmit the geographic coordinates of the tracking unit to a remote monitoring unit. The tracking unit also includes a motion detector that outputs a motion signal when the animal is on the move. A motion signal “wakes up” the processor that wakes up the GPS receiver and the GSM transmitter to begin calculating and transmitting the geographic coordinates of the tracking unit. The tracking unit also includes electrical generators configured to transduce mechanical motion of the tracking unit into electrical energy to recharge a battery and power devices. The portable tracking unit is fabricated monolithically in silicon with circuitry integrated with silicon micro-machined motion sensor, as well as power generators, and packaged through silicon wafer bonding. A remote computing device receives the geographic coordinates of the tracking device and indicates to a user the position of the tracking device in relation to a map. An alert may also be provided if the location of the tracking device is outside a programmed safe zone.
Owner:CARBON GLOBAL
System and method for analog cellular radio geolocation
InactiveUS6845240B2Reduce data volumeEfficiently and accurately geolocatingSpatial transmit diversityDirection finders using radio wavesFourier transform on finite groupsGeolocation
A system and method for determining the geolocation of autonomous mobile appliances emitting analog waveforms is disclosed. More specifically, the inventive system and method is used to geolocate FM analog signals such as those used in the AMPS cellular radio air standard by using a time difference of arrival (“TDOA”) approach. The inventive system and method uses a novel approach to minimize the amount of data sent between location sensors and the central location processor comprising adaptive signal combining from N channel to a single channel, FM demodulation to reduce bandwidth, Fourier transformation for signal compression, and segmentation of the location sensors into primary and secondary modes to allow for parallel processing to ease the computational burden on the central location processor.
Owner:ANDREW CORP +1
Estimation of position, speed and bearing using time difference of arrival and received signal strength in a WLAN positioning system
InactiveUS20080248808A1Network topologiesRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsArrival timeMultilateration
A method of estimating the speed of a WLAN-enabled device in a WLAN positioning system is provided. A method of estimating a speed of travel of a WLAN-enabled device includes the WLAN-enabled device receiving signals transmitted by a WLAN access point in range of the WLAN-enabled device. The signals include a first message and a second message. The method also includes estimating an expected time of arrival of the second message based on an actual arrival time of the first message and determining an actual time of arrival value of the second message. The method further includes determining a time difference of arrival value for the second message based on the actual time of arrival of the second message and the expected time of arrival of the second message and estimating the speed of travel of the WLAN-enabled device based on the time difference of arrival value.
Owner:SKYHOOK WIRELESS
Navigation unit and base station
InactiveUS20080234930A1Accurately determine its locationFast updatePosition fixationNavigation instrumentsMultilaterationWide band
The present invention relates to a navigation unit and base station used for determining location. A plurality of base stations are initialized to determine their location relative to each other. At the navigation unit, the time of arrival of at least one signal from each of the plurality of base stations is measured. From this, the location of the navigation unit relative to the plurality of base stations may be directly calculated using a closed solution. In one embodiment, a time of arrival technique is used and in another embodiment a time difference of arrival technique is used. Preferably an ultra-wide band frequency is utilized.
Owner:HAILO TECH LLC
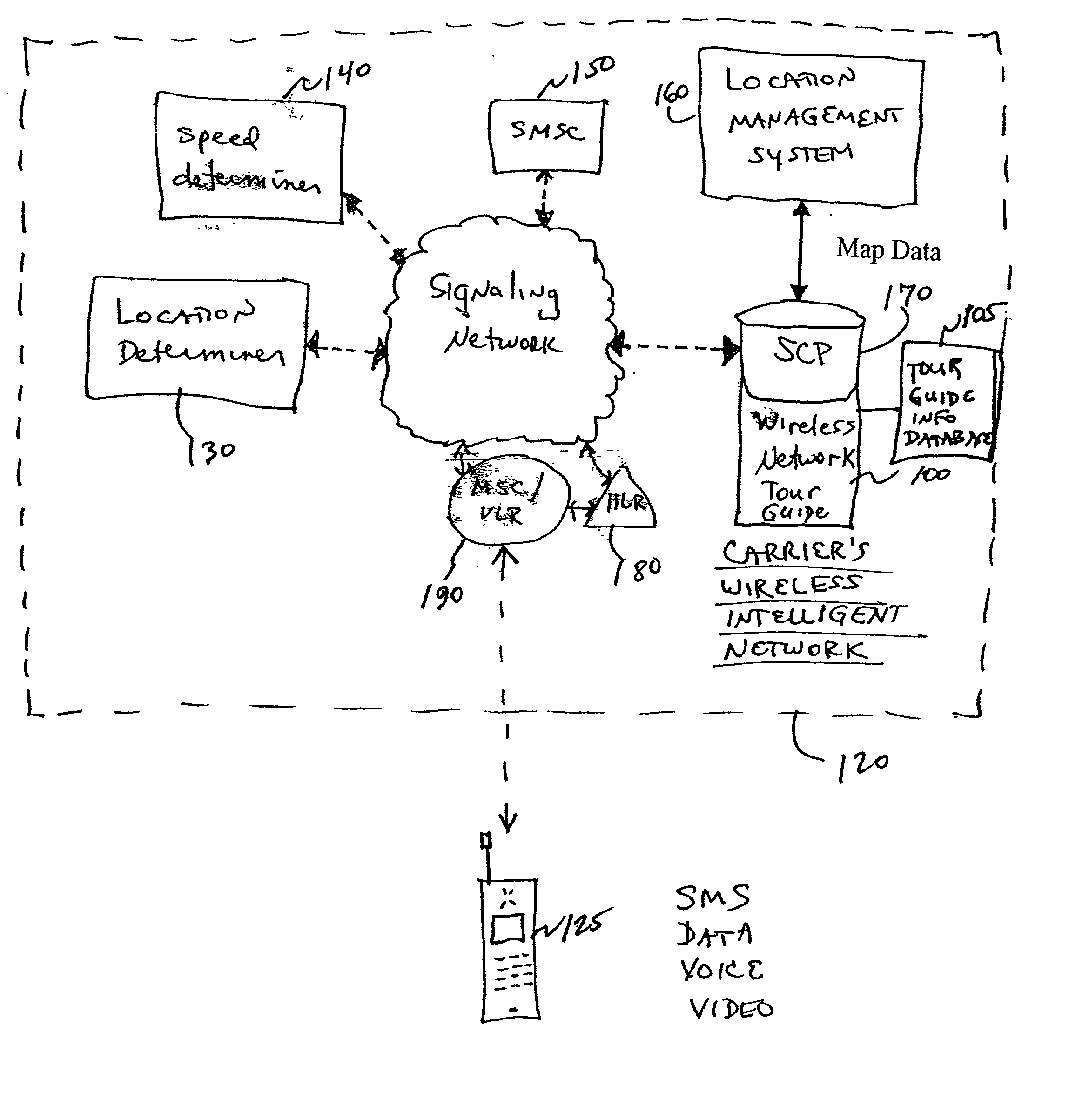
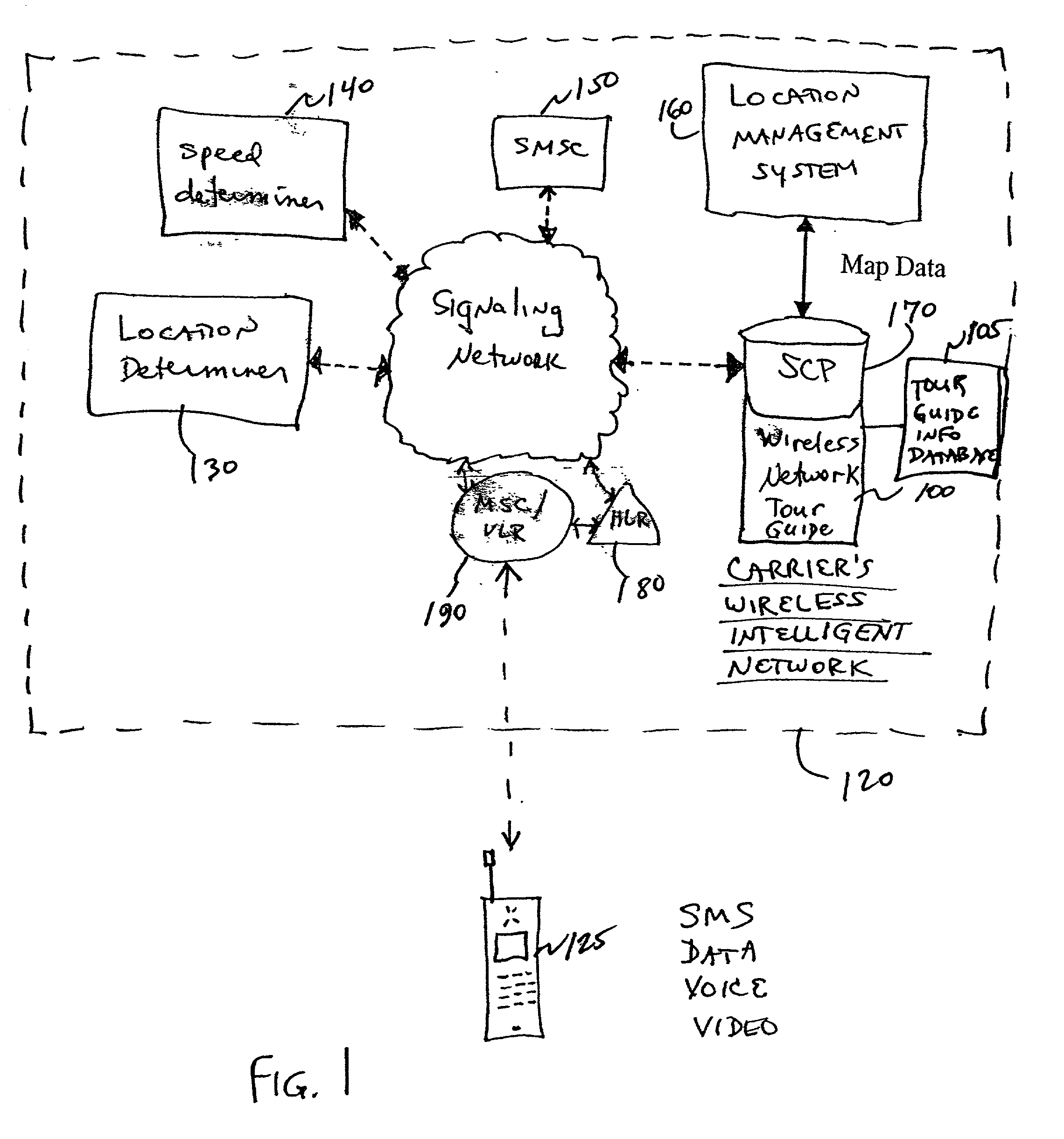
Wireless network tour guide
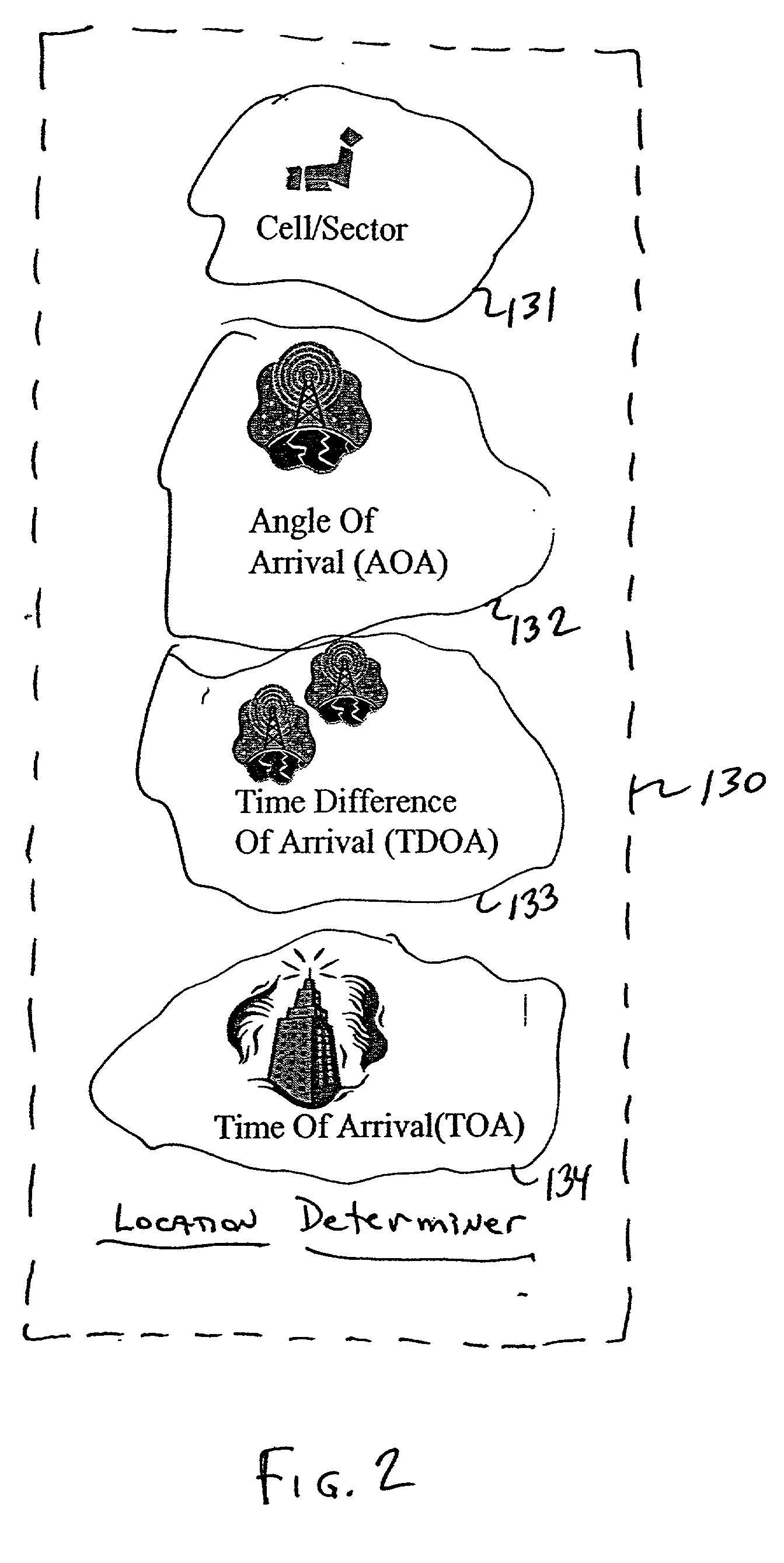
Location based wireless services in a service provider's network are intertwined with a message database (text and / or audio) to automatically provide location information regarding the subscriber to the message database, without requiring the wireless device itself to provide the location information. A location management system is provided to perform the location management functions of determining subscriber location (e.g., by call / sector ID, angle of arrival (AOA), time difference of arrival (TDOA), time of arrival (TOA)), and of mapping the location to the desired text and / or audio. Speed information may also be determined by the location management system, or the subscriber may be prompted to input a particular mode of transportation, or generally indicate their speed. Of course, the slower the speed of the subscriber, the fewer location updates will be required, lessening the burden on the tour guide system in the wireless network.
Owner:TELECOMM SYST INC
Three dimensional (3-D) object locator system for items or sites using an intuitive sound beacon: system and method of operation
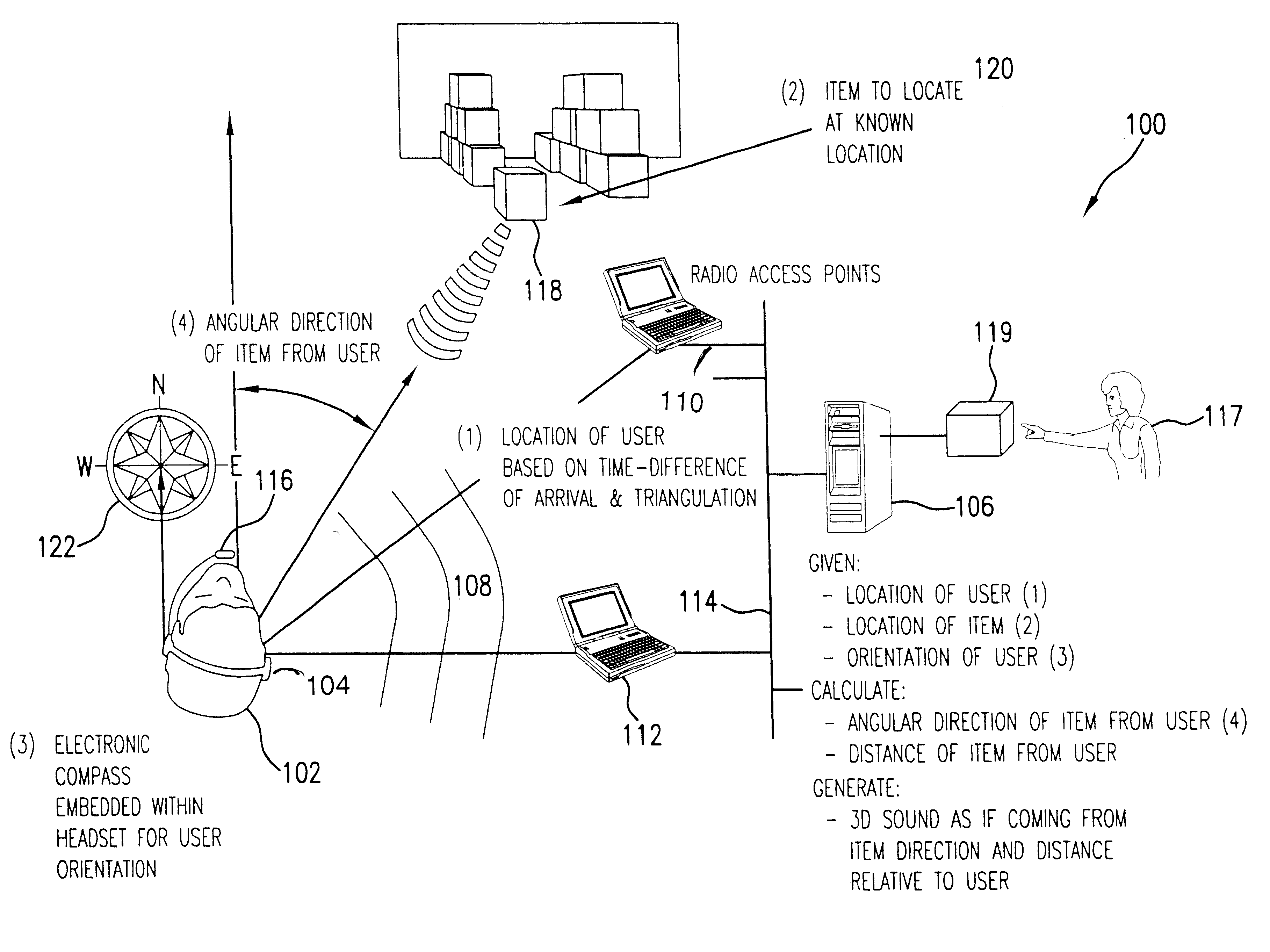
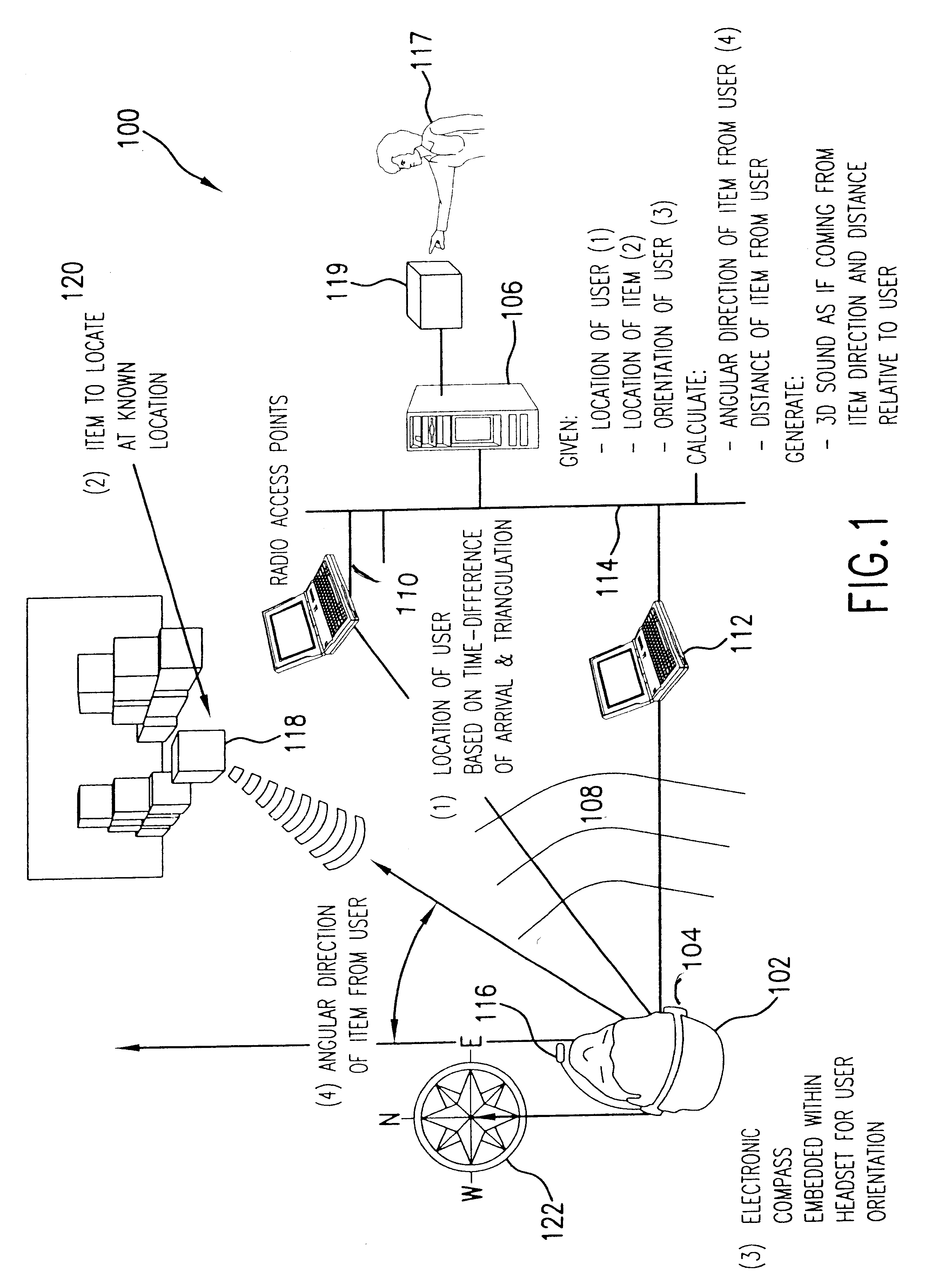
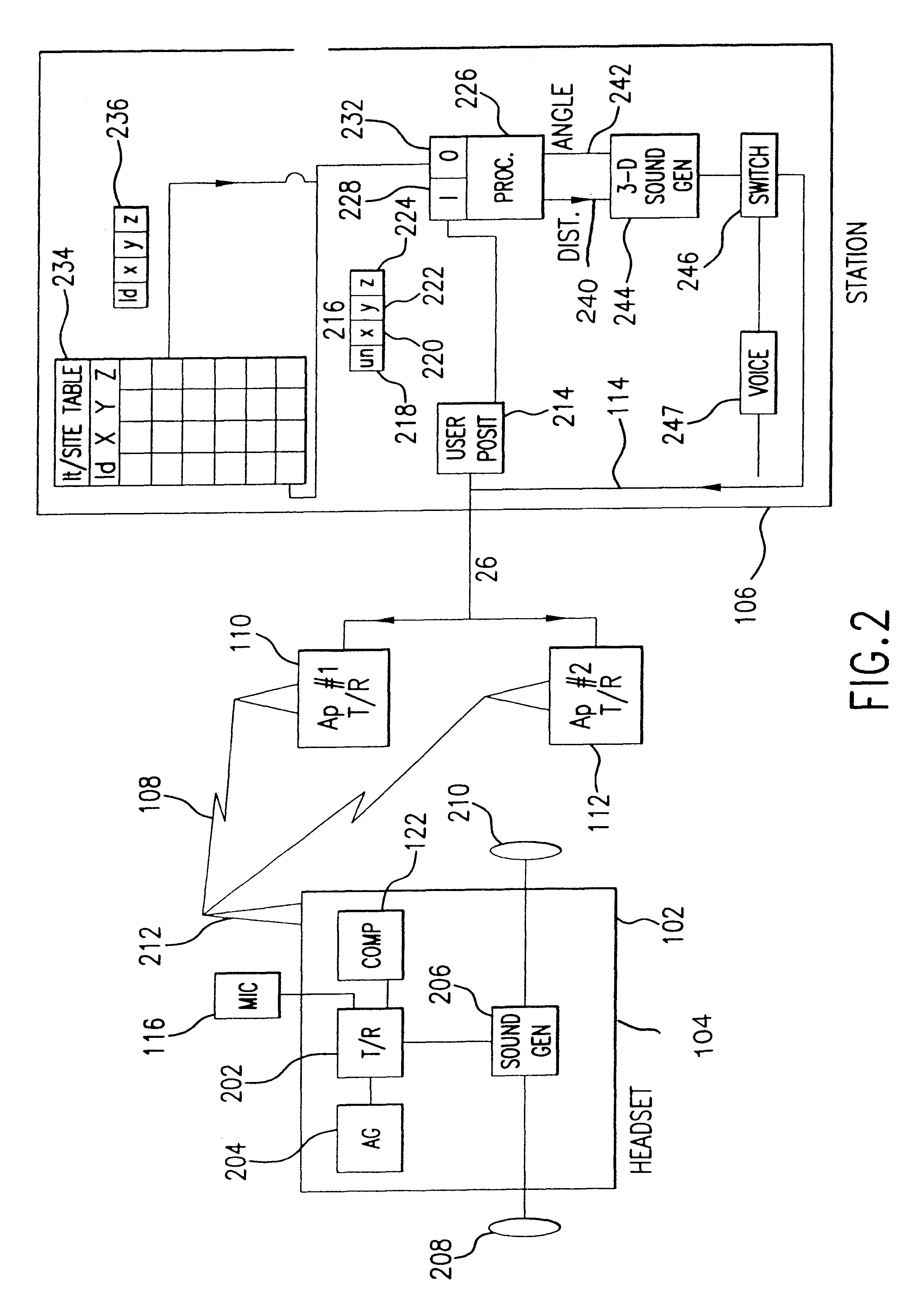
InactiveUS6684176B2Instruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlTransceiverAccelerometer
An object locator system generates an audio signal as if emanating from the object as a user varies angular orientation and distance from an object or site to be located within an area. A computer linked to an access transceiver receives transmissions from a user wearing a headset including a transceiver and electronic compass. The compass provides a signal indicative of the user orientation. An access transceiver receives the signal and calculates the location of the user based on the time difference of arrival of the RF signal and triangulation of the user movement. An accelerometer in the headset continuously tracks user movement. The location of the object in a vertical direction is provided by a directory or other reference source stored in the computer. Based on the angular orientation, horizontal and vertical distance of the object or site relative to the user, the computer maps the location information into sounds in the form of pulse amplitude or frequency modulated sound. The audio signal is perceived by the user as emanating from the object or site.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH LLC
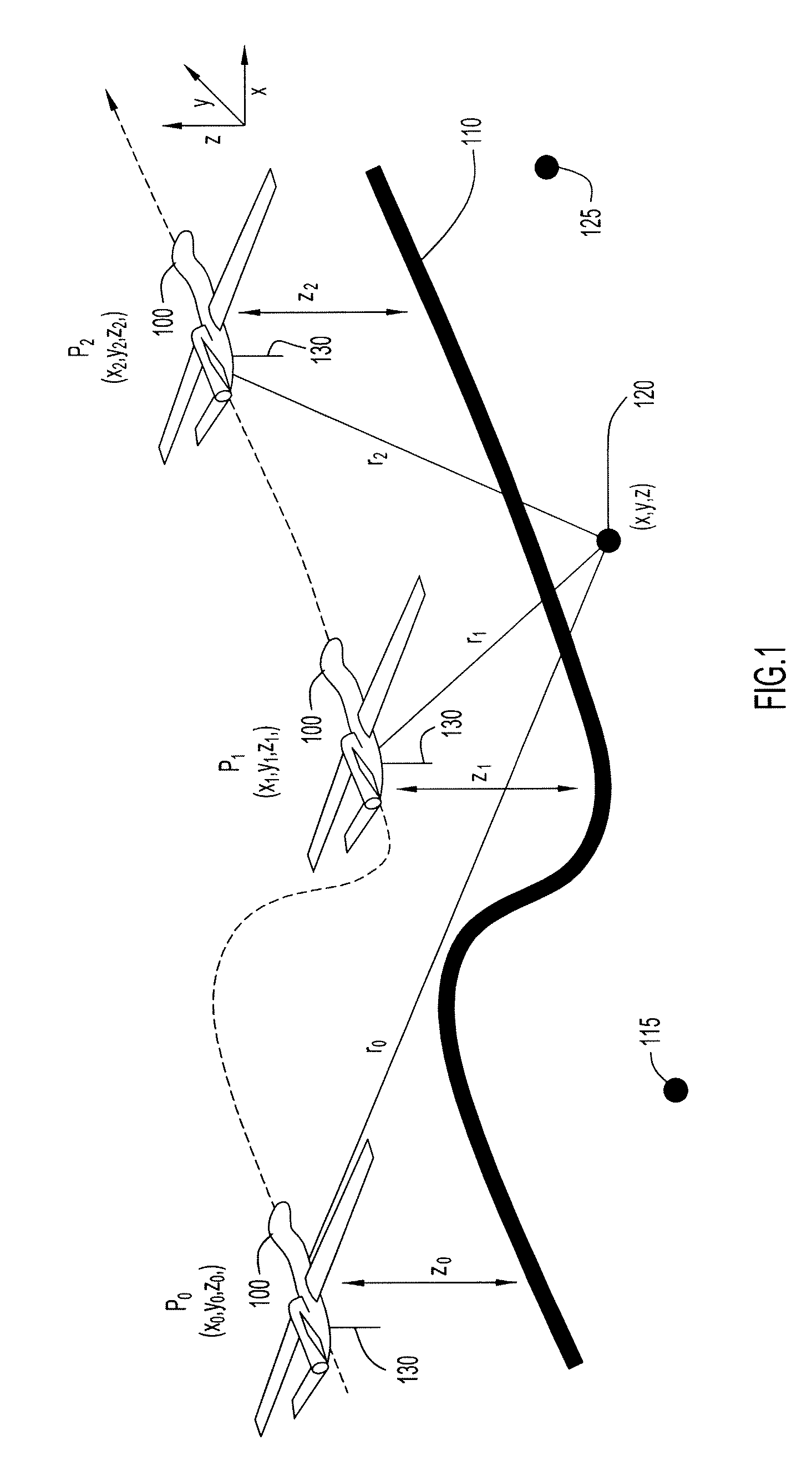
System and method for multilaterating a position of a target using mobile remote receiving units
ActiveUS20070247368A1Direction finders using radio wavesPosition fixationTarget signalMultilateration
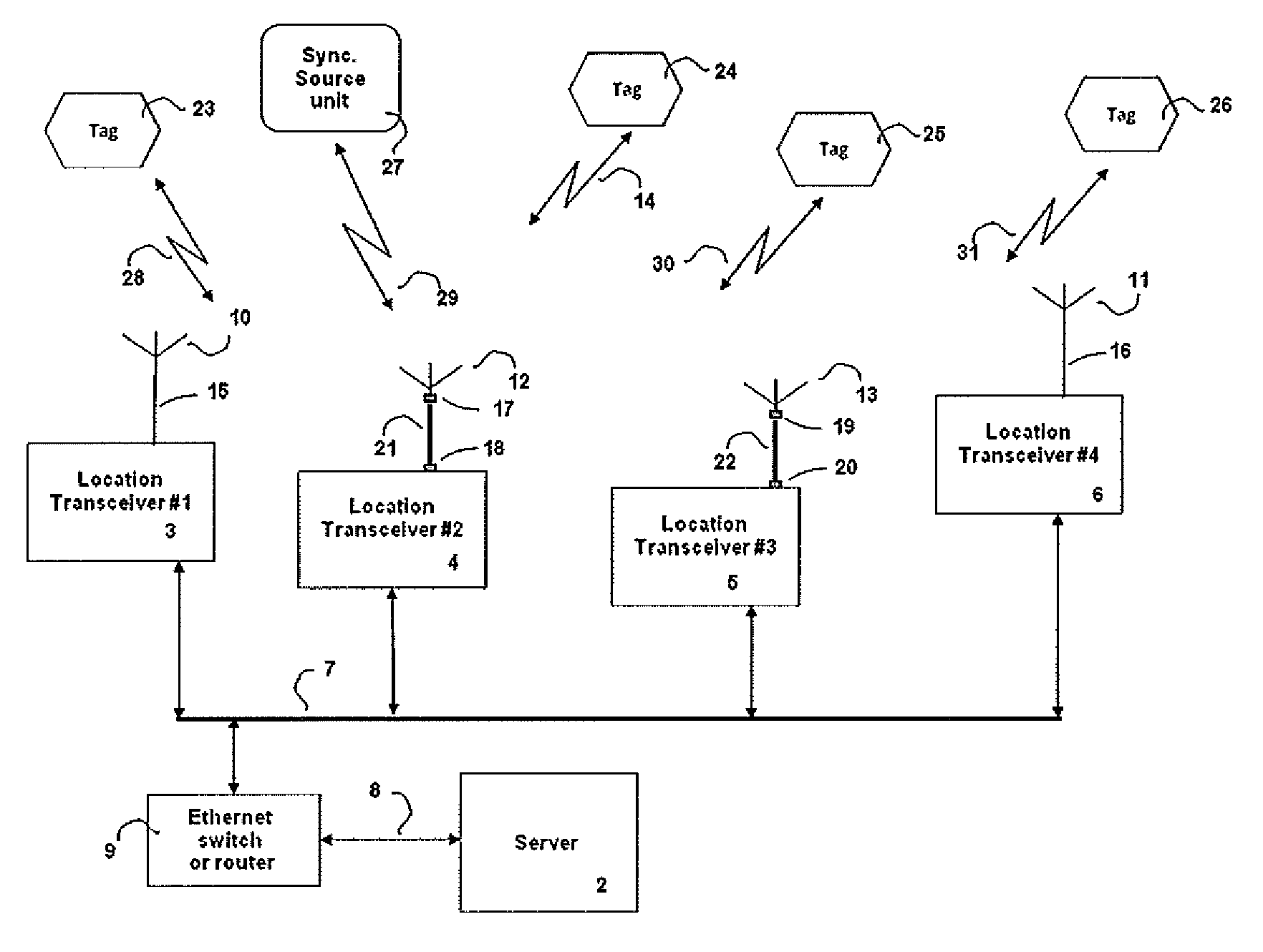
A method of multilaterating the position of a target, including the steps of deploying a plurality of time synchronized receiving units in a network that allows the receiving units to communicate with a central processor; receiving a target signal from the target at each receiving unit; determining a time of arrival for the target signal at each receiving unit; determining position data for each receiving unit at the time when the target signal is received at each respective receiving unit; and using the time of arrival and position data for each receiving unit to determine the position of the target by multilateration. A system for carrying out the method is also disclosed.
Owner:SAAB INC
System and Method for Allocating Jamming Energy Based on Three-Dimensional Geolocation of Emitters
ActiveUS20120309288A1Rapid identificationMaximize overall jamming effectWave based measurement systemsTelephonic communicationGeolocationEnergy based
According to an embodiment of the present invention jamming energy is allocated to a plurality of emitters based on a three-dimensional (3-D) emitter geolocation technique that determines the geolocation of radio frequency (RF) emitters based on energy or received signal strength (RSS) and / or time differences of arrival (TDOAs) of transmitted signals. The three-dimensional (3-D) emitter geolocations are used to rank emitters of interest according to distance and available radio frequency (RF) jamming energy is allocated to the emitters in rank order. The techniques may be employed with small unmanned air vehicles (UAV), and obtains efficient use of jamming energy when applied to radio frequency (RF) emitters of interest.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
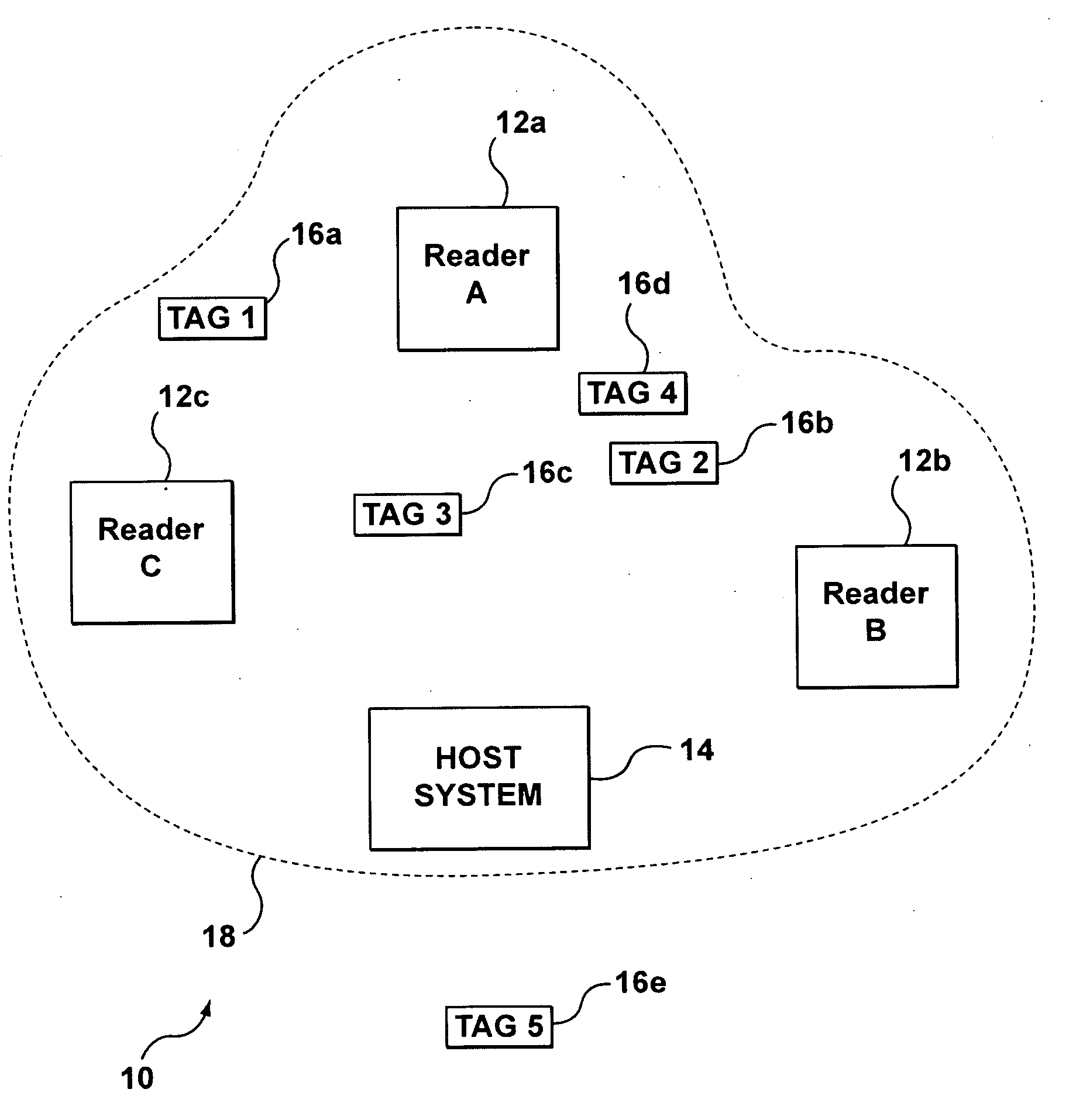
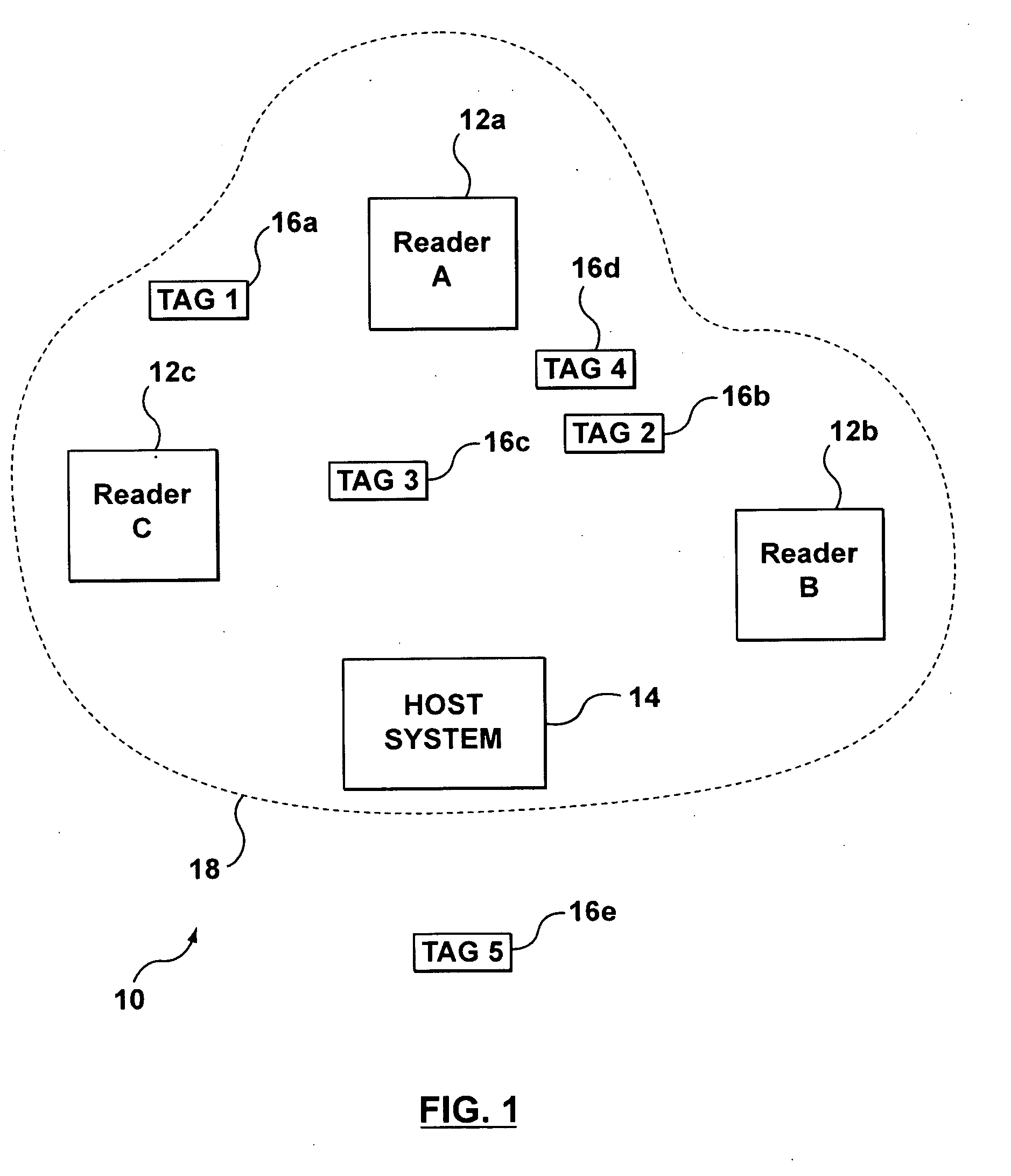
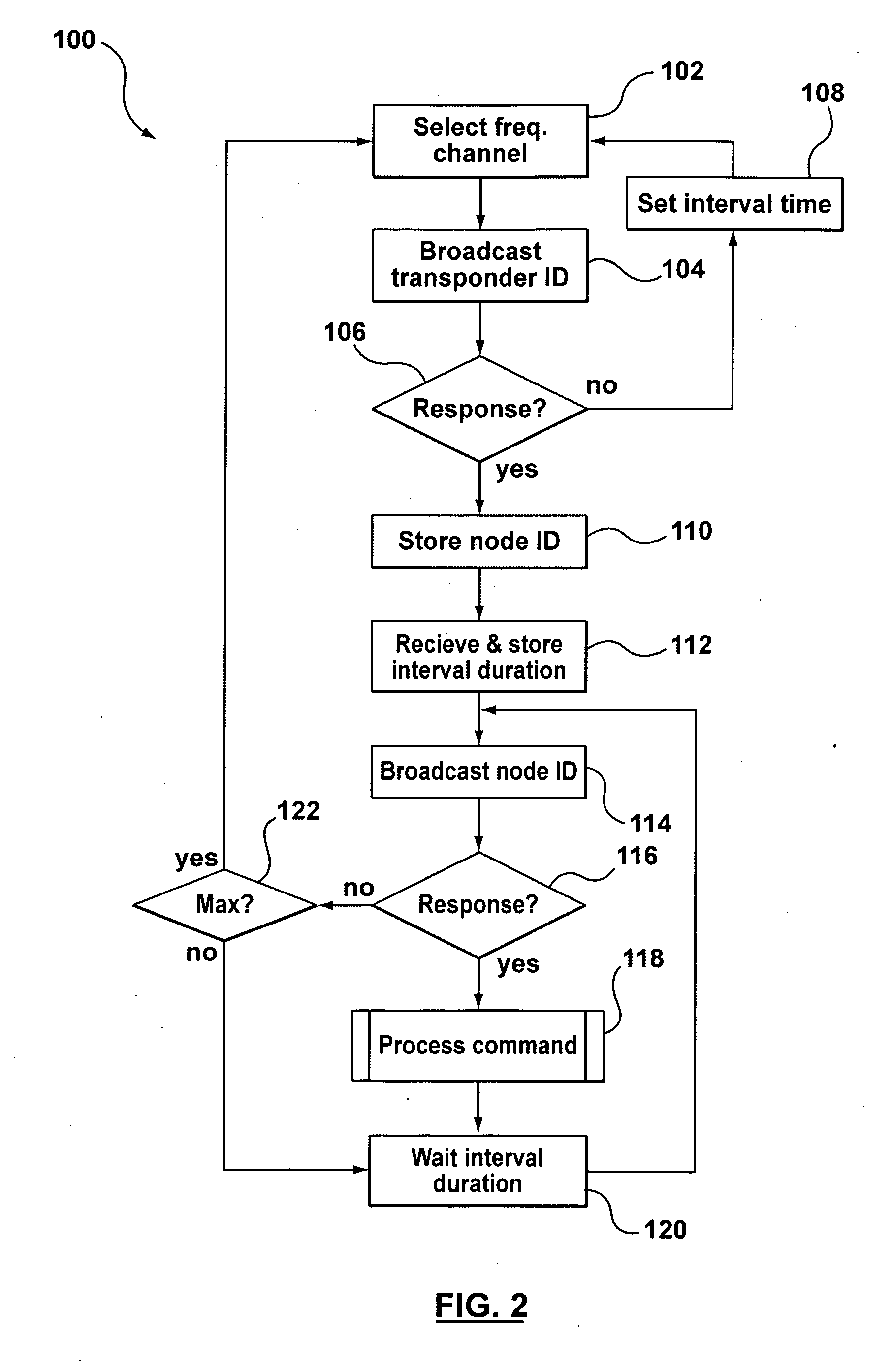
Real-Time Location Systems and Methods
InactiveUS20090201169A1Eliminate the effects ofElectric/electromagnetic visible signallingAlarmsMultilaterationReal-time locating system
A real-time location system for identifying and locating tagged items. The system may include an identification protocol that tracks in-network transponders and assigns dynamic in-network identification numbers to in-network transponders. The system includes a locator function that employs time-of-arrival analysis. Rather than attempt to synchronize the time base at each reader, the system and process eliminate the need to sync the readers and also eliminate the impact of differential receive delays in the respective readers. Both the transponder and a master reader transmit locate signals, which are measured at slave readers. The system relies on differences in time-of-arrival of the two signals at the respective slave readers to determine the likely location of the transponder.
Owner:MARK IV INDS
Apparatus and method for estimating position of mobile communication terminal
InactiveUS7057557B2Function increaseDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationComputer terminalArrival time
A position estimating method and apparatus are disclosed that determine an angle of arrival of a signal received from a terminal; determine a distance of the terminal, using an arrival time difference between the arrival time of the signal and a reference time; and determine a position of the terminal based on the determined angle of arrival and distance.
Owner:HIGHBRIDGE PRINCIPAL STRATEGIES LLC AS COLLATERAL AGENT
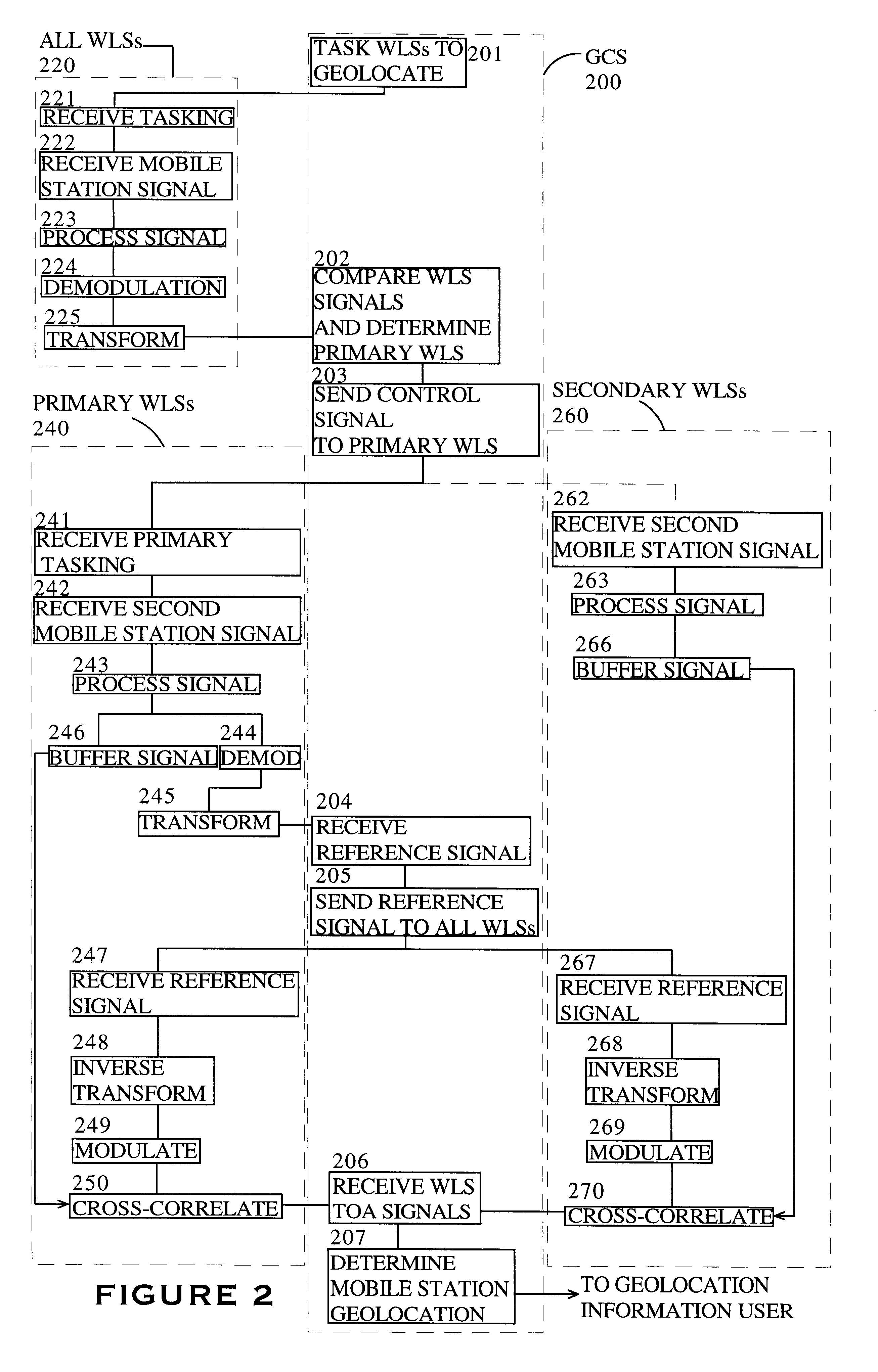
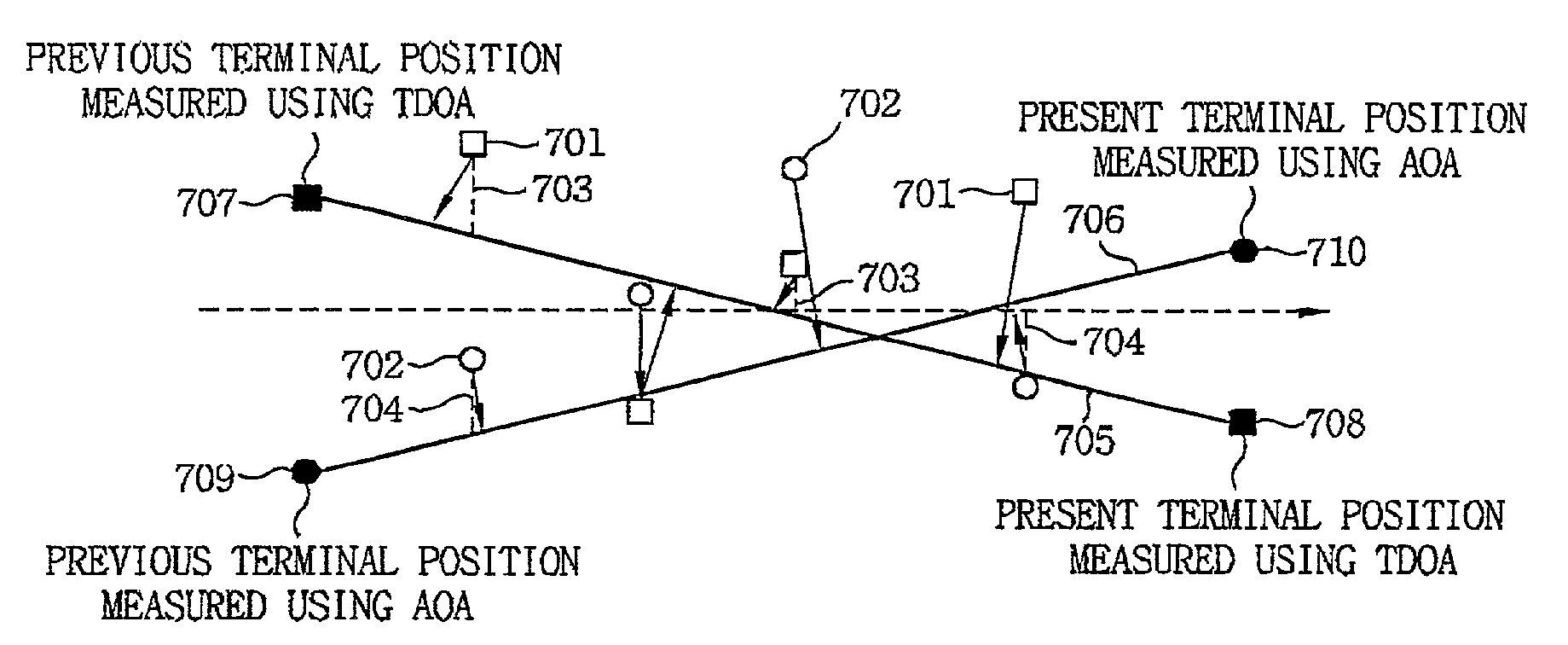
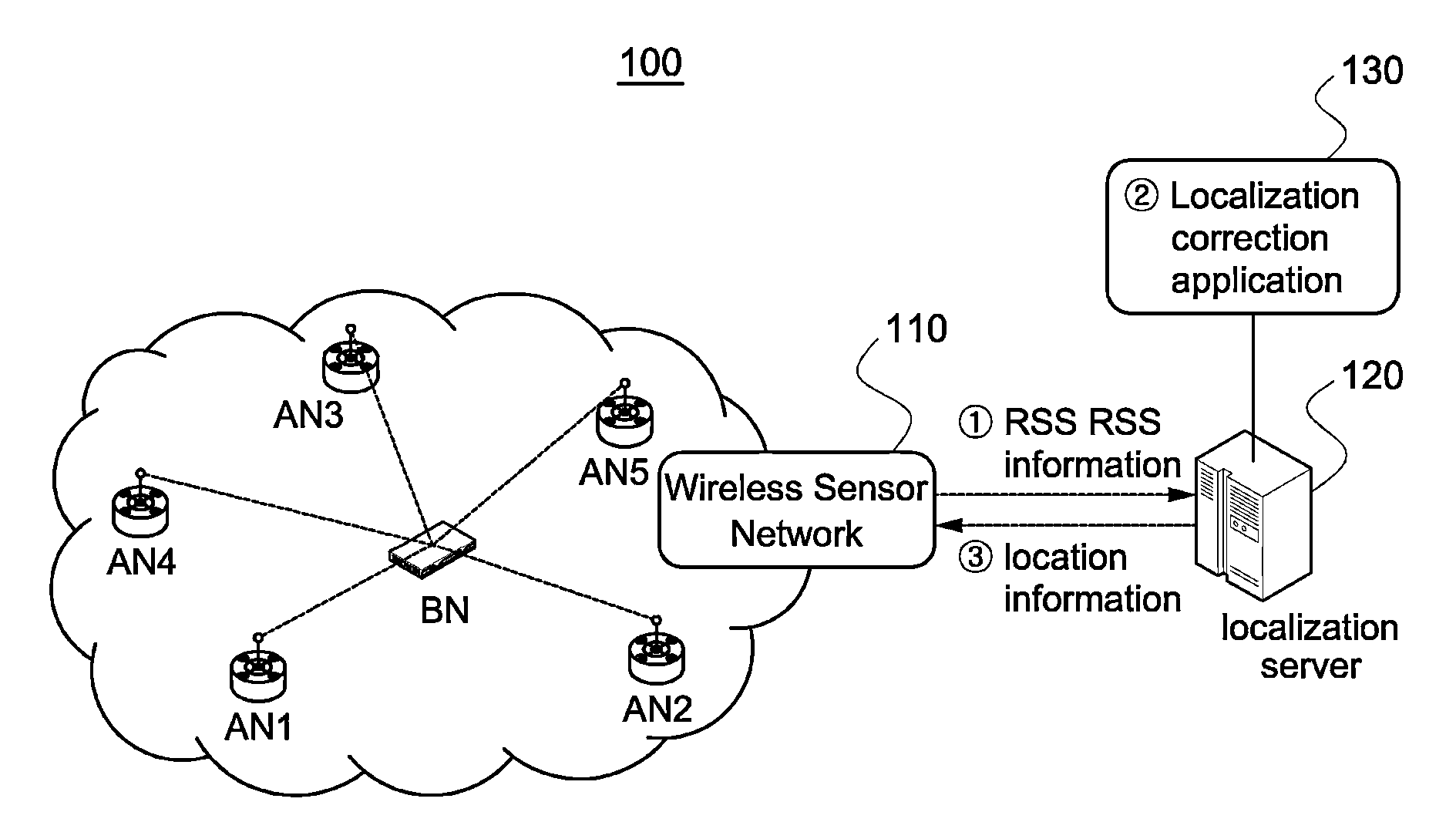
Wireless localization method based on an efficient multilateration algorithm over a wireless sensor network and a recording medium in which a program for the method is recorded
ActiveUS20130045750A1Improve estimation accuracyDistance can be inaccurateDirection finders using radio wavesSpecial service for subscribersWireless mesh networkWireless sensor networking
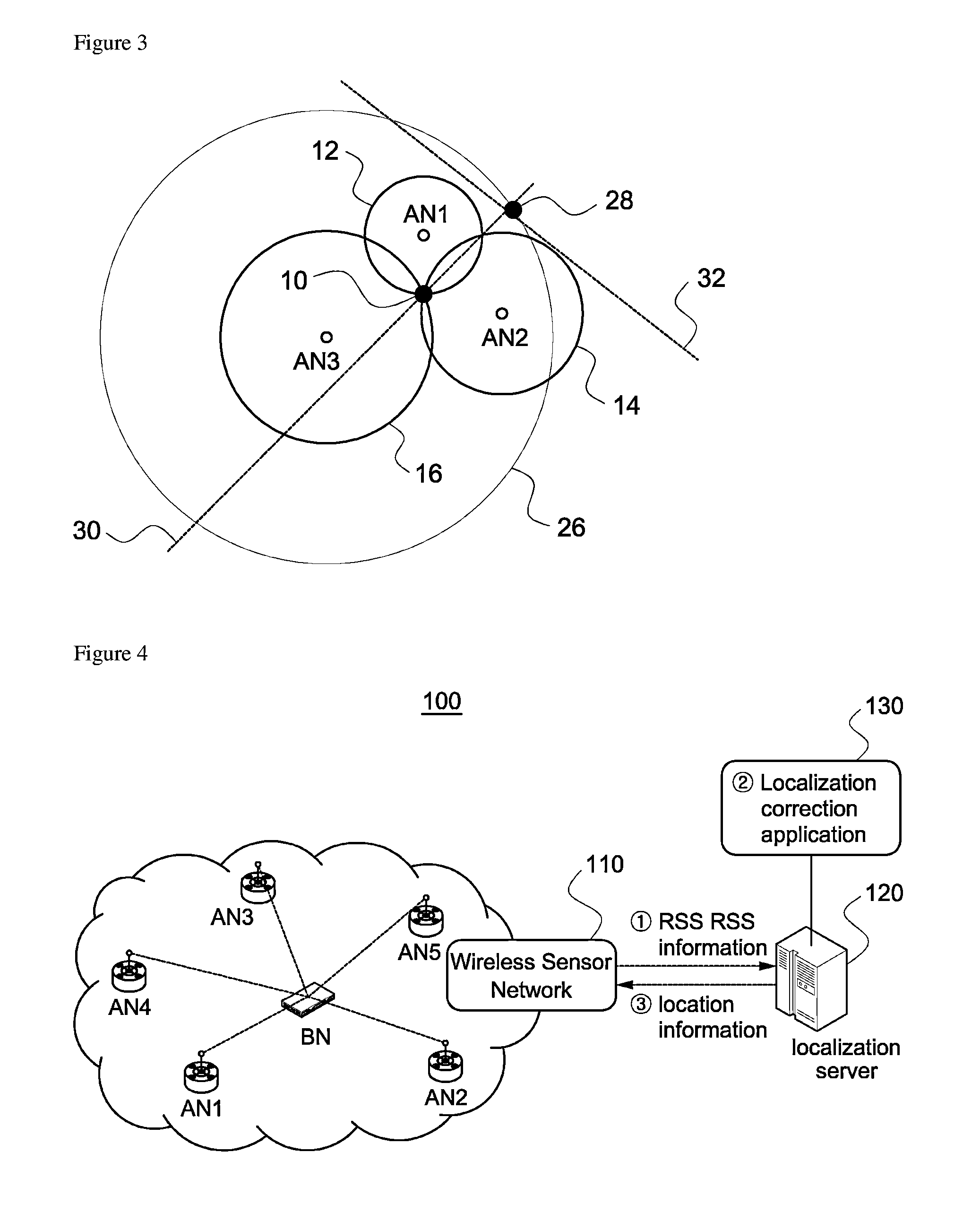
A wireless localization technology using efficient multilateration in a wireless sensor network is disclosed. After calculating estimated distances from each of at least three reference nodes to a blind node using received signal strength of wireless signals that the at least three reference nodes received from the blind node, the estimated location of the blind node is obtained through multilateration using the calculated estimated distances. To correct error in the estimated location, the estimated distances are used, and the error correction direction and error correction distance for the estimated location are calculated by applying a largest weight to the reference node closest to the estimated location. The error of the estimated location is corrected by move the estimated location of the blind node by the calculated error correction direction and error correction distance. Calculation for the error correction is very simple and fast.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Method and system for synchronizing location finding measurements in a wireless local area network
InactiveUS20040072582A1Echo effect reductionDirection finders using radio wavesKaiman filterMultilateration
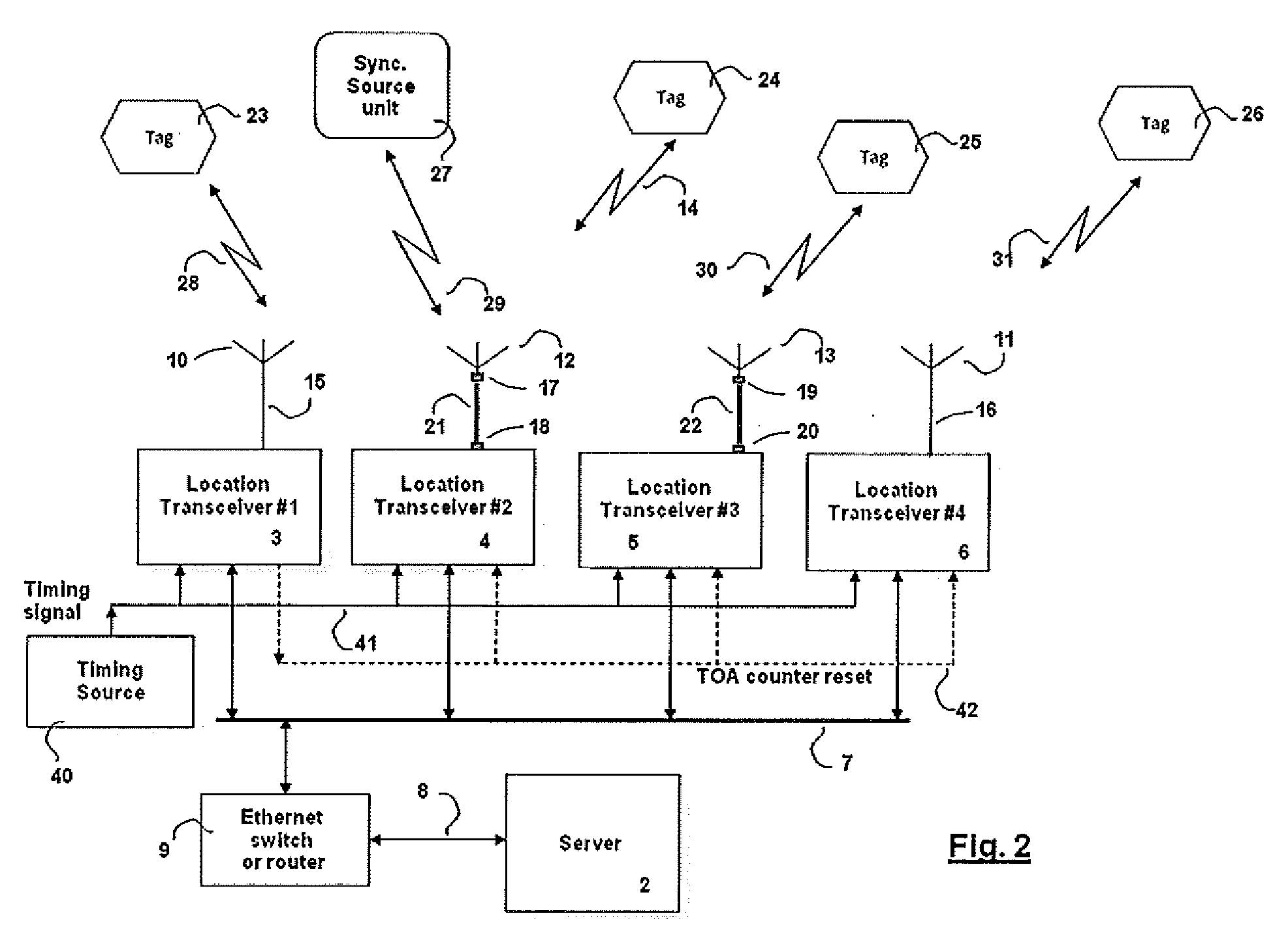
A method and system for synchronizing location finding measurements in a wireless local area network (WLAN) provides a low cost mechanism for correcting location measurements within a WLAN location finding system. Multiple location receivers compute the time-of-arrival (TOA) of a reference transmitter signal, which is generally a beacon signal. The TOAs are collected and reported to a master unit that contains stored predetermined position information for the location receivers. The master unit computes the time-differences-of-arrival (TDOA) between multiple receivers and computes differences between the measured TDOAs and theoretical TDOAs computed in conformity with the predetermined position of each location receiver. The deviations between theoretical and measured TDOAs are collected in a statistical sample set and Kalman filters are used to produce a model of location receiver timebase offset and drift over multiple received beacon signals. The filter outputs are used to then either correct subsequent TDOA measurements for each location receiver, improving the accuracy of subsequent and / or prior TDOA measurements, or commands are sent to the location receivers to calibrate the timebases within the location receivers in order to improve the accuracy of subsequent TOA measurements.
Owner:AEROSCOUT
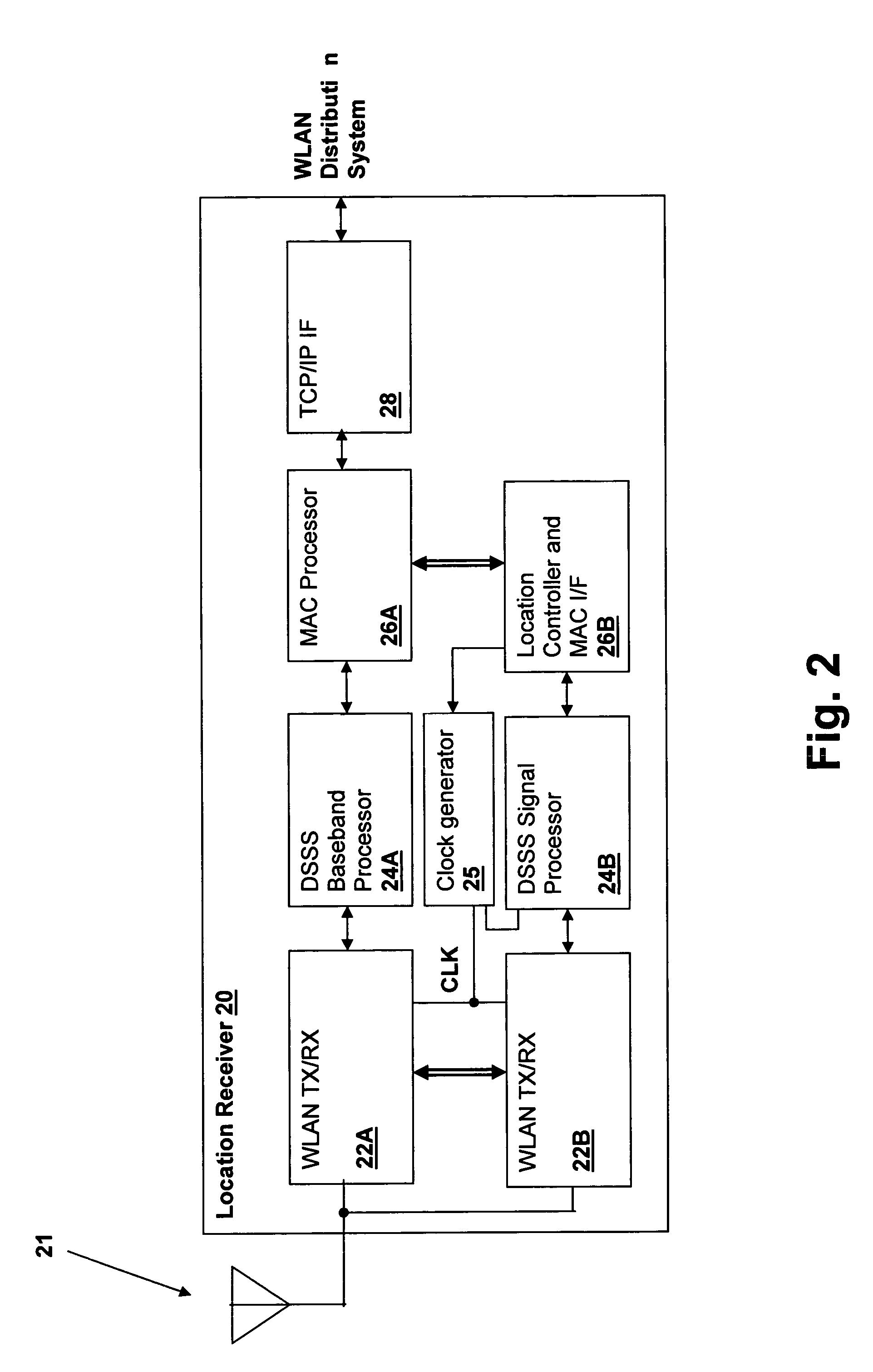
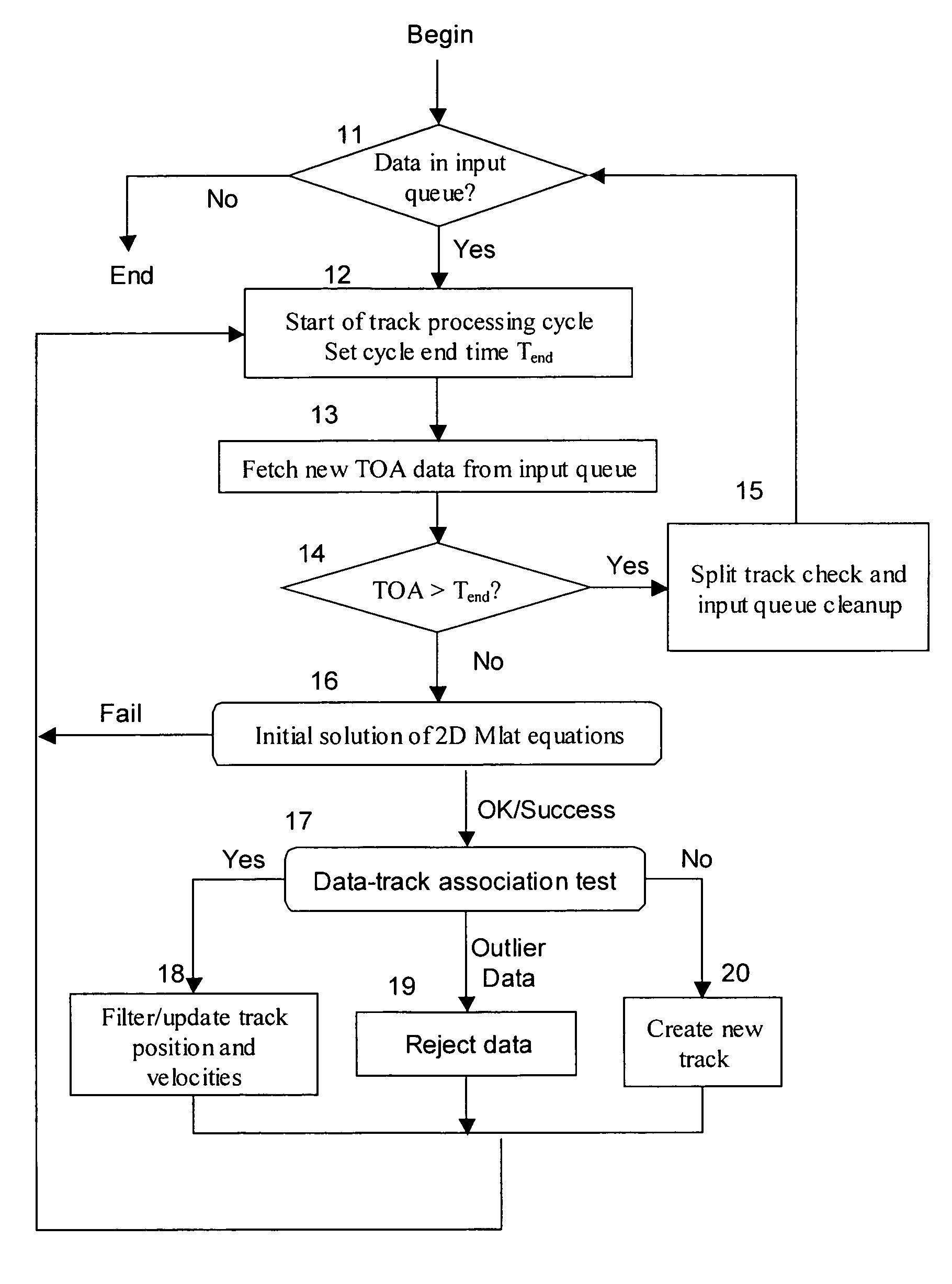
Method and apparatus for accurate aircraft and vehicle tracking
InactiveUS7132982B2Improve vertical accuracyGood HDOPDirection finders using radio wavesBeacon systemsFlight vehicleMultilateration
A direct multilateration target tracking system is provided with the TOA time stamp as an input. A technique of tracking targets with varying receiver combinations is provided. Methods of correlating and combining Mode A, Mode C, and Mode S messages to enhance target tracking in a passive surveillance system are provided. A direct multilateration target tracking system is provided by TOA tracking and smoothing. A technique for selecting best receiver combination and / or solution of multilateration equations from a multitude of combinations and / or solutions is provided. A technique for correcting pseudorange values with atmospheric conditions is provided. A technique for improving height determination for regions of poor VDOP in a 3D multilateration system is provided.
Owner:SRA INTERNATIONAL
Multilateration enhancements for noise and operations management
InactiveUS20060191326A1Data augmentationGood serviceDirection finders using radio wavesSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementNoise monitoringMultilateration
Multilateration techniques are used to provide accurate aircraft tracking data for aircraft on the ground and in the vicinity of an airport. From this data, aircraft noise and operations management may be enhanced. Aircraft noise may be calculated virtually using track data in real-time and provided to a user to determine noise violations. Tracking data may be used to control noise monitoring stations to gate out ambient noise. Aircraft emissions, both on the ground and in the air may be determined using tracking data. This and other data may be displayed in real time or generated in reports, and / or may be displayed on a website for viewing by airport operators and / or members of the public. The system may be readily installed in a compact package using a plurality of receivers and sensor packages located at shared wireless communication towers near an airport, and a central processing station located in or near the airport.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Location system and method with a fiber optic link
InactiveUS20110050501A1Simple processSimplifying the fiber optic link and the transpondersPosition fixationBeacon systemsFiberTransceiver
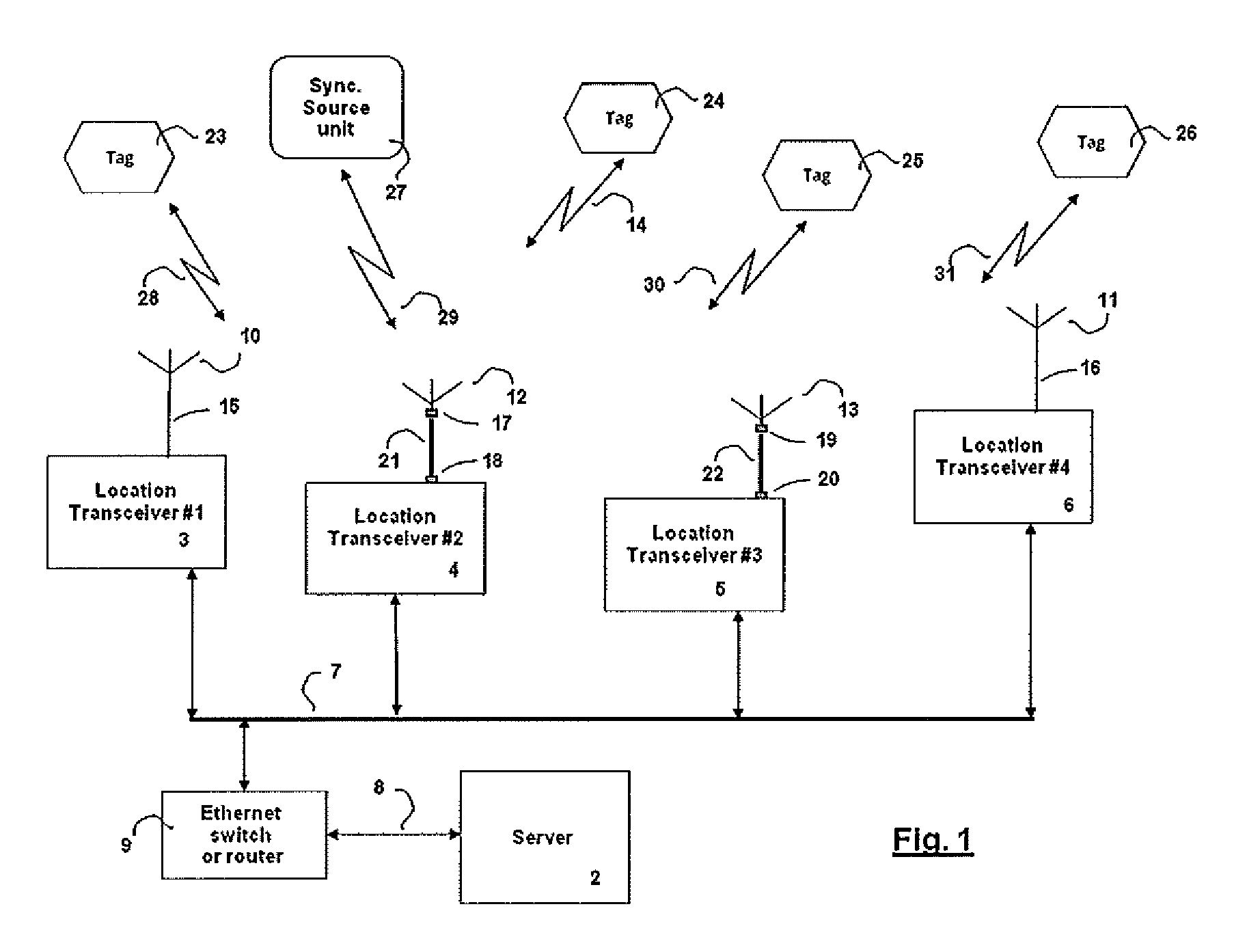
A TDOA (time difference of arrival) location system, in which mobile wireless devices broadcast wireless signals which are received by two or more transceivers deployed in the vicinity of the mobile wireless device. Each transceiver measures the TOA (time of arrival) of the received broadcasted signal and reports the TOA to a central server. The central server then calculates the mobile device position using multi-lateration of TDOA values. The system uses fiber optic links between the antennas and the transceivers deployed in the location area to provide unique advantages that couldn't be achieved using RF coaxial cables.
Owner:AEROSCOUT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com